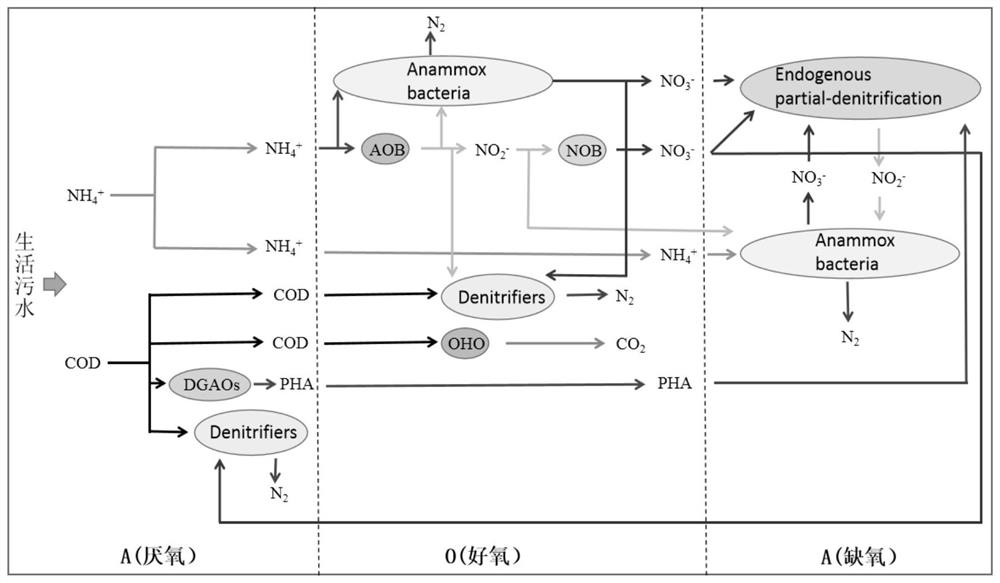
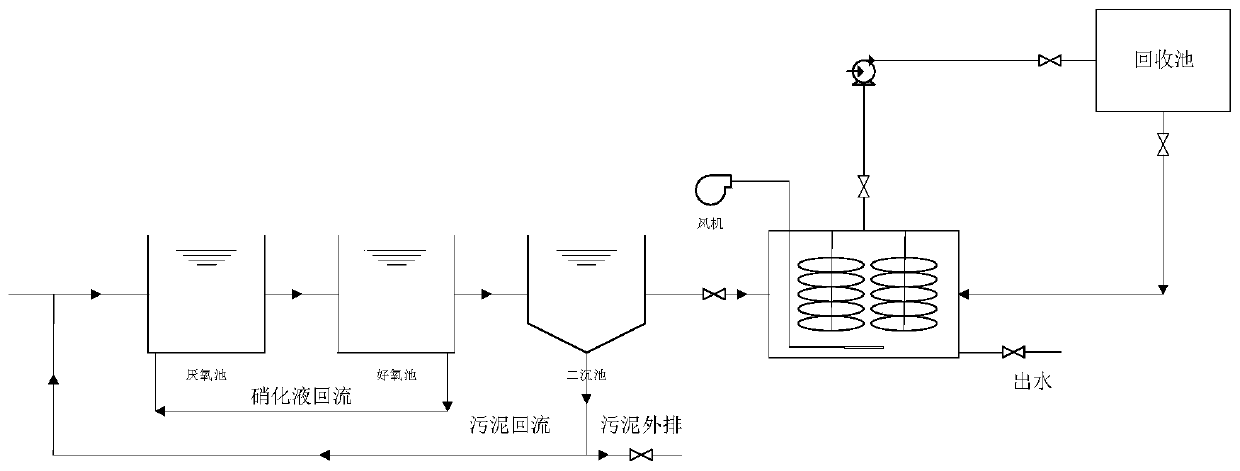
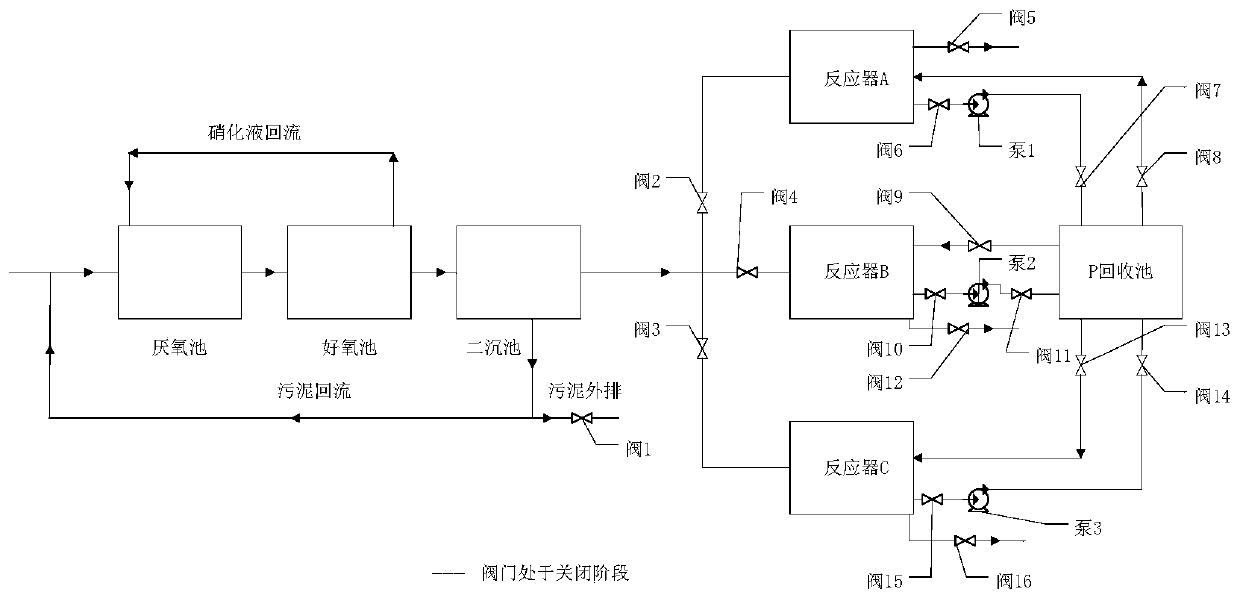
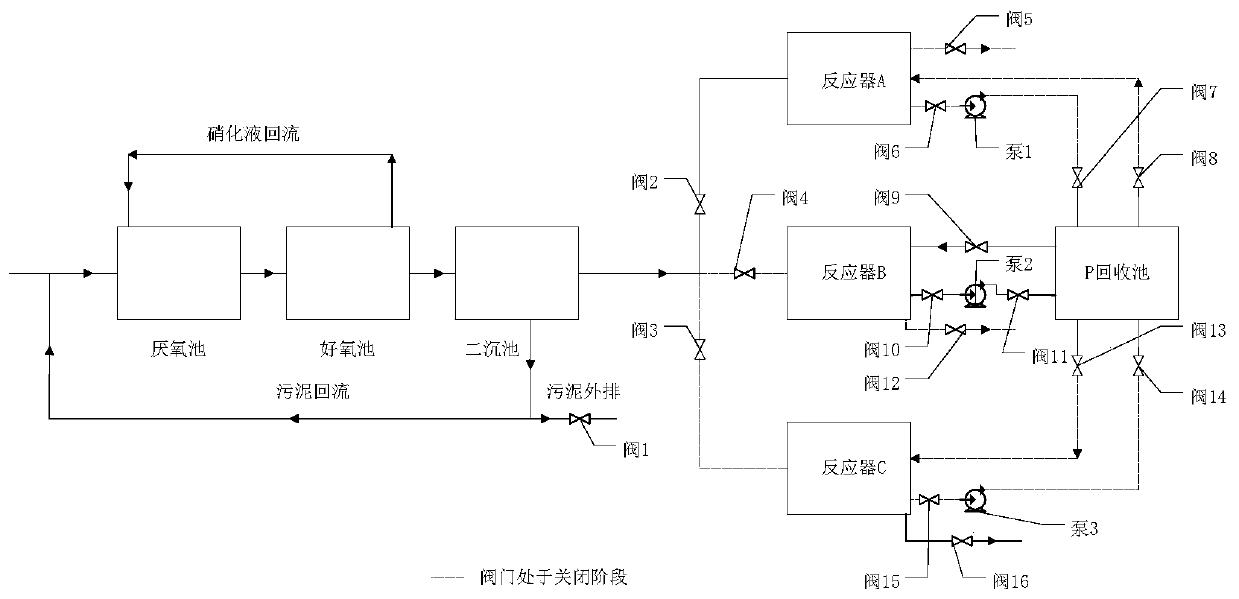
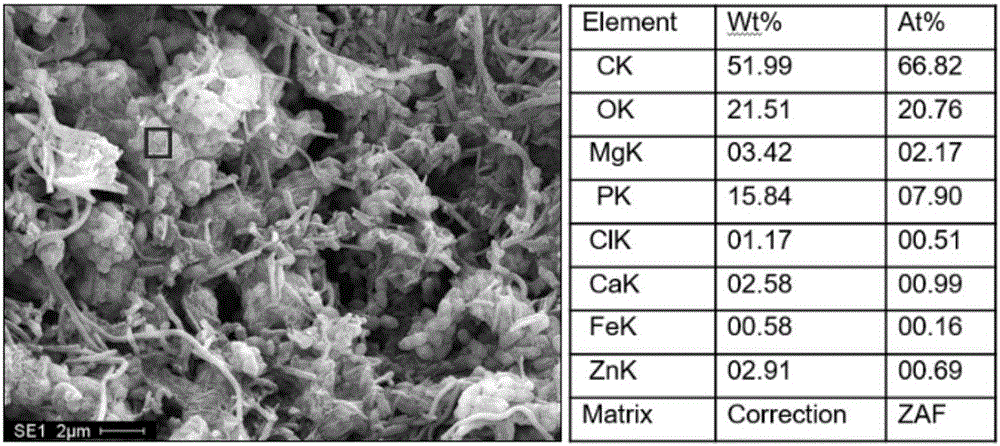
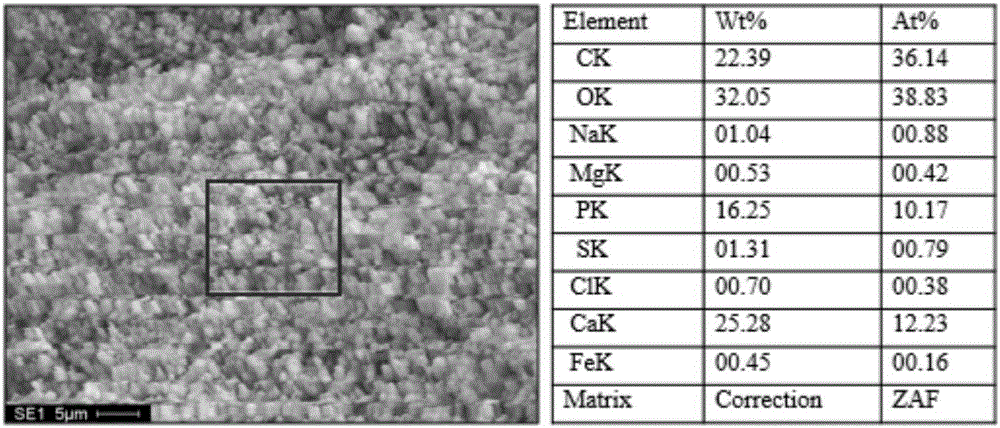
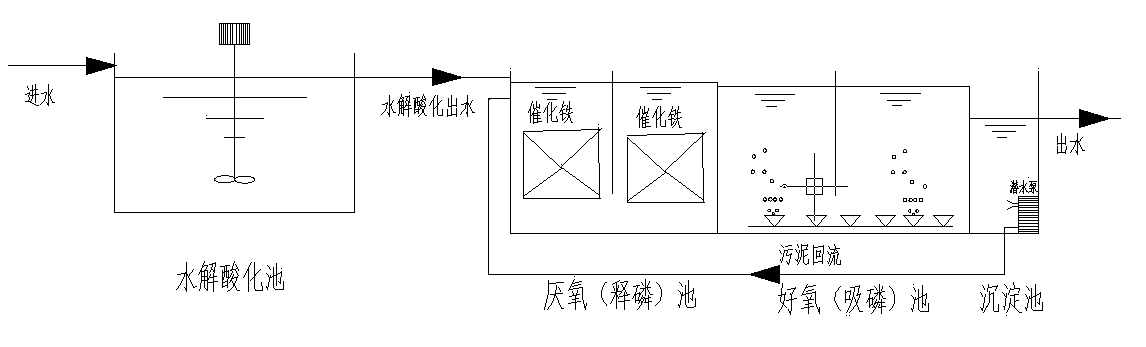
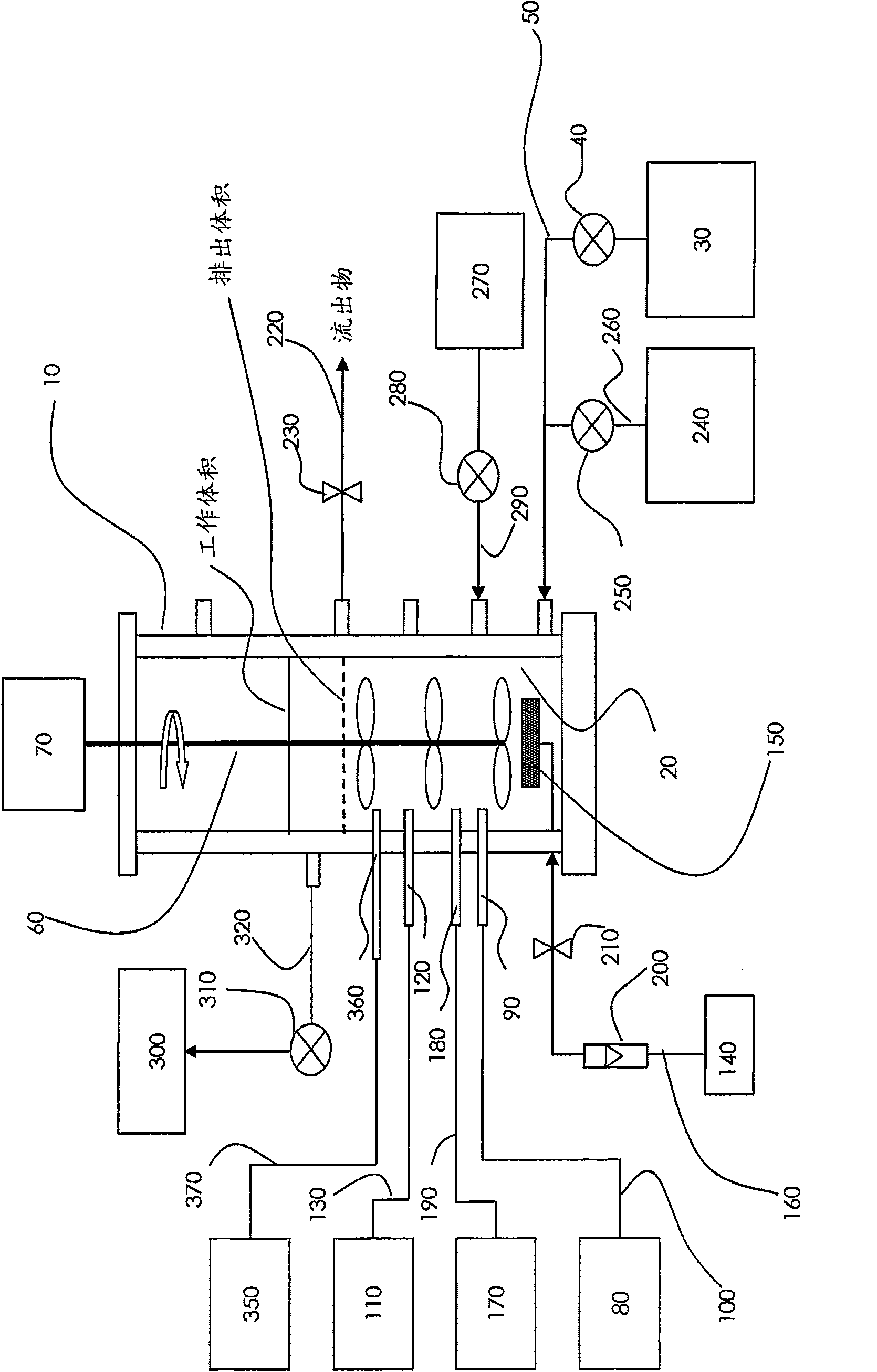
Patents
Literature
164 results about "Polyphosphate-accumulating organisms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
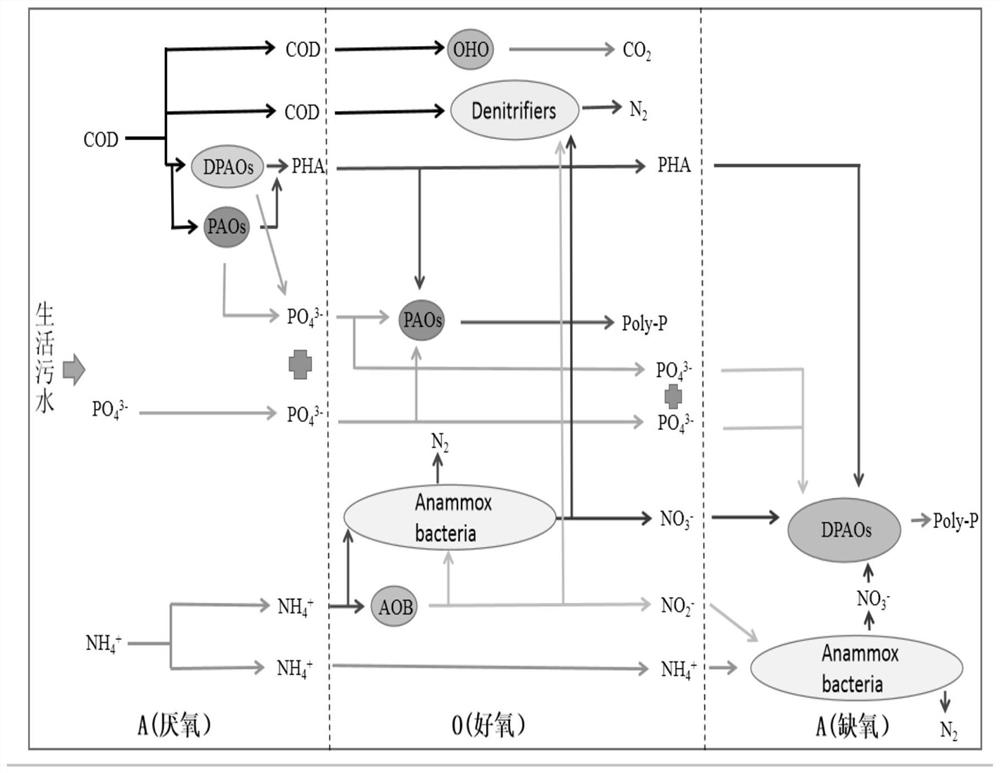
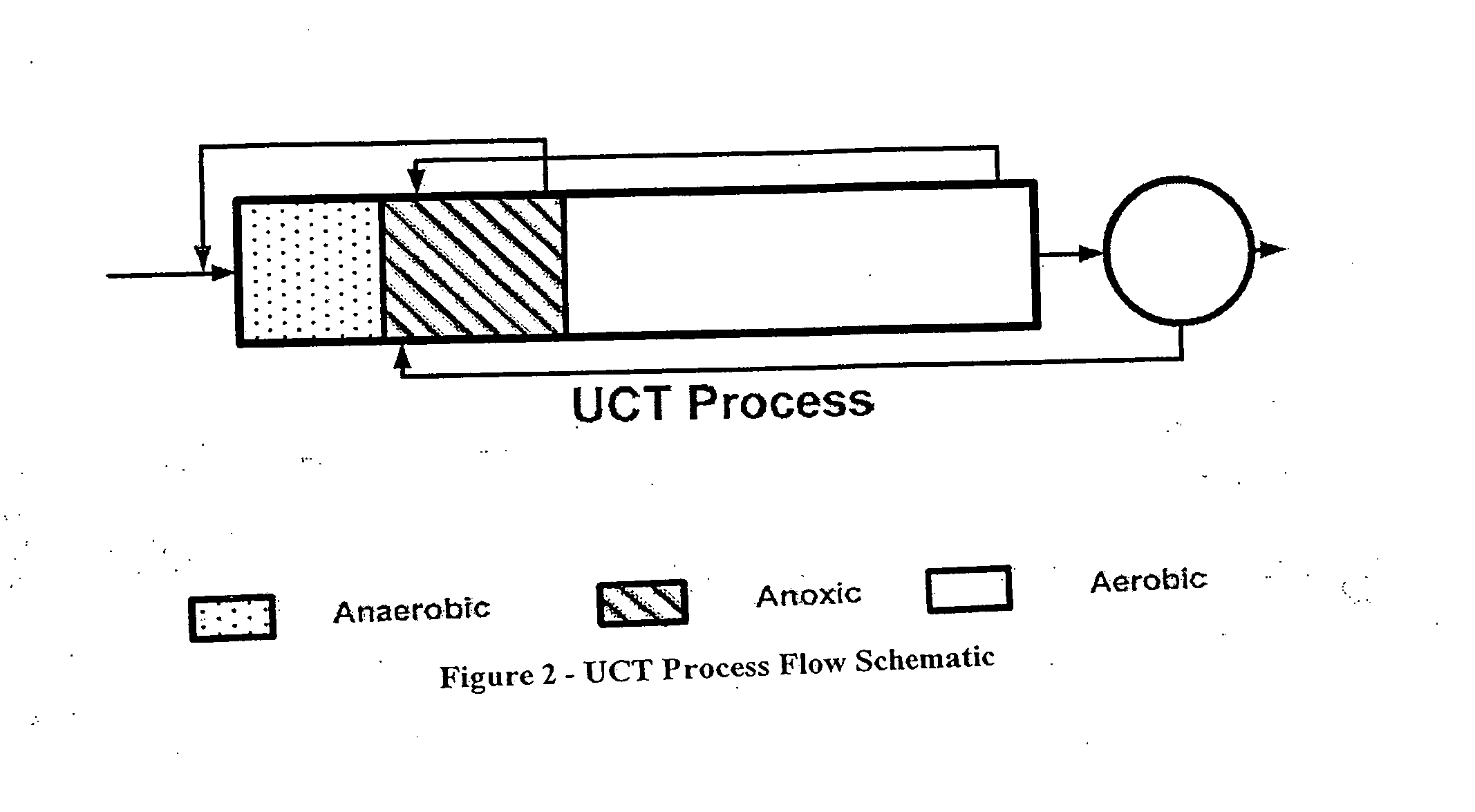
Polyphosphate-accumulating organisms (PAOs) are a group of bacteria that, under certain conditions, facilitate the removal of large amounts of phosphorus from wastewater in a process, called enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR). PAOs accomplish this removal of phosphate by accumulating it within their cells as polyphosphate. PAOs are by no means the only bacteria that can accumulate polyphosphate within their cells and in fact, the production of polyphosphate is a widespread ability among bacteria. However, the PAOs have many characteristics that other organisms that accumulate polyphosphate do not have, that make them amenable to use in wastewater treatment. Specifically, this is the ability to consume simple carbon compounds (energy source) without the presence of an external electron acceptor (such as nitrate or oxygen) by generating energy from internally stored polyphosphate and glycogen. Most other bacteria cannot consume under these conditions and therefore PAOs gain a selective advantage within the mixed microbial community present in the activated sludge. Therefore, wastewater treatment plants that operate for enhanced biological phosphorus removal have an anaerobic tank (where there is no nitrate or oxygen present as external electron acceptor) prior to the other tanks to give PAOs preferential access to the simple carbon compounds in the wastewater that is influent to the plant.
