Patents
Literature
88 results about "Capacitive storage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
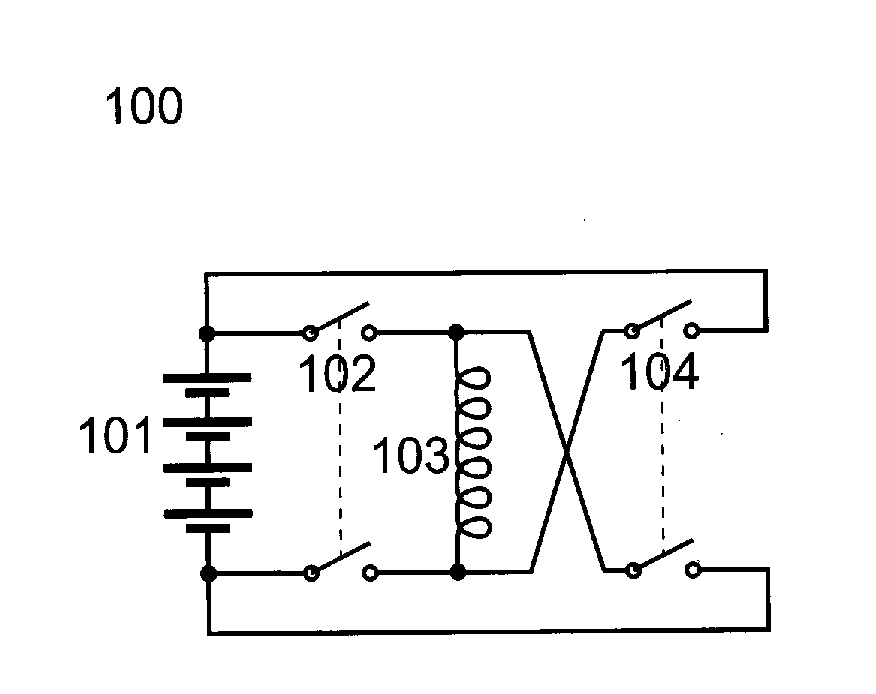
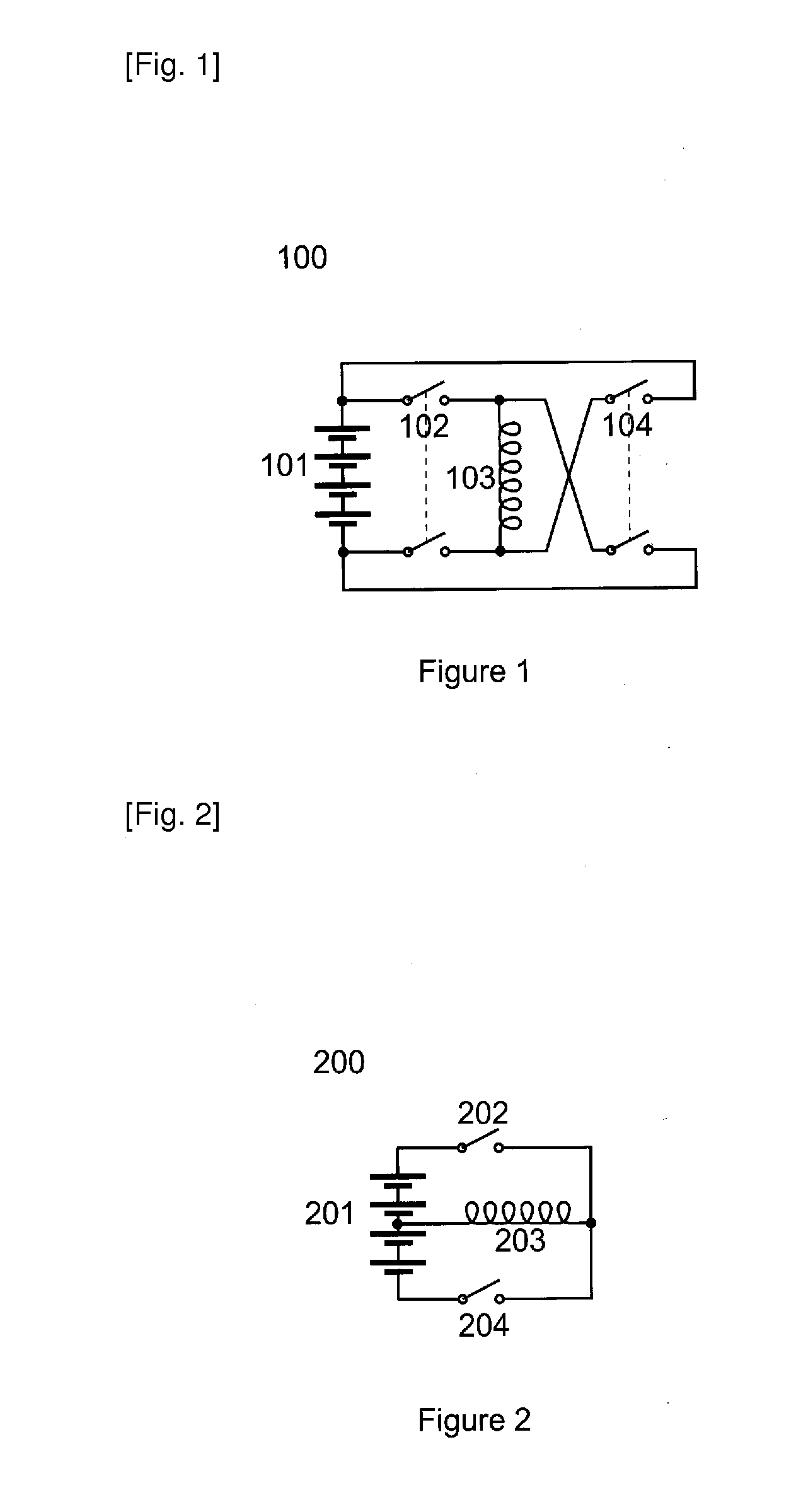
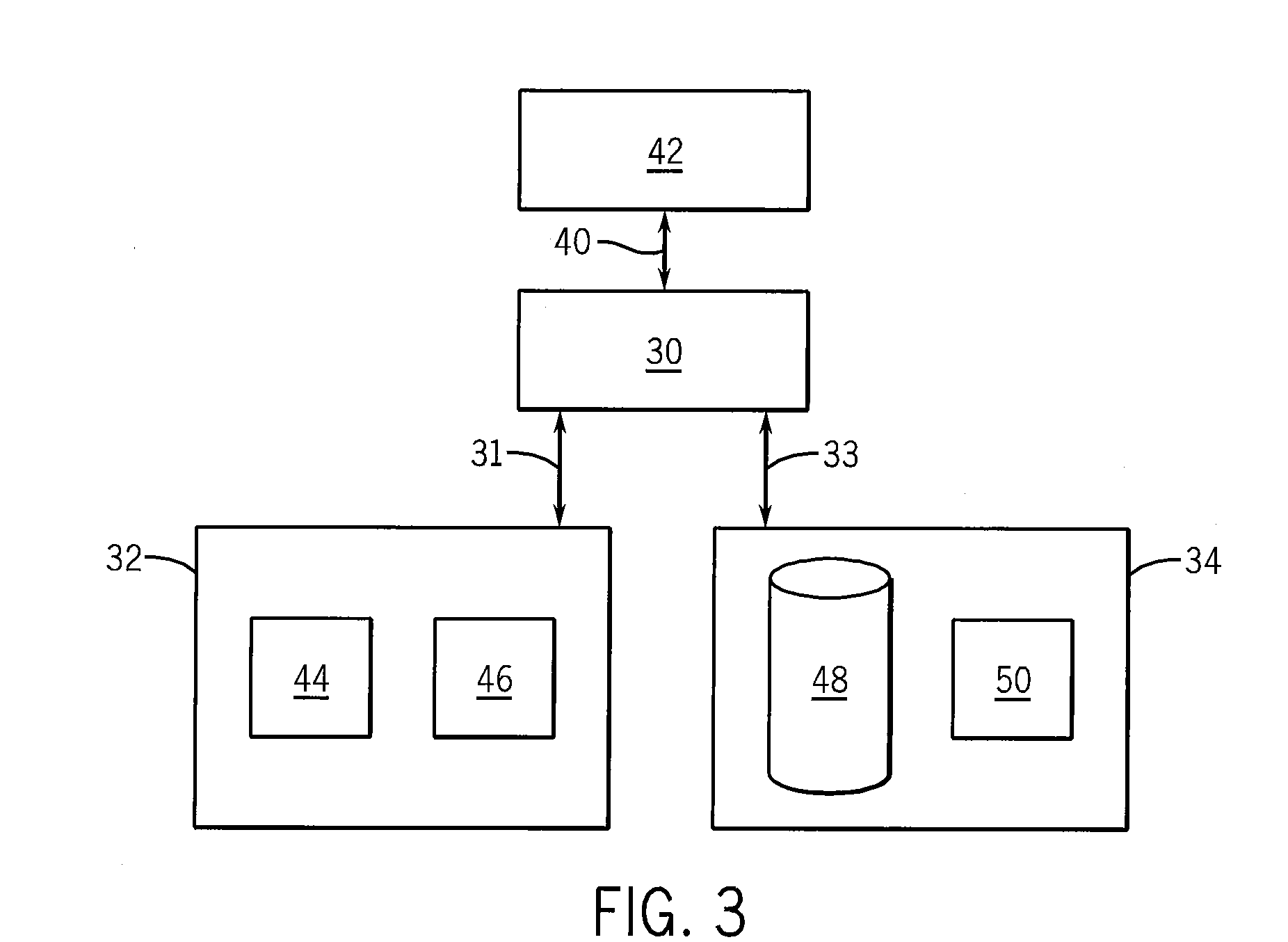
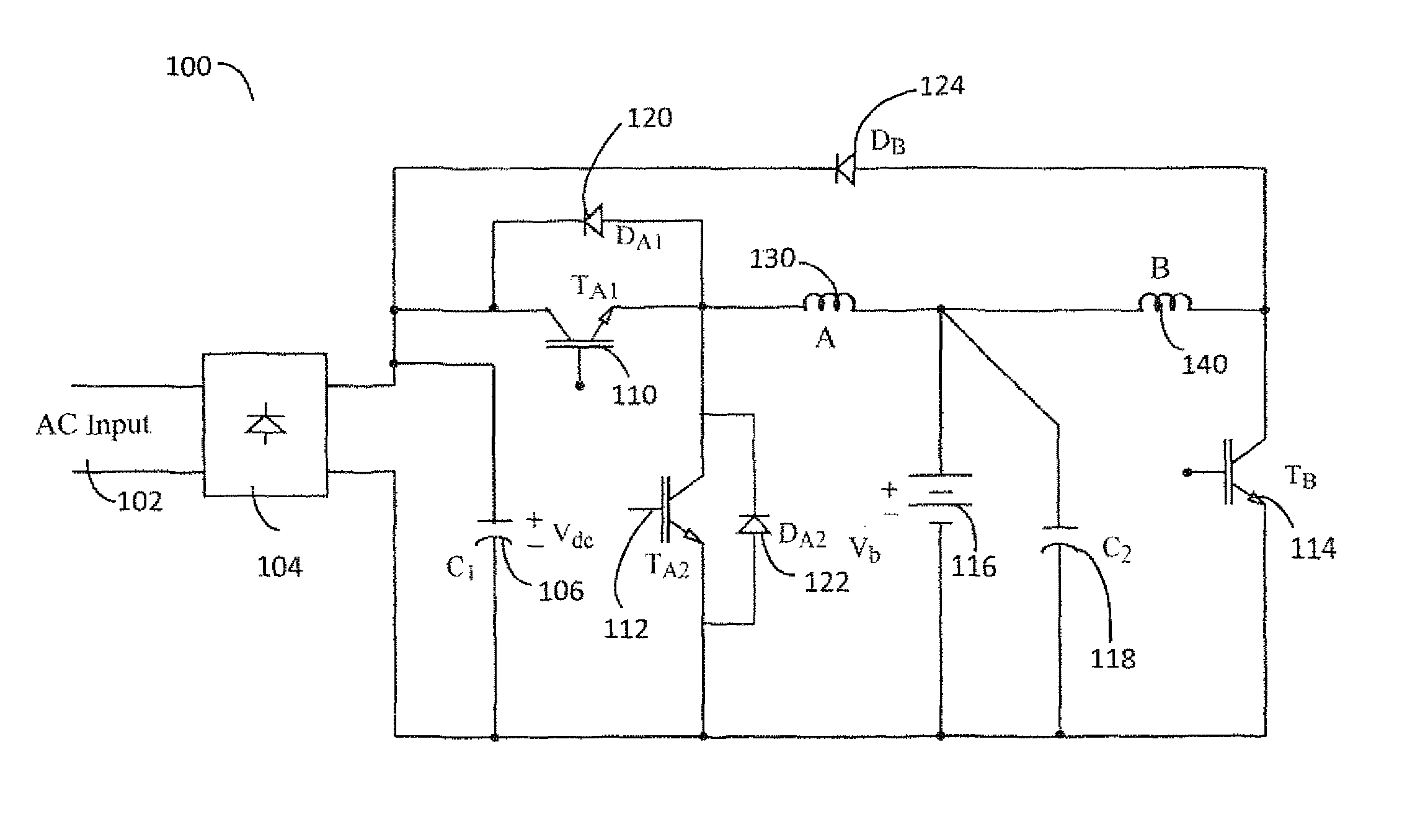
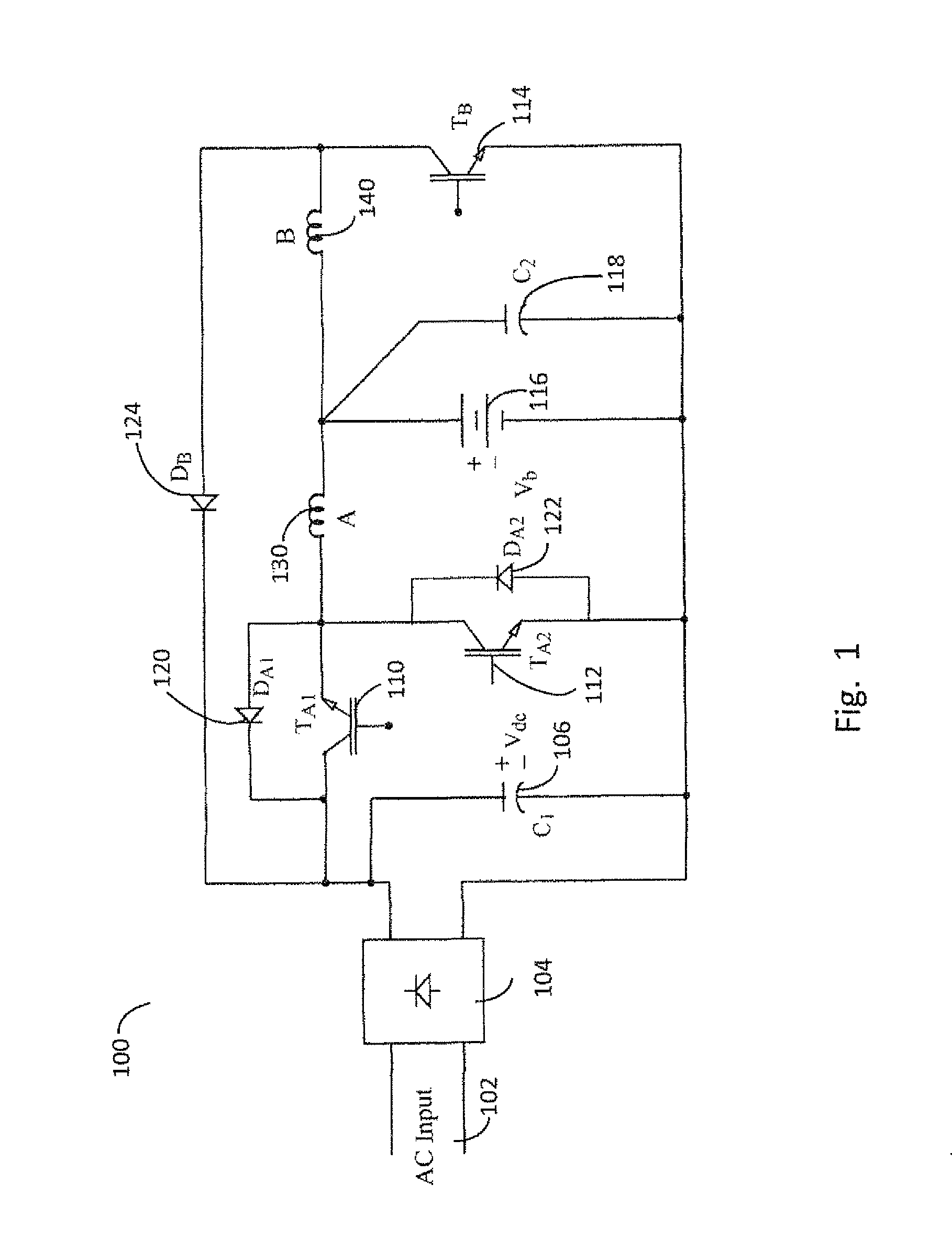
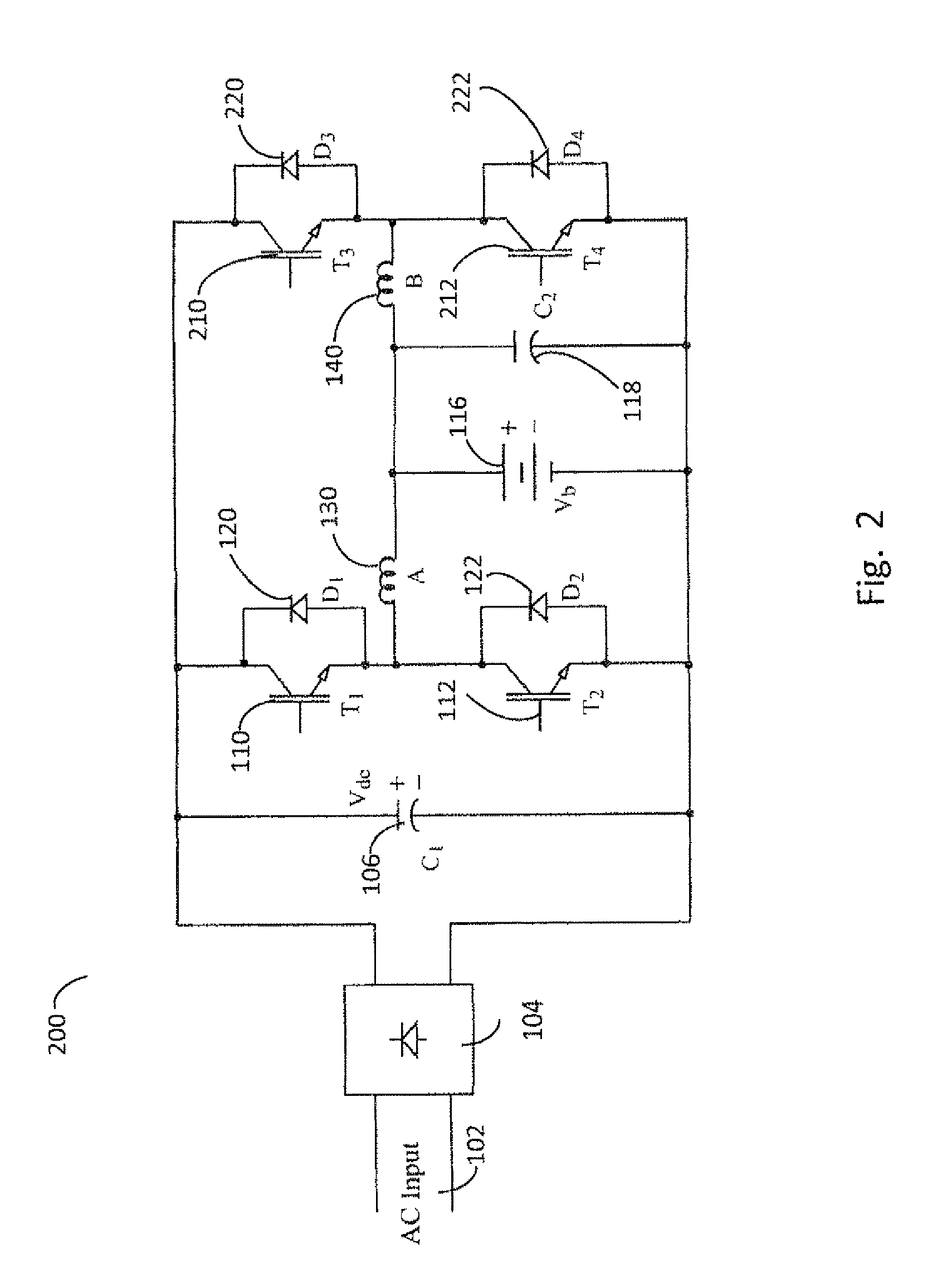
Charge balancing systems and methods
InactiveUS6841971B1Easy to scaleCharge equalisation circuitSecondary cells charging/dischargingCapacitanceCapacitive storage
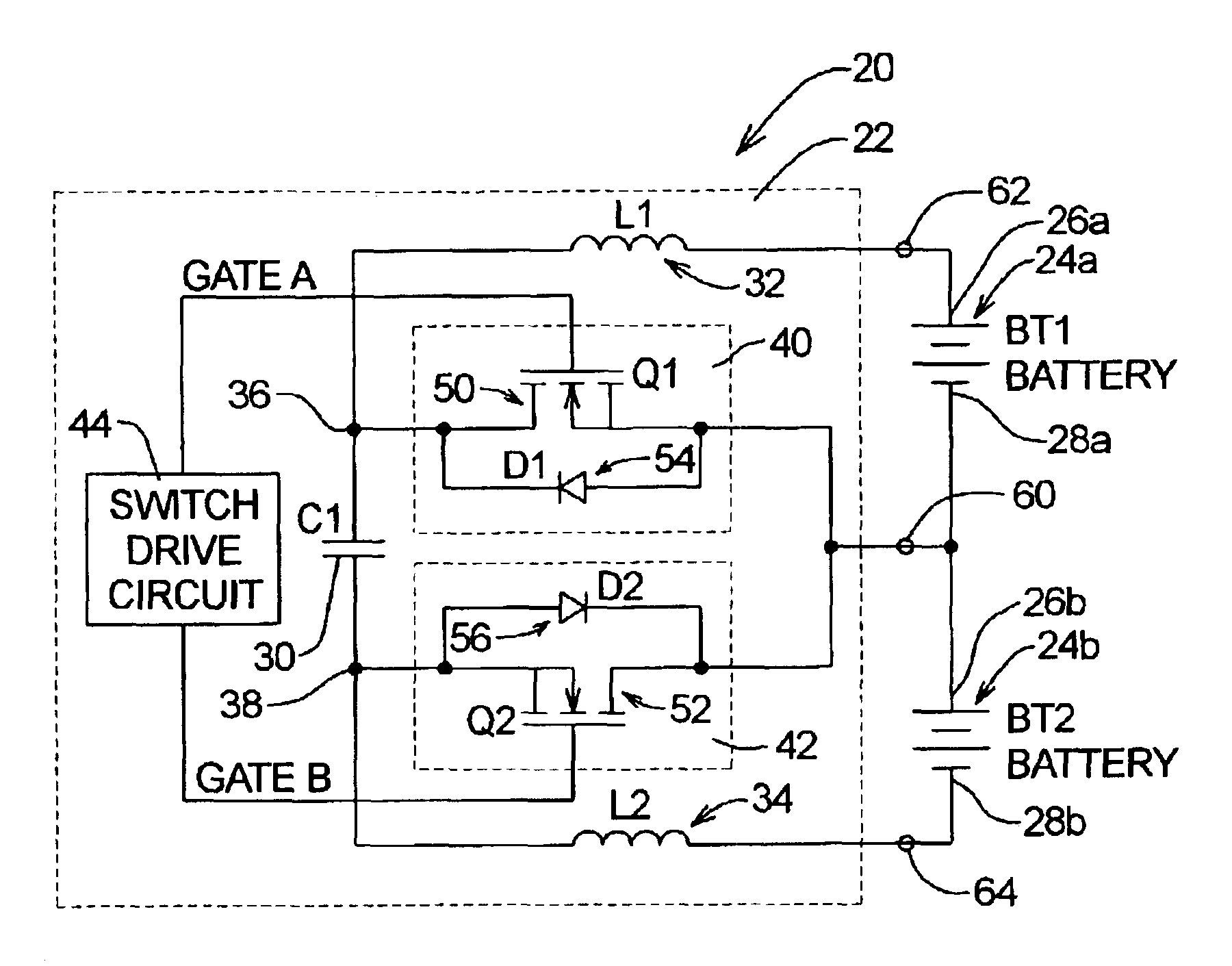
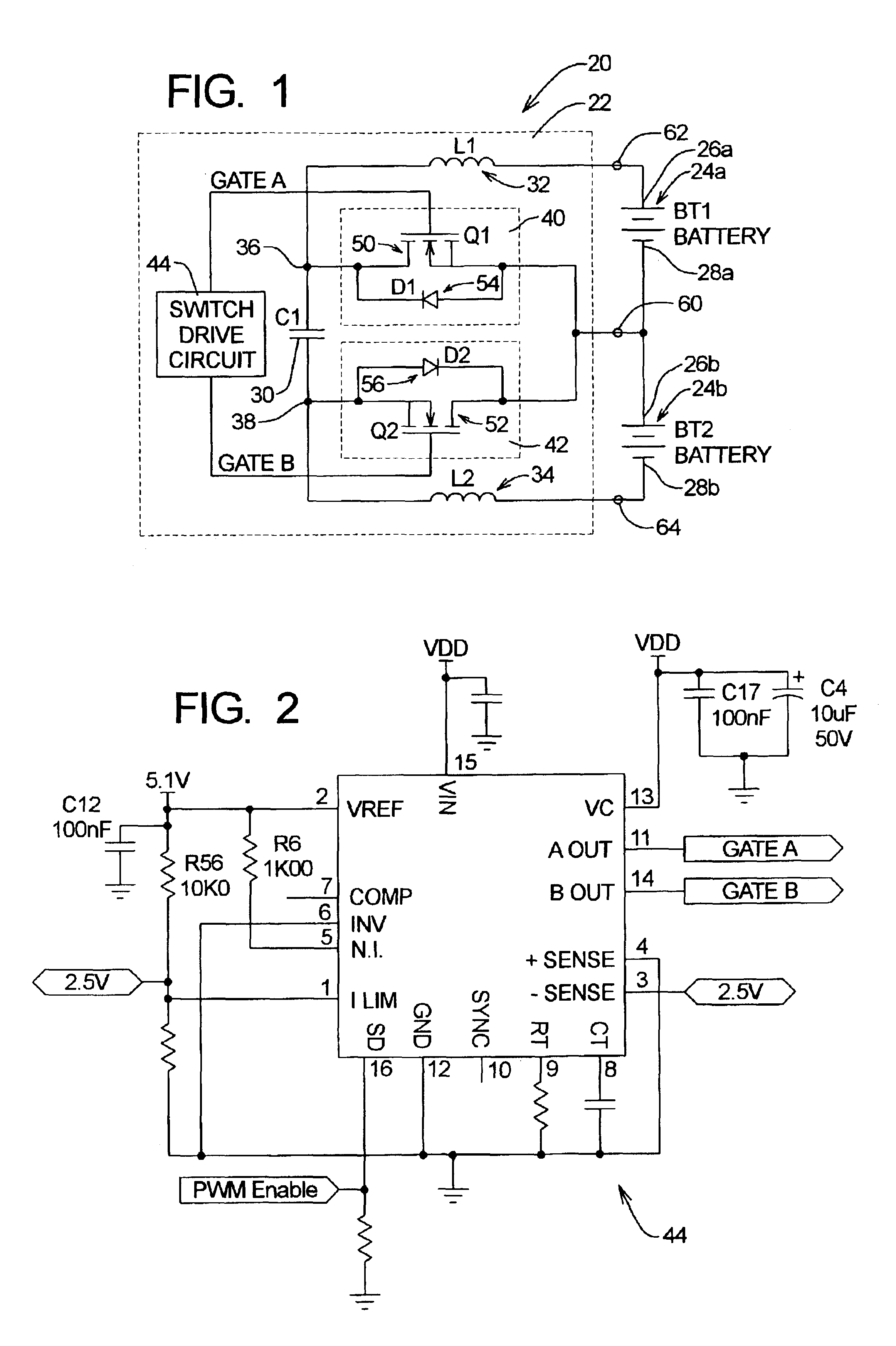
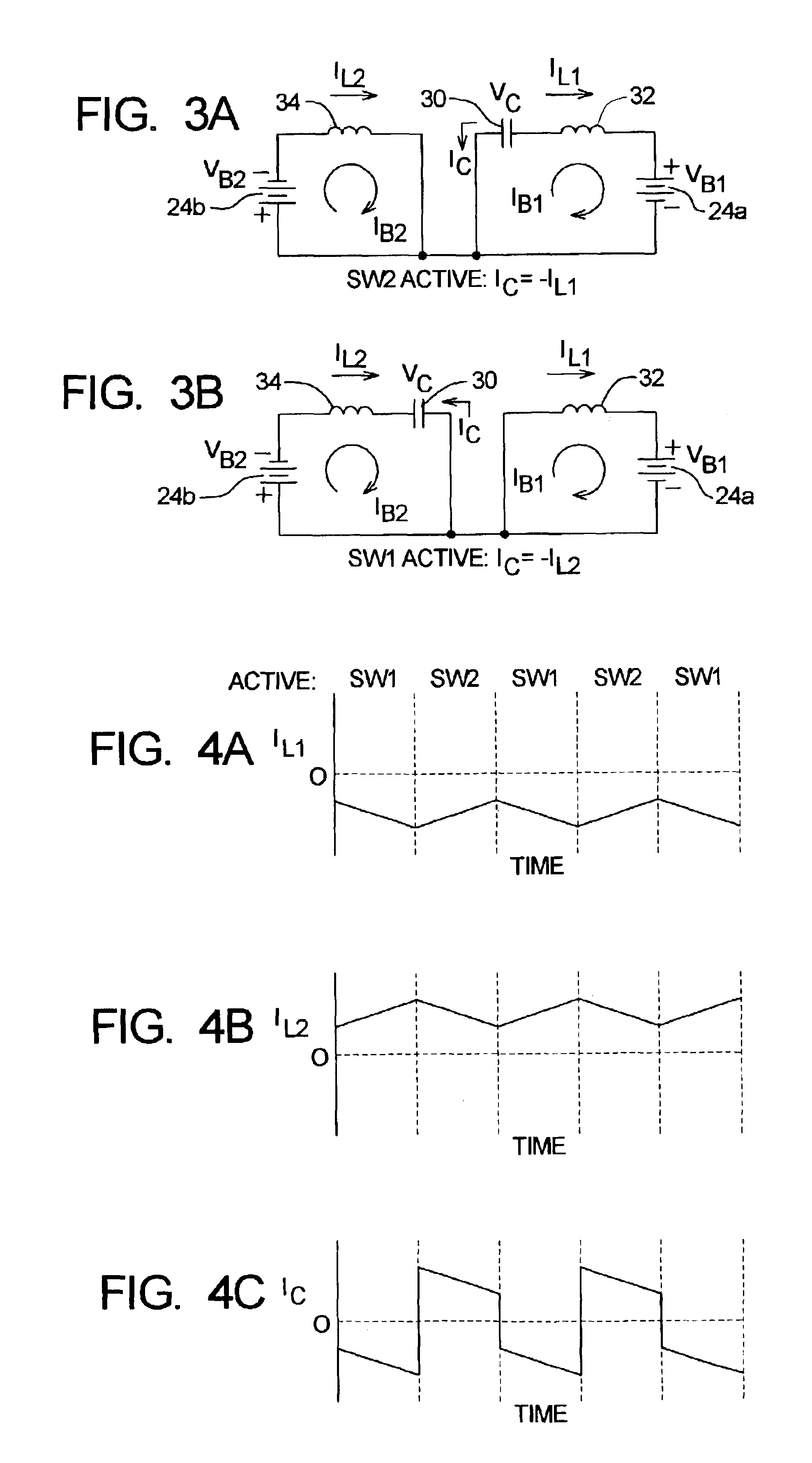
A system for equalizing the voltages across first and second batteries coupled in series at a common terminal comprising a capacitive storage element, first and second inductive storage elements, first and second switch circuits, and a control unit. The capacitive storage element is coupled to first and second nodes. The first inductive storage element is coupled between the first node and the first battery. The second inductive storage element is coupled between the second node and the second battery. The first switch circuit is coupled between the first node and the common terminal. The second switch circuit is coupled between the second node and the common terminal. The control circuit operates the first and second switch circuits to control current flow to the first and second batteries.
