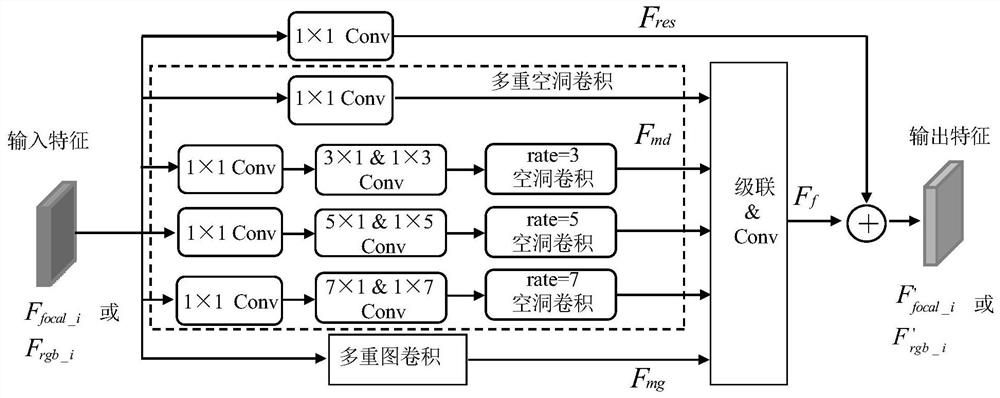
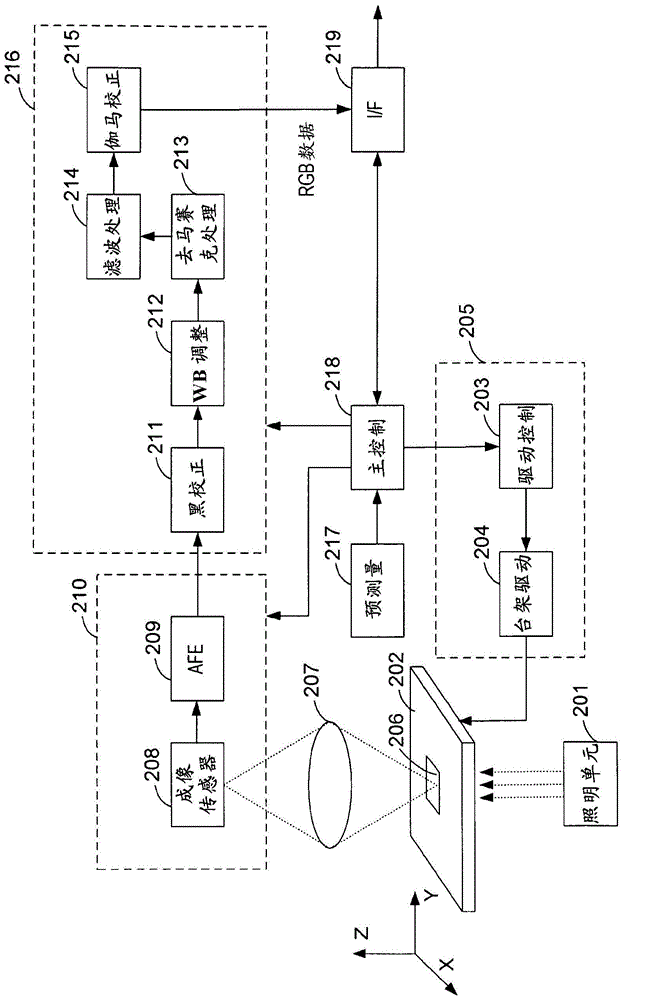
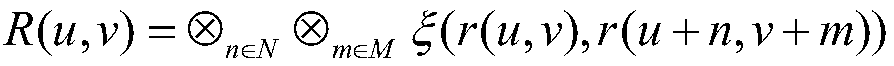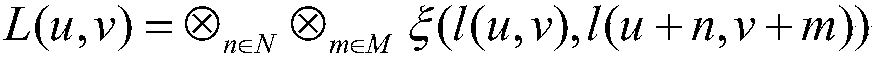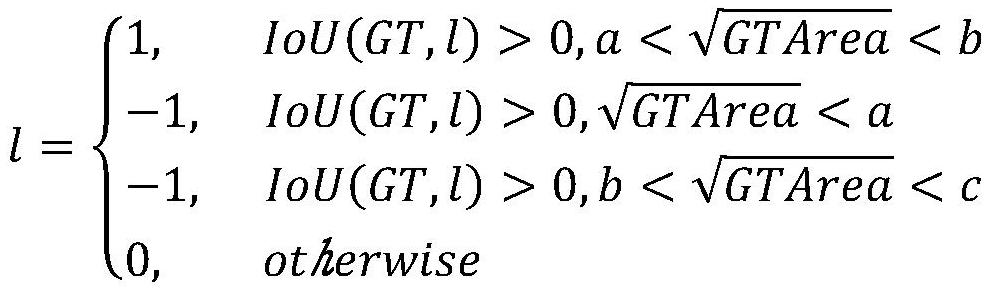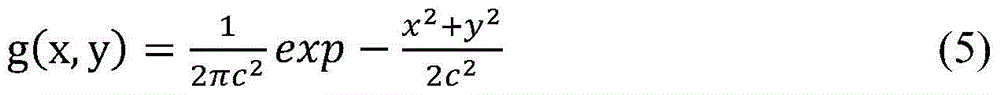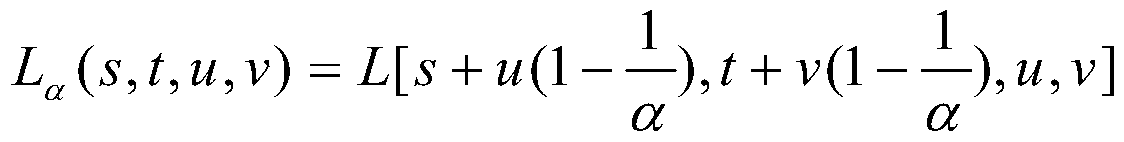Patents
Literature
70 results about "Focus stacking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
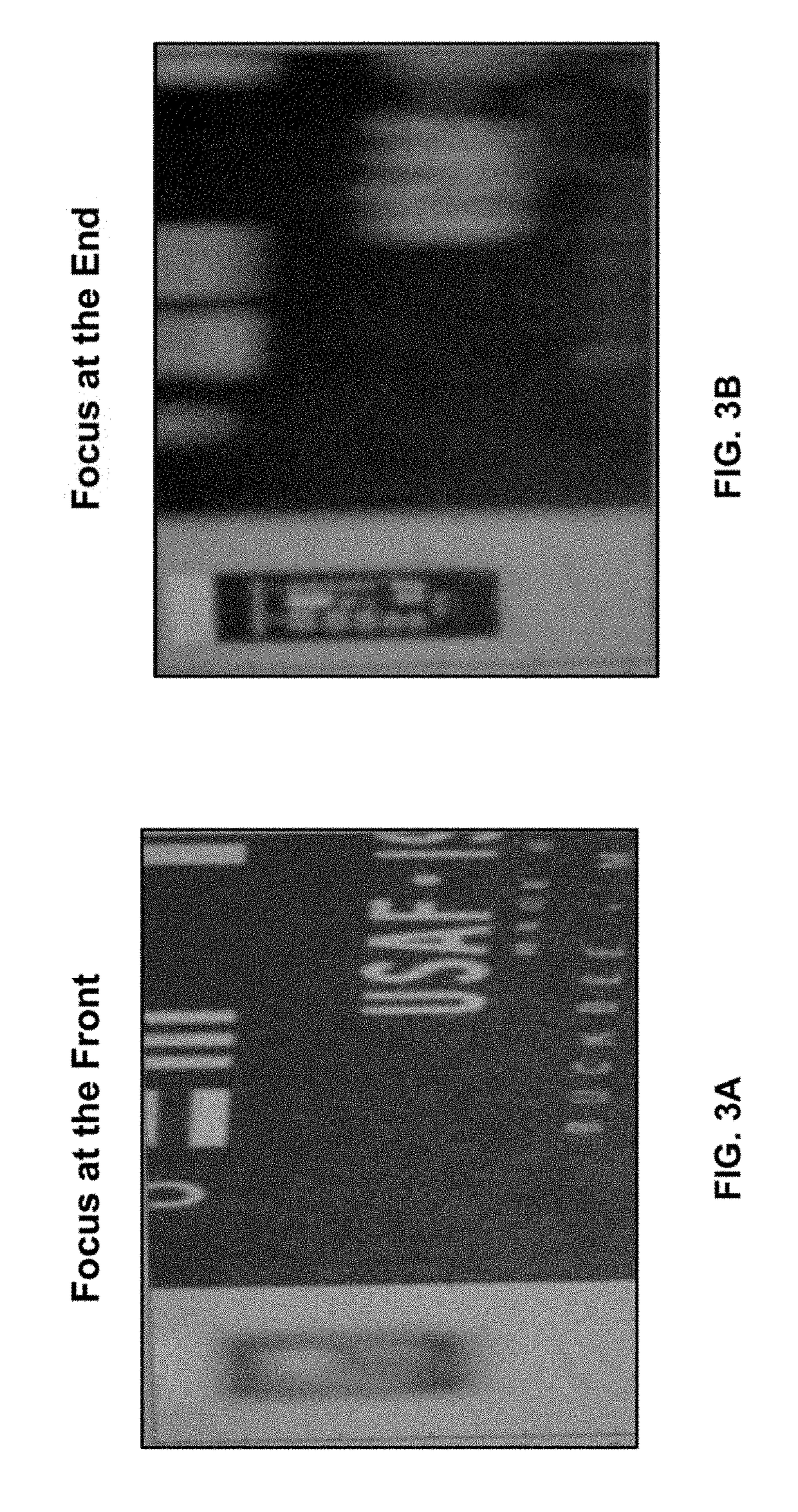
Focus stacking (also known as focal plane merging and z-stacking or focus blending) is a digital image processing technique which combines multiple images taken at different focus distances to give a resulting image with a greater depth of field (DOF) than any of the individual source images. Focus stacking can be used in any situation where individual images have a very shallow depth of field; macro photography and optical microscopy are two typical examples. Focus stacking can also be useful in landscape photography.
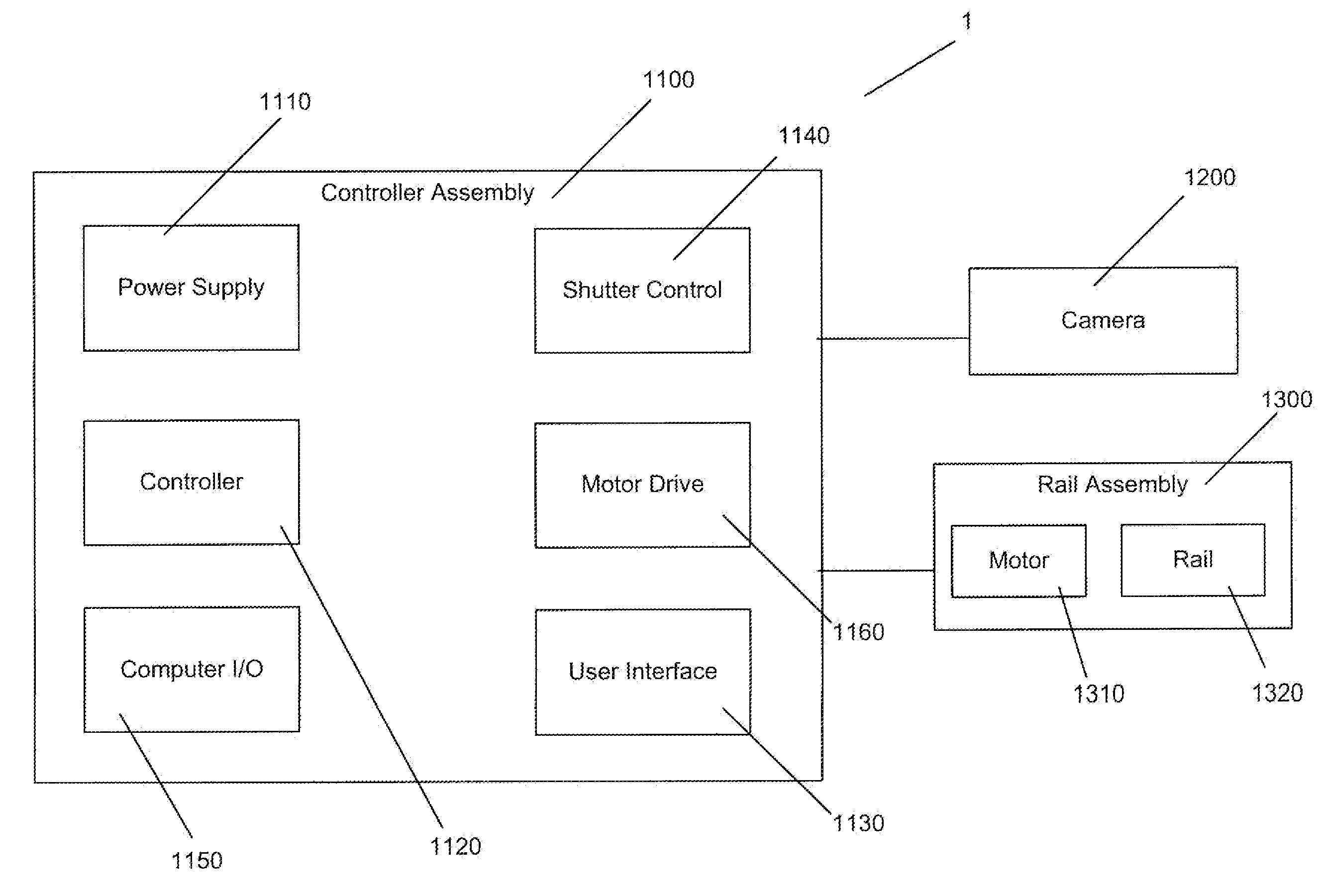
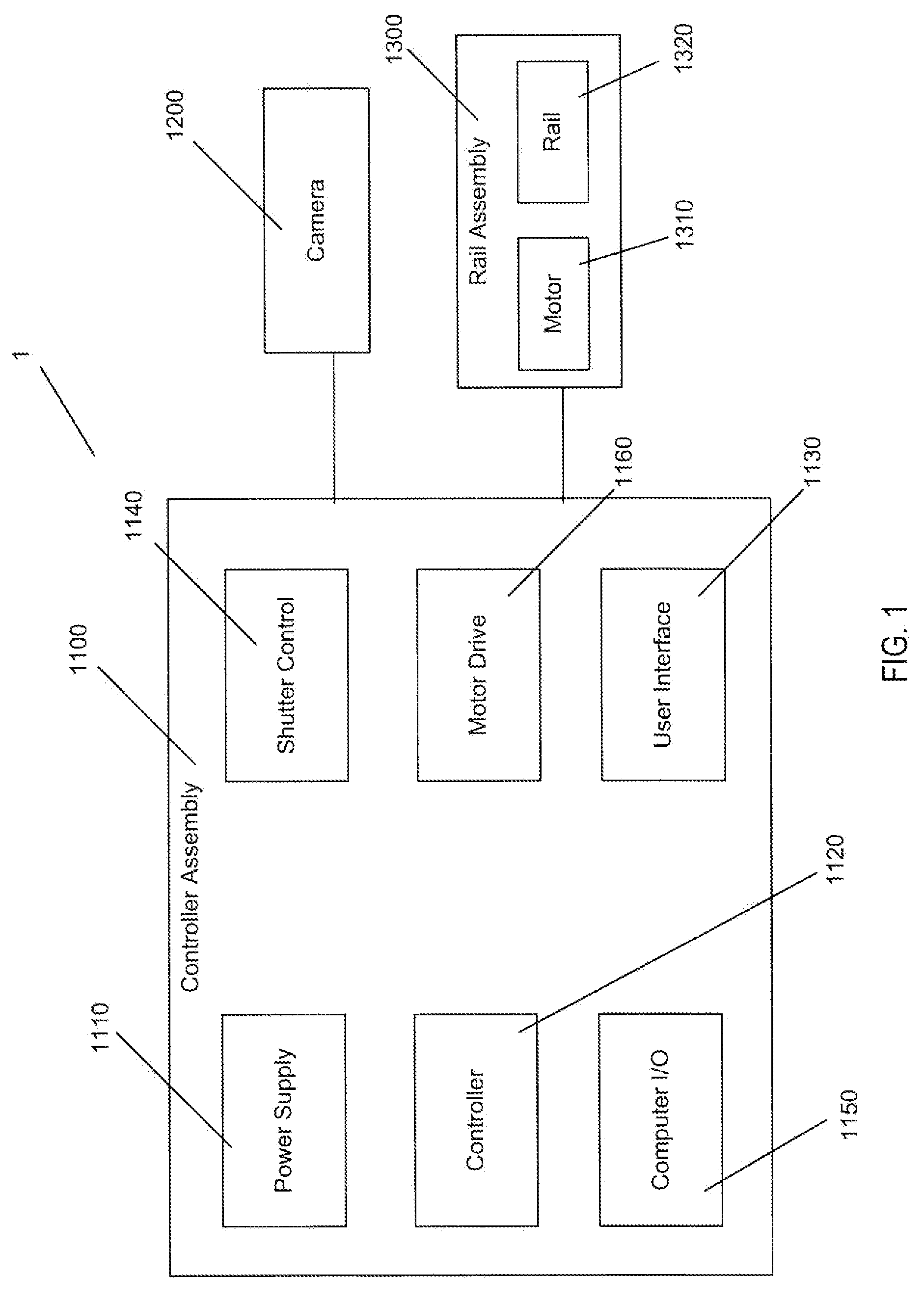
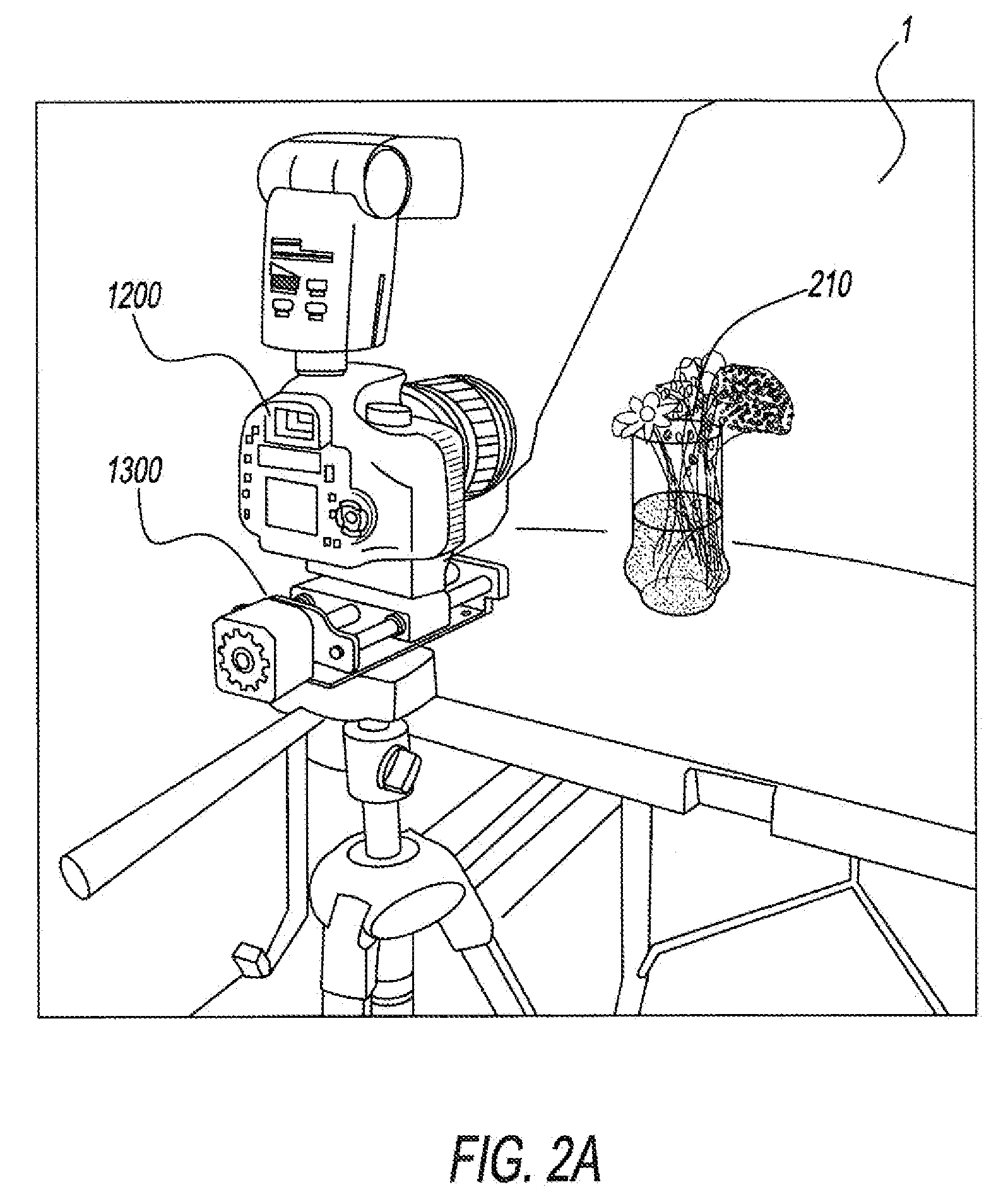
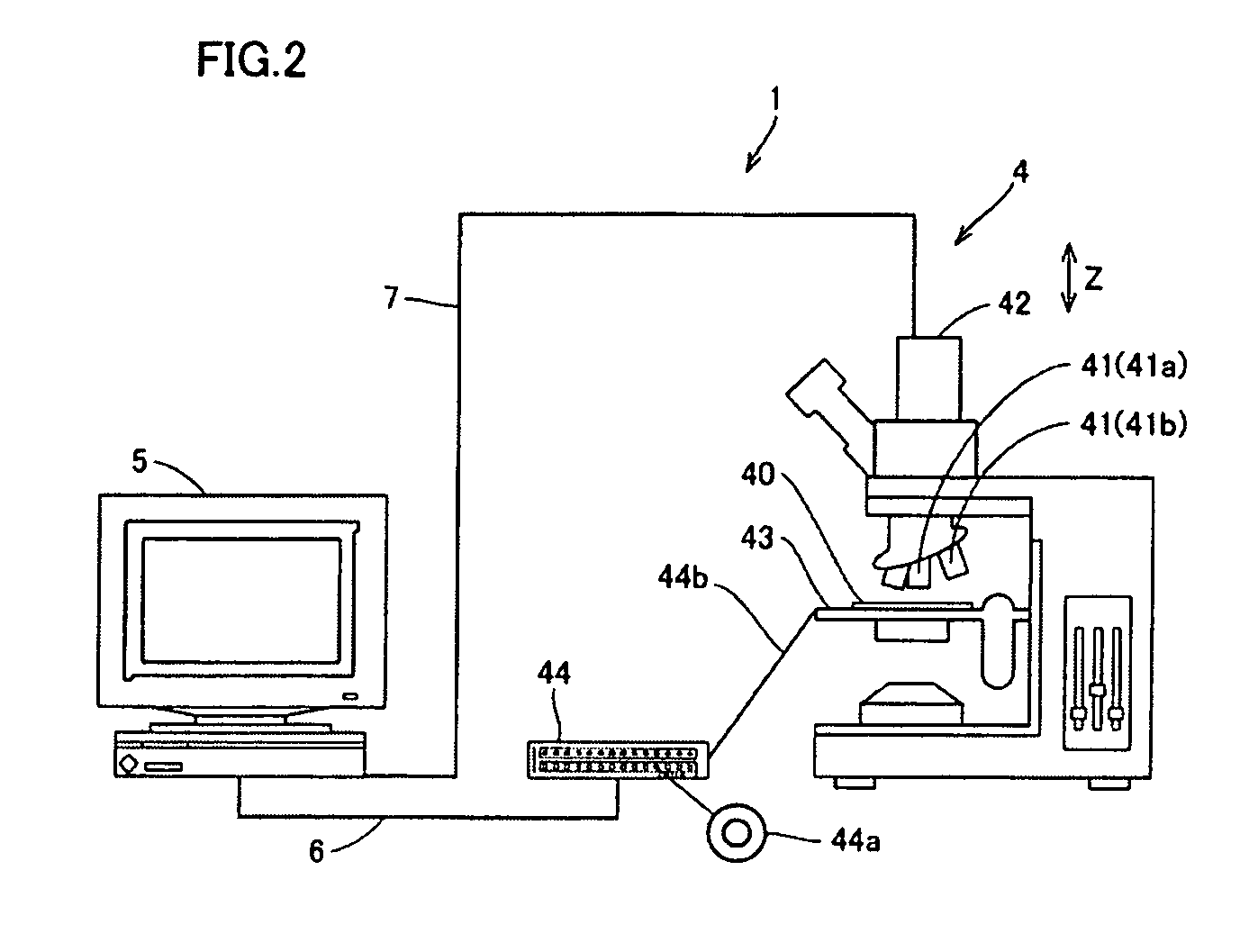
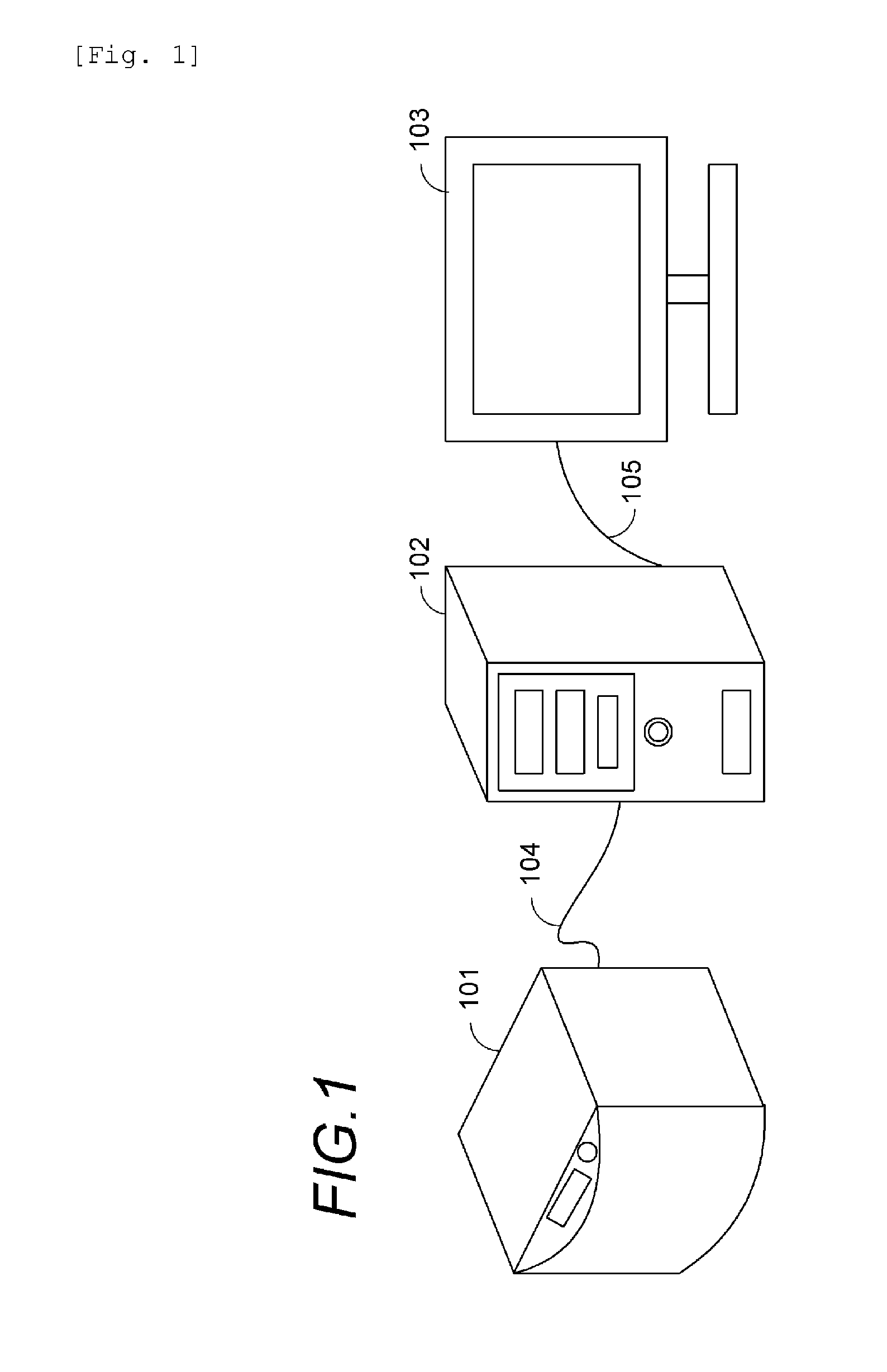
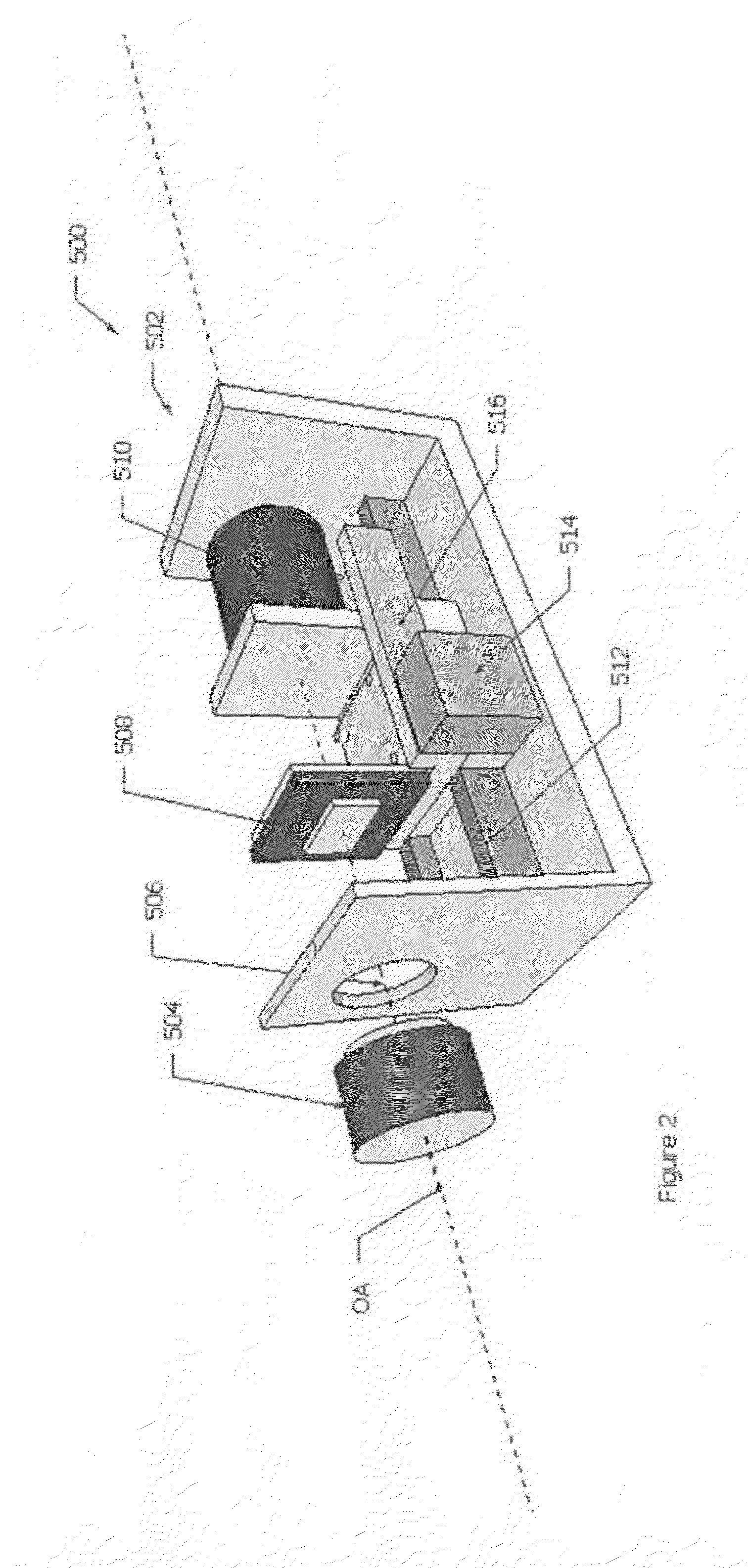
Motor controlled macro rail for close-up focus-stacking photography
ActiveUS20110123188A1Simplification and improvement of processTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensClose-up
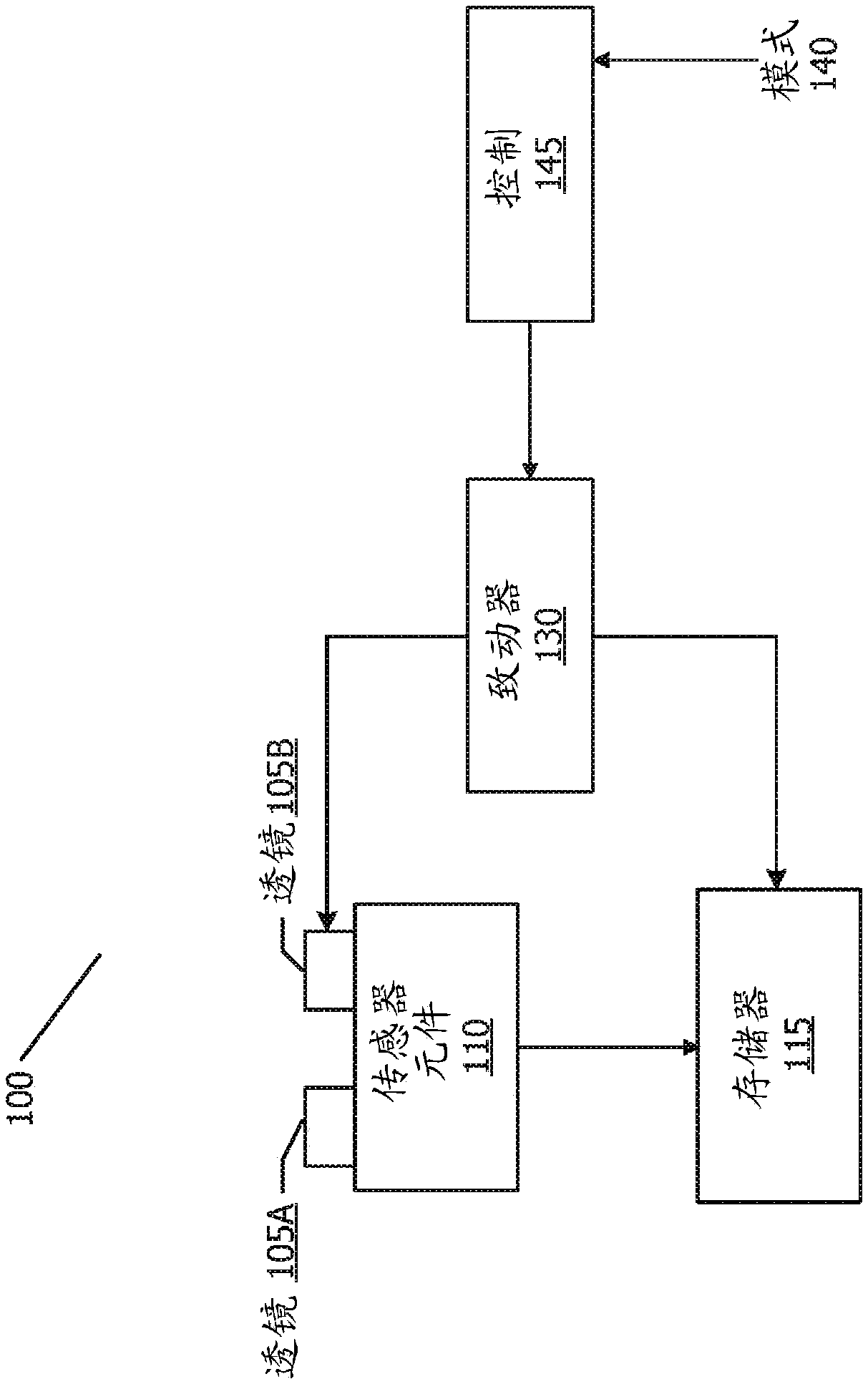
A motor controlled rail assembly is provided which simplifies and automates the process of taking focus-stacked pictures. This device can be used to incrementally move a camera or other photographic device a programmable distance forward or backward in precise steps relative to an external object to facilitate focus-stacked photography. The device may include a motor-driven macro rail assembly, a controller assembly and a camera, which, generally speaking, are configured as follows: a camera is attached to a macro rail carriage which is driven by the motor and controller. The device may have different modes of operation (an automatic step mode, an automatic distance mode, a total distance mode, a distance per step mode, a continuous mode and a manual mode) to yield improved results in different situations.
Owner:DEZEEUW PAUL +2
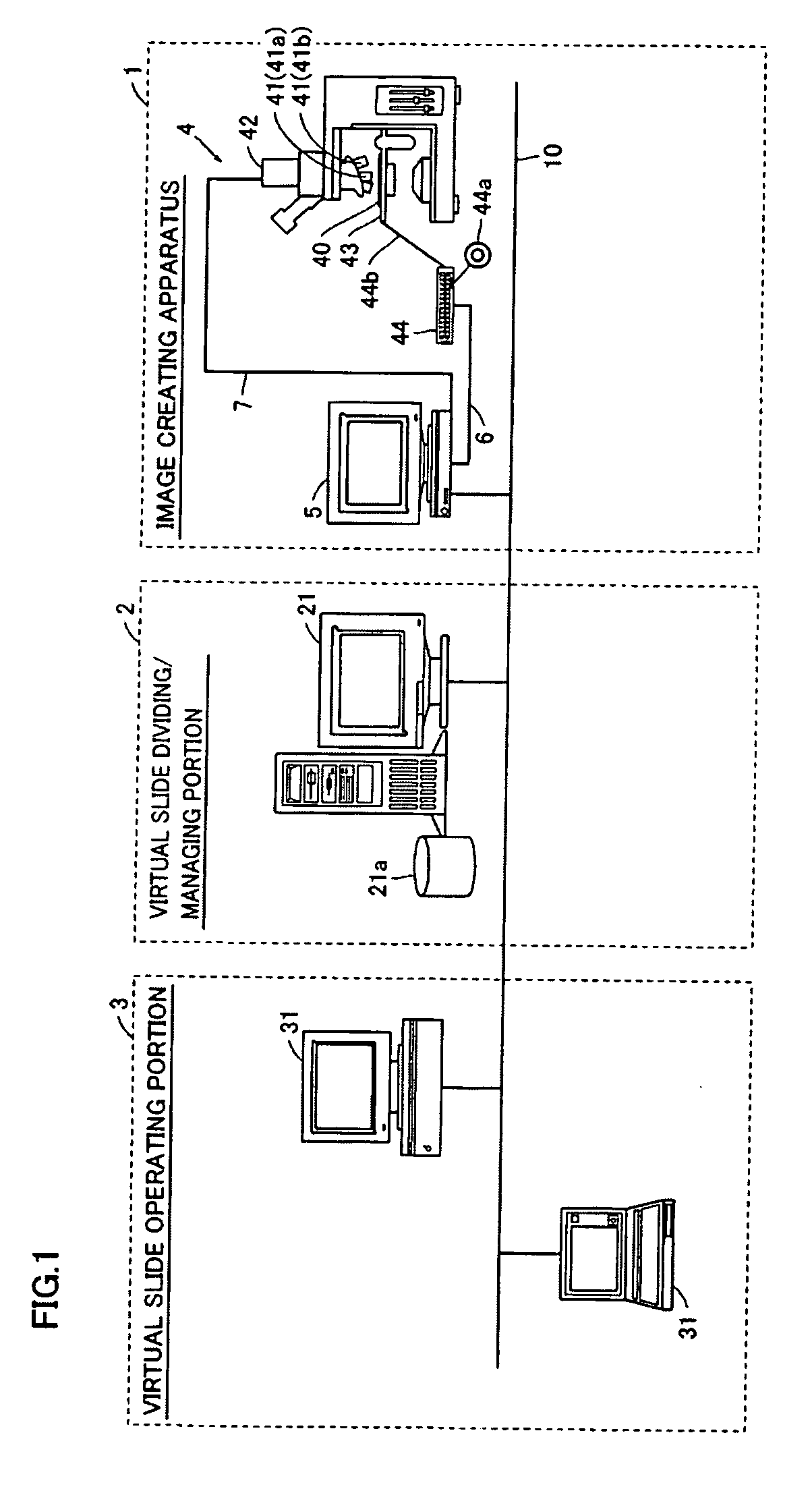
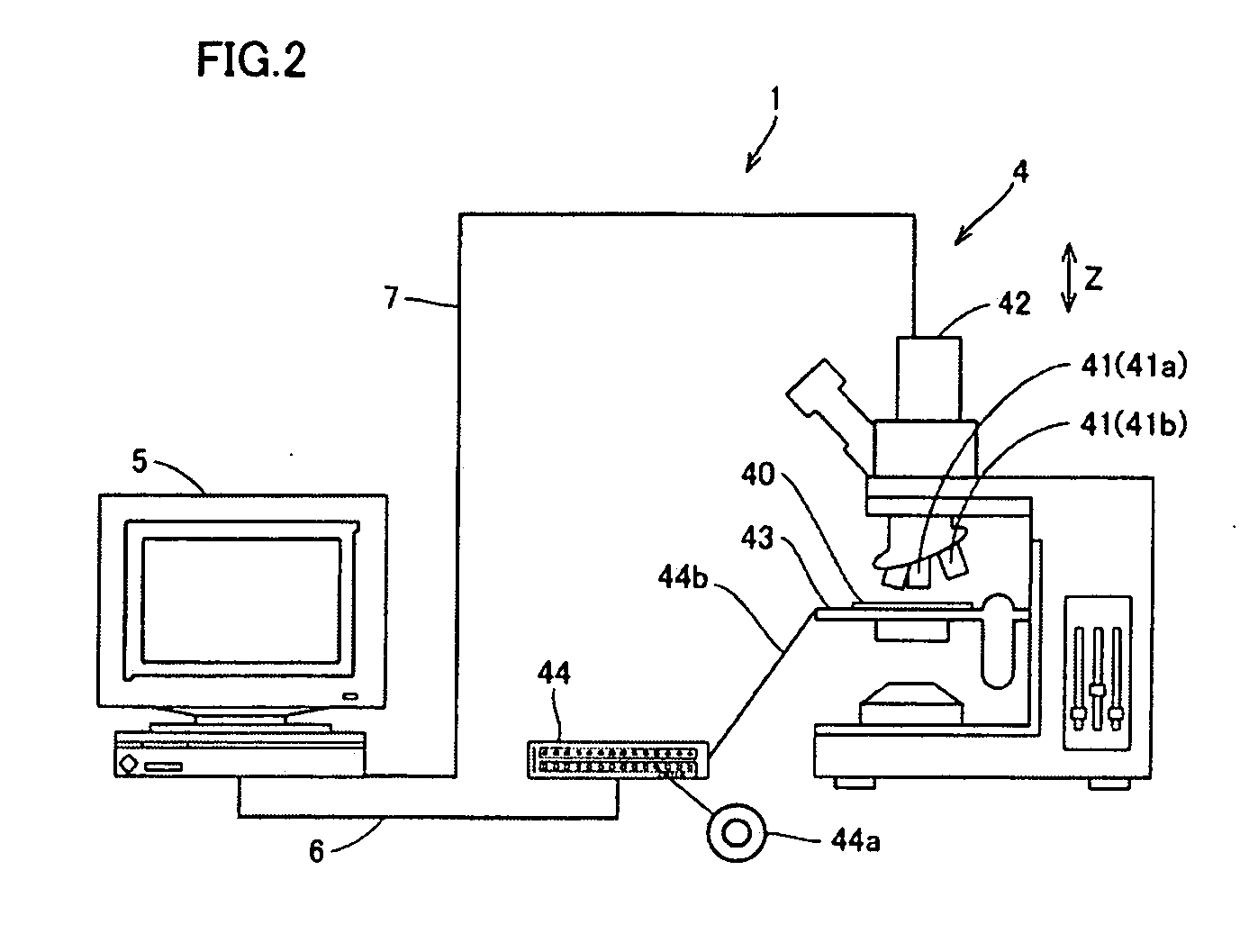
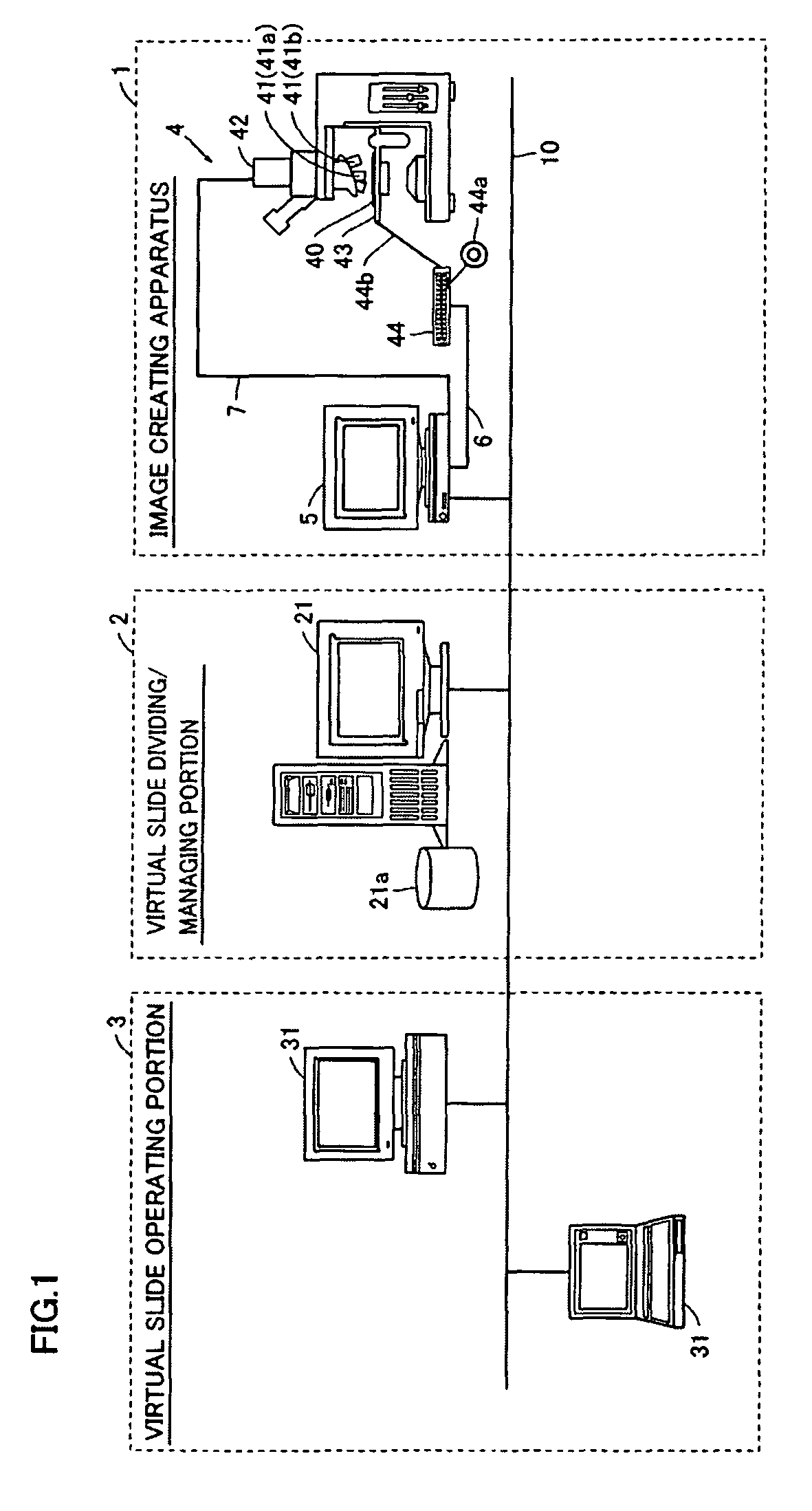
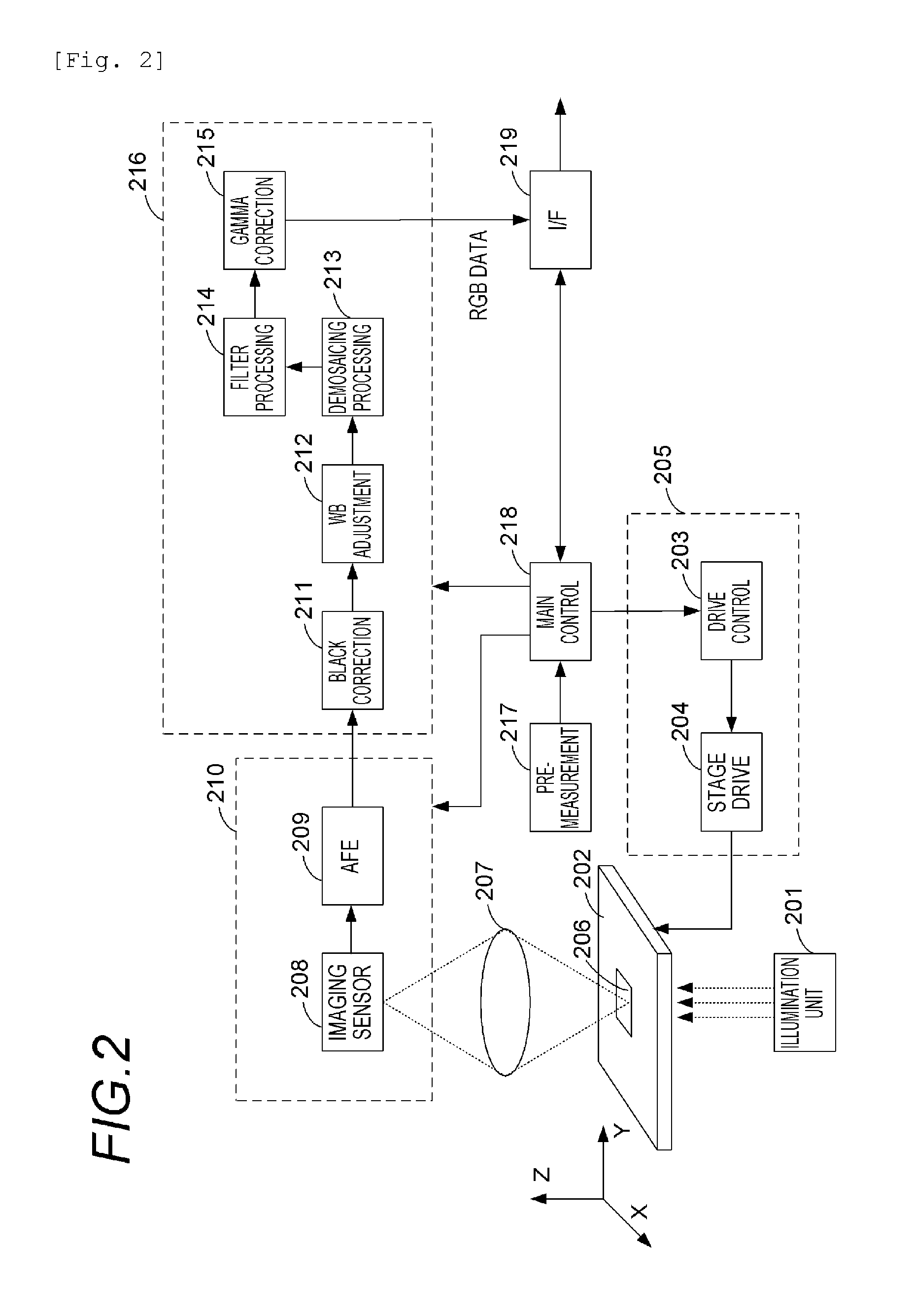
