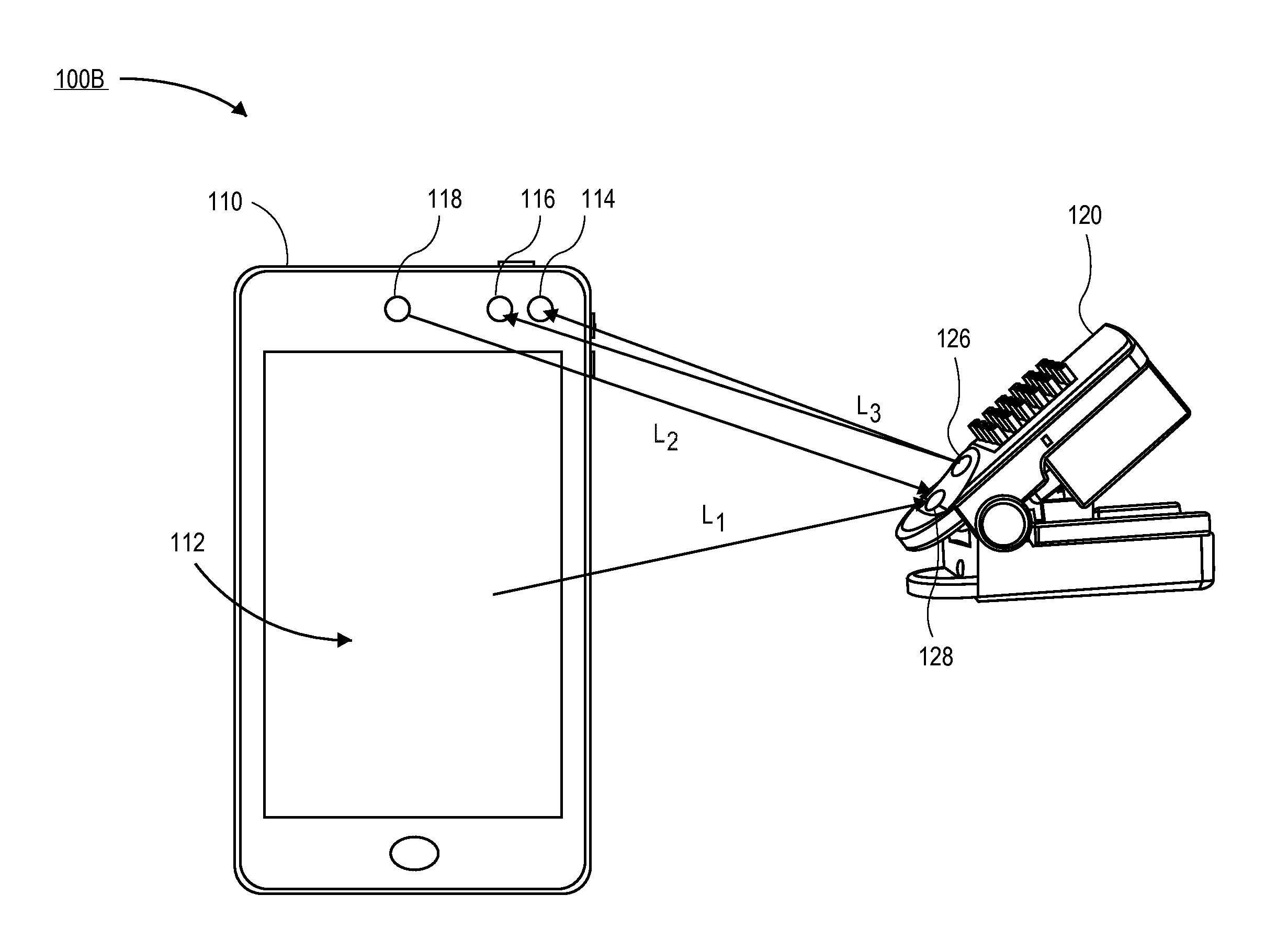
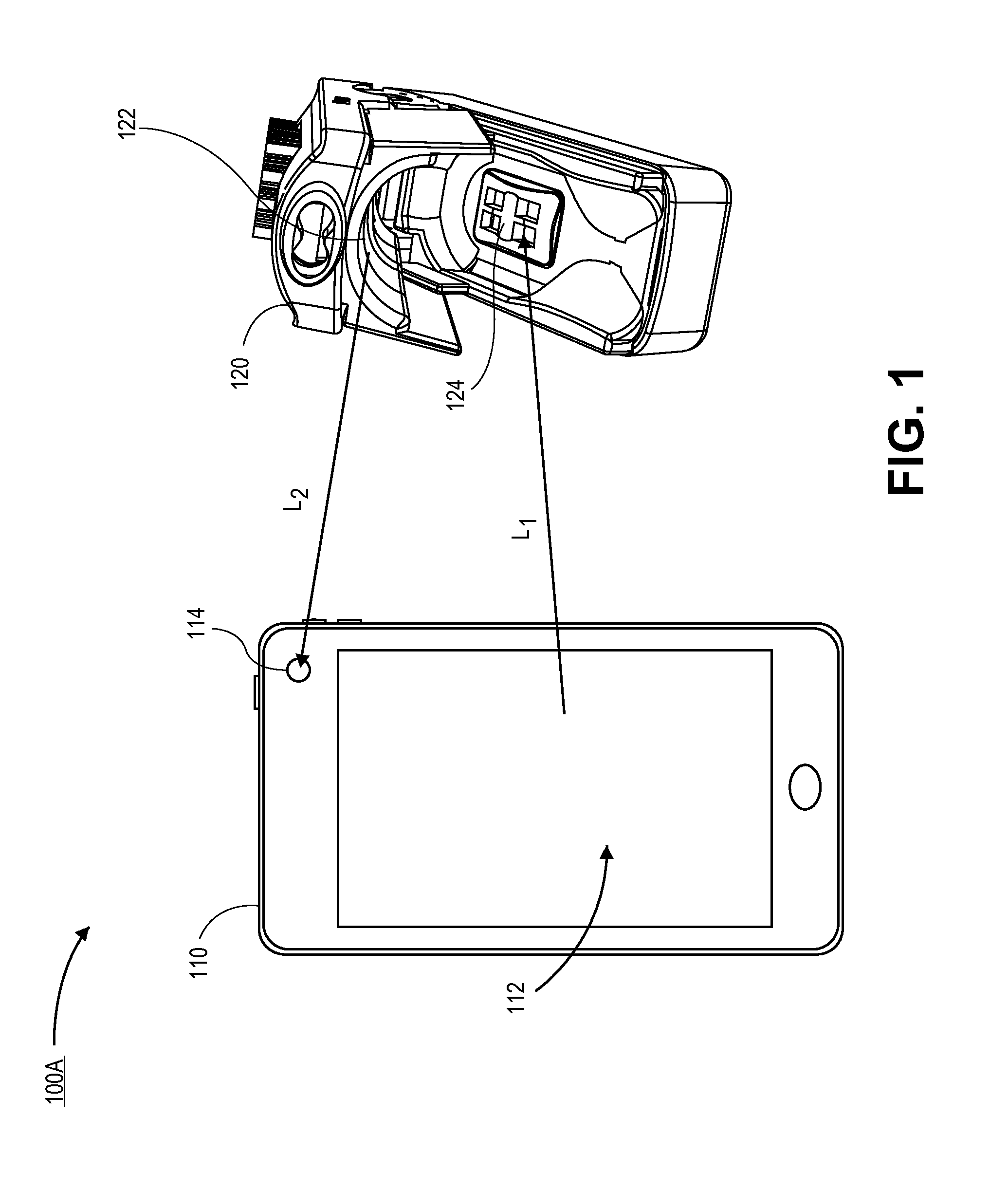
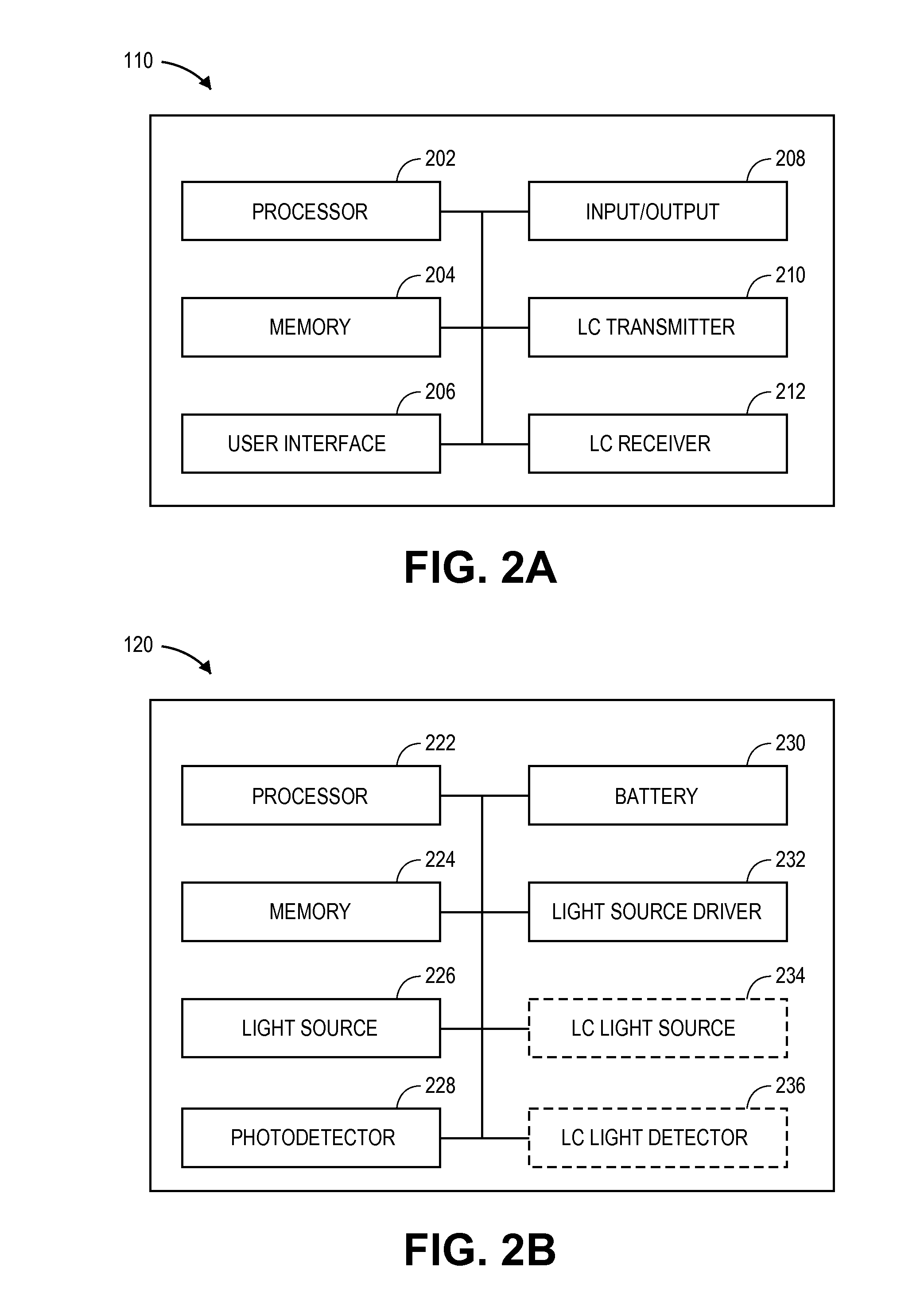
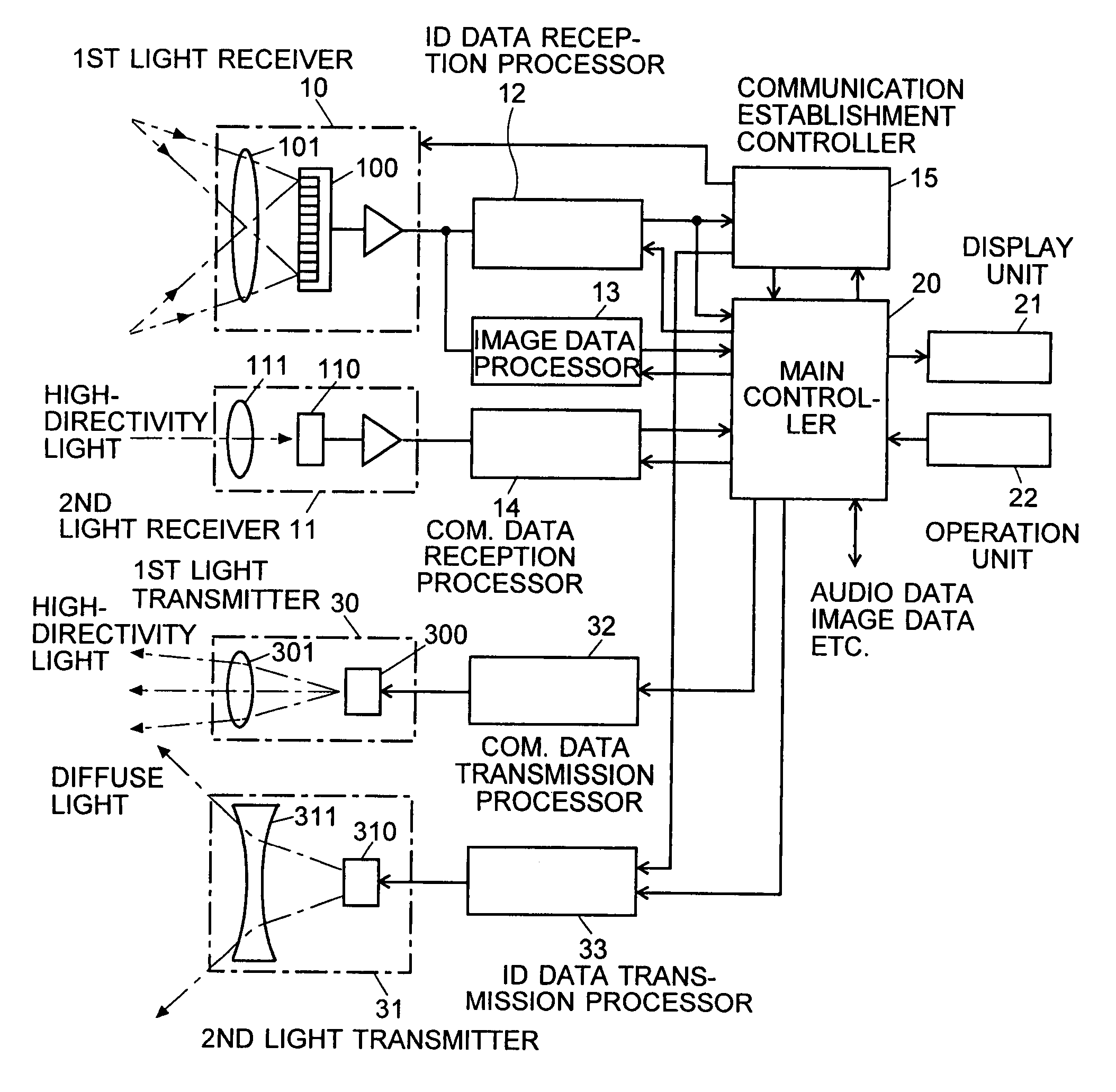
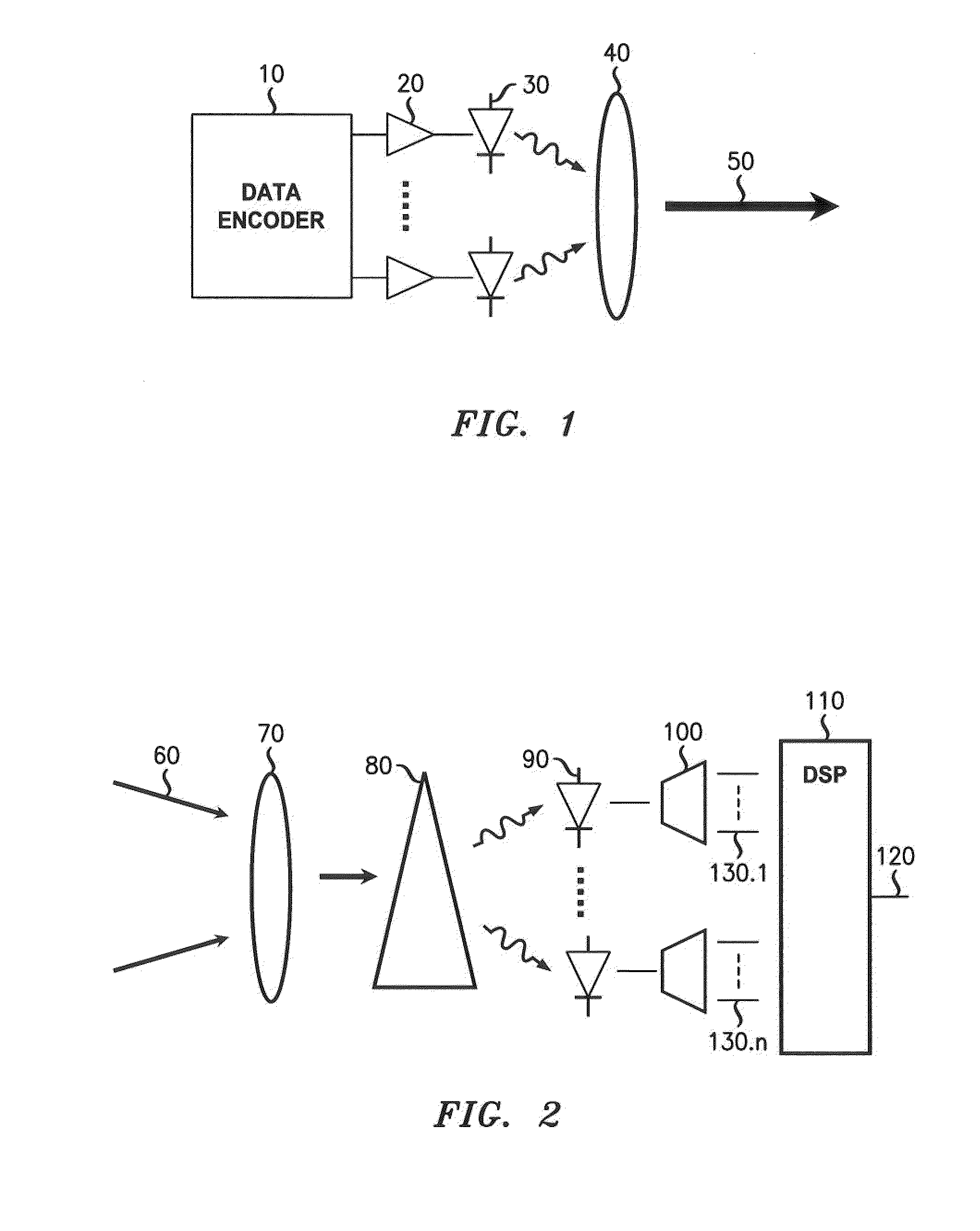
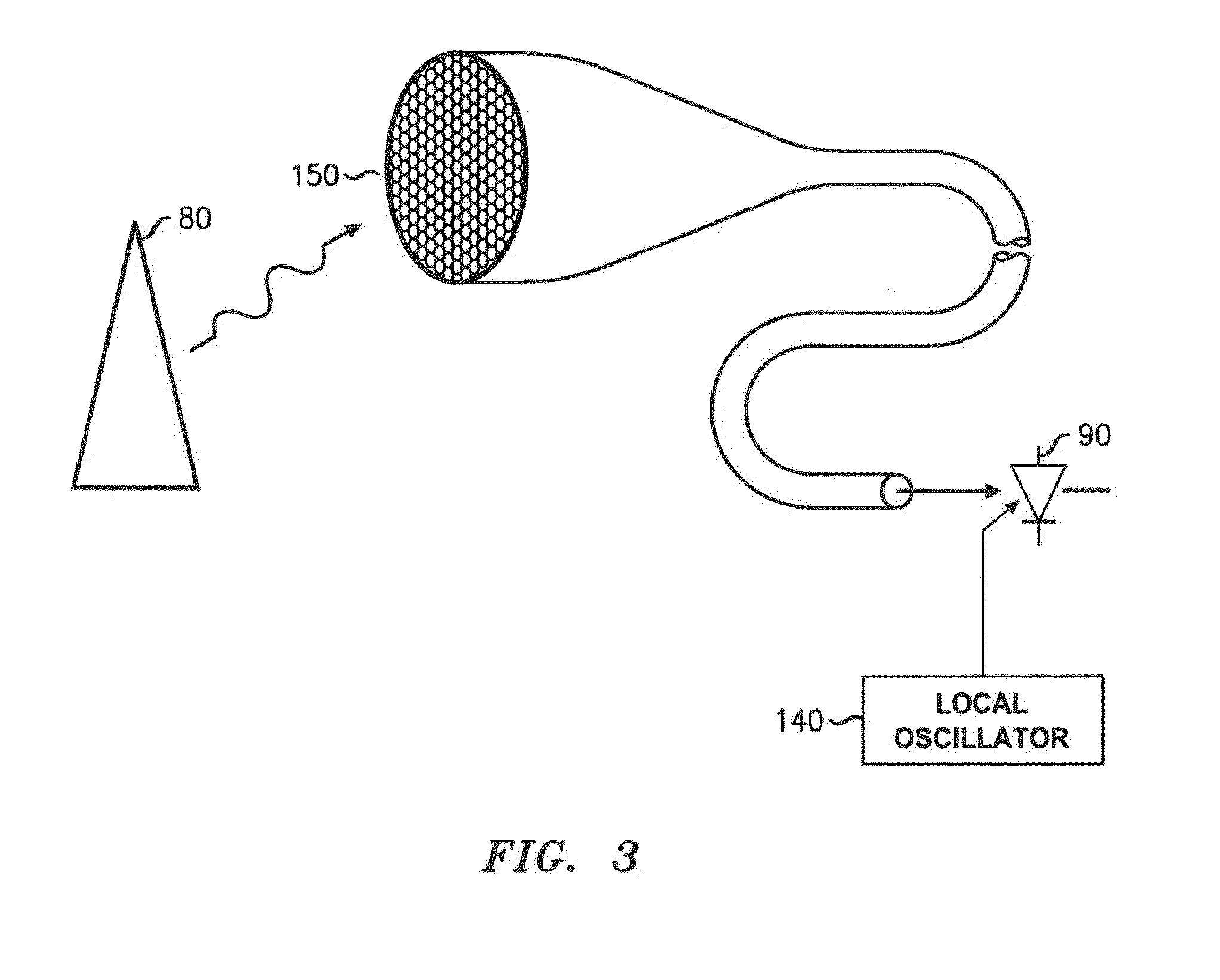
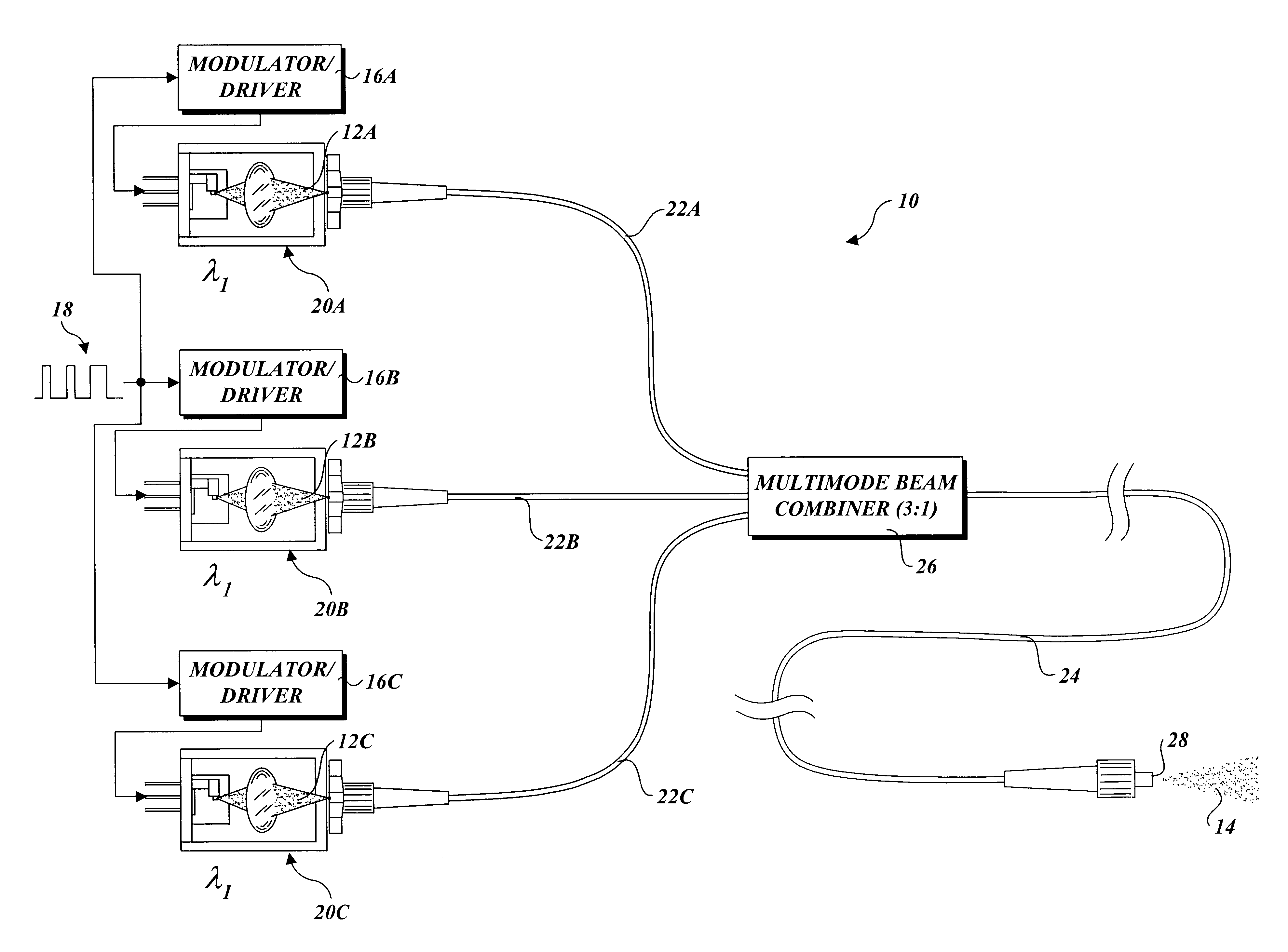
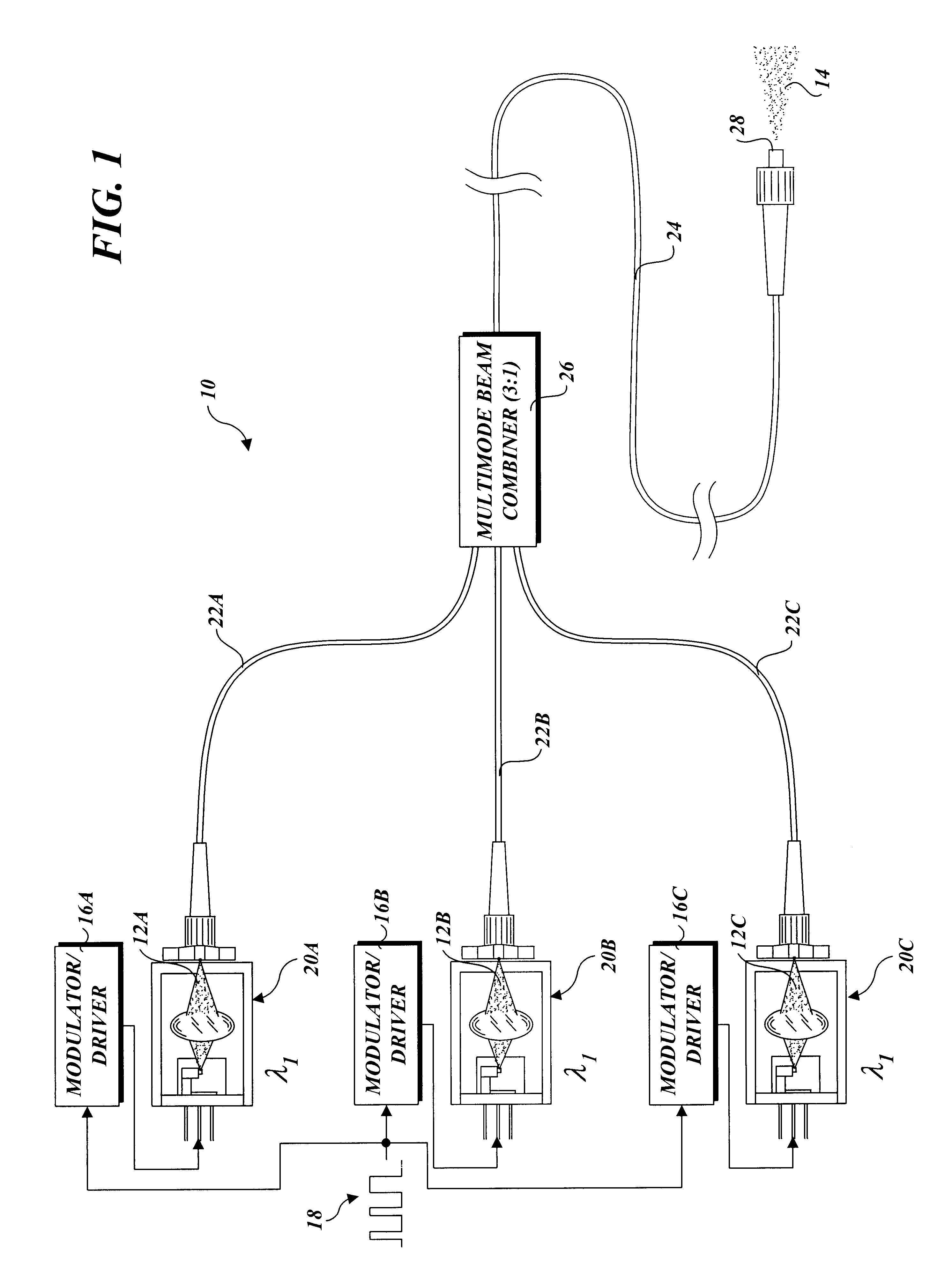
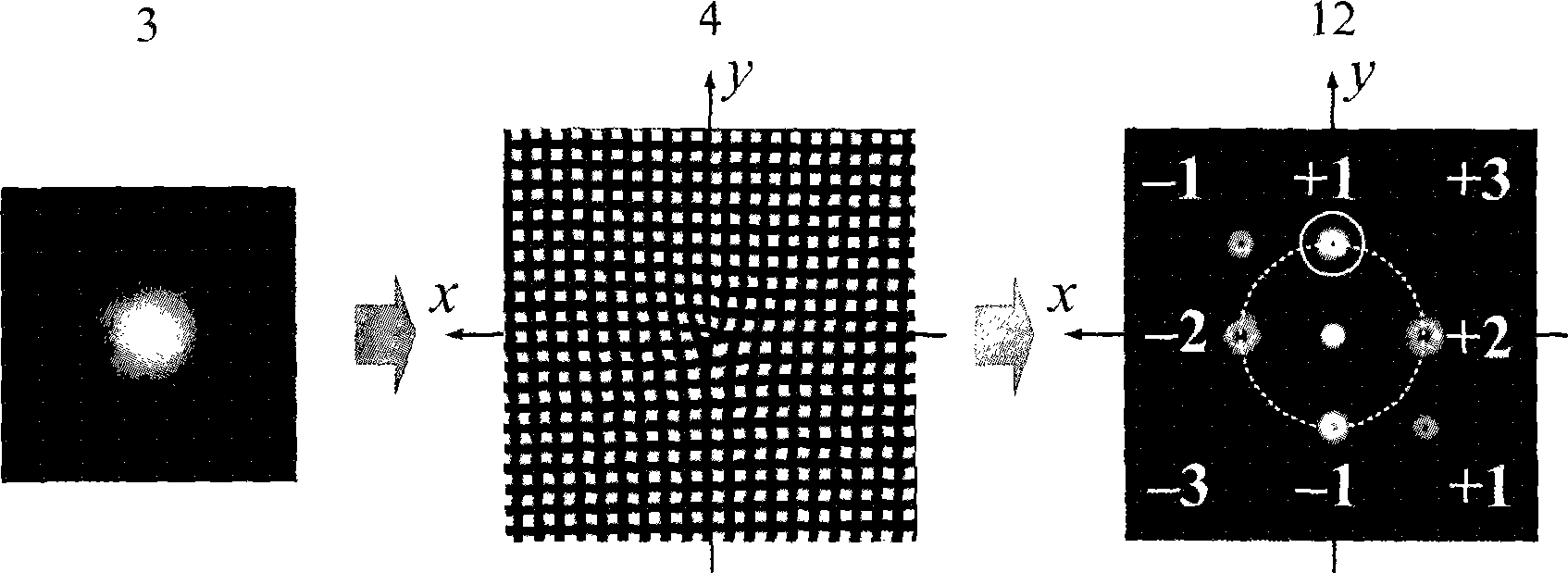
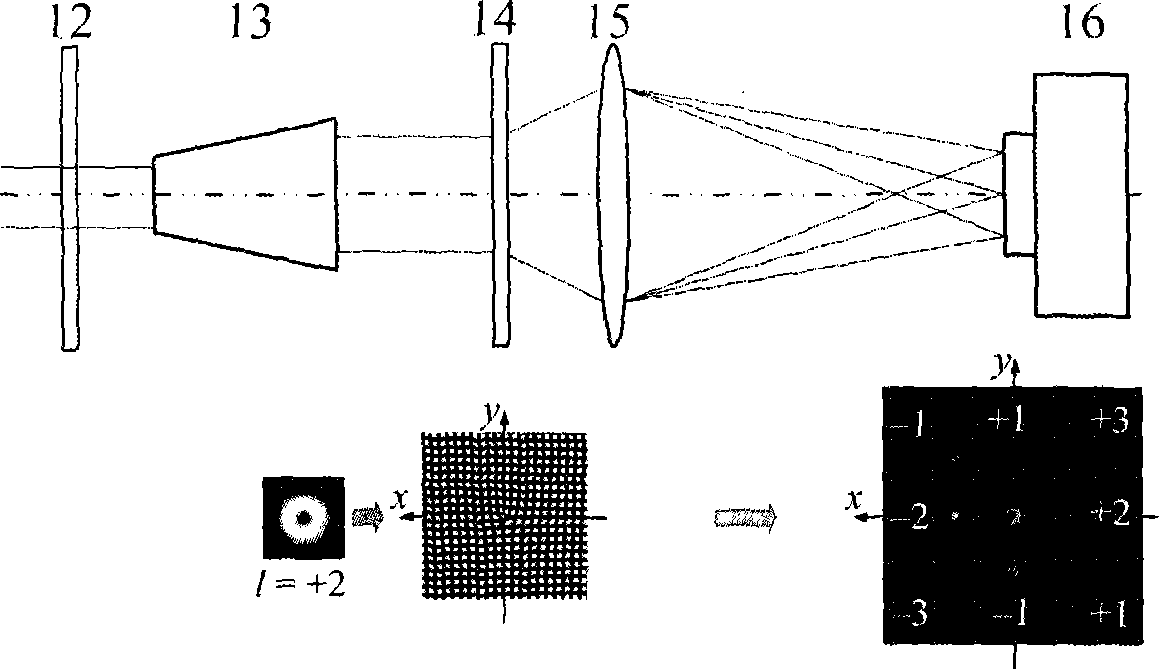
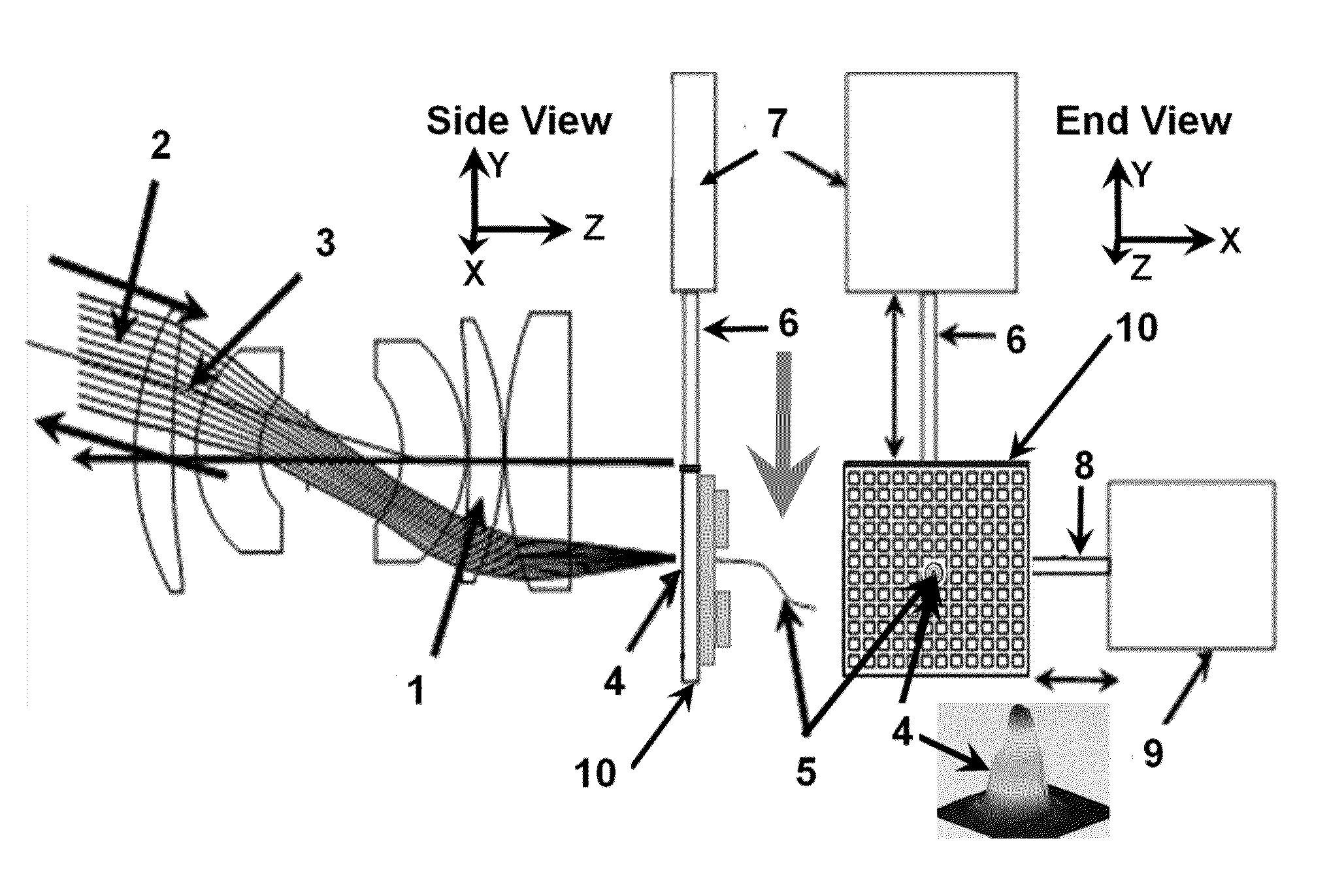
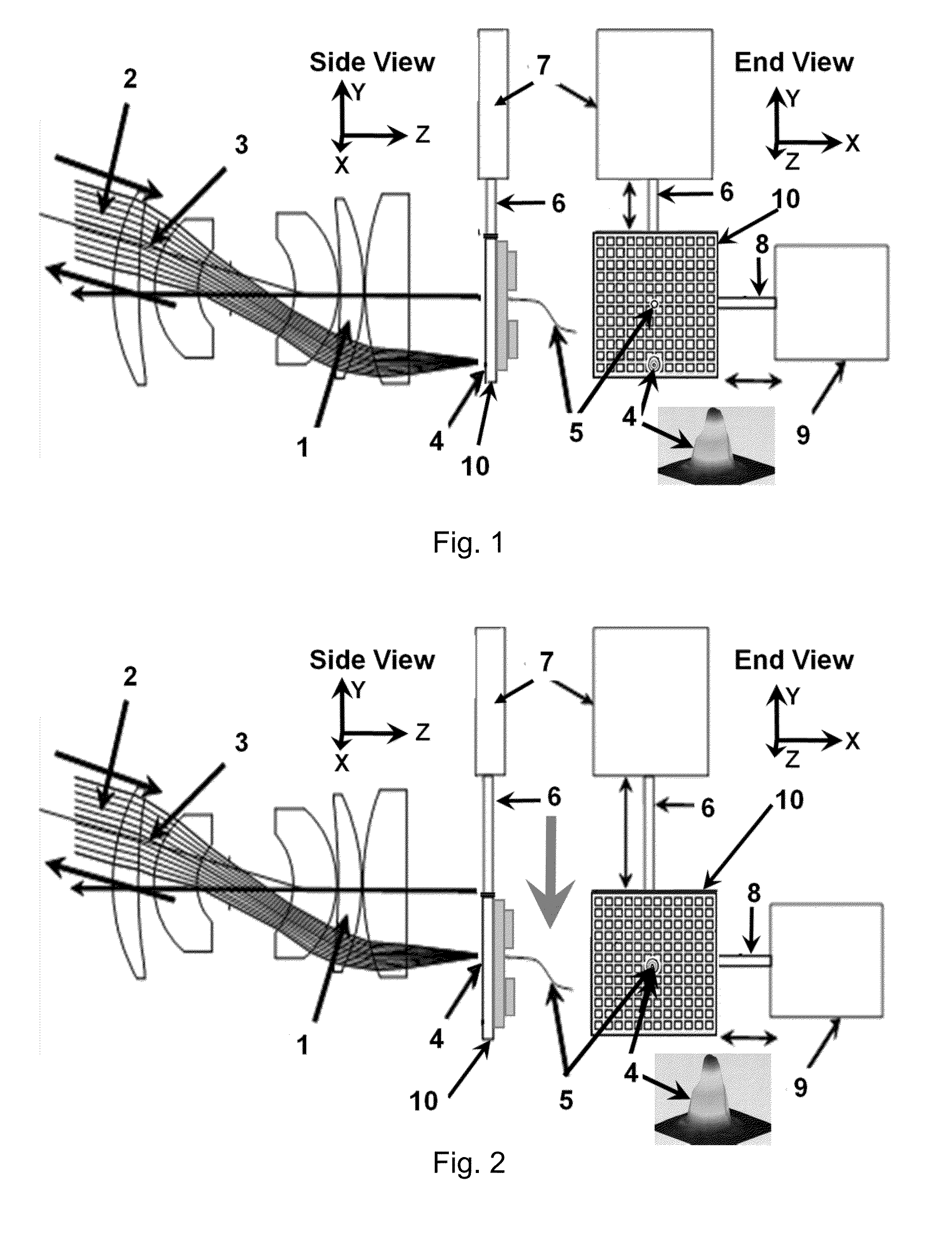
Patents
Literature
554 results about "Free-space optical communication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
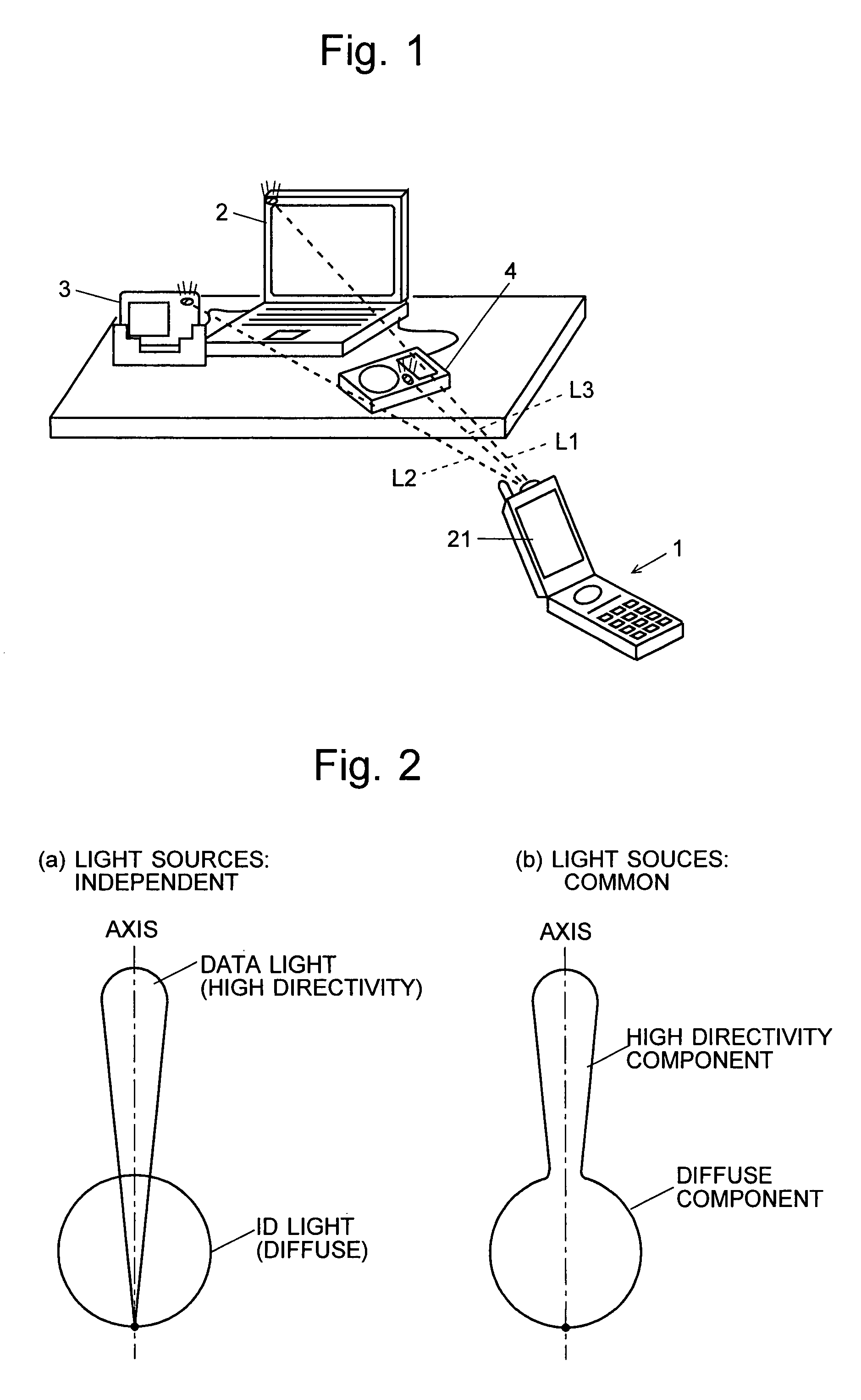
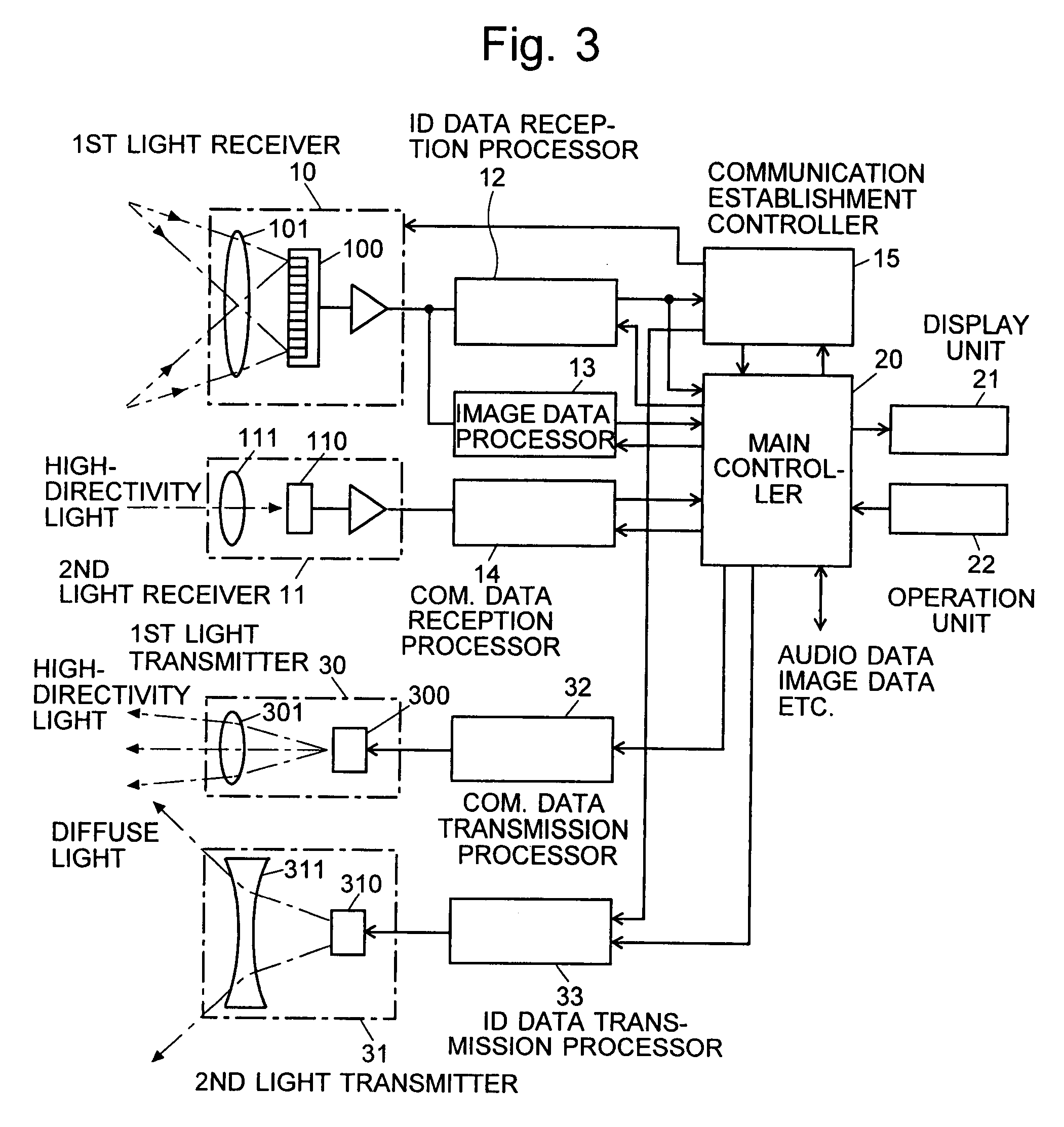
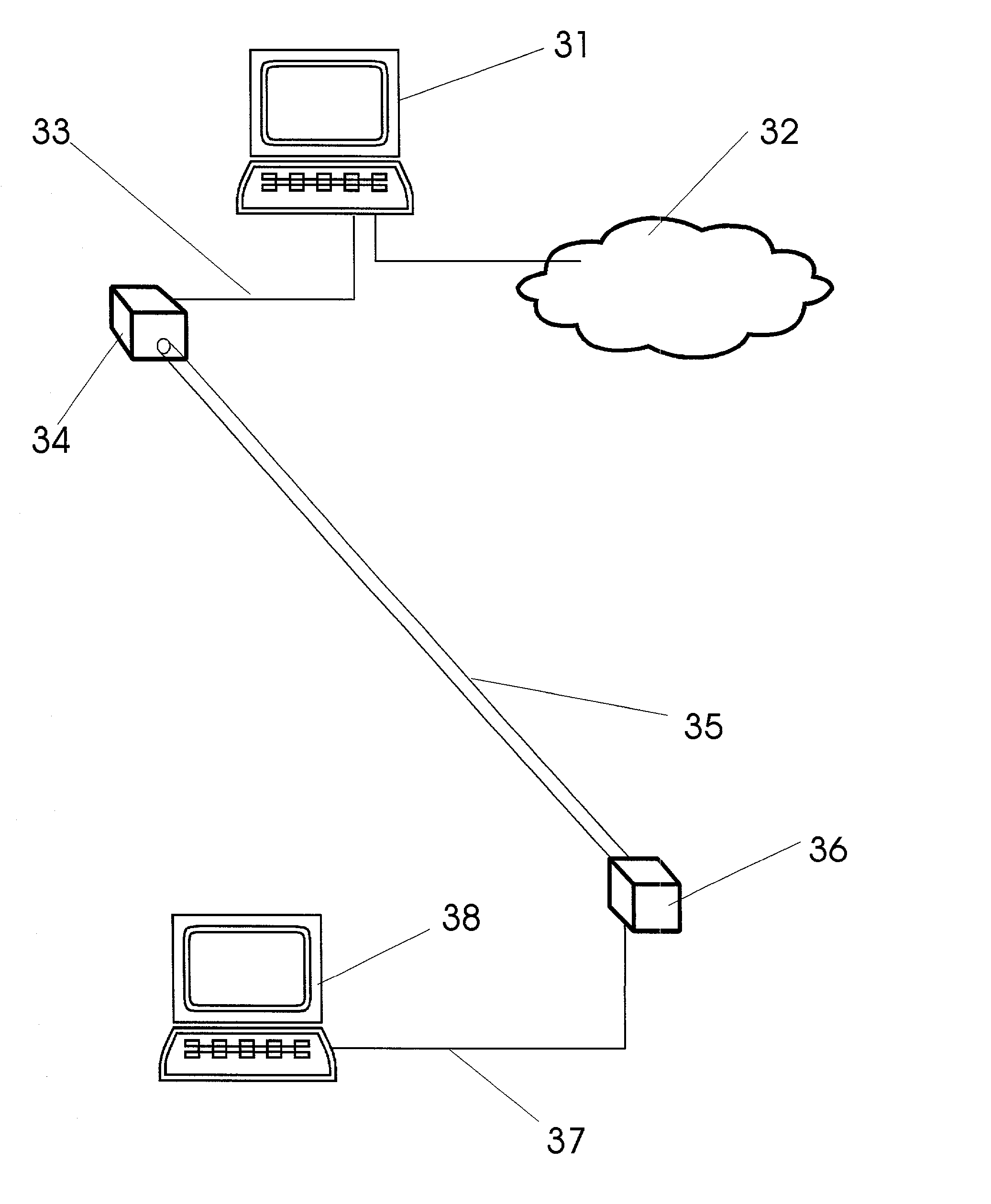
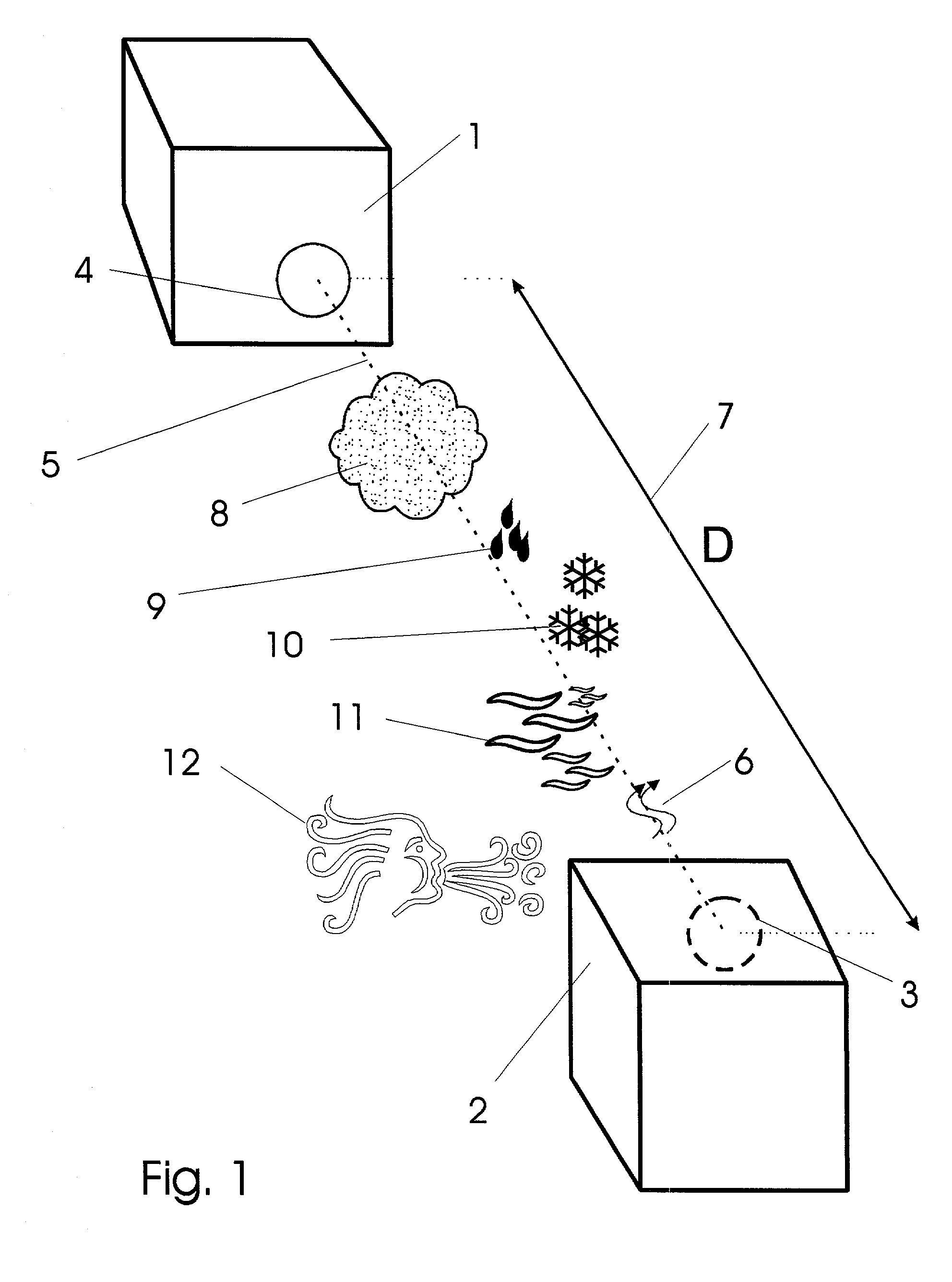
Free-space optical communication (FSO) is an optical communication technology that uses light propagating in free space to wirelessly transmit data for telecommunications or computer networking. "Free space" means air, outer space, vacuum, or something similar. This contrasts with using solids such as optical fiber cable.
Wireless optical communication between noninvasive physiological sensors and patient monitors
InactiveUS20140275871A1Reduced portabilityReduce compactnessClose-range type systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringPatient monitorComputer science
Embodiments of the disclosure include a noninvasive physiological patient sensor and a patient monitor capable of wireless communication with one another. An optical communication path can be used to provide the communication path between the noninvasive physiological patient sensor and the patient monitor. The path can be maintained by one or more light sources and detectors traditionally associated with noninvasive optical sensors or by one or more additional dedicated light sources and detectors.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Information-processing system using free-space optical communication and free-space optical communication system
InactiveUS7715723B2Suppress power consumptionSmall sizeNetwork topologiesConnection managementInformation processingImaging data
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Free space optical communications link tolerant of atmospheric interference
InactiveUS20040208602A1Improve reliabilityIncrease resistanceElectromagnetic transmissionUltrasound attenuationTransceiver
Free space optical communications systems which resist atmospheric attenuation of optical beams is presented. Very long link distances remain highly reliable despite fog and other inclement weather conditions which otherwise tend to hamper optical transmissions in an atmospheric air column. Systems include primary elements as follows: a plurality of transceivers and at least one air column optical path. Each transceiver includes specialized light sources which produce radiation in the Mid-IR spectral region. In addition, these sources are very compact and well organized in view of their intended deployment environment. Further, special modulation means are joined with particular light sources to address high bandwith needs. In addition, specialized detection strategies are presented whereby sensitivity is improved. Alternative versions and configurations directed to specialized function are also described in detail.
Owner:PLANTE JAMES
Information-processing device and information-processing system
InactiveUS20070070060A1Reduce in quantityReduce the number of timesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsInformation processingFourier transform on finite groups
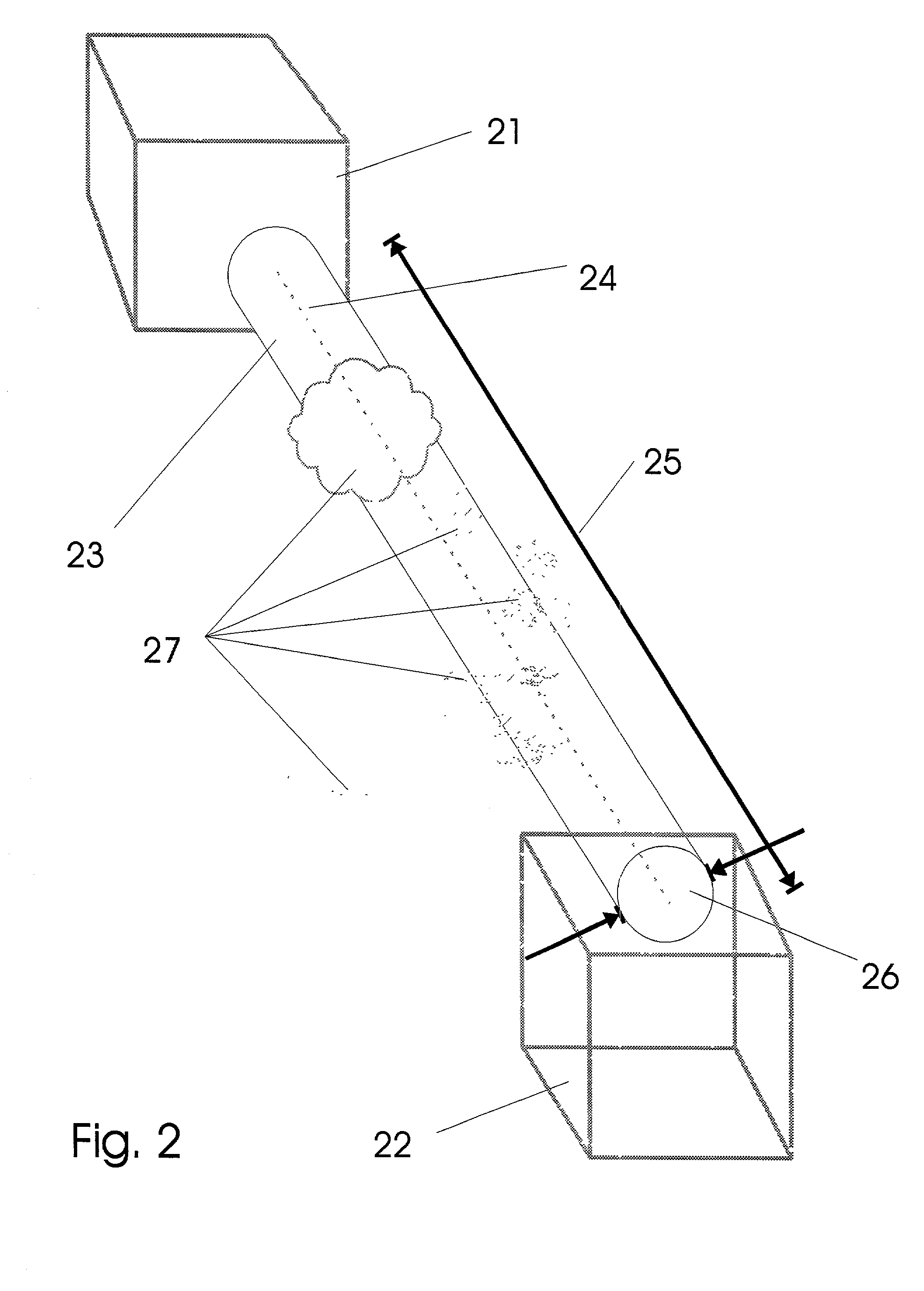
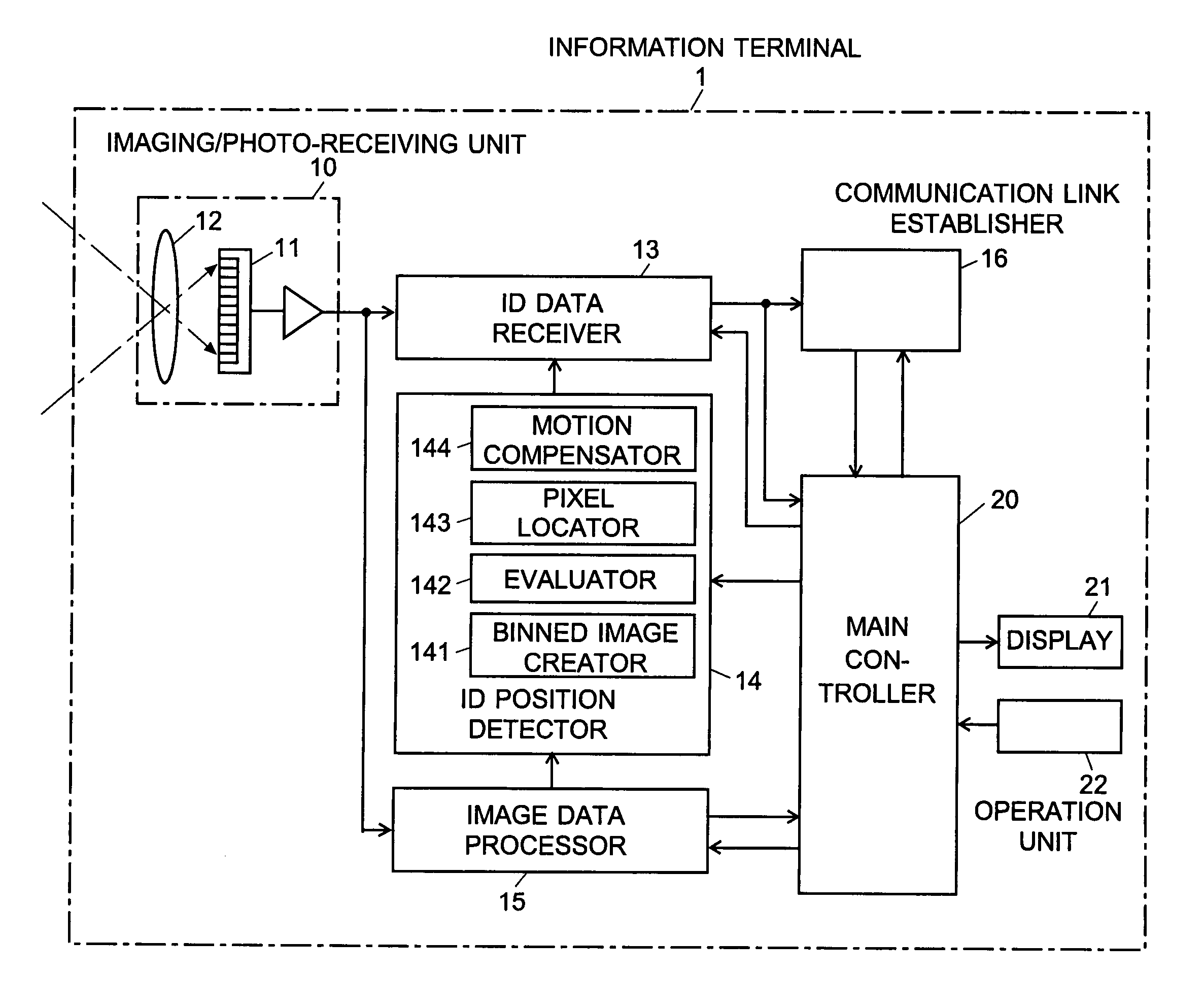
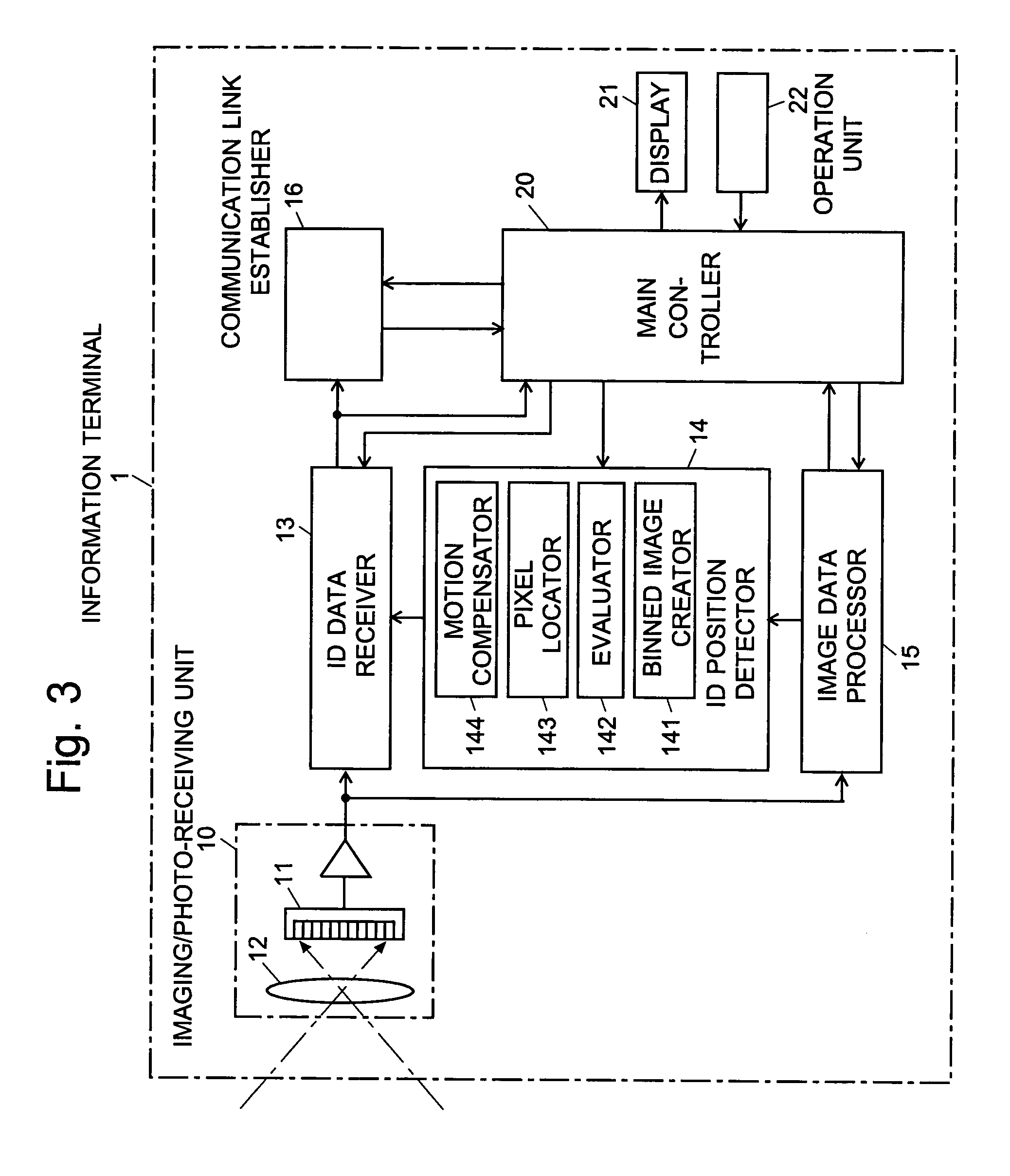
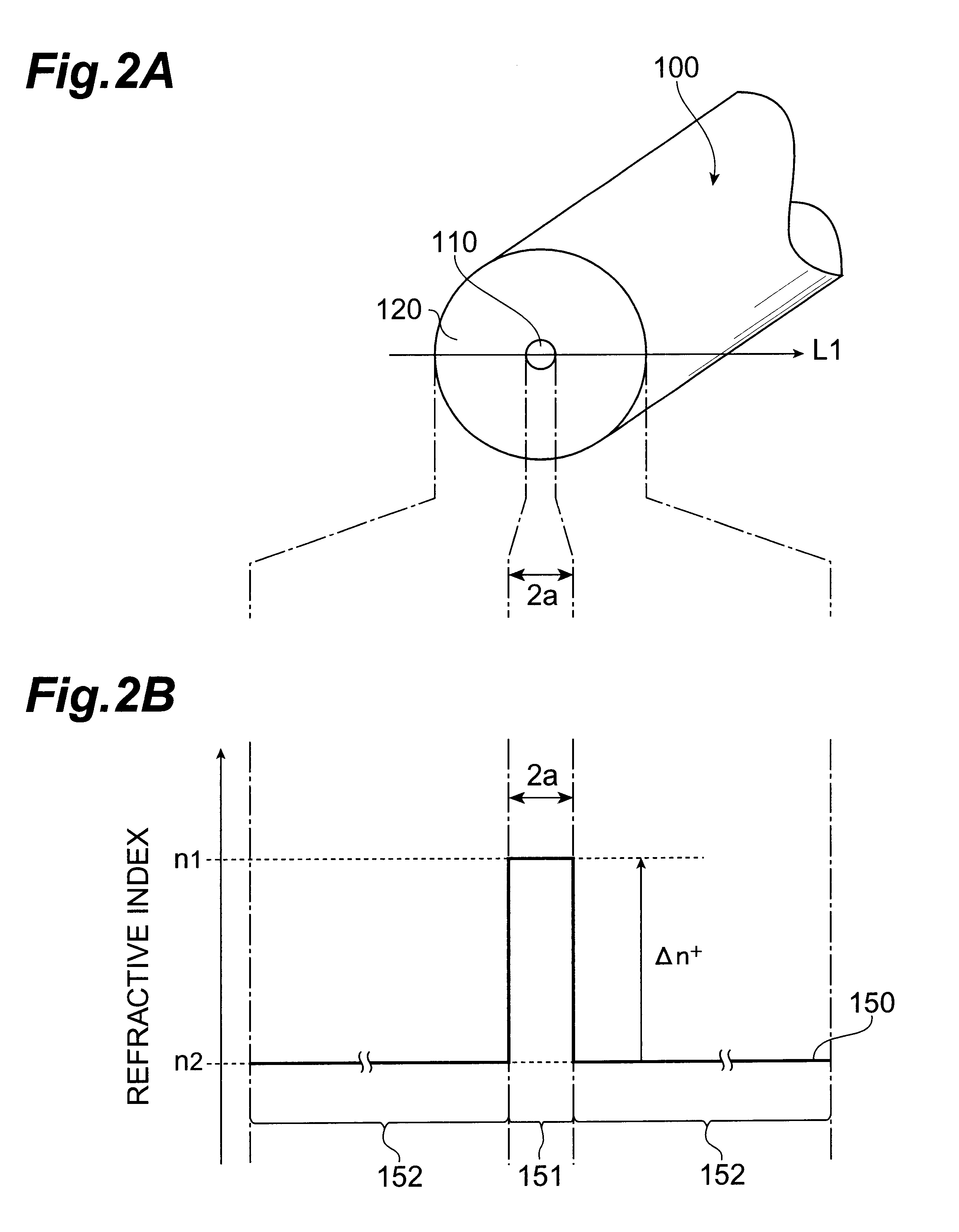
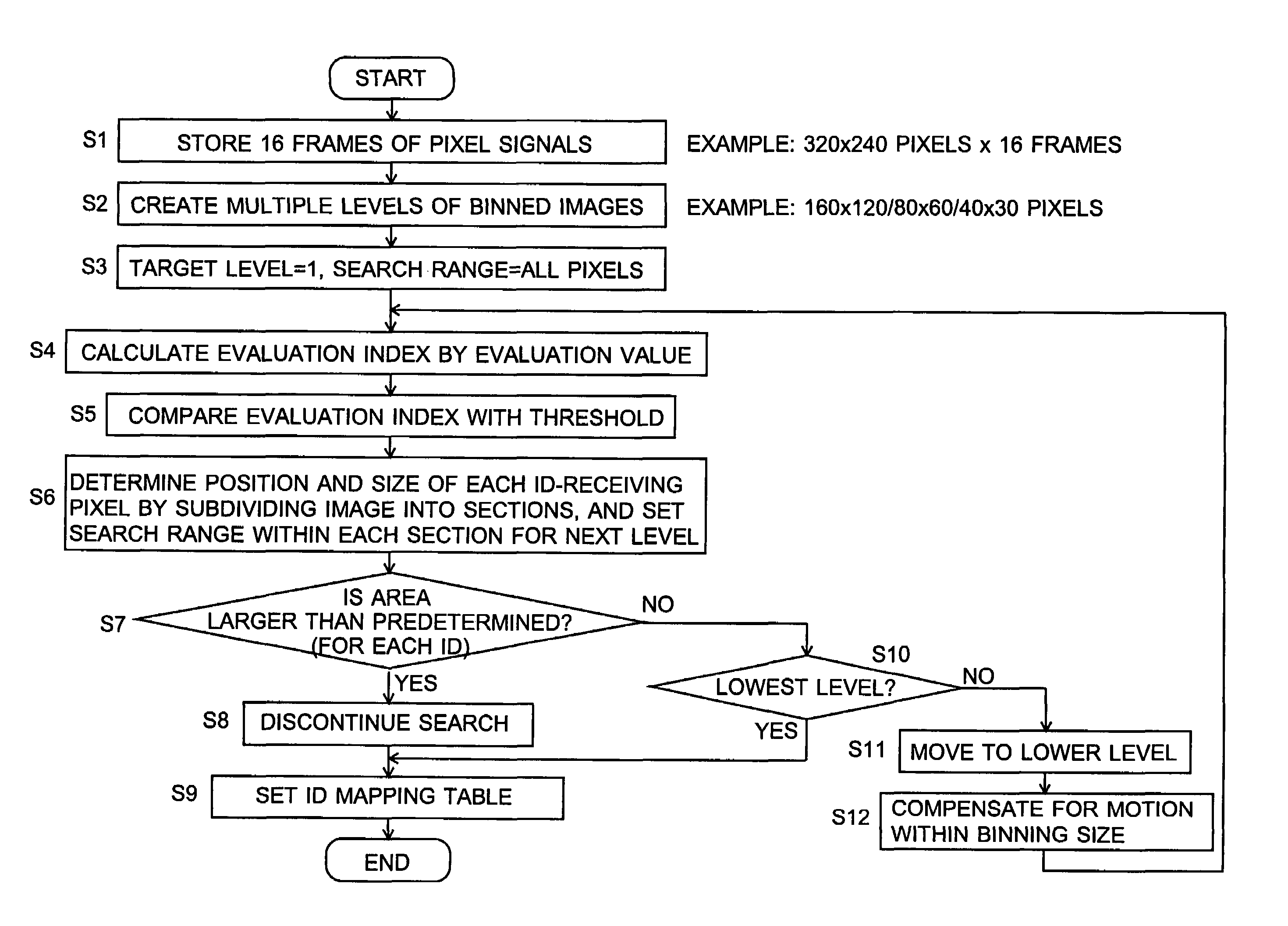
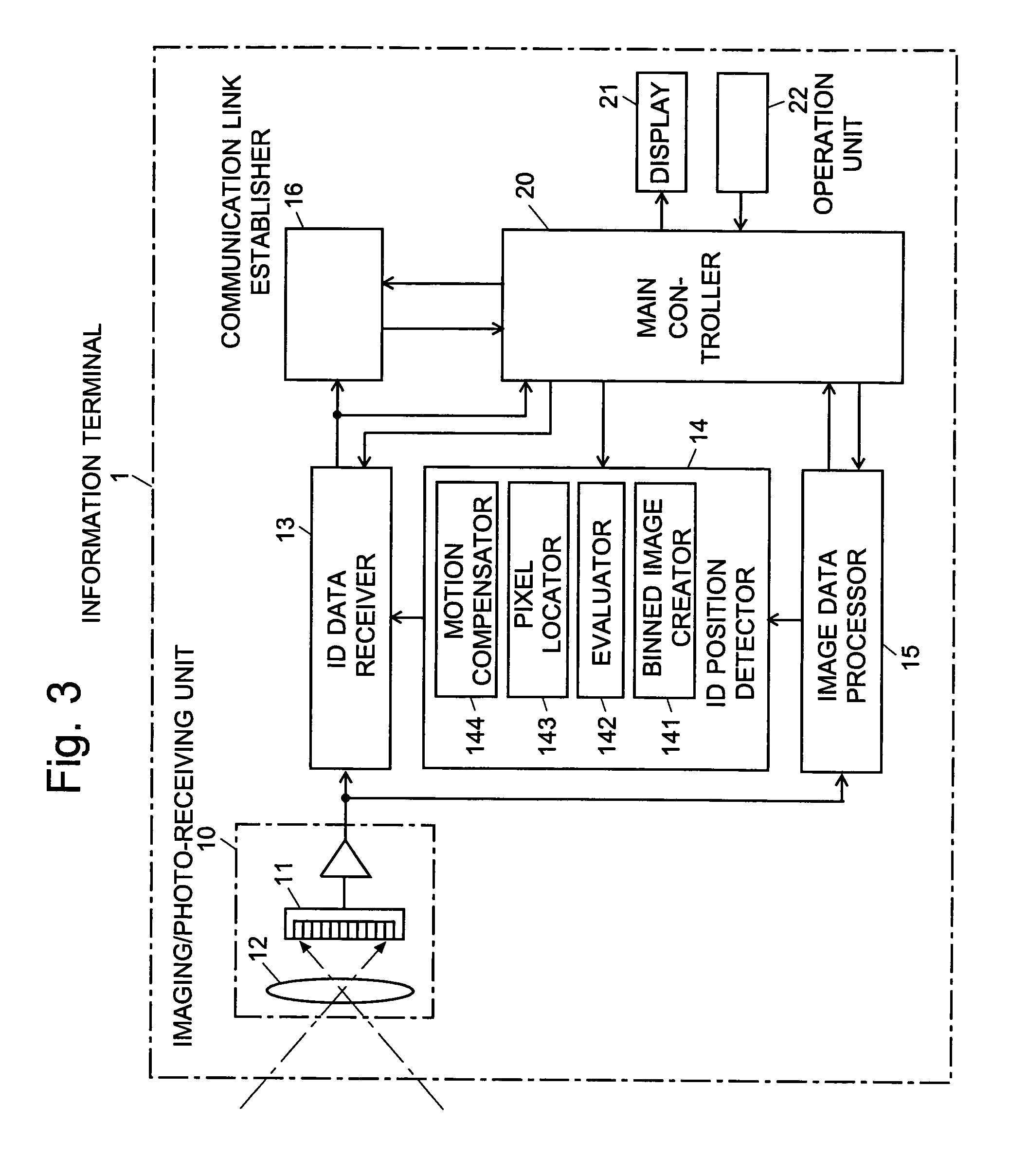
