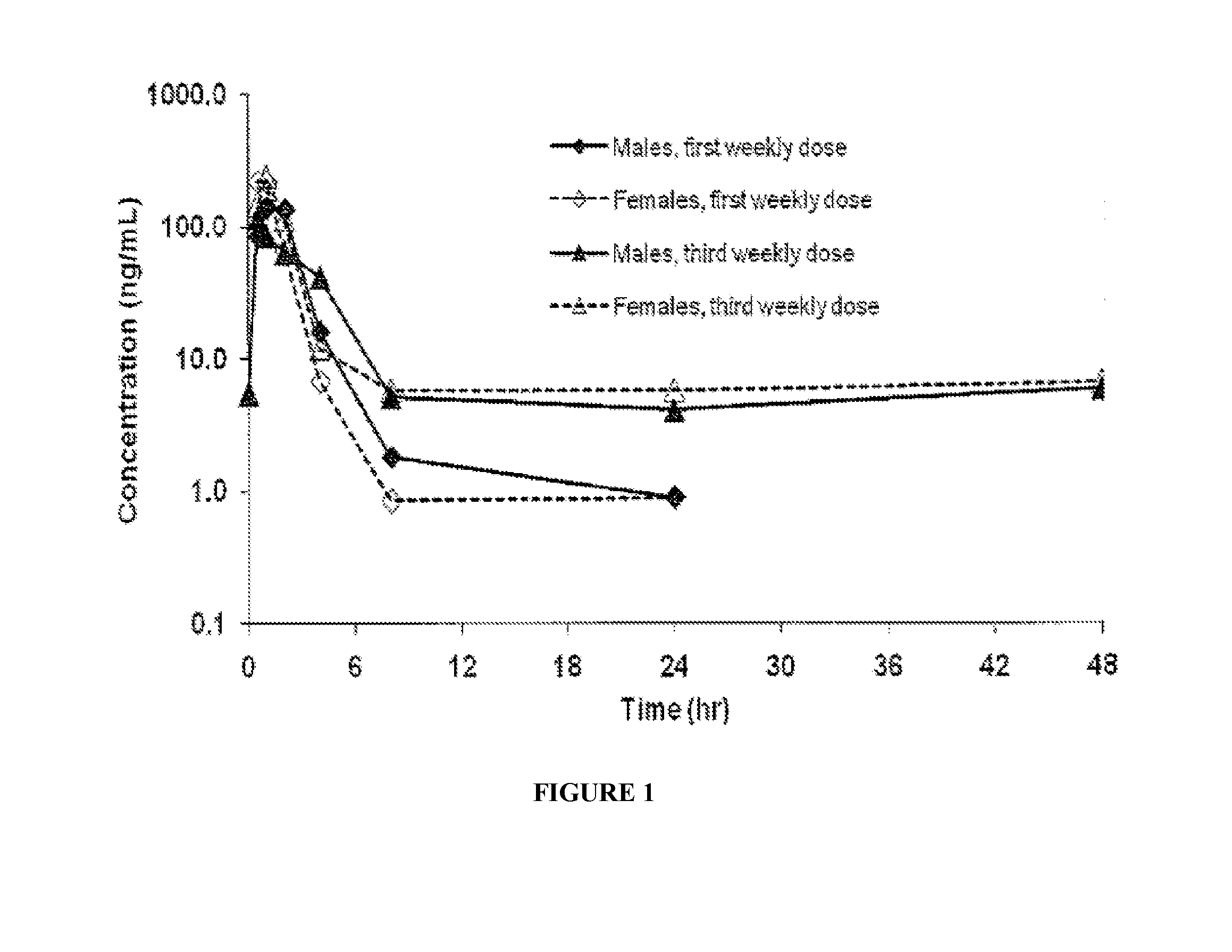
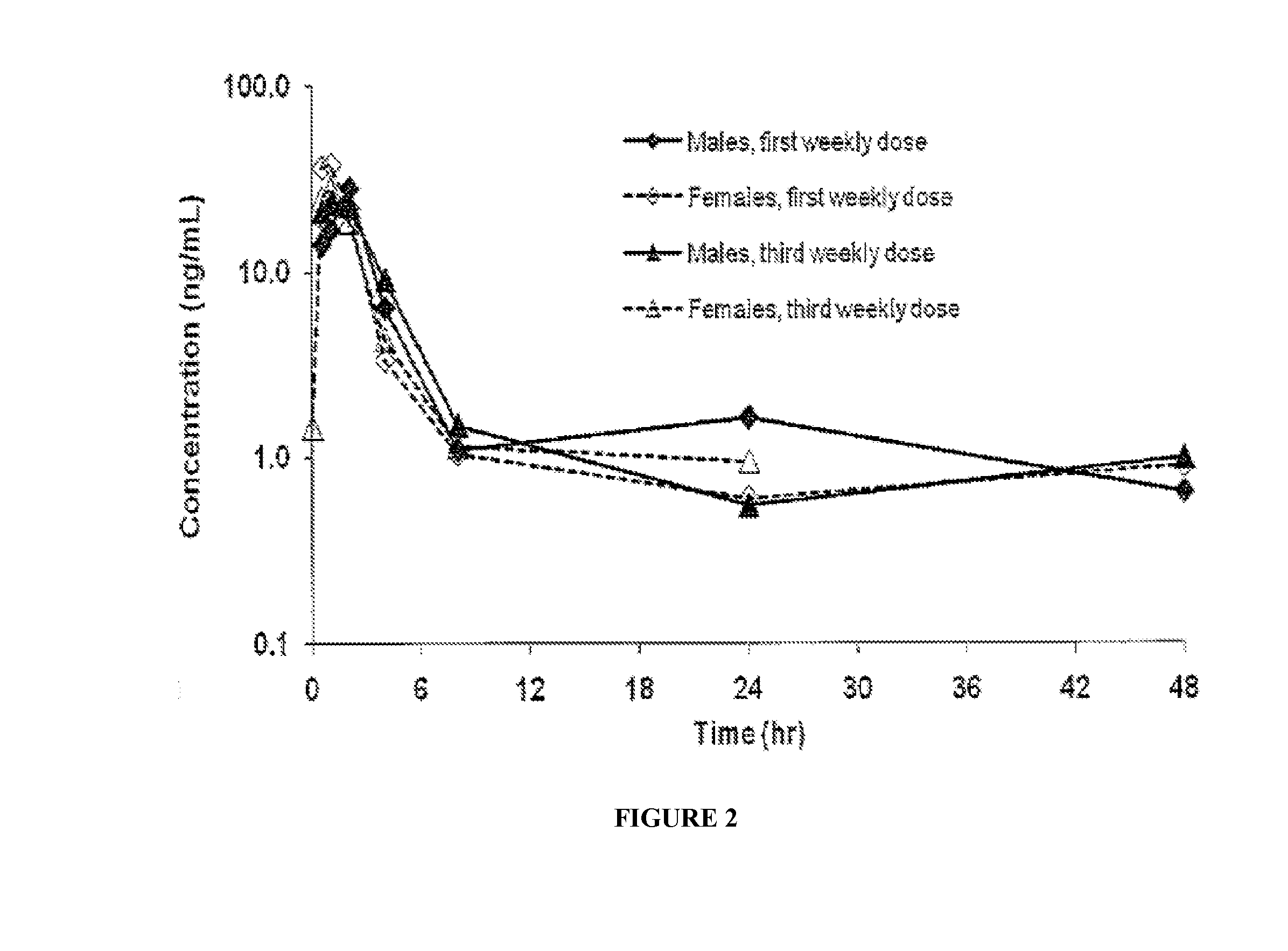
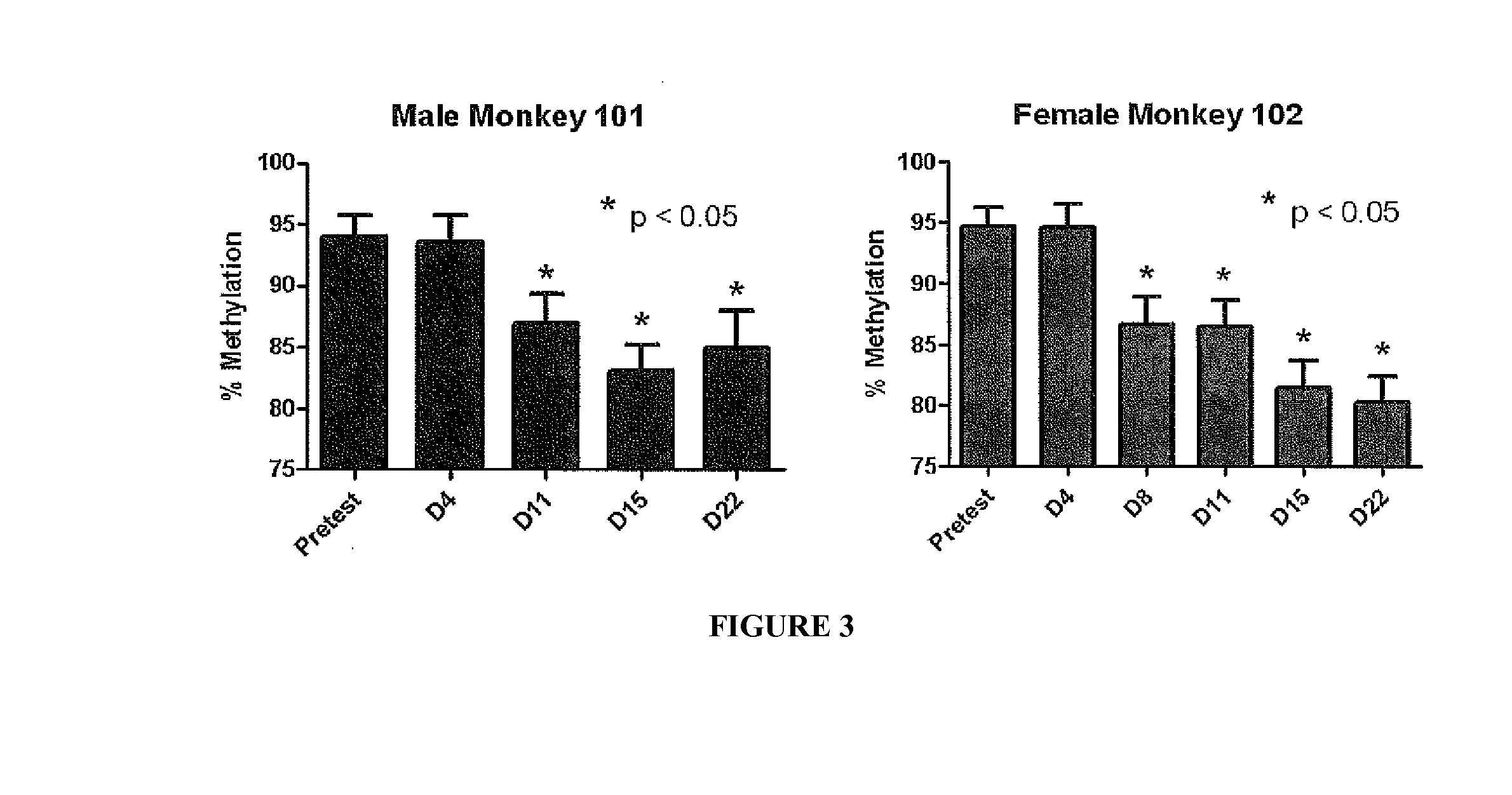
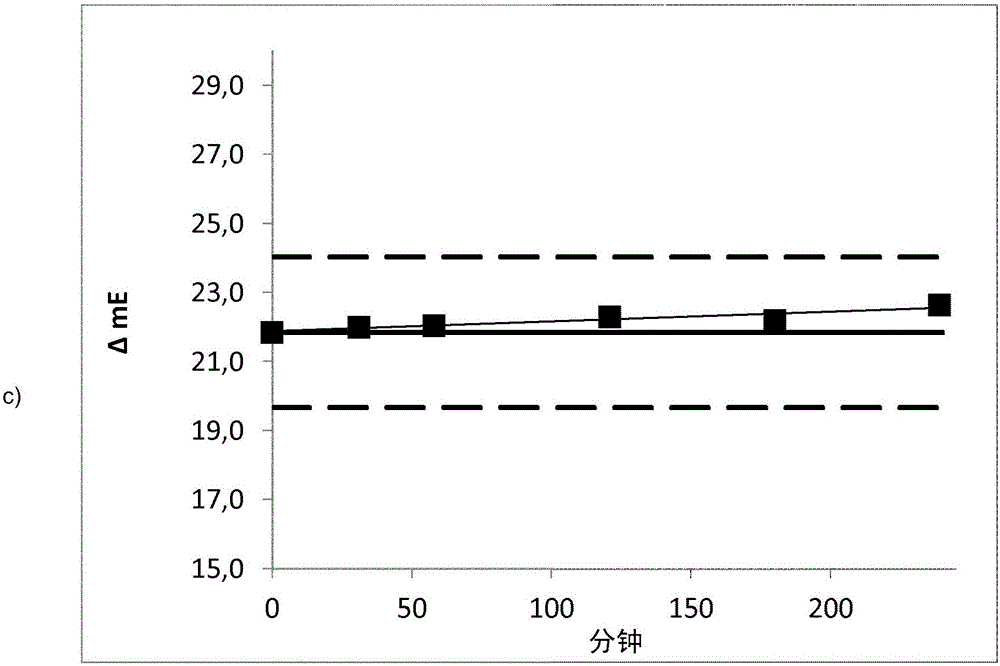
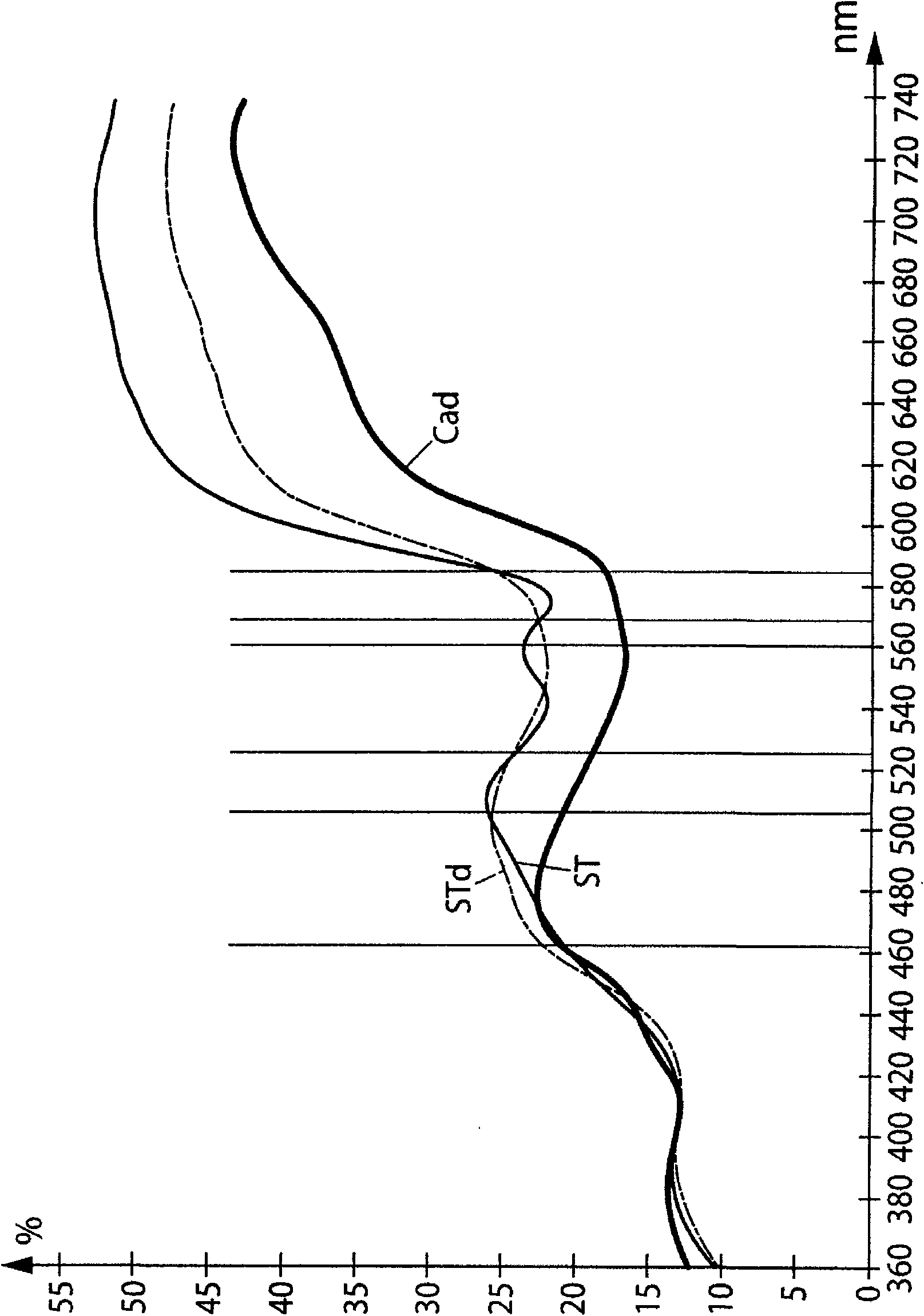
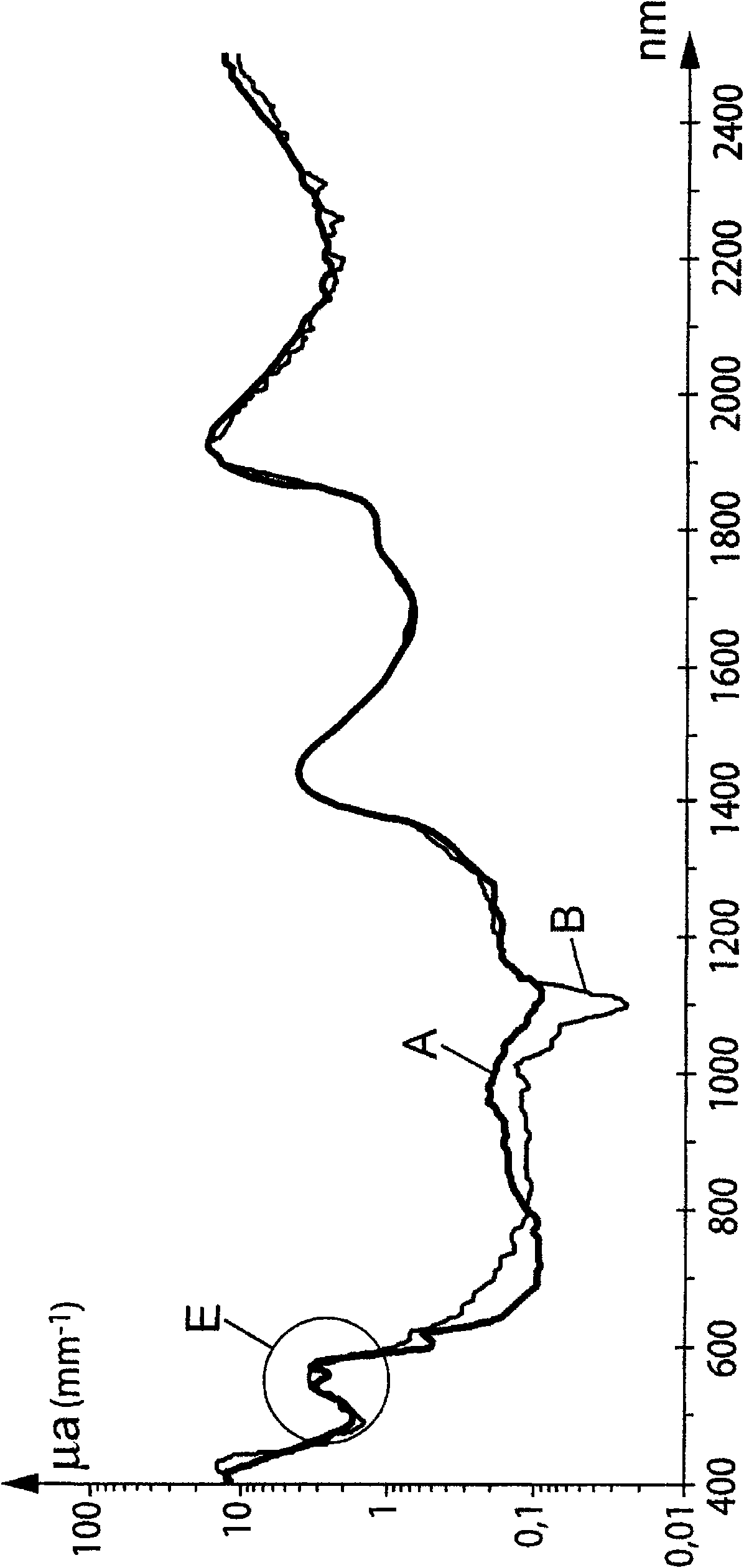
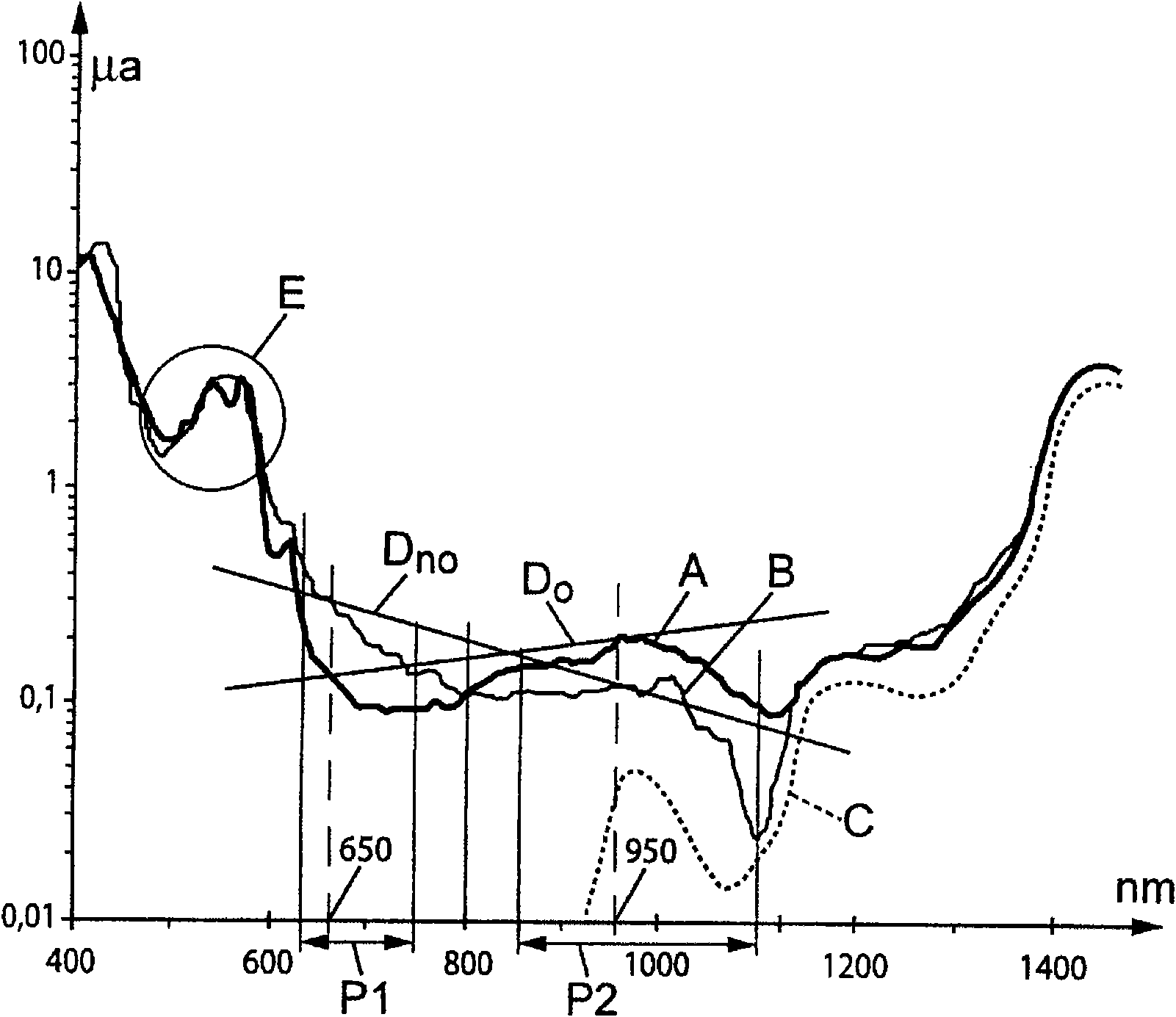
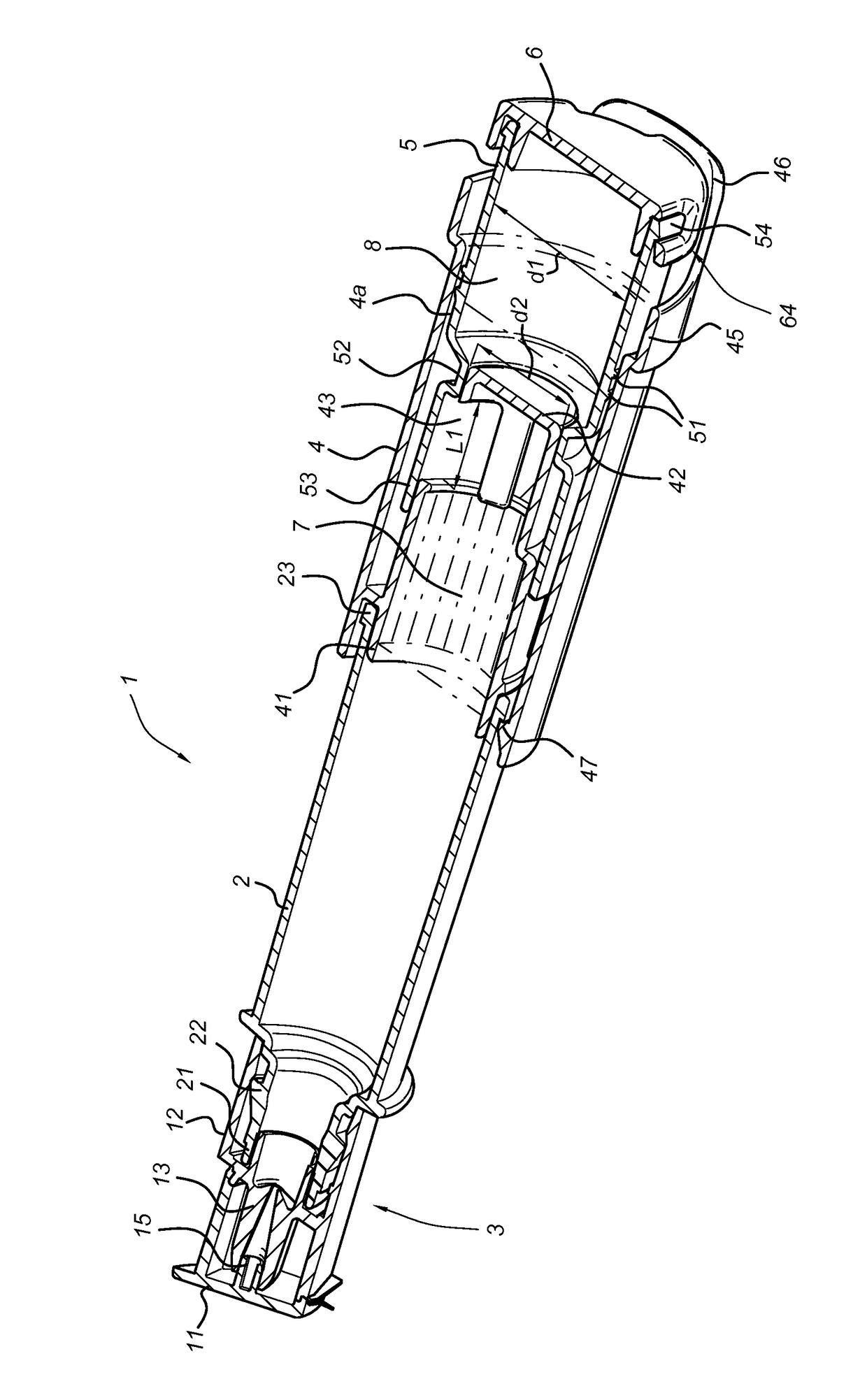
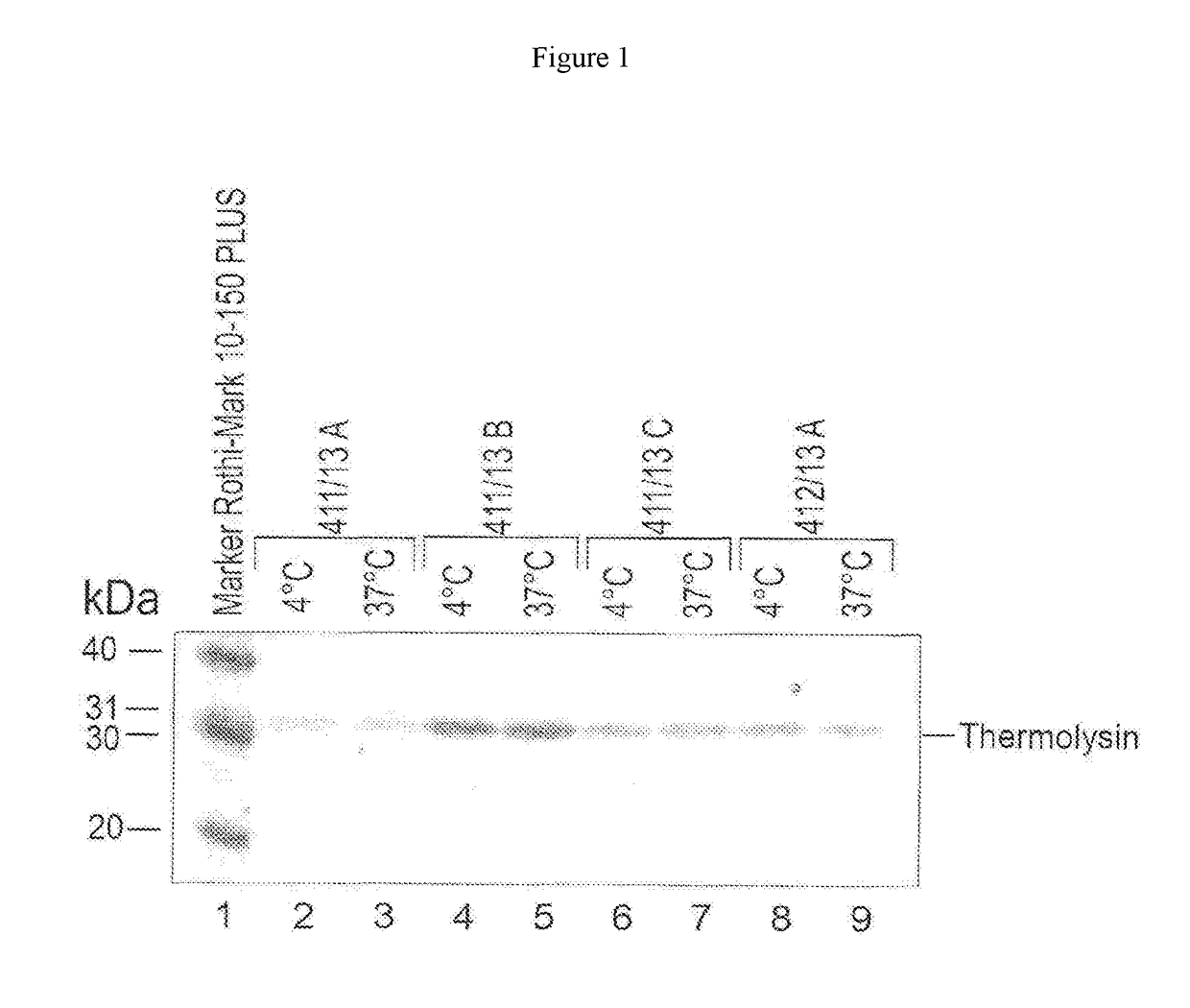
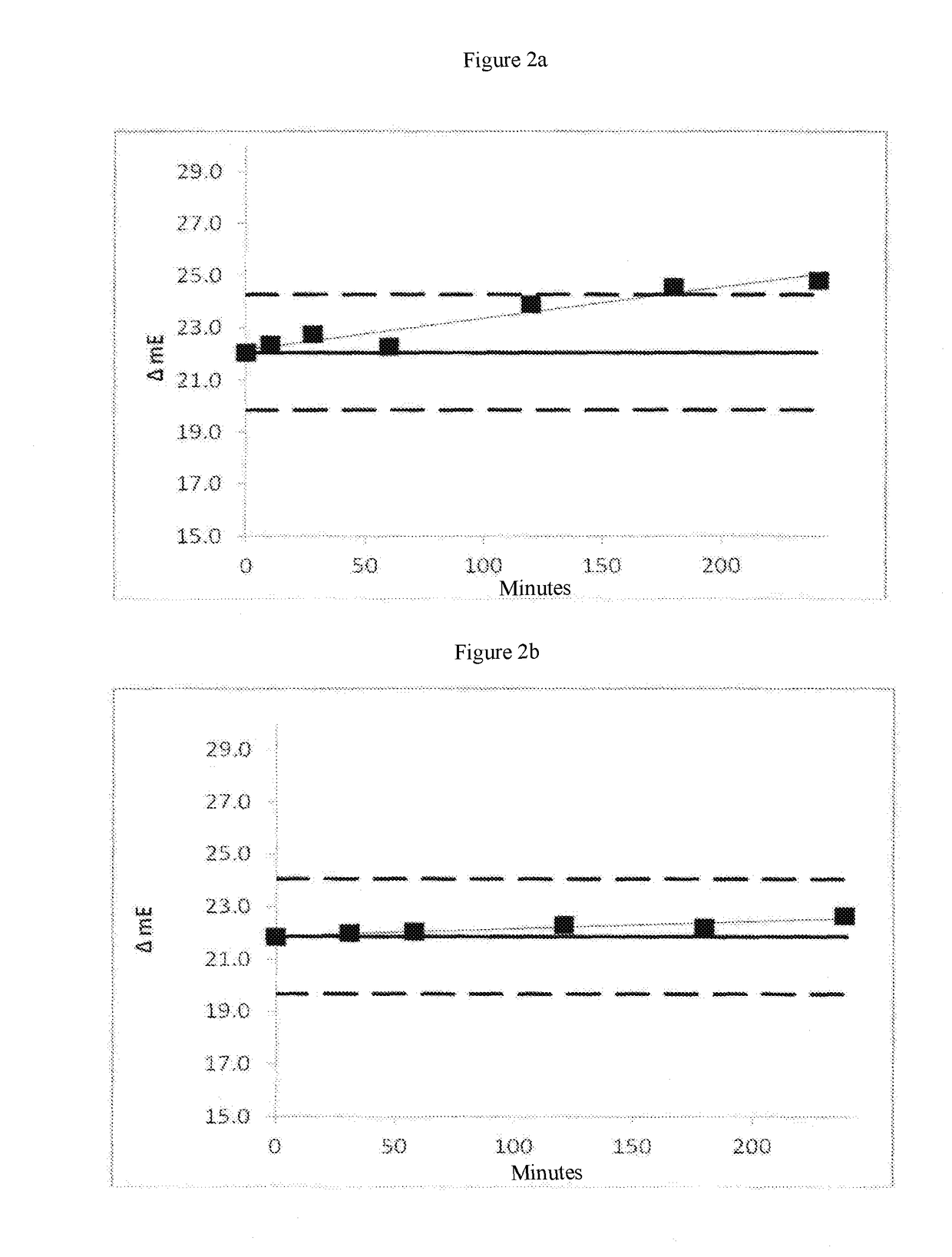
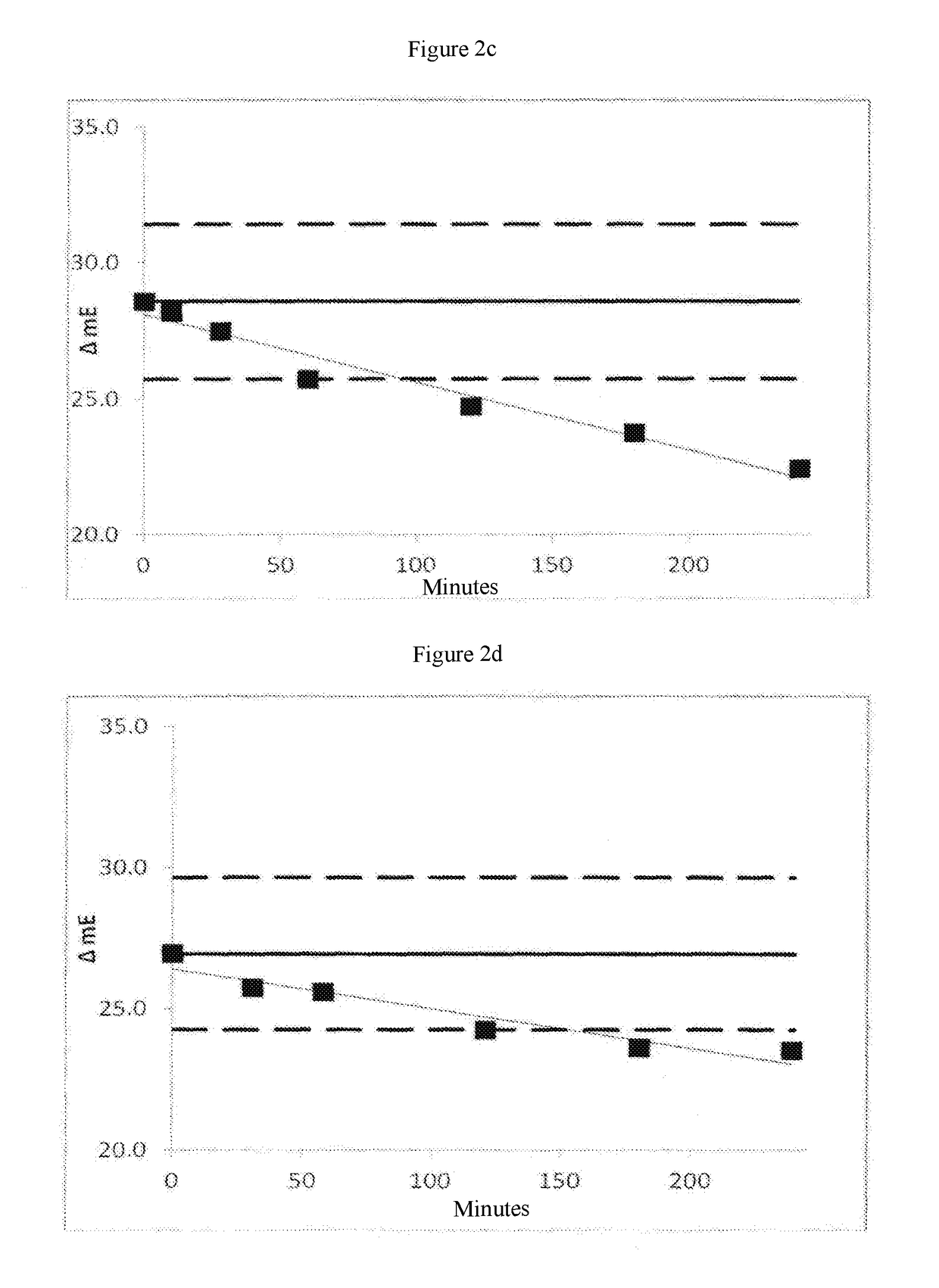
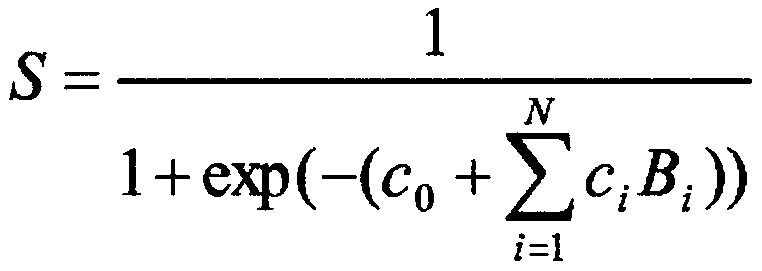Patents
Literature
37 results about "Haemoglobin Suresnes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Drug combinations
InactiveUS20160015805A1Good effectLow toxicityBoron compound active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseHaematological disorders
The invention provides combinations of derivatives of decitabine and other active agents, including T-cell activating agents, cancer vaccines, and adjuvants. Some derivatives of decitabine exhibit superior chemical stability and shelf life, with similar physiological activity. Methods of treating one or more myelodysplasia syndromes, cancers, haematological disorders, or diseases associated with abnormal haemoglobin synthesis using the combinations are described.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Pig haemoglobin glycopeptide with anti-oxidizing activity and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106749634AImprove antioxidant functionIncreased sensitivityHaemoglobins/myoglobinsAccessory food factorsMaillard reactionGlycopeptide
The invention relates to the field of animal protein processing, and particularly discloses pig haemoglobin glycopeptide with anti-oxidizing activity and a preparation method and application thereof. The pig hemoglobin glycopeptide has the advantages that the pig hemoglobin is used as raw material, and