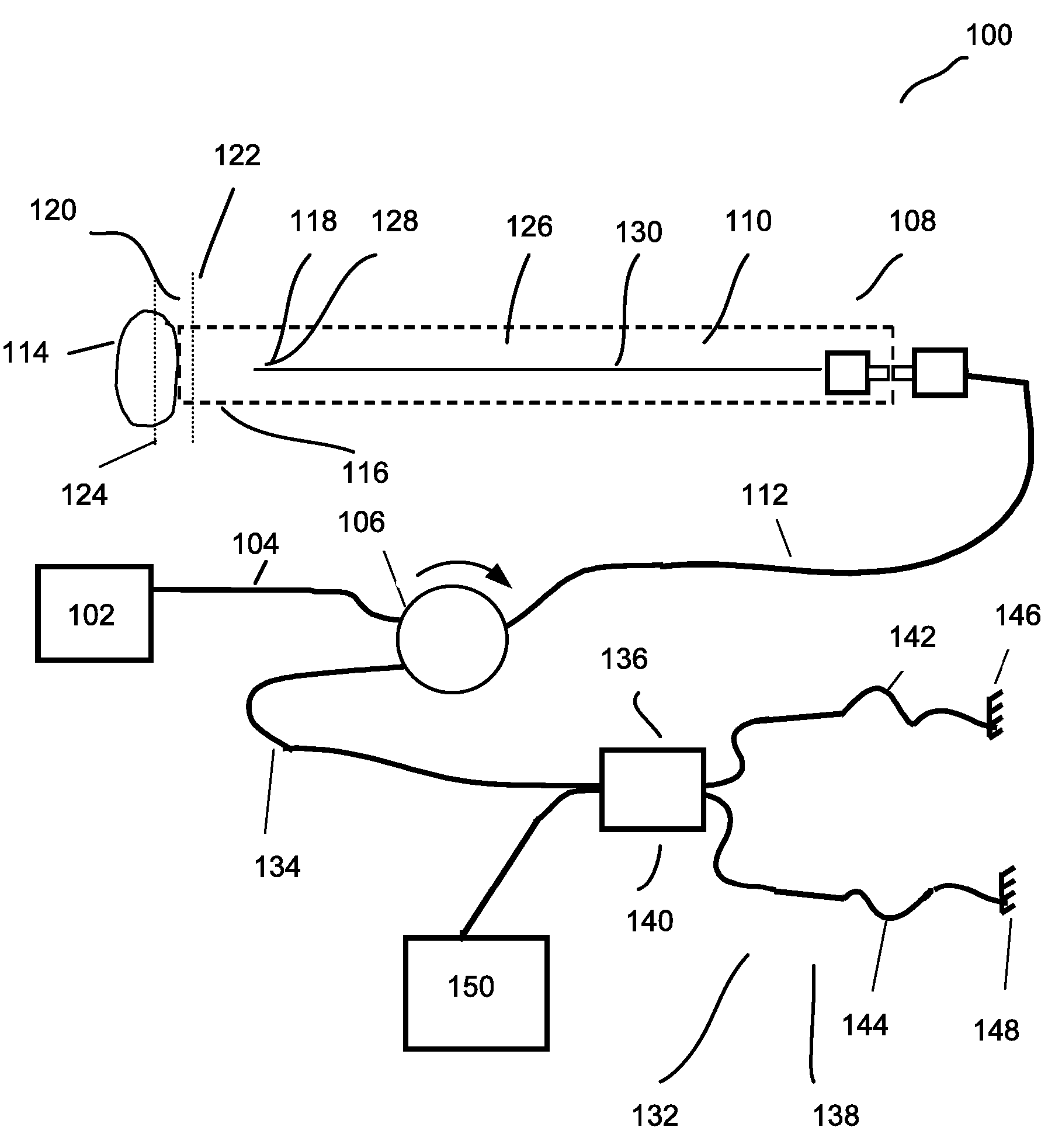
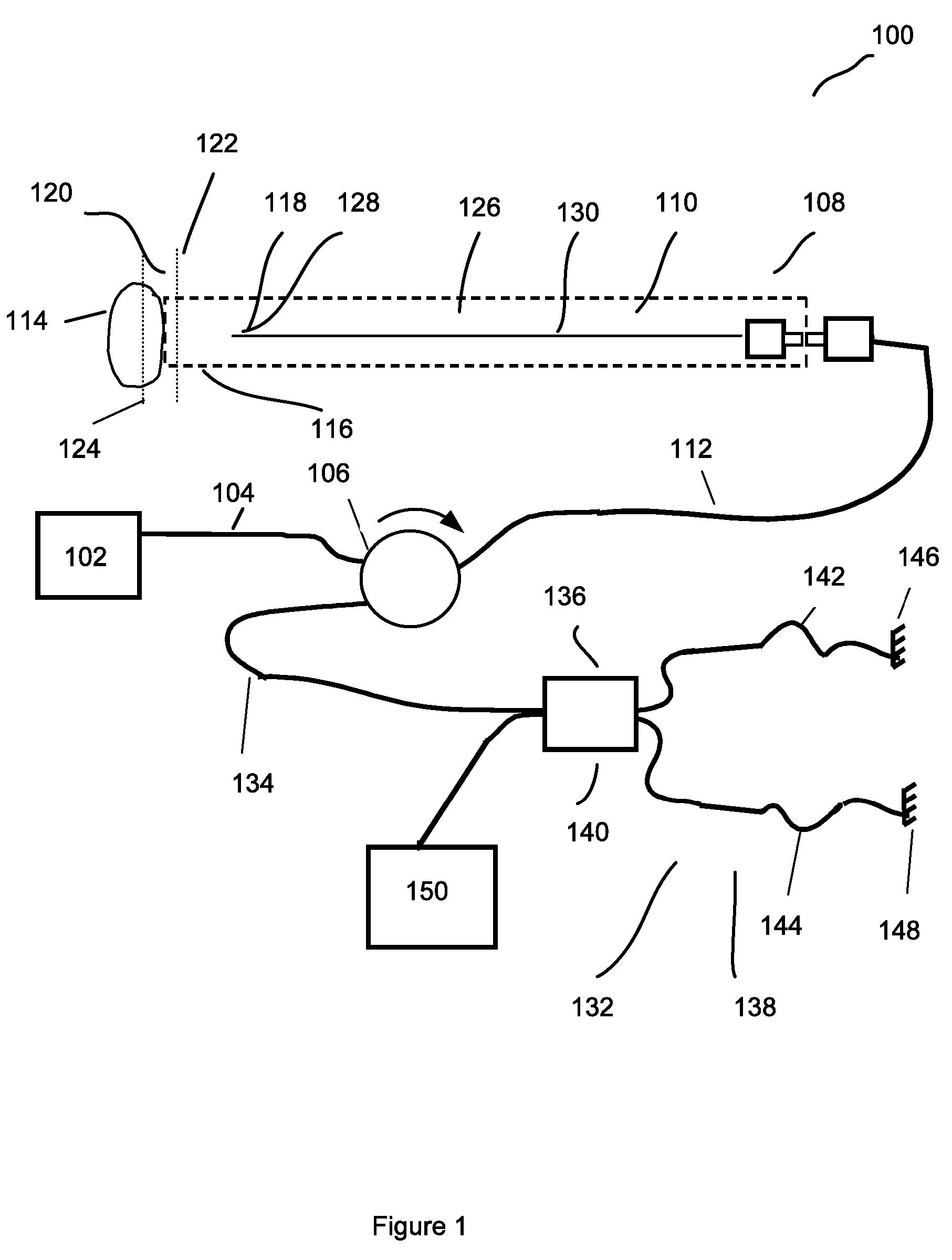
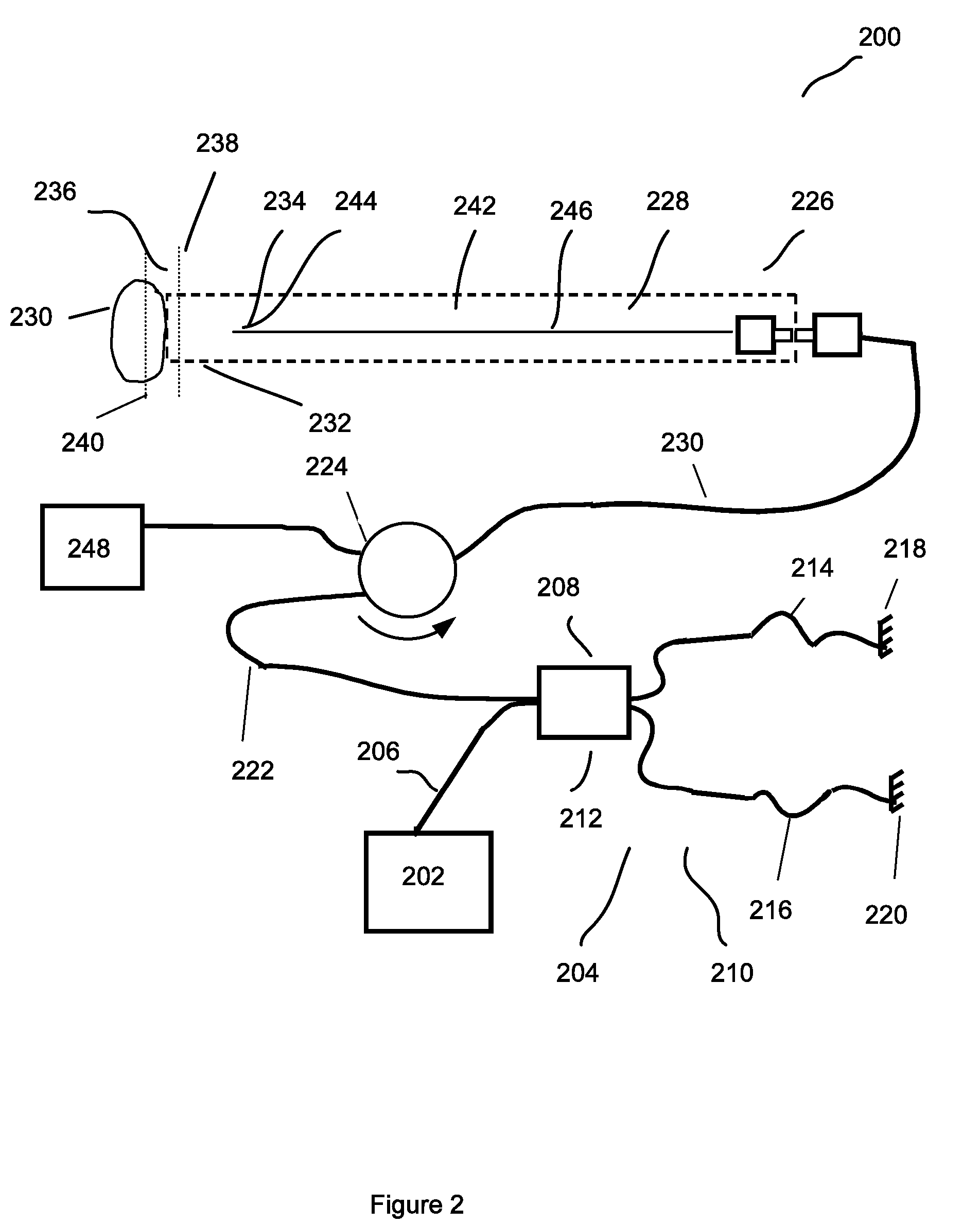
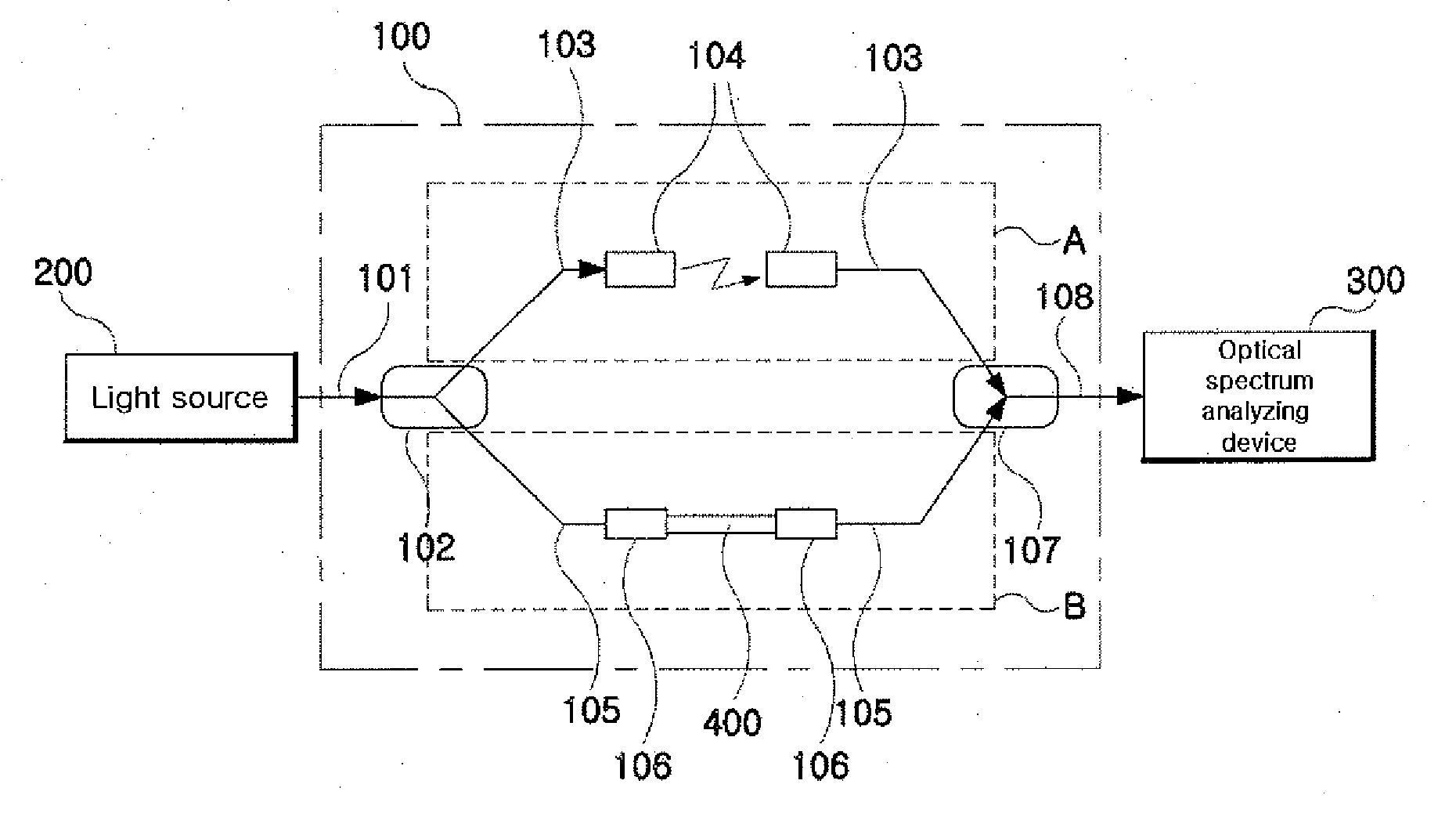
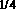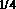Patents
Literature
44 results about "Astronomical interferometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
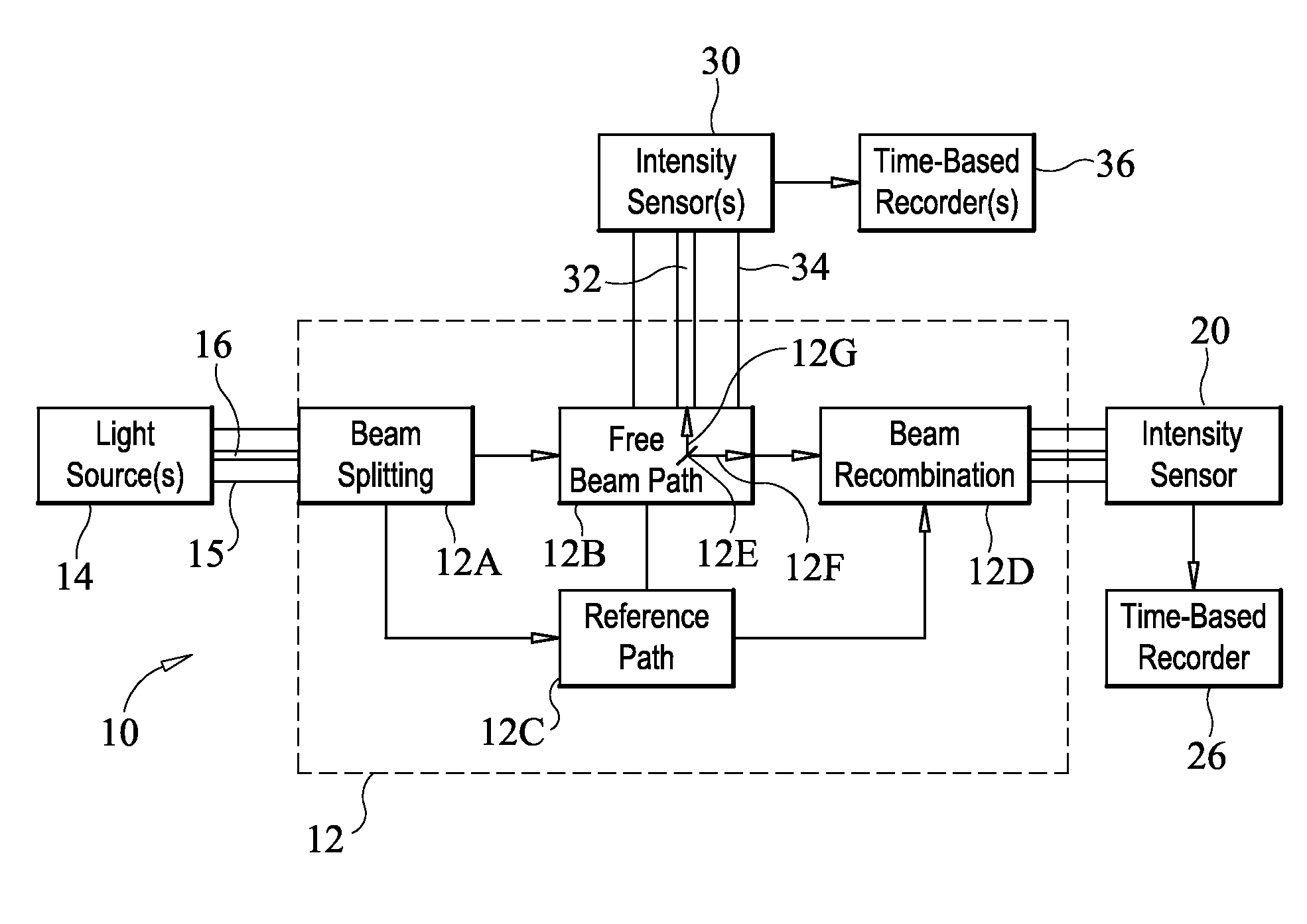
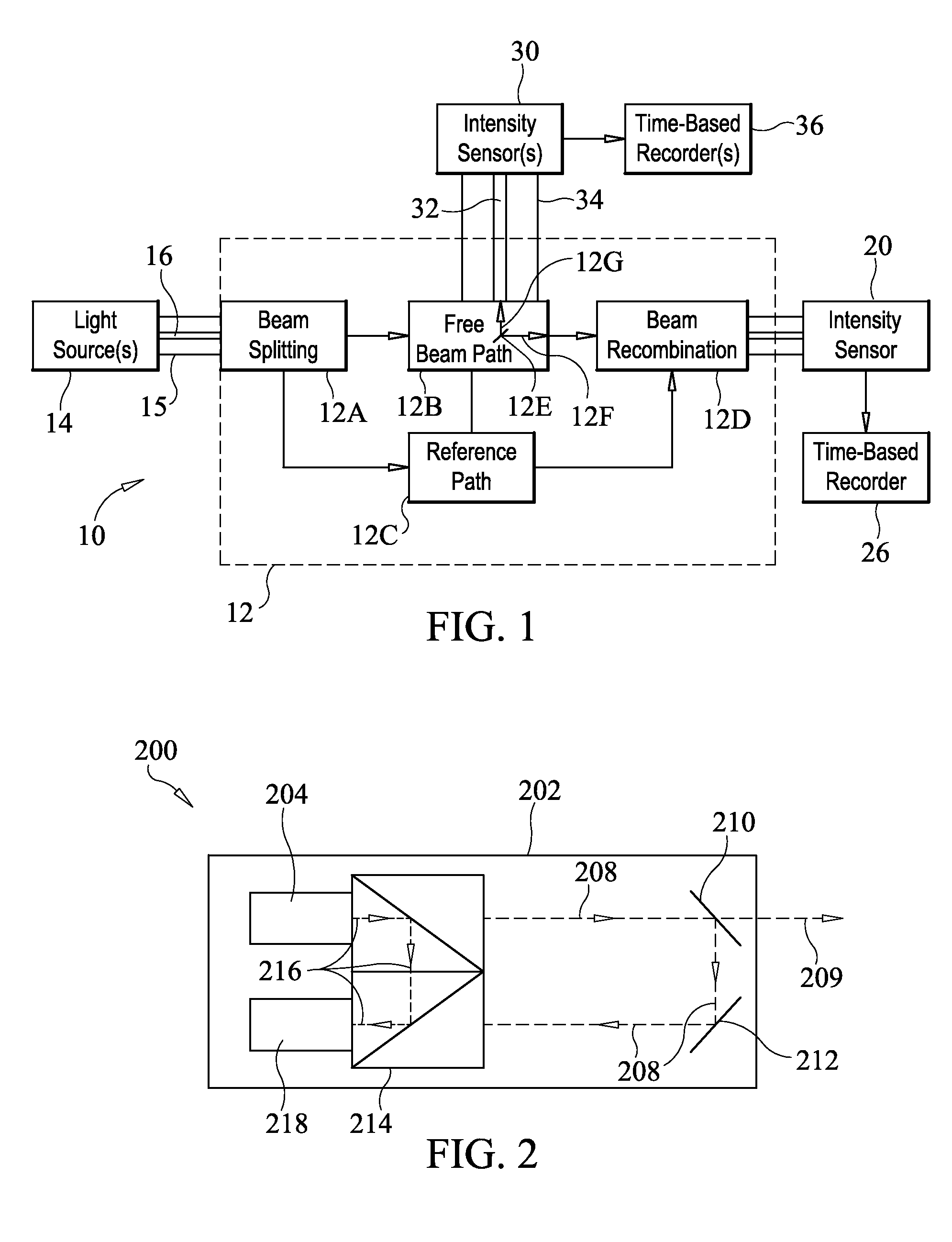
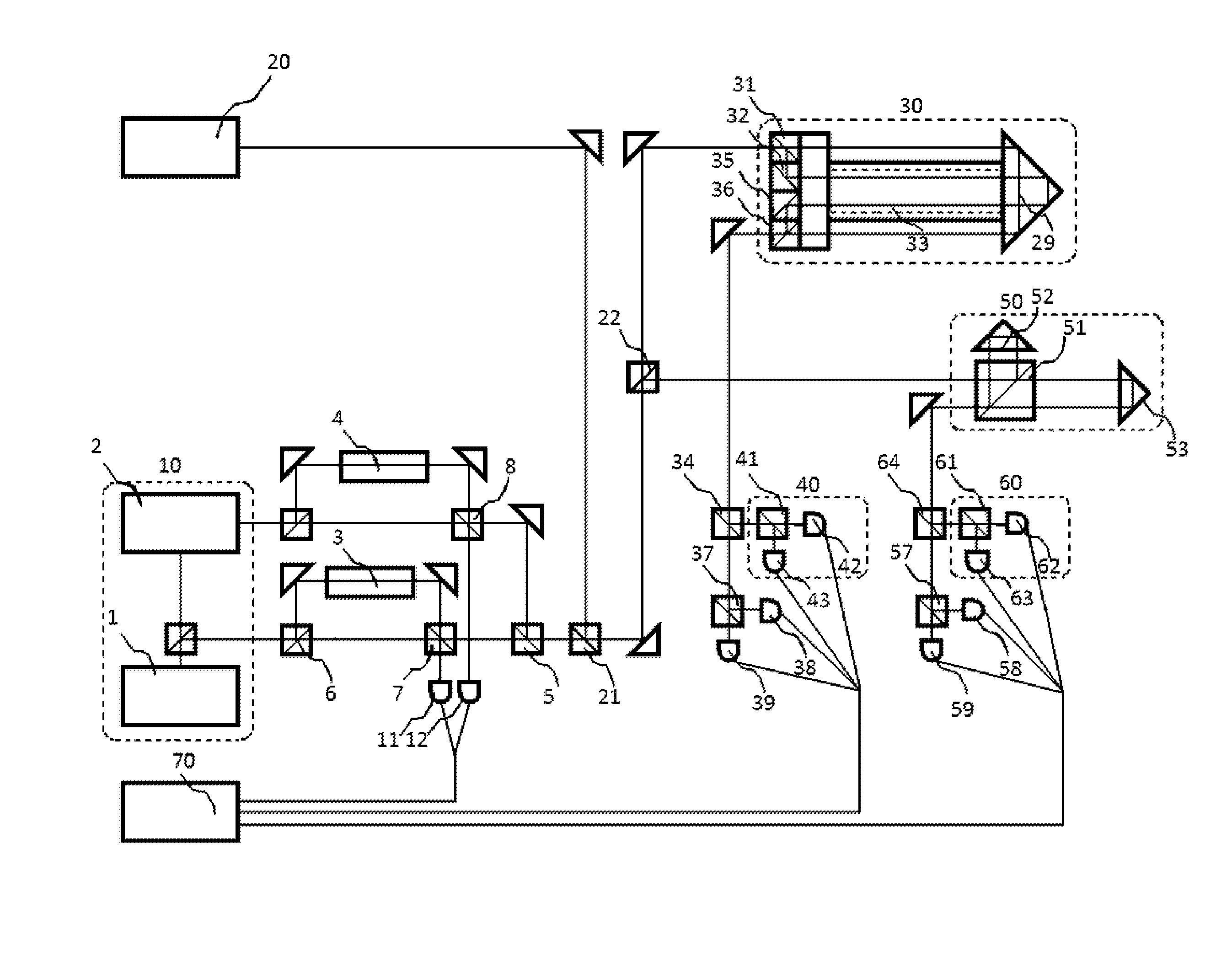
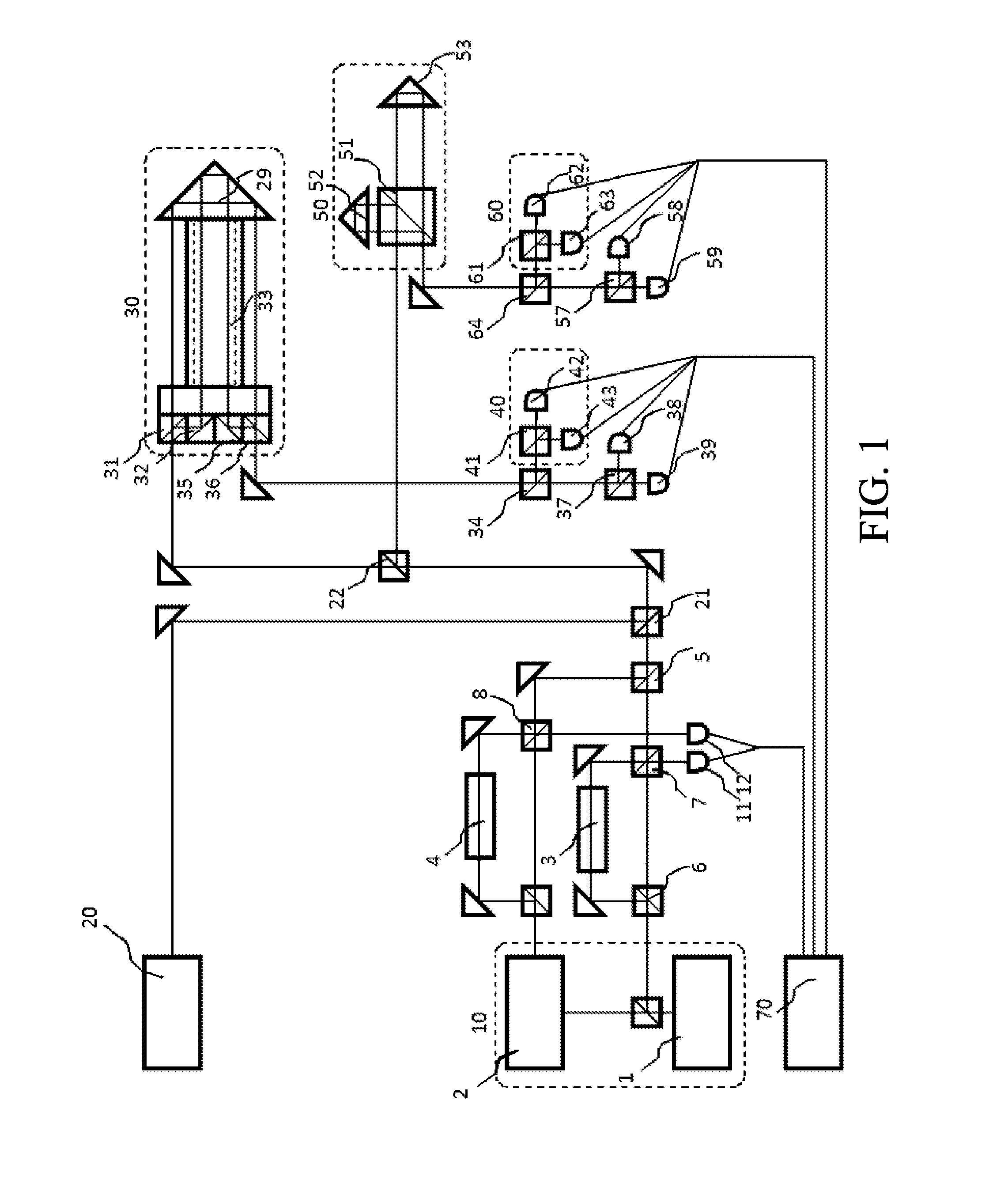
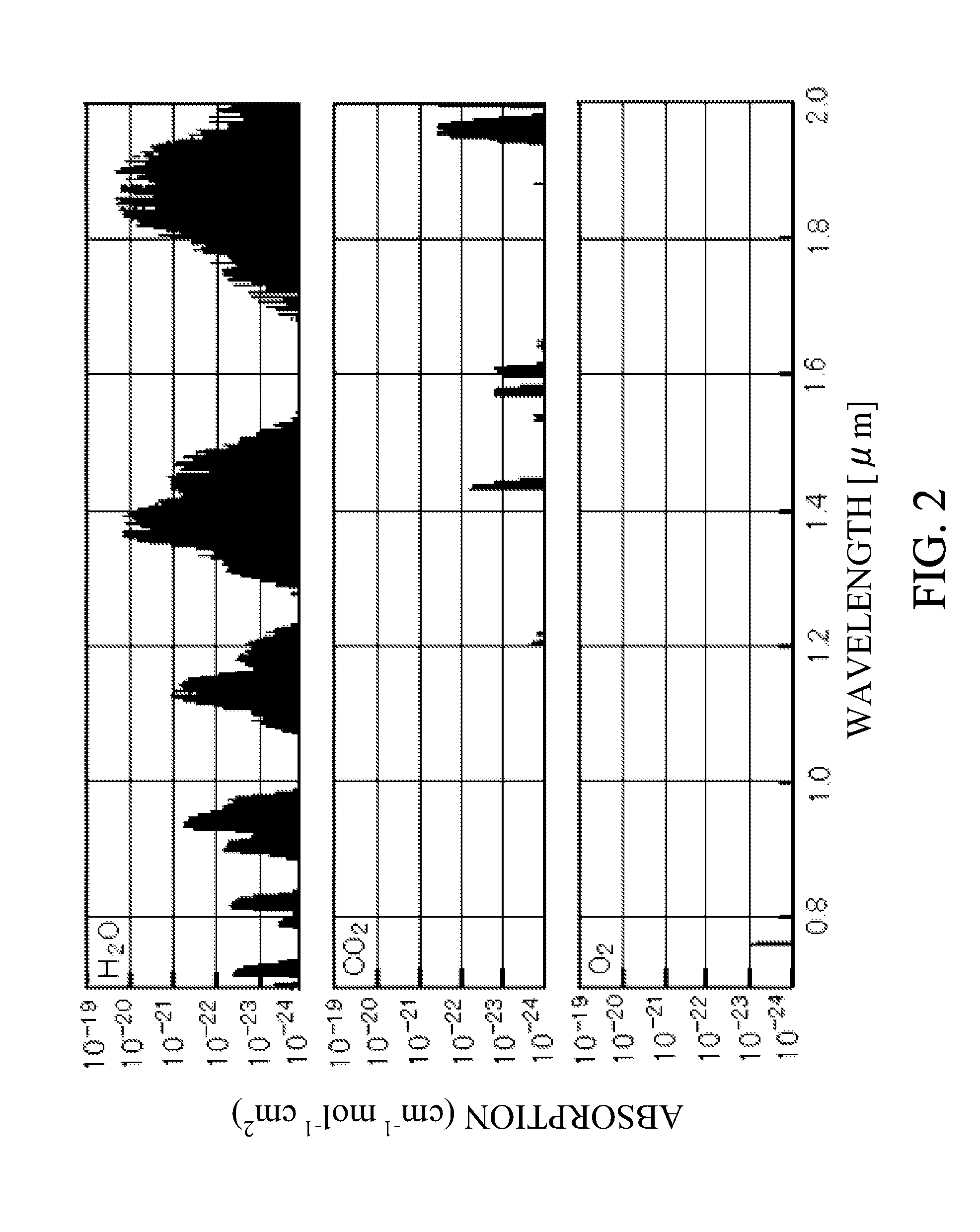
An astronomical interferometer is an array of separate telescopes, mirror segments, or radio telescope antennas that work together as a single telescope to provide higher resolution images of astronomical objects such as stars, nebulas and galaxies by means of interferometry. The advantage of this technique is that it can theoretically produce images with the angular resolution of a huge telescope with an aperture equal to the separation between the component telescopes. The main drawback is that it does not collect as much light as the complete instrument's mirror. Thus it is mainly useful for fine resolution of more luminous astronomical objects, such as close binary stars. Another drawback is that the maximum angular size of a detectable emission source is limited by the minimum gap between detectors in the collector array.
