Patents
Literature
86 results about "Gaussian frequency-shift keying" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
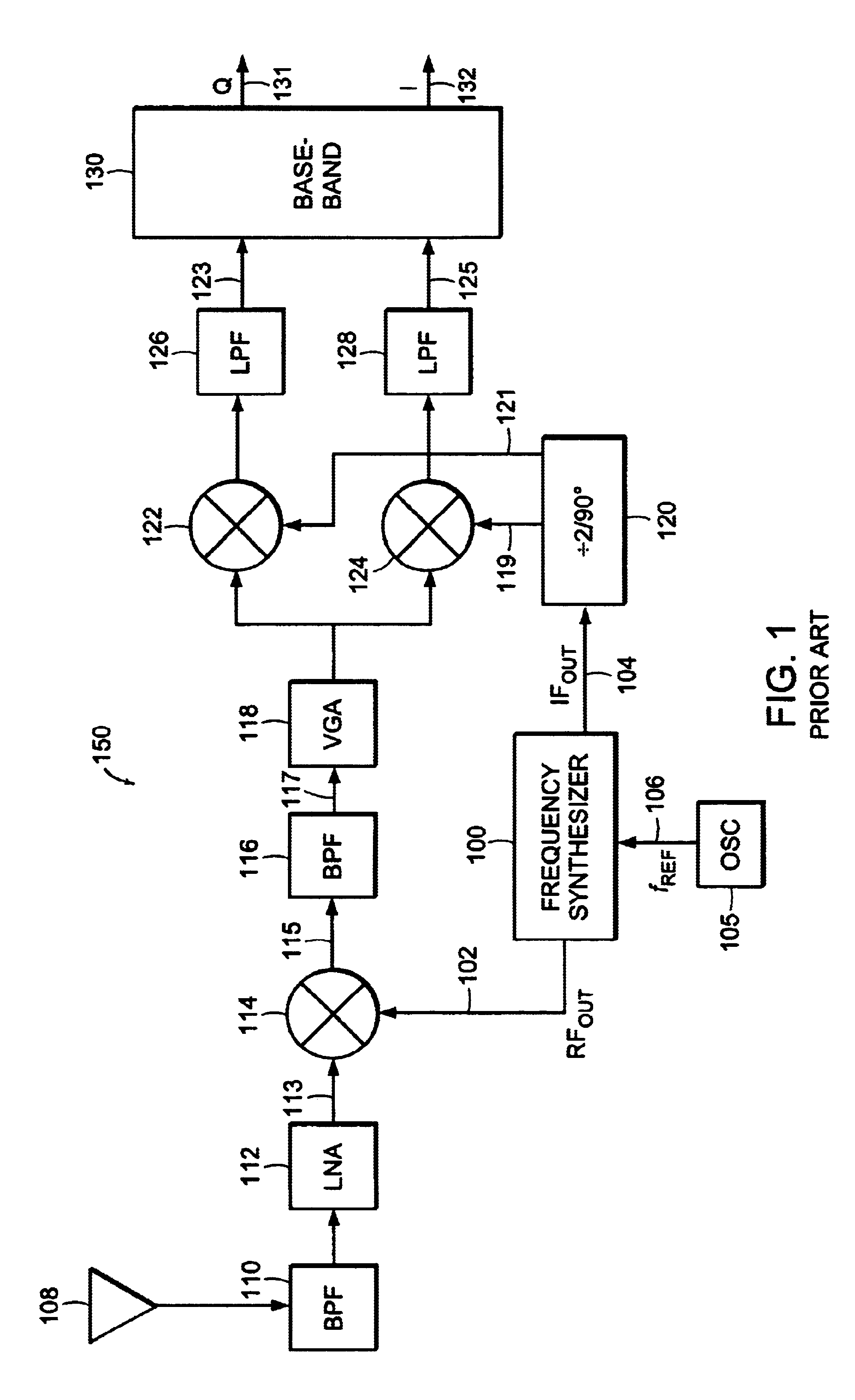
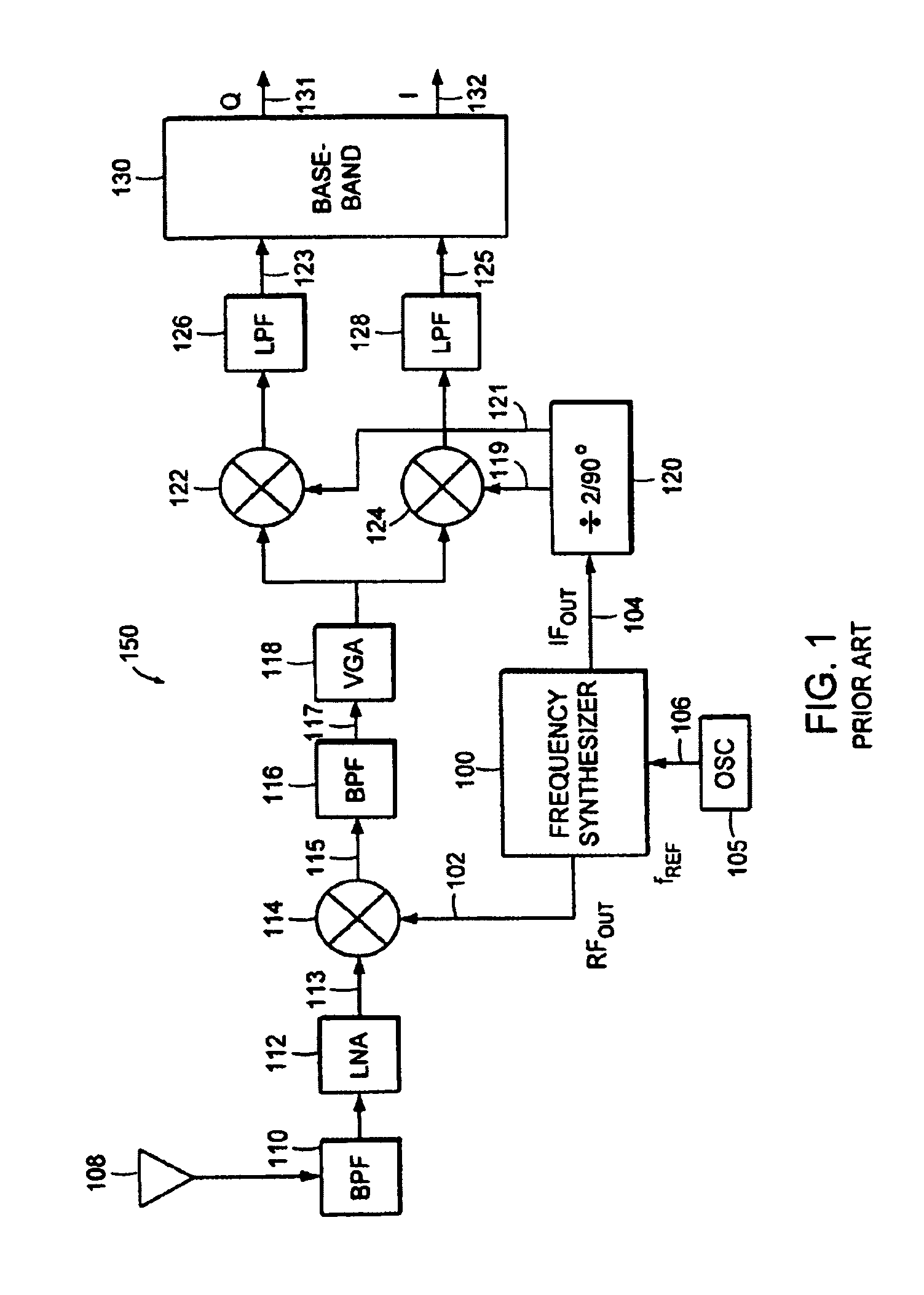
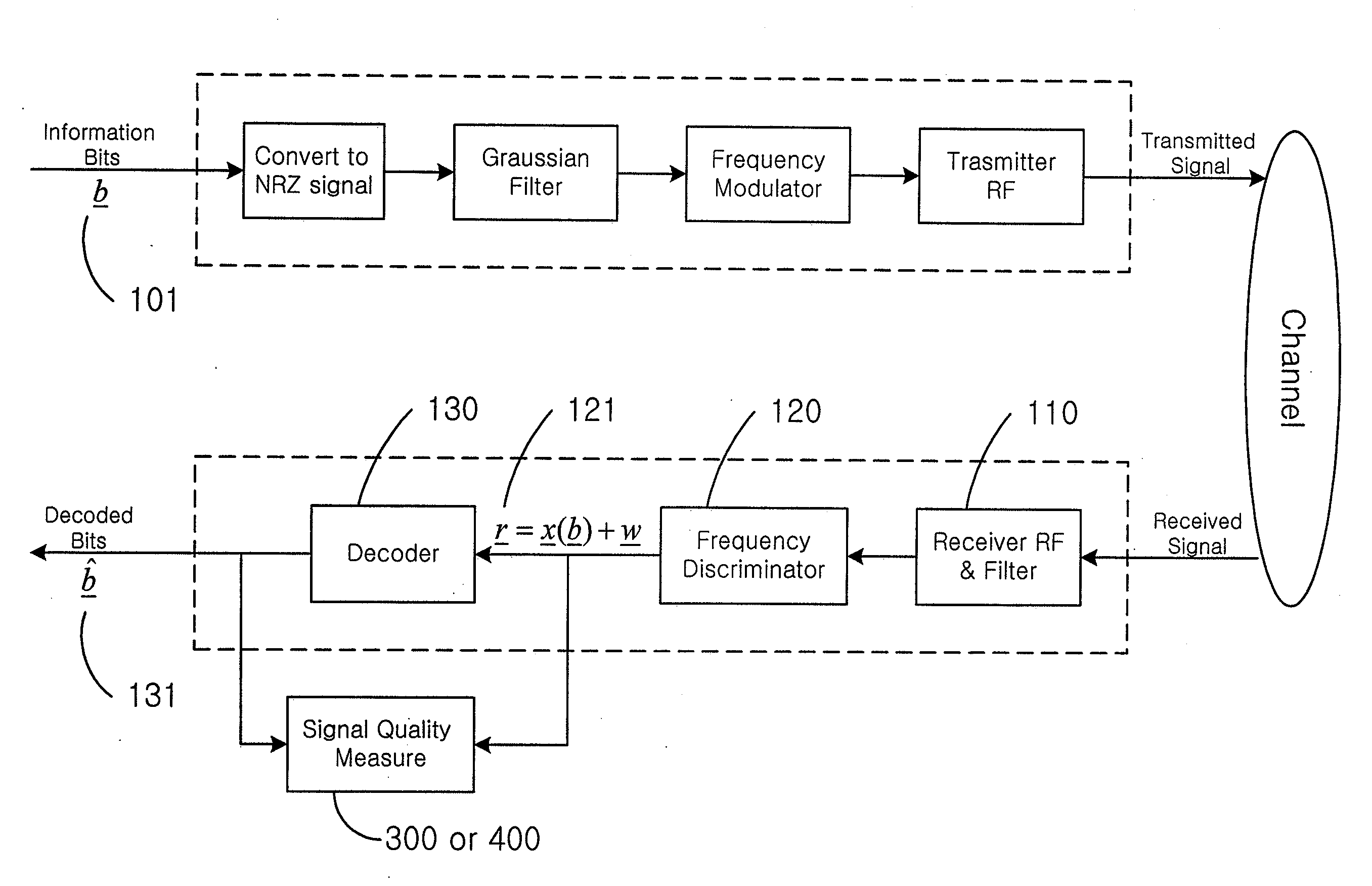
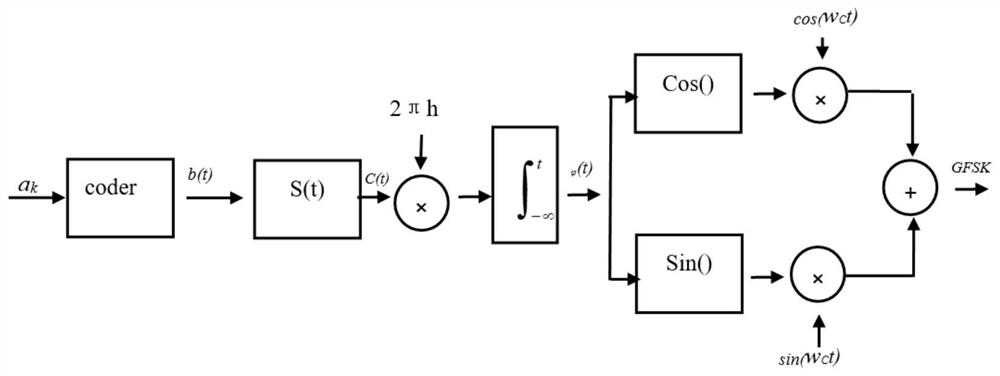
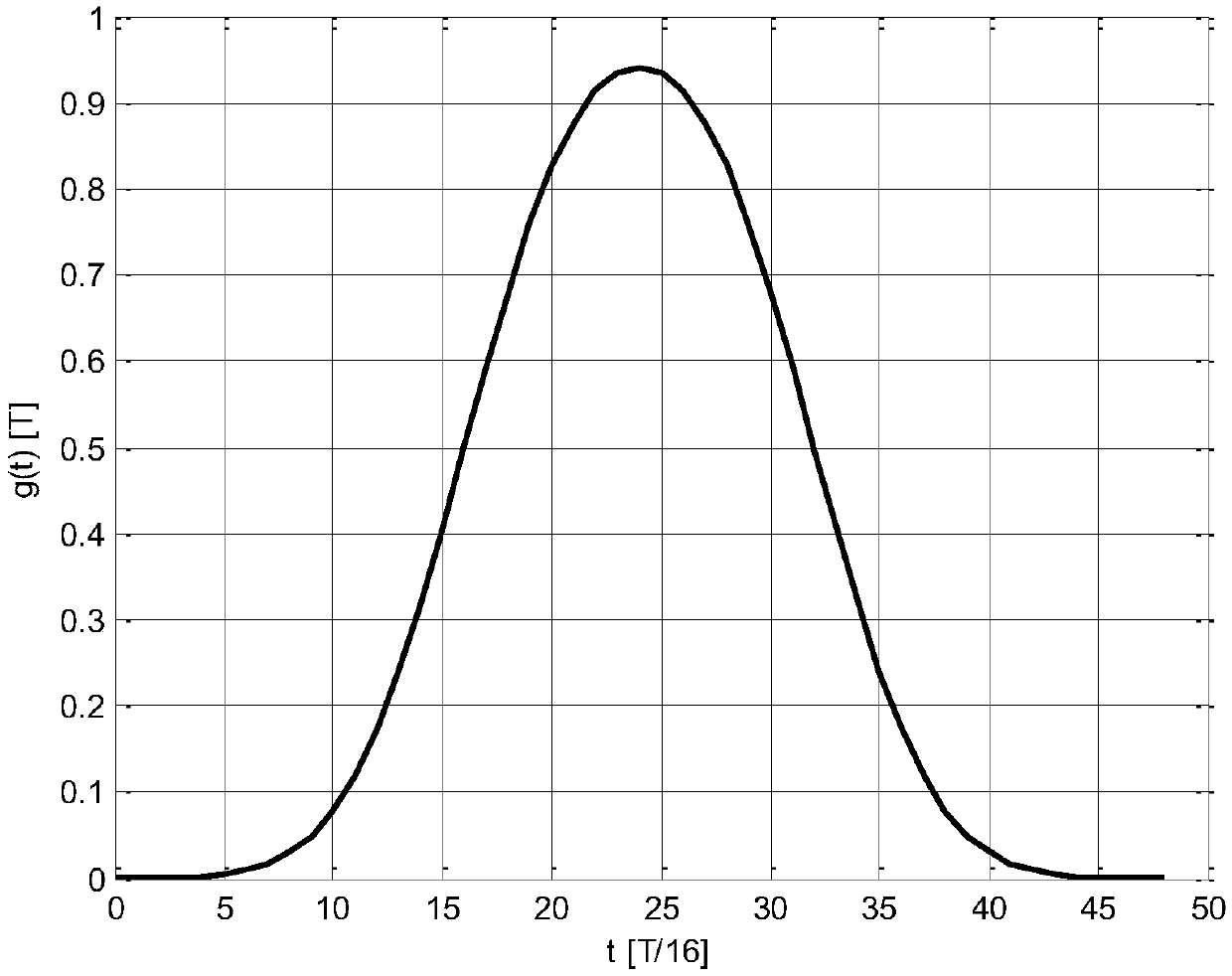
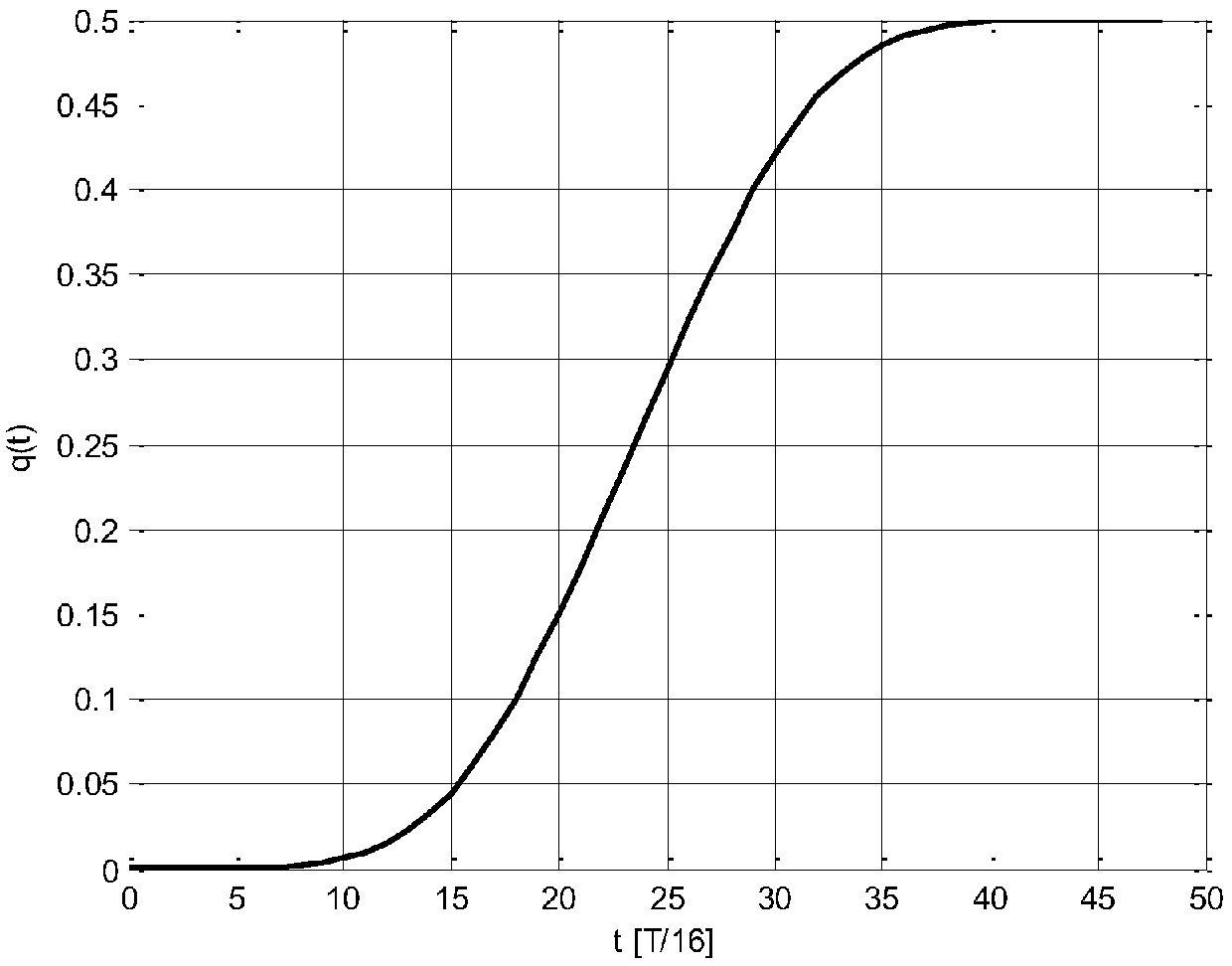
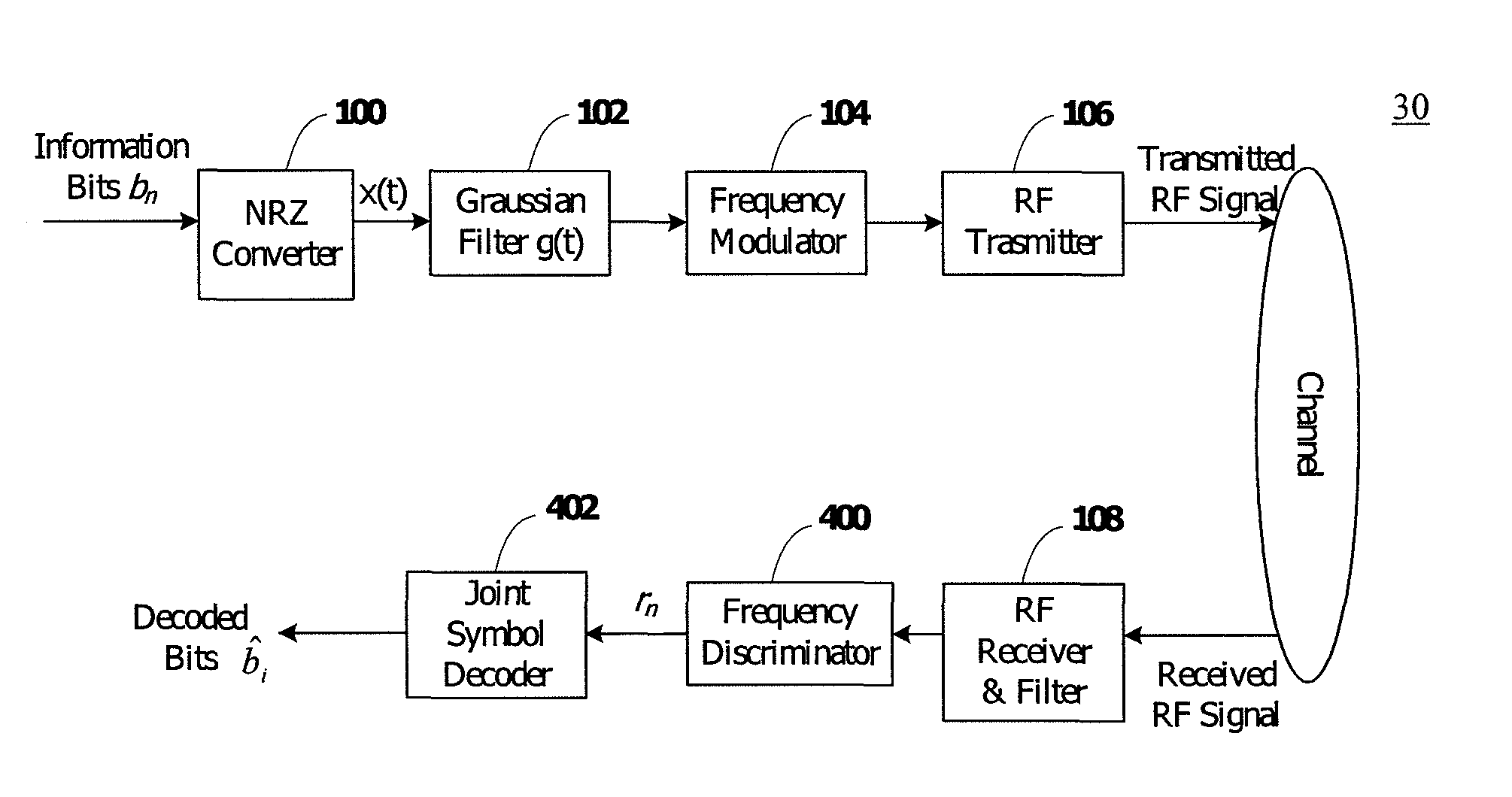
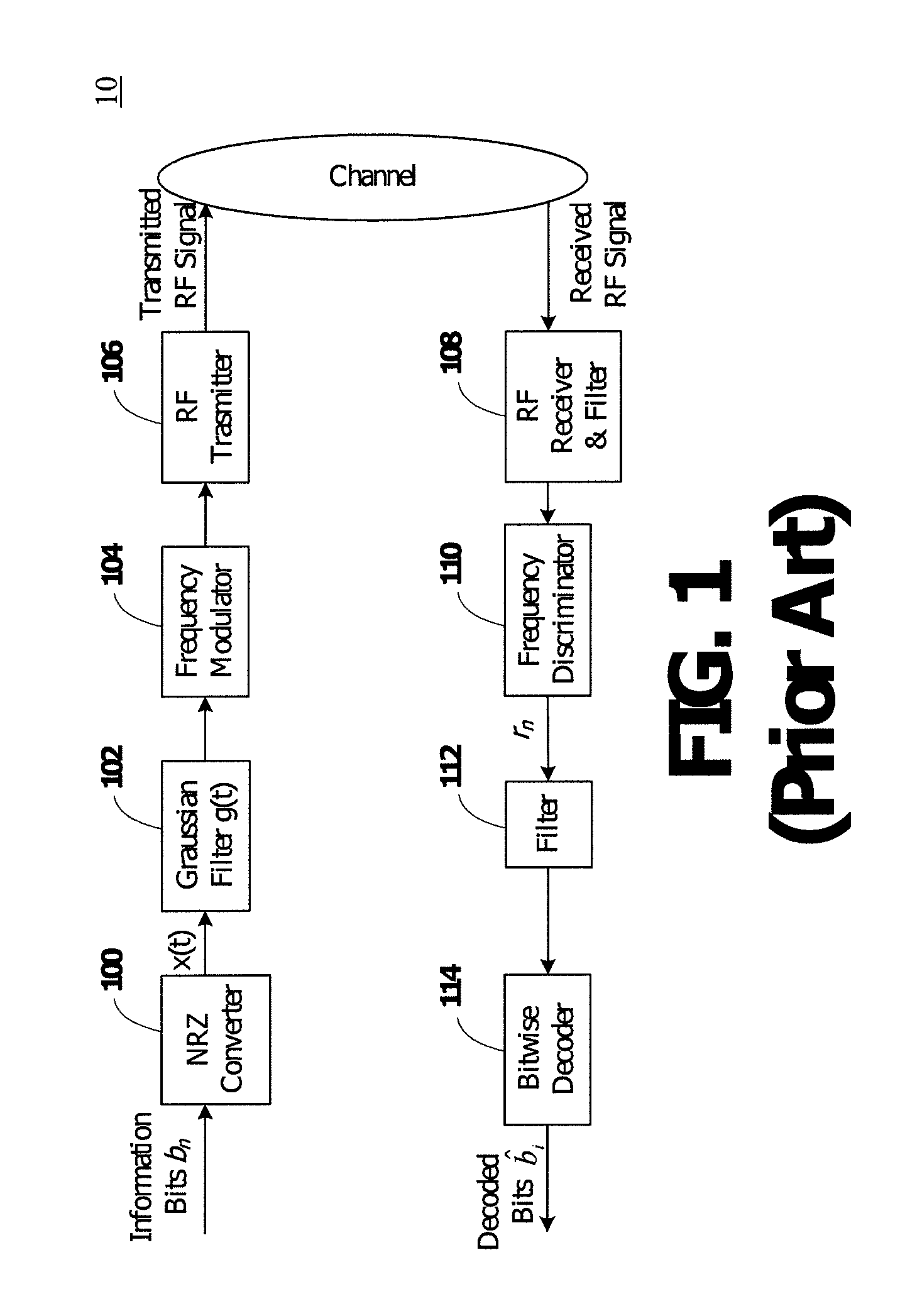
Gaussian frequency-shift keying is a type of frequency shift keying modulation that uses a Gaussian filter to smooth positive/negative frequency deviations, which represent a binary 1 or 0. It is used by DECT, Bluetooth, Cypress WirelessUSB, Nordic Semiconductor, Texas Instruments LPRF, Z-Wave and Wavenis devices. For basic data rate Bluetooth the minimum deviation is 115 kHz.
