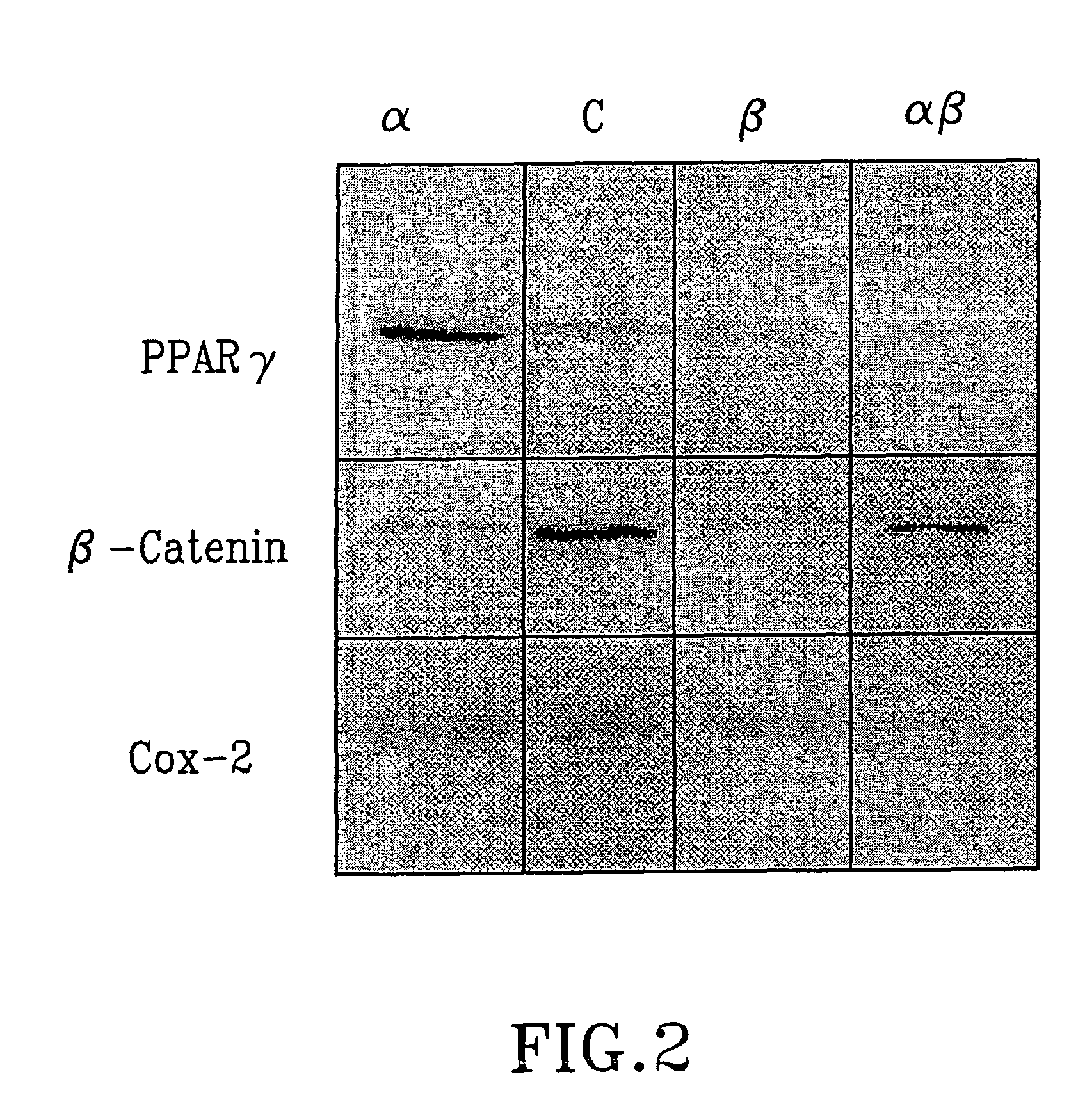
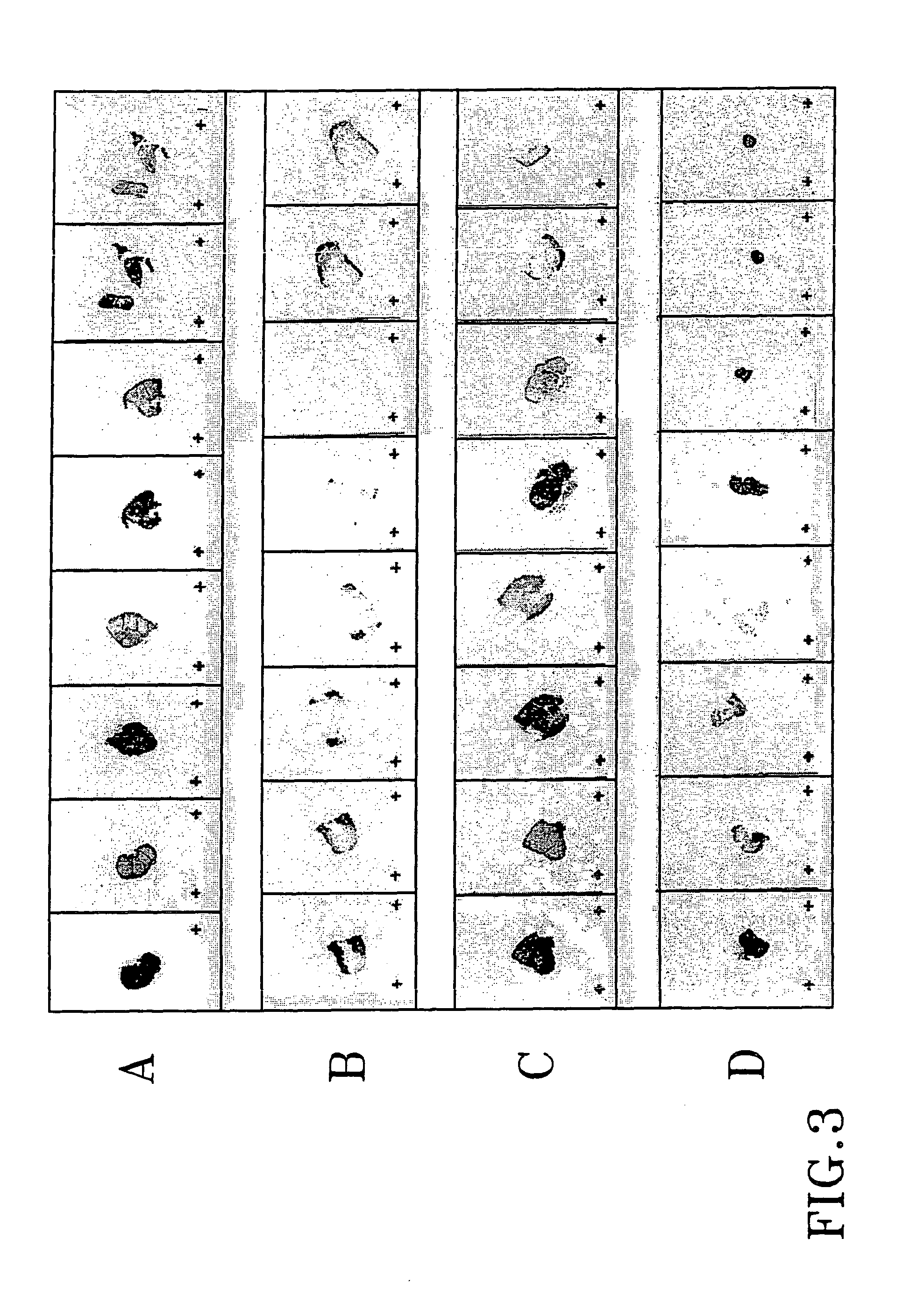
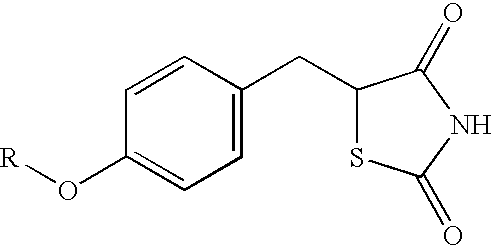
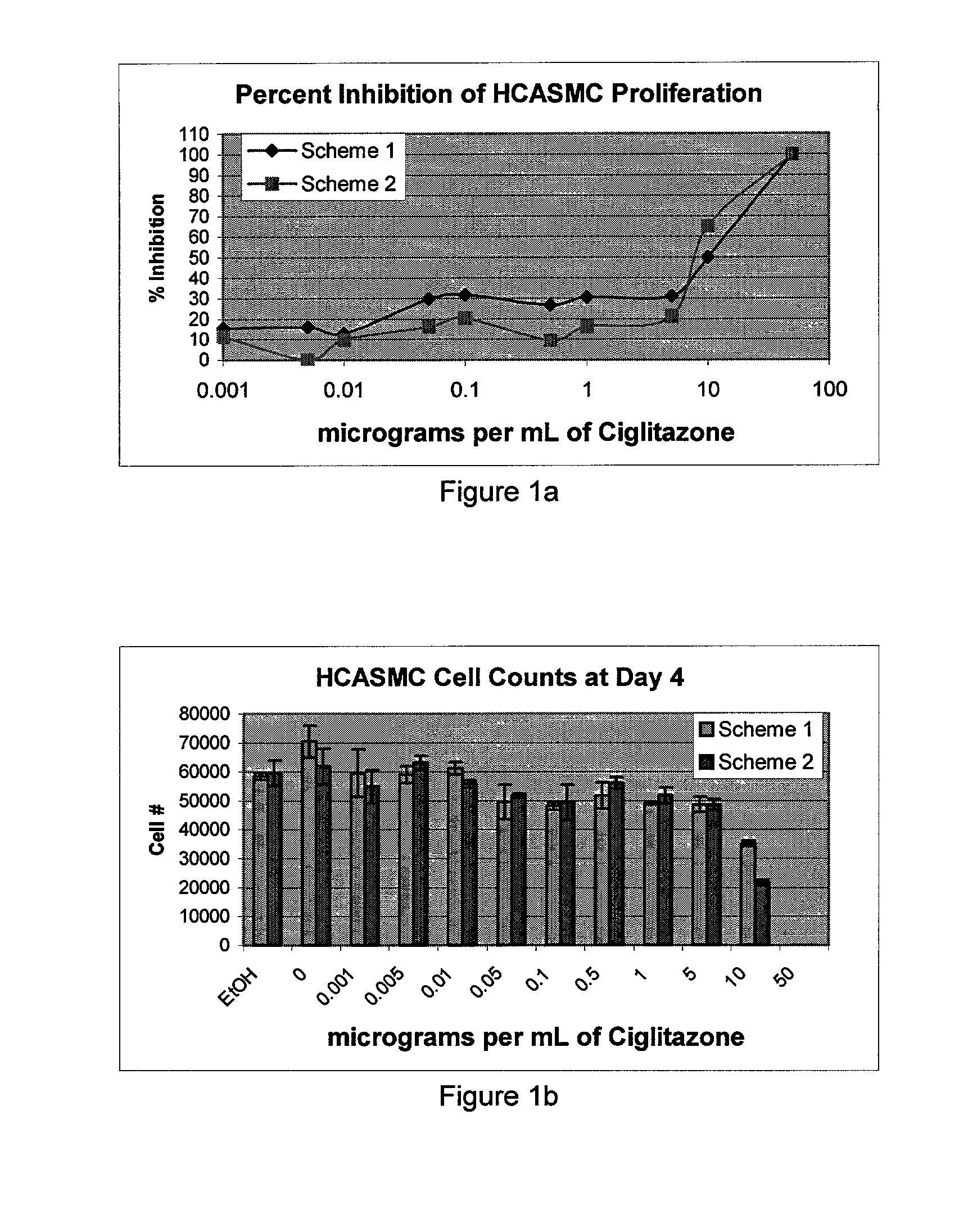
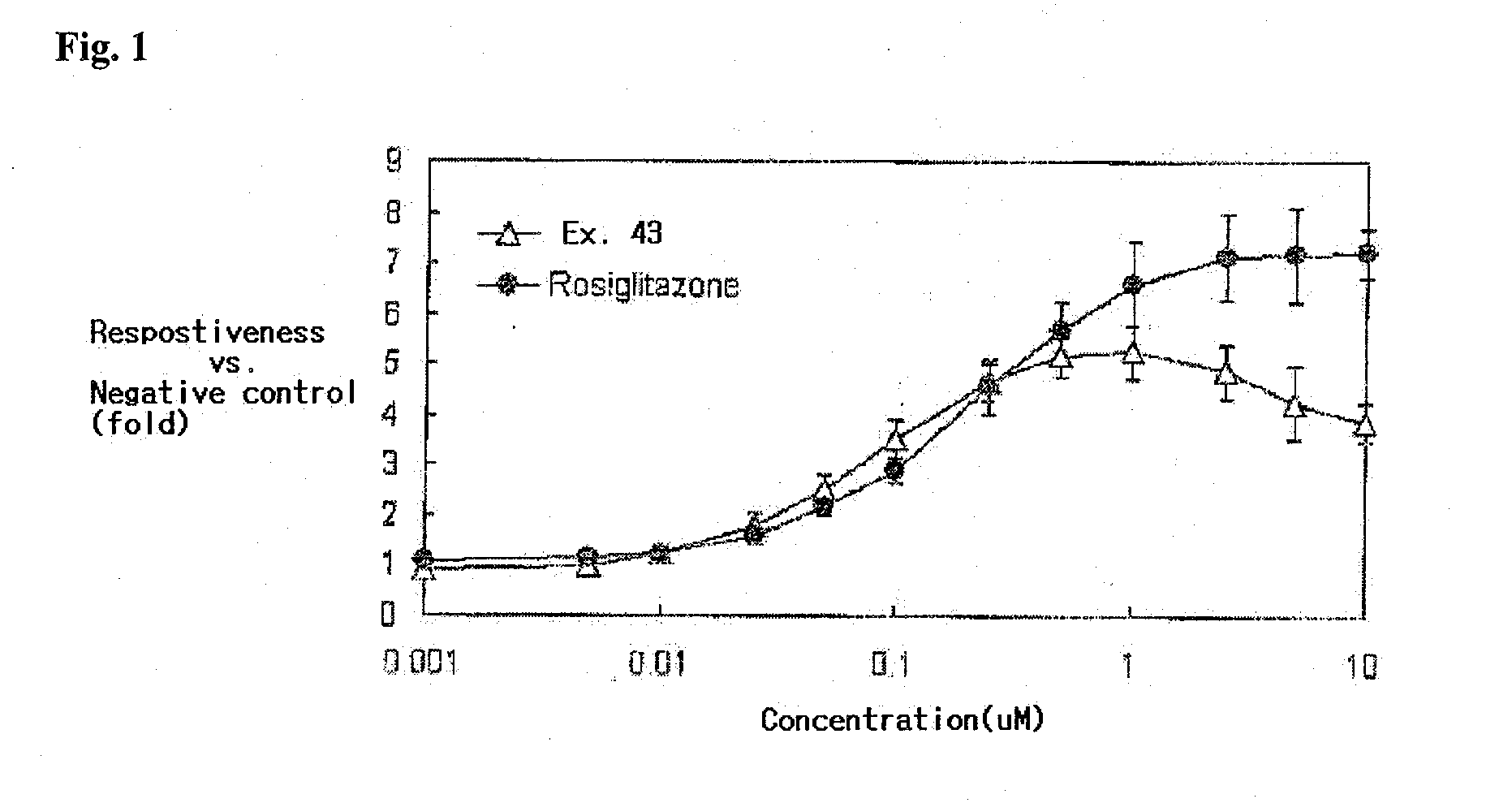
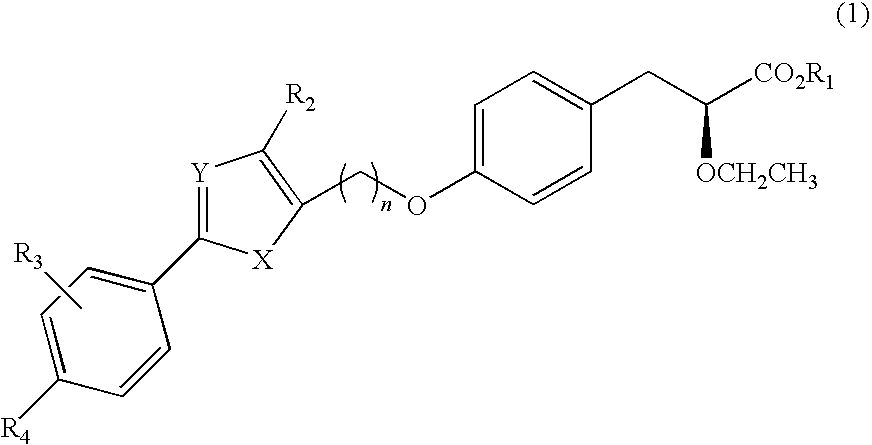
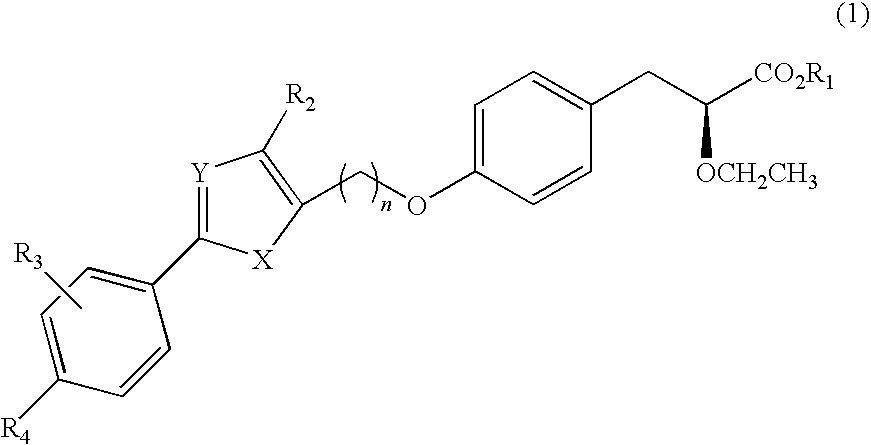
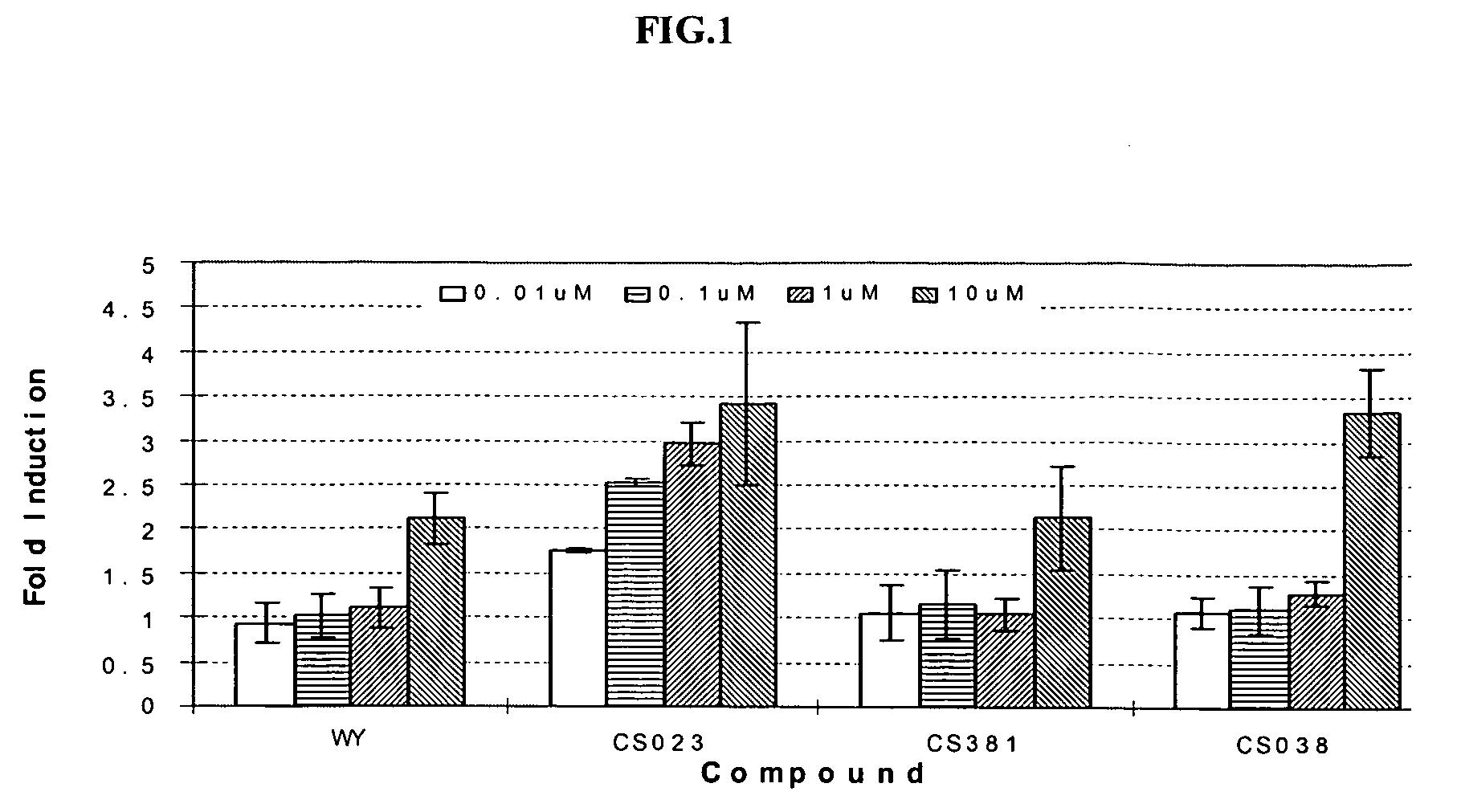
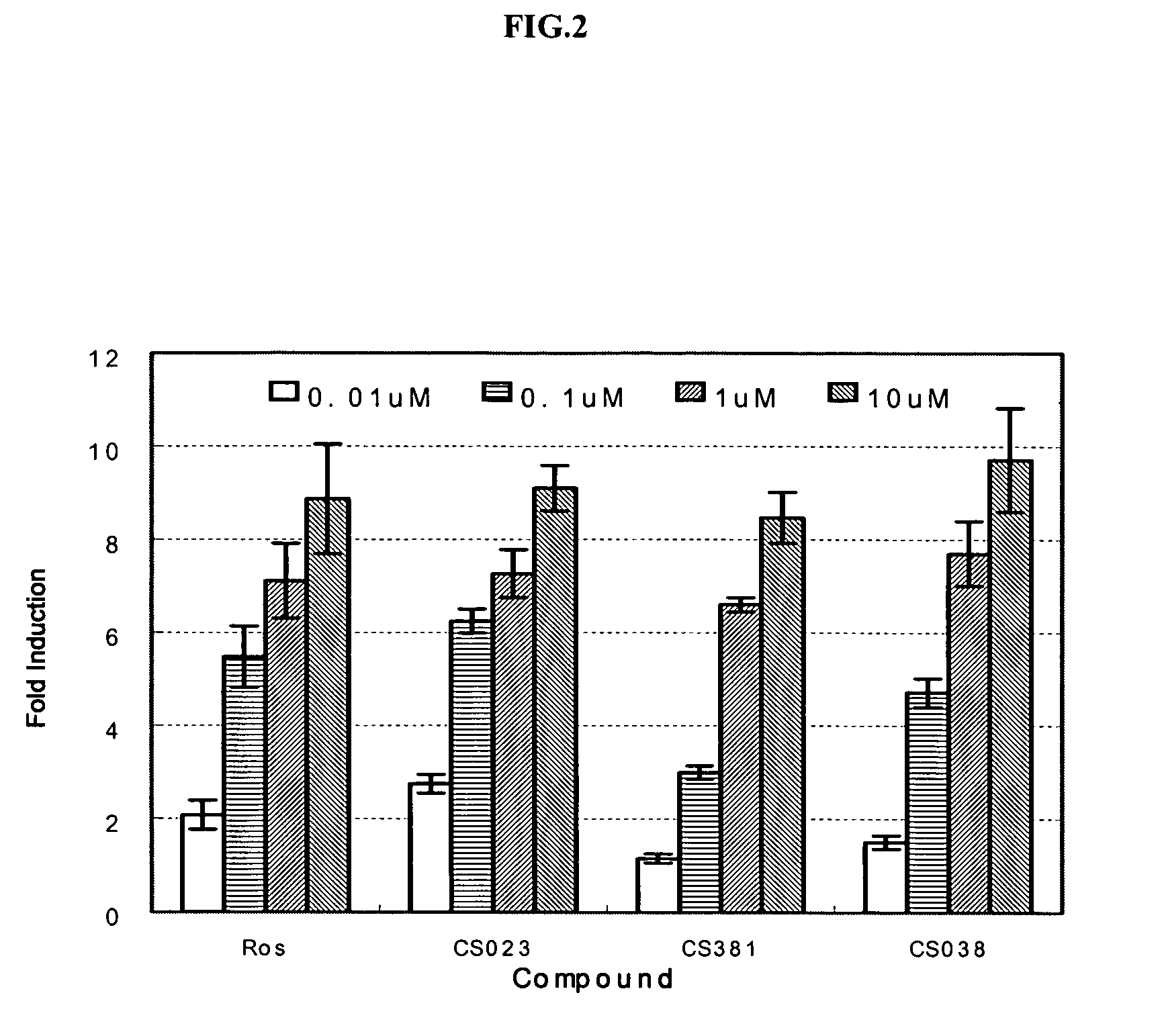
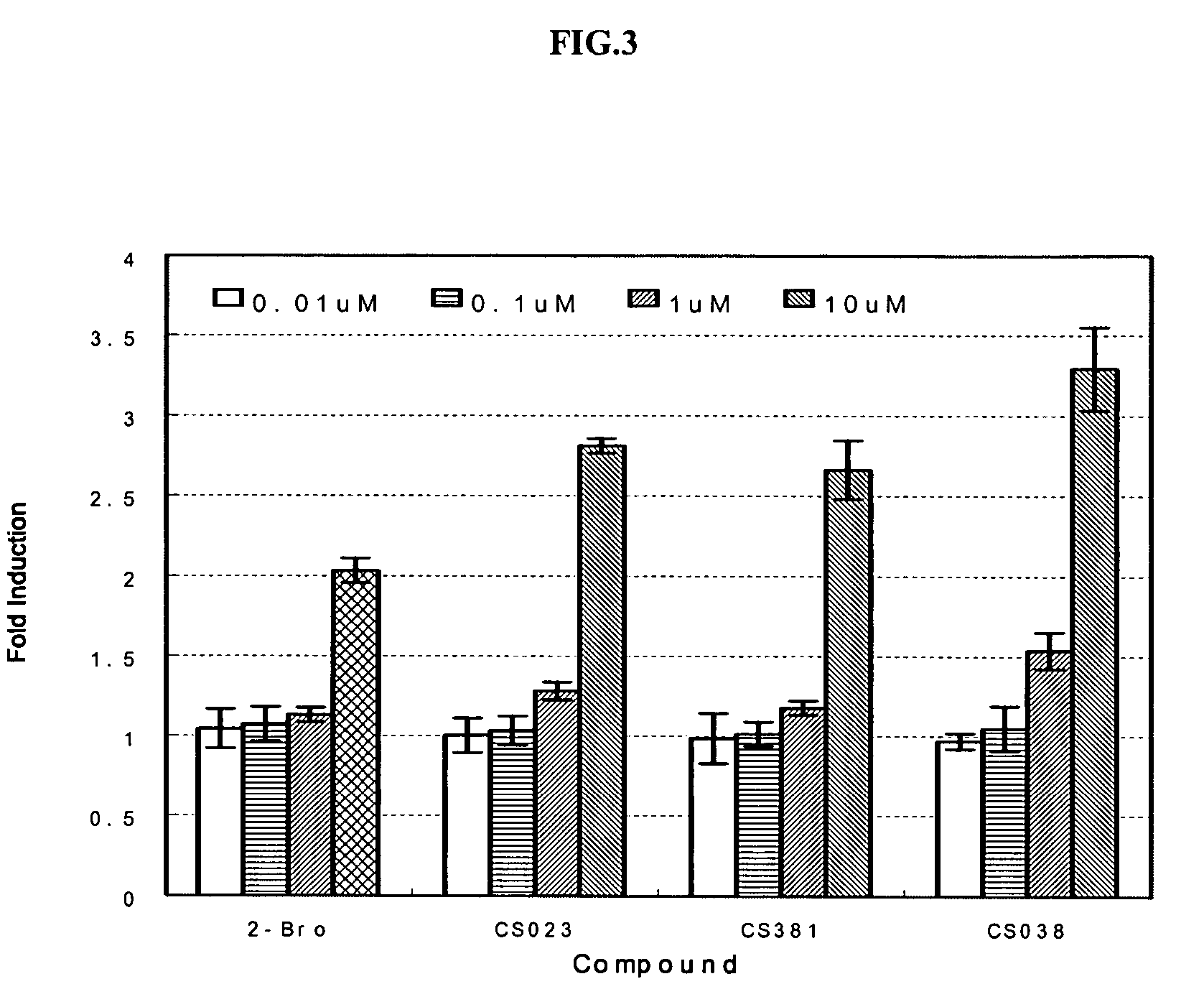
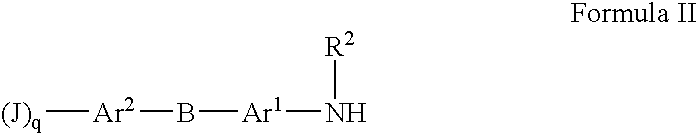
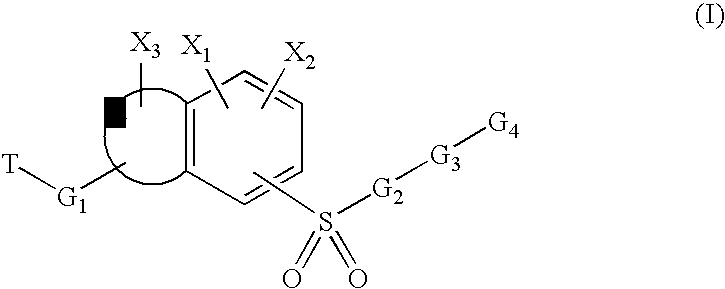
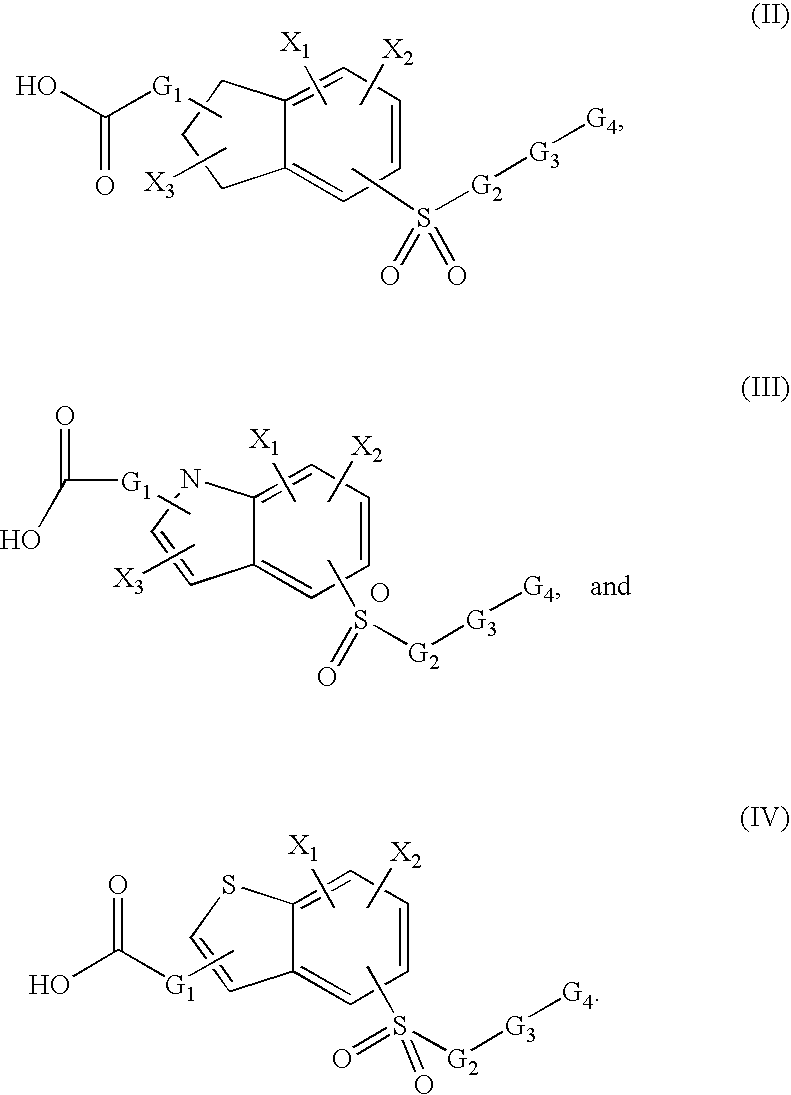
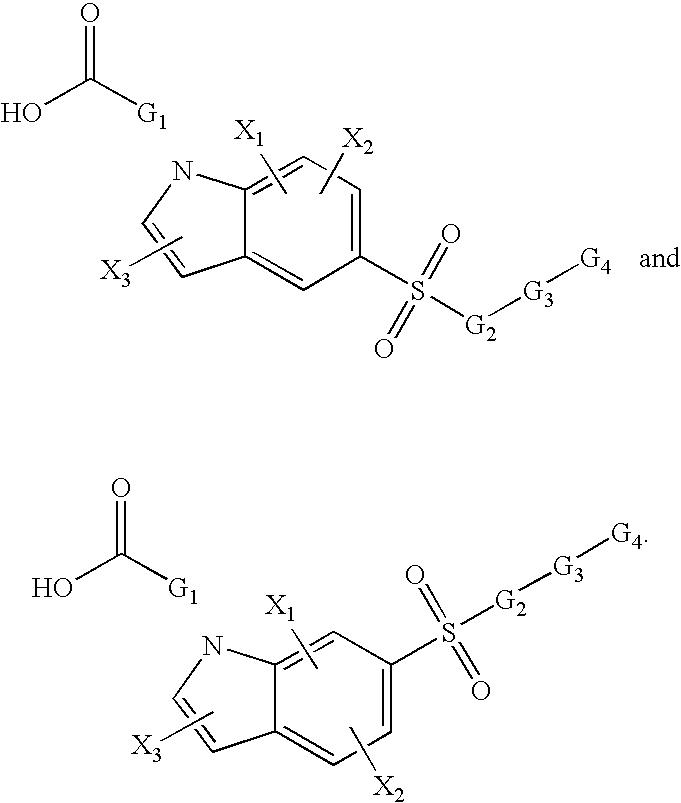
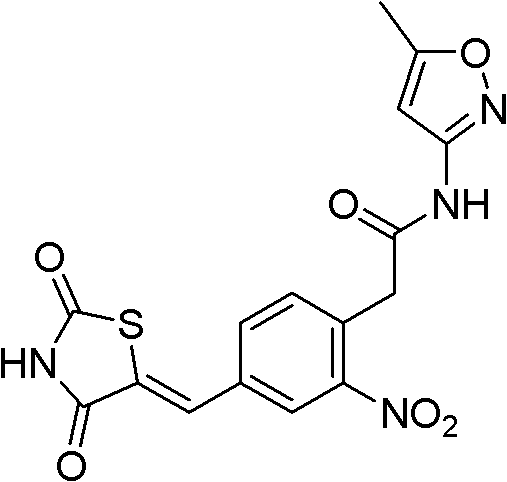
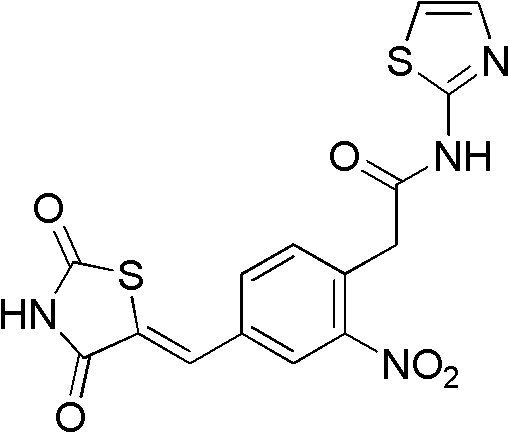
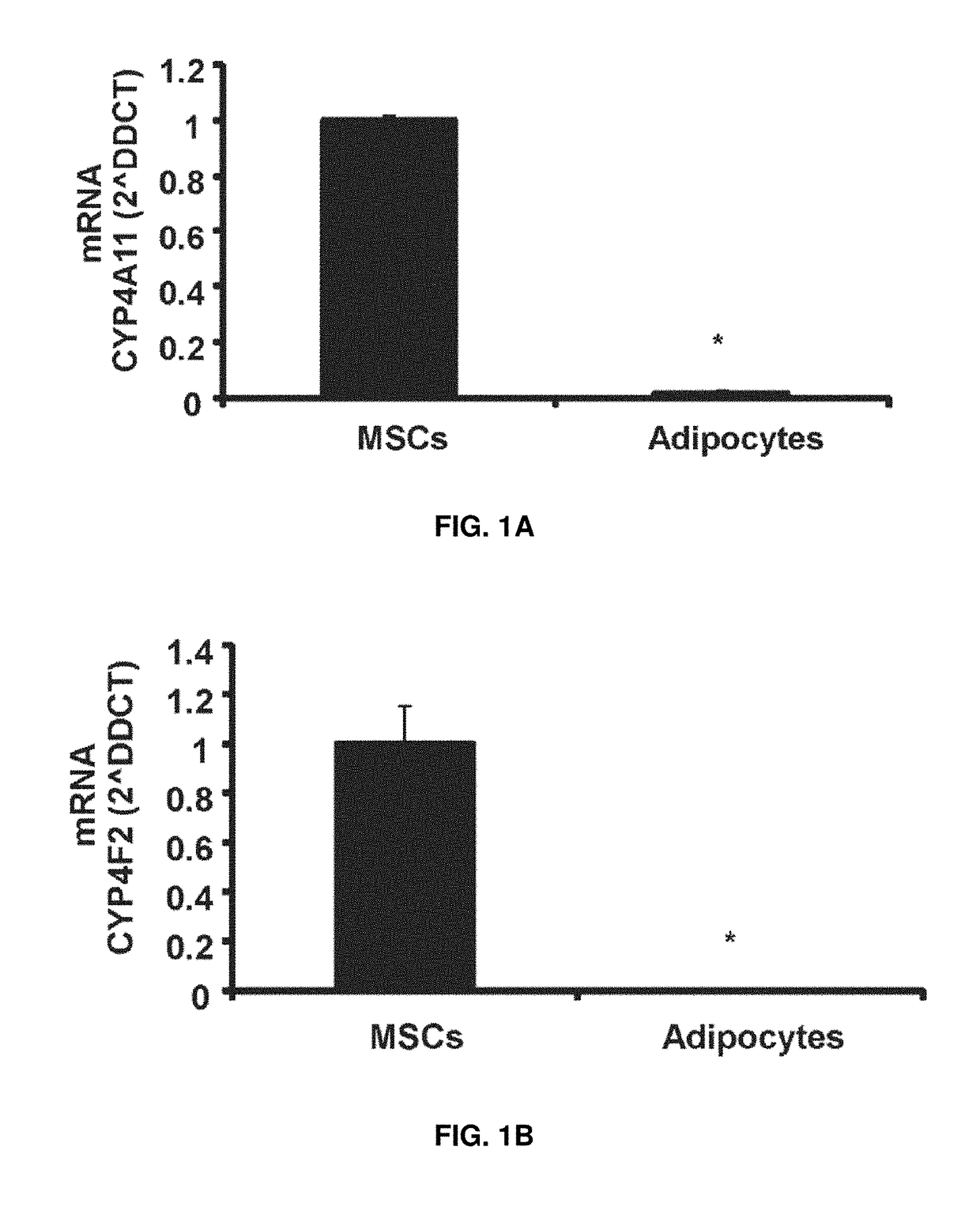
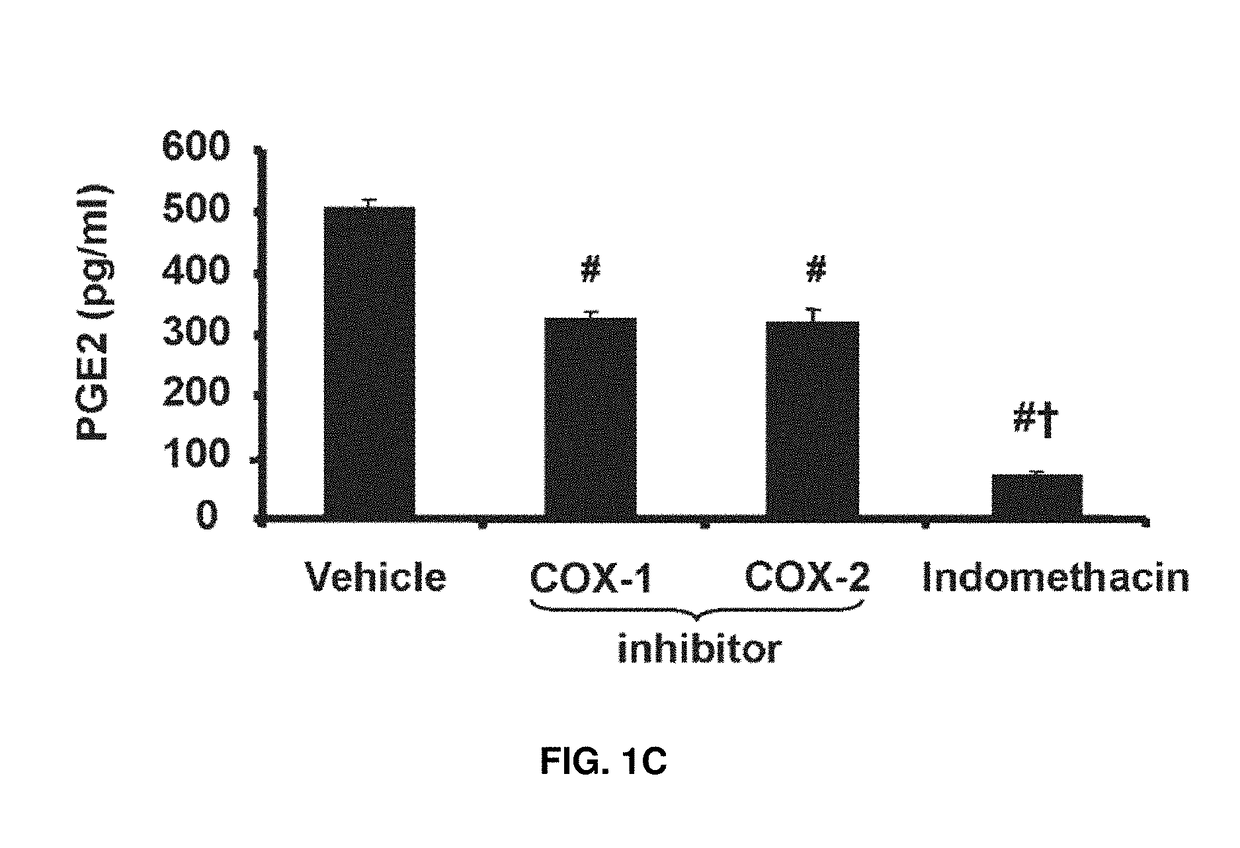
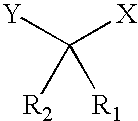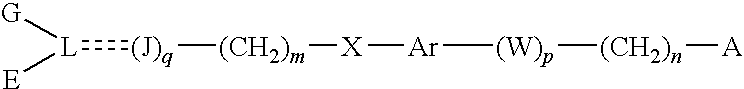Patents
