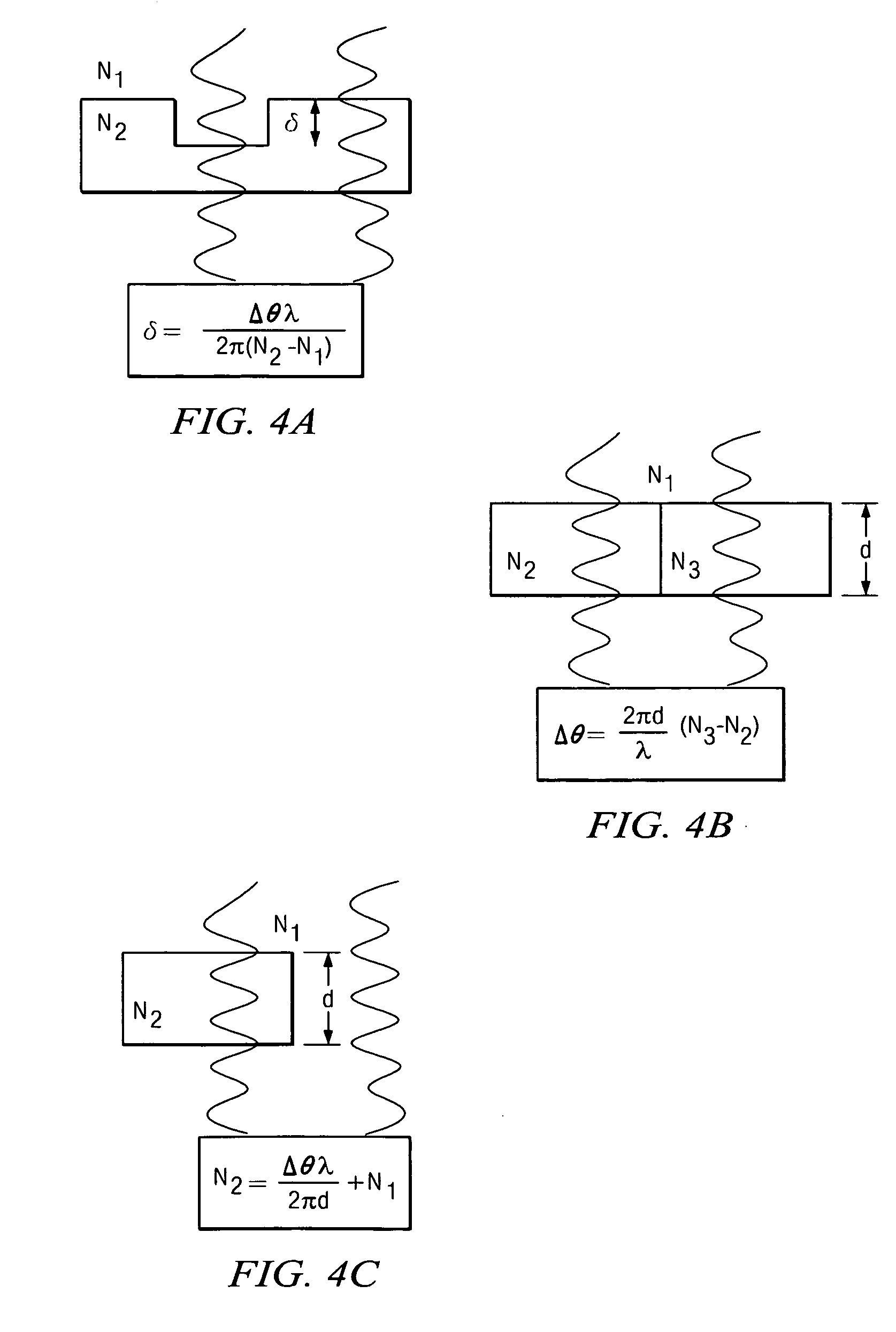
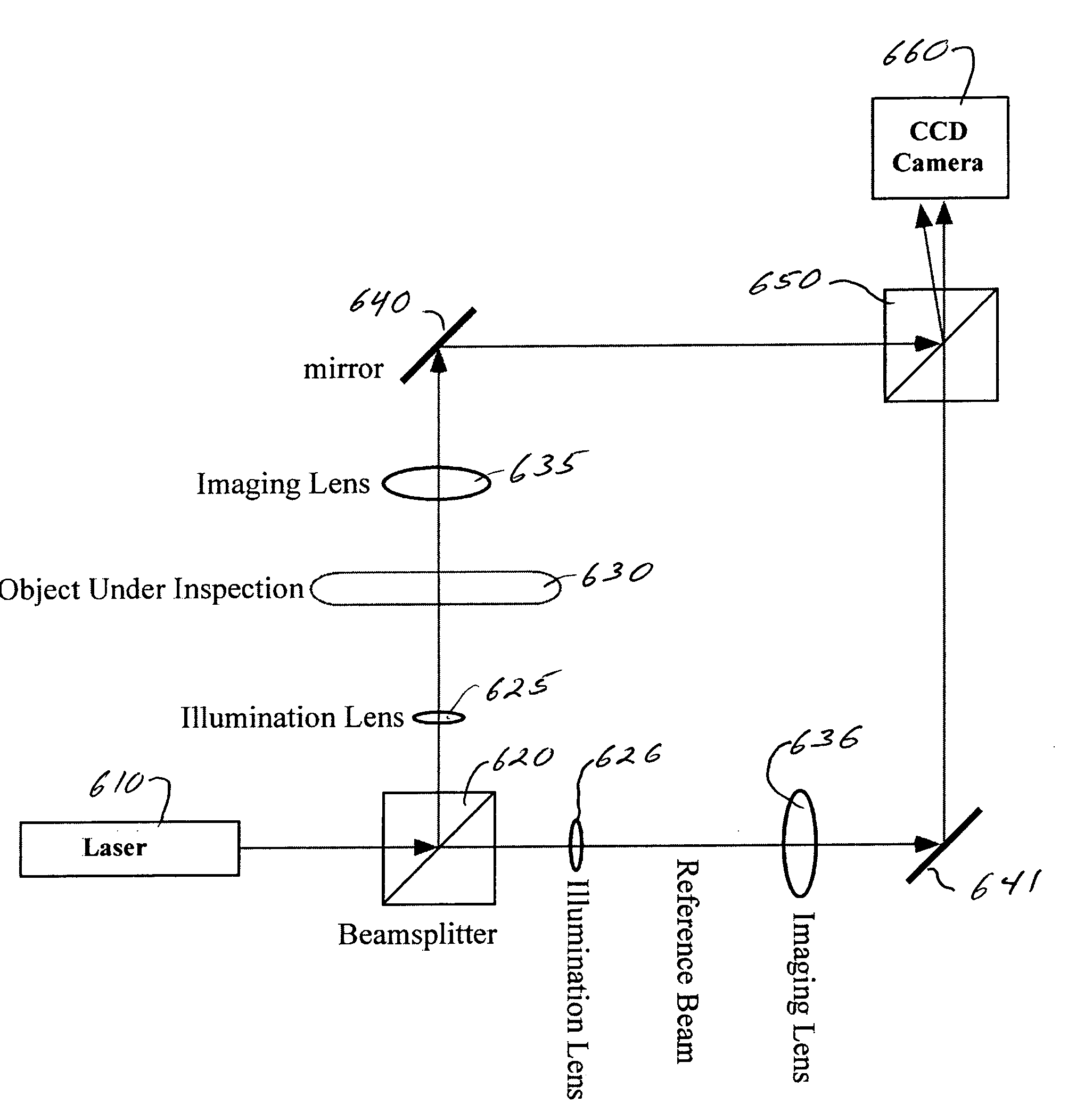
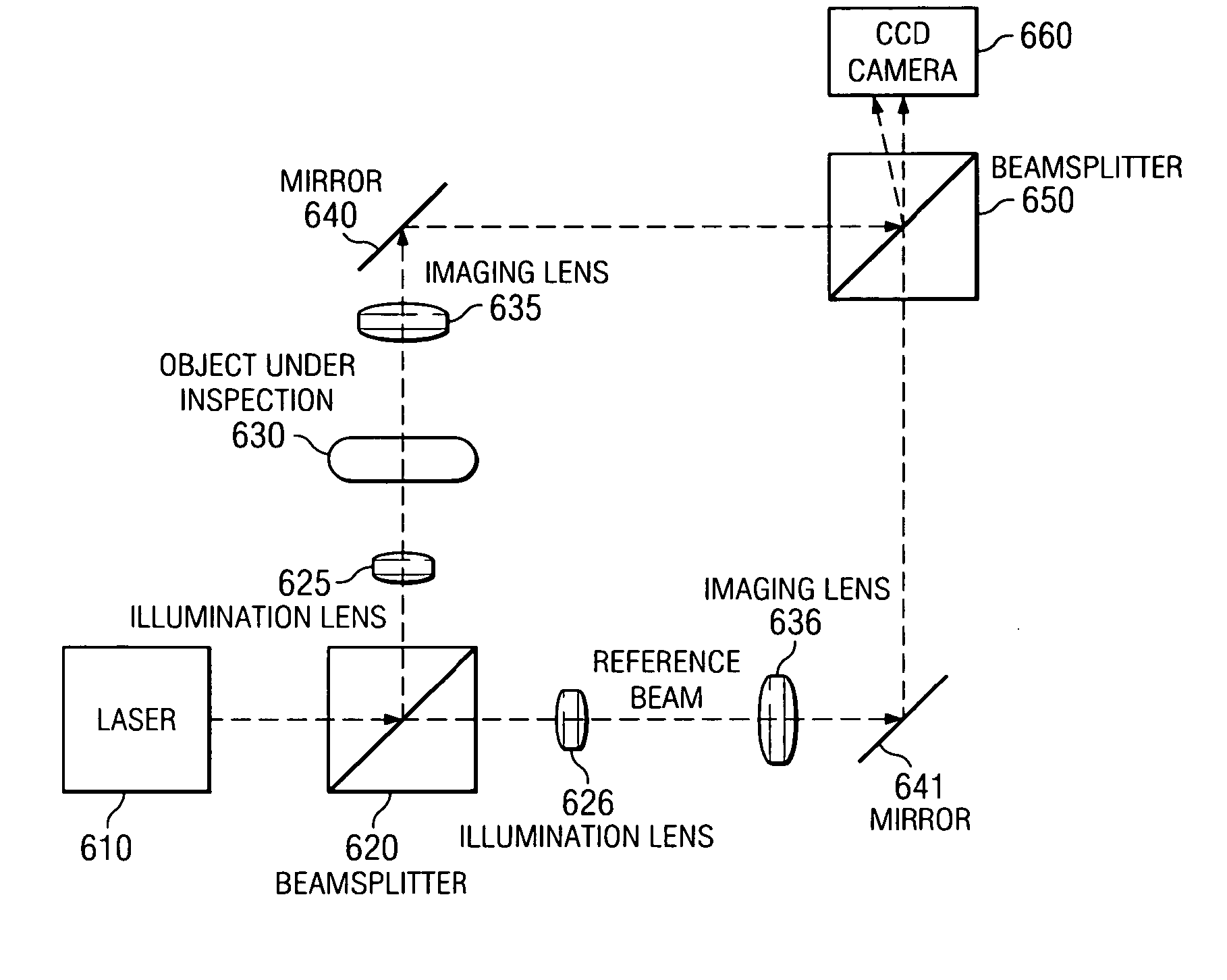
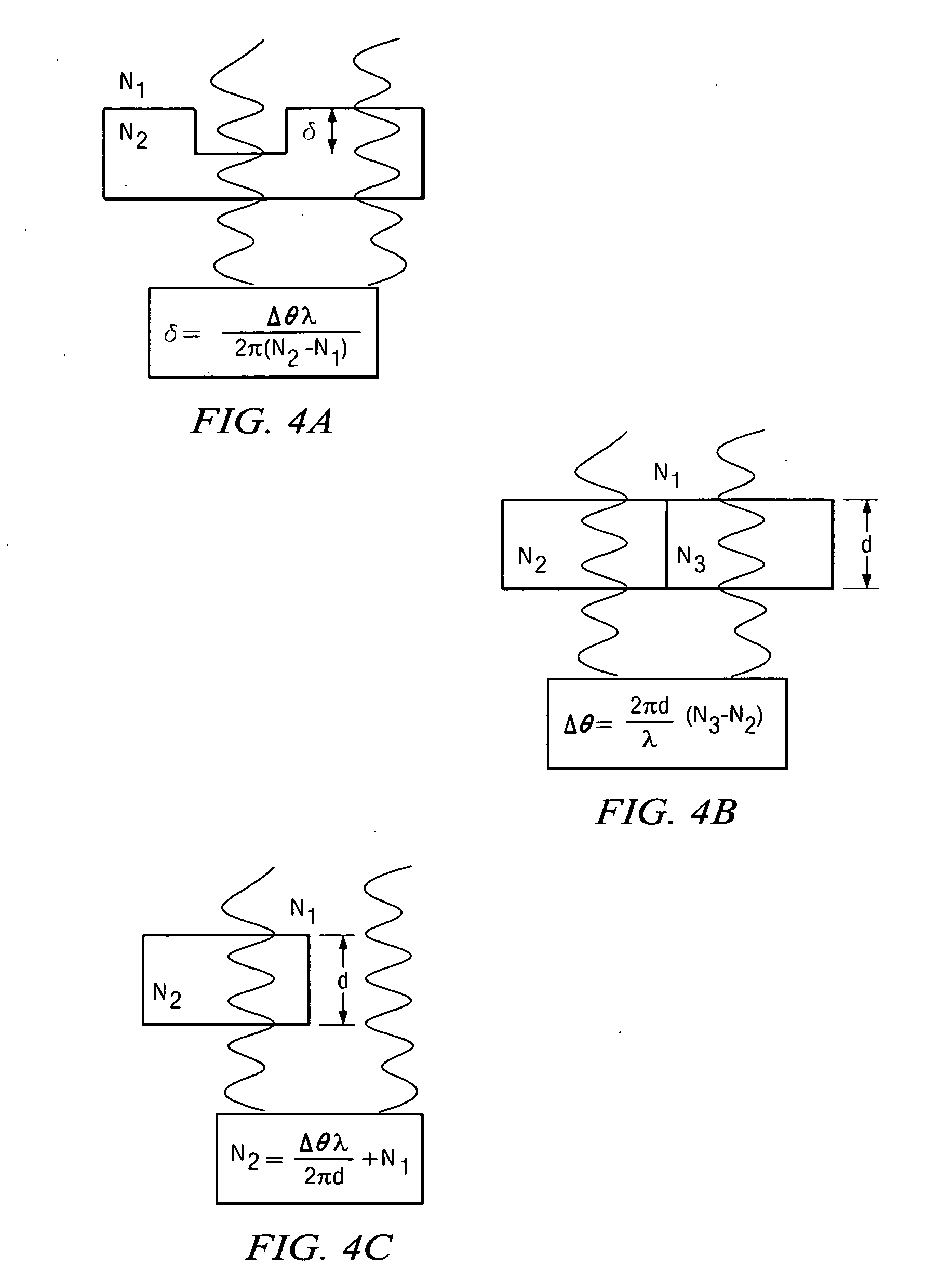
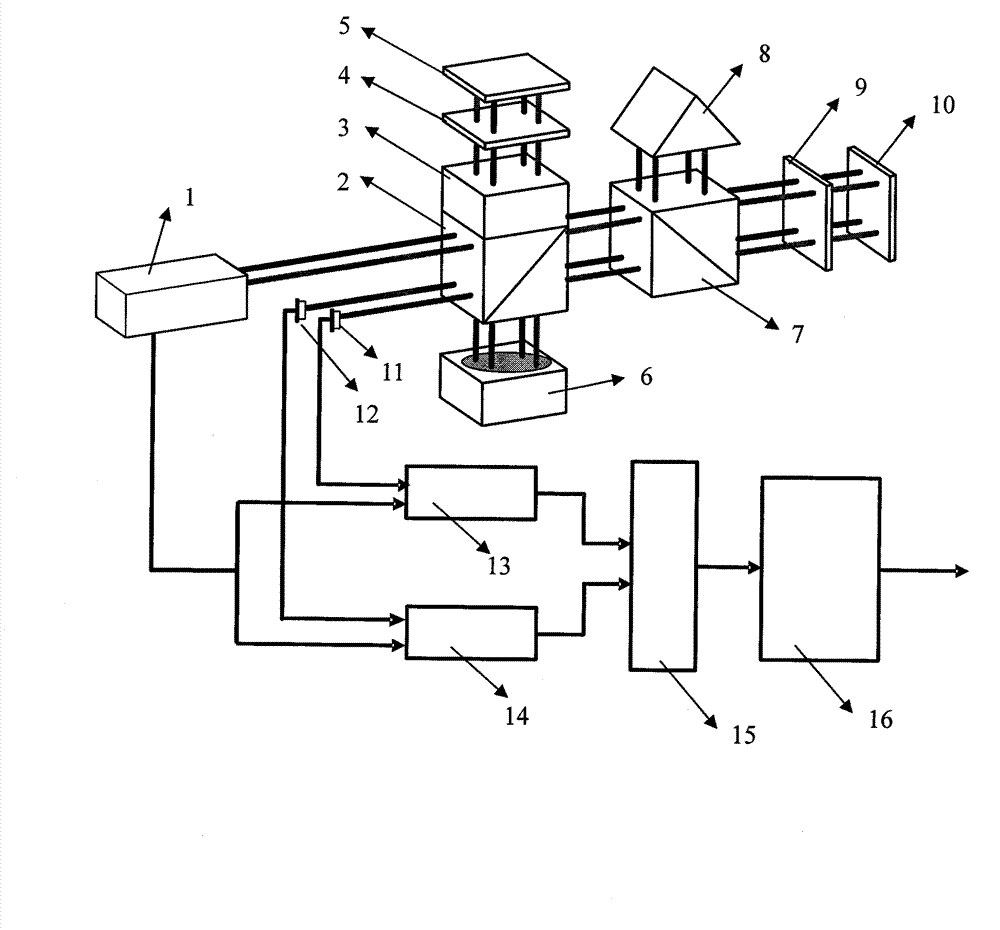
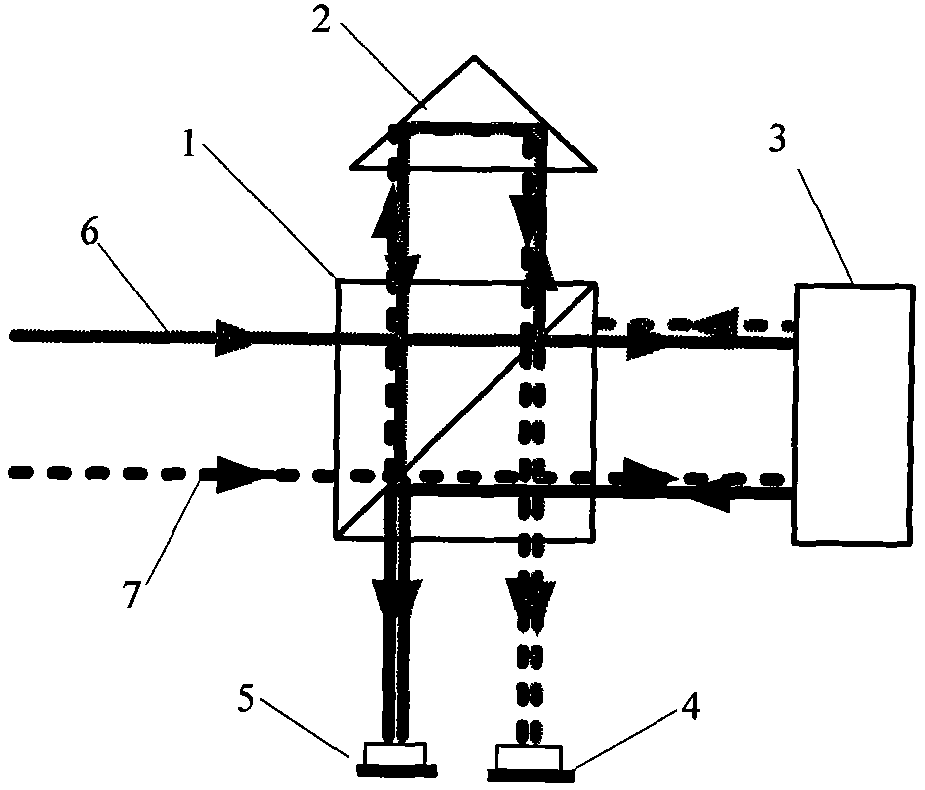
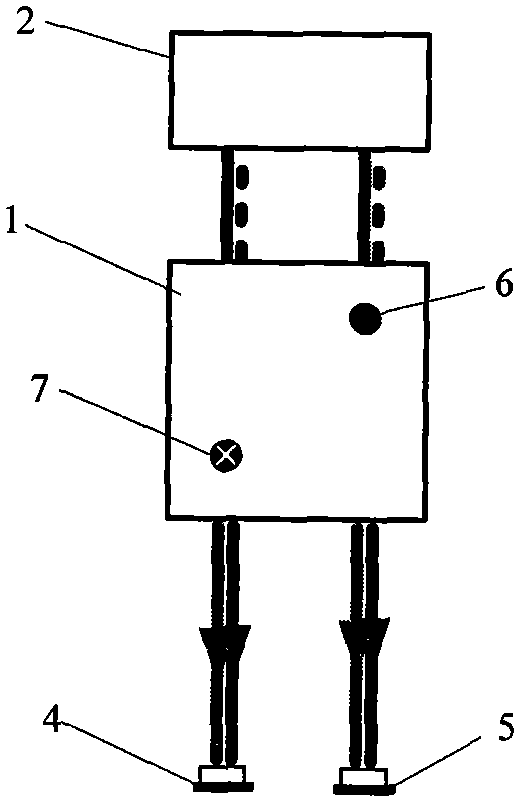
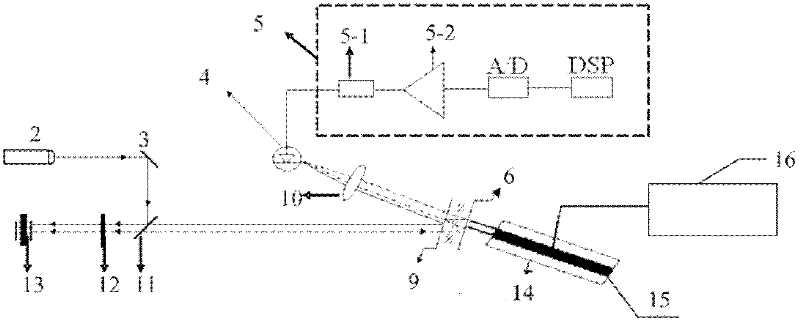
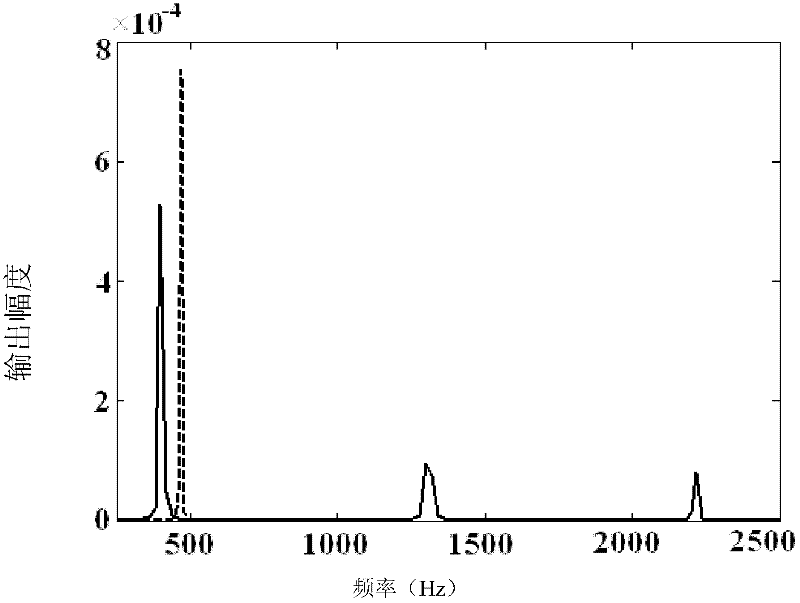
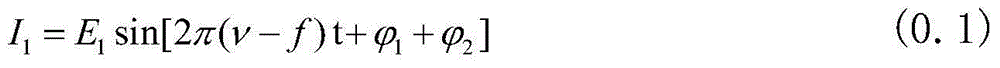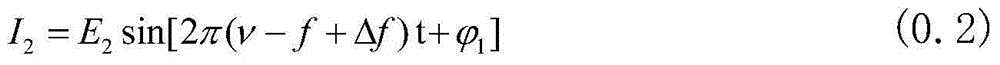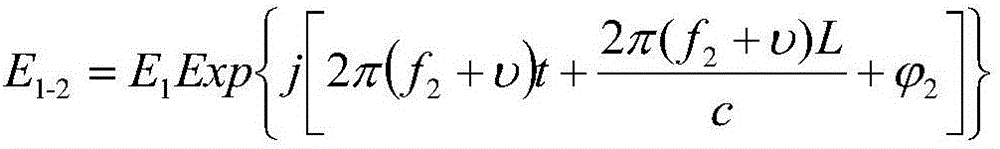Patents
Literature
89 results about "Heterodyne interferometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
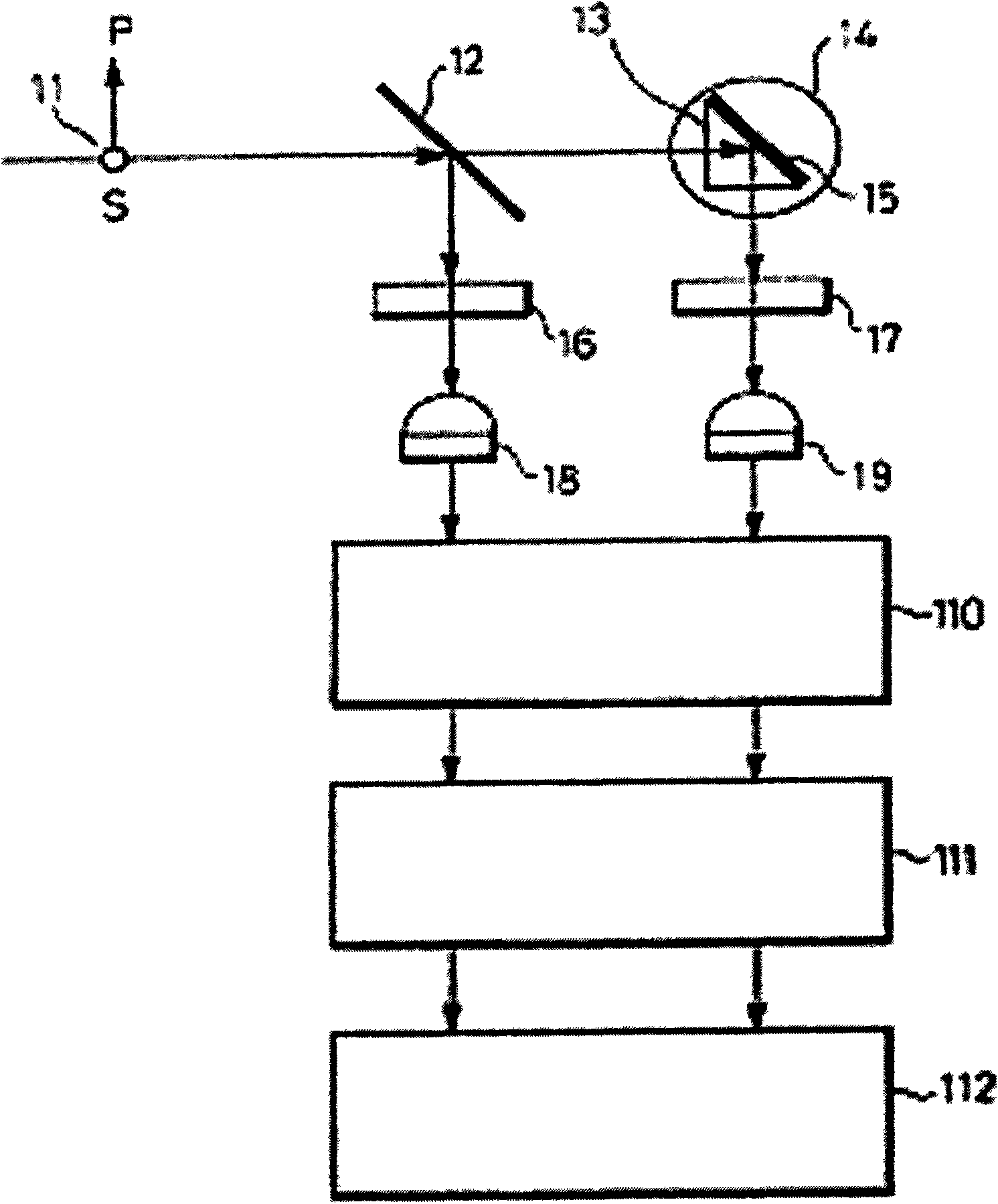
Laser heterodyne interference linearity measuring device and laser heterodyne interference linearity measuring method with six-degree-of-freedom detection
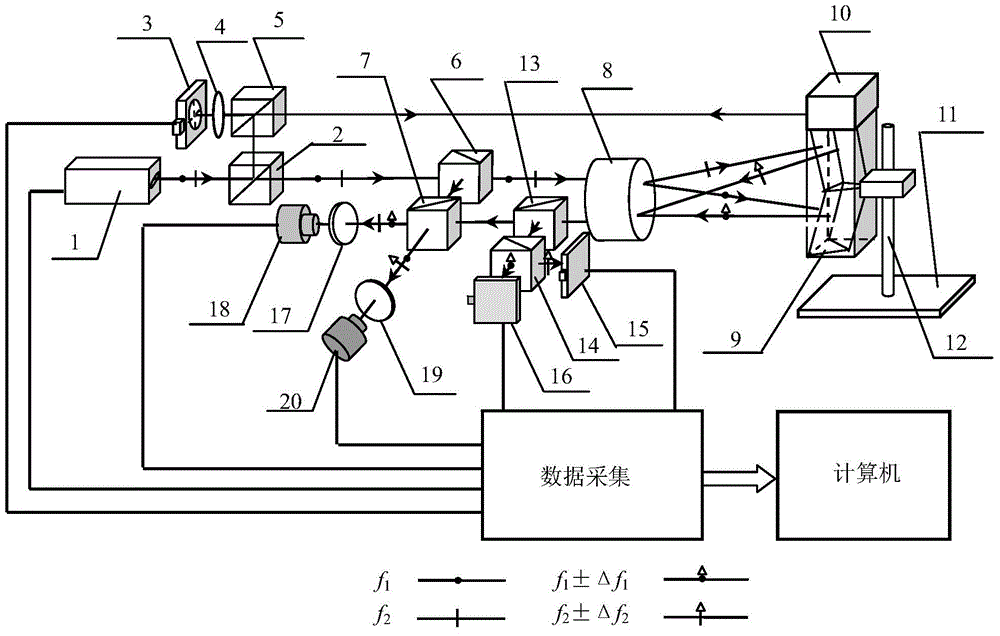
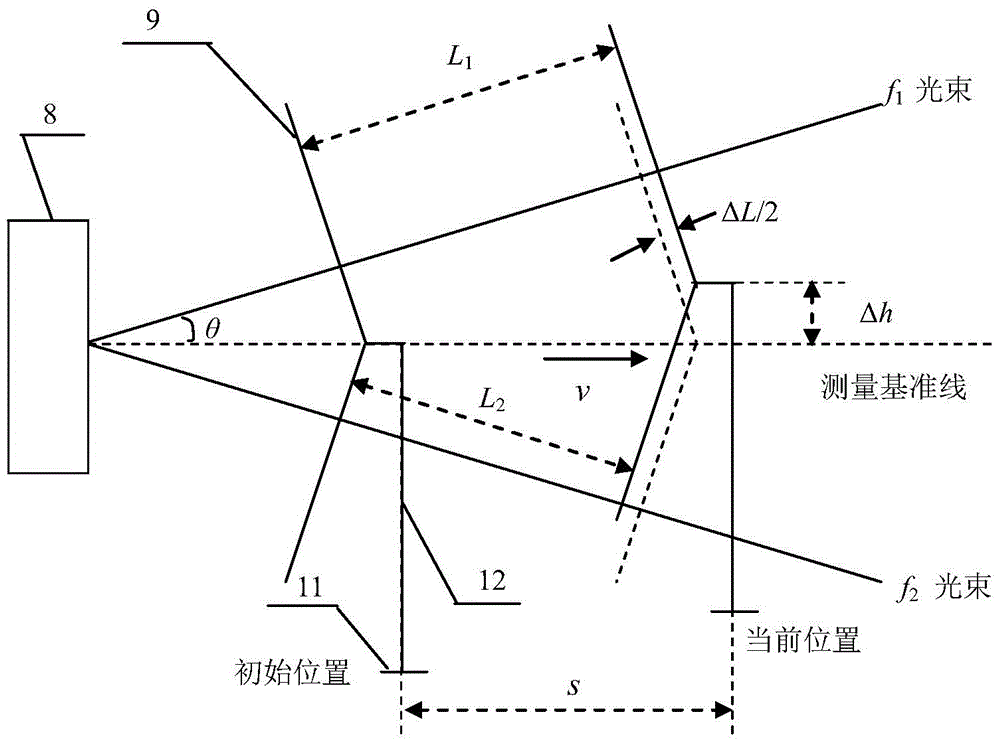
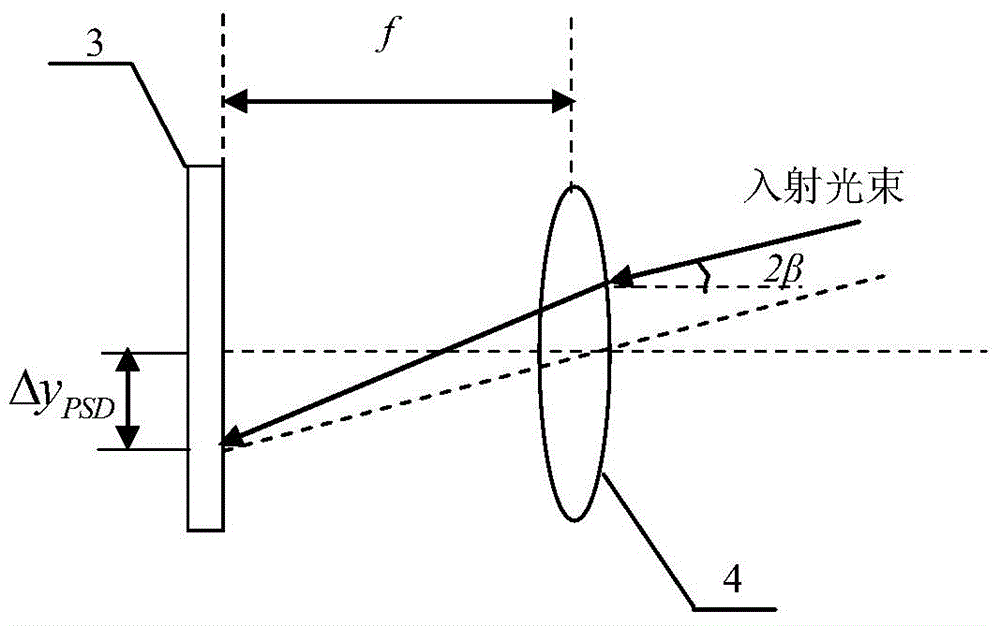
ActiveCN104634283AAchieving Simultaneous DetectionEasy to detectUsing optical meansBeam splitterMeasurement device
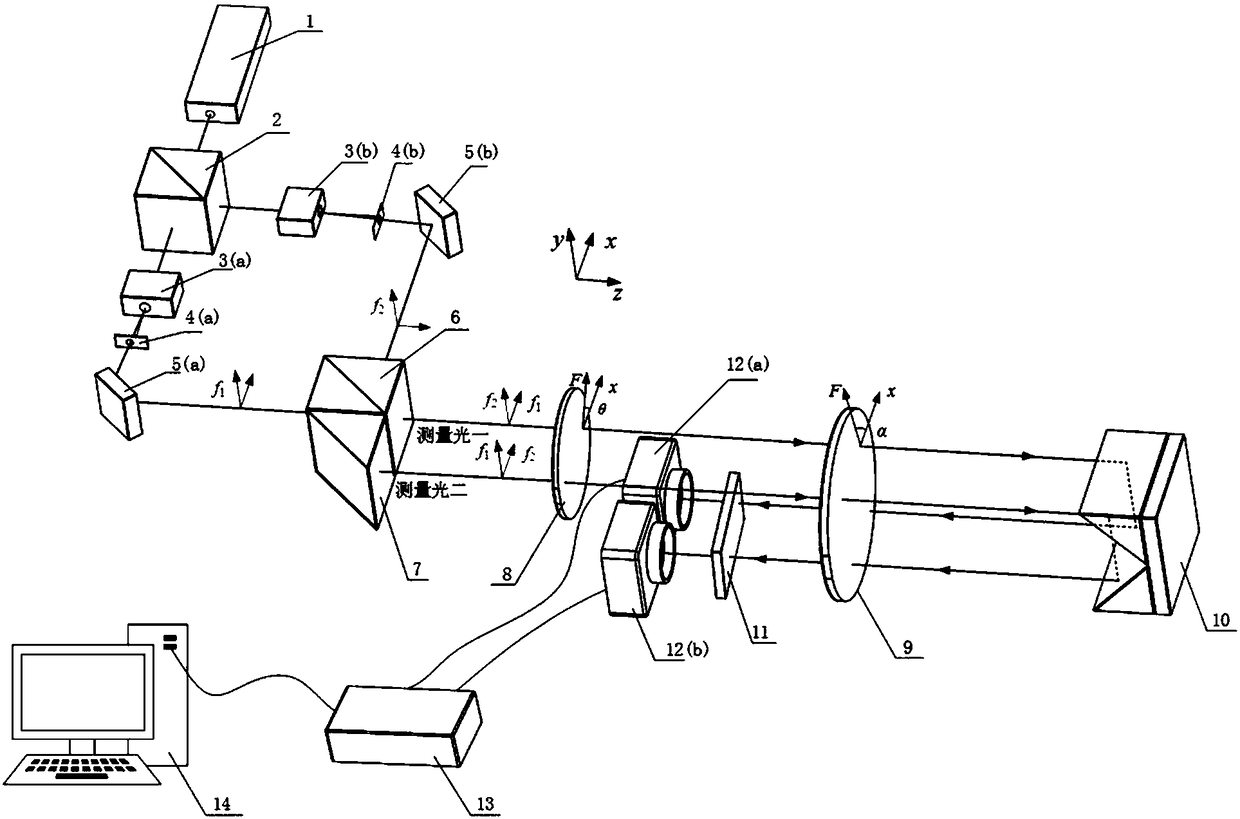
The invention discloses a laser heterodyne interference linearity measuring device and a laser heterodyne interference linearity measuring method with six-degree-of-freedom detection. The laser heterodyne interference linearity measuring device comprises a laser heterodyne interference linearity and position detection part and an error detection and compensation part; a four-degree-of-freedom error detection light path consisting of three ordinary beam splitters, a polarizing beam splitter, a plane reflecting mirror, a convex lens, a position sensitive detector and two four-quadrant detectors is additionally arranged in a light path structure of the laser heterodyne interference linearity and position detection part. By utilizing a method for integrating the laser heterodyne interferometry and a laser spot detection method, the simultaneous six-degree-of-freedom detection of a deflection angle, a pitch angle, a rolling angle, horizontal linearity, vertical linearity and linearity position of a measured object can be realized, the error compensation is carried out for the vertical linearity and the vertical linearity position, the influence of rotation error of the measured object on a measurement result in the linearity measuring process can be eliminated, and the measurement precision of the laser heterodyne interference linearity and the position of the laser heterodyne interference linearity can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
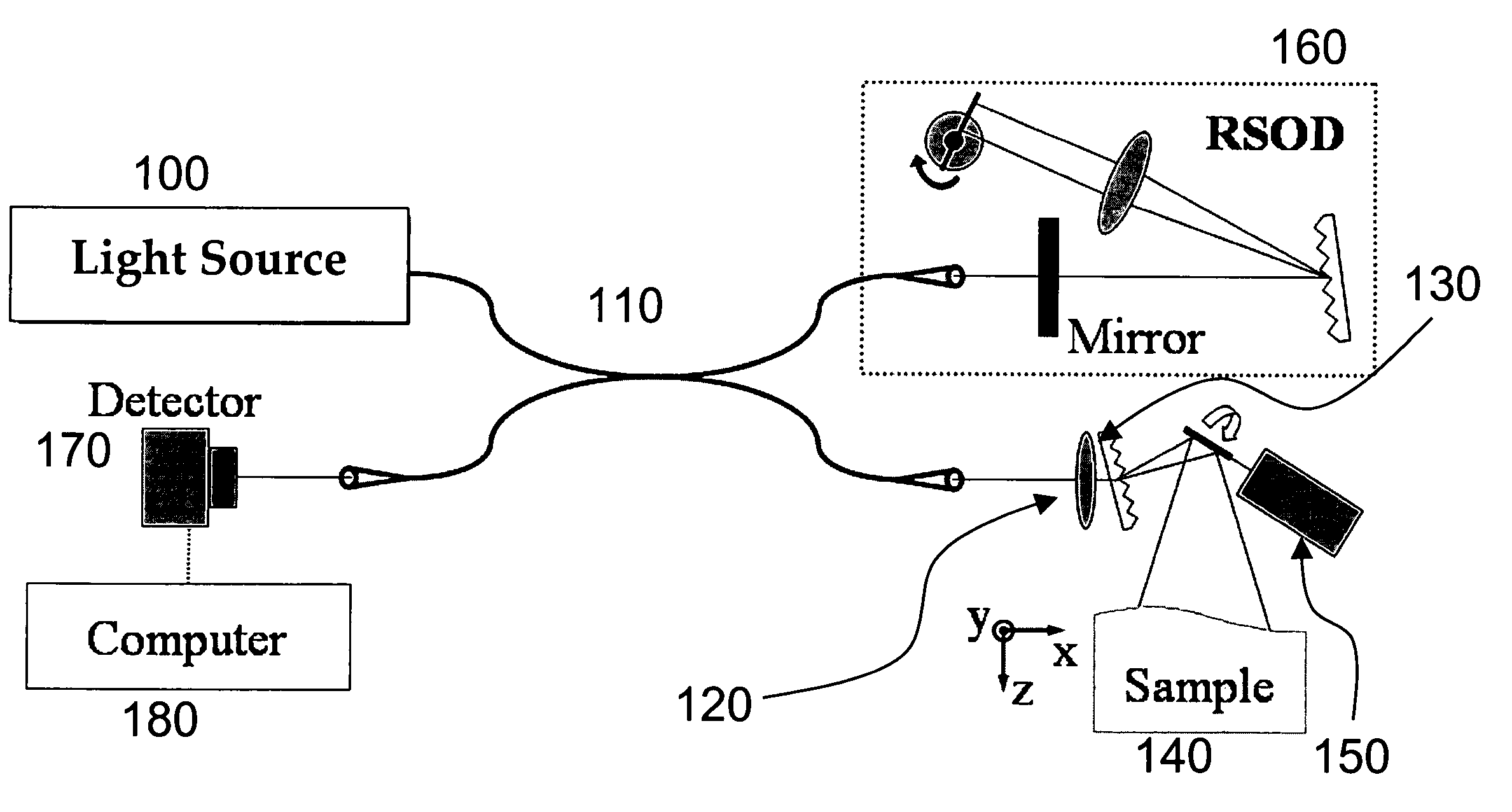
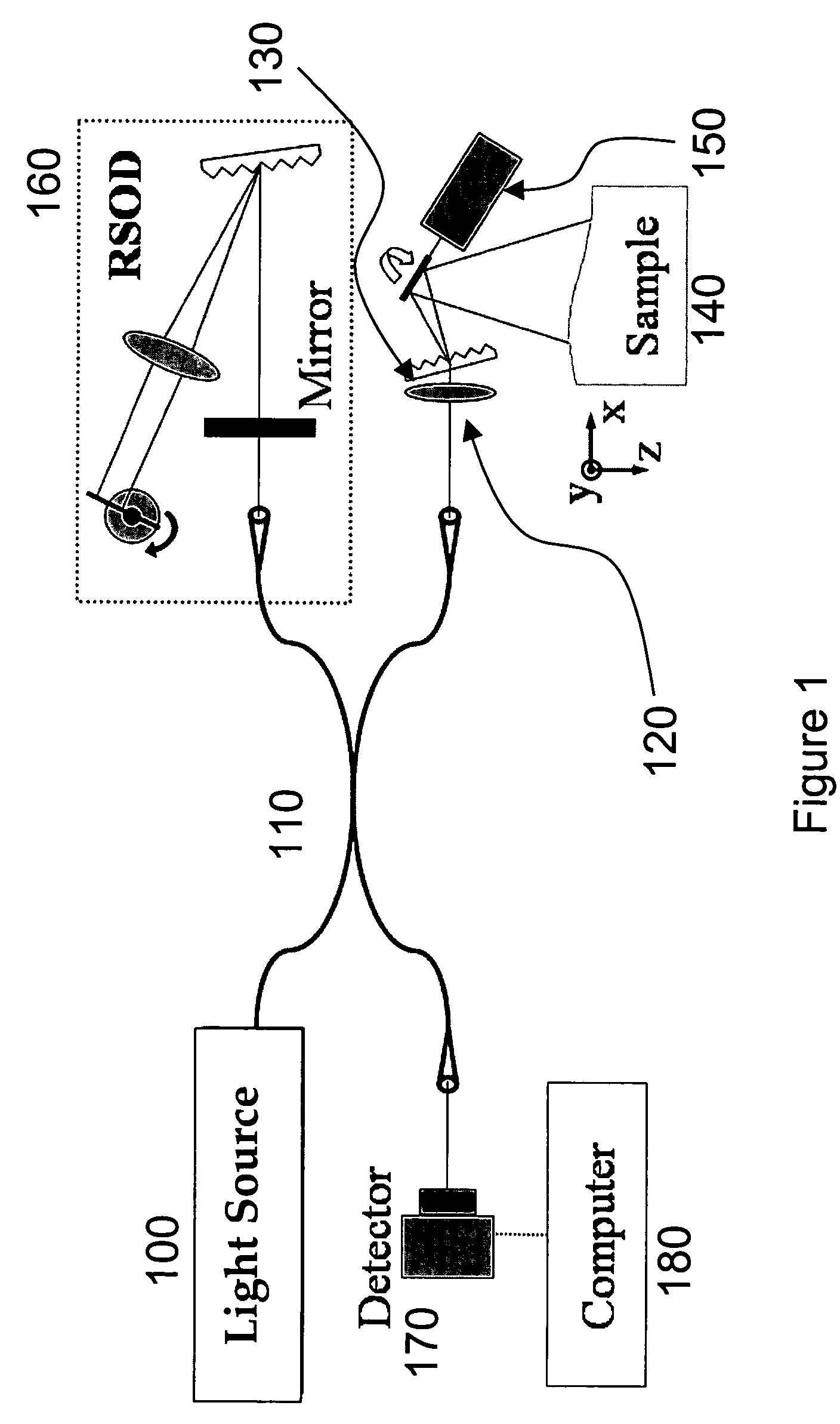
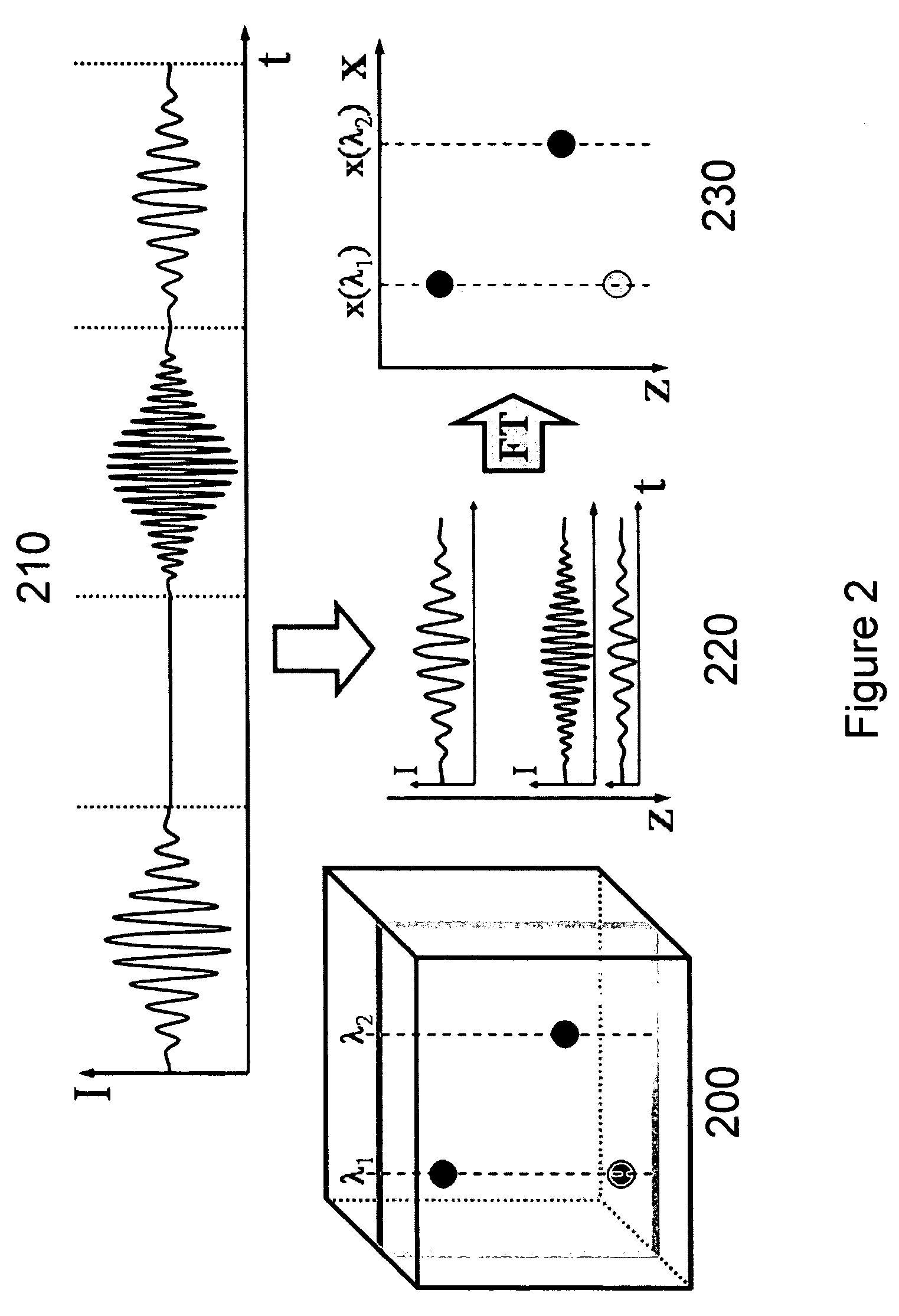
System, method and arrangement which can use spectral encoding heterodyne interferometry techniques for imaging
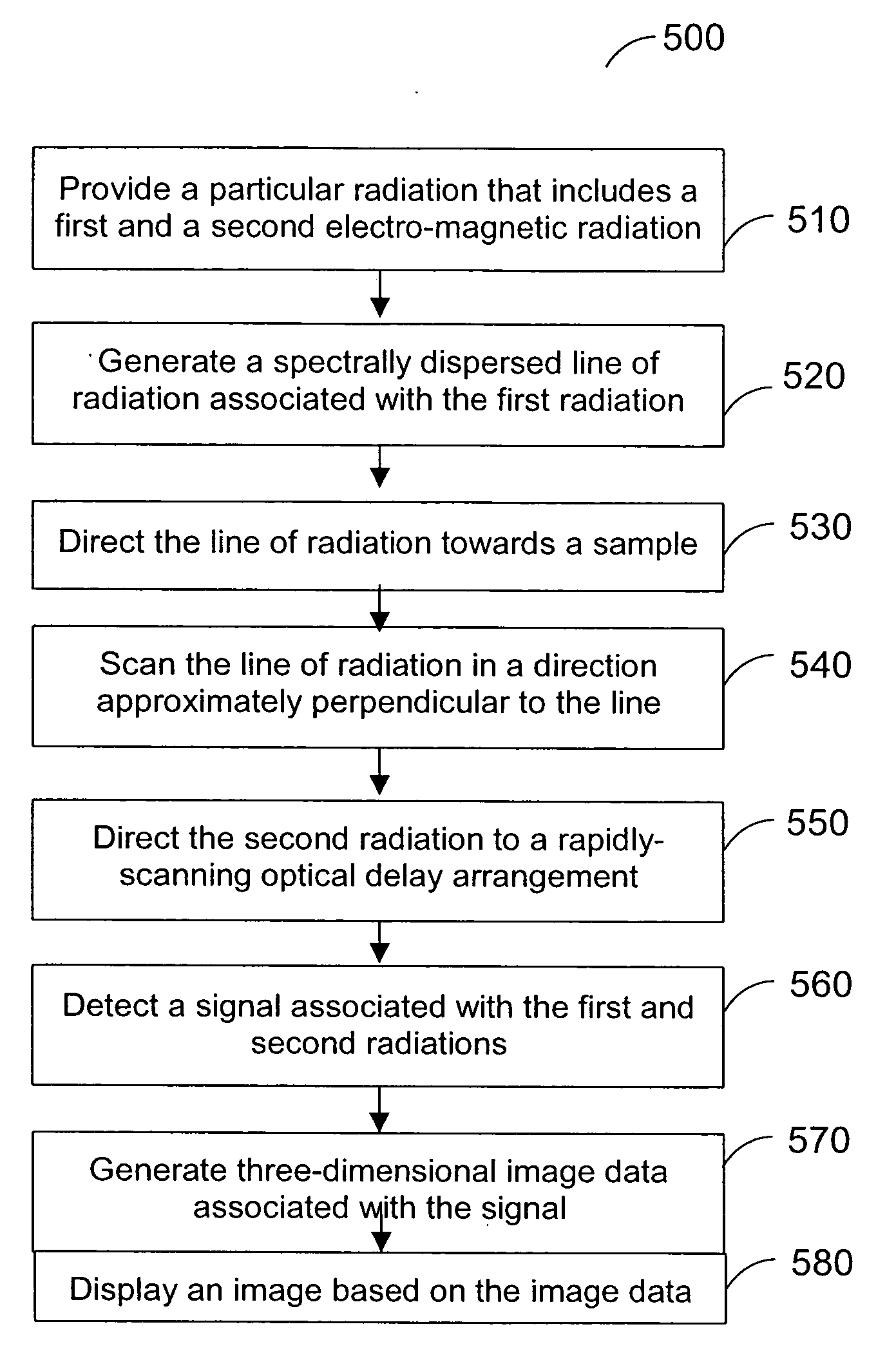
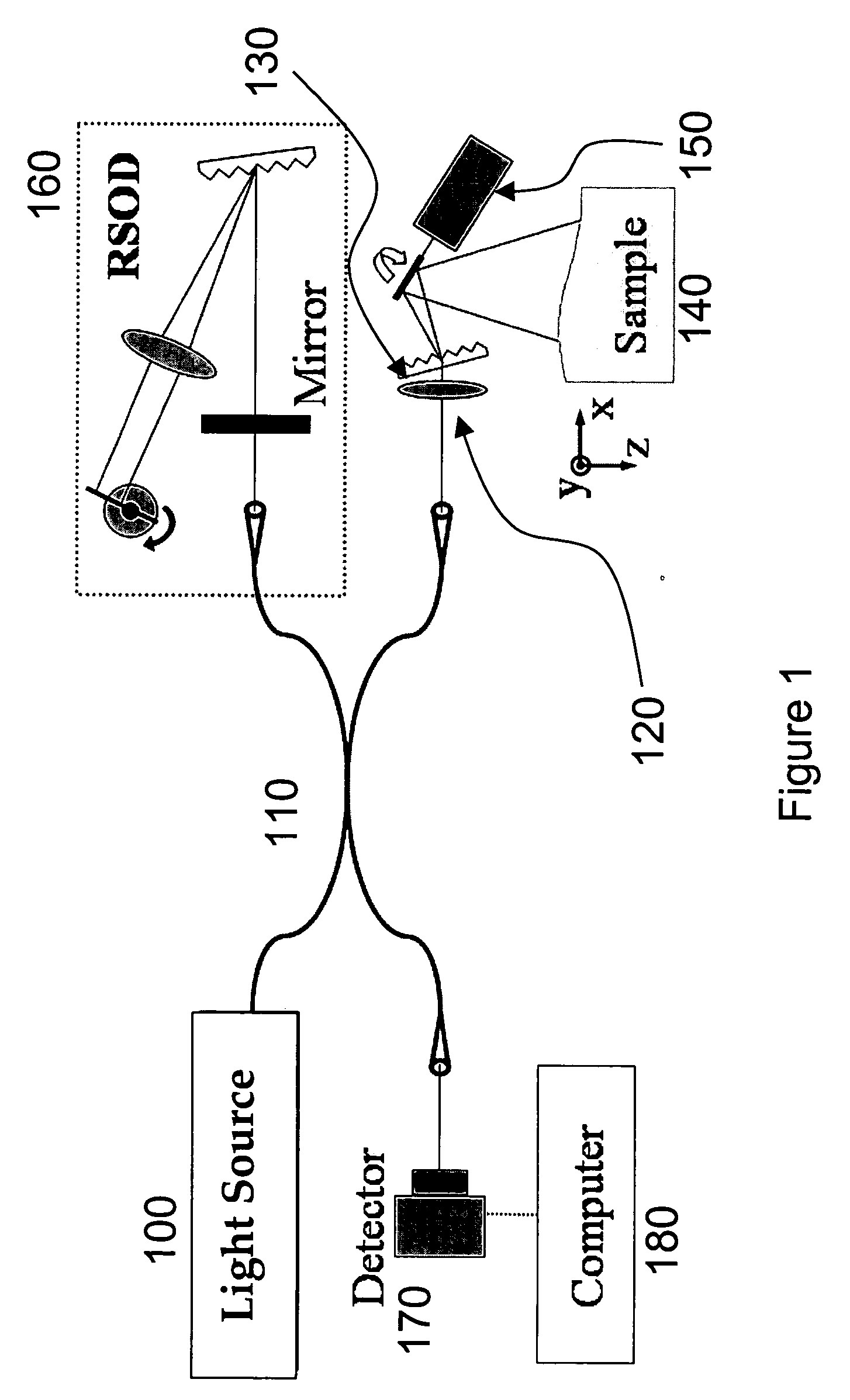
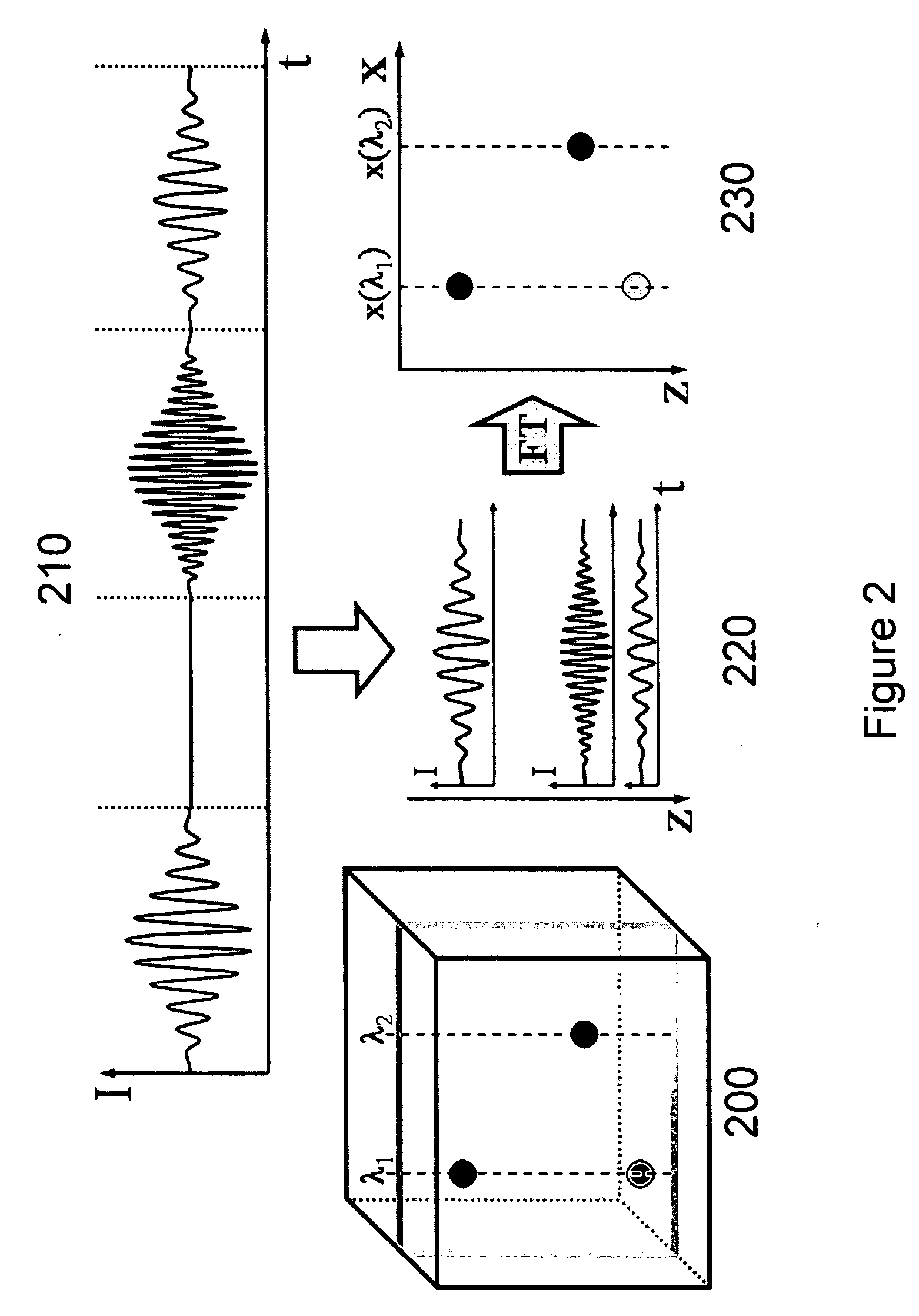
Systems, arrangements and methods for obtaining three-dimensional imaging data are provided. For example, a broadband light source can provide a particular radiation. A first electro-magnetic radiation can be focused and diffracted, and then provided to at least one sample to generate a spectrally-encoded line. A second electro-magnetic radiation may be provided to a reference, which may include a double-pass rapidly-scanning optical delay, where the first and second electro-magnetic radiations can be based on the particular radiation. An interference between a third electro-magnetic radiation (associated with the first electro-magnetic radiation) and a fourth electro-magnetic radiation (associated with the second electro-magnetic radiation) can be detected. The spectrally-encoded line may be scanned over the sample in a direction approximately perpendicular to the line. Image data containing three-dimensional information can then be obtained based on the interference. The exemplary imaging methods and systems can be used in a small fiber optic or endoscopic probe.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