is pretreated by ultrasonic waves and the like, the multiple proteases are used for composite enzymatic hydrolysis under the condition of no adding of any acid and alkaline, and the membrane separating technique is adopted, so as to obtain a certain molecular weight of hemoglobin; the hemoglobin and lactose generate Maillard reaction under the milder condition, so as to develop the pig hemoglobin glycopeptide with anti-oxidizing function and better color and flavor. A simple and high-efficiency preparation method of the pig haemoglobin glycopeptide is established.
Owner:北京鸿顺养源生物科技有限公司
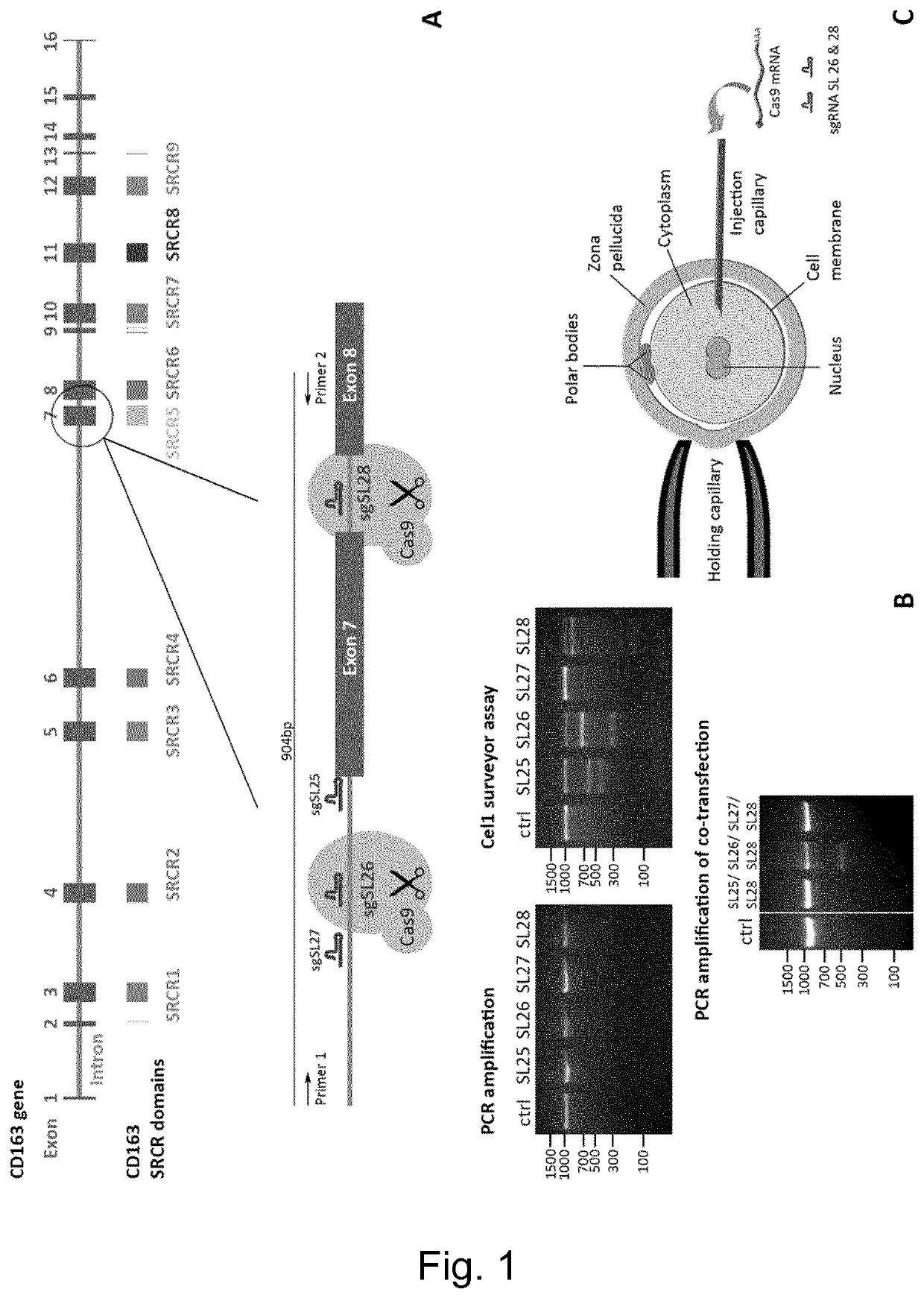
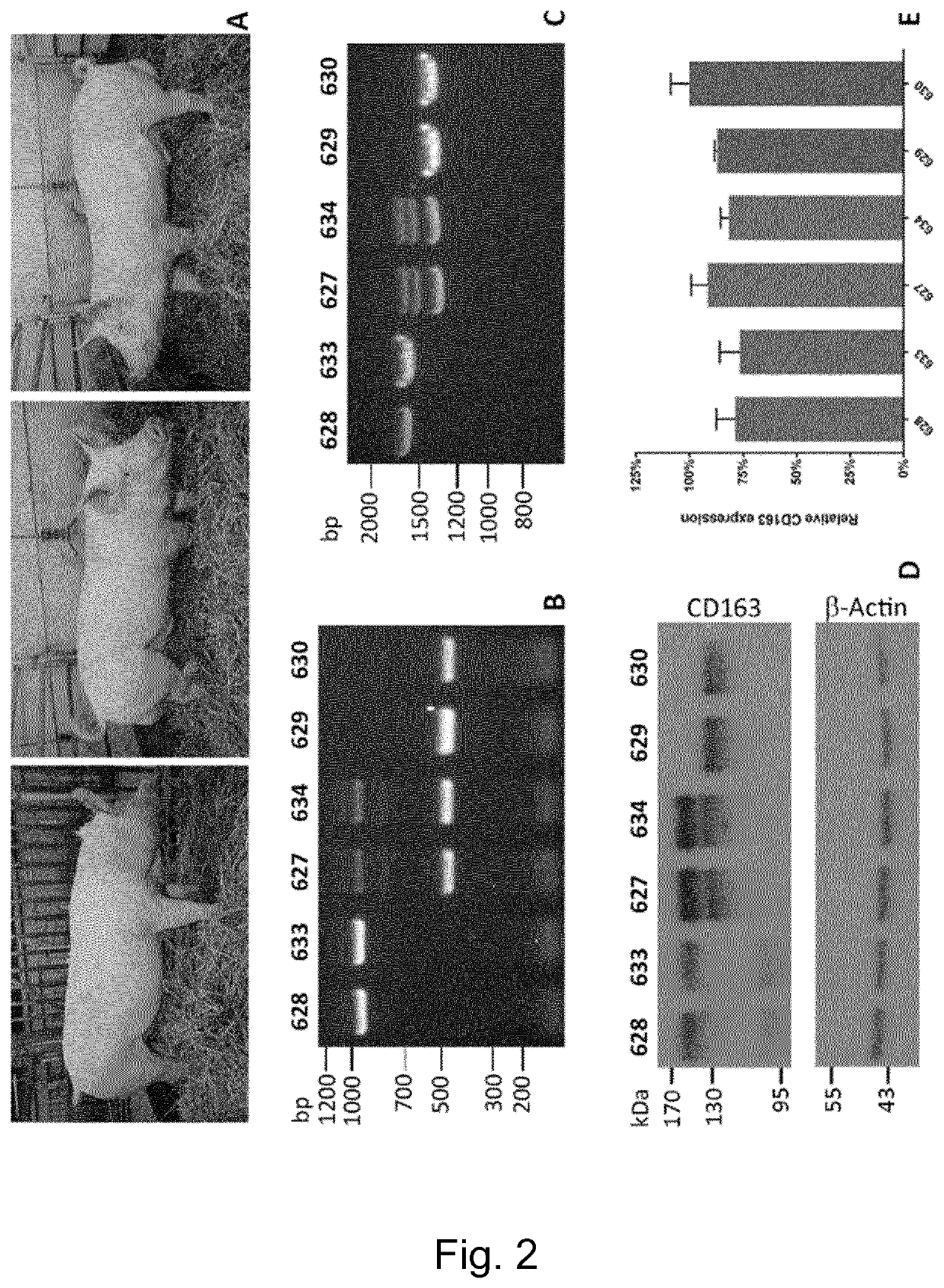
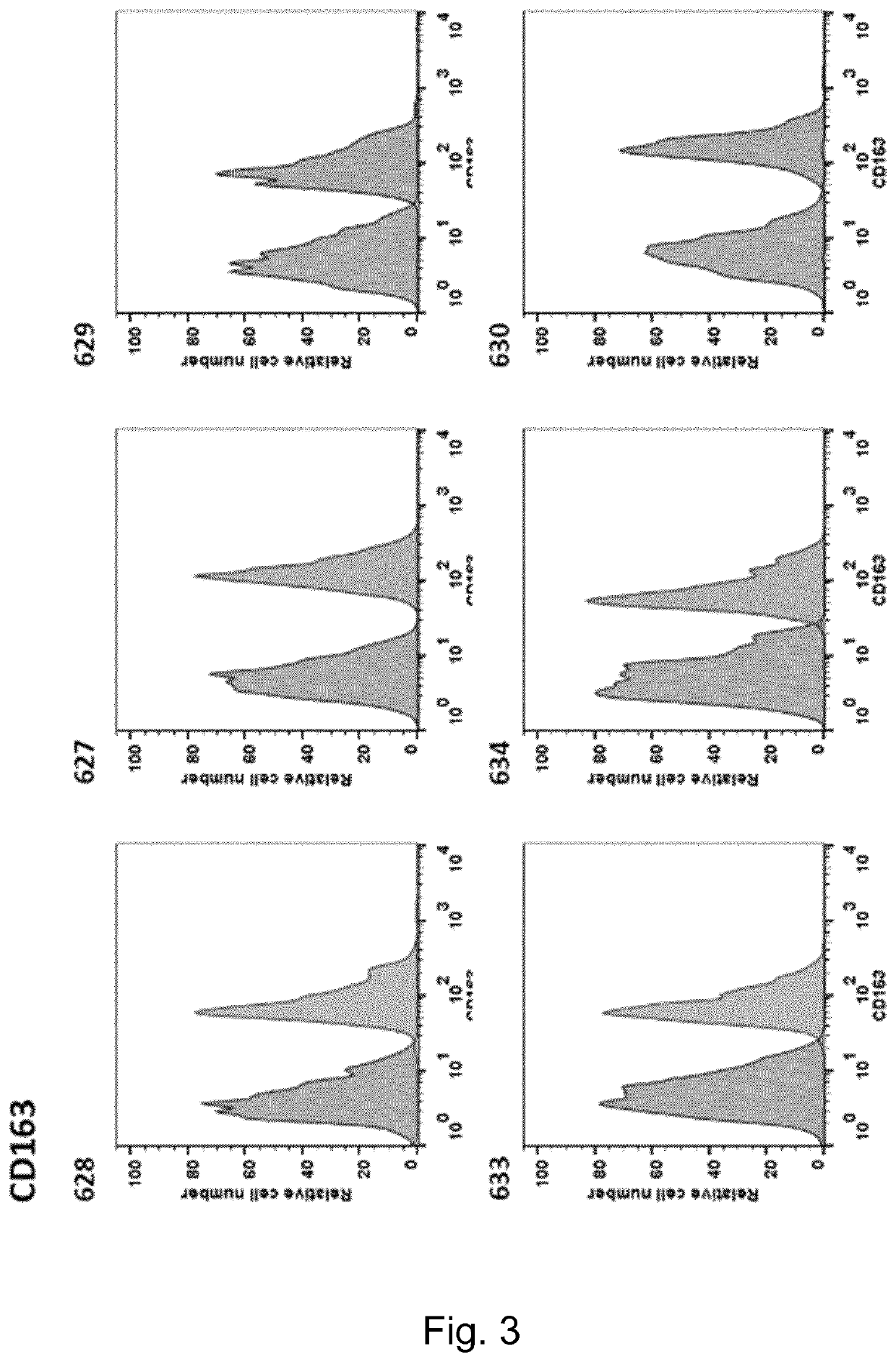
Swine Comprising Modified CD163 and Associated Methods
InactiveUS20200045945A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsGenetically modified cellsScavenger receptorCoboglobin
The present invention relates to genetically edited swine which produce CD163 protein in which the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich 5 (SRCR5) domain (also known as CD163 domain 5) has been deleted. Such swine have been found to be healthy and do not exhibit negative properties, and are resistant to PRRSV infection. CD163 expressed in the edited swine also demonstrates retention of the ability to function as a haemoglobin-haptoglobin scavenger. Methods of producing such swine are also provided.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF EDINBURGH
Method
InactiveUS20100216664A1Improve the level ofGood effectNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyIntergenic region
