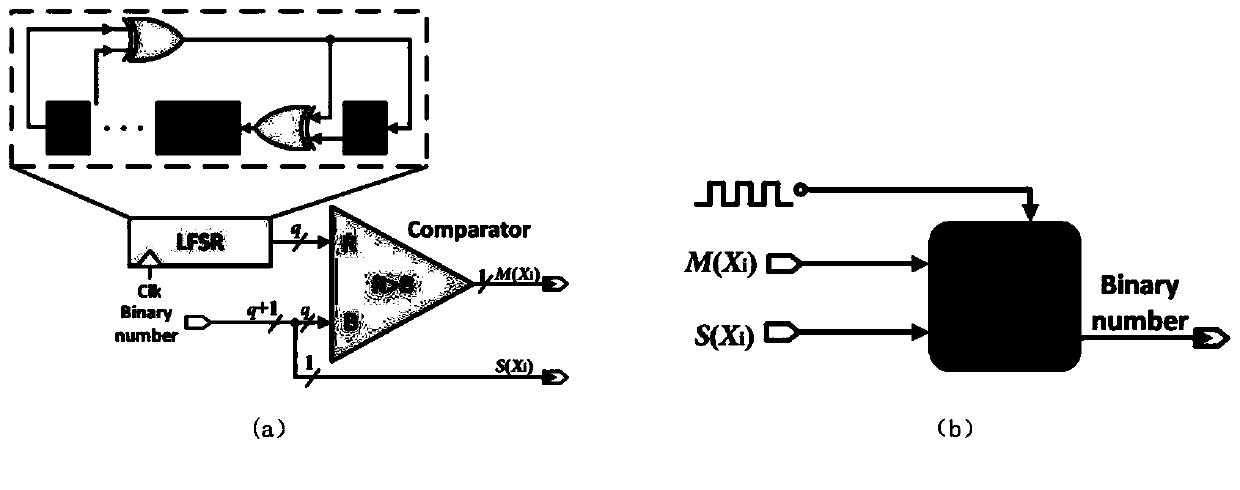
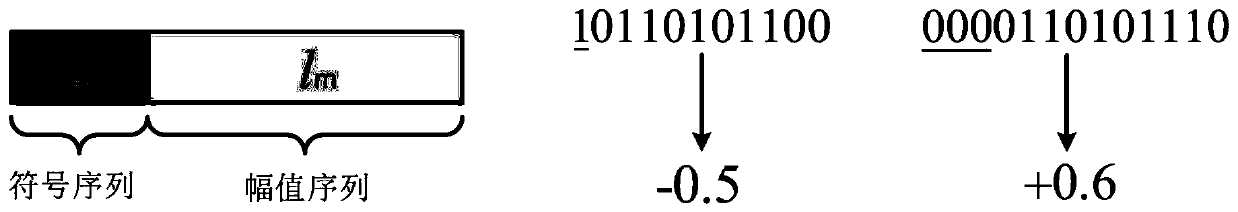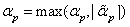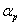Patents
Literature
43 results about "Stochastic computing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stochastic computing is a collection of techniques that represent continuous values by streams of random bits. Complex computations can then be computed by simple bit-wise operations on the streams. Stochastic computing is distinct from the study of randomized algorithms.
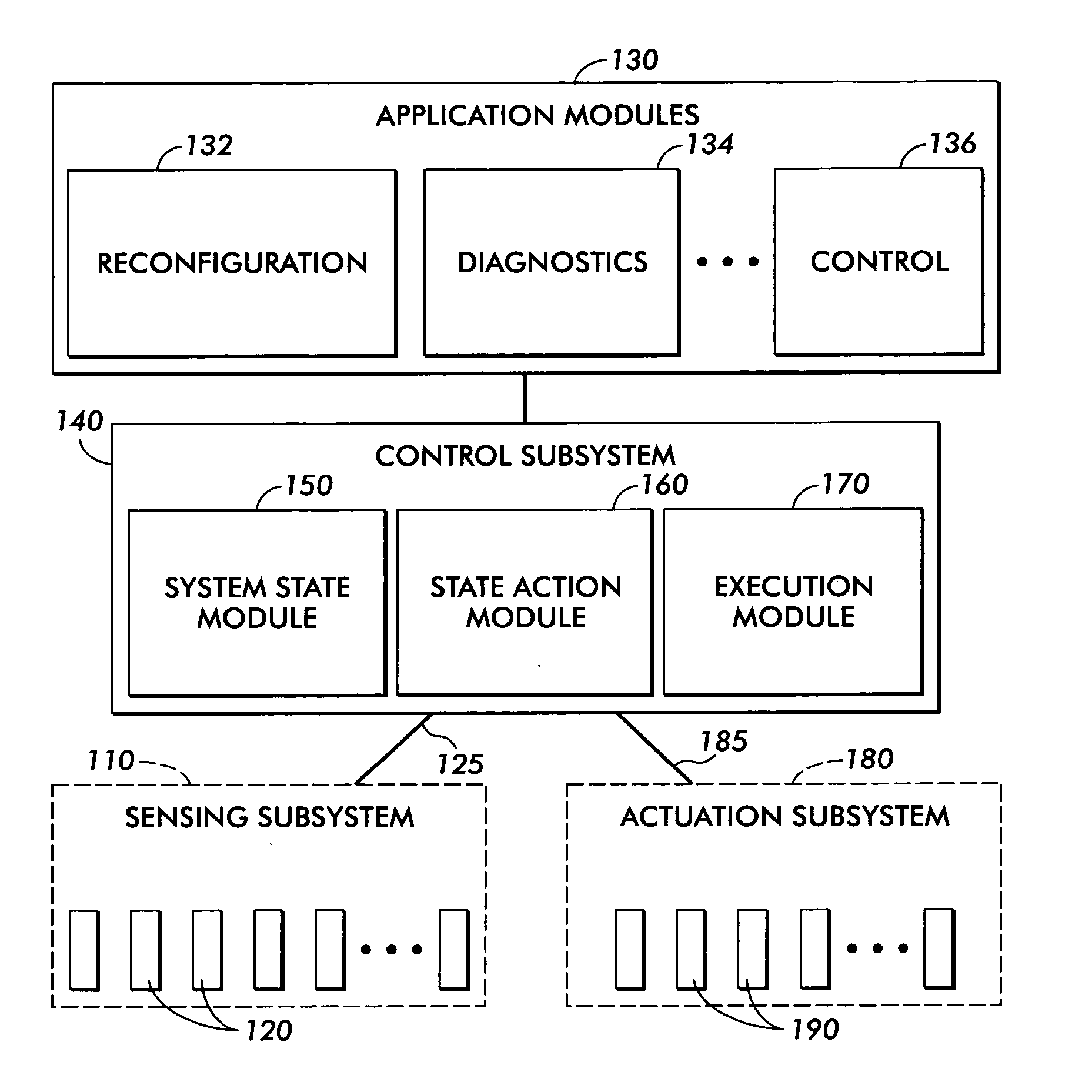
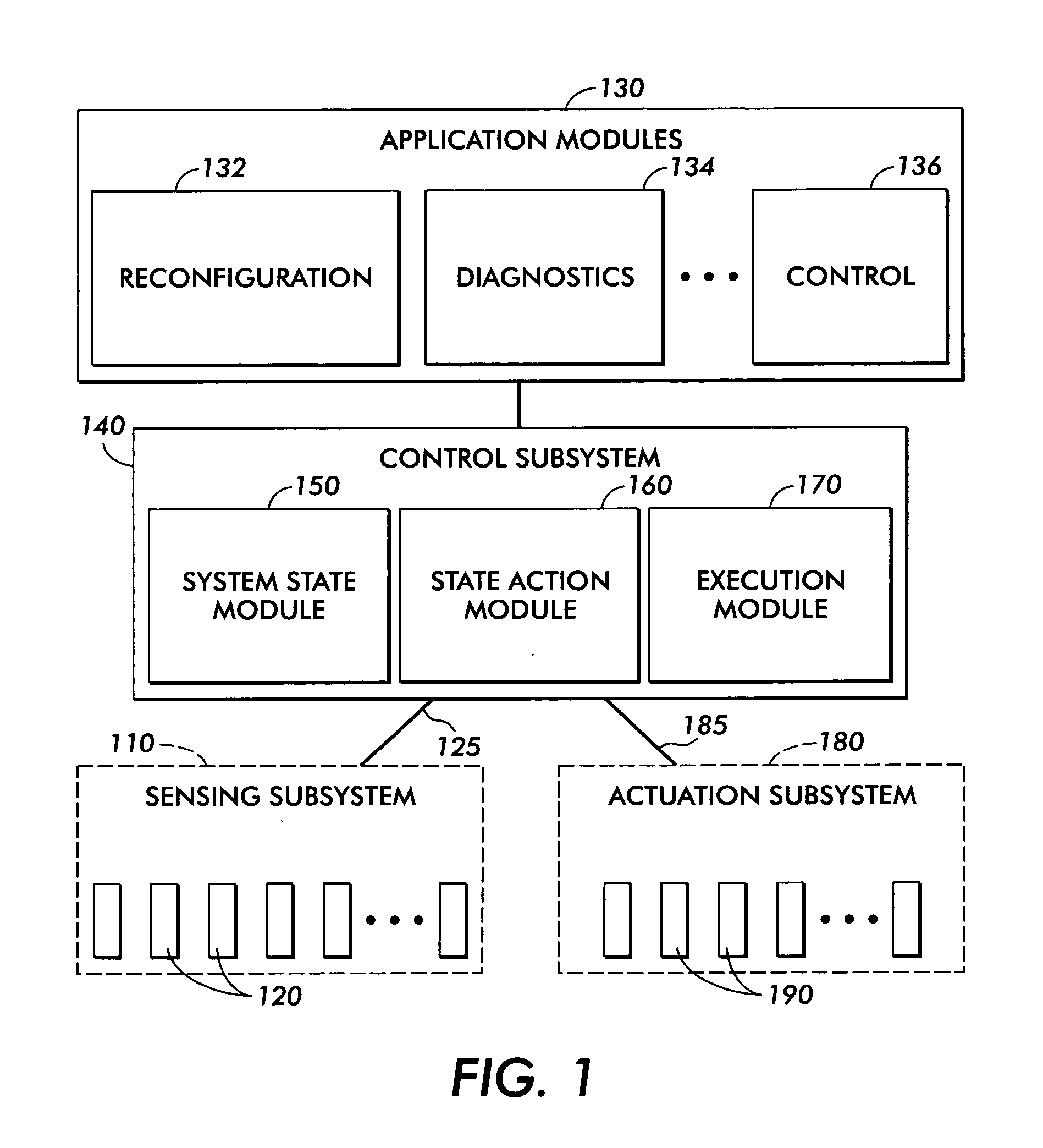
System and method for implementing real-time applications based on stochastic compute time algorithms
InactiveUS20050203643A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceError detection/correctionAlgorithmStochastic computing
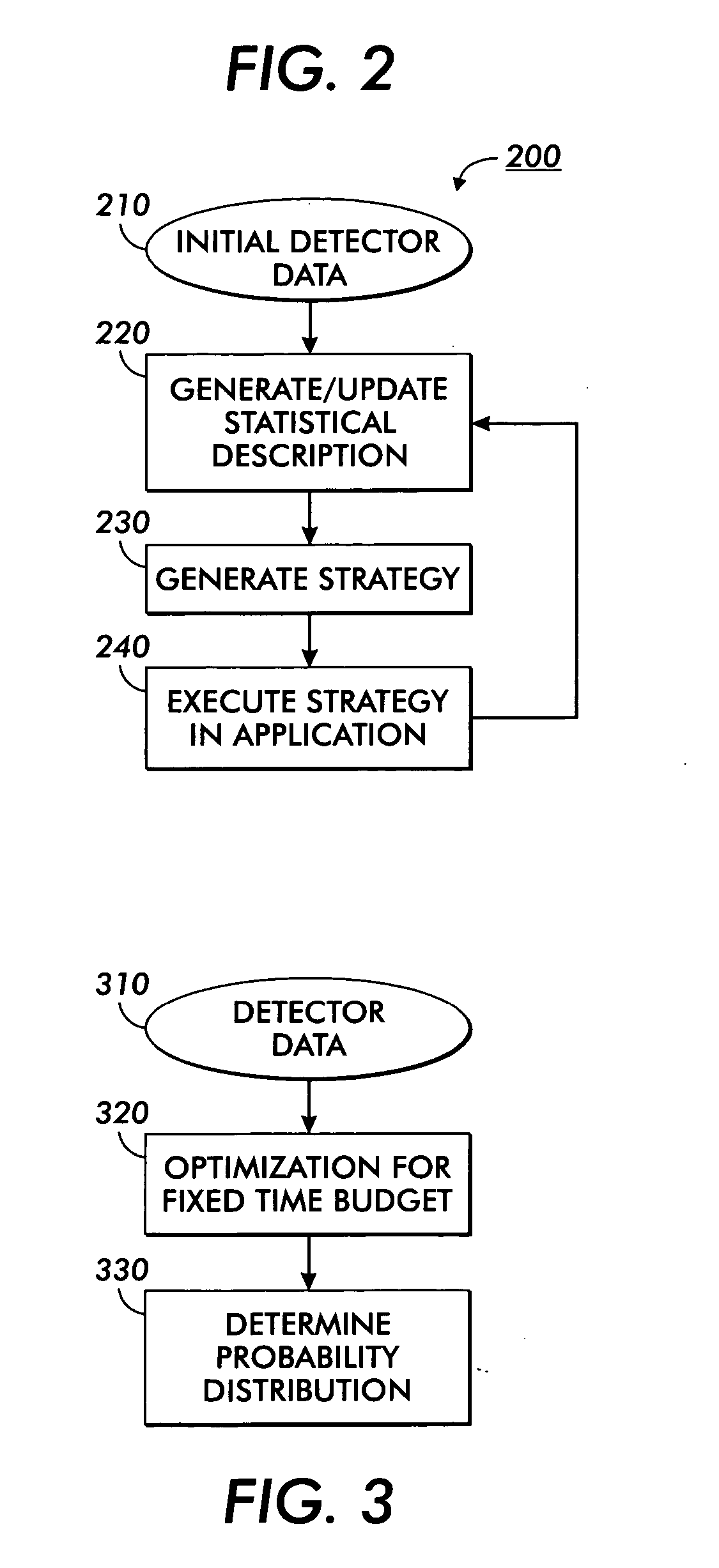
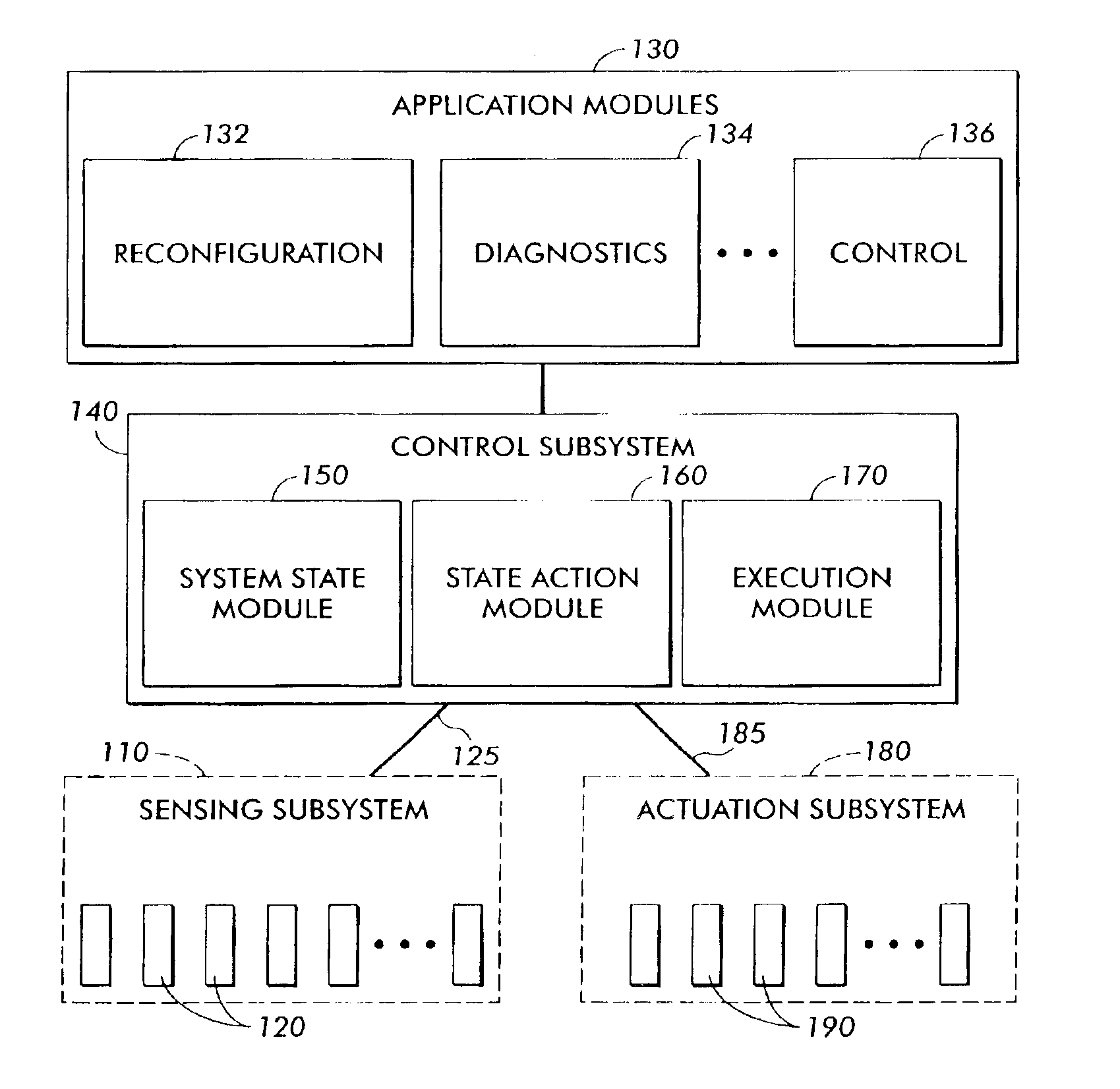
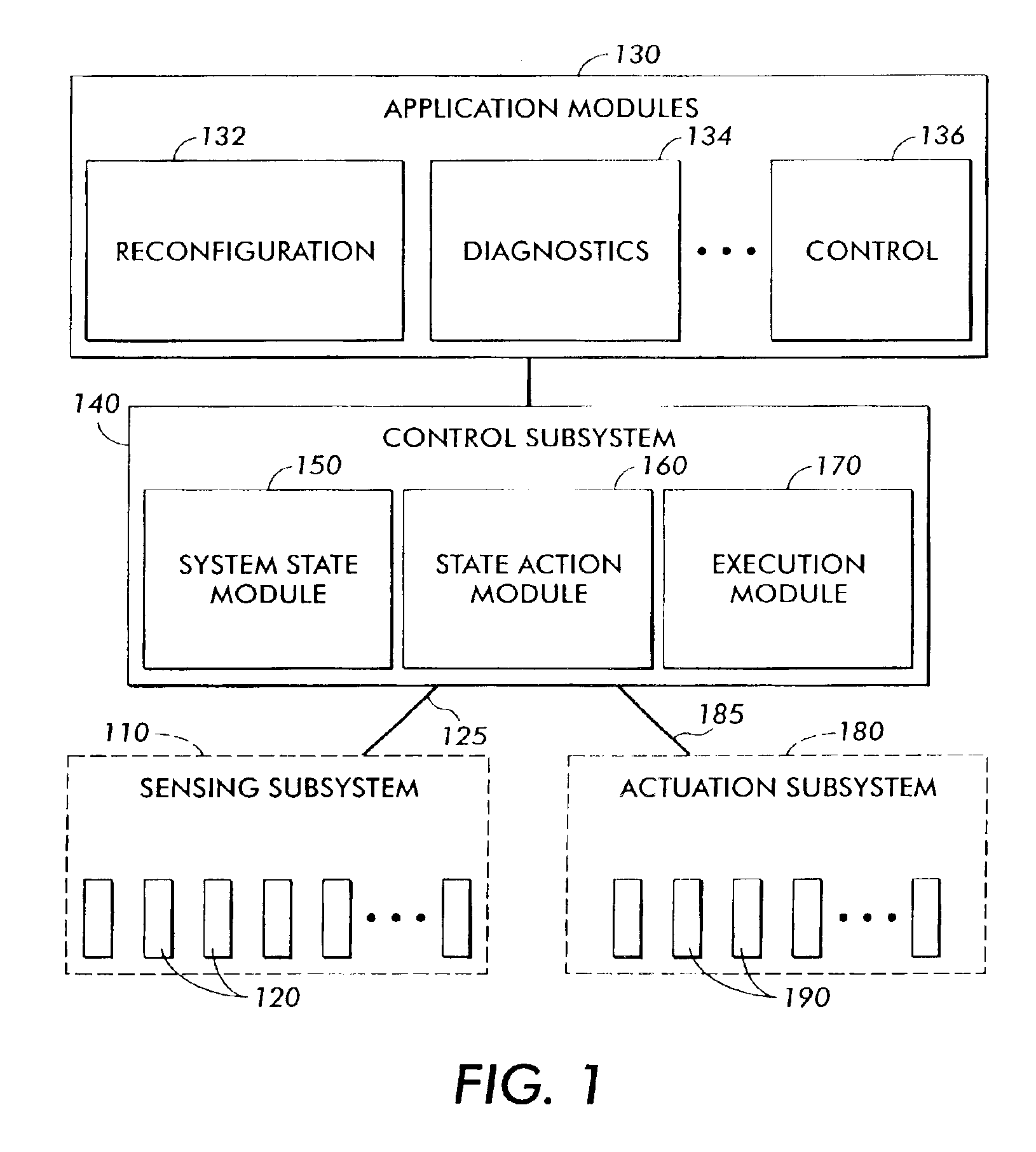
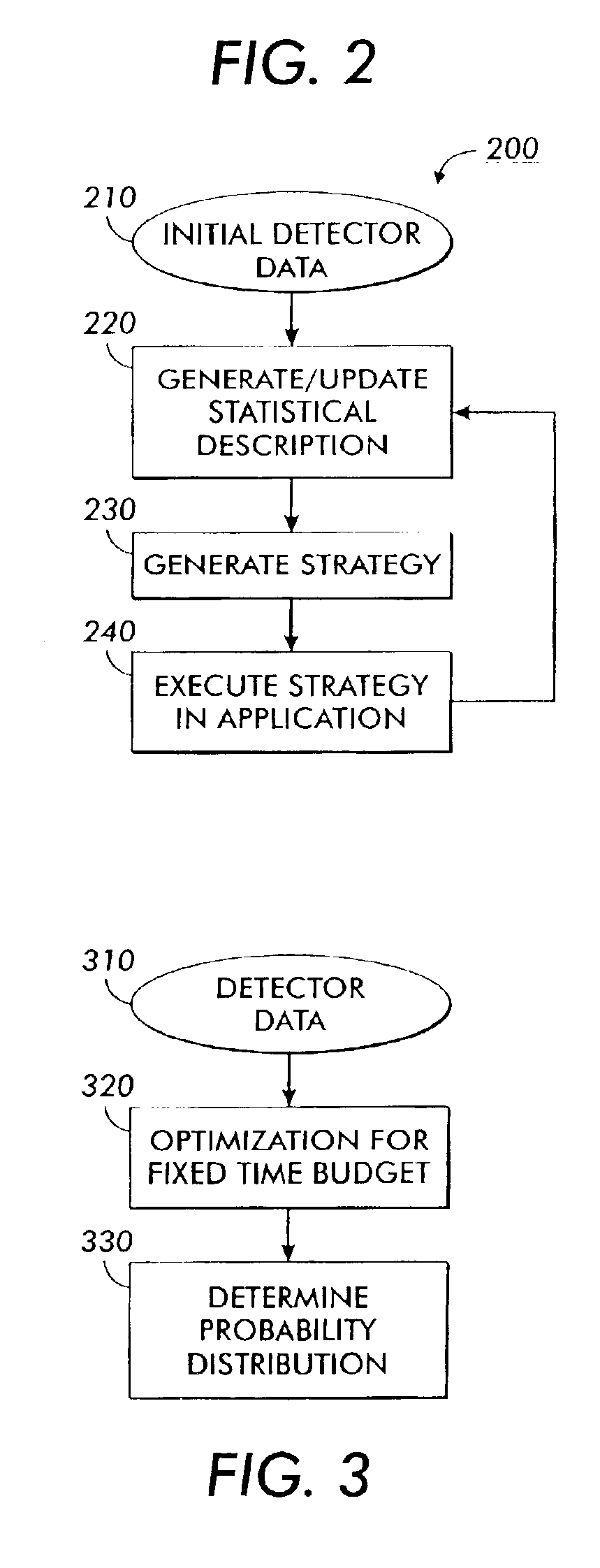
A method for developing and using real time applications for a dynamic system having a sensing subsystem, actuation subsystem, a control subsystem, and an application subsystem utilizes stochastic compute time algorithms. After optimization functions, desired state and constraints are received and detector data has been provided from a sensor subsystem, a statistical optimization error description is generated. From this statistical optimization error description a strategy is developed, including the optimization errors, within the control subsystem. An execution module within the control subsystem then sends an execution strategy to various actuators within the actuation subsystem.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Countermeasure method in an electronic component which uses an RSA-type public key cryptographic algorithm
InactiveUS7123717B1Public key for secure communicationVolume/mass flow measurementComputer hardwareCountermeasure
A countermeasure method in an electronic component which uses an RSA-type public key cryptographic algorithm. A first countermeasure method uses a random calculation for each new execution of the decryption algorithm with CRT. The calculations are made modulo p*r and q*t, r and t being random numbers. A second countermeasure makes the recombination random using the CRT theorem.