Image creating apparatus and image creating method
ActiveUS20060239534A1Reliable determinationCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsFocal positionFocus stacking
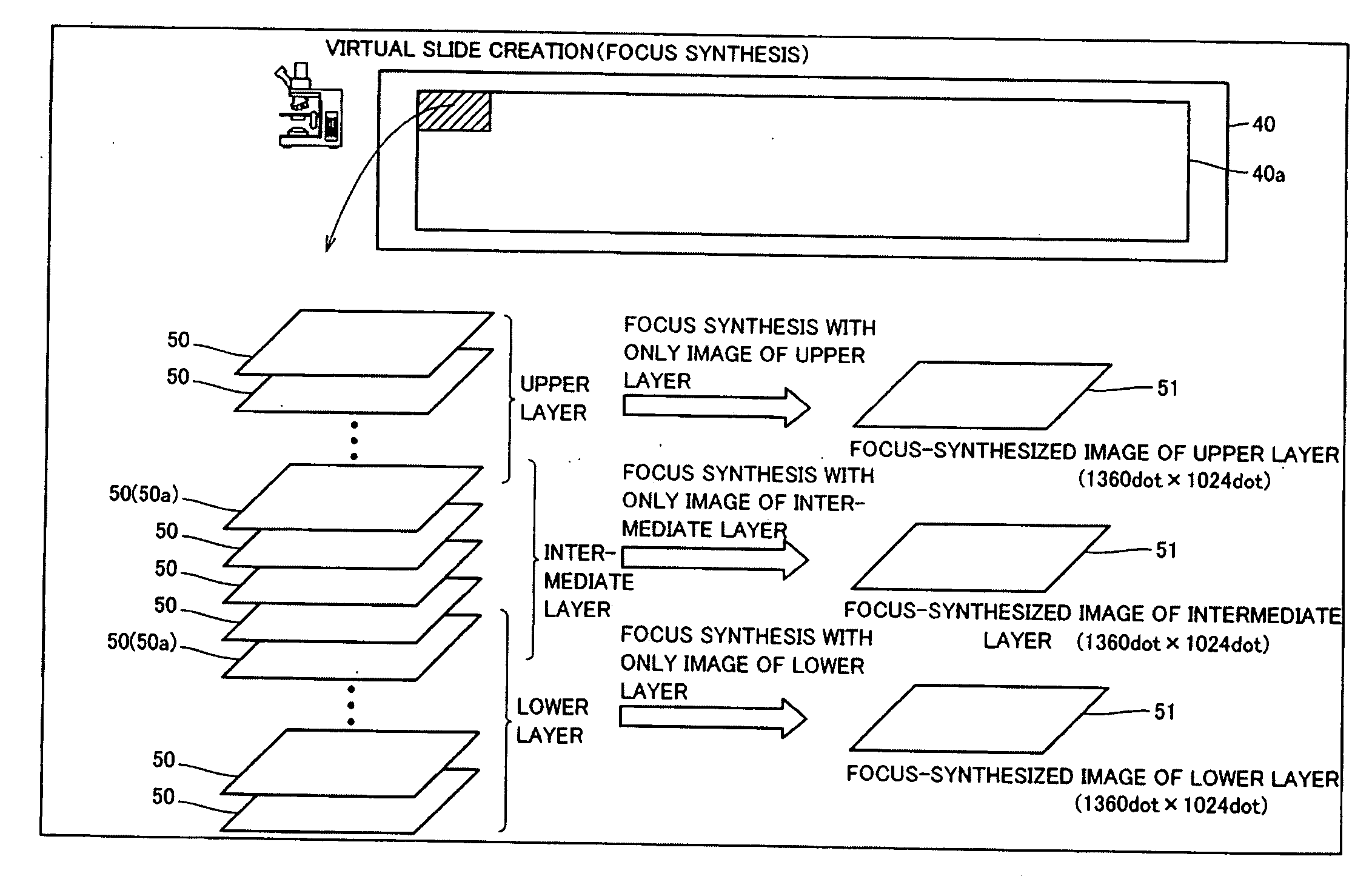
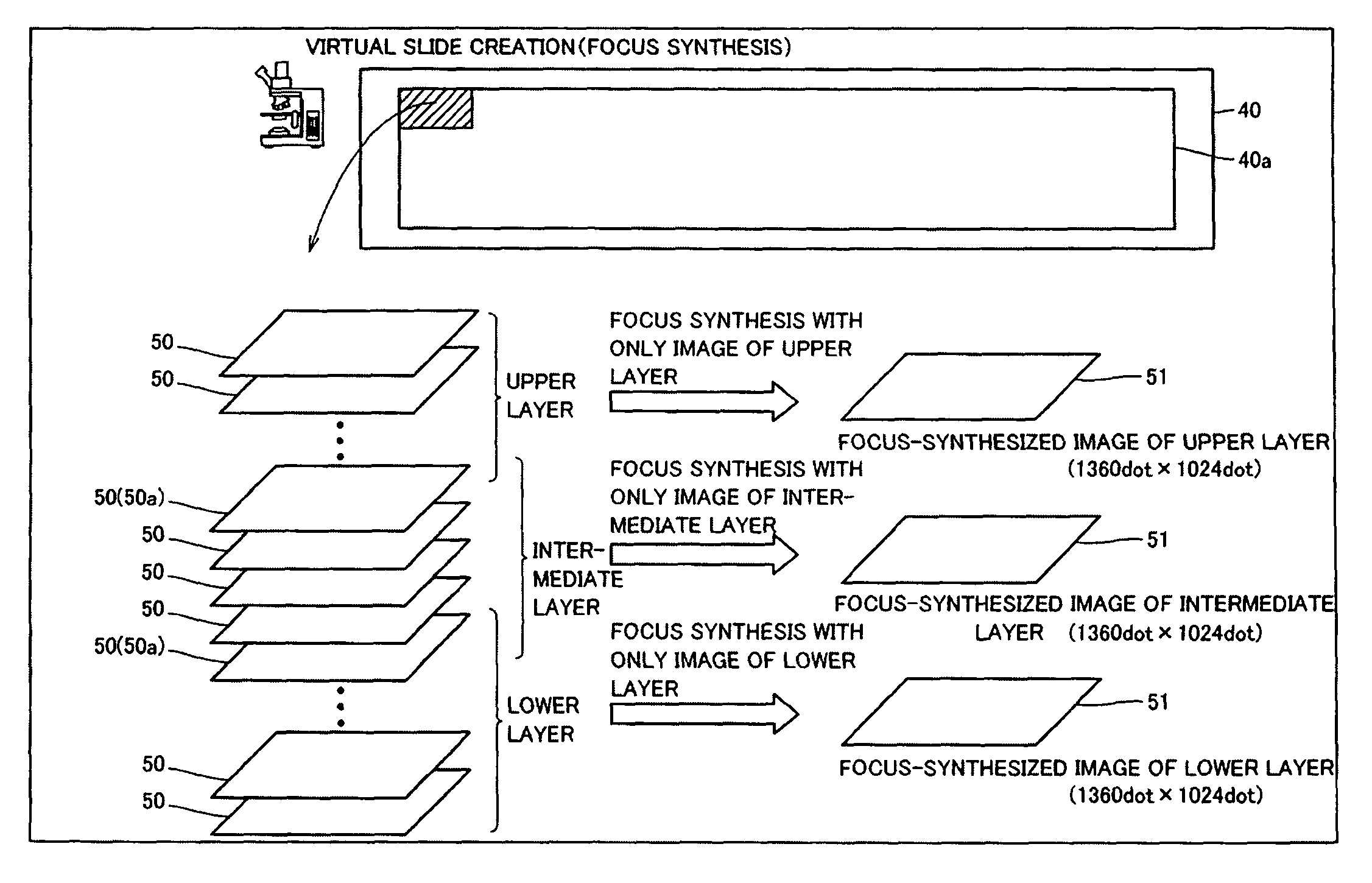
An image creating apparatus capable of creating cell images allowing reliable determination of cell structures in a cell is provided. This image creating apparatus comprises an image pickup portion picking up a plurality of images of a cell on different focal positions and an image synthesizing portion classifying the plurality of images picked up by the image pickup portion into a plurality of depth ranges as to the focal direction and synthesizing the plurality of images belonging to the respective ones of the plurality of depth ranges every plurality of depth ranges thereby creating focus-synthesized images in focus over corresponding depth ranges every plurality of depth ranges.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Image creating apparatus and image creating method
InactiveUS8044974B2Reliable determinationCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsFocal positionFocus stacking
An image creating apparatus capable of creating cell images allowing reliable determination of cell structures in a cell is provided. This image creating apparatus comprises an image pickup portion picking up a plurality of images of a cell on different focal positions and an image synthesizing portion classifying the plurality of images picked up by the image pickup portion into a plurality of depth ranges as to the focal direction and synthesizing the plurality of images belonging to the respective ones of the plurality of depth ranges every plurality of depth ranges thereby creating focus-synthesized images in focus over corresponding depth ranges every plurality of depth ranges.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
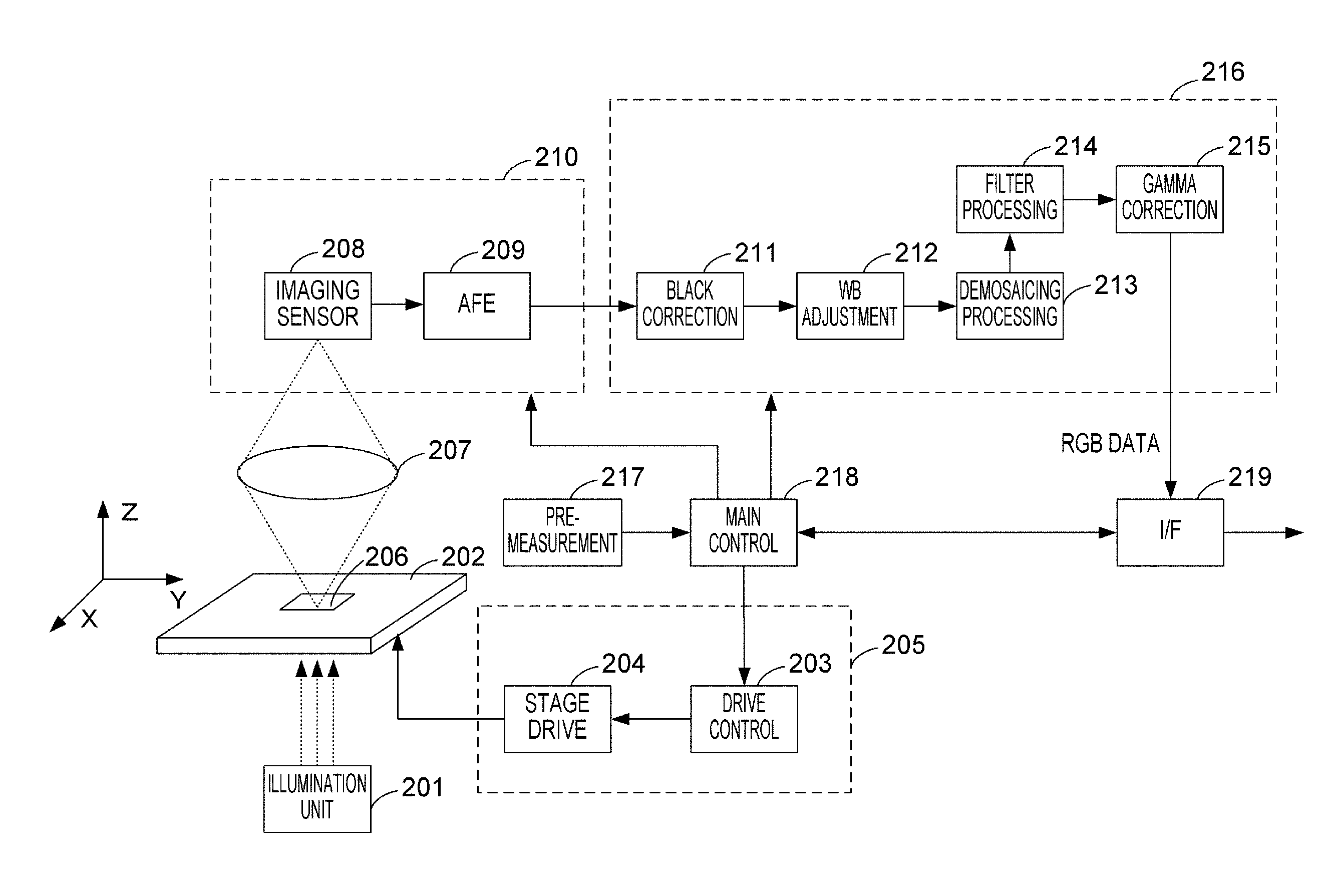
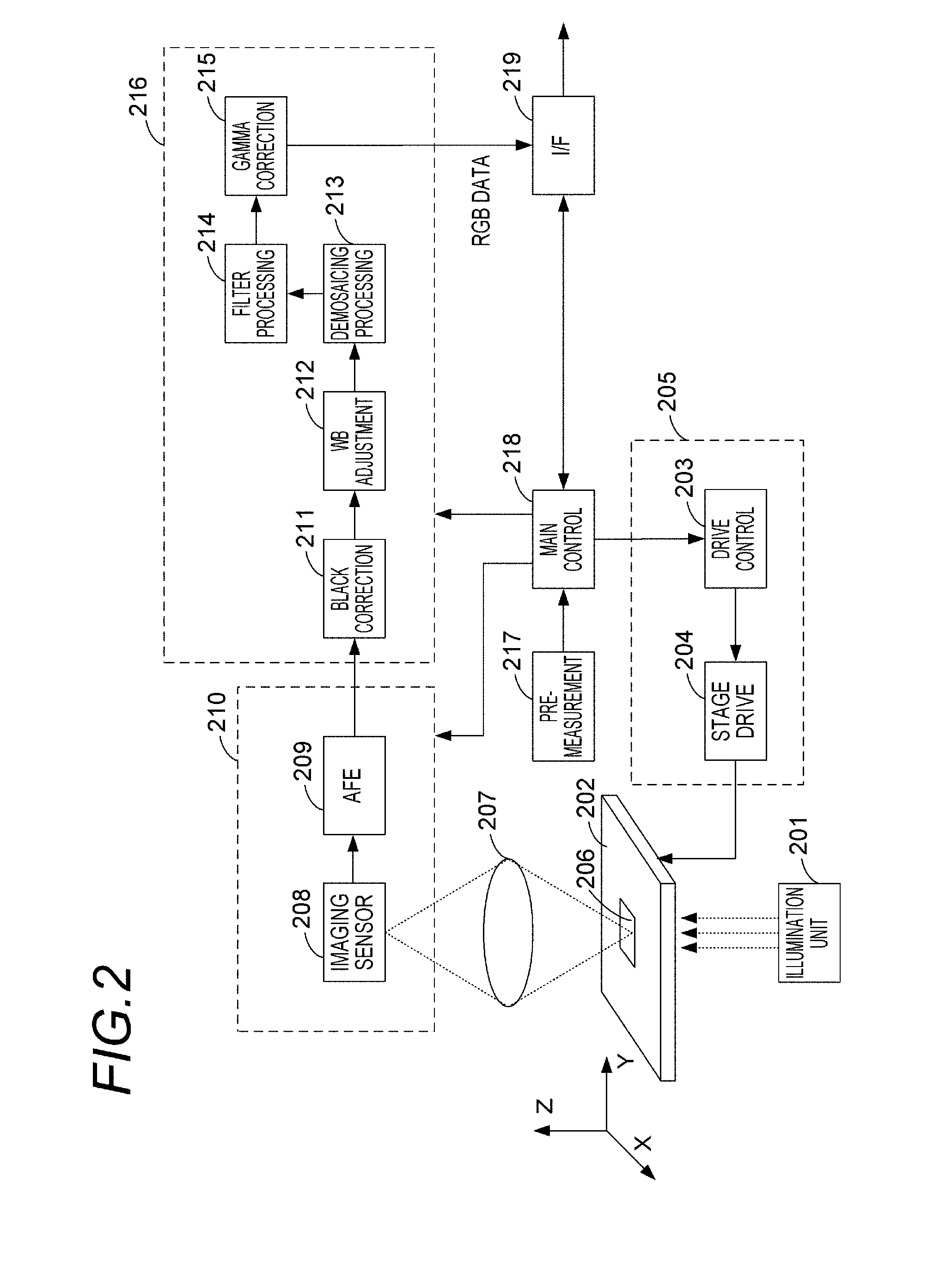
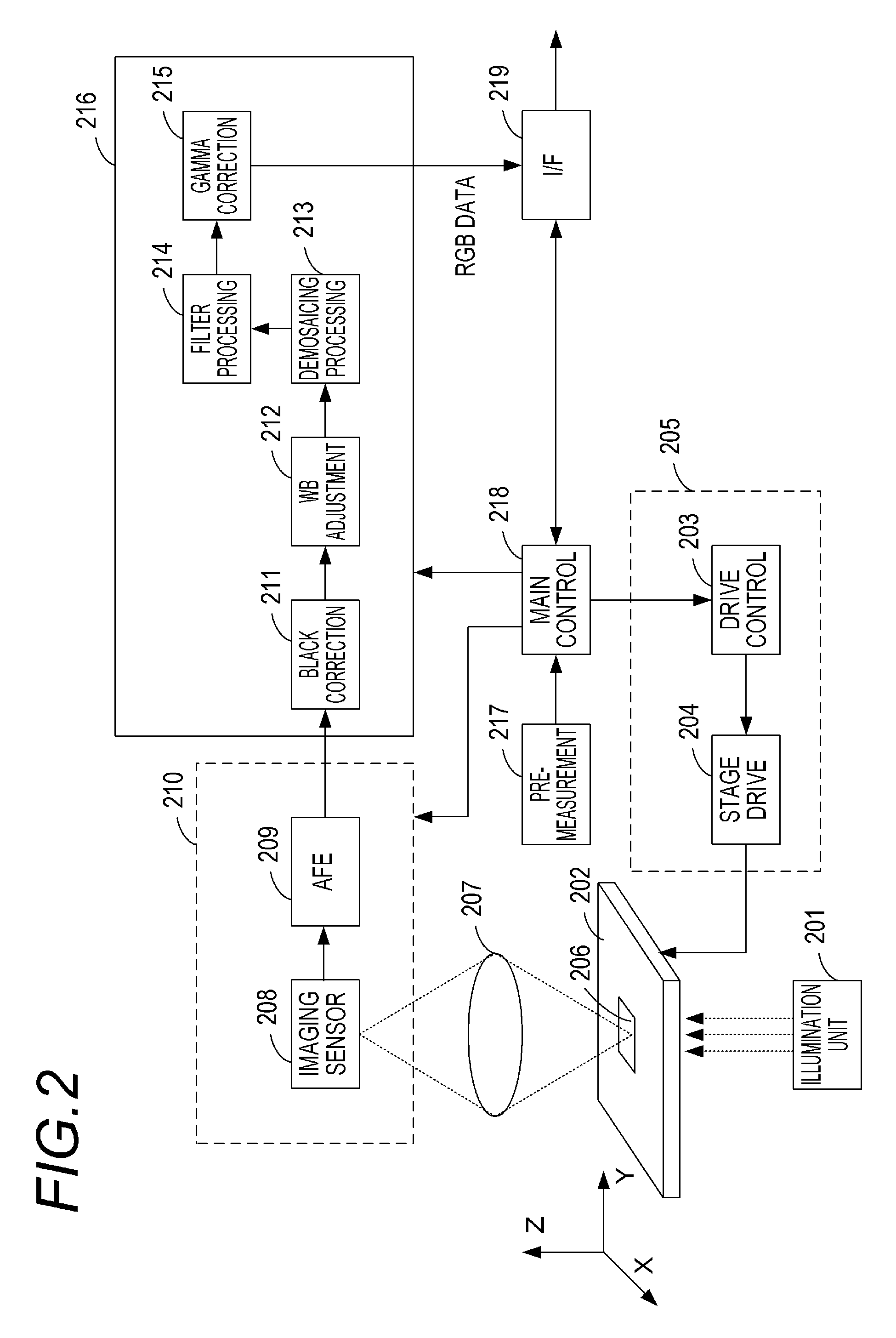
Image processing apparatus, imaging system, and image processing system
InactiveUS20140015933A1Little blurPartly suitableMicroscopesImage acquisitionImaging processingDisplay device