Common path frequency domain optical coherence reflectometer and common path frequency domain optical coherence tomography device
InactiveUS7426036B2Improve fluencyImprove signal-to-noise ratioInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansData acquisitionHandling system
Common path frequency domain optical coherence reflectometry / tomography devices with an additional interferometer are suggested. The additional interferometer offset is adjusted such, that it is ether less than the reference offset, or exceeds the distance from the reference reflector to the distal boundary of the longitudinal range of interest. This adjustment allows for relieving the requirements to the spectral resolution of the frequency domain optical coherence reflectometry / tomography engine and / or speed of the data acquisition and processing system, and eliminates depth ambiguity problems. The new topology allows for including a phase or frequency modulator in an arm of the additional interferometer improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the devices. The modulator is also capable of substantially eliminating mirror ambiguity, DC artifacts, and autocorrelation artifacts. The interference signal is produced either in the interferometer or inside of the optical fiber probe leading to the sample.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
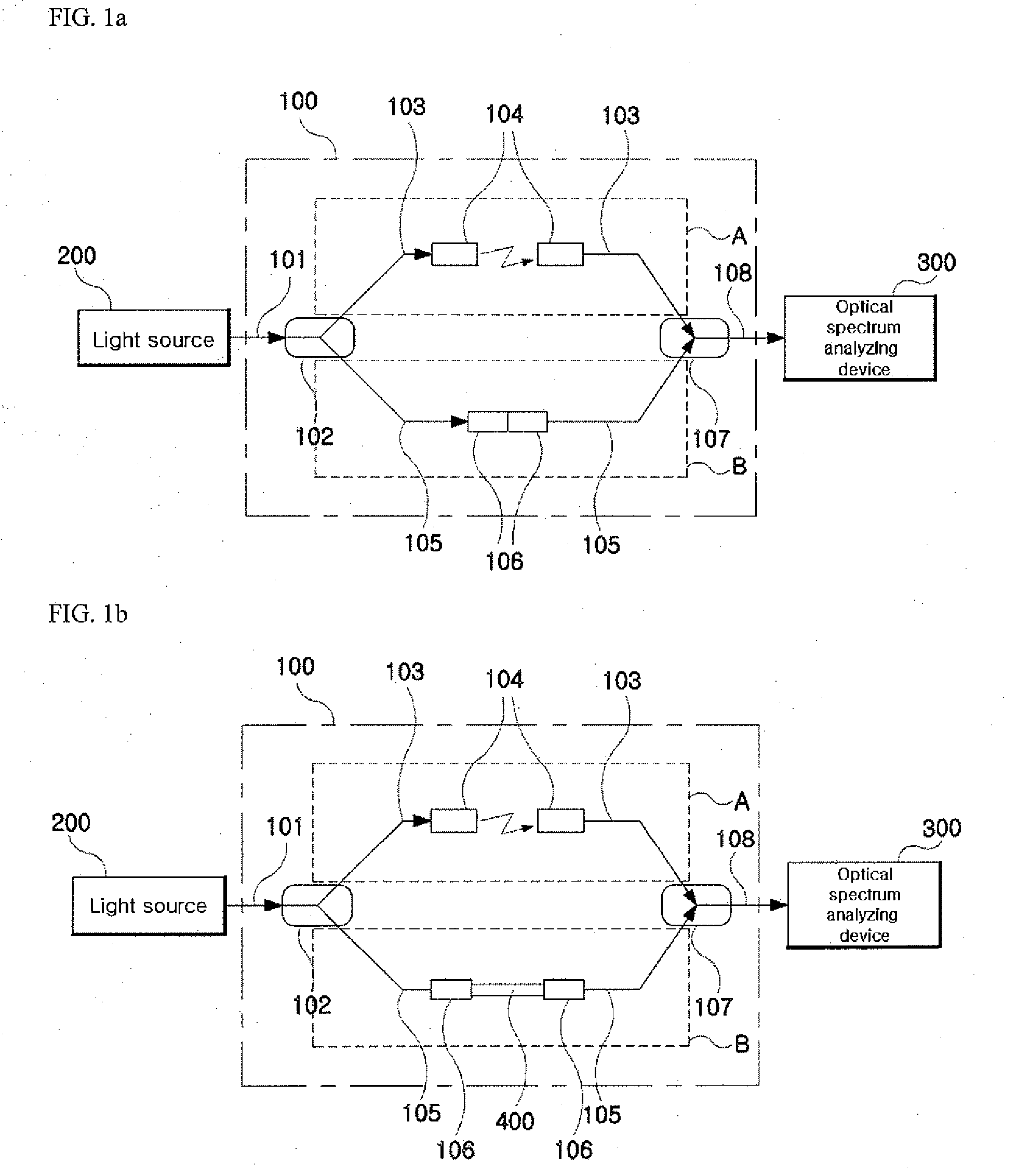
Measurement method of chromatic dispersion of optical beam waveguide using interference fringe measurement system
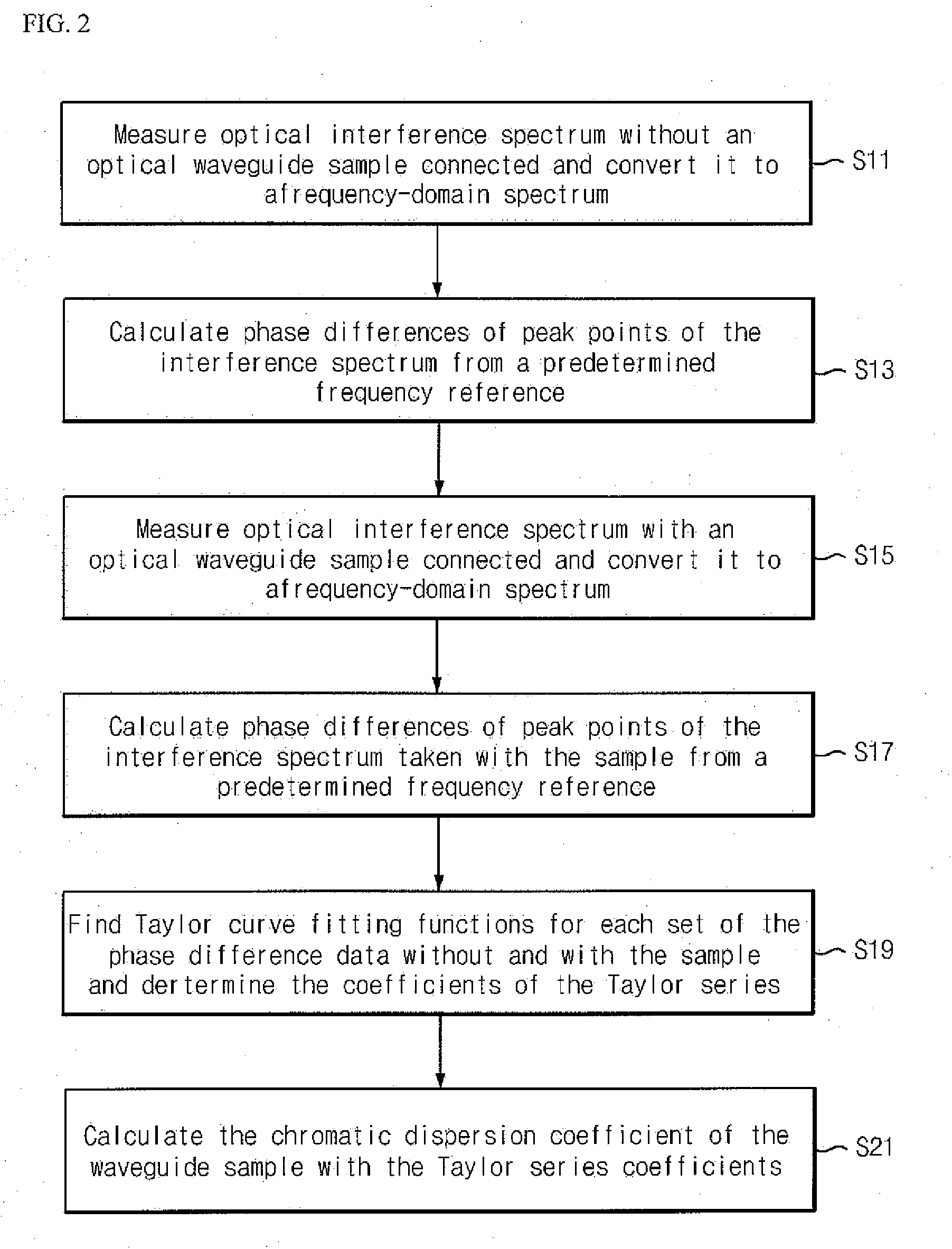
The present invention relates to a measurement method of the chromatic dispersion of an optical waveguide using an optical interferometer with a broadband multi-wavelength light source and an optical spectrum analyzing apparatus, wherein one arm, called “reference arm” of the interferometer's two arms has an adjustable air spacing and the other arm, called “sample arm” can contain said optical waveguide to be measured, and including the following measurement and analysis steps: measuring interference spectra of the optical beam output exiting from the said interferometer with an optical spectrum analyzing apparatus when said optical waveguide is connected to said sample arm, and when said optical waveguide is not connected to said sample arm respectively; by adjusting the reference arm length for appearance of clear interference patterns; converting the wavelength-domain interference spectra into frequency-domain interference spectra and calculating phase difference values of the interference peaks of one of the spectra from a predetermined reference peak as a function of the frequency change by counting the interference peak (or valley) points; finding a Taylor series curve fit function for each set of the phase difference value data corresponding to each of the two interference spectra; and calculating a chromatic dispersion coefficient of the optical waveguide by using the coefficients of the Taylor series curve fit functions.
Owner:INHA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION
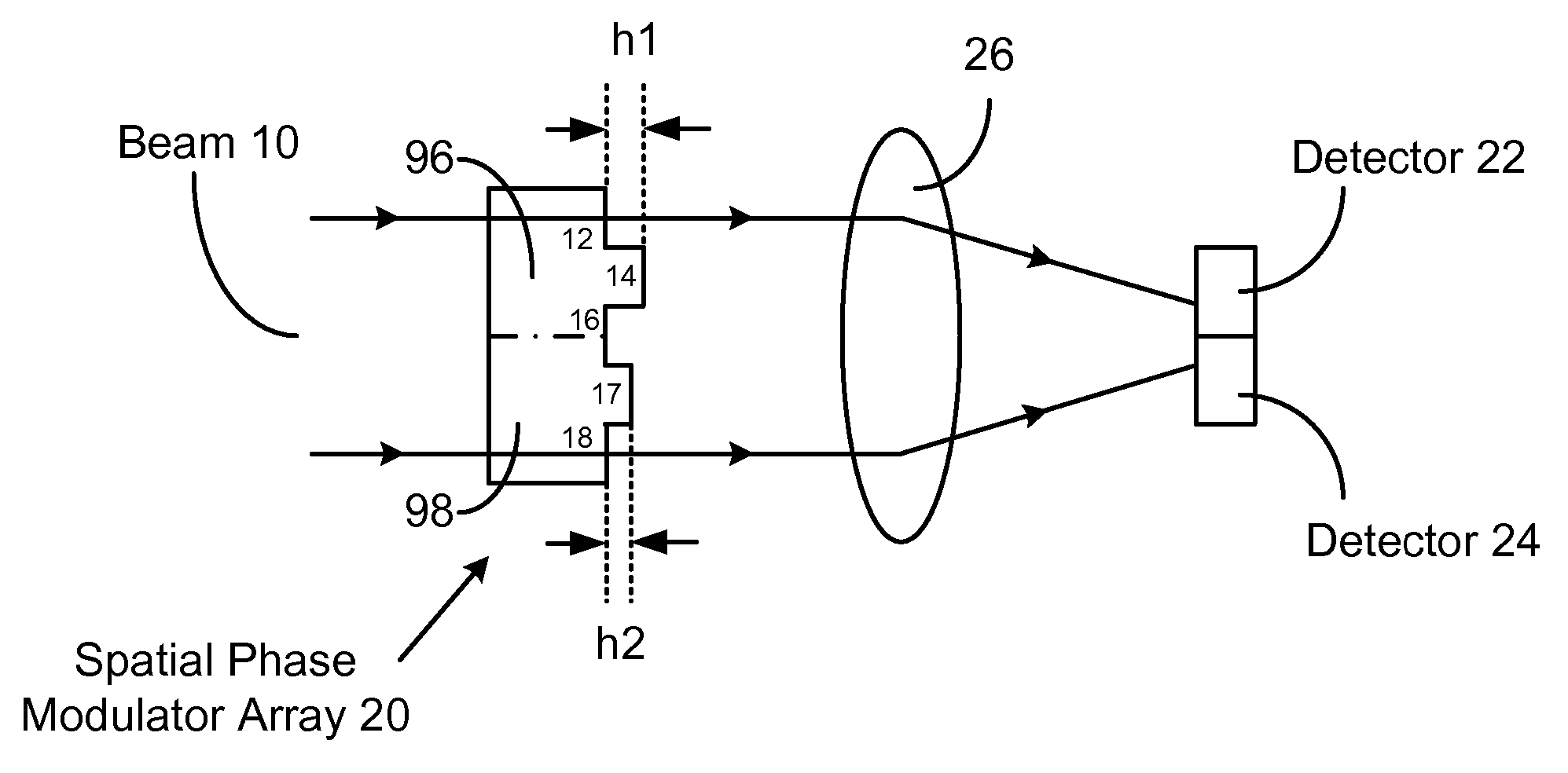
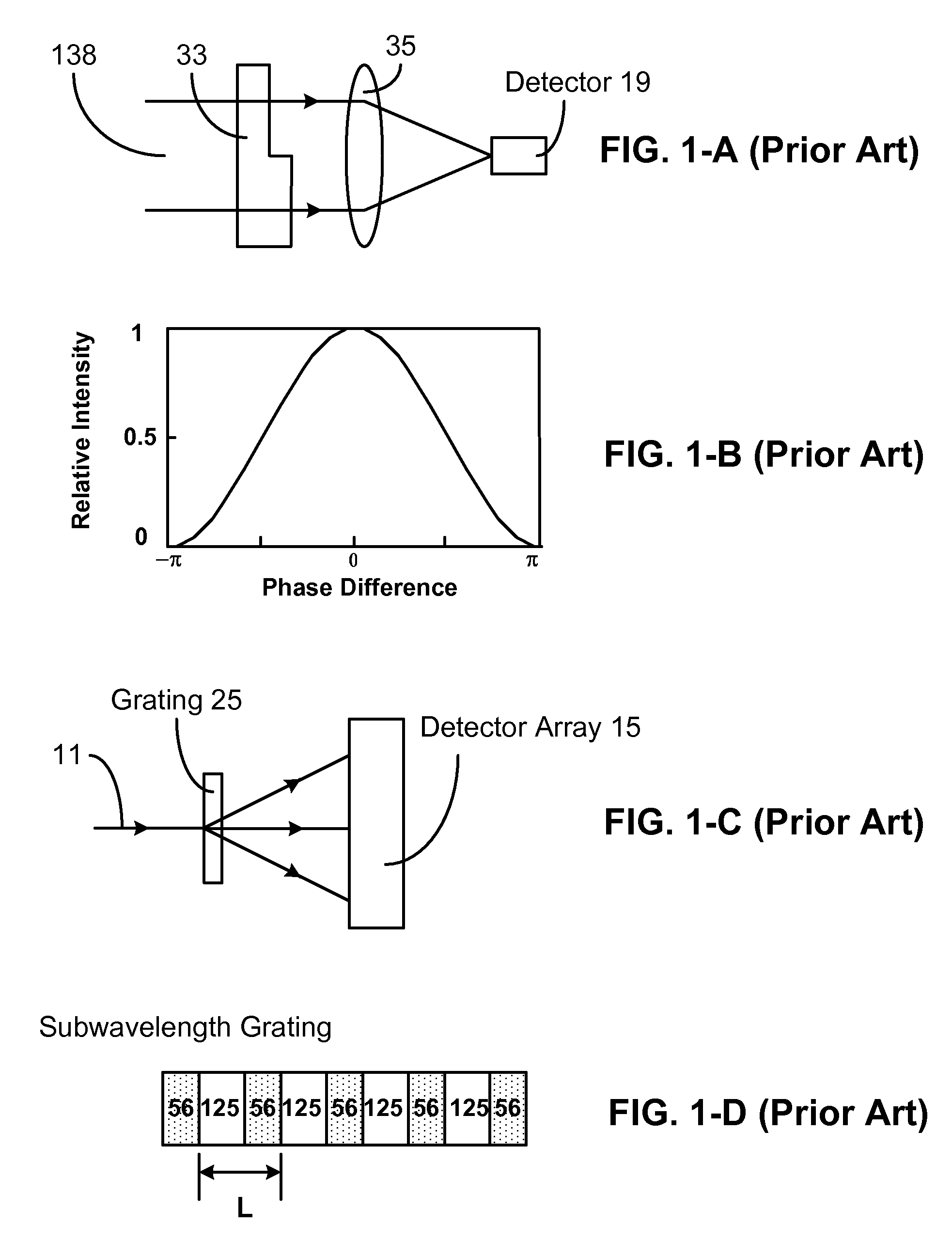
Optical interferometer and method
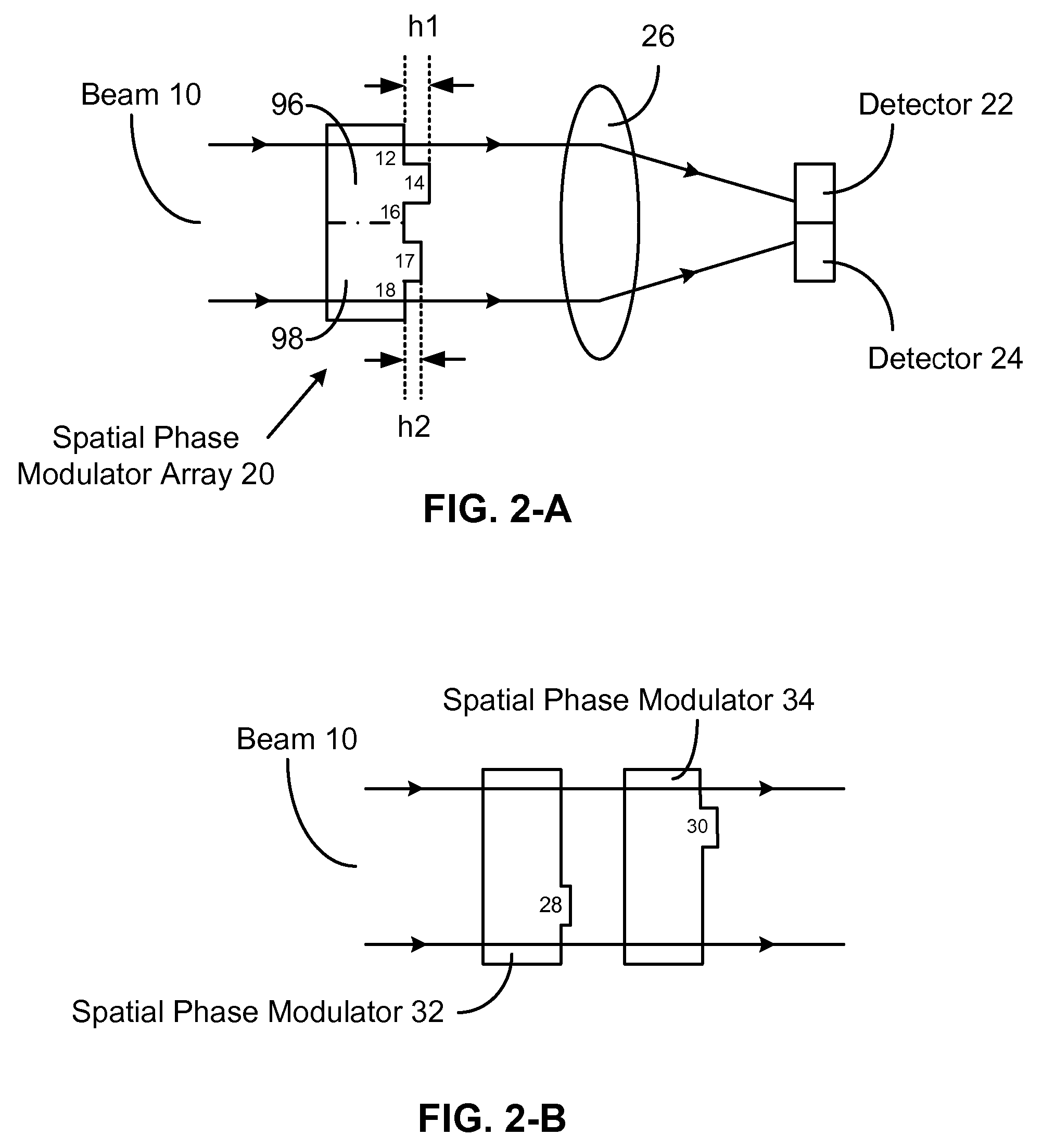
Disclosed are compact optical interferometer array, miniature optical interferometer array, and miniature optical interferometer. The interferometer arrays contain a spatial phase modulator array and a detector array. They are used for conducting multiple measurements. The miniature interferometer has only one component—a spatial phase modulator. Without passing through any focus lens, beam portions coming out of the modulator spread and merge together by themselves. Size of the miniature interferometer can reach subwavelength or even nanoscale. The interferometer array and miniature interferometer find applications in miniature spectrometer, color filter, display, adjustable subwavelength grating, etc.