Owner:GEMPLU
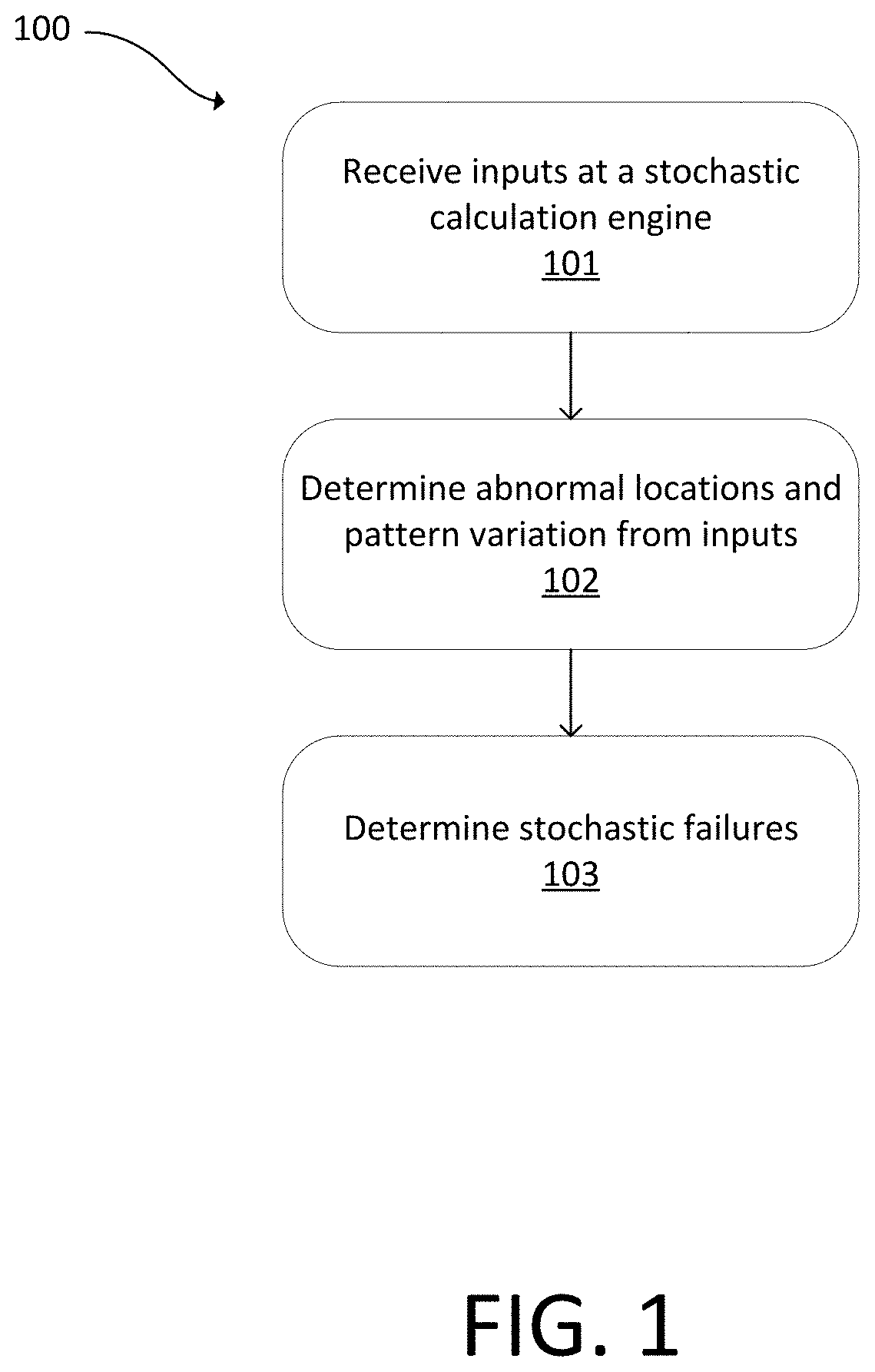
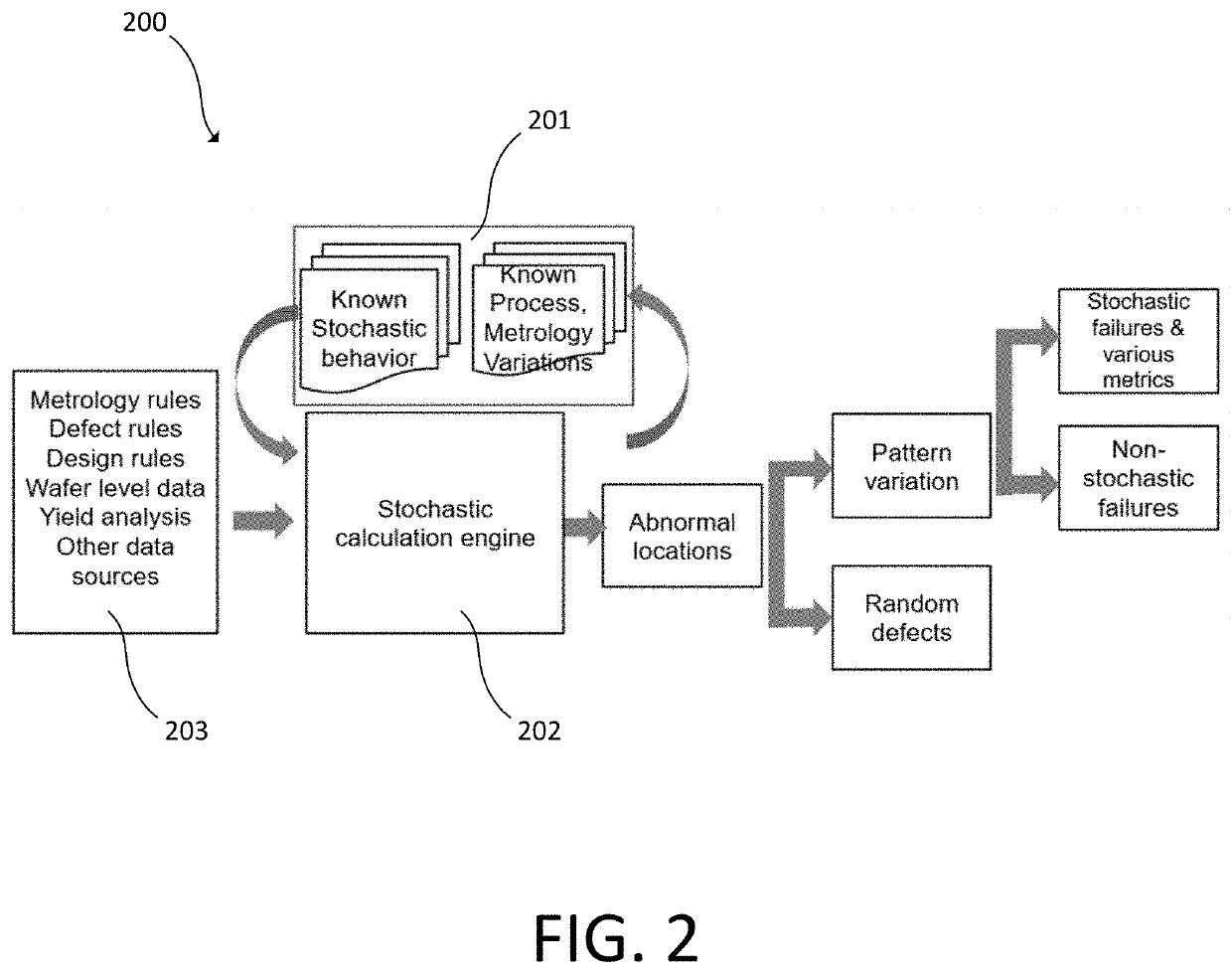
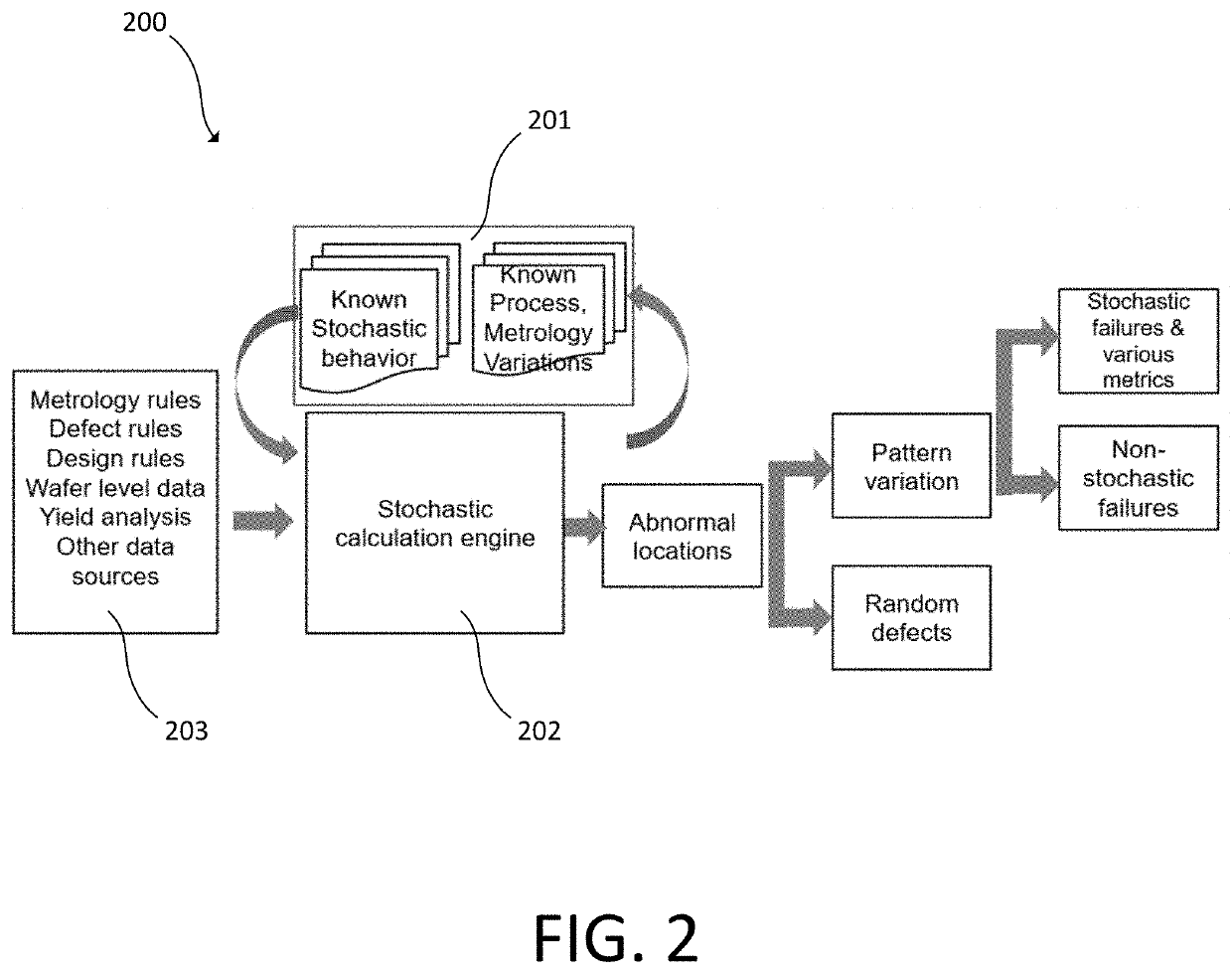
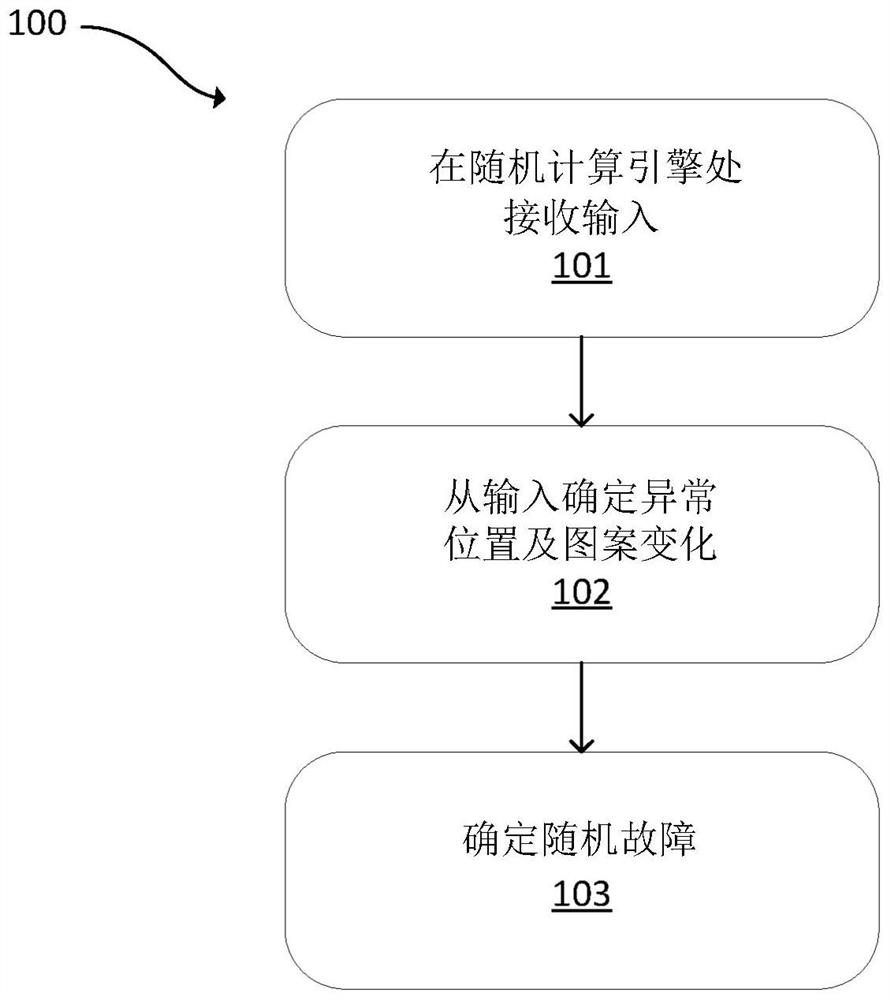
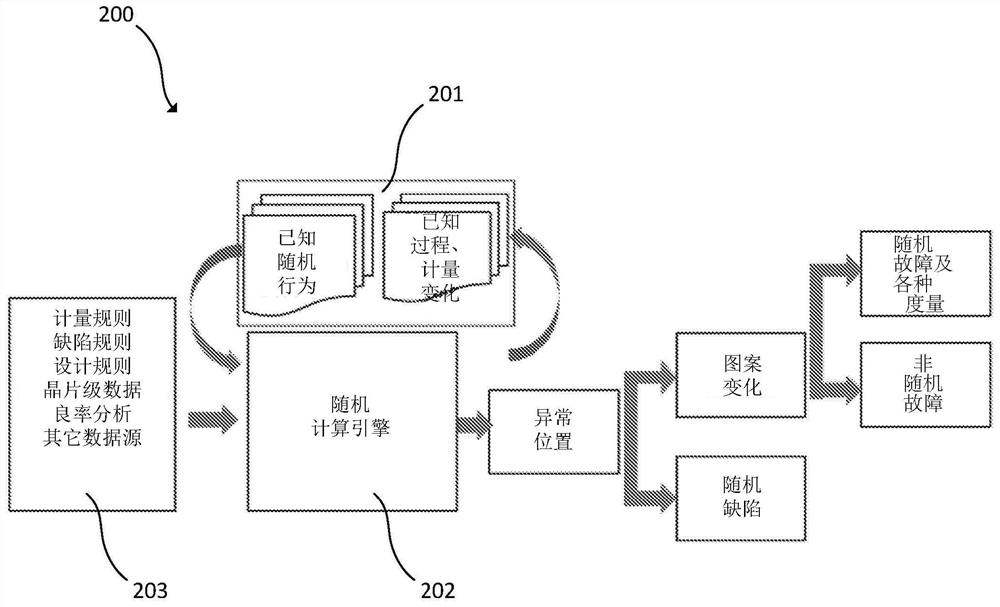
Using stochastic failure metrics in semiconductor manufacturing
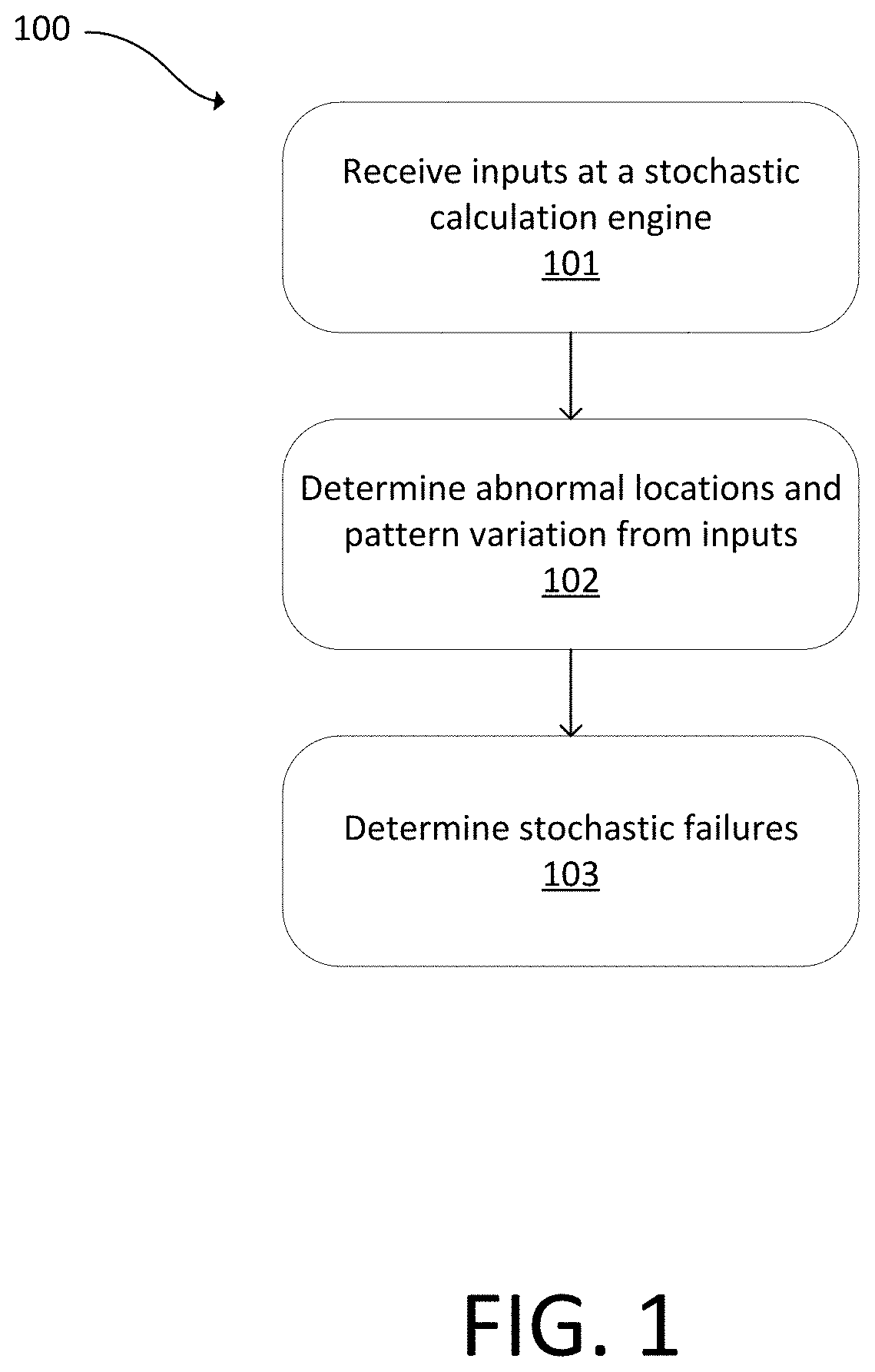
A stochastic calculation engine receives inputs from a semiconductor inspection tool or semiconductor review tool. The stochastic calculation engine determines abnormal locations and pattern variation from the inputs and determines stochastic failures from the inputs. An electronic data storage unit connected with the stochastic calculation engine can include a database with known stochastic behavior and known process metrology variations. The stochastic calculation engine can flag stochastic features, determine a failure rate, or determine fail probability.
