Patents
Literature
222results about "Hot plugging-unplugging power/load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Point of load regulator having a pinstrapped configuration and which performs intelligent bus monitoring
ActiveUS20060149396A1Low costVolume/mass flow measurementHardware monitoringPoint of loadVoltage converter
A new system-level approach to managing the delivery of DC voltage and current. Several system level functions may be enabled without requiring separate ICs to perform those functions. Supervisory functions for a voltage converter may be performed by a central control module or chip that may be coupled to point-of-load voltage converters comprised in digital power management devices (DPMD) through a serial digital bus. The DPMDs may also use the high-speed serial digital bus to provide real-time feedback information to the central control module or chip. Single DPMDs may be combined together in a current sharing configuration in a “plug-and-play” fashion, where the control logic in each DPMD is capable of automatically establishing control loops required a multi-phase supply. Feedback necessary for establishing control may be transmitted across the digital bus coupling the devices. The supervisory functions may be included in each DPMD, which may communicate with each other over a serial digital bus, where the DPMDs singly or together may operate to perform control of their respective POLs, enabling configurations that do not require a central control module.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
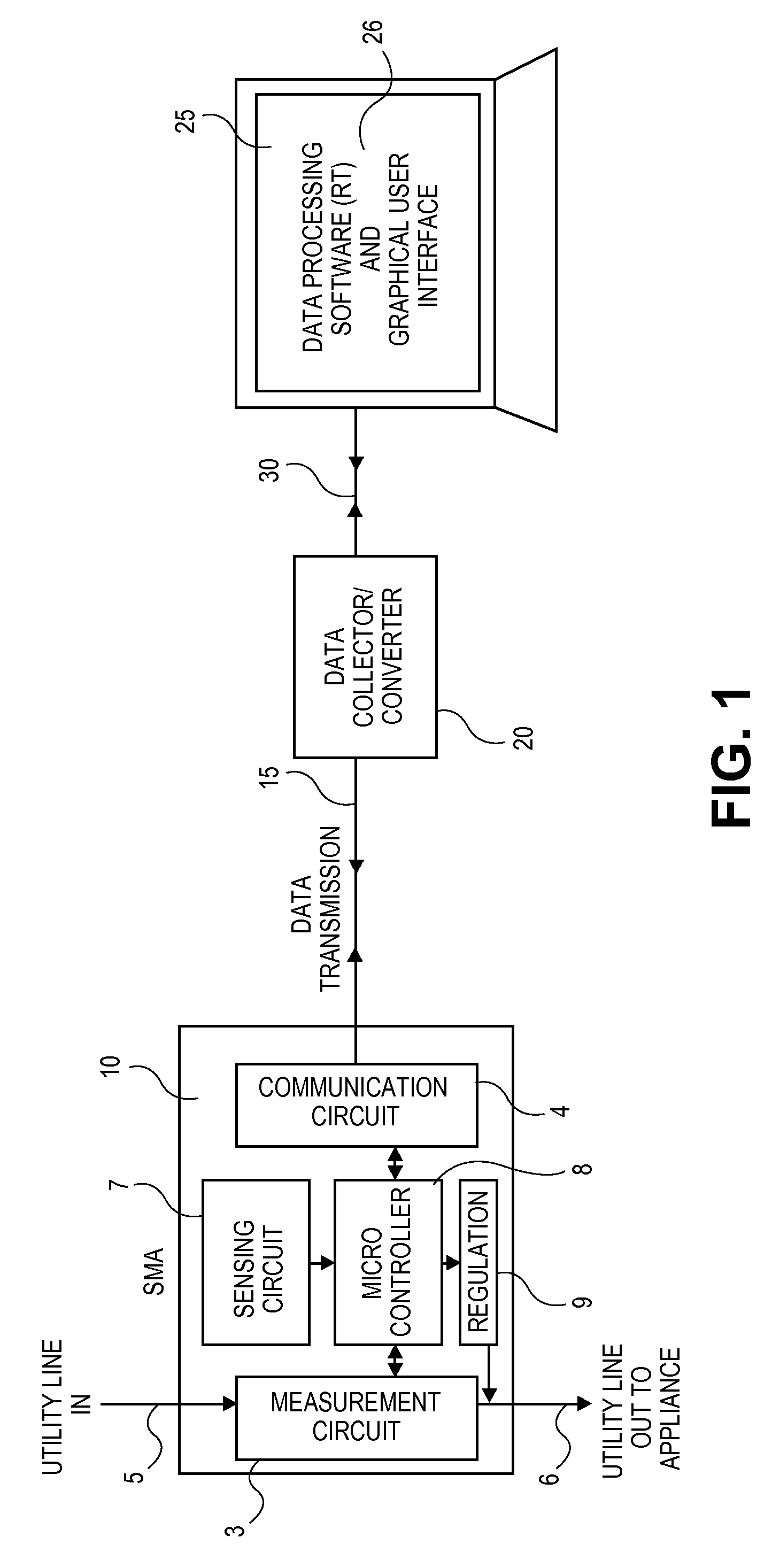
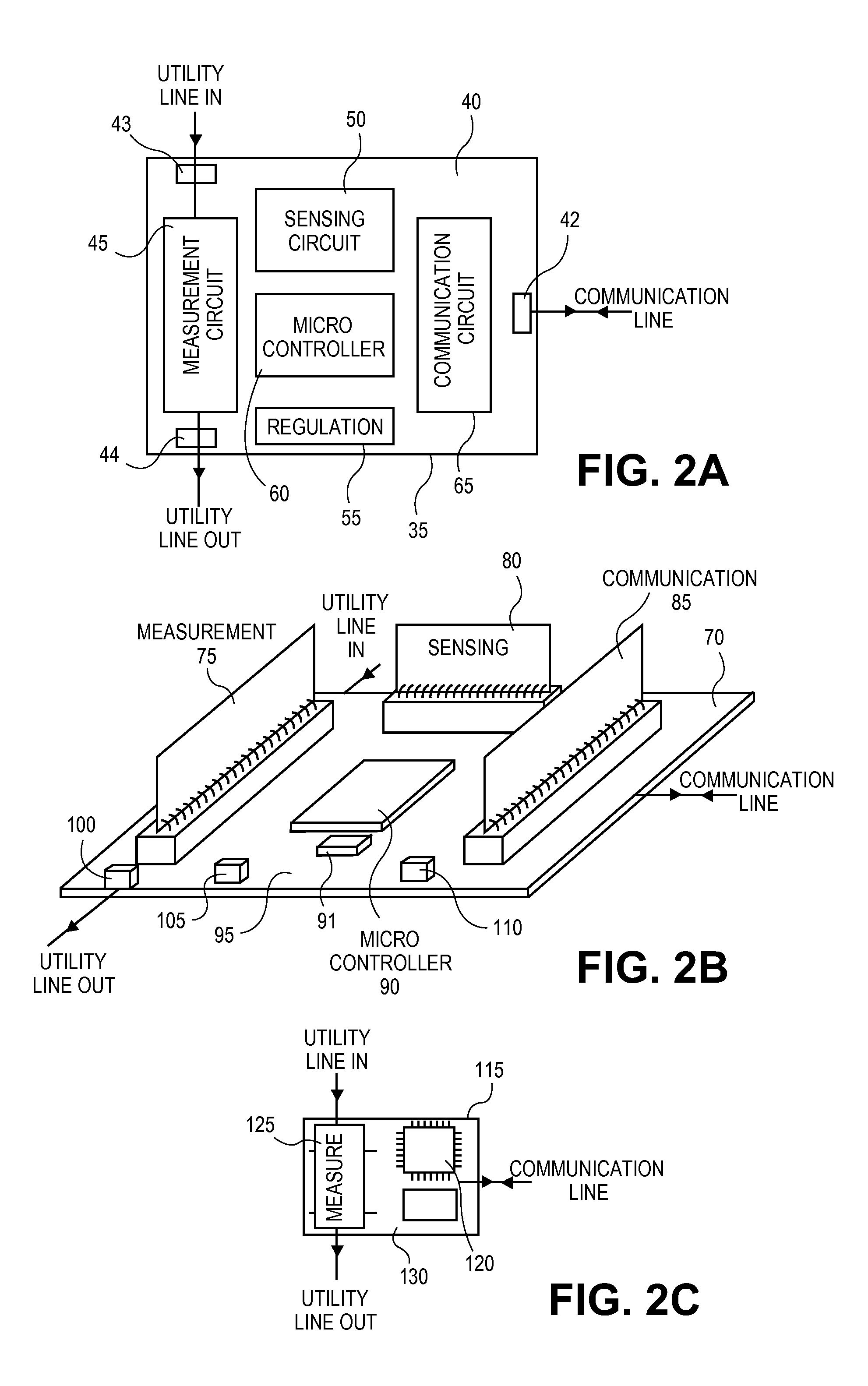
Optimizing Utility Usage by Smart Monitoring
InactiveUS20110082599A1Not cause excessive noiseStreamline data collectionLevel controlVolume/mass flow measurementUnique identifierSmart surveillance
A system for optimizing utility usage is described. The system comprises a monitoring device adapted to be connected to a utility point, a utility consuming device and a central processing unit (CPU). The monitoring device is configured to regulate utility usage information of the utility consuming device and is further configured to assign a unique identifier to the monitoring device. The monitoring device comprises a measurement circuit for measuring utility usage information, wherein the measurement circuit is coupled to the utility point. The monitoring device is configured to communicate with the CPU, wherein the monitoring device is configured to transmit utility usage information of the utility consuming device to the CPU on the unique identifier and wherein the monitoring device is configured to receive utility usage information of the utility consuming device and wherein the CPU is configured to process the utility usage information based on the unique identifier.
Owner:SHINDE MAKARAND +2
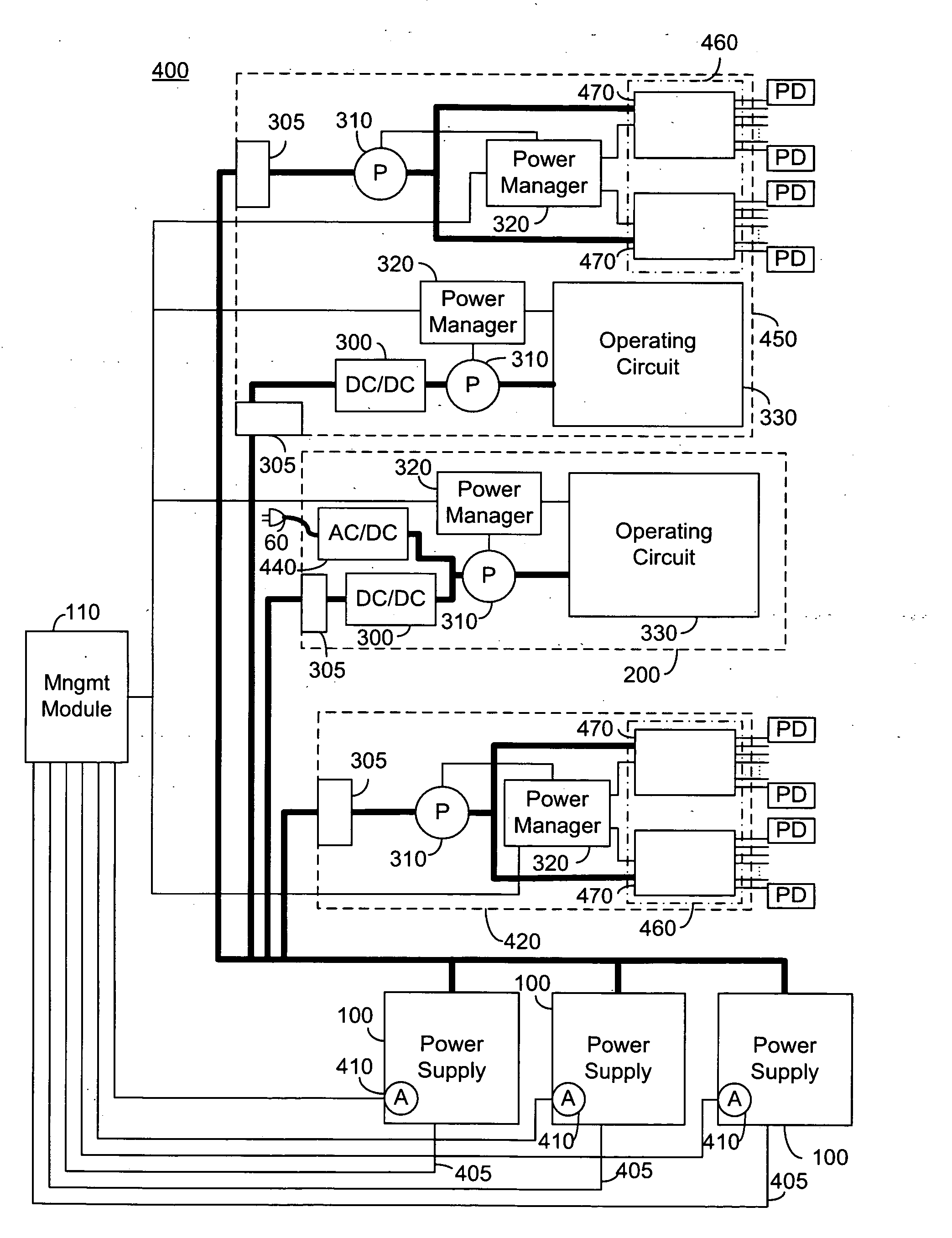
Rack level power management
InactiveUS20060082222A1Reduce power consumptionServersLoad balancing in dc networkEngineeringPower budget
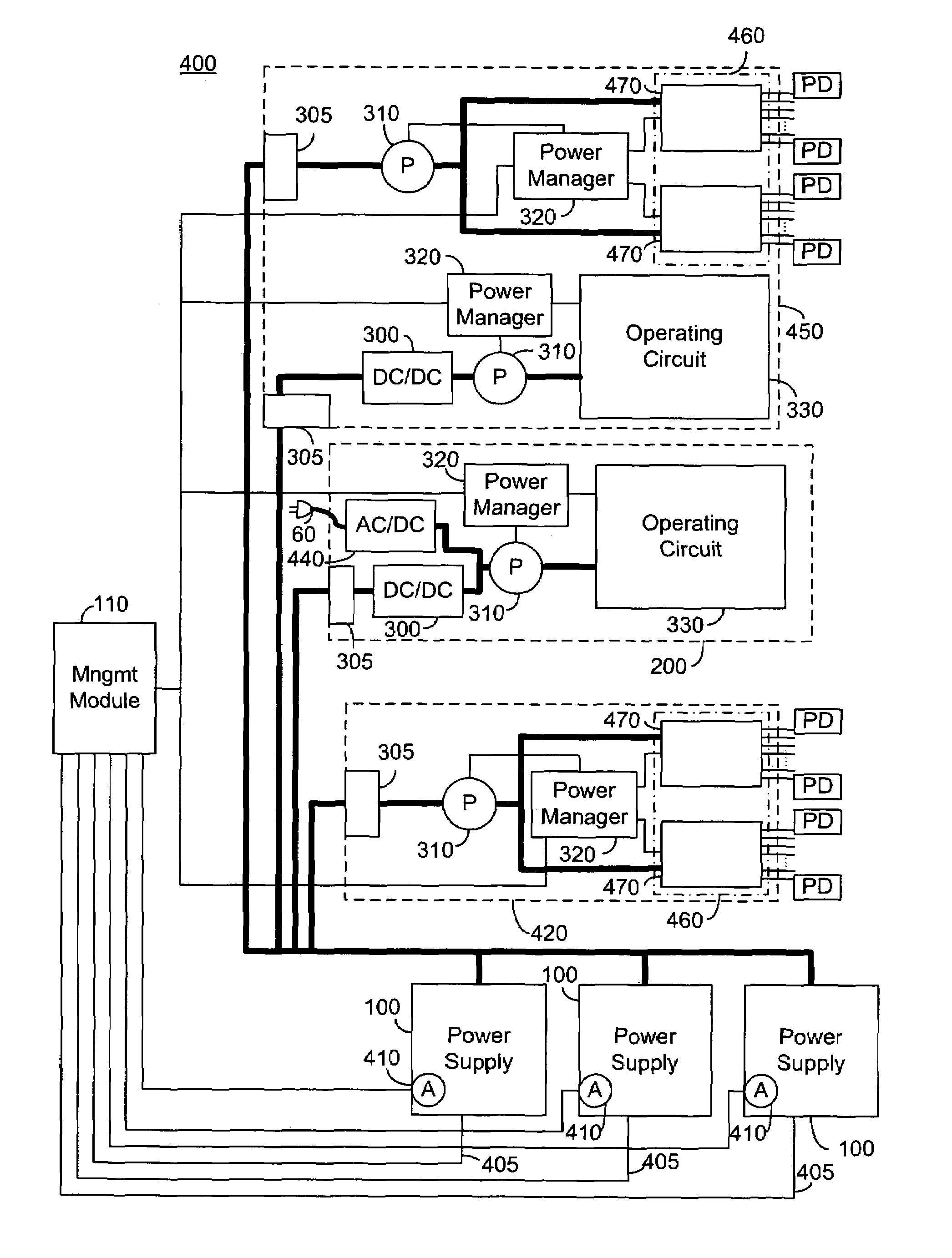
A system for rack level power management, the system comprising: at least one power source; a management module; and a plurality of power managed modules in communication with the management module and connected to draw power from the at least one power source, each of the plurality of power managed modules comprising a power manager and an operating circuit, the operating circuit being operable at a plurality of power drawing levels responsive to the power manager, the management module being operative to allocate a power budget to each of the plurality of power managed modules and communicate the allocated power budgets to the power managers, each of the power managers being operative to control the operating circuit of the power managed module to be operable at a power drawing level within the allocated budget.
Owner:NEVERMORE SOLUTIONS
Modular power supply
InactiveUS6121695AIncrease profitBatteries circuit arrangementsVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityCoupling
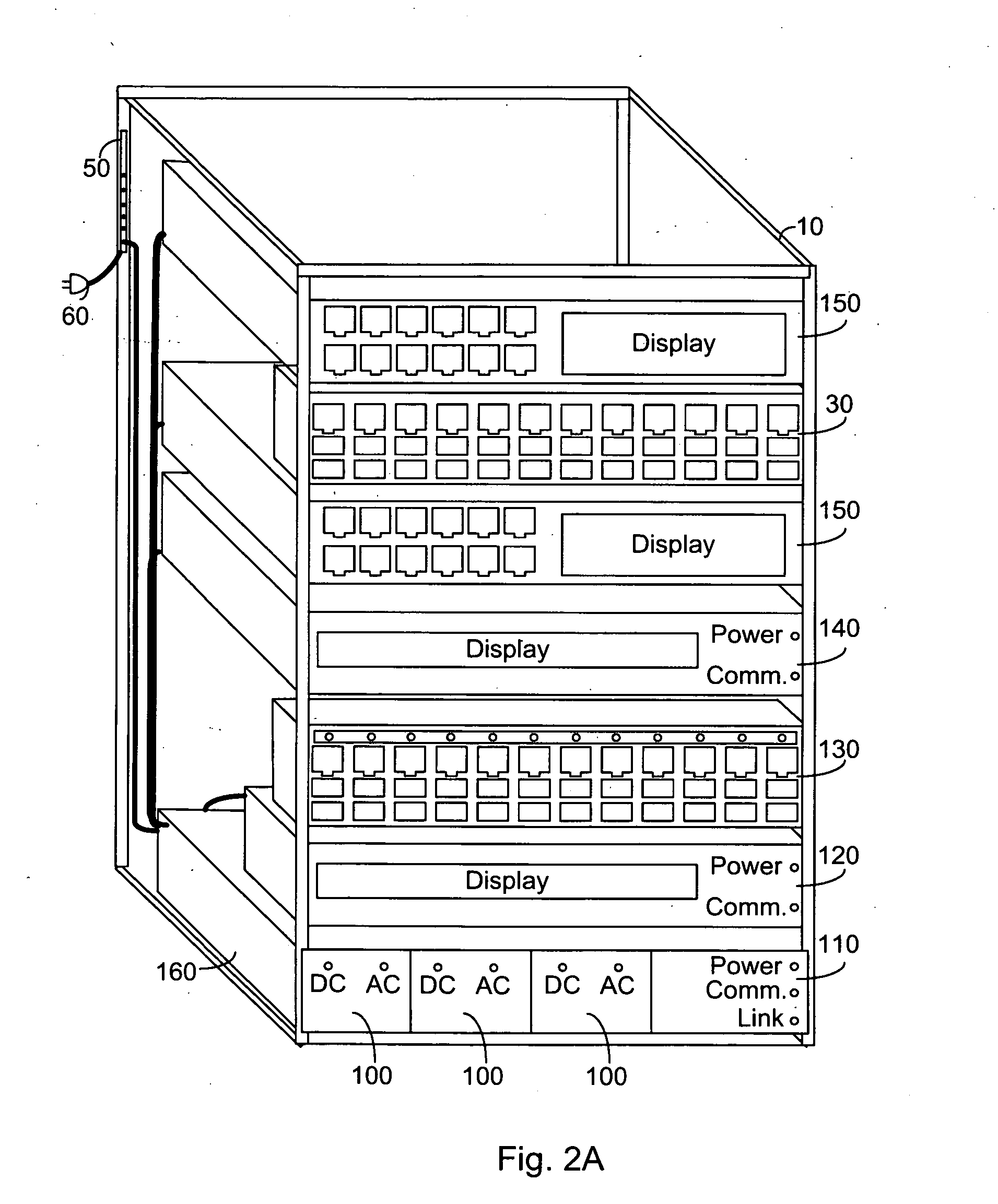
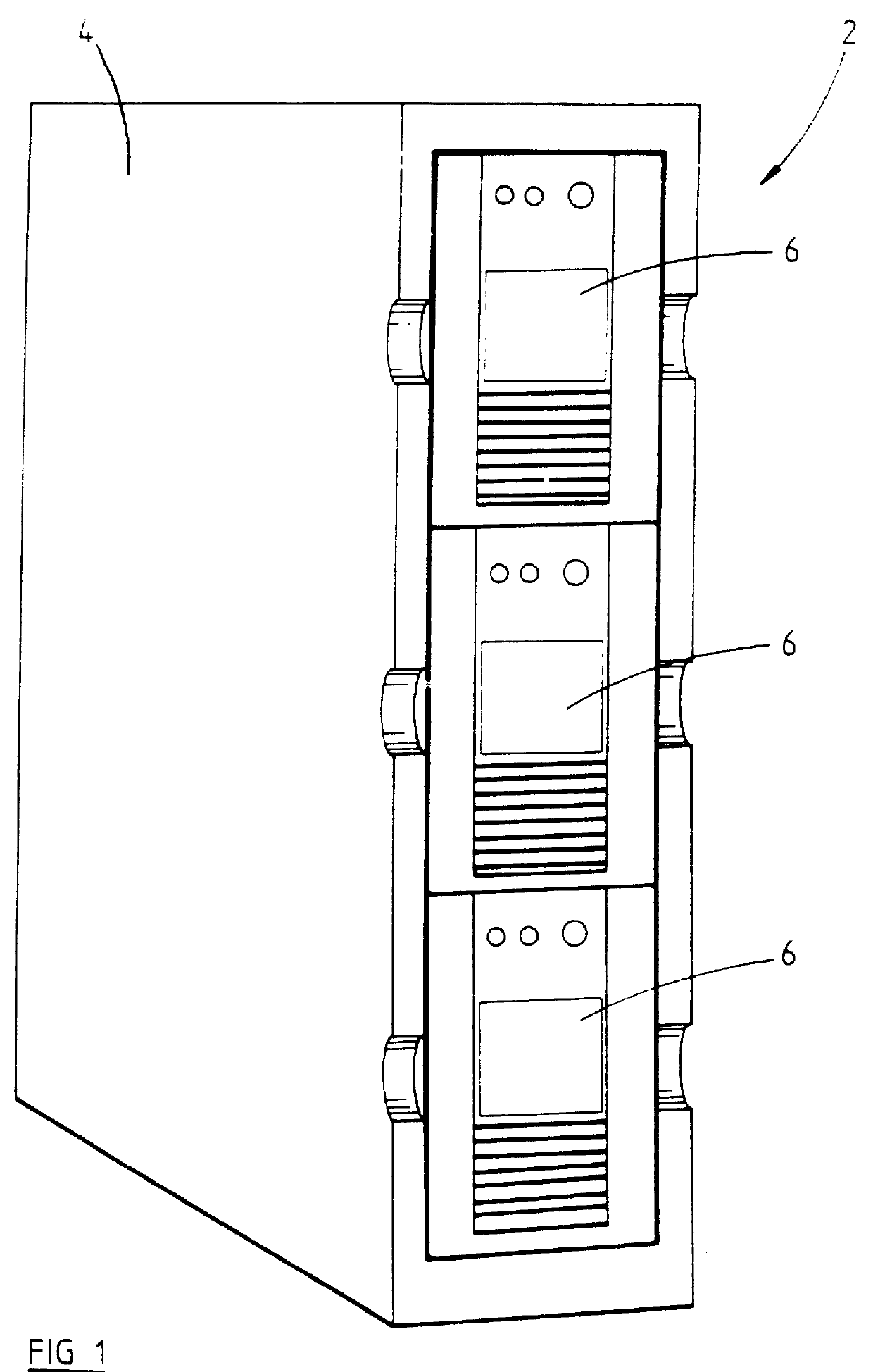
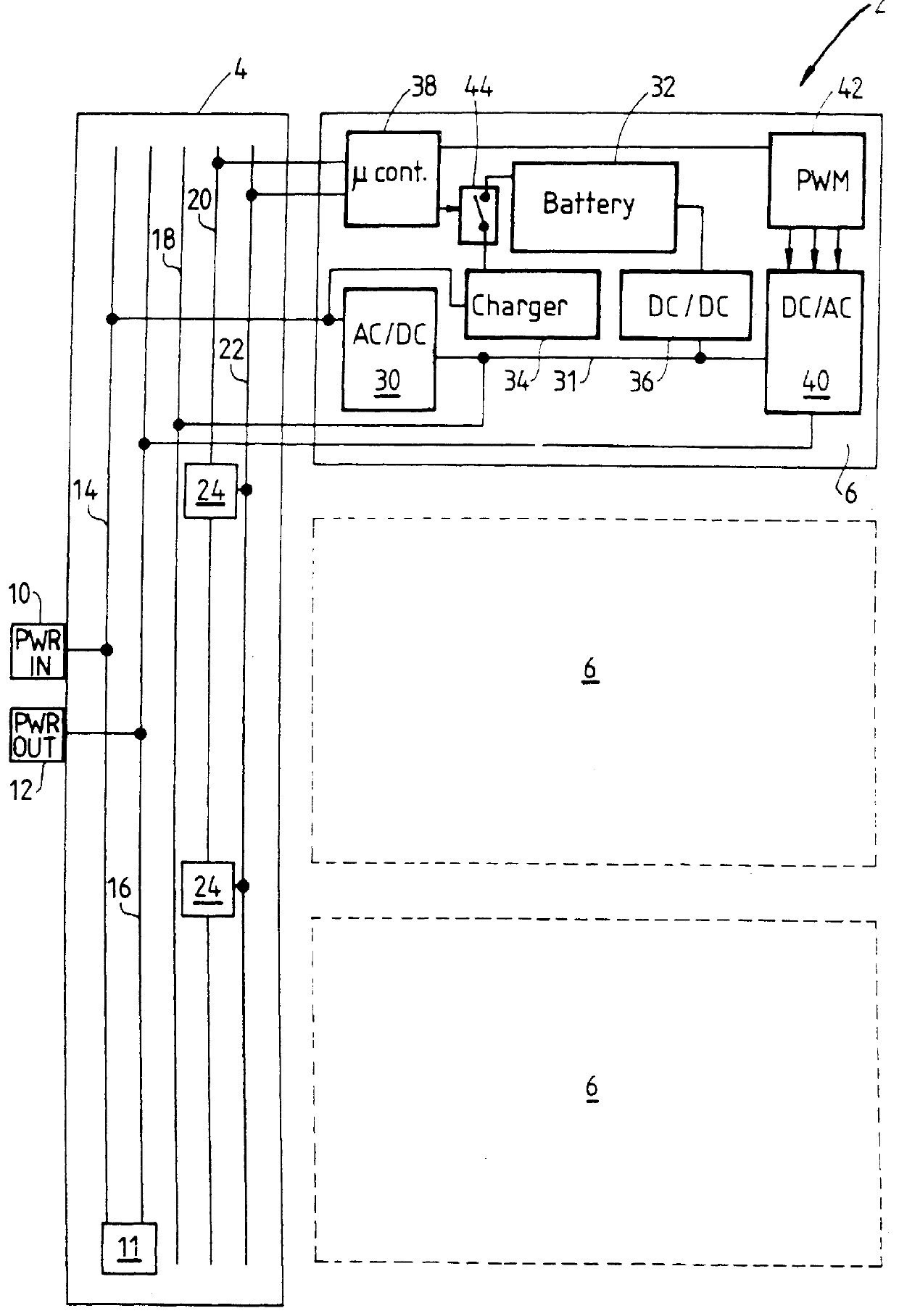
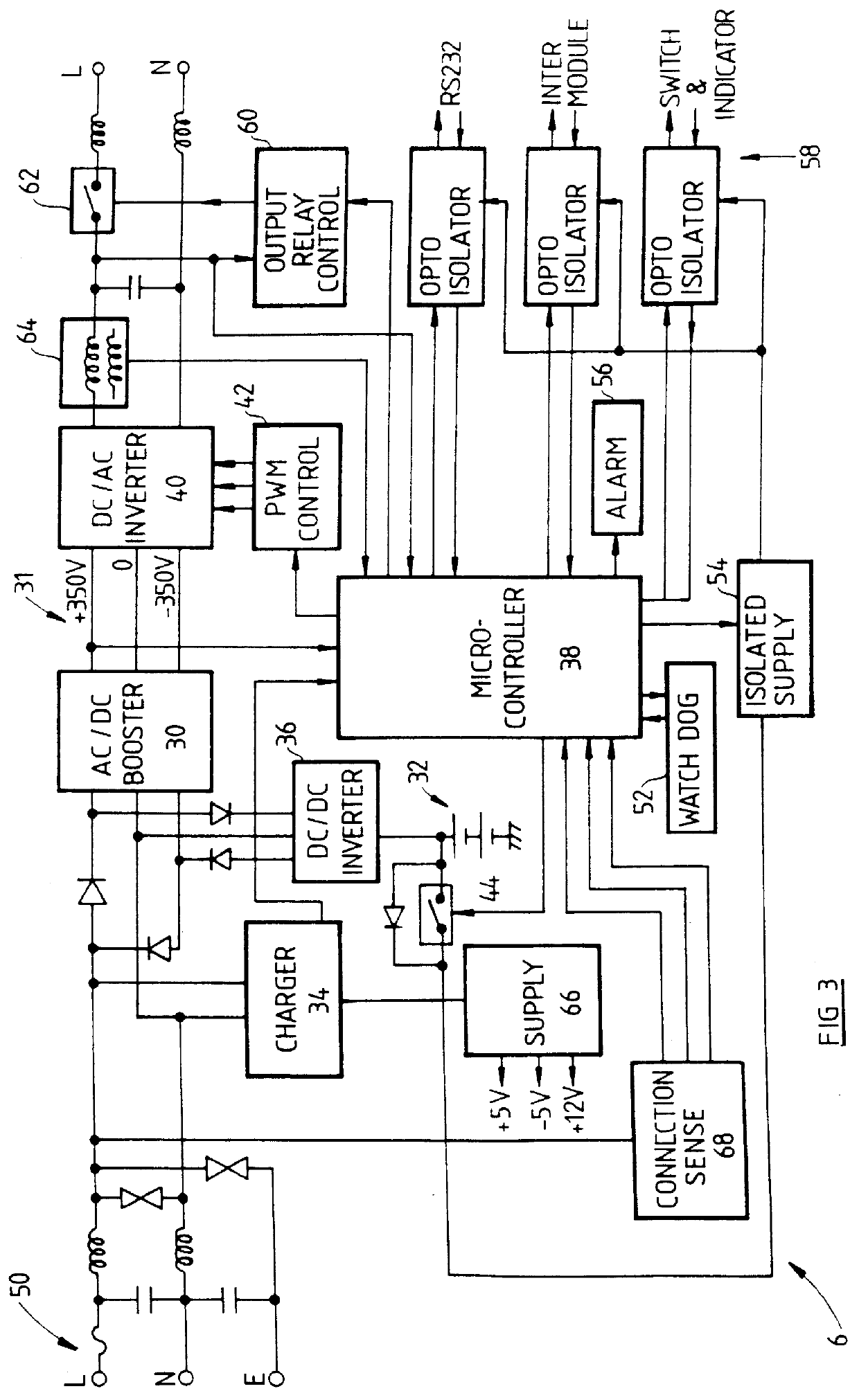
PCT No. PCT / AU96 / 00637 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 23, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 23, 1998 PCT Filed Oct. 10, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 14206 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 17, 1997A modular power supply (2) suitable for application as an uninterruptable power supply for use with electrical equipment such as computers. A module (6) of the power supply may include a battery (32), a charging circuit for the battery (34), a power supply circuit coupled to mains electricity and the battery (30, 36, 40), and a control circuit (38) for selectively providing power to the electrical equipment (12) by way of the power supply circuit from either mains electricity (10) or the battery as source. The module is also provided with a coupling which is adapted to connect the module in parallel with at least one other module. A housing may be provided to receive a plurality of modules, which are connected together in parallel by way of plugs and sockets when received in the housing. The plugs and sockets and the control circuit may be adapted to enable "hot-swapping" of the modules from the housing. The modules may also be interconnected in the housing by way of a control line (20) which enables communication of the modules for making a majority rules decision concerning the provision of power from the mains or battery on the basis of fluctuations in the electrical mains supply.