FMOD transceivers including continuous and burst operated TDMA, FDMA, spread spectrum CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA
InactiveUS6928101B2Improve performanceLow costAsymmetric modulation circuitsPhase-modulated carrier systemsModem deviceFrequency spectrum
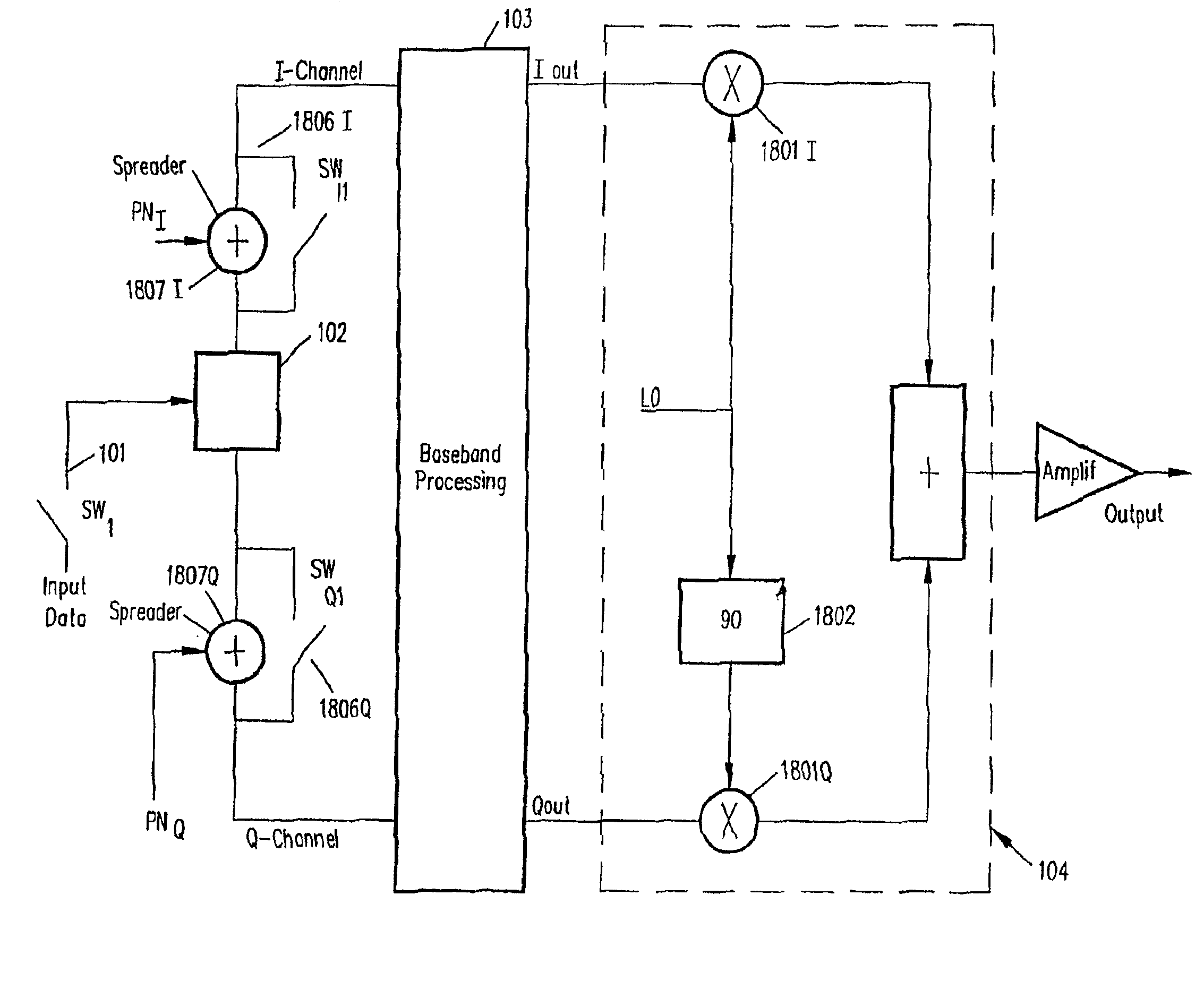
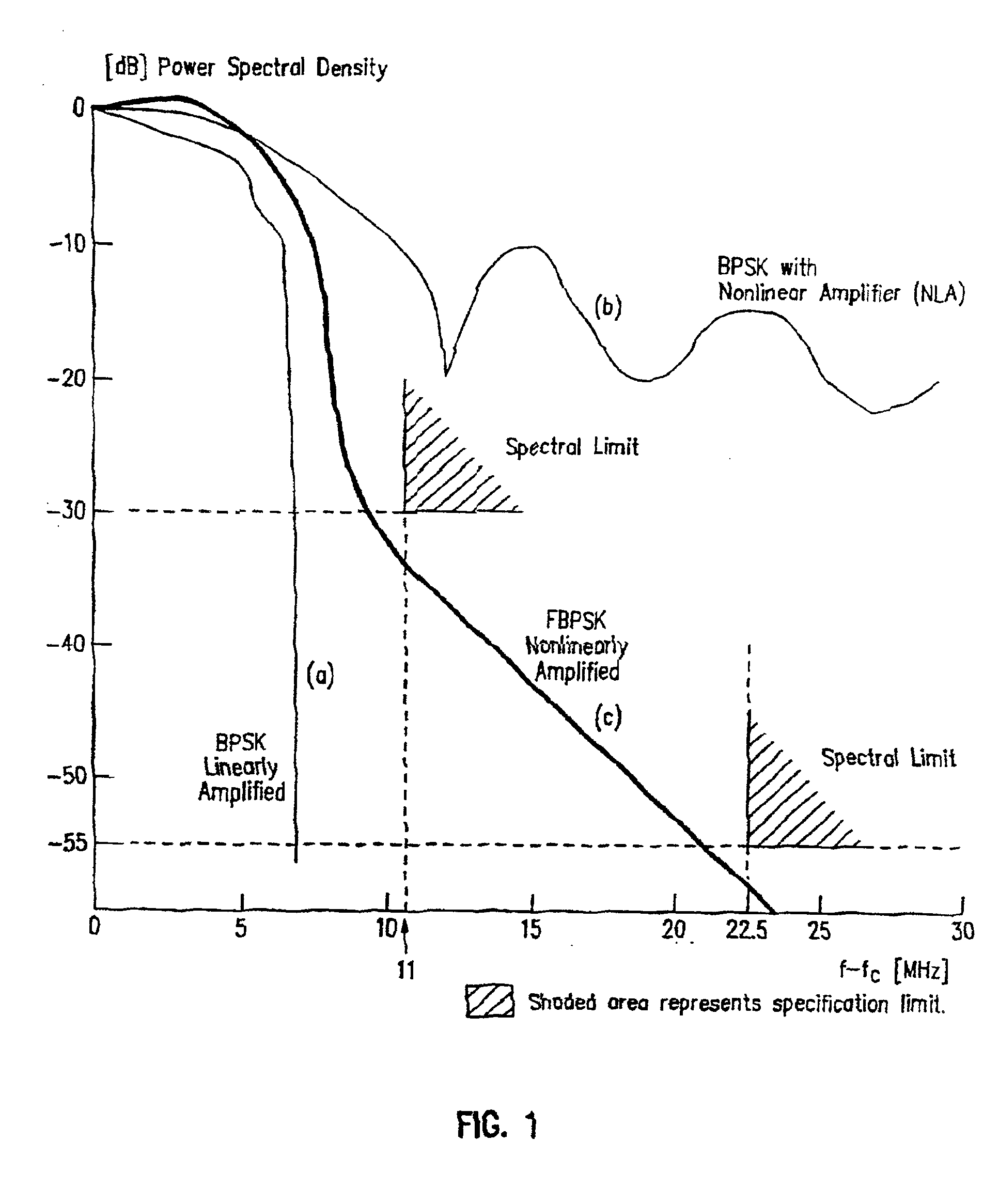
Binary and Quadrature Feher's Modulation (F-Modulation, or FMOD) Transmitter-Receiver systems and circuits exhibit reduced envelope fluctuation and peak radiation, and increased efficiency. A subclass of these systems has a constant envelope. They advantageously provide lower power operation with improved performance including robust BER performance, and compatibility with both linearly and nonlinearly amplified narrow spectrum, and without disadvantages of conventional BPSK, DBPSK QPSK and pi / 4-QPSK. Feher's BPSK (FBPSK) is an improved efficiency transmitter which is compatible with conventional BPSK receivers. FBPSK modems are based on using quadrature structure where Q-channel data is inserted in quadrature with I-channel data for certain applications. The Q-channel data may be “offset” from the I-channel data by an amount selectable between zero and a specified time. Further improvement in the spectrum is attained using correlation between I and Q channels. FBPSK modem is shown to meet the IEEE 802.11 specified spectral direct sequence spread spectrum mask (−30 dB point) for wireless LAN, and leads to an output power gain of 6.5 dB over conventional BPSK modems. The cross-coupled quadrature FMOD structure is also suitable for continuous mode and for burst operated TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA Frequency Modulation Quadrature AM (QAM), QPSK and offset QPSK, as well as pi / 4-shifted QPSK modems / processors. Reduced modulation index Gaussian FSK (GFSK), multilevel FM and cross-coupled Quadrature Amplitude Modulated (QAM) transmitters and combinations of these modulations and corresponding coherent demodulators are disclosed. Controlled rise and fall time descriptions of burst operated systems are included.
Owner:INTEL CORP
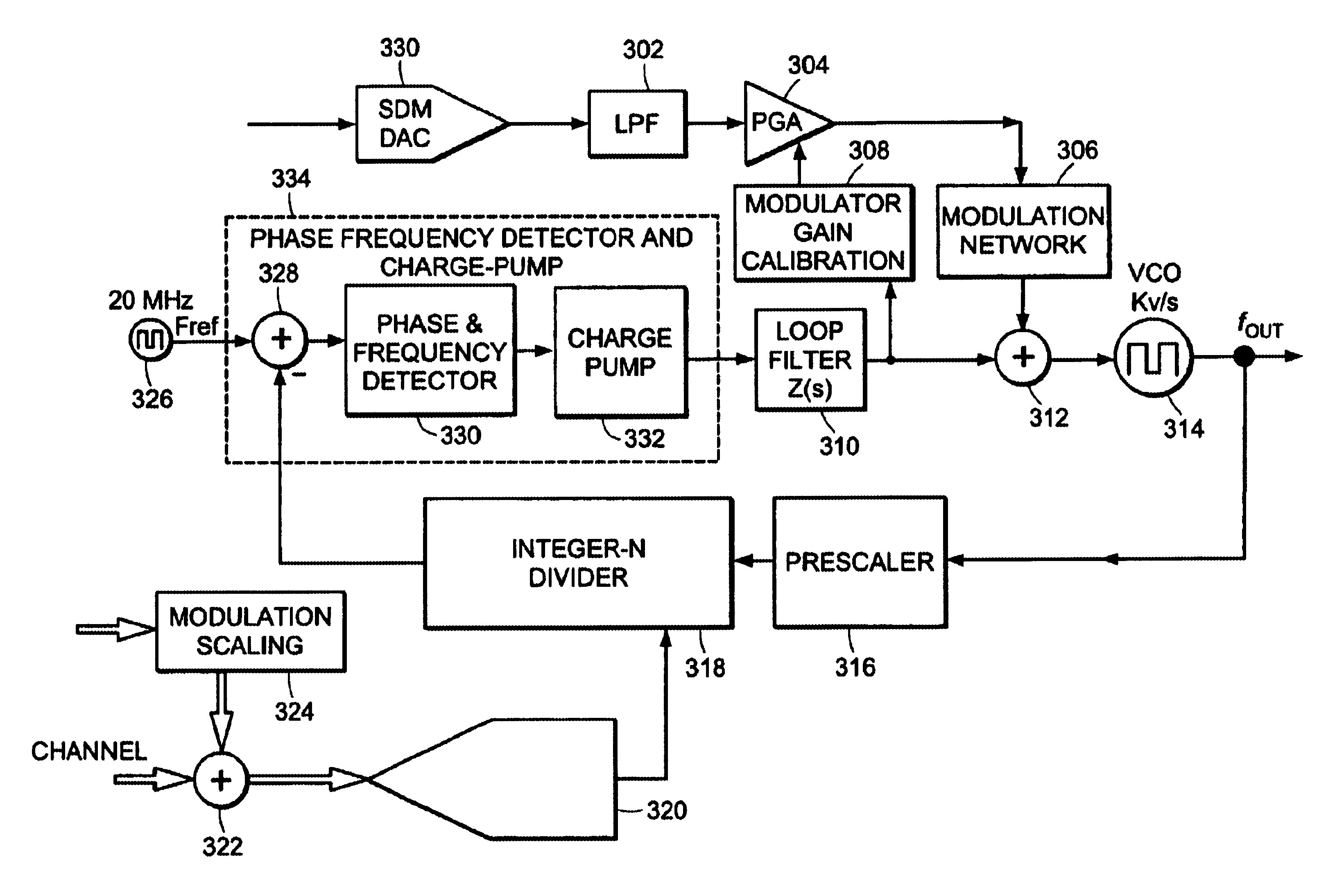
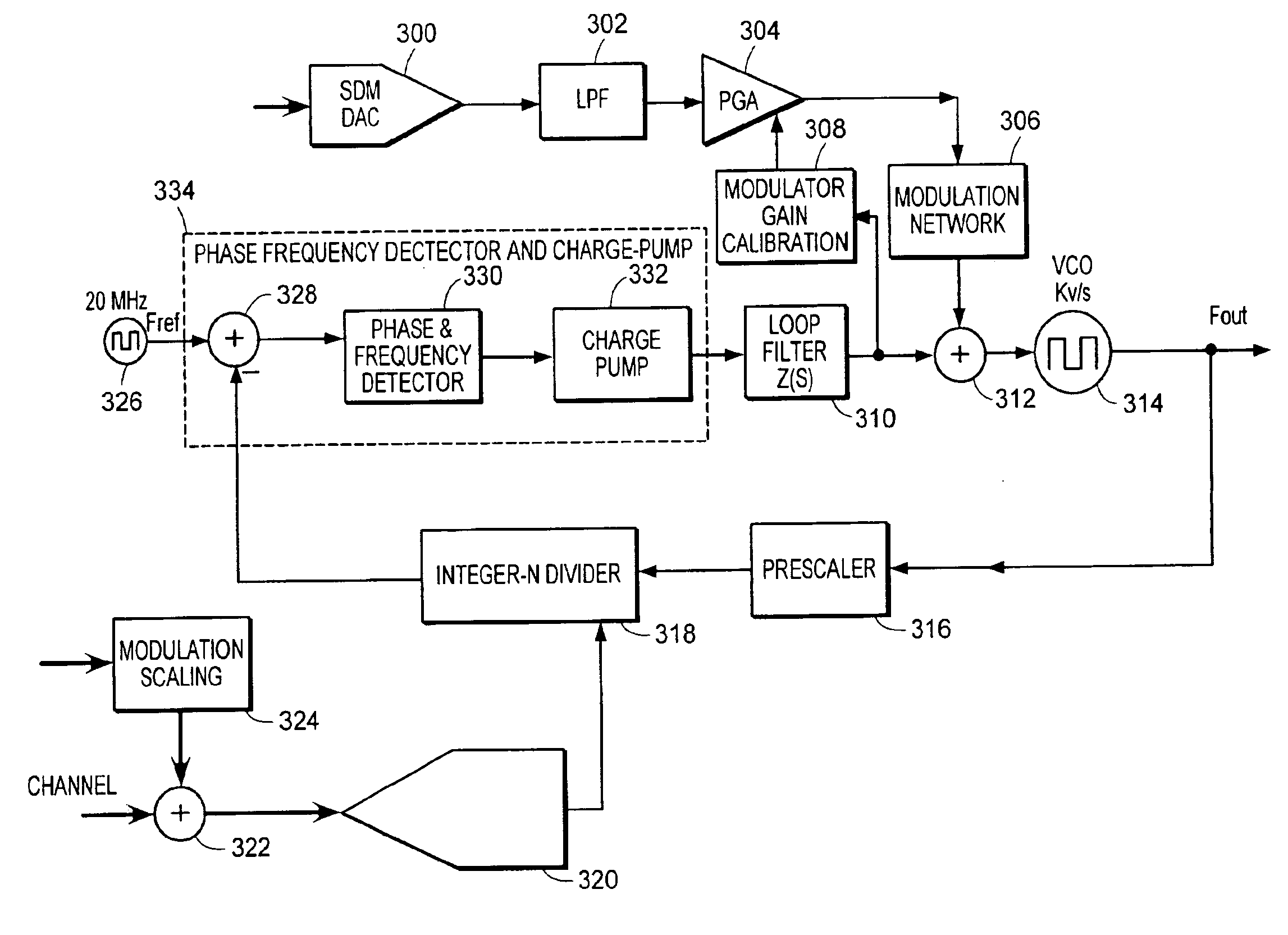
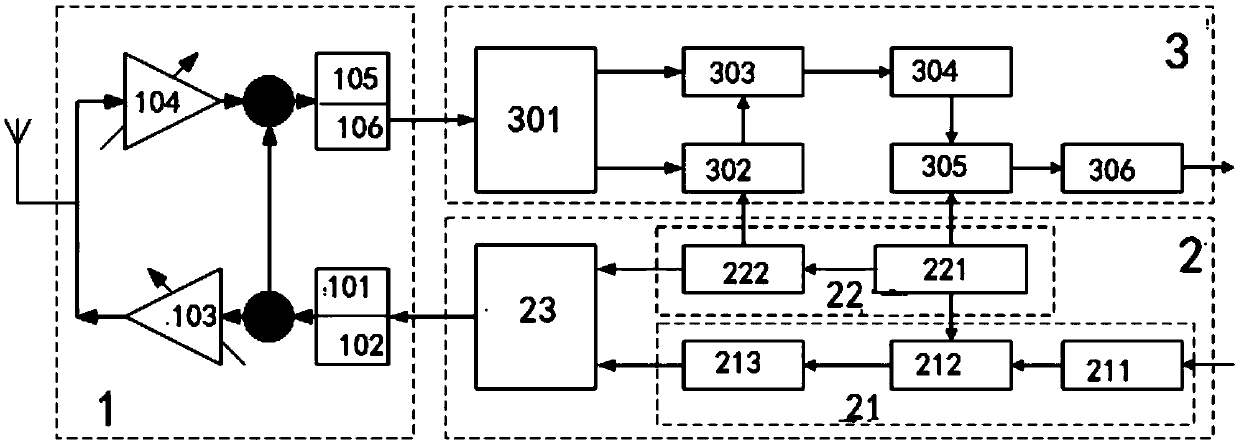
Method of modulation gain calibration and system thereof
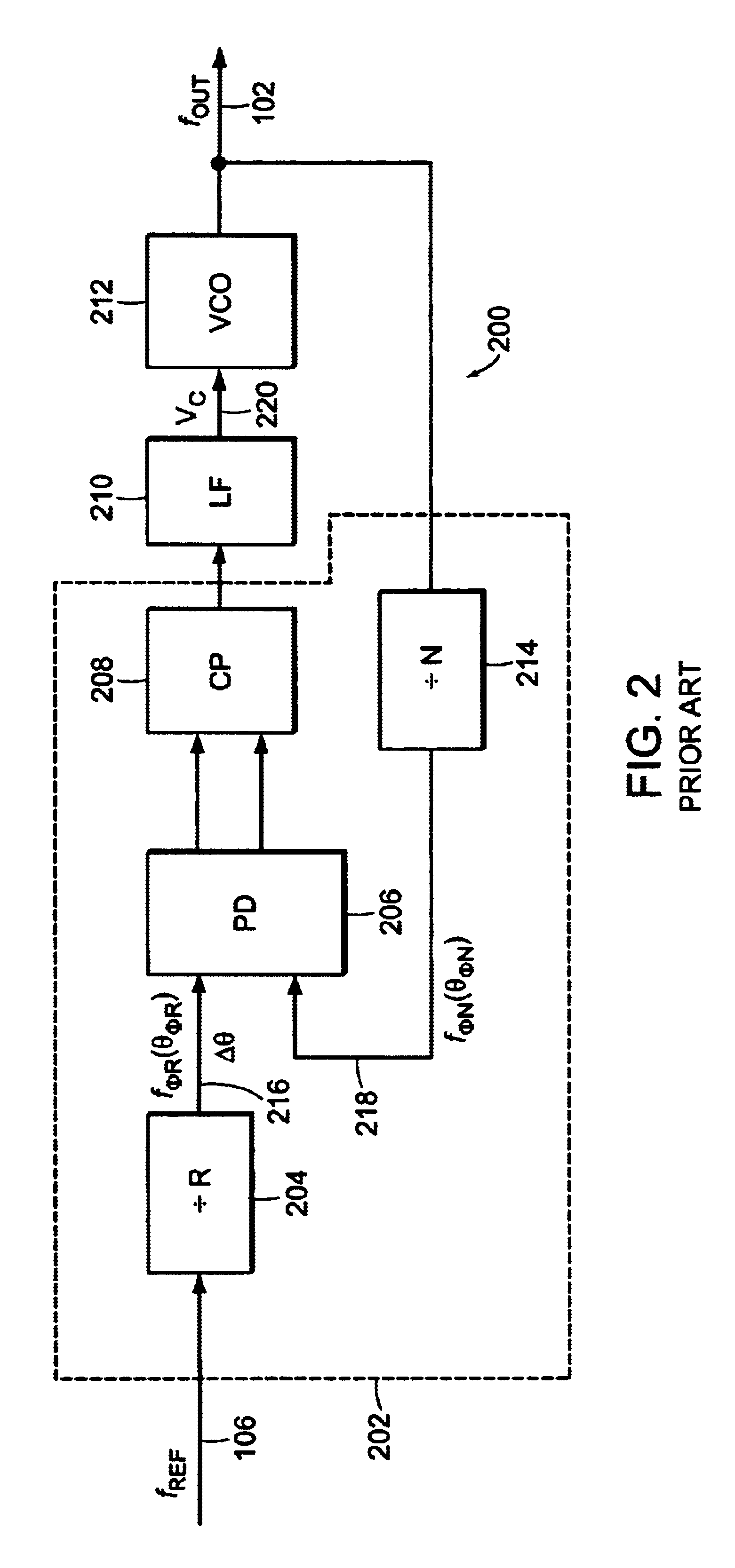
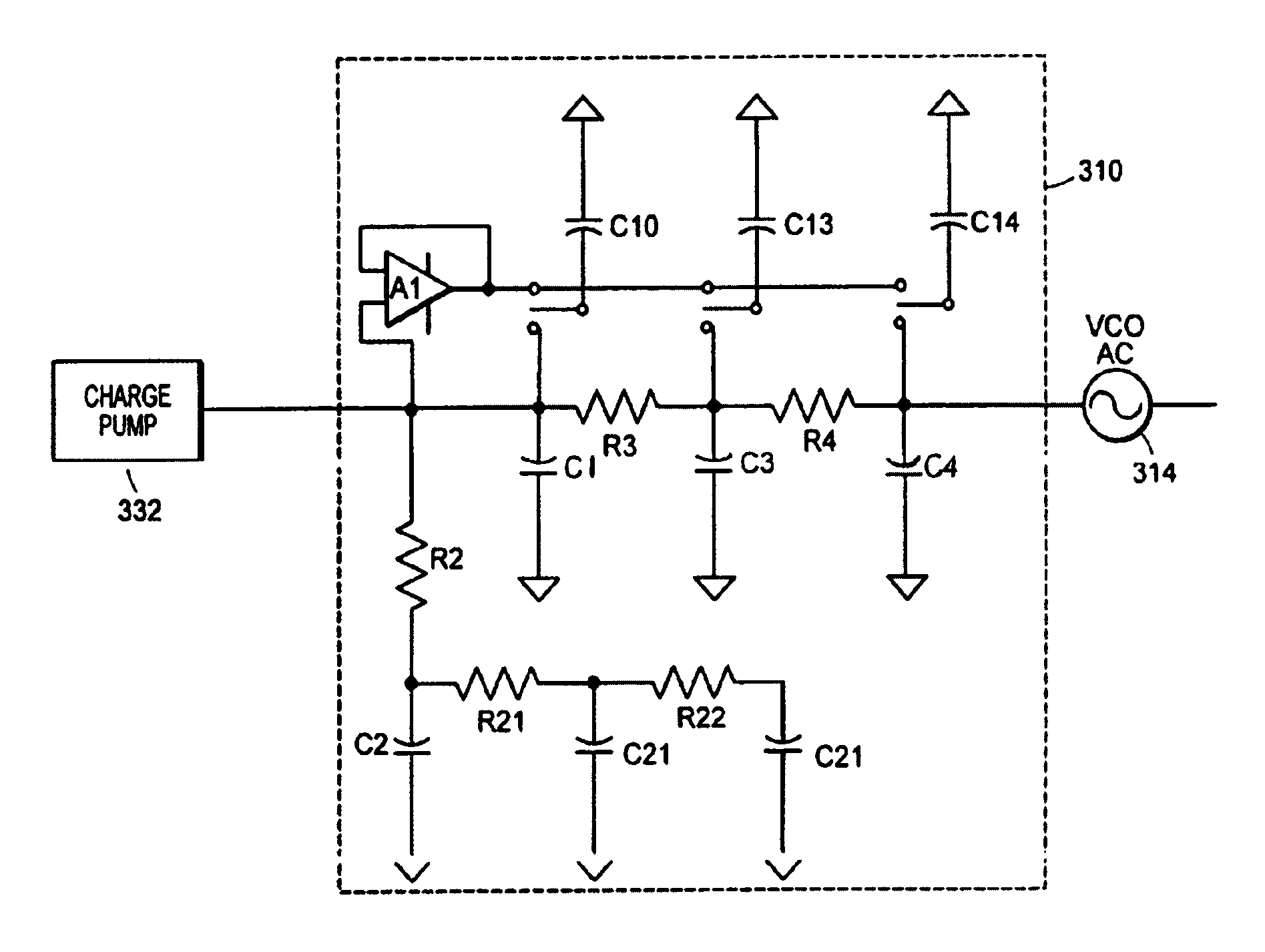
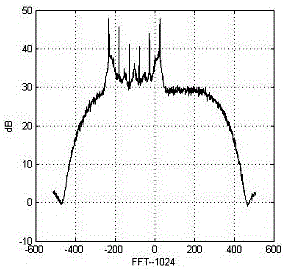
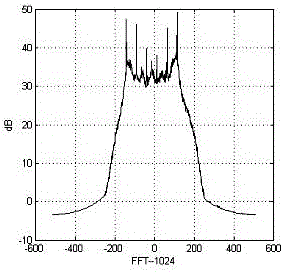
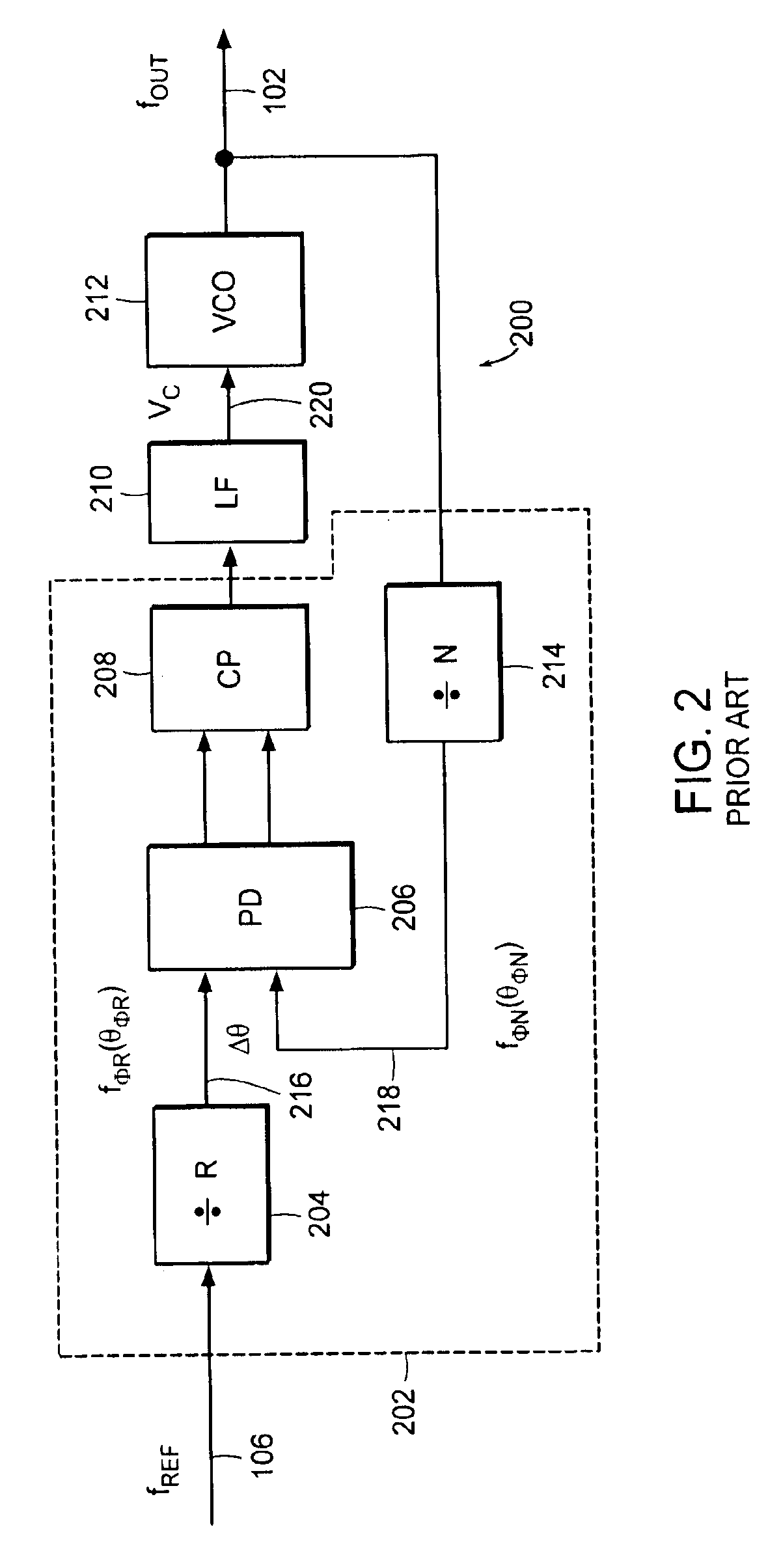
A wideband impedance attenuator includes a phase-locked loop filter, a voltage-controlled oscillator connected to the phase-locked loop filter during transmit, and an impedance circuit connected to the phase-locked loop filter and the voltage controlled oscillator. The impedance circuit is a scaled version of the phase-locked loop filter. Moreover, the wideband impedance attenuator attenuates a Gaussian frequency shift key modulation signal by a factor of 1 / (N+1) using the impedance circuit, which has an impedance of N*Z(s), and the phase-locked loop filter, which has an impedance of Z(s). An output frequency is generated using a voltage-controlled oscillator wherein the output frequency corresponds to the attenuated Gaussian frequency shift key modulation signal. In addition, a comparator compares a voltage of an output from the programmable gain amplifier with a voltage necessary to produce a predetermined frequency shift in a voltage-controlled oscillator to produce a gain signal. A gain controller, in response to the gain signal produced by the comparator, controls a gain of the programmable gain amplifier.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Phase-locked loop filter with out of band rejection in low bandwidth mode
