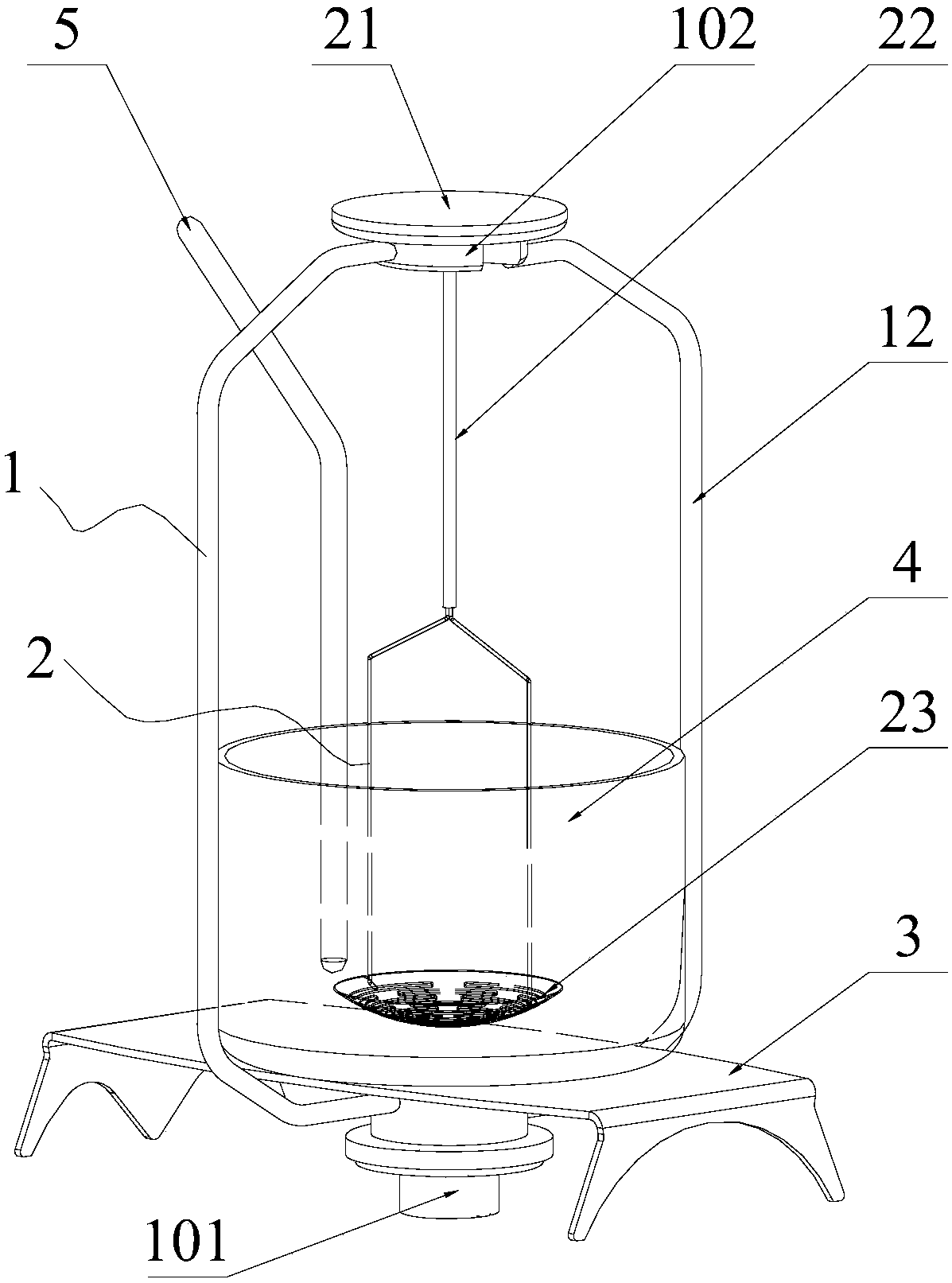
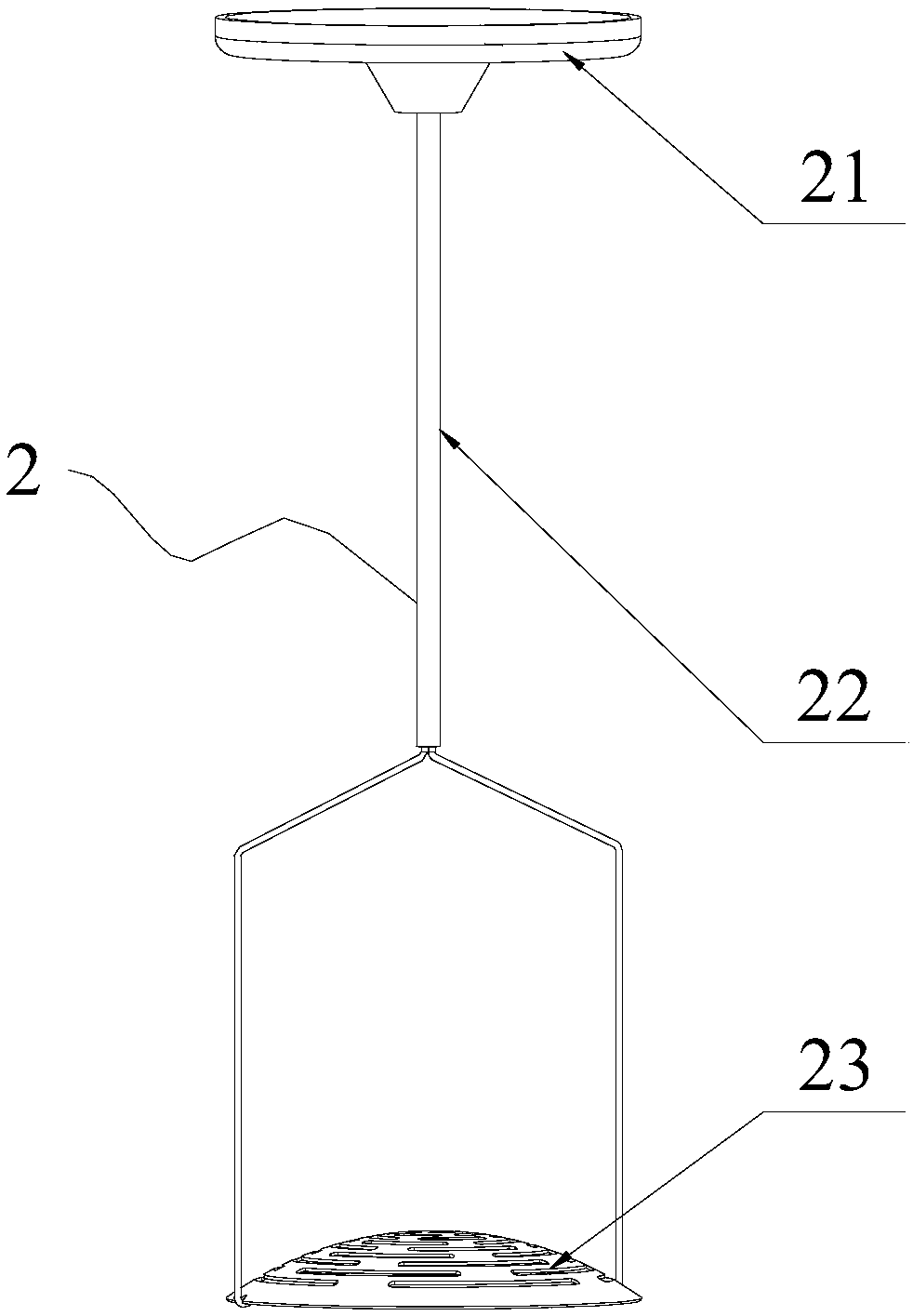
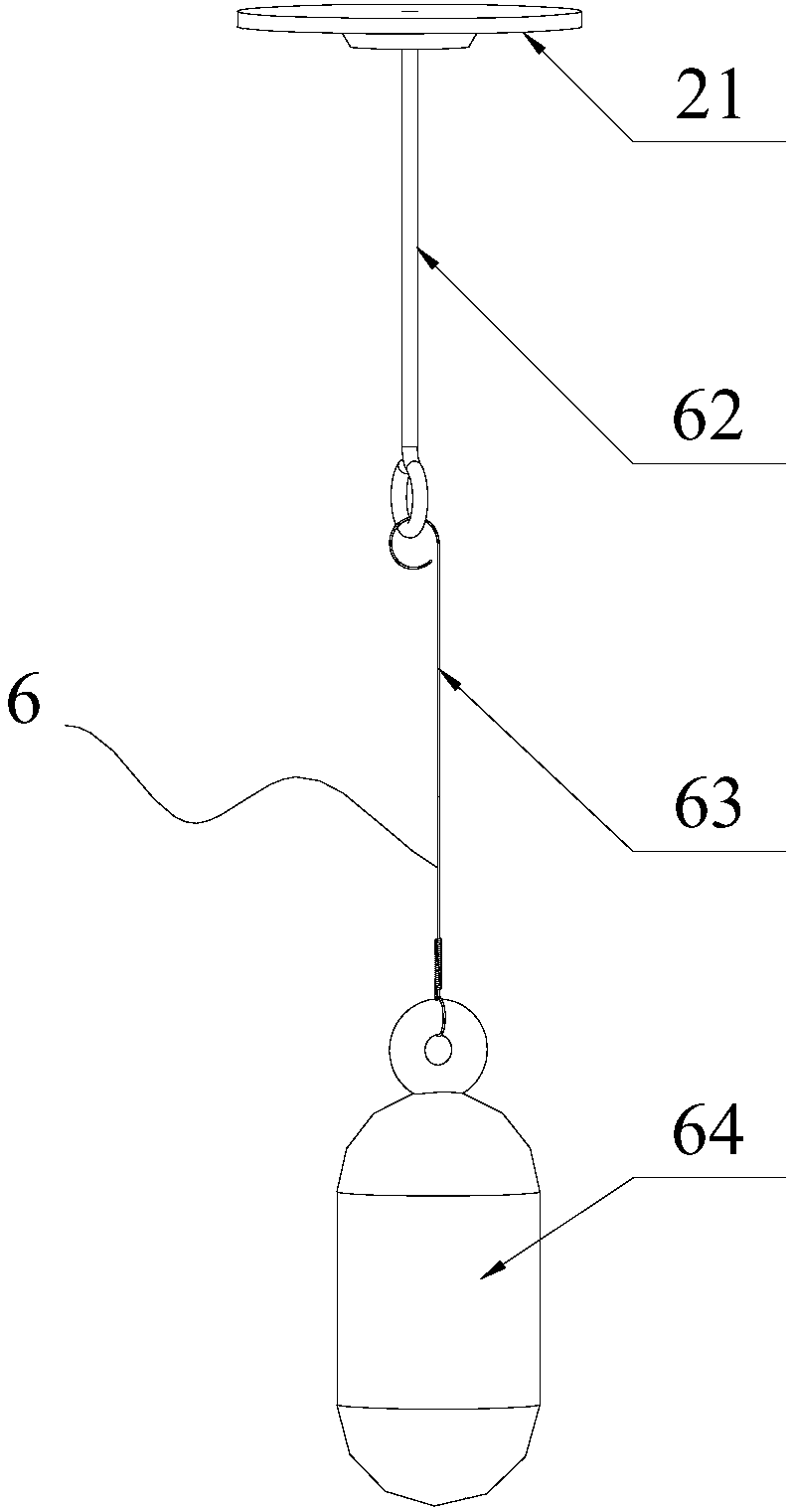
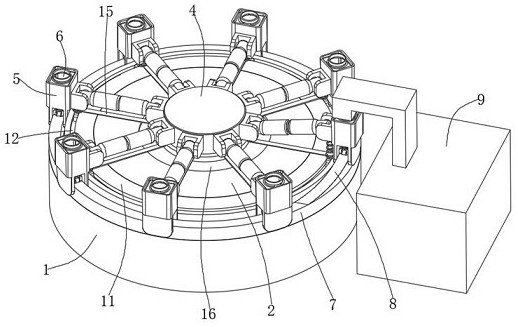
Patents
Literature
105 results about "Kit device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Analyte measurement kit
InactiveUS6994825B2Easy to measureAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSamplingAnalyteMeasuring instrument
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
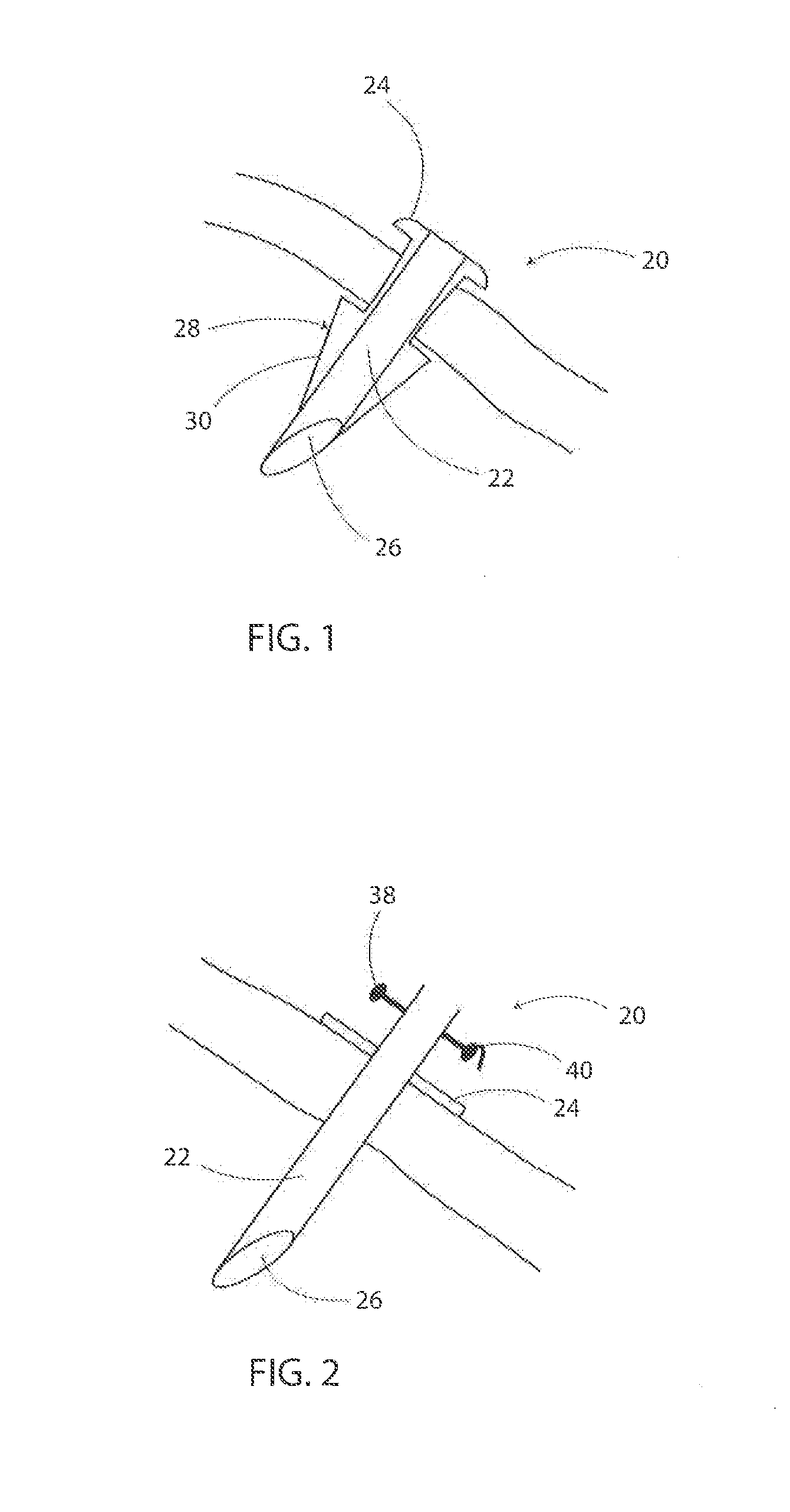
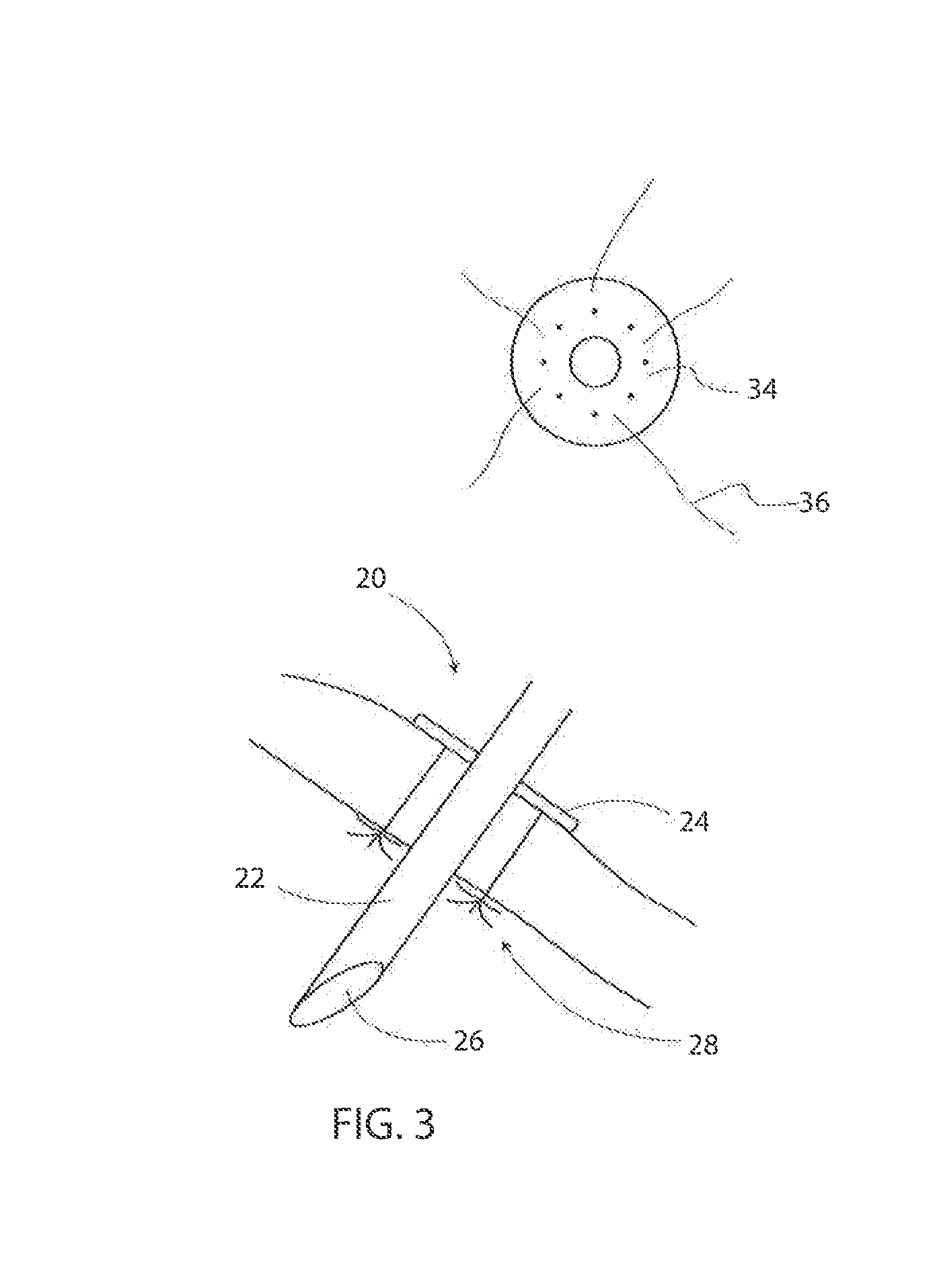
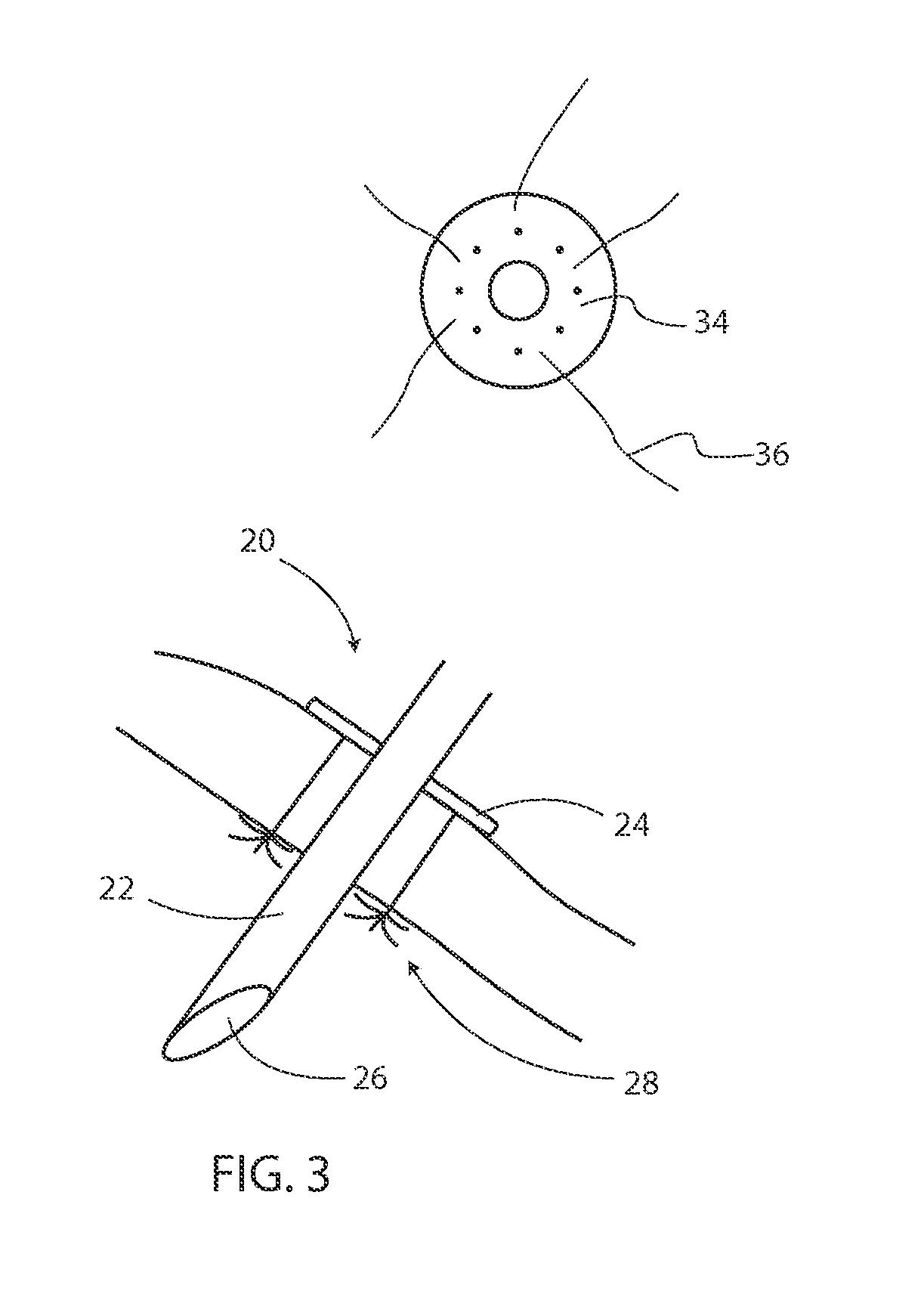
Surgical tools and methods for their use
InactiveUS20150032140A1Promote resultsSignificant complicationSuture equipmentsMammary implantsRaspKit device
Surgical tools and kits for performing methods include a grommet with cylindrical shaft, cutting tip, annular flange with suture retaining anchoring fixture; a grommet jig for extending between adjacent grommets and guiding a needle therebetween; a family of needles with single and double pointed ends, reinforced eyelets, stops to limit inadvertent exiting, double shaft construction with a longitudinal gap and sharpened, slicing ends, including a “J” shape embodiment; a bone anchor with ring to secure sutures about a patient's clavicle; a tissue dissector having radially extending cones to nick taut connecting tissues; a tissue rasp having a series of crisscrossing grooves along an end; a tissue mesher comprising one or more blocks having a matrix of holes for clamping a plurality of needles and a supporting framework; and a kit device and a method of surgically inserting an internal mesh brassiere under the breast skin.