For an information terminal to be operated by users for collecting predetermined pieces of information from remote information devices by free-space optical communication, the present invention provides a technique for suppressing the power consumption of the information terminal by minimizing the amount of calculation performed to collect the aforementioned information. According to the present invention, each information device emits ID light on which a low-frequency pilot signal is superimposed. The information terminal captures a series of frames of images including the ID light and locates the ID light within the images by the following steps: (1) creating multiple levels of binned images having different resolutions for each frame of the image; (2) calculating an evaluation index for each pixel within a target range of the binned images at each level, from the lowest to the highest resolution, where the target range is narrowed every time the process switches over to a lower level. In (2), the evaluation index is calculated by an evaluation function including fast Fourier transformation performed throughout the series of frames of images. The evaluation index thus calculated is compared with a threshold to determine whether the pixel concerned is receiving ID light. The present technique significantly reduces the number of pixel to be analyzed and evaluated, thereby decreasing the total number of arithmetic operations to be performed using the evaluation function. Thus, the power consumption is suppressed.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +2
Agile-beam laser array transmitter
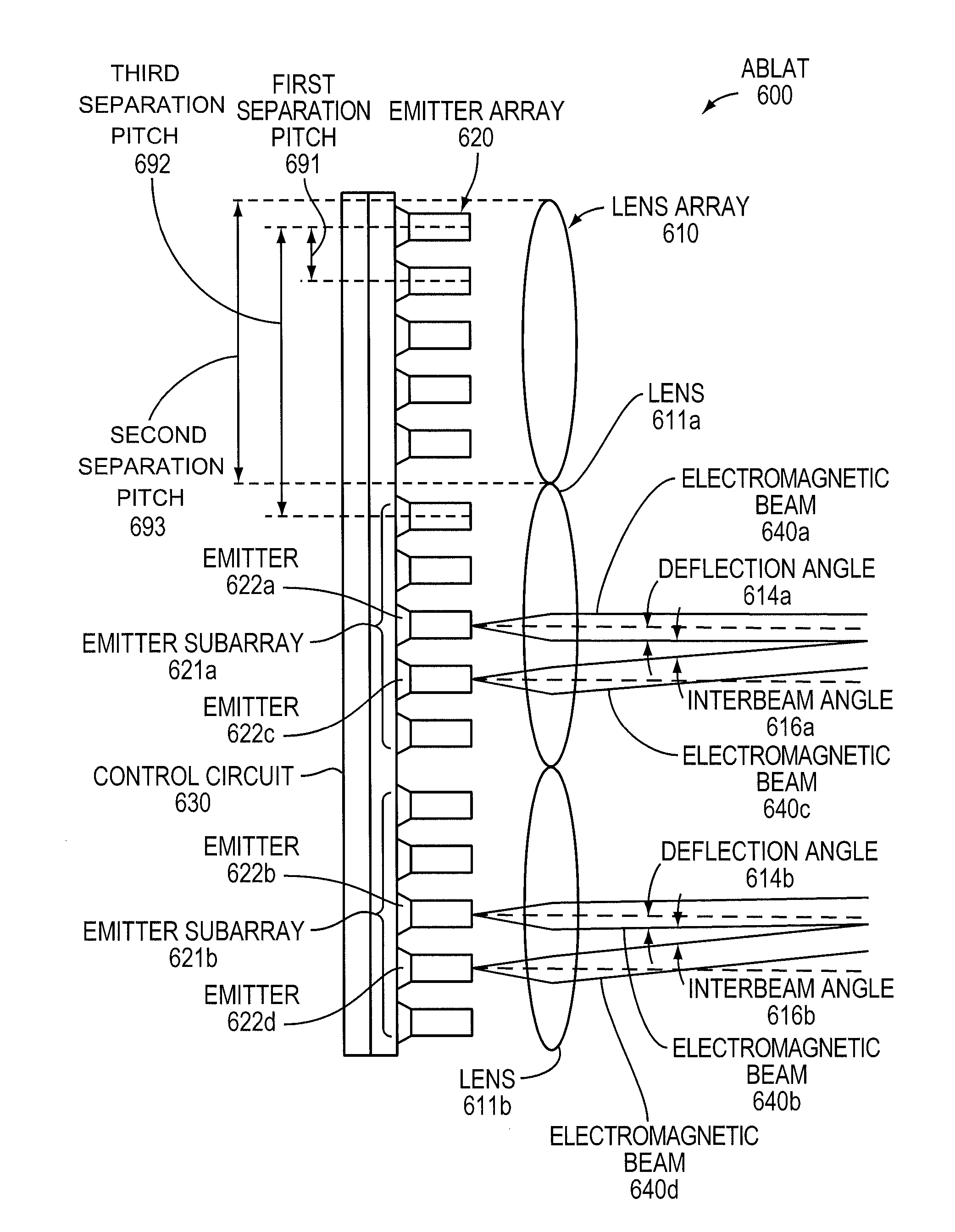
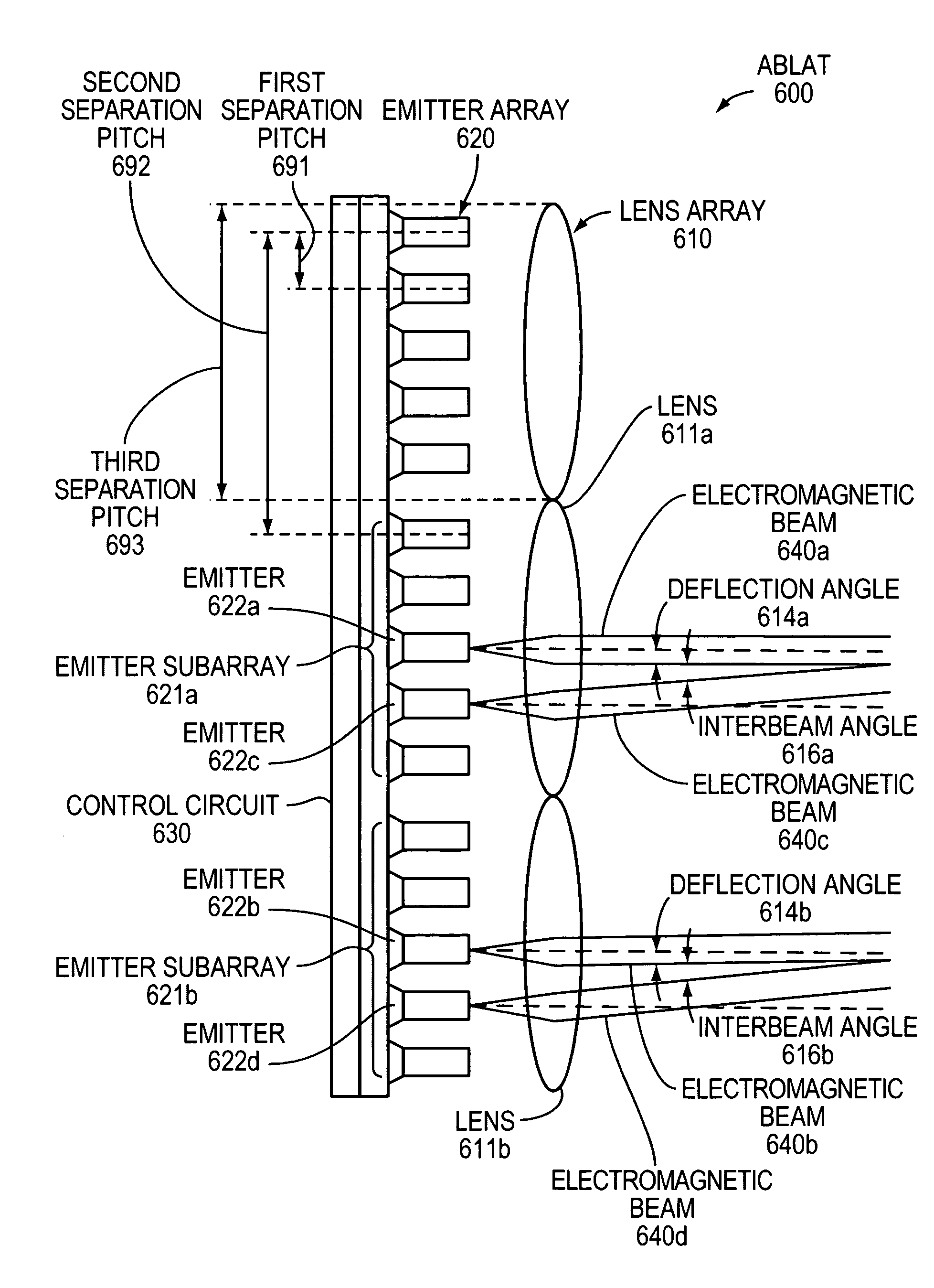
ActiveUS8301027B2Turn fasterWave based measurement systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLaser arrayBeam steering
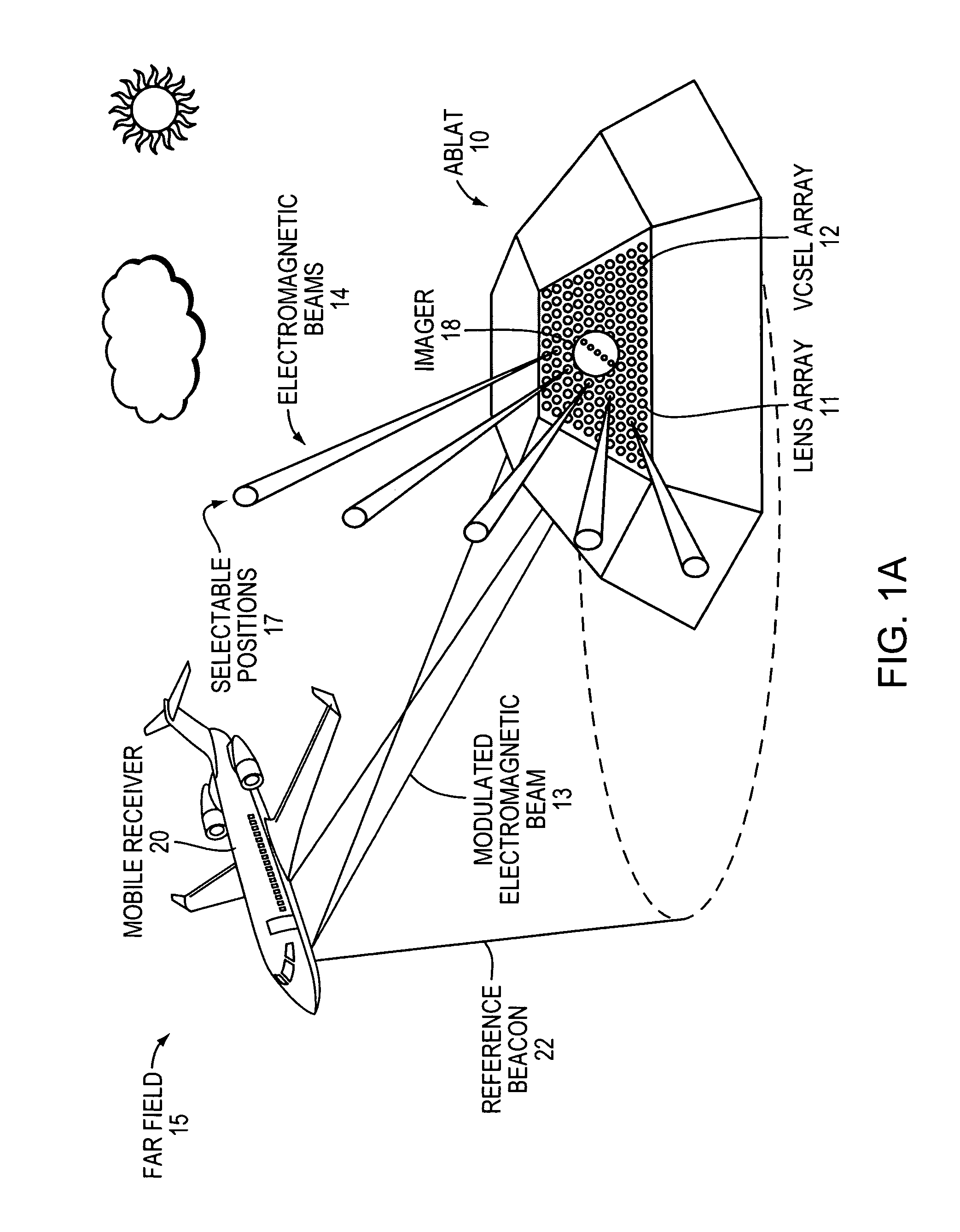
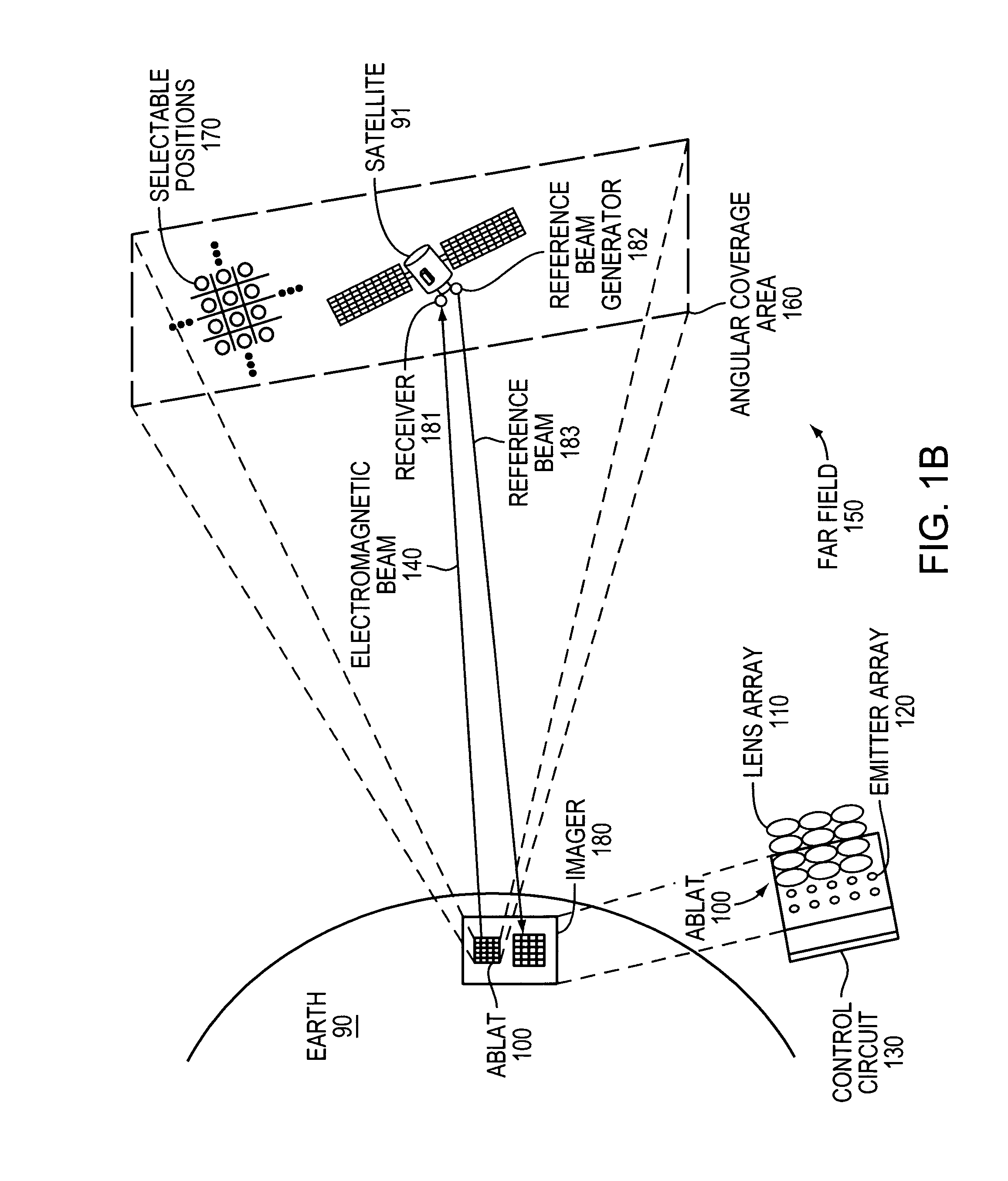
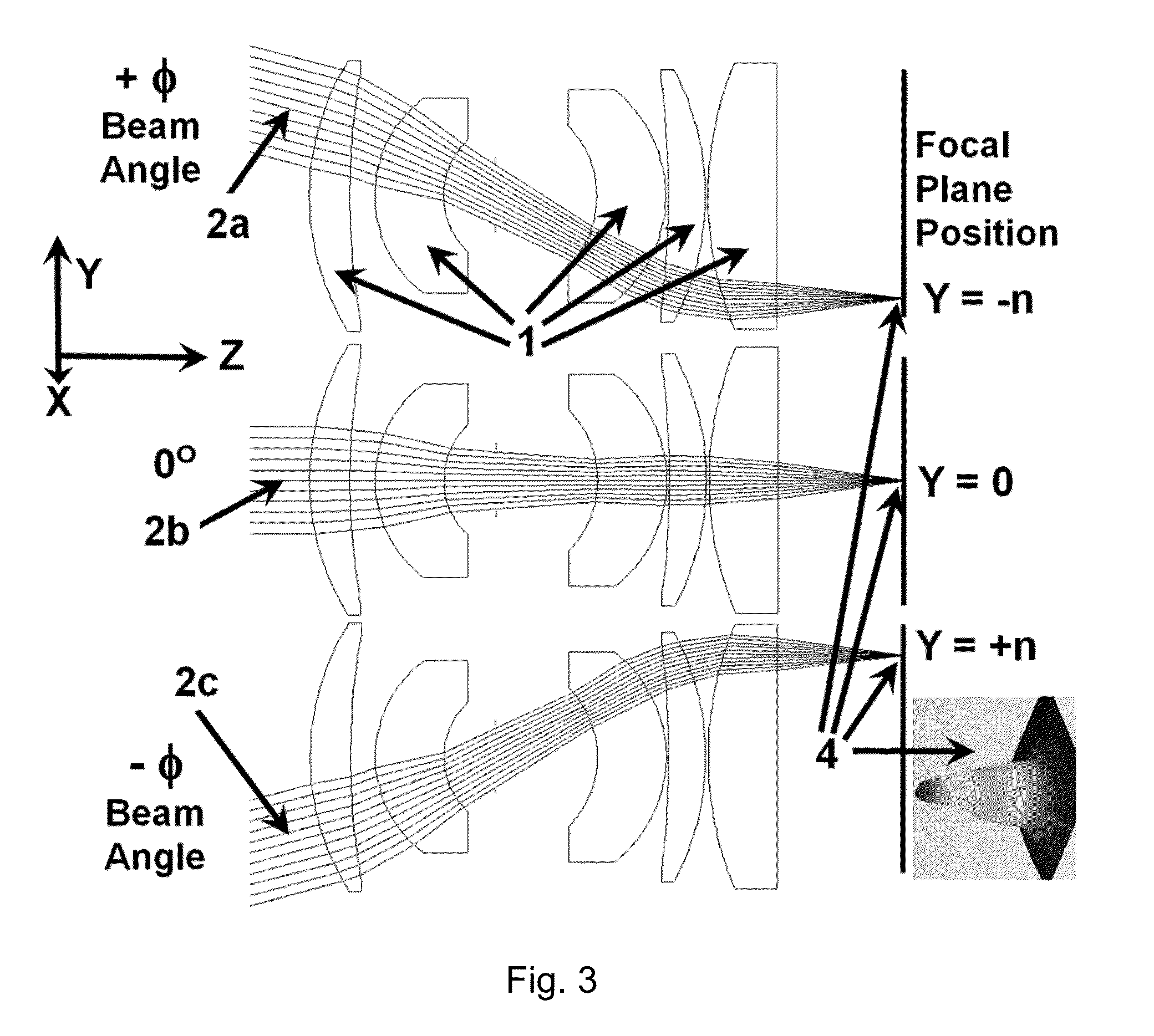
An Agile-Beam Laser Array Transmitter (ABLAT) uses an array of emitters and an array of lenses to project electromagnetic beams over a wide angular coverage area in the far field. Differences in the separation pitches of the two arrays allows the ABLAT to project beams to contiguous and / or overlapping positions, depending on the ratio of the separation pitches and the lens focal length. Compared to other beam steering technology, the ABLAT is a smaller, lighter, and more efficient means of projecting beams over wider angular coverage areas. Various embodiments can be used in any beam steering application, including, but not limited to: free-space optical communications; light detection and ranging (lidar); optical scanning (e.g., retinal or bar-code scanning); display projection; image capture; optical character recognition; scanning laser microscopy; non-destructive testing; printing; facsimiles; map making; web inspection; color print processing; phototypesetting and platemaking; laser marking; material processing; DNA analysis; and drug discovery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Agile-beam laser array transmitter
ActiveUS20100046953A1Turn fasterWide field of viewWave based measurement systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLaser arrayColor printing
An Agile-Beam Laser Array Transmitter (ABLAT) uses an array of emitters and an array of lenses to project electromagnetic beams over a wide angular coverage area in the far field. Differences in the separation pitches of the two arrays allows the ABLAT to project beams to contiguous and / or overlapping positions, depending on the ratio of the separation pitches and the lens focal length. Compared to other beam steering technology, the ABLAT is a smaller, lighter, and more efficient means of projecting beams over wider angular coverage areas. Various embodiments can be used in any beam steering application, including, but not limited to: free-space optical communications; light detection and ranging (lidar); optical scanning (e.g., retinal or bar-code scanning); display projection; image capture; optical character recognition; scanning laser microscopy; non-destructive testing; printing; facsimiles; map making; web inspection; color print processing; phototypesetting and platemaking; laser marking; material processing; DNA analysis; and drug discovery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Optical fiber and optical communication system including the same
InactiveUS6658190B2Increase the effective areaRestrains nonlinear optical phenomenaOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCommunications systemEngineering
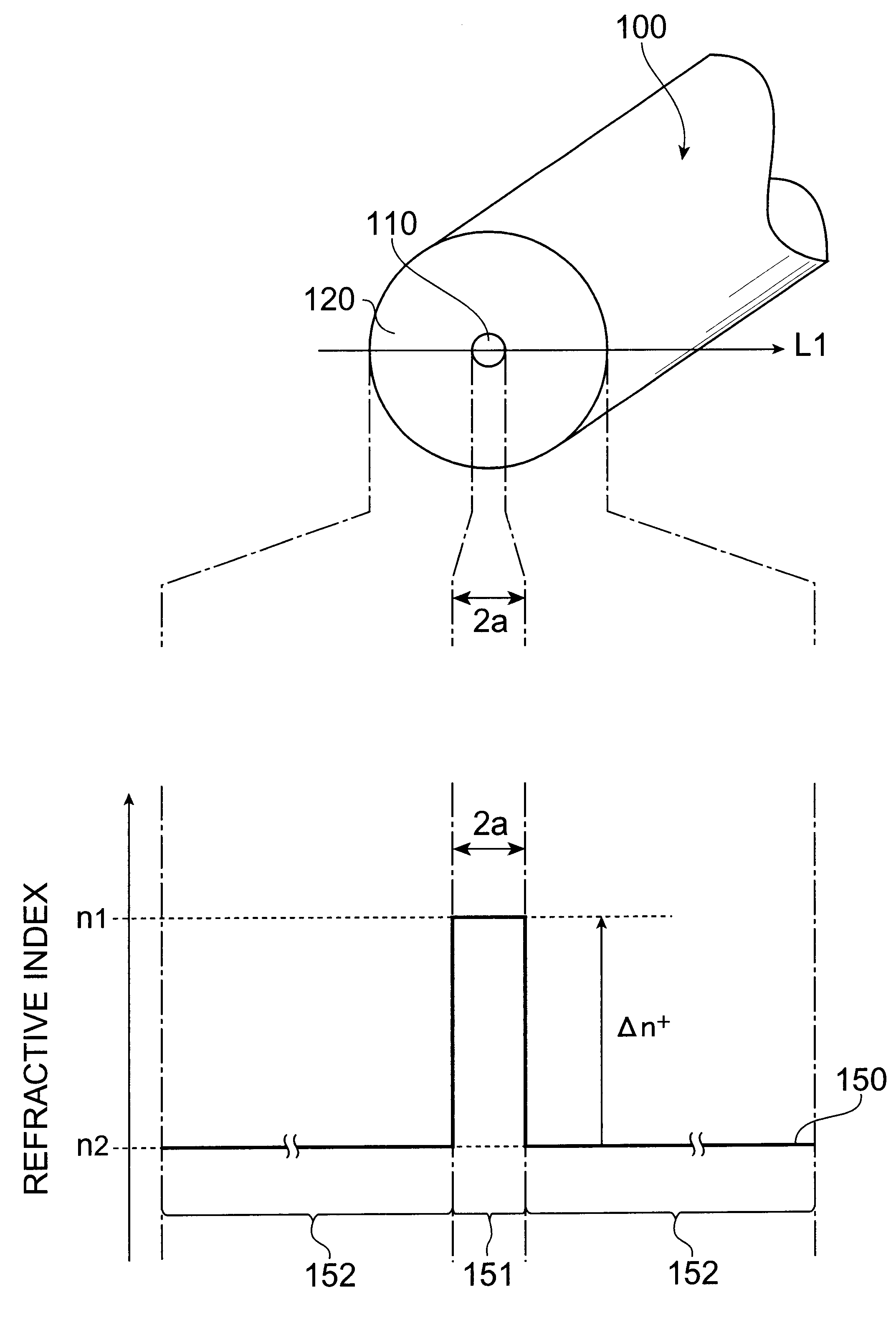