A wideband impedance attenuator includes a phase-locked loop filter, a voltage-controlled oscillator connected to the phase-locked loop filter during transmit, and an impedance circuit connected to the phase-locked loop filter and the voltage controlled oscillator. The impedance circuit is a scaled version of the phase-locked loop filter. Moreover, the wideband impedance attenuator attenuates a Gaussian frequency shift key modulation signal by a factor of 1 / (N+1) using the impedance circuit, which has an impedance of N*Z(s), and the phase-locked loop filter, which has an impedance of Z(s). An output frequency is generated using a voltage-controlled oscillator wherein the output frequency corresponds to the attenuated Gaussian frequency shift key modulation signal. In addition, a comparator compares a voltage of an output from the programmable gain amplifier with a voltage necessary to produce a predetermined frequency shift in a voltage-controlled oscillator to produce a gain signal. A gain controller, in response to the gain signal produced by the comparator, controls a gain of the programmable gain amplifier.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
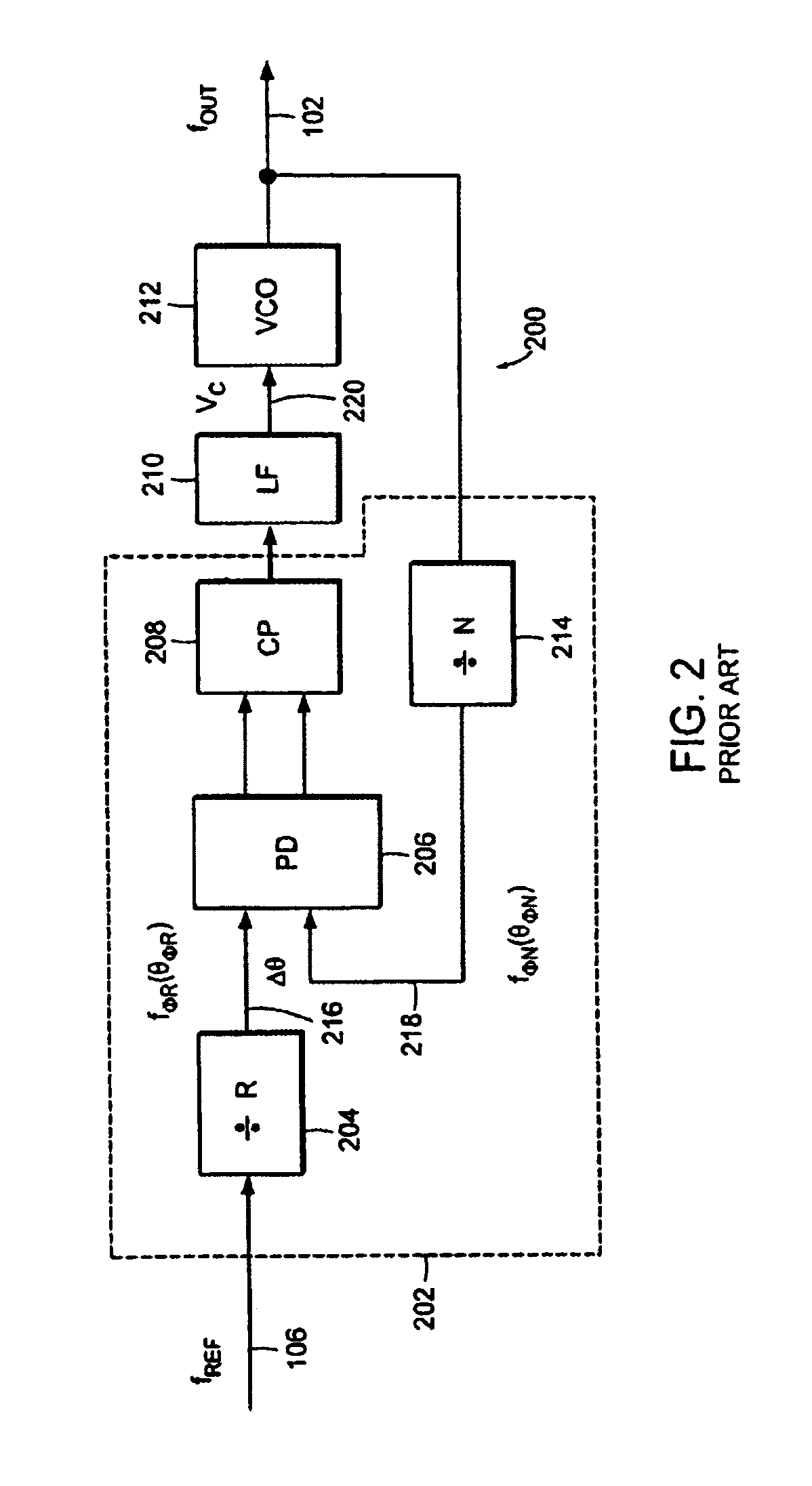
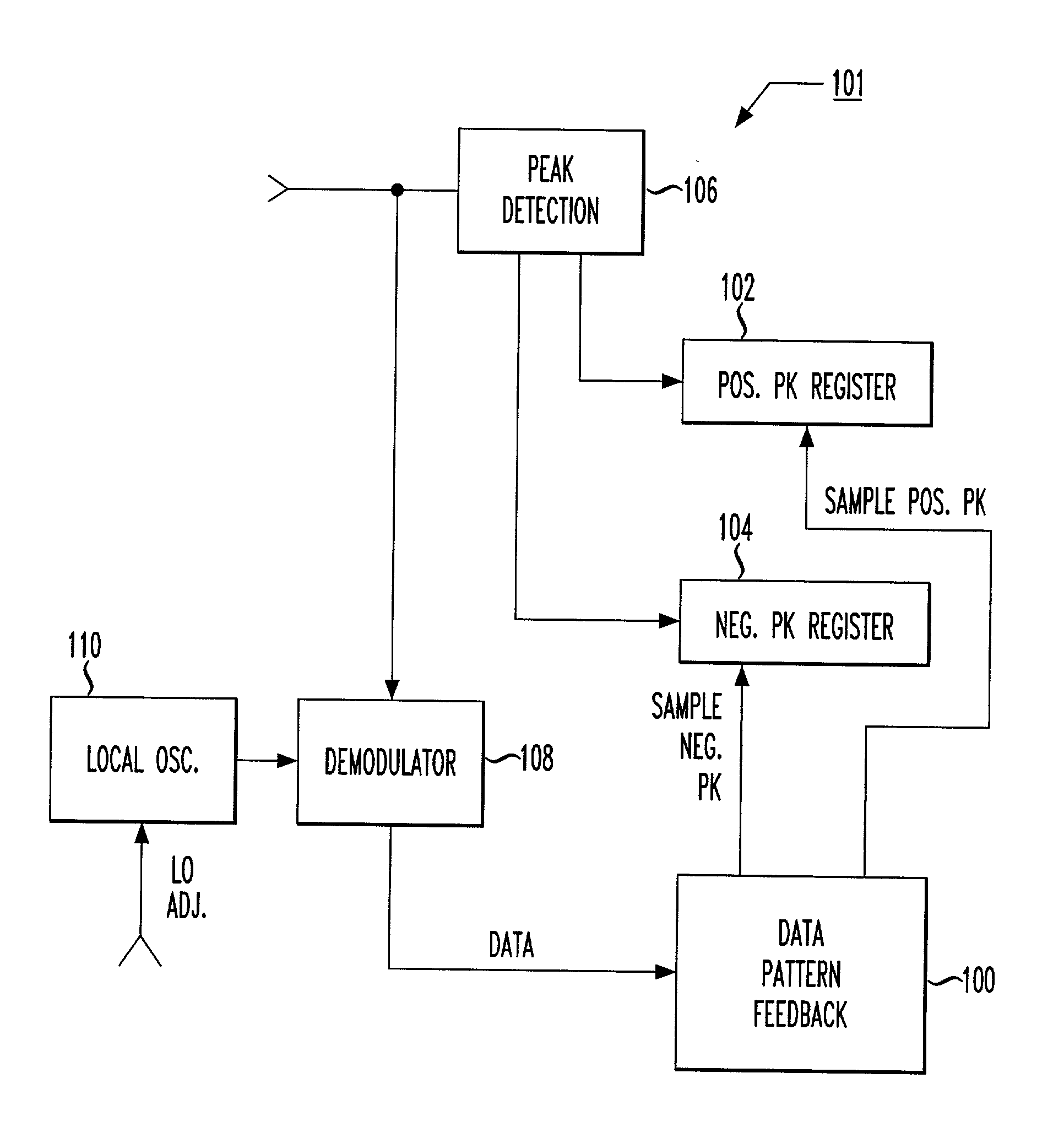
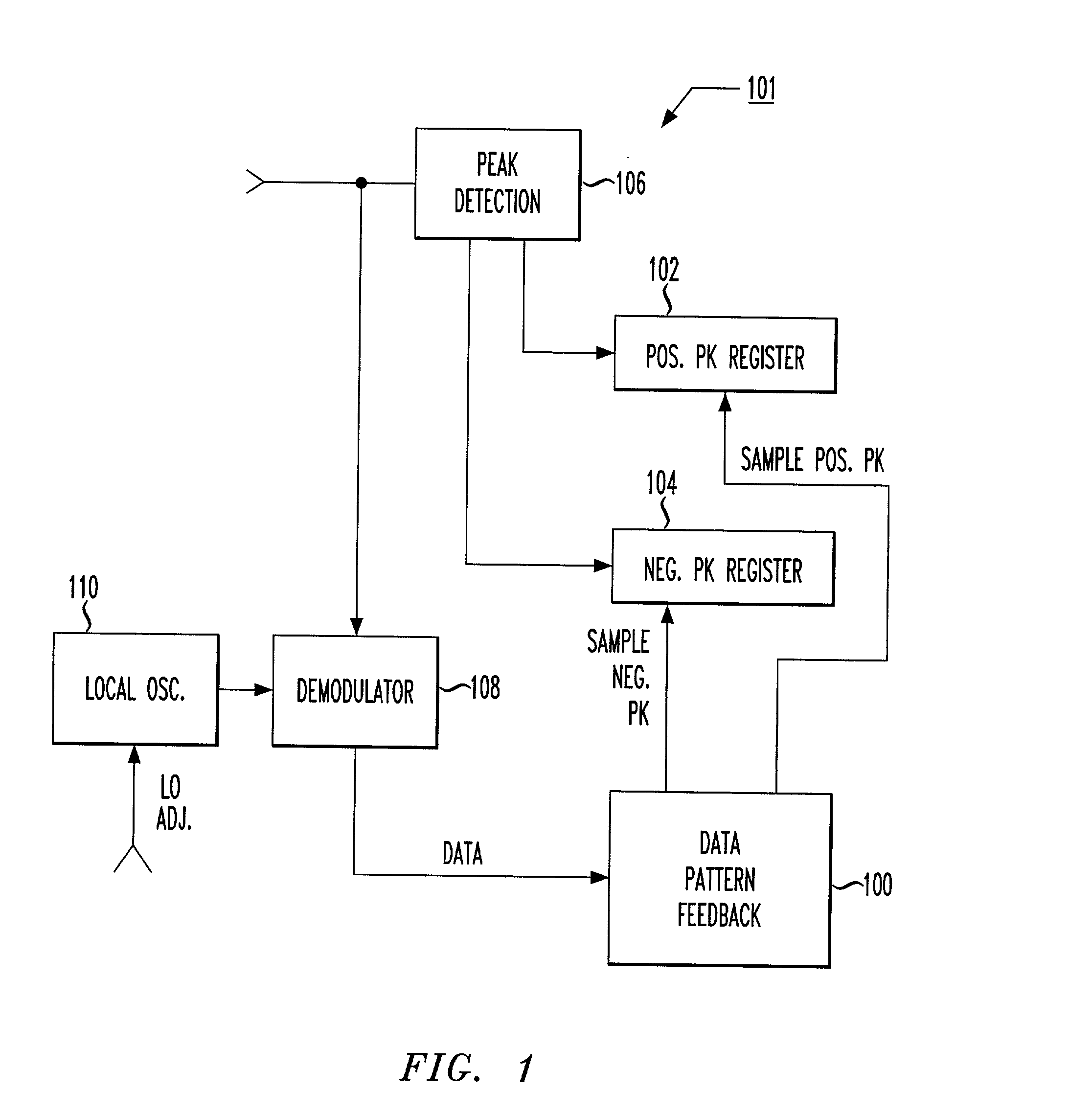
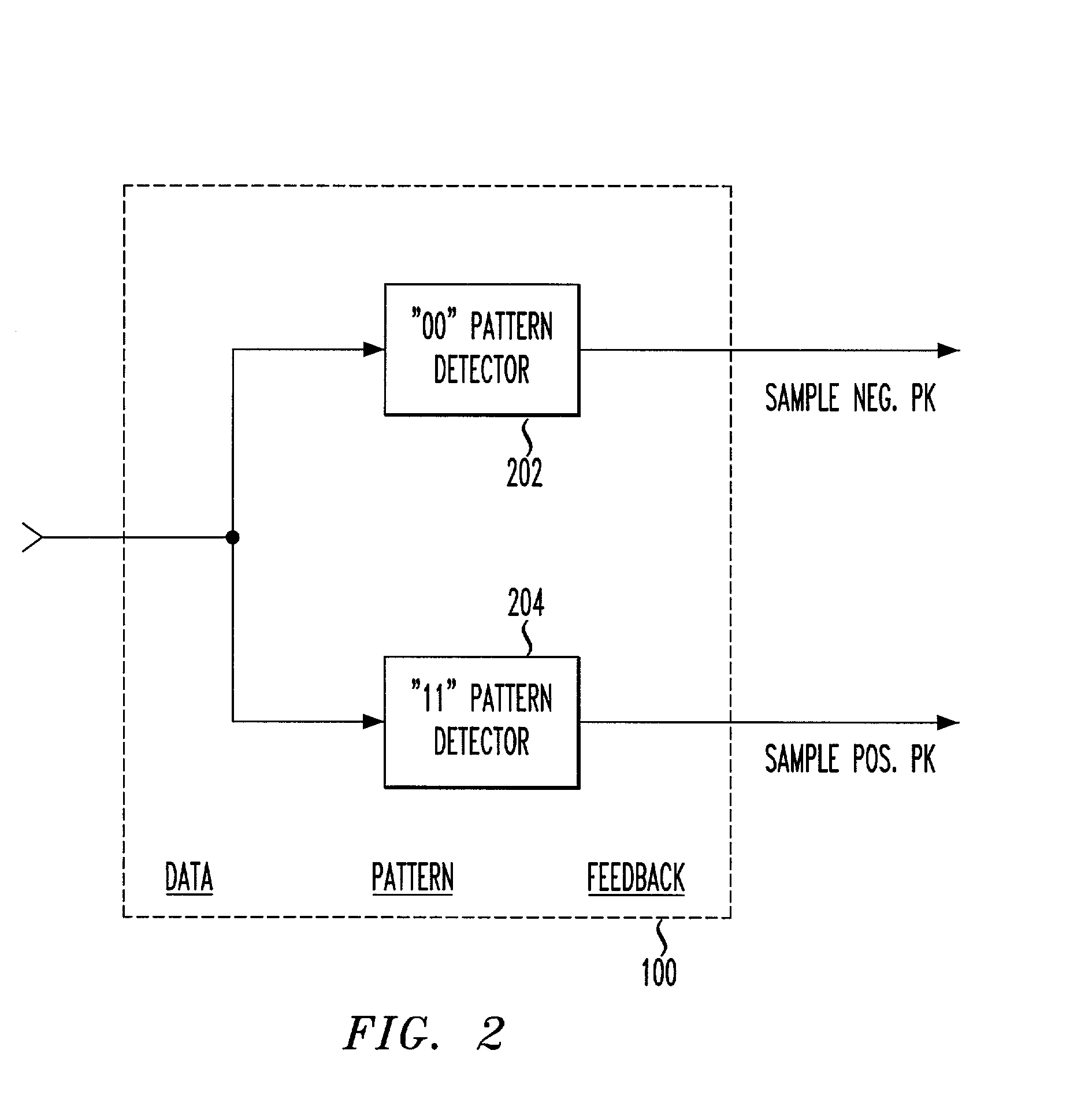
Fine-stage automatic frequency compensation in post-detection BLUETOOTH applications
InactiveUS20030203729A1Network topologiesAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency compensationLocal oscillator
A data-pattern feedback mechanism is introduced into the peak detection process of an automatic frequency compensation system in a Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying (GFSK) modulated system, providing fast and accurate fine-stage automatic frequency compensation (AFC). Maximum positive and negative peak registers are updated with new values as necessary based on detection during a sequence of identical binary bit values (e.g., during a "00" for detection of maximum negative peak frequency, or during a "11" for detection of maximum positive peak frequency), in a particular data frame. As soon as an initial value is determined for both the maximum positive and negative peak frequencies (e.g., after the first occurrence of a "11" and a "00", in any order), fine-stage automatic frequency compensation can be initiated. Subsequent adjustments to the VCO of the local oscillator will further refine the frequency offset towards the ideal of zero. Quick determination of the maximum positive and negative peak frequencies is made based on data pattern feedback in accordance with the principles of the present invention, allowing for a fast and accurate fine-stage automatic frequency compensation adjustment of a local oscillation clock signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Gfsk receiver architecture and methodology
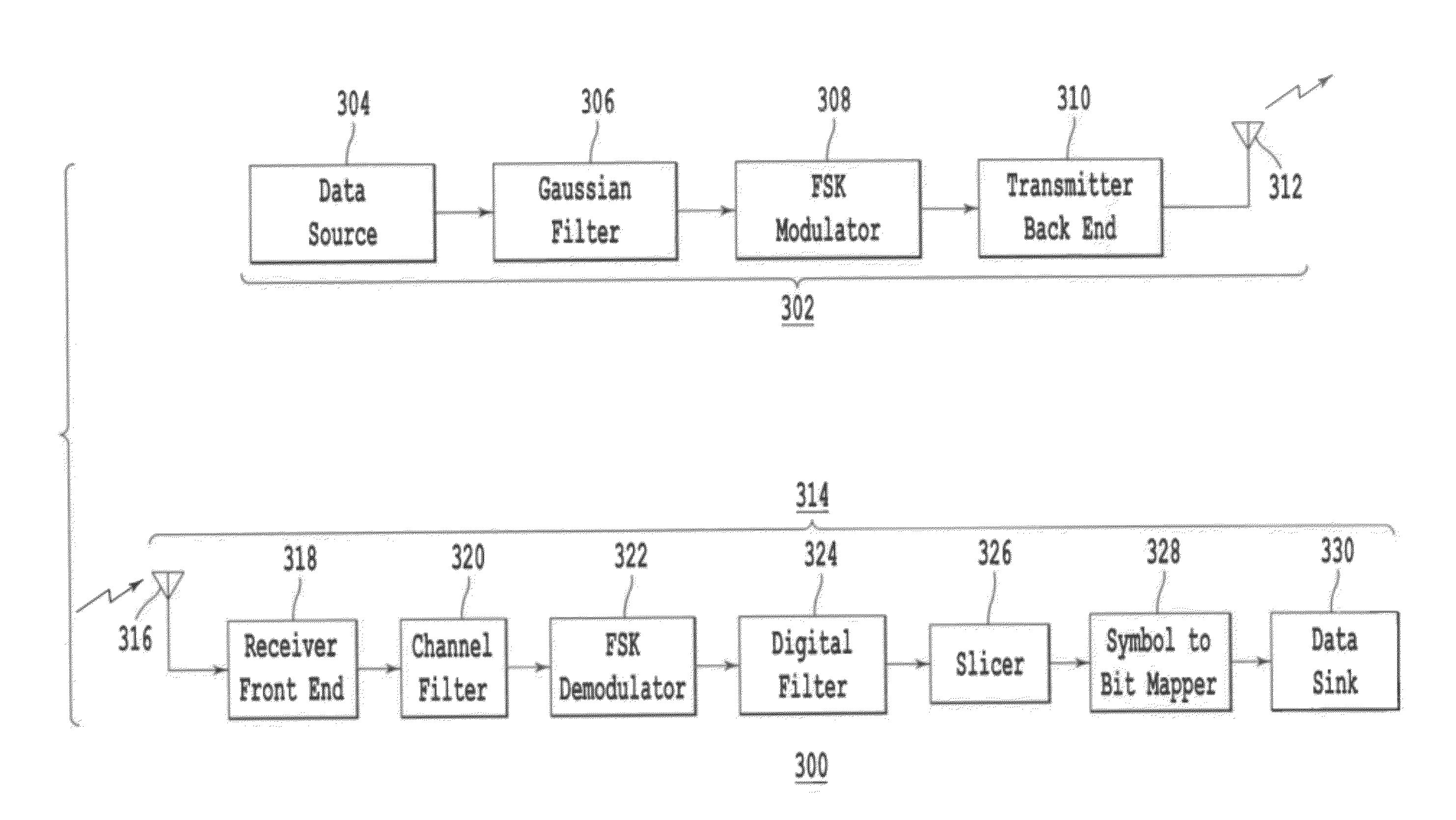
ActiveUS20120027132A1Simple and cost-effective approachImprove throughputError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionDigital filterFrequency modulation
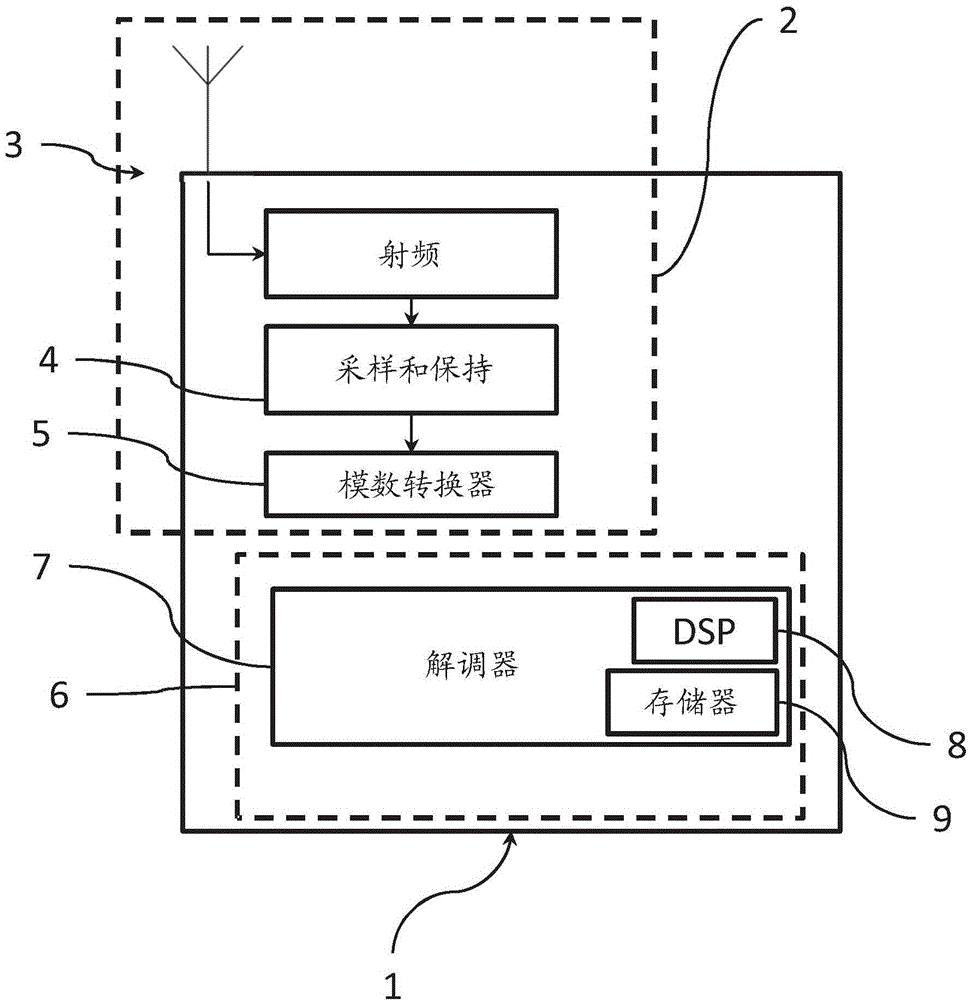
A Gaussian Frequency Shift Key (GFSK) receiver includes a receiver front end to receive a GFSK-modulated signal and convert the received GFSK-modulated signal to a baseband frequency modulated signal, a channel filter to reduce channel interference which is adjacent to a desired channel of the baseband frequency modulated signal, a demodulator to demodulate the channel filtered baseband modulated signal and to recover a sequence of symbols, a digital filter to reduce inter-symbol interference (ISI) from the sequence of symbols, a slicer to produce symbol decisions based on the filtered sequence of symbols, and a symbol-to-bit mapper to map the symbol decisions to data bits.
