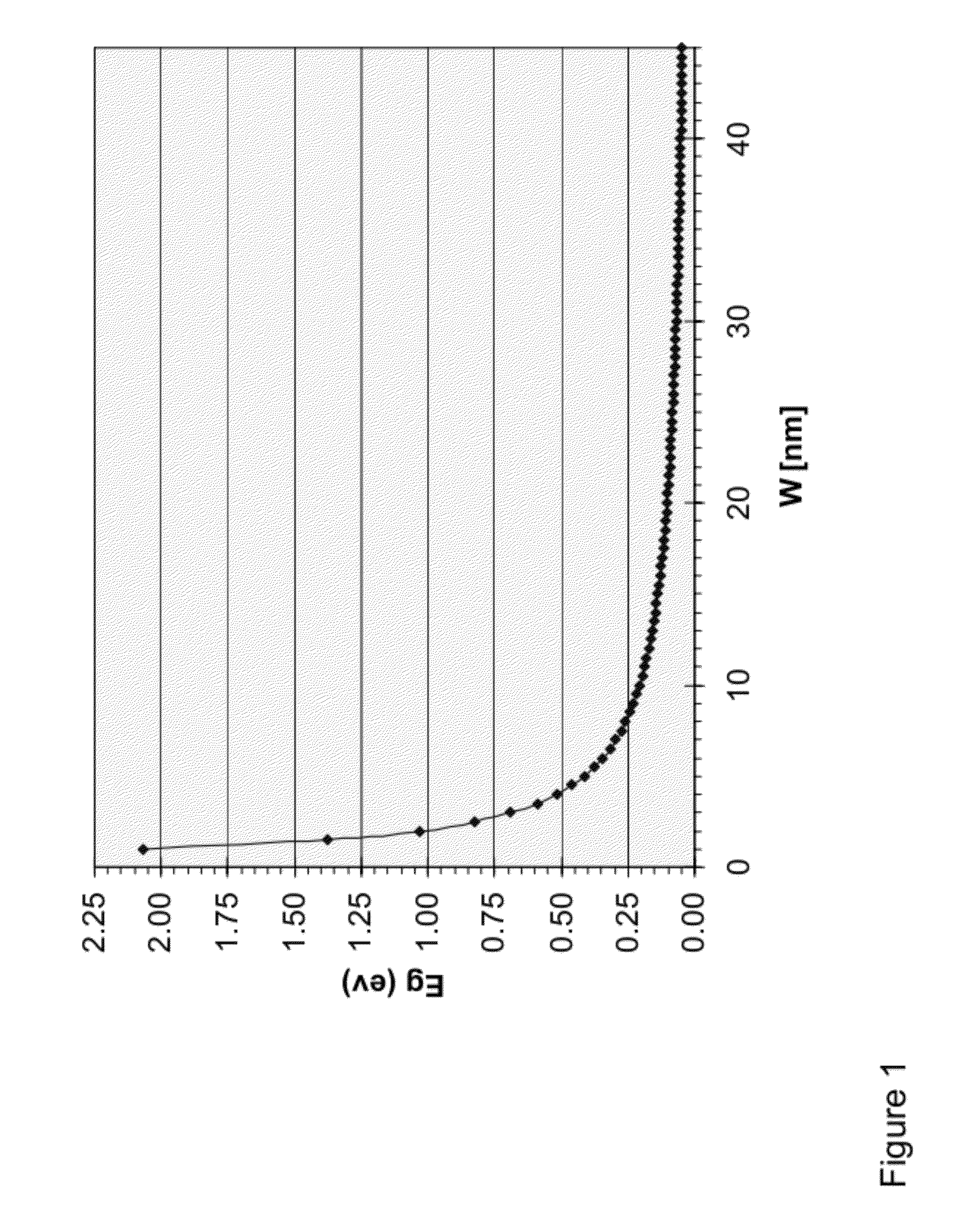
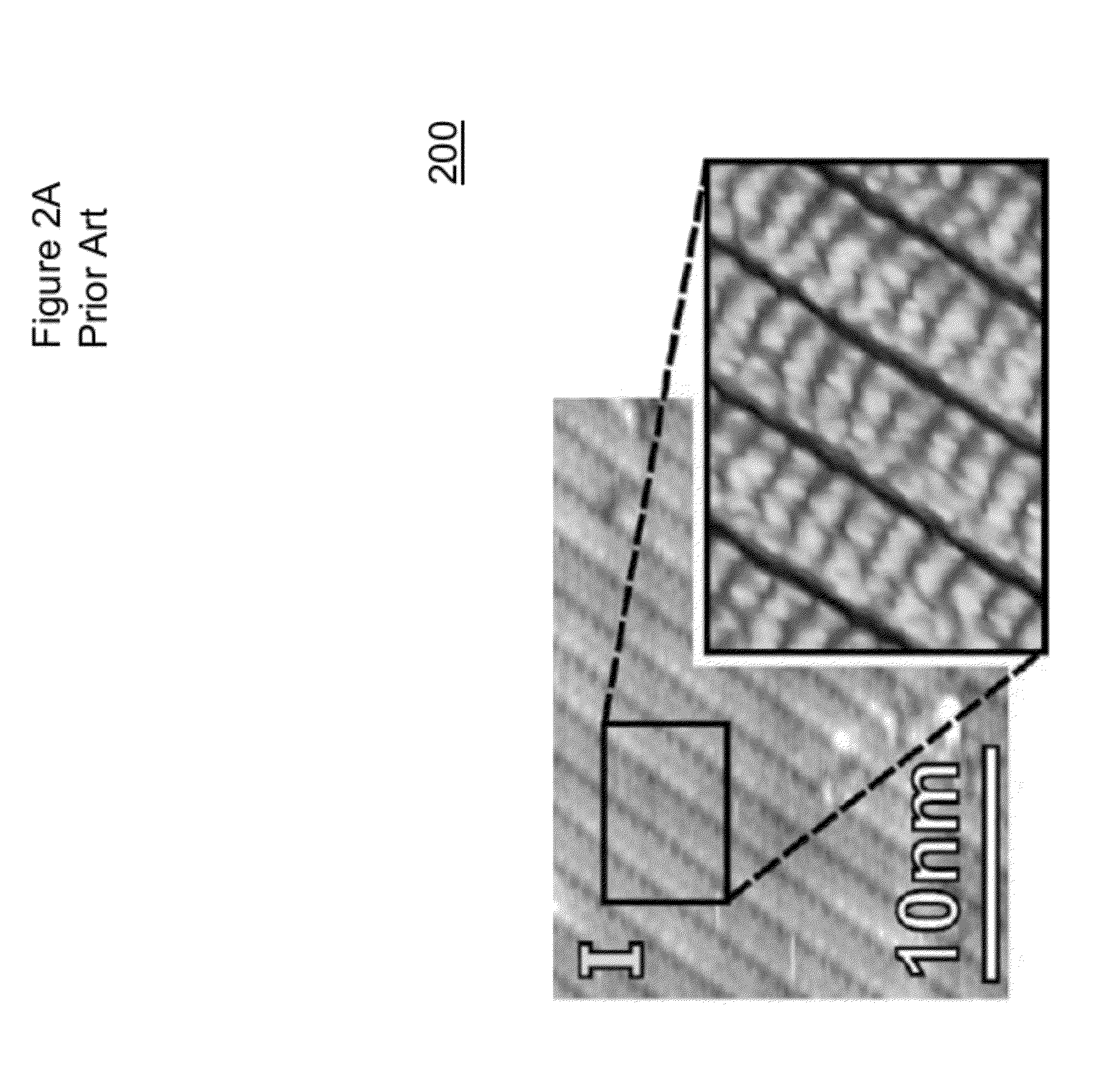
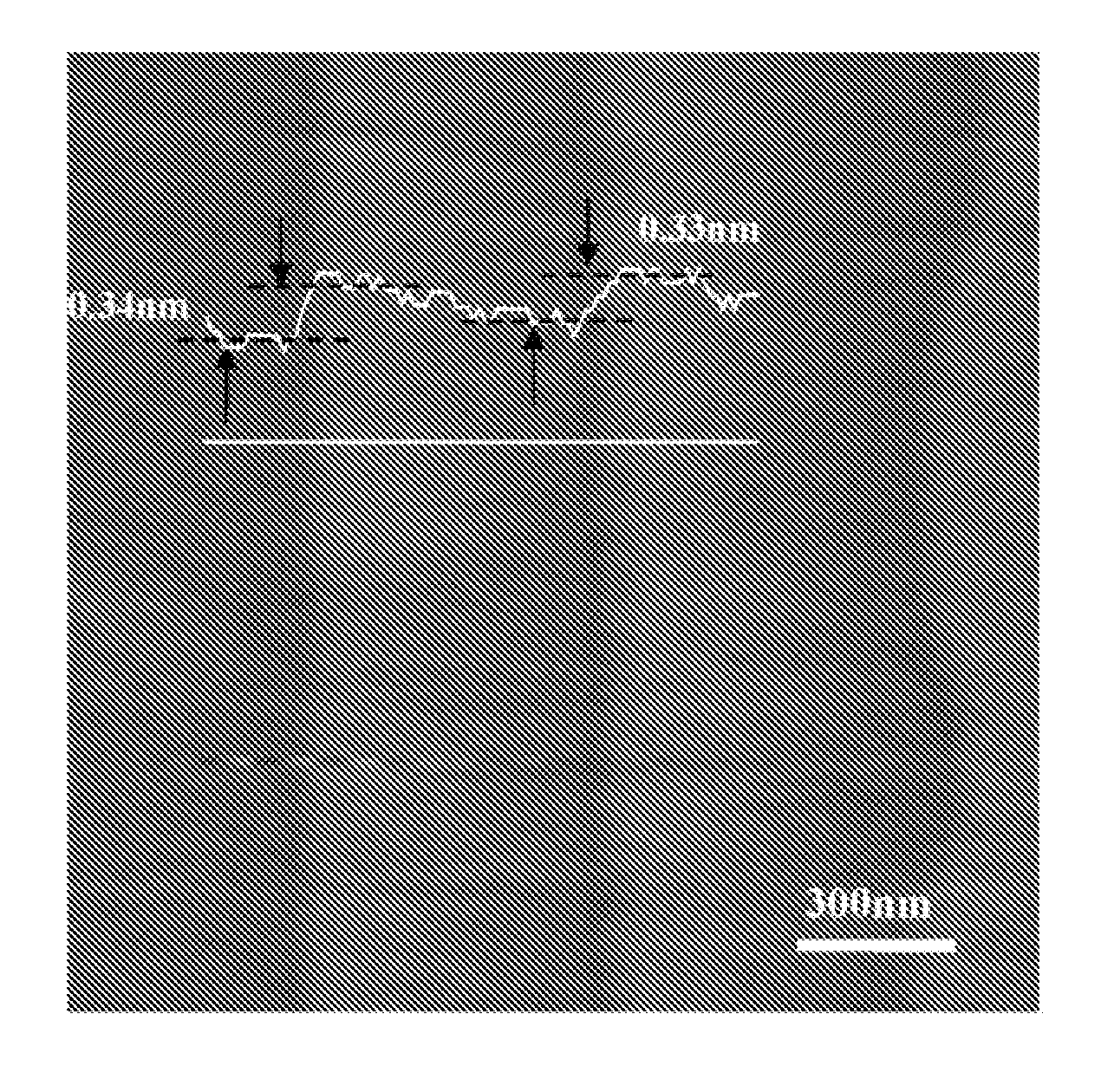
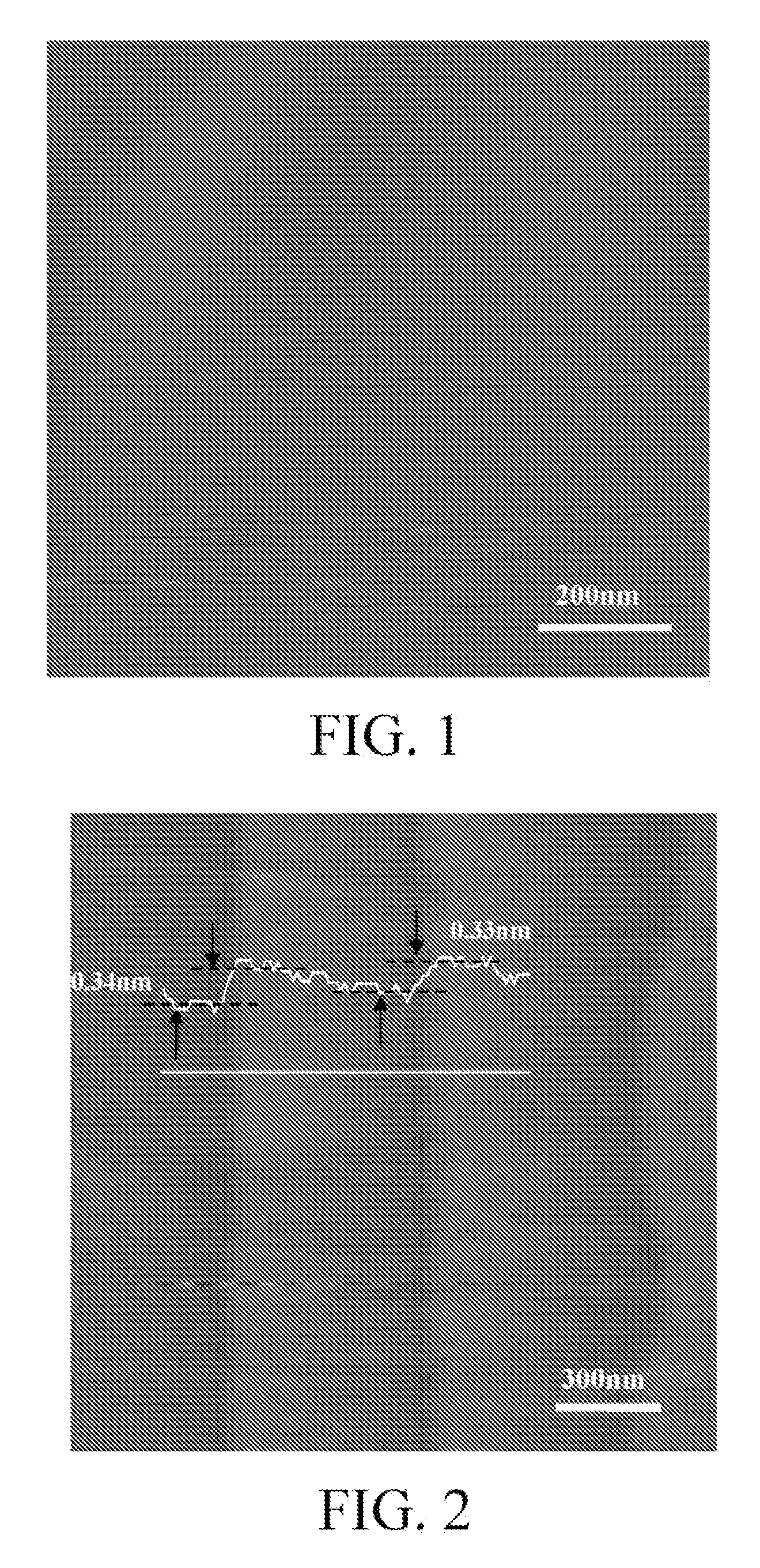
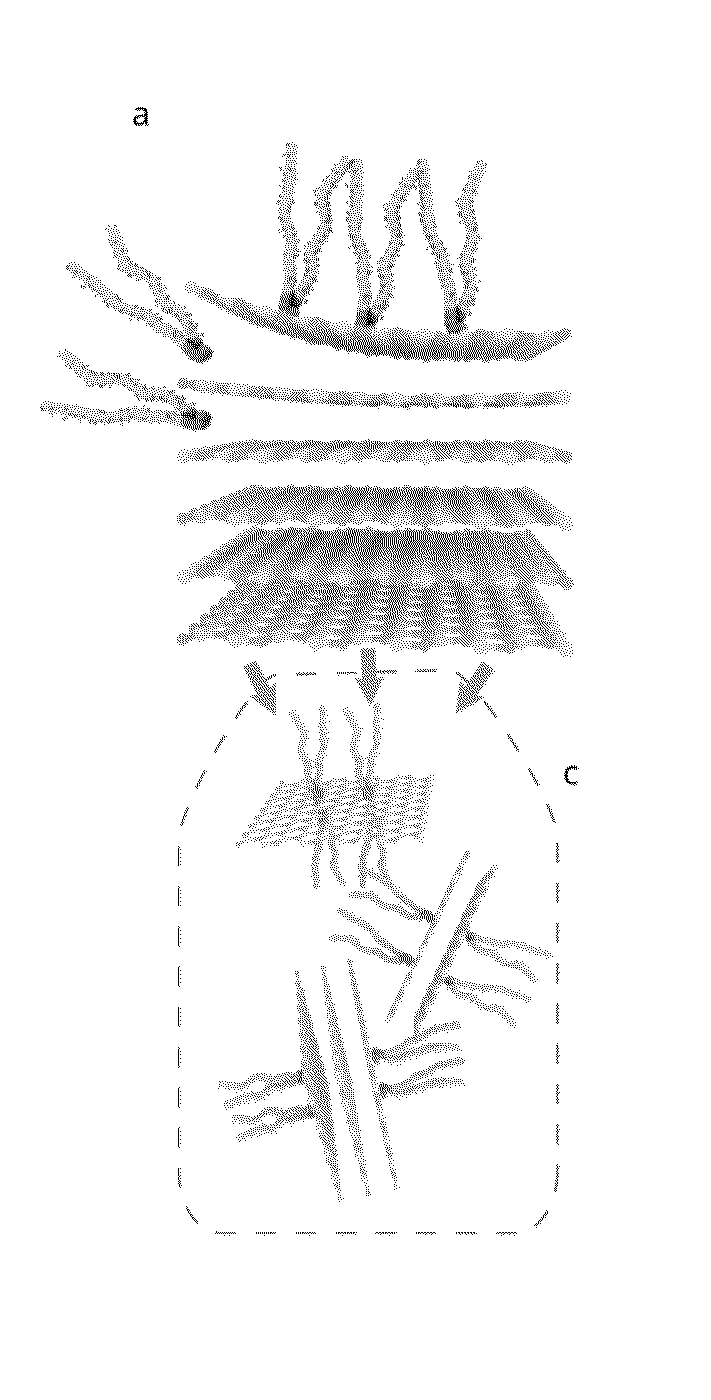
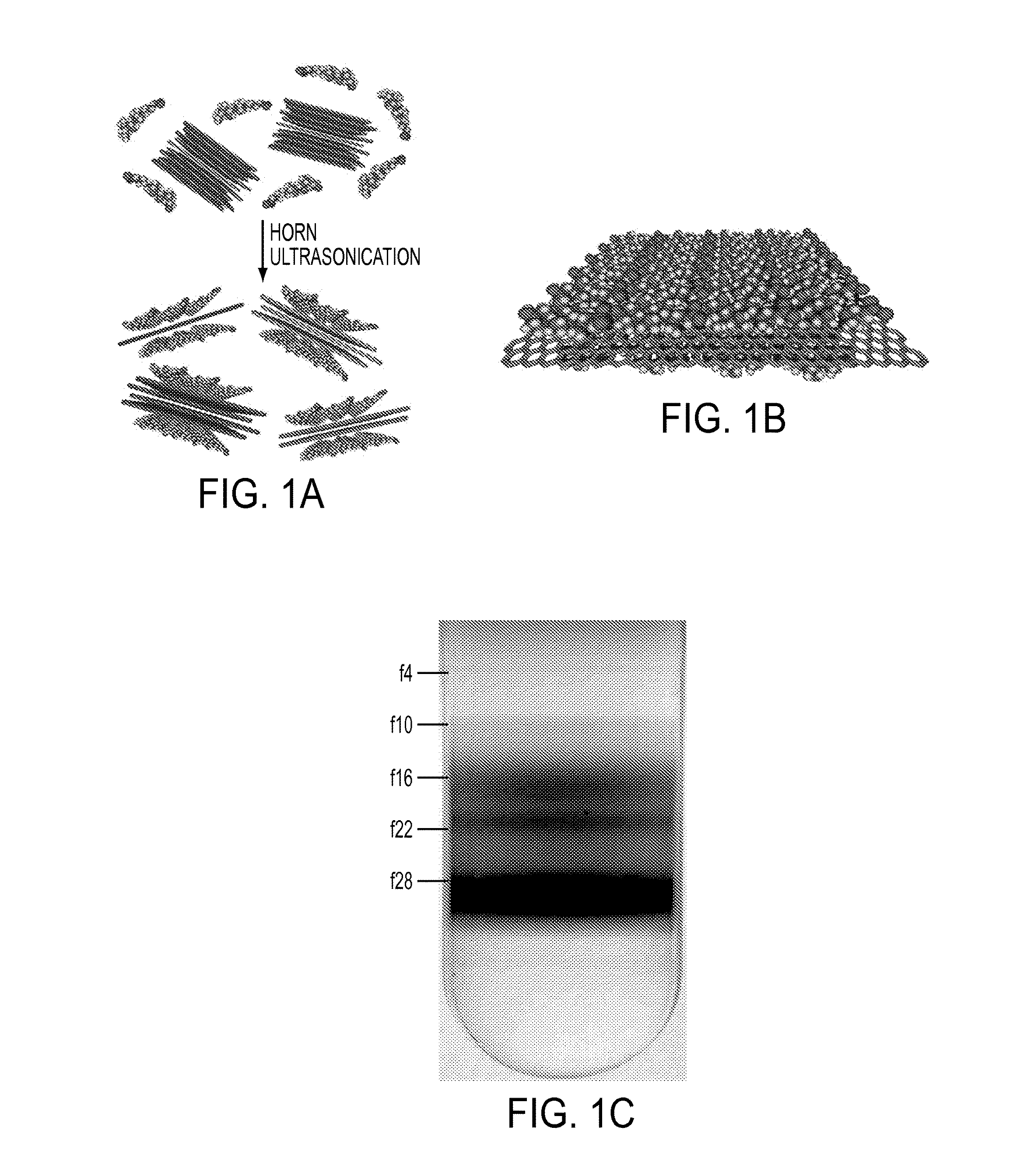
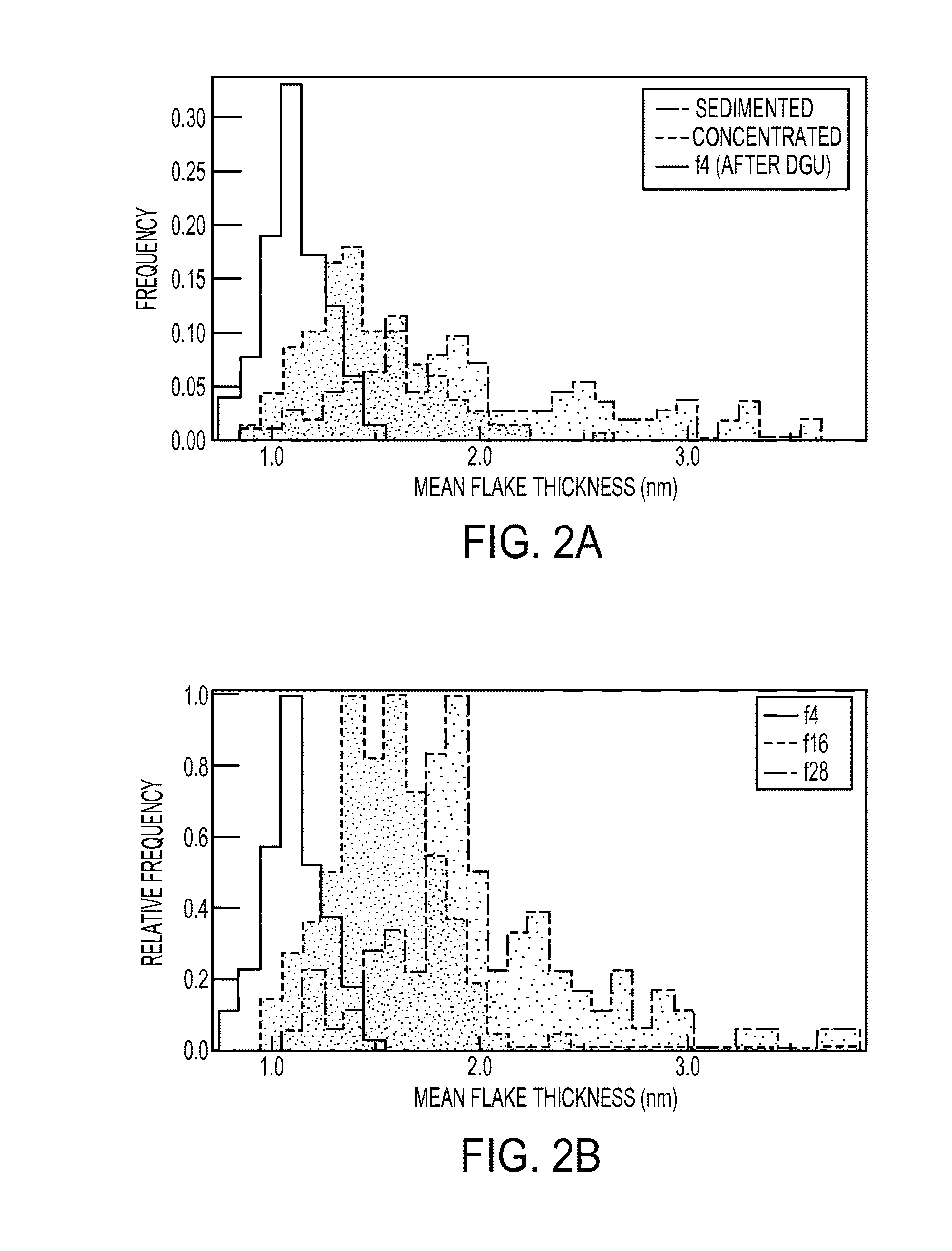
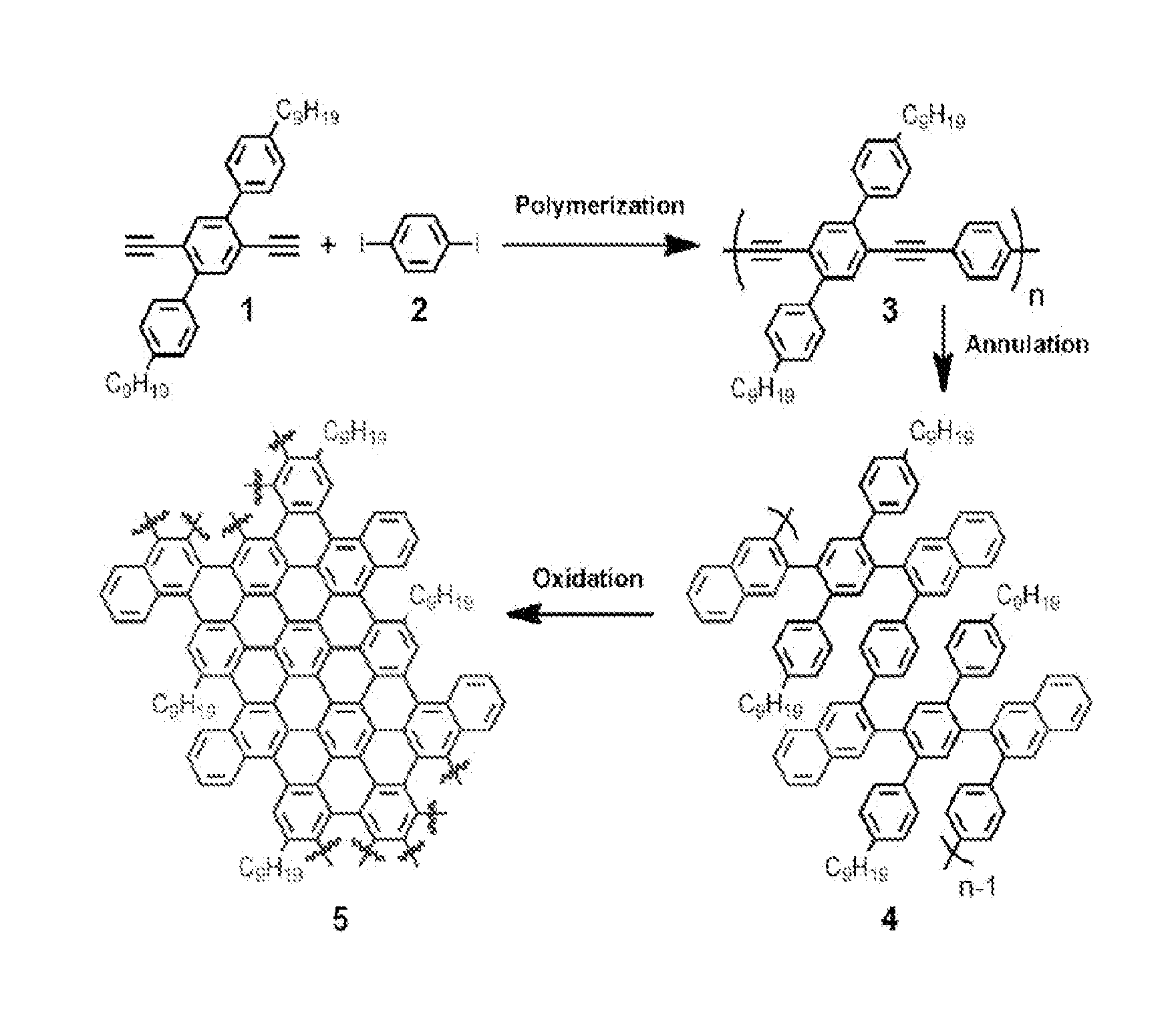
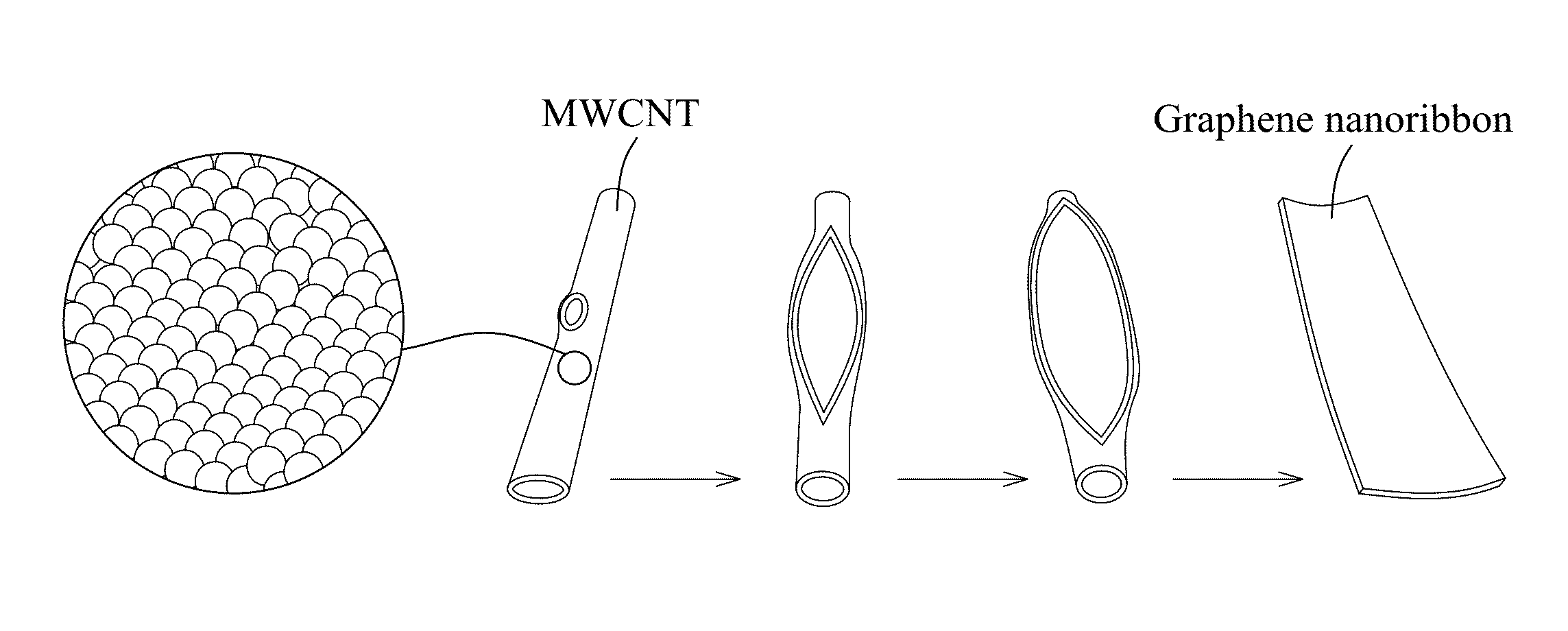
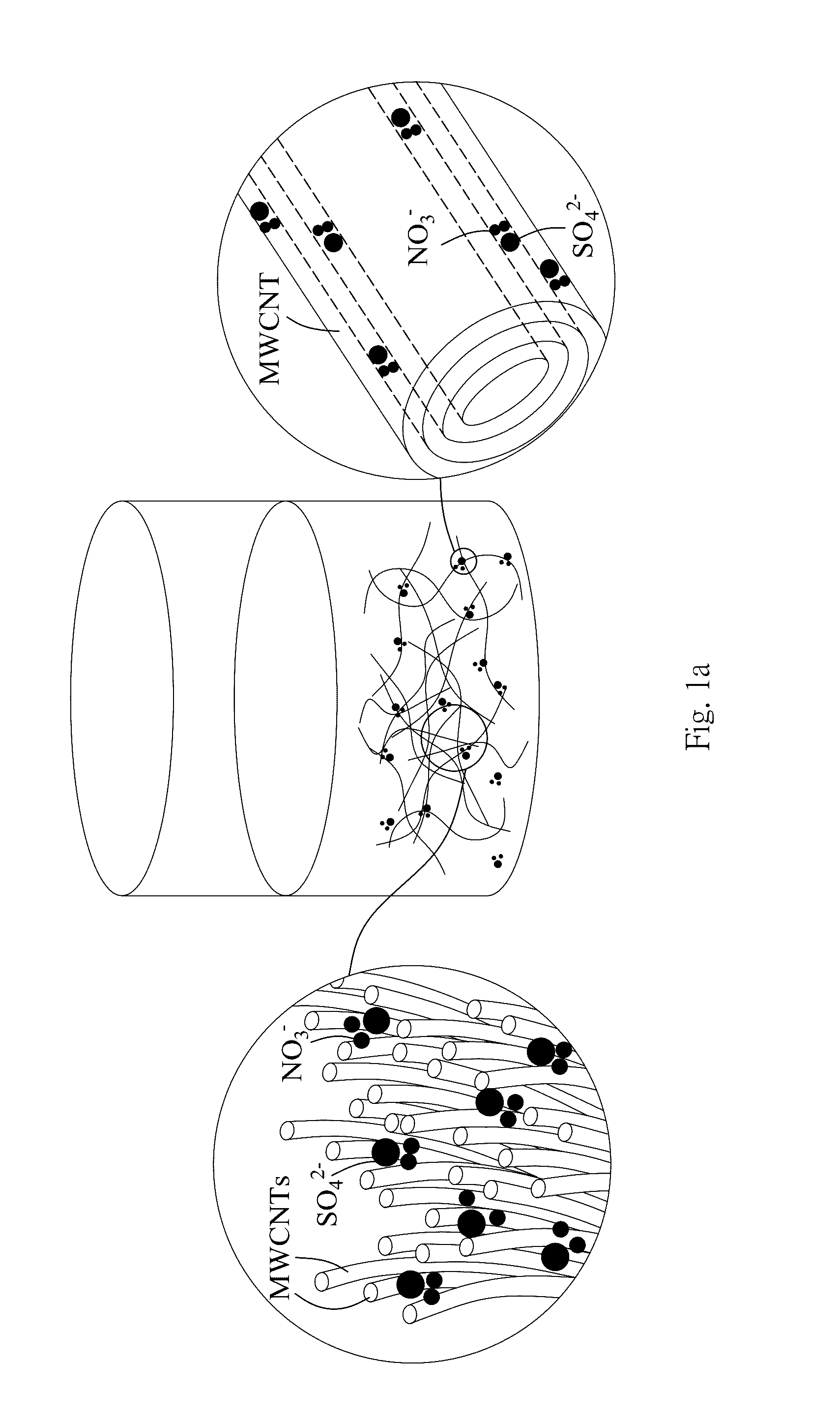
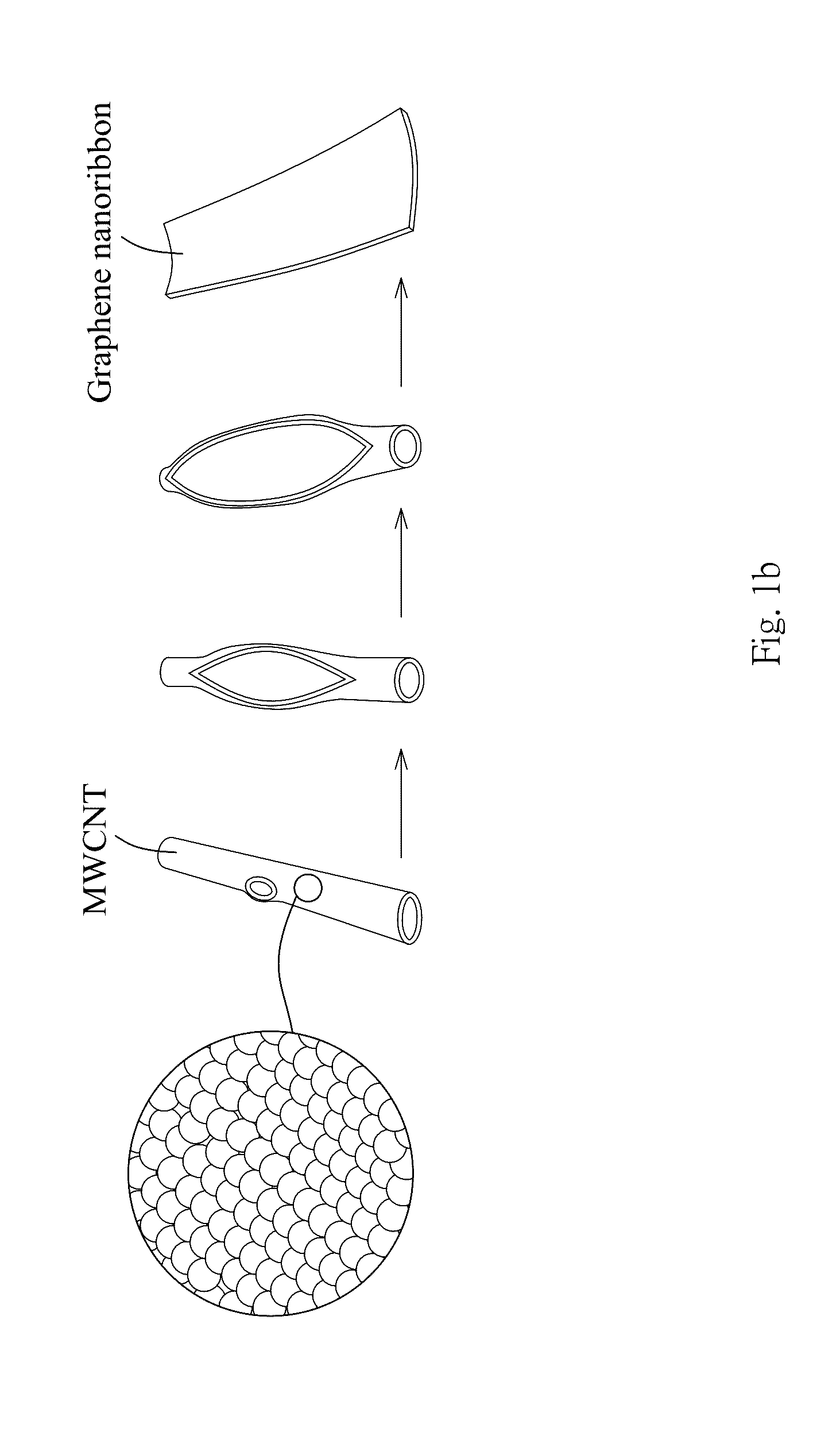
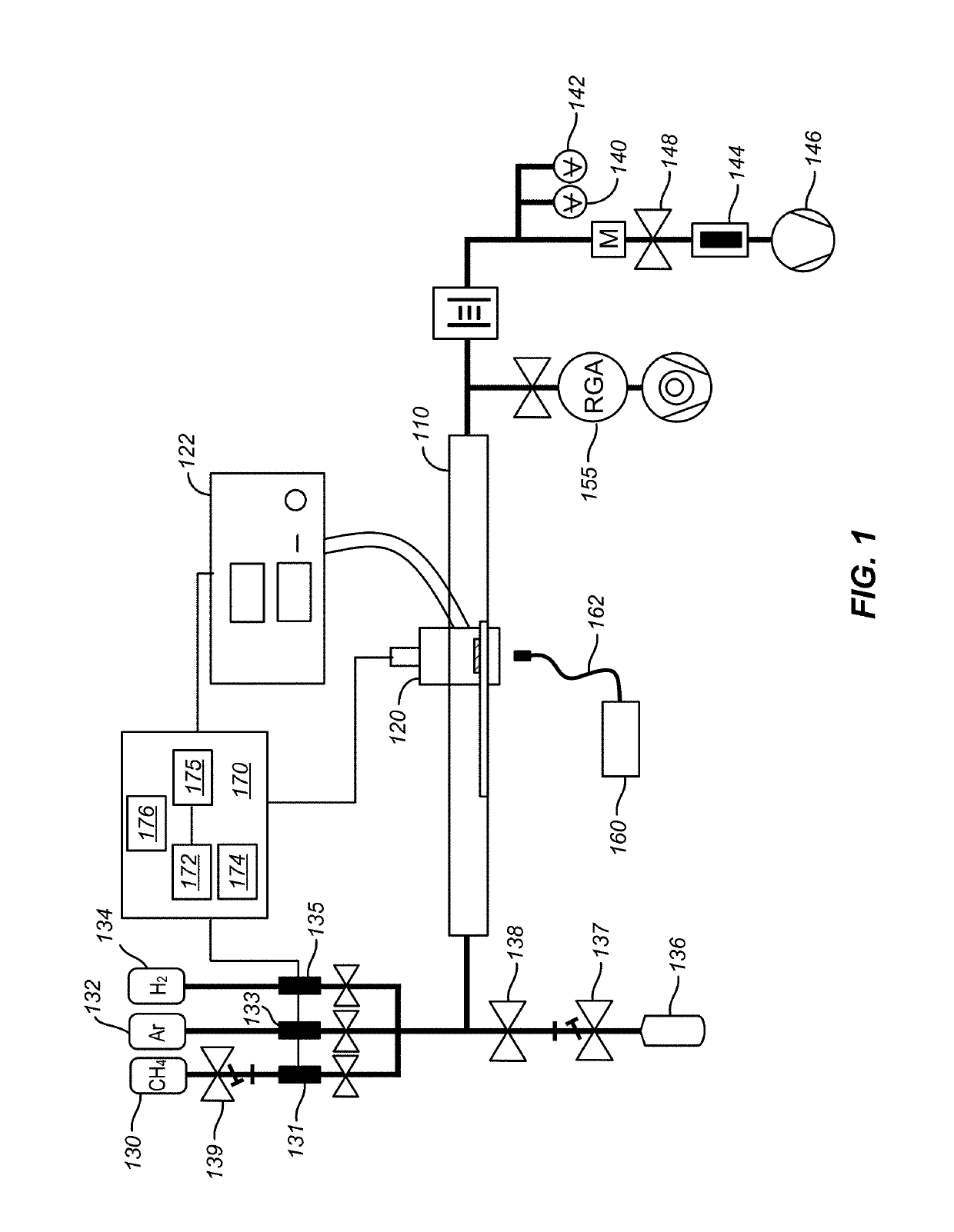
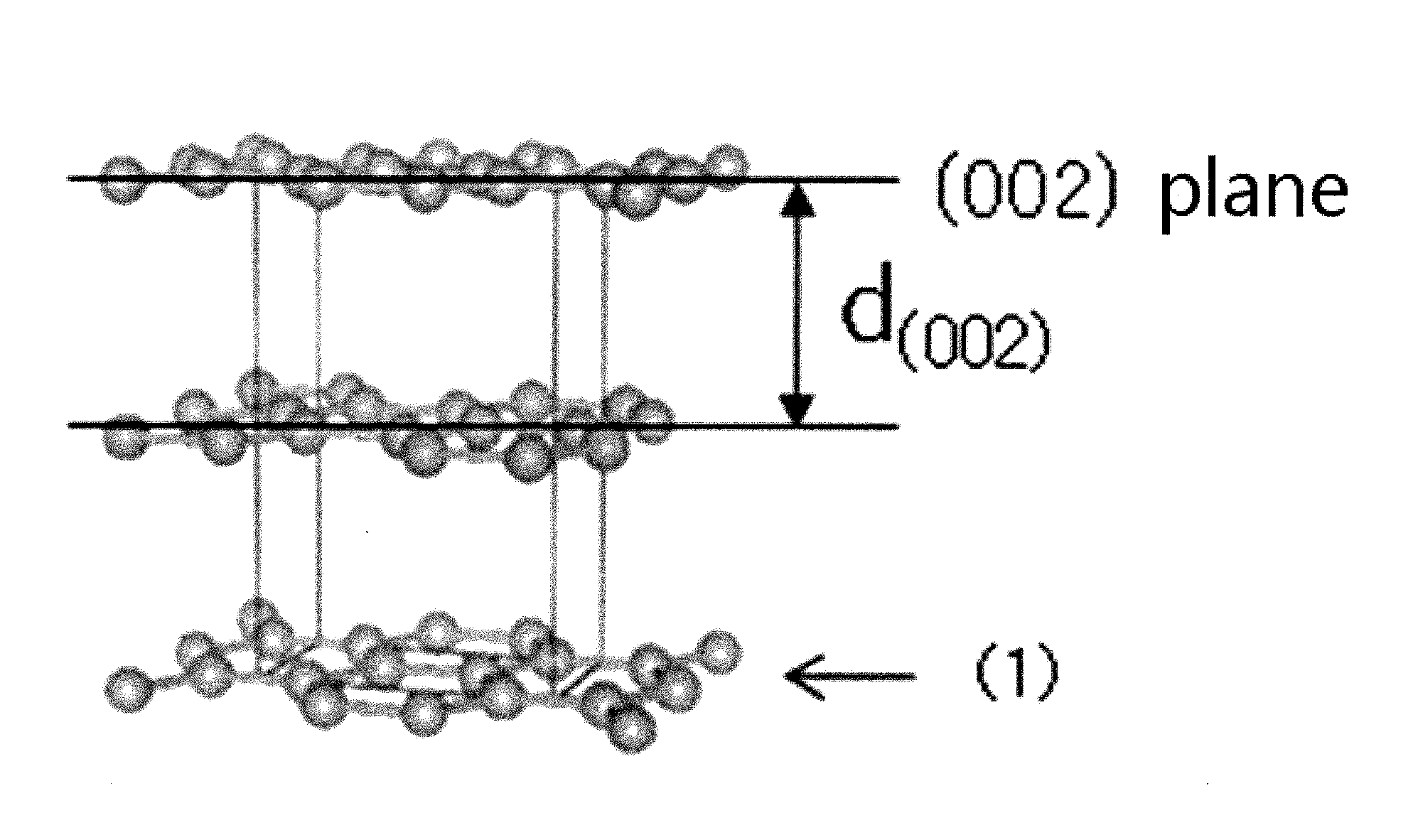
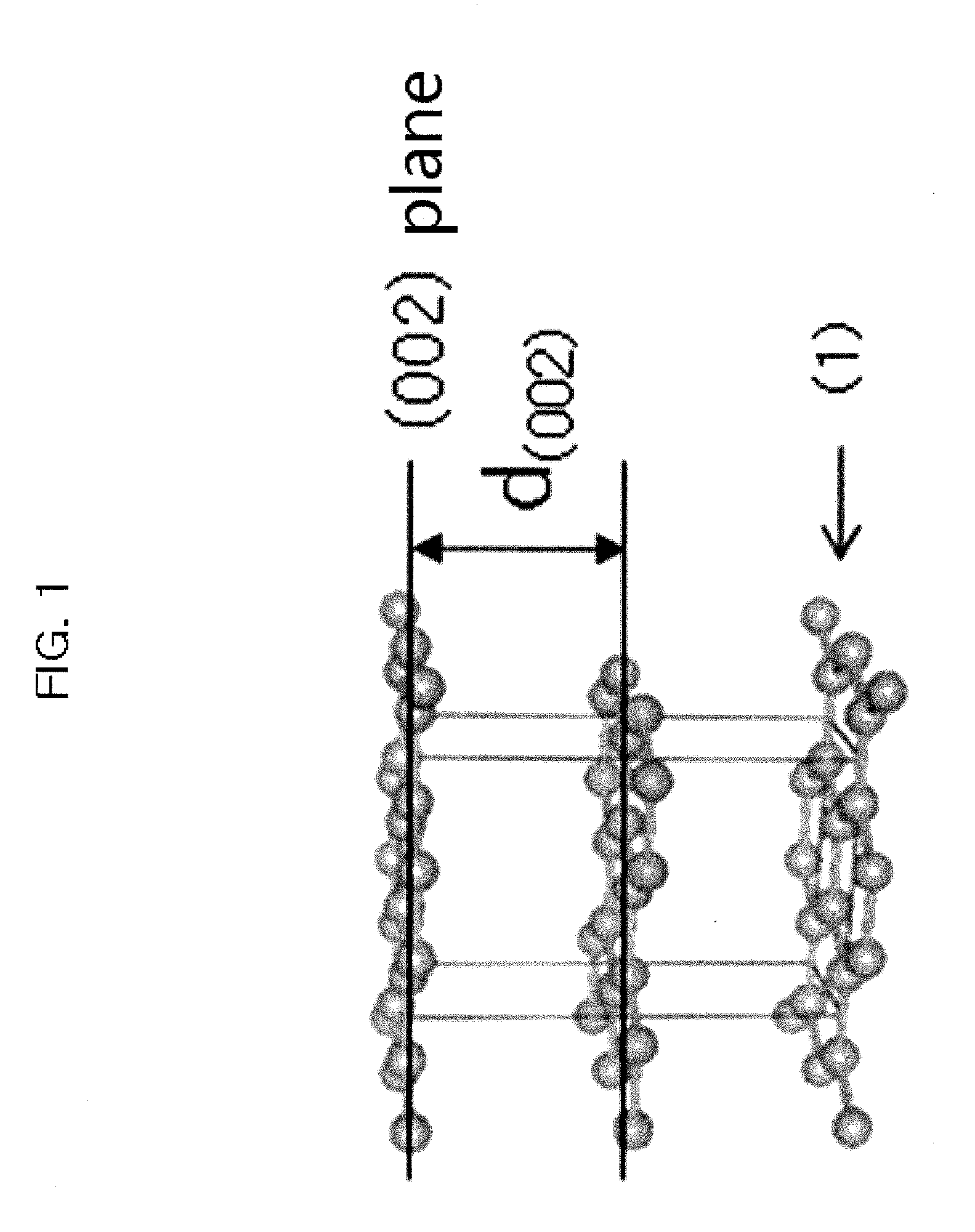
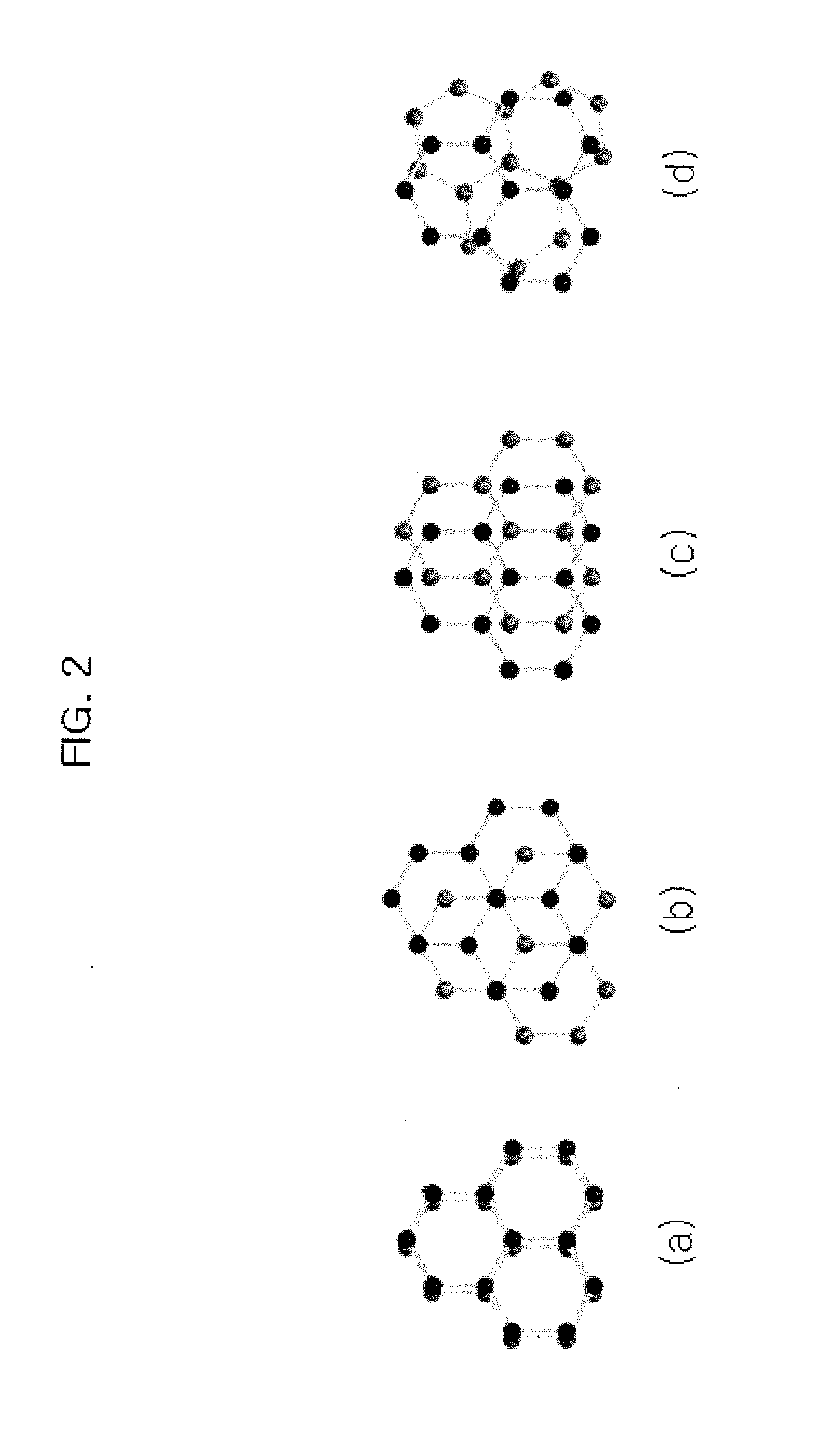
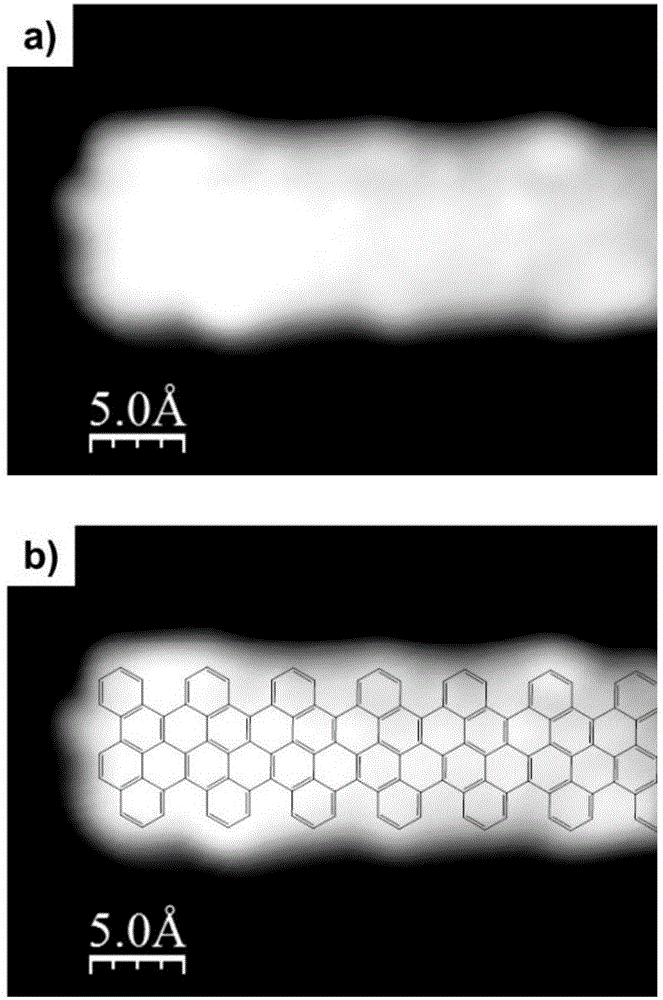
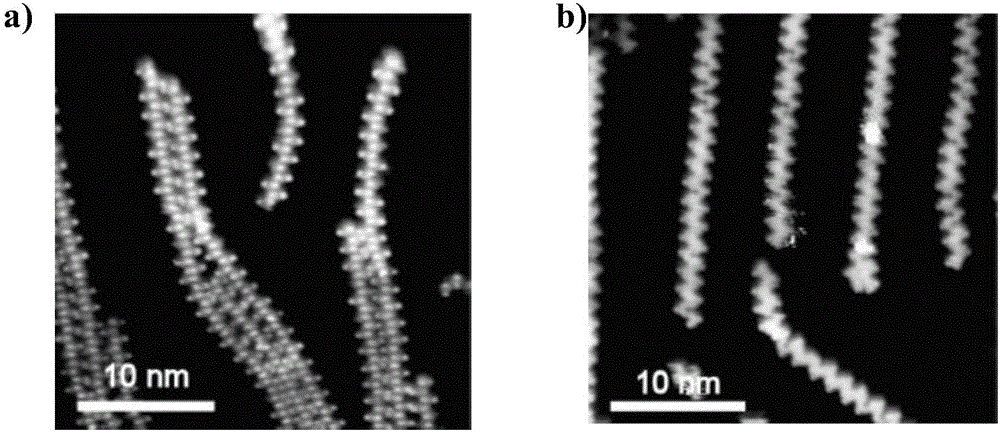
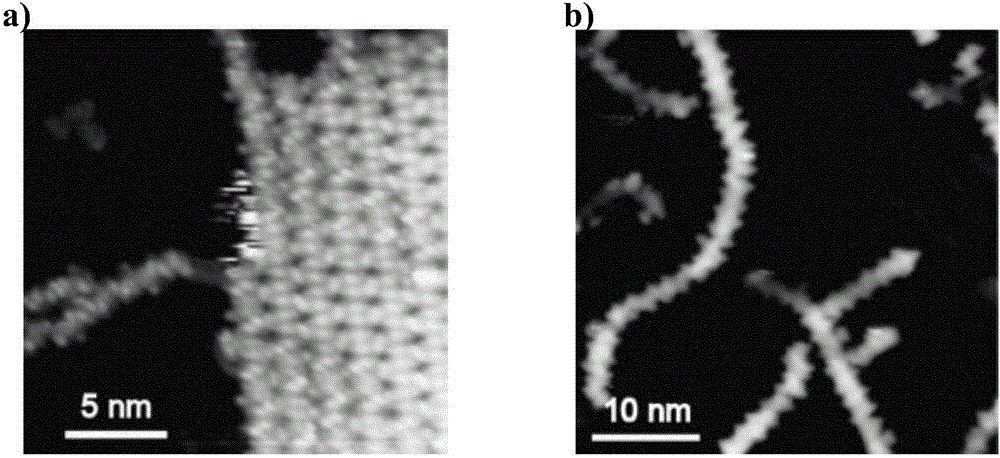
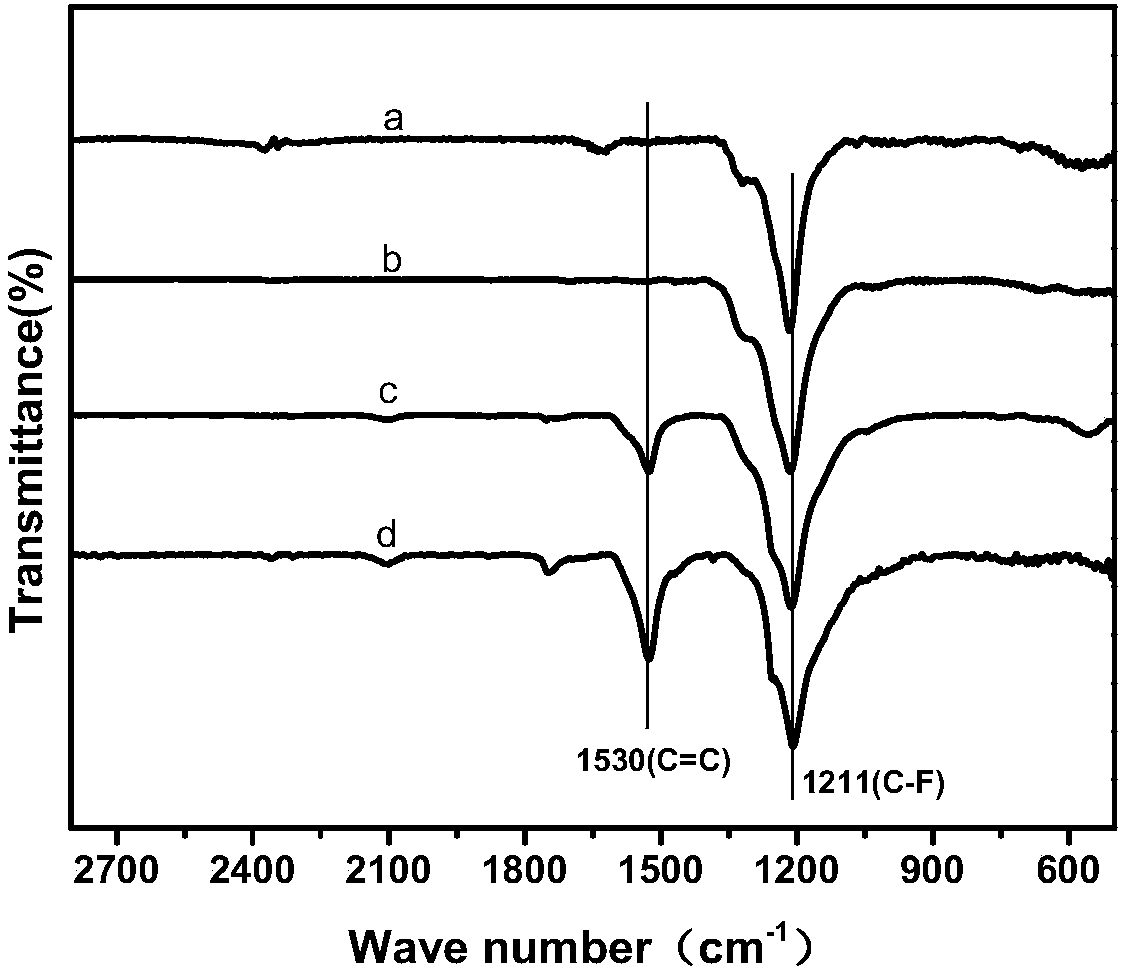
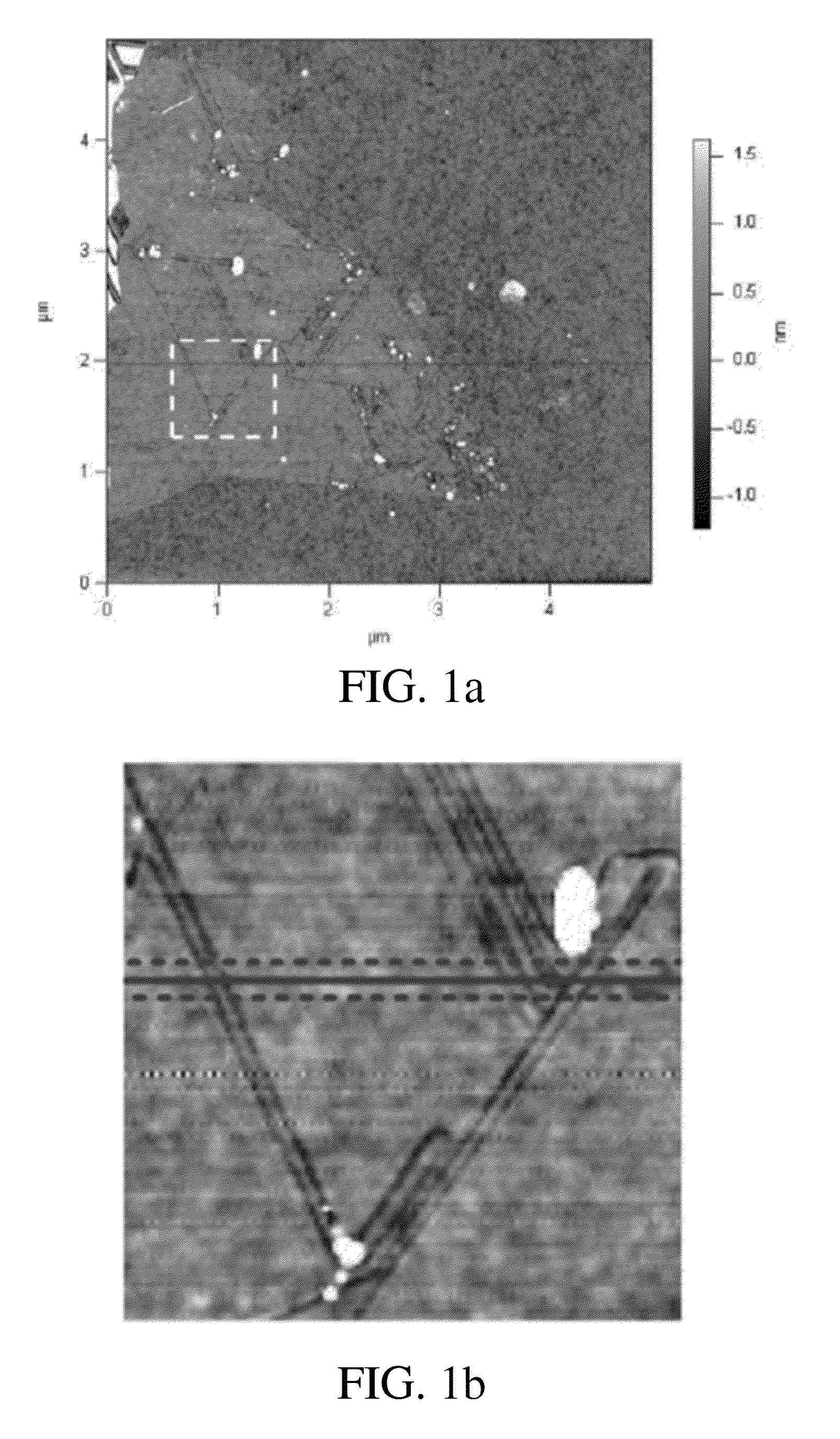
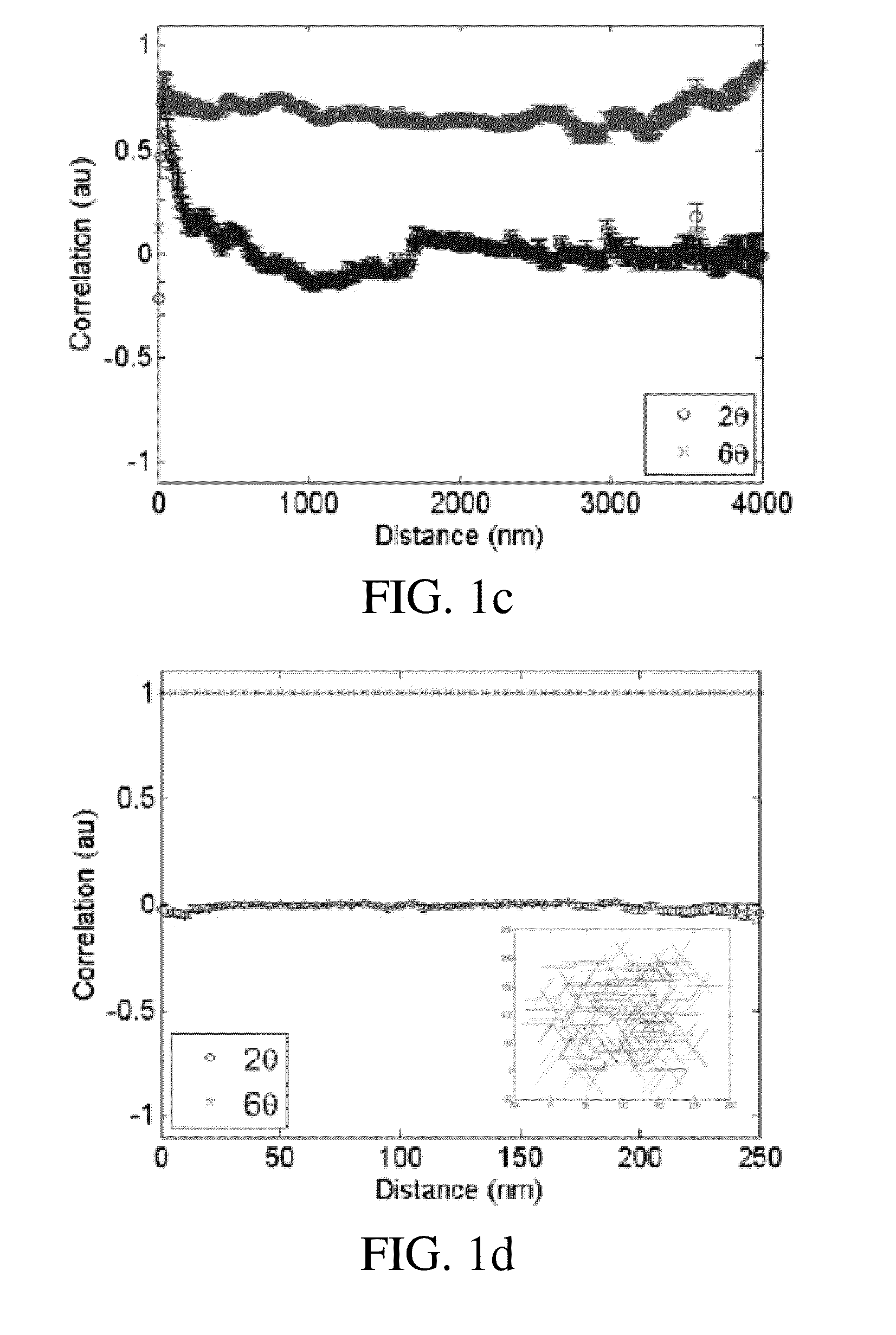
Patents
Literature
63results about "Graphene nanoribbons" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for preparing graphene ribbons
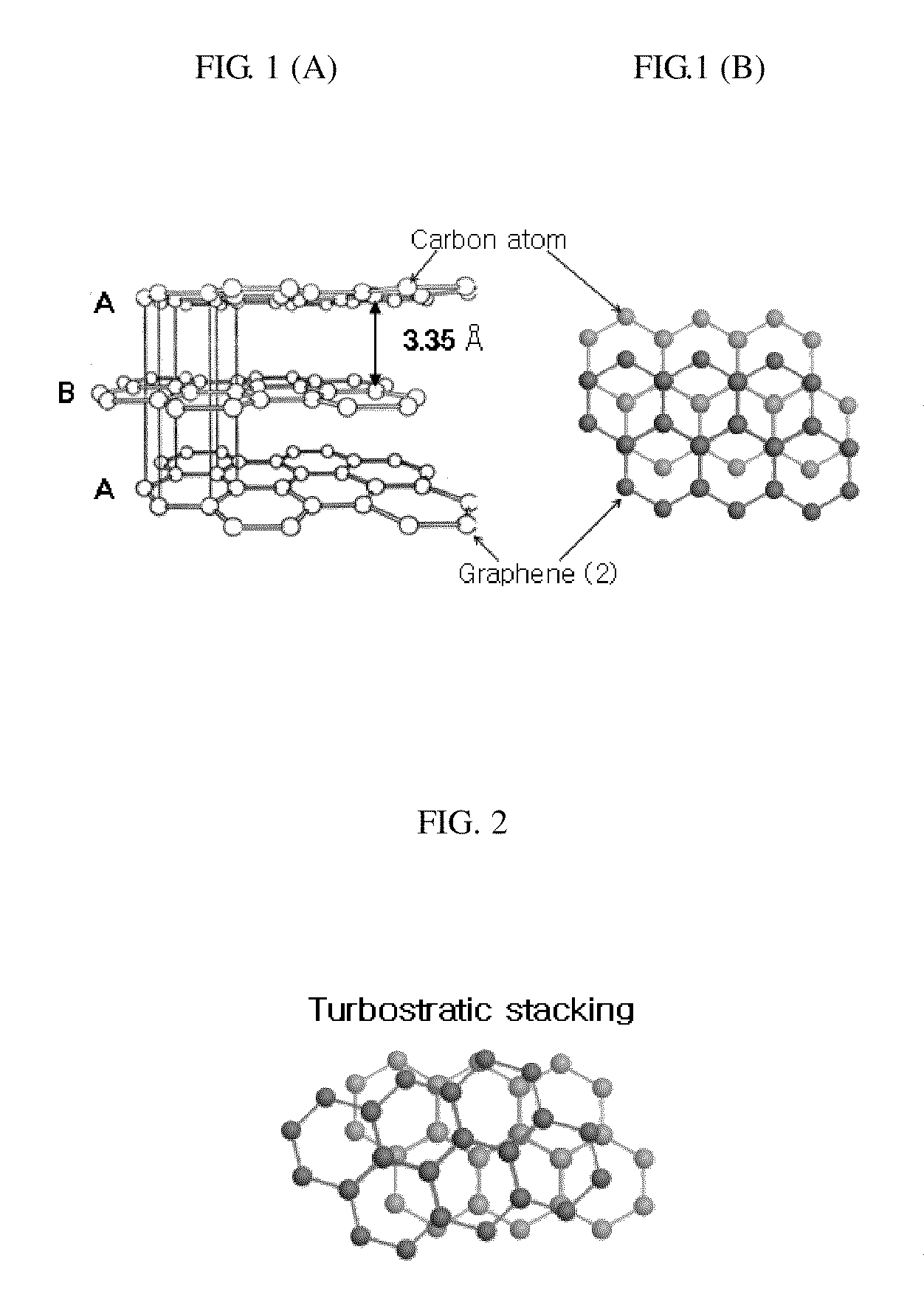
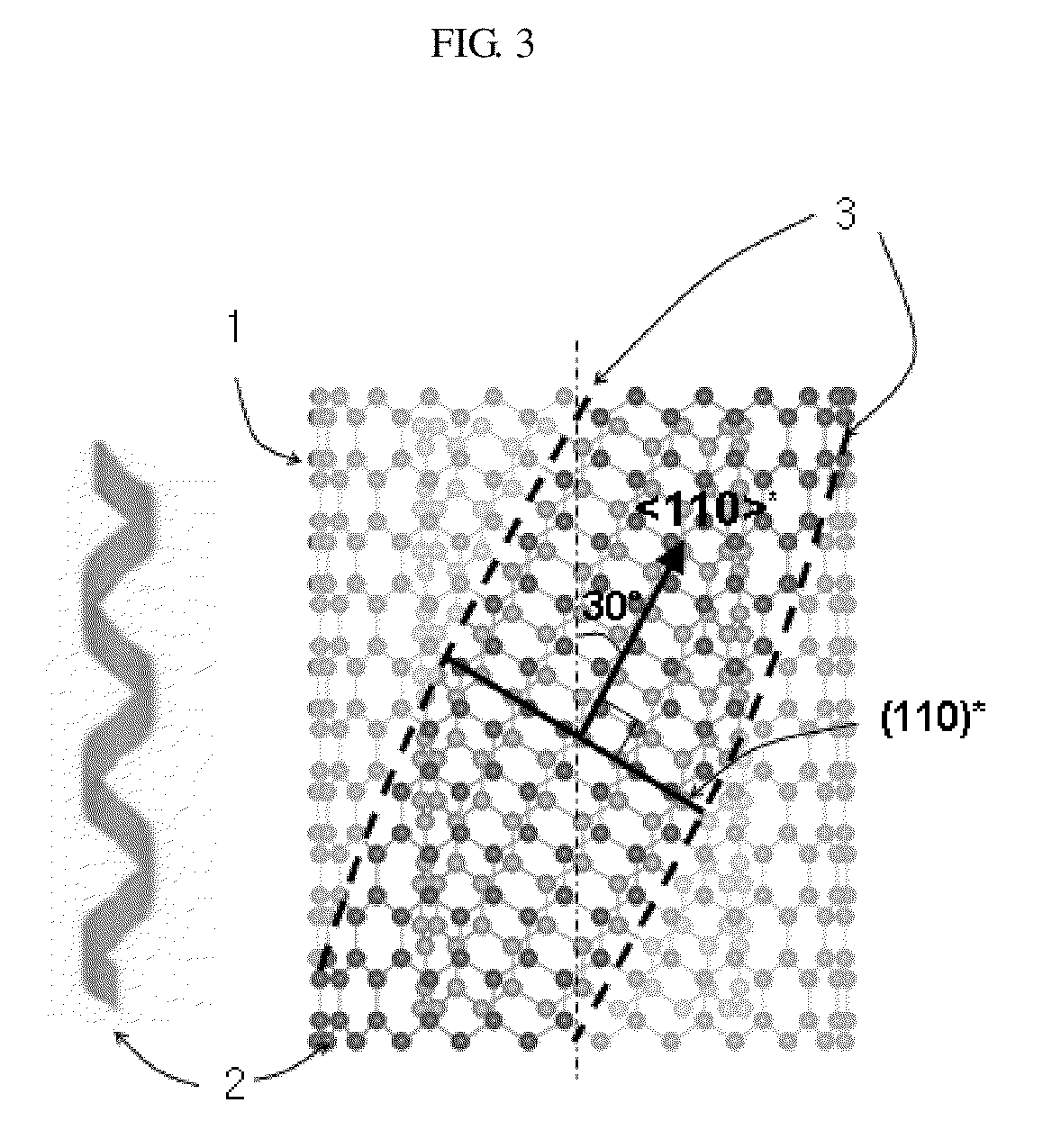