Owner:LI CHIAN CHIU
Apodization of beams in an optical interferometer
InactiveUS7095504B1Diffraction reductionAvoid diffractionUsing optical meansLight beamAstronomical interferometer
An interferometry apparatus comprises one or more beam generators, a detector, and a plurality of optical paths along which one or more beams of light propagate. Disposed along at least one of the optical paths is an apodization mask to shape one of the beams.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
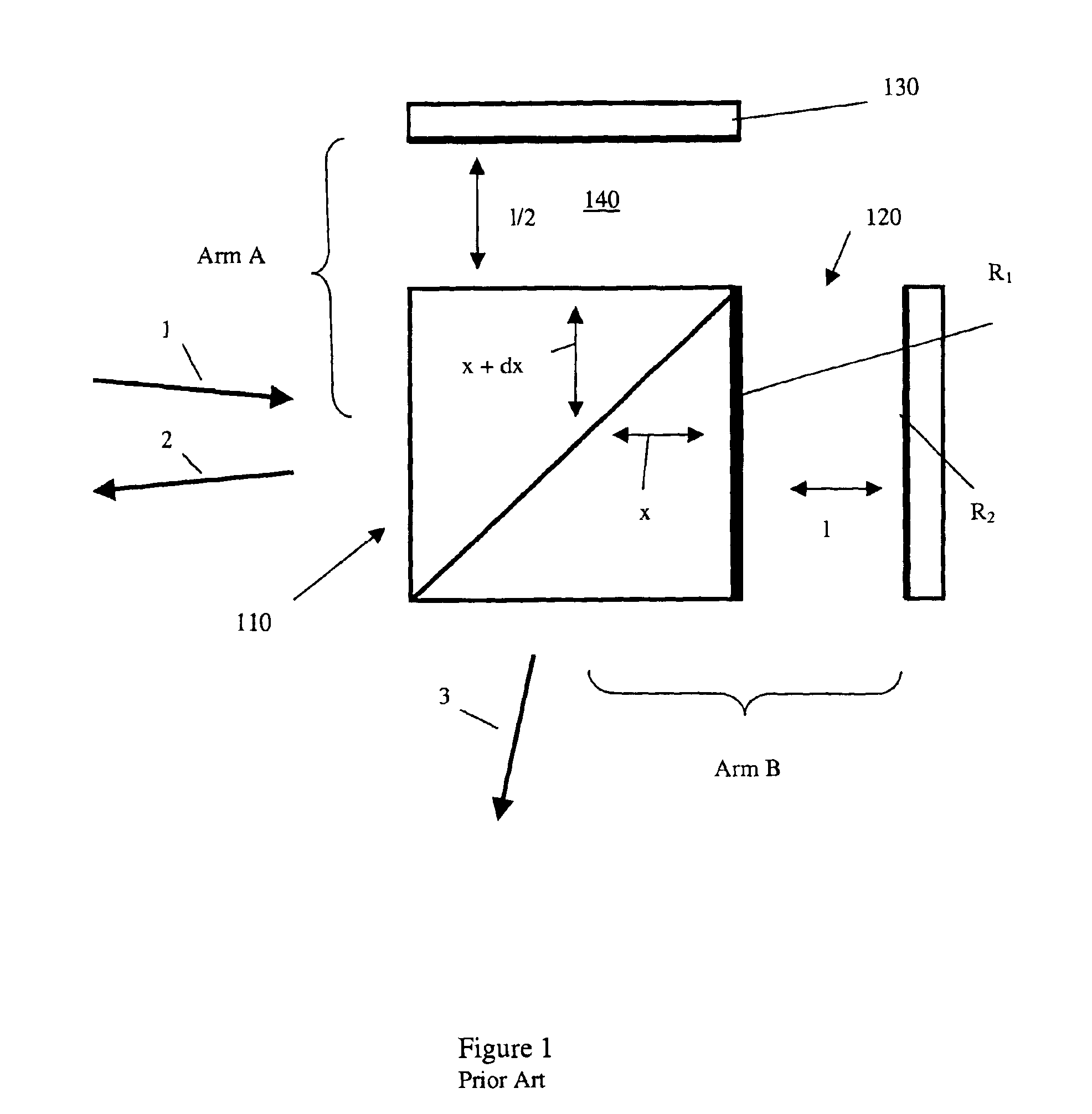
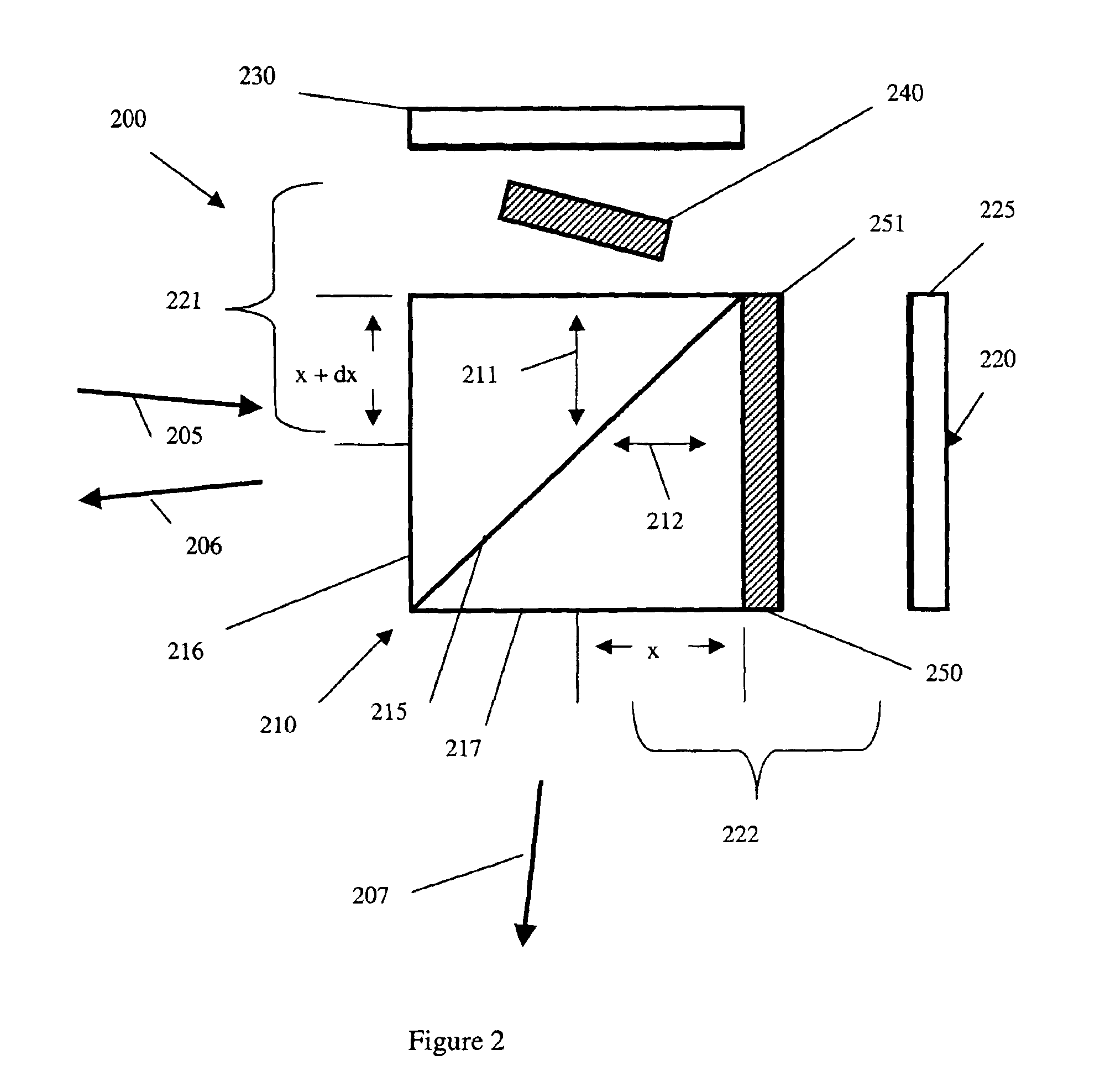
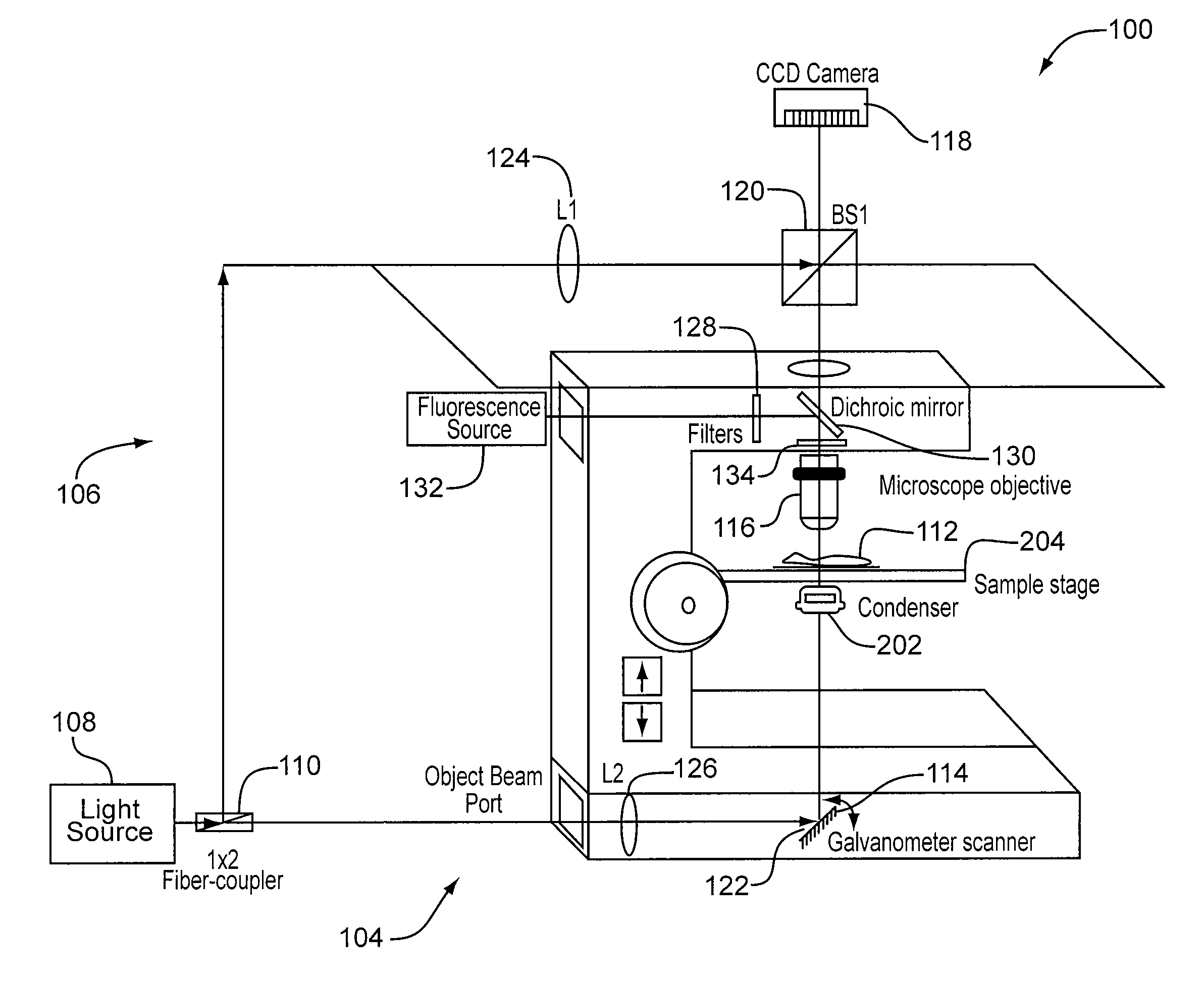
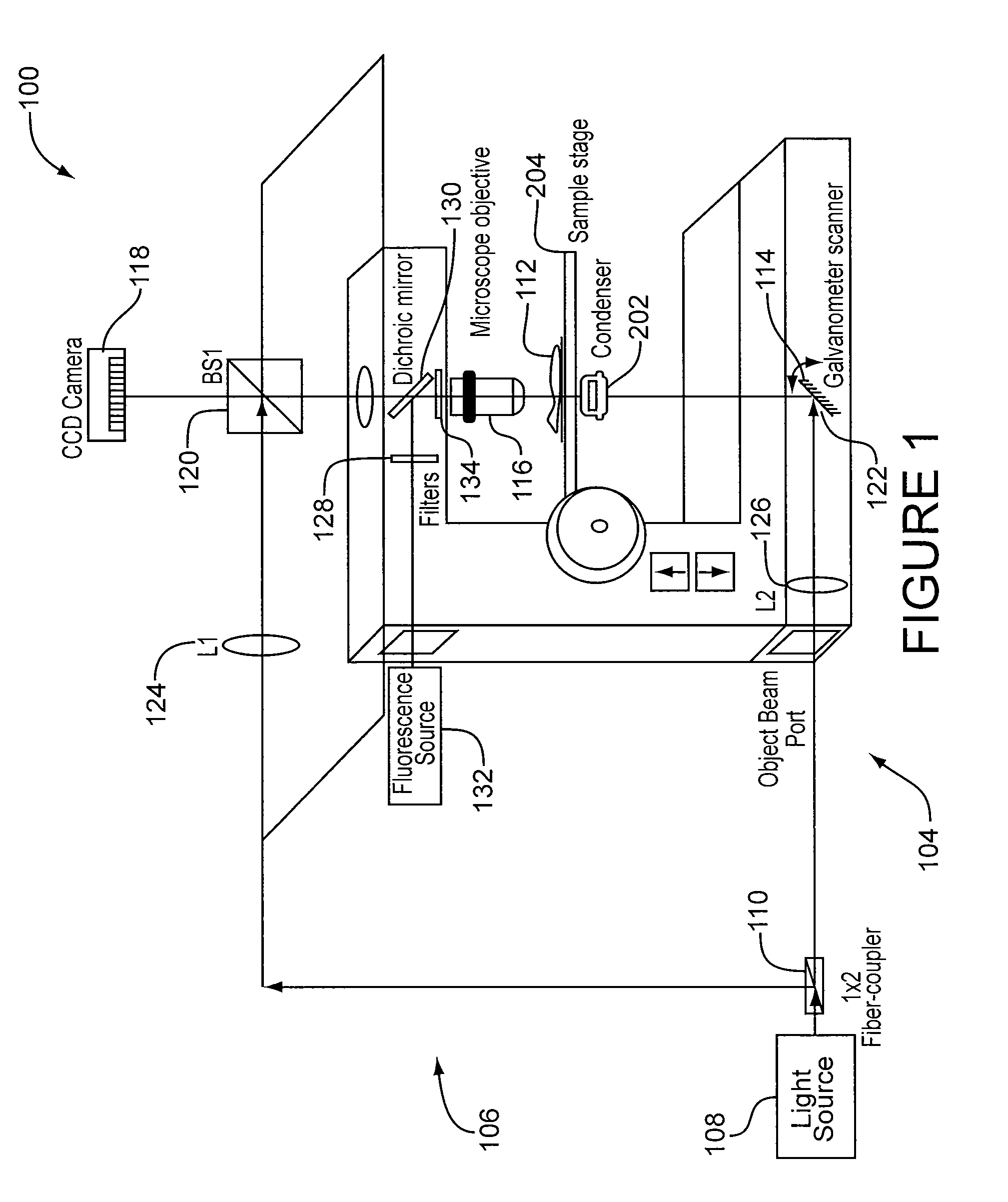
Quantitative phase-imaging systems
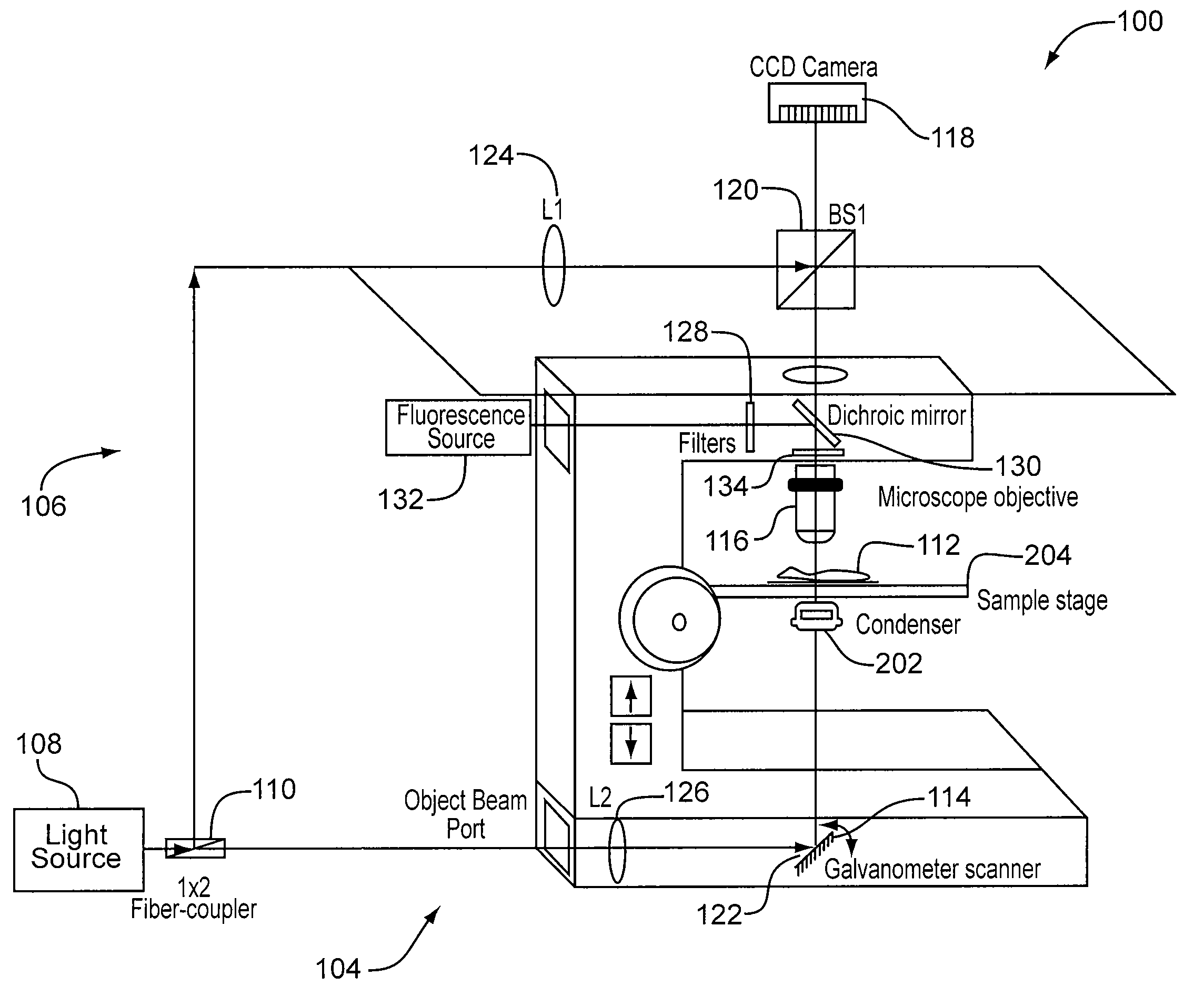
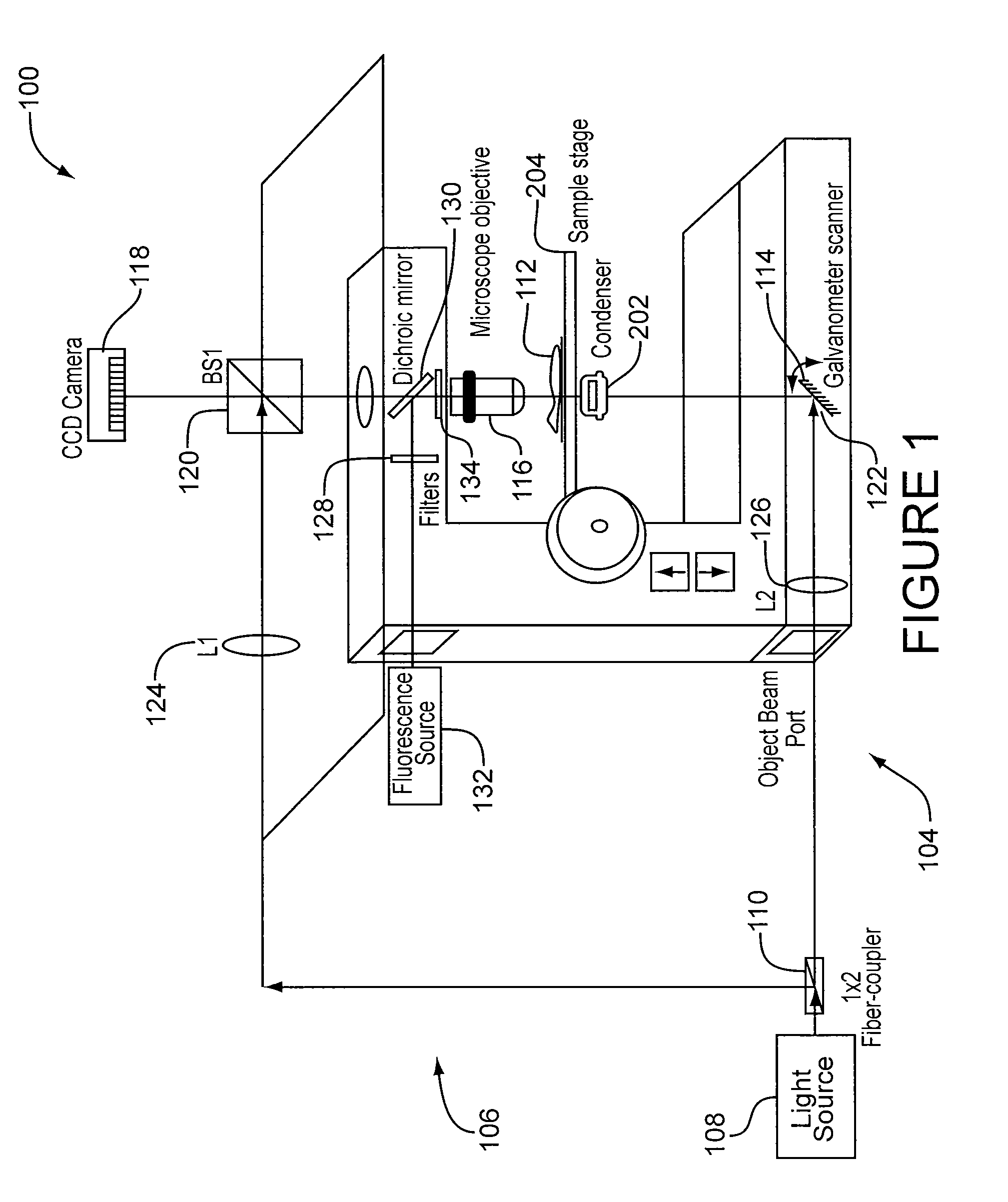
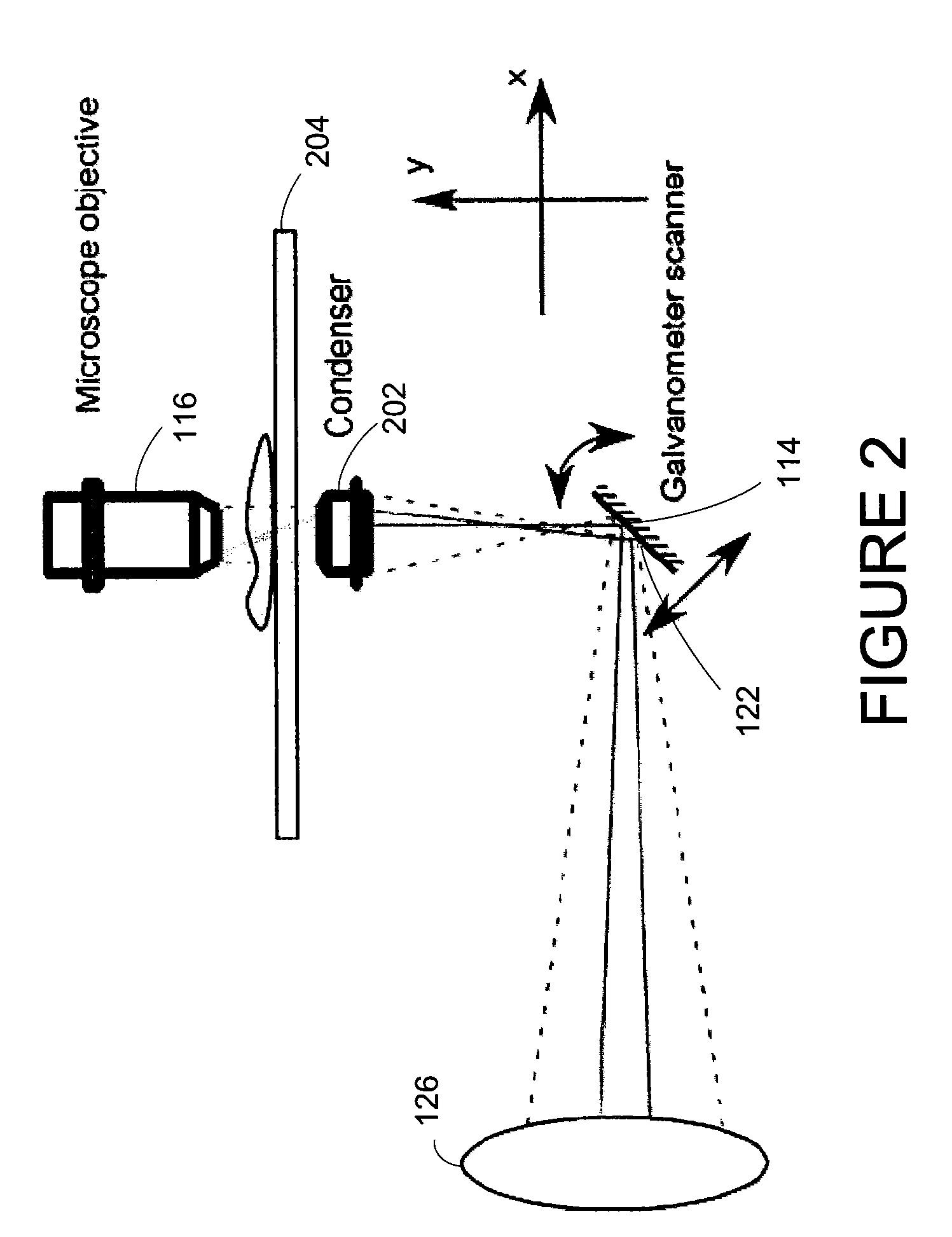
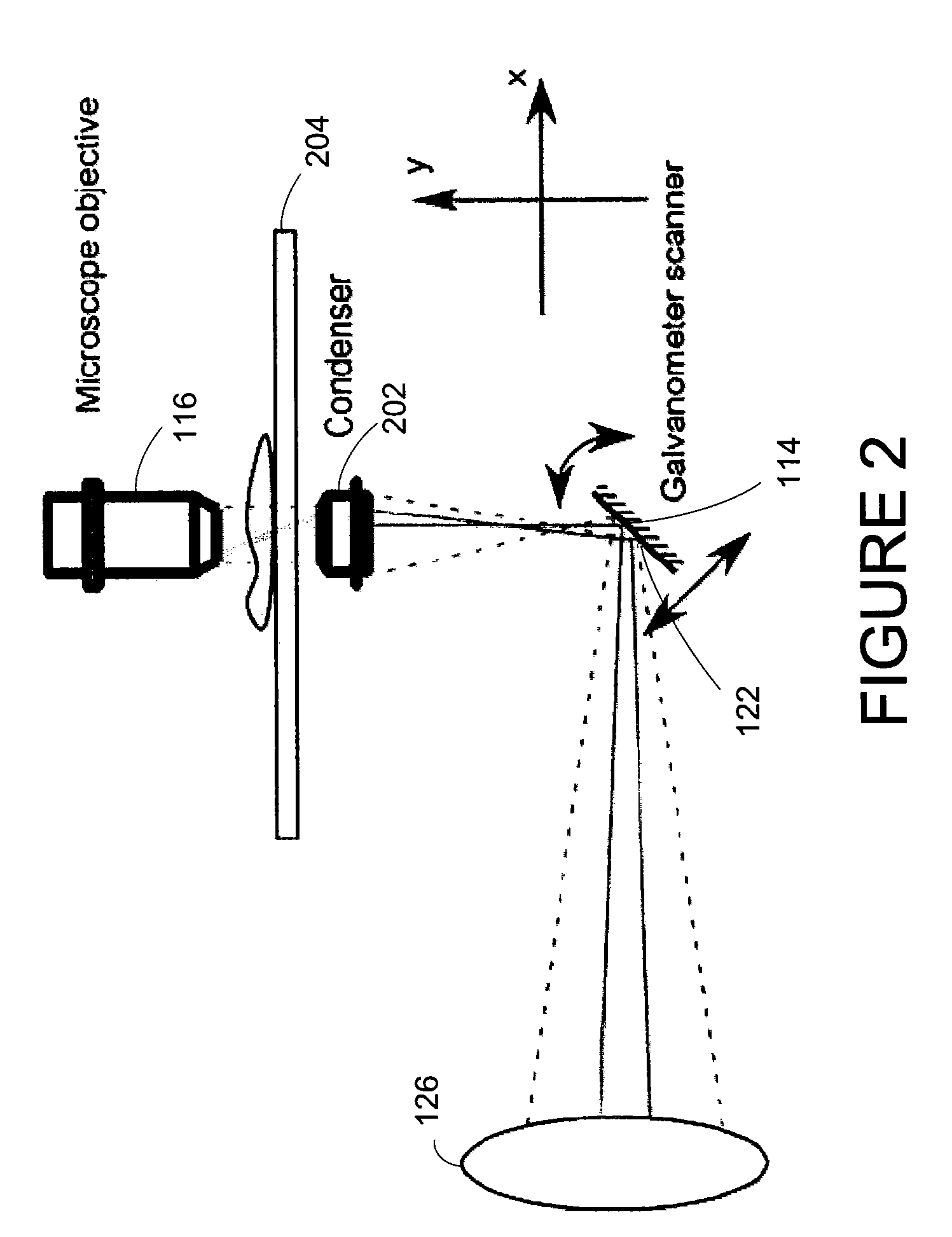
InactiveUS20100231895A1Phase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansGalvanometerAstronomical interferometer
An optical system performs imaging in a transmissive and reflective mode. The system includes an optical interferometer that generates interference phenomena between optical waves to measure multiple distances, thicknesses, and indices of refraction of a sample. Measurements are made through a galvanometer that scans a pre-programmed angular arc. An excitation-emission device allows an electromagnetic excitation and emission to pass through an objective in optical communication with the sample. An electromagnetic detector receives the output of the optical interferometer and the excitation-emission device to render a magnified three dimensional image of the sample.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Optical interferometer
InactiveUS6636317B2Avoid interferenceMeasurement stabilityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBeam splitterLight beam
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Photo-thermal interferometer for monitoring concentration of particulate matters in atmosphere and monitoring method of photo-thermal interferometer
ActiveCN104237088APhase-affecting property measurementsParticle suspension analysisParticulatesBeam splitting
The invention discloses a photo-thermal interferometer for monitoring the concentration of particulate matters in the atmosphere and a monitoring method of the photo-thermal interferometer. The photo-thermal interferometer comprises a laser, a first quarter wave plate, a parallel panel pair, an aerosol chamber, a corner reflecting prism, a modulation laser, a non-depolarization beam splitting prism and a polarization beam splitting prism photoelectric detection device. The monitoring method comprises the steps of filtering sampled air by utilizing filter paper to form dust-containing filter paper, and illuminating the dust-containing filter paper by virtue of modulated laser to cause the variation of surface air temperature and refractive index. If components of the particulate matters in the air are constant, the mass of particulate matters on the filter paper is acquired by measuring the variation of the air refractive index, and the mass of particulate matters on the filter paper is equivalent to the mass concentration of the particulate matters in the air by virtue of a sampling volume.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
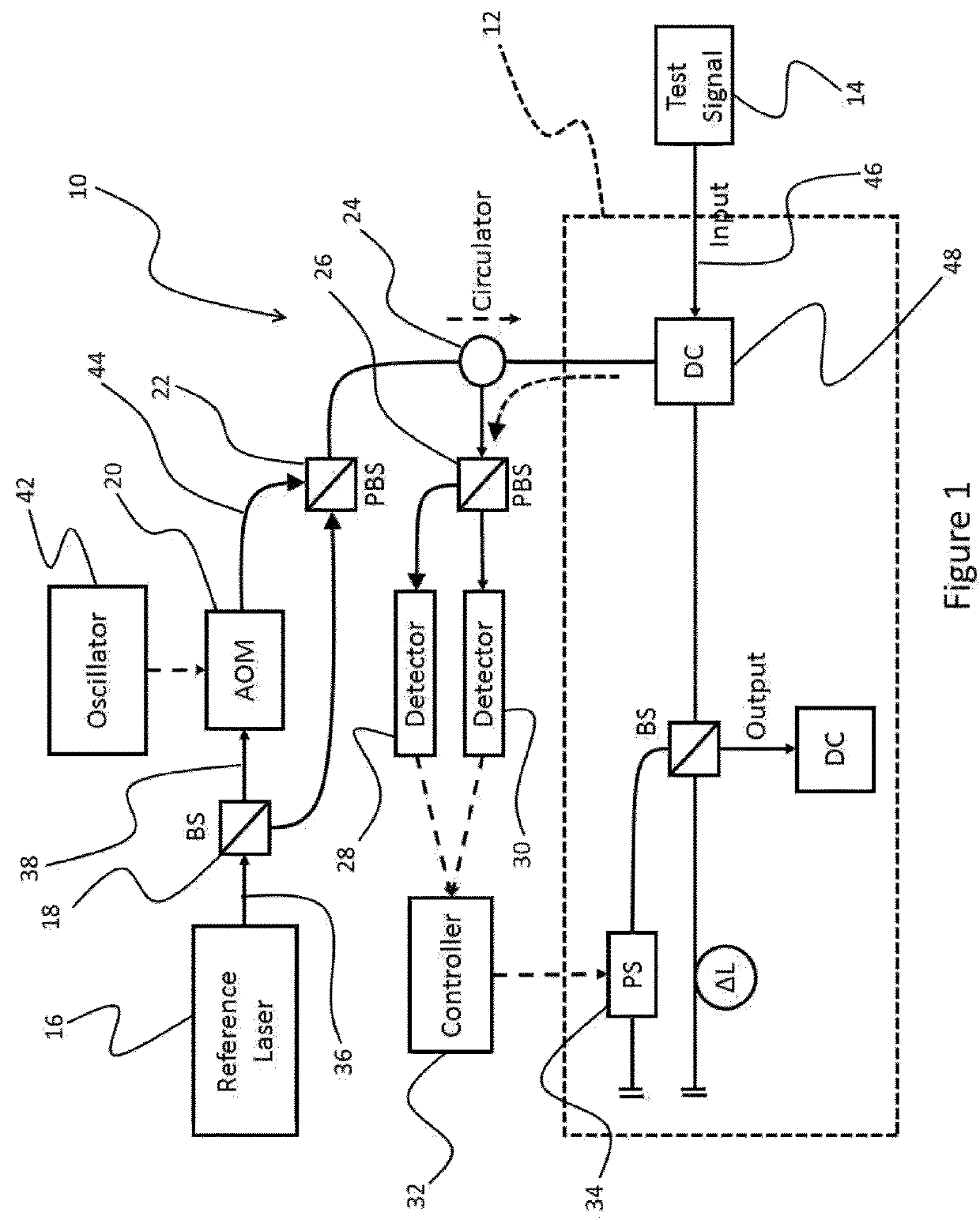
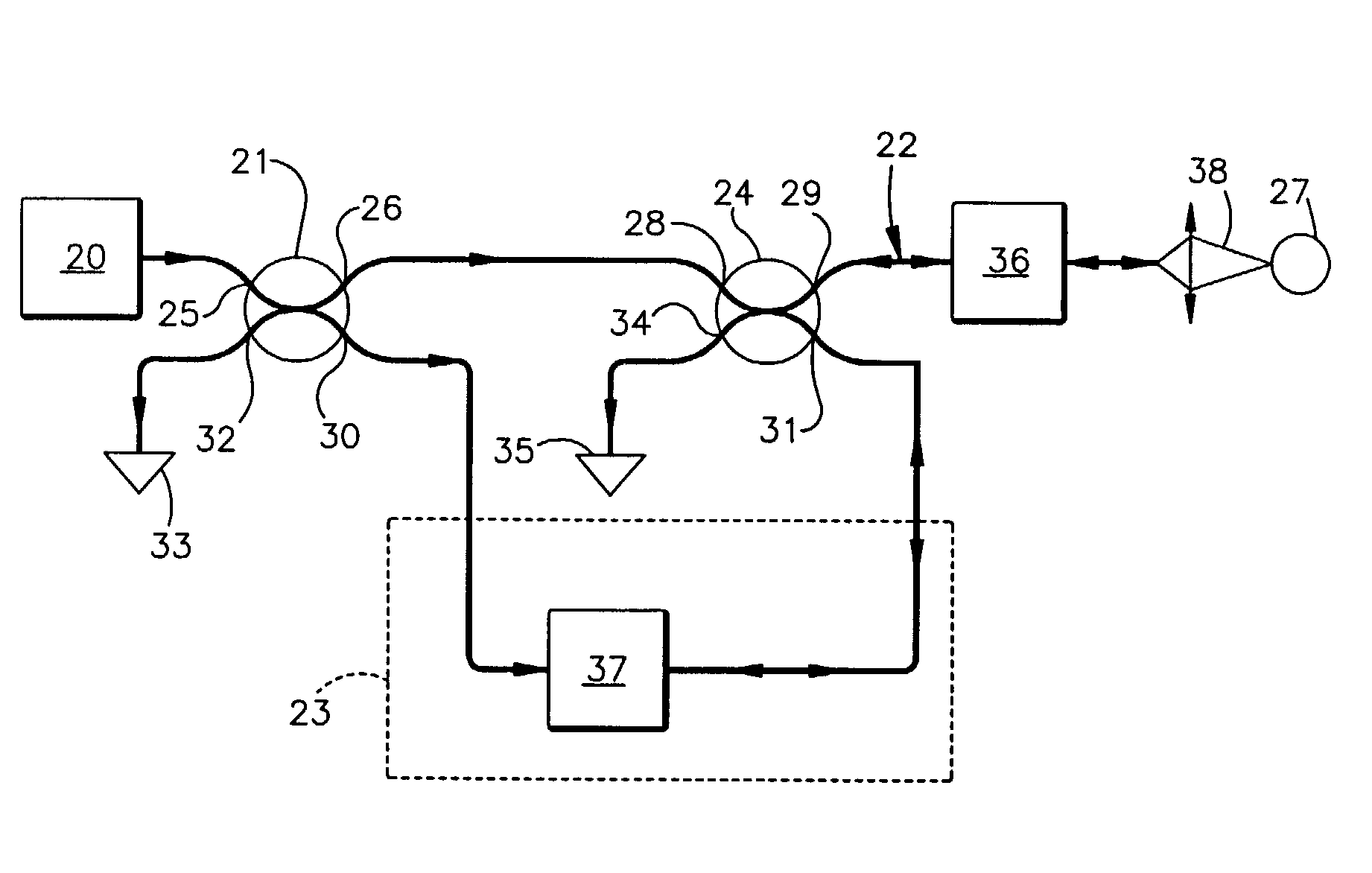
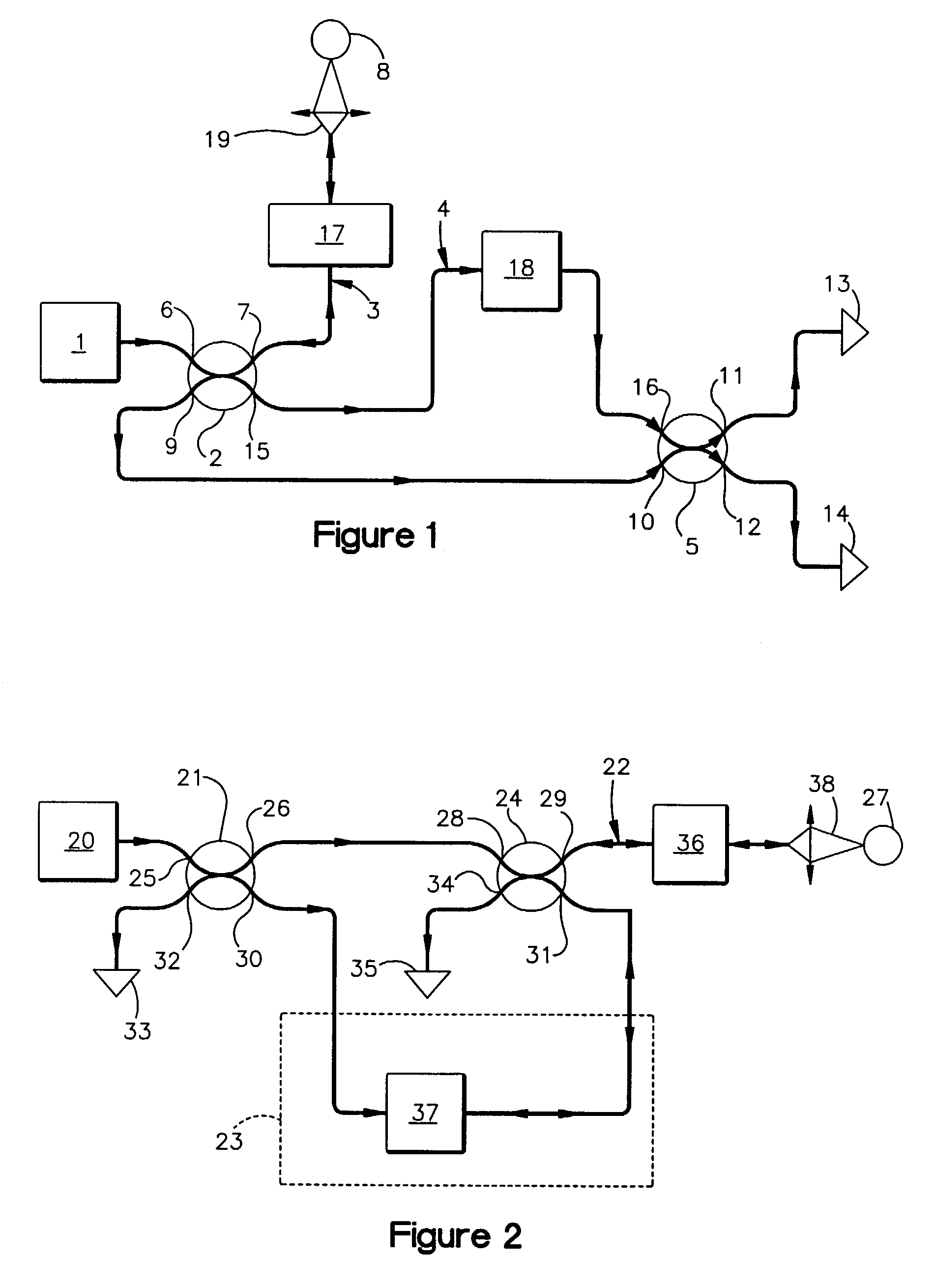
System and method for phase-readout and active stabilization of optical interferometers
ActiveUS20180180401A1Easy to separateEasy to combineOptical measurementsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementPolarization multiplexedAmbiguity
A system and method for phase-readout / control and active stabilization on arbitrary interferometric phase in the optical interferometer platform is disclosed. The method makes use of a bi-colored polarization-multiplexed reference laser scheme. The disclosed scheme is based on two phase-locked reference signals with different frequencies that together remove the phase ambiguity. The two signals are polarization-multiplexed (either in free-space or optical fiber implementations) to enable easy separation and combining of these two signals through the use of polarization beam-splitters. The disclosed scheme provides a one-to-one map between phase and feedback signal levels, and enables phase-readout and stabilization even when one of the feedback-signals is at a maximum / minimum.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
Athermal interferometer
InactiveUS6909511B2Using optical meansCoupling light guidesRefractive indexAstronomical interferometer
An apparatus is described for controlling the optical path length in an optical device, e.g. an interferometer, and more importantly to maintaining the optical path length difference in an interferometer. The apparatus may include an adjustable plate optically coupled with a beamsplitter. The plate may be rotated such that its surface receives light propagated from the beamsplitter at a non-zero incident angle. In one embodiment, temperature sensitivity is addressed by ensuring that the refractive index of the plate is greater than the refractive index of the beamsplitter. In another embodiment, the apparatus includes combination spacers having a component selected in dependence upon a composition, thickness, and orientation of the adjustable plate.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Quantitative phase-imaging systems
InactiveUS8248614B2Phase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansInterference phenomenonGalvanometer
An optical system performs imaging in a transmissive and reflective mode. The system includes an optical interferometer that generates interference phenomena between optical waves to measure multiple distances, thicknesses, and indices of refraction of a sample. Measurements are made through a galvanometer that scans a pre-programmed angular arc. An excitation-emission device allows an electromagnetic excitation and emission to pass through an objective in optical communication with the sample. An electromagnetic detector receives the output of the optical interferometer and the excitation-emission device to render a magnified three dimensional image of the sample.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method for studying a sample and optical interferometer for doing the same
InactiveUS6992776B2Easy to useRaise the ratioPhase-affecting property measurementsInterferometersOptical radiationBeam splitter
The present invention relates to the study of internal structure of objects by optical means. The invention presents a bi-directional sampling optical path for the low coherent optical radiation directed to the sample, i.e. a bi-directional sampling arm, and two unidirectional reference beams directed along a reference path designed as a loop. One of the reference beams propagates clockwise and the other propagates counterclockwise in the reference loop. The beam splitters non-reciprocal or polarization-dependent and by placing polarization-changing elements between the beam splitters and / or into the sampling arm and the reference loop. Thus the developed method and optical interferometer make possible to ensure highly efficient use of optical source power together with optimal signal-to-noise ratio for a given optical source power and are simple and cost effective.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