Owner:ALPHA TECHNOLOGIES SERVICES INC
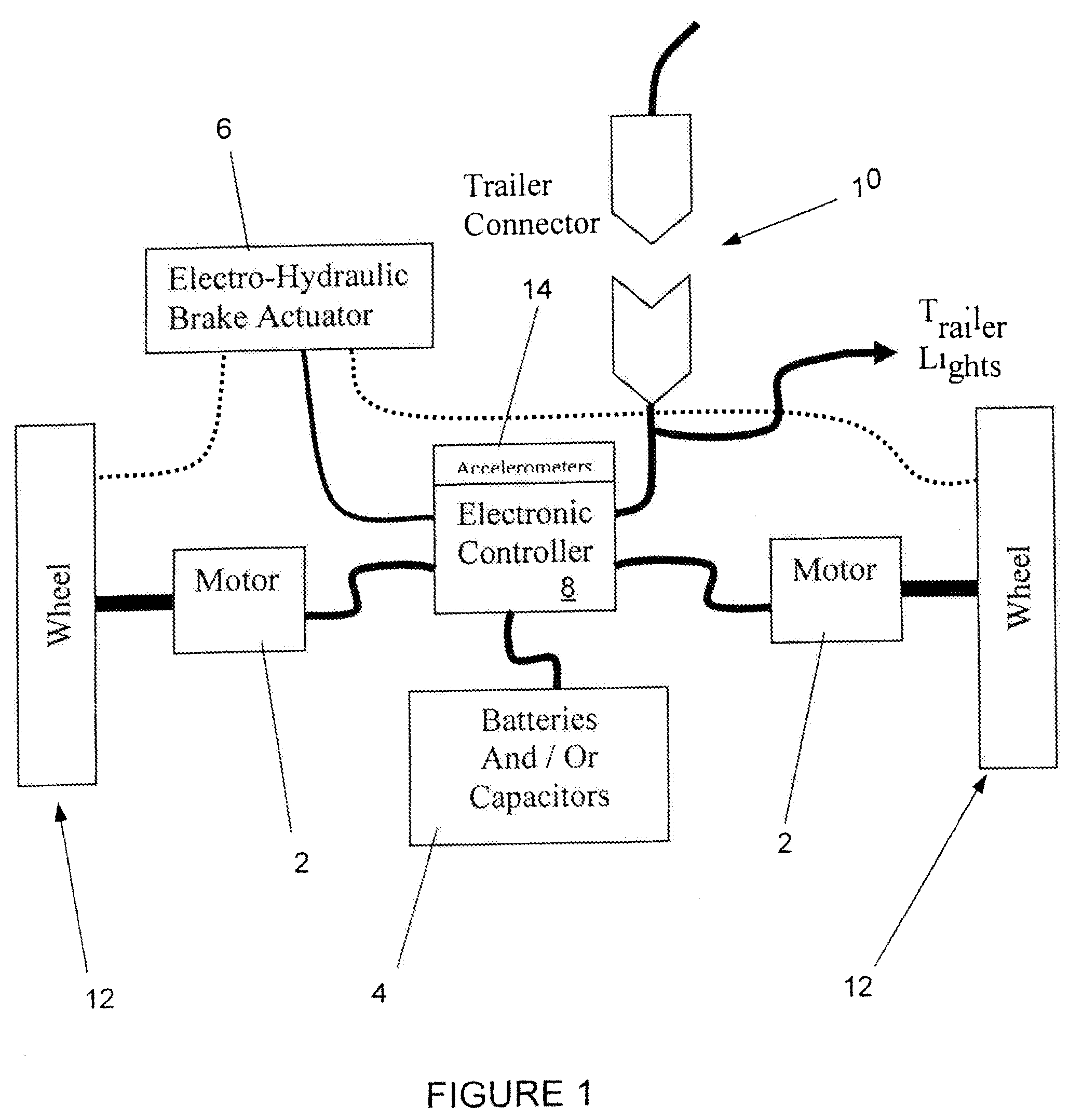
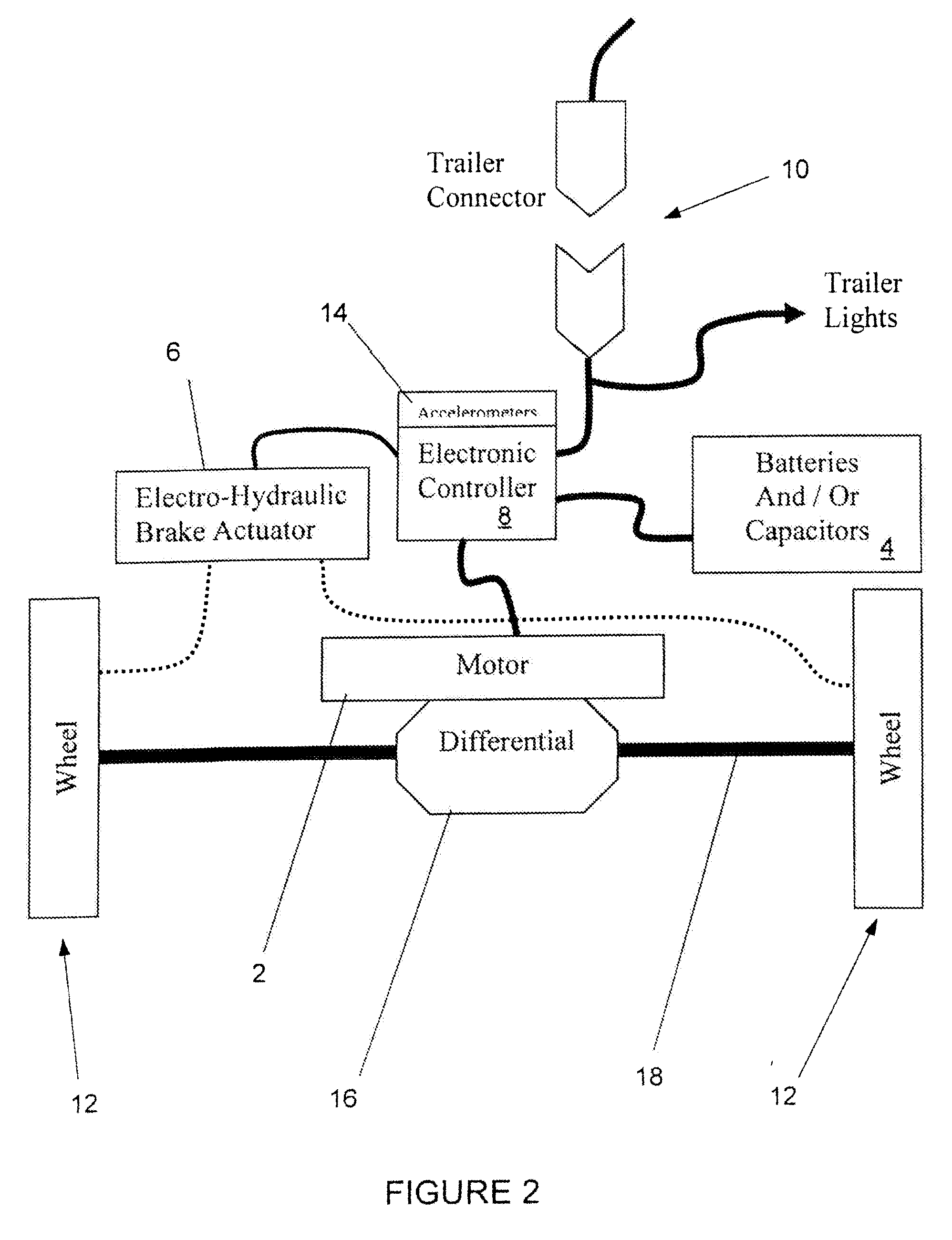
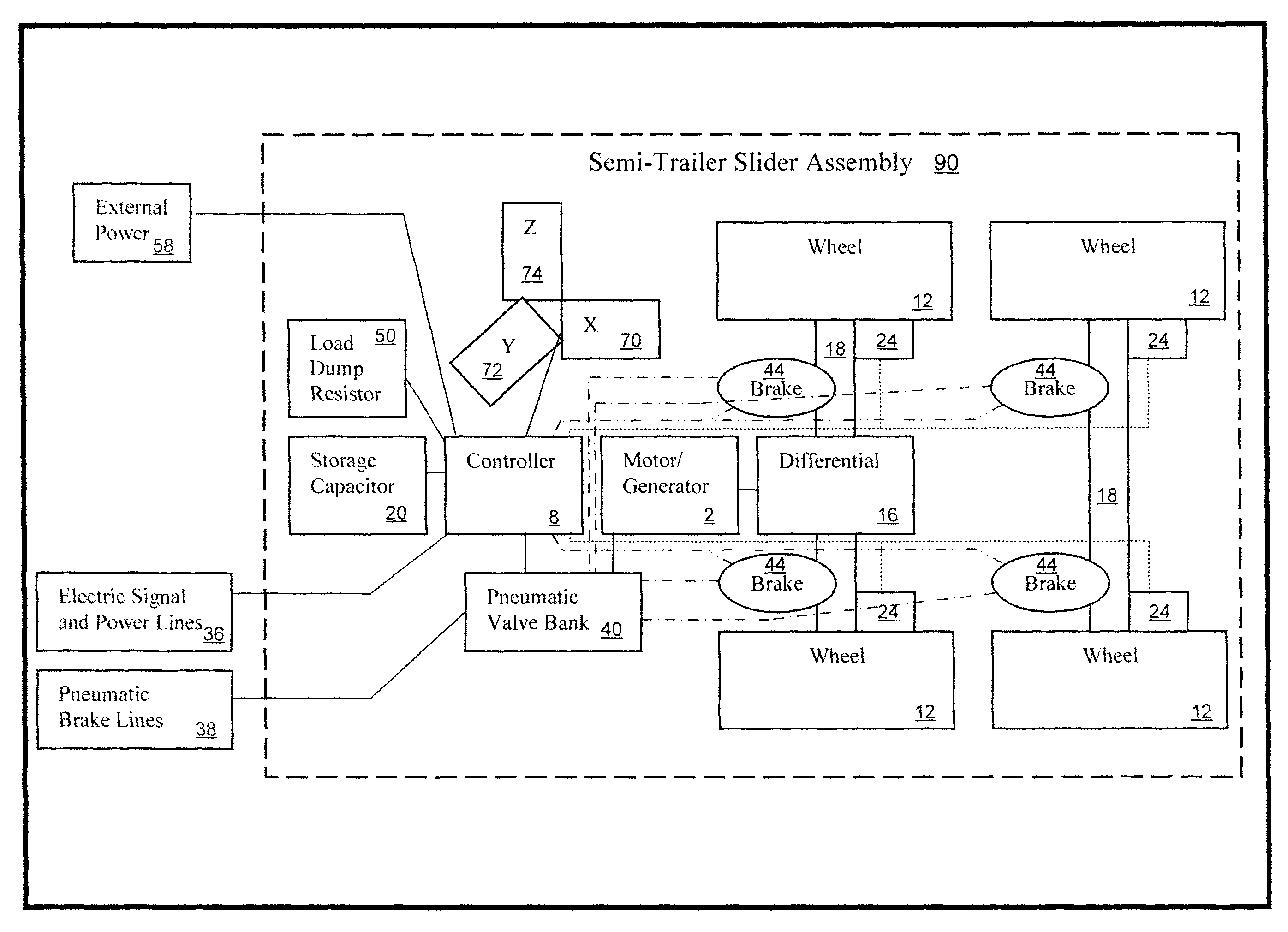
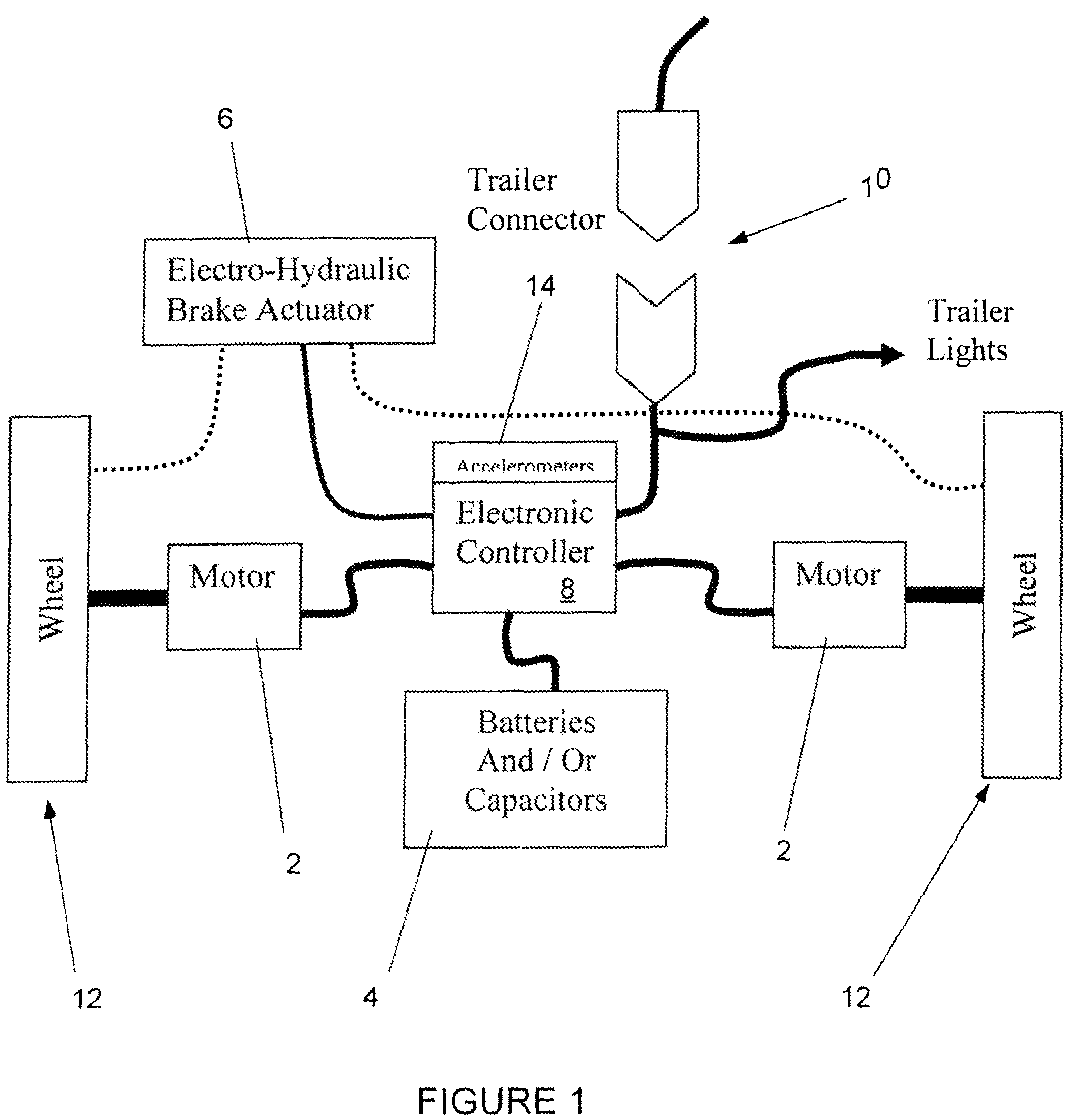
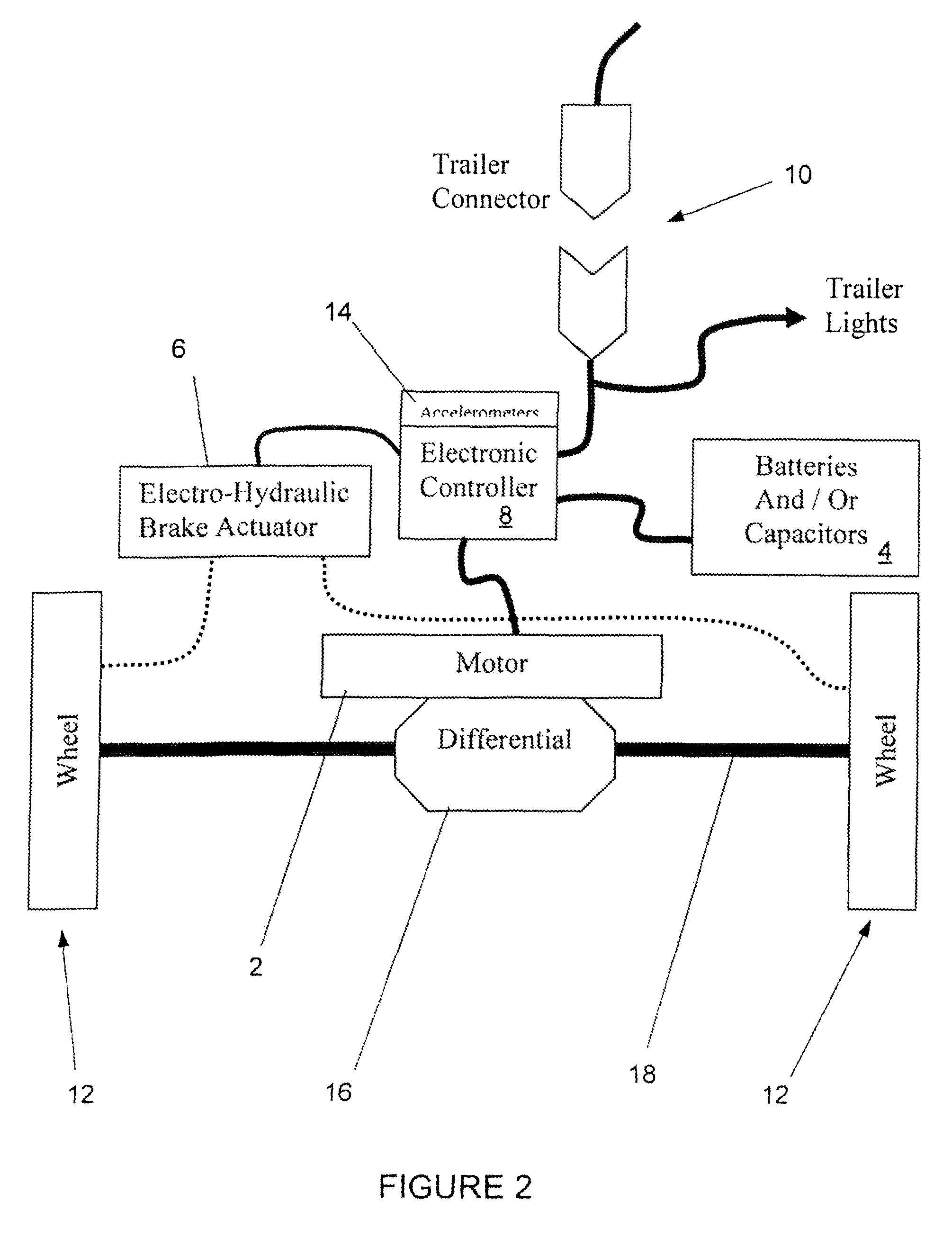
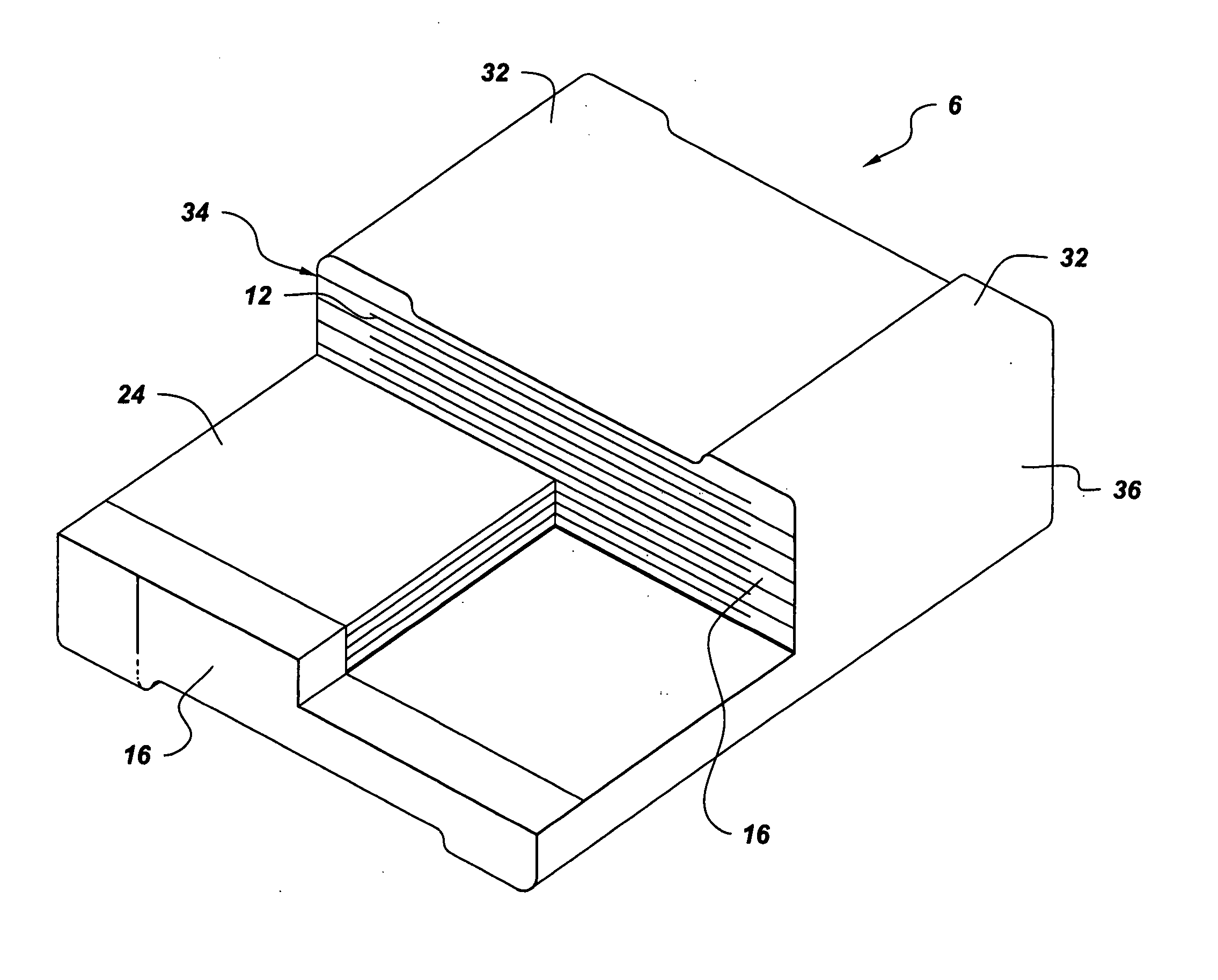
Hybrid trailer system
InactiveUS20080169144A1Easily retrofit into new and used trailerReduce maintenanceAuxillary drivesConvertible cyclesCapacitanceCapacitive storage
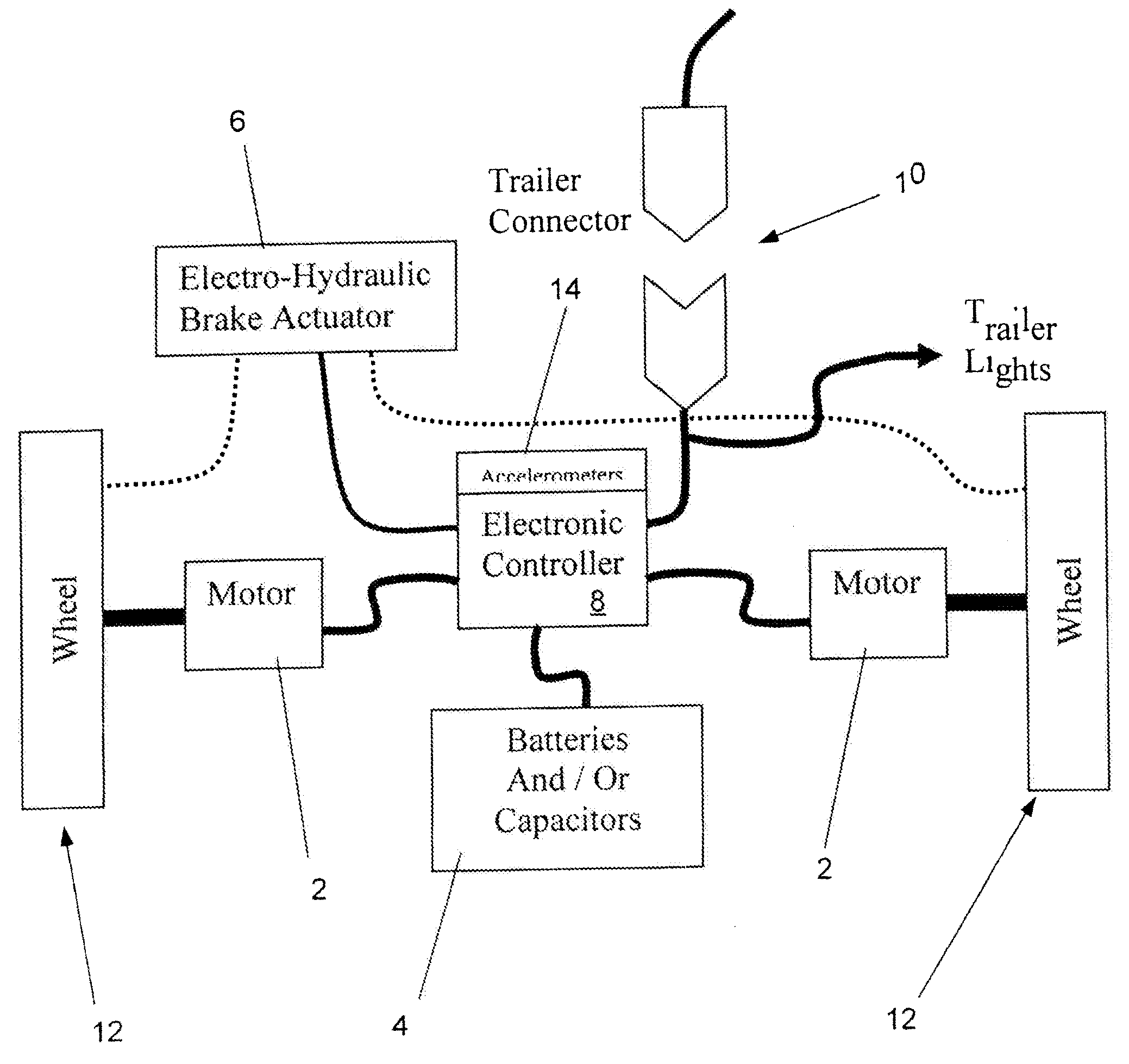
A system and related method for a regenerative braking system on a towed vehicle, such as a trailer or semi-trailer. The system provides power and braking to the respective trailer wheels, as needed, to help stabilize the trailer. Power is regenerated during braking. While batteries may be used to store the energy, the system also may use capacitive storage units, which charge and discharge large amounts of energy at a fast rate. A multiple-axis sensor system in conjunction with wheel sensors, load sensors, and proportional control of the brakes and motor power to the axles and wheels, is used to achieve superior load stabilization. The invention can be easily retrofit into new or used trailers, and is self-contained with low maintenance.
Owner:DEGRAVE KEN +1
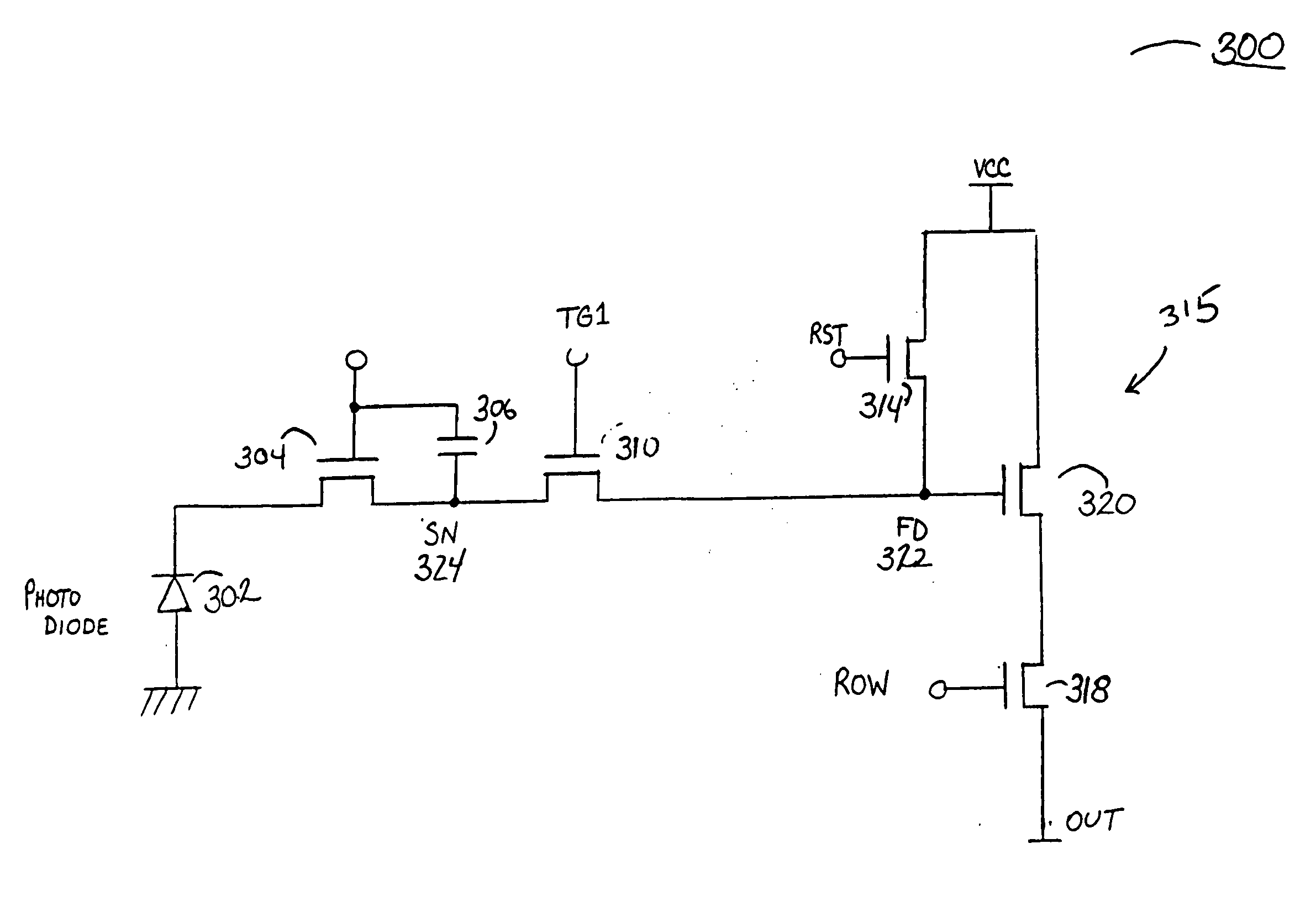
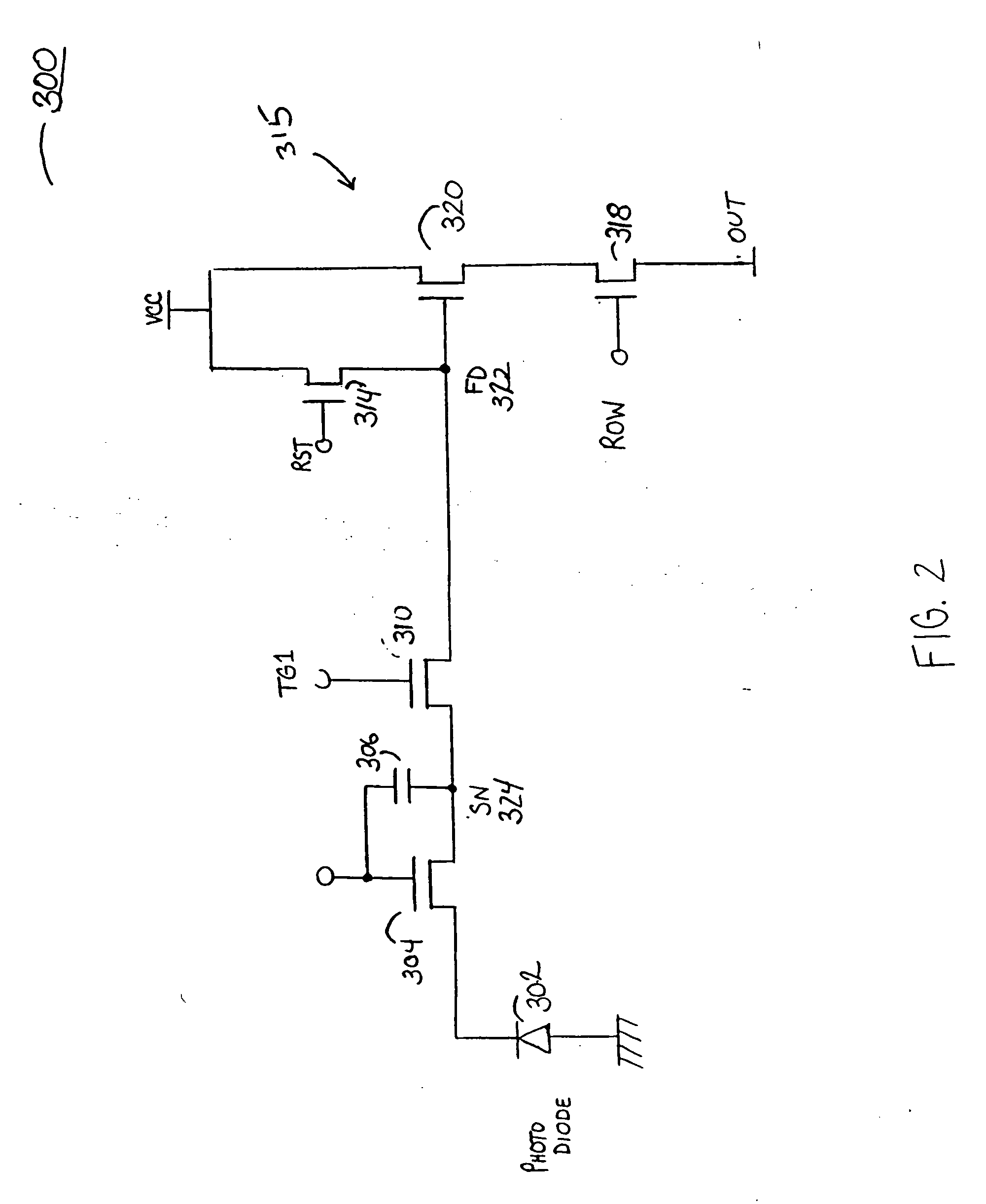
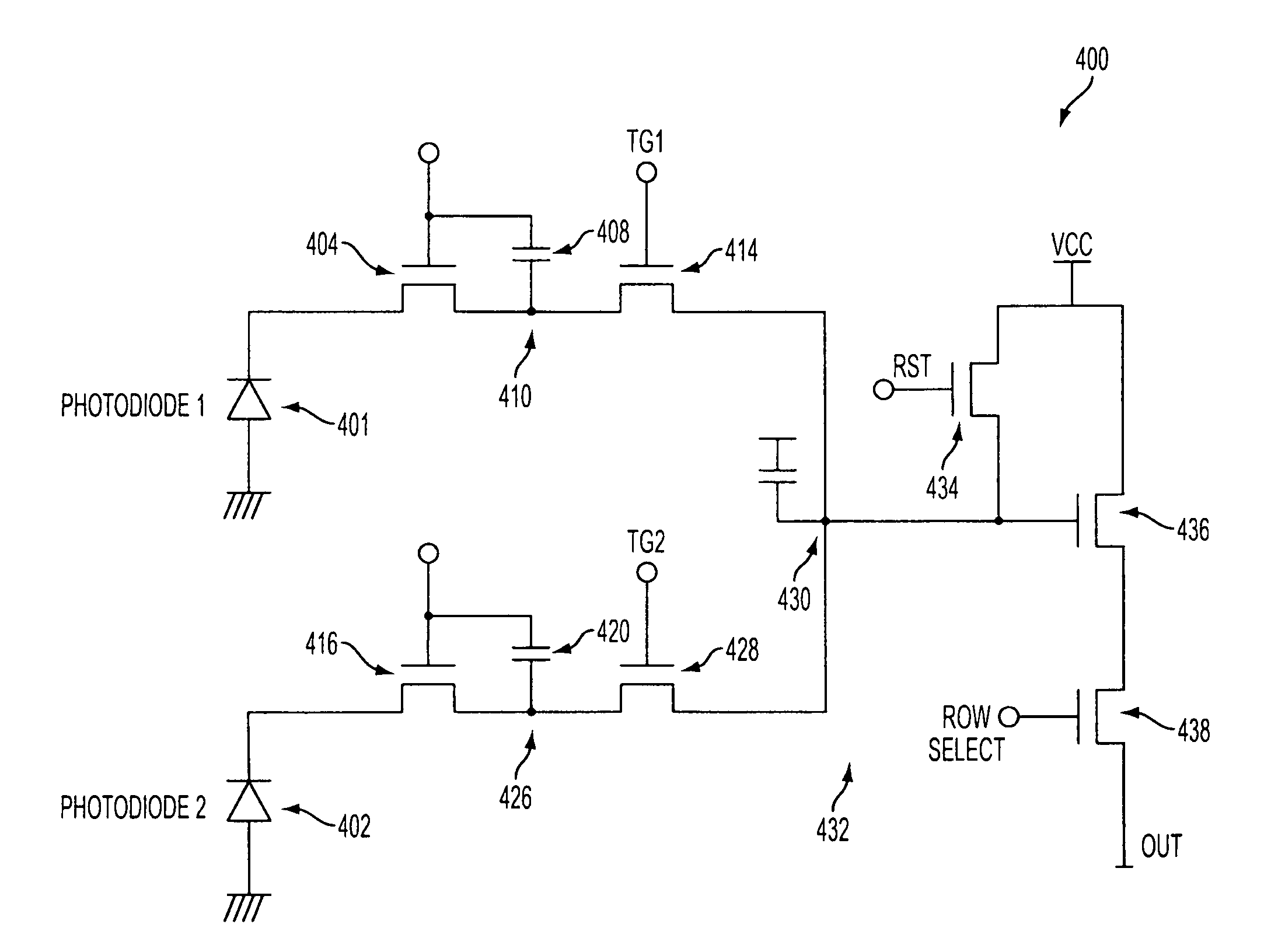
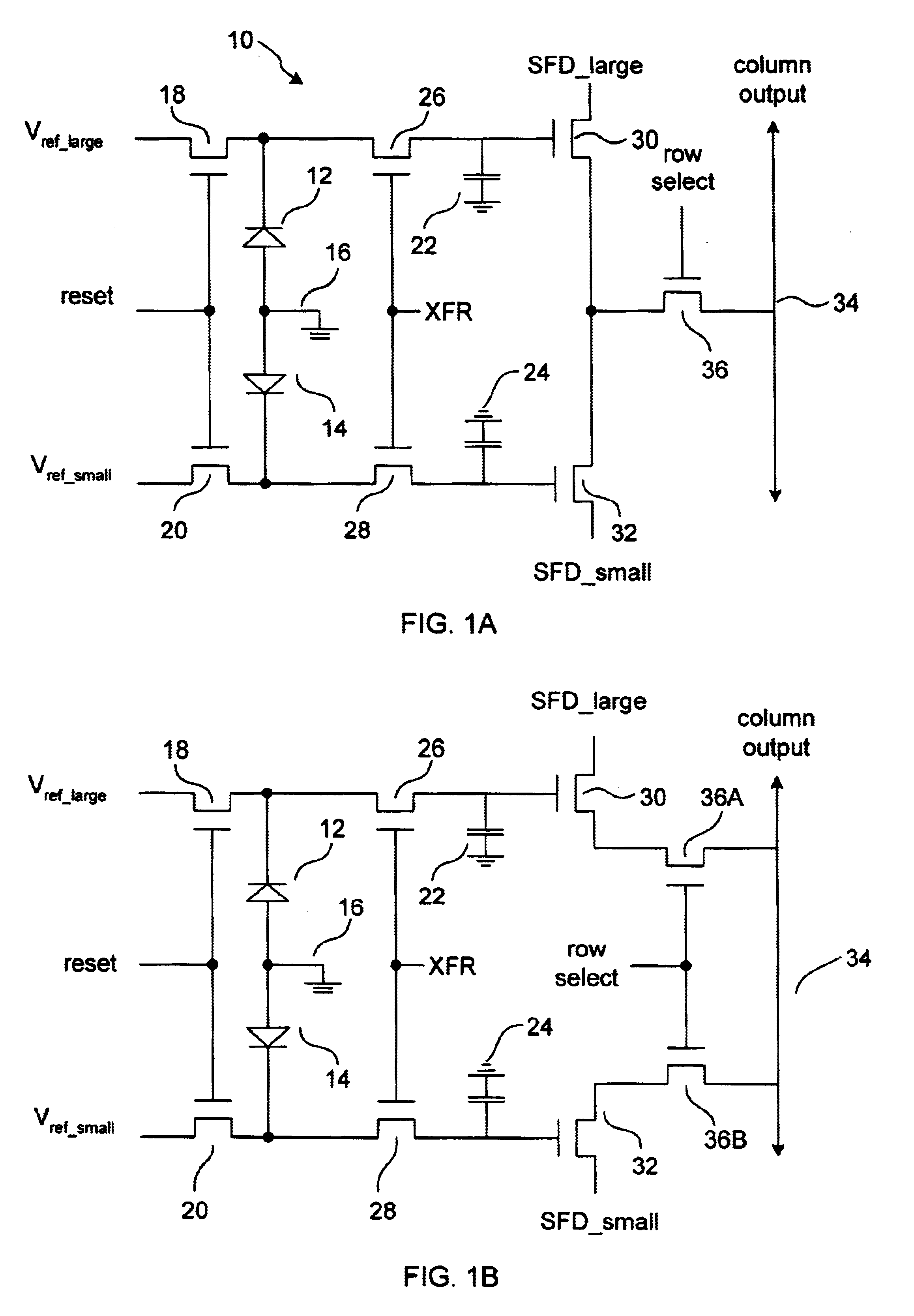
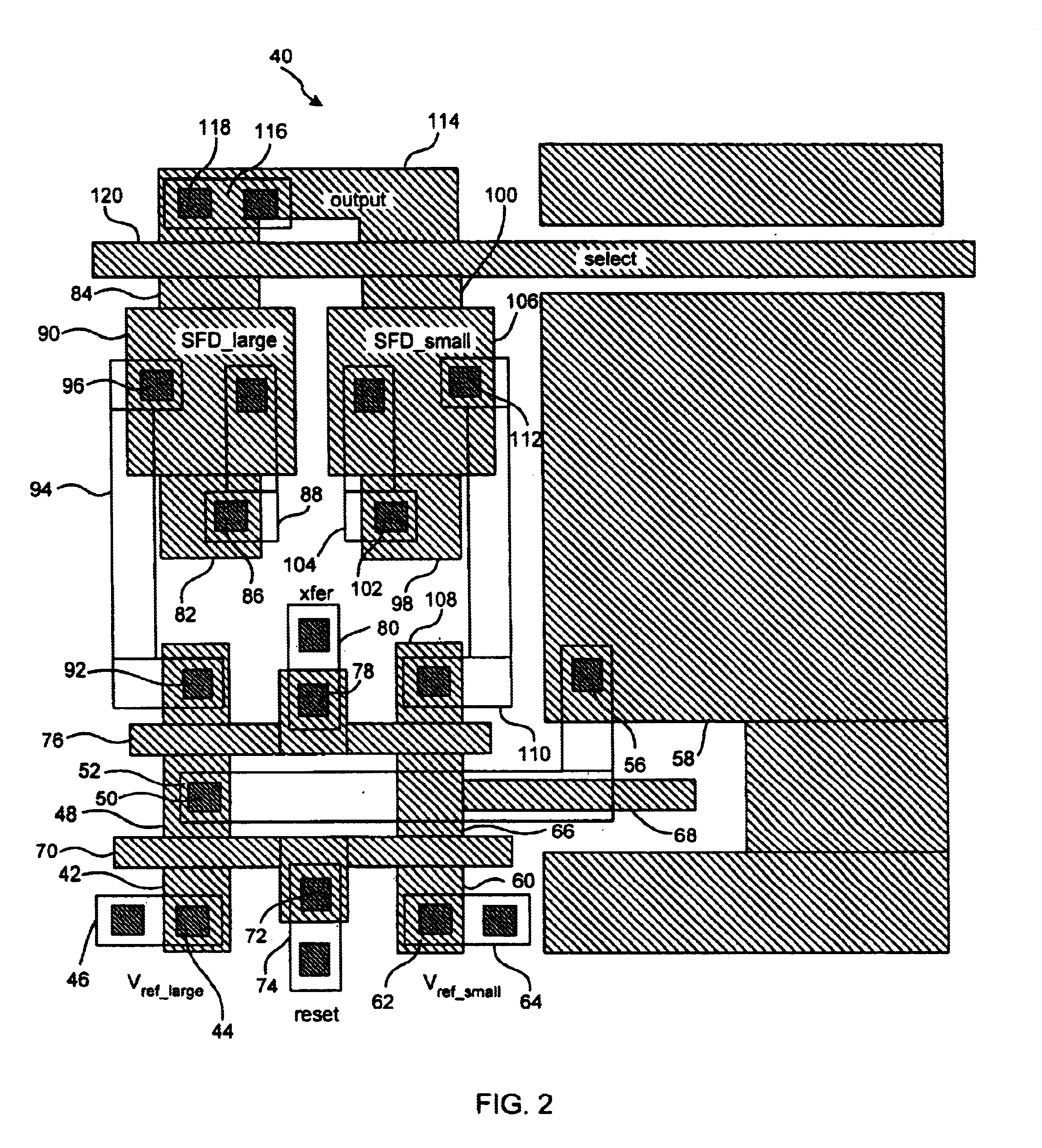
Image sensor with a capacitive storage node linked to transfer gate
ActiveUS20050110884A1Increases charge generating areaIncrease costTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceCMOS
A CMOS imaging system with increased charge storage capacitance of pixels yet decreased physical size, kTC noise and active area. A capacitor is linked to the transfer gate and provides a storage node for a pixel, allowing for kTC noise reduction prior to readout. The pixel may be operated with the shutter gate on during the integration period to increase the amount of time for charge storage by a pixel.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
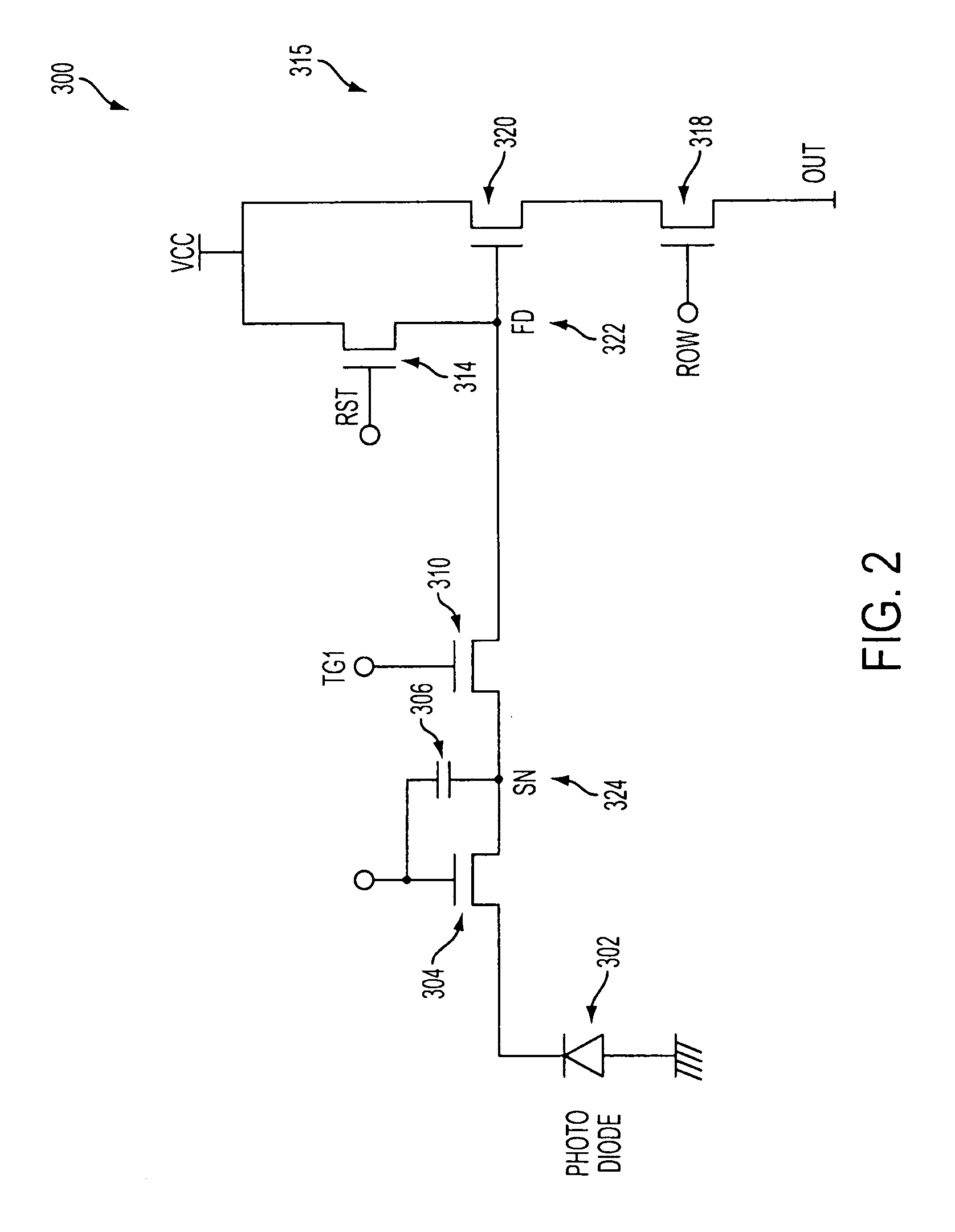
Intra-pixel frame storage element, array, and electronic shutter method suitable for electronic still camera applications
InactiveUS6741283B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceElectronic shutter
A storage pixel sensor disposed on a semiconductor substrate comprises a capacitive storage element having a first terminal connected to a fixed potential and a second terminal. A photodiode has an anode connected to a first potential and a cathode. A semiconductor reset switch has a first terminal connected to the cathode and a second terminal connected to a reset potential. A semiconductor transfer switch has a first terminal connected to the cathode and a second terminal connected to the second terminal of the capacitive storage element. A semiconductor amplifier has an input connected to the capacitive storage element and an output. The semiconductor reset switch and the semiconductor transfer switch each have a control element connected to a control circuit for selectively activating the semiconductor reset switch and the semiconductor transfer switch. A light shield is disposed over portions of the semiconductor substrate comprising a circuit node including the second terminal of the semiconductor transfer switch, the second terminal of the capacitive storage element and the input of the semiconductor amplifier and to prevent substantially all photons from entering the circuit node. Structures are present for preventing substantially all minority carriers generated in the semiconductor substrate from entering the circuit node. A plurality of storage pixel sensors are disposed in an array.