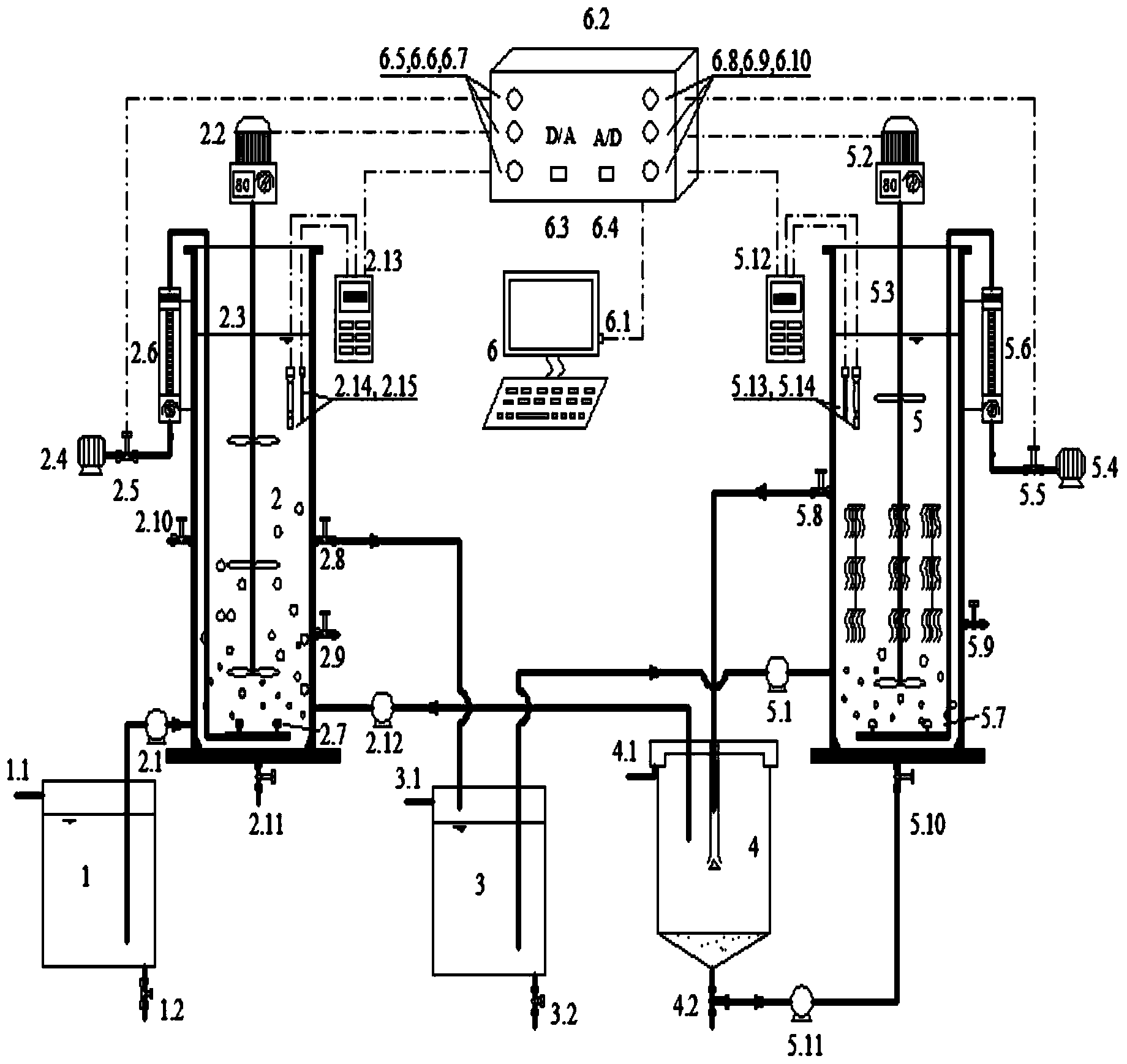
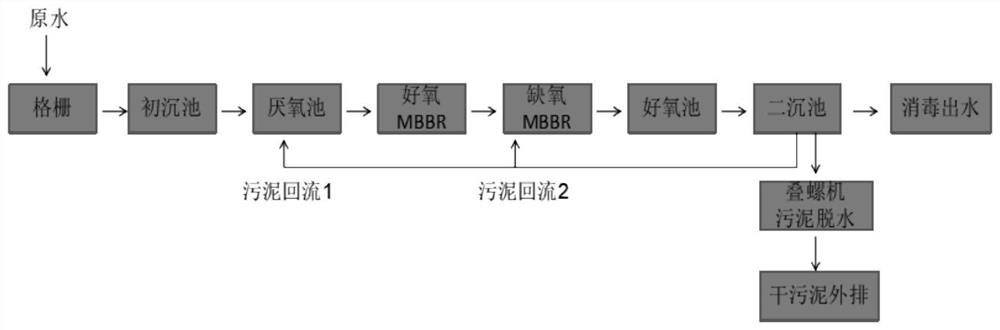
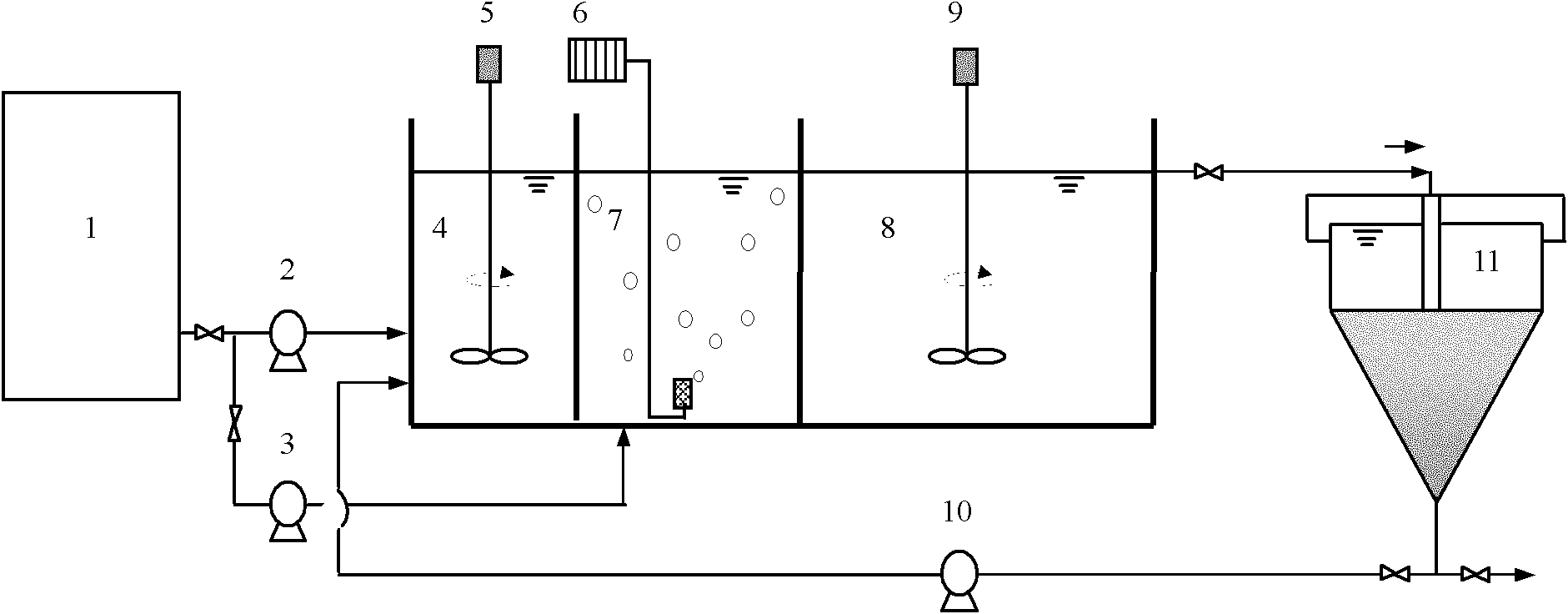
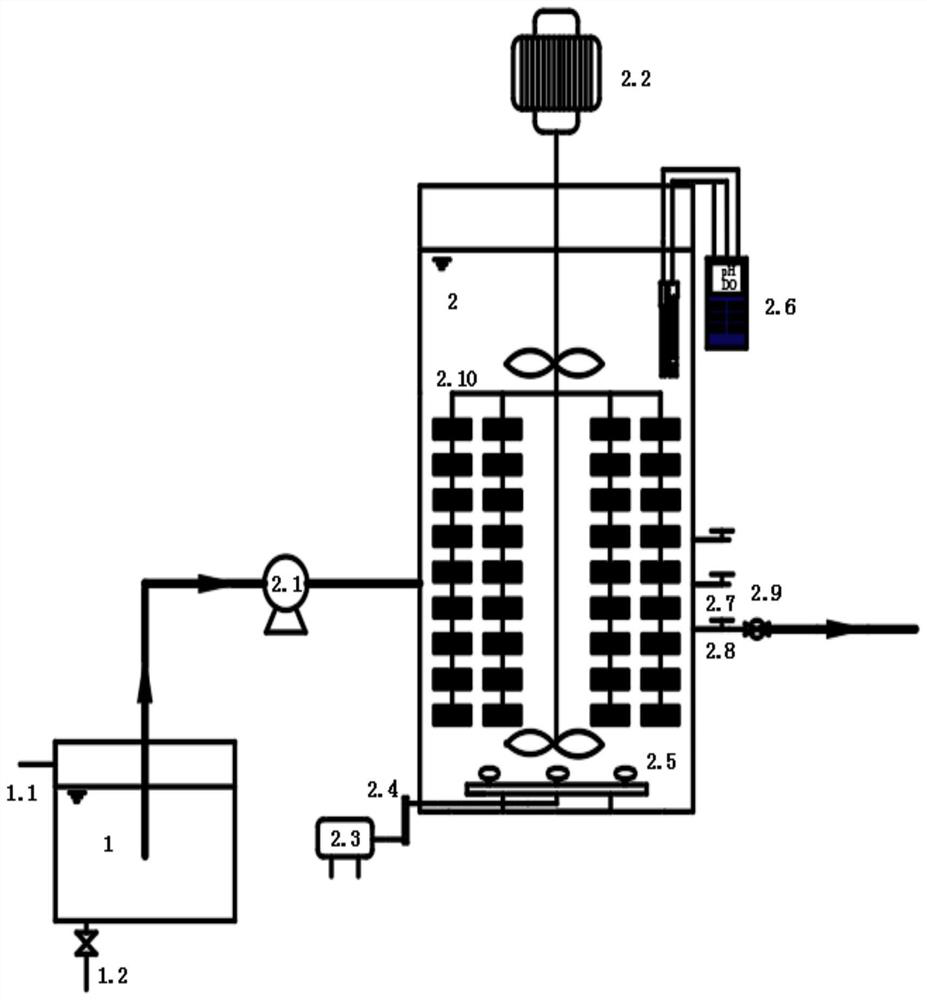
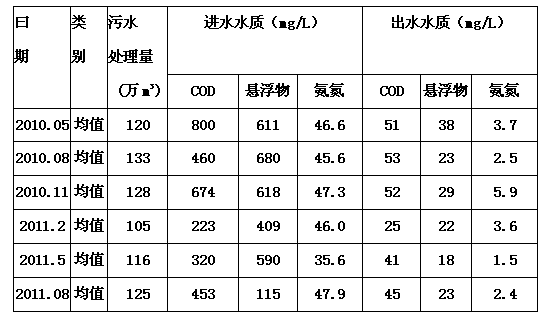
Device and method for nitrogen and phosphorus removal for low CN ratio urban sewage through nitrosation and anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupling denitrifying phosphorus removal intensification
ActiveCN103663862AUnified denitrificationUnified phosphorus removal processMultistage water/sewage treatmentMunicipal sewageAmmonia
The invention discloses a device and a method for nitrogen and phosphorus removal for low CN ratio urban sewage through nitrosation and anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupling denitrifying phosphorus removal intensification, and belongs to the field of biological sewage treatment. The device comprises an urban sewage raw water tank, a denitrifying phosphorus removal reactor, an adjusting water tank, a sedimentation tank, and an integrated partial nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation reactor; when the urban sewage enters the denitrifying phosphorus removal reactor, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria utilizes organic carbon source in the urban sewage for anaerobic phosphorus release, sedimentation and water drainage are performed, the amount of output water is adjusted by the adjusting water tank, then the output water enters the integrated partial nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation reactor, contained NH4<+>-N is converted into N2 to be effectively removed through partial nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation, contained PO4 <3-> and a small amount of NO3<->-N produced in the anaerobic ammonia oxidation flow back with the output water to the denitrifying phosphorus removal reactor for denitrifying phosphorus removal, and then micro-aeration is carried out for a period of time. The method reduces oxygen consumption and energy consumption, improves the nitrogen and phosphorus removal rate, and avoids the problem of insufficient carbon source.
