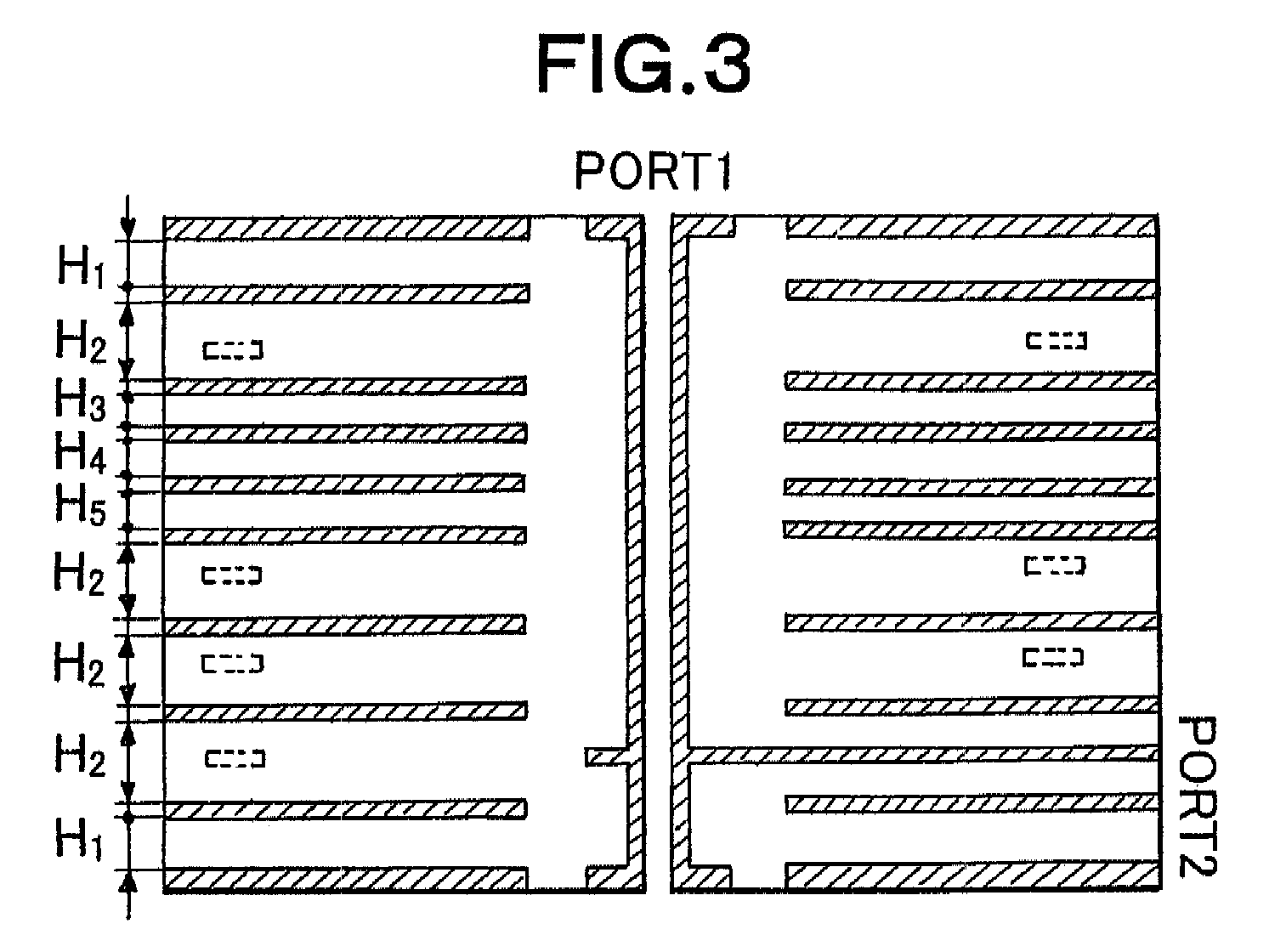
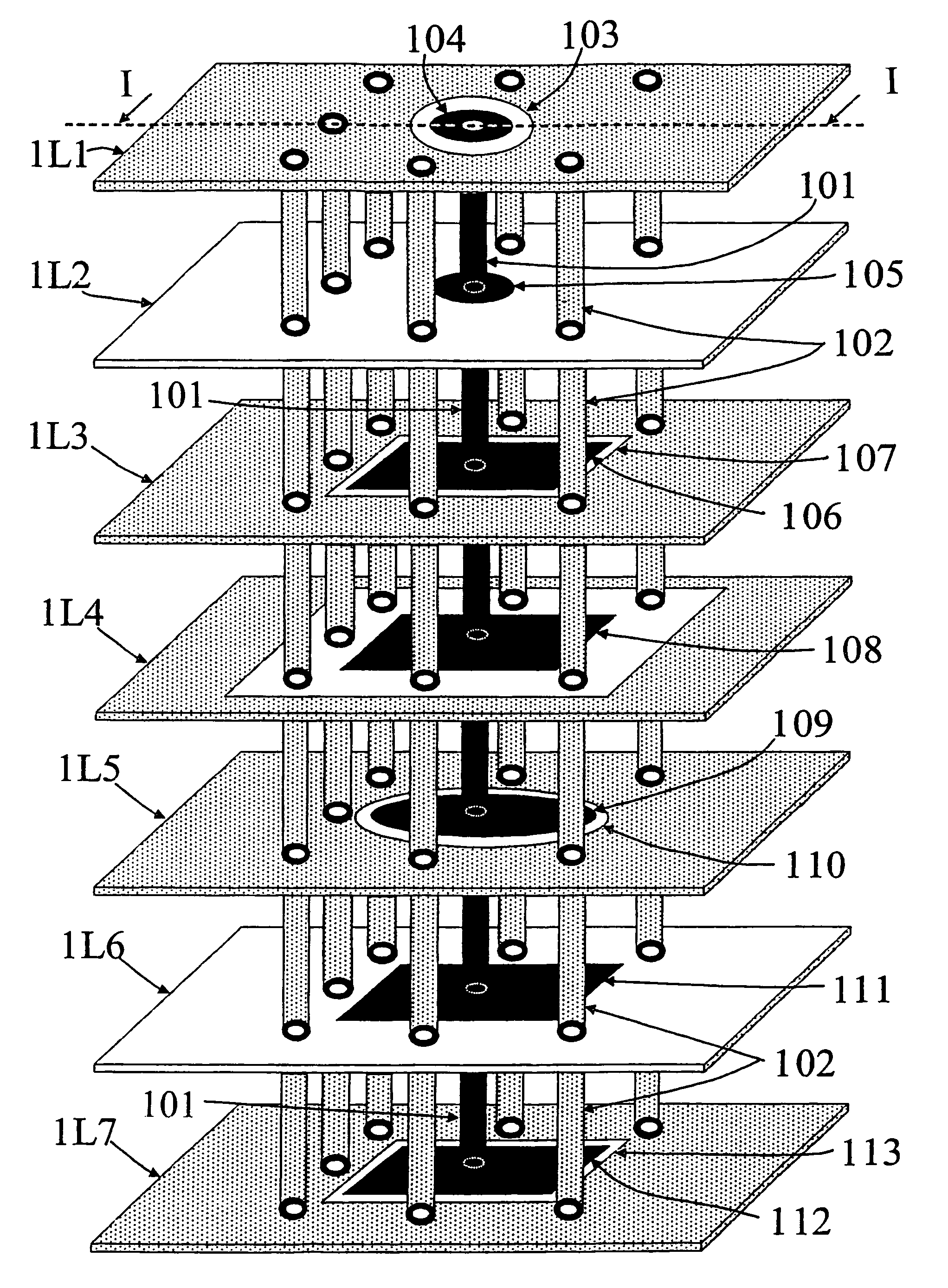
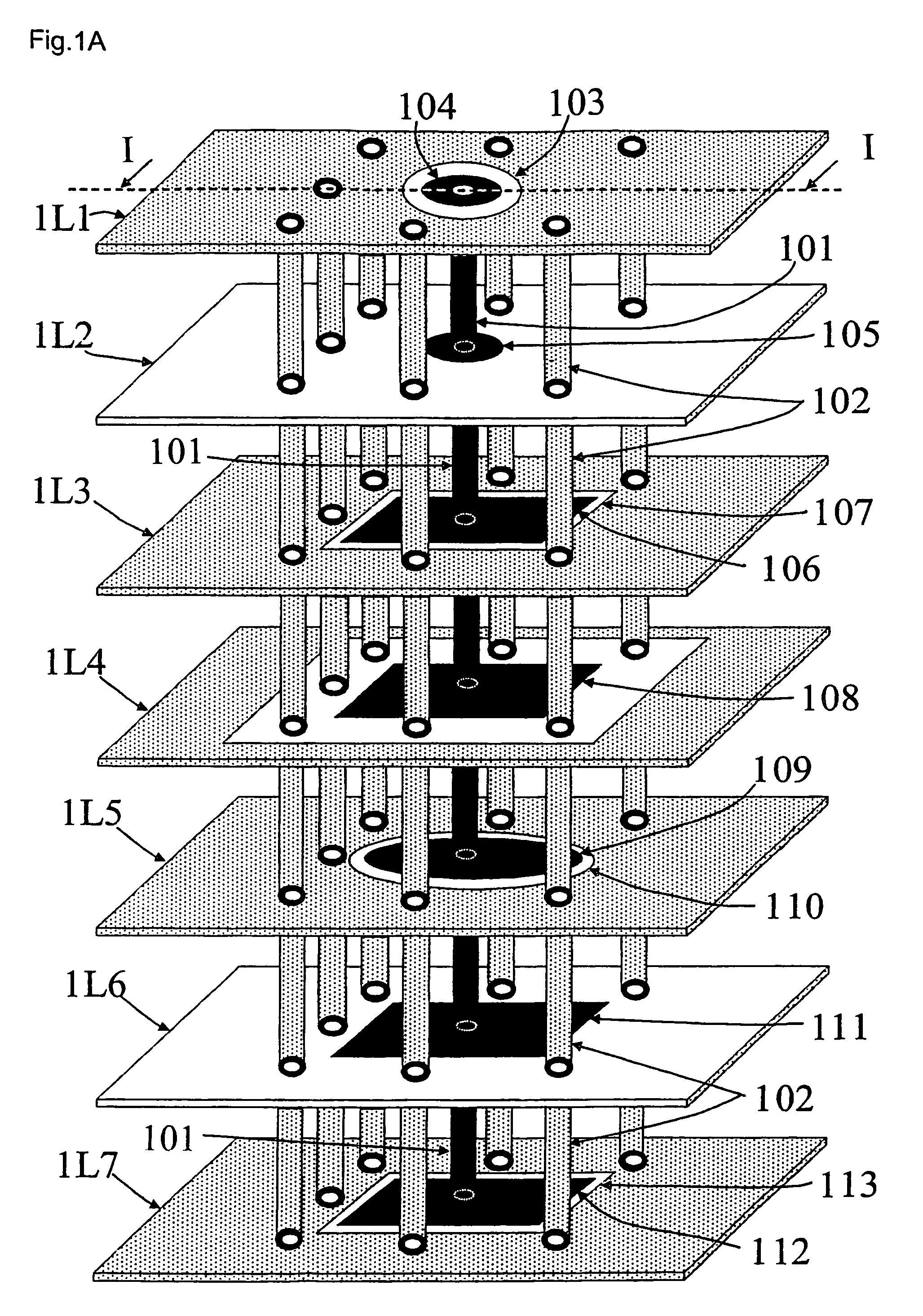
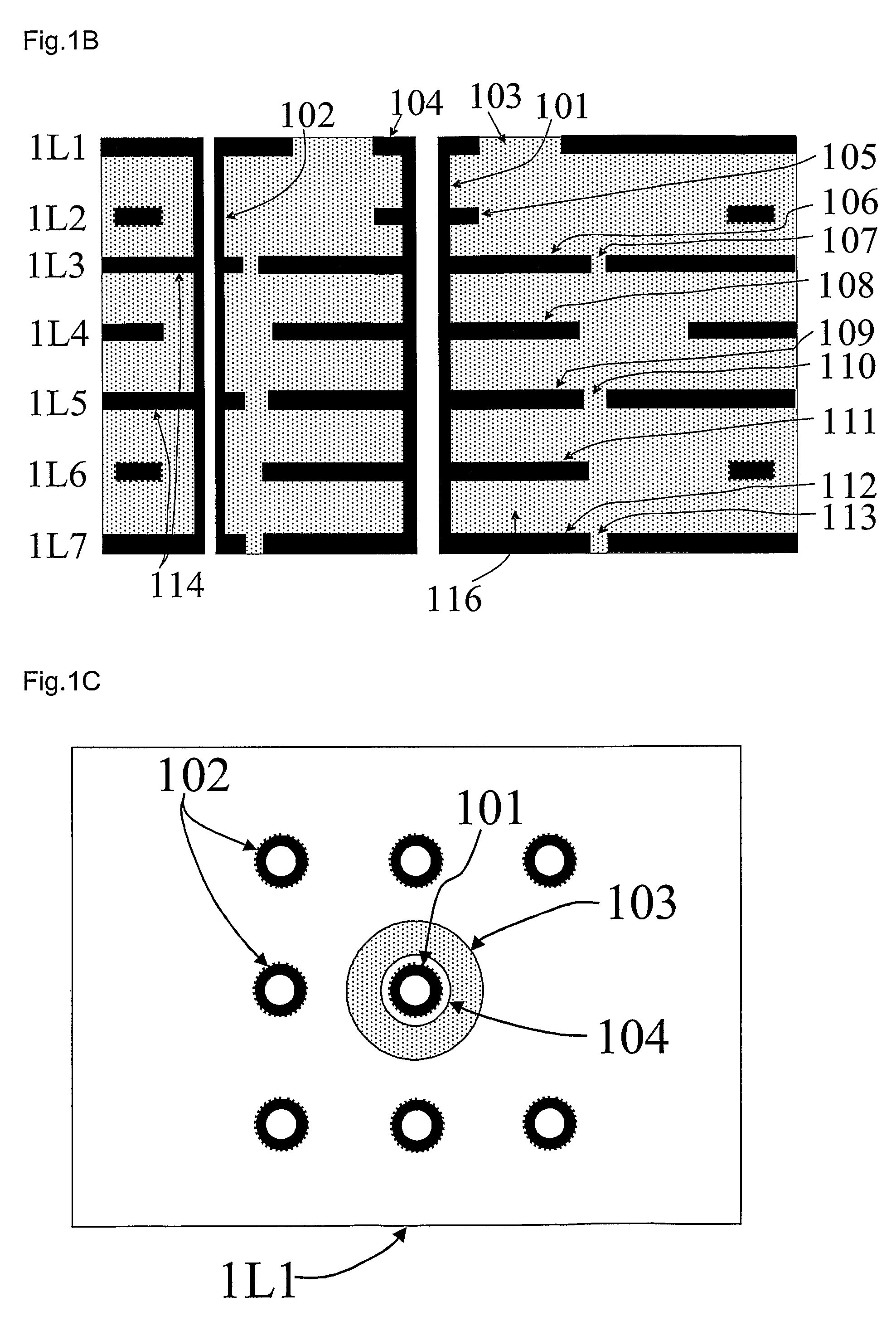
Patents
Literature
104 results about "Planar transmission lines" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
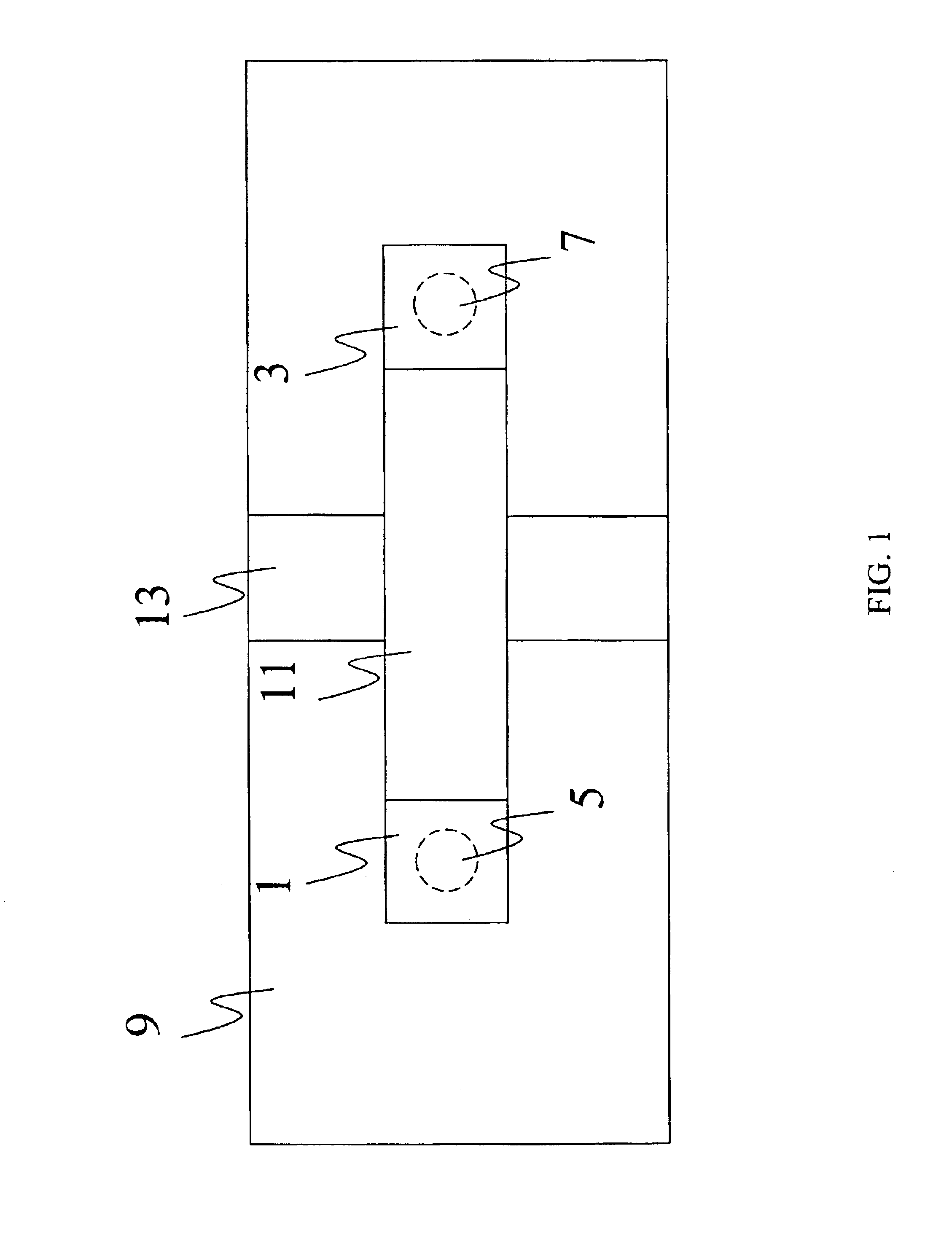
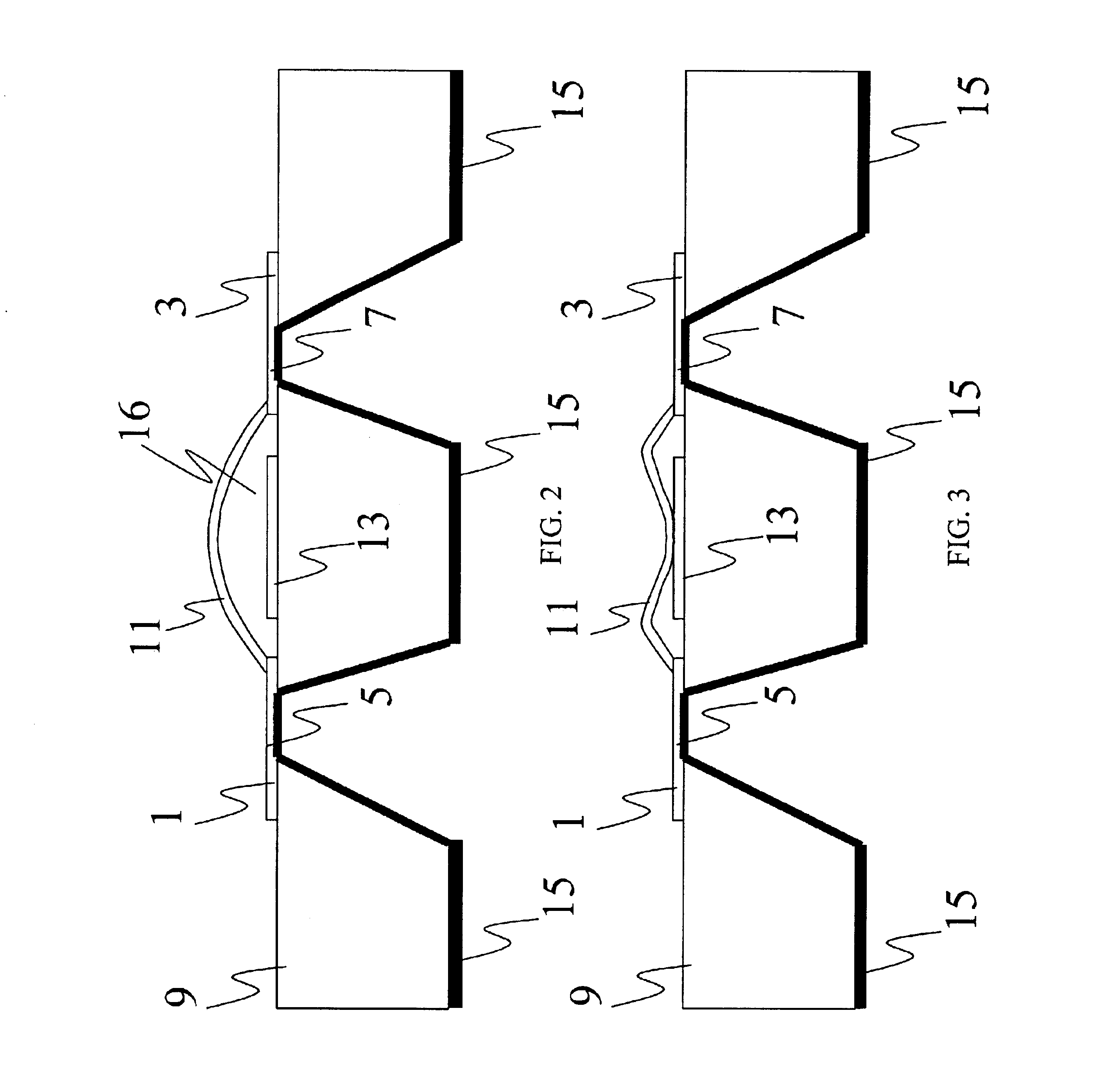
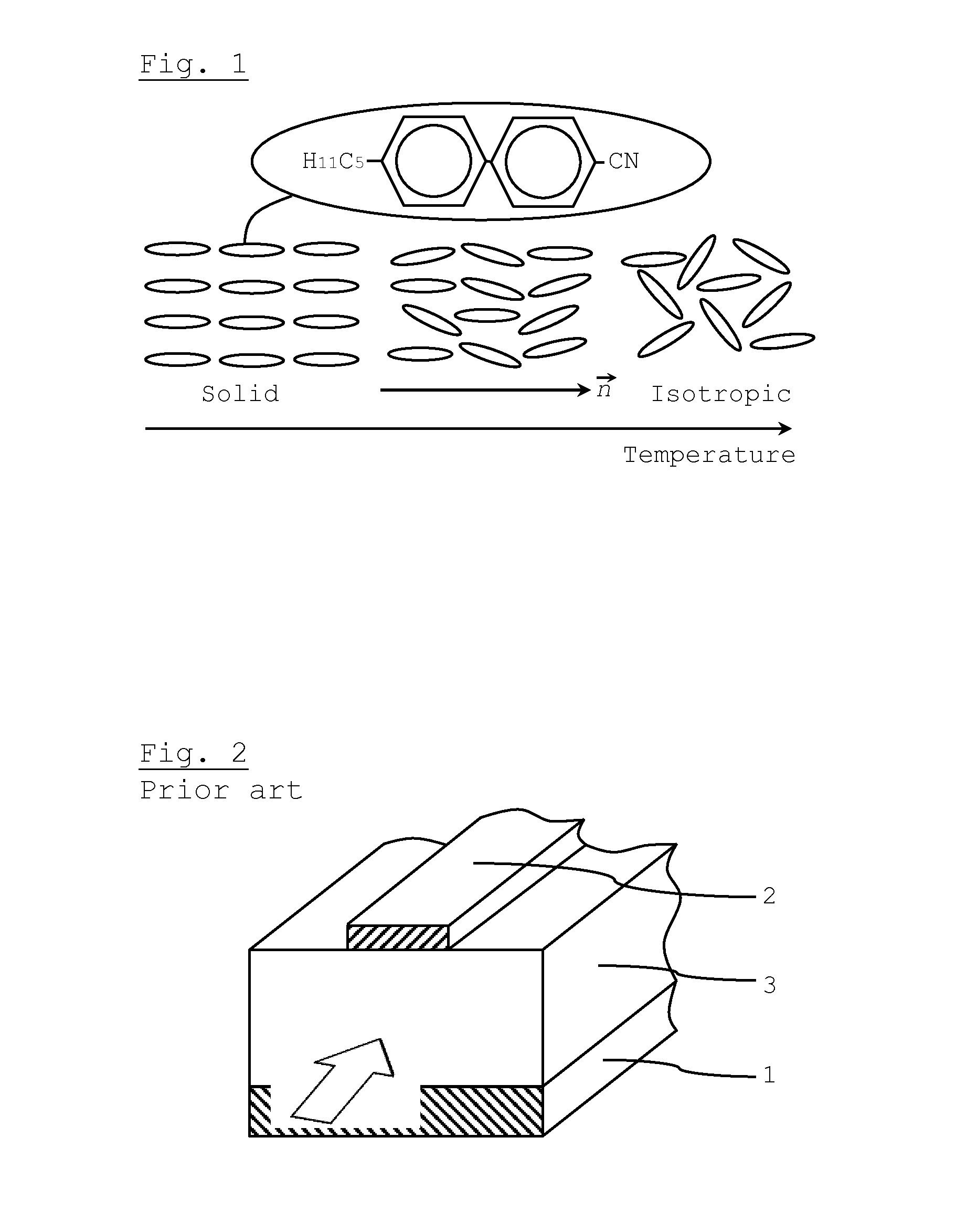
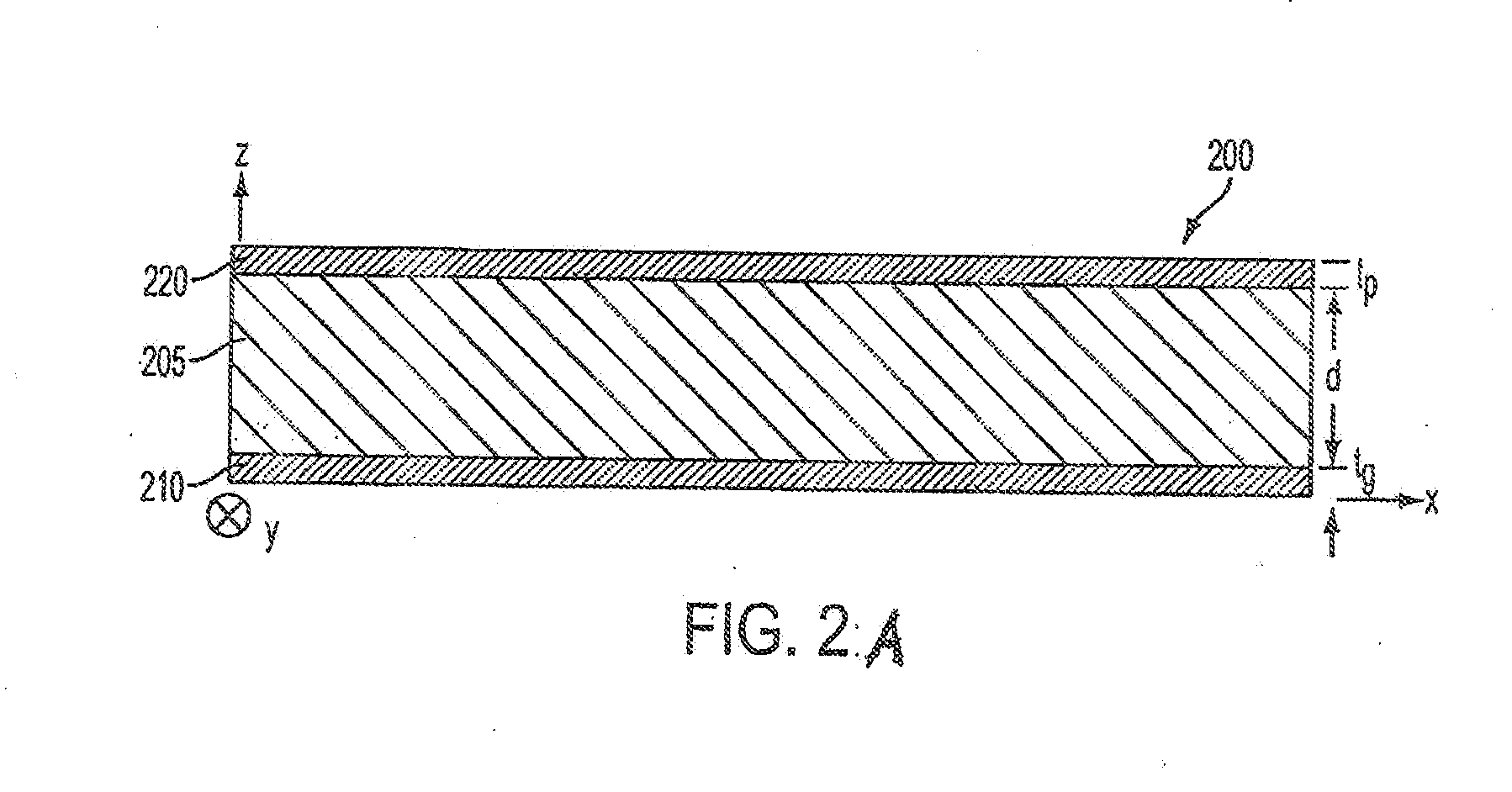
Planar transmission lines are those transmission lines in which the conductors are essentially flat. The conductors consist of flat strips, and there are usually one or more ground planes parallel to the flat surface of the conductors.
