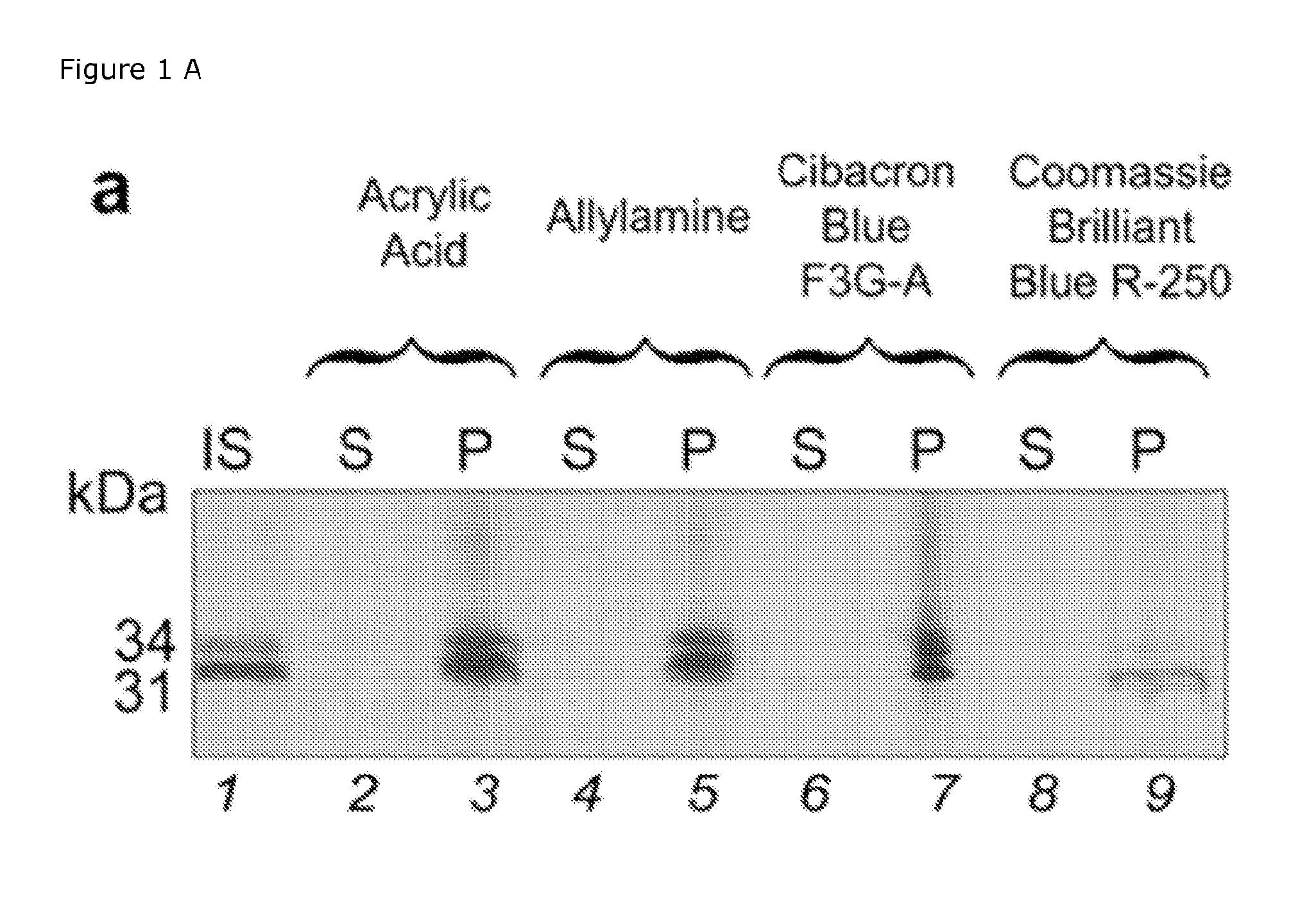
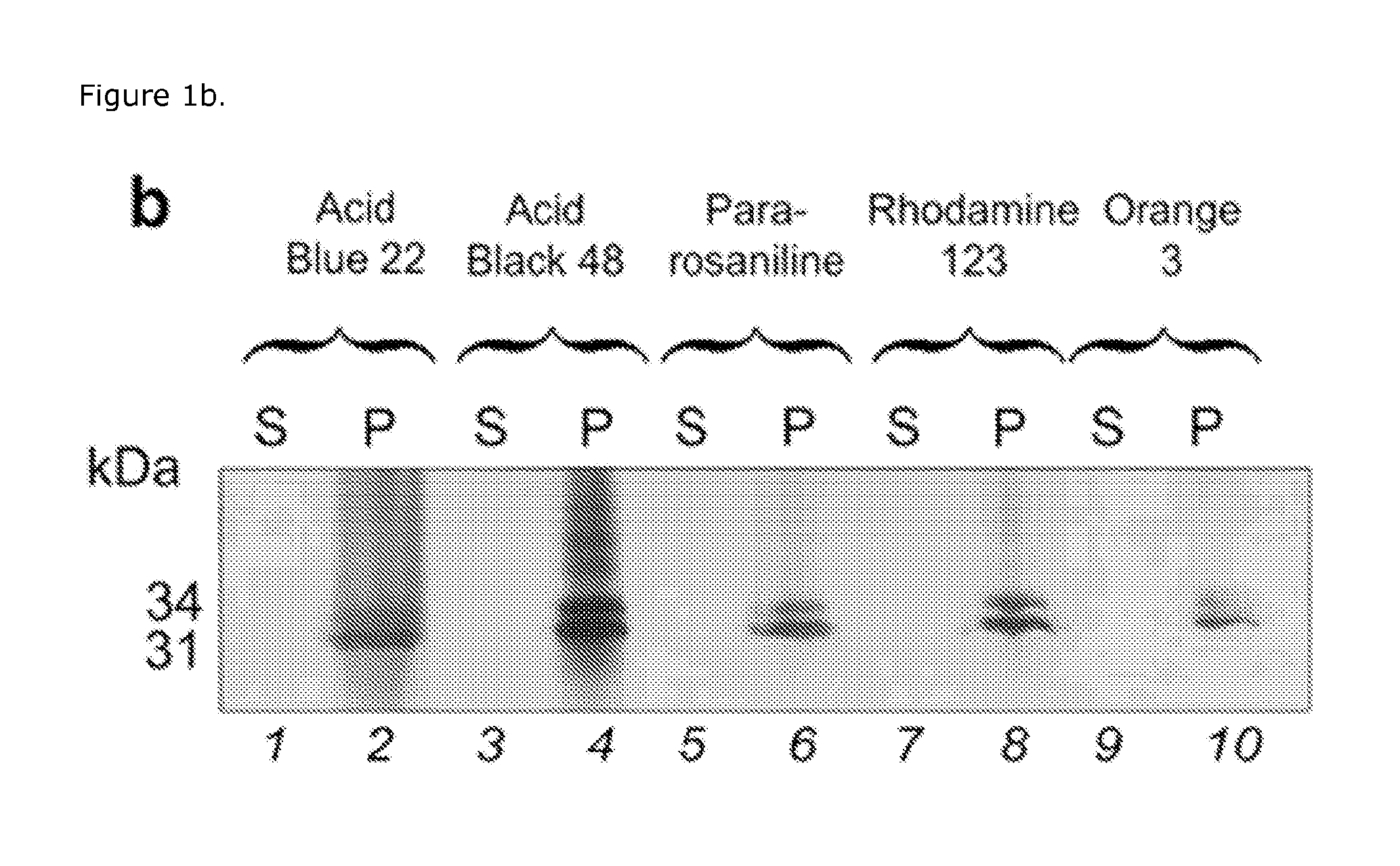
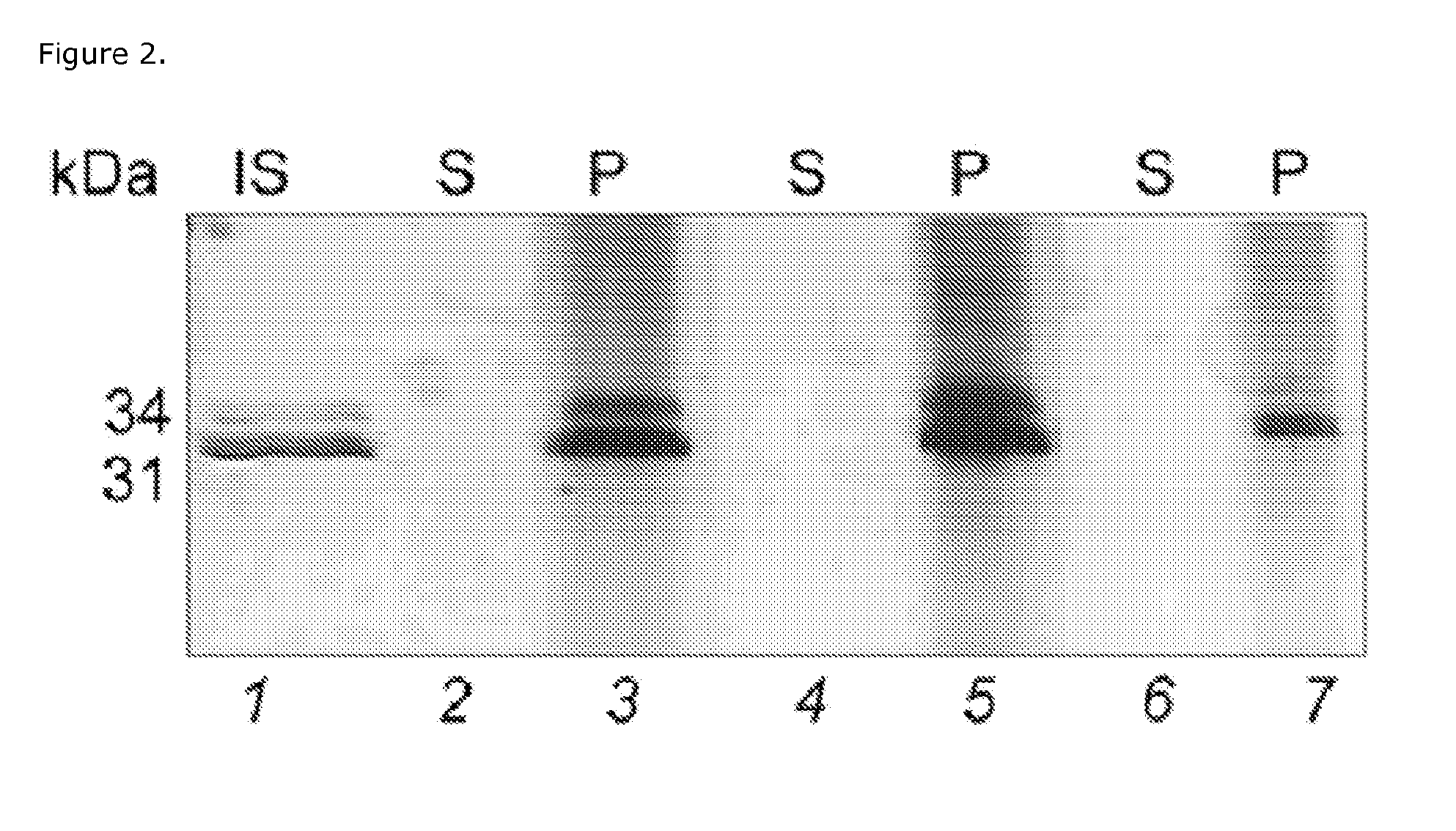
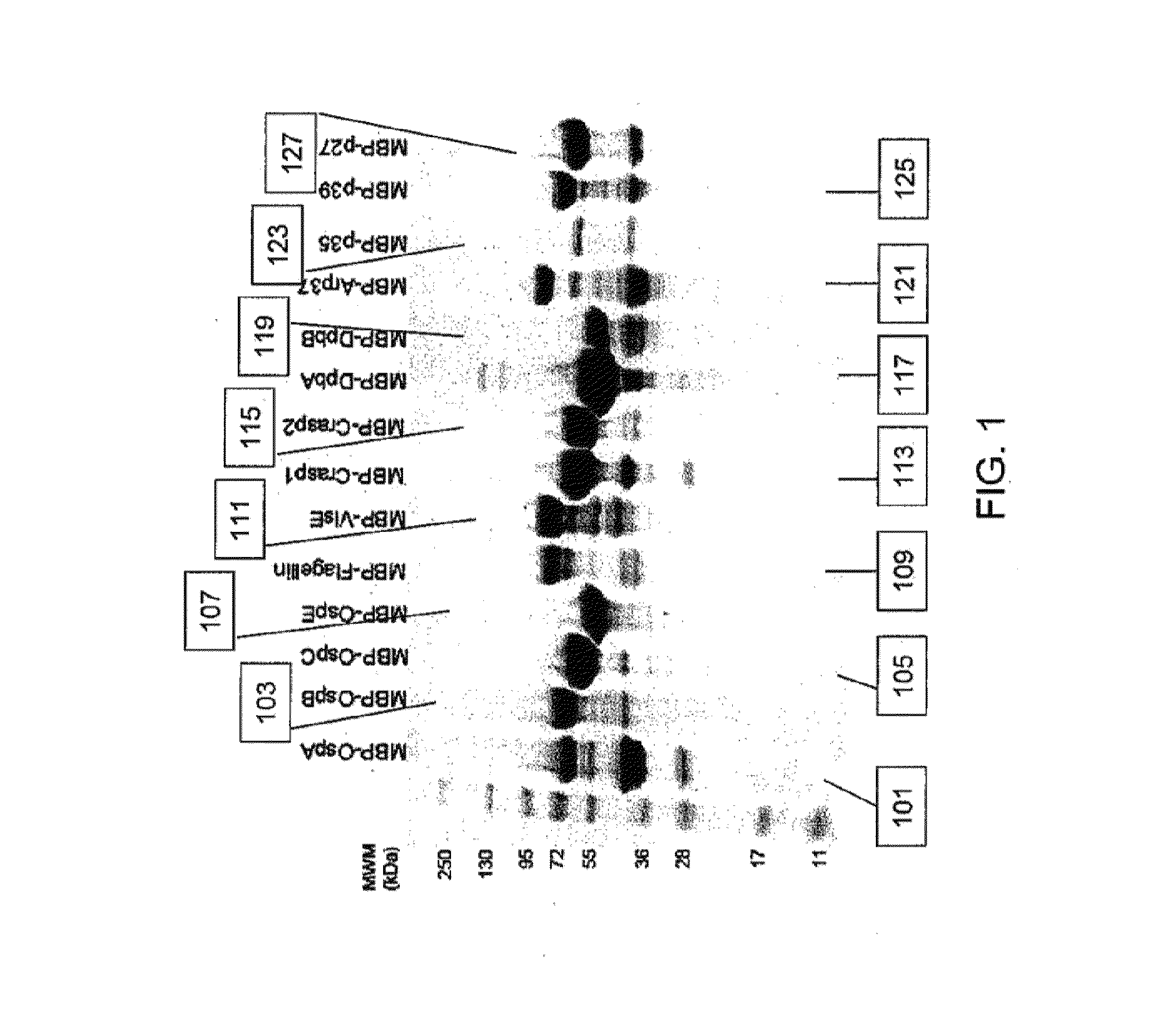
Patents
Literature
58 results about "Lyme's disease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
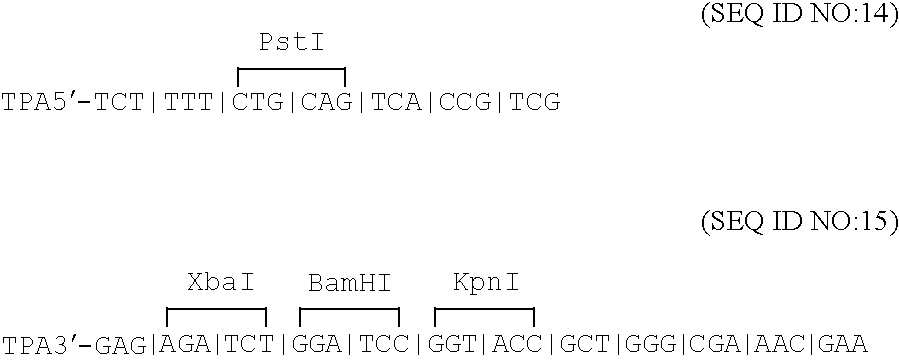
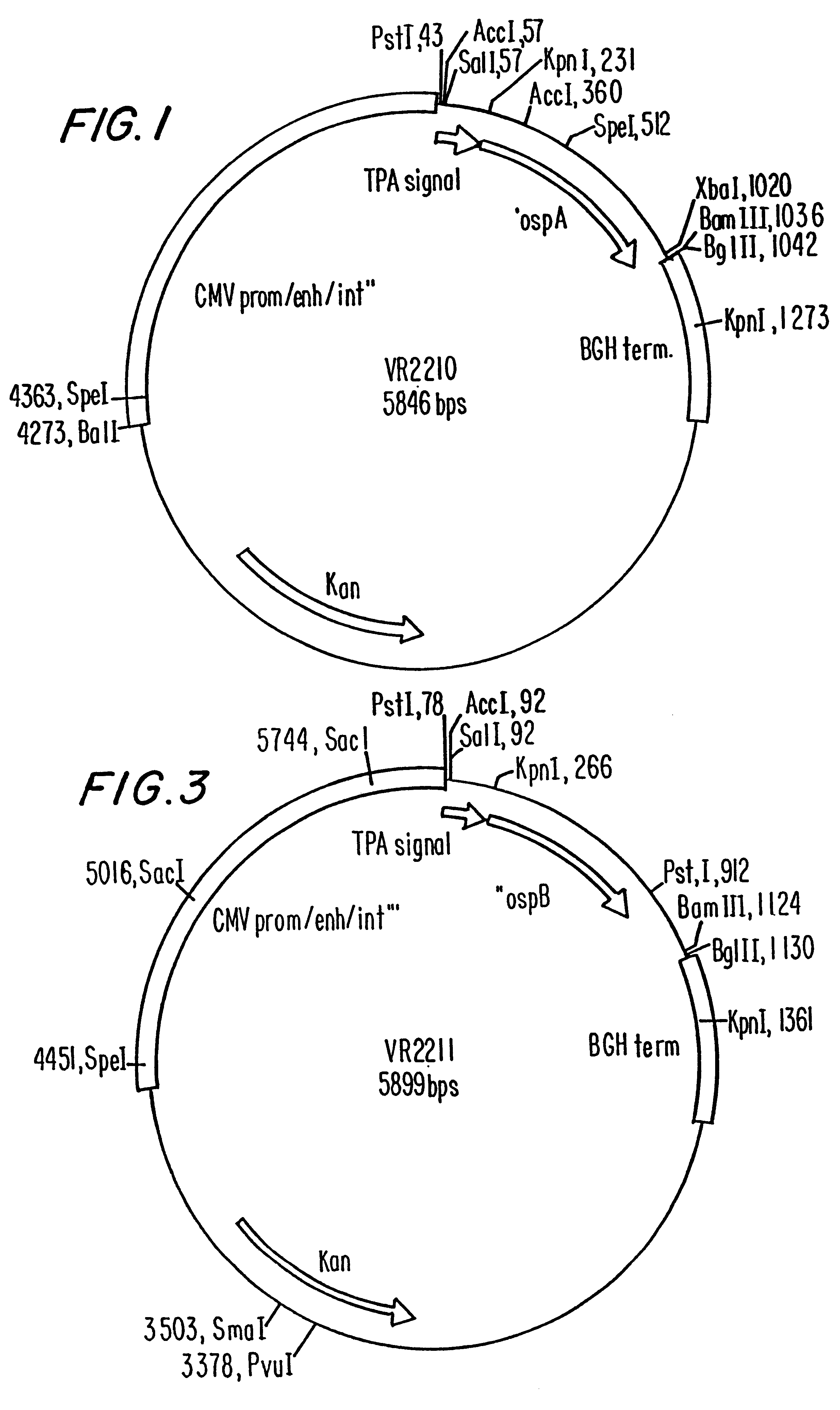
Compositions and methods for administering Borrelia DNA
Disclosed is a vaccine against Lyme Disease or its causative agent Borrelia burgdorferi (sensu stricto or sensu lato) containing a plasmid a DNA encoding a promoter for driving expression in a mammalian cell, DNA encoding a leader peptide for facilitating secretion / release of a prokaryotic protein sequence from a mammalian cell, a DNA encoding Borrelia OspA or OspB, and a DNA encoding a terminator. Disclosed too is an immunogenic composition against Lyme Disease or its causative agent Borrelia burgdorferi (sensu stricto or sensu lato) containing a plasmid comprising a DNA encoding a promoter for driving expression in a mammalian cell, DNA encoding a leader peptide for facilitating secretion / release of a prokaryotic protein sequence from a mammalian cell, a DNA encoding a Borrelia OspC, and a DNA encoding a terminator. And, methods for making and using such vaccines and the immunogenic composition are also disclosed.