Owner:FOVEON
Hybrid trailer system
InactiveUS8215436B2Easily retrofit into new and used trailerReduce maintenanceAuxillary drivesConvertible cyclesCapacitanceCapacitive storage
A system and related method for a regenerative braking system on a towed vehicle, such as a trailer or semi-trailer. The system provides power and braking to the respective trailer wheels, as needed, to help stabilize the trailer. Power is regenerated during braking. While batteries may be used to store the energy, the system also may use capacitive storage units, which charge and discharge large amounts of energy at a fast rate. A multiple-axis sensor system in conjunction with wheel sensors, load sensors, and proportional control of the brakes and motor power to the axles and wheels, is used to achieve superior load stabilization. The invention can be easily retrofit into new or used trailers, and is self-contained with low maintenance.
Owner:DEGRAVE KEN +1
Self Heating Battery System
ActiveUS20120126753A1Supply will become excessiveHigh switching rateBatteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cellsCapacitanceCapacitive storage
A battery self heating system for batteries that experience battery impedance or internal battery resistance when temperature drops. The system comprises an energy storage element applied to the battery terminals to draw energy from the battery. The energy is stored in a magnetic or capacitive storage device. The system is self-resonant so that energy transfer from the storage device to the battery will occur at a frequency and load level that is compatible with the current state of the battery. Internal heating of the battery is accomplished by a cycle comprising the out flux and influx of energy through the impedance of the battery. Energy losses due to battery impedance are converted to heat thereby heating the battery internally.
Owner:STRYTEN ENERGY LLC
1T/0C RAM cell with a wrapped-around gate device structure
A memory device and a method of forming the memory device. The memory device comprises a storage transistor at a surface of a substrate comprising a body portion between first and second source / drain regions, wherein the source / drain regions are regions of a first conductivity type. The storage transistor also comprises a gate structure that wraps at least partially around the body portion in at least two spatial planes. A bit line is connected to the first source / drain region and a word line connected to the gate structure. The memory device does not require an additional capacitive storage element.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Image sensor with a capacitive storage node linked to transfer gate
ActiveUS7542085B2Increase storage capacityIncrease capacitanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceCMOS
A CMOS imaging system with increased charge storage capacitance of pixels yet decreased physical size, kTC noise and active area. A capacitor is linked to the transfer gate and provides a storage node for a pixel, allowing for kTC noise reduction prior to readout. The pixel may be operated with the shutter gate on during the integration period to increase the amount of time for charge storage by a pixel.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
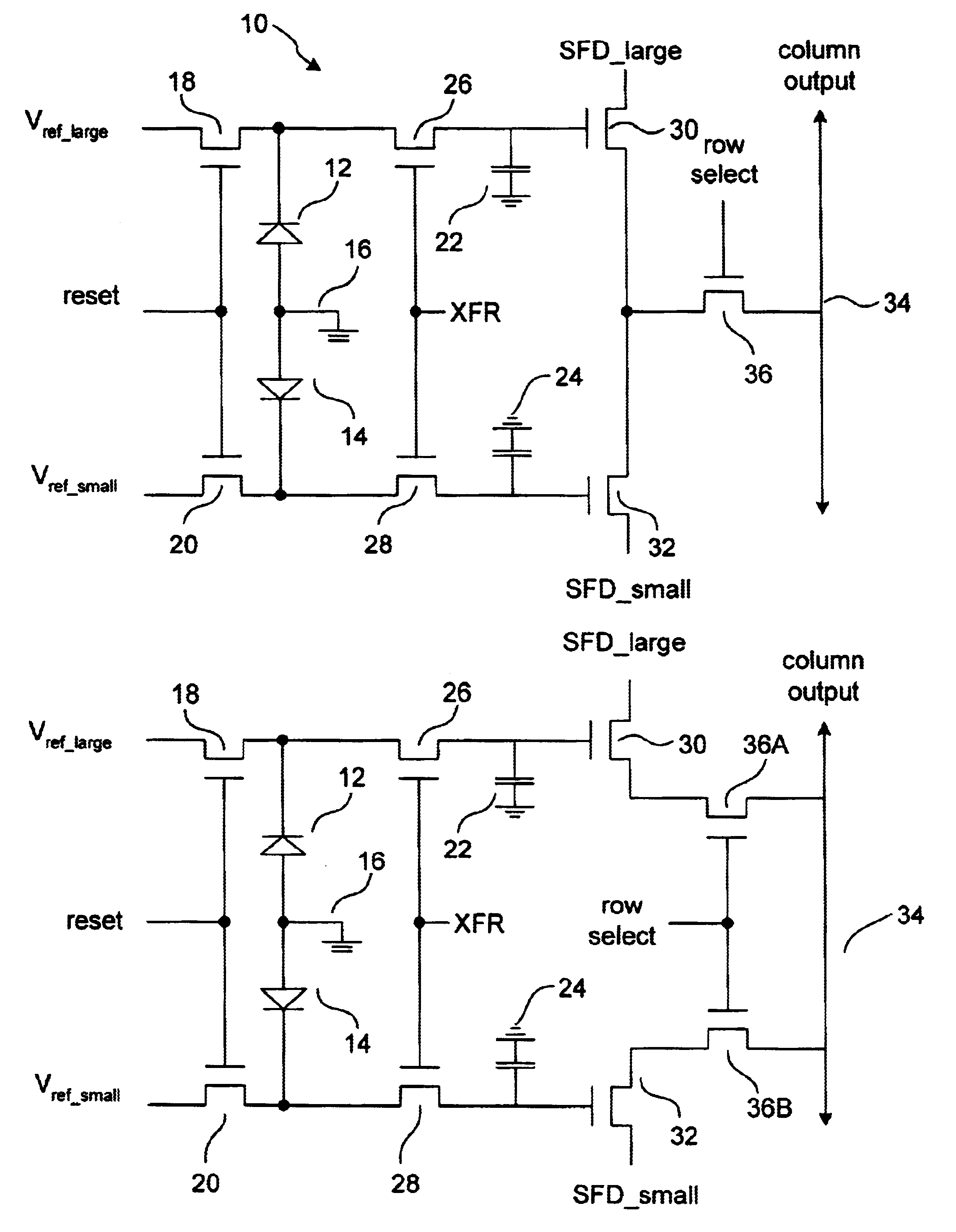
Triple slope pixel sensor and arry
InactiveUS6697114B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceCMOS sensor
A triple-slope MOS active pixel sensor disposed on a semiconductor substrate comprises first and second capacitive storage elements each having a first terminal connected to a fixed potential and a second terminal. First and second photodiodes each have a first terminal connected to a fixed potential and a second terminal. The second photodiode is smaller than the first photodiode. First and second semiconductor reset switches each have a first terminal connected respectively to the second terminal of the first and second photodiodes and a second terminal connected respectively to first and second reset potentials that reverse bias the photodiodes. First and second semiconductor transfer switches each have a first terminal connected respectively to the second terminals of the first photodiode and a second terminal connected respectively to the second terminals of the first and second capacitive storage elements. First and second semiconductor amplifiers each have an input connected respectively to the second terminals of the first and second capacitive storage elements and have their outputs connected together. The first and second semiconductor reset switches and the first and second semiconductor transfer switches each have a control element connected to a control circuit for selectively activating the first and second semiconductor reset switches and the first and second semiconductor transfer switches.
Owner:FOVEON
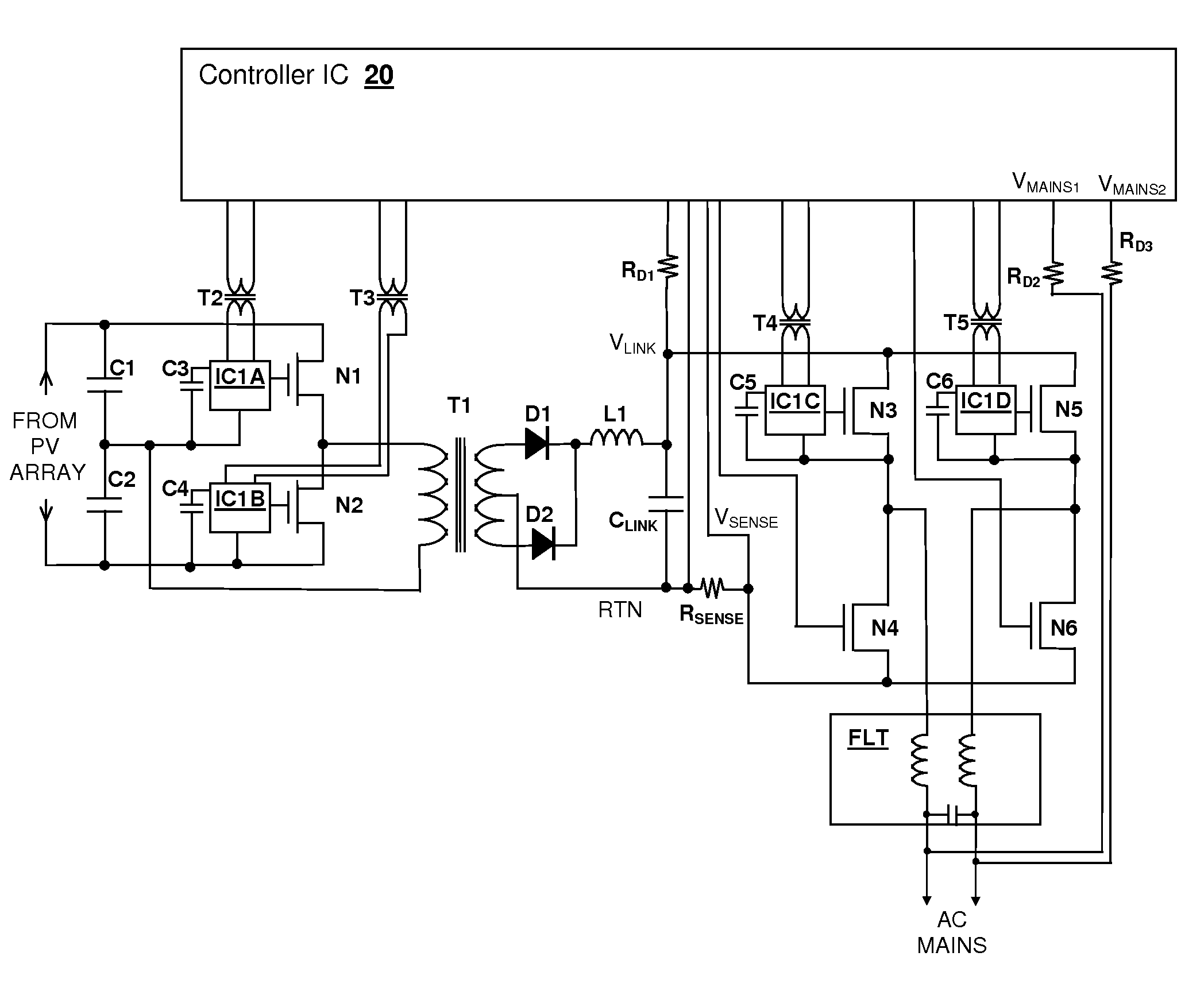
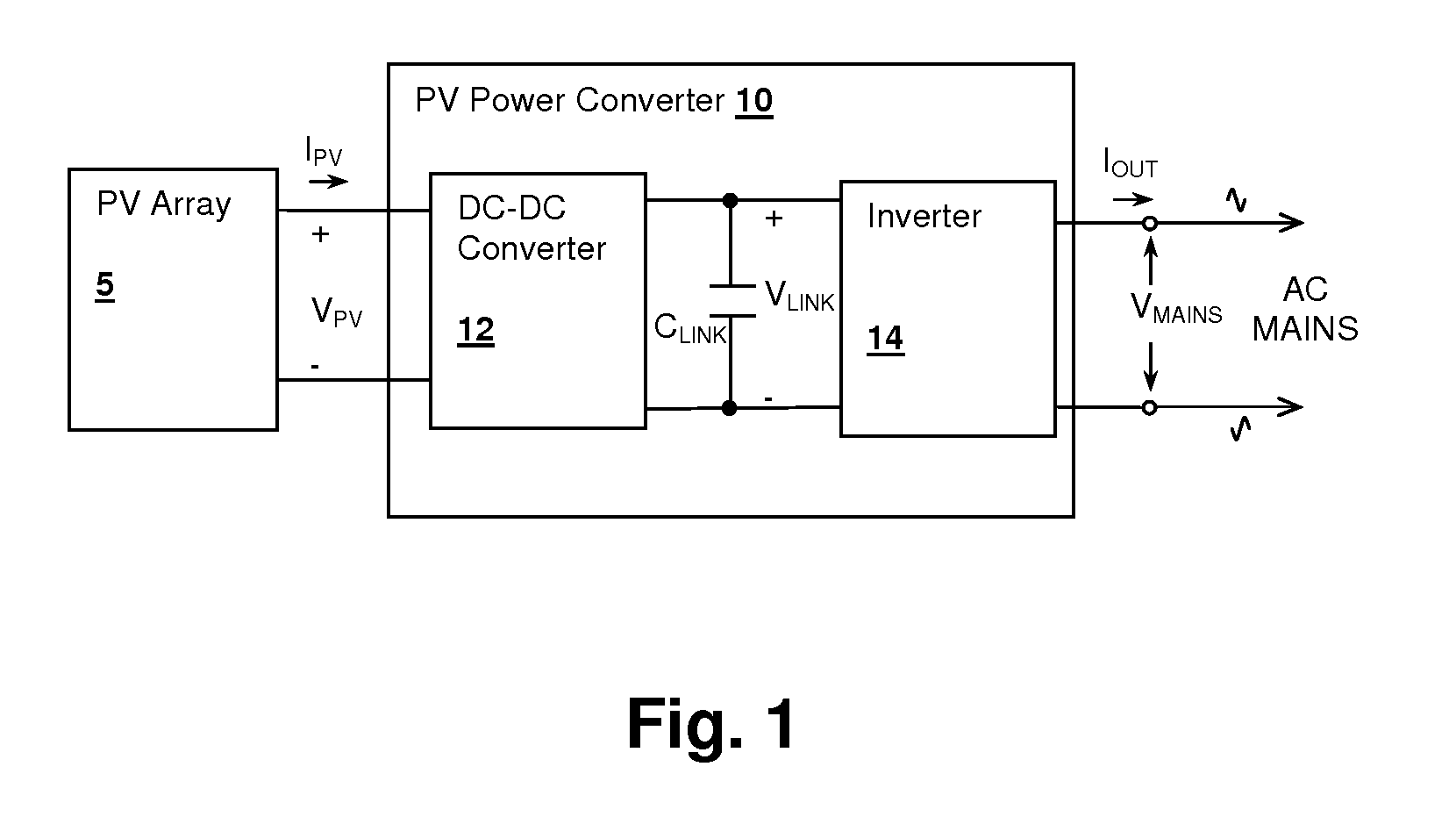