Literature
64 results about "Peroxisome proliferators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Treatment of tumours
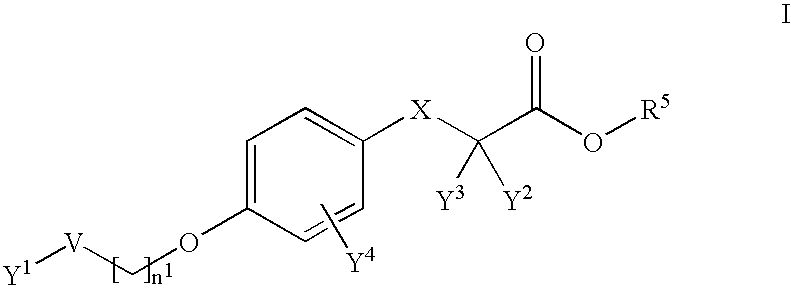
InactiveUS20050192262A1Good curative effectSquelching unwanted PPARγ-activityOrganic active ingredientsSteroidsDiseaseAndrostane
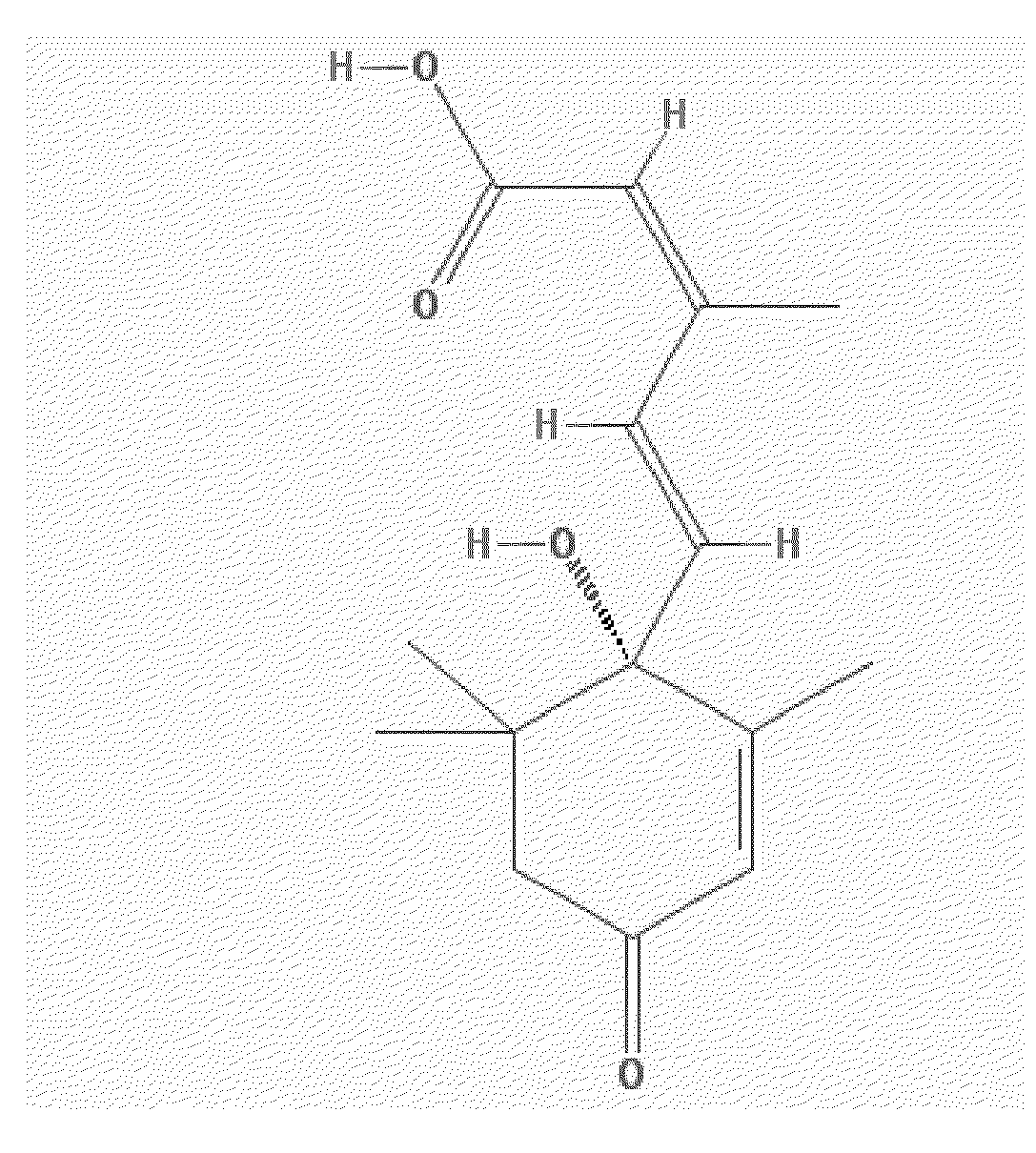
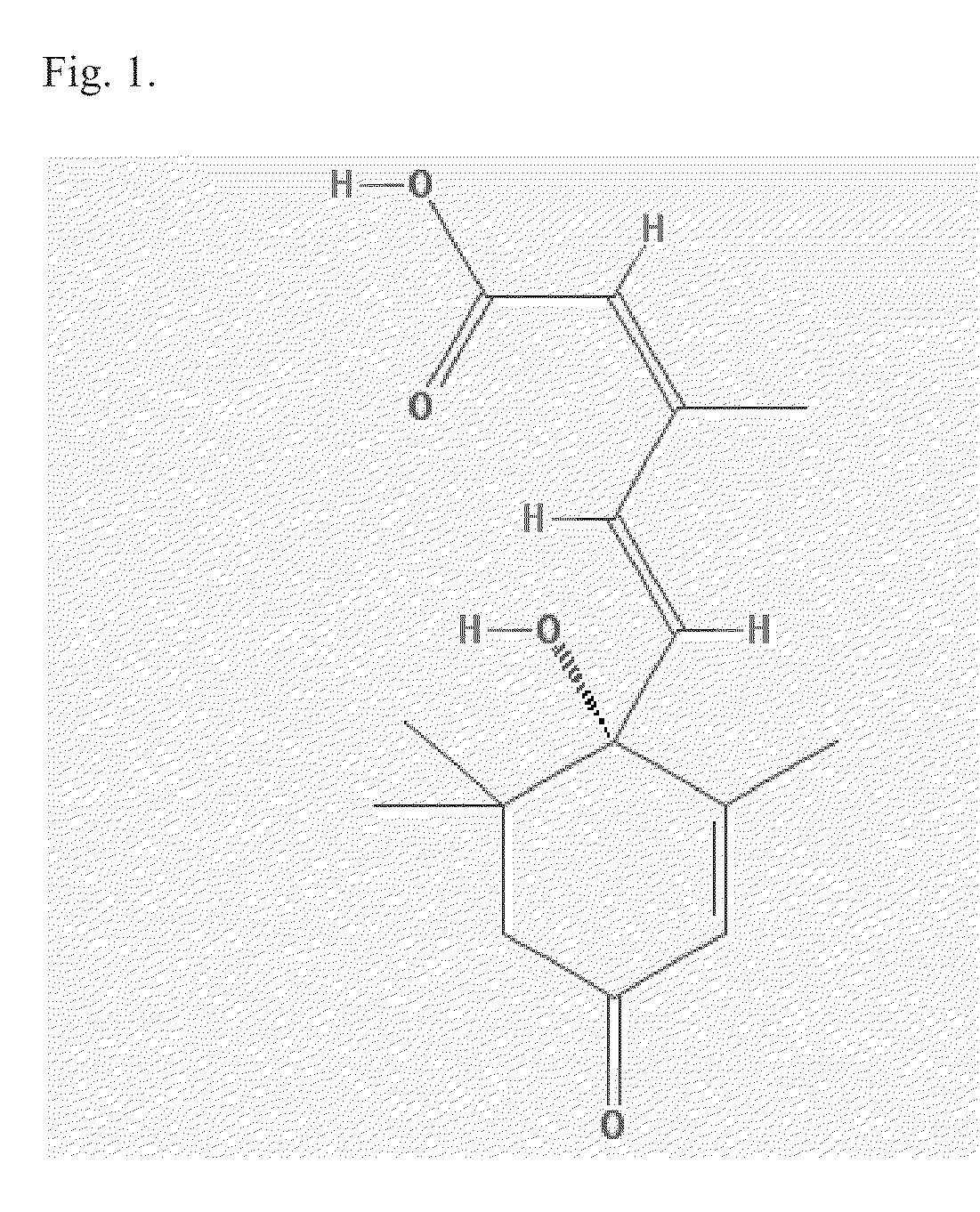
The present invention refers to steroid derivatives for use as medicaments. More specifically, the invention also relates to the use of a steroid derivative of 5-androstene-, 5-pregnenolone or corresponding saturated derivatives (androstane- or pregnane-) in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of a benign and / or malignant tumour, which medicament is capable of interrupting disturbances in Wnt-signaling, such as cell-cycle arrest in G1-phase, and / or providing an angiostatic effect. Examples of such steroid derivatives are -5-androstene-17-ol, androstane-17-ol-pregnane-17-ol or pregnane-17-ol derivatives. In a further aspect, the invention relates to a method of producing a medicament for the treatment of a benign and / or malignant tumour and / or an inflammatory condition comprising the steps of contacting 5-androstane-3β,17-diol or androstane-3β-diol, an enzyme and a sulfotransferase to provide 5-androstene-17-ol-3β-sulfate or corresponding andros tane derivative (17-AEDS or 17-AADS); and mixing the 17-AEDS or 17-AADS so produced with a suitable carrier; whereby a medicament which is capable of acting as a ligand to peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-(PPAR) is produced.
