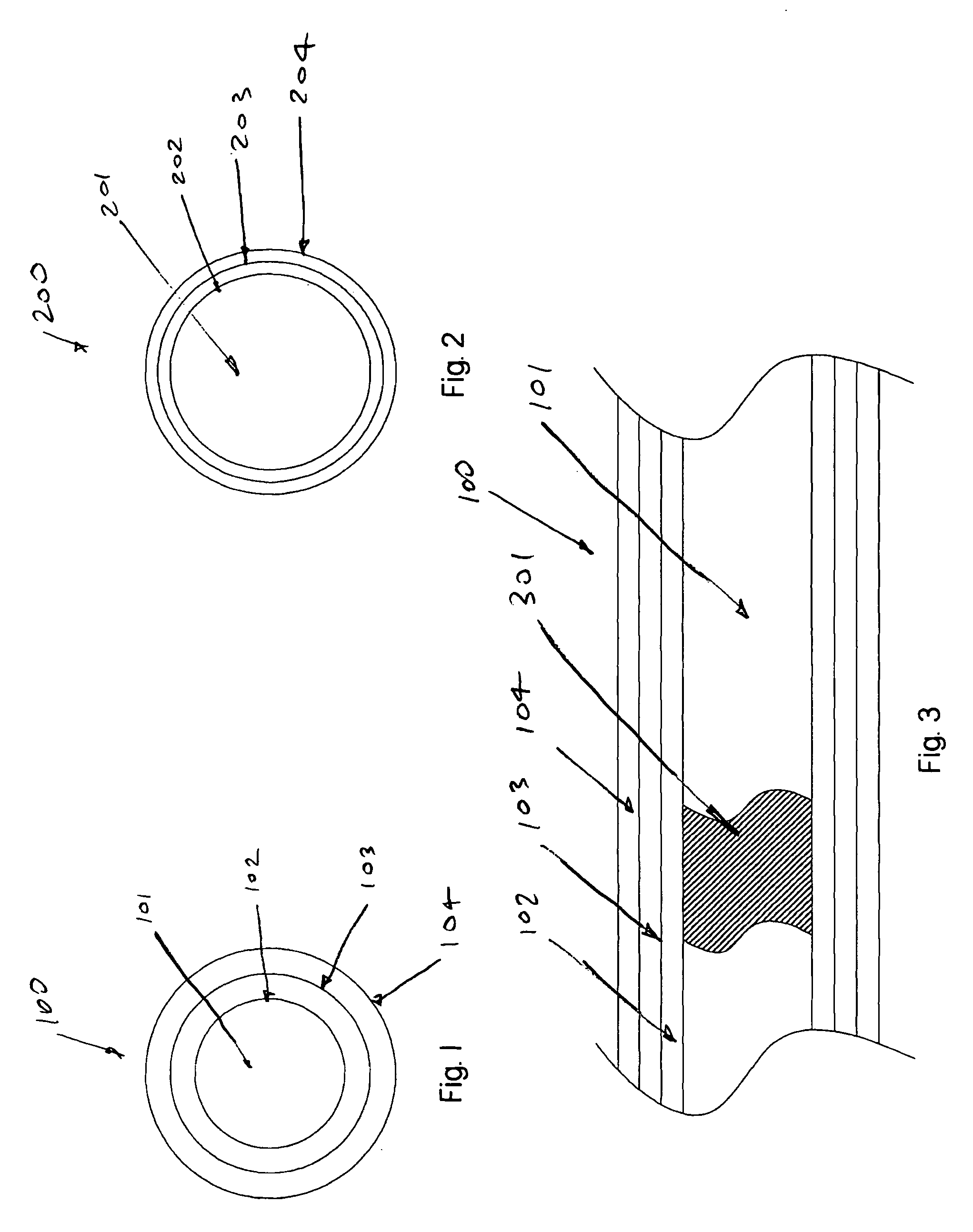
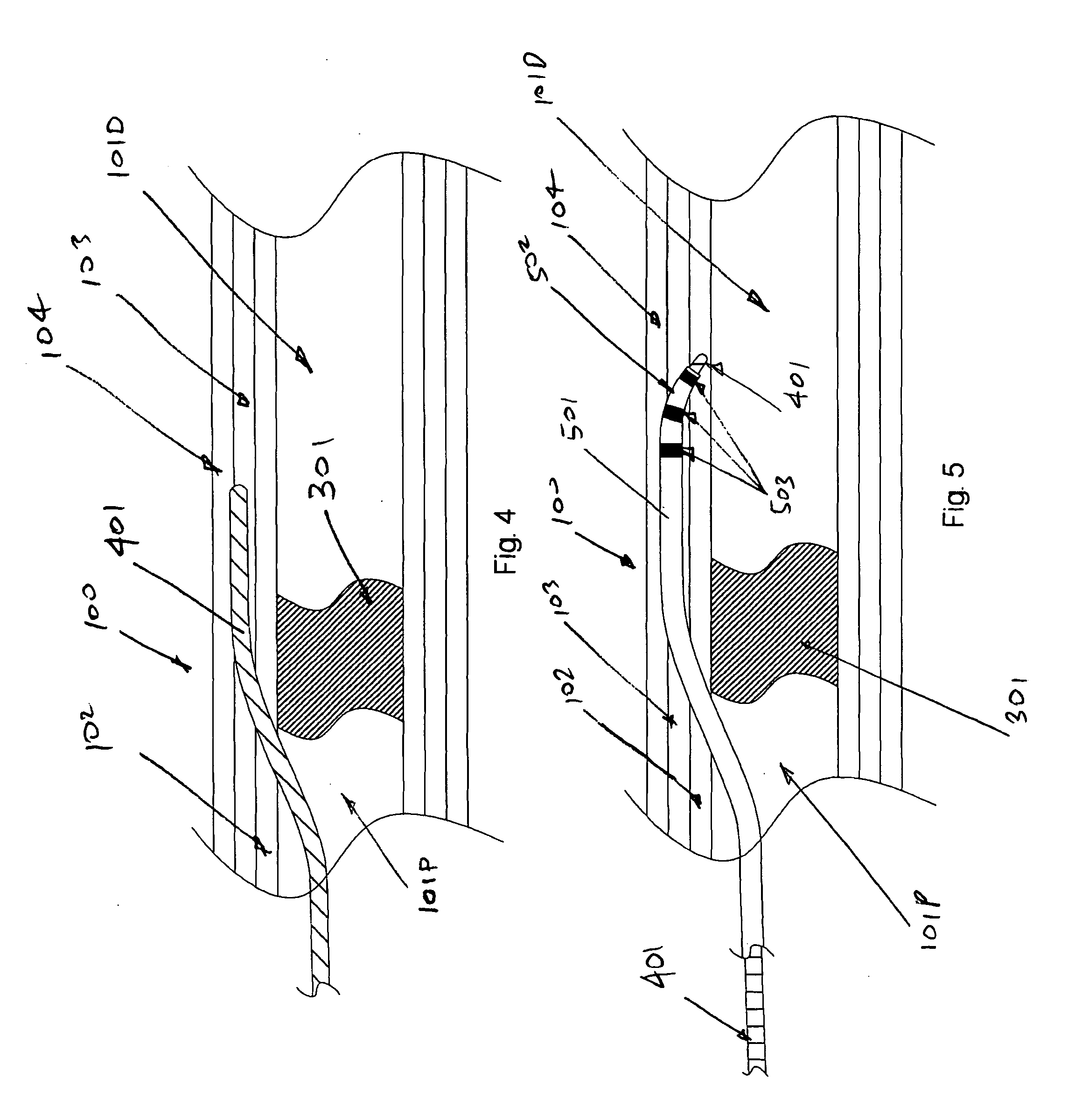
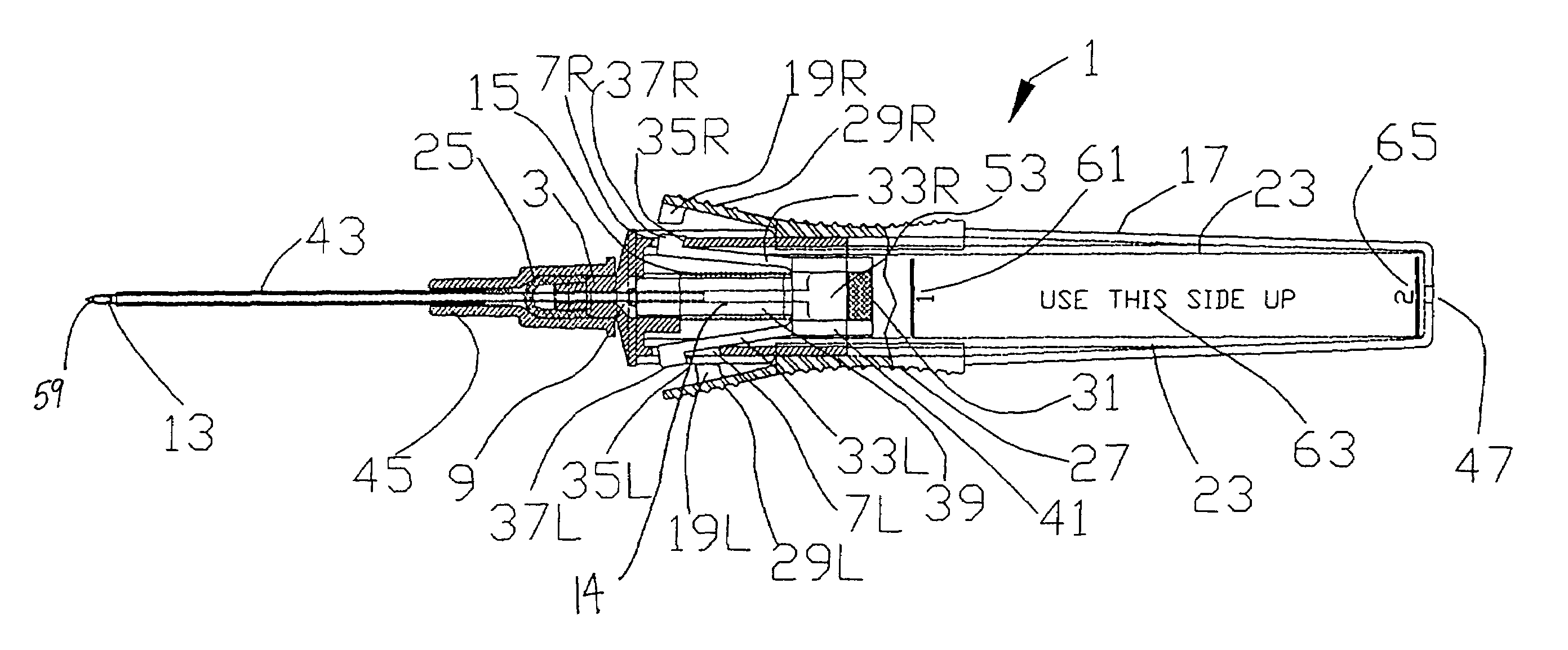
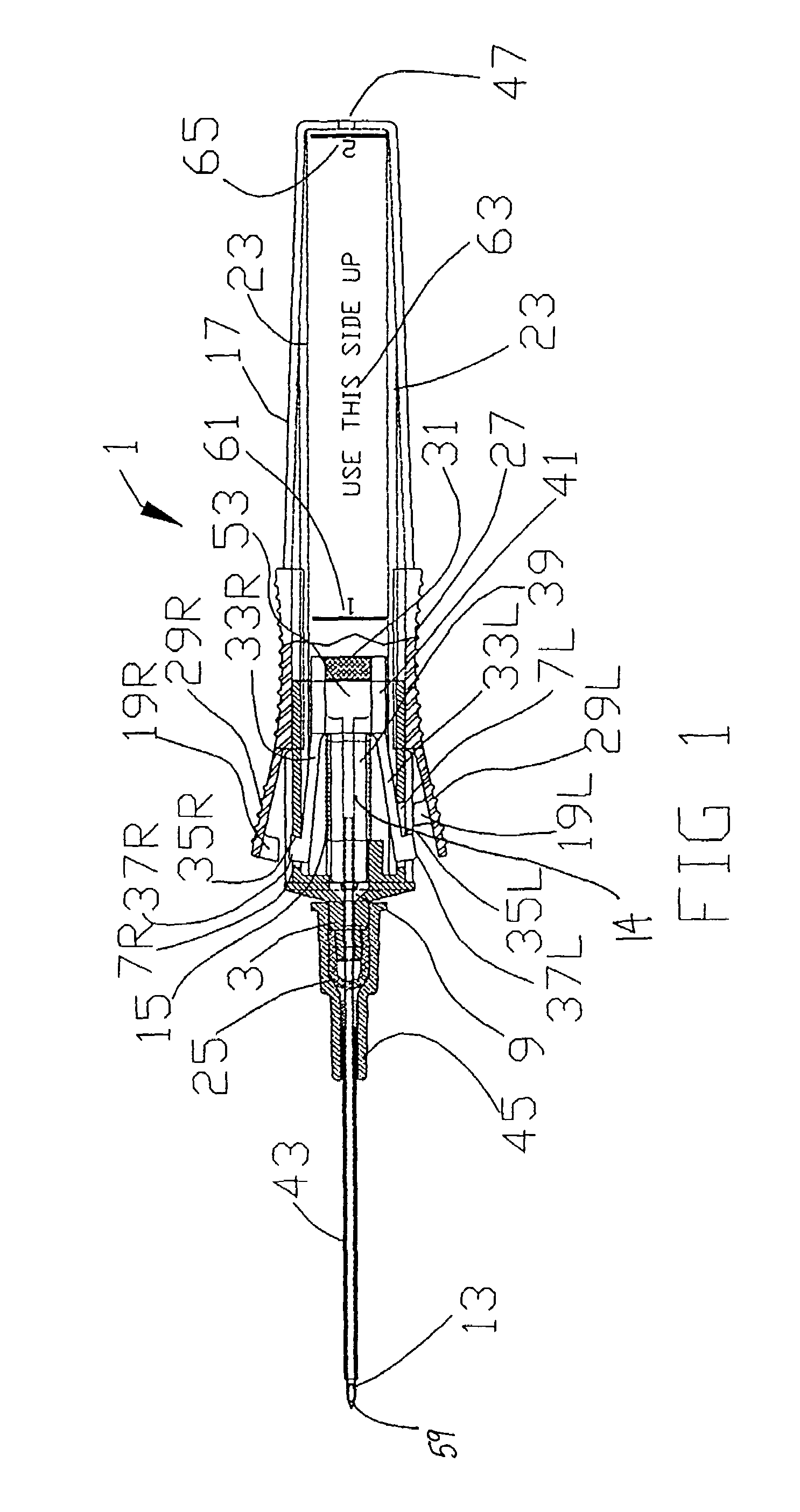
Patents
Literature
152 results about "Catheter placement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Minimally Invasive Aortic Valve Replacement
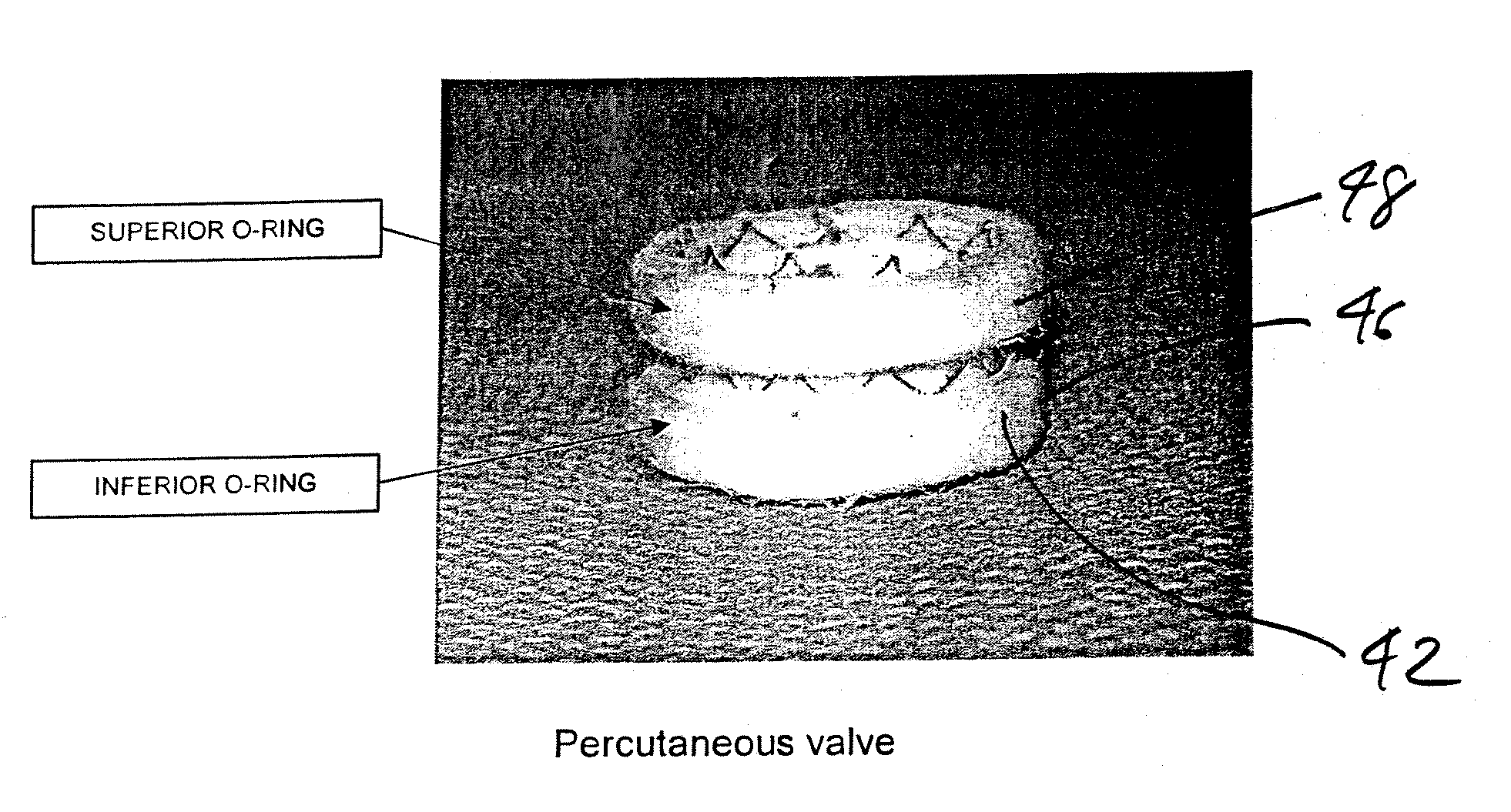
A replacement cardiac valve for placement adjacent the native annulus comprises a valve body having a multi-leaflet valve, a supporting stent surrounding and operatively coupled to the valve body, a superior O-ring and an inferior O-ring spaced from one another to span the native annulus, the O-rings surrounding the valve body and operatively coupled the valve body or the supporting stent, the valve body, the supporting stent, and the O-rings adapted for transcatheter placement using a deployment catheter.
Owner:TEHRANI HASSAN
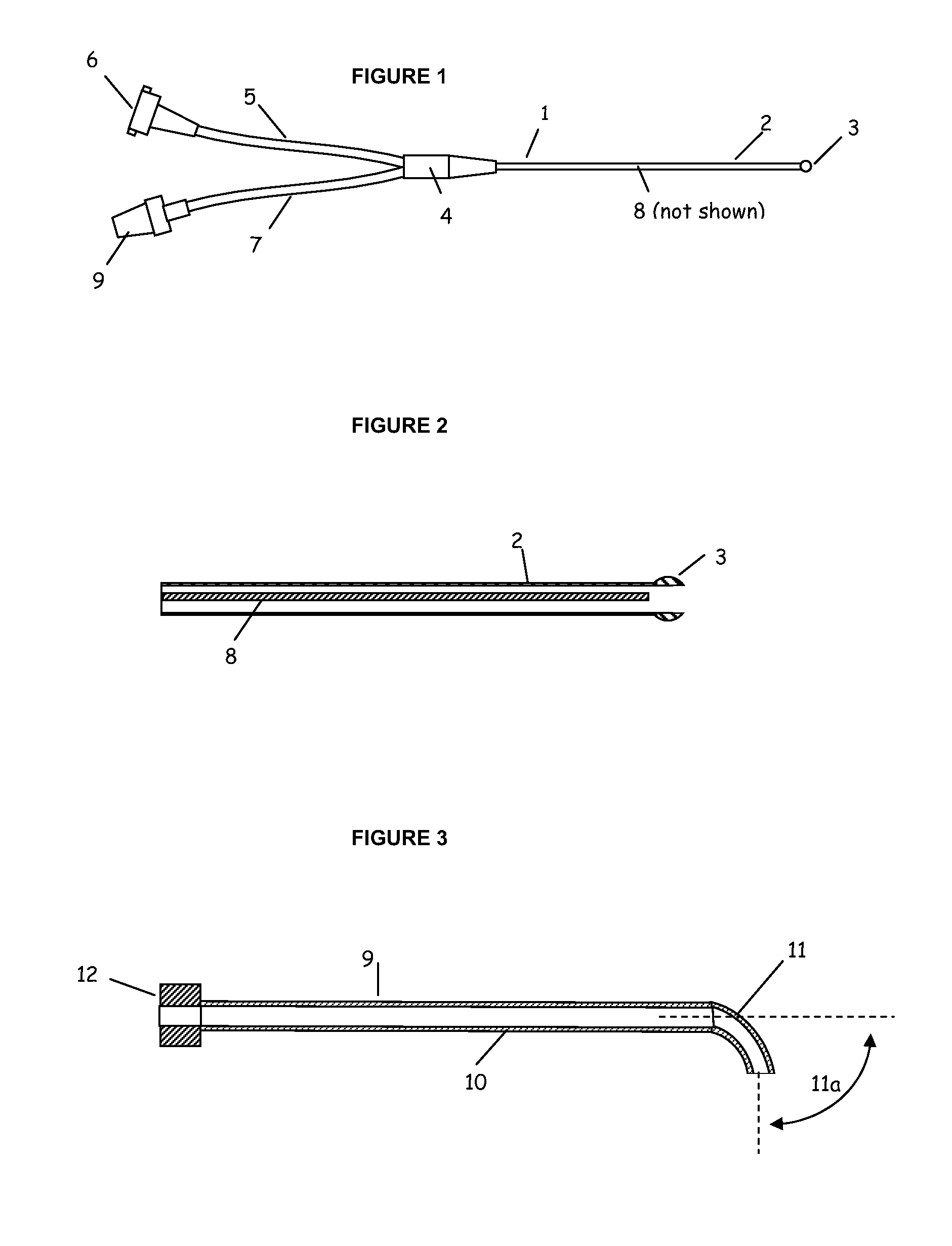
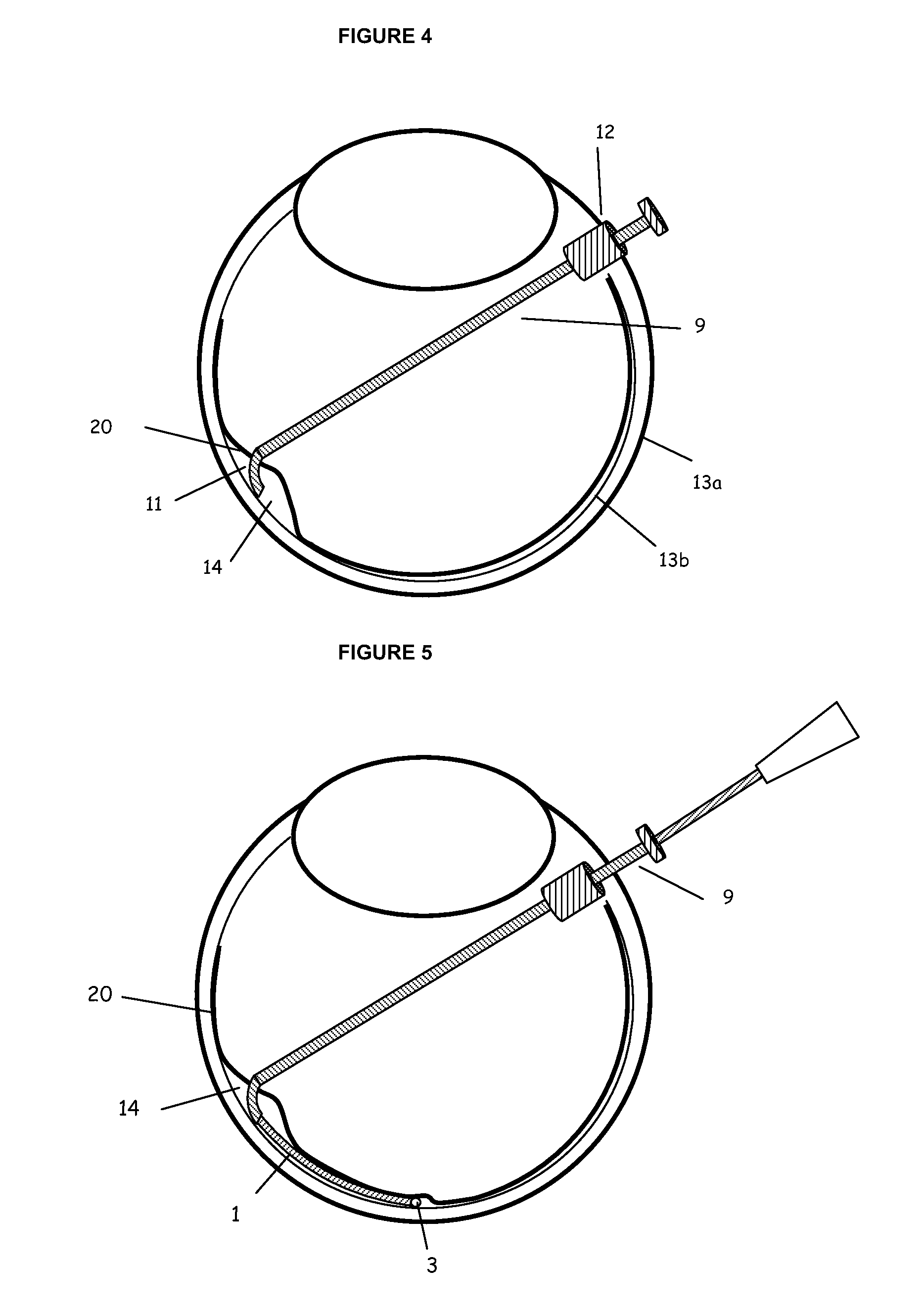
Methods and apparatus for sub-retinal catheterization
Devices and methods are provided for access to the sub-retinal space that lies between the retina and the choroid in order to introduce therapies to the retina and more specifically to the sensory retina and RPE, particularly in the region of the macula. The devices comprise a catheter that incorporates advantageous size, flexibility and tip features to properly, accurately and atraumatically access the sub-retinal space. Ancillary devices to assist in placing catheters into the sub-retinal space are also provided. The catheter devices incorporate a lumen for delivery of therapeutic substances or devices into the eye.