Owner:KHOURI ROGER
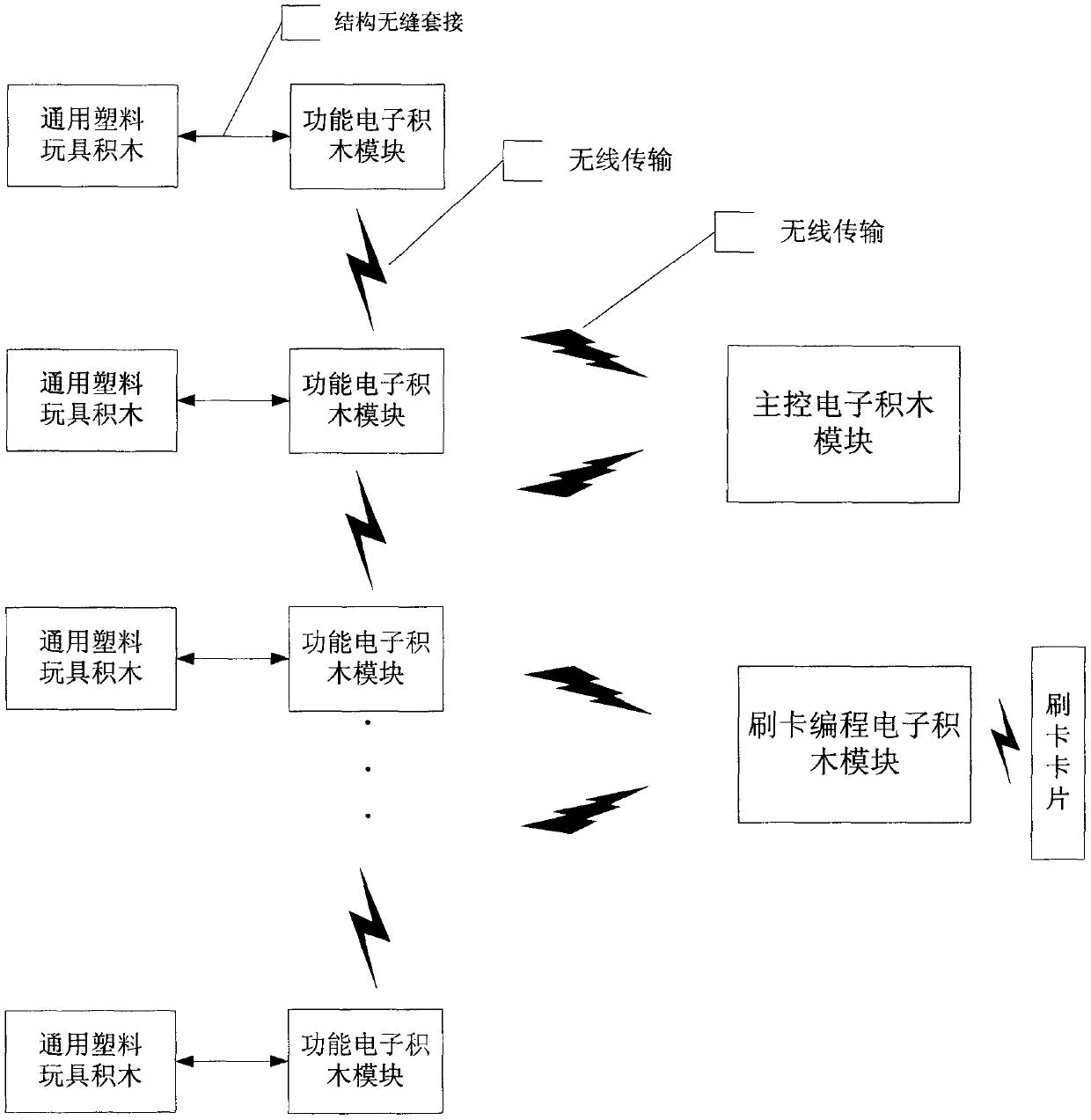
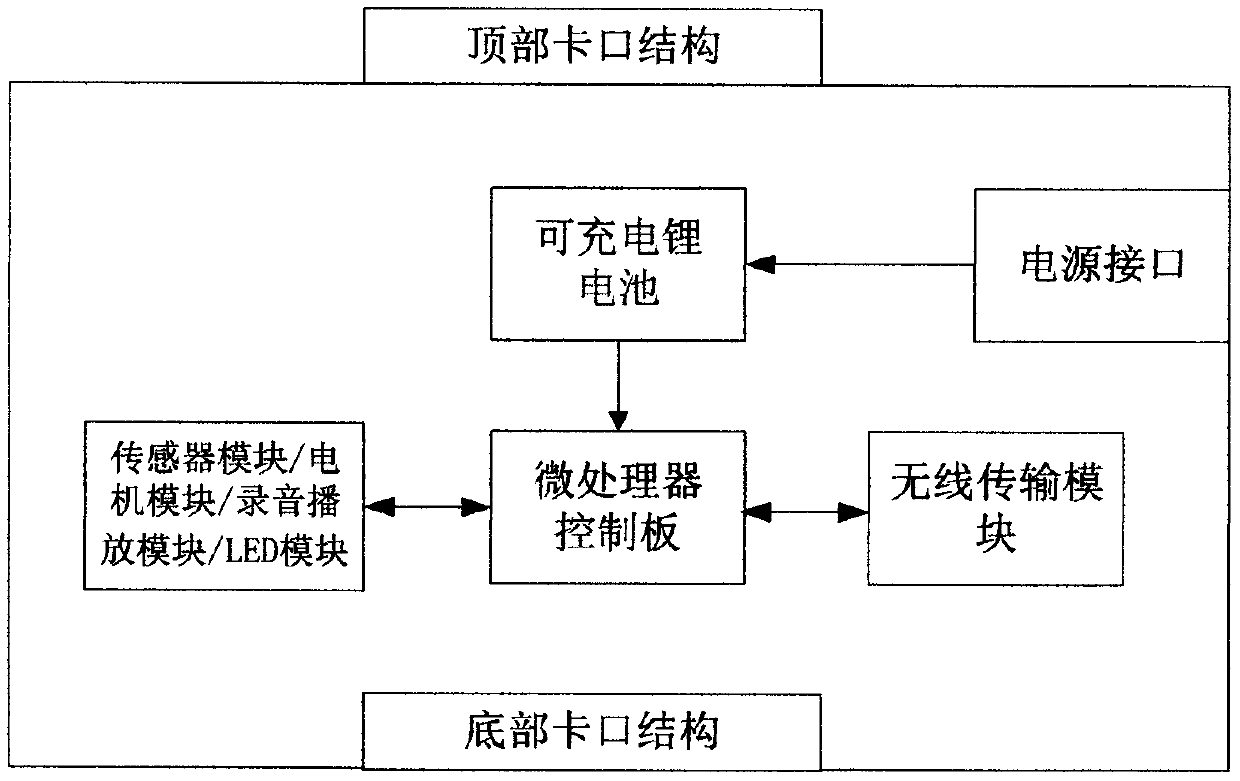
Integrated wireless ad hoc network electronic building block kit device with card swiping programming function
The invention discloses an integrated wireless ad hoc network electronic building block kit device with a card swiping programming function, and relates to the field of intelligent electronic toy products. The integrated wireless ad hoc network electronic building block kit device is characterized in that the appearance structure design of the kit device can be in structural sleeve joint connection with common building block toys in the market, so that building block scenes can be built together, scientific thinking of children can be inspired while entertainment is performed, and programmingideas can be cultivated; the kit device comprises three parts: a main control electronic building block module, a functional electronic building block module, a card-swiping programming electronic building block module and a card-swiping card, wherein the electronic building block modules can be wirelessly connected; the main control electronic building block module achieves overall networking configuration and behavior control of the building block device; the functional electronic building block module achieves different functional operations; the card-swiping programming electronic buildingblock module can control the operation of the functional electronic building block module through a card-swiping instruction; the kit device can more flexibly exert the imagination of a user to buildvarious building block scenes and intelligently control the building block scenes.