Owner:HAGSTROM TOMAS
Peroxisome proliferator-acitvated receptor gamma ligand eluting medical device
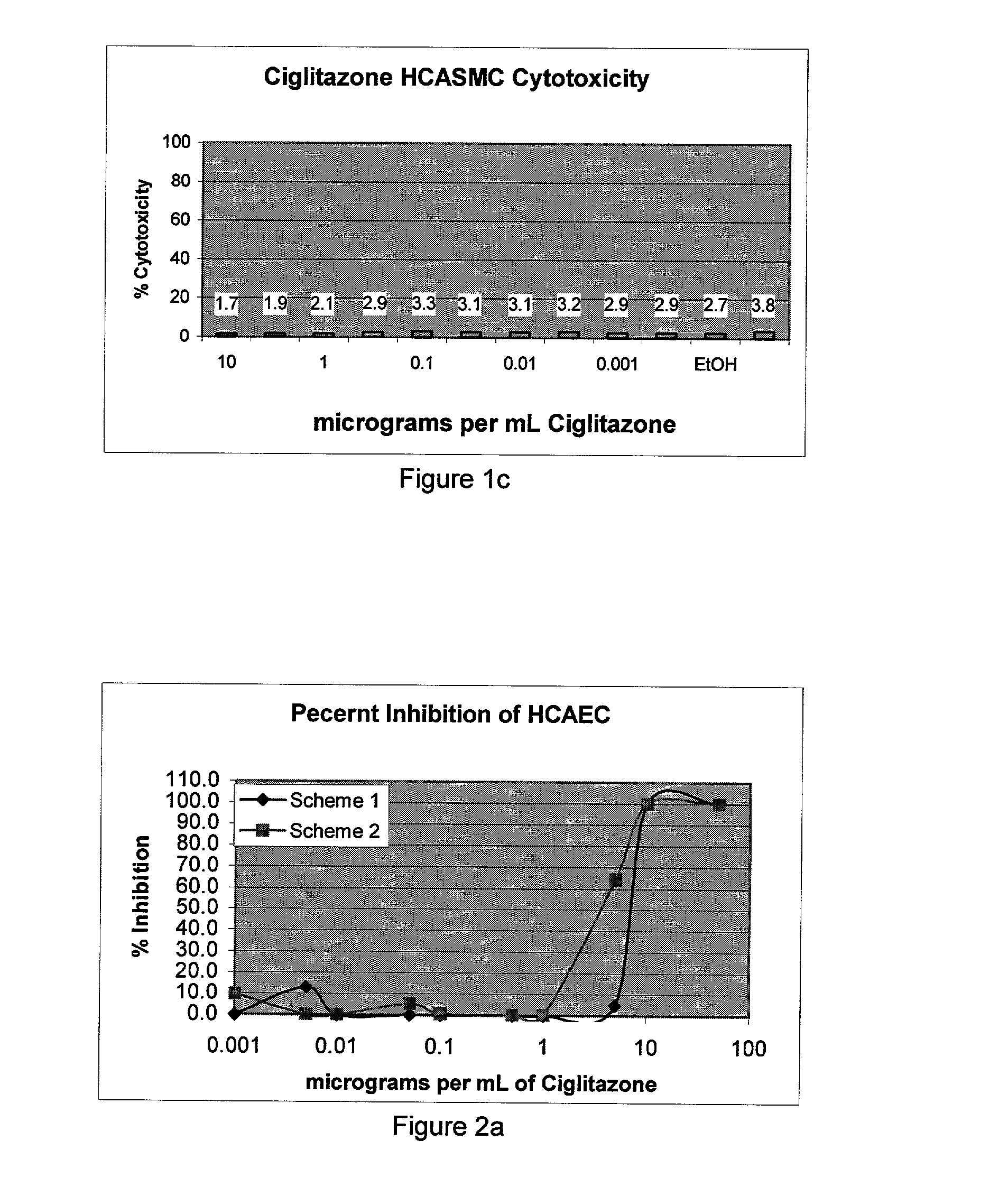
Implantable medical devices having an anti-restenotic coatings are disclosed. Specifically, implantable medical devices having coatings of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR.gamma.) agonists are disclosed. The anti-restenotic PPAR.gamma. ligands include thiazolidinedione compounds including ciglitazone. The anti-restenotic medial devices include stents, catheters, micro-particles, probes and vascular grafts. The medical devices can be coated using any method known in the art including compounding the thiazolidinedione with a biocompatible polymer prior to applying the coating. Moreover, medical devices composed entirely of biocompatible polymer-thiazolidinedione blends are disclosed. Additionally, medical devices having a coating comprising at least one thiazolidinedione in combination with at least one additional therapeutic agent are also disclosed. Furthermore, related methods of using and making the anti-restenotic implantable devices are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
Lanthionine synthetase component c-like proteins as molecular targets for preventing and treating diseases and disorders
ActiveUS20110275558A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsThiazolidinedioneAutoimmune disease
The present invention relates to the field of medical treatments for diseases and disorders. More specifically, the present invention relates to the use of the lanthionine synthetase component C-like (LANCL) proteins as therapeutic targets for novel classes of anti-inflammatory, immune regulatory and antidiabetic drugs. This includes but it is not limited to abscisic acid (ABA), ABA analogs, benzimidazophenyls, repurposed drugs or drug combinations, including thiazolidinediones (TZDs); naturally occurring compounds such as conjugated diene fatty acids, conjugated triene fatty acids, isoprenoids, and natural and synthetic agonists of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors that activate this receptor through an alternative mechanism of action involving LANCL2 or other membrane proteins to treat or prevent the common inflammatory pathogenesis underlying type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis, cancer, some inflammatory infectious diseases such as influenza and autoimmune diseases including but not limited to inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease and Ulcerative colitis), rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes and other chronic inflammatory conditions.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
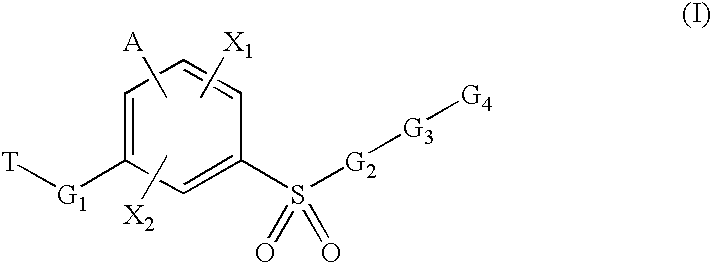
Sulfonyl-Substituted Aryl Compounds as Modulators of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptors
InactiveUS20090143396A1Useful PPAR-modulating activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryArylDisease
Compounds as modulators of peroxisome proliferator activated receptors, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same, and methods of treating disease using the same are disclosed.
Owner:MALECHA JAMES W +3
Cyclic amino benzoic acid derivative
InactiveUS7902367B2Improve abilitiesReduced activityBiocideOrganic chemistryBenzoic acidOrtho position
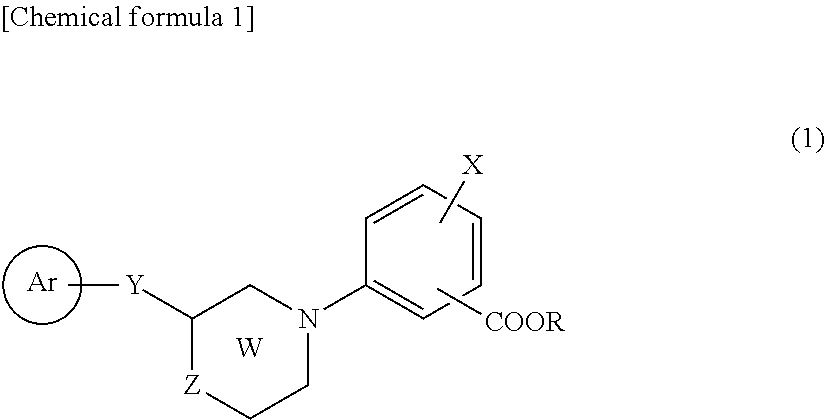
The present invention relates to cyclic amino benzoic acid derivatives which are effective in therapy of lipid metabolism abnormality, diabetes and the like as a human peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor (PPAR) agonist, in particular, as an agonist against human PPARα isoform, and addition salts thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds.A cyclic amino benzoic acid derivative represented by the general formula (1)[wherein a ring Ar represents an aryl group which may have substituent, or the like; Y represents a C1-C4 alkylene, C2-C4 alkenylene, C2-C4 alkynylene, or the like; Z represents an oxygen atom, sulfur atom or —(CH2)n— (n represents 0, 1 or 2); X represents a hydrogen atom, halogen atom, lower alkyl group which may be substituted with a halogen atom, or the like; R represents a hydrogen atom or lower alkyl group, and —COOR substitutes for an ortho position or metha position of binding position of ring W] or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:KYORIN PHARMA CO LTD
Substituted benzylthiazolidine-2, 4-dione derivatives
The invention provides novel substituted benzylthiazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives that bind to receptor to activate as ligands of human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) and exhibit blood glucose-decreasing action and lipid-decreasing action, and processes for preparing them.It relates to substituted benzylthiazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives represented by the general formula (1)[wherein the bond mode of A denotes -CH2CONH-, -NHCONH-, -CH2CH2CO- or -NHCOCH2-, and B denotes a lower alkyl group with carbon atoms of 1 to 4, lower alkoxy group with carbon atoms of 1 to 3, halogen atom, trifluoromethyl group, trifluoromethoxy group, phenyl group which is unsubstituted or may have substituents, phenoxy group which is unsubstituted or may have substituents or benzyloxy group which is unsubstituted or may have substituents], their medicinally acceptable salts, their hydrates and processes for preparing them.
Owner:KYORIN PHARMA CO LTD
Novel phenylpropionic acid derivatives as peroxisome proliferator-activated gamma receptor modulators, method of the same, and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same
InactiveUS20100063041A1Effective preventionEffective treatmentBiocideOrganic chemistryDisease3-phenylpropanoic acid
The present invention provides a novel phenylpropionic acid derivative and a PPAR-γ modulator comprising the same as an active ingredient. The phenylpropionic acid derivative of the present invention has modulatory action on function of PPAR-γ and then exhibits hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic and insulin resistance-reducing effects on PPAR-mediated diseases or disorders. Therefore, the present invention is prophylactically or therapeutically effective for diabetes and metabolic diseases.
Owner:DONG A PHARMA +1
Alpha-substituted omega-3 lipids that are activators or modulators of the peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor (PPAR)
InactiveUS20100035990A1Lose weightWeight increaseCompounds screening/testingBiocideLipid formationAcyl group
Omega-3 lipid compounds of the general formula (I):wherein R1 and R2 are the same or different and may be selected from a group of substituents consisting of hydrogen, a hydroxy group, an alkyl group, a halogen atom, an alkoxy group, an acyloxy group, an acyl group, an alkenyl group, an alkynyl group, an aryl group, an alkylthio group, an alkoxycarbonyl group, a carboxy group, an alkylsulfinyl group, an alkylsulfonyl group, an amino group, and an alkylamino group; X represents a carboxylic acid or a derivative thereof, a carboxylate, a carboxylic anhydride or a carboxamide; and Y is a C6 to C22 alkene with two or more double bonds, having E and / or Z configuration, are disclosed. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions and lipid compositions comprising such compounds, and to such compounds for use as medicaments in particular for the treatment of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
Owner:PRONOVA BIOPHARMA NORGE
Substituted arylalcanoic acid derivatives as PPAR pan agonists with potent antihyperglycemic and antihyperlipidemic activity
ActiveUS7268157B2Decrease hyperglycemiaDecrease hypertriglyceremiaBiocideOrganic chemistryAcute hyperglycaemiaCoronary artery disease
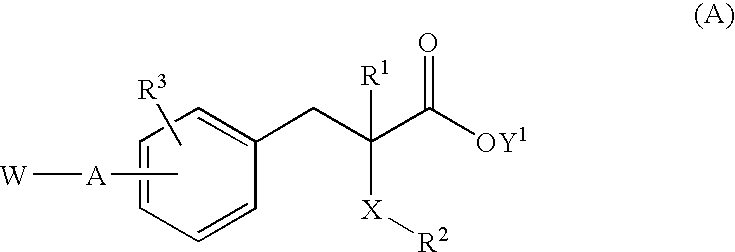
Disclosed is the preparation and pharmaceutical use of substituted arylalcanoic acid derivatives of Formula I, wherein ring A, ring B, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, X, Alk1, Alk2, Ar1, and Ar2 are as defined in the specification. These compounds, as selective agonists activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR), in particularly the RXR / PPARalpha, RXR / PPARgamma, and RXR / PPARdelta heterodimers, are useful in the treatment and / or prevention of type 2 diabetes and associated metabolic syndrome such as hypertension, obesity, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, and other cardiovascular disorders with improved side effects profile commonly associated with conventional PPARgamma agonists.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHIPSCREEN BIOSCIENCES CO LTD
Compounds, their preparation and use
Novel compounds of the general formula (I), the use of these compounds as pharmaceutical compositions, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds and methods of treatment employing these compounds and compositions. The present compounds may be useful in the treatment and / or prevention of conditions mediated by Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPAR), in particular the PPARδ suptype.