An image processing apparatus includes: an image acquisition unit for acquiring original images obtained by imaging an object at different focal positions; an image generation unit for generating a plurality of observation images from the original images, the observation images being mutually different in at least either focal position or DOF; and an image displaying unit for displaying the observation images on a display device. The image generation unit generates the observation images by performing combine processing for selecting two or more original images from the original images and focus-stacking the selected original images to generate a single observation image, for plural times while differing a combination of the selected original images. The image displaying unit selects the observation images to be displayed, when the observation images displayed on the display device are switched, such that the focal position or the DOF changes sequentially.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and apparatus for analyzing and/or repairing of an EUV mask defect
ActiveUS20130156939A1Maximizes process windowImage analysisParticle separator tubesMask inspectionComputational physics
The invention relates to a method for analyzing a defect of a photolithographic mask for an extreme ultraviolet (EUV) wavelength range (EUV mask) comprising the steps of: (a) generating at least one focus stack relating to the defect using an EUV mask inspection tool, (b) determining a surface configuration of the EUV mask at a position of the defect, (c) providing model structures having the determined surface configuration which have different phase errors and generating the respective focus stacks, and (d) determining a three dimensional error structure of the EUV mask defect by comparing the at least one generated focus stack of the defect and the generated focus stacks of the model structures.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Image processing apparatus, imaging system, and image processing system
InactiveUS20150153559A1Little blurPartly suitableColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsImaging processingFocus stacking
An image processing apparatus includes: an image acquisition unit configured to acquire layer images obtained by imaging different positions of an object by using a microscope; an image generation unit for generating a plurality of observation images from the layer images. The image generation unit generates the observation images by performing combine processing for focus-stacking two or more layer images selected from among the layer images to generate a single observation image, for plural times.