Owner:武汉壹加创新智能科技有限公司
Surgical tools and methods for their use
InactiveUS20150032143A1Promote resultsSignificant complicationSuture equipmentsMammary implantsRaspKit device
Surgical tools and kits for performing methods include a grommet with cylindrical shaft, cutting tip, annular flange with suture retaining anchoring fixture; a grommet jig for extending between adjacent grommets and guiding a needle therebetween; a family of needles with single and double pointed ends, reinforced eyelets, stops to limit inadvertent exiting, double shaft construction with a longitudinal gap and sharpened, slicing ends, including a “J” shape embodiment; a bone anchor with ring to secure sutures about a patient's clavicle; a tissue dissector having radially extending cones to nick taut connecting tissues; a tissue rasp having a series of crisscrossing grooves along an end; a tissue mesher comprising one or more blocks having a matrix of holes for clamping a plurality of needles and a supporting framework; and a kit device and a method of surgically inserting an internal mesh brassiere under the breast skin.
Owner:KHOURI ROGER
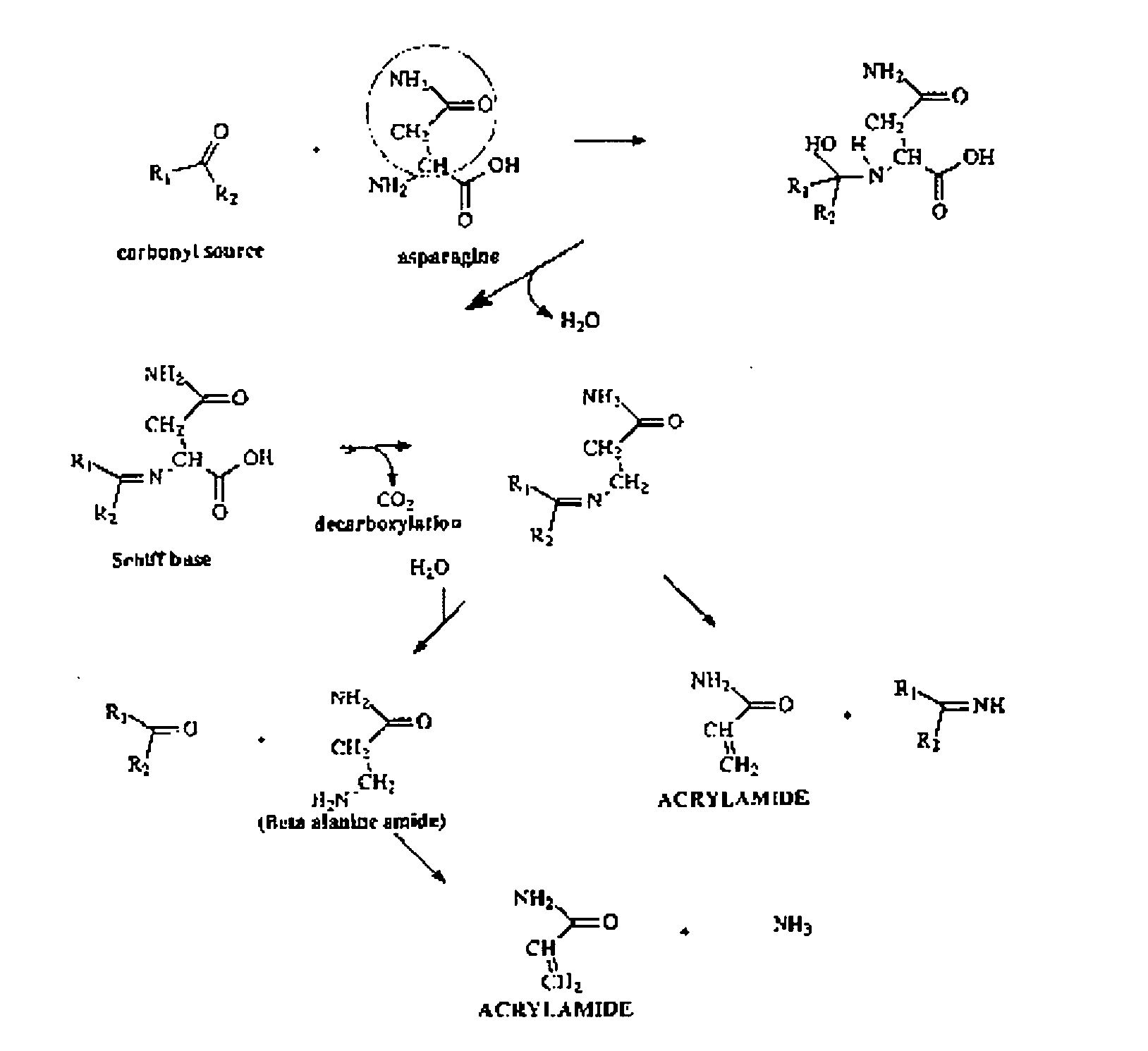
Devices and methods for the rapid, reliable detection and determiniation of acrylamide concentration in food substances and prevention of acrylamide formation in the same
ActiveUS20060029992A1Quickly and easily ascertainEliminate and greatly reduce formation of acrylamideMicrobiological testing/measurementFood preparationHigh concentrationForms of energy
The present invention includes a device and associated analytical method to use for the sensitive detection and accurate, rapid determination of acrylamide in food substances. The present invention also relates to the use of a kit device and associated analytical method in which a user can quickly and easily ascertain the amount of acrylamide in food substances with ease and in any location, including a non-laboratory environment. Such detection device and method may be comprised of a sample collection area on which a sample of food, after being mixed in a solution, is placed for example on the substrate of a biochip that includes an enzyme that along with a co-enzyme or form of energy or catalyst, facilitates the conversion of either acrylamide to acrylonitrile or the conversion of acrylamide to ammonia. If acrylamide is detected in the sample food substance, the resultant concentration, as determined on the calorimetric scale, provides the consumer of the food substance an opportunity to reject or discard the substance prior to digestion, thus promoting good health and avoiding potential ingestion of relatively high concentrations of carcinogenic potent acrylamides. Another variation of the detection device above may utilize pH balance meter and system similar to the calorimetric system utilized above, but which allows a numeric or digital reading of the concentration of acrylamides present in the sample of food. Another variation of the detection device may utilize infrared (IR) detection using an IR sensor to measure a sample and quantify the concentration of acrylonitrile within the sample by an absorption peak of the carbon-nitrogen (C≡N) triple bond in acrylonitrile in an IR spectra at 2250 cm−1 wavelength.
Owner:EPATENTMANAGER COM
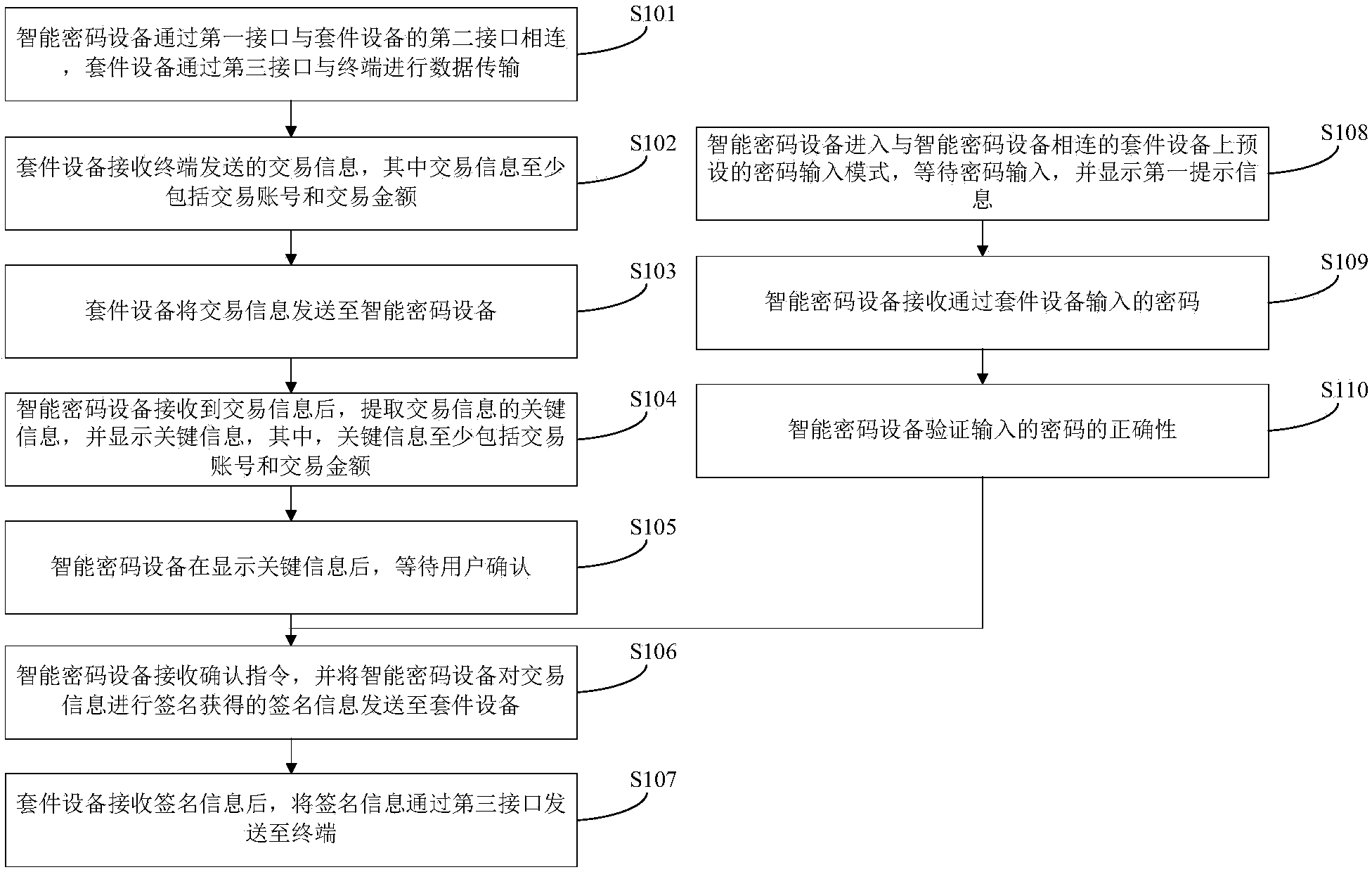
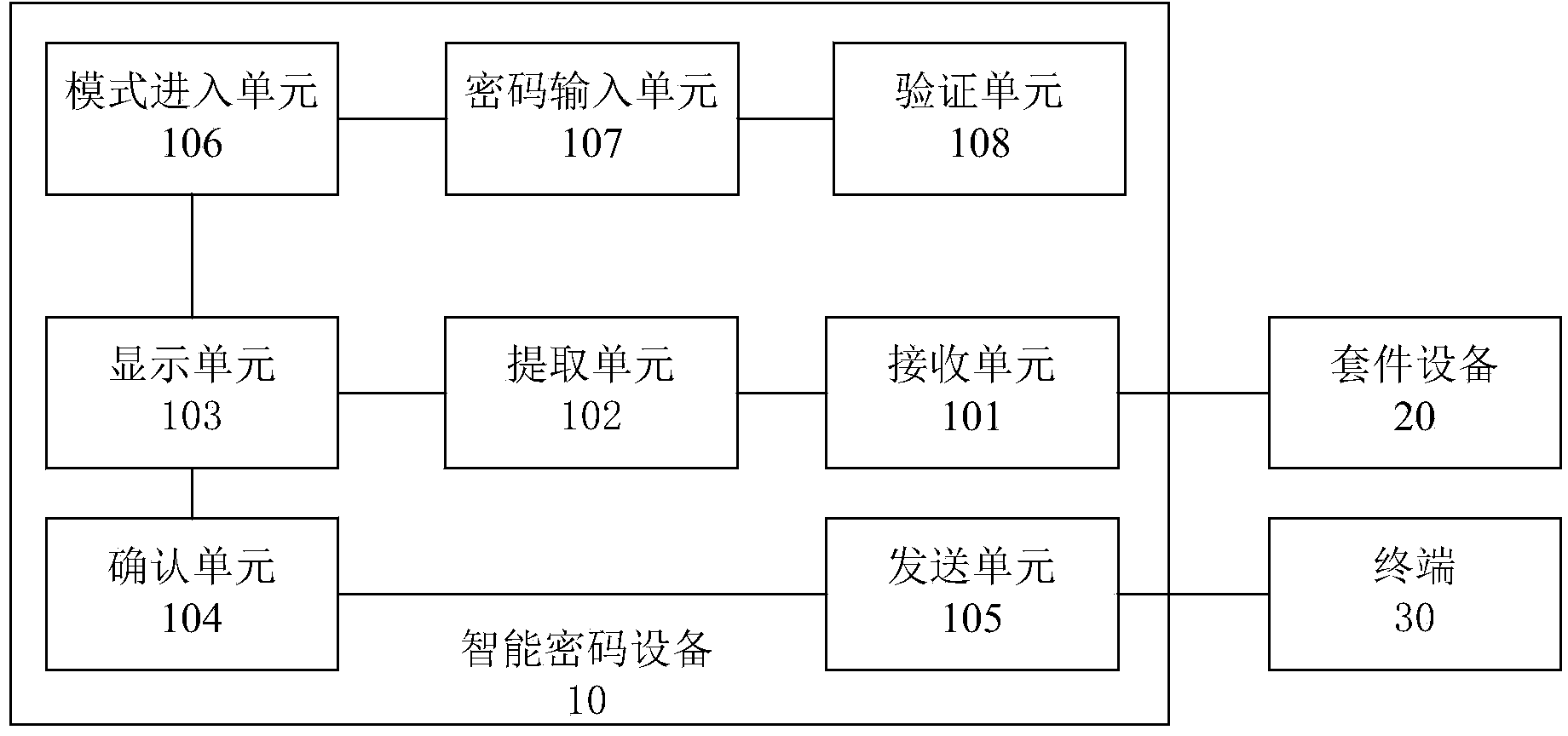
Data transmission method and system
ActiveCN103731273AImprove securityAvoid unsafe hazardsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwarePassword
The invention provides a data transmission method and system. The data transmission method comprises steps that an external member device receives trade information sent by a terminal and transmits the trade information to a smart password device; the smart password device extracts key information of the trade information and displays key information to be verified by users; the smart password device receives a verification instruction and transmits signing information to the external member device; the external member device transmits the signing information to the terminal; wherein before the smart password device receives the verification instruction, the smart password device enters a password input mode preset on the external member device, receives passwords input by the external member device, and verifies correctness of the passwords. Therefore, the passwords can be input by means of the password input mode preset on the external member device, different external member devices can be used according to different security levels of password input modes preset on the external member devices, and security of password input is improved.