Owner:贵州筑信水务环境产业有限公司
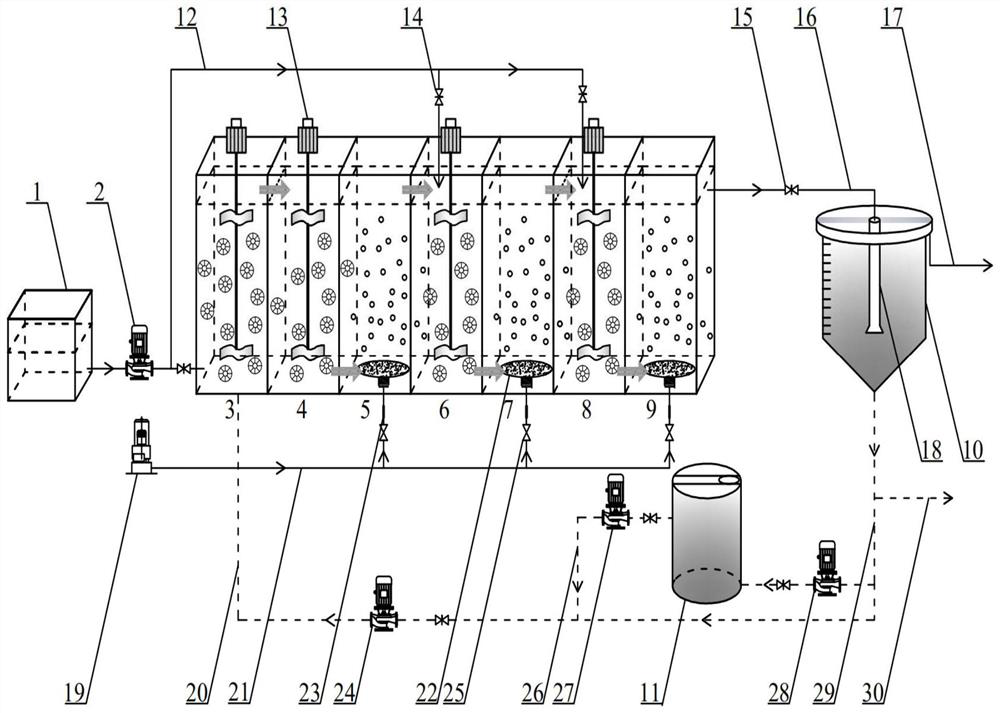
Device and method for nitrogen and phosphorus removal treatment by denitrification on high-ammonia nitrogen anaerobic ammonia oxidation effluent and domestic sewage
ActiveCN103539317AReduce outputLess oxygen consumptionMultistage water/sewage treatmentNitrifying bacteriaSedimentation
The invention discloses a device and method for nitrogen and phosphorus removal treatment by denitrification on high-ammonia nitrogen anaerobic ammonia oxidation effluent and domestic sewage, belonging to the field of biological sewage treatment. The device comprises a high-ammonia nitrogen inflow water tank, an integrated partial nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation reactor, a sedimentation tank, a domestic sewage inflow water tank, a denitrification nitrogen and phosphorus removal reactor and an effluent water tank sequentially connected in series. The method comprises the following steps: in the integrated reactor, effectively removing nitrogen of the high-ammonia nitrogen wastewater through the effect of partial nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation; in the denitrification nitrogen and phosphorus removal reactor, performing anaerobic phosphorus release by phosphorus-accumulating bacteria by use of an organic carbon source in the domestic sewage, and performing hypoxia denitrification phosphorus removal by use of nitrate nitrogen in the anaerobic ammonia oxidation effluent; and finally, further absorbing phosphorus at the aerobic zone in accompany with the nitrification effect generated by the nitrification bacteria. According to the method, the nitrogen removal by anaerobic ammonia oxidation and phosphorus removal by denitrification are coupled into a biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal system for sewage, the nitrate nitrogen generated in the anaerobic ammonia oxidation process is effectively utilized, and the oxygen consumption and energy consumption are greatly reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for achieving partial short-cut nitrification-Anammox/denitrification of sewage by using sludge fermentation materials
ActiveCN108439595ARealize deep denitrificationAchieve reductionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAmmonia-oxidizing bacteriaNitrogen gas
The invention provides a method for achieving partial short-cut nitrification-Anammox / denitrification of sewage by using sludge fermentation materials, and belongs to the field of treatment of sewagesludge. A device used by the method comprises a raw water tank, an SBR reactor, a sludge fermentation material storage tank and a residual sludge fermentation tank. The method comprises mixing residual sludge fermentation materials with domestic sewage for treating, and achieving the short-cut nitrification by using the sludge fermentation materials, wherein the inhibition of the sludge fermentation materials on nitrite oxidizing bacteria is far greater than the inhibition of the sludge fermentation materials on ammonia oxidizing bacteria. The method is specifically characterized in that in ananaerobic phase, polyphosphate accumulating bacteria are used for releasing phosphorus by using the sludge fermentation materials and carbon sources in raw water, and storing the inner carbon sources, in an aerobic phase, the partial short-cut nitrification is achieved through real-time control on DO and pH, in an anoxic phase, anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria are used for converting ammonianitrogen and nitrite nitrogen into nitrogen and nitric nitrogen, and heterotrophic bacteria are used for reducing residual nitrite nitrogen and the generated nitric nitrogen into nitrogen by using theinner carbon sources. Through the method, the aeration intensity is reduced; meanwhile, the deep denitrification of the domestic sewage with a low C / N ratio and the reduction of exogenous sludge areachieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Two-stage backflow simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal device and technology for denitrification phosphorus removal, shortcut nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation of municipal sewage
ActiveCN103588352AAlkalinity balanceEmission reductionMultistage water/sewage treatmentChemical oxygen demandNitration
The invention discloses two-stage backflow simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal device and technology for denitrification phosphorus removal, shortcut nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation of municipal sewage, and belongs to the field of sewage treatment. Municipal sewage enters an anaerobic / anoxic reactor after passing through a regulating reservoir; phosphorus-accumulating bacteria finish storage and phosphorus release of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) by using inflow chemical oxygen demand (COD) under an anaerobic condition; phosphorus-rich supernatant enters inside a middle reservoir through a water decanter, and is injected into a moving bed membrane bioreactor by a lift pump after the water quantity is adjusted; autotrophic nitrogen removal of the shortcut nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation is achieved by alternate operation of low-oxygen aeration and anoxic agitation; the processed effluent enters the anaerobic / anoxic reactor again under the action of a suction pump; denitrification phosphorus removal is achieved after phosphorus-accumulating sludge containing the PHB and autotrophic denitrification effluent containing nitrate nitrogen are mixed. Simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal of low-carbon municipal sewage is achieved by using coupling of three functional microorganisms for denitrification phosphorus removal, shortcut nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation, and the two-stage backflow simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal device has the advantages of being high-efficiency and energy-efficient, stable to run, and low in sludge yield.
Owner:贵州筑信水务环境产业有限公司
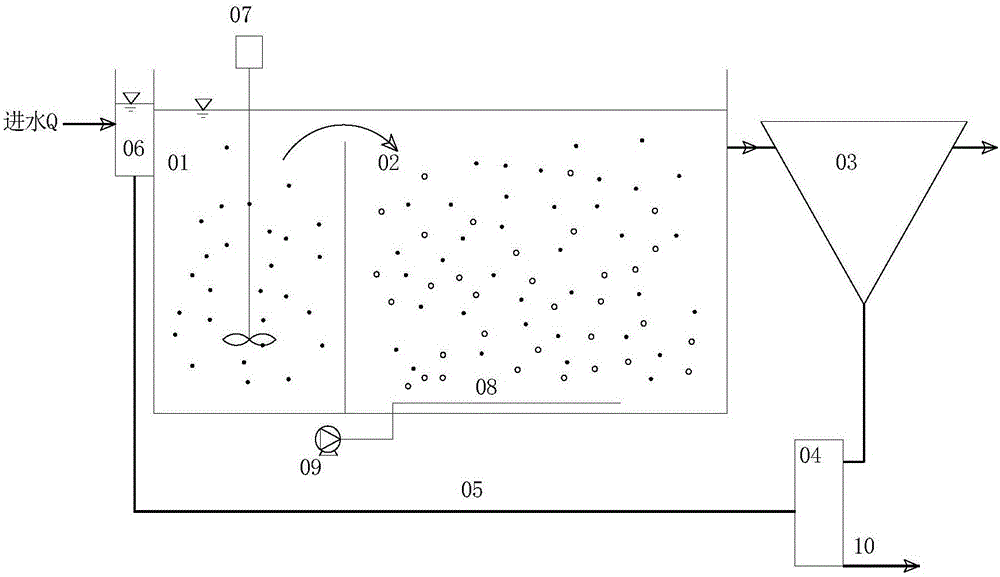
Rear denitrifying sewage treatment device and process
InactiveCN102153236AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiencyTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentSludgeAir pump
The invention discloses a rear denitrifying sewage treatment device and process. A water inlet bucket, a biochemical tank, a sedimentation tank and a water outlet bucket are connected with each other in sequence; the biochemical tank comprises three parts, such as an anaerobic zone, an aerobic zone and an anoxic zone; blenders are arranged in the aerobic zone and the anoxic zone; the anaerobic zone is connected with the anoxic zone by a carbon source shunt pipe; an aerator is arranged in the aerobic zone; the aerator, a gas flowmeter and a gas pump are connected with each other in sequence; the sedimentation tank comprises a central pipe, a reflective plate, a tank body, a water outlet weir and a water outlet; and the bottom of the sedimentation tank is connected with the anaerobic zone of the biochemical tank by a sludge backflow pipe. By using a single-sludge system, the device and process, disclosed by the invention, operate in the form of continuous flow according to an anaerobic-aerobic-anoxic mode. A mixed solution rich in polyhydroxyalkanoate in the anaerobic zone is shunted to the aerobic zone to provide phosphorus-accumulating bacteria with a carbon source so that the denitrifying phosphorus removal is realized in the aerobic zone. The device and process, disclosed by the invention, have the advantages of good nitrogen and phosphorus removal effect, simple process flow, low operation energy consumption, high carbon source utilization rate and the like, and are applicable to treatment of sewage (wastewater) with low C / N (Carbon / Nitrogen) ratio and low C / P (Carbon / Phosphorus) ratio.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Whole process low-oxygen aeration SBMBBR synchronous denitrification and dephosphorization method
ActiveCN107010727AGood denitrification and phosphorus removalHigh organic loadWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSequencing batch reactorMoving bed biofilm reactor
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Non-excess activated sludge discharged printing and dyeing wastewater processing equipment and operation method thereof
InactiveCN101139155AEasy to handleReduce outputTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeDenitrifying bacteria
A printing and dyeing wastewater treatment device and operation method of no excess active sludge discharge belongs to the field of environment protection. The device consists of a regulating tank (1), an overhead tank (2), a NO. 1 hydrolyzing and acidification reactive tank (3), a NO. 2 hydrolyzing and acidification reactive tank (4), a dephosphorization tank (17), a multilevel contact oxidation tank (5) and a solid-liquid separation stillpot (6). A screw carrier of the multilevel contact oxidation tank forms an anaerobic and facultative space. The anaerobic and facultative space plus two-level hydrolyzing and acidification section before the aerobic tecchnics leads three different environment conditions of anaerobic, oxygen-poor and aerobic technics to alternately carry through simultaneously and various microbe groups like denitrifying bacteria and nitrobacteria can coexist in the same sludge system. The goal of effective dephosphorization is reached by strengthening the phosphorus releasing action of the anaerobic section phosphorus-accumulating bacteria through the operation mode of two-level hydrolyzing and acidification and adding chemical phosphate removing agent in the dephosphorization tank. The present invention has the advantages of simple technics, low operation cost, effective dephosphorization, high anti-impact load capacity, convenient operation and management and no excess active sludge discharge.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
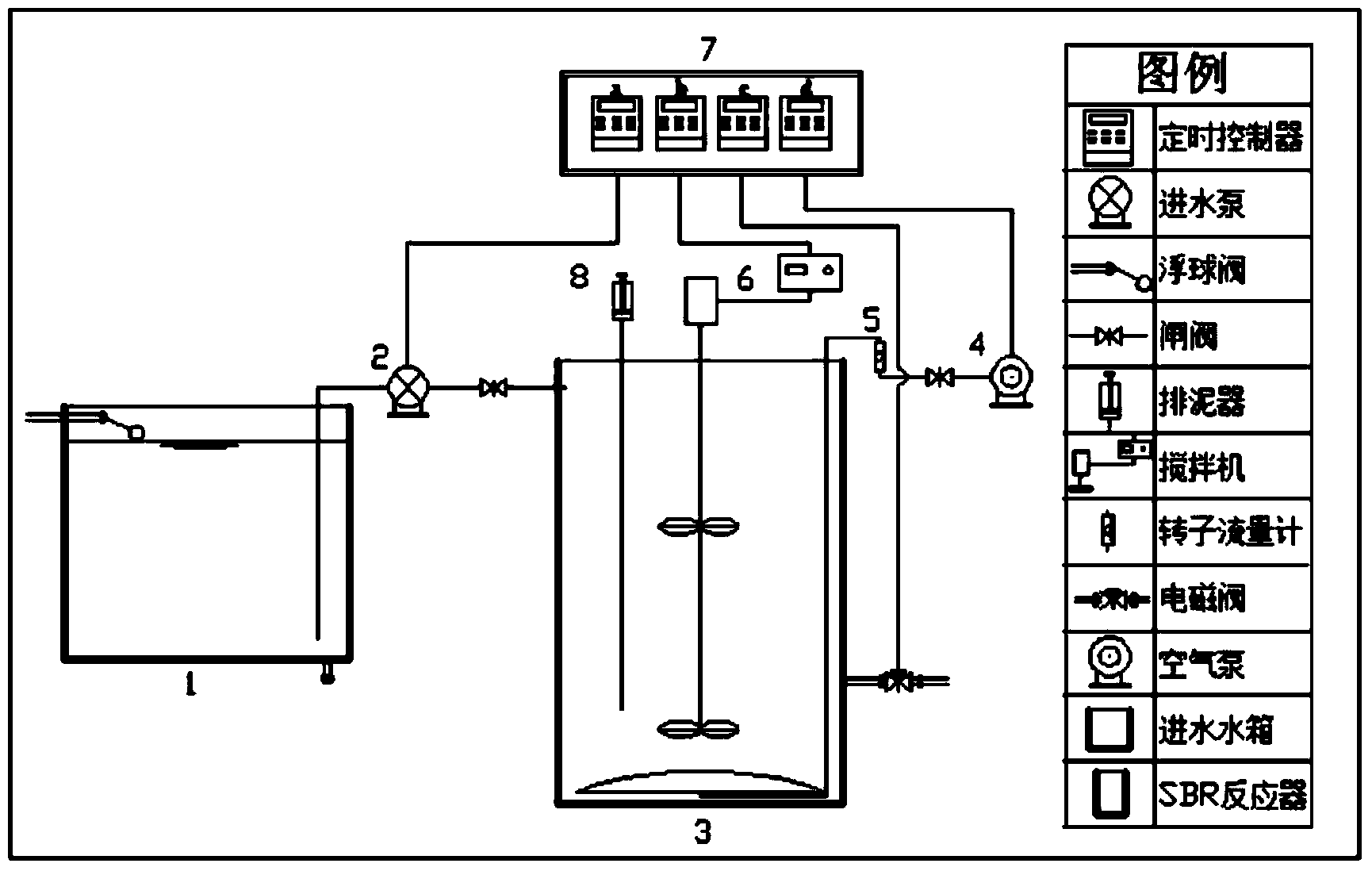
Quick starting method of SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) for synchronously denitrifying and removing phosphor
InactiveCN103588300AReduce startup timeEffective proliferationBacteriaTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSequencing batch reactorFungicide
The invention discloses a quick starting method of an SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) for synchronously denitrifying and removing phosphor, and belongs to the field of sewage treatment. The quick starting method using a batch-injection chronological sequencing batch reactor comprises the following steps: (1), operating the SBR system under an anaerobic / aerobiotic alternation condition, and domesticating and enriching phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, so that the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria intake phosphor under the aerobiotic condition and release phosphor under the anaerobic condition; removing phosphate in water by removing mud; (2), changing an operating way of the system, and enriching denitrifying phosphate-accumulating organisms; increasing an anoxic zone and shortening the aeration time, so that the denitrifying phosphate-accumulating organisms utilize an intracellular carbon source and use nitrate / nitrite as an electron acceptor to intake phosphor; (3), adding a compound fungicide into the reaction, so that biological enhancement is repeatedly coupled with anaerobic / aerobiotic / anoxic / aerobiotic starting method, DPB (Denitrifying Phosphorus-removal Bacteria) are effectively proliferated, glycogen accumulating organisms are restrained, the starting time of the reactor is shortened, and the water outlet effect is improved. The starting way disclosed by the invention operates about 50 days in total, can be used for saving about 30 days and saving the aeration time by about 30% in comparison with an anaerobic / aerobiotic / anoxic starting method.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Municipal domestic sewage AOA mud-membrane mixed deep nitrogen and phosphorus removal system
InactiveCN113173642AImprove settlement performanceEasy to useWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeDenitrifying bacteria
The invention discloses a municipal domestic sewage AOA mud-membrane mixed deep nitrogen and phosphorus removal system, which comprises the following operation steps that municipal domestic sewage enters a biochemical system and is mixed with first reflux sludge in an anaerobic tank, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and glycogen-accumulating bacteria in the sludge utilize a carbon source in raw water to synthesize an internal carbon source in vivo, then the sludge enters an aerobic zone, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria in the aerobic zone perform aerobic excessive phosphorus absorption to completely absorb phosphorus in the domestic sewage while activated sludge in the aerobic zone and nitrifying bacteria on a filler perform nitrification under the aerobic condition, at the moment, the mixed liquid and the sludge reflux to enter the anoxic zone, and the activated sludge and endogenous denitrifying bacteria on the filler perform deep denitrification on nitrate nitrogen in the sewage by utilizing an internal carbon source accumulated in the anaerobic zone. According to the invention, the system consists of a pretreatment unit, an AOA mud-membrane mixed reactor, a secondary sedimentation tank and a disinfection system, and the effluent reaches the four-class standard.
