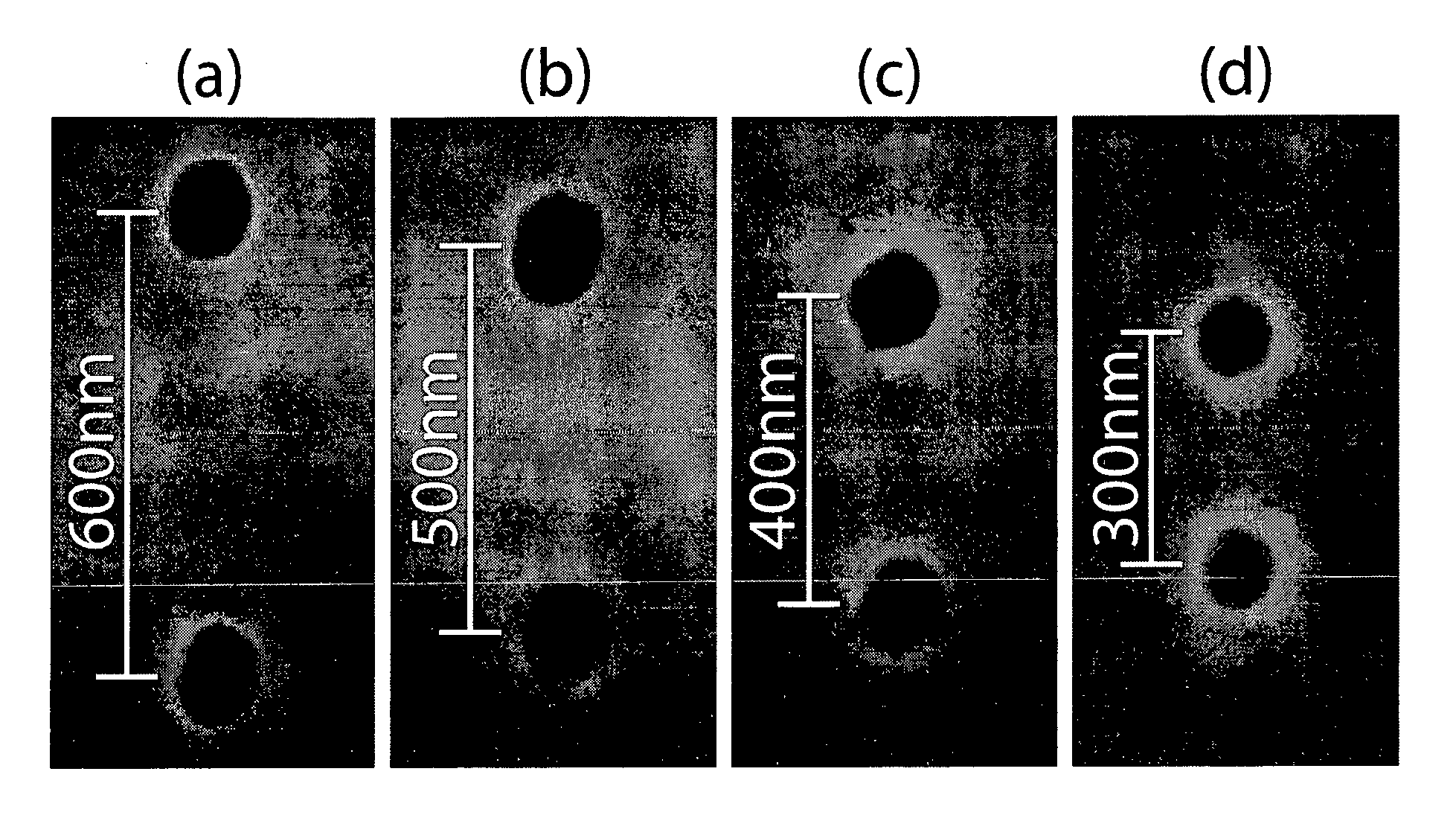
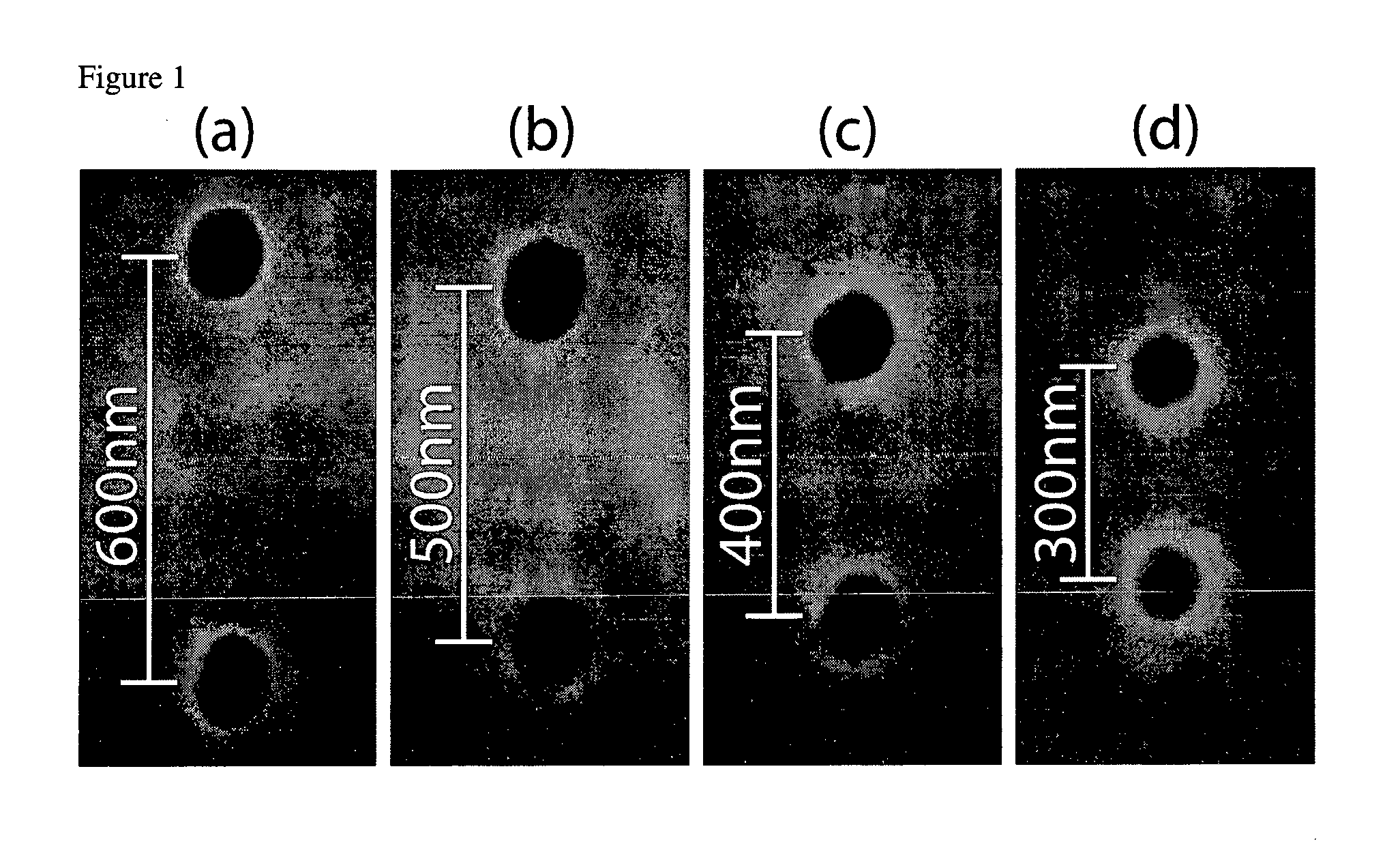
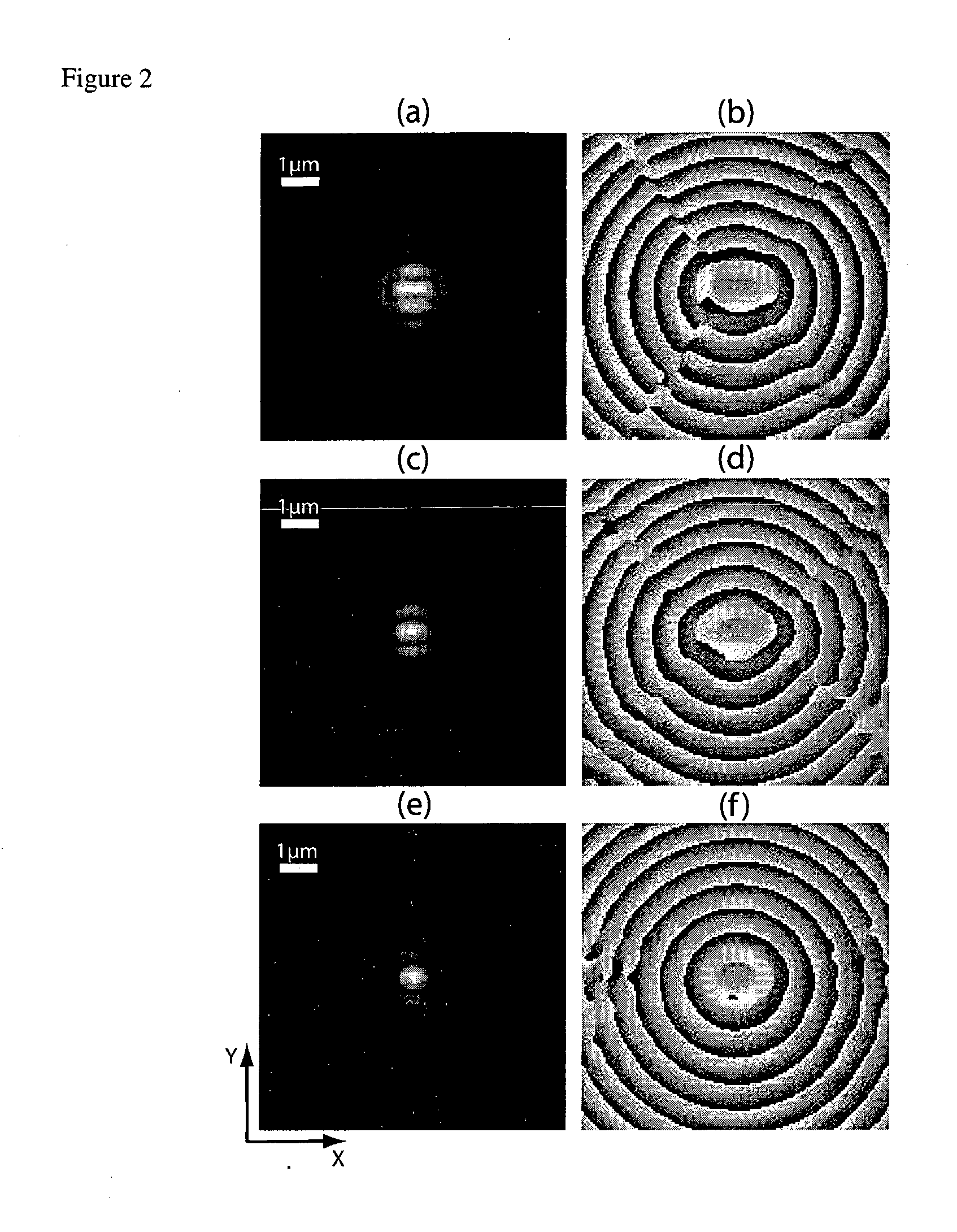
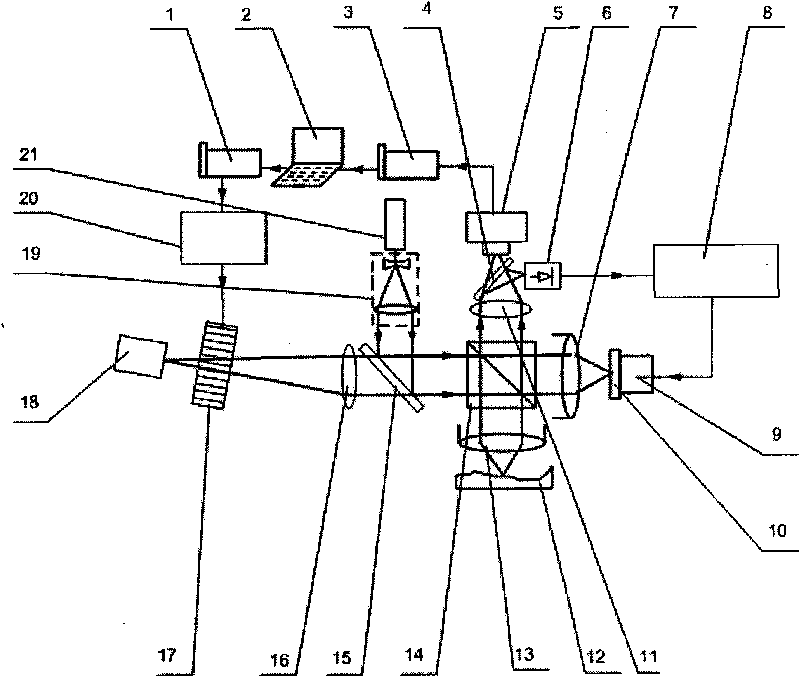
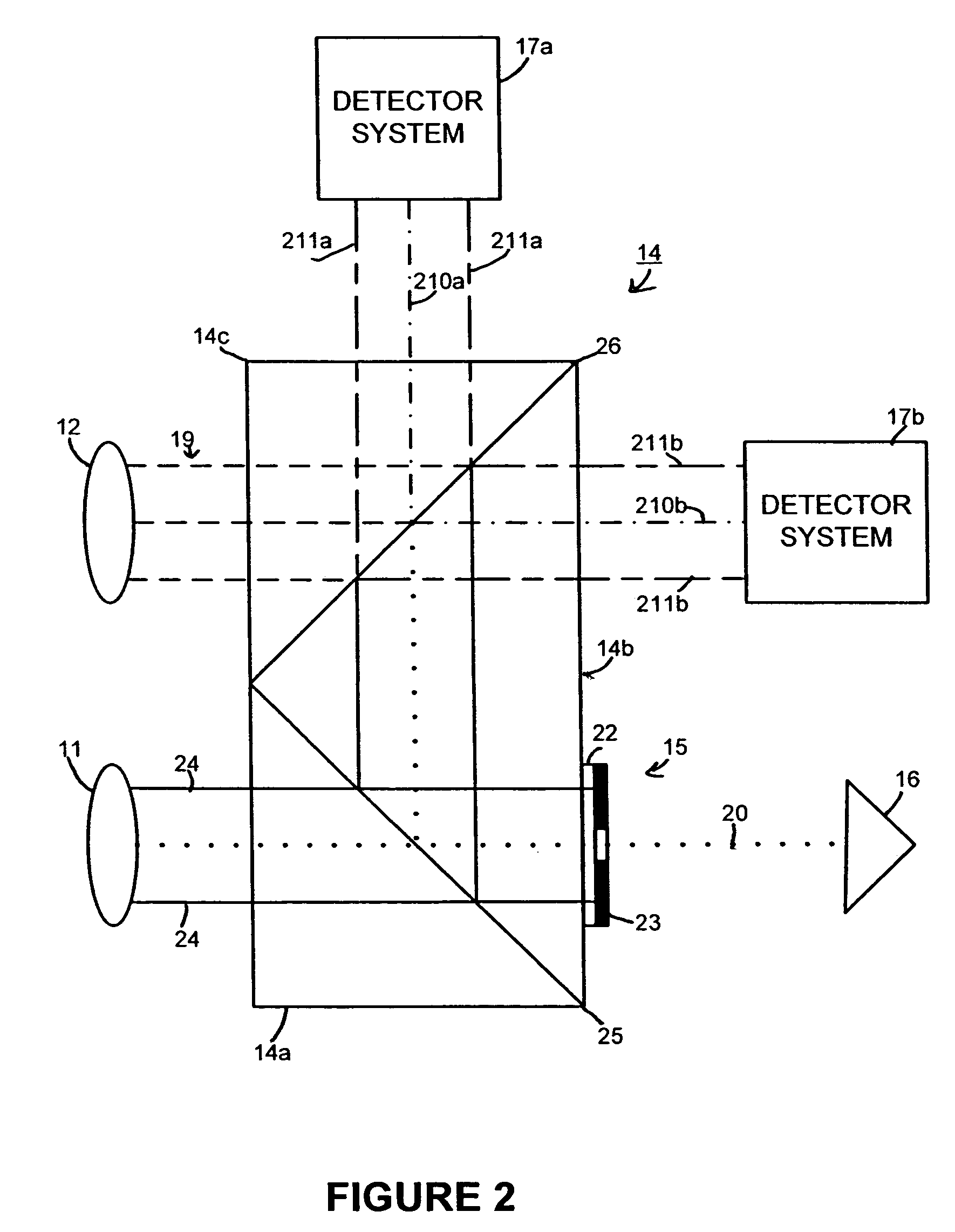
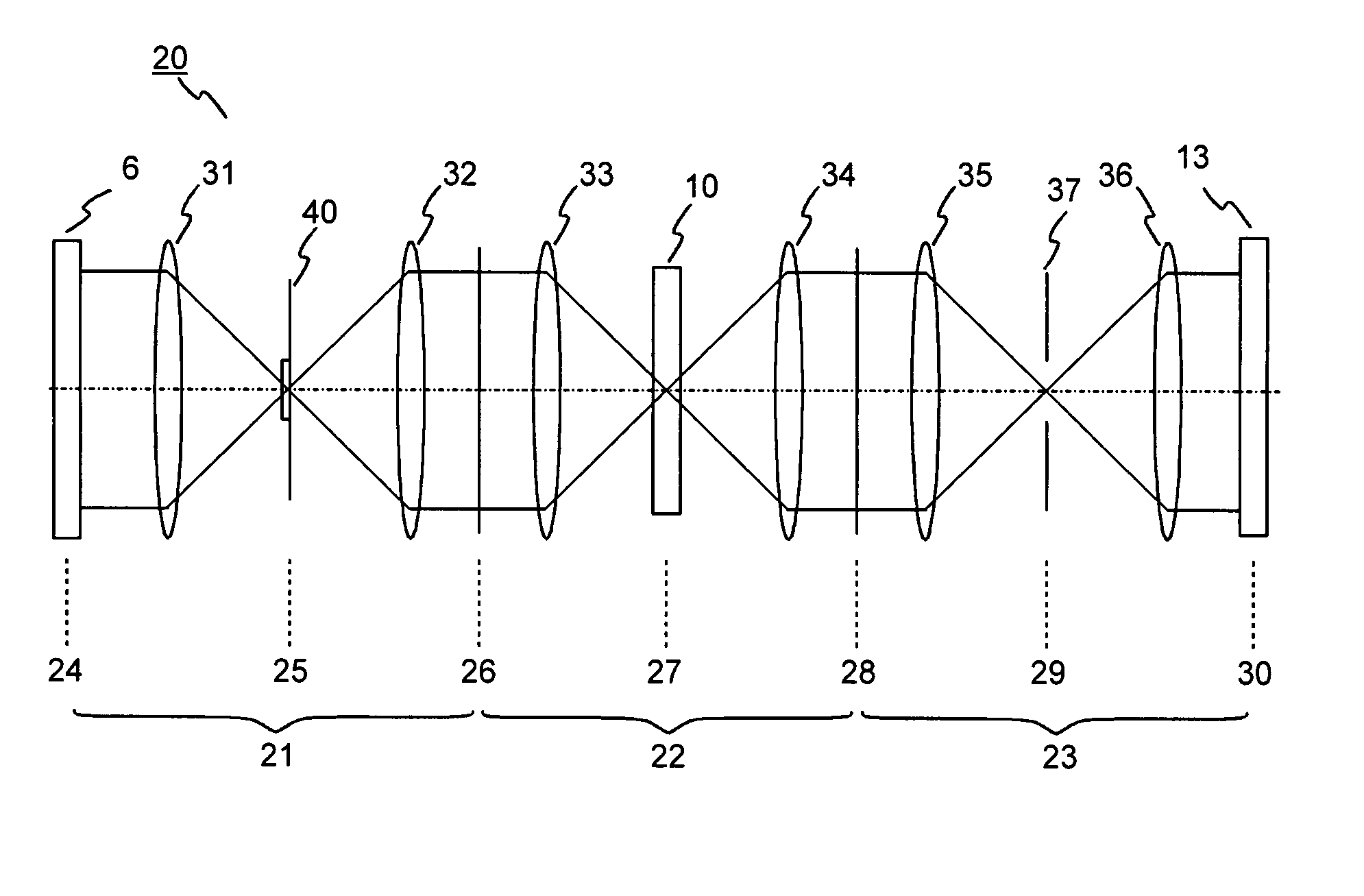
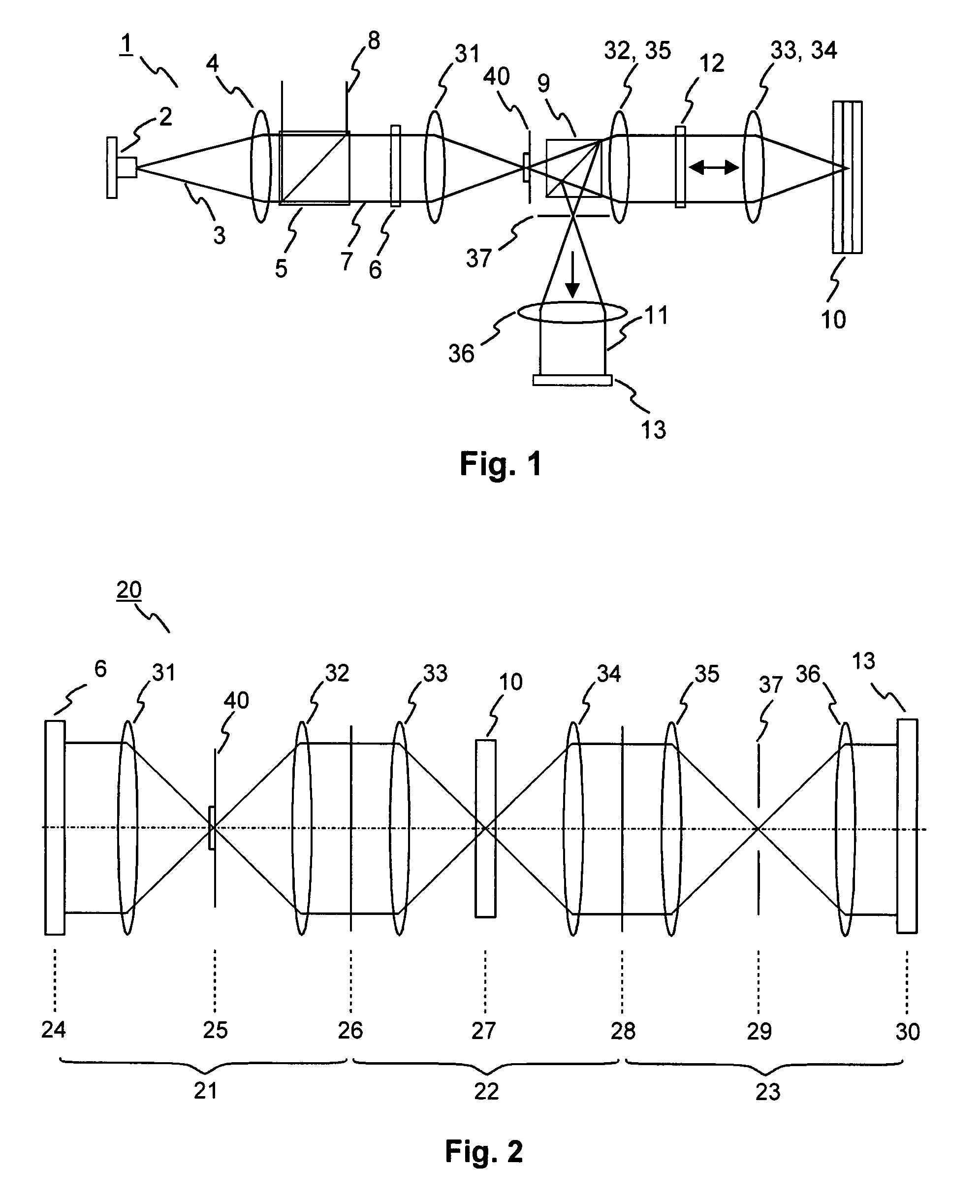
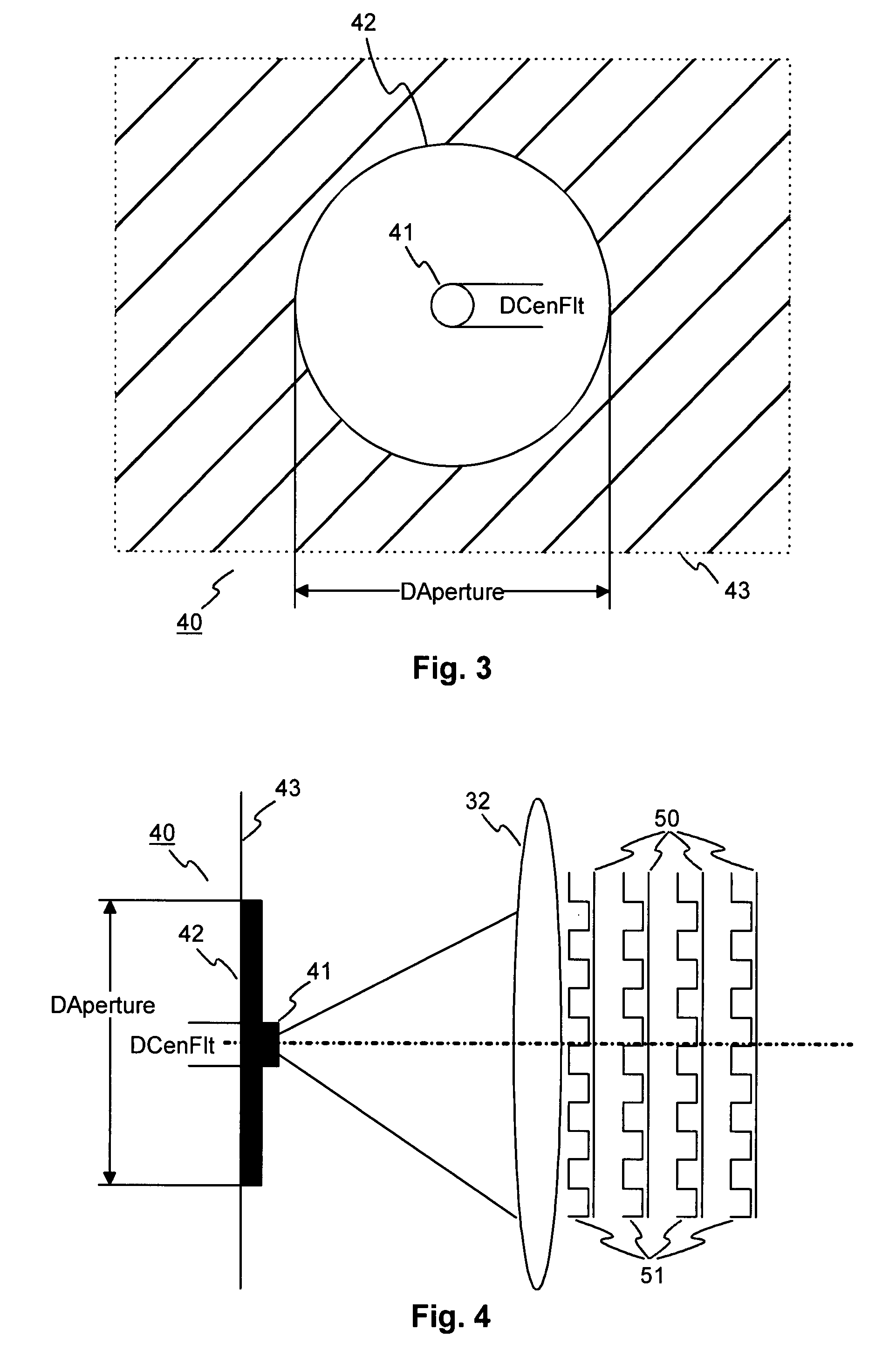
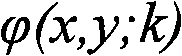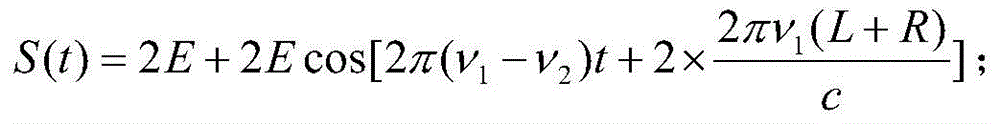Patents
Literature
31 results about "Common-path interferometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
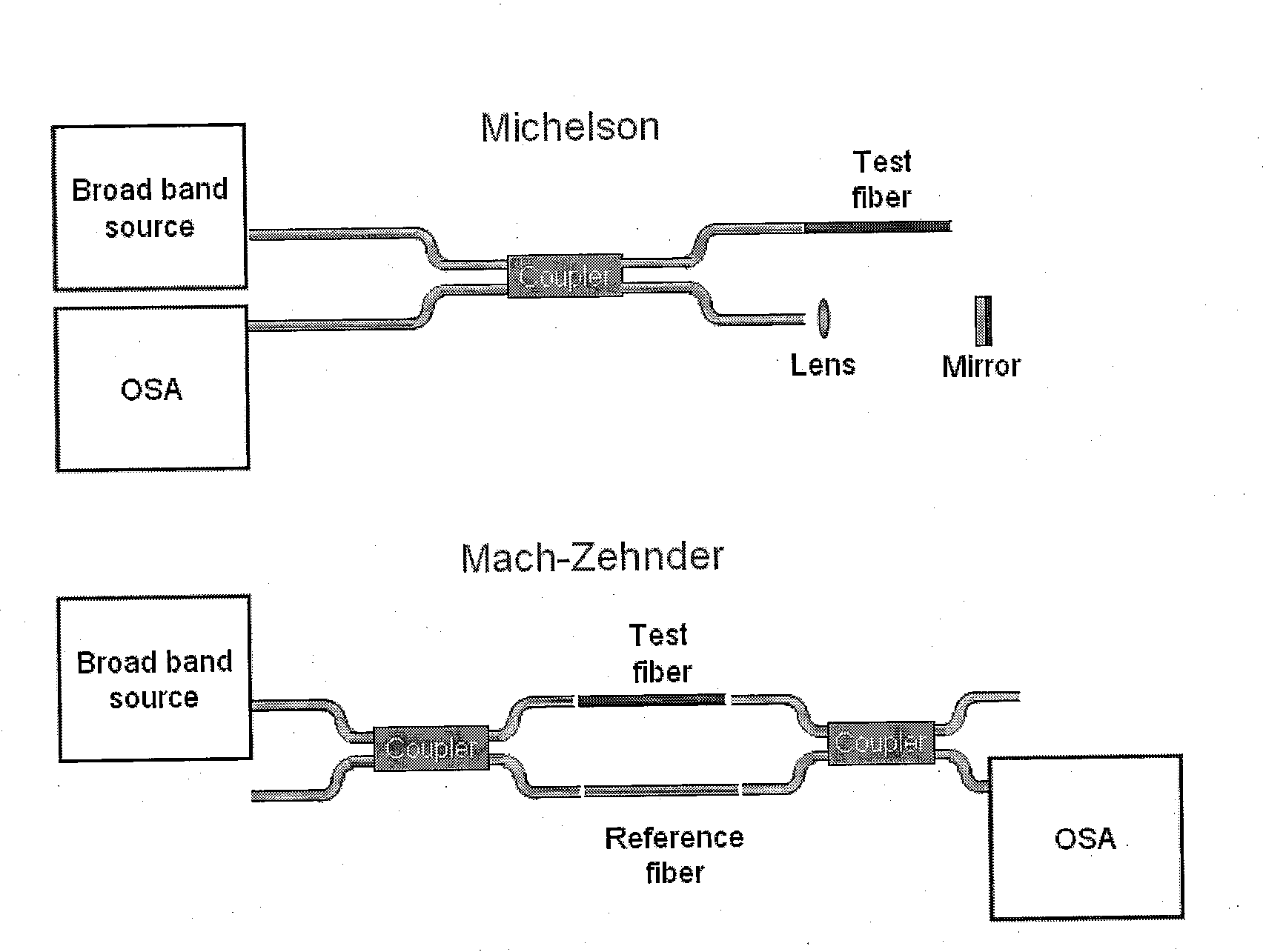
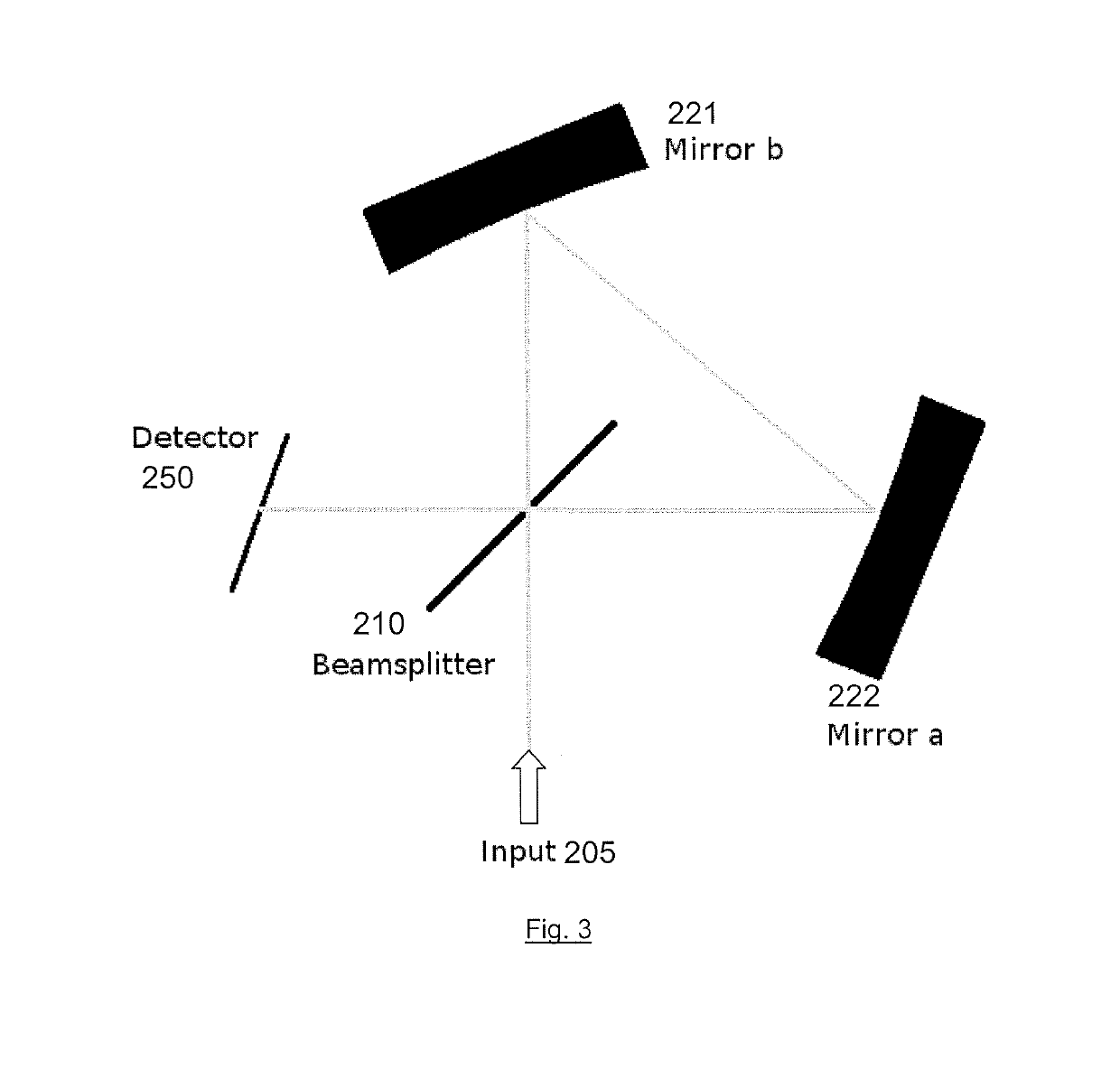
A common-path interferometer is a class of interferometers in which the reference beam and sample beams travel along the same path. Examples include the Sagnac interferometer, Zernike phase-contrast interferometer, and the point diffraction interferometer. A common-path interferometer is generally more robust to environmental vibrations than a "double-path interferometer" such as the Michelson interferometer or the Mach–Zehnder interferometer. Although travelling along the same path, the reference and sample beams may travel along opposite directions, or they may travel along the same direction but with the same or different polarization.