Owner:TENDYRON CORP
Universal Bioabsorbable Nasal Implant Kit
Novel bioabsorbable, universal kits used to form nasal implants are disclosed. The implants are useful in rhinoplasty and nasal reconstruction surgical procedures. The kit devices have a universal configuration and can be converted by the surgeon in the field into one or more individual nasal implant devices having different configurations and applications. The kits may have outlines of nasal implants thereon.
Owner:ETHICON INC
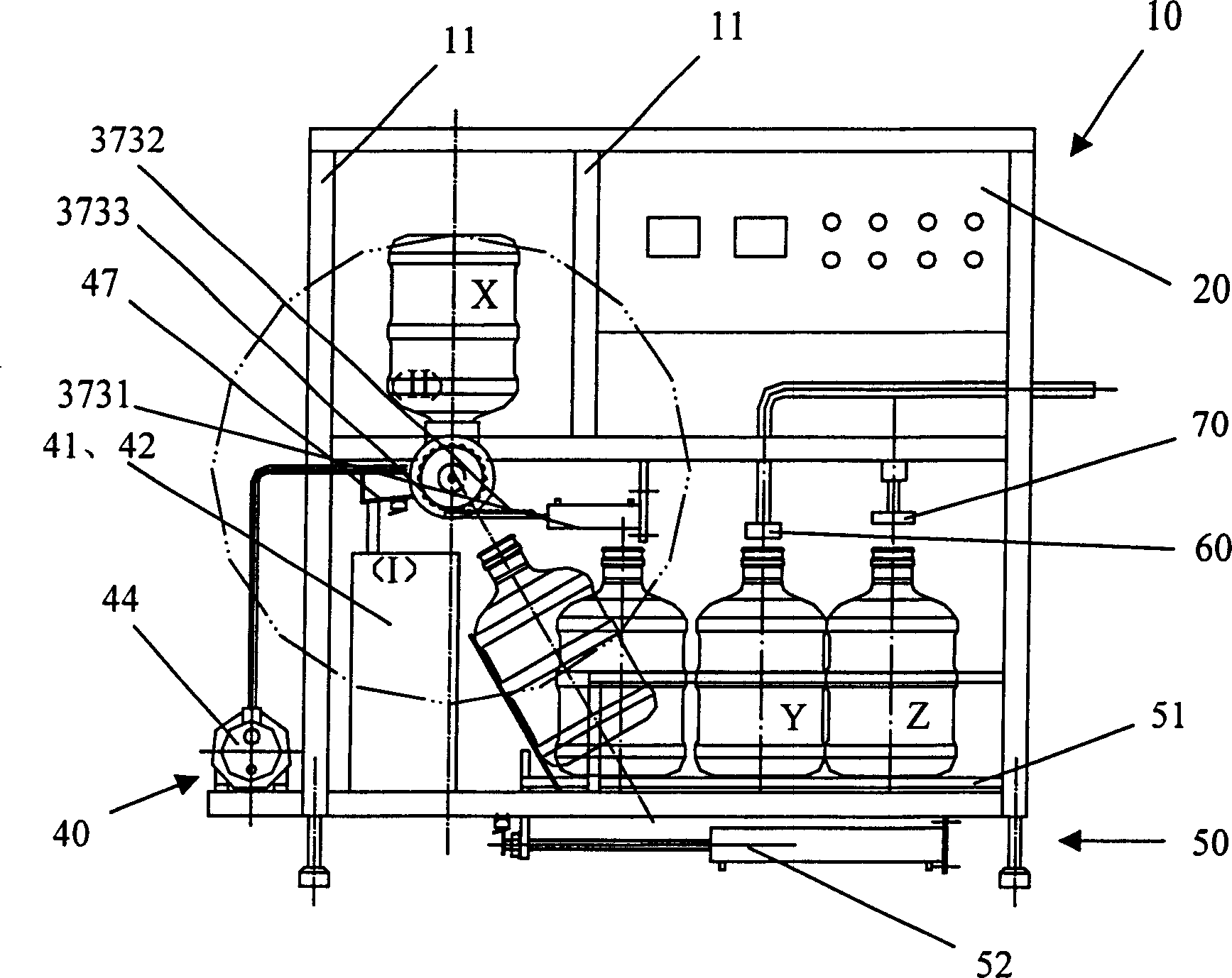
Miniaturized integrated equipment of drinking water filling machine
InactiveCN1803574ASmall form factorSmall footprintBottle-handling machinesMiniaturizationElectric machinery
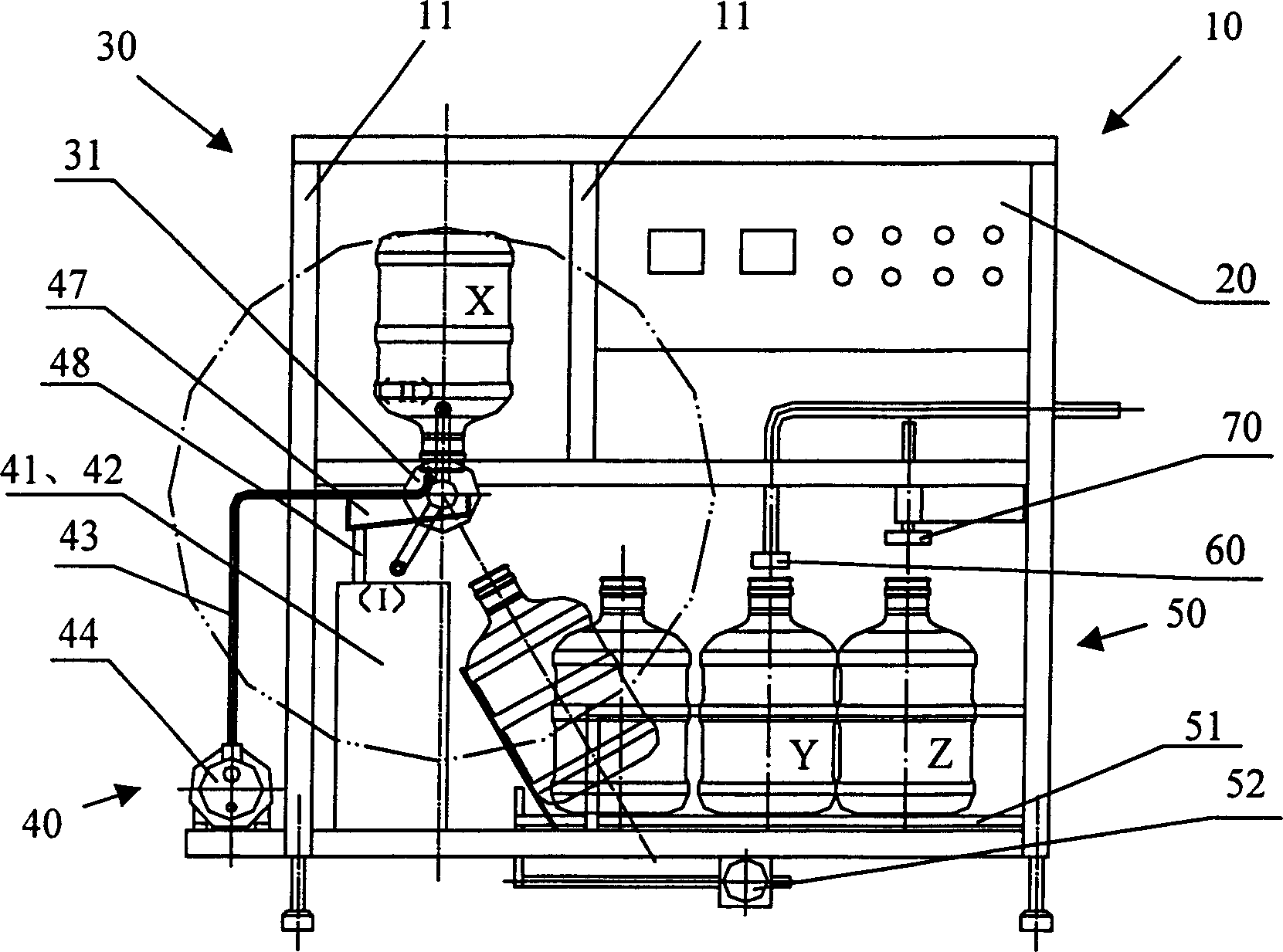
The invention discloses a mini-kit device of drinking water bottler, which comprises the following parts: frame, electric control cabinet, pouring and gland device, drinking water turnover device, disinfection cleaning device under the drinking water turnover device and bottle-dragging device, wherein the drinking water turnover device is set on one side of frame, which combines four stations into one station; the bottle-dragging device is set under the frame, which conveys the water barrel to the pouring and gland procedure position. The invention simplifies the pipe to reduce cost, which controls the barrel moving distance and lid.