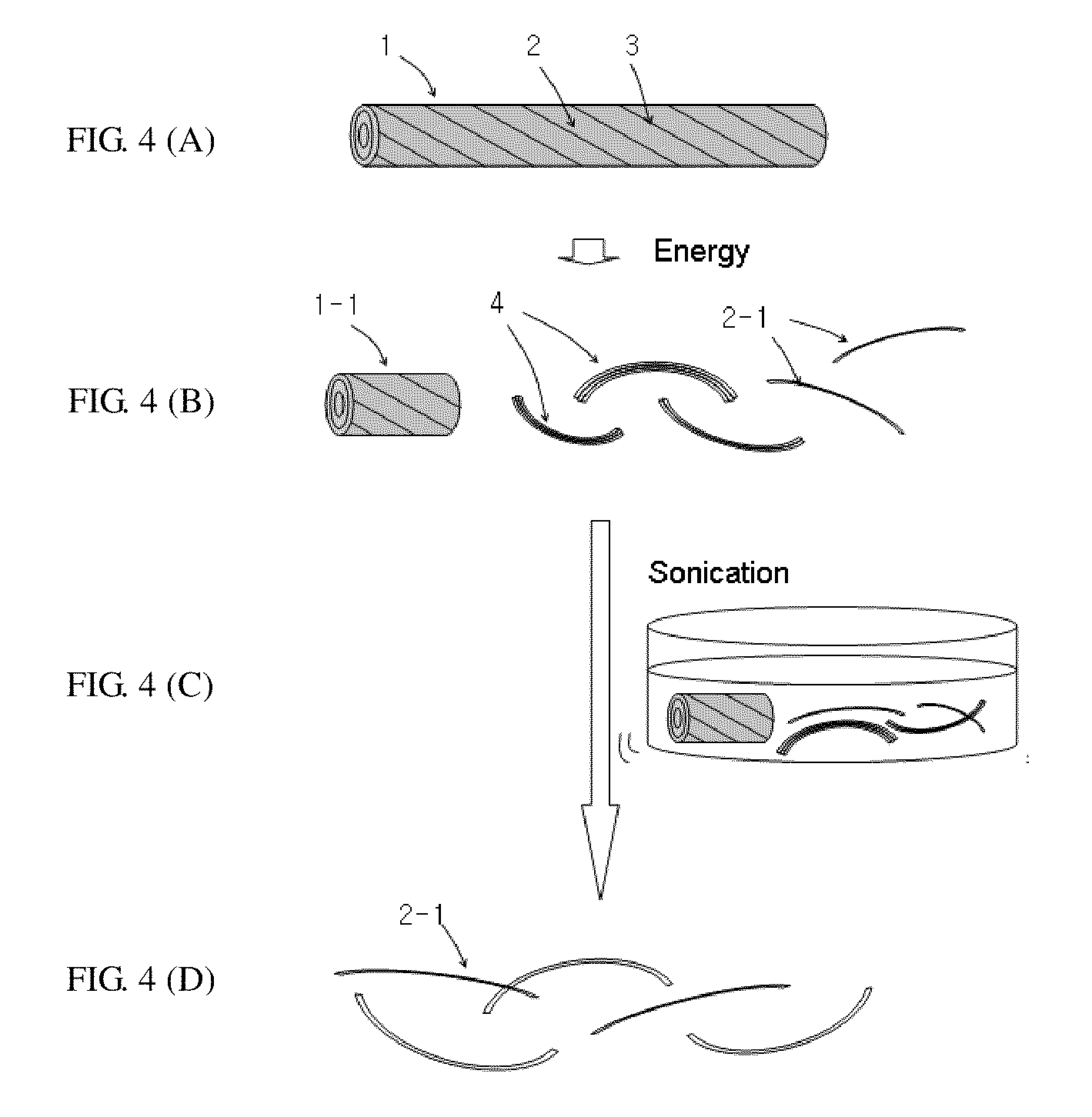
Disclosed is a method for fabricating graphene ribbons, comprising: preparing a graphitic material comprising stacked graphene helices; and cutting the graphitic material in a short form by applying energy to the graphitic material; and simultaneously or afterward, decomposing the graphitic material into short graphene ribbons. This method provides a mass production route to graphene ribbons.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Structure and method of making graphene nanoribbons
InactiveUS20120261644A1Increase the number ofMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsGraphene nanoribbonsPolyaromatic hydrocarbon
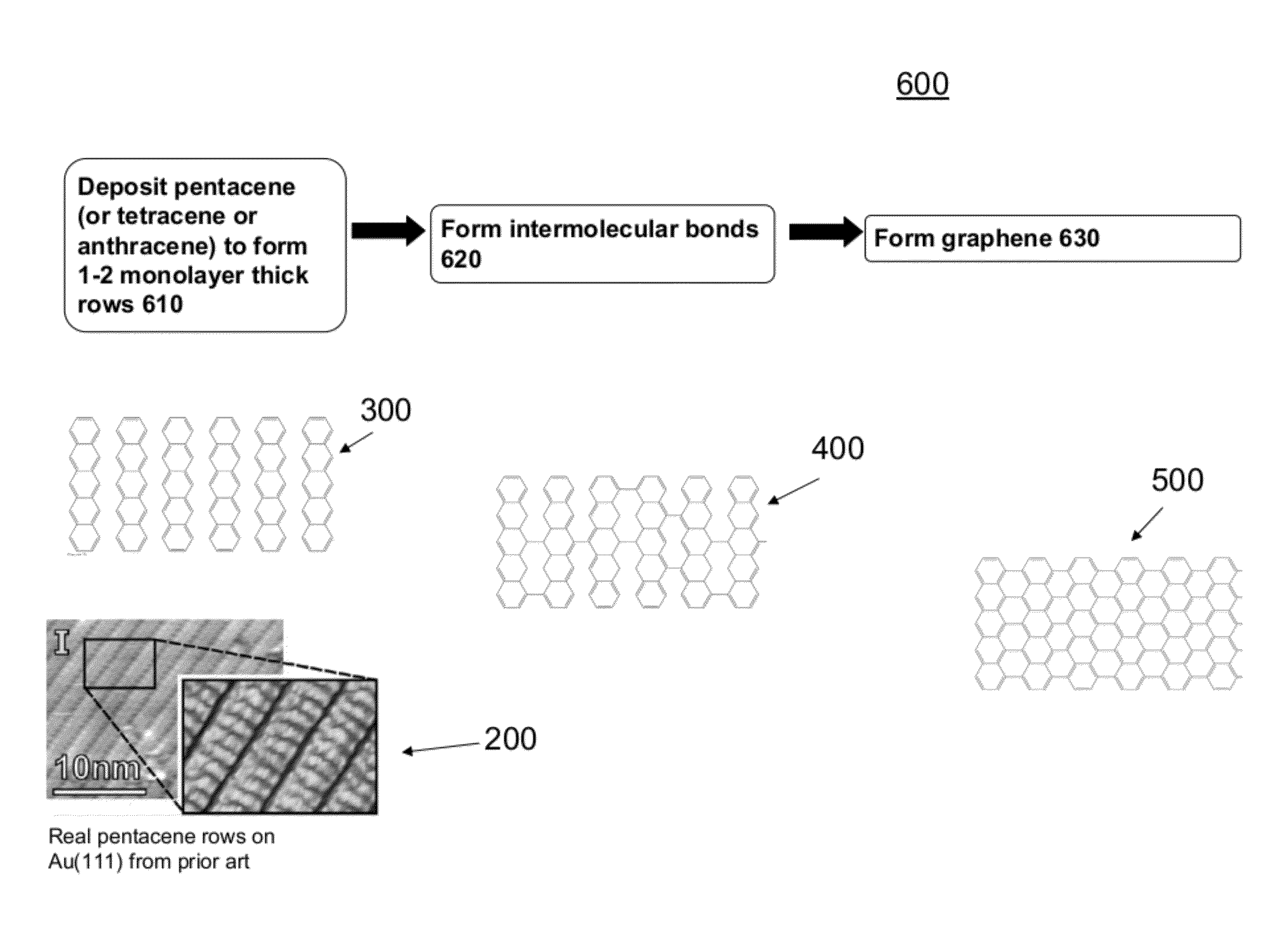
Disclosed is a ribbon of graphene less than 3 nm wide, more preferably less than 1 nm wide. In a more preferred embodiment, there are multiple ribbons of graphene each with a width of one of the following dimensions: the length of 2 phenyl rings fused together, the length of 3 phenyl rings fused together, the length of 4 phenyl rings fused together, and the length of 5 phenyl rings fused together. In another preferred embodiment the edges of the ribbons are parallel to each other. In another preferred embodiment, the ribbons have at least one arm chair edge and may have wider widths.The invention further comprises a method of making a ribbon of graphene comprising the steps of:a. placing one or more polyaromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) precursors on a substrate;b. applying UV light to the PAH until one or more intermolecular bonds are formed between adjacent PAH molecules; andc. applying heat to the PAH molecules to increase the number of intermolecular bonds that are formed to create a ribbon of graphene.The invention further comprises an electrical device structure having two or more ribbons of graphene in surface to surface contact with a non conductive substrate. Each of the ribbons has a width less than 3 nm and each of the ribbons has edges that are parallel to one another. In a preferred embodiment the ribbons comprise a channel in a Field Effect Transistor (FET).