Owner:JIANGSU YULONG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
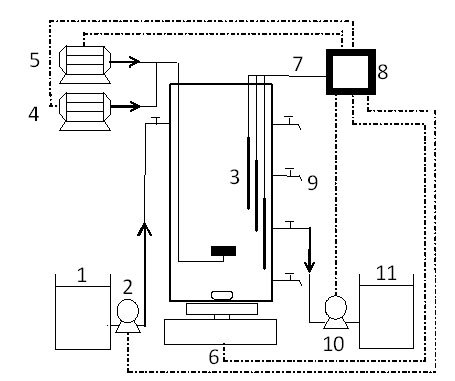
Method for quickly enriching phosphorus accumulating organisms (PAOs) in activated sludge
InactiveCN102079578AFor anaerobic phosphorus releaseTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSequencing batch reactorNitrate nitrogen
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
AOA (Angles-Of-Arrival) continuous flow biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal process for sewage treatment
ActiveCN102086061AEasy to transformSimple structureTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesContinuous flowOxygen
The invention relates to an AOA (Angles-Of-Arrival) continuous flow biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal process for sewage treatment, relating to a sewage treatment process and solving the problems of low efficiency, great operation energy consumption and great carbon source dosage of synchronous nitrogen and phosphorus removal existing in traditional sewage treatment. The process comprises the following steps that: (1) the yielding water of a primary sedimentation tank respectively enters an anaerobic tank and an aerobic tank and the mud of a secondary sedimentation tank is refluxed to the initial end of the anaerobic tank to form a muddy water mixture; and (2) the muddy water mixture enters the aerobic tank from the anaerobic tank in a flow-pushing mode, then enters an anoxic tank and finally enters the secondary sedimentation tank to precipitate and drain. The process provided by the invention comprises the series connection of anaerobism, aerobism and anaerobism, original intake shunted in two parts enters the anaerobic tank and the aerobic tank so that polyphosphate accumulating organisms accumulate a great amount of intracellular polymers by utilizing carbon source in the original intake, the exogenous denitrification and denitrification phosphorus removal of inner carbon sources can be realized in the subsequent anoxic tank, and the synchronous nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency is improved. The process does not adopt a digestive juice reflux unit, has lower operation energy consumption than a traditional process and saves the carbon source dosage.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
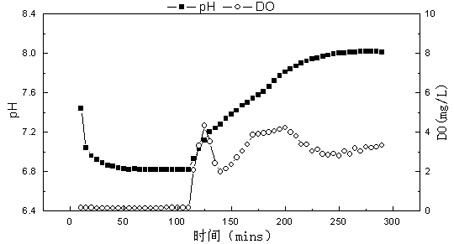
Sequencing batch reaction device and method for carrying out dephosphorization and partial nitrification on low-carbon urban sewage in single-sludge system
ActiveCN103708615ASimple structureEasy to operateTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSequencing batch reactorAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention relates to a sequencing batch reaction device and method for carrying out dephosphorization and partial nitrification on low-carbon urban sewage in a single-sludge system and belongs to the fields of urban sewage treatment and resource regeneration. The device comprises a sequencing batch reactor, a stirring mill and an aerator. The device comprises the following steps: controlling the sludge age, selectively discharging sewage, maintaining the low dissolved oxygen, carrying out time-controlled semi-nitrosation, preserving phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, inhibiting nitrite-oxidizing bacteria, enriching ammonia oxidizing bacteria, rapidly starting a microorganism system led by the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and the ammonia oxidizing bacteria, and optimizing a microenvironment in which the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and the ammonia oxidizing bacteria coexist, so as to enable the contents of water and phosphorus to reach a first-stage standard A, wherein the specific value of nitrite nitrogen to ammonia nitrogen is about 1:1; after carrying out precipitation and water discharging, creatively carrying out anaerobic stirring on the precipitated sewage, and restoring the residual nitrite nitrogen into nitrogen by virtue of endogenous denitrification. According to the device and the method, the problem that the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and the ammonia oxidizing bacteria cannot harmoniously coexist in a single sewage system is solved, and a novel thought is provided for dephosphorization and autotrophic nitrogen removal processes.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device and method for realizing advanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal of municipal sewage by coupling integrated short-cut nitrification with anaerobic ammonia oxidation denitrification phosphorus removal
InactiveCN112250176ASimple processAchieving auto-oxygen denitrificationWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesPhosphateEnvironmental chemistry
The invention discloses a device and a method for realizing advanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal of municipal sewage by coupling integrated short-cut nitrification with anaerobic ammonia oxidationdenitrification phosphorus removal. The device comprises a municipal sewage raw water tank and a short-cut nitrification coupling anaerobic ammonia oxidation denitrification phosphorus removal reactor. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, municipal sewage enters a short-cut nitrification coupled anaerobic ammonia oxidation denitrification phosphorus removal reactor, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and denitrifying phosphorus-accumulating bacteria store an internal carbon source and release phosphorus at the same time, and denitrifying glycogen-accumulating bacteria take in organic matters and convert the organic matters into PHAs to be stored in vivo; then steps of low-oxygen aeration, phosphorus absorbing by phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, converting of part of ammonia nitrogen into nitrite nitrogen are carried out, and anaerobic ammonia oxidation is performed on the residual ammonia nitrogen and the generated nitrite nitrogen to realize denitrification; and the generated nitrate nitrogen is used as an electron acceptor of denitrifying phosphorus-accumulating bacteria to perform excessive absorption of phosphate, thereby achieving the effect of synchronous nitrogen and phosphorus removal. After the stage is completed, anoxic stirring is performed for advanced treatment, and the method can stably realize advanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal of low-C / N municipal sewage.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Grating coupler and package structure incorporating the same
A method for removing phosphorus and nitrogen from an activated sludge wastewater treatment system is provided consisting of one or more anaerobic zones followed by two or more activated sludge reactors operating in parallel each having independent aeration / mixing means, whereby the utilization of the influent organic carbon under anoxic conditions, and thereby, the selection of denitrifying phosphate accumulating organisms (DNPAOs) over non-denitrifying phosphate accumulating organisms (PAOs), is maximized in order to further maximize the removal of phosphorus and nitrogen in the wastewater treatment system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
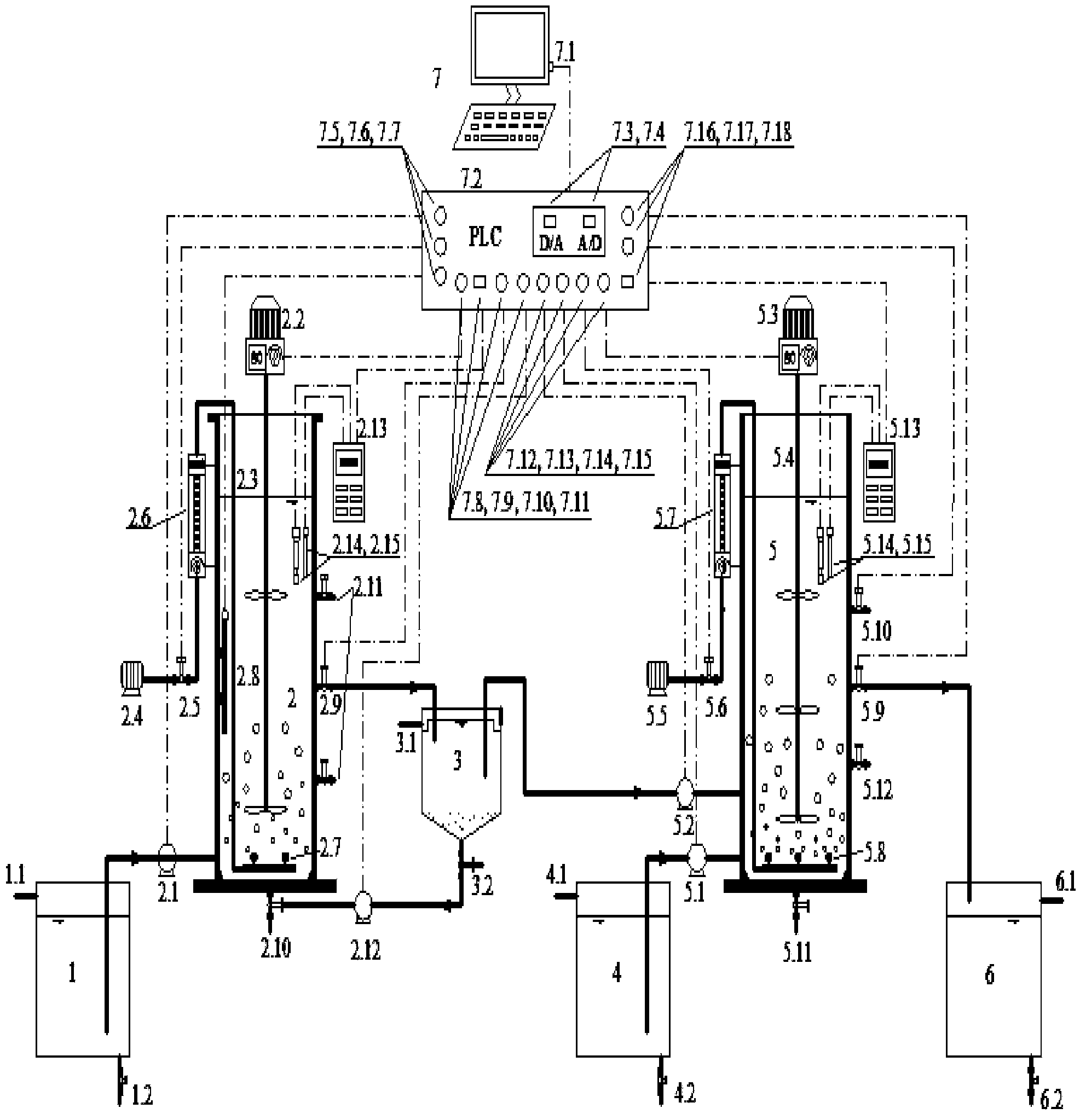
Segmented drainage type short-cut nitrification parallelly-connected anaerobic ammonia oxidation denitrifying phosphorous removal coupled endogenous denitrification device and method thereof
ActiveCN110002587AHas the function of nitrogen and phosphorus removalHigh processing loadTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMunicipal sewageOrganic matter
The invention discloses a segmented drainage type short-cut nitrification parallelly-connected anaerobic ammonia oxidation denitrifying phosphorous removal coupled endogenous denitrification device and a method thereof. Municipal sewage firstly enters a short-cut nitrification phosphorous removal reactor, denitrifying glycogen accumulating bacteria ingest the organic matter and store it as PHAs, and phosphorus-accumulating bacteria store internal carbon source and simultaneously release phosphorous; then, phosphorus is absorbed and ammonia nitrogen is converted to nitrite nitrogen under the hypoxia aeration mode, and nitrosated sewage undergoes first water draining and enters an intermediate water tank; and after anaerobic stirring and denitrification, secondary water draining is carried out. A part of raw water enters an anaerobic ammonia oxidation denitrifying phosphorus removal coupled endogenous denitrification reactor, denitrifying glycogen accumulating bacteria store PHAs, and denitrifying phosphorus accumulating bacteria store an internal carbon source and release phosphorous. After the stage, nitrite nitrogen-containing sewage in the intermediate water tank enters the anaerobic ammonia oxidation denitrifying phosphorus removal coupled endogenous denitrification reactor to realize deep nitrogen and phosphorus removal. By the method, municipal sewage deep nitrogen and phosphorus removal with low C / N ratio can be stably realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Germ composite polluted water treatment agent
InactiveCN103130335APollutedNo pollution in the processBiological water/sewage treatmentBacilliPhotosynthetic bacteria
The invention discloses a germ composite polluted water treatment agent. The germ composite polluted water treatment agent is characterized by comprising 5-20 parts of nitrifying bacteria, 5-20 parts of denitrifying bacteria, 5-15 parts of phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, 5-20 parts of bacillus, 5-20 parts of photosynthetic bacteria, and 1-20 parts of saccharomycetes based on counting weight parts, and each gram medium of a single bacterium contains 1.0-3.5 hundreds of millions of bacteria. The germ composite polluted water treatment agent has the advantages of being high-efficiency, free of pollution, low in sewage treatment cost, little in investment, low in operation cost, strong in adaptability, low in mud output, and capable of possessing good economic and social benefit.