Owner:ALLIANCE TRUSTEE BERHAD
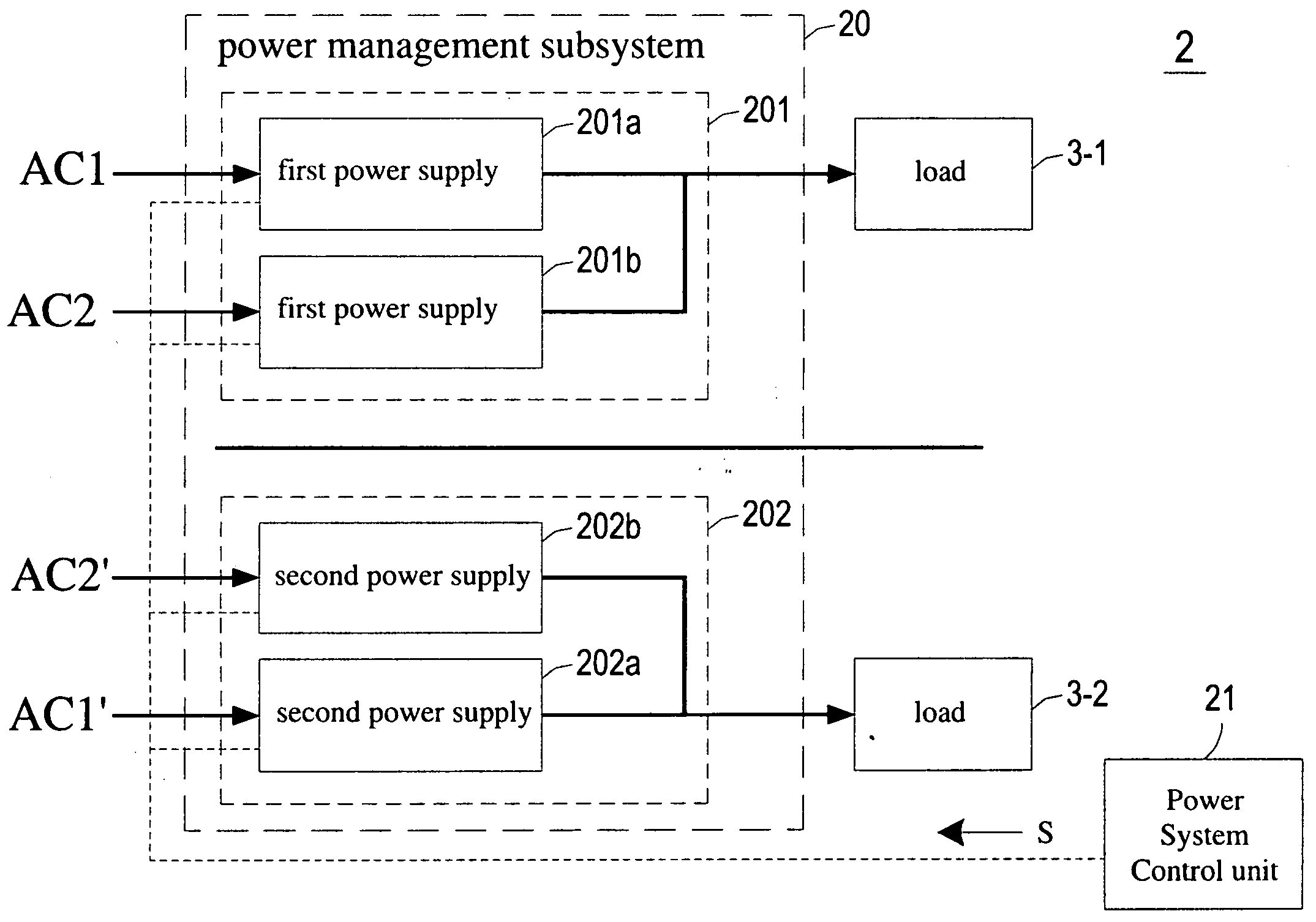
Power management system capable of saving power and optimizing operating efficiency of power supplies for providing power with back-up or redundancy to plural loads
ActiveUS20090271642A1Save powerOperating efficiency is optimizedBatteries circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsOne passEngineering
The present invention relates to a power management system comprising at least one power management subsystem. Each power management subsystem comprises a first power module coupled to a first load and comprising at least one first power supply for supplying power to the first load; a second power module coupled to a second load and comprising at least one second power supply, wherein at least one second power supply is retractably installed in the second power module and selectively coupled to the second load; and a pass-through module comprising at least one pass-through unit retractably installed in the second power module to replace with the at least one second power supply and selectively connecting the first power module to the second load for allowing the first power module to supply power to the second load.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for integrated active-diode-ORing and soft power switching
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
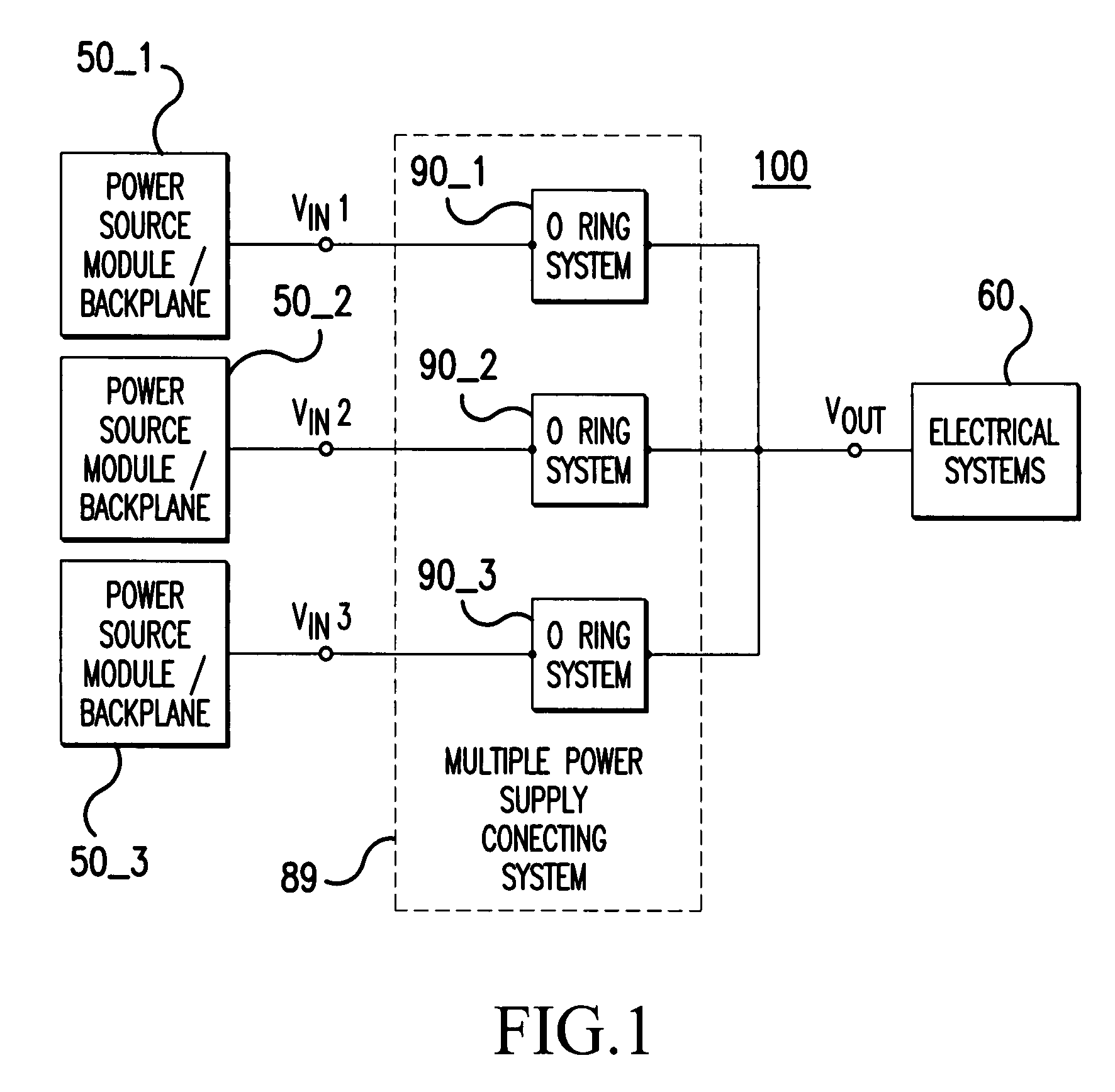
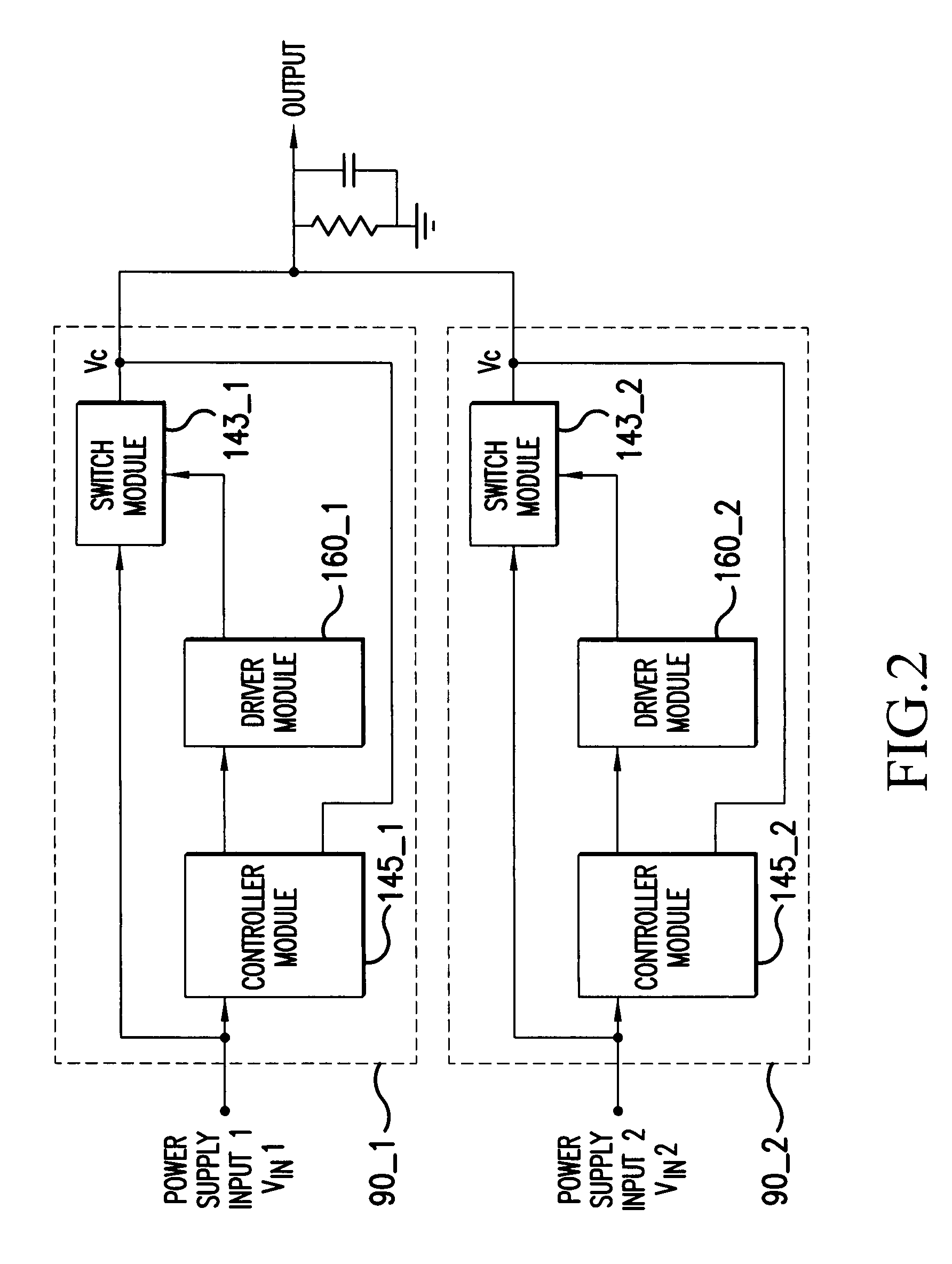
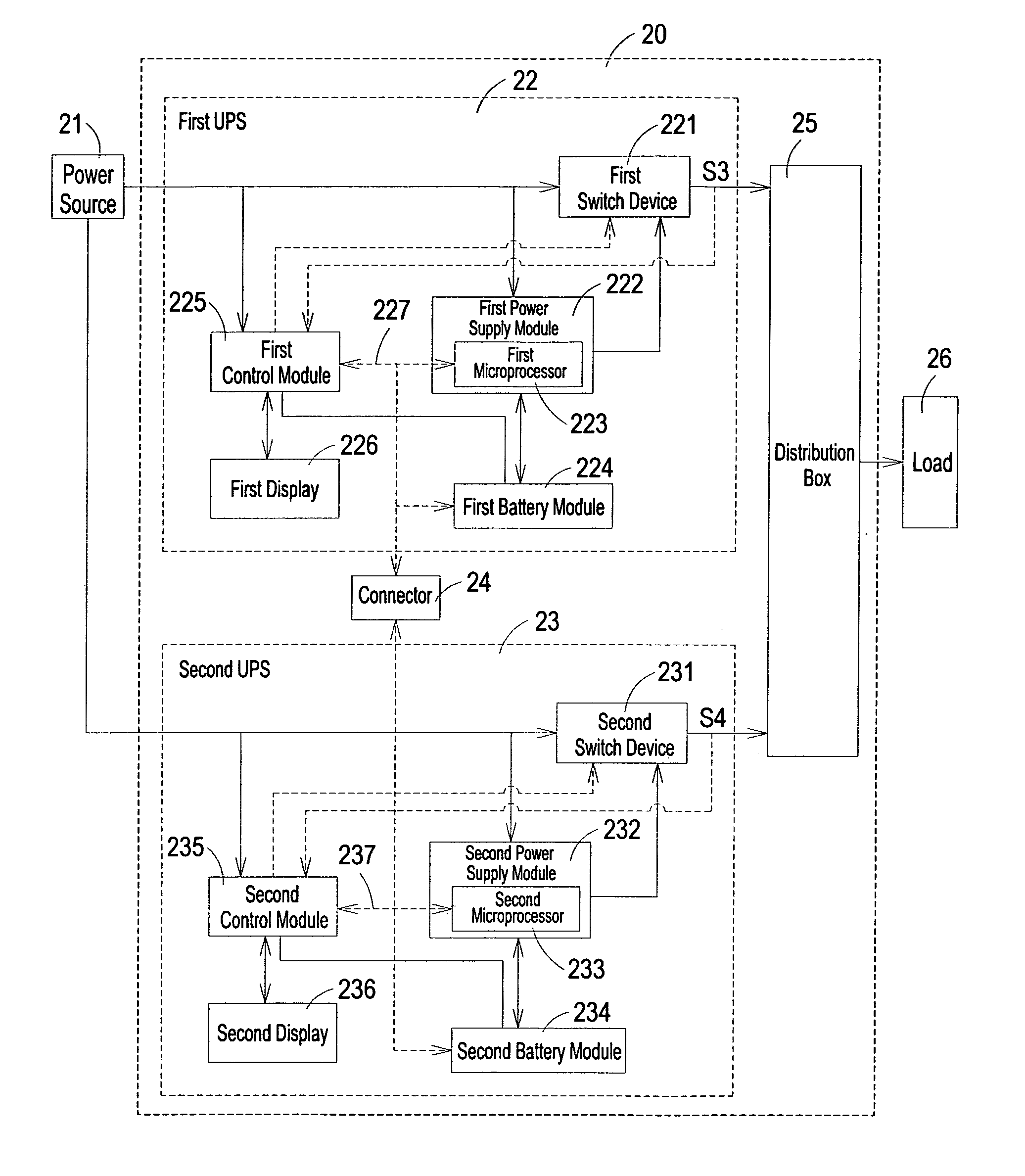
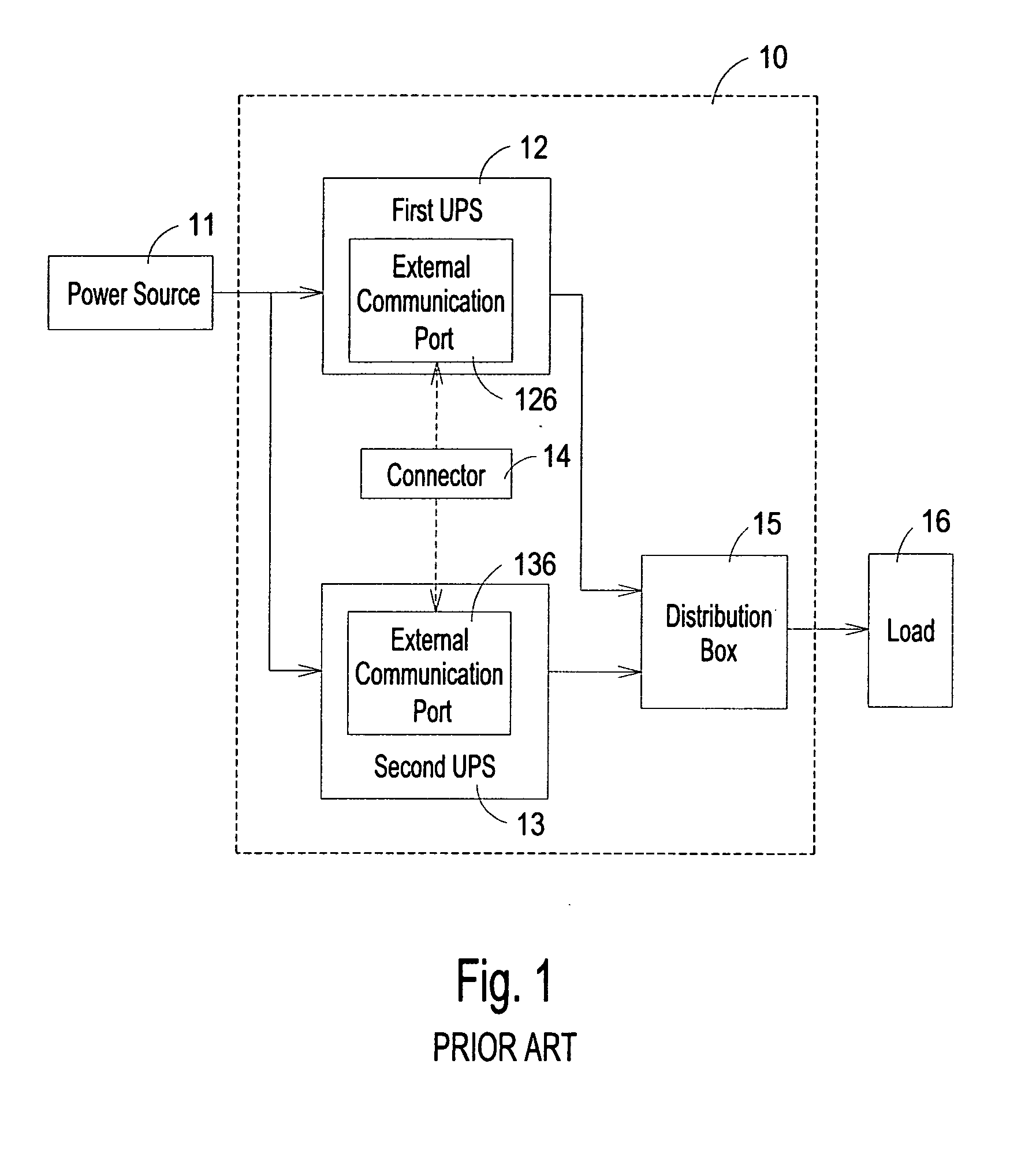
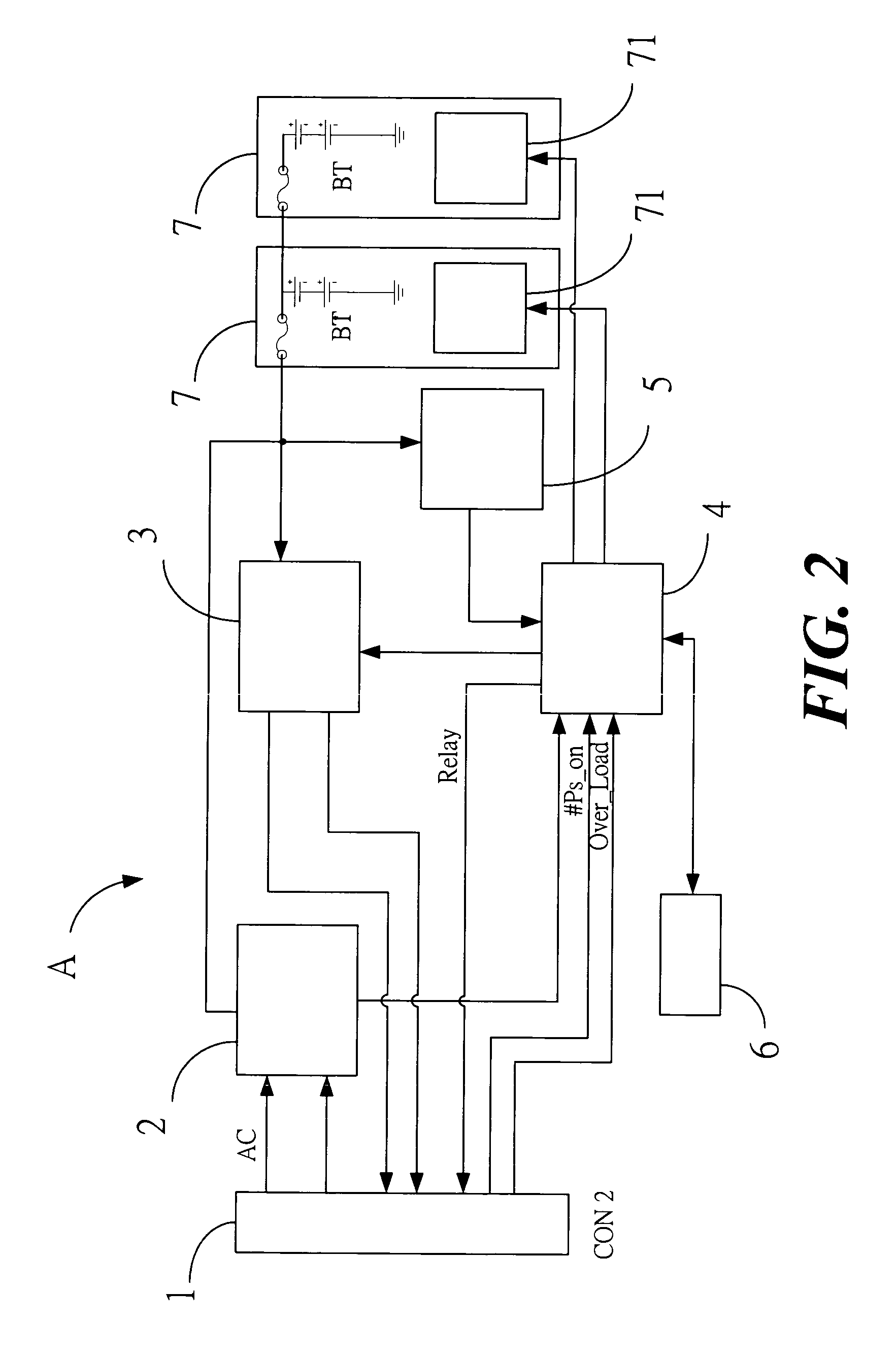
Parallel uninterruptible power supply system
InactiveUS20070114852A1Fast signal transmission rateShort response timeBatteries circuit arrangementsDc source parallel operationData signalEngineering
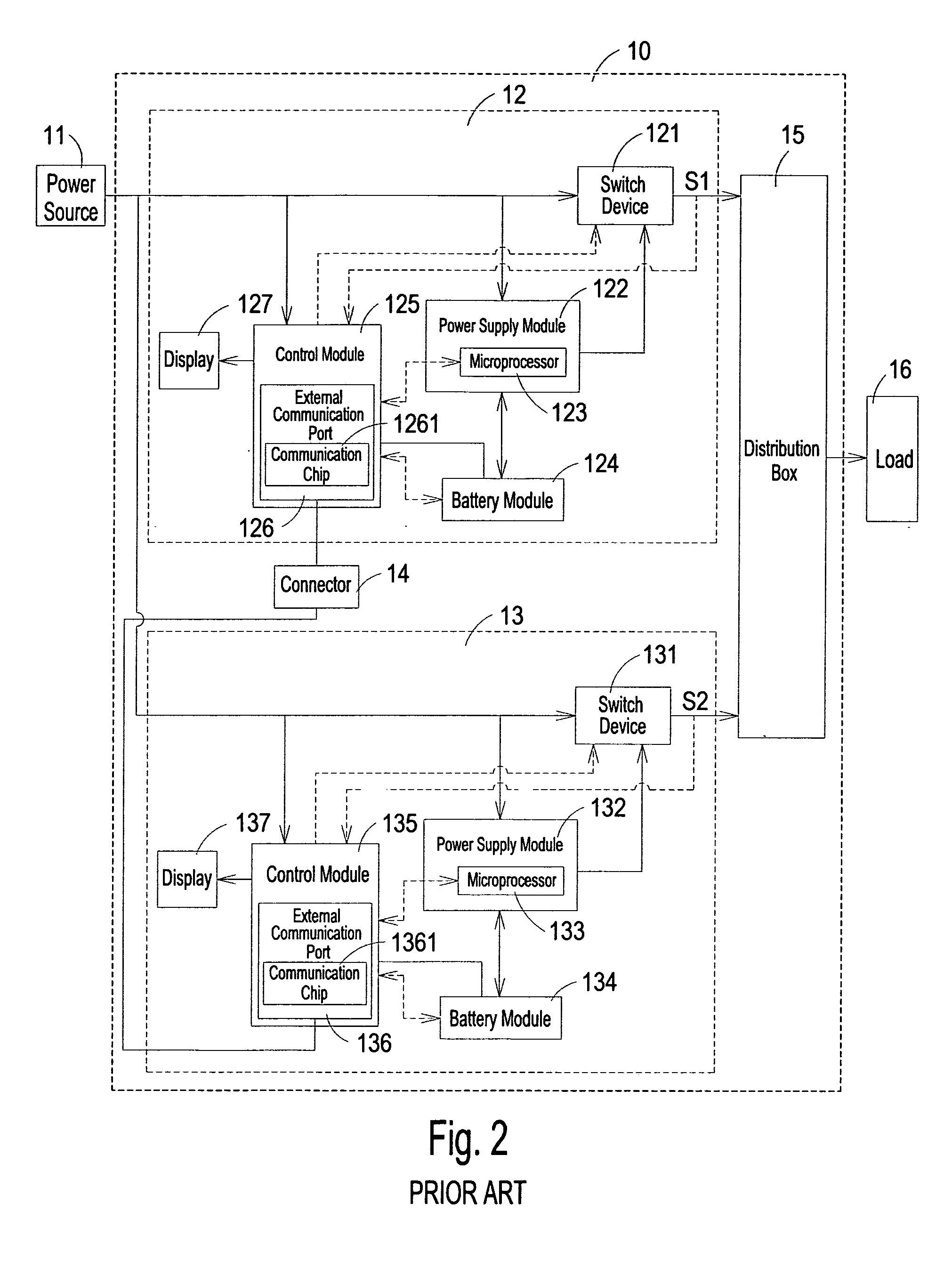
Provided is a parallel uninterruptible power supply system including a first uninterruptible power supply and a second uninterruptible power supply connected in parallel with each other, and a connector interconnecting a first signal transmission line of the first uninterruptible power supply and a second signal transmission line of the second uninterruptible power supply. A first control module of the first uninterruptible power supply can directly receive data signal outputted from a second power supply module and a second battery module of the second uninterruptible power supply, and a second control module of the second uninterruptible power supply can directly receive data signal outputted from a first power supply module and a first battery module of first uninterruptible power supply, so that the first uninterruptible power supply and the second uninterruptible power supply can communicate directly with each other.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Rack level power management
InactiveUS7400062B2Reduce power consumptionServersLoad balancing in dc networkPower budgetElectric power
A system for rack level power management, the system comprising: at least one power source; a management module; and a plurality of power managed modules in communication with the management module and connected to draw power from the at least one power source, each of the plurality of power managed modules comprising a power manager and an operating circuit, the operating circuit being operable at a plurality of power drawing levels responsive to the power manager, the management module being operative to allocate a power budget to each of the plurality of power managed modules and communicate the allocated power budgets to the power managers, each of the power managers being operative to control the operating circuit of the power managed module to be operable at a power drawing level within the allocated budget.
Owner:NEVERMORE SOLUTIONS
More compact and higher reliability power source system
InactiveUS20050180181A1Reduce rippleEasy dischargeDc source parallel operationPower supply for data processing
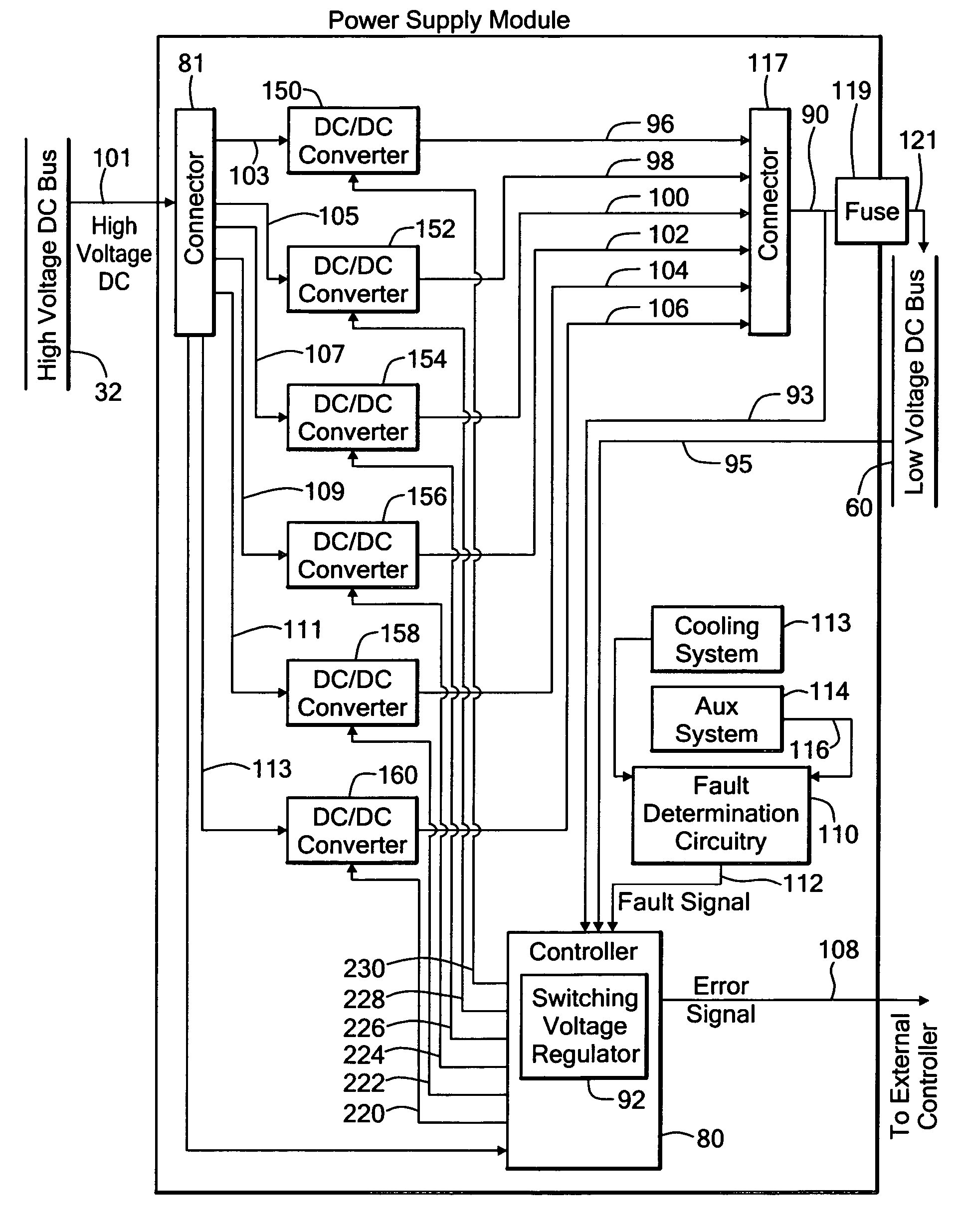
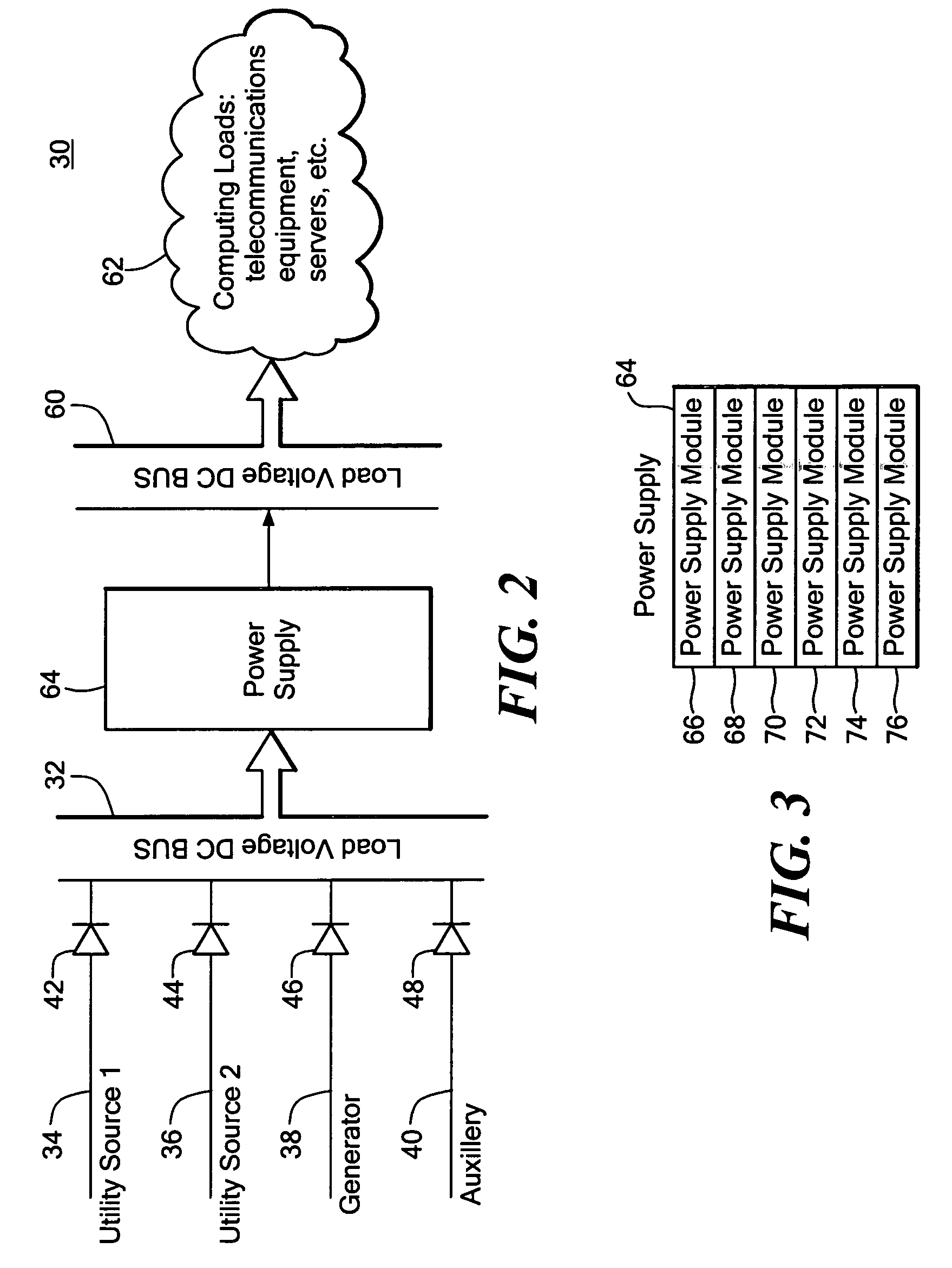
This invention features a more compact and higher reliability power source system for computing loads, the system including a high voltage DC bus connected to a number of DC sources each connected to the high voltage DC bus by a switch configured to deliver to the high voltage DC bus the DC source with the highest DC voltage, a low voltage DC bus connected to the computing loads, and a power supply including a number of DC / DC converters connected in parallel between the high voltage DC bus and the low voltage DC bus, and a controller configured to modulate each DC / DC converter to convert the high voltage on the high voltage DC bus to a low voltage output on the low voltage DC bus.