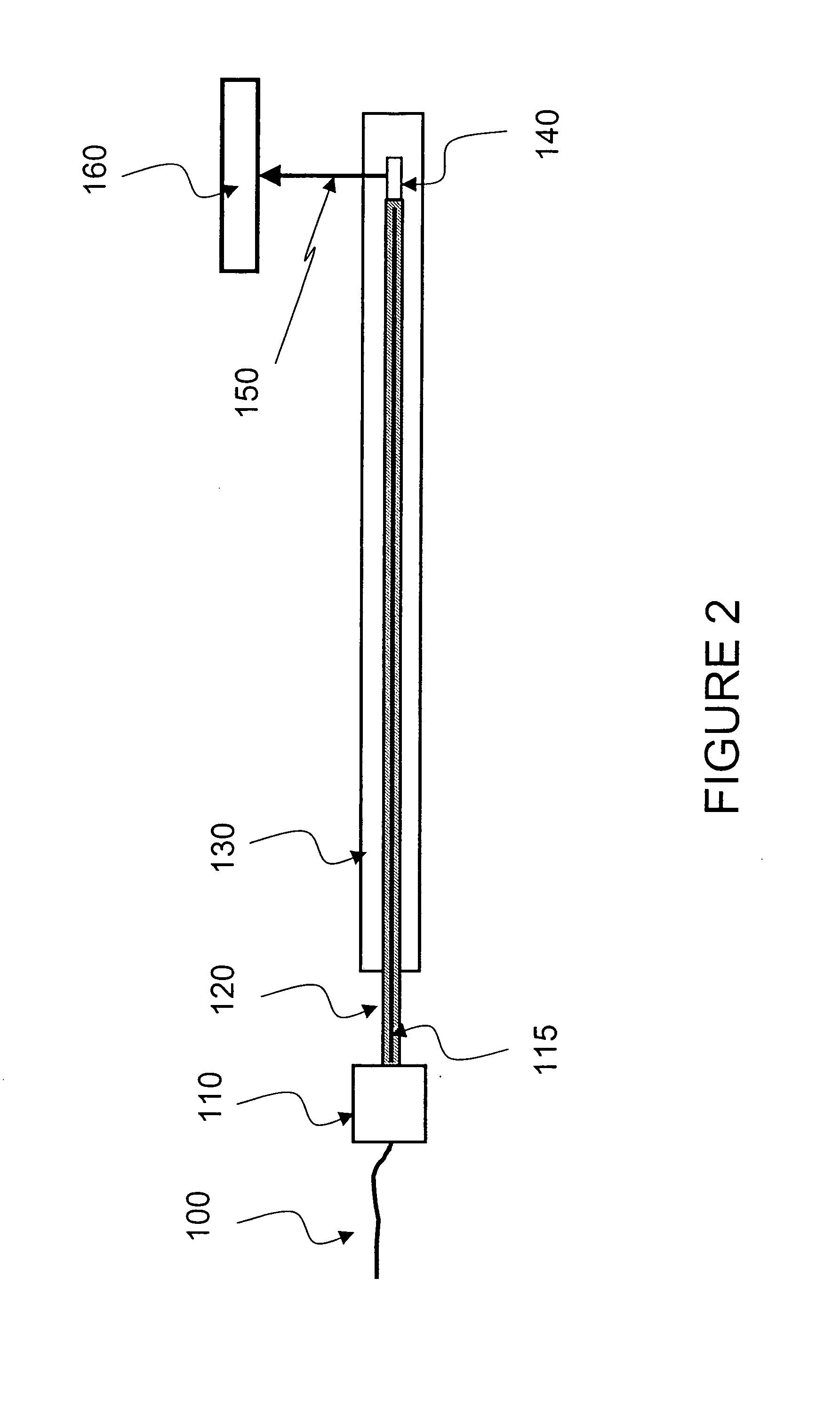
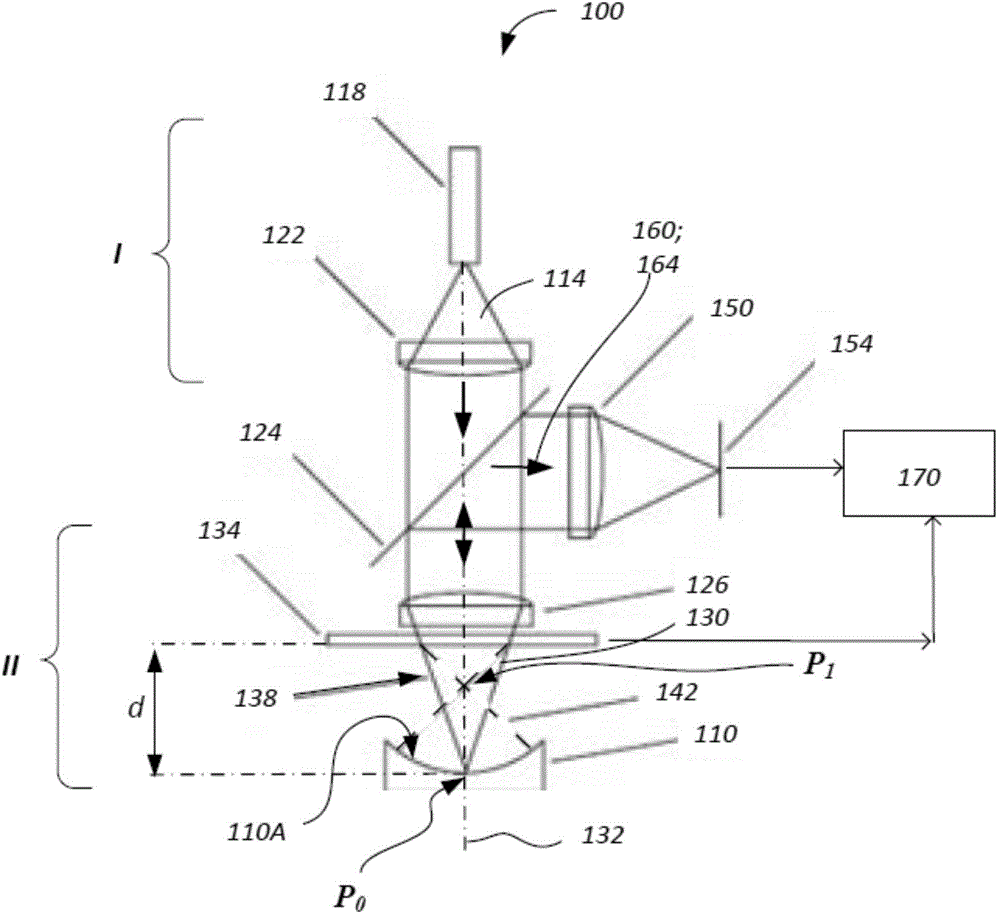
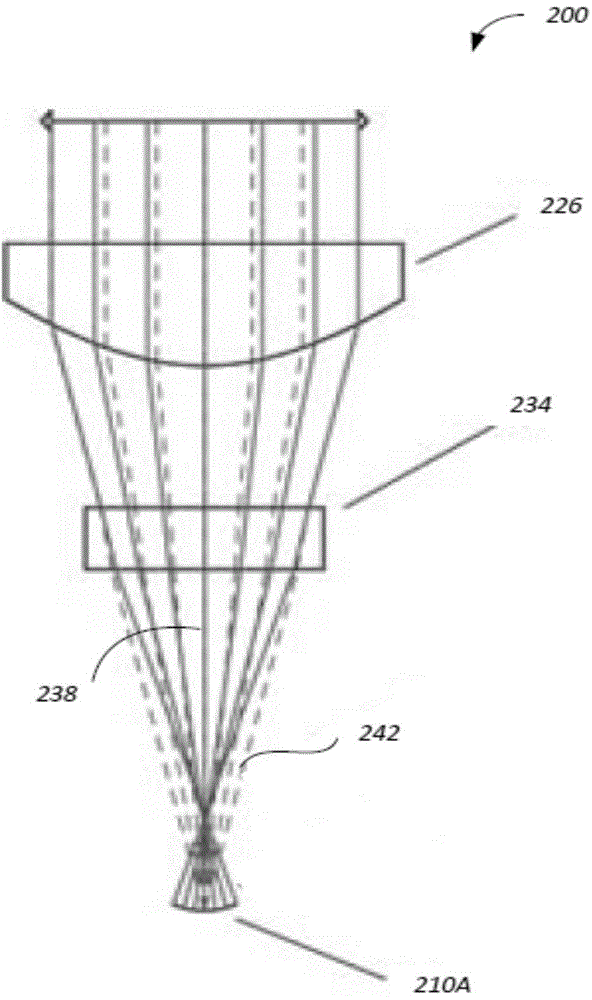
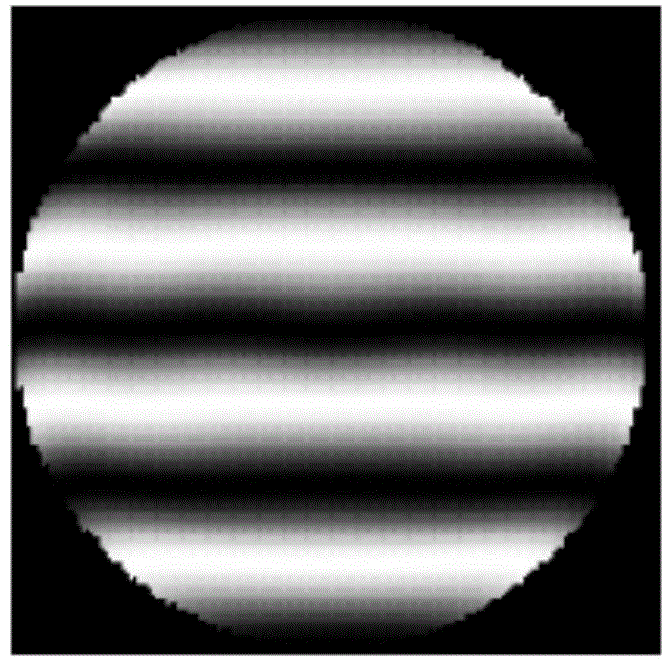
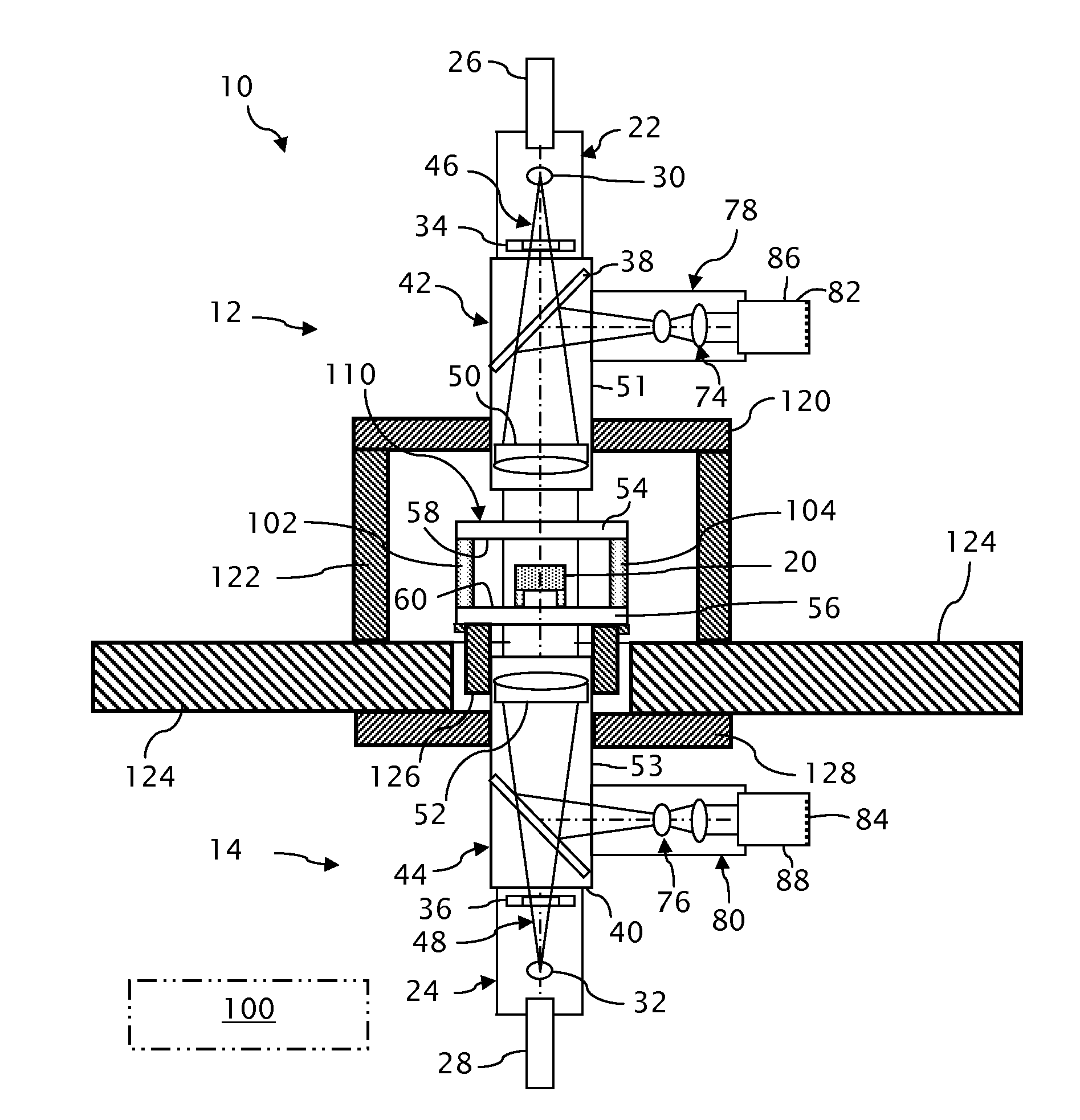
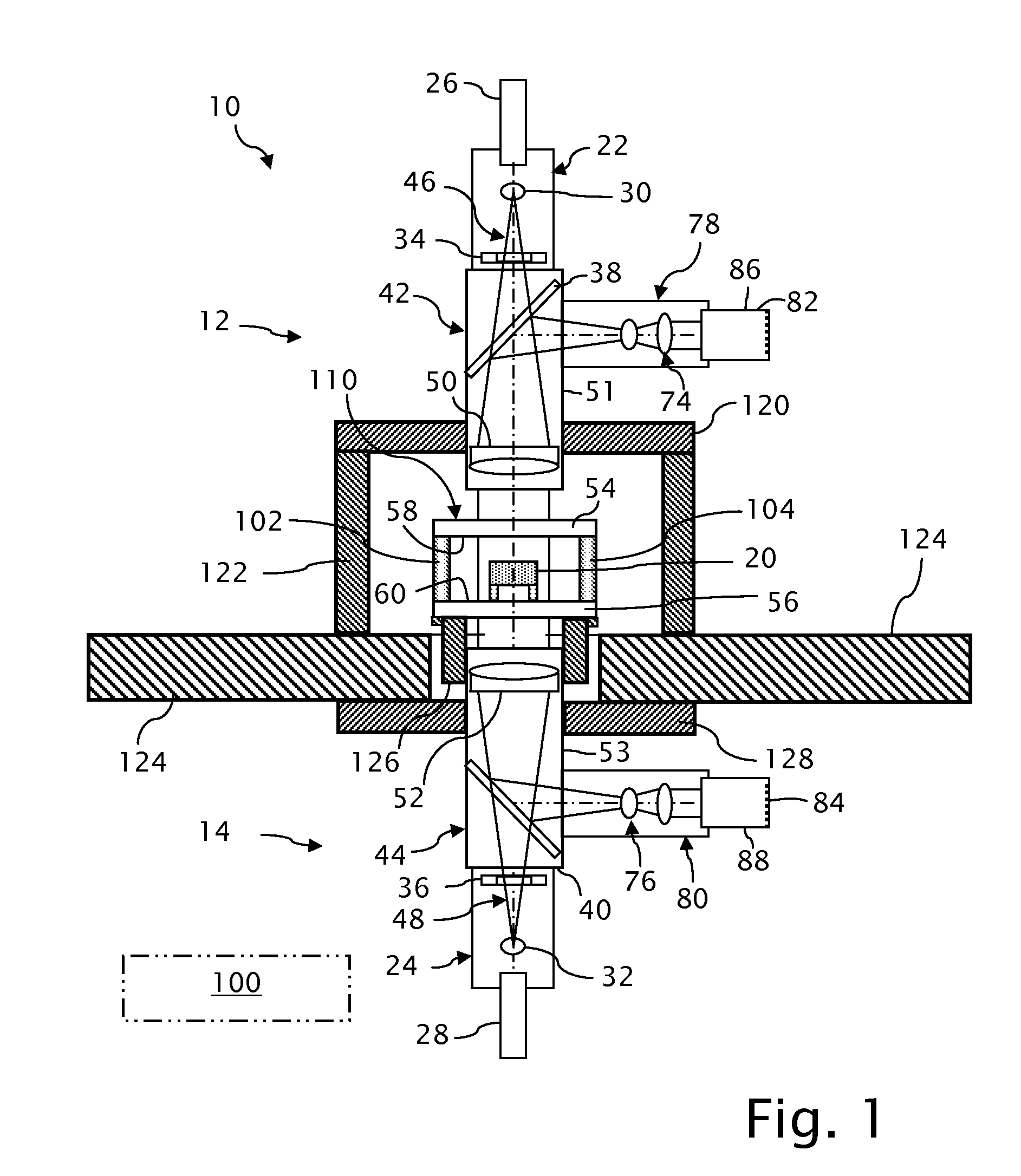
Devices and arrangements for performing coherence range imaging using a common path interferometer
ActiveUS7995210B2InterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
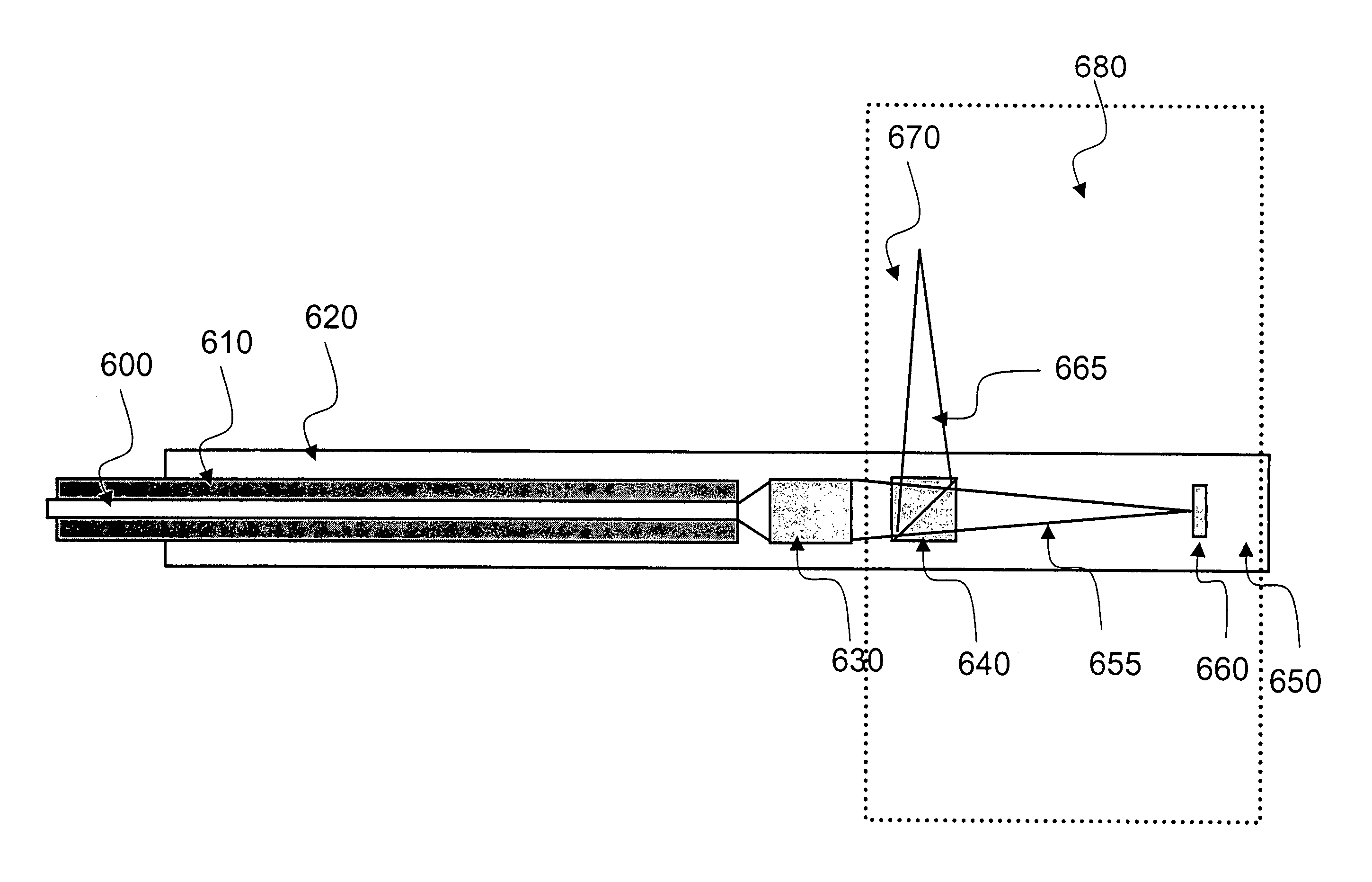
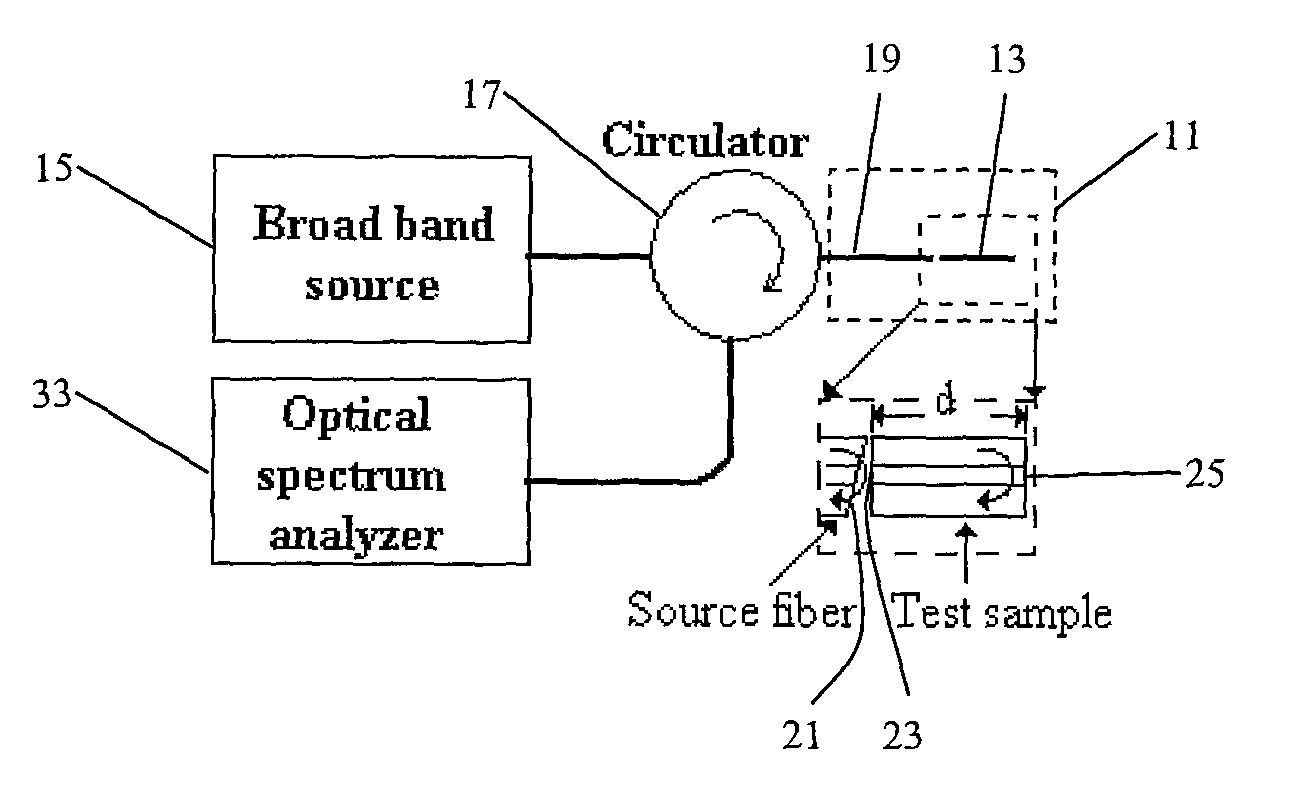
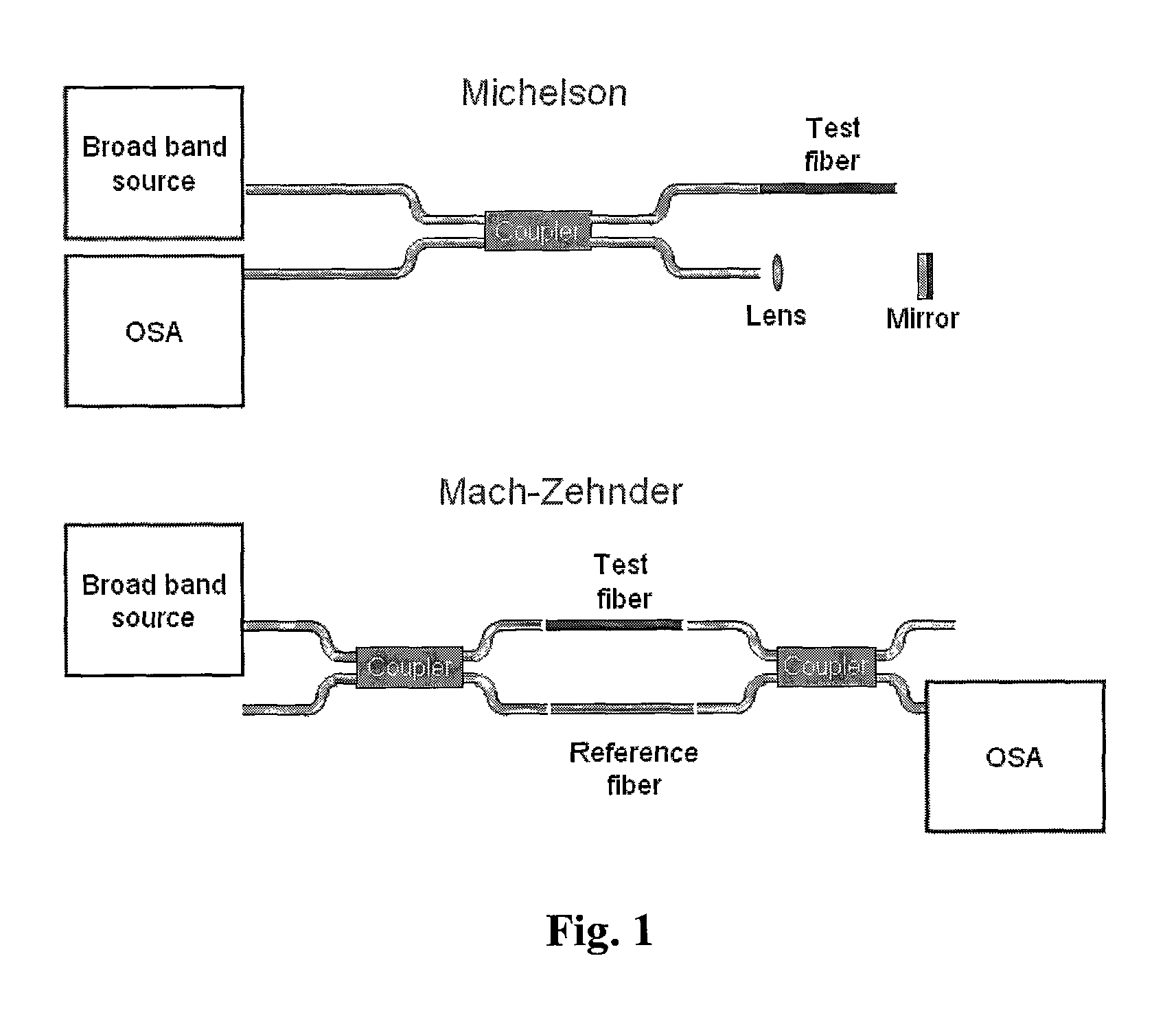
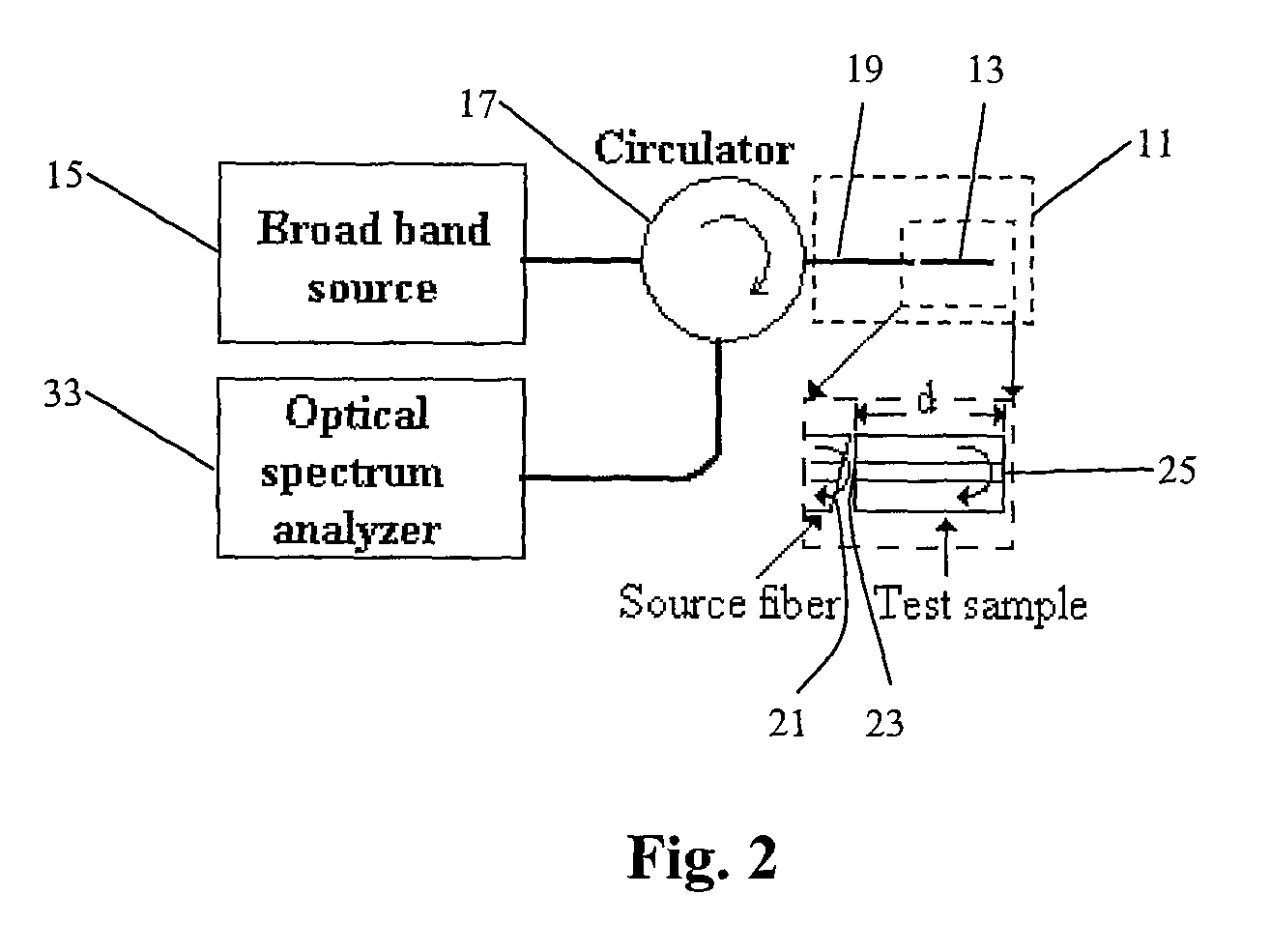
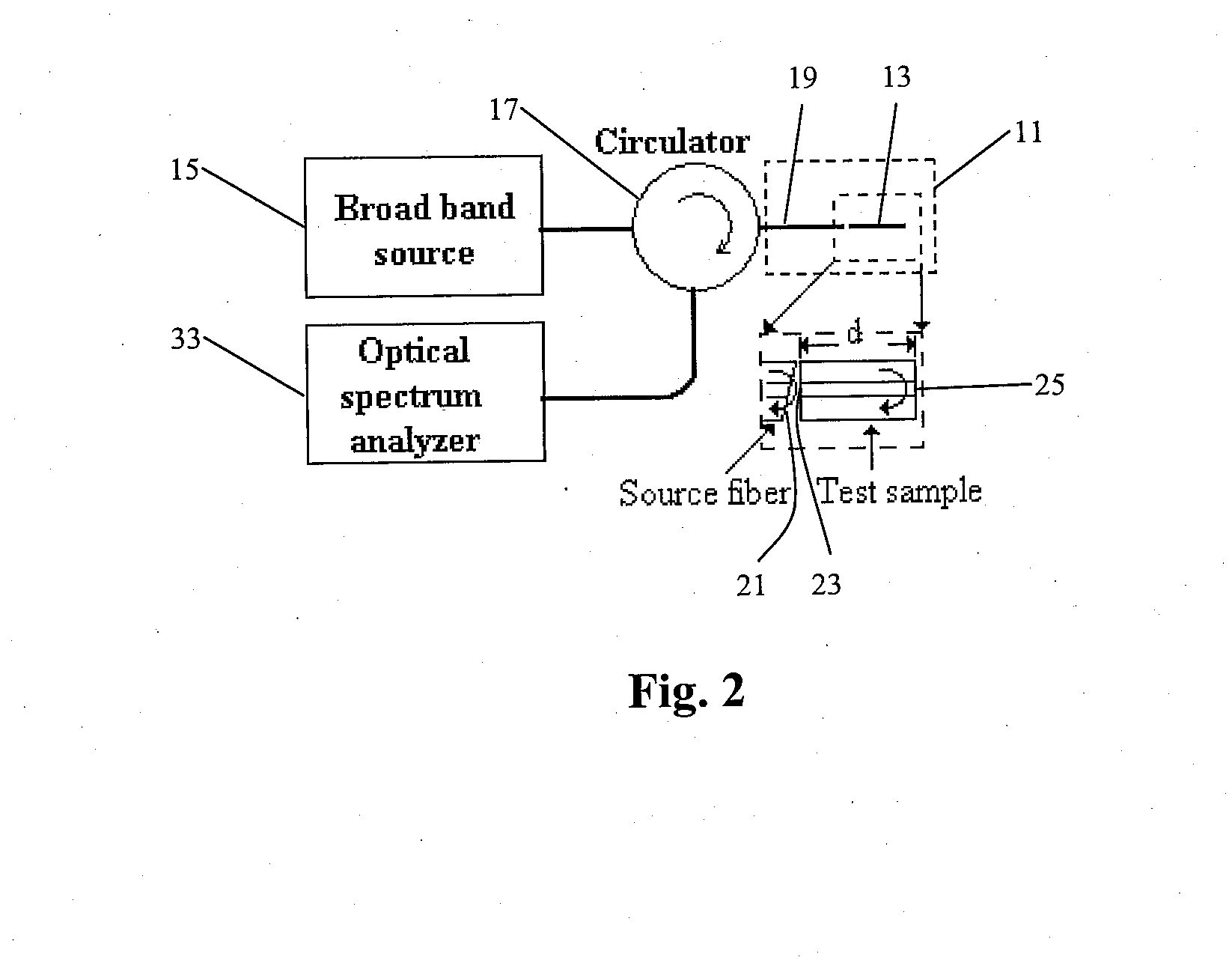
System and method to determine chromatic dispersion in short lengths of waveguides using a common path interferometer
InactiveUS7787127B2Material analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansReflected wavesIncident wave
The present invention relates to a system and method to determine chromatic dispersion in short lengths of waveguides using a two wave interference pattern and a common path interferometer. Specifically the invention comprises a radiation source operable to emit radiation connected to a means for separating incident and reflected waves; the means for separating incident and reflected waves possessing an output arm adjacent to a first end of the waveguide; and the means for separating incident and reflected waves further connected to an optical detector operable to record an interference pattern generated by a reflected test emission from the radiation source. The interference pattern consists of two waves: one reflected from a first facet of a waveguide and the second reflected from a second facet of the same waveguide.
Owner:GALLE MICHAEL +2
Devices and arrangements for performing coherence range imaging using a common path interferometer
ActiveUS20060109478A1Path length mismatchDispersion mismatchInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic radiationLength wave
Devices, arrangements and apparatus adapted to propagate at least one electro-magnetic radiation are provided. In particular, a probe housing, a sample arm section and a reference arm section can be included. For example, the sample arm section can be at least partially situated within the probe housing, and configured to propagate a first portion of the electro-magnetic radiation that is intended to be forwarded to a sample. The reference arm section can be at least partially situated within the probe housing, and configured to propagate a second portion of the electro-magnetic radiation that is intended to be forwarded to a reference. In addition or as an alternative, an interferometer may be situated within the probe housing. The first and second portions may travel along substantially the same paths, and the electro-magnetic radiation can be generated by a narrowband light source that has a tunable center wavelength. Further, the first and second portions may be at least partially transmitted via at least one optical fiber. A splitting arrangement may be provided which splits the electro-magnetic radiation into the first and second portions, and positioned closer to the sample than to the source of the electro-magnetic radiation, and the first and second portions may be adapted to propagate in different directions. An apparatus may be provided that is configured to control an optical path length of the second portion.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Overlapping common-path interferometers for two-sided measurement
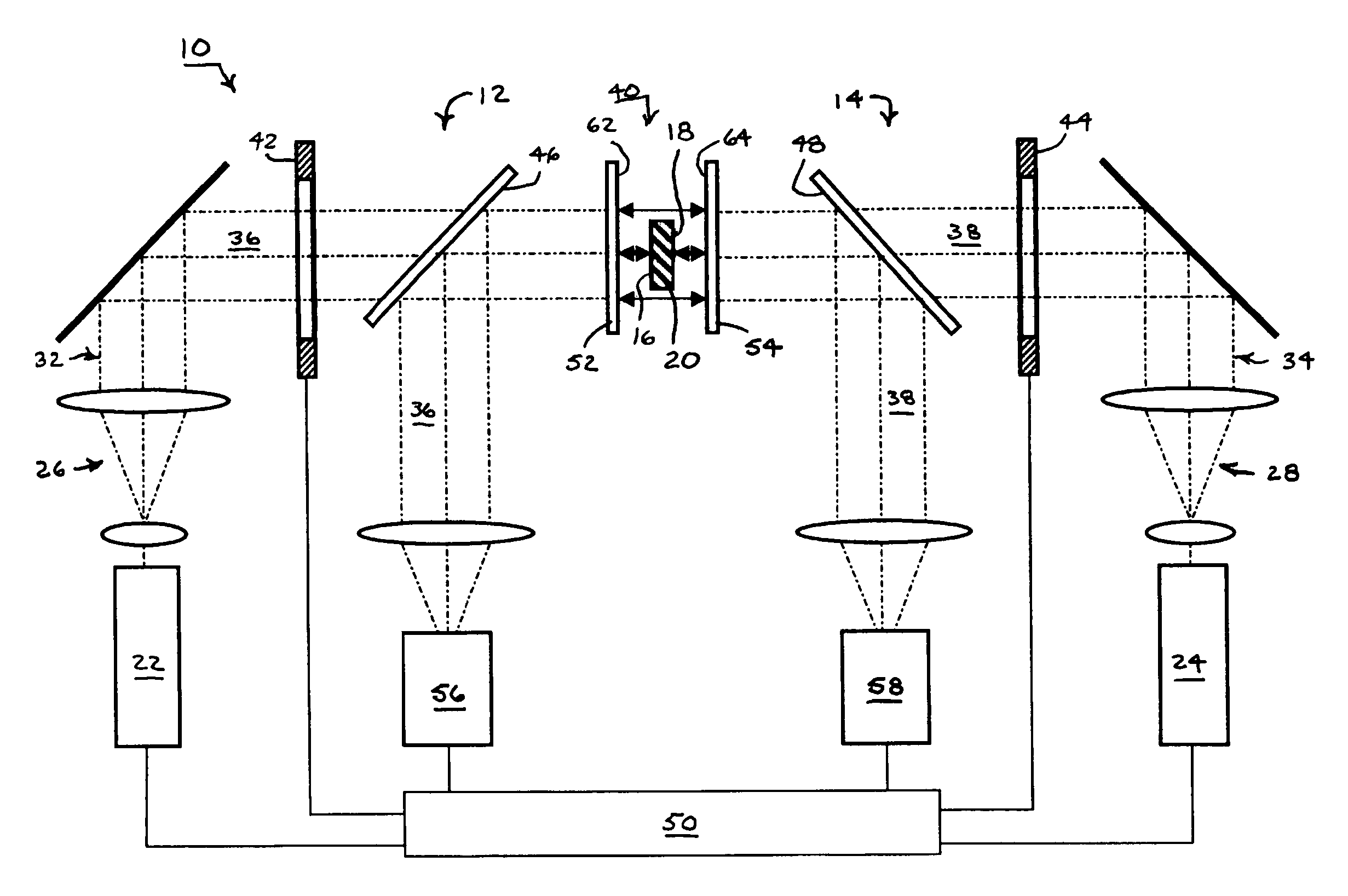
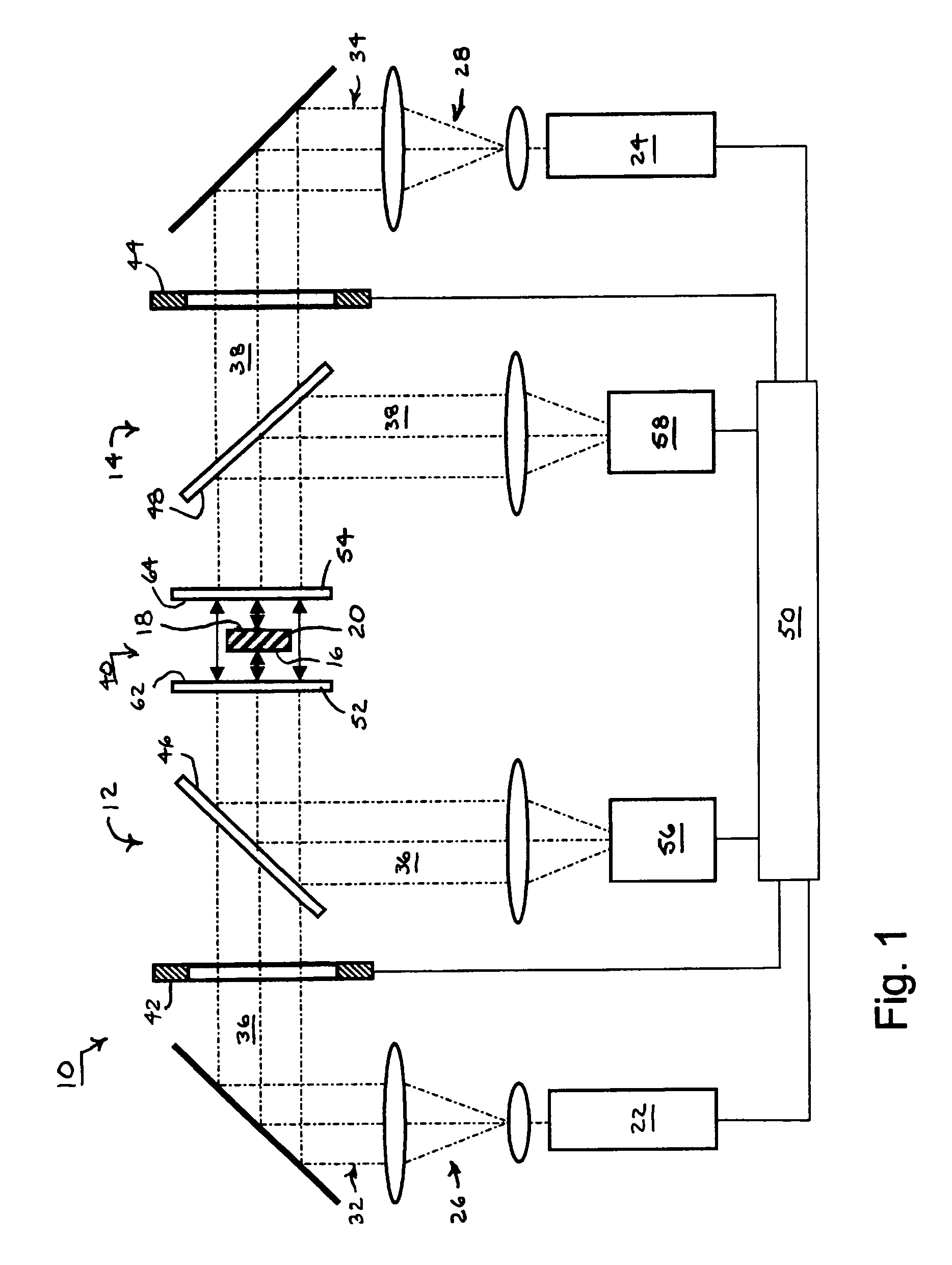
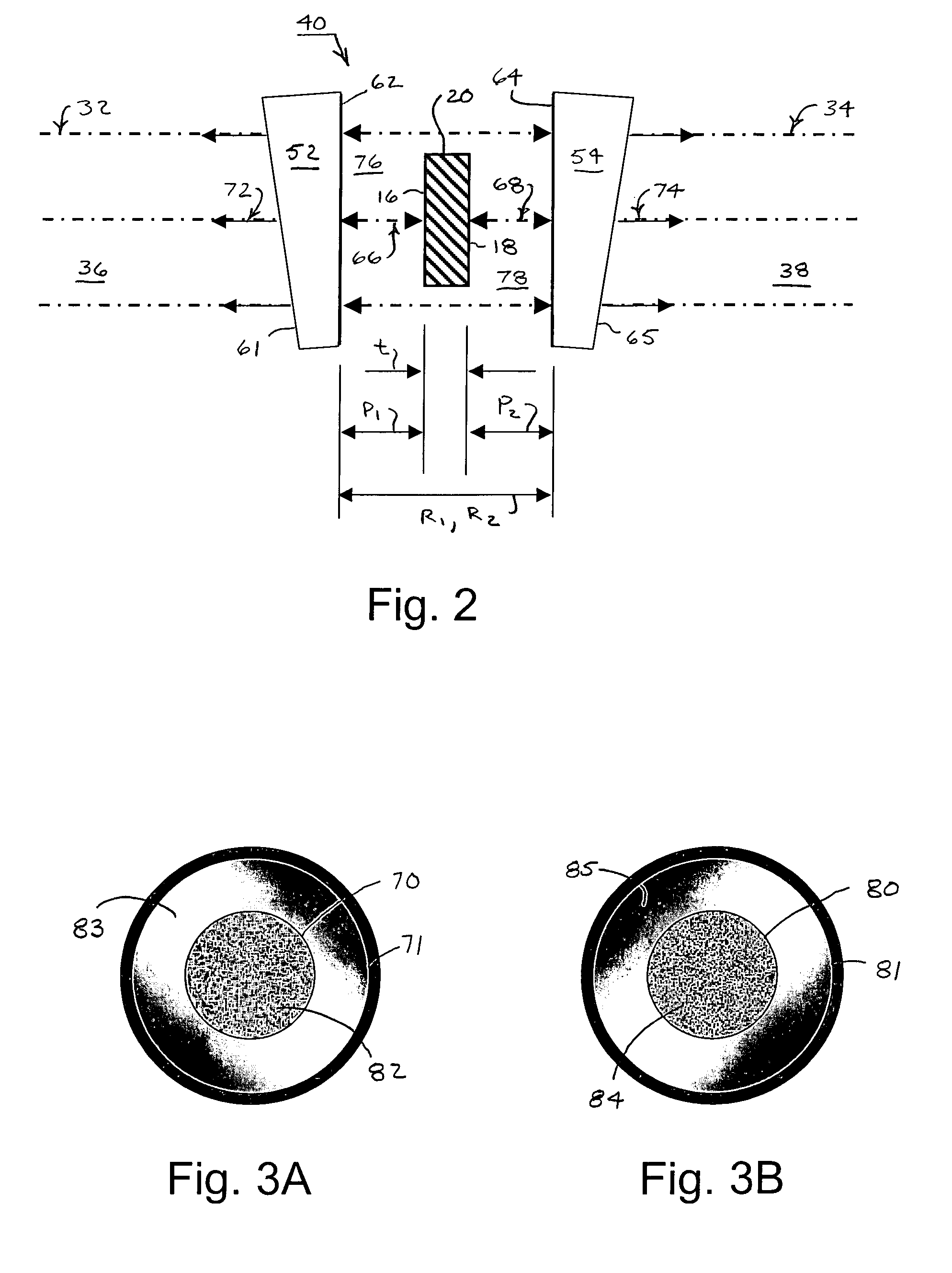
InactiveUS20060139656A1High precisionAvoid mistakesInterferometersUsing optical meansCommon pathCommon-path interferometer
Two common-path interferometers share a measuring cavity for measuring opposite sides of opaque test parts. Interference patterns are formed between one side of the test parts and the reference surface of a first of the two interferometers, between the other side of the test parts and the reference surface of a second of the two interferometers, and between the first and second reference surfaces. The latter measurement between the reference surfaces of the two interferometers enables the measurements of the opposite sides of the test parts to be related to each other.
Owner:CORNING INC
Complex index refraction tomography with sub lambda/6-resolution