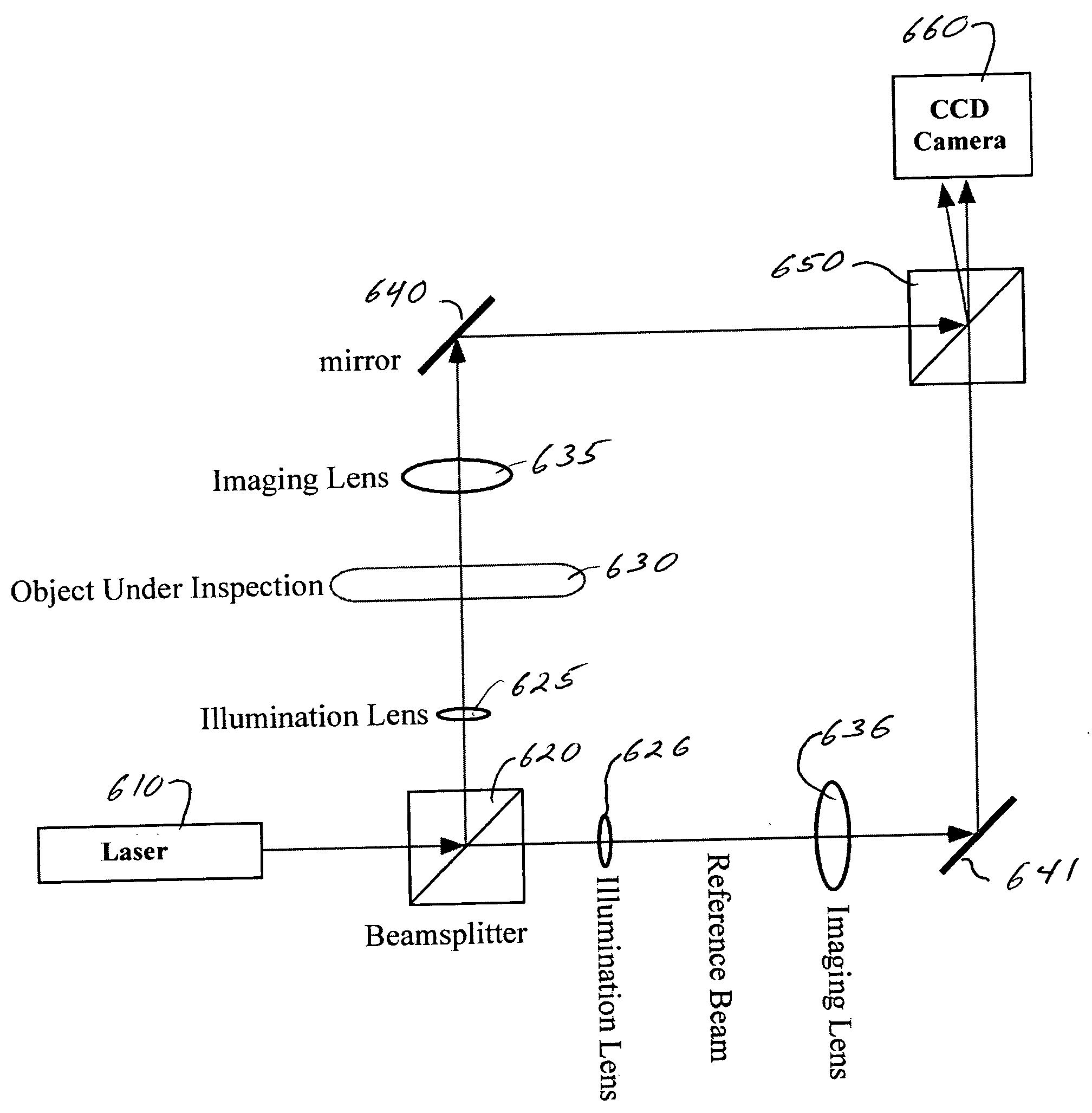
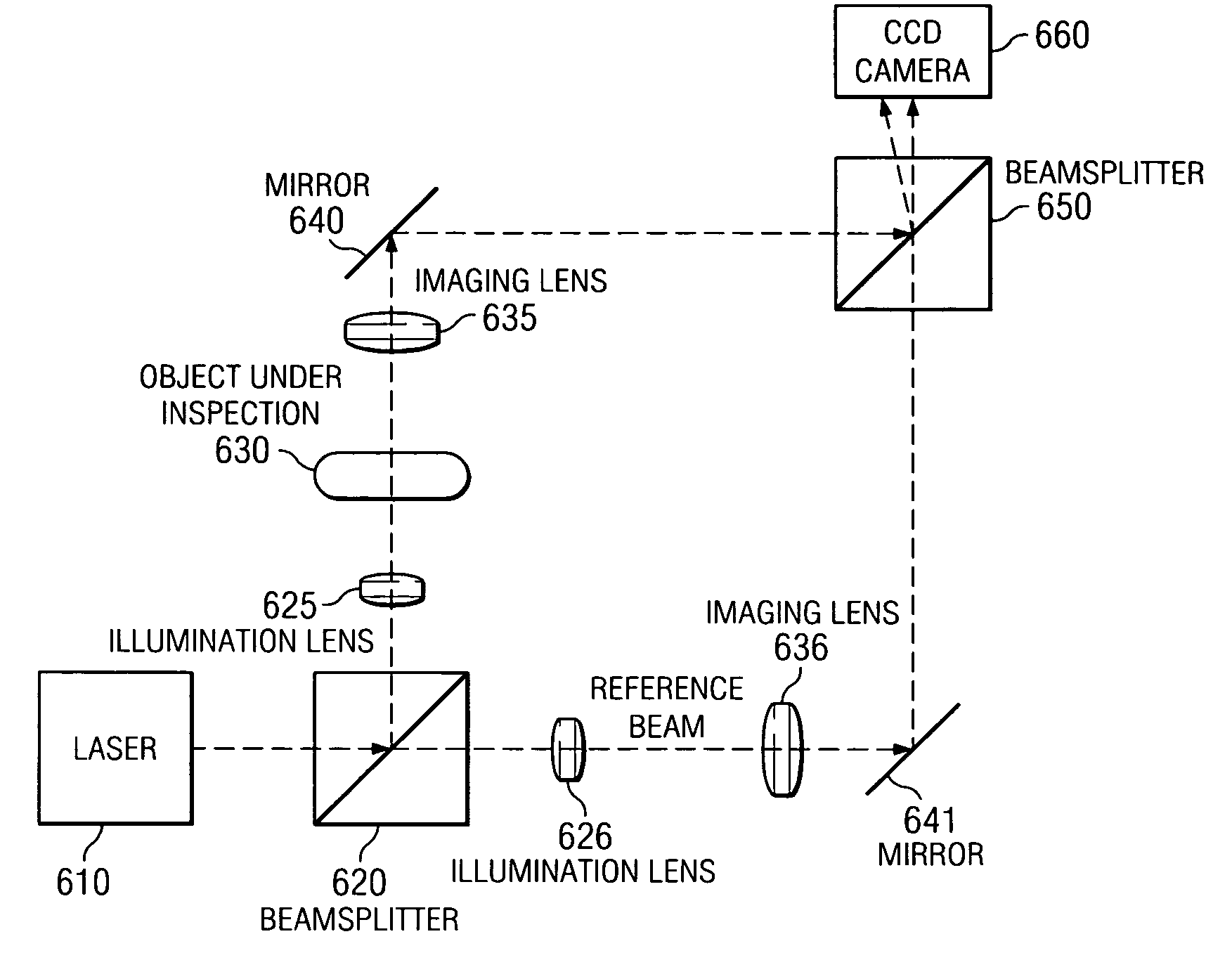
Spatial-heterodyne interferometry for reflection and transmission (SHIRT) measurements
InactiveUS20050046858A1Holographic object characteristicsUsing optical meansLight beamReference beam
Systems and methods are described for spatial-heterodyne interferometry for reflection and transmission (SHIRT) measurements. A method includes digitally recording a first spatially-heterodyned hologram using a first reference beam and a first object beam; digitally recording a second spatially-heterodyned hologram using a second reference beam and a second object beam; Fourier analyzing the digitally recorded first spatially-heterodyned hologram to define a first analyzed image; Fourier analyzing the digitally recorded second spatially-heterodyned hologram to define a second analyzed image; digitally filtering the first analyzed image to define a first result; and digitally filtering the second analyzed image to define a second result; performing a first inverse Fourier transform on the first result, and performing a second inverse Fourier transform on the second result. The first object beam is transmitted through an object that is at least partially translucent, and the second object beam is reflected from the object.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method for eliminating or reducing nonlinearity errors in laser heterodyne interferometry
InactiveCN101893448AEliminate or substantially reduce adverse effectsEliminate or substantially reduce non-linear errorsPolarising elementsMitigation of undesired influencesLight beamOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a method for eliminating or reducing nonlinearity errors in laser heterodyne interferometry, which belongs to the technical field of light heterodyne interferometry in precision measuring technology. The method comprises a step of adding new light rays after amplitude adjustment and phase adjustment into laser beams participating in interferences, wherein the new light rays has the same frequency and amplitude as those of light signals generating the nonlinearity errors, and has reverse phases with the light signals generating the nonlinearity errors so as to counteract the interferences generated by the light signals generating the nonlinearity errors to the laser heterodyne interferometry. The method has the advantages of effectively eliminating or reducing the nonlinearity errors and improving the measurement precision.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving measurement precision by using acousto-optic device in optical heterodyne interferometry
InactiveCN101660924AEliminate or significantly reduce interfering light componentsEliminate or substantially reduce non-linear errorsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansOptoelectronicsSignal light