Owner:DIVERSIFIED TECH INC
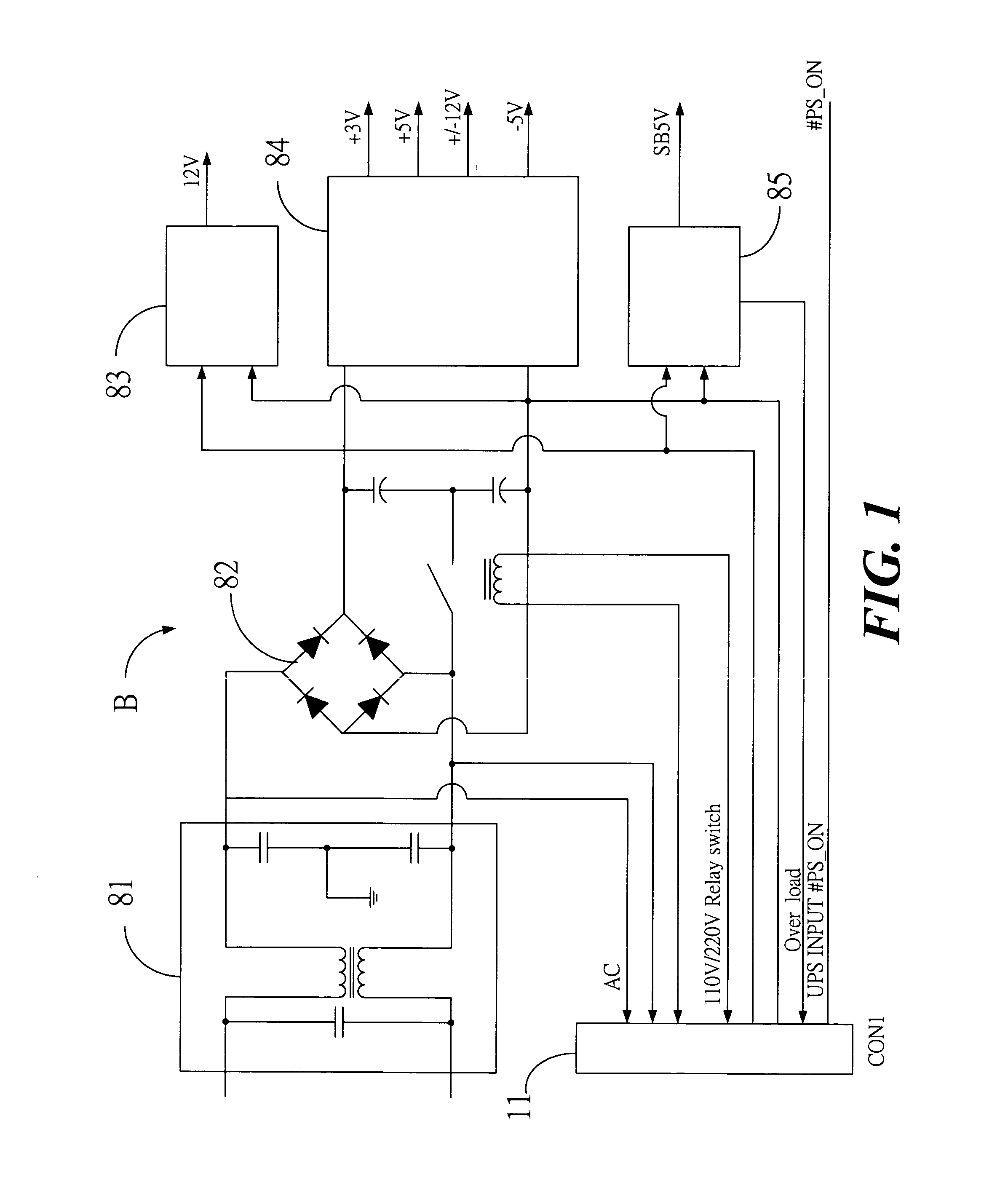
Uninterruptible power supply circuit having hot swappable battery module
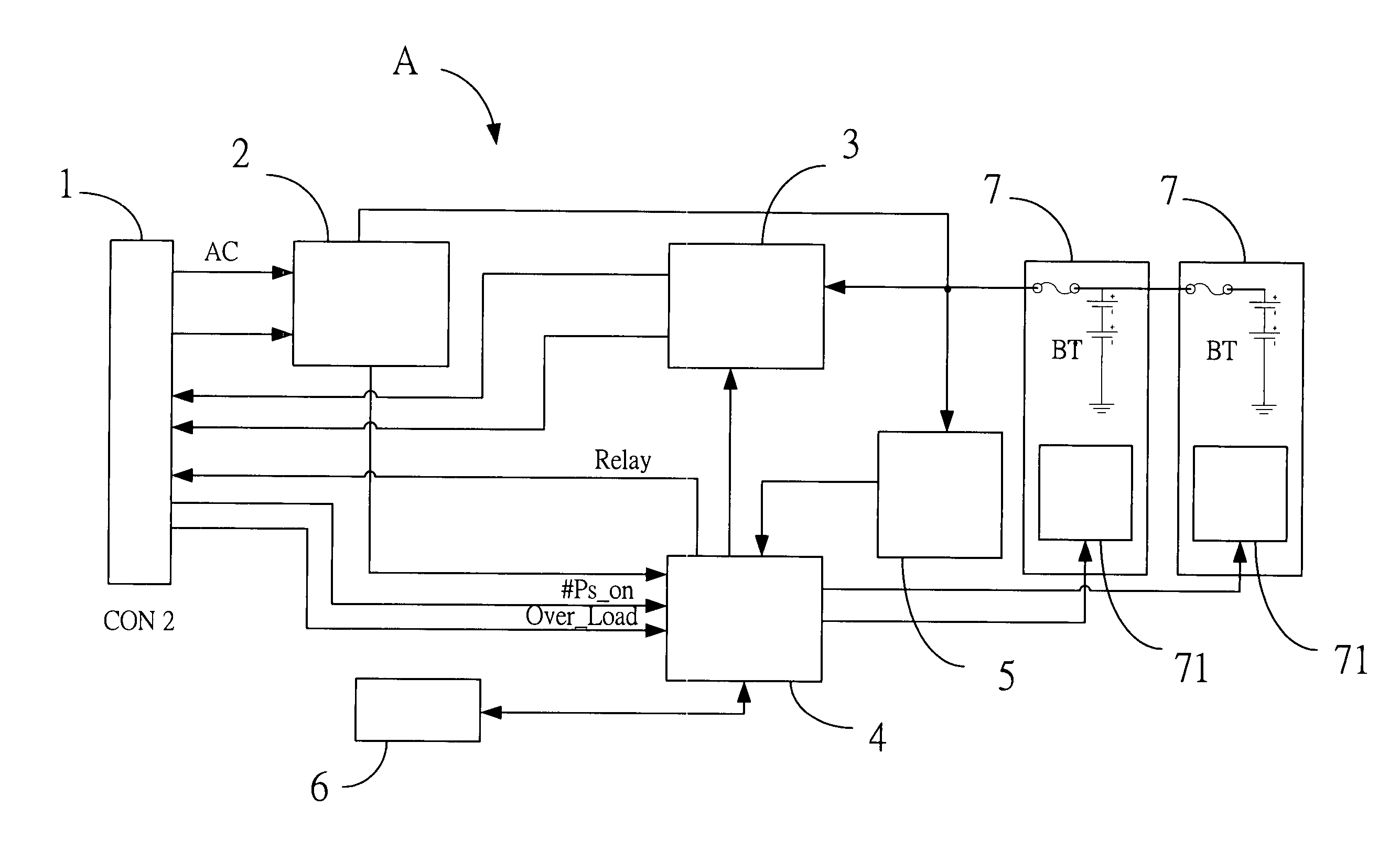
An improved uninterruptible power supply circuit having a hot swappable battery module is connected with internal connectors of a UPS power supply circuit via external connectors of the power supply circuit. When the supply of the commercial AC power is abnormal, the backup battery provides power to the power supply circuit via the internal connectors in response to signals from the UPS power supply circuit, thereby instantly providing power to the computer and avoiding power interruption, wherein the backup battery is provided in a removable battery box, and several backup batteries can be connected in parallel by means of the removable battery box so as to provide power to the computer in case of long-term power failure.
Owner:DIGIPOWER MFG
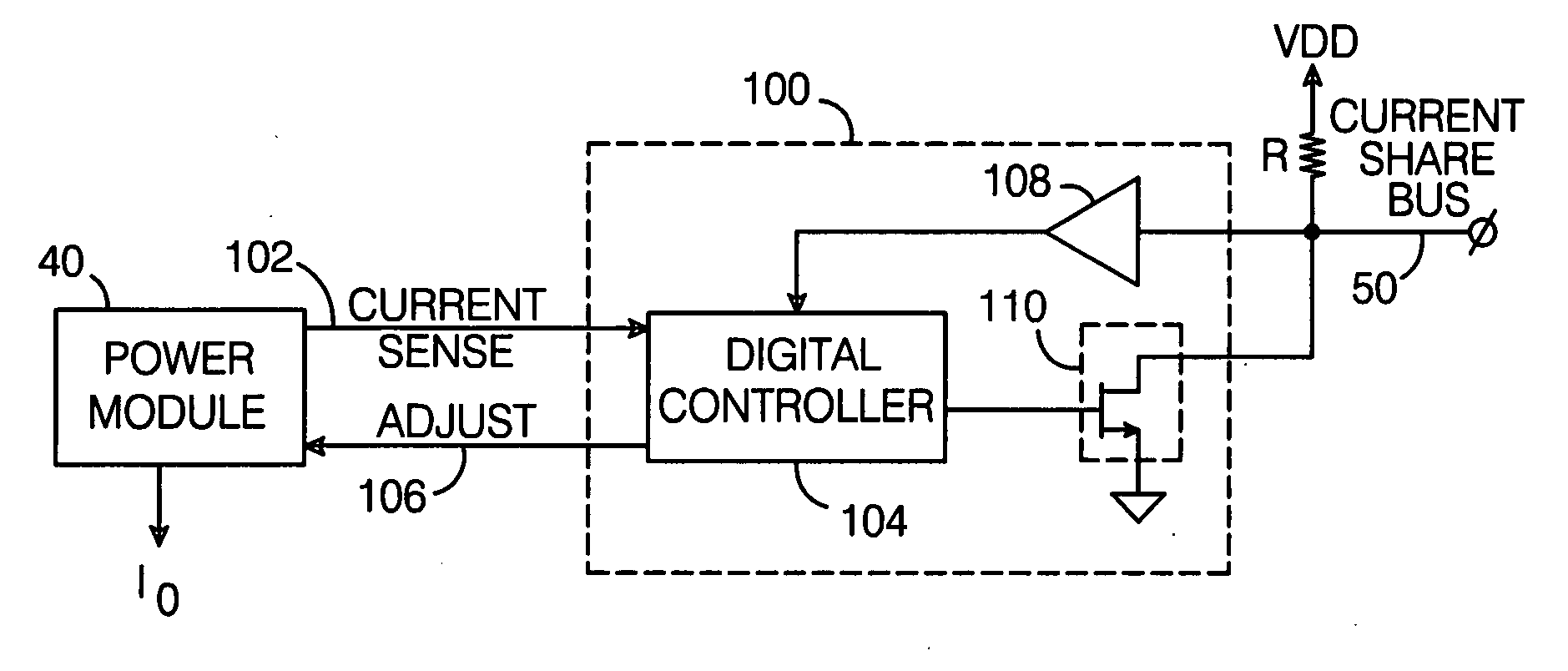
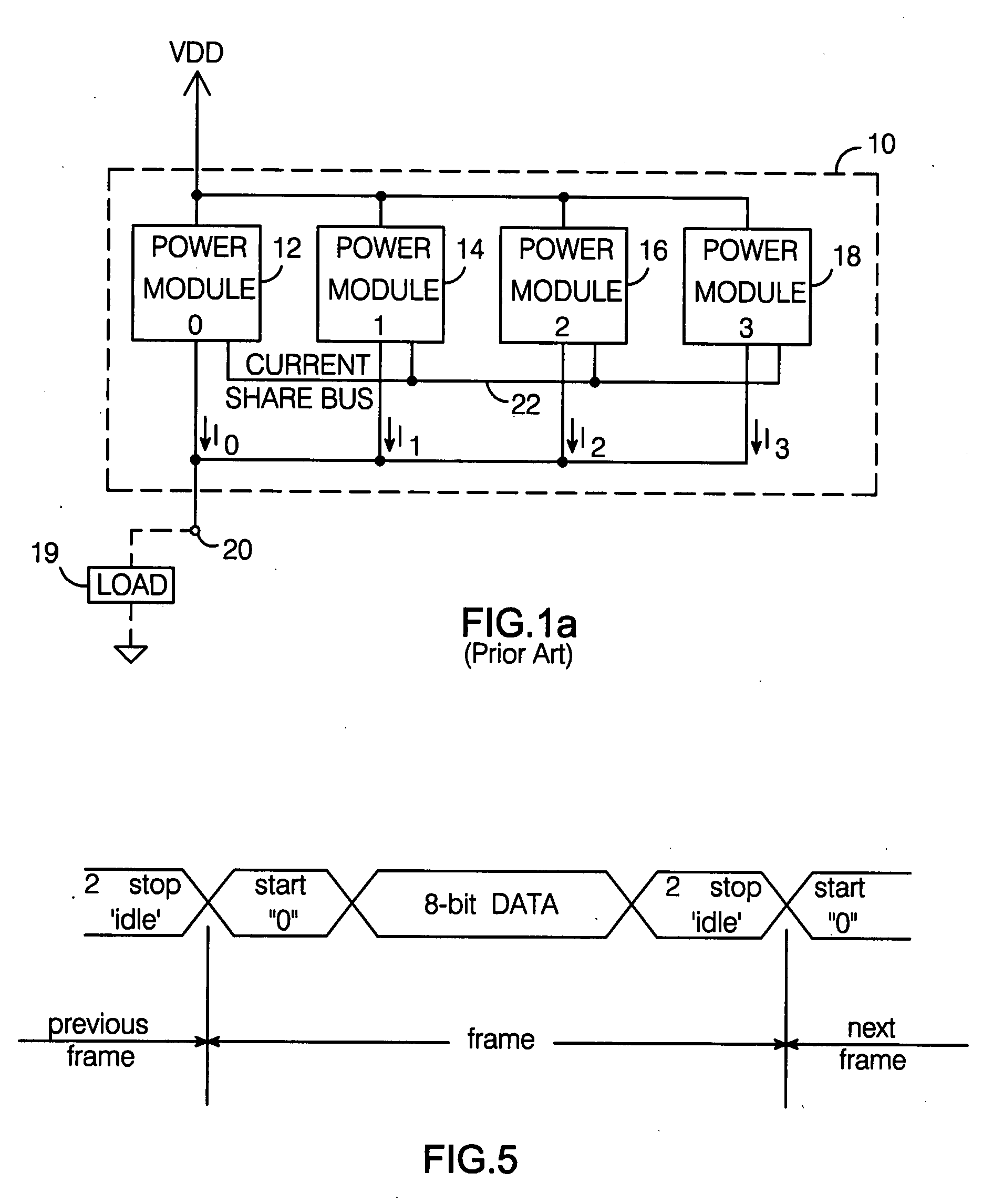
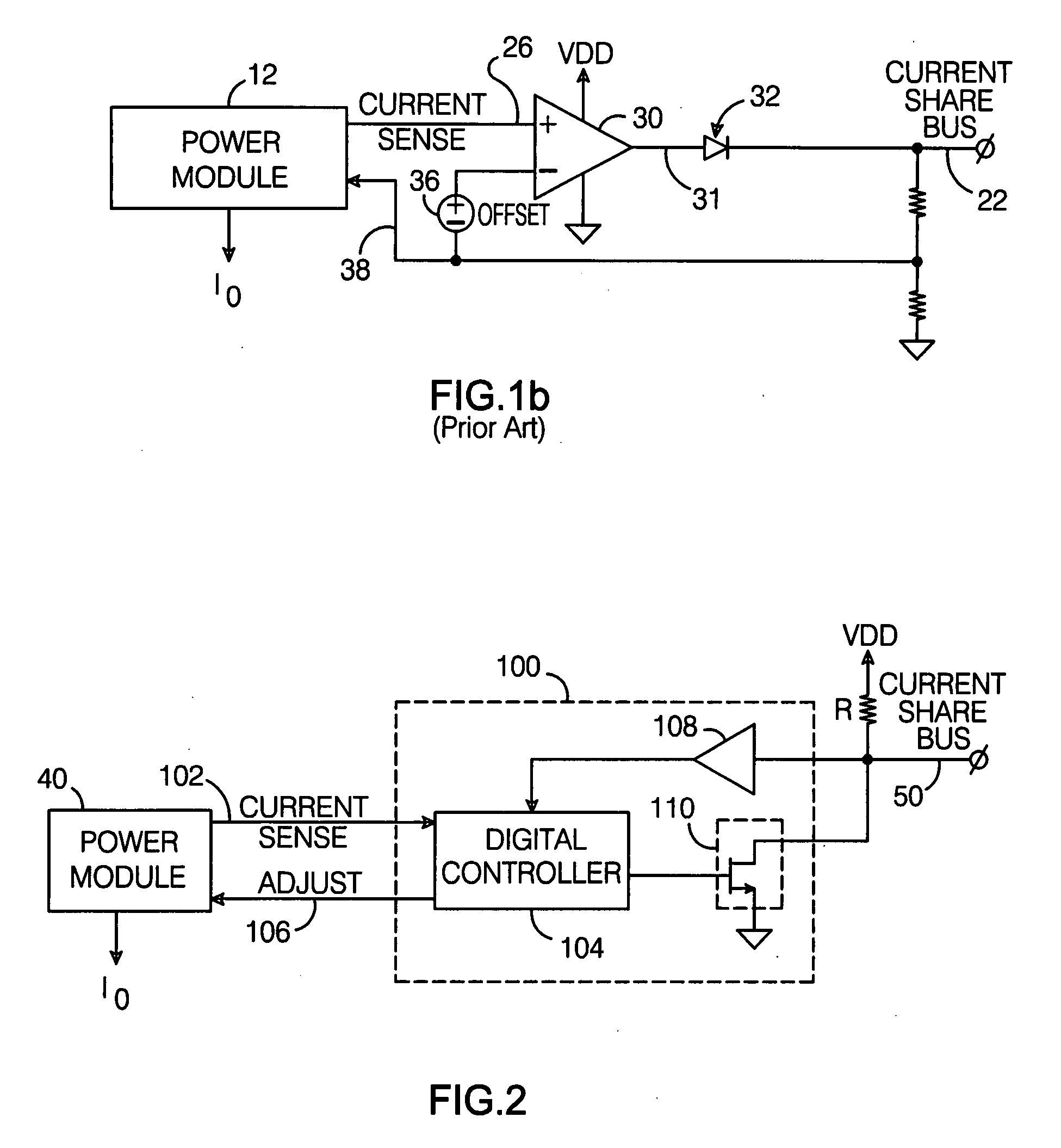
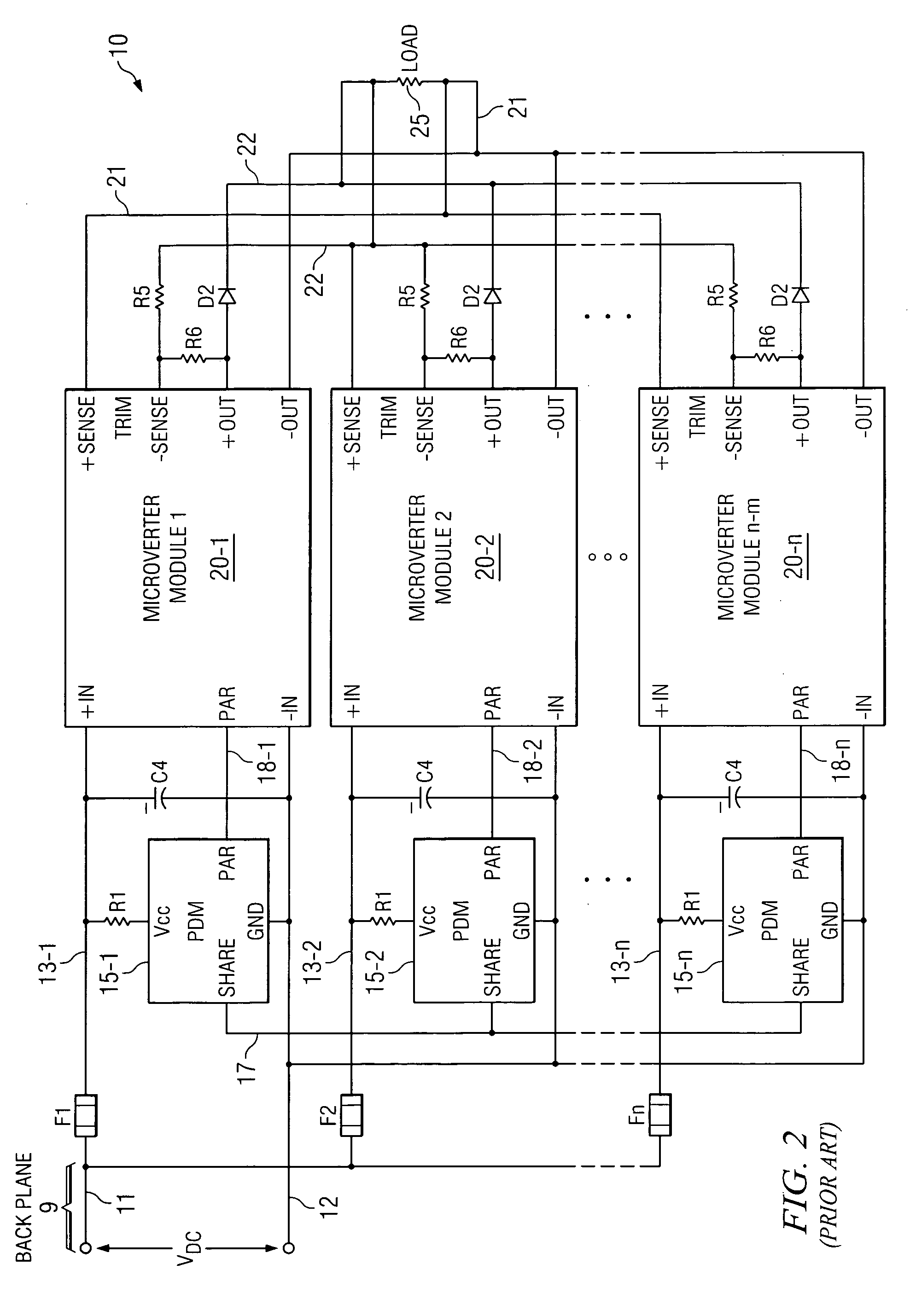
Digital current share bus interface
A digital current share bus interface connects to a power module which provides a signal representative of its output current, and adjusts the module's output current in response to a control signal received from the interface. A data formatting module receives the output current signal and generates a digital word that varies with the current; the bits of the word are coupled to a current share bus. A comparator module receives digital words conveyed via the bus and generated by the data formatting module at respective inputs, and provides the control signal to the power module so as to adjust its output current to match the current value represented by the digital word on the bus. In a typical implementation, multiple power modules are coupled to the current share bus via respective interfaces, with the output currents of all the power modules connected in parallel.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
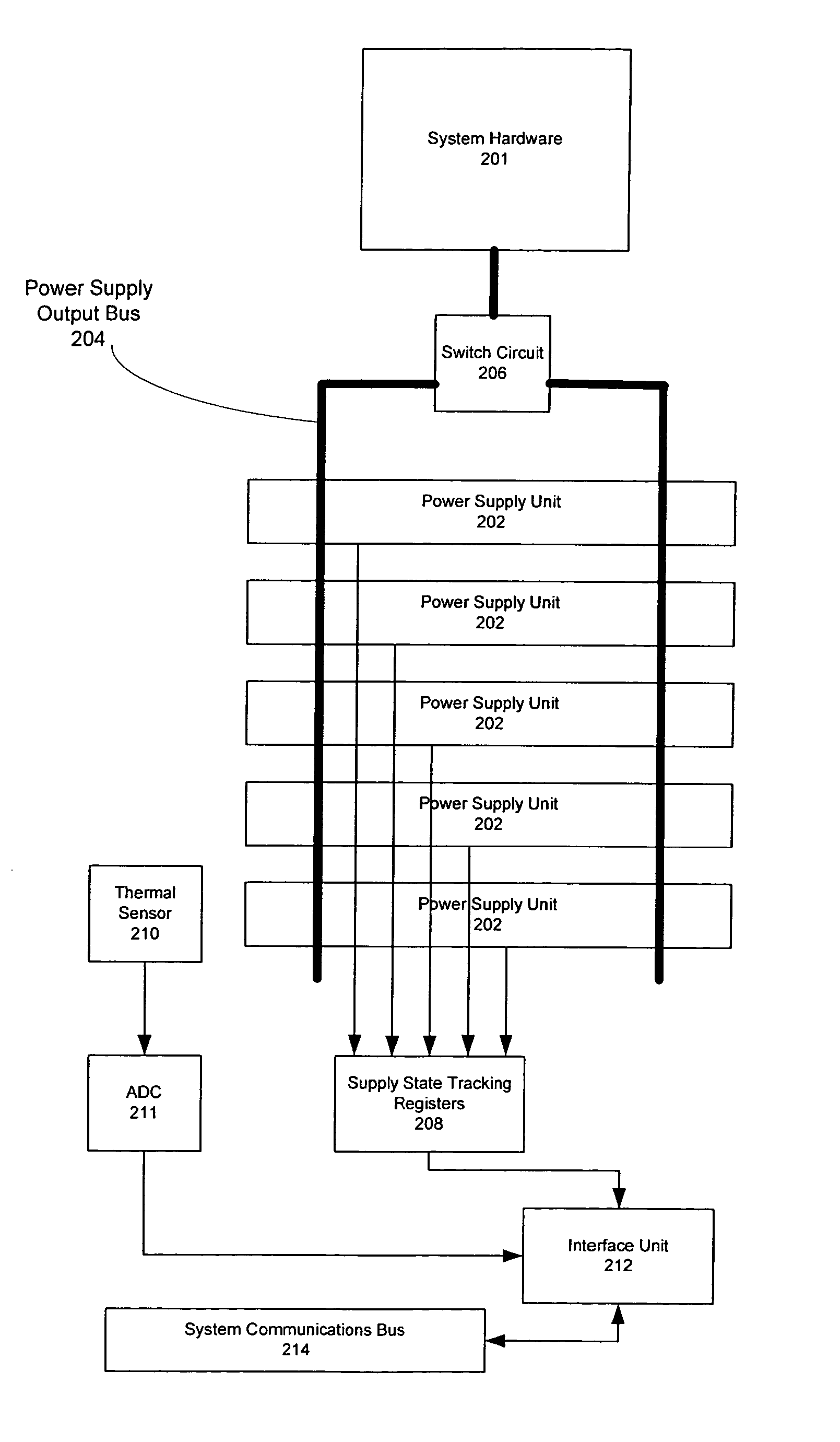
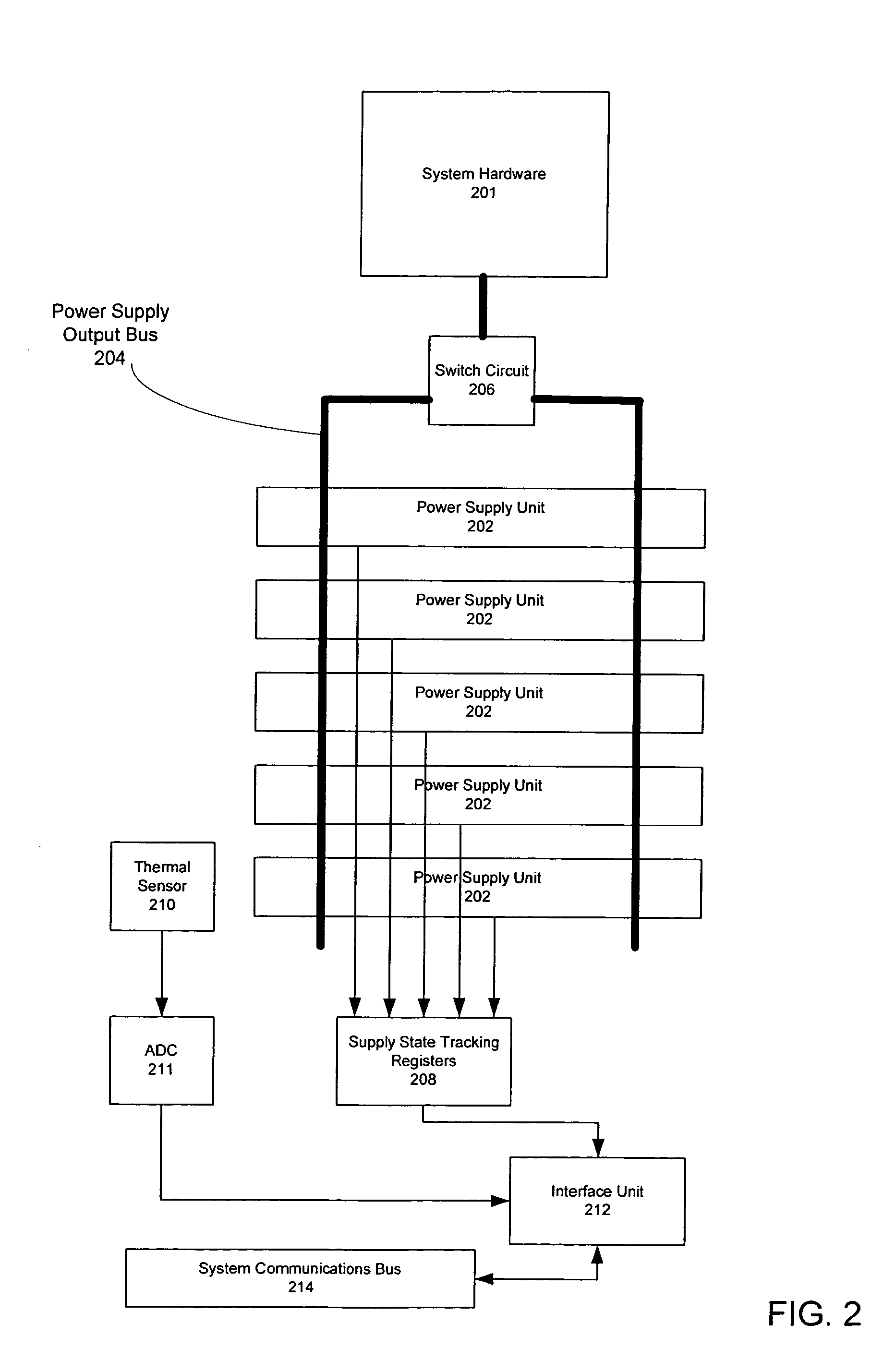
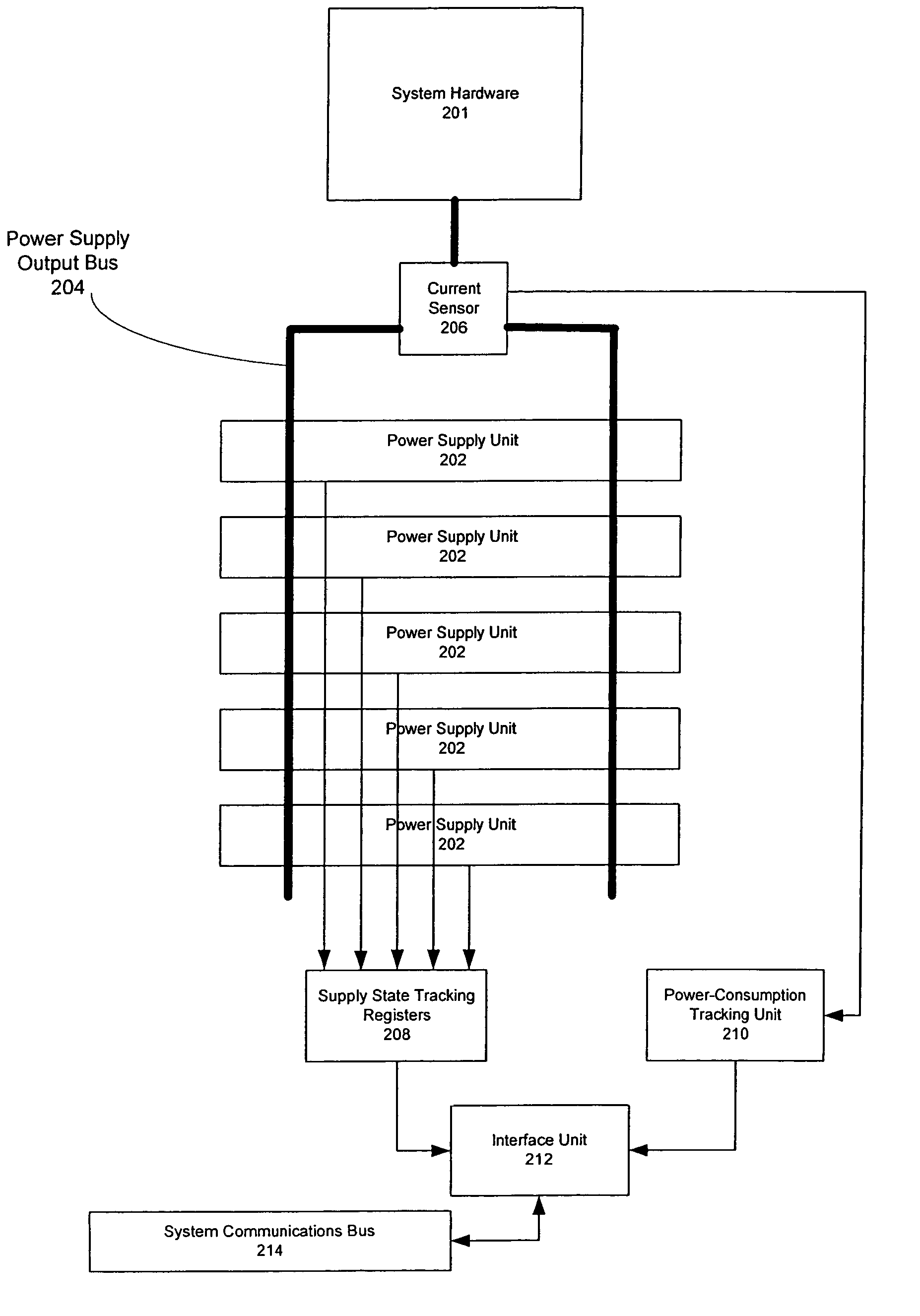
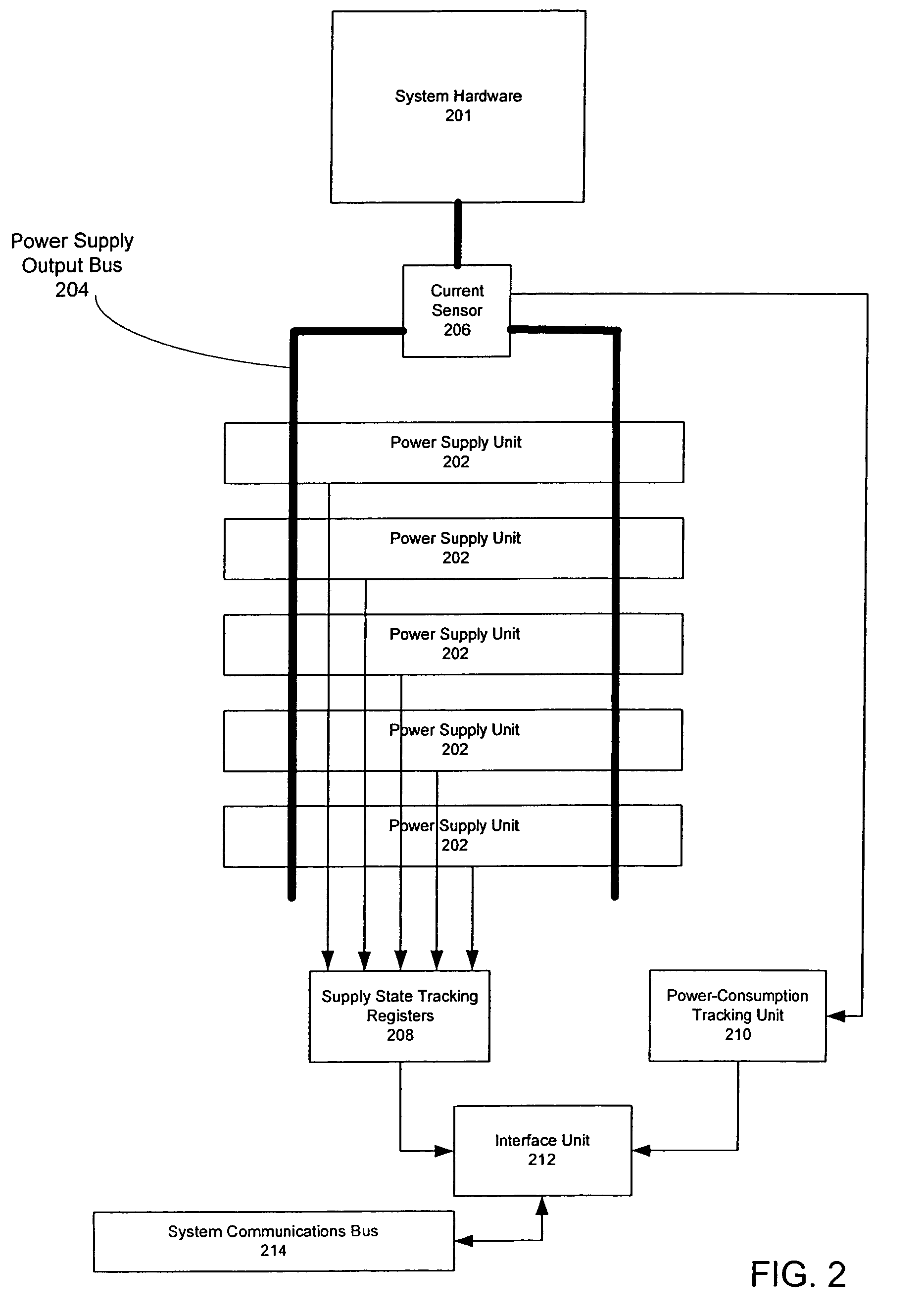
Method for determining number of dynamically temperature-adjusted power supply units needed to supply power according to measure operating temperature of power supply units
ActiveUS7222246B2Error detection/correctionVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringOperating temperature
One embodiment disclosed relates to a method of providing dynamic temperature-adjusted power redundancy for a system. Tracking is performed of the number of power supply units, n, that are presently in an up state. The temperature in which the power supply units are operating is measured, and a temperature-adjusted number of power supply units, N, which are presently needed to supply power to the system, is dynamically determined.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
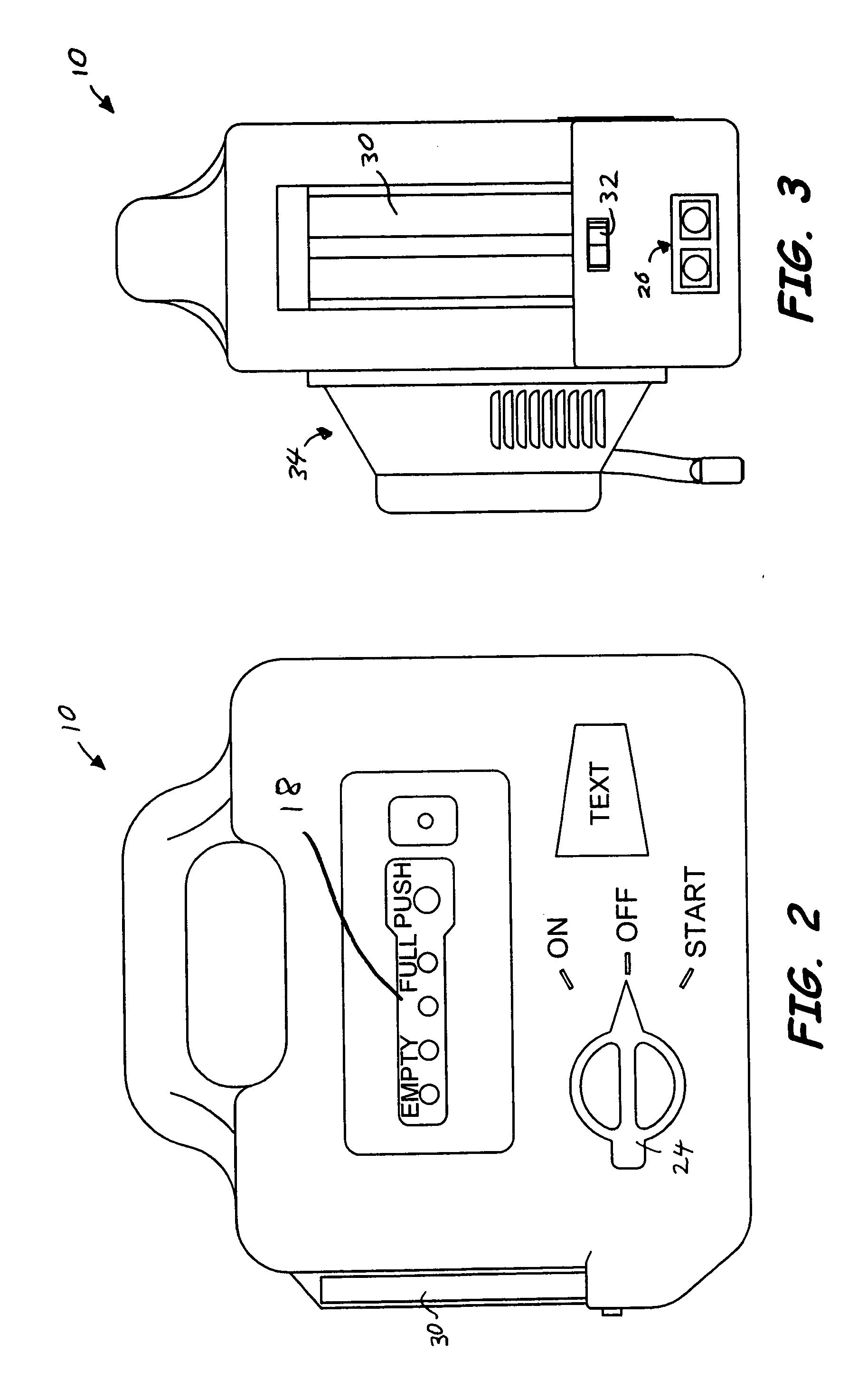
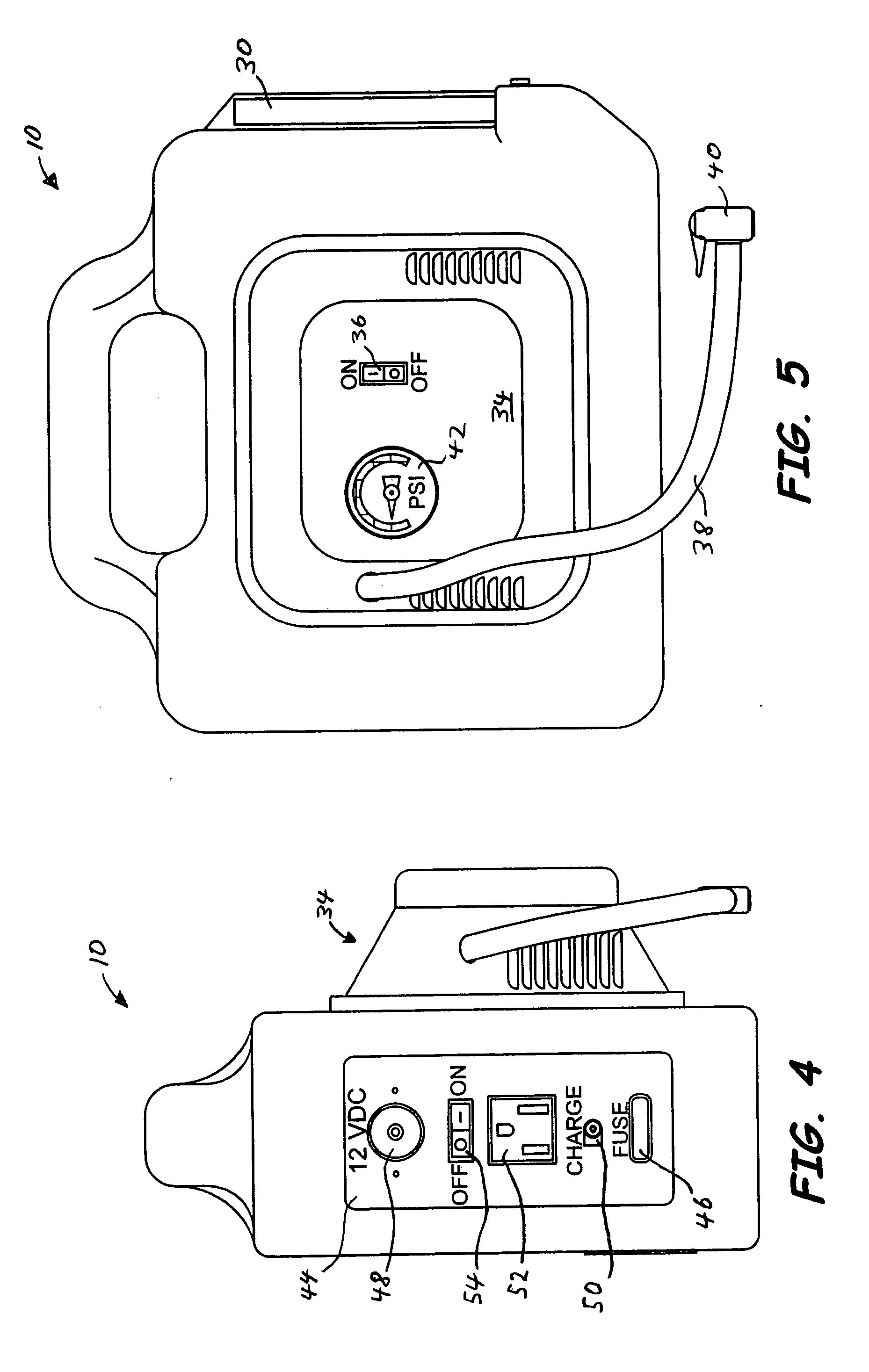
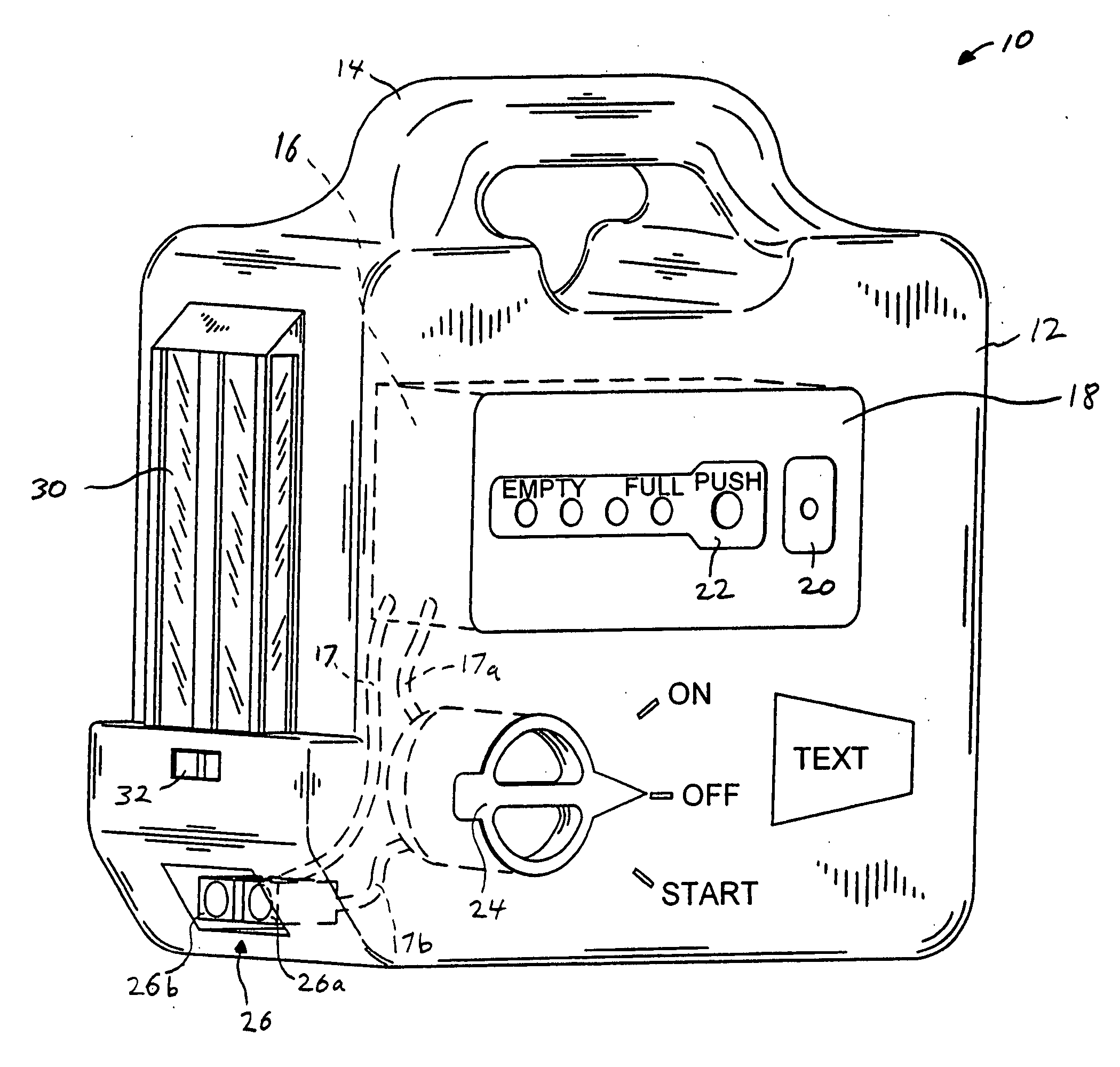
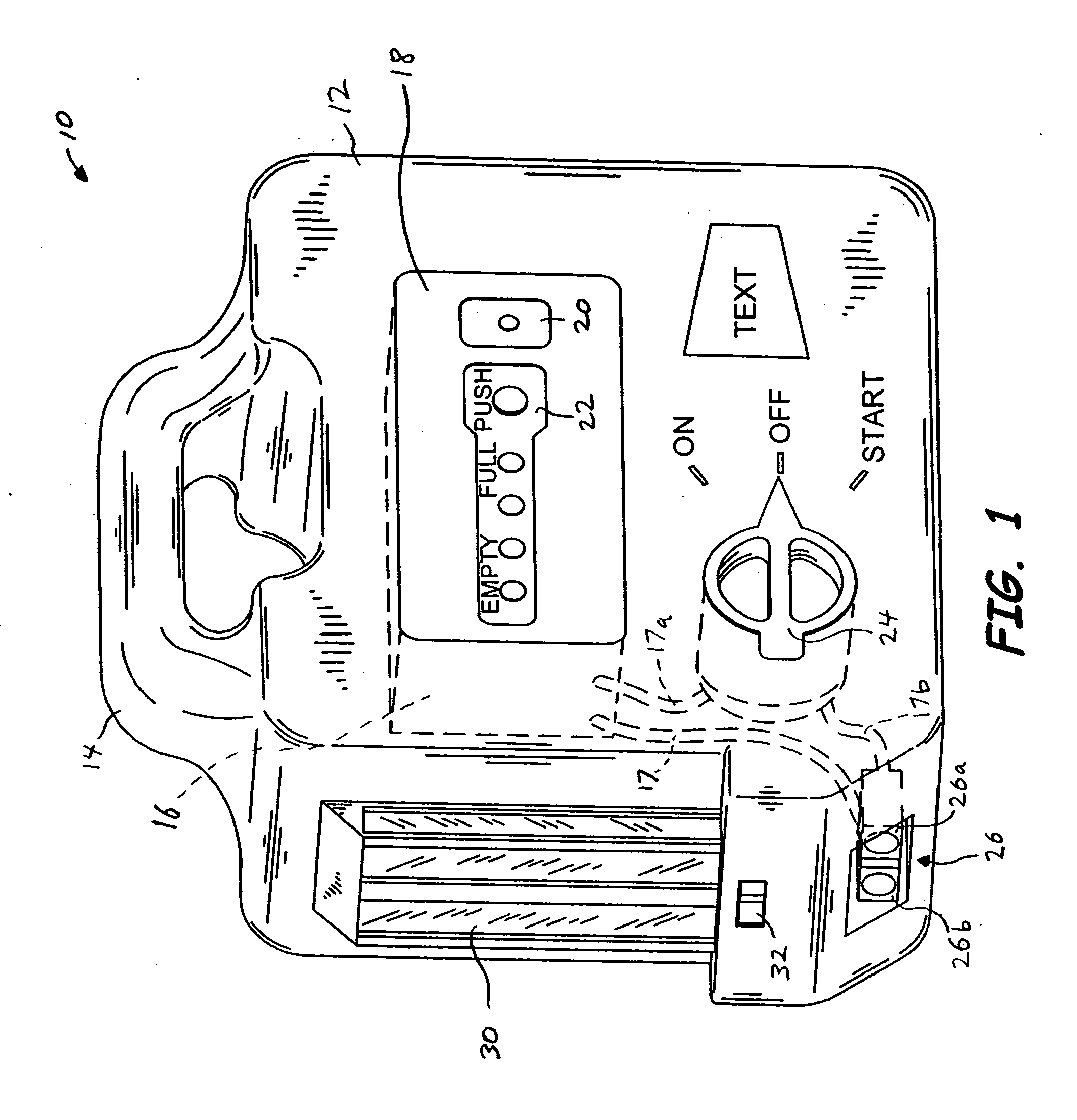
