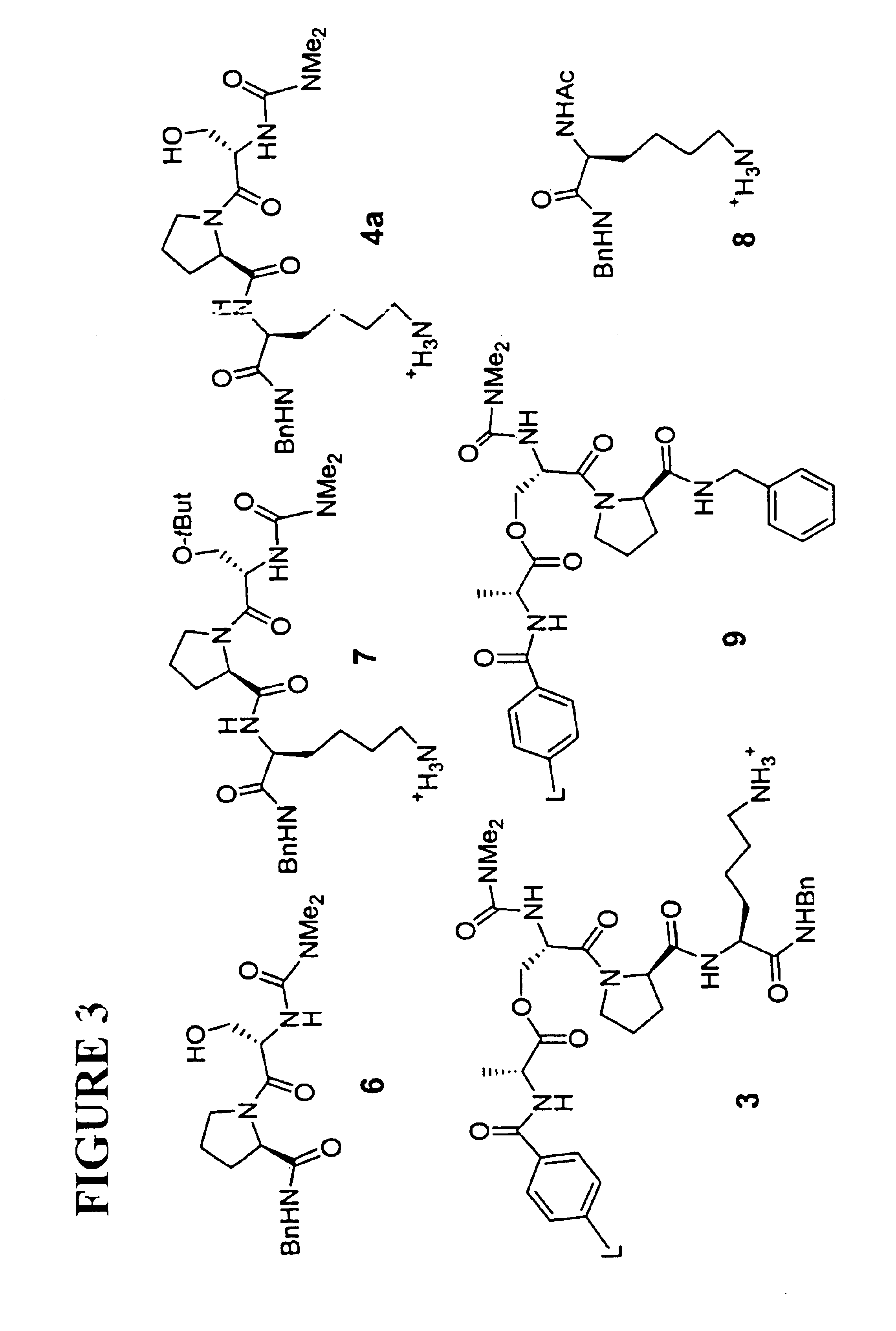
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Vancomycin resistant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A vancomycin resistant staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) infection is caused by bacteria. These bacteria are resistant to the antibiotic medicine vancomycin. The infection can spread easily from person to person.