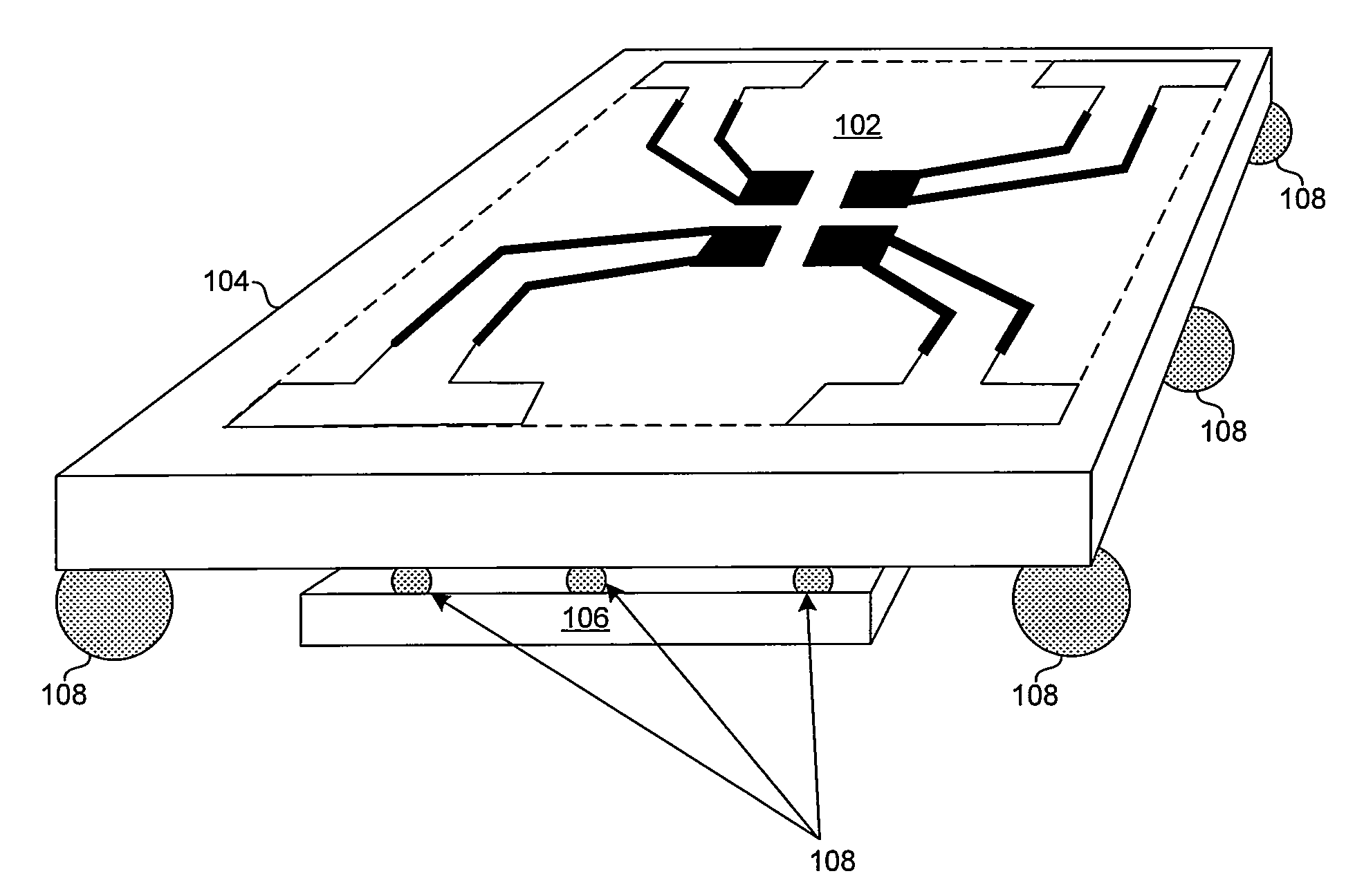
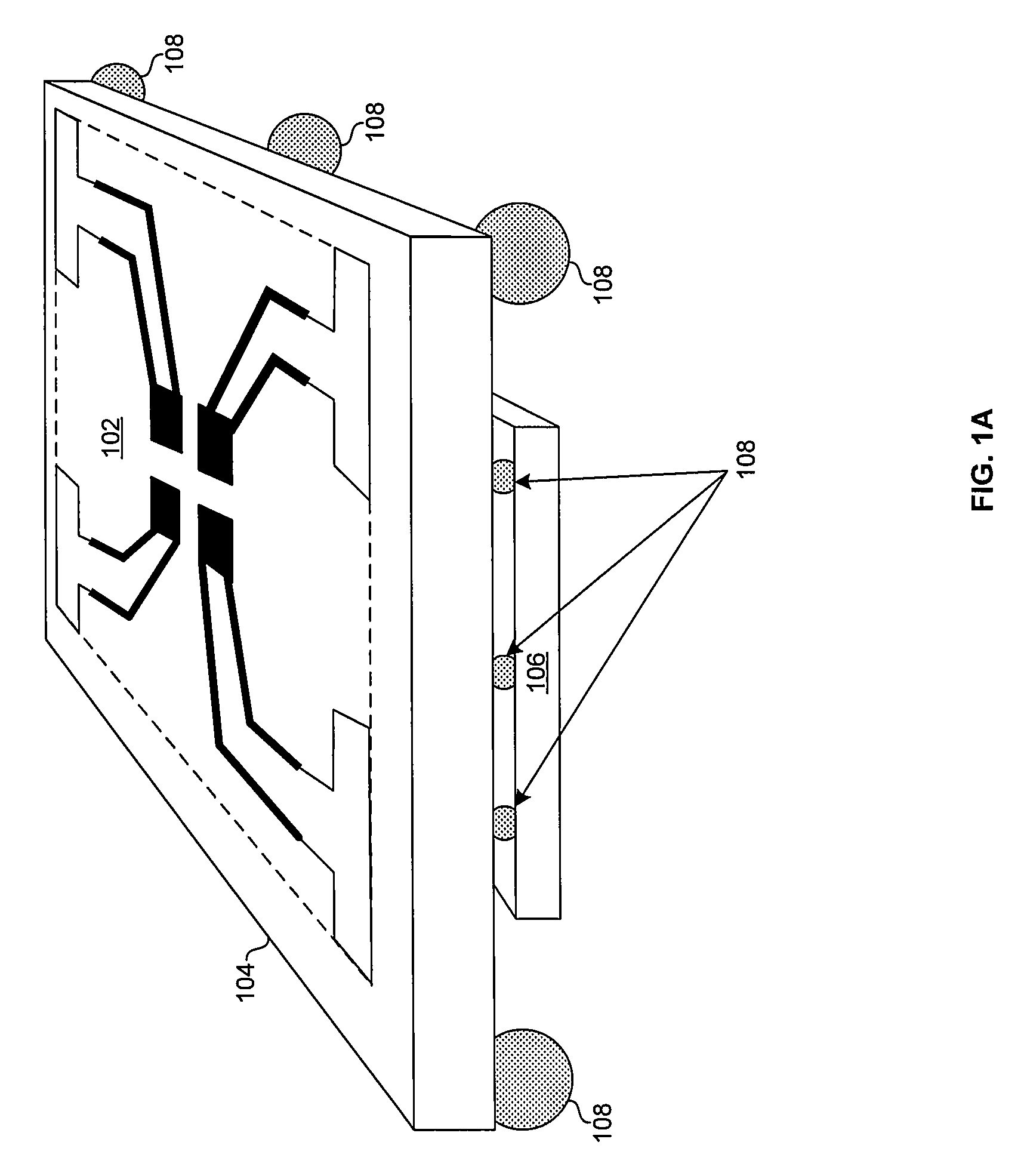
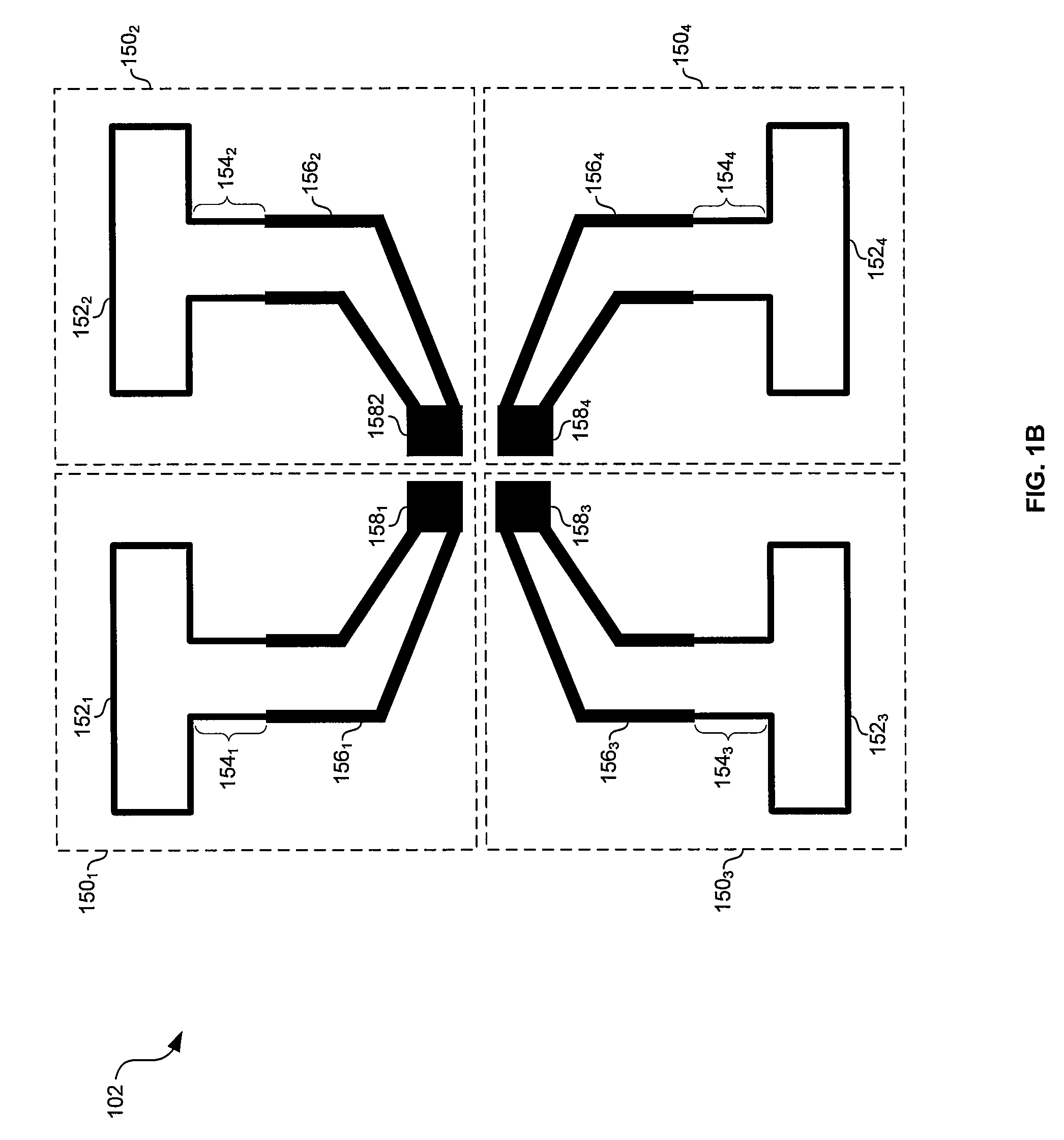
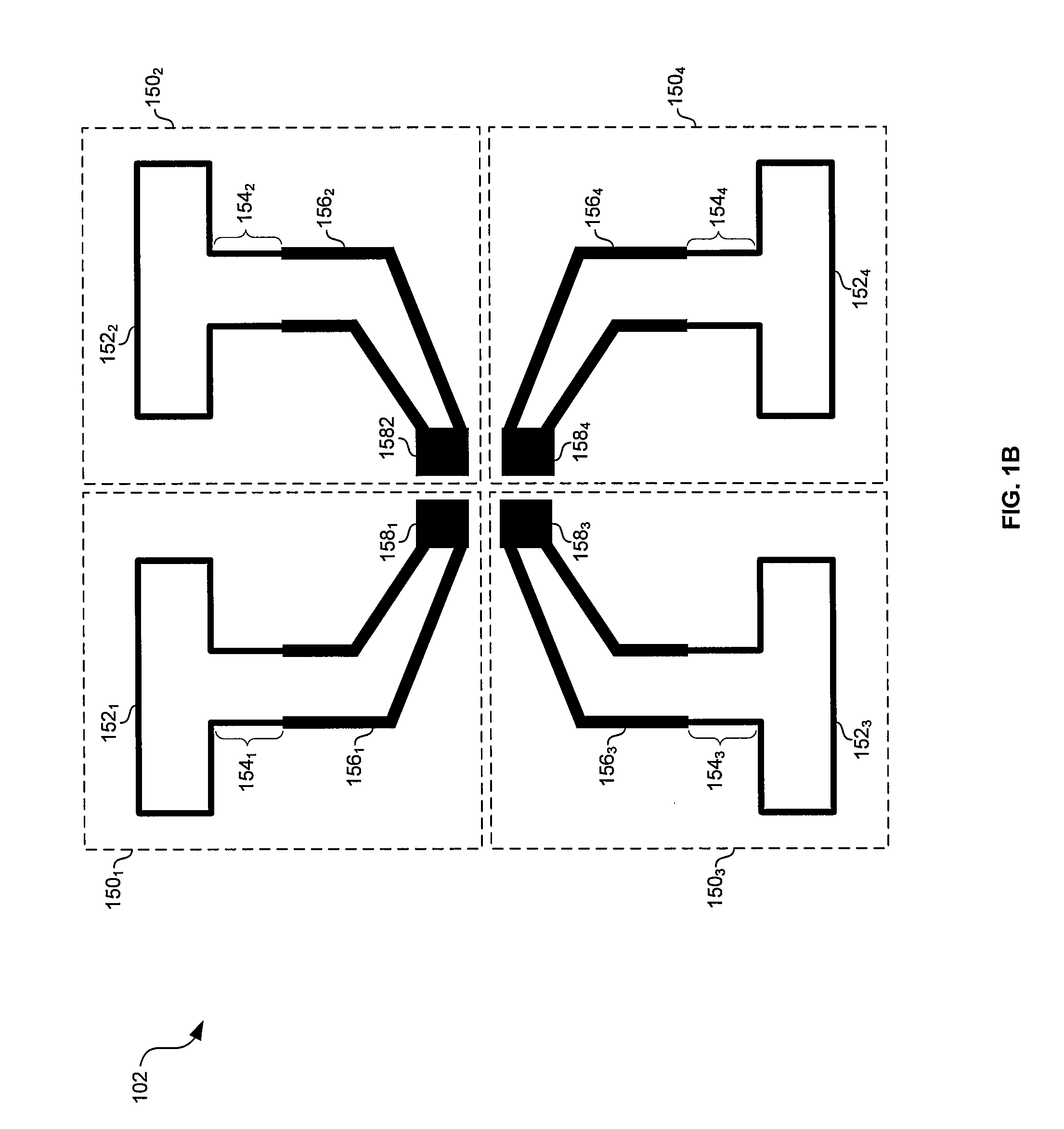
Method and system for a phased array antenna embedded in an integrated circuit package
ActiveUS7880677B2Simultaneous aerial operationsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhase shiftedTransformer
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
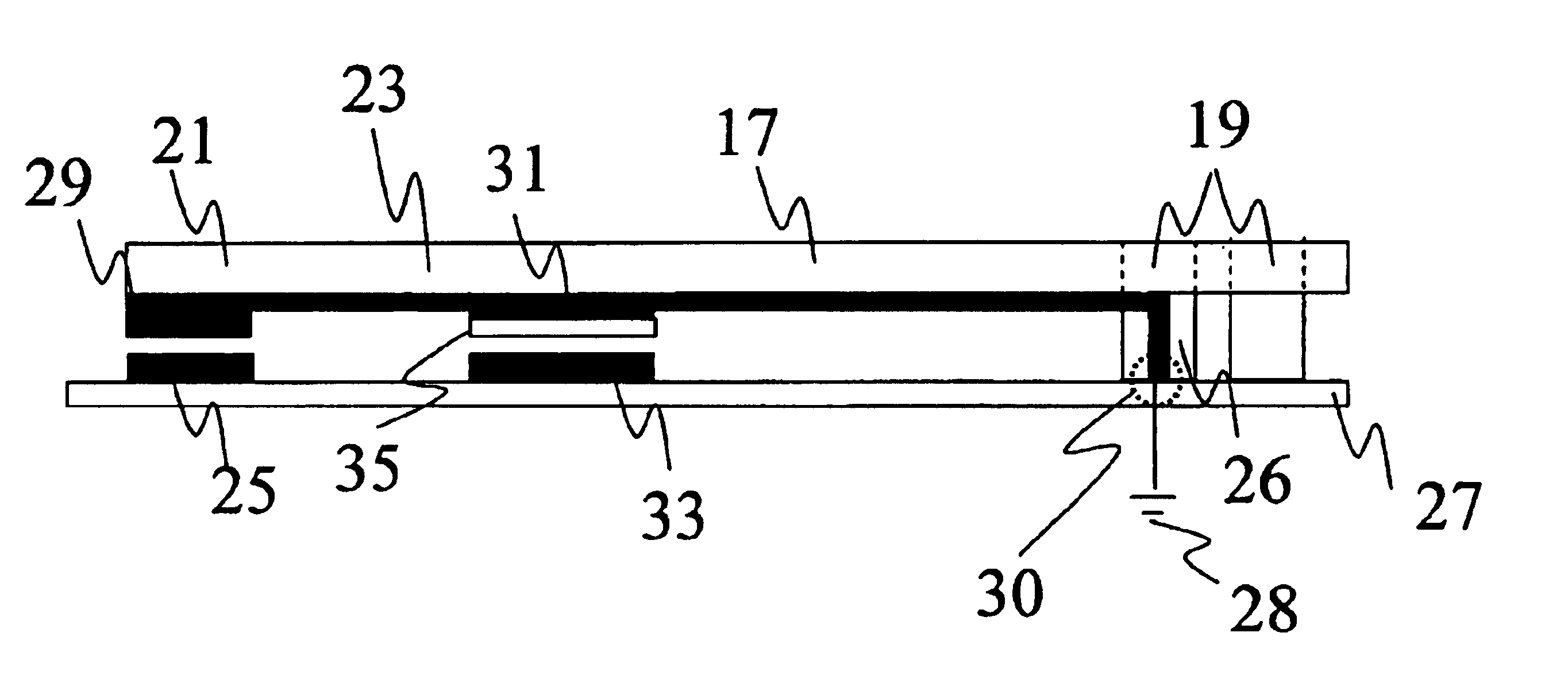
Microelectromechanical RF and microwave frequency power regulator
InactiveUS6847266B2Electrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysCurrent interference reductionContact padEngineering
Microelectromechanical RF and microwave frequency power limiter and electrostatic protection devices for use in high-speed circuits are presented. The devices utilize an airbridge or a cantilever arm including a contact pad positioned operatively adjacent to an electrically conductive and substantially planar transmission line. When the power level in the transmission line exceeds a particular threshold, the airbridge or cantilever arm yields due to force between the contact pad and the transmission line, directing undesired power away from active devices. This characteristic can either serve as a method by which to limit the amount of power passing through the transmission line to a determined value or as a method by which to protect devices along the transmission line from damage due to large electrostatic bursts.
Owner:HRL LAB
Method and system for a phased array antenna embedded in an integrated circuit package
ActiveUS20090153428A1Antenna supports/mountingsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhase shiftedTransformer
Aspects of a method and system for configurable antenna in an integrated circuit package are provided. In this regard, a phased array antenna embedded in a multi-layer integrated circuit (IC) package may be utilized for transmitting and / or receiving signals. An IC enabled to transmit and / or receive signals may be bonded to the multi-layer IC package and may communicate a reference signal and / or one or more phase shifted versions of said reference signal to the antenna. One or more phase shifters (fabricated, for example, in planar transmission line) may be embedded in the multi-layer IC package and may be controlled via an IC bonded to the multi-layer IC package. The phased array antenna may comprise a plurality of antenna elements which may each comprise an interconnection for communicatively coupling to an associated transmitter and / or receiver, a feeder line, a quarter wavelength transformer, and a radiating portion (e.g., a folded dipole).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
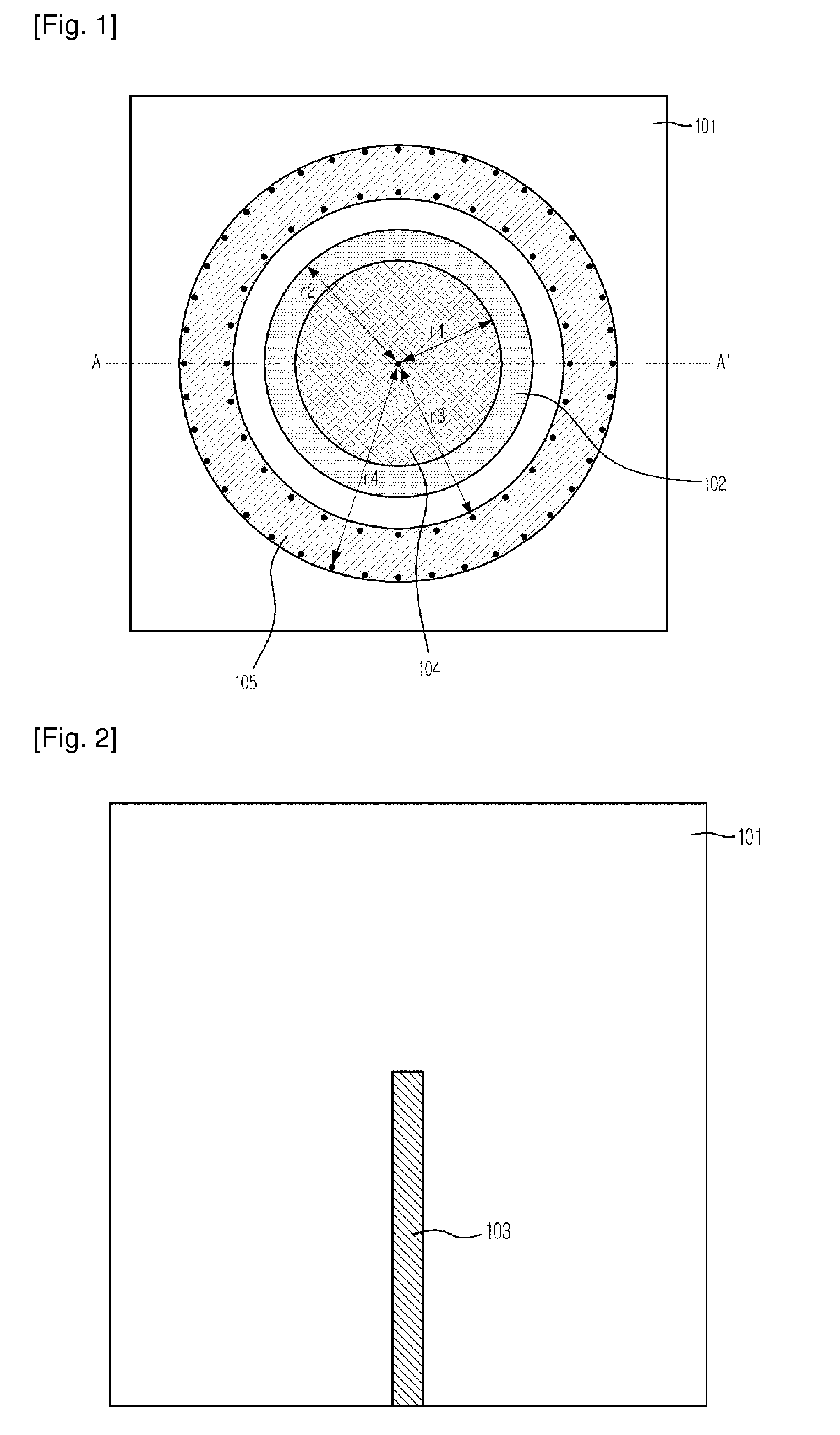
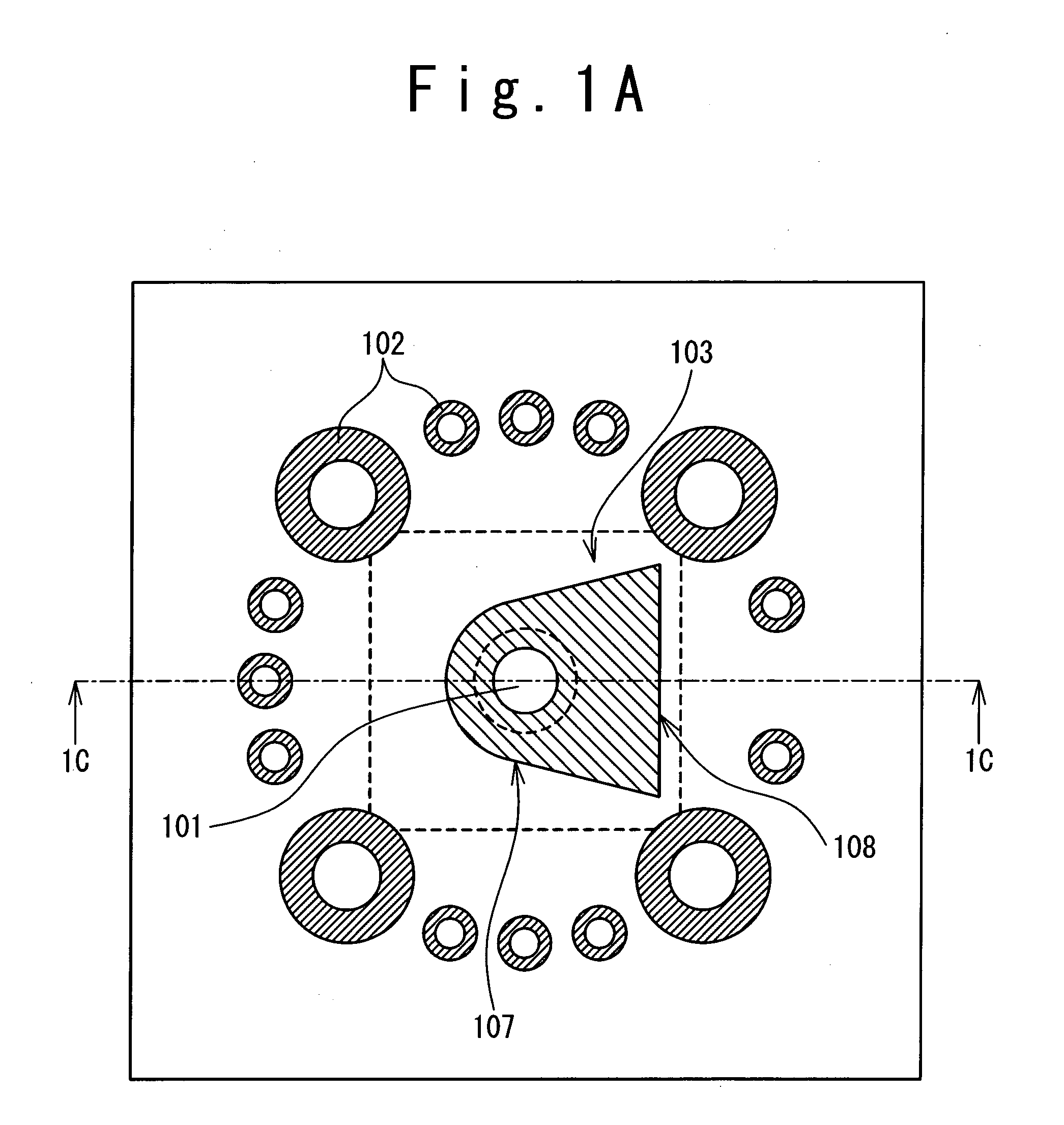
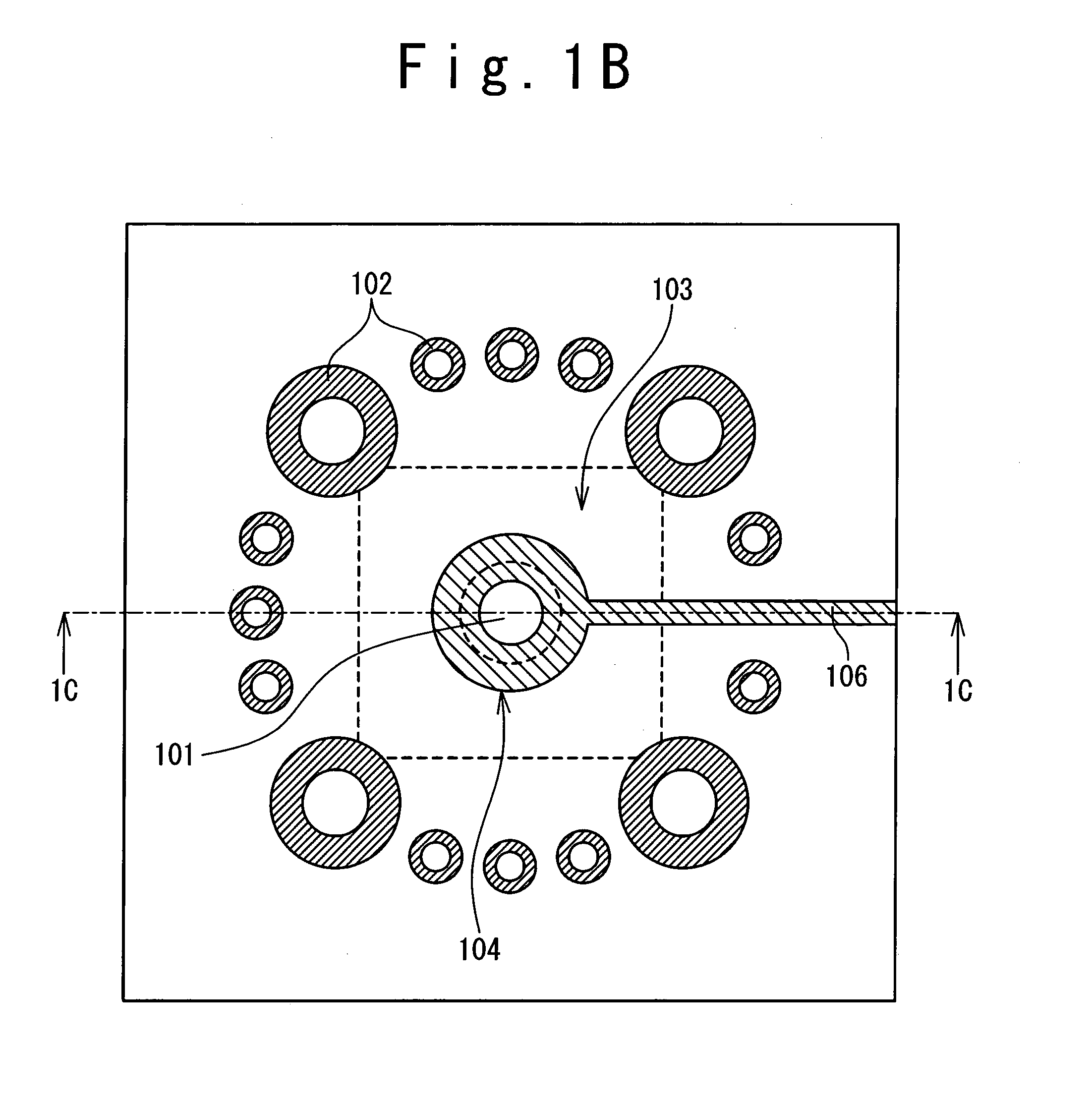
Omni-directional planar antenna
InactiveUS20100090903A1Easy to integrateEasy to implementSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDielectric substrateDirectional antenna
Provided is a planar antenna having omni-directional radiation patterns. The planar antenna includes a circular patch located on one dielectric substrate of the plurality of dielectric substrates; a planar transmission line applied with signals from the exterior; a signal via for coupling the circular patch with the planar transmission line and supplying the signals incoming through the planar transmission line to the circular patch; and a metal ground plane having a slot having a certain shape through which the signal via passes, and located on the dielectric substrate.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Arrangement and method for contactless energy transmission with a coupling-minimized matrix of planar transmission coils
ActiveUS20140091640A1Minimize couplingSimplifies design and optimizationNear-field transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic couplingElectrical conductor
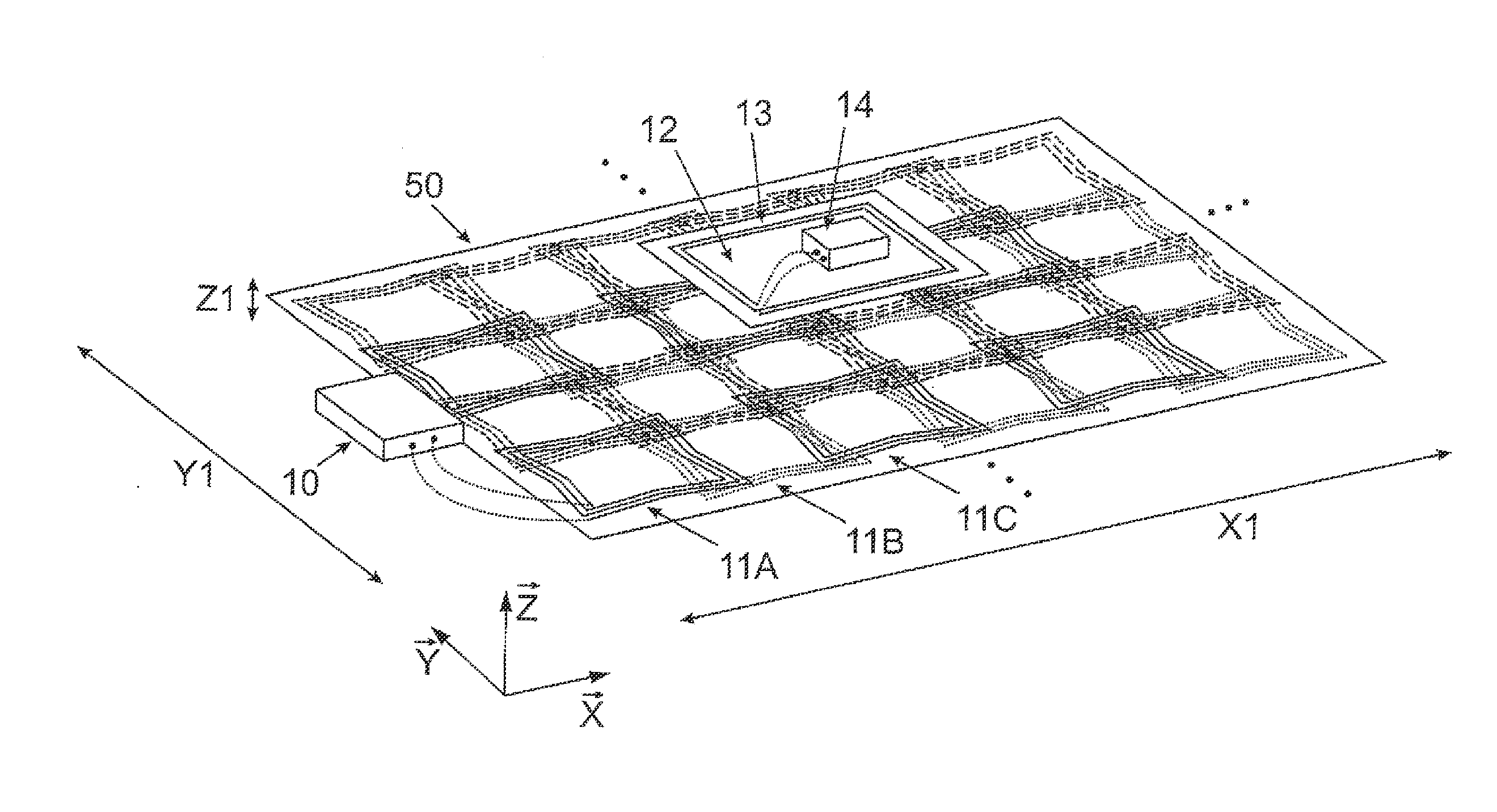
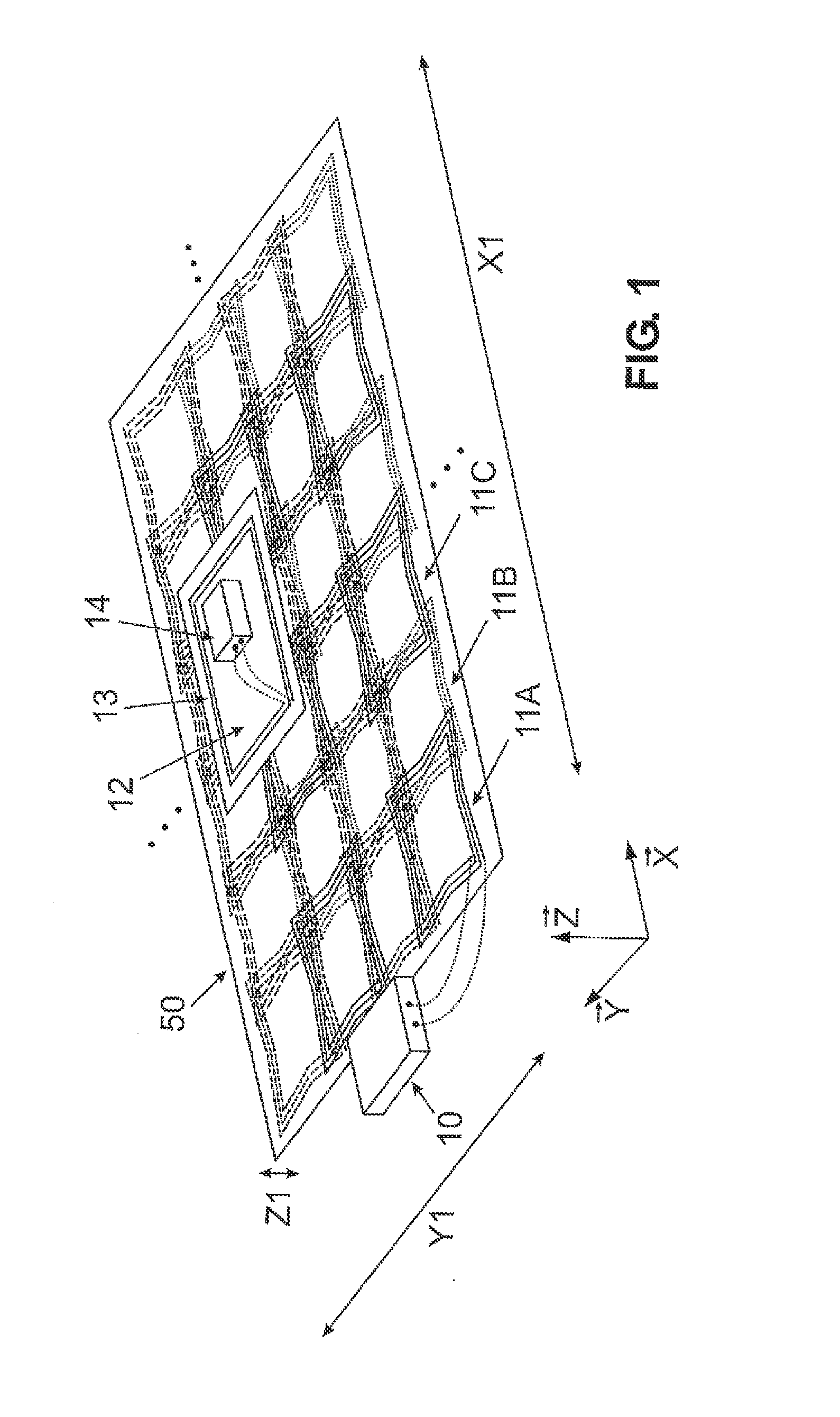
The invention relates to an arrangement and a method for contactless energy transmission by means of induction. There are a plurality of coils arranged in a matrix, the coils having at least one conductor that surrounds a central axis of the coil at least once in one turn. The central axis stands vertically on the surface surrounded by the conductor in the geometric center of area of the surrounded surface. The coils are arranged adjacent to one another in a planar unit that extends in a first dimension, in a second dimension, and in a third dimension. The extension of the planar unit in the first dimension and in the second dimension is significantly greater than in the third dimension. The central axis of each coil stands at least locally at least nearly perpendicular to the surface spanned by the first dimension and the second dimension. The coils are also arranged in a regular manner within the planar unit in rows and / or columns such that each coil has at least two or three immediately adjacent coils. The distances between geometric centers of area of the coils and the shape and the extension of the at least one turn per coil are selected such that the mutual electromagnetic coupling between coils is minimal for all pairs of immediately adjacent coils in the planar unit.