The present invention relates to an optical fiber having a structure suitable for long-distance optical communications, and an optical transmission line including the same. The optical fiber in accordance with the present invention comprises a core region extending along a predetermined axis, and a cladding region disposed so as to surround the outer periphery of the core region; and, as characteristics at a wavelength of 1.55 mum, an effective area of at least 110 mum<2>, a dispersion of 18 to 23 ps / nm / km, and a dispersion slope of 0.058 to 0.066 ps / nm<2> / km.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Information-processing device and information-processing system
InactiveUS7502053B2Reduce in quantityReduce the number of timesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsInformation processingInformation device
For an information terminal to be operated by users for collecting predetermined pieces of information from remote information devices by free-space optical communication, the present invention provides a technique for suppressing the power consumption of the information terminal by minimizing the amount of calculation performed to collect the aforementioned information. According to the present invention, each information device emits ID light on which a low-frequency pilot signal is superimposed. The information terminal captures a series of frames of images including the ID light and locates the ID light within the images by the following steps: (1) creating multiple levels of binned images having different resolutions for each frame of the image; (2) calculating an evaluation index for each pixel within a target range of the binned images at each level, from the lowest to the highest resolution, where the target range is narrowed every time the process switches over to a lower level. In (2), the evaluation index is calculated by an evaluation function including fast Fourier transformation performed throughout the series of frames of images. The evaluation index thus calculated is compared with a threshold to determine whether the pixel concerned is receiving ID light. The present technique significantly reduces the number of pixel to be analyzed and evaluated, thereby decreasing the total number of arithmetic operations to be performed using the evaluation function. Thus, the power consumption is suppressed.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +2
Techniques for secure free space laser communications
Techniques for establishing a free-space optical communications link between a local terminal and a remote terminal include determining that a remote terminal is within a wide field of view associated with a micromechanical mirror in a local terminal. The risk of an undesirable effect which imposes a performance or security problem is also determined to occur within the wide field of view. The micromechanical mirror is pointed by including the remote terminal within a narrow field of view that is narrower than the wide field of view, and by reducing the risk that the undesirable effect is within the narrow field of view.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Multiple-Input Method And Apparatus Of Free-Space Optical Communication
An approach is provided that uses diversity to compensate fading of free-space optical (FSO) signals propagating through an environment characterized by atmospheric scintillation. One embodiment involves collecting at least one FSO beam, demultiplexing the beam by wavelength into at least two sub-beams, detecting each sub-beam to produce an electrical output therefrom, and recovering a signal using complementary information from at least two of the electrical outputs. Another embodiment involves collecting the FSO beam onto an array of spatially separated sub-apertures, detecting the light entering each sub-aperture to produce an electrical output therefrom, and recovering a signal using complementary information from at least two of the electrical outputs. This second embodiment enables both electronic adaptive processing to coherently integrate across the sub-apertures and in the case of multiple transmit apertures a free space optical Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) system.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS
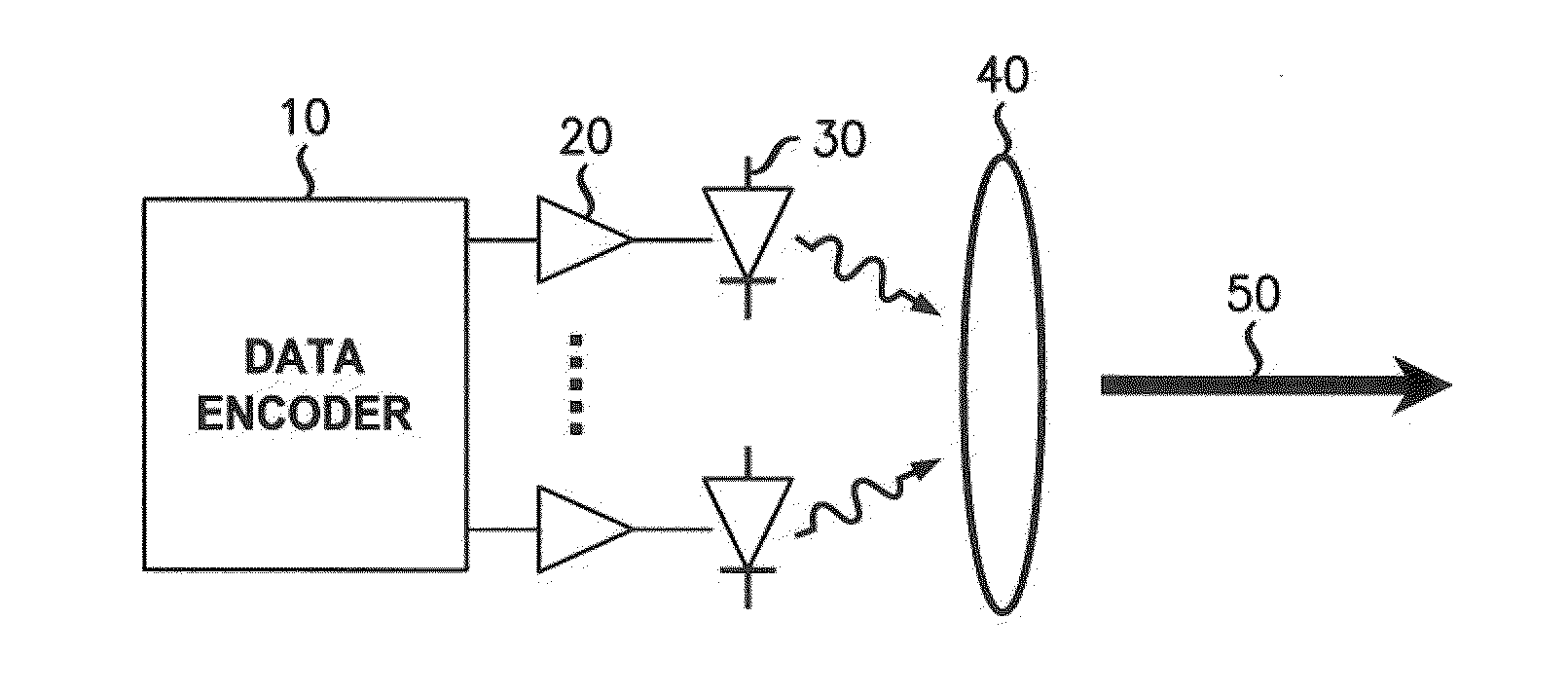
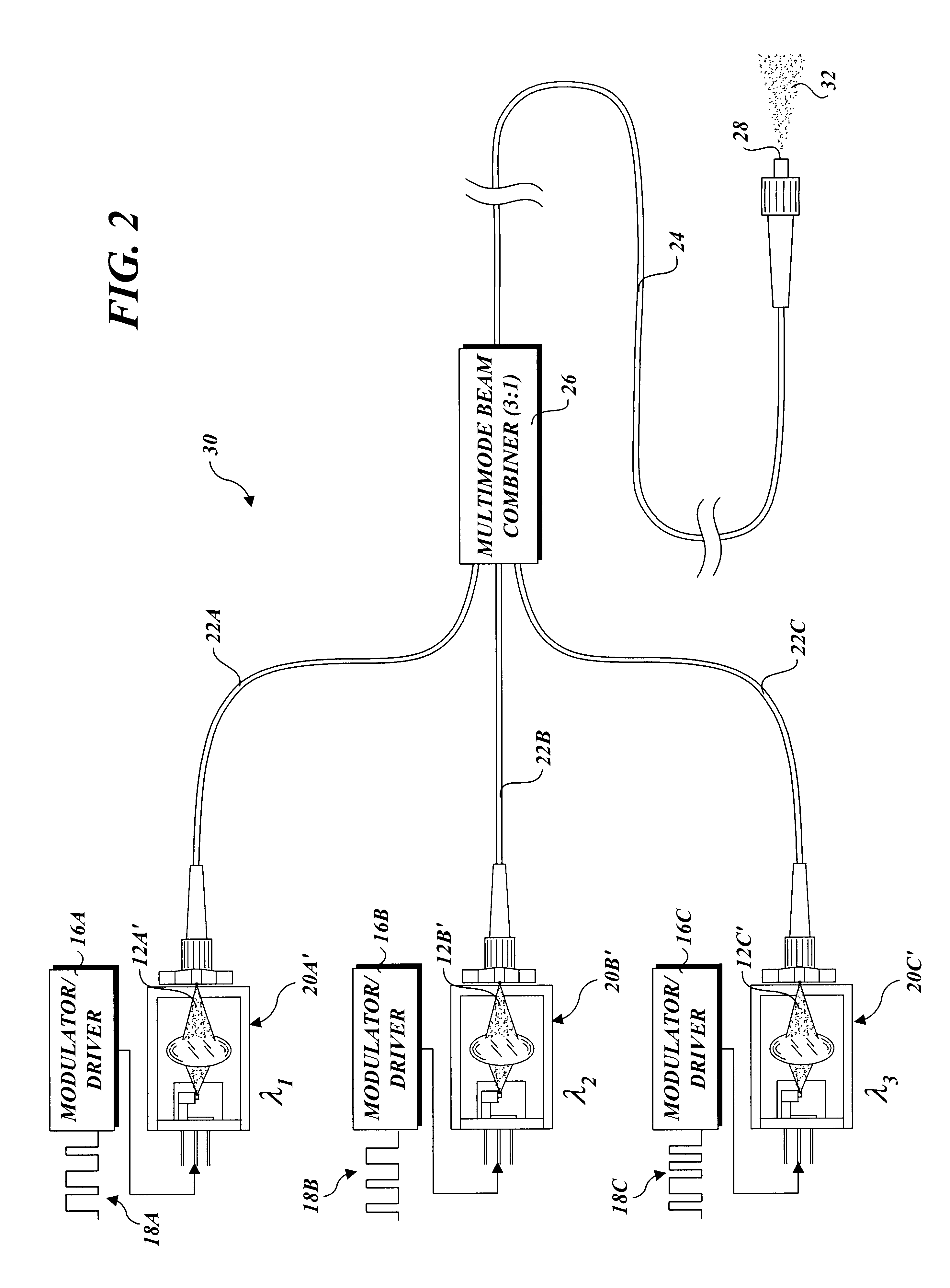