Owner:KLA CORP
Neural network random number generator sharing circuit, sharing method and processor chip
PendingCN112698811AAccurate statisticsScale efficientlyRandom number generatorsNeural architecturesActivation functionAlgorithm
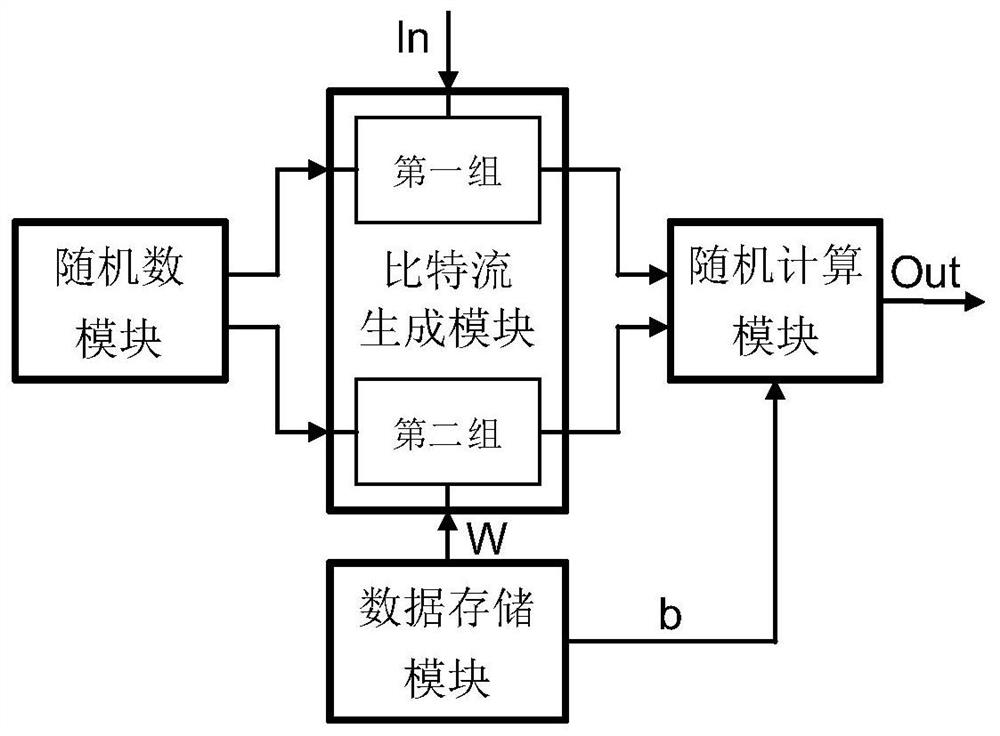
The invention discloses a neural network random number generator sharing circuit, a sharing method and a processor chip, belongs to the technical field of novel calculation, and is applied to an artificial neural network circuit. The system comprises a random number module, a bit stream generation module, a random calculation module and a data storage module. The random calculation module comprises a plurality of neural calculation units, each neural calculation unit comprises a multiplication circuit, a scaled addition circuit and an activation function circuit, and the scaled addition circuit is based on a parallel accumulator, so that the requirement of an operation circuit on input bit stream non-correlation can be reduced; therefore, the random number generator can be shared in the whole artificial neural network circuit, and one complete neural network only needs one random number generator. Compared with an existing neural network circuit based on random calculation, hardware resources are greatly saved, power consumption is reduced, and meanwhile operation precision is improved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
System and method for implementing real-time applications based on stochastic compute time algorithms
A method for developing and using real time applications for a dynamic system having a sensing subsystem, actuation subsystem, a control subsystem, and an application subsystem utilizes stochastic compute time algorithms. After optimization functions, desired state and constraints are received and detector data has been provided from a sensor subsystem, a statistical optimization error description is generated. From this statistical optimization error description a strategy is developed, including the optimization errors, within the control subsystem. An execution module within the control subsystem then sends an execution strategy to various actuators within the actuation subsystem.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Using stochastic failure metrics in semiconductor manufacturing
A stochastic calculation engine receives inputs from a semiconductor inspection tool or semiconductor review tool. The stochastic calculation engine determines abnormal locations and pattern variation from the inputs and determines stochastic failures from the inputs. An electronic data storage unit connected with the stochastic calculation engine can include a database with known stochastic behavior and known process metrology variations. The stochastic calculation engine can flag stochastic features, determine a failure rate, or determine fail probability.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Address allocation method for LoRaWAN terminal equipment
ActiveCN111711708AReduce the probability of conflictAvoid confictTransmissionTerminal equipmentEngineering
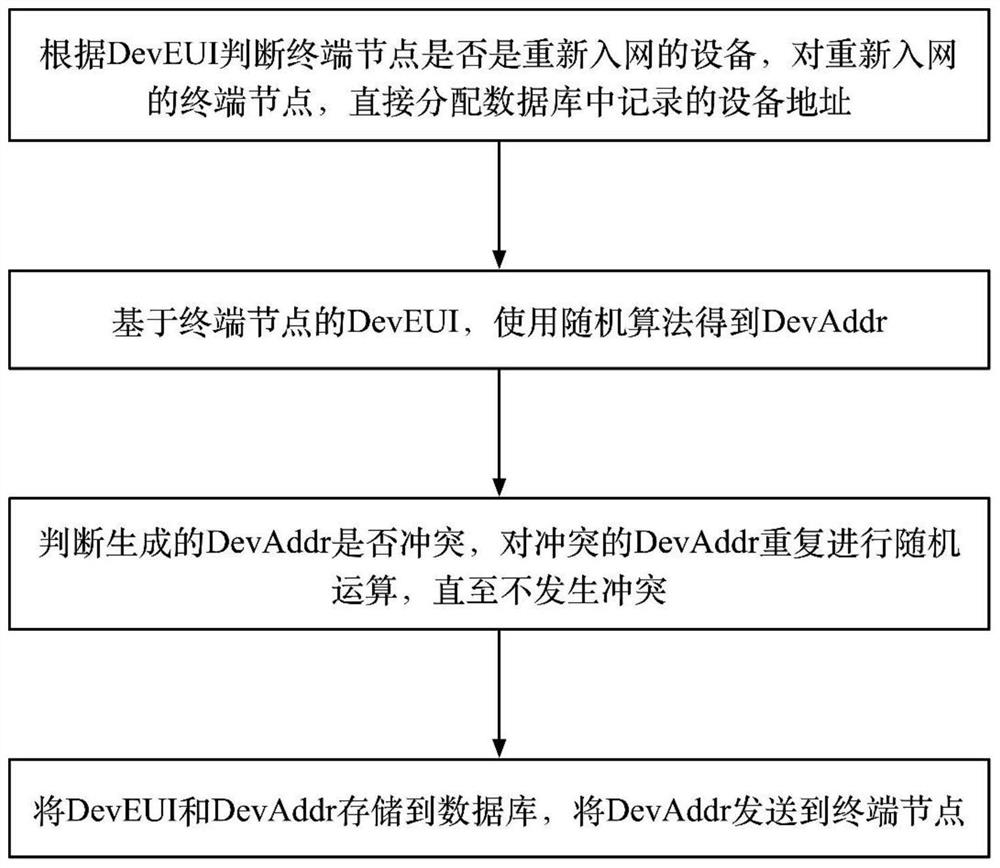
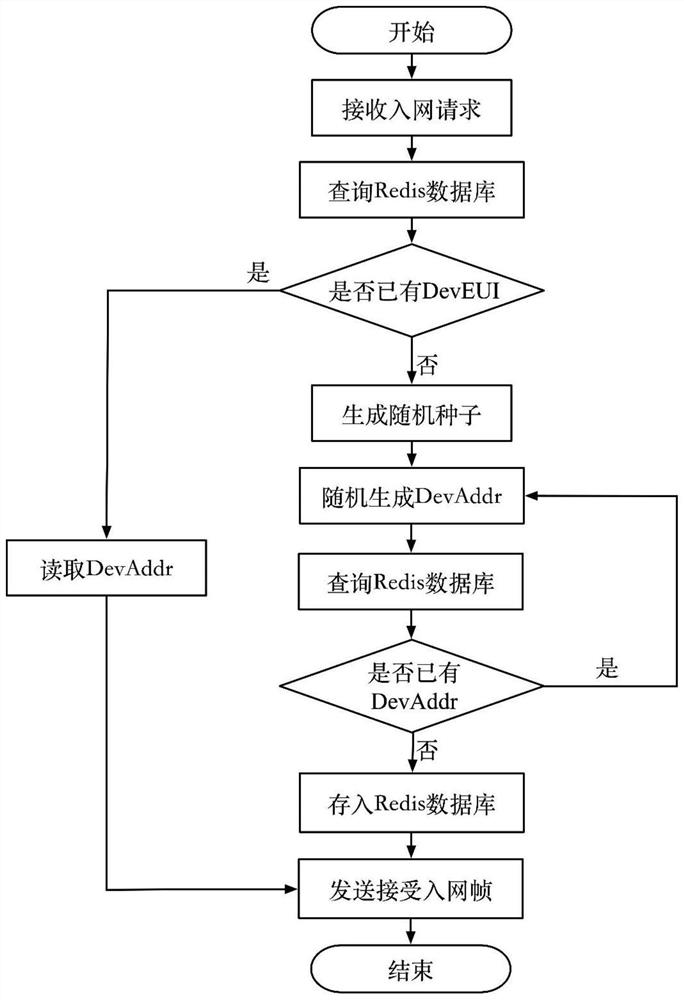
The invention discloses an address allocation method for LoRaWAN terminal equipment, and aims to solve the problems that when the number of terminal nodes in a LoRaWAN network is large, equipment addresses conflict, and the equipment addresses change when the network is accessed again. The method comprises the steps of storing equipment identifiers and equipment addresses of networked terminal nodes by using a database; enabling the network server to query a database according to the equipment identifier of the terminal node to judge whether the terminal node is the equipment which accesses the network again, and quickly allocate the same equipment address to the equipment which accesses the network again; for newly accessed equipment, calculating and generating the equipment address of the terminal node according to the equipment identifier of the terminal node; querying the database to judge whether the generated equipment addresses conflict or not, and avoiding the equipment addressconflict by using multiple random calculations.
Owner:成都慧简联信息科技有限公司
Embedded stochastic-computing accelerator architecture and method for convolutional neural networks
PendingUS20210256357A1Reduce computing timeImprove energy consumptionDigital data processing detailsNeural architecturesAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
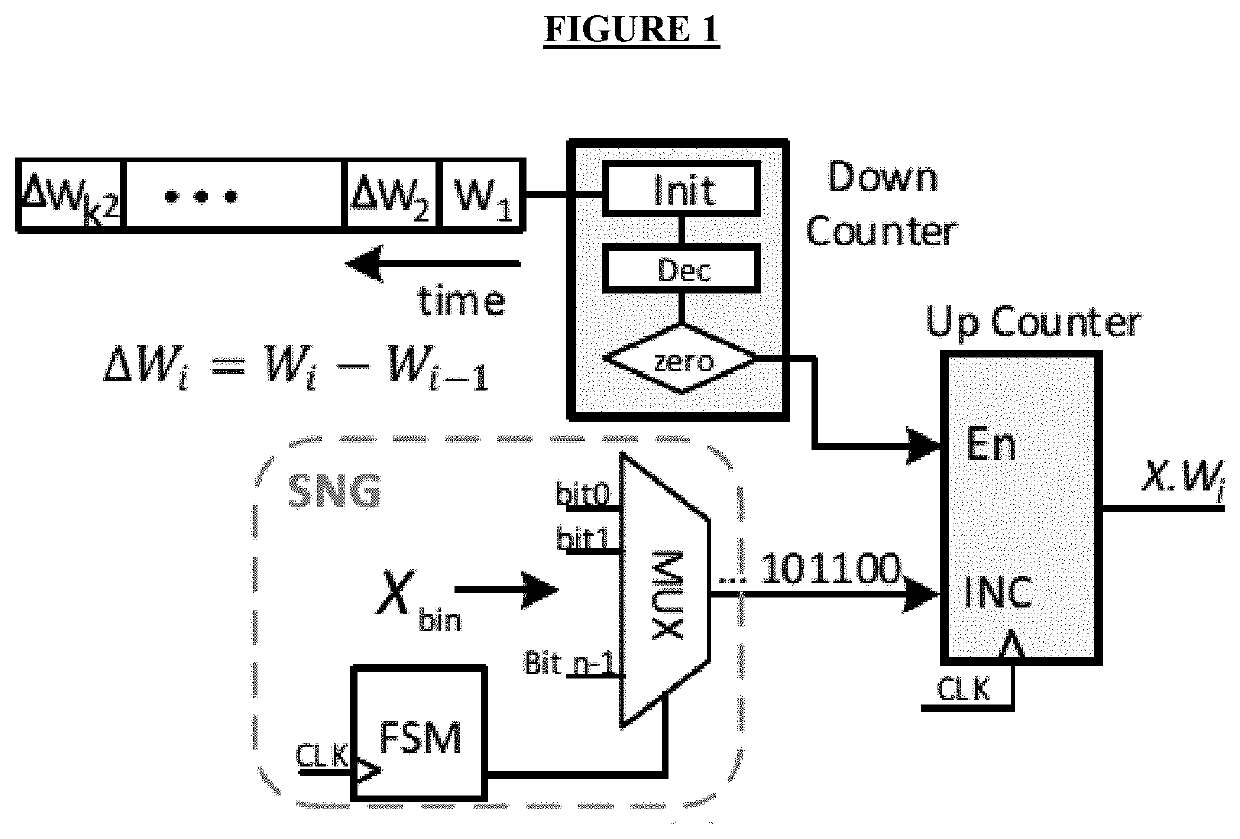
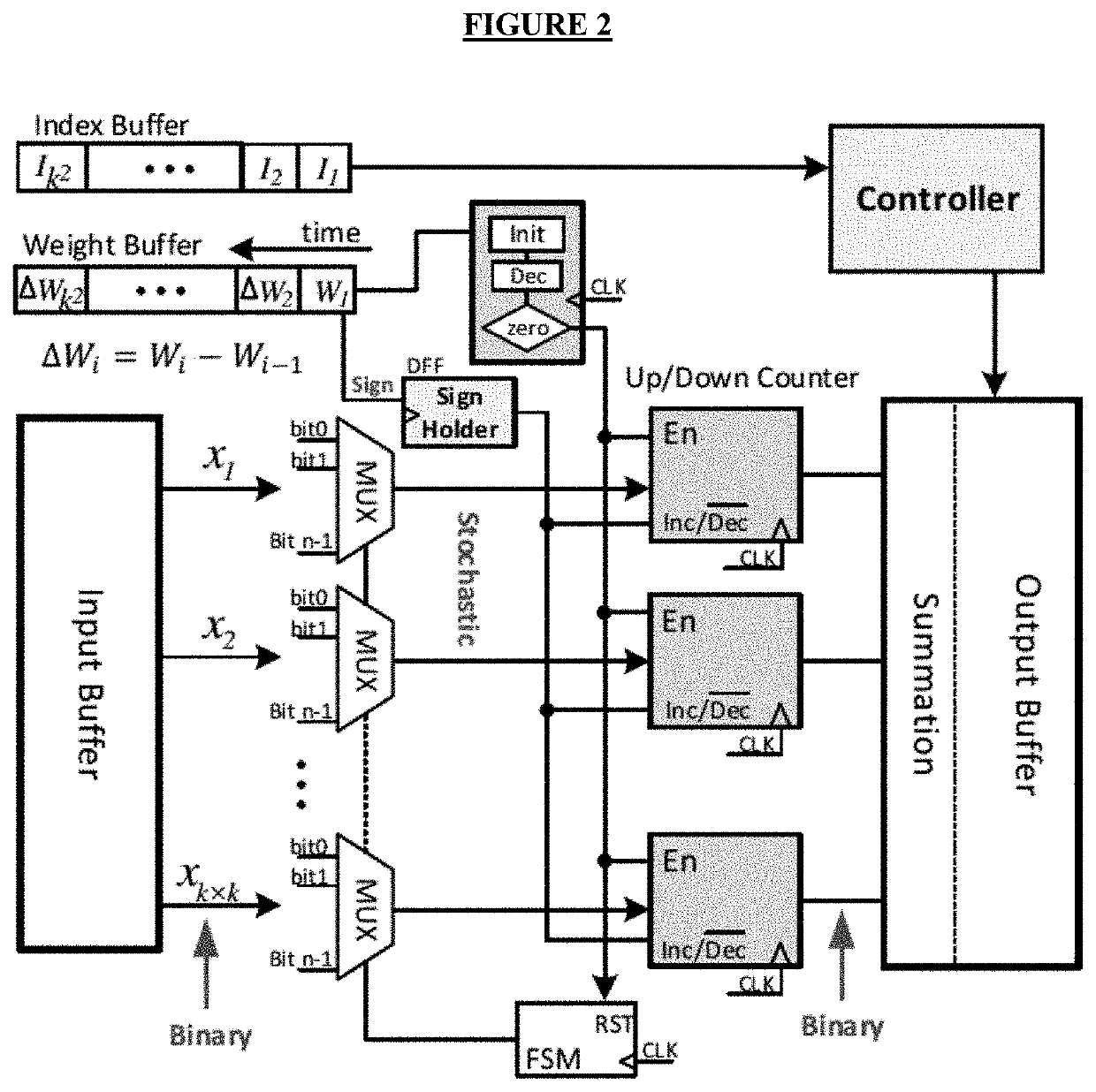
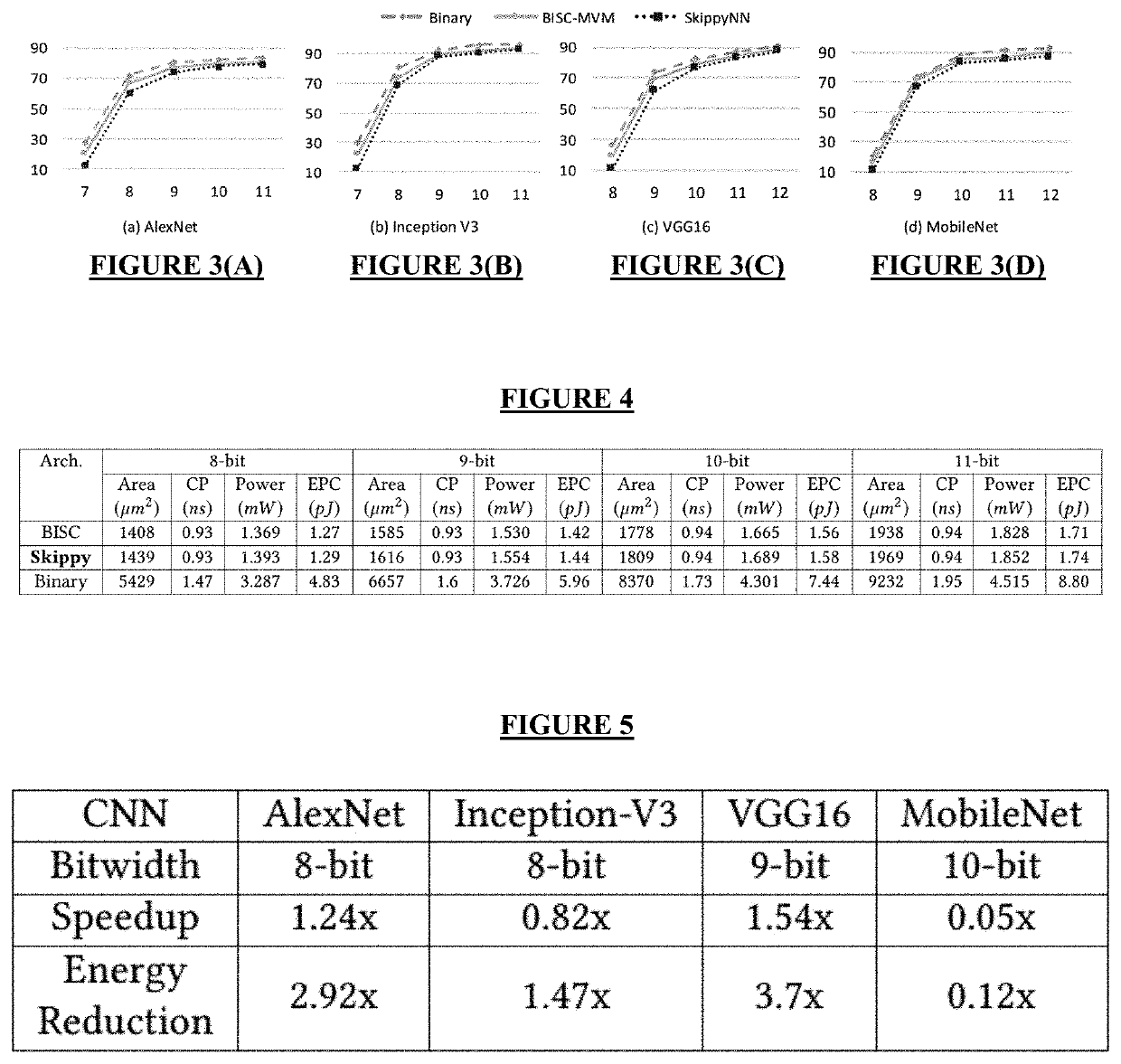
The disclosed invention provides a novel architecture that reduces the computation time of stochastic computing-based multiplications in the convolutional layers of convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Each convolution in a CNN is composed of numerous multiplications where each input value is multiplied by a weight vector. Subsequent multiplications are performed by multiplying the input and differences of the successive weights. Leveraging this property, disclosed is a differential Multiply-and-Accumulate unit to reduce the time consumed by convolutions in the architecture. The disclosed architecture offers 1.2× increase in speed and 2.7× increase in energy efficiency compared to known convolutional neural networks.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LOUISIANA AT LAFAYETTE
Low-complexity convolutional neural network based on symbol random calculation
PendingCN110555519AAvoid calculation errorsImprove throughputNeural architecturesPhysical realisationCalculation errorStochastic computing
The invention discloses a low-complexity convolutional neural network based on symbol random calculation. The system comprises a symbol random calculation module and an efficient convolution layer, apooling layer and a nonlinear excitation layer which are constructed based on the symbol random calculation module, the symbol random calculation module comprises a forward conversion module and a backward conversion module, the efficient convolution layer comprises a random processing unit and a random adder matrix, and the pooling layer is connected to the output end of the efficient convolutionlayer. According to the invention, a special sign bit is introduced; symbol random calculation is formed, the problem that the traditional random calculation can only represent positive numbers is solved; the calculation error caused by scaling coding is avoided, a novel parallel fast convolutional neural network architecture is provided based on the random calculation mode, the throughput rateof random convolution is increased while the hardware consumption is reduced, and the delay of random convolution calculation is reduced to a certain extent.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
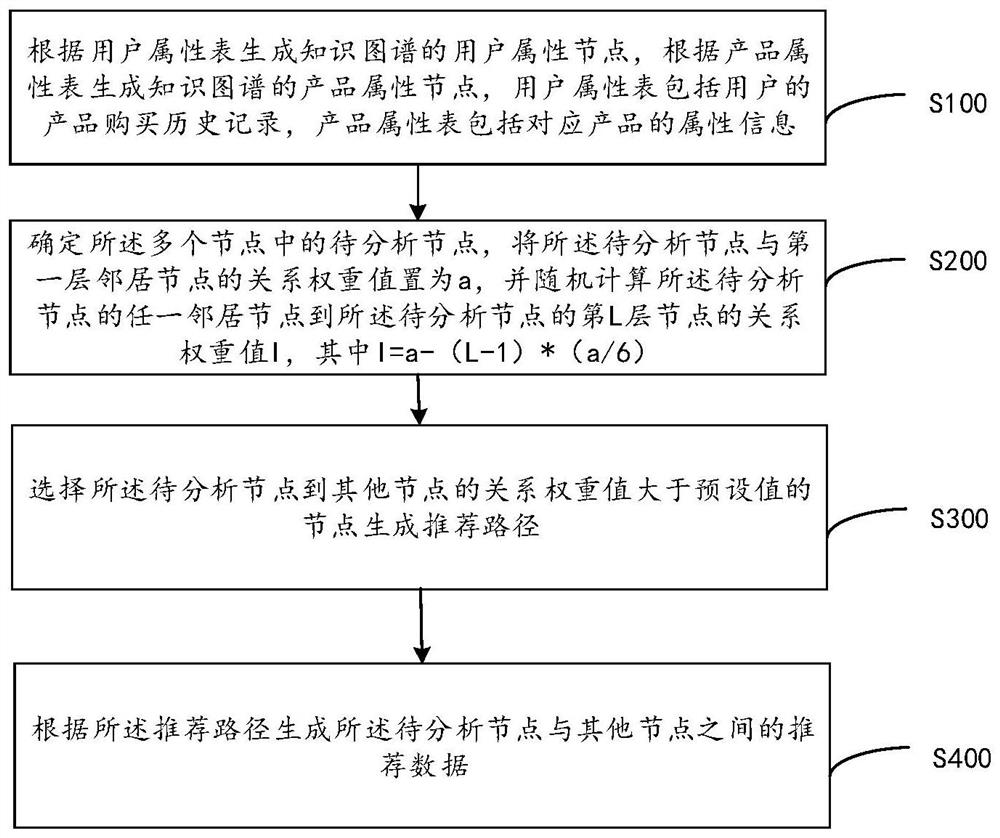
Knowledge graph-based recommendation method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN111966912ASolve the problem of not being able to obtain accurate recommendation results with high efficiency and low costSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic tool creationPathPingTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a knowledge graph-based recommendation method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: determining a to-be-analyzed node in the plurality of nodes, setting a relationship weight value between the to-be-analyzed node and a first-layer neighbor node as a, and randomly calculating a relationship weight value I from any neighbor node of the to-be-analyzed node to an Lth-layer node of the to-be-analyzed node, wherein I = a-(L-1) * (a / 6); selecting the node of which the relationship weight value from the to-be-analyzed node to other nodes is greater than a preset value to generate a recommended path; generating recommendation data between the to-be-analyzed node and other nodes according to the recommendation path. According to the method, the knowledge graph nodes are randomly calculated for multiple times, the relationship strength values of the other nodes are obtained from the single node, then the nodes meeting the preset relationship strength value are selected to generate the recommendation path, and therefore the problem that an accurate recommendation result cannot be obtained with high efficiency andlow cost is solved.