Owner:ISCI INTERVENTIONAL CORP
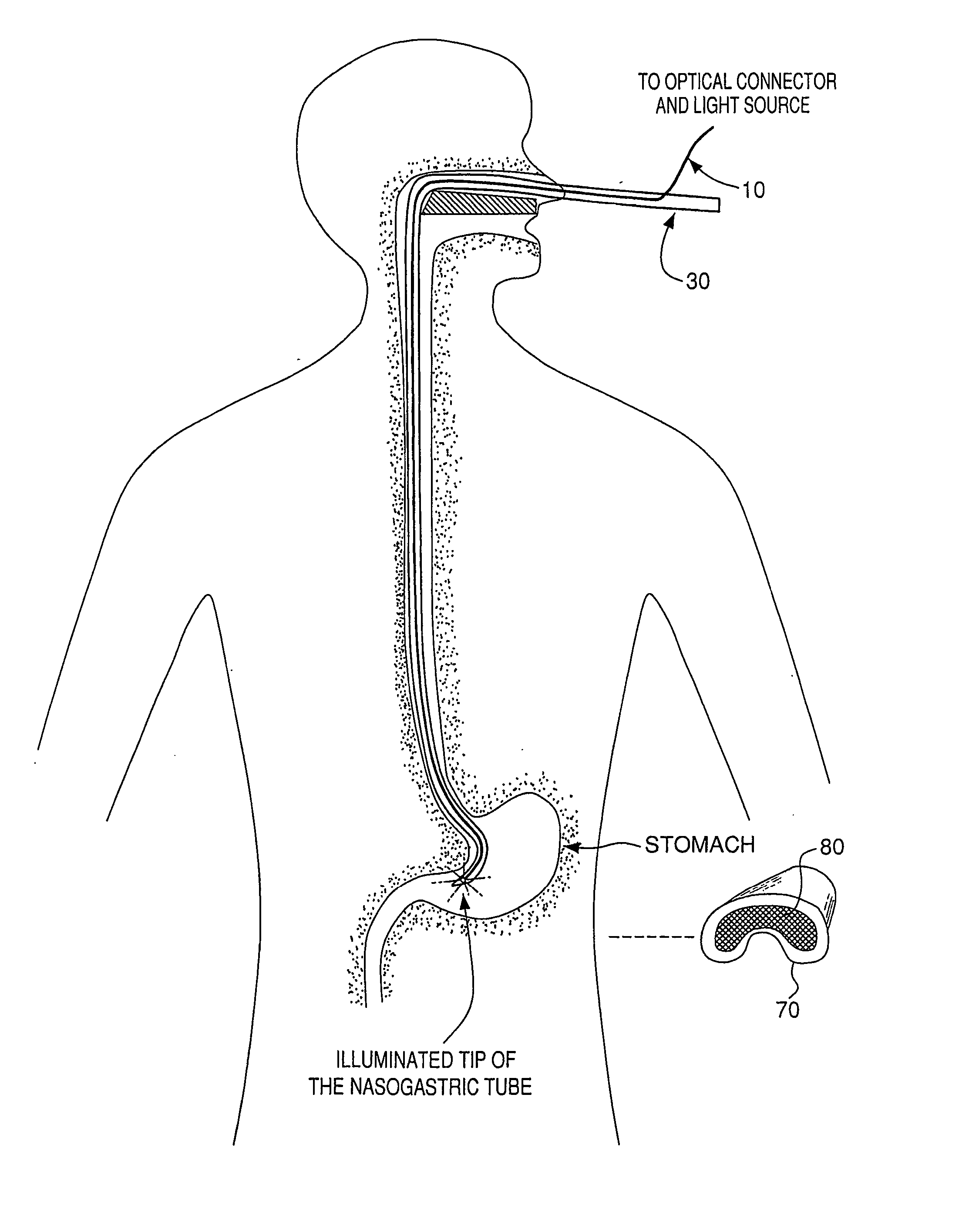
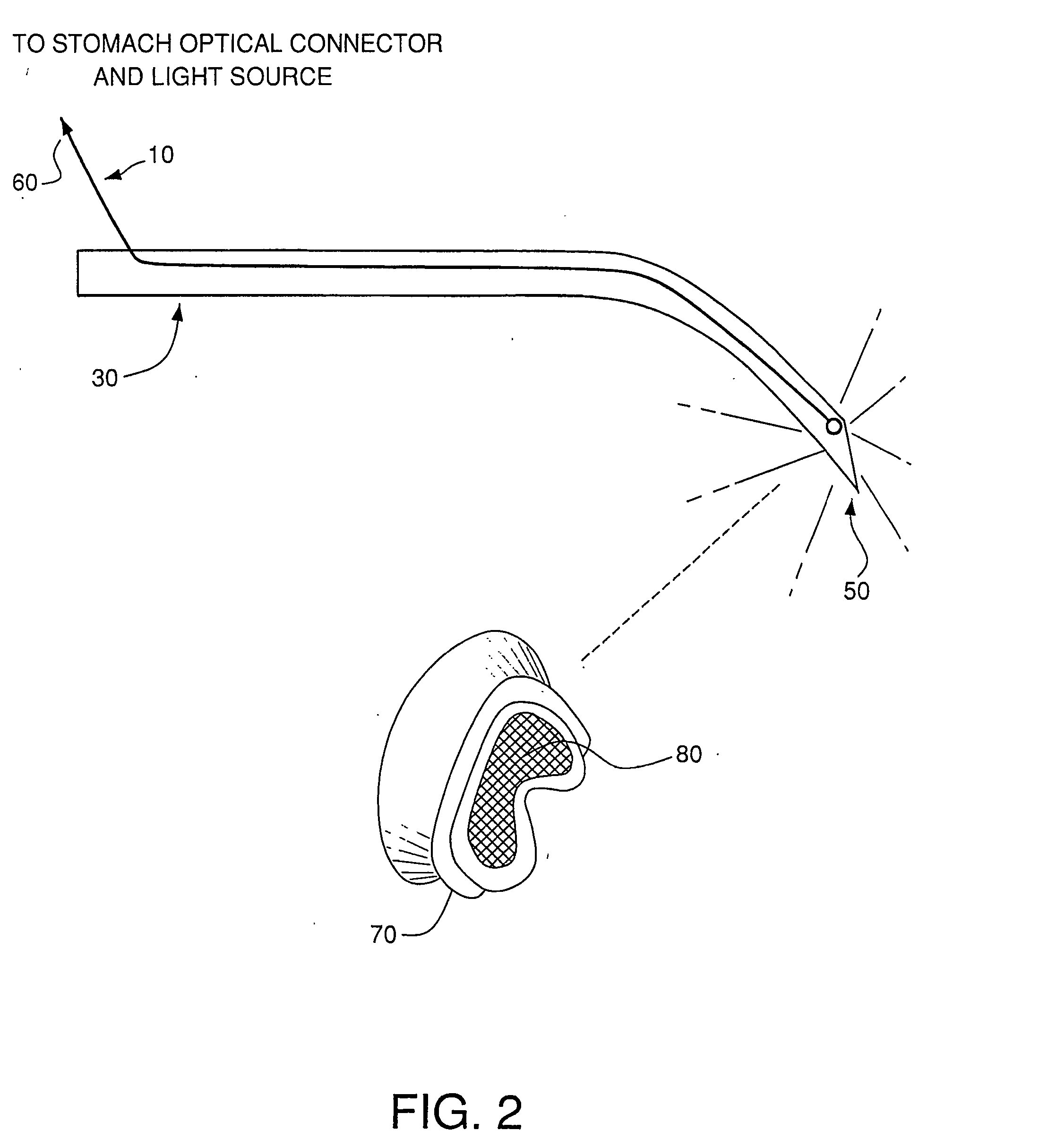
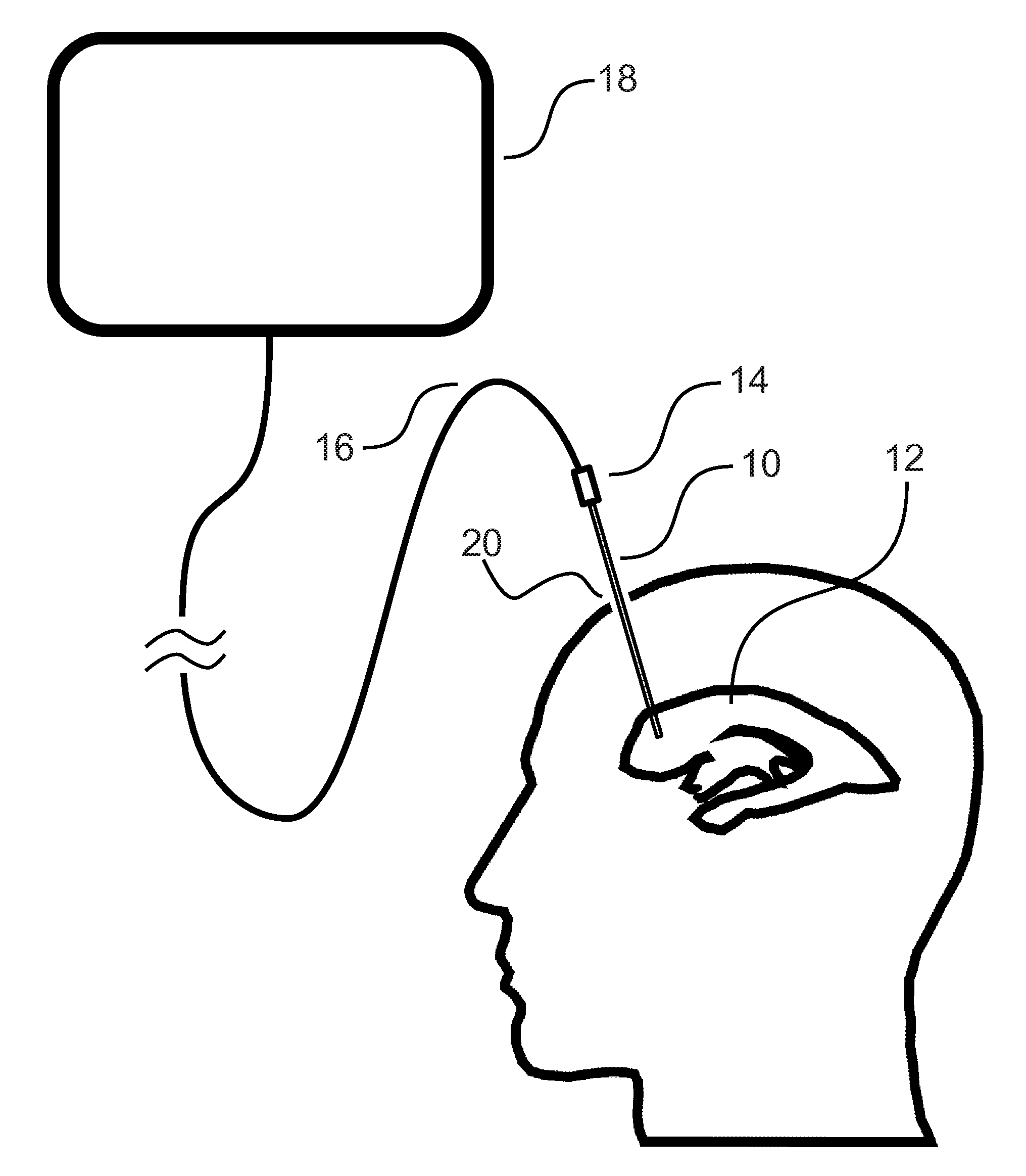
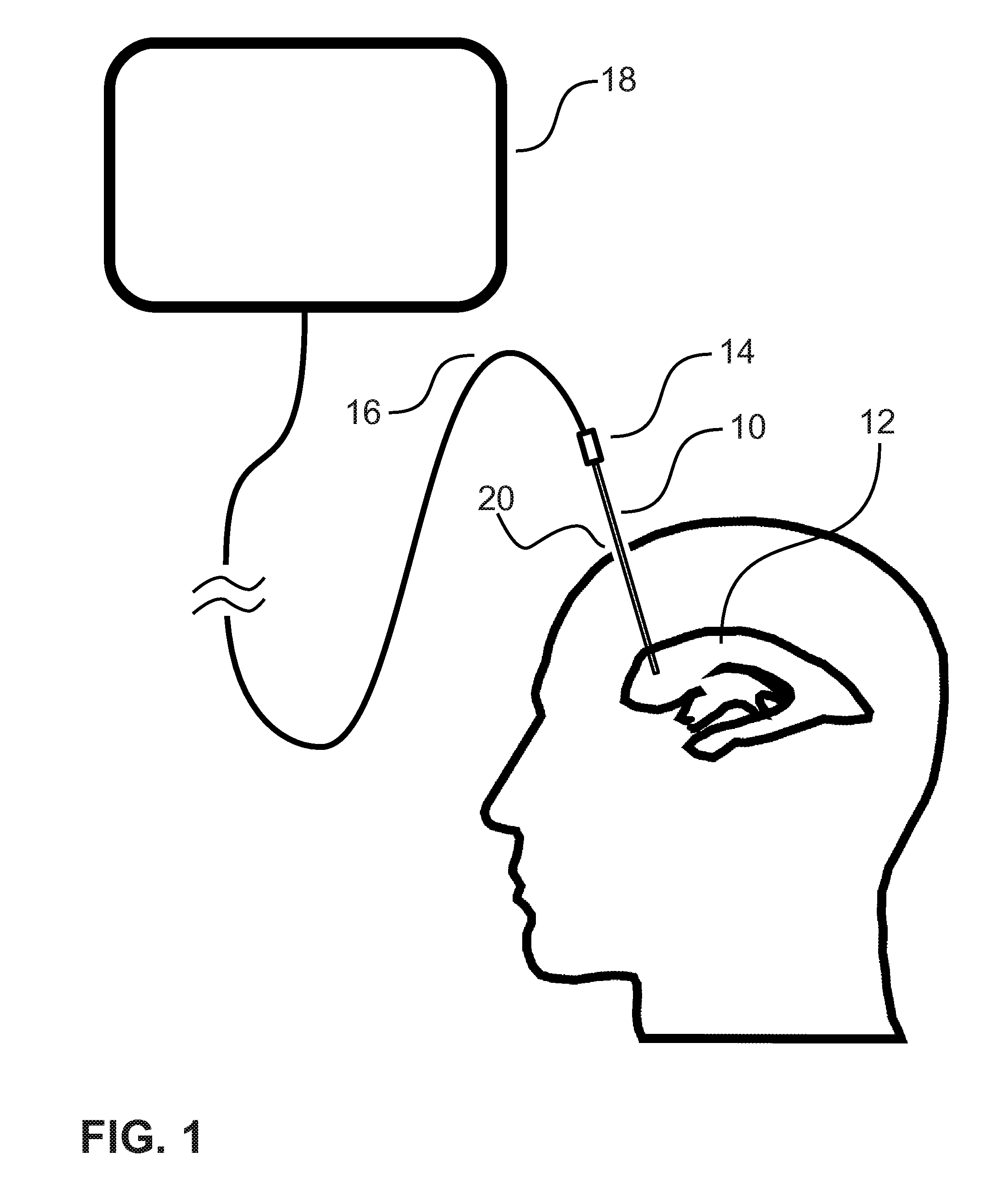
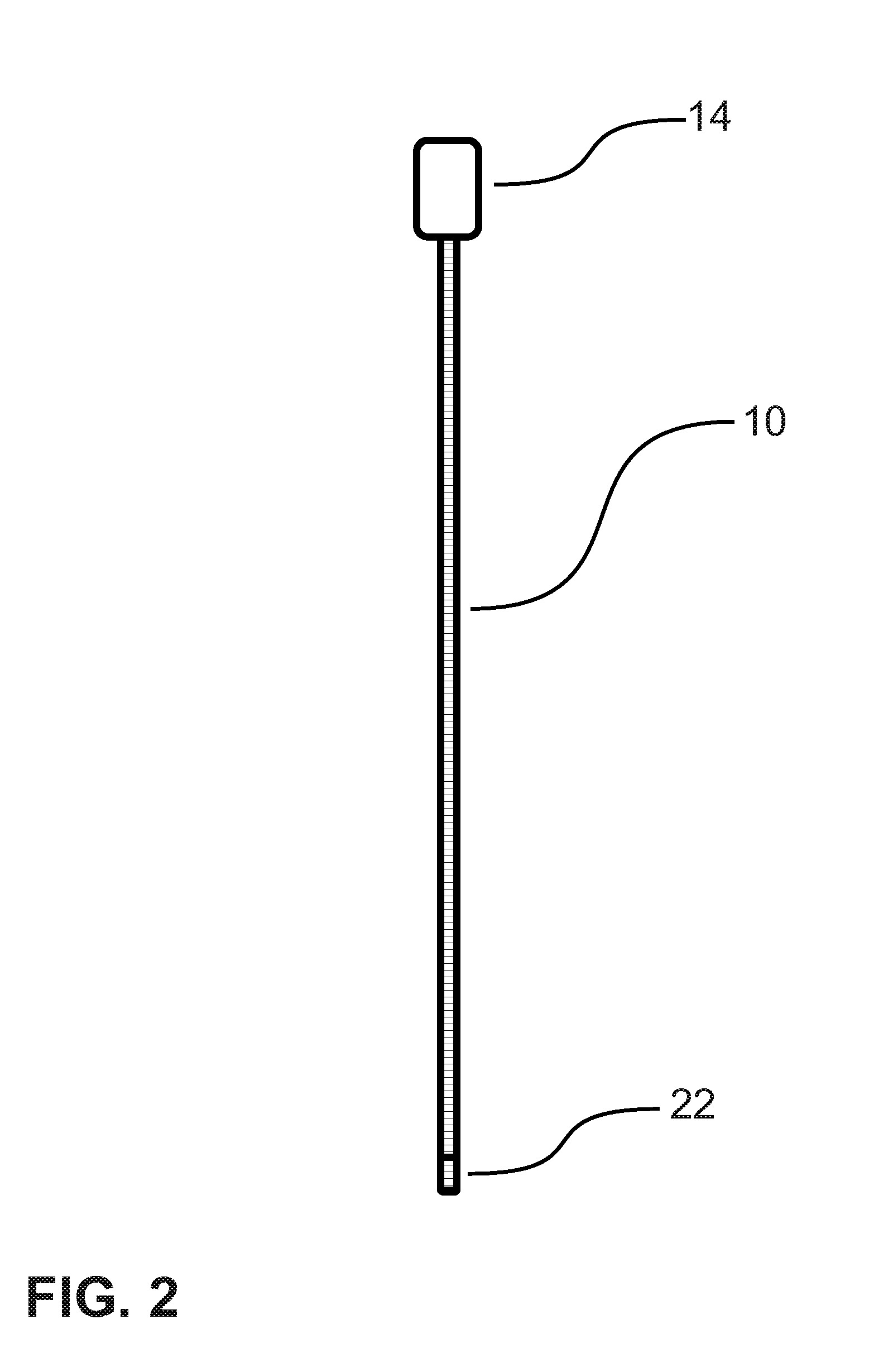
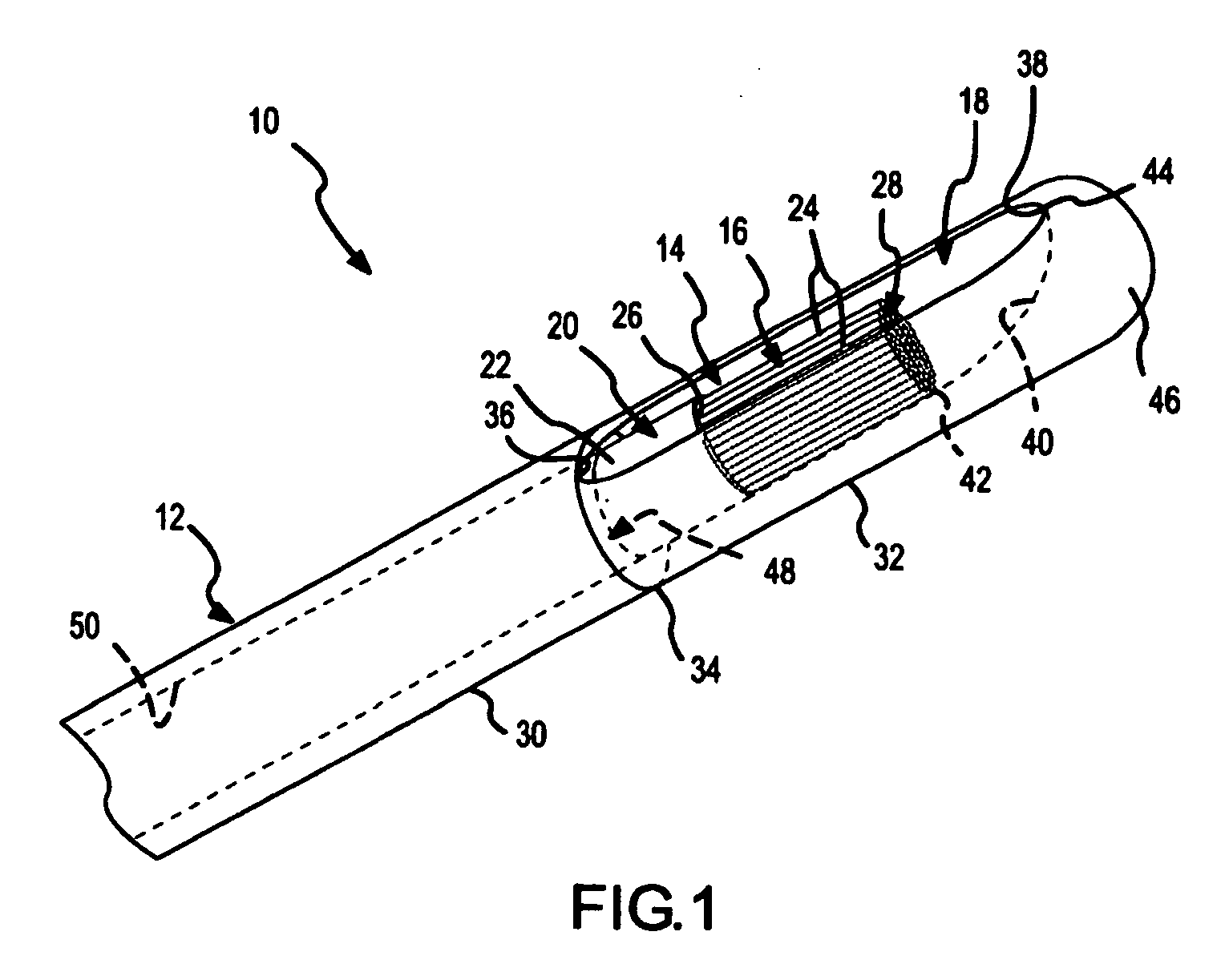
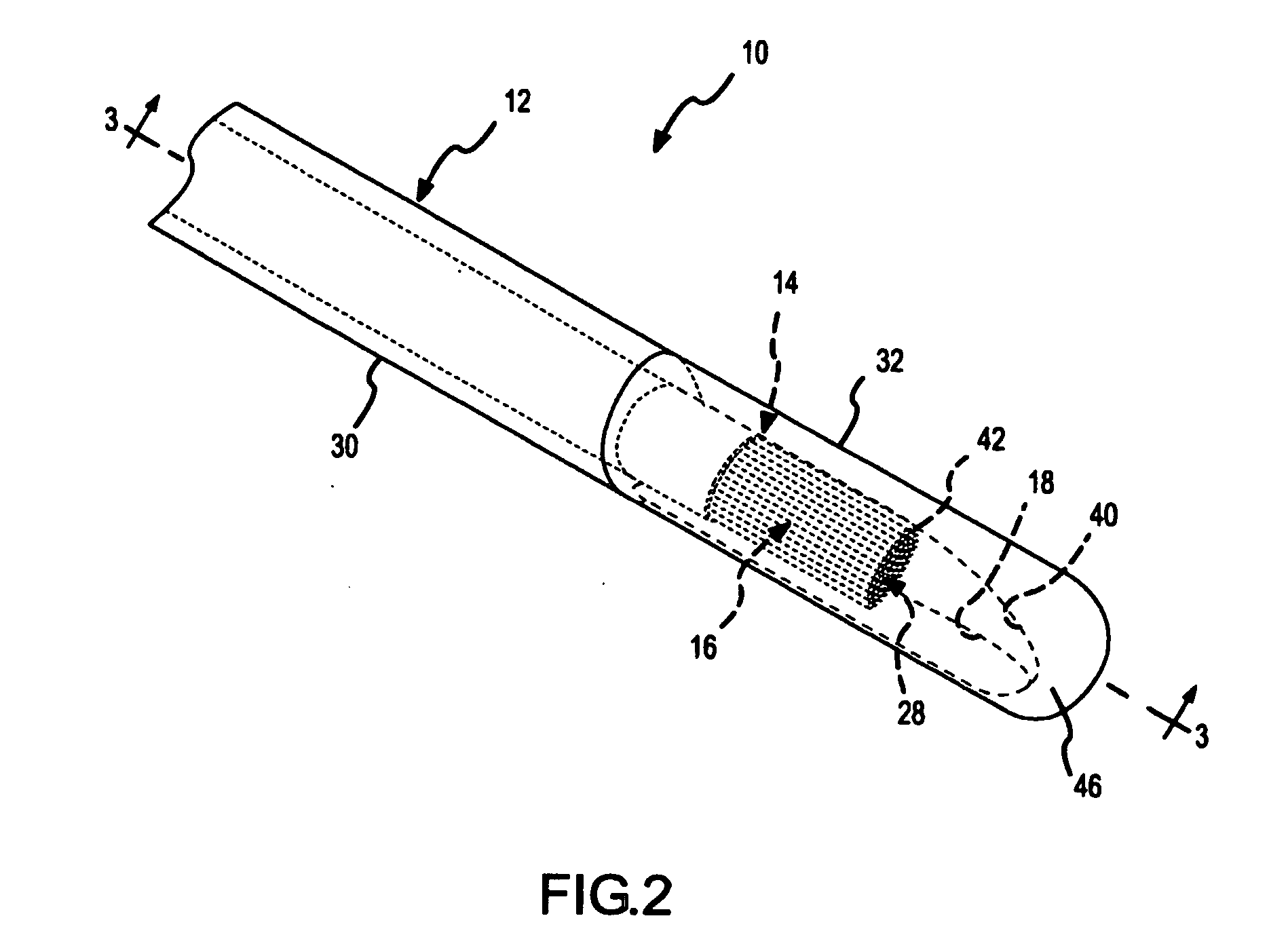
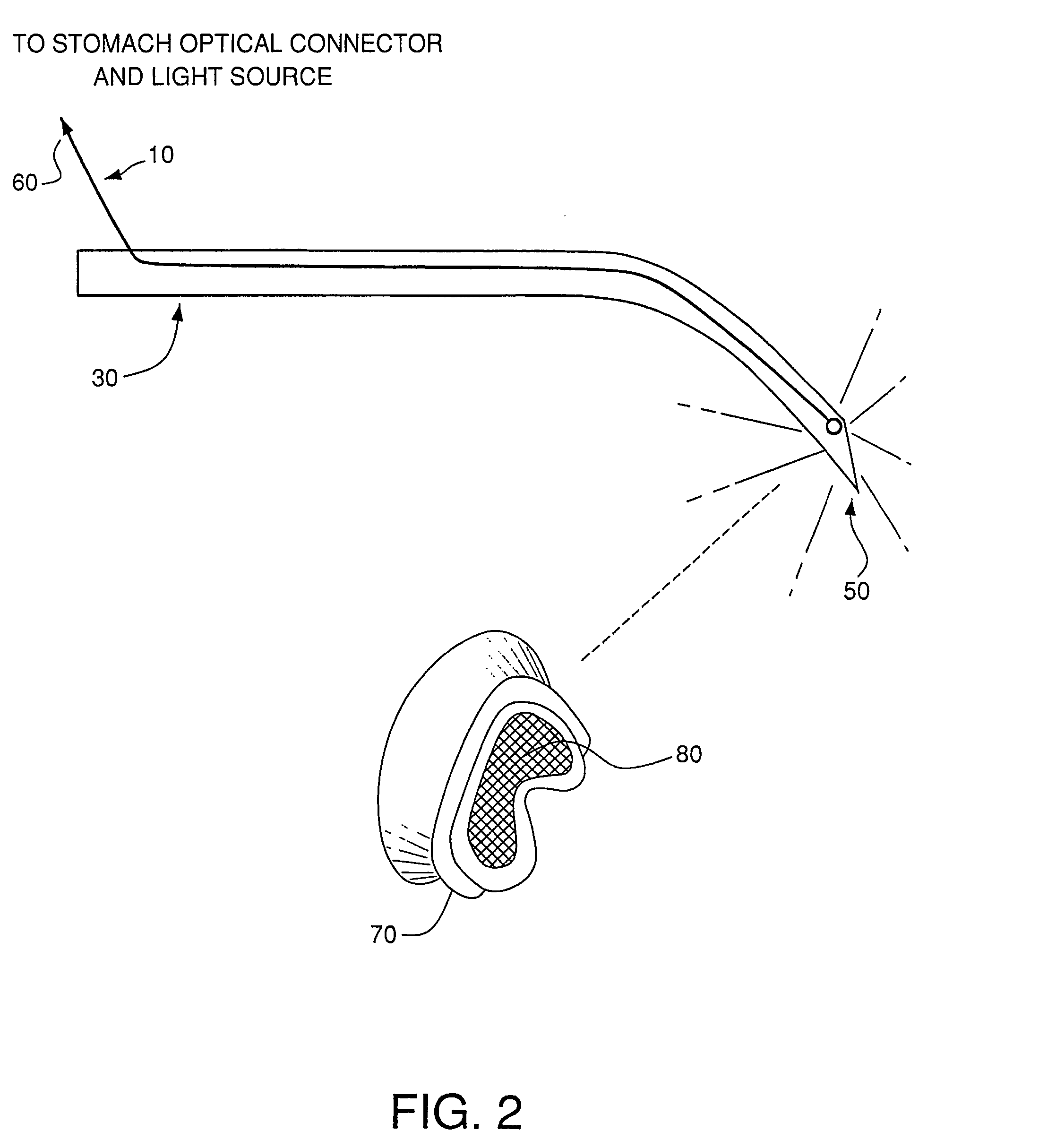
Three-dimensional optical guidance for catheter placement
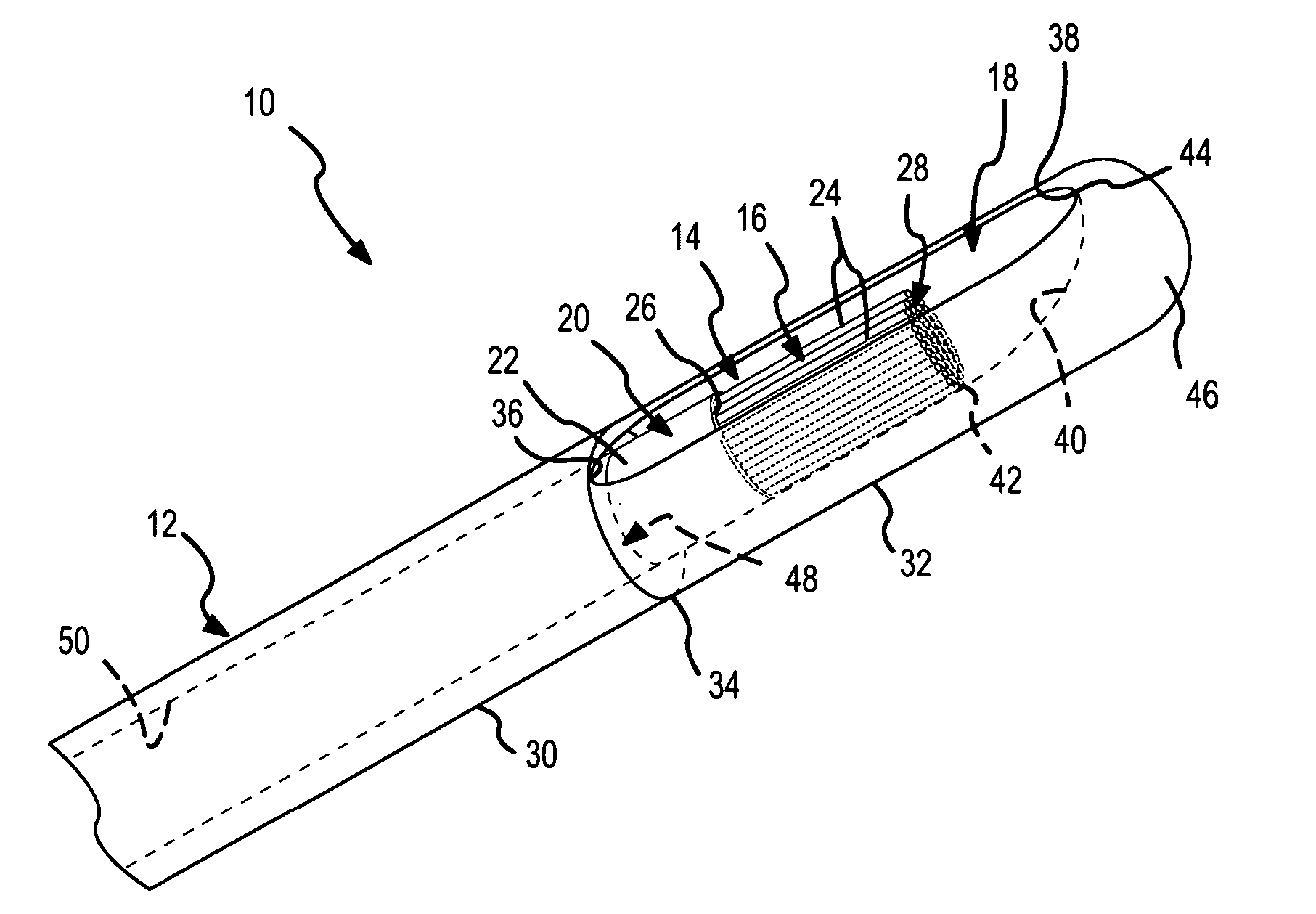
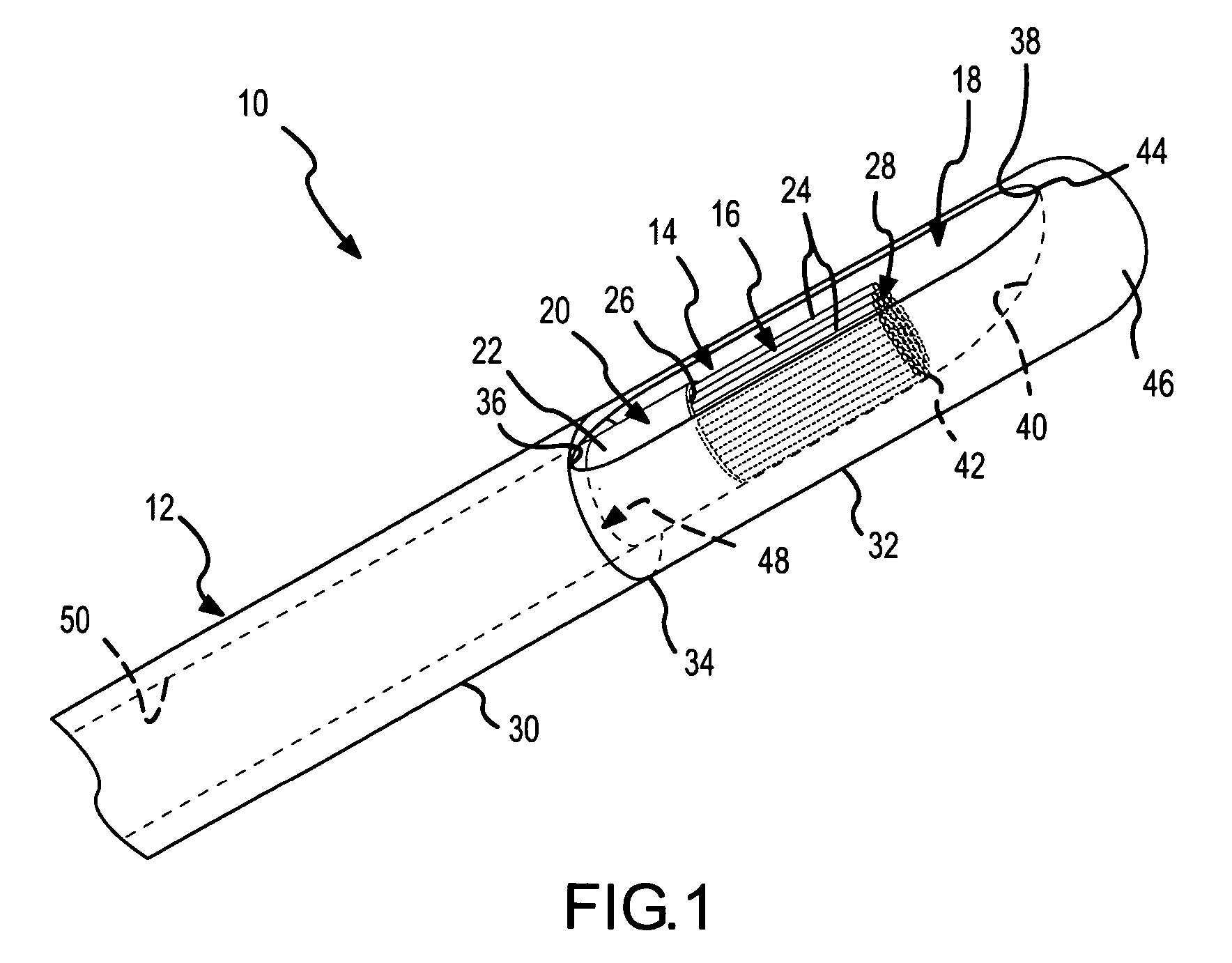
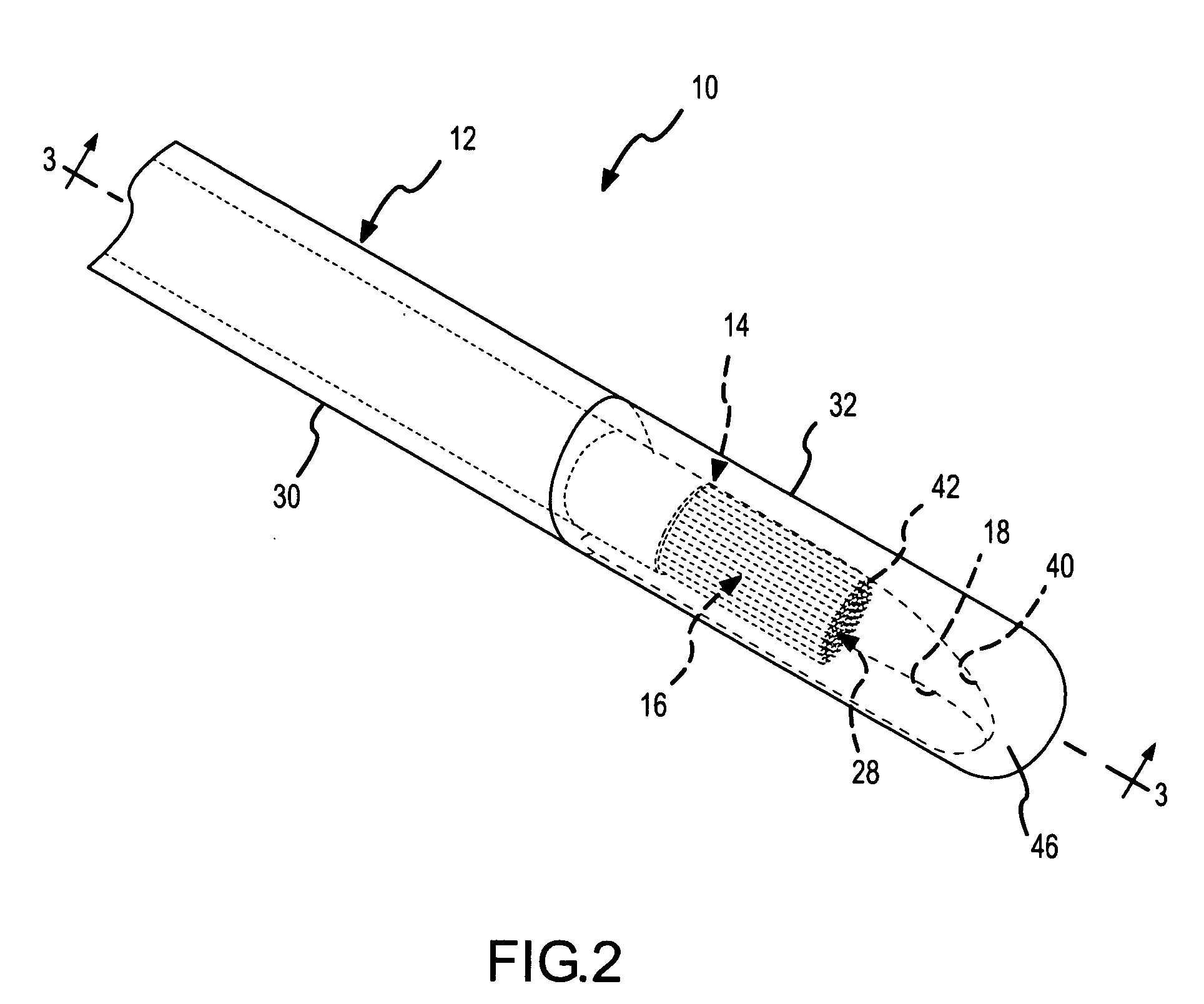
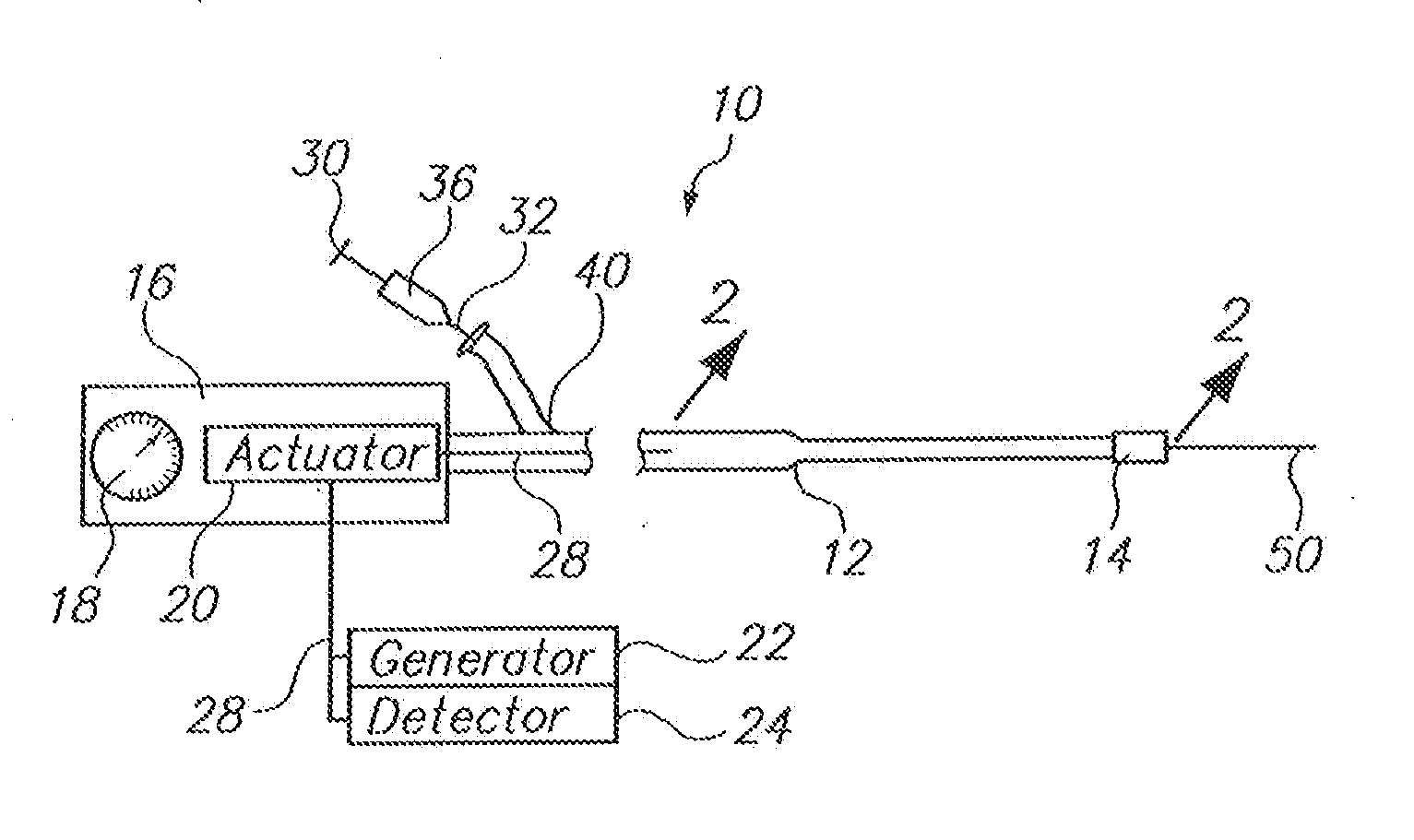
InactiveUS20080039715A1Quick placementAccelerated settlementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLight emitting deviceCatheter placement
A system is provided comprising an optically-guided catheter having a proximal end, a distal end, and at least one lumen. A light-emitting means is coupled to the catheter, the catheter is inserted into place in the patient, and light is emitted as a point or points from a selected location, usually the distal tip, of the catheter to which it is coupled. The system further comprises an external detection device that detects the transdermally projected light, emitted by the light-emitting point from within the patient, thereby indicating precise placement of the catheter within the patient. A system and method for three-dimensional visualization using an internally positioned light emitter and an externally positioned detection array are also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Magnetic navigation manipulation apparatus