Cascaded switching power converter for coupling a photovoltaic energy source to power mains
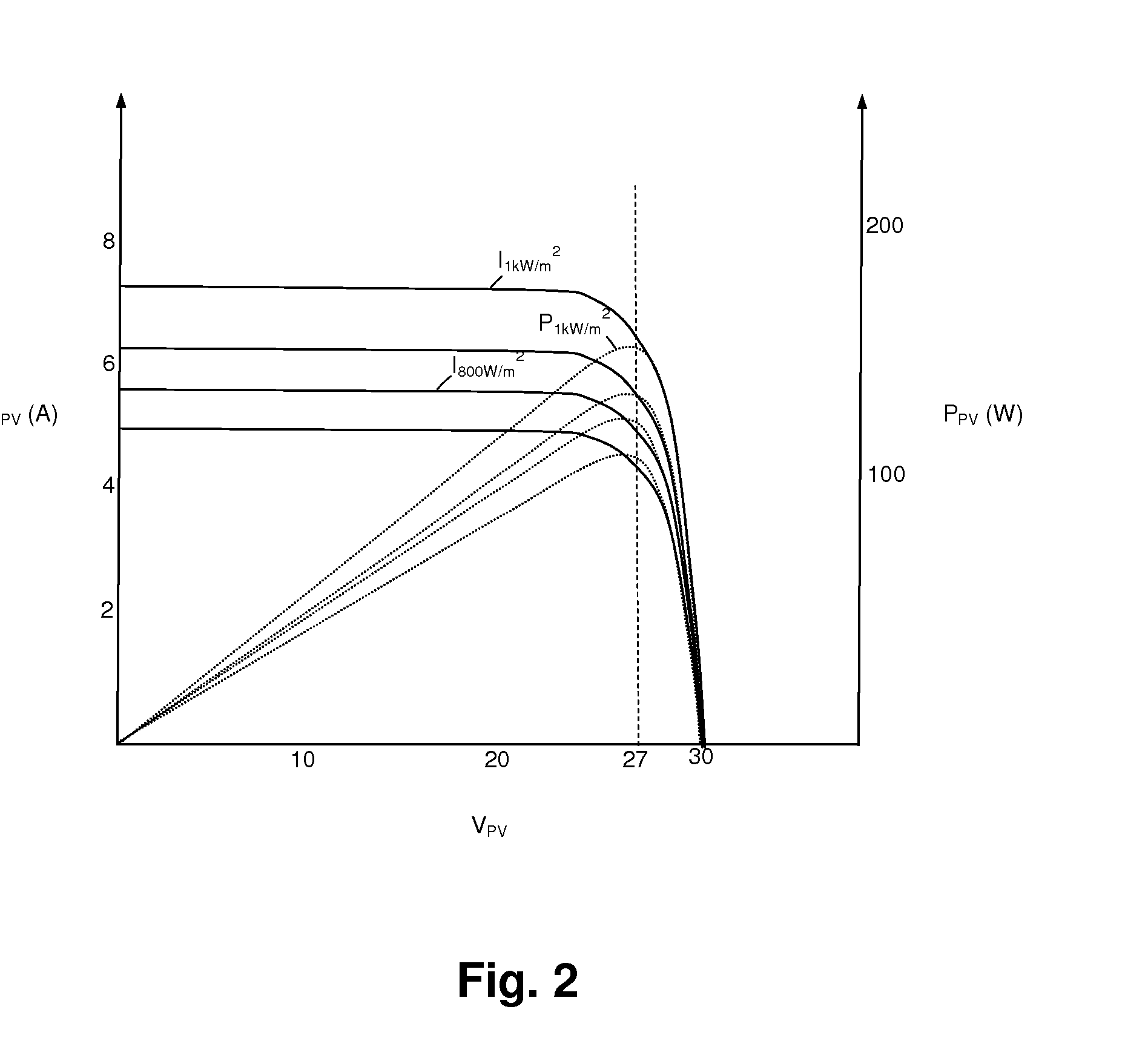
InactiveUS20110032734A1High energyLarge outputAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsCapacitanceCapacitive storage
A cascaded switching power converter for coupling a photovoltaic (PV) energy source to power mains provides a high-efficiency and a potentially simple control mechanism for AC solar energy conversion systems. The PV energy source charges a capacitive storage element through a DC-DC converter, and an inverter couples energy from the capacitive storage element to the mains supply. The DC-DC converter is controlled so that ripple present on the capacitive storage element due to current drawn by the inverter is not reflected at the input of the DC-DC converter, which is accomplished by varying the conversion ratio of the DC-DC converter with the ripple voltage present across the capacitor. The average voltage of the capacitor can also be increased with increases in the available power output from the PV energy source, so that a corresponding increase in power is transferred to the mains supply.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
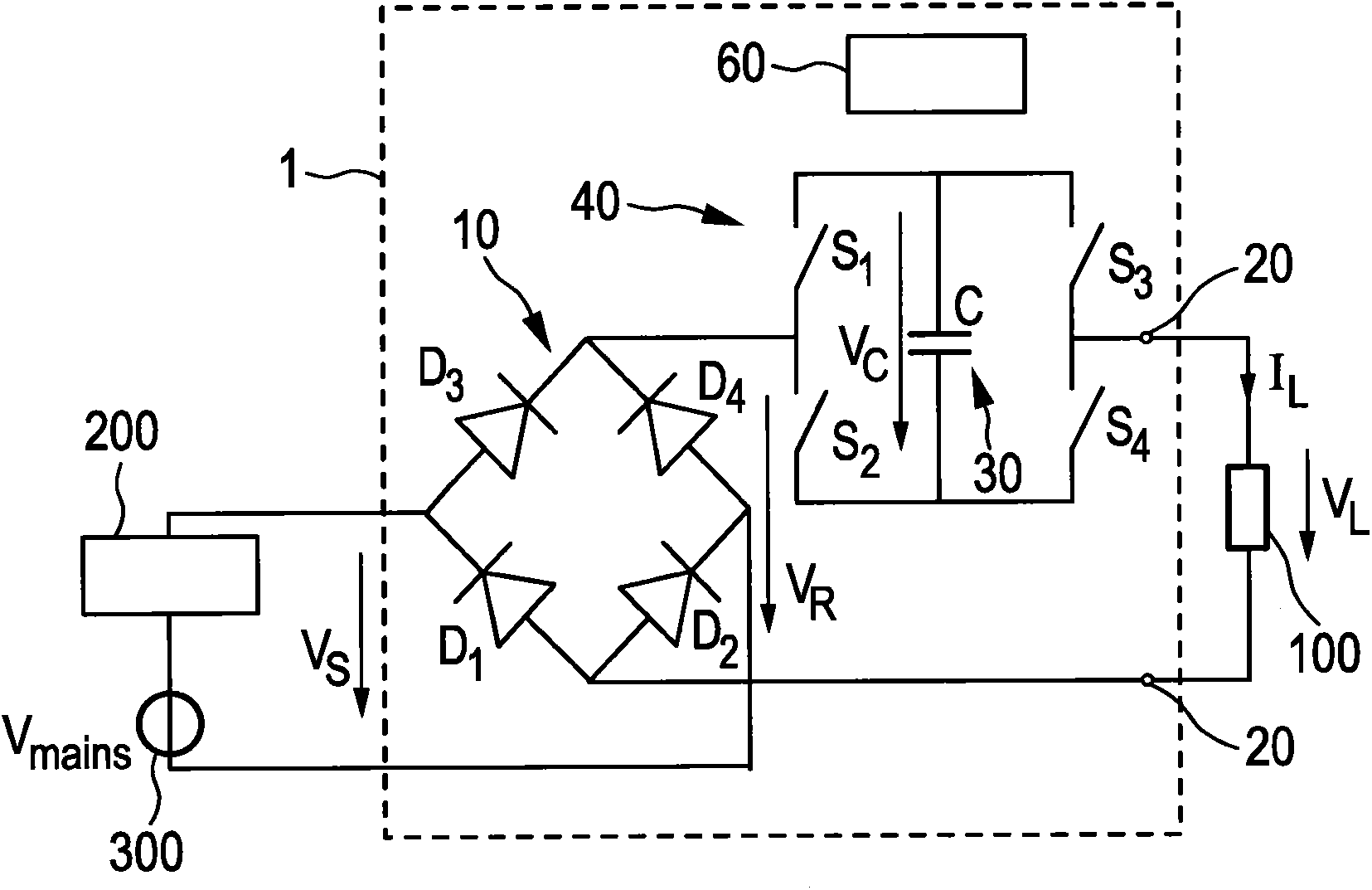
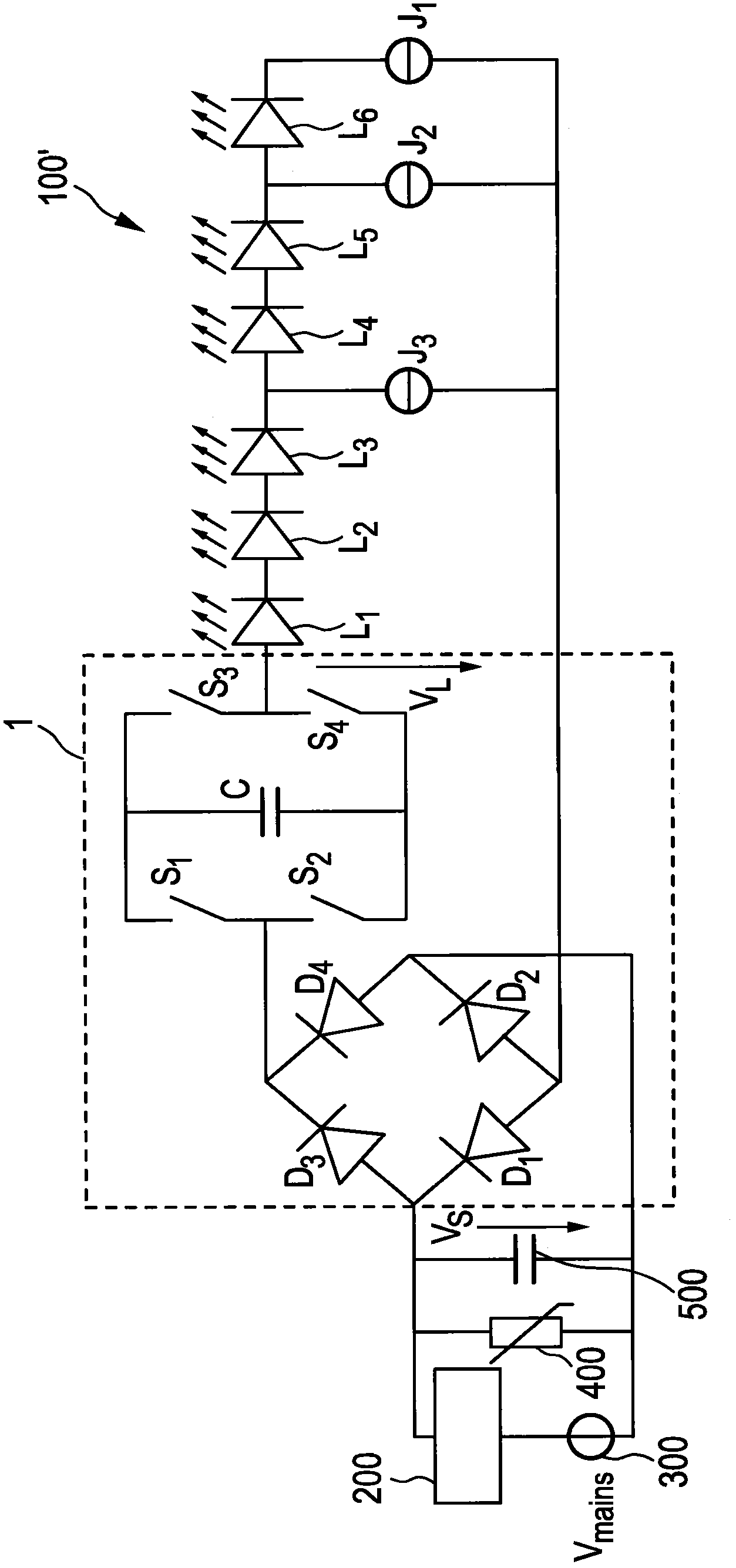
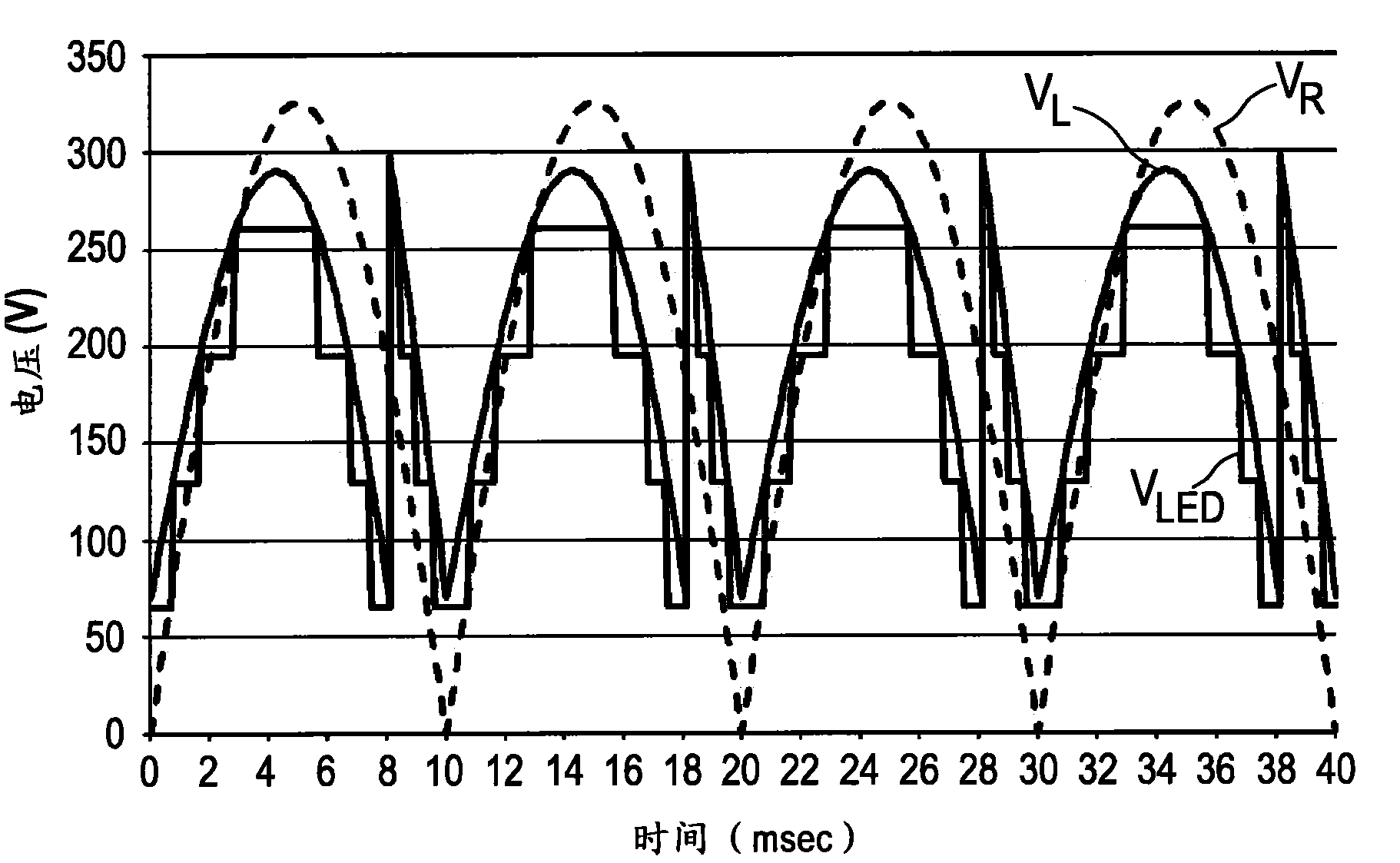
Driving device and method for driving a load, in particular an LED assembly
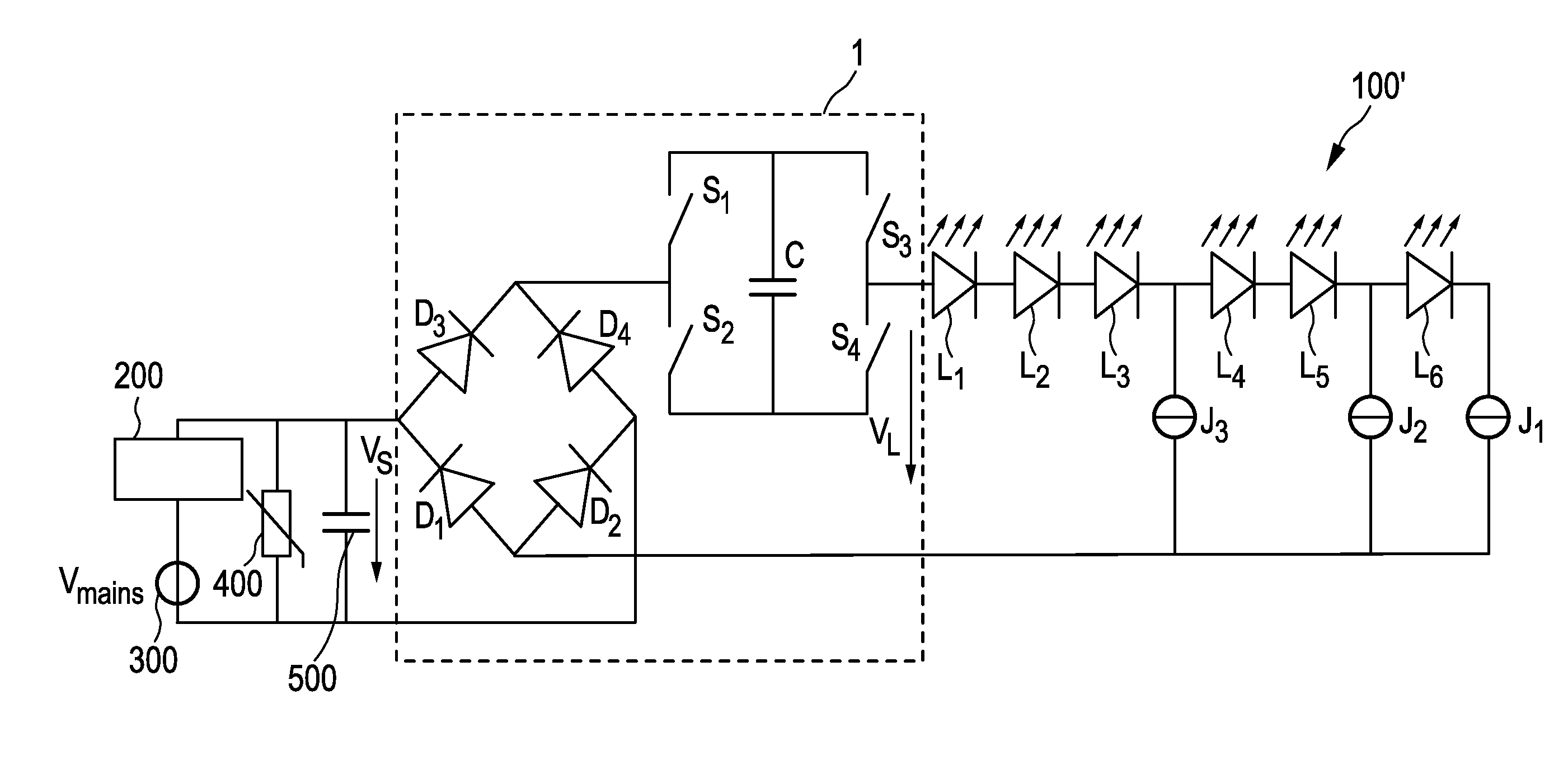
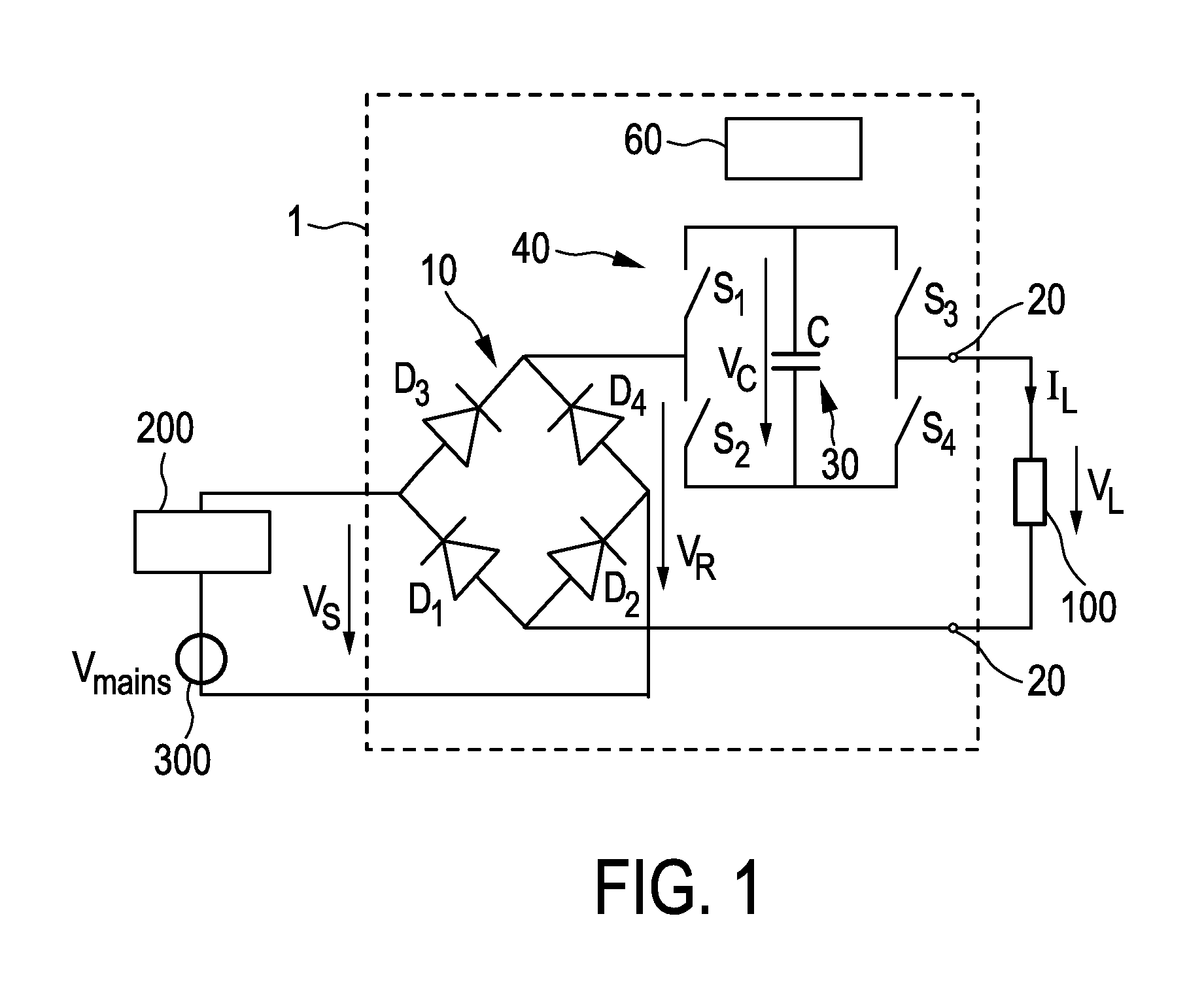
ActiveUS20140049174A1Large series capacitor value rangeImprove compatibilityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentCapacitance
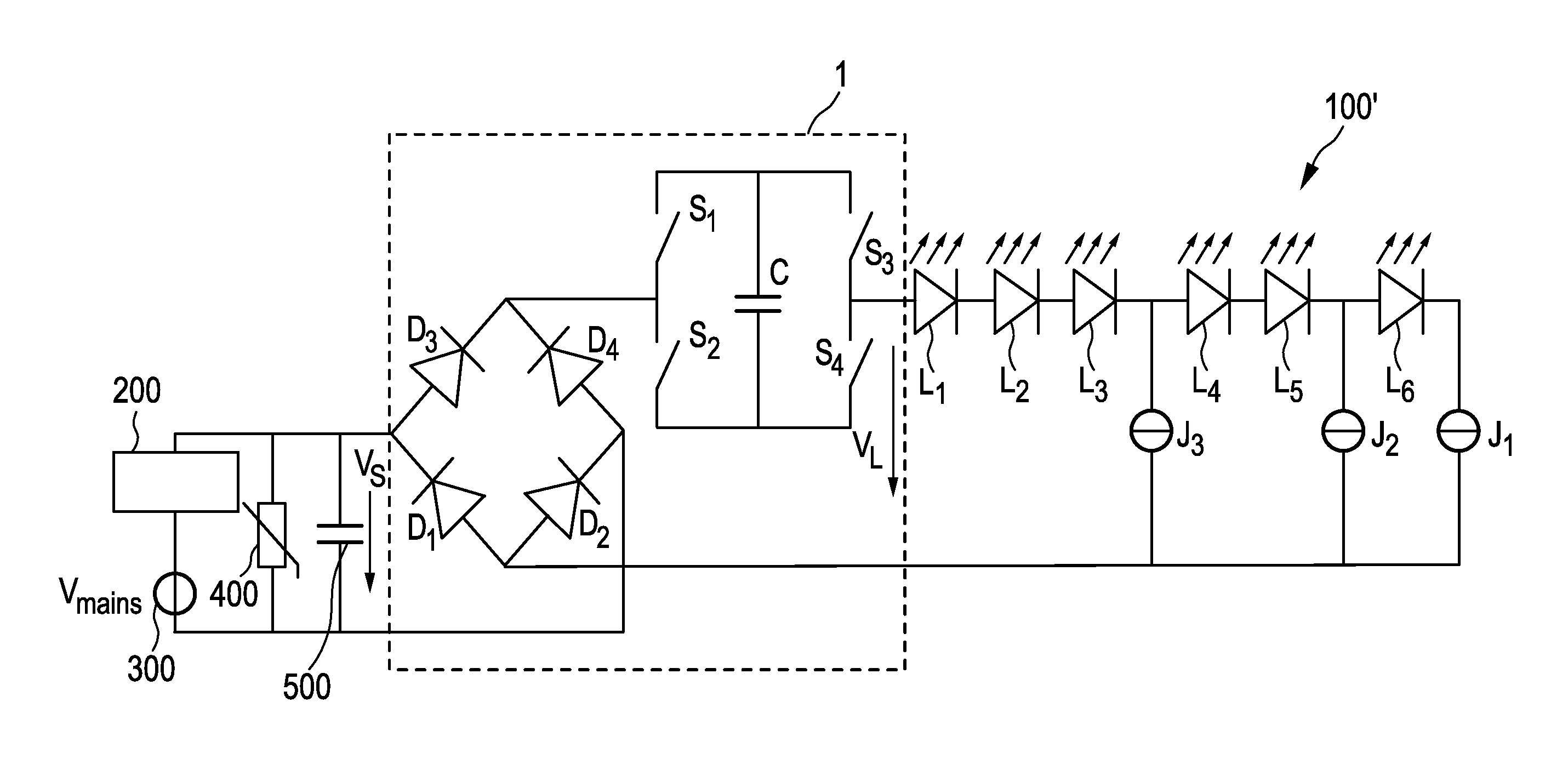
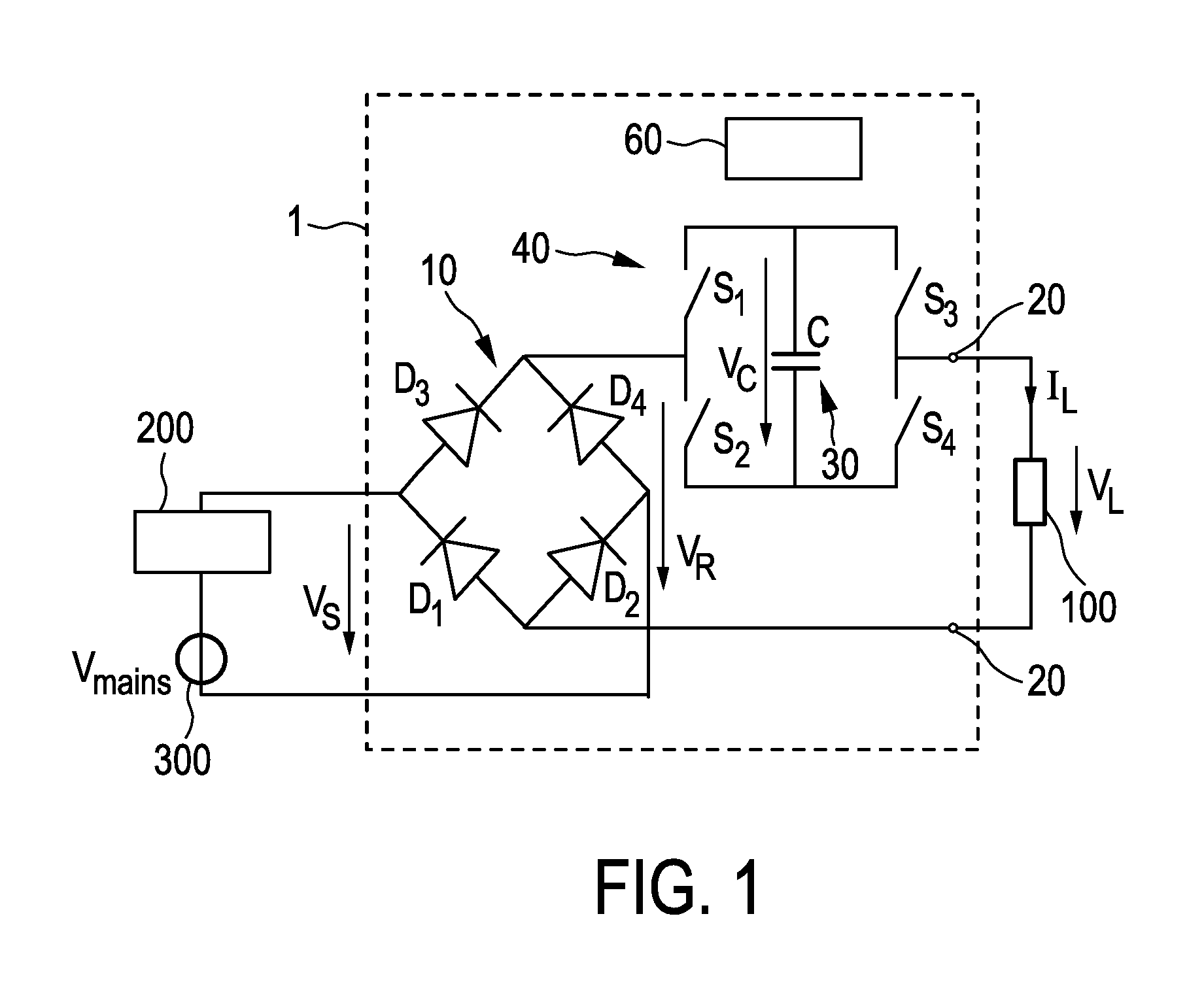
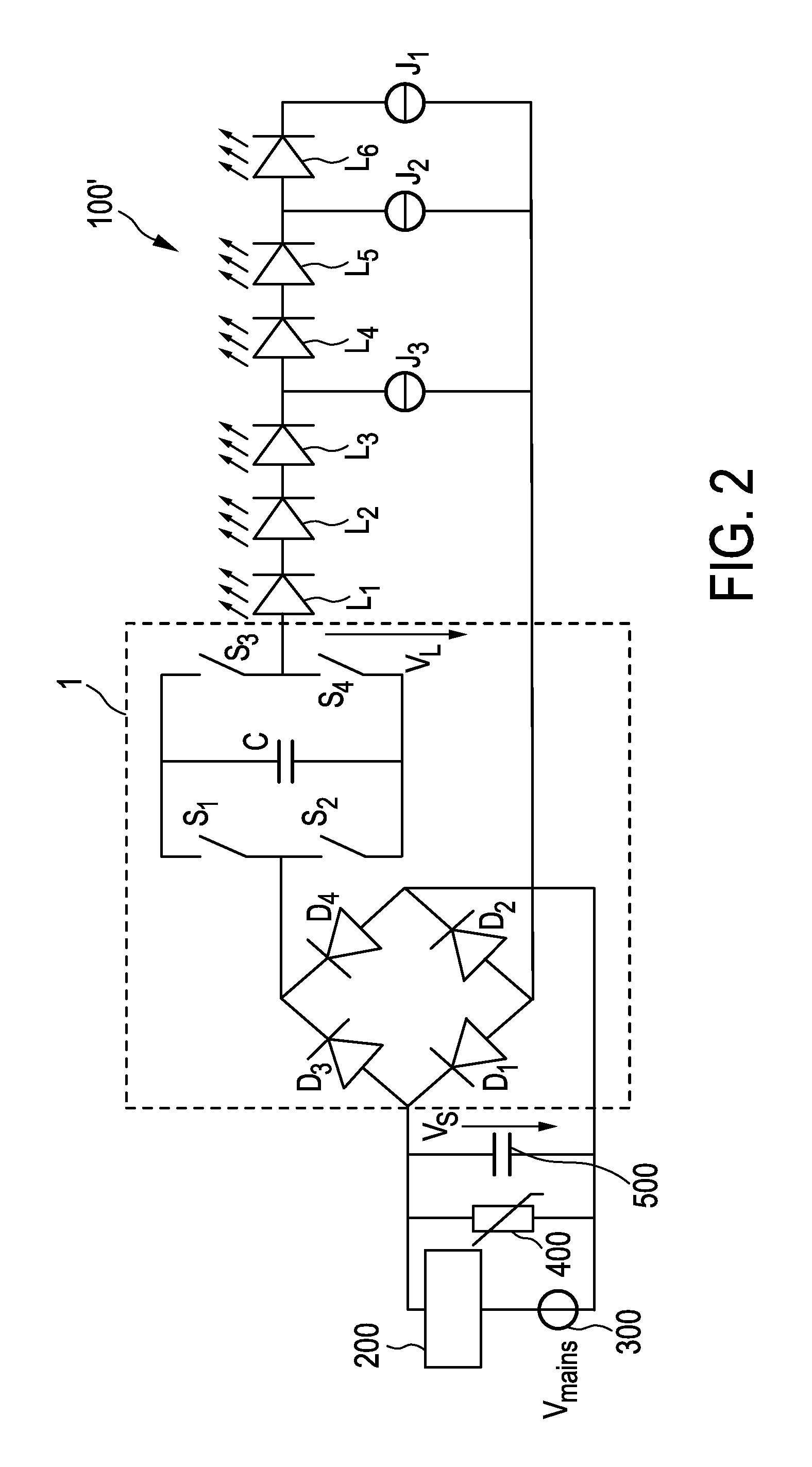
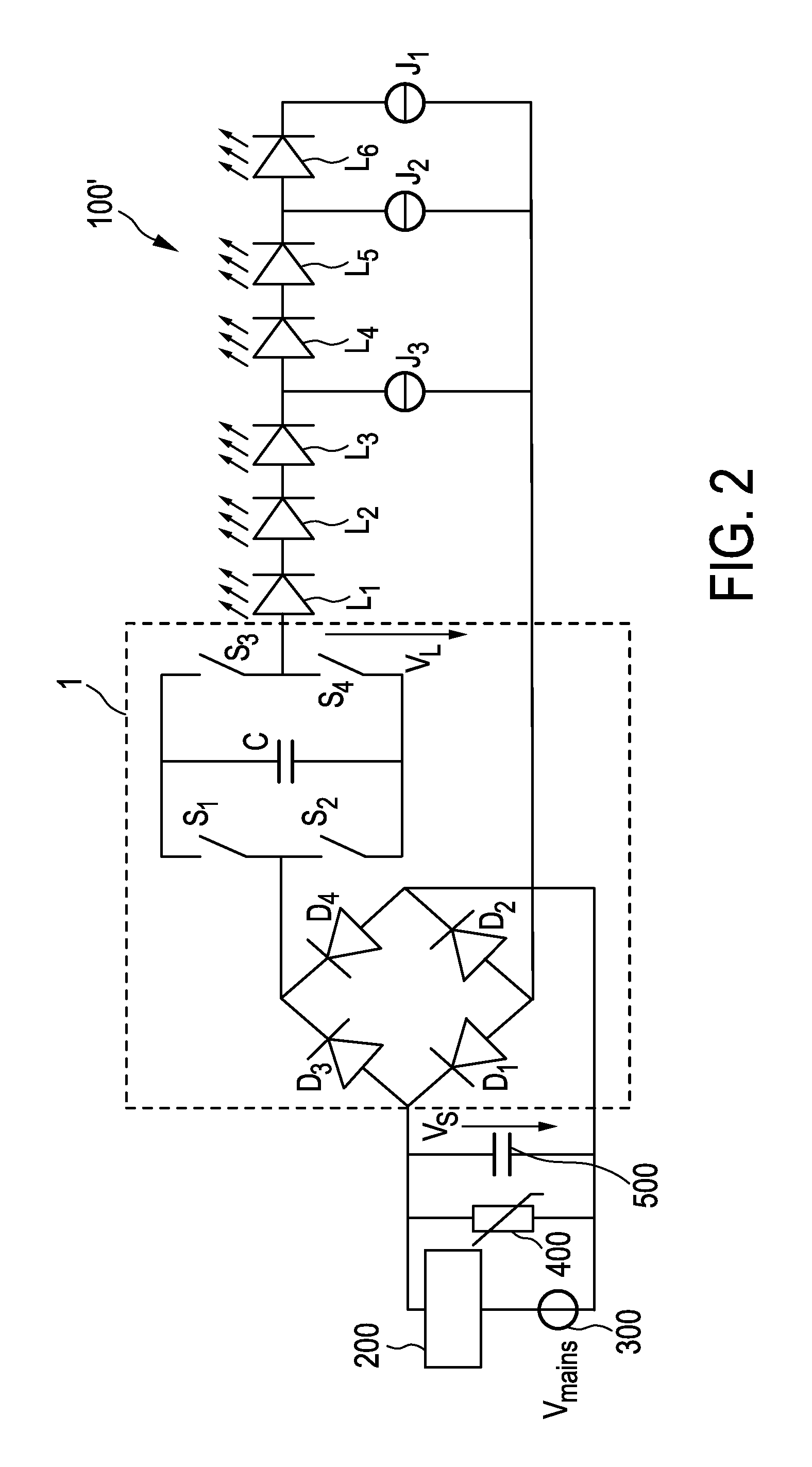
Driver device and a corresponding driving method for driving a load, in particular an LED assembly comprising one or more LEDs. To provide a better performance, better cost-efficiency, improved power factor and reduced losses, a driver device (1,1′, 2, 2′) is provided comprising a rectifier unit (10) for rectifying a received AC supply voltage (VS), load terminals (20) for providing a drive voltage (VL) and / or a drive current (IL) for driving said load, a capacitive storage unit (30) coupled between said rectifier unit and said load terminals for storing electrical energy provided by said rectifier unit and providing electrical energy to said load, and a bridge switching unit (40) coupled between said rectifier unit and said load for switching said capacitive storage unit into a load current path from said rectifier unit to said load terminals with a desired polarity and for switching said capacitive storage unit out of said load current path.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
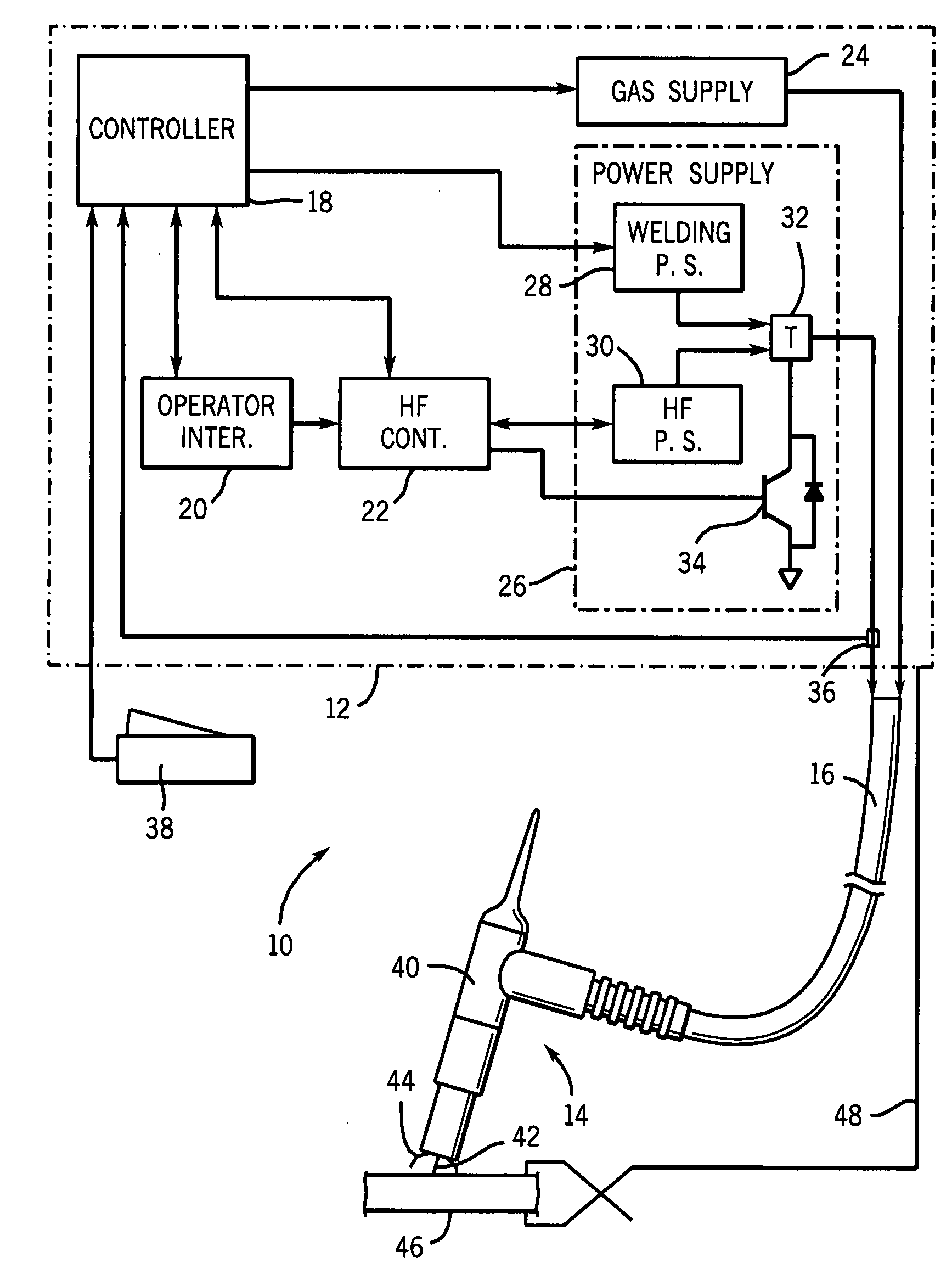
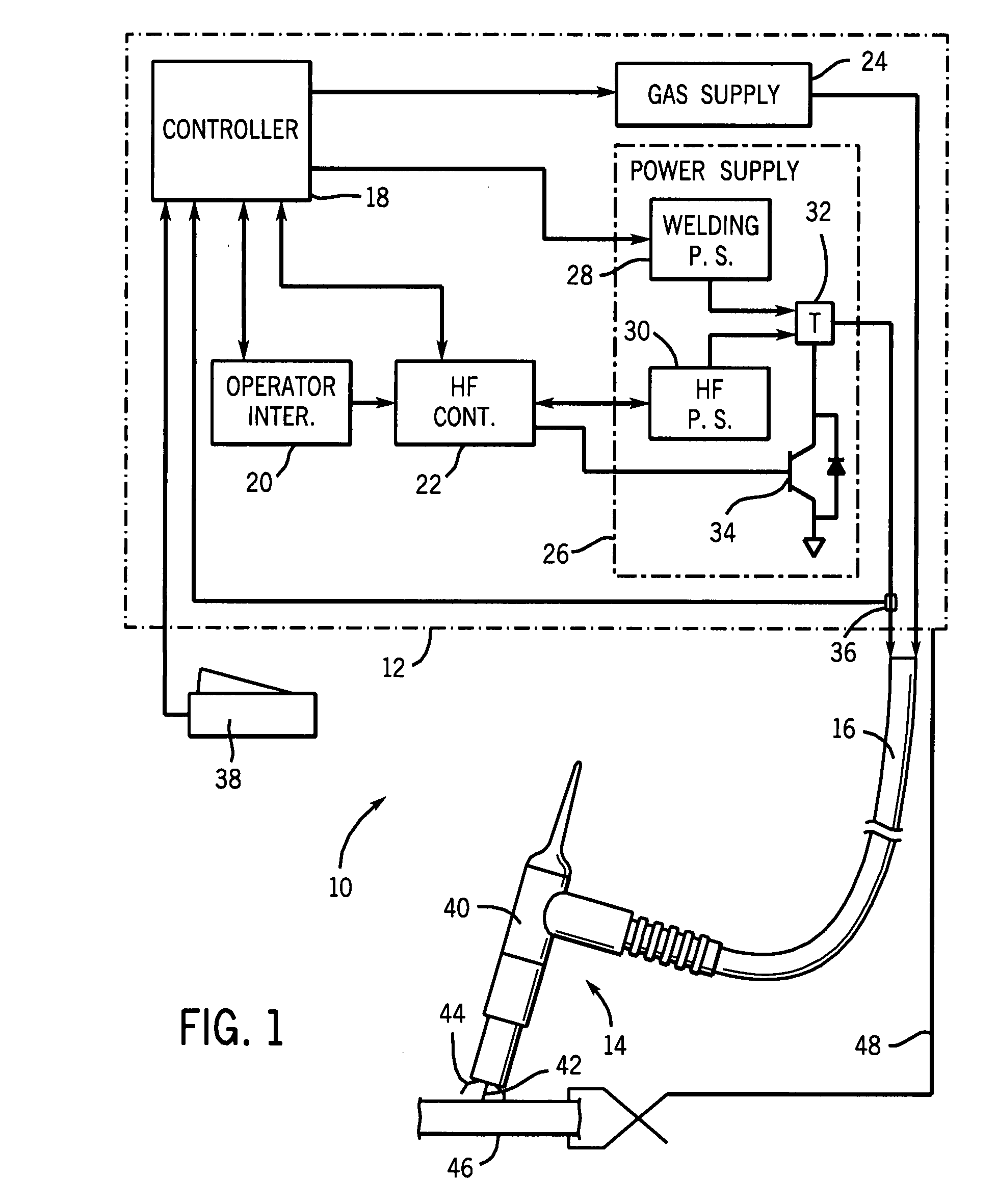
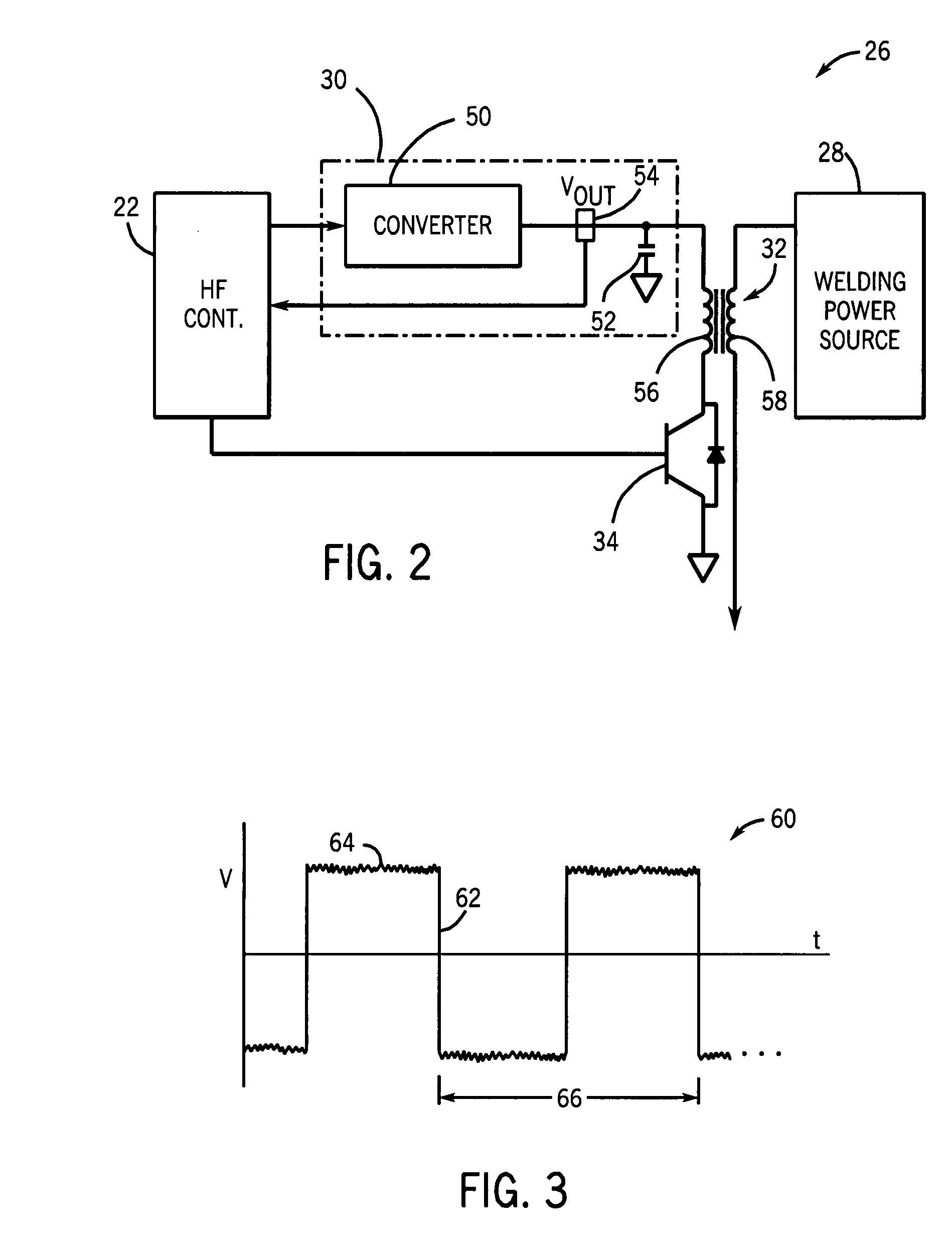
Welding power source with automatic variable high frequency
ActiveUS20080264915A1Improve the level ofImproved arc performanceArc welding apparatusCapacitanceCapacitive storage
A high frequency power source configured to provide a variable voltage output is described such as for use in welding systems. The high frequency power source charges a capacitive storage device. A transformer having a primary winding coupled to the output of the high frequency power source and establishing a resonant frequency signal with the capacitive storage device, and a secondary winding coupled to the welding power supply, superimposes the resonant frequency signals onto the welding power signal of the welding power supply during periods of the resonant rings. By varying the voltage output from the high frequency power source, the high frequency energy delivered to the welding torch can be optimized for a variety of welding applications.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
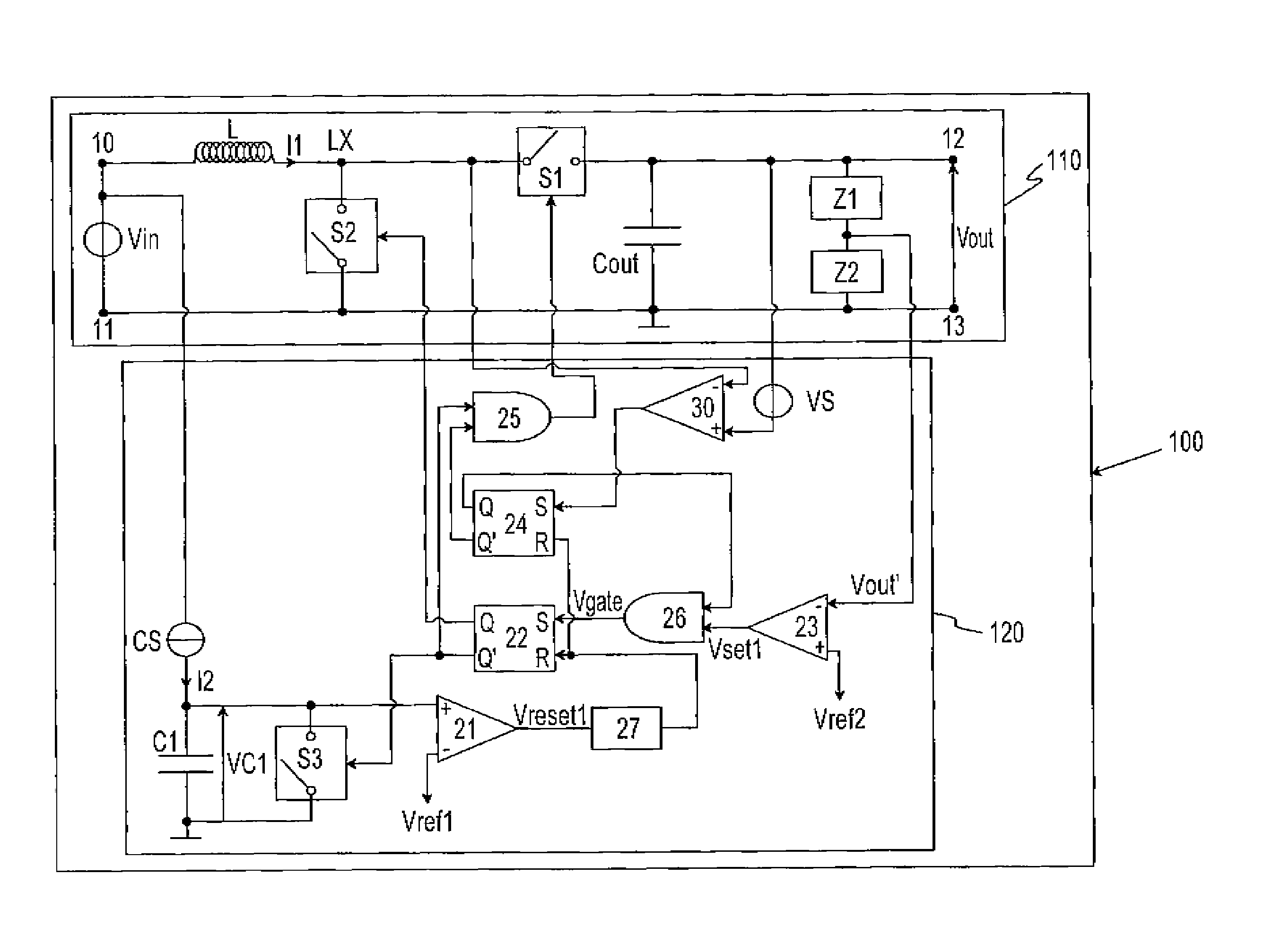
Lower power controller for DC to DC converters
InactiveUS20110001460A1Save power consumptionImprove noiseEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionPower controllerCapacitance
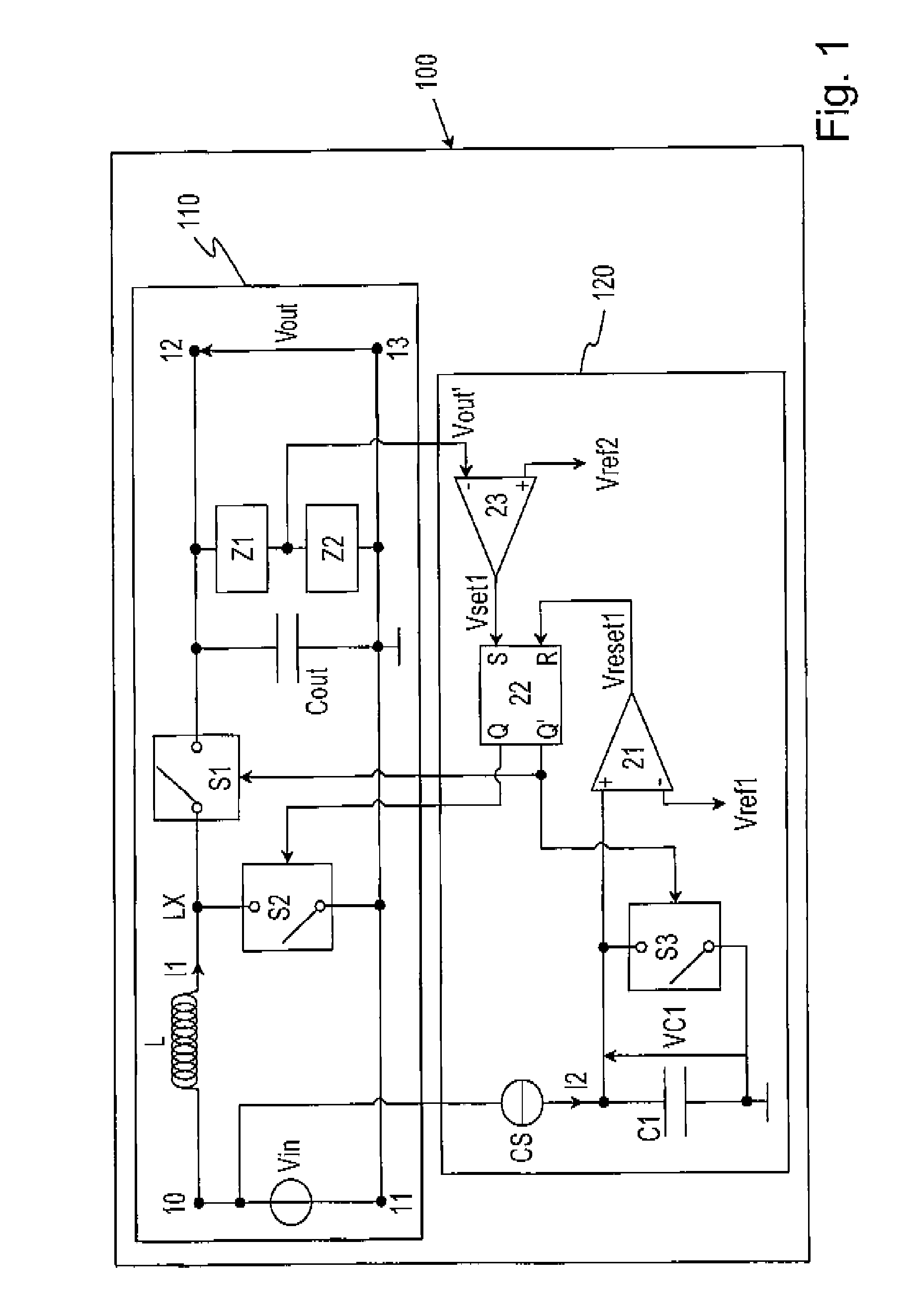
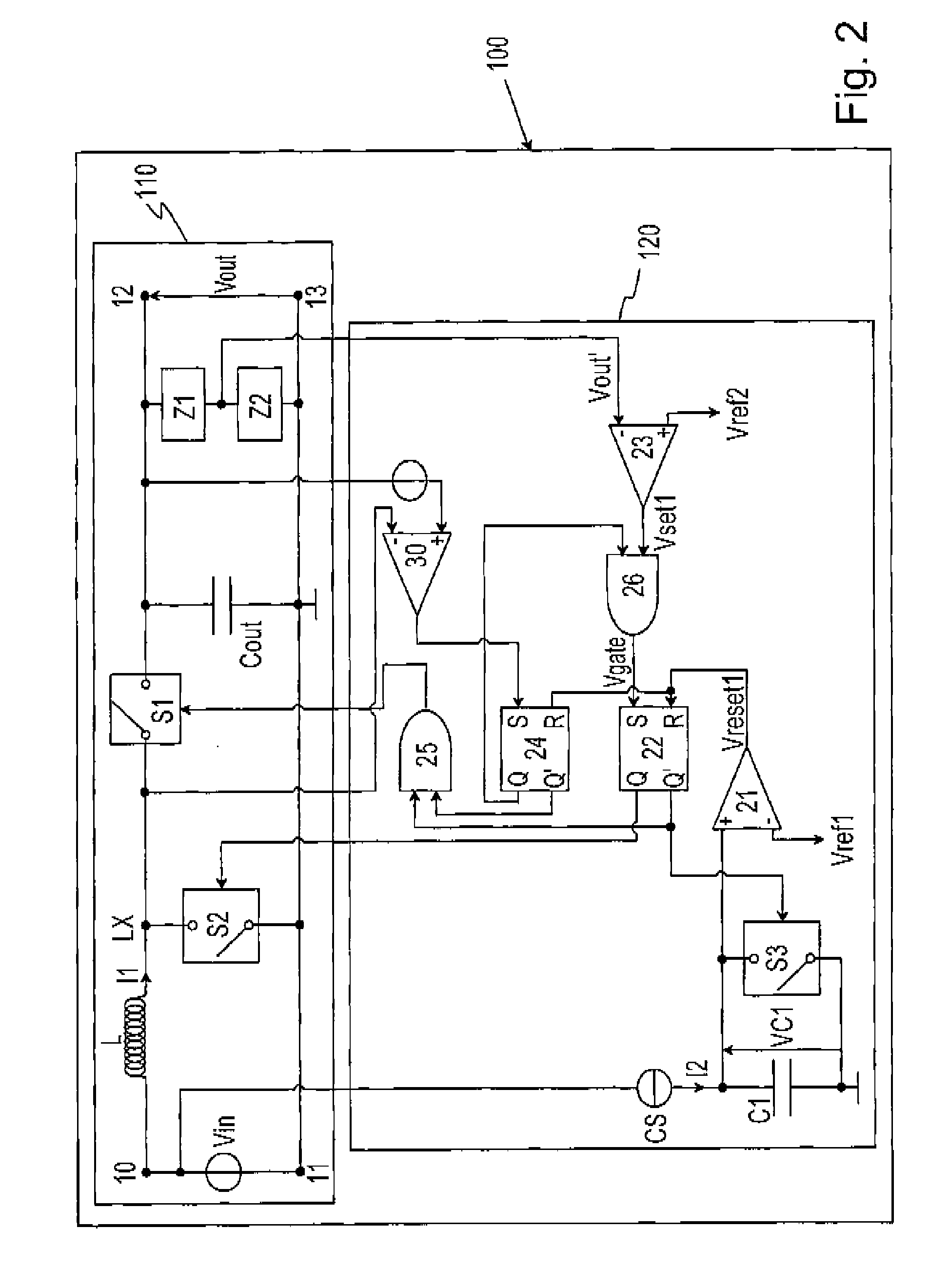
The present invention relates to a DC to DC converter system (100), which comprises converter means (110) and control means (120). The switching sequence of the first, second and third switching means (S1, S2, S3) is controlled by the control means (120) in such a manner that, during the on-time of the second switching device (S2), the first current (II) that flows through the inductive storage element (L) of the converter means (110) can be indirectly measured through the first voltage (VC1) across the capacitive storage element (C1), which is being charged with a second current (12) proportional to the input voltage (Vin) of the converter means (110) and provided by the current source (CS). Thus, the on-time of the second switching means (S2) varies inversely proportional to the input voltage (Vin).