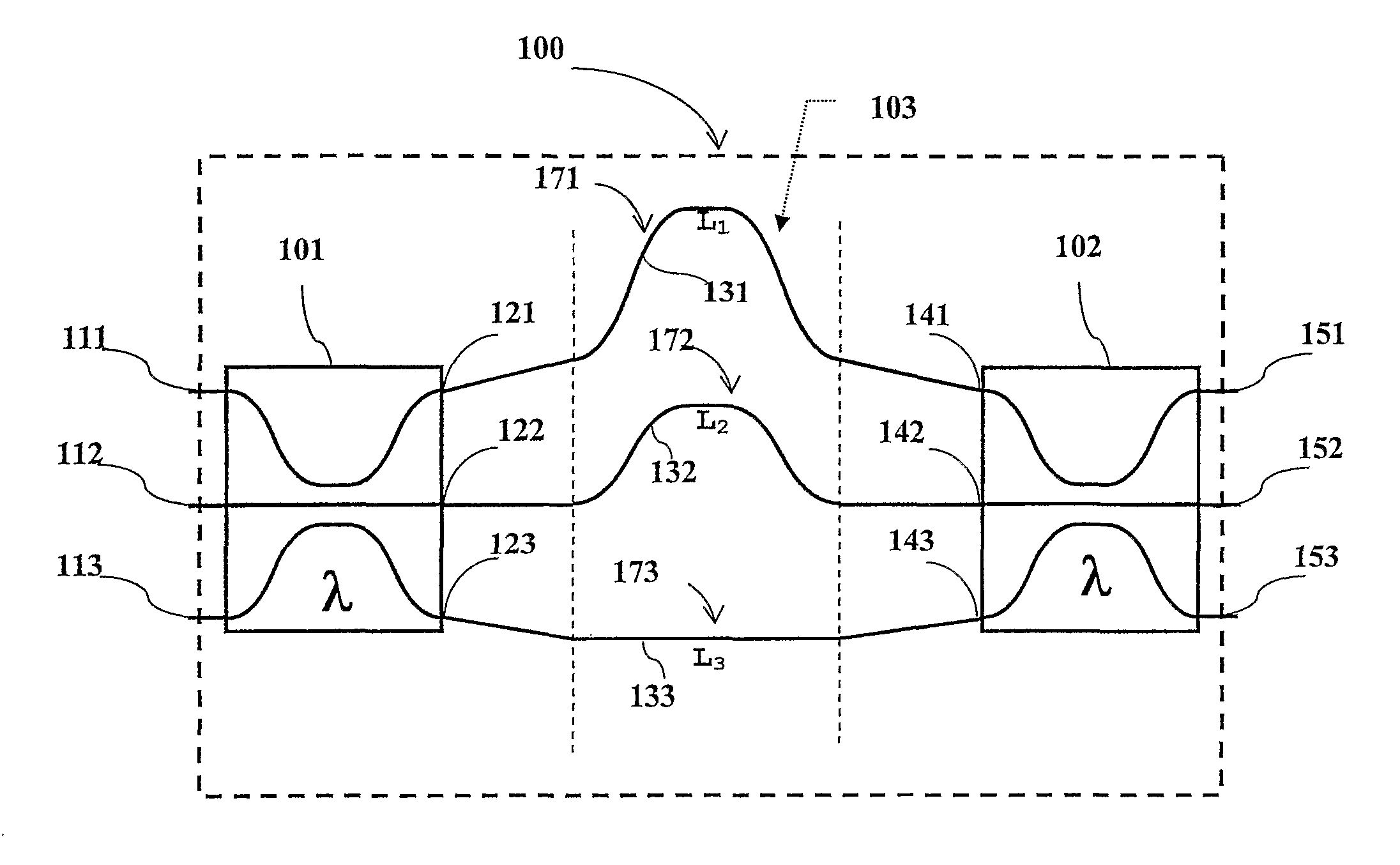
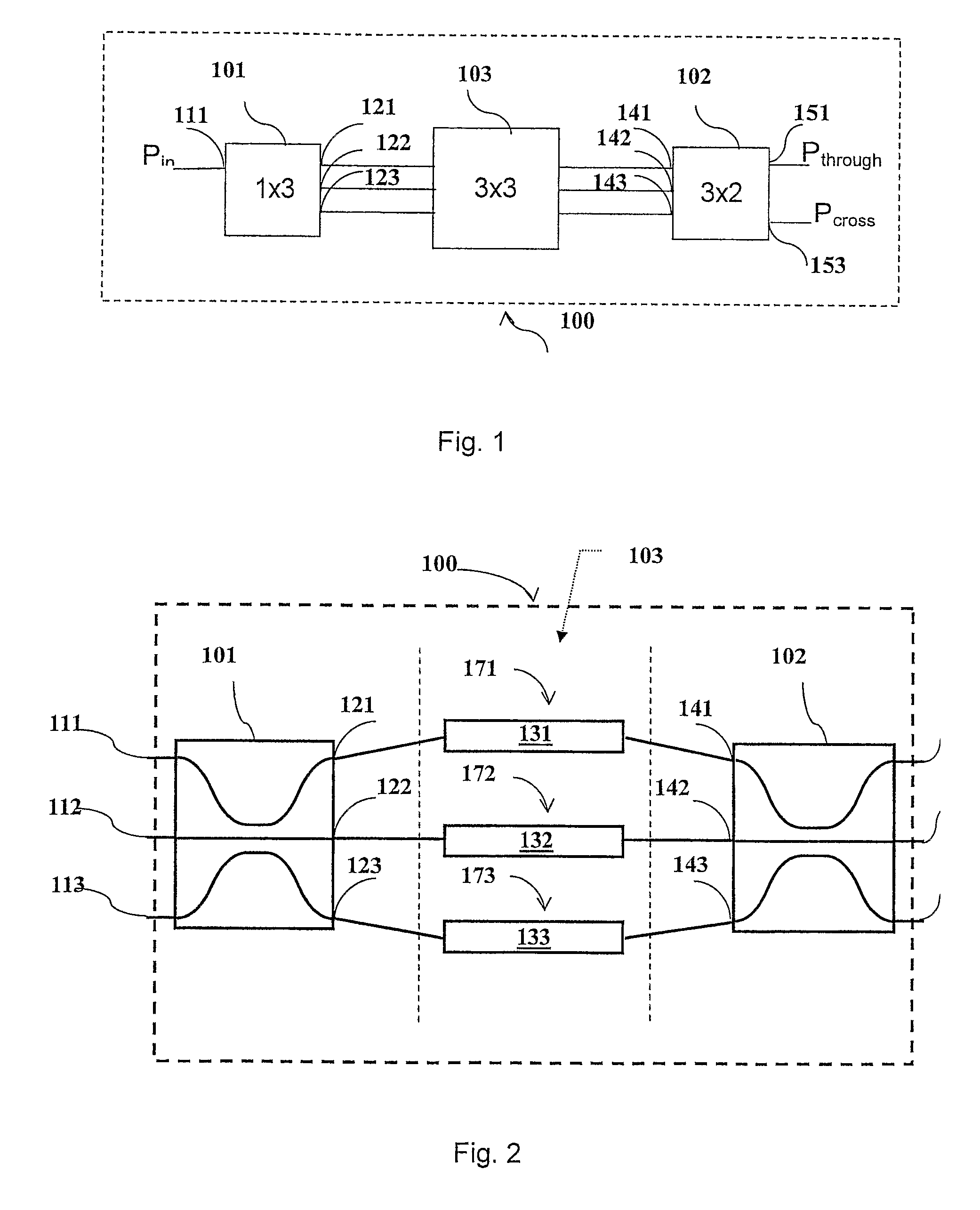
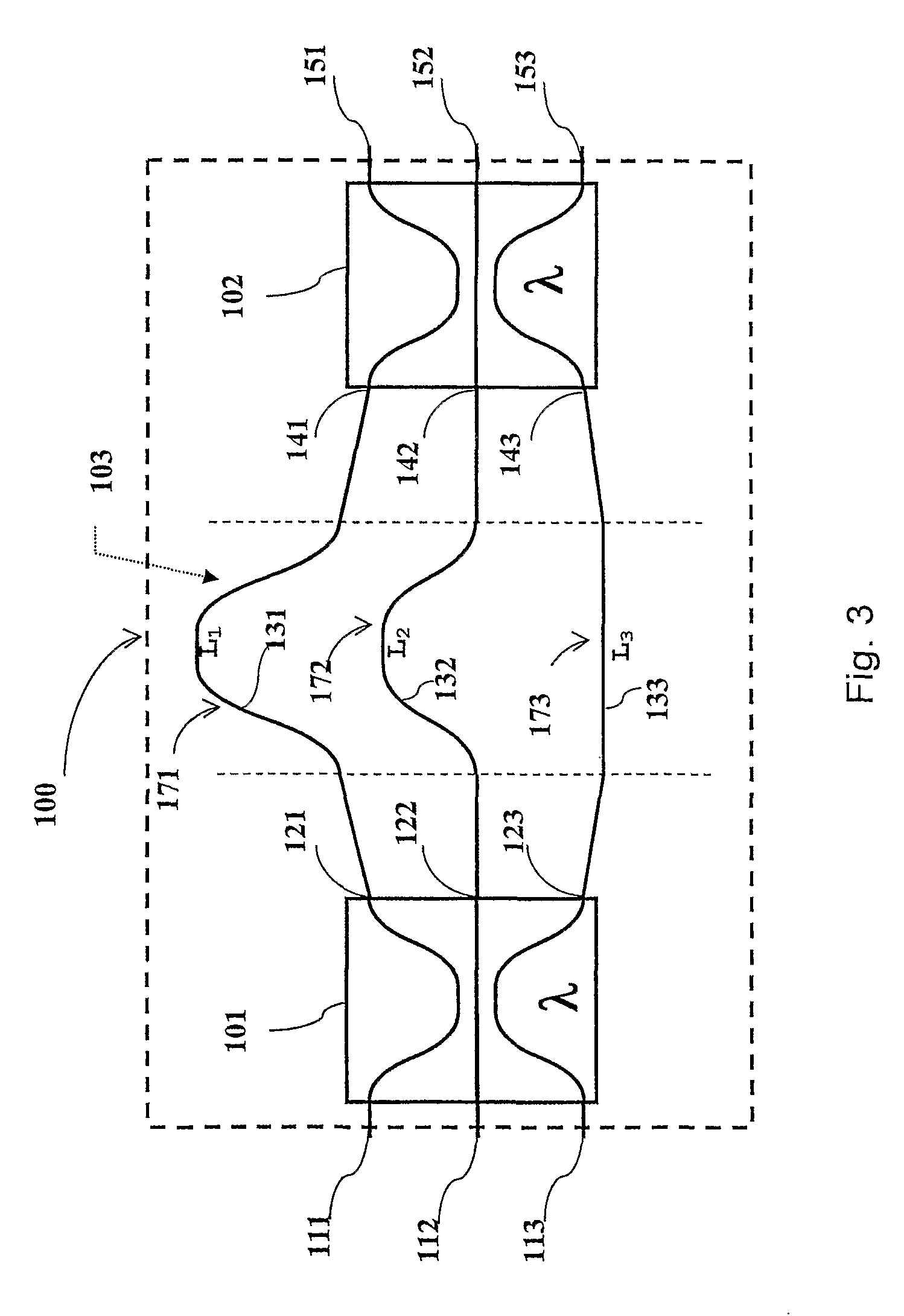
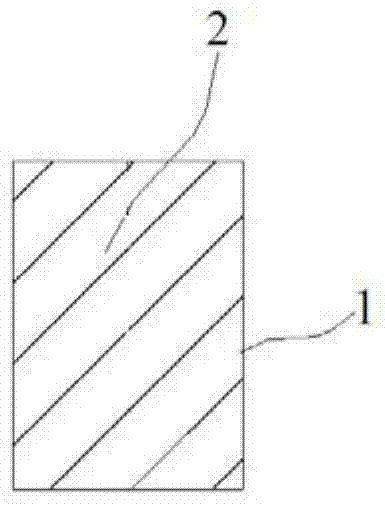
Optical band splitter/combiner device comprising a three-arms interferometer
InactiveUS8023822B2Strong toleranceReduce alignmentWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMach–Zehnder interferometerAstronomical interferometer
A three-arm-Mach-Zehnder interferometer for splitting / combining a first and a second wavelength band, wherein the optical device includes: a first and second optical splitting / combining element; a differential optical delay device comprising a first, a second and a third optical path; each of the first and second optical splitting / combining elements, is of the (25-50-25%)λx(0-0-100%)λy type, wherein λx is a wavelength with the first optical band and λy is a wavelength with the second optical band, and the first, second and third optical paths of the differential optical delay device are configured to introduce, at a wavelength λz within the first optical band, a phase delay Δφ of 2πm.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Optical interferometer used for detecting outer surface of cylinder
ActiveCN103615971AImprove test efficiencyHigh precisionUsing optical meansTest efficiencyBeam splitter
The invention discloses an optical interferometer used for detecting the outer surface of a cylinder. A condensation convex lens is located between a laser and a collimation convex lens, and the focus of the condensation convex lens and the focus of the collimation convex lens coincide; a beam splitter located between the condensation convex lens and the collimation convex lens is used for dividing light of an auto-collimation convex lens into a first light beam and a second light beam; a standard optical flat is located on one side, back to the beam splitter, of the collimation convex lens, and the surface, back to the collimation convex lens, of the standard optical flat is a standard surface; an annular reflection inclined surface located at the center of an annular inclined surface reflector is arranged on the inner side in the circumferential direction of the annular inclined surface reflector, the to-be-detected cylinder is located in the annular inclined surface reflector, a rotary shaft of the annular inclined surface reflector, the axis of the cylinder and the axis of the optical flat coincide, and the annular reflection inclined surface of the annular inclined surface reflector and the outer surface of the cylinder are placed oppositely. According to the optical interferometer, the feature information of the inner surface of the whole stereoscopic cylinder can be obtained at a time, and test efficiency, accuracy and reliability are also greatly improved.
Owner:苏州慧利仪器有限责任公司 +2
Wavelength locker and laser package including same
A wavelength locker may include a first optical detector configured to detect light, wherein the first optical detector is at least partially transparent to the light. The wavelength locker may further include an optical interferometer optically coupled to the first optical detector and to a second optical detector. The optical interferometer is configured to selectively filter the light that passes through the first optical detector and the second optical detector detects the filtered light. An optical module or package may include the wavelength locker coupled to a laser for locking an emission wavelength of the laser.
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
Optical interferometer for detecting outer arc surface of annular guide rail
InactiveCN103697806AImprove test efficiencyHigh precisionUsing optical meansTest efficiencyBeam splitter
The invention discloses an optical interferometer for detecting the outer arc surface of an annular guide rail. A condenser convex lens is positioned between a laser and a collimating convex lens, and the focus of the condenser convex lens is coincided with the focus of the collimating convex lens. A beam splitter is positioned between the condenser convex lens and the collimating convex lens and is used for dividing a light ray from the collimating convex lens into a first light beam and a second light beam, the surface, which is opposite to the collimating convex lens, of a reference lens is a convex surface, and the surface, which is back-to-back with the convex surface, of the reference lens is a standard reference surface; an annular reflecting slope which is arranged in the middle of an annular slope reflector is arranged in the peripheral direction and is arranged on the inner side, the annular guide rail to be detected is positioned in the annular slope reflector, a rotating axle of the annular slope reflector is coincided with the respective axes of the annular guide rail and the reference lens, and the annular guide rail is arranged outside the focus of the reference lens. All the stereoscopic appearance information of the outer arc surface of the annular guide rail can be obtained in a one-time manner, and meanwhile, the test efficiency, accuracy and reliability are greatly improved.
Owner:苏州慧利仪器有限责任公司 +2
Optical interferometer used for detecting inner surface of hollow cylinder
InactiveCN103615972AImprove test efficiencyHigh precisionUsing optical meansTest efficiencyBeam splitter
The invention discloses an optical interferometer used for detecting the inner surface of a hollow cylinder. The inner surface is located on the inner side or the outer side in the circumferential direction of the hollow cylinder, a condensation convex lens of the inner surface is located between a laser and a collimation convex lens, and the focus of the condensation convex lens and the focus of the collimation convex lens coincide; a beam splitter located between the condensation convex lens and the collimation convex lens is used for dividing light of an auto-collimation convex lens into a first light beam and a second light beam; a standard optical flat is located on one side, back to the beam splitter, of the collimation convex lens, the surface, facing the collimation convex lens, of the standard optical flat is a convex surface, and the surface, back to the convex surface, of the standard optical flat is a standard reference surface; a conical reflector is located in the hollow cylinder to be detected, and a rotary shaft of the conical reflector, the axis of the hollow cylinder and the axis of the standard optical flat coincide. According to the optical interferometer, feature information of the inner surface in the whole stereoscopic hollow cylinder can be obtained at a time, and test efficiency, accuracy and reliability are also greatly improved.