The present invention relates, in one aspect, to a method for determining the severity of a disease attributed to at least one genetic mutation in one or more of the genes encoding haemoglobin polypeptide chains, comprising the steps of: (a) providing a sample from said subject; and (b) determining the presence of one or more diagnostic markers:(i) within a 127 kb segment on chromosome 2p15;(ii) within MYB and / or HBSIL and / or the intergenic region between MYB and HBSIL located on the 6q23 QTL interval; and / or(iii) within one of the chromosomal loci given in Table 14; wherein the presence of said marker(s) in said sample is indicative that the severity of said disease in said subject will be or is less severe in said subject in comparison to a subject that does not possess said marker(s).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Device and method for detection of haemoglobin and its complexes
ActiveCN107405115AConcentration Accurate MeasurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDiagnostic recording/measuringGlycated haemoglobinReceptor
An electrochemically active device is provided for collecting and retaining a blood sample with at least a two-electrode member connected to conductive tracks. A receptor with an integral receptor-membrane arranged on the two-electrode member, to receive non-electrochemically active heamoglobin bioanalyte and its complexes from red blood cells (RBC) of said blood sample, through a lysing agent and convert the non-electrochemically active heamoglobin bioanalyte and its complexes, into an electrochemically active bioanalyte and its electrochemically active complexes. The present invention also provides a point-of-care biosensor incorporated with the device of the present invention and method of measuring for the detection and quantitative measurement of concentrations of haemoglobin (Hb), glycated haemoglobin (GHb), methaemoglobin (MetHb) and myoglobin, in reduced volumes of blood samples, by determining redox current values in the reduced volumes of blood samples.