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
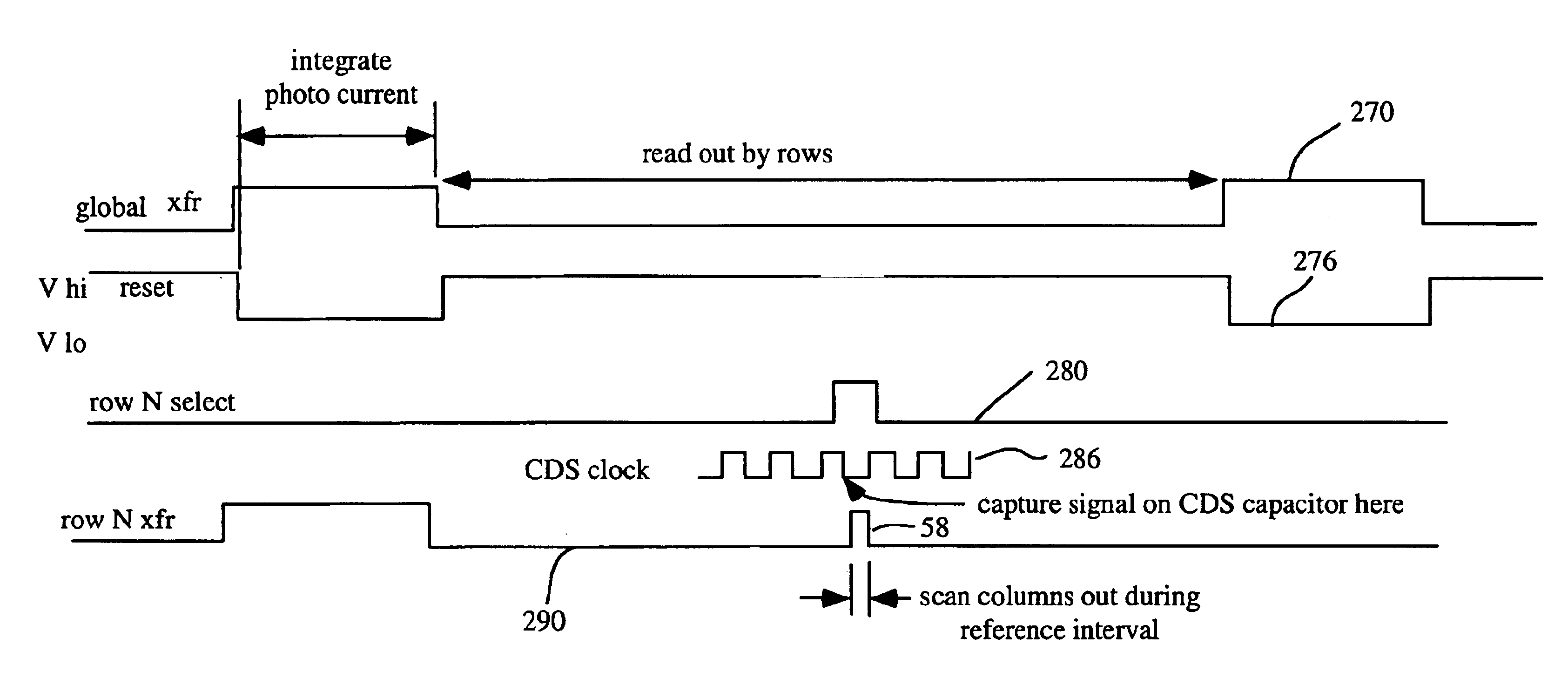
High-sensitivity storage pixel sensor having auto-exposure detection
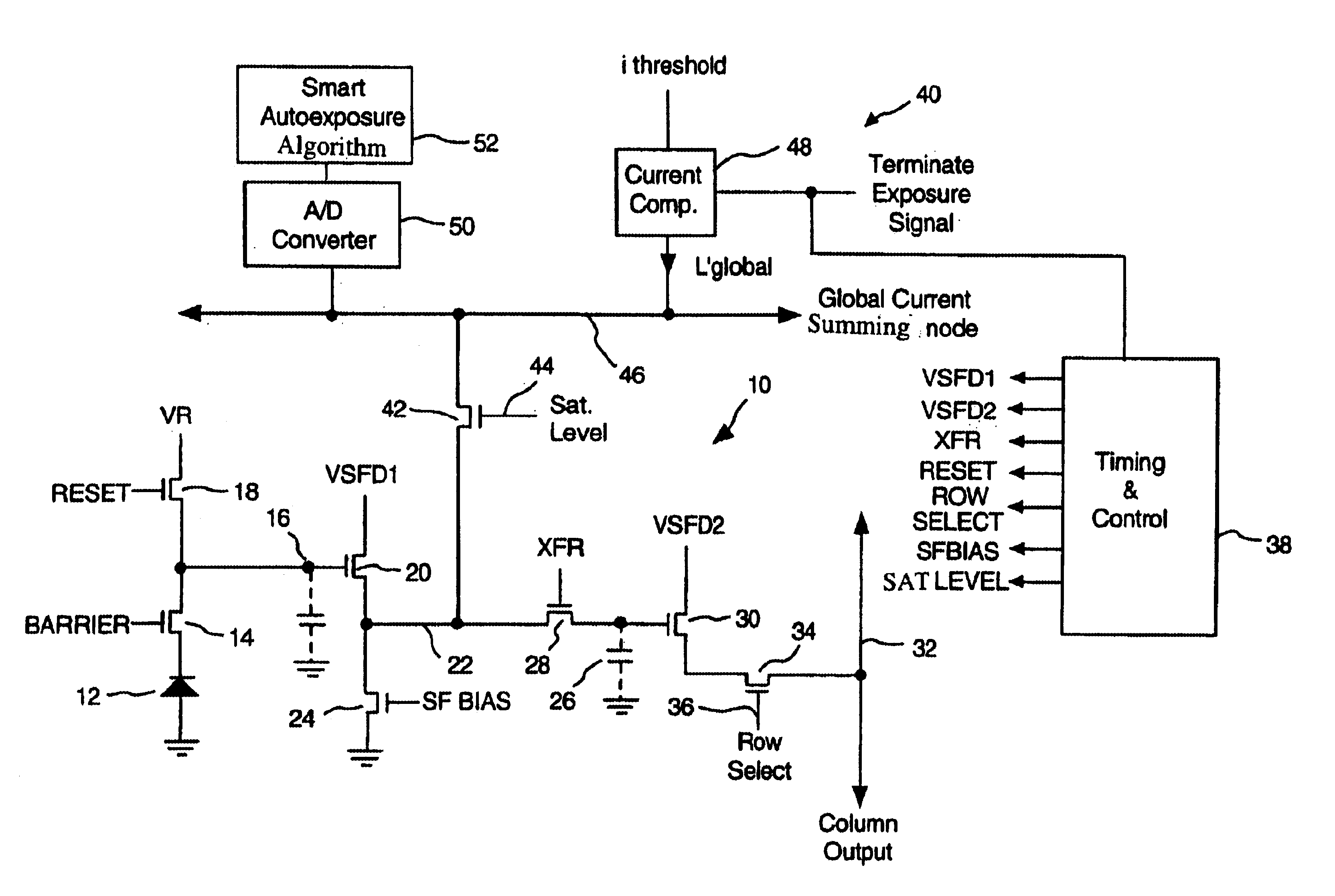
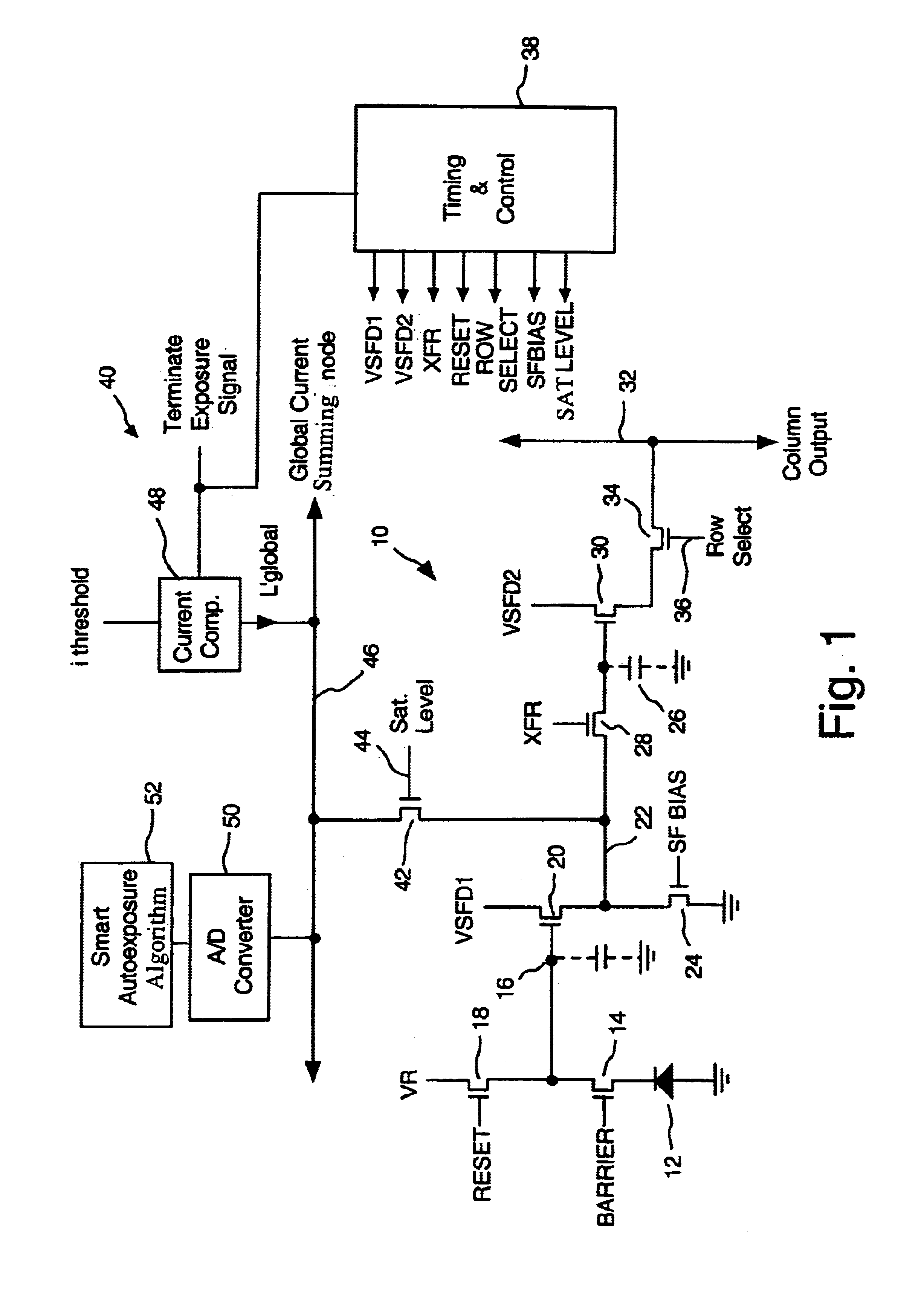
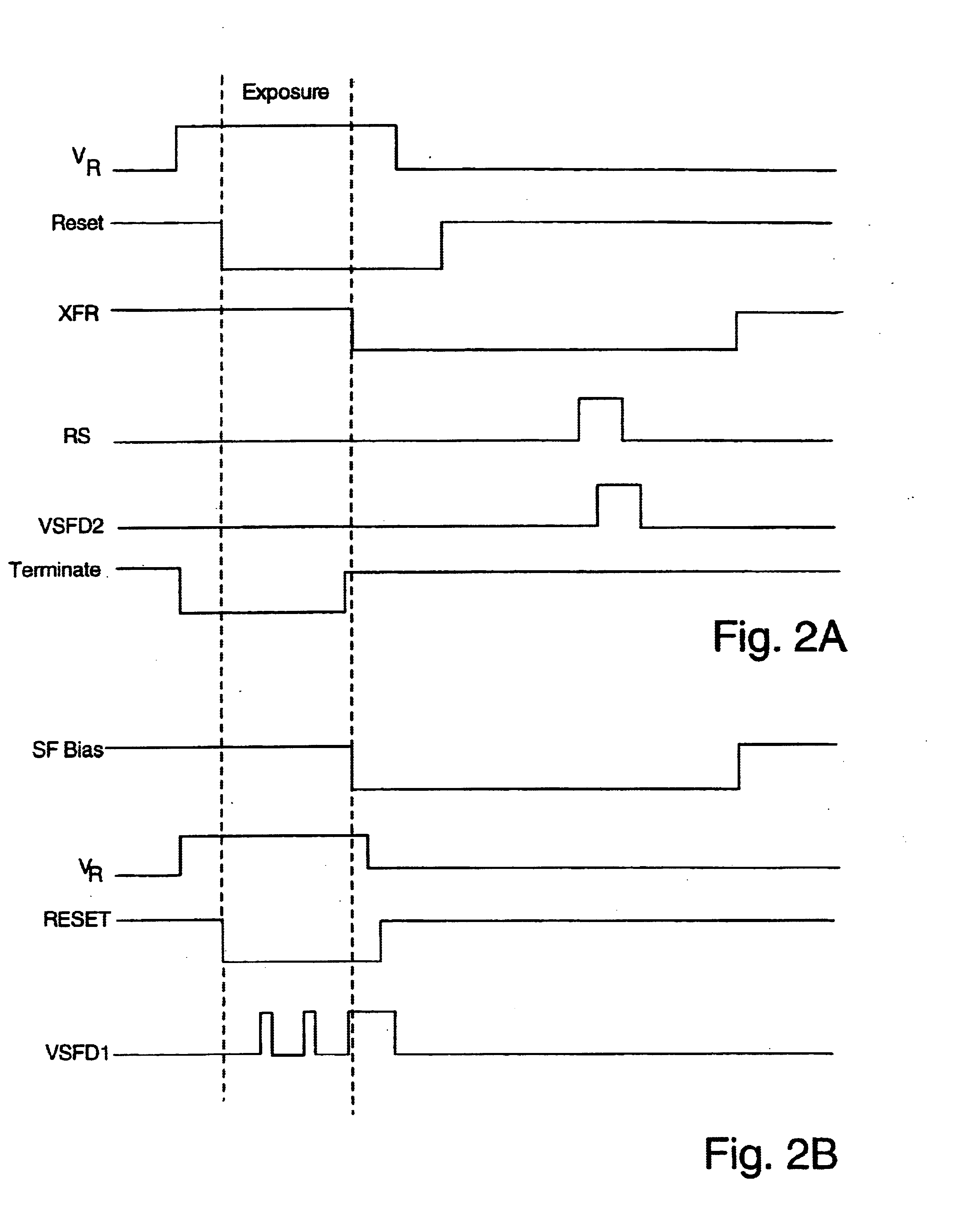
InactiveUS6882367B1High sensitivityReduce noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceCapacitive storage
A storage pixel sensor disposed on a semiconductor substrate comprises a photodiode having a first terminal coupled to a first potential and a second terminal. A barrier transistor has a first terminal coupled to the second terminal of the photodiode, a second terminal and a control gate coupled to a barrier set voltage. A reset transistor has a first terminal coupled to the second terminal of the barrier transistor, a second terminal coupled to a reset reference potential that reverse biases the photodiode, and a control gate coupled to a source of a RESET signal. A photocharge integration node is coupled to said second terminal of said barrier transistor. The photocharge integration node comprises the control gate of a first source-follower transistor. The first source-follower transistor is coupled to a source of bias current and has an output. A capacitive storage node is coupled to the output of the first source-follower transistor and comprises the control gate of a second source-follower transistor having an output. An exposure transistor is coupled between the output of the first source-follower transistor and a global current-summing node and has a control gate coupled to a saturation level voltage.