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for preparing graphene nanoribbon on insulating substrate
ActiveUS20130022813A1Inhibit transferEnsure performanceMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsActivated carbonGraphene nanoribbons
A method for growing a graphene nanoribbon on an insulating substrate having a cleavage plane with atomic level flatness is provided, and belongs to the field of low-dimensional materials and new materials. The method includes the following steps. Step 1: Cleave an insulating substrate to obtain a cleavage plane with atomic level flatness, and prepare a single atomic layer step. Step 2: Directly grow a graphene nanoribbon on the insulating substrate having regular single atomic steps. In the method, a characteristic that nucleation energy of graphene on the atomic step is different from that on the flat cleavage plane is used, and conditions, such as the temperature, intensity of pressure and supersaturation degree of activated carbon atoms, are adjusted, so that the graphene grows only along a step edge into a graphene nanoribbon of an adjustable size. The method is mainly applied to the field of new-type graphene optoelectronic devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for forming graphene nanoribbons
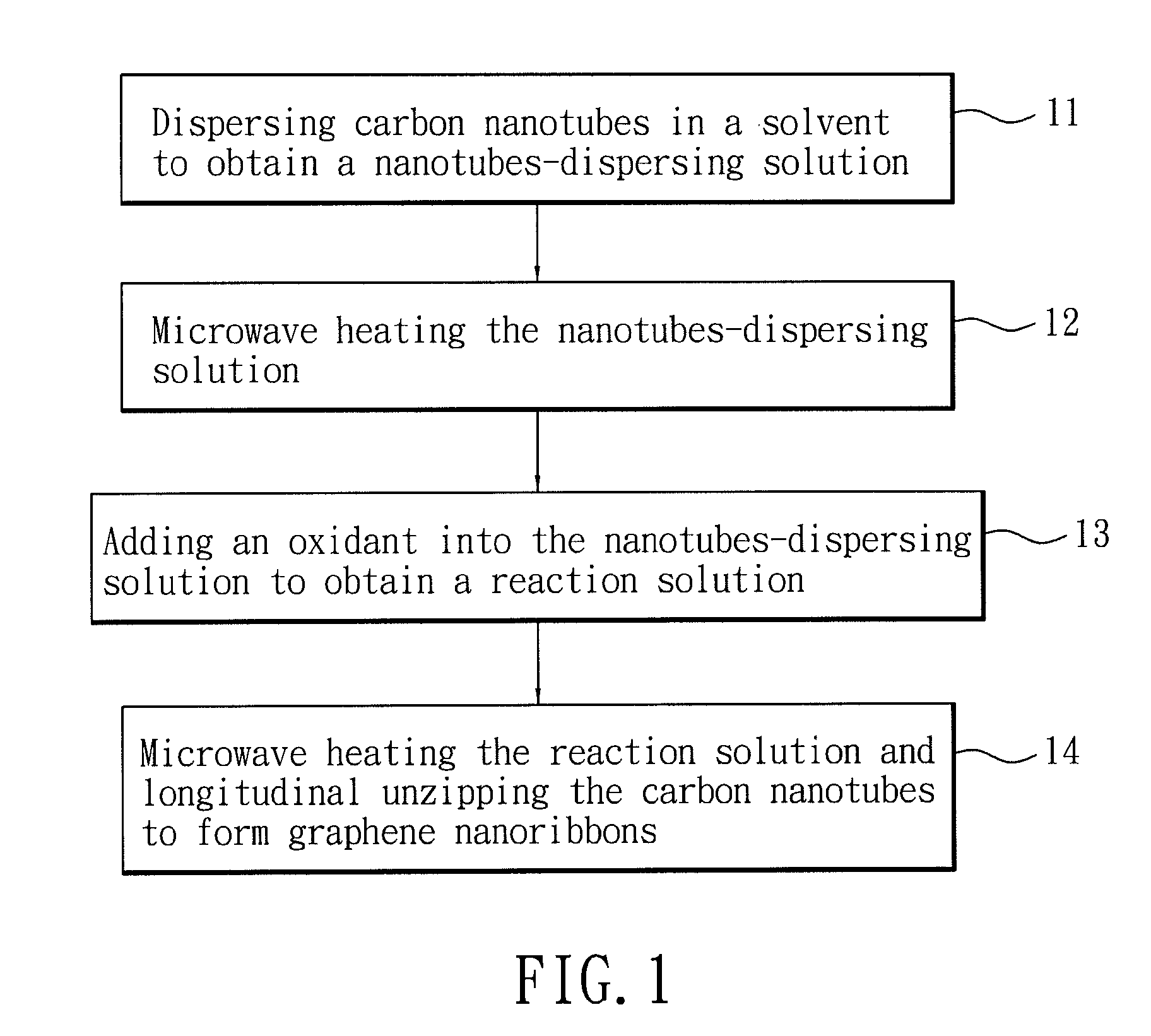
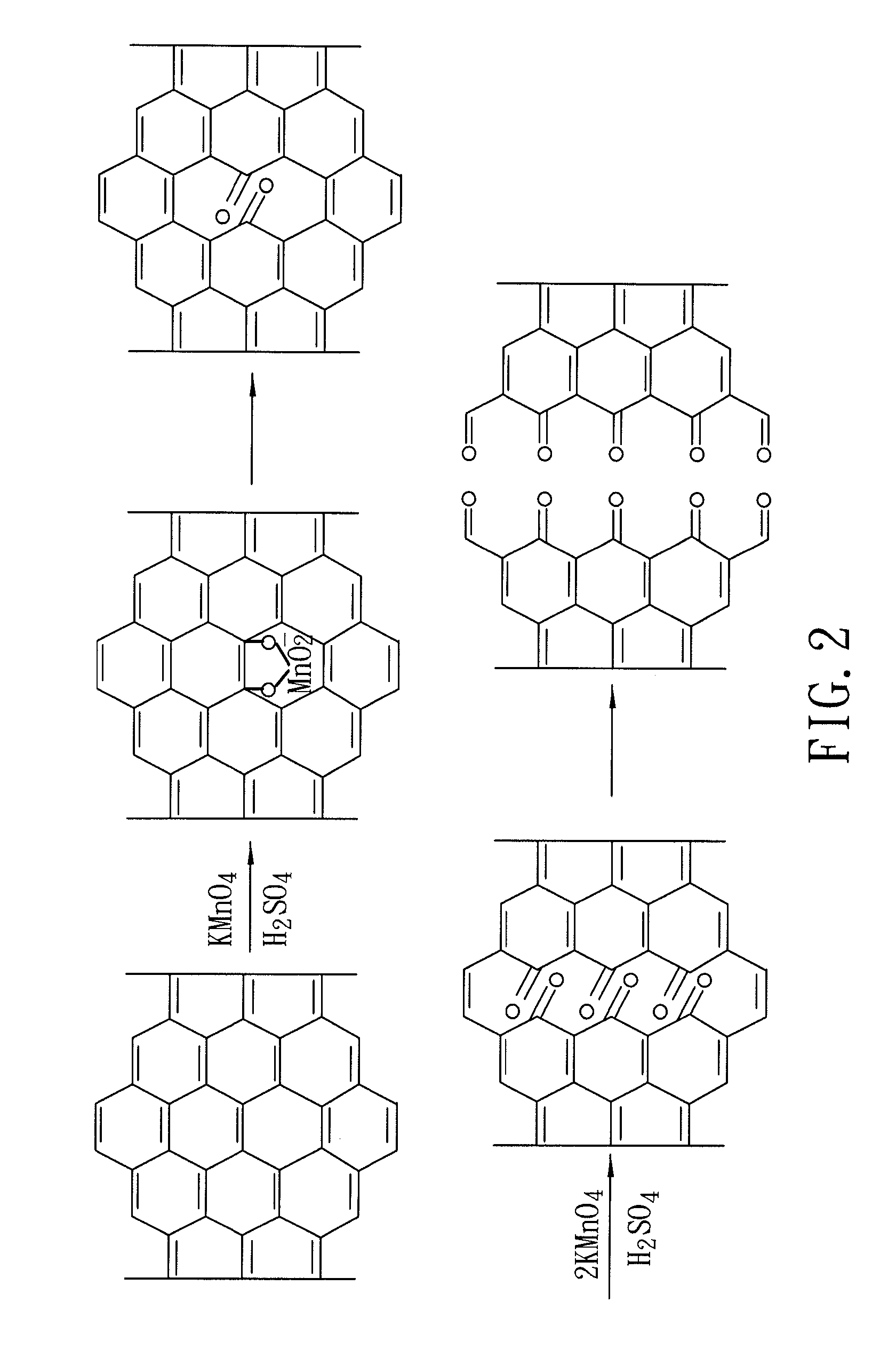
A method for forming graphene nanoribbons includes: (a) dispersing carbon nanotubes in a solvent to obtain a nanotube-dispersing solution; (b) adding an oxidant into the nanotube-dispersing solution to obtain a reaction solution; and (c) microwave heating the reaction solution and longitudinally unzipping the carbon nanotubes to form graphene nanoribbons.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
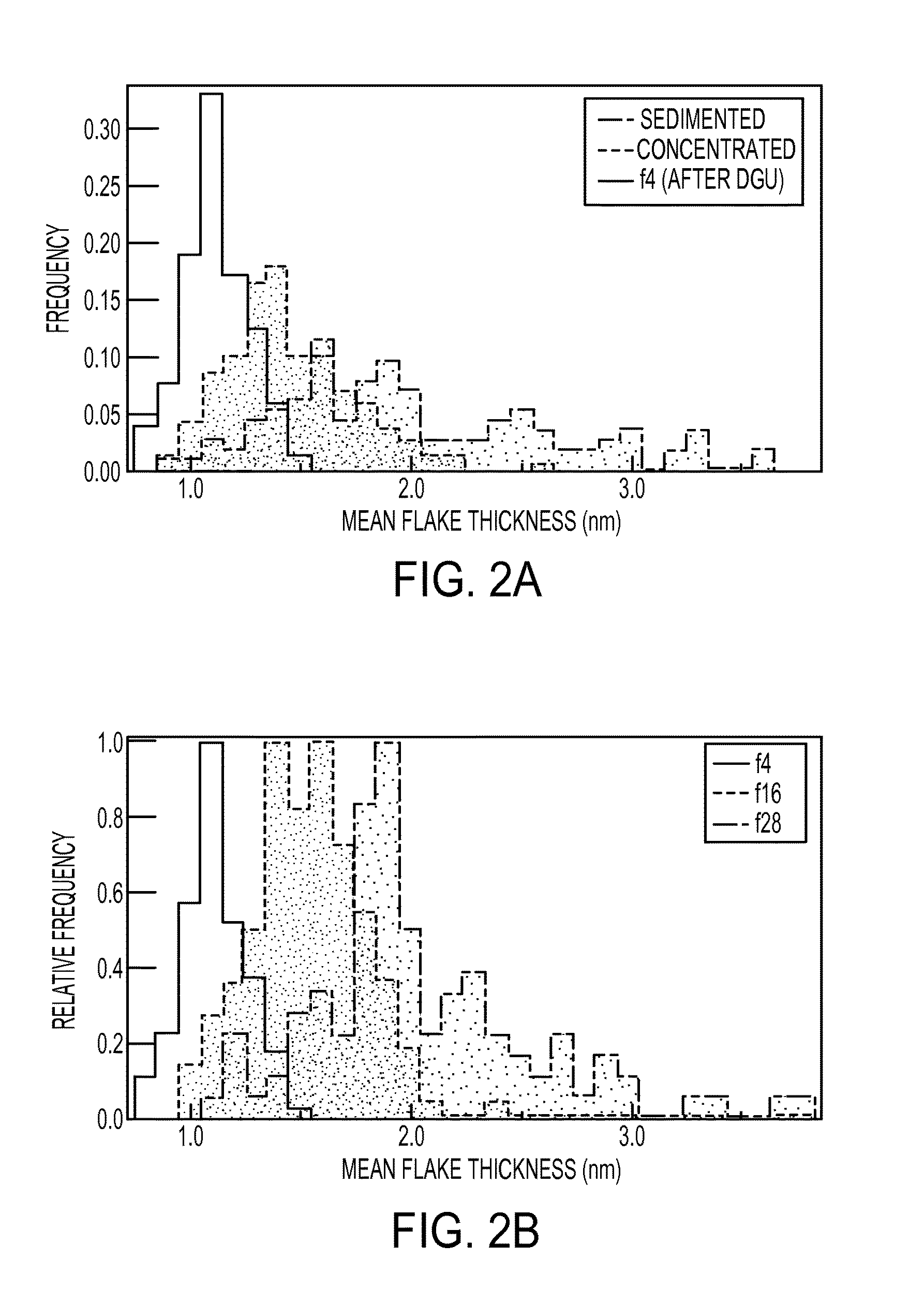
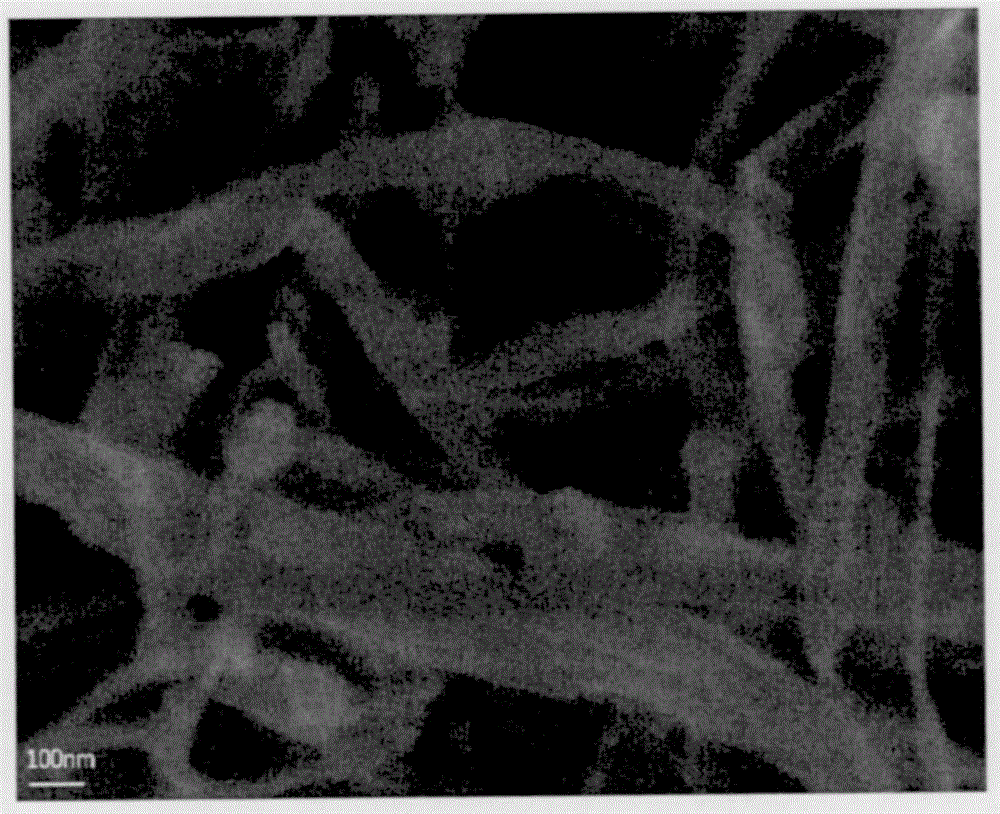
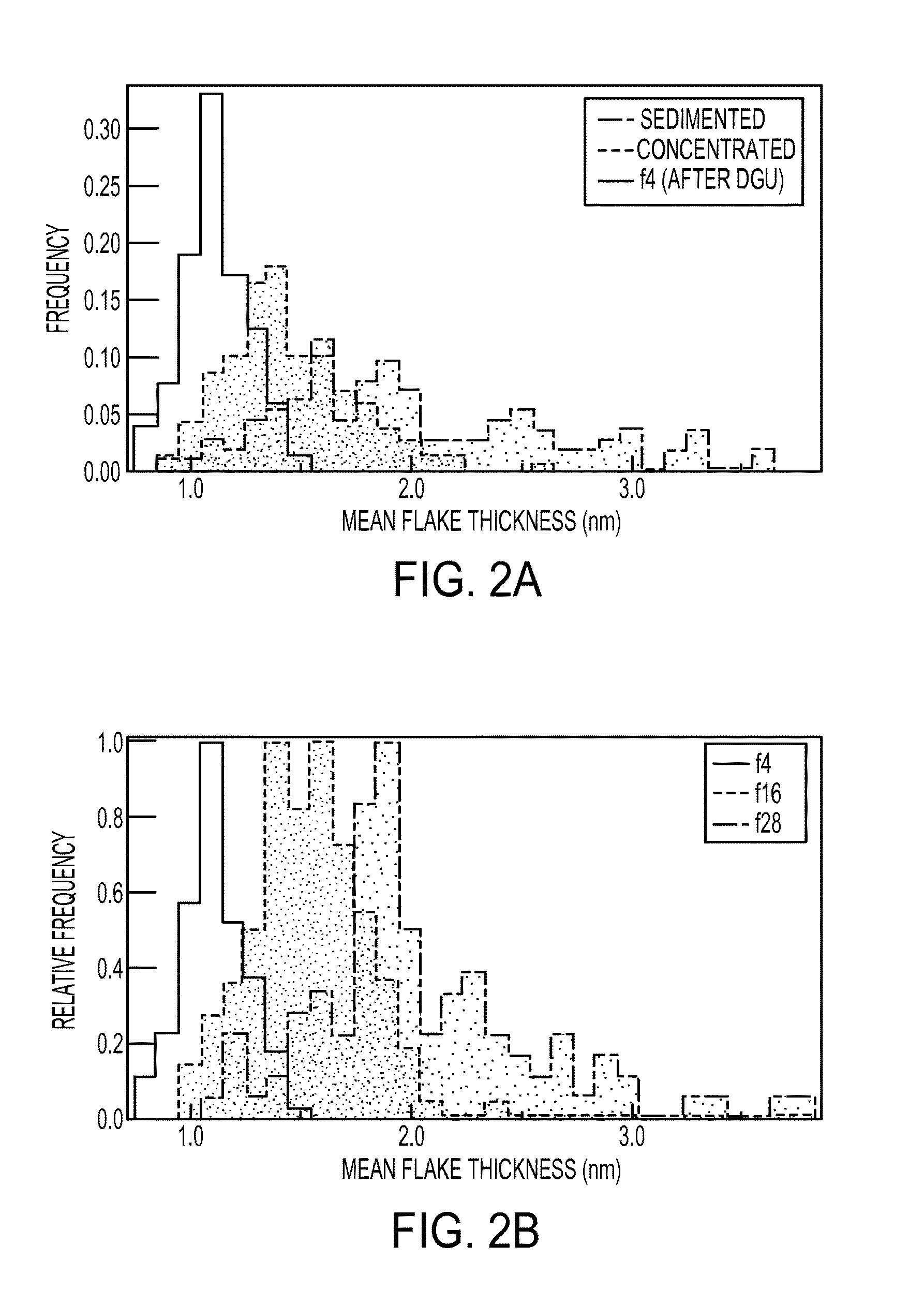
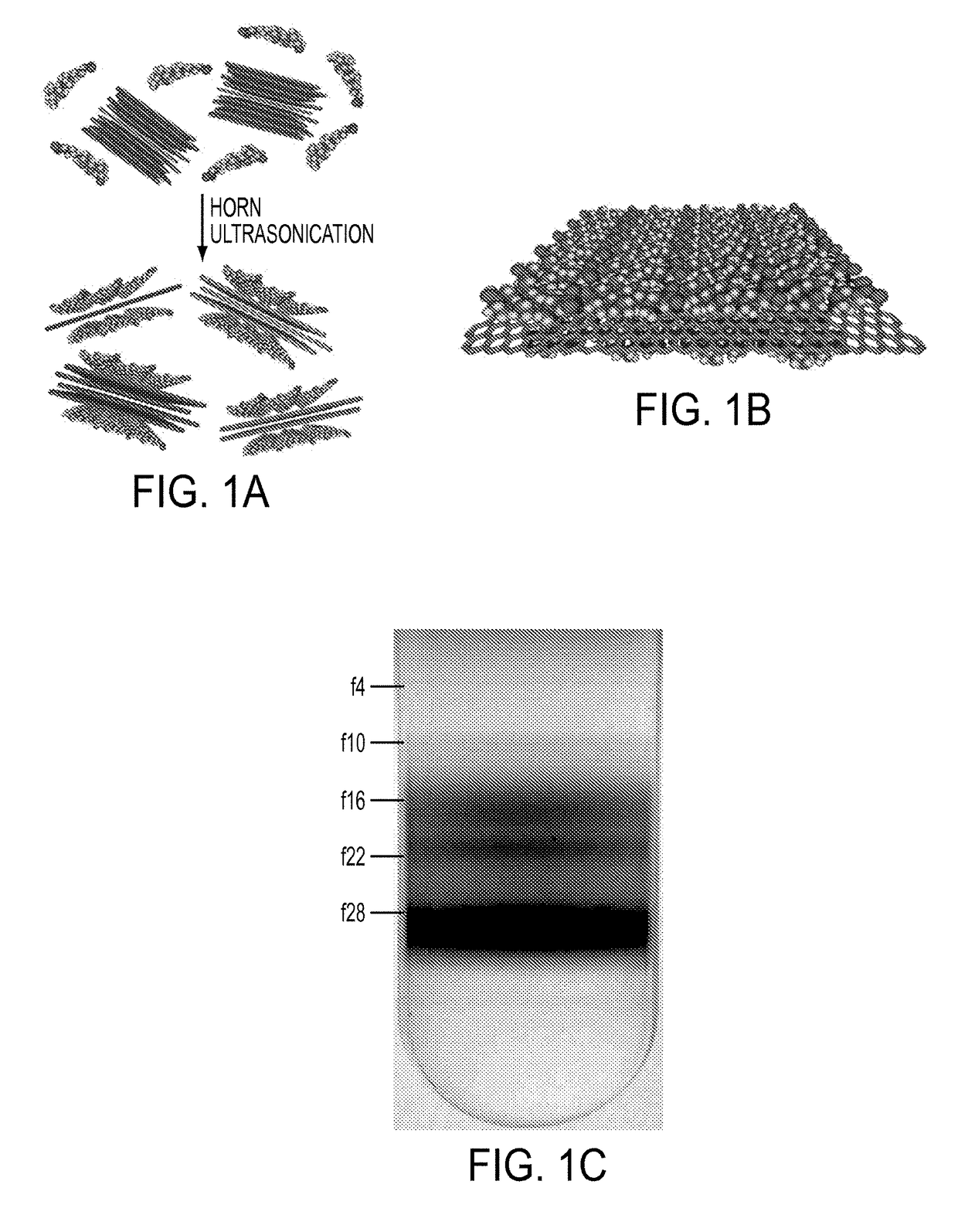
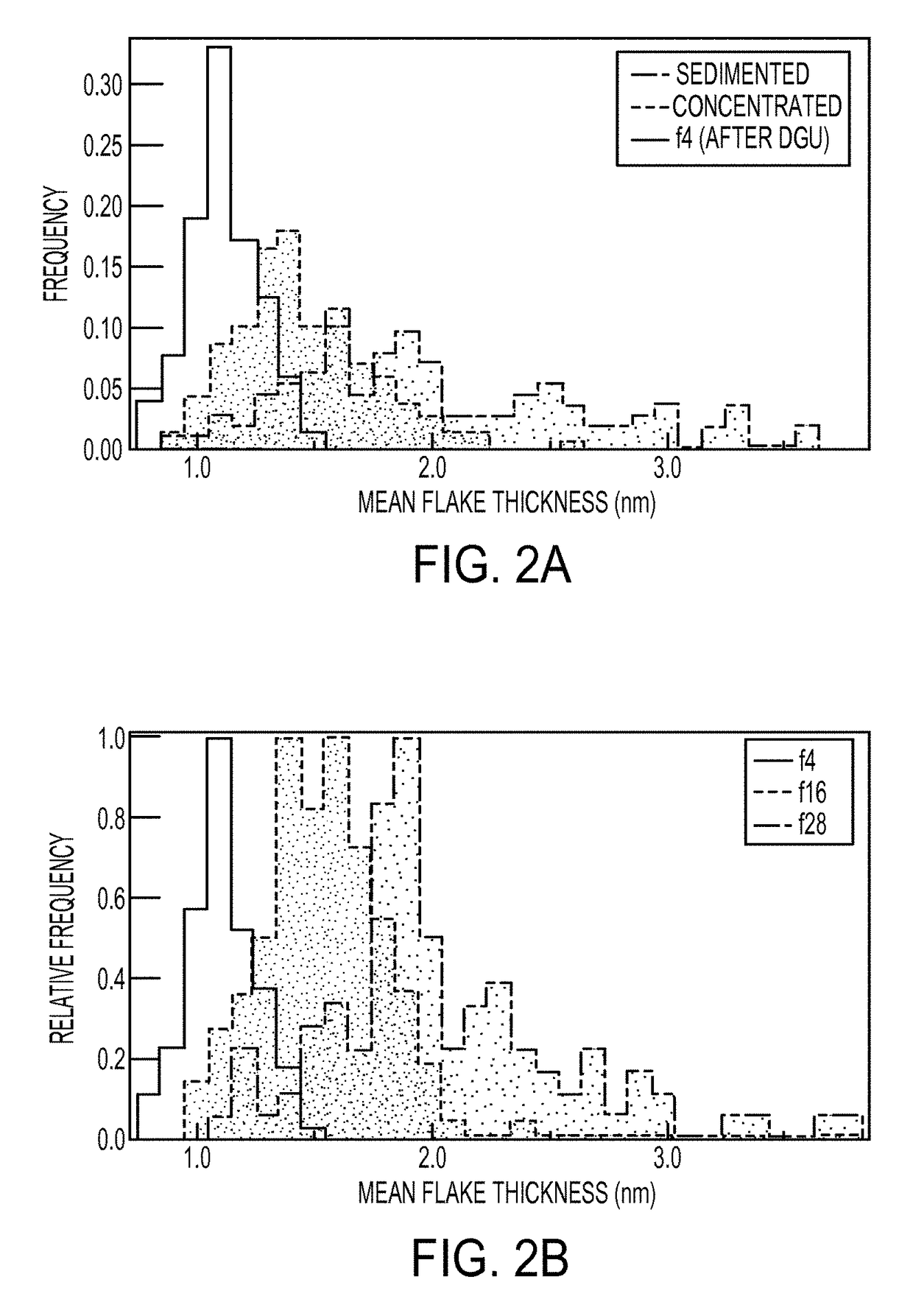
Sorting Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials by Thickness
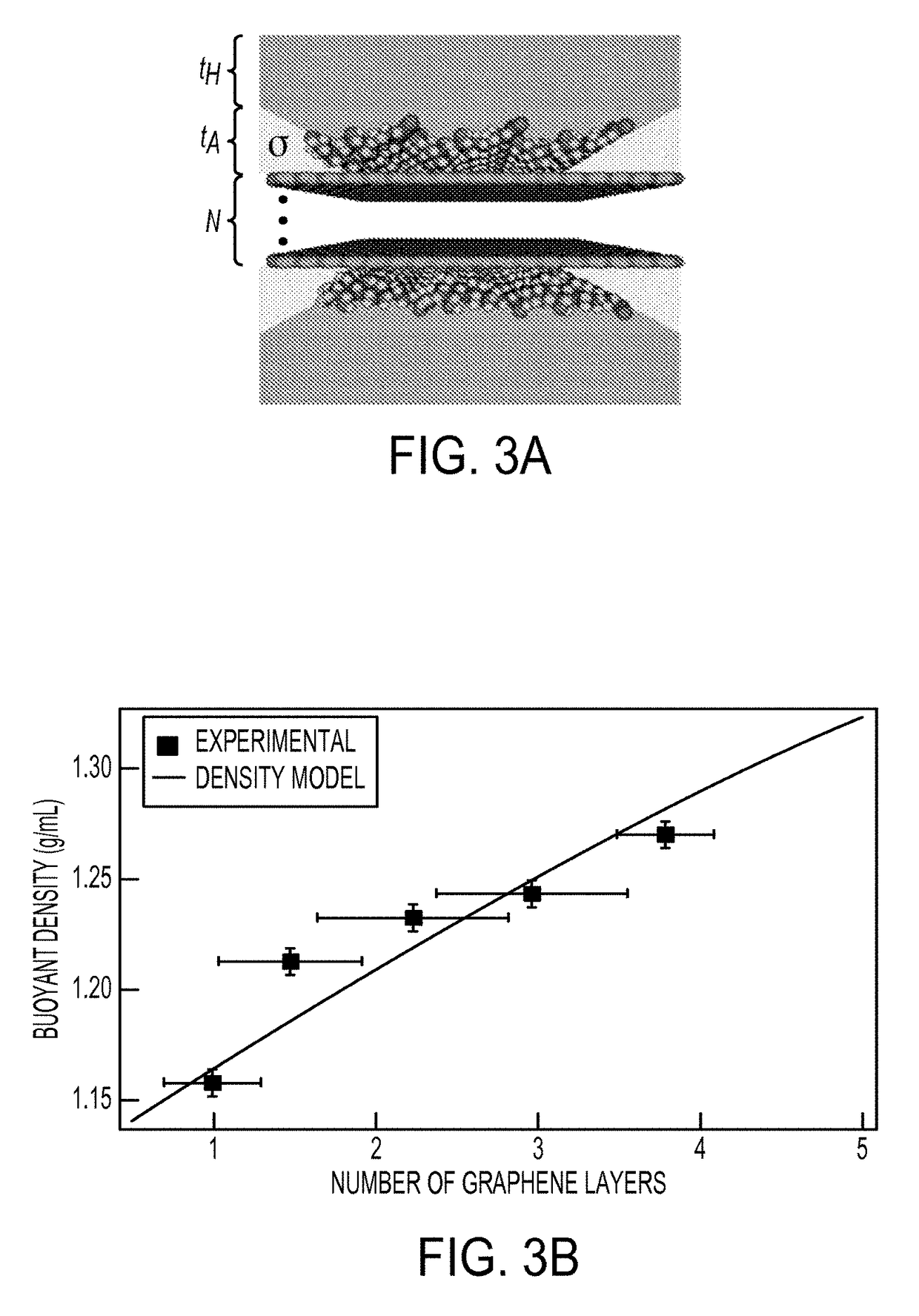
ActiveUS20160016796A1Different buoyant densityEffective dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsBoron nitrideLayer thickness
The present teachings provide, in part, methods of separating two-dimensional nanomaterials by atomic layer thickness. In certain embodiments, the present teachings provide methods of generating boron nitride nanomaterials having a controlled number of atomic layer(s).