Owner:CANON KK
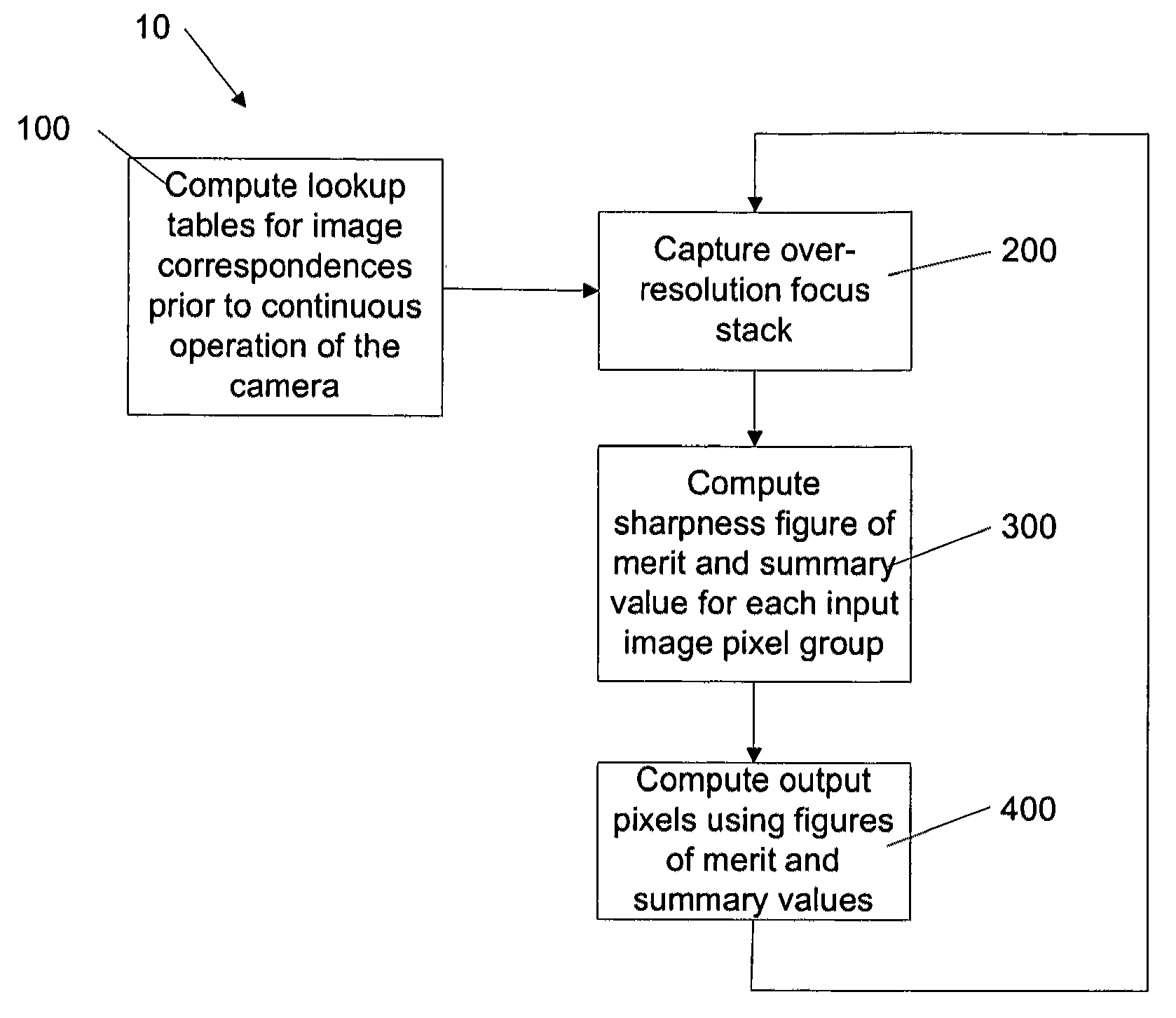
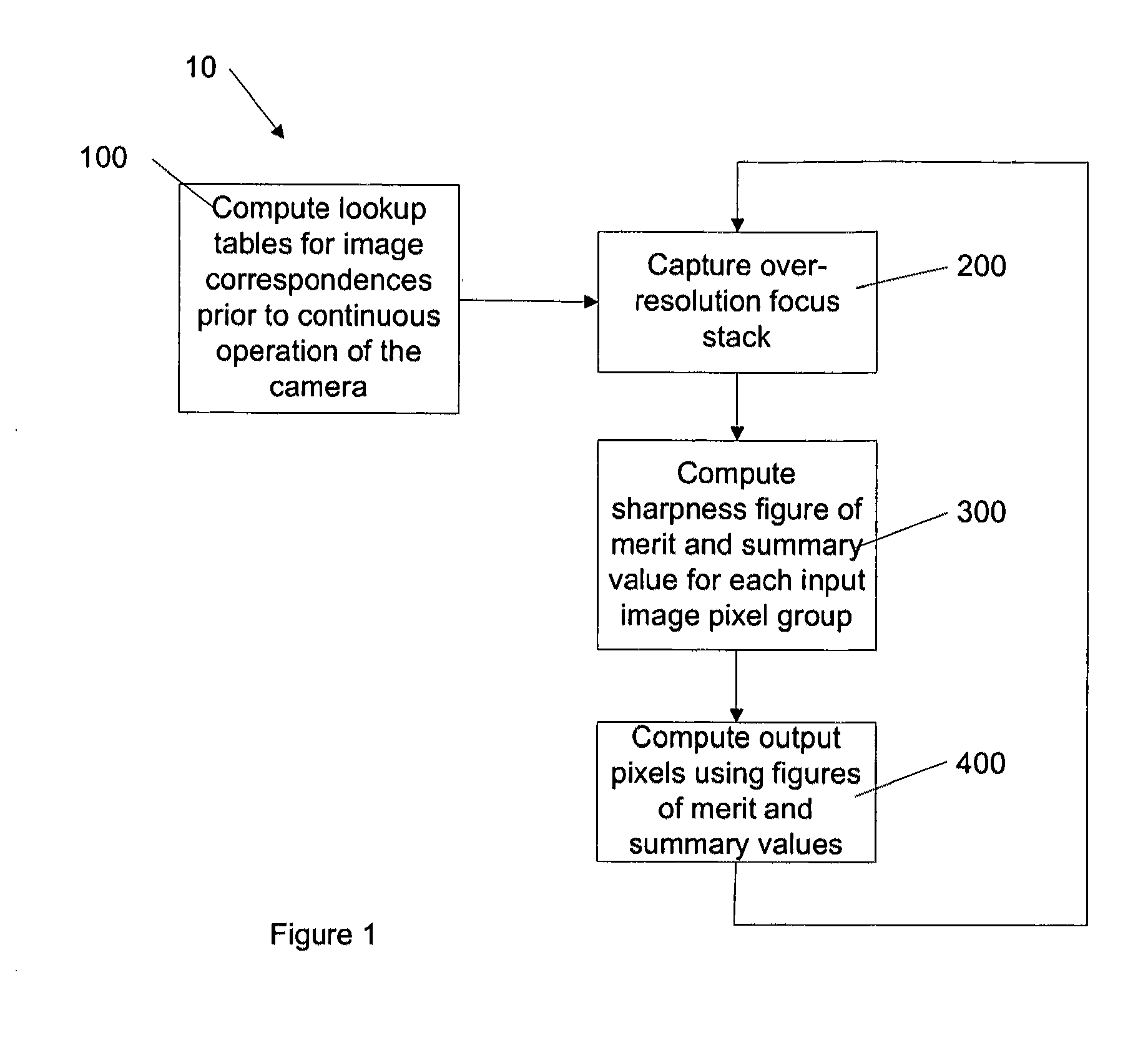
Producing universally sharp images
InactiveUS20120098947A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionFigure of merit
A method for producing an output image defined by output pixels comprises capturing a focus stack of input images, each input image defined by input pixels and having a resolution higher than the output image, determining a group of input pixels in each input image corresponding to one of the output pixels, calculating a figure of merit and a summary pixel value for each group of input pixels, and computing a value for each output pixel by mathematically combining the figures of merit and the summary pixel values corresponding to each output pixel. The output image values are calculated such that the entire output image is sharply in focus.
Owner:WILKES DAVID ROBERT
Image processing apparatus, imaging system, and image processing system
InactiveCN103460684AObserve in detailTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImaging processingDisplay device
An image processing apparatus includes: an image acquisition unit for acquiring original images obtained by imaging an object at different focal positions; an image generation unit for generating a plurality of observation images from the original images, the observation images being mutually different in at least either focal position or DOF; and an image displaying unit for displaying the observation images on a display device. The image generation unit generates the observation images by performing combine processing for selecting two or more original images from the original images and focus-stacking the selected original images to generate a single observation image, for plural times while differing a combination of the selected original images. The image displaying unit selects the observation images to be displayed, when the observation images displayed on the display device are switched, such that the focal position or the DOF changes sequentially.
Owner:CANON KK
Depth estimation method for light field image
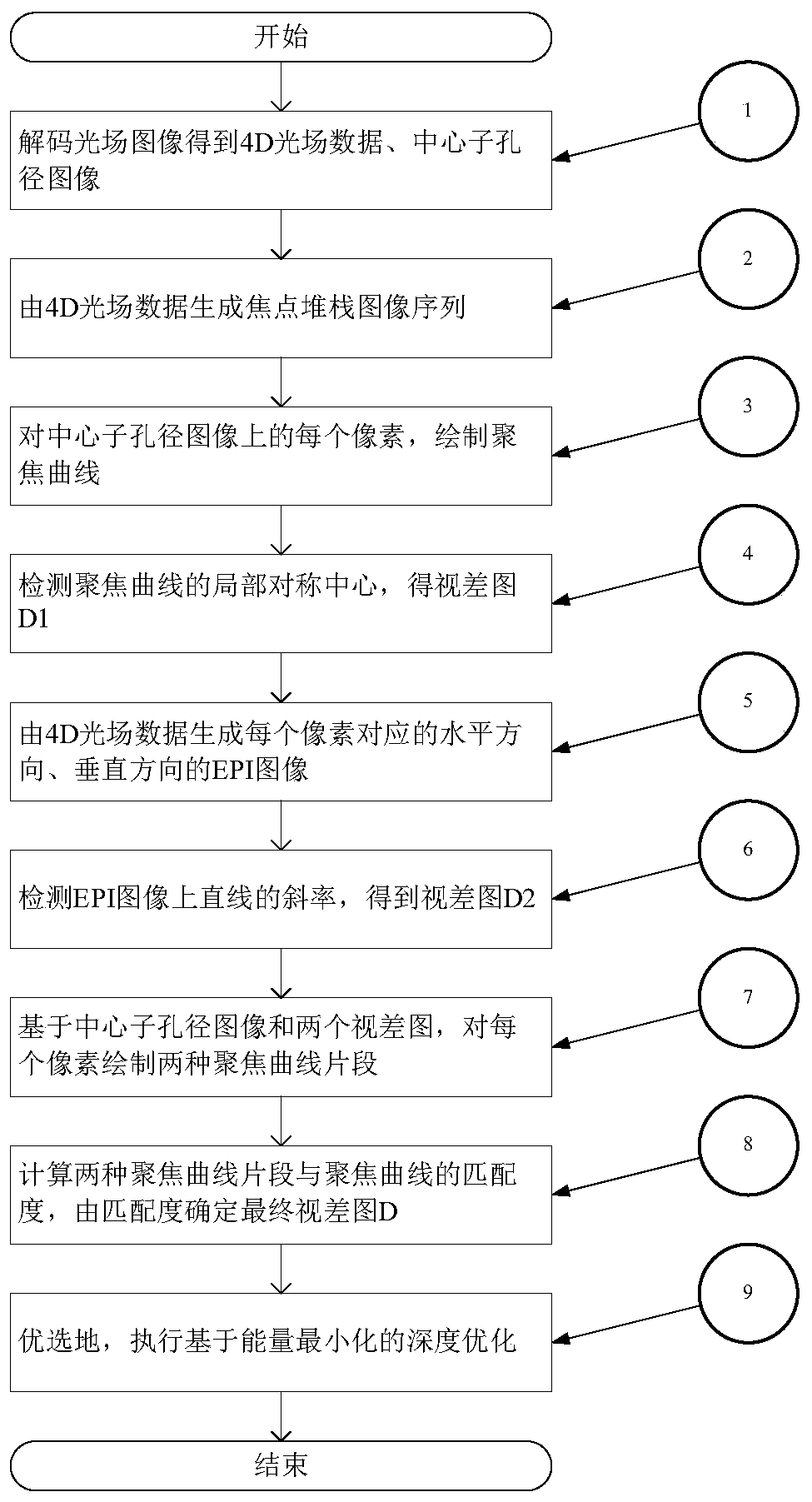
The invention discloses a depth estimation method for a light field image. The depth estimation method comprises the following steps: decoding the light field image to obtain 4D light field data and acentral sub-aperture image; generating a focus stack image sequence through the 4D light field data; drawing a focusing curve for each pixel on the central sub-aperture image; detecting a local symmetry center of the focusing curve to obtain a disparity map D1; generating an EPI image in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction corresponding to each pixel through the 4D light field data; detecting the slope of a straight line on the EPI image to obtain a disparity map D2; based on the central sub-aperture image and the two disparity maps, drawing two focusing curve segments for each pixel; calculating the matching degrees of the two focusing curve segments and the focusing curve, and determining a final disparity map D according to the matching degrees; performing deep optimization based on energy minimization. A depth estimation result of the method is high in accuracy, and has high robustness for outdoor noise scenes, complex shielding scenes and the like.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
A hybrid depth estimation method based on light field data
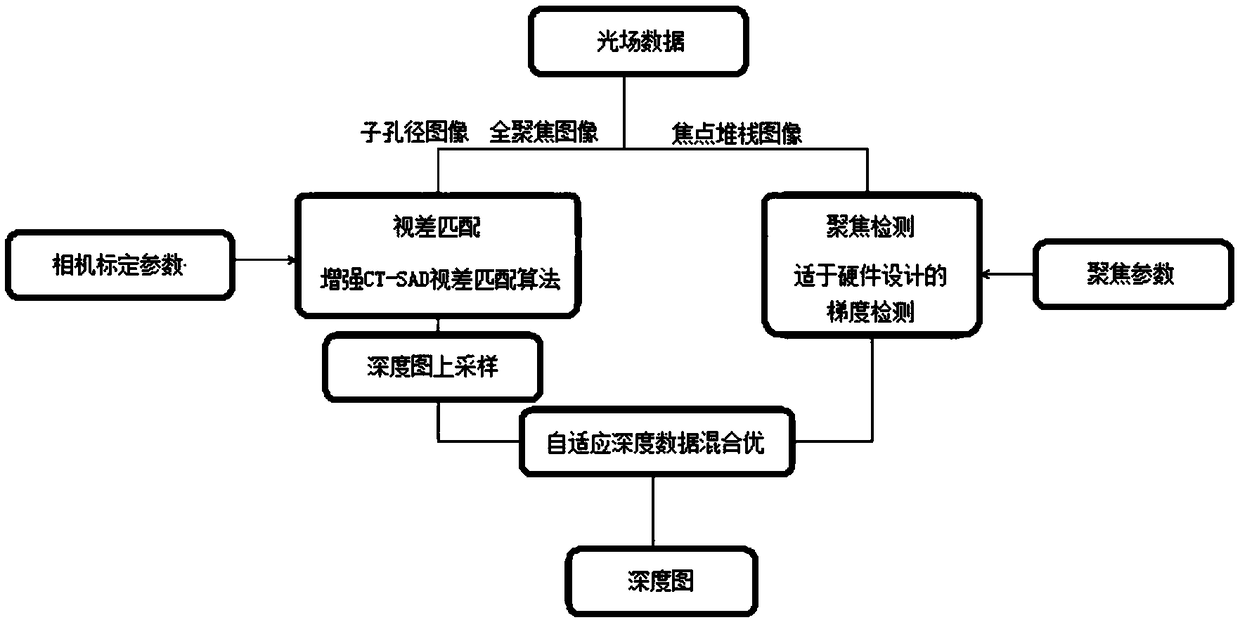
The invention discloses a hybrid depth estimation method based on light field data. The method includes: using a hybrid depth estimation method, the focus stack image to perform the hybrid depth estimation based on the parallax and the blur detection on the sub-image and the all-focus image obtained by the light field camera are collected, and the sub-image with the angle difference is used for fusion matching. The method performs parallax analysis, performs focus detection on the simultaneously acquired focus stack image to obtain a depth image, and uses a classification and an adaptive hybrid method to fuse the depth map obtained based on the parallax and the depth map based on the focus; after upsampling the sub image Perform a fusion of depth maps. The invention can obtain the scene depth information by using only one light field camera, and the algorithm is simple and accurate.
Owner:AVIC SHANGHAI AERONAUTICAL MEASUREMENT CONTROLLING RES INST
Method, device and system for detecting object in image
ActiveCN110751160AImprove accuracyImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesActivation functionSaliency map
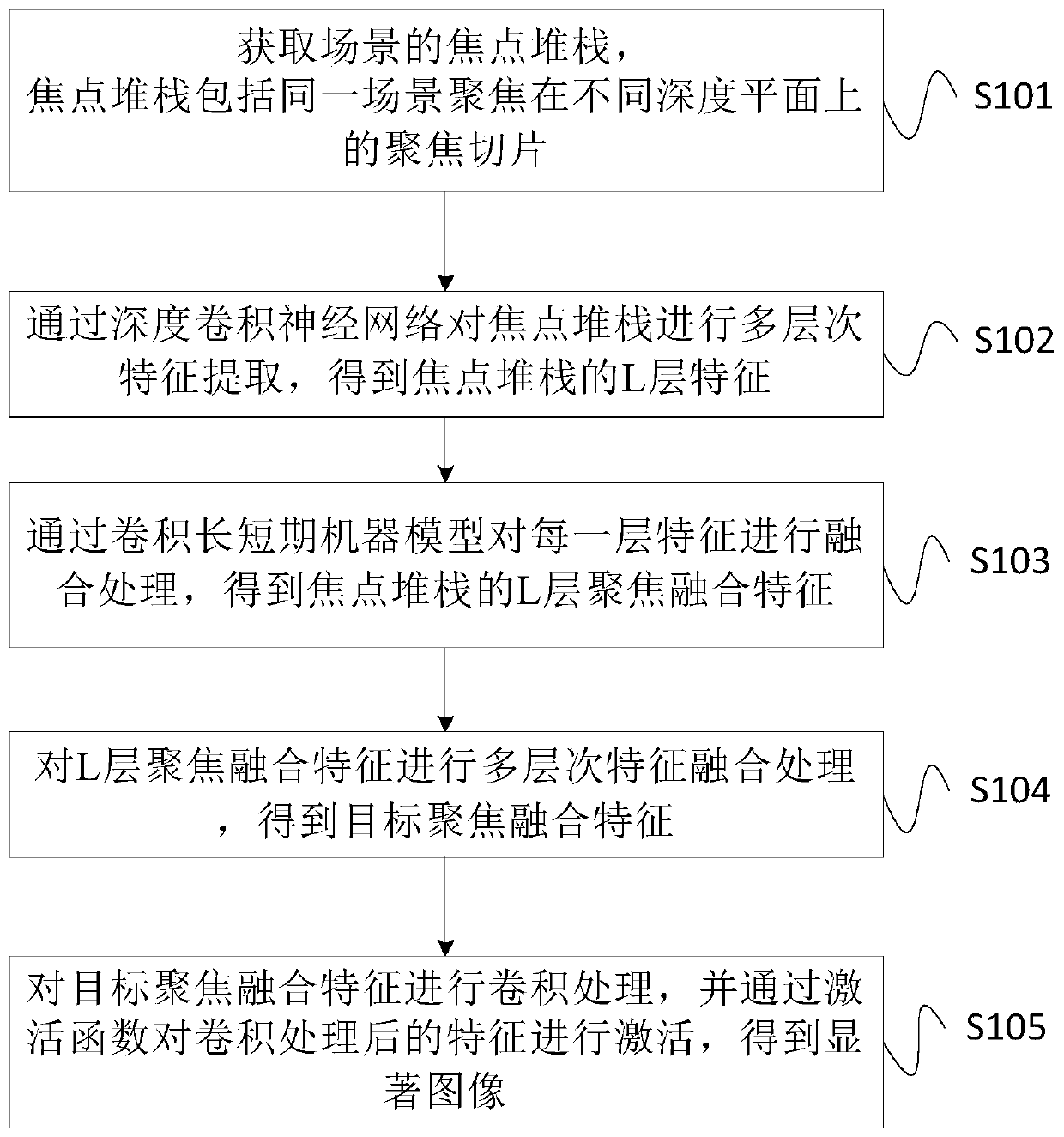
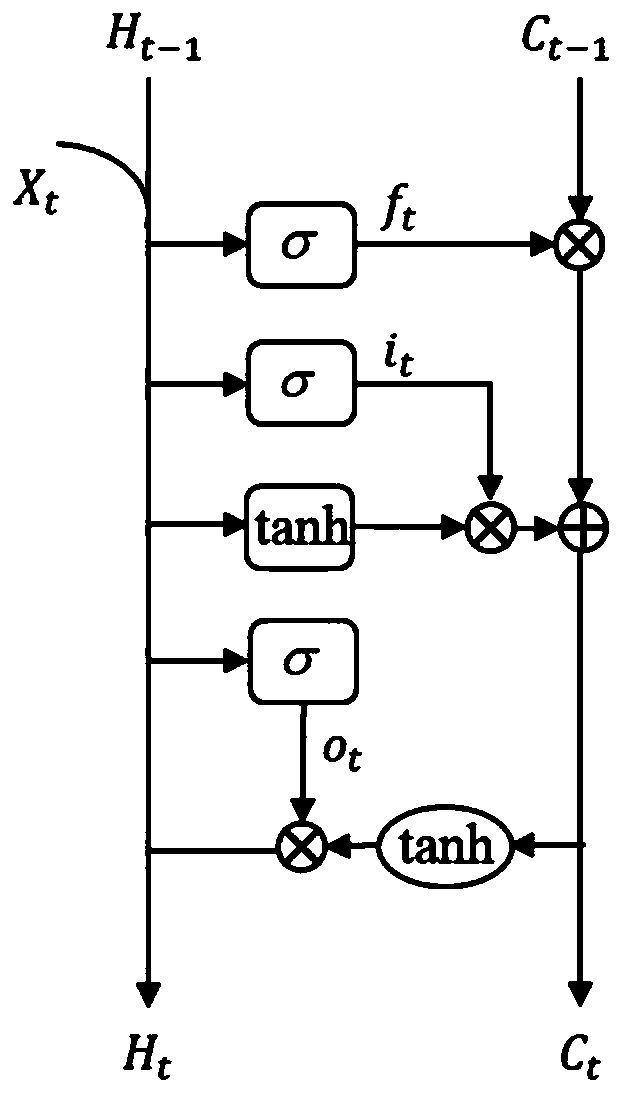
The invention provides a method, a device and a system for detecting an object in an image. The method comprises the steps that a focus stack of a scene is acquired, the focus stack comprises focusingslices, focused on different depth planes, of the same scene, multi-level feature extraction is conducted on the focus stack through a deep convolutional neural network, and L-layer features of the focus stack are obtained, wherein L is a natural number greater than 1; fusion processing is performed on each layer of features through a convolution long-short-term machine model to obtain L layers of focusing fusion features of the focus stack; and multi-level feature fusion processing is performed on the L-layer focusing fusion features to obtain target focusing fusion features, convolution processing is performed on the target focusing fusion features, and the features are activated after convolution processing through an activation function to obtain a significant image. Therefore, the accuracy and robustness of object detection in a complex environment scene image are improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
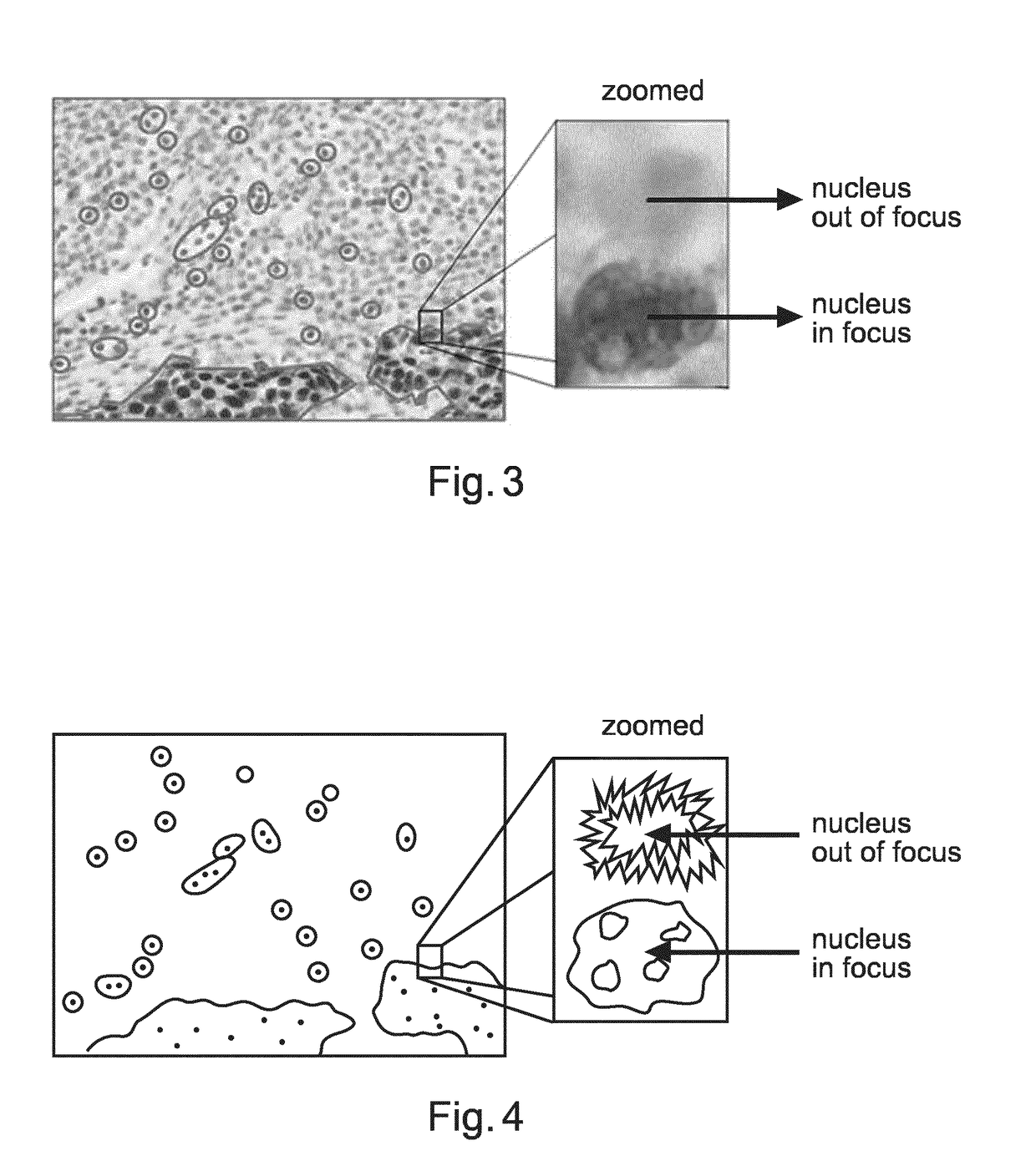
Focus stacking image processing apparatus, imaging system, and image processing system
An image processing apparatus comprises: an image acquisition unit for acquiring a plurality of original images acquired by imaging a specimen including a structure in various focal positions using a microscope apparatus; an image generation unit for generating, on the basis of the plurality of original images, a first image on which blurring of an image of the structure has been reduced in comparison with the original images; and an analysis unit for obtaining information relating to the structure included in the first image by applying image analysis processing to the first image. The image generation unit selects a part of the original images having focal positions included within a smaller depth range than a thickness of the specimen from the plurality of original images obtained from the specimen, and generates the first image using the selected original images.