A method for improving measurement precision by using an acousto-optic device in optical heterodyne interferometry belongs to the field of measurement precision by using acousto-optic device in optical heterodyne interferometry in precise measurement technology. In the measurement precision by using acousto-optic device in optical heterodyne interferometry by using the acousto-optic device, by changing the polarization direction of the part light beam output during an acoustic-optic interaction process, for instance, by utilizing abnormal Gragg diffraction, the polarization direction of the first-order diffraction light with frequency converted is vertical to other light beams, particularly the polarization direction of the zero-order light with the frequency unconverted; therefore, the crosstalk light is extremely easy to be filtered. Alternatively, the polarization direction of the reference light beam can be adjusted so that the polarization direction of the reference light component in the signal light beam is vertical to the polarization direction of the reference light beam, thus leading the interference signal output by a detector to be the minimum. In conclusion, the difference among the useful light beam, the crosstalk light and the noise light on the polarization direction can be caused; by utilizing the difference, the method can inhibit the effect of the interference light effectively, so as to reduce nonlinearity, improve signal-to-noise ratio and improve the measurement precision by magnitude.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spatial-heterodyne interferometry for reflection and transmission (SHIRT) measurements
InactiveUS6999178B2Holographic object characteristicsUsing optical meansLight beamHeterodyne interferometry
Systems and methods are described for spatial-heterodyne interferometry for reflection and transmission (SHIRT) measurements. A method includes digitally recording a first spatially-heterodyned hologram using a first reference beam and a first object beam; digitally recording a second spatially-heterodyned hologram using a second reference beam and a second object beam; Fourier analyzing the digitally recorded first spatially-heterodyned hologram to define a first analyzed image; Fourier analyzing the digitally recorded second spatially-heterodyned hologram to define a second analyzed image; digitally filtering the first analyzed image to define a first result; and digitally filtering the second analyzed image to define a second result; performing a first inverse Fourier transform on the first result, and performing a second inverse Fourier transform on the second result. The first object beam is transmitted through an object that is at least partially translucent, and the second object beam is reflected from the object.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Spatial-heterodyne interferometry for transmission (SHIFT) measurements
InactiveUS20050046857A1Holographic object characteristicsUsing optical meansFourier transform on finite groupsLight beam
Systems and methods are described for spatial-heterodyne interferometry for transmission (SHIFT) measurements. A method includes digitally recording a spatially-heterodyned hologram including spatial heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis using a reference beam, and an object beam that is transmitted through an object that is at least partially translucent; Fourier analyzing the digitally recorded spatially-heterodyned hologram, by shifting an original origin of the digitally recorded spatially-heterodyned hologram to sit on top of a spatial-heterodyne carrier frequency defined by an angle between the reference beam and the object beam, to define an analyzed image; digitally filtering the analyzed image to cut off signals around the original origin to define a result; and performing an inverse Fourier transform on the result.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Four-channel detection technology based method for inter-satellite displacement measurement through weak-light phase lock and device for realizing same