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
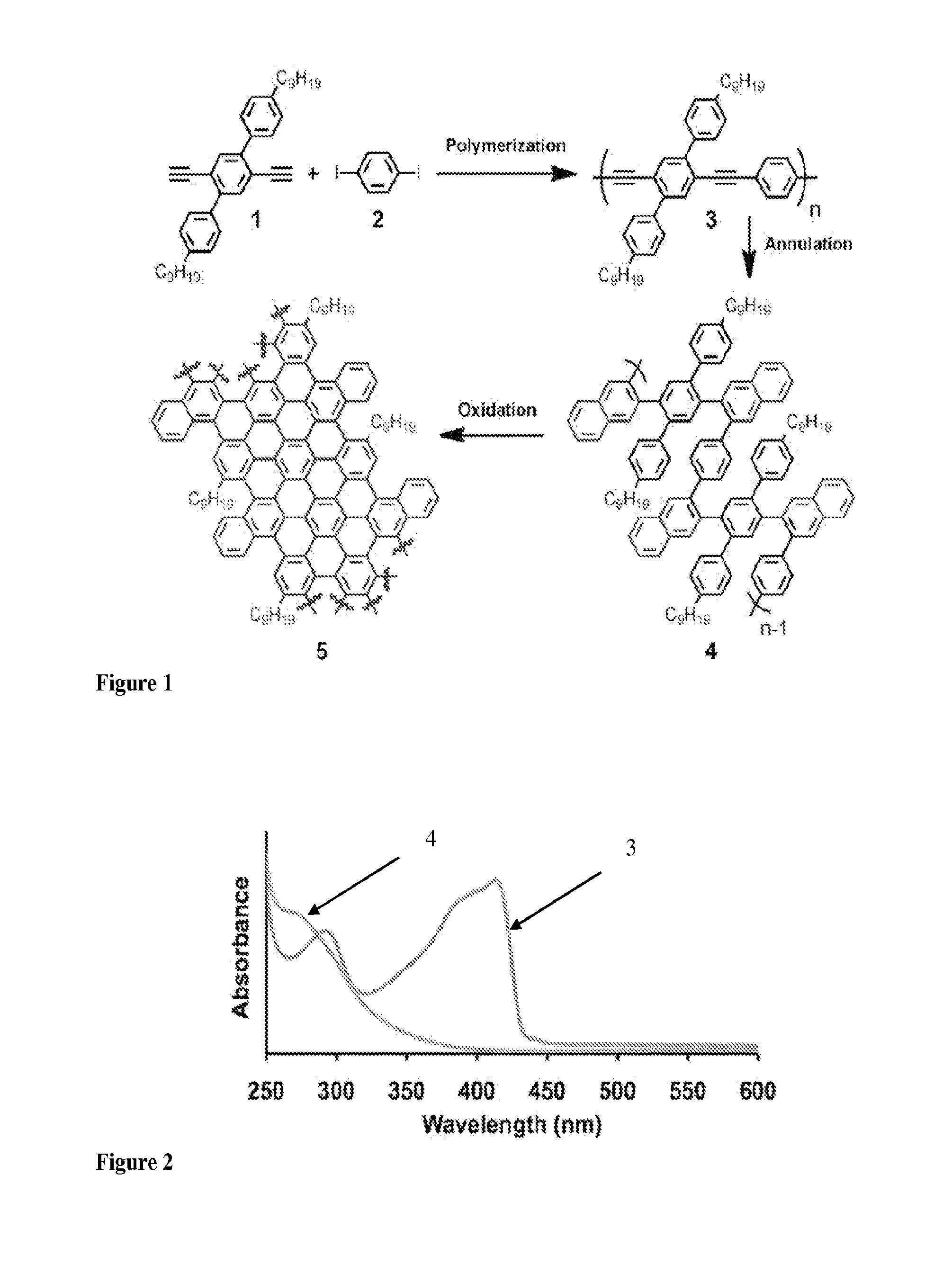
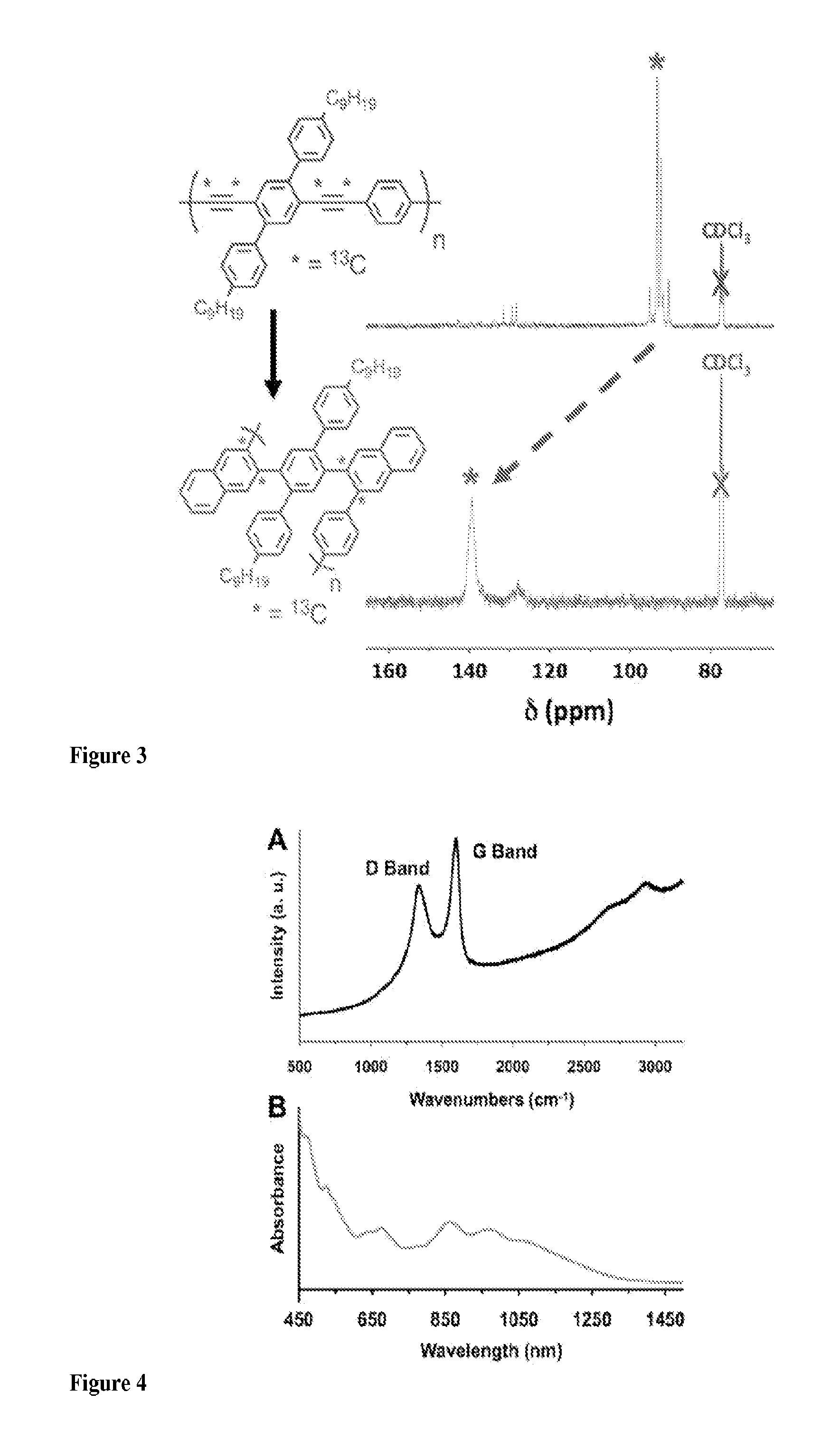
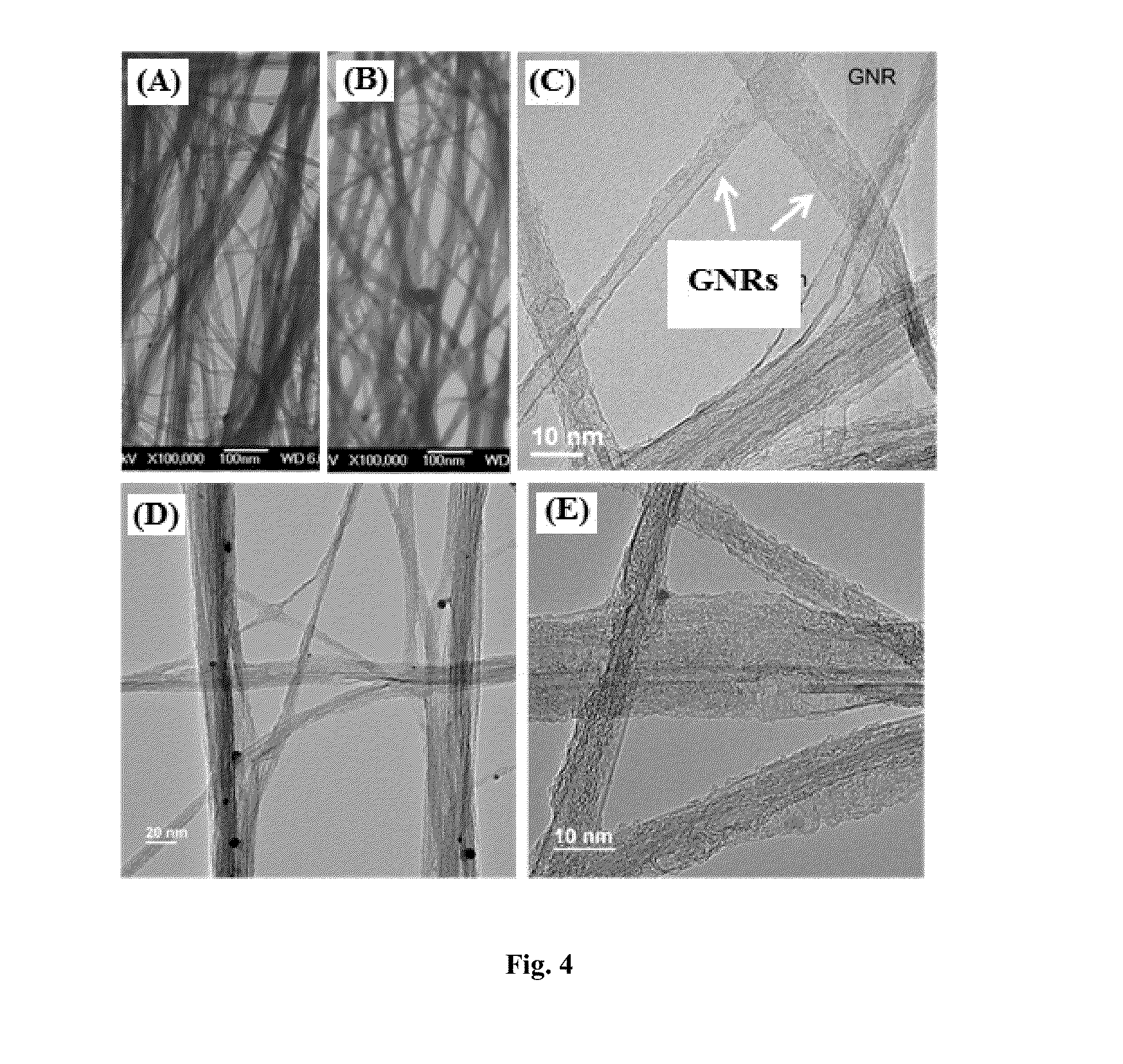
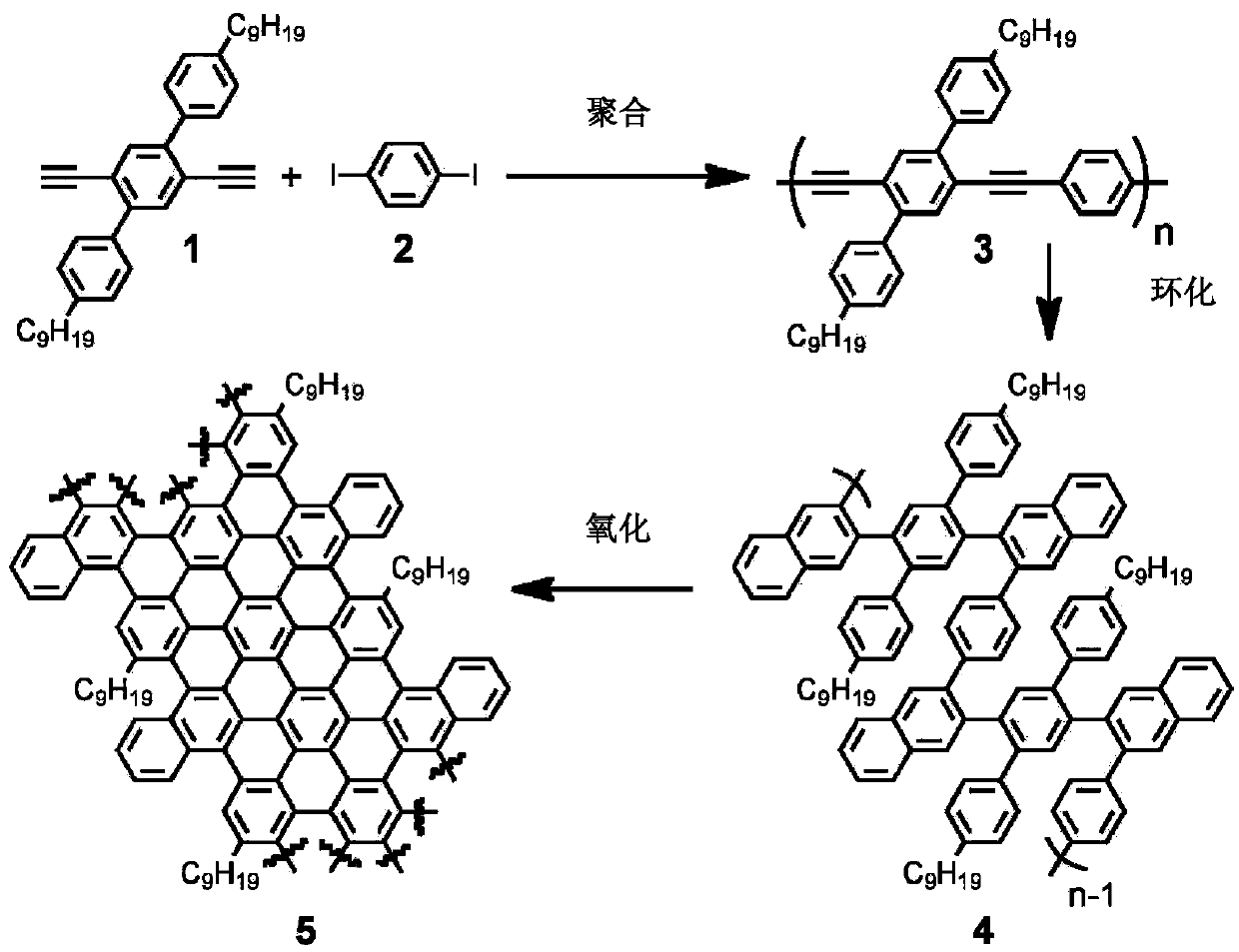
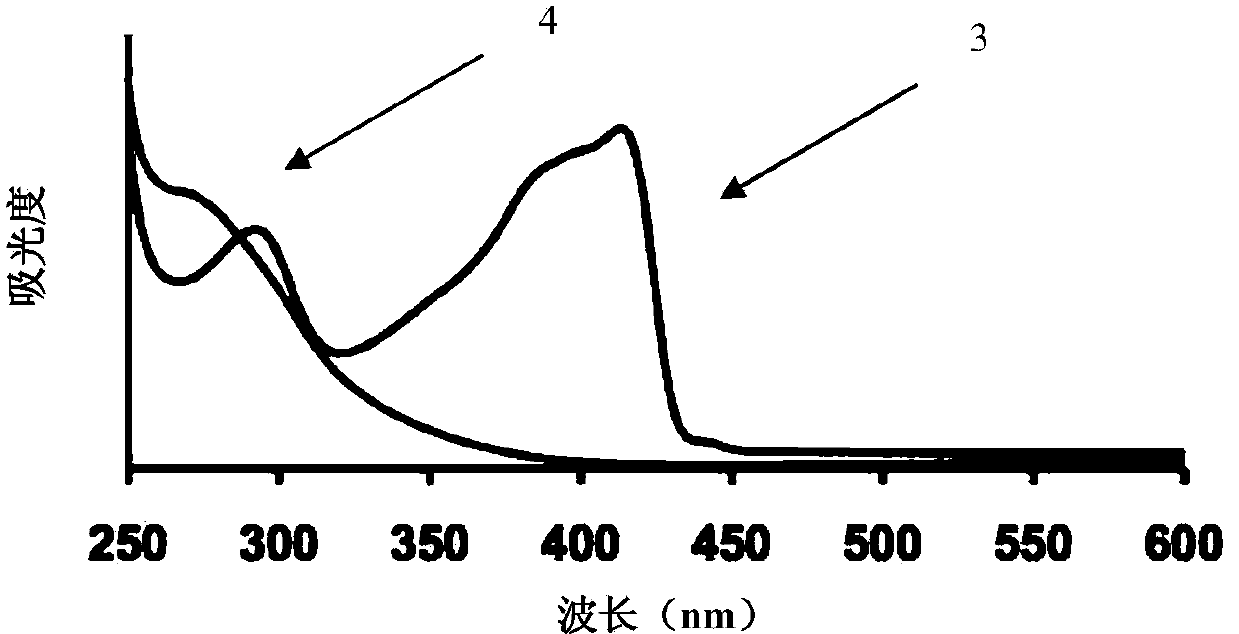
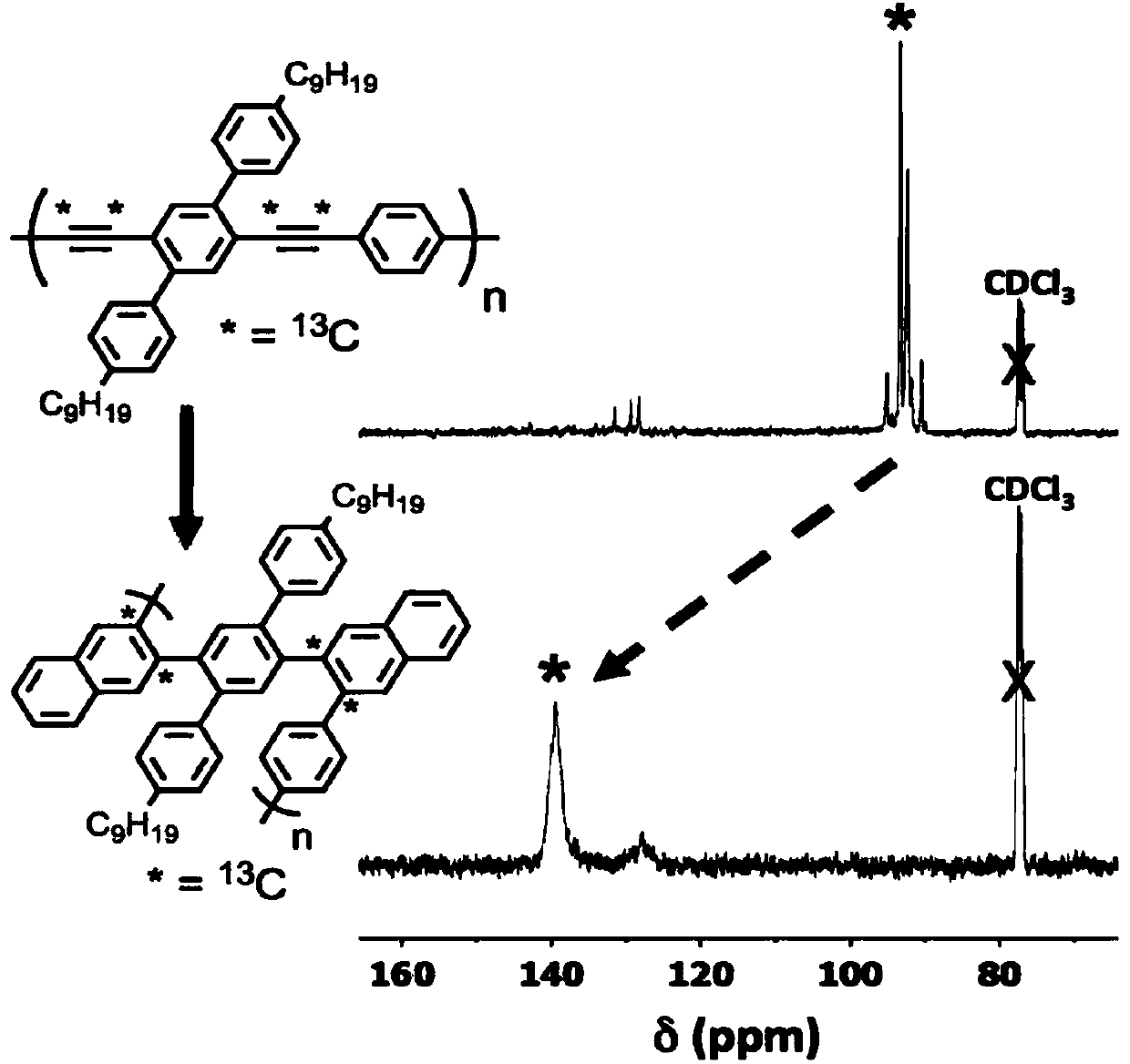
Graphene nanoribbons, methods of making same, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140212668A1Increase added valuePredict and controlMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsGraphene nanoribbonsCycloaddition
Provided are graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), methods of making GNRs, and uses of the GNRs. The methods can provide control over GNR parameters such as, for example, length, width, and edge composition (e.g., edge functional groups). The methods are based on a metal catalyzed cycloaddition reaction at the carbon-carbon triple bonds of a poly(phenylene ethynylene) polymer. The GNRs can be used in devices such a microelectronic devices.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Sorting Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials by Thickness
ActiveUS20150283482A1Quality improvementIncreasingly enriched separation fractionMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsGrapheneLayer thickness
The present teachings provide, in part, methods of separating two-dimensional nanomaterials by atomic layer thickness. In certain embodiments, the present teachings provide methods of generating graphene nanomaterials having a controlled number of atomic layer(s).