Owner:苏州慧利仪器有限责任公司 +2
Optical parametric oscillator with optimized output coupling
InactiveUS8498043B2Improve stabilityWide wavelength rangeLaser detailsLight demodulationCouplingComputational physics
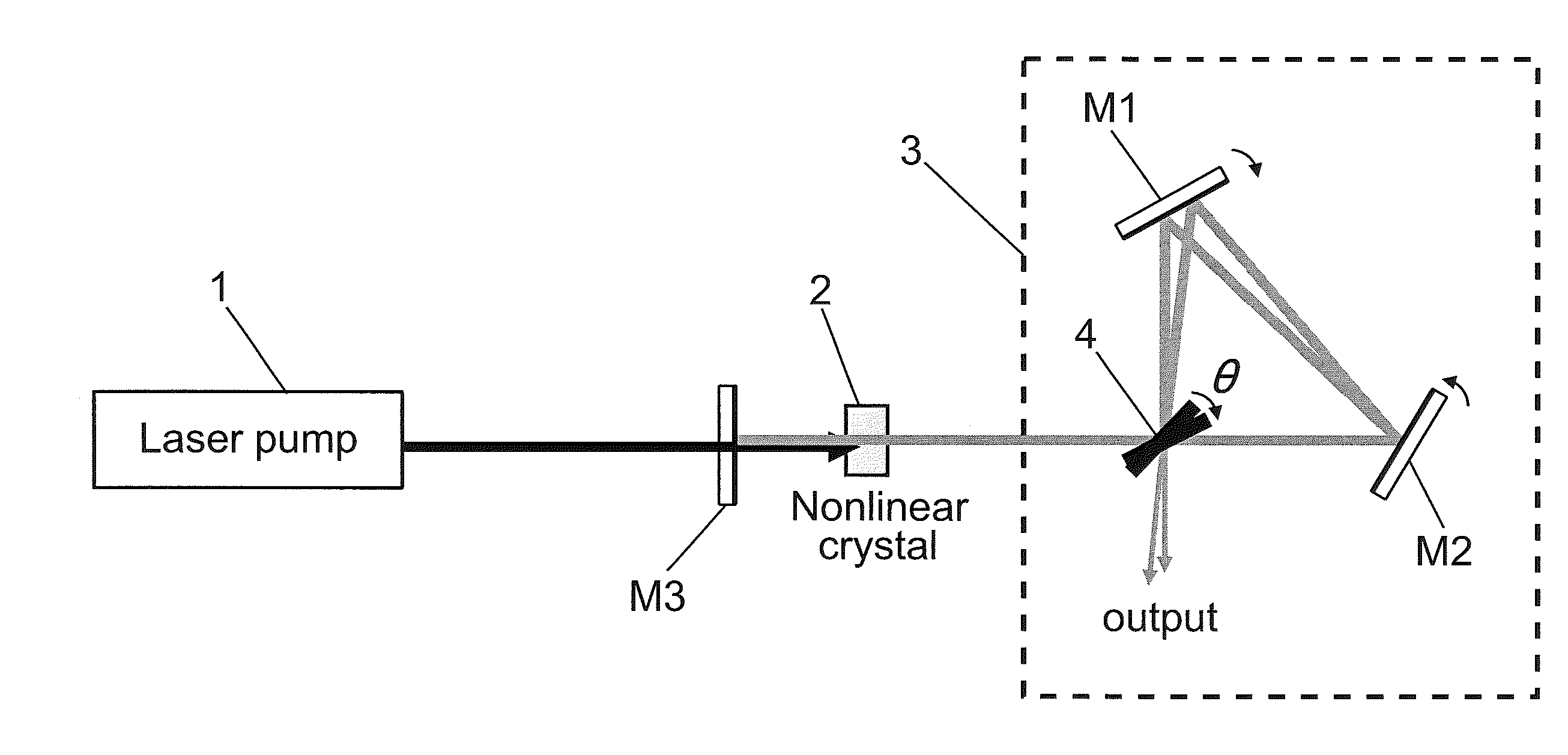
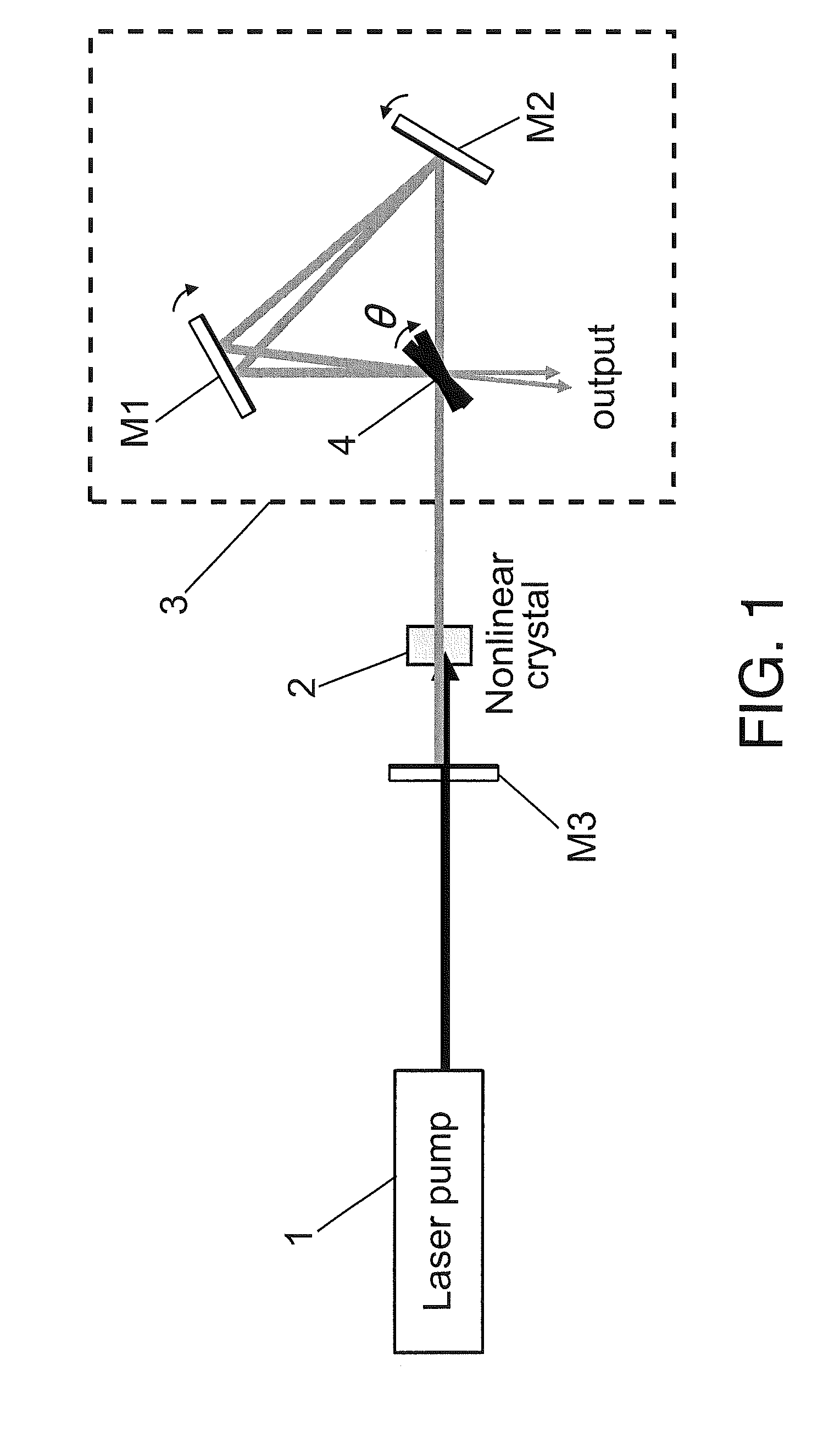
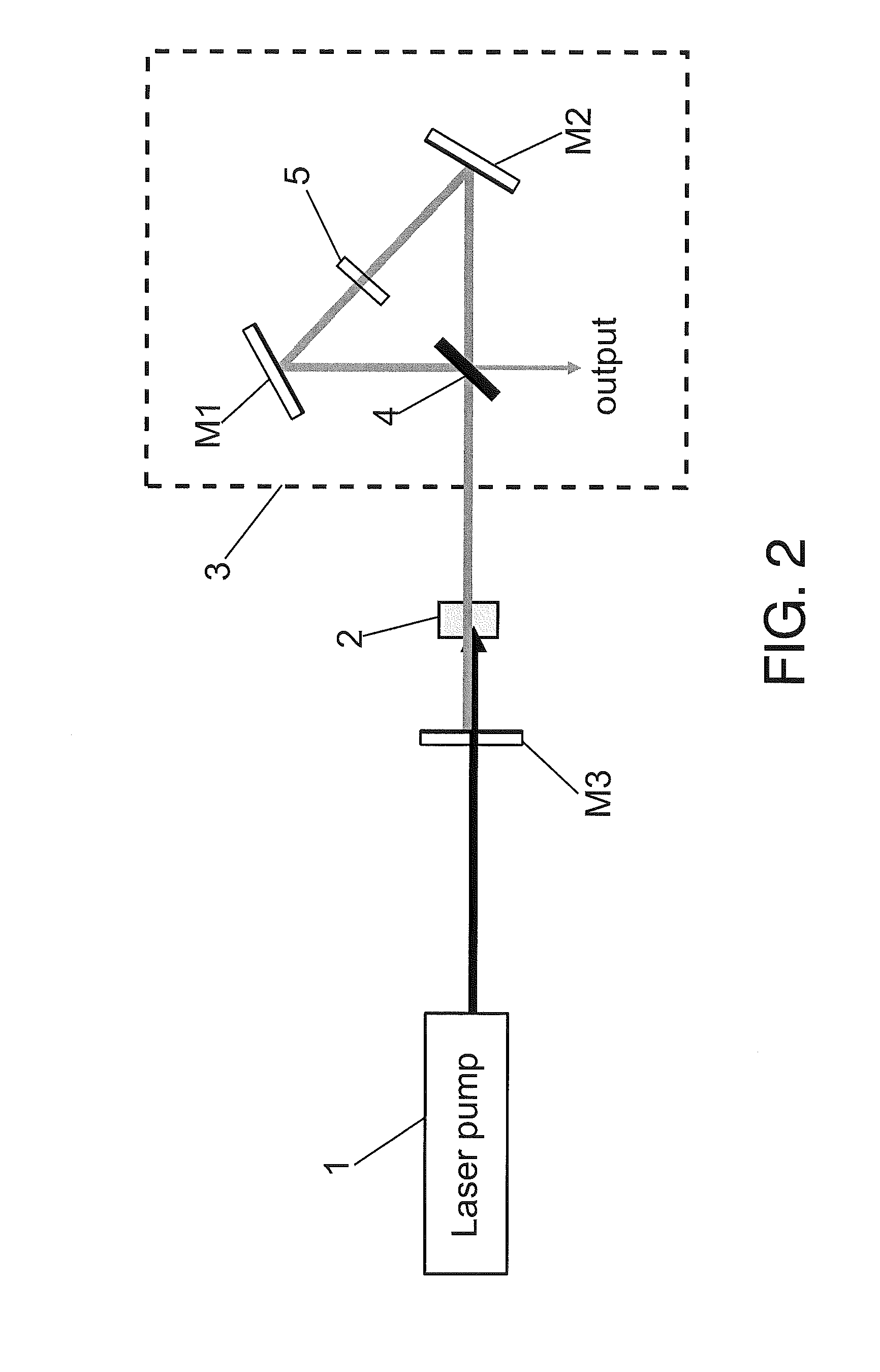
An optical parametric oscillator including a nonlinear crystal pumped by a laser source and an optical resonator, including an optical interferometer, which determines a level of output coupling of the oscillator, allowing high stability, broad wavelength tuning, and output power level optimization.
Owner:FUNDACIO INST DE CIENCIES FOT NIQUES +1
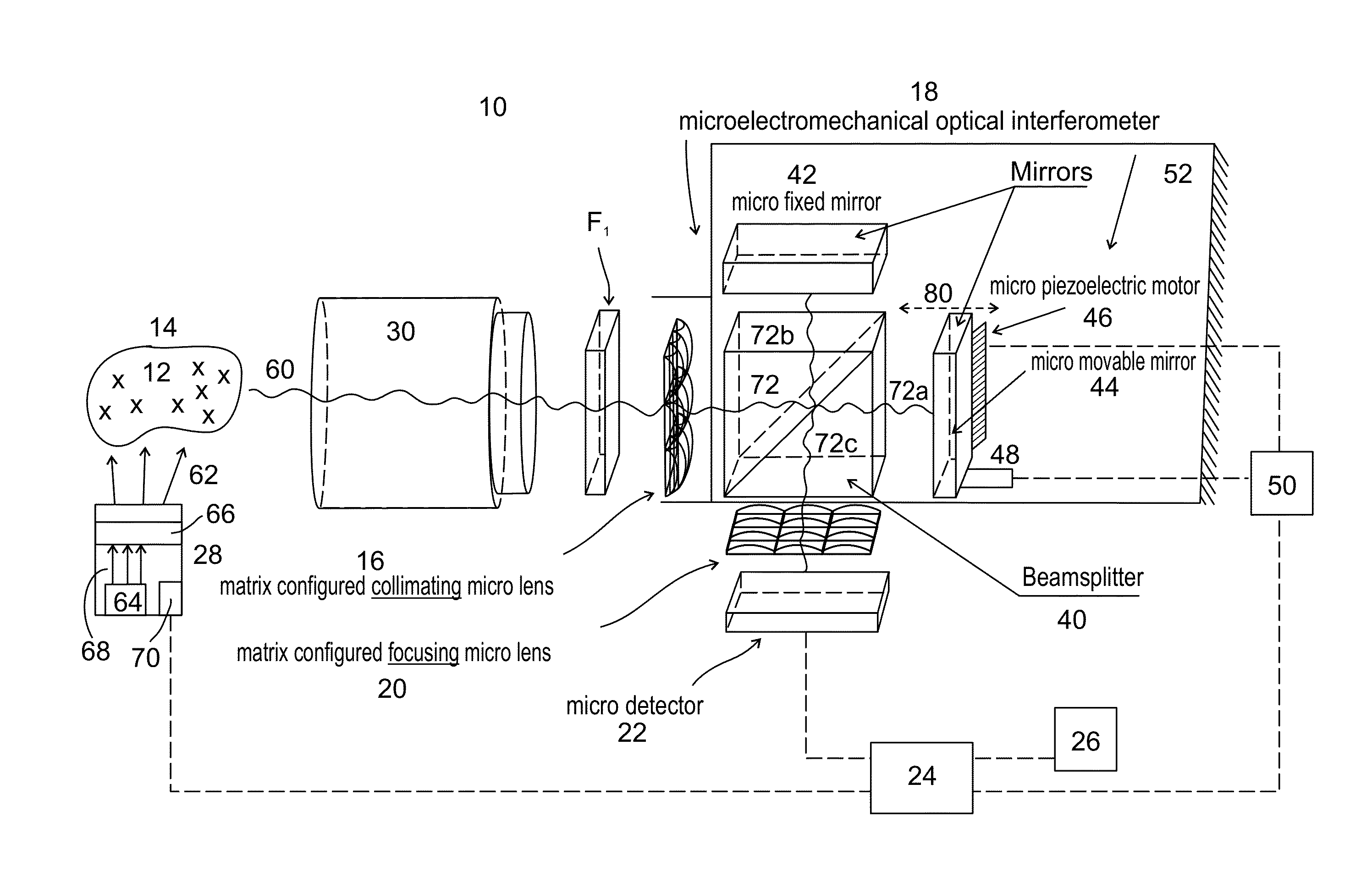
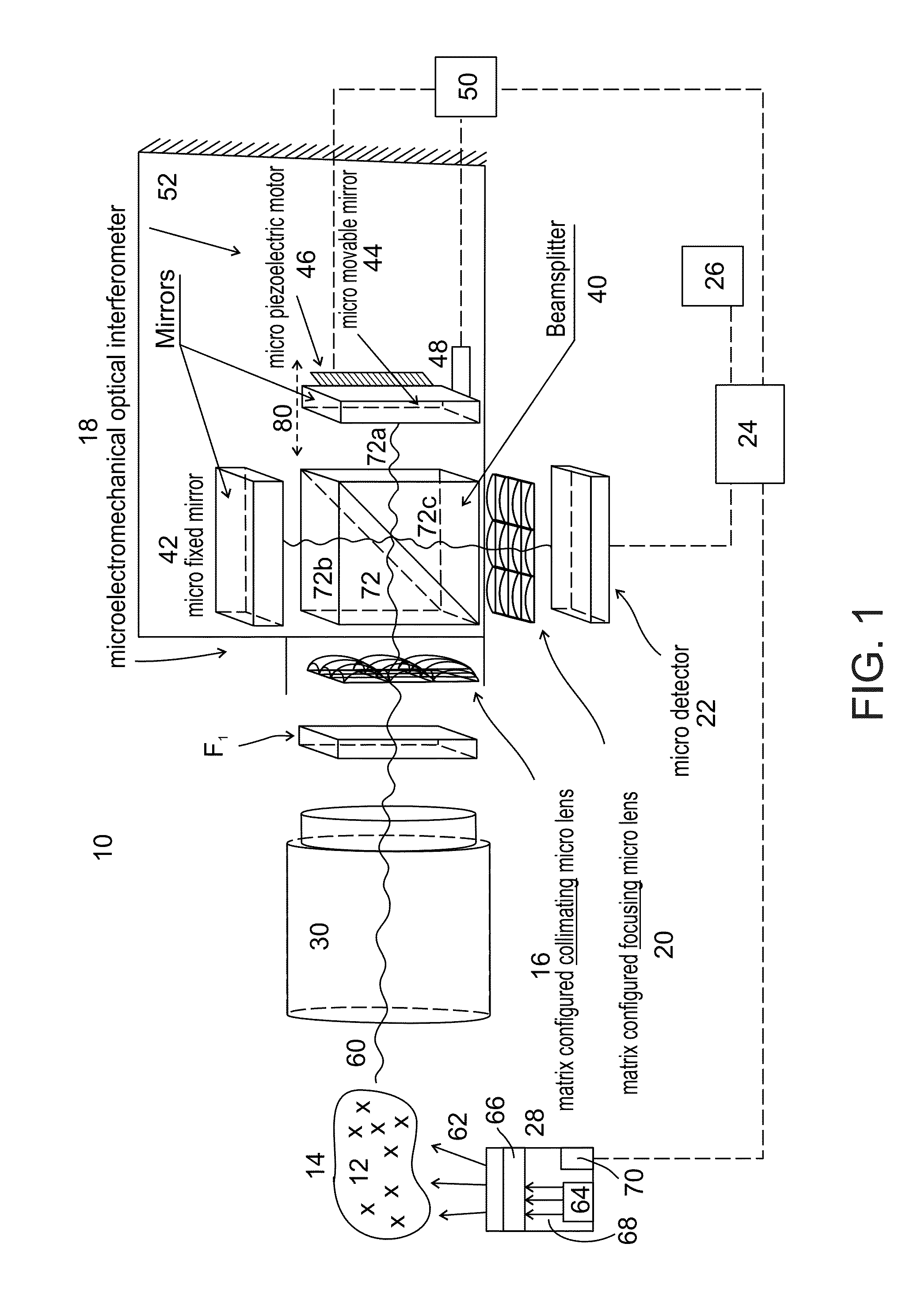
Microelectromechanical system (MEMS) and (MEM) optical interferometer for hyper-spectral imaging and analysis
InactiveUS20140078509A1Television system detailsRadiation pyrometryBiophysical chemistryMicroelectromechanical systems
A microelectromechanical system (MEMS) (10), and a microelectromechanical (MEM) optical interferometer (18), for hyper-spectral imaging and analysis. System (10) includes matrix configured collimating micro lens (16), for receiving and collimating electromagnetic radiation (60) emitted by objects (12) in a scene or sample (14); microelectromechanical optical interferometer (18), for forming divided collimated object emission beam (72) having an optical path difference, and for generating an interference image exiting optical interferometer (18); matrix configured focusing micro lens (20); micro detector (22), for detecting and recording generated interference images; and micro central programming and signal processing unit (24). Applicable for on-line (e.g., real time or near-real time) or off-line hyper-spectral imaging and analyzing, on a miniaturized or ‘micro’ (sub-centimeter [1 cm (10 mm) or less], or sub-millimeter) scale, essentially any types or kinds of biological, physical, or / and chemical, (i.e., biophysicochemical) objects.
Owner:GREENVISION SYST
Optical interferometer and signal synthesizer using the interferometer
InactiveUS6587278B1Optical measurementsElectromagnetic transmittersSpatial light modulatorOptical frequencies
An optical signal synthesizer having an optical slab waveguide constructed from three layers in which optical pulses are introduced. A first cut-away portion of the optical slab waveguide has a plano-concave shape serving as a plano-convex lens which collimates the introduced optical pulses, a second cut-away portion of the optical slab waveguide serving as a diffraction grating for parallel light beams in which the optical pulses are separated into every frequency, and a third cut-away portion of the optical slab waveguide has a plano-concave shape serving as a plano-convex lens by which the separated optical pulses are focused on a different spatial position associated with each frequency. A spatial light modulator is fabricated at the focusing position in the optical slab waveguide which allows the optical pulses subjected to optical modulation every frequency to pass therethrough according to an applied electrical signal. A fourth cut-away portion of the optical slab waveguide has a plano-concave shape serving as a plano-convex lens which collimates each modulated optical frequency component individually, and a fifth cut-away portion of the optical slab waveguide serving as a diffraction grating for the modulated optical pulses restores the modulated optical pulses to the parallel light beams.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