Owner:FOVEON
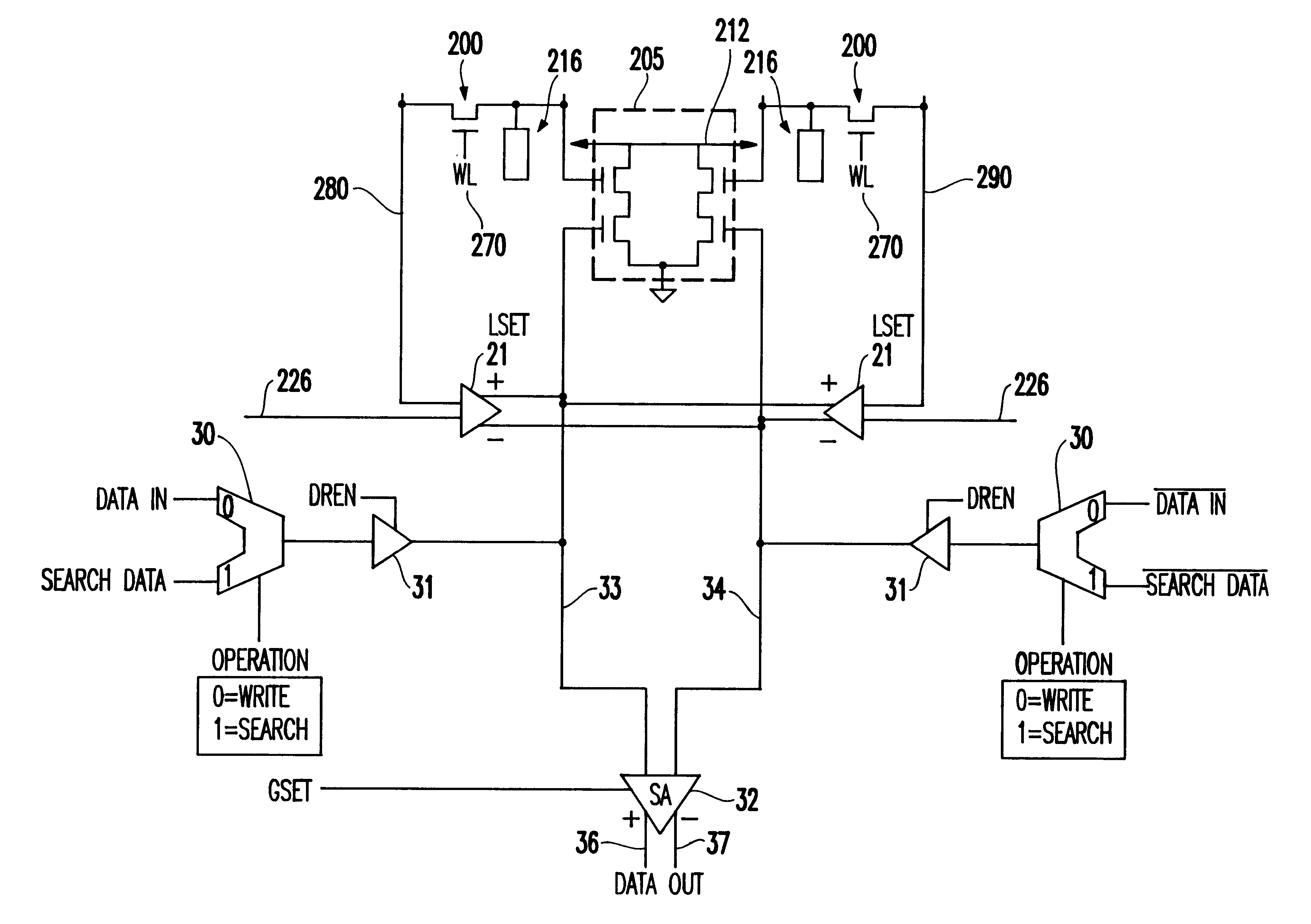
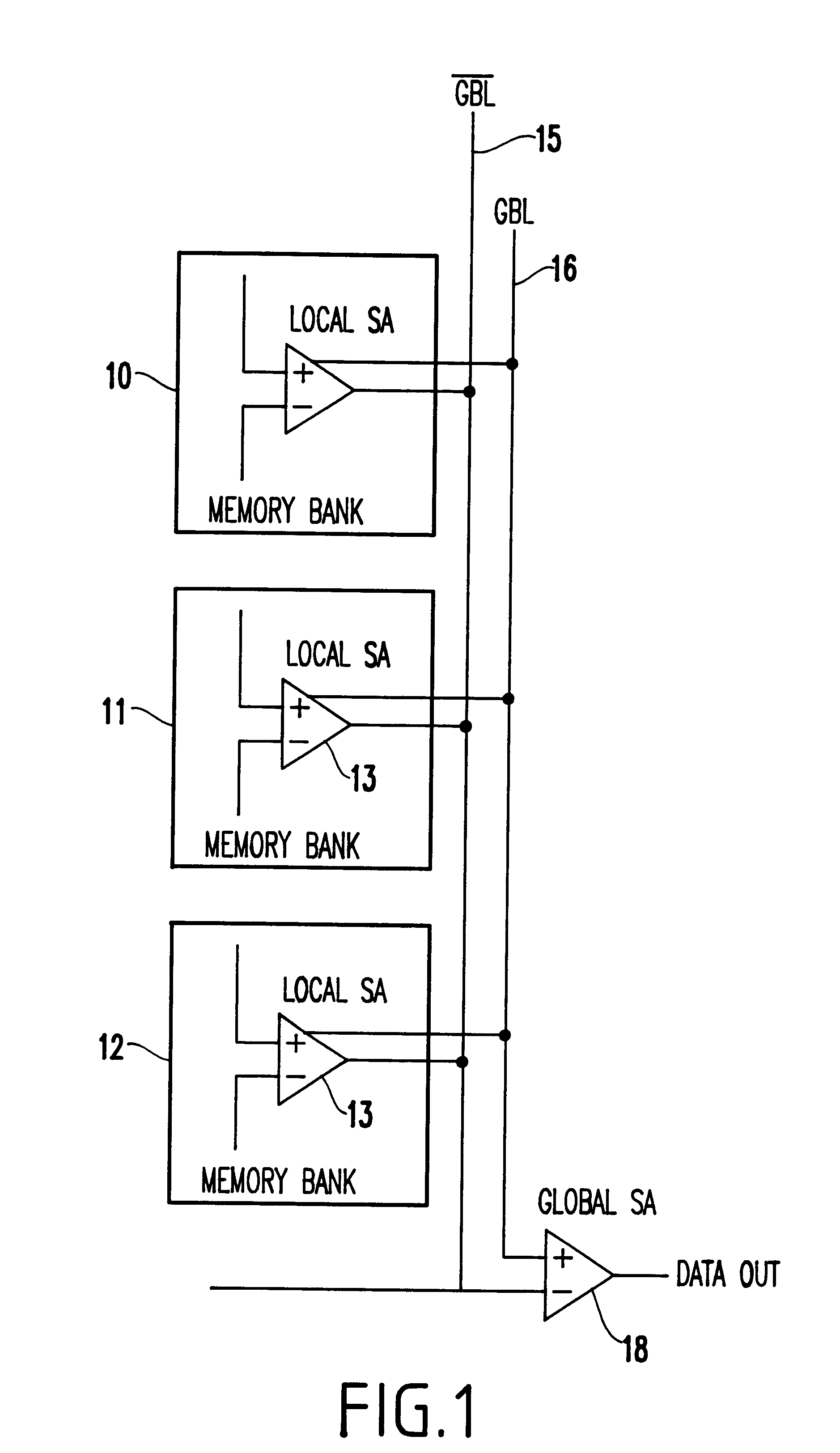
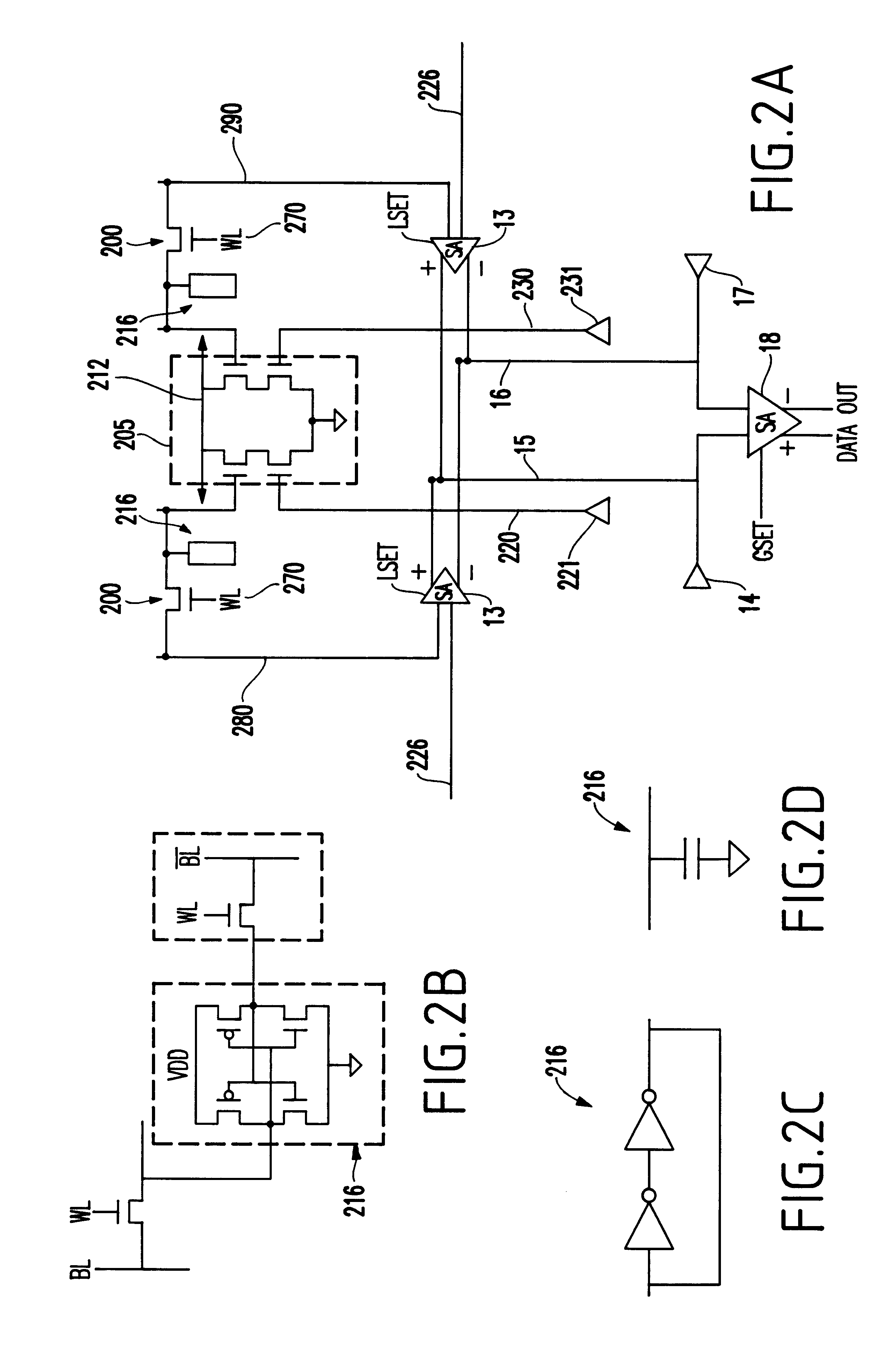
Use of search lines as global bitlines in a cam design
A method and structure for a content addressable memory (CAM) array having a plurality of memory cells. Each of the memory cells has capacitive storage devices, transistors connected to the storage devices, a wordline connected to and controlling the transistors, bitlines connected to the storage devices through the transistors, combined search and global bitlines connected to the capacitive storage devices. These cells are further arranged into columns, each containing multiplexers connected to the combined search and global bitlines, data-in lines connected to the multiplexers, and search-data lines connected to the multiplexers. Further, the multiplexers select between the data-in lines and the search-data lines to allow the combined search and global bitlines to be alternatively used as data lines and search lines. Also, in the invention each of the columns further has drivers between the multiplexers and the combined search and global bitlines. The drivers drive signals between the multiplexers and the combined search and global bitlines during search and write operations.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method of forming a memory device having a storage transistor
A memory device and a method of forming the memory device. The memory device comprises a storage transistor at a surface of a substrate comprising a body portion between first and second source / drain regions, wherein the source / drain regions are regions of a first conductivity type. The storage transistor also comprises a gate structure that wraps at least partially around the body portion in at least two spatial planes. A bit line is connected to the first source / drain region and a word line connected to the gate structure. The memory device does not require an additional capacitive storage element.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
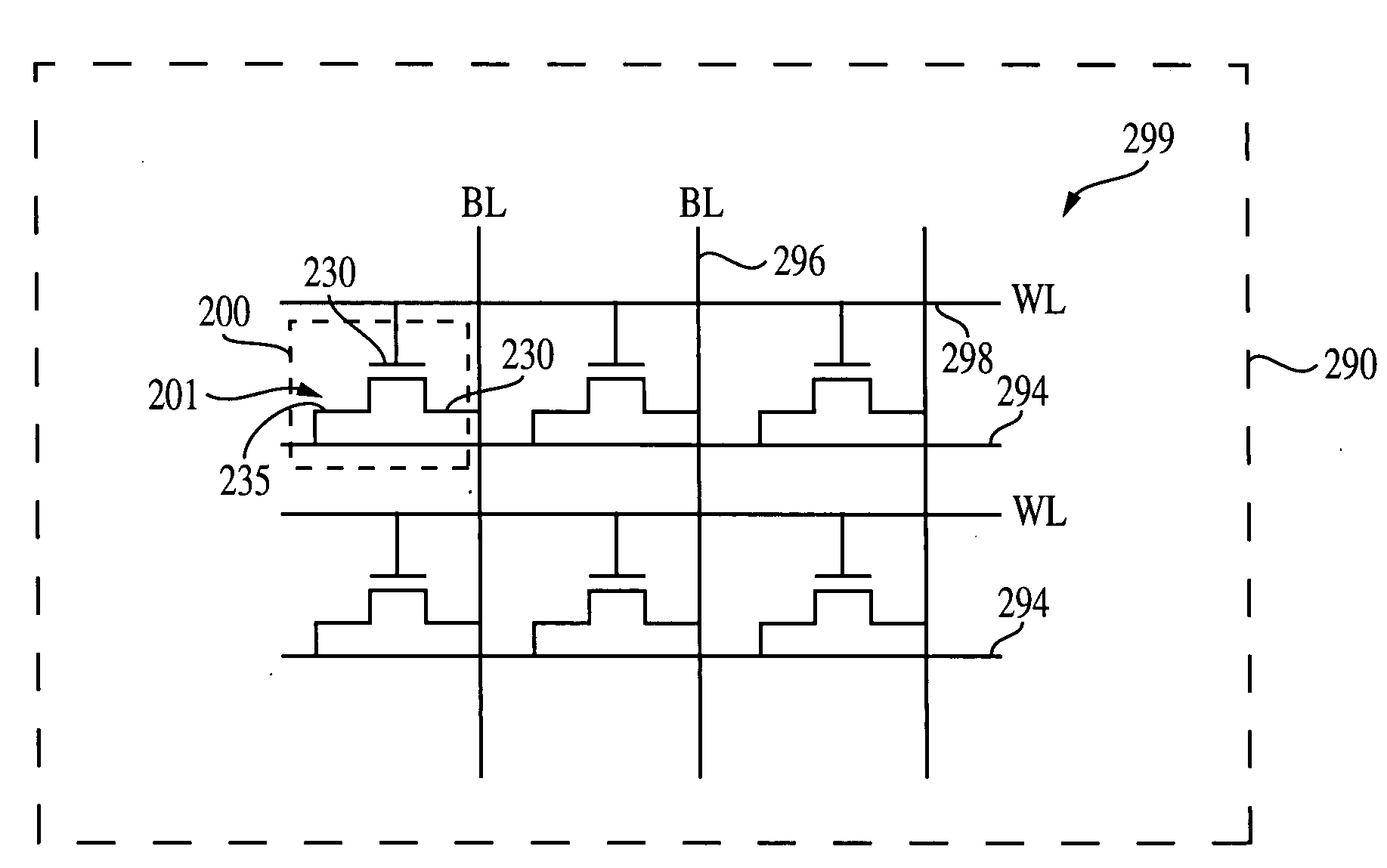
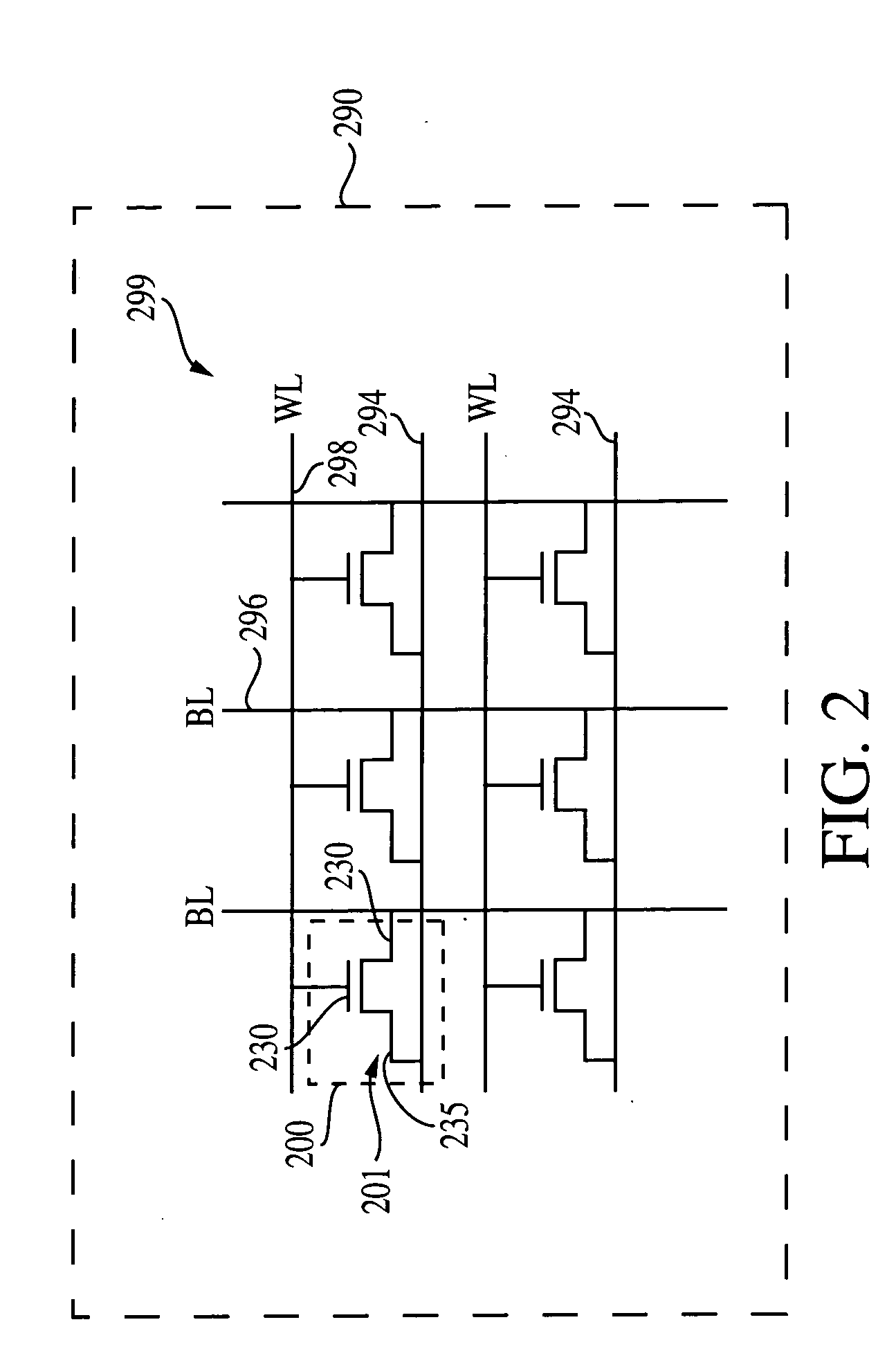
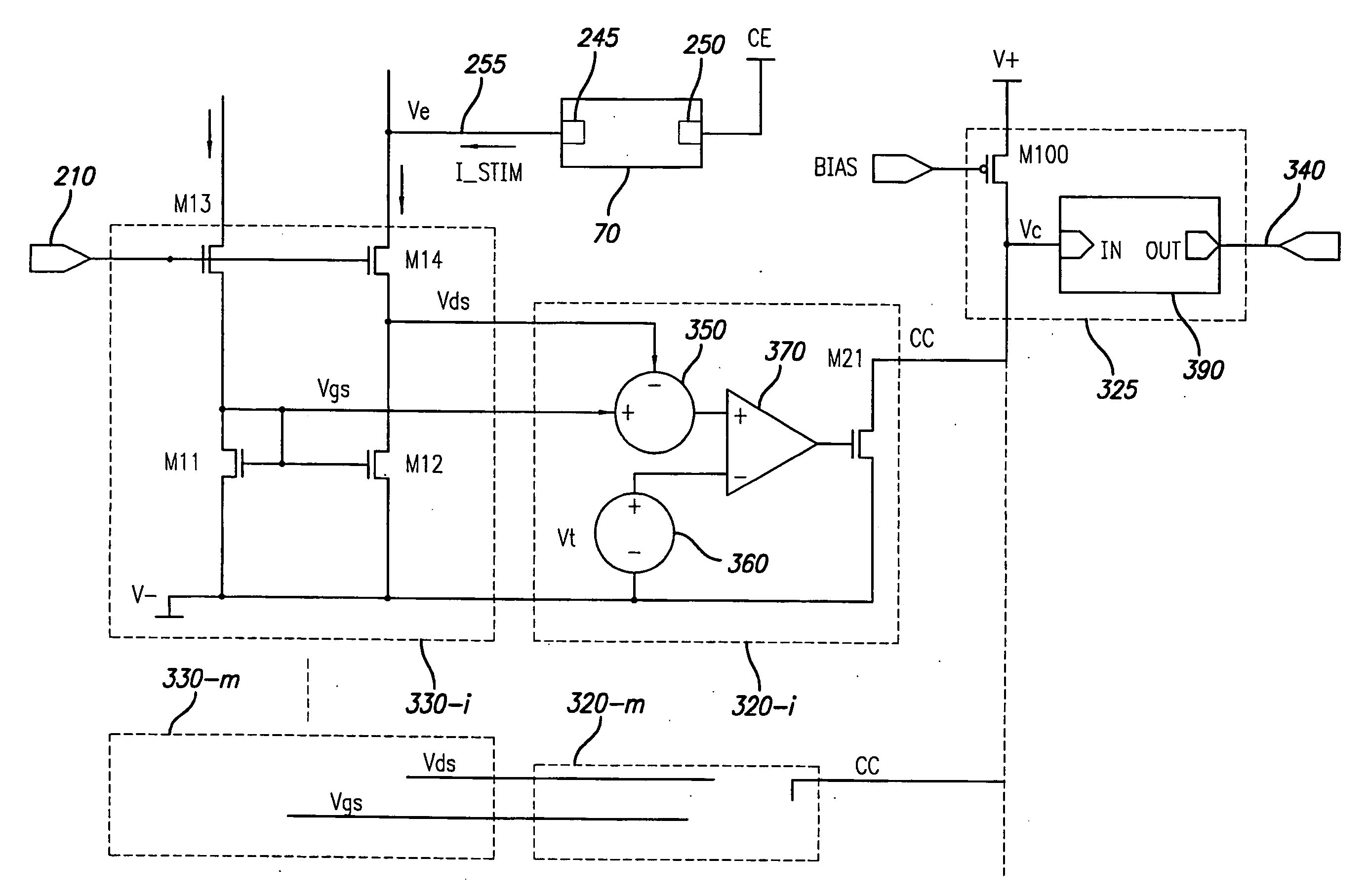
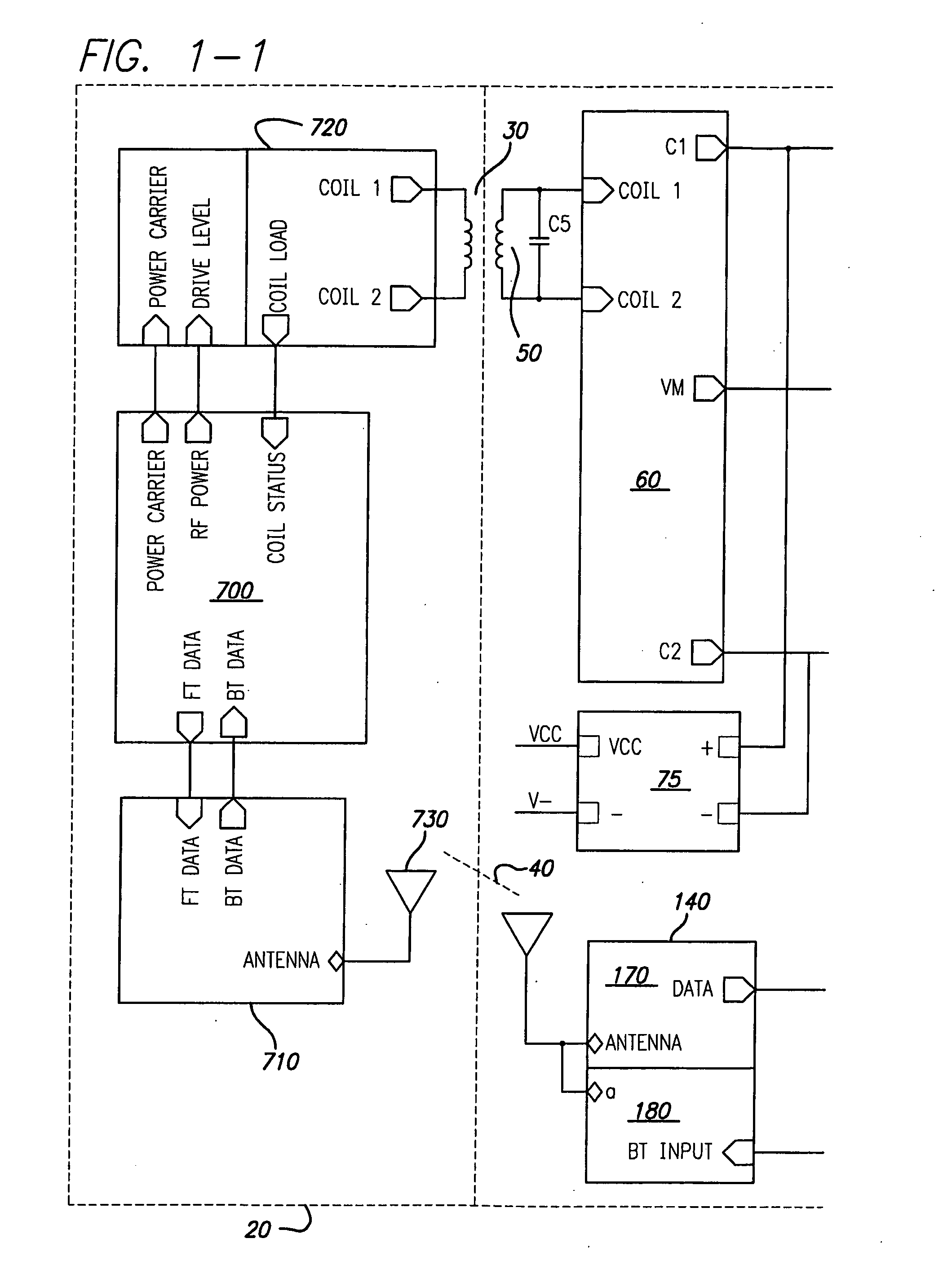
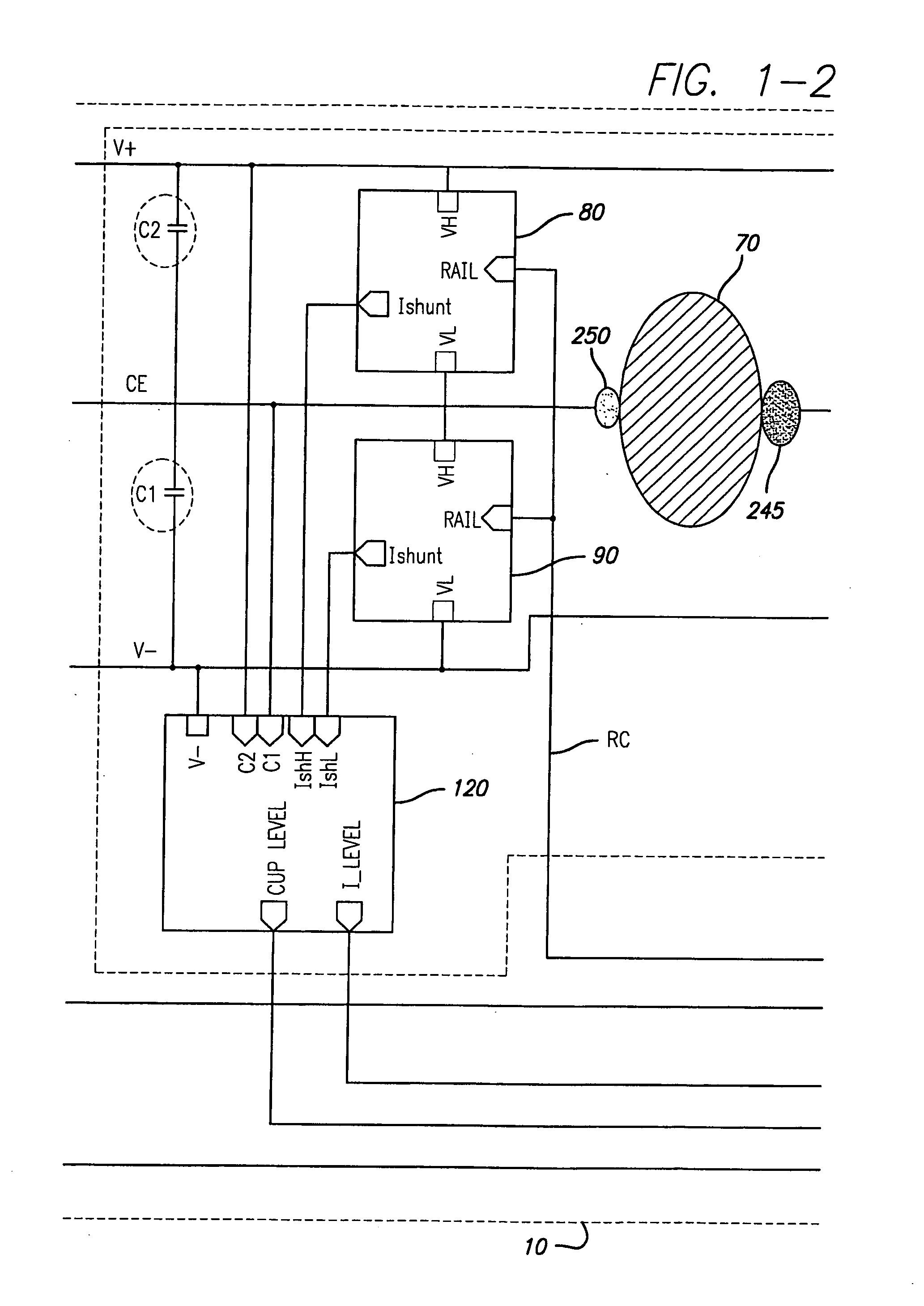
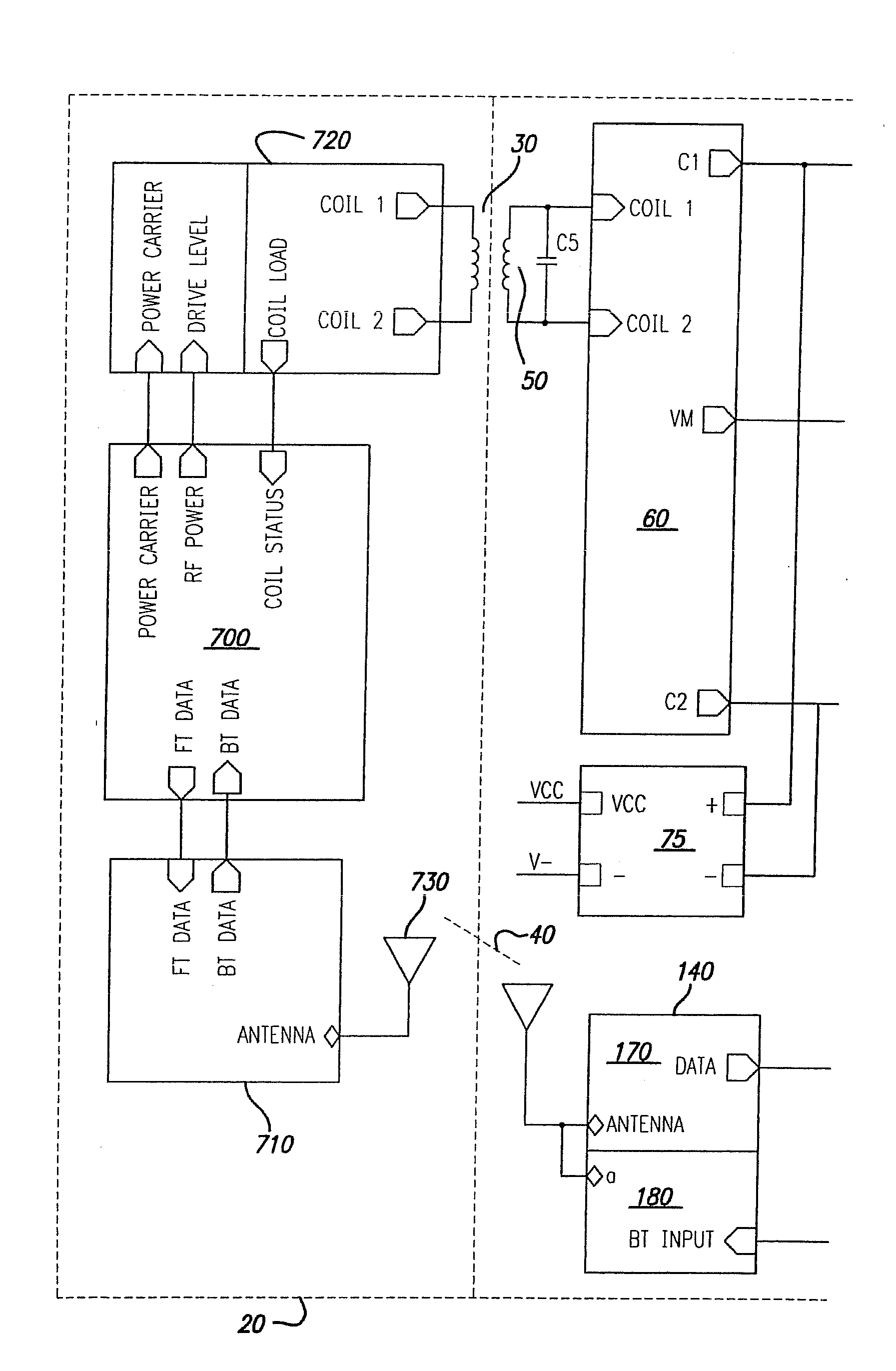
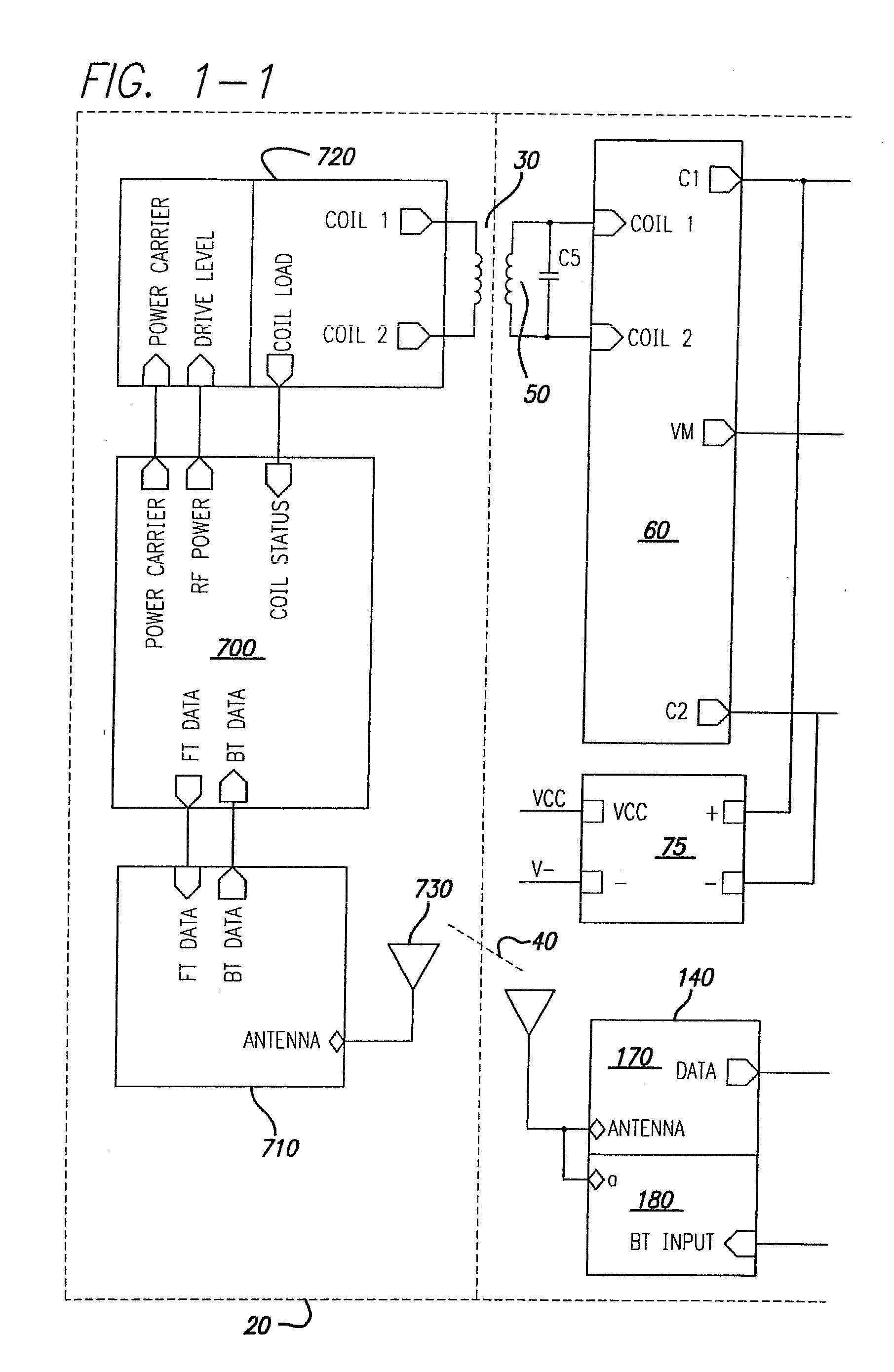
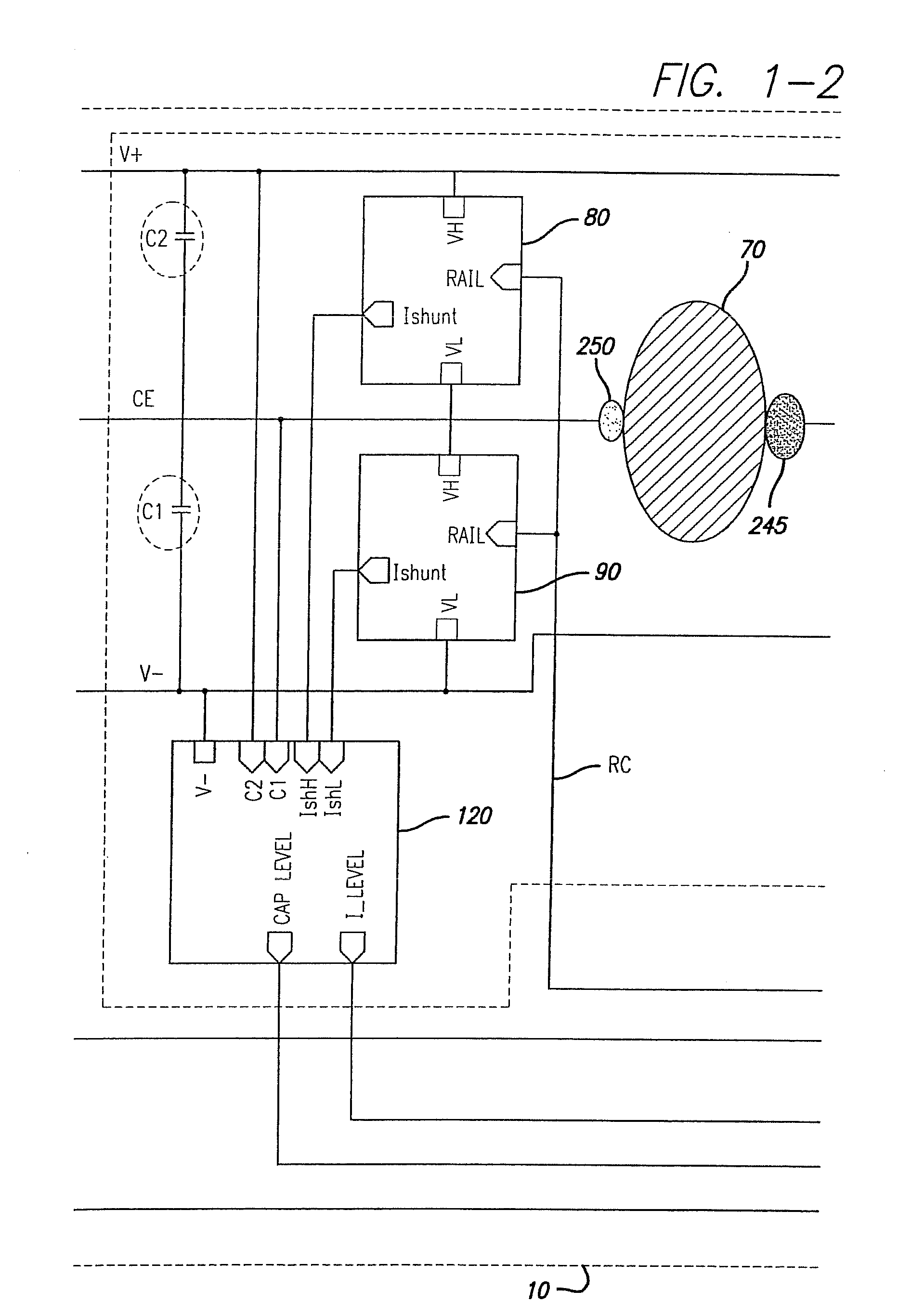
Power Scheme for Implant Stimulators on the Human or Animal Body
A power scheme for an implant on a human or animal body comprises: a charging circuit to provide power to deliver controlled stimulation currents to a body tissue; a capacitive storage arrangement connected with the charging circuit and charged by the charging circuit; a shunting arrangement to limit voltage on the capacitive storage arrangement; a driver array configured to transfer charges from the capacitive storage arrangement to the tissue; and an electrode array connected with the driver array and the tissue.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
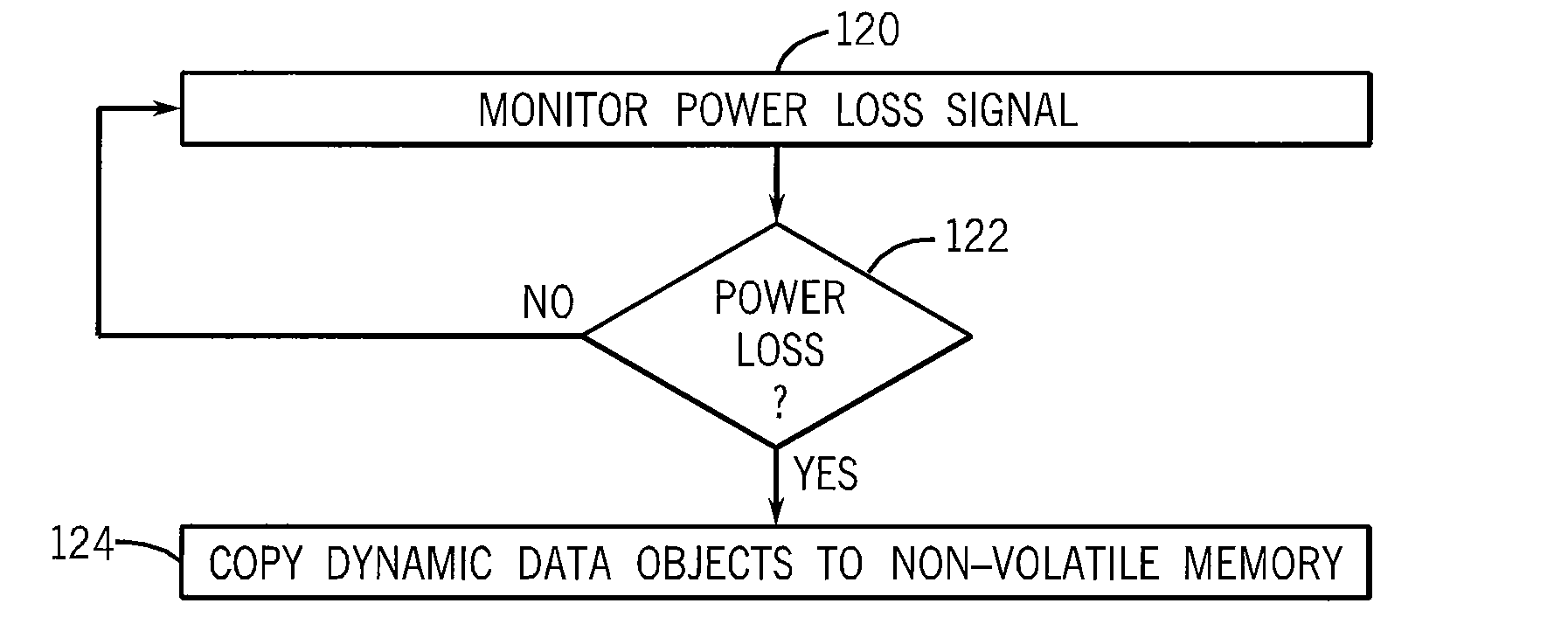
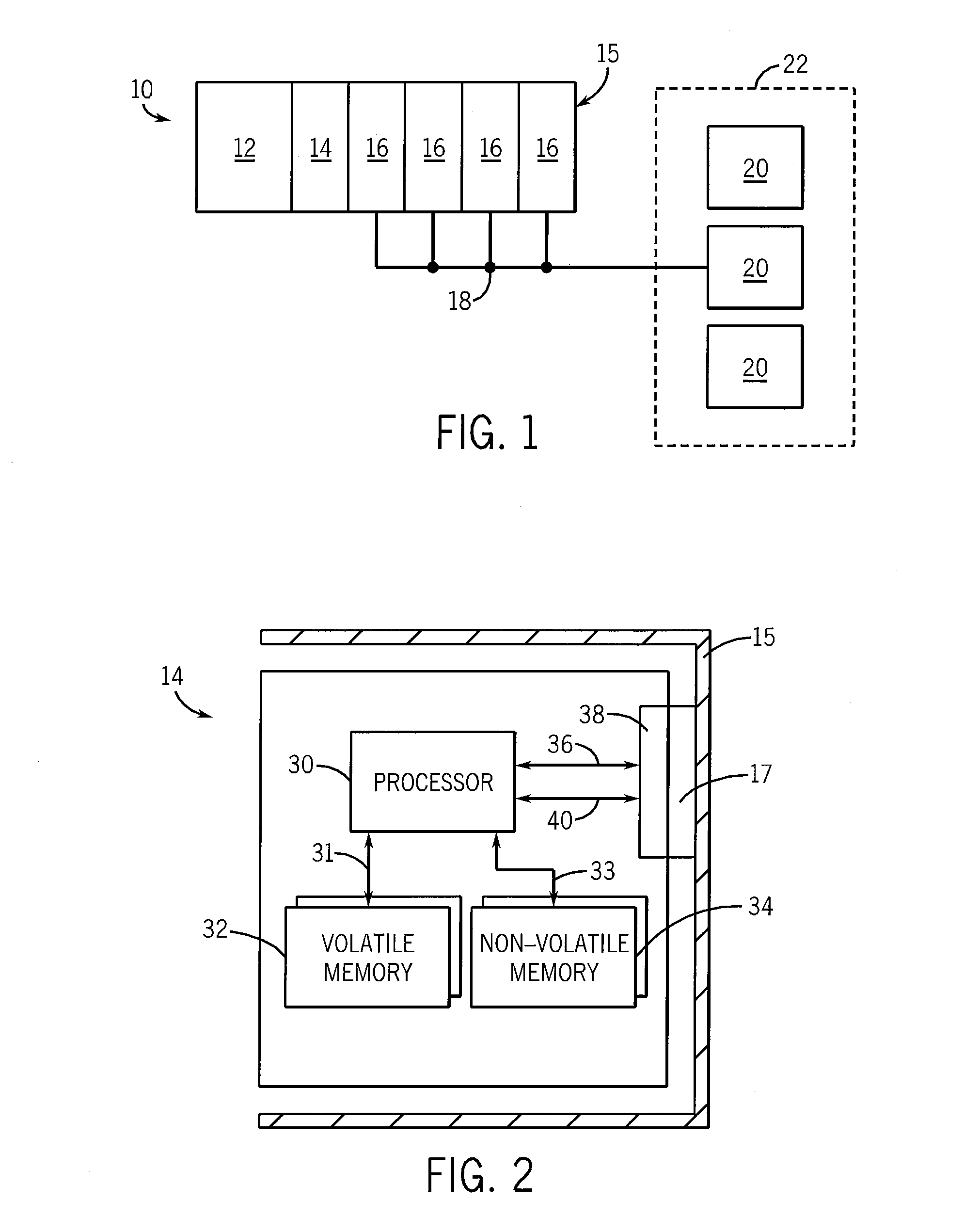
Method to Separate and Persist Static and Dynamic Portions of a Control Application
ActiveUS20110283070A1Minimal numberEasy to storeProgramme controlMemory loss protectionCapacitanceCapacitive storage
The subject matter disclosed herein describes a method of allocating and persisting memory in an industrial controller without requiring a battery backup or a large capacitive storage system. Each data object is identified as static or dynamic. Static objects are further classified by whether frequent access of that data object is required. Each of the data objects is stored in non-volatile memory. The dynamic data objects and static data objects requiring frequent access are stored in volatile memory. A record of static data objects is maintained in non-volatile memory and a record of dynamic data objects is maintained in volatile memory. Upon power loss, the present value of each dynamic data object is copied to non-volatile memory. When power is restored, the values of both the dynamic data objects and the static data objects that require frequent access at run-time are copied from non-volatile memory to volatile memory.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