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Electrochemical process for synthesis of graphene
InactiveUS20130175182A1Few defectUniform layer thicknessMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolysis componentsGraphene nanoribbonsCarbon nanotube
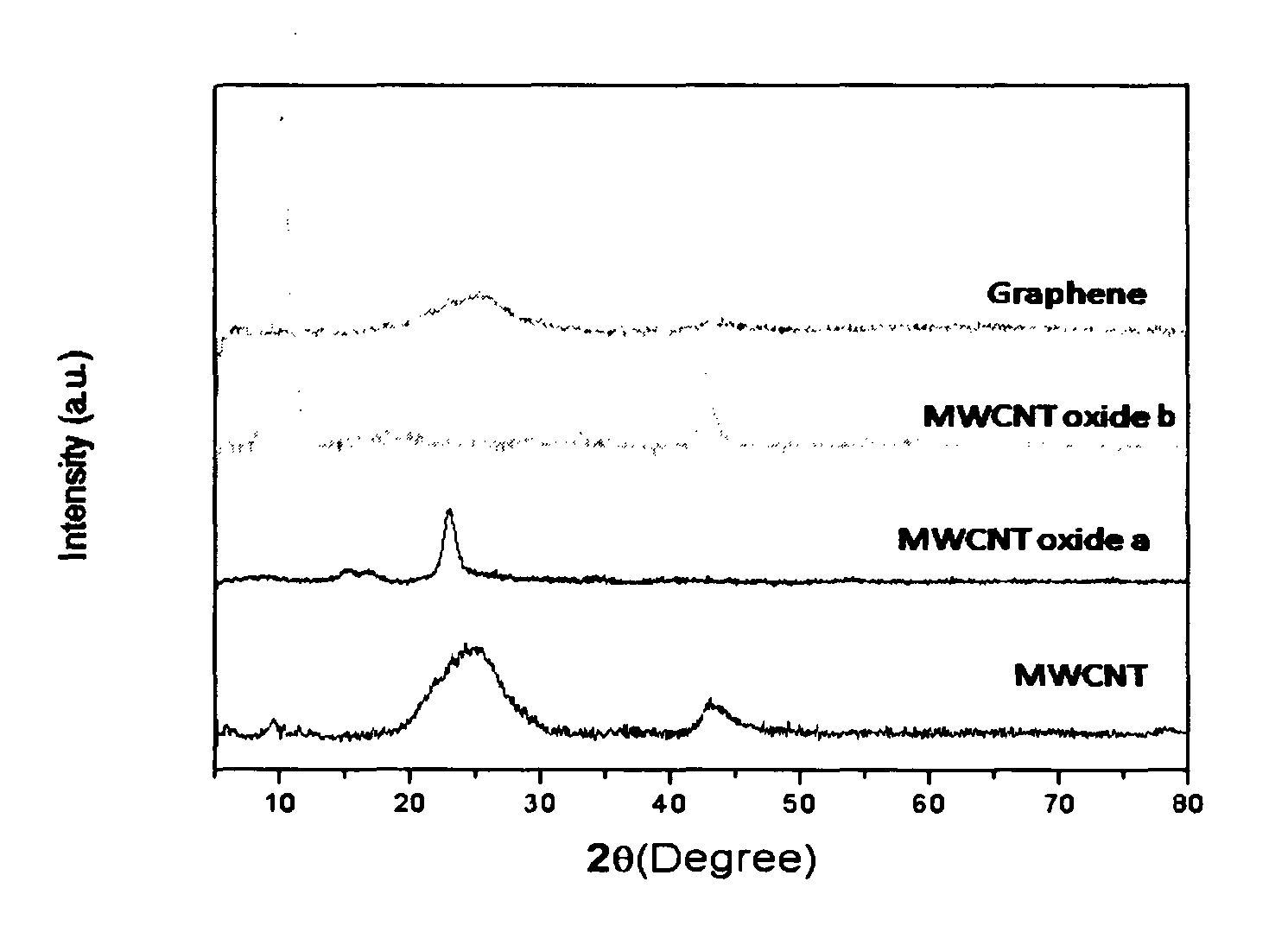
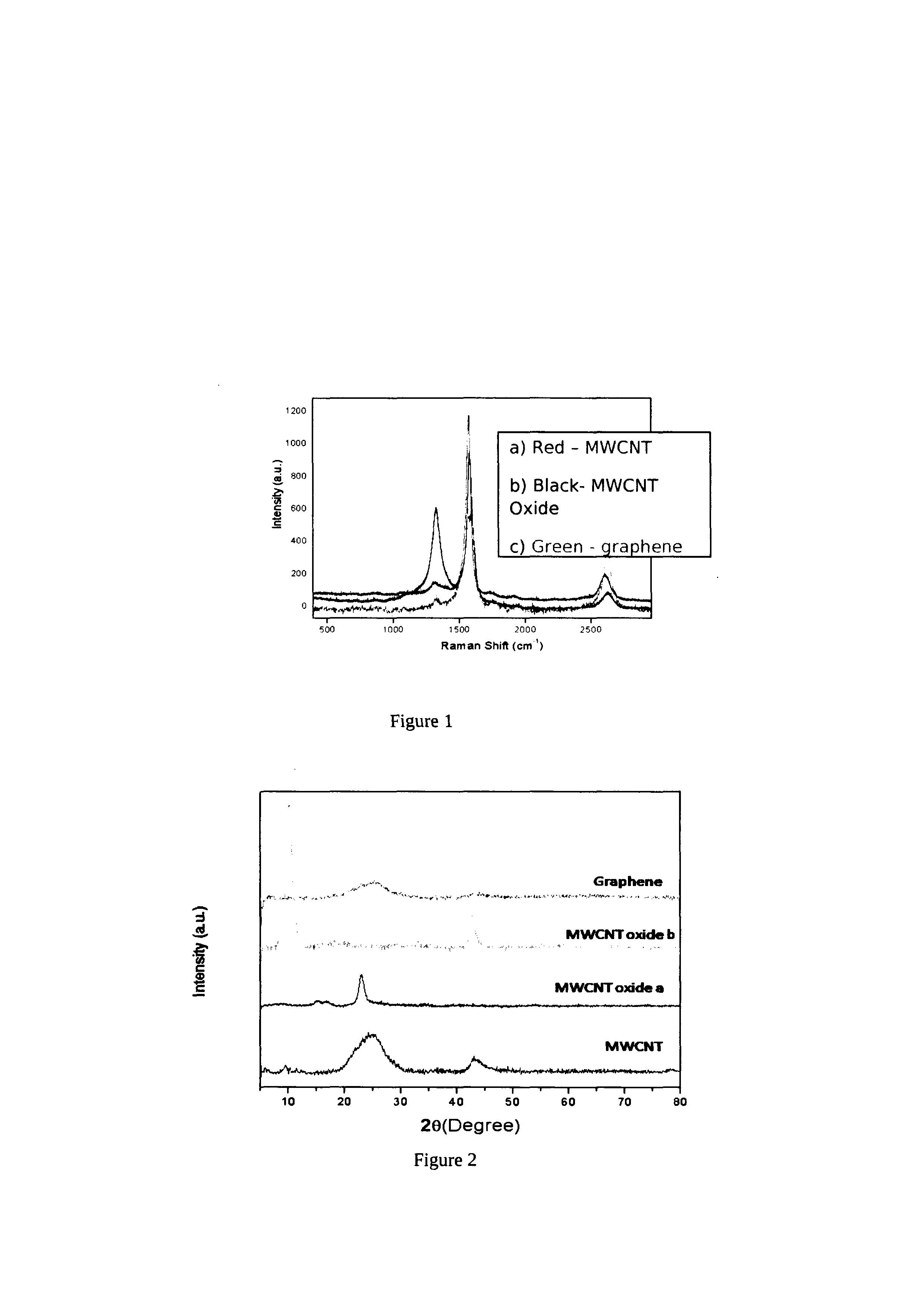
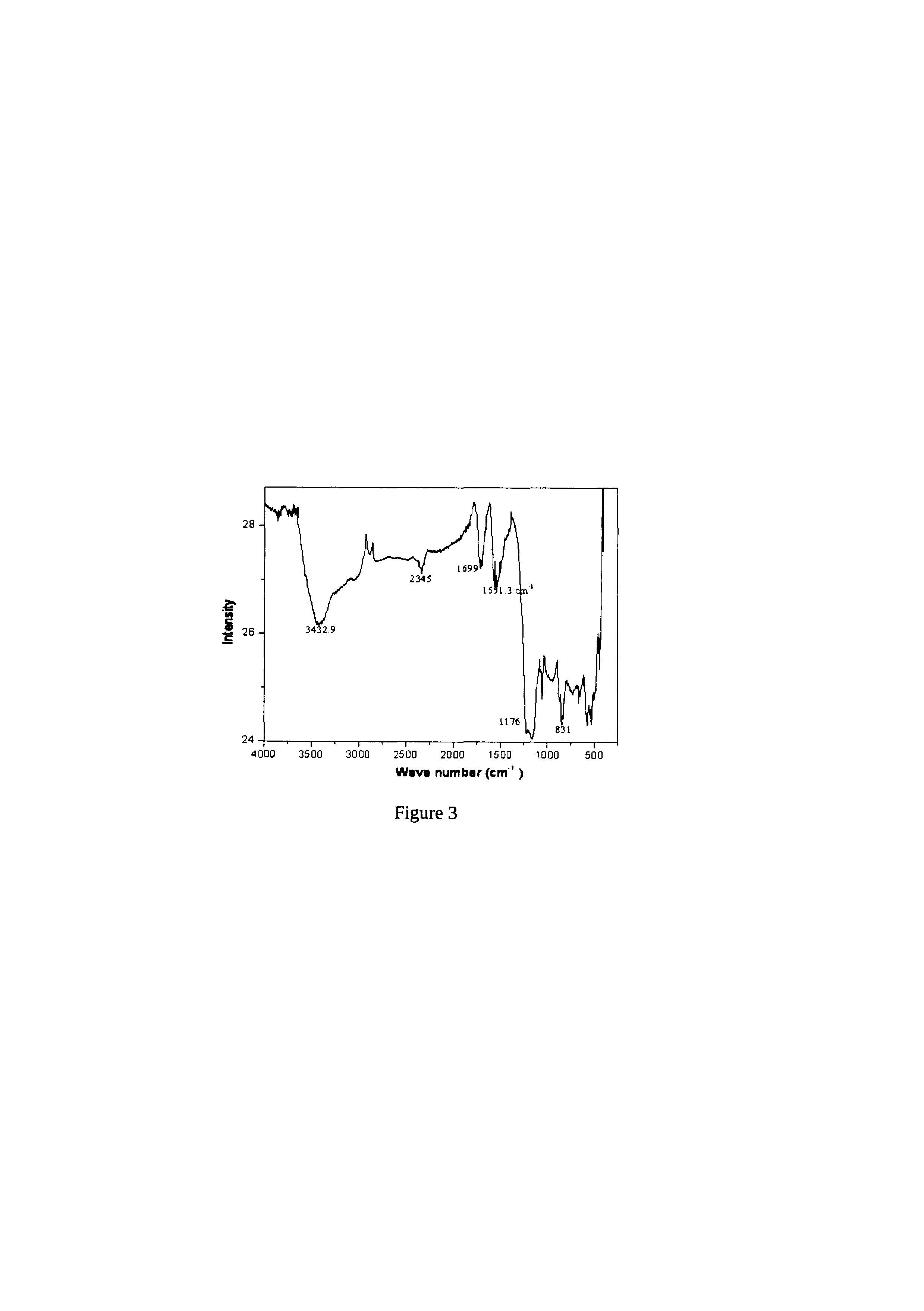
A process for the transformation of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to nanoribbons composed of a few layers of graphene by a two-step electrochemical approach is disclosed in this invention. This consists of the oxidation of CNTs at controlled potential, followed by reduction to form graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) having smooth edges and fewer defects, as evidenced by multiple characterization techniques, including Raman spectroscopy, atomic force micro-scopy, and transmission electron microscopy. This type of ‘unzipping” of CNTs (single-walled, multi-walled) in the presence of an interfacial electric field provides unique advantages with respect to the orientation of CNTs, which might make possible the production of GNRs with controlled widths and fewer defects. The extent of oxidation was confirmed by various characterization techniques like XRD, XPS and Raman spectroscopy. In the second step of experiments, the CNT oxide were reduced for different periods such as 4, 8, 12 hours at fixed negative potentials of −0.5 V, so as to get layers of graphene ribbons as tabulated herein.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Modified Graphene, Method for Producing a Modified Graphene and Applications Thereof
ActiveUS20160347619A1Optimizing material dispersion% reductionGraphiteGraphene nanoribbonsStrong acidsOxygen
Provided is a method for producing a modified graphene, comprising the steps of intercalating or inserting a mixture of intercalating agents in a spacing between interlayers of carbon substrates or between carbon substrates, whereby the binding force between the interlayers of the carbon substrates or between the carbon substrates is weaken; and then exfoliating the pretreated carbon substrates to form the modified graphene. Upon environmental friendly purpose, the method according to the present invention is useful for reducing the total amount of strong acid. Therefore, the amount of the generated oxygen-containing functional groups attached on the modified graphene is modulated to avoid defects and maintain a yield over 80%.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
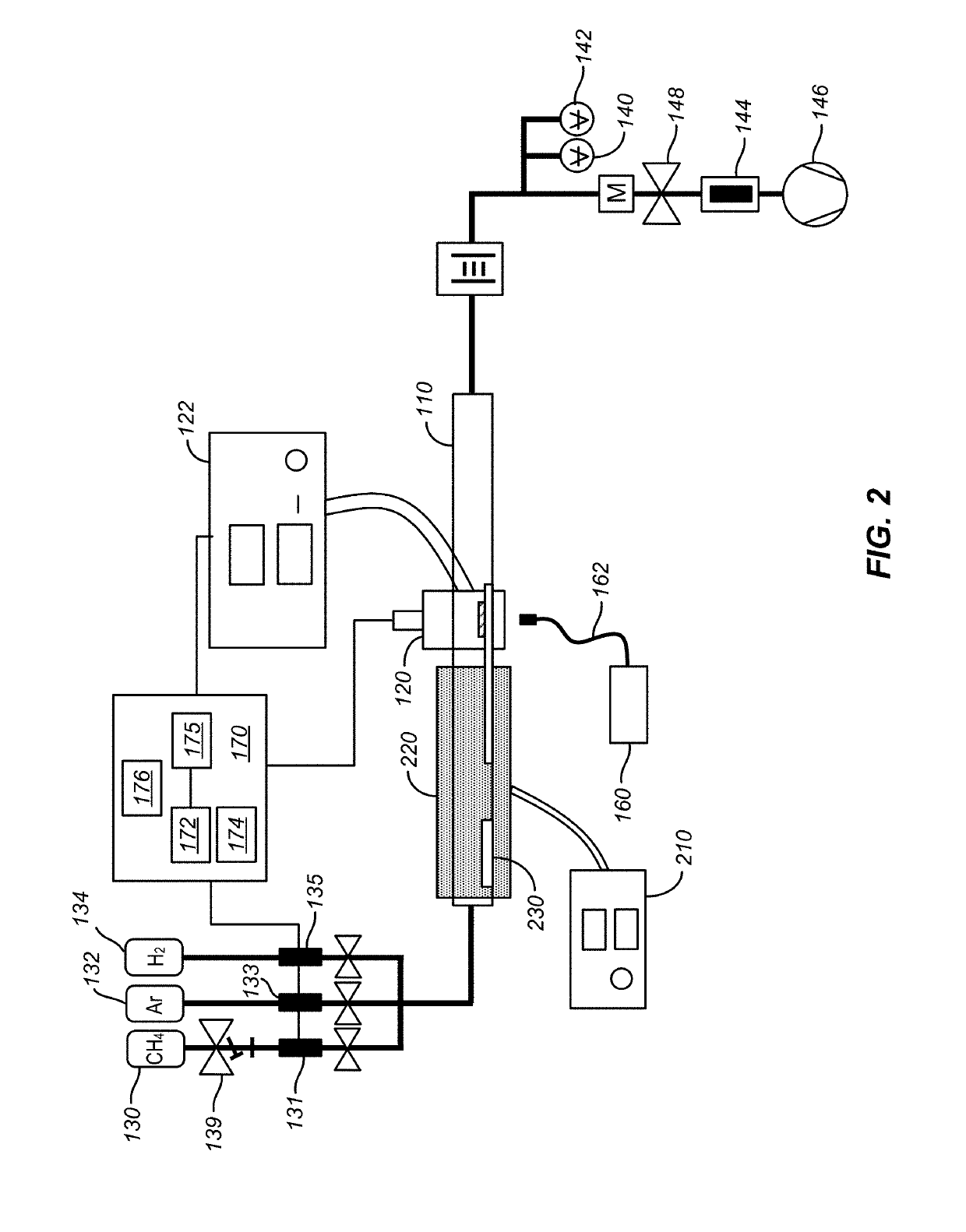
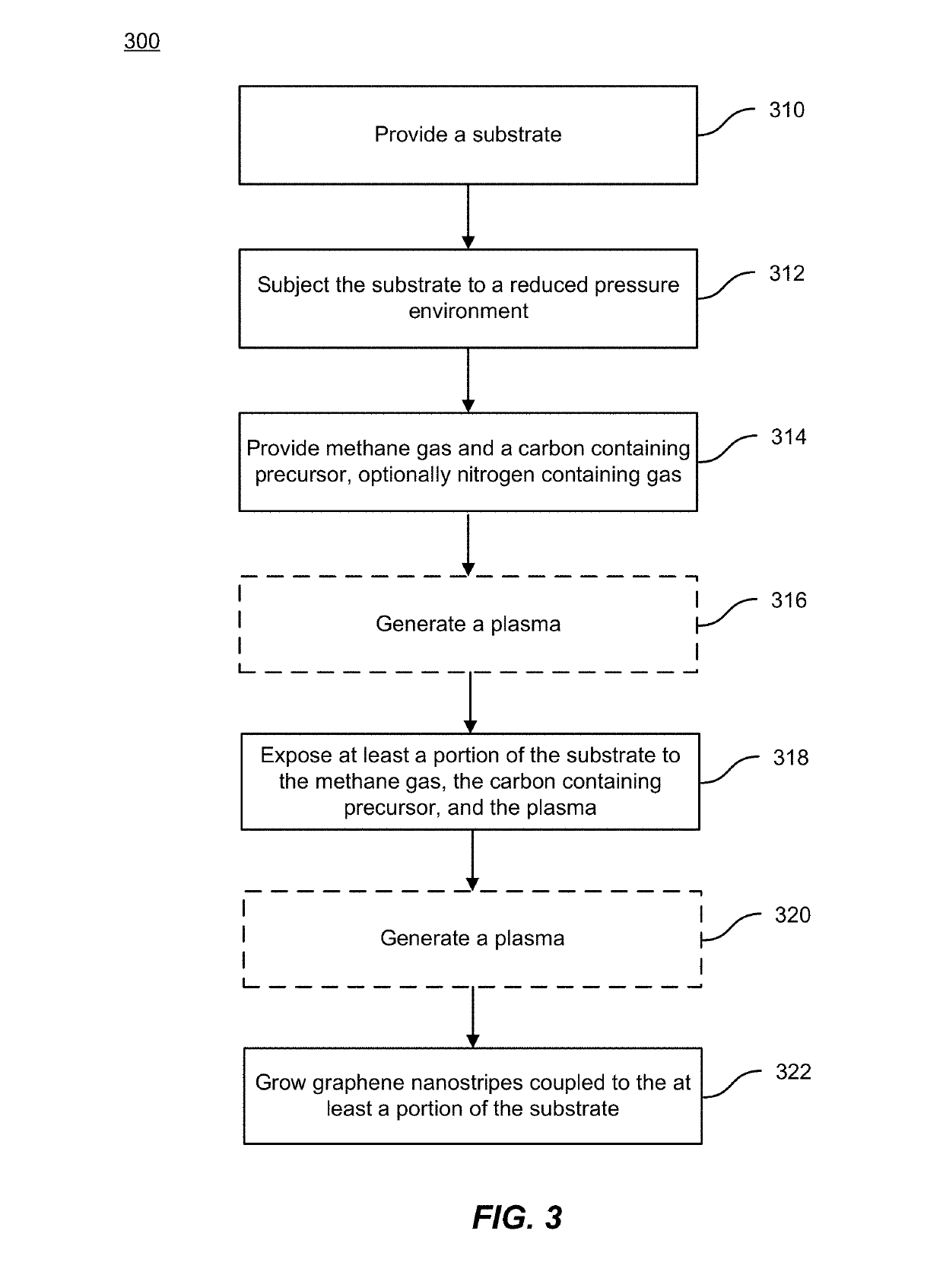
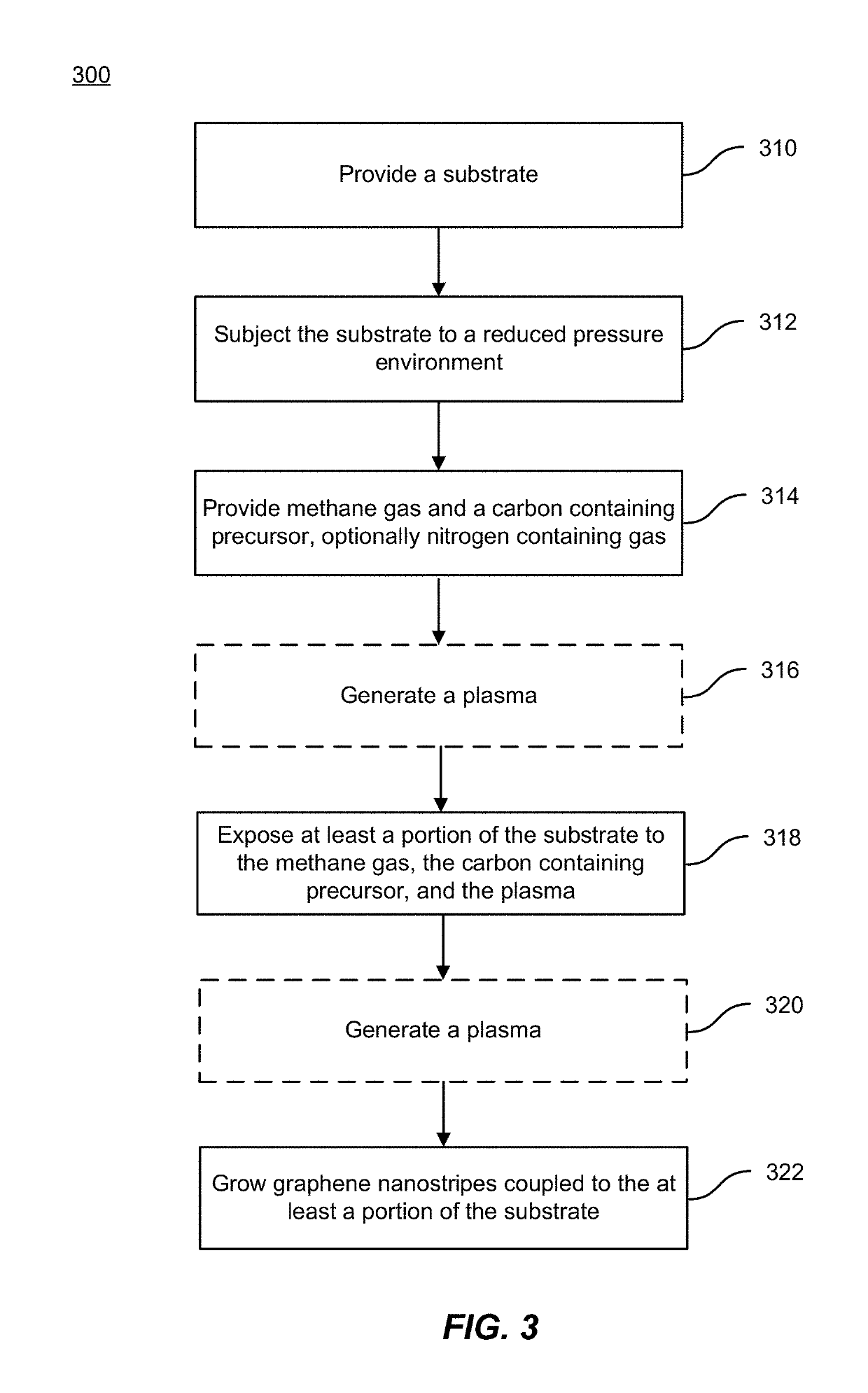
Method and system for growth of graphene nanostripes by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition
ActiveUS20190093227A1High yieldEnhanced vapor depositionChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideMaterial nanotechnologyGraphene nanoribbonsGas phase
A method of forming graphene nanostripes includes providing a substrate comprising at least one of copper foil or nickel foam and subjecting the substrate to a reduced pressure environment in a processing chamber. The method also includes providing methane gas and 1,2-dichlorobenzene (1,2-DCB) gas, flowing the methane gas and the 1,2-DCB into the processing chamber, and establishing a partial pressure ratio of 1,2-DCB gas to methane gas in the processing chamber. The partial pressure ratio is between 0 and 3. The method further includes generating a plasma, thereafter, exposing the at least a portion of the substrate to the methane gas, the 1,2-DCB gas, and the plasma, and growing the graphene nanostripes coupled to the at least a portion of the substrate.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Graphene Nanoribbons and Methods
Methods are provided for fabricating graphene nanoribbons. The methods rely on laser irradiation that is applied to a carbon nanotube film to unzip one or more carbon nanotubes of the carbon nanotube film. Graphene nanoribbons can be cross-linked via laser irradiation to form a graphene nanoribbon network.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Graphene nanoribbons, methods of making same, and uses thereof
ActiveCN103635423AReasonable designPrecise structureMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureGraphene nanoribbonsCycloaddition
Provided are graphene nanoribbons (GNR), methods of making GNR, and uses of the GNR. The methods can provide control over GNR parameters such as, for example, length, width, and edge composition (e.g., edge functional groups). The methods are based on a metal catalyzed cycloaddition reaction at the carbon-carbon triple bonds of a poly(phenylene ethynylene) polymer. The GNR can be used in devices such as microelectronic devices.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of graphene nanoribbon
PendingCN106587014ALower requirementEasy to operateGraphene nanoribbonsDispersityGraphene nanoribbons
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene nanoribbon and belongs to the technical field of carbon nano functional materials. According to the preparation method of the graphene nanoribbon, a final product is prepared from a carbon nanotube as a raw material through two-step lengthwise cutting with a reduction method and an oxidation method. The method adopts a simple process, is convenient to operate, low in production cost and environment-friendly and facilitates large-scale production. The graphene nanoribbon prepared with the method has a complete structure, is high in dispersity, electric conductivity and heat conductivity and can be widely applied to synthesis of nanocomposites.
Owner:重庆锦添翼新能源科技有限公司 +1
Sorting two-dimensional nanomaterials by thickness
ActiveUS9221064B2Different buoyant densityEffective dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsGrapheneLayer thickness
The present teachings provide, in part, methods of separating two-dimensional nanomaterials by atomic layer thickness. In certain embodiments, the present teachings provide methods of generating graphene nanomaterials having a controlled number of atomic layer(s).
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Random graphite and fabrication method thereof using graphene nanoribbon
InactiveUS20120171109A1Reduce the temperaturePigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyGraphene nanoribbonsGraphite
Random graphite which is a type of graphite comprising three-dimensionally random graphene layers, and a fabrication method thereof at a low temperature as below 100° C. are disclosed. Random graphite may have a large volume of an empty space due to the feature of the presence of the three-dimensionally random graphene nanoribbons. Thus, it can be applied to Graphitic Intercalation Compound (GIC) such as electrodes for Li-ion battery.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of fluorinated graphene nanobelt
ActiveCN108383110ASimple post-processingExcellent superhydrophobic propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon nanotubesGraphene nanoribbonsChemical stability