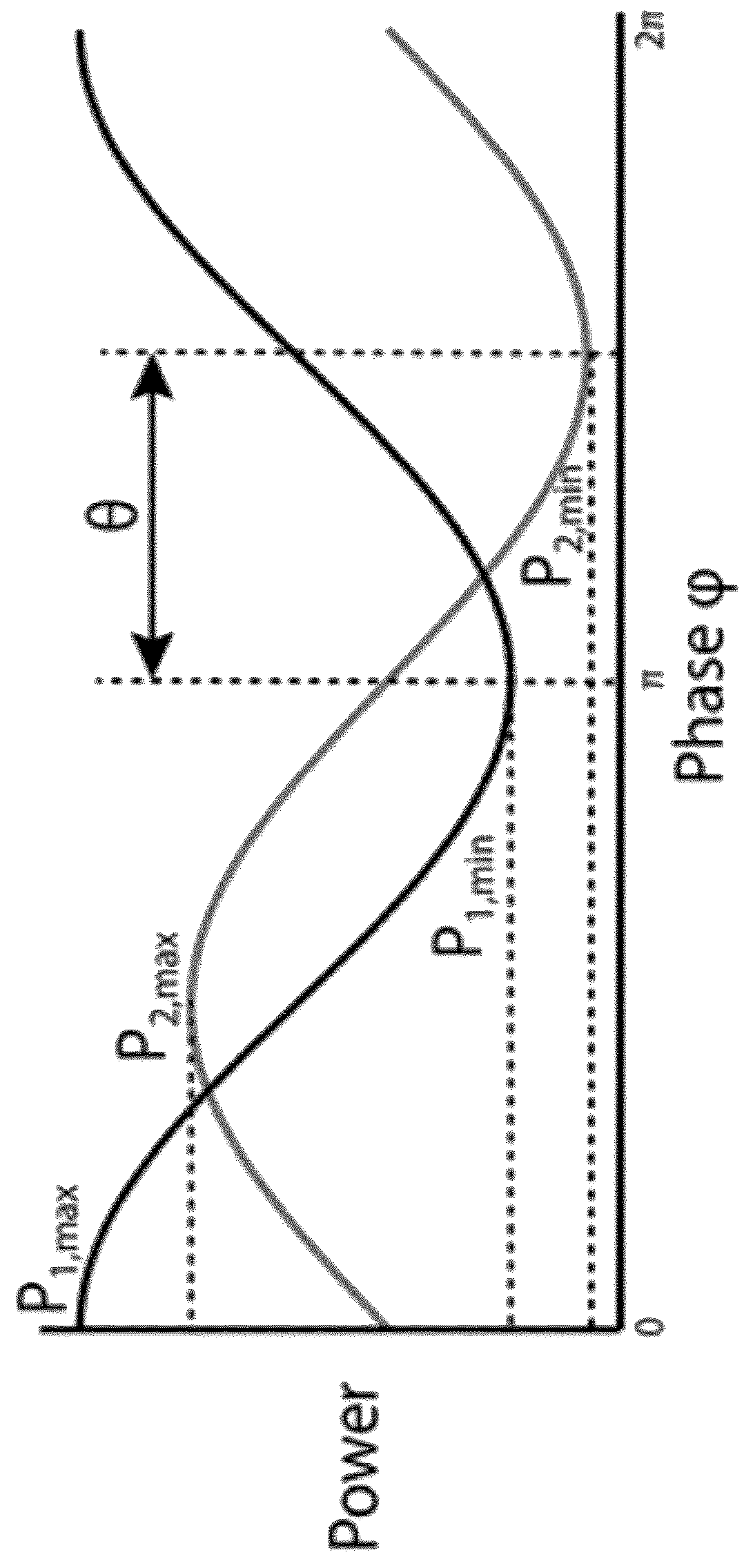
Optical interferometer with a casing and an optical part that is movable with respect to the casing
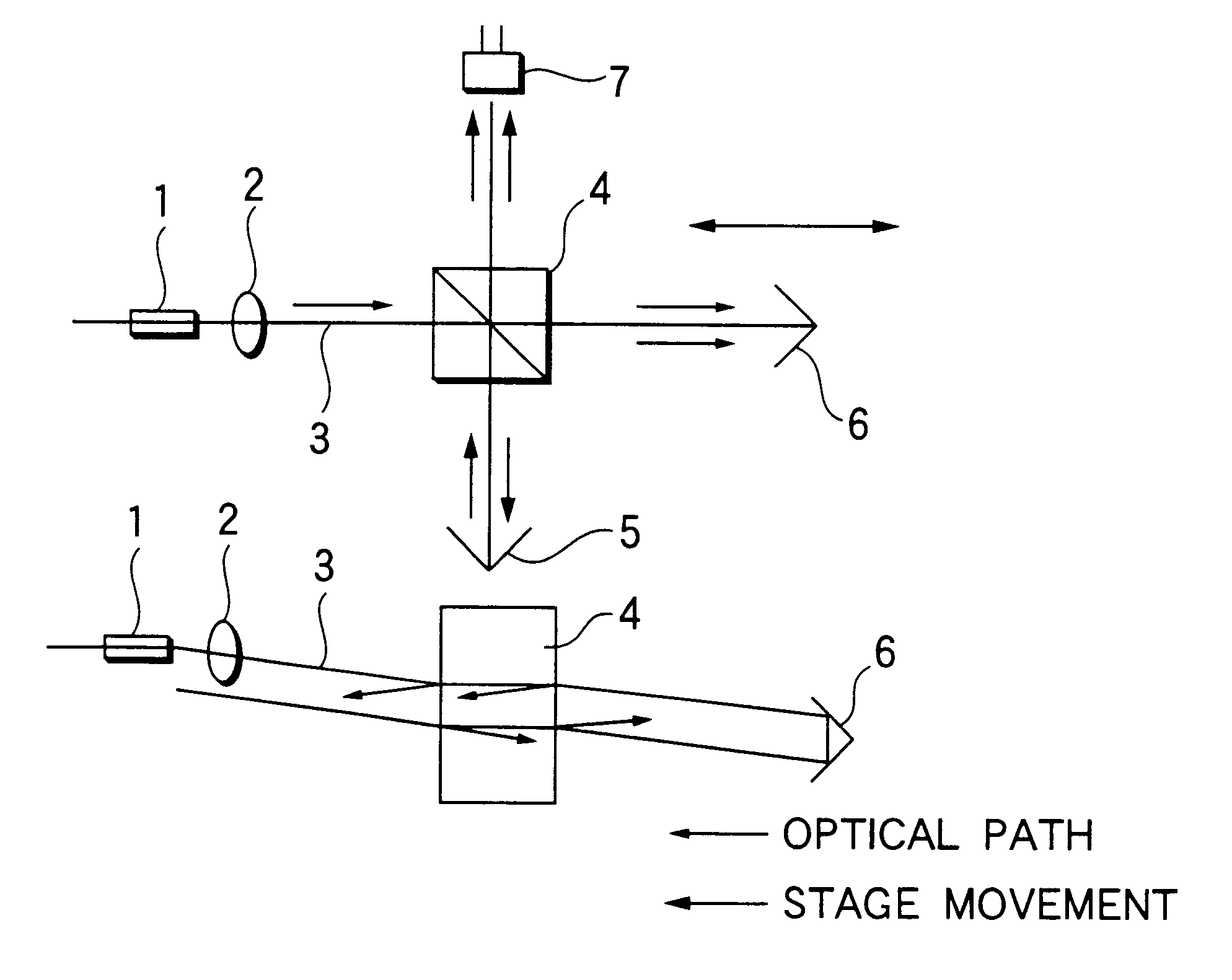
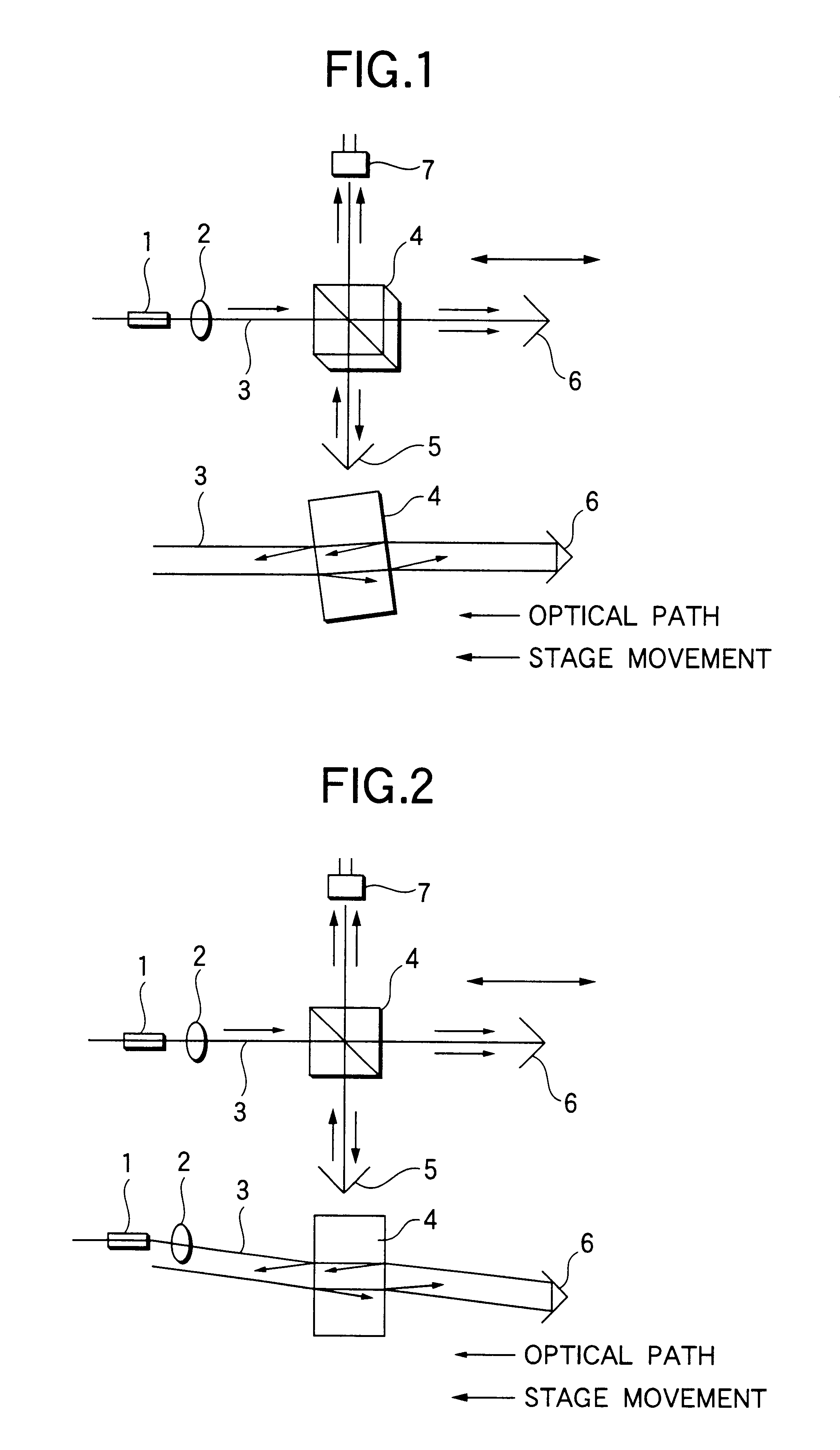
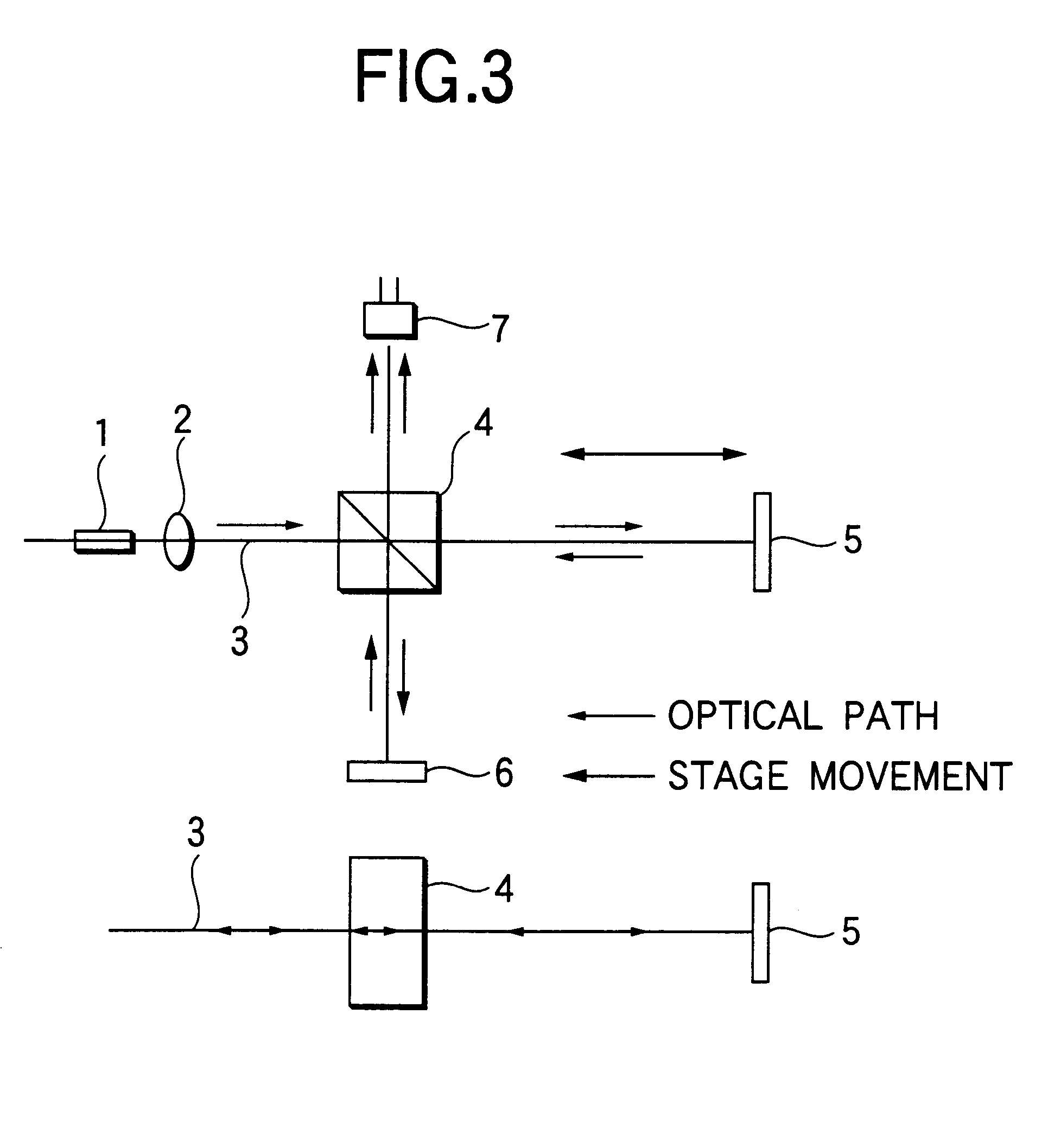
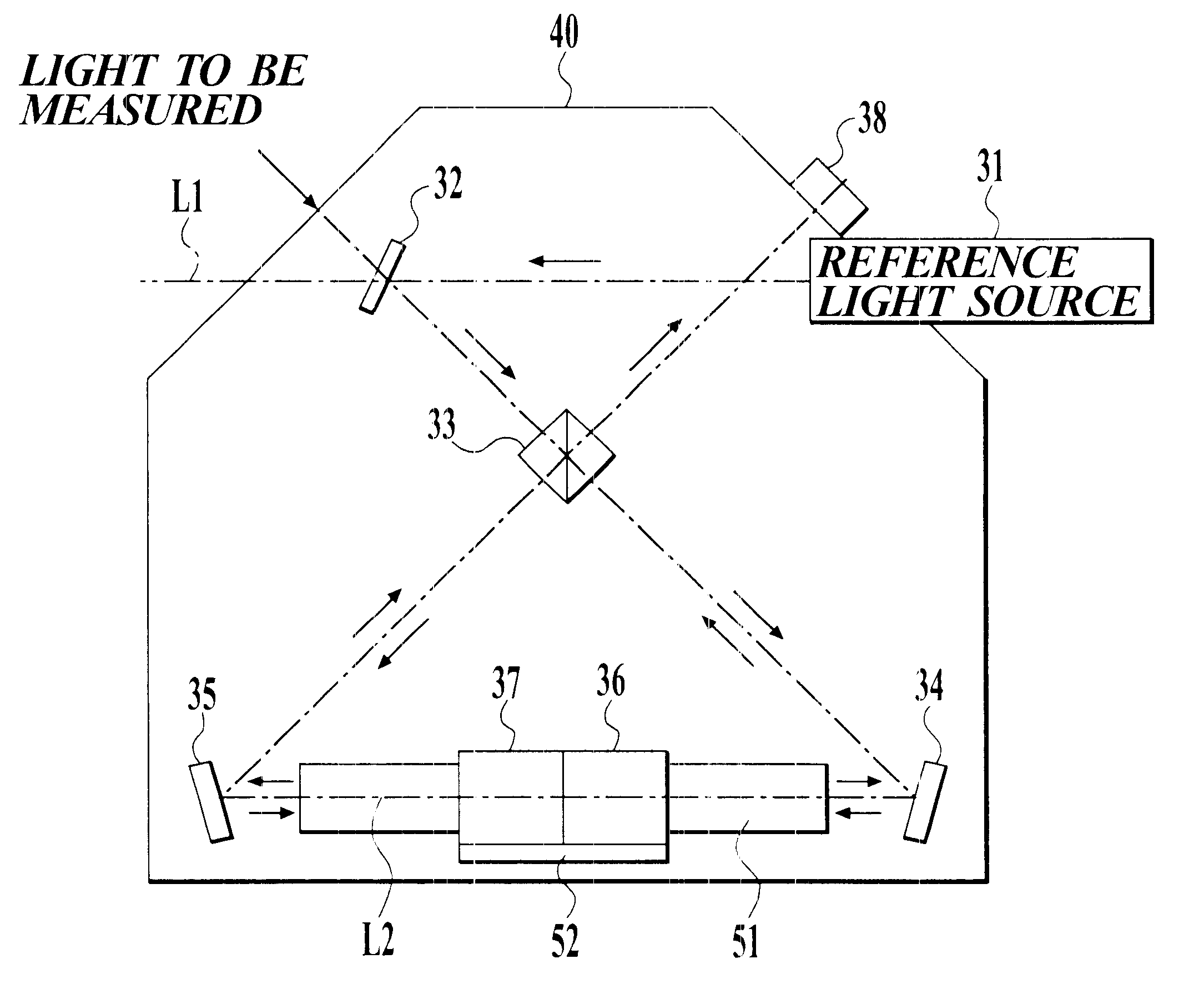
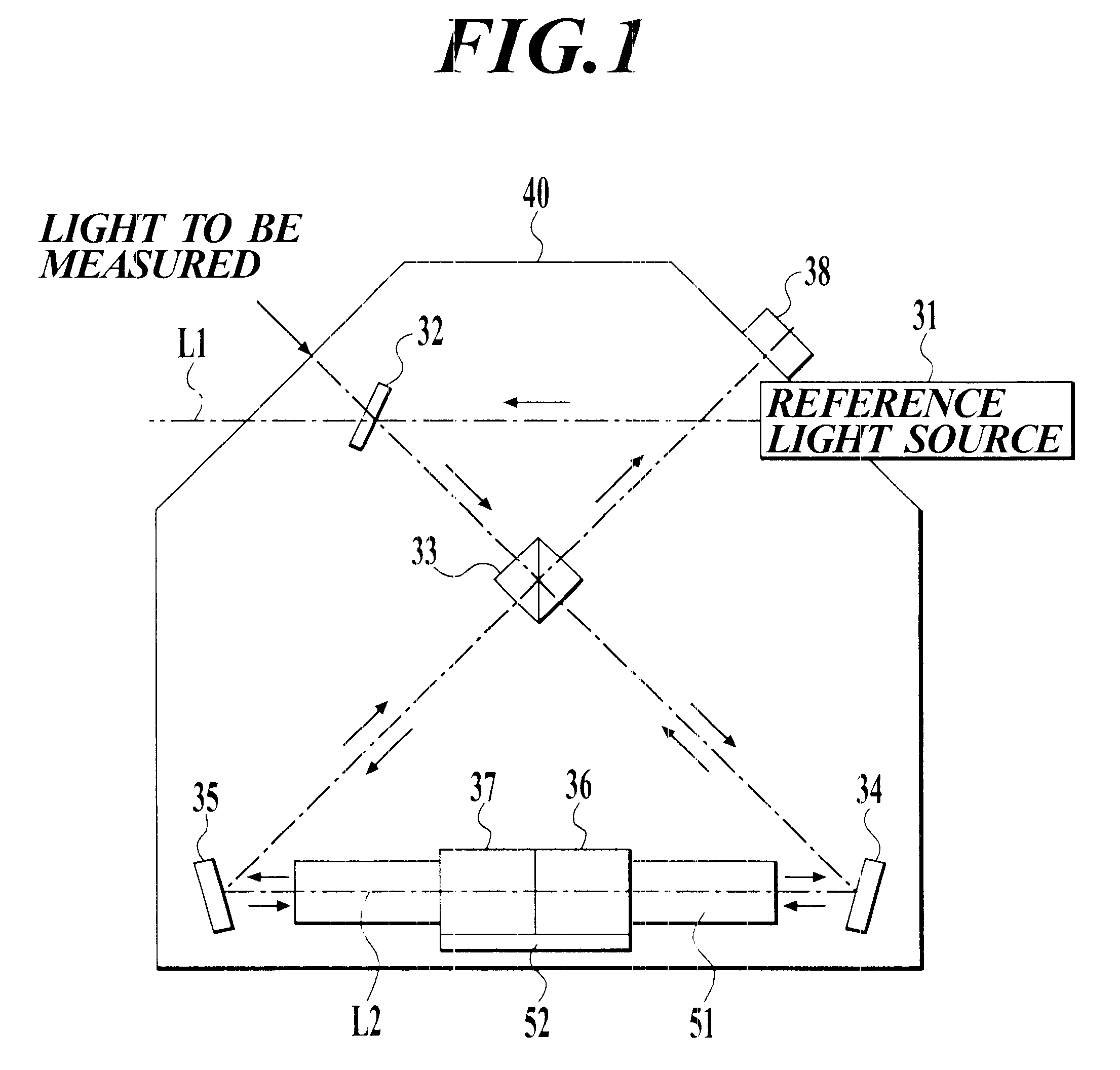
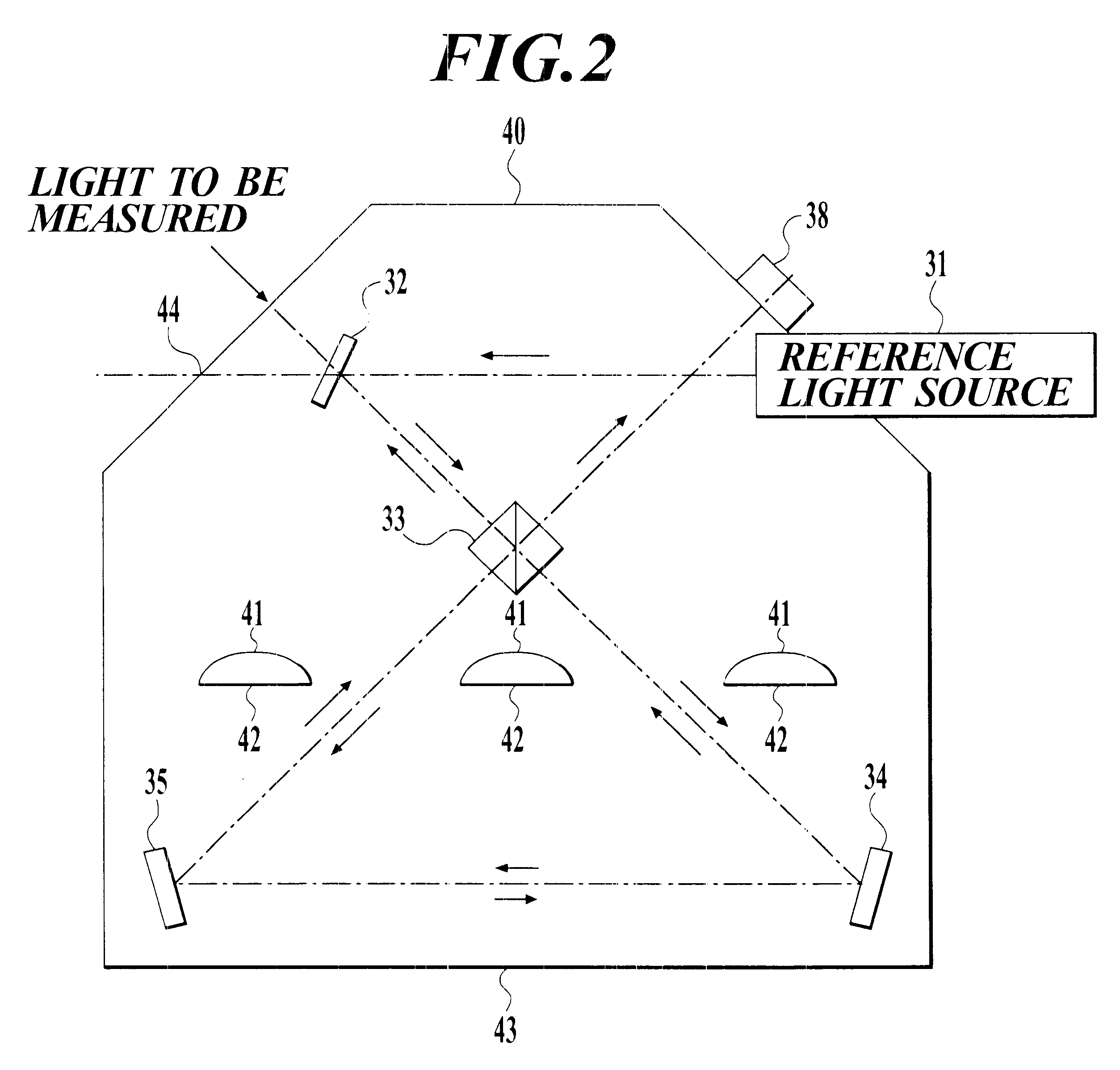
InactiveUS6504613B1Optical measurementsRadiation pyrometryAstronomical interferometerOptical interferometer
An optical interferometer in which a reference light and a light to be measured interfere with each other includes a casing, a movable optical part which is movable with respect to the casing, a fixed optical part which is fixed to the casing, and an attachment emember for attaching the movable optical part to the casing and for removing the movable optical part form the casing.
Owner:ANDO ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Compact optical modulator
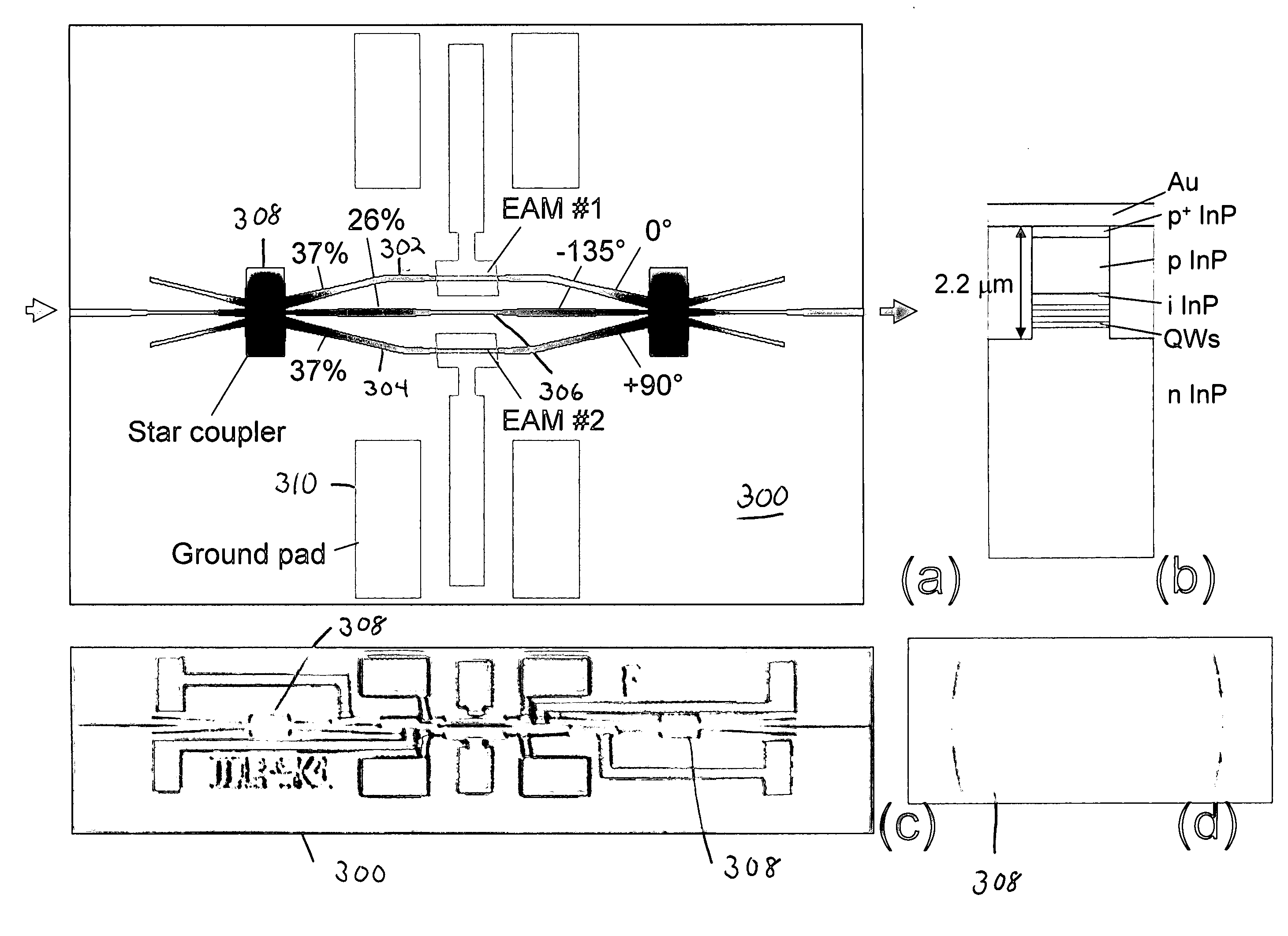
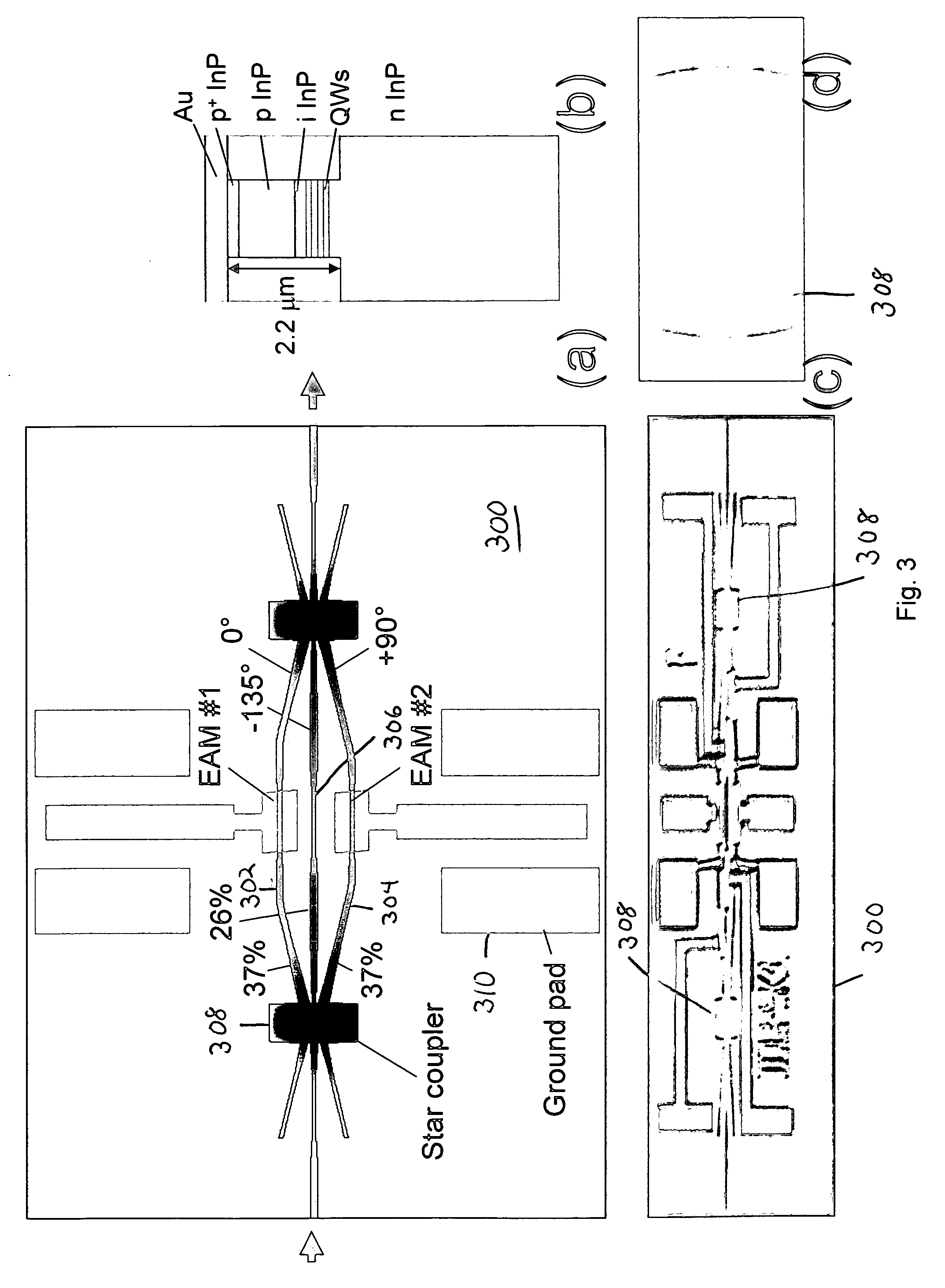
ActiveUS20080166083A1Highly compact DQPSKElectromagnetic transmissionNon-linear opticsDifferential quadrature phase shift keyingEngineering
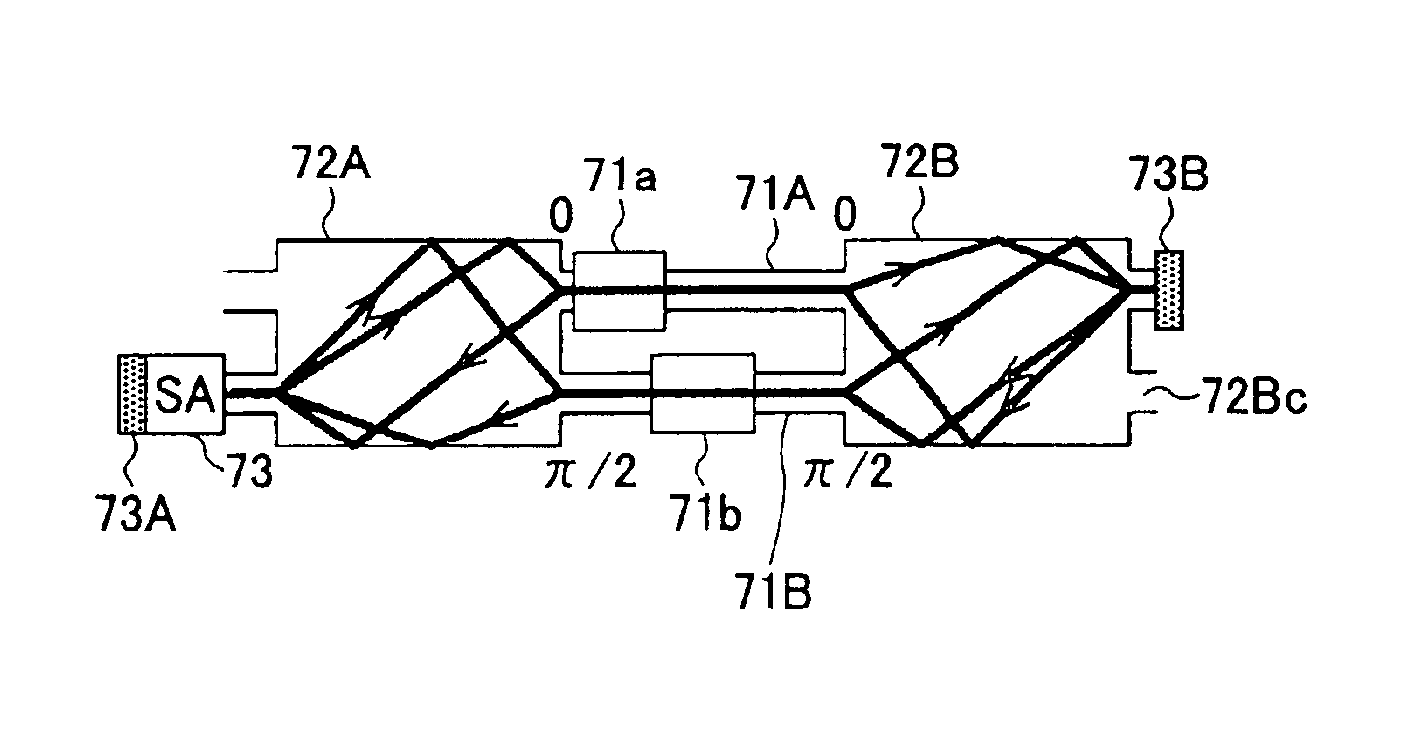
We present a novel design for an optical differential quadrature phase shift keying modulator comprised of two intensity modulators in a three-arm interferometer.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
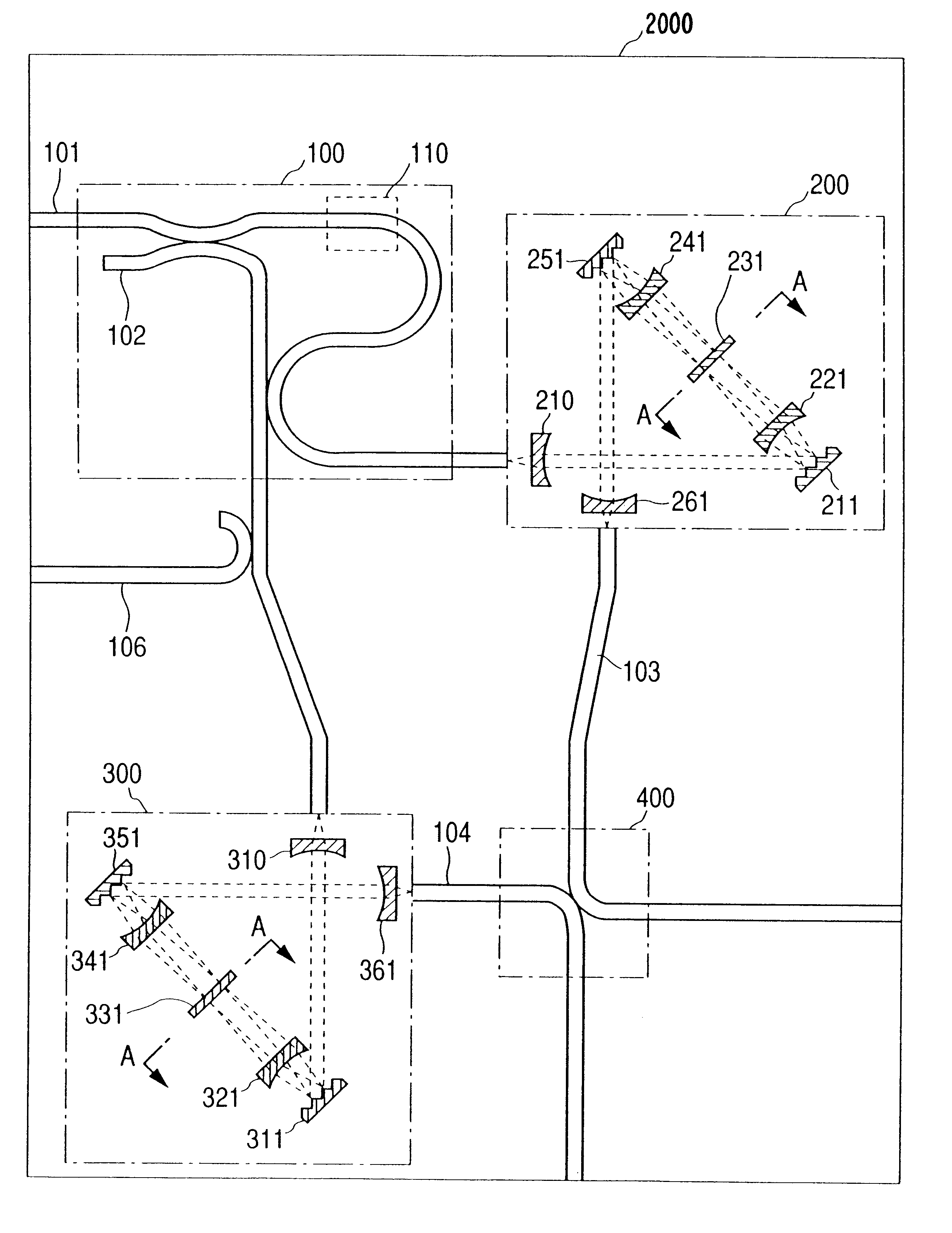
Dual polarization interferometers for measuring opposite sides of a workpiece
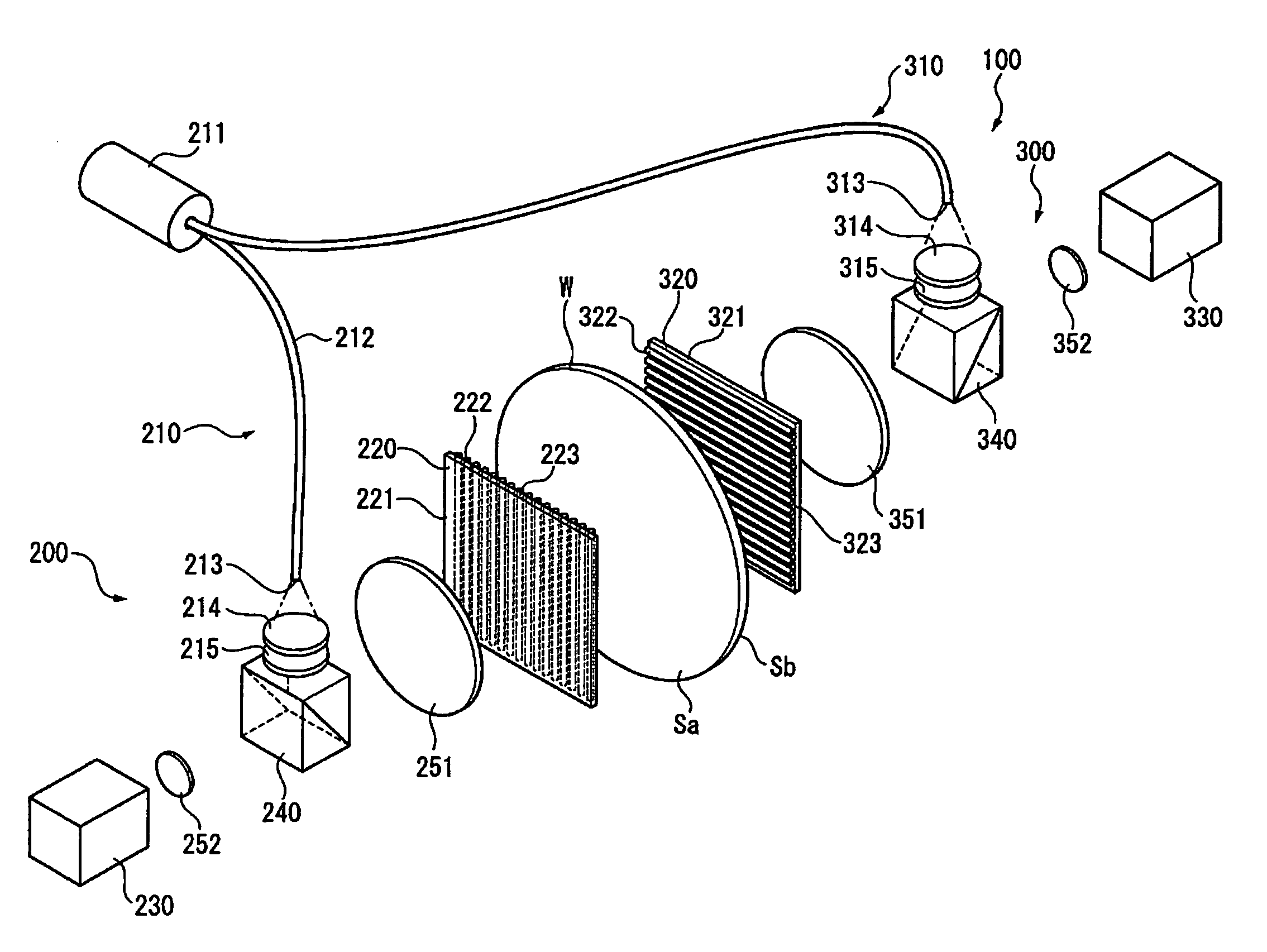
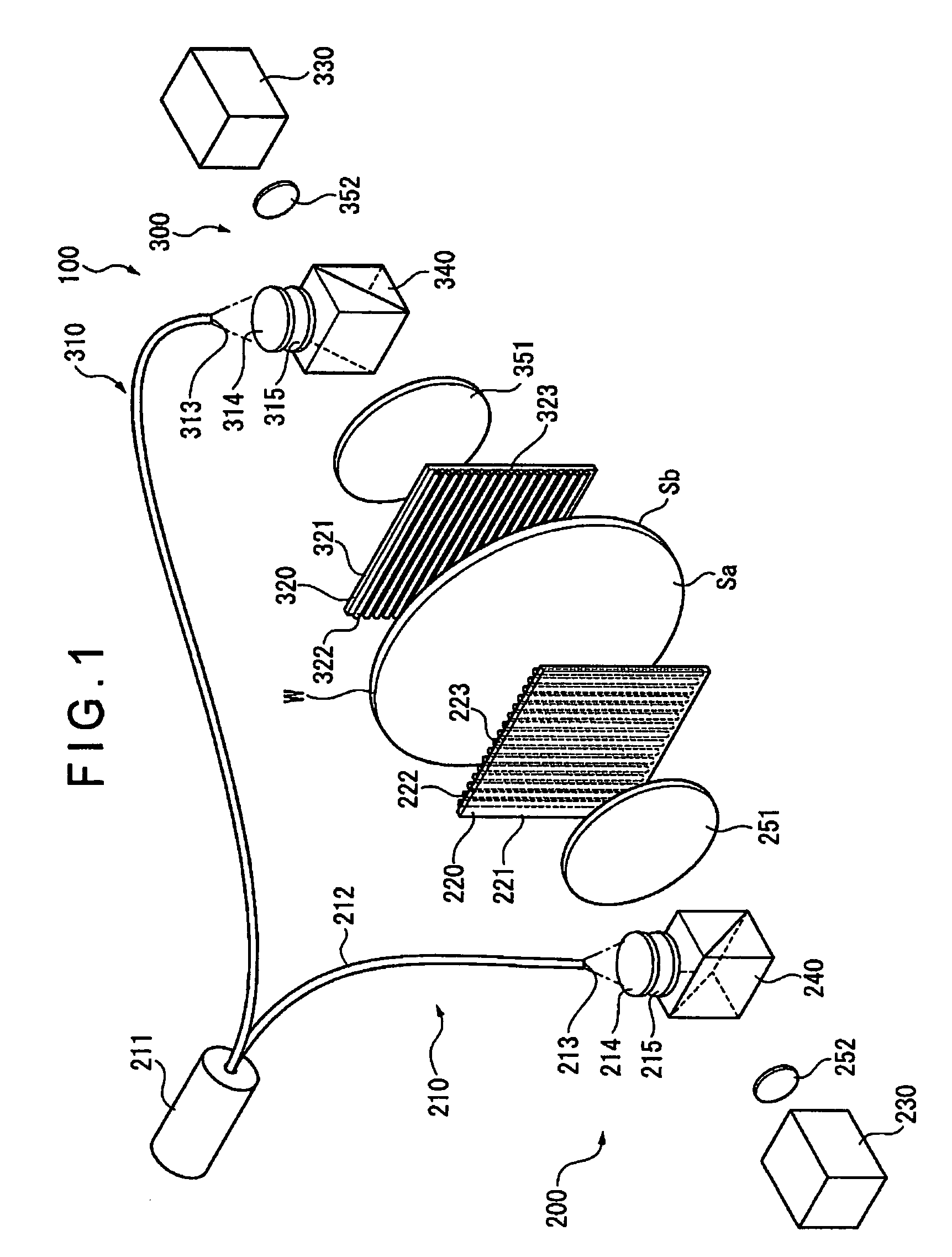
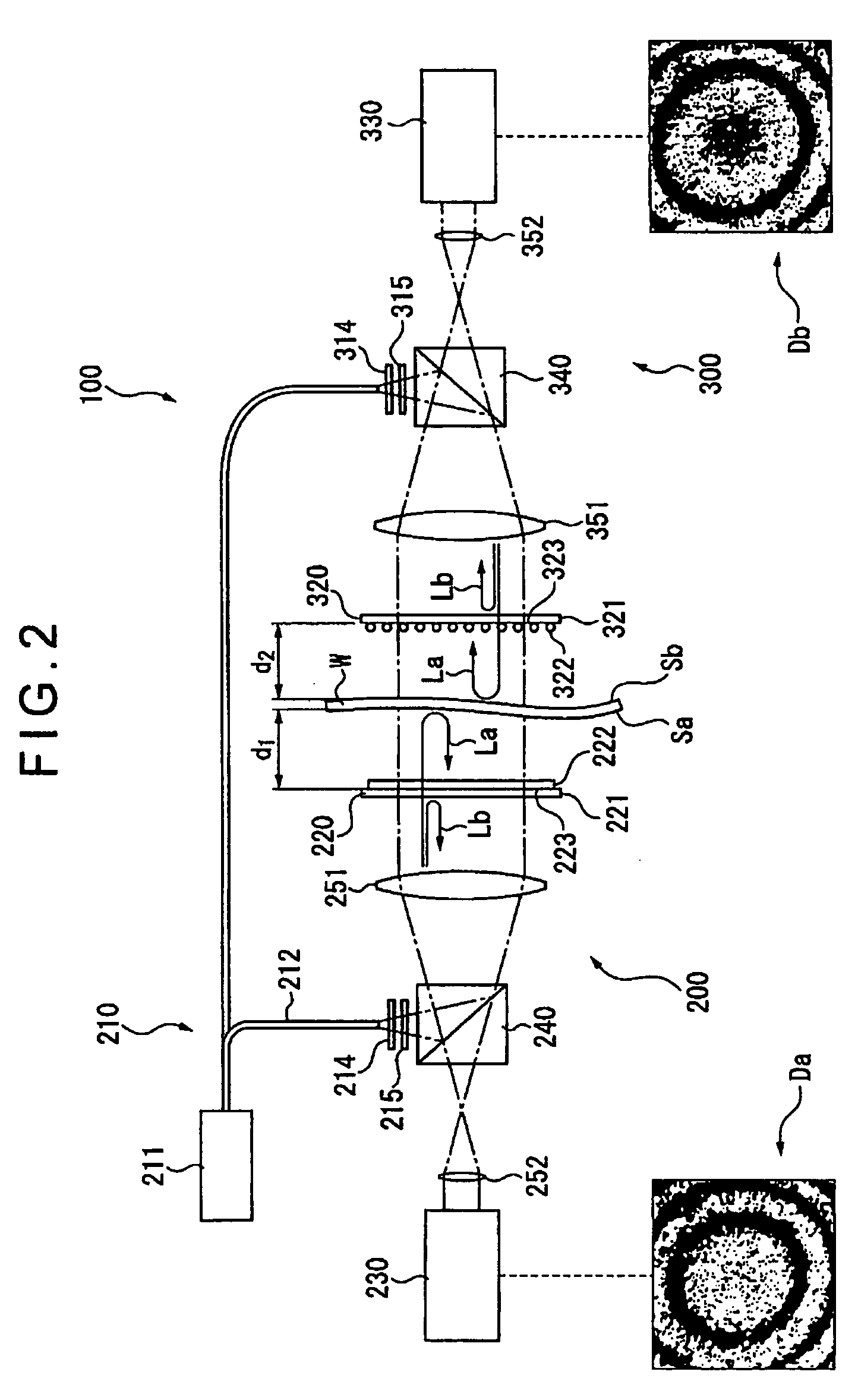
ActiveUS7471396B2Precise changeChange thicknessInterferometersUsing optical meansWire gridComputational physics
An optical interferometer (100) includes a first optical interferometer (200) disposed on a front surface side of a workpiece (W) and a second optical interferometer (300) disposed on a rear surface side of the workpiece (W). The first optical interferometer (200) and the second optical interferometer (300) each include a light emitting section (210, 310), a wire grid (220, 320) and an interference fringe sensor (230, 330). Wire alignment directions of the wire grid (220) of the first optical interferometer (200) and the wire grid (320) of the second optical interferometer (300) are orthogonal to each other. When no workpiece (W) is set, the wire grid (220) of the first optical interferometer (200) reflects light from the second optical interferometer (300) to generate object light and the wire grid (320) of the second optical interferometer (300) reflects light from the first optical interferometer (200) to generate object light.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
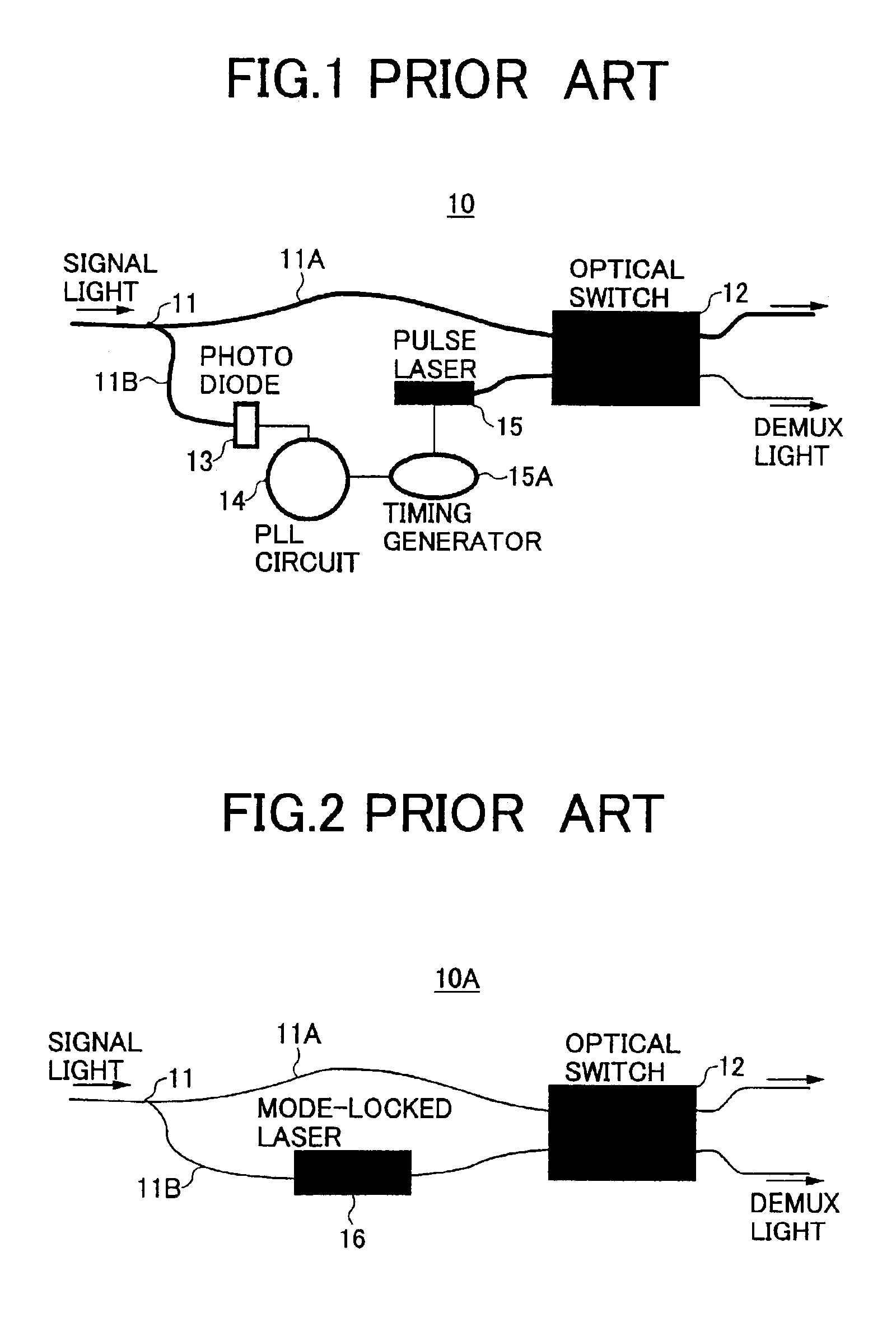
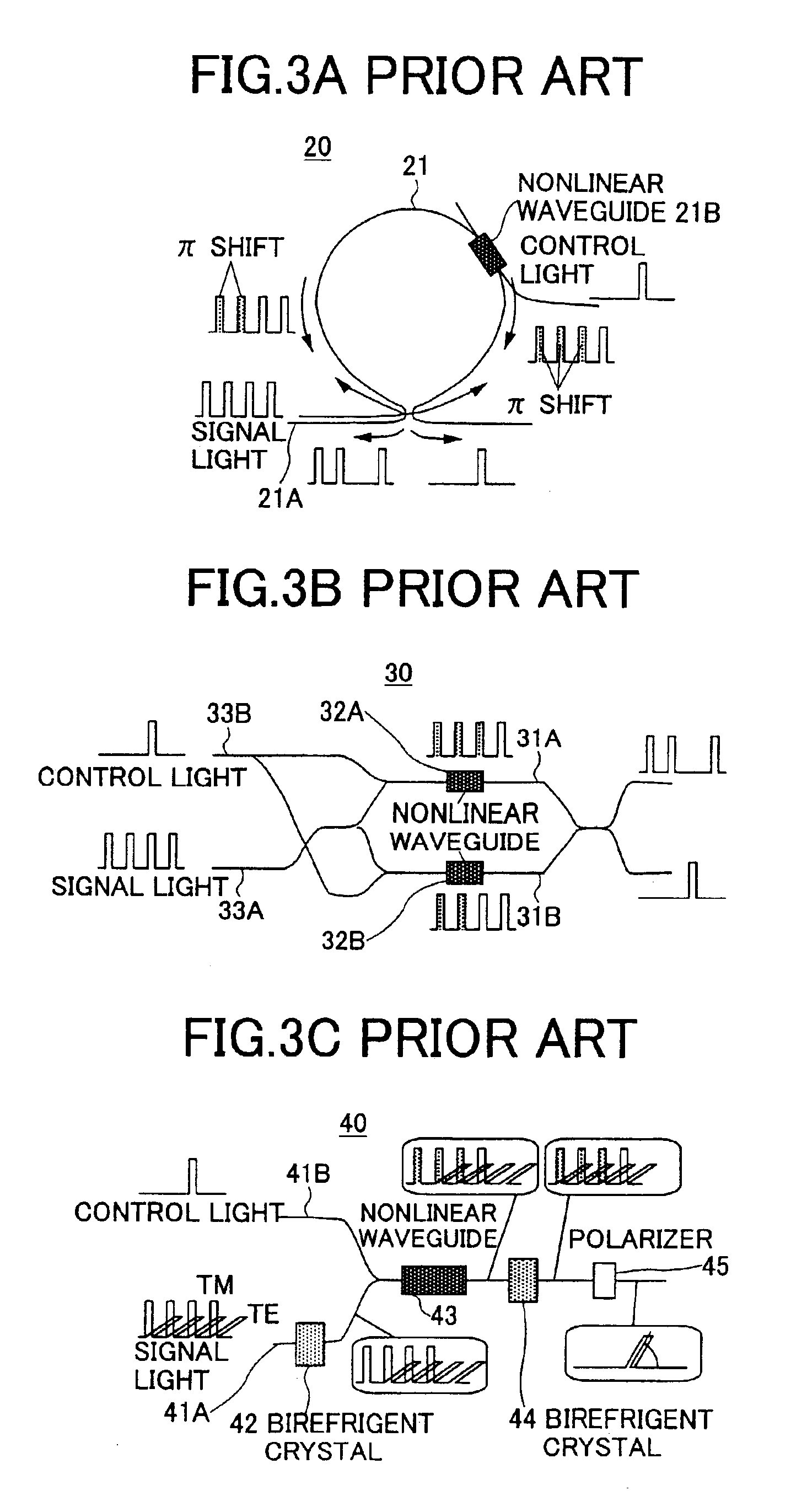
Optical interferometer generating a mode-locked laser oscillation, all-optical switch, all-optical asymmetric demultiplexer and all optical pulse reshaping apparatus
InactiveUS6856716B2Eliminate the problemEasy-fabricated configurationLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlOptical cavityPulse shaping