Owner:HIGH POINT PHARMA
Compounds and methods for inhibiting nhe-mediated antiport in the treatment of disorders associated with fluid retention or salt overload and gastrointestinal tract disorders
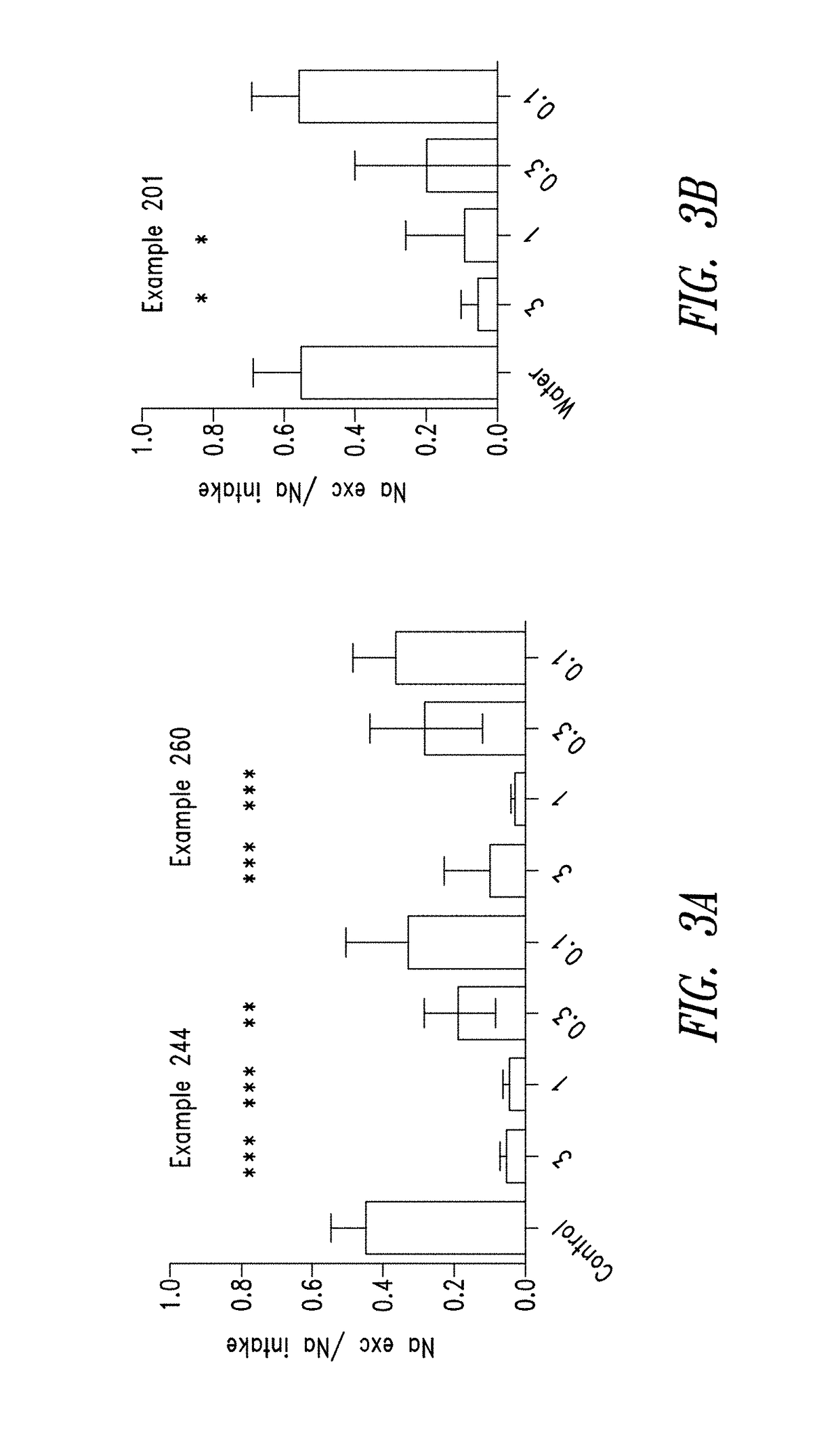
ActiveUS20170340623A1Reduce interdialytic weight gainMore palatable dietPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsIntestinal tract diseasesDisease
The present disclosure is directed to compounds and methods for the treatment of disorders associated with fluid retention or salt overload, such as heart failure (in particular, congestive heart failure), chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, liver disease, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma agonist-induced fluid retention. The present disclosure is also directed to compounds and methods for the treatment of hypertension. The present disclosure is also directed to compounds and methods for the treatment of gastrointestinal tract disorders, including the treatment or reduction of pain associated with gastrointestinal tract disorders. The methods generally comprise administering to a mammal in need thereof a pharmaceutically effective amount of a compound, or a pharmaceutical composition comprising such a compound, that is designed to be substantially active in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract to inhibit NHE-mediated antiport of sodium ions and hydrogen ions therein. More particularly, the method comprises administering to a mammal in need thereof a pharmaceutically effective amount of a compound, or a pharmaceutical composition comprising such a compound, that inhibits NHE-3, -2 and / or -8 mediated antiport of sodium and / or hydrogen ions in the GI tract and is designed to be substantially impermeable to the layer of epithelial cells, or more specifically the epithelium of the GI tract. As a result of the compound being substantially impermeable, it is not absorbed and is thus essentially systemically non-bioavailable, so as to limit the exposure of other internal organs (e.g., liver, heart, brain, etc.) thereto. The present disclosure is still further directed to a method wherein a mammal is administered such a compound with a fluid-absorbing polymer, such that the combination acts as described above and further provides the ability to sequester fluid and / or salt present in the GI tract.
Owner:ARDELYX
Isomers of inositol niacinate and uses thereof
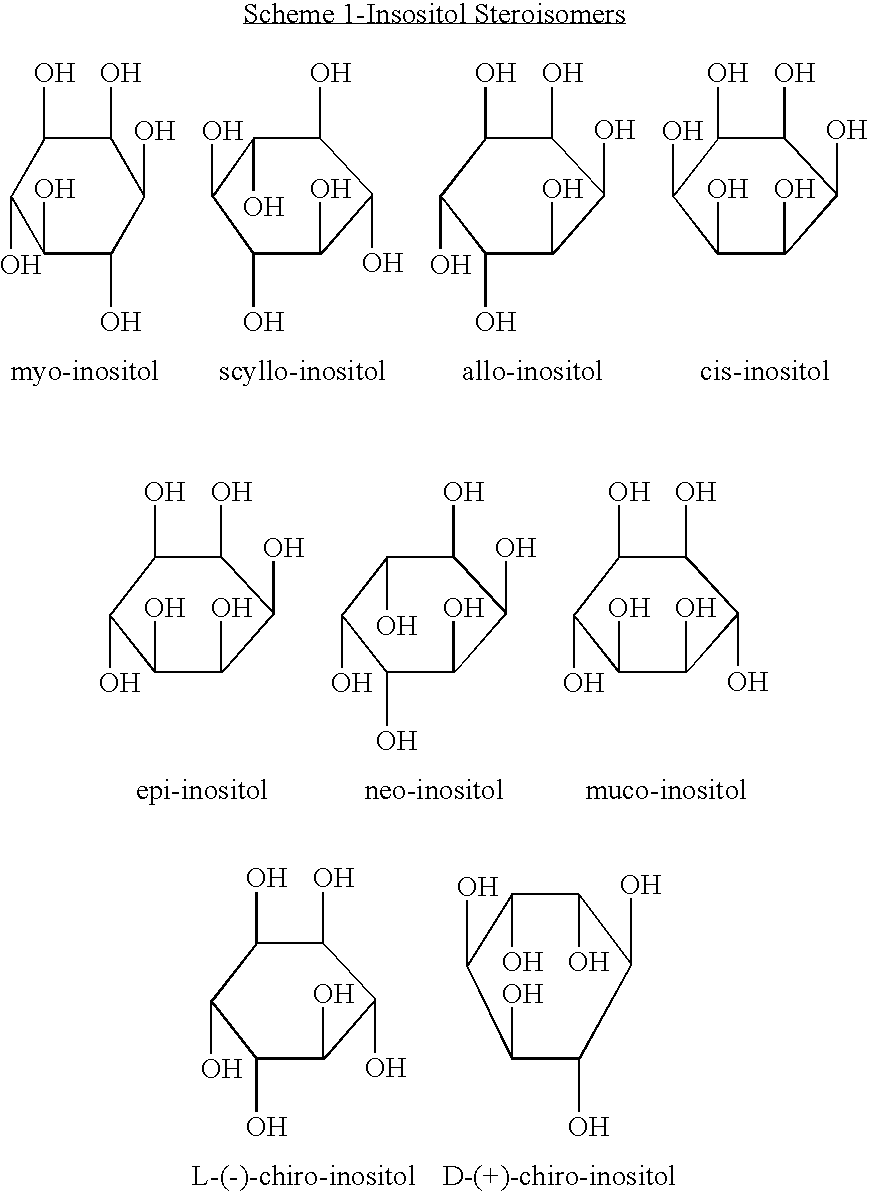
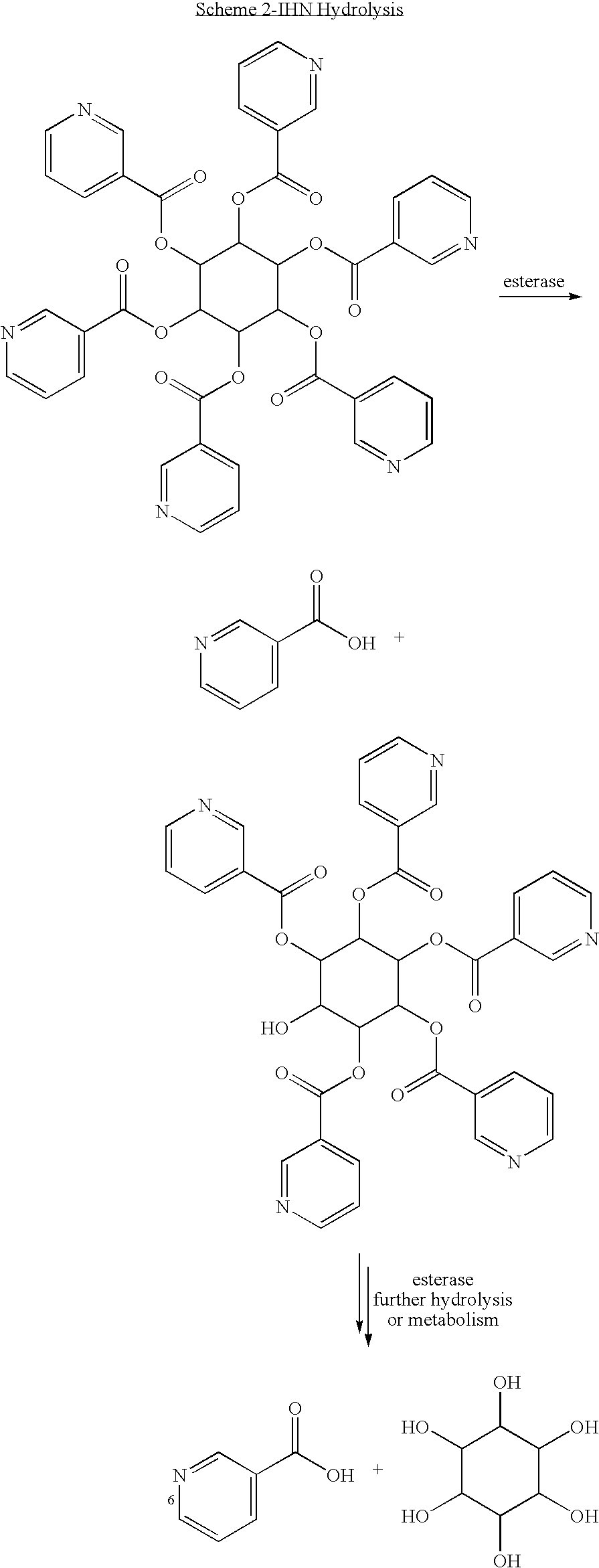
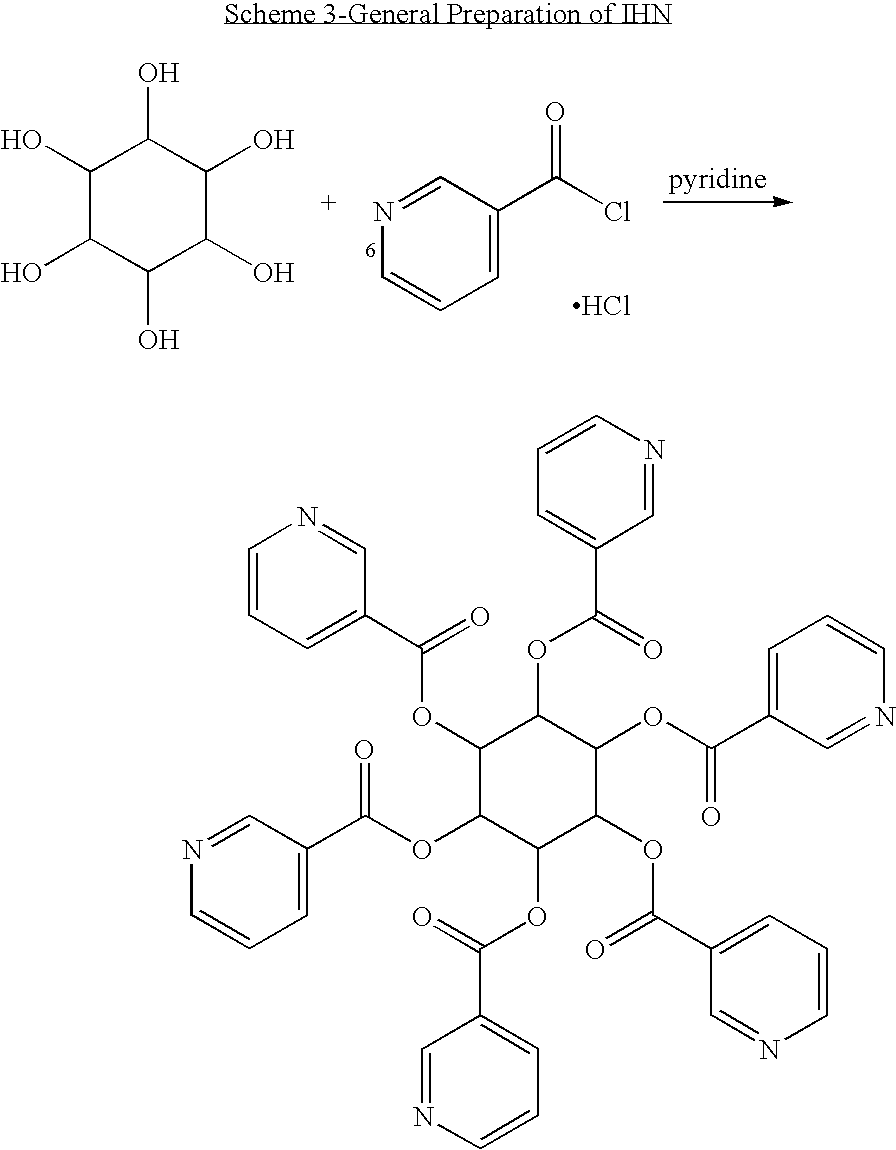
InactiveUS20090326013A1Reduce cardiovascular riskPrevent liver damageBiocideNervous disorderHMG-CoA reductaseAllo-Inositol
An ester formed from an inositol or an inositol derivative and niacin, wherein the inositol or the inositol derivatives comprises a stereoisomer selected from allo-inositol, cis-inositol, epi-inositol, muco-inositol, neo-inositol, scyllo-inositol, D-chiro-inositol and L-chiro-inositol, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. Examples of esters include inositol hexaniacinates such as allo-inositol hexaniacinate and cis-inositol hexaniacinate. The esters can be used to treat any disorder that is treatable with niacin therapy such as dyslipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemia or cardiovascular disease. The esters can be administered with other agents such as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, statins, fibrates, activators of peroxisome proliferator activated receptors poli-cosanol, phytosterols, tocotrienols, calcium, bile acid sequestrants, guar gum and free niacin. The invention includes pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds.