Owner:XIAN REJE BIOLOGICAL TECH
Medicament for repairing polluted soil and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108728108AShorten repair timeRestoration of physical and chemical propertiesFungiAgriculture tools and machinesLactic acid bacteriumMicrobiology
The invention discloses a medicament for repairing polluted soil and a preparation method thereof. The medicament is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 5 to 100 parts of microorganism bacterium agent and 1 to 200 parts of chemical agent, wherein the microorganism bacterium agent is prepared from indigenous microorganism culture, nitrifying bacterium culture, denitrifying bacterium culture, phosphorus accumulating bacterium culture, saccharomycetes culture and lactic acid bacterium culture; the weight ratio of the indigenous microorganism culture to the nitrifying bacterium culture to the denitrifying bacterium culture to the phosphorus accumulating bacterium culture to the saccharomycetes culture to the lactic acid bacterium culture is (5 to 10) to (10 to 15) to (10to 15) to (5 to 10) to (10 to 15) to (5 to 10); the chemical agent is prepared from a heavy metal passivating agent and a curing agent; the weight ratio of the heavy metal passivating agent to the curing agent ranges from (1 to 30) to (3 to 170). According to the medicament disclosed by the invention, polluted soil is treated through adopting a physical-chemical-biological combined treatment technology; the medicament has a good repairing effect on the polluted soil.
Owner:SHANDONG LYUZHIXING ENVIRONMENT ENG CO LTD
Device and method for realizing deep denitrification of municipal sewage by coupling integrated short-cut nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation with endogenous short-cut denitrification
ActiveCN112250175ARealize deep denitrificationSolve difficult problems such as high energy consumption, insufficient carbon source, and large sludge outputWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesGlycogenEnvironmental chemistry
The invention discloses a device and a method for realizing deep denitrification of municipal sewage by coupling integrated short-cut nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation with endogenous short-cut denitrification. The device comprises a municipal sewage raw water tank, a short-cut nitrification anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupling endogenous short-cut denitrification reactor and a water outlet tank. The method comprises the following steps: municipal sewage firstly enters a short-cut nitrification anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupling endogenous short-cut denitrification reactor, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and denitrifying glycogen-accumulating bacteria release phosphorus while storing an internal carbon source, and the denitrifying glycogen-accumulating bacteria take in organic matters and convert the organic matters into PHAs to be stored in vivo; then low-oxygen aeration is carried out to convert part of ammonia nitrogen into nitrite nitrogen; anaerobic ammonia oxidation is performed on the residual ammonia nitrogen and the generated nitrite nitrogen to realize denitrification; and the generated nitrate nitrogen is used as an electron acceptor of denitrifying glycan-accumulating bacteria to perform endogenous short-cut denitrification, and the generated nitrite nitrogen can be continuously utilized for anaerobic ammonia oxidation. The method can stably realizelow C / N municipal sewage deep denitrification.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Continuous biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal recovery system and continuous biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal recovery technology
ActiveCN110668560AOptimizing the Performance of Biological Nitrogen and Phosphorus RemovalSolve the problem of large amount of mud dischargeWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesBiofilmNitrogen removal
The invention discloses a continuous biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal recovery system. The system comprises an A / O system and a plurality of bio-membrane reactors arranged behind the A / O system in parallel, an aeration device is arranged in each bio-membrane reactor, and each bio-membrane reactor is rich in phosphorus-accumulating bacteria; the plurality of bio-membrane reactors are allcommunicated with the A / O system, and valves for controlling on-off are arranged on passages; and a phosphorus recovery tank is arranged behind the bio-membrane reactors and is communicated with the plurality of bio-membrane reactors. The invention also provides a continuous biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal recovery technology. The continuous biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal recovery technology has a good nitrogen removal effect, and synchronously achieves removal of phosphorus and enrichment of a phosphate solution.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Tubular membrane and rear anoxic endogenous denitrification combined nitrogen and phosphorous deep removal device
ActiveCN109485150AIncrease profitEasy to separateWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsSludgeNitration
A tubular membrane and rear anoxic endogenous denitrification combined nitrogen and phosphorous deep removal device belongs to the technical field of biological sewage treatment. According to the tubular membrane and rear anoxic endogenous denitrification combined nitrogen and phosphorous deep removal device, domestic sewage enters into the anaerobic section of an AOA (anaerobic / aerobic / anoxic) reactor via a raw sewage tank, glycogen accumulating organisms and polyphosphate accumulating organisms in the anaerobic section can fully absorb and convert external carbon sources in raw sewage into an internal carbon source (PHA, polyhydroxyalkanoates) which is stored in cells, and meanwhile, the polyphosphate accumulating organisms perform anaerobic phosphorous release; then mixed solution is pushed into an aerobic section of nitrification, and polyphosphate accumulating organisms in active silt perform aerobic phosphorous absorption to complete phosphorous absorption; then the mixed solution is pushed into the anoxic section, the glycogen accumulating organisms and the polyphosphate accumulating organisms perform endogenous denitrification on nitrate nitrogen; lastly, the mixed solutionis pushed into a tubular membrane system for slit-water separation, filtered water serves as final effluent for discharging, slit is returned to the anaerobic section and the anoxic section of the AOA reactor. According to the tubular membrane and rear anoxic endogenous denitrification combined nitrogen and phosphorous deep removal device, the anoxic section is arranged at the rear to make full use of the internal carbon source for denitrification nitrogen removal; the tubular membrane system solves the problem of large silt reflux amount, different silt-water separation and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Germ water purifying agent
InactiveCN103130333APollutedNo pollution in the processBiological water/sewage treatmentBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a germ water purifying agent. The germ purifying agent is characterized by comprising 5-12 parts of denitrifying bacteria, 5-12 parts of denitrifying bacteria, 5-12 parts of bacillus, 5-12 parts of photosynthetic bacteria, 8-12 parts of phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, 5-10 of saccharomycetes, and 2-8 parts of actinomycetes based on counting weight parts, and each gram medium of a single bacterium contains 2.5-3.2 hundreds of millions of bacteria. The germ water purifying agent has the advantages of being high-effciency, free of pollution, low in sewage treatment cost, little in investment, low in operation cost, strong in adaptability, low in mud output, and capable of possessing good economic and social benefit.