ActiveCN102419441ARealize high-precision phase-locked trackingImprove anti-interference abilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationLight beamOptoelectronics
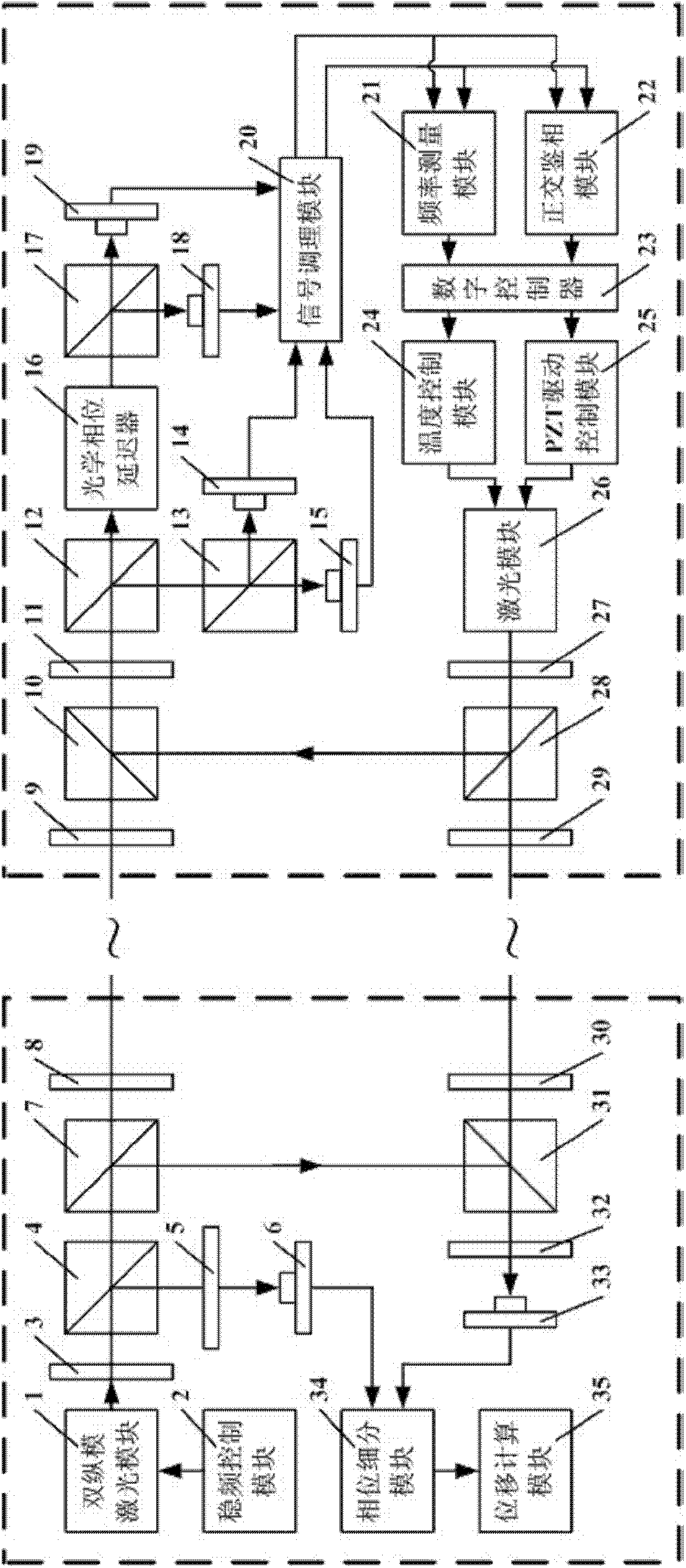
The invention relates to a four-channel detection technology based method for inter-satellite displacement measurement through weak-light phase locking and a device for realizing the same, belongs to the field of optics, and solves the problem that light beam energy can hardly meet the measurement requirement in the inter-satellite displacement measurement of ultralong distance. The method is used for measuring a displacement between two satellites, both of which are respectively called as a target end and a measurement end, and comprises the steps of: outputting a laser containing two longitudinal mode laser components with mutually vertical polarization states by using a double longitudinal mode laser module at the measurement end; regulating the laser and then transmitting the regulated laser to the target end as a measurement laser, and forming a reference signal Sref; after processing the measurement laser at the target end, combining the processed measurement laser with a laser transmitted by a laser module at the target end; returning a formed return laser to the measurement end; combining the return laser with the reference laser and performing frequency mixing to obtain ameasurement signal Smeas obtained through a heterodyne interferometry; and after respectively inputting the reference signal Sref and the measurement signal Smeas into a phase subdivision module, resolving the displacement of the target end relative to the measurement end according to an accumulated phase value by a displacement calculating module.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
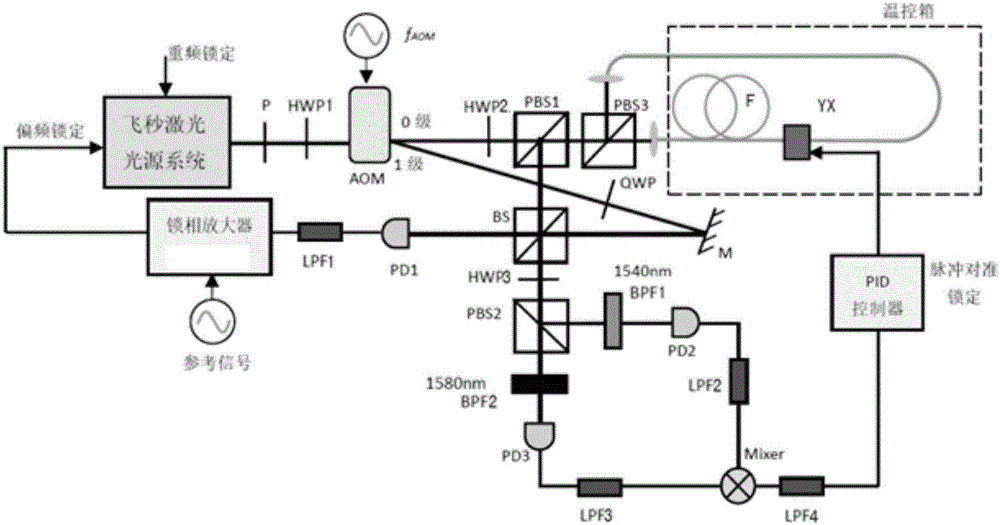
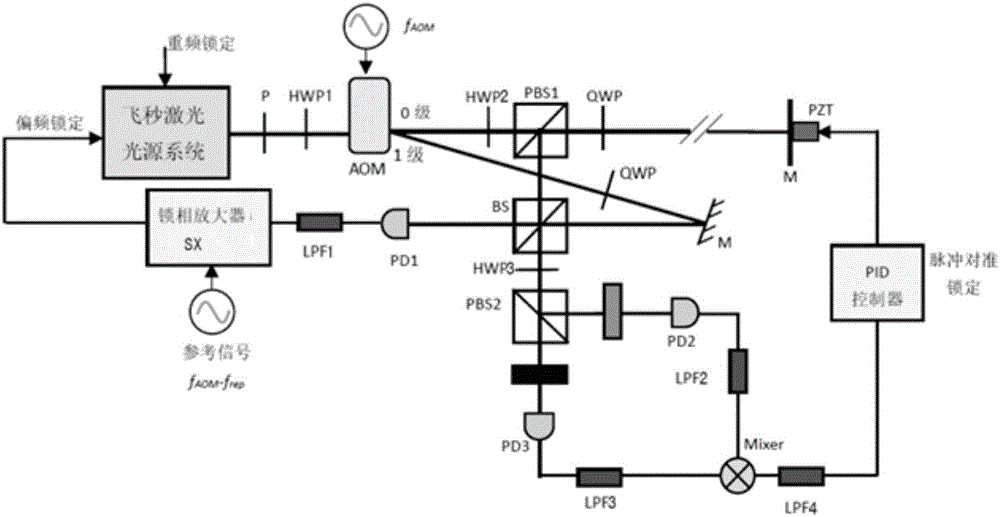
Femtosecond laser carrier envelope offset frequency lock system based on heterodyne interferometric method
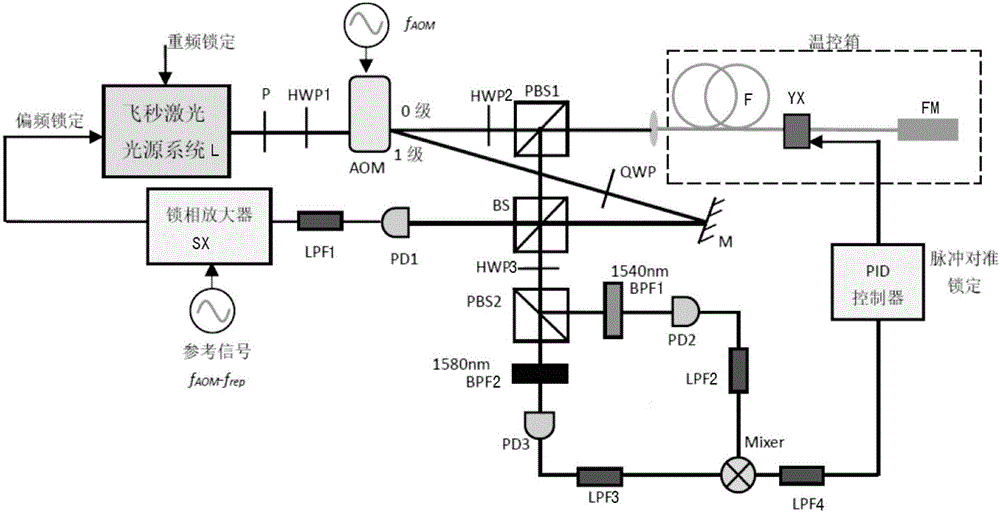
The invention relates to a femtosecond laser carrier envelope offset frequency lock system based on a heterodyne interferometric method. The system is characterized by comprising a femtosecond laser light source system, an acousto-optic modulator, a controllable optical path retardation device, a light splitting prism, a first photoelectric detector, a phase lock amplifier, a phase difference voltage conversion device and a PID controller. Heterodyne interferometry can be conducted on first-level phase-shift diffraction light modulated by the acousto-optic modulator and zero-level diffraction light which is not modulated, and after mixing of interference signals with different wavelengths, direct-current level lock pulse envelope alignment is achieved; optical frequency comb envelope offset frequency is locked by means of interference signal phase, the linear process does not exist, high non-linear optical fibers, frequency doubling crystals and the like are not needed, and the system is simple in structure and low in requirement for laser energy.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Dual-wavelength superheterodyne-interference wide-range high-precision real-time displacement measuring system and method