InactiveUS20060144407A1Shorten the timeEasy accessCatheterSurgical manipulatorsMarine navigationBlood vessel
The inventive apparatus may be inserted into a guiding catheter or other thru-lumen catheters and tubing to assist in navigating and placing the distal end of the guiding catheter or other thru-lumen catheters and tubing at a target location within a patient, by utilizing an externally applied magnetic field to align a plurality of magnetically responsive elements on the apparatus towards the target location. The guiding catheter or other thru-lumen catheters and tubing is then advanced and guided by the apparatus, which facilitates access of the guiding catheter or other thru-lumen catheters and tubing to the target vessel to save time during the catheter placement procedure. The apparatus in combination with magnetic navigation also provides support to hold the guiding catheter or other thru-lumen catheters and tubing in place to resist back out of the catheter.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
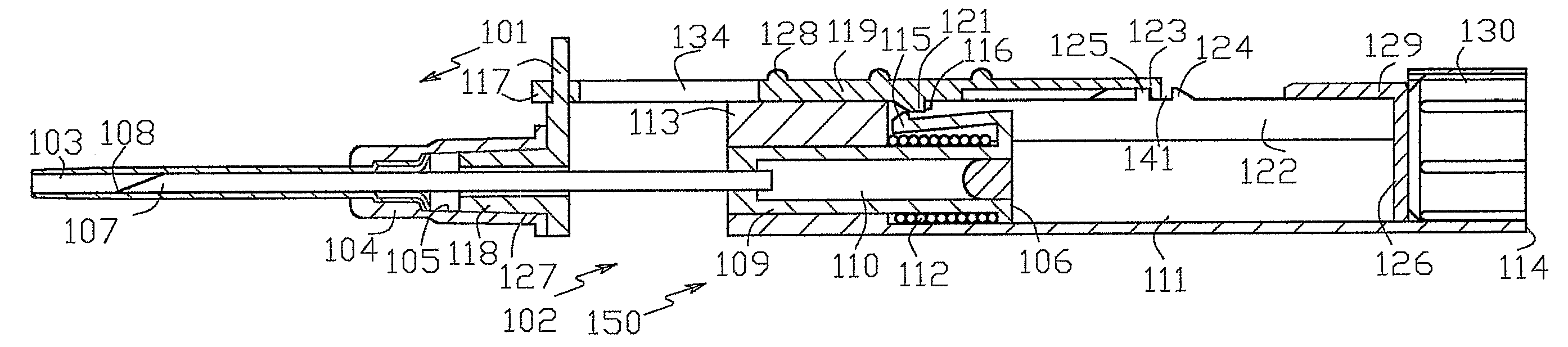
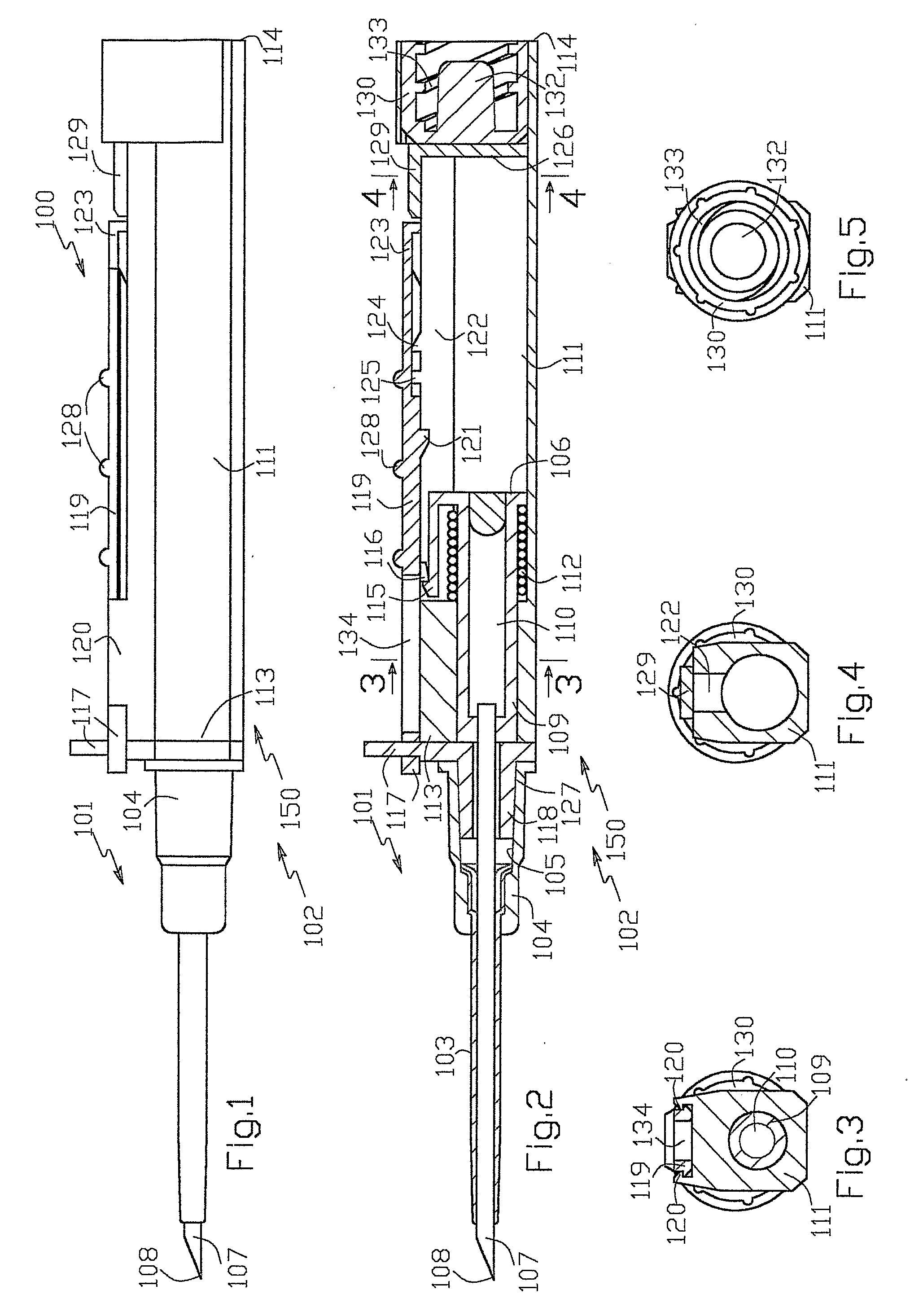
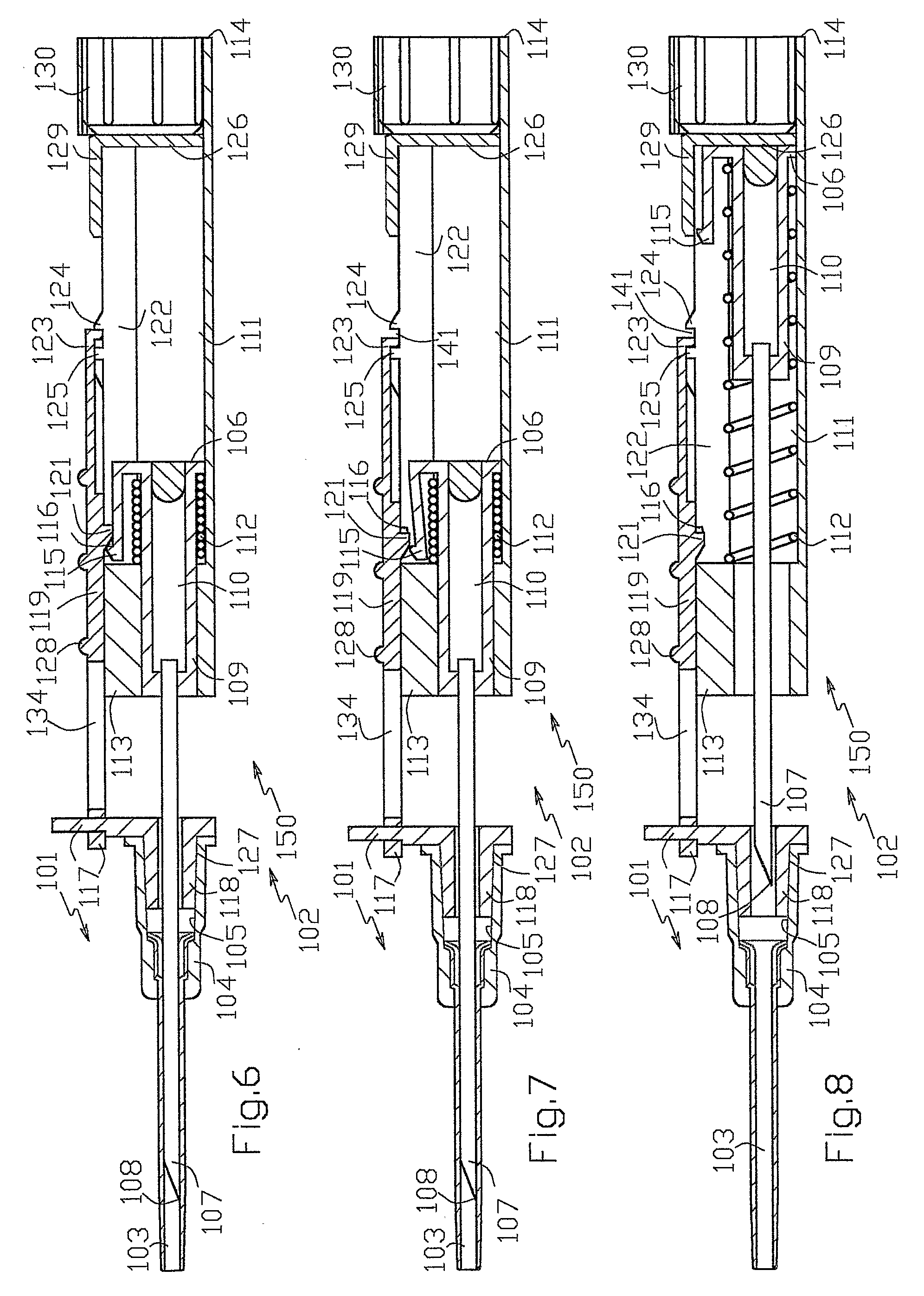
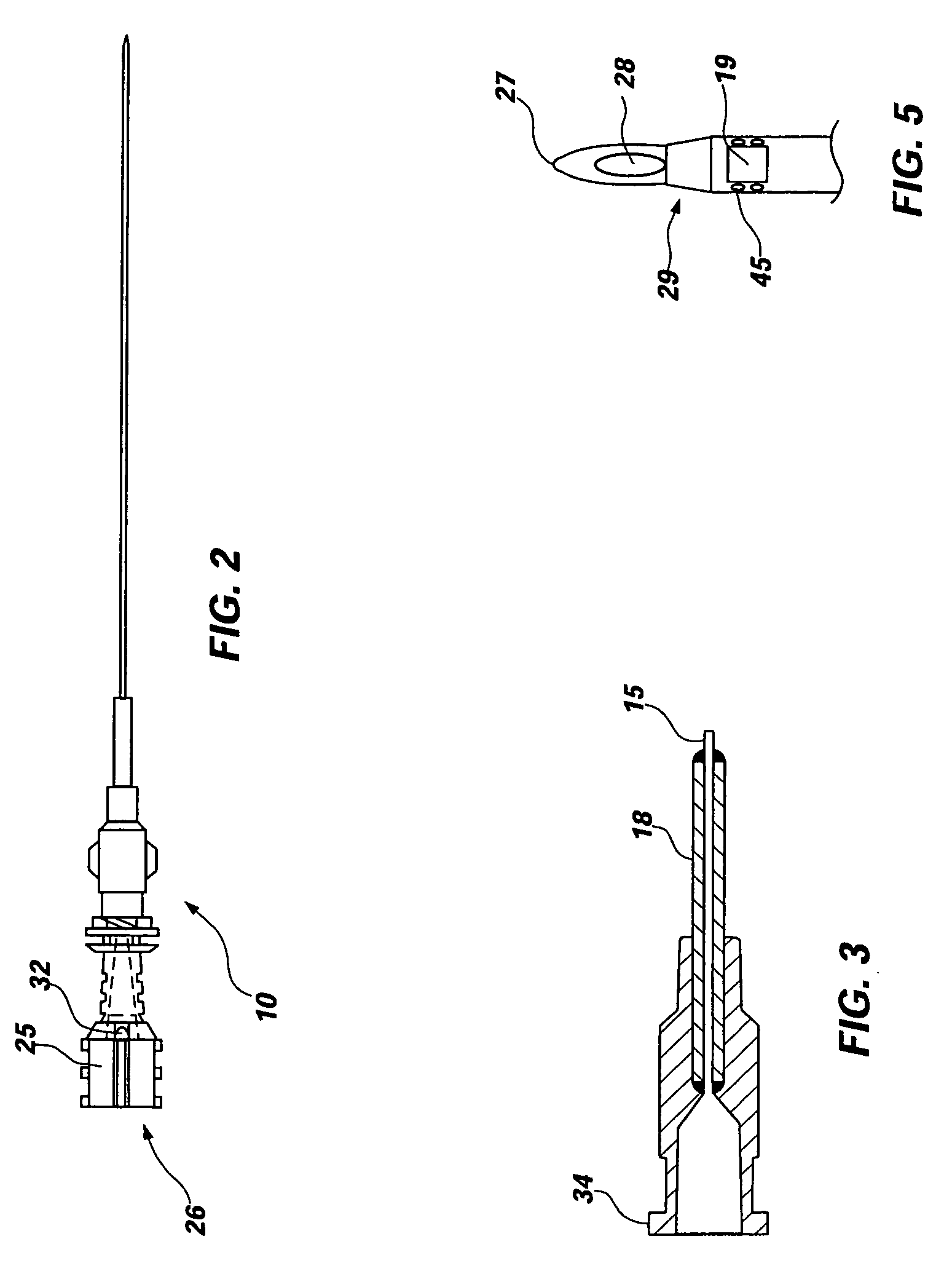