Owner:PHOENIX CONTACT GMBH & CO KG
Phase shift device
ActiveUS20150380789A1Easy and cost-saving fabricationFast and cheap fabricationCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricDelay linesMetal-insulator-metalElectricity
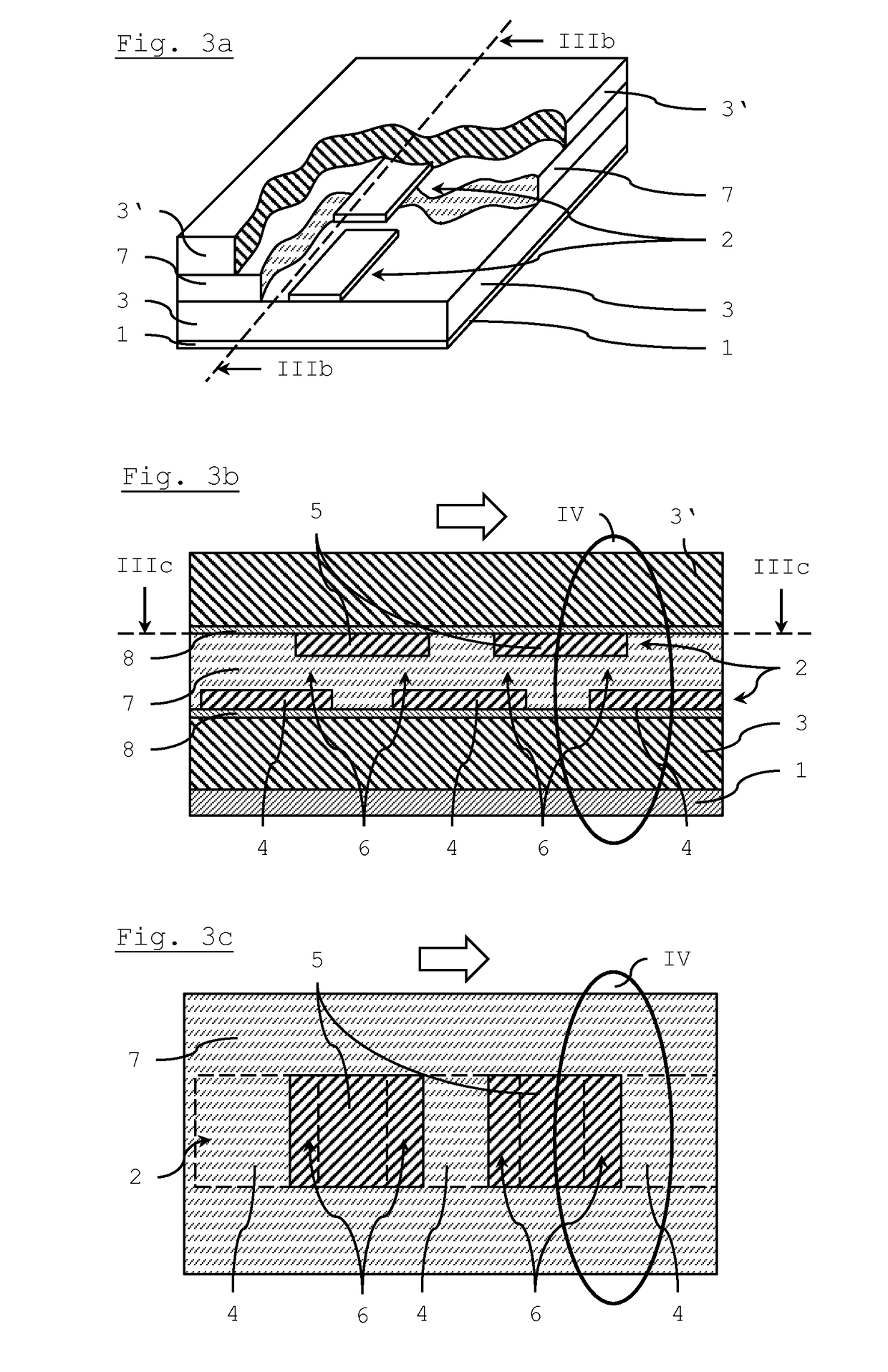
A phase shift device includes a planar transmission line that is formed by a signal electrode and a ground electrode which are separated by a dielectric substance, whereby the signal electrode of the planar transmission line is divided into several pieces and includes overlapping areas of adjacent pieces that are filled with a tunable liquid crystal material, thereby forming a dielectric tunable component (varactor) with a metal-insulator-metal type capacitor. The several pieces of the signal electrode are arranged at two or more different distance levels with respect to the ground electrode. The tunable liquid crystal material is arranged as a continuous layer between several pieces of the signal electrode that are arranged at two different distance levels.
Owner:ALCAN SYST GMBH
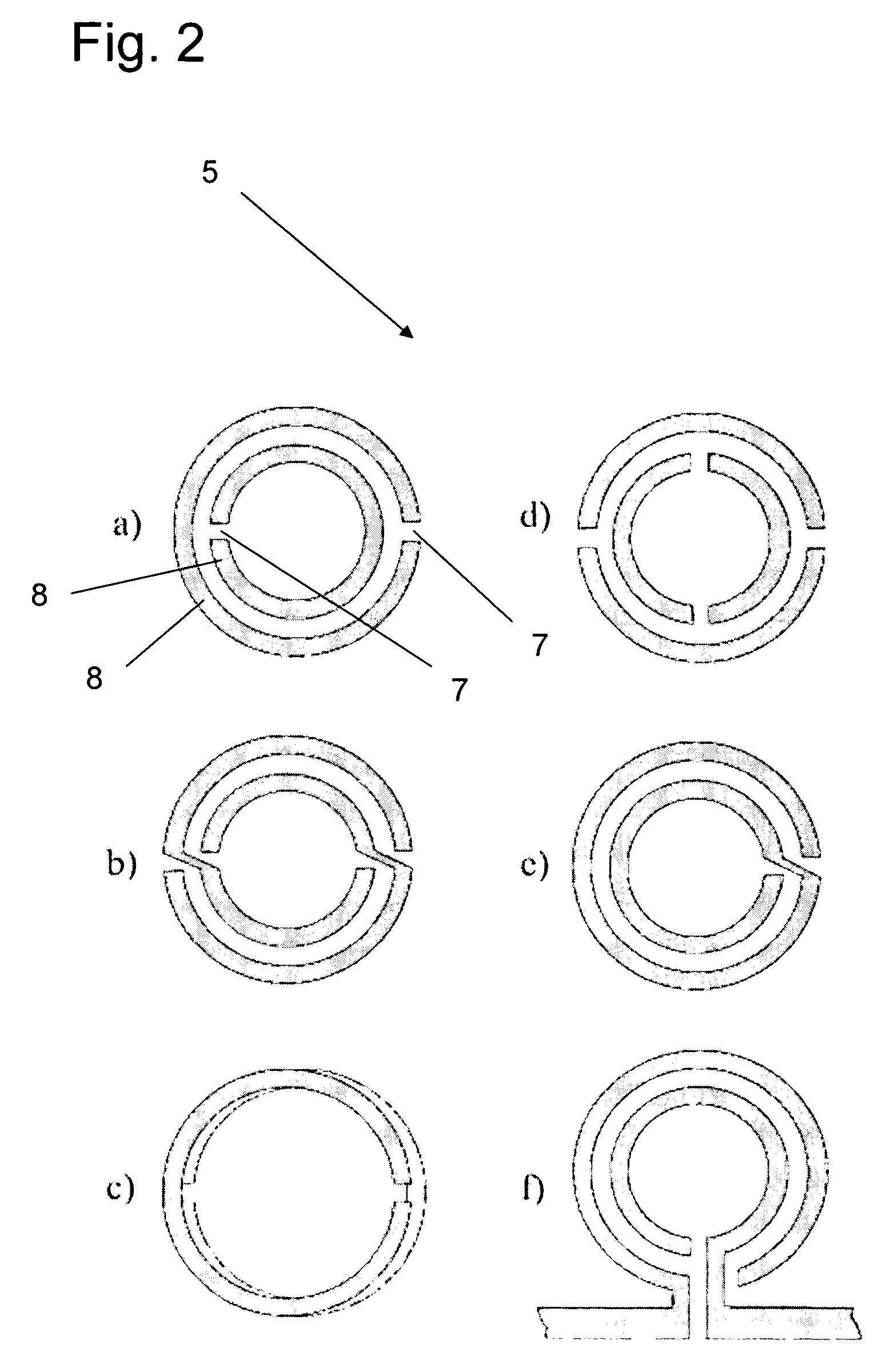
Filters and antennas for microwaves and millimetre waves, based on open-loop resonators and planar transmission lines
InactiveUS20070024399A1Good level of directivityGood level of polarisationResonatorsLoop antennasElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
Filter for microwaves and millimetER waves, characterised in that it comprises a planar transmission medium (1) that it includes a conductor strip (3), metallic ground plane (4) and dielectric substrate (2) and in that it includes at least one split rings resonator (5a, 5b, 5c, 5d, 5e and 5f)
Owner:AUTONOMOUS UNIVERSITY OF BARCELONA
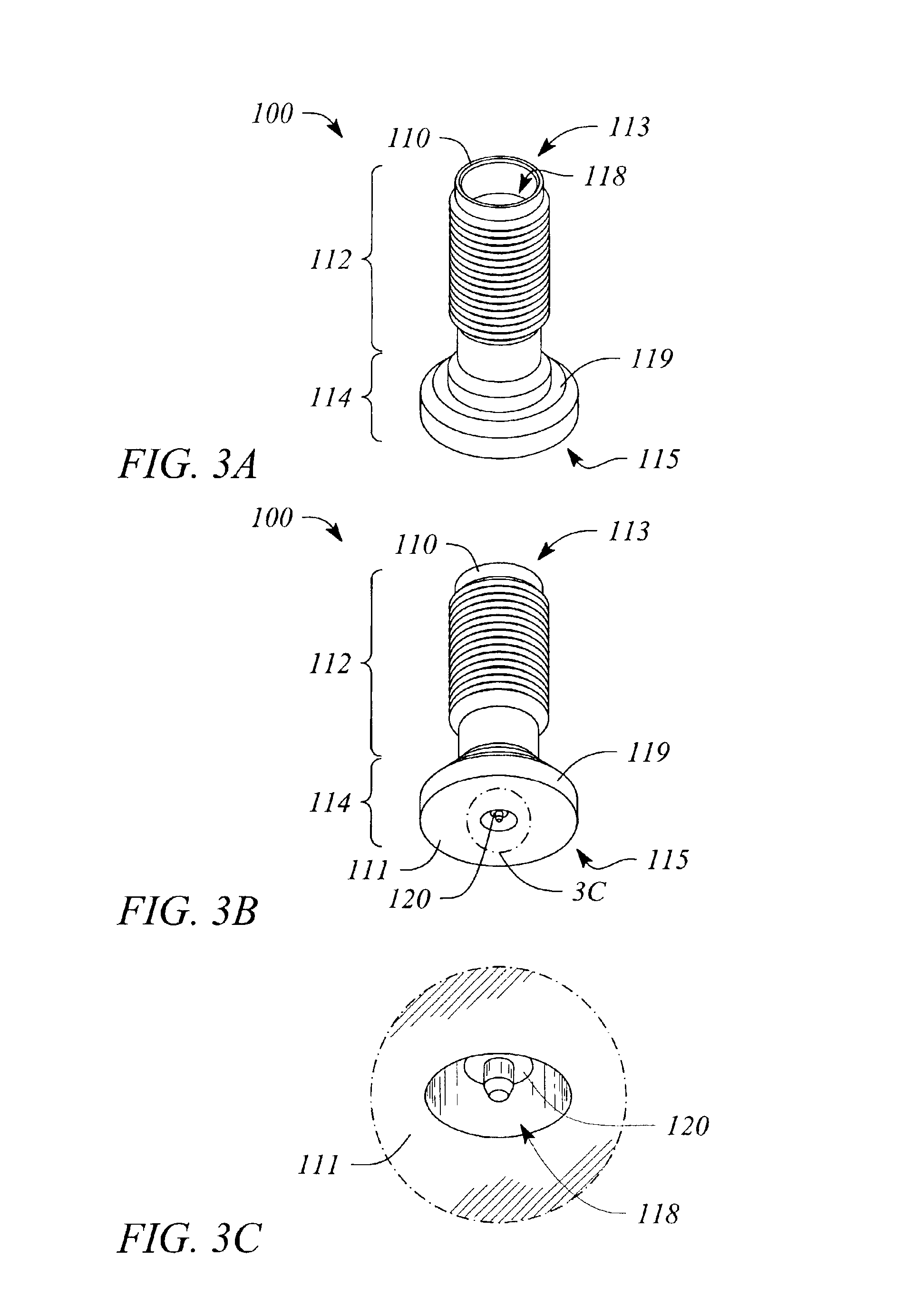
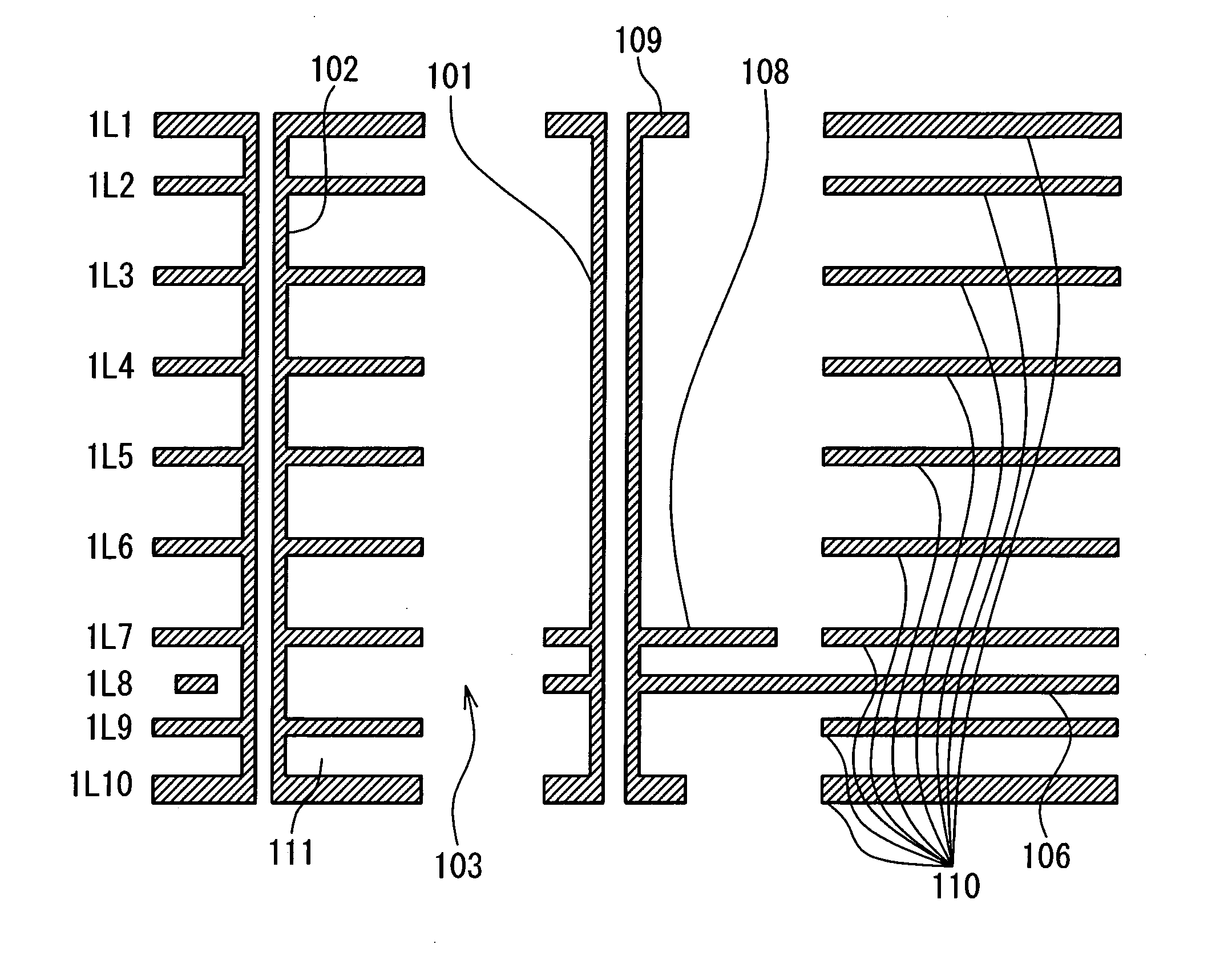
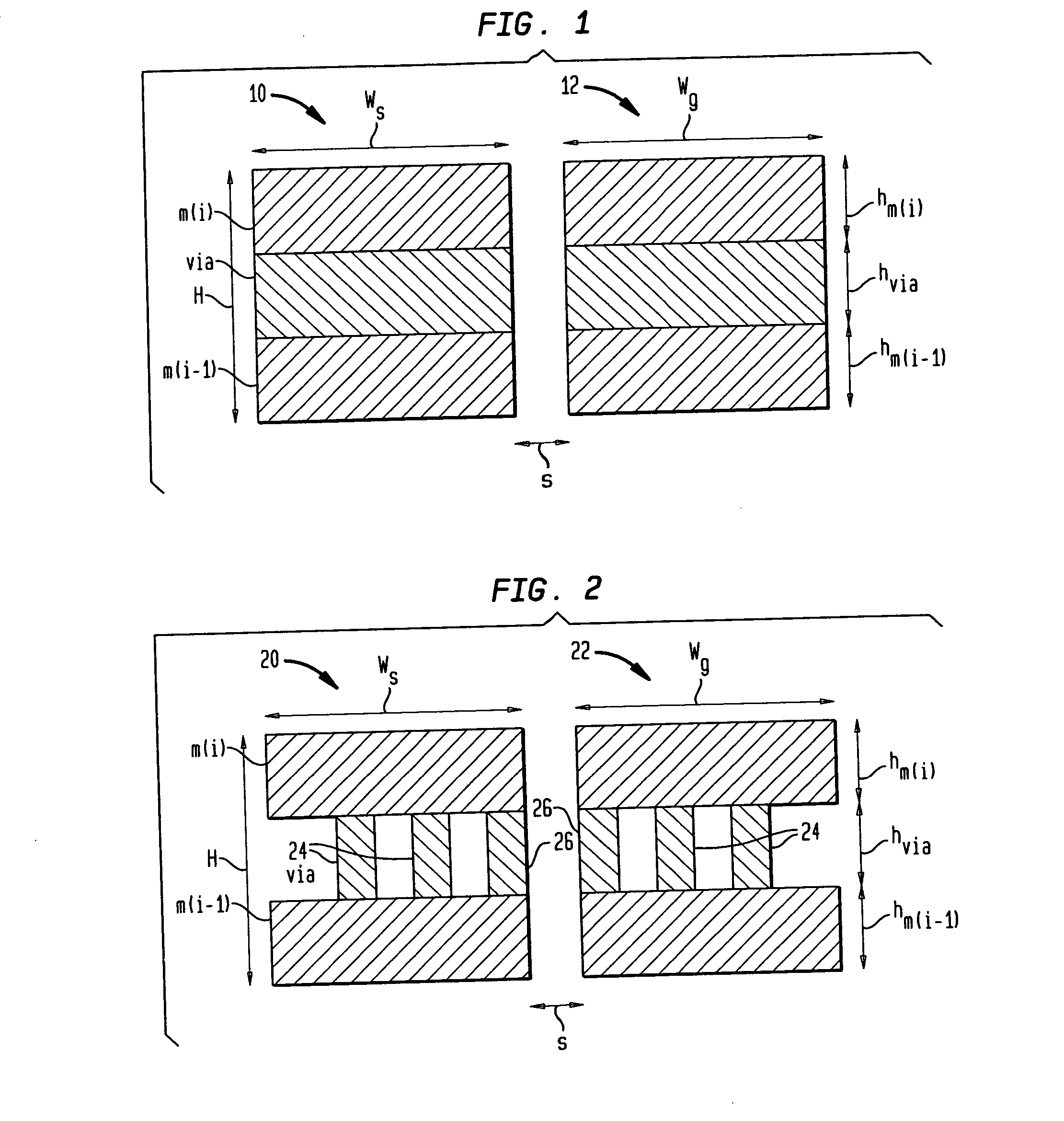
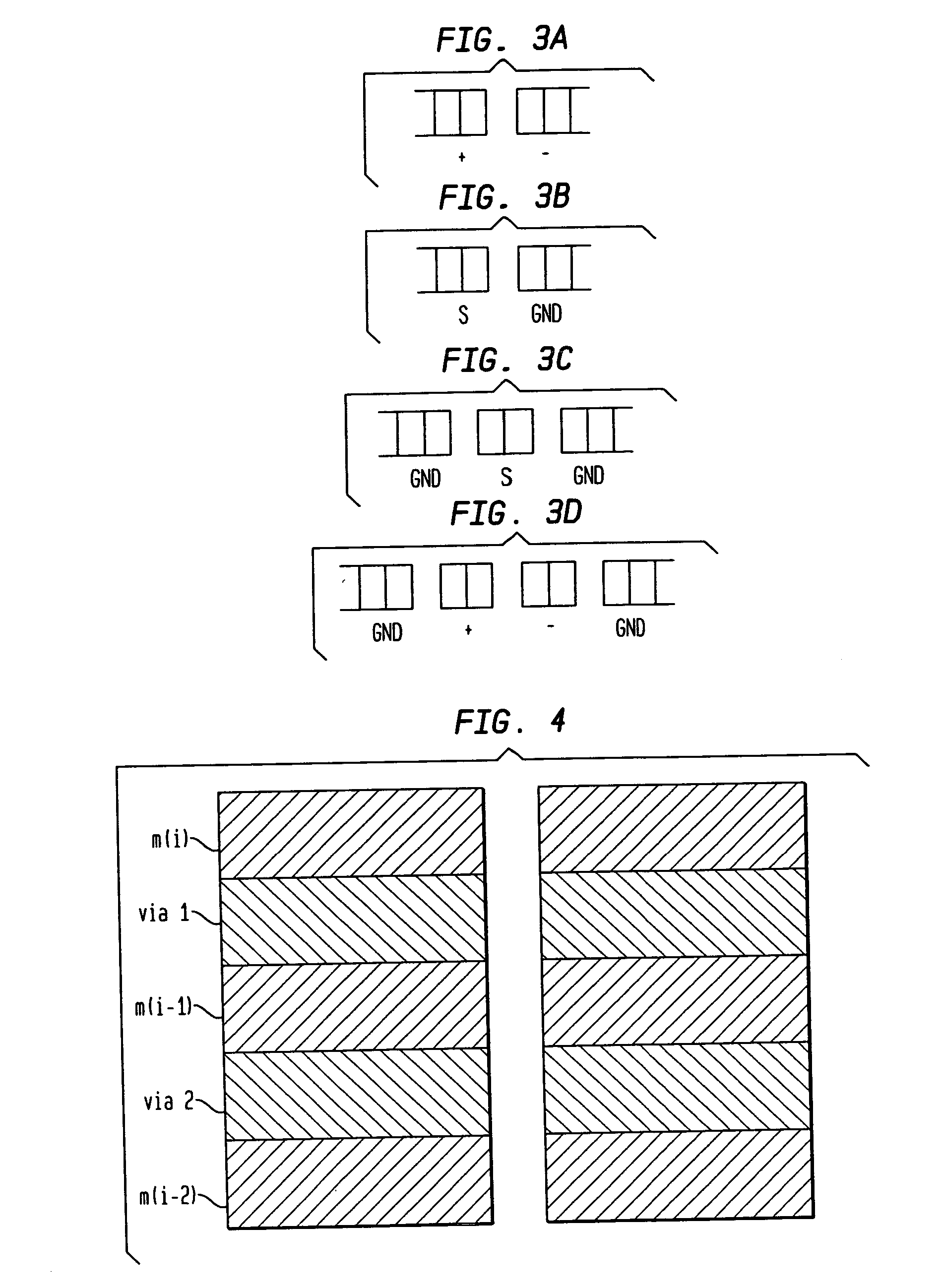
Composite Via Structures and Filters in Multilayer Printed Circuit Boards
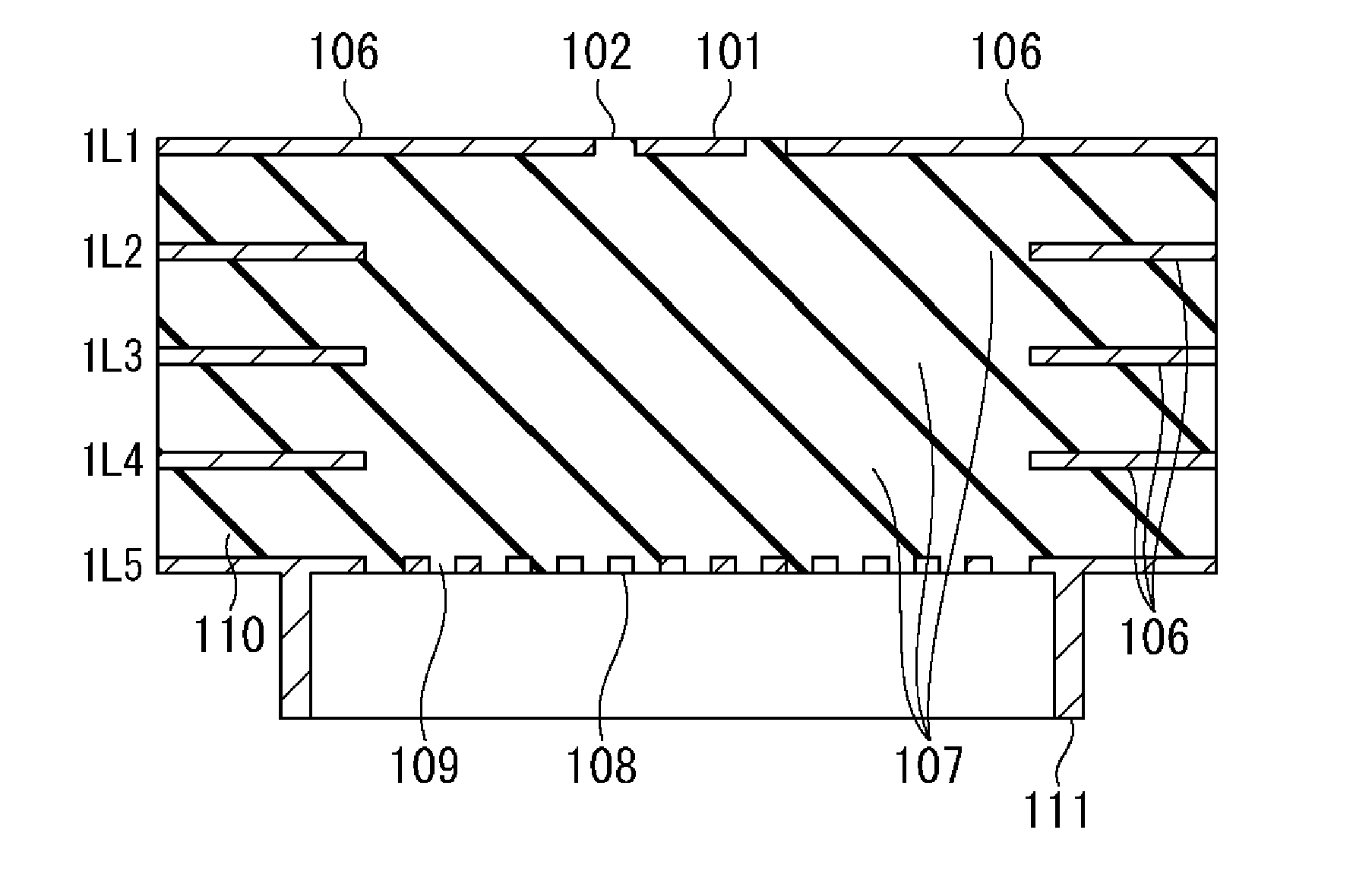
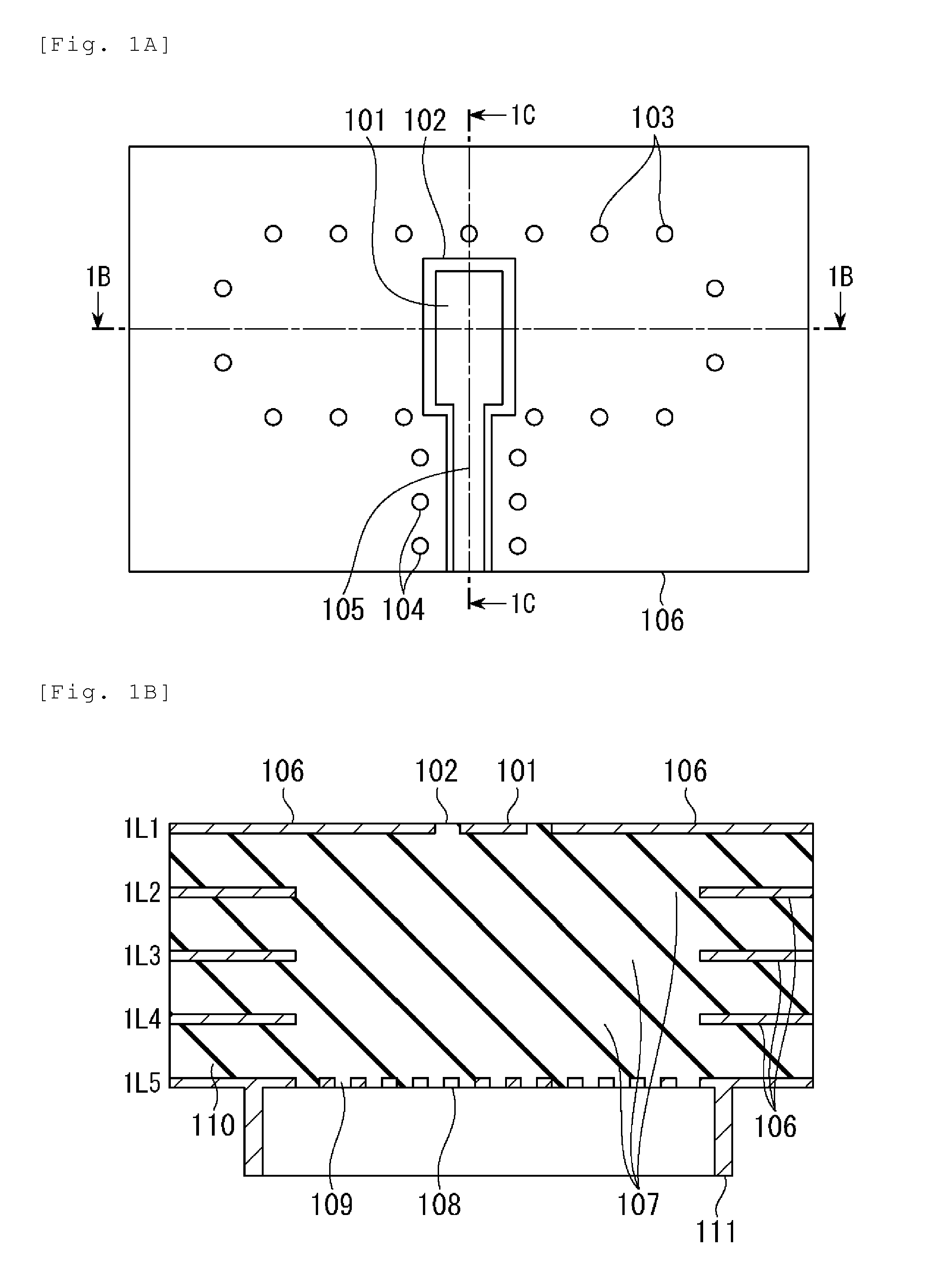
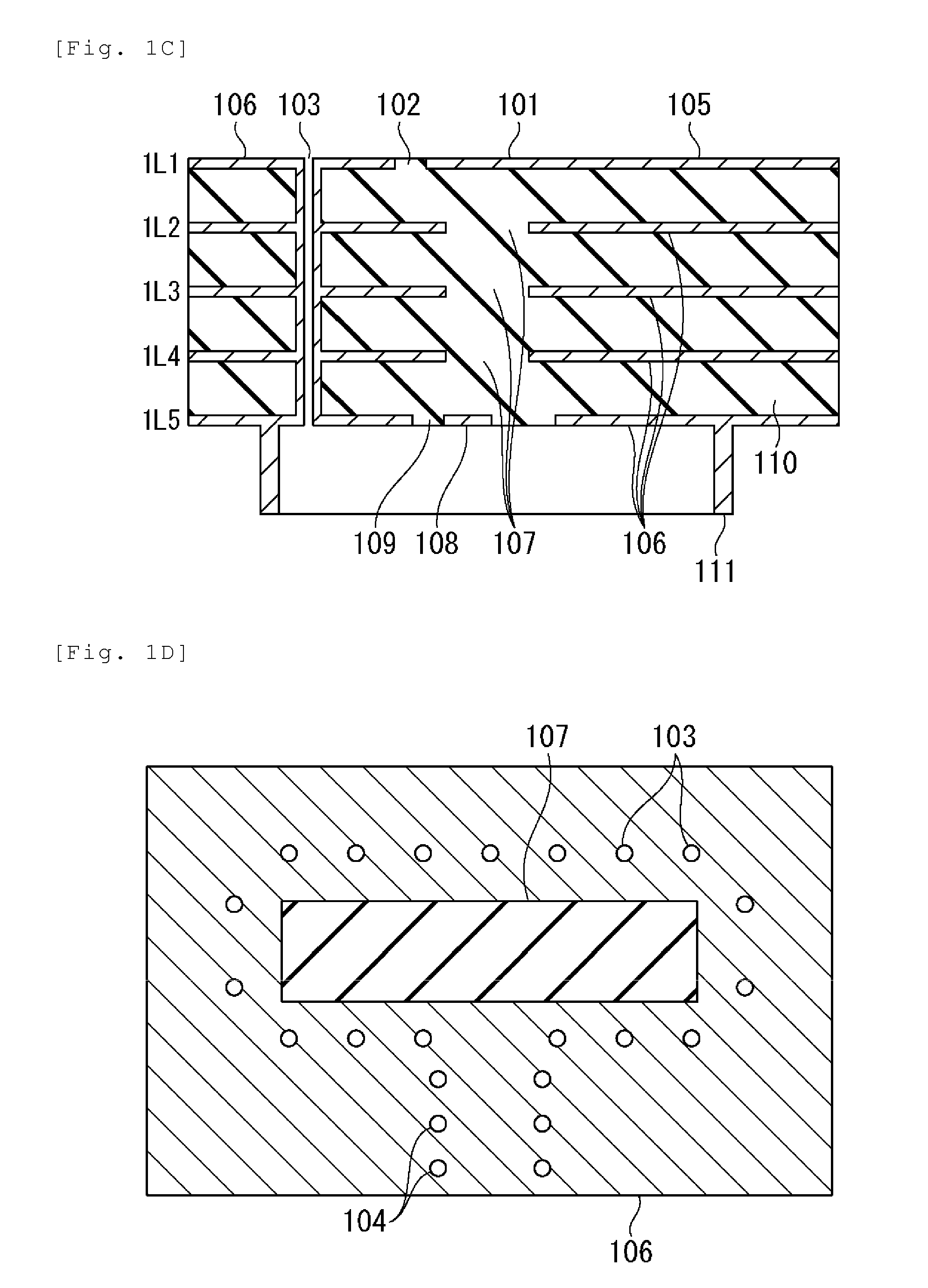
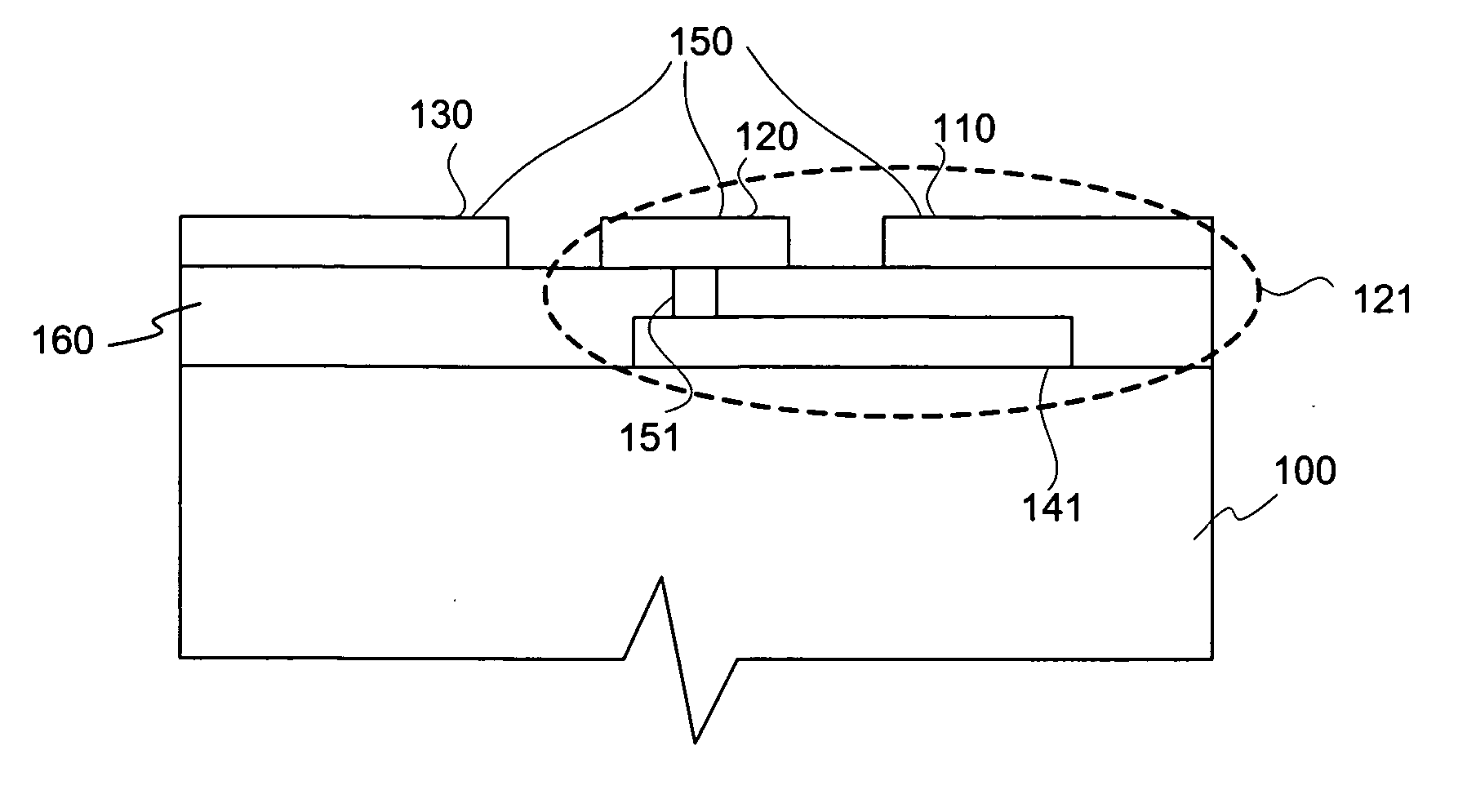
InactiveUS20080093112A1Improve electrical performancePrinted electric component incorporationPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringPlanar transmission lines
A composite via structure in a multilayer printed circuit board (PCB) and also compact and shielded filters formed by the use of composite via structures as building blocks are provided. The composite via structure consists of two functional parts. The first functional part is designed to form an interconnected circuit with low return and leakage losses between the first pad disposed at the one side of the PCB and the special pad serving for a connection to a planar transmission line. The second functional part of the composite via structure serves to form a shielded open- or short-circuited resonant length (stub) extended in the vertical direction from the special pad to the second pad disposed at the opposite side of the PCB.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Wideband transition between a planar transmission line and a waveguide
A wideband transition between a planar transmission line and a waveguide of this invention comprises a substrate, a segment of the planar transmission line and a section of the waveguide. The substrate includes a plurality of conductor-layers stacked from top to bottom and isolated by an insulating material. The segment of the planar transmission line is disposed in a top conductor-layer of the plurality of conductor-layers. The section of the waveguide is disposed on a bottom conductor-layer of the plurality of conductor-layers by a first end. The substrate comprises a conductive patch and a conductive dispersion plate. The conductive patch is disposed in the top conductor-layer and connected to a first end of said segment. The conductive dispersion plate is disposed in the bottom conductor-layer and under the conductive patch. The conductive dispersion plate comprises a corrugation.