Portable power source
A portable power source for starting a variety of outdoor power equipment. The portable power source generally includes a housing, an electrochemical power supply, a switch having an ON position with a fixed contact and a START position with a momentary contact, and a connector connected to the switch. The switch may be electrically connected to the electrochemical power supply and, using a cable, the connector is operable to be electrically connected to a starter motor associated with the outdoor power equipment. Actuation of the switch to the START position electrically connects the electrochemical power supply to the starter motor. The portable power source is adapted to be used as a primary power source and an auxiliary power source. The portable power source also includes an integrated light, an air compressor, a power supply indicator, and one or more inputs and outputs to receive and provide direct current (“DC”) and alternating current (“AC”).
Owner:BRIGGS & STRATTON
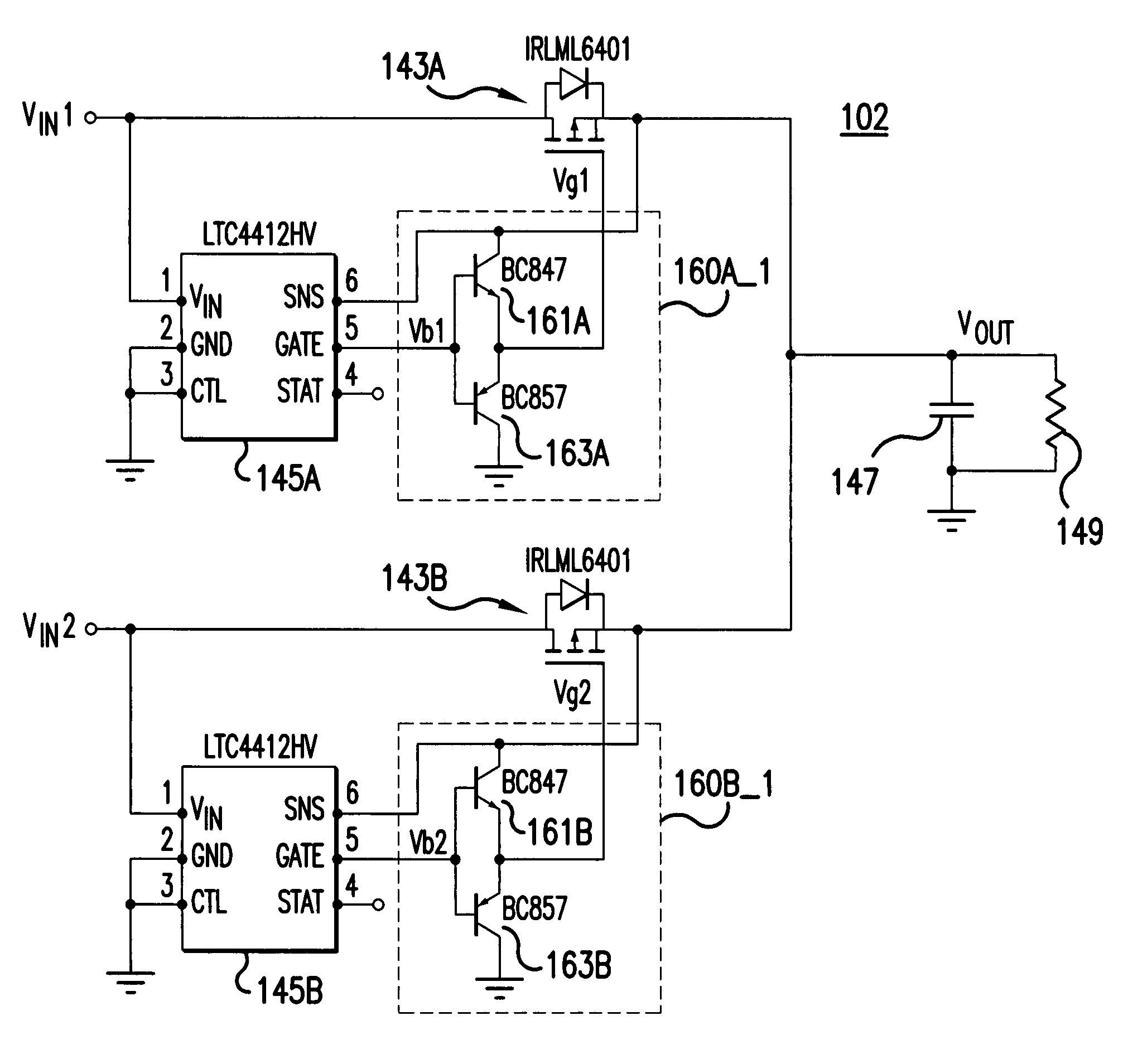
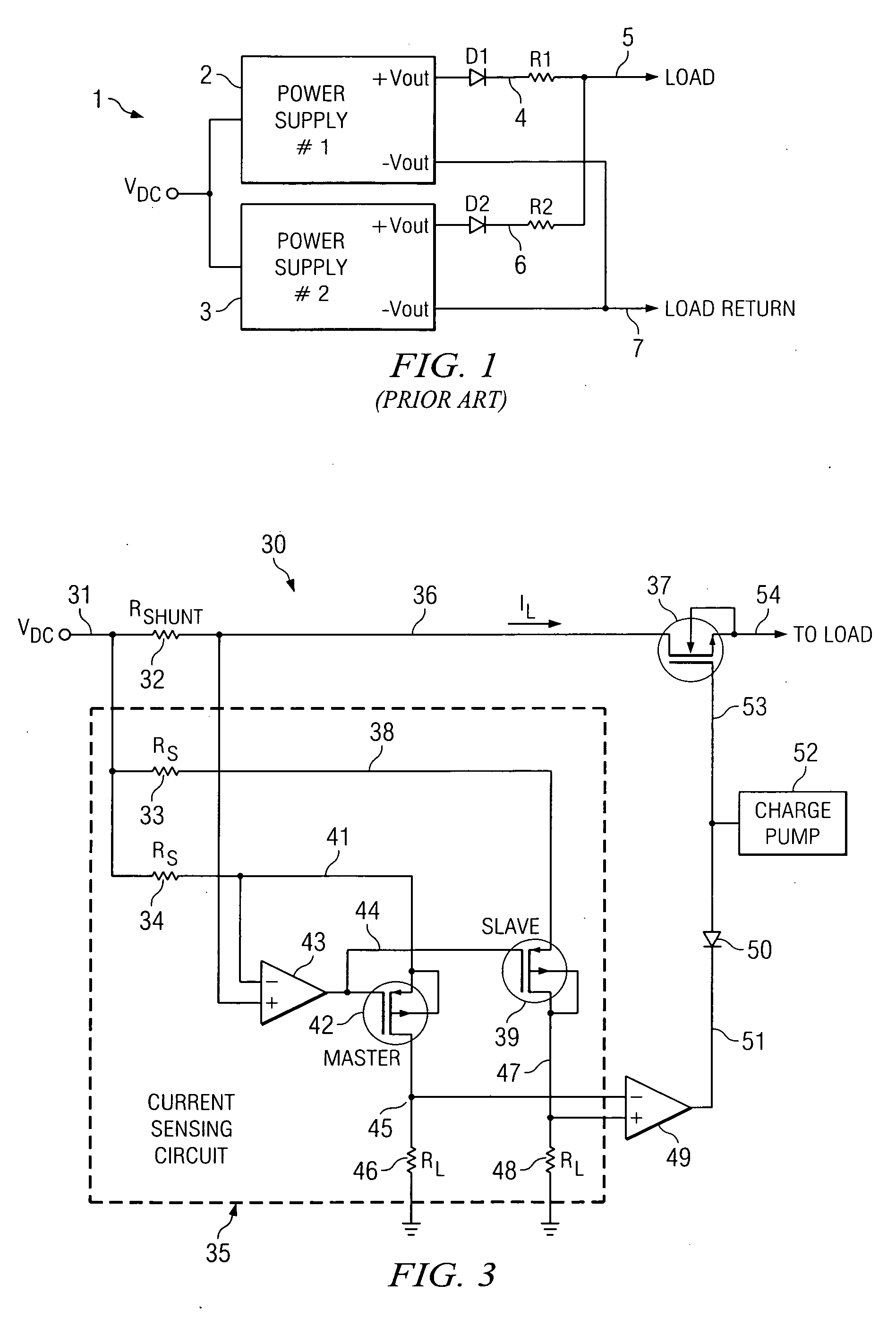
Active impendance current-share method
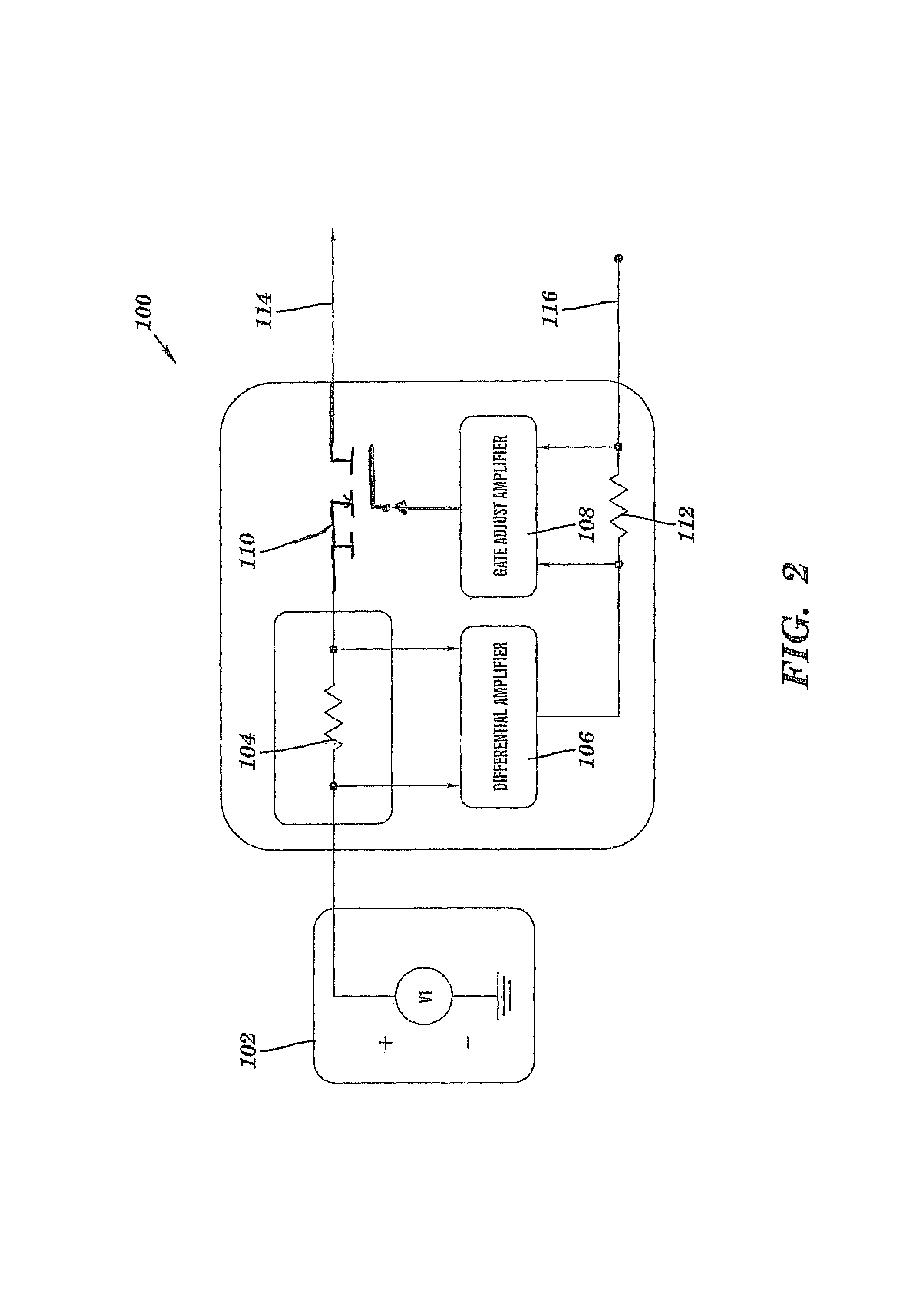
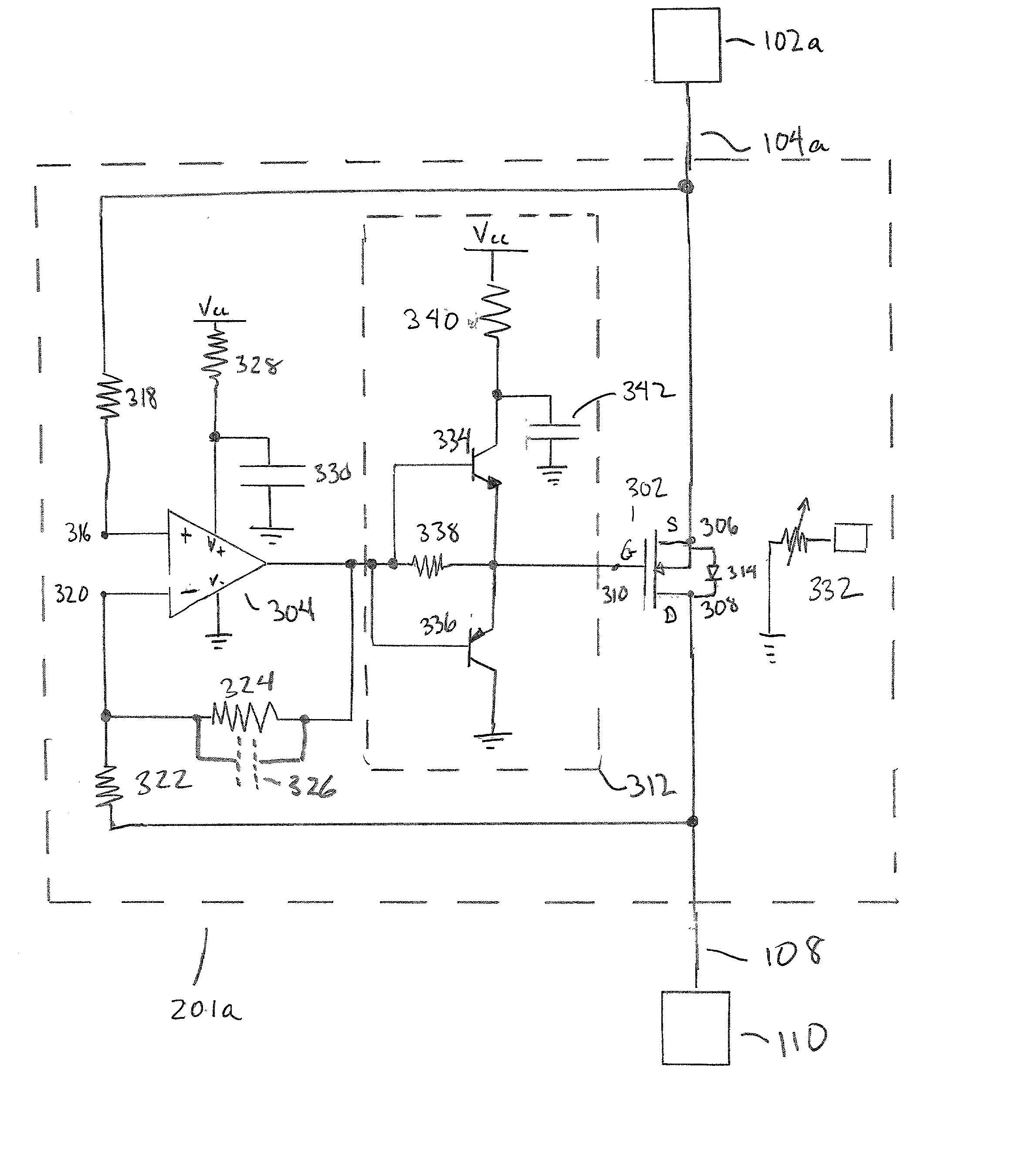
InactiveUS7282899B1Highly accurateImprove reliabilityDc source parallel operationHot plugging-unplugging power/loadMOSFETElectricity
Exemplary embodiments include An active impedance current-sharing circuit including: a power supply in electrical communication with a current sense resistor; a differential amplifier in electrical communication with the current sense resistor; a gate adjust amplifier in electrical communication with the differential amplifier; an ORing MOSFET in electrical communication with the gate adjust amplifier and the current sense resistor; a current share resistor in electrical communication with a current share bus and the gate adjust amplifier; and a current share output in electrical communication with the ORing MOSFET, wherein the circuit allows two or more power supplies that are not designed for current share to be connected in parallel and current share by actively modulating the ORing MOSFET between its linear and fully enhanced regions.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
System and method providing output signal control for a power supply
InactiveUS20020125865A1Increase the resistance valueLower the resistance valueElectric signal transmission systemsBatteries circuit arrangementsControl systemControl signal
A control system for selectively isolating a power supply from a common bus is provided. The control system comprises a connection to an output path of an output signal of the power supply and a resistive element providing a variable resistance between an input terminal and an output terminal. The input terminal is connected to the connection and the output terminal is connected to the common bus. The resistive element further comprises a control terminal allowing adjustment of the variable resistance. A control element provides a control signal to the control terminal; the control element is responsive to current flowing between the output path and the common bus.