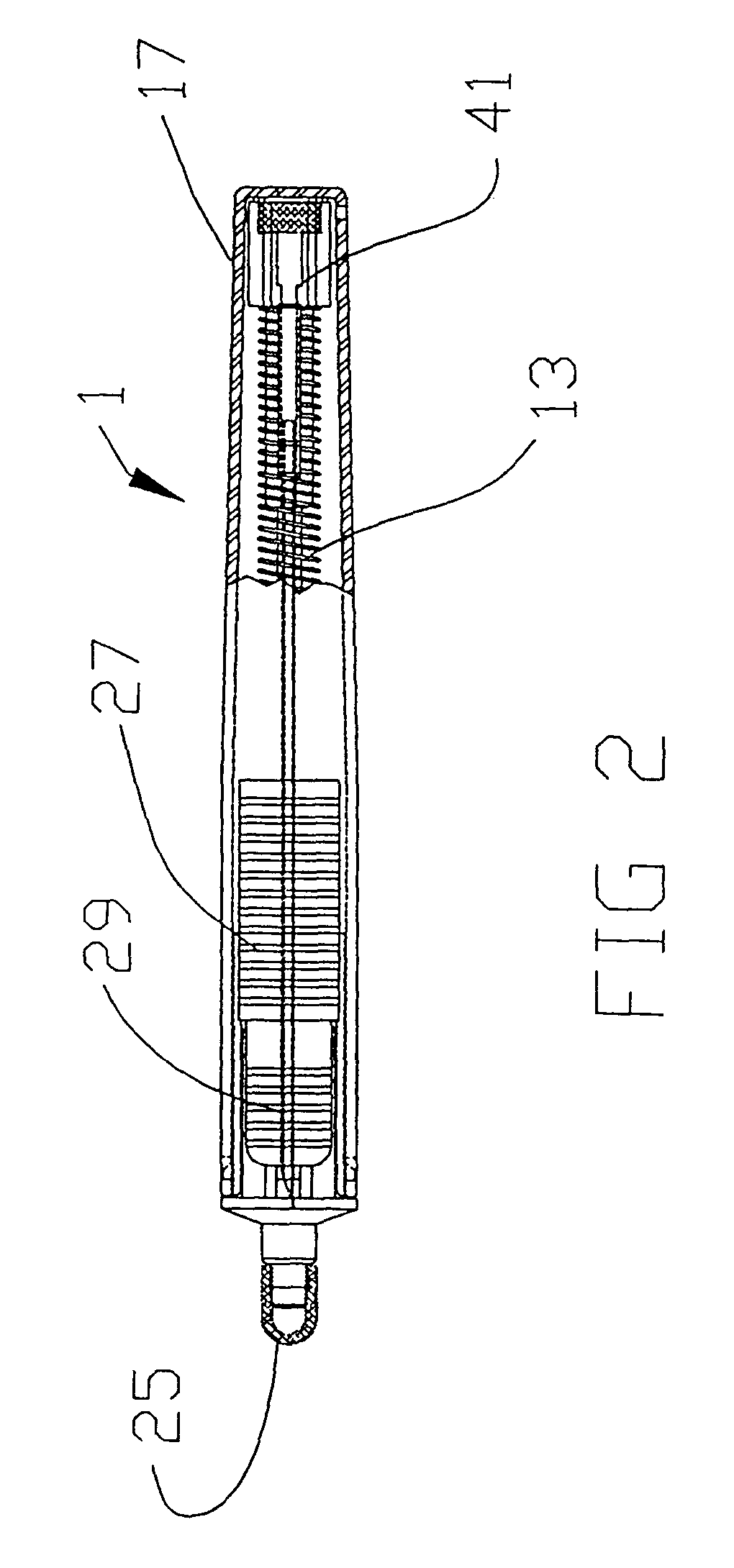
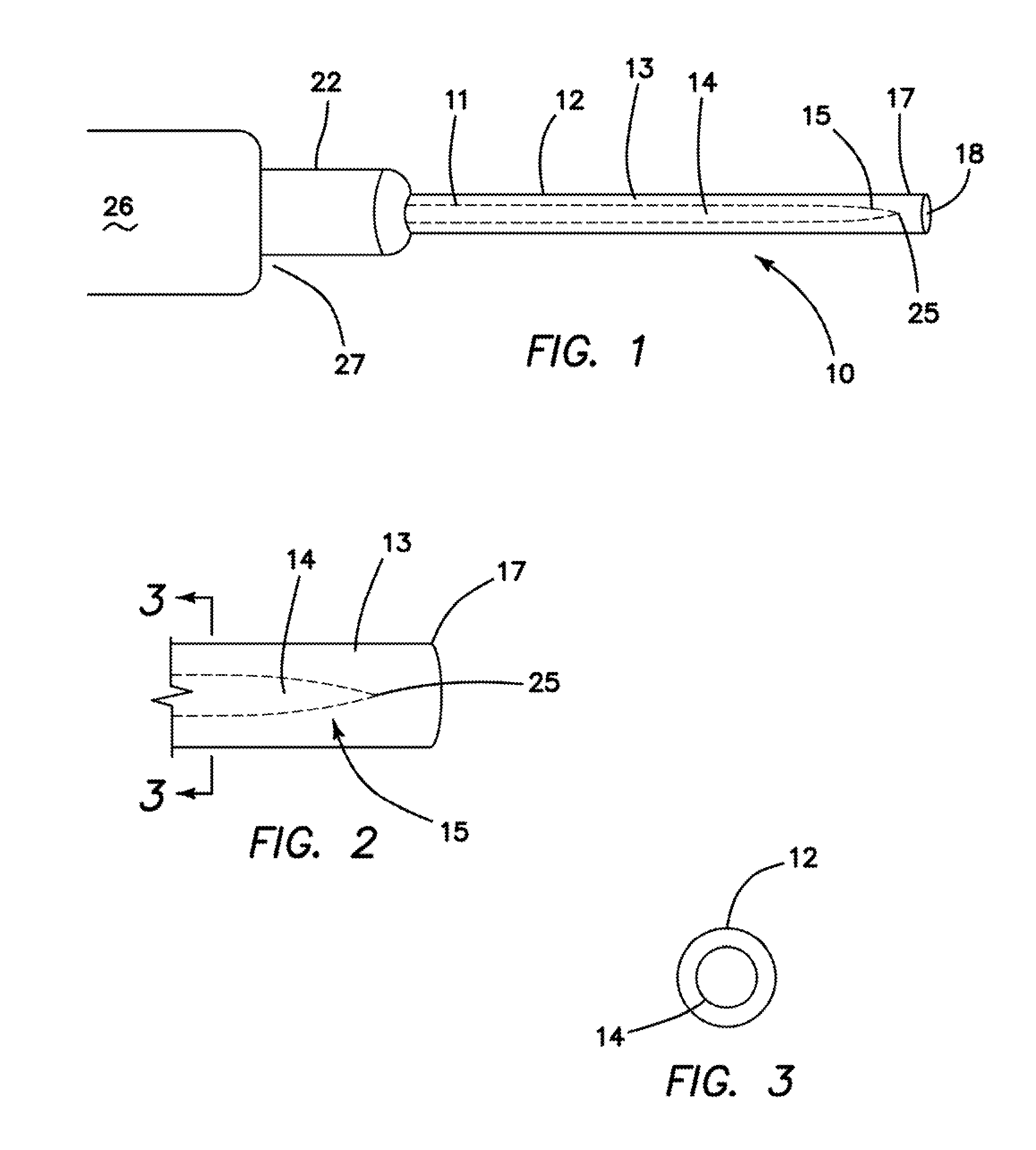
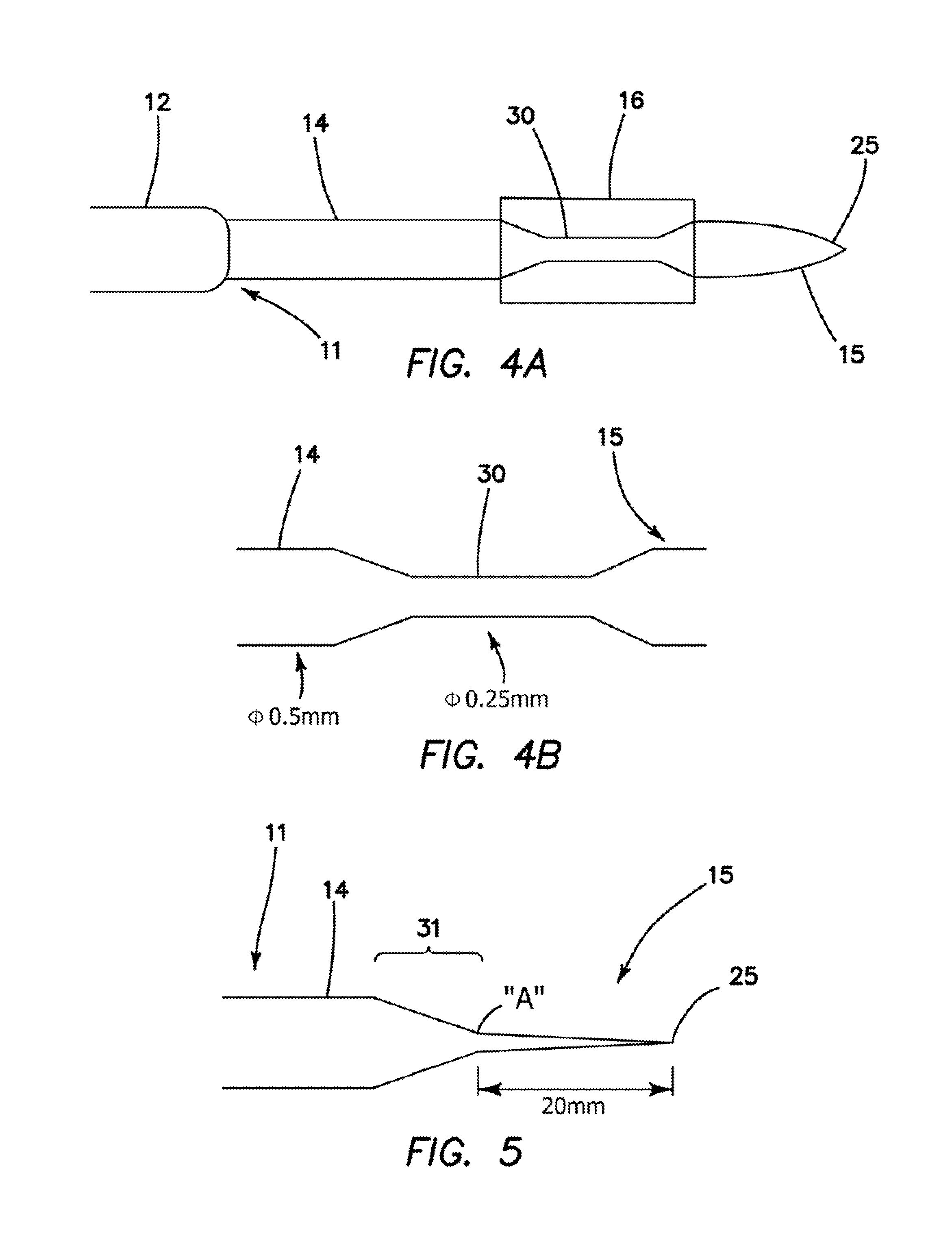
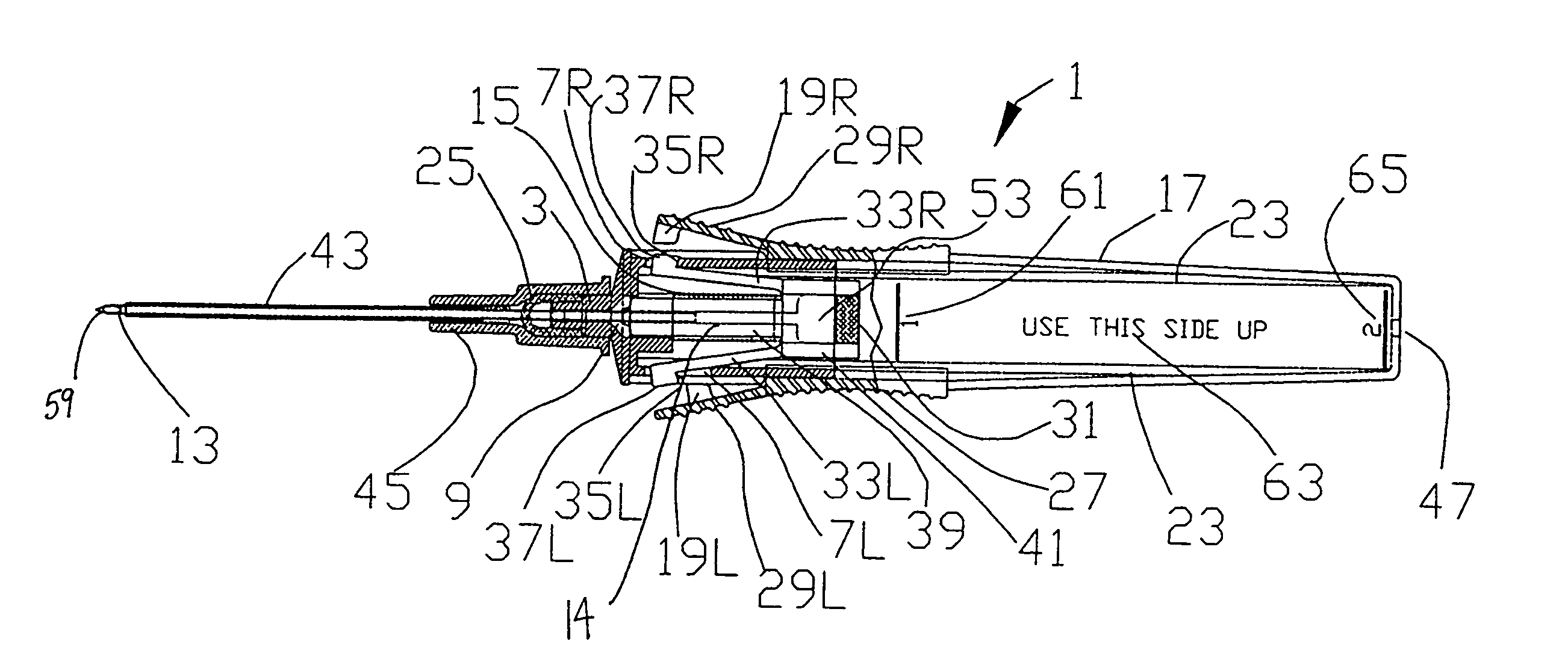
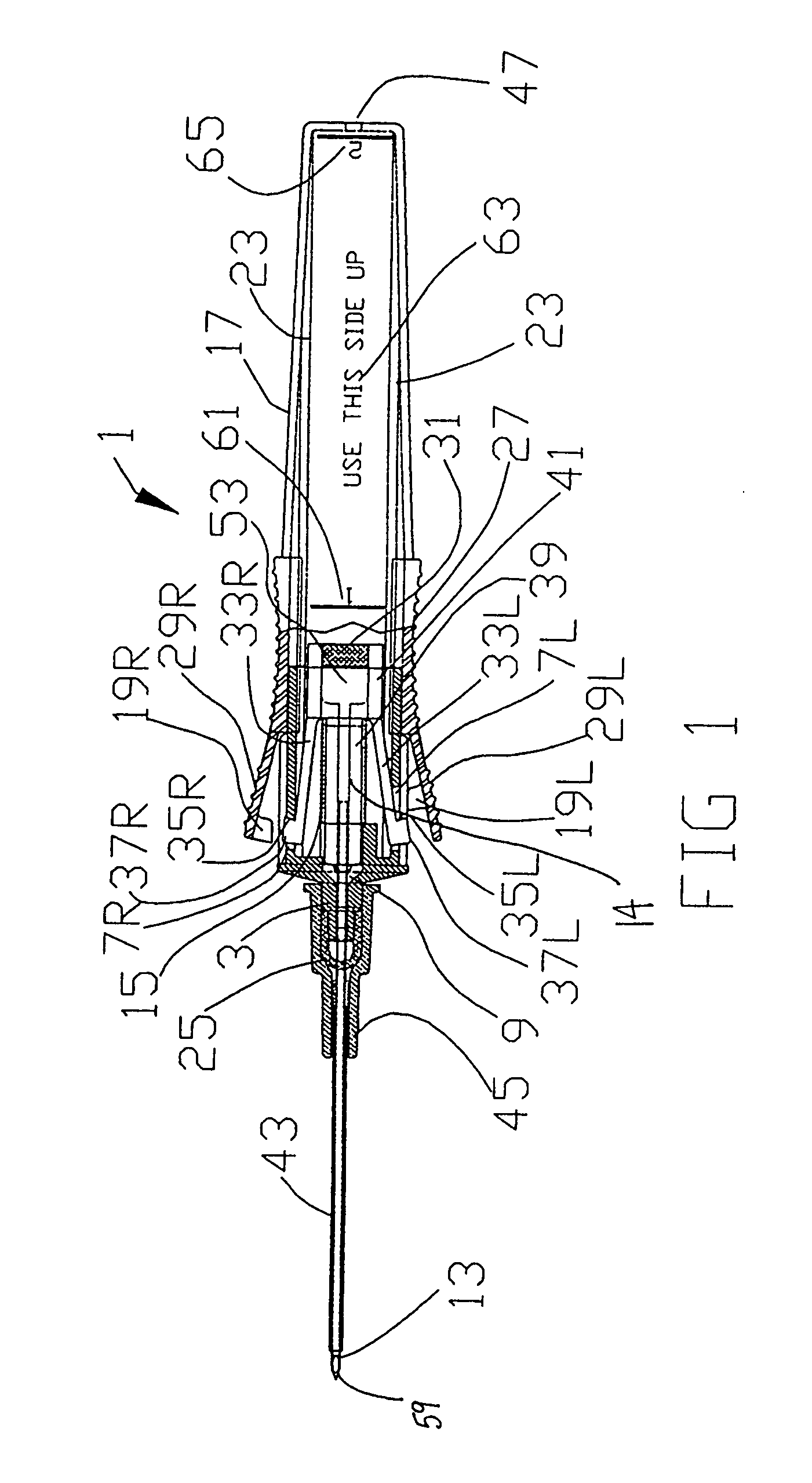
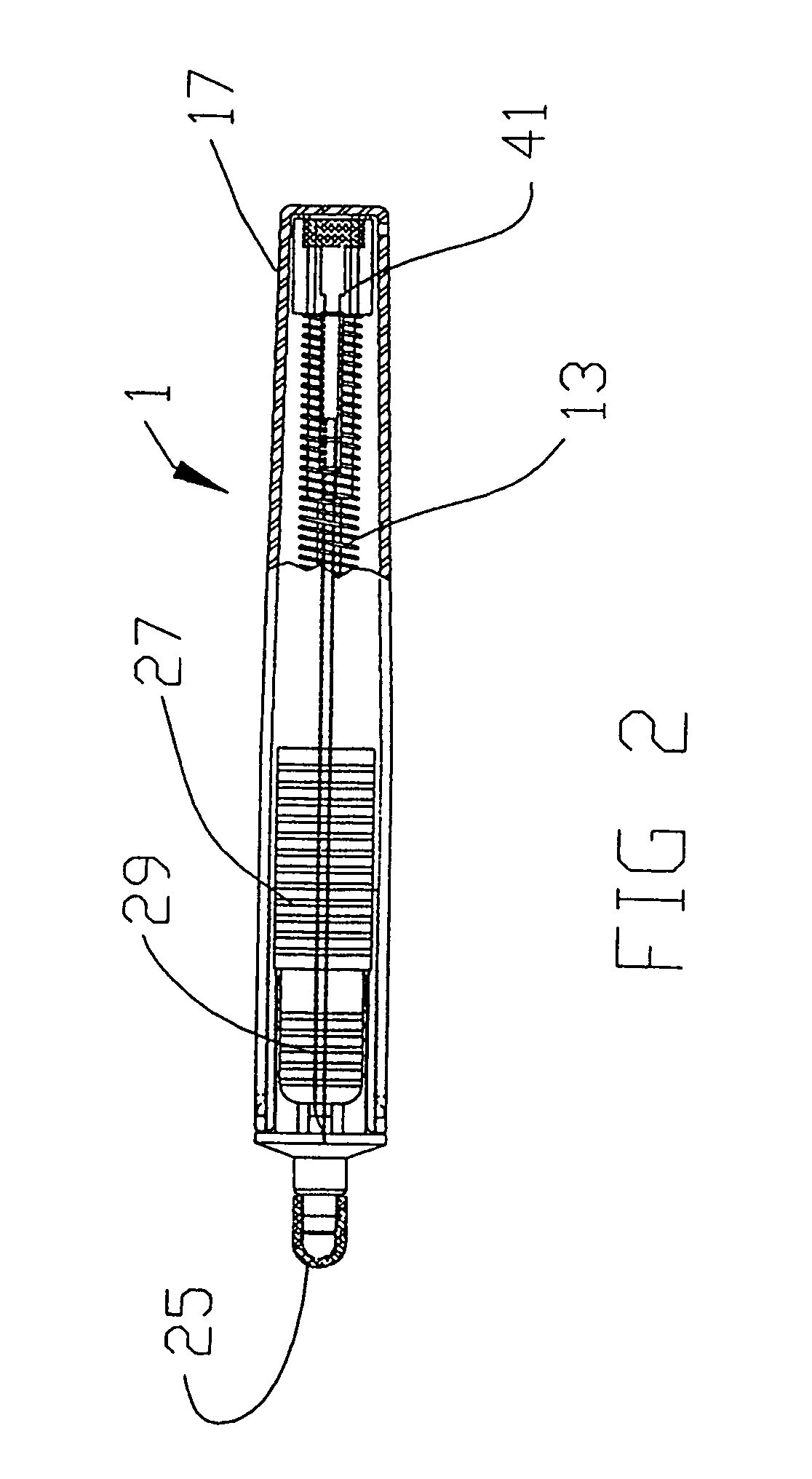
Catheter placement device
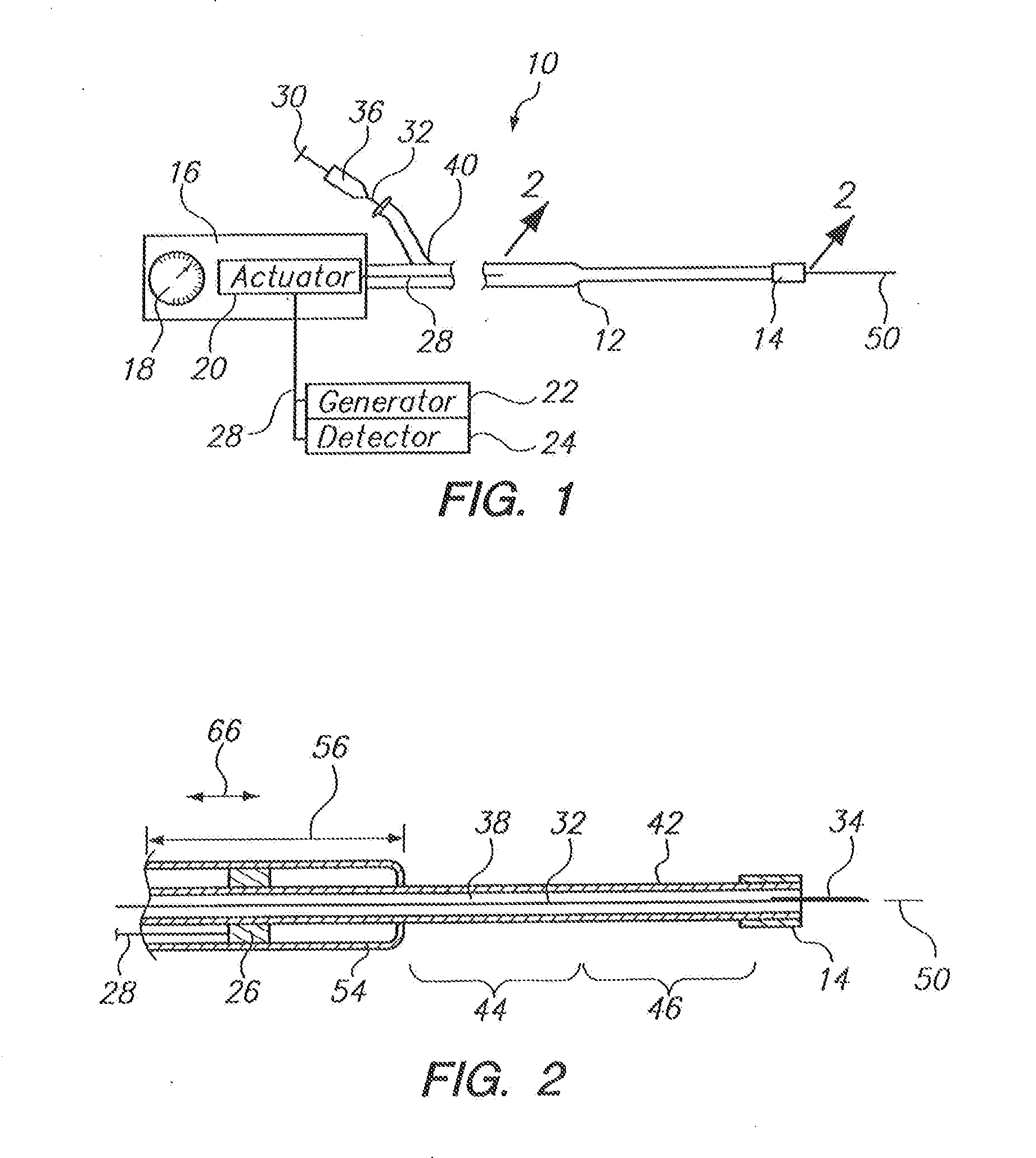
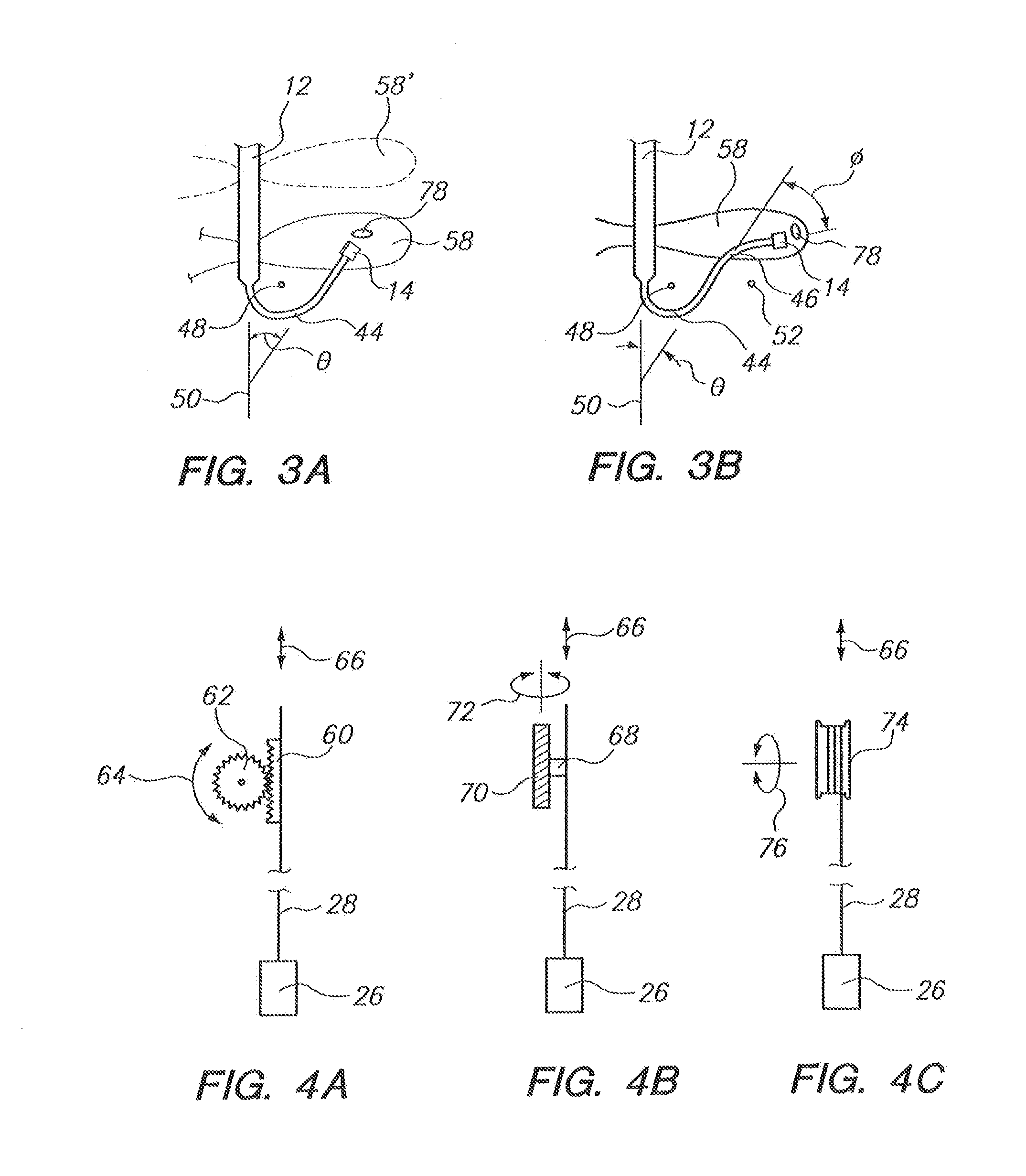
InactiveUS20090131872A1Avoiding catheter bleedingGood for observationGuide needlesInfusion syringesVeinCam
Abstract A catheter placement device (see FIG. 2) includes a needle unit, which in an initial position is releasably engaged with a housing distal end and has a sharp needle passing through a catheter and protruding distally of it. There is also a telescopic protector including guard unit, which is sliding in a housing guide. After inserting the needle into patient's vein, operator one-handedly pushes the guard unit distally, thereby emplacing the catheter, displacing the protector into a full length position and locking therein, and passively disengaging the needle unit from the hosing by a trigger cam located on the guard unit. As a result, a retracting spring moves a needle into retracted position, wherein it is protected from any contact with personal. Then, operator disconnects the guard from the catheter, turns the housing and occludes the catheter entrance with a cap, which was detachably mounted on the housing.