Owner:NEC CORP
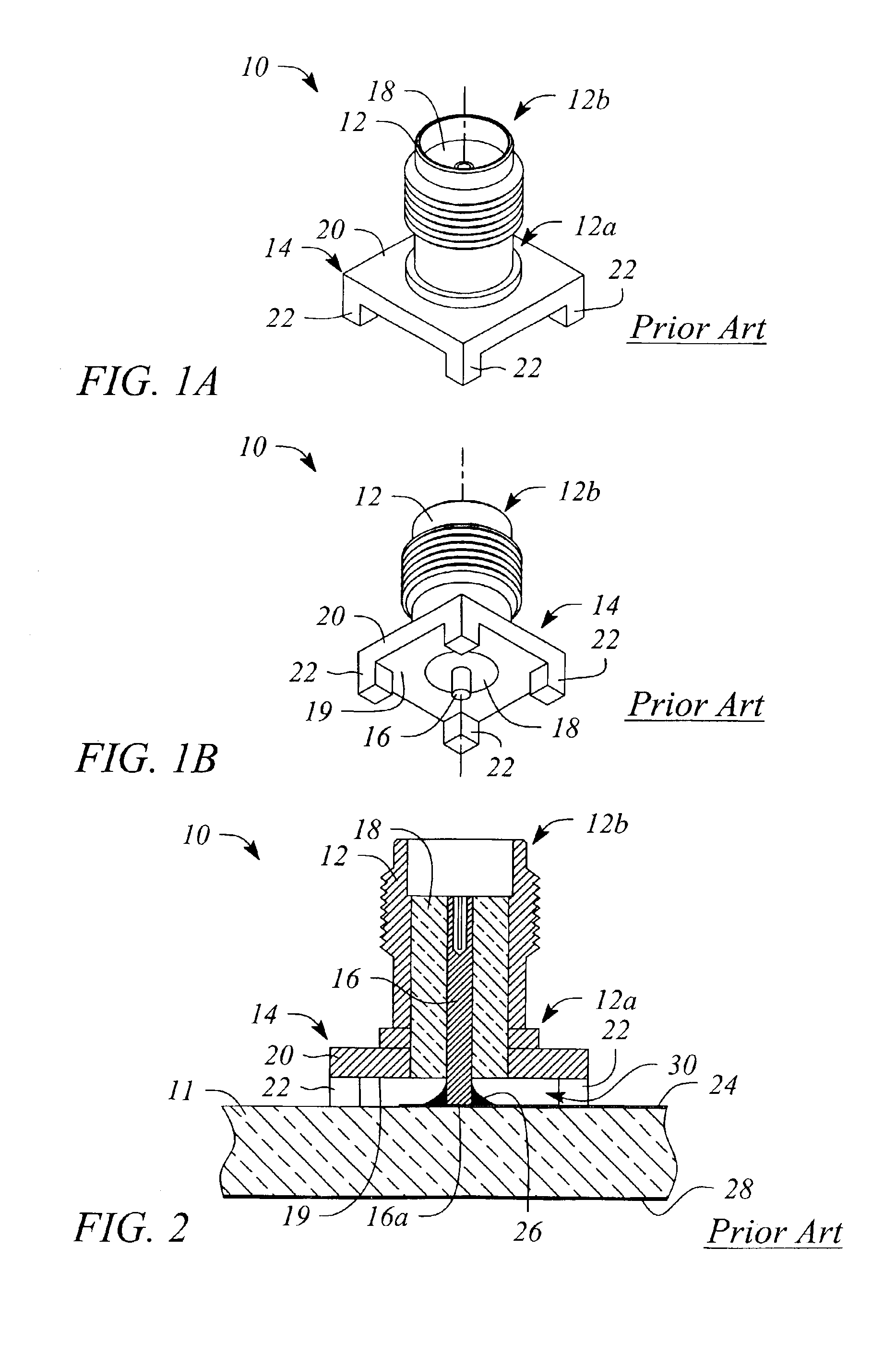
Shielded surface mount coaxial connector
InactiveUS6992544B2Reduces spurious electromagnetic radiationReduce Impedance DiscontinuitiesMultiple-port networksElectrically conductive connectionsMicrowave frequency rangeSurface mounting
A coaxial connection is electromagnetically shielded at an interface between a surface mountable coaxial connector and a planar circuit operating in the radio frequency (RF) and microwave frequency ranges. In addition or alternatively, the coaxial connection reduces a potential impedance mismatch associated with attaching a coaxial transmission line of the coaxial connector to a planar transmission line of the planar circuit.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
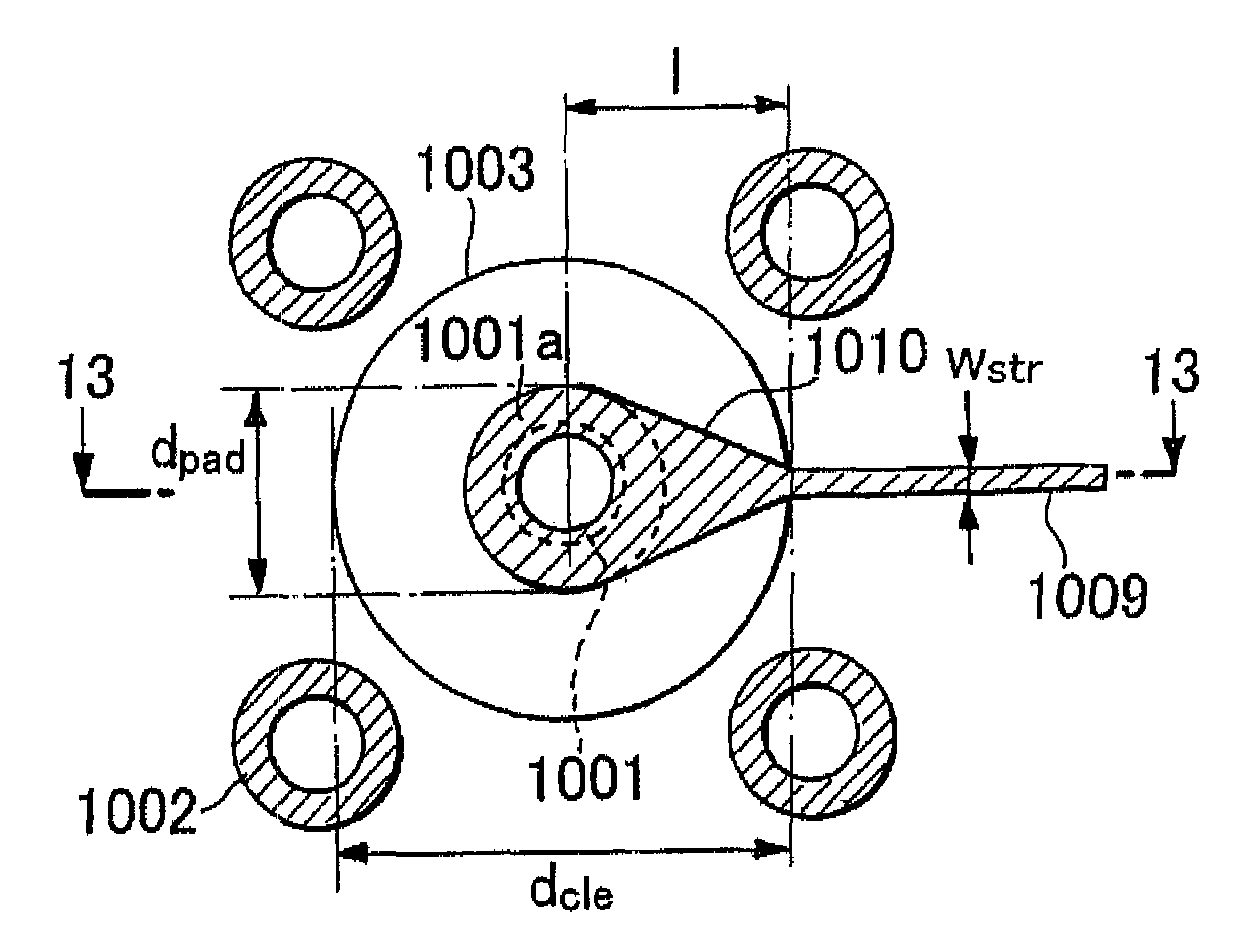
Broadband transition from a via interconnection to a planar transmission line in a multilayer substrate
ActiveUS20090015345A1Improve electrical performanceMultiple-port networksCross-talk/noise/interference reductionTime domainElectrical conductor
According to one embodiment, a broadband transition to joint a via structure and a planar transmission line in a multilayer substrate is formed as an intermediate connection between the signal via pad and the planar transmission line disposed at the same conductor layer. The transverse dimensions of the transition are equal to the via pad diameter at the one end and strip width at another end; The length of the transition can be equal to the characteristic dimensions of the clearance hole in the direction of the planar transmission line or defined as providing the minimal excess inductive reactance in time-domain according to numerical diagrams obtained by three-dimensional full-wave simulations.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
Composite via structures and filters in multilayer printed circuit boards
InactiveUS7705695B2Improve electrical performancePrinted electric component incorporationPrinted circuit aspectsPlanar transmission linesPrinted circuit board
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Apparatus and methods for constructing and packaging waveguide to planar transmission line transitions for millimeter wave applications
ActiveUS20070229182A1High performance couplingSuppressing undesired waveguide modesOne-port networksWaveguidesCouplingBroadband
Apparatus and methods are provided for constructing waveguide-to-transmission line transitions that provide broadband, high performance coupling of power at microwave and millimeter wave frequencies. More specifically, exemplary embodiments of the invention include wideband, low-loss and compact CPW-to-rectangular waveguide transition structures and ACPS (or CPS)-to-rectangular waveguide transition structures that are particularly suitable for microwave and millimeter wave applications.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
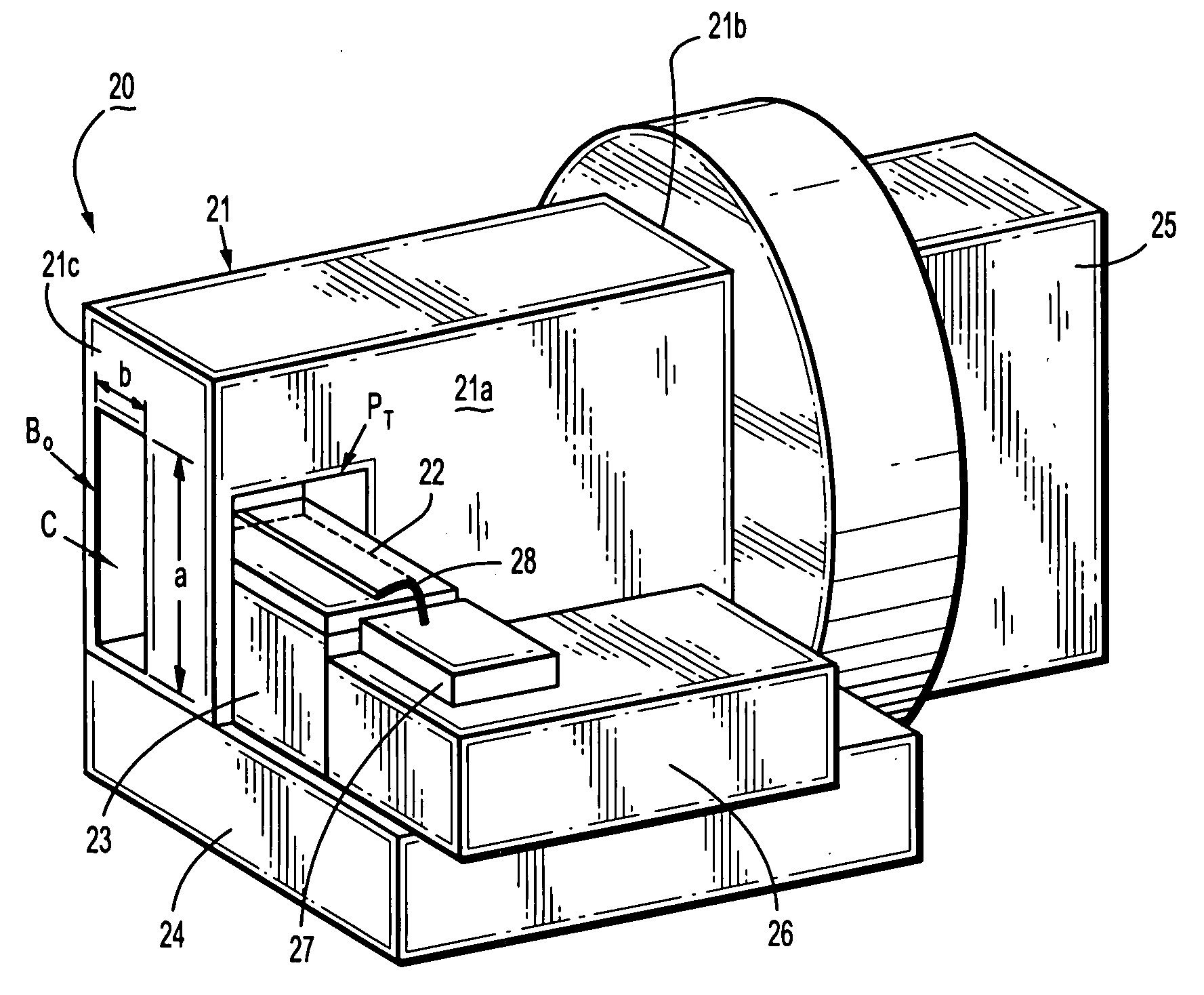
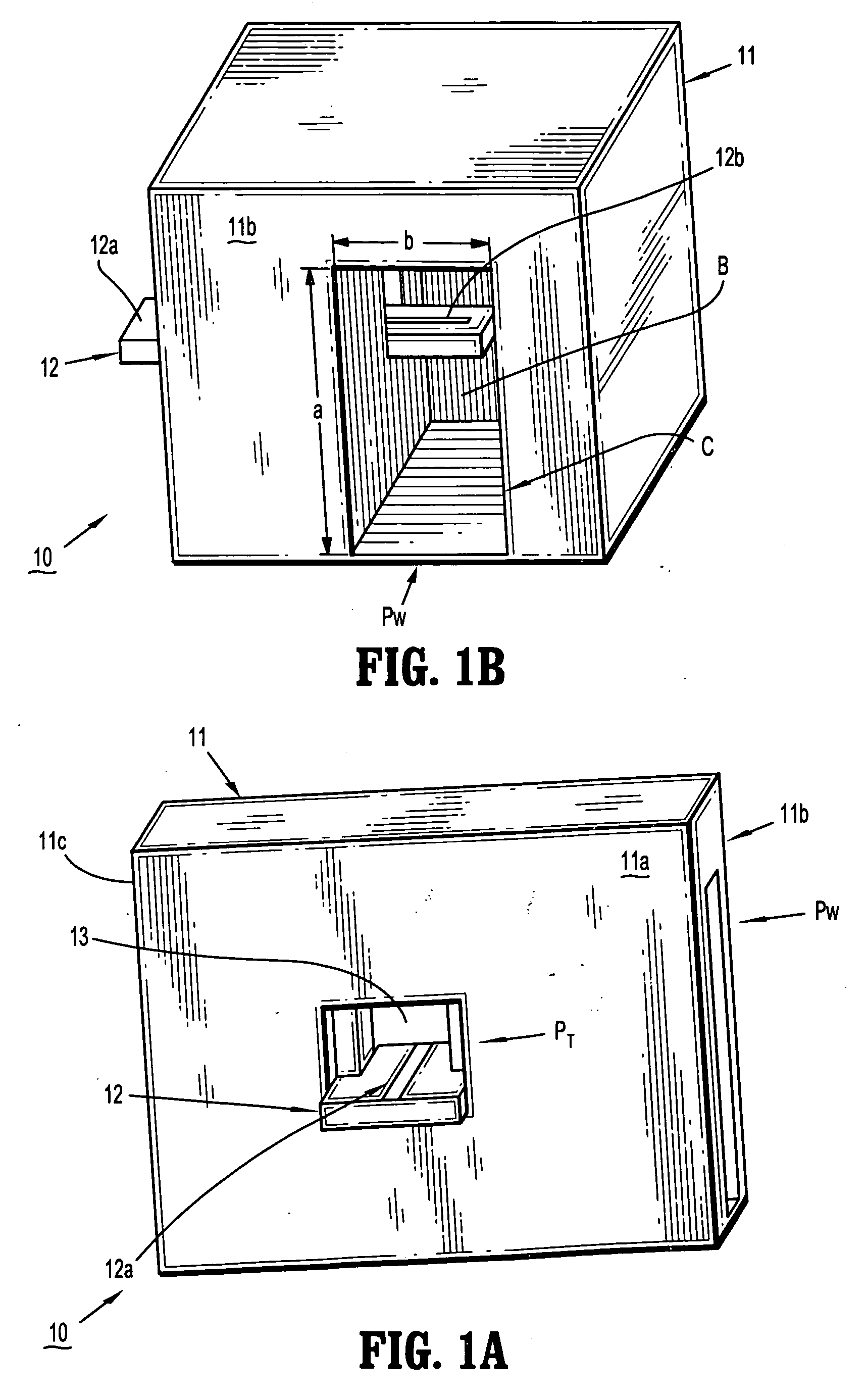
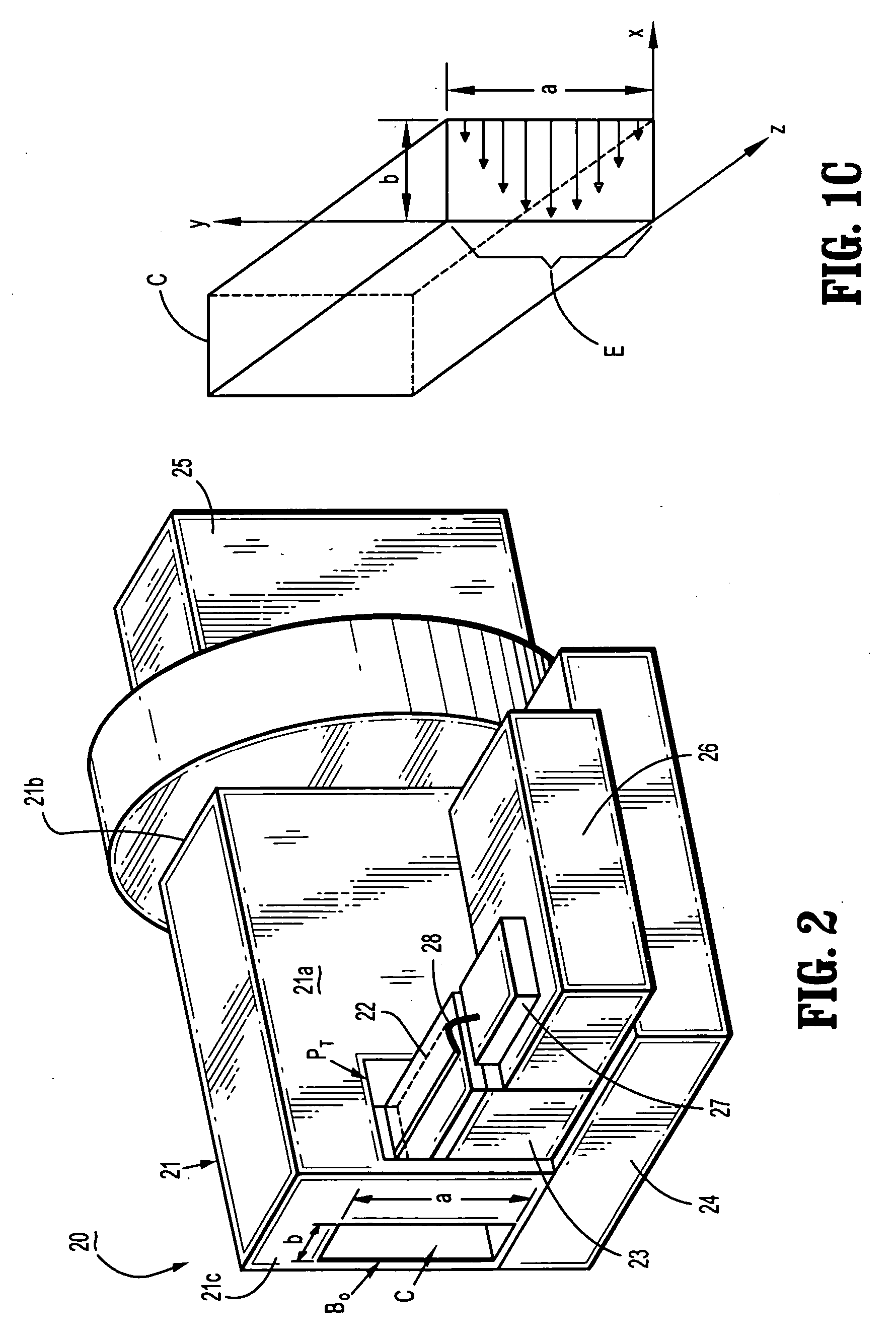
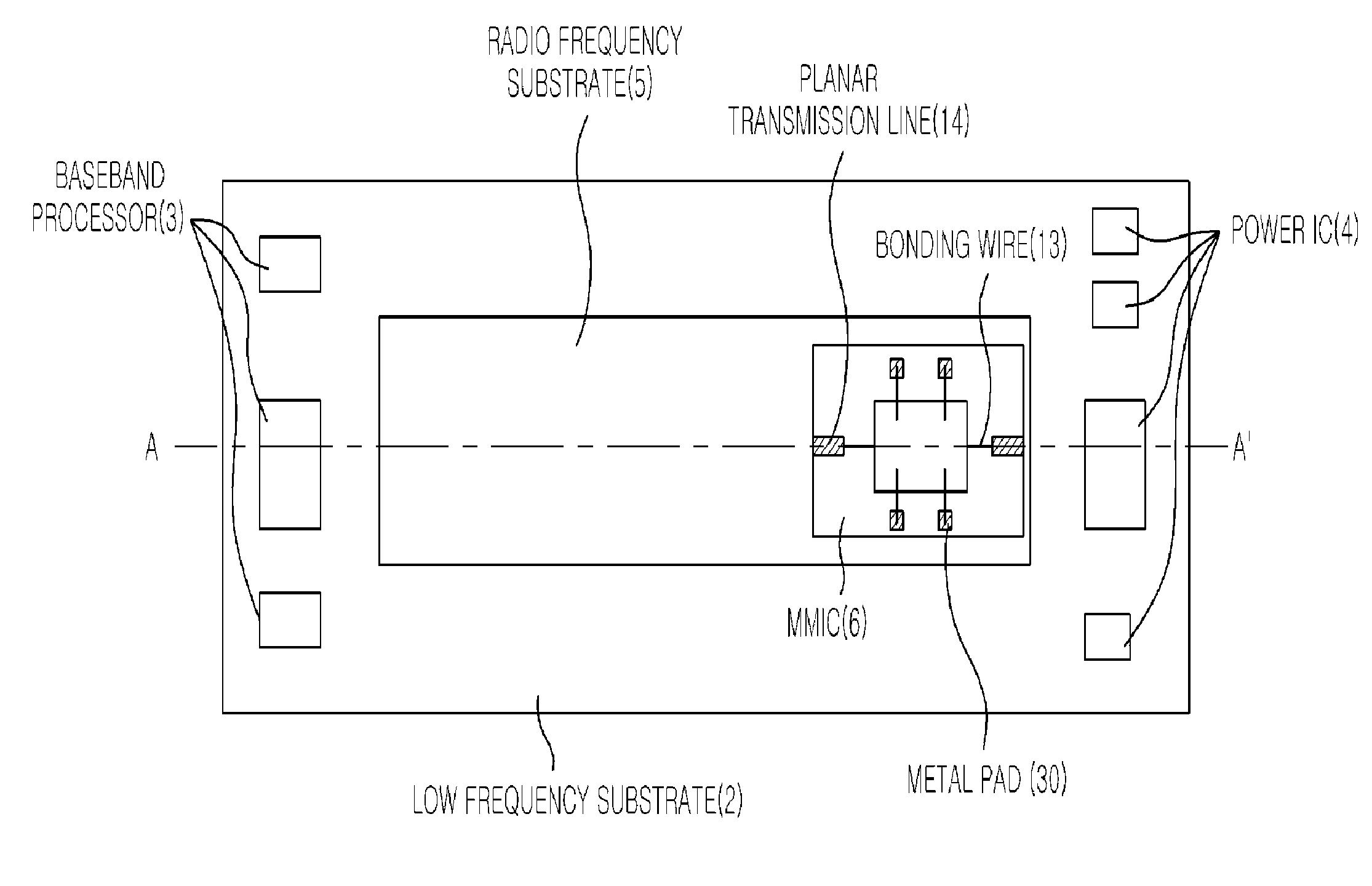
Mode Transition Circuit for Transferring Radio Frequency Signal and Transceiver Module Having the Same