Owner:SENSUS USA
GFSK baseband digital receiver and baseband synchronization and demodulation method of the GFSK baseband digital receiver
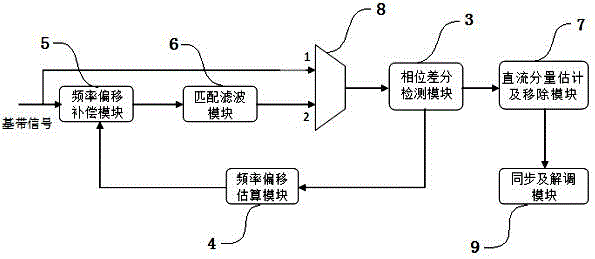
ActiveCN105812303AImprove performanceReduce overheadFrequency-modulated carrier systemsSequence signalPhase difference
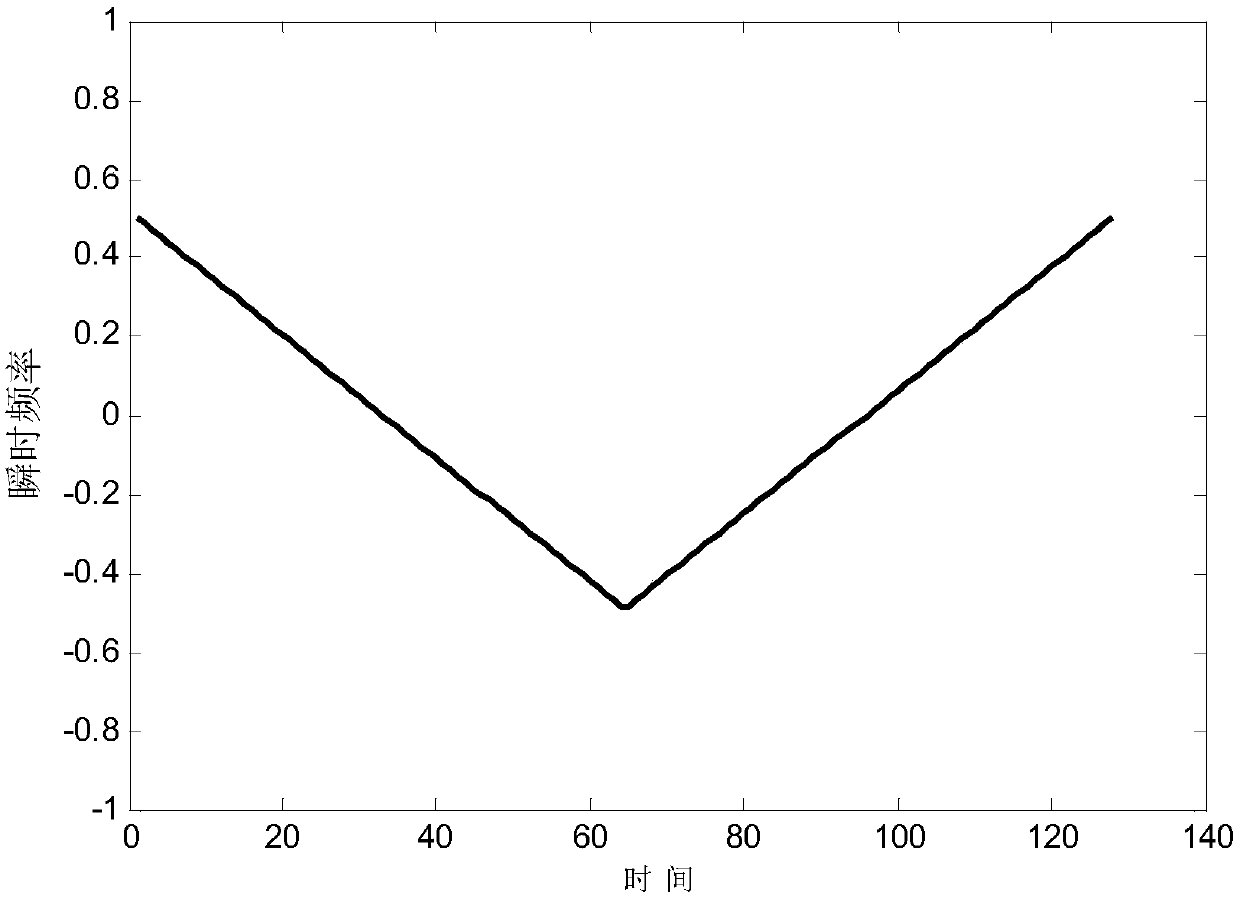
The invention discloses a GFSK baseband digital receiver and a baseband synchronization and demodulation method of the GFSK baseband digital receiver. The receiver comprises a phase difference detection module, a frequency shift estimation module, a frequency shift compensation module, a matched filtering module, a direct current component estimation and removing module, a selector and a synchronization and demodulation module. According to the receiver and the method, DFT operation of a specific frequency point is carried out on code element envelope signals output through phase difference detection; whether there are leader sequence signals or not is judged; moreover a corresponding frequency shift is calculated; frequency compensation and matched filtering are carried out on follow-up baseband signals; code element envelope is output through difference detection; and at this time, the direct current component estimation and removing module and the synchronization and demodulation module of the backward stage start working. The receiver is equipped with a frequency shift estimation and compensation circuit, thus improving the performance of the receiver; signal demodulation and code element judgment are carried out in a phase domain; the symbol synchronization and sampling clock synchronization of the receiver are realized based on a counter; and the receiver is simple and reliable in structure and can adapt to various different data rates.
Owner:SUZHOU ZHUOZHI CHUANGXIN ELECTRONICS TECH
Wideband modulation summing network and method thereof
A wideband impedance attenuator includes a phase-locked loop filter, a voltage-controlled oscillator connected to the phase-locked loop filter during transmit, and an impedance circuit connected to the phase-locked loop filter and the voltage controlled oscillator. The impedance circuit is a scaled version of the phase-locked loop filter. Moreover, the wideband impedance attenuator attenuates a Gaussian frequency shift key modulation signal by a factor of 1 / (N+1) using the impedance circuit, which has an impedance of N*Z(s), and the phase-locked loop filter, which has an impedance of Z(s). An output frequency is generated using a voltage-controlled oscillator wherein the output frequency corresponds to the attenuated Gaussian frequency shift key modulation signal. In addition, a comparator compares a voltage of an output from the programmable gain amplifier with a voltage necessary to produce a predetermined frequency shift in a voltage-controlled oscillator to produce a gain signal. A gain controller, in response to the gain signal produced by the comparator, controls a gain of the programmable gain amplifier.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Demodulation and timing synchronization combined method for GFSK (Gauss Frequency Shift Key)
InactiveCN102170414ASimplify complexityReduce overheadSynchronisation arrangementFrequency-modulated carrier systemsLoop filterFilter tuning
The invention relates to a demodulation and timing synchronization combined method for a GFSK (Gauss Frequency Shift Key). In the invention, an oversampling signal is used as an input of a demodulation and synchronization loop; after a phase of the sampling signal is adjusted by an interpolation filter, conjugate multiplication is carried out on the sampling signal by every two continuous sampling values to obtain a phase difference; and the phase difference is used as an input of timing error detection. With a difference between front and back phase values as a direction of error adjustment,a middle phase value of every three continuously calculated phase values is used as a size of the error adjustment. A timing error is fed back to the interpolation filter after passing through a loopfilter, and a new sampling value is adjusted again and again. By using the invention, the realization complicatedness of hardware is simplified and the use of a square error detection algorithm is avoided under an oversampling situation; and the demodulation and timing synchronization combined method for the GFSK, provided by the invention, has the advantages of small hardware cost and good timing detection performance.
Owner:浙江瑞讯微电子有限公司
Receivers and symbol decoders thereof
ActiveUS20110142173A1Frequency-modulated carrier systemsAngle demodulationSymbol decodingCommunications system
A receiver capable of decoding a symbol based on information on a previous symbol, the symbol and a next symbol in a Gaussian frequency shift keying (GFSK) communication system is provided. The receiver includes a discriminator to generate a symbol for each bit in a bit sequence, a first lookup table (LUT) to store a number of bit patterns and mapping patterns, wherein each of the bit patterns is in the form of a set of consecutive bits in the bit sequence and corresponds to a respective one of the mapping patterns, and wherein each of the mapping patterns includes a set of entries and each of the entries results from an operation of attribute values at a sample time in the waveform of a symbol, a calculator to receive a set of consecutive symbols from the discriminator and calculate a distance value between the set of consecutive symbols and each of the mapping patterns, and a comparator to identify one of the mapping patterns with a minimum distance value by comparing among the distance values from the calculator.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
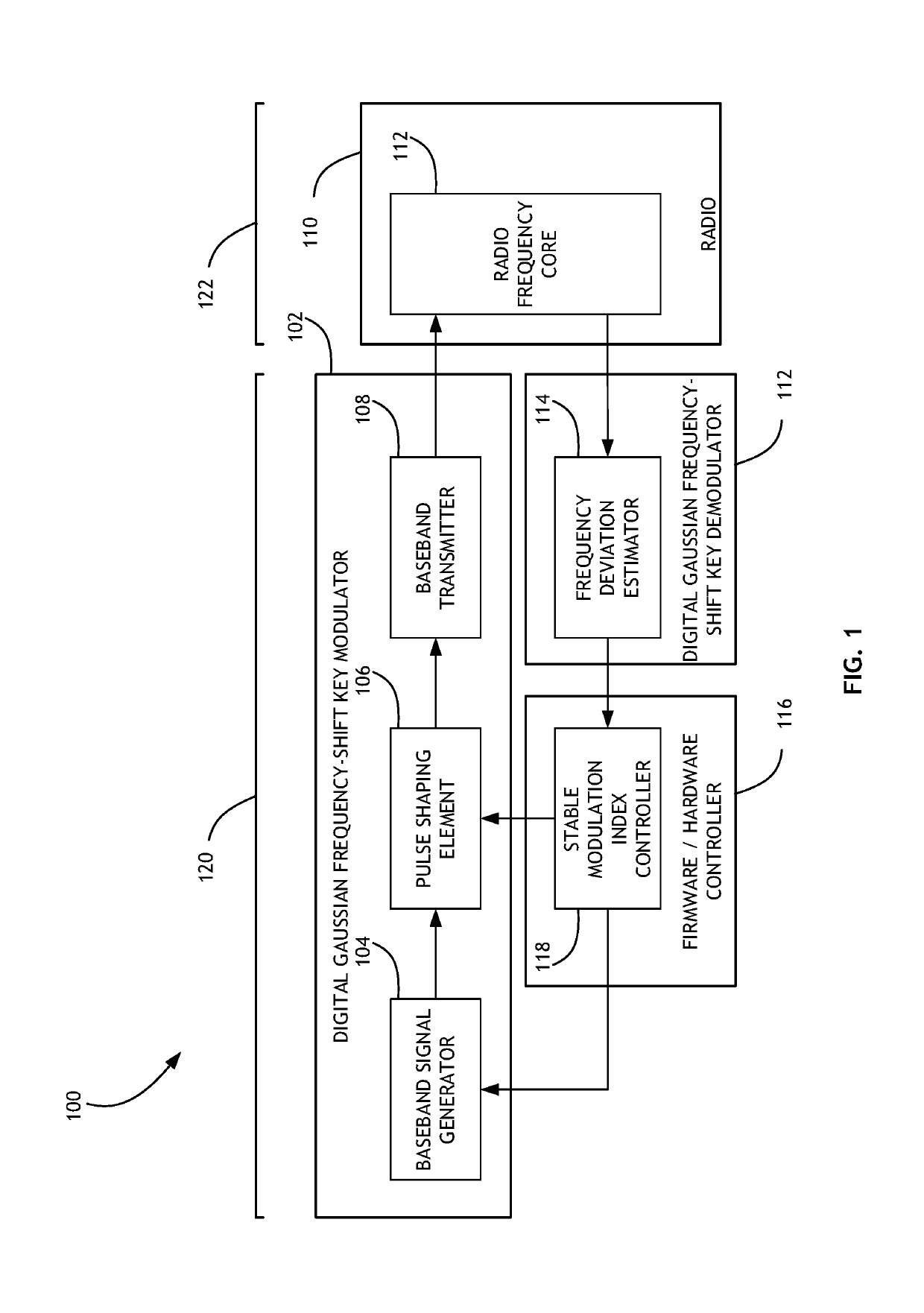
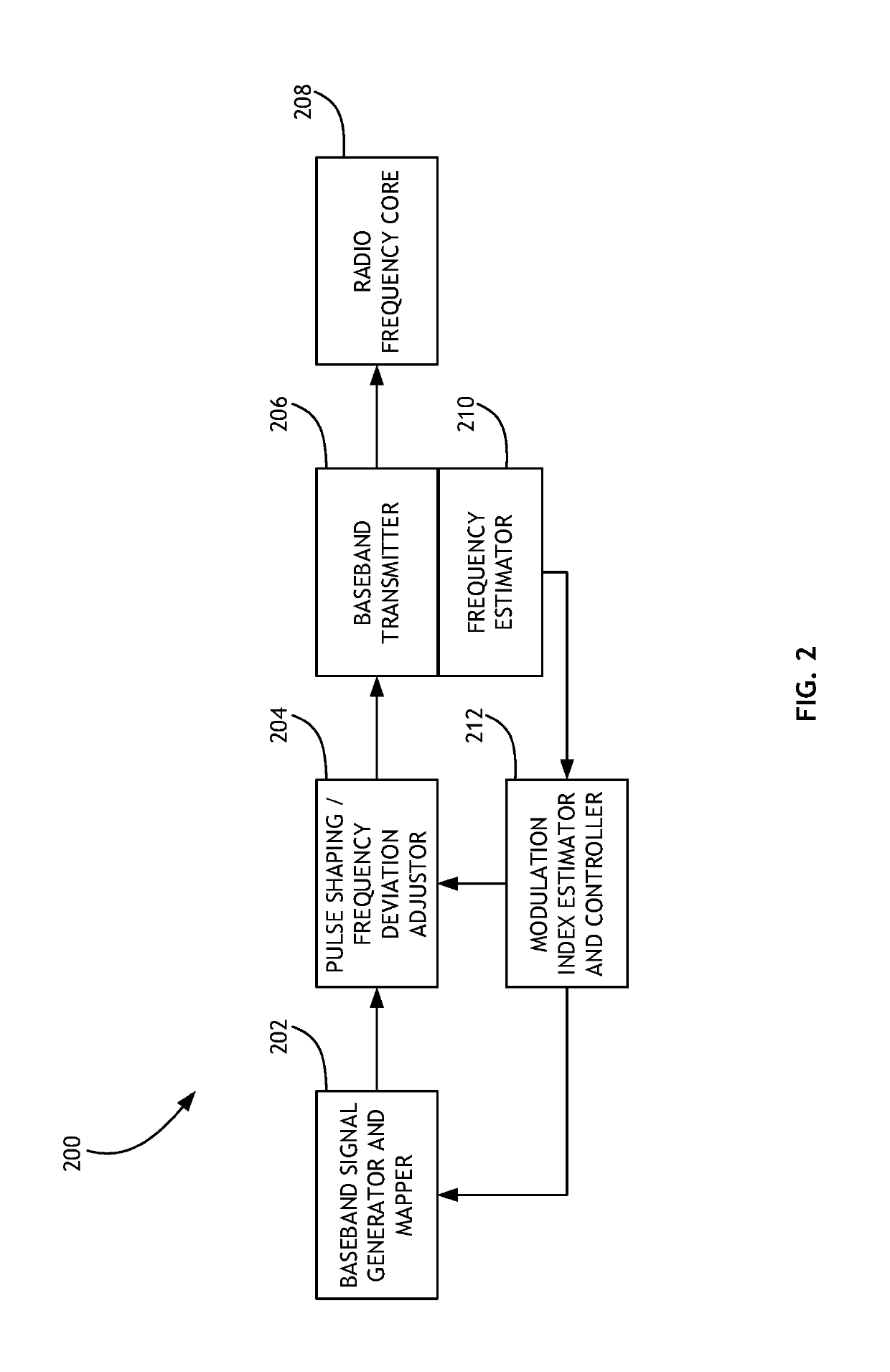
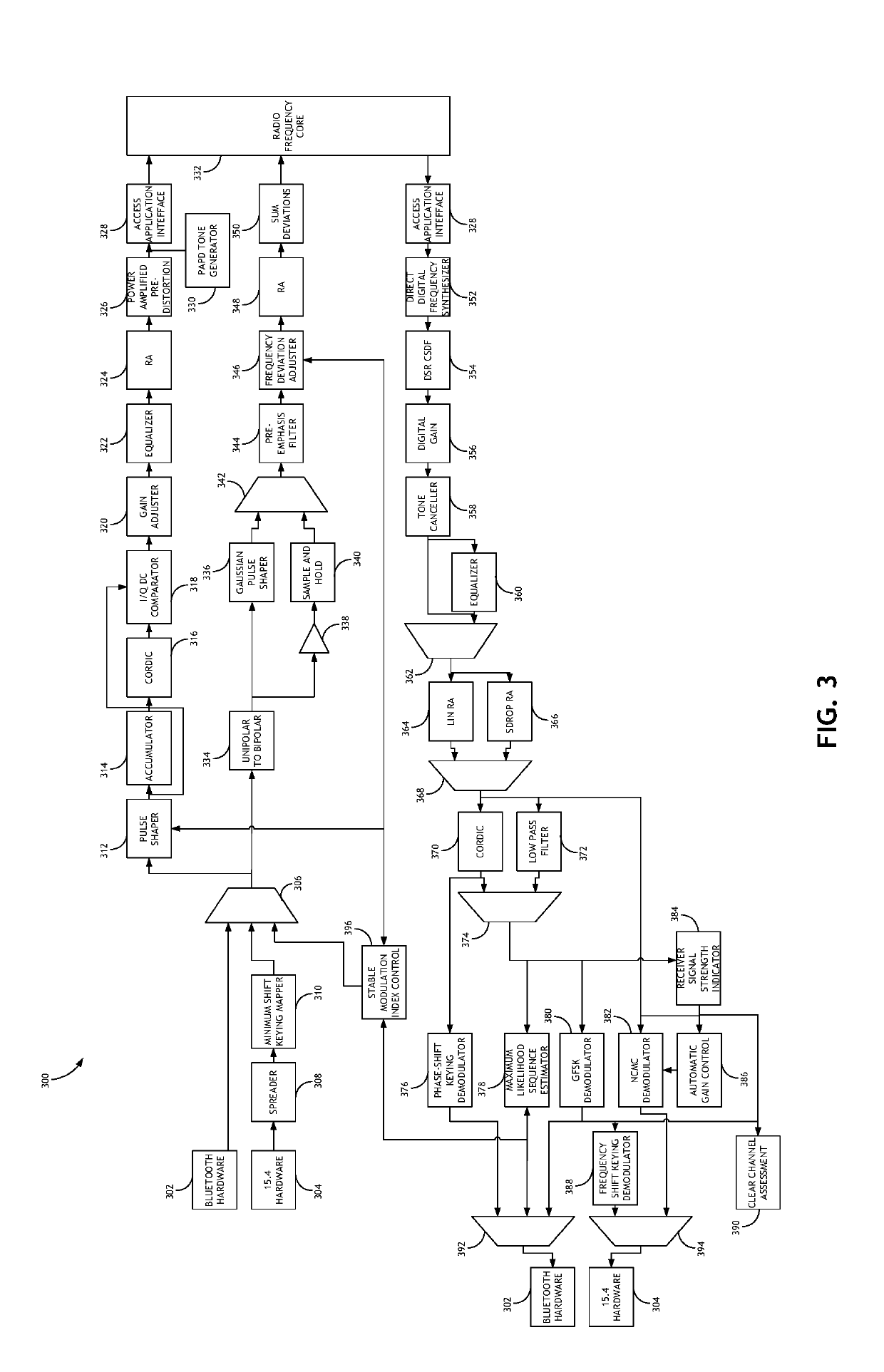
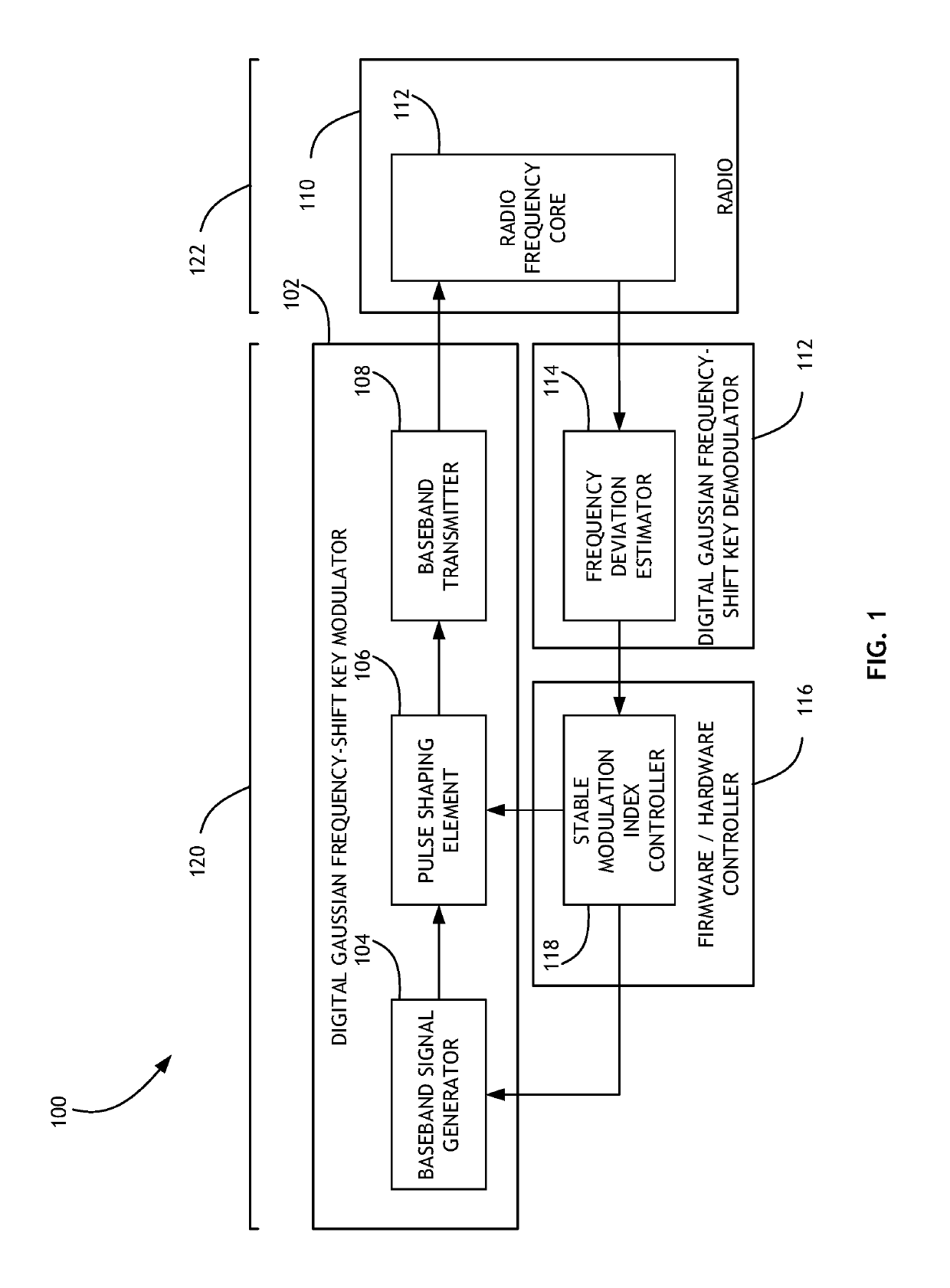
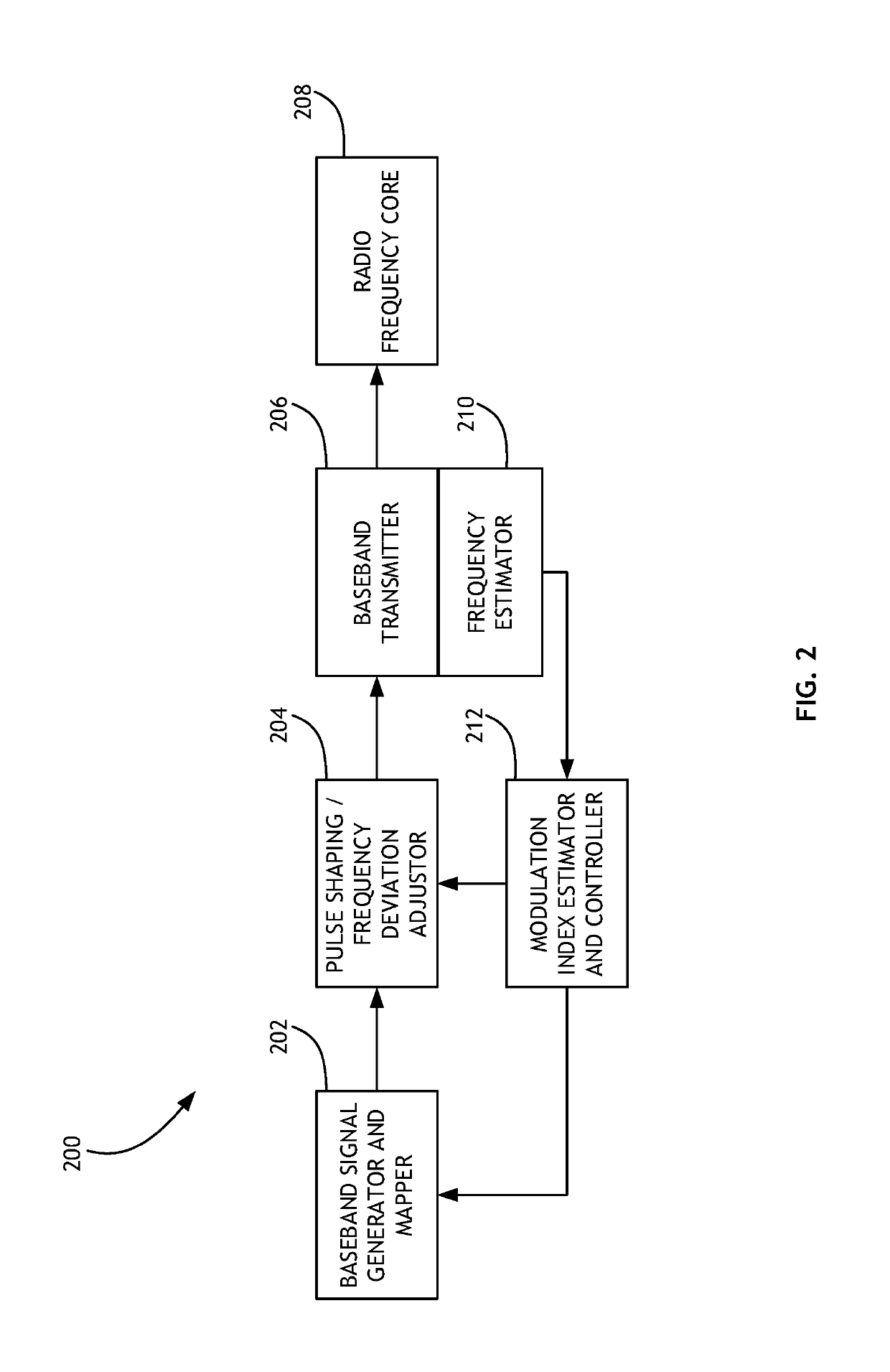
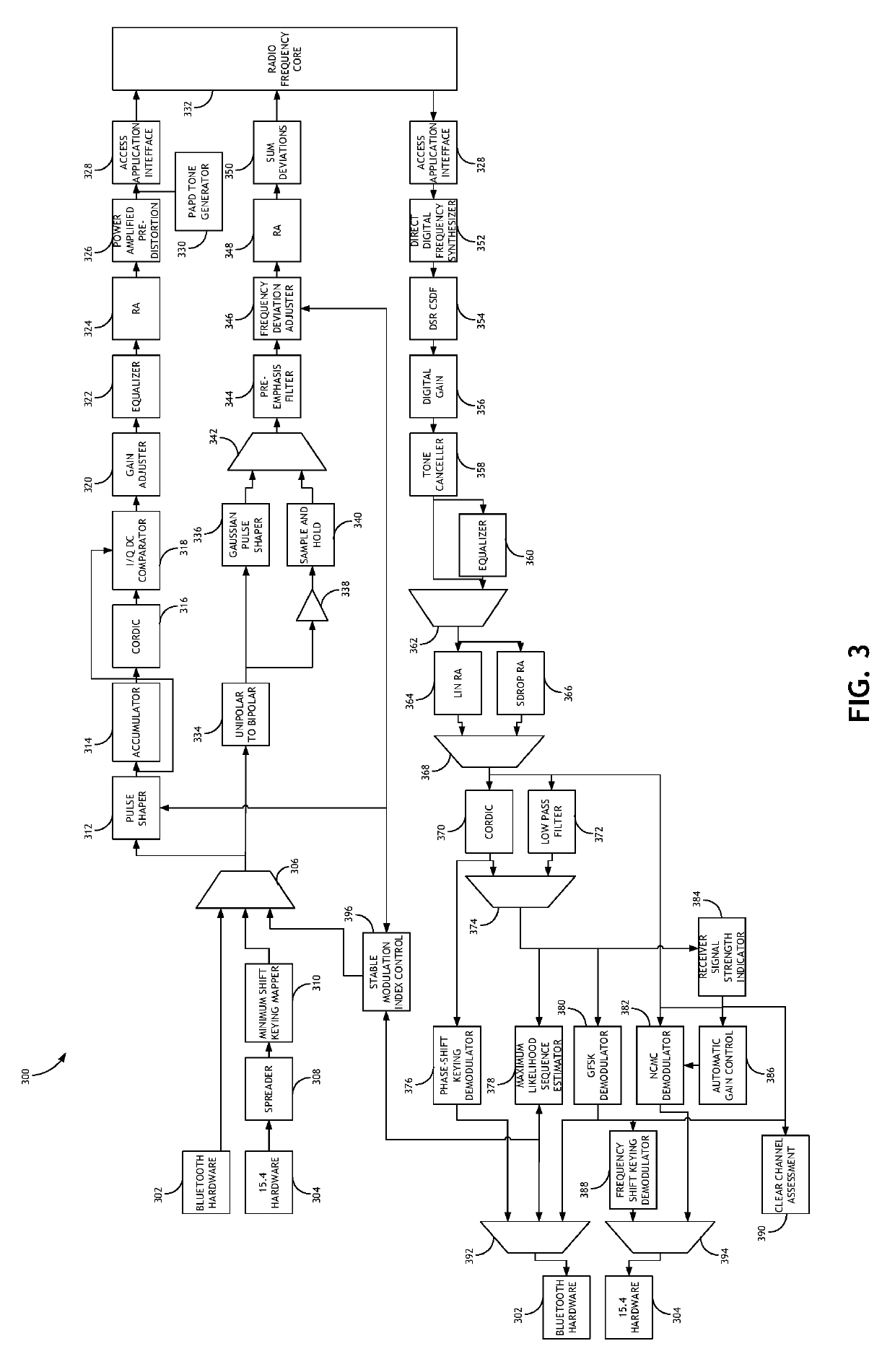
Stable Modulation Index Calibration and Dynamic Control
Calibrating a Gaussian frequency-shift keying modulation index includes generating a training sequence of bits, shaping a pulse from the training sequence according to an initial modulation index, and converting the shaped signal to a transmission signal. The transmission signal is then either looped through a radio frequency core or processed by frequency deviation estimation hardware to determine a frequency deviation. The frequency deviation is converted to a new modulation index, and potentially a ratio between a target modulation index and a measured modulation index as a scaling factor. The process is then iteratively repeated until a threshold frequency deviation is achieved.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Apparatus and method for receiving signal in communication system supporting gaussian frequency shift keying modulation scheme