Owner:CANON KK
System for generating a synthetic 2d image with an enhanced depth of field of a biological sample
ActiveUS20190075247A1Increase depth of fieldTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImaging dataFocus stacking
The present invention relates to a system for generating a synthetic 2D image with an enhanced depth of field of a biological sample. It is described to acquire (110) with a microscope-scanner (20) first image data at a first lateral position of the biological sample and second image data at a second lateral position of the biological sample. The microscope-scanner is used to acquire (120) third image data at the first lateral position and fourth image data at the second lateral position, wherein the third image data is acquired at a depth that is different than that for the first image data and the fourth image data is acquired at a depth that is different than that for the second image data. First working image data is generated (130) for the first lateral position, the generation comprising processing the first image data and the third image data by a focus stacking algorithm. Second working image data is generated (140) for the second lateral position, the generation comprising processing the second image data and the fourth image data by the focus stacking algorithm. The first working image data and the second working image data are combined (150), during acquisition of image data, to generate the synthetic 2D image with an enhanced depth of field of the biological sample.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and system for measuring focus drift distance of microscopic image and computer equipment
ActiveCN111551117AImprove robustnessHigh speedUsing optical meansNeural architecturesMicroscopic imageSingle image
The invention discloses a method for measuring the focus drift distance of a microscopic image. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a microscopic image sequence; calculating a radial average logarithm power spectrum value of each incoherent focus stack image, and obtaining a focusing position of a microscope objective lens according to the radial average logarithm power spectrum value; marking each coherent focus stack image according to the focusing position; dividing the marked coherent focus stack image into a training set and a verification set; training a pre-constructed convolutional neural network model by using the training set, and verifying the trained convolutional neural network model by using the verification set to obtain a trained convolutional neural networkmodel; and measuring the focus drift distance of the microscopic image to be measured by using the trained convolutional neural network model. According to the method provided by the invention, the focus drift distance can be measured only through a single image, the speed is high, the precision is high, and the robustness of the convolutional neural network model is high.
Owner:湖南国科智瞳科技有限公司
High-performance multi-scale target detection method based on deep learning
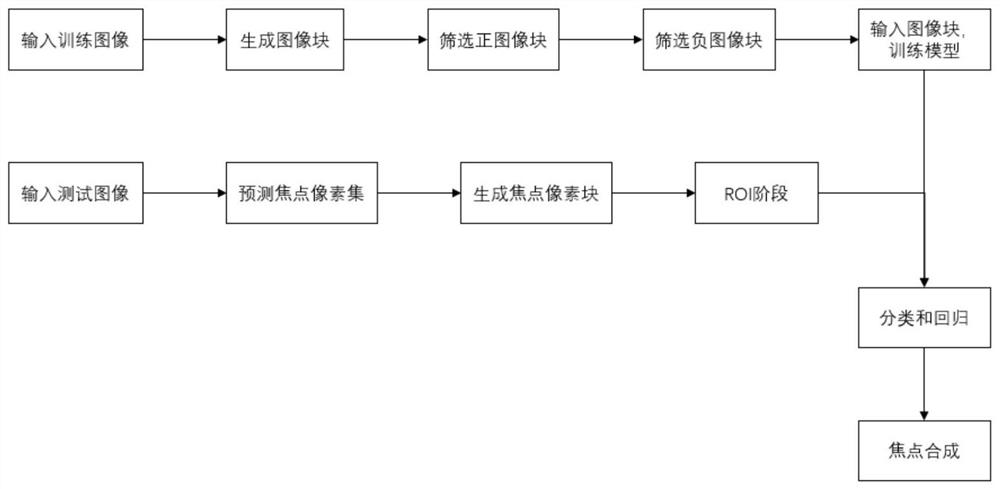
PendingCN112149665ASmall amount of calculationBreak through the bottleneck that cannot be put into practical applicationImage enhancementImage analysisRegion selectionEngineering
The invention discloses a high-performance multi-scale target detection method based on deep learning, and the method comprises a training process and a detection process, and the training process comprises the following steps: 1.1, inputting a picture, and generating an image block; 1.2, screening positive image blocks; 1.3, screening negative image blocks; 1.4, inputting image blocks, and training a model; the detection process is as follows: 2.1, predicting a focus pixel set; 2.2, generating a focus image block; 2.3, a RoI stage; 2.4, carrying out classification and regression; 2.5, carrying out focus synthesis. According to the method, a brand new candidate region selection method is provided for the training process, meanwhile, a shallow-to-deep method is adopted for the detection process, regions which cannot possibly contain targets are ignored, and compared with a conventional detection algorithm for processing the whole image pyramid, the calculation amount of the multi-scaledetection method is remarkably reduced, and the detection accuracy is improved. The detection rate is greatly improved, and the bottleneck that the conventional multi-scale detection algorithm cannotbe put into practical application is broken through.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
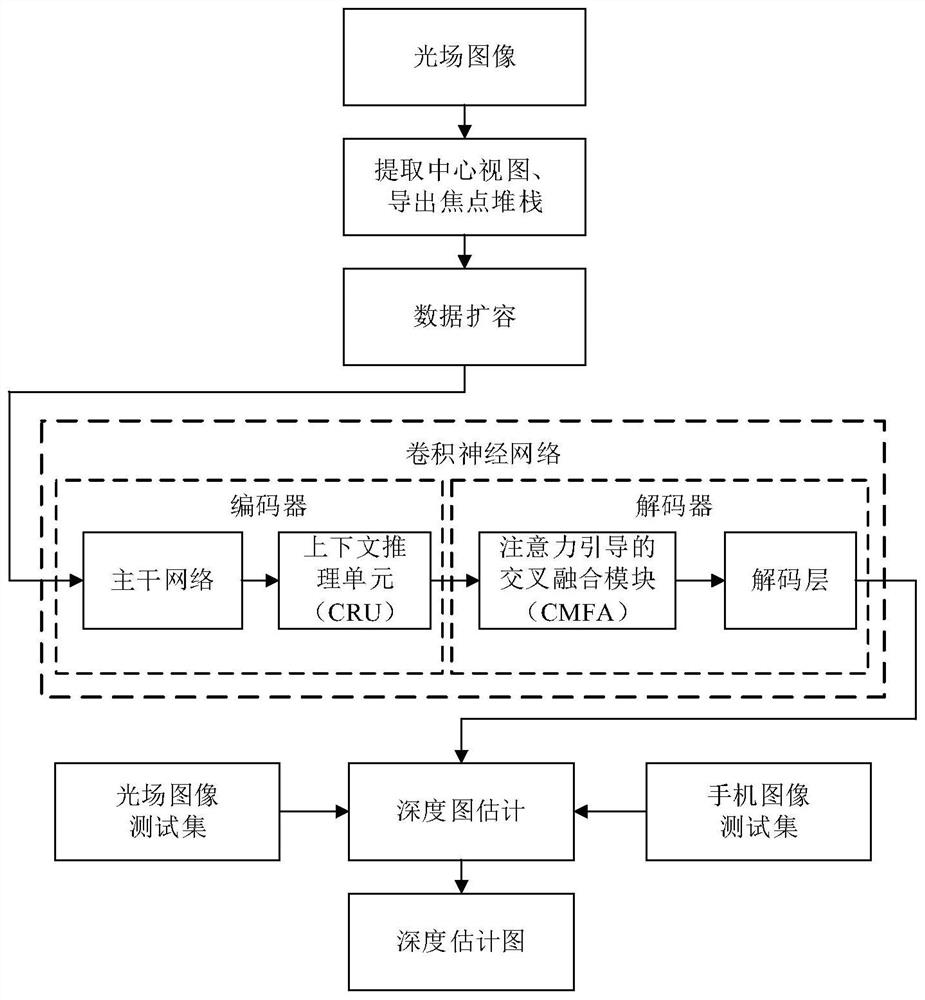
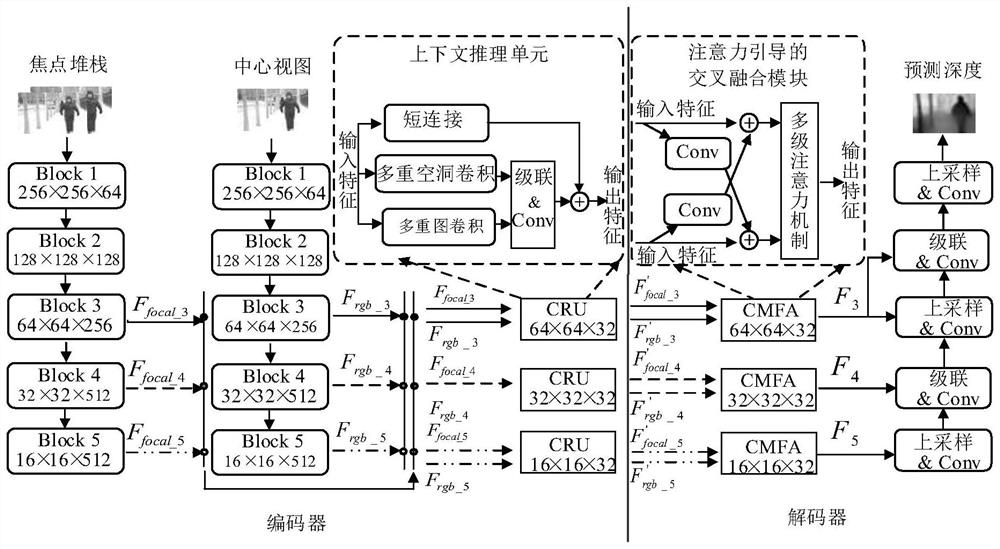
Multi-modal information-based light field depth estimation method
ActiveCN112767466AEfficient captureEfficient use ofImage enhancementImage analysisData expansionData set
The invention discloses a multi-modal information-based light field depth estimation method, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring light field image data by using a light field camera based on a micro-lens array to obtain a four-dimensional light field image array, extracting a centermost visual angle image as a central view, exporting a group of focus slices as a focus stack, and carrying out data expansion; constructing a convolutional neural network, taking the focus stack and the corresponding center view as the input of a network model, and obtaining the input tensor of a focus stack flow and the input tensor of a center view flow; training the constructed convolutional neural network; and testing on the light field test set by using the trained neural network, and carrying out verifying on an actual focusing slice acquired by the mobile phone. According to the light field depth estimation method provided by the invention, multi-mode information of the light field can be fully utilized, and more accurate depth estimation is realized on a light field data set; the obtained depth information is more complete, and the edge is clearer; and practical application of a common consumer-level mobile phone terminal can be achieved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Focus stack photo fusing method based on image reconstruction
The invention discloses a focus stack photo fusing method based on image reconstruction. The focus stack photo fusing method includes acquiring a plurality of focus stack photos same in scenes, focal lengths and apertures but different in field depth of focusing; calculating definition of each pixel in the acquired focus stack photos; continuously fitting definition of the corresponding pixels to obtain the maximum value of the fitted curve as the optimal focusing field depth of this position; calculating the optimal field depth and camera parameter of the pixel in each corresponding position to obtain dispersion degree of this position; deconvoluting the pixel of each corresponding position to obtain pixels after definition is recovered, so as to obtain a fused clear photo. The focus stack photo fusing method can fuse clear photos and can be applied to clear shooting occasions requiring high field depth and quality and large apertures.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Image processing apparatus, imaging system, and image processing system
An image processing apparatus includes: an image acquisition unit configured to acquire layer images obtained by imaging different positions of an object by using a microscope; an image generation unit for generating a plurality of observation images from the layer images. The image generation unit generates the observation images by performing combine processing for focus-stacking two or more layer images selected from among the layer images to generate a single observation image, for plural times.
Owner:CANON KK
Focus stacking of captured images
ActiveUS20180253877A1Well formedImage enhancementImage analysisProgram instructionComputerized system
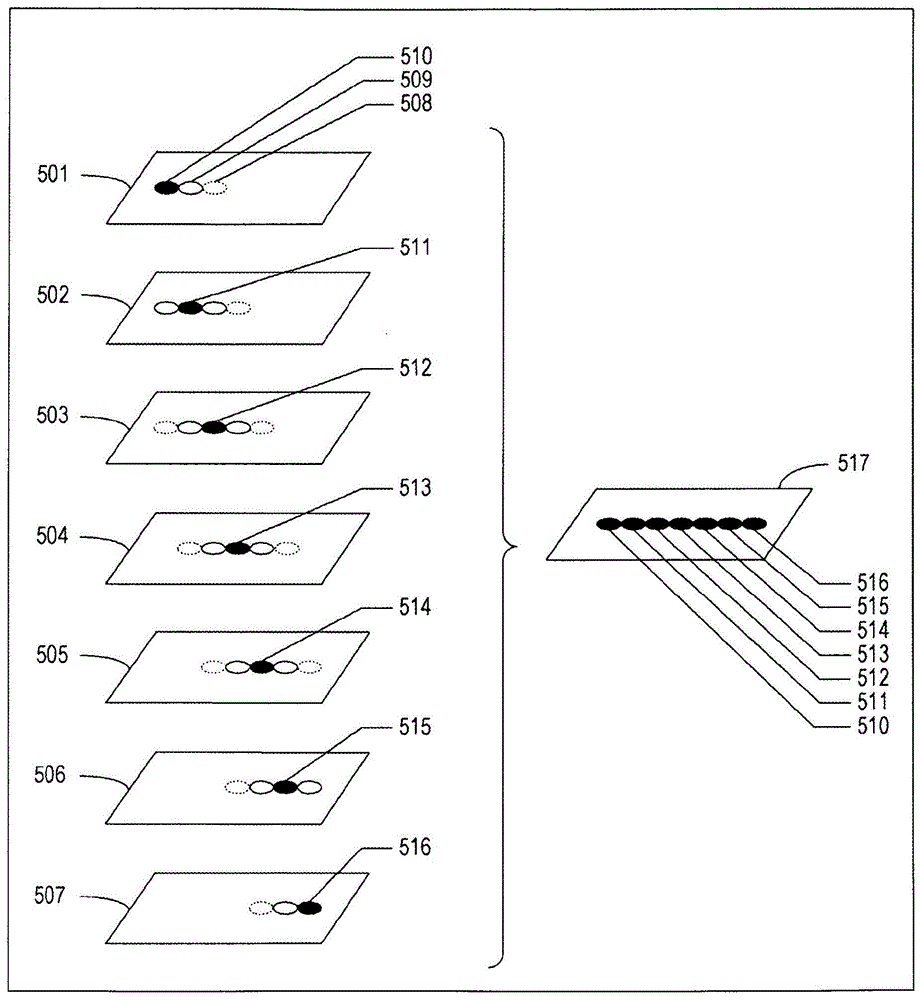
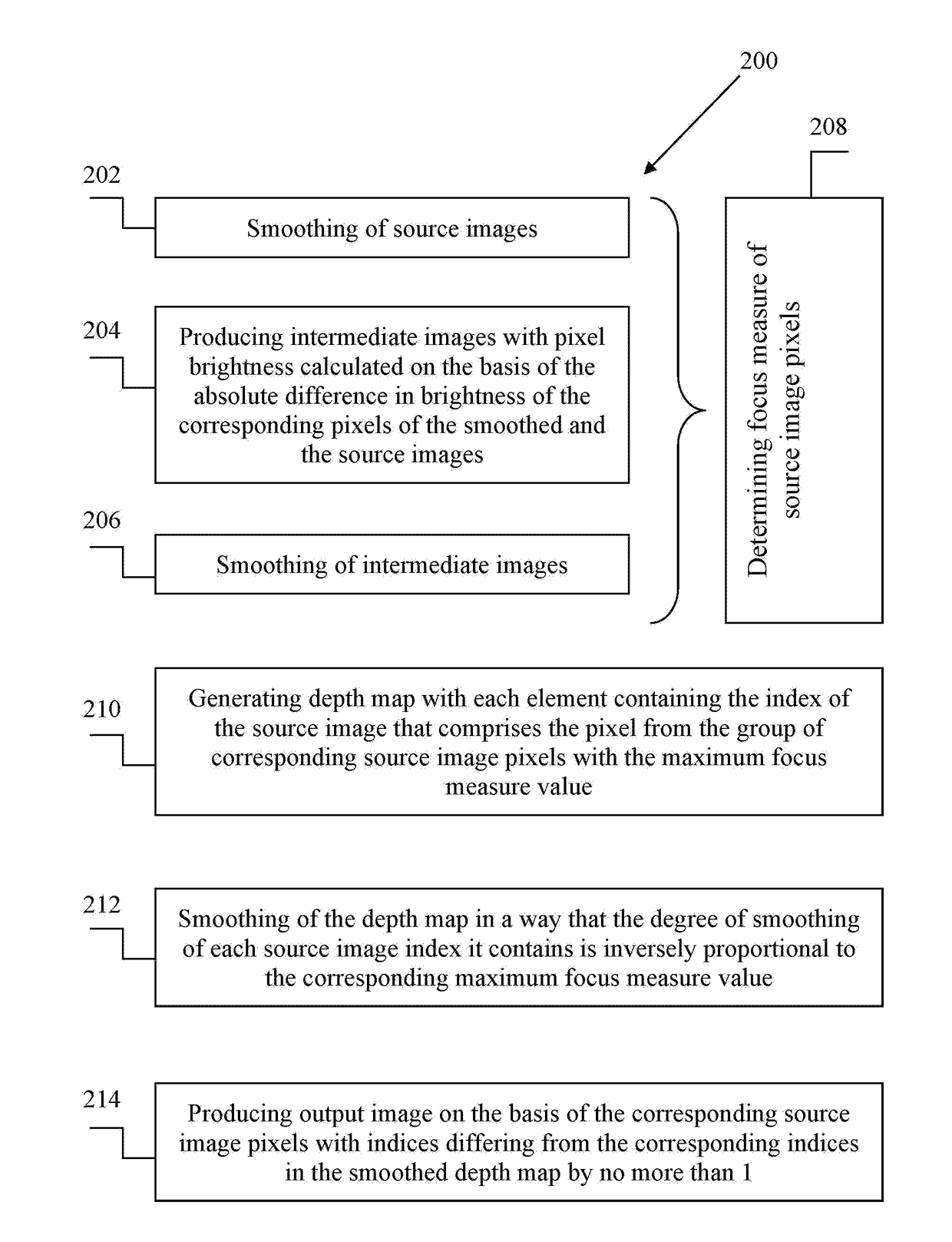
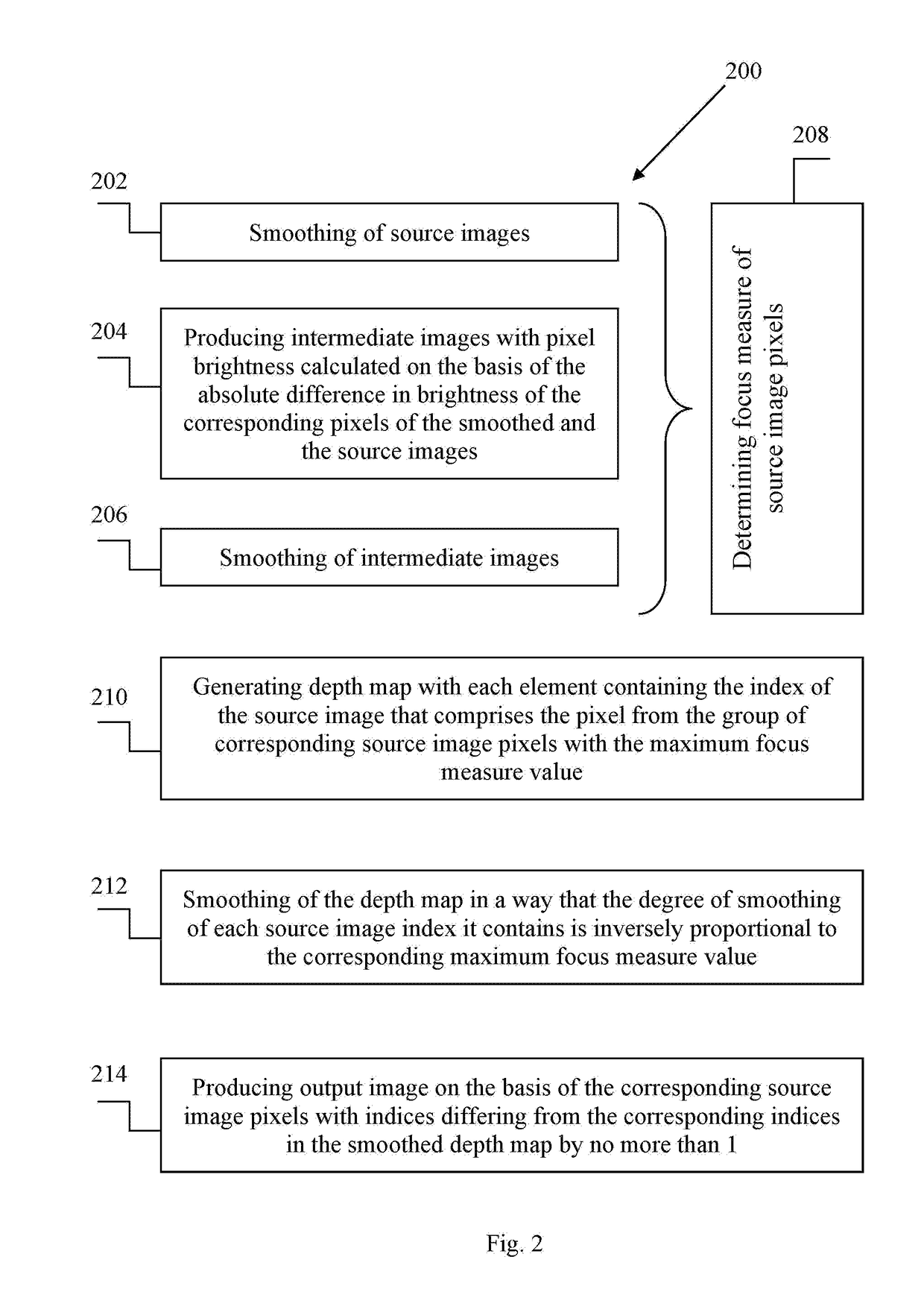
A digital image processing, in particular to the method of producing the output image with extended depth of field from a group of source images of the same scene, captured with a shift of depth of field. The method of producing the output image with extended depth of field form a group of at least two source images of substantially the same scene captured with a shift of depth of field, comprises determining focus measures of source image pixels; generation of a depth map with elements comprising source image indices; smoothing of the depth map in a way that the degree of smoothing of source image indices it contains is inversely proportional to the corresponding focus measure values; producing an output image using the smoothed depth map. A computer system that implements said method, and a computer readable medium comprising program instructions allowing for implementing said method.