ActiveUS20080297283A1Minimize signal lossReduce manufacturing costOne-port networksCoupling devicesTransceiverRadio frequency signal
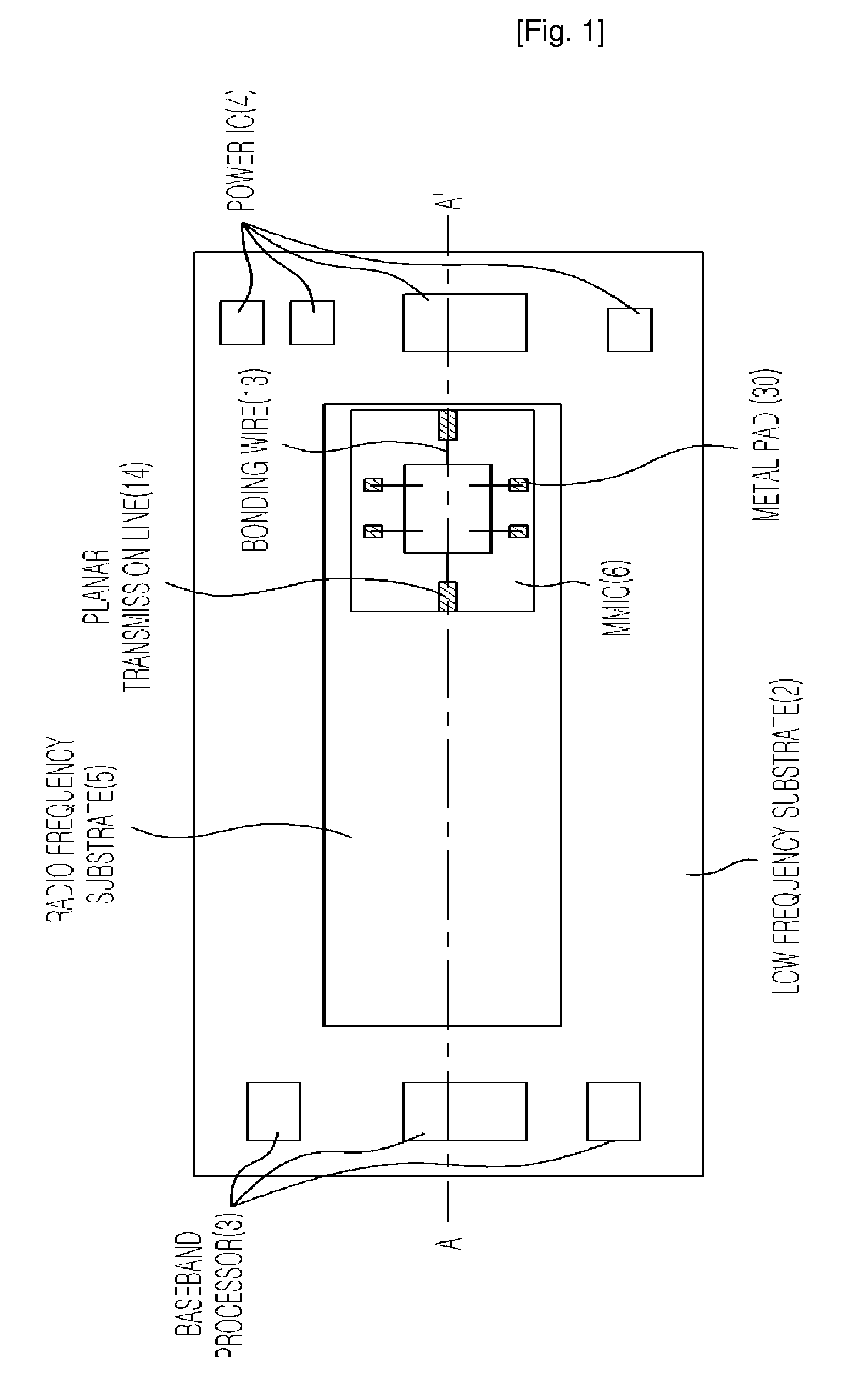
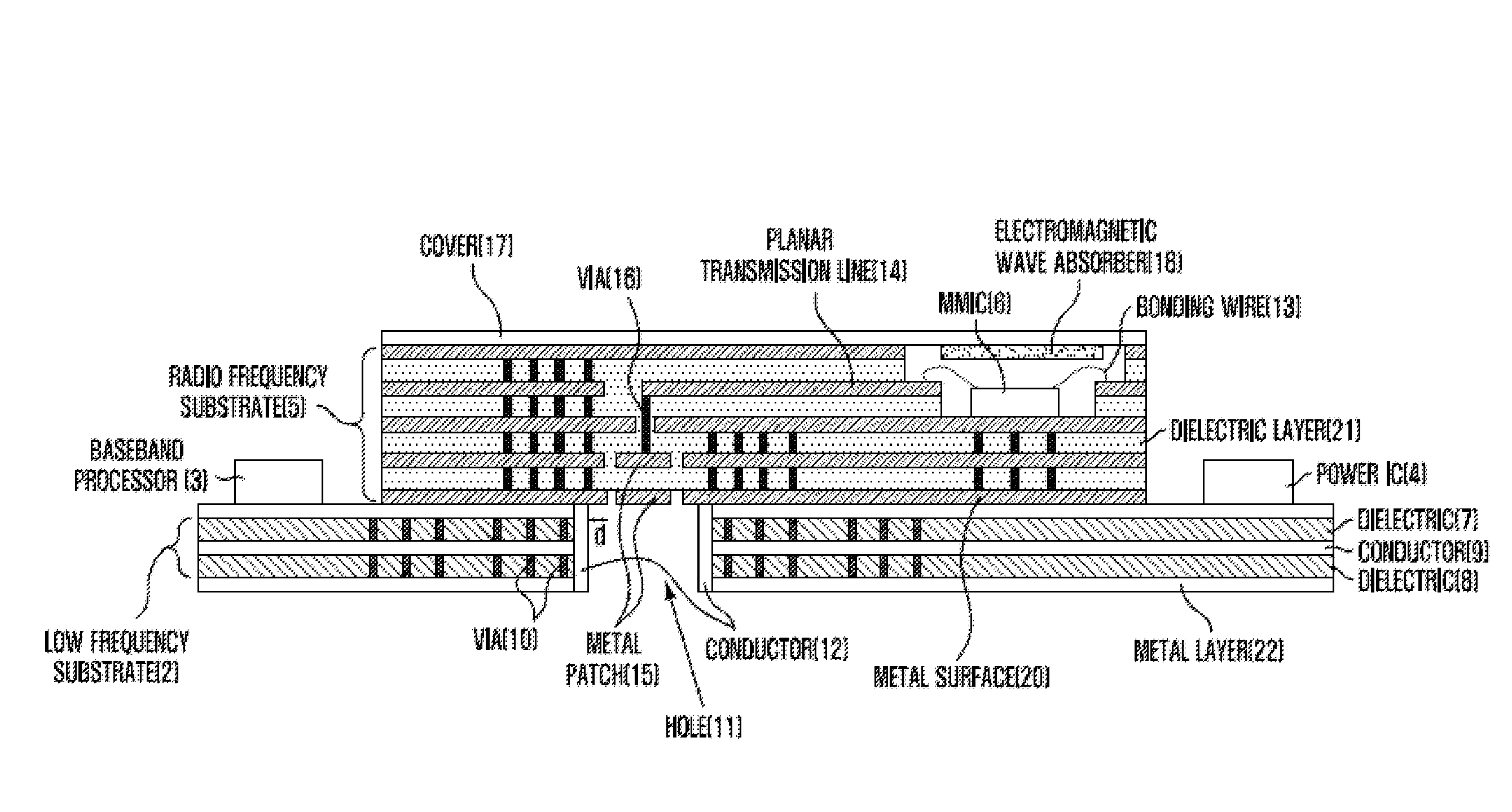
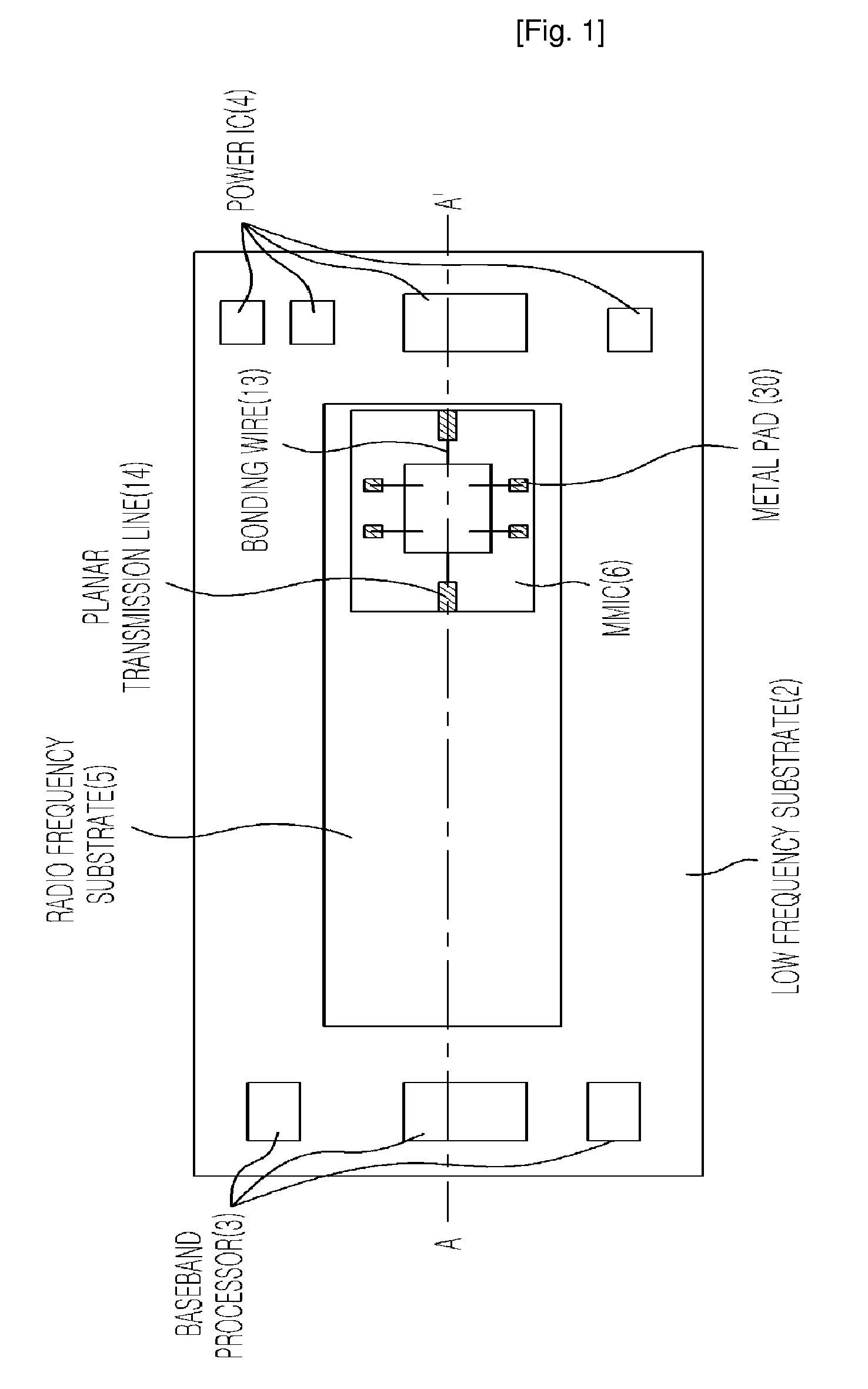
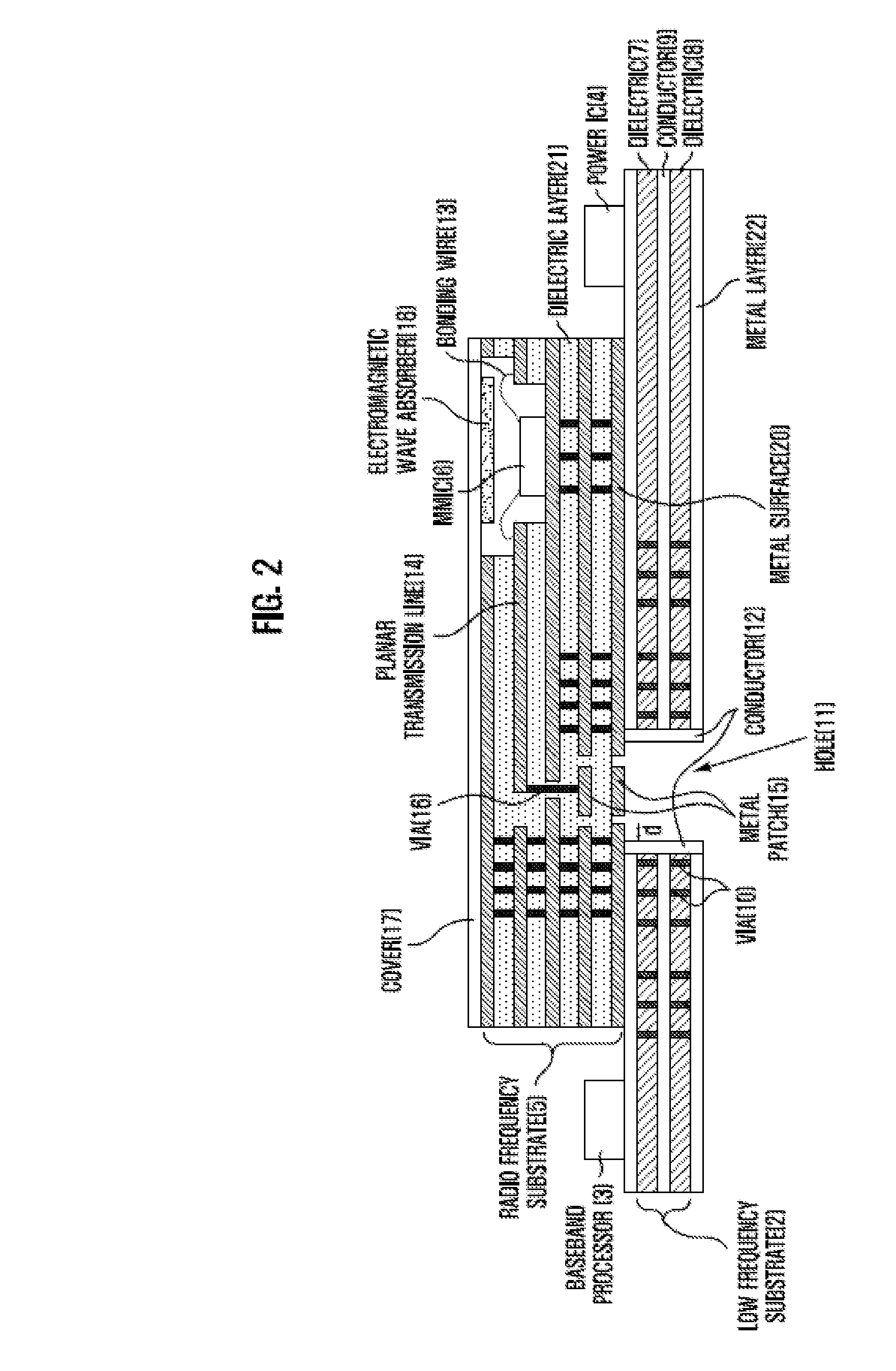
Provided is a mode transition circuit for transferring a RF signal and a transceiver module having the same. The mode transition circuit includes: a planar transmission line mounted at a RF substrate for receiving a RF signal from a RF signal generating unit; a via formed inside the RF substrate and connected to one side of the planar transmission line for receiving the RF signal from the planar transmission line; at least one of metal patches formed inside the RF substrate and connected to the one side of the via for receiving the RF signal from the via; and a hole formed inside a low frequency substrate and connected to one side of the metal patch for receiving the RF signal from the metal patch.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Microelectromechanical slow-wave phase shifter device and method
InactiveUS7259641B1Improve performanceReduce lossDelay linesWaveguidesCapacitanceMicroelectromechanical systems
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for a monolithic device utilizing cascaded, switchable slow-wave CPW sections that are integrated along the length of a planar transmission line. The purpose of the switchable slow-wave CPW sections elements is to enable control of the propagation constant along the transmission line while maintaining a quasi-constant characteristic impedance. The device can be used to produce true time delay phase shifting components in which large amounts of time delay can be achieved without significant variation in the effective characteristic impedance of the transmission line, and thus also the input / output return loss of the component. Additionally, for a particular value of return loss, greater time delay per unit length can be achieved in comparison to tunable capacitance-only delay components.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
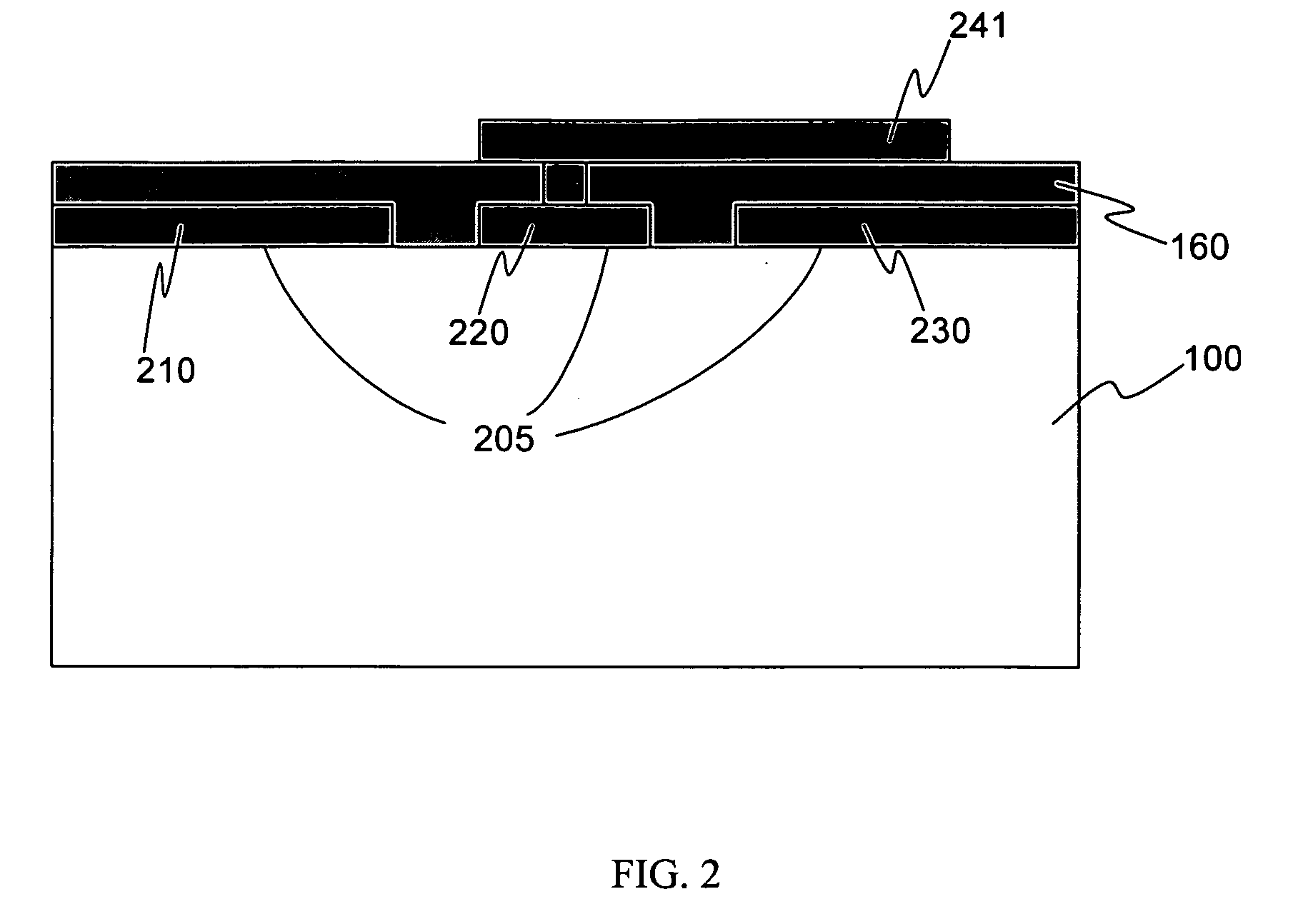
Arrangement relating to electronic circuitry
InactiveUS6501181B2Increase productionLess expensiveSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCross-talk/noise/interference reductionElectrical conductorCapacitive coupling
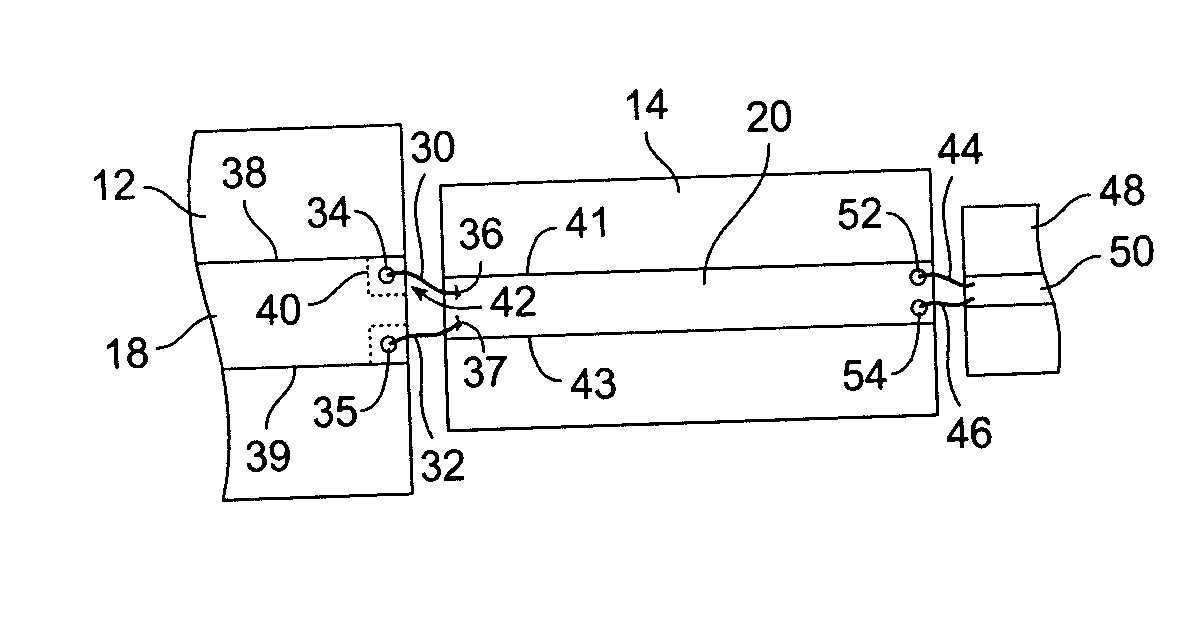
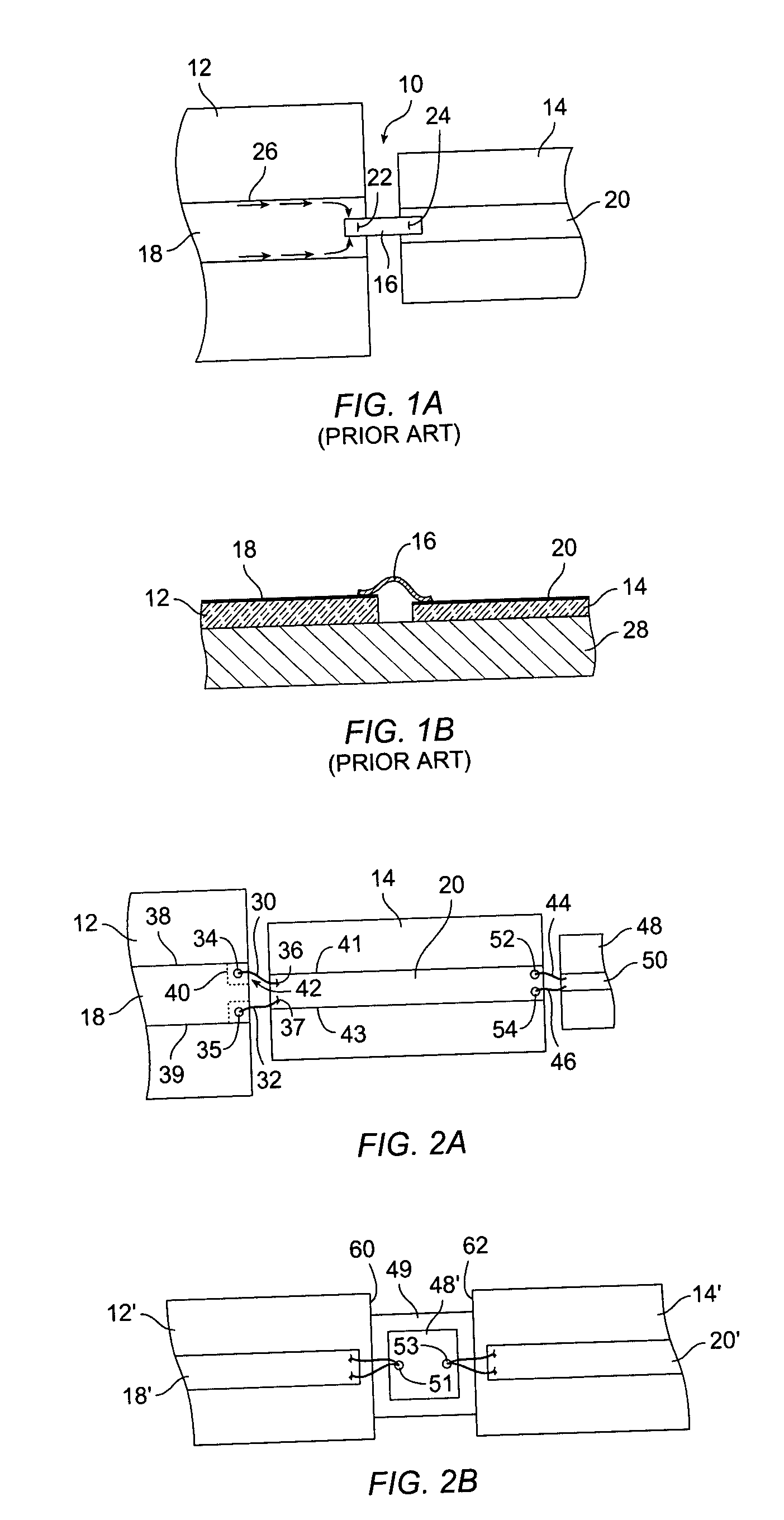
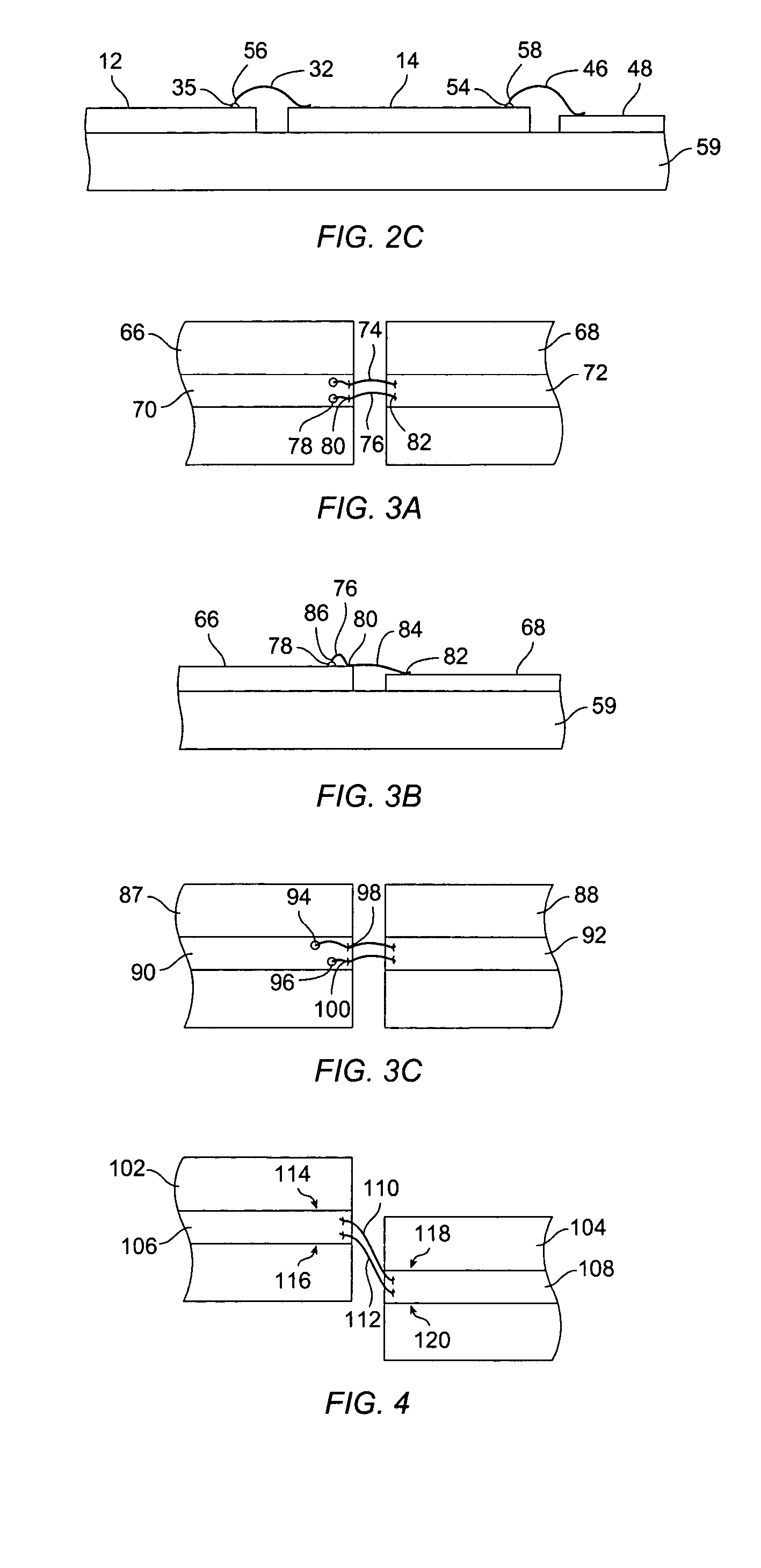
The present invention relates to an arrangement in a multilayered electronic circuit. In a transition between two planar transmission lines, a compensating element is used to keep the average capacitance per length unit more constant during the transition. A via conductor the passes near an edge of a planar conductor pattern, the via conductor and the planar conductor having a mutual capacitive coupling within a predetermined range. A compensating conductor is formed between the planar conductor and the via conductor, which conductor is connected to the planar conductor by a compensating via. If the segment of the via conductor which belongs to the same via hole pattern as the compensating via is displaced, the compensating via is also displaced. The compensating planar pattern is then disconnected from the planar conductor. This improves yield in a given multilayer process.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
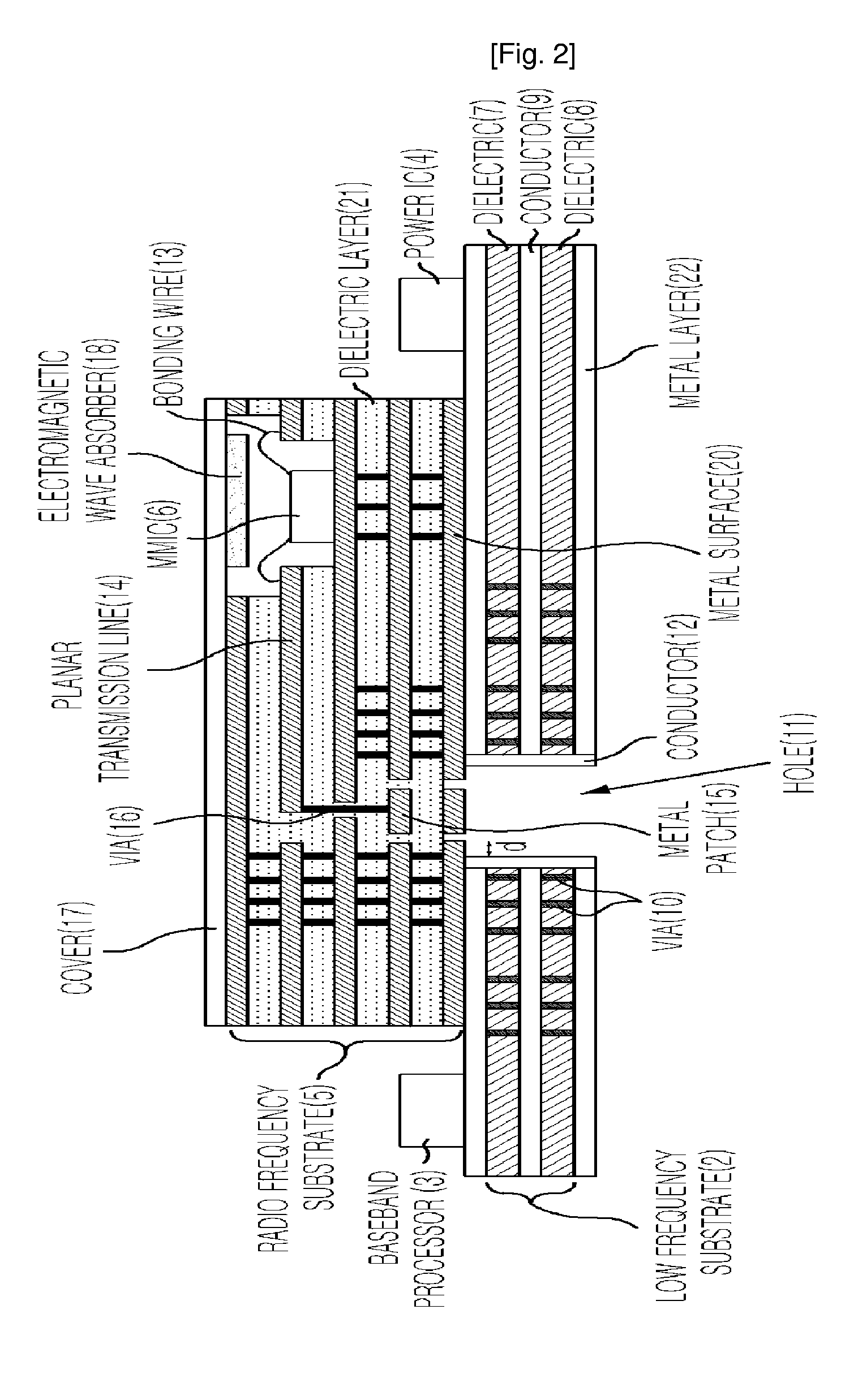
Mode transition between a planar line and a waveguide with a low loss RF substrate and a high loss low frequency substrate
ActiveUS7911292B2Minimize signal lossReduce manufacturing costOne-port networksCoupling devicesTransceiverRadio frequency signal