Owner:PASTEUR MERIEUX SERUMS & VACCINS SA
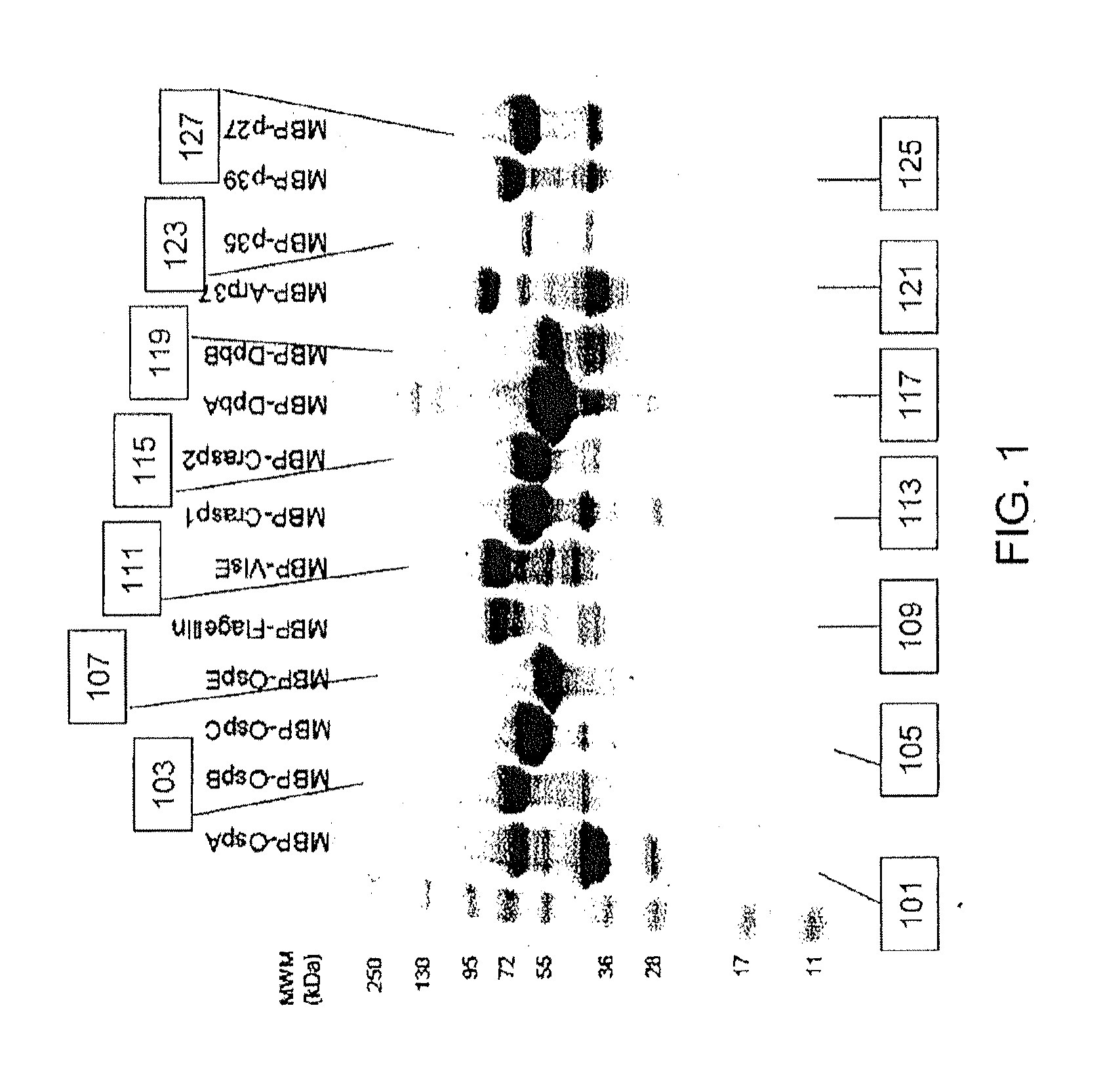
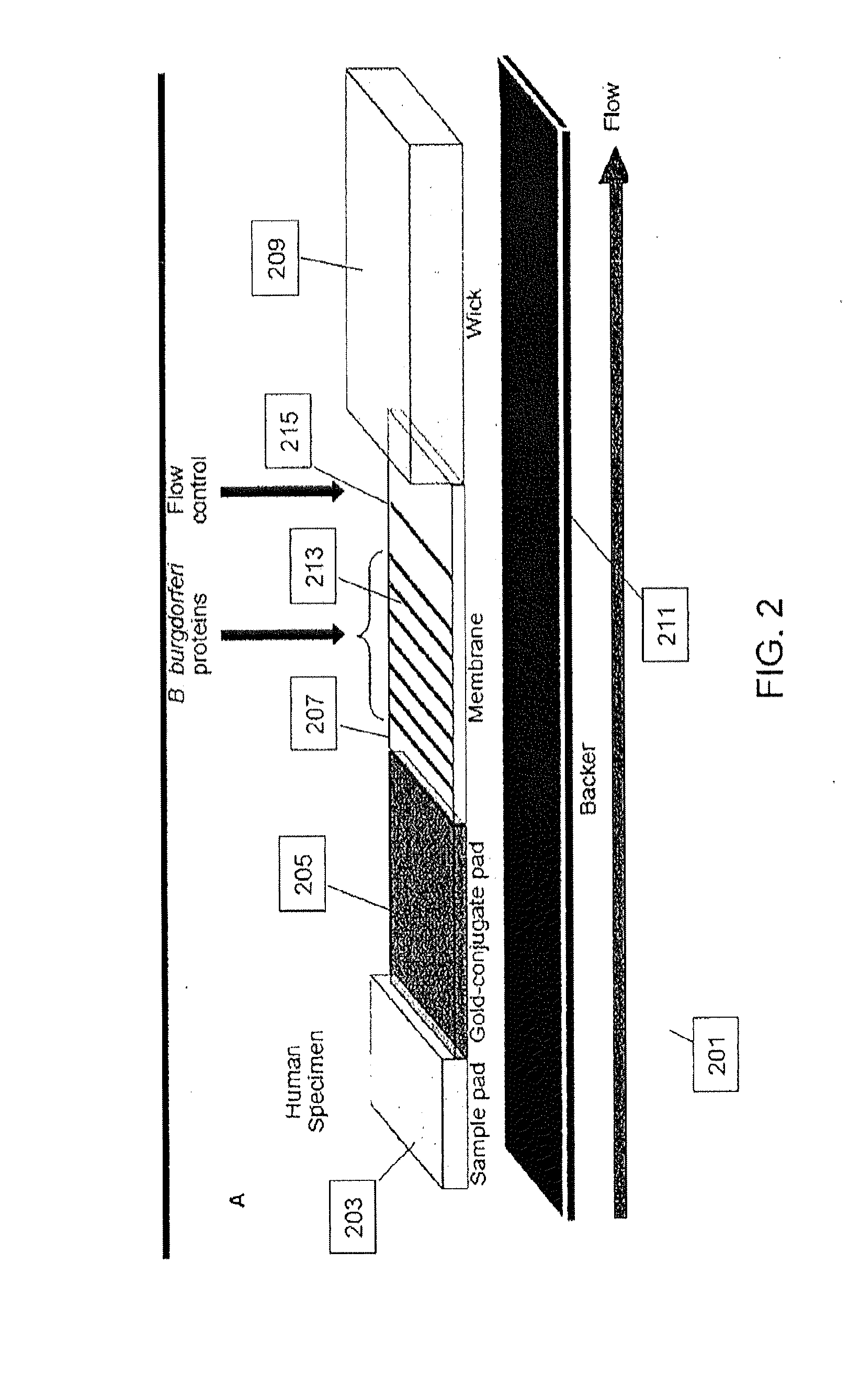
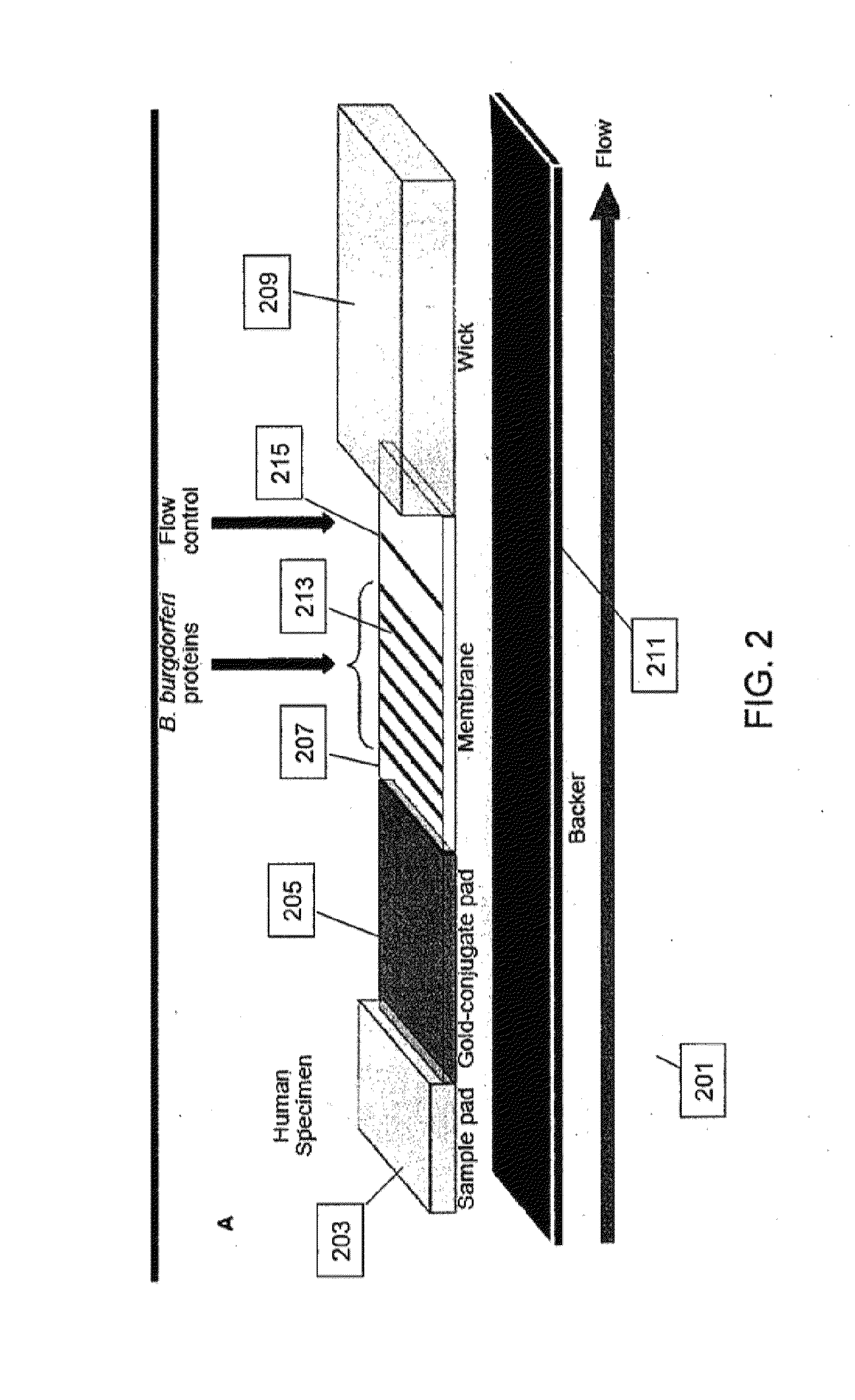
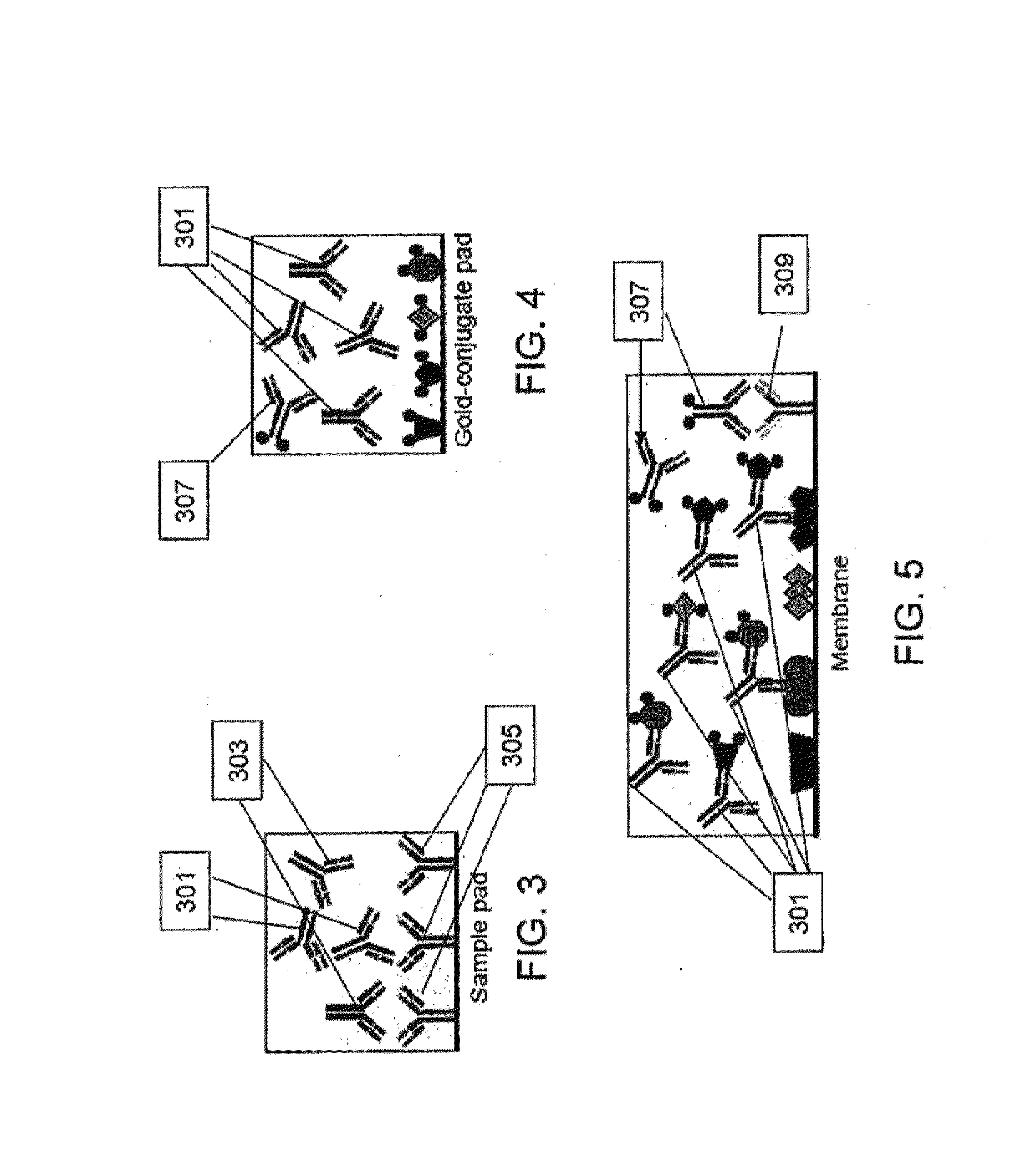
Proteins and method for detection of lyme disease
InactiveUS20120142023A1Accurate detectionCost-effectiveDisease diagnosisBiological testingGold ColloidCapture antibody
Recombinant B. burgdorferi proteins, representative of the life cycle, are membrane-immobilized to capture antibodies in biological samples. Lateral flow technology incorporating gold colloid deposition results in band visualization indicative of a positive test.