The invention provides a method for preparing a fluorinated graphene nanobelt by taking fluorine gas as a fluorine source. The method comprises the step: fluorinating an anhydrous carbon nanotube under the conditions of -0.07 to 0 MPa and 280 to 450 DEG C and under the atmosphere of fluorine gas to obtain the fluorinated graphene nanobelt. The method provided by the invention is simple to operate,wide in raw material source, low in cost and high in yield; the yield can reach dozens of milligrams, even hundreds of milligrams; and furthermore, aftertreatment is simple, and the fluorinated graphene nanobelt can be prepared through one-step reaction. The prepared fluorinated graphene nanobelt has high super-hydrophobicity and chemical stability, can be applied in the fields of protective iceand the like and has a very good application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Soluble graphene nanoribbon as well as synthetic method and application thereof
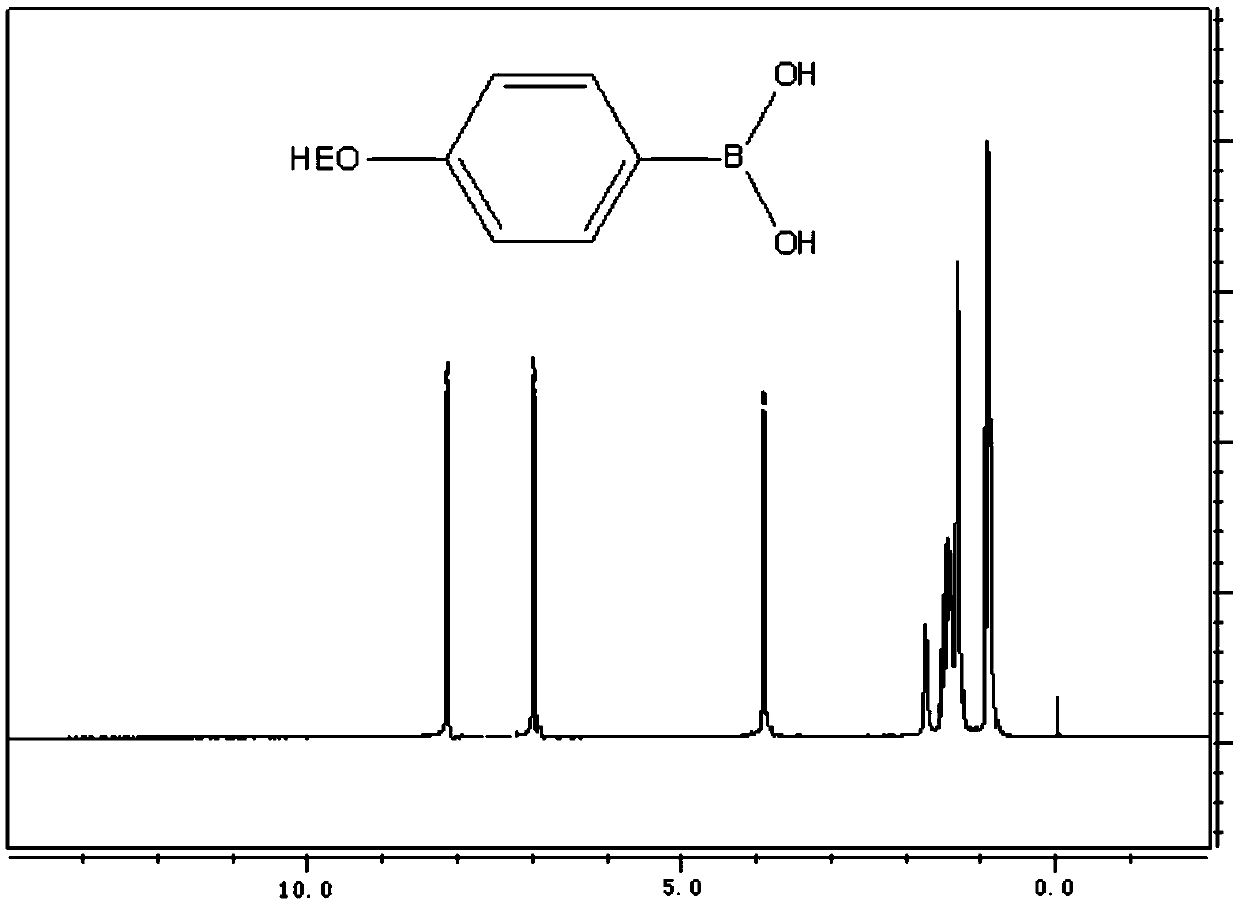
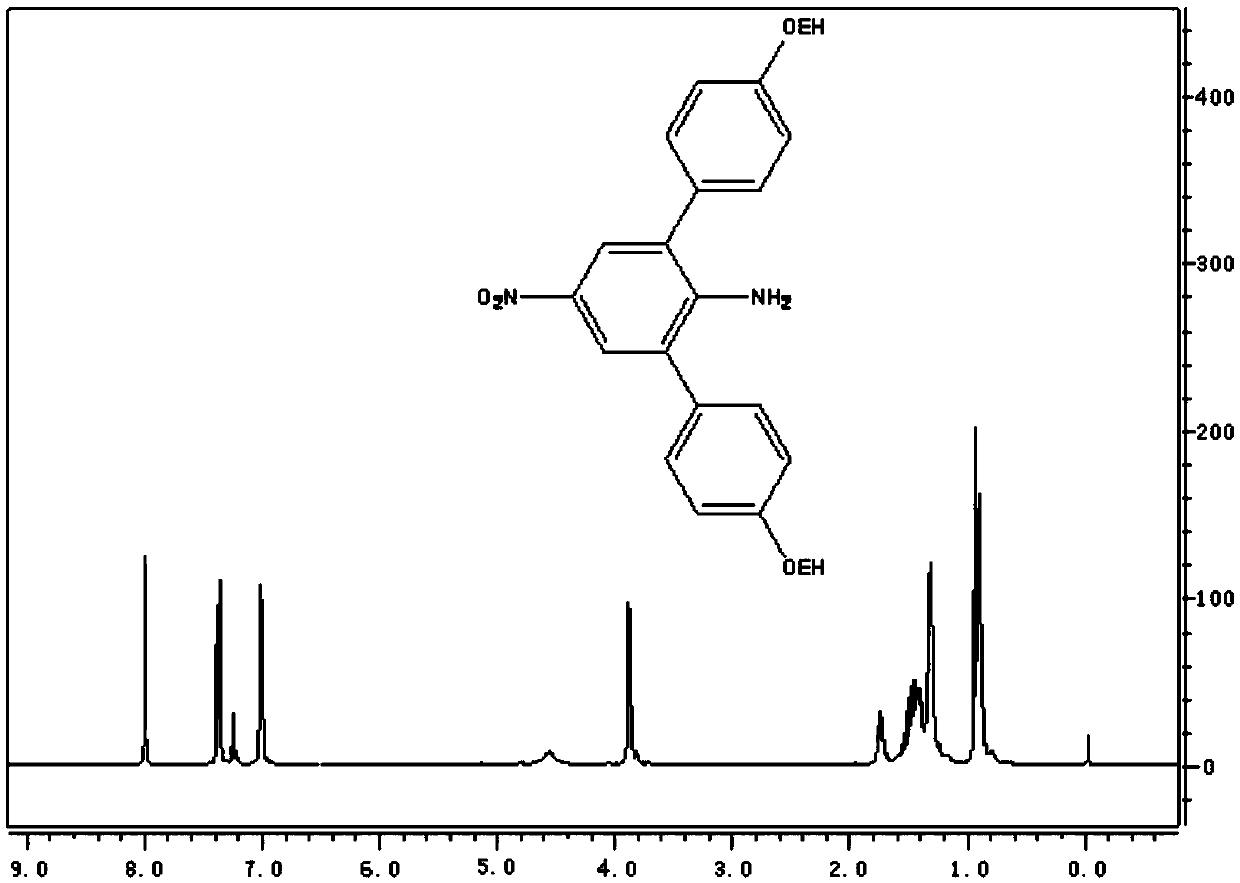
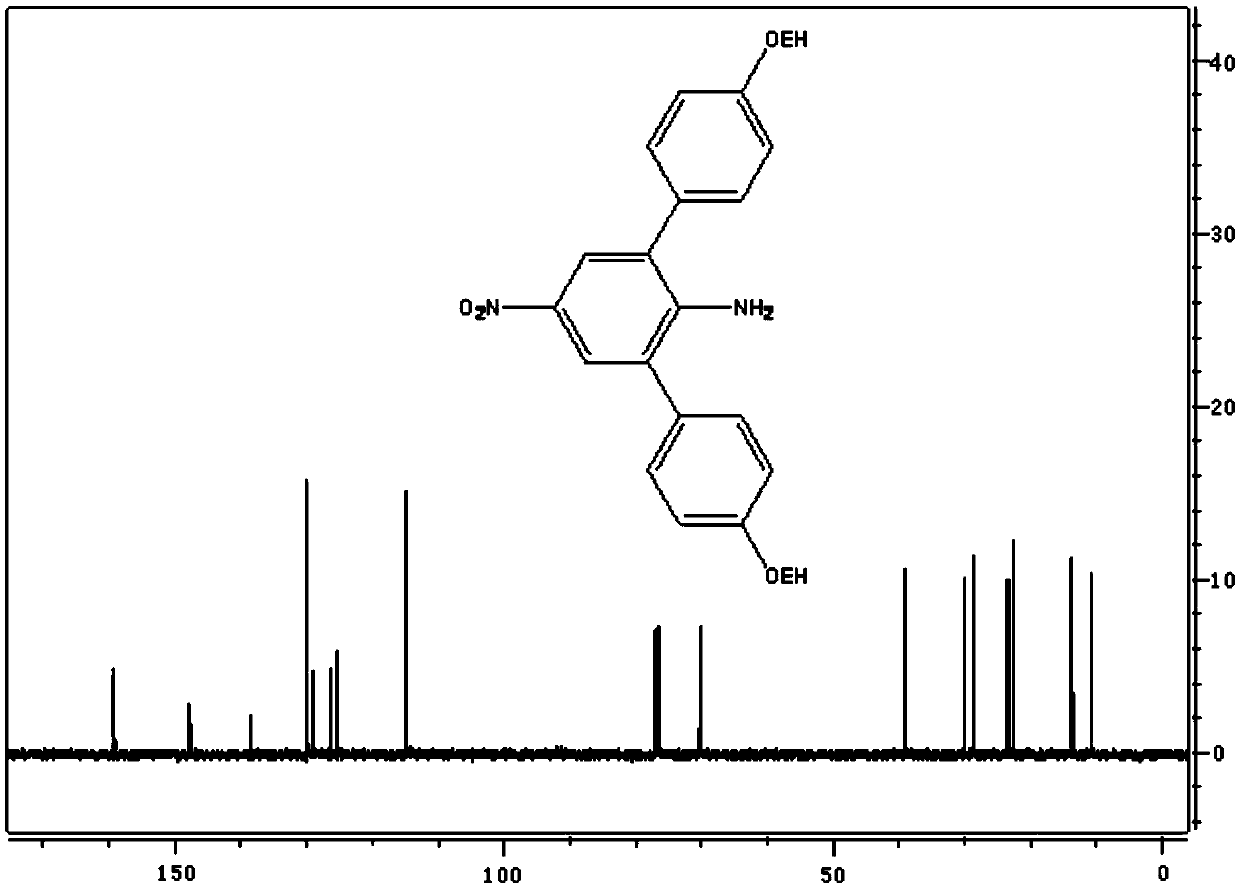
InactiveCN105502351AEasy to gatherLower bandgapMaterial nanotechnologyGraphene nanoribbonsBoronic acidDehydrogenation
The invention belongs to the technical field of functional materials and discloses a soluble graphene nanoribbon as well as a synthetic method and an application thereof. The synthetic method comprises the steps that 2,6-dibromo-4-nitroaniline and alkyl / alkoxy arylboronic acid have a Suzuki coupling reaction, 2,6-bis(4-alkyl / alkoxy benzene)-4-nitroaniline is obtained and reduced, 2,6-bis(4-alkyl / alkoxy benzene)-1,4-phenylenediamine is obtained and has halogenation, 2,6-bis(4-alkyl / alkoxy benzene)-1,4-dibromo / iodobenzene is obtained and has an Miyaura borylation reaction, and 2,6-bis(4-alkyl / alkoxy benzene)-4-boronic acid pinacol ester-1-bromo / iodobenzene is obtained; then a poly-para-phenylene derivative is generated through the Suzuki coupling reaction, and a product is obtained through oxidative dehydrogenation. The soluble graphene nanoribbon can be applied to the fields of field effect transistors, photovoltaic cells, non-linear optics and sensing.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Few-layer graphene nanoribbon and a method of making the same
InactiveUS20140004327A1Material nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsGraphene nanoribbonsNanoparticle
A method of preparing graphene nanoribbons from a few-layer graphene film includes the steps of growing or placing a few-layer graphene film on a substrate, applying nanoparticles to a surface of the few-layer graphene layer on the substrate and performing chemical vapor etching. The resulting few-layer graphene nanoribbon has a thickness of between about 0.3 nm and about 50.0 nm and a width of between about 1.0 nm and about 20.0 nm.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
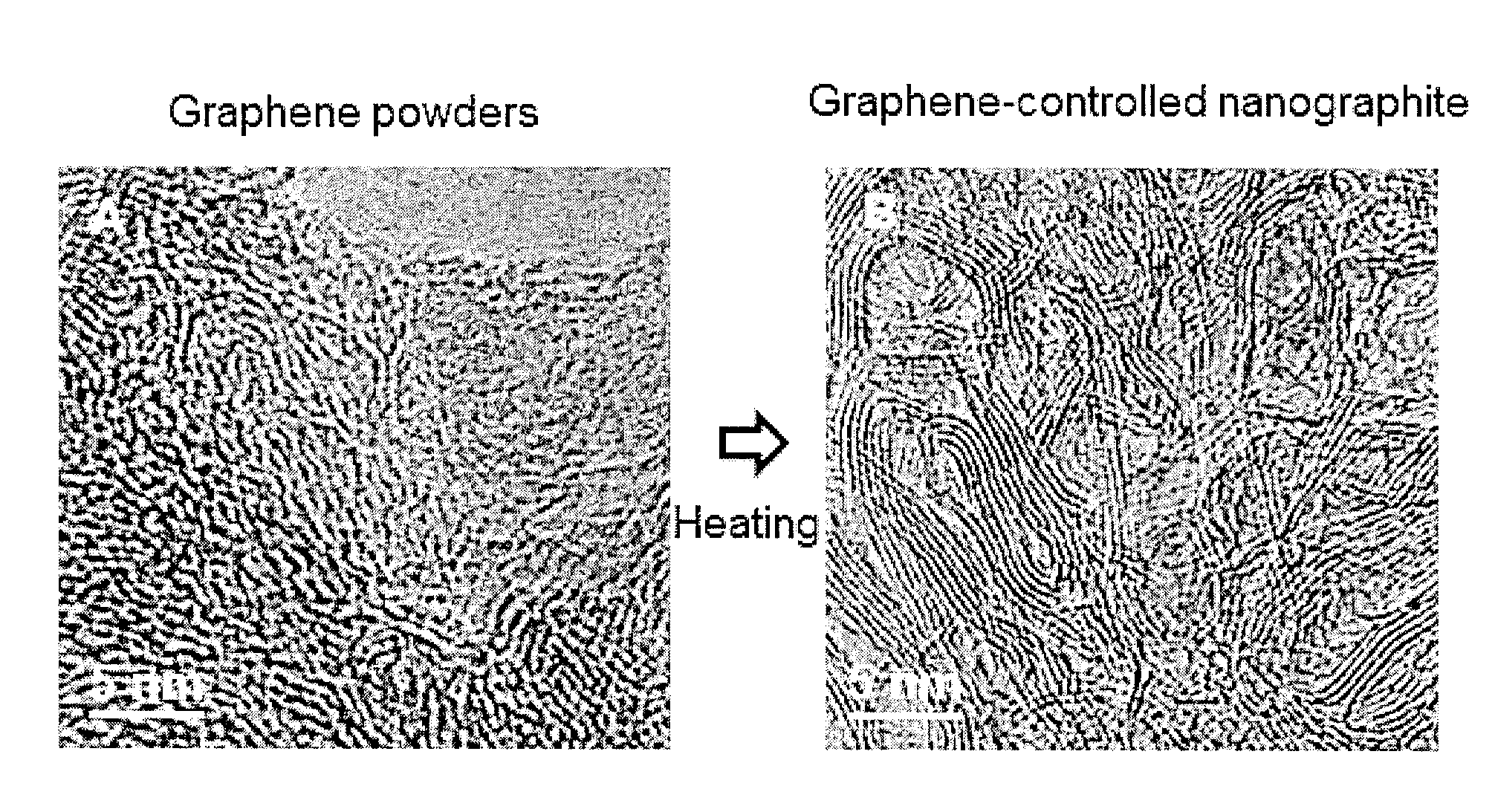
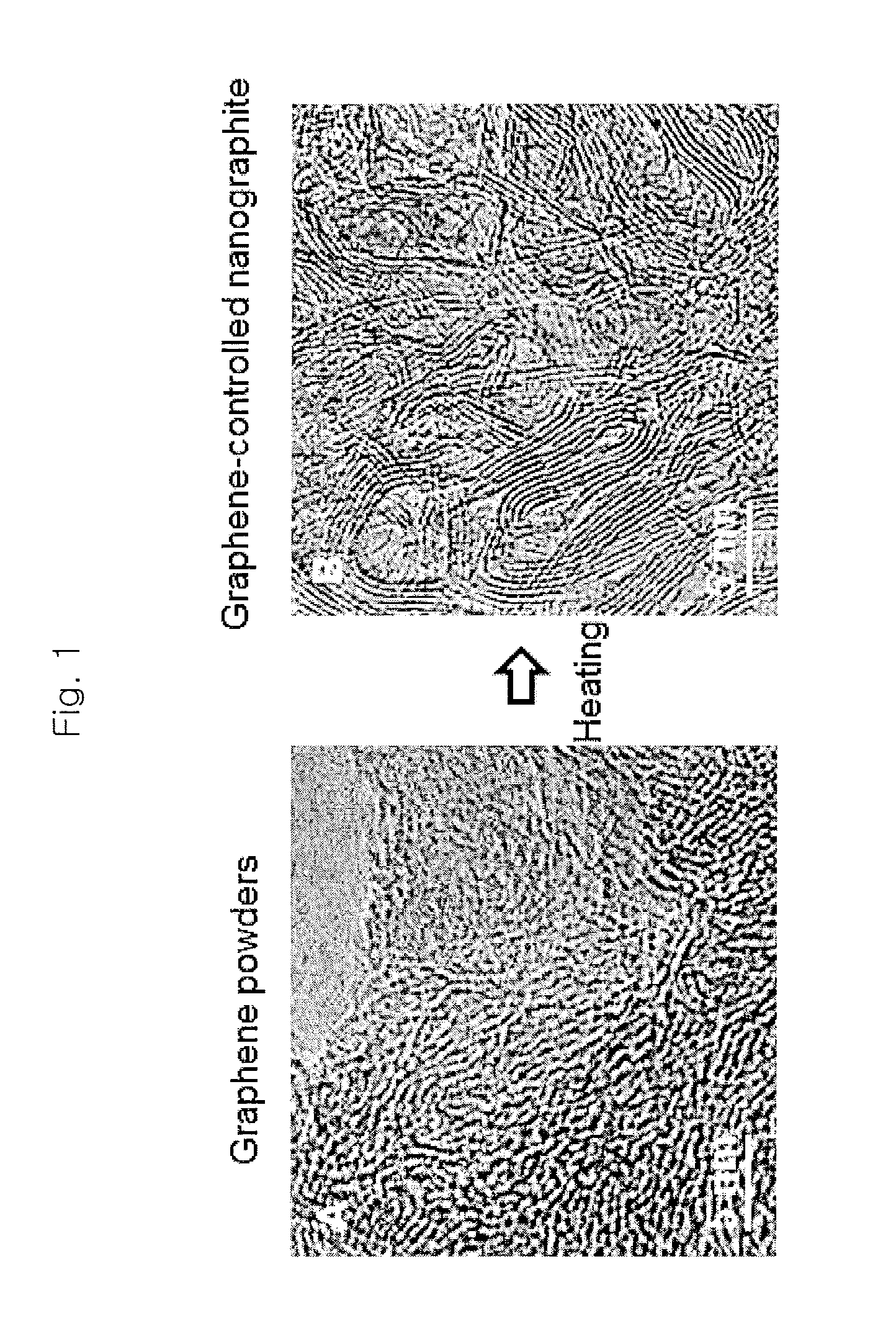
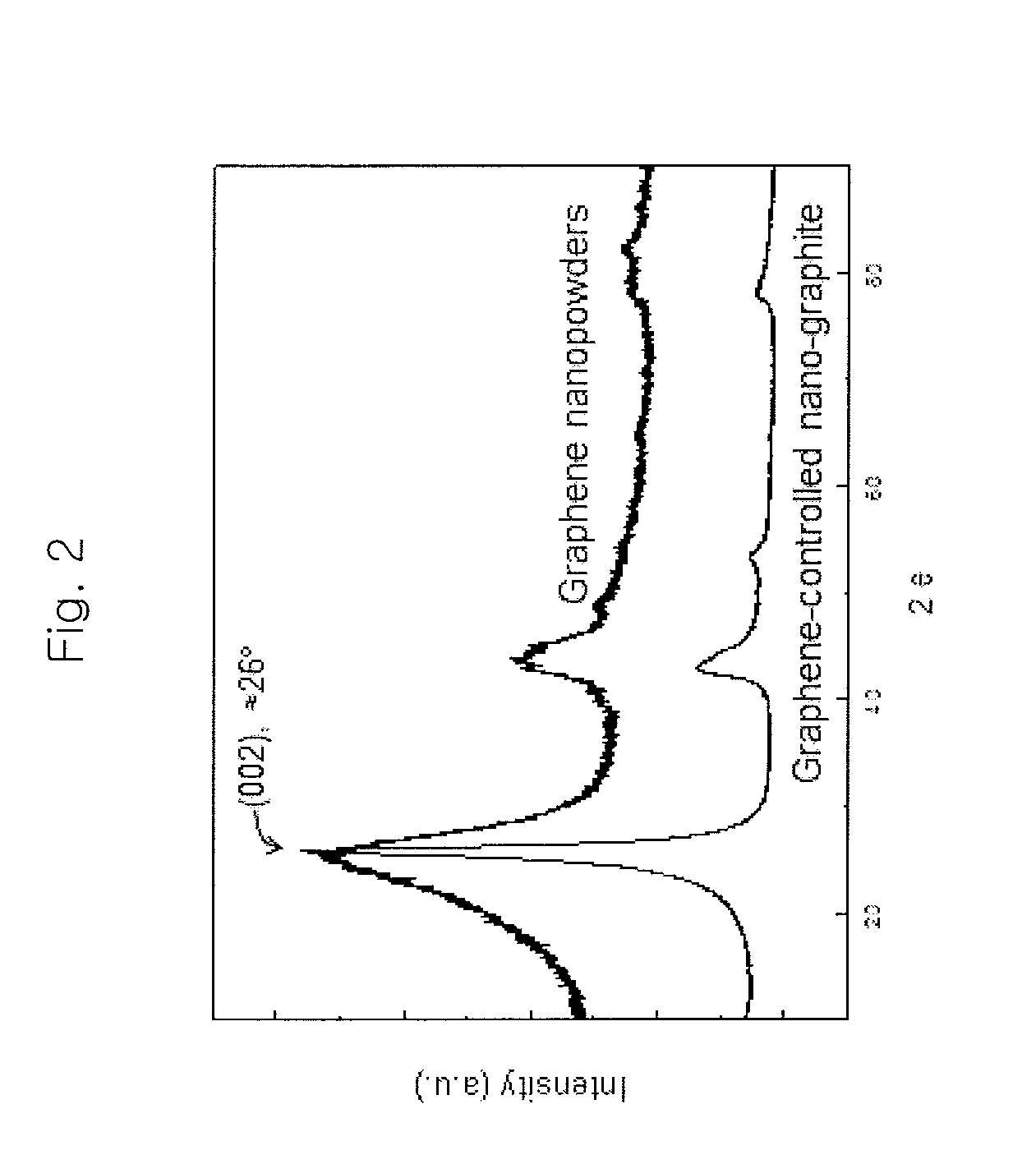
Fabrication method of graphene-controlled nano-graphite
InactiveUS20120295107A1Good flexibilityRaise the ratioMaterial nanotechnologySpecific nanostructure formationGraphiteGraphene
The present invention relates to a method of fabricating a carbon material and, more particularly, to a method for fabricating graphite having a nano-ribbon shape (hereinafter, referred to as a ‘graphene-controlled nano-graphite’) through a heat treatment of graphene nano-powders, and a graphene-controlled nano-graphite fabricated through the method. The method for fabricating graphene-controlled nano-graphite includes a preparation step of preparing graphene powders and a fabrication step of fabricating graphene-controlled nano-graphite through heat treatment of the graphene powders. The graphene powder may be fabricated by disintegrating crystalline graphite.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of graphene nanoribbon on h-BN
ActiveUS9570294B2Improve electrical performanceQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGraphene nanoribbonsGraphene nanoribbonsCvd graphene
A preparation method of a graphene nanoribbon on h-BN, comprising: 1) forming a h-BN groove template with a nano ribbon-shaped groove structure on the h-BN by adopting a metal catalysis etching method; 2) growing a graphene nanoribbon in the h-BN groove template by adopting a chemical vapor deposition method. In the present invention, a CVD method is adopted to directly prepare a morphology controllable graphene nanoribbon on the h-BN, which helps to solve the long-term critical problem that the graphene is difficult to nucleate and grow on an insulating substrate, and to avoid the series of problems introduced by the complicated processes of the transferring of the graphene and the subsequent clipping manufacturing for a nanoribbon and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for growth of graphene nanostripes by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition
ActiveUS10465291B2High yieldHigh aspect ratioChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideMaterial nanotechnologyGraphene nanoribbons2-dichlorobenzene
A method of forming graphene nanostripes includes providing a substrate comprising at least one of copper foil or nickel foam and subjecting the substrate to a reduced pressure environment in a processing chamber. The method also includes providing methane gas and 1,2-dichlorobenzene (1,2-DCB) gas, flowing the methane gas and the 1,2-DCB into the processing chamber, and establishing a partial pressure ratio of 1,2-DCB gas to methane gas in the processing chamber. The partial pressure ratio is between 0 and 3. The method further includes generating a plasma, thereafter, exposing the at least a portion of the substrate to the methane gas, the 1,2-DCB gas, and the plasma, and growing the graphene nanostripes coupled to the at least a portion of the substrate.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
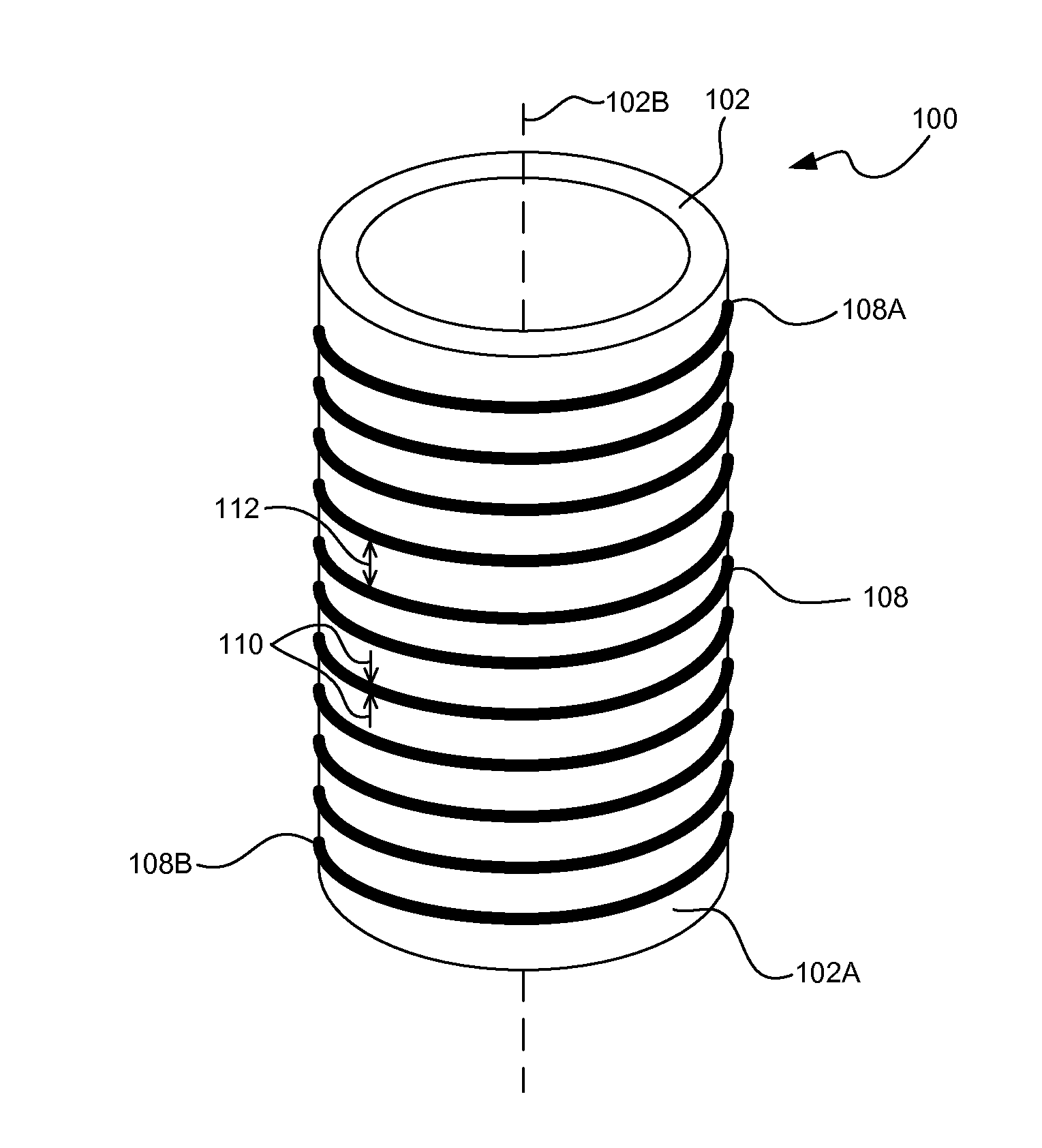
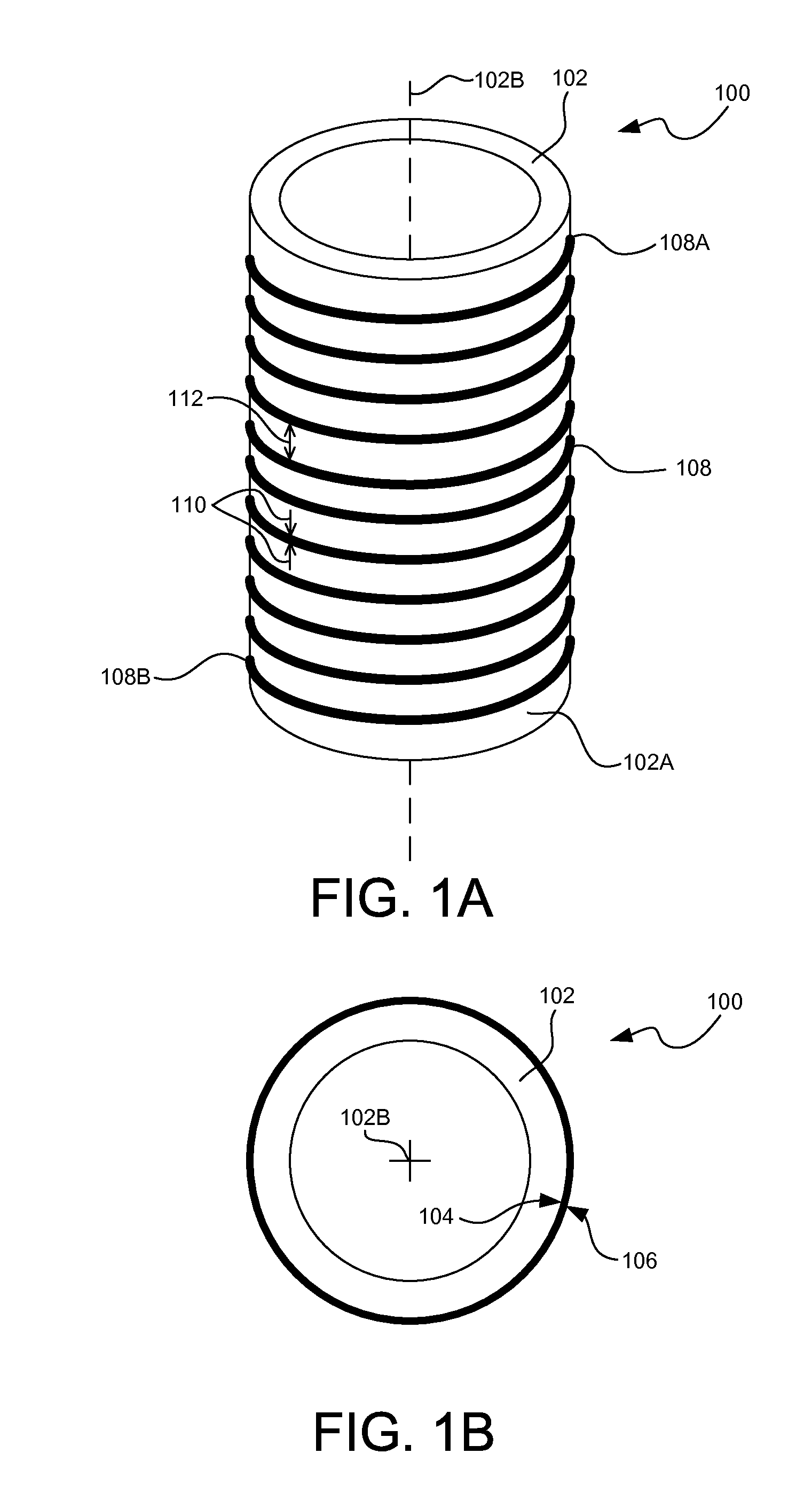
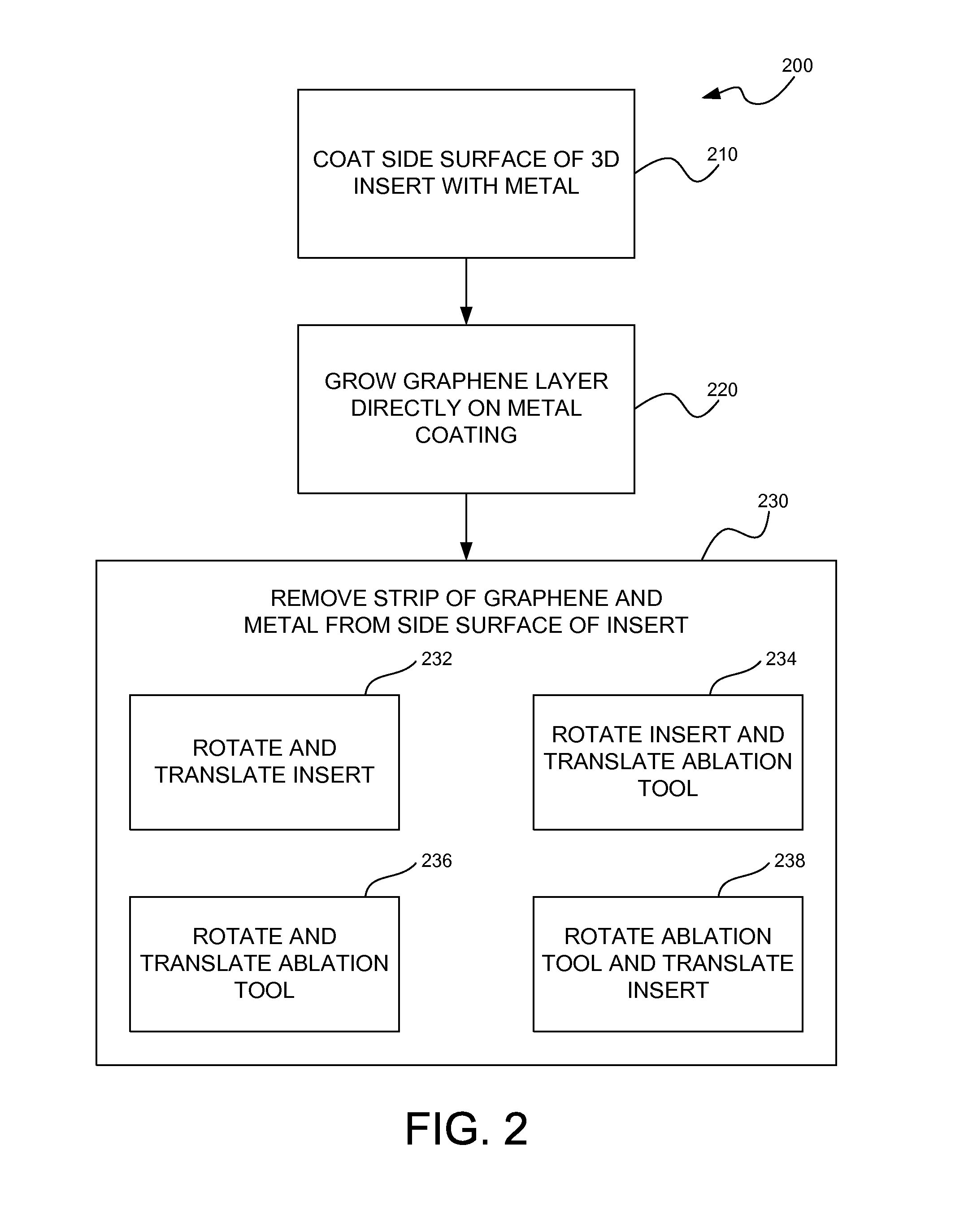
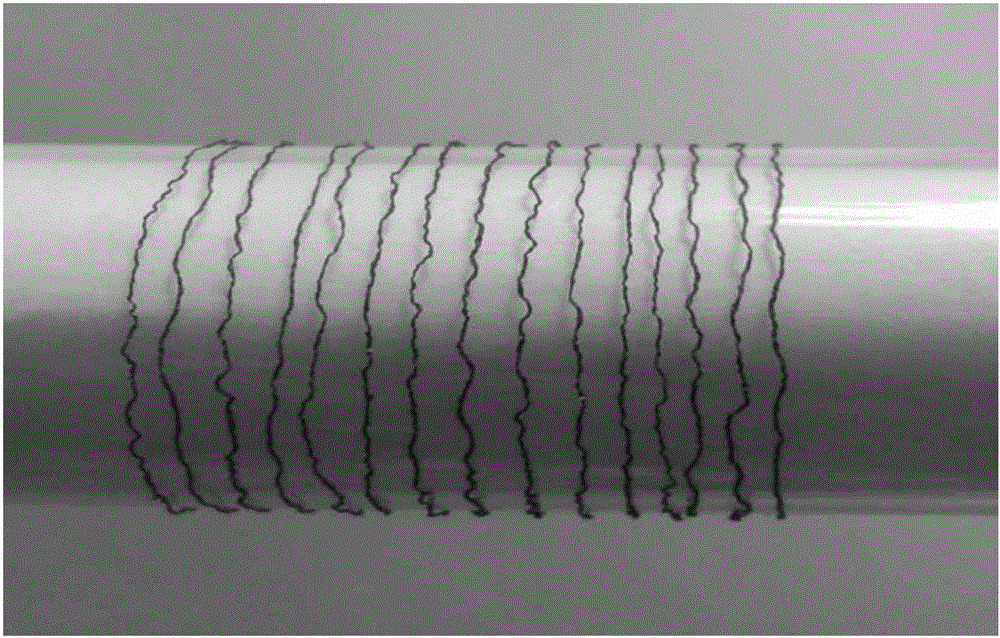
Cylindrical graphene nanoribbon on metal
InactiveUS20150024201A1Easy to useRadiation applicationsLayered productsMetal coatingGraphene nanoribbons
Three-dimensional (3D) graphene nanoribbons and methods for fabricating 3D graphene nanoribbons that may readily function as solenoid windings and the like. In one embodiment, a method of fabricating a 3D graphene nanoribbon (100) may include coating a side surface (102A) of a 3D insert (102) with a metal (104) appropriate for graphene growth thereon. The method may also include growing a layer (106) of graphene directly on the metal coating. The method may also include removing a strip of the graphene layer and metal coating (106 / 104) to expose the side surface (102A) of the insert (102) while leaving a line (108) of graphene on metal winding around the insert (102) and extending continuously from a first end (108A) of the line (108) to a second end (108B) of the line (108).