Provided is a mode transition circuit for transferring a RF signal and a transceiver module having the same. The mode transition circuit includes: a planar transmission line mounted at a RF substrate for receiving a RF signal from a RF signal generating unit; a via formed inside the RF substrate and connected to one side of the planar transmission line for receiving the RF signal from the planar transmission line; at least one of metal patches formed inside the RF substrate and connected to the one side of the via for receiving the RF signal from the via; and a hole formed inside a low frequency substrate and connected to one side of the metal patch for receiving the RF signal from the metal patch.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
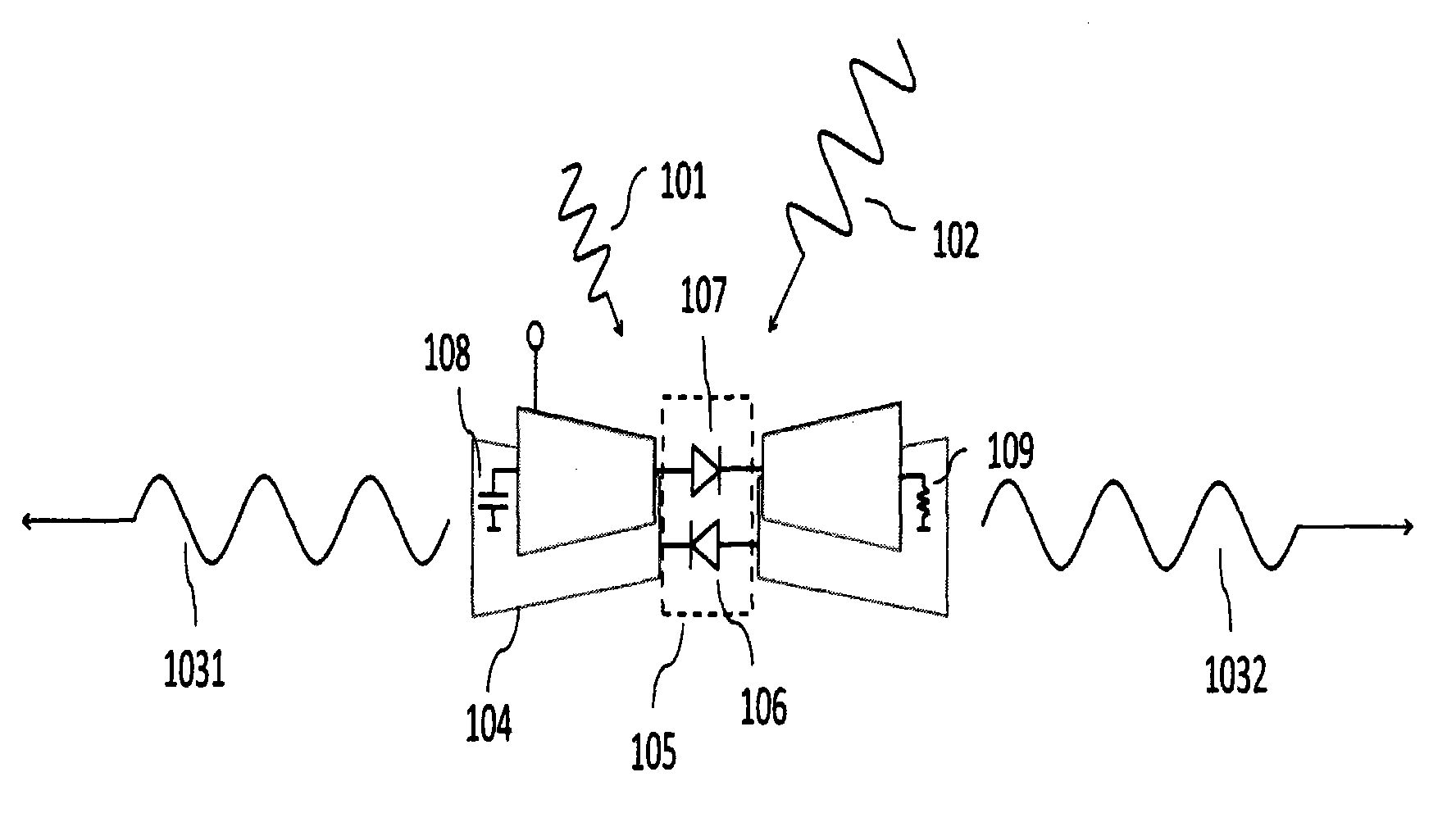
Terahertz frequency mixing antenna and quasi-optical frequency mixing module
ActiveCN102983388ASimple structureFirmly connectedSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsCapacitanceIntermediate frequency
The invention provides a terahertz frequency mixing antenna and a quasi-optical frequency mixing module. The terahertz frequency mixing antenna comprises a first schottky diode, a second schottky diode, a planar antenna and a blocking condenser, wherein a negative pole of the first schottky diode is connected with a positive pole of the second schottky diode through the blocking condenser, and a positive pole of the first schottky diode is connected with a negative pole of the second schottky diode directly or through a resistance. The schottky diodes are arranged on radio frequency feed ports of the planar antenna, a radio frequency signal and a local oscillating signal are fed in a space coupling mode through the planar antenna, and an intermediate frequency signal is output after the frequency mixing of the schottky diodes and is output in a guided current mode from the outermost side of the planar antenna. The quasi-optical frequency mixing module comprises the terahertz frequency mixing antenna, a bias and intermediate frequency circuit and a planar transmission line. The terahertz frequency mixing antenna and the quasi-optical frequency mixing module are capable of being operated in a sub-harmonic frequency mixing mode or a fundamental wave frequency mixing mode, and being connected with a standard circuit port easily. Due to the fact that direct current bias is loaded on the frequency mixing antenna, requirements of local oscillating power is reduced.
Owner:杭州太睿康科技有限公司
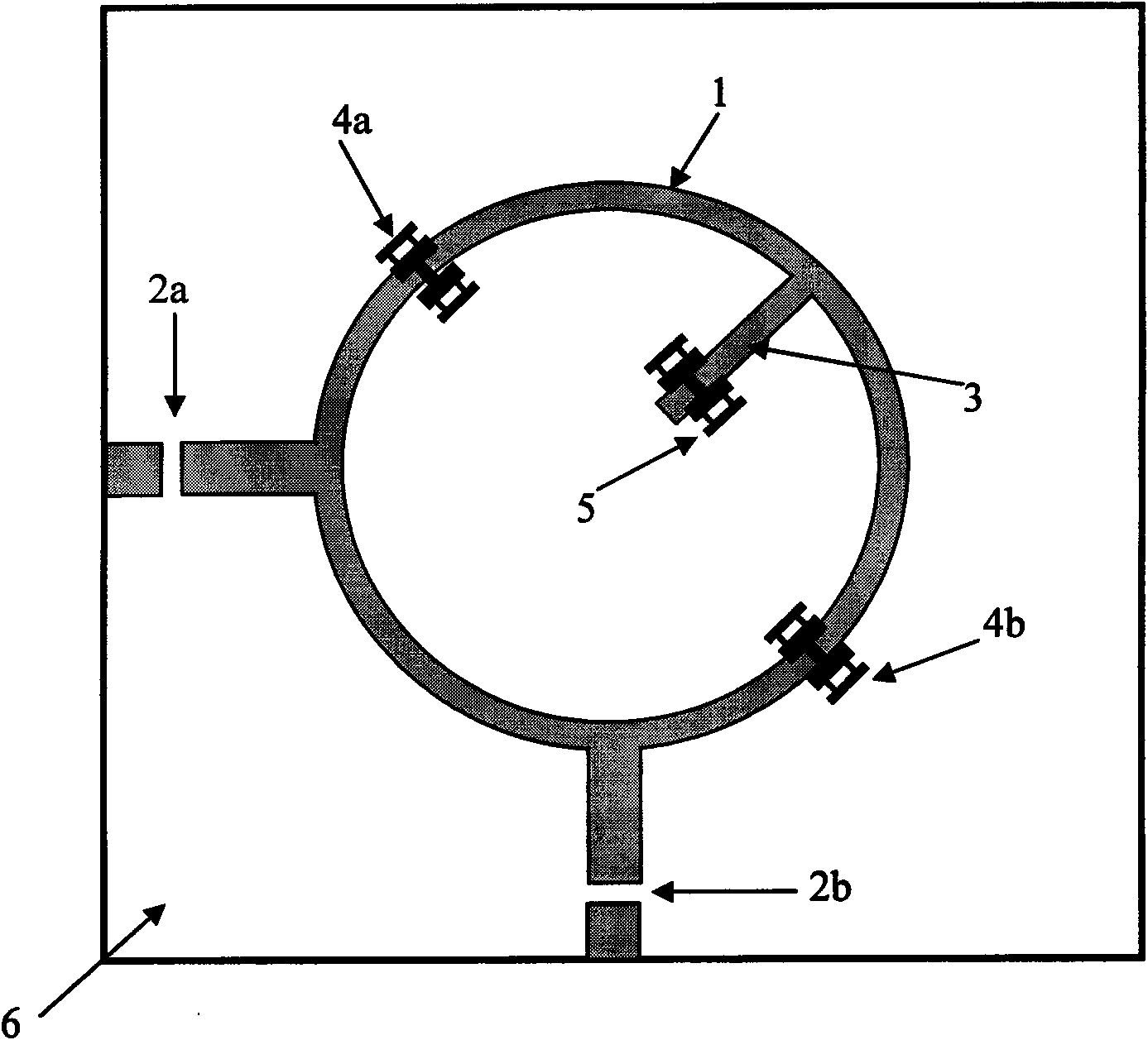
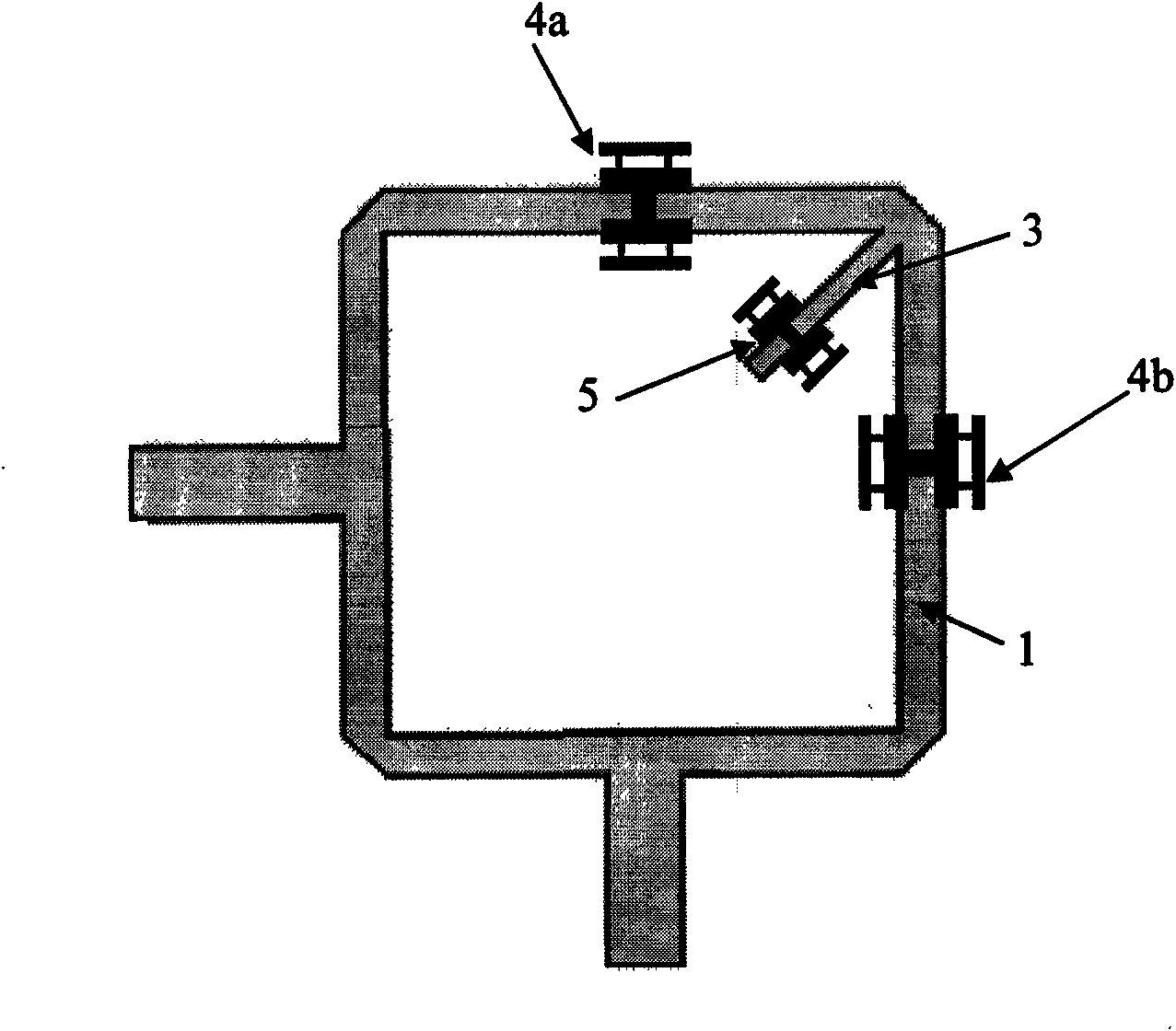
Adjustable microwave band-pass filter
InactiveCN101593863AEasy loadingHigh Q valueTelevision system detailsImpedence networksCapacitanceDual mode
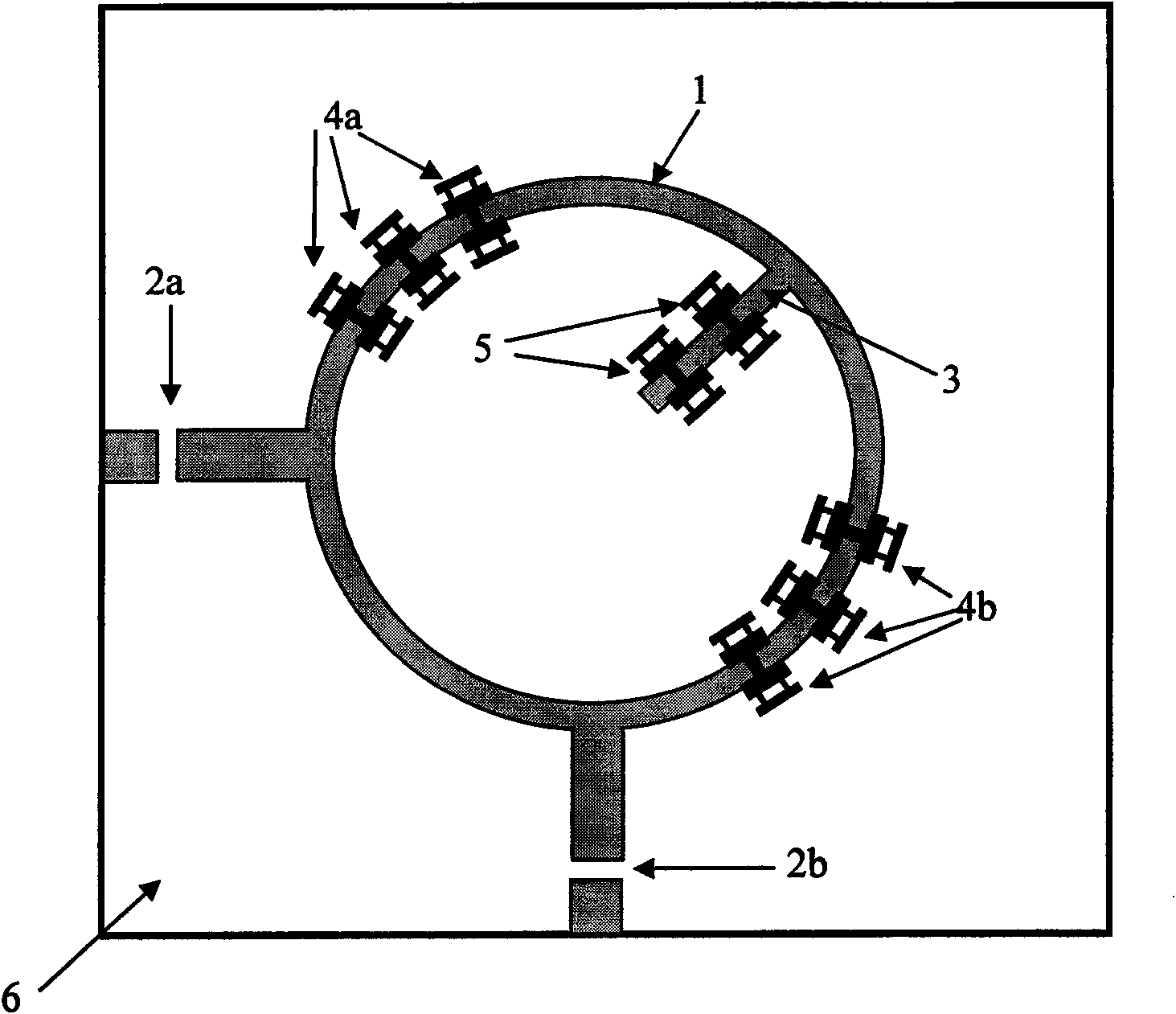
The invention discloses an adjustable microwave band-pass filter. A microwave circuit substrate is provided with a double-resonance modal annular resonator and a corresponding input coupling unit, an output coupling unit and a disturbance unit, wherein an even number of micro mechanical bridge films are placed on the resonator in a mirror symmetry mode to adjust a center frequency; and one or more micro mechanical bridge films are placed on the disturbance unit to adjust the bandwidth. The filter uses a variable capacitance effect generated by a capacitance loading structure of the micro machined bridge films to load a dual-mode resonator and a disturbance structure thereof, so that the adjustment of filtering characteristics, such as the passband center frequency, the passband bandwidth and the like can be realized by fewer micro mechanical bridge films and less chip area occupation. Compared with the prior dual-mode filter and the micro mechanical adjustable band-pass filter, the adjustable microwave band-pass filter has the advantages of more flexible structure, lower technology complexity and better device overall performance, and is suitable for filtering devices based on planar transmission lines and on-chip waveguide at the same time.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