Owner:ONE CONNECT SMART TECH CO LTD SHENZHEN
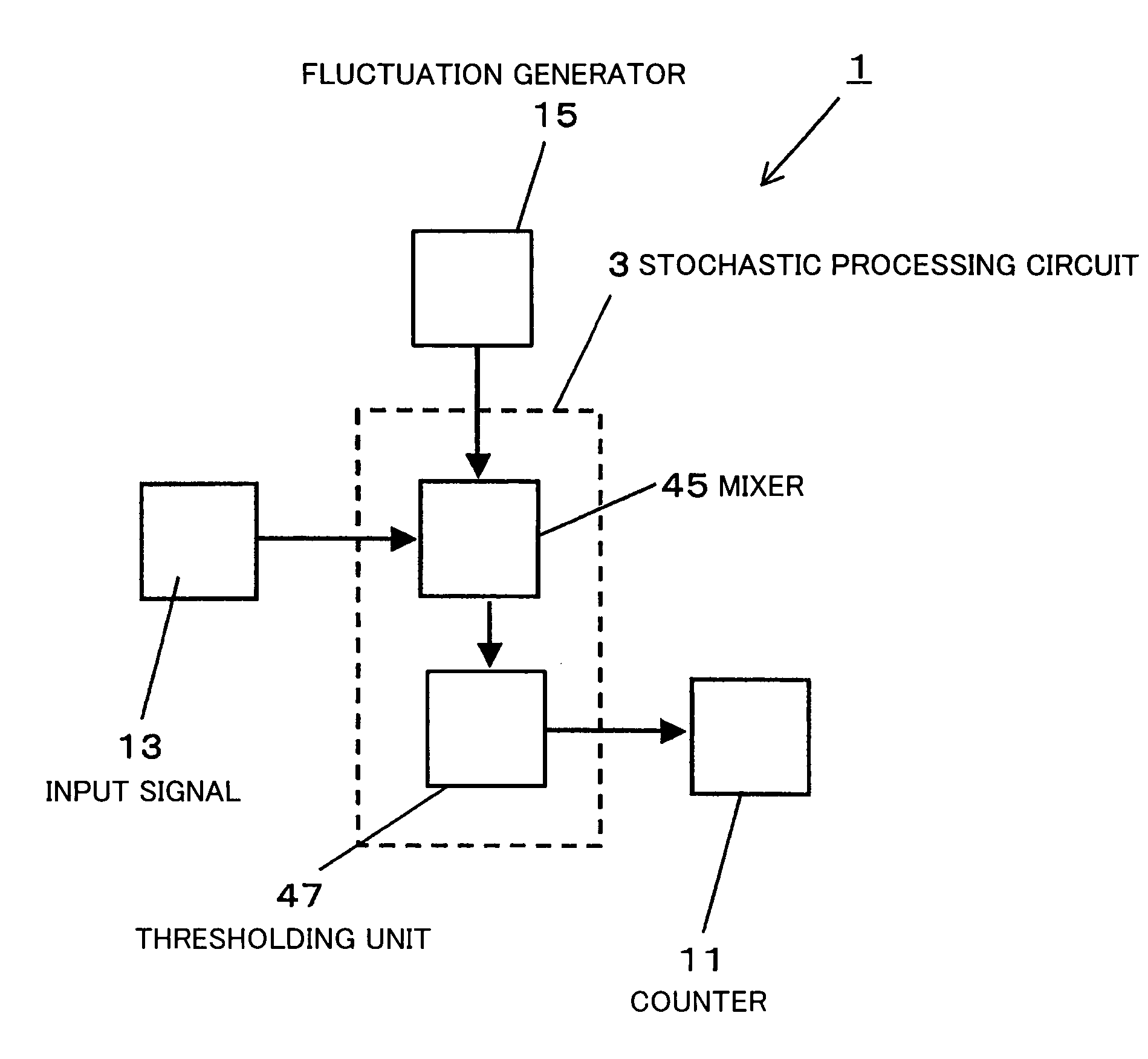
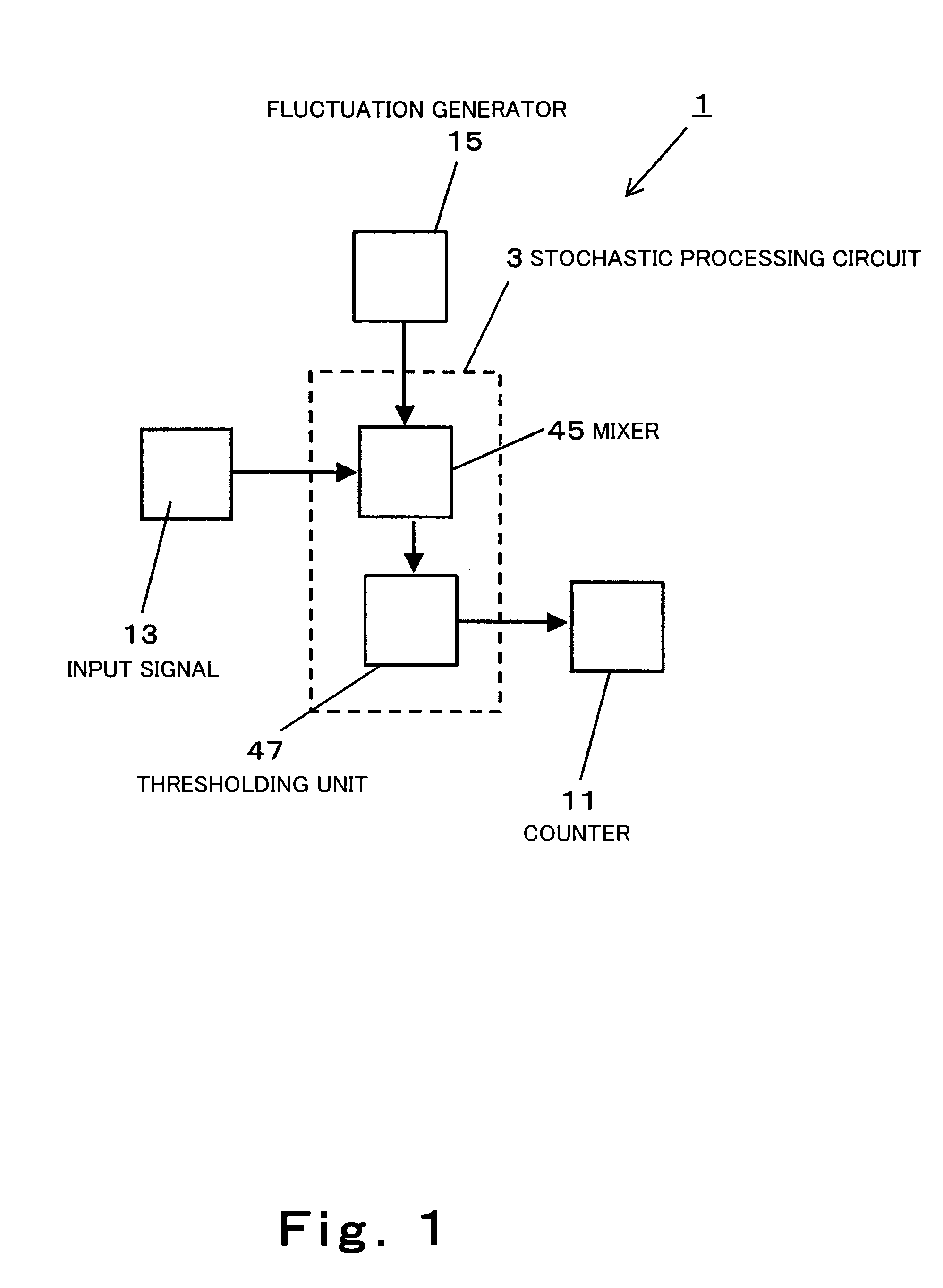
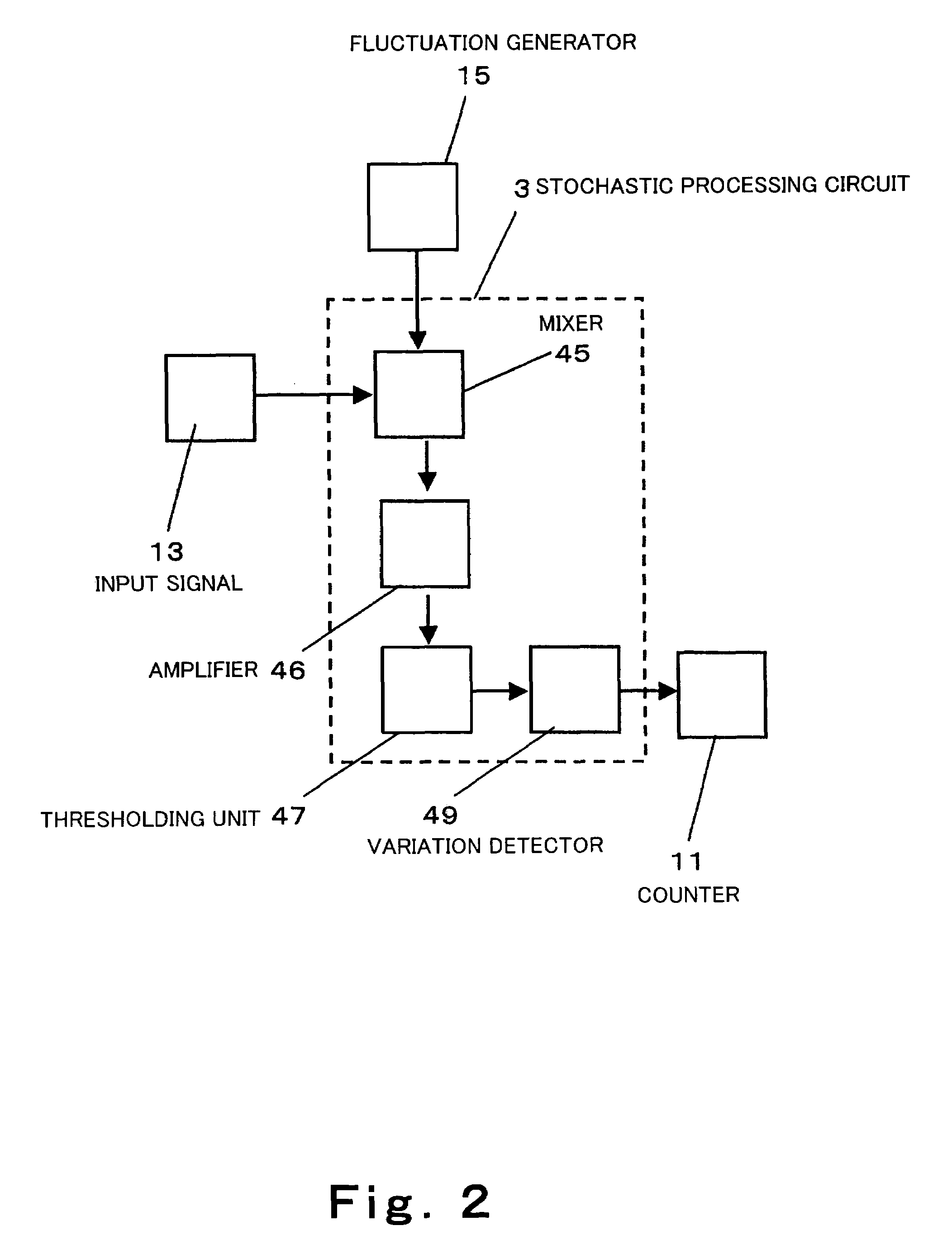
Stochastic processor and stochastic computer using the same
A stochastic processor and a stochastic computer comprises a fluctuation generator configured to generate and output analog quantity having fluctuation comprised of chaos of tent mapping, a mixer configured to output a fluctuation superposed signal with the analog quantity output from the fluctuation generator superposed on an input signal represented by analog quantity and a thresholding unit configured to perform thresholding on the fluctuation superposed signal output from the mixer to generate and output a pulse.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Error-free adder based on random calculation
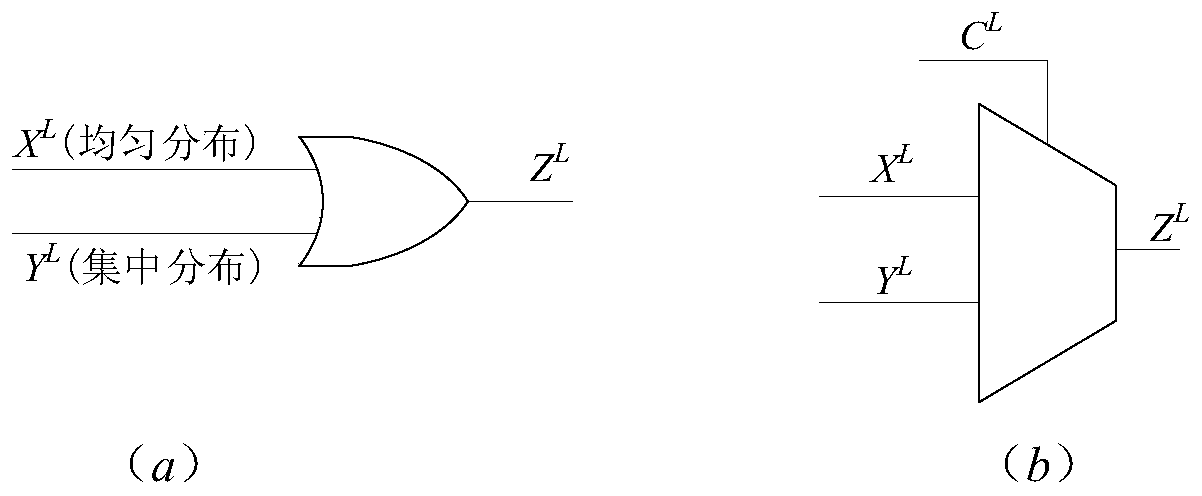
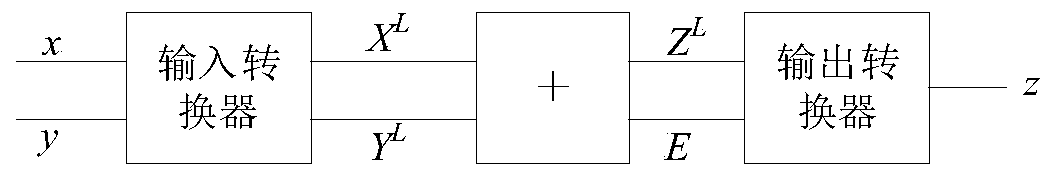
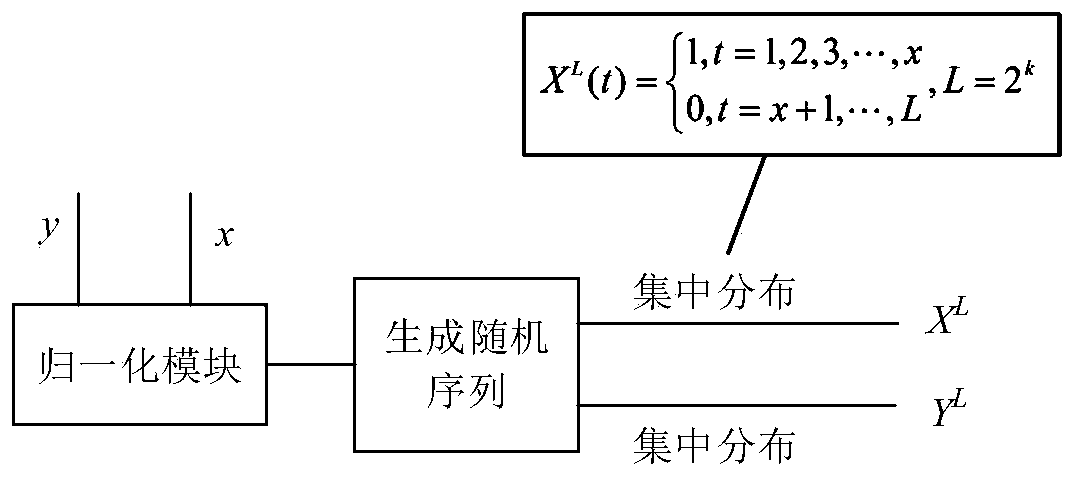
ActiveCN110705196AReduce resource consumptionSave resourcesCAD circuit designConvertersStochastic computing
The invention discloses an error-free adder based on random calculation, which is applied to the field of digital circuit optimization design. Aimed at the error problem of an existing random adder, the error-free adder comprises an input converter, a random adder and an output converter. The input converter is used for converting input data into a random sequence, '0' and '1' in the random sequence of the input random adder can be at any position, the random adder is used for completing the additive operation of the random sequence, and the output of the random adder comprises an additive result and an error. The output converter is used for converting the addition result back to the traditional binary numerical domain through accumulation, and performing shift operation and accumulationon the error according to the cascade stage number of the error to compensate to obtain a final error-free result. The error-free adder disclosed by the invention has good universality.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Random computing method for importance degree of wavelet coefficient of two-dimensional image
The invention discloses a random computing method for an importance degree of a wavelet coefficient of a two-dimensional image. The present method is very rough and is generally used for only dividing foreground and background coefficients or appointing one importance degree to each code block. The random computing method comprises the following steps: firstly, initializing alpha as a 0 matrix and generating a random matrix r, wherein the row number and the line number are consistent with beta and the elements are uniformly distributed on a coordinate (-1, 1); defining beta'=sgn(r)*beta and performing wavelet conversion W on beta', thereby obtaining alpha': alpha'=W(beta'); finally, updating alpha:alphap=max(alphap, absolute value of alphap') and performing p0 on each position; and if alpha no longer changes, ending and outputting alpha. According to the random computing method provided by the invention as a middle step of a JPEG2000 implicit ROI encoding process, the importance degree of each element on an image space is converted into the importance degree of each coefficient on a wavelet domain. According to the random computing method provided by the invention, the more accurate control on the ROI area and importance degree of a JPEG2000 compressed image is realized.