The present invention discloses a method to improve the image resolution of a microscope. This improvement is based on the mathematical processing of the complex field computed from the measurements with a microscope of the wave emitted or scattered by the specimen. This wave is, in a preferred embodiment, electromagnetic or optical for an optical microscope, but can be also of different kind like acoustical or matter waves. The disclosed invention makes use of the quantitative phase microscopy techniques known in the sate of the art or to be invented. In a preferred embodiment, the complex field provided by Digital Holographic Microscopy (DHM), but any kind of microscopy derived from quantitative phase microscopy: modified DIC, Shack-Hartmann wavefront analyzer or any analyzer derived from a similar principle, such as multi-level lateral shearing interferometers or common-path interferometers, or devices that convert stacks of intensity images (transport if intensity techniques: TIT) into quantitative phase image can be used, provided that they deliver a comprehensive measure of the complex scattered wavefield. The hereby-disclosed method delivers superresolution microscopic images of the specimen, i.e. images with a resolution beyond the Rayleigh limit of the microscope. It is shown that the limit of resolution with coherent illumination can be improved by a factor of 6 at least. It is taught that the gain in resolution arises from the mathematical digital processing of the phase as well as of the amplitude of the complex field scattered by the observed specimen. In a first embodiment, the invention teaches how the experimental observation of systematically occurring phase singularities in phase imaging of sub-Rayleigh distanced objects can be exploited to relate the locus of the phase singularities to the sub-Rayleigh distance of point sources, not resolved in usual diffraction limited microscopy. In a second, preferred embodiment, the disclosed method teaches how the image resolution is improved by complex deconvolution. Accessing the object's scattered complex field—containing the information coded in the phase—and deconvolving it with the reconstructed complex transfer function (CTF) is at the basis of the disclosed method. In a third, preferred embodiment, it is taught how the concept of “Synthetic Coherent Transfer Function” (SCTF), based on Debye scalar or Vector model includes experimental parameters of MO and how the experimental Amplitude Point Spread Functions (APSF) are used for the SCTF determination. It is also taught how to derive APSF from the measurement of the complex field scattered by a nanohole in a metallic film. In a fourth embodiment, the invention teaches how the limit of resolution can be extended to a limit of λ / 6 or smaller based angular scanning. In a fifth embodiment, the invention teaches how the presented method can generalized to a tomographic approach that ultimately results in super-resolved 3D refractive index reconstruction.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
System for quickly measuring surface quality
InactiveCN101718520AShort reaction timeFast measurementUsing optical meansEnvironmental noiseAcousto-optics
The invention discloses a system for quickly measuring surface quality. The system comprises two sets of common-path interferometers, wherein one set of reference interferometer for noise compensation is specially used for detecting noises such as vibration, air disturbance and the like in environment, and eliminating the influence of interference of the background noises through negative feedback; and the other set of main interferometer for measurement controls wavelength of optical wave incident to the interferometers by using an acousto-optic filter, and can quickly acquire a three-dimensional feature of a surface to be measured by processing a generated interference signal by using large-scale parallel computation based on GPGPU. The system can measure the surface quality in real time, does not need mechanical light path scanning in the process of measurement, and can reach a high measurement speed. The system can be updated one time in 1 to 2 seconds on average, and can be updated more frequently after being optimized. The system can reduce influence of environmental noise on the measurement by adding the active optical path compensation technology, achieves measurement accuracy of sub-nano range, reduces cost, saves a usually expensive high-precision translation stage and can be used for processing workshops with more interference.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Sagnac delay-line interferometer for DPSK demodulation
InactiveUS8270067B1Lower requirementUsing optical meansElectromagnetic transmittersBeam splitterLight beam
A DPSK demodulator is implemented in Sagnac interferometer configuration with a delay line element introduced in one or both of the optical paths of the transmitted and reflected beams. Because the two reflected and transmitted beams travel on the same optical path (though in opposite directions), the Sagnac interferometer provides all the advantages of a common-path interferometer, is thermally and mechanically stable, and the phase requirements are greatly reduced. In its simplest form, the Sagnac DPSK demodulator. In the preferred embodiment, the beam-splitting surface and one of the mirrors are combined into a rhomb beam-splitter structure and the other two mirrors into a right-angle prism. In a DQPSK embodiment, the input beam is split by an upfront beam splitter into two parallel beams that are then directed toward the rhomb-beam-splitter / right-angle-prism combination of the invention.