Owner:INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE
Strain, and construction method and application thereof
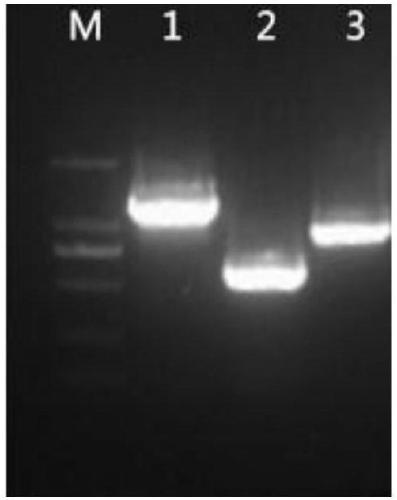
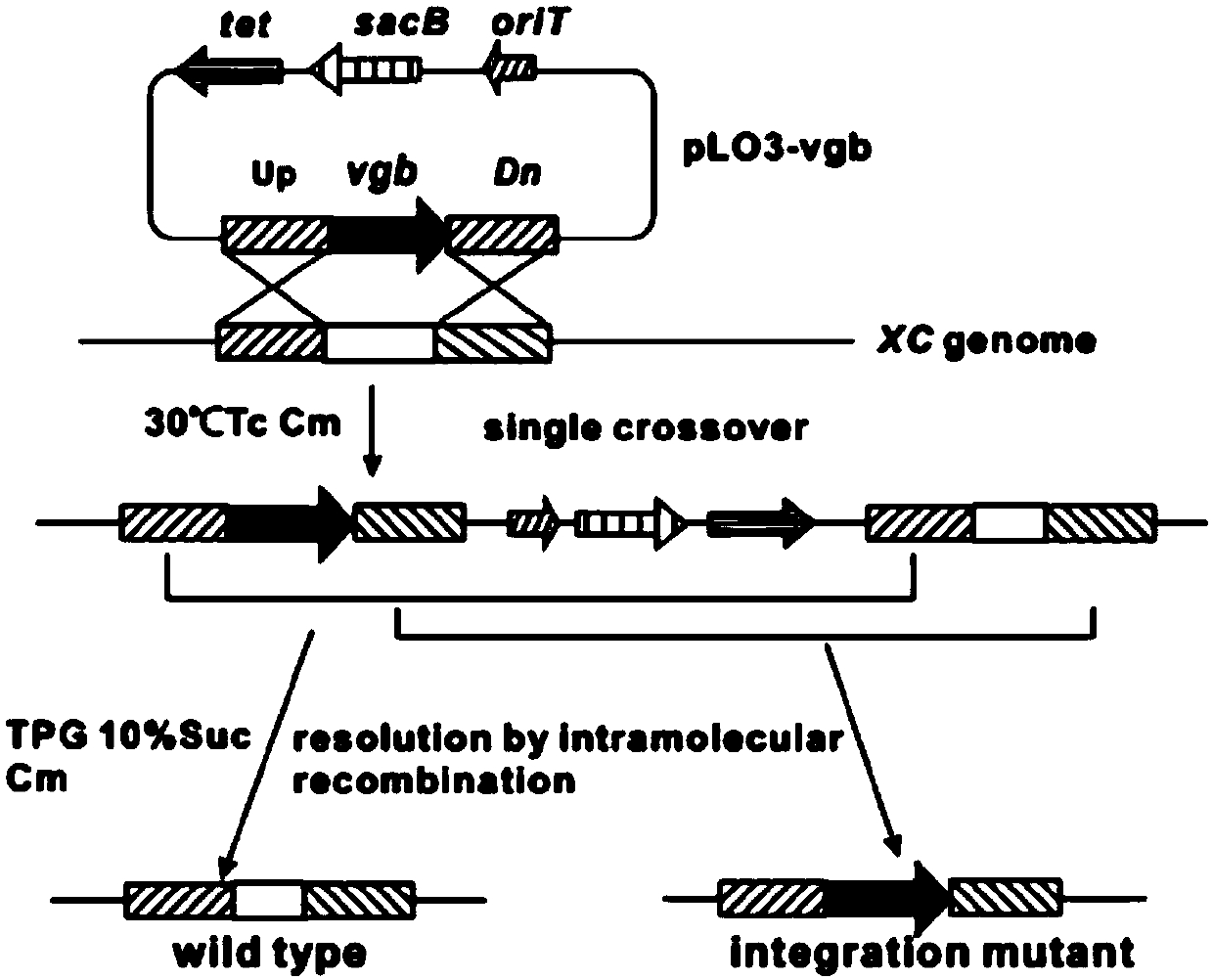
The invention relates to the field of microorganism genetic engineering, in particular to a strain, and a construction method and application thereof. Xanthomonas campestris is used an original strain, a key gene pigA of an xanthomonadins synthesis way is inactivated through a genetic engineering technique, a haemoglobin vgb gene is introduced, and a xanthan gum white mutant (the strain is authorized to the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center for preservation with the preservation number being CGMCC No.14771) is constructed. White xanthan gum can be produced, synthesized xanthan gum basically excludes the xanthomonadins, side effects of unknown mutation to strains can be reduced, the usage quantity of ethanol can be massively reduced, resources and the production cost can be saved, and the strain has great industrial application value.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Assay method
InactiveCN103492881AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementCoboglobinAssay
The invention provides an assay method for determining a level of haptoglobin in a sample comprising the steps of: (i) mixing haemoglobin with the sample to be assayed so as to form a haptoglobin-haemoglobin complex with haptoglobin present in the sample; (ii) contacting the product of step (i) with reagents for generating hydrogen peroxide and one or more chromogens which undergo a spectroscopically detectable change when peroxidase activity is present, in the presence of a buffer, under conditions in which hydrogen peroxide is generated from said reagents and forms a substrate for the peroxidise activity of the haptoglobin-haemoglobin complex present, and wherein the pH of the buffer is within a range which is sufficiently low that the peroxidise activity of any uncomplexed haemoglobin is substantially suppressed but sufficiently high that hydrogen peroxide generation occurs; (iii) determining the peroxidase activity of the haptoglobin-haemoglobin complex by measuring the change in an optical property of the reaction mixture; and (iv) correlating the level of peroxidise activity of the haptoglobin-haemoglobin complex with the amount of haptoglobin in the sample. A kit for use in such a method is also provided.
Owner:REACTIVLAB
Diagnosis of mild or severe periodontitis
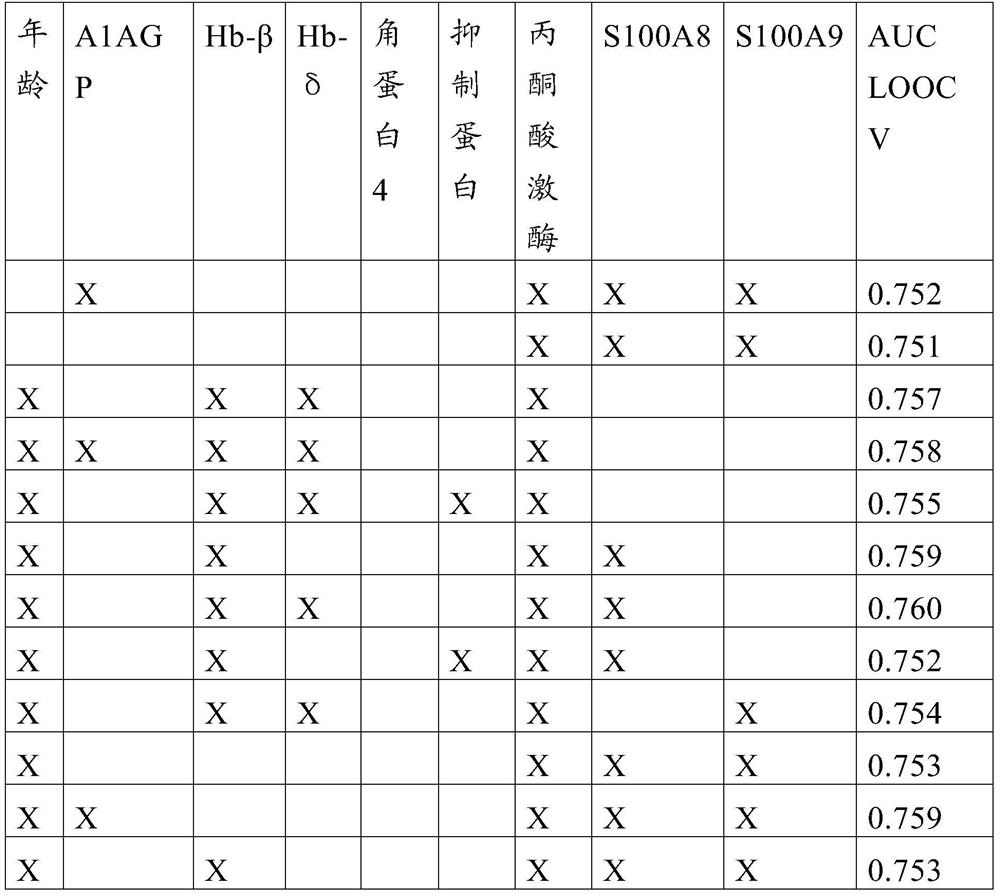