Owner:CONCOURSE HEALTH SCI
Modulators of peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (ppar)
The present invention is directed to a compound of formula I, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, hydrates or stereoisomer thereof, which are useful in treating Syndrome X, Type II diabetes, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, obesity, coagaulopathy, hypertension, arteriosclerosis, and other disorders related to Syndrome X as well as cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
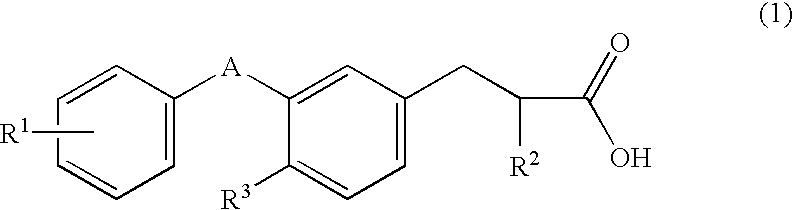
Substituted phenylpropionic acid derivatives
The invention provides novel substituted phenylpropionic acid derivatives that bind to the receptor as ligands of human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) to activate and exhibit potent lipid-decreasing action, and processes for preparing them.It relates to substituted phenylpropionic acid derivatives represented by a general formula (1)[wherein R1 denotes a lower alkyl group with carbon atoms of 1 to 4, lower alkoxy group with carbon atoms of 1 to 3, trifluoromethyl group, trifluoromethoxy group, phenyl group which is unsubstituted or may have substituents, phenoxy group which is unsubstituted or may have substituents or benzyloxy group which is unsubstituted or may have substituents, R2 denotes a hydrogen atom, lower alkyl group with carbon atoms of 1 to 4 or lower alkoxy group with carbon atoms of 1 to 3, R3 denotes a lower alkoxy group with carbon atoms of 1 to 3, and the binding mode of A portion denotes —CH2CONH—, —NHCOCH2—, —CH2CH2CO—, —CH2CH2CH2—, —CH2CH2O—, —CONHCH2—, —CH2NHCH2—, —COCH2O—, —OCH2CO—, —COCH2NH— or —CHCH2CO—], their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and their hydrates, and processes for preparing them.
Owner:KYORIN PHARMA CO LTD
Substituted Heteroaryl- and Phenylsulfamoyl Compounds
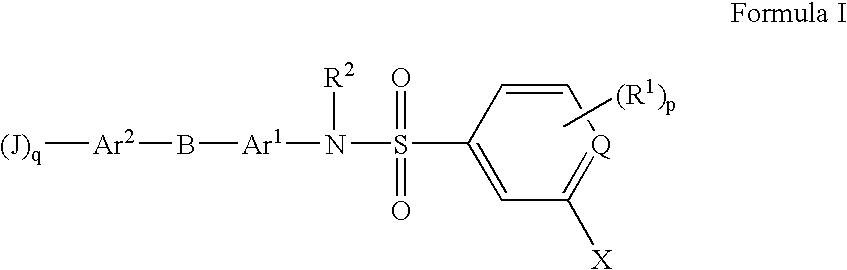
InactiveUS20060258723A1Negative energy balanceExcessive accumulation of triglycerides in liver tissue is prevented or alleviatedBiocideNervous disorderMammalBlood plasma
The present invention is directed at substituted heteroaryl and phenylsulfamoyl compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds and the use of such compounds as peroxisome proliferator actuator receptor (PPAR) agonists. PPAR alpha activators, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds and the use of such compounds to elevate certain plasma lipid levels, including high density lipoprotein-cholesterol and to lower certain other plasma lipid levels, such as LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and accordingly to treat diseases which are exacerbated by low levels of HDL cholesterol and / or high levels of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides, such as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases, in mammals, including humans. The compounds are also useful for the treatment of negative energy balance (NEB) and associated diseases in ruminants.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Sulfonyl-substituted bicyclic compounds as modulators of PPAR
Compounds as modulators of peroxisome proliferator activated receptors, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same, and methods of treating disease using the same are disclosed.
Owner:KALYPSYS INC
Method for improving pig meat quality
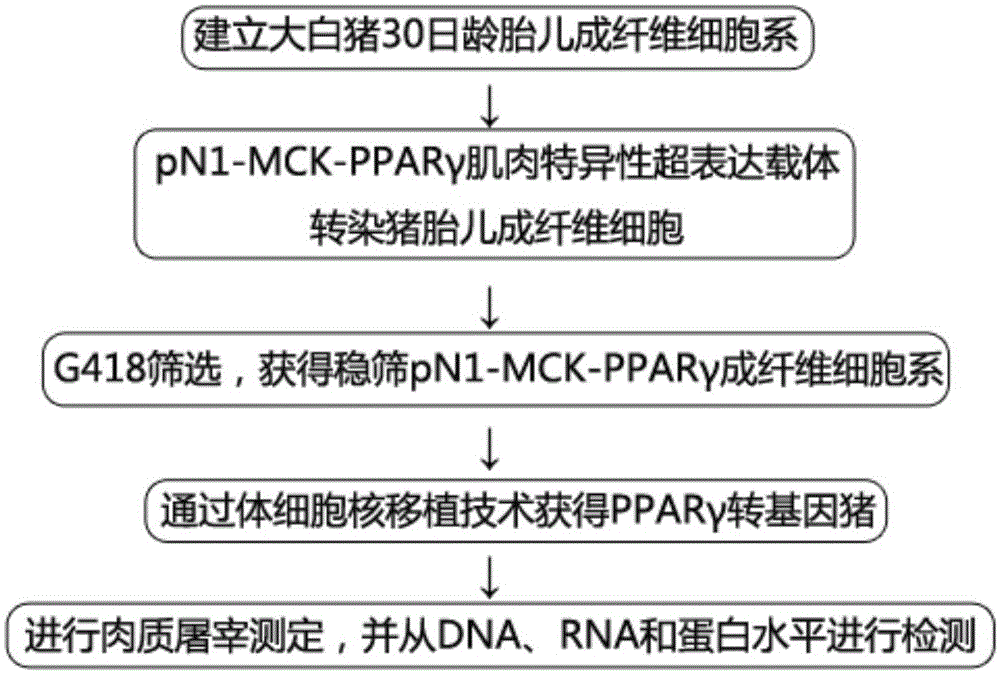
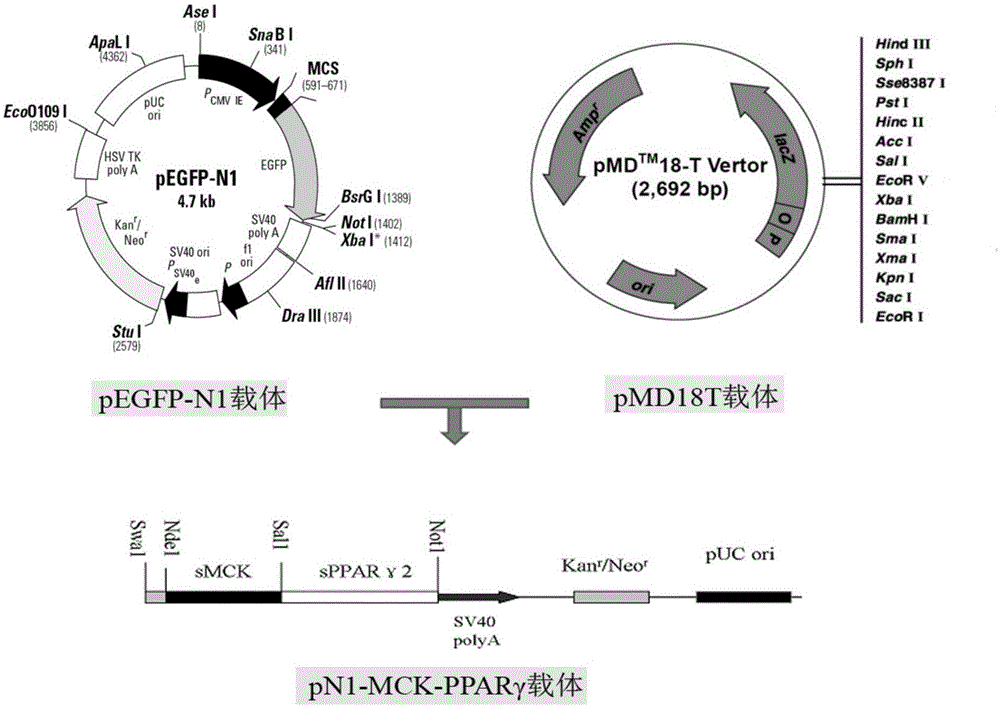
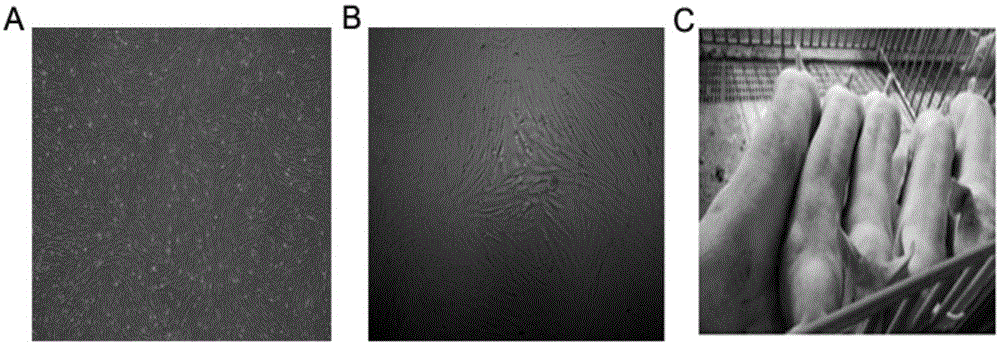
InactiveCN105039402AImprove qualityHigh in fatFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyMuscle tissue
The invention belongs to the technical field of animal genetic engineering and particularly relates to a method for improving pig meat quality. The method is characterized in that a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma gene serves as an important candidate gene for improving the meat quality, a fibroblast cell line of a 30-day-old fetus of a large white pig is established, a SwaI linearized pN1-MCK-PPAR gamma2 expression vector is shifted to the 30-day-old fetus fibroblast cell line of the large white pig through an electrotransfection method, and a PPAR gamma transgenic pig is prepared in a method of somatic nucleus transplantation. The influence of muscle tissue overexpression PPAR gamma genes on meat traits such as intramuscular fat deposition is verified in a transgenic pig, the contradiction of simultaneously selecting meat quality and meat quantity in conventional animal breeding is overcome, and the novel method is provided for cultivating lean meat pigs with good meat quality.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
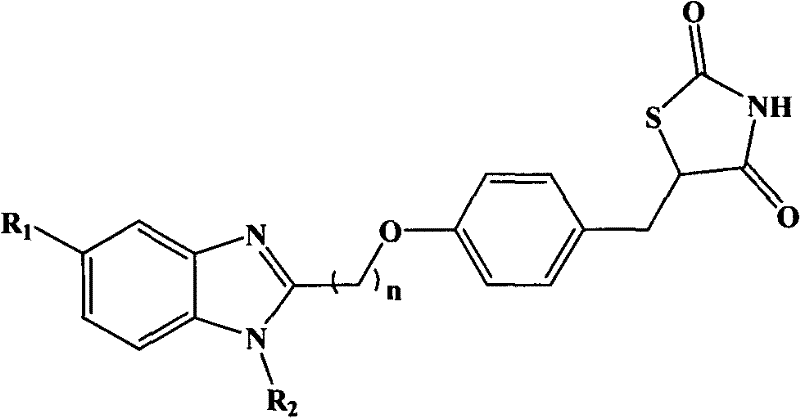
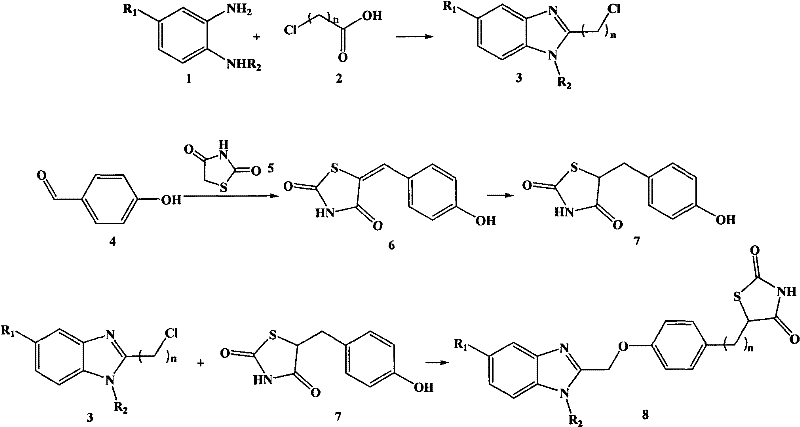
Benzimidazolyl thiazolidinone compounds and synthesis method thereof
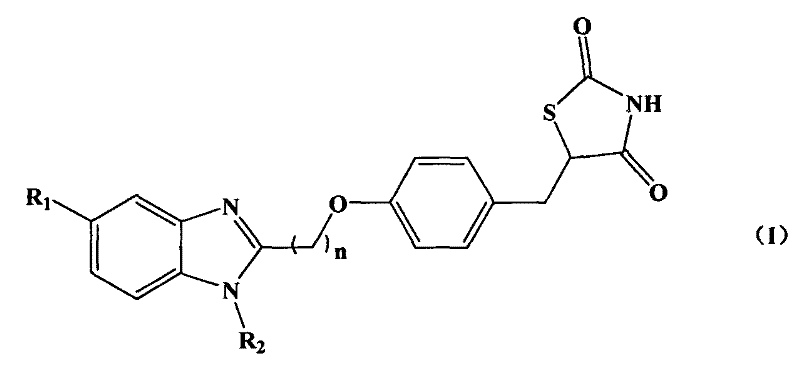
InactiveCN102250082AGood water solubilityFacilitate throughNervous disorderOrganic chemistrySolubilitySynthesis methods
The invention relates to benzimidazolyl thiazolidinone compounds and a synthesis method thereof. The compounds have a structure shown by a general formula (I), wherein R1 and R2 may be methyl, ethyl, benzyl, alkyl or hydrogen; and n is an integer between 1 and 5. The benzimidazolyl thiazolidinone compounds provided by the invention are high-affinity ligands having specificity against peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR-gamma), by improving glucose absorption by cells and lowering output of glycogen, the sensitivity of cells to insulin is increased and the antagonism of tissues against glucose; and the compounds, compared with the conventional thiazolidinones PPAR-gamma activating agent, has high lipid solubility, is easier to pass through blood brain barrier, improves the sensitivity of insulin in brain, and can be used for treating neurological diseases caused by diabetes and neuroprotection.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Exercise and diet program
A method of individualized weight management for a subject includes obtaining a biological sample from the subject; detecting the presence or absence of polymorphisms associated with at least seven genes comprising fatty acid-binding protein 2 (FABP2), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG), beta-2-adrenergic receptor (ADRB2), beta-3-adrenergic receptor (ADRB3), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), alpha-actinin-3 (ACTN3), and proton-linked monocarboxylate transporter (MCT1) in the biological sample to obtain genotype pattern data for the subject; wherein the polymorphisms are indicative of at least one nutritional trait and at least one fitness trait and preparing a nutritional and fitness program based on the subject's genotype pattern data; wherein the fitness program comprises sequences of resistance, cardio, and excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) training routines.
Owner:ALDO CONSULTING & PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Composition comprising peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma
InactiveUS20130331332A1Increase volumeGood effectCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsDermatologyPeroxisome proliferators
An injectable composition comprising peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma for subcutaneous administration and a method for improving imperfections of the skin, wherein the injectable composition is subcutaneously administered at the area of skin imperfections comprising the steps: a) identifying an area of skin imperfections, b) administering a safe and cosmetically effective amount of the composition subcutaneously to the area of skin imperfections.