Owner:POPOV
Microelectrode catheter for mapping and ablation
InactiveUS7047068B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyMicroelectrodeCatheter placement
Catheter for mapping and / or ablation, and methods of using the same. According to one embodiment, catheter includes a metallic cap having a plurality of apertures and at least one electrode disposed in each aperture of the plurality of apertures. According to another embodiment, the catheter includes a non-conductive cap having a plurality of apertures and at least one electrode disposed in each aperture of the plurality of apertures. Electrodes may be paired, arranged along the length of the cap, or circumferentially arranged on the cap, according to various embodiments. According to a further embodiment, a method for treating a condition of a heart includes placing a catheter inside the heart, mapping a region of the heart using mapping electrodes on the catheter, and ablating using an ablation electrode disposed about the mapping electrodes of the catheter.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Safety spinal catheter
InactiveUS20050090801A1Simple and straightforward catheter insertionEasy and faster flowGuide needlesInfusion syringesSpinal columnCatheter Gauge
An apparatus and method to insert a spinal catheter and minimize incidence of post dural puncture headache. The apparatus typically includes a support needle with a non-cutting piercing tip and an exteriorly mounted catheter. The catheter gauge is reduced, while ease of use is increased by the exterior mounting. The catheter may include a kink sleeve that protects against kinking when bent during use. A central stylet maybe included to prevent entry of matter into the support needle opening during insertion. Methods using a single stick insertion procedure allow for catheter placement to be determined and adjusted based on physical feedback obtained during the single stick insertion.
Owner:CUSTOM MEDICAL APPL
Port stem marking for catheter placement
InactiveUS20050124980A1Minimize failureEasy to optimizeMedical devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismIn vivoAccess port
An access port having a marking located on the port stem to aid the physician in placing the catheter correctly onto the port stem, wherein a fluid channel is provided to allow liquid from the inner lumen of the catheter to flow into the chamber located inside the access port. In one variation, the marking indicates to the physician the proper distance to advance the port stem into the catheter for optimal connection. A catheter lock or other locking sleeves may be placed over the catheter and port stem connection to secure the catheter on the port stem. Since the preferred location for the placement of catheter may differ depending on the design of the port stem, such a marker may facilitate the placement of the catheter and avoid problems associated with physicians placing the catheter incorrectly, which could potentially result in in vivo leakage from the catheter.
Owner:CR BARD INC
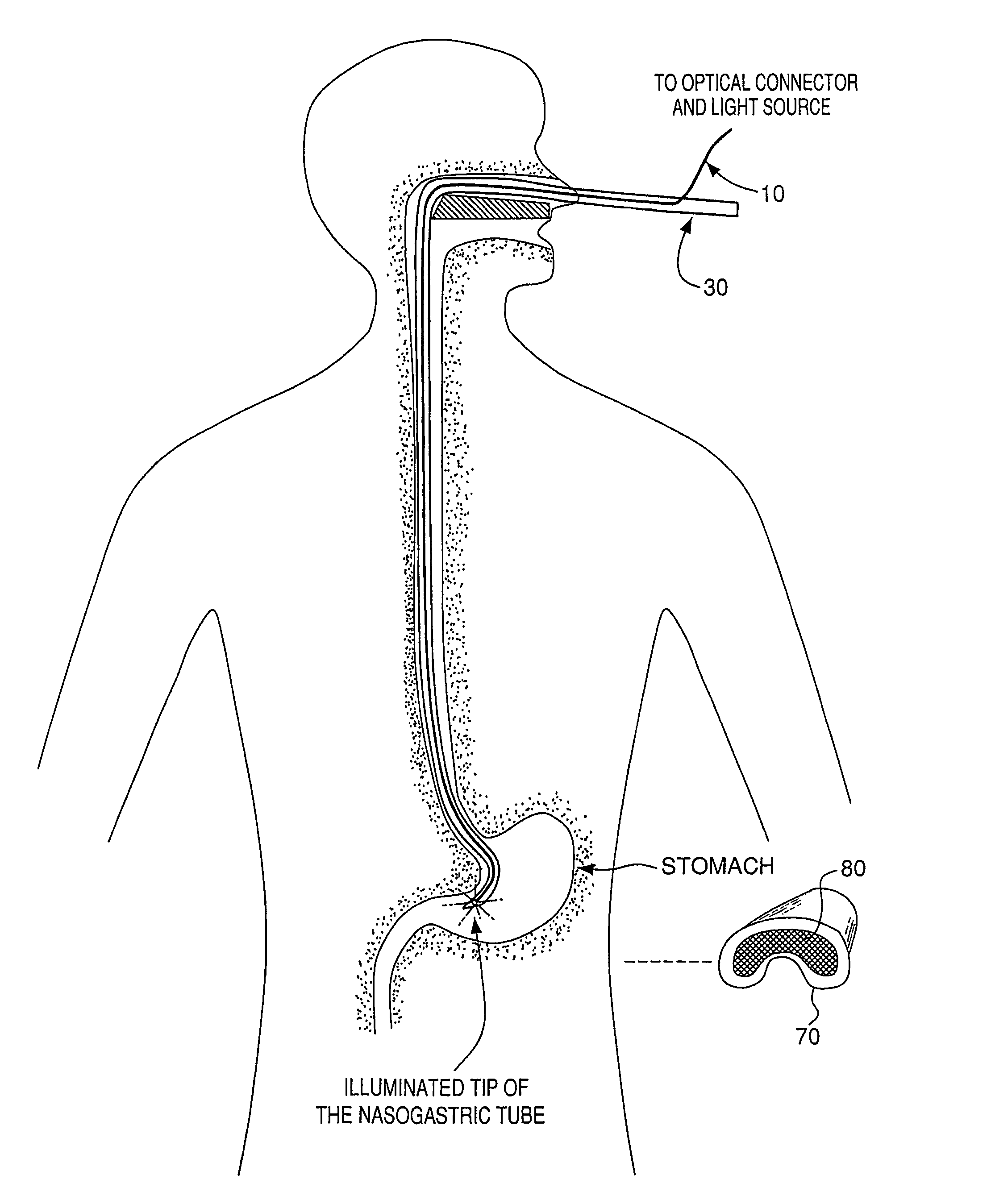
Optical guidance system for invasive catheter placement
Light from a small laser diode is inserted in a distal end of a catheter and passed through an optical fiber that is either included in the lumen or incorporated into the wall of an invasive catheter tube during manufacture. The light is selected to be of a wavelength that is minimally absorbed by tissue, preferably in the range from about 620 nm to 1100 nm. 780 nm is preferably used as this is where the tissue absorption is near a minimum. The light passes out the end of the fiber (at the proximal end of the catheter) and through the tissue to the outside of the patient's skin where it is measured. The light pattern is observed by night vision goggles that filter out other frequencies of light. The detected light permits location of the end of the fiber, the positional accuracy depending on the thickness of tissue between the fiber tip and the exterior of the body. The method is highly accurate for small children and for catheters within a few centimeters of the skin surface of adults.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Device and method for vascular re-entry
ActiveUS20100317973A1Facilitating re-entrySimple methodUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChiropractic devicesUltrasound deviceRe entry
In a method for re-entry from extraluminal space into the central lumen of a vessel, a guidewire is advanced into the extraluminal space of the vessel, and then a directional catheter is advanced over the guidewire through the extraluminal space. Thereafter, the guidewire is removed from the directional catheter, an ultrasound device is placed through the directional catheter, and the ultrasound device is advanced through the extraluminal space into the central lumen and then activated.
Owner:FLOWCARDIA
Retractable I-V catheter placement device
InactiveUS6942652B1Improve securityMinimize the possibilityGuide needlesInfusion syringesVeinIntravenous catheter
An intravenous catheter placement device having a hollow body and a nose on one end of the hollow body. A needle hub fits within the nose and contains a needle embedded therein. A catheter is free to slide along the needle and substantially covers the shaft of the needle. Winged beams on the needle hub include catches and release tabs that cooperate with slots in the nose to retain the needle hub in the nose. A magnified transparent verification cavity in the needle hub provides for viewing blood flash in the cavity to verify that the intravenous catheter is inserted into the correct location. An energy storage device in contact with the needle hub releasably retains the needle hub to prevent premature projection of the needle hub into the hollow body. Upon insertion of the intravenous catheter and introducer needle into a patient, depressing the release tabs triggers the needle hub and blunts the needle within the catheter and projects the needle hub and embedded needle into the hollow body.
Owner:MEDSAFE TECH
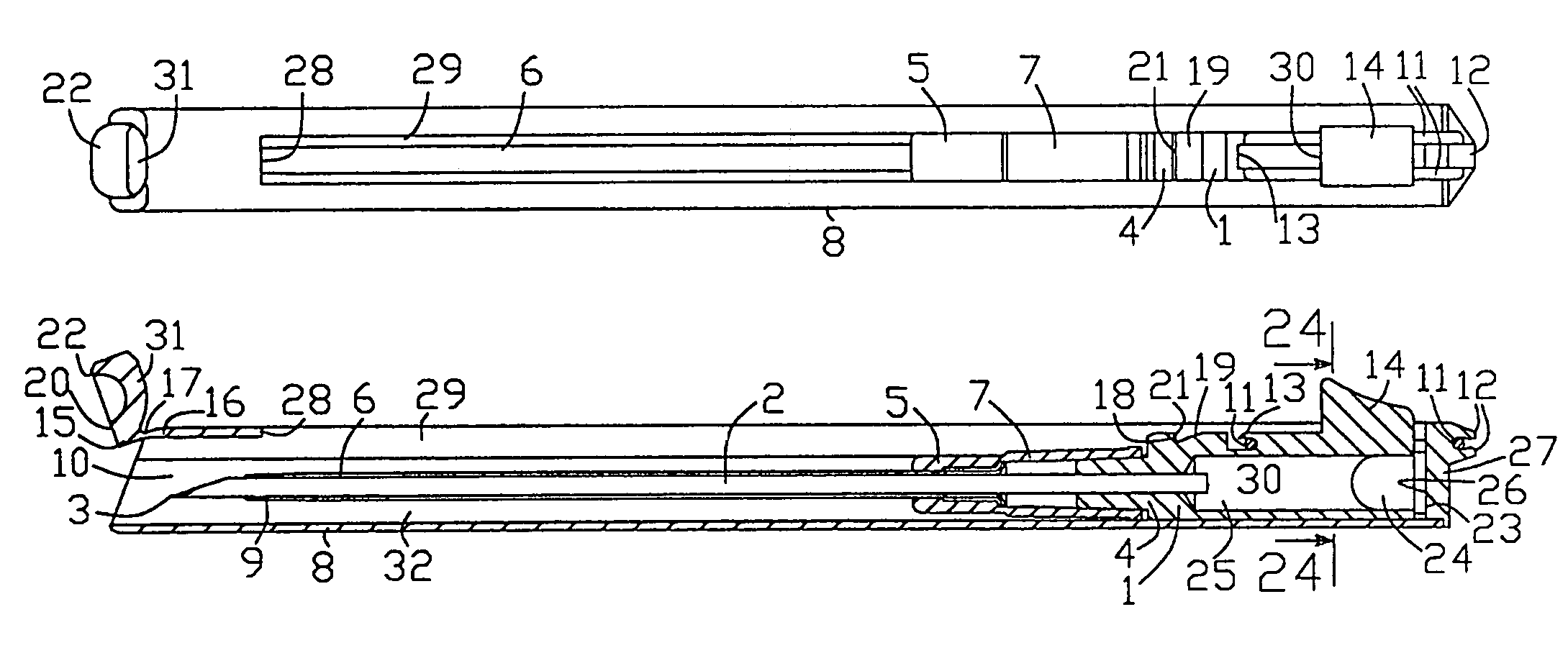
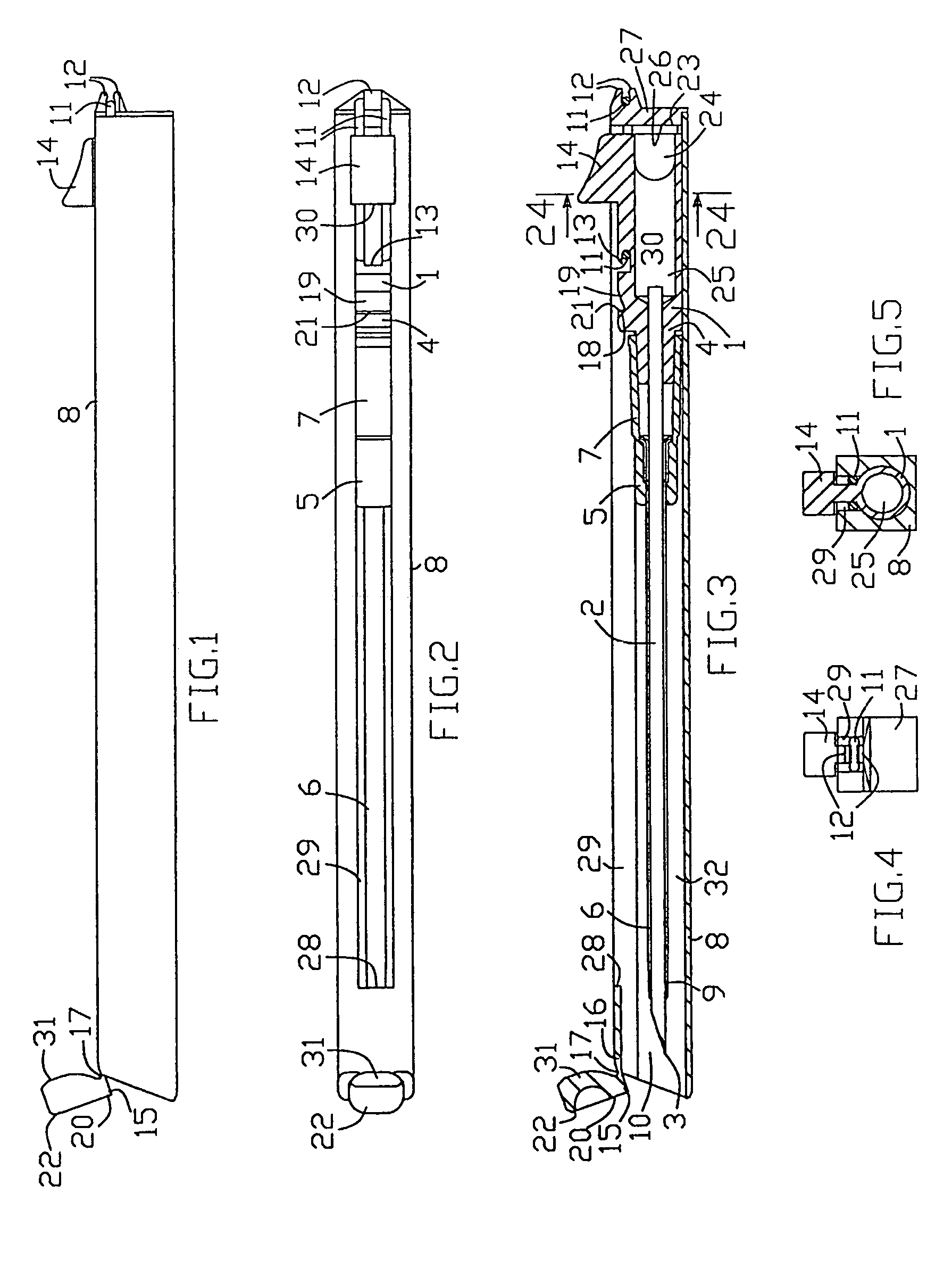
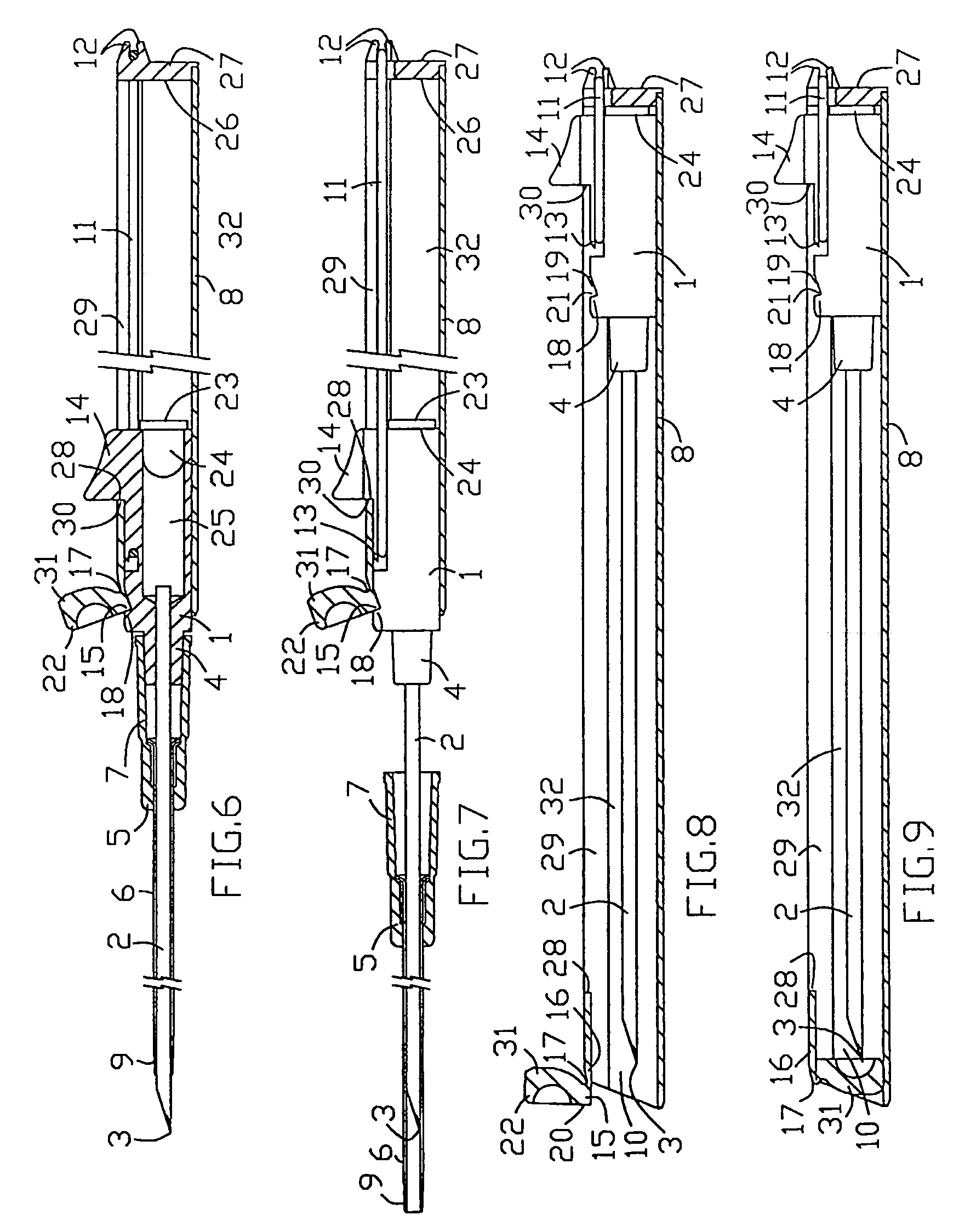
Compact catheter insertion apparatus
InactiveUS7422572B2Reduce transportationReduce packaging expenseGuide needlesInfusion syringesVeinCatheter hub
Invention relates to catheter placement devices for peripheral blood vessel catheterization with protected needle tip and shortened length in a transport position (see FIG. 31). In the transport position (FIG. 9), the needle and catheter units (1 and 5) are held inside the handle (8). User transposes the needle and catheter units into a duty ready position (FIG. 6), wherein the needle unit is engaged with the handle distal end and a catheter hub (7) protrudes distally out of the handle. After catheter insertion into patient vein, user disconnects the needle unit and handle allowing the needle unit retraction by a resilient member (11) into the protection position. The trigger and transposing means (22) location enables the apparatus single handed control. The fixation means (31) in the protection position eliminates repeated needle unit advance. It can be used rubber or spiral spring resilient members and the catheter hubs with foldable side wings and side port.