Owner:ROCKLAND IMMUNOCHEM
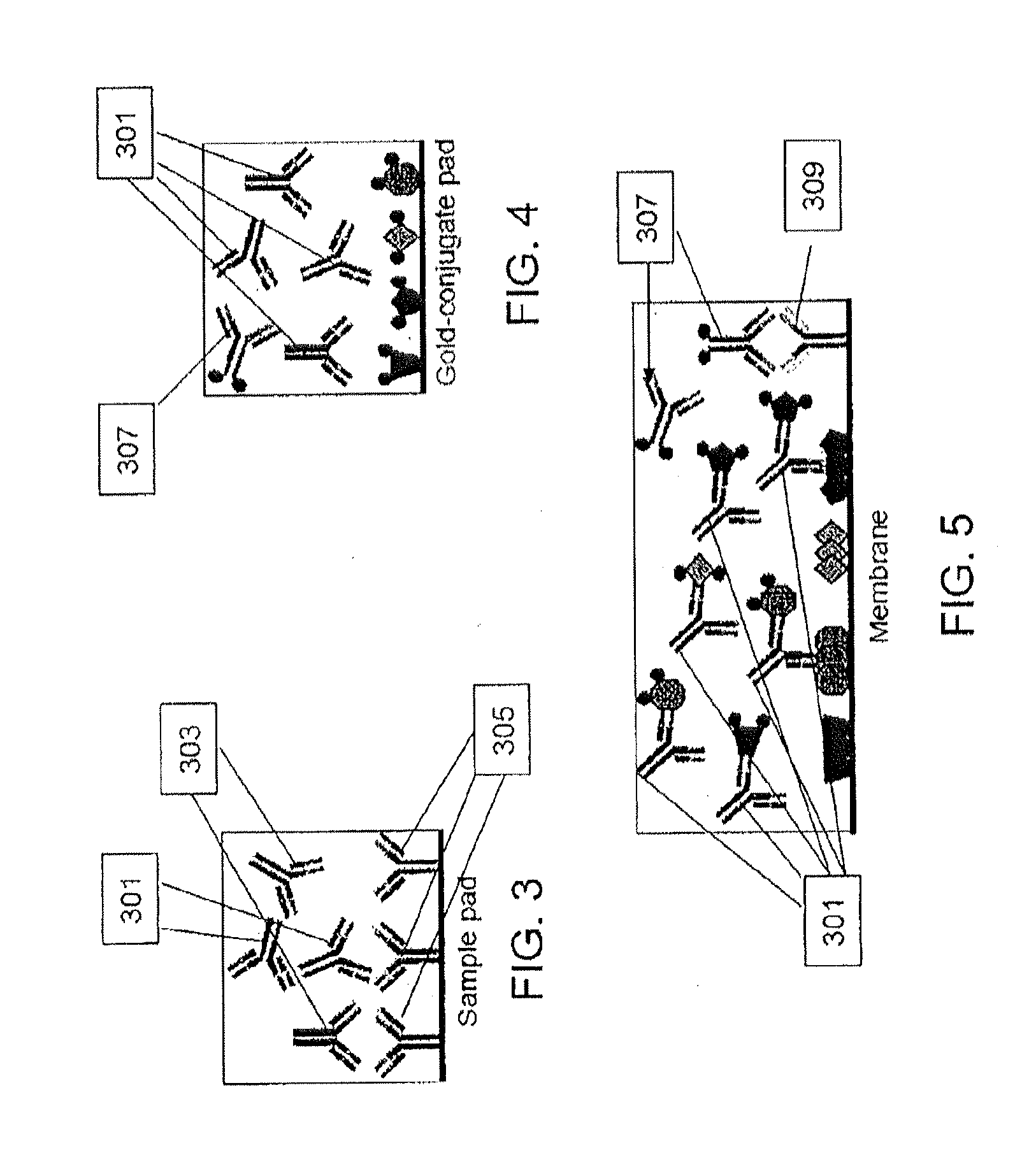
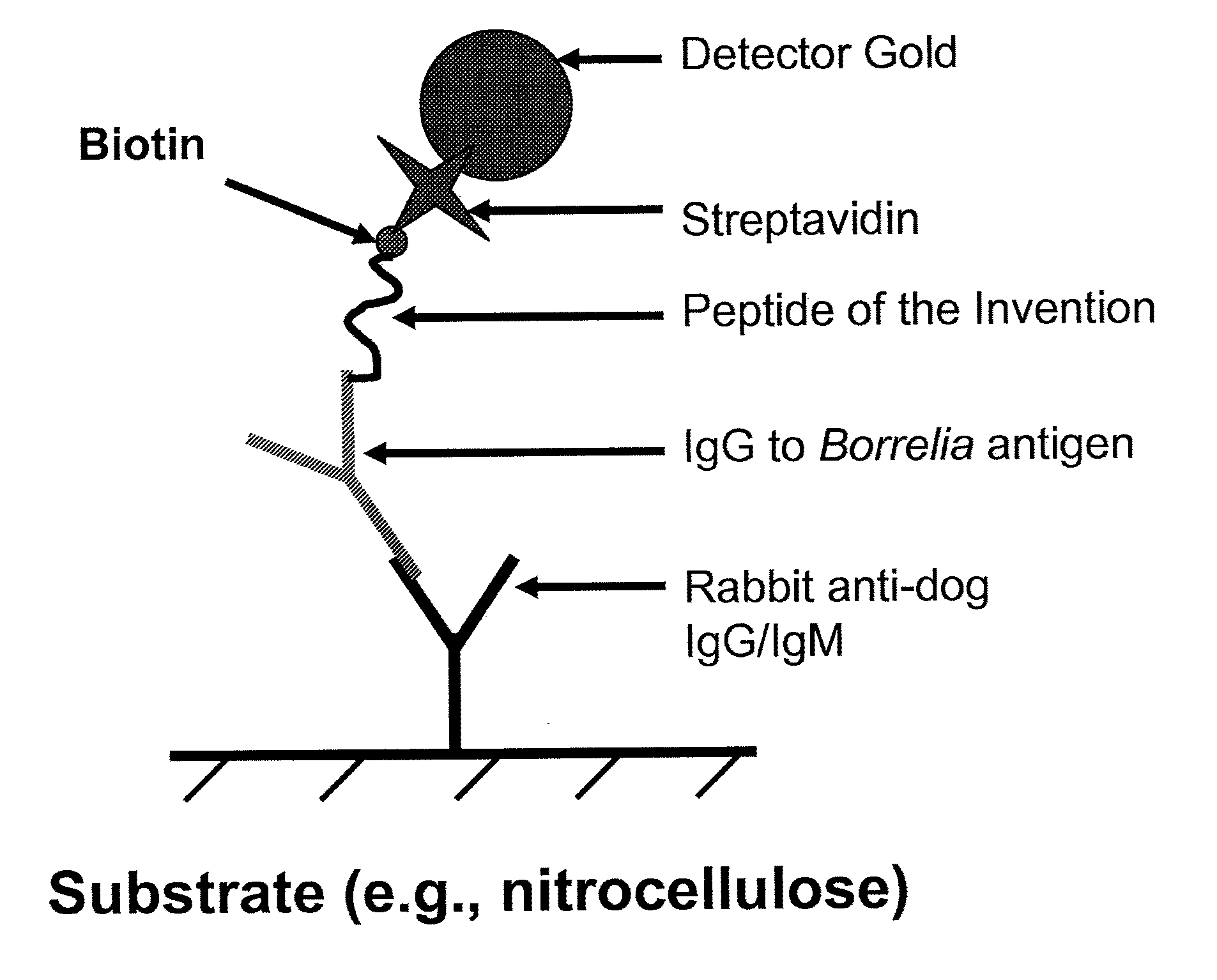
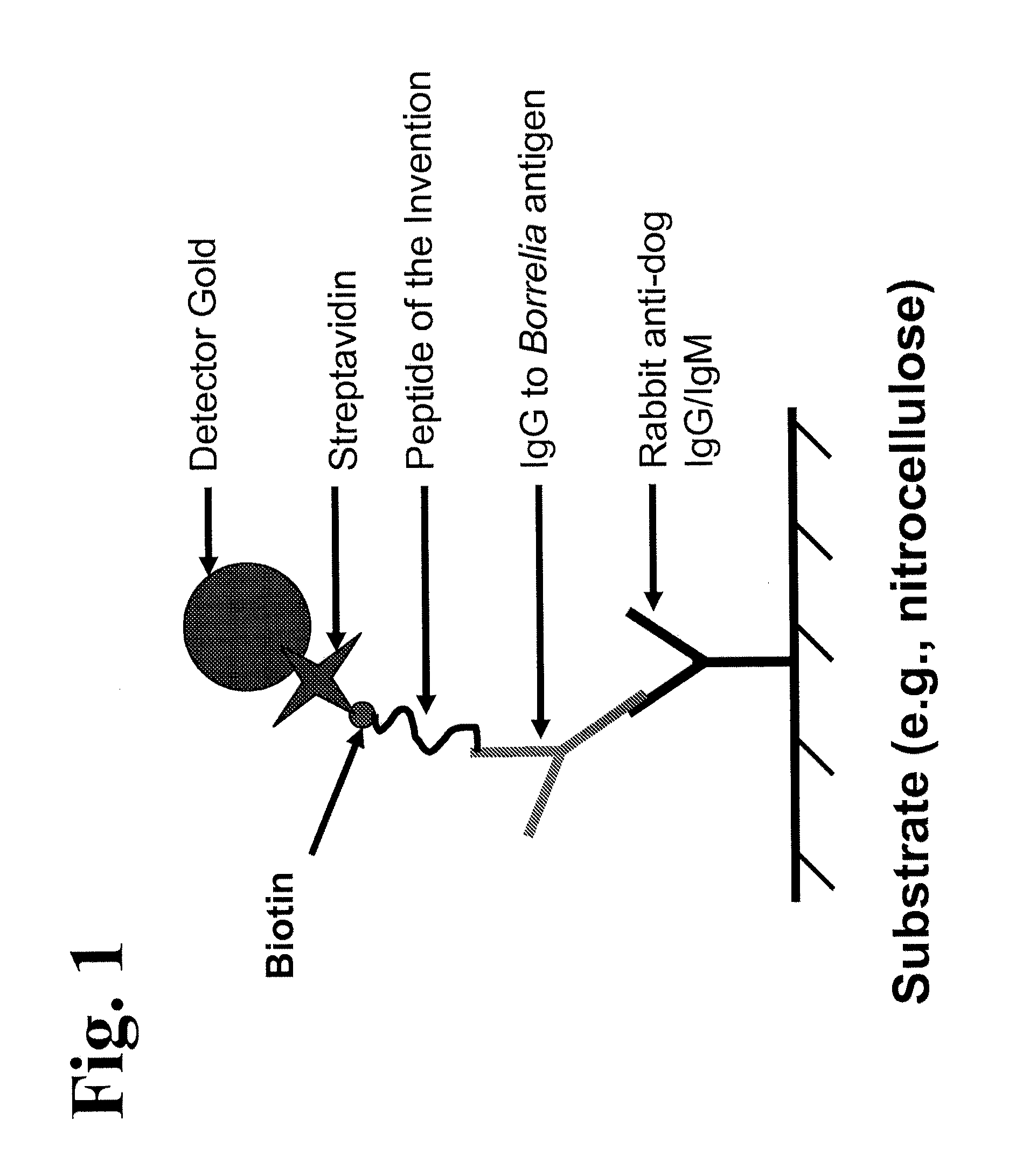
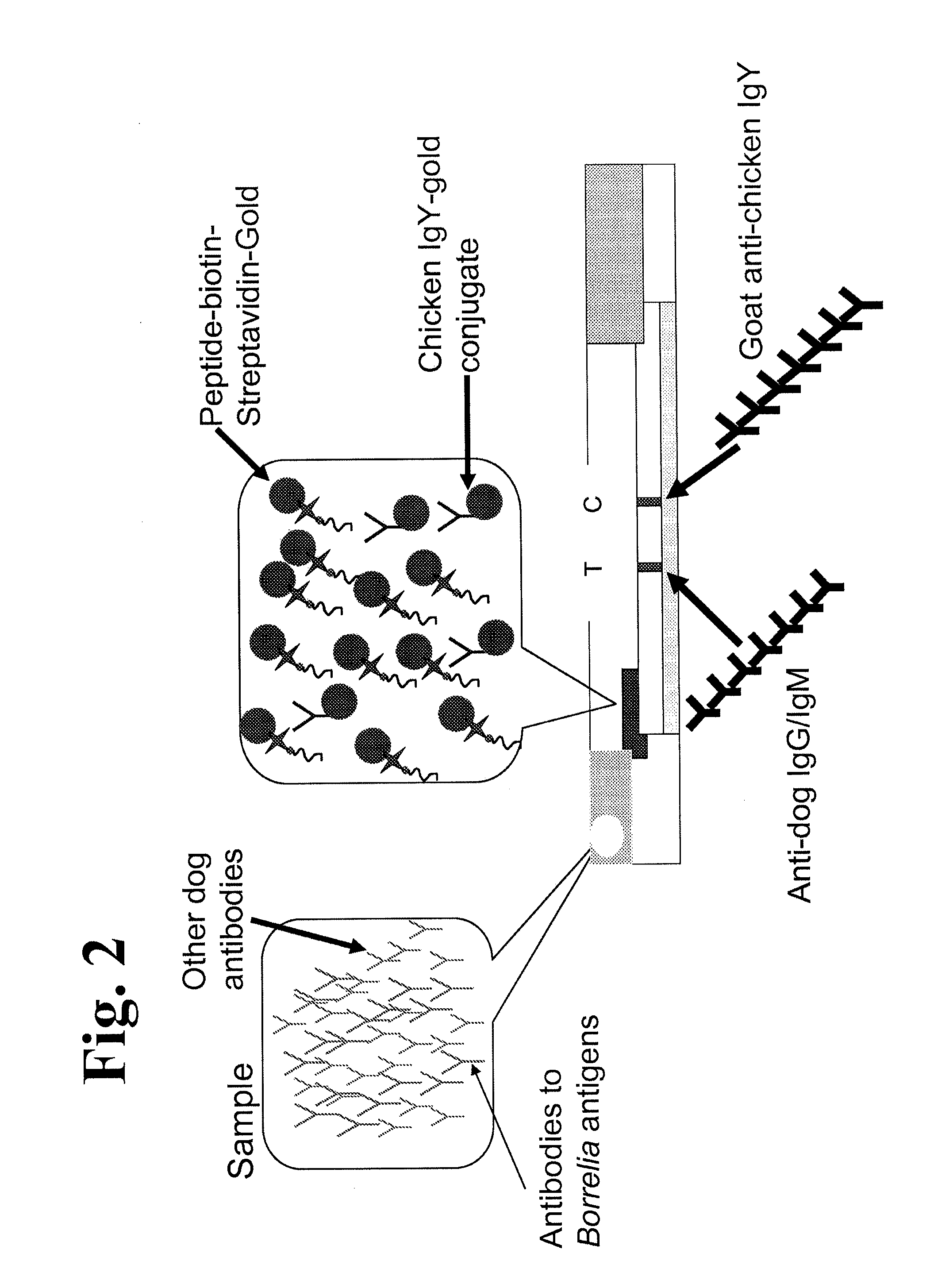
Peptides and methods for the detection of lyme disease antibodies
ActiveUS20110136155A1Robust detectionSimple and inexpensive and rapid and sensitive and accurate detectionPeptide/protein ingredientsLaboratory glasswaresBorrelia antigenAntigen
The invention provides compositions (e.g., peptide compositions) useful for the detection of antibodies that bind to Borrelia antigens. The peptide compositions comprise polypeptide sequences comprising variants in the IR6 domain of the Borrelia VlsE protein. The invention also provides devices, methods, and kits comprising such peptide compositions and useful for the detection of antibodies that bind to Borrelia antigens and the diagnosis of Lyme disease.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Herbal remedy for treating Lyme disease
The present invention is directed to a composition for the treatment of Lyme disease, comprising: Uncaria tomentosa (Cat's Claw); Pau d'arco; Scutellaria baicalensis (Baikal Scullcap); Artemisinin; and Sambucus nigra (Elderberry).
Owner:BROWN PAUL R
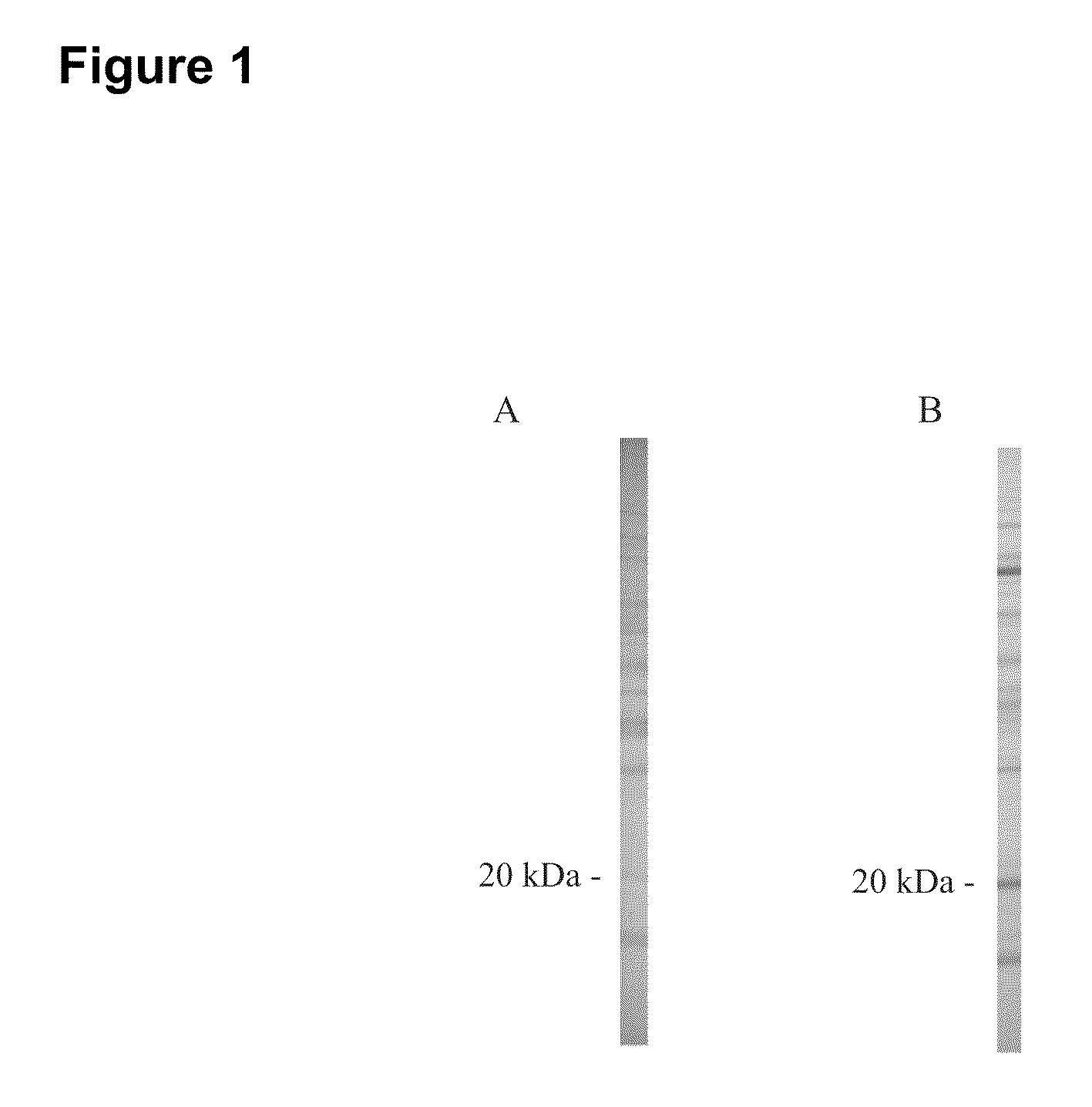
Early detection of canine lyme disease by specific peptides and antibodies
ActiveUS20100184086A1Useful in detectionSuitable for detectionBacterial antigen ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsVirologyAntibody
The present invention relates, in one aspect, to the detection of Lyme disease in canines by detecting the peptide or antibodies to an infection specific peptide after challenge with B. burgdorferi. The 20 kDa peptide is not detectable in human sera samples after challenge or infection with B. burgdorferi and, as such, appears to be specific for canines and suitable for the consistent detection of Lyme disease in canines at time points earlier that possible with prior art methods.