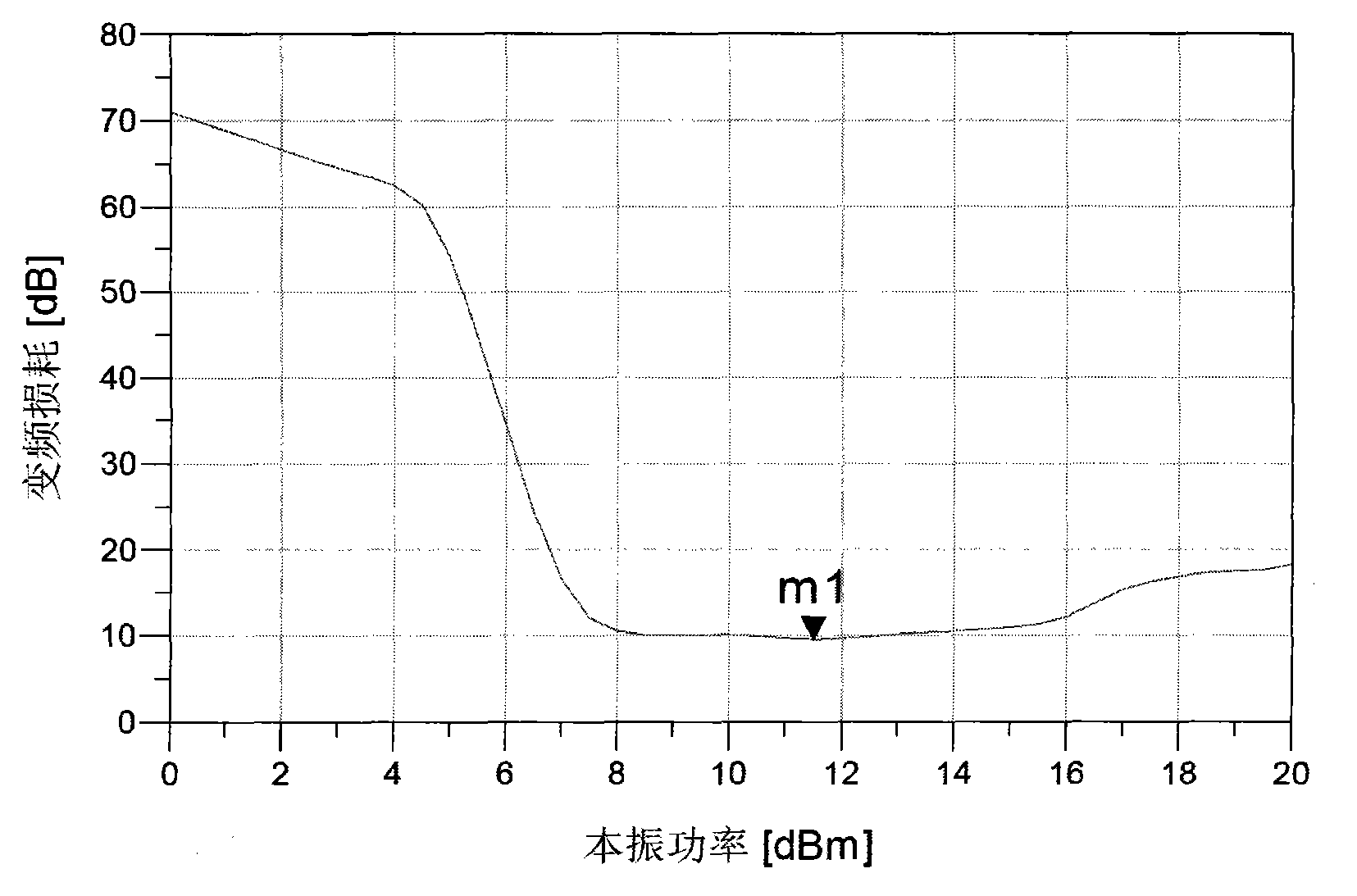
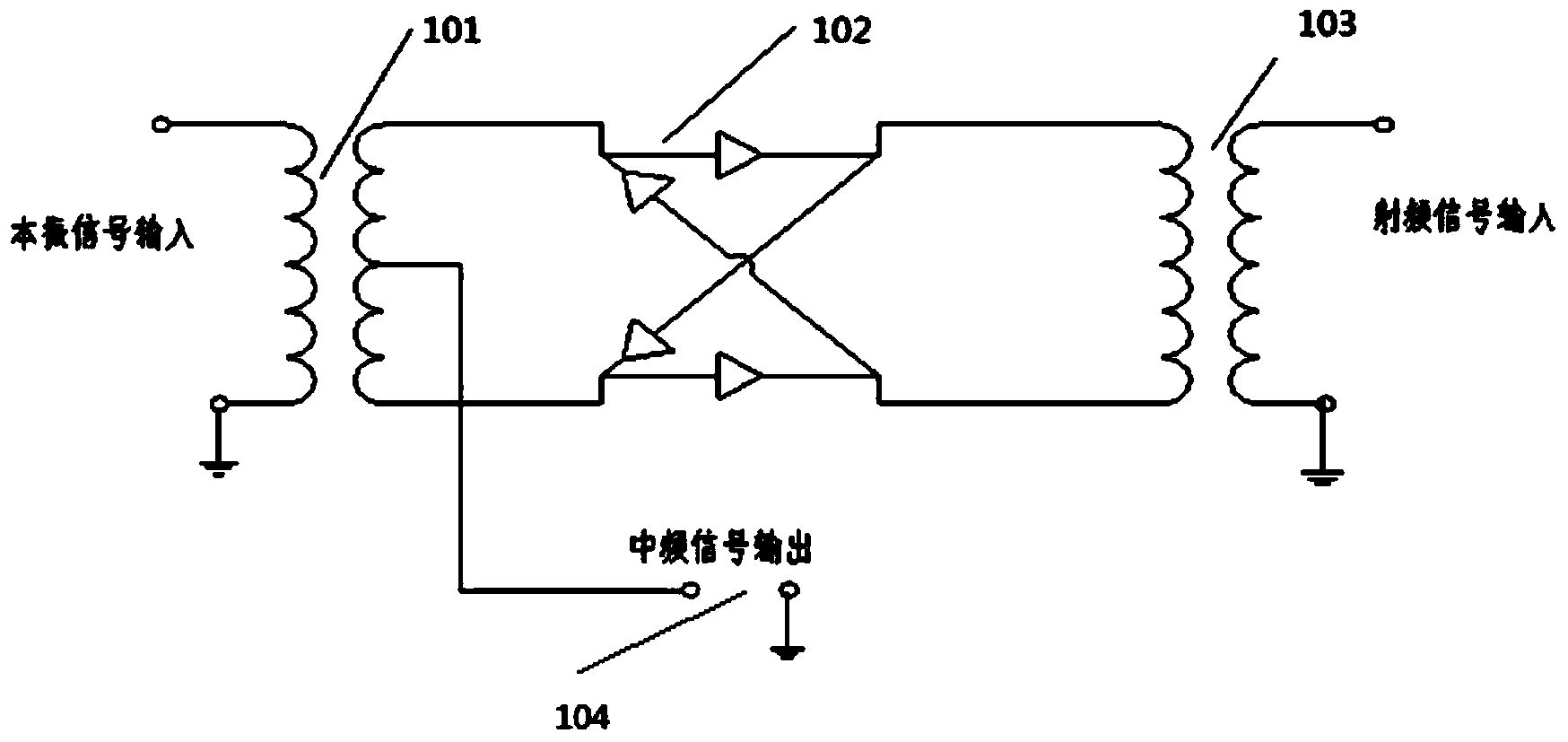
Ultra-wideband frequency mixer
InactiveCN103633943AAchieve ultra-wideband frequency coverageReduce lossMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferenceUltra-widebandLocal oscillator signal
The invention provides an ultra-wideband frequency mixer. The ultra-wideband frequency mixer comprises transition sections from a broadside coupling balun and a broadside coupling strip line of a local oscillator channel to a plane transmitting line, a coplanar waveguide of a radiofrequency channel, a medium frequency output channel and a frequency mixing diode pair, wherein the frequency of a local oscillator signal and the frequency of a radio frequency signal are mixed by input frequency mixing diodes of the local isolator channel and input frequency mixing diodes of the radiofrequency channel respectively; generated medium signals are outputted via the medium frequency output channel; the broadside coupling balun is used for converting unbalanced ultra-wideband local isolator signals into balanced ultra-wideband local isolator signals; after the balanced local isolator signals are converted into input frequency mixing diodes of the plane transmitting line via the transition section, generated medium signals step across the coplanar waveguide by using a gold wire inductor and then are outputted via a microstrip line. By using the scheme, the working frequency can cover an ultra-wide frequency range of 0.01GHz-110GHz; the ultra-wideband frequency mixer can work in a fundamental wave frequency mixing mode in a frequency range of 0.01GHz-70GHz, and the frequency conversion loss and a noise coefficient index can be lower than 12dB; and the ultra-wideband frequency mixer can work in a frequency range of 70GHz-110GHZ in a triple frequency harmonic frequency mixing mode, and the frequency conversion loss and the noise coefficient index can be lower than 30dB.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
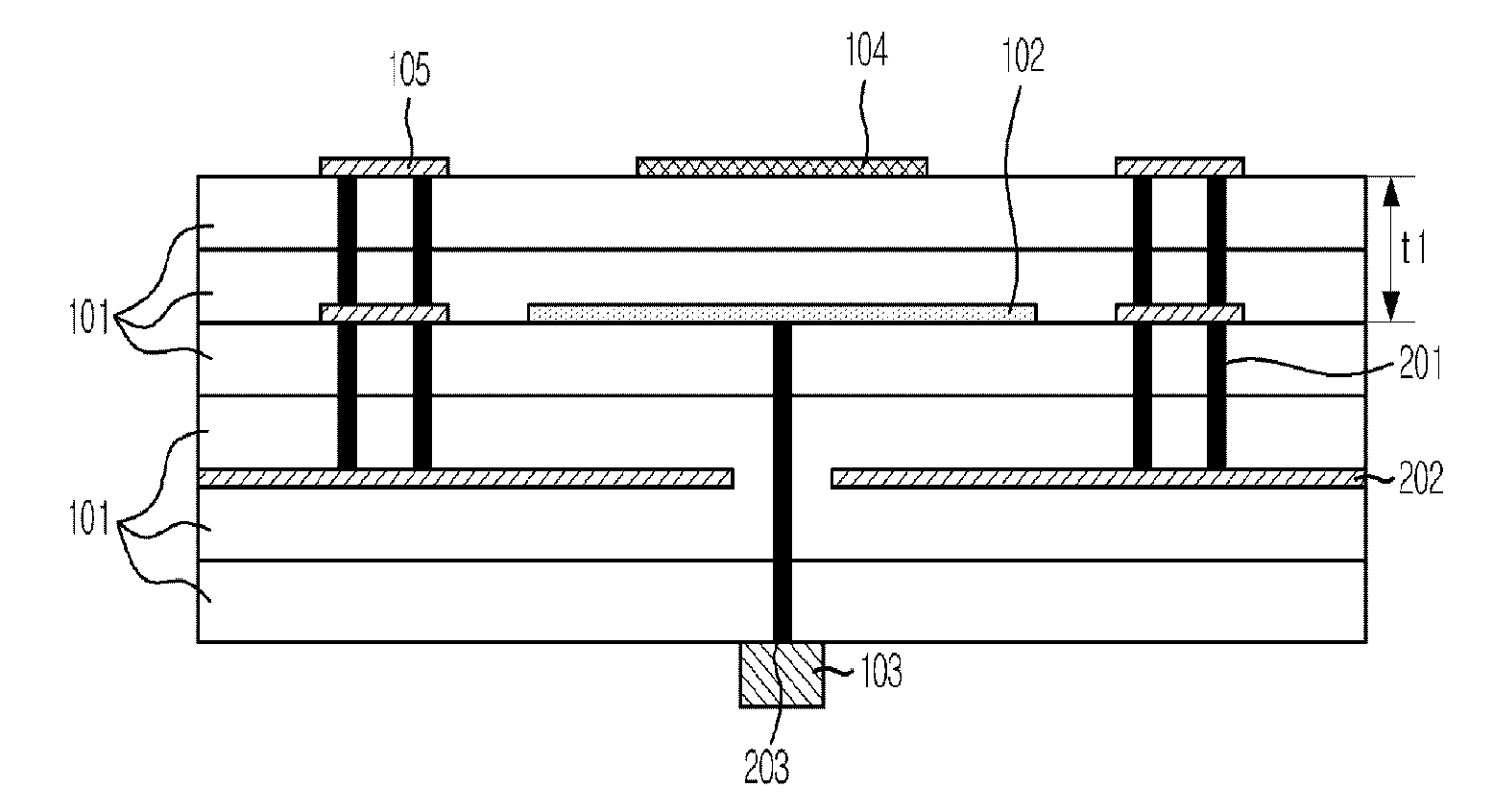
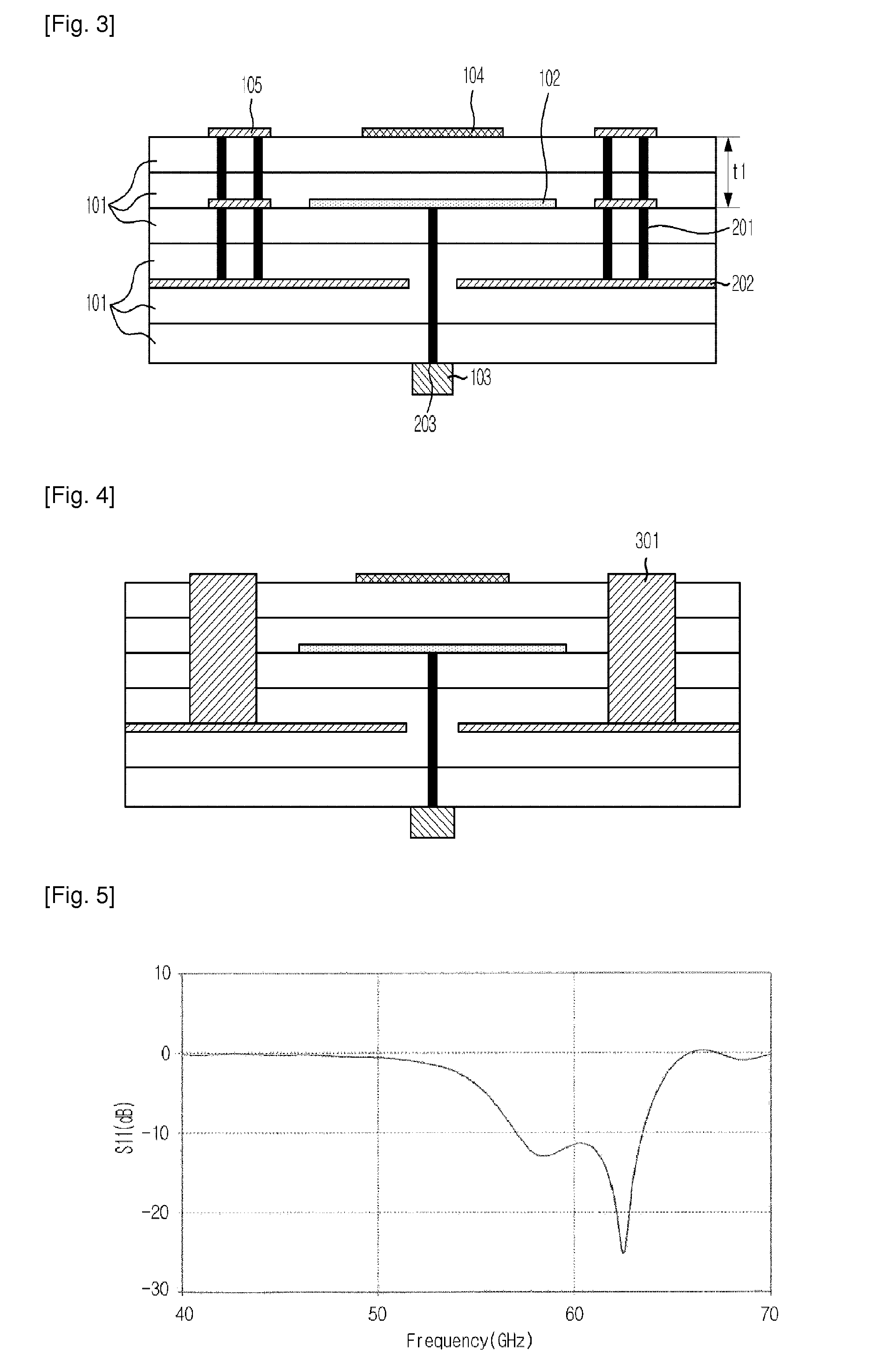
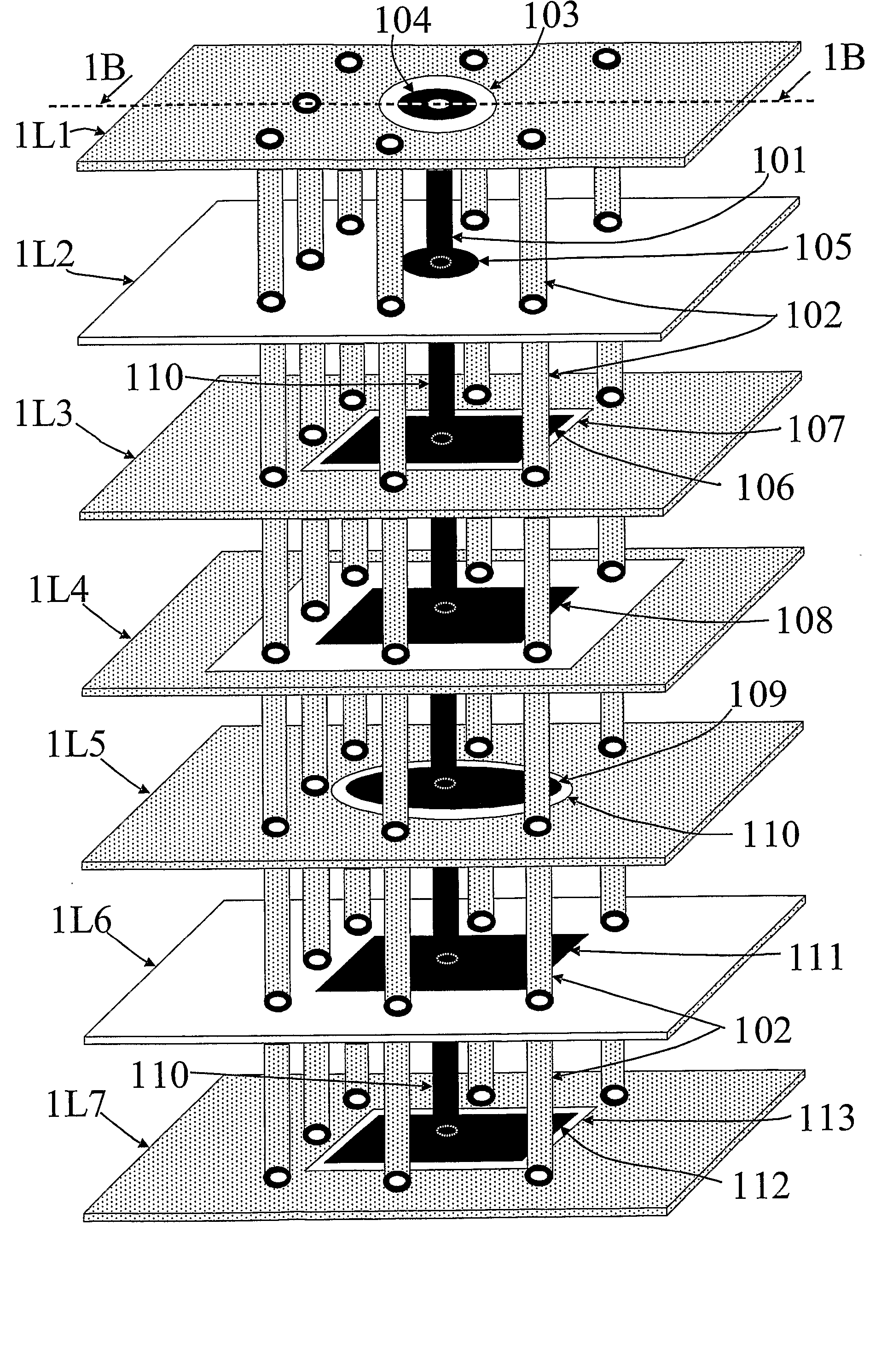
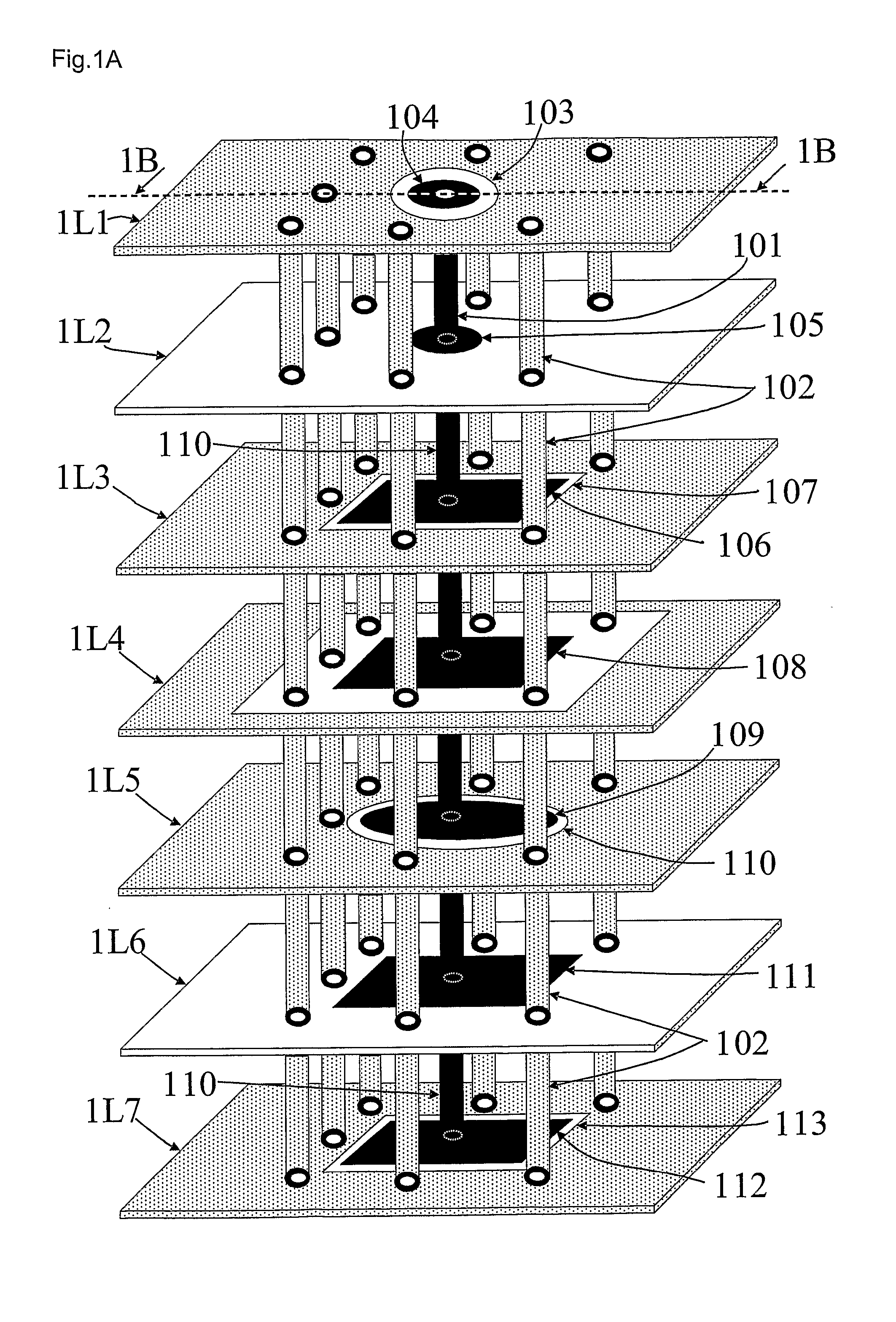
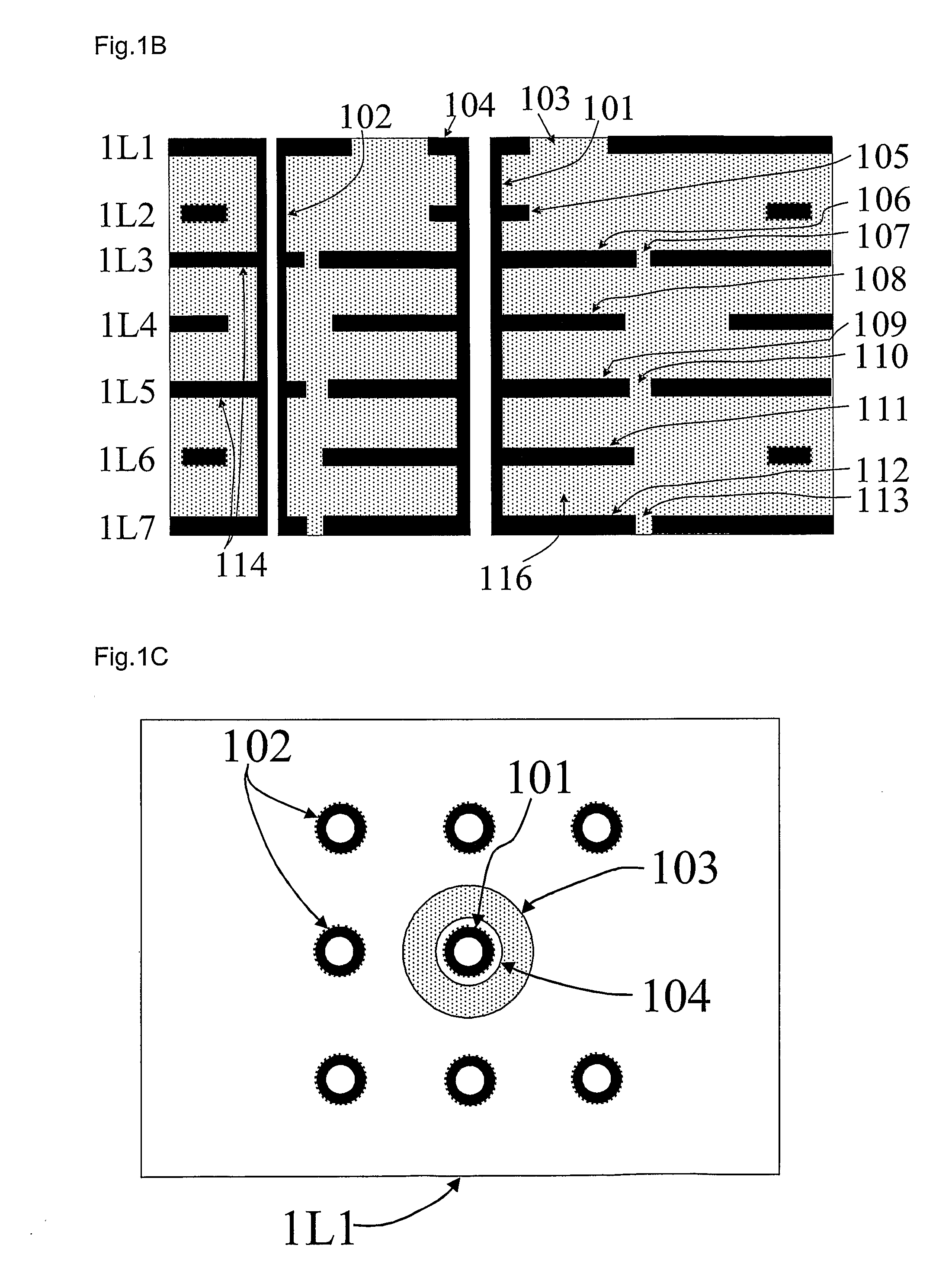
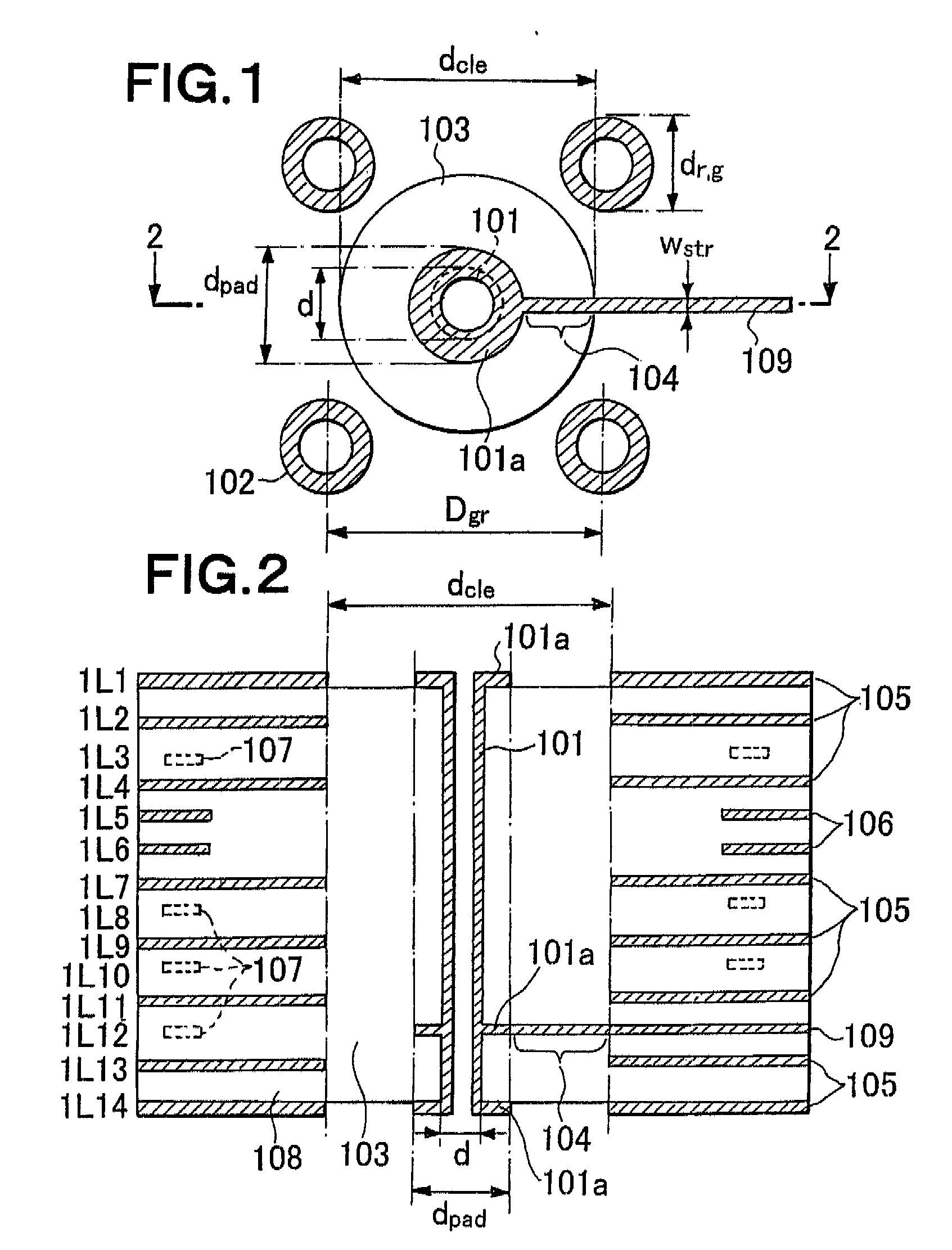
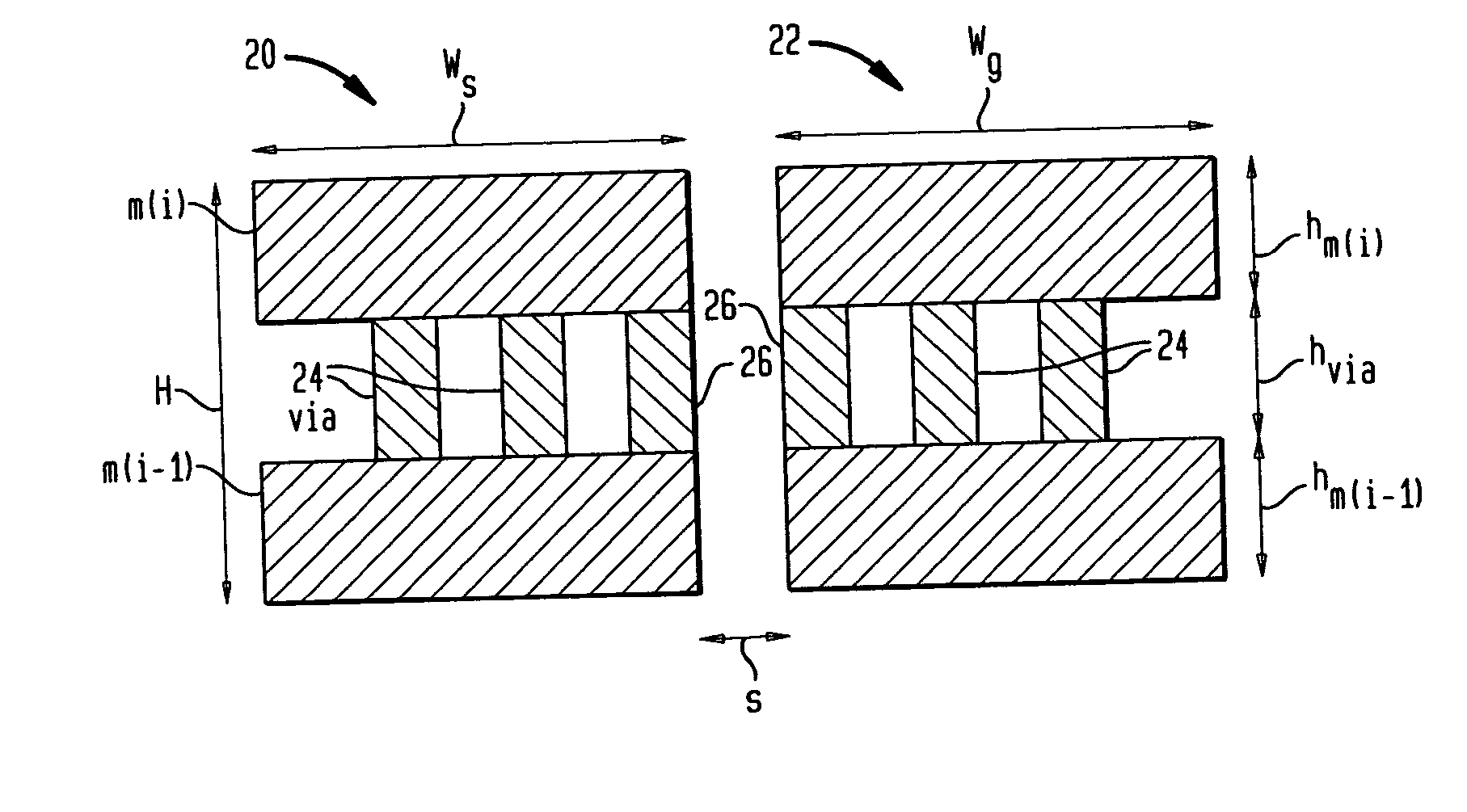
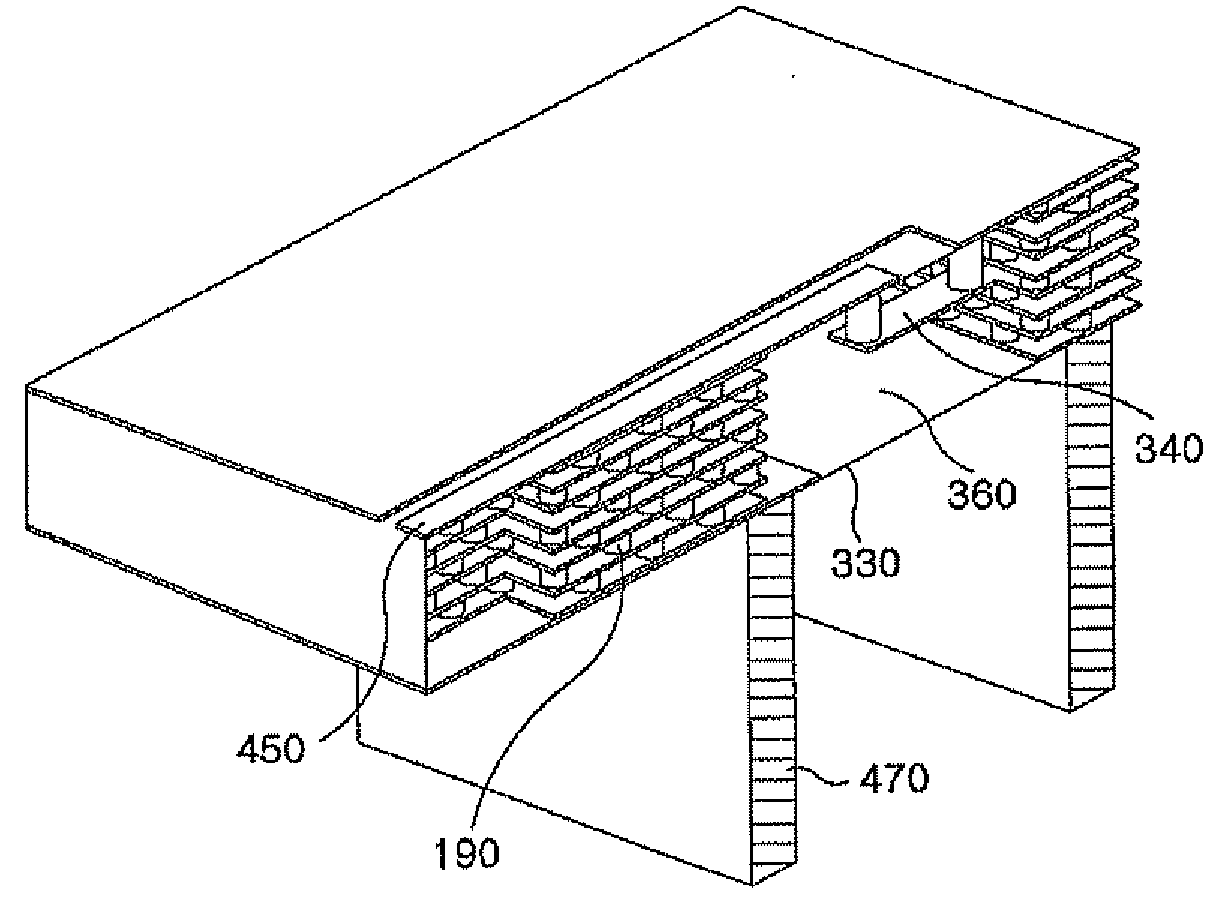
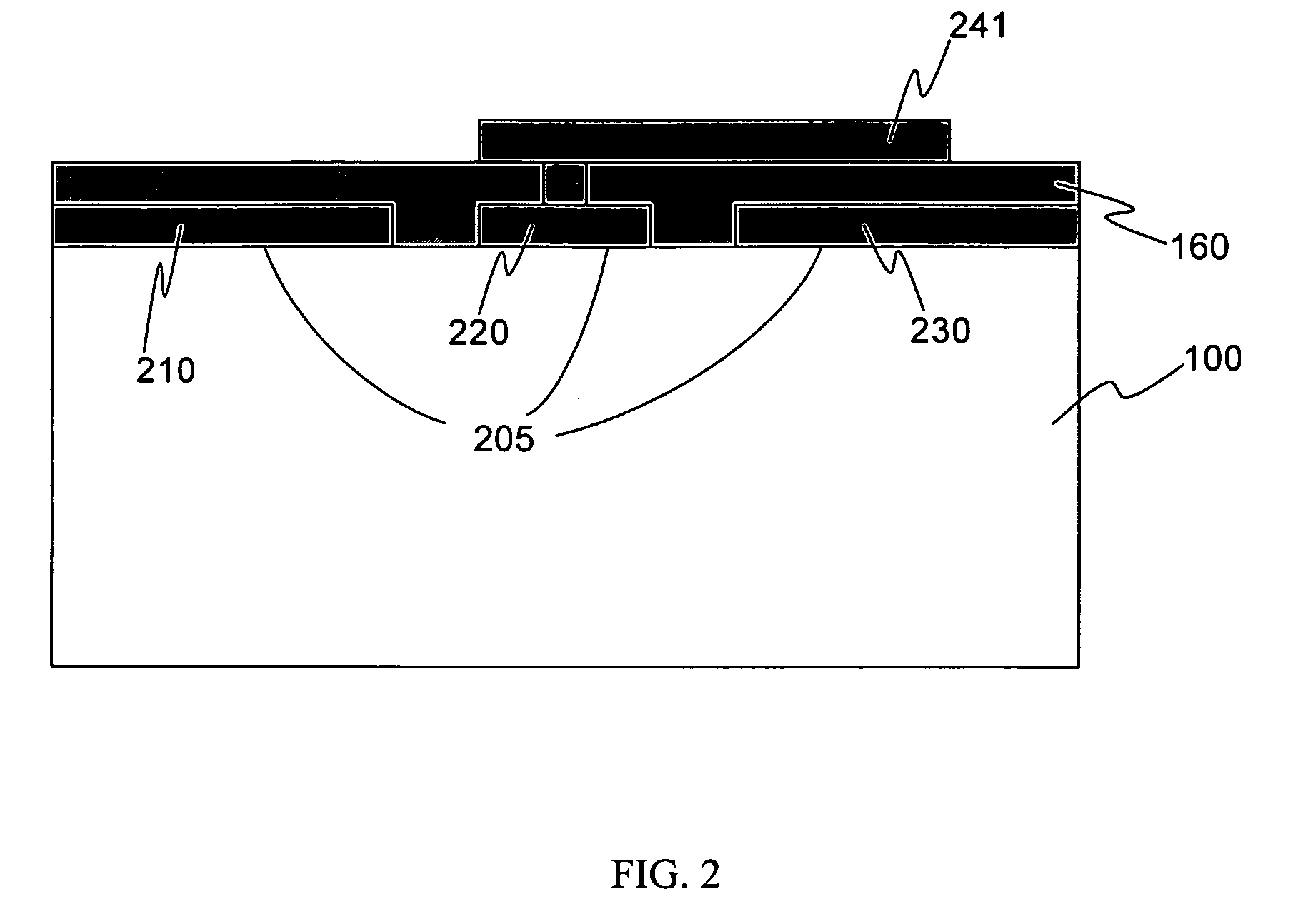
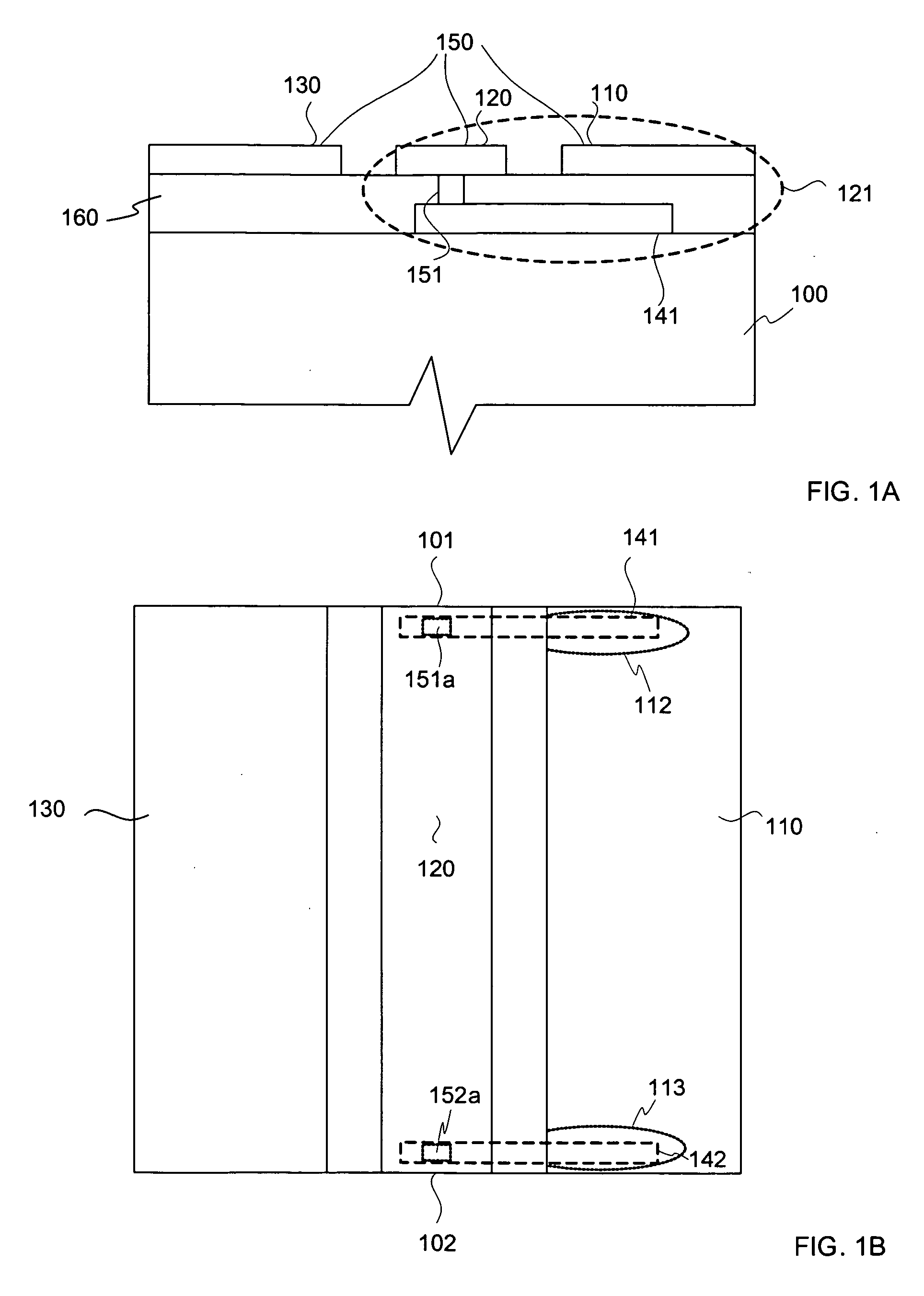
Multi-layer substrate
ActiveUS20100282503A1Lower overall renovationCross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted circuit aspectsElectrical conductorEngineering
A multi-layer substrate includes a planar transmission line structure and a signal via, which are connected by a multi-tier transition. The multi-tier transition includes a signal via pad configured to serve for a full-value connection of the signal via and the planar transmission line; and a dummy pad connected to the signal via, formed in an area of a clearance hole in a conductor layer disposed between a signal terminal of the signal via and the planar transmission line, and isolated from the conductor layer.