Owner:SHANGHAI LIGHT IND RES INST
Kit apparatus and method for decorating a body
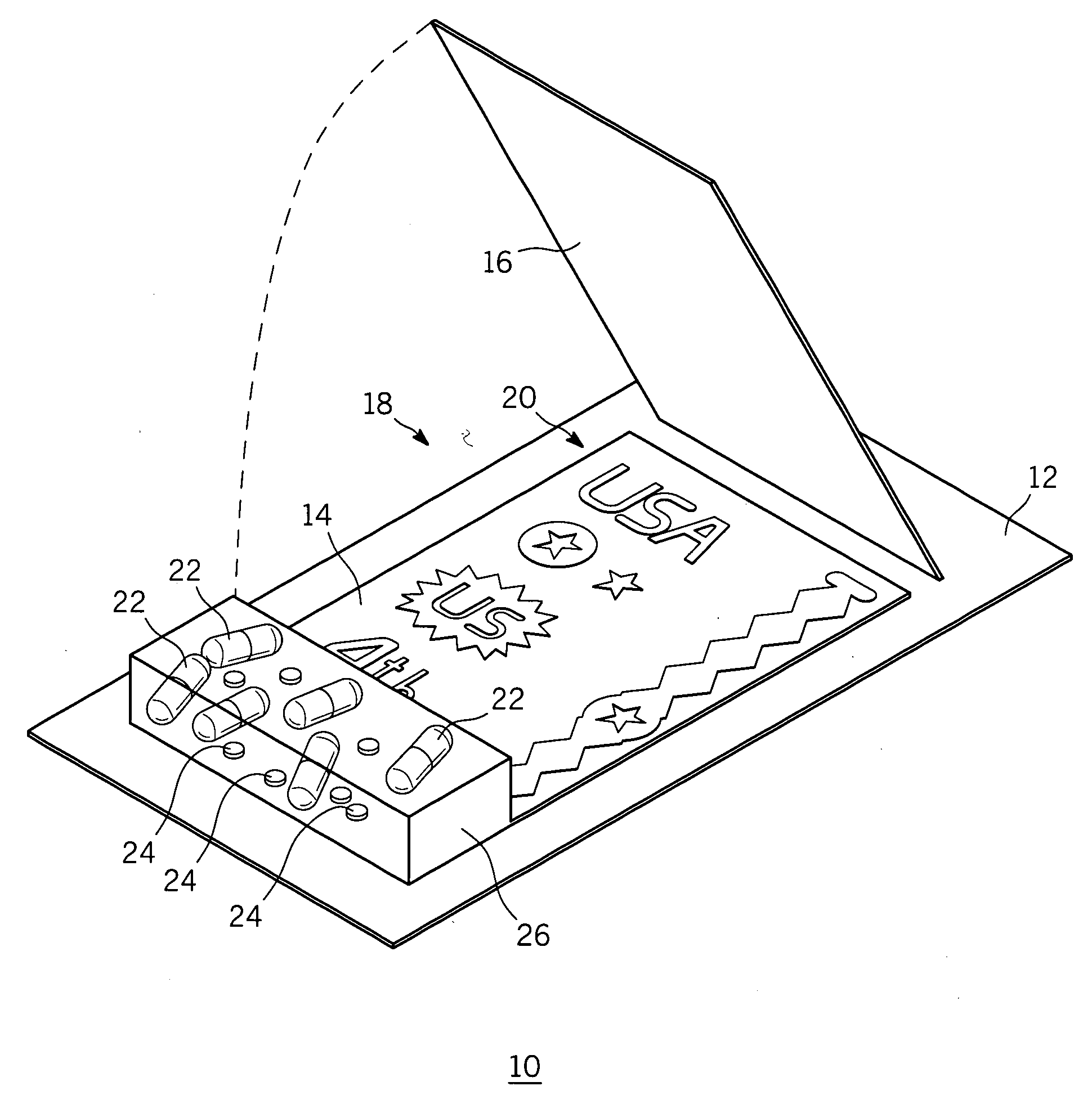
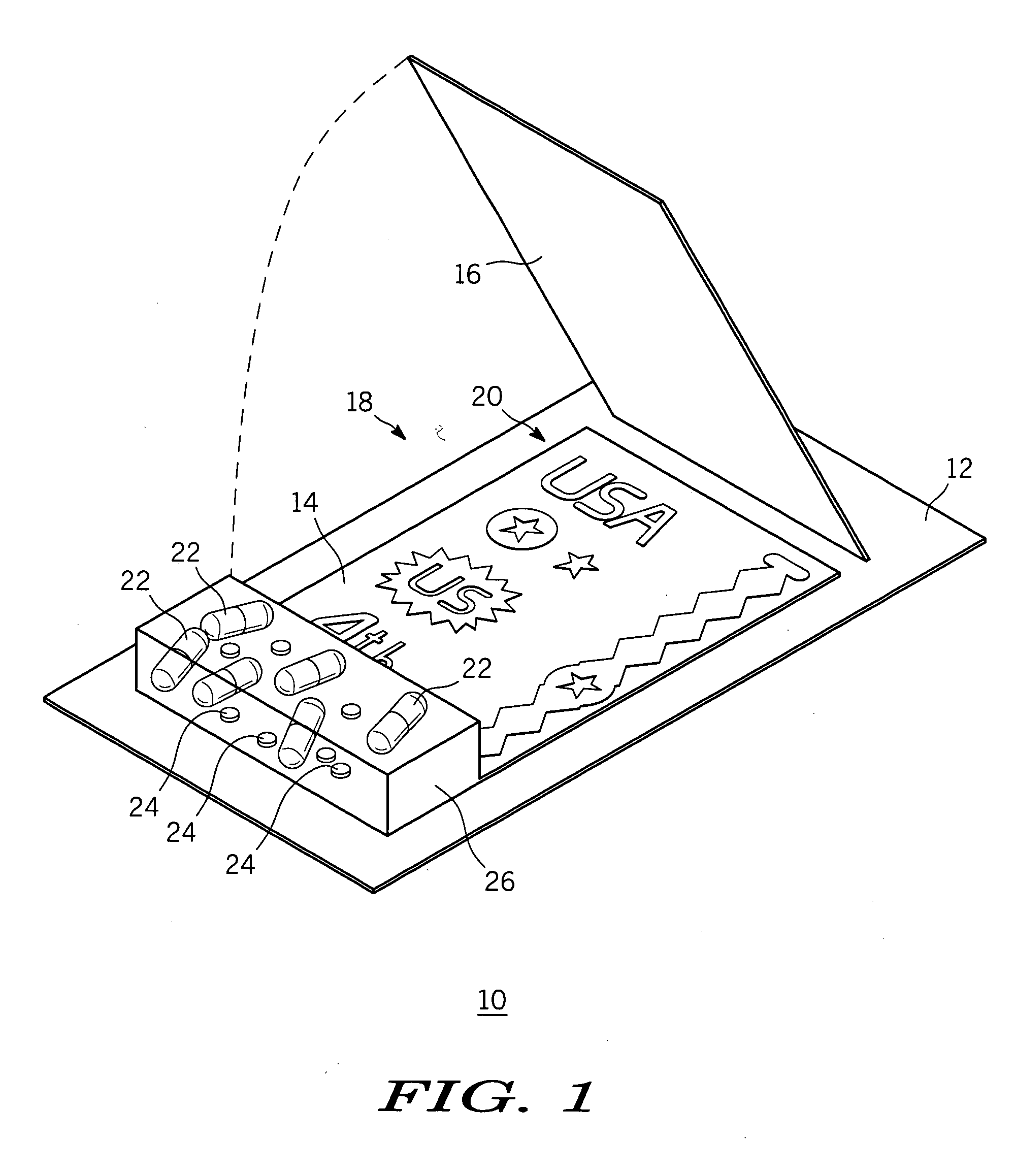
InactiveUS20050016211A1Reusable and visually dramaticImprove adhesionDecorative surface effectsSpecial ornamental structuresHuman bodyKit device
The disclosed invention provides a kit apparatus for decorating a body with temporary body art that is reusable and visually dramatic. The kit apparatus includes a number of patterned transfer sheets having a plurality of releasable themed ornamental patterns thereon, a plurality of capsules containing one or more sprinkle-able decorative materials, a plurality of ornamental studs, and an instruction sheet. Each of the number of patterned transfer sheets includes a double-sided medical grade adhesive material sandwiched between two release liners and die cut into themed ornamental patterns suitable for placement on the human body. The sprinkle-able decorative materials include one or a combination of colored sand, colored cosmetic grade glitter, or glow-in-the-dark powder. Each of the plurality of ornamental studs may include any one or more of metal spikes, metal studs, and pseudo-jewels, colored or otherwise, having a flat back surface for optimal adherence to the adhesive material.
Owner:SCOZZAFAVA FR CHARLES
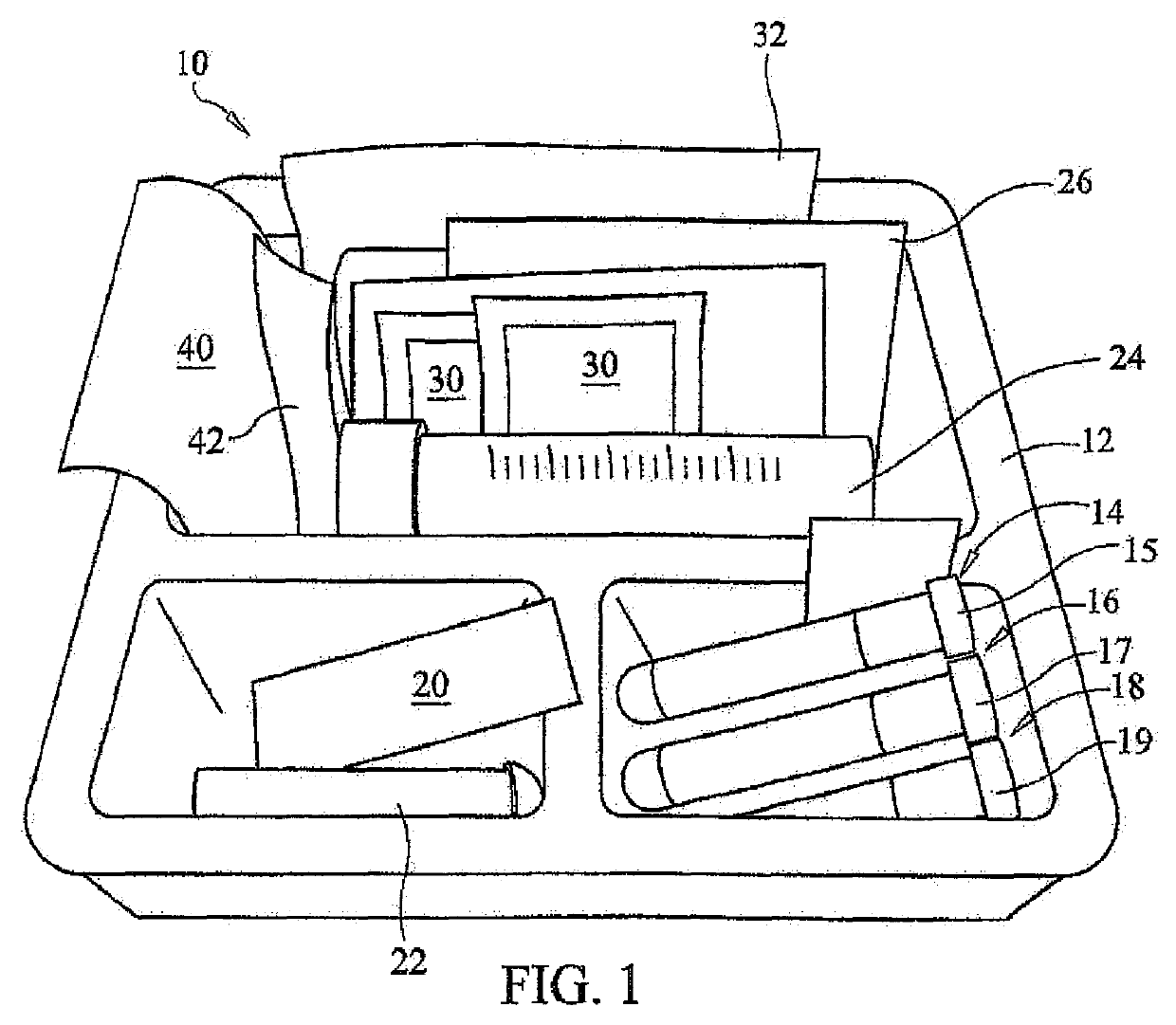
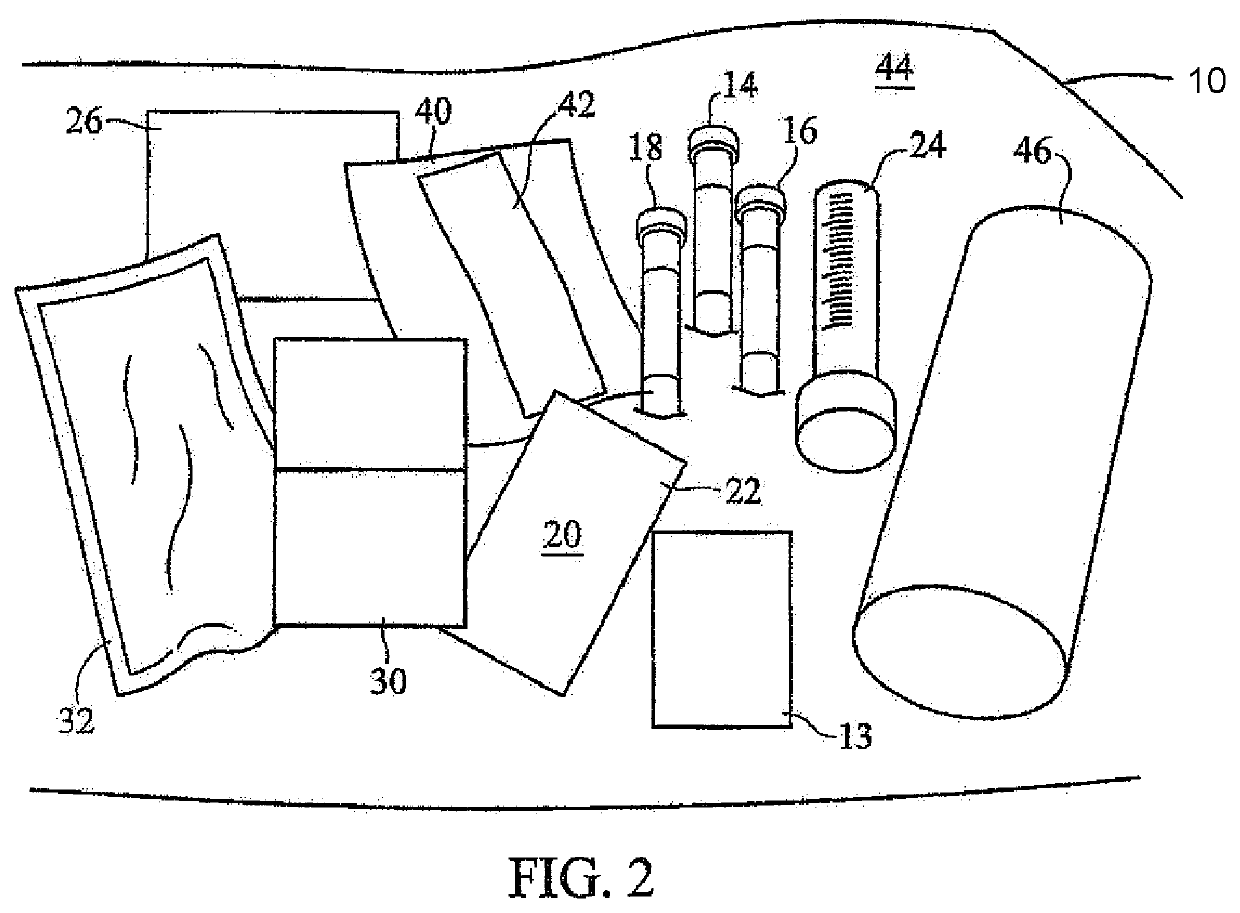
Methods and Apparatus for Preparing Autologous Blood Eye Drops
ActiveUS20200337946A1Improve sterilitySufficient materialSurgical furniturePharmaceutical containersKit deviceAutologous blood
Methods and apparatus for preparing autologous blood serum eye drops within a potentially contaminating environment are disclosed. Key convenience kit apparatus providing novel methodology includes a plastic bag in which an innovative tray securely holds a plurality of empty eye drop bottles and associated caps disposed and sealed therein. Providing the only access pathway into the bag is a sterilizing filter appliance which filters all fluid entering the bag and provides a nozzle for dispensing into bottles disposed in the tray. The key convenience kit apparatus is sterilized prior to use, assuring all components disposed within the bag are within a desired sterility assurance level. The sterilized state of items associated with the key apparatus is maintained by the single pathway for fluid. Capping and sealing the bottles before opening the bag permits delivery of sterile product for use outside the bag.