Owner:GUNDERSEN LUTHERAN MEDICAL FOUND
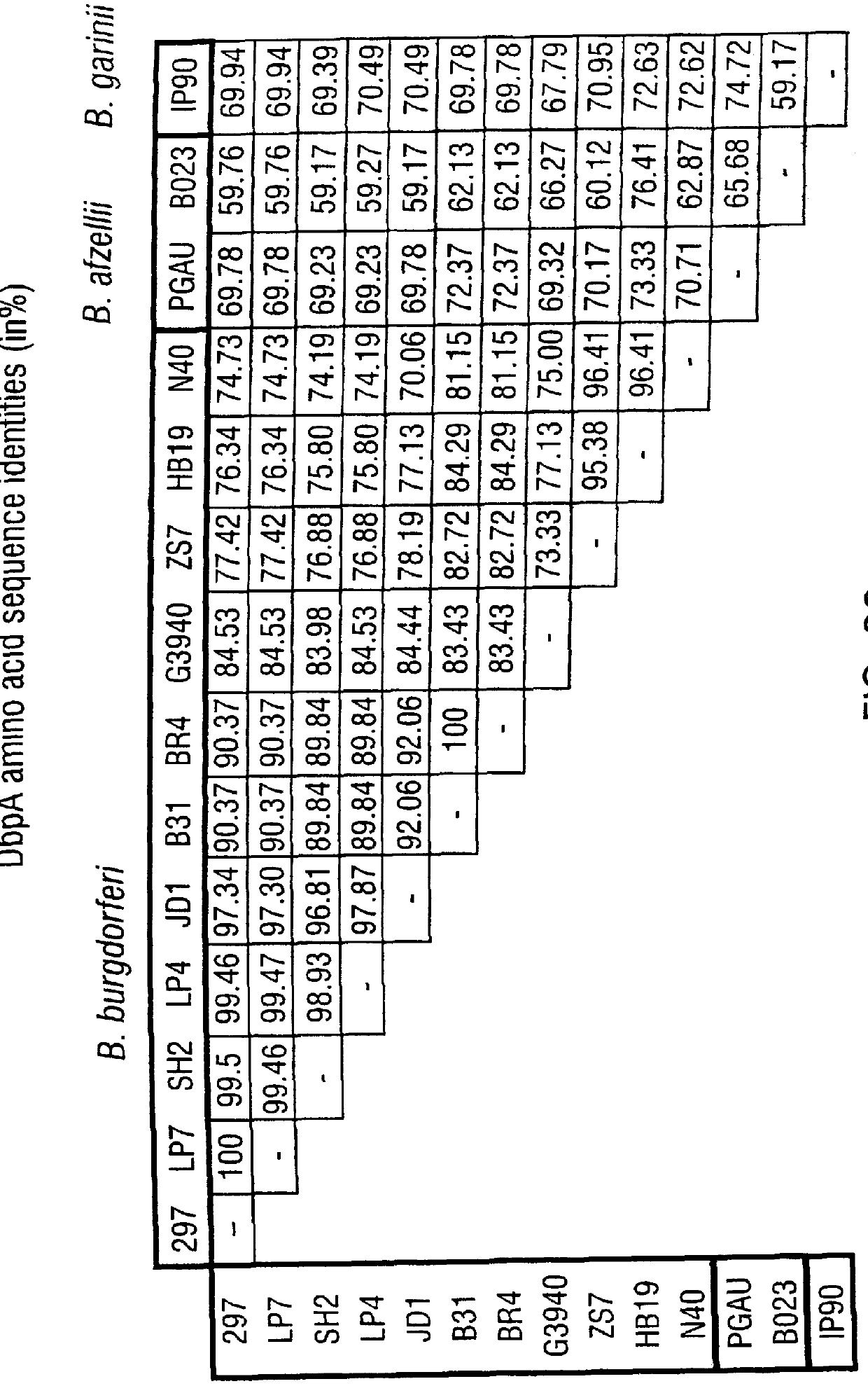
DbpA compositions
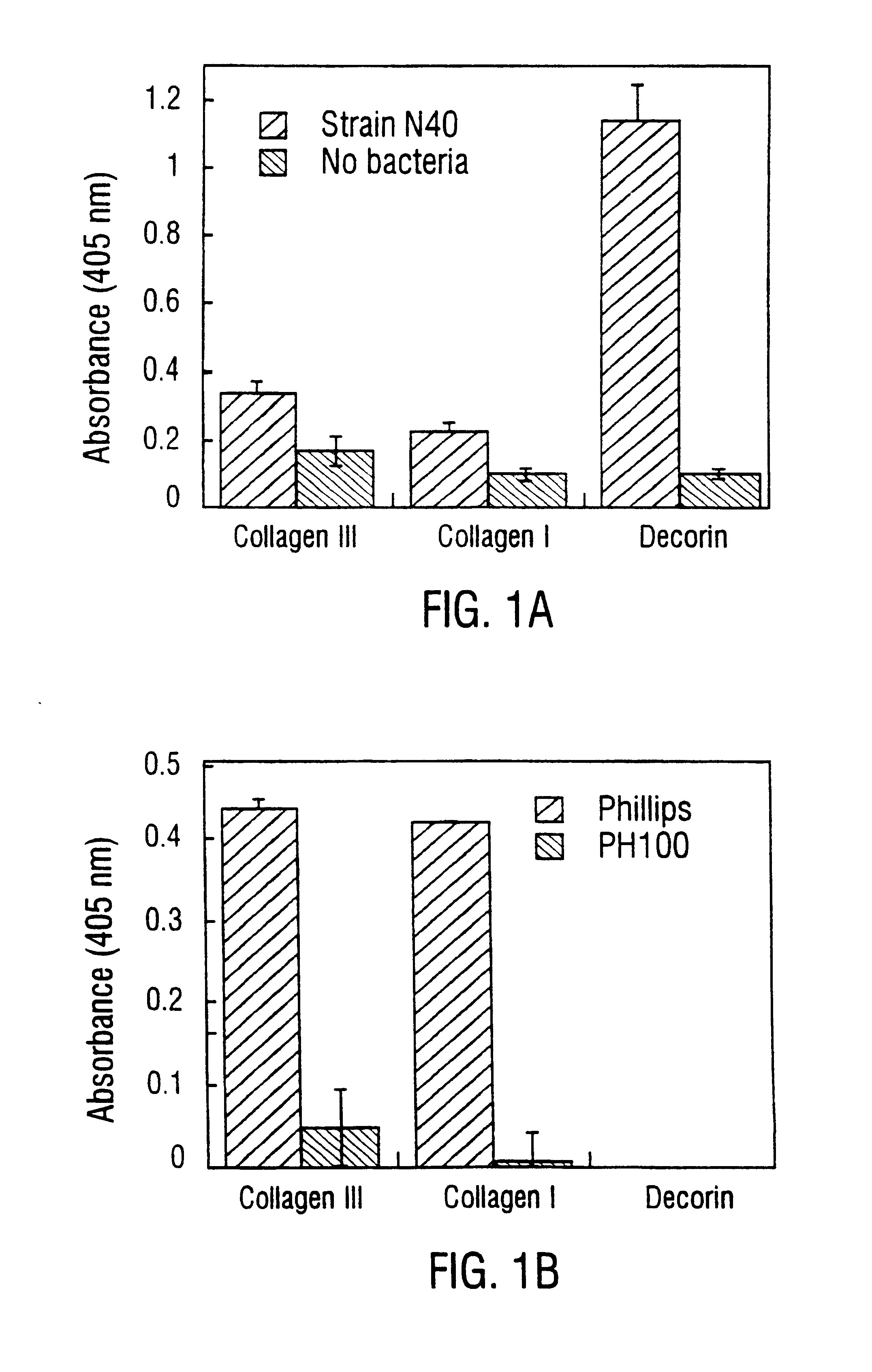
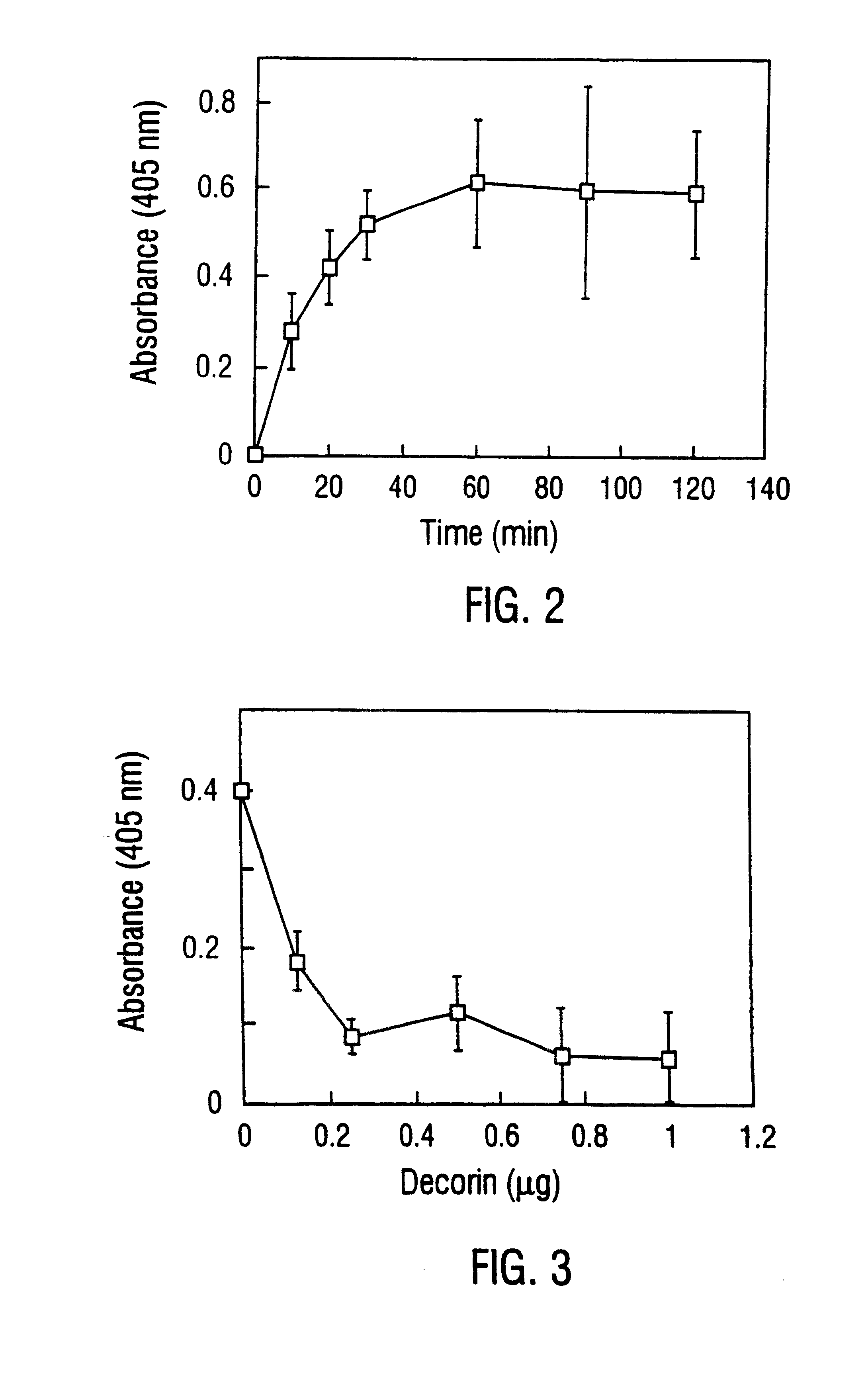
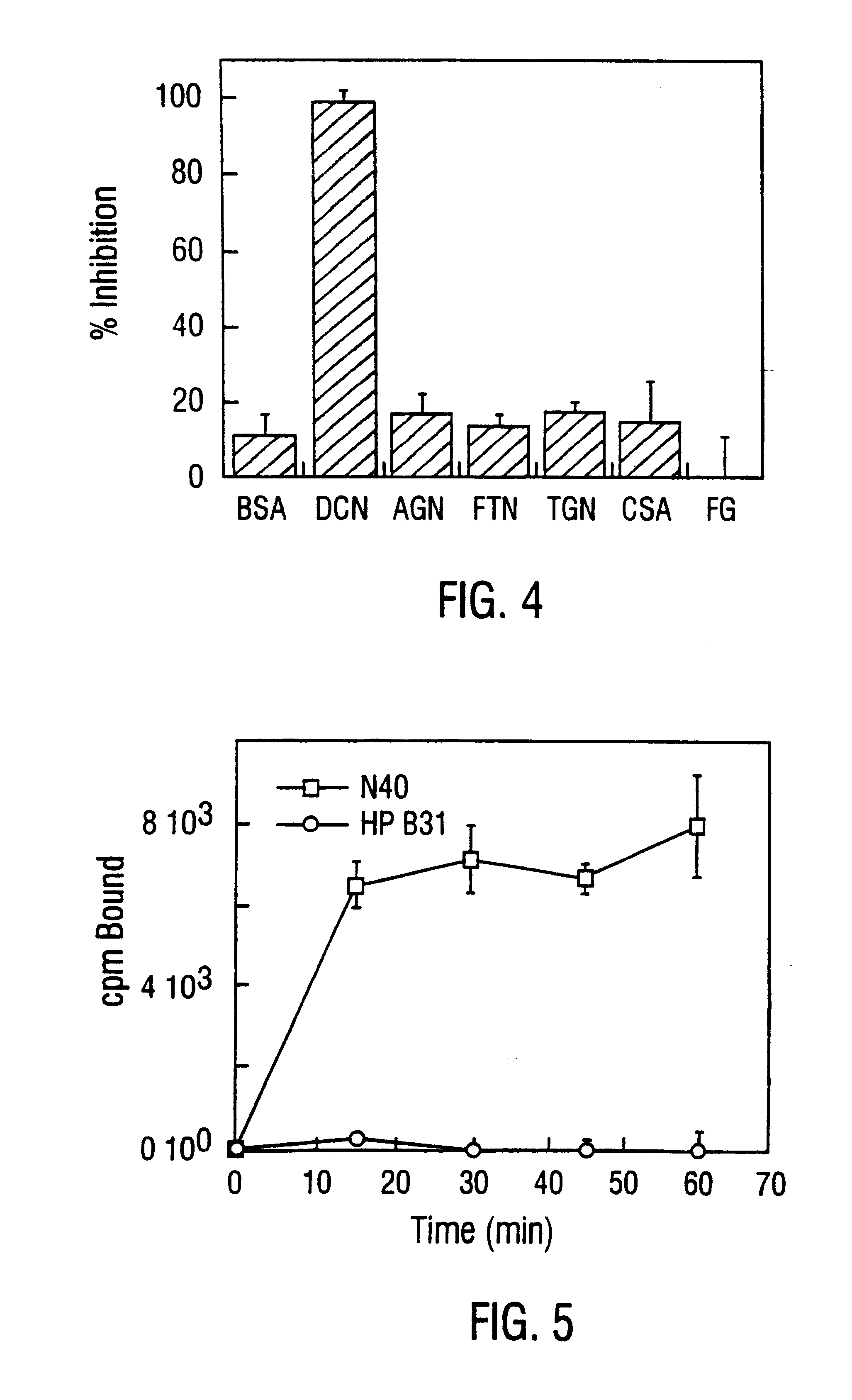
Disclosed are the dbp gene and dbp-derived nucleic acid segments from Borrelia burgdorferi, the etiological agent of Lyme disease, and DNA segments encoding dbp from related borrelias. Also disclosed are decorin binding protein compositions and methods of use. The DBP protein and antigenic epitopes derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the treatment of pathological Borrelia infections, and in particular, for use in the prevention of bacterial adhesion to decorin. DNA segments encoding these proteins and anti-(decorin binding protein) antibodies will also be of use in various screening, diagnostic and therapeutic applications including active and passive immunization and methods for the prevention of Borrelia colonization in an animal. These DNA segments and the peptides derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the preparation of vaccines and, also, for use as carrier proteins in vaccine formulations, and in the formulation of compositions for use in the prevention of Lyme disease.
Owner:MEDIMMUNIE +1
Vmp-like sequences of pathogenic borrelia species and strains
The present invention relates to DNA sequences encoding Vmp-like polypeptides of pathogenic Borrelia, the use of the DNA sequences in recombinant vectors to express polypeptides, the encoded amino acid sequences, application of the DNA and amino acid sequences to the production of polypeptides as antigens for immunoprophylaxis, immunotherapy, and immunodiagnosis. Also disclosed are the use of the nucleic acid sequences as probes or primers for the detection of organisms causing Lyme disease, relapsing fever, or related disorders, and kits designed to facilitate methods of using the described polypeptides, DNA segments and antibodies.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Test for lyme disease
InactiveUS6838247B2Bacterial antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBorrelia antigenBorrelia burgdorferi
The present invention provides an accurate method to identify and quantify the Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb) antigen, the cause of Lyme Disease, in a sample of whole blood, body tissues and fluids of a subject, a human or animal subject. The qualitative method provides a quick, easy and accurate method of detection of the Bb antigen. The quantitative method allows for monitoring of treatment in conjunction with severity of clinical signs and symptoms.
Owner:BOWEN RES & TRAINING
Protein chip for lyme disease flagellin antigen immunoserology diagnosis and preparation method and application of protein chip
InactiveCN104374921AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityBiological testingAgainst vector-borne diseasesSerodiagnosesADAMTS Proteins
The invention discloses a protein chip for lyme disease flagellin antigen immunoserology diagnosis and a preparation method and application of the protein chip. The protein chip is characterized in that borrelia burgdorferi recombination flagellin antigen probes are fixed on the surface of a solid phase carrier in a dot matrix mode; the solid phase carrier is a 16-amino-1-hexadecyl mercaptan modified gold foil chip which is combined with 4-(N-maleinimide methyl) cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid succinimide ester and 4-(dimethylamino) pyridine. The protein chip disclosed by the invention can accurately detect an anti-flagellin antigen IgG antibody and an anti-flagellin antigen IgM antibody in serums of lyme disease patients, the operation is simple, and the detection result is stable.