Owner:OPTOPLEX CORP
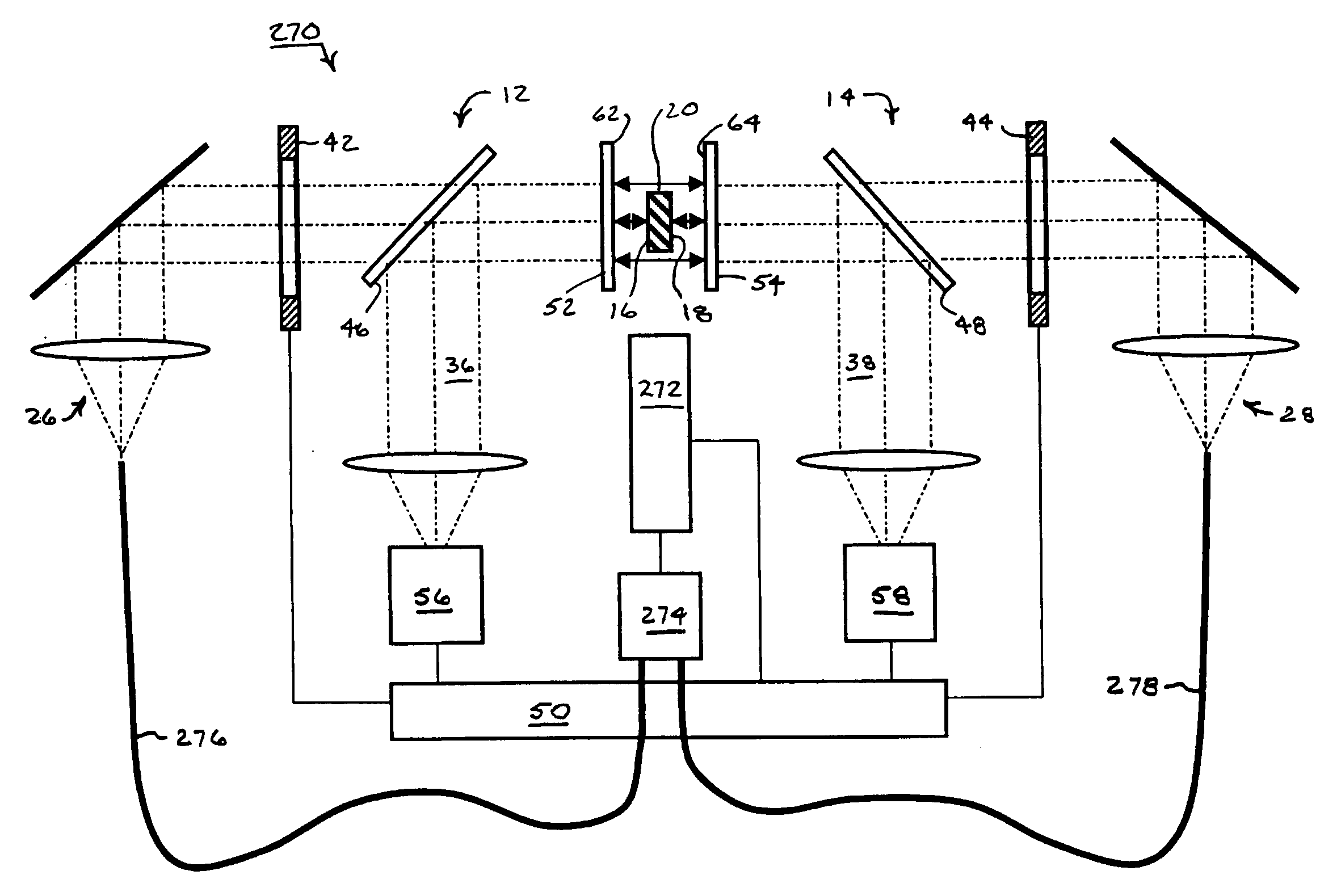
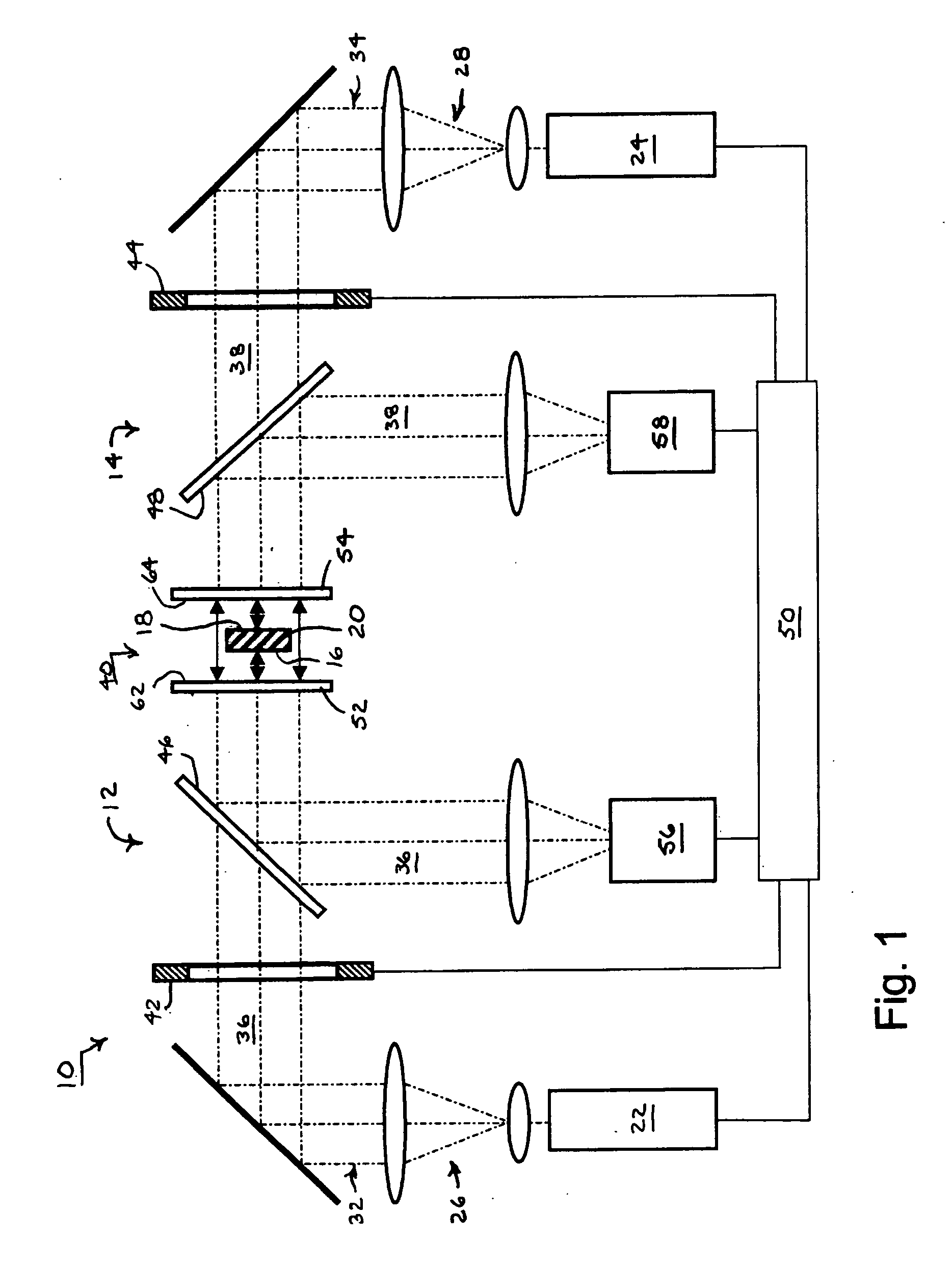
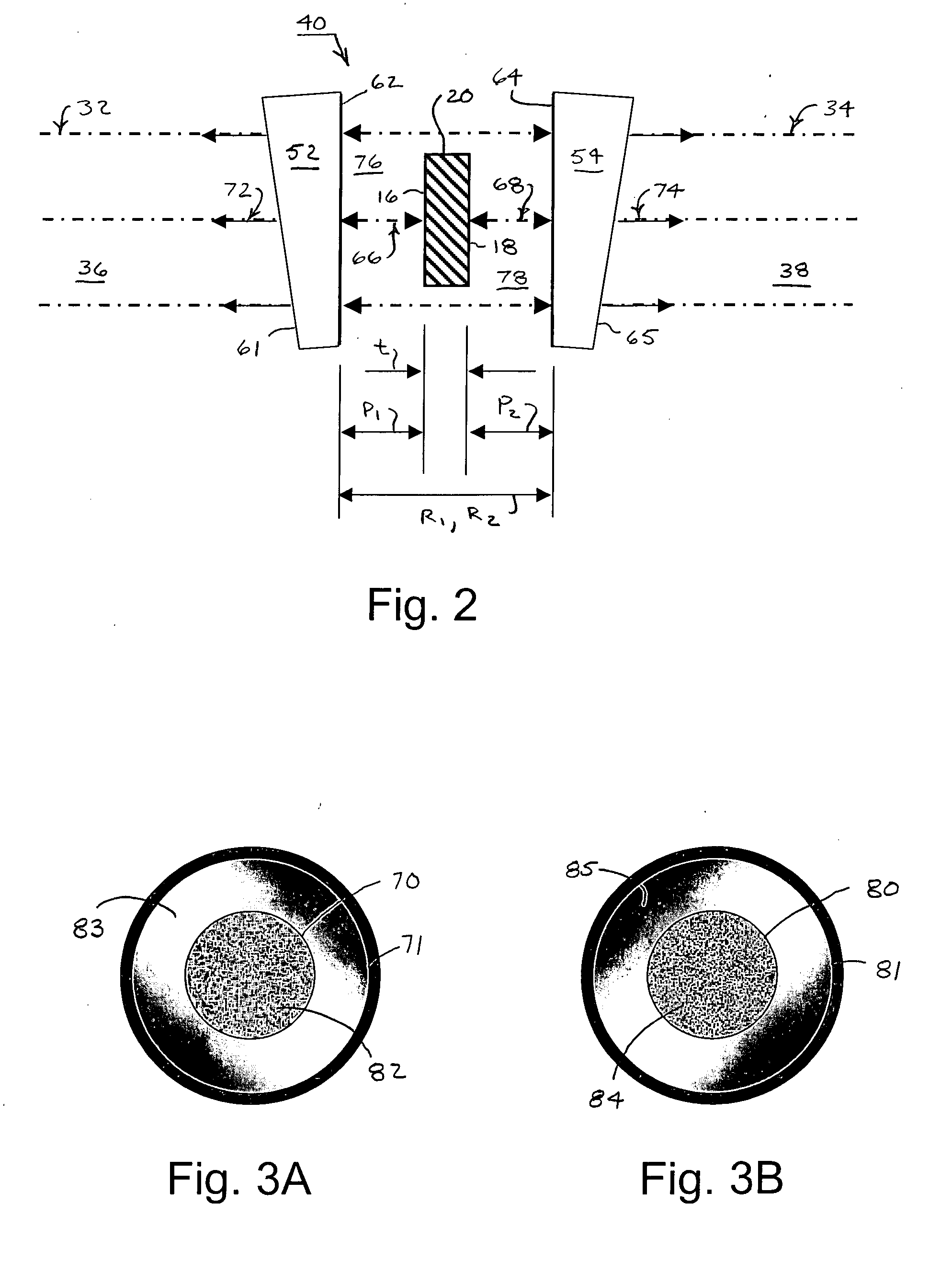
Overlapping common-path interferometers for two-sided measurement
InactiveUS7268887B2High precisionAvoid mistakesInterferometersUsing optical meansEngineeringMechanical engineering
Two common-path interferometers share a measuring cavity for measuring opposite sides of opaque test parts. Interference patterns are formed between one side of the test parts and the reference surface of a first of the two interferometers, between the other side of the test parts and the reference surface of a second of the two interferometers, and between the first and second reference surfaces. The latter measurement between the reference surfaces of the two interferometers enables the measurements of the opposite sides of the test parts to be related to each other.
Owner:CORNING INC
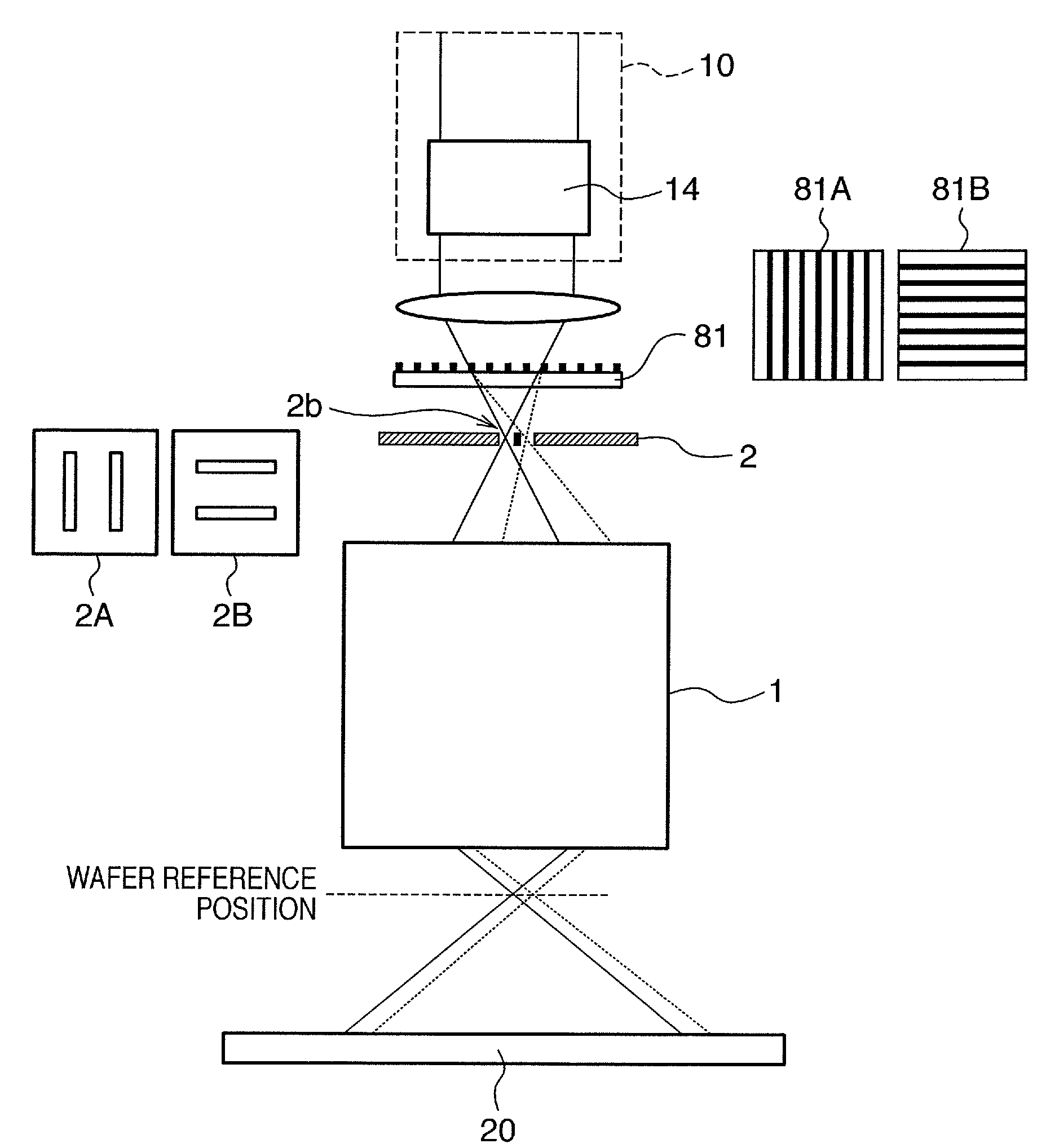
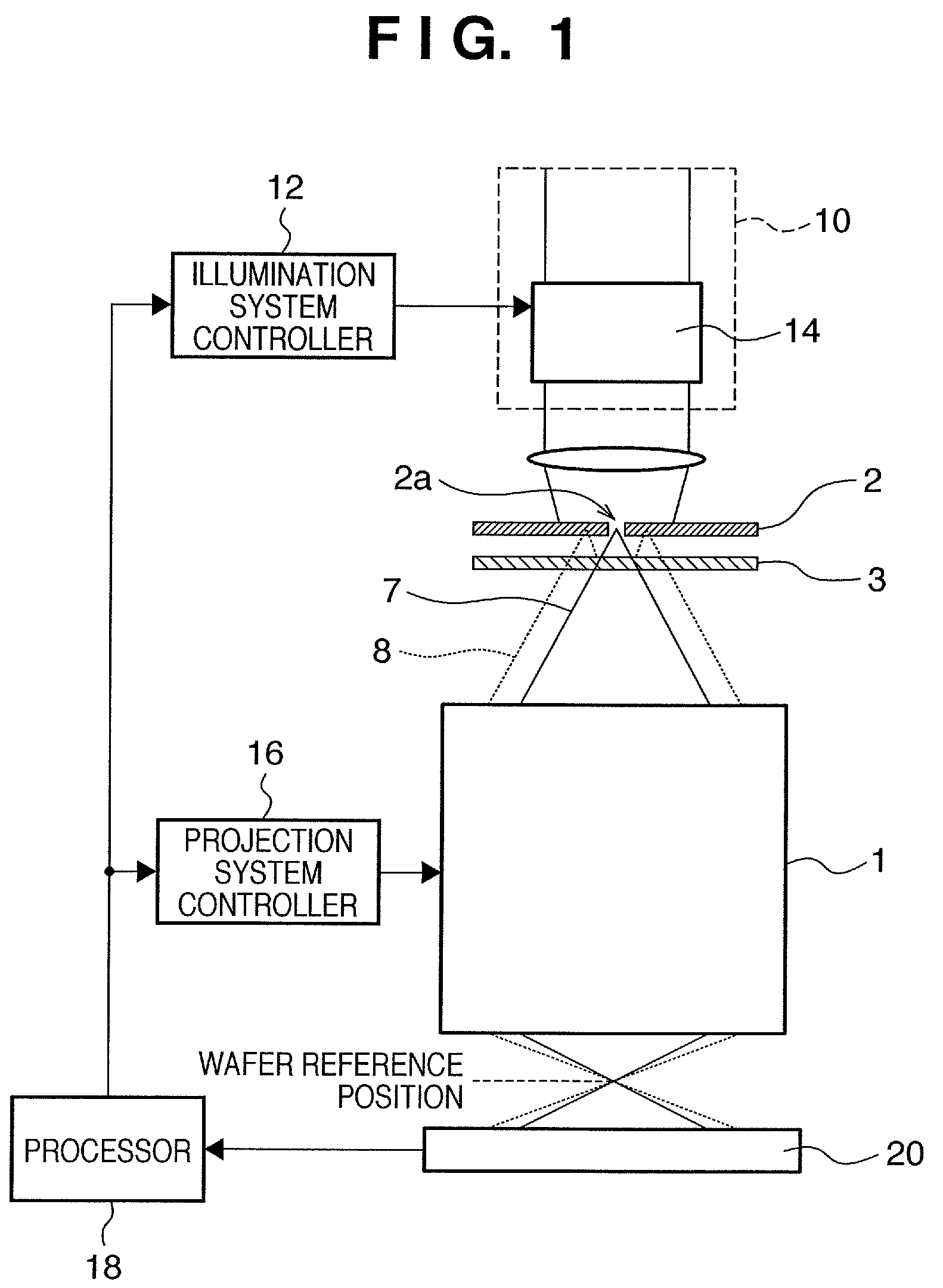
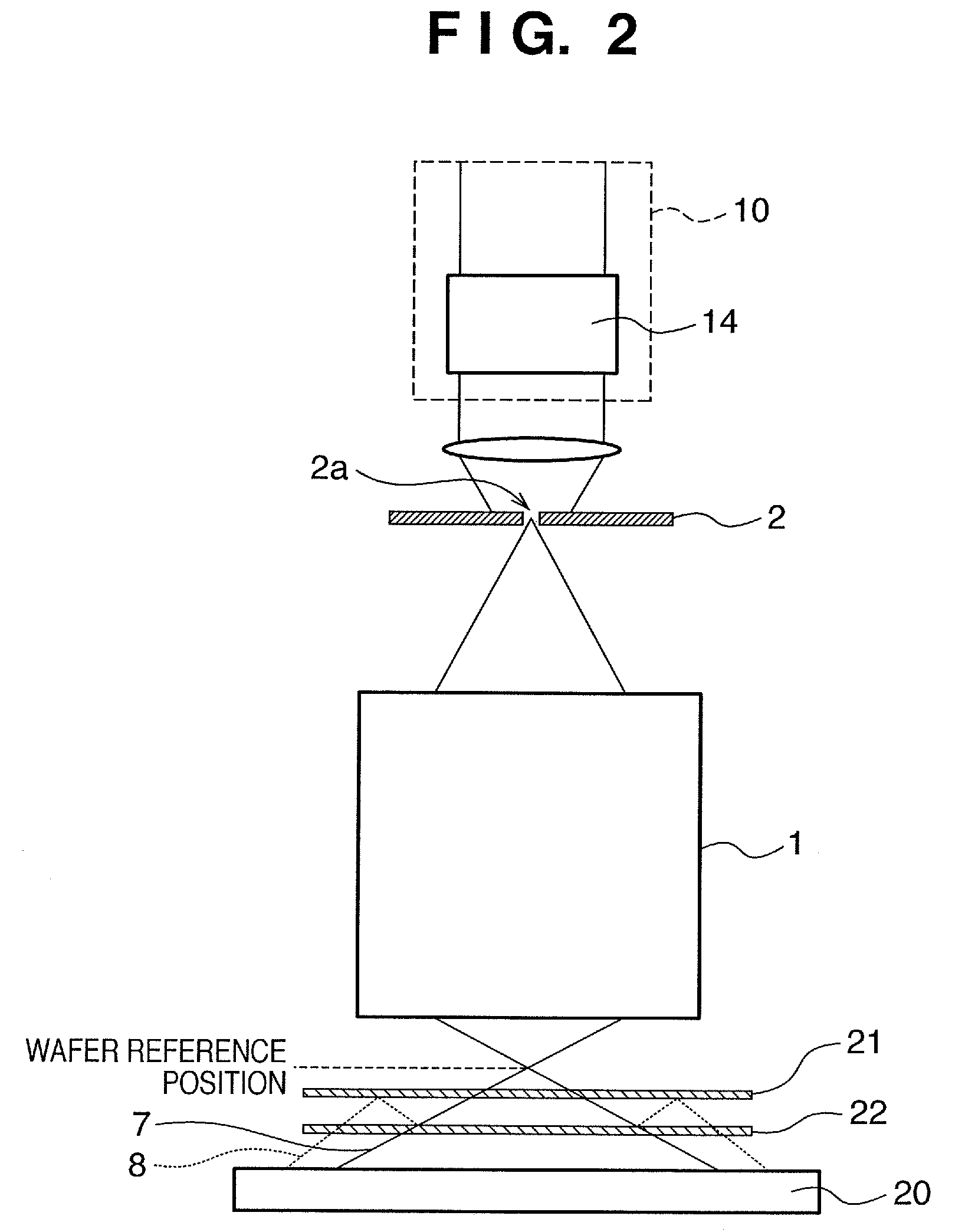
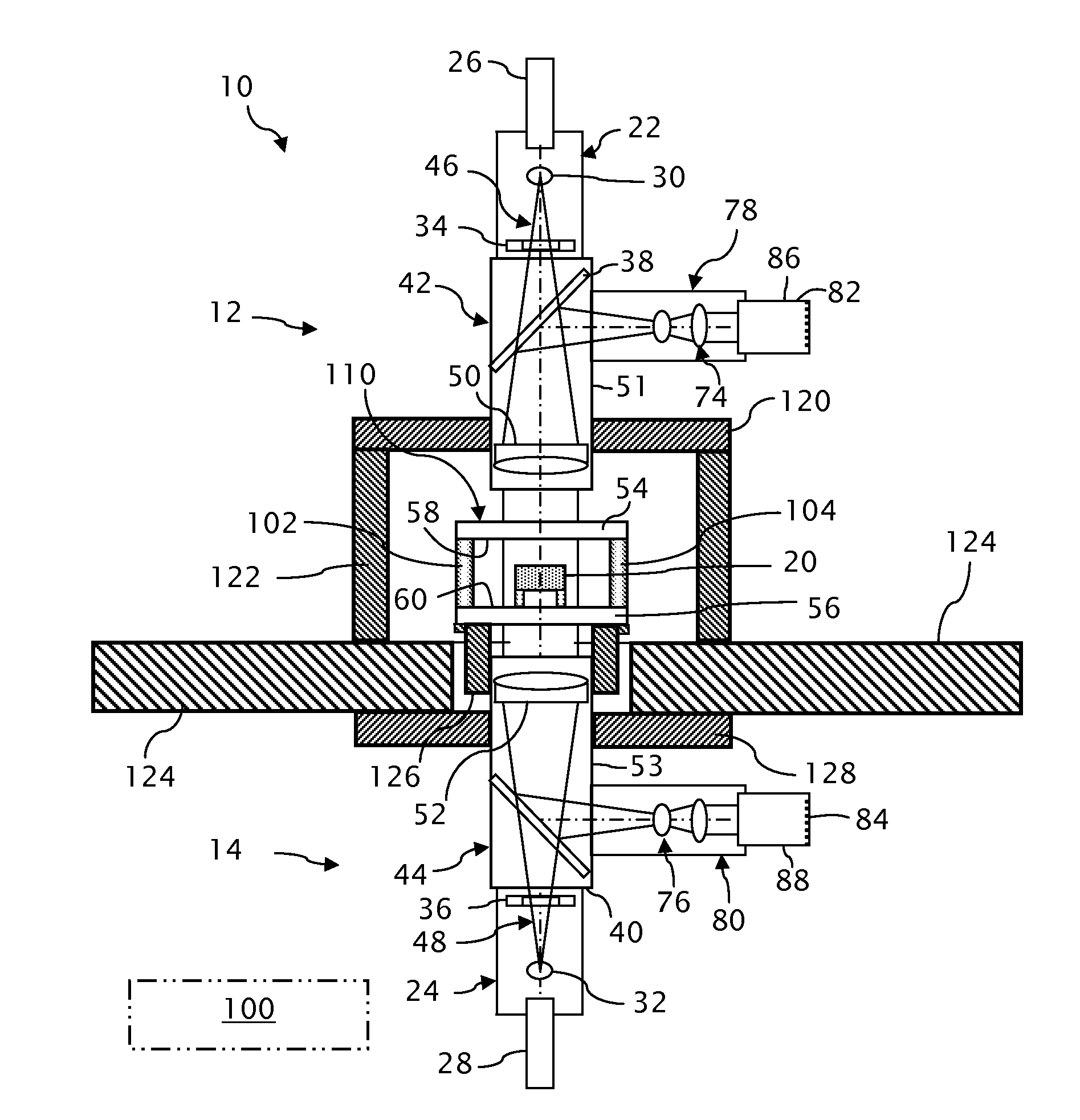
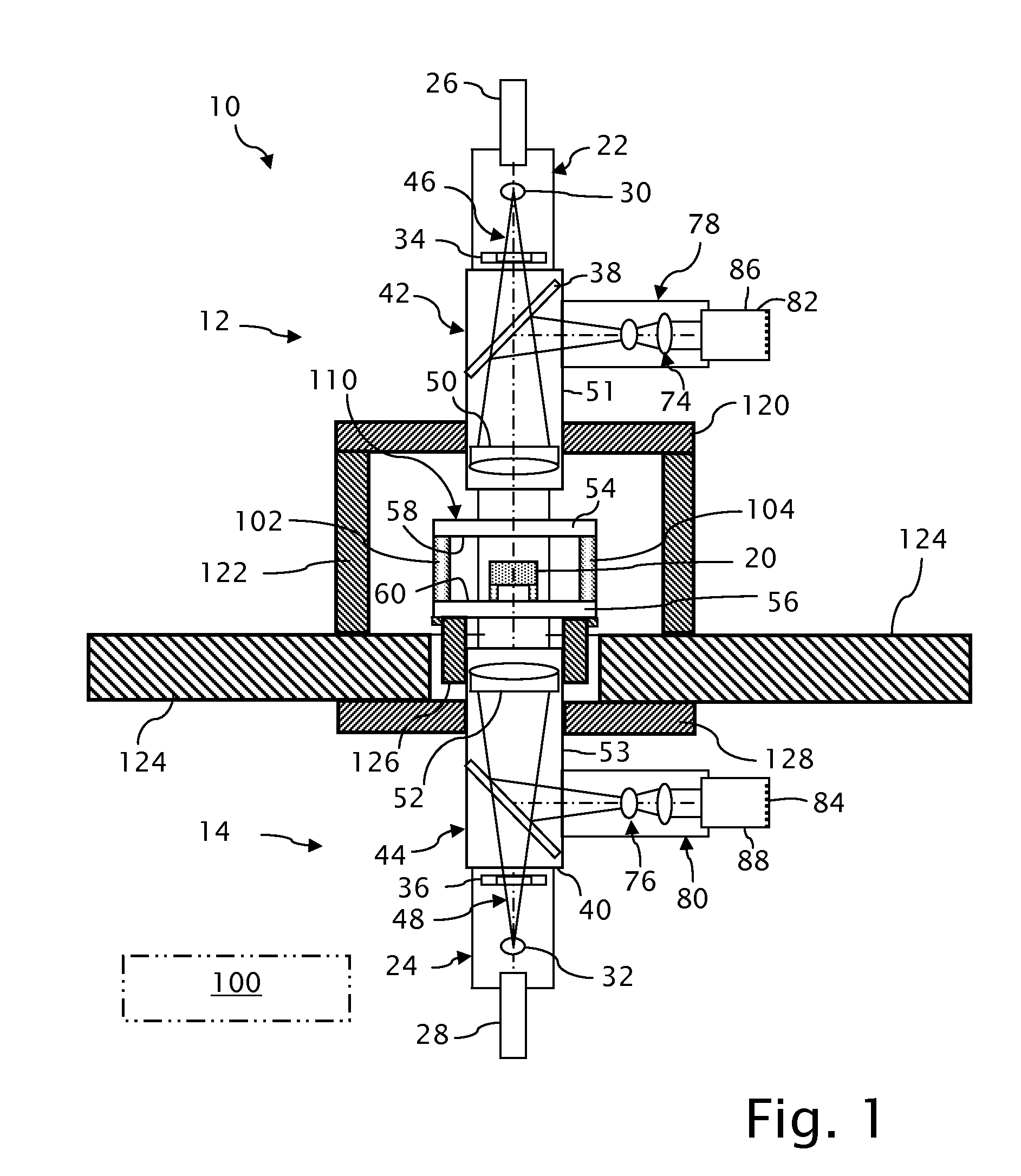
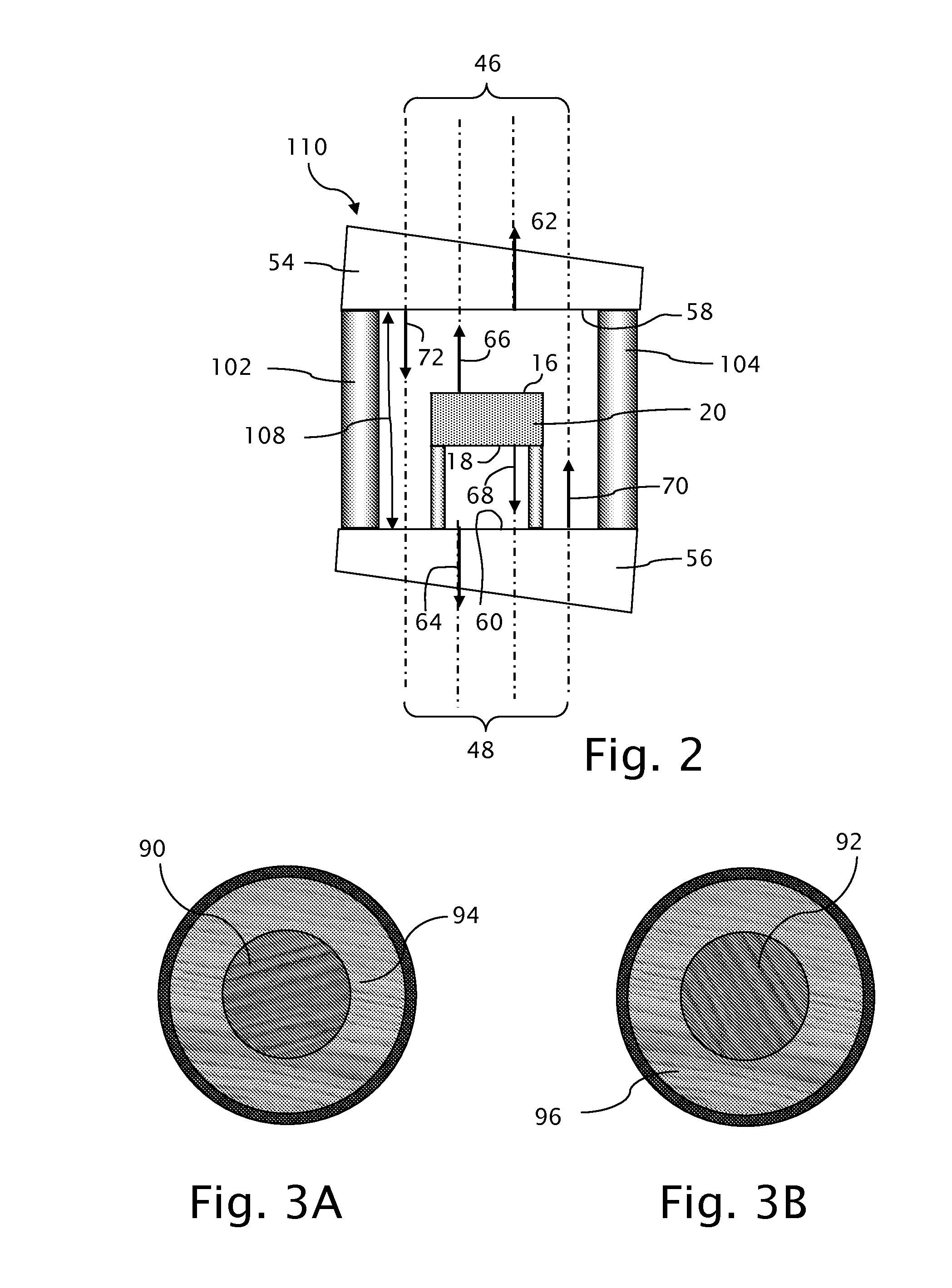
Exposure apparatus and device manufacturing method using a common path interferometer to form an interference pattern and a processor to calculate optical characteristics of projection optics using the interference pattern
An exposure apparatus including an illumination system which illuminates an original, and projection optics which project a pattern of the original illuminated by the illumination system onto a substrate. The apparatus includes an interferometer which forms an interference pattern including aberration information on the projection optics using a polarized light beam emitted from the illumination system, in which the interferometer is a common path interferometer in which two light beams forming interference pattern pass along a path in the projection optics, and a processor which calculates optical characteristics of the projection optics on the basis of the interference pattern formed by the interferometer. The illumination system including a polarization controller which sequentially generates at least three difference polarized light beams with respective polarization states different from each other. The processor separates first aberration and second aberration from wavefront aberration represented by the interference patterns sequentially formed by the interferometer using the at least three different polarized light beams, by calculating a data of the interference patterns, the first aberration being aberration which does not change dependent on a polarization state of polarized light beam entering the projection optics. The second aberration is aberration which changes dependent on the polarization state of the polarized light beam entering the projection optics.