Owner:MURATA POWER SOLUTIONS
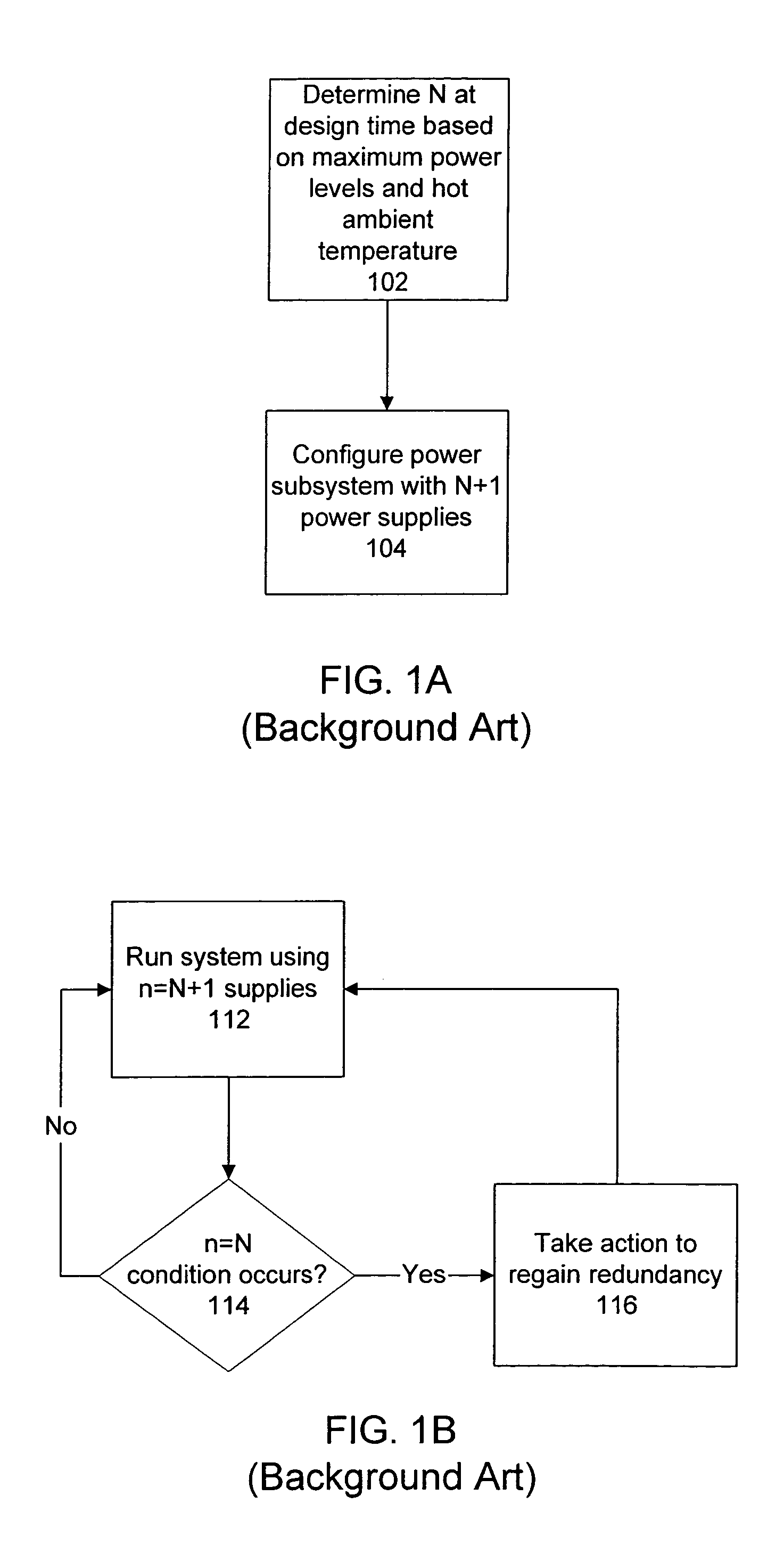
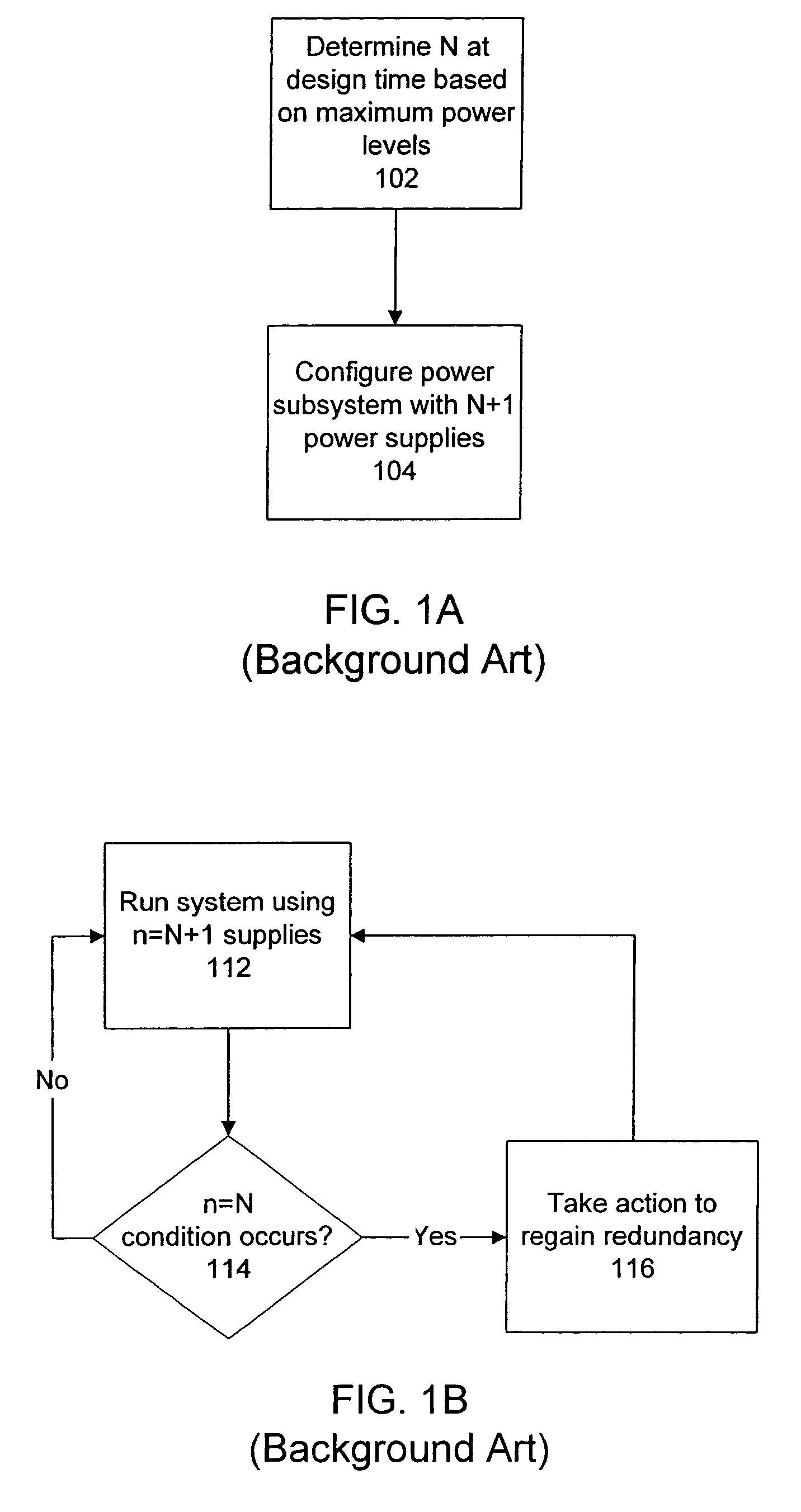
Method of providing dynamic power redundancy based on a difference of current power units and currently needed power units
One embodiment disclosed relates to a method of providing dynamic power redundancy for a system. A number of power supply units, n, that are presently in an up state is tracked. In addition, a number of power supply units, N, that are presently needed to supply power to the system is dynamically determined. If a margin of safety corresponding to a difference between n and N reaches a minimum acceptable level, then action is taken to increase the margin of safety.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
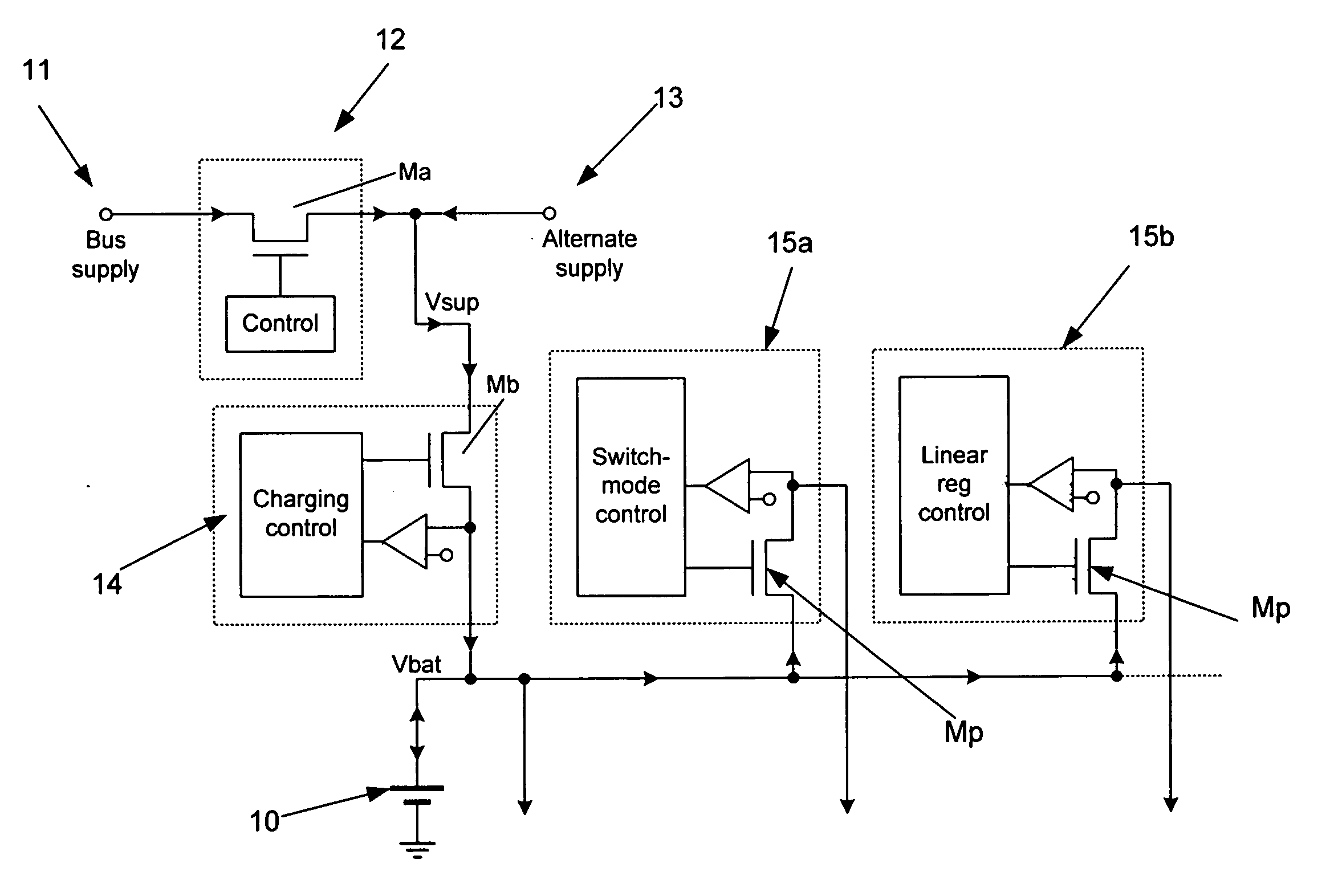
Power supply circuit for portable battery powered device
ActiveUS20060022640A1Reduce voltage dropImprove effective battery lifeThree-or-more-wire dc circuitsElectric powerEngineeringVoltage source
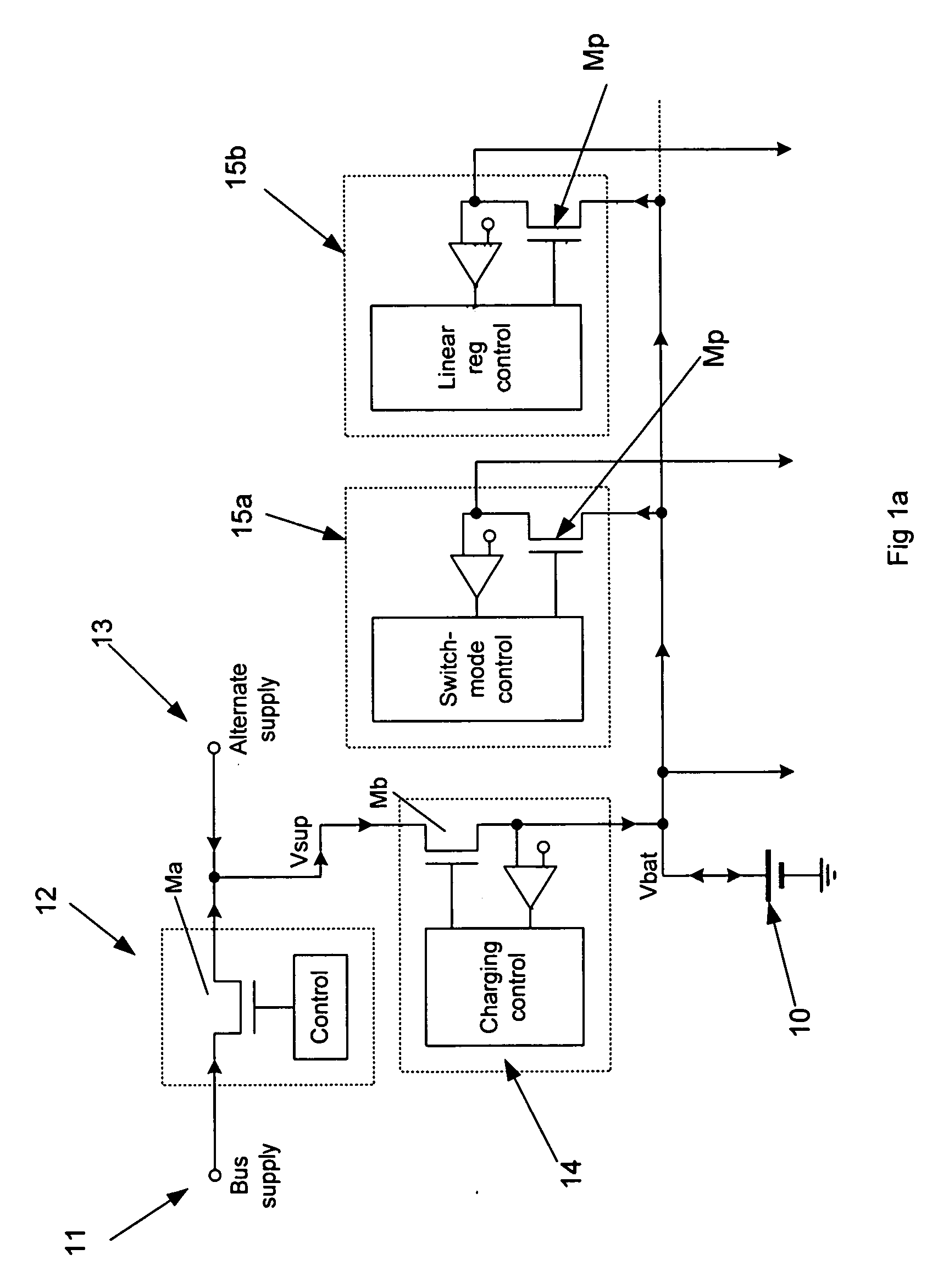
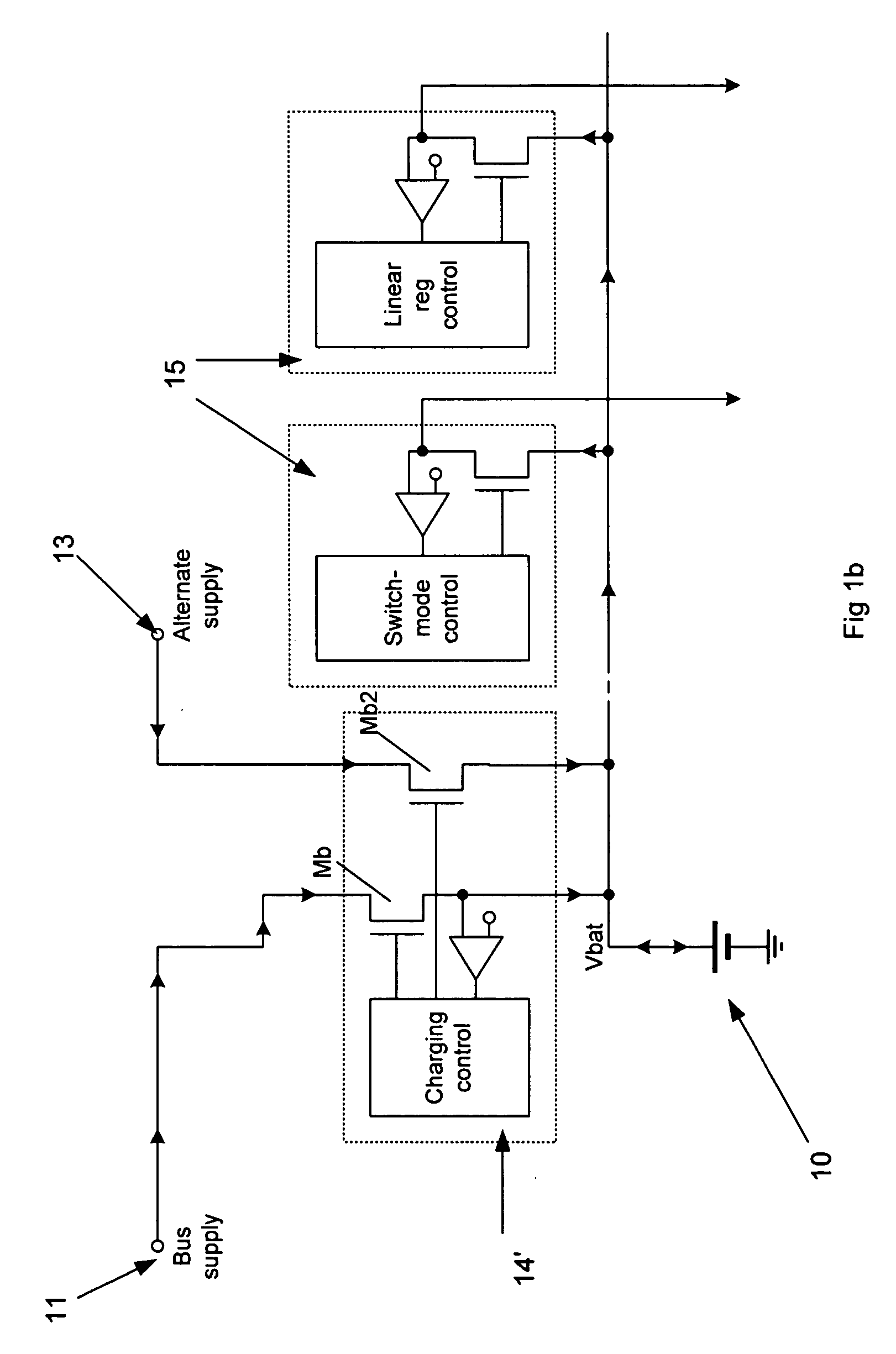
The present invention relates to battery power peripheral devices such as MP3 players which are also periodically connected to another power source such as a mains wall socket or USB cable power bus. In particular, but not exclusively, the present invention relates to regulation of these voltage sources. In general terms the present invention provides a multiple supply rail for the load regulators of a power supply circuit for a battery powered device. One supply rail is coupled to the battery, and another is coupled to a non-battery source such as an external mains regulated source and / or a bus power wire from a USB cable or similar. The regulators have multiple inputs, each for taking their input voltage from one of these supply rails.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Method of and system for starting engine-driven power equipment
InactiveUS20050082833A1Batteries circuit arrangementsElectric motor startersElectricityElectrical conductor
A portable power source for starting a variety of outdoor power equipment, particularly a portable generator. The portable power source generally includes a housing, an electrochemical power supply, a switch, and a connector connected to the switch. The switch may be electrically connected to the electrochemical power supply and, using a conductor (e.g., a cable), the connector is operable to be electrically connected to a starter motor associated with the outdoor power equipment. The portable power source is adapted to be used as a primary power source and as an auxiliary power source. The portable power source can also includes an integrated light, an air compressor, a power supply indicator, and one or more inputs and outputs to receive and provide direct current (“DC”) and alternating current (“AC”).
Owner:BRIGGS & STRATTON
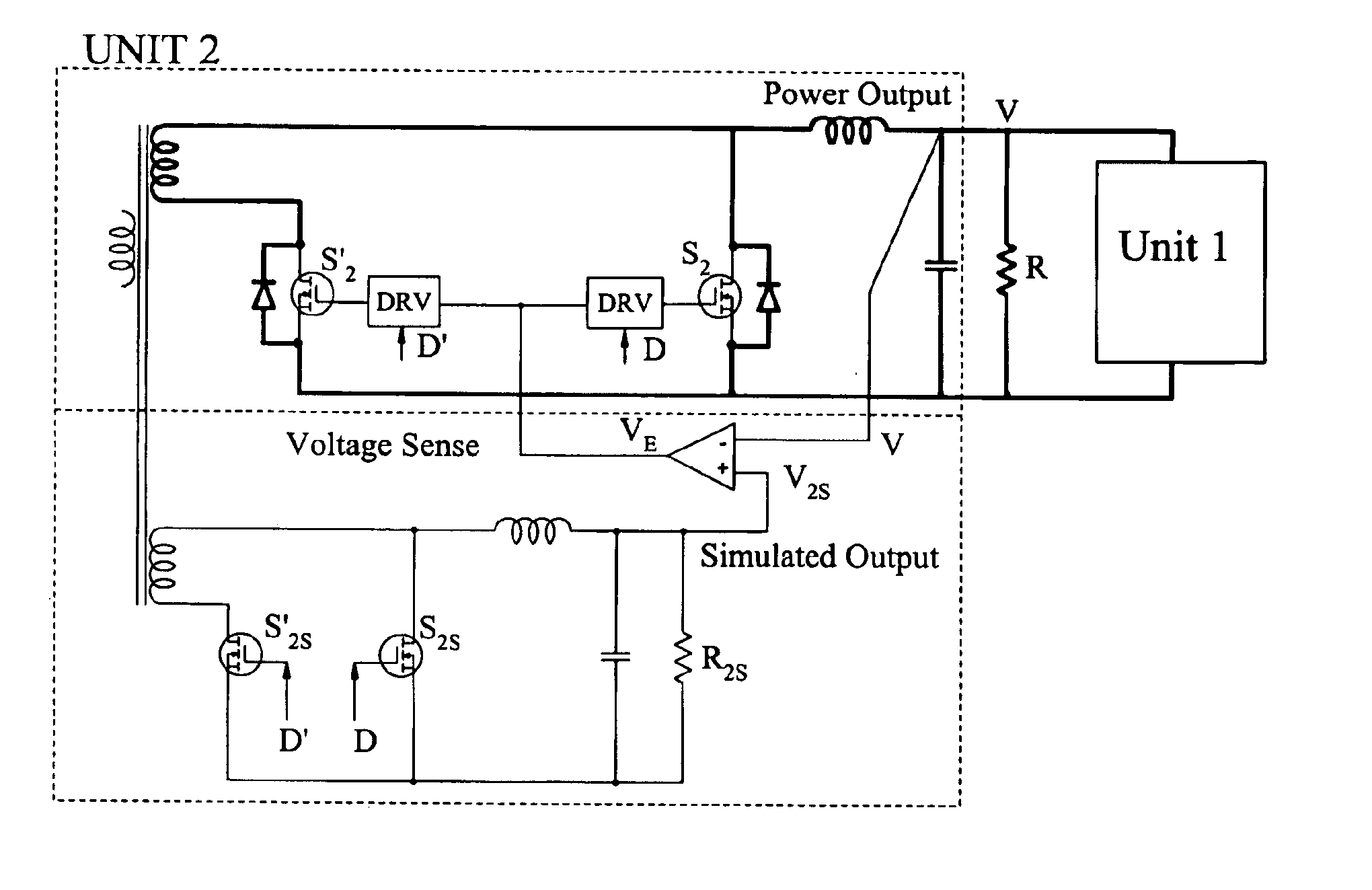
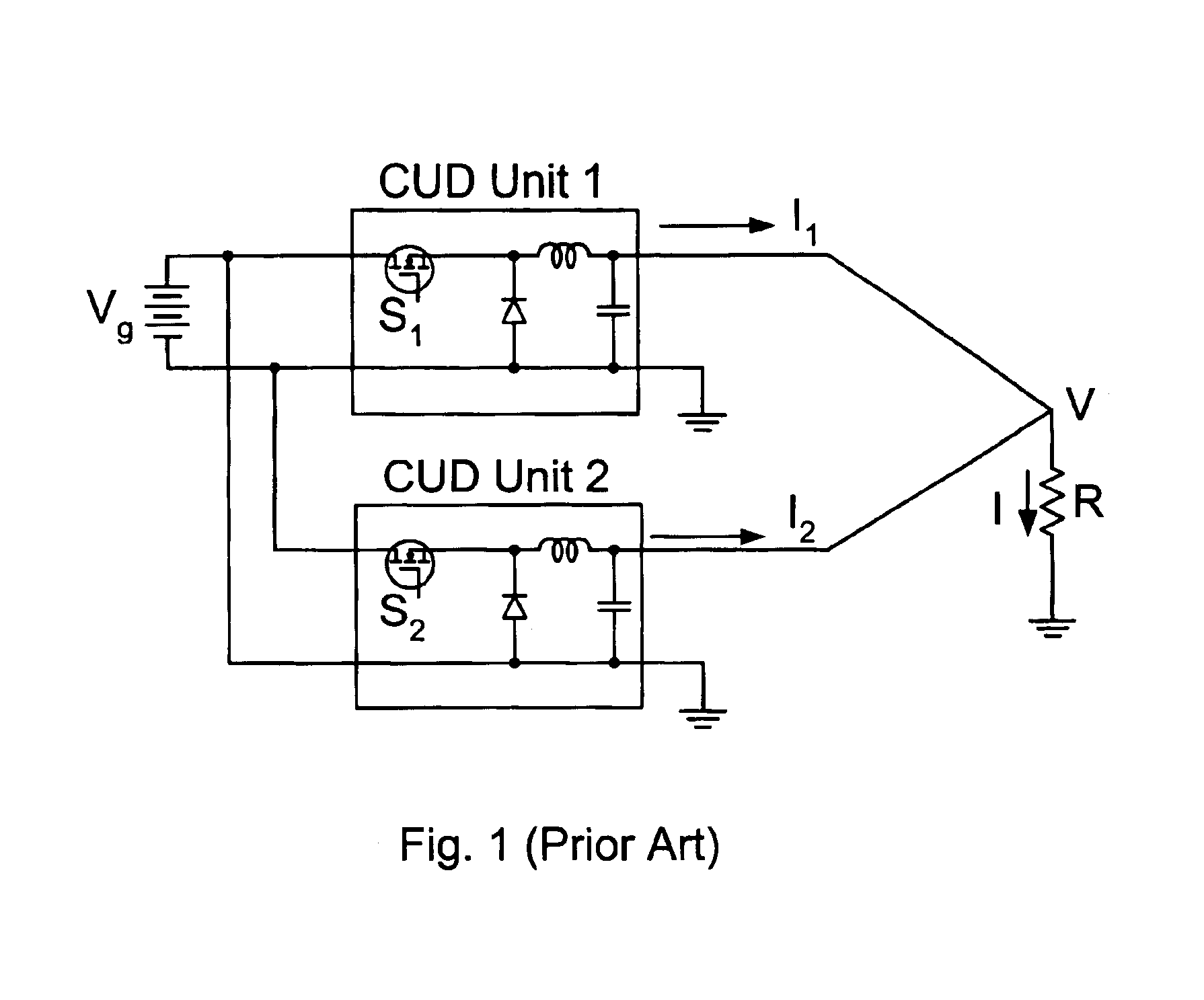
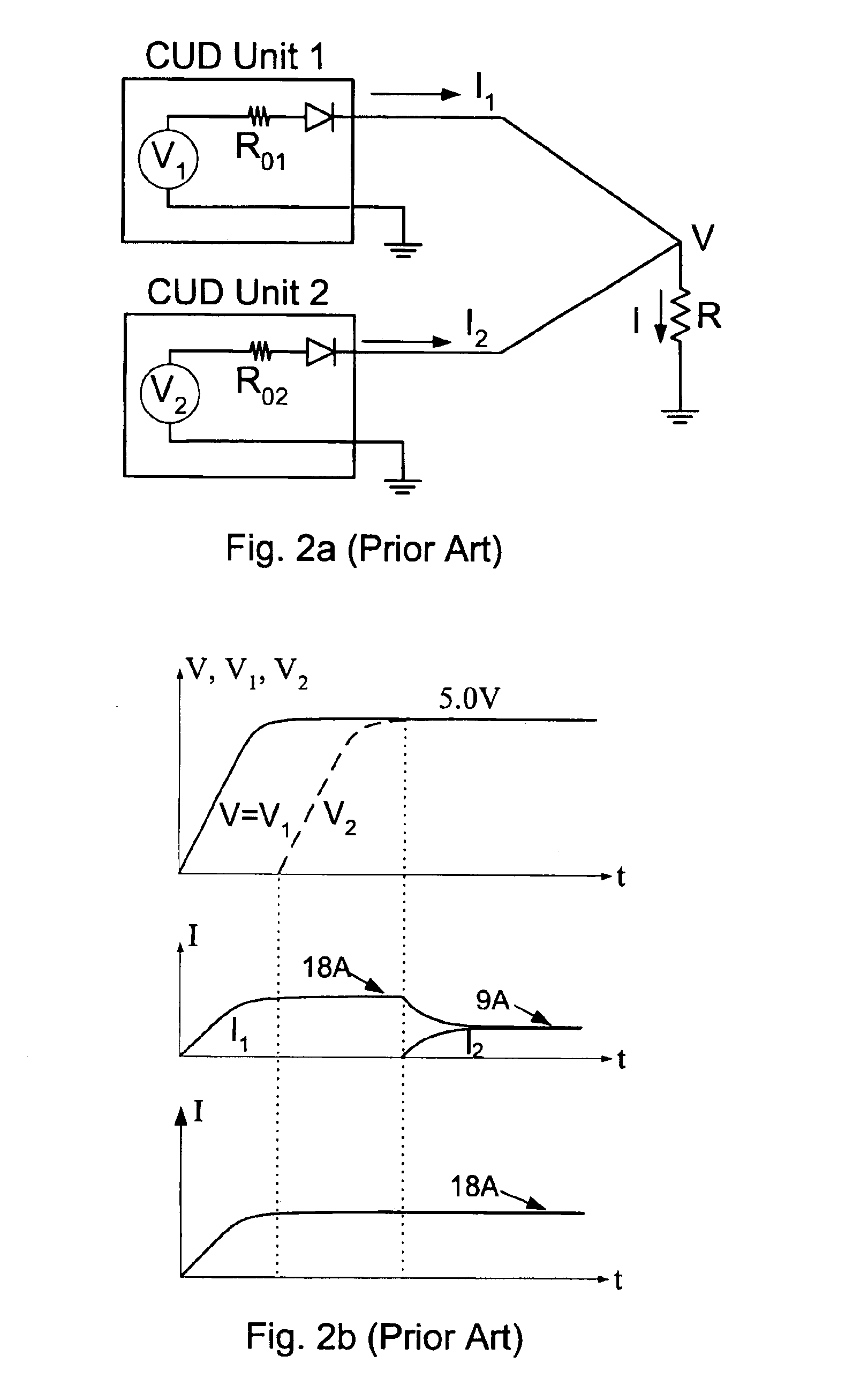
Voltage sense method and circuit which alleviate reverse current flow of current bi-directional converters
InactiveUS6853562B2Eliminate stressHigh pressureEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsVoltage overshootReverse current
The Voltage Sense Method is introduced and a number of its implementations using Voltage Sense Circuit are demonstrated to solve problems associated with the start-up of parallel switching converters, each converter having output synchronous rectifiers or more general Current Bi-directional Switches: prevention of the excessive reverse current, elimination of the excess voltage stress of the input switches and elimination of the voltage overshoot in the common output voltage. The Voltage Sense circuit added to each converter generates a Simulated Output Voltage, which predicts how would the output voltage of each particular unit rise during the start-up with enabled synchronous rectifiers if that particular unit were to operate alone. When the simulated output voltage of one converter reaches the actual common output voltage, synchronous rectifiers / CBS switches of that particular converter are all enabled so that their body-diodes, used up until that time to prevent reverse current flow, are by-passed eliminating all start-up problems. The introduced Voltage Sense Method and a number of its Voltage Sense Circuitries are also applicable to solve problems associated with the start-up of the current bi-directional converters with a battery load.
Owner:TESLACO
High reliability DC power distribution system
ActiveUS20060097578A1Increase speedHigh DC outputBatteries circuit arrangementsLoad balancing in dc networkElectric forceFlywheel energy storage
A high voltage DC power distribution system that eliminates static switches and batteries. Flywheel energy storage devices and extremely reliable, high power DC / DC converters provide at a lower cost, more reliable, noise and harmonic free, critical electrical power directly at equipment racks at 48 VDC, 24 VDC, 6 VDC, 2 VDC, or any other desired DC voltage level.