ActiveCN107192336ALarge rangeImprove real-time performanceUsing optical meansSignal processing circuitsPolarizer
The invention discloses a dual-wavelength superheterodyne-interference wide-range high-precision real-time displacement measuring system and method. The system is composed of two lasers between which the wavelength difference is deltalambda, three polarization splitting prisms, four splitting prisms, two acousto-optic modulators, four 1 / 4 waveplates, five planar mirrors, three Polaroids, a super-narrowband filter plate, two large-bandwidth transimpedance photoelectric detectors, two low-bandwidth high-sensitivity photoelectric detectors, a reference reflector, a measured reflector, a signal processing circuit and a host computer. According to the invention, a synthesized wavelength interference signal generated by dual wavelengths is used to improve the measuring range of the system, so that the measuring range of the system is greater than the range of single-wavelength interference; a superheterodyne interference method is used to demodulate and filter output signals, the phase of the synthesis wavelength can be measured directly, and real-time measurement is realized; and the super-narrowband filter plate is used to collect single-wavelength interference signals, and the precision of single-wavelength interference measurement is ensured while the measuring range is widened.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
System, method and arrangement which can use spectral encoding heterodyne interferometry techniques for imaging
ActiveUS20060270929A1High-speed imagingMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterFiberElectromagnetic radiation
Systems, arrangements and methods for obtaining three-dimensional imaging data are provided. For example, a broadband light source can provide a particular radiation. A first electro-magnetic radiation can be focused and diffracted, and then provided to at least one sample to generate a spectrally-encoded line. A second electro-magnetic radiation may be provided to a reference, which may include a double-pass rapidly-scanning optical delay, where the first and second electro-magnetic radiations can be based on the particular radiation. An interference between a third electro-magnetic radiation (associated with the first electro-magnetic radiation) and a fourth electro-magnetic radiation (associated with the second electro-magnetic radiation) can be detected. The spectrally-encoded line may be scanned over the sample in a direction approximately perpendicular to the line. Image data containing three-dimensional information can then be obtained based on the interference. The exemplary imaging methods and systems can be used in a small fiber optic or endoscopic probe.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
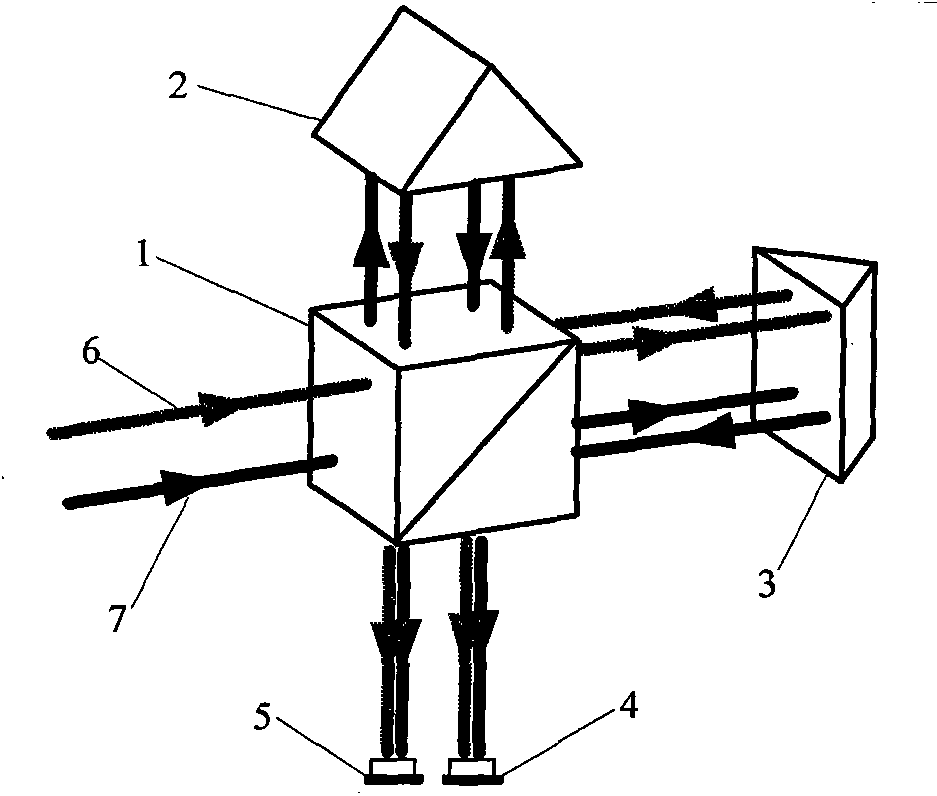
Common-optical-path laser heterodyne interference method roll angle high-precision measuring device and method
ActiveCN108168465AReduce distractionsReduce optical path differenceUsing optical meansPhase differenceBeam splitting