Owner:XIAN REJE BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for removing nitrate nitrogen and total phosphorus in printing and dyeing wastewater by denitrifying poly-phosphorus accumulating organisms (B8)
InactiveCN104232543AEfficient removalUnderstand the spiritual essenceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPseudomonas putidaNitrate nitrogen
The invention belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment, and particularly relates to a method for removing nitrate nitrogen and total phosphorus in printing and dyeing wastewater by denitrifying poly-phosphorus accumulating organisms (B8). The denitrifying poly-phosphorus accumulating organisms (B8) are preserved in the CGMCC (China general microbiological culture collection center) with the preservation number of CGMCC NO.9168. The denitrifying poly-phosphorus accumulating organisms are proved to be pseudomonas putida sp. 10% of a bacterium solution prepared by bacteria in percentage by mass is fed into printing and dyeing wastewater and treated by an anaerobic-aerobiotic process or an anaerobic-anoxic process for 9-25 hours at the temperature of 26-30 DEG C respectively, and nitrate nitrogen and total phosphorus in the printing and dyeing wastewater can be effectively removed.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Device and method for enhancing nitrogen and phosphorus removal by combining multistage AO short-cut denitrification coupling Anammox with sludge hydrolytic acidification
ActiveCN112645449AStable carbon sourceAchieve removalWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention discloses a device and method for enhancing nitrogen and phosphorus removal by combining multistage AO short-cut denitrification coupling Anammox with sludge hydrolytic acidification, and belongs to the technical field of activated sludge process sewage treatment. The system comprises a water tank, a water pump, a biochemical reaction area, a hydrolytic acidification tank and the like, raw water is injected into the reaction area in a segmented manner by a multi-stage AO segmented water inlet pipeline, so that the efficient utilization of organic matters in the raw water is ensured; biological membrane carriers are added into an anaerobic zone and an anoxic zone to enrich anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria, nitrite nitrogen is generated through short-cut denitrification to provide a substrate for the anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria, and nitrogen autotrophic removal is achieved; nitrification and phosphorus-accumulating bacteria aerobic phosphorus absorption are carried out in an aerobic zone; and part of residual sludge in a secondary sedimentation tank enters the hydrolytic acidification tank to convert macromolecular organic matters into micromolecular organic matters, a hydrolytic acidification mixture and the residual sludge in the secondary sedimentation tank synchronously flow back to the anaerobic zone, and the micromolecular organic matters serving as a high-quality carbon source can promote short-cut denitrification. The system provides a new method for efficient and energy-saving treatment of urban sewage.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for removing and recycling phosphorus from sewage based on aerobic granular sludge
ActiveCN106219754AAchieve removalAchieve recyclingWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMagnesium ammonium phosphateChemistry
The invention discloses a method for removing and recycling phosphorus from sewage based on aerobic granular sludge. The method comprises the following steps: forming magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitate in the granular sludge in an anaerobic reaction zone, and additionally arranging a granular sludge selecting zone behind a secondary sedimentation tank for selecting granules with higher sedimentation rate, discharging the selected granules out of a system and recycling magnesium ammonium phosphate; refluxing the aerobic granular sludge which is enriched with phosphorus-accumulating bacteria into the anaerobic zone to release phosphorus, and forming the magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitate in the granules; subsequently, enabling the granular sludge mixed solution to pass through the aerobic zone, wherein the granular sludge absorb the phosphorus in the sewage excessively through the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria; after sludge is separated from water in the secondary sedimentation tank, enabling the granules to enter the granular sludge selecting zone, so that the magnesium ammonium phosphate-containing granular sludge with higher sedimentation rate is selected and discharged out of the system to recycle the phosphorus. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a phosphorus recycling system is simplified; the phosphorus is recycled by utilizing an aerobic granular sludge technology; the system is simple and energy-saving, and has practical application and popularization values on the transformation of a sewage phosphorus removal process.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
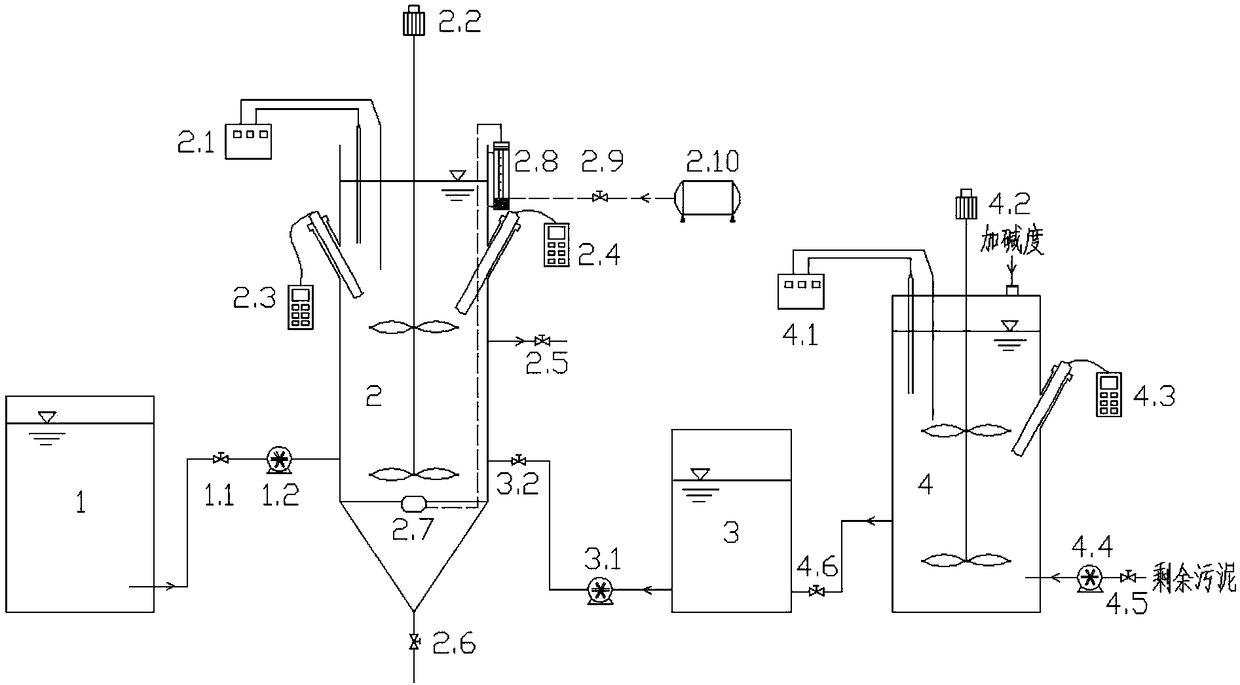
Hydrolytic acidification-catalyzed iron/anaerobic-aerobic biological dephosphorization coupling process
ActiveCN103663686AImprove stabilityImprove efficiencyTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentPhosphate ionPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a hydrolytic acidification-catalyzed iron / anaerobic-aerobic biological dephosphorization coupling process which is realized by a hydrolytic acidification-catalyzed iron / anaerobic-aerobic biological dephosphorization coupling device. The device is composed of a hydrolytic acidification tank, an anaerobic tank and a catalyzed iron filler therein, an aerobic tank and a precipitation tank which are sequentially connected. The process specifically comprises the following steps: sewage is fed into the hydrolytic acidification tank, and the hydraulic retention time is controlled to be 2-6 hours; the effluent water after hydrolytic acidification reaction is fed into the anaerobic tank, sludge in the anaerobic tank is refluxed by the aerobic tank, the reflux liquid brings dissolved oxygen to destroy the anaerobic phosphorus release environment of phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, and the catalyzed iron can effectively remove the dissolved oxygen and simultaneously form ferrous ions; the effluent water of the anaerobic tank passes through the aerobic tank, and the ferrous ions are oxidized to become ferric ions and be combined with phosphate ions to form precipitates, thus achieving dephosphorization effect; and the effluent water of the aerobic tank is precipitated in the precipitation tank, the effluent water is discharged, and part of sludge is refluxed to the anaerobic tank. The process provided by the invention greatly makes up the limitation of the current biological dephosphorization process, and has favorable application prospects.
Owner:相出净流智能科技(上海)有限公司
Wastewater treatment
InactiveCN101573302AWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsBiological bodyTotal nitrogen