Owner:BALDWIN TECH
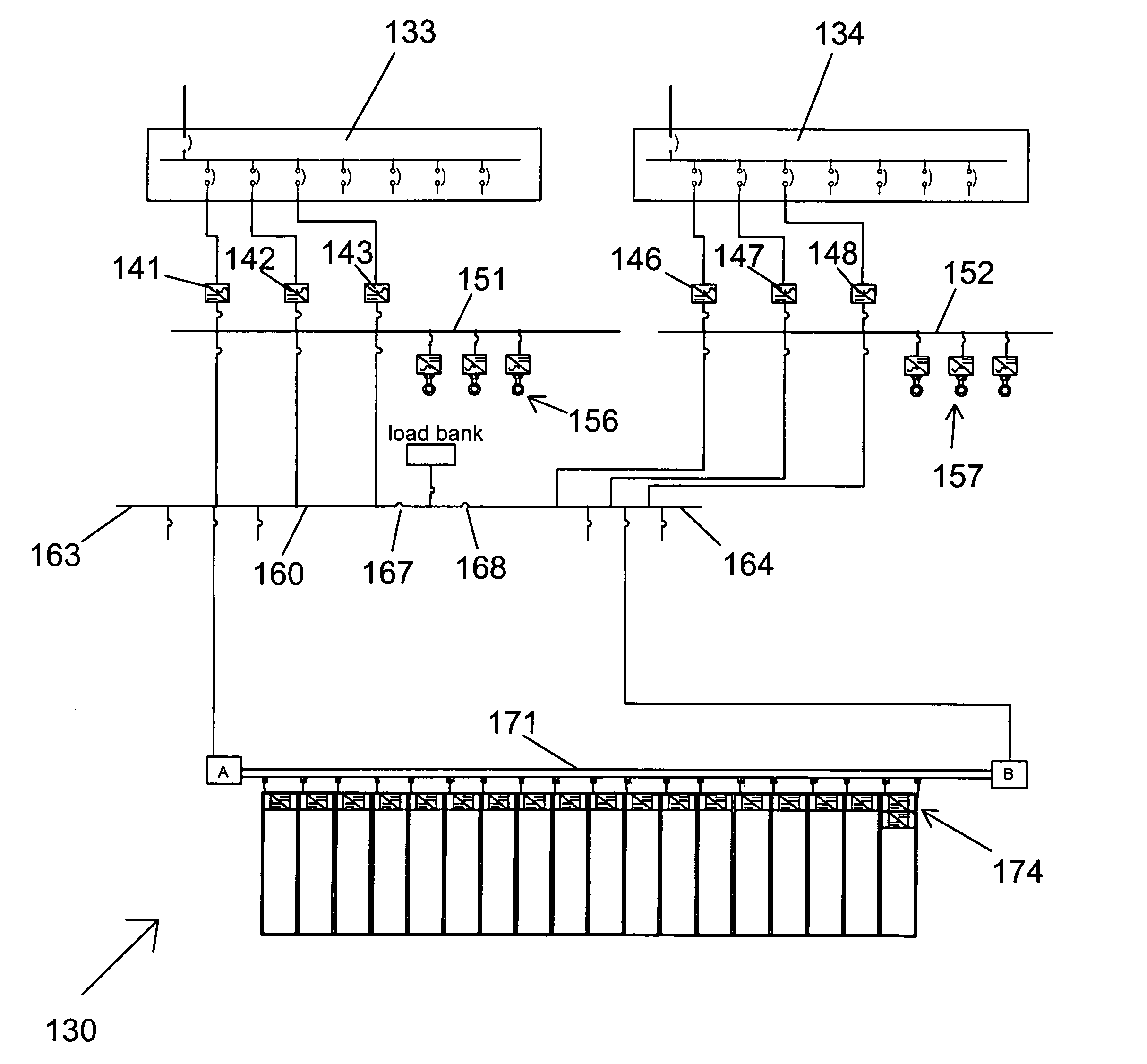
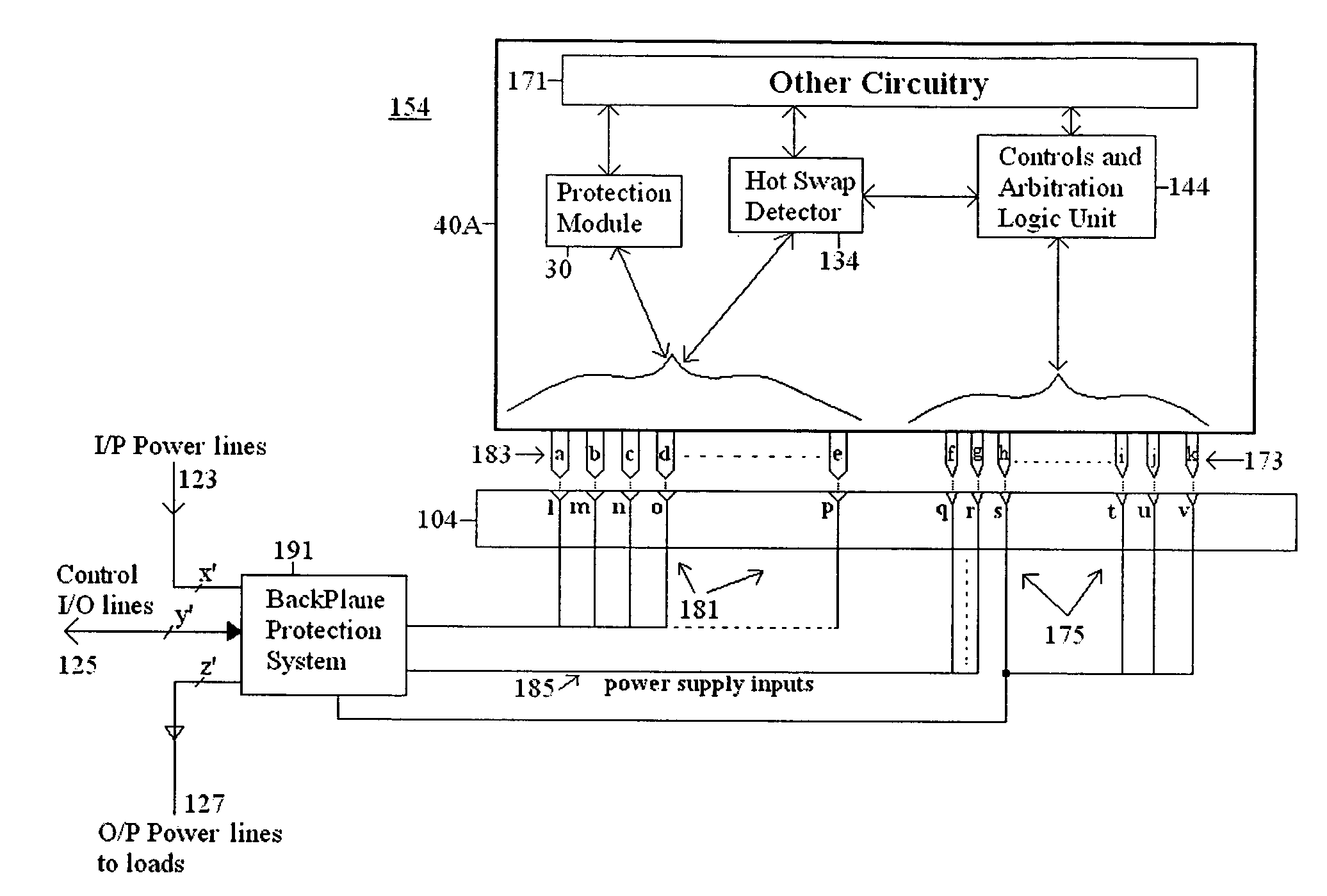
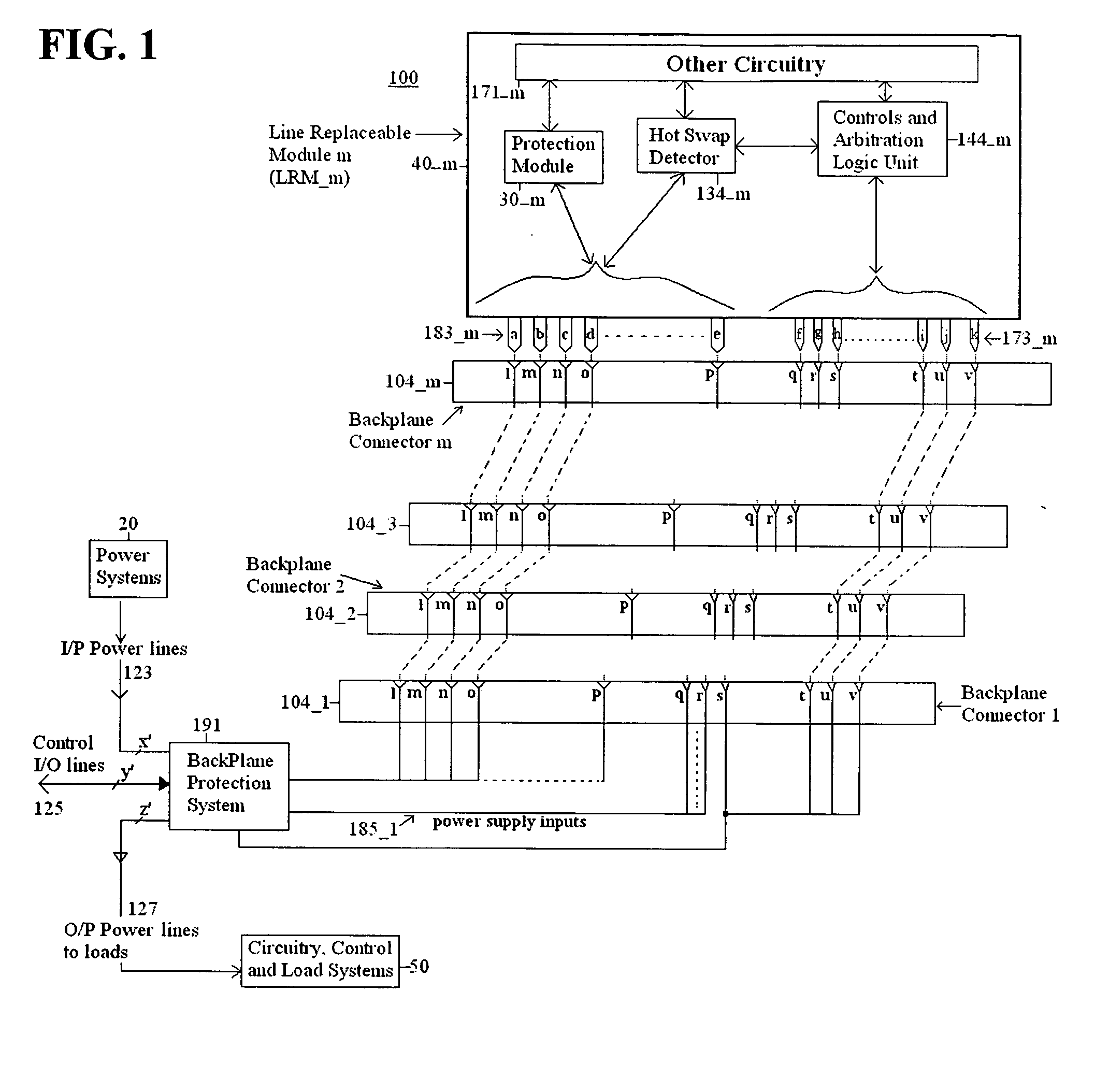
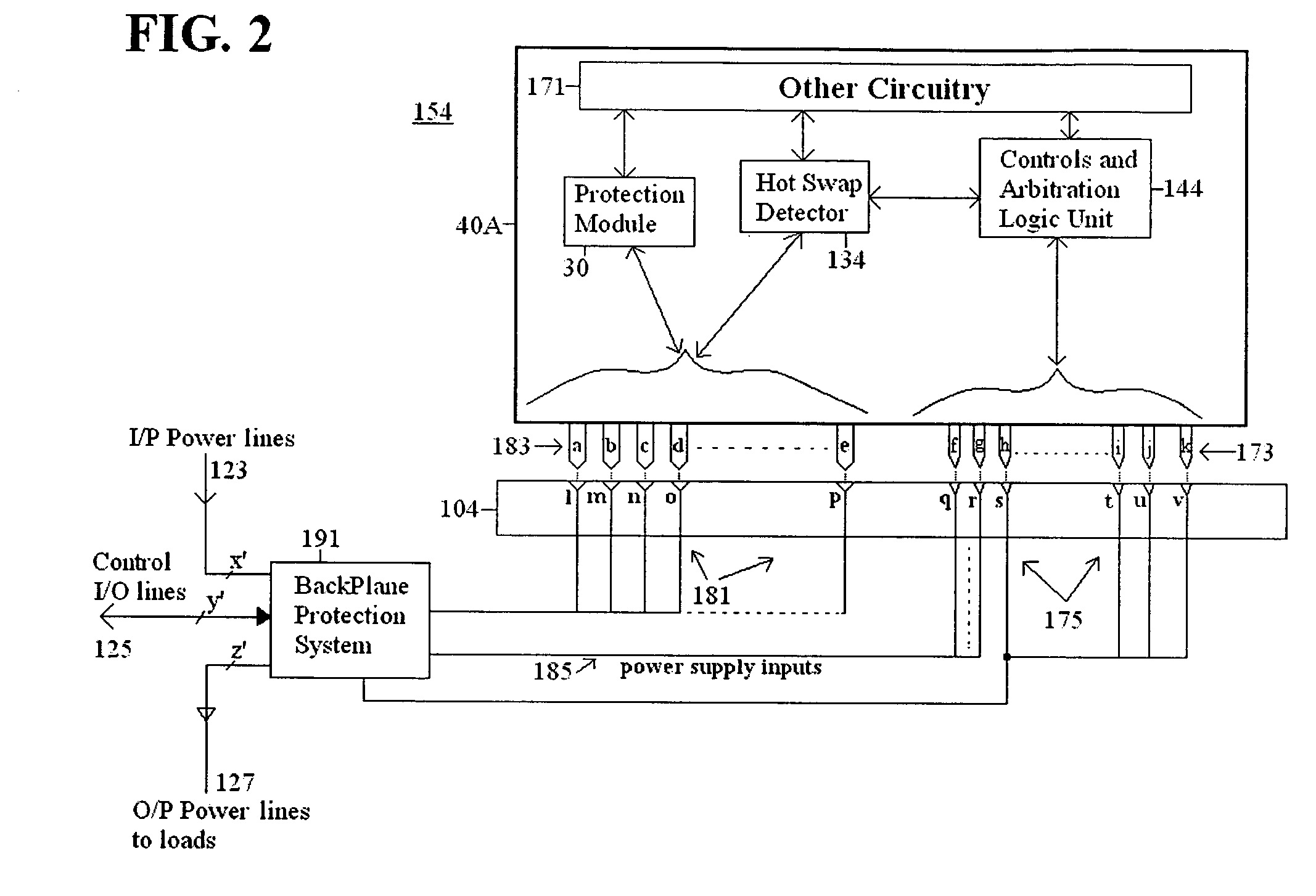
Method and apparatus for hot swap of line replaceable modules for AC and DC electric power systems
InactiveUS20070271403A1Total current dropIncrease resistanceEnergy efficient board measuresEfficient propulsion technologiesElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh resistance
A method and an apparatus are used in hot swap of AC or DC line replaceable modules (40A). The apparatus according to one embodiment comprises a pin assembly (183), the pin assembly (183) being connectable to a module (40A) and connectable to a backplane (104), the pin assembly (183) resistively reducing a current associated with the module (40A) during disconnection of the module (40A) from the backplane (104), and presenting a high resistance to the module (40A) during connection of the module (40A) to the backplane (104), and a low resistance to the module (40A) at completion of the connection of the module (40A) to the backplane (104); and a hot swap detector (134) connectable to the pin assembly (183), the hot swap detector (134) detecting the disconnection of the module (40A) from the backplane (104), and detecting the connection of the module (40A) to the backplane (104). In one embodiment, the method and apparatus provide a main advantage of preventing electrical arcs and damage to mating pins (183). Embodiments for the method and apparatus prevent any excessive voltage and / or current transients that would disturb the operation of other connected subsystems.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
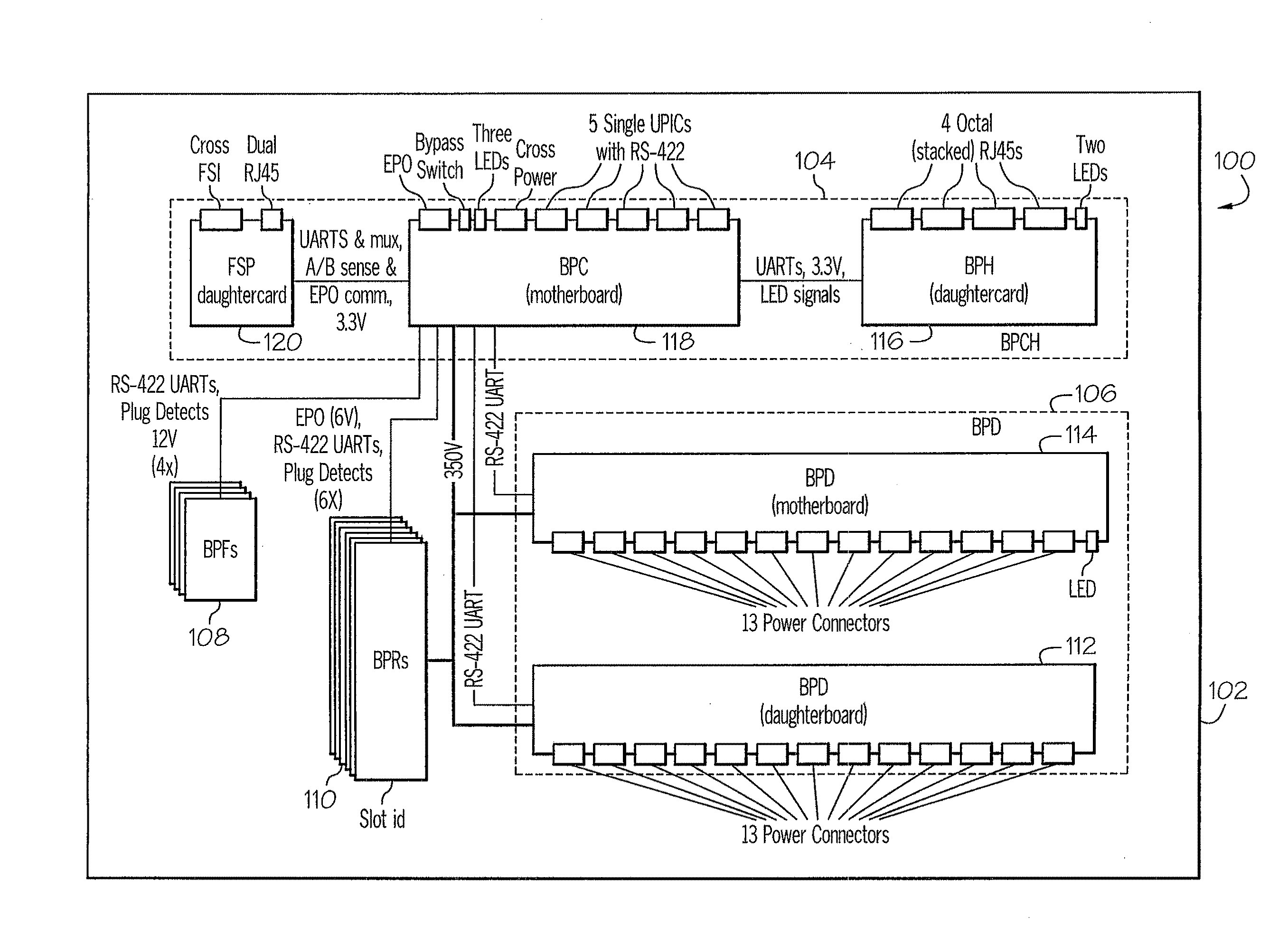
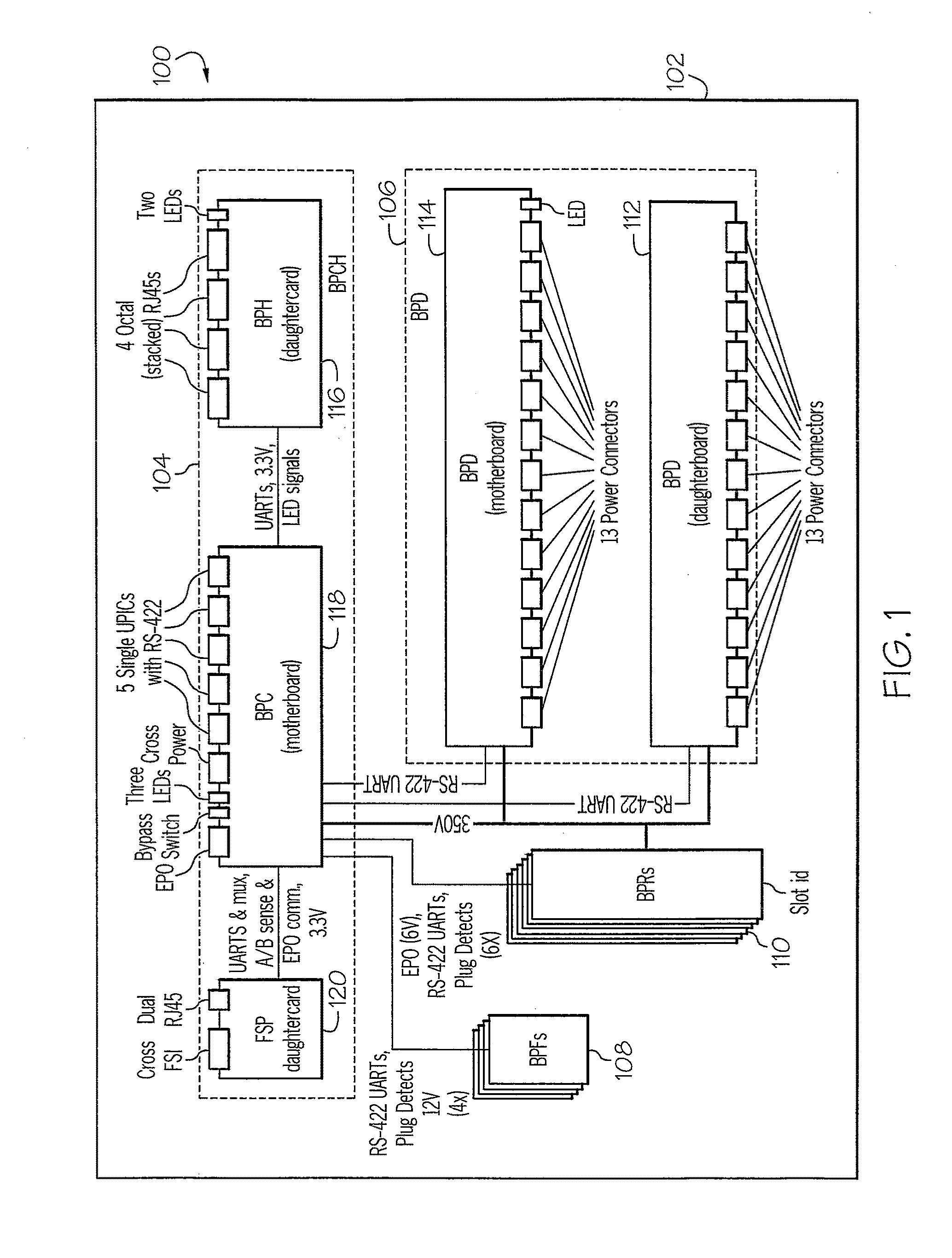
Power conversion, control, and distribution system
InactiveUS20100264731A1Single network parallel feeding arrangementsAc-dc network circuit arrangementsPower controllerDistribution power system
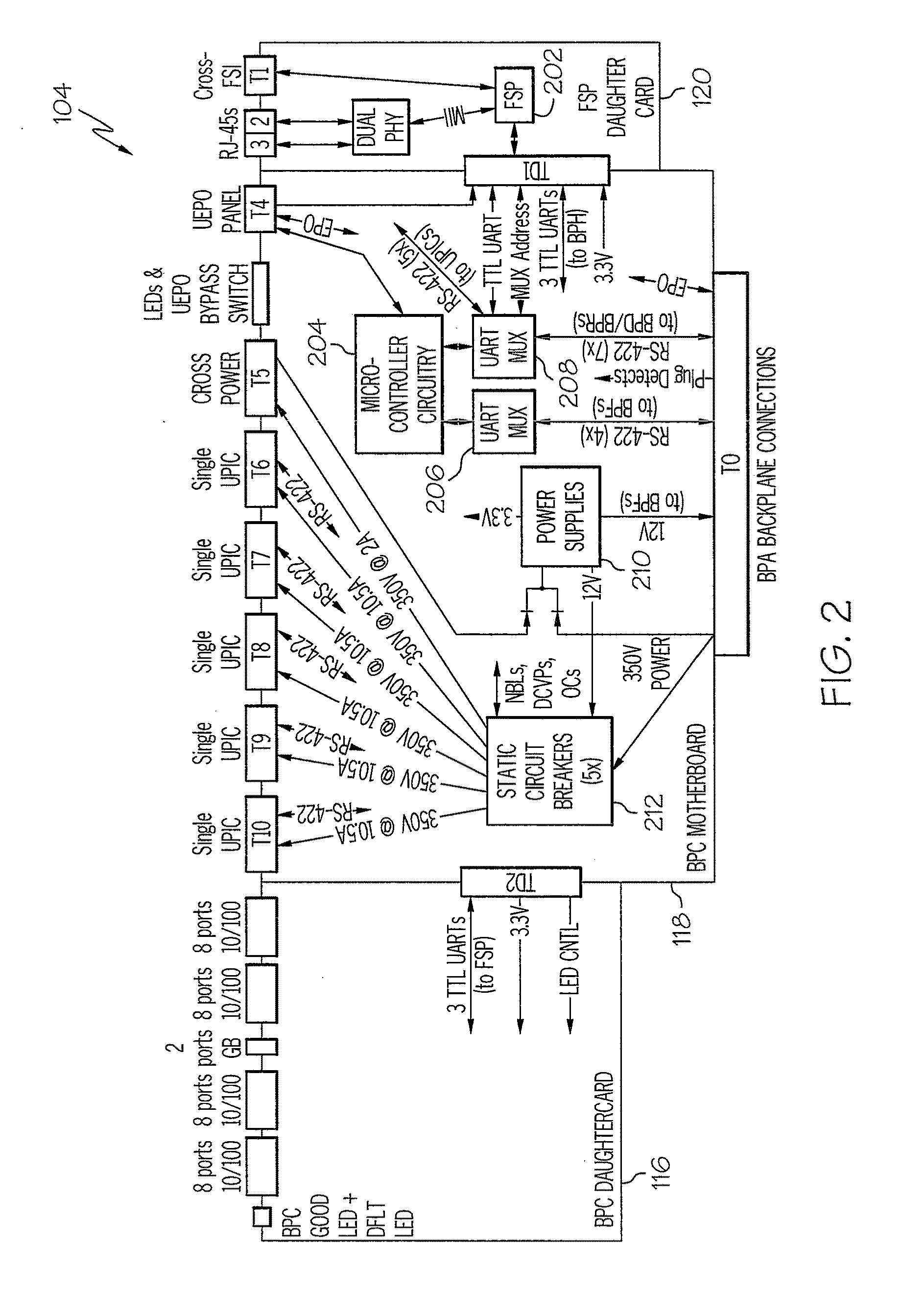
A power conversion, control, and distribution system includes multiple bulk power regulator (BPR) subassemblies, a bulk power distribution (BPD) subassembly, and a bulk power controller and hub (BPCH) subassembly. The BPR subassemblies are each configured to provide regulated DC power from both AC input power and DC input power. The BPD subassembly is configured to distribute the regulated DC power. The BPCH subassembly is coupled to the multiple BPR subassemblies and the BPD subassembly. The BPCH subassembly is configured to monitor and control the BPR assemblies and the BPD assembly.
Owner:IBM CORP
Variable fuel cell power system for generating electrical power
InactiveUS7261962B1Reduce decreaseMaintain energy balanceBatteries circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsElectrical batterySystem configuration
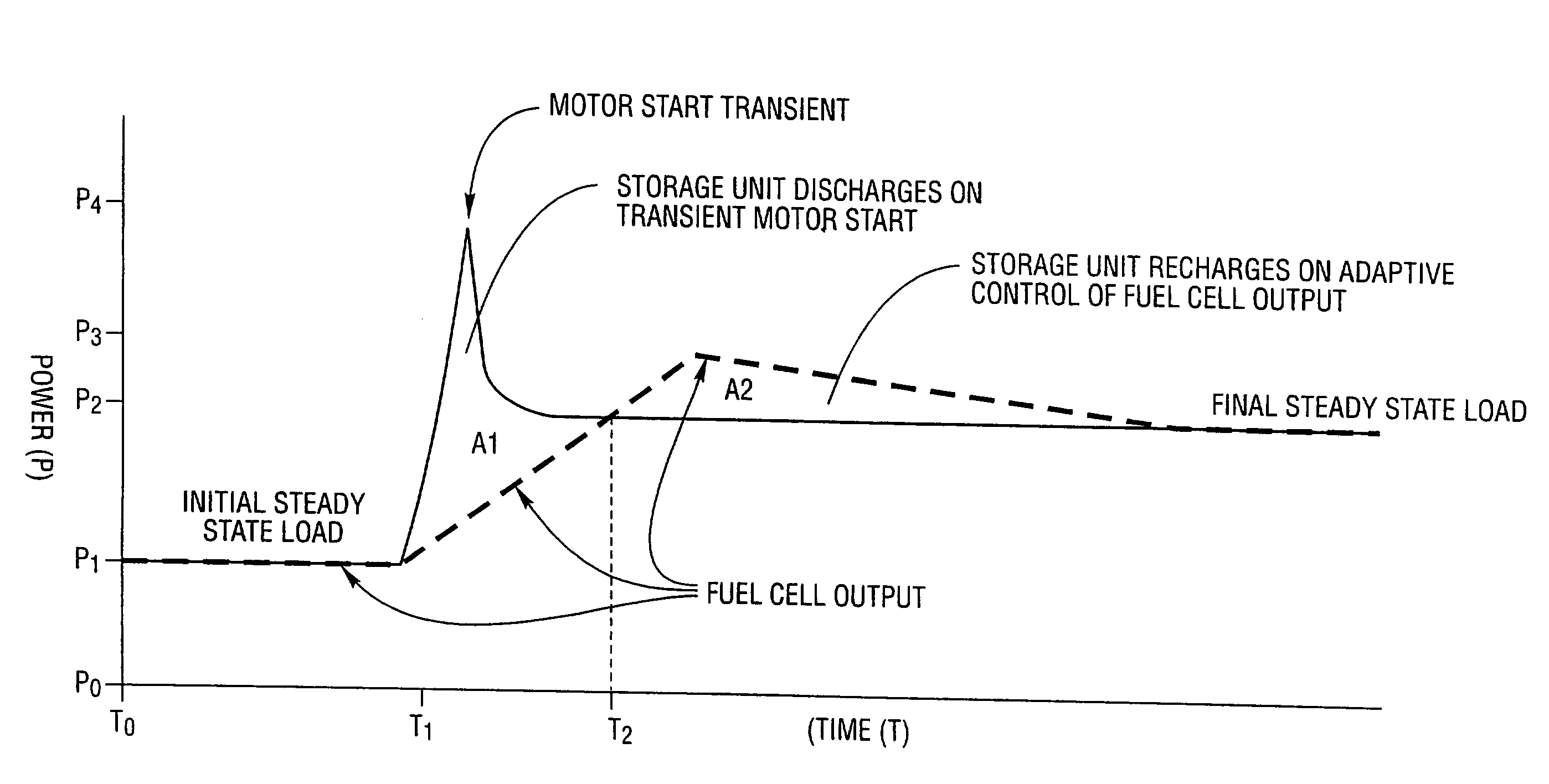
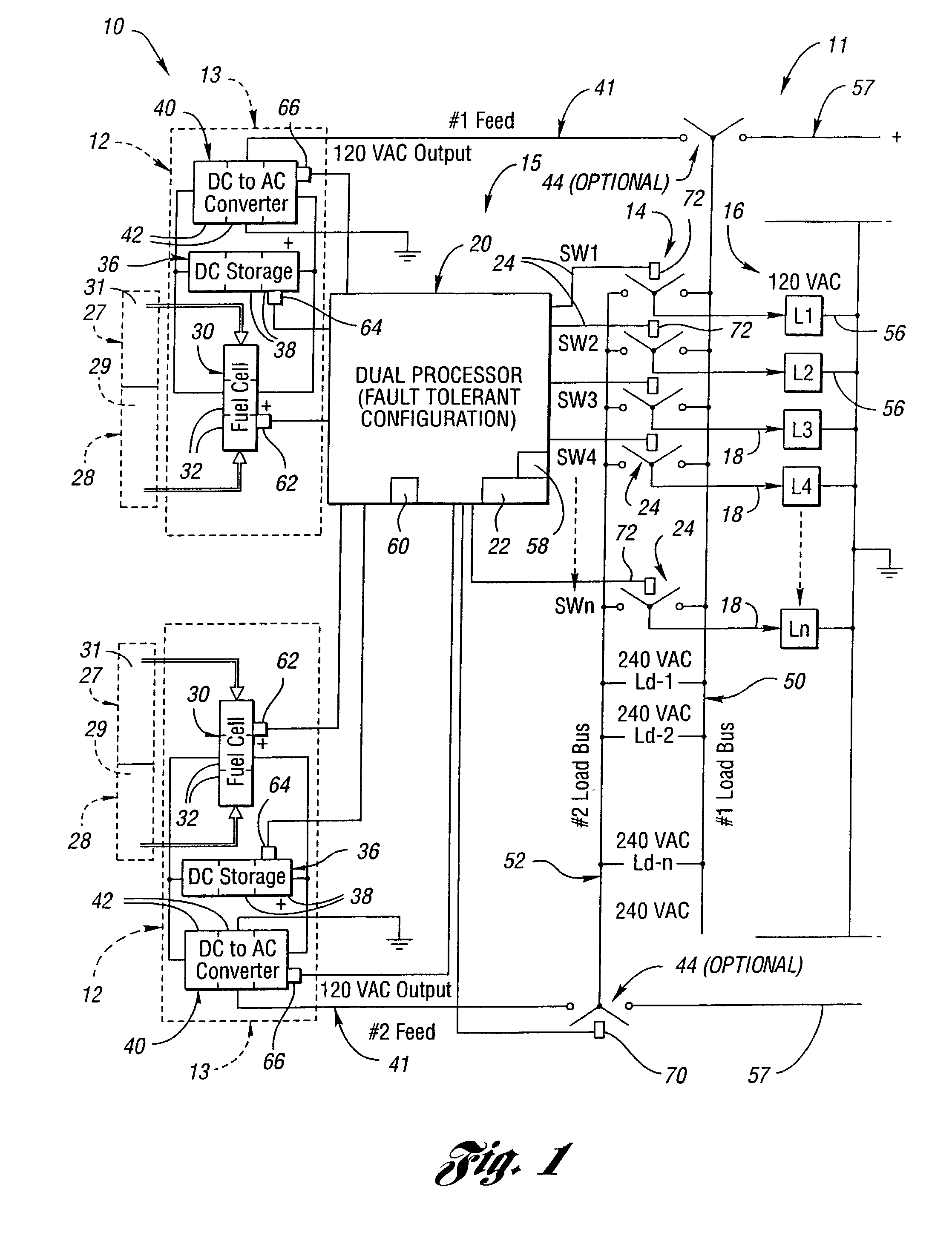
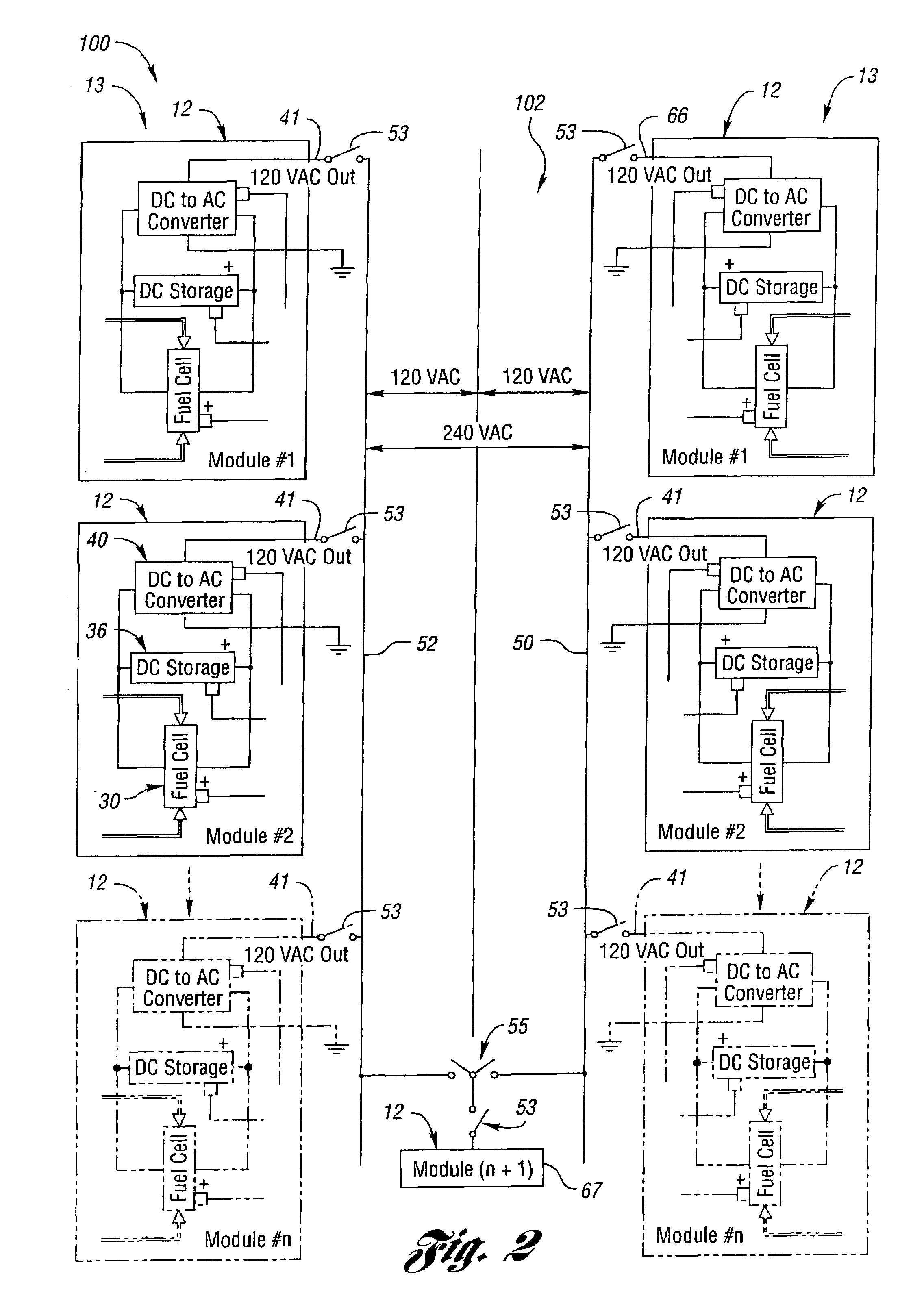
The present invention provides an apparatus and methods for variably supplying power from a stand-alone fuel cell power supply system including a power conversion unit, a power switching unit and a load control unit. Preferably, a controller manages system configuration to switch the loads, the power conversion and the delivery between the two without reducing capacity by redundantly backing up each individual portion with a bank of at least two modules for each unit. Preferably, controller actuated devices are triggered automatically in response to monitors that sense performance operating parameters and detect values operating outside a threshold range. Preferably, each of the units and the components in each unit are banked in a plurality of modular units so that individual converters may be interchanged, individual fuel cells may be interchanged, individual controllers may be interchanged, and individual storage units such as batteries may be interchanged to ensure proper operation of each bank despite changes or failures in individual components of the bank. The power system may include couplers for connecting the system to dedicated outlets such as an NEC standard 120 / 240 volt building circuitry. The invention monitors multiple elements from fuel supply, fuel cells, converters, storage units, and controls as well as the loads for balanced, reliably robust, high power quality, and independent power supply.