Owner:CANON KK
System and Method to Determine Chromatic Dispersion in Short Lengths of Waveguides Using a Common Path Interferometer
InactiveUS20090097036A1Material analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansReflected wavesIncident wave
The present invention relates to a system and method to determine chromatic dispersion in short lengths of waveguides using a two wave interference pattern and a common path interferometer. Specifically the invention comprises a radiation source operable to emit radiation connected to a means for separating incident and reflected waves; the means for separating incident and reflected waves possessing an output arm adjacent to a first end of the waveguide; and the means for separating incident and reflected waves further connected to an optical detector operable to record an interference pattern generated by a reflected test emission from the radiation source. The interference pattern consists of two waves: one reflected from a first facet of a waveguide and the second reflected from a second facet of the same waveguide.
Owner:GALLE MICHAEL +2
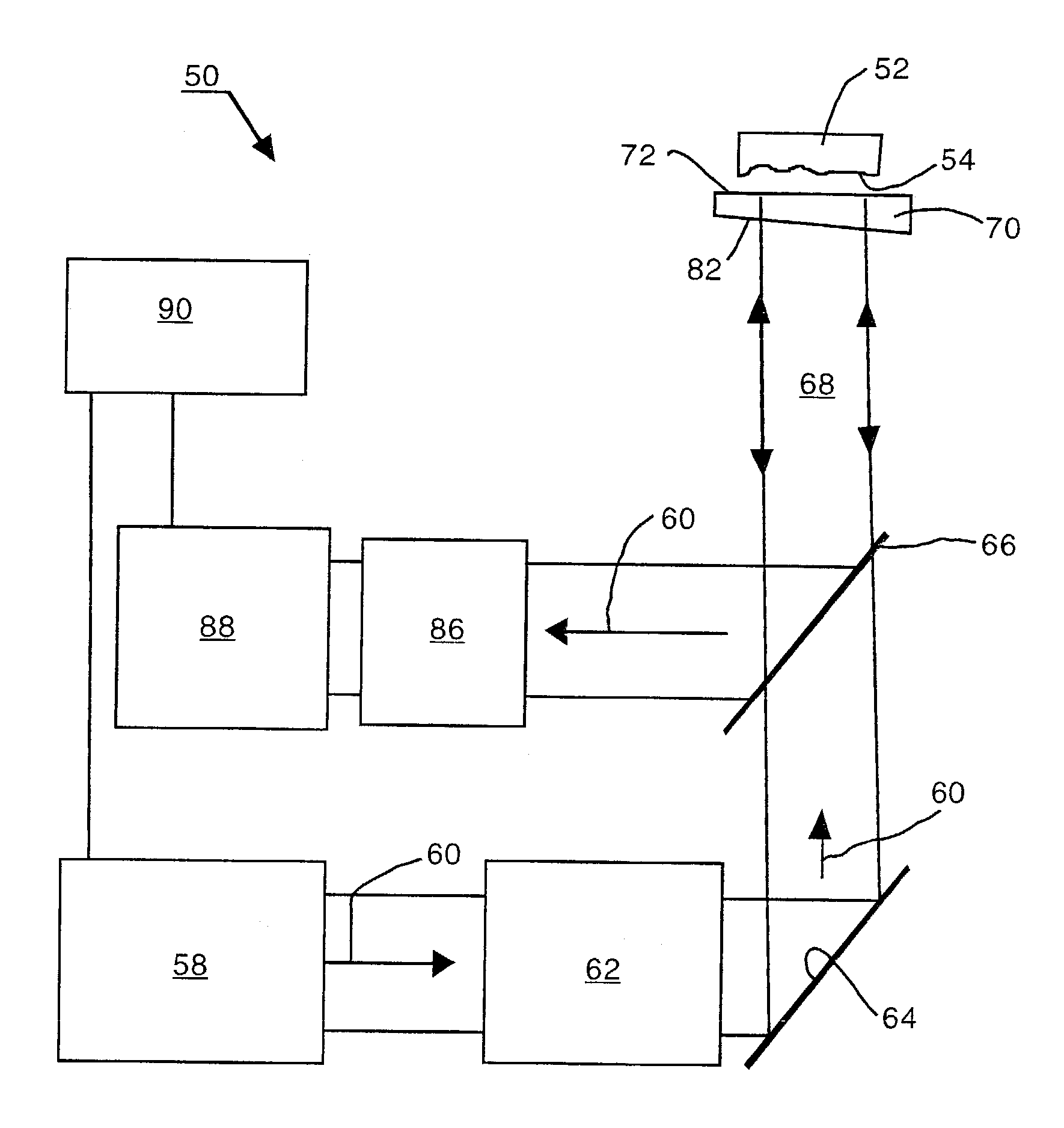
Systems, methods, devices, and computer readable media for terahertz radiation detection
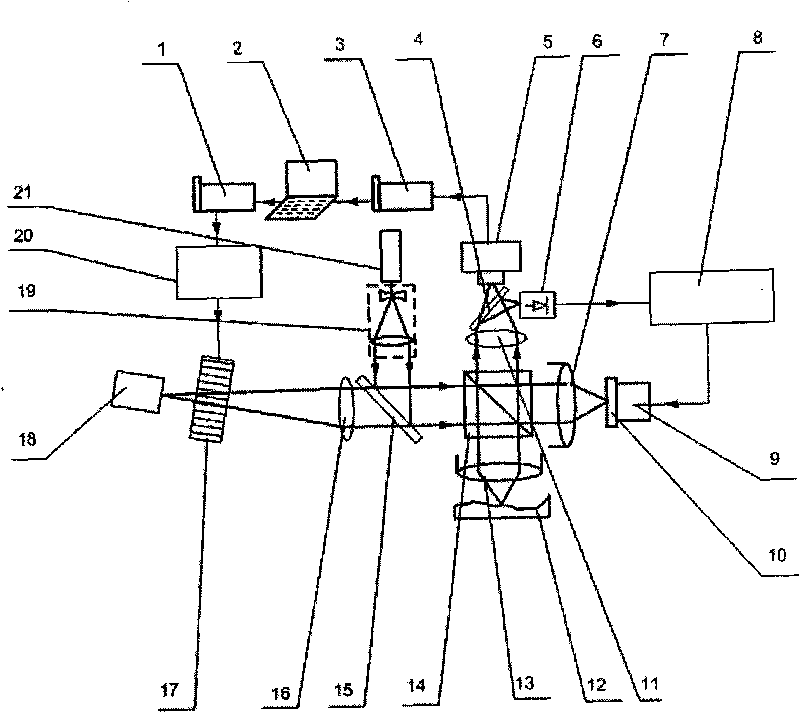
Systems, devices, methods, and computer-readable media relating to terahertz radiation detection are disclosed. A method of detecting terahertz radiation may include transmitting a reference beam and a signal beam through a common-path interferometer. The method may further include transmitting a terahertz beam through a target object. Furthermore, the method may include causing the signal beam and the terahertz beam to simultaneously propagate through an electro-optical element within the common-path interferometer after transmitting the terahertz beam through the target object to induce a phase delay between the signal beam and the reference beam. In addition, the method may include calculating the phase delay and calculating an amplitude of an electric field of the terahertz beam from the phase delay.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Common-path integrated low coherence interferometry system and method therefor
ActiveUS20190003820A1Improve performanceLow wavelength dependenceUsing optical meansSignaling systemLength wave
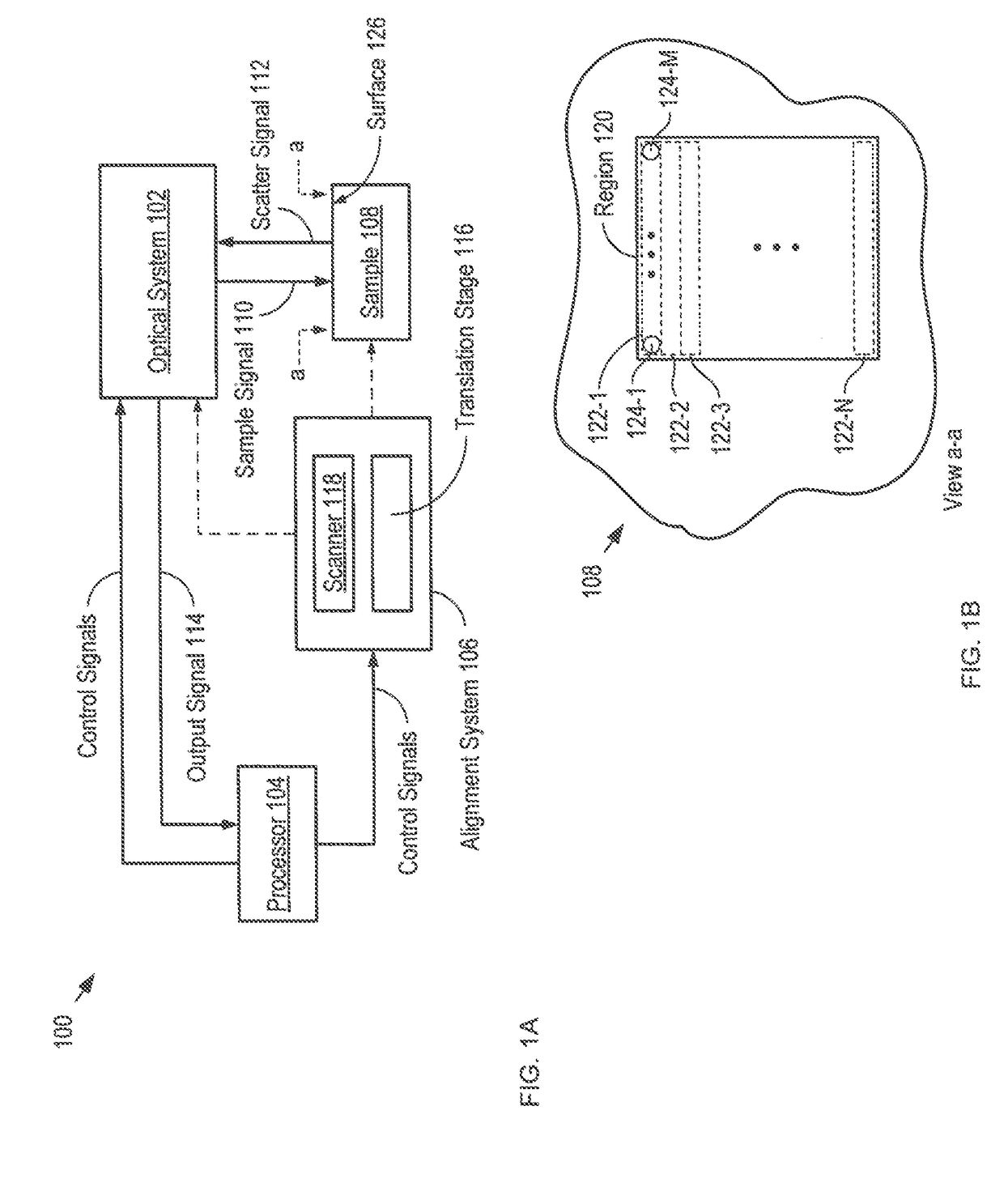
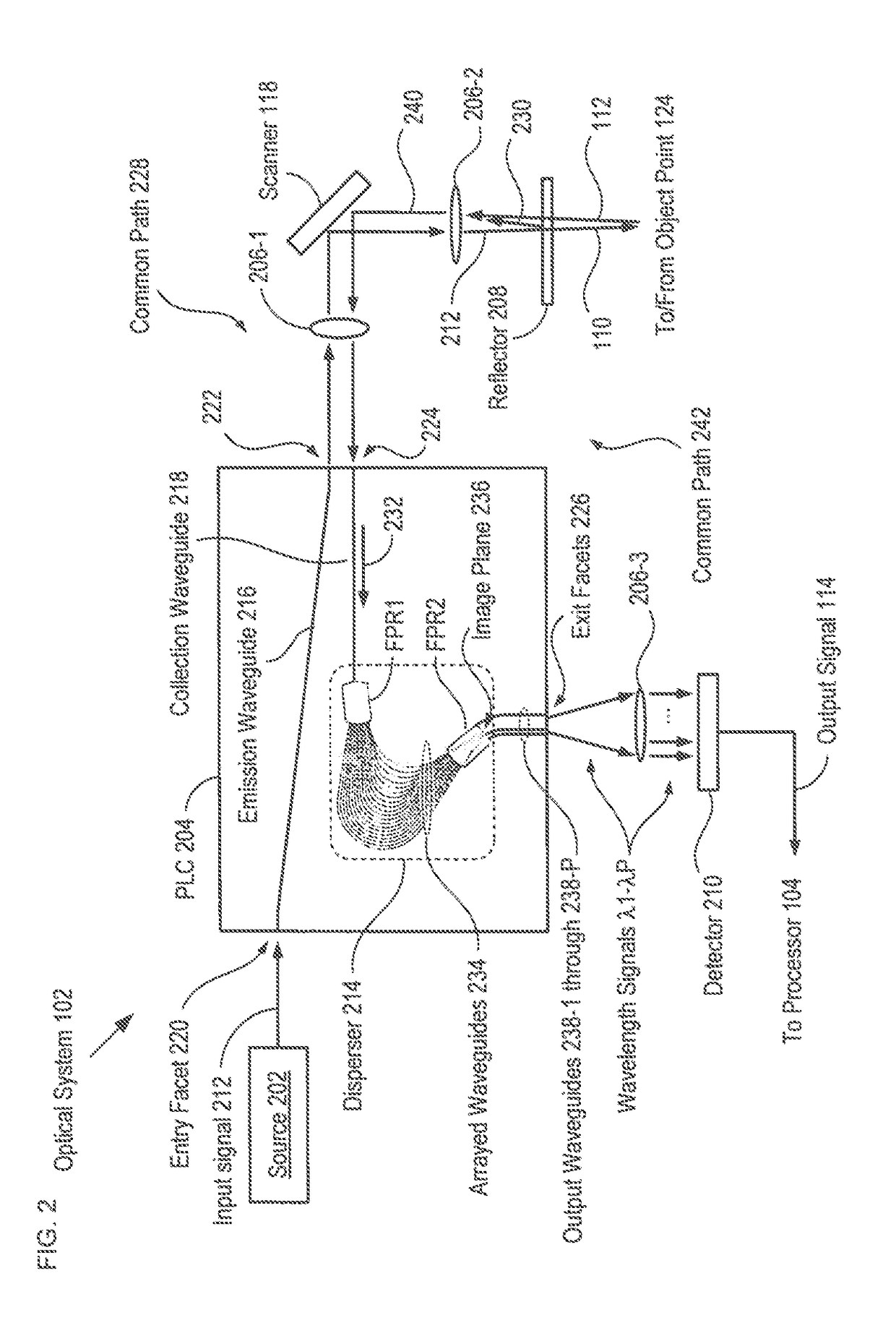
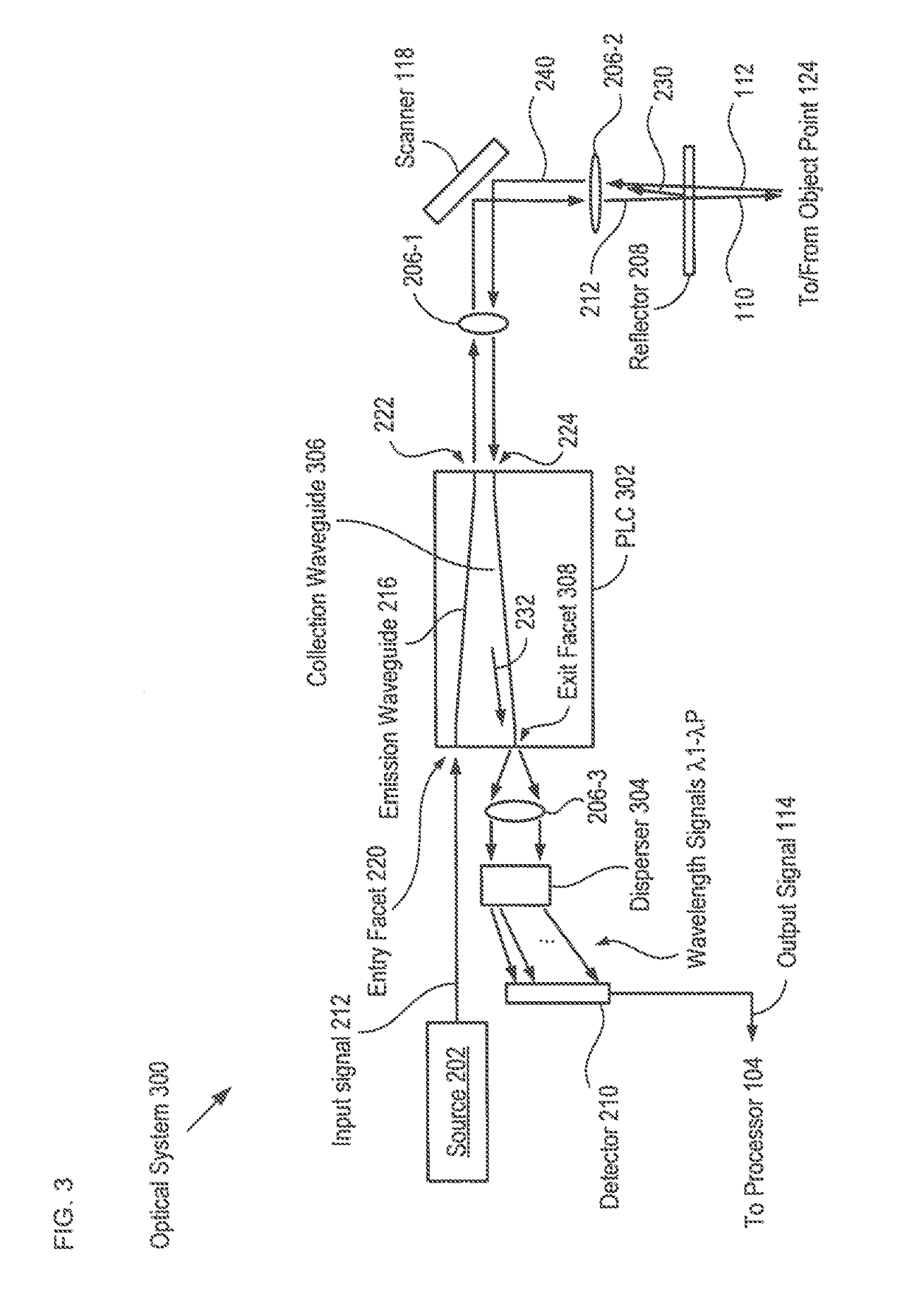
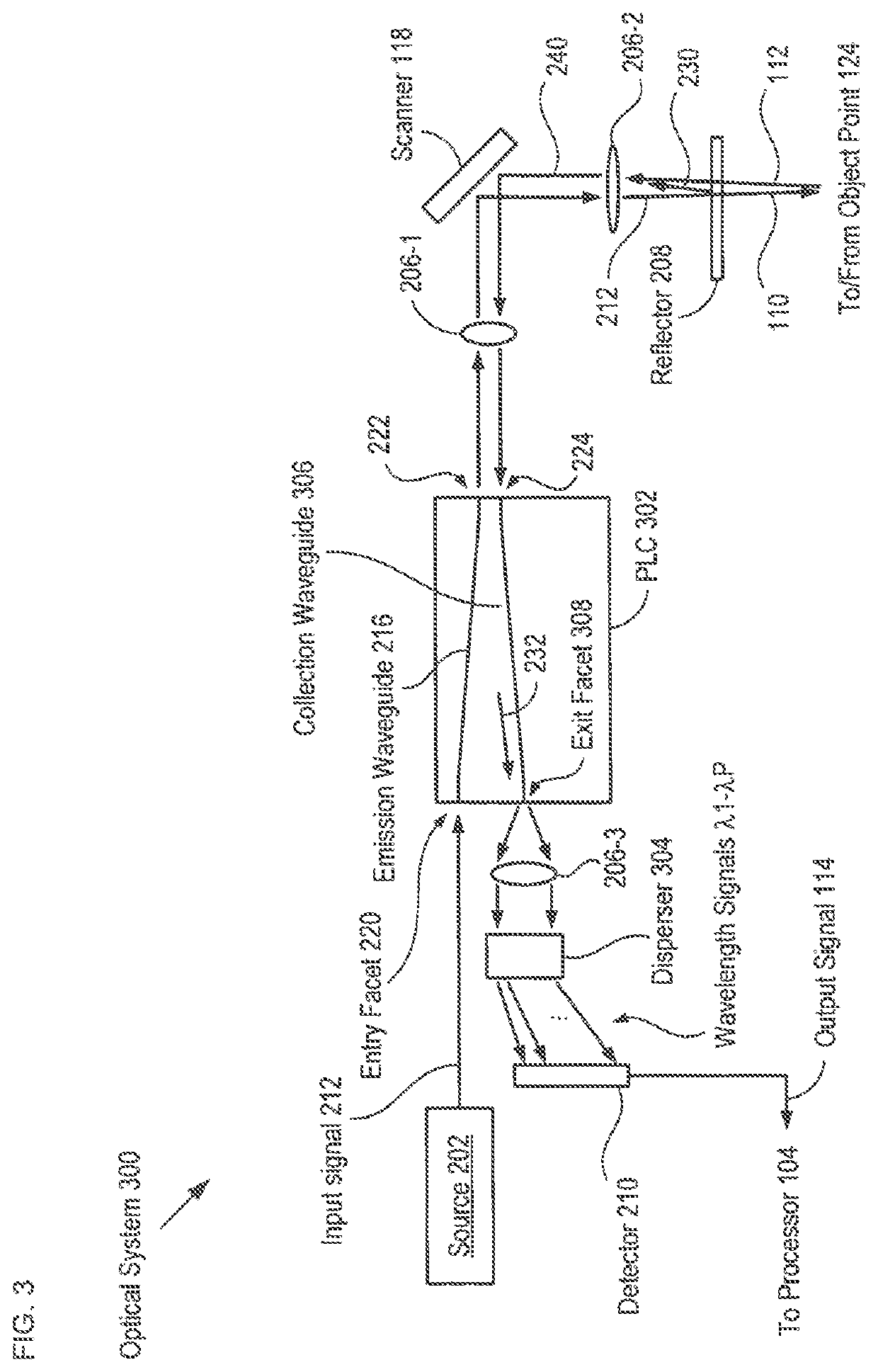
A low coherence interferometry imaging system comprising a common-path interferometer that is at least partially integrated as part of a planar lightwave circuit is disclosed. Imaging systems in accordance with the present invention are implemented in integrated optics without the inclusion of highly wavelength-sensitive components. As a result, they exhibit less wavelength dependence than PLC-based interferometers of the prior art. Further, the common-path interferometer arrangement of the present invention avoids polarization and wavelength dispersion effects that plague prior-art PLC-based interferometers. Still further, an integrated common-path interferometer is smaller and less complex than other integrated interferometers, which makes it possible to integrate multiple interferometers on a single chip, thereby enabling multi-signal systems, such as plane-wave parallel OCT systems.