Owner:THORNE INTPROP HLDG LLC
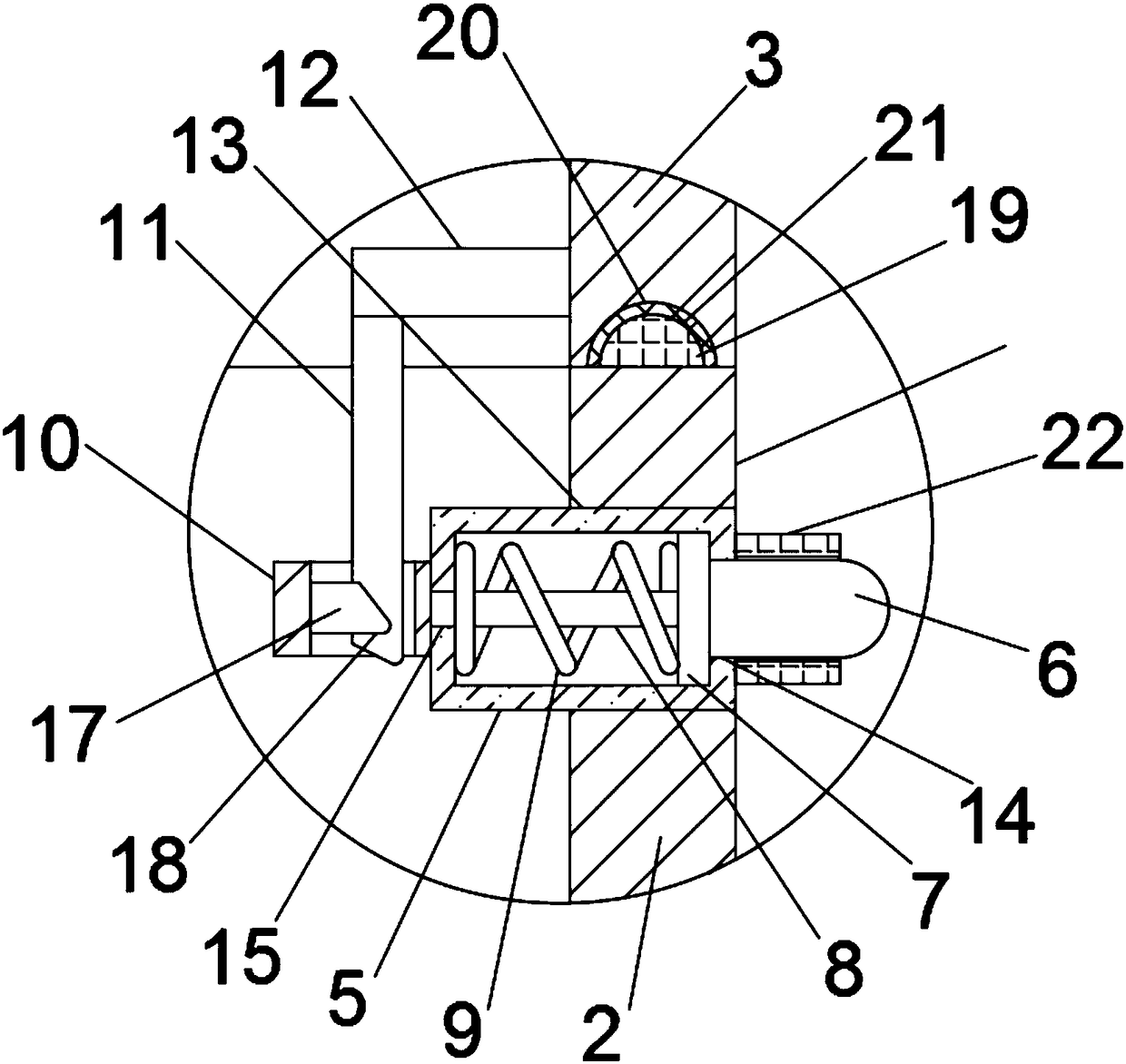
Medicine kit device of old people nursing robot
ActiveCN107081770ASolve the problem of not being able to automatically deliver medicineSolve the problem of dispensing drugsManipulatorOlder peopleKit device
The invention discloses a medicine kit device for an old people nursing robot. The medicine kit device comprises medicine storage boxes arranged in the robot and medicine plates capable of stretching out of the robot and exposing contained medicines. Corrugated pipes capable of stretching and contracting communicate between the medicine plates and the medical storage boxes. One-way valves only allowed for sending medicines to the medicine plates are arranged at the connecting positions between the corrugated pipes and the medicine plates. Multiple sets of corresponding medicine plates, medicine storage boxes and corrugated pipes are arranged. The medicine plates are integrally formed. Electric push rods used for pushing the medicine plates to stretch out of the robot are connected to the medicine plates. Each set of medicine storage box is provided with a medicine inlet for medicines to be inserted therein. By means of the medicine kit device of the old people nursing robot, an automatic medicine sending function and an automatic medicine distributing function can be achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING YOUBANJIA TECH CO LTD
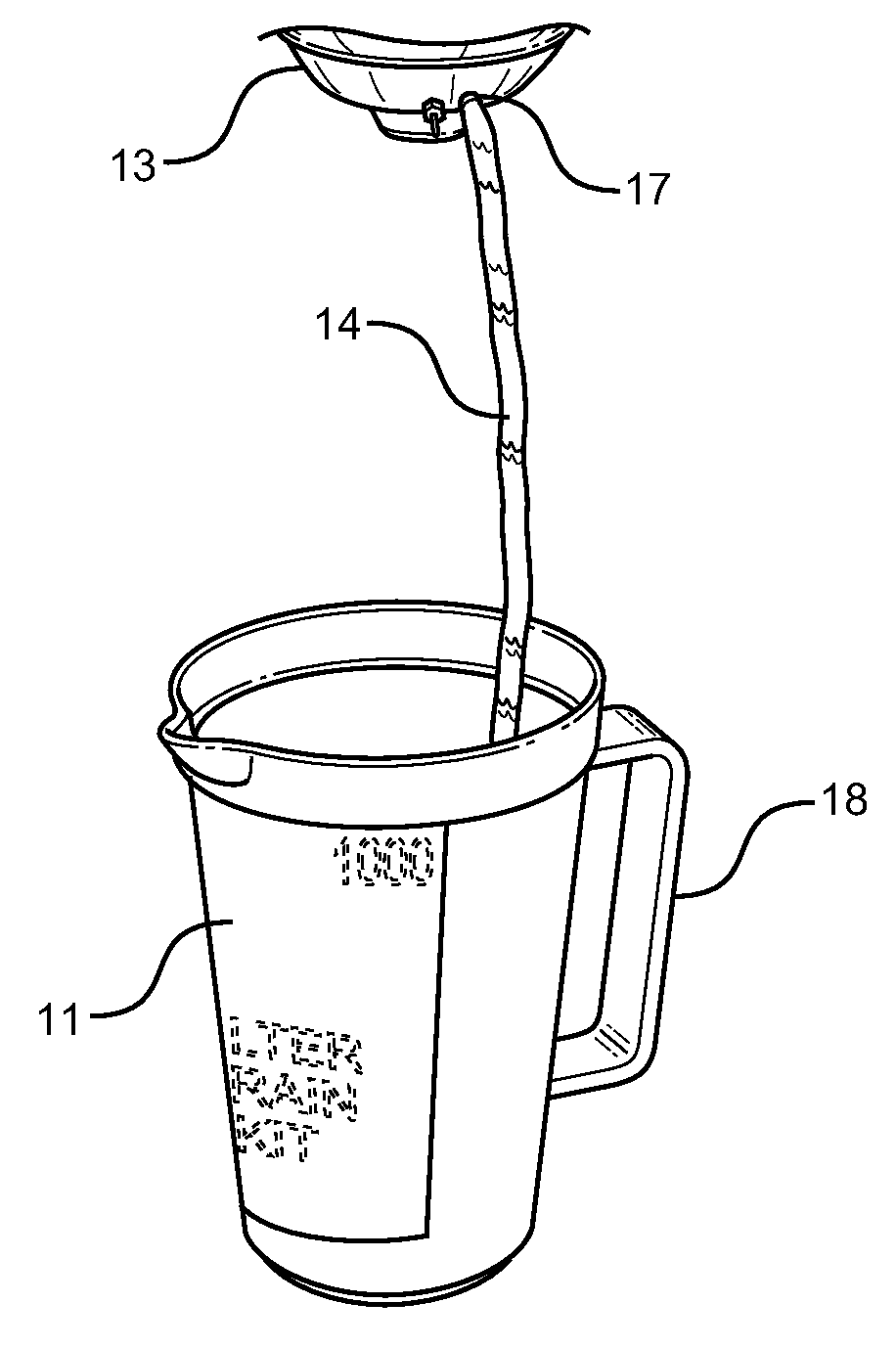
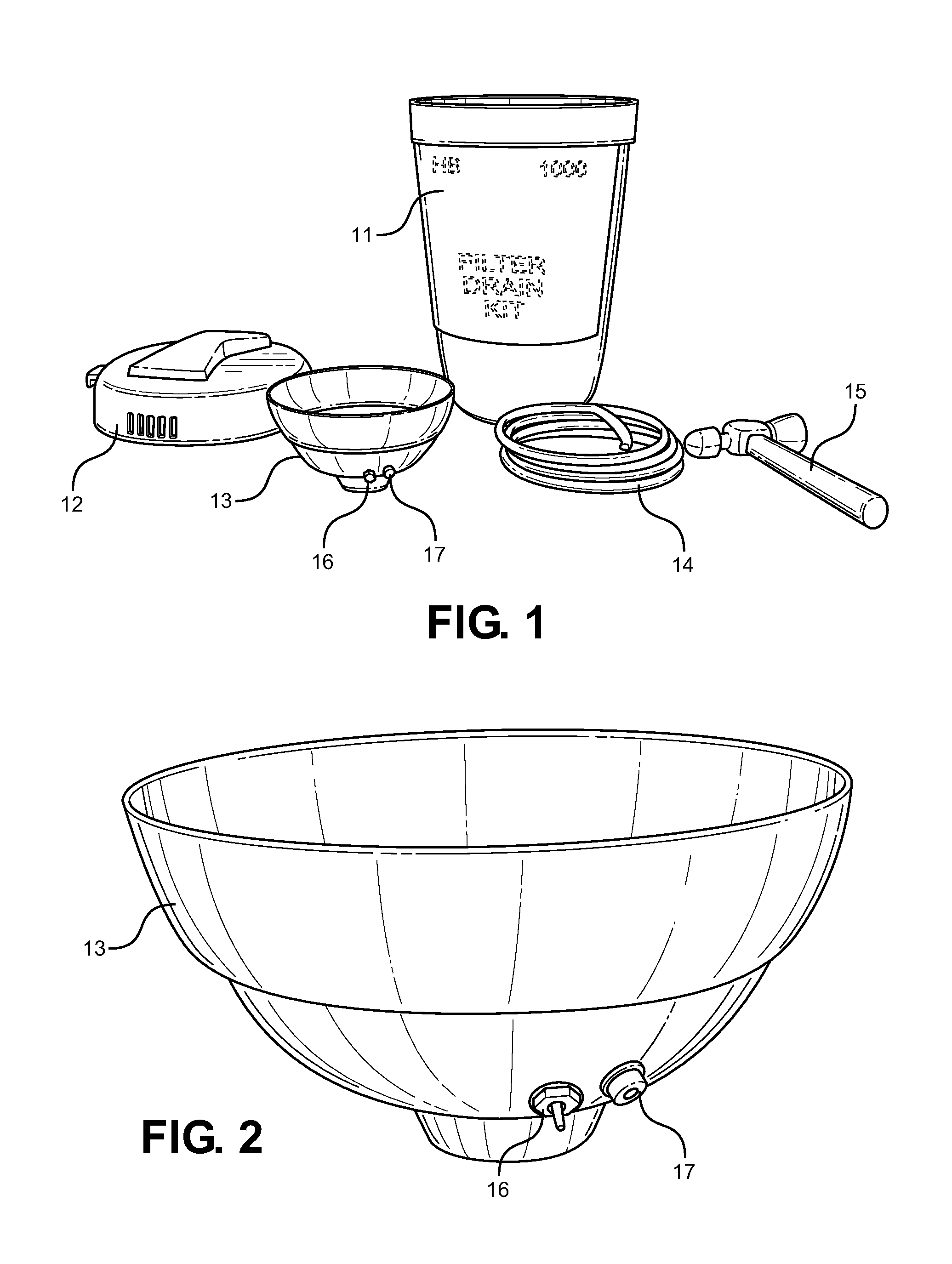
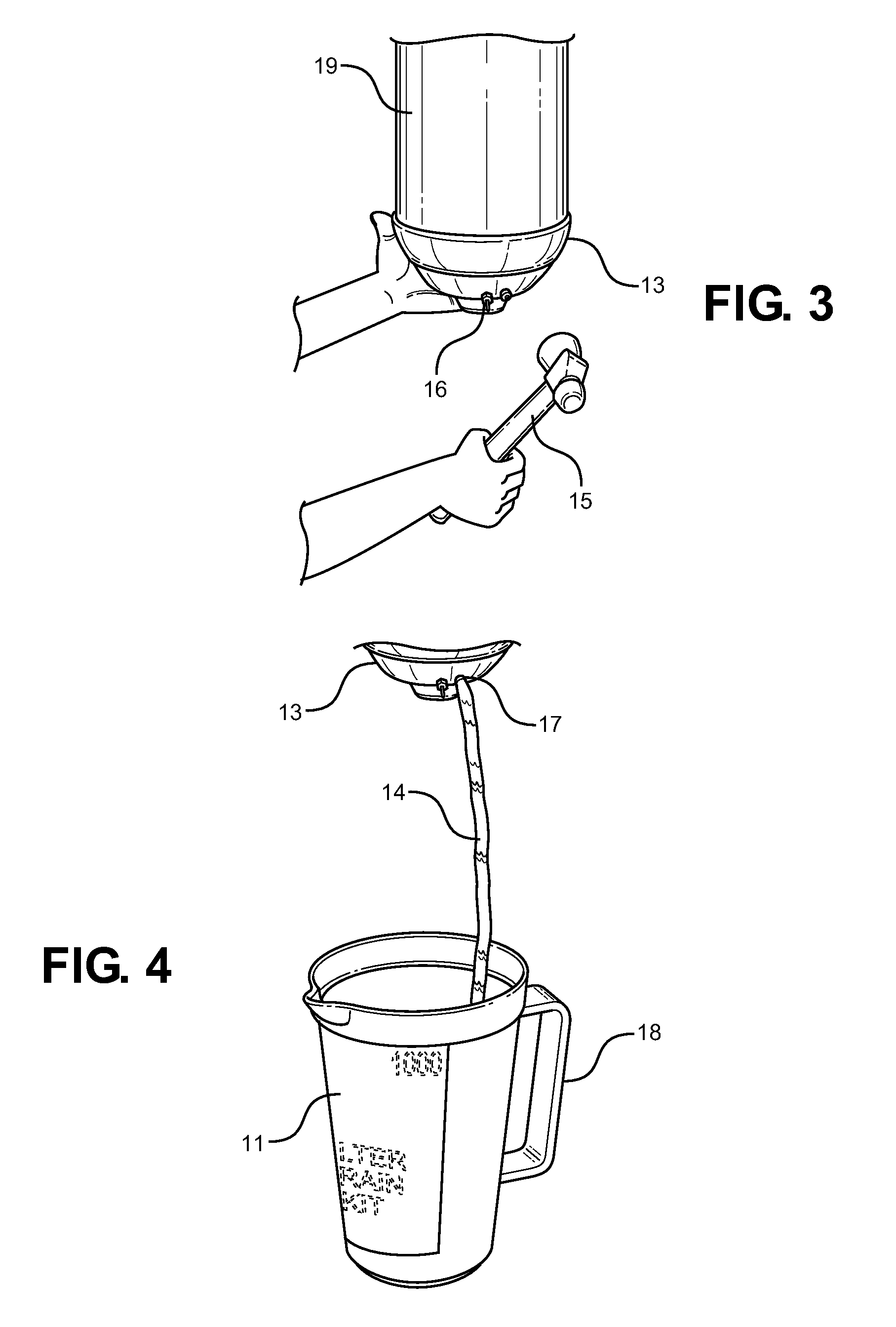
Filter Drain Kit and Method
A filter drain kit device is provided having a cylindrical storage container with a lid and handle that holds a flexible drain cup. The cup includes a puncture device and drain fitting. The kit also includes a clear plastic drain hose to fit the drain fitting, and a striking hammer. The items within the kit allow for a method of removing oil from an oil filter without the spillage that normally accompanies this process. The components of the kit are meant to be wiped clean after use and placed back into the storage container, thereby allowing for reusability and ease of storage while not in use.