The present invention provides a biological process for reducing the levels of nitrogen and phosphorous in wastewater, wherein said wastewater comprises at least 100mg / L total nitrogen wherein said process comprises feeding said wastewater into a reaction vessel in at least two steps, wherein said reaction vessel comprises an active biomass comprising nitrifying and denitrifying organisms and polyphosphate accumulating organisms (PAOs), wherein at least the first feed step is followed by a non-aerated period of sufficient duration to result in sufficiently low concentrations of NOx species in the wastewater to allow for accumulation of polyhydroxyalkanoates in the PAOs, and at least the first non-aerated period is followed by an aerated period of sufficient duration to allow for ammonium oxidation by the nitrifying organisms and assimilation by the PAOs of at least a portion of the phosphorous in the wastewater.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL BIOTECH CRC
Novosphingobium and application thereof in wastewater phosphorus removal
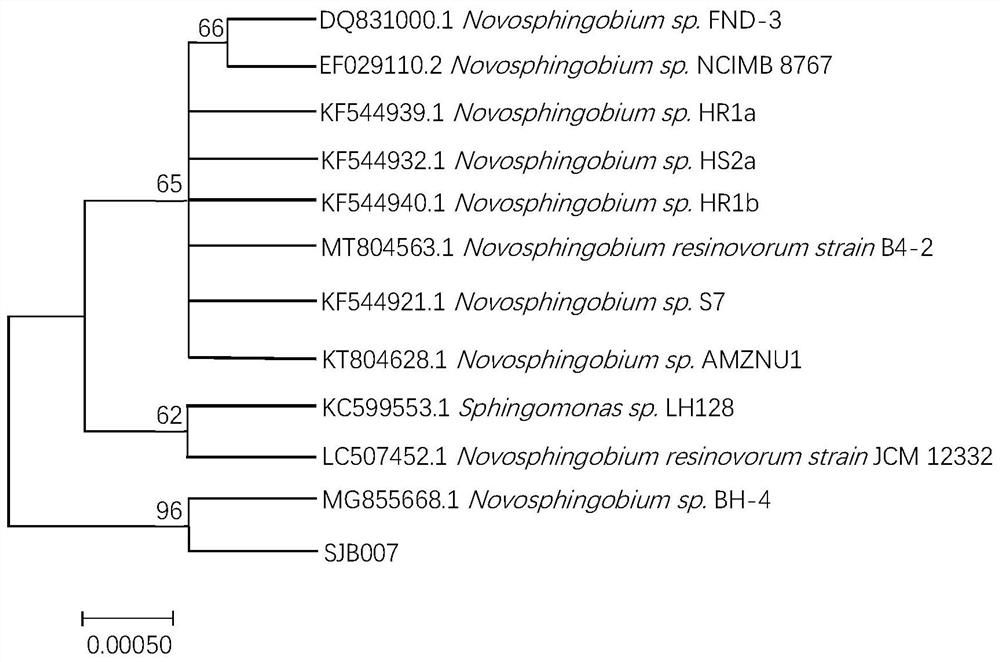
ActiveCN113444661AWide range of temperature adaptationHigh removal rateBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyNovosphingobium sp.
The invention relates to Novosphingobium and application thereof in wastewater phosphorus removal. The bacterial strain is Novosphingobium sp. SJB007 and preserved in the general microbiological center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.21177. The invention further discloses an application of the Novosphingobium sp. SJB007 in removal of phosphorus in sewage. The application comprises the following steps that (1), strain culture is carried out, specifically, a preservation strain, namely Novosphingobium sp. SJB007, is inoculated into a seed culture medium, culturing is carried out for 24 hours under the conditions of 30 DEG C and 160rpm, centrifuging is carried out to obtain thalli, and the thalli are washed with sterile water to prepare a bacterial suspension with OD600 of 0.50-0.60; and (2), fermenting is carried out to remove phosphorus, specifically, the bacterial suspension prepared in the step (1) is inoculated into phosphorus-containing sewage according to the proportion of 2%, and fermenting is carried out under the conditions that the pH is 4-8 and the temperature is 15-35 DEG C to remove phosphorus. According to the efficient phosphorus-accumulating strain Novosphingobium sp. SJB007, when the concentration of phosphorus in sewage is 10-30mg / L under a proper condition, the removal rate exceeds 97%, and a relatively high removal rate is achieved.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
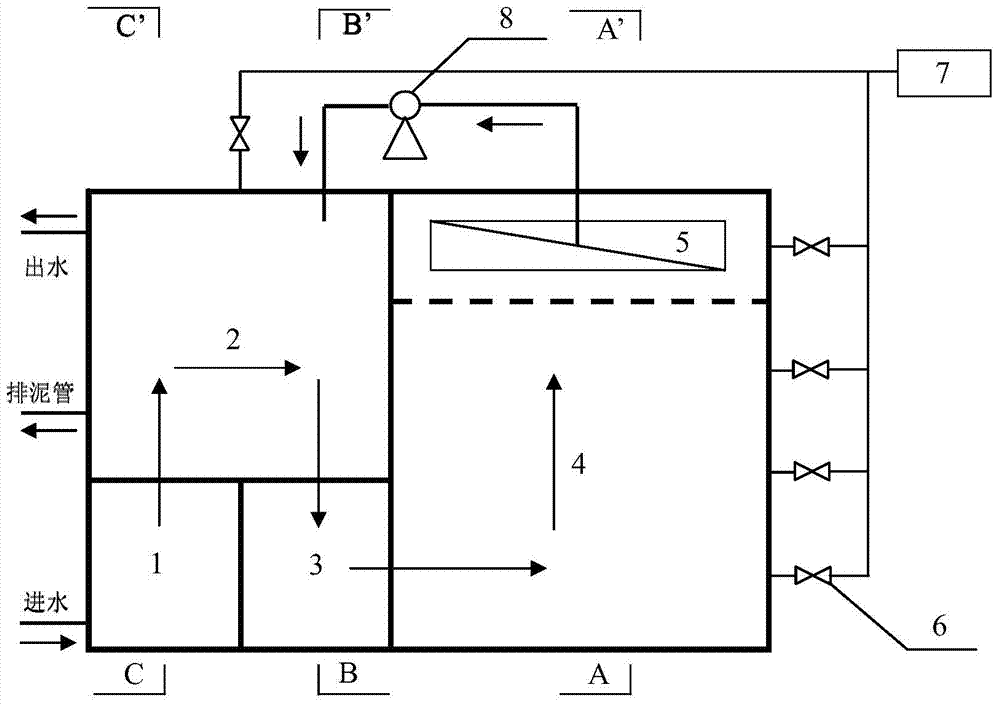
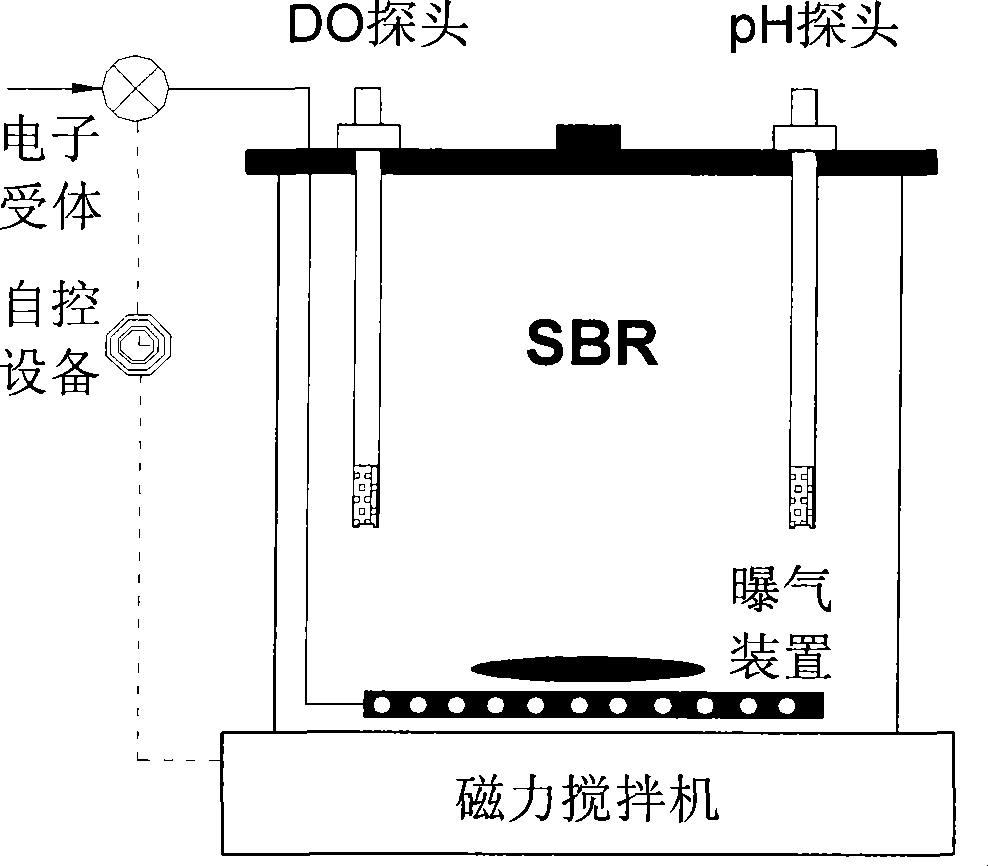
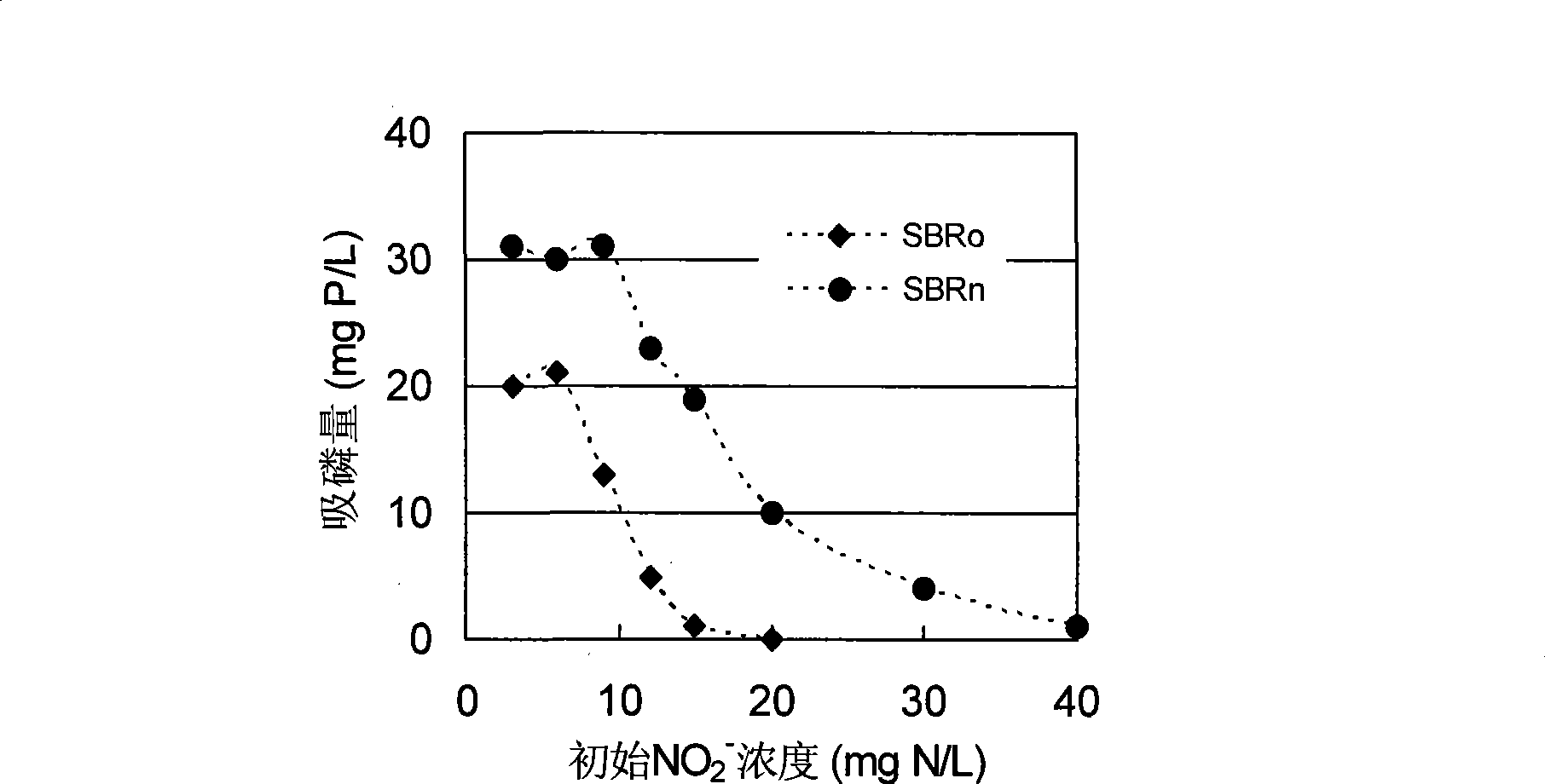
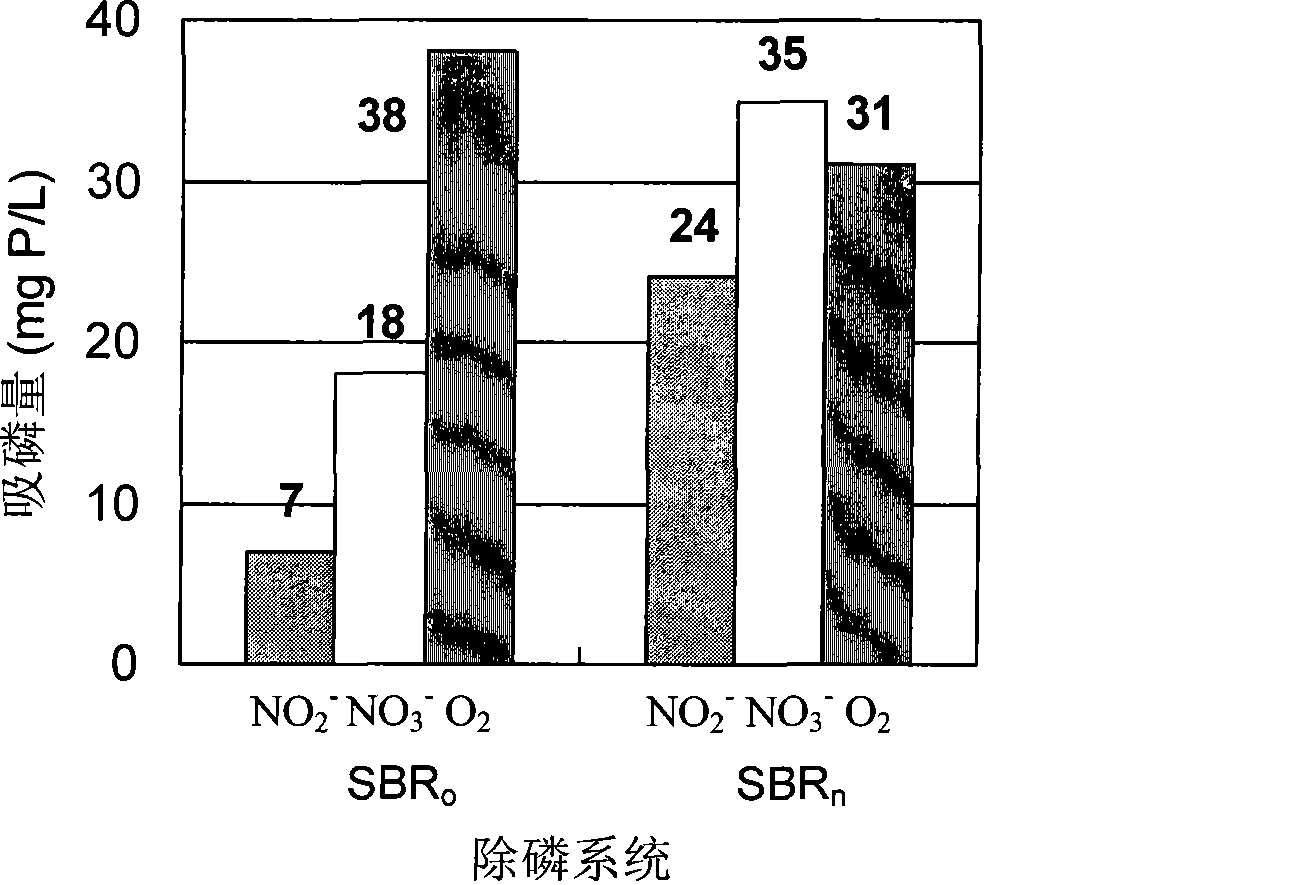
Detection method for diagnosing phosphate accumulating organisms constitute in sewage water phosphorus removal system
InactiveCN101418333AImprove efficiencyThe detection method is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementWater treatment systemSludge
The invention provides a detection method for diagnosing the structure of Poly-P Accumulating Organisms (PAO) in a sewage disposal system. The method comprises two operational phases of an NO2<-> suppressant check test and a phosphorus uptake determination test, wherein in the first phase, the highest NO2<-> concentration which sludge can bear is determined by examination of the influence of different NO2<-> initial concentrations on denitrifying phosphorus uptake of the tested sludge; and in the second phase, the sludge is subjected to aerobic or anoxic phosphorus uptake reaction under the condition of three different electron acceptors of O2, NO3<-> and NO2<-> respectively, and the phosphorus uptake MO, the phosphorus uptake MON and the phosphorus uptake MONn are obtained. Moreover, the quantitative proportion of various PAOs such as aerobic PAO (a-PAO), denitrifying PAO (d-PAO), facultative PAO (f-PAO), obligative aerobic PAO (oa-PAO) and obligative anoxic PAO (od-PAO) in the sludge is mastered according to the computing formula and the application scope of the sludge on the basis, so that the detection method is favorable for diagnosing and improving the operating efficiency of a phosphorus removal system in time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
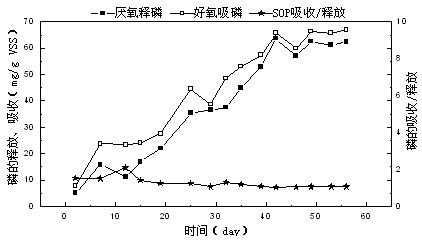
Device and method for enhancing biological phosphorus removal based on synergistic effect of double phosphorus-accumulating bacteria
ActiveCN111995049AReduce dependenceReduce doseWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesPeristaltic pumpVolatile fatty acids
A device and a method for enhancing biological phosphorus removal based on synergistic effect of double phosphorus-accumulating bacteria belong to the technical field of biological sewage treatment. The device comprises a water inlet tank, a biological phosphorus removal reactor, a peristaltic pump, a sludge storage tank and an air pump. According to the method, residual sludge is taken as a matrix and enters the biological phosphorus removal reactor together with wastewater, and in an anaerobic stage, a phosphorus-accumulating bacterium Tetrasphaera with fermentation capability generates volatile fatty acid (VFA) by using residual sludge as a matrix and supplies the volatile fatty acid (VFA) to the traditional phosphorus-accumulating bacteria Candidatus Accumulibacter for utilization, stores an internal carbon source and releases phosphate; and in an aerobic stage, phosphate in sewage can be excessively absorbed by the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria Tetrasphaera and Candidatus Accumulibacter together, so that the synergistic phosphorus removal is realized. By utilizing the synergistic effect of the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria Tetrasphaera and Candidatus Accumulibacter, thedependence on inlet water VFA can be reduced, meanwhile, phosphorus is absorbed by the phosphorus-accumulating Tetrasphaera and Candidatus Accumulibacter at the same time in an aerobic stage, biological phosphorus removal can be effectively enhanced, and a brand-new process solution is provided for treatment of sewage lack of carbon sources in many regions.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device and method for side-flow enhanced biological phosphorus removal process developed based on carbon source in excess sludge
InactiveCN112174317ALow running costReduce doseWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsVolatile fatty acidsPhosphate
The invention discloses a device and a method for a side-flow enhanced biological phosphorus removal process developed based on a carbon source in excess sludge, and belongs to the field of biologicalsewage treatment. According to the method, a part of returned sludge in a secondary sedimentation tank enters a side-flow fermentation zone, activated sludge is used as a matrix of phosphorus-accumulating bacteria Tetrosphaera with fermentation capability, phosphate is released, an internal carbon source is absorbed and stored, and volatile fatty acid VFA is produced by fermentation and is used by other heterotrophic bacteria. The other part of the returned sludge, the effluent of the side-flow fermentation zone and municipal sewage inflow enter an anoxic zone of a main-flow reaction zone together, denitrification nitrogen and phosphorus removal are achieved by utilizing an internal carbon source absorbed and stored in the fermentation zone and volatile fatty acid VFA generated in the fermentation zone, and the effluent of the anoxic zone flows into an aerobic zone for aerobic phosphorus absorption and nitrification. According to the invention, a side-flow continuous flow process is utilized, a front anaerobic zone is omitted, the addition of a carbon source is greatly saved, and the dependence on inlet water VFA is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com