ActiveUS20150280951A1Reduce processLower implementationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsAngle demodulationCommunications systemEngineering
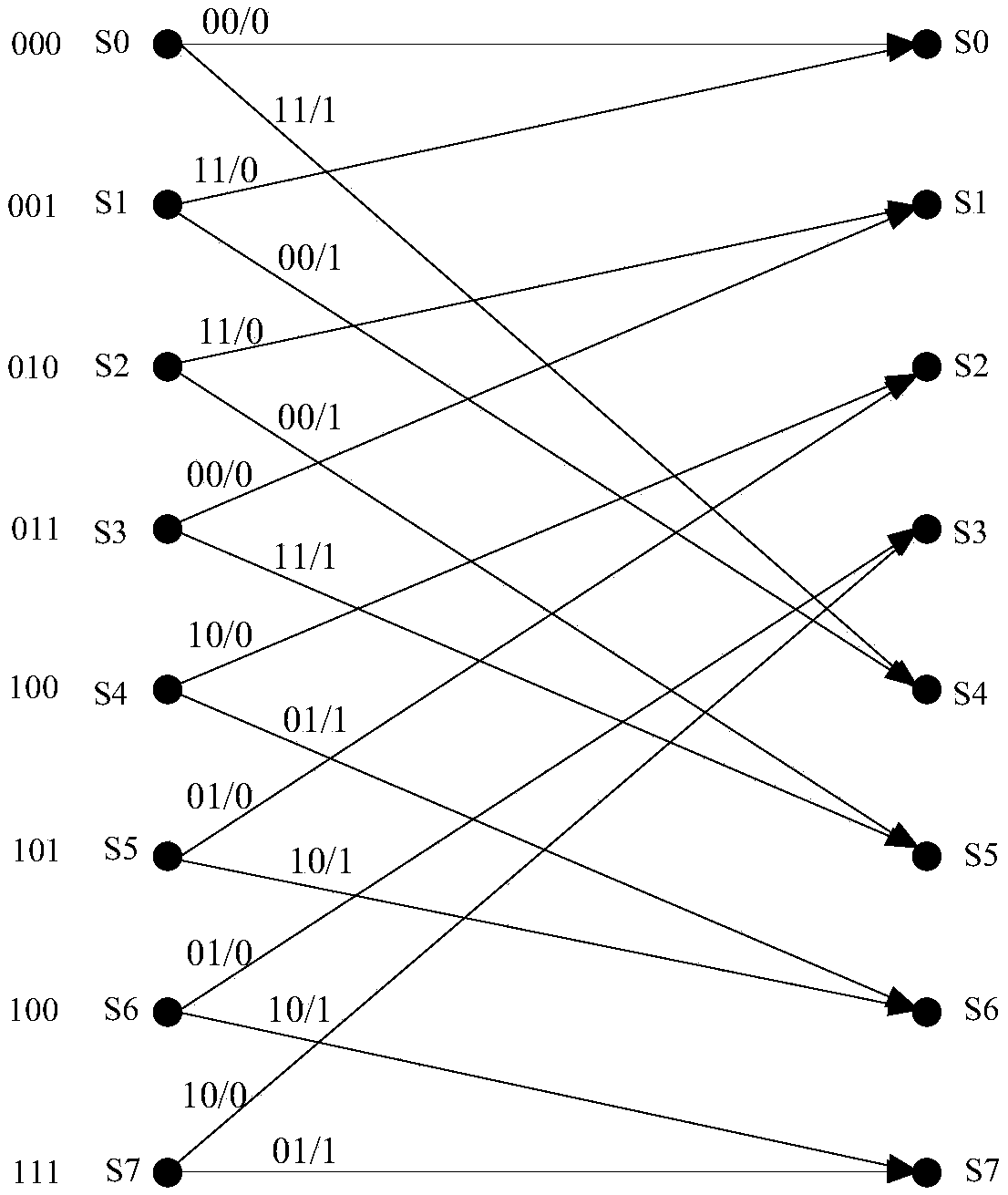
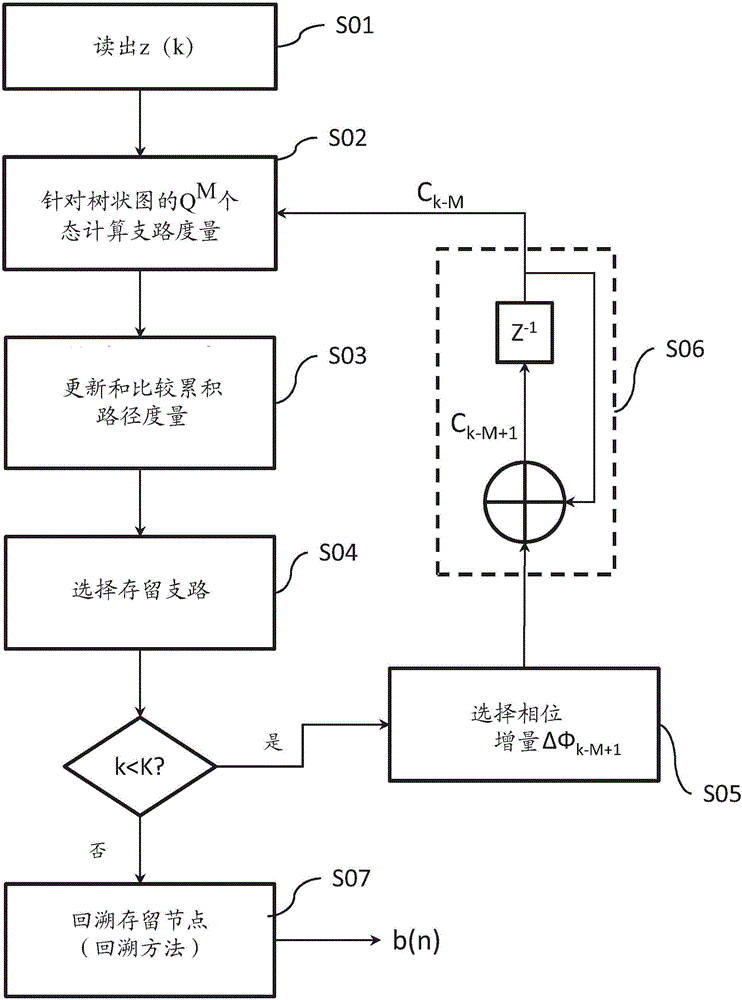
An apparatus and a method are provided for receiving a signal in a communication system supporting a Gaussian frequency shift keying (GFSK) modulation scheme. The method includes receiving the signal; and estimating a codeword vector by performing a signal detecting operation based on a GFSK-maximum likelihood sequence estimation (MLSE) scheme, which is based on a GFSK modulation scheme and an MLSE scheme, on the received signal. States of a Viterbi trellis that are used in the GFSK-MLSE scheme are determined based on the GFSK modulation scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Gaussian frequency shift keying digital demodulator
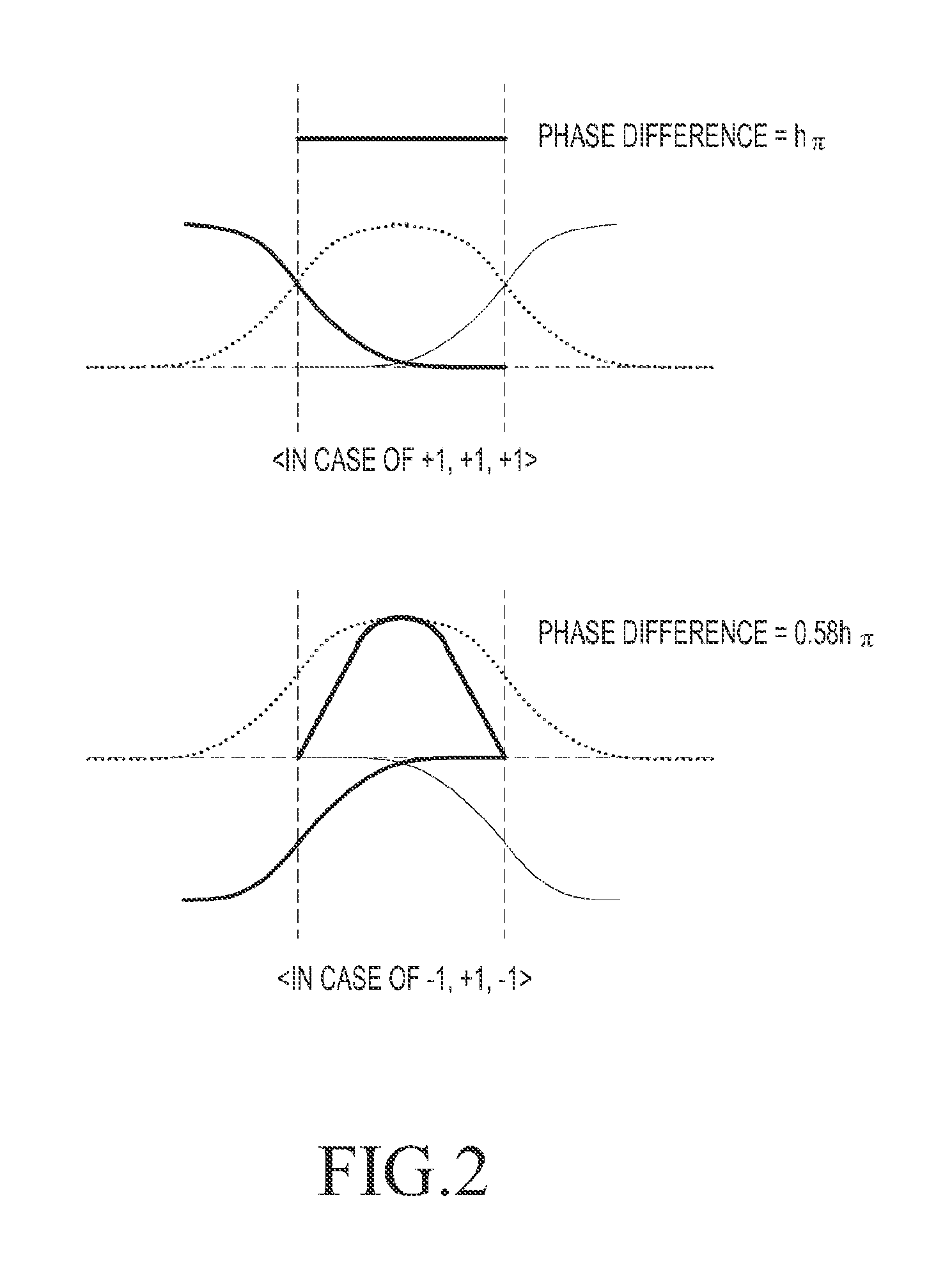
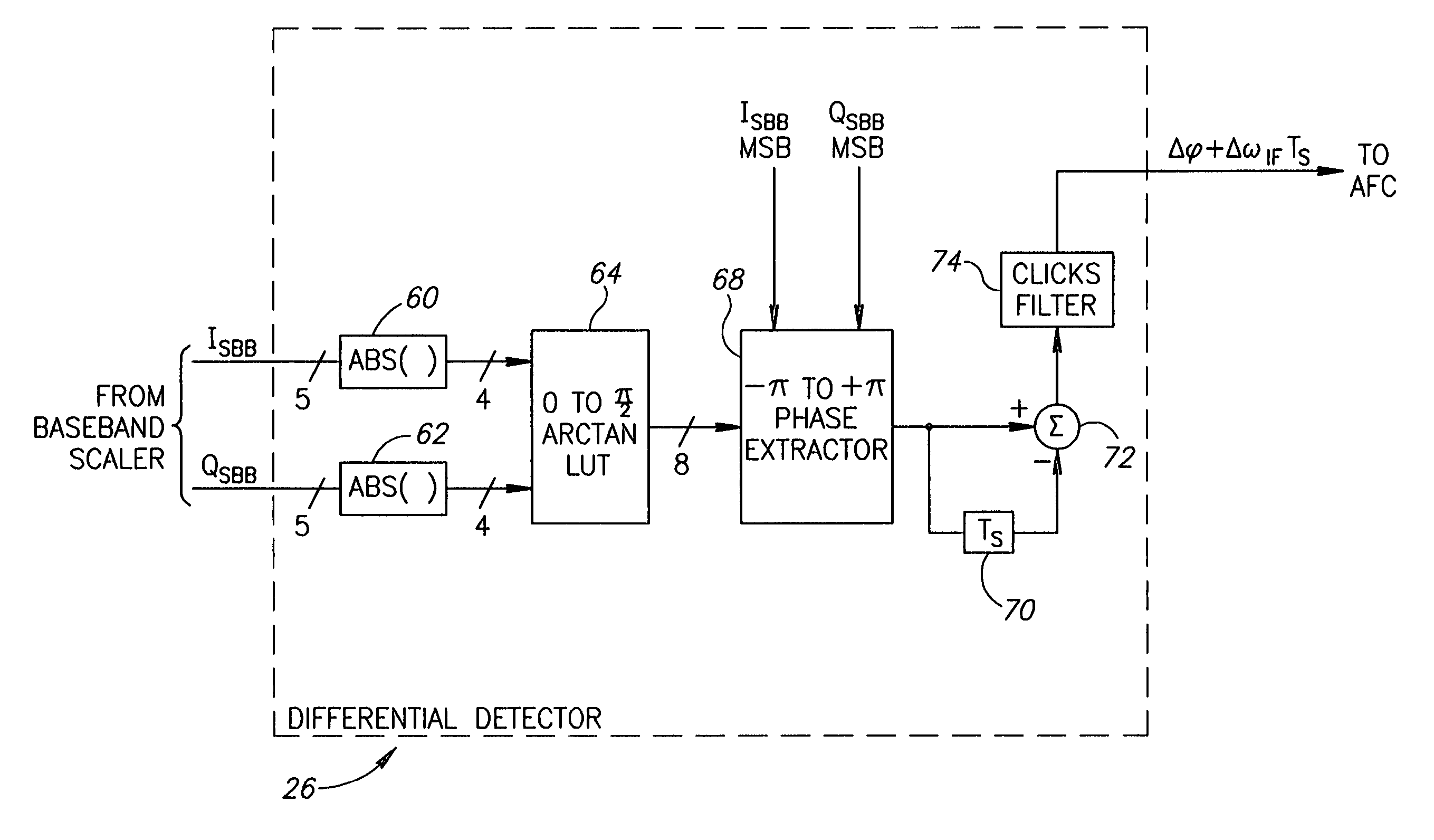
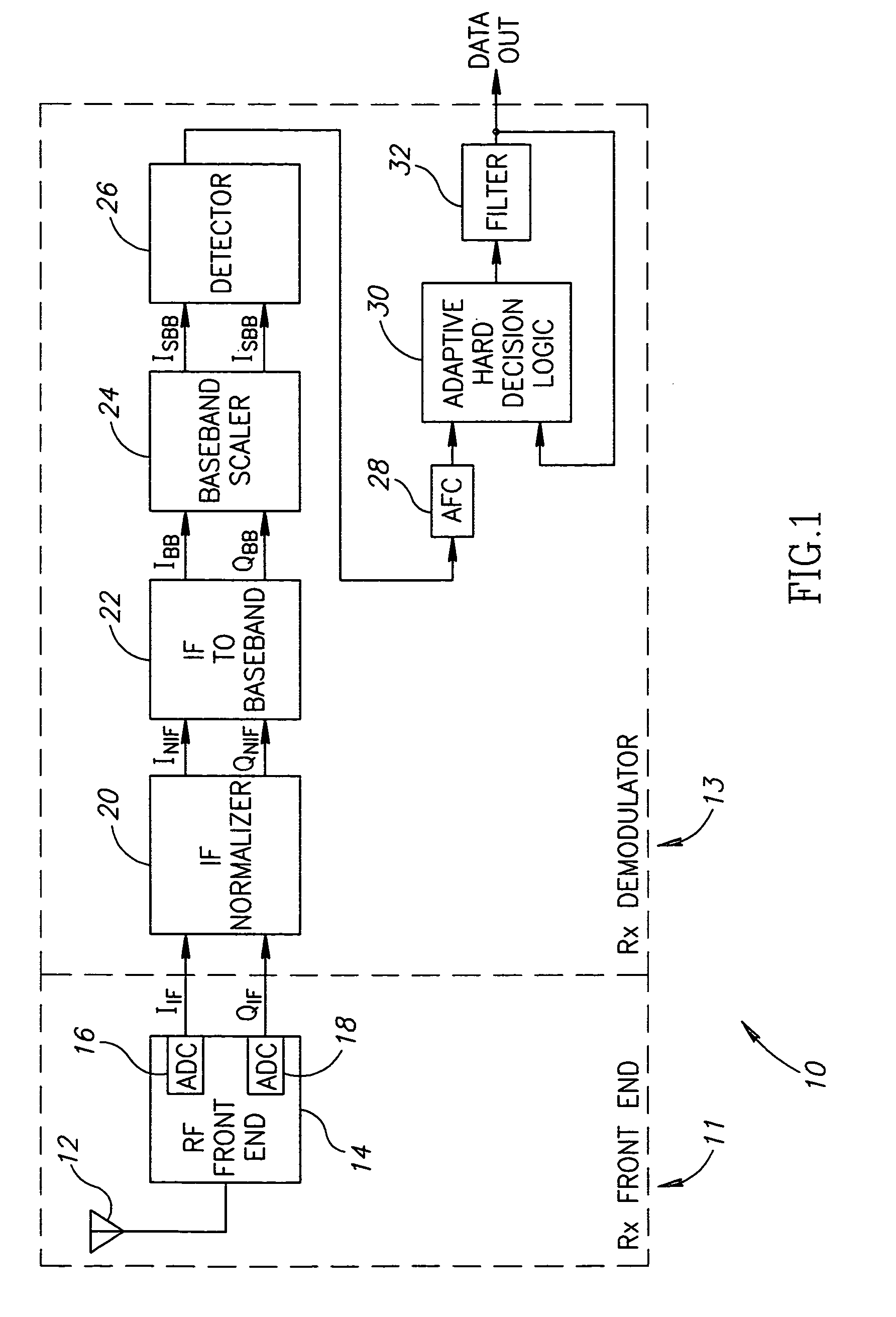
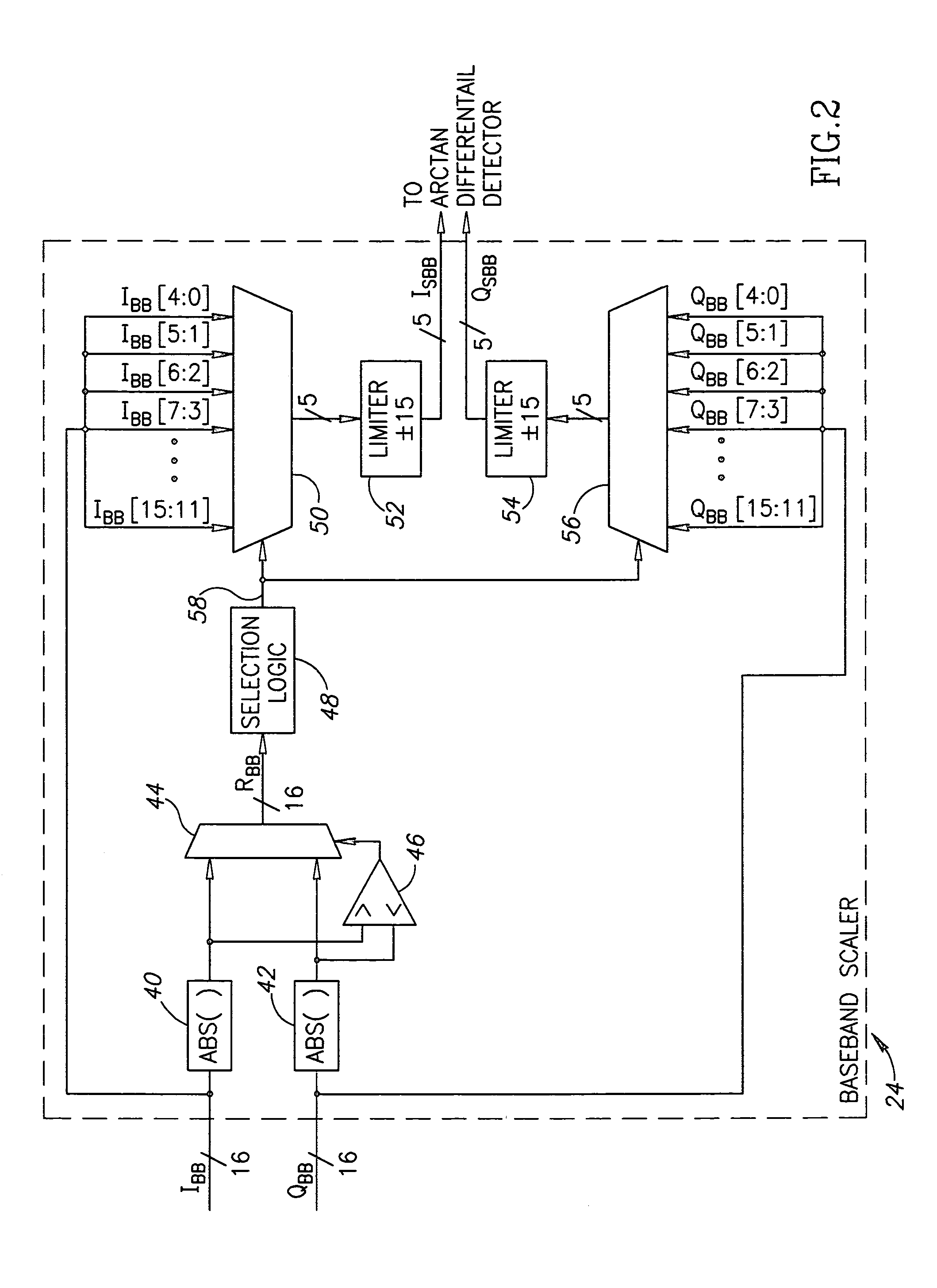
ActiveUS7110477B2Small sizeLow costFrequency-modulated carrier systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsPhase differenceReduced size
A digital demodulator employing a digital differential detection mechanism based on extracting phase differences directly from the I and Q signals after downconversion to zero-IF and image rejection are performed. The phase of the input I and Q signals is determined using the principle that the phase is equivalent to arctan(QI).A lookup table stores the values of the arctan function preferably in a reduced size format. The size of the lookup table can be reduced significantly by storing arctan values for the first quadrant only (i.e. 0 to 90°) and taking advantage of the fact that the phase values for the other three quadrants can be derived from those of the first with some correction applied depending on the signs of the I and Q input samples. Phase extraction logic is provided that is operative to map the phase into the entire 0 to 360° range of phase values (i.e. −π to +π radians) based on the signs of the I and Q signals. The phase difference between a current phase value and the previous phase value is then calculated. It is these phase differences that reflect the frequency deviations present in the transmitted signal which represent the original modulating signal. A ‘click’ removal filter circuit is provided to remove the discontinuities in the phase difference output that occur when the 2π radians value is crossed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Stable modulation index calibration and dynamic control
Calibrating a Gaussian frequency-shift keying modulation index includes generating a training sequence of bits, shaping a pulse from the training sequence according to an initial modulation index, and converting the shaped signal to a transmission signal. The transmission signal is then either looped through a radio frequency core or processed by frequency deviation estimation hardware to determine a frequency deviation. The frequency deviation is converted to a new modulation index, and potentially a ratio between a target modulation index and a measured modulation index as a scaling factor. The process is then iteratively repeated until a threshold frequency deviation is achieved.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Chirp-GFSK combined spectrum spreading modulation and demodulation system
ActiveCN109547059AReduce complexityReduce sync timeFrequency-modulated carrier systemsRadio frequencyChirp
The invention discloses a Chirp-GFSK combined spectrum spreading modulation and demodulation system, and relates to the technical field of wireless communication. The system comprises a radio frequency part, a baseband modulator and a baseband demodulator; the baseband modulator comprises a data modulator, a frame synchronization header generator and a data frame forming module; and the data demodulator comprises a whitening module, a spectrum spreading module and a GFSK modulation module. At a transmitter, the system dynamically generates and sends a Chirp waveform to serve as a frame synchronization signal according to a GFSK spectrum spreading mode, and then data is sent by the GFSK modulation module; and at a receiver, a symbol and a frequency deviation of the signal in the channel transmission are estimated according to the frame synchronization signal Chirp by adopting a multi-threshold synchronization algorithm, a spectrum spreading GFSK signal is subjected to GFSK demodulationand signal dispreading after the frequency deviation of spectrum spreading GFSK is compensated, and a sending signal is obtained through recovery. According to the system, the advantages of the Chirpmodulation and the advantages of the spectrum spreading GFSK modulation signal are integrated, the complexity of signal synchronization is reduced, the synchronization time of a weak signal is shortened, the channel symbol and frequency deviation are overcome, and the signal demodulation complexity is reduced while low power consumption is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI PANCHIP MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
GFSK digital double-channel demodulation method
ActiveCN106603454AReduce occupancyCarrier regulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsFast Fourier transformProcessor register
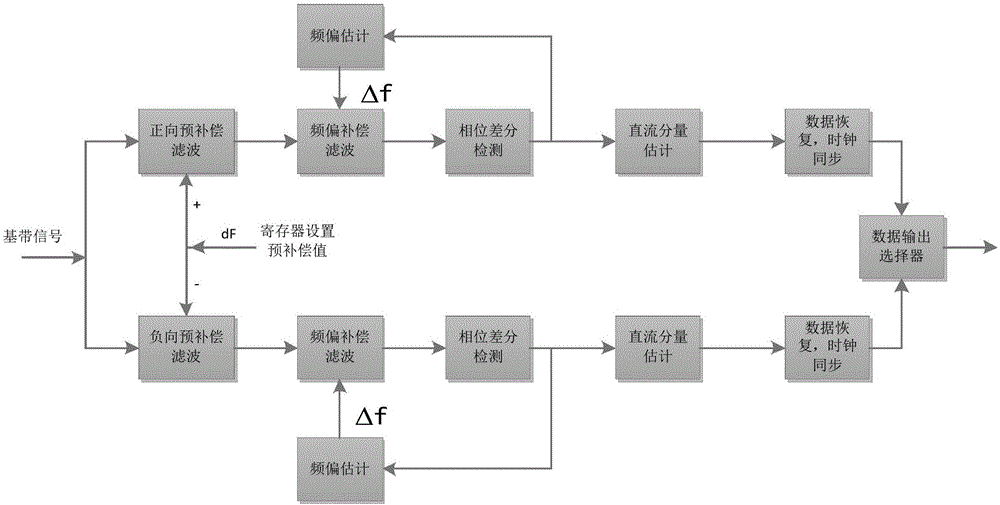
The invention discloses a GFSK (Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying) digital double-channel demodulation method. The method comprises the following steps: enabling baseband signals to pass through a positive pre-compensation filter module and a negative pre-compensation filter module respectively at the same time, setting a pre-compensation value by a register and setting different pre-compensation values dF according to a carrier offset range tolerable for a system; performing pre-compensation filtering on the baseband signals respectively, then performing precise estimation on signal frequency deviations, and then performing compensation filtering; then, performing differential operation to obtain a result which refers to enveloping of modulation signals of a transmitting terminal; after phase differentiation, enabling the baseband signals to pass through a module without direct-current components; processing input signals by a data recovery clock synchronization module to generate serial bit decoding output and also generate a corresponding clock signal to ensure that a latter stage can make use of the clock signal directly to perform sampling processing on bit signals; and then selecting to output which path of signals according to the quality of leading signals by a number follower. The GFSK digital double-channel demodulation method not only achieves utilization of the demodulation performance of an FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) module, but also occupies less hardware resources, and is easy to implement.