Owner:NEC CORP
Vertically-stacked co-planar transmission line structure for IC design
InactiveUS20050062137A1Improve performanceWide rangeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorPlanar transmission lines
A vertically stacked coplanar transmission line structure for an IC (integrated circuit) is provided which has superior loss and reflection characteristics relative to conventional on-chip transmission line designs. A simple embodiment of the vertically stacked coplanar transmission line structure comprises a micro-strip pair of first and second vertically stacked coplanar conductors, each comprising a metal layer, a next metal layer down, and an intermediate connecting via layer in between the metal layer and the next metal layer down.
Owner:IBM CORP
Planar transmission line-to-waveguide transition apparatus and wireless communication module having the same
InactiveUS20100001808A1Relatively large bandwidthLow insertion lossMultiple-port networksOne-port networksComputer moduleEngineering
A wireless communication module includes a plurality of monolithic millimeter-wave integrated circuits (MMICs) for signal processing attached to the top surface of a multi-layer low temperature co-fired ceramic substrate; a planar transmission line formed on the top surface of the multi-layer substrate for communications between the MMICs; a metal base attached to the bottom surface of the multi-layer substrate and having an opening to which an antenna is attached; a plurality of vias for connecting the metal base and the planar transmission line within the multi-layer substrate to establish a uniform potential on a ground plane of the multi-layer substrate; an embedded waveguide formed in the opening surrounded with the vias within the multi-layer substrate; and a planar transmission line-to-waveguide transition apparatus for the transition of waves between the planar transmission line and the embedded waveguide.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
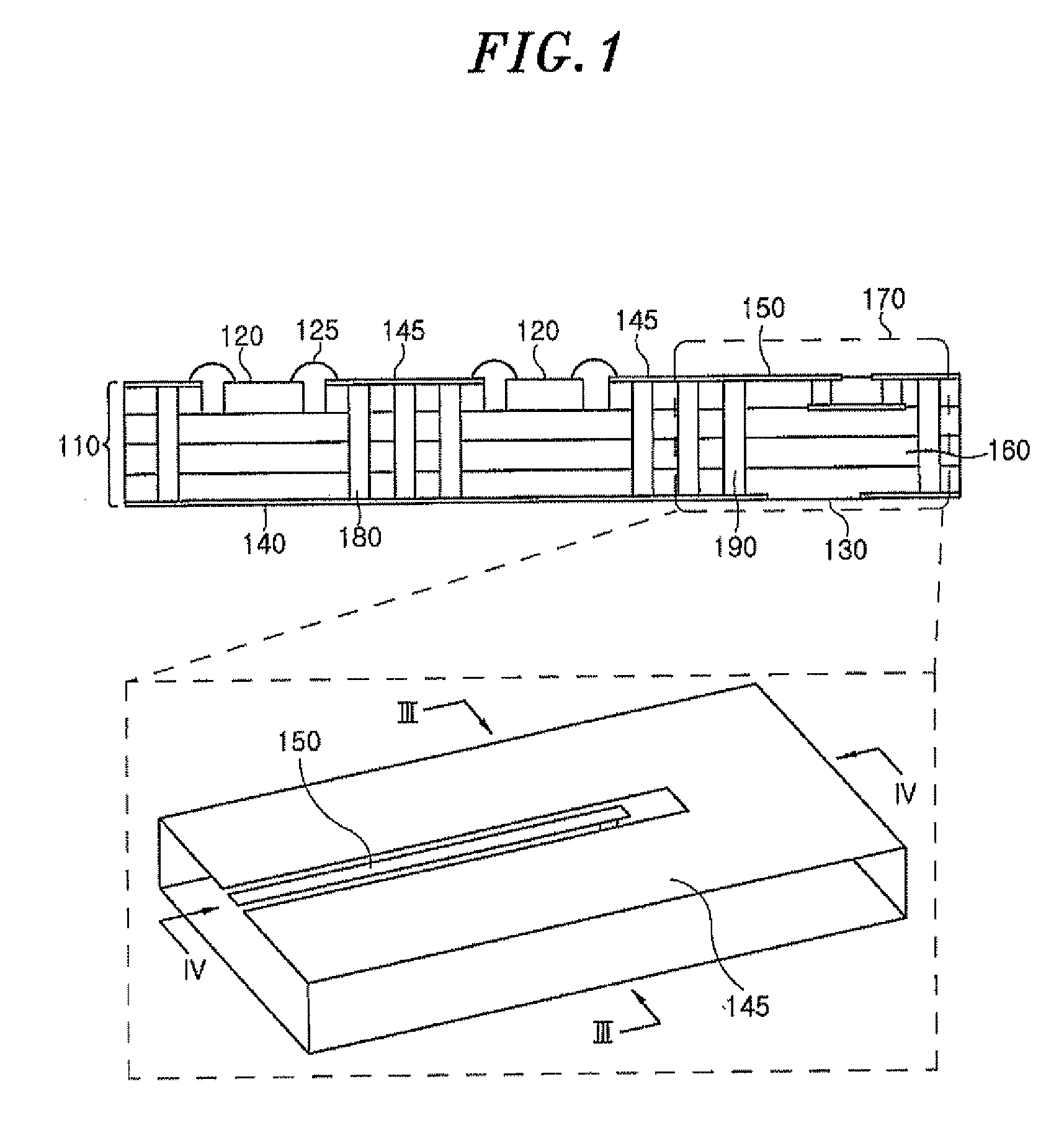
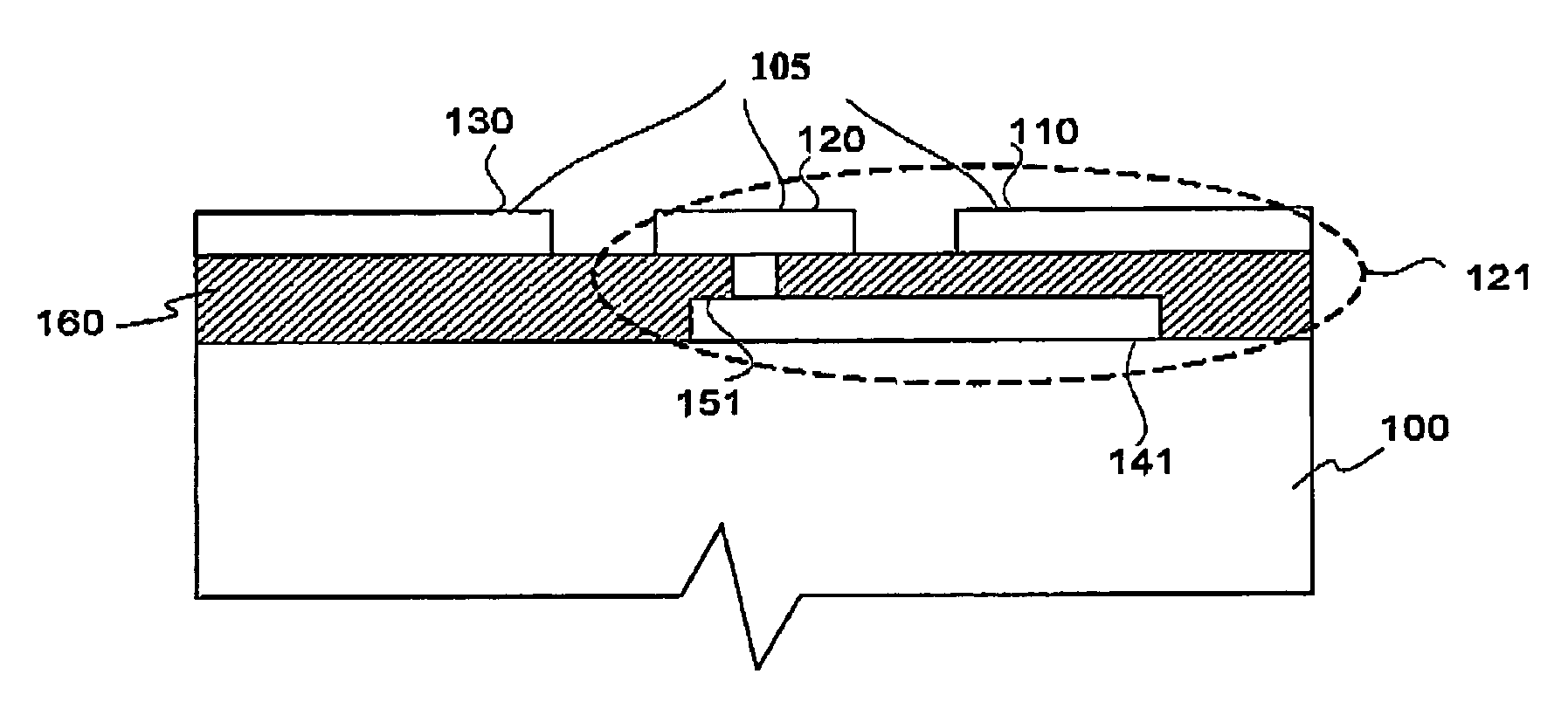
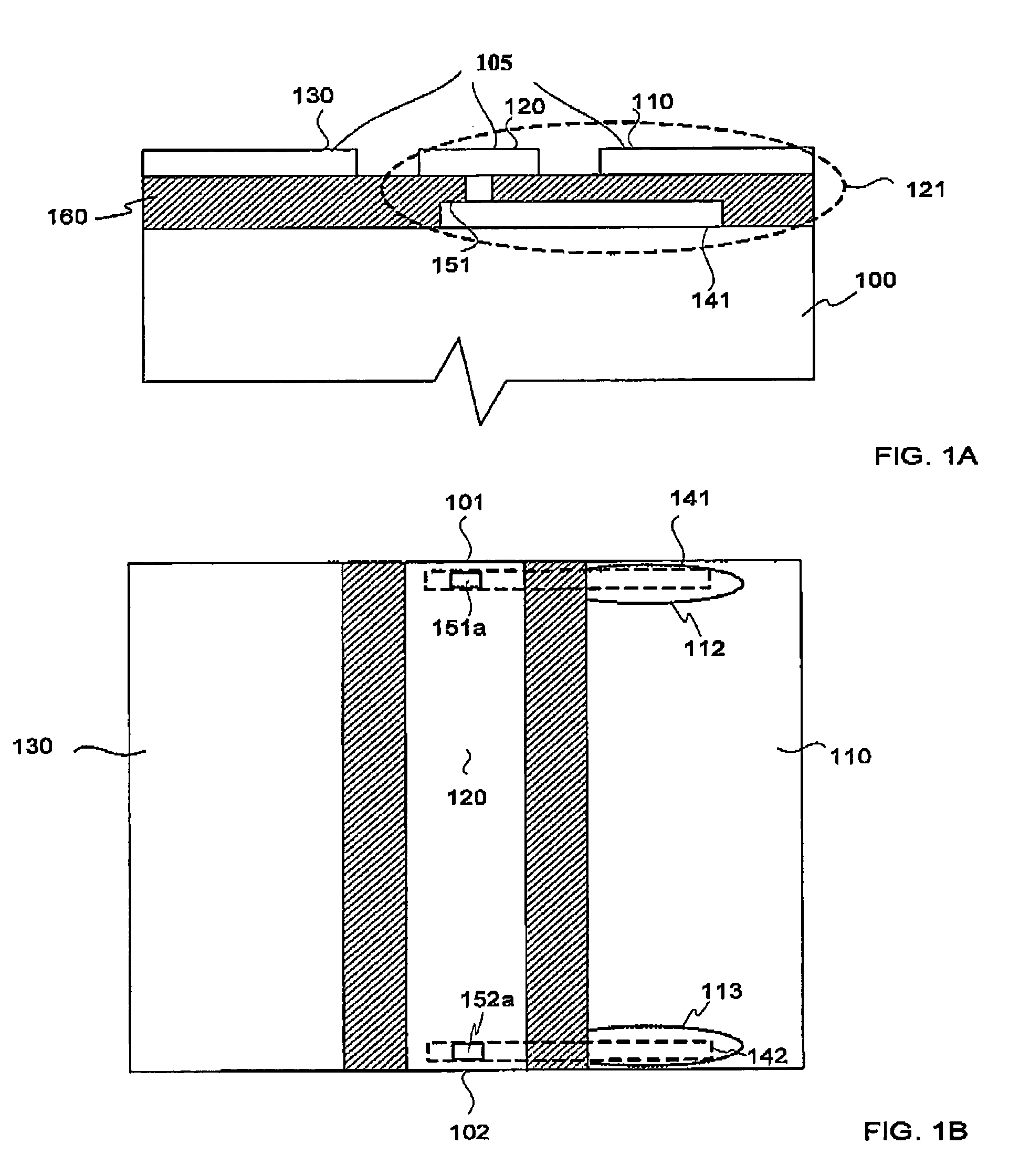
Electrical interconnection for high-frequency devices
InactiveUS20050083153A1Improve impedance continuityPrinted electric component incorporationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLead bondingElectrical devices
Wire bonds connect current-carrying edges of high-frequency planar conductors to other electrical devices. In one embodiment, planar transmission lines are interconnected using two wire bonds. One bond wire extends from an edge of a first center conductor to a corresponding edge of a second center conductor, and a second bond wire extends from the other edge of the first center conductor to the other edge of the second center conductor. Embodiments include center conductors at different heights and having different widths, and different electrical devices, such as semiconductor integrated circuits. In a particular embodiment, ball bonding is used. In some embodiments, a tack bond is included after a ball bond to allow closer attachment of the bond wire to the edge of the conductor.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Reduced size transmission line using capacitive loading
InactiveUS7190244B2Increase electrical lengthSize-reducedMultiple-port networksWaveguidesCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A capacitively loaded multilevel transmission line network for operation at a microwave frequency f is disclosed wherein microstrip conductors are disposed over or under a uniplanar transmission line (UTL), electrically connected thereto at or near opposing ends of the UTL and coupled to portions of the UTL separated therefrom by a thin dielectric film. The microstrip conductors and the portions of the UTL coupled thereto form thin-film microstrip (TFMS) shunt stubs capacitively loading the ends of the UTL for increasing its electrical length. The present invention enables considerable size reduction of microwave circuits having uniplanar transmission lines.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Phase shift device
ActiveUS10141620B2Improve insertion lossHigh metallic loss of the CPWCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricWaveguide type devicesMetal-insulator-metalPhase shifted
A phase shift device includes a planar transmission line that is formed by a signal electrode and a ground electrode which are separated by a dielectric substance, whereby the signal electrode of the planar transmission line is divided into several pieces and includes overlapping areas of adjacent pieces that are filled with a tunable liquid crystal material, thereby forming a dielectric tunable component (varactor) with a metal-insulator-metal type capacitor. The several pieces of the signal electrode are arranged at two or more different distance levels with respect to the ground electrode. The tunable liquid crystal material is arranged as a continuous layer between several pieces of the signal electrode that are arranged at two different distance levels.
Owner:ALCAN SYST GMBH
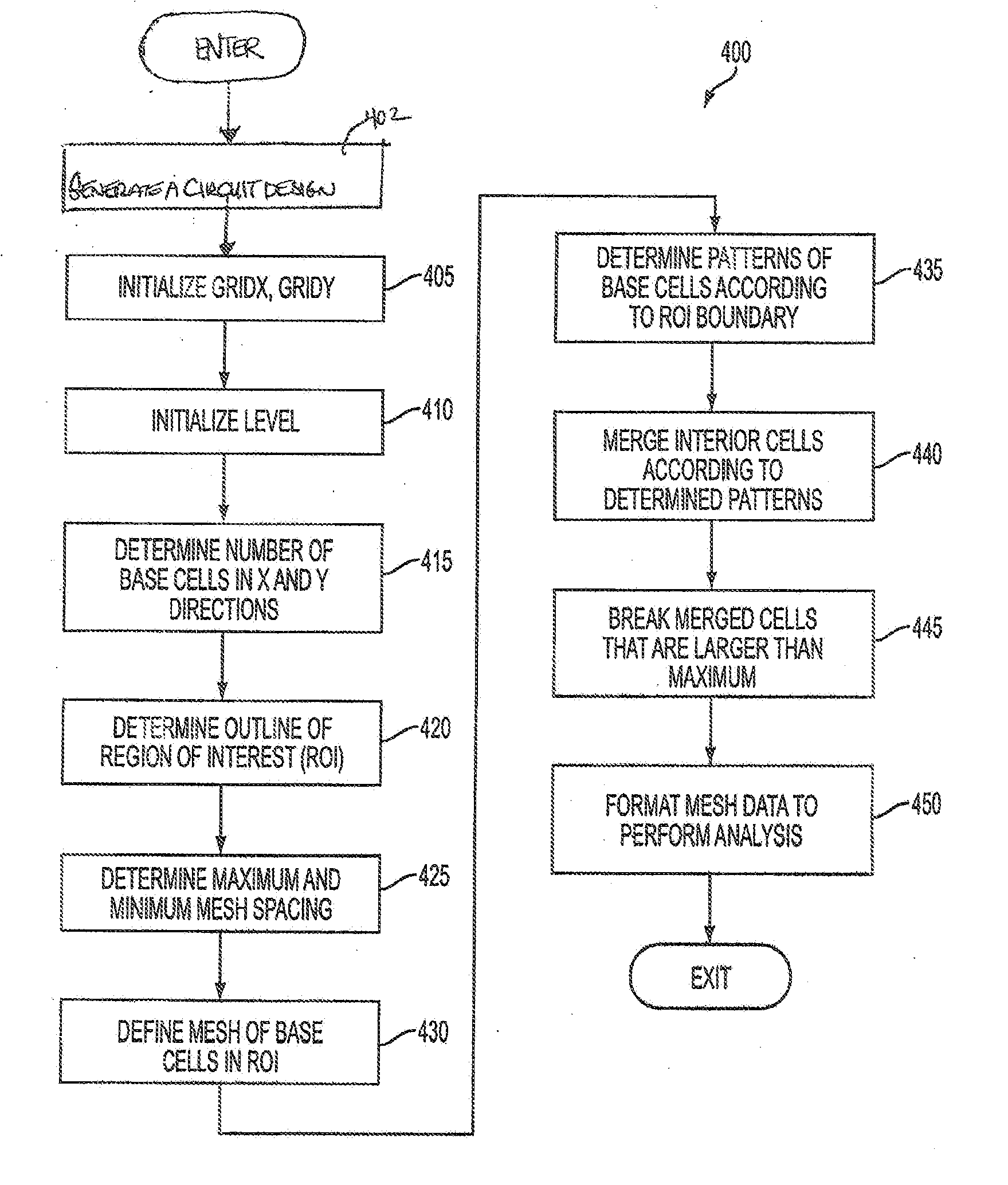
Adaptive mesh resolution in electric circuit simulation and analysis
ActiveUS20100205572A1Reduce computational overheadReduced simulation timeDesign optimisation/simulationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationImage resolutionResonance
An adaptive mesh of virtual nodes is provided to analyze the performance of a power / ground plane pair having an irregular shape. Plane transmission line characteristics and regional modal resonances can be modeled accurately, and with a significant decrease in simulation time as compared to traditional methods. A variable-sized cell structure is constructed with smaller cells in irregular regions and with larger cells in uniform regions. Grid nodes may thus stay aligned along length and width to allow parameters of equivalent circuit models to be scaled appropriate to the cell size.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Apparatus and methods for constructing and packaging waveguide to planar transmission line transitions for millimeter wave applications
ActiveUS7479842B2Suppressing undesired waveguide modes and resonancesOne-port networksWaveguidesCouplingCoplanar waveguide
Apparatus and methods are provided for constructing waveguide-to-transmission line transitions that provide broadband, high performance coupling of power at microwave and millimeter wave frequencies. More specifically, exemplary embodiments of the invention include wideband, low-loss and compact coplanar waveguide-to-rectangular waveguide transition structures and asymmetric coplanar stripline (or coplanar stripline)-to-rectangular waveguide transition structures that are particularly suitable for microwave and millimeter wave applications.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Reduced size transmission line using capacitive loading
InactiveUS20060103482A1Increase electrical lengthSize-reducedMultiple-port networksWaveguidesCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A capacitively loaded multilevel transmission line network for operation at a microwave frequency ƒ is disclosed wherein microstrip conductors are disposed over or under a uniplanar transmission line (UTL), electrically connected thereto at or near opposing ends of the UTL and coupled to portions of the UTL separated therefrom by a thin dielectric film. The microstrip conductors and the portions of the UTL coupled thereto form thin-film microstrip (TFMS) shunt stubs capacitively loading the ends of the UTL for increasing its electrical length. The present invention enables considerable size reduction of microwave circuits having uniplanar transmission lines.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
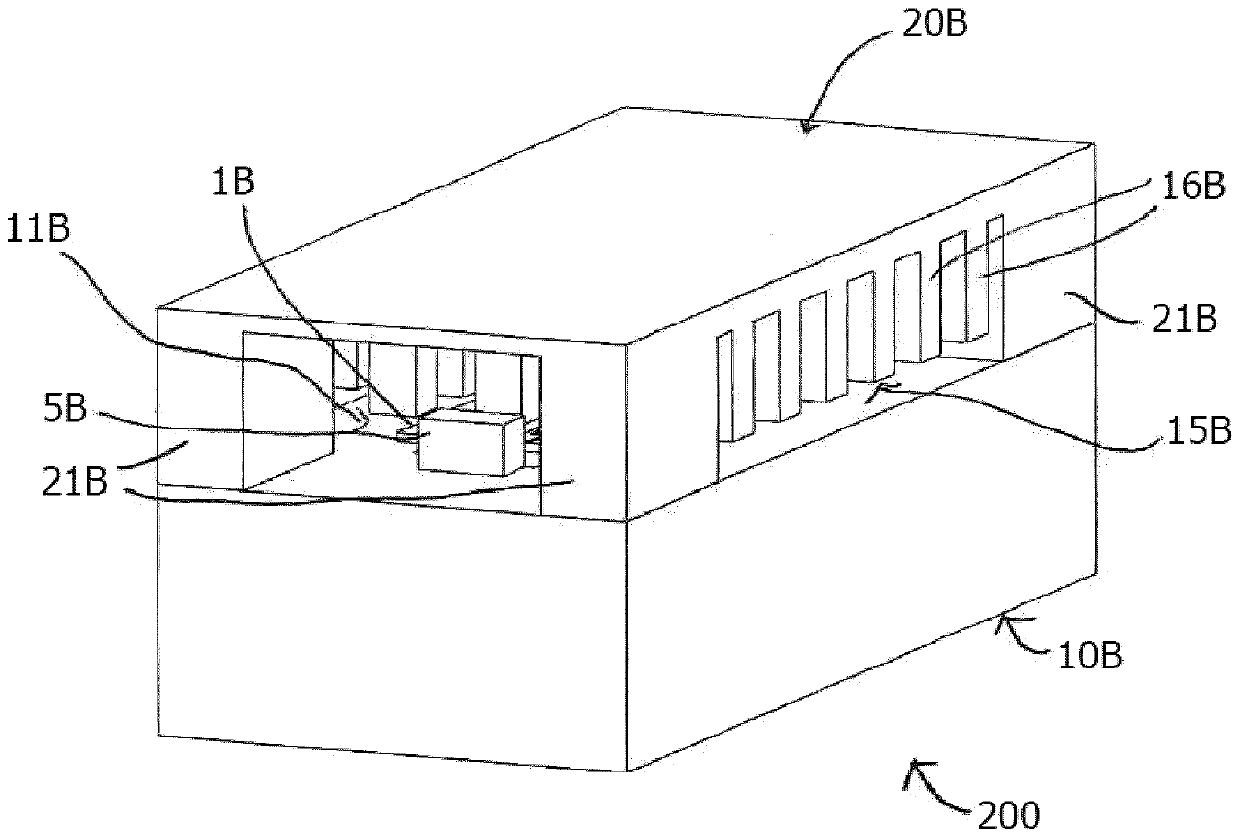
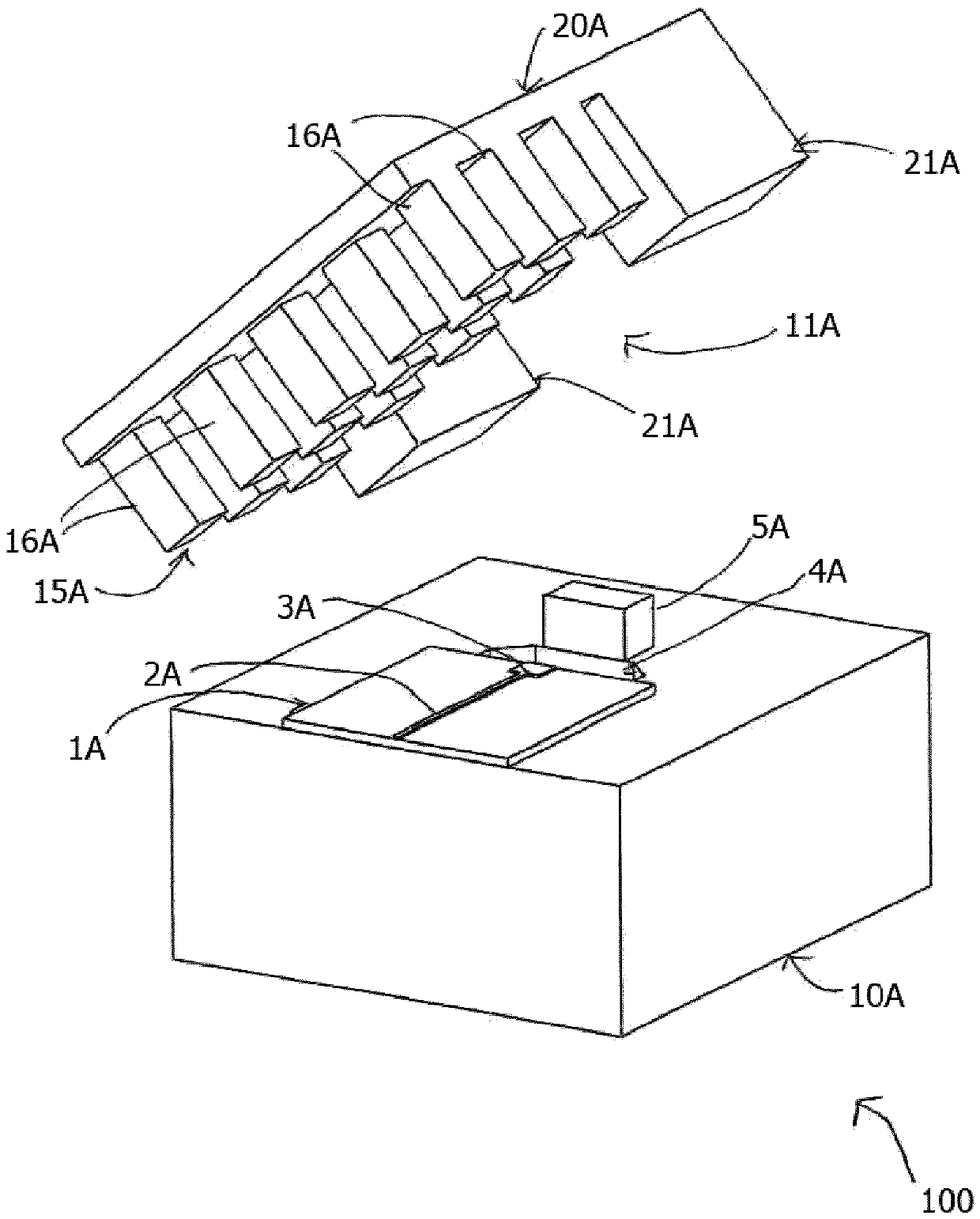
Packaging structure comprising at least one transition forming contactless interface
ActiveCN109792102AOvercoming Interconnect Issues Associated with InterconnectsQuick measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringPlanar transmission lines
The present invention relates to a packaging structure (100)comprising a split-block assembly with a first and a second conducting block section (10A, 20A) and at least one transition between a firstplanar transmission line (2A) and a second transmission line (11A), and one or more input / output ports. The first transmission line (2A) is arranged on a substrate, e.g. an MMIC (1A), disposed on thefirst conducting block section (10A) and comprises a coupling section (3A), the first conducting block (10A) comprises a cavity (4A) with a cavity opening in an upper surface of the first conducting block section (10A) so arranged that, in an assembled state of the split-block assembly, the coupling section (3A) will be located above, or in, the opening of the cavity (4A), the second transmissionline (11A) being in line with the first transmission line (2A) and located on an opposite side of the opening of the cavity (4A).The second conducting block section (20A) acts as a lid in an assembledstate of the packaging structure. One of the conducting block sections is provided with a high impedance surface (15A) in a transition region along or facing the first (2A) and second (11A) transmission lines, a narrow gap being provided between the high impedance surface region (15A) and the opposing surface of the other conducting block section (10A) at least in the transition region such thatthe transition will be contactless without any galvanic contact between the first and second transmission lines (2A, 11A).
Owner:GAPWAVES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com