Owner:BROADWAY THOMAS
Electronic balance density measurement kit device
PendingCN108225974AHigh strengthAvoid deformationSpecific gravity measurementMeasurement deviceKit device
The invention relates to the field of density measurement devices, and discloses an electronic balance density measurement kit device. The electronic balance density measurement kit device comprises asupport frame, a sample holding mechanism and / or buoyancy mechanism and a beaker bracket, wherein the support frame has an axisymmetric structure with a symmetrical central line, and the bottom end can be connected to a scale seat of an electronic balance; the support frame is connected to the scale seat of the electronic balance in such a manner that the center of gravity of the support frame and the weighing center of the electronic balance are positioned on the symmetrical central line of the support frame; the sample holding mechanism and / or buoyancy mechanism can be arranged on the support frame, and extends towards the bottom end of the support frame along the symmetrical central line of the support frame; the beaker bracket can be supported on a panel of the electronic balance; a gap is formed between the beaker bracket and the support frame. By adopting the electronic balance density measurement kit device, the center of gravity of a measured object can be controlled within asmaller radius region which takes the weighing center of the electronic balance as a dot, so that the measurement result of the electronic balance is more accurate.
Owner:SARTORIUS SCI INSTR BEIJING CO LTD
Humanized/sexual genetic engineering antibody kit device
The invention discloses a humanized / sexual genetic engineering antibody kit device, and relates to the technical field of antibody reagent filling. The device comprises a main body, a fixing frame is fixedly arranged on the inner side of the top of the main body, a motor with an upward output end is mounted at the bottom end in the fixing frame, a rotating frame is fixedly arranged at the output end of the motor, and a plurality of groups of rotating supporting mechanisms are uniformly and fixedly arranged on the outer side of the rotating frame. According to the device, the motor drives the rotating frame to rotate, the multiple groups of rotating supporting mechanisms matched with sliding rails and protruding fixing blocks are evenly and fixedly arranged on the outer side of the rotating frame, when one set of rotating supporting mechanism rotates to the top of the corresponding protruding fixing block, a containing frame is passively jacked up and ascends to a certain height, a kit placed in the containing frame can be better matched with a filling head, so that bacteria are effectively prevented from polluting an antibody reagent in the filling process, and the sealing effect in the whole filling process is better.
Owner:SUZHOU GUOCHEN BIOTEK CO LTD
Surgical tools and methods for their use
ActiveUS20150157450A1Significant complicationSignificant failureSuture equipmentsMammary implantsRaspKit device
Surgical tools and kits for performing methods include a grommet with cylindrical shaft, cutting tip, annular flange with suture retaining anchoring fixture; a grommet jig for extending between adjacent grommets and guiding a needle therebetween; a family of needles with single and double pointed ends, reinforced eyelets, stops to limit inadvertent exiting, double shaft construction with a longitudinal gap and sharpened, slicing ends, including a “J” shape embodiment; a bone anchor with ring to secure sutures about a patient's clavicle; a tissue dissector having radially extending cones to nick taut connecting tissues; a tissue rasp having a series of crisscrossing grooves along an end; a tissue mesher comprising one or more blocks having a matrix of holes for clamping a plurality of needles and a supporting framework; and a kit device and a method of surgically inserting an internal mesh brassiere under the breast skin.
Owner:LIPOCOSM LLC
Multifunctional kit for environmental detection
InactiveCN111774120AEffective protectionPrevent slipping outHeating or cooling apparatusTest tube stands/holdersPhysicsKit device
The invention discloses a multifunctional kit for environmental detection, relates to the technical field of kit devices, and aims to solve the problem that a reagent tube is easy to break when a reagent is carried by an existing multifunctional kit for environmental detection. According to the multifunctional kit, an inner box is mounted in a reagent placement box; a damping device is mounted below the inner box; a storage battery is mounted on one side of the damping device; a temperature control device is mounted on one side of the storage battery; a reagent placing groove is formed in theinner box; a friction fixing block is arranged on the inner wall of the reagent placing groove; electric telescopic rods are mounted at the upper ends of the two sides of the interior of the inner box; a fixing plate is installed above the electric telescopic rods, a through hole is formed in the fixing plate, a tweezer containing groove is formed in one side of the fixing plate, a dropper containing groove is formed in one side of the tweezer containing groove, and a detection cup containing groove is formed in one side of the dropper containing groove.
Owner:邓婧
Functional medicine first-aid kit for outdoors
PendingCN111671576AClear irradiationIrradiation allows the wounded to be treated outdoors clearlyPlanar light sourcesSurgical furnitureKit first aidLight equipment
The invention discloses a functional medicine first-aid kit for outdoors, and relates to the technical field of a medicine kit device for medical care. A kit cover is arranged above a kit body, a clipis mounted on one side of the kit body and one side of the box cover, and is fixedly connected with the kit body and the kit cover, the kit body is rotatably connected with the kit cover through a first hinge, a belt is arranged below the kit body, a frame body is mounted above the kit body, second hinges are respectively arranged on two sides of the frame body, a third hinge is arranged on one sides of the second hinges, a fourth hinge is arranged on the other side of the third hinge, emergency lighting equipment is arranged above the frame body, the upper end of the third hinge is located at the middle of two sides of the emergency lighting equipment, and a handle is arranged on one side of the kit cover. The problems that the inner part of the medical kit is free from a light source and medicines are disorderly classified, are solved, the light source can be fixed to any positions as needed, the limitation of the medical kit while in use can be improved, and the functions of the medical kit are increased.
Owner:南京宇赛科技发展有限公司
Novel dustproof phospholipase A2 testing kit
The invention discloses a novel dustproof phospholipase A2 testing kit which comprises a kit body and a locking device. The kit body comprises a placement tank, a sealing cover and the locking device,one side of the sealing cover is rotatably connected with the placement tank through a hinge while the other side of the same is in clamping connection with the placement tank through the locking device, and the locking device comprises a mounting shell, a button, a connecting plate, a connecting shaft, a compression spring, a clamping connection block, and a fixing shaft and a fixing block. Thekit body is sealed, so that outside dust and steam are prevented from entering the kit body, and pollution of kit devices in the kit body caused by impurities is prevented.
Owner:天津中标招标代理有限公司
Arthrocentesis kit device
ActiveUS11213365B1Reliable resultsImprove performanceSurgical furnitureIntravenous devicesExcess fluidsDiagnosis laboratory
An arthrocentesis kit and method for using the kit including a procedure tray having all the necessary contents in one tray to reliably perform an arthrocentesis procedure and deliver the fluid samples to a laboratory for analysis, allowing the physician to order delivery of the tray and perform the procedure at the bedside of the patient by using the tray to simultaneously collect and send the synovial fluid collected to a laboratory for all diagnostic testing, thus enhancing the reliability of proper diagnosis thereby allowing crucial orthopedic surgeons, rheumatologists, internists, emergency room physicians and family practitioners to minimize mistakes caused by delays and mistakes attributable to not having all the arthrocentesis kit tools together and readily available for bedside or emergency room treatment. The instant invention also allows a physician to dispose safely excess fluid in the reservoir, which takes advantage of the fact that bodily fluids quickly solidify into waste fluid for controlled disposal.
Owner:TRIKALA LAB A LLC
Improved type medical kit device
The invention discloses an improved type medical kit device. The improved type medical kit device comprises a medical kit and a locking device, wherein the locking device is used for fixing the medical kit; the medical kit is internally provided with a chamber body; the right end wall of the chamber body is provided with an upper empty opening and a lower empty opening which communicate with the outer end; the lower empty opening is rotationally equipped with a covering door through a hinge shaft; the covering door is equipped with an electronic lock for locking the covering door; the upper ends of the front end rear end walls in the chamber body are provided with a first sliding chamber extending in the left-right direction; the first sliding chamber is equipped with a sliding block capable of sliding leftwards and rightwards; a straight plate and an obliquely-arranged plate are fixedly installed inside the chamber body; the straight plate is positioned at the left end of the middle end of the chamber body; the obliquely-arranged plate is positioned at the upper right of the straight plate; an interval is kept between the straight plate and the obliquely-arranged plate; a push plate is fixedly arranged at the lower end face of the sliding block; and the lower end of the push plate leans against the upper end face of the straight plate.
Owner:广州爵诺医疗器械有限公司
Medical kit device used for elementary school classroom
The invention provides a medical box device used in elementary school classrooms, which includes a fixing plate, a fixing seat, a fixing groove, a box body, a cover door, an upper clamping column, a locking device and an elastic band. The rear end of the fixing seat is equipped with a fixing plate, the top of the fixed base is provided with a fixed groove, the fixed groove is provided with a box body, the top rear end of the box body and the cover door are movably connected through a hinge, and a handle is installed on the top of the cover door, so An upper card post is installed in the middle of the front end of the cover door, and a fixing hole is arranged on the upper card post. A storage bag is provided inside the cover door, and an elastic band is provided at the opening of the storage bag. The front side of the box body A lower post is installed in the middle of the top, and a fixing hole is arranged on the lower post. The invention makes the storage of the box simple and easy to take through the flexible connection of the box body and the fixed groove, and the use of the locking device prevents primary school students from randomly taking the medical supplies inside, resulting in the lack of medical supplies.
Owner:张景玉
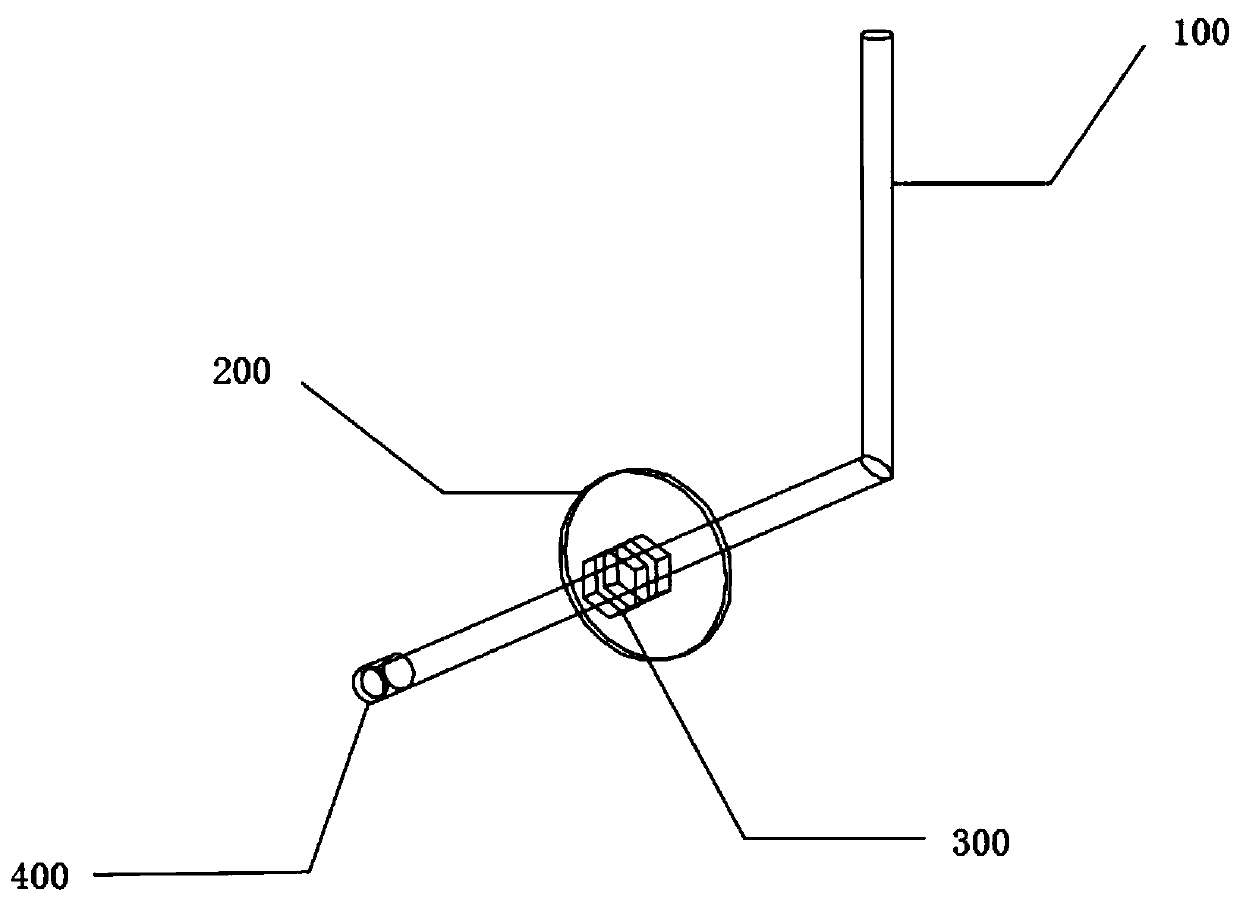
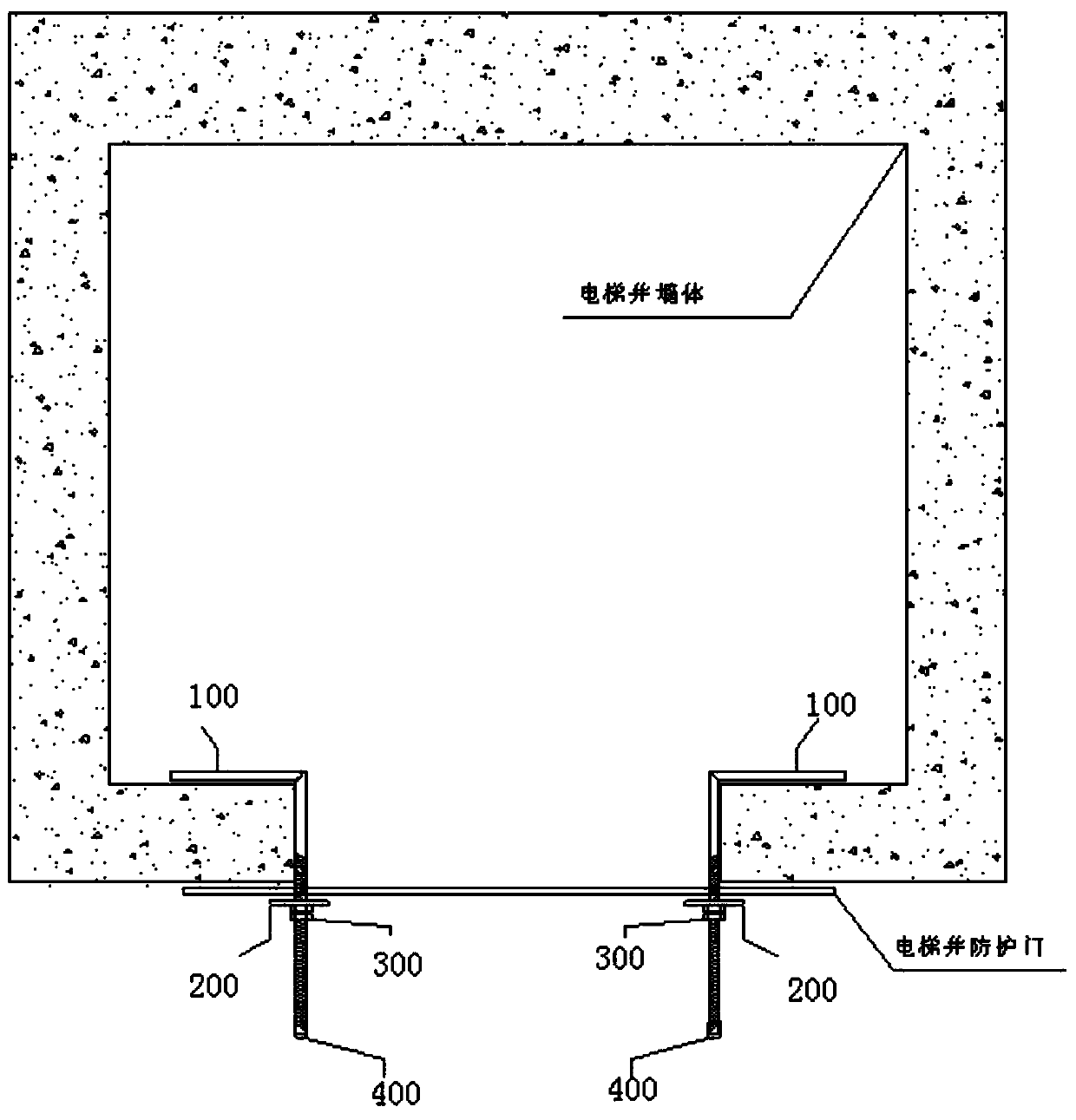
Setting elevator door fixed kit device
PendingCN111441599ASimple preparation processEasy to installBuilding material handlingKit deviceHouse building
The invention discloses a setting elevator door fixed kit device. The device comprises a main rod, a round gasket, a screw cap and a rubber cap, the main rod is bent to 90 degrees, a straight segmentof the main rod is provided with a thread, the straight segment of the main rod is sleeved with the round gasket and is in threaded connection with the screw cap, the rubber cap is mounted on the upper end of the straight segment of the main rod, the device is formed through assembling of the main rod, the round gasket, and the screw cap, and compared with the prior art, the device has the advantages that design is scientific, manufacturing is easy, cost is low, manufacturing materials can be taken in a construction site, operation is easy, the construction period is quickened, construction cost is reduced, the device can be widely applied to various buildings of house buildings, construction buildings and the like, a bending machine can carry out bending and cutting at the same time, andwork efficiency is improved.