Owner:CHINA GRIDCOM +2
Bluetooth signal frame synchronous detection method for wireless general measuring instrument
ActiveCN105657739ARealize synchronous detectionGuaranteed synchronization accuracyModulated-carrier systemsWireless commuication servicesMeasuring instrumentSynchronous detection
The invention provides a Bluetooth signal frame synchronous detection method for a wireless general measuring instrument. The method comprises the following steps: step S1, inputting a signal; step S2, coarsely synchronizing frame power judgment; step S3, calculating a phase angle; step 4, differentiating; step S5, filtering; step S6, eliminating an initial frequency offset, and obtaining a sequence f (n); step S7, an initial position is n, and the length of each symbol is Ts, and performing a GFSK (Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying) demodulation judgment on every 5 GFSK symbols; step S8, if ''10101'' or ''01010'' is found, then entering the next step; and if ''10101'' or ''01010'' is not found, then n=n+1 and returning to step S7; and step S9, taking points from (n+(1 / 3) *Ts) to (n+(2 / 3) *Ts) as initial points, and orderly performing a sliding judgment on 5 symbols. The Bluetooth signal frame synchronous detection method for the wireless general measuring instrument provided by the invention has the following beneficial effects: Bluetooth signal frame synchronous detection of the wireless general measuring instrument can be realized, an MAC address is not depended, and certain synchronization accuracy can be guaranteed.
Owner:深圳市极致汇仪科技有限公司
Low complexity, high performance GFSK signal multi-bit demodulation method
ActiveCN101047677AReduce complexityImprove performanceFrequency-modulated carrier systemsModem devicePhase change
This invention provides a simple and high performance multi-bit demodulation method for GFSK signals including the following steps: 1, converting the frequency change form when modulating to a phase change form, 2, using the DPSK modem method in the GFSK demodulation, 3, making parameters concrete to carry out iterative judgment to get the demodulation resut.
Owner:豪威国际控股有限公司
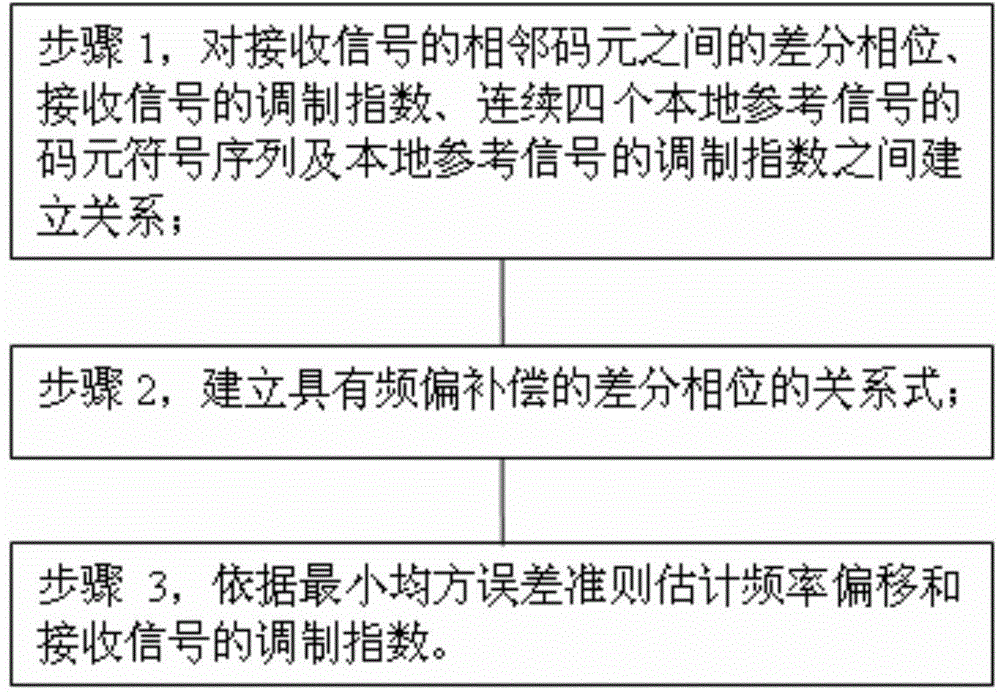
Method and system for estimating modulation index and frequency offset
ActiveCN105827551AFrequency-modulated carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksDifferential phaseElectronic communication
The invention relates to the technical field of electronic communication, and particularly relates to a method for estimating a modulation index and frequency offset. The method is applied to a Bluetooth wireless receiving system and comprises the steps of S1, establishing an operation relation among a differential phase delta theta<ndiff> between adjacent code elements of received signals, a modulation index h of the received signals, a code element symbol sequence I<n-1>, In, I<n+1>, I<n+2> of four successive local reference signals, and a modulation index h0 of the local reference signals, S2, establishing a relation expression provided with a differential phase with frequency offset compensation, wherein the relation expression is as follows: delta theta<n>=delta phi+delta theta<ndiff>, delta theta<n> is the differential phase with frequency offset compensation, and delta phi is frequency offset of the received signals, and S3, estimating the frequency offset and the modulation index of the received signals according to a minimum mean square error criterion. The method provided by the invention realizes simultaneous estimation for the modulation index and the frequency offset through establishing the relation between the modulation index and the differential phase, and is suitable for signal estimation of the Bluetooth basic data rate and frequency offset and modulation index estimation of other GFSK (Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying) signals.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
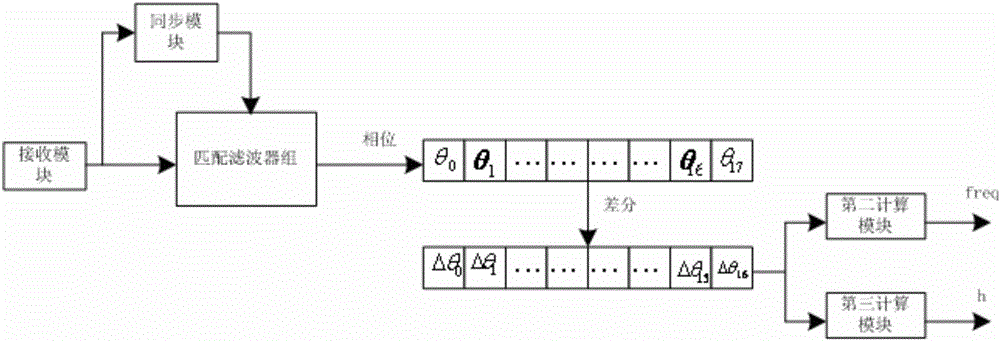
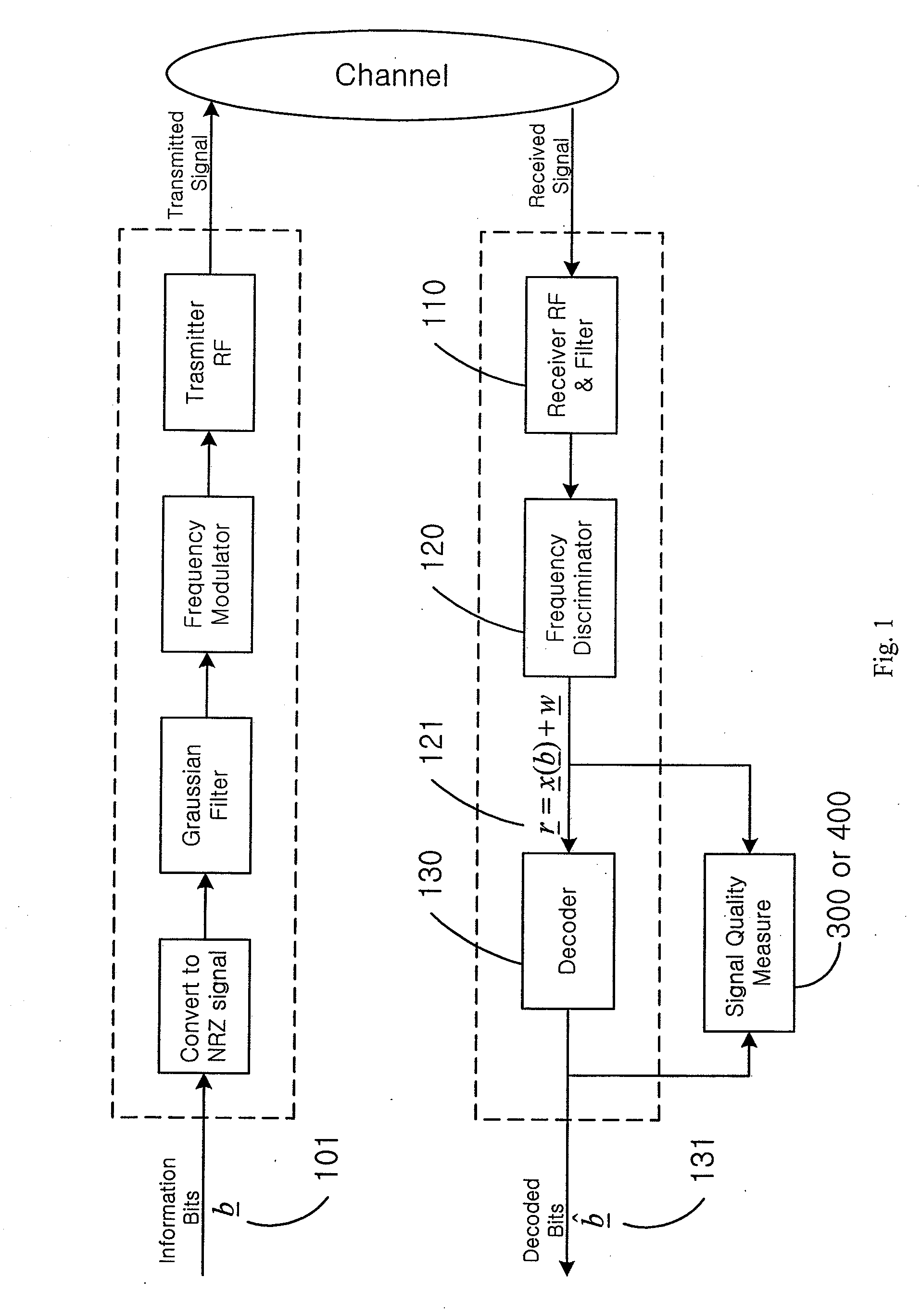
Apparatus and method for signal quality measurement on gfsk signals
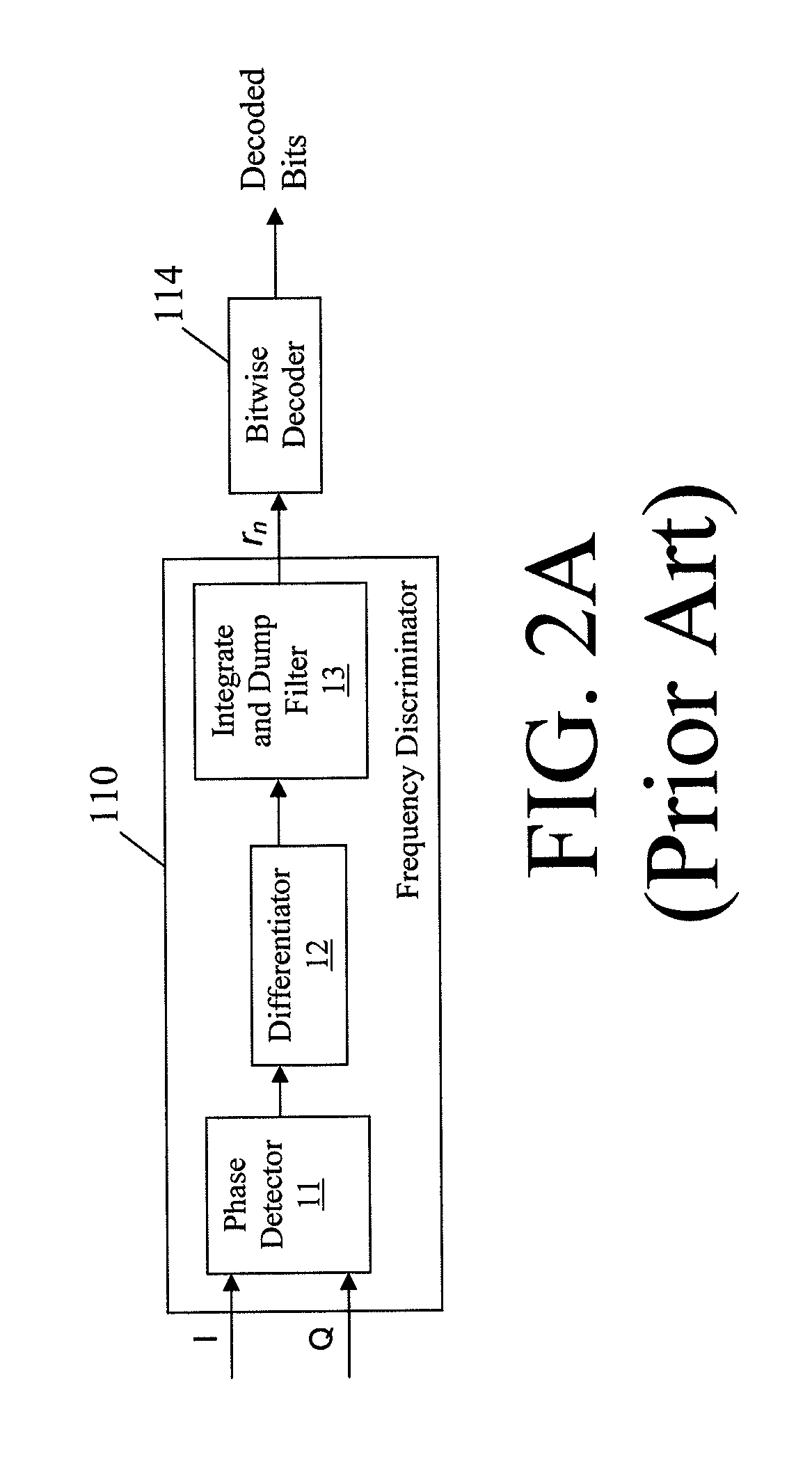
ActiveUS20110090944A1Accurately indexedNoise power become accurate and reliableDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionFrequency-modulated carrier systemsDiscriminatorSignal quality
The present invention discloses an effective apparatus and method to measure the received signal quality for a GFSK modulated signal with (or without) an unknown modulation index. The signal quality measurements are based on the decoded (unknown or known) bits and the trellis of the frequency discriminator output. This trellis is pre-calibrated with a reference Rx. The transmitted modulation index is also accurately estimated in this invention.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
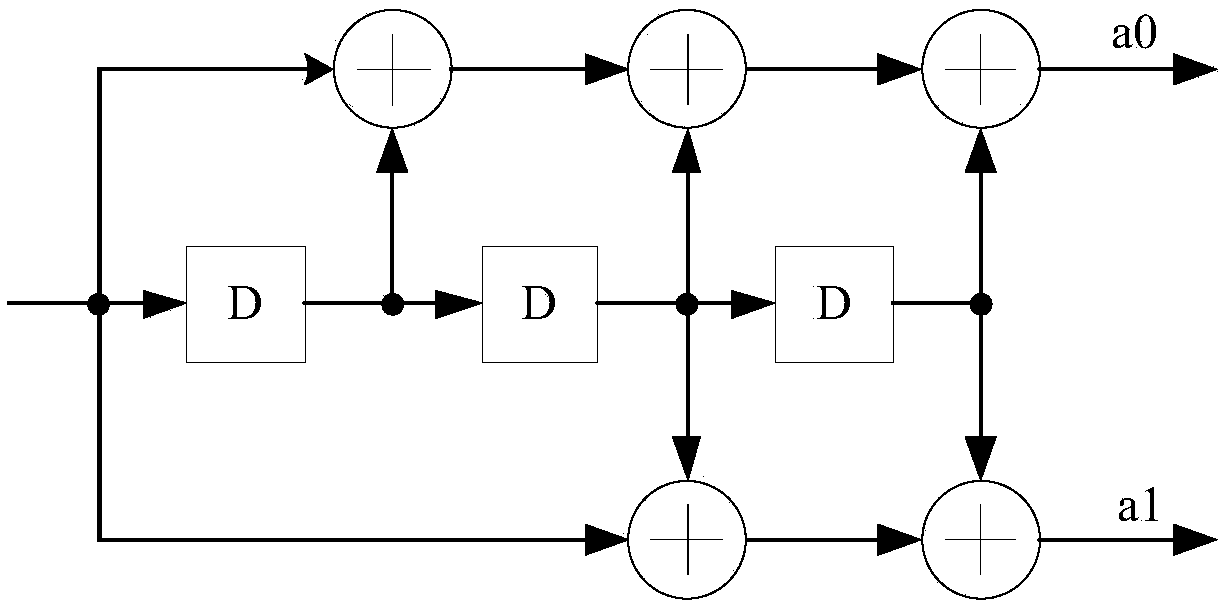
Joint demodulation and decoding method for convolutionally encoded Gaussian frequency shift keying (GFSK) signals
ActiveCN108881088ASimple calculationReduce complexityError correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionComputation complexitySignal on
The invention, which relates to the field of wireless communication technologies, discloses a joint demodulation and decoding method for convolutionally encoded Gaussian frequency shift keying (GFSK)signals. Approximating processing is carried out on phases of GFSK signals and the phase interference between adjacent symbols is neglected, so that the path metric calculation is simplified and thusthe computational complexity of the path metric is reduced. According to a grid diagram of a convolutional code, a path metric of each surviving path is calculated based on a surviving path processingmethod. For each surviving path, one path metric and a coded sequence sum corresponding to the surviving path are kept, wherein the coded sequence sum is used for constructing a transmitting GFSK signal on the branch; correlation values a received signal and a corresponding transmitted signal on the branch are calculated to obtain a branch metric of the branch. With the joint demodulation and decoding method provided by the invention, the coded gain of the convolutional code is realized; and compared with the GFSK signal hard decision separation demodulation and decoding method, the joint demodulation and decoding method has the obvious performance gain.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Method and device for demodulating GFSK-modulated signals with Q states
ActiveCN104904171AFrequency-modulated carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksLinear filterComputer science
The invention relates to a method for demodulating and decoding at least one received signal modulated with Q states by means of Gaussian frequency-shift keying, said signal being received from a communication channel and comprising a message consisting of message symbols, said method being characterised in that, in order to determine a message symbol: a plurality of possible phase increments are estimated by the application of a linear filter to a plurality of sequences of M products of modulation with Q states by phase-shifting of possible consecutive message symbols; the cumulated phase of the preceding iterations of the method is added to each of said possible phase increments in order to provide an estimated phase; and the message symbol is determined by selecting possible consecutive symbols of which the estimated phase is the closest to the received signal.
Owner:SAGEM DEFENSE SECURITE SA
Low-voltage transformer area topology identification method based on PWM characteristic modulation current
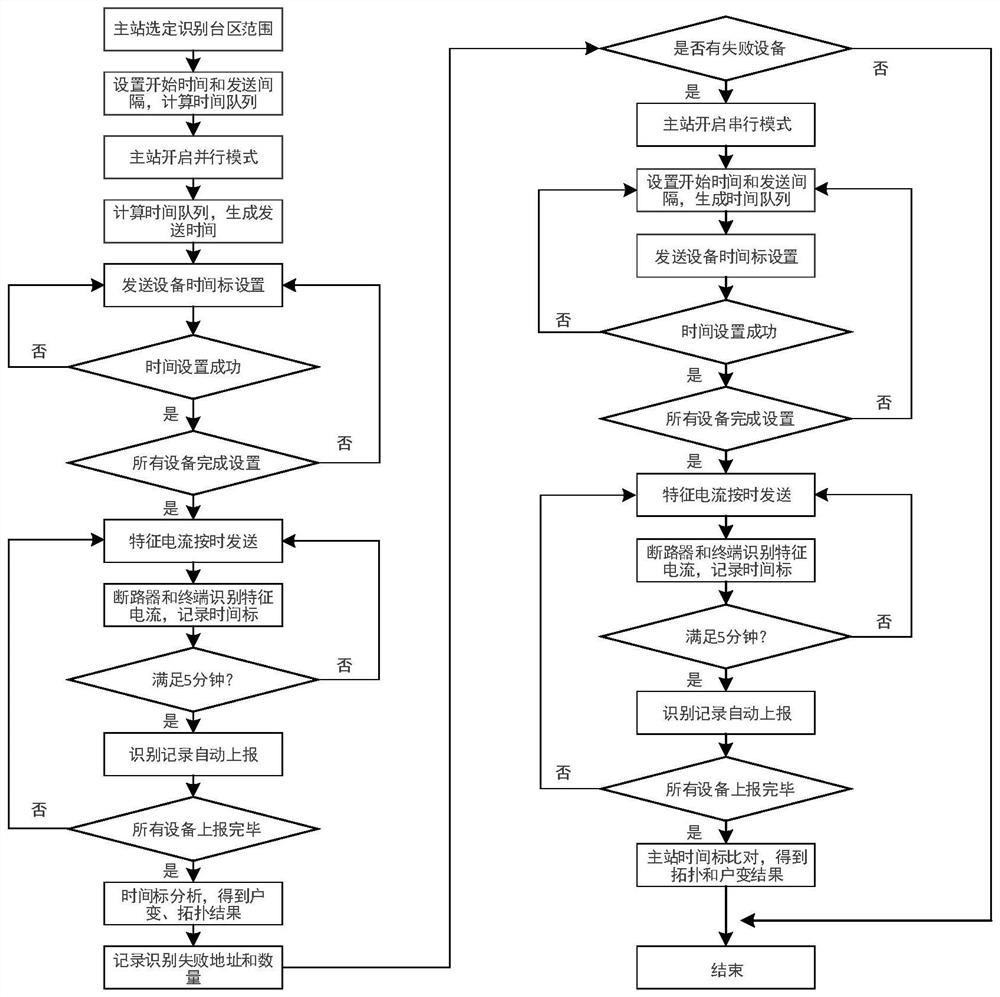
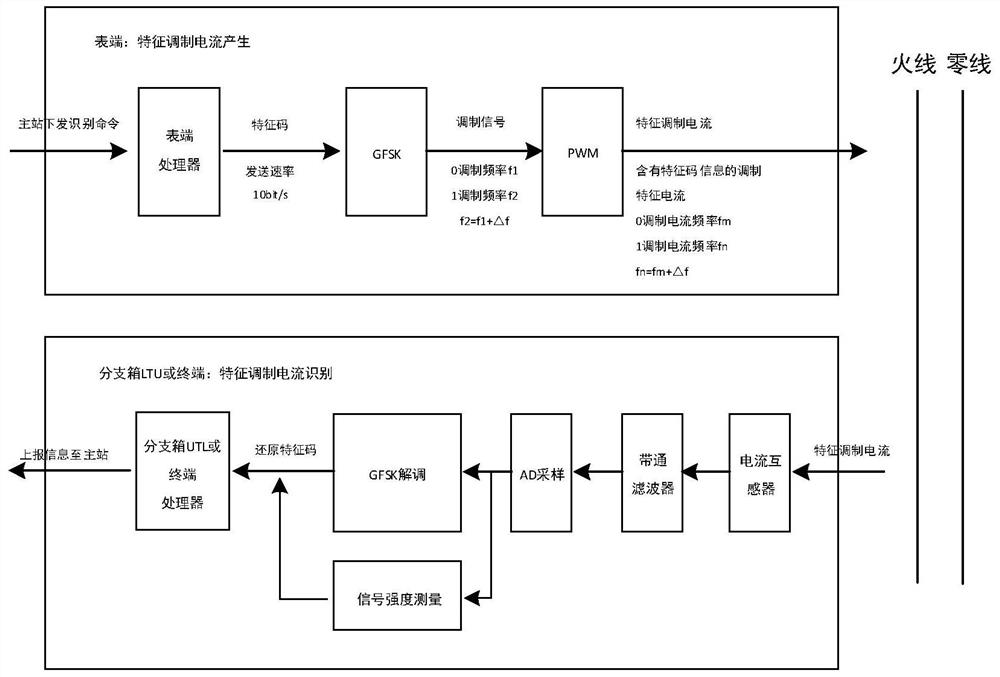
PendingCN113471967AImprove accuracyGood Spectrum Identification FeaturesElectrical testingSustainable buildingsTopology identificationFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a low-voltage transformer area topology identification method based on PWM characteristic modulation current. The method comprises the steps that a transformer area master station sends an identification command to each device in a transformer area, generates a characteristic identification code at each device, carries out the Gaussian frequency shift keying modulation of the characteristic identification code, generates a GFSK signal, carries out the pulse width modulation processing, and outputs the characteristic modulation current to the line; the line current signal is received and demodulated through related devices in the transformer area so as to restore the characteristic identification code, and the size, phase and time mark of the identified line current signal are recorded and reported to the master station; and the master station is used for drawing the physical topology of the line according to the identification information. According to the method, the processing mode of combining Gaussian frequency shift keying modulation and pulse width modulation is utilized, the characteristic modulation current with good spectrum identification characteristics and good transmission characteristics can be generated, the device can identify and capture the characteristic modulation current more easily, the accuracy of signal acquisition is high, and therefore the accuracy of topology identification is improved.