PendingCN111954818ASimple and Straightforward Diagnostic TestTransferasesLaboratory glasswaresSaliva sampleCalcium-binding protein
Disclosed is an in vitro method for assessing whether a human patient suffering from periodontitis has mild periodontitis or advanced periodontitis. The method is based on the insight to determine a selection of three bio marker proteins. Accordingly, in a sample of saliva a patient suffering from periodontitis, the concentrations are measured of the proteins Pyruvate Kinase (PK) and at least twoof Haemoglobin-beta (Hb-beta), Haemoglobin-delta (Hb-delta), S100 calcium-binding protein A8 (S100A8) and S100 calcium-binding protein A9 (S100A9). Based on the concentrations as measured, a value reflecting the joint concentrations for said proteins is determined. The value is compared with a threshold value reflecting in the same manner the joint concentrations associated with advanced periodontitis. The comparison allows assessing whether the testing value is indicative of the presence of advanced periodontitis or of mild periodontitis in the patient. Thereby, typically, a testing value reflecting a joint concentration below the joint concentration reflected by the threshold value is indicative for mild periodontitis in the patient, and a testing value reflecting a joint concentration at or above the joint concentration reflected by the threshold value, is indicative for advanced periodontitis in the patient.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
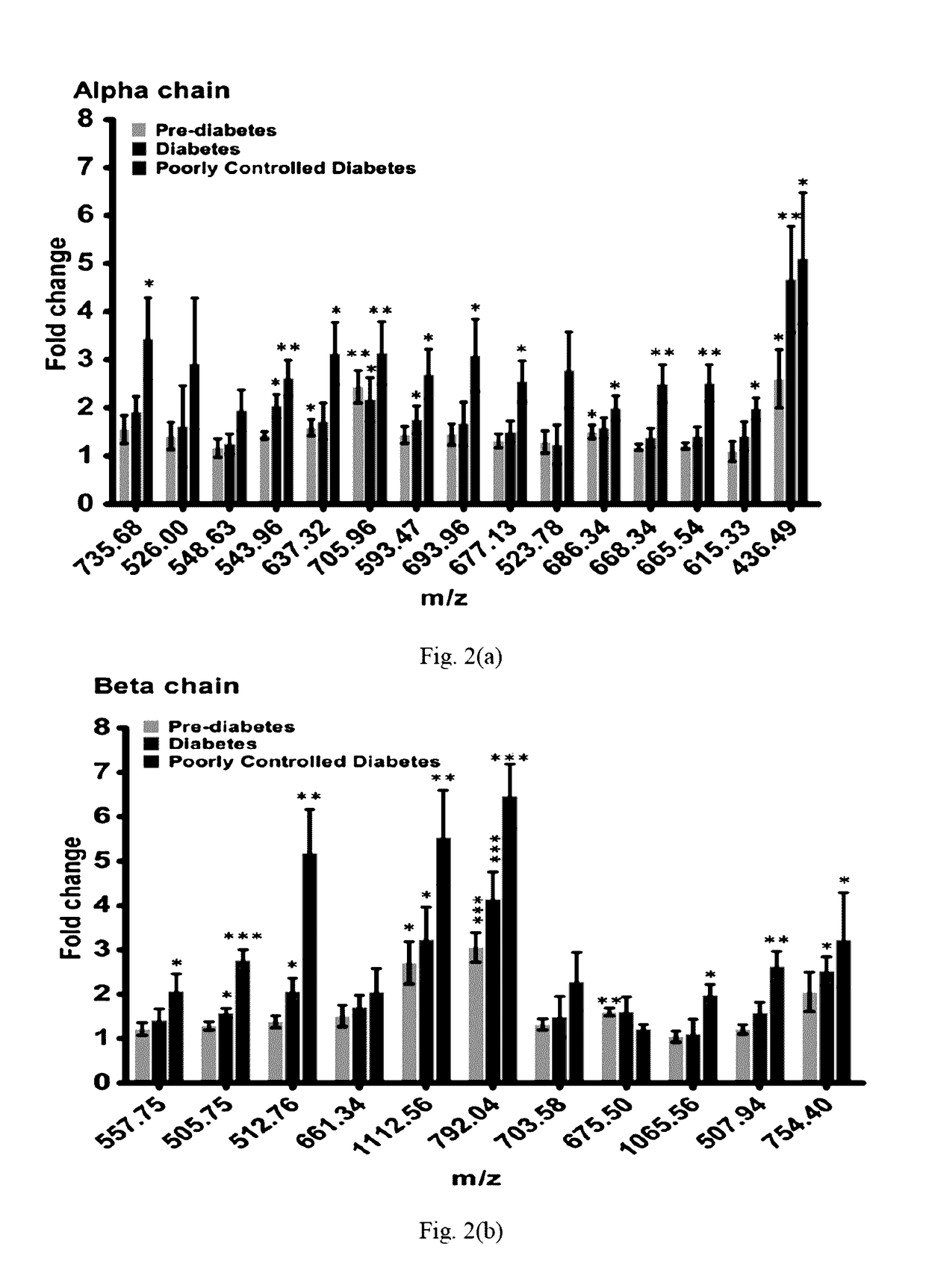
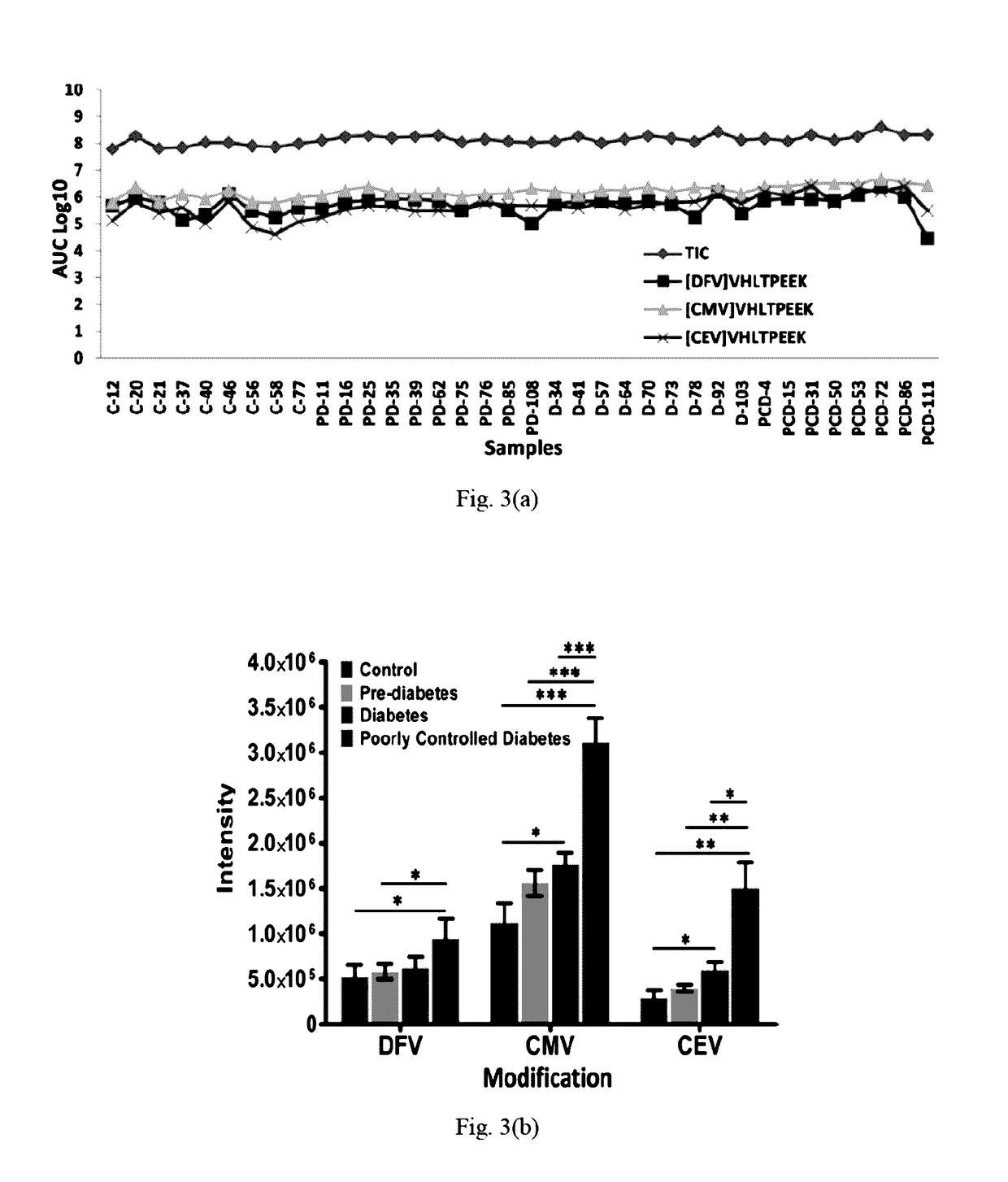
Method for identifying and quantifying carboxyethyl valine modified haemoglobin
The present invention relates to a method for identification and quantification of carboxyethylated valine modified haemoglobin to assess the extent of diabetic complications.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Cervical Sample Preparation For Reduced Variability In Raman Spectroscopy
InactiveUS20160069809A1Easy to integrateVariabilityPreparing sample for investigationRaman scatteringMedicineSpectroscopy
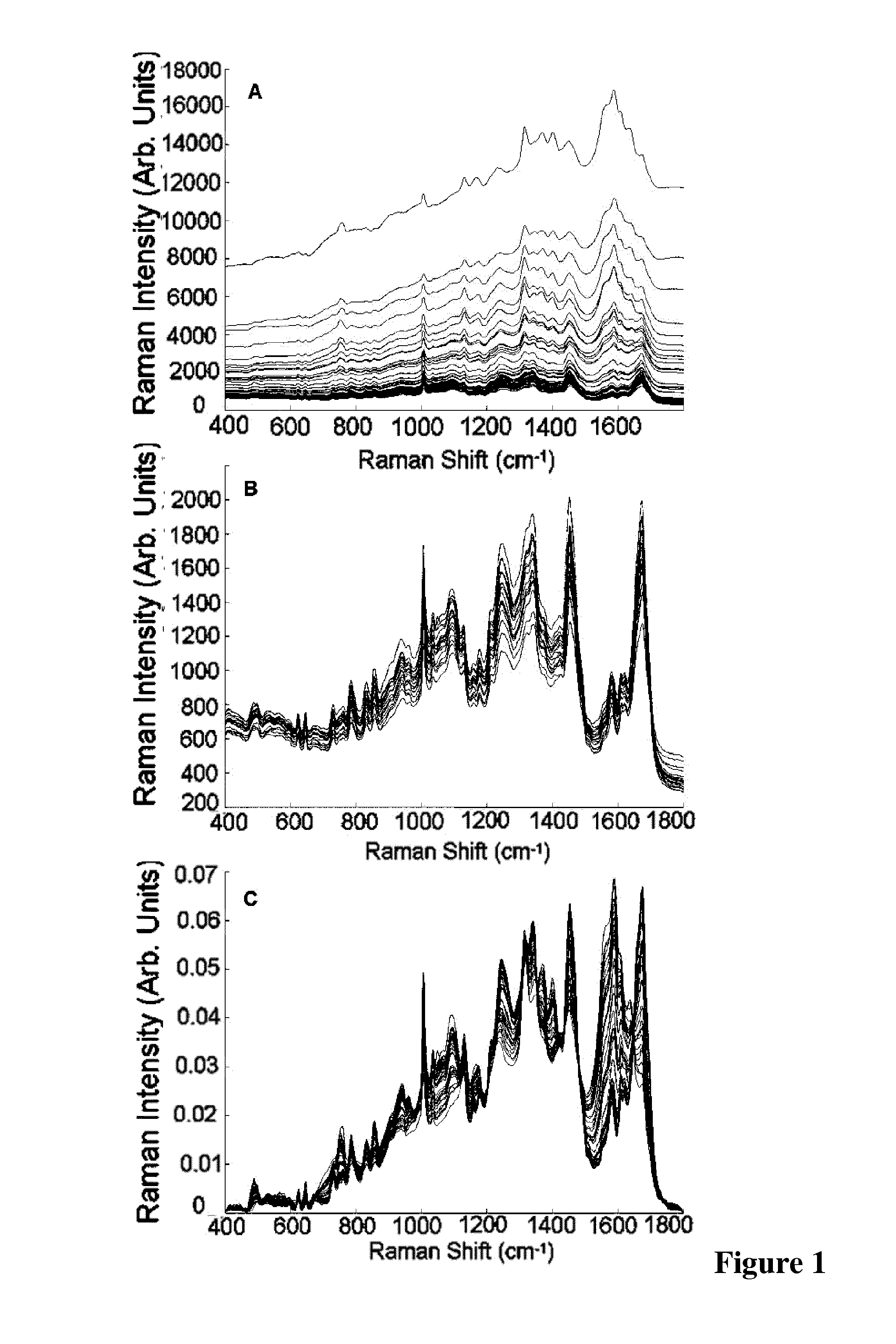
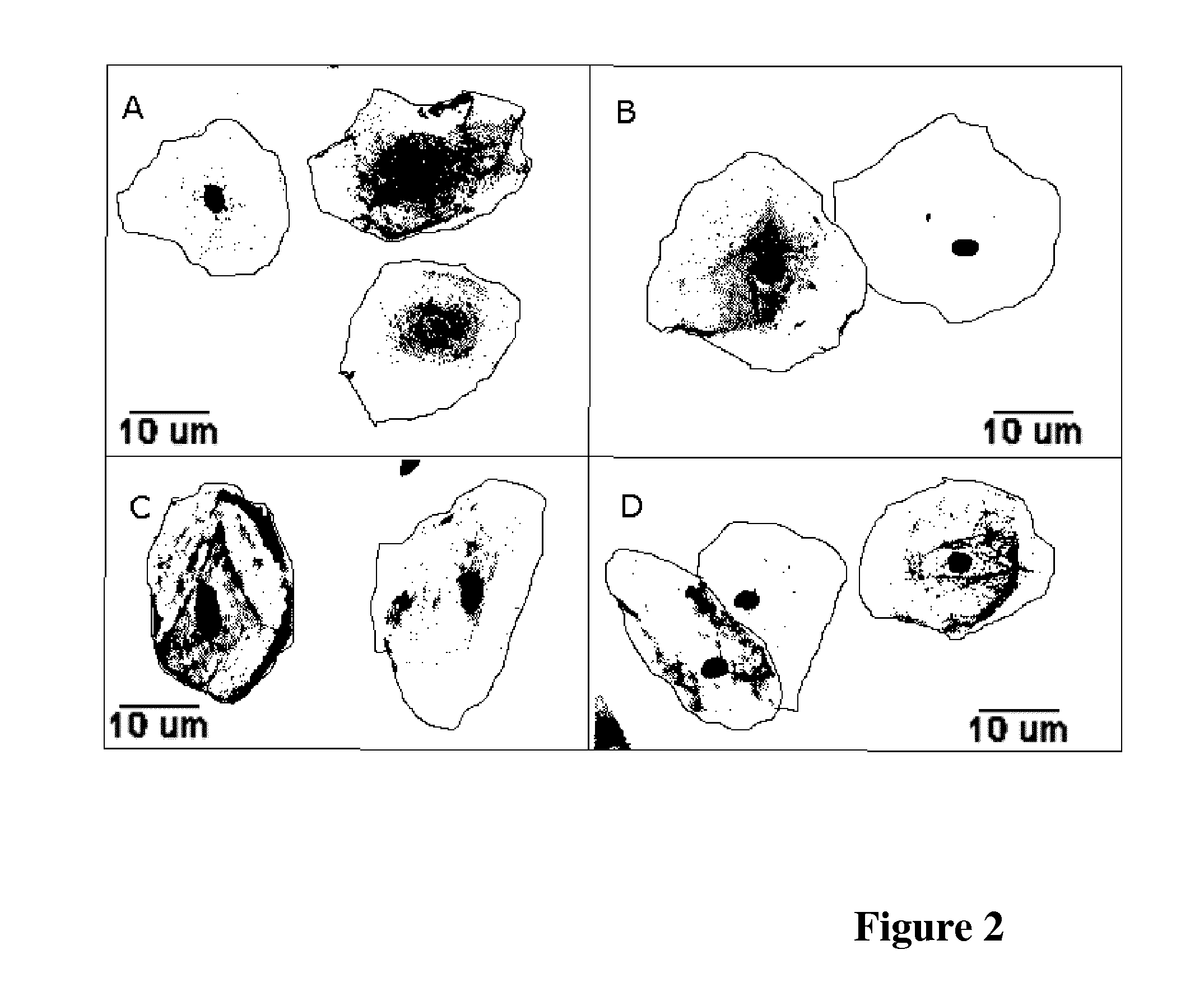
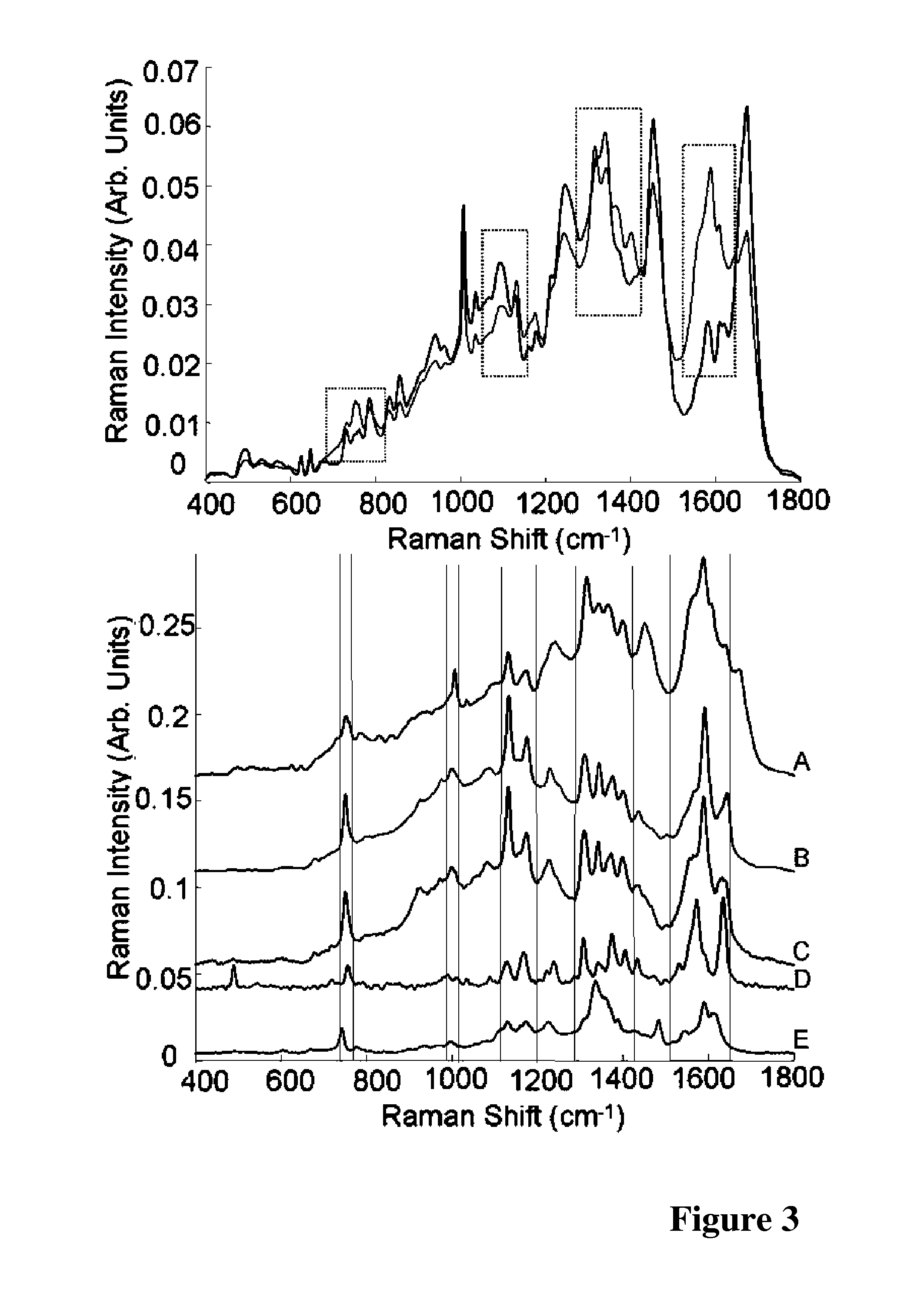
A method of performing a spectroscopy process on a fixed biological sample is described. The method comprises the steps of: (i) treating the fixed biological material to cause oxidation of haemoglobin present in the fixed biological material, and (ii) performing spectroscopy on the treated fixed biological sample. The method is particularly suitable for cervical sample preparation for reduced variability in Raman spectroscopy.