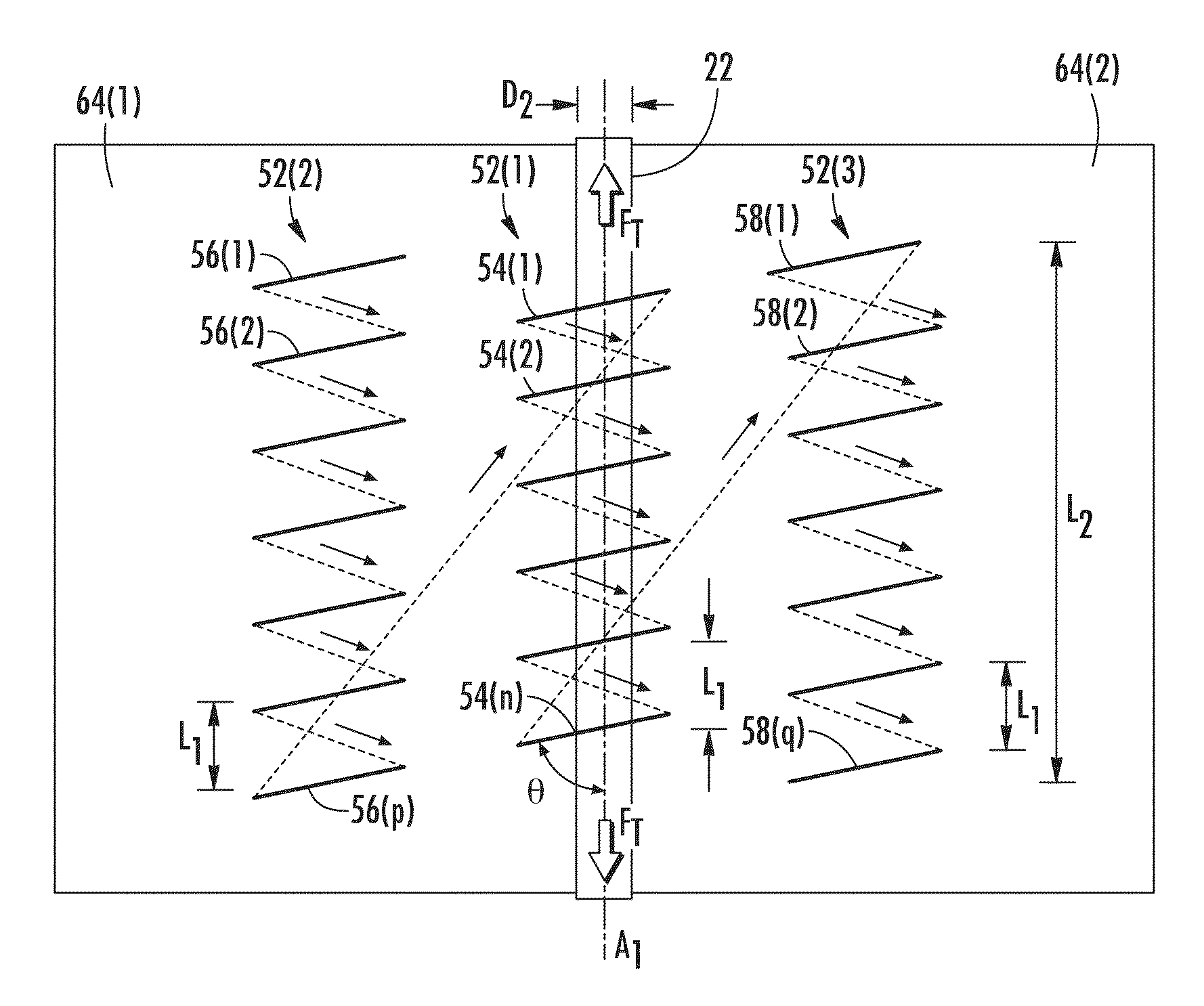
Apparatus and method for combining multiple optical beams in a free-space optical communications system
InactiveUS6868236B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersFiberCommunications system
An apparatus and method for combining multiple optical beams into mode-scrambled optical signals. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes a plurality of laser beam sources, each to produce a modulated optical beam. A plurality of input fiber segments, each comprising a multimode optical fiber core, are operatively coupled at one end to a respective laser source to receive a respective modulated optical beam. A multimode optical beam combiner is used to operatively couple the output ends of the input fiber segments to the input end of an output fiber segment having a multimode optical fiber core. The modulated optical beams produced by the laser beam sources are combined into a single mode-scrambled optical signal. The apparatus enables multiple optical beams having similar wavelengths to be combined to increase optical signal strength. It also enables multiple optical beams having different wavelengths to be combined to form a wavelength division multiplexed signal.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
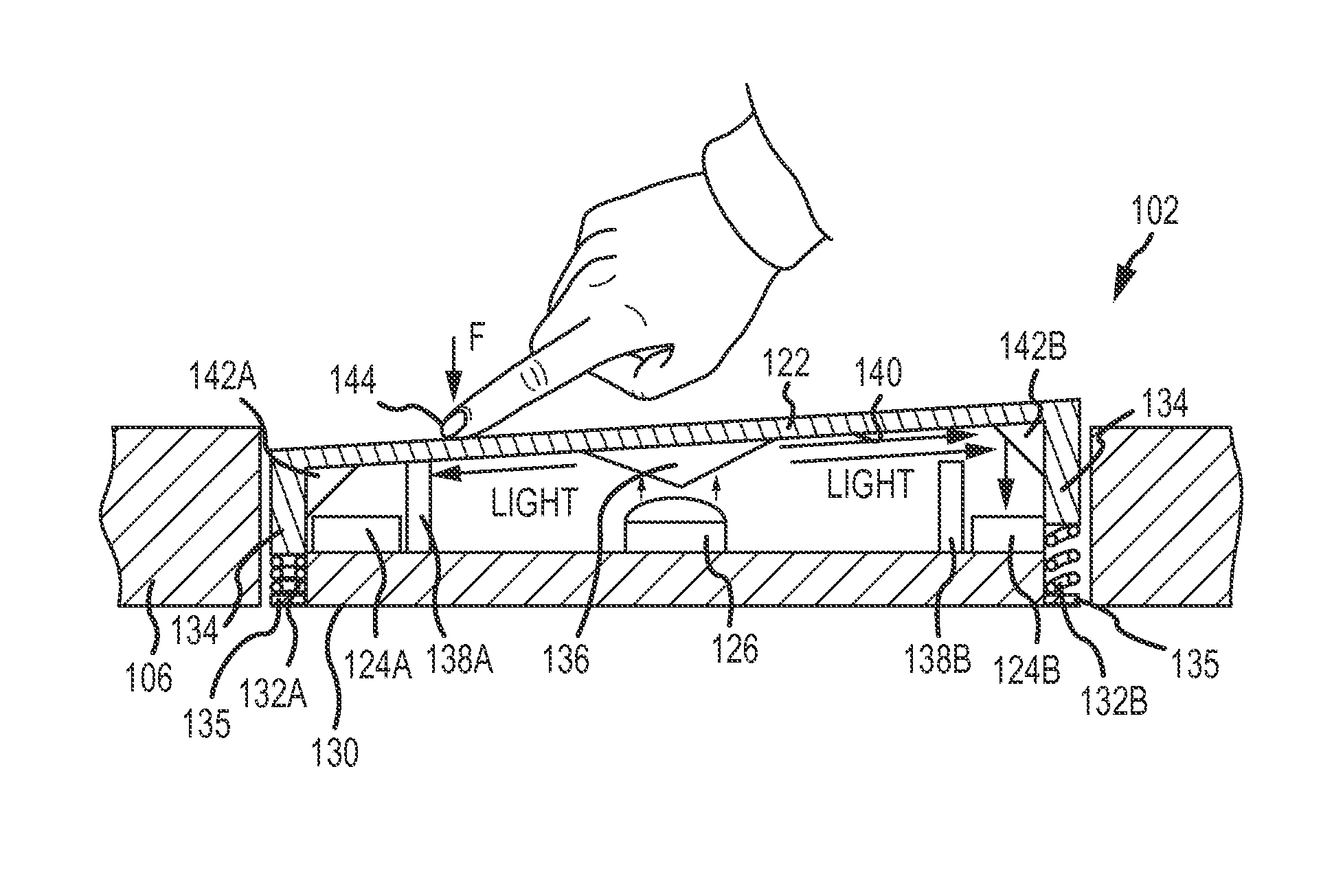
Optical sensing mechanisms for input devices
A computer or other electronic device including a processor and an input device, such as a track pad. The track pad being in communication with the processor and including a movable surface, a light source in communication with the processor, and an optical sensor in selective optical communication with the light source and in communication with the processor. The optical sensor detects movement of the movable surface by receiving light from the light source.
Owner:APPLE INC
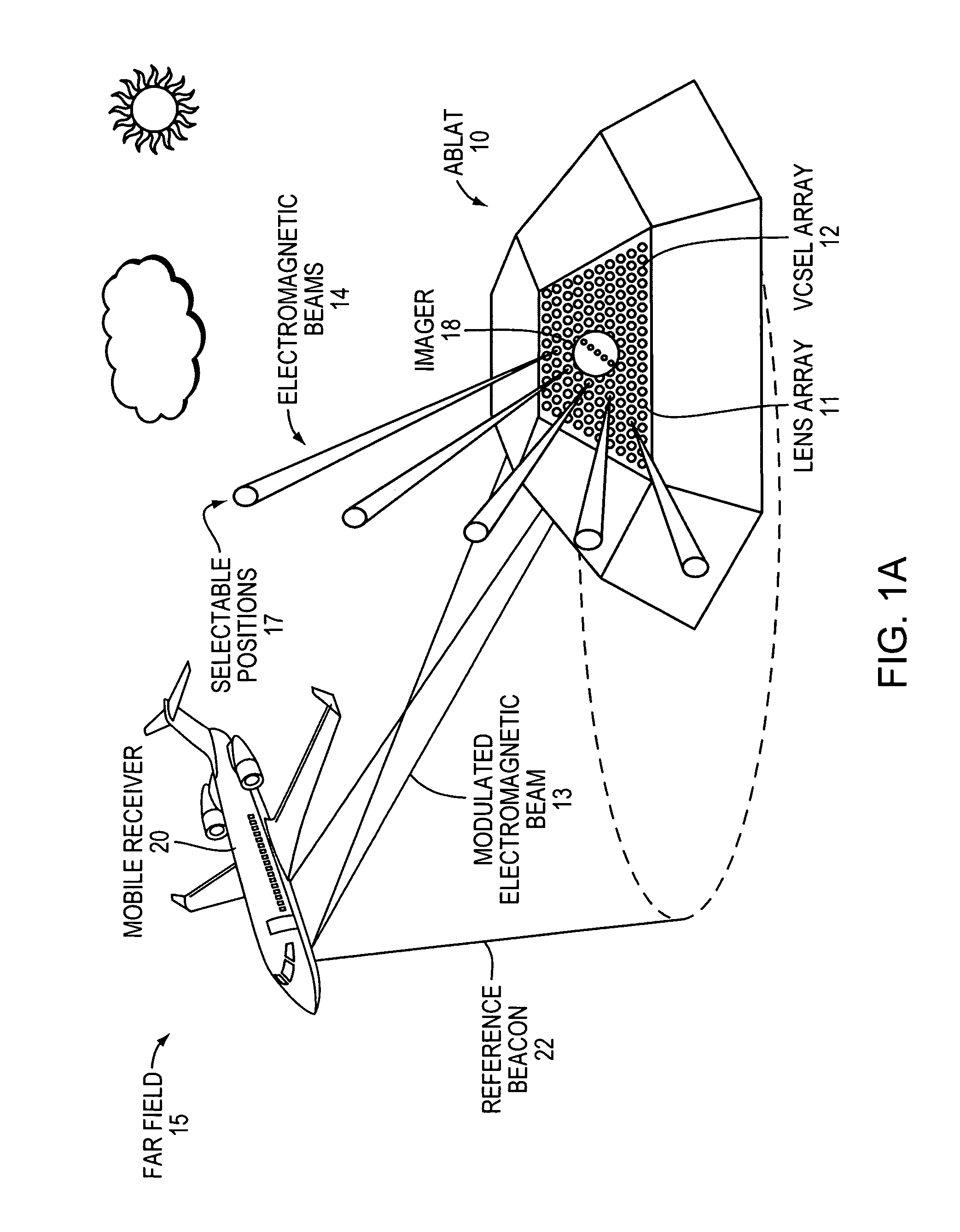
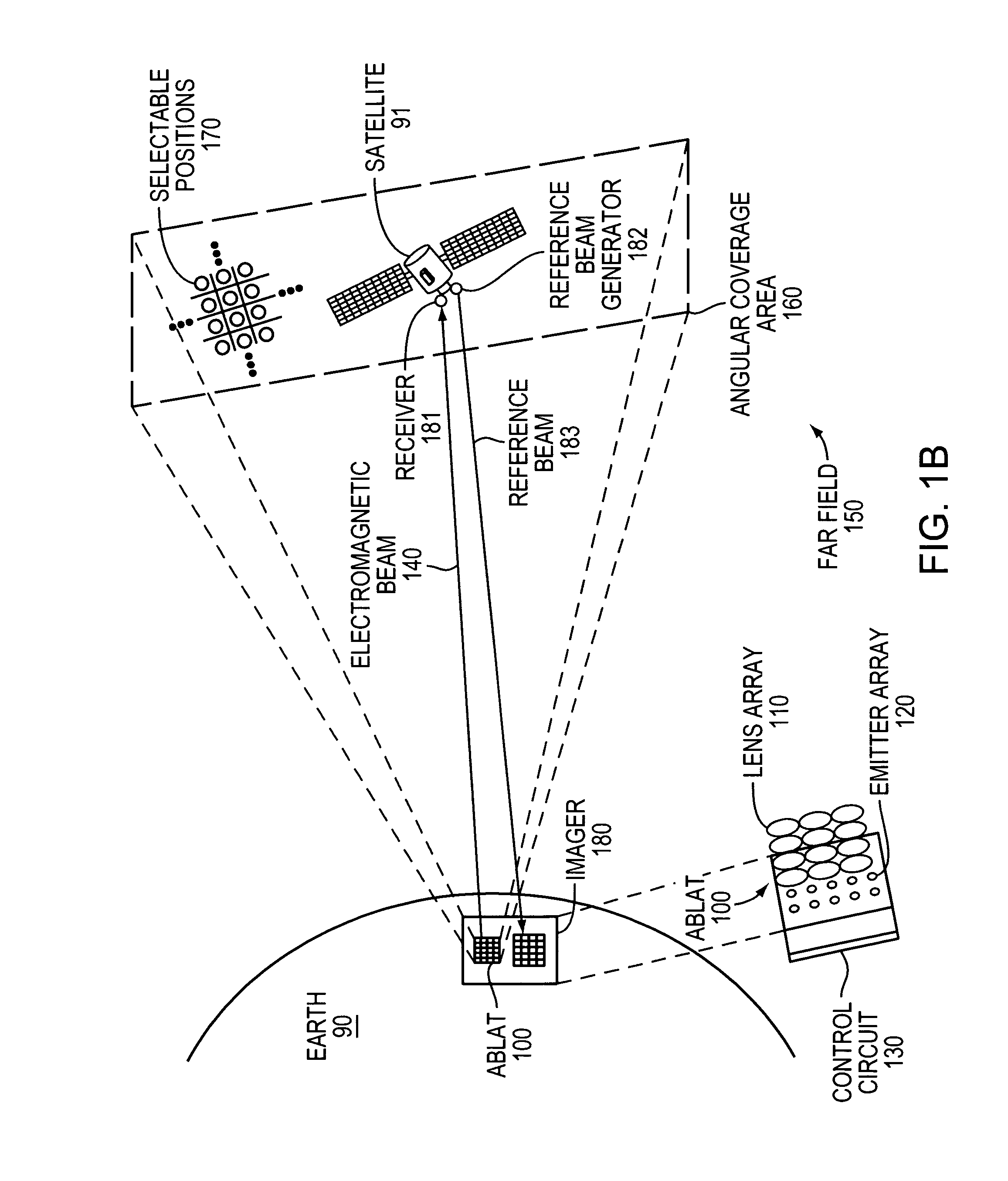
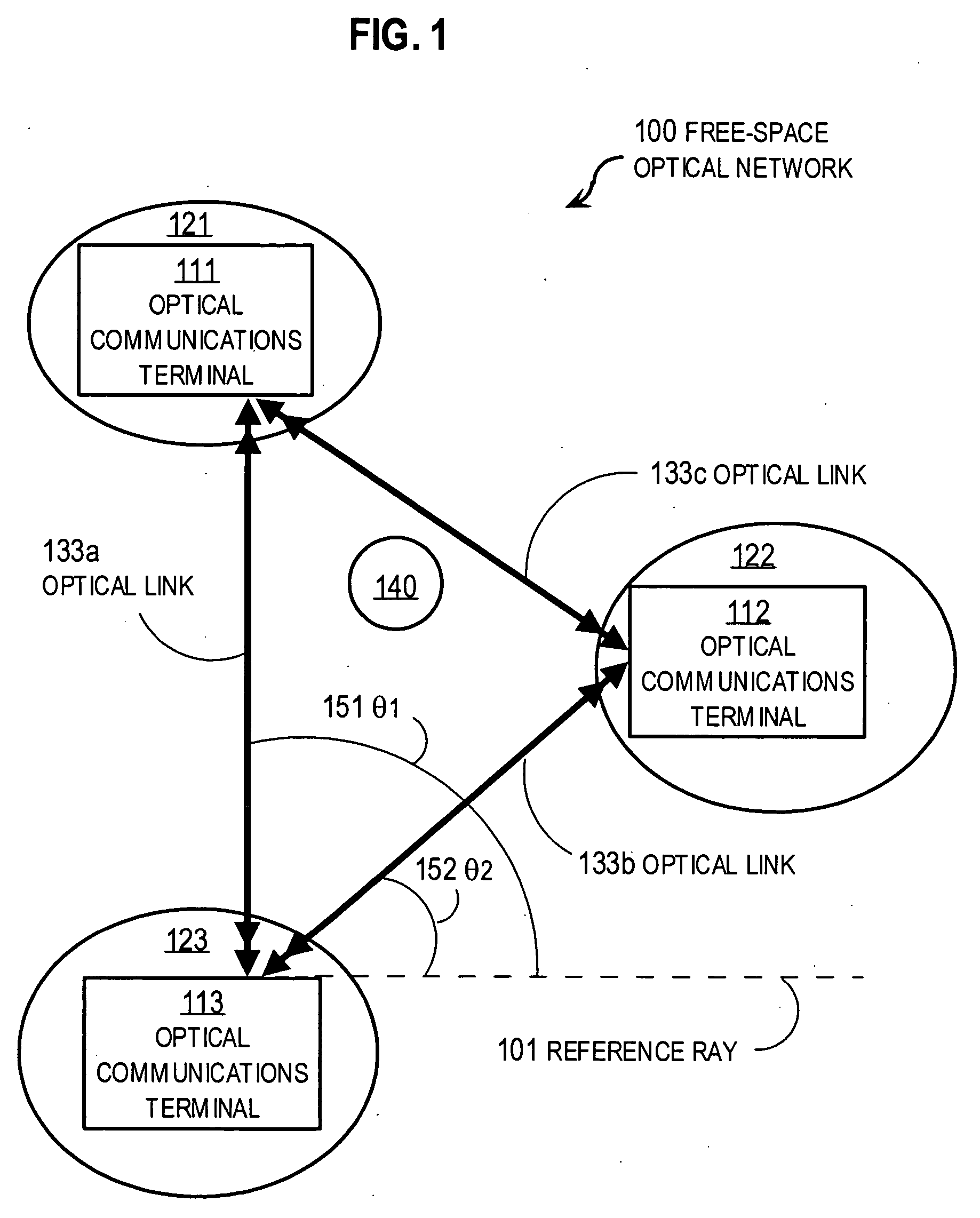
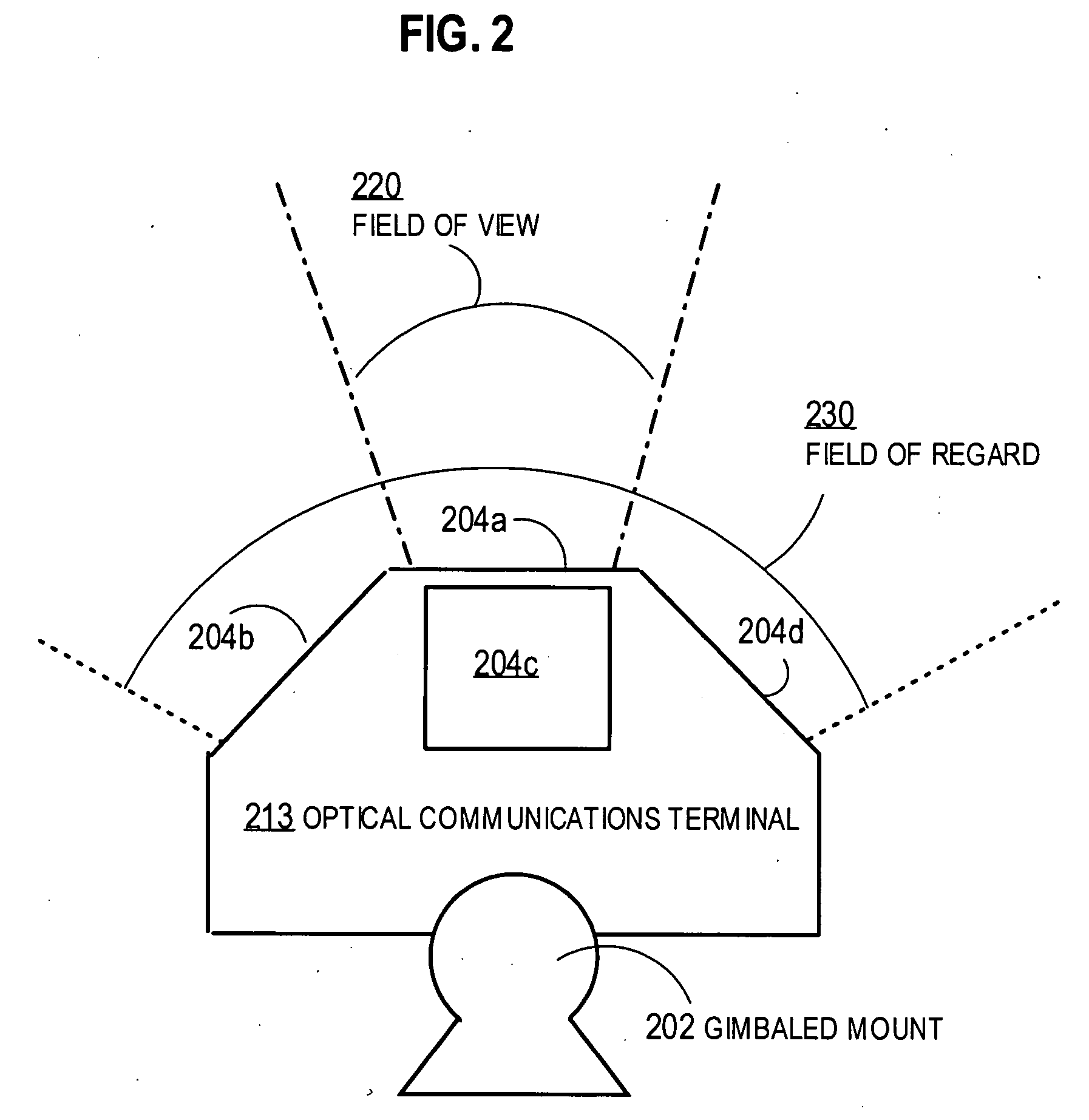
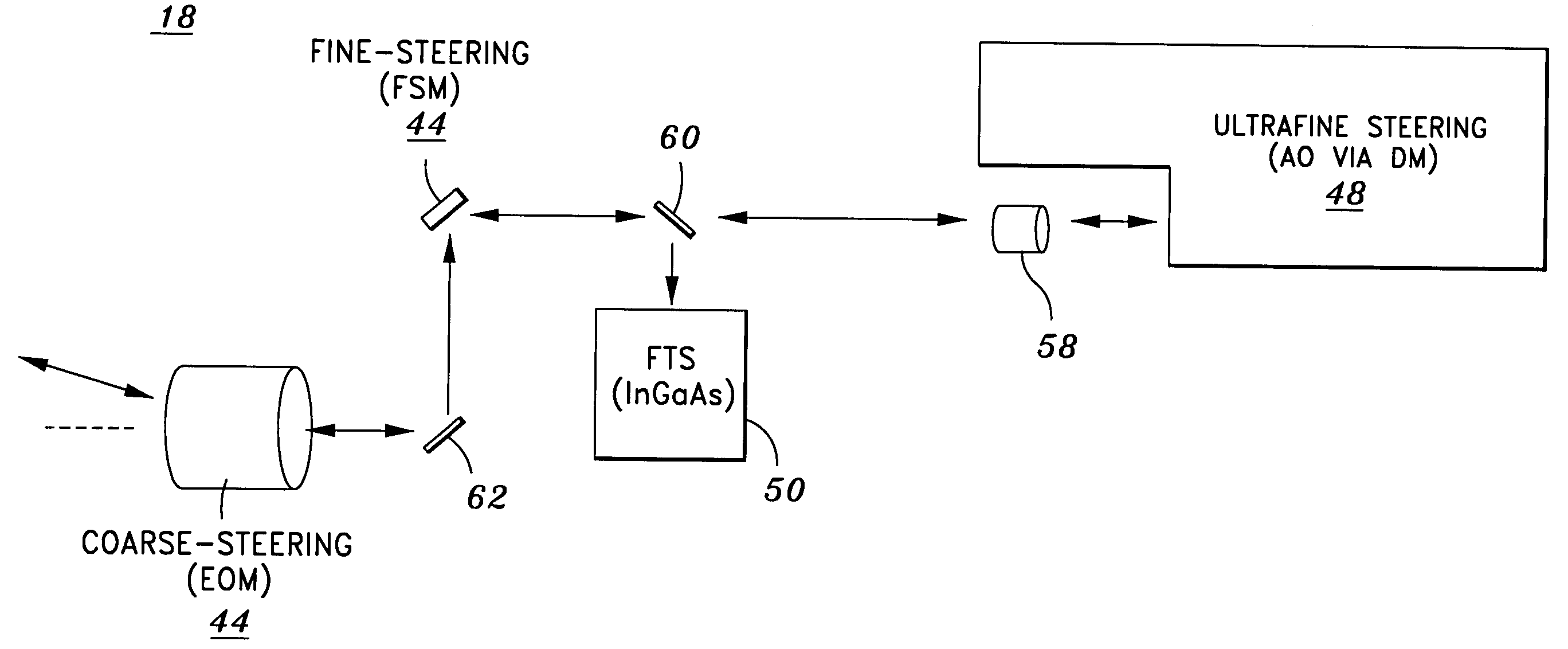
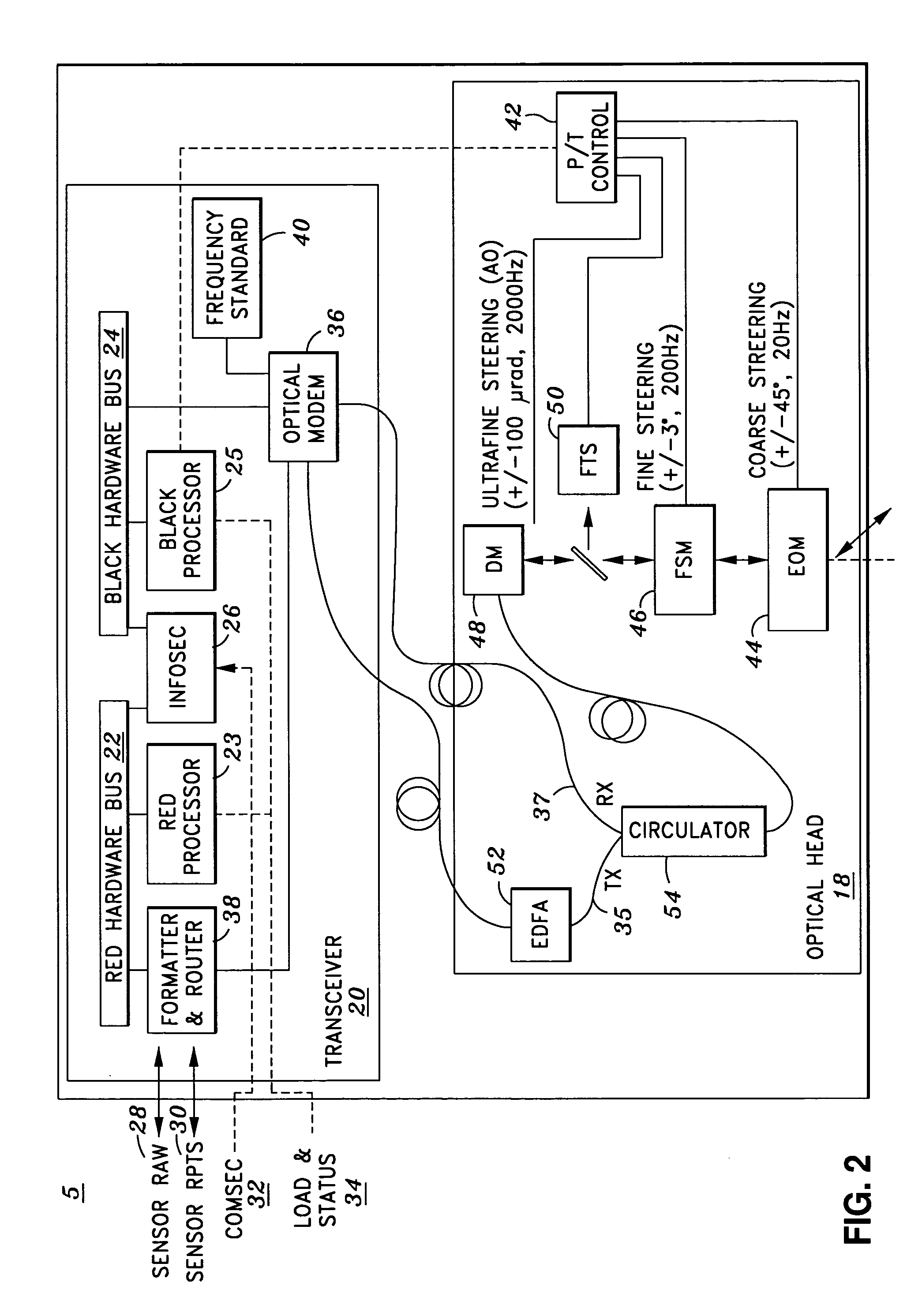
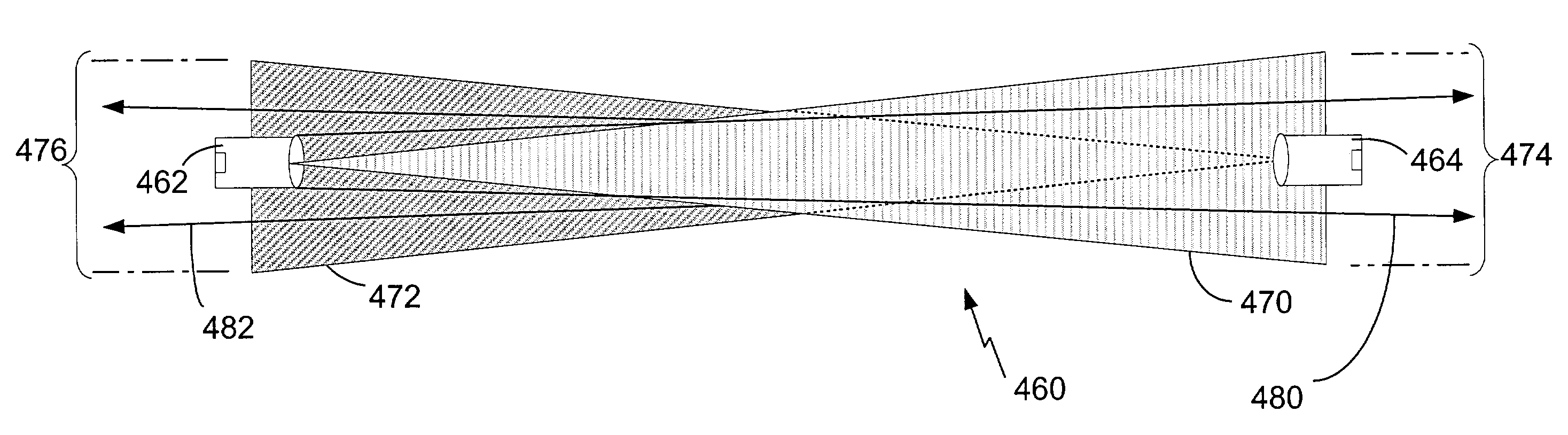
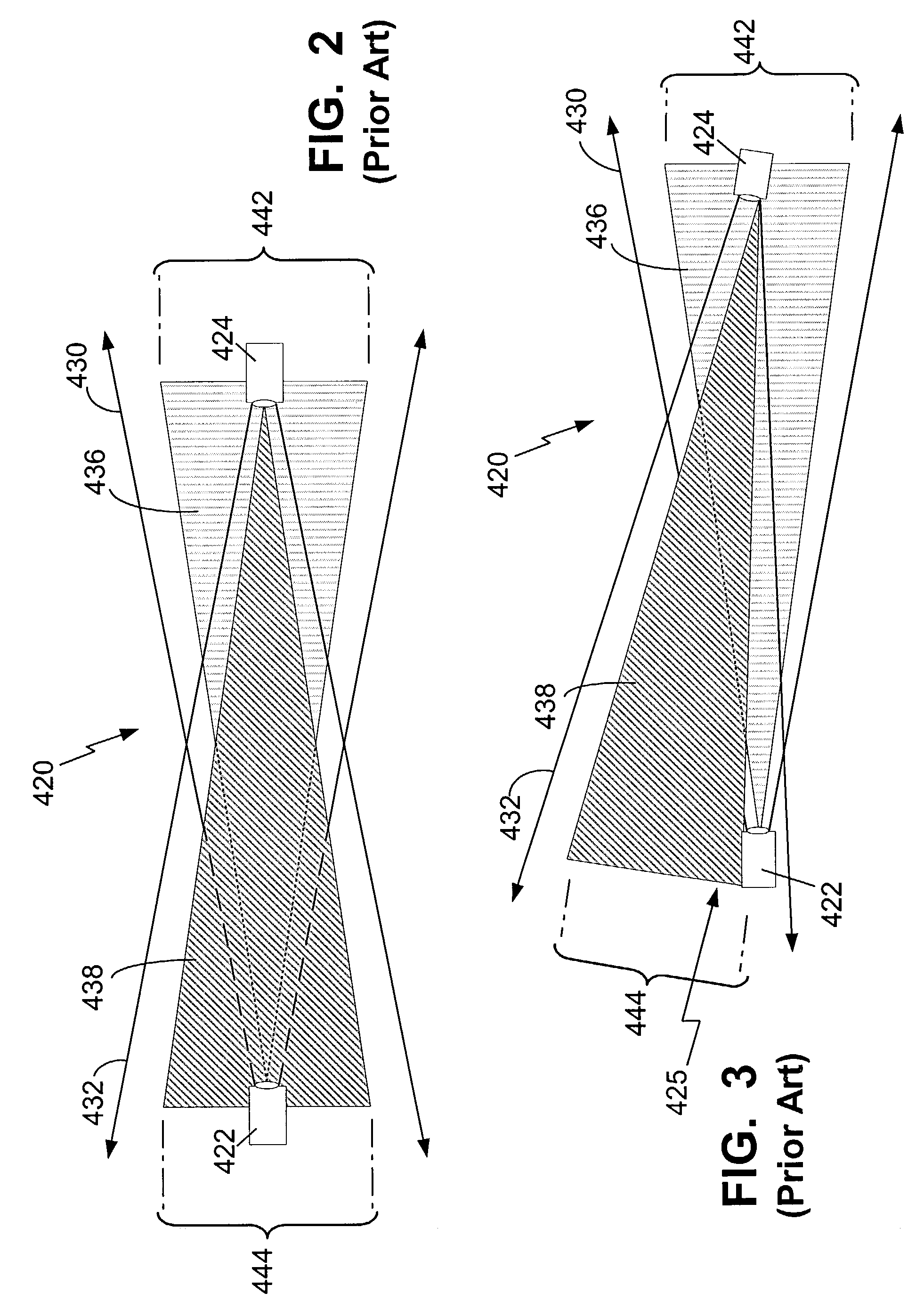
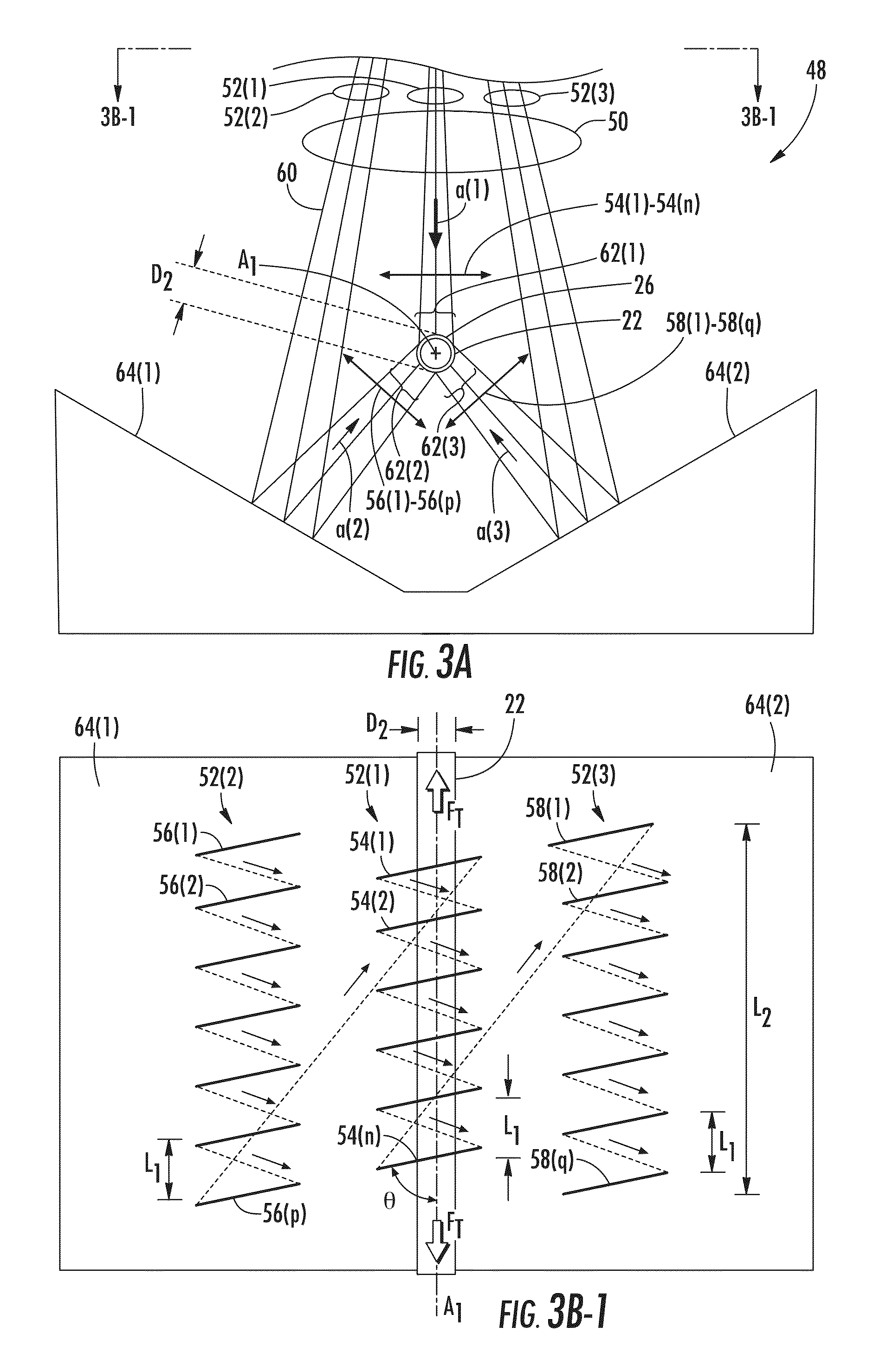
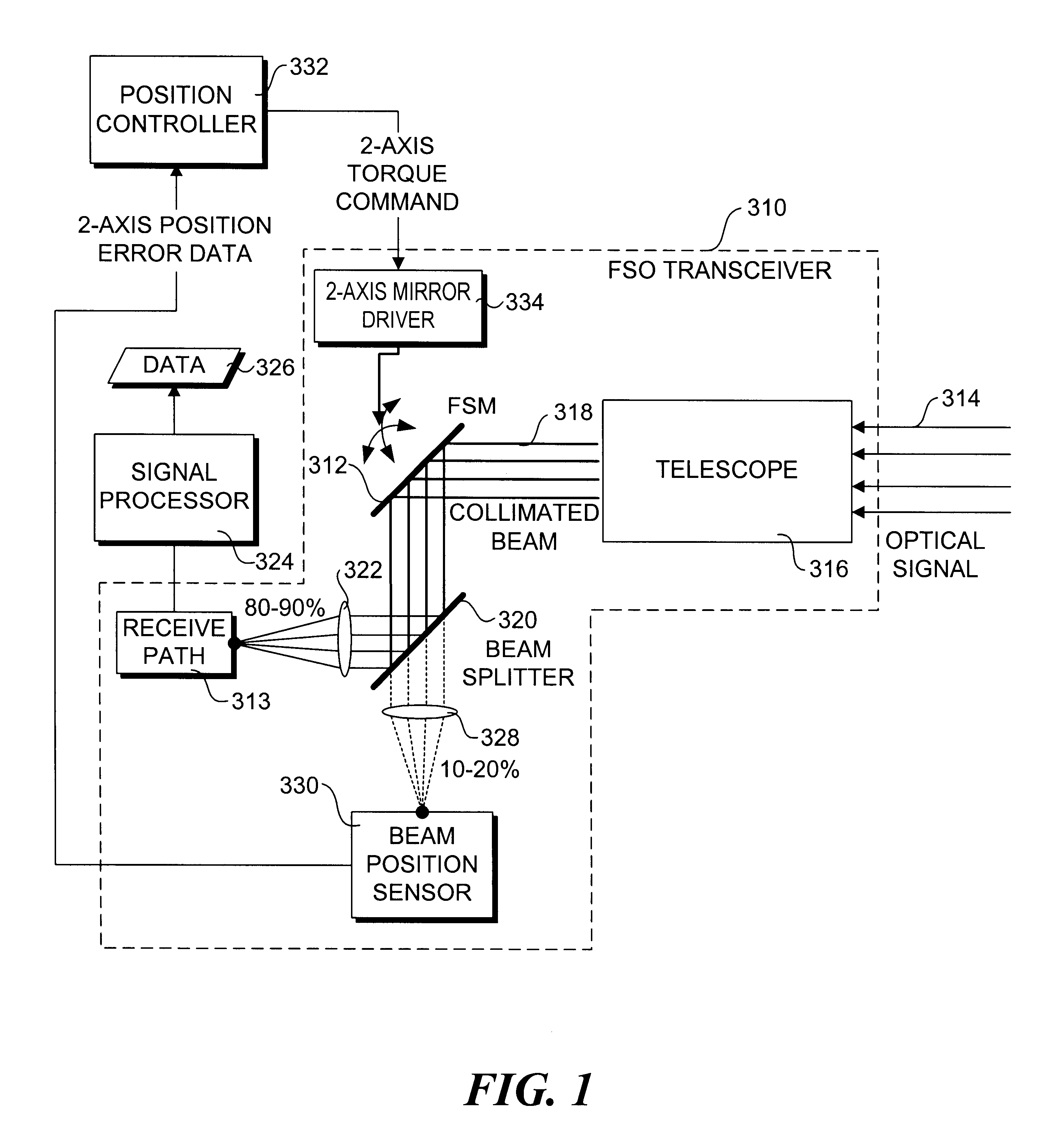
Airborne free-space-optical system utilizing three-tier, ultrafine steering
ActiveUS20050069325A1Mitigate vibration-inducedMitigate aero-optic-induced jitterSatellite communication transmissionRadio transmissionCommunications systemEngineering
An optical head is provided for a free space optical communications system. The optical head is utilized for transmitting and receiving modulated infrared laser beams. The optical head includes an optical amplifier, a circulator, an ultrafine-steering element, a fine-steering element, a course-steering element, and a fine track sensor. Additionally, a method is provided for facilitating airborne free space optical communications between an airborne host platform and a link platform. Each platform has an optical head which transmits and receives data via modulated infrared laser beams, wherein the host includes at least an optical head having a fine, coarse, and ultrafine steering element configured in a cascaded three-tier steering element architecture.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
Apparatus for implementing orbit angular momentum state super position and modulation
InactiveCN101251655AAchieve overlayGood for long-distance transmissionDiffraction gratingsNon-linear opticsBeam splittingPolarizer
The invention relates to a device for realizing superposition and modulation of orbital angular momentum states of light beams, belonging to the laser application technical field. The invention consists of a laser, a polarizer, a one-fourth wave plate, a diffraction grating, a Fourier lens, a polarized beam-splitting prism, two Dove prisms, three holophotes and a pinhole diaphragm, wherein, firstly, an optical system which takes the diffraction grating and the Fourier lens as core elements is adopted to generate a plurality of bundles of light beams which are equidistantly distributed on the circumference which takes an optical axis of incident light as the center and are positioned in different orbital angular momentum states; secondly, an optical system which consists of the polarized beam-splitting prism, the holophotes and the rotatable Dove prisms is adopted to decompose an optical field into field components which rotate towards the opposite direction; thirdly, the field components are superposed, and superposition of required orbital angular momentum states is realized and then superposition and modulation of the orbital angular momentum states are realized. The device for realizing superposition and modulation of the orbital angular momentum states of the light beams has application value in the free space optical communication field.