The invention belongs to the field of photoelectric measurement of a roll angle, in particular to a common-optical-path laser heterodyne interference method roll angle high-precision measuring device.The measuring device includes a single frequency stabilized laser, a depolarization beam splitting prism, a polarization beam splitting prism, and a right angle prism; an acousto-optic modulator anda reflector are sequentially arranged on the transmission optical axis and the reflection optical axis of the depolarization beam splitting prism; the second exit surface of the polarization beam splitting prism is sequentially provided with a quarter wave plate, a half-wave plate and a reflector, and a polarization analyzer is further arranged on the reflection optical axis of the reflector, a first photoelectric detector and a second photoelectric detector are arranged in the exit direction of the polarization analyzer; the first photoelectric detector and the second photoelectric detector are connected with a phase difference detector, and the phase difference detector is connected with a computer. The two measuring light rays in the measuring device are opposite to the phase shift generated by the same rolling, the measuring resolution is improved, the optical path difference of the two light beams is small, the influence of environmental factors is small, and the measurement result is accurate.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Confocal-scanning microscopic imaging method and system based on laser heterodyne interferometry
ActiveCN104359862ASame polarization directionImprove beat frequency efficiencyPhase-affecting property measurementsConfocal scanning microscopyFluorescence
The invention discloses a confocal microscopic imaging system based on the laser heterodyne interferometry. The confocal microscopic imaging system is characterized in that on the basis of a microscope optical system and a scanning part of the existing laser confocal microscope, a frequency-shifting part is added, and accurate measurement is realized by combination of the optical heterodyne interferometry. The confocal microscopic imaging system disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the ultrahigh lateral resolution of a confocal scanning microscope is fully utilized, and simultaneously accurate phase information is acquired for replacing intensity information, so that not only is the axial resolution increased, but also a series of problems brought by use of a fluorescent dye are avoided; and a transparent phase object can be measured under the condition without marks.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPTO MEDIC TECH CO LTD
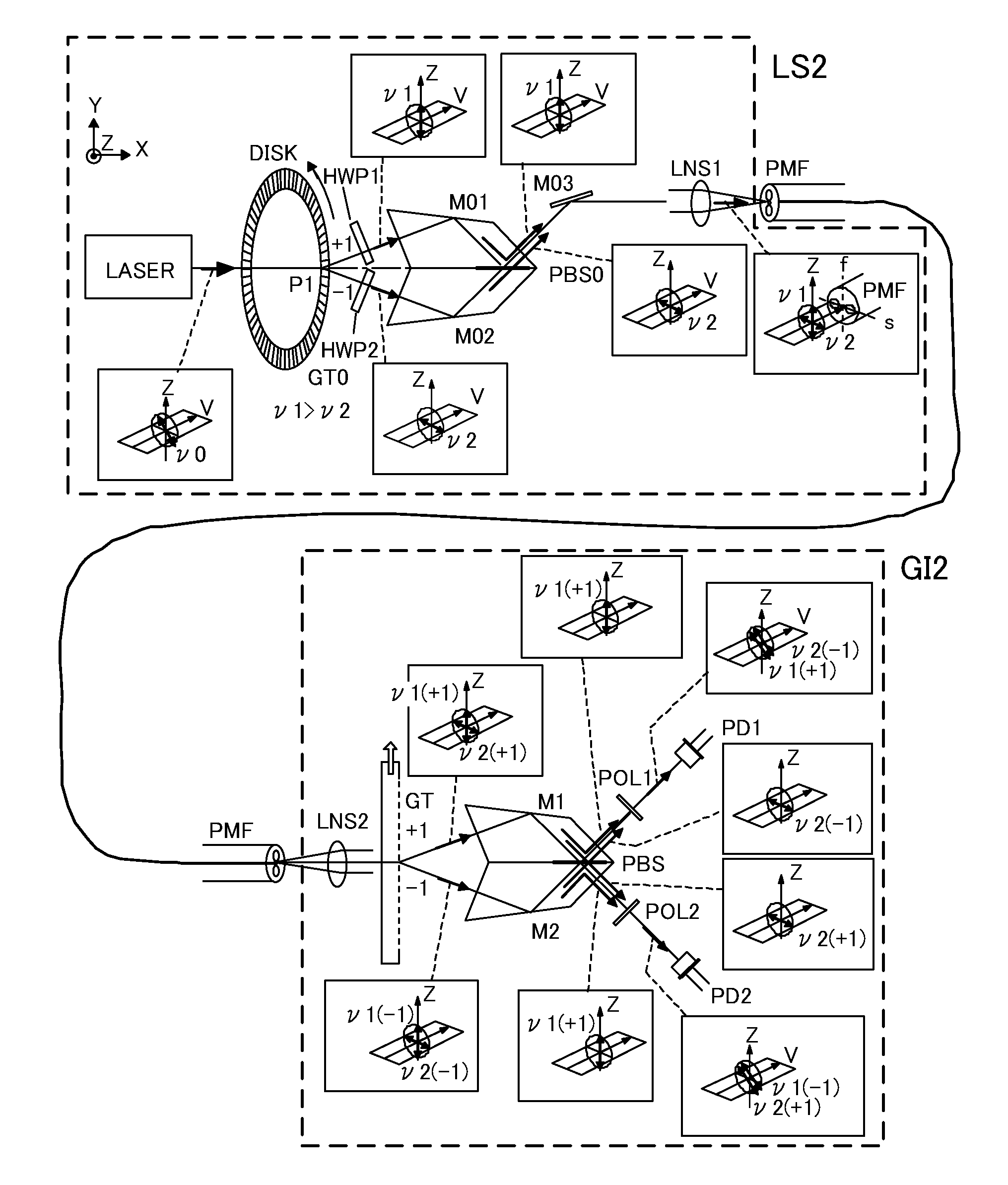
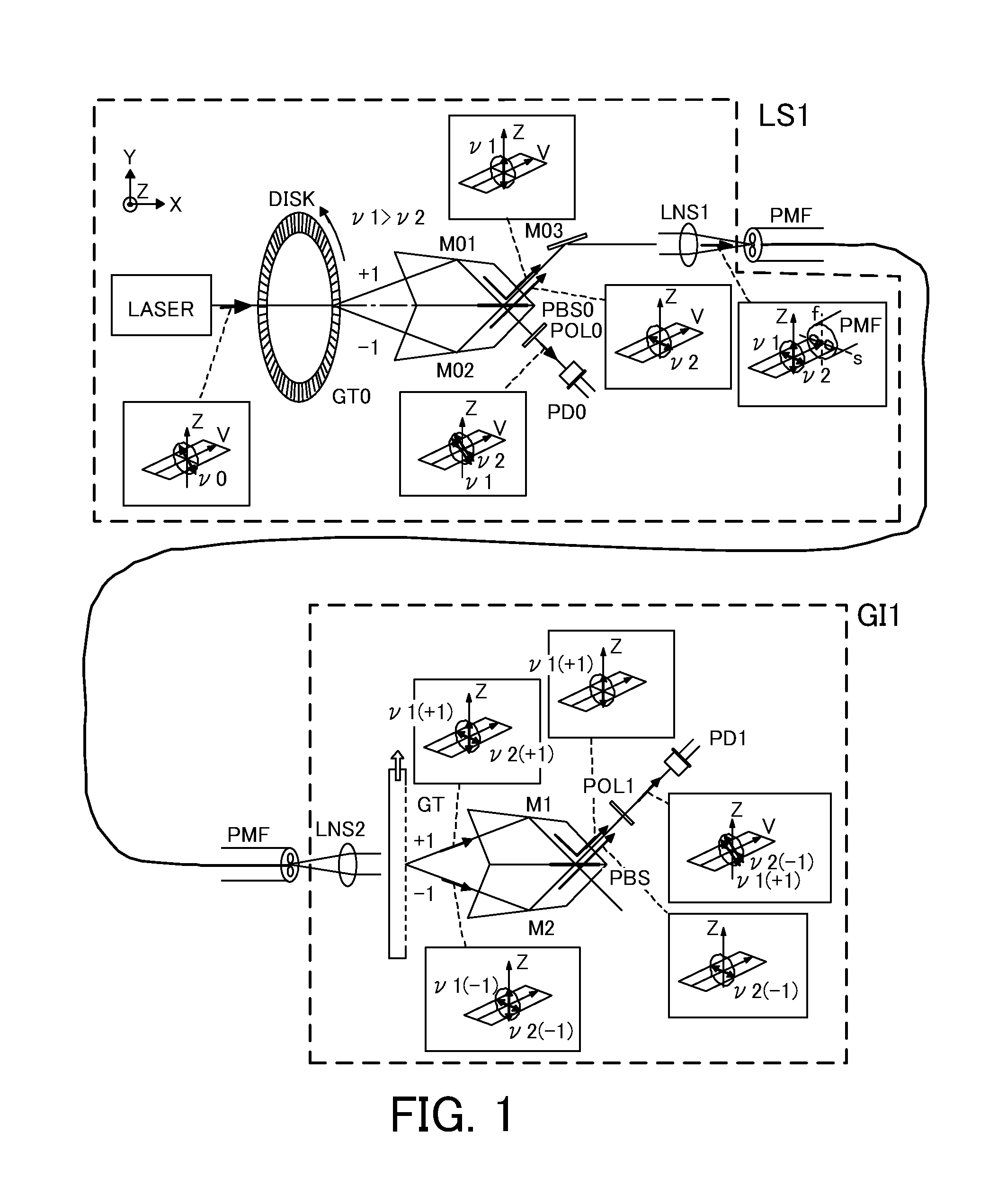
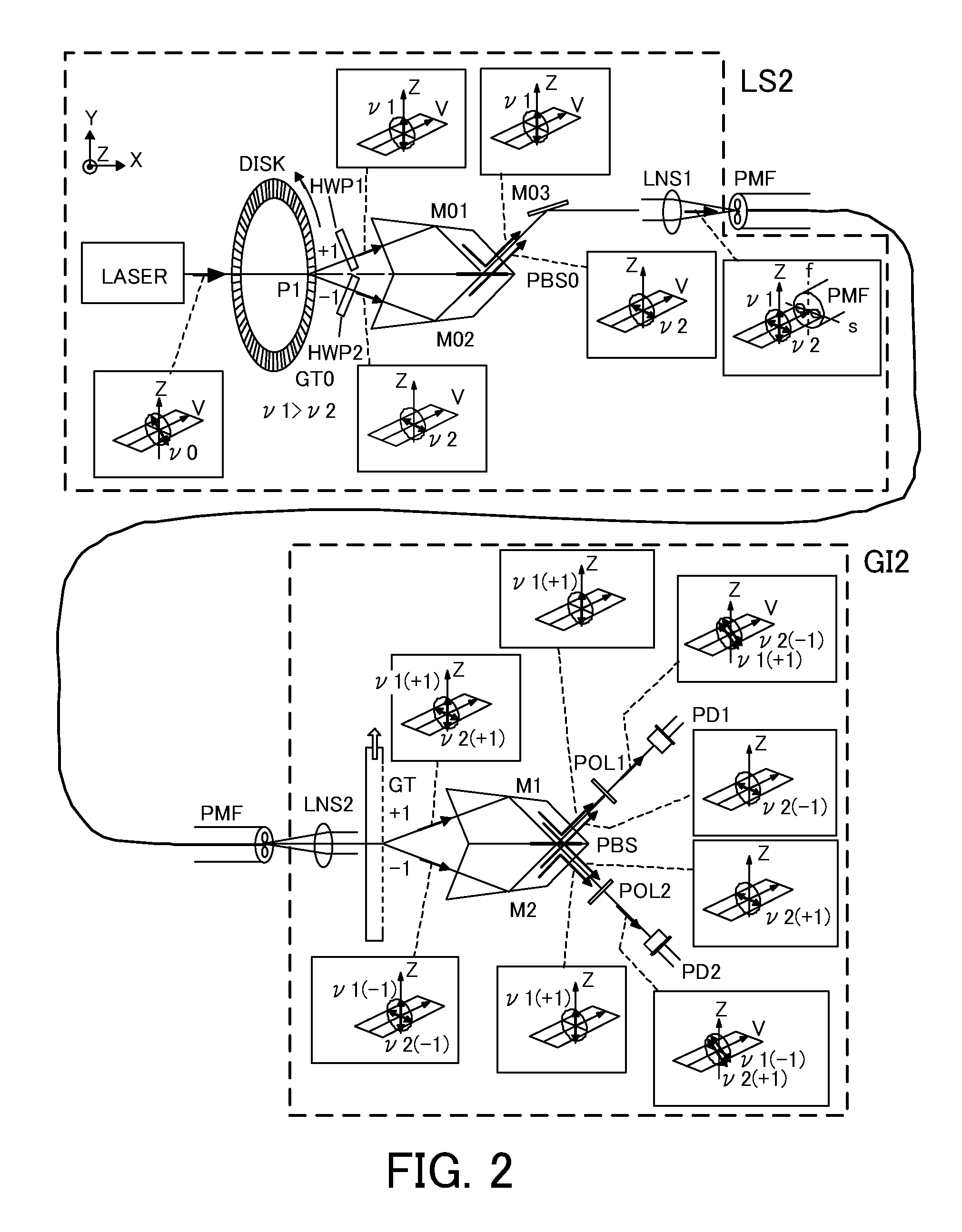
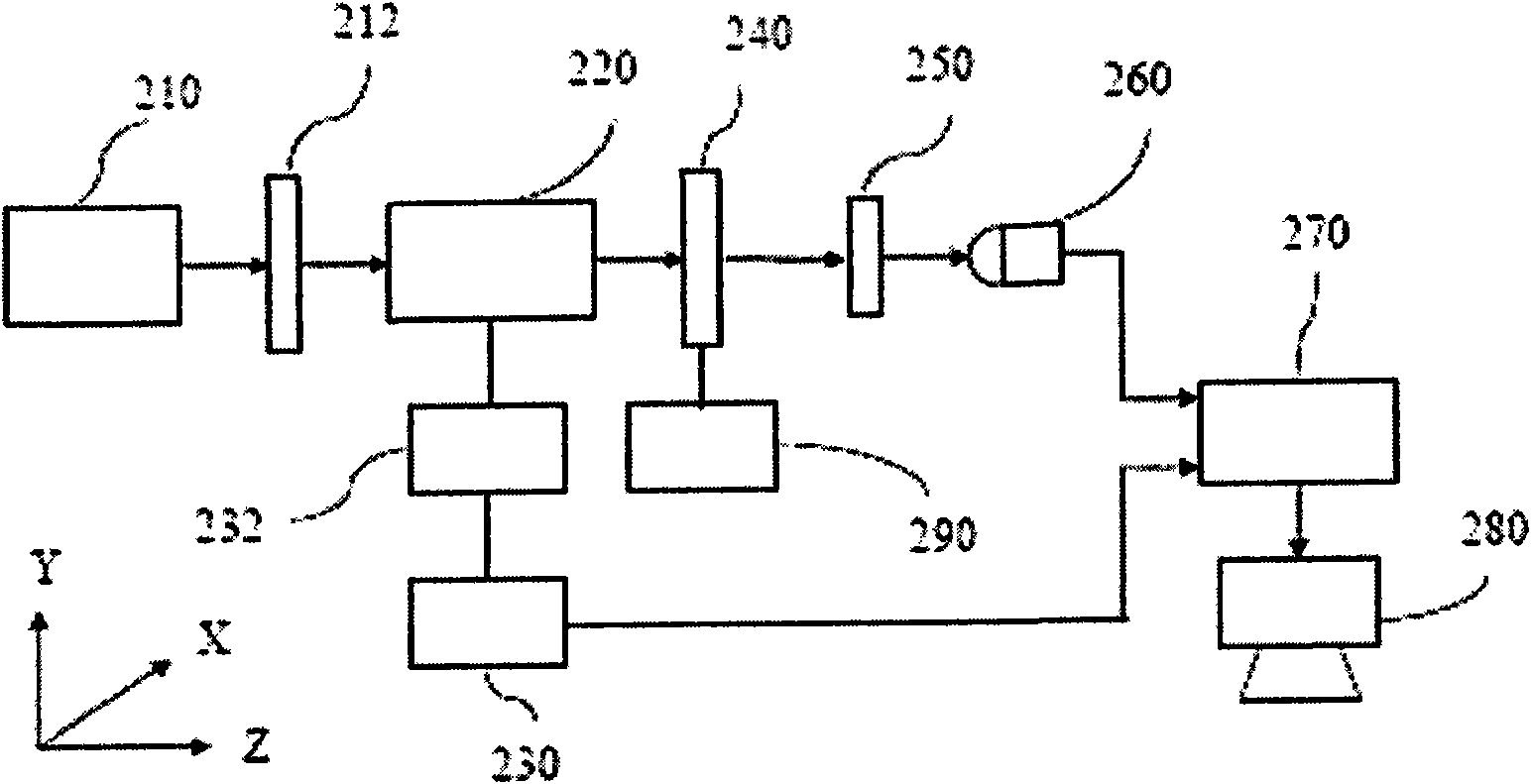
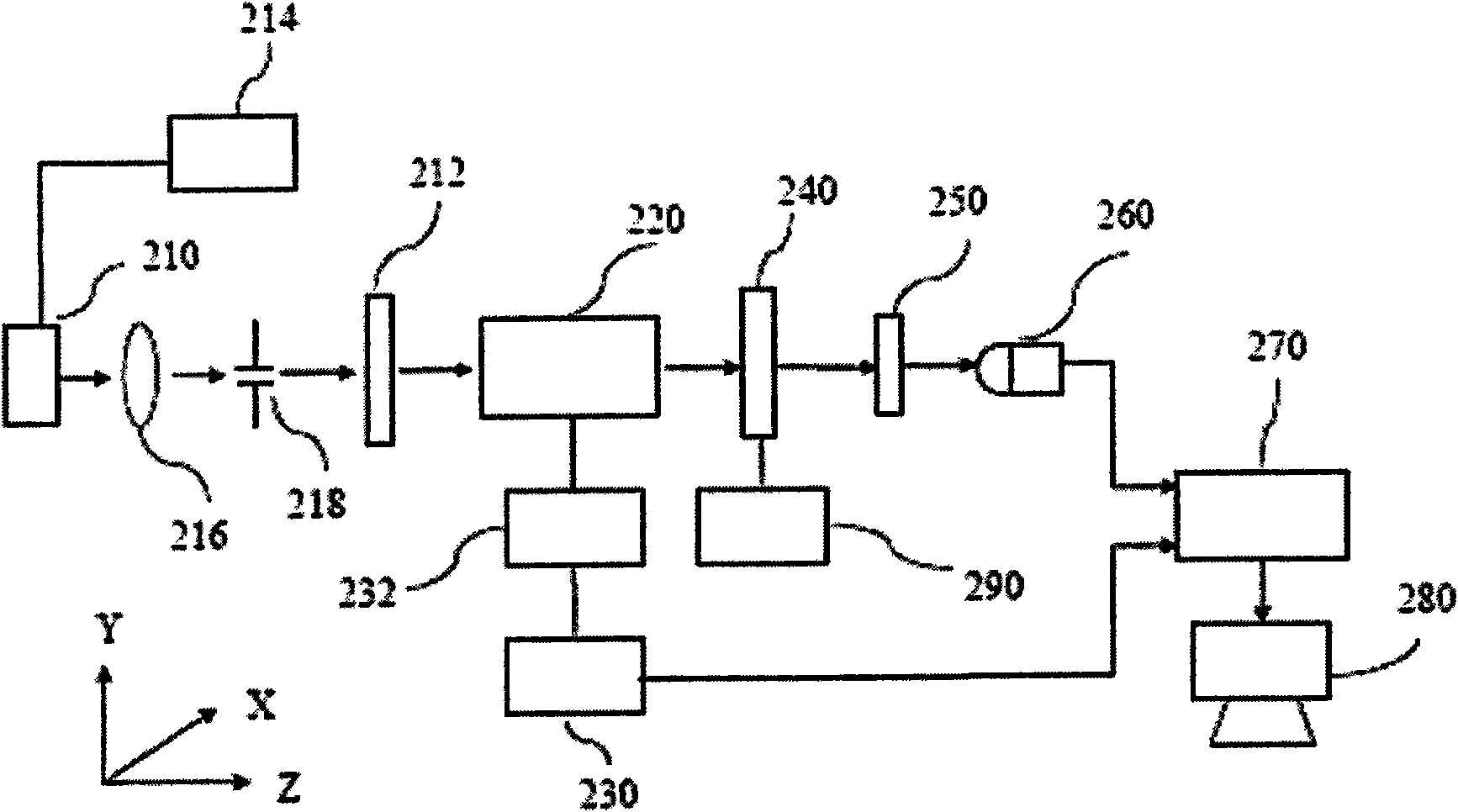
Heterodyne interferometry displacement measurement apparatus
A heterodyne interferometry displacement measurement apparatus includes a first optical system including a light source (LASER) and a diffraction grating (GT0) that generates two diffracted lights to combine the two diffracted lights to generate a combined light and that causes the two diffracted lights to interfere with each other to generate a first frequency difference signal, a second optical system that converts the combined light into two lights of which frequencies are different from each other by a second frequency difference in accordance with a displacement of an object and that causes the two lights to interfere with each other to generate a second frequency difference signal, and an output device that outputs information of a displacement amount of the object based on the first frequency difference signal and the second frequency difference signal.