Owner:CHINA CONSTR FOURTH ENG DIV +1
Grinding tool kit, equipment and method used for rolling surface finishing of tapered rollers
ActiveCN113601277AIncrease the number ofHigh dimensional consistencyLapping machinesLapping toolsKit deviceEngineering
The invention discloses a grinding tool kit, equipment and method used for rolling surface finishing of tapered rollers. The equipment comprises a main machine, an outer circulation system, the grinding tool kit and a grinding tool kit clamp. The structure of the main machine comprises a grinding strip assembly rotary type and a grinding sleeve rotary type. The outer circulation system comprises a collecting unit, an arranging unit, a feeding unit and a conveying system. The grinding tool kit comprises a grinding sleeve and a grinding strip assembly, the grinding sleeve keeps coaxial during working, the grinding strip assembly penetrates through the grinding sleeve, a cylindrical spiral groove is formed in the inner surface of the grinding sleeve, and the grinding strip assembly comprises multiple grinding strips which are distributed in a circumferential columnar array manner, and linear grooves are formed in the front faces of the grinding strips. During grinding, under the action of friction and pushing of a spiral groove working face and linear groove working faces, tapered rollers move along the linear grooves and the spiral groove while rotating along the axes of the tapered rollers, and therefore grinding of the rolling surfaces of the tapered rollers is achieved. By means of the grinding tool kit, equipment and method, the size consistency of the rolling surfaces of the tapered rollers can be improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
First-aid kit device
The invention provides a first-aid kit for first aid during field operation. The first-aid kit device is characterized by comprising a storage part and a strap part, wherein the storage part comprises a main box used for accommodating multiple first-aid articles; the strap part is connected with the storage part and allows a first-aid worker to carry the storage part; the main box comprises a box body and a cover, the upper part of the cover is connected with the upper part of the box body through a zipper, a hard isolation layer parallel to the inner wall of the main box is arranged in the main box and divides a space in the main box into two parts, and multiple fixing buckles are arranged on the inner wall of the box body, the inner wall of the cover and the front and rear walls of the hard isolation layer and used for fixing articles in the main box in the corresponding positions; the strap part comprises double shoulder straps arranged on the outer wall of the side, far away from the cover, of the box body as well as a waistband arranged below the double shoulder straps.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Methods and apparatus for preparing autologous blood eye drops
ActiveUS10940087B2Improve sterilitySufficient materialSurgical furniturePharmaceutical containersKit deviceAutologous blood
Methods and apparatus for preparing autologous blood serum eye drops within a potentially contaminating environment are disclosed. Key convenience kit apparatus providing novel methodology includes a plastic bag in which an innovative tray securely holds a plurality of empty eye drop bottles and associated caps disposed and sealed therein. Providing the only access pathway into the bag is a sterilizing filter appliance which filters all fluid entering the bag and provides a nozzle for dispensing into bottles disposed in the tray. The key convenience kit apparatus is sterilized prior to use, assuring all components disposed within the bag are within a desired sterility assurance level. The sterilized state of items associated with the key apparatus is maintained by the single pathway for fluid. Capping and sealing the bottles before opening the bag permits delivery of sterile product for use outside the bag.
Owner:THORNE INTPROP HLDG LLC
Medical kit device
InactiveCN107826428ASimple structureEasy to installDrawer-and-shell containersExternal fittingsKit deviceEngineering
The invention discloses a medical box device, which comprises a medical box and a locking structure for fixing the medical box. The locking structure includes a mounting plate, an engaging arm fixed on the right end surface of the mounting plate, and a fixing The locking arm that is installed on the right end of the engaging arm and extends upwards, the right end surface of the locking arm is provided with a first oblique inserting surface correspondingly, and the right end surface of the installation plate is provided with a mounting plate with the opening end facing right. Groove, the left end wall of the installation groove is provided with a perforation communicating with the outer end, the perforation is provided with fasteners for fixing the installation board on the wall, and the left end surface of the medical box is provided with There is an insertion groove with the opening facing left, the upper right end of the insertion groove is provided with a locking groove extending upward and matching with the locking arm, and the left end surface of the medical box is also provided with a top under the locking groove. A push slot, a slide push arm is movably installed in the push push slot, and a marking head is fixedly arranged at the left end of the slide push arm.
Owner:韩建波
Biological diagnosis kit device
ActiveCN112874992ALow efficiencyGuaranteed accuracyClosuresInternal fittingsKit deviceBatch operation
The invention discloses a biological diagnosis kit device which comprises a stirring box. A stirring cavity with an upward opening is formed in the stirring box, an annular sealing groove with an upward opening is formed in the stirring box in the circumferential direction with the stirring cavity as the center, an upper cover annular block is connected into the annular sealing groove in a rotating fit mode, and an upper cover is fixedly connected to the upper end face of the upper cover annular block; and an upper cover cavity with an opening facing downwards is formed in the upper cover, and a clutch box located below the stirring cavity is arranged in the stirring box. A mechanical device is used, so that continuous and rapid reagent adding and preparing can be carried out on a large batch of kits, and the problems that in the large-batch operation process, the efficiency of a traditional manual mode is low are solved, in the kit operation process, the reagent adding is further automatically completed by a device, the accuracy of reagent adding of each sample is ensured, and the device has a two-layer sealing protection effect, so that the sample is prevented from being polluted by air, and the reliability of a result is ensured.
Owner:广州市言康生物科技有限公司
Safety medical kit device
The invention provides a safety medical kit device. The safety medical kit device comprises a kit body used for storing medical tools, and a surrounding door body device used for shielding the kit body. A left sliding groove and a right sliding groove which stretch up and down are formed in the front end of the left end wall of the kit body and the front end of the right end wall of the kit body respectively. A left sliding block and a right sliding block are installed in the left sliding groove and the right sliding groove in a slidable mode respectively. A motor is fixedly installed at the lower end of the left sliding groove, a damping piece is arranged outside the motor and used for weakening vibration generated when the motor runs, a left screw rod is installed at the upper end of the left sliding groove in a steering mode, and the lower end of the left screw rod is fixedly connected with a power shaft of the motor.
Owner:黄龙飞
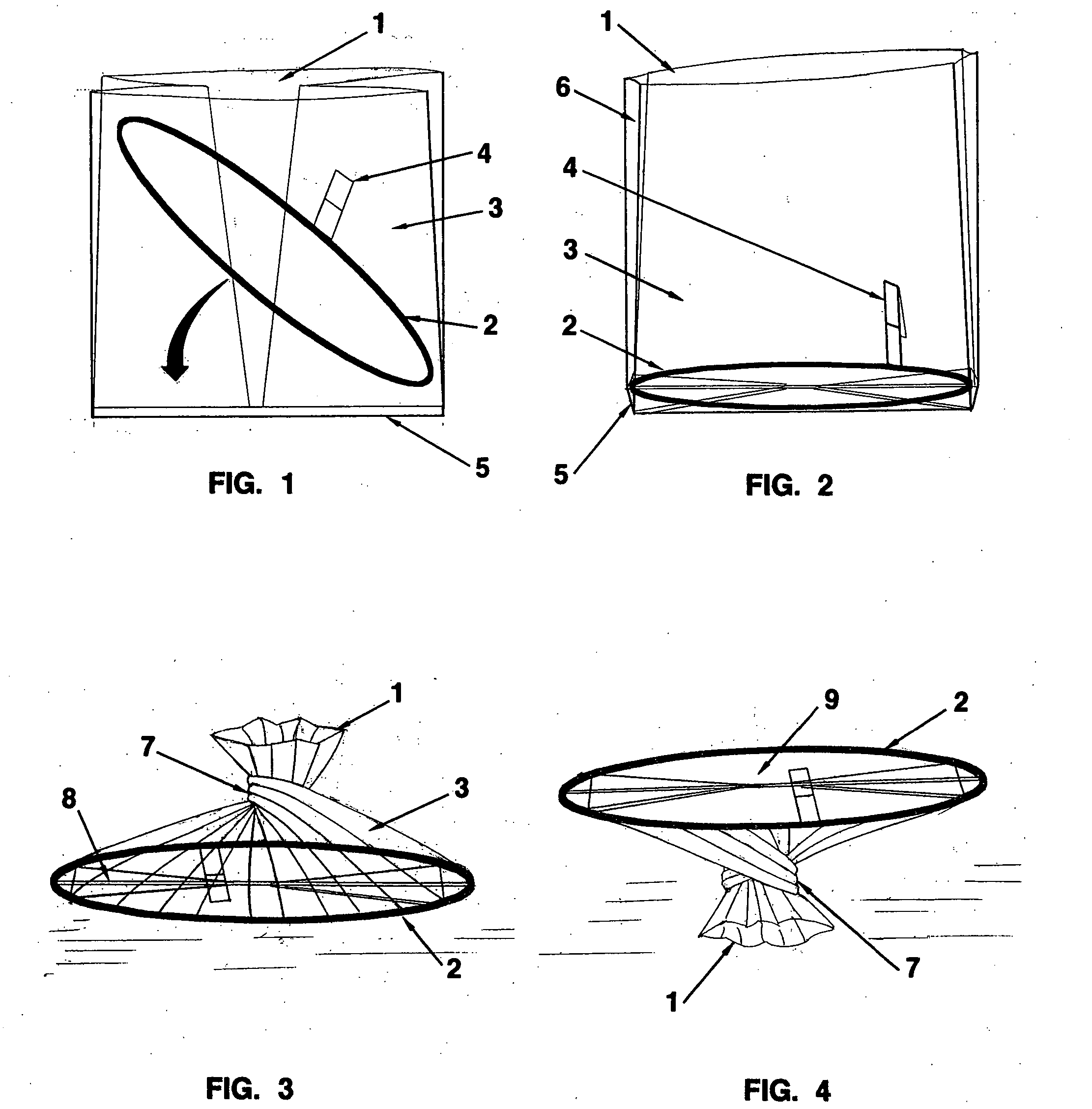
Ring kit canine waste collection and disposal method
A canine waste collection device and waste disposal method are described. The device is called the Ring Kit Canine Waste Collection and Disposal Method. The ring kit device collects canine feces before it contacts the ground and provides a sanitary means to dispose of the collected solid waste. The ring kit device consists of a chrome-plated, 10-inch in diameter, steel ring, a supply of disposable plastic bags, a steel belt clip, and complete instructions for use.
Owner:CIAVOLA ALEX WILLIAM
Underwater first-aid kit
The invention discloses an underwater first-aid kit, which relates to the technical field of first-aid kit devices. The underwater first-aid kit comprises a lock catch, a lock pin, a belt, a first-aid kit body, a first-aid kit cover, a first-aid kit hole, positioning holes, a waistband, a carrying hook, an external medicament cabin, an internal medicament cabin, an acupuncture needle cabin and isolating frames, and is characterized in that: the first-aid kit body is provided with the carrying hook; the waistband is connected with the first-aid kit body through the carrying hook; the upper part of the first-aid kit body is provided with the first-aid kit hole; one end of the waistband is connected with the lock catch; the lock catch is provided with the lock pin; 4-8 positioning holes are formed in the waistband; the top of the first-aid kit body is provided with the first-aid kit hole; three cabins are formed in the first-aid kit body; and the three cabins are isolated away from each other by using the isolating frames. Due to the adoption of the underwater first-aid: the defects in the prior art are overcome, and common unexpected diseases can be treated particularly on bathing beaches and wild lake beaches.
Owner:马荣华
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com