Owner:CONVERGENCE LLC A MICHIGAN LIMITED LIABILITY
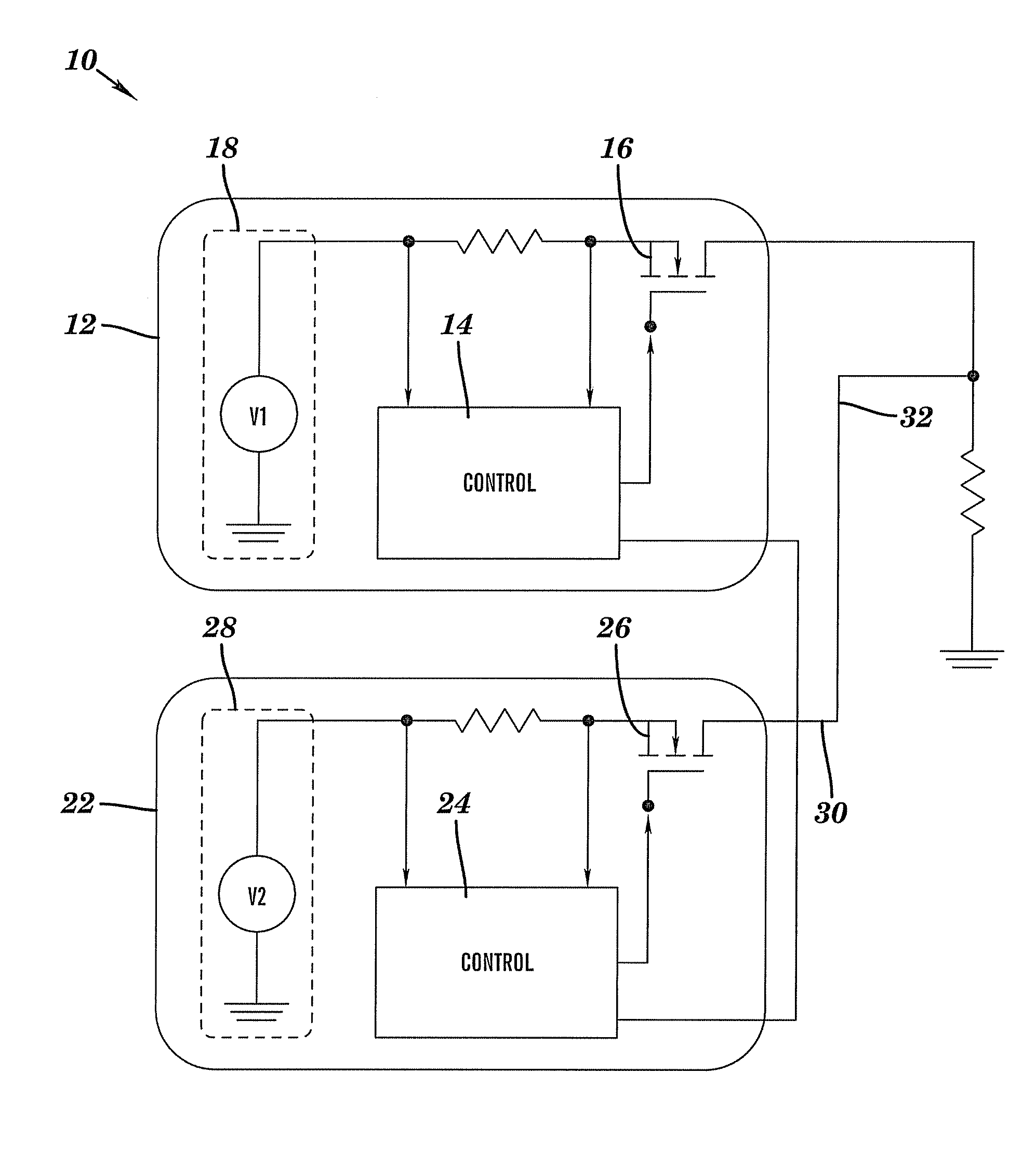
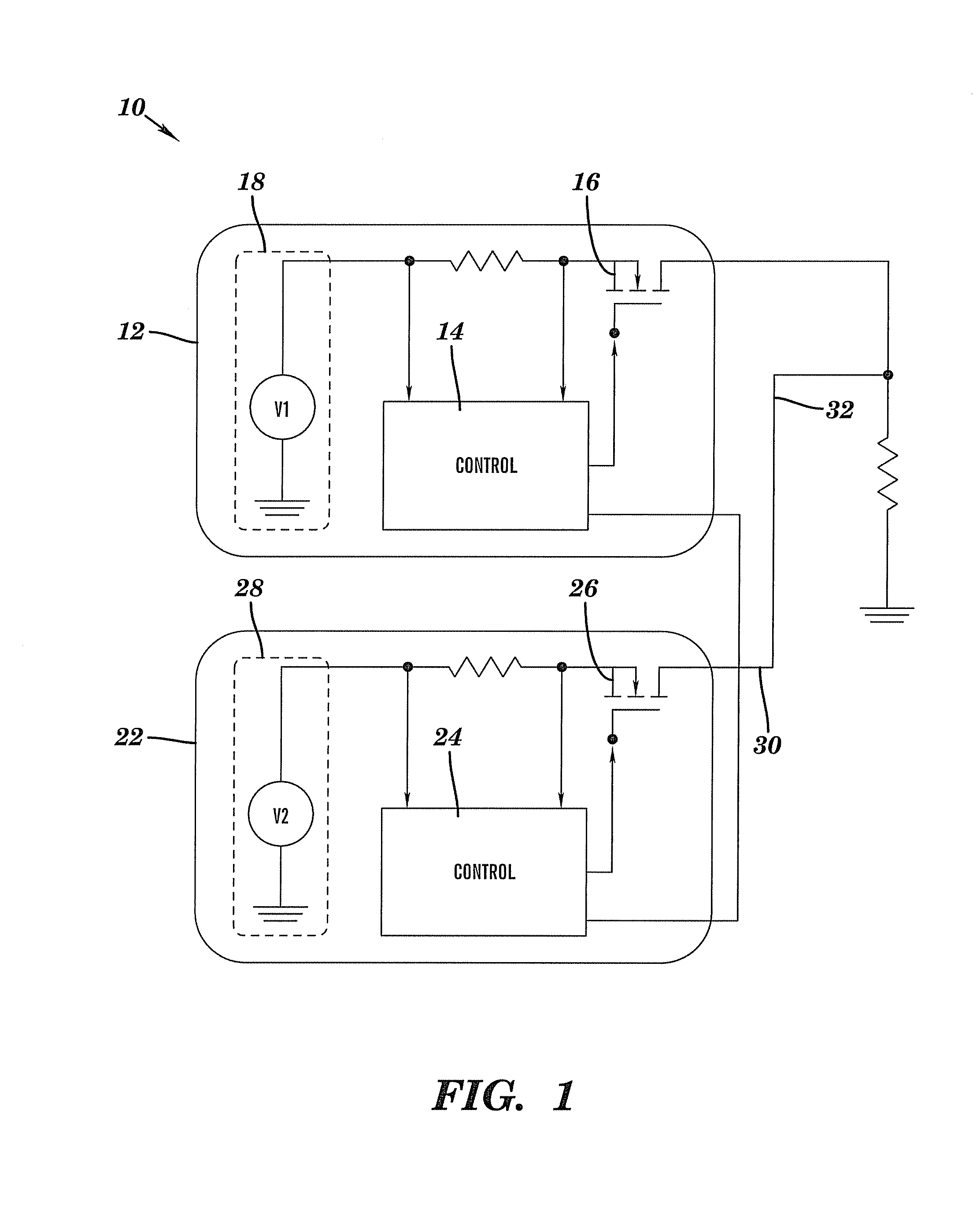
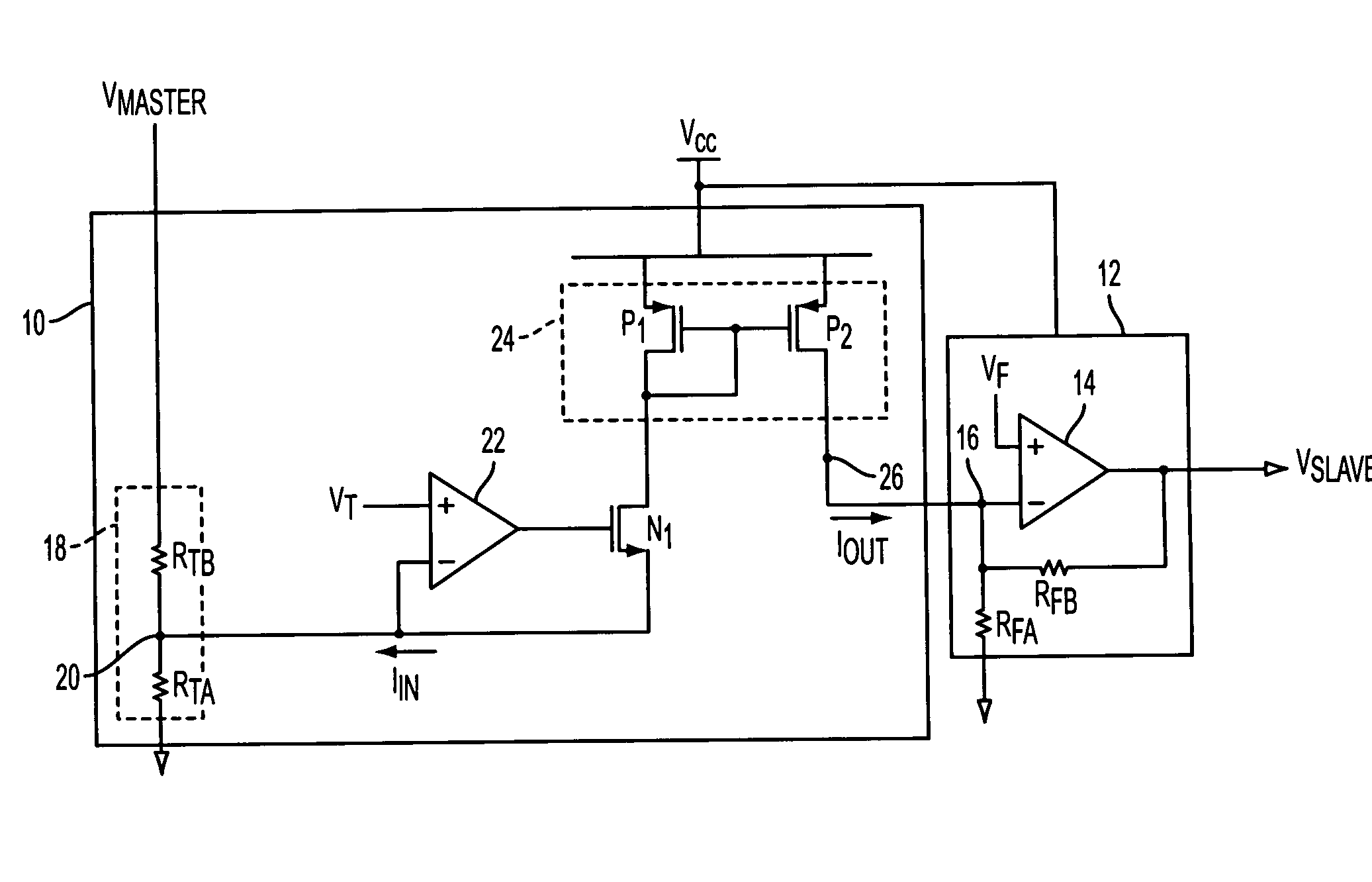
Methods and circuits for tracking and sequencing multiple power supplies
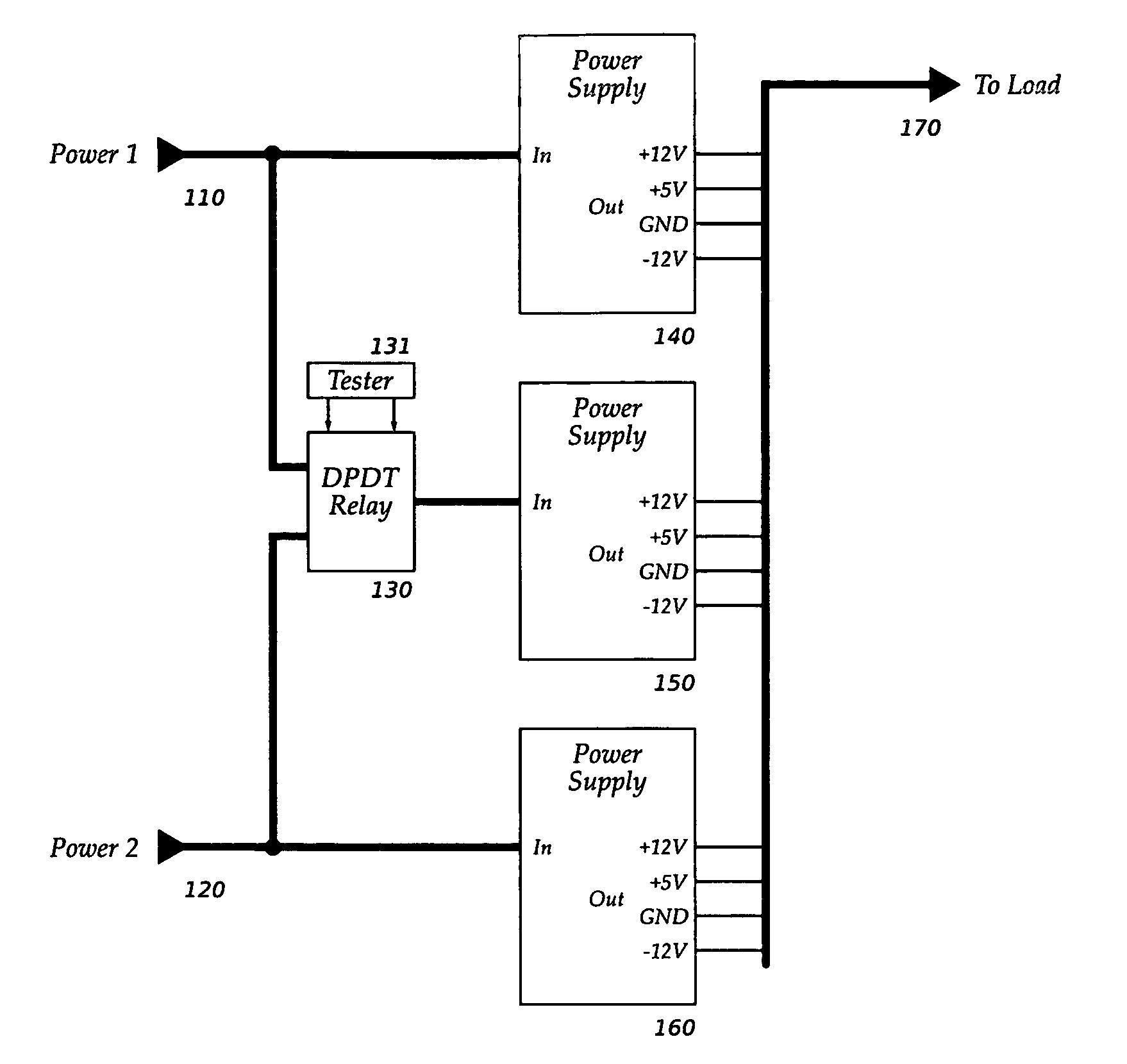
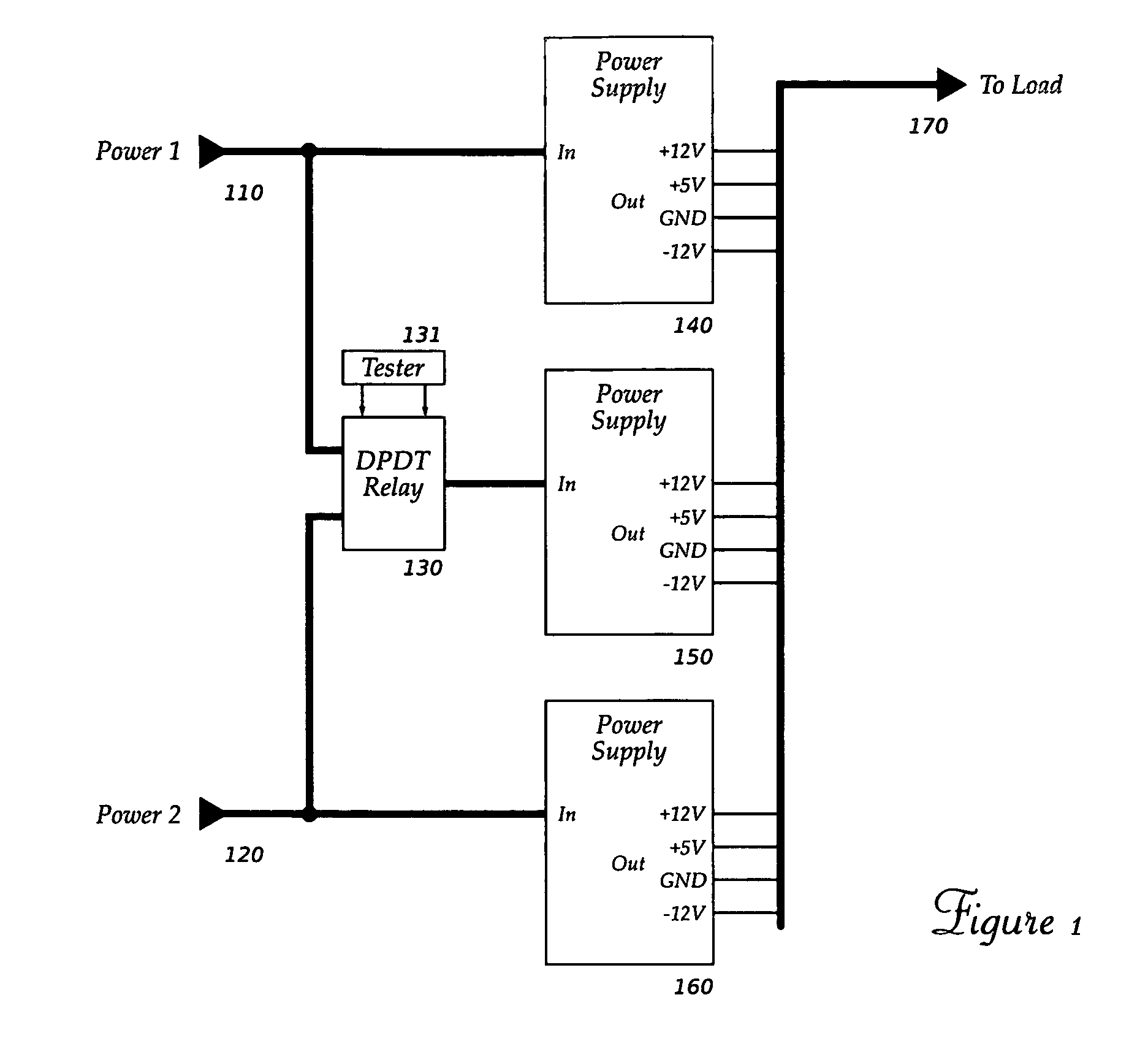
ActiveUS7342328B1High impedanceDc source parallel operationHot plugging-unplugging power/loadElectrical and Electronics engineeringDefining relationship
The present invention relates to methods and circuits for controlling outputs of one or more slave power supplies in one or more defined relationships to a master signal. The defined relationships include but are not limited to coincident tracking, offset tracking, ratiometric tracking, and supply sequencing.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
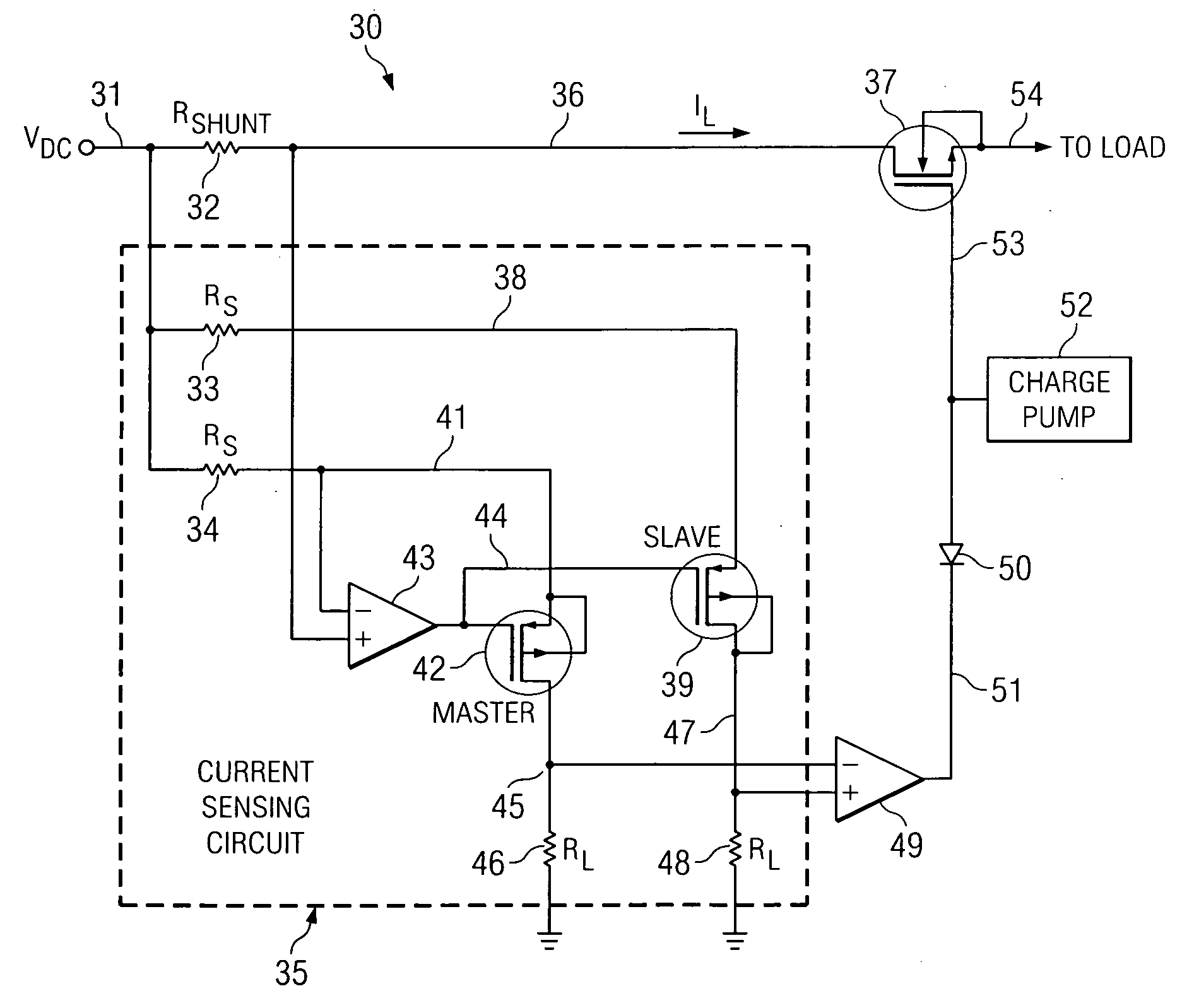
Minimum loss and wiring circuit and method for paralleling hot swap controllers
ActiveUS20100007217A1Reduce power consumptionEqual currentBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsProtective switchesAudio power amplifierControl signal
A hot swap controller includes a shunt resistor (32-1,2) and a power transistor (37-1,2) having a source coupled to a load maintains the first power transistor in a fully-turned-on condition to cause it to deliver a load current contribution (I1,2) which flows through the shunt resistor and the power transistor to the load (25). Current sensing circuitry (35-1,2) produces a first control signal (V45-1,2-V47-1,2) equal to the difference between a DC component (V47-1) proportional to a first load current contribution (IL1) flowing in the first shunt resistor and a feedback-based component (V45-1). A control amplifier (49-1,2) produces a second control signal (V51-1,2) in response to the first control signal to modify a drive signal (53-1) to the power transistor so as to reduce a channel resistance of the power transistor if the first control signal exceeds a predetermined level.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
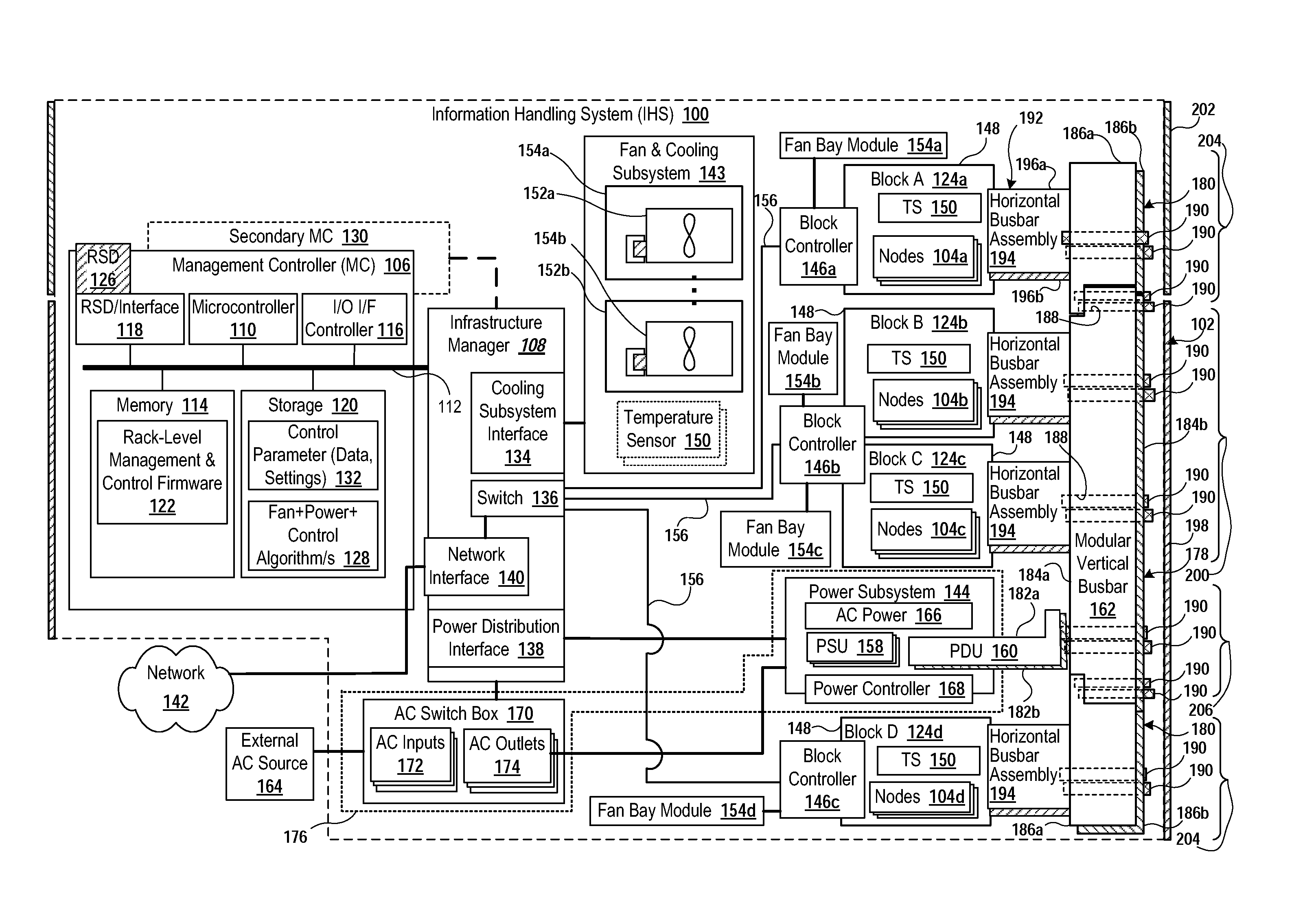
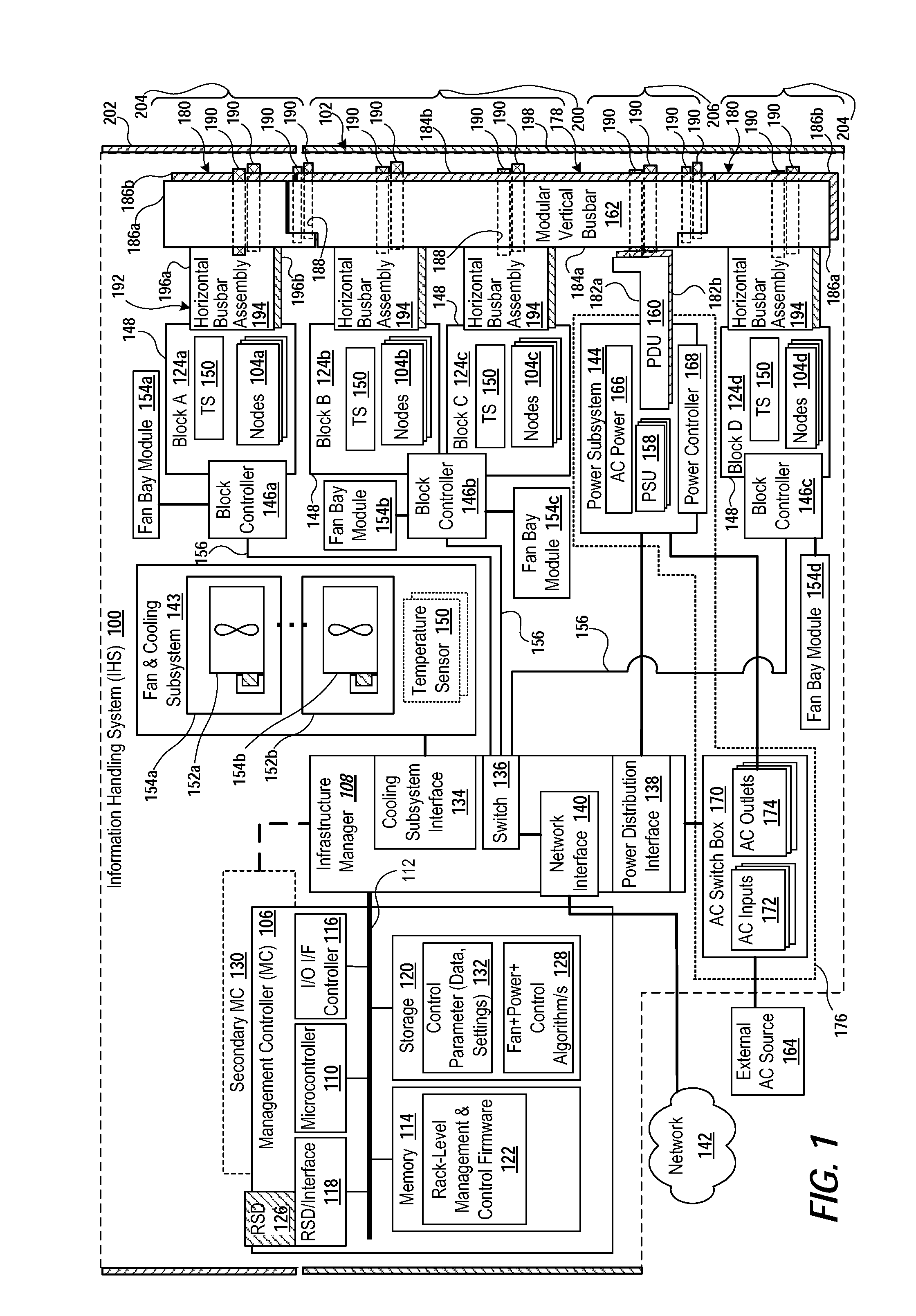
Rack power distribution via modular, expandable bus bar for modular and scalable/expandable information handling system
A rack-based information handling system (IHS) includes a rack having a modular structure that supports insertion from a front of the rack of different numbers and sizes of information technology (IT) gear to create one or more IT nodes. Power bay chassis is received in the rack with a power distribution unit directed towards a rear of the rack. A modular busbar assembly is attached to the rear of the rack. A first vertical busbar segment is in direct electrical connection with the power distribution unit and spans one or more nodes to provide hot pluggable electrical power to an aft-directed connection of an IT node inserted into the rack. A second busbar segment can be attached to the first vertical busbar to electrically communicate with the power distribution unit and span an additional node adjacent to the one or more nodes to provide electrical power to the adjacent node.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Redundant power system with no latent single failure point
ActiveUS20060208572A1Batteries circuit arrangementsError detection/correctionSingle faultElectric power
A redundant power supply system with several individual power supplies, each connected to one of several power inlets. At least one power supply can be connected to a selectable one of the several power inlets by means of a steering network.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Power conversion system and method for pre-charging dc-bus capacitors therein