Owner:ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
Methods for Diagnosing Lyme Disease
ActiveUS20130273572A1Biological material analysisPeptide preparation methodsOuter surface proteinBorrelia burgdorferi
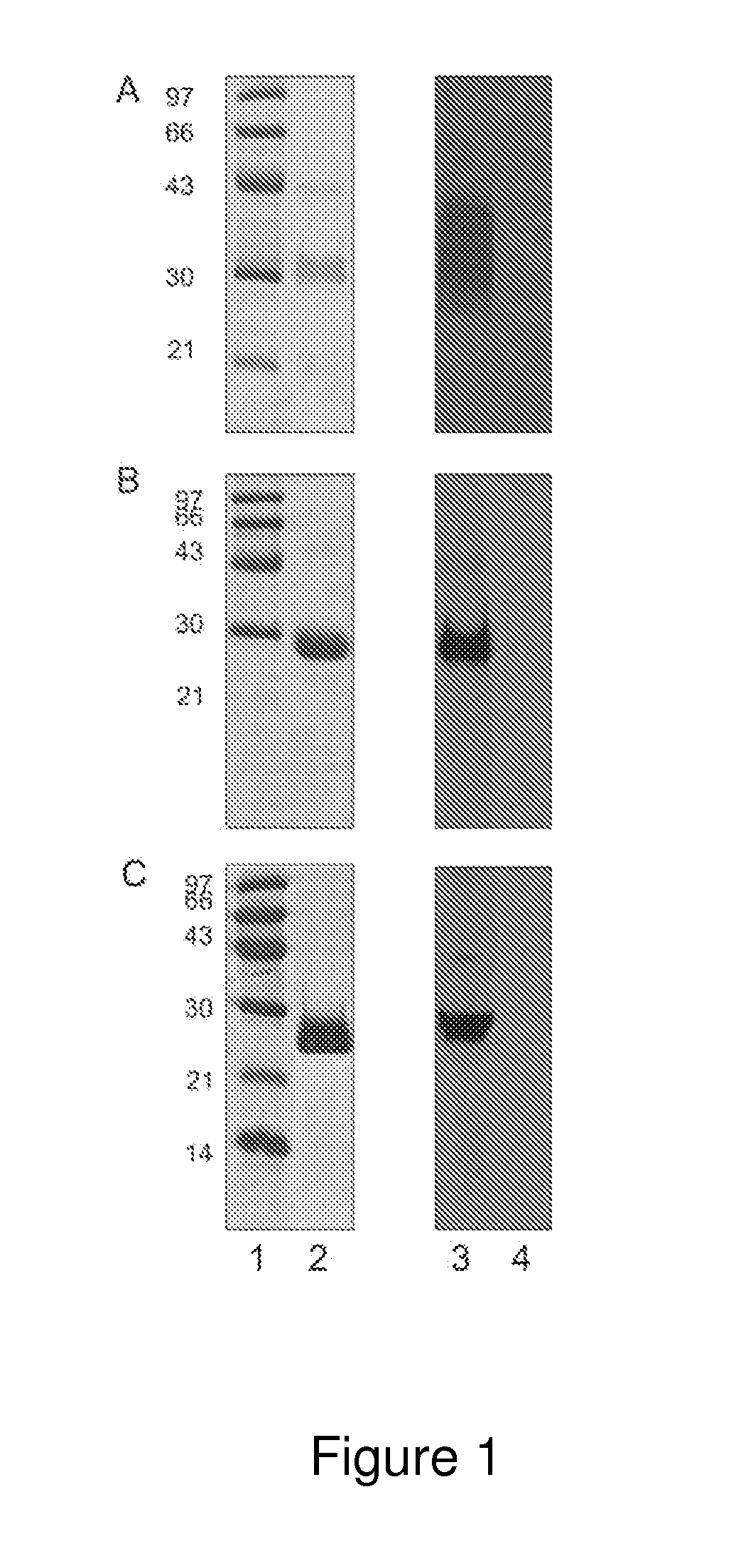
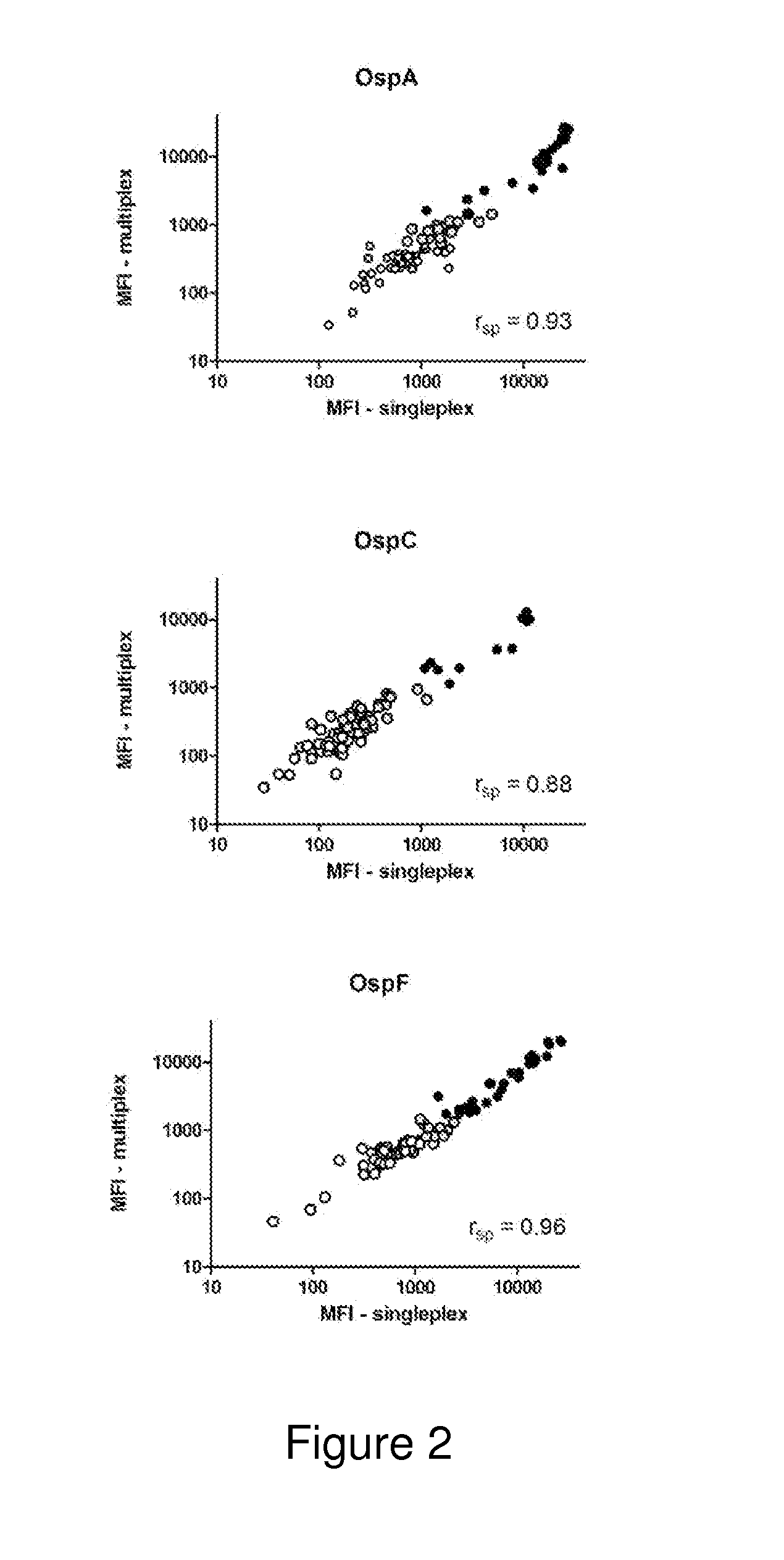
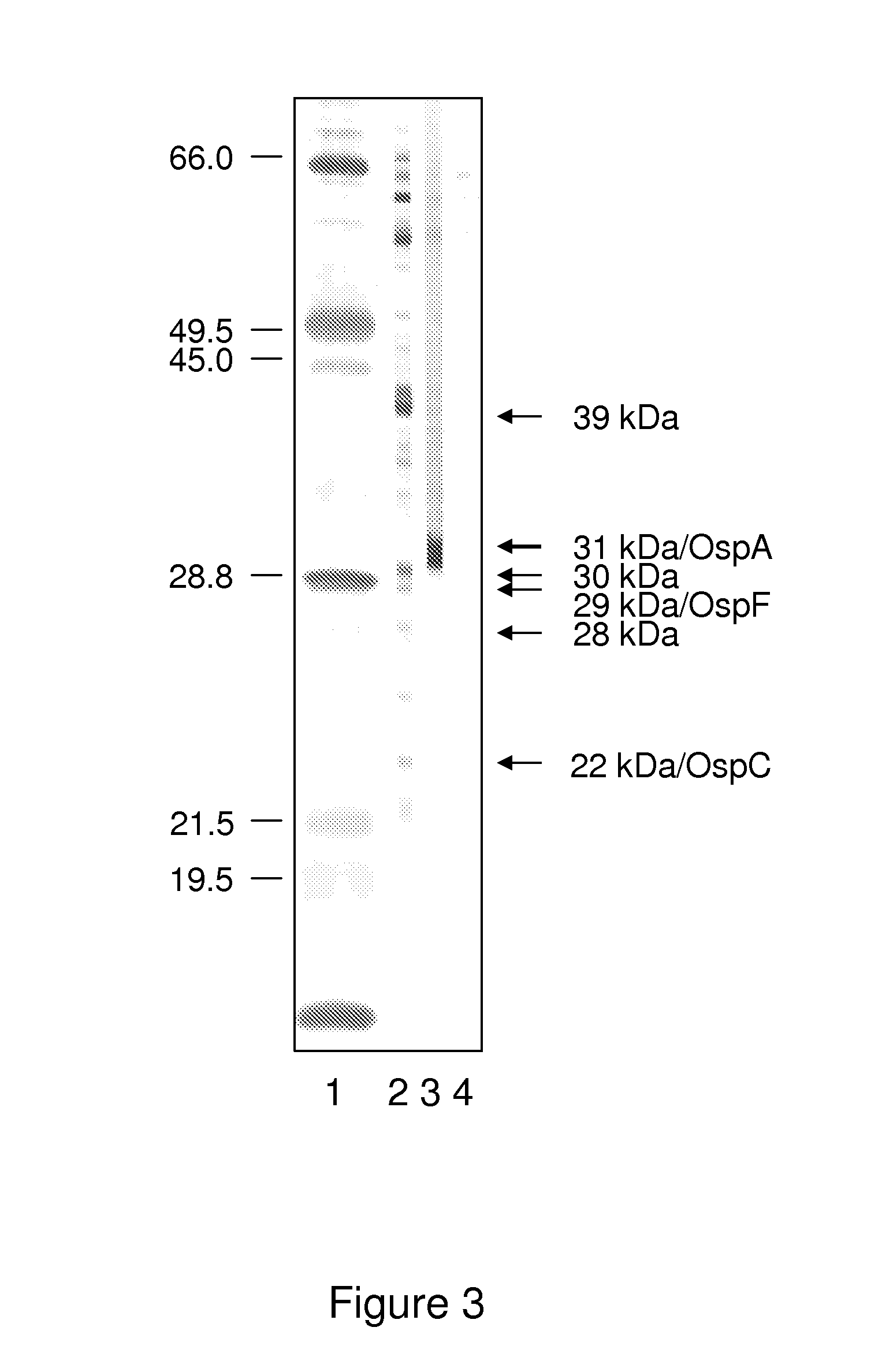
A method for diagnosing Lyme disease status in a mammal is provided. The method entails, in a biological sample obtained or derived from a mammal, determining antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi (B. burgdorferi) outer surface proteins (Osp) OspA, OspC, and OspF. Based upon determining the OspA, OspC, and OspF antibodies, the mammal can be diagnosed as vaccinated, not vaccinated, infected or not infected with B. burgdorferi. Mammals that have early, intermediate or chronic B. burgdorferi infection can also be identified. The method is particularly suited for use with horses and dogs. Isolated or recombinant B. burgdorferi antigens and compositions that contain them are also provided.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Decorin binding protein compositions and methods of use
Disclosed are the dbp gene and dbp-derived nucleic acid segments from Borrelia burgdorferi, the etiological agent of Lyme disease, and DNA segments encoding dbp from related borrelias. Also disclosed are decorin binding protein compositions and methods of use. The DBP protein and antigenic epitopes derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the treatment of pathological Borrelia infections, and in particular, for use in the prevention of bacterial adhesion to decorin. DNA segments encoding these proteins and anti-(decorin binding protein) antibodies will also be of use in various screening, diagnostic and therapeutic applications including active and passive immunization and methods for the prevention of Borrelia colonization in an animal. These DNA segments and the peptides derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the preparation of vaccines and, also, for use as carrier proteins in vaccine formulations, and in the formulation of compositions for use in the prevention of Lyme disease.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Lyme disease vaccine
InactiveUS20110262475A1Broad protectionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunodominant EpitopesBorrelia garinii
Antigenic polypeptides comprising linear immunodominant epitopes of Borrelia outer surface protein A (OspA) or Borrelia outer surface protein C (OspC) are useful as vaccines against Lyme disease, and as diagnostics for detecting Borrelia infections. The OspA and OspC antigenic polypeptides typically comprise a plurality of peptides representing epitope containing regions from multiple distinct phyletic groups. The antigenic polypeptides may also include epitopes from both Borrelia OspA and Borrelia OspC.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Borrelia burgdorferi bacterial antigen diagnosic test using polymeric bait containing capture particles
InactiveUS20130085076A1Improve abilitiesReliable, rapid, inexpensive and non-invasiveLibrary screeningImmunoassaysDiagnostic testSeroconversion
The invention relates to both a sensitive method for the capture and detection of low-abundance Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb) bacterial antigens allowing for the diagnosis of Lyme Disease using standard immunoassays. Furthermore, this invention allows the antigen to be identified in a sample of urine, serum, or other biological fluids isolated from humans and animals. The invention provides a method to capture, concentrate, separate and specifically quantify the abundance of Bb antigens using immunoassays. The detection of Bb Outer Surface Protein A is presented as an example of the disclosed invention. High sensitivity levels, low cost and easily collected biofluids allow this technology to reach patients in clinics as well as POC applications for the early detection of Lyme disease prior to seroconversion. A kit containing necessary reagents and the method for diagnosis, monitoring or assessing lyme disease using an immunoassay such as an ELISA, western blot or RPPMA is disclosed.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP INC +1
Proteins and method for detection of lyme disease
Recombinant B. burgdorferi proteins, representative of the life cycle, are membrane-immobilized to capture antibodies in biological samples. Lateral flow technology incorporating gold colloid deposition results in band visualization indicative of a positive test.
Owner:ROCKLAND IMMUNOCHEM
Luciferase co-immunoprecipitation kit for detecting mammalian lyme diseases
ActiveCN106771250AHigh sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioBiological material analysisBiological testingAntigenSurface membrane
The invention discloses a luciferase co-immunoprecipitation kit for detecting a mammalian lyme disease. The luciferase co-immunoprecipitation kit comprises the following components: (1) a sample diluent; (2) a fusion protein solution composed of ranilla luciferase and a borrelia burgdorferi surface membrane protein OspC antigen; (3) a proteinA / G-coated ELISA plate; (4) washing liquid; (5) a luciferase substrate. The luciferase co-immunoprecipitation kit disclosed by the invention adopts a luciferase co-immunoprecipitation method and can be used for detecting the lyme disease and the onset period thereof according to the fluorescence intensity. The method is quick, simple and convenient, high in sensitivity, high in signal-noise ratio, and stable and reliable in measured C:\Program Files\Youdao\Dict\7.1.0.0421\resultui\dict\value.
Owner:杭州北角医学检验所有限公司
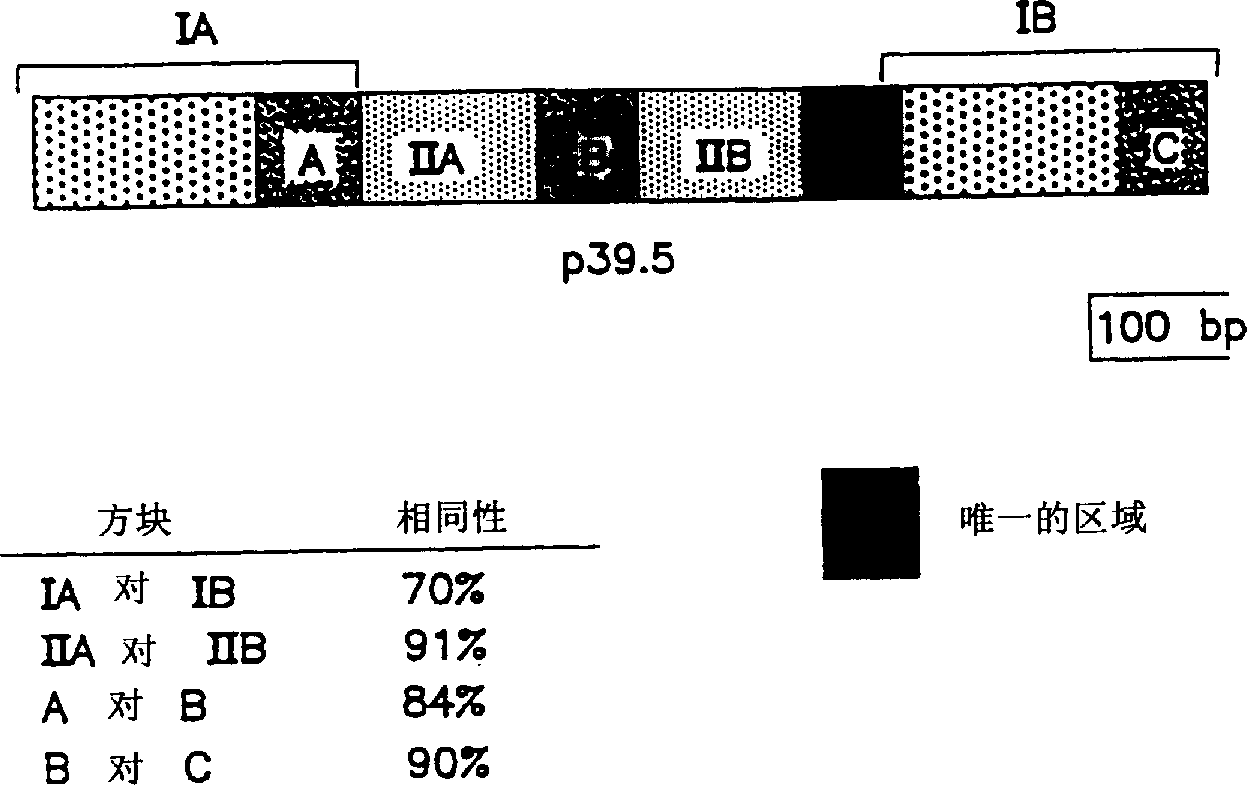
Surface antigens and proteins useful in compositions for diagnosis and prevention of lyme disease
A novel isolated Borrielia burgdorferi sensu lato surface antigen is characterized by a relative molecular mass of 39.5 kDa. This antigen is expressed in vitro by spirochetes of a B. burgdorferi sensu lato strain. This antigen induces antibodies which kill spirochetes of a B. burgdorferi sensu lato strain by ADCK in vitro. Novel Borrelia cassette string protein or fragments thereof are also useful, as is the P39.5 protein in diagnosing Lyme disease and in compositions for treatment or prophylaxis thereof.