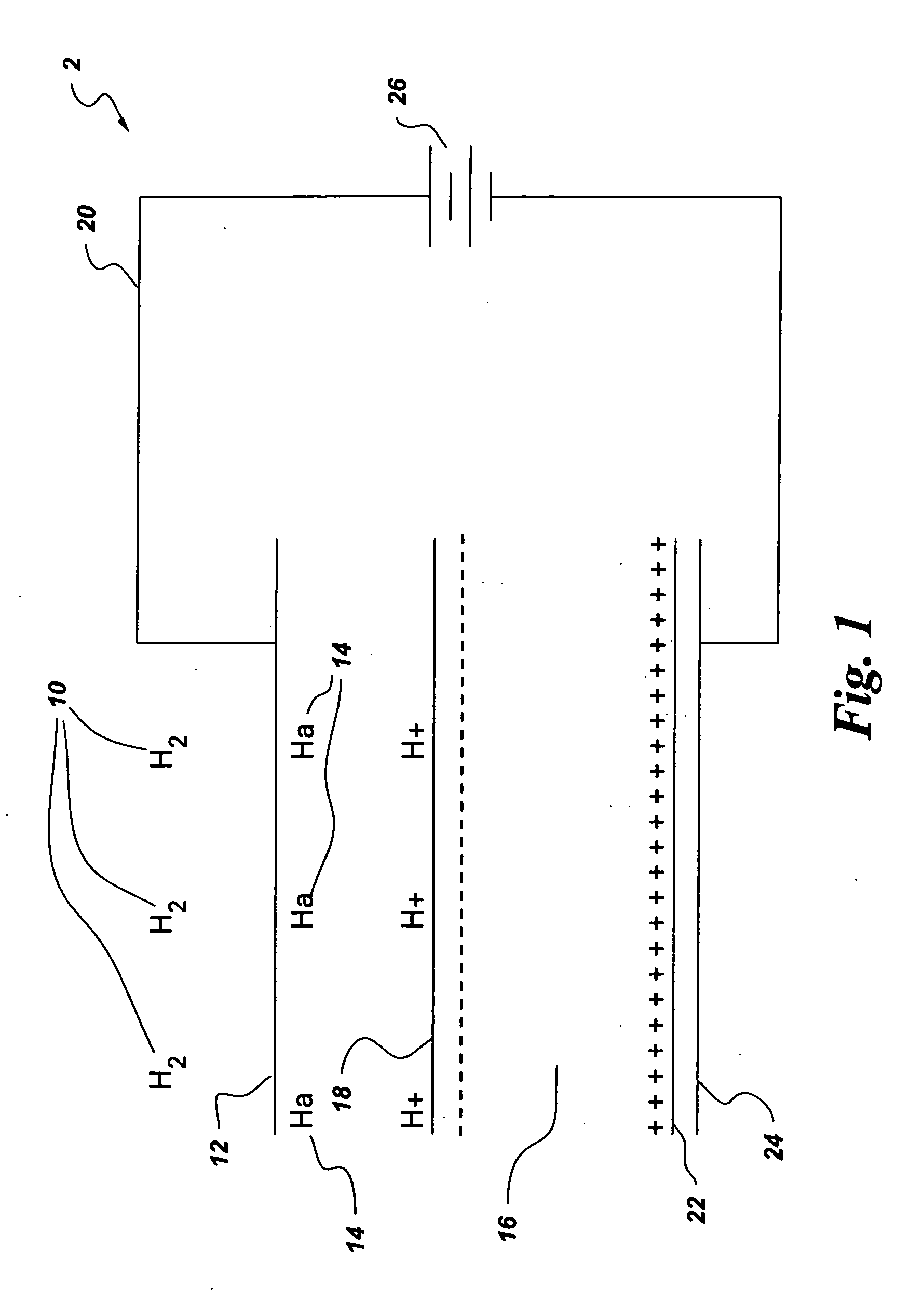
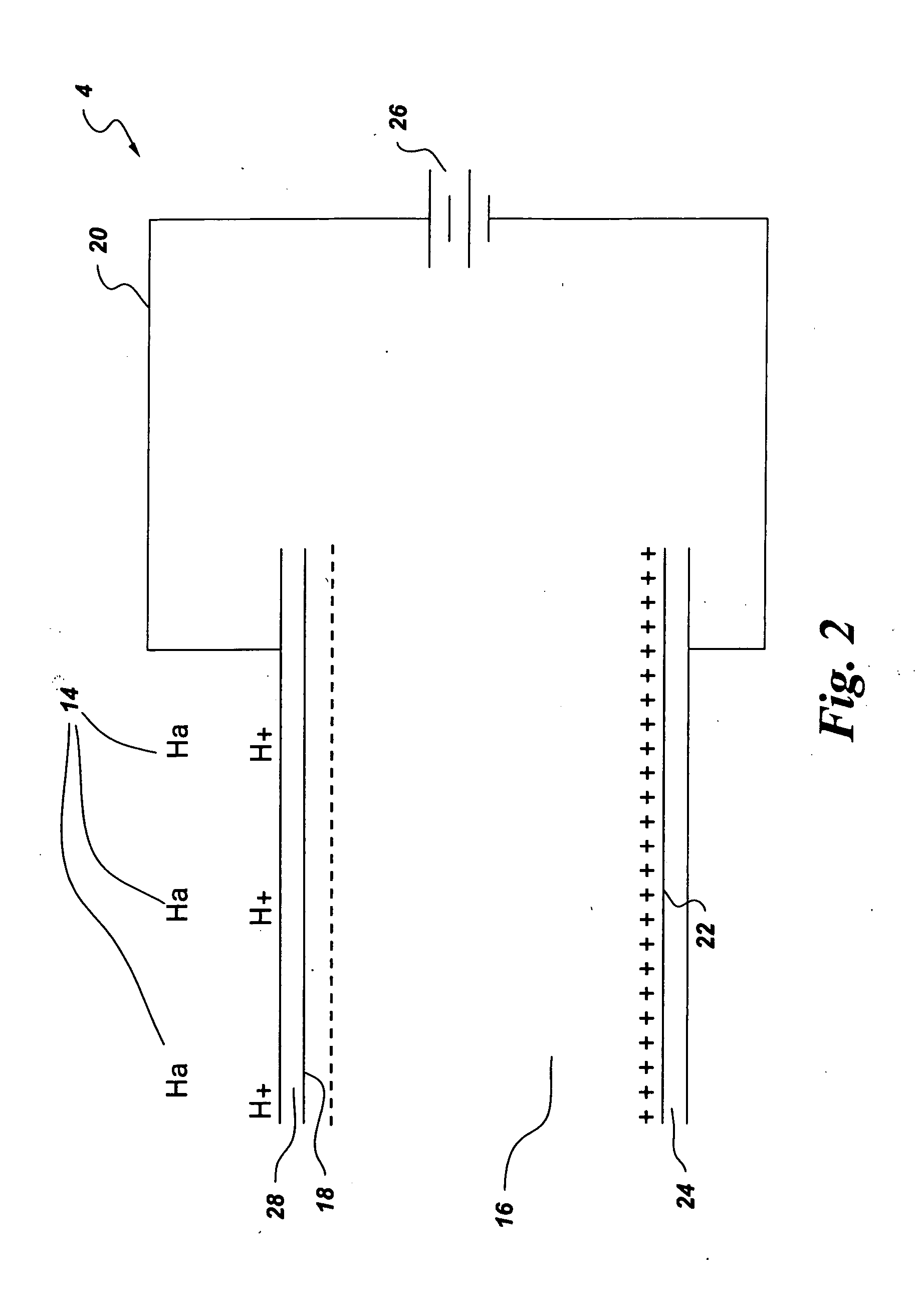
System and method for storing hydrogen and electrical energy
A hybrid capacitive storage system and method for storing electrical energy and hydrogen comprising at least a first dielectric layer, which dielectric layer is substantially impermeable to hydrogen. The hybrid storage system further comprises at least a first catalytic electrode layer disposed on at least a portion of a first surface of said first dielectric layer, which first catalytic electrode layer converts molecular hydrogen into atomic hydrogen, an electrode layer disposed on at least a portion of a second surface of said first dielectric layer, which electrode layer is selectively electrically connected to said first catalytic electrode layer; and at least one field generator for selectively applying a field to said storage system. Upon introduction of hydrogen to the storage system and activation of the at least one field generator, the hydrogen is converted to protons and electrons, wherein the electrons are permitted to flow through electrical connection to the electrode layer and the protons remain at the first catalytic electrode layer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Transmission of a power loss condition over a network
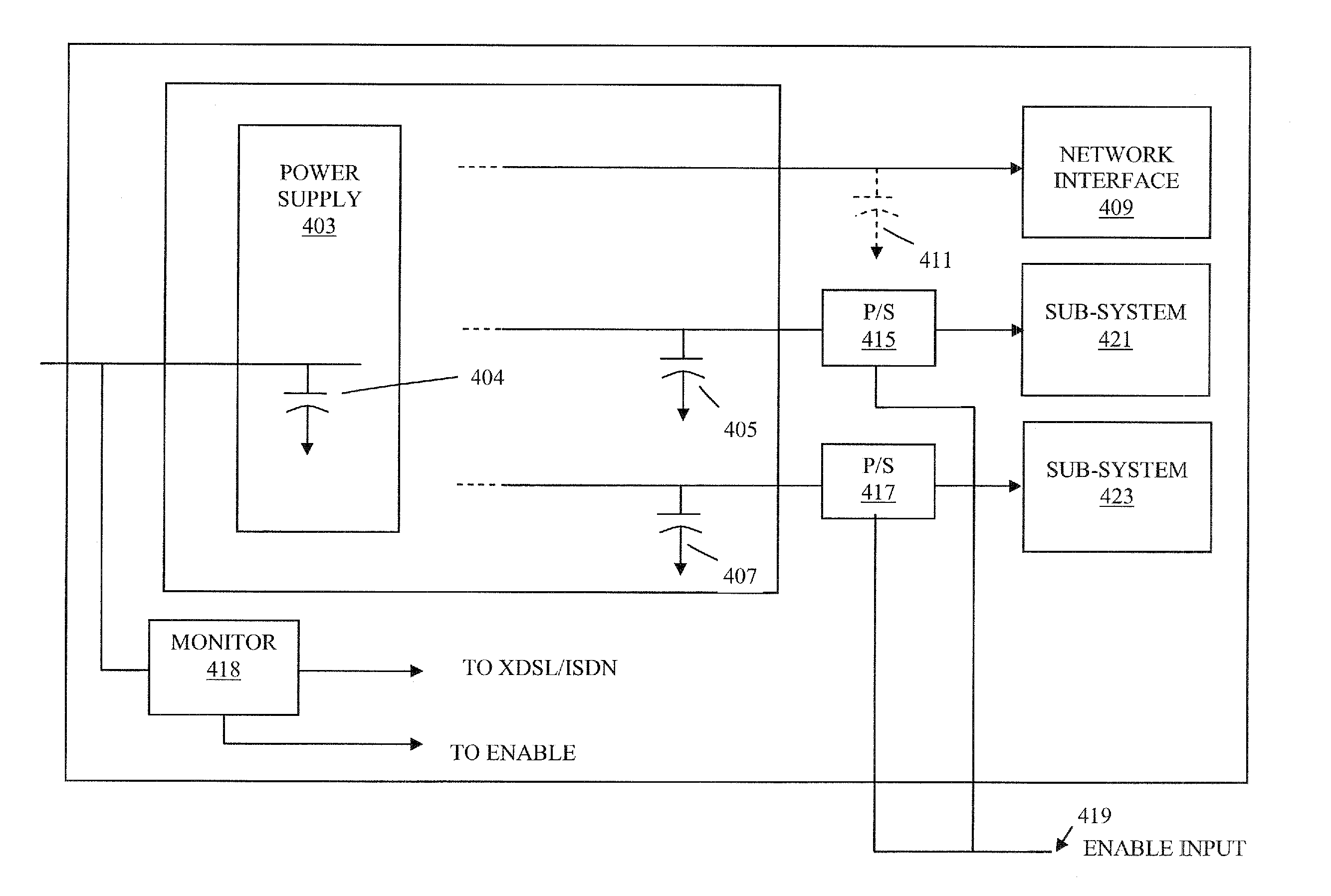
ActiveUS20080046768A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsCapacitive storage
A system is disclosed as including a power supply, a secondary capacitive storage device connected to the power supply, and multiple network devices powered by the power supply. The system further includes a designated device for transmitting a power loss condition over a network, where upon detection of an imminent interruption of power from the power supply the secondary capacitive storage device exclusively powers the designated device during transmission of the power loss condition, and the multiple network devices are intentionally powered off.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
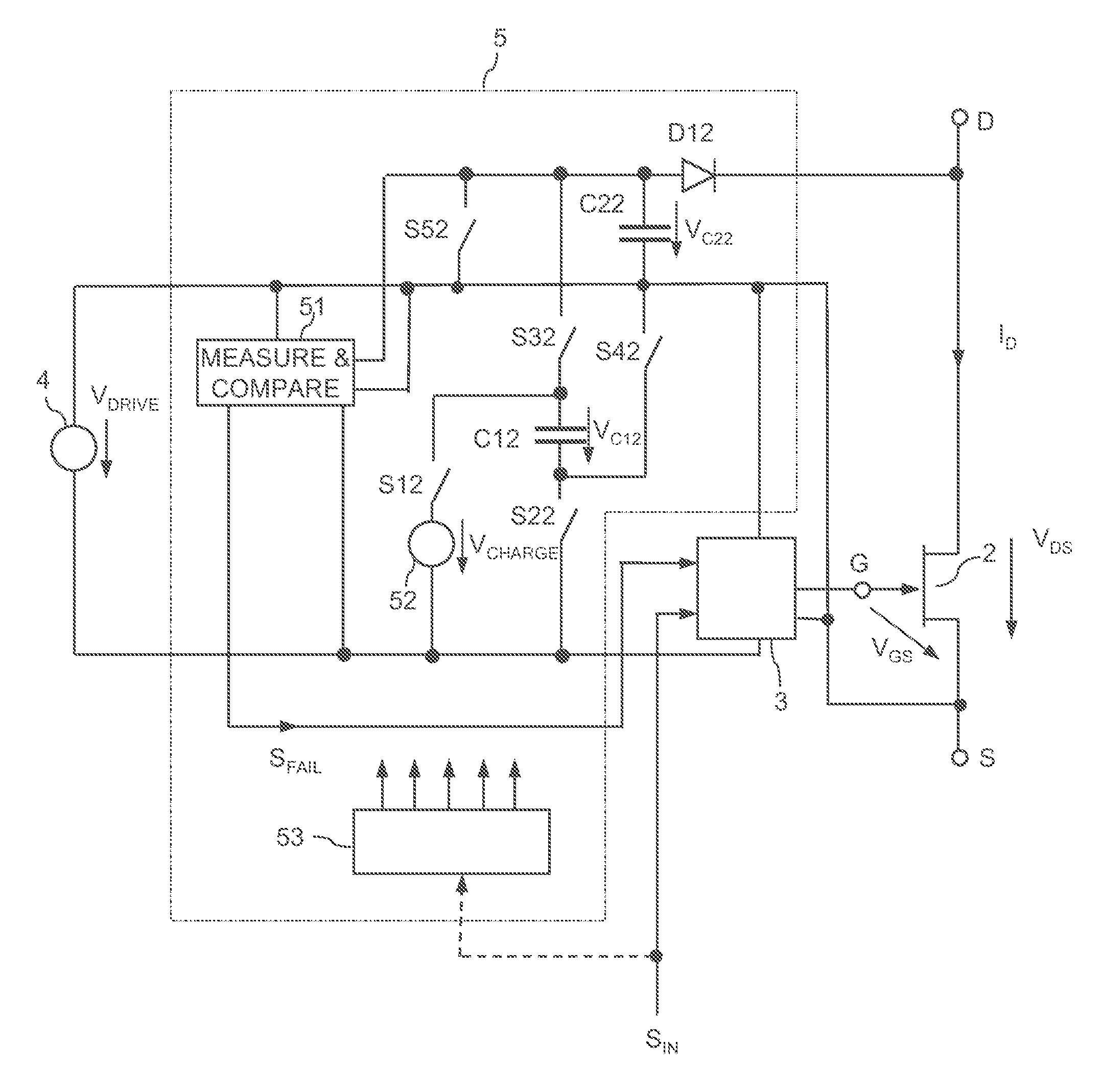
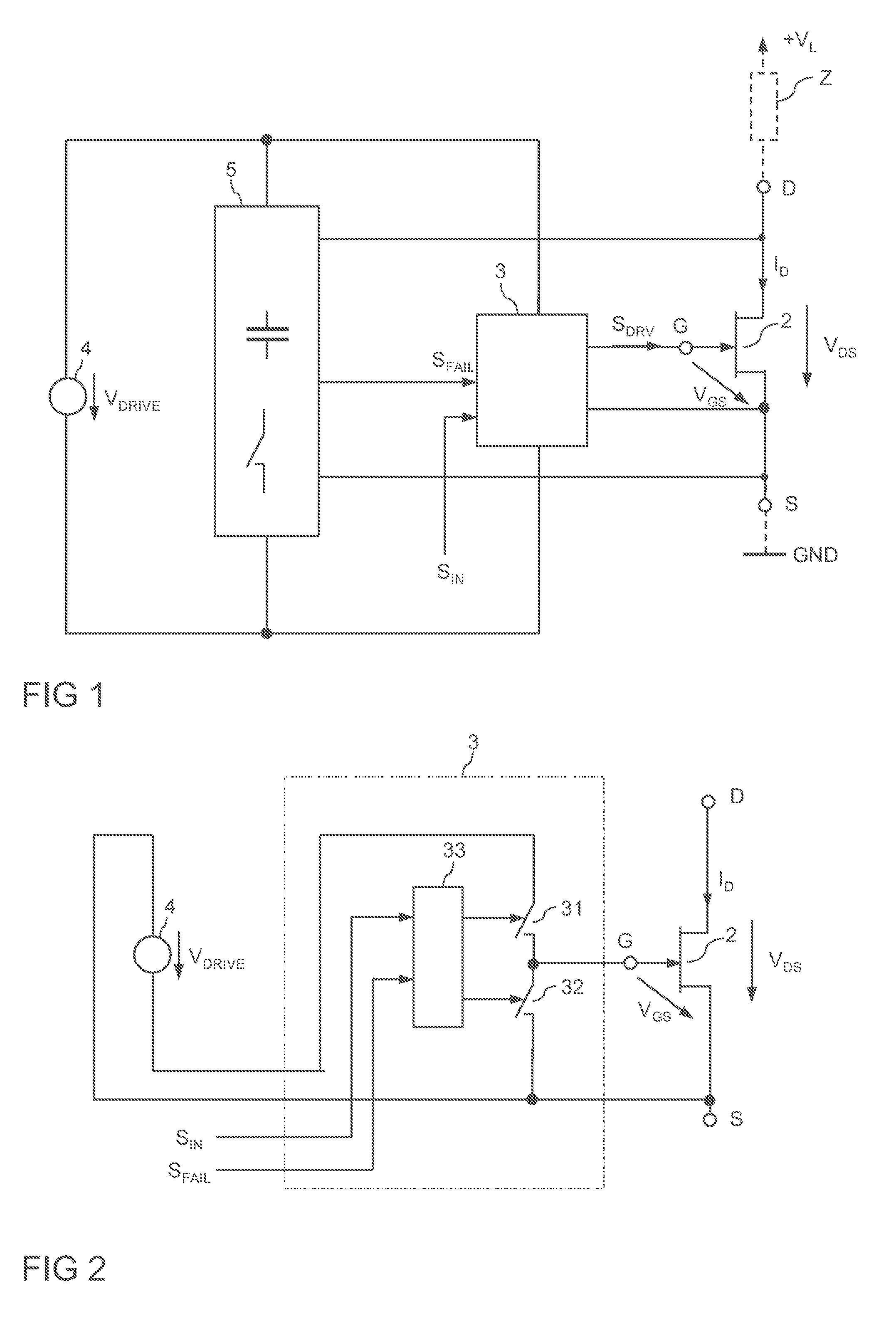
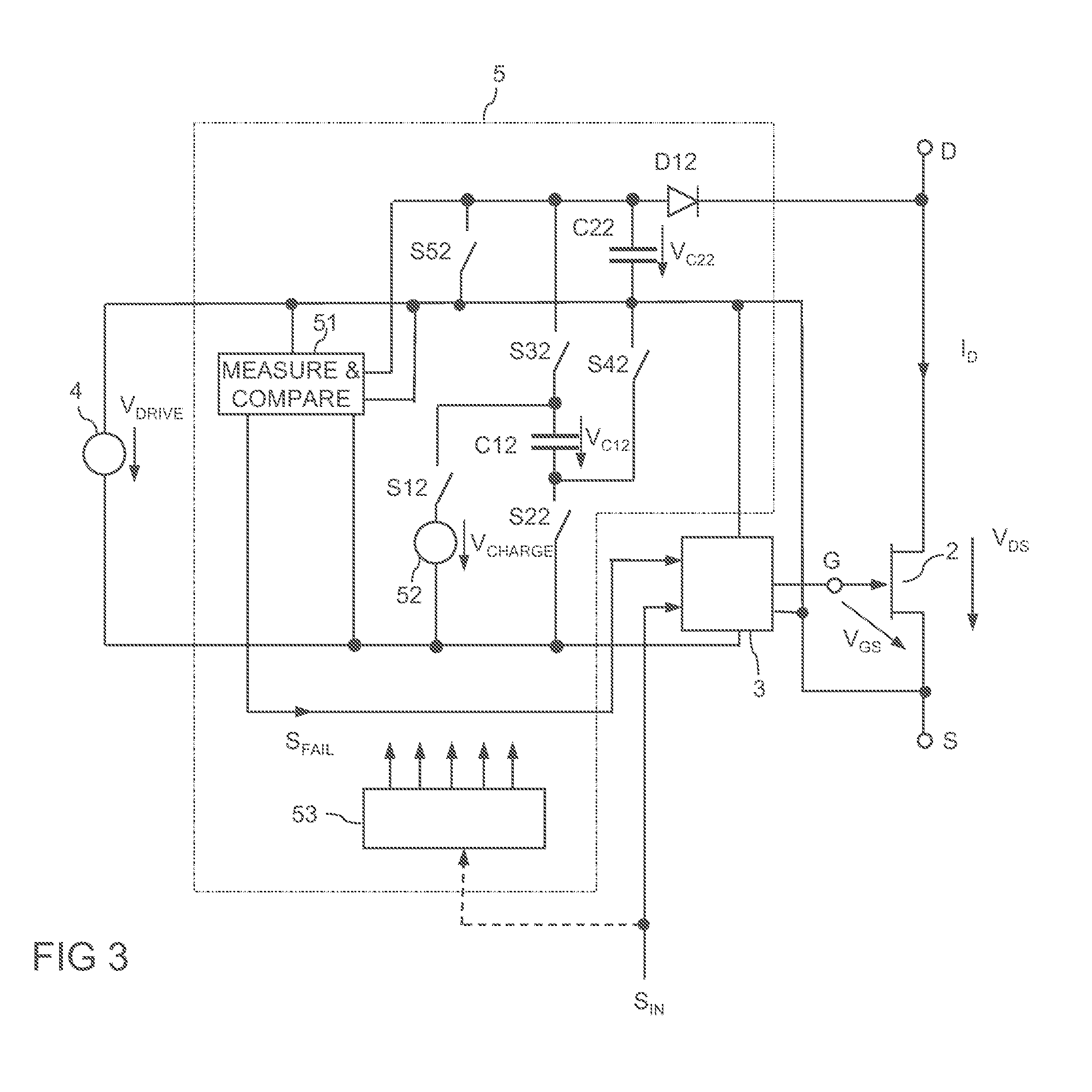
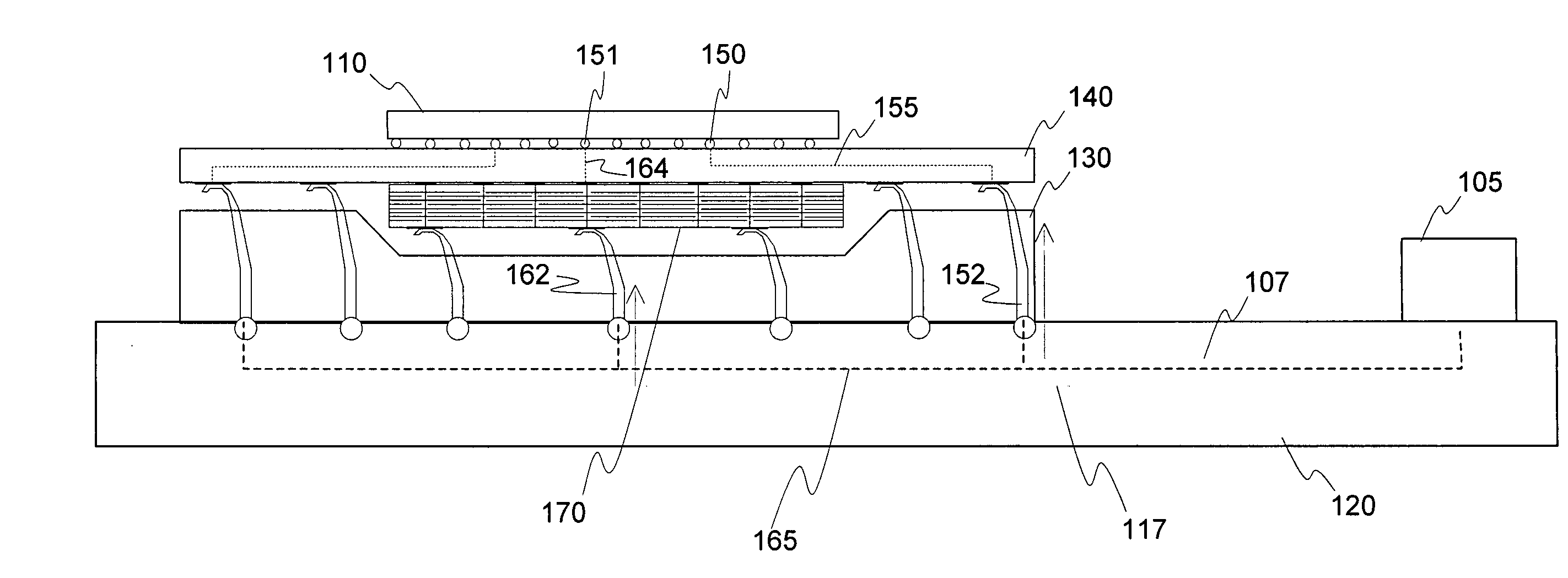
Electronic Circuit with an Electronic Switch and a Monitoring Circuit
An electronic circuit includes an electronic switch having a control terminal and a load path. A monitoring circuit includes a switched-capacitor circuit with a capacitive storage element. The switched-capacitor circuit is coupled to the load path of the electronic switch. The monitoring circuit is operable to evaluate a load voltage of the electronic switch and to generate a failure signal dependent on the evaluation. A drive circuit is operable to provide a drive signal at the control terminal of the electronic switch dependent on the failure signal.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Array capacitor with IC contacts and applications
ActiveUS20060067030A1Multiple fixed capacitorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceCapacitive storage
An apparatus comprises a first plurality of contacts on a first side of the apparatus adapted to interface with a corresponding plurality of contacts on an integrated circuit package. The apparatus further comprises a second plurality of contacts on a second side of the apparatus adapted to interface with a corresponding plurality of grid array leads and a plurality of capacitive storage structures coupled to the first and second plurality of contacts.