Owner:SPL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
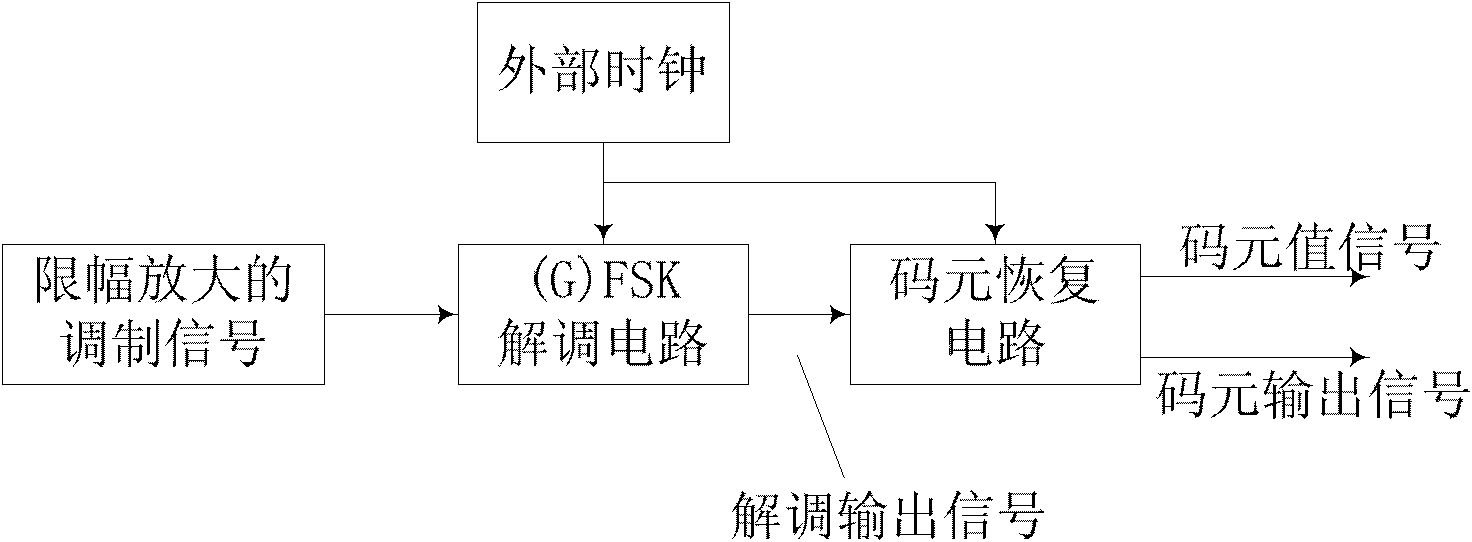
(Gauss) frequency shift keying ((G)FSK) digital demodulation device and method
InactiveCN102075470AEffective recoveryRestore resistanceFrequency-modulated carrier systemsIntermediate frequencyCoded element
The invention discloses a frequency shift keying (FSK) or a Gauss frequency shift keying (GFSK) digital demodulation device and method. The device comprises an FSK or GFSK demodulation circuit and a code element recovery circuit, wherein the FSK or GFSK demodulation circuit is used for detecting the intermediate frequency of a modulation signal so as to demodulate the modulation signal by adopting proper intermediate frequency, and outputting a demodulation result; and the code element recovery circuit is used for counting positions of a rising edge and a falling edge of the demodulated signal output by the FSK or GFSK demodulation circuit, searching for an initial position of a proper single code element and outputting an accurate code element. The FSK or GFSK digital demodulation device and the FSK or GFSK digital demodulation method have the advantages that: a bit error rate is low, and the parameter setting of a scheme is regulated according to different frequency shift tolerances so as to achieve simple structure and high flexibility; the code element can be effectively recovered and the offset of an external clock can be resisted; and only a digital circuit is adopted so as to achieve low cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
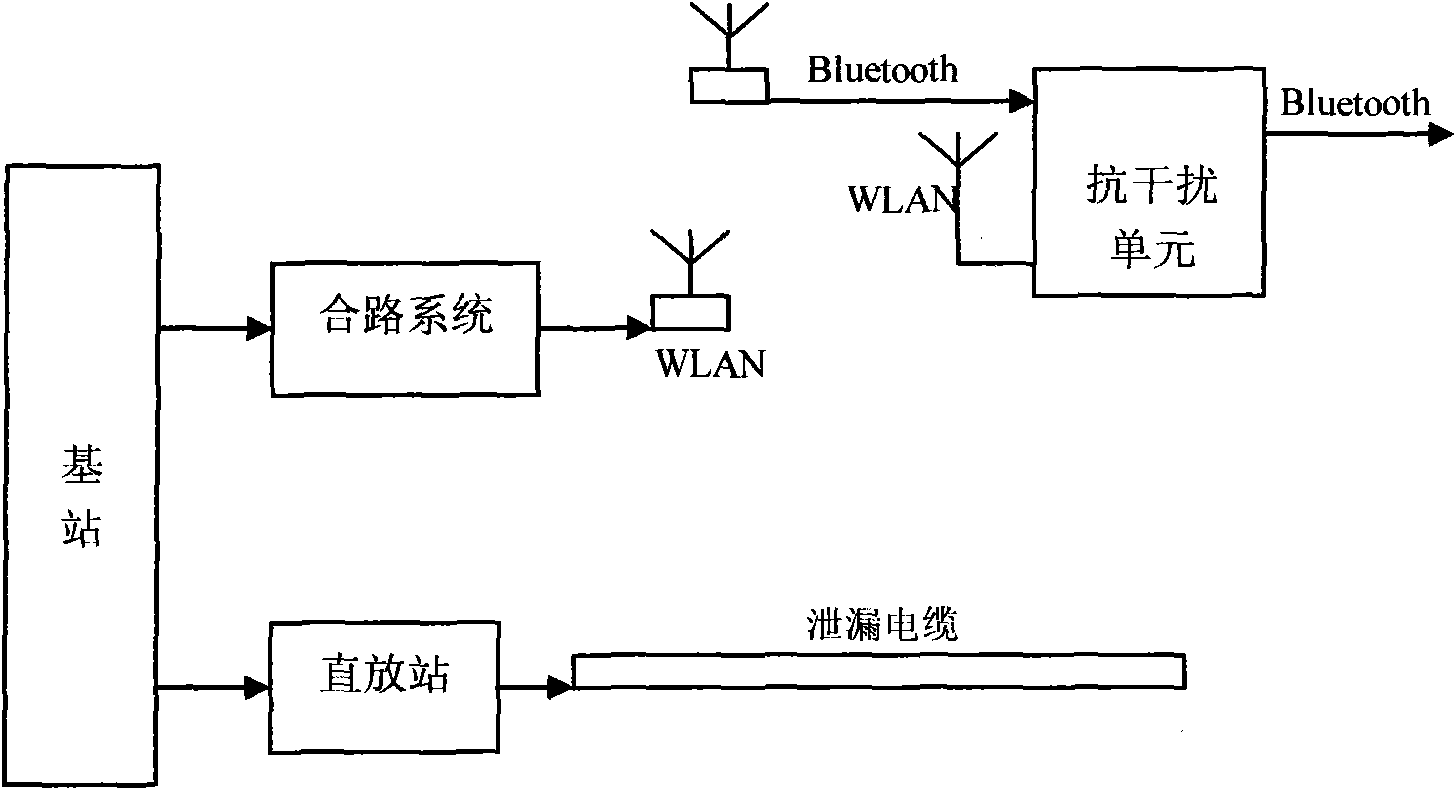
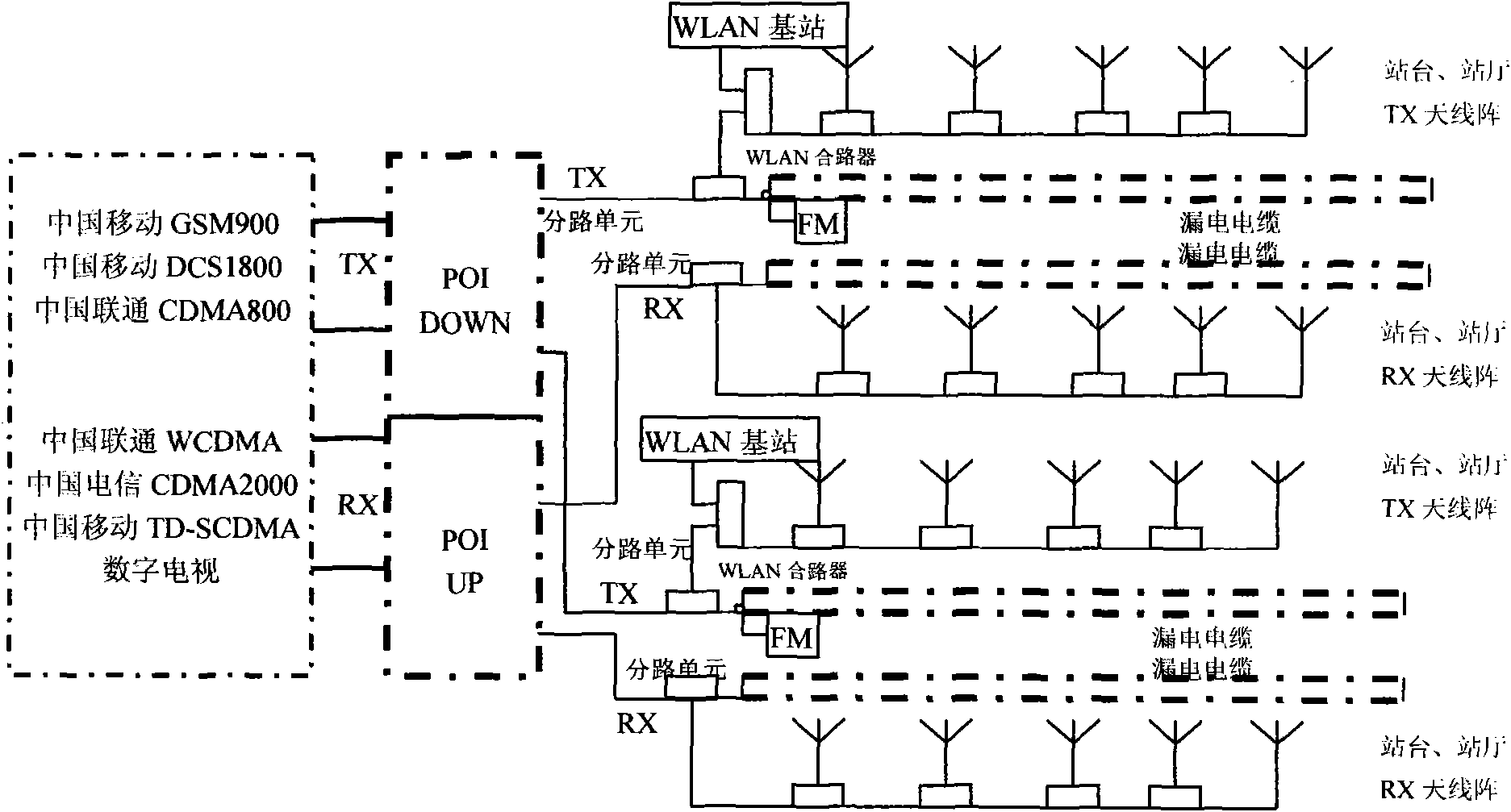
Novel wireless mobile communication combining coverage system and method
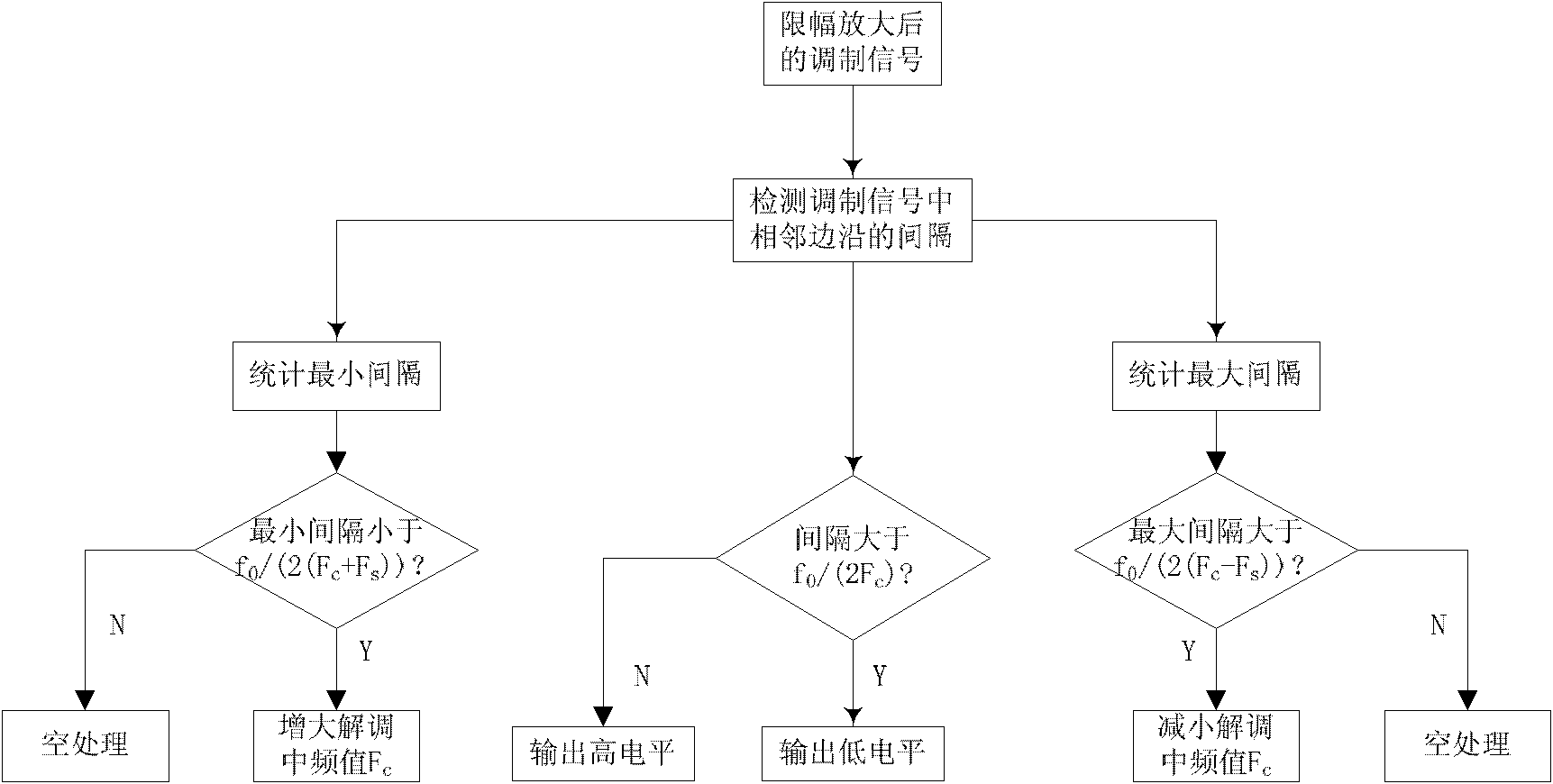
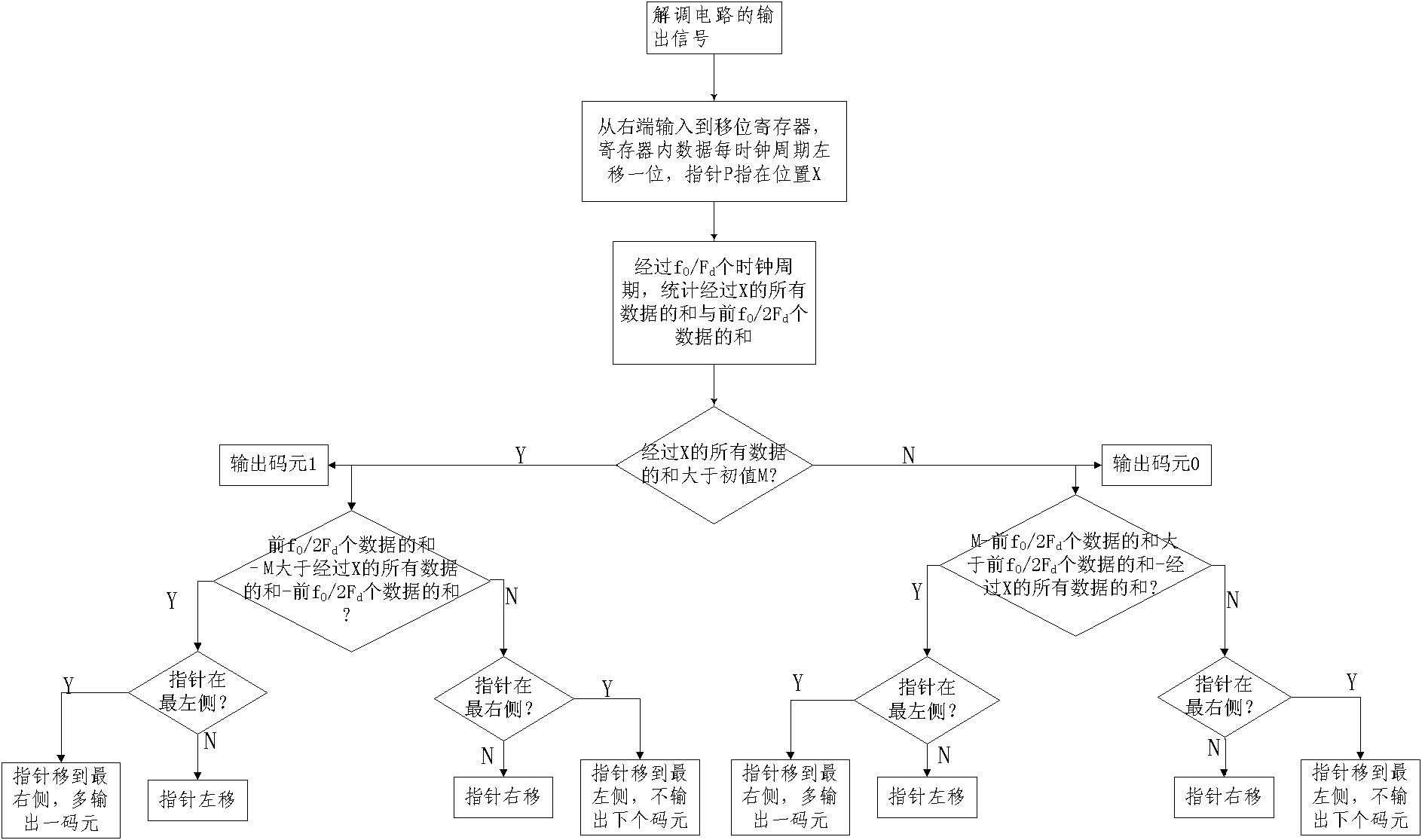
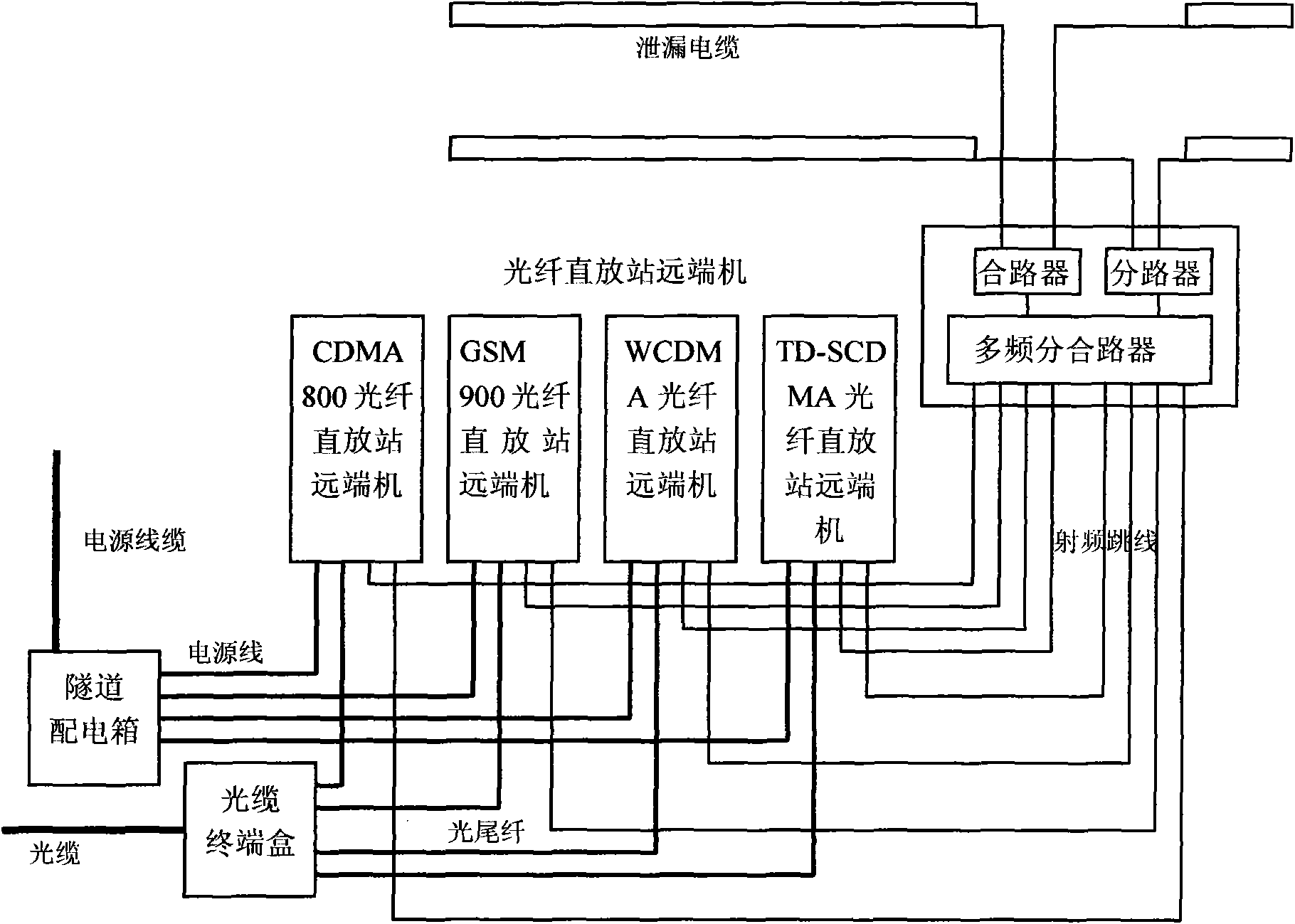
The invention relates to novel wireless mobile communication combining coverage system and method. The system comprises a combining system, a repeater and an anti-interference unit, wherein the combining system consists of an upstream signal combining platform and a downstream signal combining platform, wherein the upstream signal combining platform comprises a detection module and an upstream combiner, and the downstream signal combining platform comprises the detection module, a PHS / WCDMA (Personal Handy-phone System / Wideband Code Division Multiple Access) module and a downstream combiner; the repeater comprise an downstream repeater remote machine, a multi-band splitter / combiner and a leakage cable; and the anti-interference unit comprises a spread spectrum unit, a modulation unit, an AWGM (Array Waveguide Grate Multiplexer) channel, a frequency shift filter, a GFSK (Gaussian Frequency Shift Key) demodulation unit, an FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) de-spread unit, an integral unit and a sample judging unit. The invention solves the combining platform problem of an essential passive device in a total solution of indoor distribution of a building and achieves the purposes of enhancing the resource utilization rate of an indoor distribution system in the intensive manner and reducing the system complexity and the construction cost.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
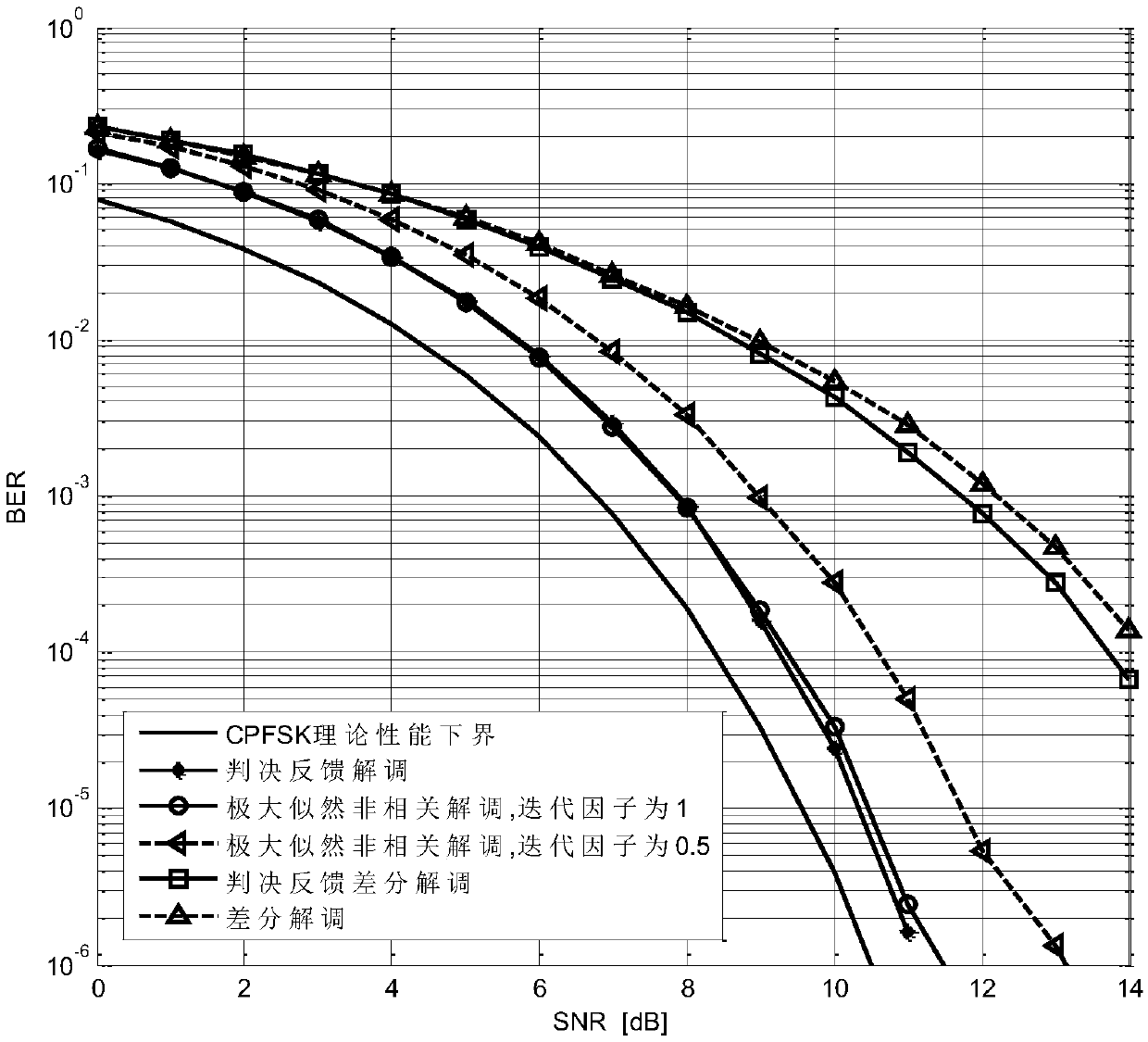
A Gaussian frequency shift keying (GFSK) signal demodulation method with low complexity based on decision feedback
ActiveCN109039966AReduce areaReduce power consumptionFrequency-modulated carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksComputation complexityComputer science
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication and discloses a Gaussian frequency shift keying (GFSK) signal demodulation method with low complexity based on decision feedback.According to the expression of GFSK signal, the phase of GFSK signal is approximated, and the phase interference between adjacent symbols is ignored, so the simplified expression of GFSK signal is obtained. Based on the principle of decision feedback, in the current sampling value of the received signal, the detected symbols are canceled to obtain the signal related to the current transmitted data symbols. On the basis of the signal, the data symbols transmitted by the current signal are judged. Compared with the traditional difference demodulation, the decision feedback difference demodulation and the maximum likelihood incoherent demodulation, the GFSK demodulation method of the invention has higher performance, and only two multiplications are required for computational complexity; When the modulation index of the GFSK signal is 0.5, the GFSK demodulation method of the invention does not need multiplication calculation, and directly decides the data symbol according to the real part or the imaginary part of the GFSK signal; Therefore, the GFSK demodulation method of the present invention is very suitable for digital integrated circuit implementation.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Method and device for demodulating signals
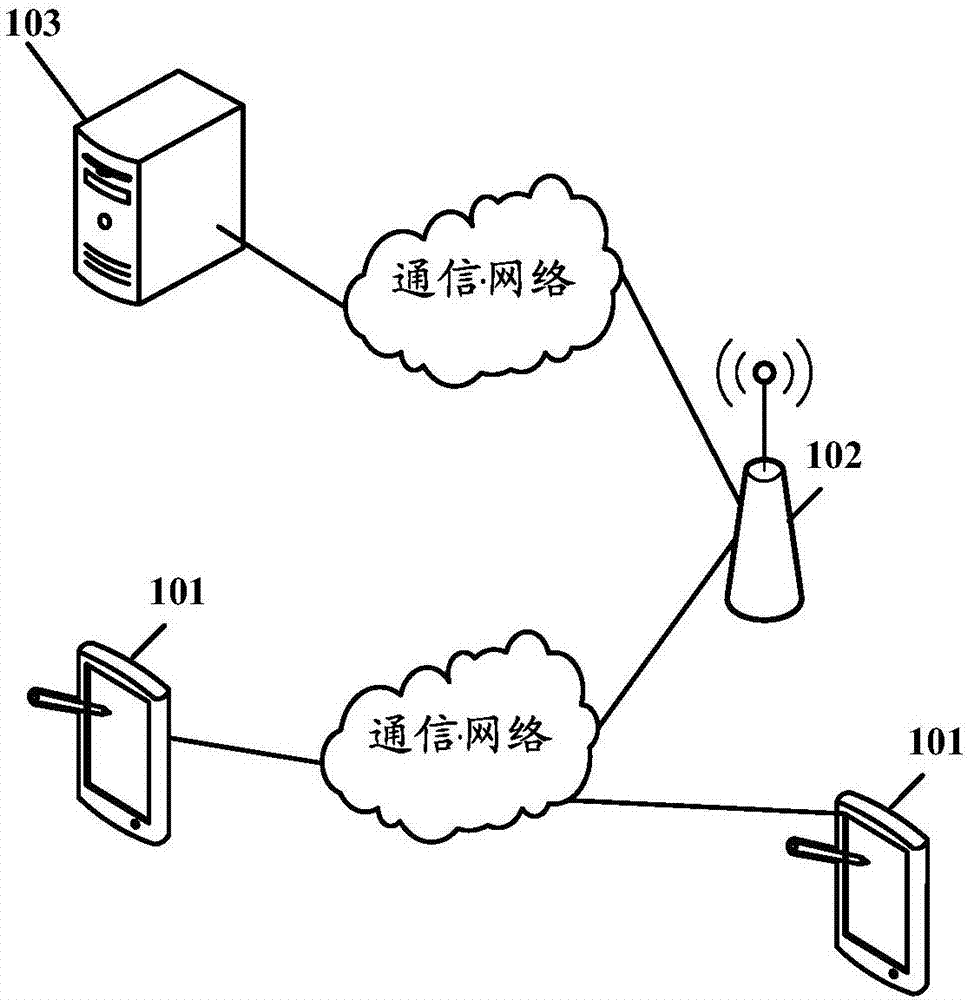
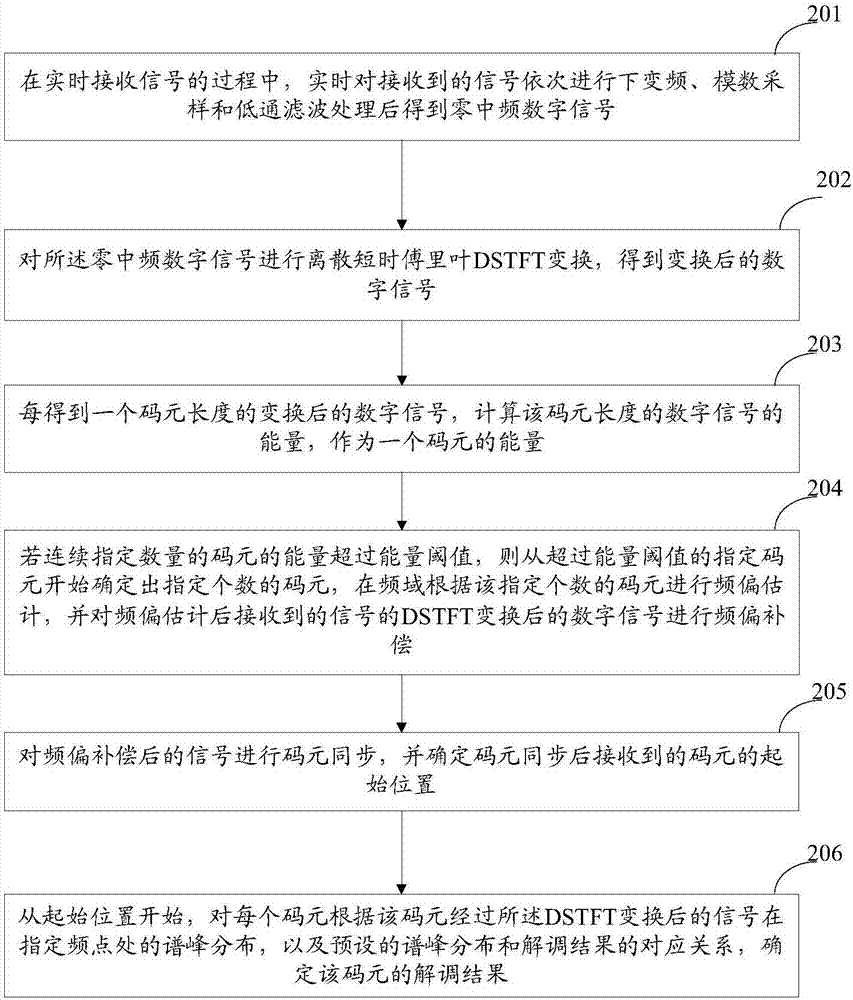
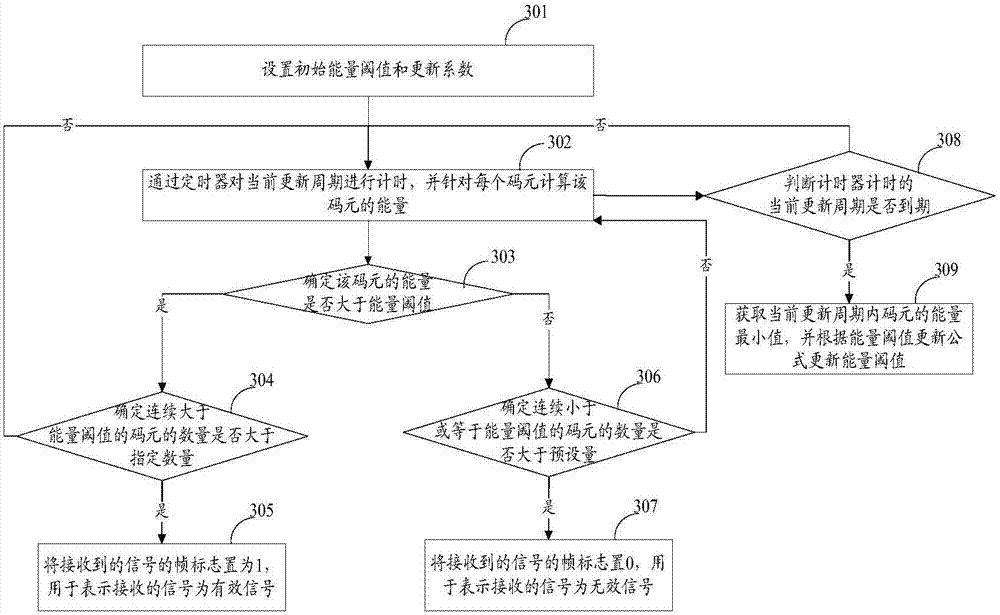
ActiveCN107404450AWith anti-interference abilitySimple demodulation methodCarrier regulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsTime domainCarrier signal
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication, in particular to the problem of how to demodulate FSK and / or GFSK signals. The invention provides a method and a device for demodulating signals. According to the embodiment of the invention, frequency offset is performed in a frequency domain, and frequency offset compensation is performed on signals subjected to DSTFT transformation, i.e., achieving frequency offset compensation in the frequency domain. Thus, compared with the time frequency-based non-coherent demodulation where frequency offset compensation is performed in time domain, the frequency offset compensation performed in the frequency domain has anti-interference ability. There is no need to recover carrier waves which have the same frequency and phase with carrier waves of a signal sending end locally, so the demodulation method is simple and requirements on hardware are not high.