Owner:SERPOMED
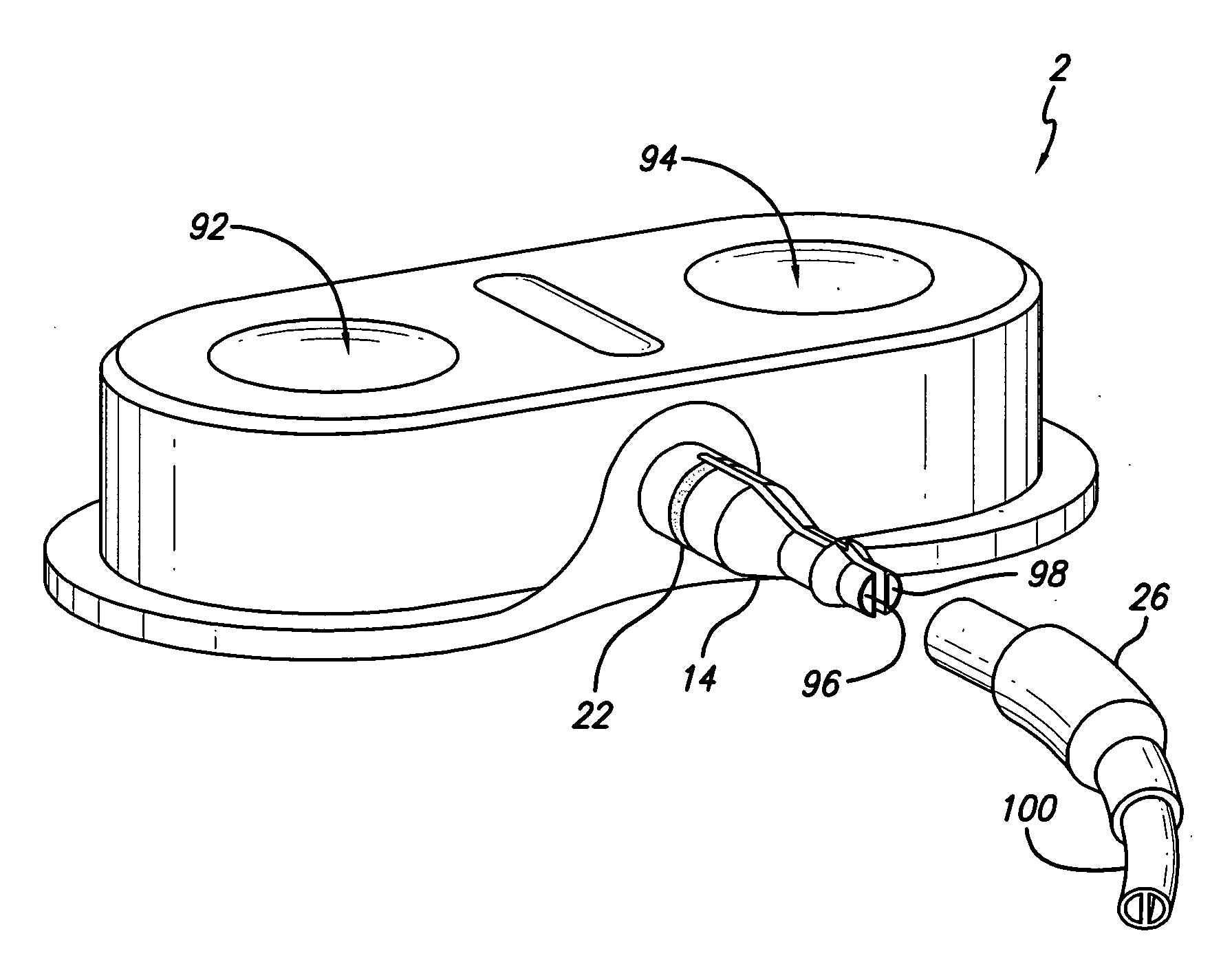
Side-port sheath for catheter placement and translation
InactiveUS20050267458A1Facilitates improved diagnosisConvenient treatmentElectrocardiographyInternal electrodesCatheter placementCatheter device
Side-port sheaths for catheter placement and translation are disclosed. The sheaths include a side-port opening through which a gliding catheter may be deployed during diagnosis or treatment of tissue. The side-port sheath may include a suspension ribbon used to deploy, or that aids in the deployment of, the embedded gliding catheter. The suspension ribbon may be slideably or fixably engaged with an outer surface of the sheath of the gliding catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
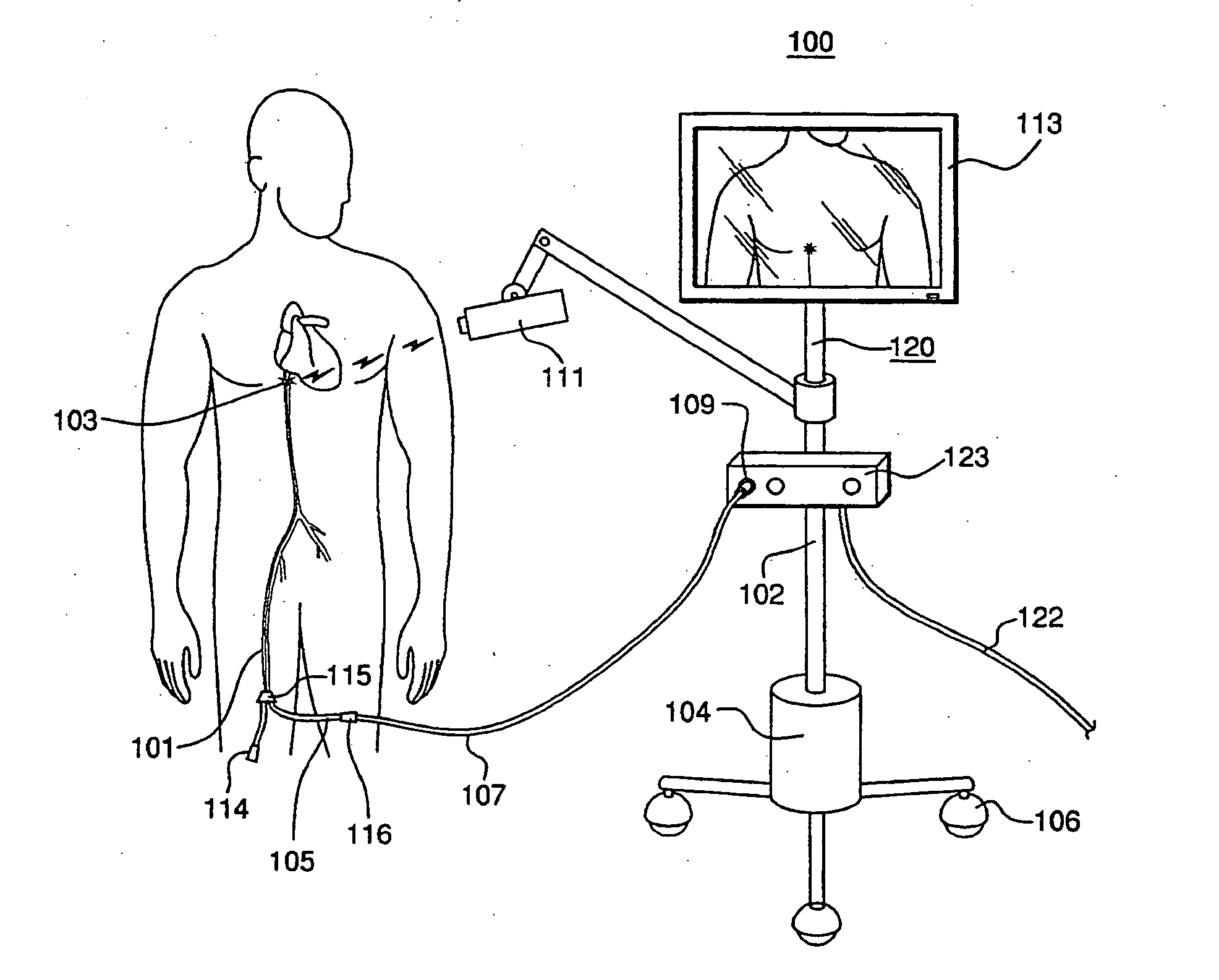
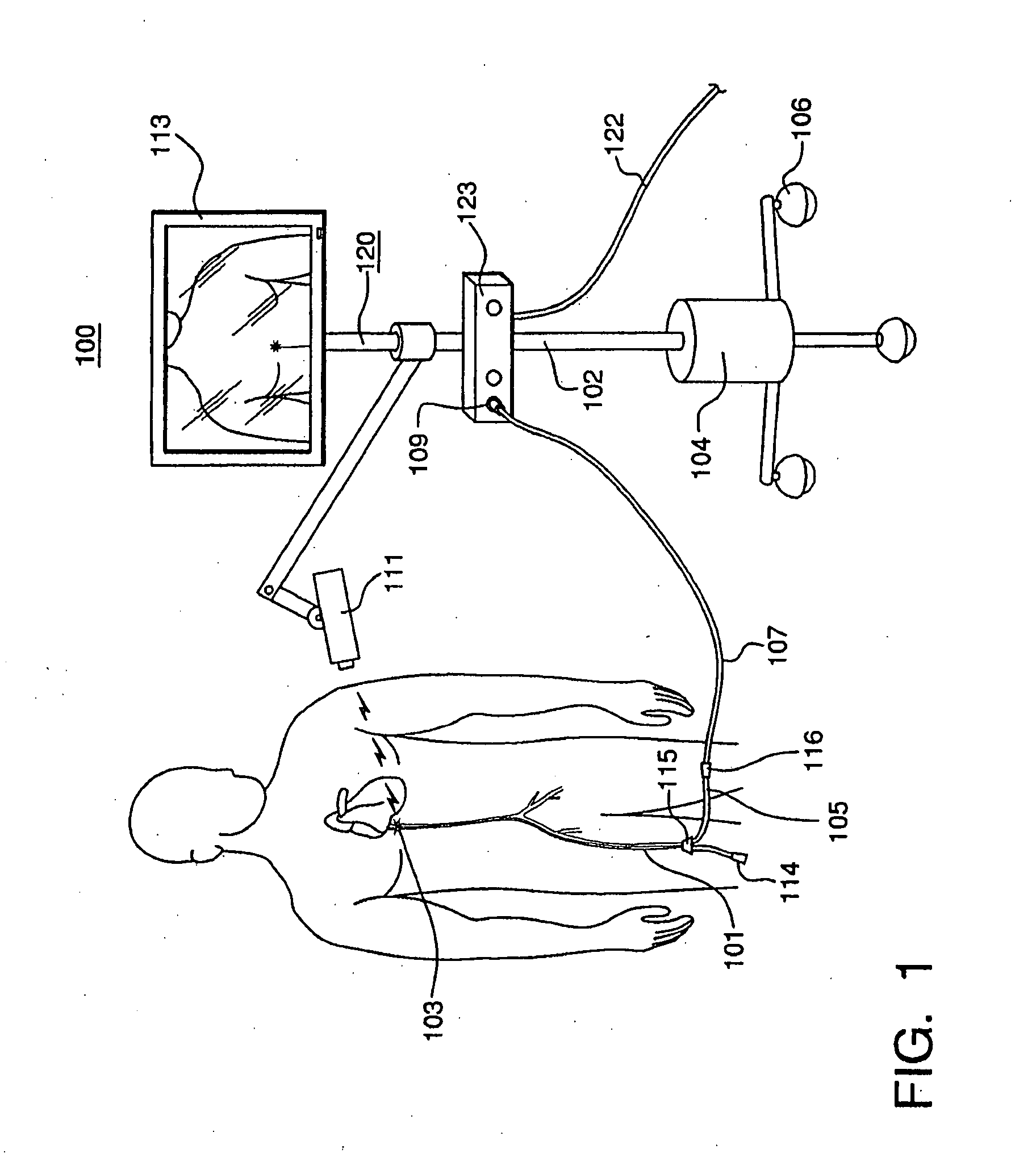
System and Method for Visualizing Catheter Placement in a Vasculature
A system for advancing a needle through a vasculature to an injection site at the heart of a patient includes a guide catheter with a reflective distal tip. Also included is an imaging unit that is mounted on the catheter to radiate an energy field. Structurally, a distal portion of the catheter is biased to bend into a predetermined configuration that will position the distal end of the catheter for interception by the energy field. If necessary, coincidence of the reflective tip with the energy field is established by moving the energy field along the length of the guide catheter. With coincidence, the reflective tip reflects a signal that is useful for advancement of the needle 34b from the guide catheter and into the injection site.
Owner:DIB ULTRASOUND CATHETER
Sonographically guided transvaginal or transrectal pelvic abscess drainage using trocar method and biopsy guide attachment
ActiveUS7981041B2Avoid relative motionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasound probeInstrumentation
A needle biopsy guide system is disclosed for attachment to an endoluminal ultrasound probe or like sonographic instrument. The device includes a biopsy-guide attachment that allows for trocar catheter placement for abscess drainage or like procedures, using the transvaginal or transrectal route under sonographic control. The device has a base portion, which is attachable to an ultrasound probe. A removable retainer is provided that slides into the base unit to hold a biopsy needle in place. A physician may locate the target area in the body with the ultrasound probe, insert the biopsy needle into the target area, and then remove the insert (retainer) from the base unit and ultrasound probe, and leave the biopsy needle in place in the body.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Controlled release endoprosthetic device
InactiveUS20050192664A1Overcome problemsVascular smooth cell proliferation caused by stents can be reducedOrganic active ingredientsStentsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTPerfusion
The invention relates to improved drug-delivery endoprosthetic device for insertion at a vascular site via catheter placement at the site, comprising: (a) a structural member into the upper and / or lower surface of which one or more micro-deepenings are engraved and / or on which a polymer member is carried, for co-expansion with the polymer member from a contracted state to an expanded state when the device is exposed to said stimulus, (b) optionally a polymer member capable of expanding from a contracted to a stable, expanded state when the polymer member is exposed to a selected stimulus, wherein the device can be delivered from a catheter, with the structural and the optional polymer members in their contracted states, and is adapted to be held in a vessel at the vascular target site by radial pressure against the wall of the vessel, with the structural and the optional polymer members in their expanded states; and wherein the micro-deepenings of said structural member and / or said polymer member comprise a pharmaceutical composition containing one or more active ingredients selected from the group consisting of agents to inhibit or at least reduce excessive proliferation of vessel wall cells, agents to enhance the downstream perfusion of tissue, agents to promote and / or to enhance the neo-formation of capillaries, agents designed to modulate the amount or activity of coagulation factors, agents to reduce the amount of Thrombin- and / or Fibrin-formation, embedded therein for release from the member, with such in its expanded state.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARM KG
Method and apparatus for measuring and controlling blade depth of a tissue cutting apparatus in an endoscopic catheter
InactiveUS20030060842A1Surgical needlesDiagnostic markersPrecut sphincterotomyCommon bile duct dilatation
According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and / or sphincterotomy of the Papilla of Vater and / or the Sphincter of Oddi is accomplished by advancing a sphincterotome (or papillotome or cannulotome) into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the sphincterotome exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the sphincterotome to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Accurate and consistent control of the length of the exposed blade is made difficult due to a number of factors. These factors include: 1) differences in the inside diameters of the outer tube and the needle knife wire, 2) the orientation of the needle knife wire within the outer tube, 3) the mismatch of tolerance of the needle knife wire and the inside diameter of the extrusion, 4) anatomy, and 5) endoscope manipulation. A sphincterotome incorporating the present invention will provide the user with an indication of the exposed blade length and will allow the physician to control the length of the exposed blade. According to one embodiment of the present invention, various visual indications are presented to the user as the needle knife is advanced from its outer sheath. These visual indications, combined with a mechanical method to hold the knife in position during catheter placement allows the user to perform precise incisions. Presently available products that may be modified according to the present invention include, but are not limited to, Boston Scientific Sphincterotomes and Needle Knives.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Side-port sheath for catheter placement and translation
InactiveUS7276064B2Reduce formationReducing of of surfaceElectrocardiographyInternal electrodesCatheter placementCatheter device
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
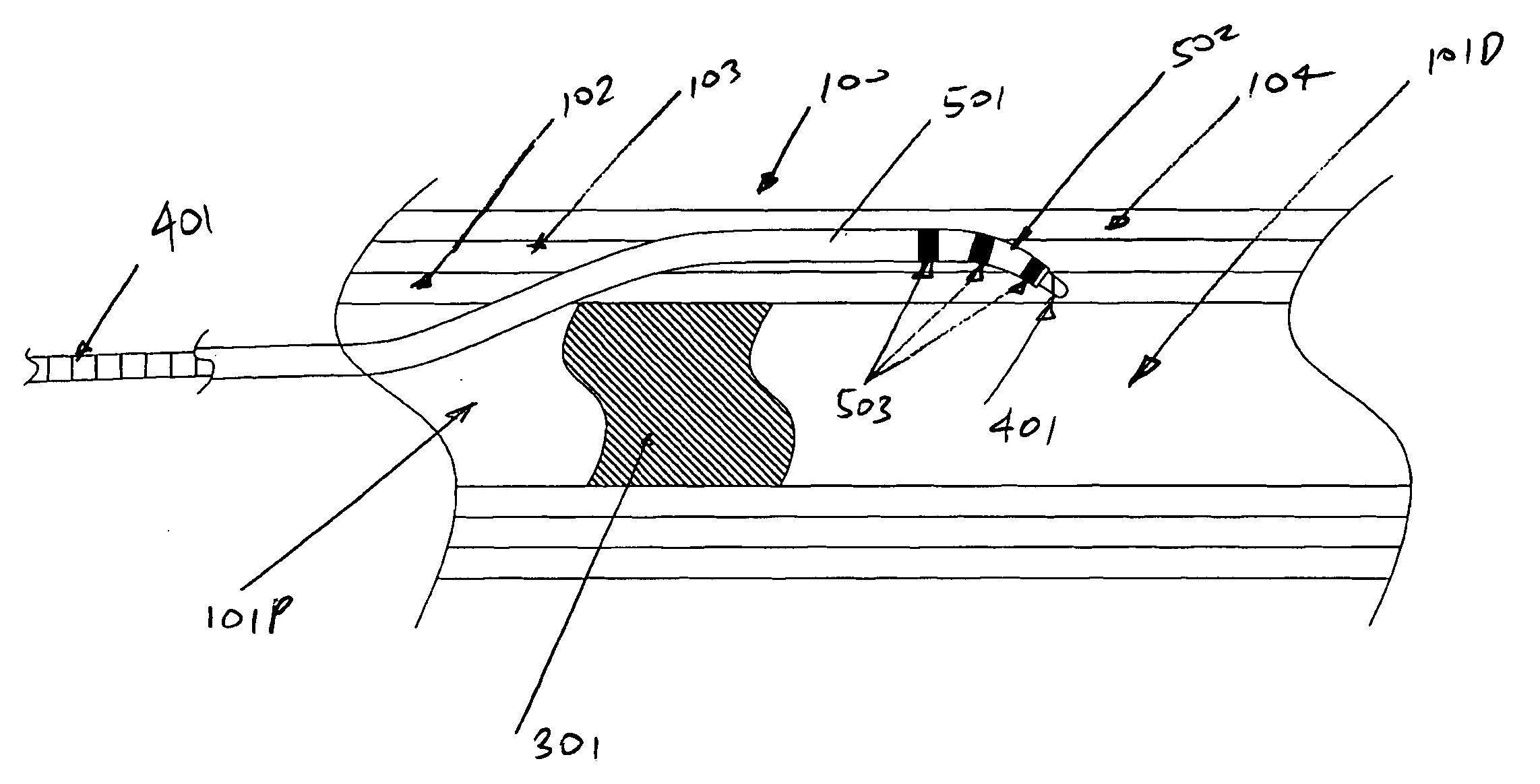
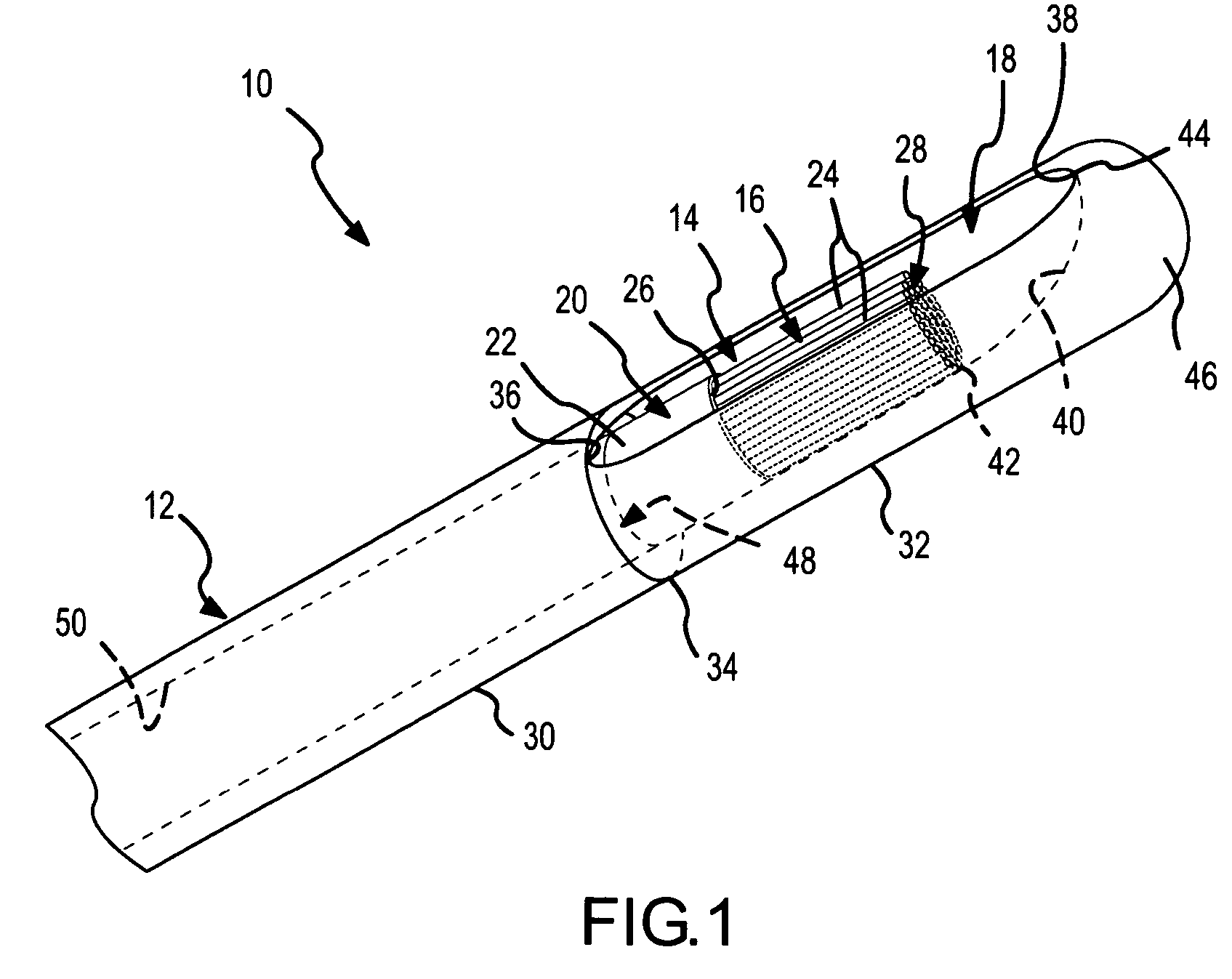
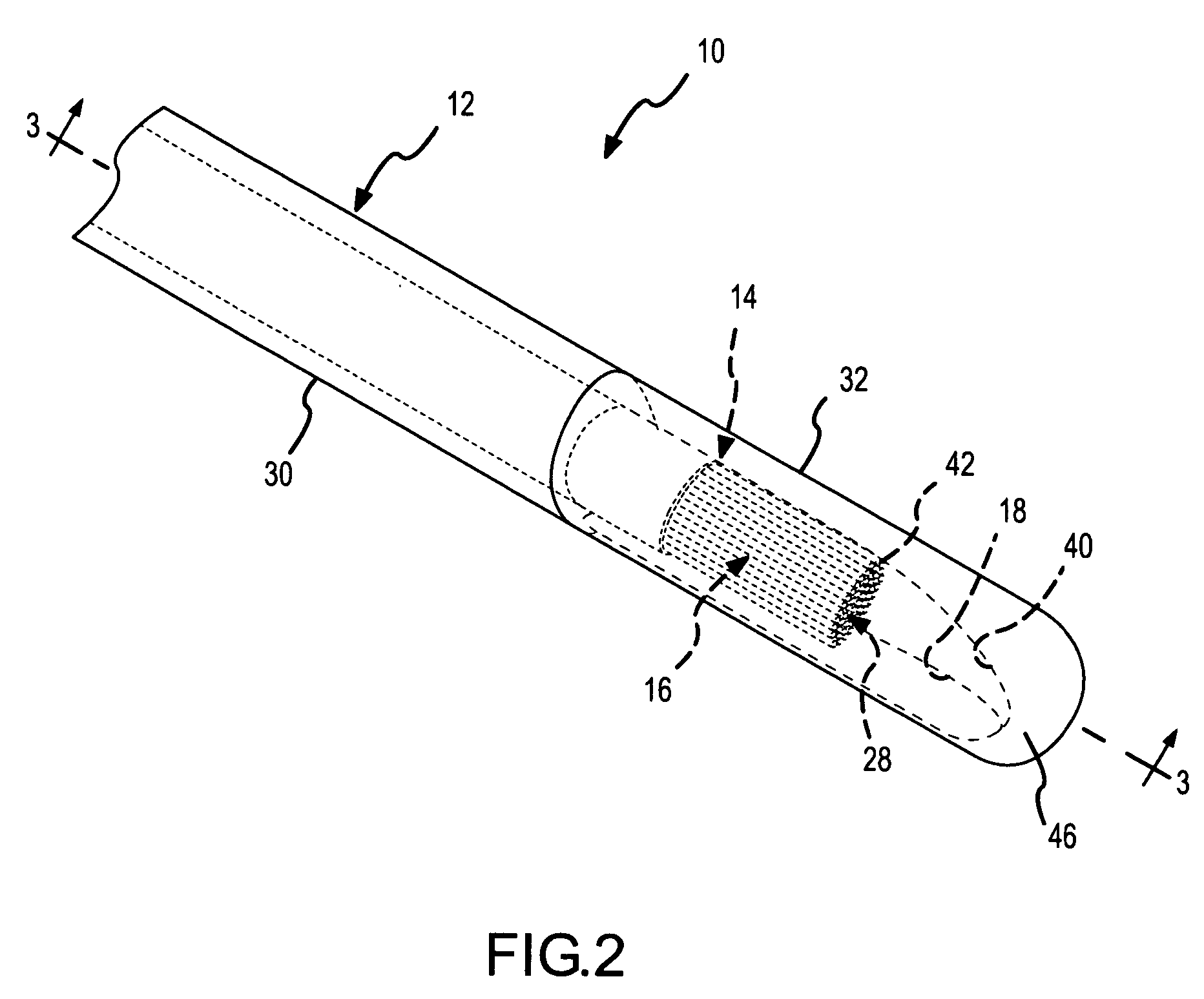
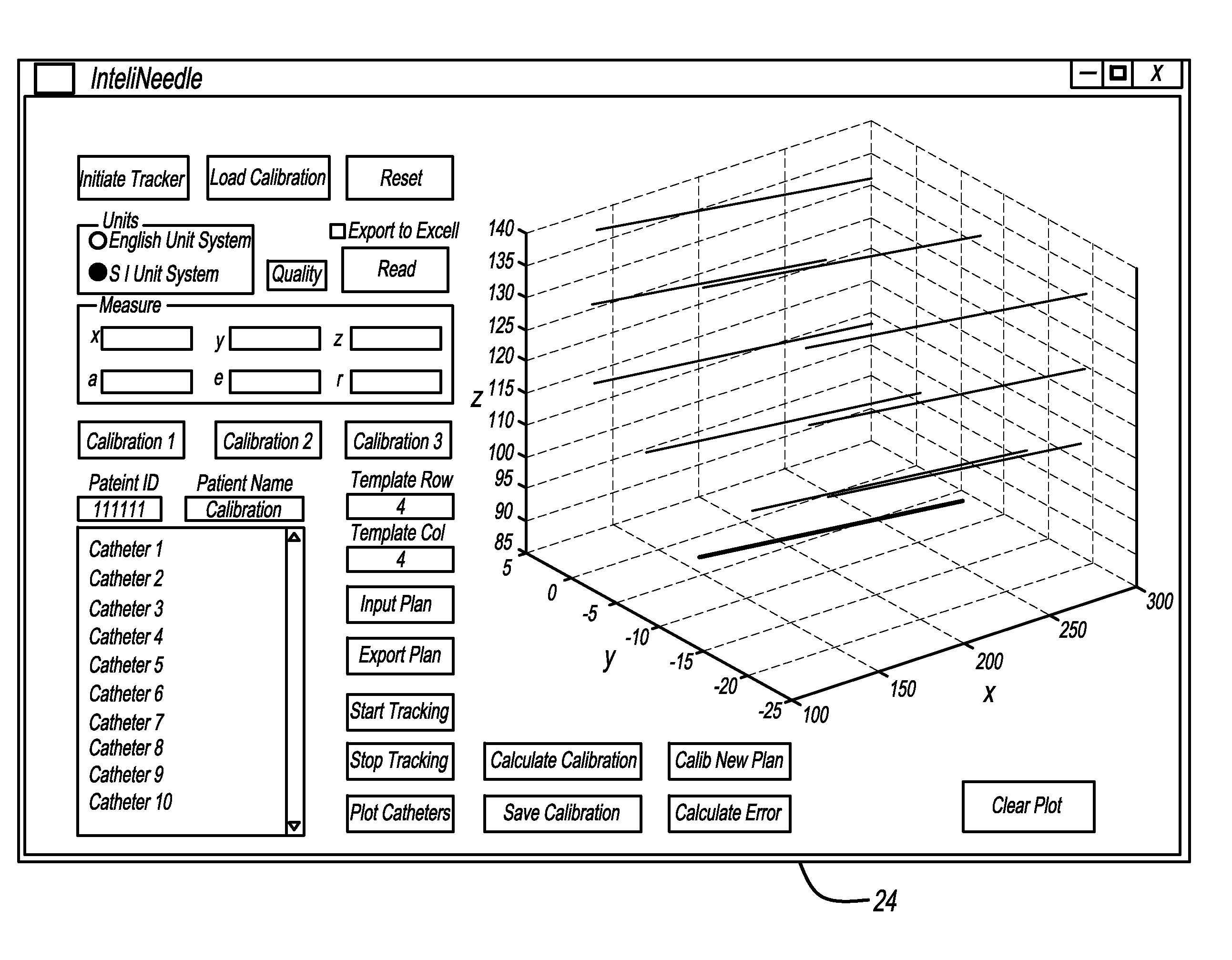
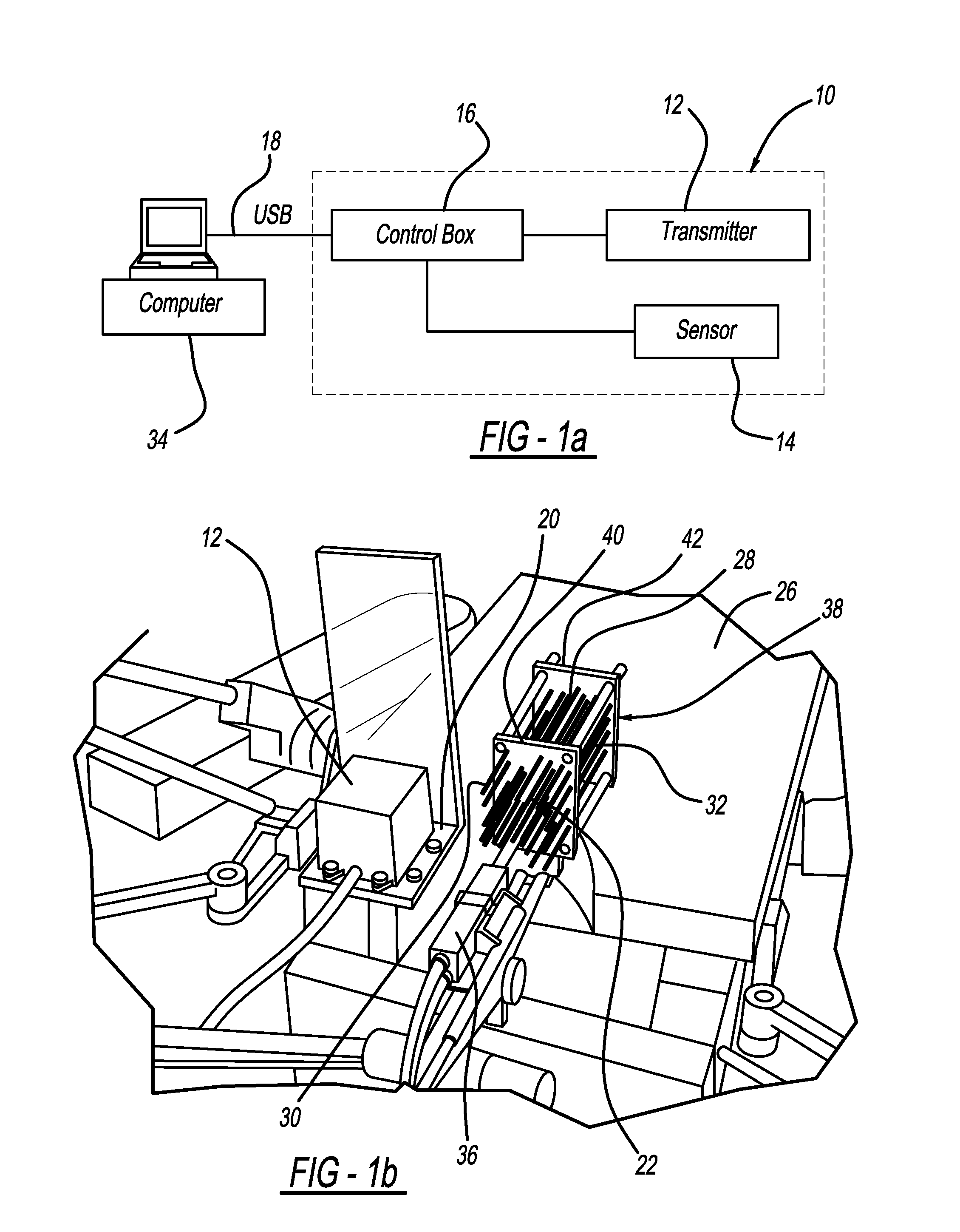
Catheter Placement Detection System and Method for Surgical Procedures
InactiveUS20140357977A1Surgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsSurgical approachElectromagnetic field
In order to increase the accuracy and speed of catheter reconstruction in surgical procedures such as an HDR prostate implant procedure, an automatic tracking system is provided preferably using an electromagnetic tracking device. The system uses a transmitter with a sensor used for catheter position. Due to substantial interference in the electromagnetic field from the surgical table, implant stepper / stabilizer etc, a calibration algorithm using a scattered data interpolation scheme is implemented to correct tracking location errors. The invention includes methods and systems used to carry out the methods.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
Systems and Methods for Needle Access to an Intervertebral Disc
ActiveUS20080312636A1Reduce intrusionReduce morbidityStentsGuide needlesDistal portionIntervertebral disk
A catheter with a balloon anchor may be sized to fit through an inner needle and introduced into the patient through the needle. The inner needle may comprise an atraumatic needle with a side port and / or a blunt tip. The catheter may include a radiopaque coil disposed over the distal portion of the catheter body to assist with catheter placement when viewed with fluoroscopy and / or x-ray. The distal portion of the catheter can be very flexible. A balloon inflation tube may terminate proximal to a proximal end of the expandable balloon anchor such that the distal portion of catheter can be flexible. This termination of the inflation tube may also position the inflation tube away from the annulus and nerve roots, so as to avoid irritation of the annulus and rubbing of the nerve roots that may potentially obscure FAD test results.