Owner:CANON KK
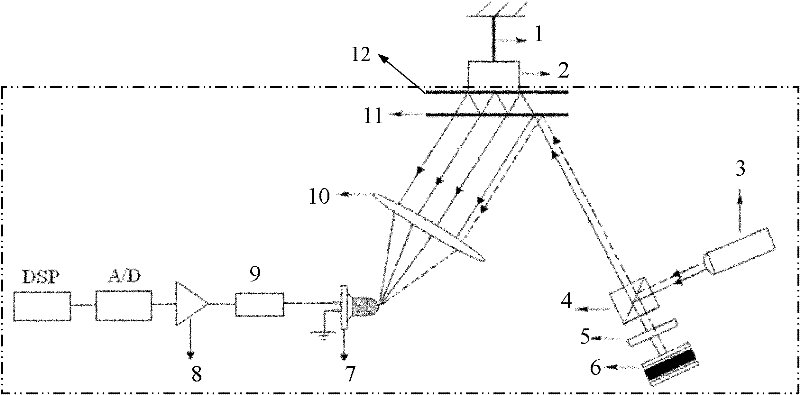
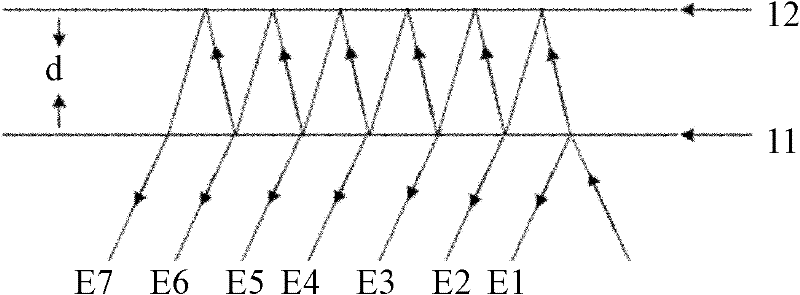
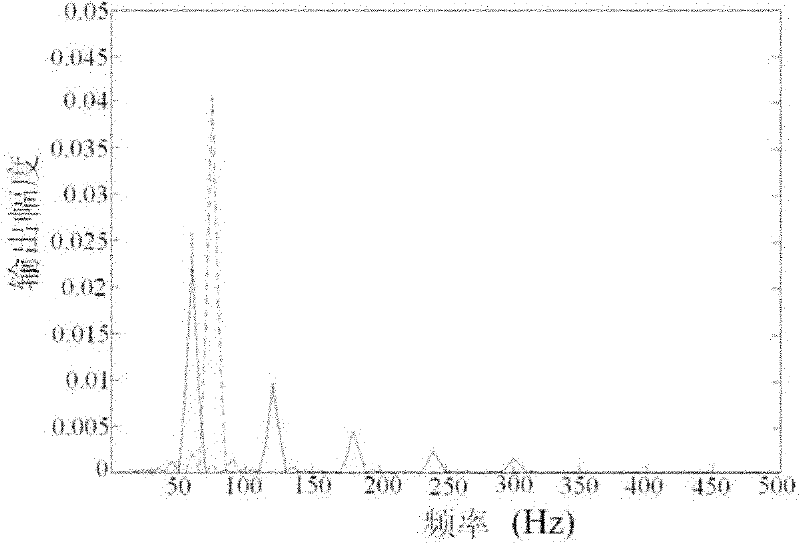
Multi-beam laser heterodyne distance measurement device and method for measuring young modulus by adopting device
InactiveCN102176022AHigh measurement accuracyImprove spatial resolutionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUsing optical meansIntermediate frequencyYoung's modulus
The invention discloses a multi-beam heterodyne distance measurement device and a method for measuring a young modulus by adopting the device, which relate to the technical field of testing and aim to solve the problem that only a single parameter value to be tested can be obtained by the conventional heterodyne interference method. The device and the method are implemented based on a laser heterodyne technology and Doppler effects. The device introduces a galvanometer into a light path to attach optical frequency to optical signals incident at different moments, and then light reflected by athin glass plate and the light reflected by a planar mirror for many times produce a multi-beam heterodyne interference signal when interference conditions are met, thereby successfully modulating information to be tested in a frequency difference of an intermediate frequency heterodyne signal. In the method, a plurality of frequency values comprising the information about metal length change amounts are obtained at the same time in a frequency domain, the signal is demodulated to obtain a plurality of length change amounts, and weighted averaging is performed to obtain the accurate amount ofchange, made along with temperature, of a sample. In a simulation experiment performed by taking a carbon steel wire as an example, a relative error of young modulus measurement is only 0.3 percent.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Spatial-heterodyne interferometry for transmission (SHIFT) measurements
InactiveUS20060192972A1Holographic object characteristicsUsing optical meansLight energyParticle physics
Systems and methods are described for spatial-heterodyne interferometry for transmission (SHIFT) measurements. An apparatus, includes: a source of coherent light energy; a reference beam subassembly optically coupled to the source of coherent light; an object beam subassembly optically coupled to the source of coherent light; a beamsplitter optically coupled to both the reference beam subassembly and the object beam subassembly; and a pixilated detection device optically coupled to the beamsplitter. The object beam subassembly includes an object that is at least partially translucent, the object transmissively optically coupled between the source of coherent light energy and the beamsplitter.
Owner:BINGHAM PHILIP R +2
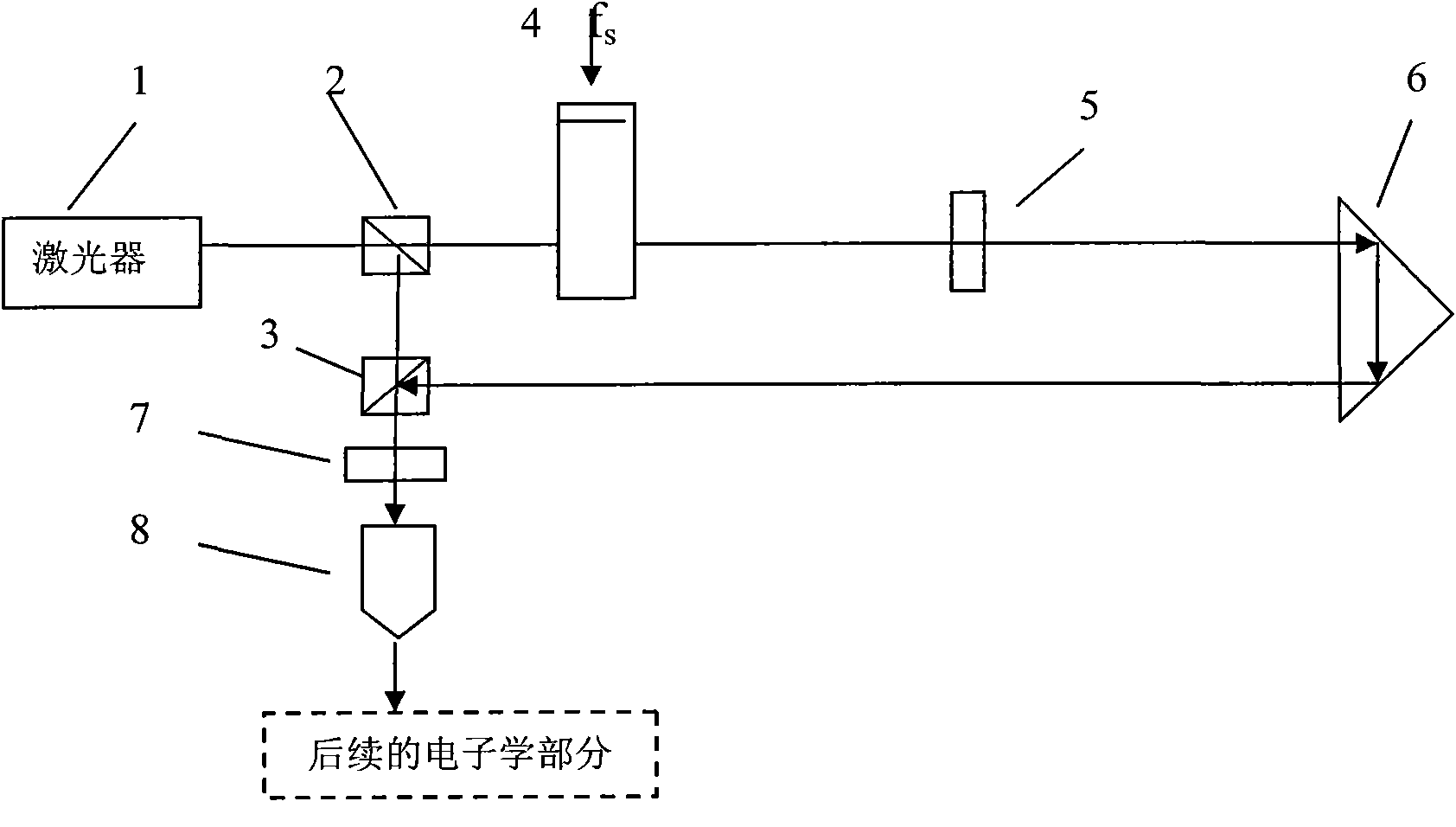
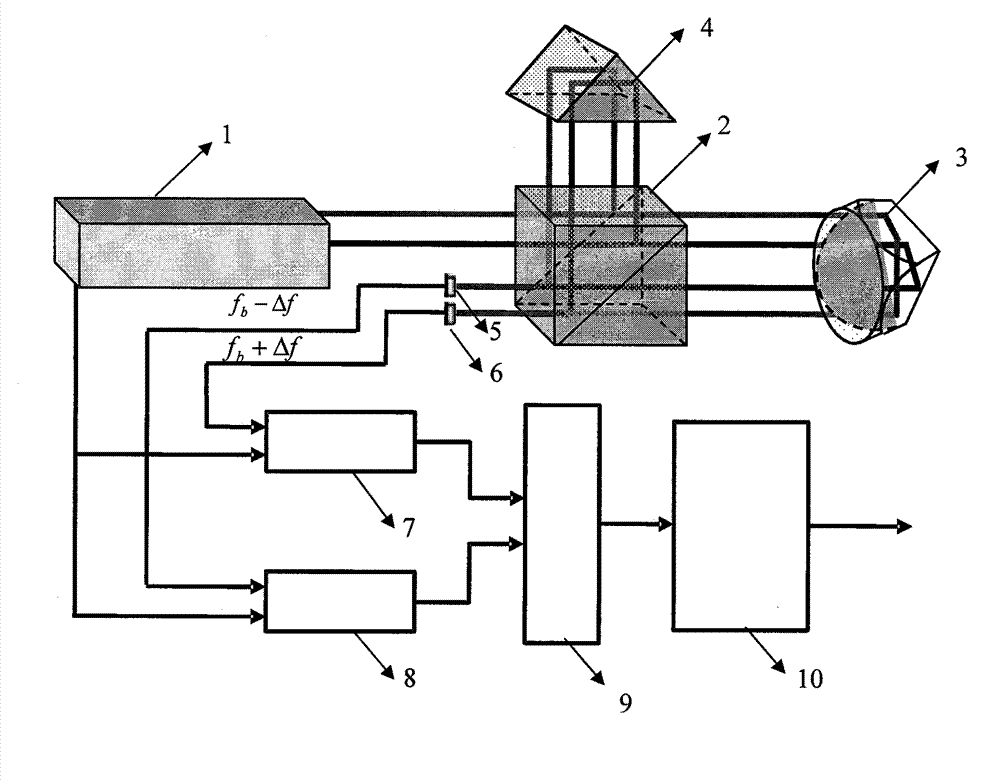
High-speed and high-resolution laser heterodyne interferometry method and high-speed and high-resolution laser heterodyne interferometry device
ActiveCN102853769AGood effectEliminate nonlinear errorsUsing optical meansOptical elementsLaser lightOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a high-speed and high-resolution laser heterodyne interferometry method and a high-speed and high-resolution laser heterodyne interferometry device, and belongs to the technical field of laser application. Reference light and measuring light which are separated from each other spatially are adopted, balance design for a measuring light path is carried out, and two interferometry signals with opposite Doppler frequency shifts are generated by the method, and are selectively used for interferometry according to the movement direction and the speed of a measured object. The high-speed and high-resolution laser heterodyne interferometry method and the high-speed and high-resolution laser heterodyne interferometry device have the advantages that influence of temperature change to measurement is reduced, frequency aliasing in an interferometer is eliminated, measurement precision of heterodyne interferometry is improved, and the problem of limitation on measuring speed due to frequency difference of laser light sources is solved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Device and method for measuring physical parameters of aeolotropic substance
The invention provides a method and a device for measuring the physical parameters of an aeolotropic substance by using the transmission type heterodyne interferometry. Two mutually orthogonal polarized light beams with slightly different frequencies pass through the aeolotropic substance to be measured, and interference is produced through an analyzer with linear polarization. An optical detector is used for detecting the interfered light and converting the interfered light into an interference signal, and a phasometer or a locking amplifier is used for acquiring the phase difference between the interference signal and a reference signal.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
Method and device for measuring novel laser heterodyne interference based on small frequency difference and beam splitting
The invention discloses a method and a device for measuring novel laser heterodyne interference based on small frequency difference and beam splitting, and belongs to the technical field of laser application. The method comprises the following steps of: using reference light and measuring light subjected to spatial isolation; and generating two interferometry signals having opposite doppler frequency shift and selectively using two measuring signals to perform interferometry according to motion direction and speed of a measured target. By utilizing the device, a traditional polarization splitting prism is replaced by a non-polarization splitting prism, and two photoelectric detectors, two phase meters and a switch circuit are additionally arranged into the device. By utilizing the method and the device, the phenomenon of mixed overlapping of the frequency in an interferometer is avoided; the measurement accuracy of the heterodyne interferometry is improved; and the problem that the measuring speed is limited by the laser light source frequency difference is solved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Device and method for measuring micro impulse by torsional pendulum method for modulating multi-beam laser heterodyne by using doppler galvanometer sine
InactiveCN102305682AHigh precisionHigh measurement accuracyApparatus for force/torque/work measurementDigital signal processingPendulum system
The invention relates to a device and a method for measuring a micro impulse by a torsional pendulum method for modulating multi-beam laser heterodyne by using doppler galvanometer sine, and belongs to the technical field of micro impulse measurement. By the device and the method, the problem that the measurement precision of parameter values to be measured is low because only one single parameter value to be measured can be acquired by the conventional heterodyne interference method for measuring the micro impulse of a micro thrustor is solved. The device consists of a digital signal processing system, a photoelectric detector, a pulse laser device, a torsional pendulum system, an H0 solid laser device, a polarization beam splitter (PBS), a quarter wave plate, a galvanometer, a plane standard lens and a convergent lens. The method comprises the following steps of: switching on driving power supplies of the H0 solid laser device and the galvanometer; exciting a working medium target by using pulse laser emitted by a pulse laser device, and making the working medium target produce plasma ejection to make the beam of a standard beam rotate; and acquiring signals emitted by the photoelectric detector by using the digital signal processing system, and processing the signals to acquire the micro impulse I' of the beam of the standard beam. The device and the method are suitable formeasuring the micro impulse of the micro thrustor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
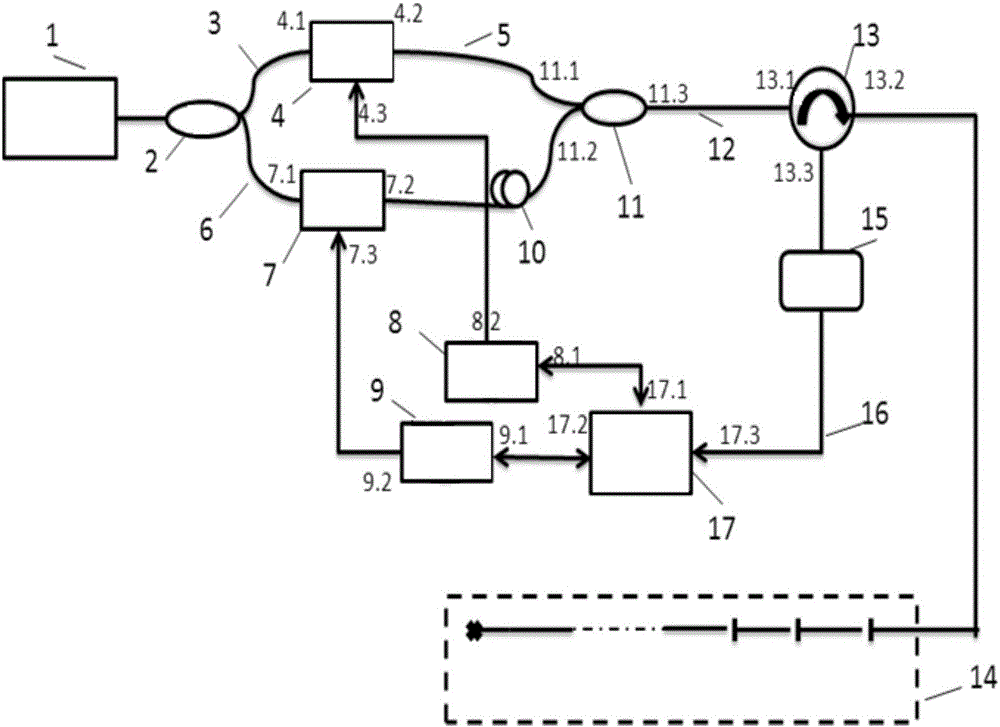
Optical fiber Fizeau interferometric array distributed vibration sensing system and method
ActiveCN105973450AReduce volumeOvercome instability and other issuesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansPhotovoltaic detectorsData acquisition
The invention discloses an optical fiber Fizeau interferometric array distributed vibration sensing system and method. The system comprises a laser light source, a first optical fiber coupler, a first optical frequency shifter, a second optical frequency shifter, a second optical fiber coupler, a delay device, an optical circulator and an optical fiber Fizeau interferometric array. The system also comprises a photoelectric detector, a data acquisition and control card, a first radio frequency signal source and a second radio frequency signal source; light emitted by the laser light source passes through the first optical fiber coupler so as to be divided into two beams of light, wherein the first beam of light and the second beam of light pass through the first optical frequency shifter and the second optical frequency shifter respectively so as to be subjected to frequency shifting, and therefore, the first beam of light and the second beam of light can be modulated into a first optical pulse and a second optical pulse with different frequencies; after the second optical pulse passes through the delay device, the second optical pulse and the first optical pulse are coupled into a pulse pair at the second optical fiber coupler; the pulse pair passes through the optical circulator and enters the optical fiber Fizeau interferometric array, and as a result, a plurality of reflected pulse pairs can be generated; the reflected pulse pairs go back to the optical circulator; and the reflected pulse pairs are subjected to heterodyne interferometry at the photoelectric detector.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
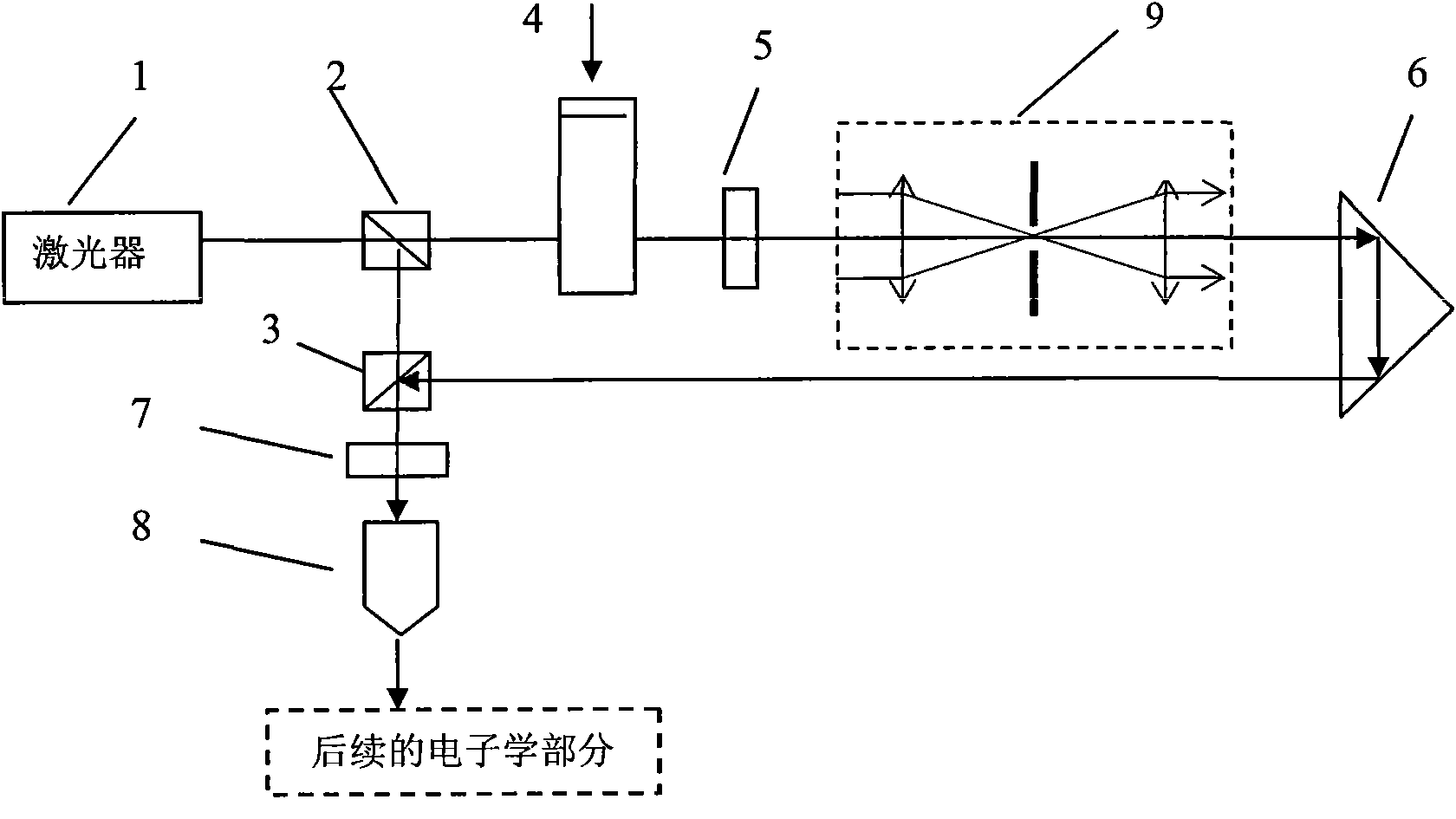
Method and device of heterodyne interferometry of incident light and laser at opposite angles based on rectangular prism