Owner:浙江锐智信息技术有限公司
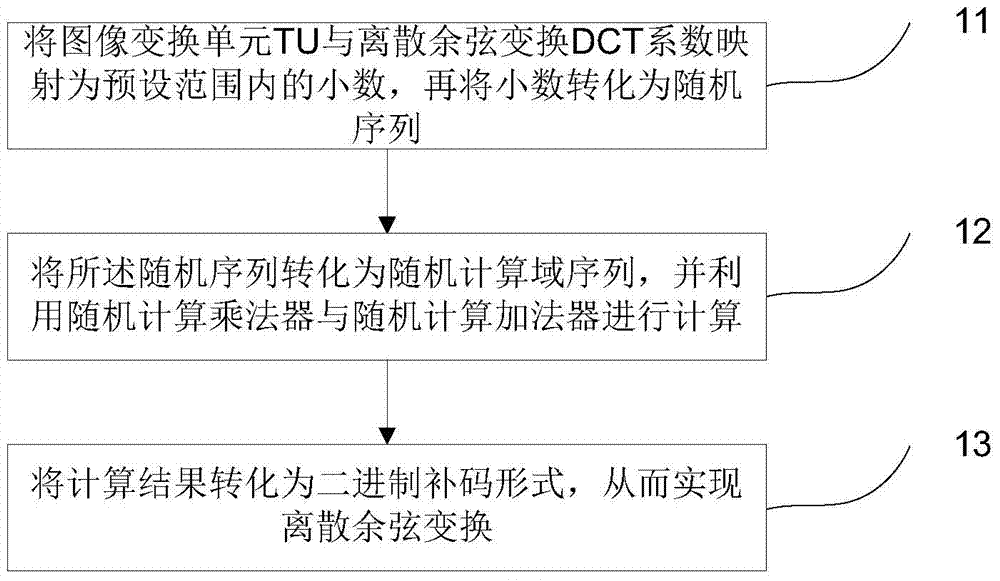
A method and system for realizing discrete cosine transform based on random calculation
ActiveCN104038770BEasy to implementIncrease the operating clock frequencyDigital video signal modificationComplex mathematical operationsBinary multiplierClock rate
The invention discloses a discrete cosine transform realization method and system based on random calculation, wherein the method includes: mapping an image transformation unit (TU) and a discrete cosine transform (DCT) coefficient to a decimal within a preset range, and then The decimals are converted into a random sequence; the random sequence is converted into a random calculation field sequence, and the random calculation multiplier and the random calculation adder are used for calculation; the calculation result is converted into a two's complement form, thereby realizing discrete cosine transformation. By adopting the method and the system disclosed in the present invention, the hardware consumption can be greatly reduced and the working clock frequency of the system can be improved at the same time.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Random computing method for importance degree of wavelet coefficient of two-dimensional image
ActiveCN102752599AEasy to controlTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationCoding blockPresent method
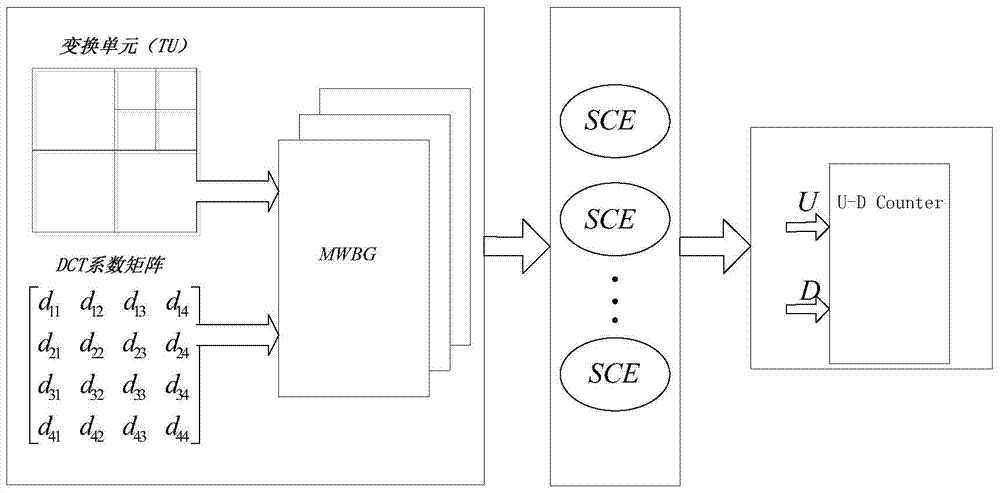
The invention discloses a random computing method for an importance degree of a wavelet coefficient of a two-dimensional image. The present method is very rough and is generally used for only dividing foreground and background coefficients or appointing one importance degree to each code block. The random computing method comprises the following steps: firstly, initializing alpha as a 0 matrix and generating a random matrix r, wherein the row number and the line number are consistent with beta and the elements are uniformly distributed on a coordinate (-1, 1); defining beta'=sgn(r)*beta and performing wavelet conversion W on beta', thereby obtaining alpha': alpha'=W(beta'); finally, updating alpha:alphap=max(alphap, absolute value of alphap') and performing p0 on each position; and if alpha no longer changes, ending and outputting alpha. According to the random computing method provided by the invention as a middle step of a JPEG2000 implicit ROI encoding process, the importance degree of each element on an image space is converted into the importance degree of each coefficient on a wavelet domain. According to the random computing method provided by the invention, the more accurate control on the ROI area and importance degree of a JPEG2000 compressed image is realized.
Owner:浙江锐智信息技术有限公司
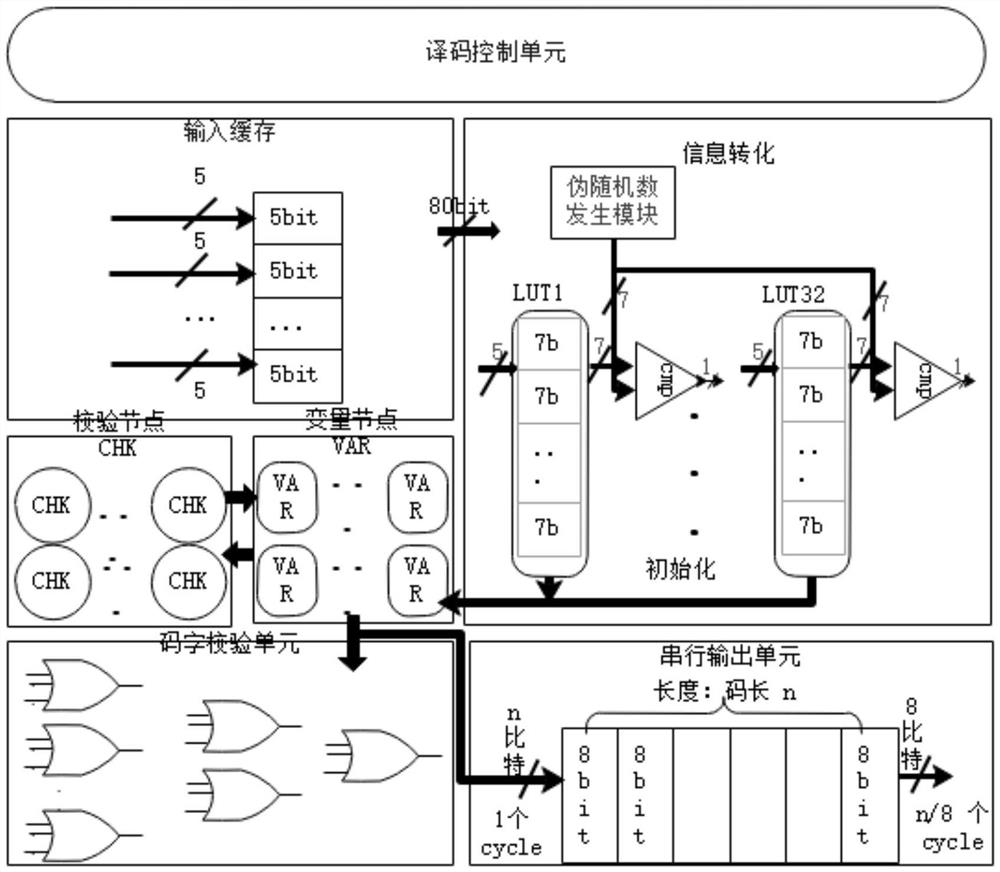
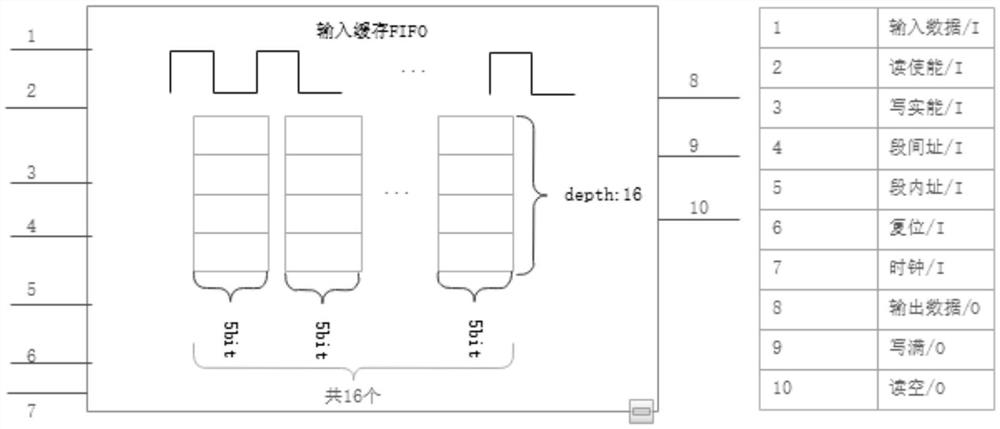
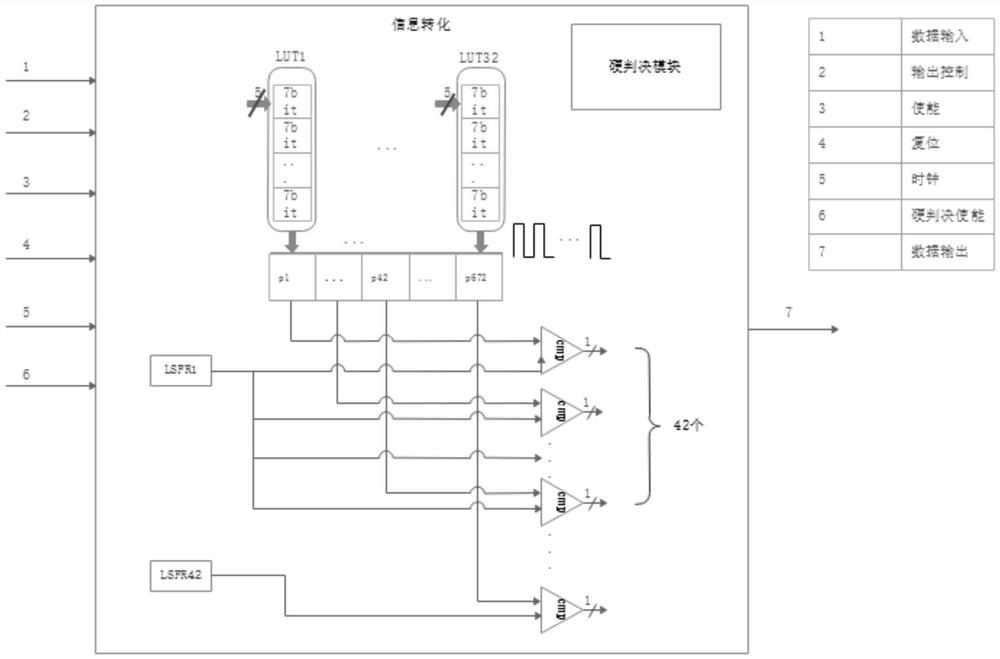
A ldpc decoder based on random bit stream update
ActiveCN108462496BDecoded correctlyImprove decoding performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionClock rateControl cell
Owner:GLORY WIRELESS CO LTD
Method for creating maps by random processing of data received from moving sensors
The application concerns a method for creating maps in an automatic manner using sub-maps created randomly and combined by statistical accumulation. The measurements from information sensors, positioned on mobile platforms, are sent to reception means disposed randomly and independent of each other and transmitting the received information to a random computer processing layer. The random processing layer, creates within same random sub-maps as the information received by the computer network becomes available, the random sub-maps being dispersed arbitrarily in the random processing layer, access pointers being associated with the random sub-maps in order to make it possible to find them. An organising layer, using the access pointers, carries out the statistical recombination of the random sub-maps dispersed in the random processing layer with a view to reconstructing the desired final map or maps. The method according to the application, in one of the applications of same, is particularly useful for the economical and swift creation of complex maps with very large coverage, as required to monitor a country, the resources of same or the economic activity thereof.
Owner:ANTIKIDIS JEAN PIERRE
Context-Aware Bit-Stream Generator for Deterministic Stochastic Computing
PendingUS20210389931A1Extended processing timeReasonable hardware cost overheadLogic circuits characterised by logic functionRandom number generatorsControl cellLeast significant bit
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LOUISIANA AT LAFAYETTE
Optimization processing unit having subunits that are programmably and partially connected
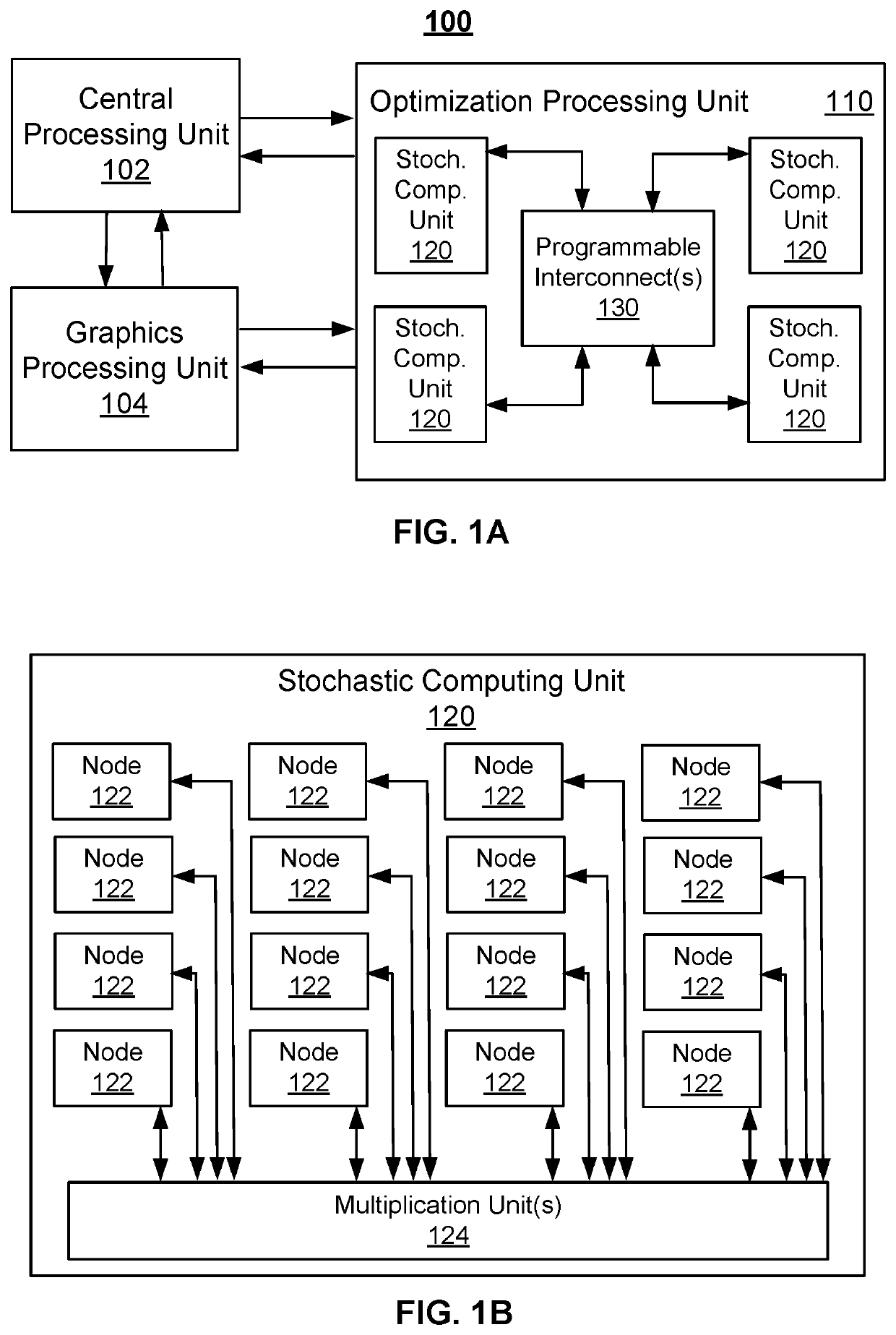
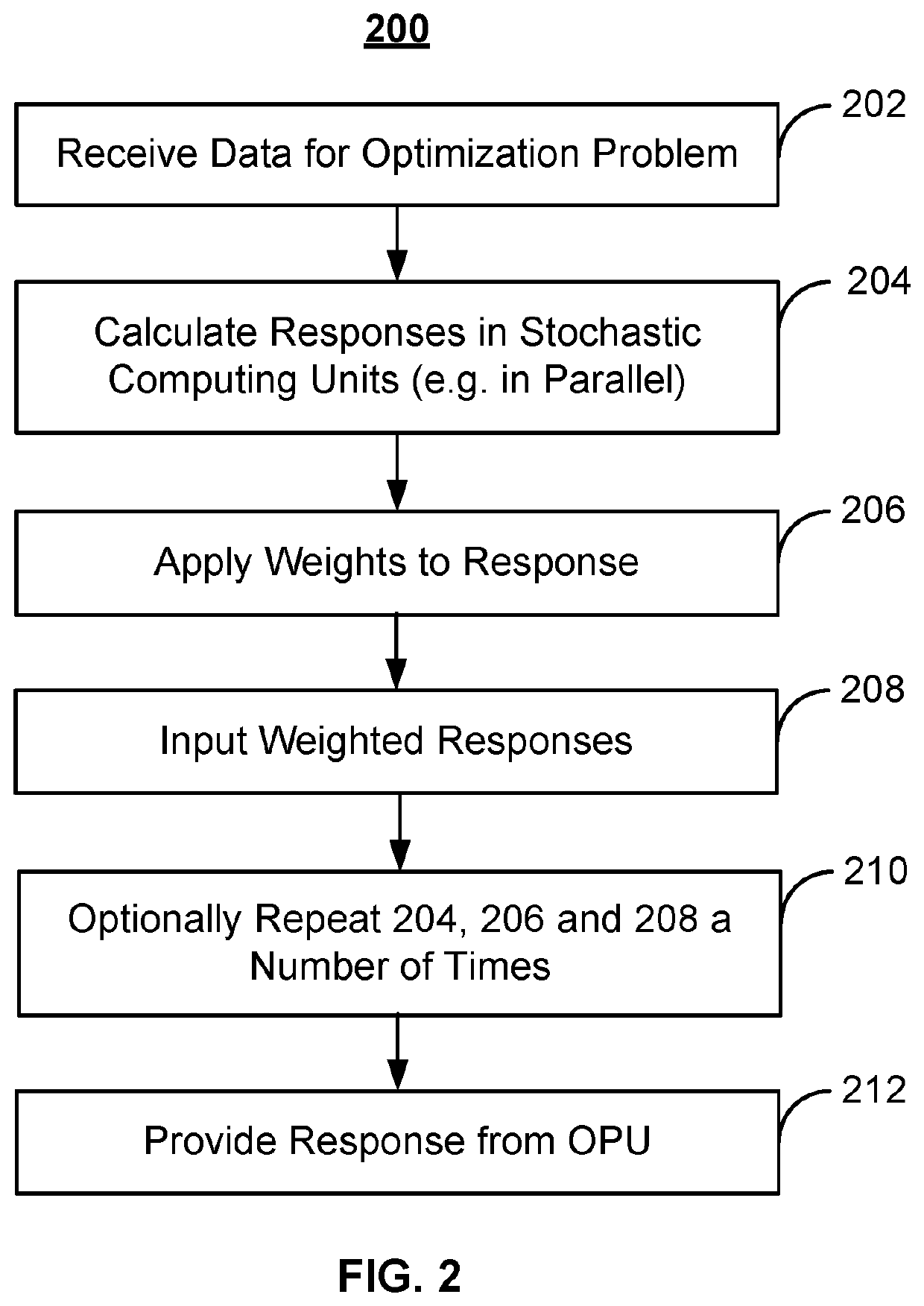
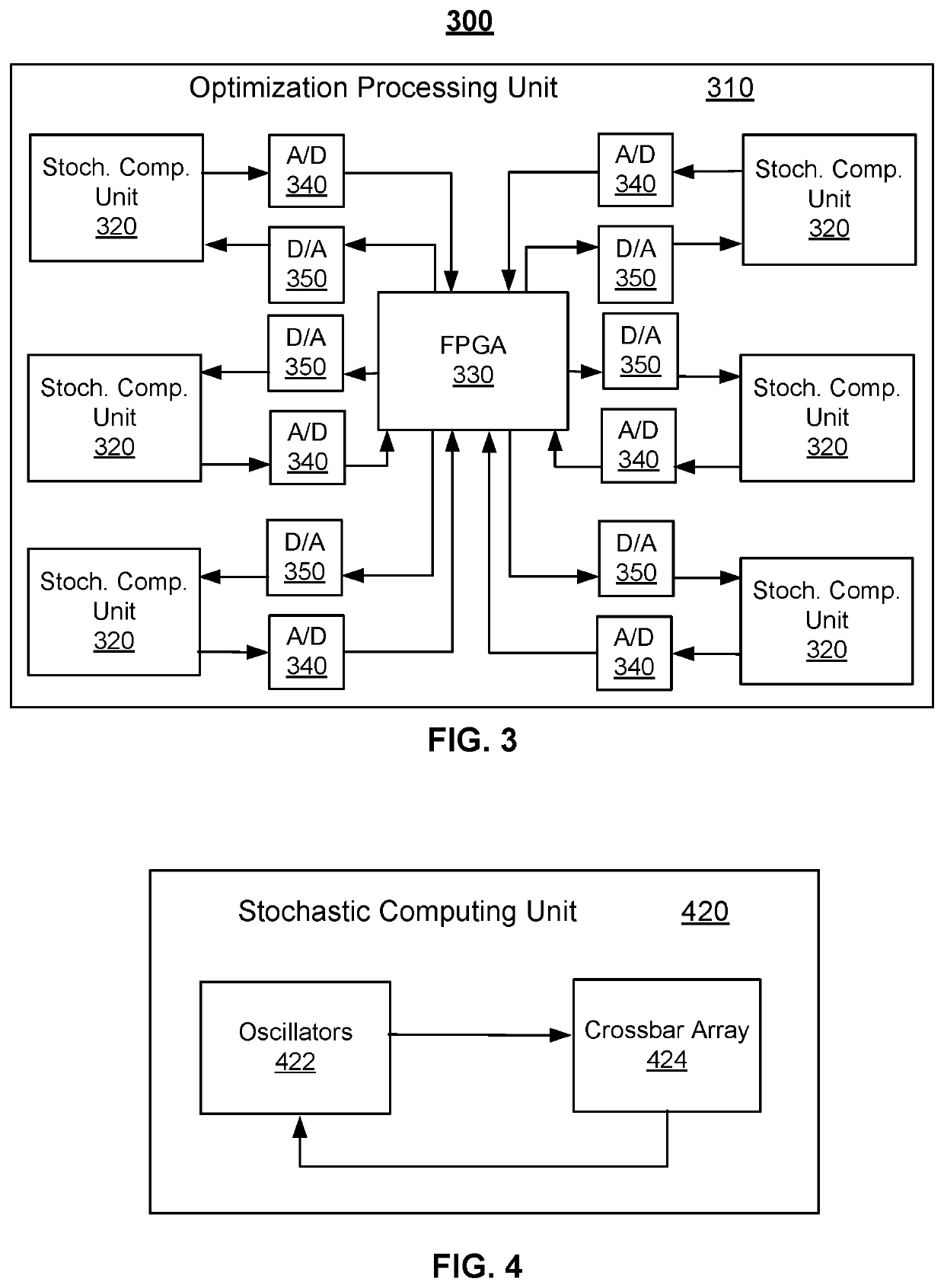
ActiveUS20210319161A1Concurrent instruction executionCAD circuit designComputer architectureEngineering
Techniques usable in optimization processing are described. A system includes an optimization processing unit (OPU). The OPU includes stochastic computing units and at least one programmable interconnect. Each of the stochastic computing units includes nodes and multiplication unit(s) configured to interconnect at least a portion of the nodes. The programmable interconnect(s) are configured to provide weights for and to selectably couple a portion of the stochastic computing units.