Owner:DUBLIN INST OF TECH
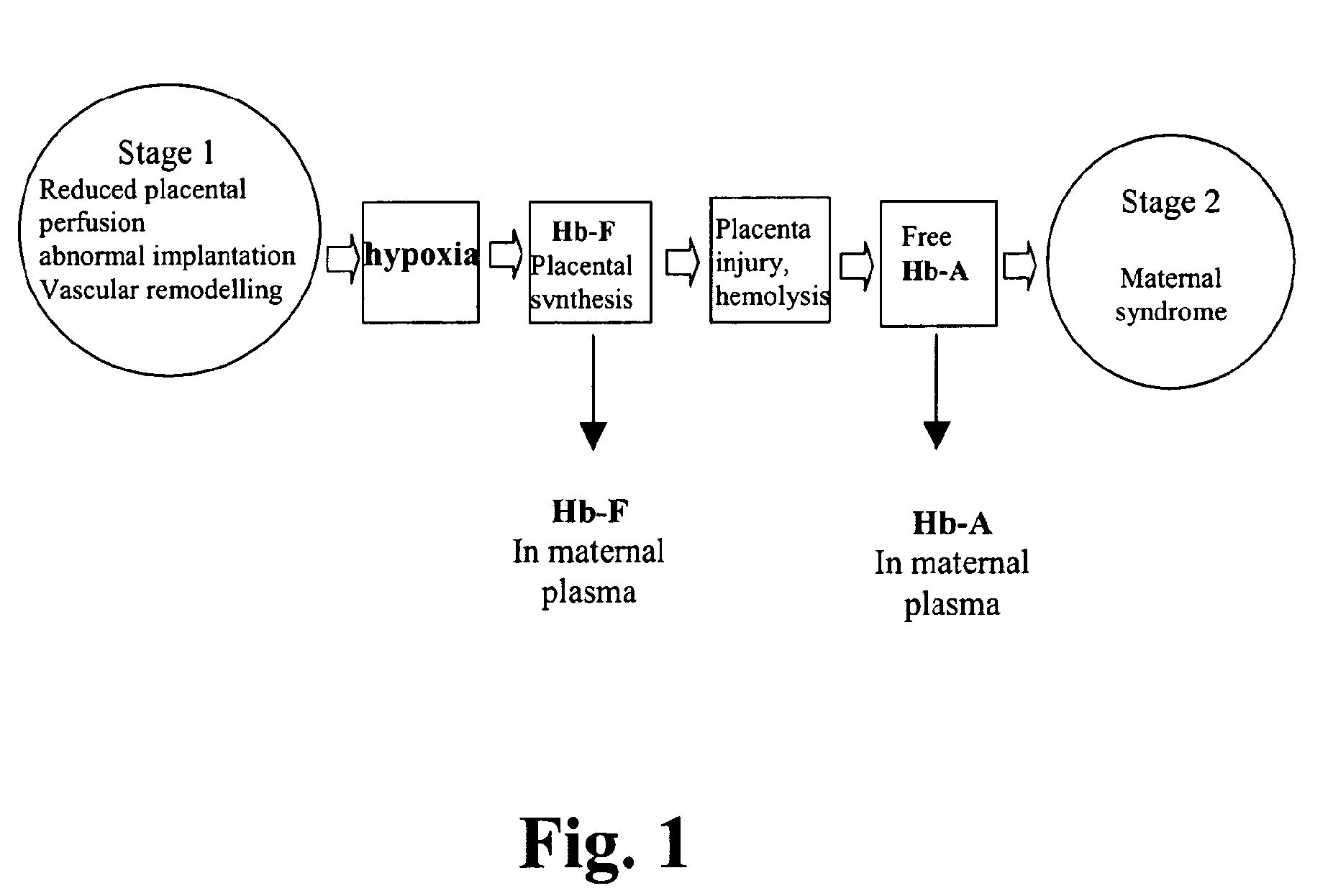
Diagnosis and treatment of preeclampsia
InactiveUS20100105070A1Avoid unnecessary hospitalisationReduce riskPeptide/protein ingredientsDisease diagnosisDiagnosis earlyFree haemoglobin
The present invention relates to biomarkers for preeclampsia as well as treatment of this disease. In particular, the invention relates to methods for diagnosis or aiding in the diagnosis of preeclampsia of a pregnant female mammal to detect elevated levels of free haemoglobin, particularly free fetal haemoglobin. This facilitates and makes possible early diagnosis and clinical intervention when a preeclamptic condition is found. In addition, the invention relates to a method to treat female mammals with preeclampsia with the purpose to reverse the pathological conditions associated with this disease.
Owner:GUARD THERAPEUTICS INT AB
Enzymatic determination of hba1c
ActiveCN106461682AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisHaemolysisGlycated haemoglobin
The present invention relates to a method for determining the amount of glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), in which -if required -the erythrocytes in a sample are haemolysed, the haemoglobin that is then released -if required -is contacted with a proteolytic agent and the glycated haemoglobin degradation products obtained in this way or otherwise are quantified. In order to provide such a process and reagents employable therein that has / have the property of sufficient stability of the chemical compounds that are essential to the reaction, the provision of the requisite proteolytic agent in the form of an inactivated protease is proposed, which is then only reactivated in situ. In particular embodiments of the invention, for the stabilization of the haemoglobin which is unfolded at a very low pH in the range from 1 to 3, at least one suitable stabilizer should be present in the haemolysis solution, and, in the embodiments of the invention in which a leuco dye is used in connection with the determination of the amount of HbA1c, it is proposed in accordance with the invention that the latter be stabilized with particular phosphine compounds and / or thio compounds.
Owner:DIASYS DIAGNOSTIC SYST
Method for validating a biometrical acquisition, mainly a body imprint
The invention relates to a method for validating a biometrical acquisition, mainly the acquisition of a body imprint of a body area such as fingerprints or a face imprint, wherein the method involves together with the biometric acquisition: lighting the body area using at least one radiation having at least two respective different wavelengths between approximately 500 nm and 1150 nm; taking at least two reflectometry measurements concerning said and at least two wavelengths for measuring the reflection index of the tissues for these wavelengths; calculating the ratio for the two measured indices; and comparing the ratio with a range of reference values characterising a haemoglobin-containing living tissue in terms of proportions of oxygenated and non-oxygenated forms characteristic of the living state for the wavelengths in question; if the ratio is included in said range, the body area is considered as living and the biometrical acquisition is validated; and conversely, if the body area is considered as not living, the biometrical acquisition cannot be validated.
Owner:MORPHO INC
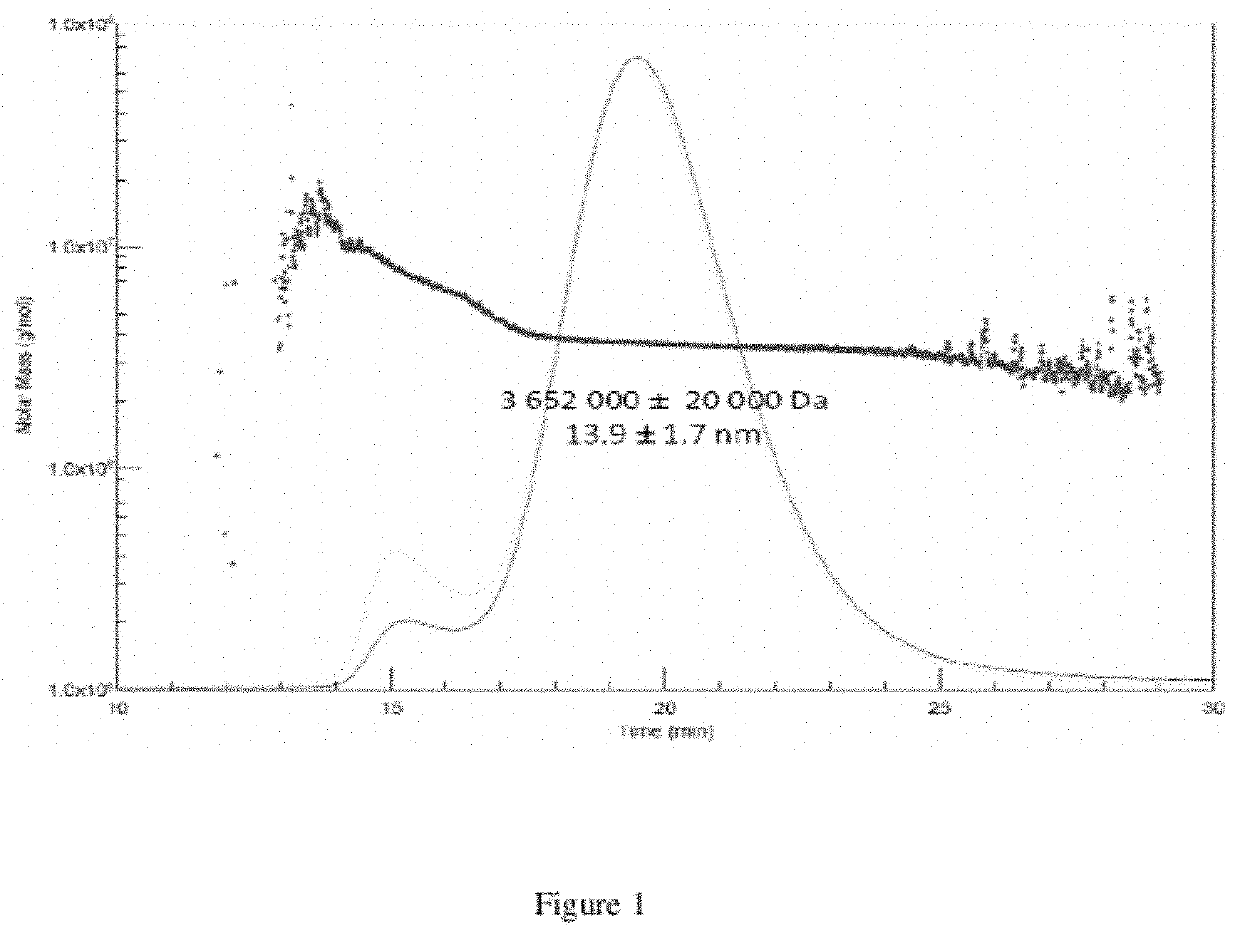
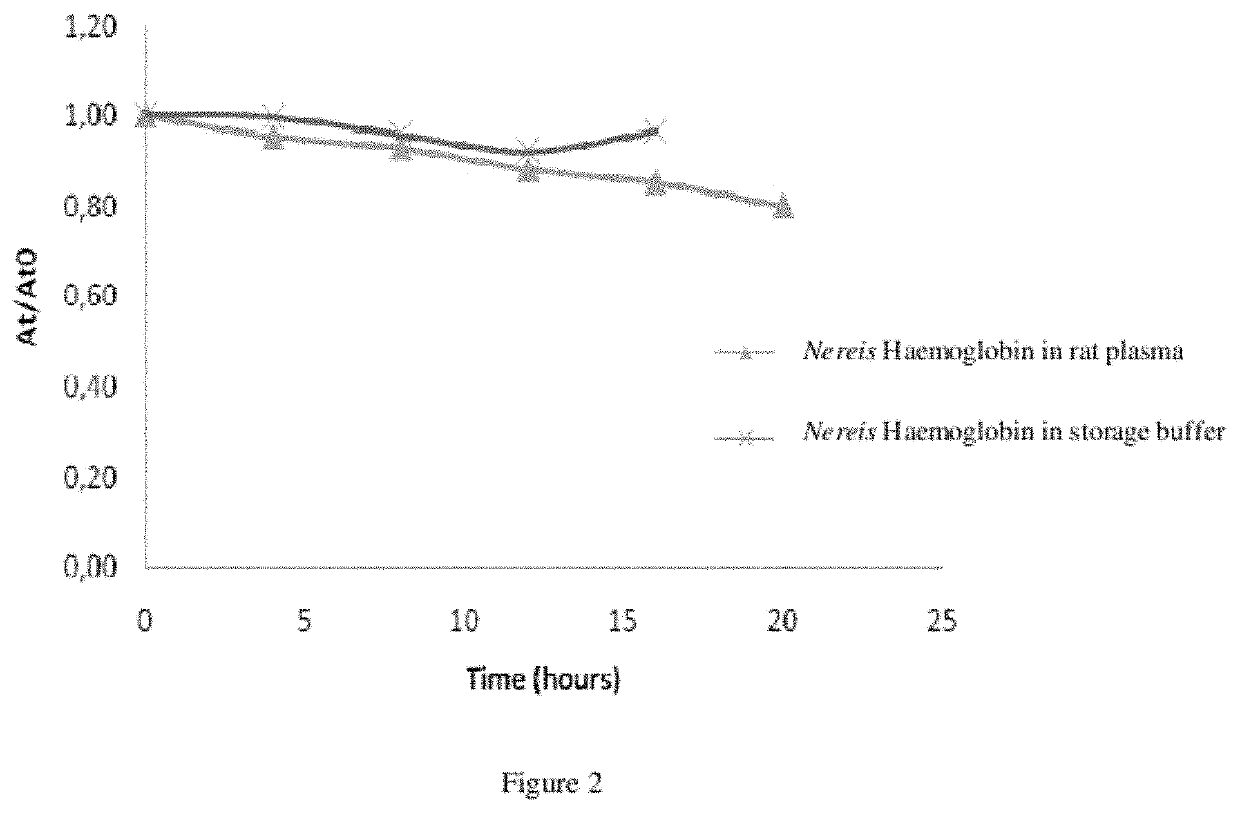
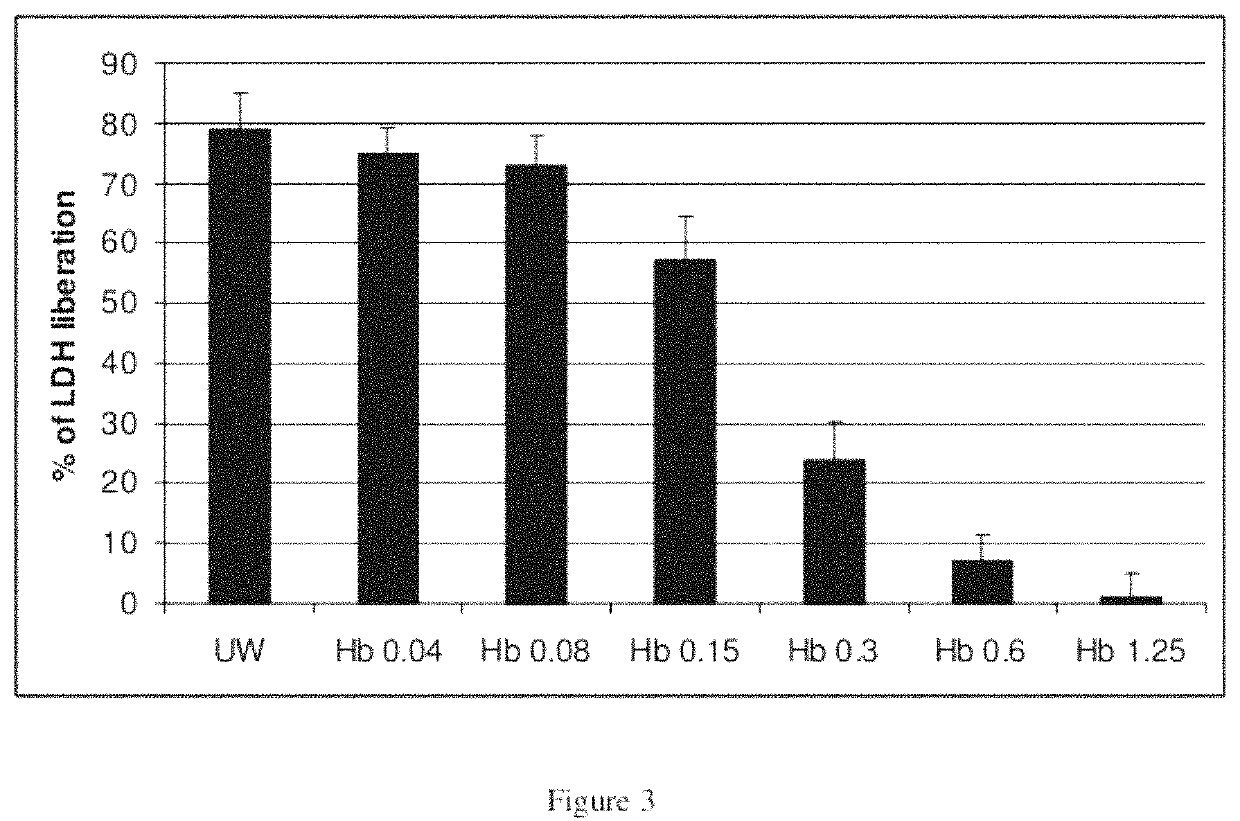
Heamoglobin and uses thereof
ActiveUS11224218B2Reduce riskConvenient amountBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyCell culture media
The present invention relates to isolated haemoglobin from worms belonging to the Nereididae family and its use in cell culture medium, in preservation solutions and as artificial oxygen carrier for transfusion.
Owner:HEMARINA
Factors
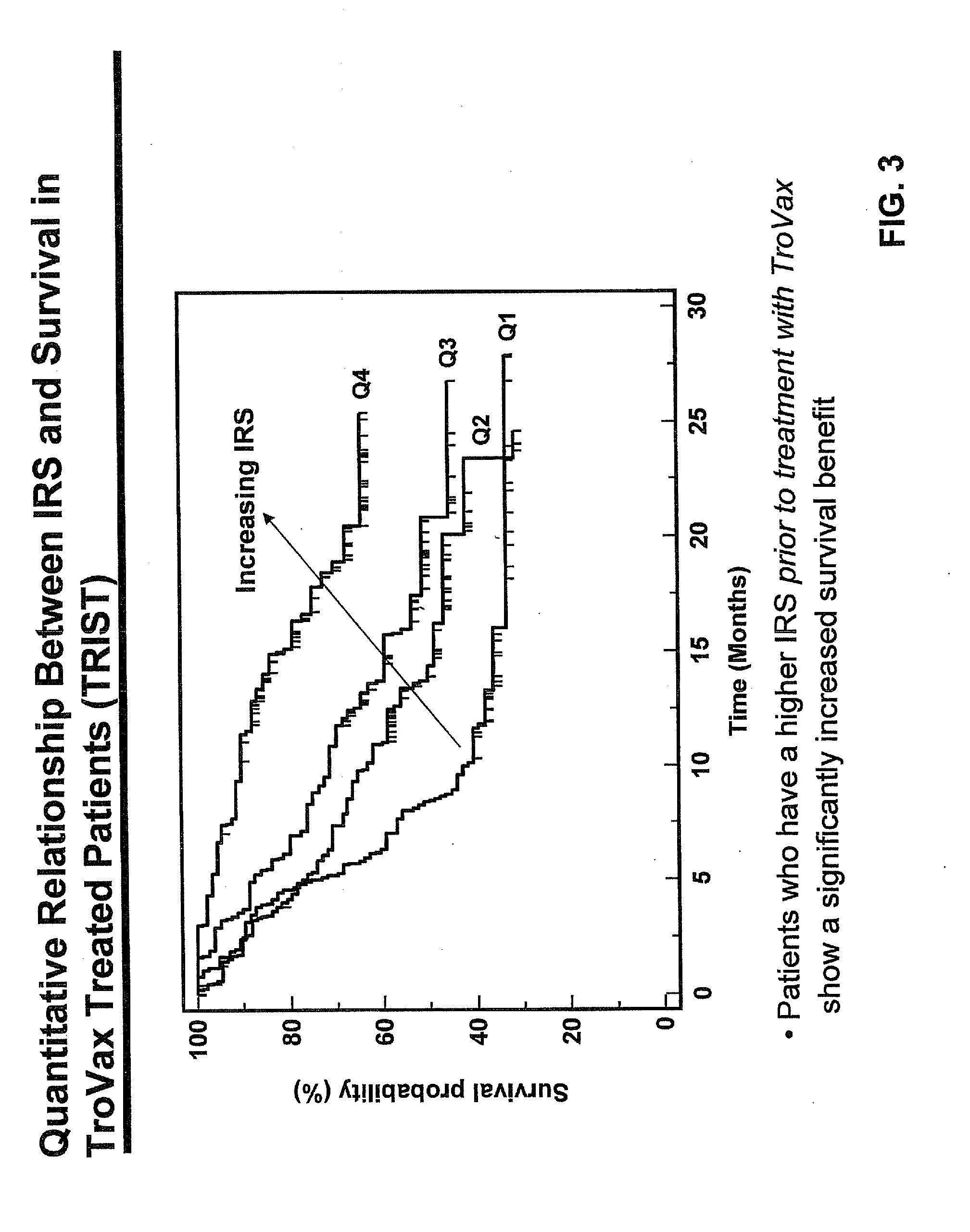
InactiveUS20120039943A1Beneficial effectGreat effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisImmunotherapyReference level
A method for determining a prognosis for benefit for a cancer patient receiving immunotherapy treatment involving (a) measuring a level of platelets and haemoglobin in a sample from the cancer patient, and (b) comparing the level of platelets in the sample to a reference level of platelets and comparing the level of haemoglobin in the sample to a reference level of haemoglobin, wherein a lower level of platelets and higher level of haemoglobin in the sample correlates with increased benefit to the patient.