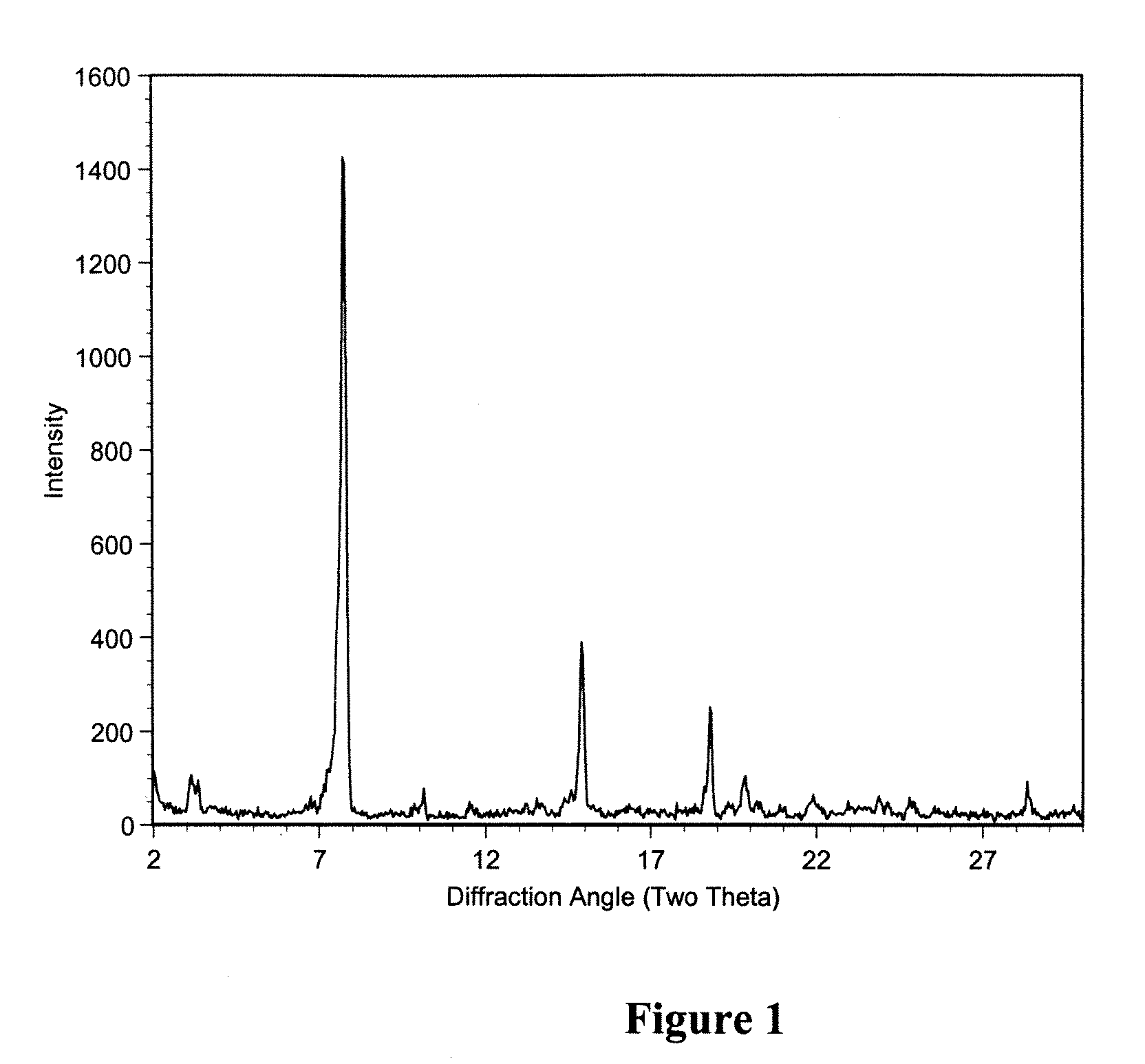
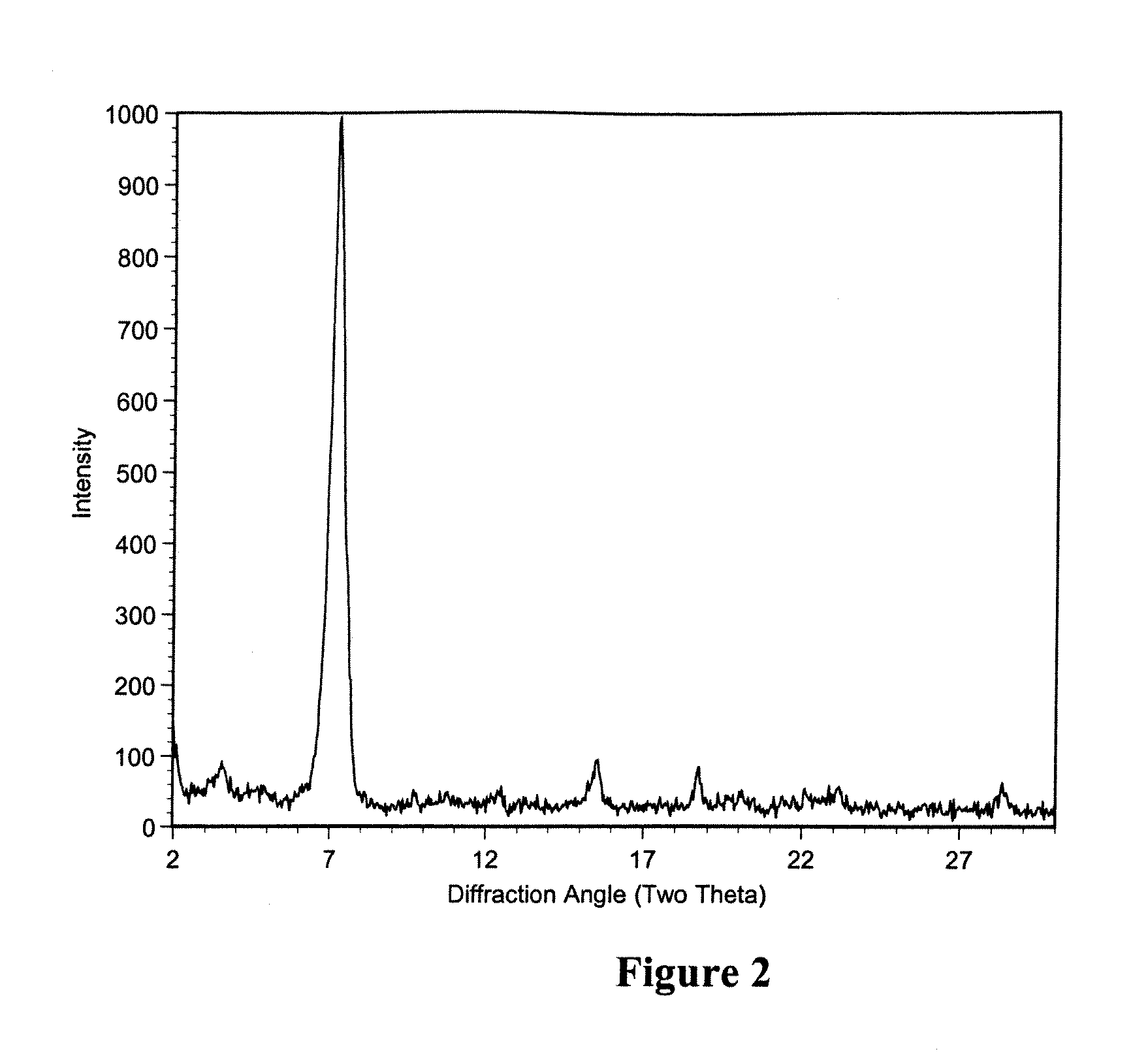
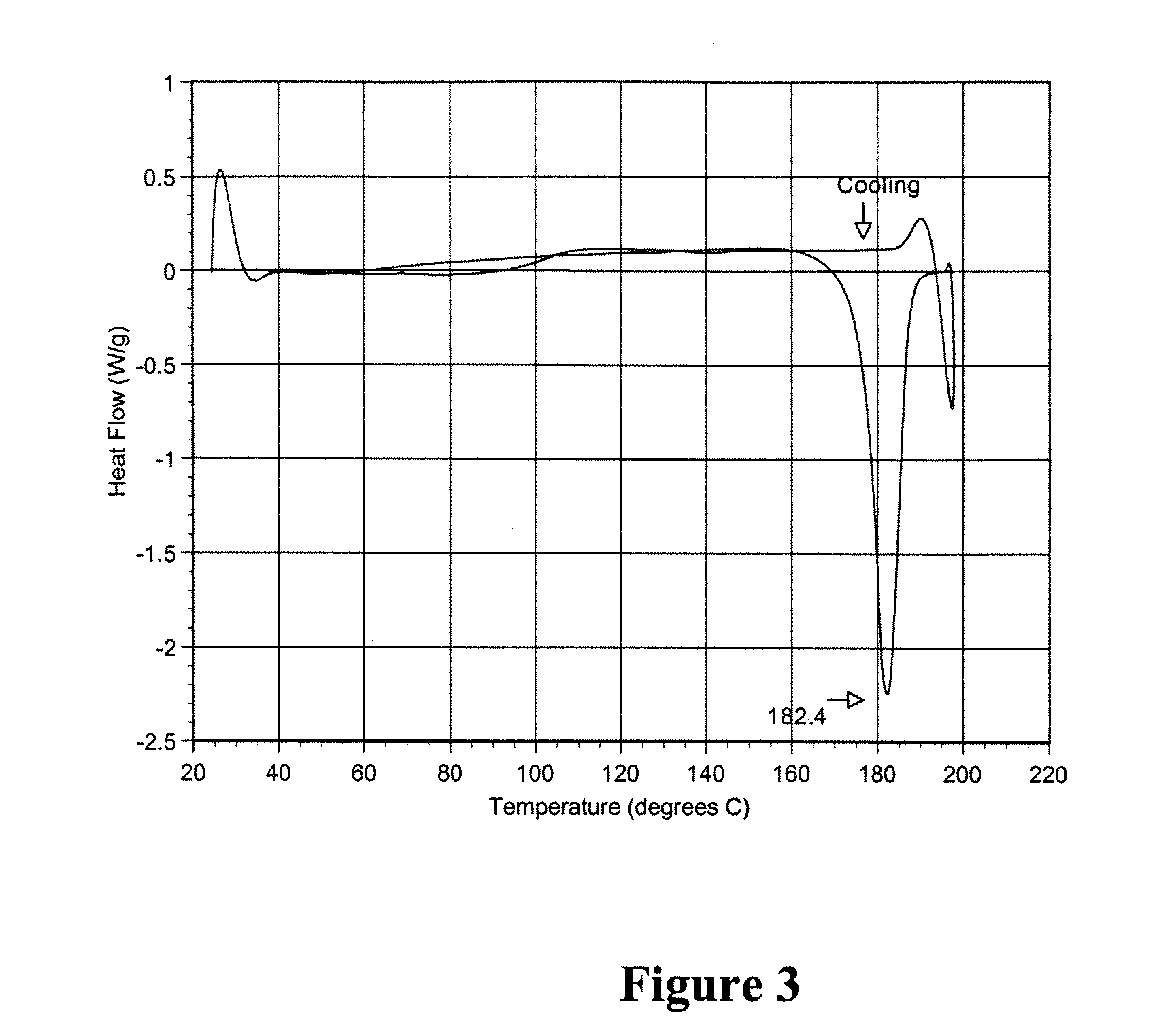
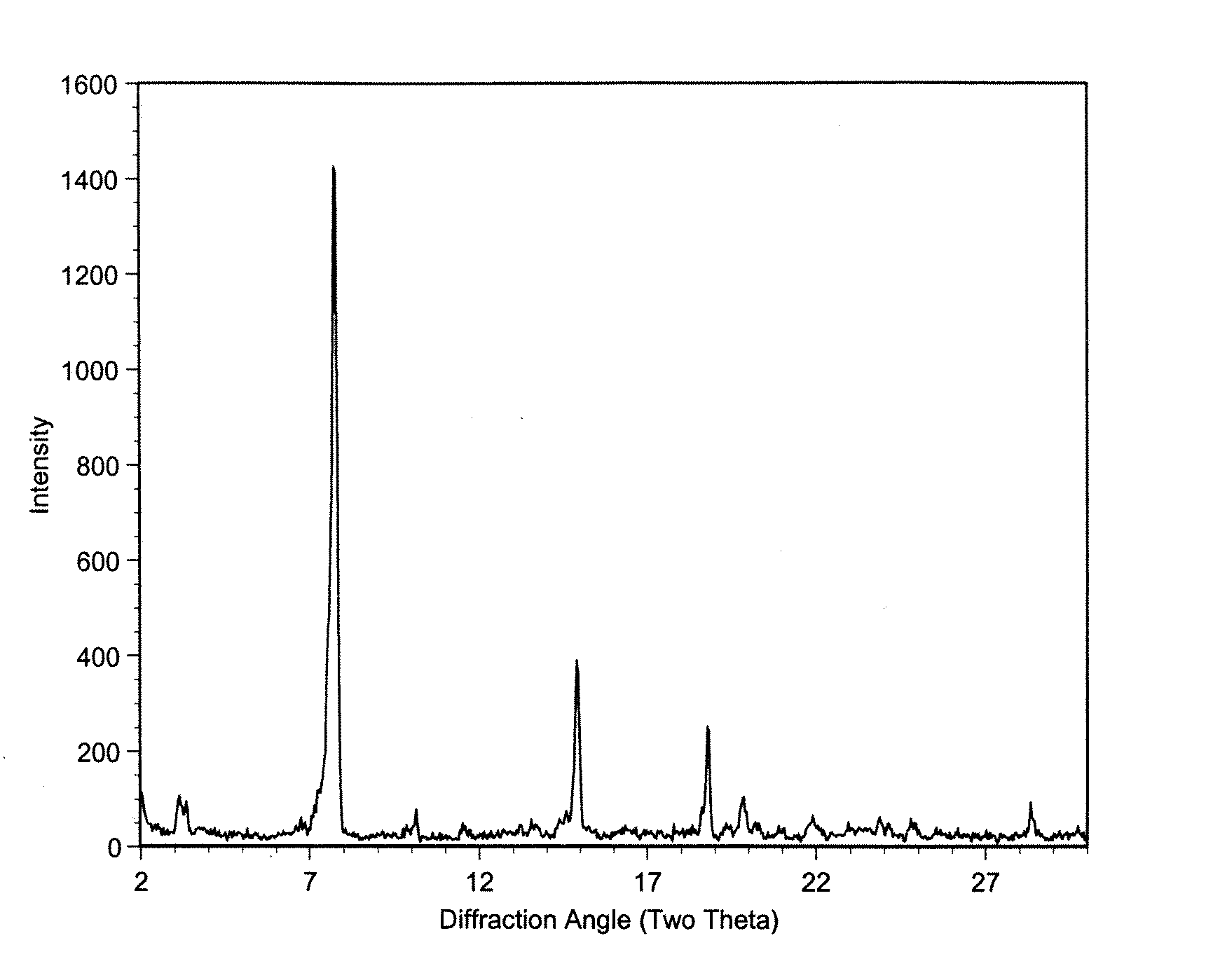
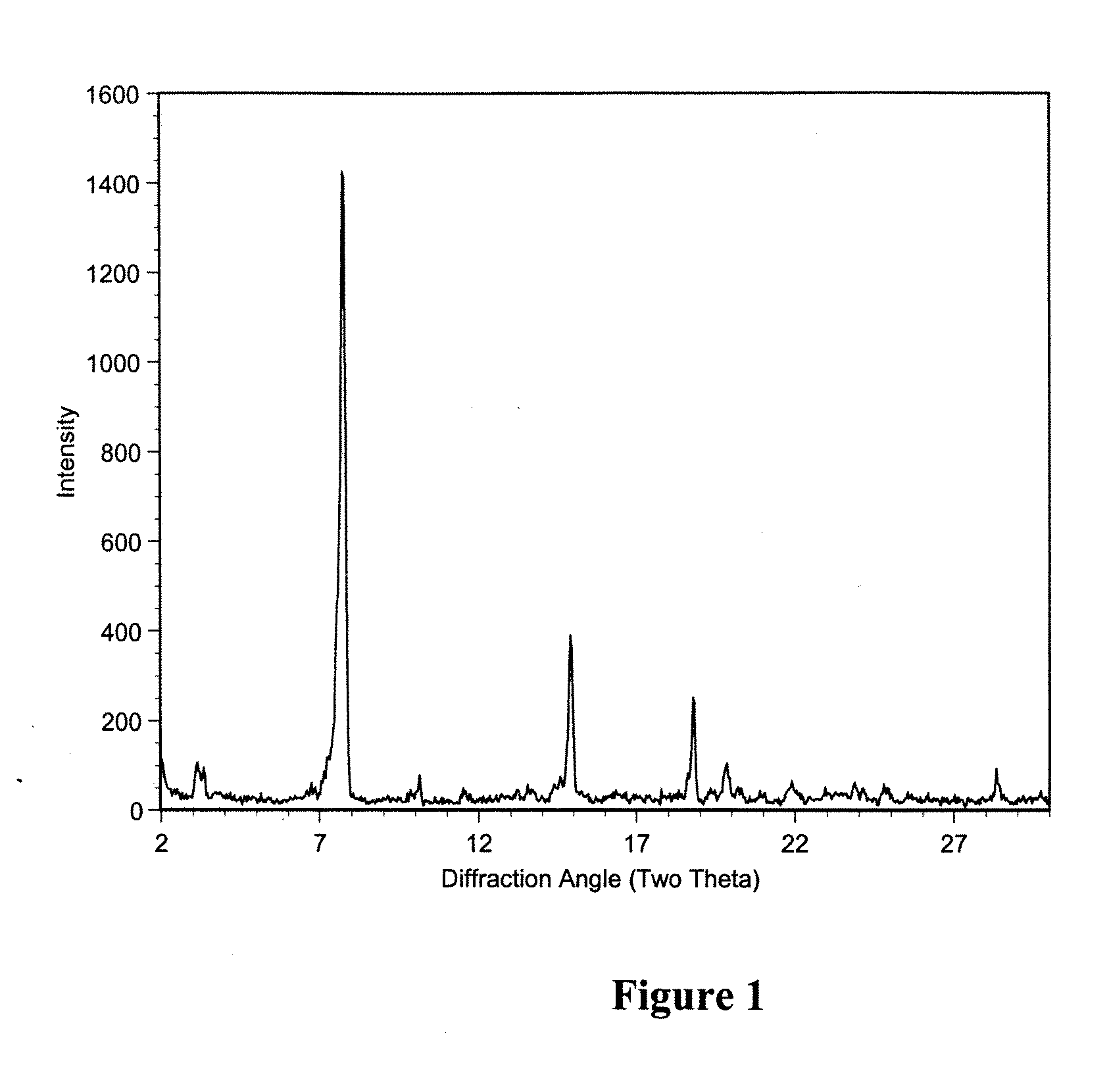