Owner:INTEL CORP
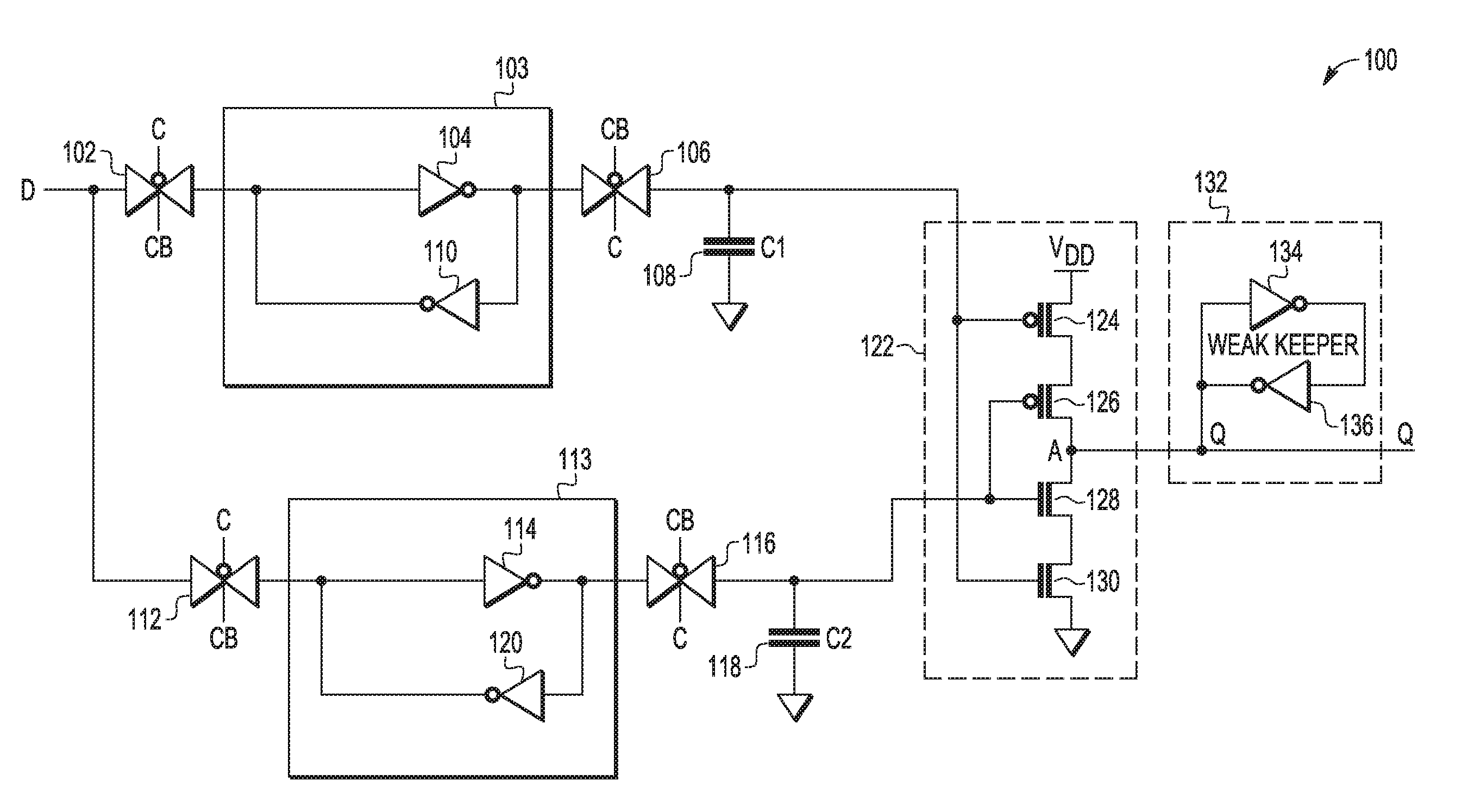
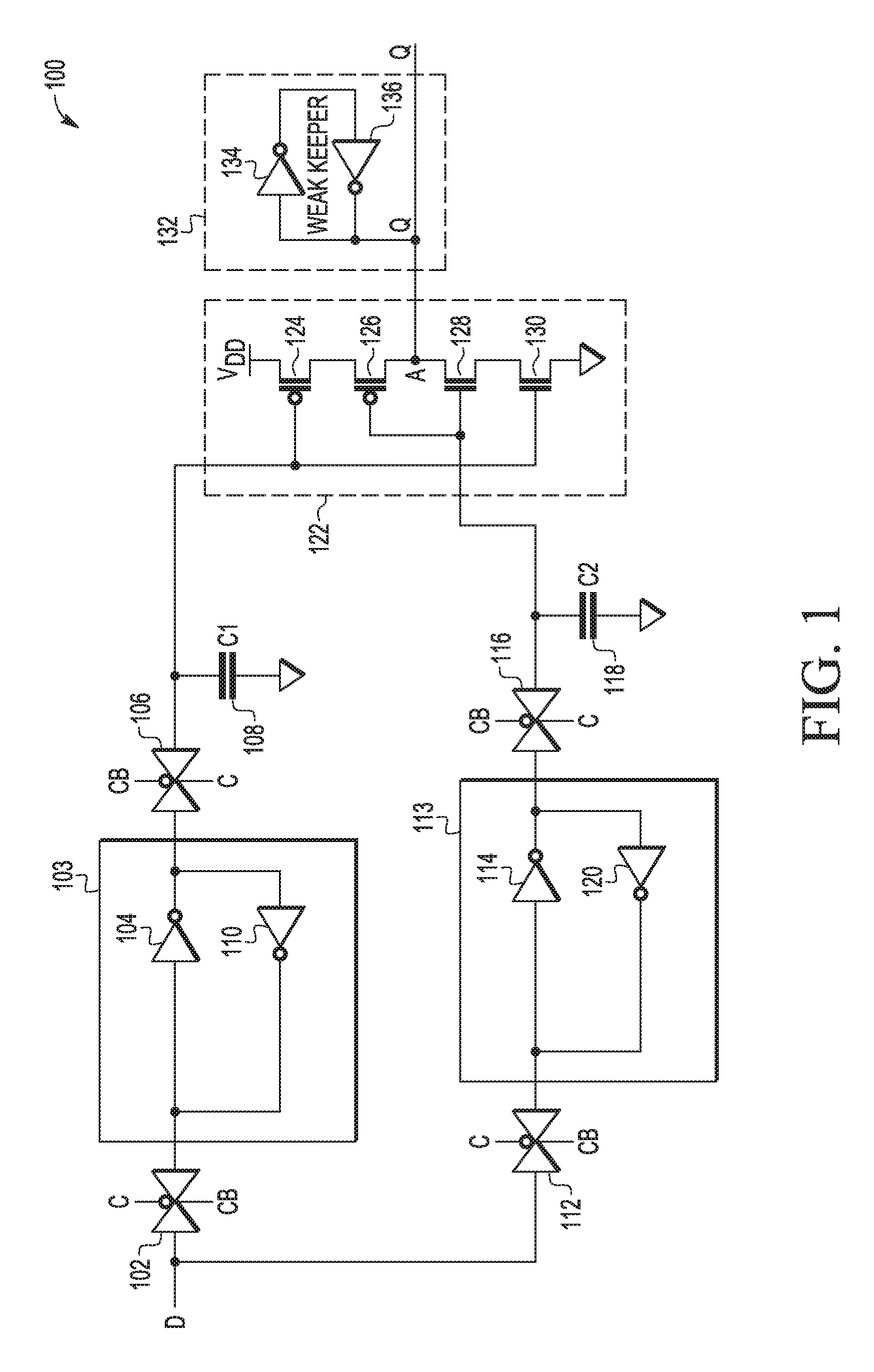
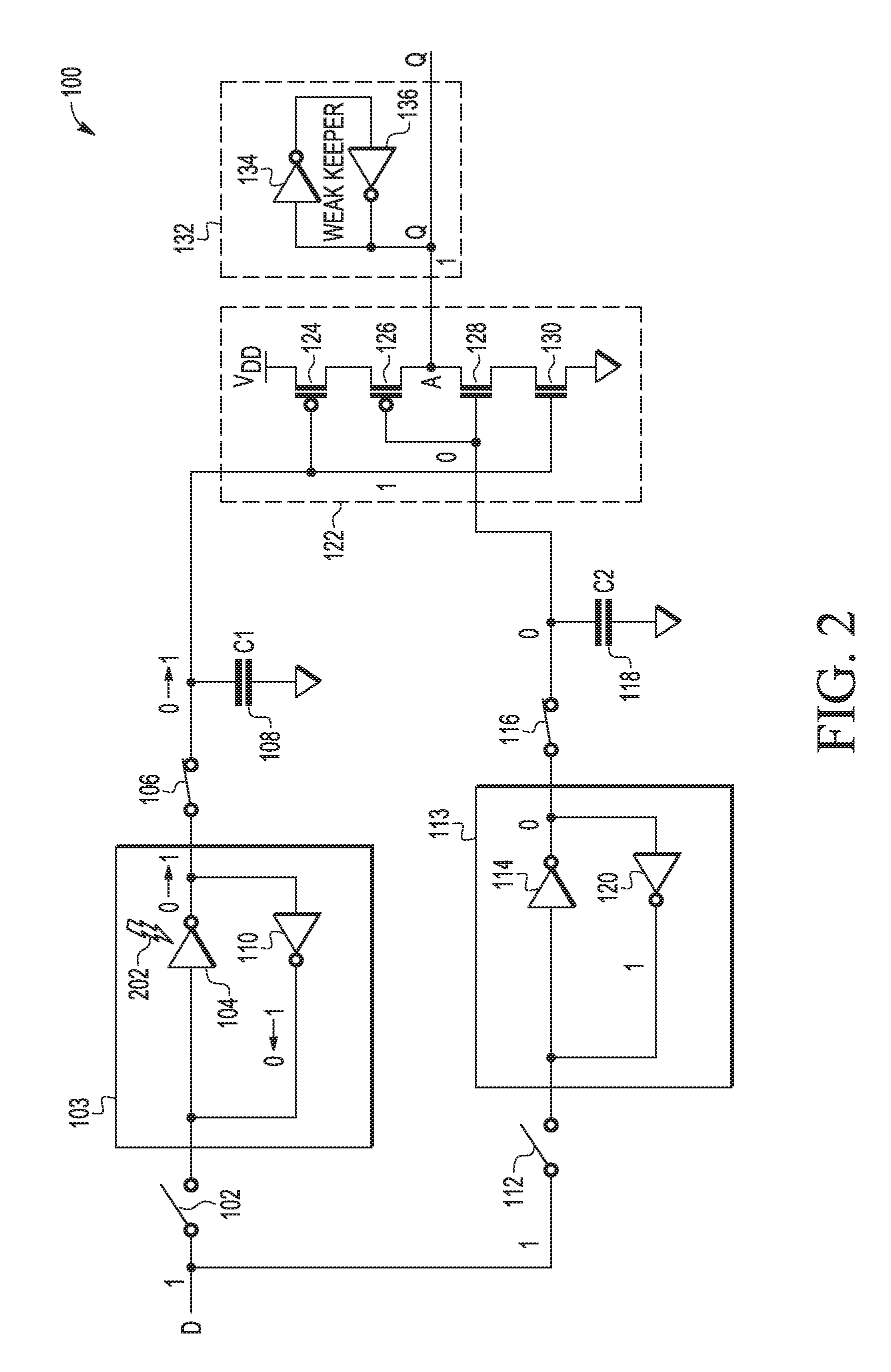
Devices and methods with capacitive storage for latch redundancy
A master slave storage circuit can include a first master portion coupled to a first master data storage node and a first slave portion coupled to a first slave data storage node. The first master portion can comprise one of a first master latch or a first master capacitive element coupled to the first master data storage node and the first slave portion comprises one of a first slave latch or a first slave capacitive element coupled to the first slave data storage node. If the first master portion comprises the first master latch, the first slave portion comprises the first slave capacitive element, and if the first master portion comprises the first master capacitive element, the first slave portion comprises the first slave latch.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Power Scheme for Implant Stimulators on the Human or Animal Body
A power scheme for an implant on a human or animal body comprises: a charging circuit to provide power to deliver controlled stimulation currents to a body tissue; a capacitive storage arrangement connected with the charging circuit and charged by the charging circuit; a shunting arrangement to limit voltage on the capacitive storage arrangement; a driver array configured to transfer charges from the capacitive storage arrangement to the tissue; and an electrode array connected with the driver array and the tissue.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Driving device and method for driving a load, in particular an LED assembly
ActiveCN103460800AReduce voltageCases without significantly changing loadElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentCapacitance
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
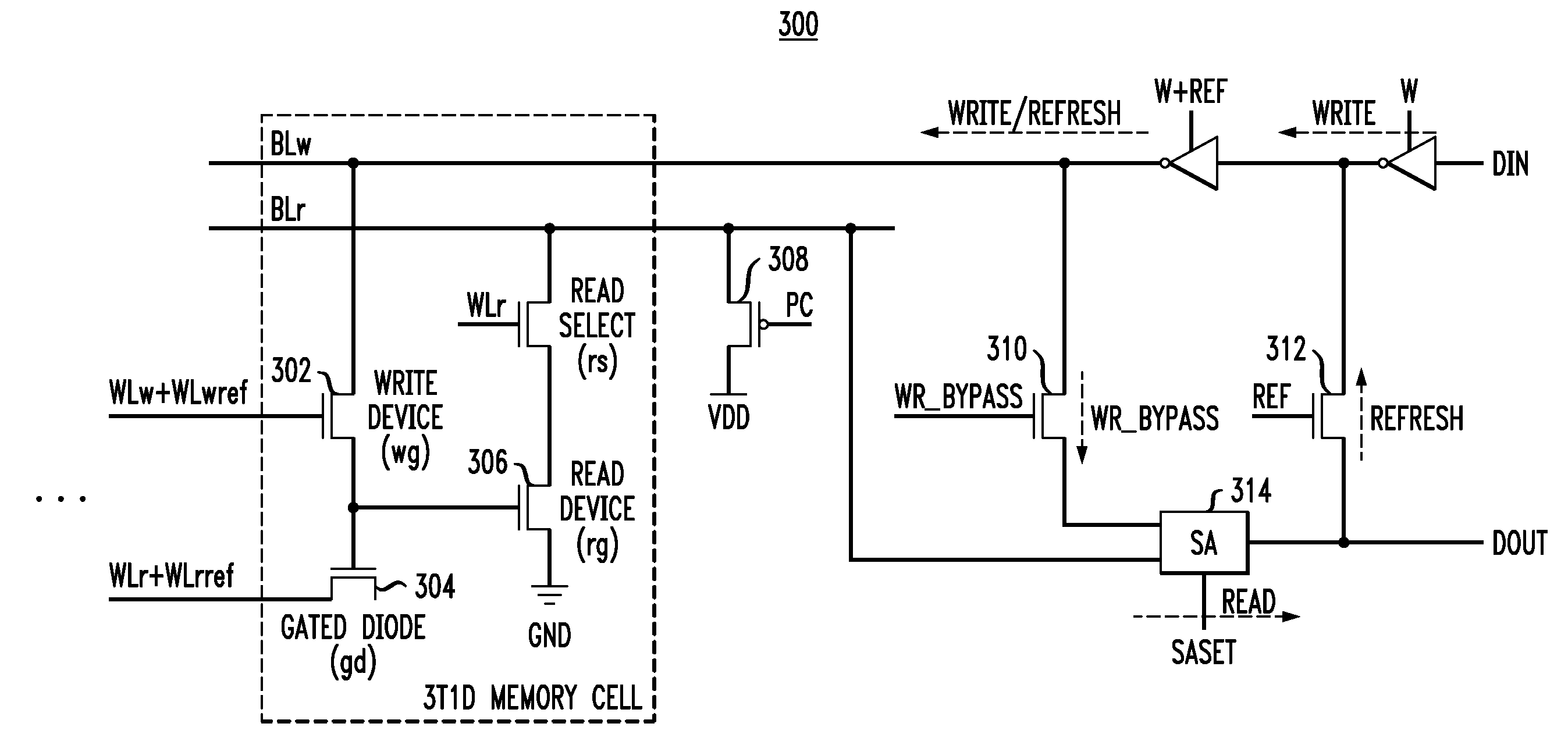
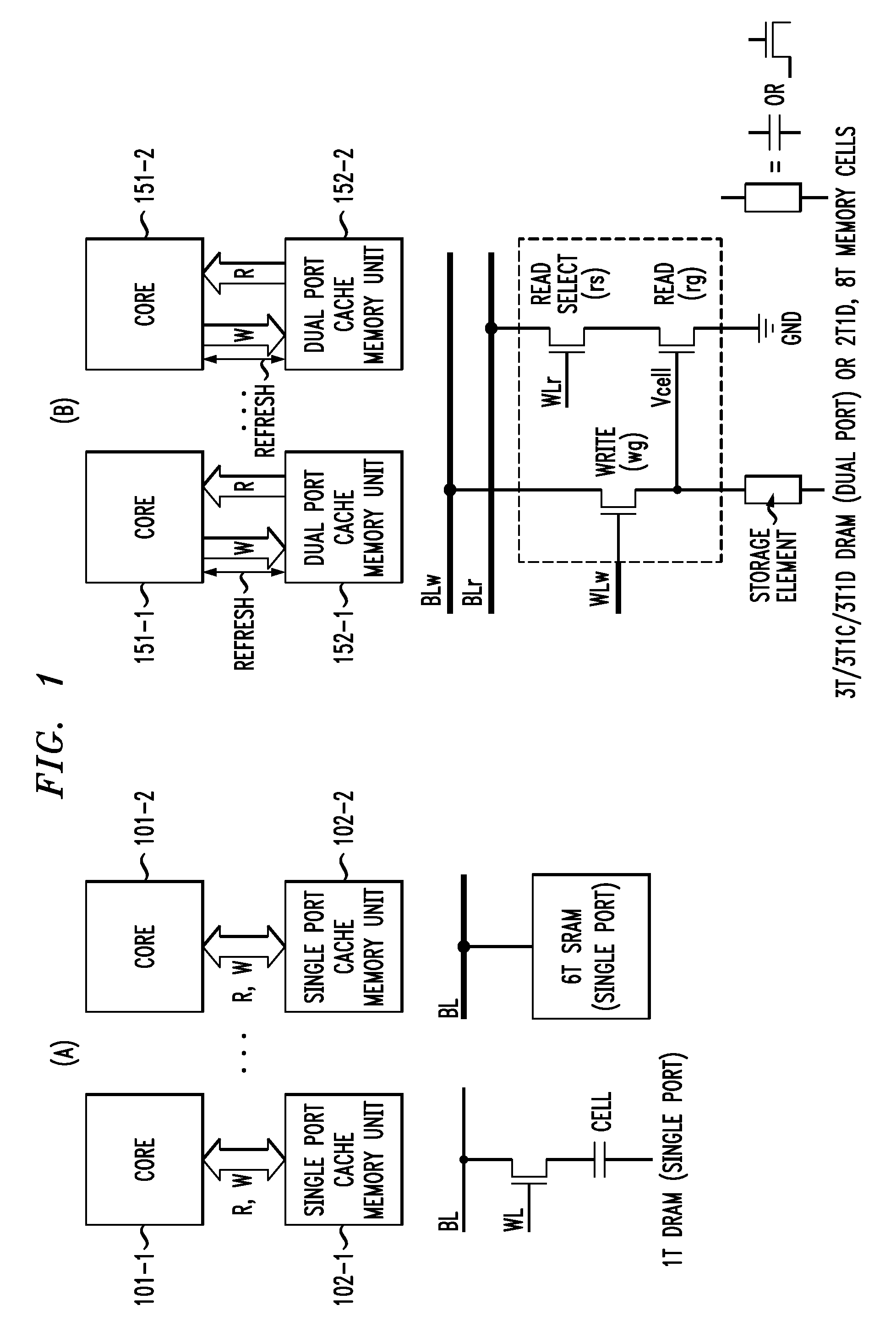
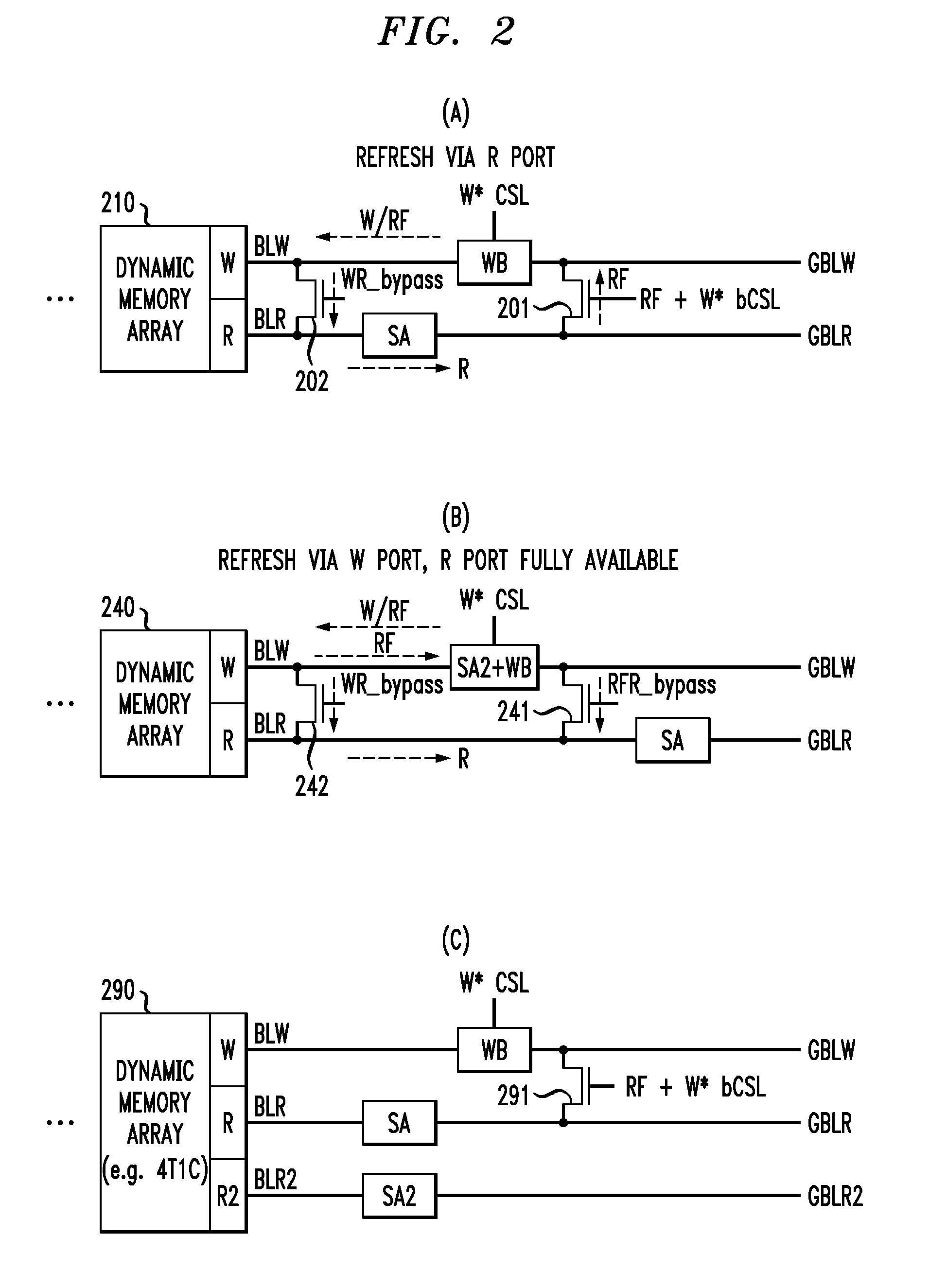
Multi-port dynamic memory structures
A dynamic random access memory circuit has at least one write bit line, at least one read bit line, a capacitive storage device, a write access device operatively coupled to the capacitive storage device and the at least one write bit line, a sense amplifier operatively coupled to the at least one read bit line and configured to generate an output signal, and a refresh bypass device operatively associated with the sense amplifier and the at least one write bit line so as to selectively pass the output signal to the at least one write bit line.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
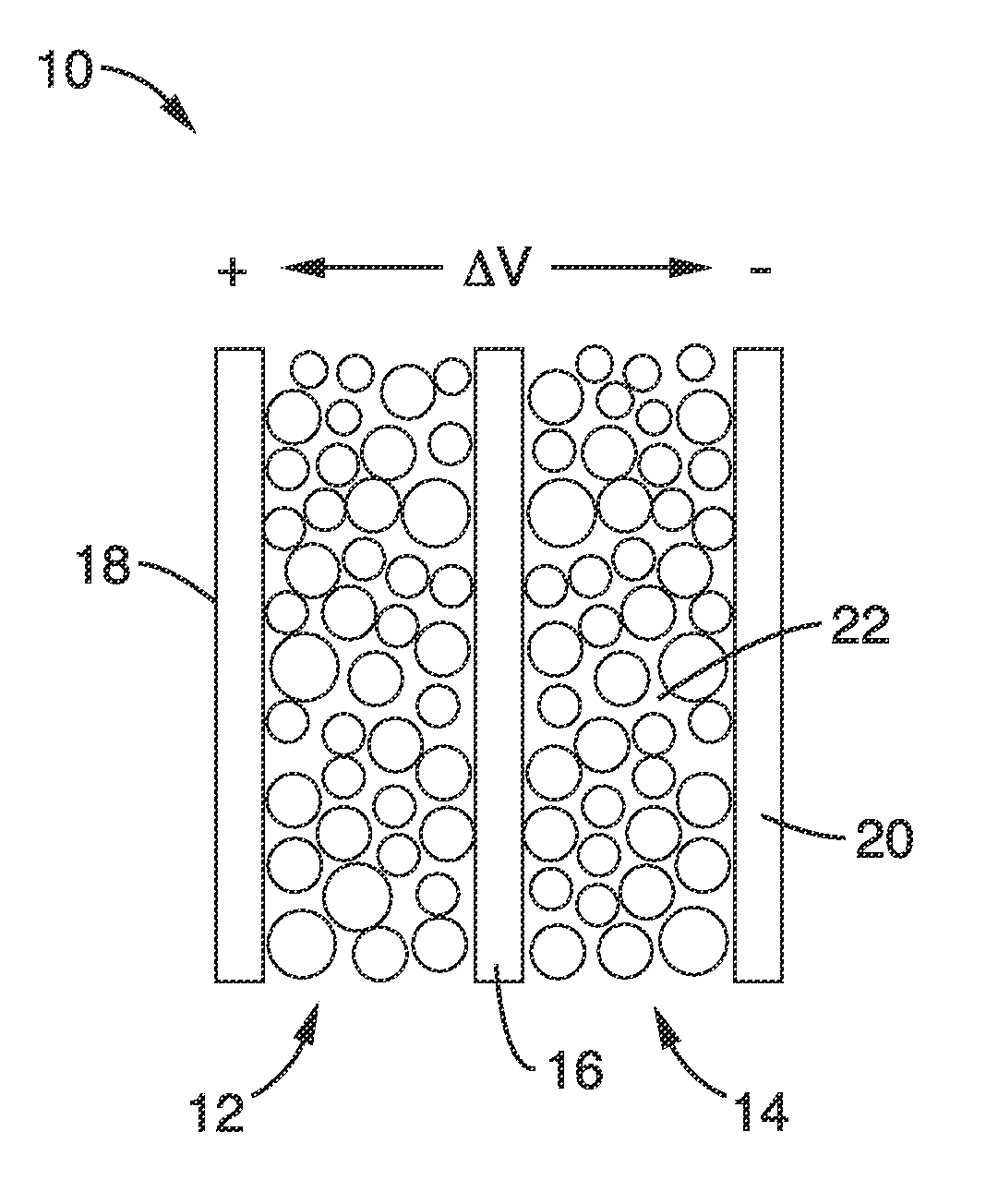
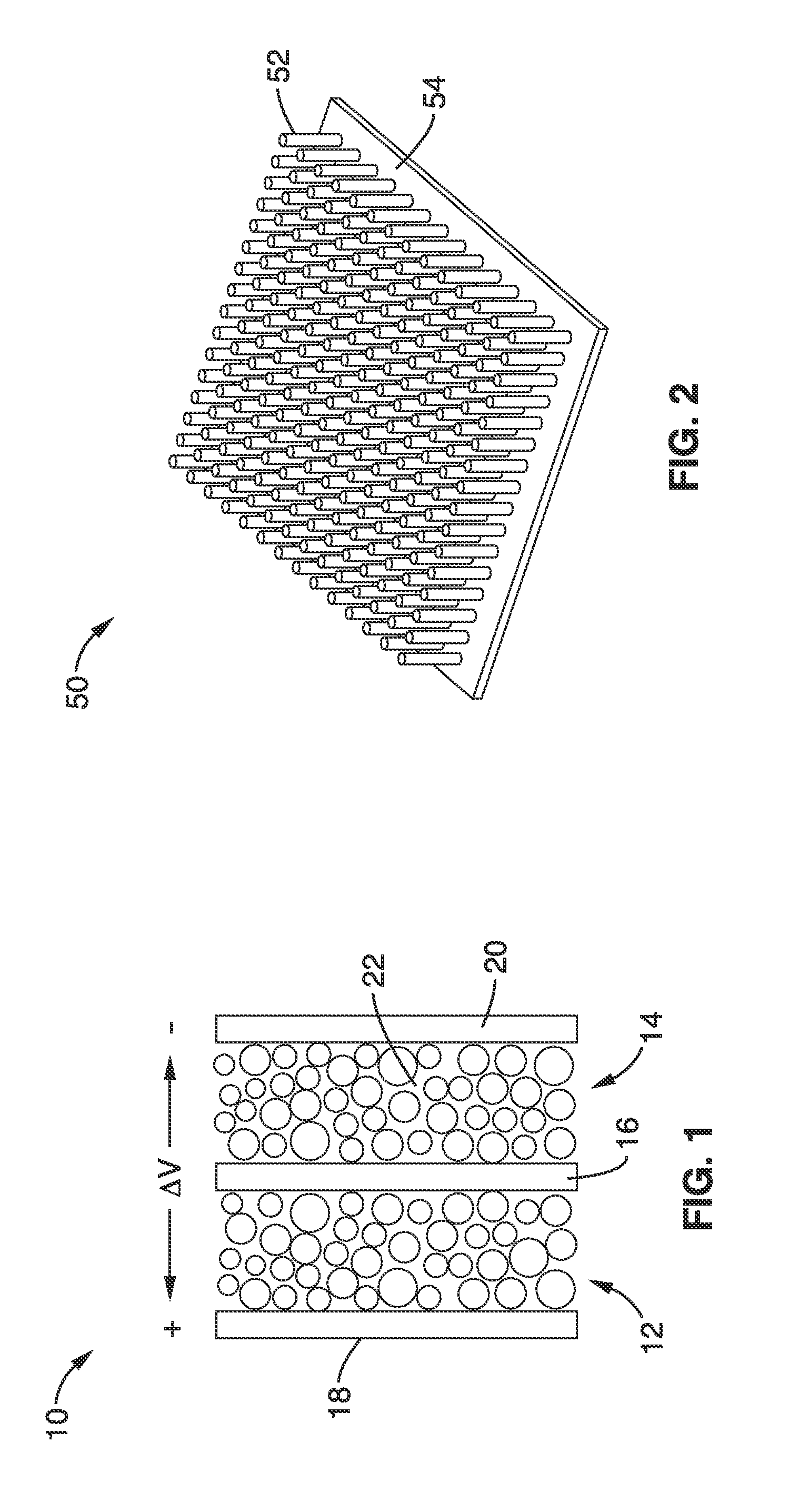
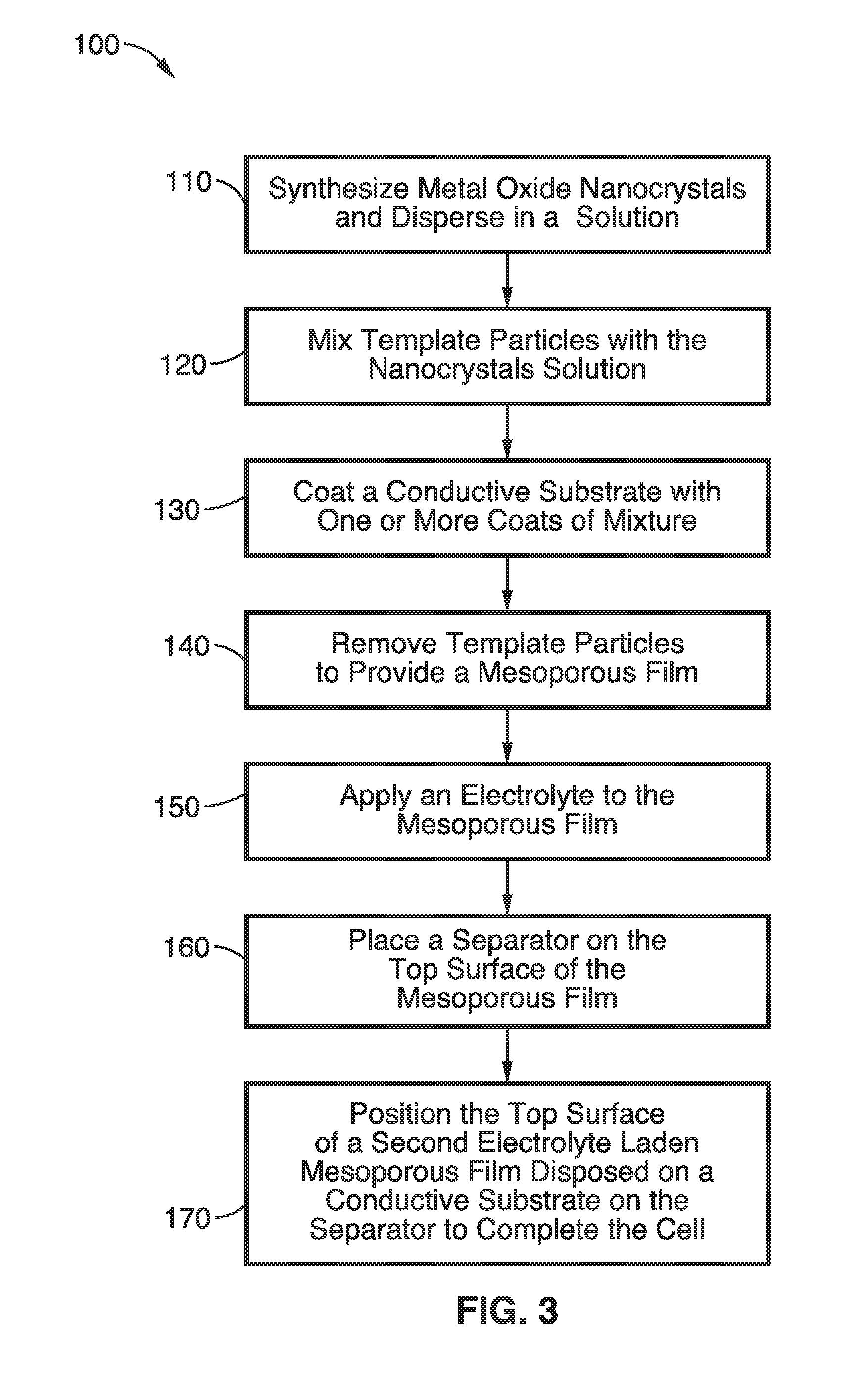
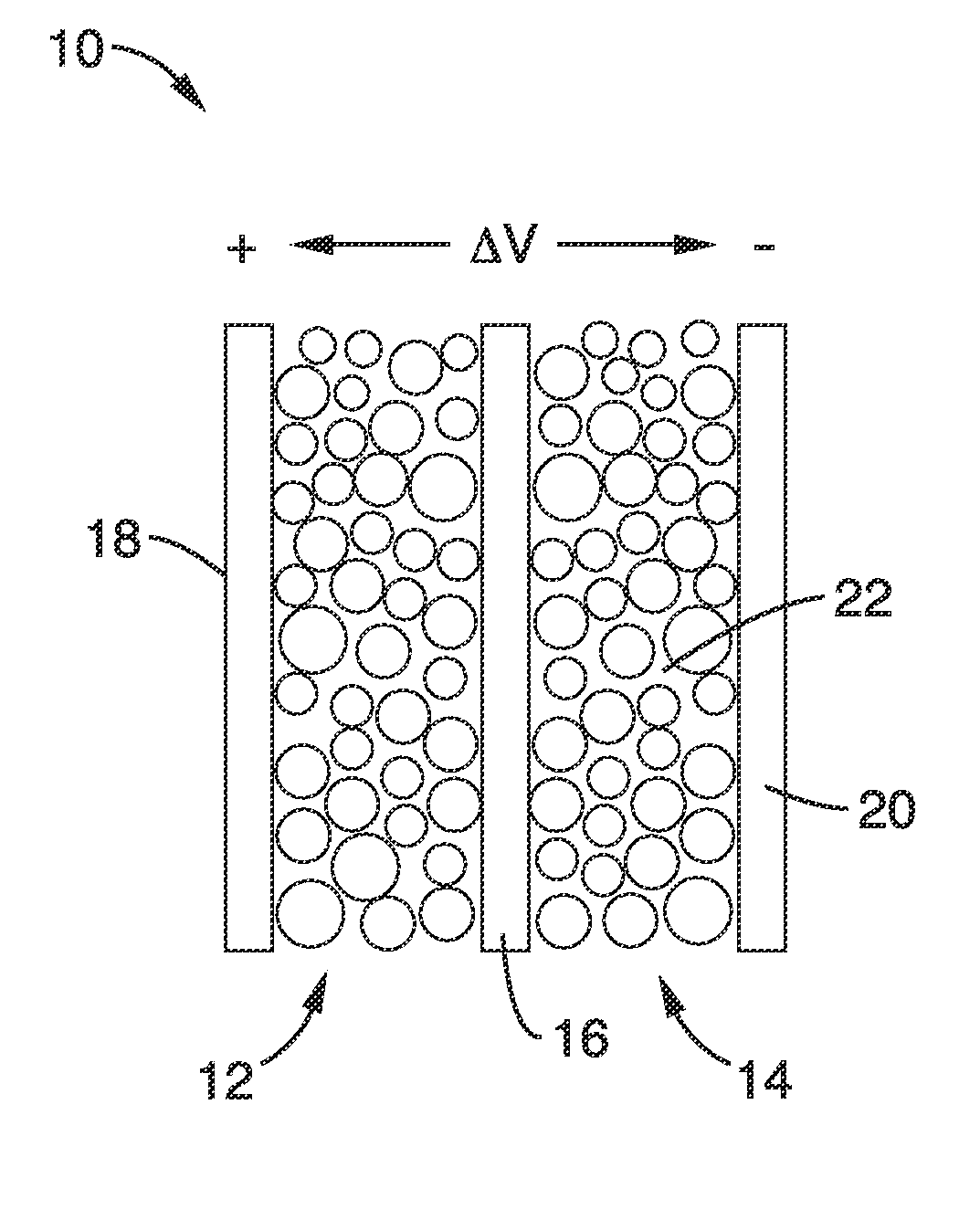
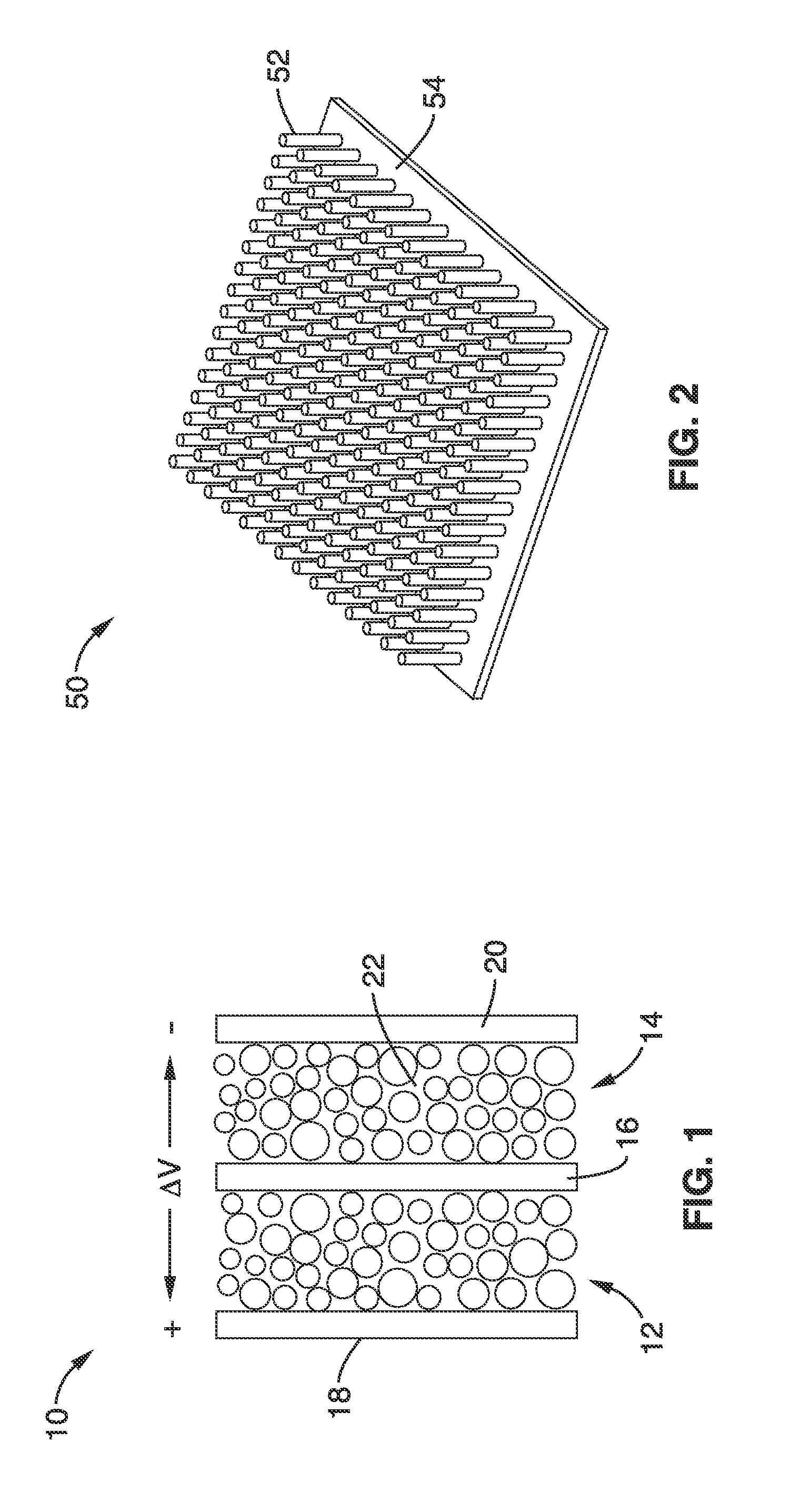
Mesoporous nanocrystalline film architecture for capacitive storage devices
ActiveUS20120026644A1Without energy densityHigh rateNanotechHybrid capacitor electrodesCapacitanceCapacitive storage
A mesoporous, nanocrystalline, metal oxide construct particularly suited for capacitive energy storage that has an architecture with short diffusion path lengths and large surface areas and a method for production are provided. Energy density is substantially increased without compromising the capacitive charge storage kinetics and electrode demonstrates long term cycling stability. Charge storage devices with electrodes using the construct can use three different charge storage mechanisms immersed in an electrolyte: (1) cations can be stored in a thin double layer at the electrode / electrolyte interface (non-faradaic mechanism); (2) cations can interact with the bulk of an electroactive material which then undergoes a redox reaction or phase change, as in conventional batteries (faradaic mechanism); or (3) cations can electrochemically adsorb onto the surface of a material through charge transfer processes (faradaic mechanism).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Switched reluctance and PM brushless DC motor drive control for electric vehicle application
InactiveUS8716961B2Enhanced electromagnetic torque operation of machineDc motor stoppersAsynchronous induction motorsCapacitive storageElectrical battery
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
Mesoporous nanocrystalline film architecture for capacitive storage devices
ActiveUS8675346B2Without energy densityHigh rateNanotechLiquid electrolytic capacitorsCapacitancePath length
A mesoporous, nanocrystalline, metal oxide construct particularly suited for capacitive energy storage that has an architecture with short diffusion path lengths and large surface areas and a method for production are provided. Energy density is substantially increased without compromising the capacitive charge storage kinetics and electrode demonstrates long term cycling stability. Charge storage devices with electrodes using the construct can use three different charge storage mechanisms immersed in an electrolyte: (1) cations can be stored in a thin double layer at the electrode / electrolyte interface (non-faradaic mechanism); (2) cations can interact with the bulk of an electroactive material which then undergoes a redox reaction or phase change, as in conventional batteries (faradaic mechanism); or (3) cations can electrochemically adsorb onto the surface of a material through charge transfer processes (faradaic mechanism).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Driving device and method for driving a load, in particular an LED assembly
ActiveUS8917027B2Improve performanceMore cost-effectiveElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentCapacitance
Driver device and a corresponding driving method for driving a load, in particular an LED assembly comprising one or more LEDs. To provide a better performance, better cost-efficiency, improved power factor and reduced losses, a driver device (1,1′, 2, 2′) is provided comprising a rectifier unit (10) for rectifying a received AC supply voltage (VS), load terminals (20) for providing a drive voltage (VL) and / or a drive current (IL) for driving said load, a capacitive storage unit (30) coupled between said rectifier unit and said load terminals for storing electrical energy provided by said rectifier unit and providing electrical energy to said load, and a bridge switching unit (40) coupled between said rectifier unit and said load for switching said capacitive storage unit into a load current path from said rectifier unit to said load terminals with a desired polarity and for switching said capacitive storage unit out of said load current path.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com