Owner:KOZUB DANYLO +1
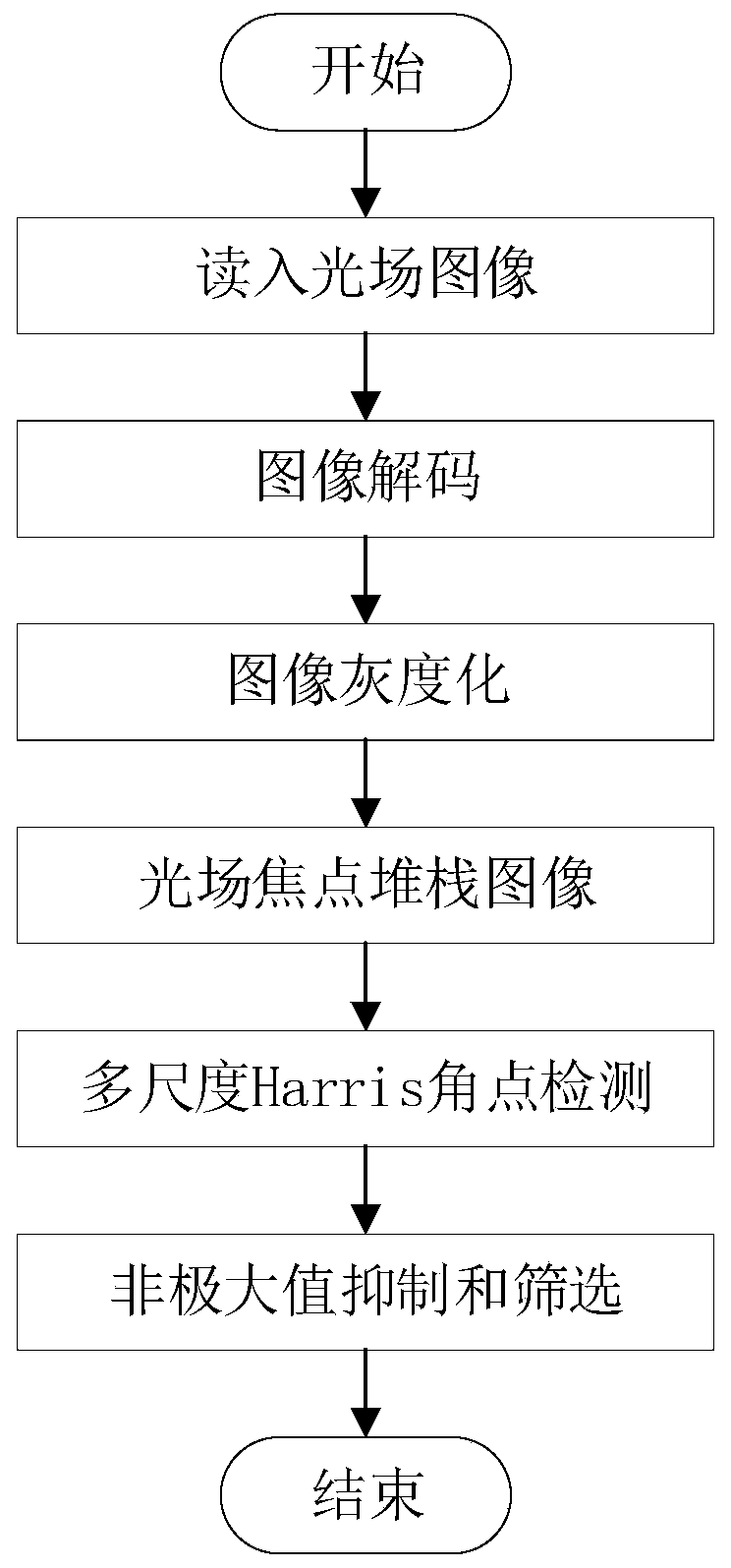
Light field image feature point detection method based on multi-scale Harris
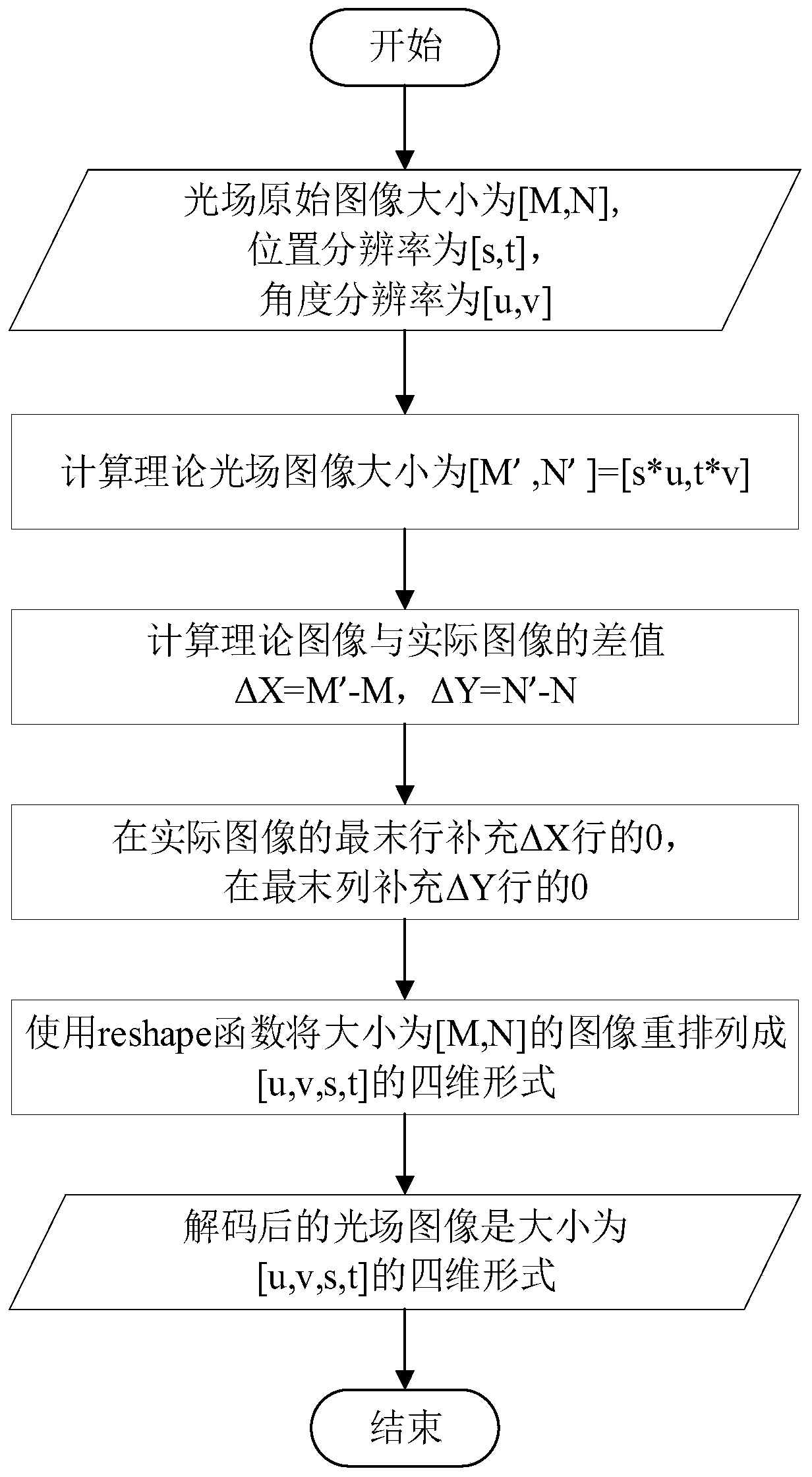
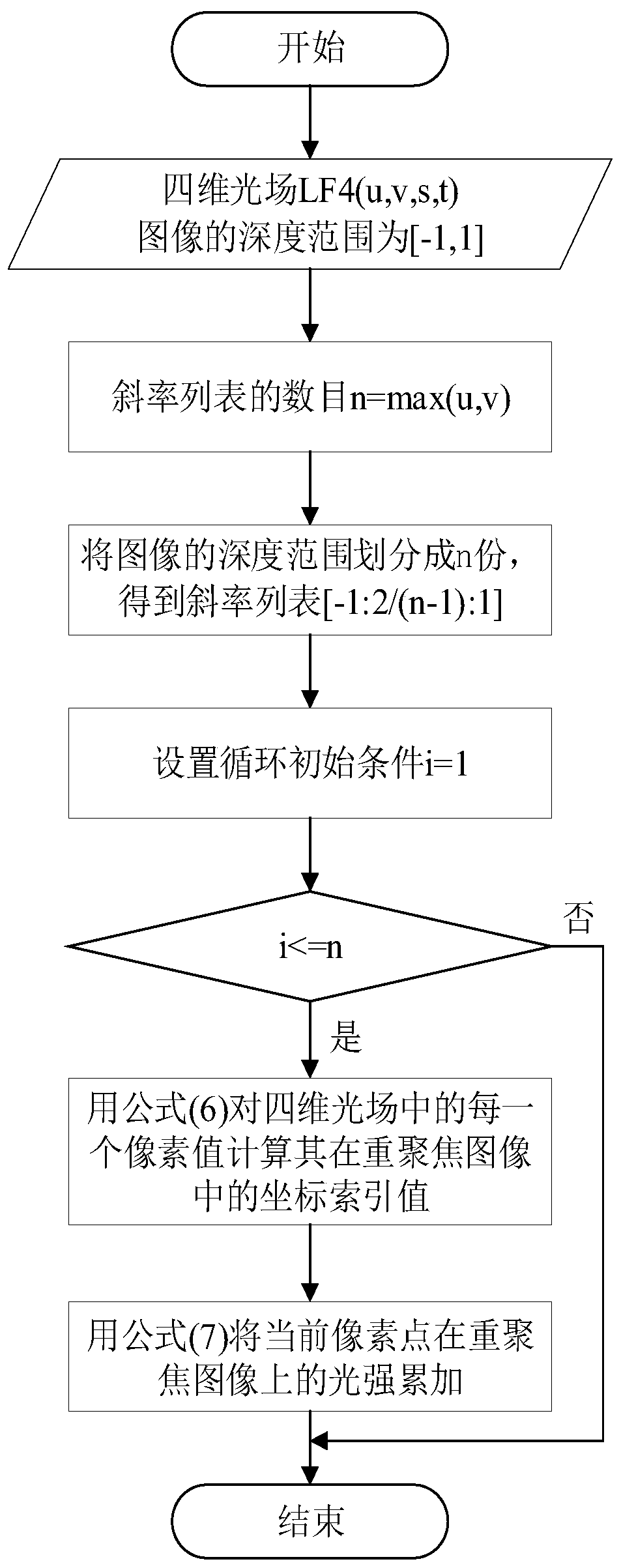
ActiveCN110490924AOvercome the shortcomings of occlusion, loss of depth, etc.Comprehensive descriptionImage enhancementImage analysisAngular pointImage resolution
The invention discloses a light field image feature detection method based on multi-scale Harris. The method specifically comprises the steps: reading a light field original image parameter file intoMATLAB, and decoding and processing the light field original image parameter file into an effective four-dimensional light field matrix; taking the maximum value in the angle resolution [u, v] as thelength n of a slope list to obtain the slope list, and refocusing each slope in the slope list to obtain a focus stack image corresponding to the slope; carrying out multi-scale Harris corner detection on each focus stack image; carrying out non-maximum suppression on the corner detected in each scale of the current corner stack, and reducing the influence of multiple responses; carrying out multi-scale judgment on the candidate corner points; if the candidate corner points appear in multiple scales, reserving the candidate corner points; otherwise, deleting, wherein the finally reserved angular points are the feature points of the light field image; obtaining the real information of the whole space by adopting the position information and the angle information in the light field image. Therefore, the defects of shielding, depth loss and the like of the traditional imaging are overcome, and the scene description is more comprehensive.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
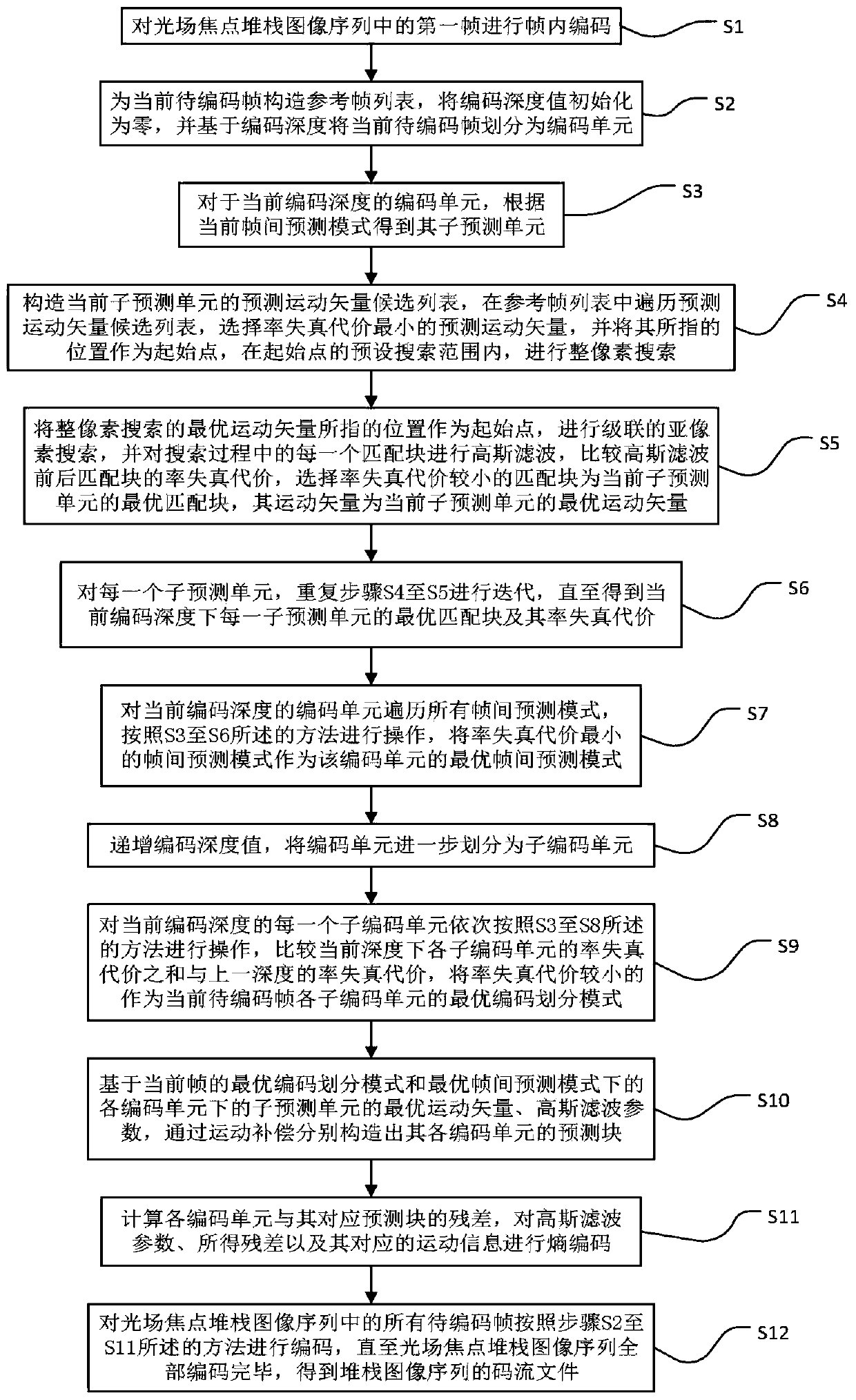
Optical field focus stack image sequence encoding and decoding method, device and system
ActiveCN110996104AEffective simulationReduce the distribution of residualsDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsRate distortion
The invention discloses an optical field focus stack image sequence encoding and decoding method, device and system, and aims to simulate out-of-focus blur regions of other frames by performing Gaussian filtering on a focusing region since each frame of a focus stack image has great correlation and only the focusing region is different from the out-of-focus blur region. According to the invention,the prediction motion vector candidate list is traversed; taking the position pointed by the prediction motion vector with the minimum distortion cost as a starting point; carrying out integer pixelsearch and cascaded sub-pixel search in sequence; gaussian filtering is carried out on each matching block in the searching process; the rate distortion cost of the matching blocks before and after Gaussian filtering is compared, the optimal matching block of the matching block with low rate distortion cost is selected, Gaussian filtering is applied to the inter-frame prediction model, residual distribution of the prediction unit and the coding unit is effectively reduced, the code rate is effectively saved, and the coding efficiency is high.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Monocular visual focusing stack acquisition and scene reconstruction method
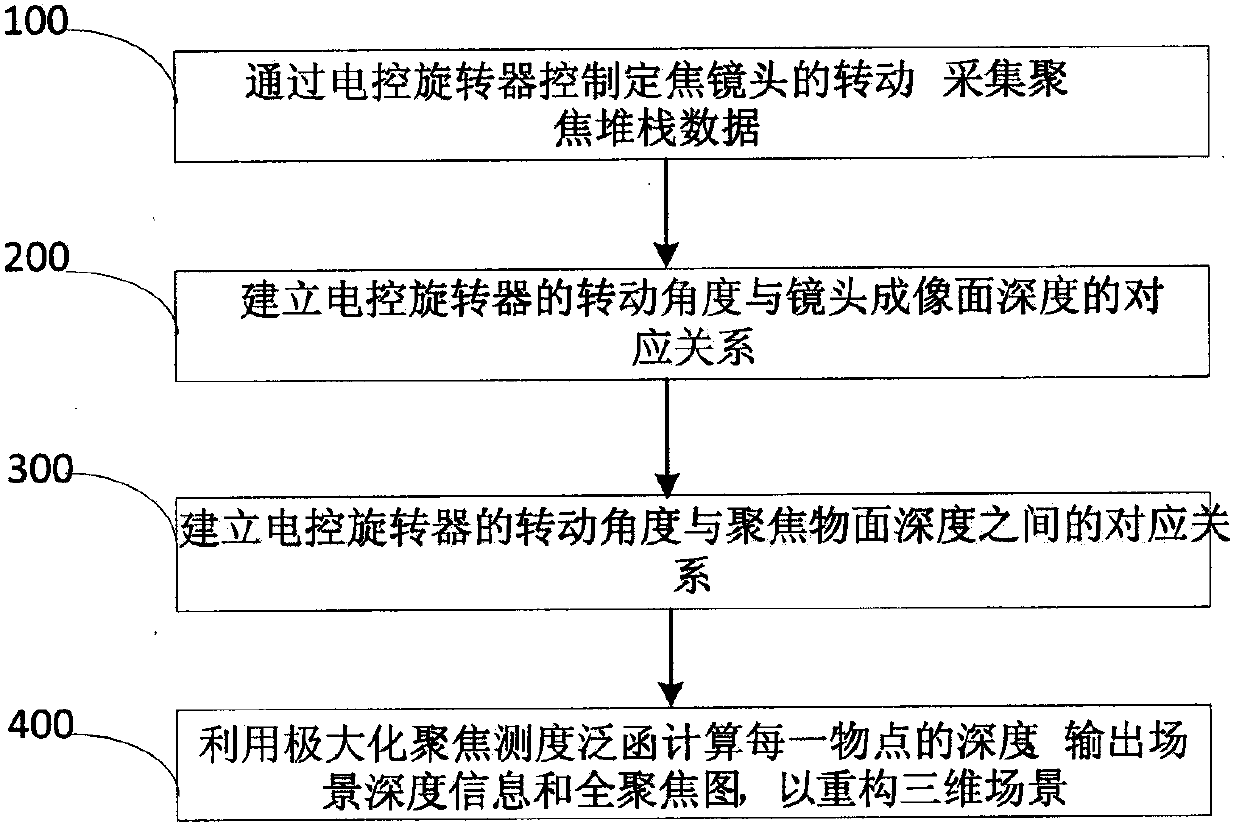
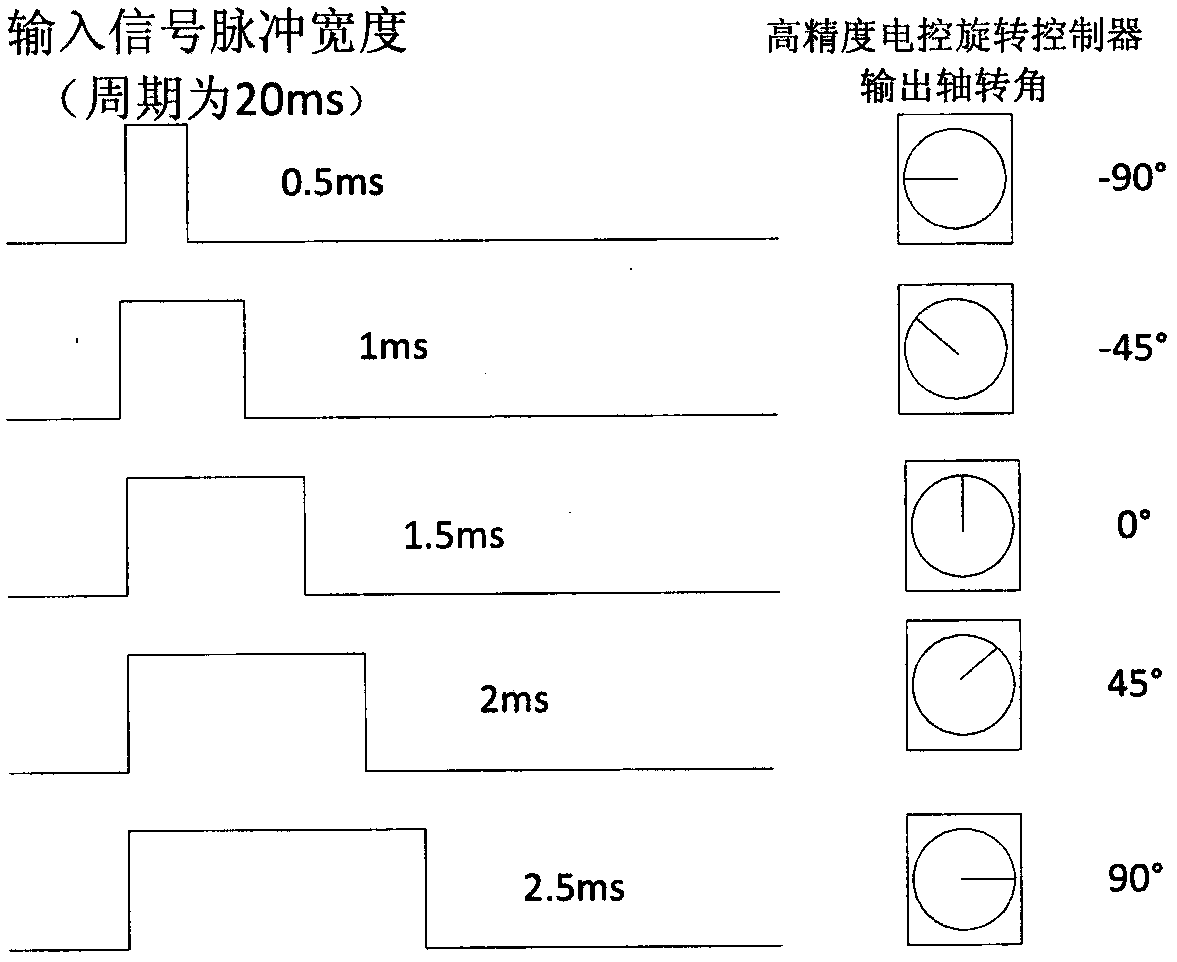
ActiveCN108053468AReduce volumeLess restrictiveTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPrime lensVisual Focusing
The invention discloses a monocular visual focusing stack acquisition and scene reconstruction method. The method comprises the following steps of: controlling rotation of a prime lens through an electric control rotator, and acquiring focusing stack data; in the rotation process of the prime lens, fixing a detector and synchronously translating the prime lens along an optical axis of a camera; establishing a corresponding relationship between a rotation angle of the electric control rotator and an imaging surface depth according to position adjustment of the prime lens; establishing a corresponding relationship between the rotation angle of the electric control rotator and a focusing object surface depth by combining an object image relationship of lens imaging according to the corresponding relationship between the rotation angle of the electric control rotator and the focusing object surface depth; and functionally calculating a depth of each object point by utilizing maximized focusing measurement according to the corresponding relationship between the rotation angle of the electric control rotator and the focusing object surface depth, and outputting a scene depth map and a full focusing map so as to reconstruct a three-dimensional scene. According to the method, the requirements for three-dimensional scene reconstruction, image depth information and full focusing under field of view (FOV) of the cameras can be satisfied, and depth images ad full focusing images can be generated.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Modulated Optical Technique for Focus Stacking Images in Imaging Systems
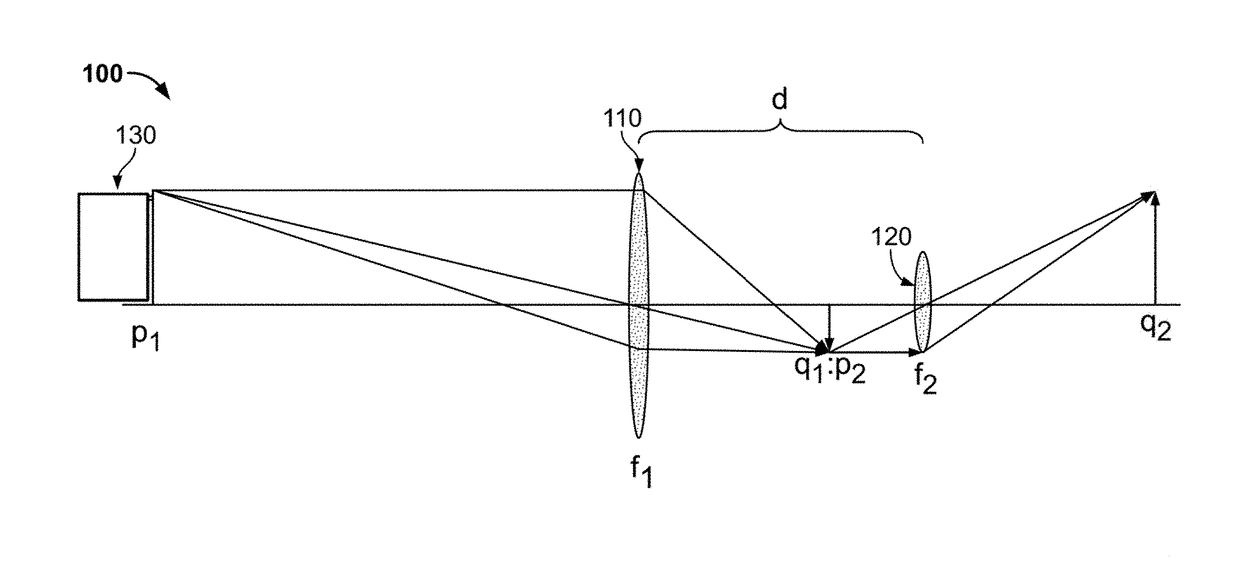
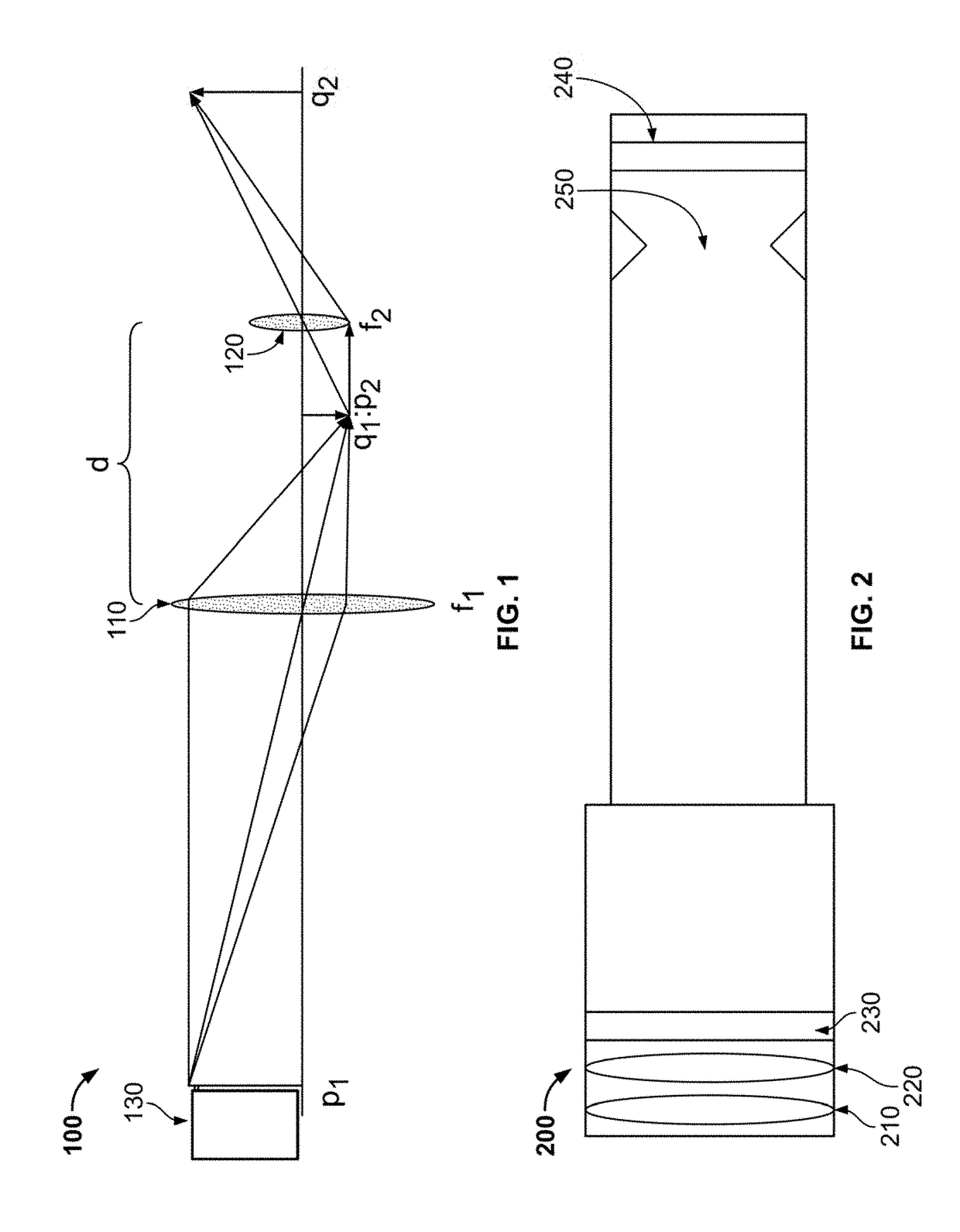
A system and method for focus-stacking images that results in a clearer image, particularly where objects in the image are at different depths of field. The system and method may be used in connection with, or made a part of, an imaging system, including a telescope, camera, binoculars or other imaging system. The system and method incorporate one or more focus-altering devices that alter the focus of an image produced by the imaging system. The system and method also incorporate a modulation device that modulates between two or focal planes, thereby resulting in a focus-stacked image that is a combination of two or more focal planes.