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
Diagnostics of gingivitis based on salivary il-1beta and hgf
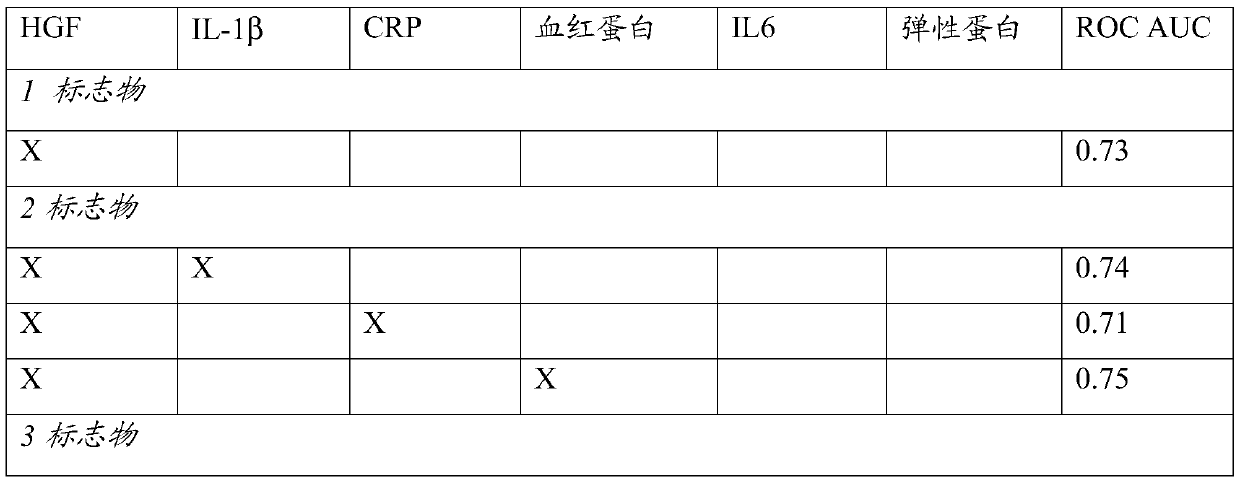
Disclosed is an in vitro method for assessing the presence of gingivitis in a human subject. The method is based on the insight to determine a selection of three biomarker proteins. Accordingly, in a saliva sample of the subject the concentrations are measured of the proteins Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and Interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and at least one of C reactive protein (CRP) and Haemoglobin. Based on the concentrations as measured, a value is determined reflecting the joint concentrations for said proteins. This value is compared with a threshold value reflecting in the same manner the joint concentrations associated with the absence of gingivitis or periodontitis. The comparison allows to assessing whether the testing value is indicative of the presence of gingivitis in said subject. Thereby, typically, a testing value reflecting a joint concentration above the joint concentration reflected by the threshold, is indicative of the presence of gingivitis.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Factors
InactiveUS20160195554A1Improve the level ofImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsPlateletImmunotherapy
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
Treatment or prevention of anaemia in pregnant non-human mammals
ActiveUS11040059B2Organic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismHaemoglobin levelsObstetrics
The present invention relates to an iron carbohydrate complex for use in a method of increasing the blood haemoglobin concentration in a pregnant non-human mammal, wherein the pregnant non-human mammal having a blood haemoglobin level of 105 g / L or less, is administered one or more doses of iron carbohydrate complex comprising an amount of elemental iron of 1800 mg or more per dose. The method relates to the further effects of decreasing the rate of stillborn offsprings from a pregnant non-human mammal having a blood haemoglobin level of 105 g / L or less, increasing the blood haemoglobin concentration of offspring litters within 3 days from birth and / or weaning, or increasing the litter size in a subsequent parity of a non-human mammal having a blood haemoglobin level of 105 g / L or less.
Owner:PHARMACOSMOS HLDG
Blood filter
ActiveUS20180015211A1Increase haemolysisWorsen haemolysisOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationHaemoglobin bindingHeme
A blood filter device having an iron-chelating molecule, a haem-binding molecule and a haemoglobin-binding molecule bound to a support. Use of the device in a vessel containing blood, for example a blood bag or a flow line, removes haemolysis-derived components from the blood.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC +1
Device for withdrawing venous thrombus from lower limb
The invention discloses a device for withdrawing a venous thrombus from a lower limb. The device comprises a thrombus withdrawing module, wherein the thrombus withdrawing module comprises a filter stand with elasticity and a thrombus withdrawing bag, the thrombus withdrawing bag is of a metallic-wire-woven reticular structure with one open end and one closed end, and the open end of the thrombus withdrawing bag is fixedly connected with the middle of the filter stand. According to the device disclosed by the invention, the problems during thrombus withdrawing such as thrombolytic drug employment, thrombus falling occurrence and haemoglobinuria occurrence can be avoided, the cost is low, the structure and operation are simple, and thus, the device has higher safety.
Owner:周汝航
Use of annelid haemoglobin for maintaining stem cells in the undifferentiated state
ActiveCN104011202AAvoid problems with immunological reactionsEpidermal cells/skin cellsArtificial cell constructsProtomerAnnelid
Owner:埃玛里纳
Establishment method of streptomyces diastatochromogenes expression system
InactiveCN103289946AImproved ability to synthesize toyocamycinImprove abilitiesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesToyocamycinPromoter
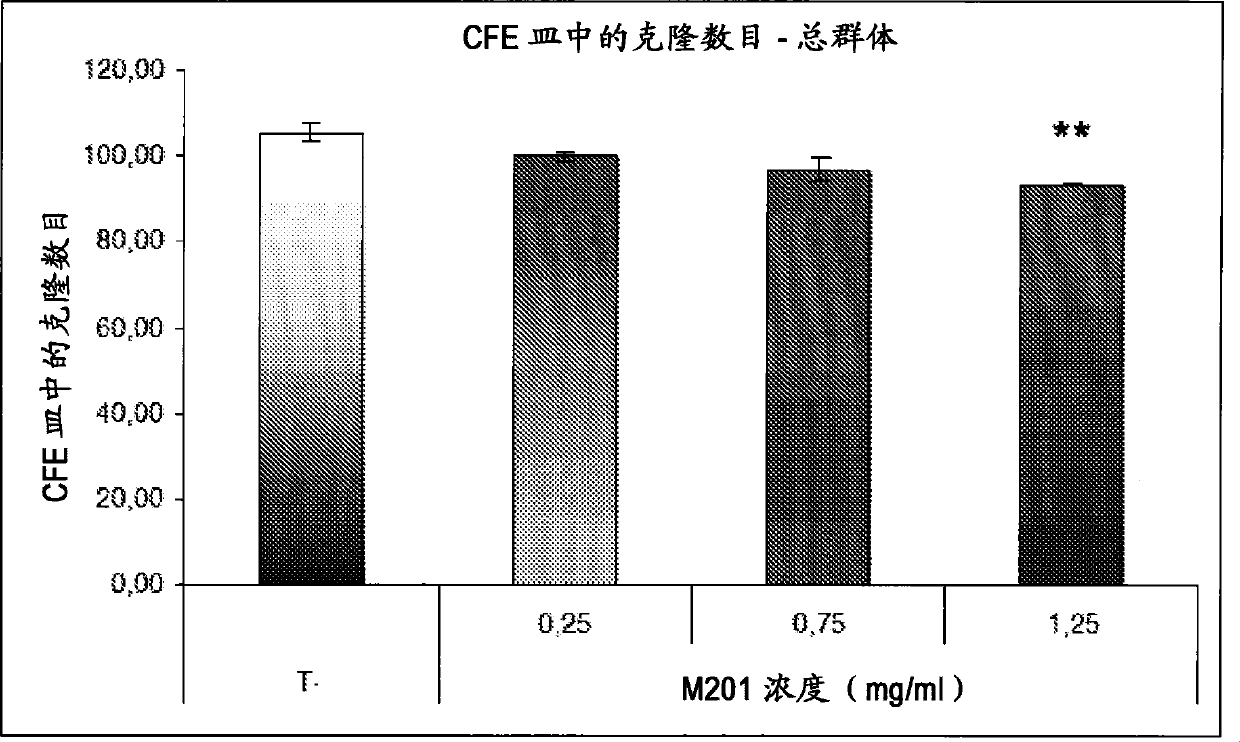
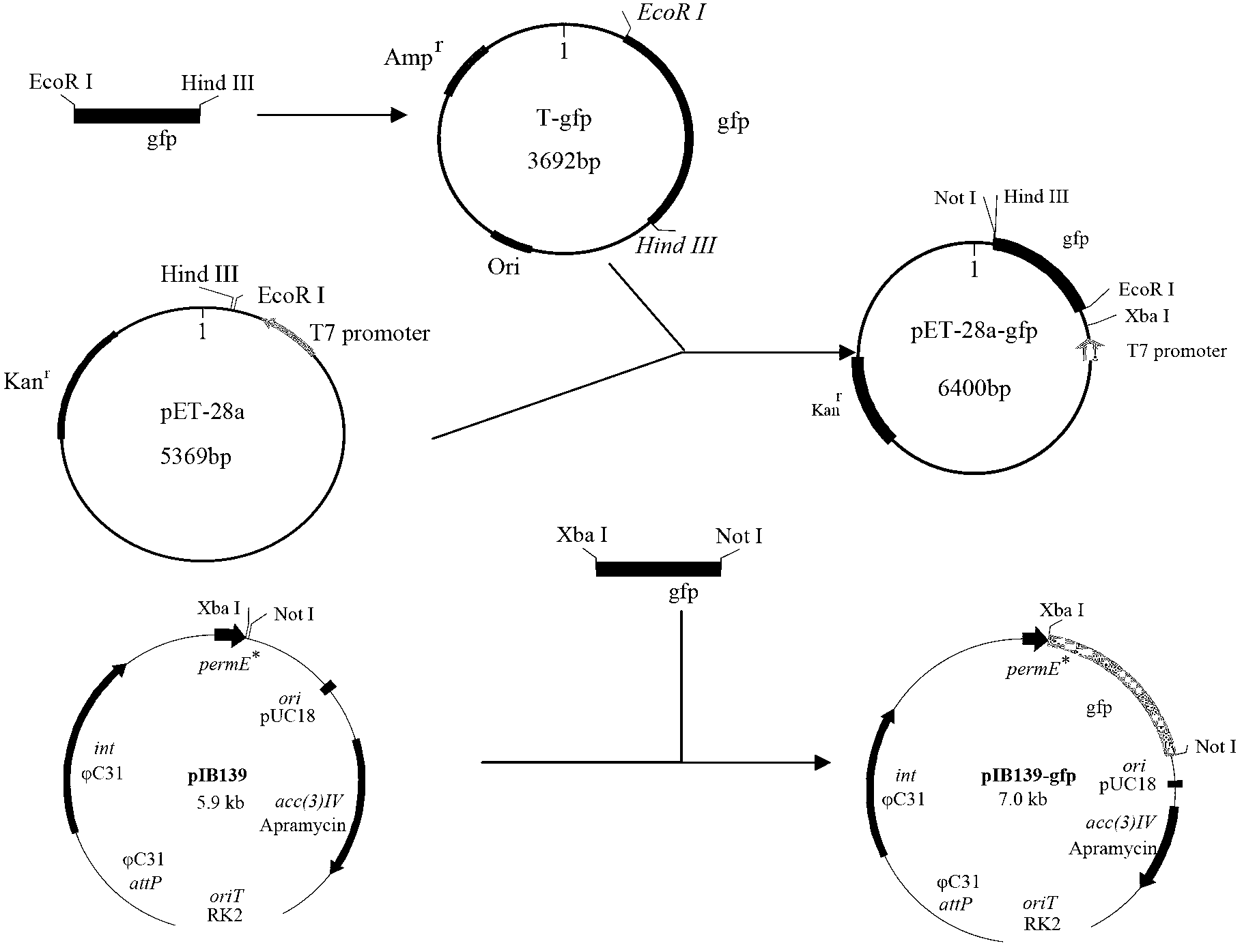
The invention discloses an establishment method of a streptomyces diastatochromogenes expression system. The establishment method comprises the following steps of: screening a necessary or efficient ingredient of the streptomyces diastatochromogenes expression system by virtue of a green fluorescent protein gene gfp at first, and then constructing the expression system of a target gene, wherein the necessary or efficient ingredient is erythromycin resistance genome constructive promoter permE*; the target gene promotes production of toyocamycin; and the target gene is a haemoglobin gene vgb. The construction processes are as follows: 1) constructing a carrier pIB139-gfp; and 2) integrating the expression carrier into a streptomyces diastatochromogenes chromosome by virtue of a conjugational transfer method, so as to obtain a recombinant bacterium. The invention provides an efficient screening method and application of the streptomyces diastatochromogenes expression system. Compared with the original strain, the recombinant bacterium has the advantages that the toyocamycin yield of the recombinant bacterium is increased by at least 21.2%, and the concentration of the recombinant bacterium is increased by 11.6%.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Container comprising haemoglobin fractions
ActiveUS20170350905A1Biological material analysisBiological testingHemeproteinReliability engineering
Owner:EUROTROL
Enzymatic determination of HbA1c
ActiveUS10202632B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisHemolysisRed blood cell
A method for determining the amount of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), in which—if required—the erythrocytes in a sample are hemolyzed, the haemoglobin that is then released—if required—is contacted with a proteolytic agent and the glycated hemoglobin degradation products obtained in this way or otherwise are quantified is disclosed. In order to provide such a process and reagents employable therein that has / have the property of sufficient stability of the chemical compounds that are essential to the reaction, the provision of the requisite proteolytic agent in the form of an inactivated protease is proposed, which is then only reactivated in situ. For the stabilization of the hemoglobin, which is unfolded at a very low pH in the range from 1 to 3, at least one suitable stabilizer should be present in the hemolysis solution, and, where a leuco dye is used in connection with the determination of the amount of HbA1c, it is proposed that the latter be stabilized with particular phosphine compounds and / or thio compounds.