An all-optical switch, an all-optical signal waveform reshaping element and an all-optical asymmetric demultiplexer are formed of an optical interferometer having a compact and simple structure. Nonlinear gain media are provided at positions different from each other in two arms of a Mach-Zehnder optical interferometer. Then, an optical cavity is formed by mounting a mirror on an optical input-output port in each of a first and a second multi-mode optical interferometers connected with the two arms. Furthermore, when a saturable absorption medium is placed on the mirror of one of the multi-mode optical interferometers, a mode-locked laser oscillation is induced.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical interferometer and signal synthesizer using the interferometer
A femtosecond pulse incident on a Mach-Zehnder interferometer is divided into two optical paths and thereafter synthesized again. The synthesized optical pulse is outputted as complementary two output optical pulses corresponding to the difference between optical paths. An optical interferometer for monitoring fluctuations of the optical path difference from one of two output optical pulses produced from an interferometer, effecting feedback on the optical path difference and providing an operation stabilized in a relation of 1 / 20 or less the central wavelength, and an optical signal synthesizer using the interferometer are provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
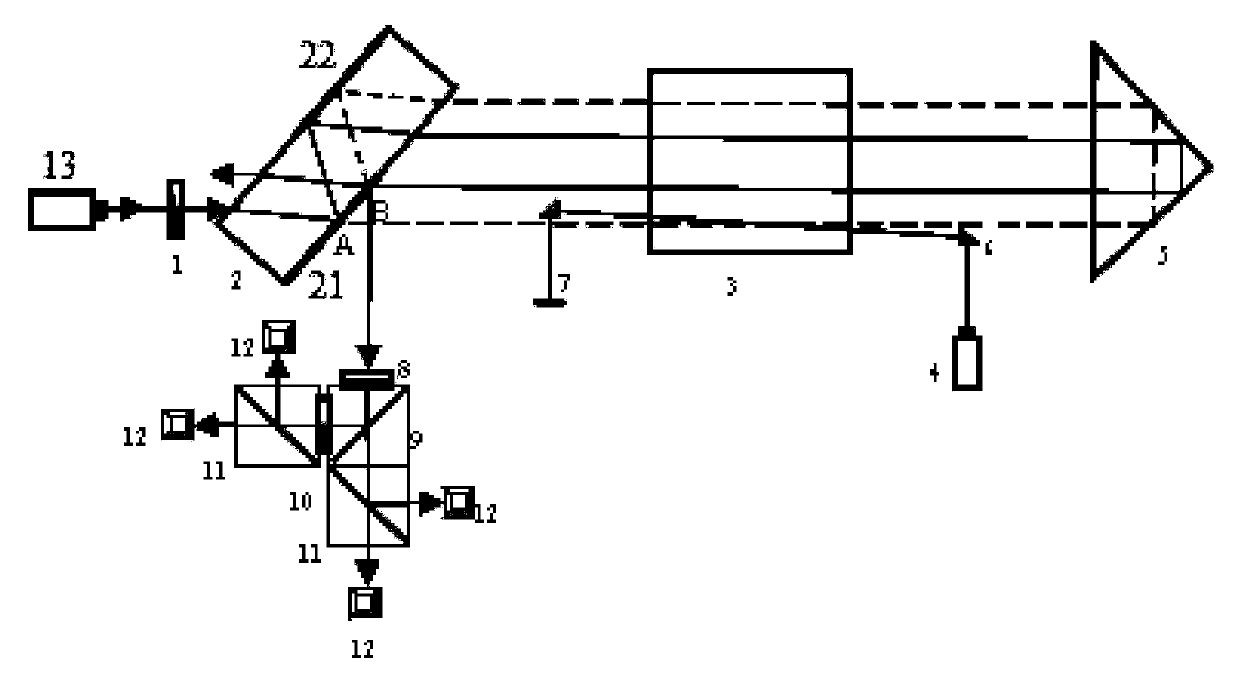
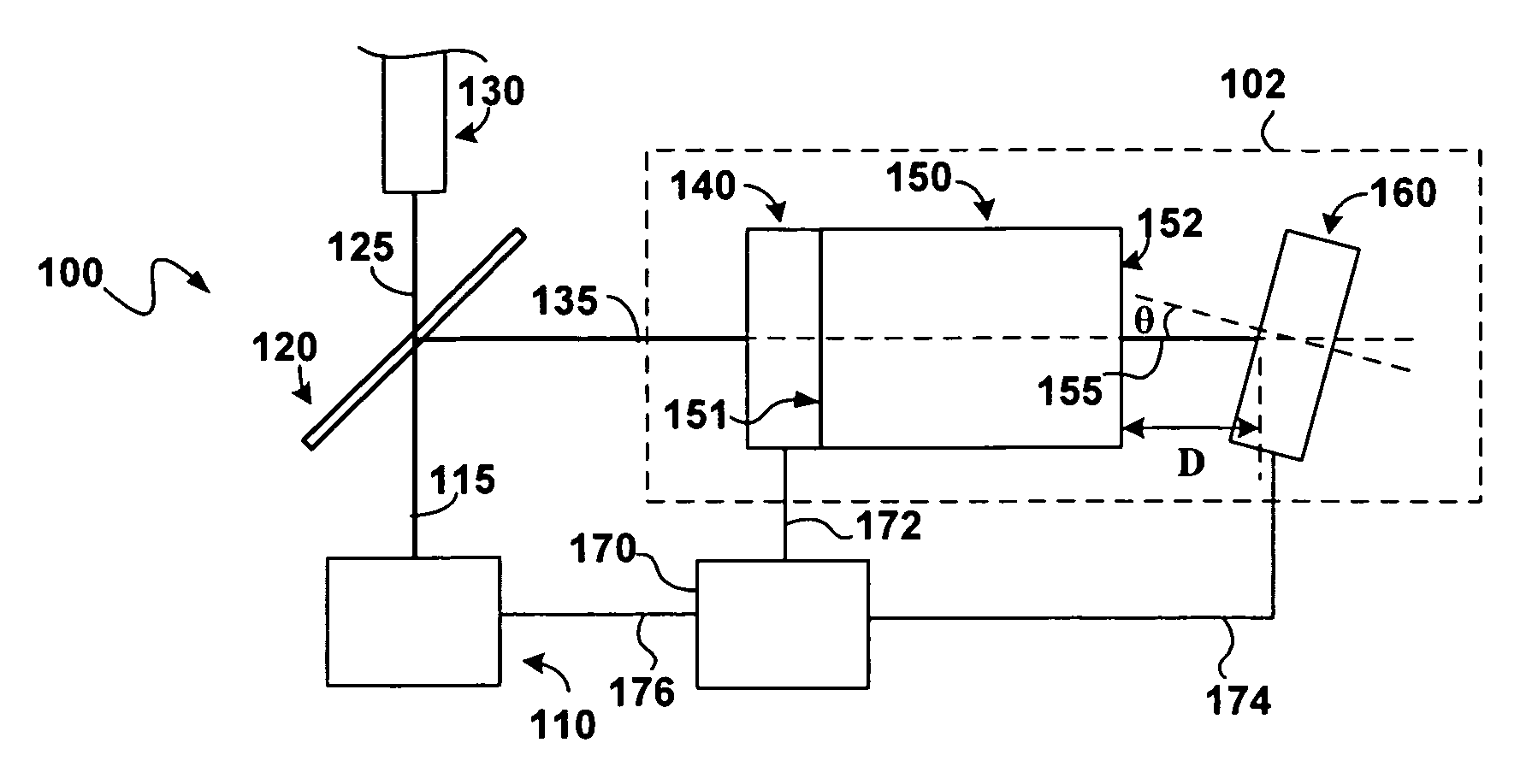
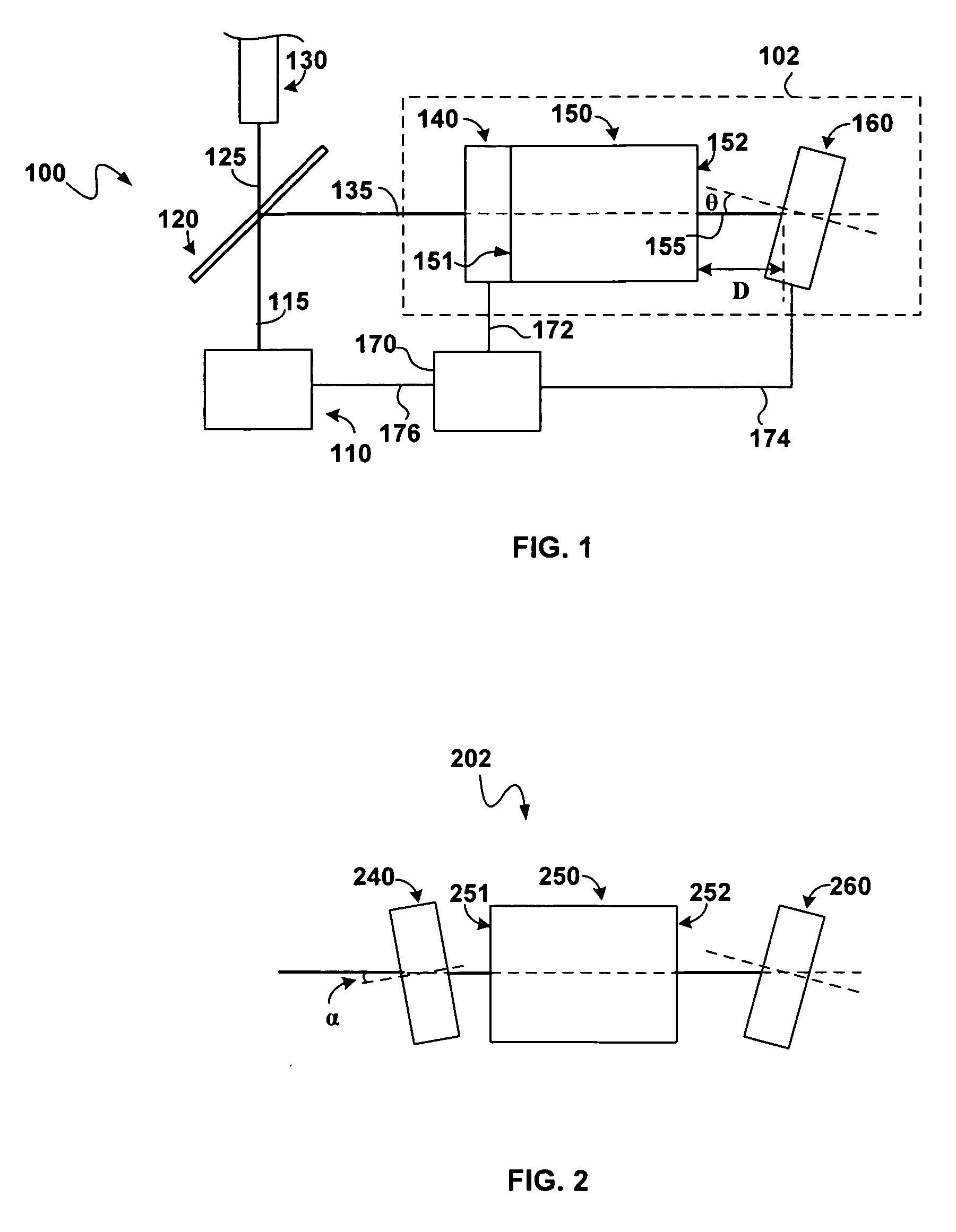
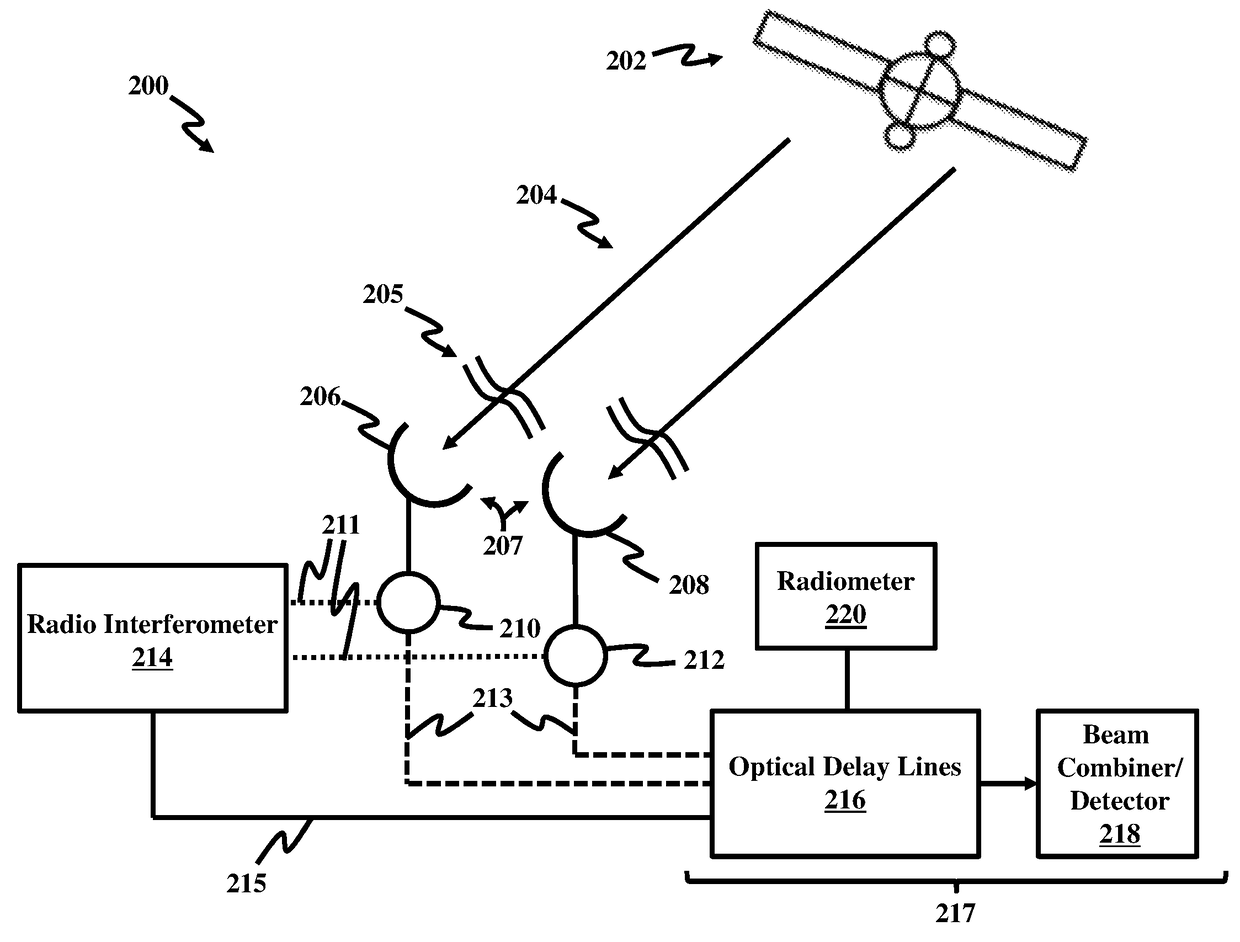
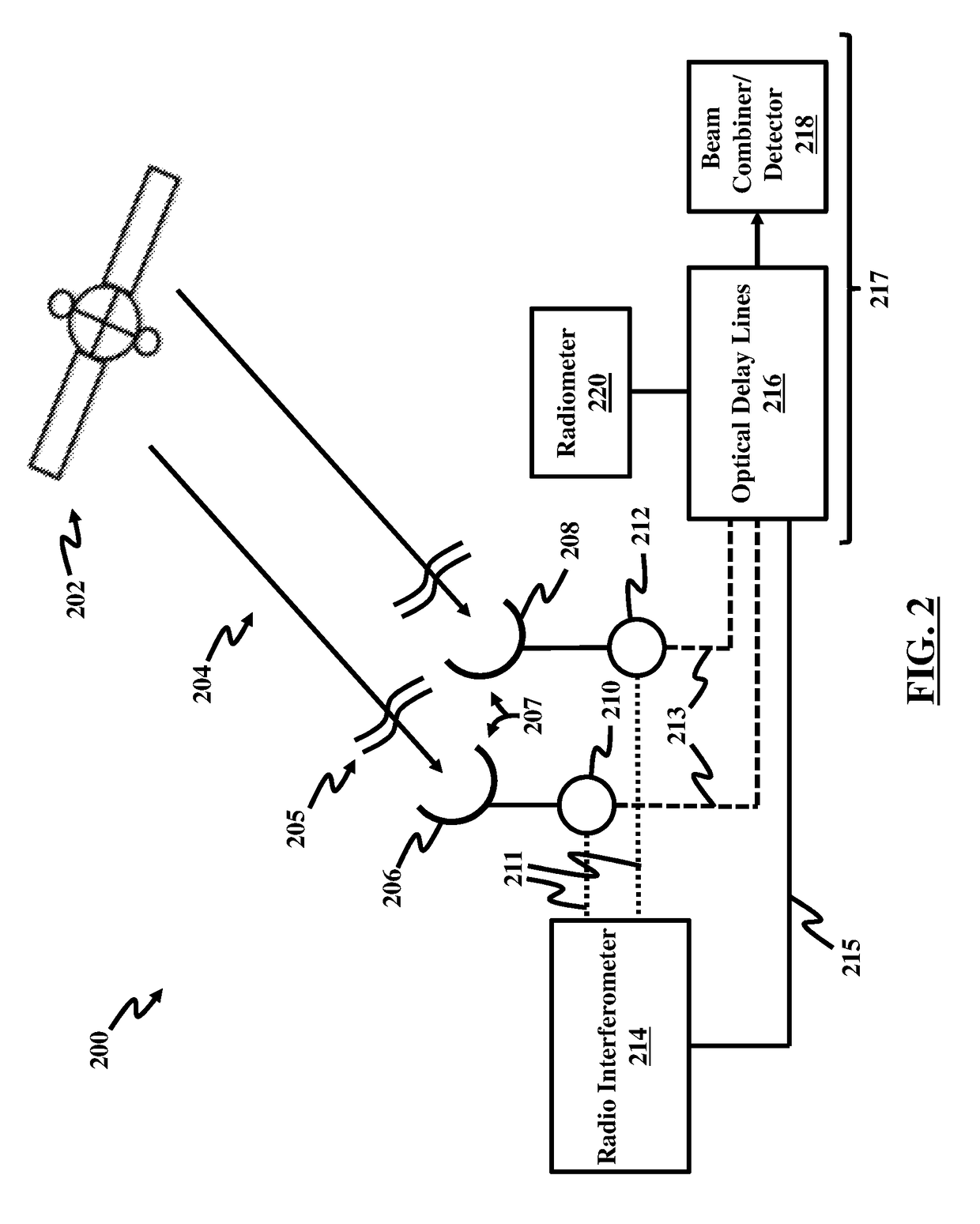
Phasing an optical interferometer using the radio emission from the target being observed
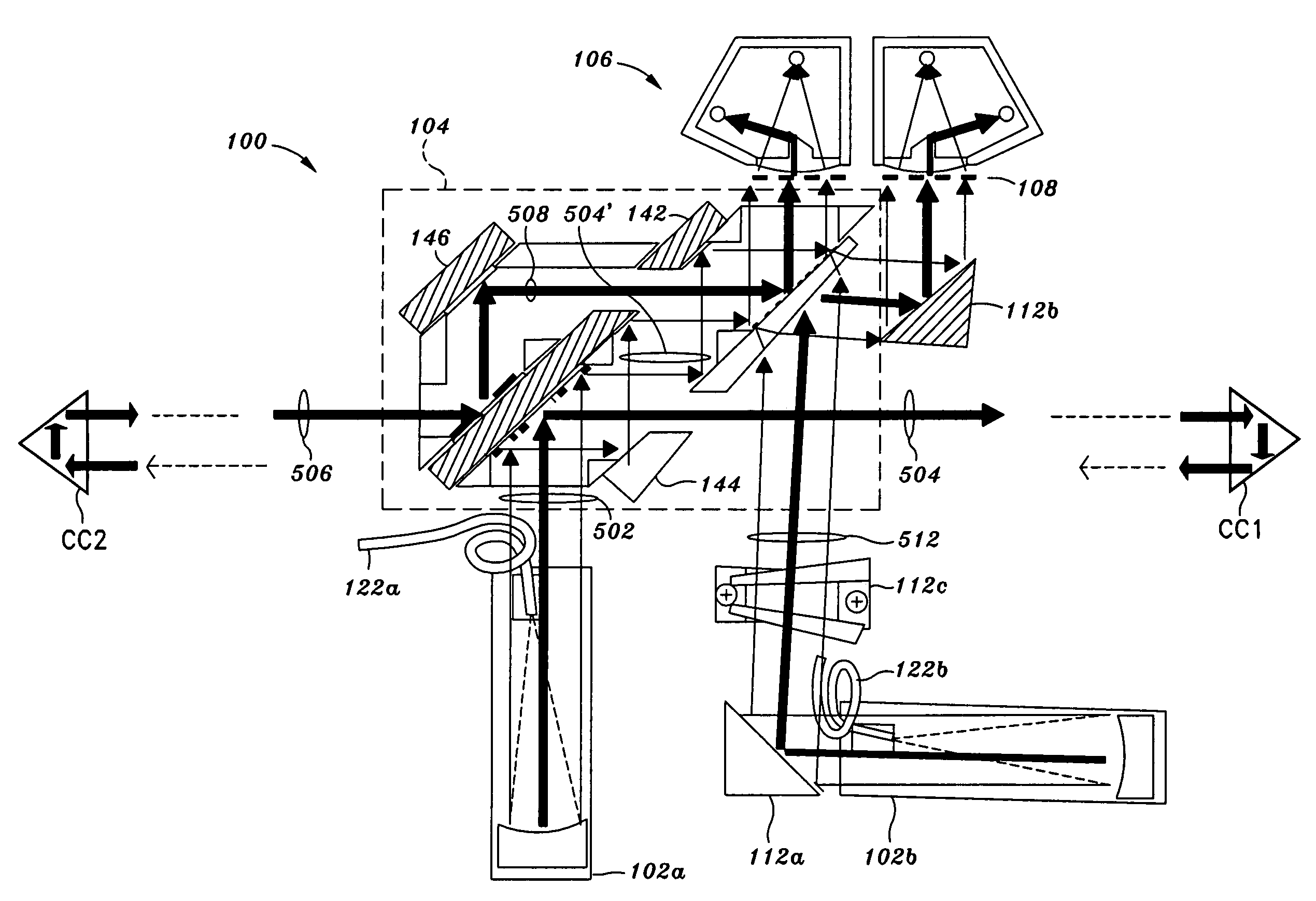
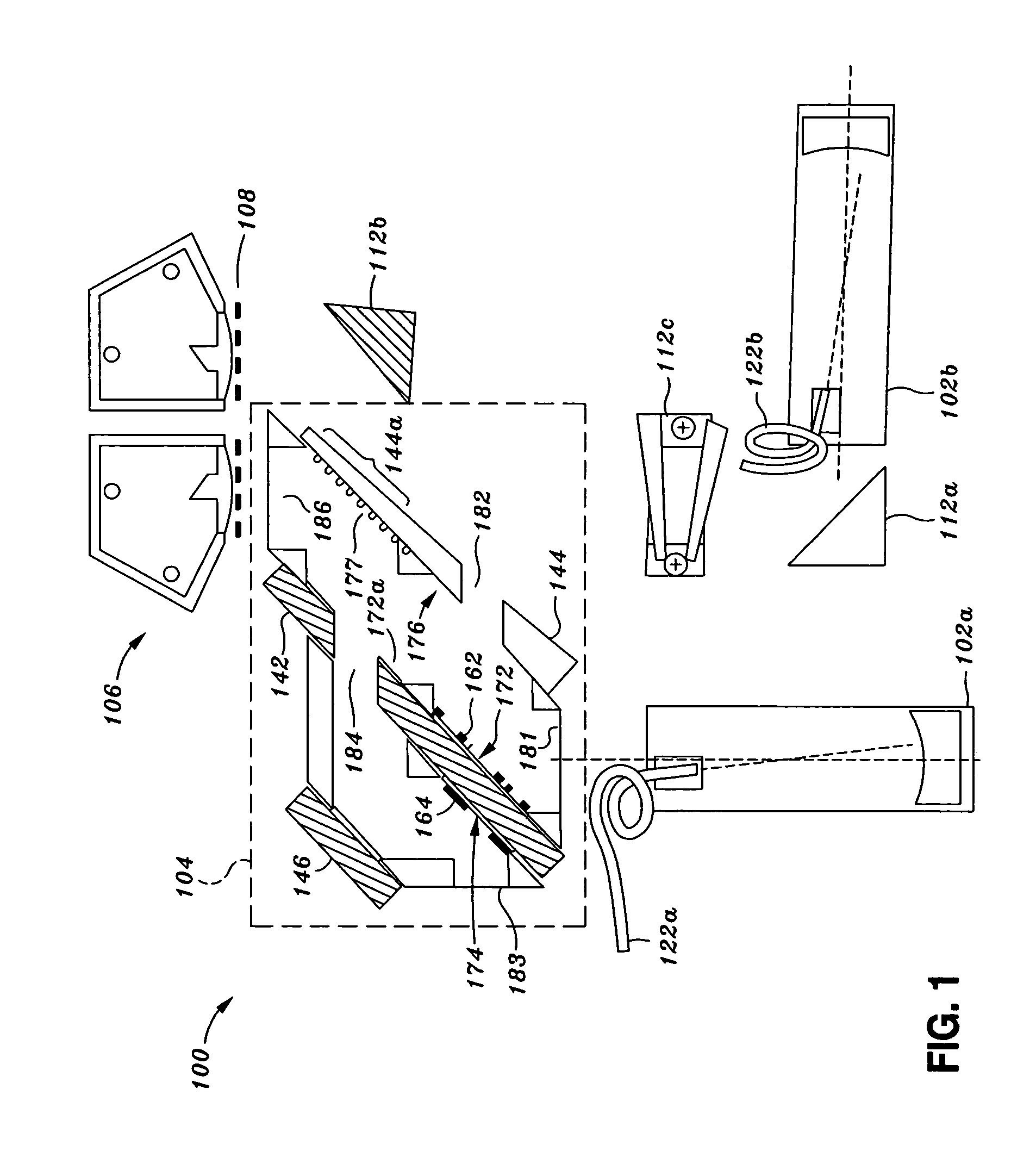
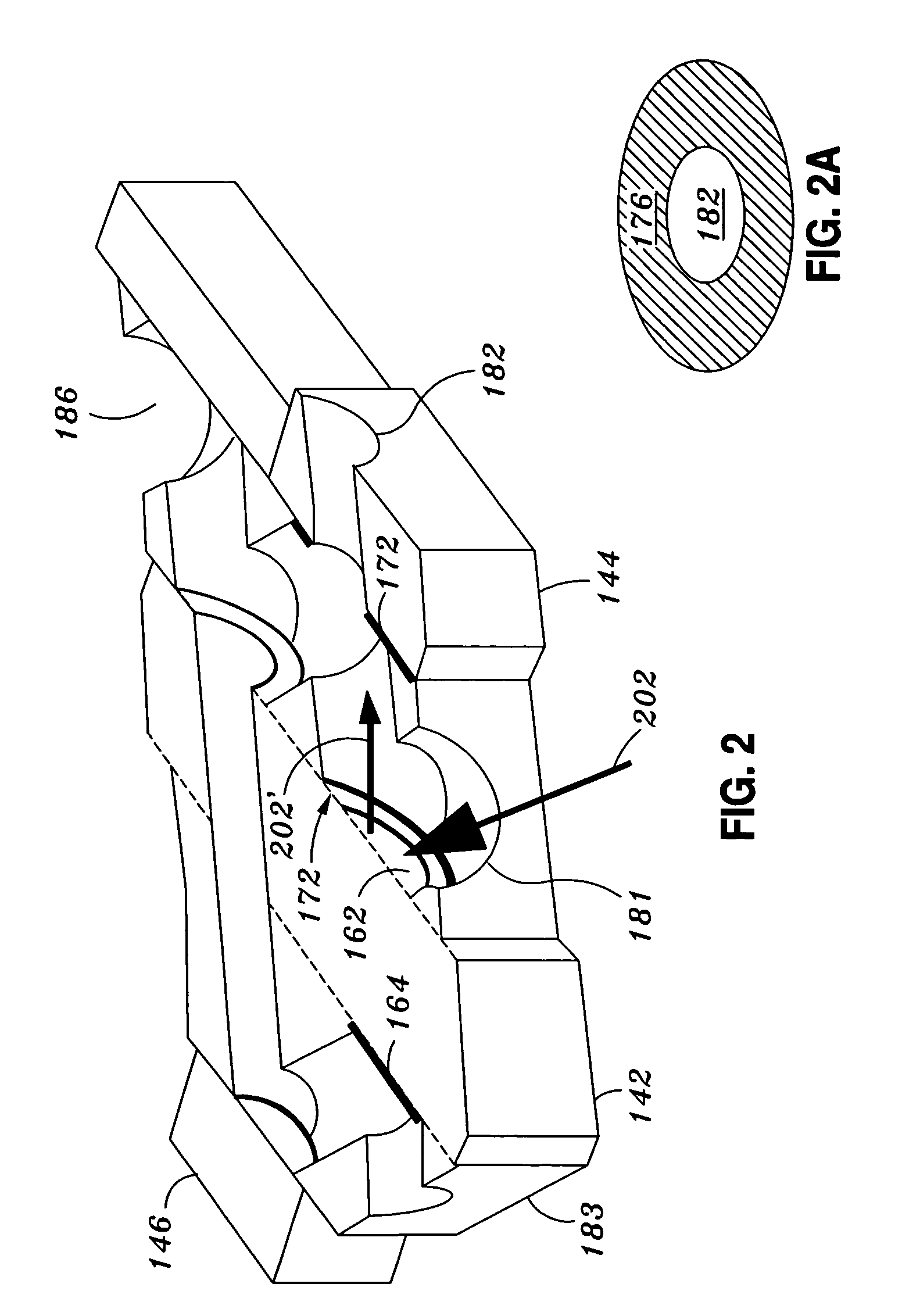
ActiveUS10082382B2Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsInterferometersBeam splitterAstronomical interferometer
An interferometry system including a first telescope for simultaneously receiving a first optical / infrared signal and a first radio signal from a target; a second telescope configured to simultaneously receive a second optical / infrared signal and a second radio signal from the target; a first beam splitter communicatively connected to the first telescope, where the first beam splitter is configured to separate the first optical / infrared signal from the first radio signal; a second beam splitter communicatively connected to the second telescope, where the second beam splitter is configured to separate the second optical / infrared signal from the second radio; and a first optical / infrared interferometer configured to detect an interferometry image of the target using the first and second optical / infrared and radio signals.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Optical multi-species gas monitoring sensor and system
ActiveUS8330961B1Photometry using reference valueInterferometric spectrometryLight energyLength wave
The system includes at least one light source generating light energy having a corresponding wavelength. The system's sensor is based on an optical interferometer that receives light energy from each light source. The interferometer includes a free-space optical path disposed in an environment of interest. The system's sensor includes an optical device disposed in the optical path that causes light energy of a first selected wavelength to continue traversing the optical path whereas light energy of at least one second selected wavelength is directed away from the optical path. The interferometer generates an interference between the light energy of the first selected wavelength so-traversing the optical path with the light energy at the corresponding wavelength incident on the optical interferometer. A first optical detector detects the interference. At least one second detector detects the light energy at the at least one second selected wavelength directed away from the optical path.