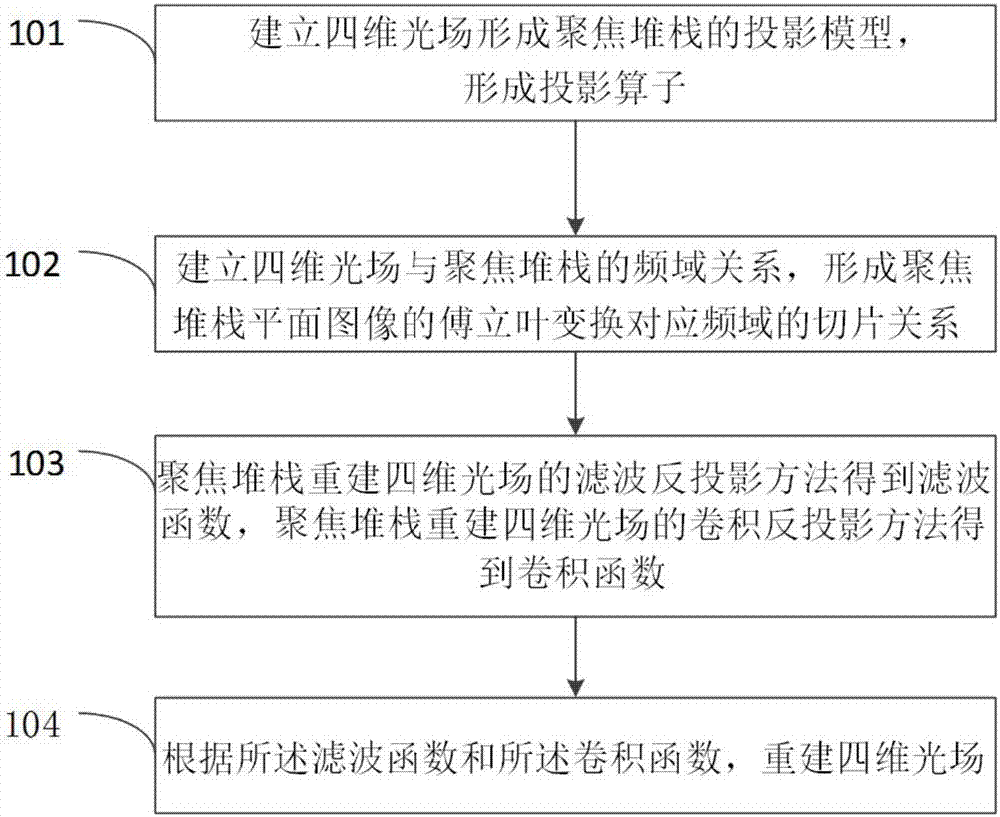
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Filtered back-projection method and apparatus for reconstructing light field by focus stack
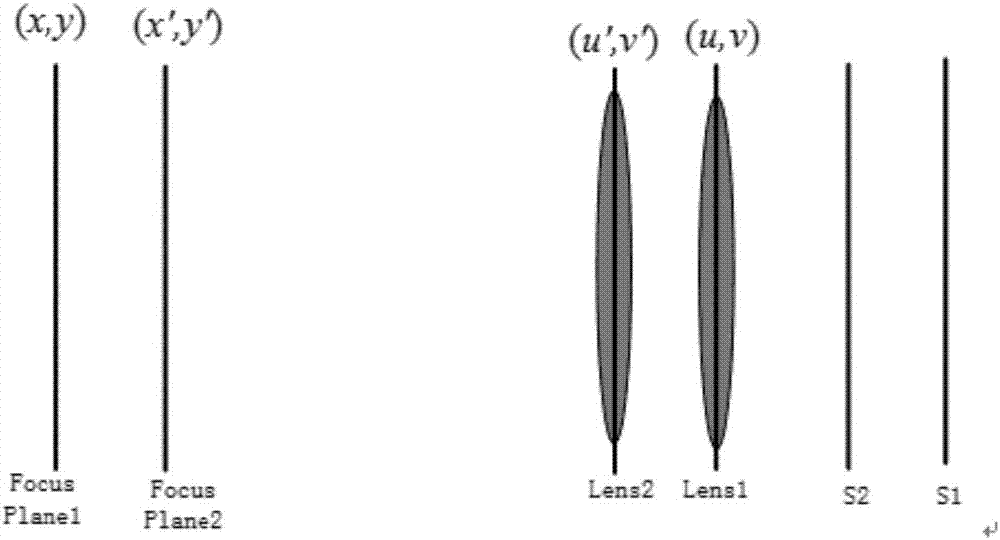
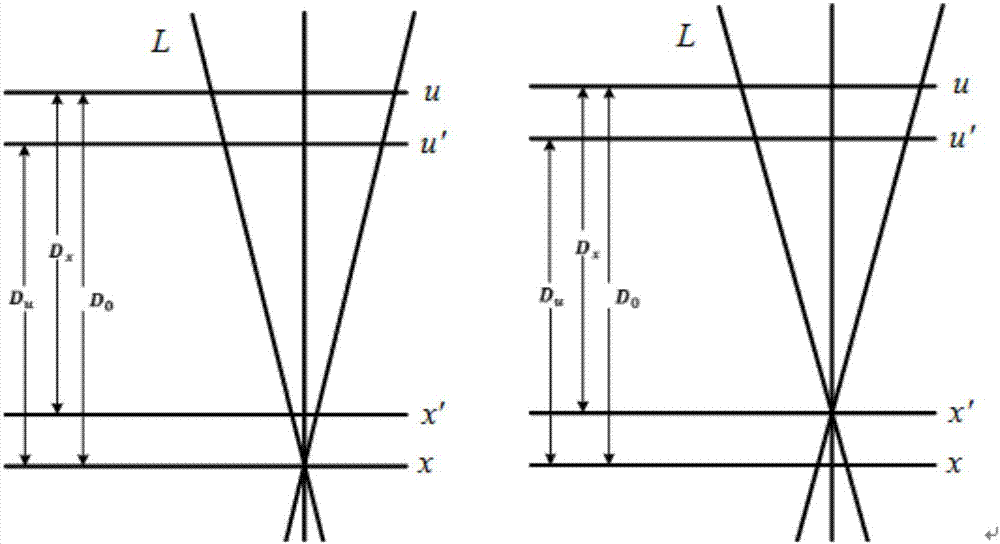
ActiveCN106934110AHigh precisionMeet needsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCamera lensRelative motion
The invention discloses a filtered back-projection method and apparatus for reconstructing a light field by a focus stack. The method mainly comprises the steps of giving out a geometric relationship of the four-dimensional light field and the focus stack, building a projection model for forming the focus stack by the light field, and forming a projection operator; based on the projection model, establishing a frequency domain relationship of the four-dimensional light field and the focus stack, and forming a Fourier slice relationship; based on the Fourier slice relationship, establishing filtered back-projection and convolution back-projection methods for reconstructing the light field by the focus stack; and selecting optimized filtering function and convolution function to reconstruct the light field. The focus stack is an image sequence collected by a relative motion of a detector and a lens, and by selecting the optimized filtering function and convolution function, the high-precision four-dimensional light field can be reconstructed. The four-dimensional light field can realize three-dimensional reconstruction under a shooting view angle of a camera, and can provide accurate three-dimensional structure information for virtual reality and geometric measurement.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Full-focusing light field image composition method and system
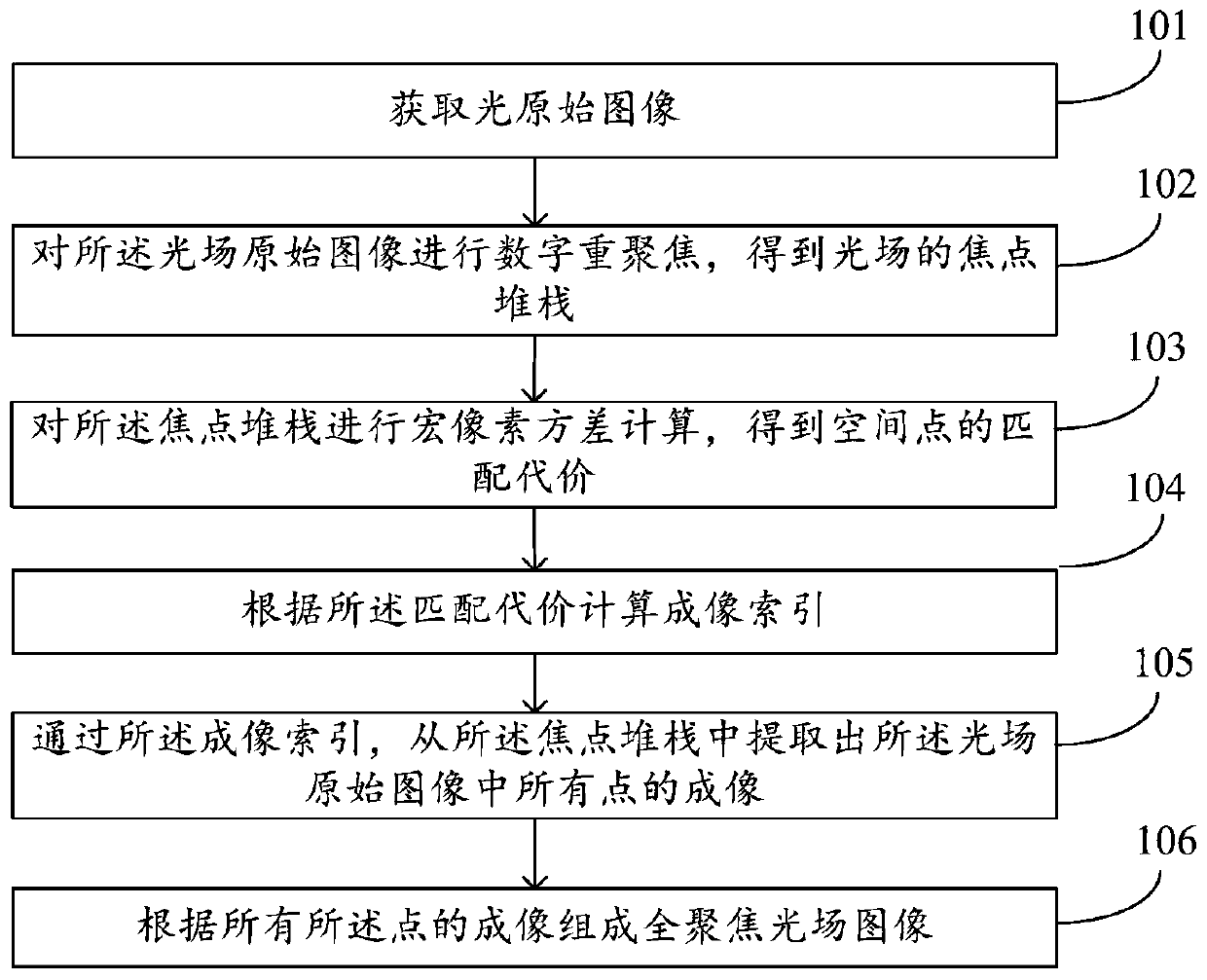
InactiveCN110246162AClear imagingNo added imaging complexityTelevision system detailsImage analysisFocus stackingLight field
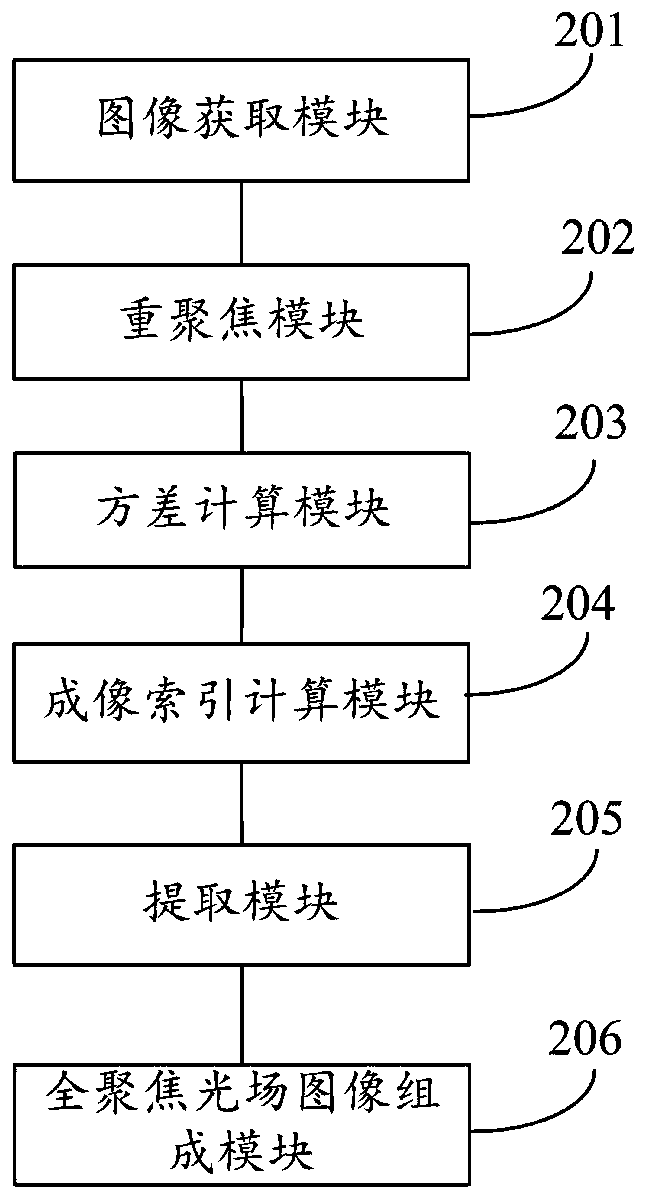
The invention discloses a full-focusing light field image composition method and system. The method comprises the steps of obtaining an optical original image; performing digital refocusing on the original image of the light field to obtain a focus stack of the light field; performing macro-pixel variance calculation on the focus stack to obtain the matching cost of spatial points; calculating an imaging index according to the matching cost; extracting images of all points in the light field original image from the focus stack through the imaging index; and forming a full-focusing light field image according to the images of all the points. According to the method, the full-focus image is solved by using the light field image, and all clear images can be obtained under the condition that the imaging complexity is not increased.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Photo-realistic shallow depth-of-field rendering from focal stacks
The invention relates to photo-realistic shallow depth-of-field rendering from focal stacks. Generating an image with a selected level of background blur includes capturing, by a first image capture device, a plurality of frames of a scene, wherein each of the plurality of frames has a different focus depth, obtaining a depth map of the scene, determining a target object and a background in the scene based on the depth map, determining a goal blur for the background, and selecting, for each pixel in an output image, a corresponding pixel from the focus stack.