Owner:SYNC COMPUTING CORP
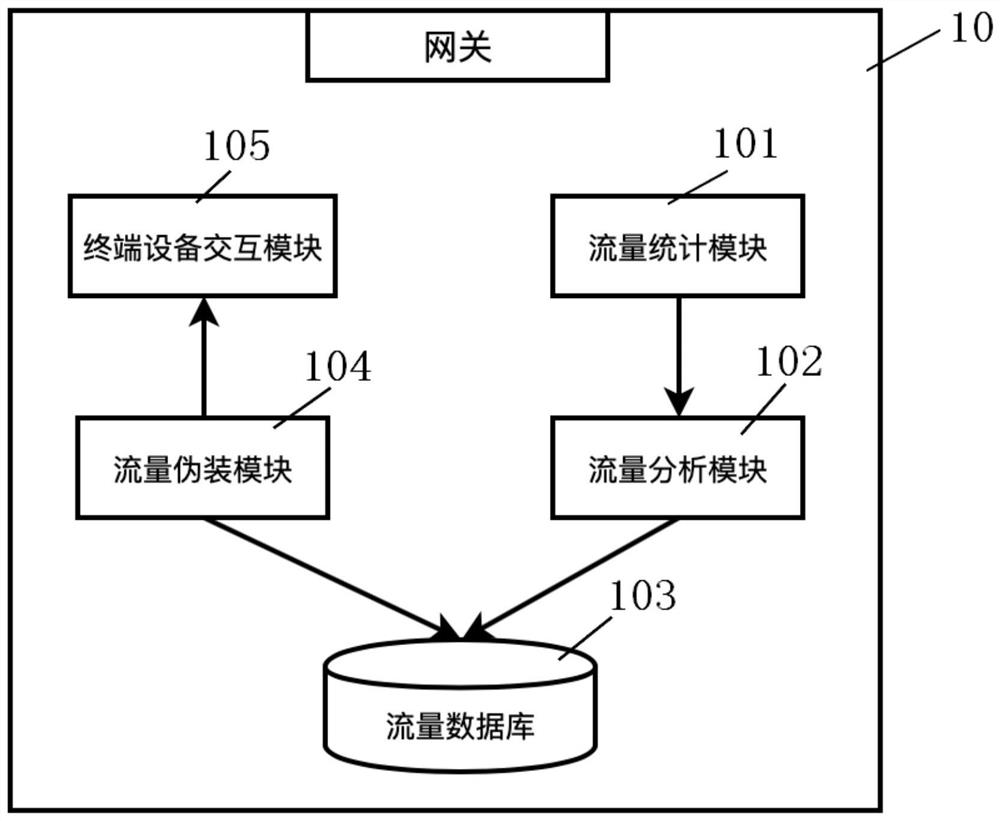
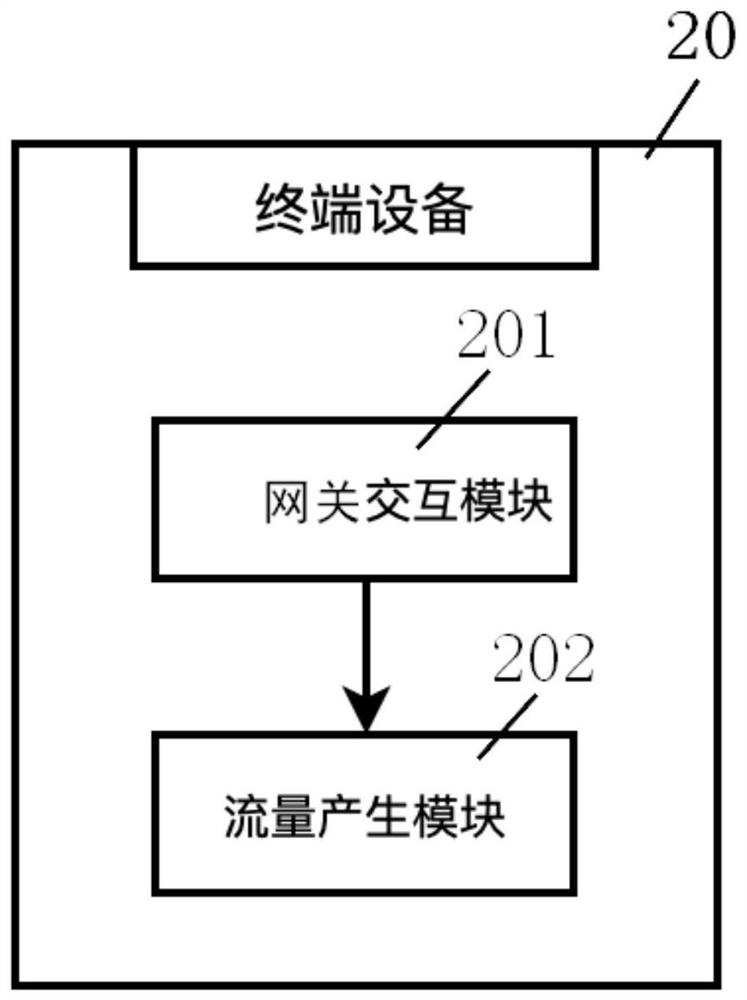
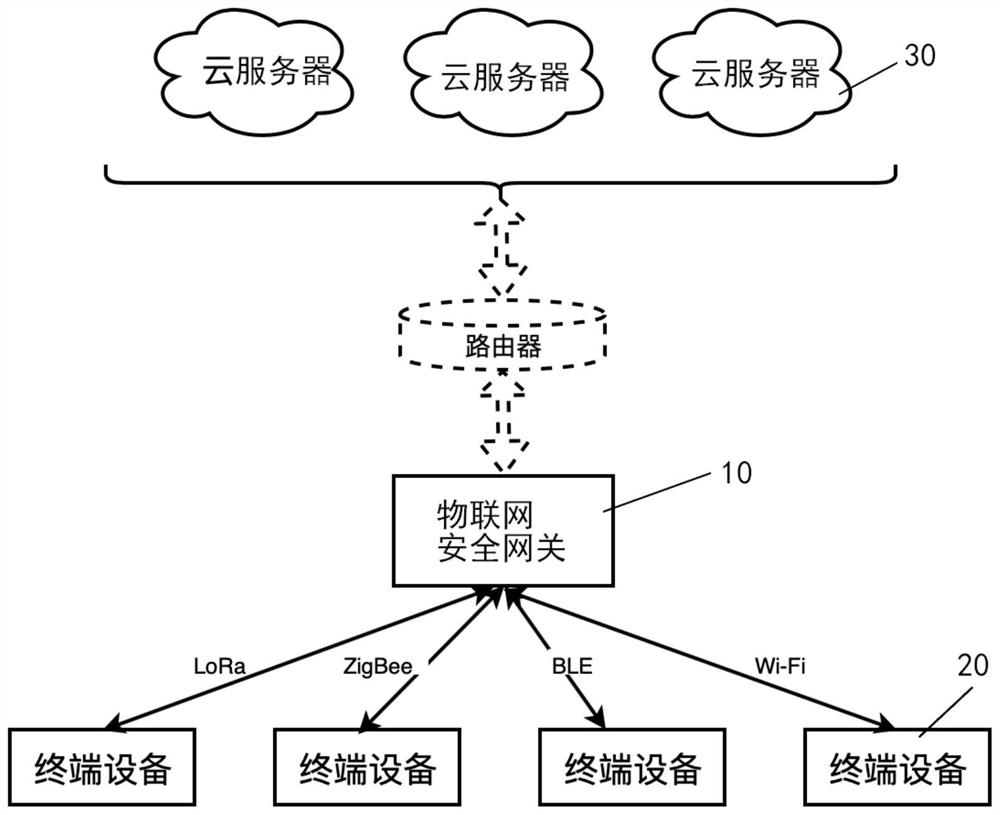
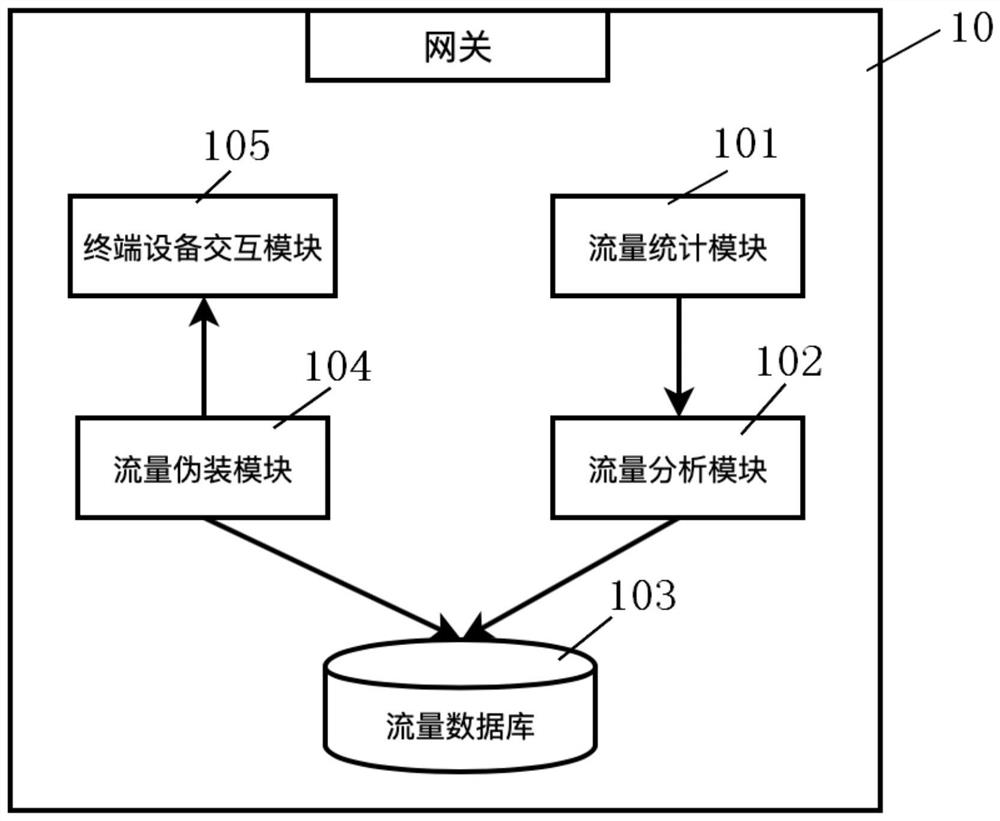
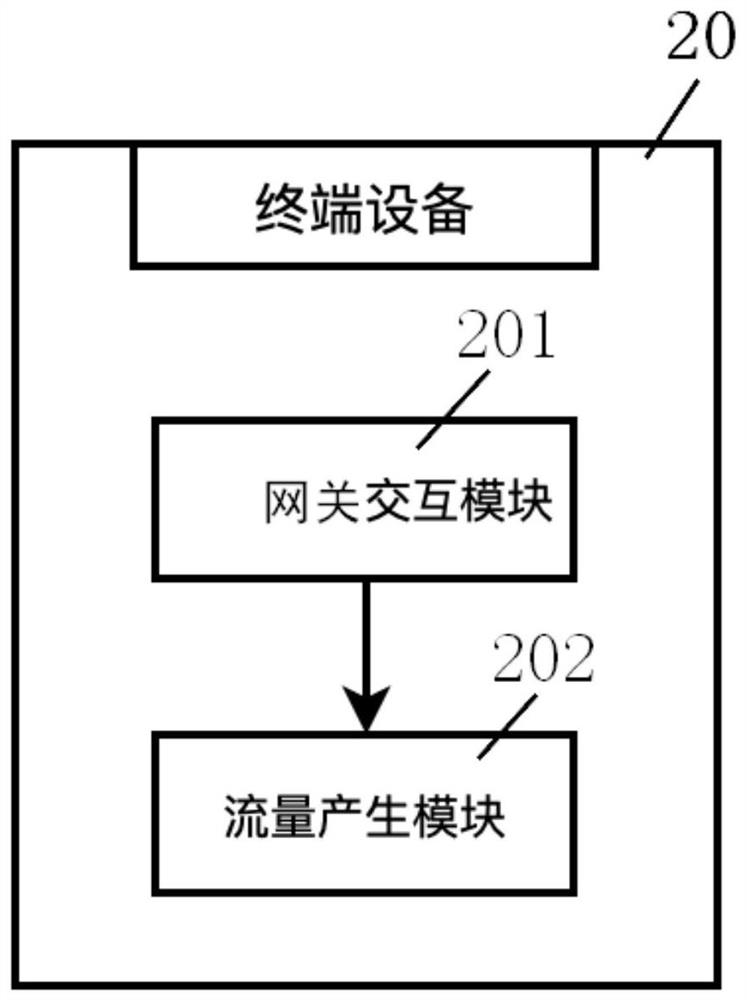
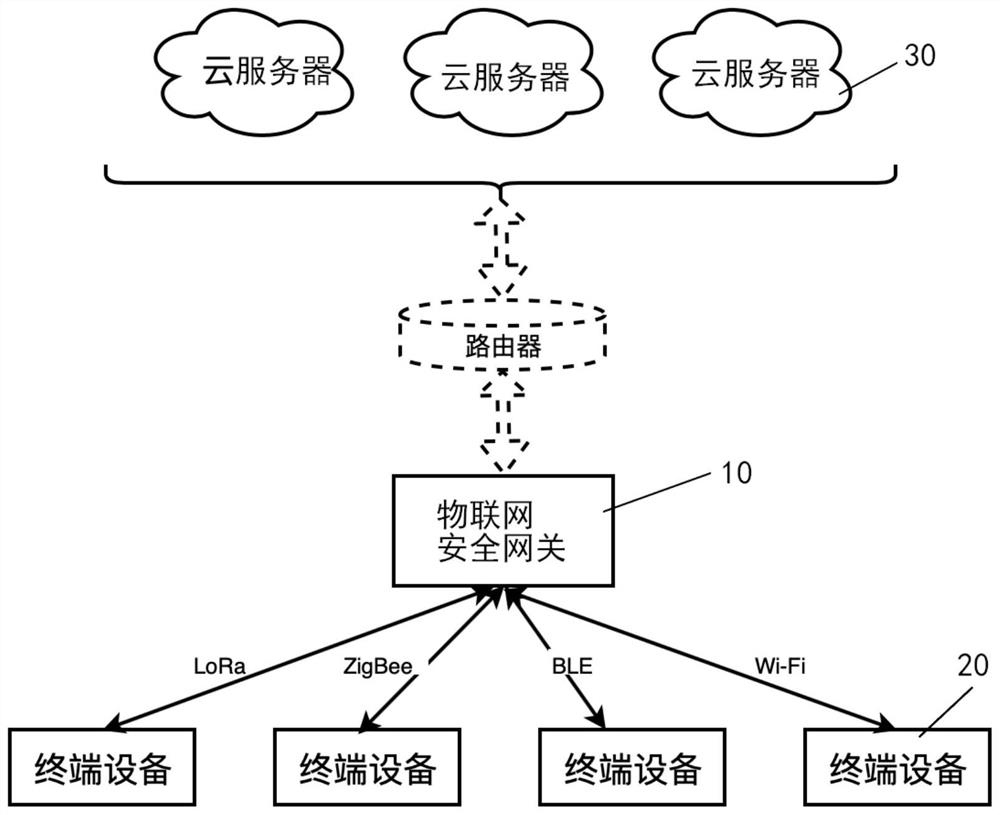
Internet of things security gateway, terminal equipment and system capable of shaping traffic
ActiveCN112040489BDoes not affect normal communicationEavesdropping attacks againstNetwork connectionsSecurity arrangementData packEngineering
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
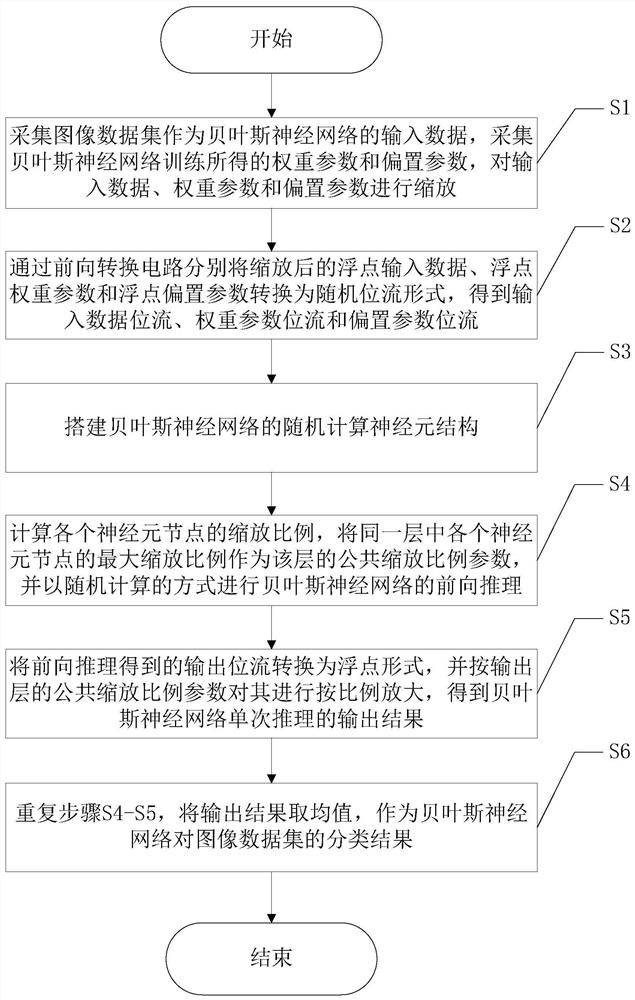
Image classification method based on random calculation Bayesian neural network error injection
ActiveCN113516172AReduce overheadReduce occupancyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesAlgorithmStochastic computing
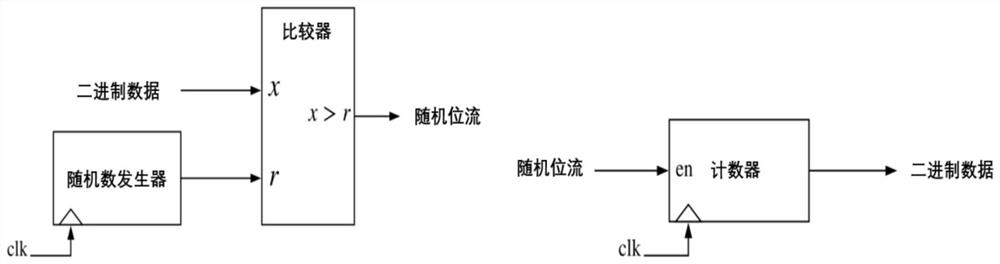
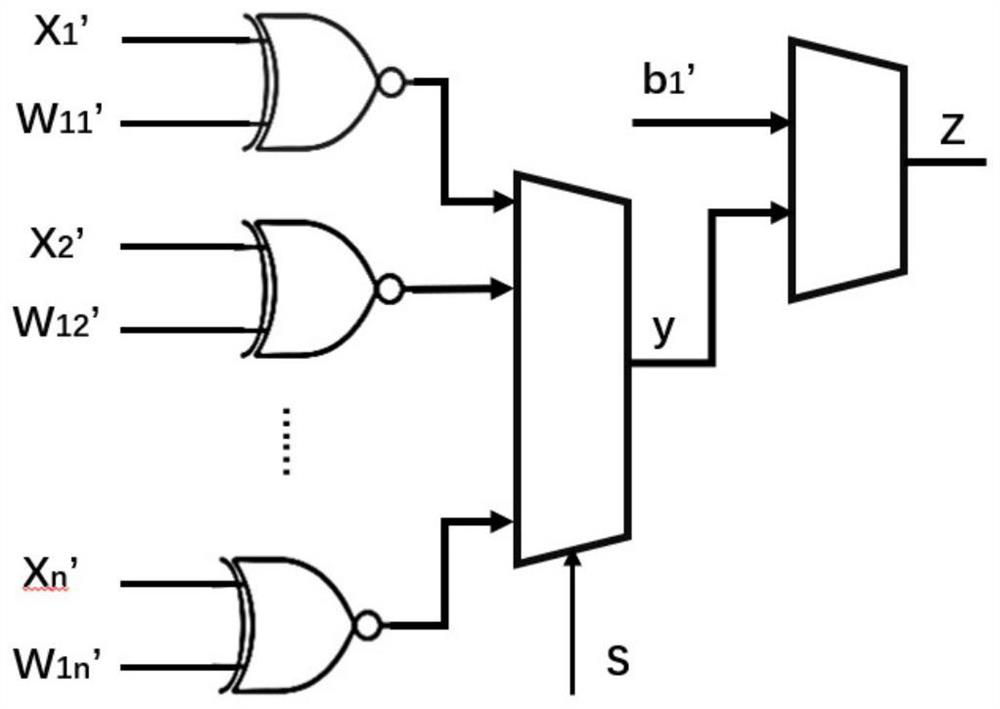
The invention discloses an image classification method based on random calculation Bayesian neural network error injection. The method comprises the following steps: S1, scaling input data, weight parameters and bias parameters; S2, converting the scaled floating point input data, the scaled floating point weight parameter and the scaled floating point bias parameter into a random bit stream form through a forward conversion circuit; S3, building a random calculation neuron structure of the Bayesian neural network; S4, calculating the scaling of each neuron node, and performing forward reasoning; S5, converting the output bit stream into a floating point form, and obtaining an output result of single reasoning; and S6, repeating the steps S4-S5, taking a mean value, and taking the mean value as a classification result. According to the image classification method based on Bayesian neural network error injection, inherent noise characteristics are calculated randomly, an additional error injection circuit does not need to be introduced, and unification of calculation and error injection in the Bayesian neural network reasoning process is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Using stochastic failure metrics in semiconductor manufacturing
A stochastic calculation engine receives inputs from a semiconductor inspection tool or semiconductor review tool. The stochastic calculation engine determines abnormal locations and pattern variation from the inputs and determines stochastic failures from the inputs. An electronic data storage unit connected with the stochastic calculation engine can include a database with known stochastic behavior and known process metrology variations. The stochastic calculation engine can flag stochastic features, determine a failure rate, or determine fail probability.