Owner:NASA
Optical interferometer
InactiveUS8576404B2High accurate correction of refractive indexInterferometersUsing optical meansTarget surfaceClassical mechanics
Owner:CANON KK
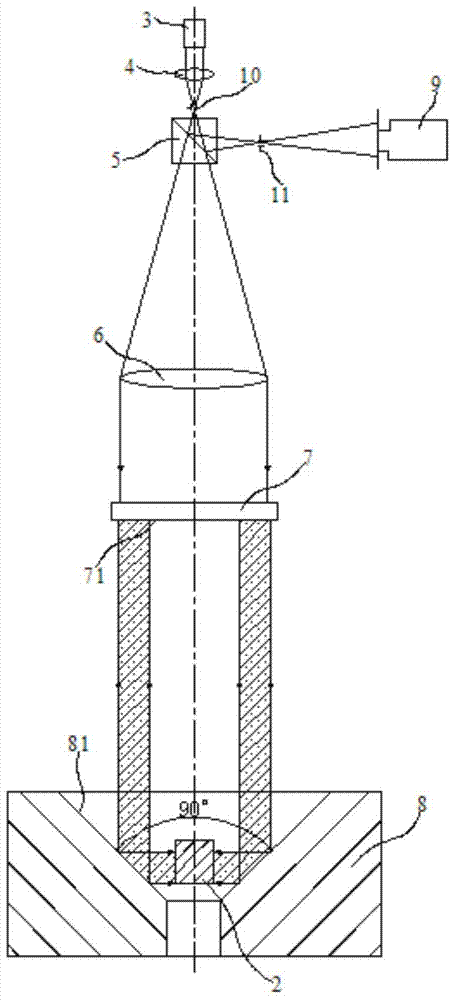
Secondary constant measuring method for aspherical mirrors
The invention relates to a secondary constant measuring method for aspherical mirrors, and belongs to the field of photoelectric technology detection. The measuring method is performed in a vertical interferometer, and mainly aims at measuring the secondary constant and the vertex curvature radius of the aspherical mirror without a hole at the center. The method comprises the steps of: firstly using the interferometer to find the position of the cat eye of the mirror to be measured as an initial position of the interferometer, vertically moving the interferometer along the optical axis, extracting the pixel radius of the zero stripe of the interferometer, working out the actual radius of the mirror by calibrated distortion, and then working out the secondary constant and the vertex curvature radius of the mirror to be measured by using the corresponding moving distance according to a formula. The method is simple in structure, flexible to use and high in accuracy.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Light reflection mechanism, optical interferometer and spectrometric analyzer
InactiveUS9291444B2Improve performanceOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryCantilevered beamLight beam
Provided is an inexpensive, high performance, compact, and energy saving light reflection mechanism comprising a first moving portion having a reflecting surface on the front surface, a supporting portion which supports the first moving portion, a first beam and a translating beam which couple the first moving portion and the supporting portion in the form of cantilever beam above and below the supporting portion, and a drive portion which moves the first moving portion, wherein a large amplitude can be obtained by small energy when the first moving portion is forced into resonance vibration in the direction perpendicular to the first reflecting surface. Also provided is an optical interferometer and a spectral analyzer.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Optical interferometer and all-fiber laser device with tunable wavelength
InactiveCN108957795ALarge wavelength tuning rangeTunable Wavelength StructureActive medium shape and constructionNon-linear opticsAstronomical interferometerLength wave
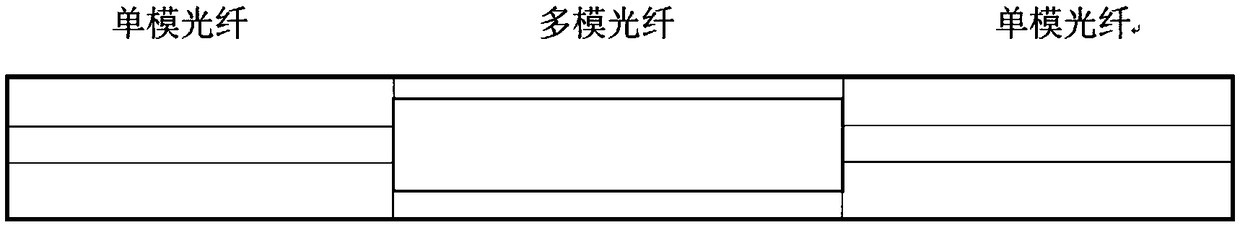
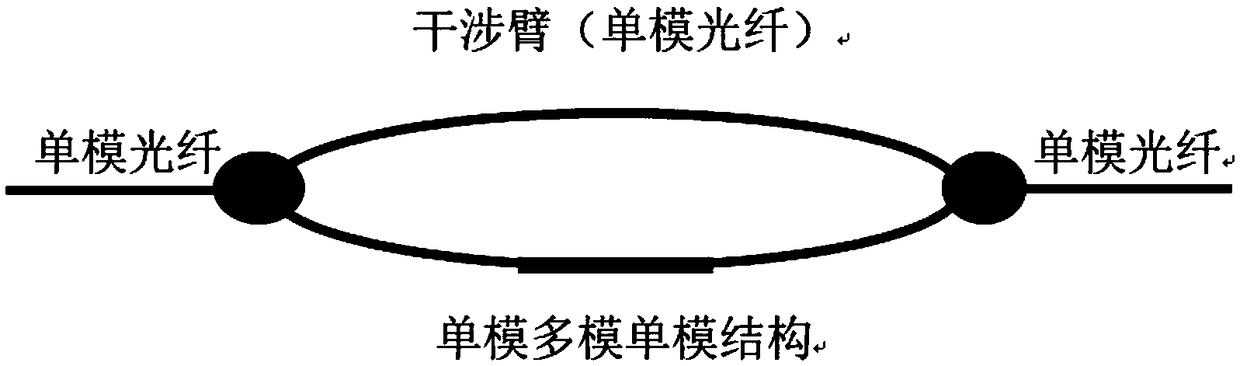
The invention provides an optical interferometer and an all-fiber laser device with a tunable wavelength. A larger tuning range is achieved by combining Mach-Zehnder and single-mode and multi-mode structures and utilizing the pattern competition between light consumption and gain, and therefore the advantages which cannot be achieved by the prior art can be achieved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com