Owner:KYPHON
System and method for inserting intracranial catheters
InactiveUS20120302875A1Avoid damageReduce system complexityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEndoscopesUltrasonic sensorIn vivo
An improved system for safely and accurately placing intracranial catheters by using techniques from the field of artificial intelligence (AI) which combine the output from in vivo ultrasonic sensors with in vivo video cameras and an embedded inertial measurement unit. The AI subsystem synthesis the output from the three sensors to determine an optimal route to the desired intracranial site while avoiding larger blood vessels en route. Additionally, by using the output from the inertial measurement unit, the catheter's complete trajectory can be recorded and made available for post-operative analysis. The entire system is portable so that it can be used outside of the hospital operating room, for example, in an intensive care unit. Compared to standard freehand methods of placing intracranial catheters, the system embodied here will reduce concomitant hemorrhaging while increasing the accuracy of catheter placement.
Owner:KOHRING GREGORY ALLEN
Side-port sheath for catheter placement and translation
InactiveUS20070293856A1Reduce formationReducing of of surfaceElectrocardiographyInternal electrodesMedicineCatheter placement
Side-port sheaths for catheter placement and translation are disclosed. The sheaths include a side-port opening through which a gliding catheter may be deployed during diagnosis or treatment of tissue. The side-port sheath may include a suspension ribbon used to deploy, or that aids in the deployment of, the embedded gliding catheter. The suspension ribbon may be slideably or fixably engaged with an outer surface of the sheath of the gliding catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Optical guidance system for invasive catheter placement
Light from a small laser diode is inserted in a distal end of a catheter and passed through an optical fiber that is either included in the lumen or incorporated into the wall of an invasive catheter tube during manufacture. The light is selected to be of a wavelength that is minimally absorbed by tissue, preferably in the range from about 620 nm to 1100 nm. 780 nm is preferably used as this is where the tissue absorption is near a minimum. The light passes out the end of the fiber (at the proximal end of the catheter) and through the tissue to the outside of the patient's skin where it is measured. The light pattern is observed by night vision goggles that filter out other frequencies of light. The detected light permits location of the end of the fiber, the positional accuracy depending on the thickness of tissue between the fiber tip and the exterior of the body. The method is highly accurate for small children and for catheters within a few centimeters of the skin surface of adults.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
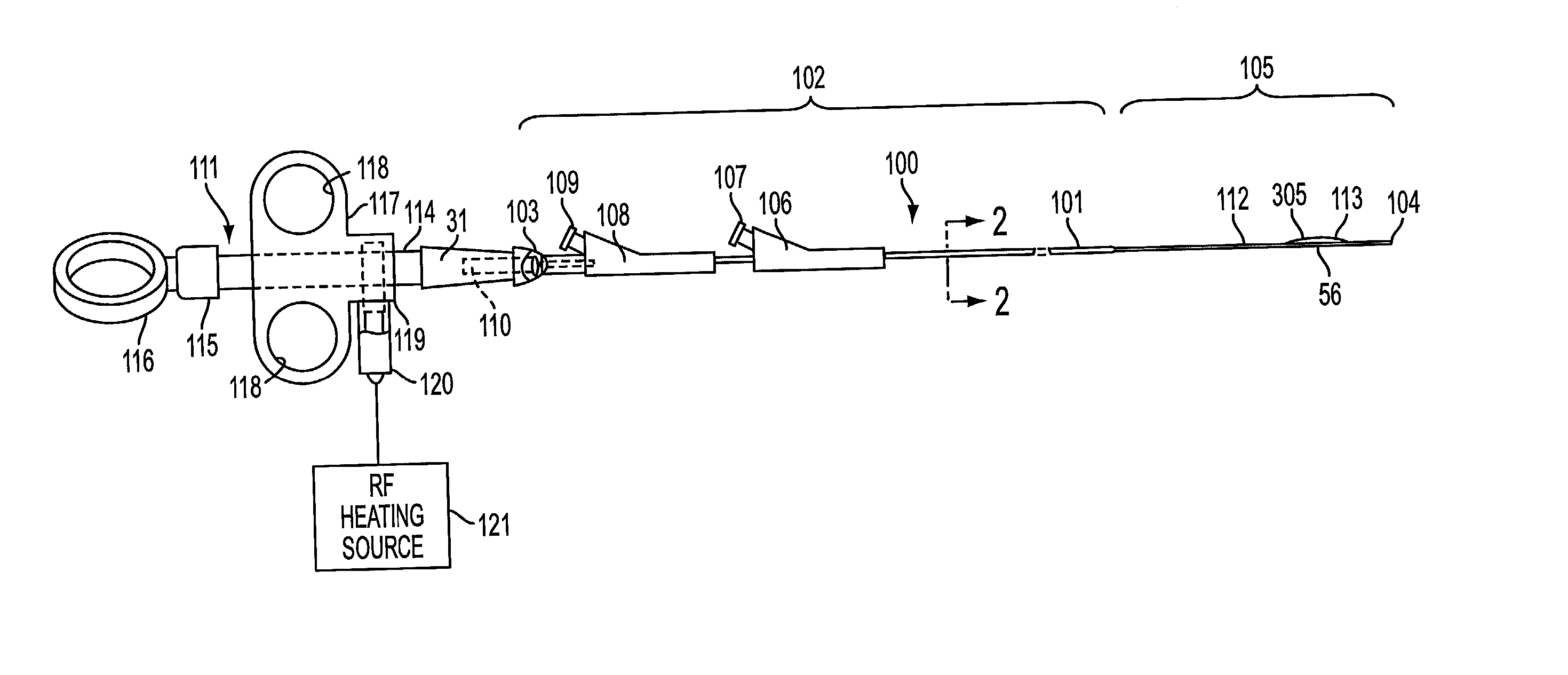
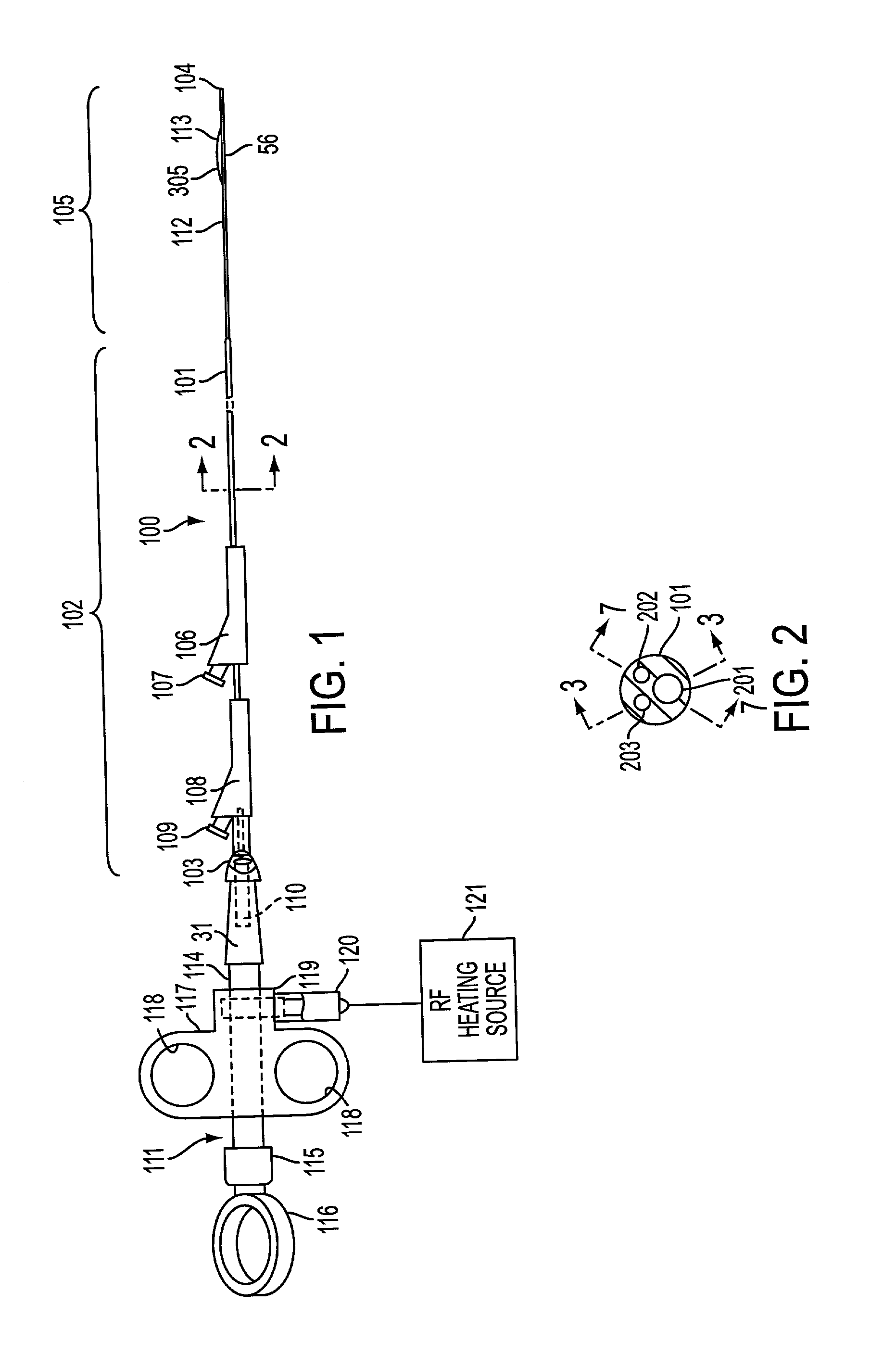
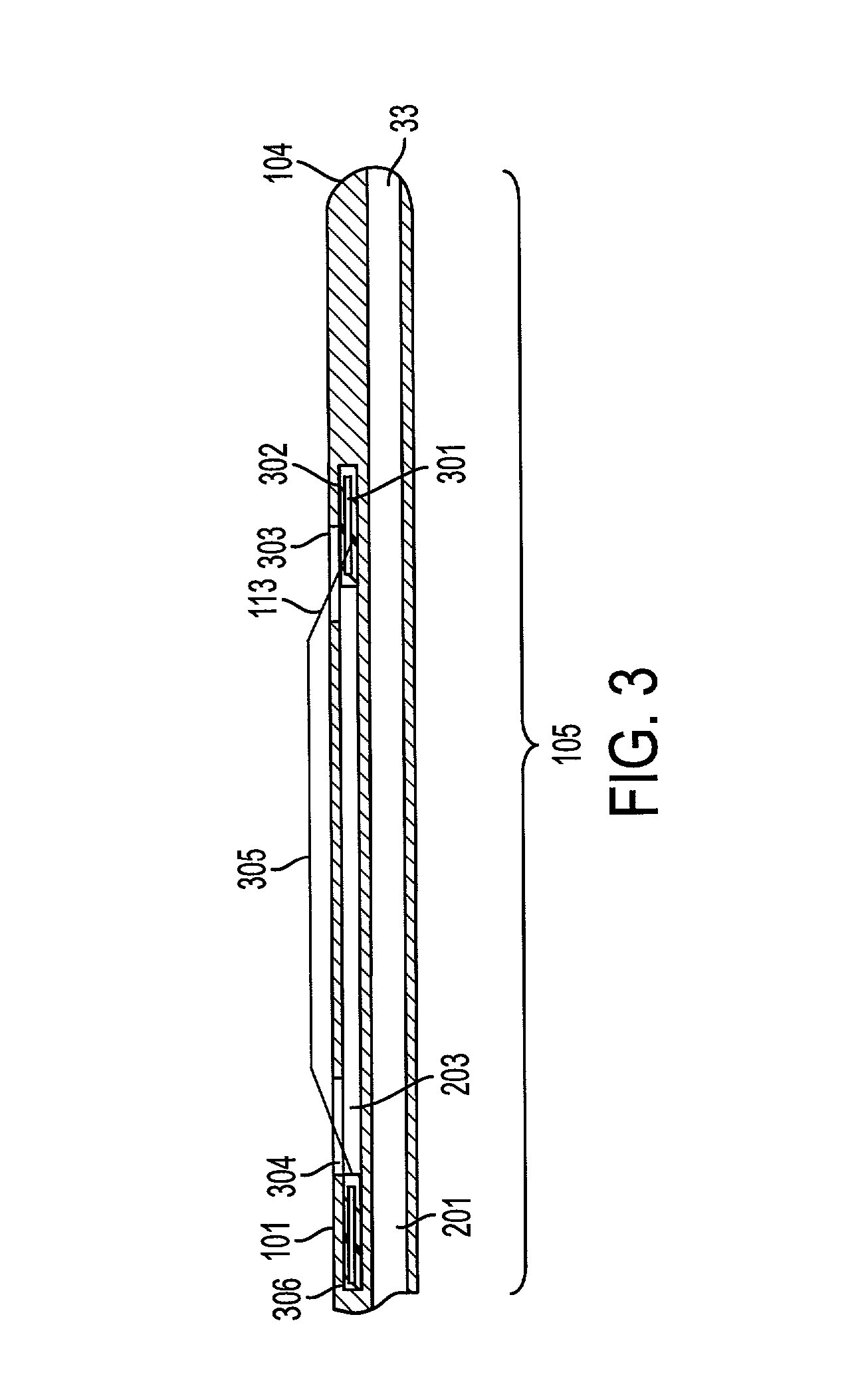
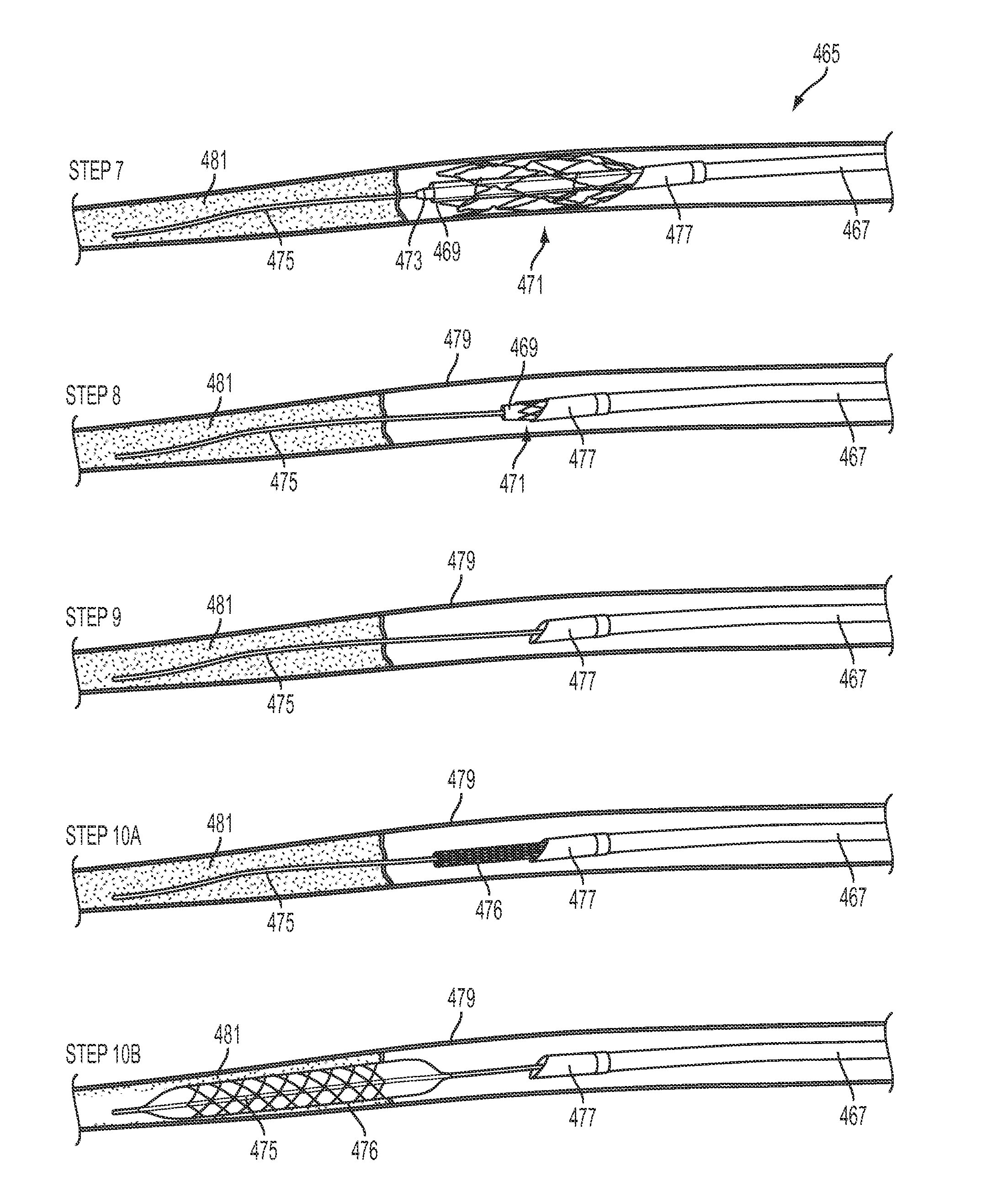
Method and apparatus for placing a catheter within a vasculature
A catheter for insertion into vasculature of a patient to a target area in the vasculature includes a hollow inner shaft, a non-occluding self-expandable scaffold coupled to the distal end of the inner shaft and disposed at the distal end of the inner shaft, and a hollow outer shaft. The outer shaft is slidable over the inner shaft and scaffold such that the scaffold is in a non-expanded state when the outer shaft is around the scaffold. The outer shaft has a state where the distal end of the outer shaft remains near the target area without the inner shaft and the scaffold being within the outer shaft. The inner shaft and the scaffold are removable through the proximal end of the outer shaft while the distal end of the outer shaft remains near the target area.