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Acquisition, Tracking, and Pointing Apparatus for Free Space Optical Communications with Moving Focal Plane Array
ActiveUS20150188628A1Simplifies FSO systemsLine-of-sight transmissionTelescopesCommunications systemDetector array
An acquisition, pointing, and tracking (ATP) apparatus for free space optical (FSO) communications systems incorporates a multi-element detector array positioned at a focal plane of an optical telescope. An optical communications element lies at the center of the detector array. In lieu of traditional beam steering, the apparatus performs pointing and tracking functions internally by first calculating a position of an optical maximum on the detector array, and then translating the detector array within the focal plane of the telescope such that the optical communications element lies at the optical maximum for transmitting and / or receiving optical communications signals.
Owner:SPACE PHOTONICS
Positioning information assisted beam control method based on intelligent reflecting surface
ActiveCN111245494AEfficient parameter configurationBeam Steering PreciseSpatial transmit diversityPassive radio relay systemsChannel state informationBeam direction
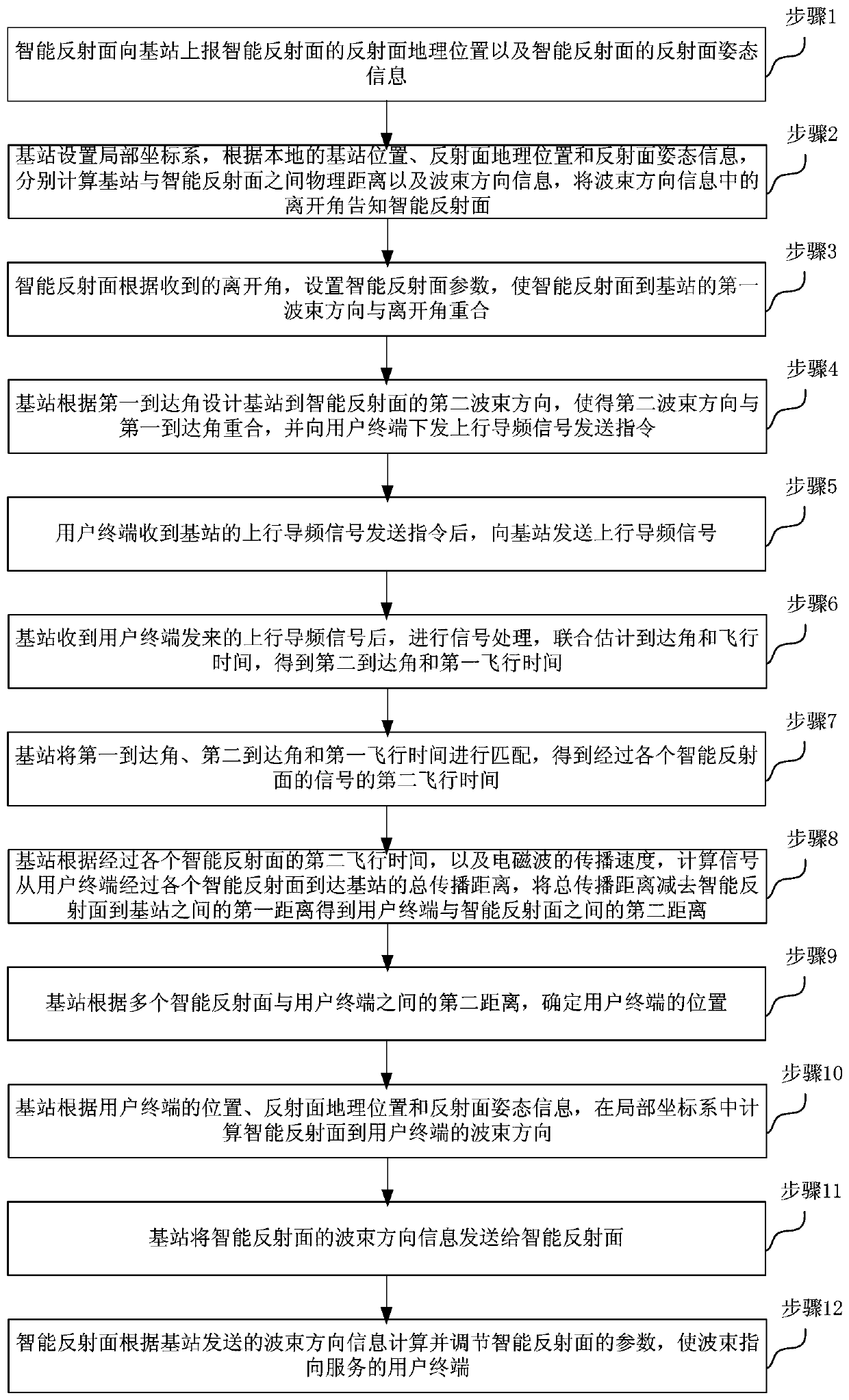
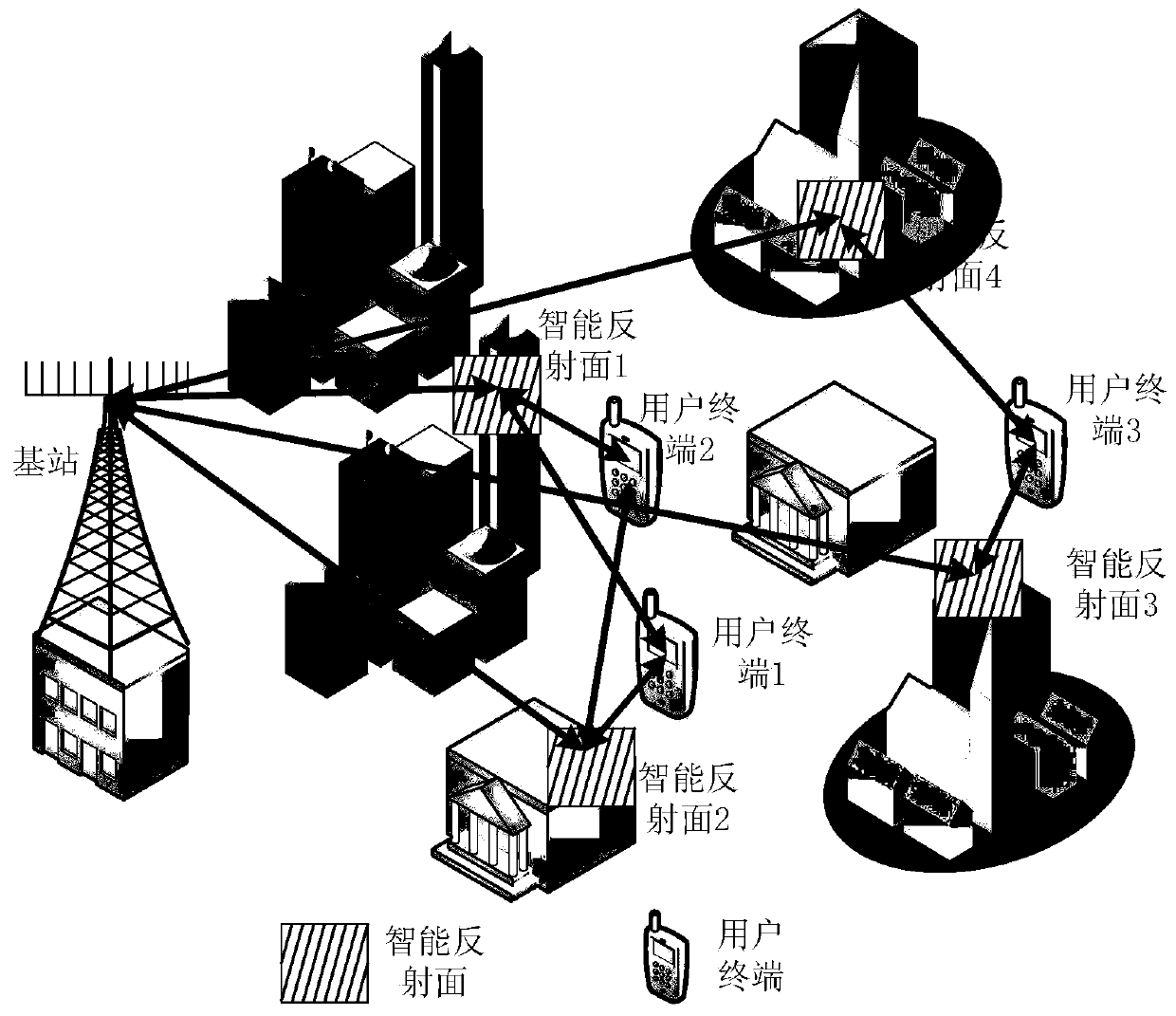
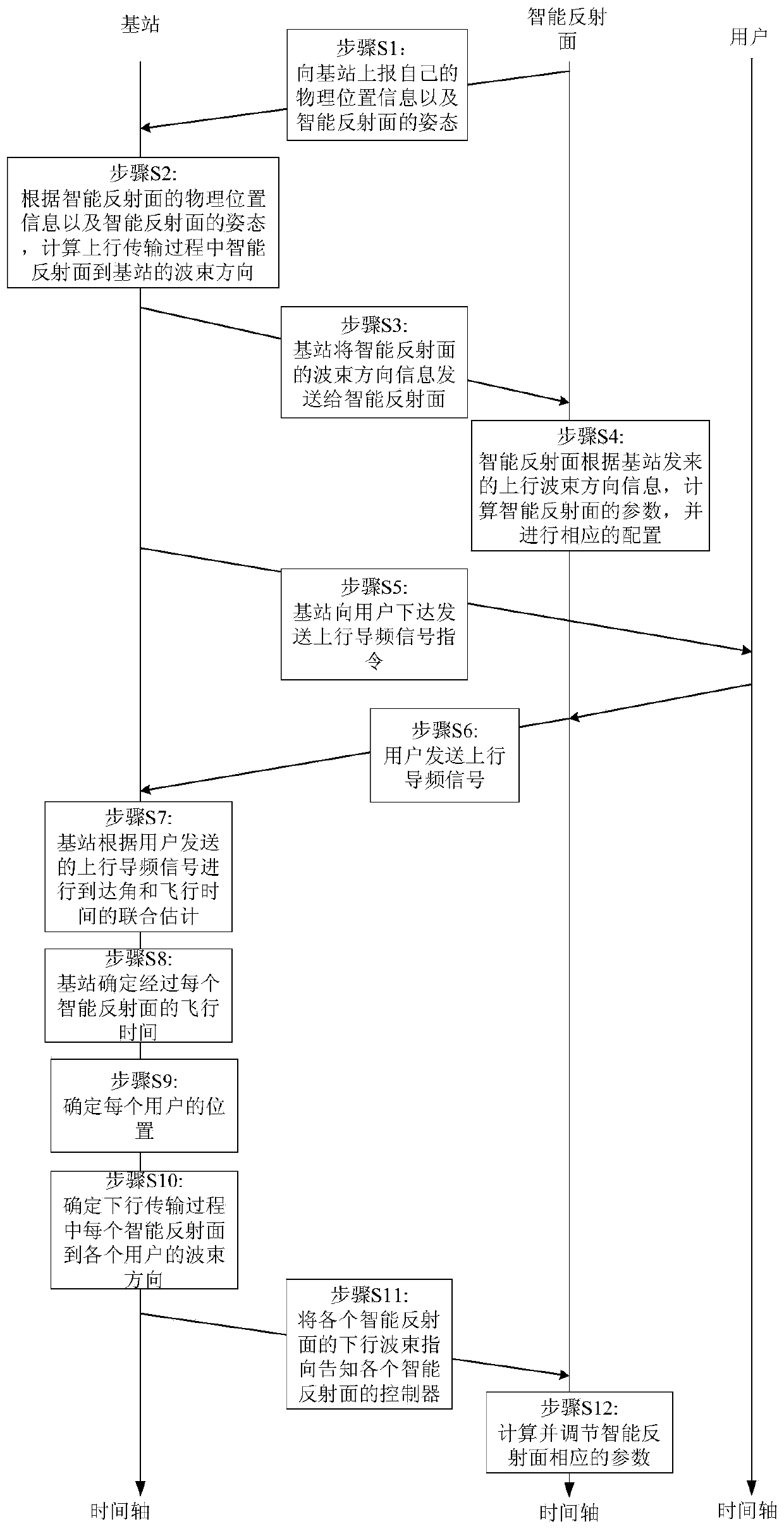
The invention discloses a positioning information assisted beam control method based on an intelligent reflecting surface. The intelligent reflecting surface can calculate and adjust the parameters ofthe intelligent reflecting surface according to the beam direction information transmitted by a base station, and enables a beam to point to a serving user terminal; the intelligent reflecting surface can perform parameter configuration efficiently, and achieves the precise beam control; in addition, a base station does not need to know complete channel state information, the base station realizes accurate positioning of the user terminal according to the results of corresponding angle estimation and flight time estimation; under the assistance of positioning information, the accurate controlof beams can be realized, the overhead of beam control can be effectively reduced, and the energy utilization rate of the system is improved. The positioning information assisted wave beam control method based on the intelligent reflecting surface is wide in application range, and is suitable for millimeter wave communication, terahertz communication and free space optical communication.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Free space optical communication system
ActiveUS20160020855A1Increase frame rateAddressing slow performanceClose-range type systemsDetector arrayLength wave
A method and system for optical communication between a transmitter and receiver, using a video camera to image the location of the remote transmitter. The comparatively slow frame rate of conventional detector arrays, which would limit communication rate, is overcome by reading only pixels in a region of interest around the transmission source image, and these pixels can then be read out and the communication information on them retrieved, at a frame rate much faster than that of the conventional full frame read-out. Custom wiring of the array can be used to enable implementation of this increased frame rate. Other methods of increasing communication speed using a video camera array detector include spreading the optical signal spatially along a row of pixels, and reading those pixels simultaneously in one frame, or wavelength multiplexing the optical information, and dispersing the different wavelengths onto successive pixels of the array.