Owner:ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT BIJ DE UNIV VAN
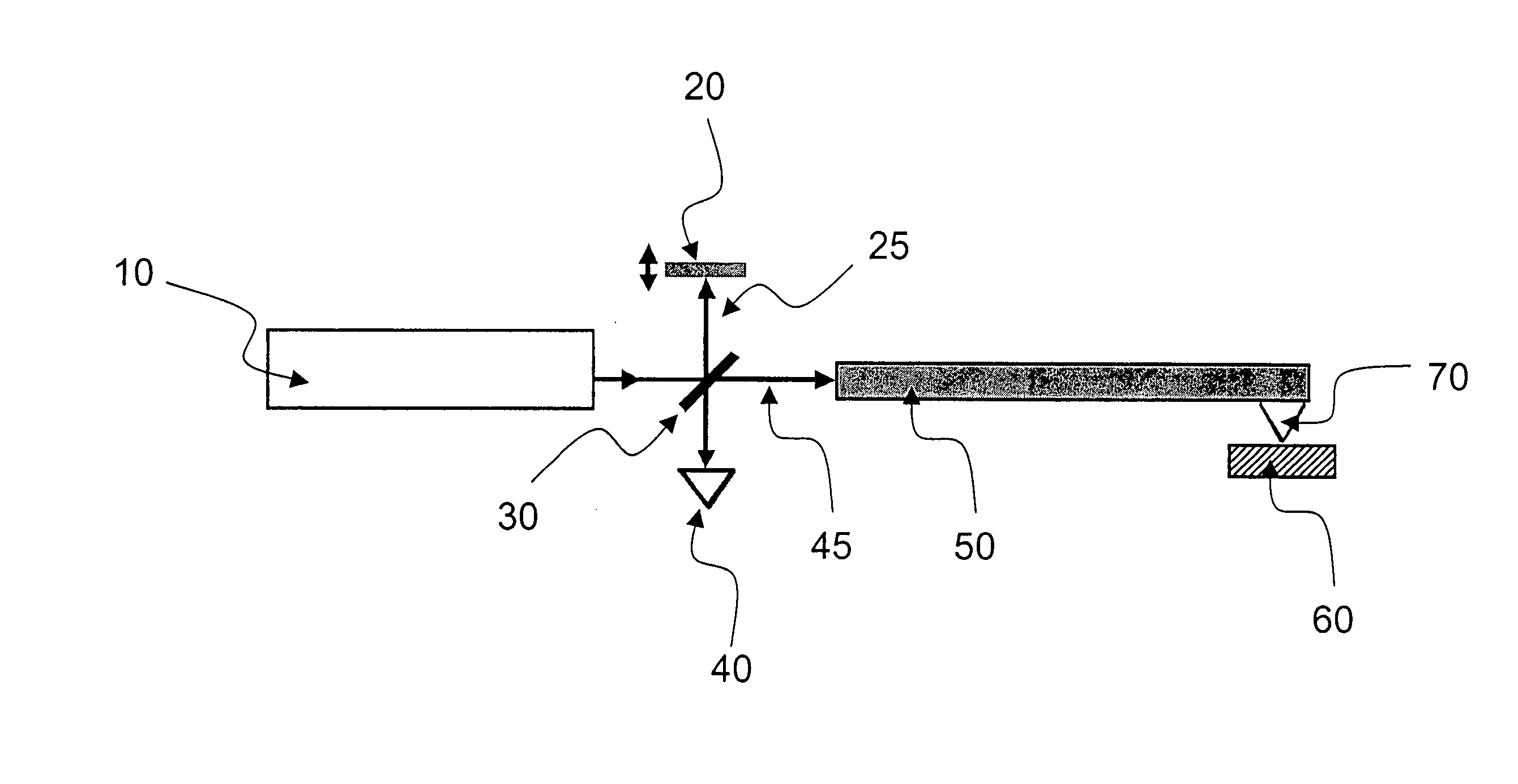
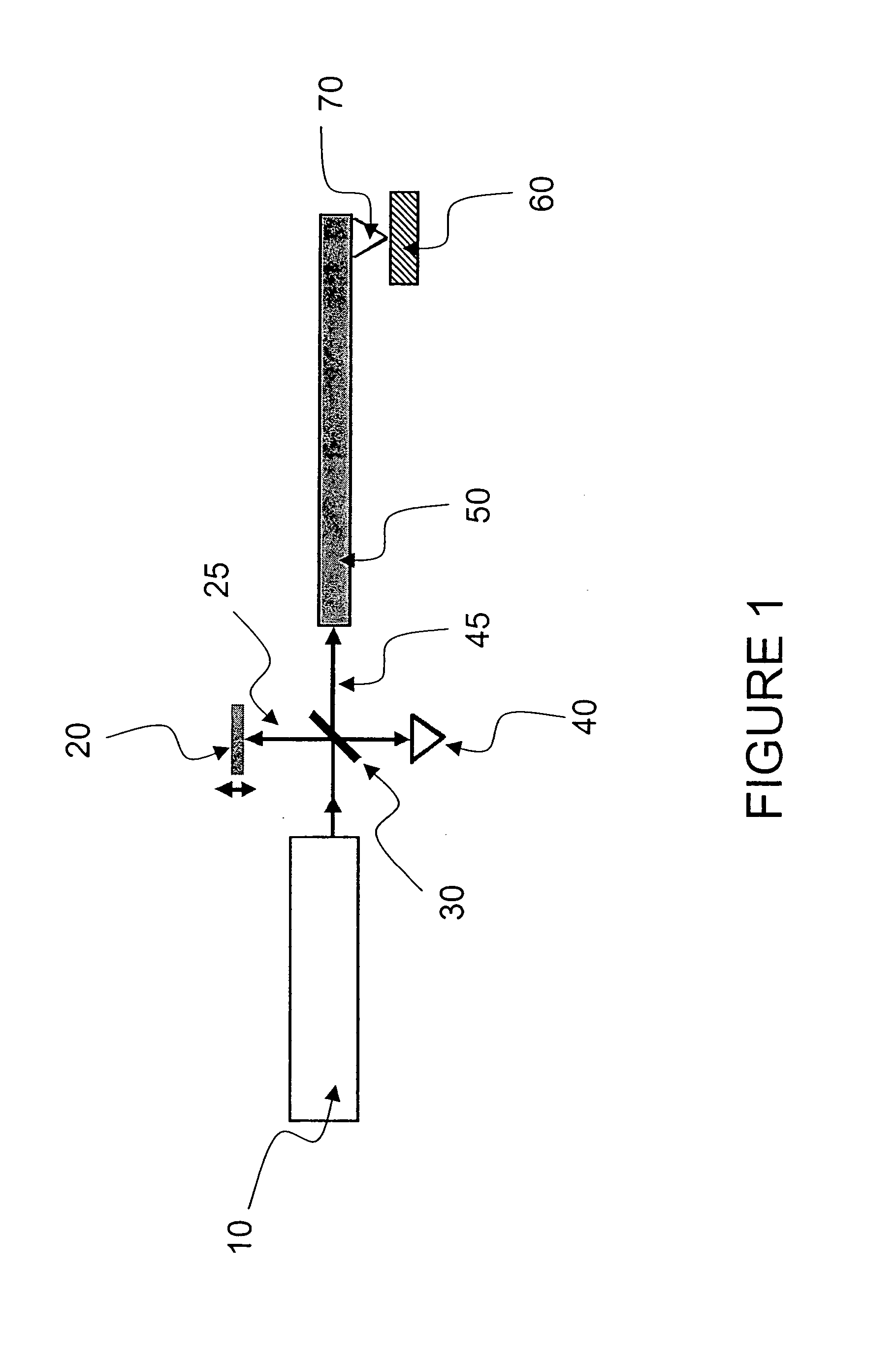
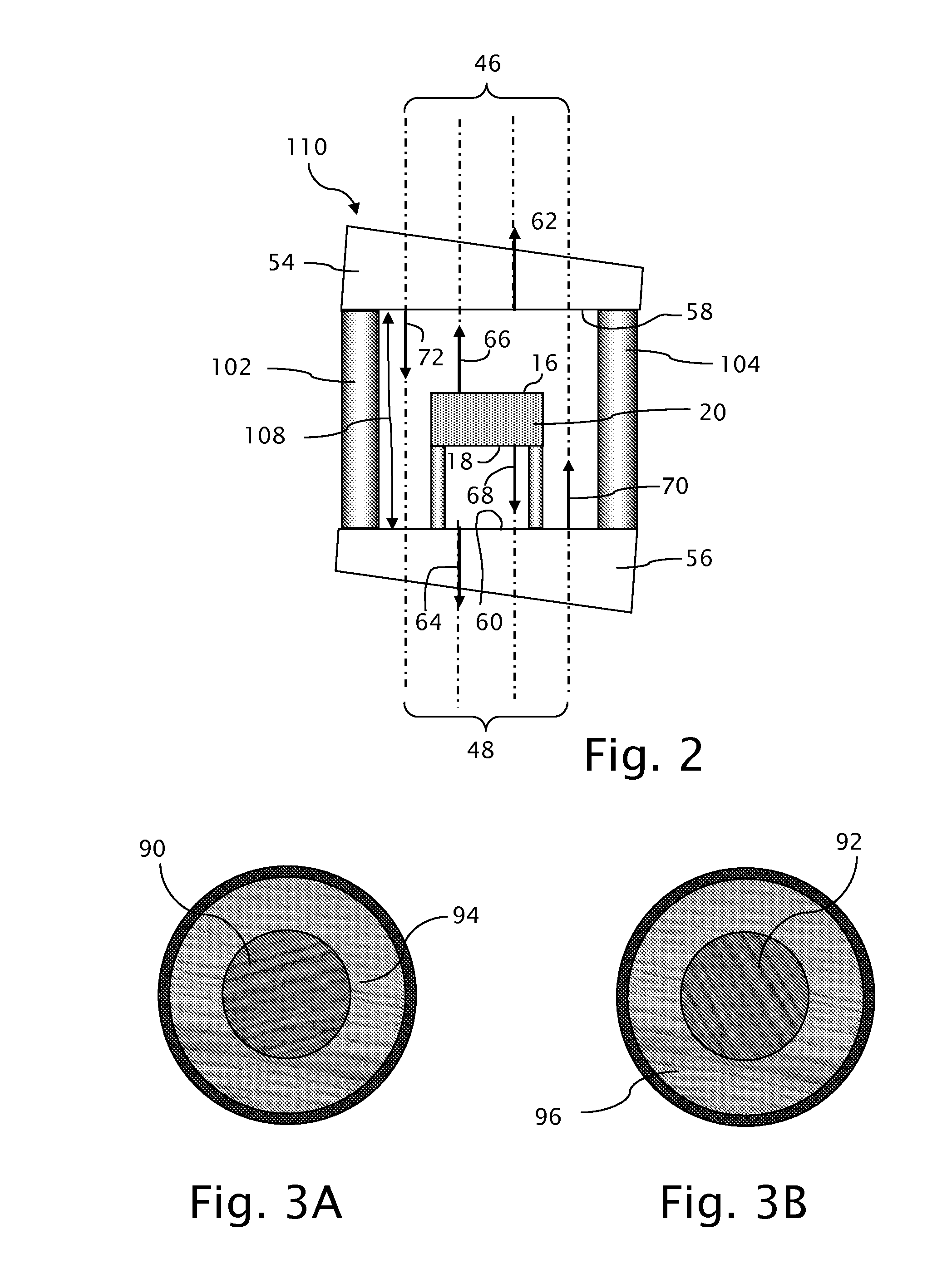
Common-path interferometer rendering amplitude and phase of scattered light
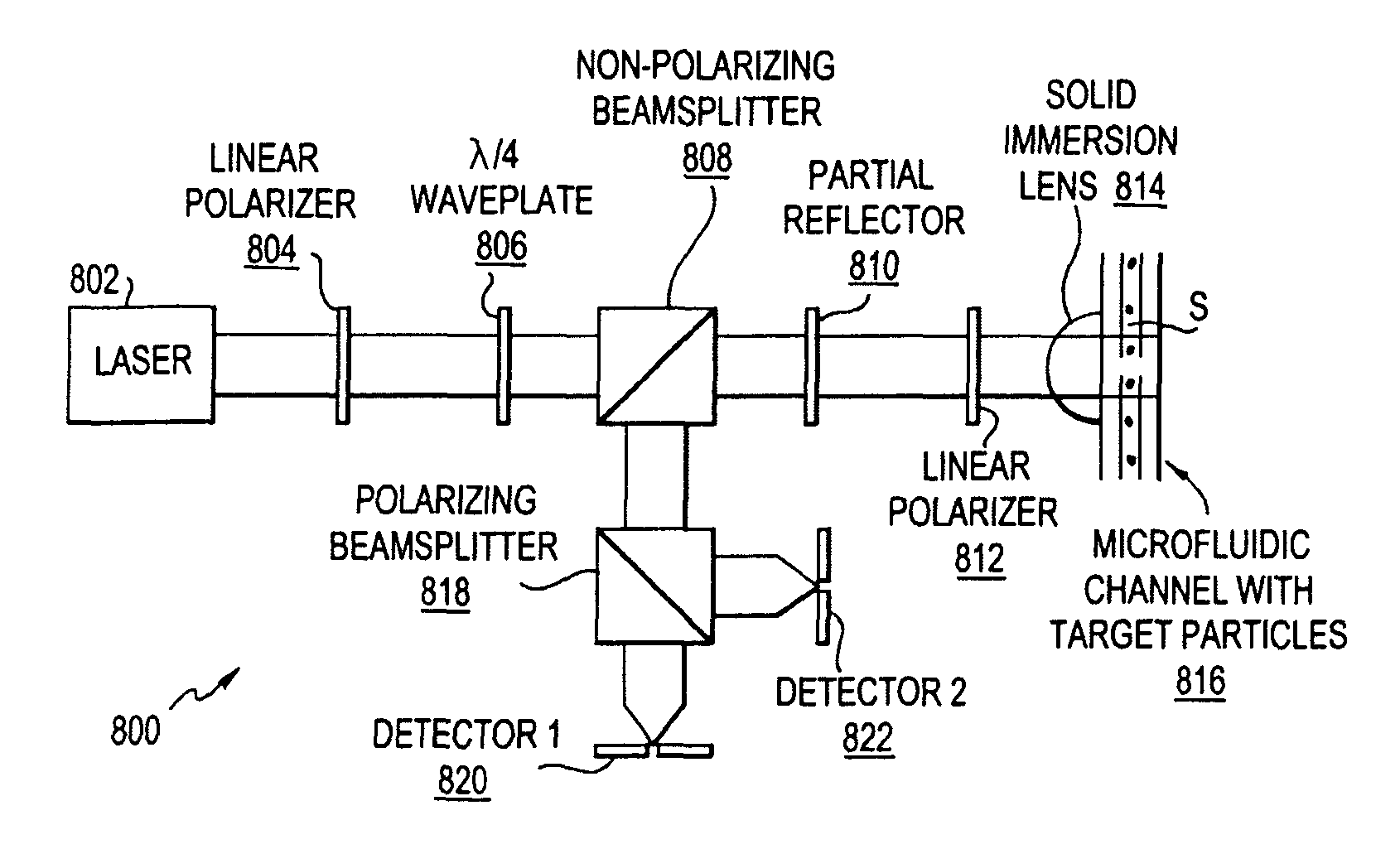
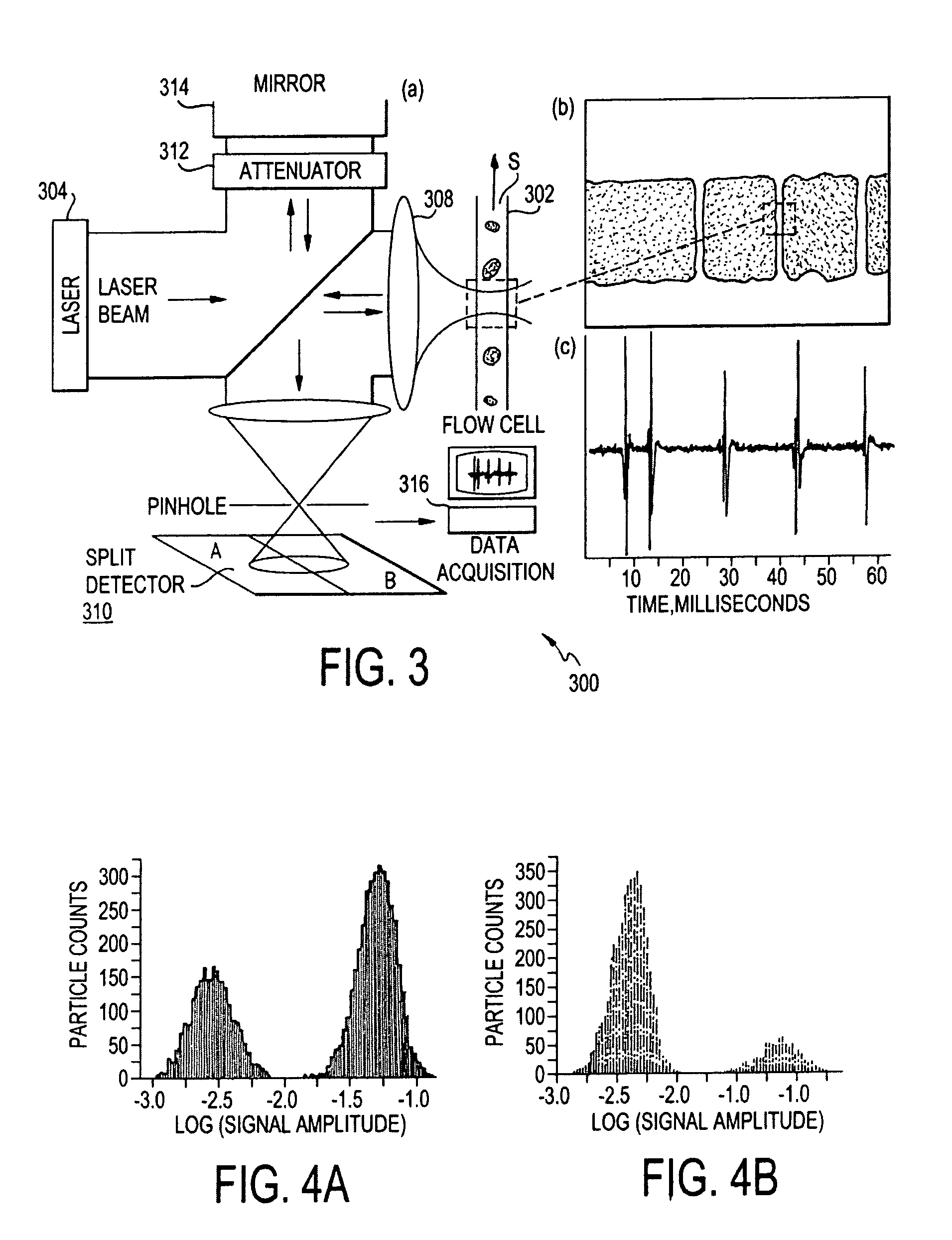
InactiveUS7876450B2Reduce phase noiseMore compactNanoparticle analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansOptoelectronicsMicroparticle
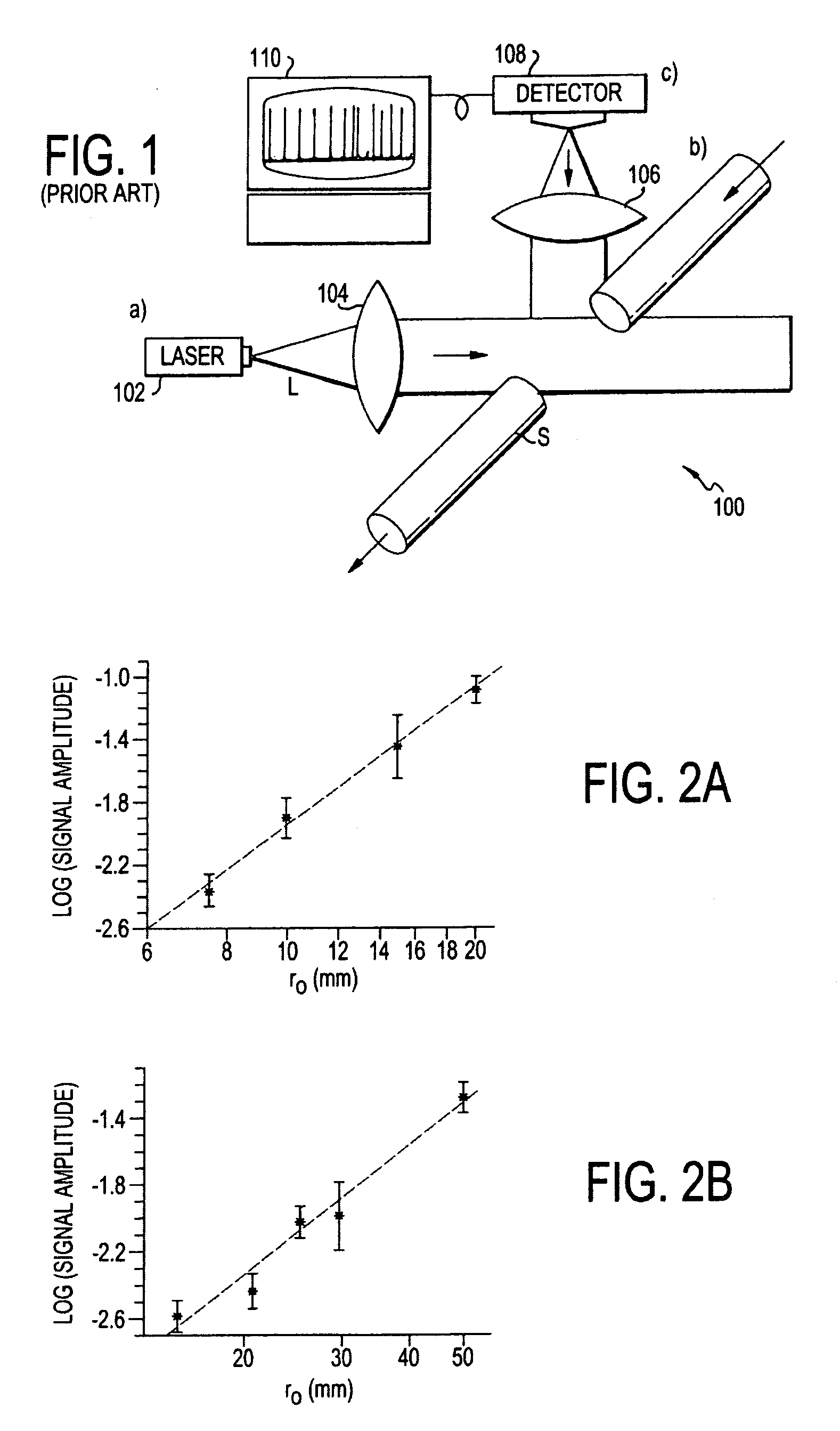
A beam of coherent laser light with linear polarization oriented at 45 degrees to vertical is expanded, and passes through a quarter-wave plate with the fast axis oriented vertically, creating circularly polarized light. The light then passes through a non-polarizing 50 / 50 beamsplitter. A partial reflector then collinearly reflects a portion of the beam, which is used as the reference beam. The transmitted light passes through a linear polarizer oriented at 45 degrees to vertical, and is focused via a lens onto the sample of interest. Light scattered from this region is re-collimated by the lens and the directed through the linear 45 degree polarizer and through the partial reflector, where it recombines with the reference beam. One use of the invention is to detect microparticles in water.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Double frequency-sweeping light source ranging system and method based on cascaded interferometer
ActiveCN110132138AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityUsing optical meansMach–Zehnder interferometerDouble frequency
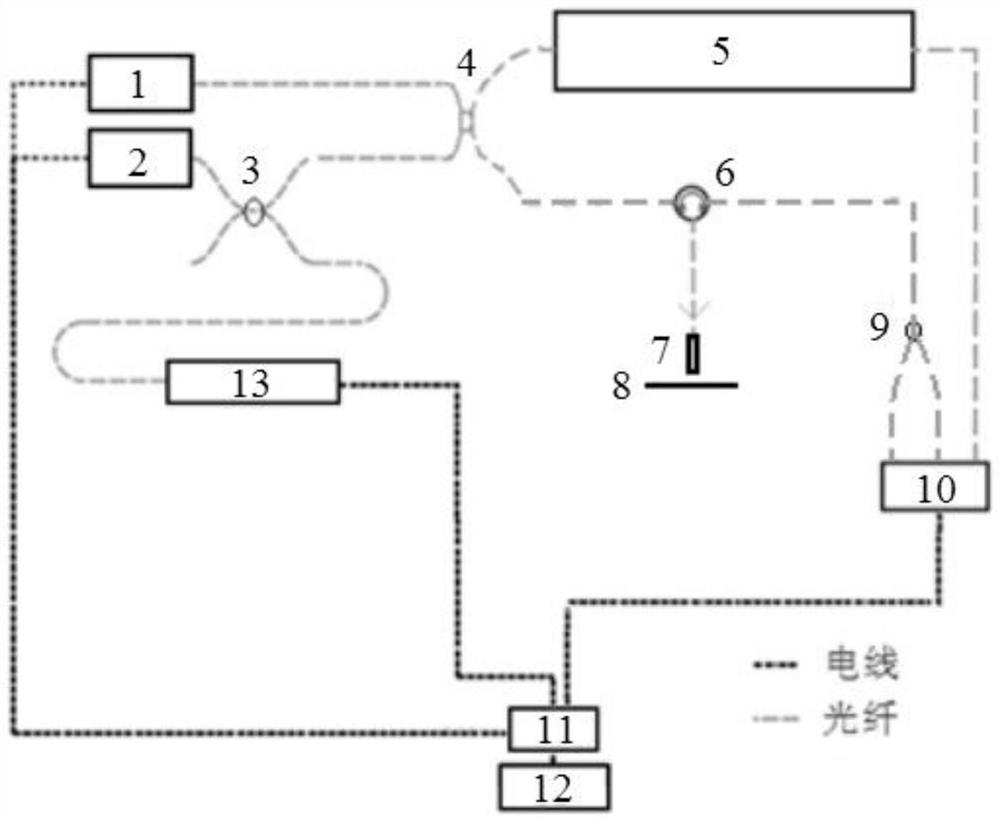
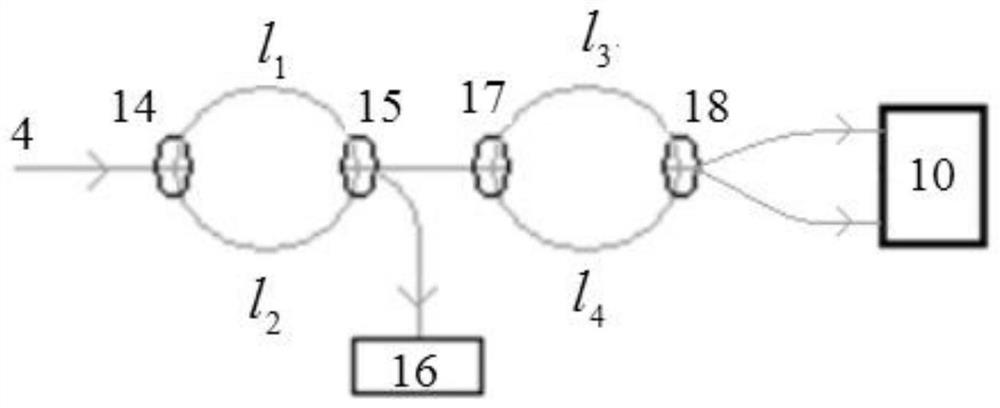
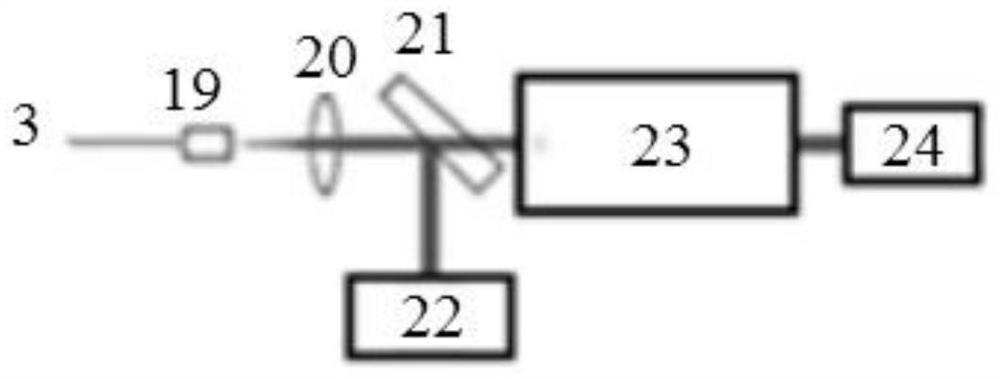
The invention relates to a double frequency-sweeping light source ranging system and method based on cascaded interferometer. Coherent light emitted by a first frequency-sweeping light source and a second frequency-sweeping light source enters an optical fiber coupler, and then respectively enters a main interferometer and a cascaded Mach-Zehnder interferometer after light-splitting; partial coherent light entering the main interferometer is first split through the optical fiber coupler, and a part reenters a common-path interferometer containing a sample through an optical fiber circulator, the returned sample interference spectrum signal and the other end output of the optical fiber coupler enter a balance detection device of the interference spectrum signal together so as to form an interference spectrum signal; and the interference spectrum signal and a reference interference signal formed in the cascaded Mach-Zehnder interferometer are synchronously collected; the light emitted bythe second frequency-scanning light source enters the optical fiber coupler, the other part of light after splitting enters a light source frequency detection unit, and a wavelength signal is synchronously collected. The accuracy and the reliability of the measurement can be improved.