Owner:DIASYS DIAGNOSTIC SYST
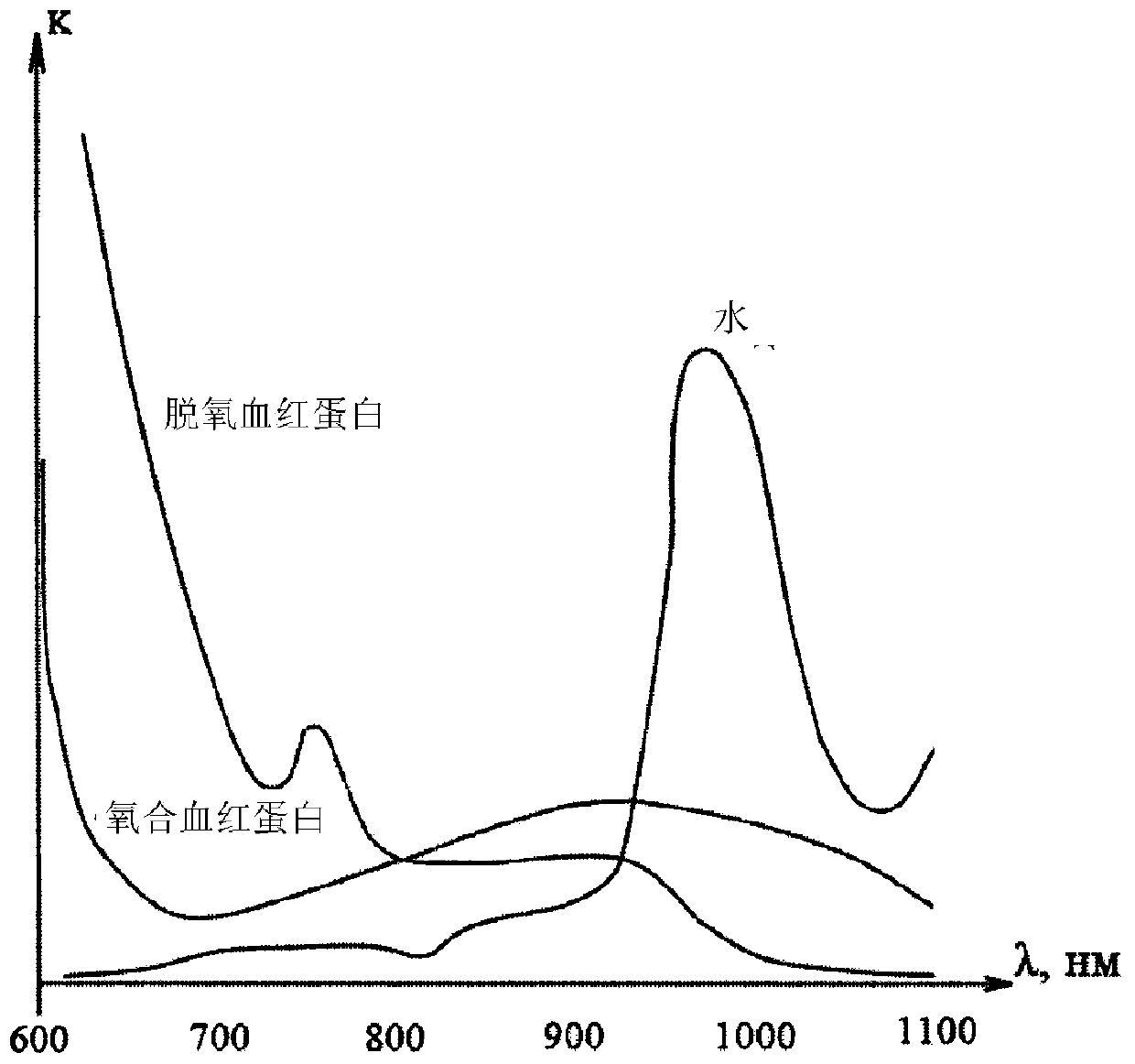
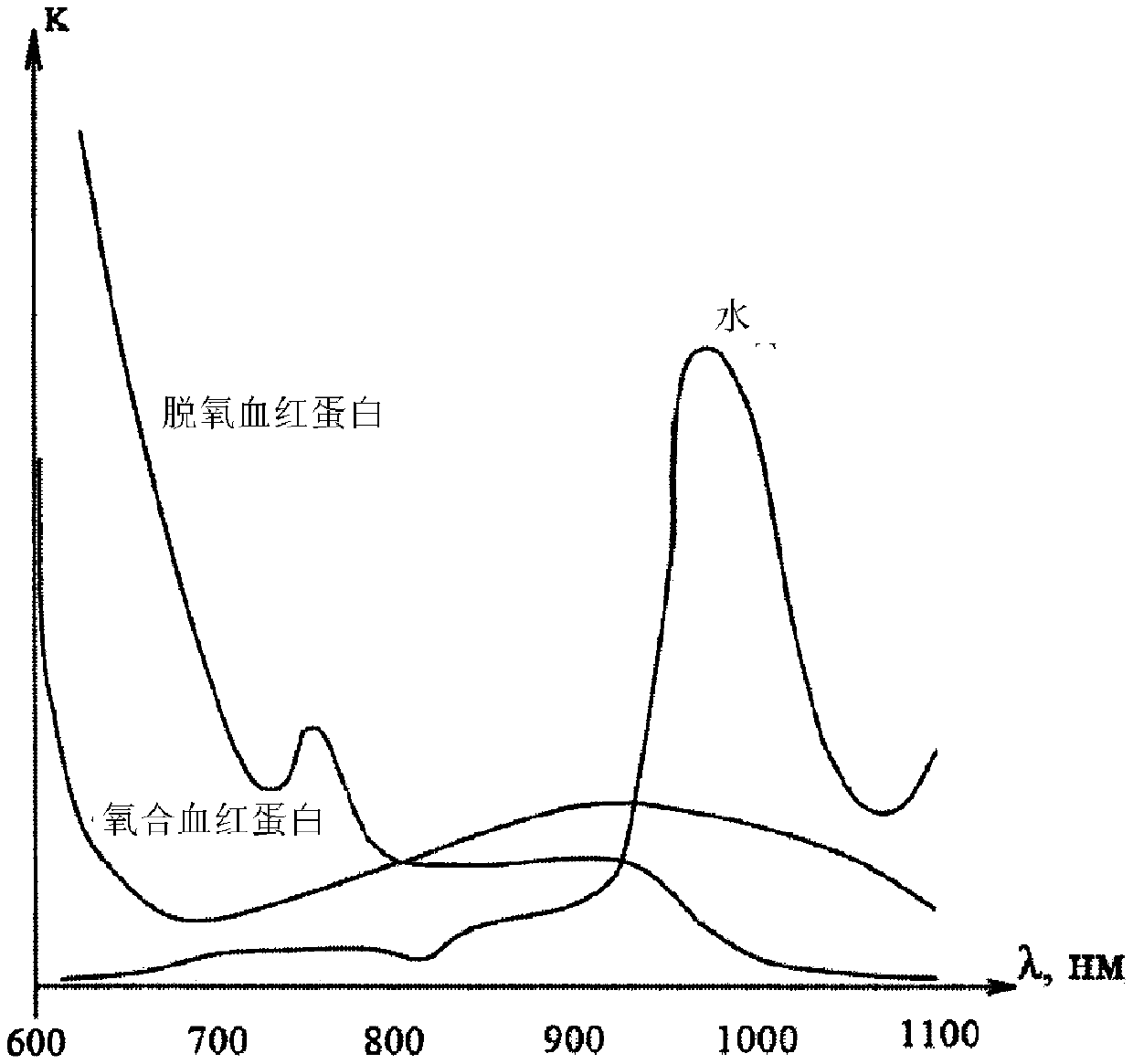
Method for non-invasively determining haemoglobin and oxygen concentrations in the blood
InactiveCN109890287AImprove accuracyAchieve technical effectsDiagnostic recording/measuringOptical sensorsOptical radiationChemical composition
The invention provides a method for non-invasively determining haemoglobin and oxygen concentrations in the blood, and relates to the field of analysis of the chemical composition of materials and canbe used in diagnostic medical equipment for non-invasively determining haemoglobin and oxygen concentrations in the blood. The method comprises exposing a biological tissue to an optical radiation infirst, second and third wavelength ranges successively, which comprise the values of 700 nm, 880 nm and 960 nm respectively; receiving the reflected optical radiation; converting the latter into an electric signal; determining the haemoglobin concentration on the basis of the sum of the electrical signals obtained during exposure to the optical radiation in the first and second wavelength ranges,which sum is reduced by a value determined by means of the electric signal obtained during exposure to the optical radiation in the third range; and determining the oxygen concentration on the basisof the difference between the electrical signals obtained during exposure to the optical radiation in the first and second wavelength ranges, which difference is reduced by a value determined by meansof the electric signal obtained during exposure to the optical radiation in the third range. The invention makes it possible, when determining haemoglobin and oxygen concentrations, to reduce inaccuracies caused by the presence of water in the biological tissue undergoing examination.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU TELEBIOMET
Container comprising haemoglobin fractions
Owner:EUROTROL
Modified haemoglobin proteins
PendingUS20200131247A1Increase ratingsEnhances reduction of at least one metallic ionPeptide/protein ingredientsHaemoglobins/myoglobinsBiochemistryProteinoid
The present invention relates to modified proteins e.g. oxygen-carrying proteins, with improved or enhanced, in comparison to a reference protein, reduction of a metal ion associated with the modified protein. The present invention also relates to methods of using such modified proteins and compositions comprising such proteins e.g. in therapy.
Owner:UNIV OF ESSEX ENTERPRISES
Diagnostics of gingivitis based on salivary il-1beta and hgf
Disclosed is an in vitro method for assessing the presence of gingivitis in a human subject. The method is based on the insight to determine a selection of three biomarker proteins. Accordingly, in asaliva sample of the subject the concentrations are measured of the proteins Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1beta), and at least one of C reactive protein (CRP) and Haemoglobin. Based on the concentrations as measured, a value is determined reflecting the joint concentrations for said proteins. This value is compared with a threshold value reflecting in the same manner the joint concentrations associated with the absence of gingivitis or periodontitis. The comparison allows to assessing whether the testing value is indicative of the presence of gingivitis in said subject. Thereby, typically, a testing value reflecting a joint concentration above the joint concentration reflected by the threshold, is indicative of the presence of gingivitis.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Enzymatic determination of HBA1c
ActiveUS10093959B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisGlycated haemoglobinHaemolysis
A method for determining the amount of glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), in which—if required—the erythrocytes in a sample are haemolysed, the haemoglobin that is then released—if required—is contacted with a proteolytic agent and the glycated haemoglobin degradation products obtained in this way or otherwise are quantified is disclosed. In order to provide such a process and reagents employable therein that has / have the property of sufficient stability of the chemical compounds that are essential to the reaction, for the stabilization of the haemoglobin which is unfolded at a very low pH in the range from 1 to 3, at least one suitable stabilizer is present in the haemolysis solution. Where a leuco dye is used in connection with the determination of the amount of HbA1c, it is proposed that the latter be stabilized with particular phosphine compounds and / or thio compounds, and, in particular embodiments, the requisite proteolytic agent is to be provided in the form of an inactivated protease which is then only reactivated in situ.
Owner:DIASYS DIAGNOSTIC SYST
Thermostabilized amadoriases and uses thereof
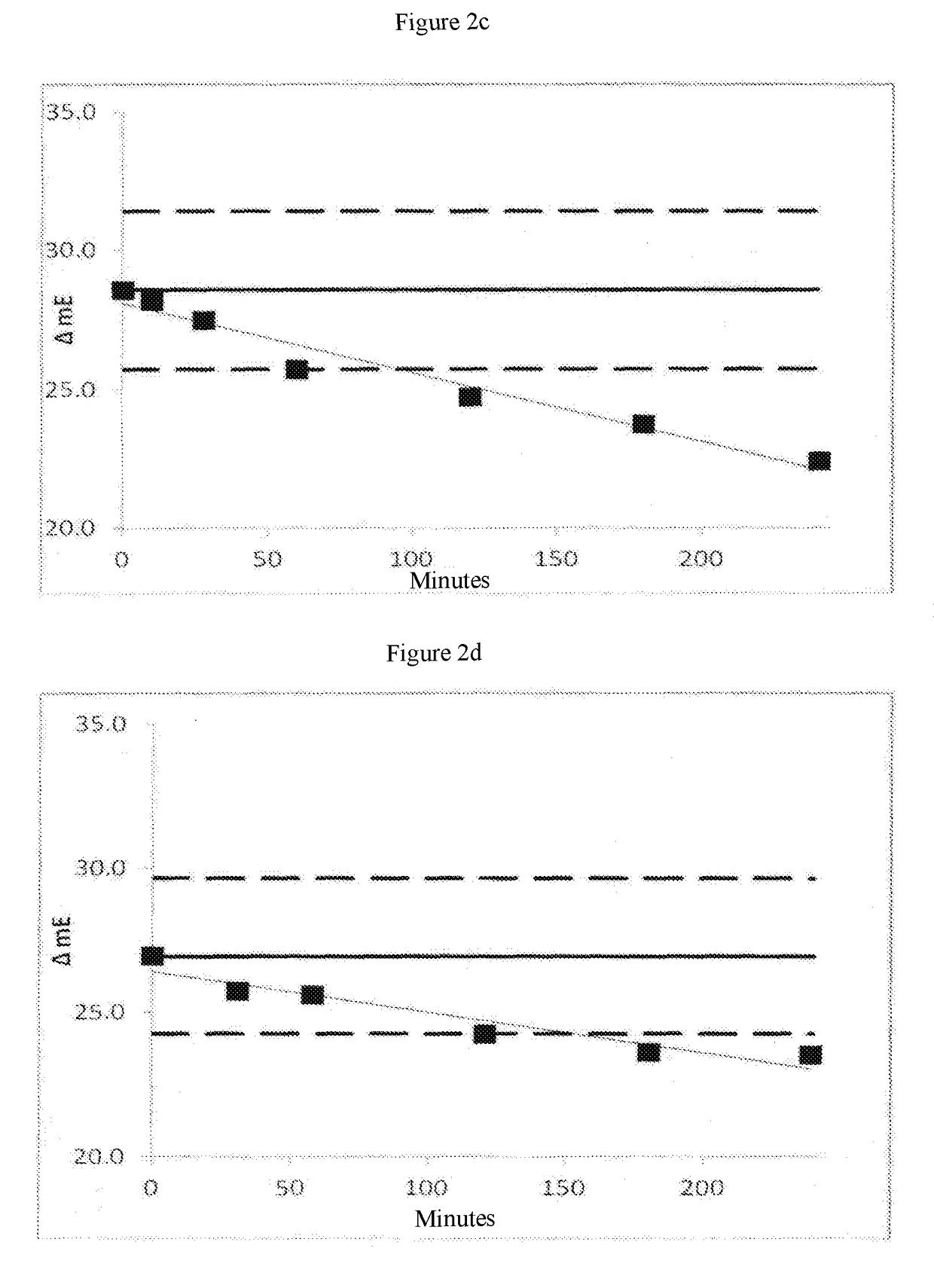
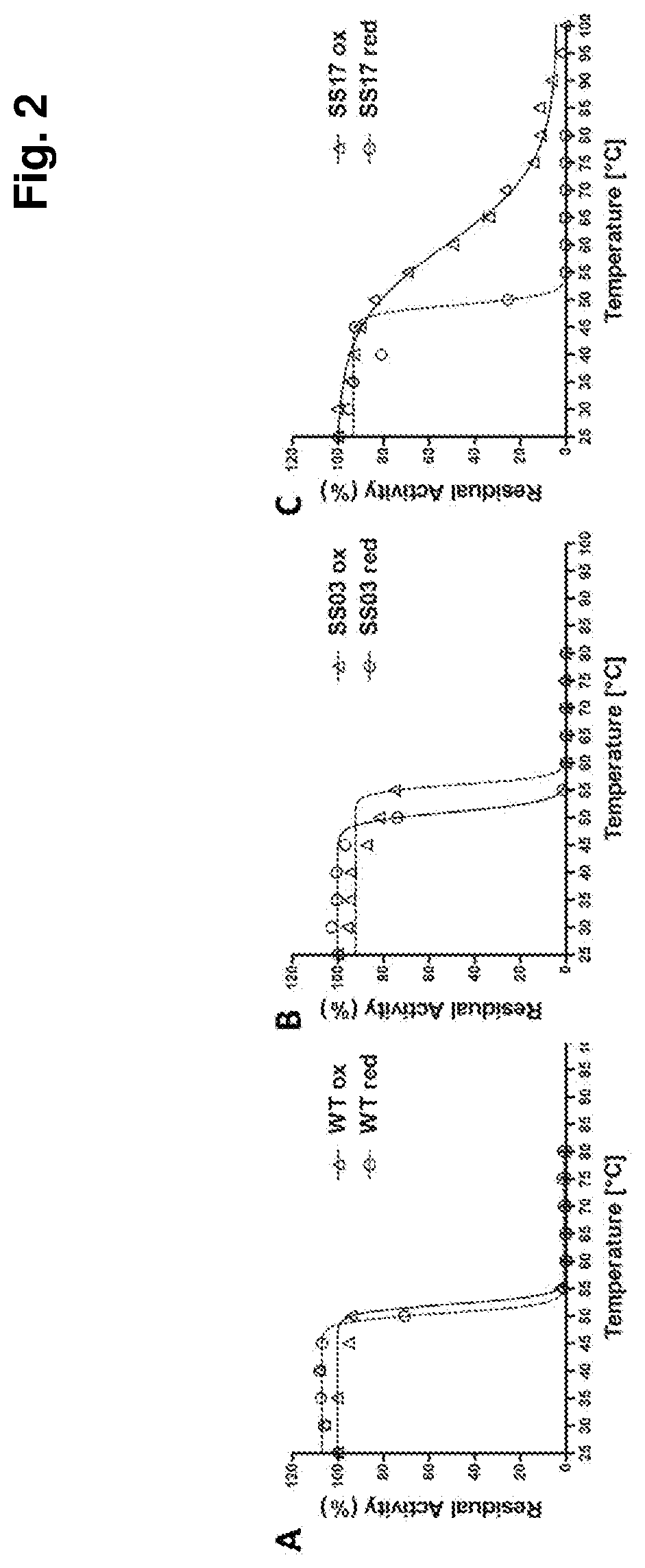
ActiveUS20210189353A1Quality lossReduce vivo glycationDisease diagnosisEnzymesBiotechnologyFood industry
The present invention refers to Amadoriase enzyme protein variants having de-glycating activity and improved thermostability compared to the wild type Amadoriase. The present invention refers also to the use of the thermostabilized Amadoriase as deglycating agent, preferably in the food industry. Moreover, the present invention refers to the use of the thermostabilized Amadoriase as diagnostic and / or therapeutic tools. Preferably, the Amadoriase enzyme protein variants of the invention can be used for determining the level of glycated haemoglobin in a biological sample and therefore for monitoring diabetes.
Owner:FOND INST ITAL DI TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com