Owner:MERZ PHARMA GMBH & CO KGAA
Thiazolidine derivant with GK and PPAR double excitation activity
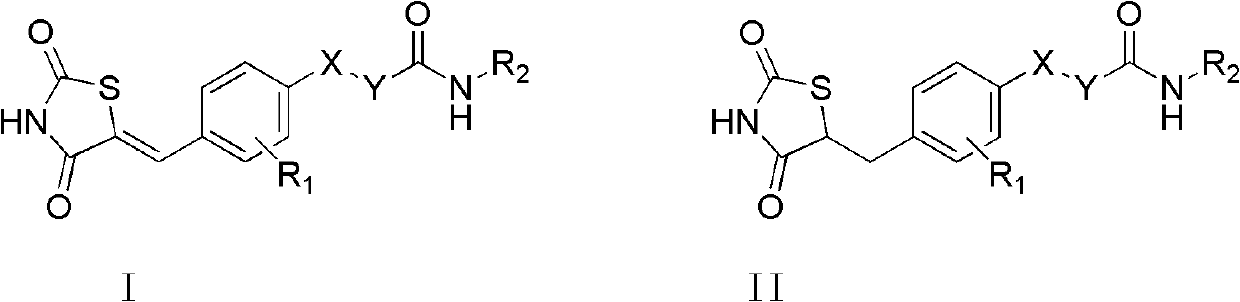
InactiveCN102558167ALower blood sugarOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseThiazolidinedione
The invention discloses a novel thiazolidine derivant and a preparation method, a medicine combination and a purpose thereof, which specifically relate to the thiazolidine derivant shown as the formula I and the formula II, officinal salt of the derivant, a precursor or a derivant with the same biological function with the thiazolidine derivant, the preparation method of the thiazolidine derivant, the combination of one or a plurality of thiazolidine derivants and the purpose of the compound in treatment on diseases related with glucokinase and a peroxisome proliferators activated receptor, such as diabetes mellitus and obesity.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Analogs of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) agonists, and methods of using the same
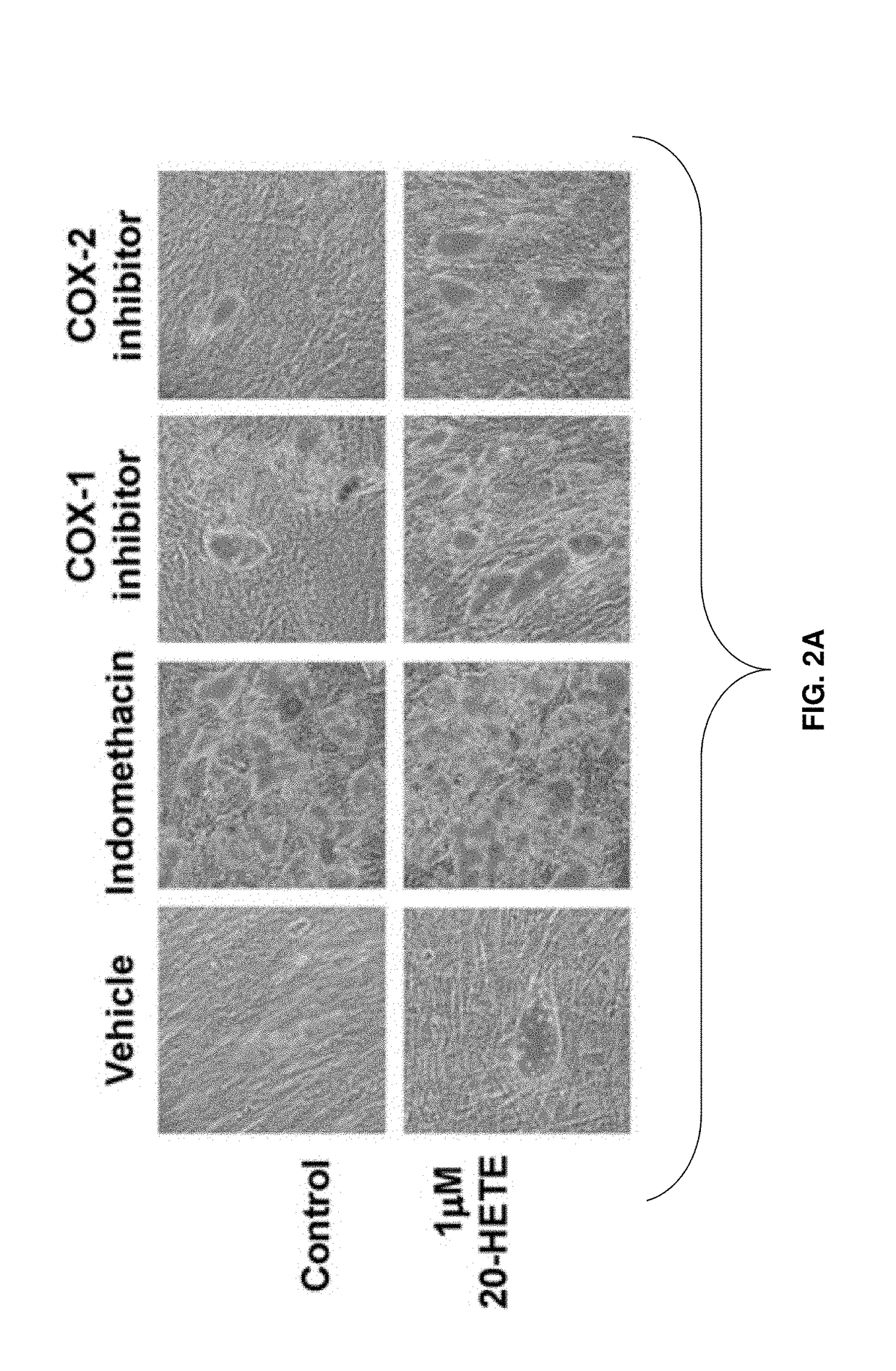
Analogs of PPAR5 and analogs of 20-OH-PGE2, which are PPAR5 agonists and 20-OH-PGE2 antagonists, respectively, and methods of using the same for inducing osteogenesis or chondrogenesis, are disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Thiazole and oxazole derivatives as activators of human peroxisome proliferator activated receptors
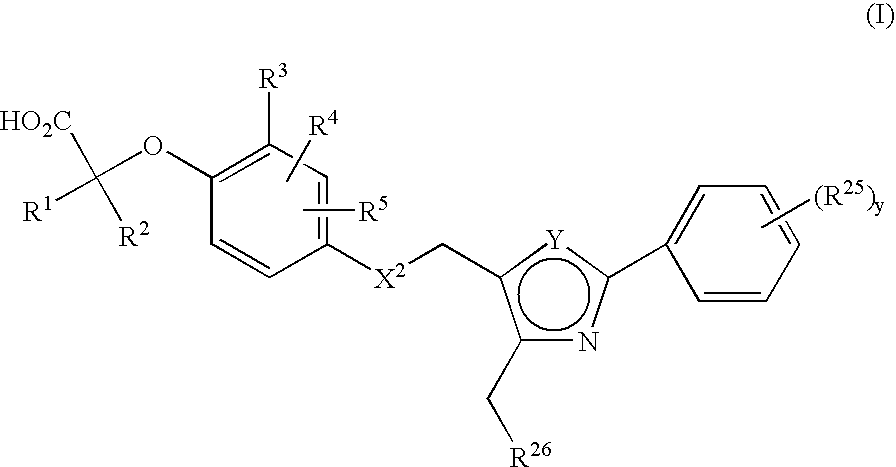
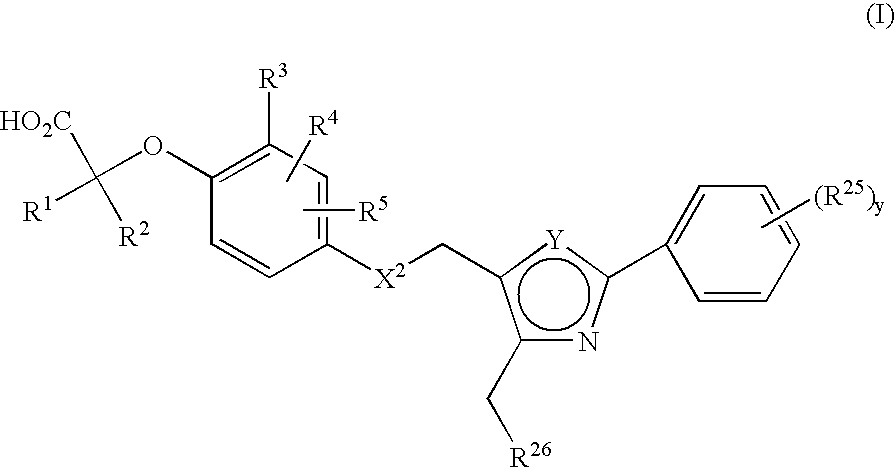
The present invention provides a compound of formula (I): wherein R1-R5, R25, R26, Y, y, and X2 are as defined herein. The compounds activate human peroxisome proliferater activated receptors (hPPARs) and are useful for the treatment of associated disorders such as dyslipidemia, syndrome X, hypercholesteremia, type II diabetes mellitus, type I diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia, and obesity.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Treatment of Acne and Other Diseases
Owner:WEIDNER MORTEN SLOTH
Methods of using peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha target genes
InactiveUS20050191668A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPeroxisome proliferatorsActivating receptors
This invention features the identification of novel target genes for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha (PPARα) in human, and their use in treating or monitoring the treatment of metabolic abnormalities, as well as in identifying compounds useful for treating metabolic abnormalities.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Treatment of tumours
InactiveUS20070111973A1Good curative effectSquelching unwanted PPARγ-activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseAndrostane
The present invention refers to steroid derivatives for use as medicaments. More specifically, the invention also relates to the use of a steroid derivative of 5-androstene-, 5-pregnenolone or corresponding saturated derivatives (androstane- or pregnane-) in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of a benign and / or malignant tumour, which medicament is capable of interrupting disturbances in Wut-signaling, such as cell-cycle arrest in G1-phase, and / or providing an angiostatic effect. Examples of such steroid derivatives are -5-androstene-17-ol, androstane-17-ol-pregnane-17-ol or pregnane-17-ol derivatives. In a further aspect, the invention relates to a method of producing a medicament for the treatment of a benign and / or malignant tumour and / or an inflammatory condition comprising the steps of contacting 5-androstane-3B,17-dio 1 or androstane-3B-diol, an enzyme and a sulfotransferase to provide 5-androstene-17-ol-3B-sulfate or corresponding andros tane derivative (17-AEDS or 17-AADS); and mixing the 17-AEDS or 17-AADS so produced with a suitable carrier; whereby a medicament which is capable of acting as a ligand to peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor—(PPAR) is produced.
Owner:HAGSTROM TOMAS +2
Compounds, their preparation and use
Novel compounds of the general formula (I), the use of these compounds as pharmaceutical compositions, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds and methods of treatment employing these compounds and compositions. The present compounds may be useful in the treatment and / or prevention of conditions mediated by Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPAR), in particular the PPARδ subtype.
Owner:HIGH POINT PHARMA
Construction and application of medicine screening model on the basis of PPAR (Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors) gamma signal channel
InactiveCN107779454AEasy to operateEffectiveCompound screeningApoptosis detectionNucleotideHigh flux
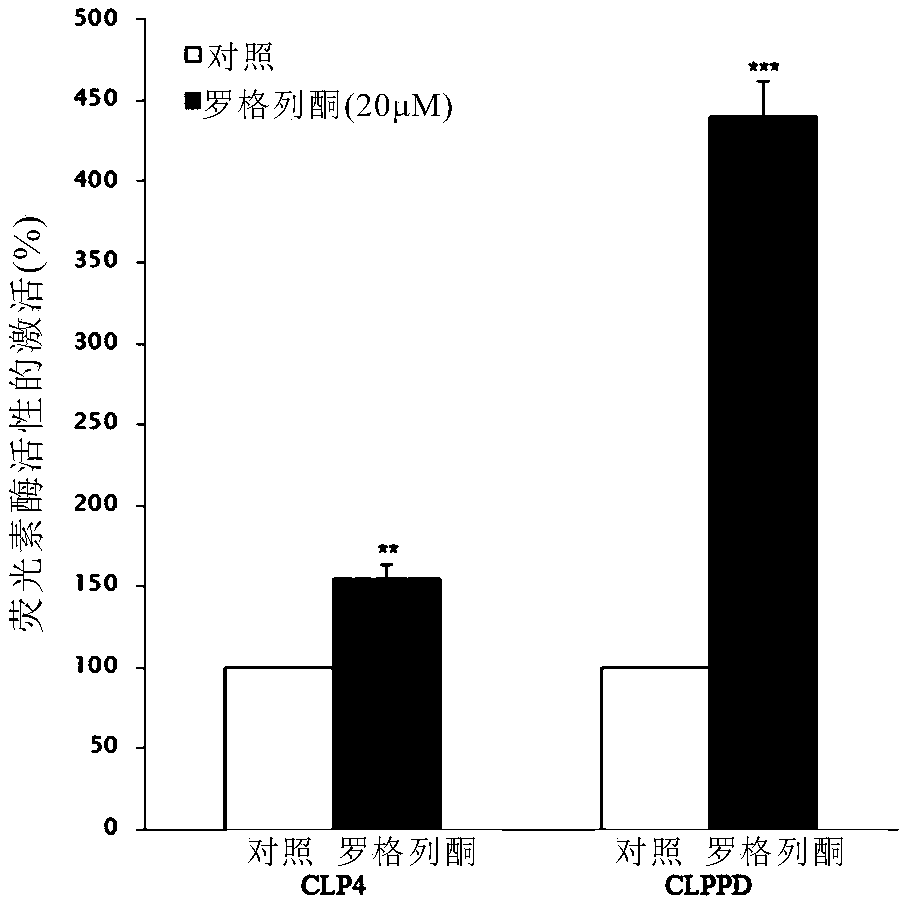
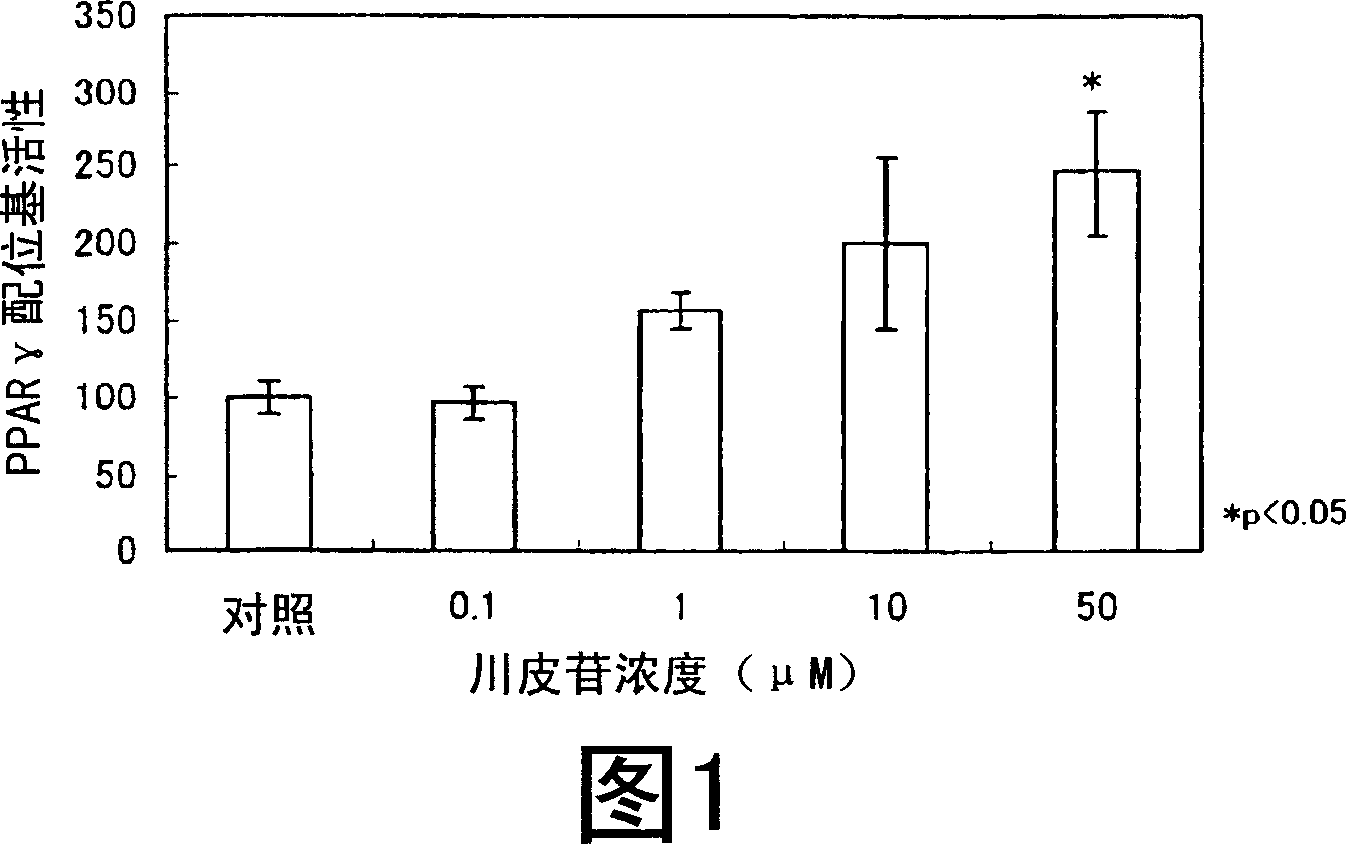
The invention relates to construction and application of a medicine screening model on the basis of a PPAR (Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors) gamma signal channel. Specifically, the invention provides a polynucleotide sequence which is selected from N1-(AGGTCA-N-AGGTCA)m-N2 and the complementary sequence thereof, wherein N1, N, N2 and m are disclosed in the invention. The invention alsoprovides a reporter vector which contains the polynucleotide sequence and a luciferase reporter gene, a kit which contains the reporter vector, a cell in which the reporter vector is transferred, a preparation method of the cell and the application of the polynucleotide, the kit and the cell. The screening system is stable, is convenient in operation and is more suitable for screening high-flux medicines, and a screening period is shortened.