Owner:宁波核芯光电科技有限公司
Compound interferometer with monolithic measurement cavity
ActiveUS20120300213A1Reducing undesirable cross influenceRealized benefitsInterferometersUsing optical meansMeasurement testCoupling
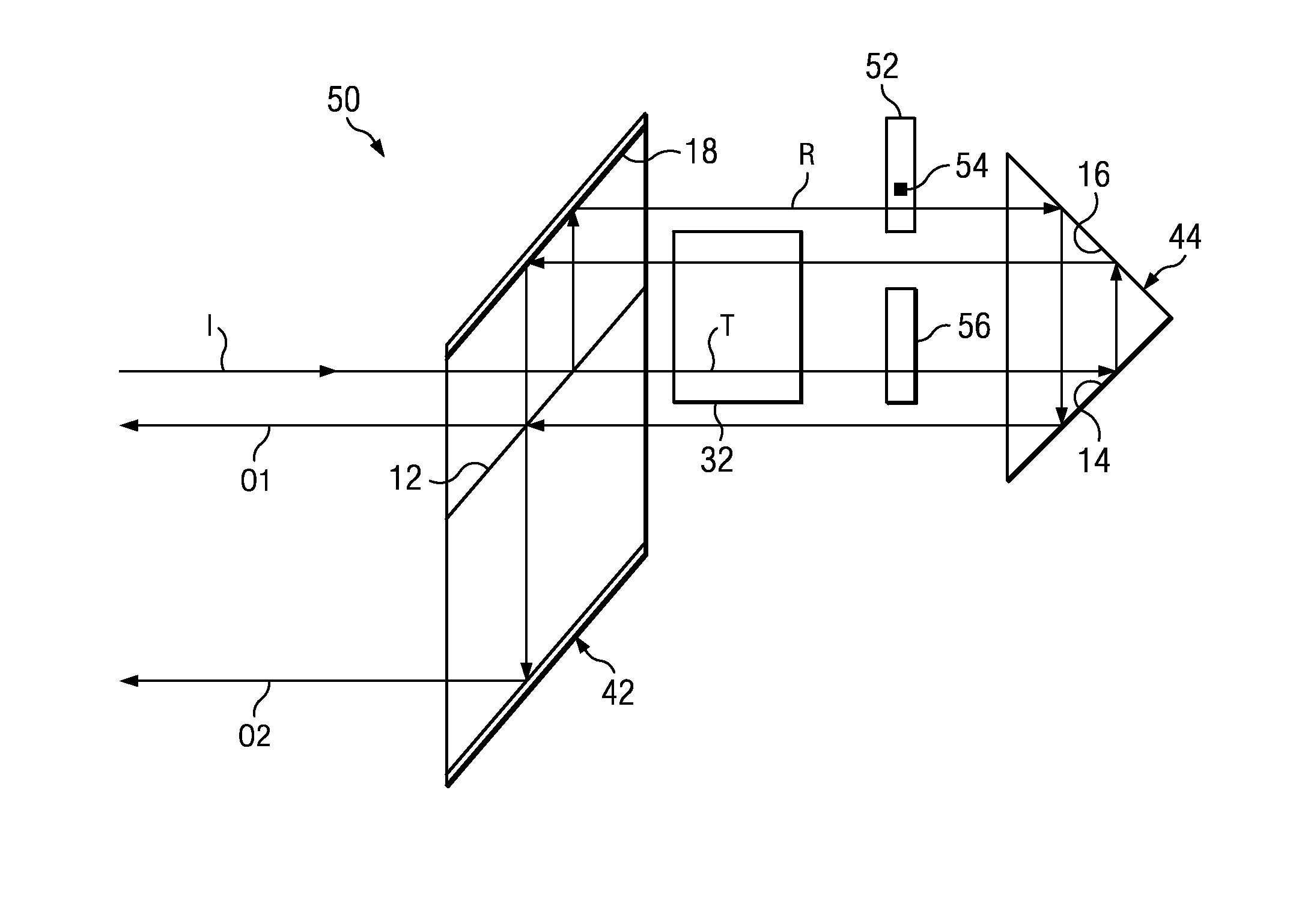
A compound common-path interferometer including first and second measurement arms for measuring a test object is arranged so that a reference optic of the first measurement arm is disconnected from a remainder of the first measurement arm and a coupling between the reference optics of the first and second measurement arms forms a monolithic measurement cavity for maintaining reference surfaces of the reference optics at a fixed spacing and orientation. Separate supports are provided for the monolithic measurement cavity and the remainder of the first measurement arm.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method and system of performing interference testing on aspheric surface optical element
The invention discloses a method and system of performing interference testing on an aspheric surface optical element. In reflection, a diffractive element horizontally arranged on an optical axis of a common path interferometer forms two diffraction beams (with different diffraction items). The first diffraction beam keeps a wave surface irradiating to the diffractive element; the second diffraction beam has a wave surface corresponding with a surface to be detected. The first diffraction beam can be reflected by a surface in a cat eye device; the second diffraction beam can be reflected by a surface of a confocal surface. The surface to be detected can be adjusted to balance the intensity of the first diffraction beam and the second diffraction beam reflected to the surfaces.
Owner:帝麦克斯(苏州)医疗科技有限公司
Common-path frequency-scanning interferometer
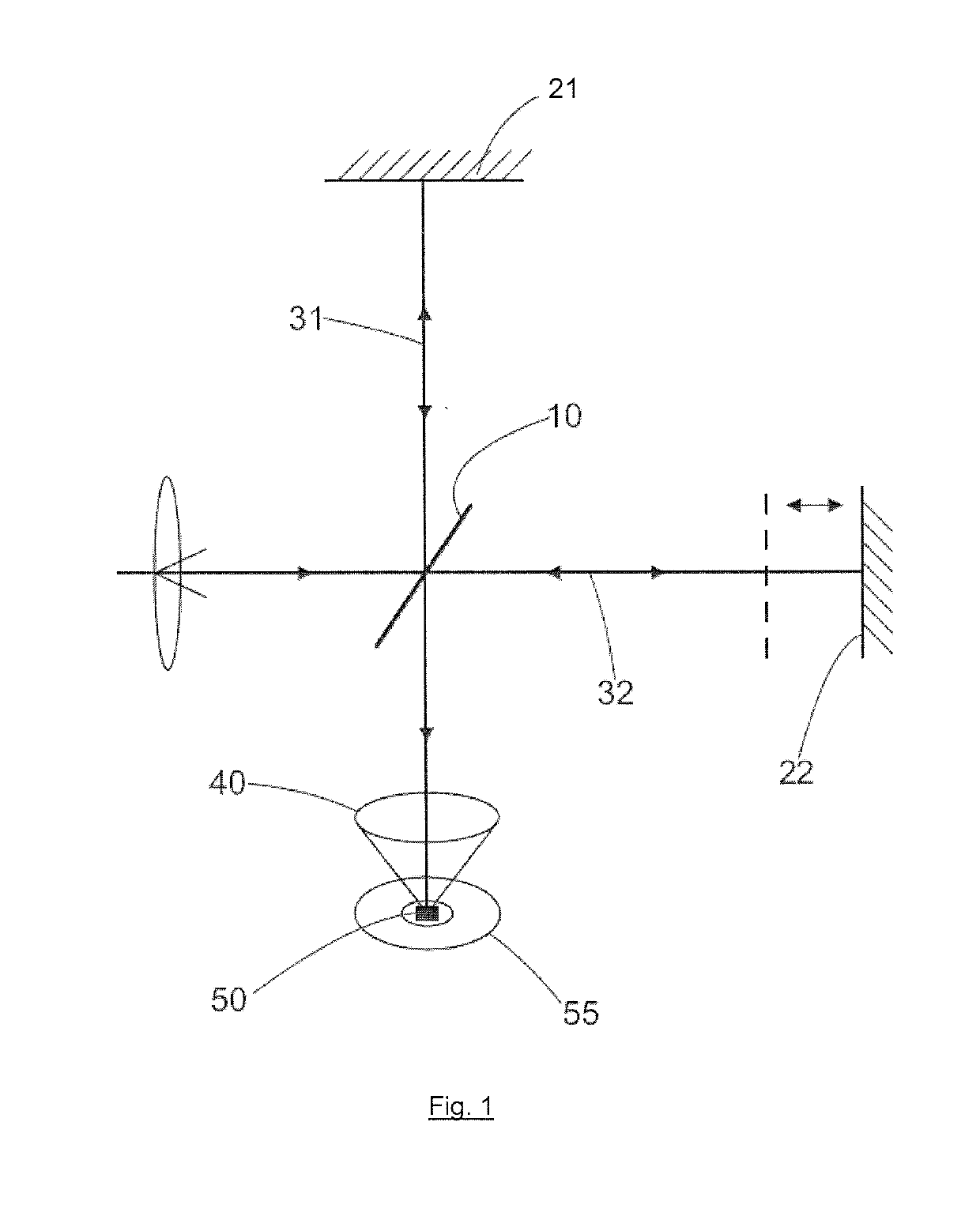
Frequency-scanning interferometry is applied to common-path interferometers for measuring topographical features of test objects. A reference element located adjacent to a test object functions as both a beamsplitter and a reference surface. A first portion of a measuring beam reflects from the reference surface of the reference element as a reference beam, and a second portion of the measuring beam transmits through the reference element to and from a surface of the test object as an object beam. Both beams are conveyed along a common path to a detector that records a plurality of intensity variations produced by constructive and destructive interference between localized portions of the object and reference beams associated with different transverse coordinates on the test object surface. An illumination frequency of the measuring beam is incrementally modified through a range of different frequencies sufficient to alternate the intensity variations between conditions of constructive and destructive interference, which occur at modulation frequencies sensitive to path length differences between corresponding points on the surfaces of the test object and reference element.
Owner:LIGHTGAGE
Monolithic, spatially-separated, common path interferometer
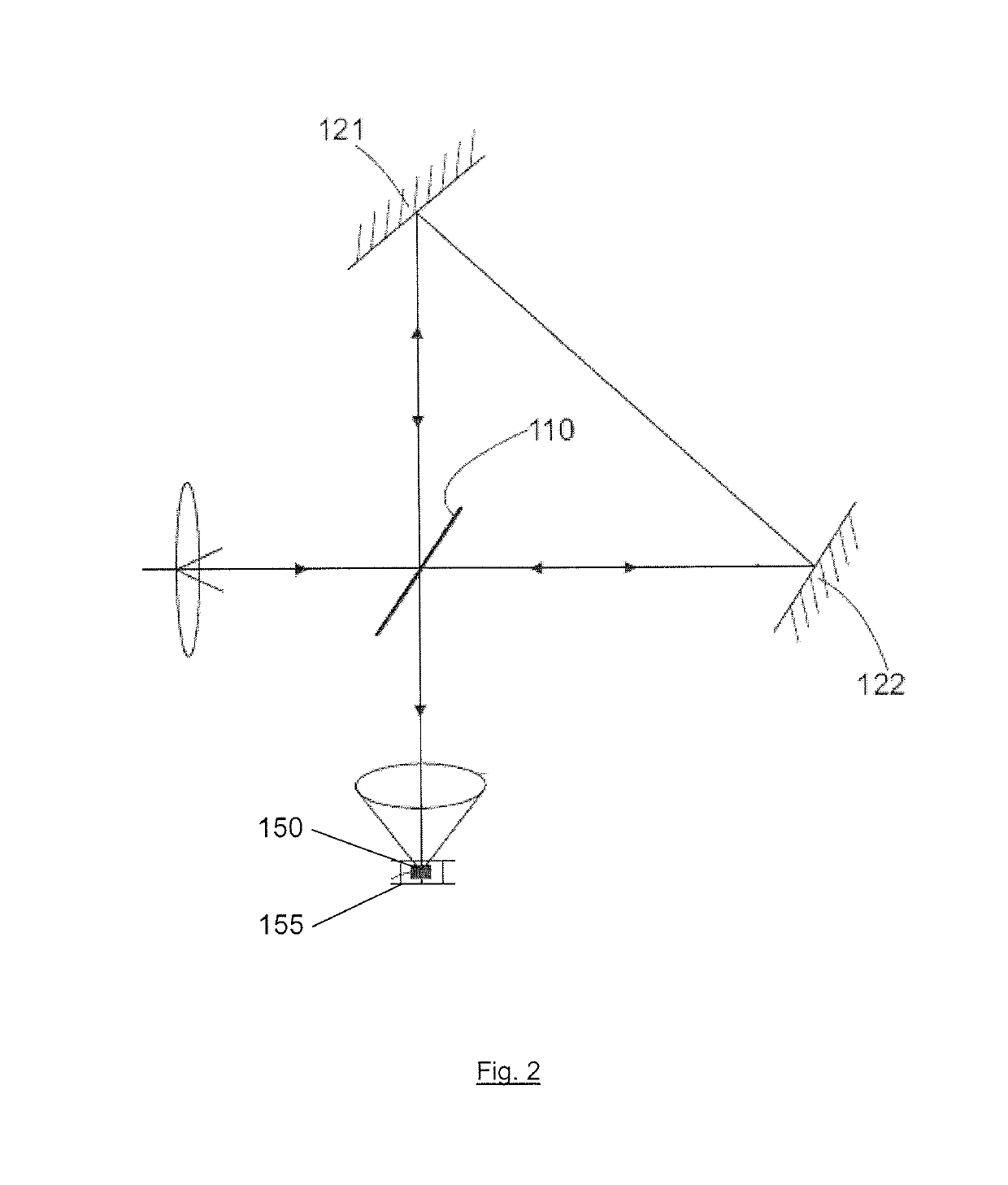
ActiveUS7372577B1Simplify deploymentEasy maintenanceRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBeam splitterHeterodyne interferometer
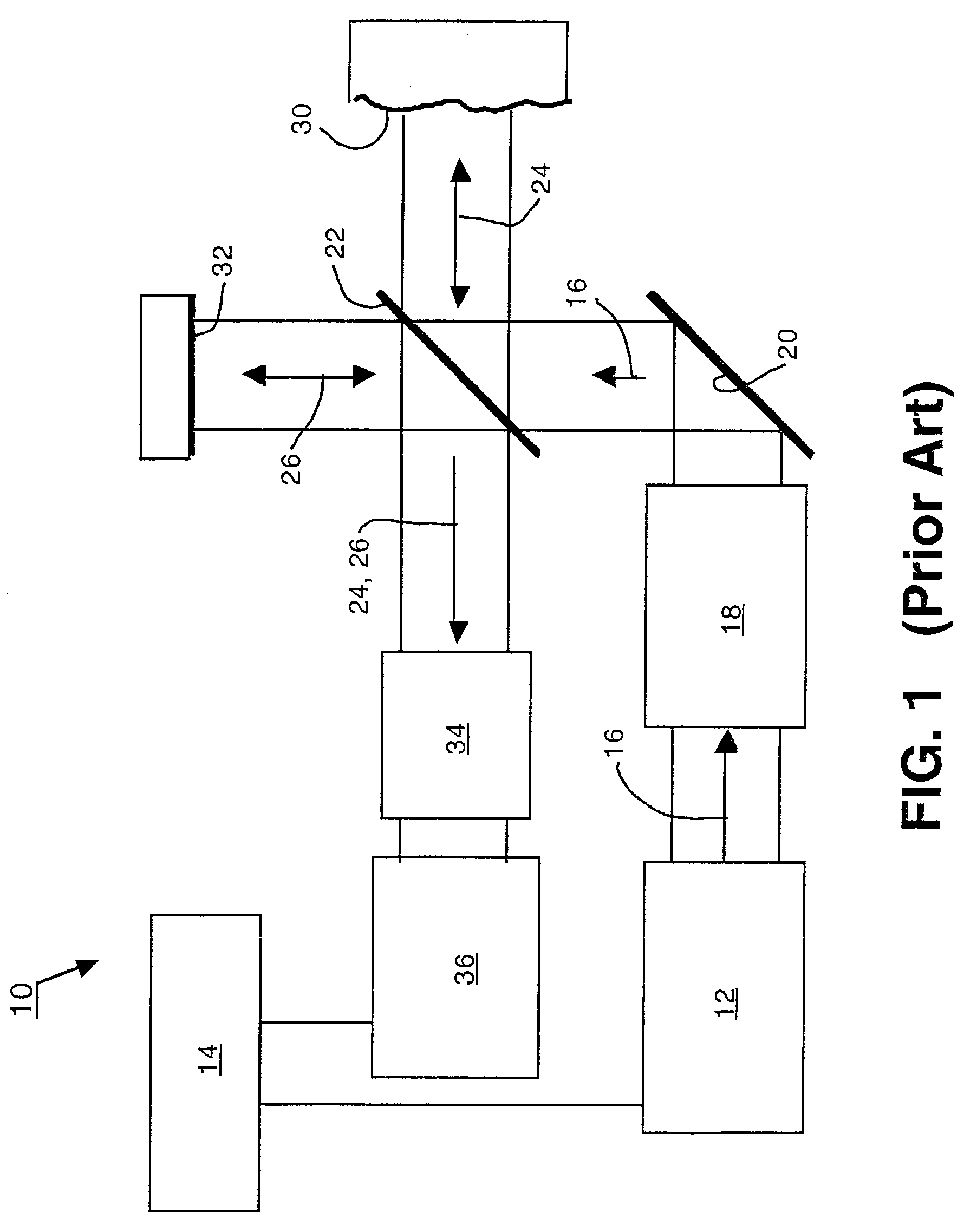
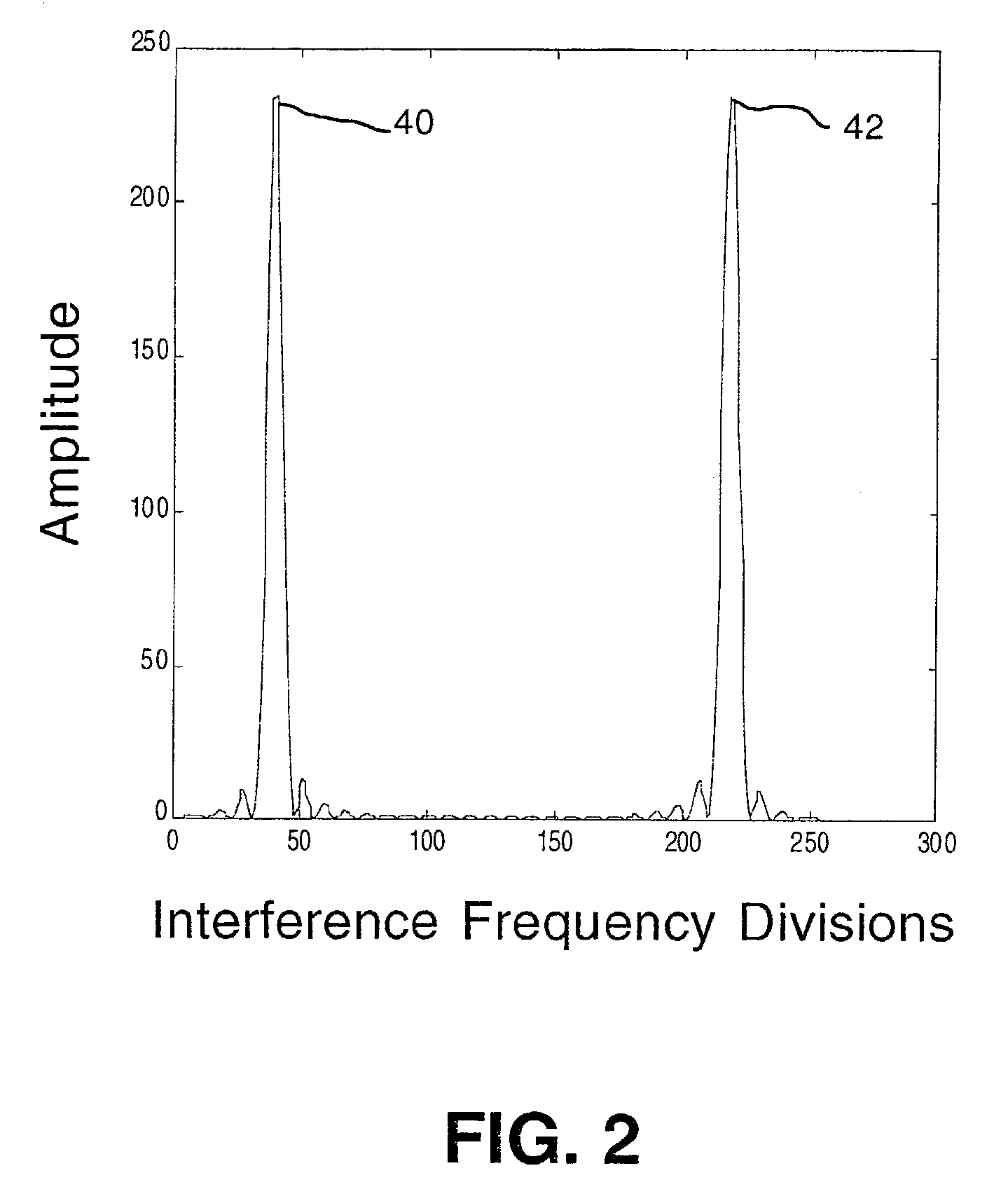
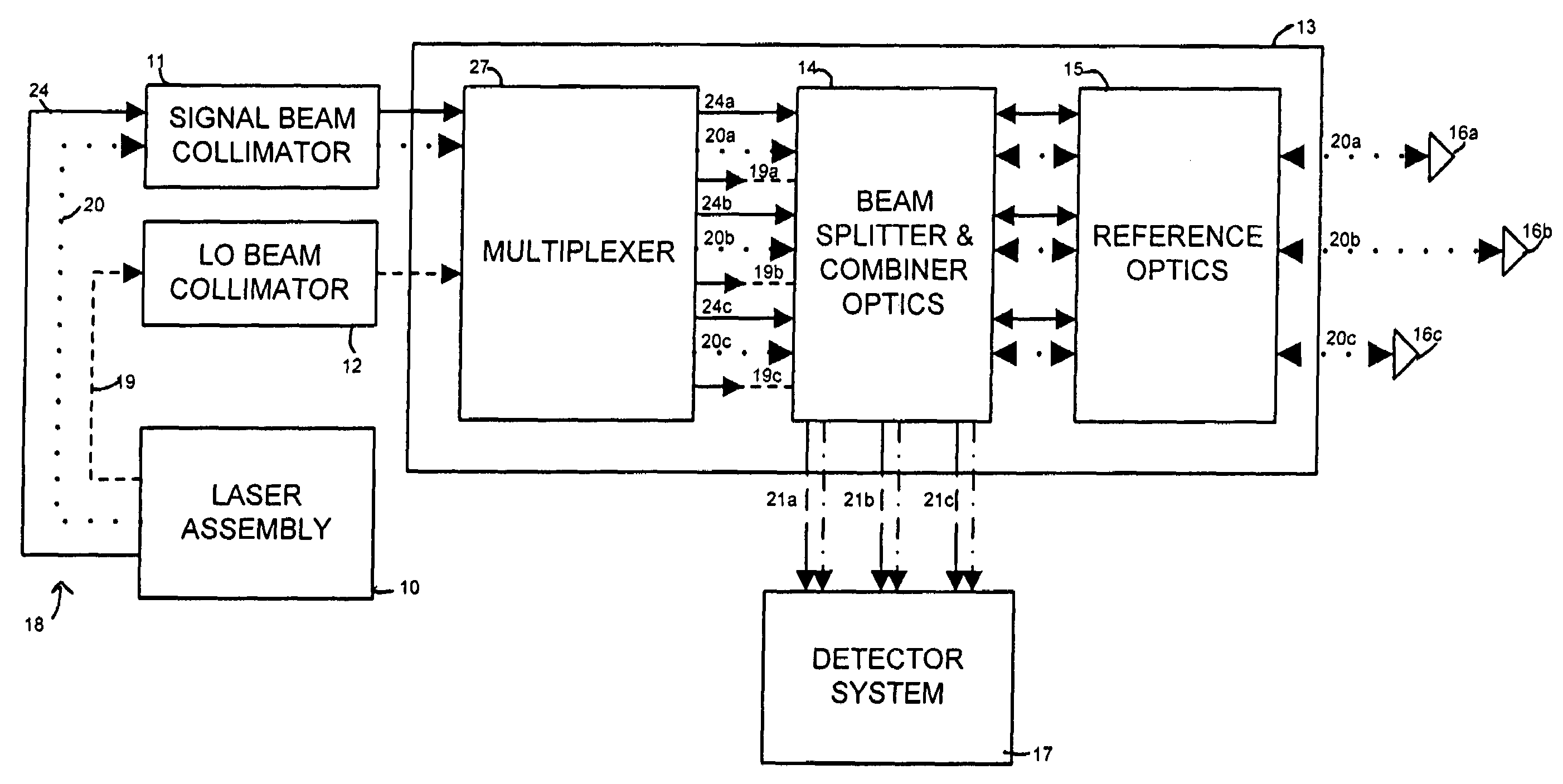
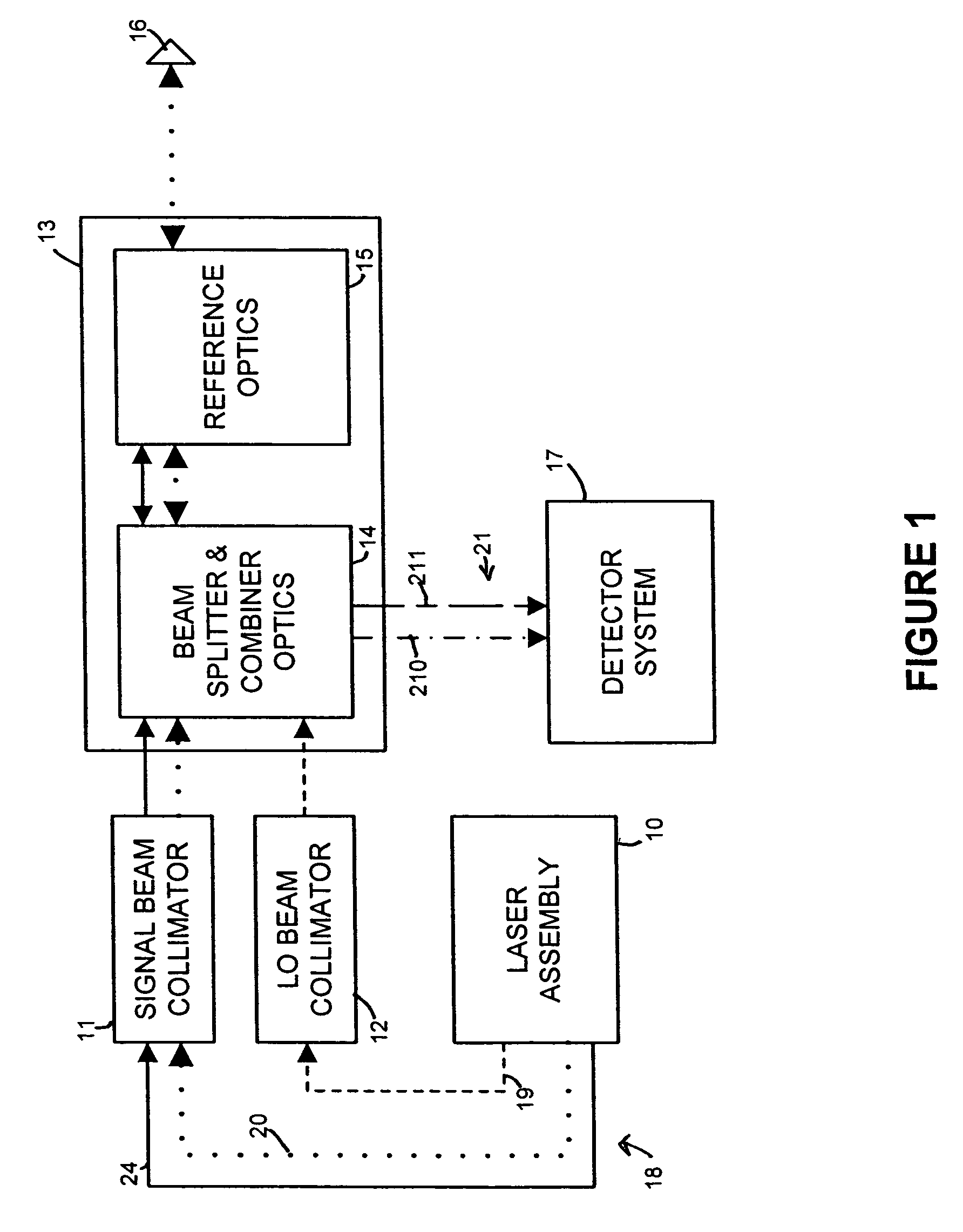
Spatially-separated heterodyne interferometer architecture is combined with monolithic glass construction techniques to provide a monolithic, spatially-separated, common-path interferometer. The monolithic interferometer includes multiple optical components bonded together into a monolithic structure. The bonded components provide both optics and structure for the interferometer, thereby producing a small, compact, and light-weight interferometry system. Beam splitters and combiners are provided on the interfaces between the optical components to direct and combine signal measurement, signal reference and local oscillator beams used in the interferometry system. The spatially-separated architecture reduces cyclic error values below those of polarization-separated interferometers. In addition, the monolithic architecture of the interferometer minimizes the impact of mechanical, thermal, and optical variations within the system.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Holographic storage system based on common path interferometry
InactiveUS7830572B2Improve data transfer rateImprove lighting efficiencyRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansHolographic storageSpatial light modulator
The present invention relates to a holographic storage system, and more specifically to a holographic storage system using a phase spatial light modulator.According to the invention a holographic storage system with a phase SLM for imprinting a 2-dimensional phase data pattern onto an object beam includes a common path interferometer for converting the phase data pattern of the object beam into an intensity data pattern.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Assembly for Increasing the Resolution of a Laser Scanning Microscope
ActiveUS20200026050A1Easy to carryLow production costMicroscopesLaser scanning microscopeBeam splitter
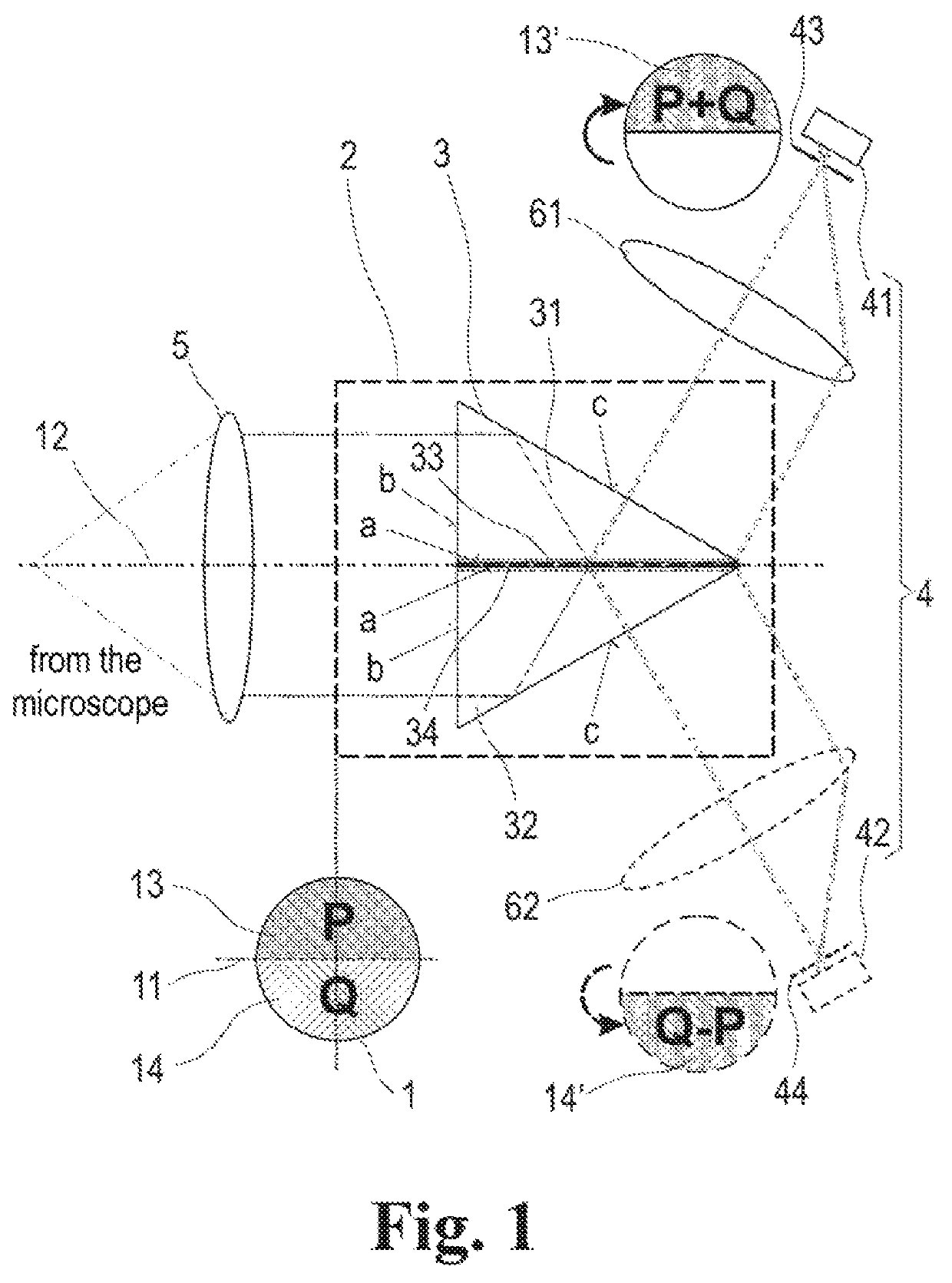
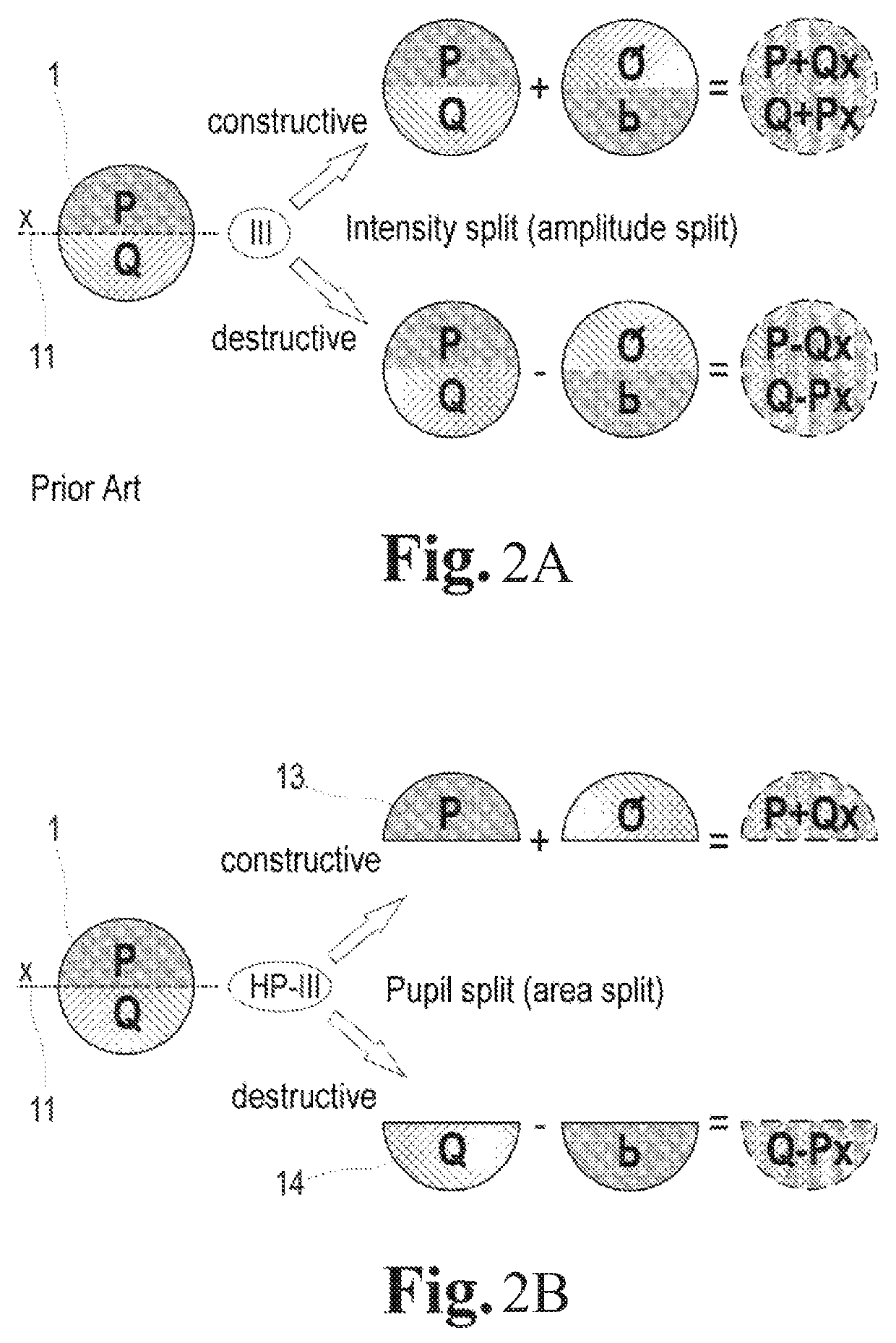
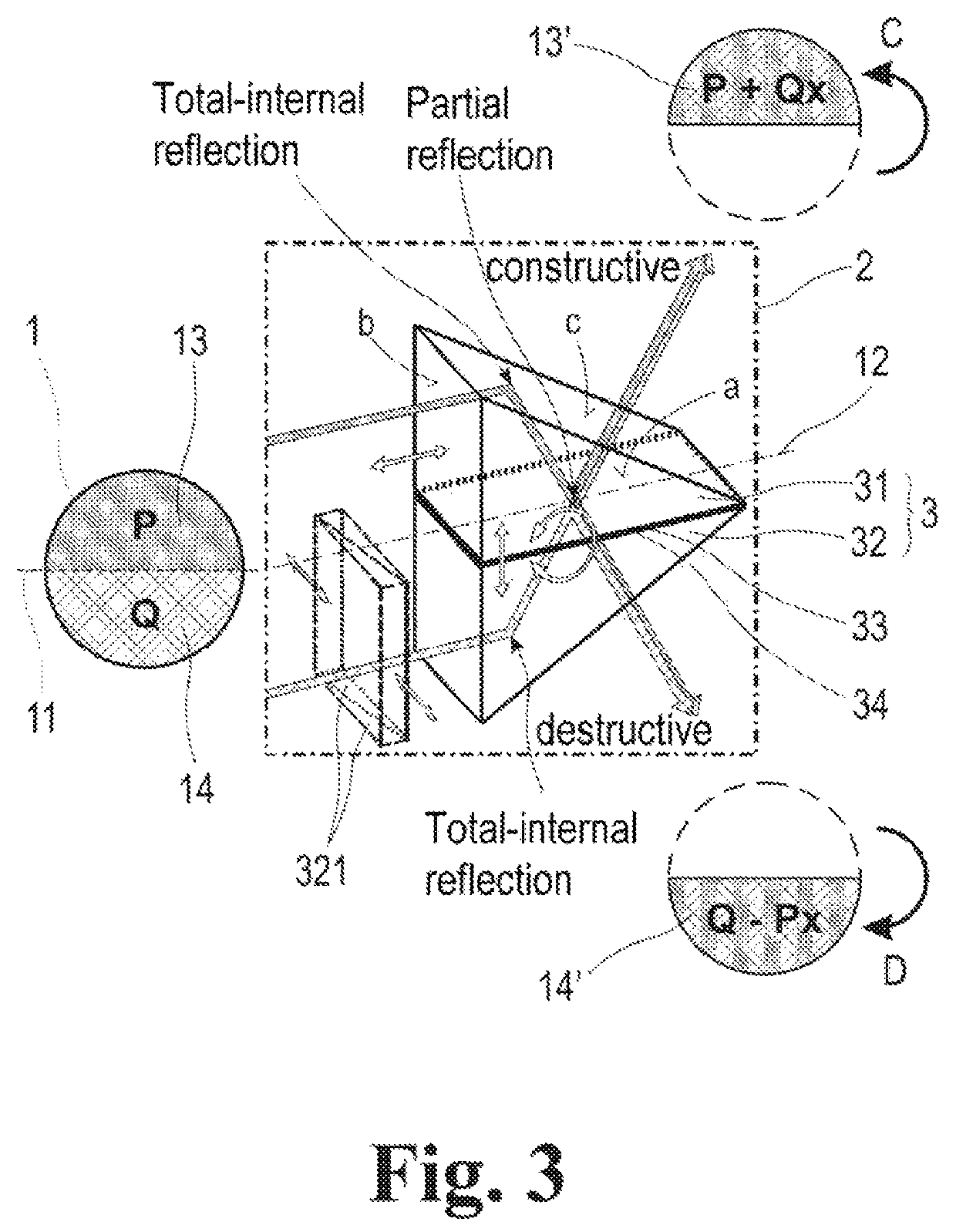
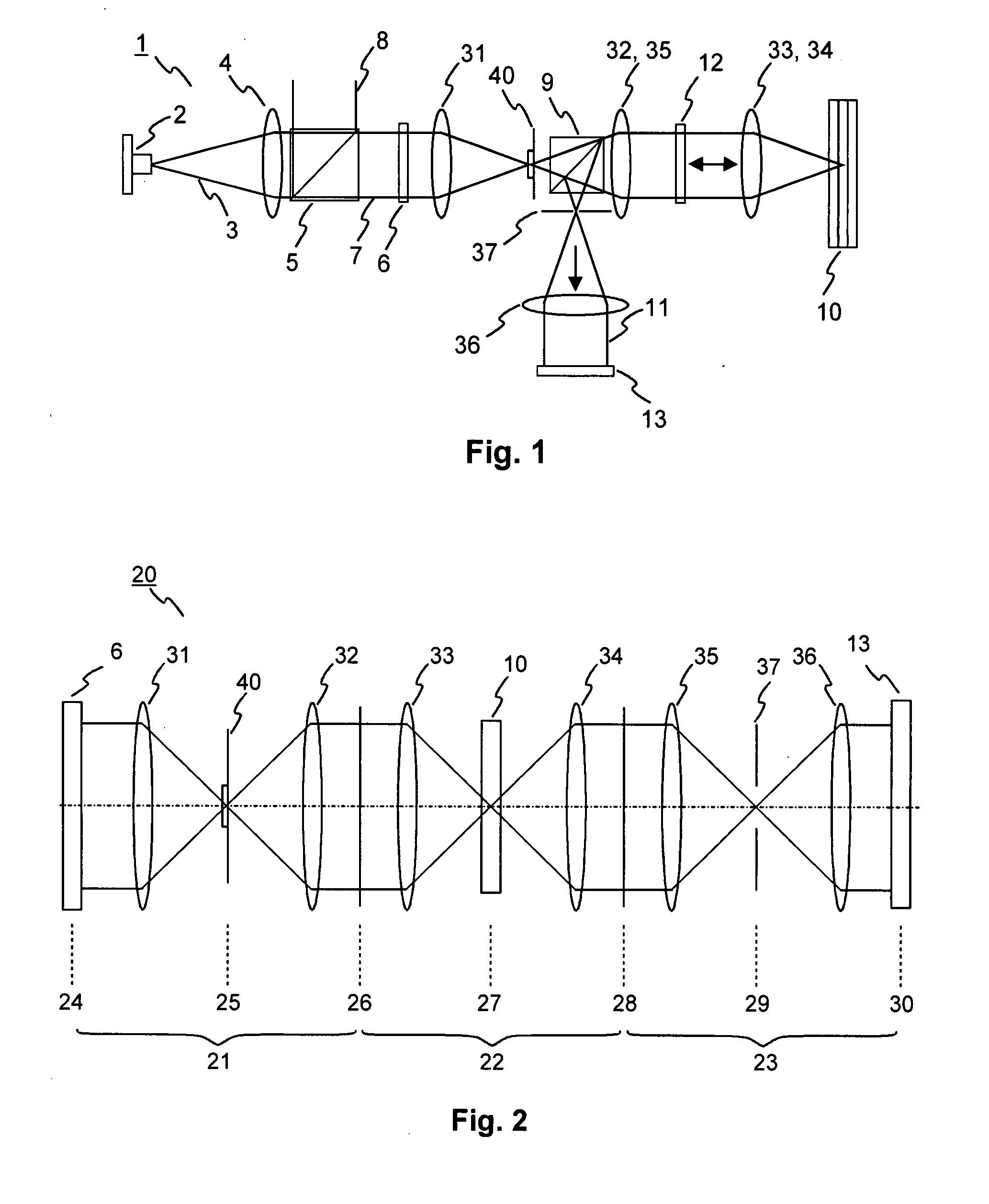
An arrangement for increasing resolution of a laser scanning microscope has a simplified adjustment and lower susceptibility to errors. The pupil beam from the laser scanning microscope is coupled into a shortened common path interferometer, to make wavefronts of a pupil image mirrored at at least one axis and wavefronts of an unchanged pupil image interfere. The area of a pupil from the pupil beam is split into two complementary portions P and Q producing two partial beams separately supplied to at least one beam deflection means by total-internal reflection along the common path interferometer. The light of the interferometer branches from transmitted light of the one interferometer branch and reflected light of the other interferometer branch is made to interfere at a partly transmissive beam splitter layer to cause constructive interference C and destructive interference D of the wavefronts from the two different portions P and Q of the pupil.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Holographic storage system based on common path interferometry
InactiveUS20070297030A1Improve data transfer rateImprove lighting efficiencyRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansHolographic storageSpatial light modulator
The present invention relates to a holographic storage system, and more specifically to a holographic storage system using a phase spatial light modulator.According to the invention a holographic storage system with a phase SLM for imprinting a 2-dimensional phase data pattern onto an object beam includes a common path interferometer for converting the phase data pattern of the object beam into an intensity data pattern.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Compact Interferometer Spectrometer
ActiveUS20190178715A1Compact size and stabilityArea of detector can be bestRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsLight beamOptoelectronics
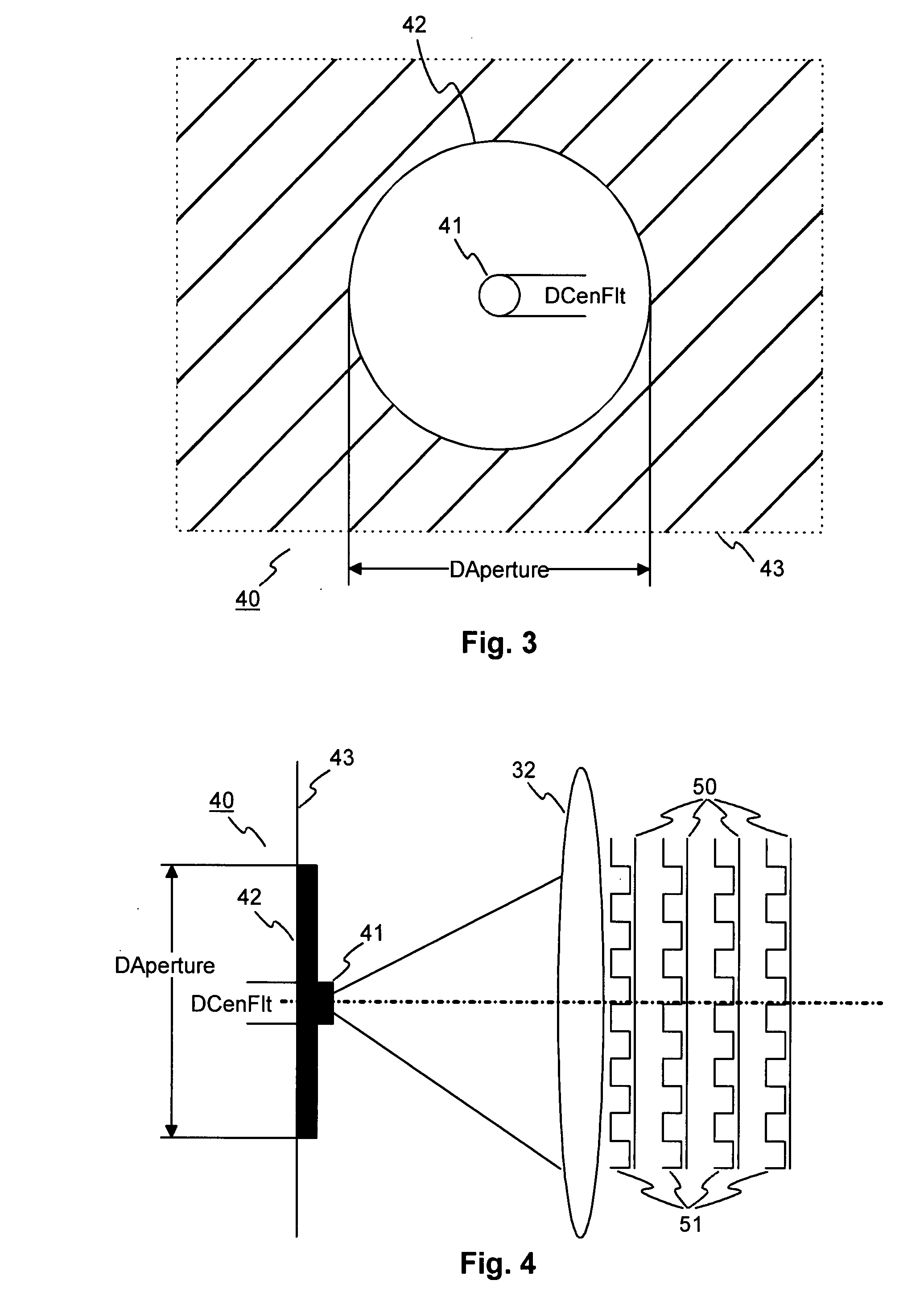
A common path interferometer is disclosed. The interferometer is arranged to divide an input beam into first and second beam portions directed in opposite directions around a cyclic path to form an interference pattern at a detector. The cyclic path is defined by at least two mirror regions curved in the plane of the cyclic path, such that the interference pattern represents path difference variations between the first and second beam portions. The interferometer further includes an input optic arranged in the beam path before division of the input beam into the beam portions. The input optic is configured to provide convergence to reduce the extent transversely to the plane of the cyclic path of the interference pattern at the detector. The beam and beam portions have different convergence requirements in the plane of, and transverse to the plane of, the cyclic path, which are addressed separately by the mirror regions and the input optic.