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
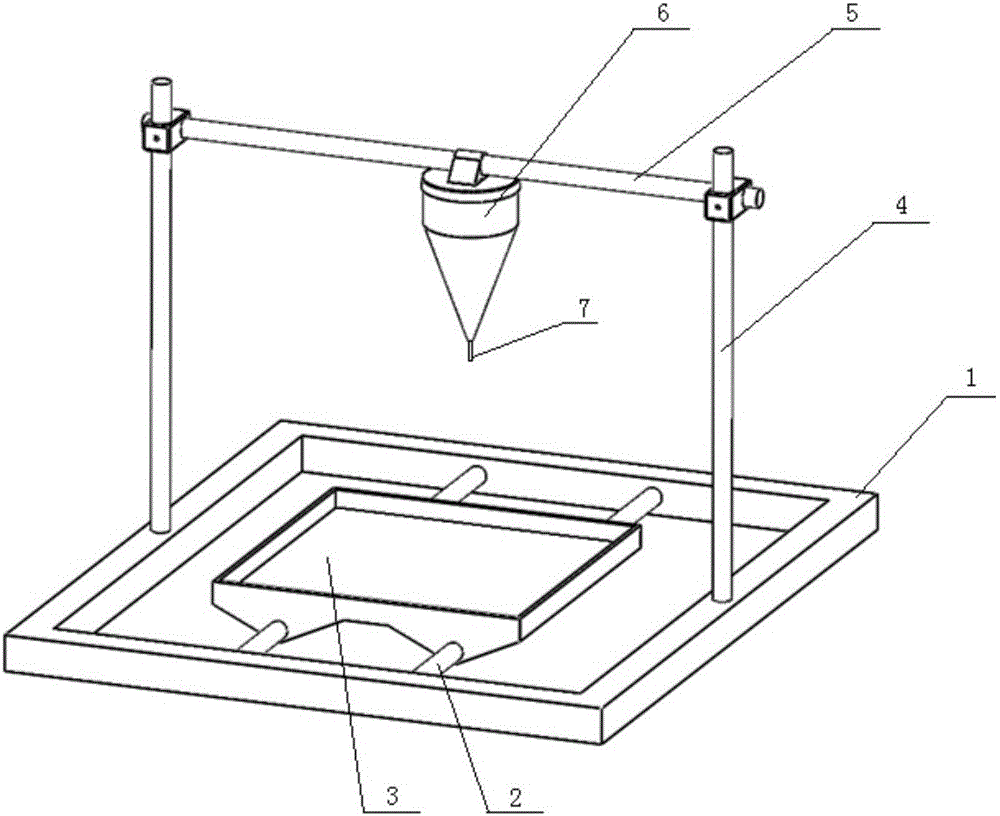
Method for preparing graphene nanobelt fibers with 3D solution printing technology
ActiveCN106006608AImprove flexibilityHigh precisionMaterial nanotechnologyAdditive manufacturing apparatusFiberPolymer science
The invention discloses a method for preparing graphene nanobelt fibers with a 3D solution printing technology, and relates to a method for preparing fibers with a 3D printing technology. The method aims at solving the technical problems that an existing graphene fiber processing method is complex in technology and long in production period, and includes the steps that 1, graphene nanobelts are prepared from multi-wall carbon nanotubes; 2, the graphene nanobelts are dispersed into high-purity deionized water to obtain a printing solution, the printing solution is printed to an ethyl acetate coagulating bath through a spraying head of a printer body of a 3D liquid printer, the cured product is taken out and dried, and the graphene nanobelt fibers are obtained. The method is simple in technology and high in accuracy, the shape and the size can be modified and adjusted, industrial production can be achieved, the tensile strength of the prepared graphene nanobelt fibers can be 90 MPa to 100 MPa, and meanwhile the graphene nanobelt fibers have high flexibility and can be used for the fields of energy storage devices, photovoltaic devices, sensors and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Sorting two-dimensional nanomaterials by thickness
ActiveUS9890043B2Different buoyant densityEffective dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsBoron nitrideLayer thickness
The present teachings provide, in part, methods of separating two-dimensional nanomaterials by atomic layer thickness. In certain embodiments, the present teachings provide methods of generating boron nitride nanomaterials having a controlled number of atomic layer(s).
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
PREPARATION METHOD OF GRAPHENE NANORIBBON ON h-BN
ActiveUS20160260604A1Improve electrical performanceQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGraphene nanoribbonsGraphene nanoribbonsBand shape
A preparation method of a graphene nanoribbon on h-BN, comprising: 1) forming a h-BN groove template with a nano ribbon-shaped groove structure on the h-BN by adopting a metal catalysis etching method; 2) growing a graphene nanoribbon in the h-BN groove template by adopting a chemical vapor deposition method. In the present invention, a CVD method is adopted to directly prepare a morphology controllable graphene nanoribbon on the h-BN, which helps to solve the long-term critical problem that the graphene is difficult to nucleate and grow on an insulating substrate, and to avoid the series of problems introduced by the complicated processes of the transferring of the graphene and the subsequent clipping manufacturing for a nanoribbon and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coating of Graphene
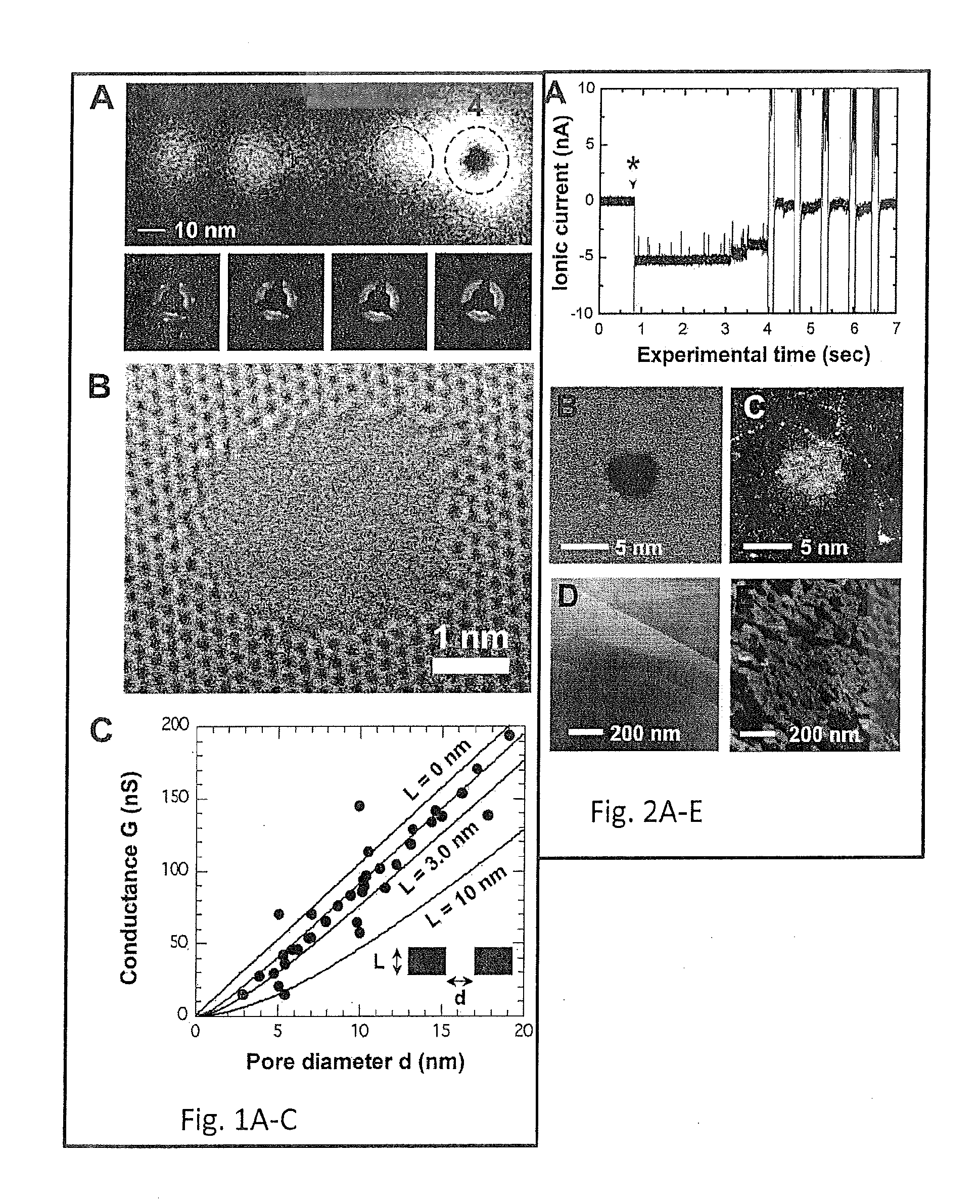
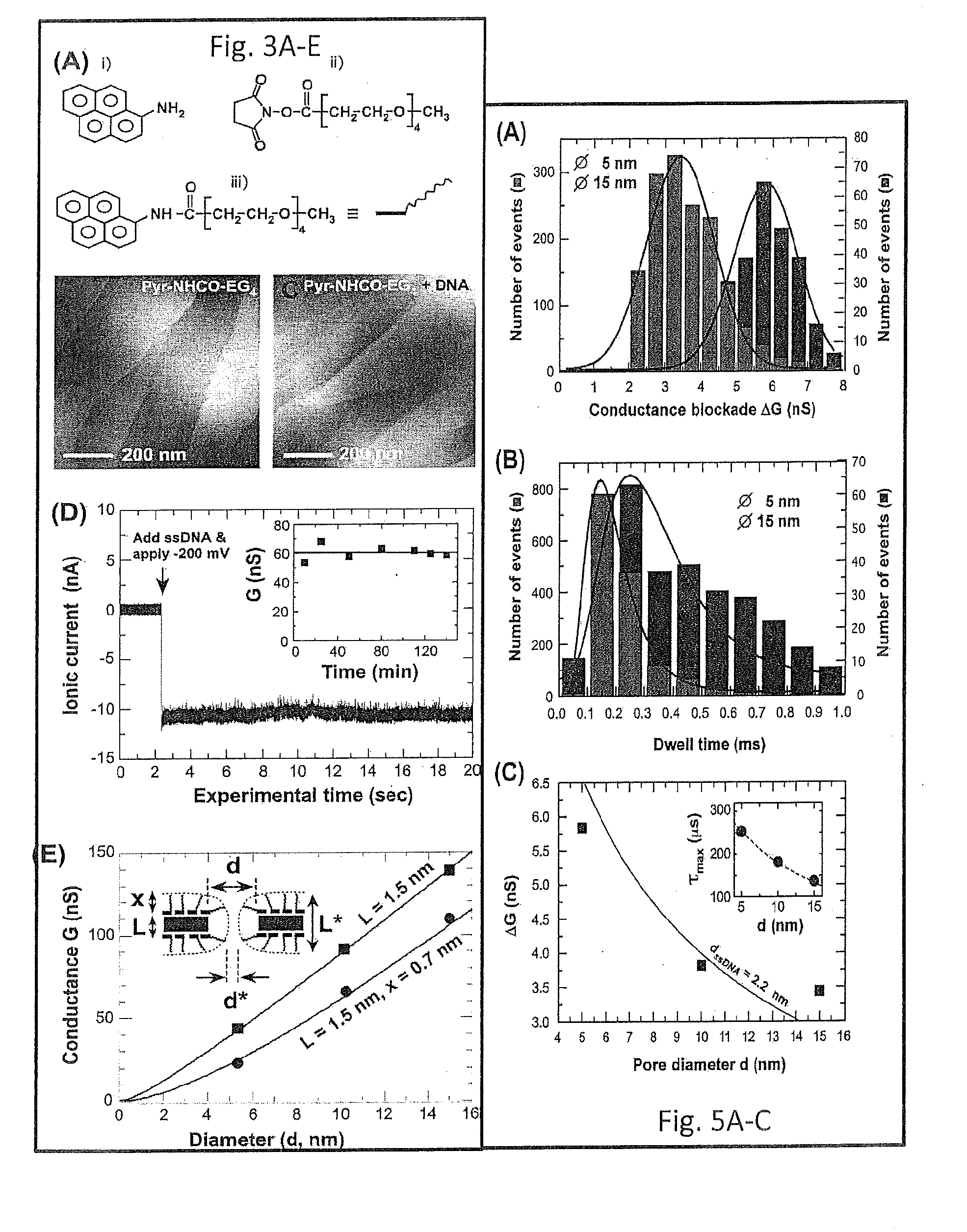
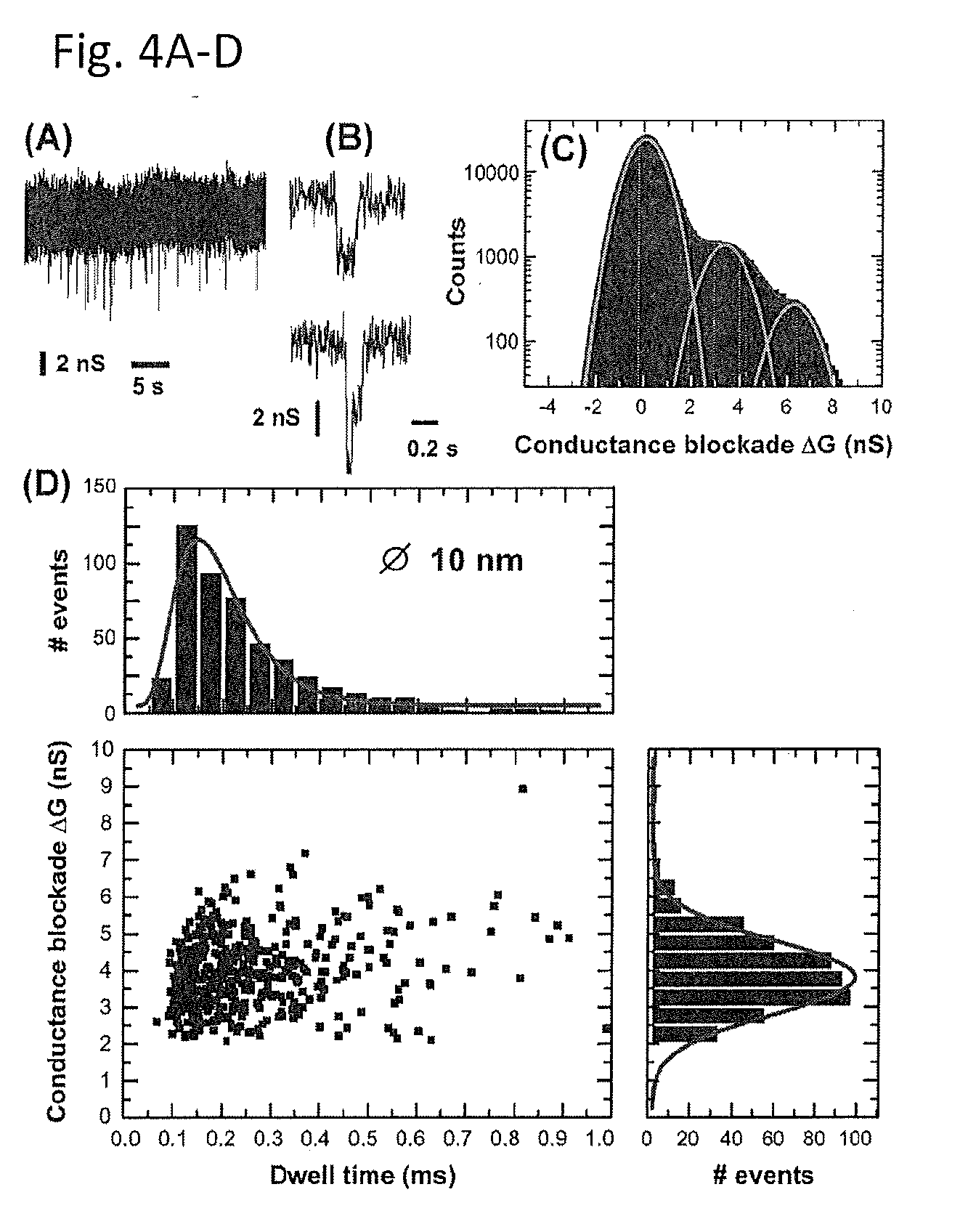
InactiveUS20160060124A1Stronger DNA clogging of the pore is inducedQuality improvementLayered productsSingle layer grapheneGraphene coatingCvd graphene
Owner:TECH UNIV DELFT
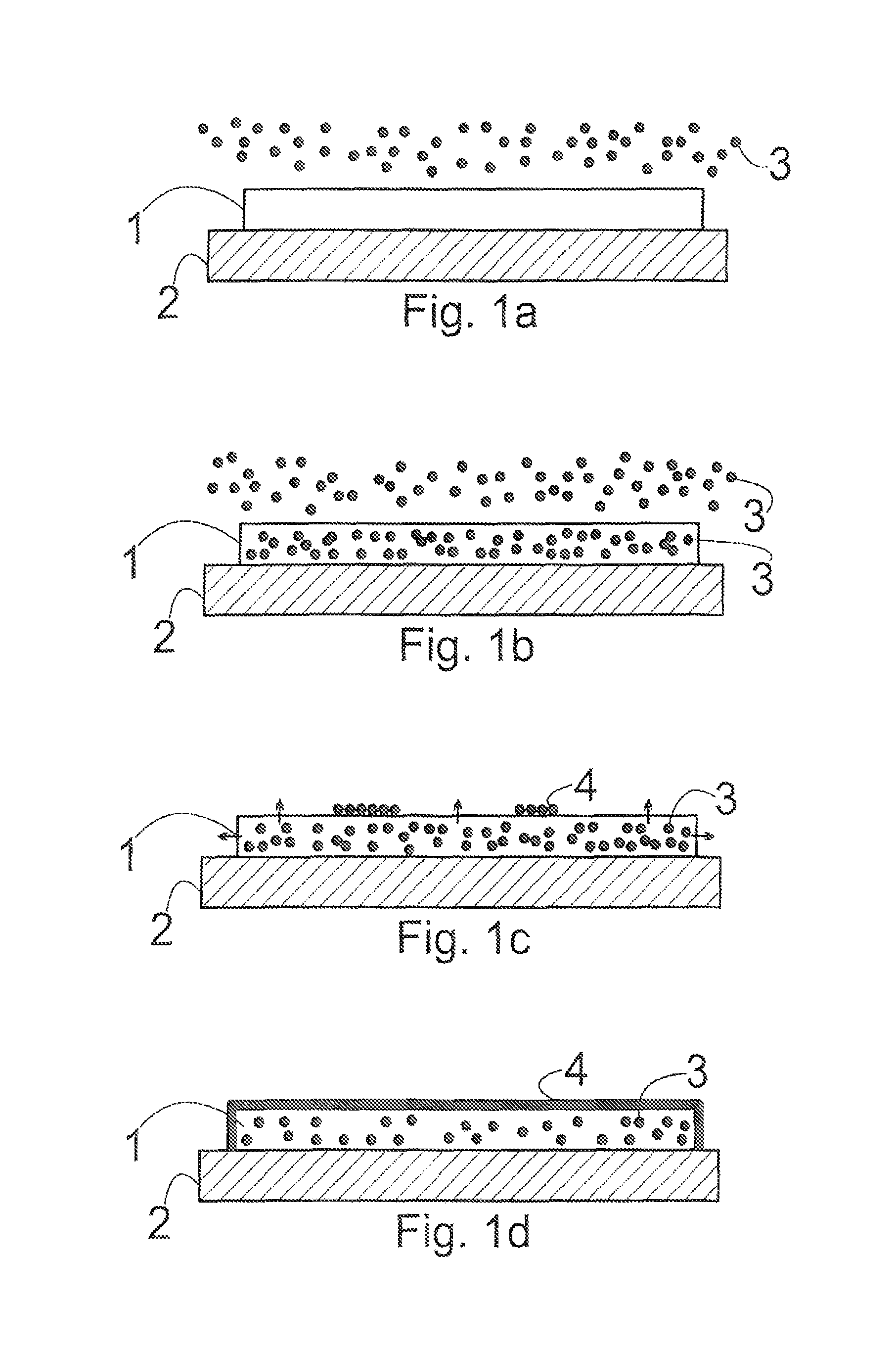
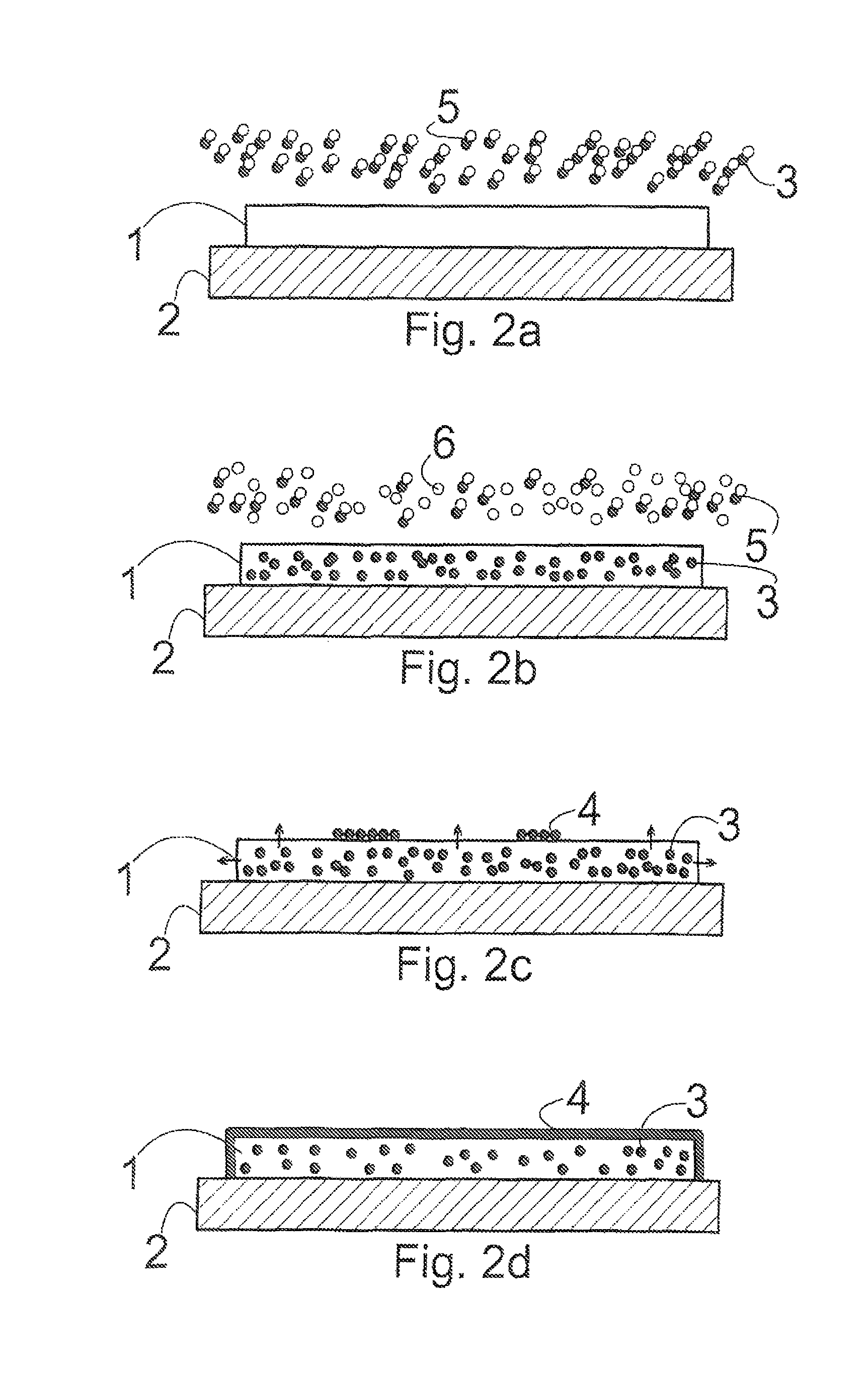
Crystalline surface structures and methods for their fabrication
InactiveUS9394599B2Simpler and cheap and more versatile methodLow costMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureCrystal structureSurface structure
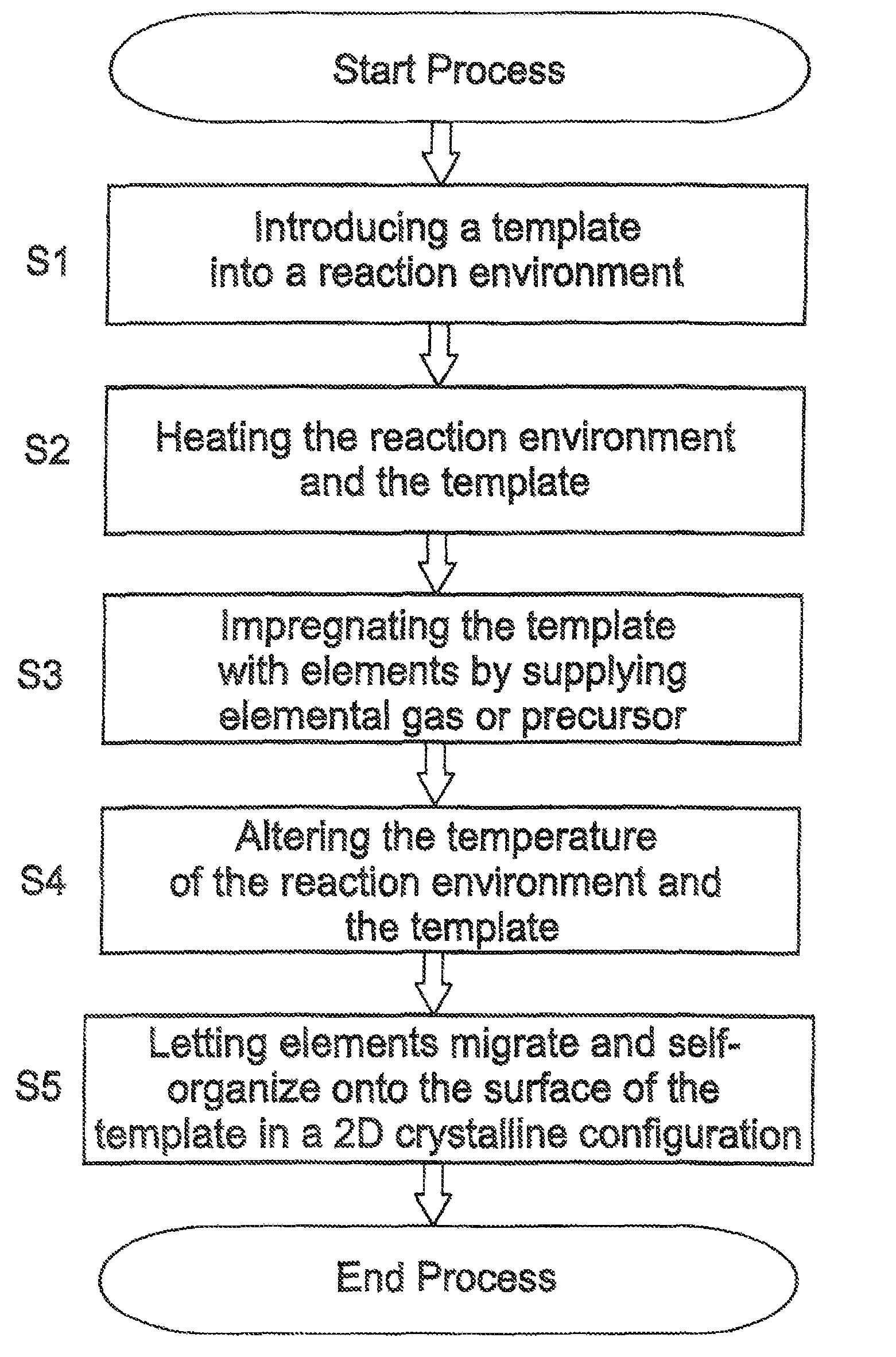
A method for fabricating crystalline surface structures (4) on a template (1). The method comprises the steps of providing a template (1) into a reaction environment, wherein one or more elements (3) required for the formation of the crystalline surface structure (4) are contained within the template (1); heating the template (1) inside the reaction environment to increase the mobility of the element (3) within the template (1), and to increase the surface diffusion length of the element (3) on the template-environment interface; and activating the template (1) by altering the conditions within the reaction environment, to make the mobile element (3) slowly migrate towards the template-environment interface and to make the element (3) organize on the surface of the template (1) as a crystalline structure (4).
Owner:CANATU OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com