Owner:KLA CORP
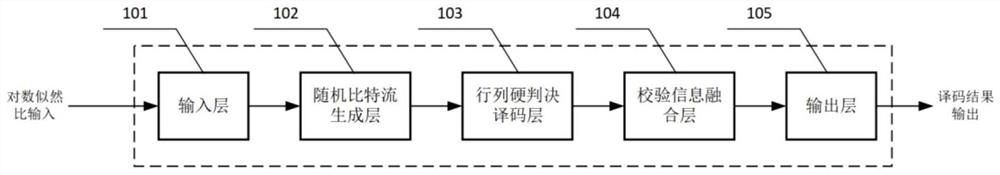
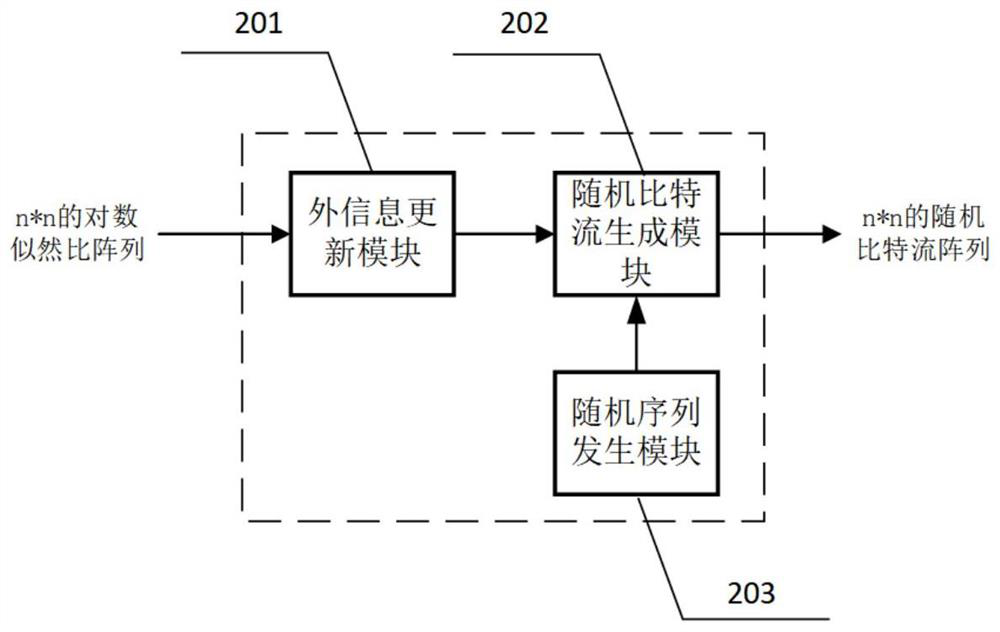
Probability calculation-based TPC iterative decoding method and decoder
PendingCN114421976AReduce implementation complexitySimple structureCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresTheoretical computer scienceLogit
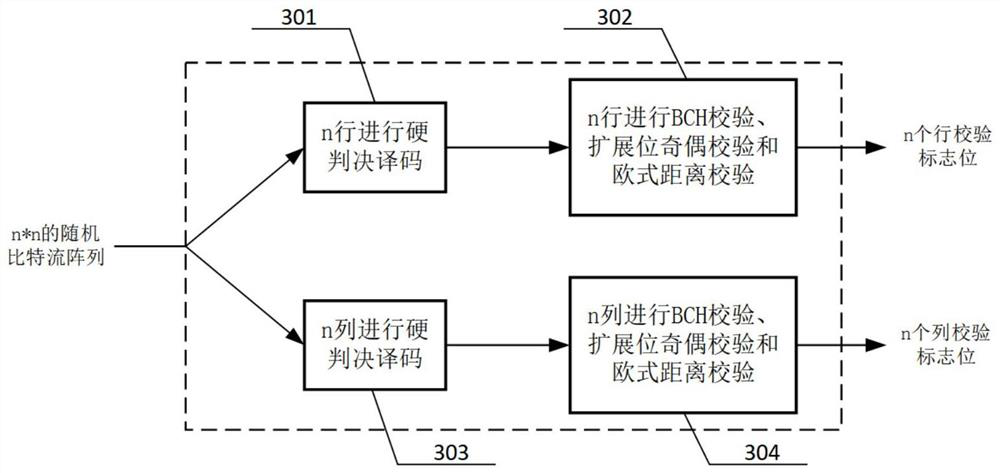
The invention discloses a TPC iterative decoding method and decoder based on probability calculation, and relates to the field of wireless communication, and the technical scheme is characterized in that a log-likelihood ratio matrix is fused with external information, and a random bit stream and a random number generated randomly are compared and judged; performing BCH codeword self-check, extended bit parity check and Euclidean distance check on the initial hard decision row decoding result and the initial hard decision column decoding result to obtain initial row check information and initial column check information; performing fusion check updating on the initial row check information and the initial column check information according to the zone bit distribution condition to obtain row fusion check information and column fusion check information; and performing iterative processing. By means of probability calculation and extrinsic information updating strategies, complex test pattern generation can be achieved through a simple random calculation method, complete TPC iterative decoding is achieved, the structure is simple, implementation is easy, hardware implementation complexity is greatly reduced, and hardware efficiency is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
RTL-level circuit reliability measurement method based on random and parallel computing strategy
PendingCN111597765AAccurate calculationQuick calculationArtificial lifeDesign optimisation/simulationConcurrent computationCircuit reliability
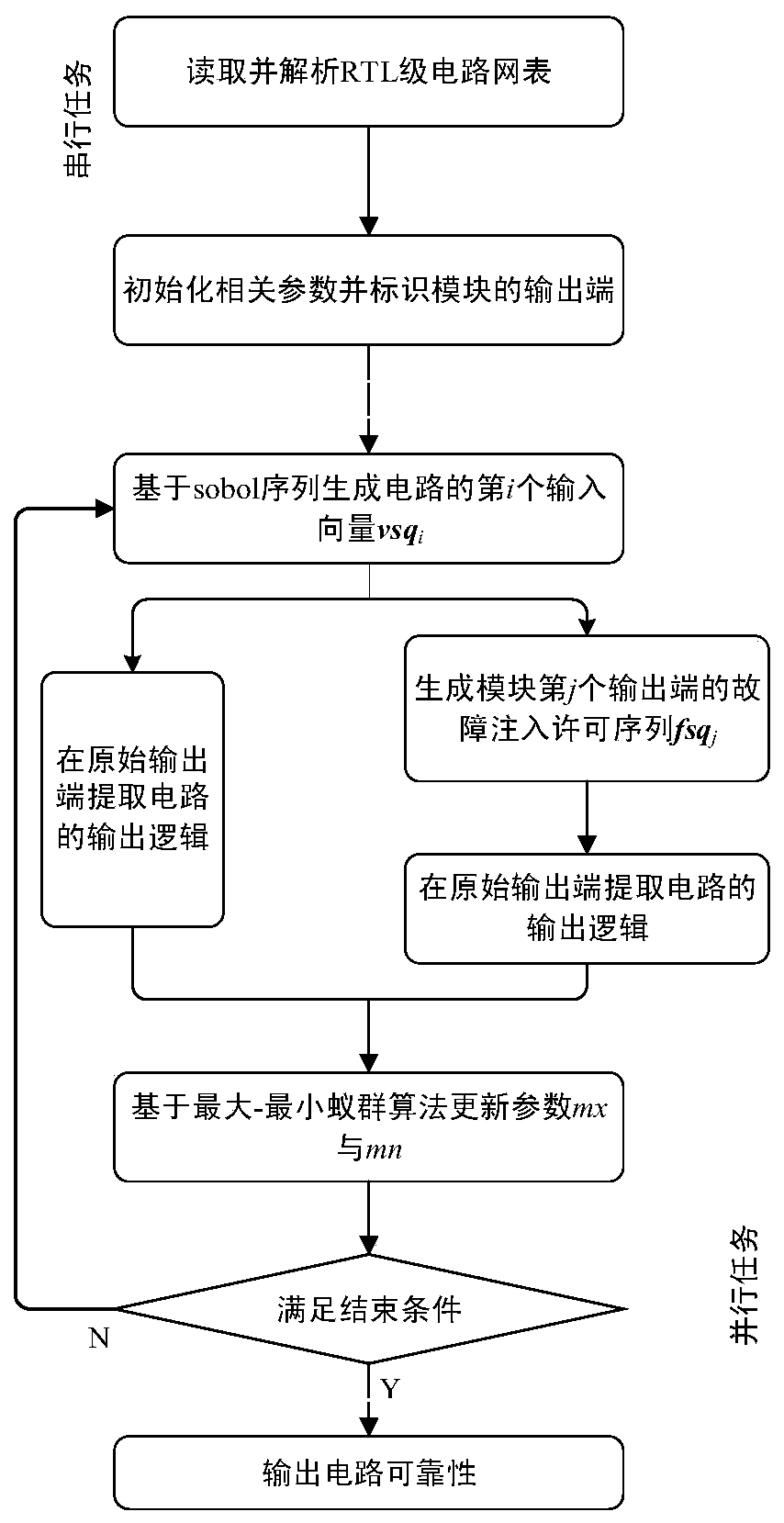
An RTL-level circuit reliability measurement method based on a random and parallel computing strategy comprises the steps: firstly, analyzing a netlist, initializing related quantities, and making preparation for follow-up computing; then, constructing a generation method of a uniform non-Bernoulli sequence based on the sobol sequence, and constructing a circuit input vector with the length of lsand a module output end-oriented fault injection permission sequence by utilizing a parallel computing strategy based on the sequence generation method; then, based on a random calculation strategy, respectively calculating circuit logic output of each input vector under different conditions in parallel; and finally, realizing adaptive convergence of the algorithm through a maximum-minimum ant colony algorithm. The evaluation precision and the calculation speed are effectively considered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Attribute encryption method, device, equipment and storage medium in cloud environment
ActiveCN112953946BReduce computational overheadImprove encryption efficiencySecuring communicationCiphertextPassword
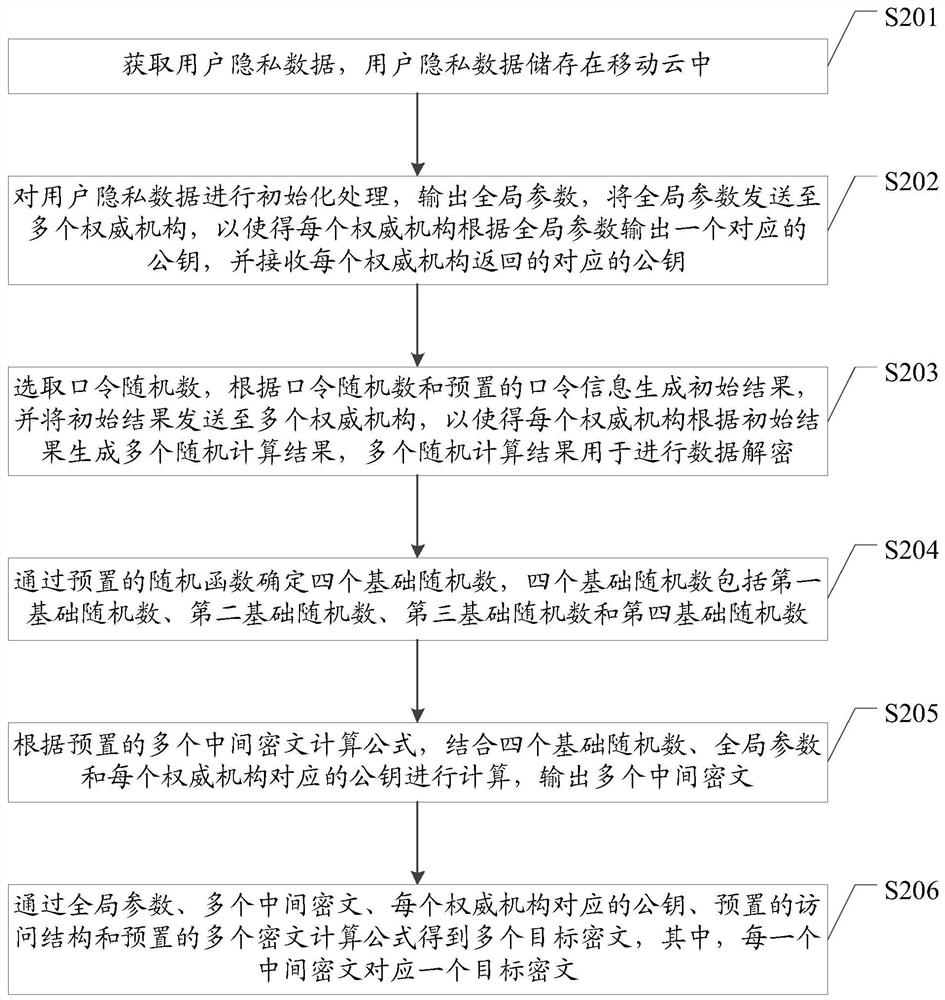
The invention relates to the field of information security, and discloses an attribute encryption method, device, equipment and storage medium in a cloud environment, which are used for data encryption based on a multi-mechanism algorithm, which reduces the computational overhead of encryption and improves the efficiency and security of encryption sex. The attribute encryption method in the cloud environment includes: obtaining user privacy data; outputting global parameters, sending the global parameters to multiple authorities, so that each authority outputs a corresponding public key according to the global parameters; The password information generates the initial result, and sends the initial result to multiple authorities, so that each authority generates multiple random calculation results according to the initial result; randomly selects multiple basic random numbers, generates multiple intermediate ciphertexts, and generates multiple intermediate ciphertexts according to Multiple intermediate ciphertexts and preset ciphertext calculation formulas generate multiple target ciphertexts. In addition, the present invention also relates to block chain technology, and the target ciphertext can be stored in the block chain.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Internet of things security gateway, terminal device and system capable of shaping flow
ActiveCN112040489ADoes not affect normal communicationEavesdropping attacks againstNetwork connectionsSecurity arrangementCommunications securityData pack
The invention discloses an Internet of Things security gateway, terminal device and system capable of shaping flow, and the gateway comprises a flow statistics module which is used for obtaining and filtering a data packet transmitted to a cloud server, and obtaining a tuple set; a flow analysis module for calculating related data based on the obtained tuple set; a flow database which is used forstoring related data; a camouflage flow calculation module which can randomly calculate and select related data in a flow database according to time and frequency characteristics to obtain a decisioninstruction of camouflage burst flow at the moment; a terminal device interaction module which can distribute the determination instruction of the camouflage burst flow obtained by the camouflage flowcalculation module to all connected Internet of Things terminal devices at the moment, and notify each Internet of Things terminal device to send an analog data packet; wherein each received analog data packet is not processed, and the related ACK packet is sent only according to the corresponding protocol. The communication security of the Internet of Things can be improved with less simulationflow.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
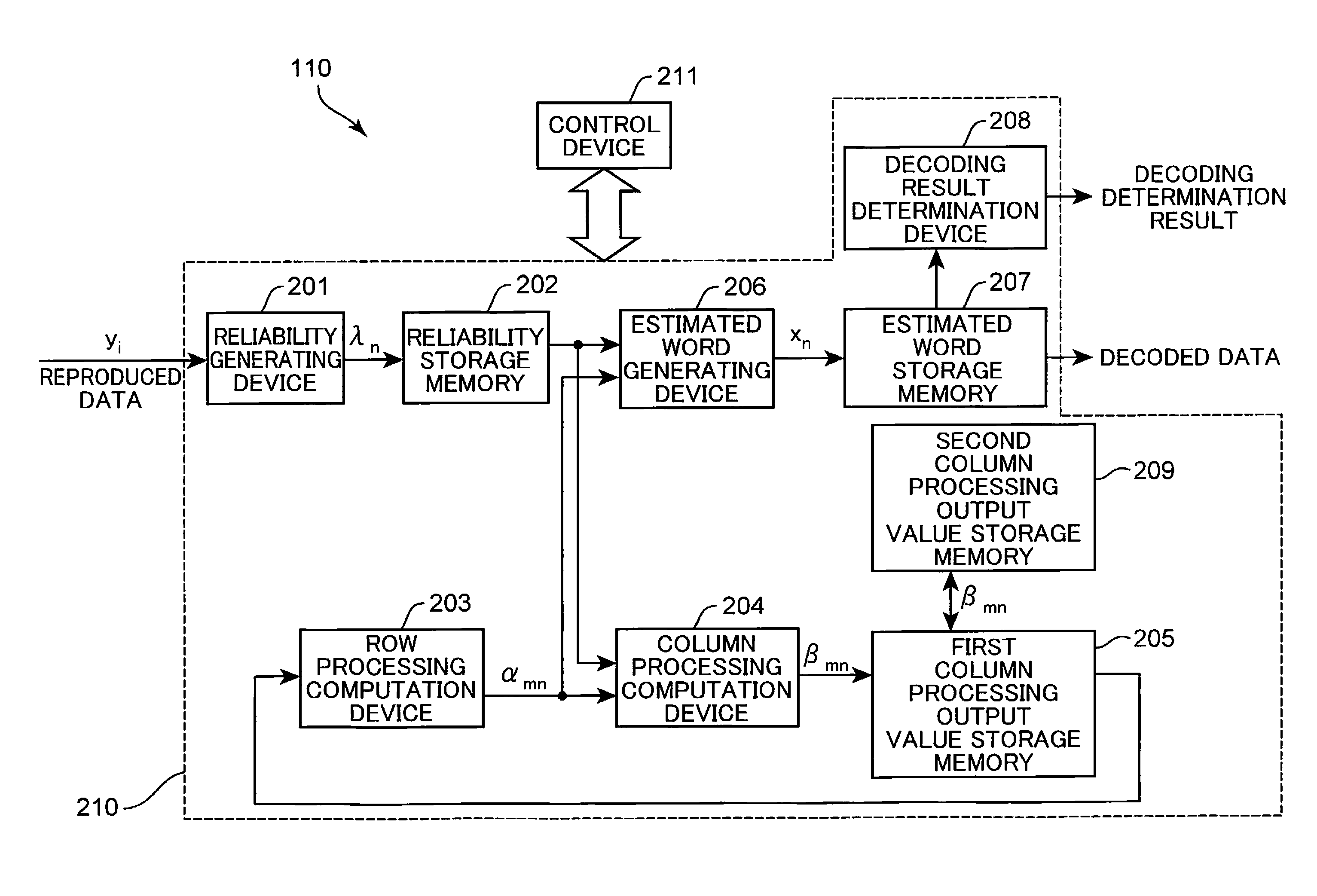