Owner:RUIJIE NETWORKS CO LTD
Receivers and symbol decoders thereof
ActiveUS8259862B2Frequency-modulated carrier systemsAngle demodulationDiscriminatorCommunications system
A receiver capable of decoding a symbol based on information on a previous symbol, the symbol and a next symbol in a Gaussian frequency shift keying (GFSK) communication system is provided. The receiver includes a discriminator to generate a symbol for each bit in a bit sequence, a first lookup table (LUT) to store a number of bit patterns and mapping patterns, wherein each of the bit patterns is in the form of a set of consecutive bits in the bit sequence and corresponds to a respective one of the mapping patterns, and wherein each of the mapping patterns includes a set of entries and each of the entries results from an operation of attribute values at a sample time in the waveform of a symbol, a calculator to receive a set of consecutive symbols from the discriminator and calculate a distance value between the set of consecutive symbols and each of the mapping patterns, and a comparator to identify one of the mapping patterns with a minimum distance value by comparing among the distance values from the calculator.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
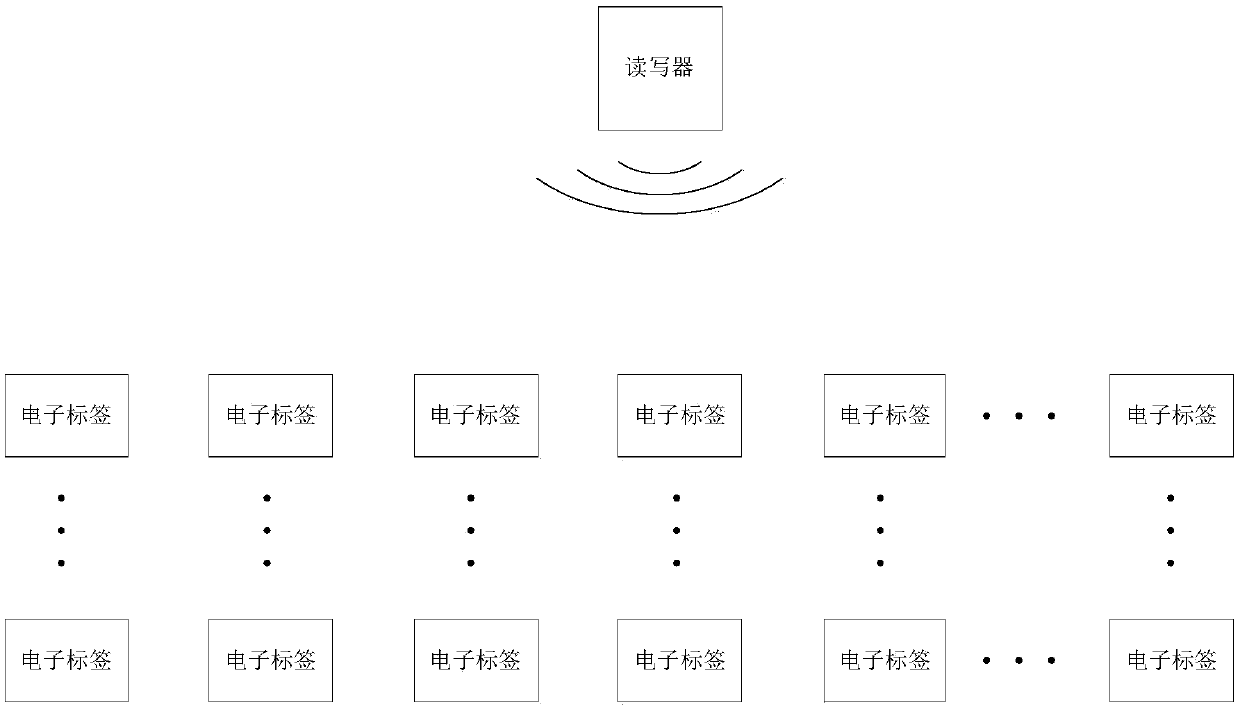
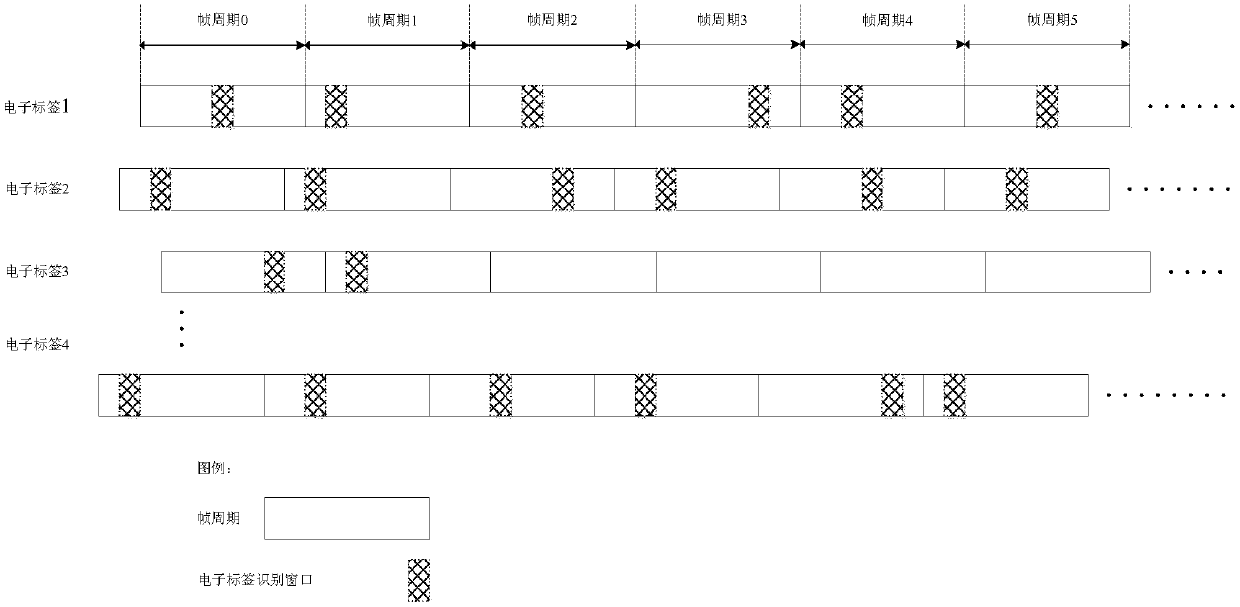
Anti-collision method of 2.4G active-electronic-tags (RFID)
InactiveCN107766764AImprove recognition rateSave energySensing by electromagnetic radiationBroadcast packetWireless communication protocol
The invention discloses an anti-collision method of 2.4G active-electronic-tags (RFID). The anti-collision method of the 2.4G active-electronic-tags includes a wireless communication protocol of a reader-writer and the electronic tags and an anti-collision method. Gaussian frequency shift keying (GFSK) is adopted to modulate the reader-writer and the electronic tags, and a work frequency band is 2.4 GHz-2.4835 GHz; the electronic tags are in a cycle transmitting state by default; the reader-writer contains a plurality of simultaneously working radio frequency chips, which respectively use a plurality of wireless channels, and are in a receiving state by default; time is divided into a plurality of frame cycles; the electronic tag randomly selects a moment and a radio frequency channel to broadcast an identity data packet in each frame cycle; The reader-writer can then send a correct response to the tag if any radio frequency chip of the reader-writer correctly receives the data packet;the tag can be in a sleeping state in the next frame cycles after the correct response is received; and the broadcast packet can be continuously sent if the electronic tag does not receive the correct response after the broadcast packet is completely sent at every turn. According to the anti-collision method of the 2.4G active-electronic-tags, the plurality of quickly moved electronic tags can besimultaneously identified, and collision probability is lower.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Method for communicating with mobile phone based on low-cost GFSK chip
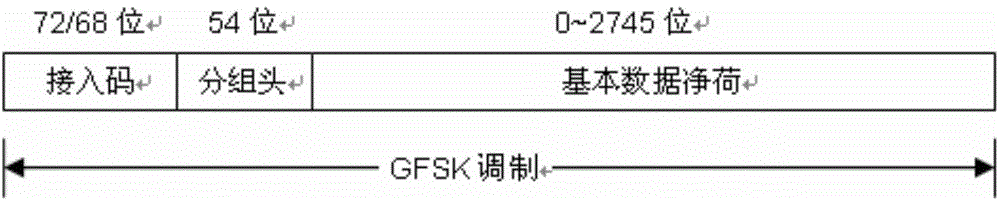
InactiveCN108924804ASolve the problem of industry barriersEasy to useBroadcast service distributionSignalling characterisationBroadcast packetRadio pack
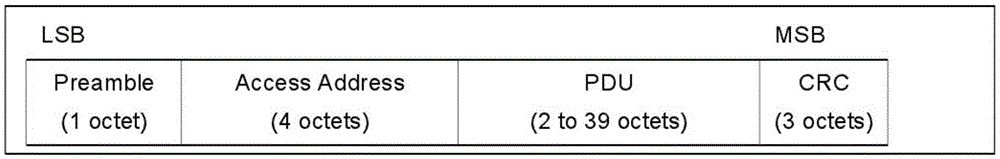
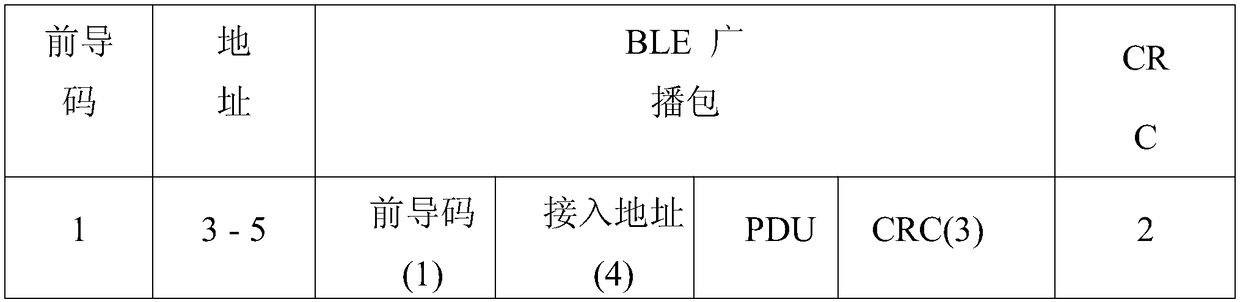
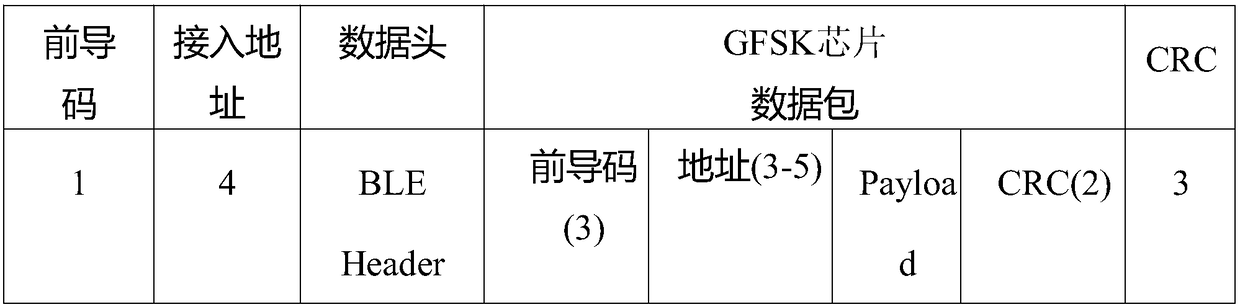
The invention relates to a method for communicating with a mobile phone with a low-cost GFSK chip. The method comprises the following steps: S1, GFSK chip-mobile phone receiving: a, a GFSK chip sendsout a first data packet, wherein the first data packet comprises a BLE broadcast packet, and the BLE broadcast packet comprises a preamble 1 Byte, access address 4 Byte, data PDU and CRC check 3 Byte;and b, the mobile phone Bluetooth receives the first data packet after scanning the BLE radio packet; S2, the mobile phone sending-GFSK chip receiving: a, the mobile phone sends out the second data packet which comprises a GFSK chip data packet, the GFSK chip data packet comprises the preamble 3 Byte, the access address 3-5 Byte, data Payload and CRC check 2 Byte; and b, the GFSK chip receives the second data packet. Through the method disclosed by the invention, the industry barrier problem caused by high-cost Bluetooth chip is solved, and the low-cost chip can realize the bidirectional communication with the mobile phone.
Owner:苏州澜普智能技术有限公司
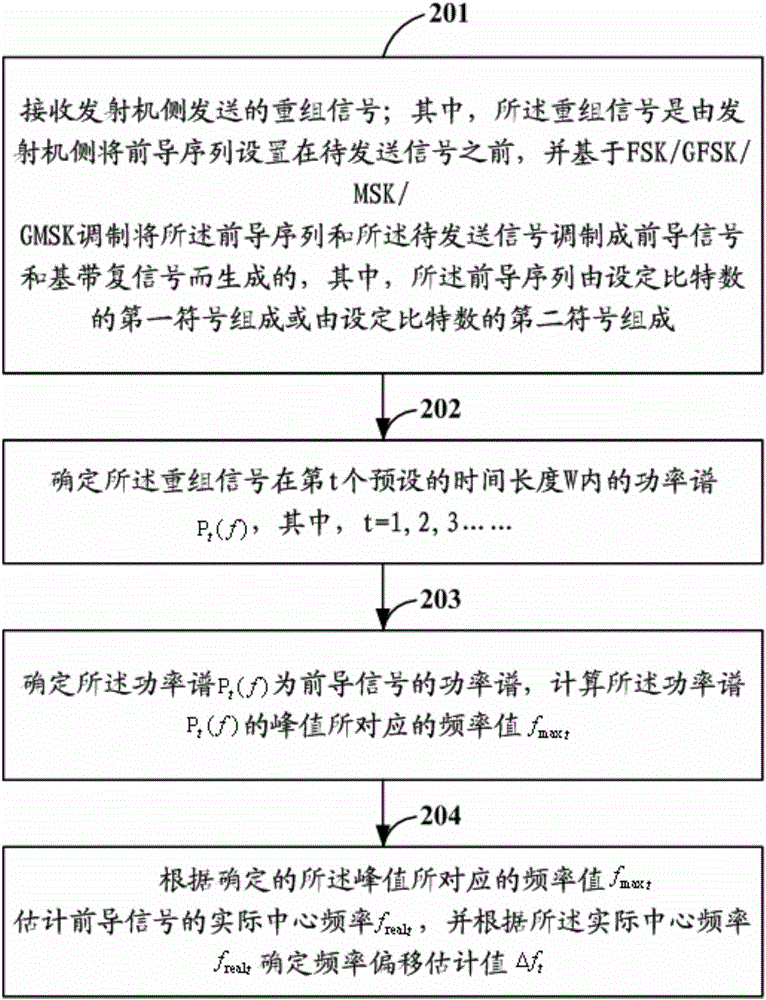
Frequency offset estimation methods, transmitter, receiver and communication system
ActiveCN106254289AIncrease redundancyImprove anti-interference abilityCarrier regulationMulti-frequency code systemsEngineeringFrequency shift
The present invention relates to frequency offset estimation methods based on frequency shift keying (FSK) / Gaussian FSK (GFSK) / minimum shift keying (MSK) / Gaussian MSK (GMSK) modulation, a transmitter, a receiver, and a communication system. A preamble sequence consisting of set symbols can be set as a preamble signal of a baseband complex signal, power spectrum analysis is performed on the preamble signal so as to estimate a frequency offset value of the baseband complex signal, and the receiver does not need to generate or pre-store the preamble signal, nor perform demodulation operation on the received preamble signal, so that the complexity of the algorithm and the communication system is lowered. In addition, the preamble sequence consisting of the same symbols improves the redundancy and anti-interference capability of the preamble signal, so that a frequency offset estimation result calculated according to the preamble signal is more accurate.
Owner:RUIJIE NETWORKS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com