Owner:APPLE INC
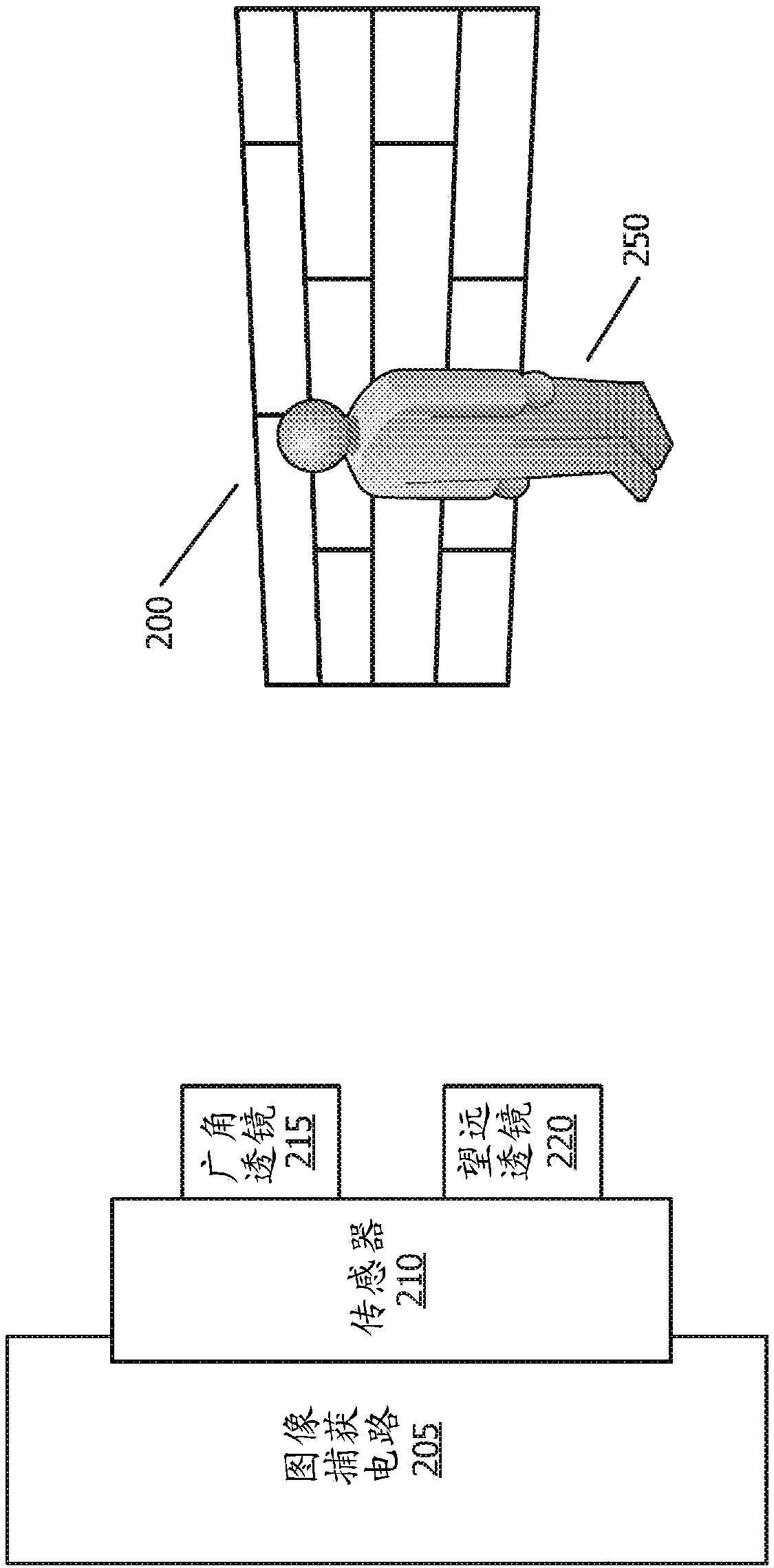
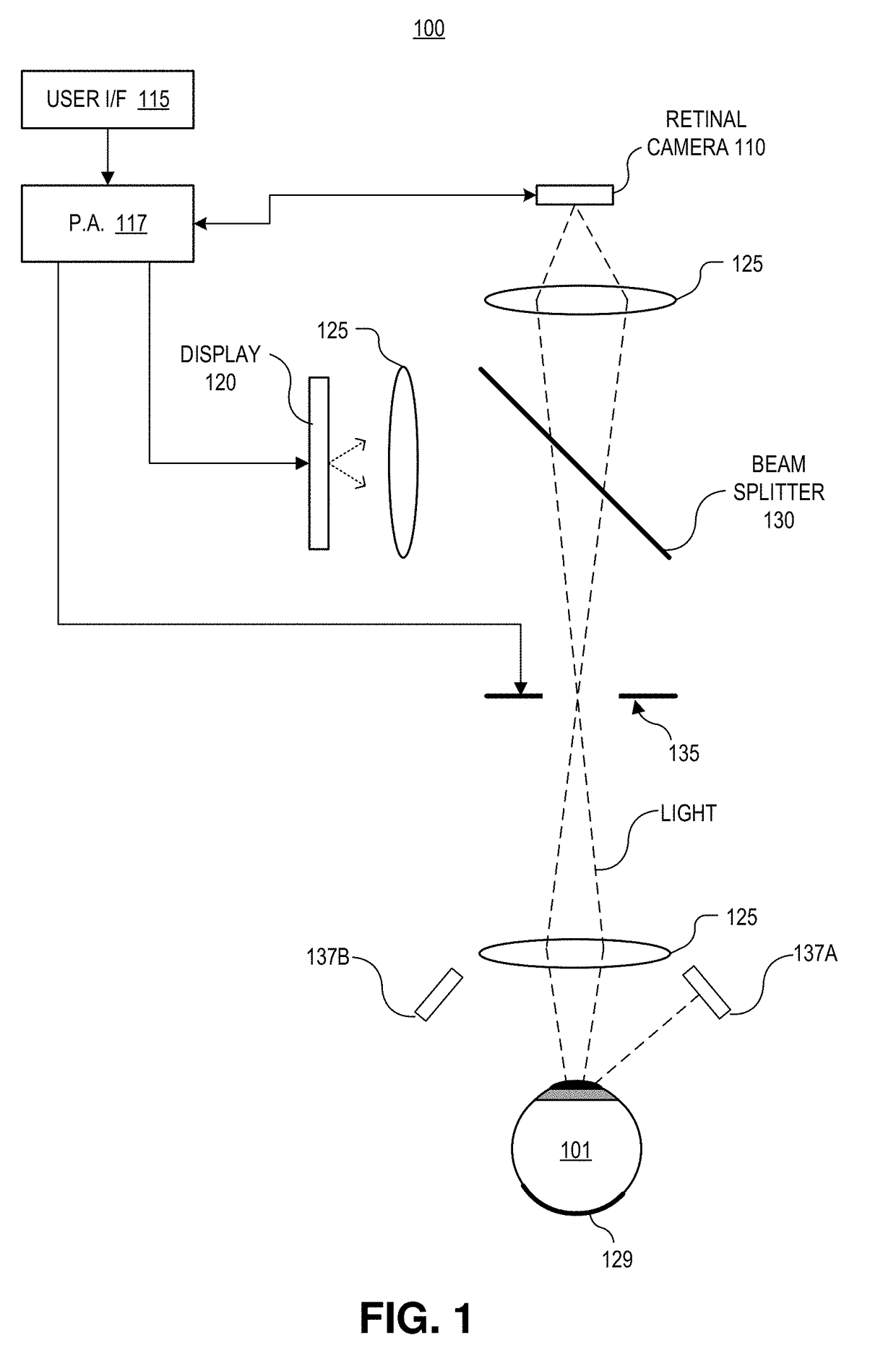
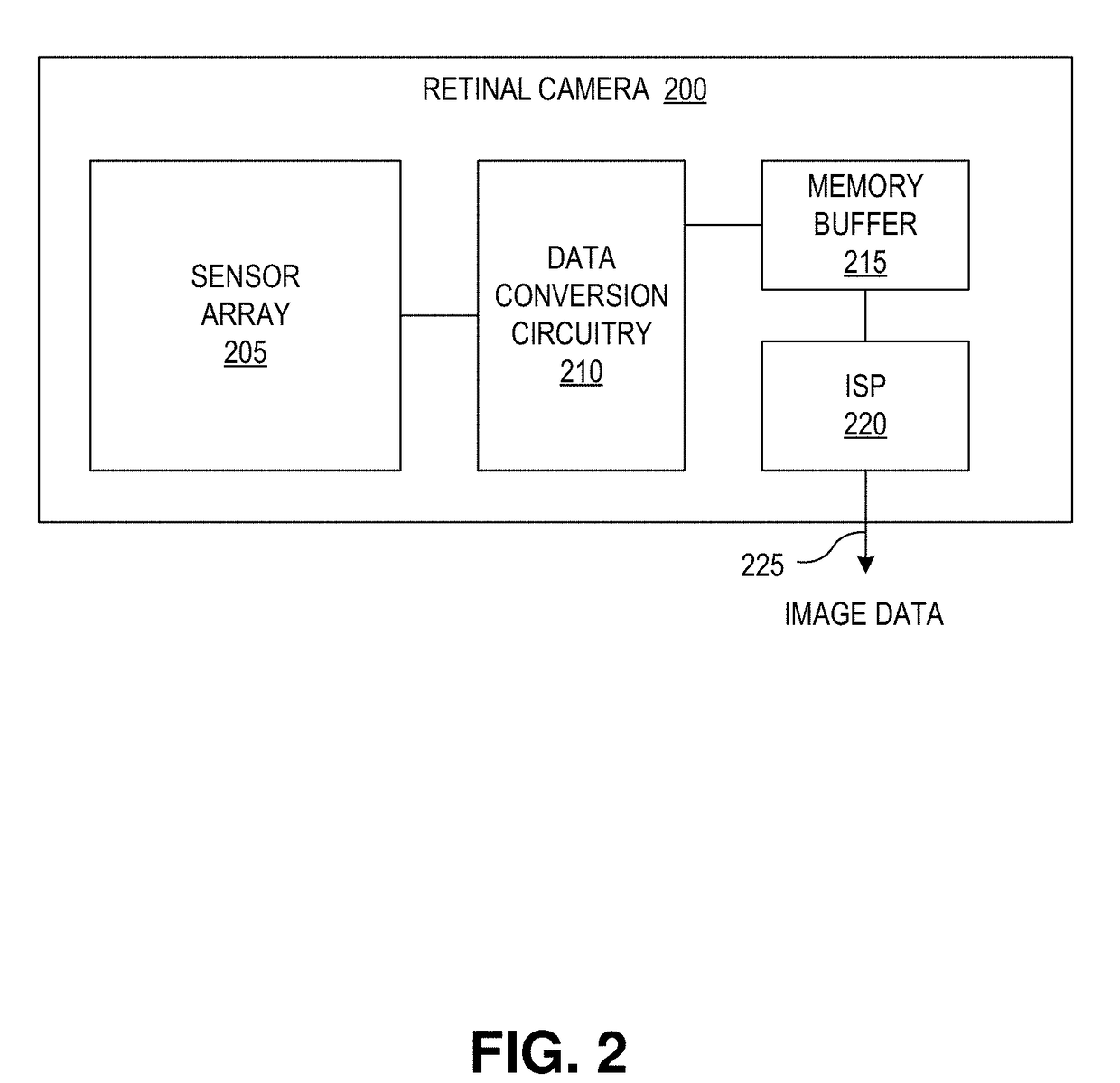
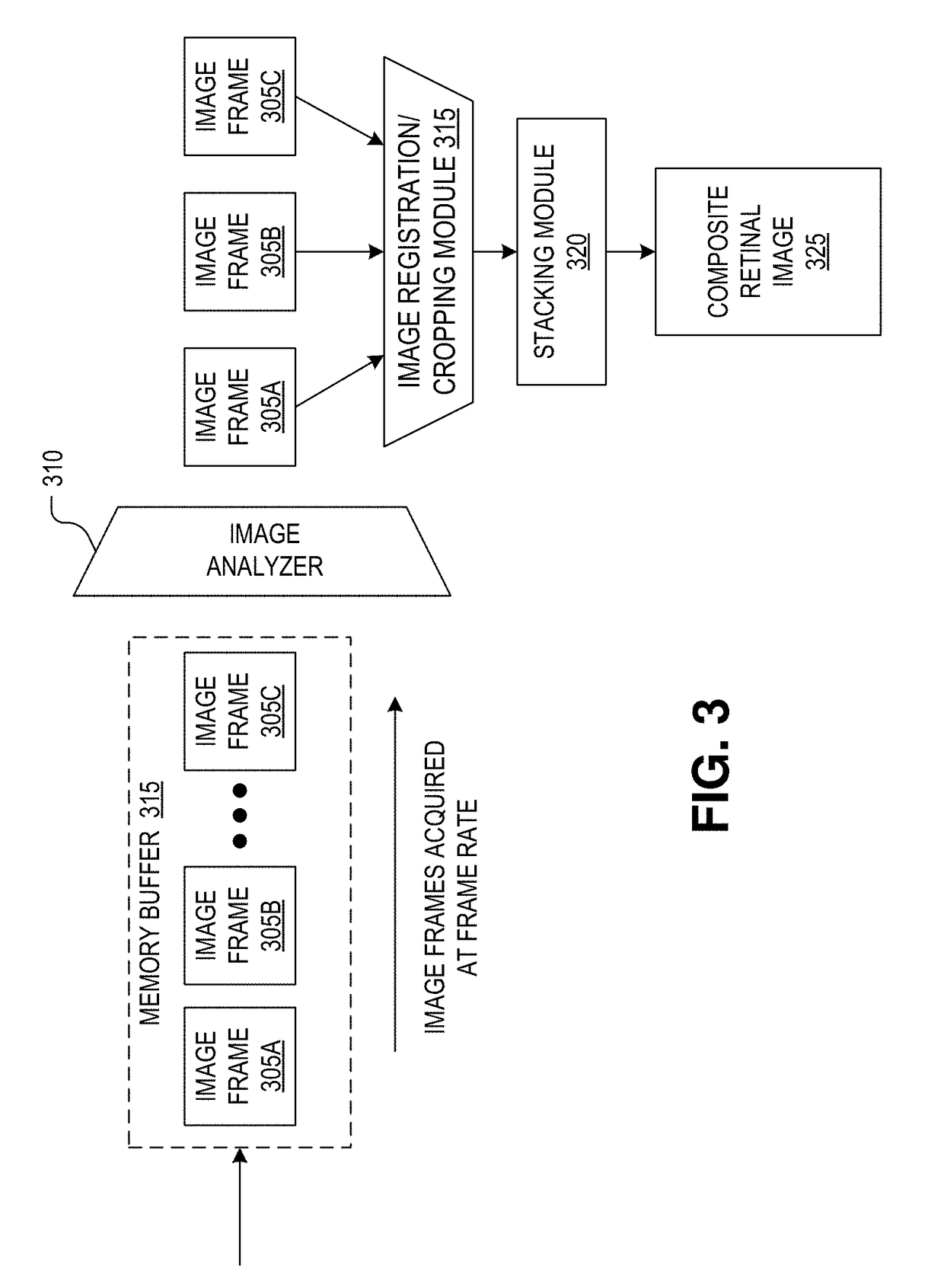
Focus stacking for retinal imaging
A method of imaging an interior of an eye includes illuminating the interior of the eye with one or more beams of light from a light source, and said illuminating is configured to trigger a change to a pupil of the eye. An image sensor captures a sequence of images of light reflected by the interior of the eye during an expected timeframe when a width of the pupil is changing in response to said illuminating. A processing apparatus combines images in the sequence of images to form a composite image having a larger depth of field than a depth of field of each of the images in the sequence of images. The depth of field for each of the images corresponds to the width of the pupil when each of the images is captured.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
Focusing stack imaging system presetting position calibration method based on focusing measurement
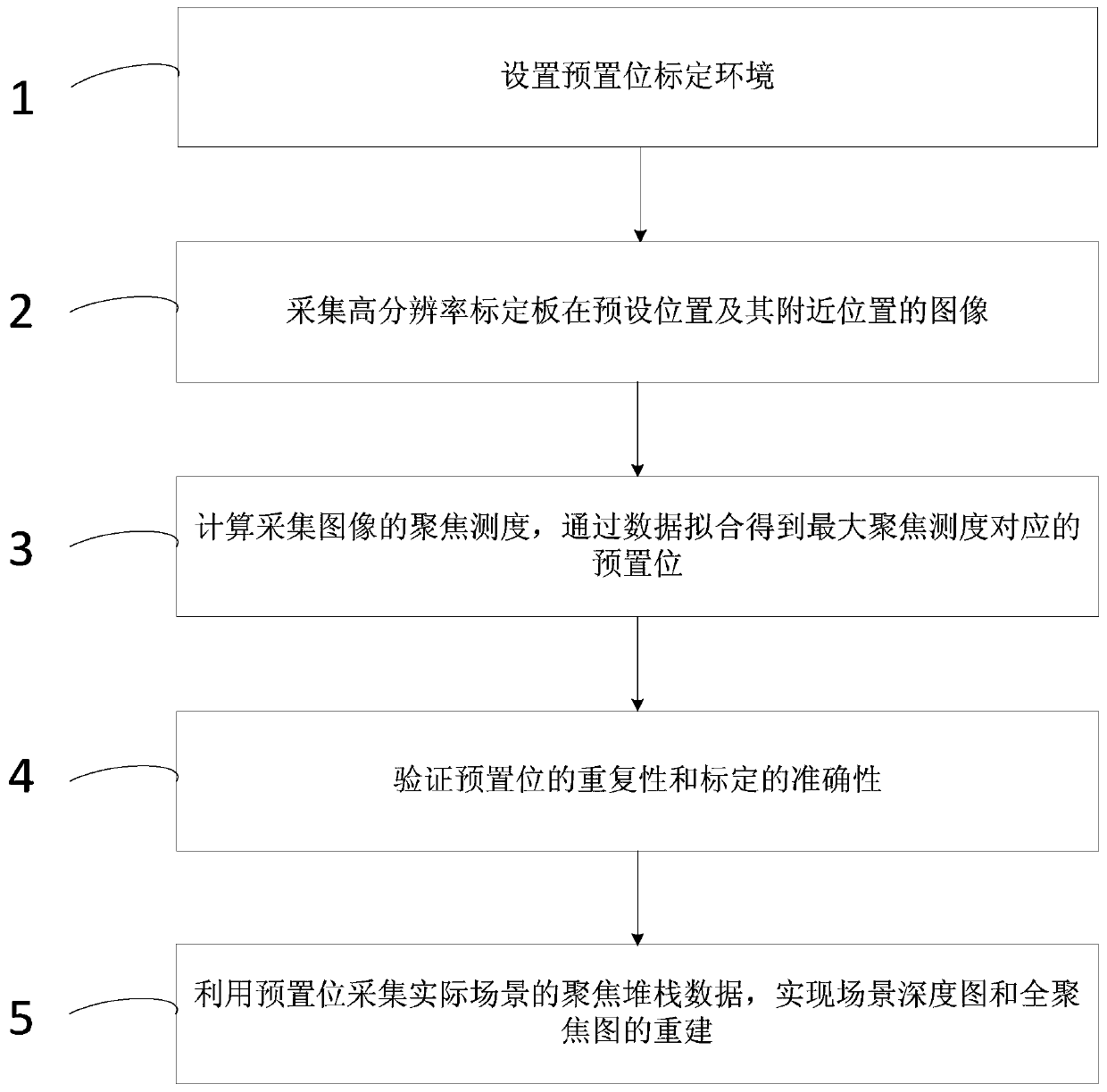
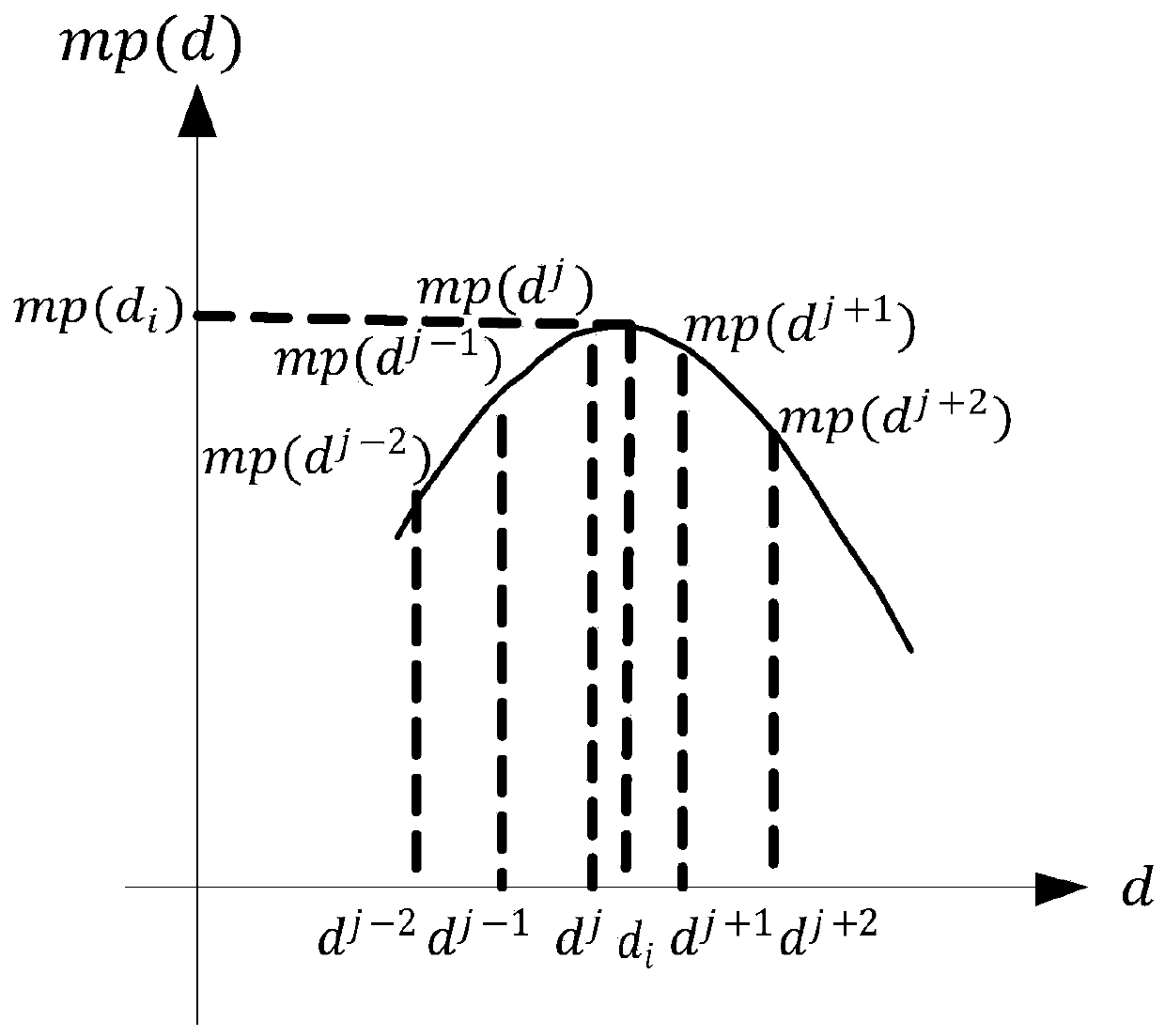
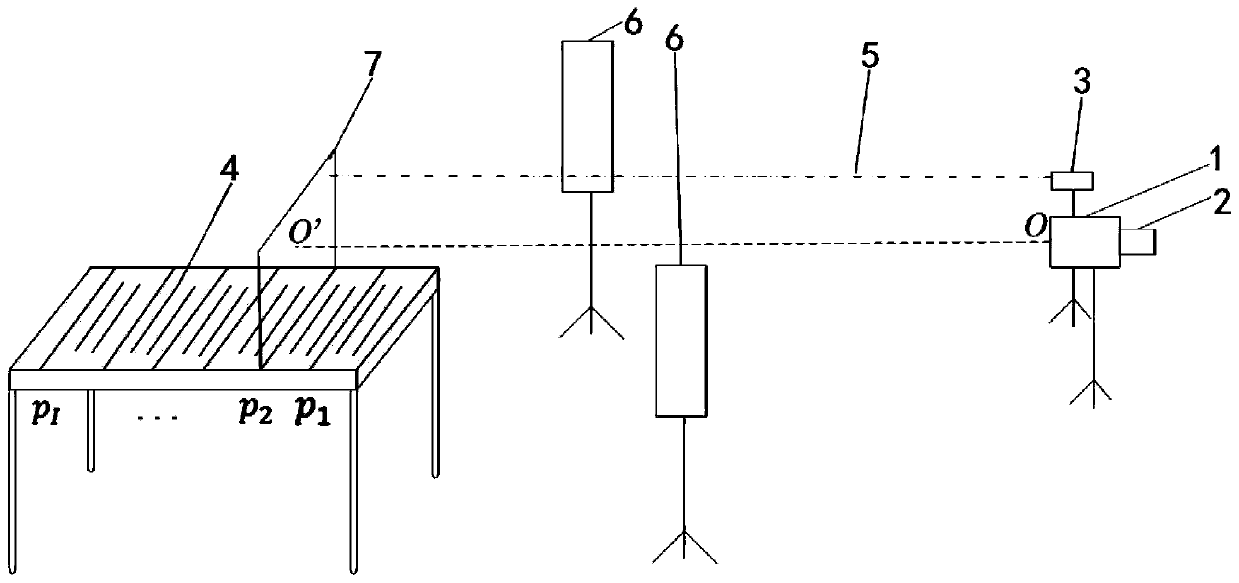
PendingCN110956668AImprove collection efficiencyAchieve high-precision reconstructionImage enhancementImage analysisRadiologyCalibration result
The invention discloses a focusing stack imaging system presetting position calibration method based on focusing measurement. The focusing stack imaging system presetting position calibration method comprises the following steps: 1, setting a presetting position calibration environment; 2, collecting images of a calibration plate in a presetting position calibration environment at a presetting position and a corresponding II-type identification line; 3, calculating the focusing measure of each collected image, and obtaining a presetting position corresponding to the maximum focusing measure through data fitting; 4, verifying the repeatability and calibration accuracy of the mean value and variance presetting positions of multiple calibration results by adopting a method of calibrating thesame presetting position for multiple times; and 5, acquiring focusing stack data of an actual scene by using the calibrated presetting position, and reconstructing a scene depth map and a full-focusing map. The focusing stack imaging system presetting position calibration method can improve the focusing stack data collection efficiency, achieves the high-precision reconstruction of the depth of athree-dimensional scene, and also can provide reference and theoretical basis for the building of a three-dimensional digital space and the improvement of a calculation method.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV +1
Light field semantic segmentation method and system, electronic terminal and storage medium
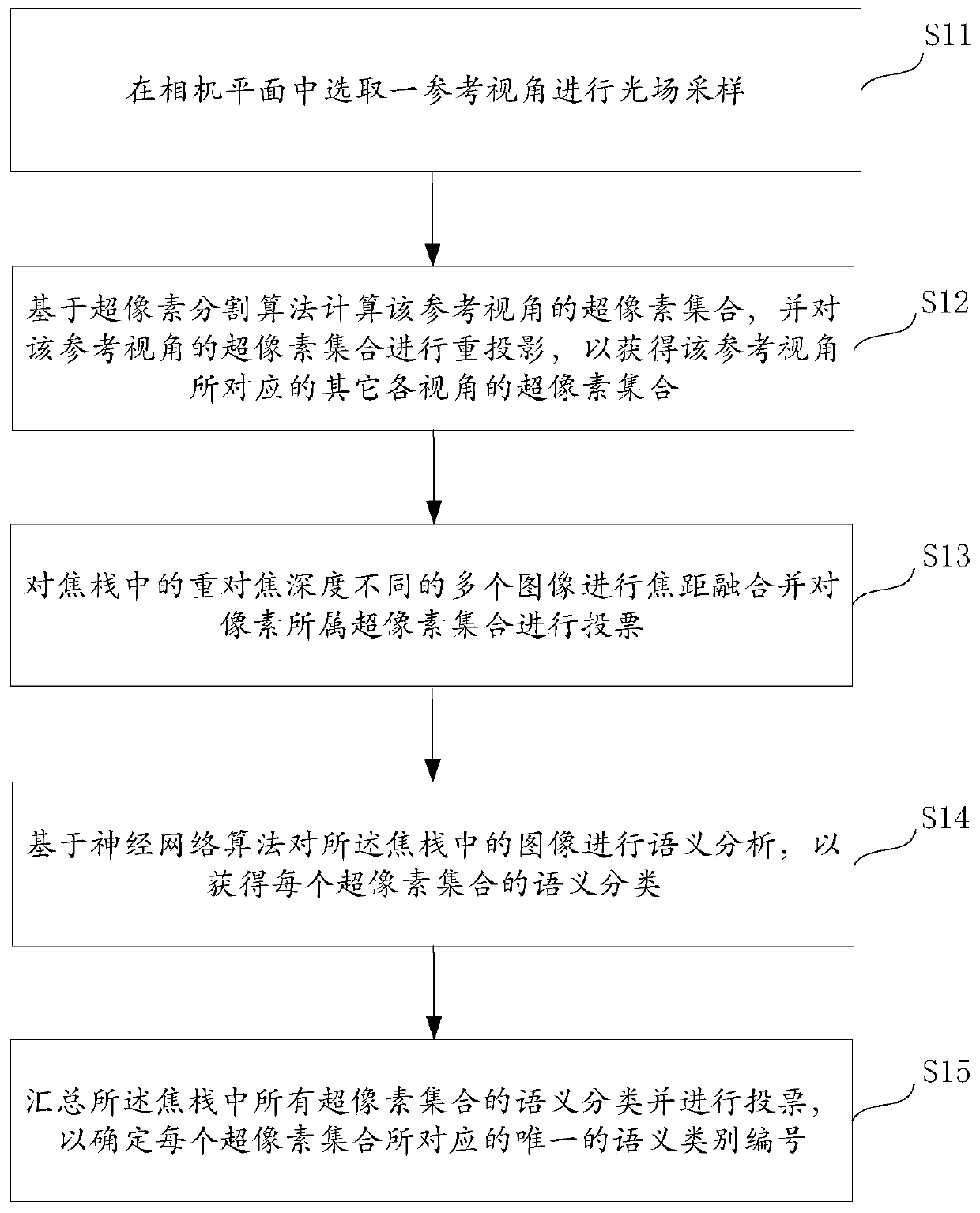
ActiveCN111382753ADeletion no longer restrictedEffectively identify occlusionCharacter and pattern recognitionMedicineSuperpixel segmentation
The invention provides a light field semantic segmentation method and system, an electronic terminal and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps that: a reference view angle is selected froma camera plane so as to perform light field sampling; the superpixel set of the reference view angle is obtained based on a superpixel segmentation algorithm, and reprojection is performed on the superpixel set of the reference view angle to obtain superpixel sets of other view angles corresponding to the reference view angle; focal length fusion is carried out on a plurality of images with different re-focusing depths in a focusing stack, and the superpixel sets to which pixels belong are voted; semantic analysis is performed on the images in the focusing stack based on a neural network algorithm to obtain the semantic classification of each superpixel set; and the semantic classifications of all the superpixel sets in the focusing stack are summarized, and voting is performed, so that aunique semantic category number corresponding to each superpixel set is determined. The method is no longer limited by depth information loss caused by projection transformation, and effectively recognizes occlusion so as to perform correct category prediction on the pixel points of an occluded object.
Owner:YAOKE INTELLIGENT TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
Super-high temperature solar compound lens focus-stacking condenser
A super-high temperature solar compound lens focus-stacking condenser belongs to the technical fields of application of modern solar energy technologies, ultra-glare light electrolysed water hydrogen production, metal smelting, refining of new special substance, manufacture and welding of oversized equipment, modern house building, in-situ sinter molding and the like. The invention discloses a super-high temperature condenser with ultra-glare light on focal points, a single lens in the prior art comprises an old convex lens, a Fresnel lens and a recently-invented liquid lens which do not reach the super-high temperature degree of fuel oil, natural gas, laser and the like, and new energy resources indulge in empty talk if the problem is not solved. The super-high temperature solar compound lens focus-stacking condenser is formed by composting a multi-face disk prism and a plurality of convex lenses or Fresnel lenses, produces a focus-stacking phenomenon that self-adaption focal points are coincident and is a novel super-high temperature single condenser converting sunlight into the ultra-glare light and mainly used for smelting iron and steel, non-ferrous metals, natural gemstones and diamonds and refining silicon materials and unknown special mineral substance.
Owner:孙言明
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com