Owner:TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
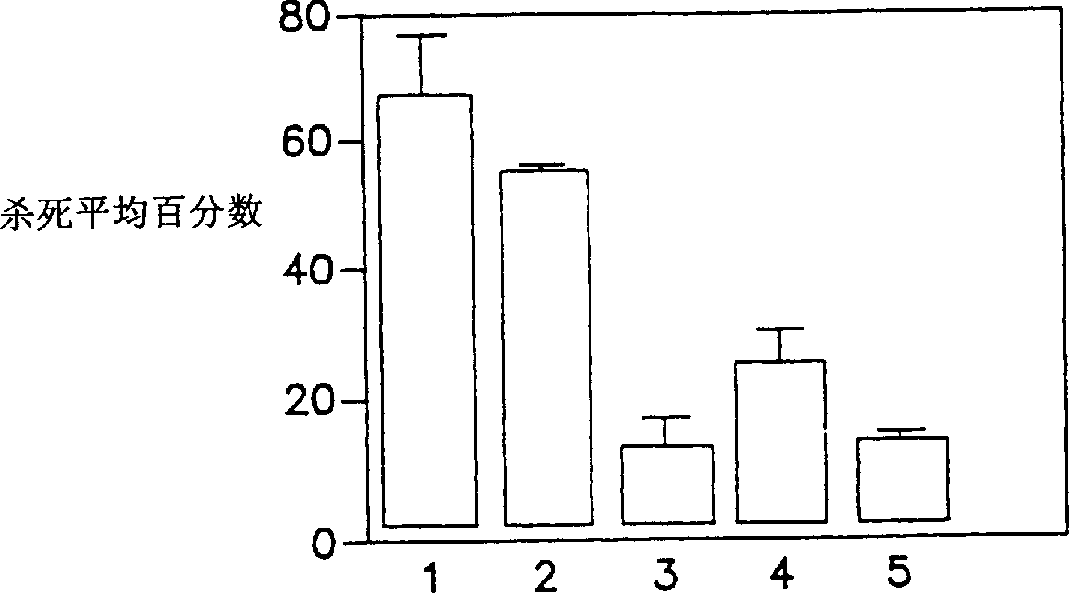
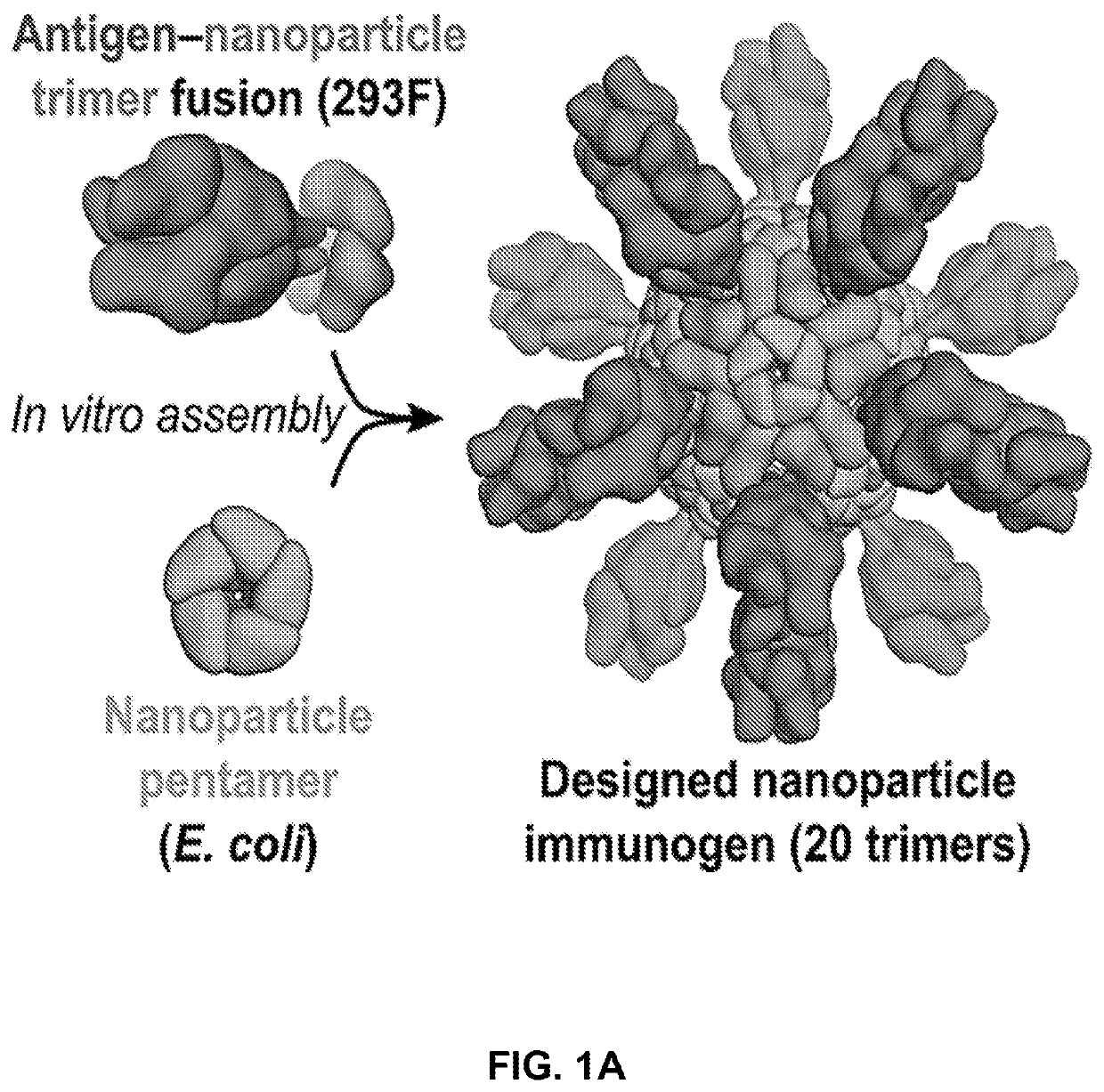
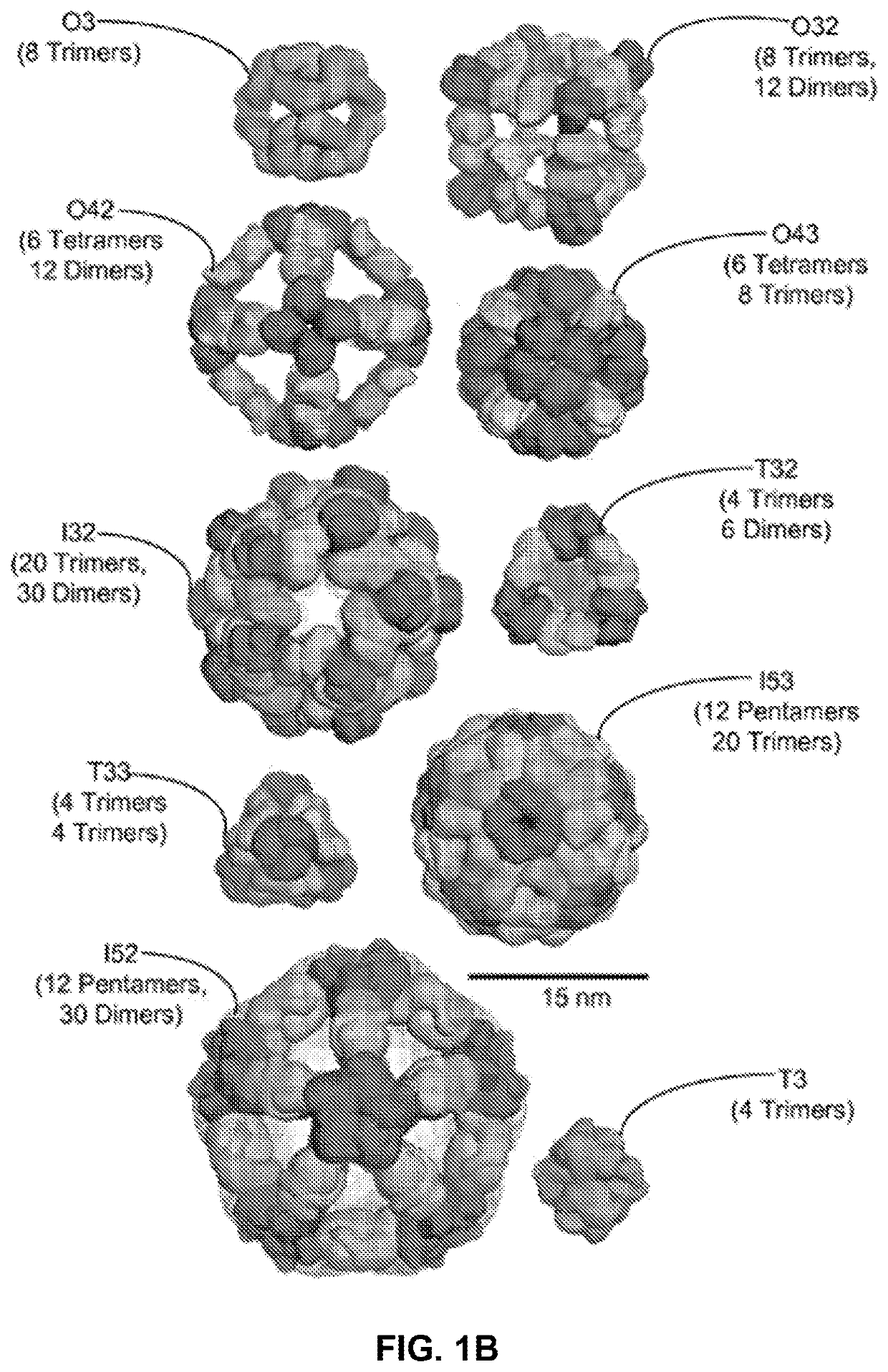
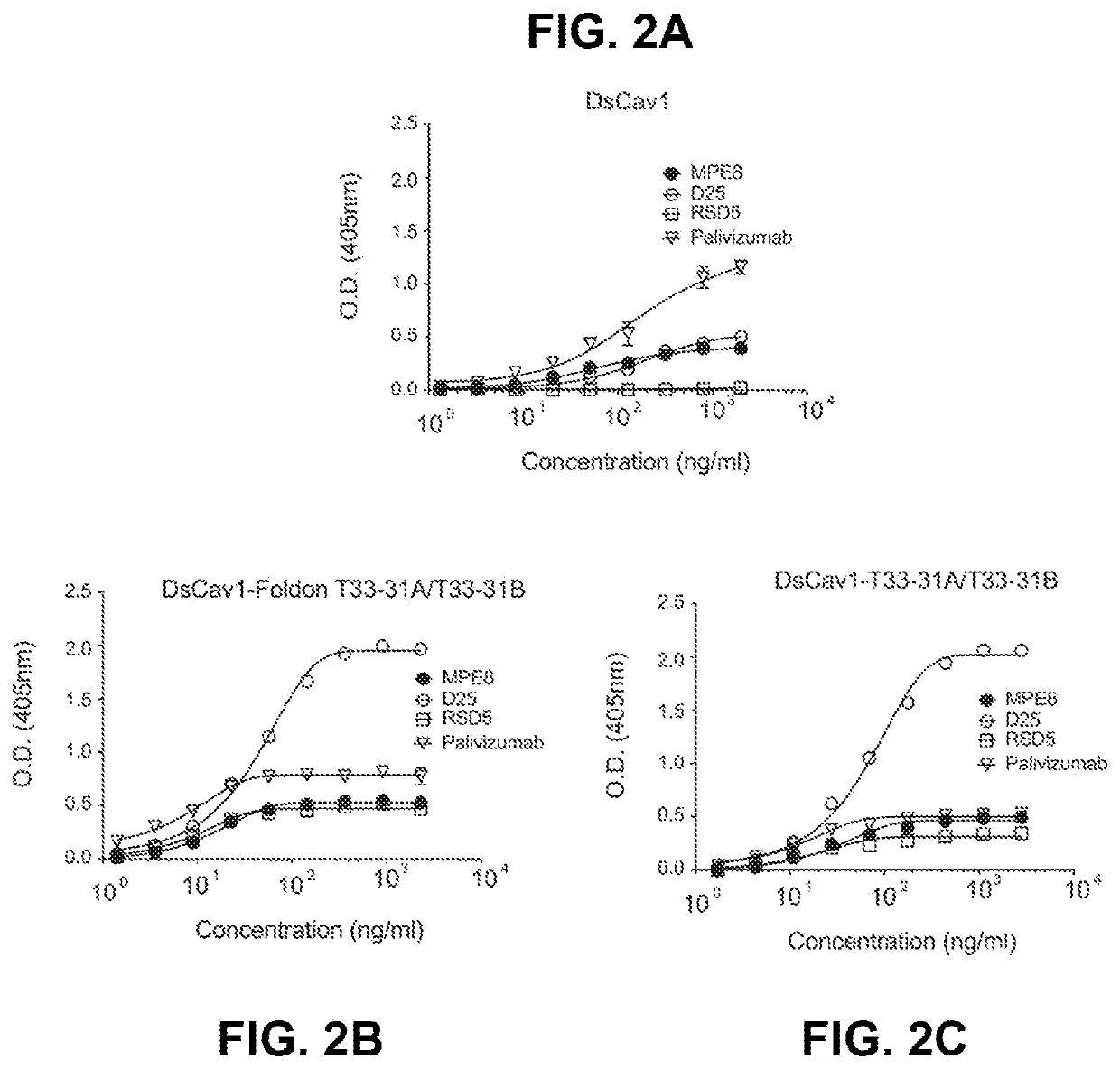
Self-asssembling nanostructure vaccines
The present disclosure provides nanostructures and nanostructure-based vaccines. Some nanostructures of the present disclosure display antigens capable of eliciting immune responses to infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, and pathogens. Some vaccines of the present disclosure are useful for preventing or decreasing the severity of infection with an infectious agent, including, for example and without limitation, lyme disease, pertussis, herpes virus, orthomyxovirus, paramyxovirus, pneumovirus, filovirus, flavivirus, reovirus, retrovirus, meningococcus, or malaria. The antigens may be attached to the core of the nanostructure either non-covalently or covalently, including as a fusion protein or by other means disclosed herein. Multimeric antigens may optionally be displayed along a symmetry axis of the nanostructure. Also provided are proteins and nucleic acid molecules encoding such proteins, vaccine compositions, and methods of administration.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
VMP-like sequences of pathogenic Borrelia
The present invention relates to DNA sequences encoding Vmp-like polypeptides of pathogenic Borrelia, the use of the DNA sequences in recombinant vectors to express polypeptides, the encoded amino acid sequences, application of the DNA and amino acid sequences to the production of polypeptides as antigens for immunoprophylaxis, immunotherapy, and immunodiagnosis. Also disclosed are the use of the nucleic acid sequences as probes or primers for the detection of organisms causing Lyme disease, relapsing fever, or related disorders, and kits designed to facilitate methods of using the described polypeptides, DNA segments and antibodies.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Biomarker signatures for lyme disease and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS10274491B2Low rate of successBacterial antigen ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsDiseaseAnalyte
Owner:VERAMARX
Compositions for treating infective arterial diseases and related conditions
PendingUS20210052557A1Enhance host defence mechanismAntibacterial agentsTetracycline active ingredientsDiseaseMycoplasma penetrans
In alternative embodiments, provided are pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment, amelioration and prevention of infection-associated blood vessel diseases, and also for the treatment, amelioration and prevention of non-vessel diseases affected by infective agents which can be treated by these compositions. In alternative embodiments, one common pathogen targeted by compositions and methods as provided herein is Chlamydia and Chlamydophila species, including pneumoniae, trachomatis and psittaci species which infect humans, including Chlamydophila penumoniae which also infects humans. In alternative embodiments, pathogens targeted and infections (diseases) treated ameliorated, or prevented by compositions and methods as provided herein include Mycoplasma, Listeria, Leptospirosis, Q fever or Coxiella burnetii infection, Lyme disease or Lyme borreliosis or any Borrelia infection, and Bartonella or of the family Bartonellaceae, including cat scratch disease.
Owner:CENT FOR DIGESTIVE DISEASES PTY LTD
Artemisinin with berberine compositions and methods of making
An all-natural herbal composition and methods of preparing the same are provided. The novel Artemisinin Combination Therapy (ACT) consists of artemisinin and its derivatives and berberine, the two active substances mixed with various selected excipient compounds to form a single pill, tablet or capsule for treatment and prevention of malaria, dengue fever, yellow fever, dysentery, Lyme disease, babesiosis, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, Helicobacter Pylori, and colitis, in adults and children. A tablet or pill for children is formulated to be chewable.