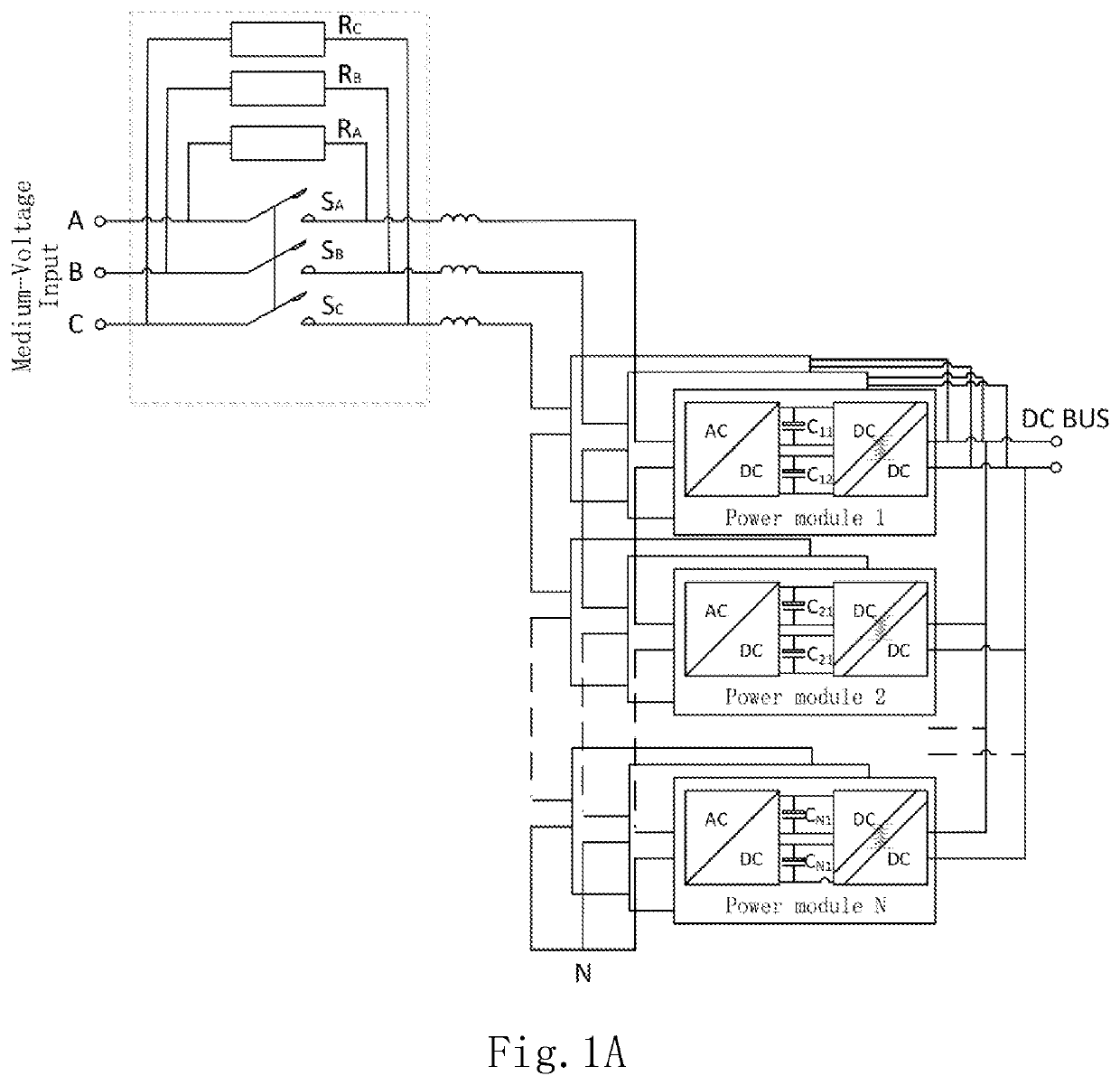
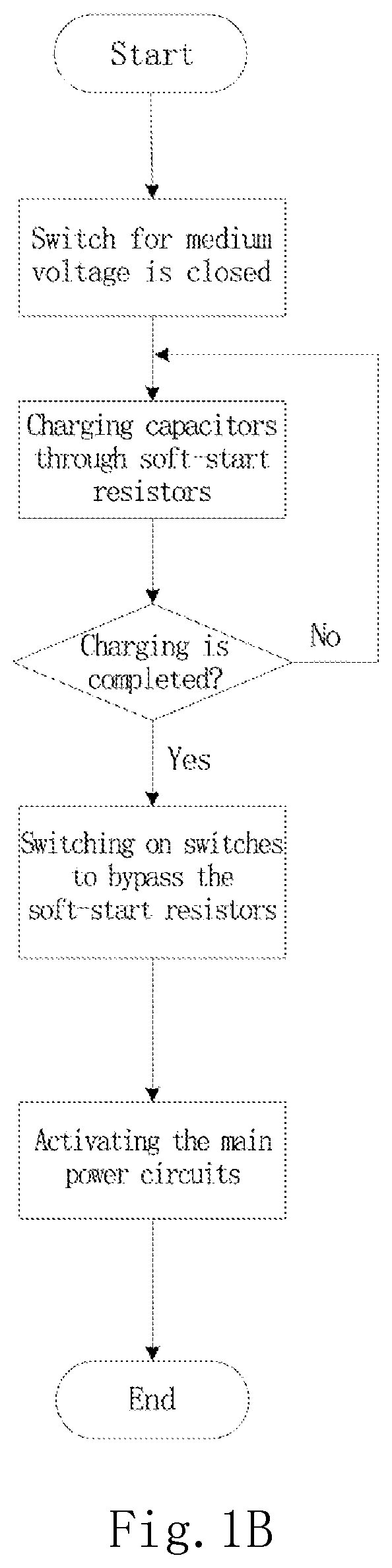
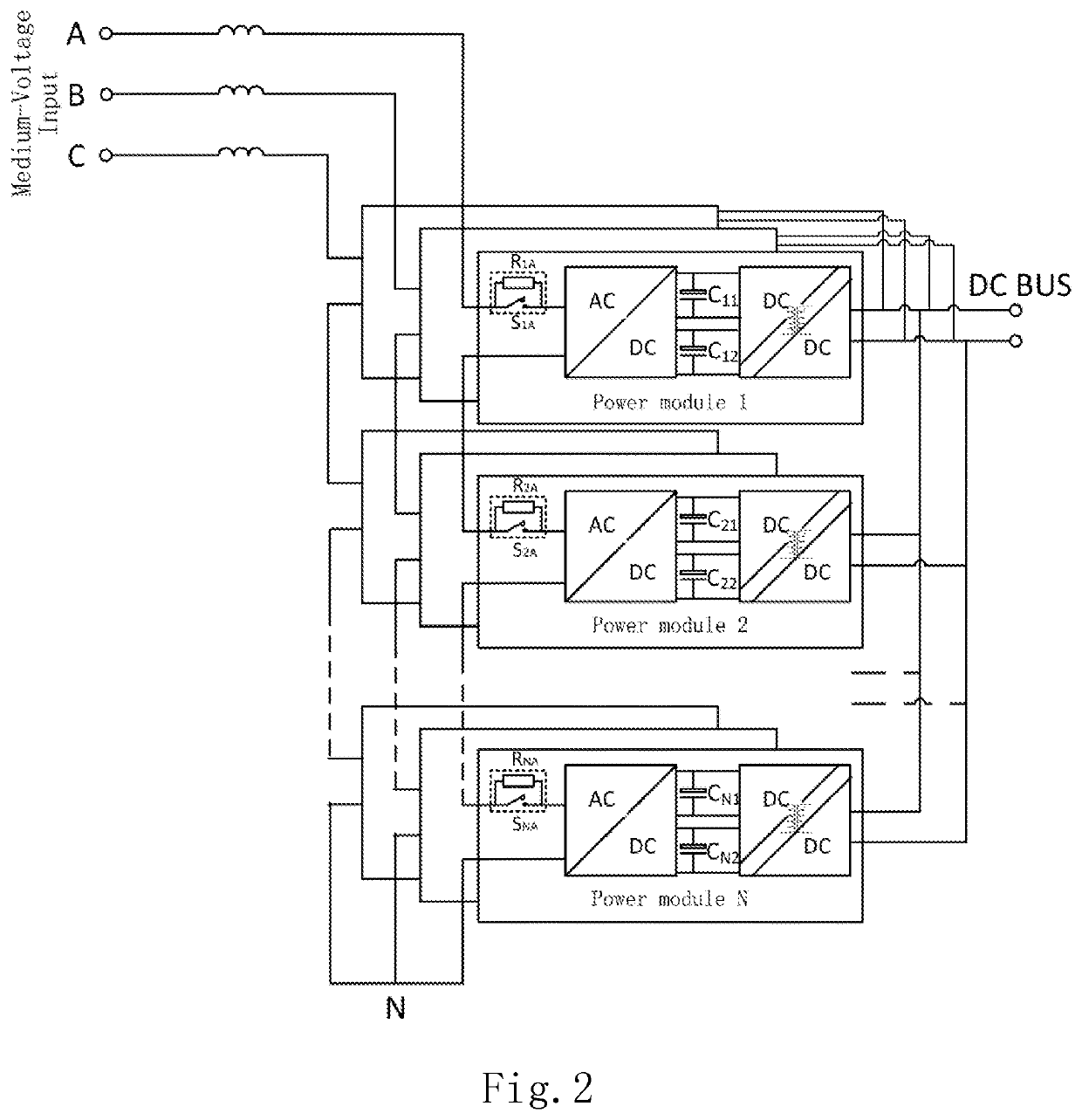
ActiveUS20200006970A1Small sizeEffectively pre-charge DC-Bus capacitorsBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalCapacitanceDC - Direct current
The present invention discloses a power conversion system and a method for pre-charging DC-Bus capacitors therein. The power conversion system comprises a plurality of power modules, each including a power input end; a charging input end; a power output end; at least one power conversion unit, each of the power conversion unit including at least one DC-Bus capacitor and being electrically connected to the power input end and the power output end; and a pre-charging unit electrically connected to the charging input end for receiving direct current and electrically connected to the DC-Bus capacitor for pre-charging the DC-Bus capacitor. The power input ends of the plurality of power modules are connected in series and then electrically connected to an AC power source, and the power output ends of the plurality of power modules are connected in parallel.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
DC power supply device, and control method for DC power supply device
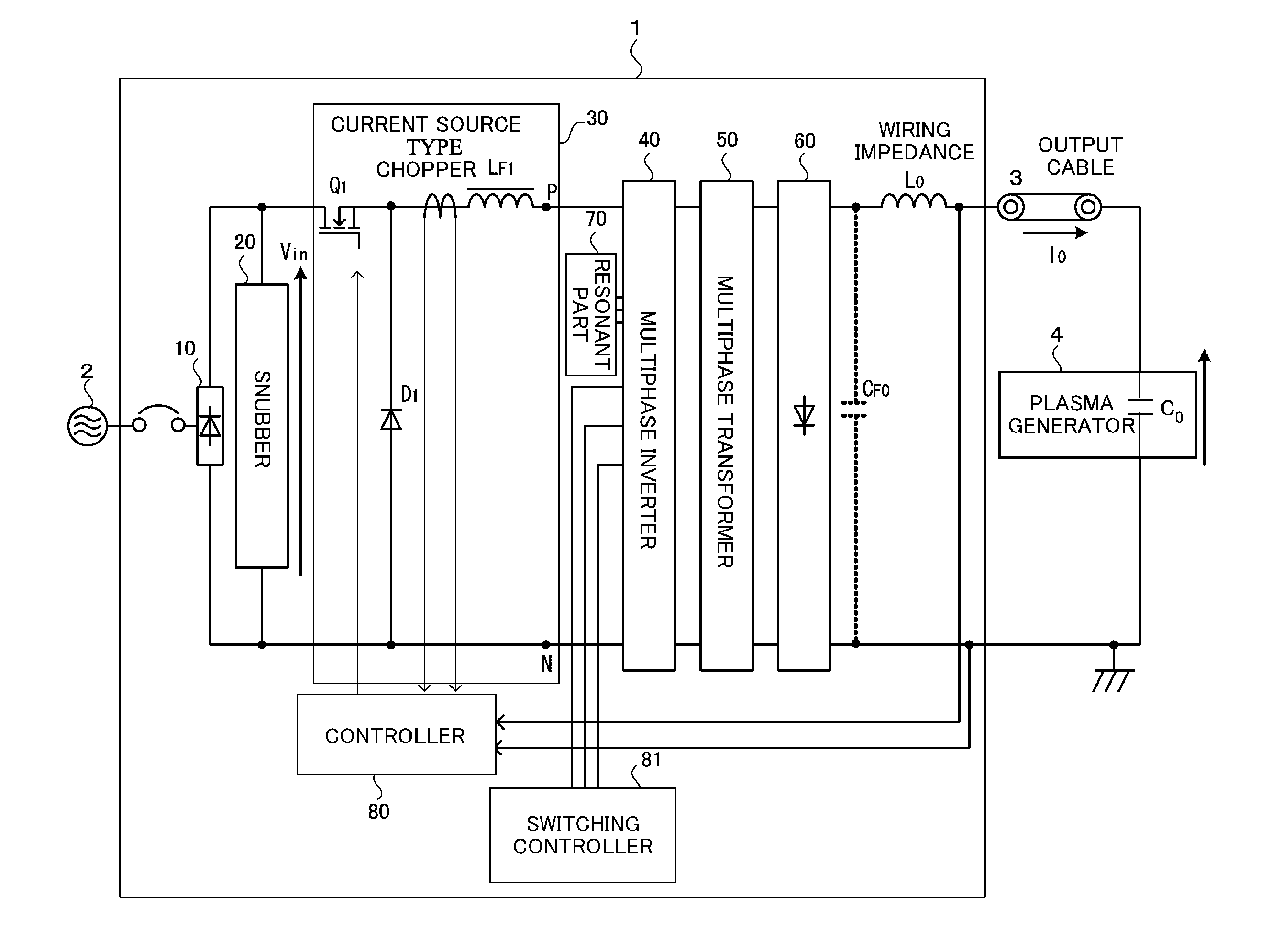
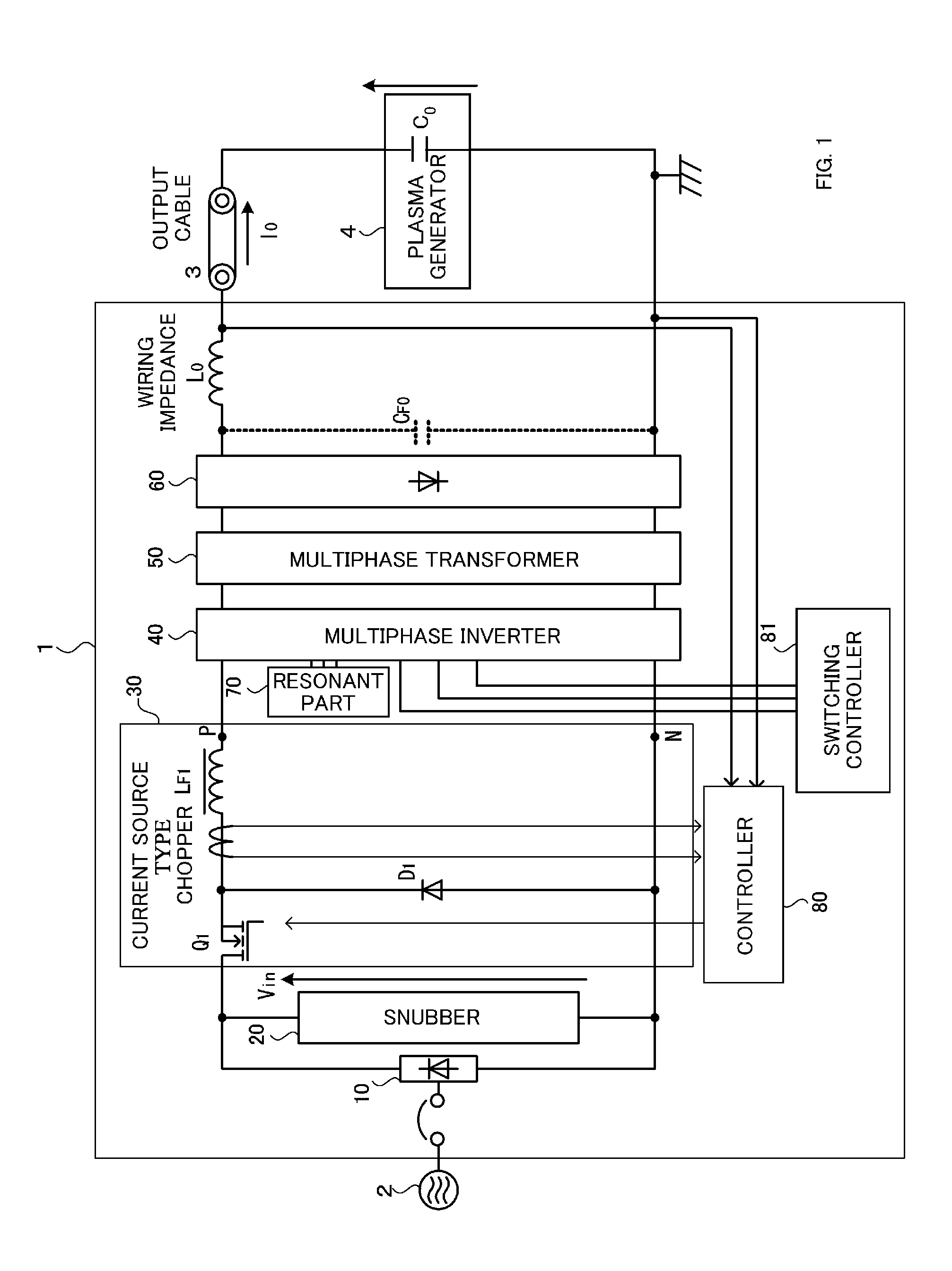
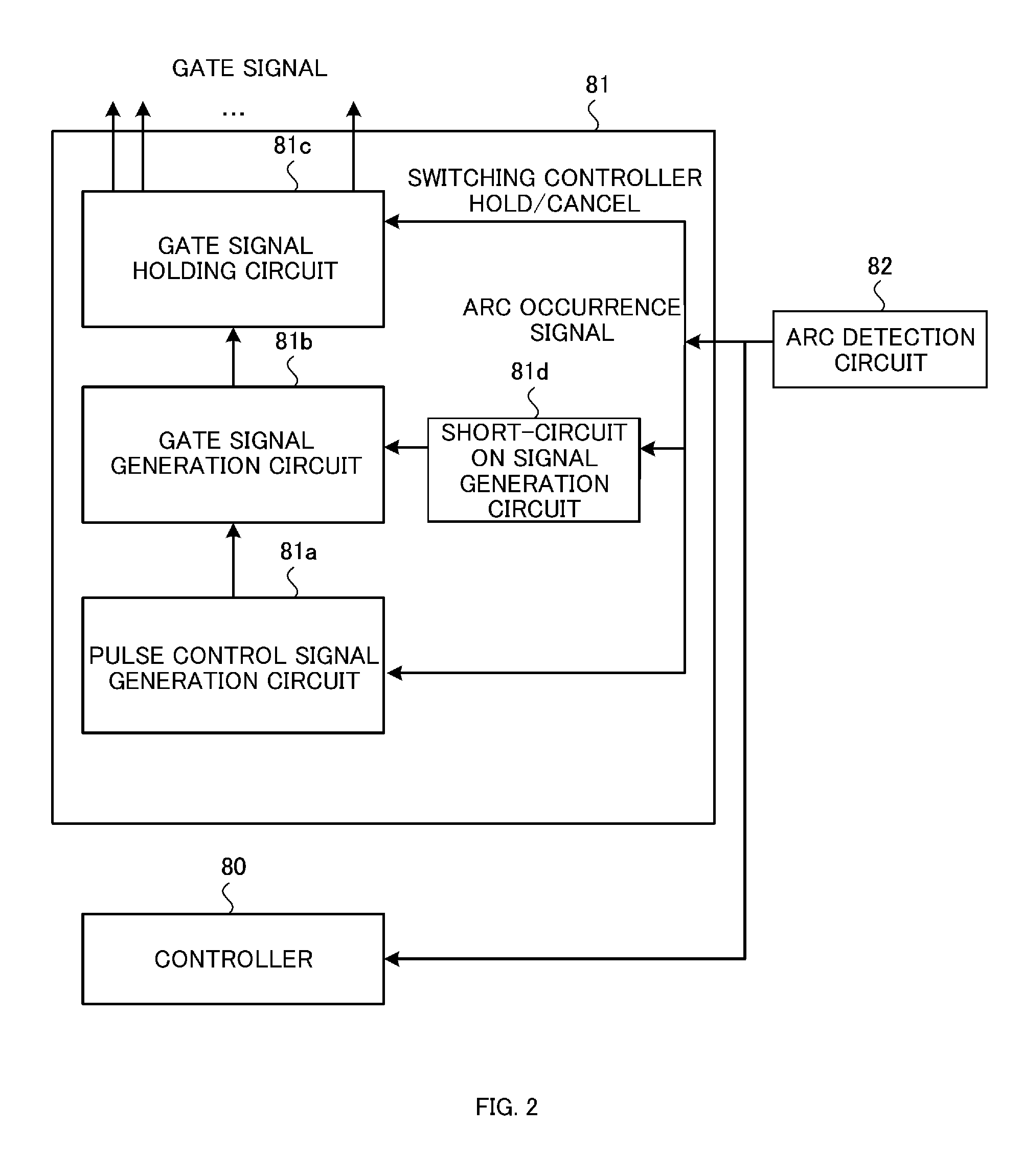
ActiveUS20150180346A1Suppresses fluctuations in output voltageSuppresses voltage fluctuationsSpark gap detailsElectric discharge tubesPower inverterPulse control
A phase of the pulse control signal upon restarting is synchronized with the phase of the pulse control signal upon suspending, thereby suppressing fluctuations of output voltage in each phase of the inverter upon restarting and further suppressing fluctuations of voltage supplied to the load. Upon supplying DC power to a plasma generator, when arc discharge occurs in the plasma generator, supplying of the DC power is suspended to reduce damage on the electrodes and substrate, and further upon extinguishing of the arc discharge, supplying of the DC power is restarted. In suspending and resuming the DC output, the current flowing in the chopper upon suspending is held in the form of circulating current, and upon restarting the inverter, this circulating current is supplied to the load. Accordingly, it is possible to reduce a delay in supplying the DC power to the load, upon resuming the DC output.
Owner:KYOSAN ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
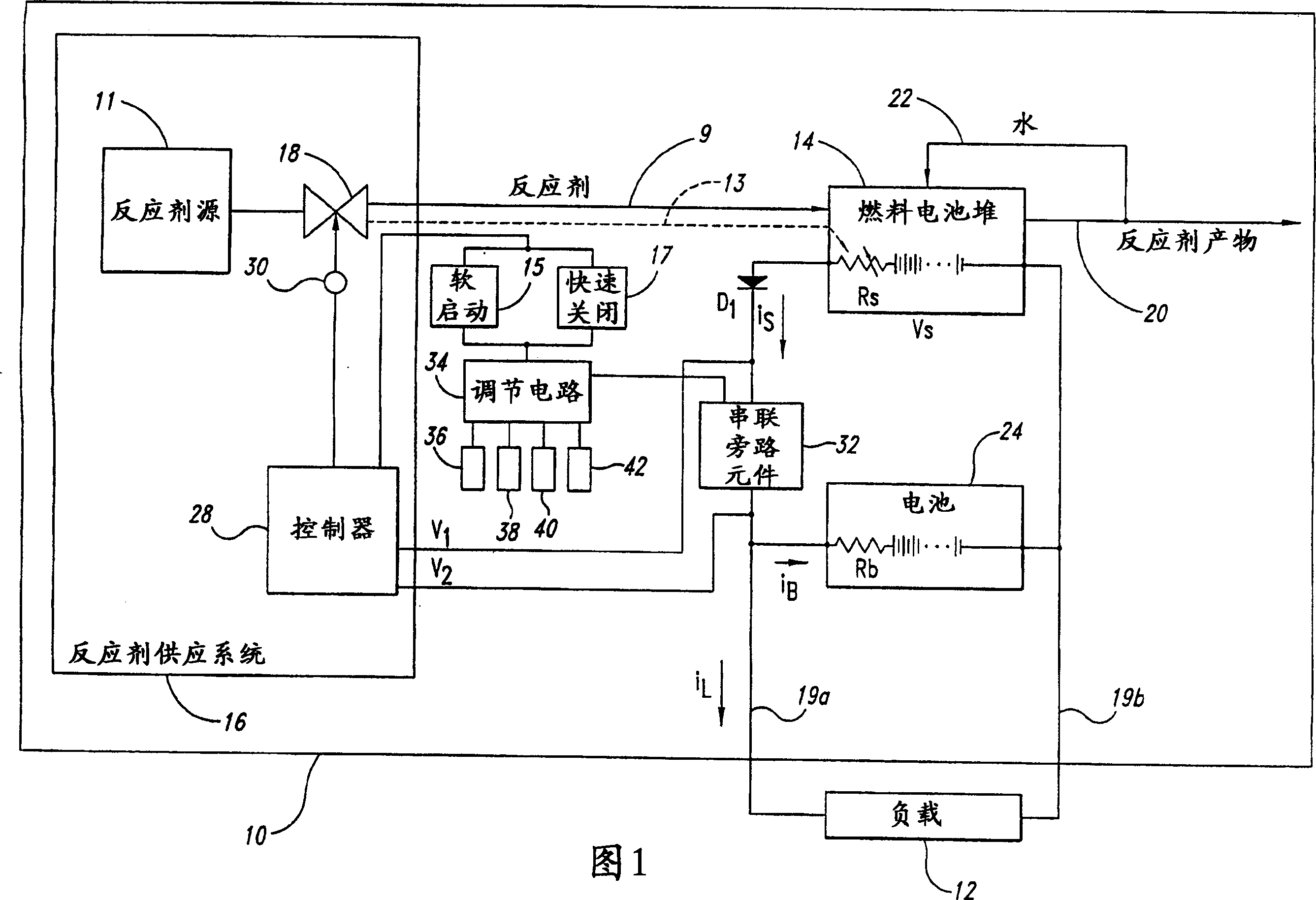
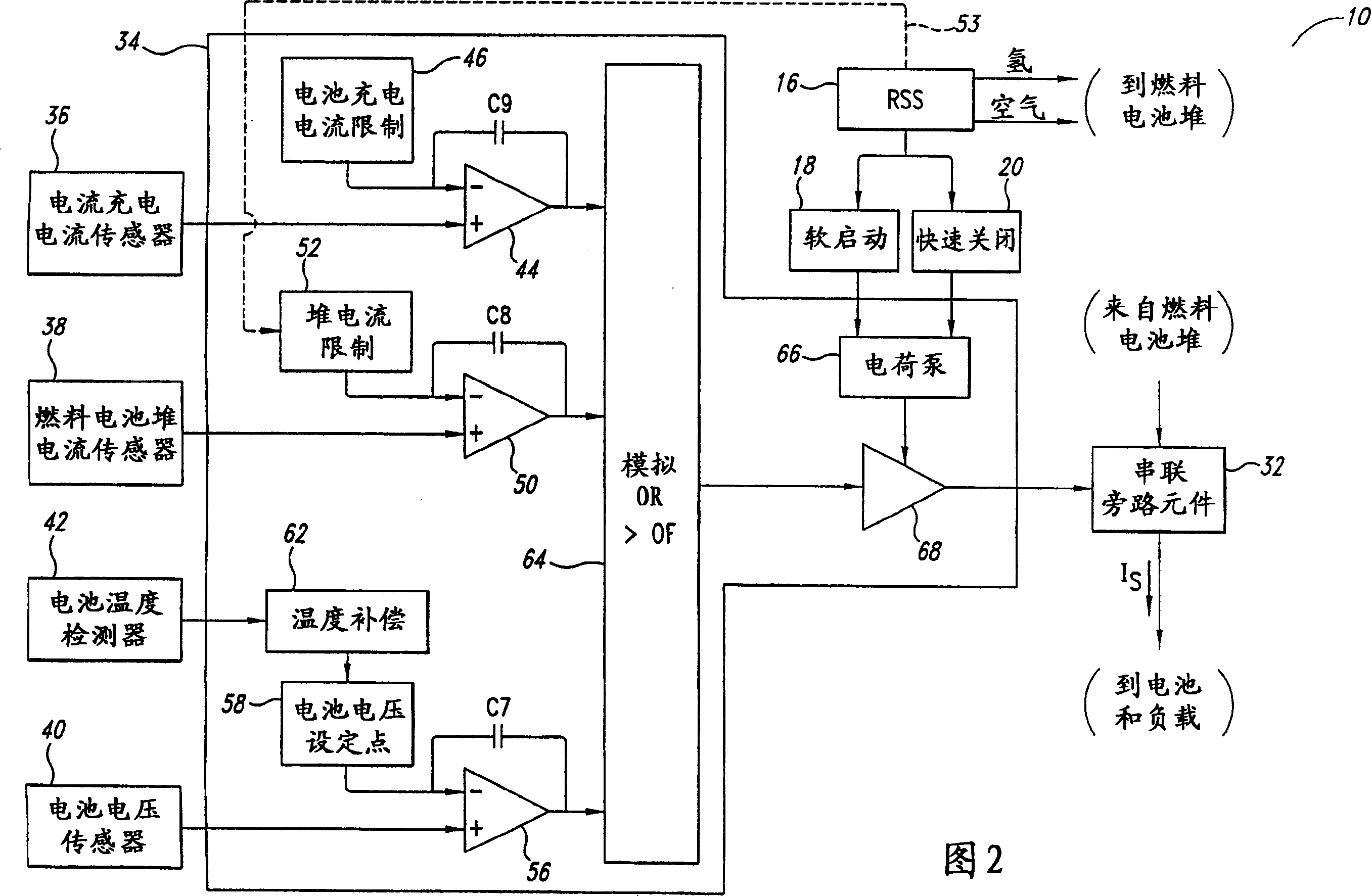
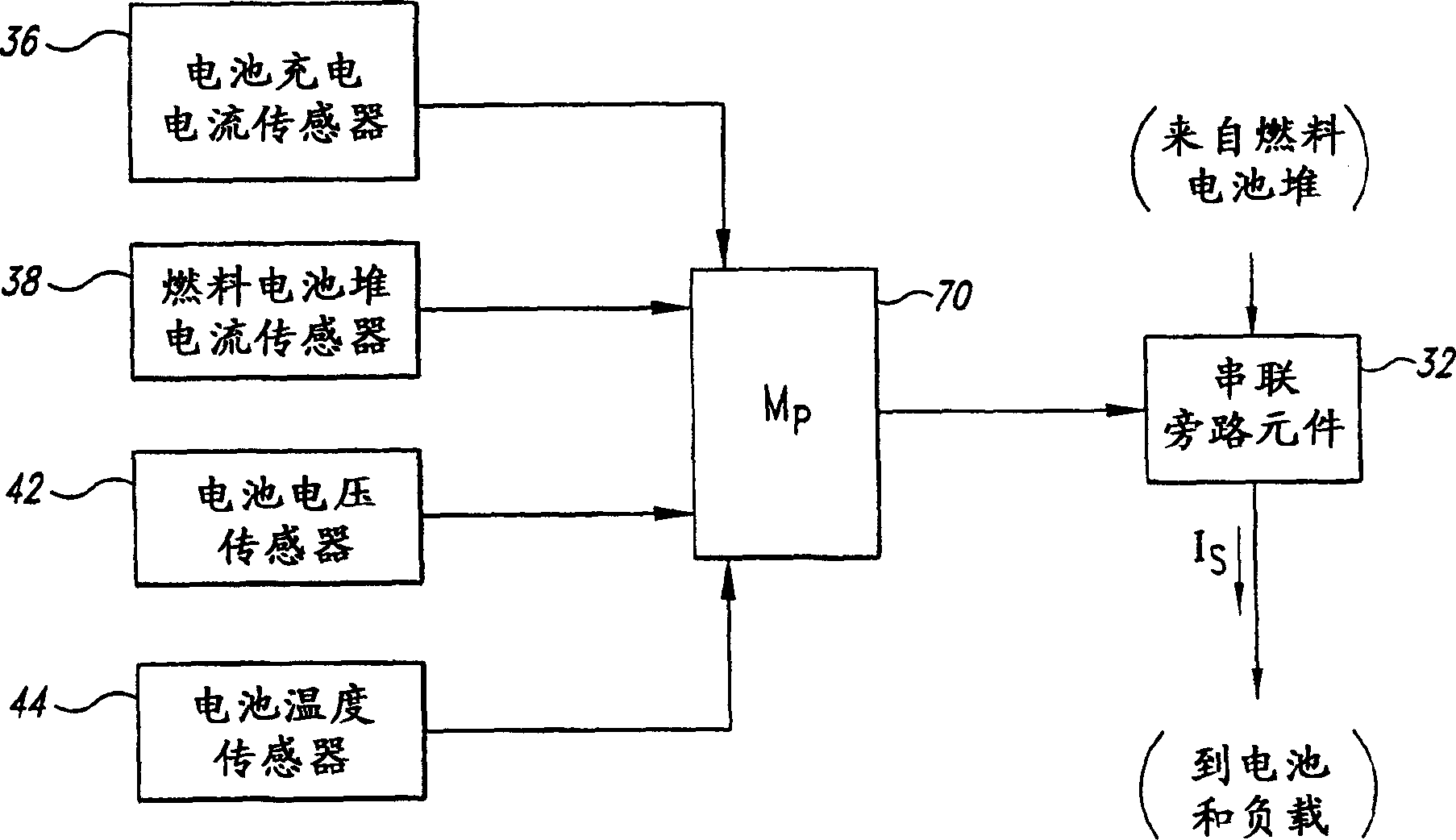
Fuel cell system
A fuel cell system having a battery employs a first stage that regulates current through a series pass element in response to a greater of a battery charging current error, a battery voltage error and a stack current error. The fuel cell system employs a second stage that controls a partial pressure of a reactant flow to the fuel cell stack based on a deviation of voltage across the series pass element, or based on a battery condition. The fuel cell system may employ either, or both, of the stages. Individual fuel cell systems can be combined in series and / or parallel to produce a combined fuel cell system having a desired output voltage and current.
Owner:BALLARD POWER SYSTEMS
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com