Owner:SHILAT OPTRONICS
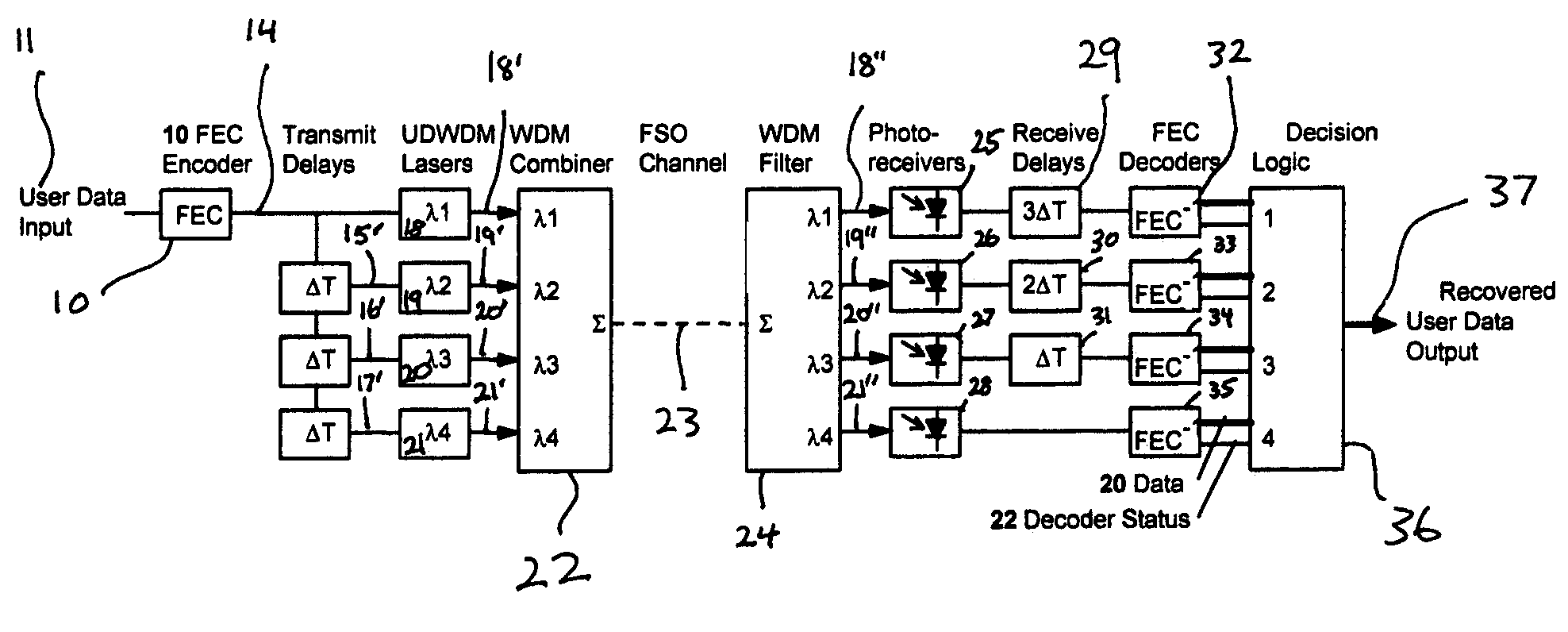
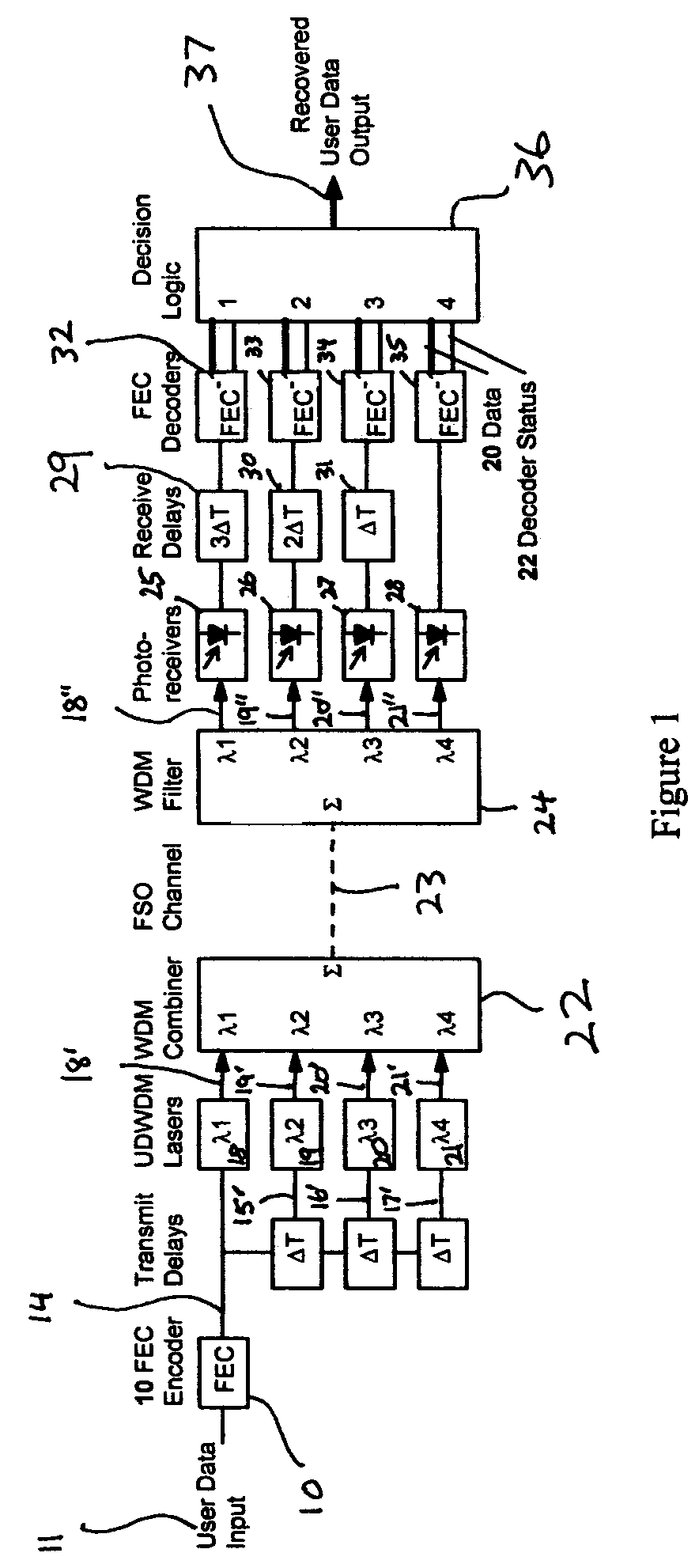
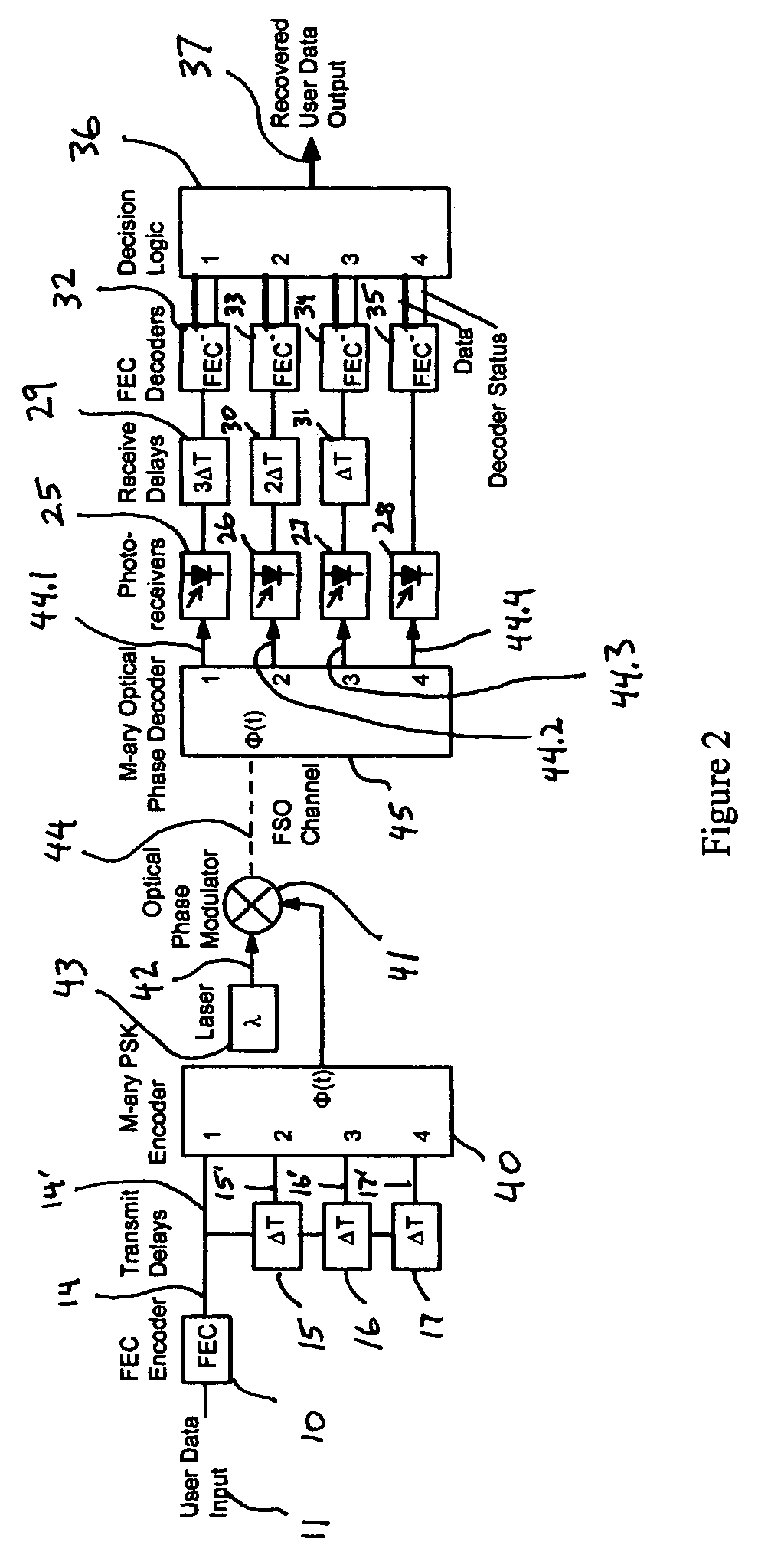
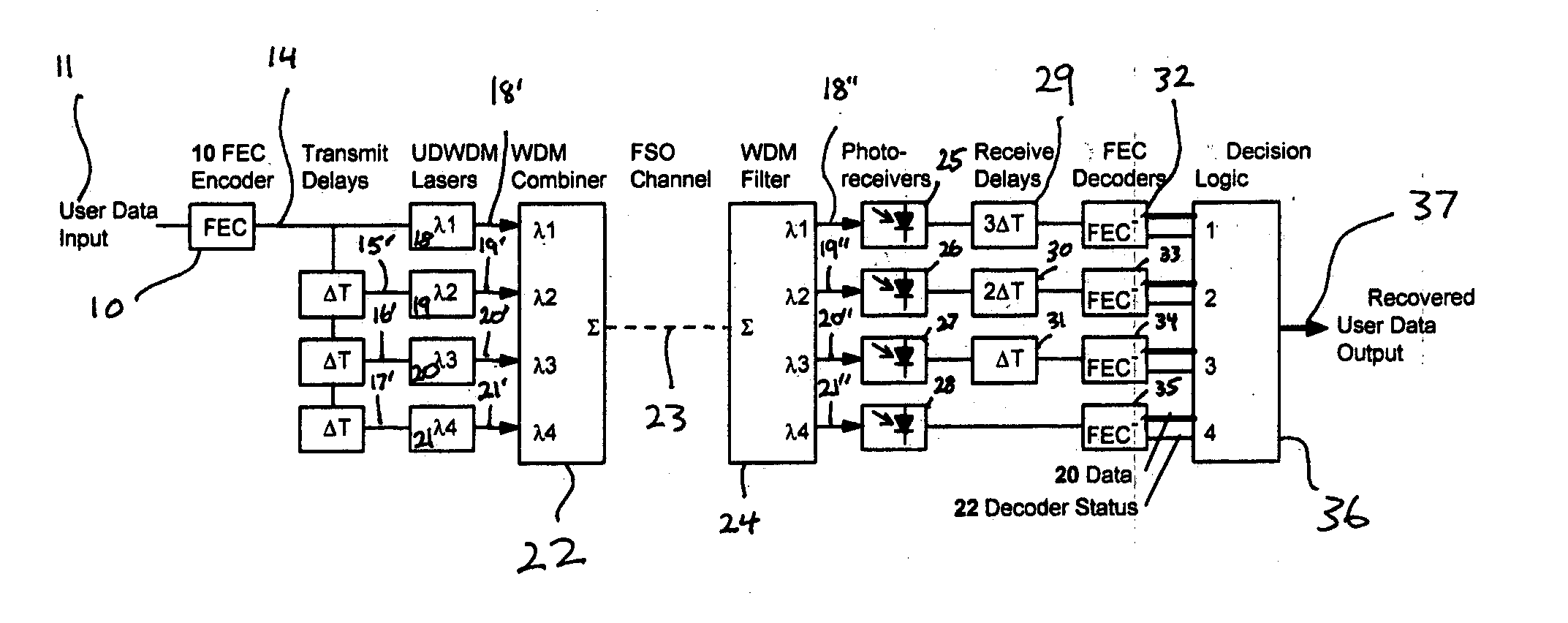
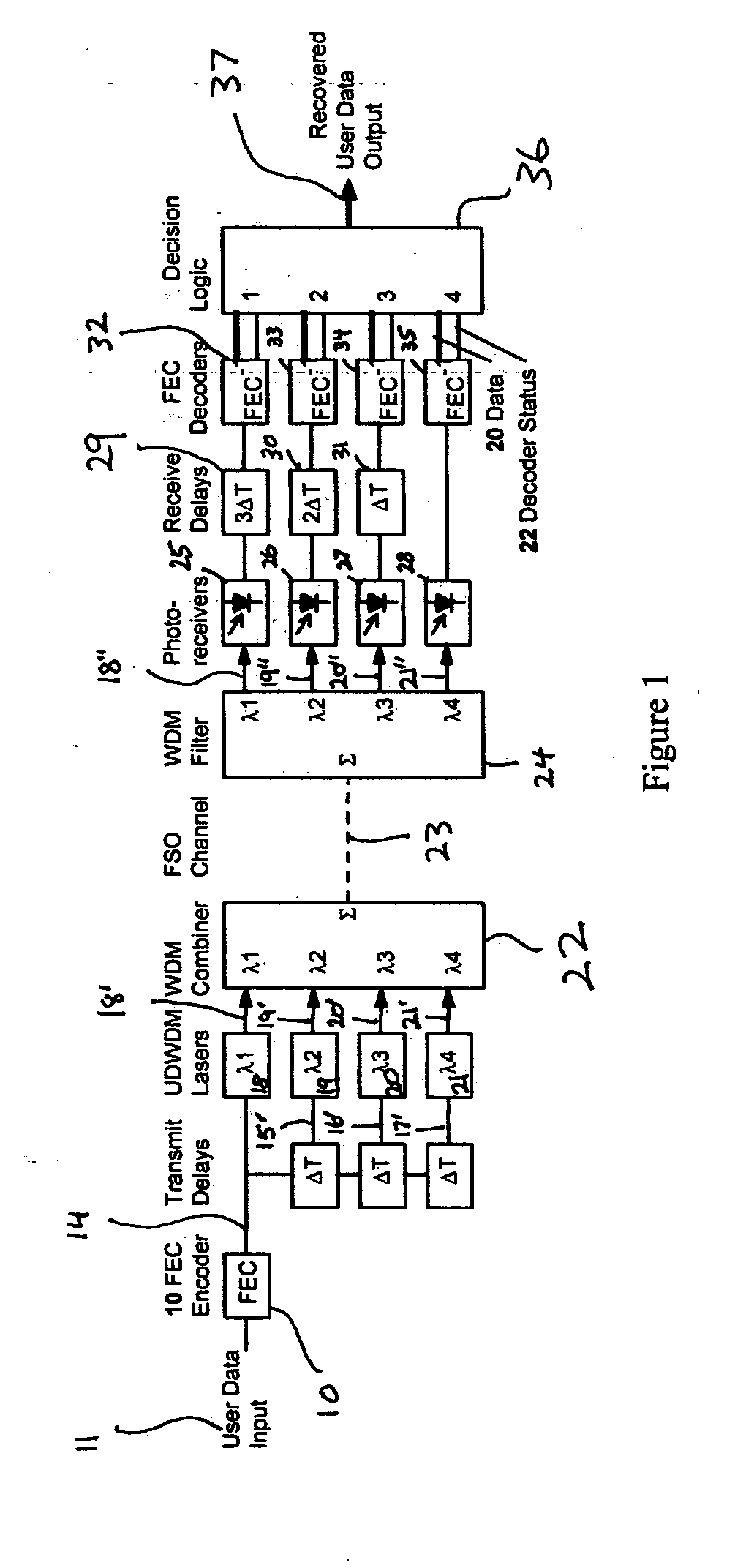
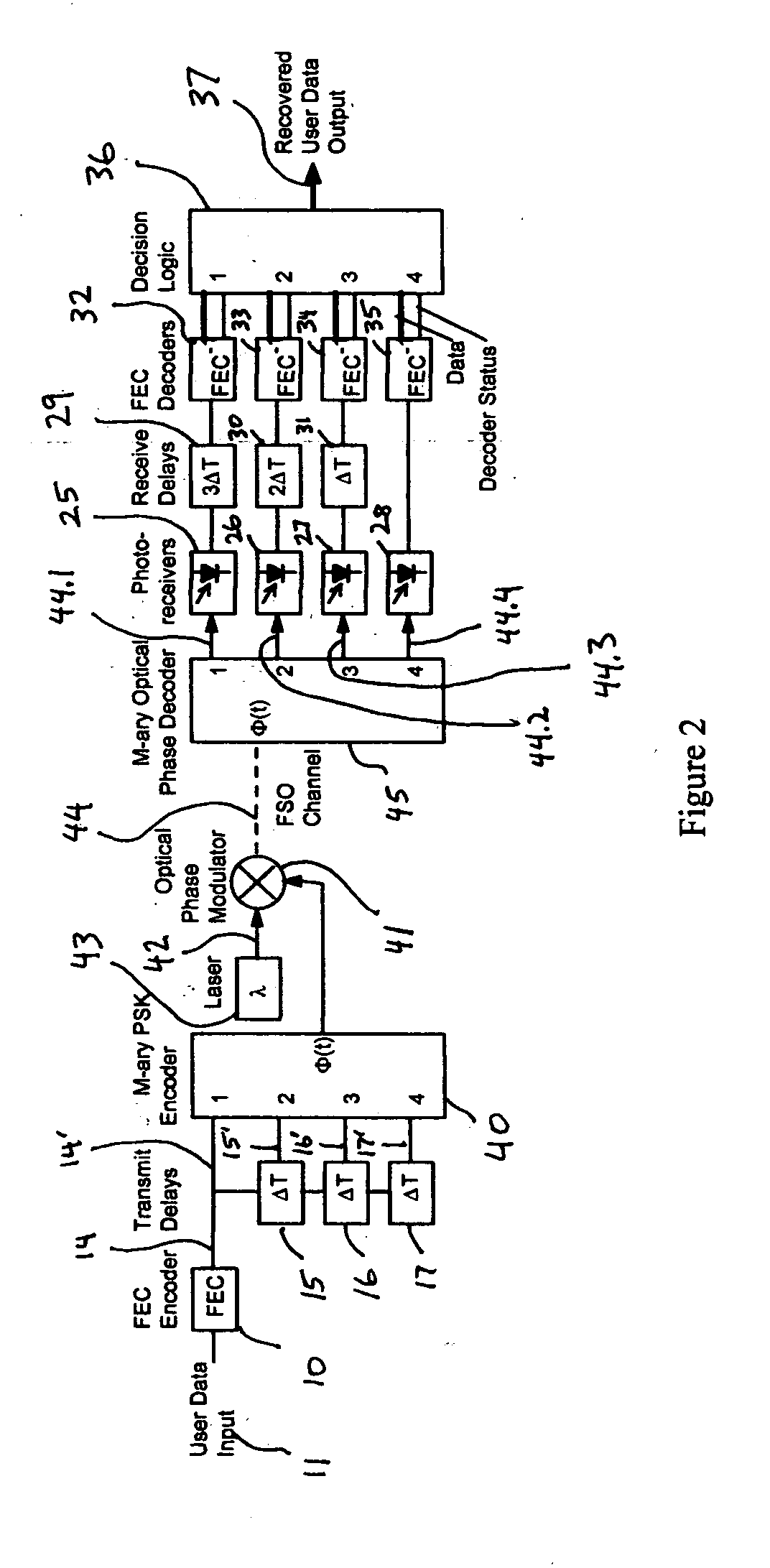
Fade-resistant forward error correction method for free-space optical communications systems
InactiveUS7277644B2Improve spectral efficiencyWide-bandwidth and secure connectionError preventionOther error detection/correction/protectionCommunications systemForward error correction
Free-space optical (FSO) laser communication systems offer exceptionally wide-bandwidth, secure connections between platforms that cannot other wise be connected via physical means such as optical fiber or cable. However, FSO links are subject to strong channel fading due to atmospheric turbulence and beam pointing errors, limiting practical performance and reliability. We have developed a fade-tolerant architecture based on forward error correcting codes (FECs) combined with delayed, redundant, sub-channels. This redundancy is made feasible though dense wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) and / or high-order M-ary modulation. Experiments and simulations show that error-free communications is feasible even when faced with fades that are tens of milliseconds long. We describe plans for practical implementation of a complete system operating at 2.5 Gbps.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Transmission of free-space optical communication signals through windows
InactiveUS6847496B1Spread the wordReduce adverse effectsDiffusing elementsElectromagnetic transmissionFilling materialsRefractive index
A method and apparatus for improving the transmission of a free-space optical communications signals through windows having surface imperfections. A void-filling material is applied to one or both surfaces of the window to fill any non-flat surface voids on those surfaces in areas through which an optical communications signal passes. In one embodiment, one or two substantially perfect optically translucent plates are mounted to the imperfect surface(s) of the window so as to capture the void-filling material between an inside surface of each optically translucent plate and the imperfect surfaces of the window. The void-filling material is selected to have an index of refraction that substantially matches an index of refraction for the window at an optical wavelength corresponding to the free-space optical communication signal. As a result, the adverse effects that would normally be caused to free-space optical communication signals that are passed through windows having surface imperfections are substantially eliminated.
Owner:PERTEX TELECOMM
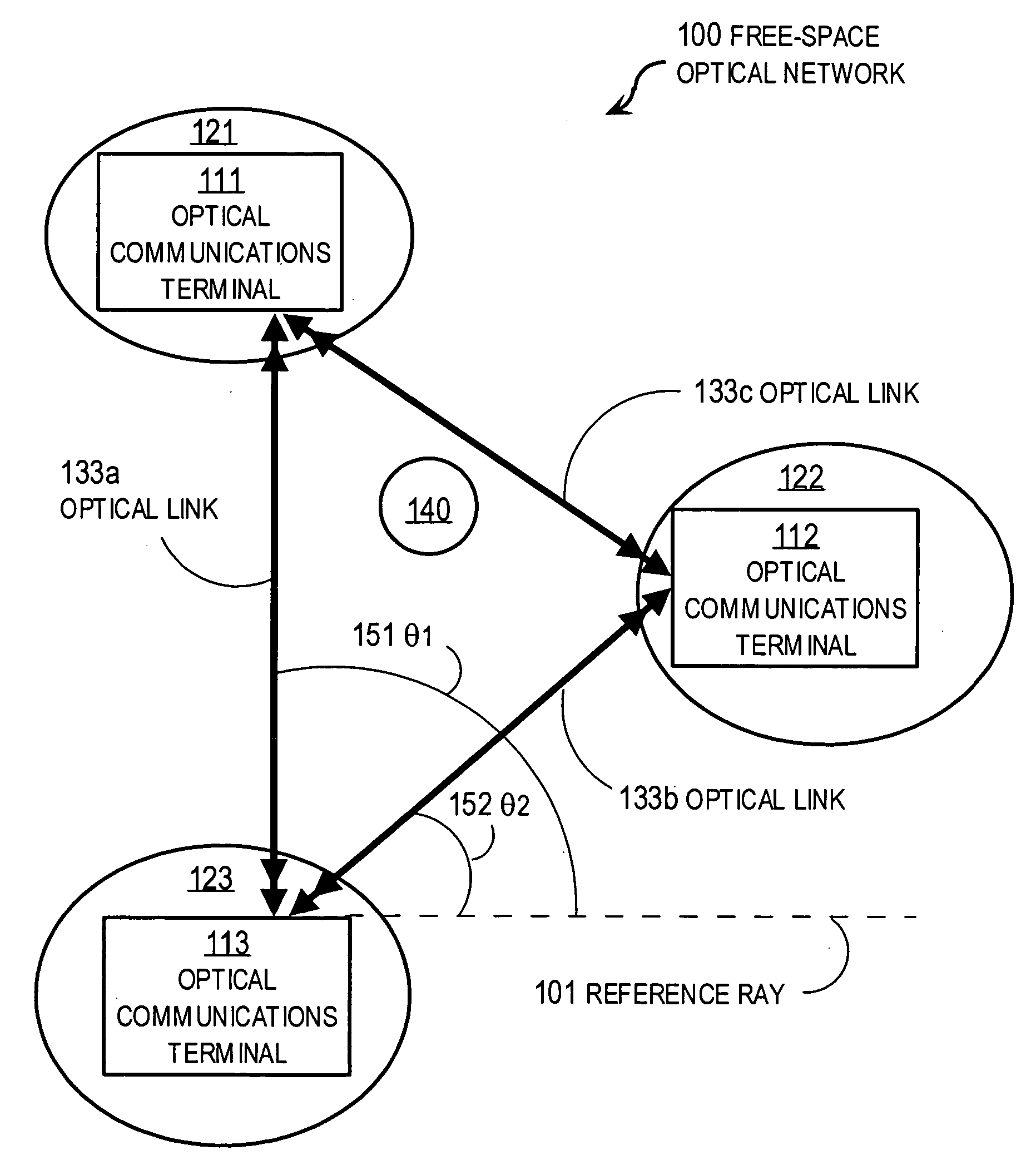
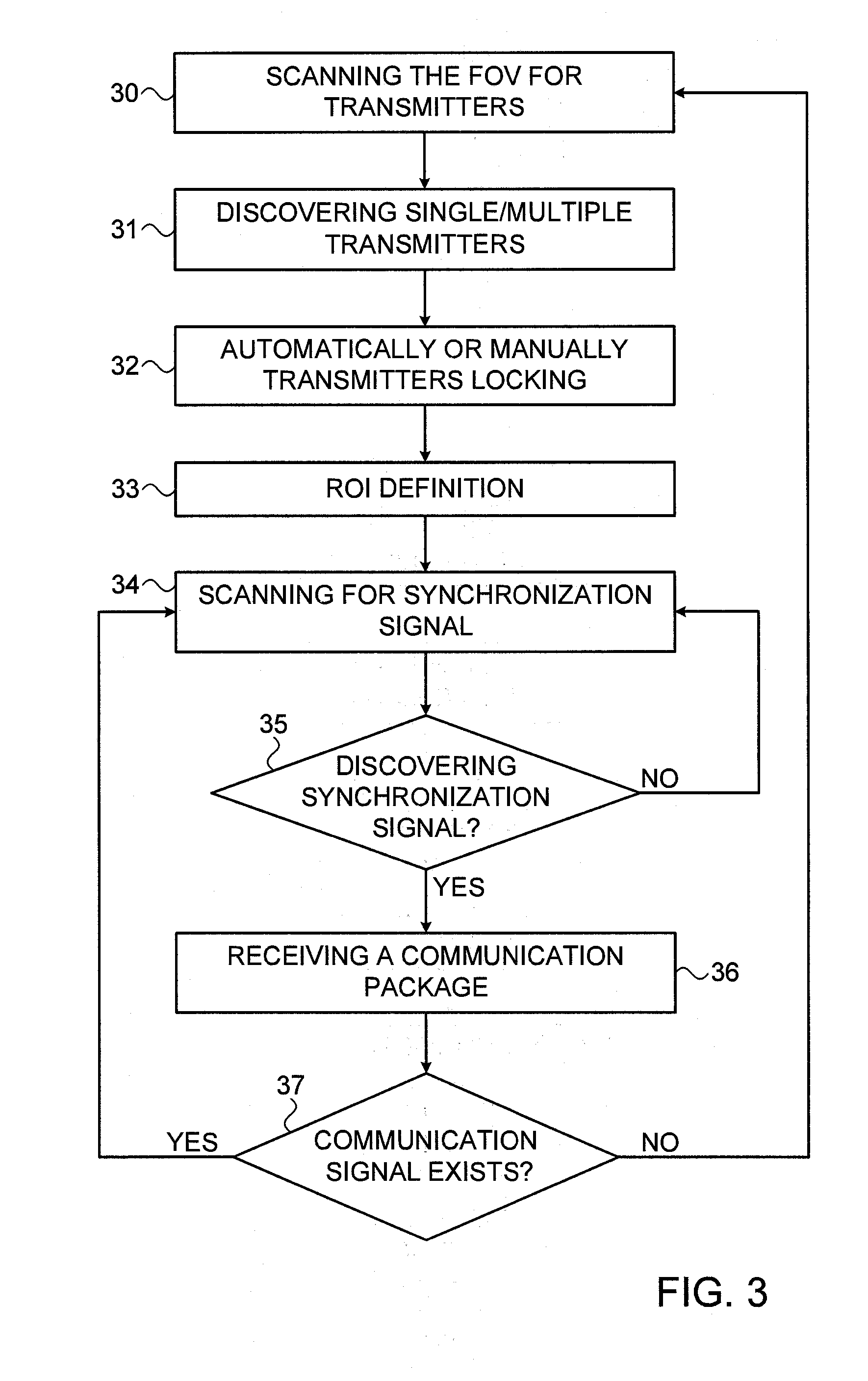
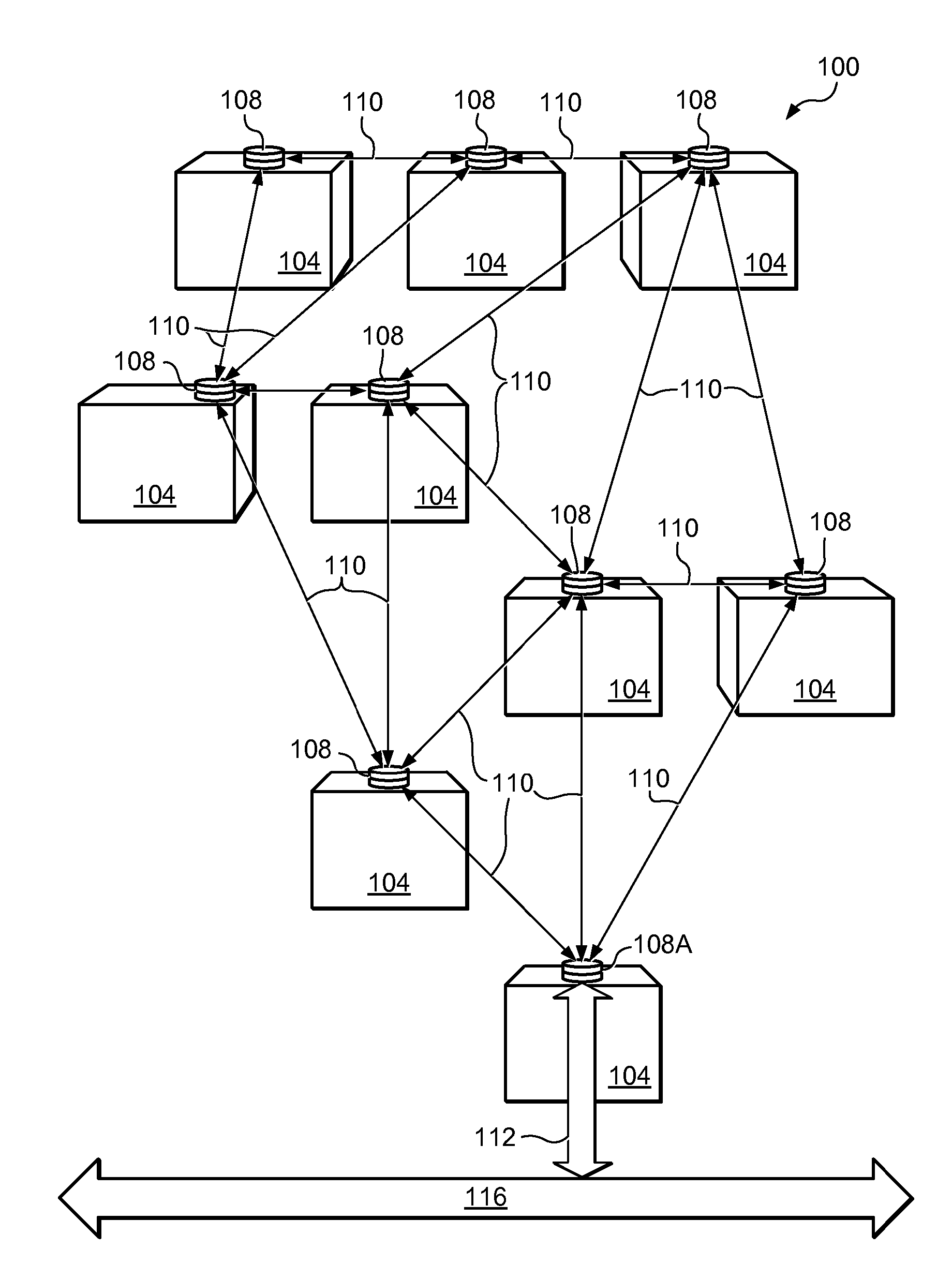
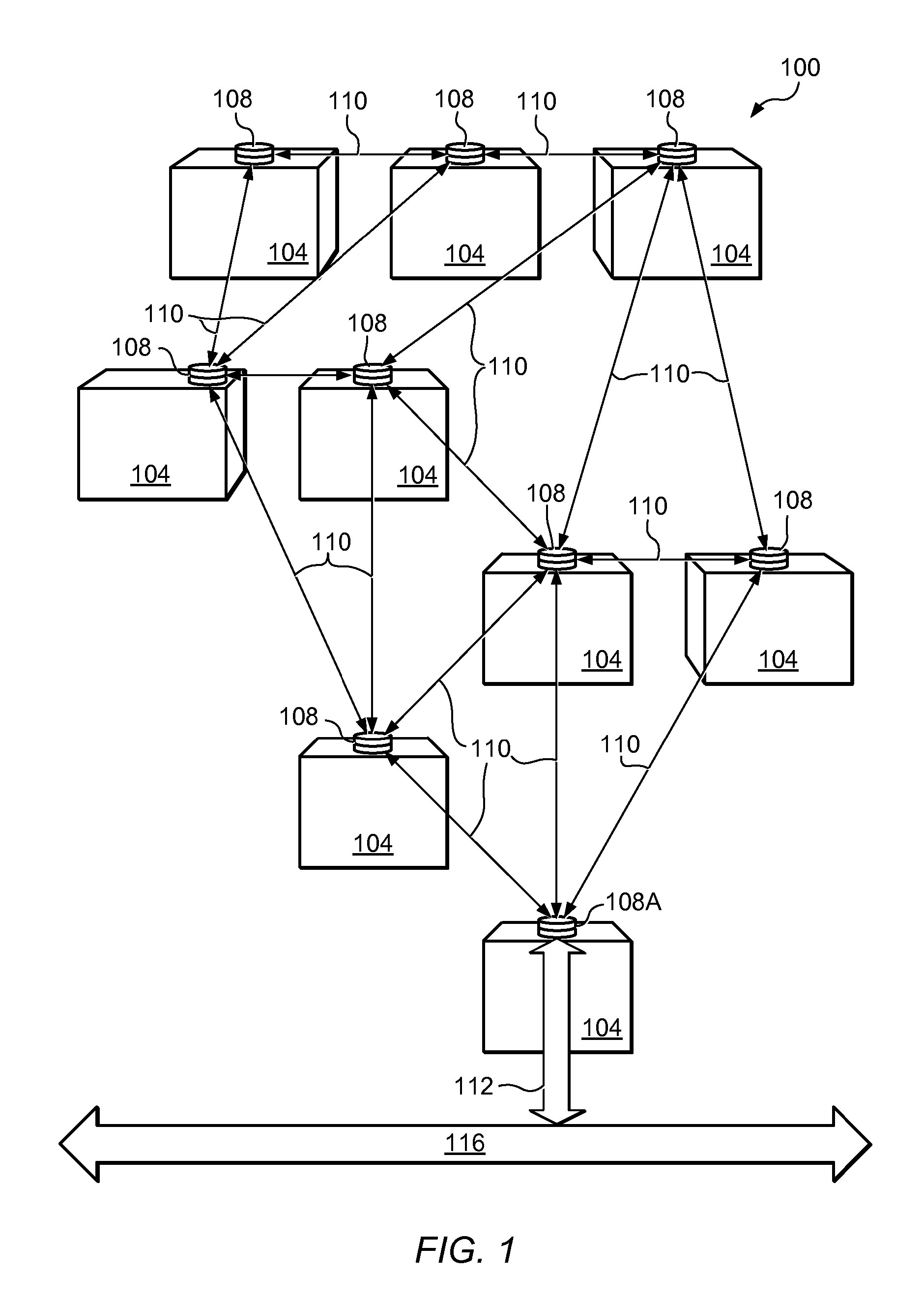
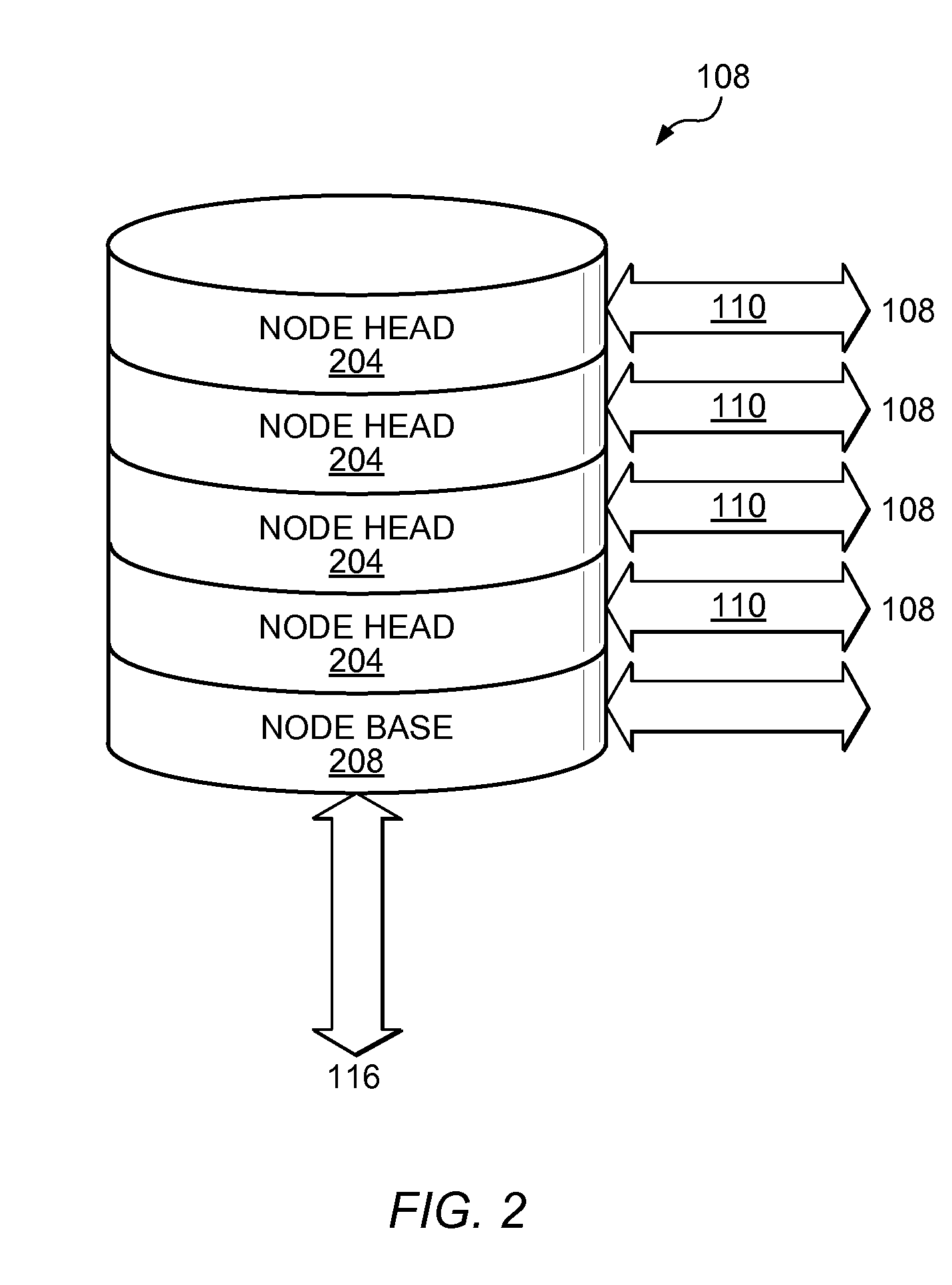
Establishment and maintenance of optical links between optical transceiver nodes in free-space optical communications networks
InactiveUS20070297808A1Add featureQuality improvementElectromagnetic transmissionTransceiverComputer network
A system and method for establishing and maintaining optical links between optical transceiver nodes in a free space optical communications network is disclosed. The system and method provide a protocol for acquisition of an optical link between transceivers in two adjacent nodes and for re-acquisition should a node be replaced or moved. The system and method also provide a protocol for tracking small movements of one or both nodes in a link. Also, the system and method provide a protocol for recovering a link that is temporarily lost.