Owner:ROSEN REECE D
Recombinant fusion protein OspC-VlsE of Lyme and application thereof
ActiveCN111018998AHigh expressionShort cycleAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid vectorEscherichia coliProtein detection
The invention discloses a recombinant fusion protein OspC-VlsE of Lyme. The recombinant fusion protein OspC-VlsE is characterized in that the amino acid sequence of the recombinant fusion protein OspC-VlsE is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. According to the invention, the recombinant fusion protein OspC-VlsE is expressed in an Escherichia coli system by utilizing a genetic engineering recombination technology, and the advantages of short production period, high yield, low cost and good specificity are obtained. The recombinant fusion protein can be used as a part of a recombinant protein detection kit for the Lyme disease.
Owner:HANGZHOU AORUI BIOMEDICINE TECH
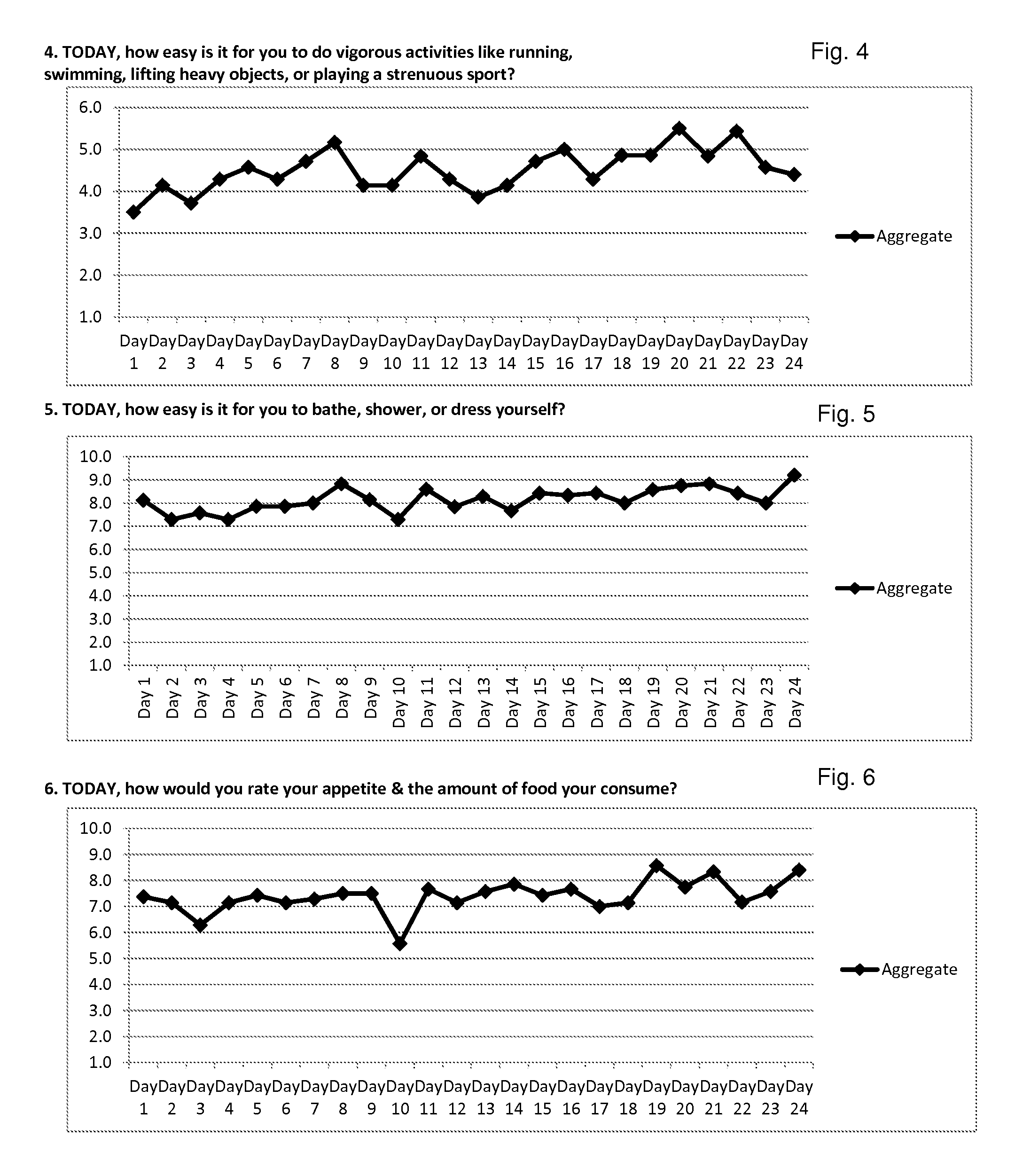
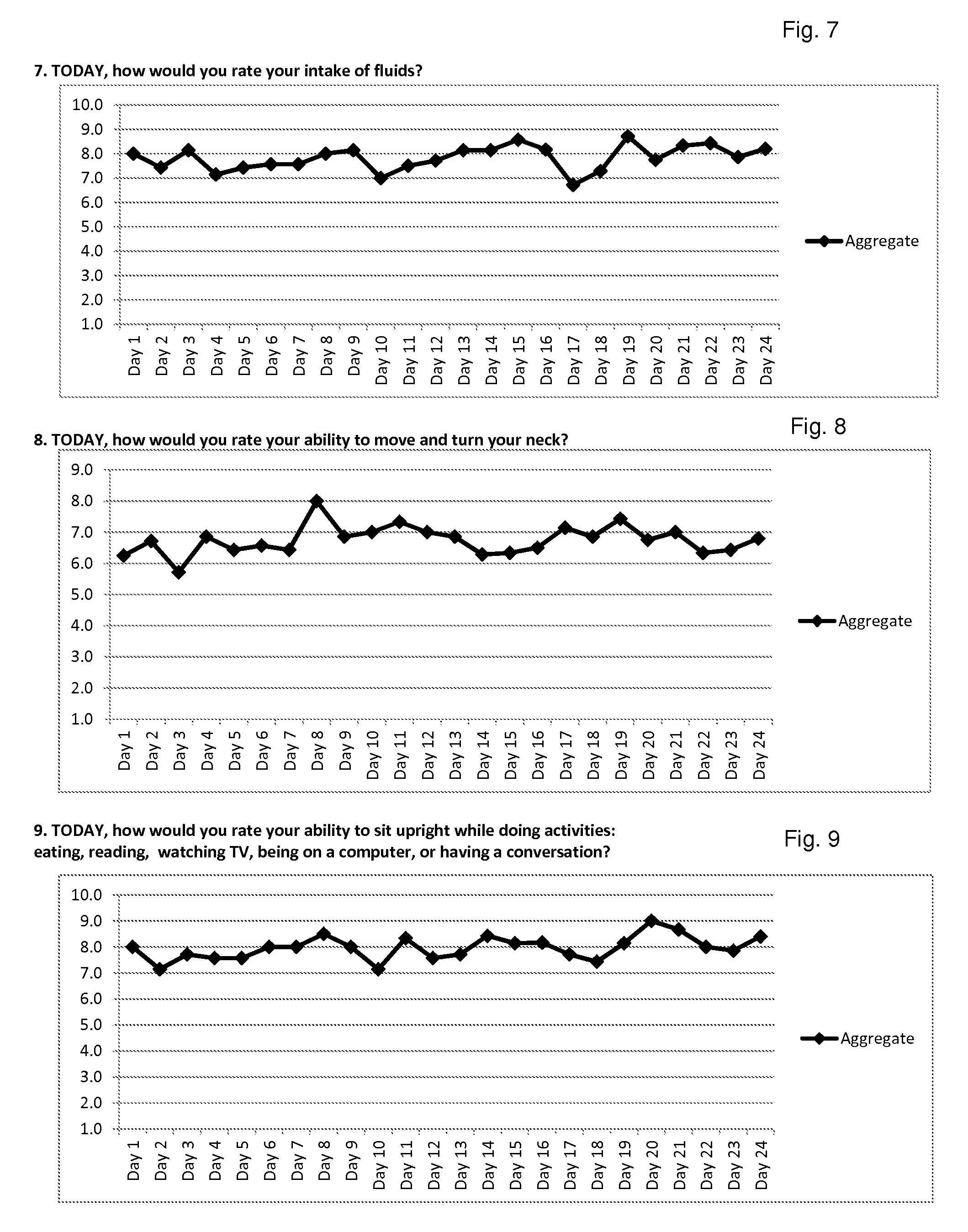
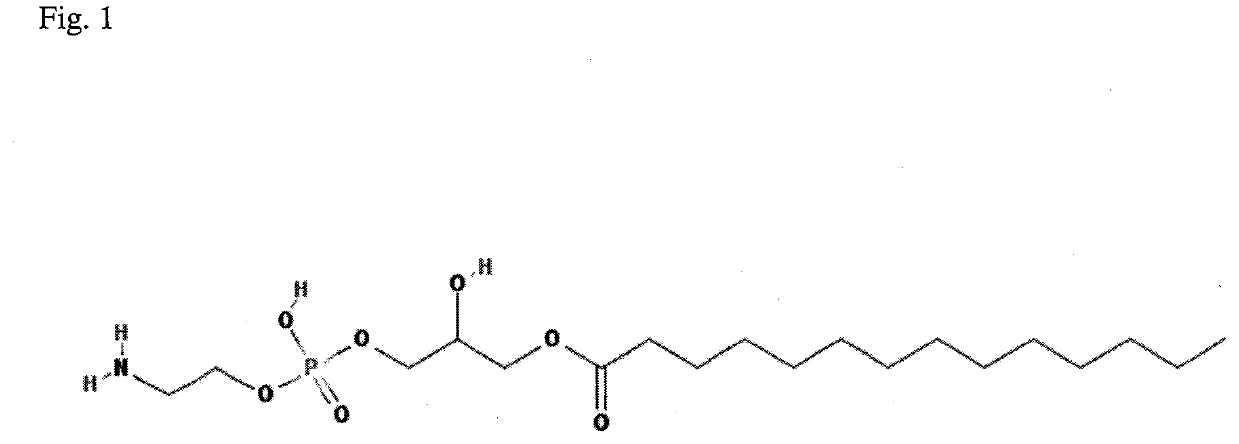
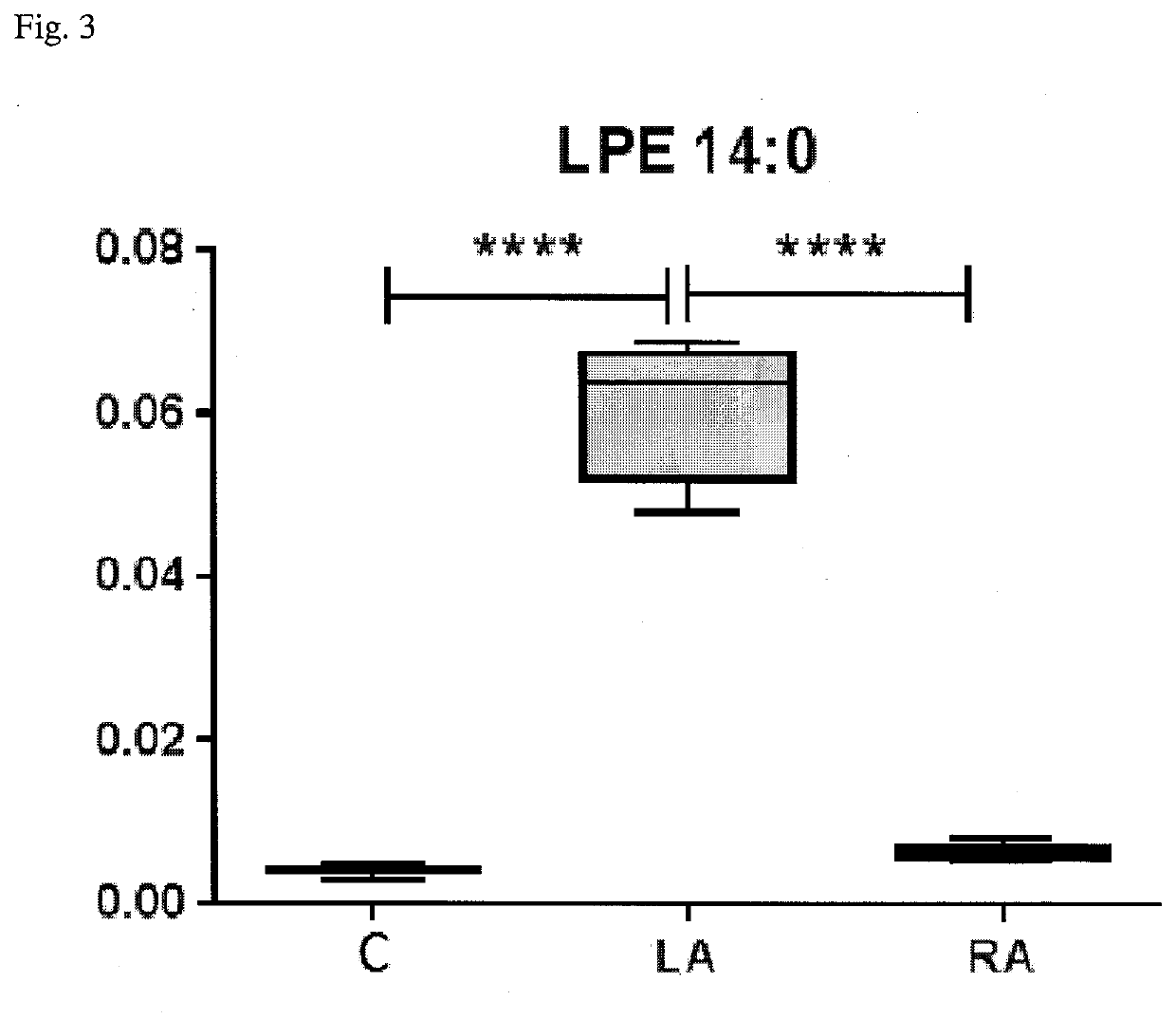
Method for diagnosis of lyme arthritis, method for differential diagnosis of lyme arthritis, lysophosphatidylethanolamine for use as biomarker, kit for diagnosis of lyme arthritis and kit for differential diagnosis of lyme arthritis
PendingUS20210255209A1Quick and precise and specific and sensitive diagnosisPrecise and easyComponent separationDisease diagnosisReference sampleSacroiliitis
The subject matter of the invention relates to a method for in vitro diagnosis of Lyme disease and a method for in vitro differential diagnosis of Lyme arthritis versus rheumatoid arthritis, in which methods, in a sample from a subject, the level of lysophosphatidylethanolamine comprising myristic acid (LysoPE(14:0)) is determined and such determined level of lysophosphatidylethanolamine is compared with the level of lysophosphatidylethanolamine comprising myristic acid in a reference sample; in wherein the level of lysophosphatidylethanolamine comprising myristic acid which is higher than the level in the said reference sample indicates that the subject suffers from Lyme disease. The subject matter of the invention further relates to lysophosphatidylethanolamine comprising myristic for use as a biomarker of Lyme disease, as a biomarker of Lyme arthritis, as a biomarker for differential diagnosis of Lyme arthritis versus rheumatoid arthritis, as a biomarker of neuroborreliosis. The subject matter of the invention also relates to a kit for in vitro diagnosis of Lyme disease and a kit for in vitro differential diagnosis of Lyme arthritis, which kits comprise a means for determining the level of lysophosphatidylethanolamine comprising myristic acid and instructions for carrying out the methods for diagnosis according to the invention.
Owner:UNIV MEDYCZNY W BIAYMSTOKU
Diagnostic peptides for lyme disease
Owner:BIOPEPTIDES LLC
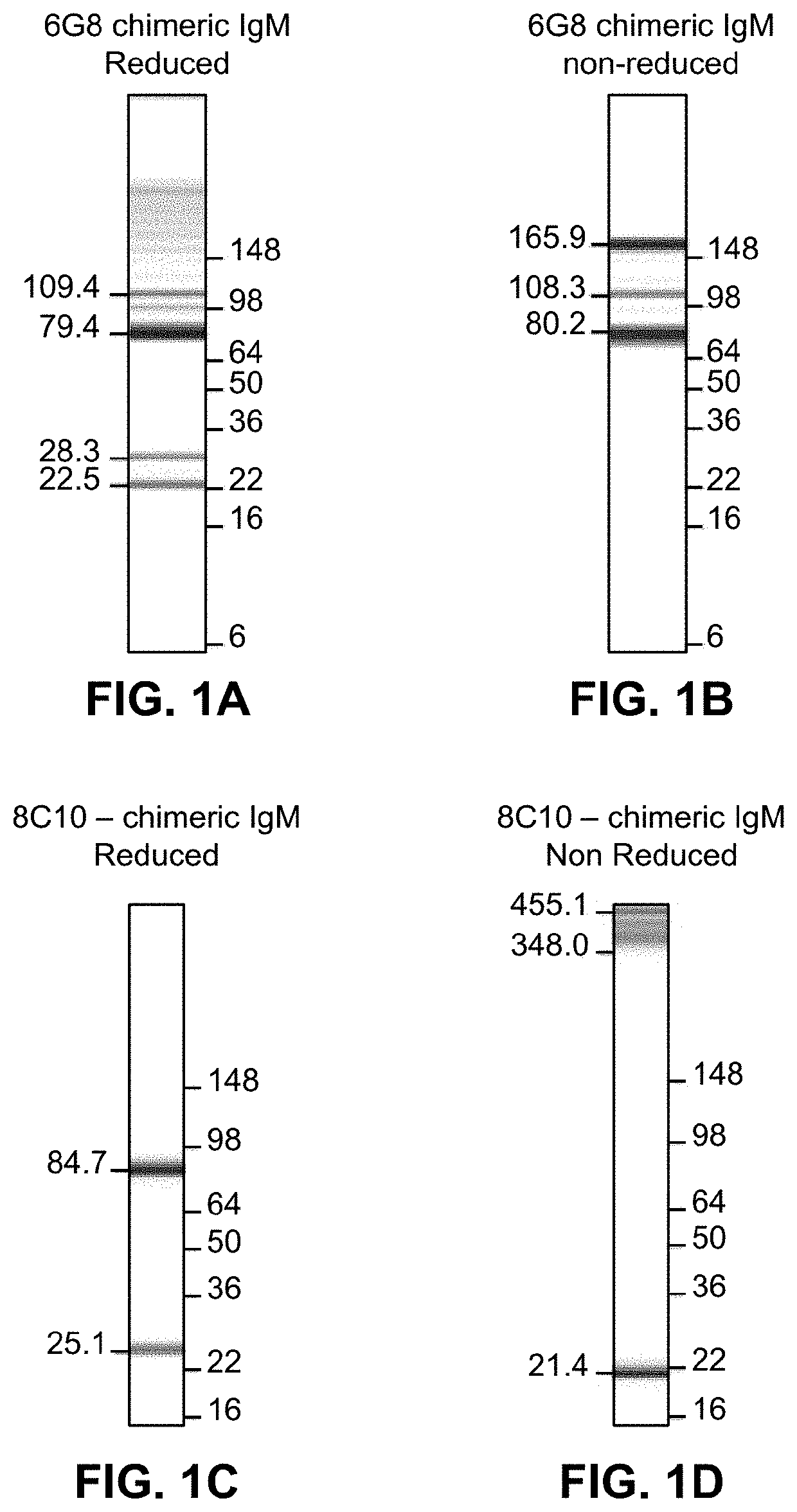
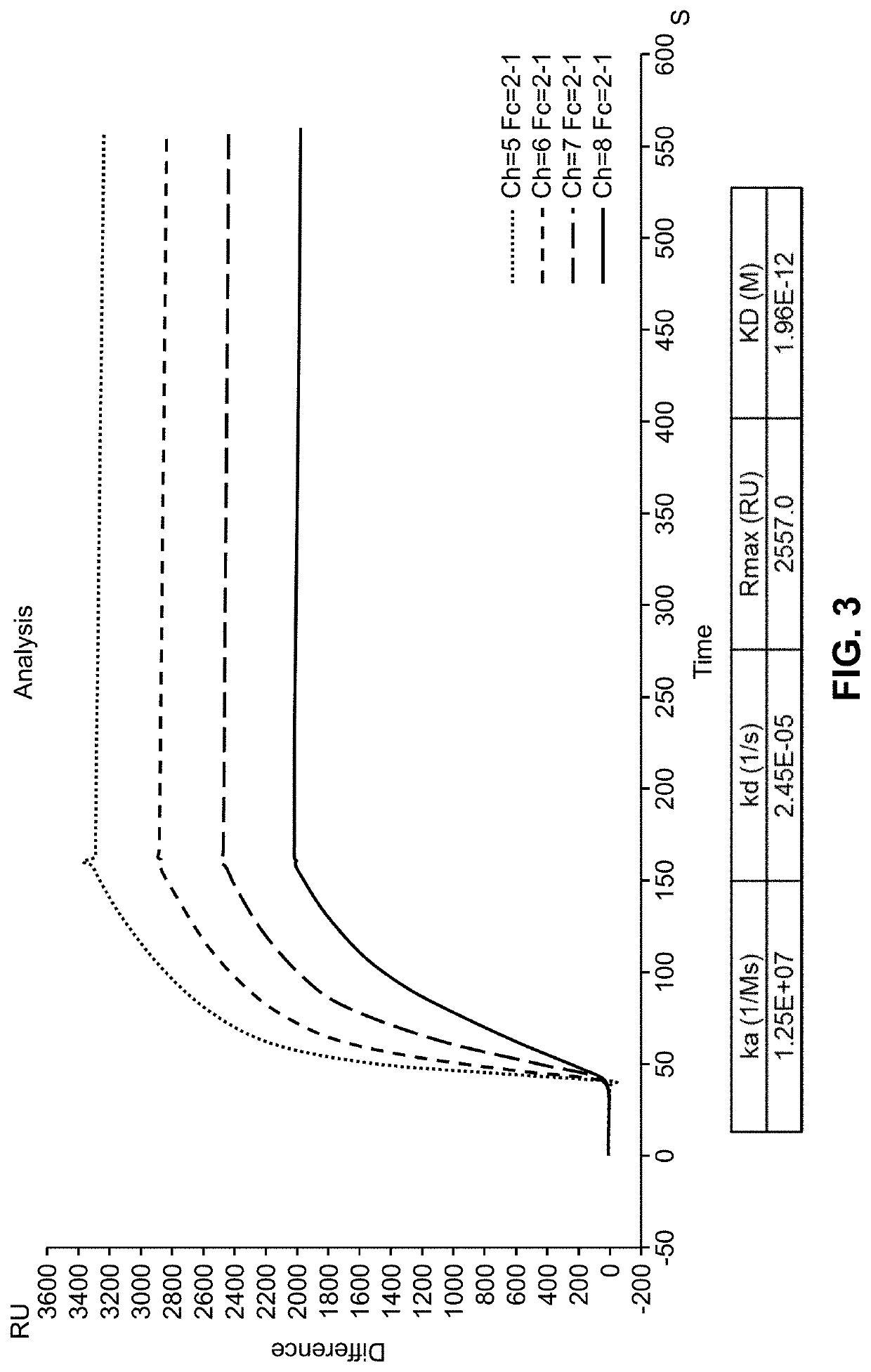
DbpA ANTIBODIES AND USES THEREOF
Embodiments of the present disclosure relate to chimeric antibodies which specifically bind to Borrelia decorin-binding protein A (DbpA) antigens and compositions or kits comprising such antibodies. The disclosure further relates to use of such antibodies in the detection of Borrelia sp. in samples, e.g., biological samples such as human blood and / or tissues of deer, ticks and other carriers of Borrelia. Embodiments of the disclosure further relate to diagnosis and / or therapy of Lyme disease using the chimeric antibodies and / or compositions containing the chimeric antibodies.