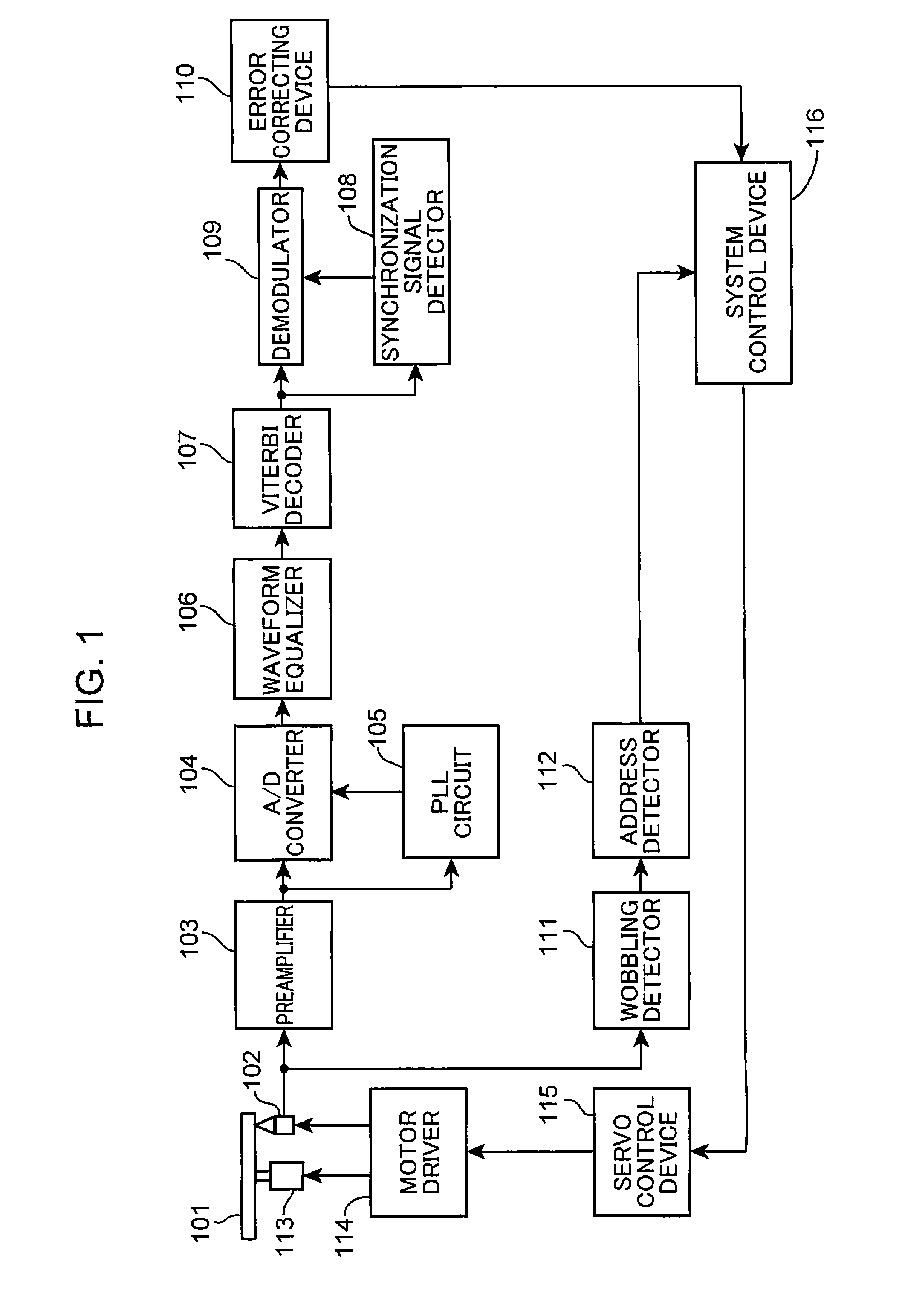
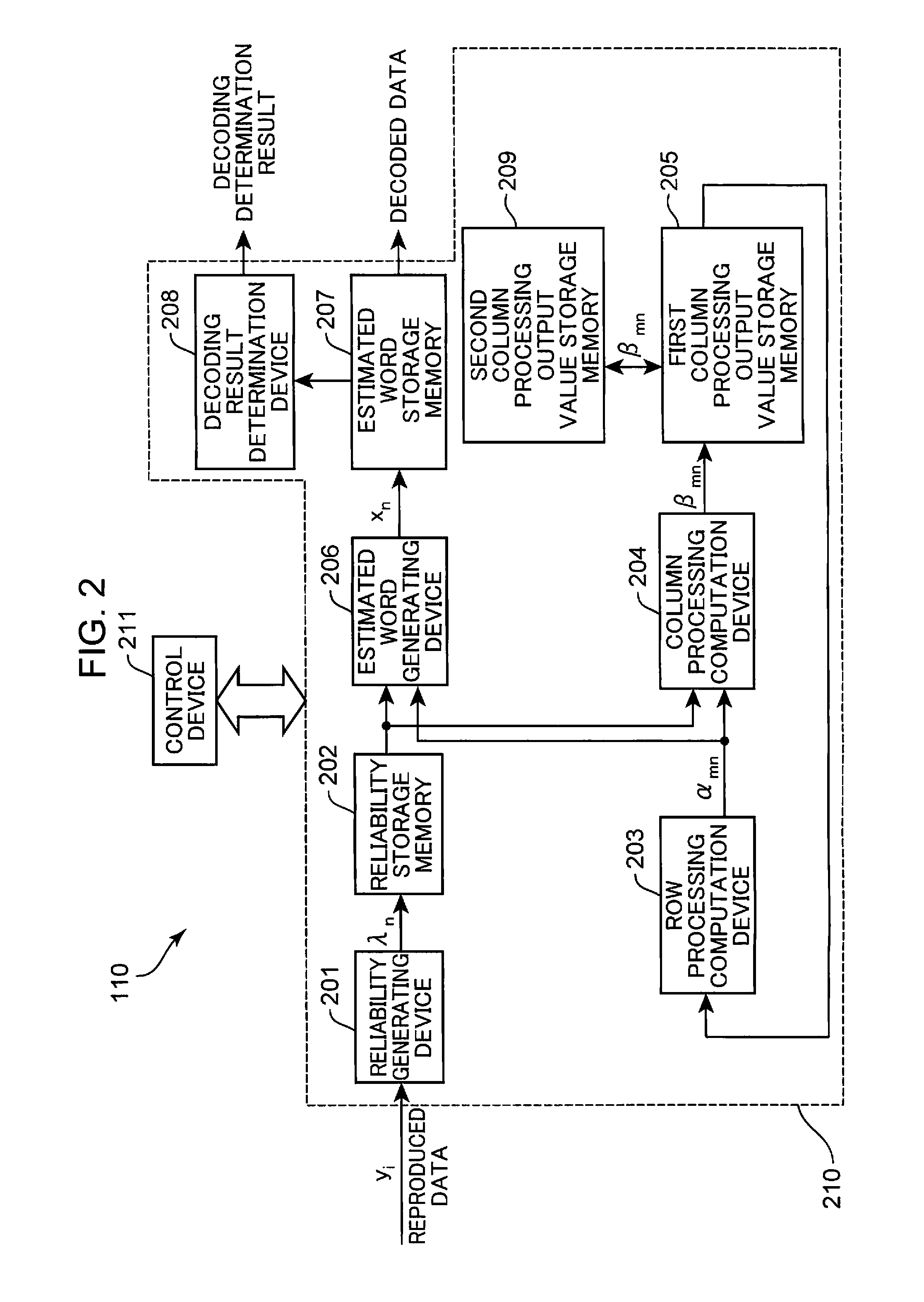
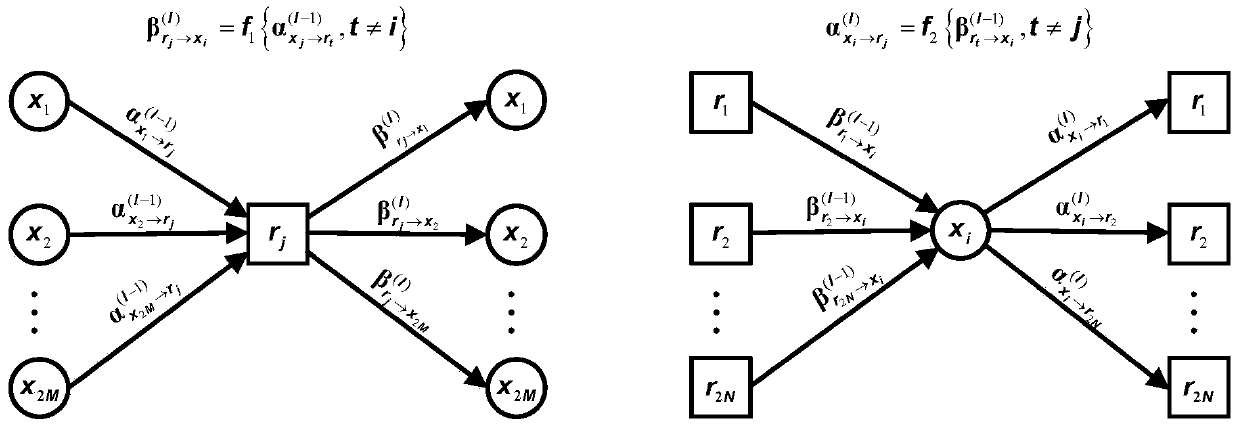
Decoding apparatus and decoding method
ActiveUS9244760B2Reduce error rateImprove signal-to-noise ratioOther decoding techniquesOptical discsDecoding methodsStochastic computing
A control device inputs reliability information on the same data block a plurality of times into a reliability storage memory. A reliability generating device generates a reliability information by performing computation processing based on a stochastic computation by using reliability information generated in the previous cycle that has been saved in the reliability storage memory and reliability information generated in the present cycle, and saves the reliability information generated in the reliability storage memory when the decoding is performed by using reliability information on the data block the same as that in the previous cycle. A column processing computation device computes a column processing output value by using the reliability information generated and saved in the reliability storage memory and a row processing output value.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
A large-scale mimo detection method and detection device
ActiveCN105515627BEasy to detectRadio transmissionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksAlgorithmStochastic computing
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) detecting method and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The large-scale MIMO detecting method comprises the steps of detecting an MIMO signal by utilizing a BP (Belief Propagation) based iterative algorithm in a real number domain; before BP iteration, firstly normalizing and quantifying all the definitive variables to enable the variables to be within a range of [-1, 1], and then representing the normalized and quantified definitive variables by using random bit streams with symbols; in the BP iteration process, finishing updating and delivery of information through random calculation; and after the BP iteration is finished, converting the random bit streams output after iteration into the definitive variables to serve as output soft information. The invention also discloses a large-scale MIMO detecting device. By combining the BP algorithm in the real number domain with random calculation, the hardware consumption and system delay just increase linearly along with the addition of the number of transmitting or receiving antennas while the detecting performance as same as that of definite detection is guaranteed, and accordingly the large-scale MIMO detecting method and device can well adapt to large-scale MIMO scenes.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A method for fast formation of Jacobian matrix in power system power flow calculation
ActiveCN109344361BFast formingImprove read and write speedData processing applicationsComplex mathematical operationsPower flowData file
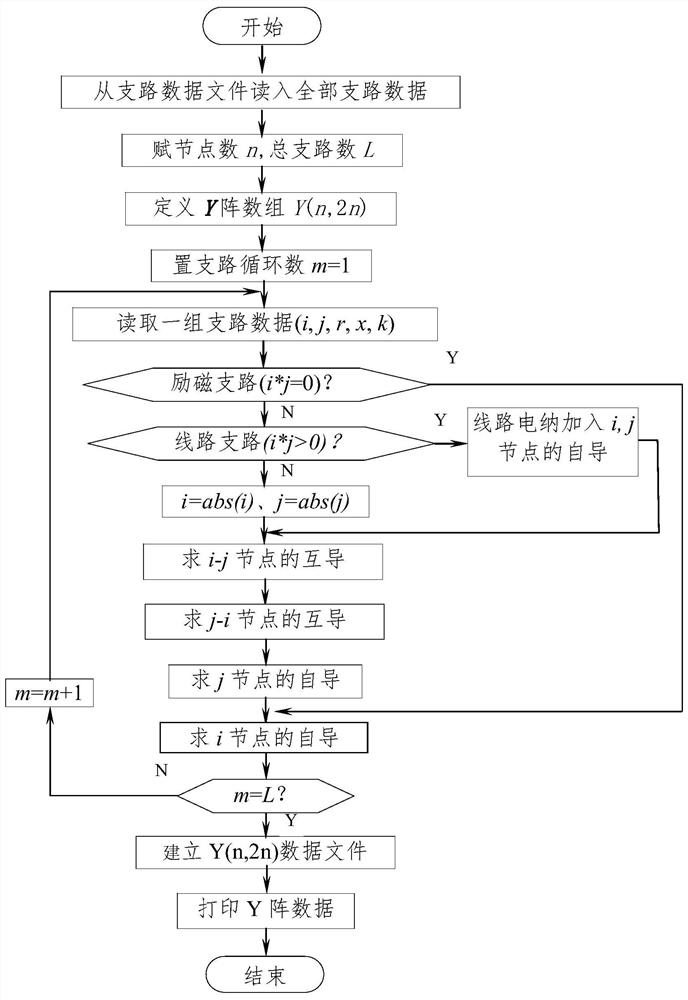
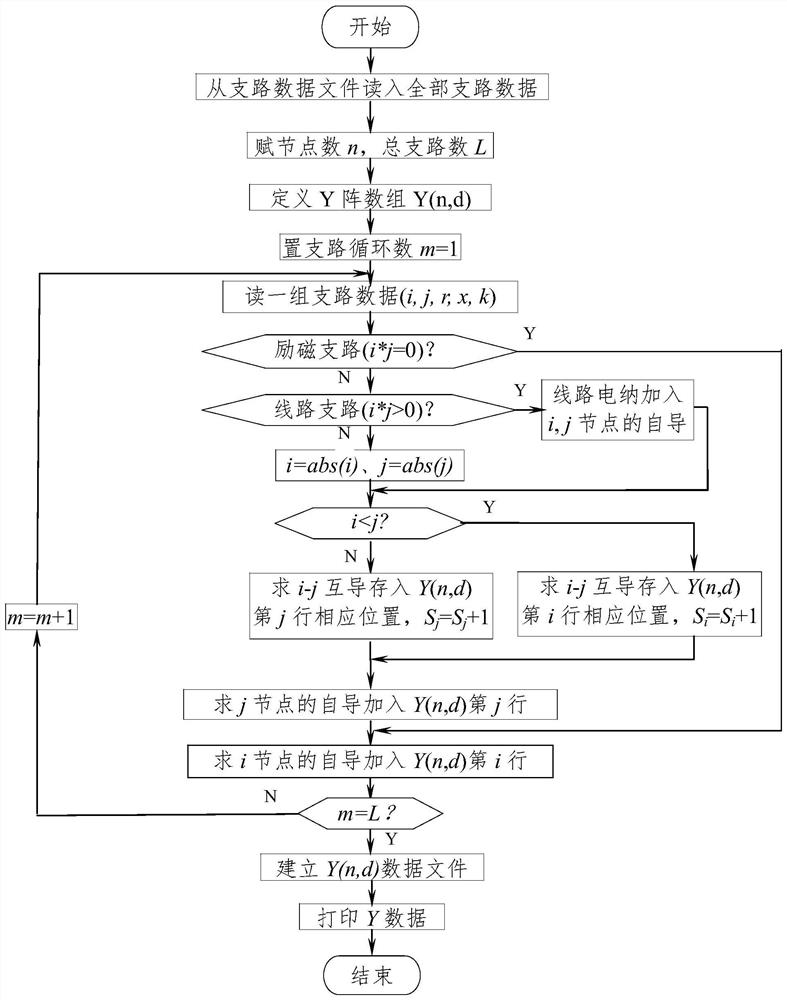
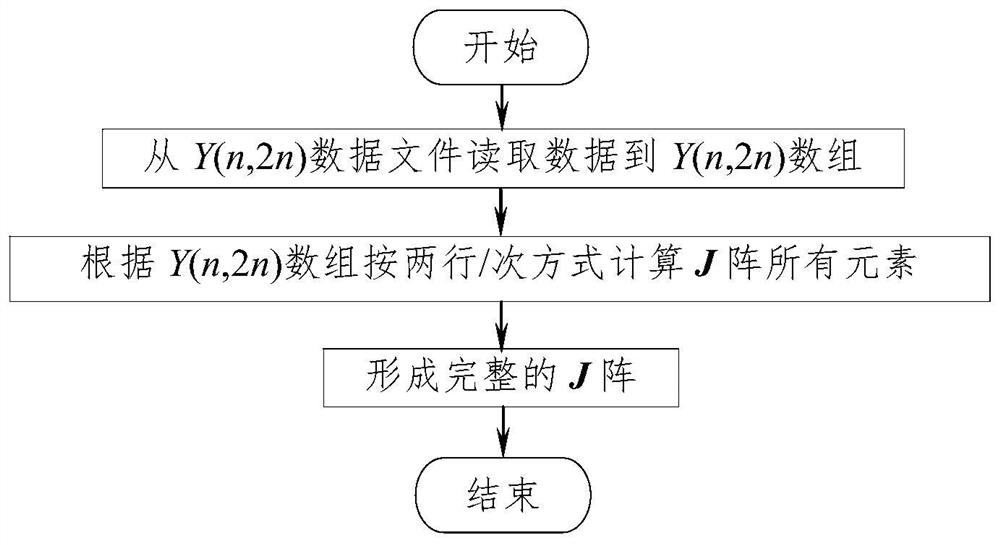
A method for quickly forming a Jacobian matrix in power system power flow calculations, comprising: establishing an array Y(n,d) that only stores triangular non-zero elements on the Y array in a random order, and controls the number of non-zero elements with the number of non-zero elements Read and apply; accumulatively calculate the self-admittance of nodes i and j; calculate the mutual admittance of nodes i and j respectively, and calculate S cumulatively according to the number of mutual admittances i ;Write the Y(n,d) array into the data file; read the Y(n,d) data file and randomly calculate the node active current I according to the parameters of the Y(n,d) array pi and reactive current I qi ;According to Y array element and J ij and J ji The corresponding relation of sub-array non-zero element position, use Y(n,d) array element, calculate J array element according to two rows + two columns at the same time; According to I pi , I qi , modify all diagonal elements to form a complete J matrix. The calculation speeds of forming and storing Y-array data files, reading Y-array data files, and forming J-array are greatly superior to those of traditional methods, and the advantages become more obvious with the increase of system scale.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
An ldpc Decoder Based on Random Computing
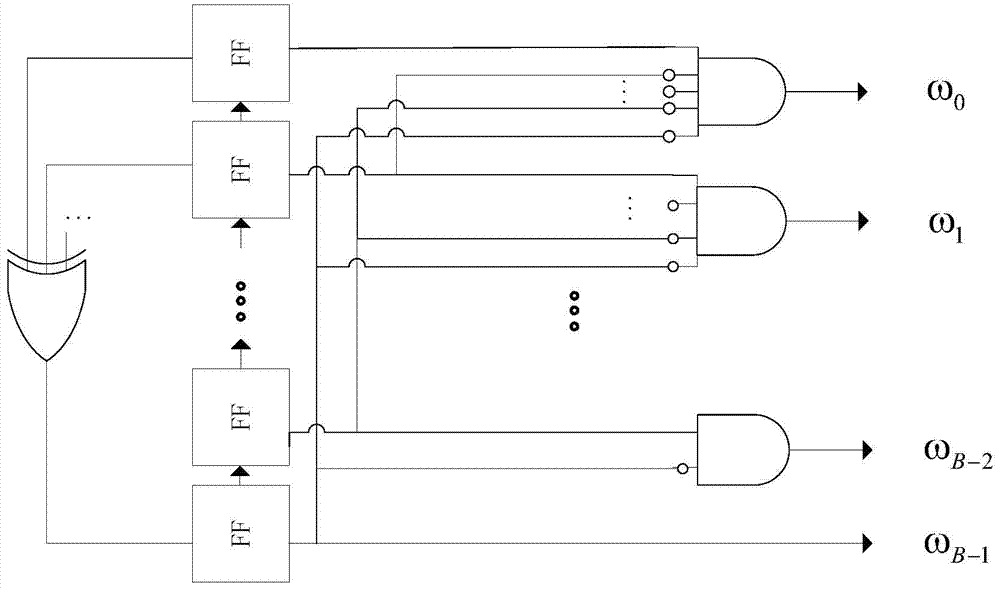
ActiveCN104283571BShorten convergence timeImprove throughputError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsStochastic computingOptical communication
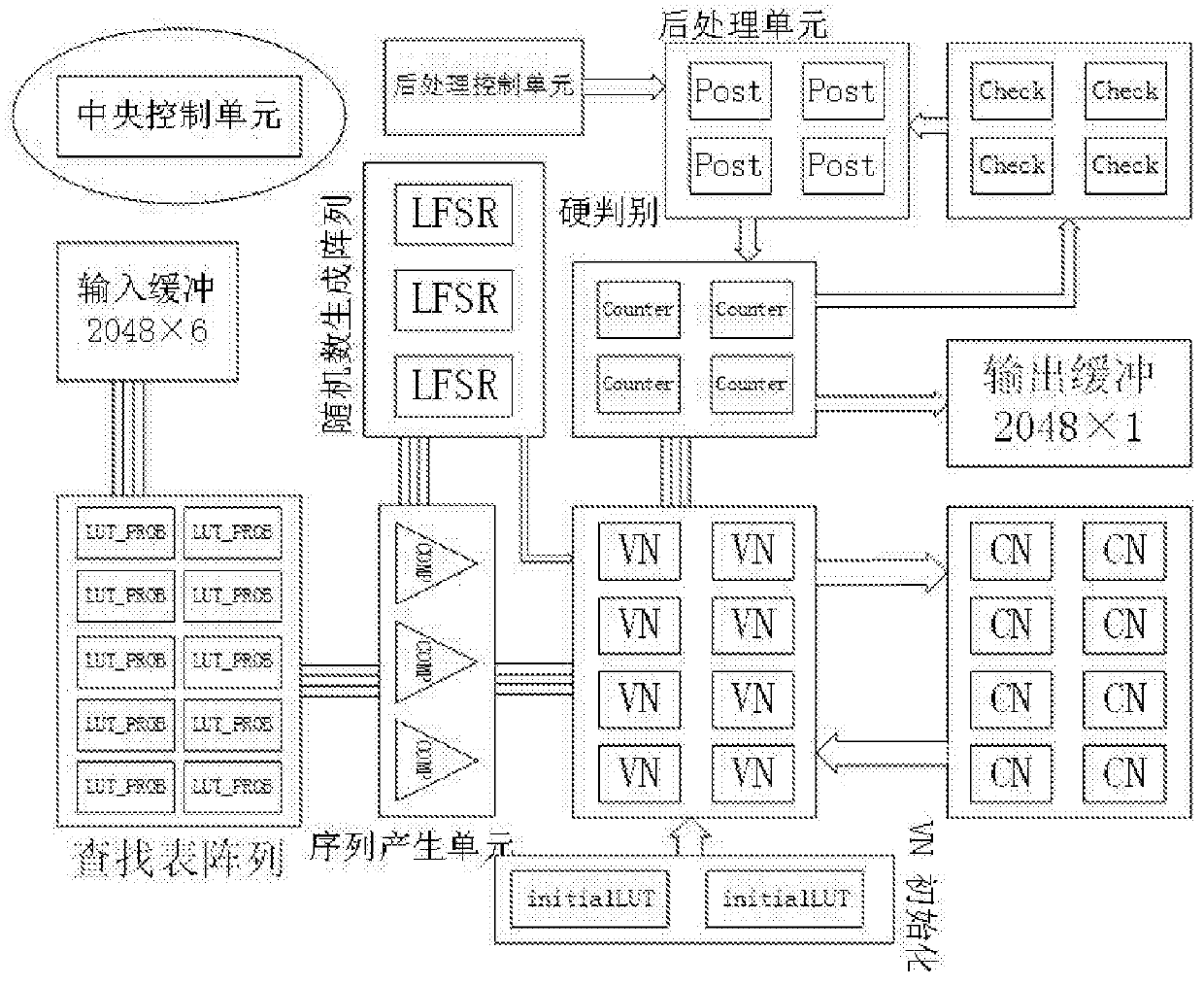
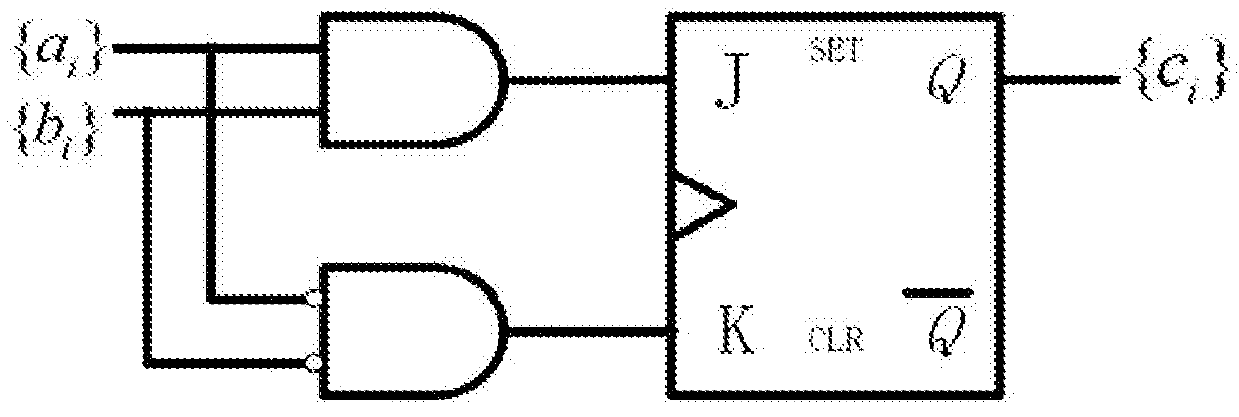
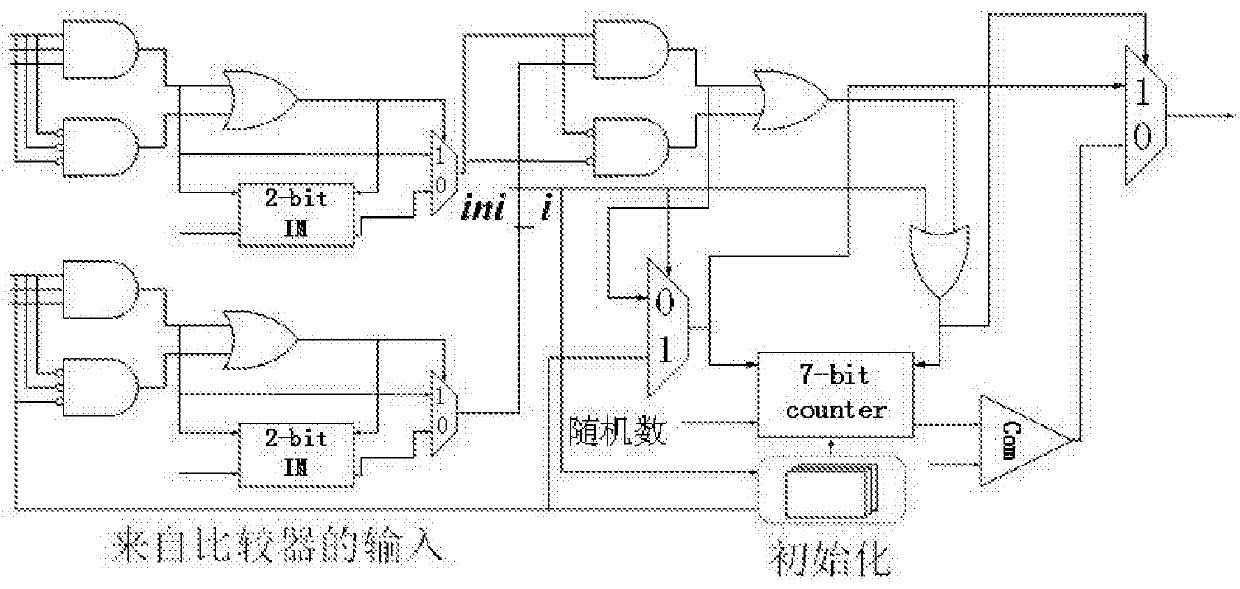
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless digital communication and broadcasting, in particular to an LDPC decoder based on random calculation. The decoder is based on the random calculation algorithm of the belief propagation algorithm in the probability domain, and its structure includes: a lookup table LUT suitable for the NDS coefficient of the (2048,1723) parity check matrix in the IEEE 802.3an (10GBASE‑T) standard Array, and three hardware structures for accelerating convergence: the initialization module of the hard discriminant counter in the array VN based on the initialization of the lookup table LUT array; After the verification result of the verification node CN reaches a certain stage, the discriminant module output by the initialization array variable node VN is flipped over; at the same time, a new VN node structure is adopted. The invention can further improve the convergence speed of the decoder, improve the throughput rate of the decoder, and provide technical solution support for optical communication whose throughput rate is required to be as high as 100 Gbps in the future.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com