Owner:KIRIBATI WIRELESS VENTURES
Method and apparatus for maintaining optical alignment for free-space optical communication
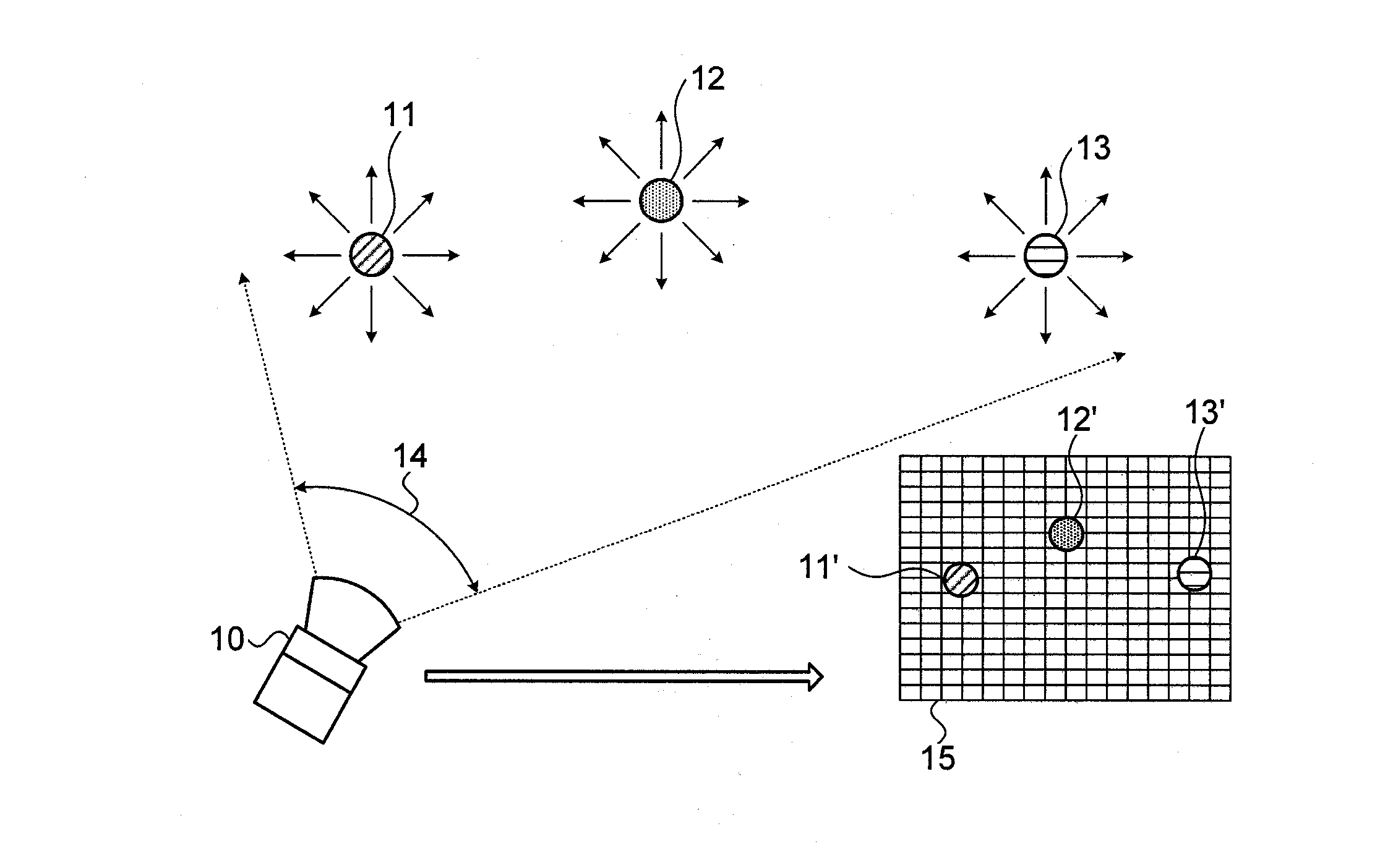
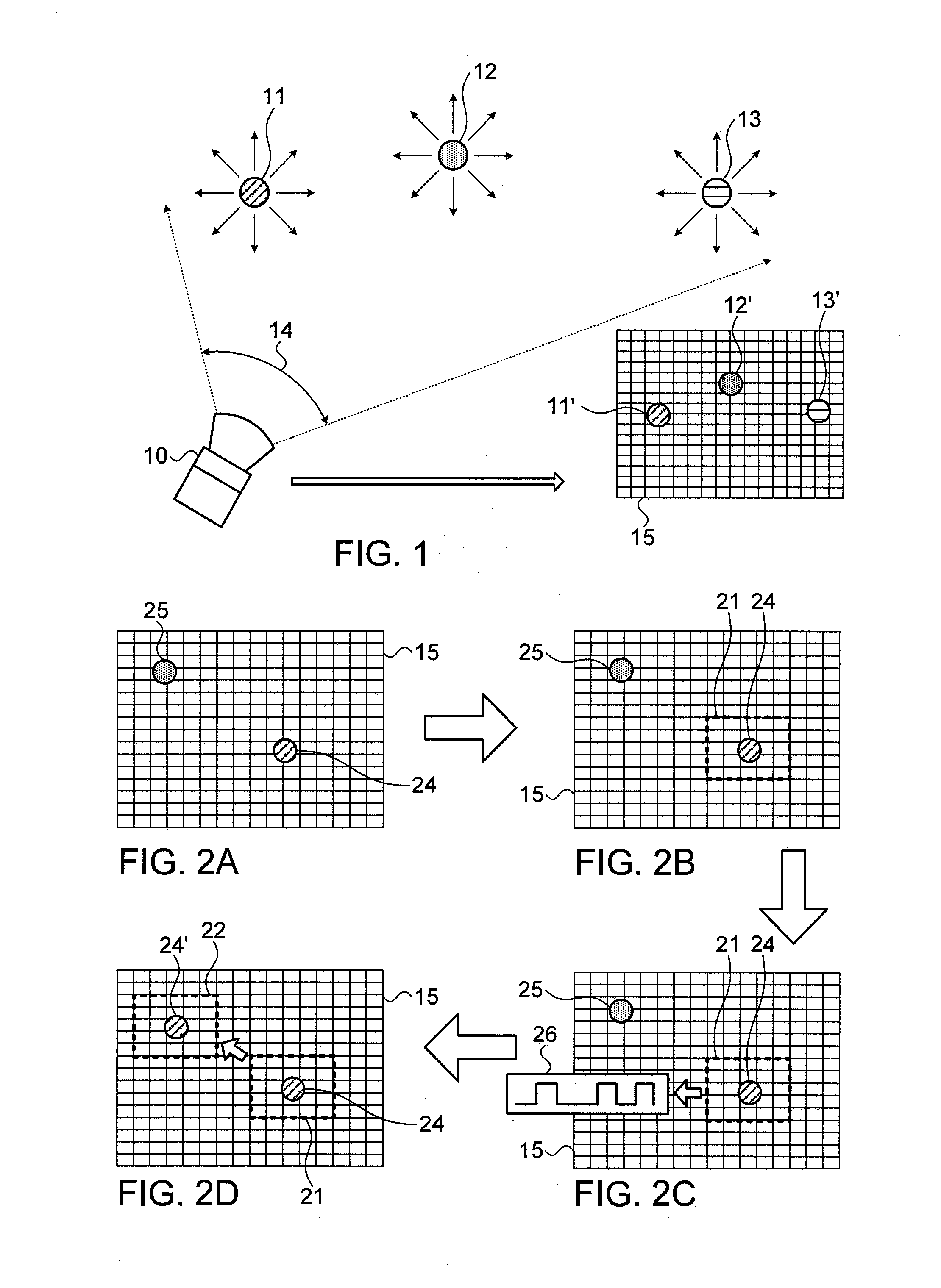
InactiveUS7120363B2Maintaining optical alignmentMaximizing received powerElectromagnetic transmissionField of viewOptical alignment
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for free-space optical communication. The method comprises the steps of receiving a receive optical beam through a narrow field of view, determining a receive power level, shifting an alignment, maximizing the receive power, and transmitting a transmit optical beam along the alignment, wherein the narrow field of view is less than a divergence of the transmit optical beam. The narrow field of view can be a narrow region of a multi-region field of view. The apparatus comprises an optical beam transmitter configured to generate a narrow diverging transmit beam, a narrow field of view optical receiver, wherein the field of view is less than the divergence of the transmit beam, and a controller configured to determine a power level of a receive beam and to determine adjustments to a direction of transmission maximizing receive power.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Coating removal systems for optical fibers
ActiveUS8755654B1Efficient removalReliable communicationCoupling light guidesWelding/soldering/cutting articlesGlass fiberLight beam
Coating removal systems for optical fibers are disclosed. An optical fiber includes a glass fiber, having a cladding and core, surrounded by a protective coating. By removing the coating at an end portion of the optical fiber, the end portion may be precisely positioned and secured in a connector to enable reliable optical communications. A laser beam may remove the protective coating while the optical fiber is under tension. In this manner, the coating may be efficiently removed while retaining tensile strength of the optical fiber.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
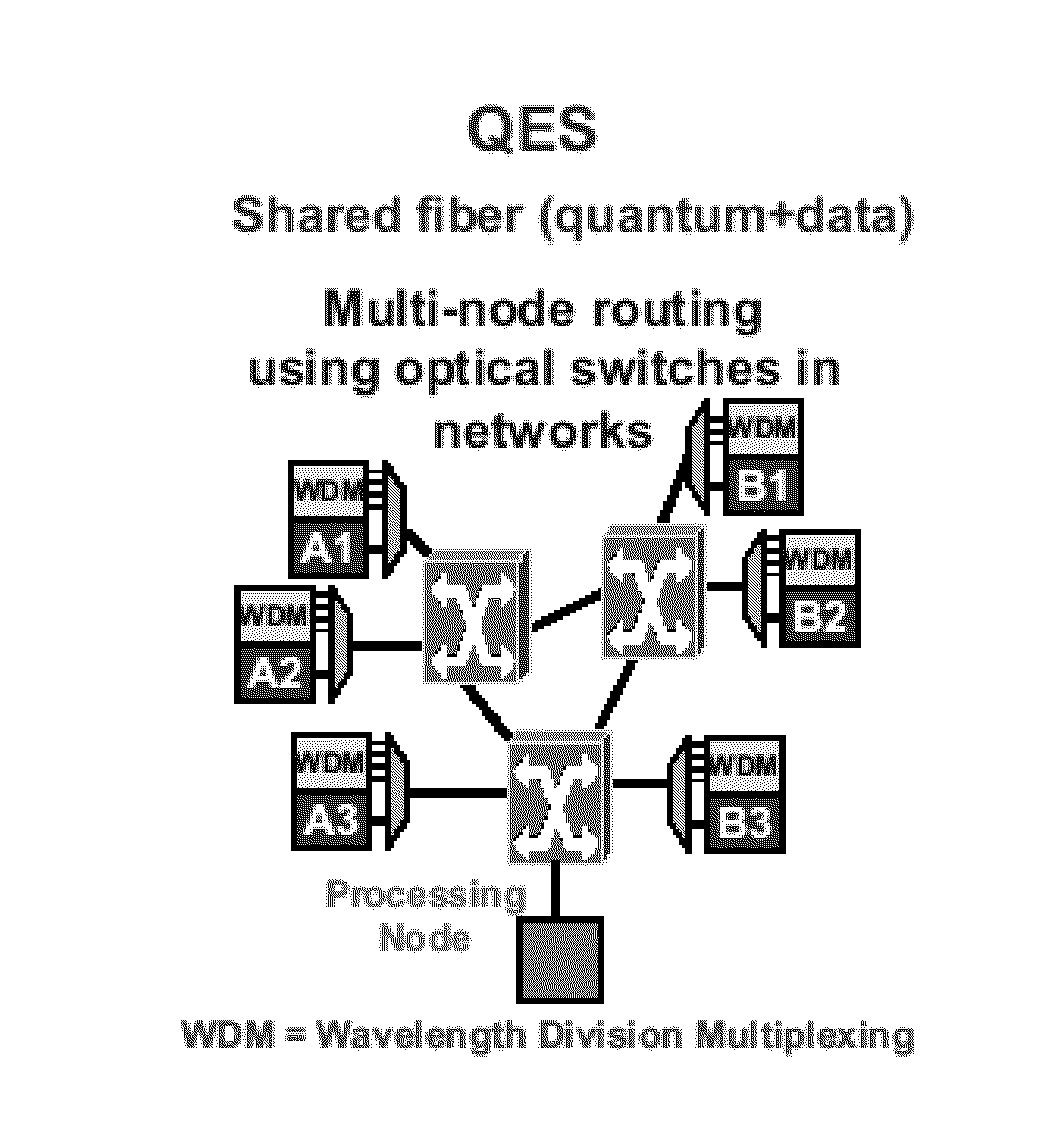
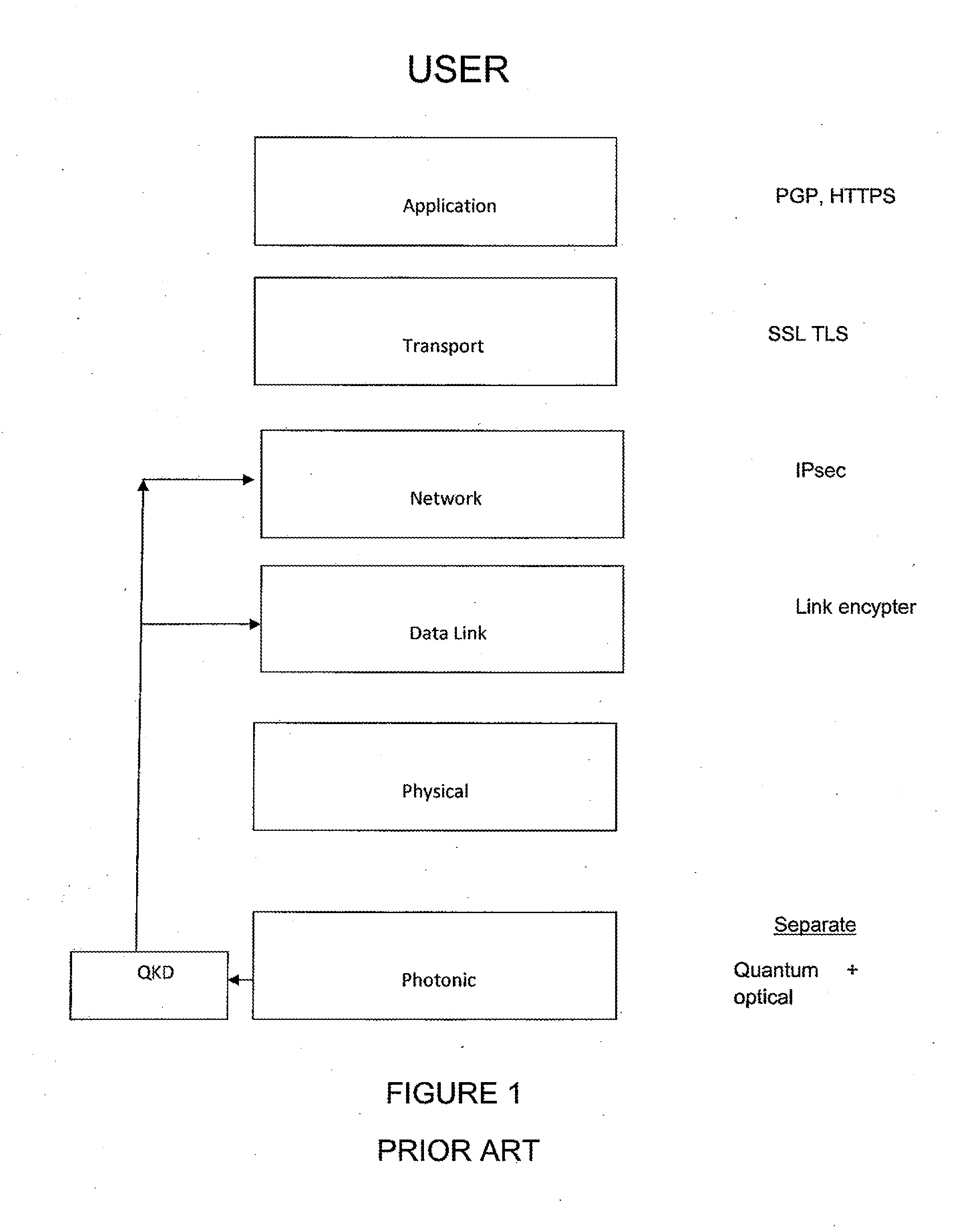
Quantum enabled security for optical communications
InactiveUS20140098955A1Recover the data faithfullyKey distribution for secure communicationWavelength-division multiplex systemsPhotonicsQuantum
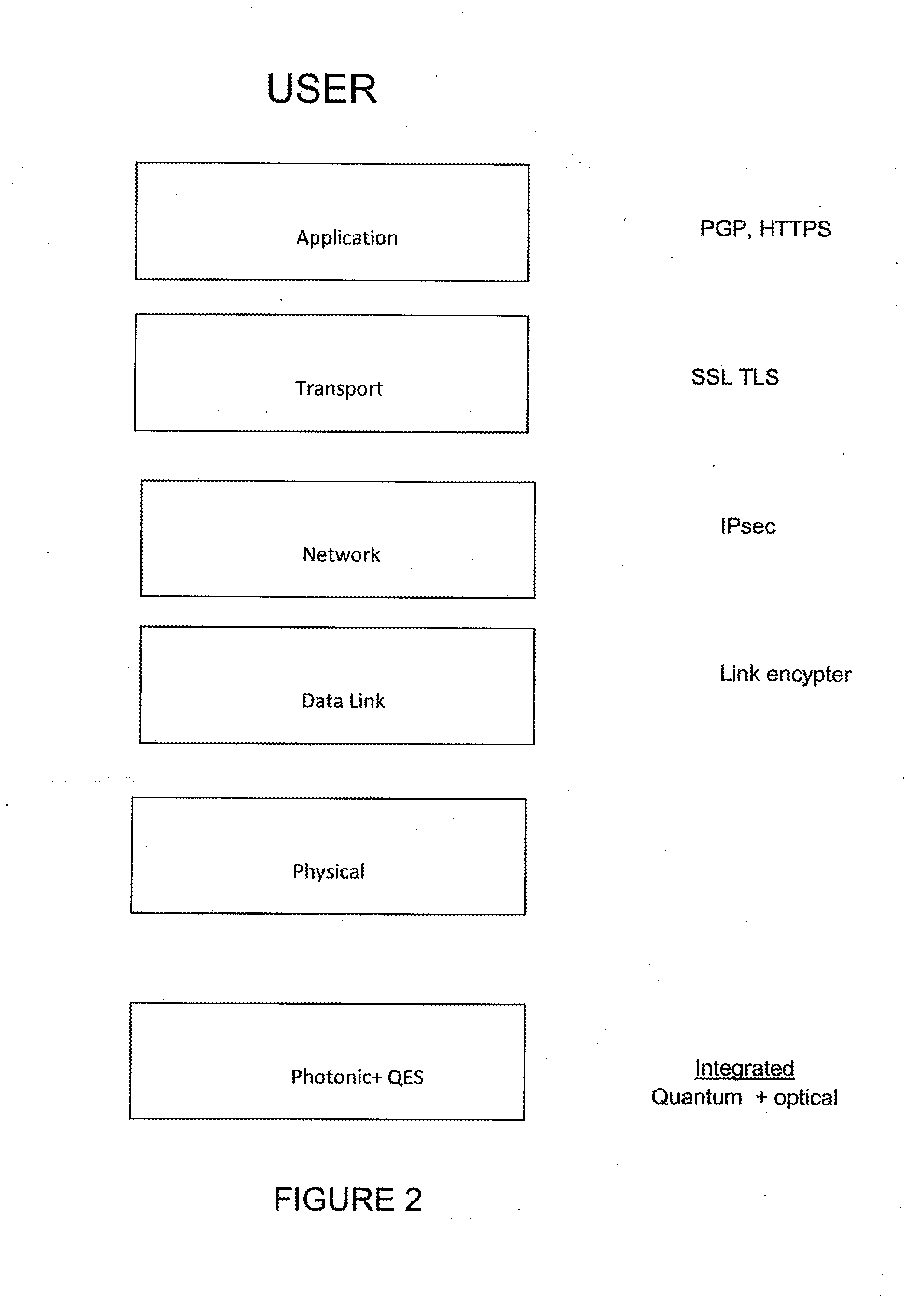
The present invention provides a quantum-enabled security (QES) protocol which creates a revolutionary new cybersecurity capability: quantum (single-photon) communications are integrated with optical communications to provide a strong, innate security foundation at the photonic layer for optical fiber networks or free-space optical communications. The new protocols will also allow the formation of ad hoc coalitions of users in order to deliver quantum-enabled security users between users who may not have direct quantum communications.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
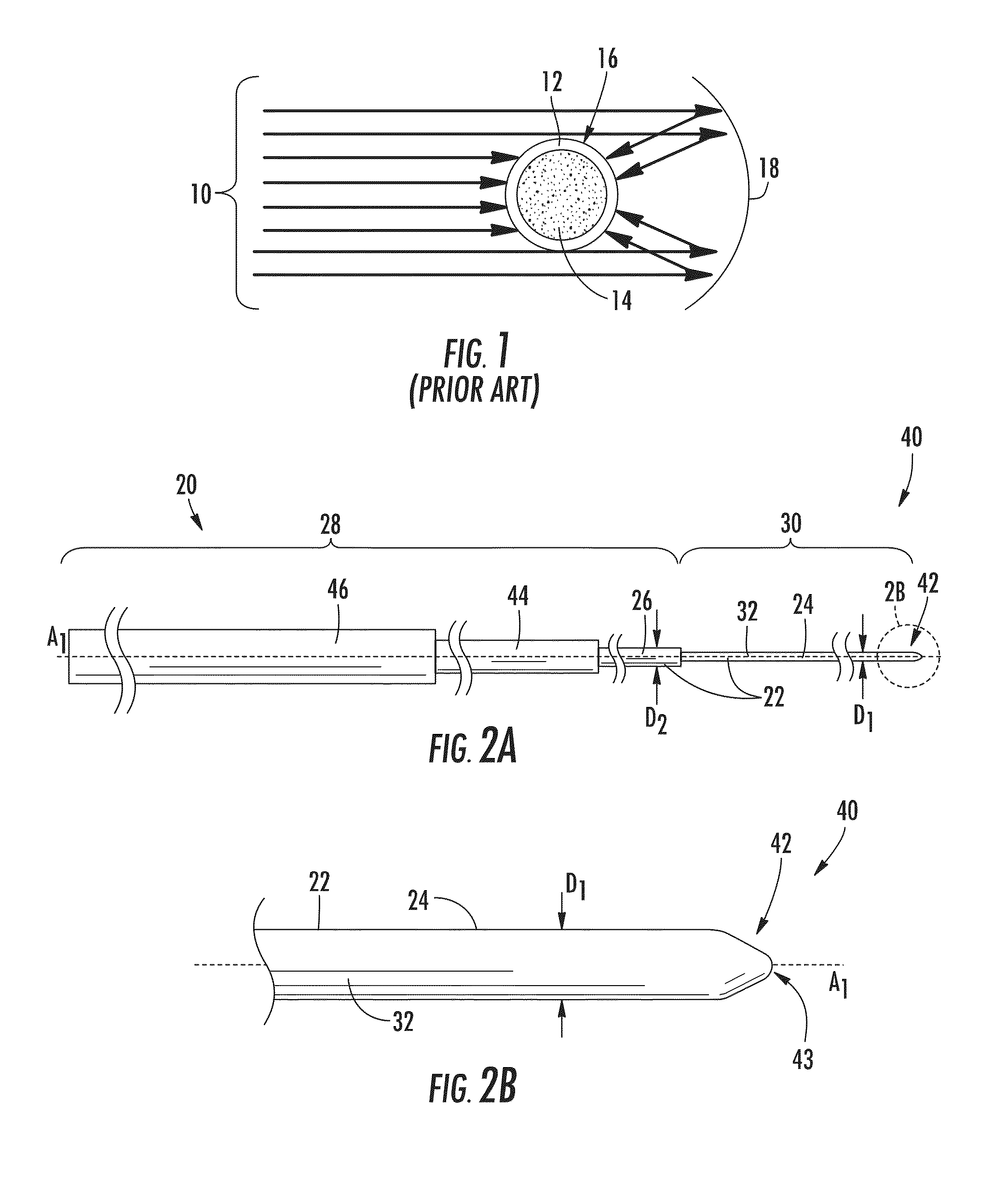
System and method for free space optical communication beam acquisition
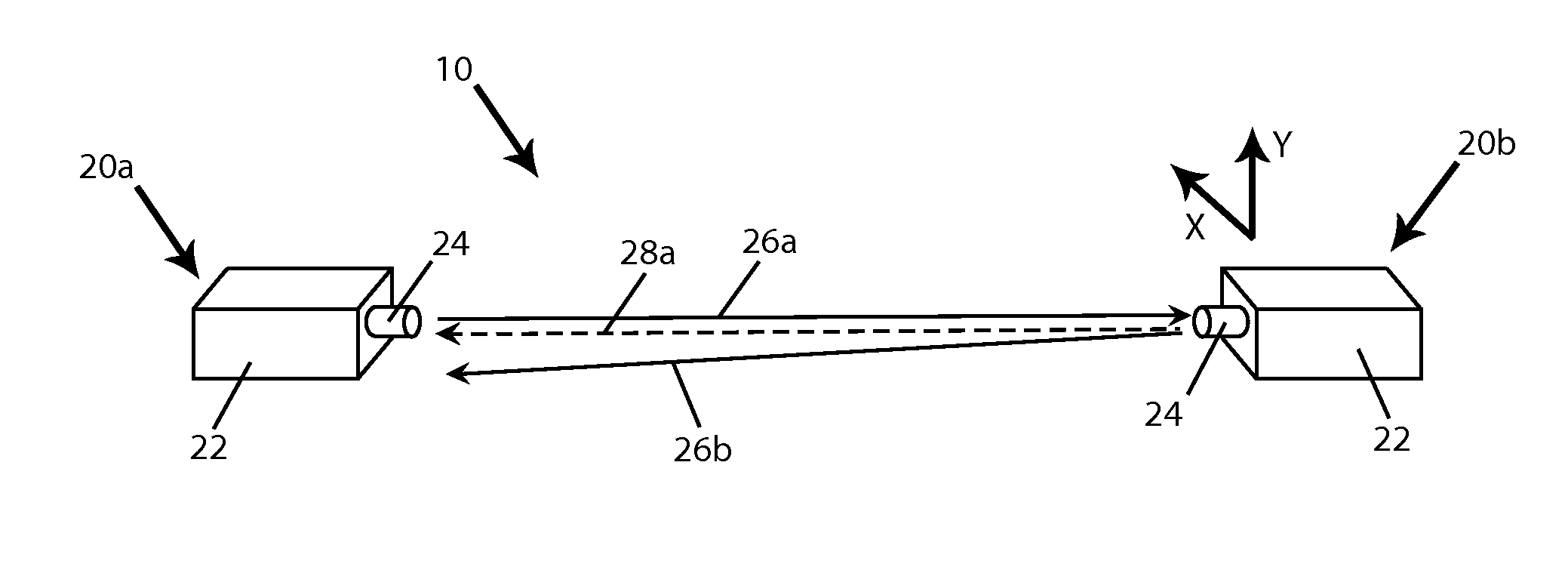
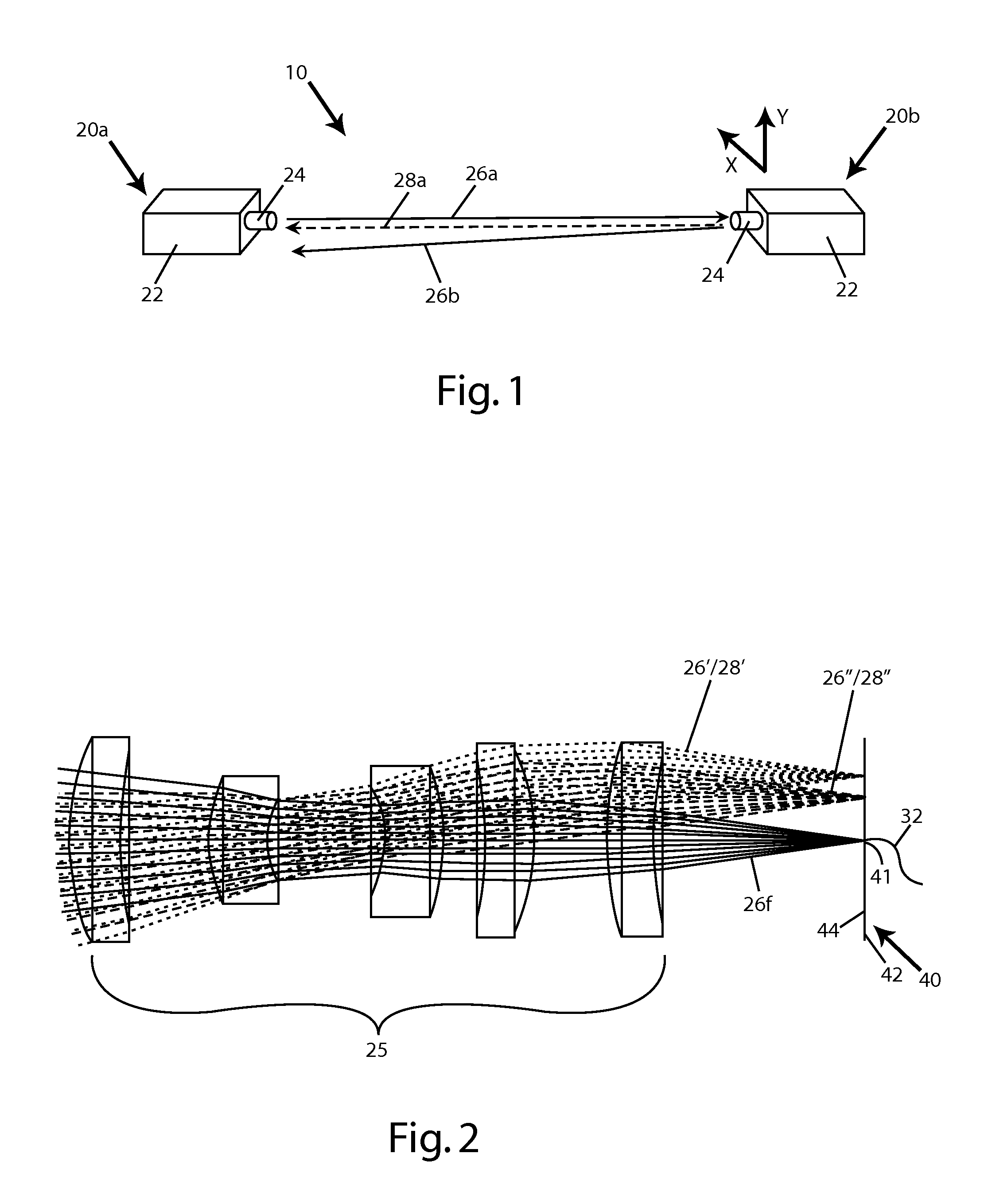
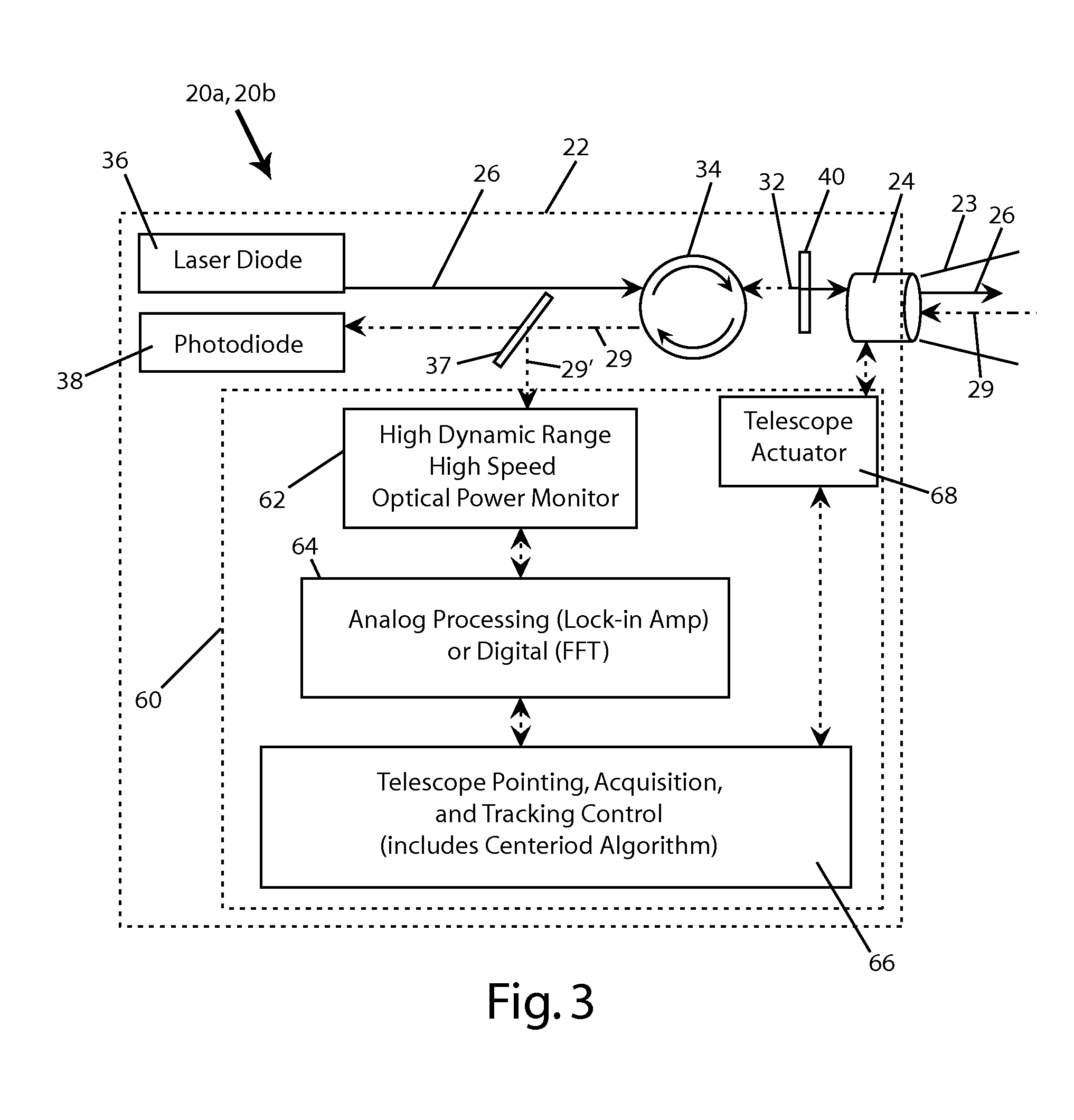
A free space optical communication system (10) including first and second mono-static transceivers (20a, 20b). Each transceiver (20a, 20b) includes a reflective assembly (40) defining a reflective surface (44) about a receiving end of a respective optical fiber (32) and configured to reflect optical signals (26) within a field of view of the transceiver (20a, 20b) as a modulated retro-reflective signal (28). Each mono-static transceiver (20a, 20b) includes an acquisition system (60) configured to detect a modulated retro-reflective signal (28) and adjust the alignment of the respective transceiver (20a, 20b) in response to a detected modulated retro-reflective signal (28). A mono-static transceiver and a method of aligning a mono-static transceiver are also provided.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Free space optical-communication APT system and method based on compressive sensing receiver
ActiveCN103326780AGuaranteed stabilityImplementing a Coarse Tracking LoopFree-space transmissionBeam splitterSpatial light modulator
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
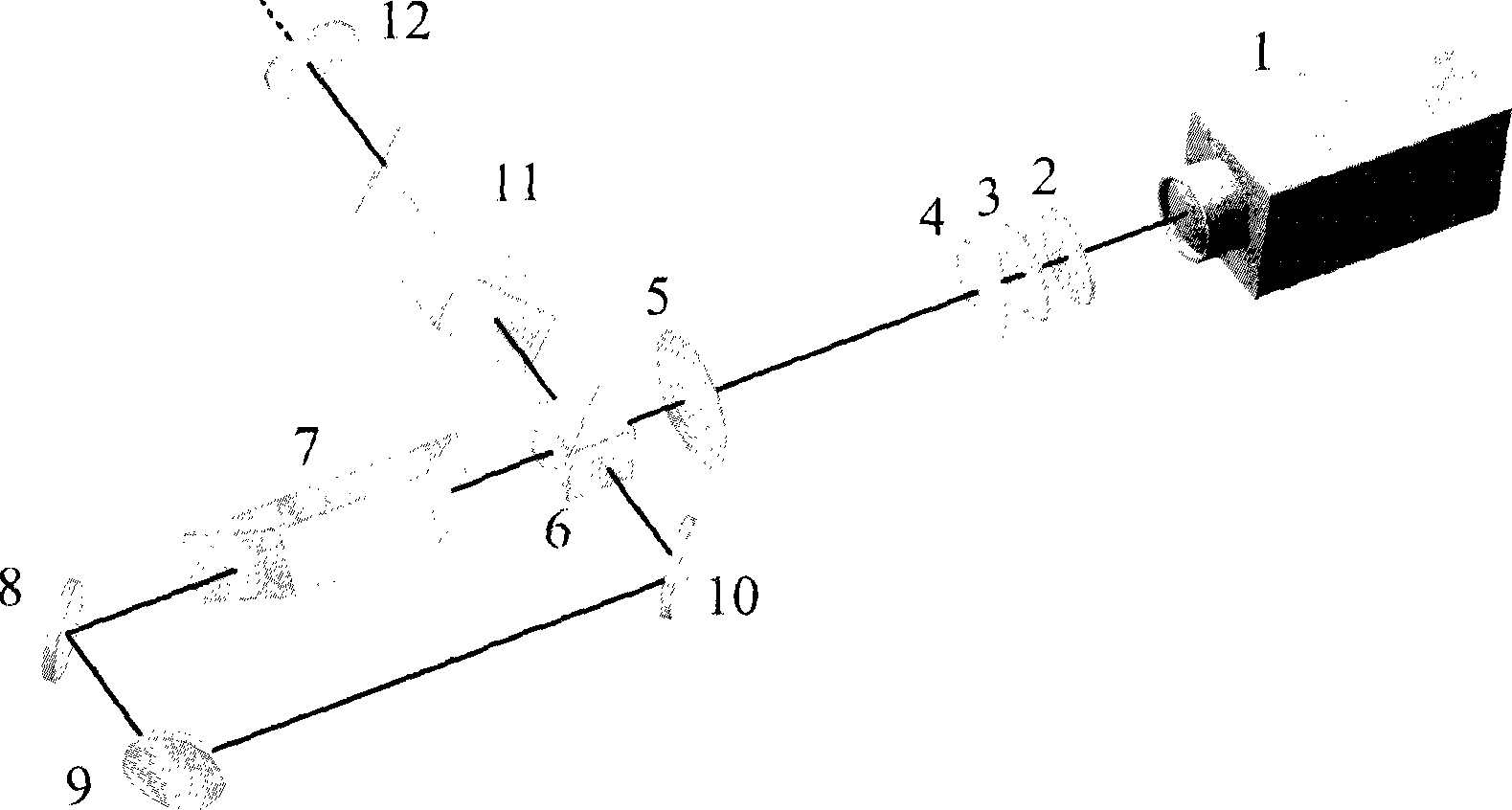
Free space laser communication system based on orbital angular momentum of light beams
InactiveCN101902276AReduce spacingImprove parallelismFree-space transmissionOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorDiffraction order
The invention relates to a free space laser communication system based on the orbital angular momentum of light beams, which belongs to the technical field of optical applications. The free space laser communication system consists of an optical fiber closely arranged laser, four convex lenses, two polarizers, a space optical modulator, a pinhole diaphragm, a beam expansion system, a composite binary amplitude grating and a CCD detector. The free space laser communication system takes the optical fiber closely arranged laser with gate control as a light source, designs a phase diffraction grating loaded onto the space optical modulator according to the distribution of the light beams emergent from the optical fiber closely arranged laser, and leads all the light beams to respectively havedifferent diffraction orders and be positioned on a central shaft of the system, thereby constructing a central diffraction light beam carrying gate information of the optical fiber closely arranged laser. When the system works, the gate control is carried out on the optical fiber closely arranged laser according to data to be transmitted for realizing the modulation loading of the data to be transmitted; and the light beams carrying data information utilize the composite binary amplitude grating to detect the orbital angular momentum state of the light beams at the receiving end of the system after transmitting for a certain distance in free space, thereby completing the demodulation of the data transmitted by the communication system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Free space MIMO optical communication system based on vertical demixing time space