Owner:QUIDEL
Serodiagnosis of lyme disease by use of two recombinant proteins in ELISA
ActiveUS10401358B1Great capacity to identifyFast and easy to performAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDepsipeptidesSerodiagnosesEscherichia coli
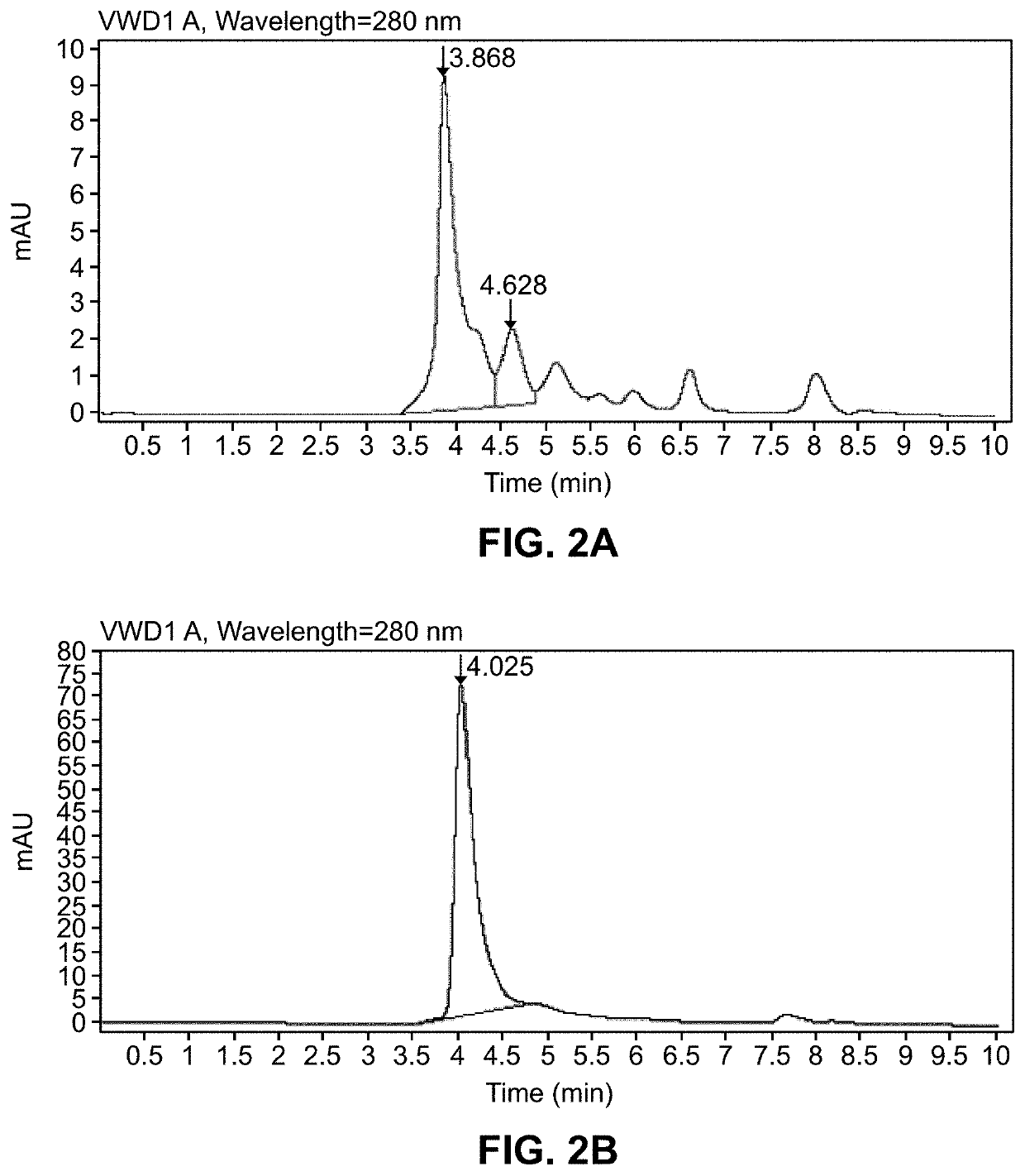
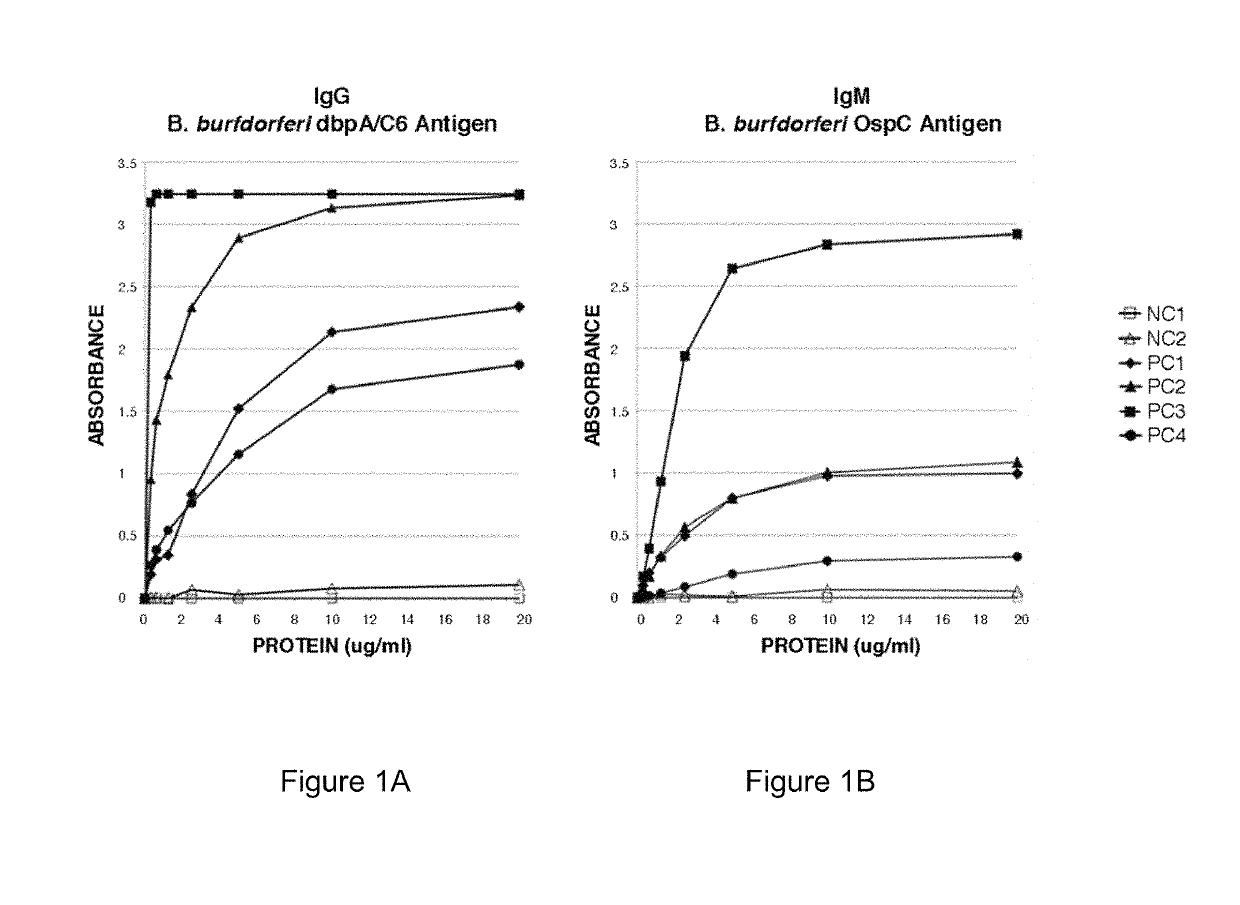
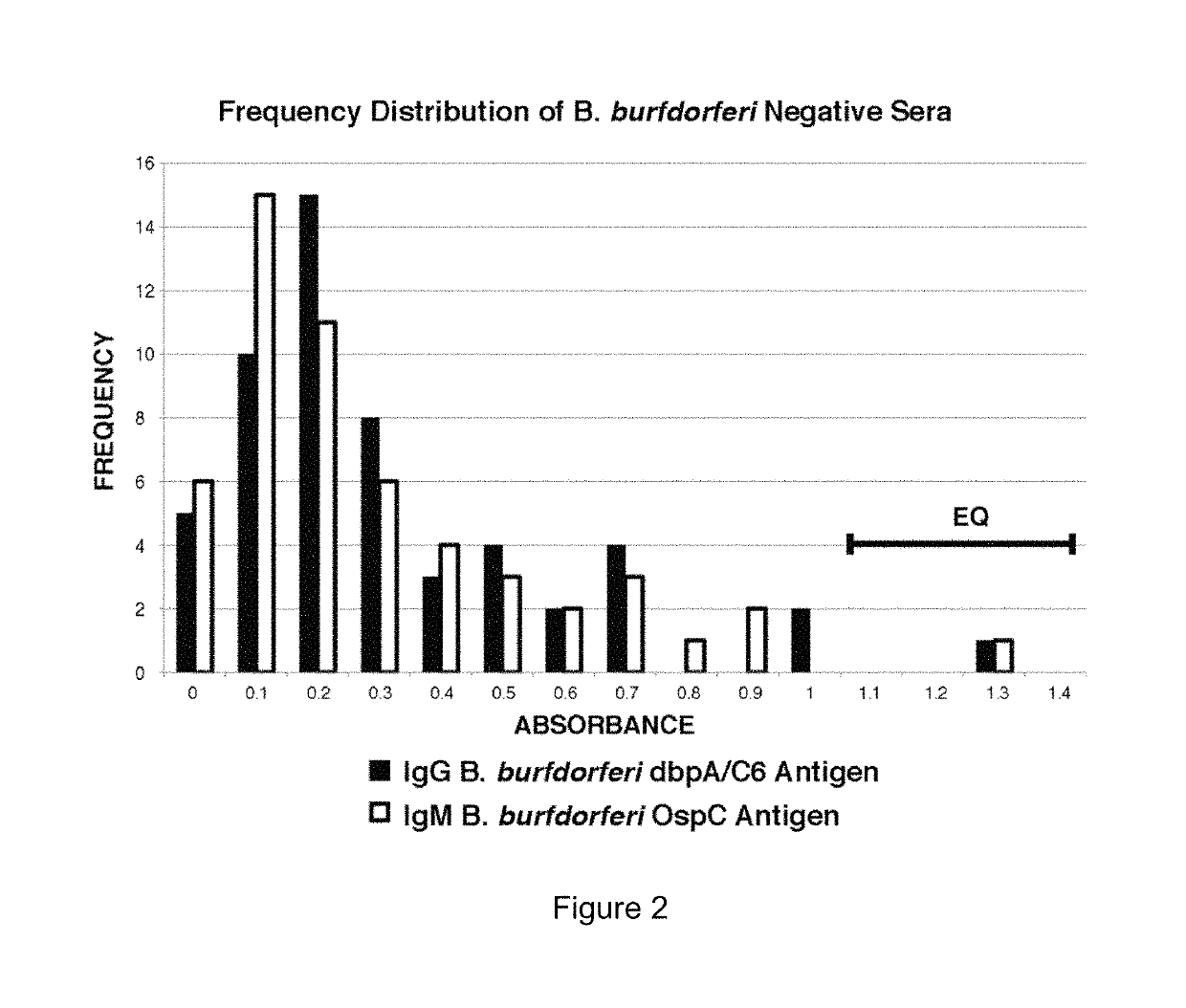
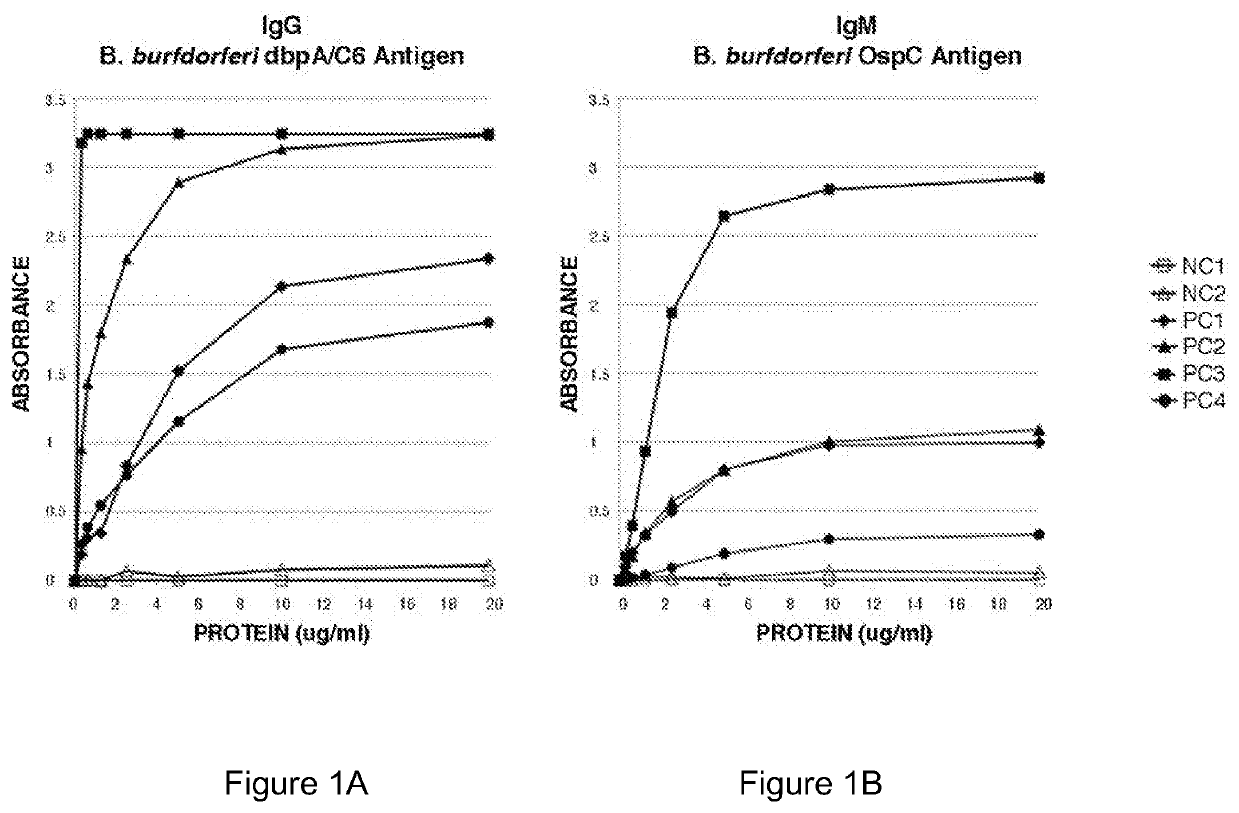
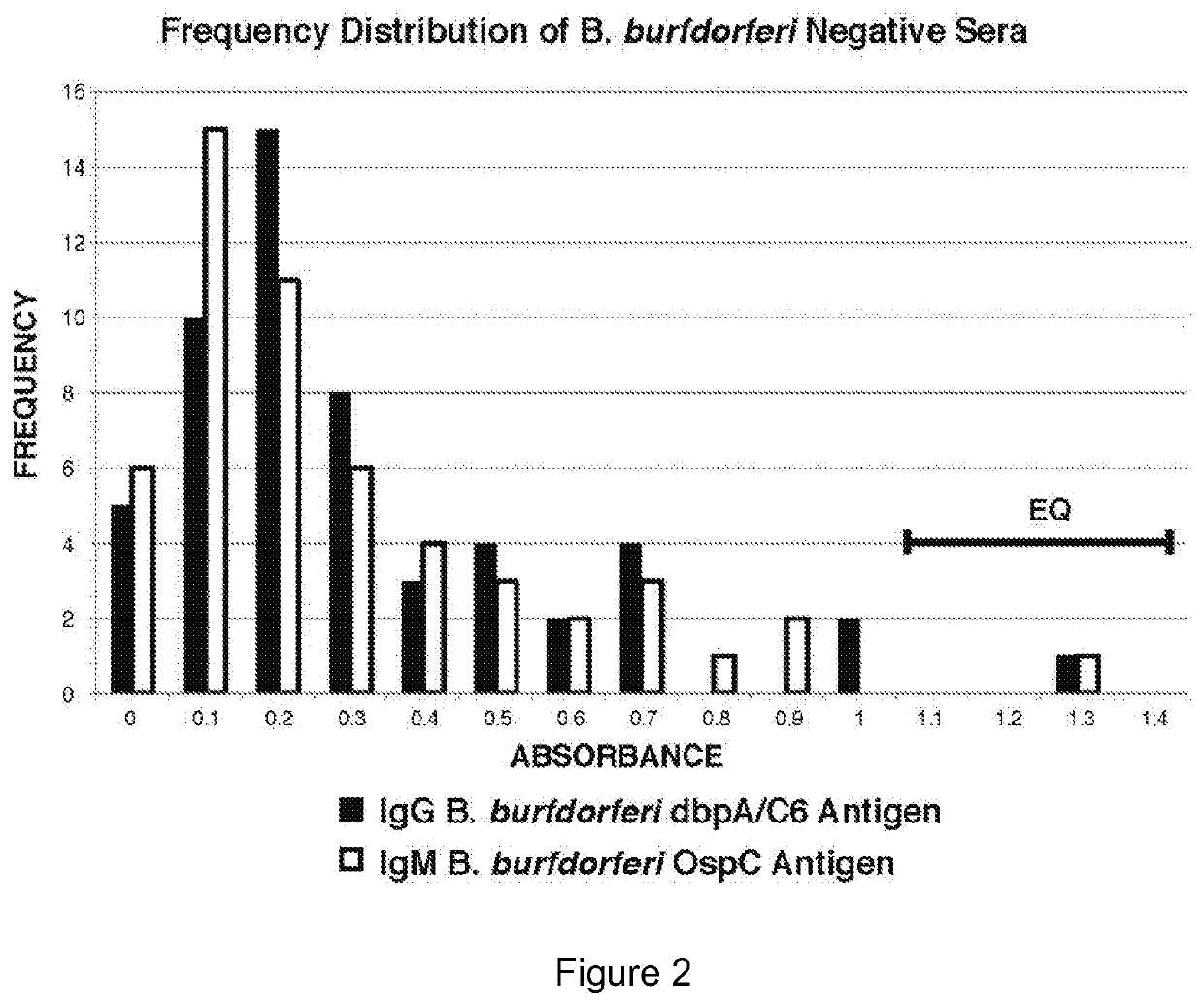
Two Borrelia burgdorferi recombinant proteins were expressed in E. coli. These two proteins were generated from (a) the full length dbpA gene combined with the invariable region 6 of the VlsE gene (dbpA / C6), and (b) the full length OspC gene combined with the coding sequence for amino acids 1-121 of the E. coli maltose binding protein gene (OspC / MBP). Methods of using these recombinant proteins for detecting anti-Borrelia burgdorferi antibodies in patient sera and diagnosis of Lyme Disease are described.
Owner:ROSS SOUTHERN LAB
Altered OSPA of Borrelia Burgdorferi
InactiveUS20140030285A1Improve stabilityLow cross-reactivityBacterial antigen ingredientsSugar derivativesBorrelia gariniiAntigenicity
Provided herein are OspA polypeptides from Lyme Disease-causing Borrelia having certain alteration(s). In one embodiment, the alteration(s) increase the conformational stability of the OspA polypeptide containing the alteration(s) while maintaining at least some of the antigenicity of the corresponding unaltered OspA polypeptide. In another embodiment, the altered OspA polypeptide has reduced cross-reactivity to hLFA-1, as compared to the corresponding unaltered OspA polypeptide.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS +2
A kind of Lyme recombinant fusion protein ospc-vlse and its application
ActiveCN111018998BShorten the production cycleIncrease productionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid vectorProtein detectionGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a Lyme recombinant fusion protein OspC-VlsE, characterized in that the amino acid sequence of the recombinant fusion protein OspC-VlsE is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The invention utilizes the genetic engineering recombination technology to express the recombinant fusion protein OspC-VlsE in the Escherichia coli system, which has the advantages of short production cycle, high yield, low cost and good specificity. The recombinant fusion protein of the invention can be used as a part of Lyme disease recombinant protein detection kit.
Owner:HANGZHOU AORUI BIOMEDICINE TECH
Serodiagnosis of Lyme disease by use of two recombinant proteins in ELISA
Two Borrelia burgdorferi recombinant proteins were expressed in E. coli. These two proteins were generated from (a) the full length dbpA gene combined with the invariable region 6 of the VlsE gene (dbpA / C6), and (b) the full length OspC gene combined with the coding sequence for amino acids 1-121 of the E. coli maltose binding protein gene (OspC / MBP). Methods of using these recombinant proteins for detecting anti-Borrelia burgdorferi antibodies in patient sera and diagnosis of Lyme Disease are described.
Owner:ROSS SOUTHERN LAB
Compositions and methods for diagnosing lyme disease and for predicting lyme disease spirochete elimination after treatment
ActiveUS20190285630A1Elicit immune responseDepsipeptidesDisease diagnosisBorrelia spWhole blood sample
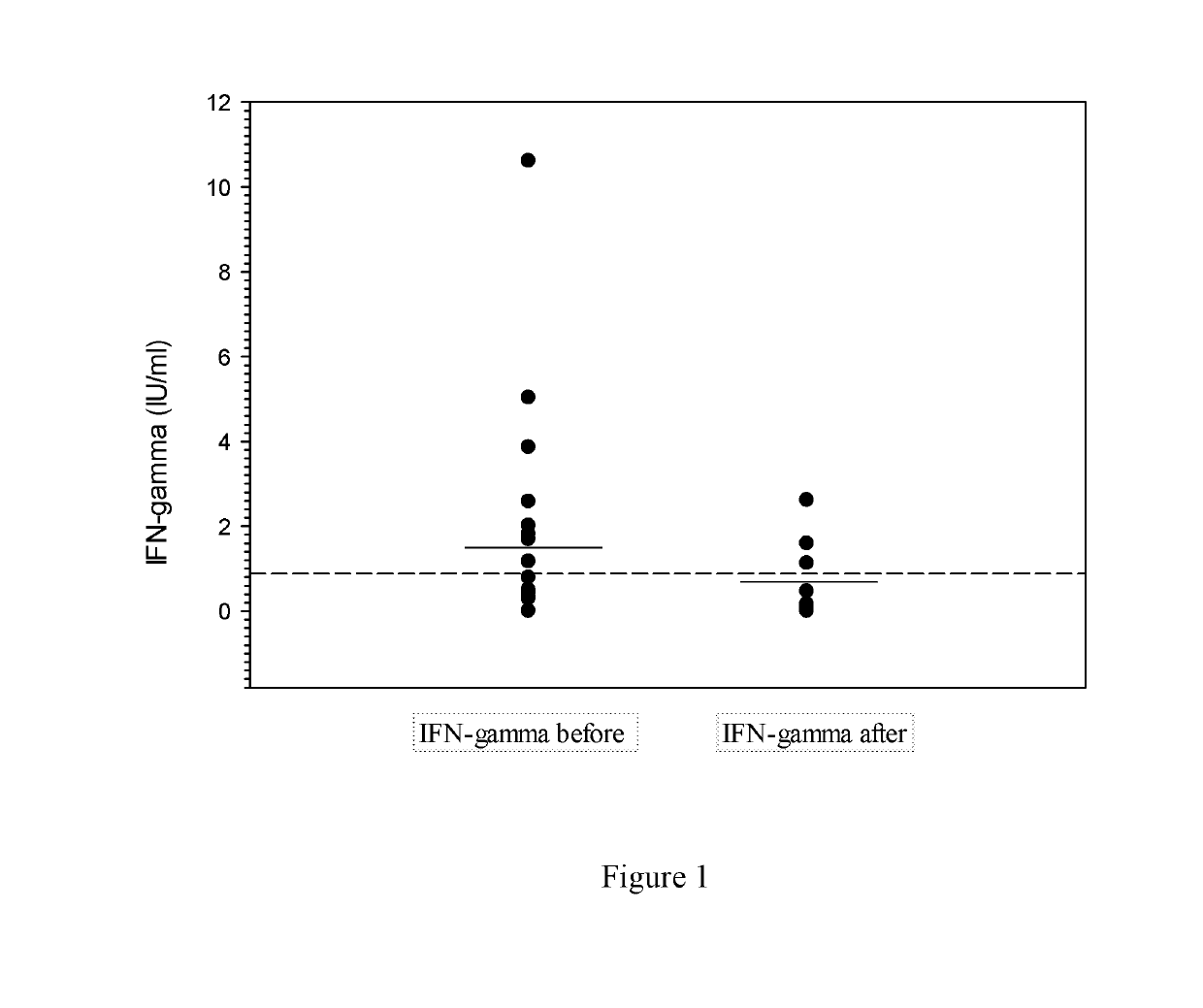
Compositions and methods are provided for detection, diagnosis and prognosis of Lyme disease (LD), including a method for confirming Borrelia spp. infection by contacting, in vitro, whole blood samples from subjects suspected of having LD with synthetic peptides comprising T-cell epitope-containing regions derived from Borrelia proteins that are expressed at different stages of Lyme disease, and indirectly detecting LD-specific activated T-cells by determining production of a T-cell immune response indicator (e.g., interferon-Y) in response to stimulation by the peptides. Also disclosed are methods for predicting elimination of LD spirochetes in LD patients who have undergone LD treatment, by exposing whole blood samples from such subjects to peptides comprising specific T-cell epitope regions of Borrelia proteins that are expressed at different stages of Lyme disease, and confirming a lack of Borrelia-specific activated T-cells in the samples by the absence of a detectable T-cell immune response indicator (e.g., interferon-Y).
Owner:QIAGEN SCIENCES LLC +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com