ActiveCN103743336AEliminate nonlinear errorsIncrease the difficulty of adjustmentUsing optical meansPrismOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a method and a device of heterodyne interferometry of incident light and laser at opposite angles based on a rectangular prism, and belongs to the technical field of laser application. The method adopts two beams of spatial isolation parallel light with different frequencies, incidence points of the two parallel beams on a non-polarization splitting prism are located on a diagonal of an incidence surface and are symmetrical about a central point of the incidence surface, and the rectangular prism is taken as a reference prism and a measuring prism; interferometry is carried out by generating two interferometry signals with opposite Doppler frequency shifts finally. According to the method and the device, the frequency aliasing phenomenon in an interferometer can be eliminated, the measuring precision of heterodyne interferometry is improved, and meanwhile, the resolution of heterodyne interferometry is doubled.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Device and method for measuring metal linear expansion coefficient by adopting Doppler galvanometer sine modulated multi-beam laser heterodyne
InactiveCN102253073AHigh precisionMaterial thermal coefficient of expansionUsing optical meansBeam splitterPlane mirror
The invention provides a device and method for measuring metal linear expansion coefficient by adopting Doppler galvanometer sine modulated multi-beam laser heterodyne, belonging to the technical field of metal linear expansion coefficient measurement. The invention aims to solve the problem that the measuring accuracy is low because only the single measured parameter value can be obtained in thetraditional methods for measuring the thermal expansion coefficients of the objects by adopting heterodyne interferometry. The device comprises an H0 solid laser, a quarter waveplate, a galvanometer,a first plane mirror, a polarizing beam splitter (PBS), a convergent lens, a thin glass plate, a second plane mirror, a metal rod to be measured, an electric heating furnace, a photoelectric detectorand a signal processing system. The method is characterized by ensuring the reflecting surface of the second plane mirror to be parallel with the thin glass plate through adjustment, adopting the electric heating furnace to uniformly heat the metal rod to be measured, opening the galvanometer and the H0 solid laser, adopting the signal processing system to acquire the electrical signal output by the photoelectric detector and processing the acquired signal to obtain the metal linear expansion coefficient. The device and the method are suitable for measurement of the metal linear expansion coefficient.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Laser Rockwell hardness standard device and measuring method
ActiveCN103487342AImplement autoloadingImprove accuracyInvestigating material hardnessControl systemClosed loop feedback
The invention relates to a laser Rockwell hardness standard device and a measuring method, discloses a Rockwell hardness device, and relates to a standard device under an international Rockwell hardness new definition, belonging to the technical field of hardness measurement. Automatic force value loading and high-accuracy real-time control are realized through an intelligent force loading closed loop feedback control system; the design and the development of the system are automatically measured through the indentation depth of a laser Michelson heterodyne interferometry principle to realize high accuracy and high reliability of the indentation measurement so as to meet the specific requirements of the international new definition on force value loading speed, force value loading accuracy, force value holding time and the like.
Owner:BEIJING CHANGCHENG INST OF METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
Micro impulse measuring apparatus using torsion pendulum method of using Doppler vibrating mirror to carry out sine modulation on multiple-beam laser heterodyne and method thereof
InactiveCN102353490AHigh precisionHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansApparatus for force/torque/work measurementDigital signal processingProperty value
The invention provides a micro impulse measuring apparatus using a torsion pendulum method of using Doppler vibrating mirror to carry out sine modulation on multiple-beam laser heterodyne and a method thereof, belonging to the micro impulse measuring technology field. According to the apparatus and the method in the invention, a problem that employing a method of using heterodyne interferometry to measure micro impulse of a micro thruster, only a single property value to be measured can be obtained, and measuring precision of the property value to be measured is low is solved. The apparatus in the invention comprises a digital signal processing system, a photoelectric detector, a pulse laser, a torsion pendulum system, an HO solid state laser, a polarization beam splitter (PBS), a quarter-wave plate, a vibrating mirror, a plane standard mirror and a convergent lens. The method comprises the following steps: opening the HO solid state laser and the vibrating mirror, and employing the pulse laser to send a pulse laser excitation working medium target to enable a crossbeam of a standard beam to rotate; collecting a signal sent by the photoelectric detector with the digital signal processing system, carrying out processing on all continuously obtained signals, and obtaining micro impulse received by the crossbeam of the standard beam. The apparatus and the method are applied to the measurement of the micro impulse.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Heterodyne spectrally controlled interferometry
Owner:OLSZAK ARTUR
Large dynamic range heterodyne interferometry type fiber optic hydrophone system
ActiveCN108225540ARaise the upper limit of dynamic rangeRaise the heterodyne carrier frequencySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansHydrophonePhotovoltaic detectors
The invention relates to a large dynamic range heterodyne interferometry type fiber optic hydrophone system which comprises a narrow linewidth laser, a first coupling, a first acoustic optical modulator, a second acoustic optical modulator, a first optical fiber delay ring, an acoustic optical modulator driver, a second coupling, a first circulator, a second circulator, a first photoelectric detector, a second photoelectric detector, a reference probe, a sensing probe and a signal demodulating module, wherein an optic signal output by the narrow linewidth laser is converted into two pieces ofpulse light with different frequencies through the first and second acoustic optical modulators, the pulse light intervenes through the probe of the fiber optic hydrophone to beat frequency to obtaina heterodyne signal of a certain frequency, and the system expands the dynamic range of the heterodyne interferometry type fiber optic hydrophone by improving the frequency of the heterodyne signal ofbeat frequency, so that the demand on measurement of large-range signals is met.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Device and method for precisely measuring laser line width on the basis of cyclic self-heterodyne interferometry
The invention discloses a device and method for precisely measuring a laser line width on the basis of cyclic self-heterodyne interferometry. The device comprises a narrow line width laser which is successively connected with an isolator, a first Y-type coupler, a first frequency shifter, a second Y-type coupler, a photoelectric detector, and a frequency spectrograph via fibers. An X-type coupler is connected between the first Y-type coupler and the second Y-type coupler via fibers. The X-type coupler is successively connected with an attenuator, a second frequency shifter, an erbium-doped fiber amplifier, a fiber band-pass filter, a polarization maintainer via fibers so that a closed loop is formed. The device and the method uses cyclic self-heterodyne interferometry based on loss compensation, and a short fiber delay line, does not require complex theoretical simulation and accurate system parameter setting, and may measure laser linewidths at a sub-kHz magnitude accurately.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Heterodyne spectrally controlled interferometry
Heterodyne interferometry is combined with spectrally-controlled interferometry (SCI) to achieve the advantages of both. Phase shifts produced by SCI produce phase-shifted correlograms suitable for heterodyne interferometric analysis, thereby enabling interferometric measurements with conventional common-path apparatus free of coherence noise and scanning-related errors, and with the precision of conventional heterodyne interferometry. A spectrum-modulating light source suitable for the invention is obtained by combining a rotating spiral grating with a multi-slit grating placed in the front focal plane of a collimating lens that propagates the light toward a blazed diffraction grating. Another exemplary spectrum-modulating light source is obtained by combining a slit spectrometer with an acousto-optic modulator.
Owner:OLSZAK ARTUR
Fiber SPR (surface plasmon resonance) sensing measuring optical circuit based on dual-frequency laser heterodyne interferometry
InactiveCN105784594ASimple structureHigh measurement accuracyPhase-affecting property measurementsDual frequencyPhase difference
The invention relates to the field of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensing measurement and laser interferometric measurement, in particular to a fiber SPR sensing measuring optical circuit based on dual-frequency laser heterodyne interferometry, comprising a dual-frequency laser source, a semi-transmitting semi-reflecting lens, a focusing lens, polarization maintaining fibers I and II, first and second polarizers, first and second detectors, and a phase measuring instrument. The laser source emits mutually orthogonal linearly polarized beams, each beam is split into two beams via the semi-transmitting semi-reflecting lens, and the transmitted beams pass through the focusing leans, the polarization maintaining fiber I (not treated), the focusing lens and the first polarizer to form a beat frequency signal that is received by the first detector and sent as a reference signal to the phase measuring instrument; the reflected beams pass through the focusing lens, the polarization maintaining fiber (the middle of which is made into SPR exciting structure), the focusing lens and the second polarizer and are received by the second detector, and the reflected beams are sent as a measurement signal to the phase measuring instrument. Through the phase measuring instrument, a phase difference Phi generated due to SPR can be acquired, and refractive index parameter of a medium to be measured can be measured according to a corresponding measuring formula.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com