Owner:上海米络凯生物科技有限公司
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) activator, and drugs, supplements, functional foods and food additives using the same
InactiveCN101052391ASecurity ConfirmationPromote combustionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryFood additiveAdiponectin secretion
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Maturation of mammalian hepatocytes
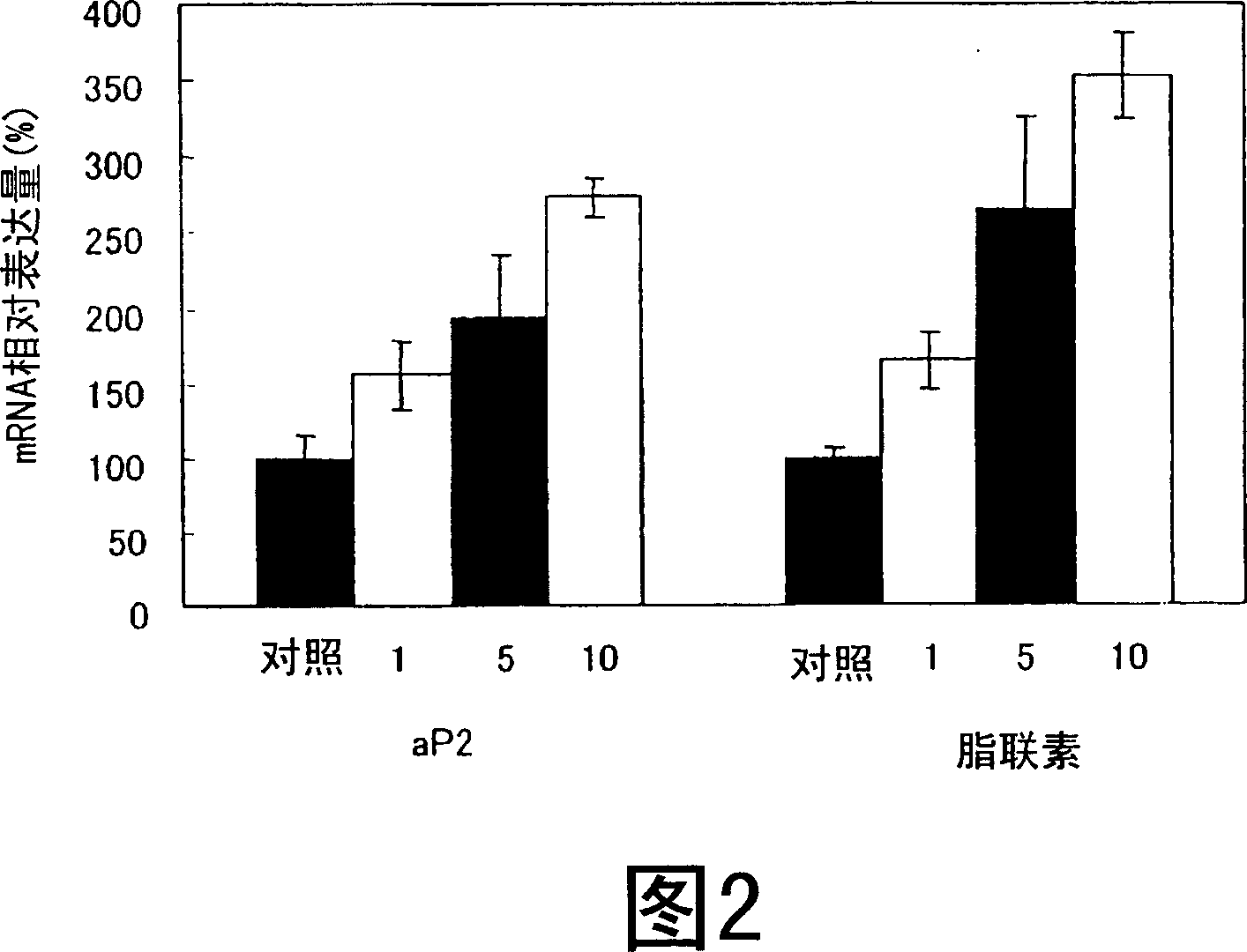
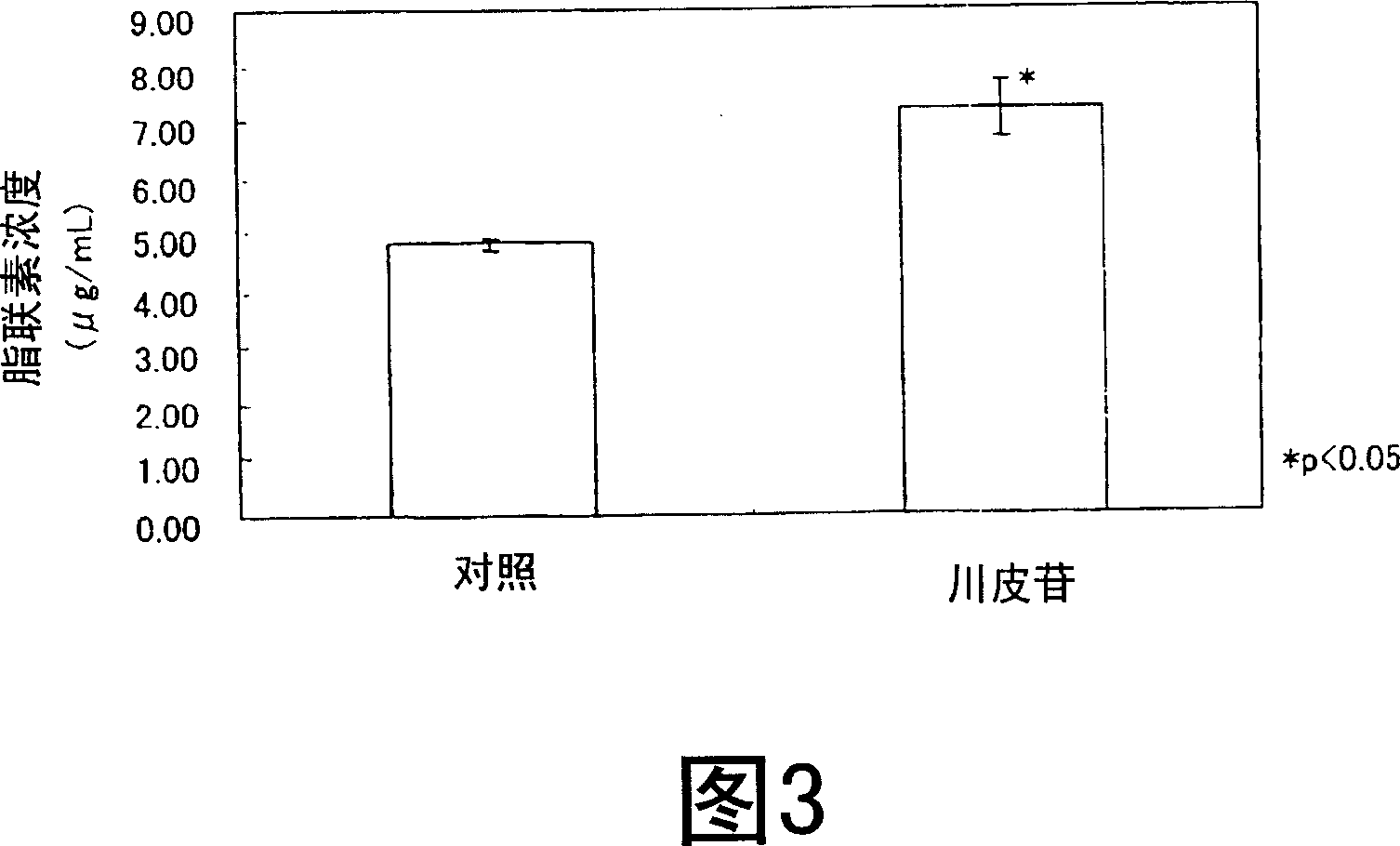
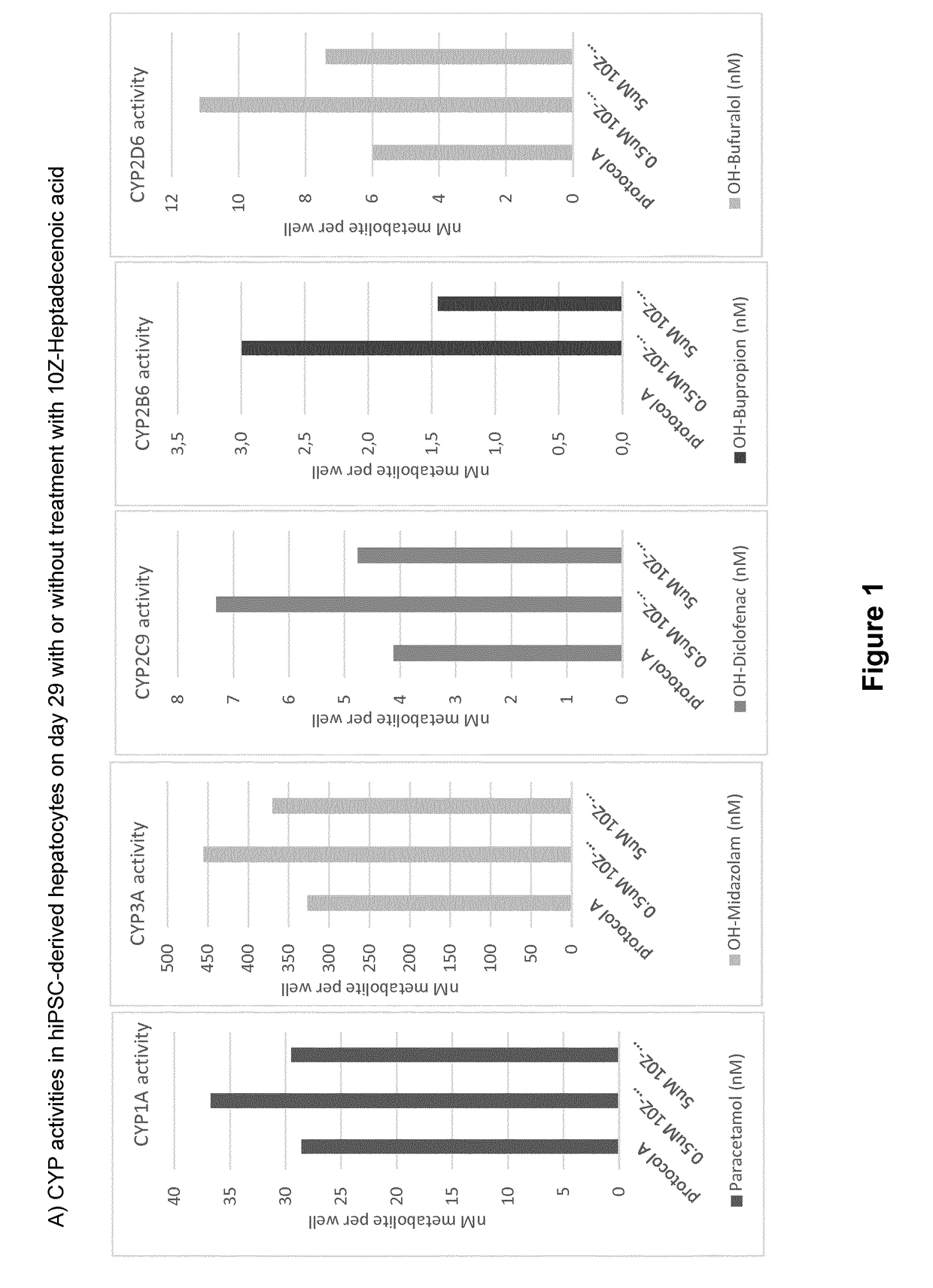
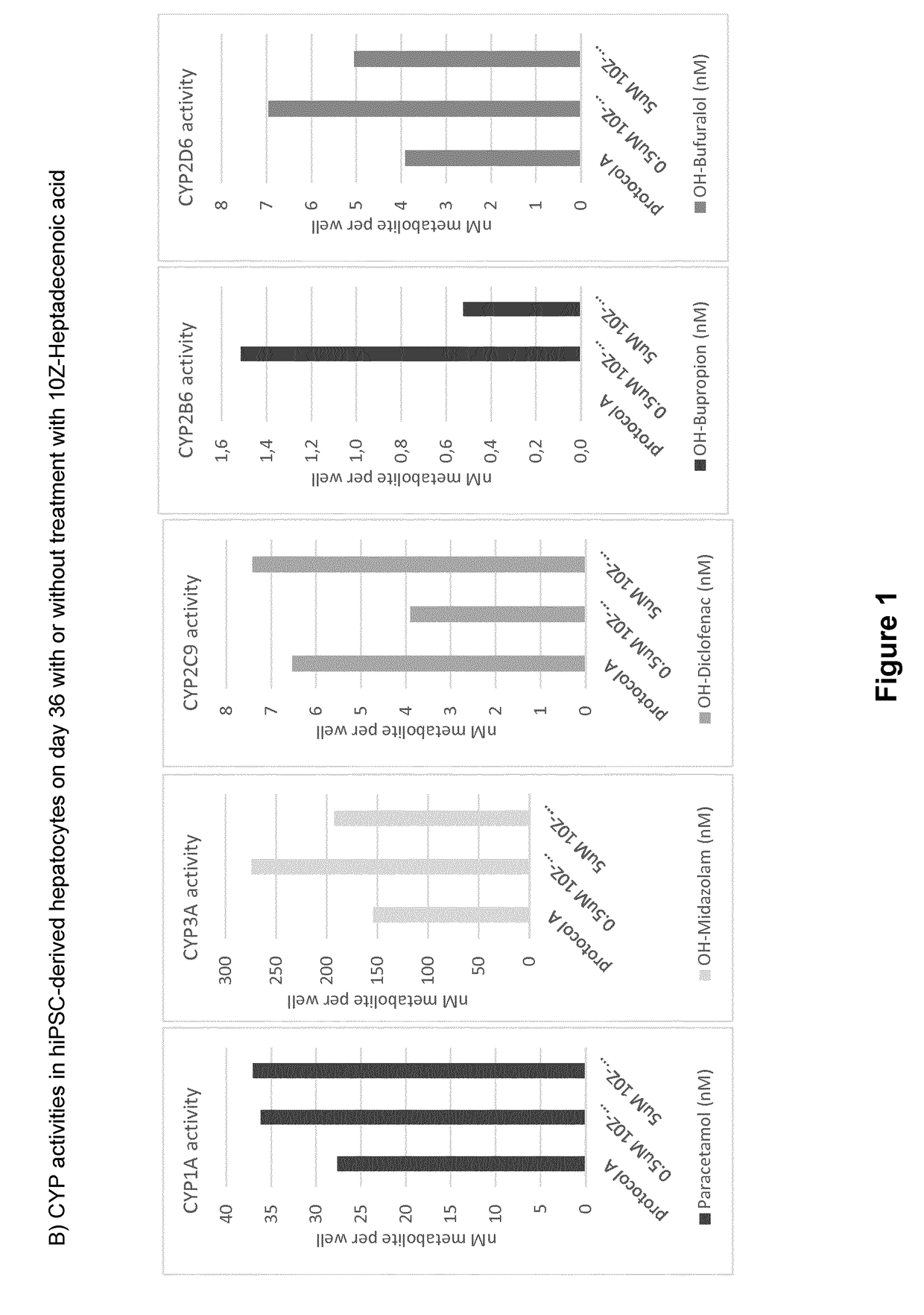
ActiveUS20190024044A1Improve the level ofRegulating trafficCulture processArtificial cell constructsMetaboliteDirected differentiation
The present invention relates to directed differentiation and maturation of mammalian hepatocytes, such as human hepatocytes. The hepatocyte obtained in accordance with the present invention show a phenotype which is more similar to that of primary hepatocytes than previously shown. In particular, the present invention relates to exposure of mammalian hepatocytes, such as human hepatocytes, to at least one maturation factor selected from the group consisting of Src kinase inhibitors, vitamin D including precursors, metabolites and analogs thereof, hypoxia inducing compounds, sphingosine and sphingosine derivatives, activators of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), platelet-activating factor (PAF), PKC inhibitors, and combinations thereof.
Owner:TAKARA BIO EURO
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com