Owner:KEIT
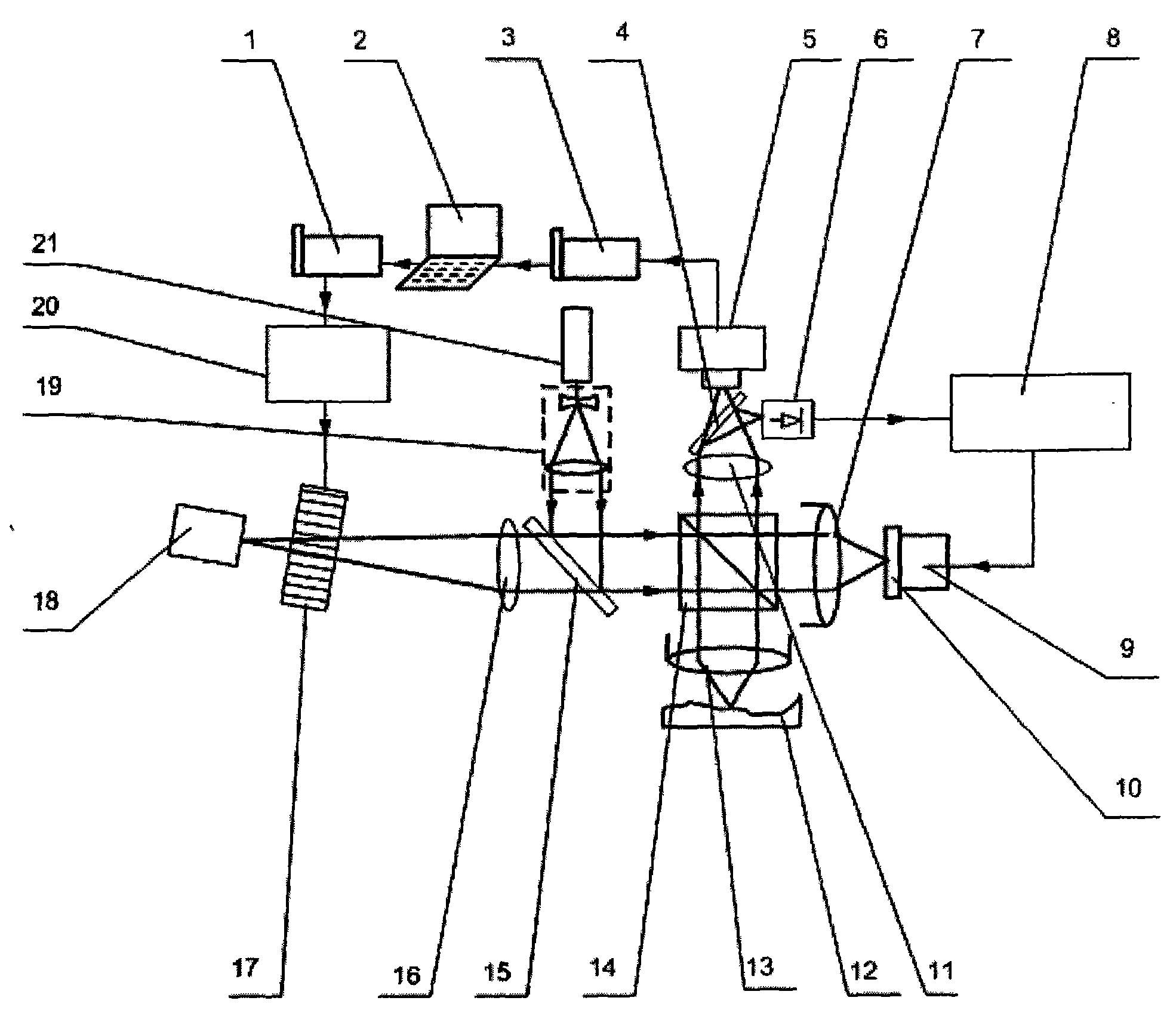
Common path interference adaptive optics oct retinal imager
ActiveCN105105707BStable imaging resultsQuality improvementOthalmoscopesWavefront sensorHorizontal and vertical
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compound interferometer with monolithic measurement cavity
ActiveUS8379219B2Undesirable influenceRealized benefitsInterferometersUsing optical meansMeasurement testingCoupling
Owner:CORNING INC
System for quickly measuring surface quality
InactiveCN101718520BFast measurementSave precious timeUsing optical meansEnvironmental noiseAcousto-optics
The invention discloses a system for quickly measuring surface quality. The system comprises two sets of common-path interferometers, wherein one set of reference interferometer for noise compensation is specially used for detecting noises such as vibration, air disturbance and the like in environment, and eliminating the influence of interference of the background noises through negative feedback; and the other set of main interferometer for measurement controls wavelength of optical wave incident to the interferometers by using an acousto-optic filter, and can quickly acquire a three-dimensional feature of a surface to be measured by processing a generated interference signal by using large-scale parallel computation based on GPGPU. The system can measure the surface quality in real time, does not need mechanical light path scanning in the process of measurement, and can reach a high measurement speed. The system can be updated one time in 1 to 2 seconds on average, and can be updated more frequently after being optimized. The system can reduce influence of environmental noise on the measurement by adding the active optical path compensation technology, achieves measurement accuracy of sub-nano range, reduces cost, saves a usually expensive high-precision translation stage and can be used for processing workshops with more interference.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A birefringent interferometer for measuring photoluminescence properties of samples
ActiveUS20210123808A1Improve stabilityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryPhotoluminescenceOptical coupling
A measurement system of photoluminescence properties of a sample, comprises a radiation source module configured to generate a first radiation, an excitation optical path coupled to the radiation source module, a support structured to support a sample to be optically coupled to excitation optical path and adapted to provide a photoluminescence radiation, and collection path coupled to the sample and configured to propagate the photoluminescence radiation. The system also includes an analysis device configured to receive the photoluminescence radiation and provide data / information on photoluminescence properties of sample. At least one path between the excitation path and the collection path comprises a respective adjustable birefringent common-path interferometer module configured to produce first and second radiations adapted to interfere with each other.
Owner:POLITECNICO DI MILANO
Endoscopic oct imaging system using optical path difference external compensation common path interference probe
ActiveCN105105717BStrong ability to resist environmental interferenceInhibition of effects on imaging resultsSurgeryEndoscopesAnti jammingData acquisition
The invention discloses an endoscopic OCT imaging system adopting an optical path difference external compensation common-path interference probe, comprising a light source, an optical path difference external compensation interferometer, first and second acousto-optic frequency shifters, an optical circulator, and an optical fiber Rotary connector, spiral scanning mechanism, endoscopic probe, glass spacer rod, Green lens, 45° cylindrical mirror, transparent sealing sleeve, metal outer sheath, window, detector, data acquisition card and computer, etc. Use the front surface of the Rigling lens of the endoscopic probe as the reference surface, and the optical path difference between it and the sample is compensated by the optical path difference external compensation interferometer; the spiral traversal scanning method is used to reduce the missed detection of lesions, and the flat window is used to To eliminate the astigmatism usually caused by the cylindrical transparent sealing sleeve, the acousto-optic frequency shifter combined with signal filtering and demodulation technology is used to eliminate the artifacts in the imaging results. The invention has the characteristics of strong anti-interference ability, plug-and-play probe, reduced missed detection of lesions, no false image interference, no astigmatism in incident sample beams, and the like.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
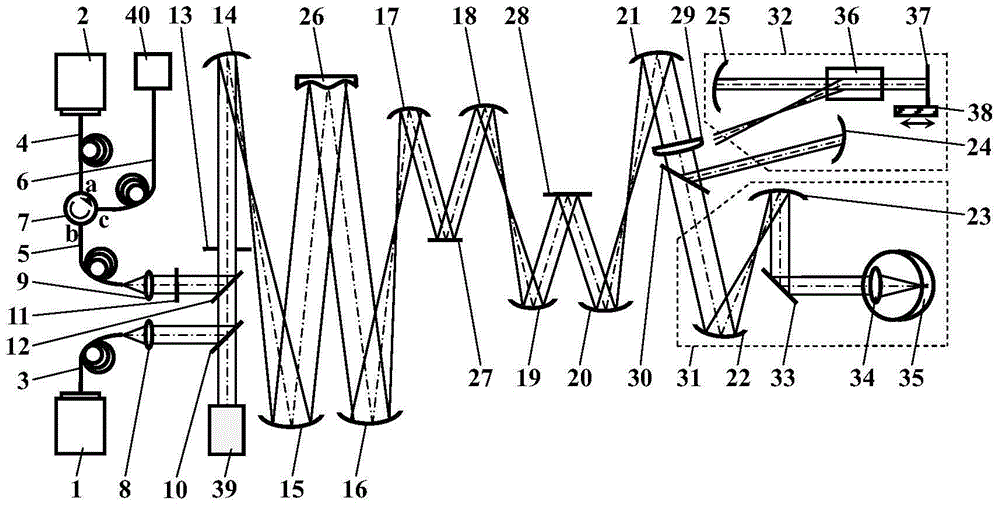
Flat crystal self-calibrating common optical path interferometer based on acousto-optic heterodyne phase shifting
ActiveCN104330021BAvoid problemsReduced precision requirementsUsing optical meansLight spotHeterodyne interferometer
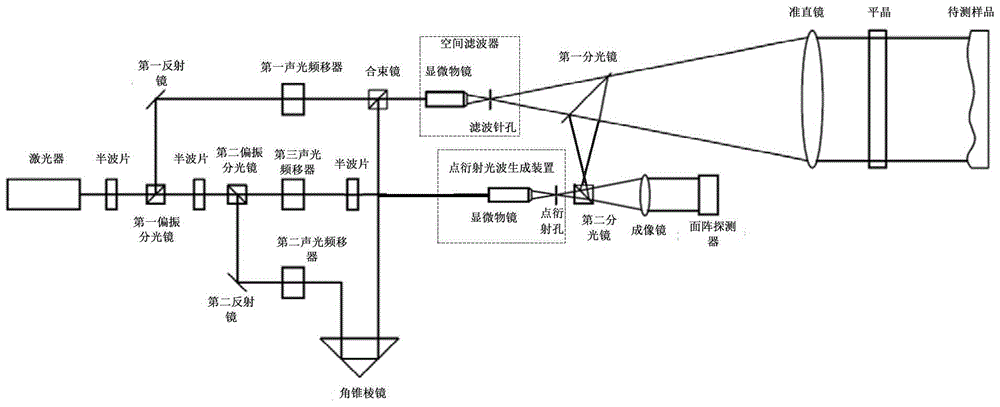
The invention discloses a flat-crystal self-calibrating common optical path interferometer based on acousto-optic heterodyne phase shifting. By adopting an acousto-optic frequency shifter for heterodyne interference phase-shifting, the presence of moving parts in the interferometer is effectively avoided, and the measurement accuracy is further improved. The interference is good, and the development difficulty and cost can be reduced, especially for the measurement of large-caliber surface shape, compared with the same advantage of mechanical drive; at the same time, using low-frequency difference heterodyne interference and continuous acquisition of high-speed area array detectors, the obtained The amount of information is richer, which is more conducive to accurately calculating the phase, and is more conducive to overcoming the influence of noise and other factors; in addition, adding point diffraction self-calibration beams, and using point diffraction light to pre-calibrate the reference mirror during measurement can reduce the accuracy of the reference mirror Requirements, and improve the accuracy of measurement, but also reduce the difficulty and cost of interferometer development.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Common-path integrated low coherence interferometry system and method therefor
ActiveUS10753724B2Improve performanceLow wavelength dependenceUsing optical meansHemt circuitsCommon path
A low coherence interferometry imaging system comprising a common-path interferometer that is at least partially integrated as part of a planar lightwave circuit is disclosed. Imaging systems in accordance with the present invention are implemented in integrated optics without the inclusion of highly wavelength-sensitive components. As a result, they exhibit less wavelength dependence than PLC-based interferometers of the prior art. Further, the common-path interferometer arrangement of the present invention avoids polarization and wavelength dispersion effects that plague prior-art PLC-based interferometers. Still further, an integrated common-path interferometer is smaller and less complex than other integrated interferometers, which makes it possible to integrate multiple interferometers on a single chip, thereby enabling multi-signal systems, such as plane-wave parallel OCT systems.
Owner:ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT BIJ DE UNIV VAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com