InactiveCN101282175ALarge capacityImprove linearityElectromagnetic transceiversError prevention/detection by diversity receptionLaser arrayDetector array
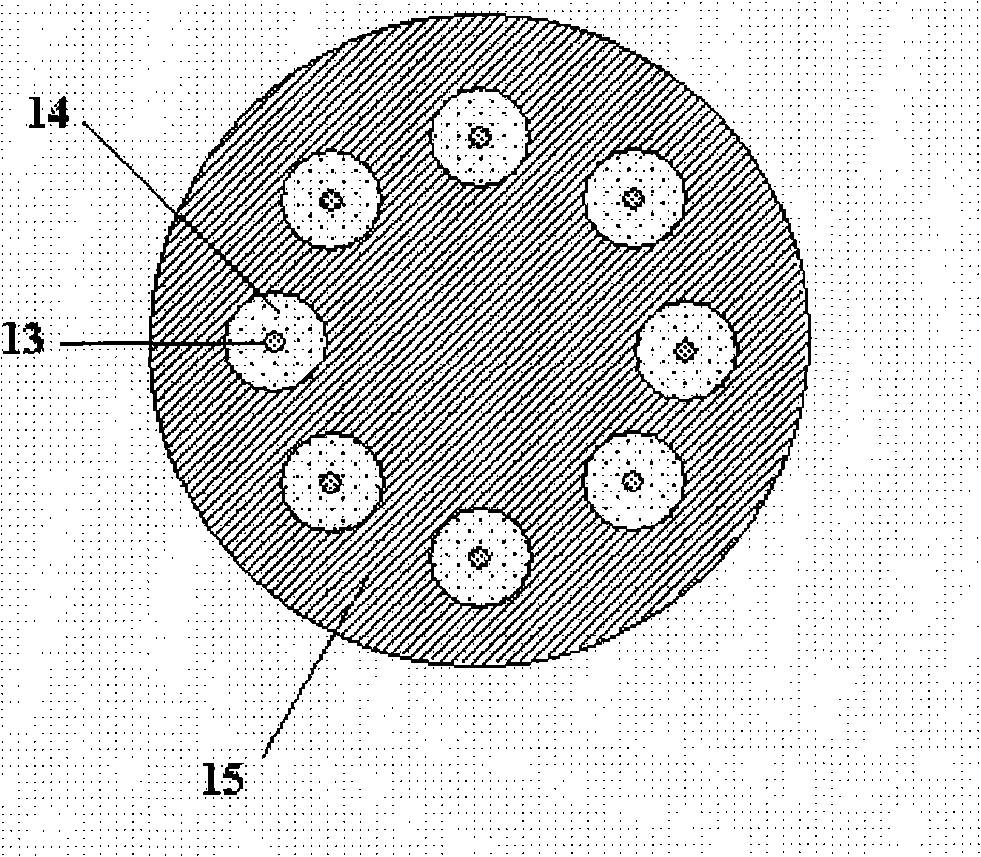
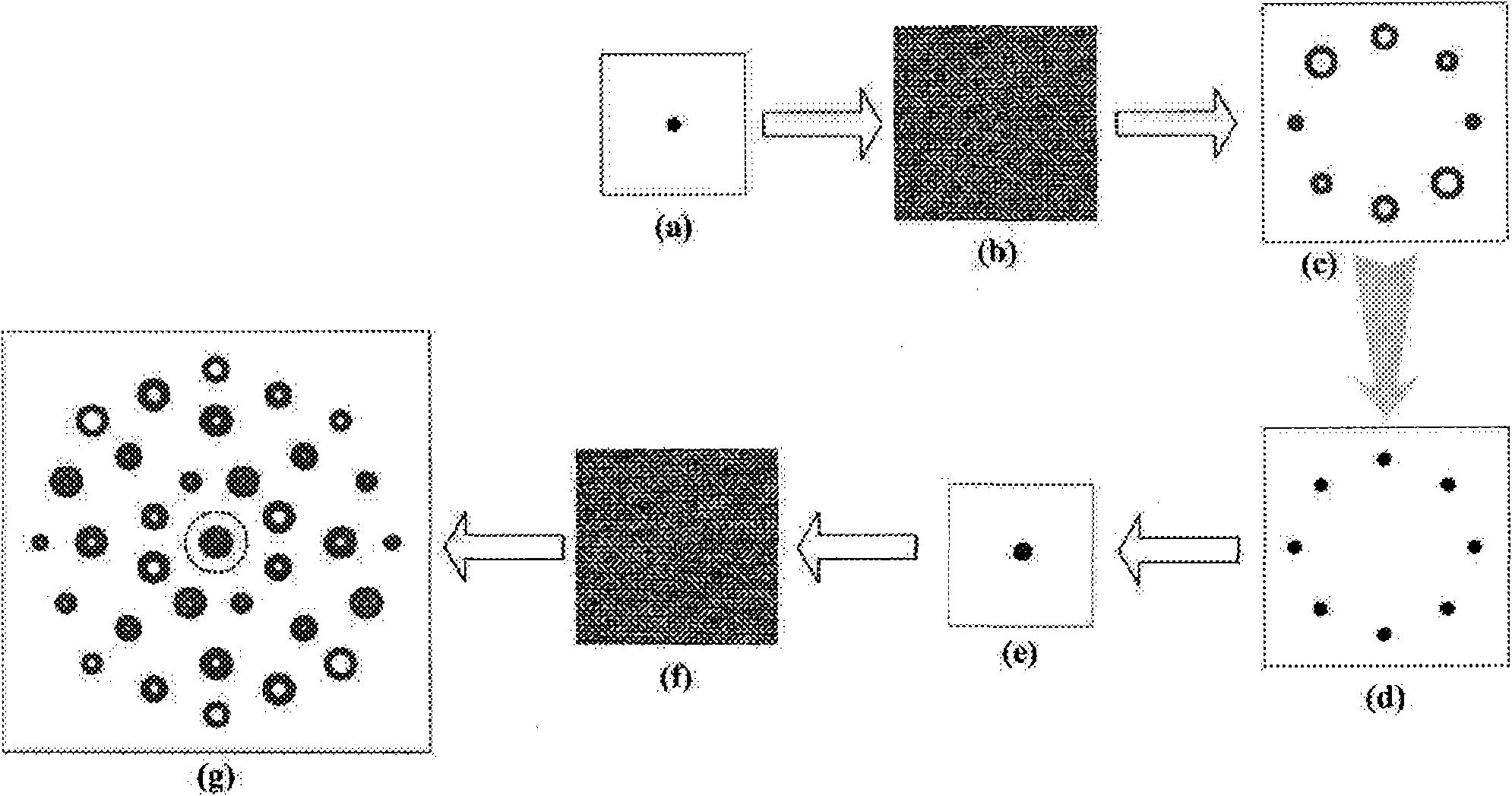
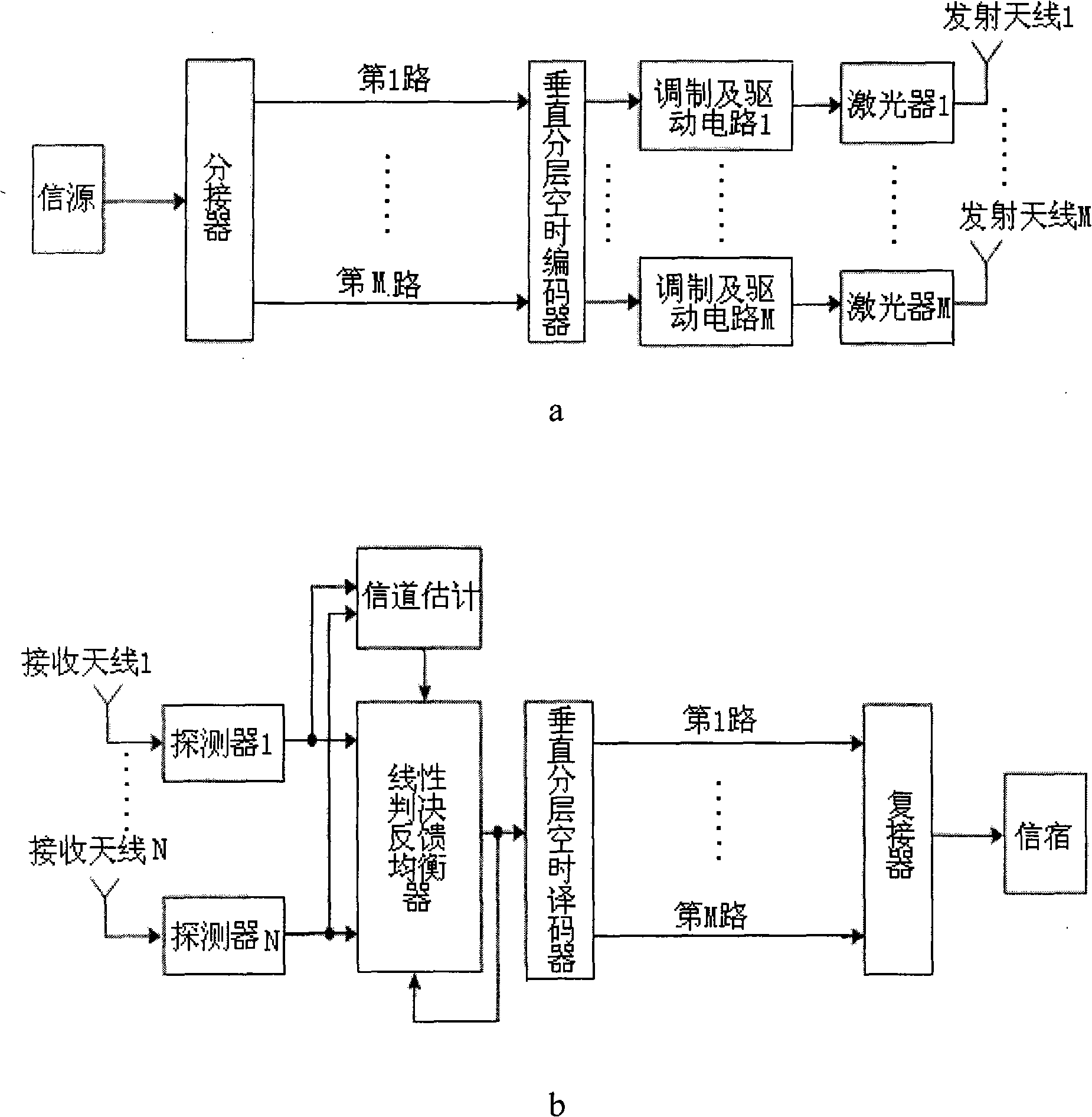
The present invention discloses a free space MIMO optical communication system based on the vertical layered space-time coding, wherein the free space MIMO optical communication system comprises a transmission terminal system and a receiving terminal system. The transmission terminal system comprises an information source, a distributing device, a layered space-time coder, a modulating and driving circuit array, a laser array and an optical transmission antenna array which are connected in series. The receiving terminal system comprises a channel estimator, and an optical receiving antenna array, a detector array, a linear decision feedback equalizer, a layered space-time coder / decoder, a multiplexer and an information sink which are connected in series. The optical transmission antenna array is composed of a plurality of pairs of parallel transmission antennae which are independent from each other. The optical receiving antenna array is composed of a plurality of pairs of optical receiving antennae which are independent from each other. The number of the optical receiving antennae is larger than or equal to that of the transmission antennae. The system according to the invention increases the speed of the communication code and the information flow-rate of the system. The communication is not affected by the atmosphere random channel.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and device for generating perfect Laguerre-Gaussian beam
InactiveCN103941405ASimple methodReliable methodOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorGaussian beam
The invention relates to a method and device for generating a perfect Laguerre-Gaussian beam. After a Gaussian beam is expanded, a spatial light modulator of a computer-generated hologram is loaded and used for regulating a light field, a first-level diffraction beam emitted by the spatial light modulator is captured, and then a hollow Gaussian beam is obtained; phase modulation is conducted through a spiral phase plate, so that a hollow beam carrying orbital angular momentum is obtained; focusing is conduced through a convex lens, so that the perfect Laguerre-Gaussian beam is obtained. According to the method and device for generating the perfect Laguerre-Gaussian beam, the perfect Laguerre-Gaussian beam is generated through the hollow beam carrying the orbital angular momentum, the method is simple and reliable, and the device is simple in structure, easy to adjust and good in stability; the generated beam can be applied to the fields such as the particle capturing field, the free space optical communication and the beam transmission characteristic research field.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
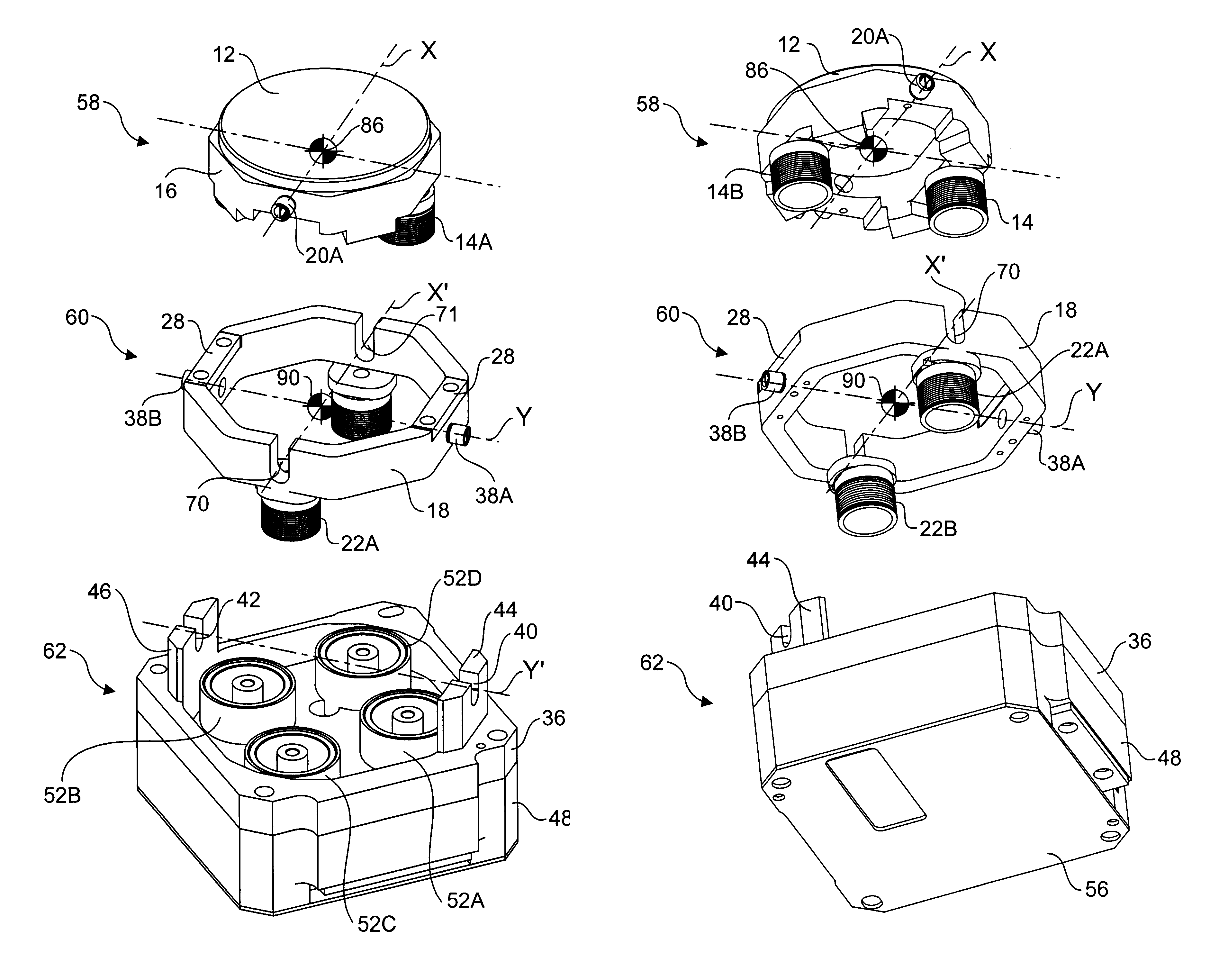
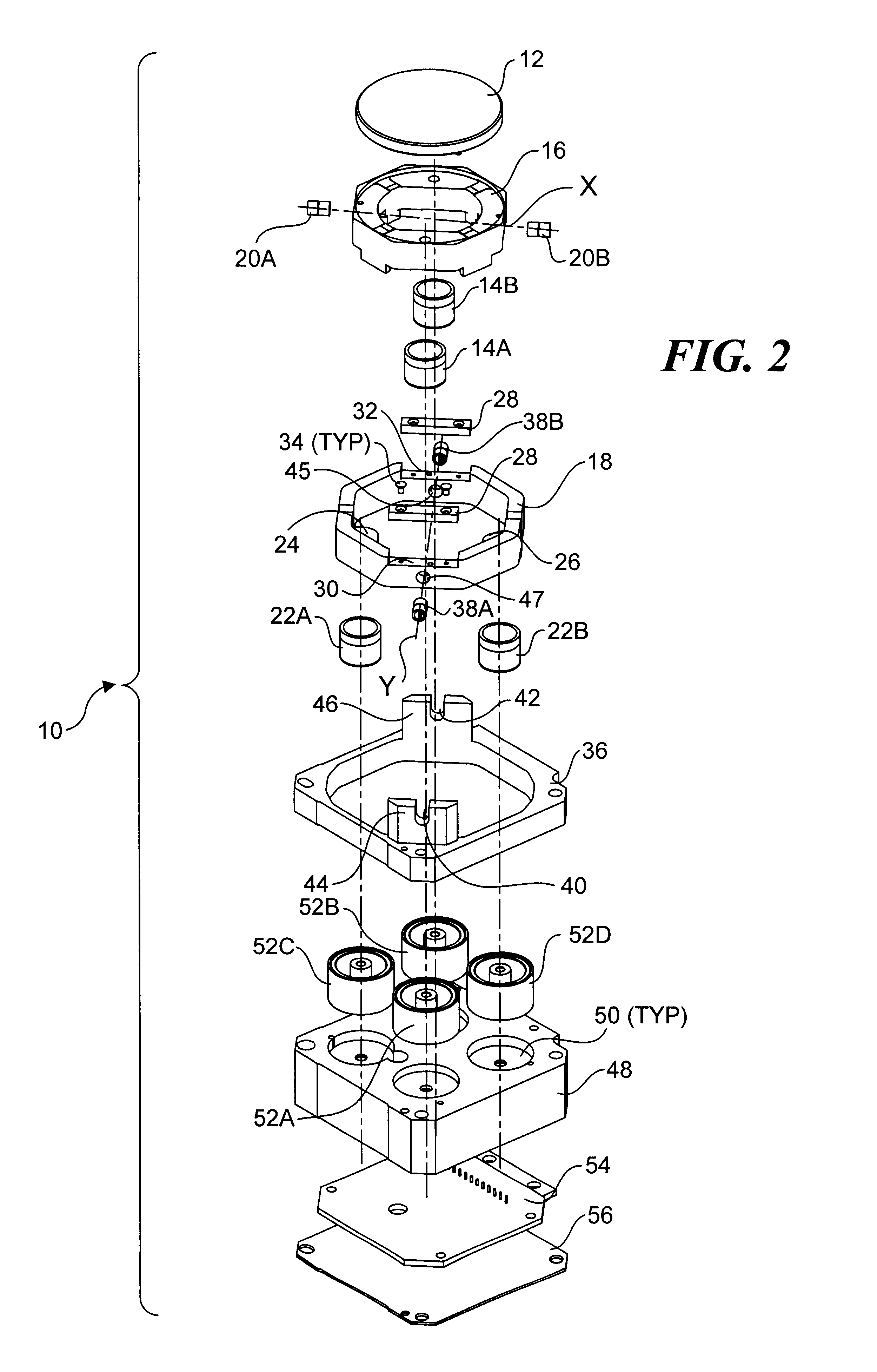
Fast steering mirror
InactiveUS6856437B2Significant performance enhancementSignificant cost reductionPicture framesDomestic mirrorsDriving currentConductor Coil
A fast steering mirror for use in free space optical communication systems. The fast steering mirror includes a gimbaled movement comprising an outer gimbal pivotally coupled to a base member and an inner gimbal pivotally coupled to the outer gimbal. A mirror that is posited by the apparatus is coupled to the inner gimbal. A first pair of voice coil drivers including a pair of magnetized stators fixedly coupled to the base member and a pair of voice coils fixedly coupled to the outer gimbal are provided along with a second pair of voice coil drivers comprising a pair of magnetized stators coupled to the base member and a pair of voice coils coupled to the inner gimbal. Selectable drive currents may be provided to the windings in the voice coils to position the mirror. In one embodiment, the fast steering mirror further includes a reference position seek mechanism.
Owner:PERTEX TELECOMM
Fade-resistant forward error correction method for free-space optical communications systems
InactiveUS20050005225A1Improve spectral efficiencyWide-bandwidth and secure connectionError preventionOther error detection/correction/protectionCommunications systemEngineering
Free-space optical (FSO) laser communication systems offer exceptionally wide-bandwidth, secure connections between platforms that cannot other wise be connected via physical means such as optical fiber or cable. However, FSO links are subject to strong channel fading due to atmospheric turbulence and beam pointing errors, limiting practical performance and reliability. We have developed a fade-tolerant architecture based on forward error correcting codes (FECs) combined with delayed, redundant, sub-channels. This redundancy is made feasible though dense wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) and / or high-order M-ary modulation. Experiments and simulations show that error-free communications is feasible even when faced with fades that are tens of milliseconds long. We describe plans for practical implementation of a complete system operating at 2.5 Gbps.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com