Owner:ROXWOOD MEDICAL
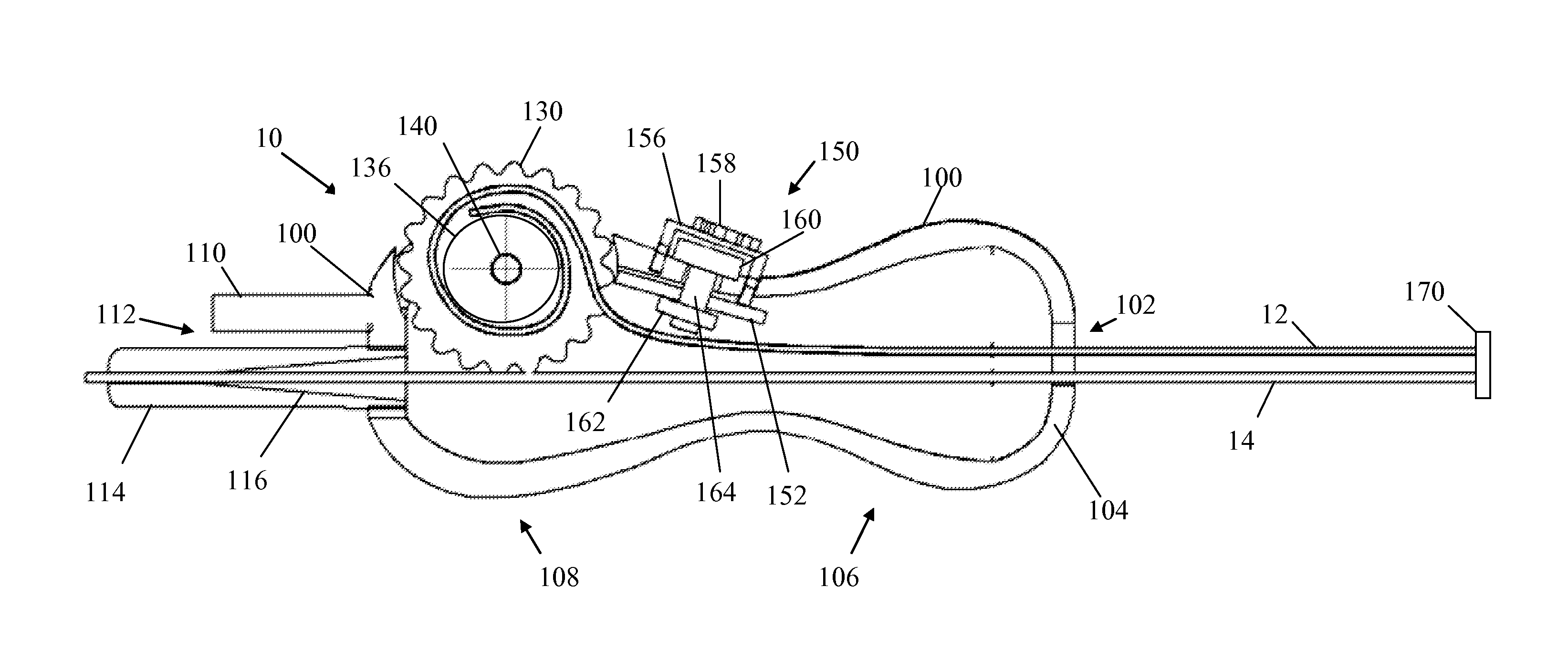
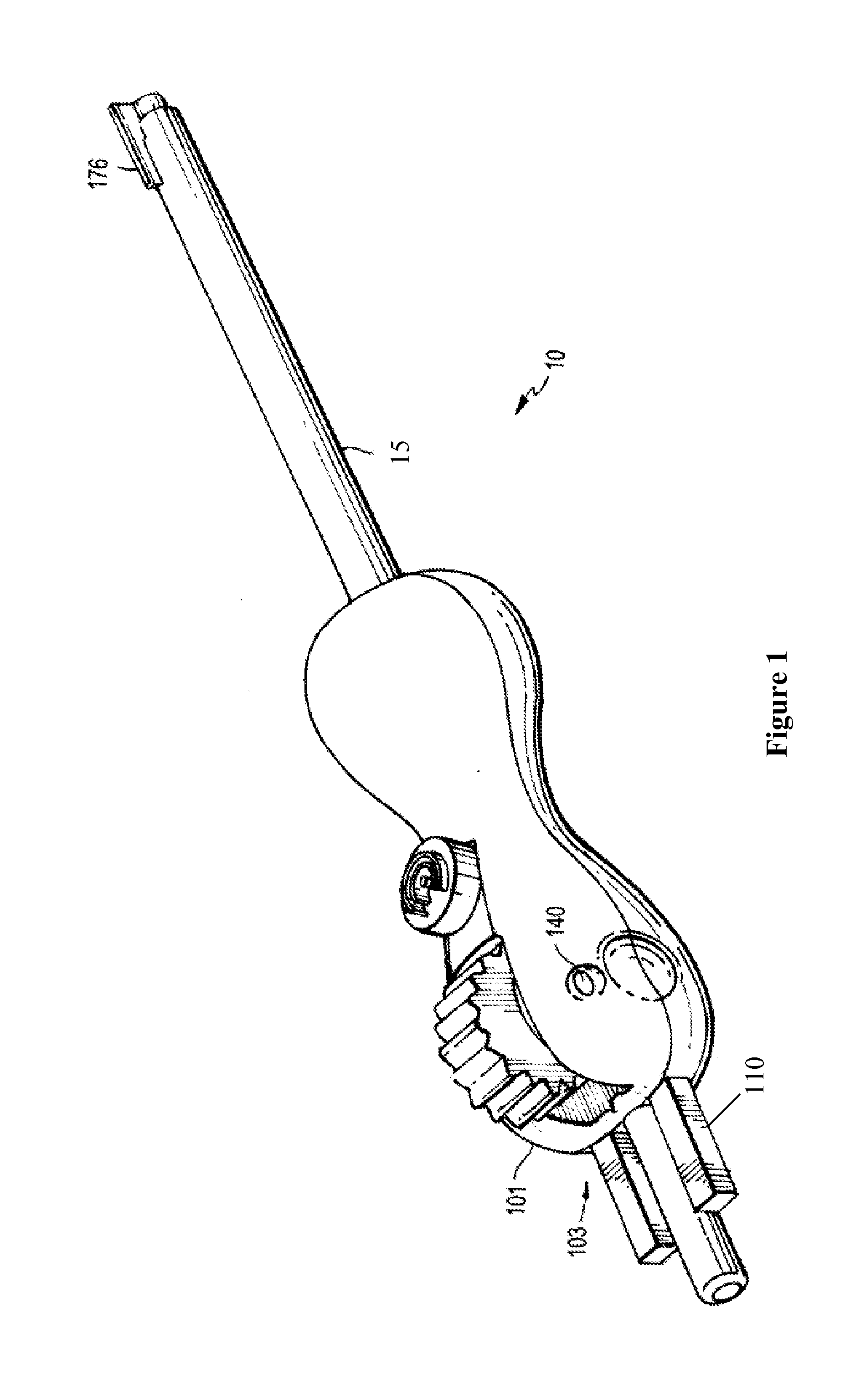
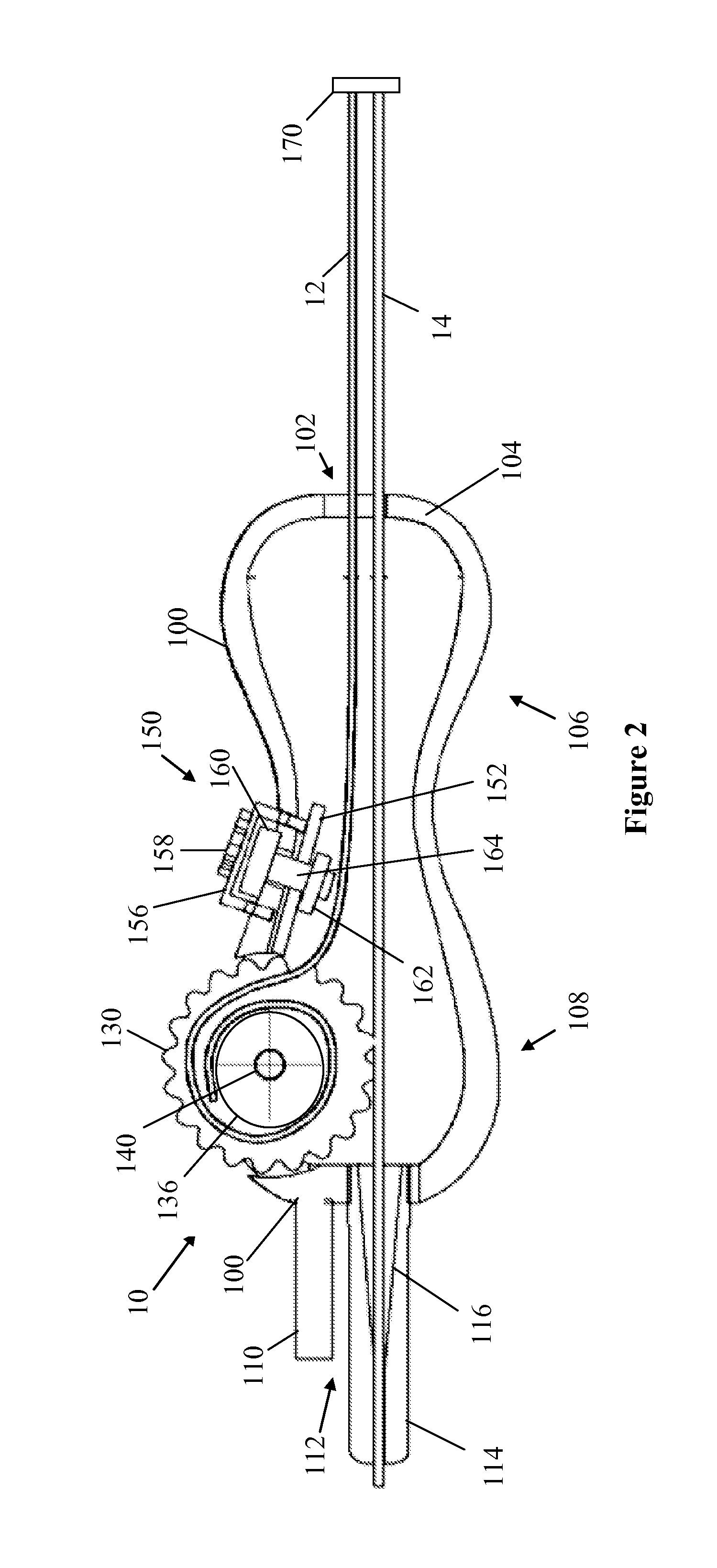
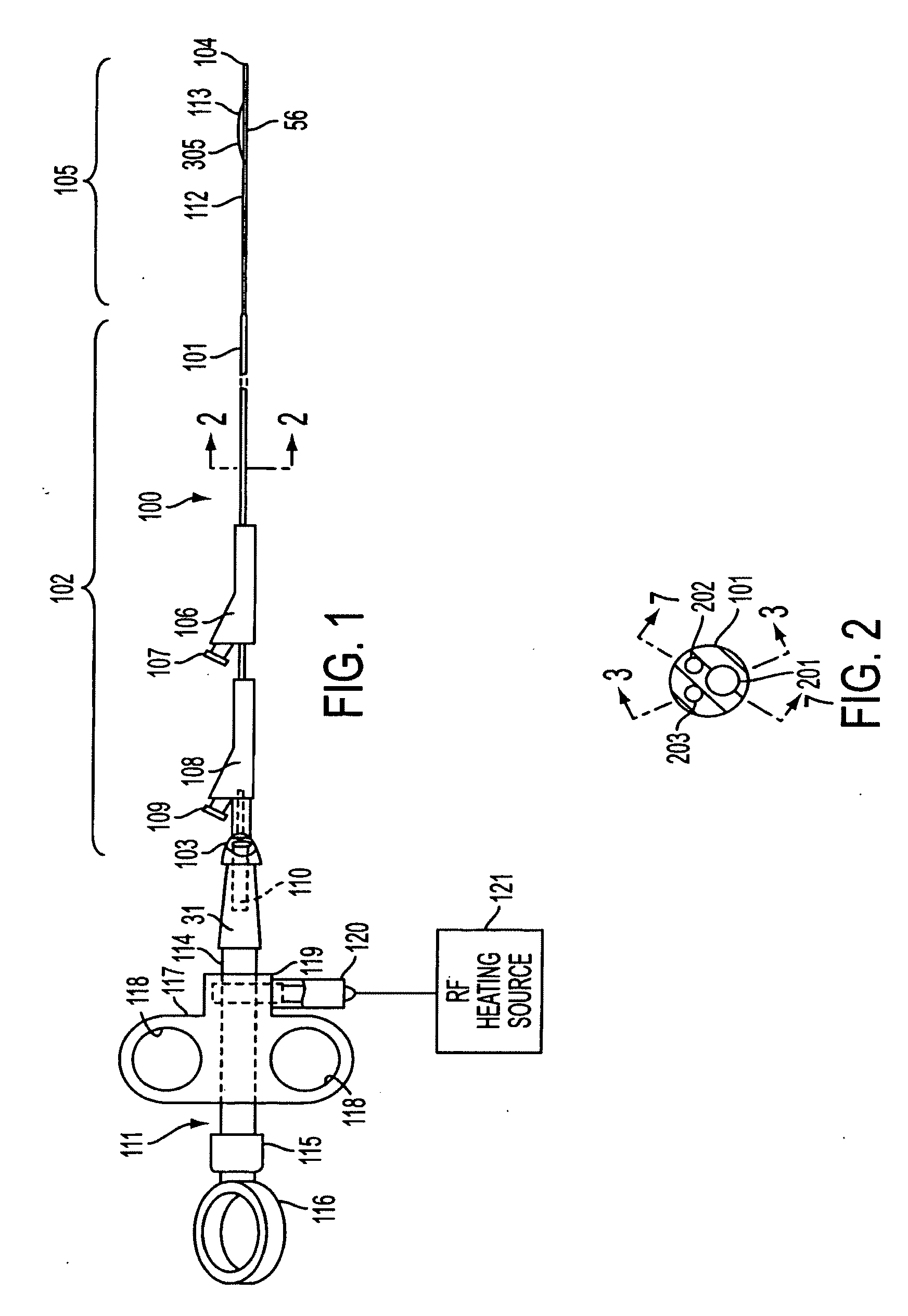
Catheter placement device
ActiveUS20160121086A1Reliable and easy to useEasy to useGuide needlesGuide wiresDrive wheelIndex finger
A deep vein intravenous introducer has a wheel located toward the front end of the device that can be rotated by the index finger of the user. After placement of the needle in the lumen of the vessel, the user rotates the wheel, which turns a drive wheel. The drive wheel has an outer surface that advances the guide wire through the center of the needle and into the patient. Once the guide wire is advanced into the vessel lumen the catheter can be advanced over the guide wire with a hub or finger tab on the catheter close to the index finger. The operation can be performed by one hand without moving the hand from its initial position.
Owner:SONOSTIK LLC
Transseptal puncture apparatus and method for using the same
Devices and methods for performing a transseptal puncture procedure using a device which includes either an untapered or tapered blunt end cannula disposed in an introducer carrying a sharp guidewire disposed longitudinally through the lumen of the blunt cannula, and a blunt end dilator wherein the guidewire is flexible and has an atraumatic shape at its tip. The cannula gives the more flexible introducer a defined shape and steerabilty allowing an ordinarily skilled physician to easily access a selected location on the septal wall of the heart for transseptal puncture and introducer placement thereacross without employing an exposed sharp end needle during the procedure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
Method and Apparatus for Measuring and Controlling Blade Depth of a Tissue Cutting Apparatus in an Endoscopic Catheter
InactiveUS20090005637A1Precise depth controlProviding resistance to movementSurgical needlesEndoscopesPrecut sphincterotomyCommon bile duct dilatation
According to the present state of the art, endoscopic cannulation of the common bile duct and papillotomy and / or sphincterotomy of the Papilla of Vater and / or the Sphincter of Oddi is accomplished by advancing a sphincterotome (or papillotome or cannulotome) into an endoscope / duodenoscope so that the distal tip of the sphincterotome exits the endoscope adjacent the sphincter muscles at the Papilla of Vater. The endoscope mechanisms are then manipulated to orient the distal tip of the sphincterotome to the desired position for proper cannulation of the duct. Accurate and consistent control of the length of the exposed blade is made difficult due to a number of factors. These factors include: 1) differences in the inside diameters of the outer tube and the needle knife wire, 2) the orientation of the needle knife wire within the outer tube, 3) the mismatch of tolerance of the needle knife wire and the inside diameter of the extrusion, 4) anatomy, and 5) endoscope manipulation. A sphincterotome incorporating the present invention will provide the user with an indication of the exposed blade length and will allow the physician to control the length of the exposed blade. According to one embodiment of the present invention, various visual indications are presented to the user as the needle knife is advanced from its outer sheath. These visual indications, combined with a mechanical method to hold the knife in position during catheter placement allows the user to perform precise incisions. Presently available products that may be modified according to the present invention include, but are not limited to, Boston Scientific Sphincterotomes and Needle Knives.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Systems and Methods for Closing a Percutaneous Vascular Puncture
A system and method for closing a percutaneous vessel puncture at the conclusion of a vascular catheterization procedure includes placement of an intravascular closure device having a tubular membrane mounted about a radially self-expandable scaffold. A tether is attached to a midpoint of the closure device and extends externally therefrom. The closure device is placed by a delivery catheter extending through the puncture site and is radially expanded in a location upstream or downstream of the puncture site. The tether extends through the vessel puncture and tension applied to the tether slides the closure device into a position covering the puncture from within the vessel.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Retractable I-V catheter placement device
An intravenous catheter placement device having a hollow body and a nose on one end of the hollow body. A needle hub fits within the nose and contains a needle embedded therein. A catheter is free to slide along the needle and substantially covers the shaft of the needle. Winged beams on the needle hub include catches and release tabs that cooperate with slots in the nose to retain the needle hub in the nose. A magnified transparent verification cavity in the needle hub provides for viewing blood flash in the cavity to verify that the intravenous catheter is inserted into the correct location. An energy storage device in contact with the needle hub releasably retains the needle hub to prevent premature projection of the needle hub into the hollow body. Upon insertion of the intravenous catheter and introducer needle into a patient, depressing the release tabs triggers the needle hub and blunts the needle within the catheter and projects the needle hub and embedded needle into the hollow body.
Owner:MEDSAFE TECH
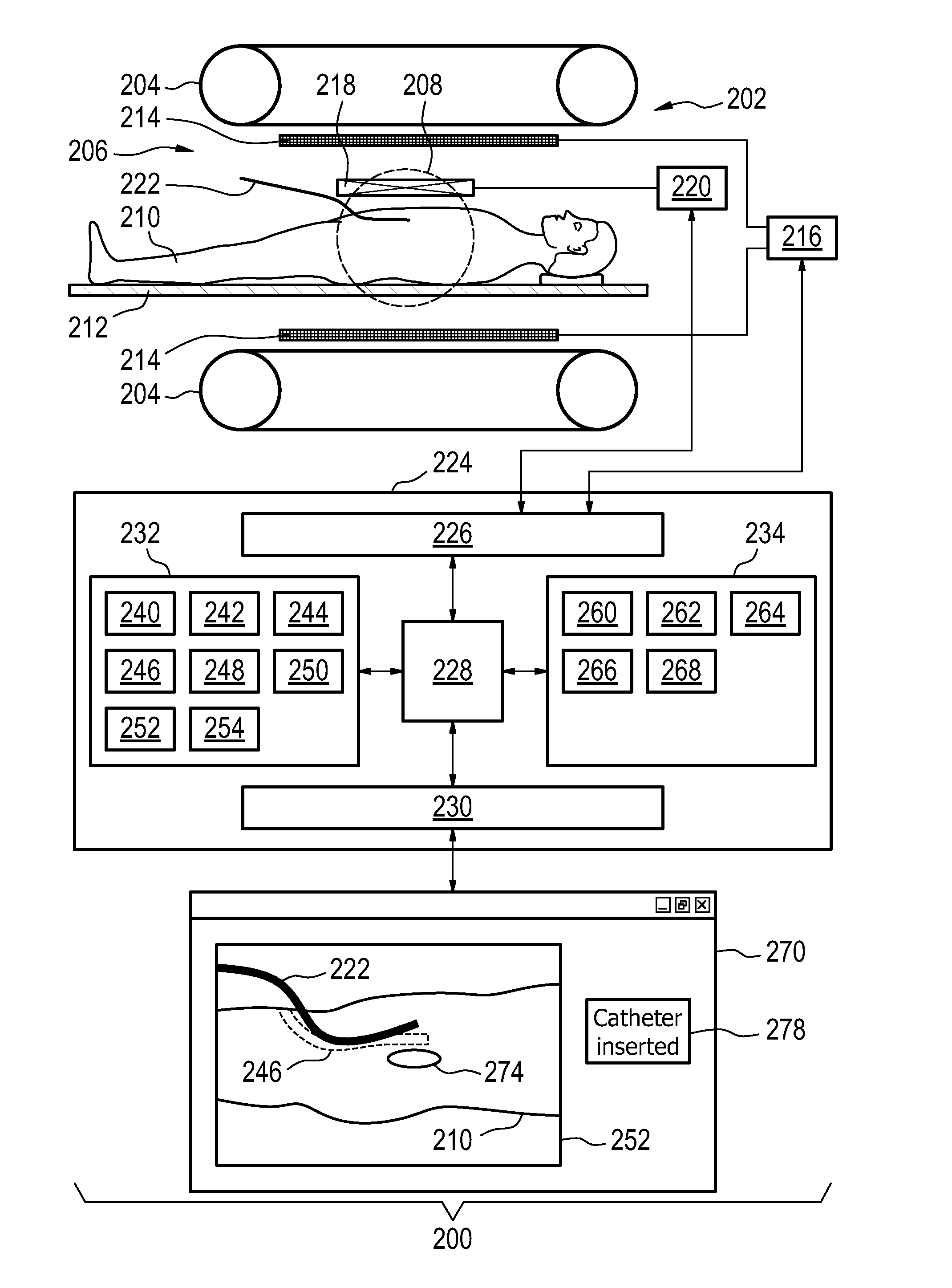
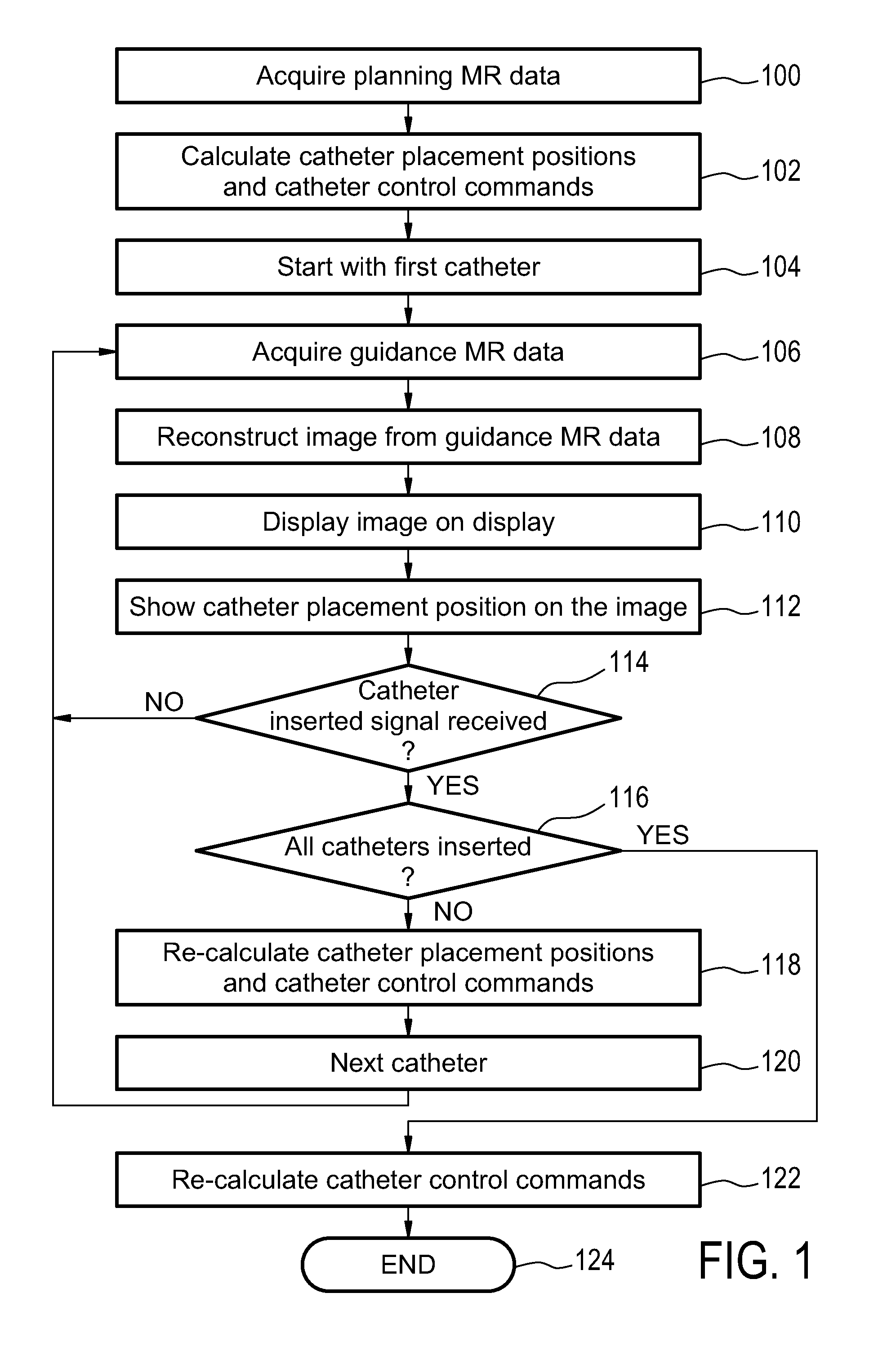
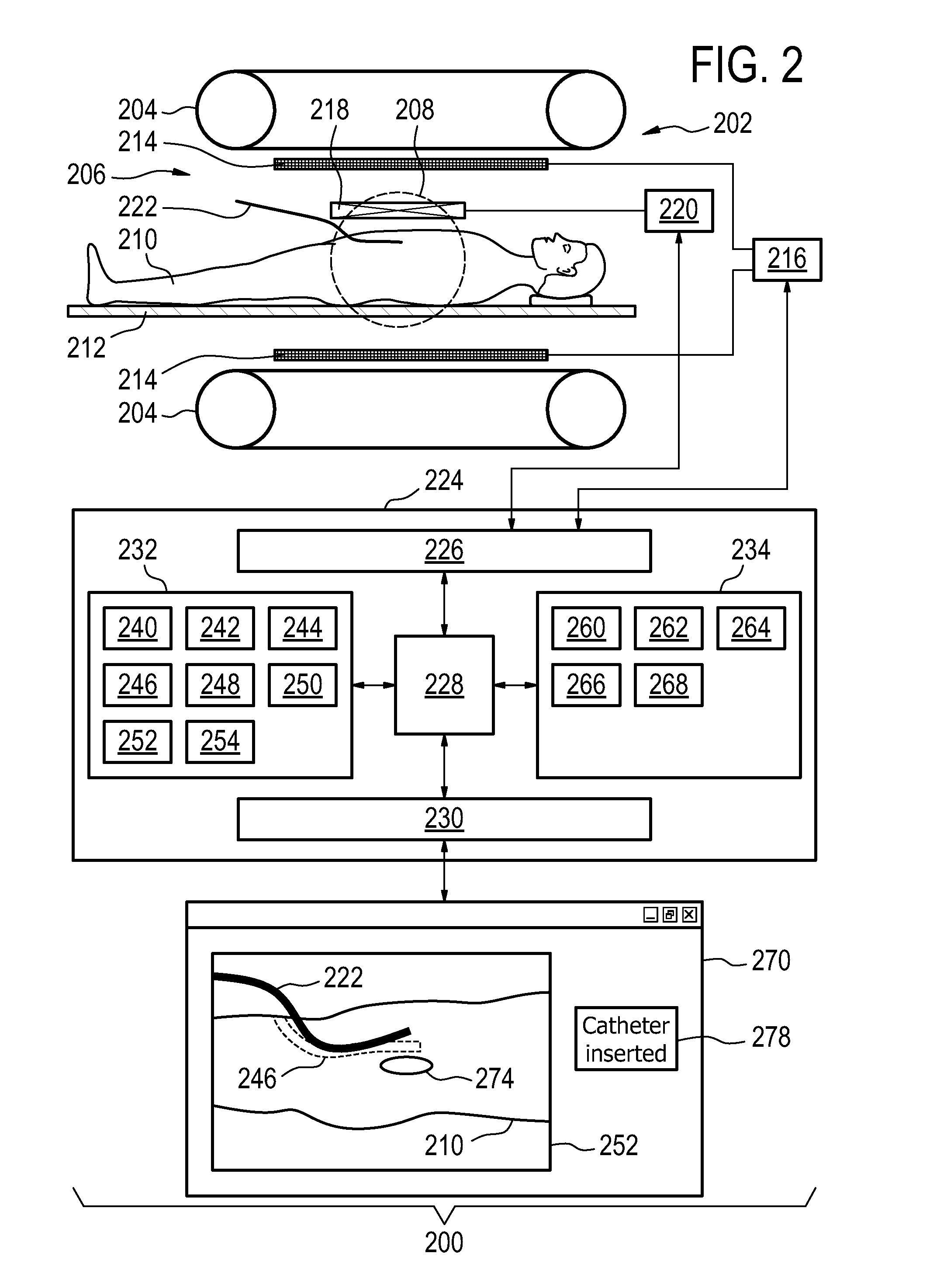
Medical apparatus for displaying the catheter placement position
InactiveUS20140303423A1Inexpensively and accurately determiningAccurate measurementX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBrachytherapyDisplay device
The invention provides for a medical apparatus (200, 300, 400) comprising: a magnetic resonance imaging system (202), a display (270), a processor (228), and a memory (234) for storing instructions for the processor. The instructions causes the processor to receive a brachytherapy treatment plan (240), acquire (100) planning magnetic resonance data (244), calculate (102) a catheter placement positions (246, 900, 902) and a catheter control commands (248) the brachytherapy catheters. The instructions cause the processor, for each catheter placement position, to repeatedly: acquire (106) guidance magnetic resonance data (250), reconstruct (108) an image (252, 500), display (110) the image and the catheter placement position on the display, receive (114) a catheter inserted signal from a user interface, segment (116) the image to determine the catheter placement position after receiving the catheter inserted signal, recalculate (116) the catheter placement positions for each remaining catheter placement position after receiving the catheter inserted signal, and recalculate (116) the catheter control command for all of the multiple catheters after receiving the catheter inserted signal.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com