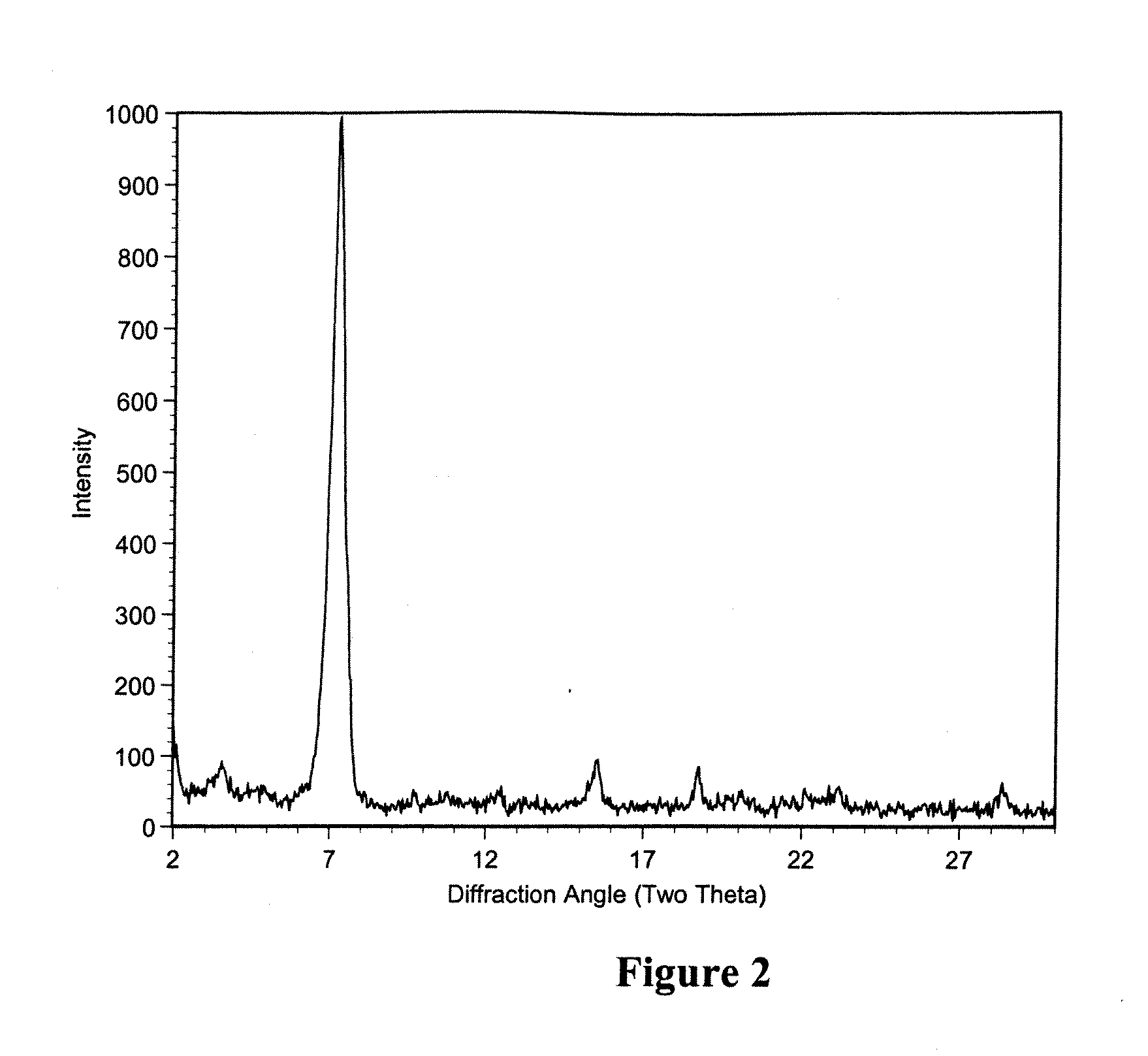
Polymorphic crystalline forms of tiacumicin B
ActiveUS7378508B2Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaDisease
The invention relates to novel forms of compounds displaying broad spectrum antibiotic activity, especially crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, compositions comprising such crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, processes for manufacture and use thereof. The compounds and compositions of the invention are useful in the pharmaceutical industry, for example, in the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with the use of antibiotics, chemotherapies, or antiviral therapies, including, but not limited to, colitis, for example, pseudo-membranous colitis; antibiotic associated diarrhea; and infections due to Clostridium difficile (“C. difficile”), Clostridium perfringens (“C. perfringens”), Staphylococcus species, for example, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus, or Enterococcus including Vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
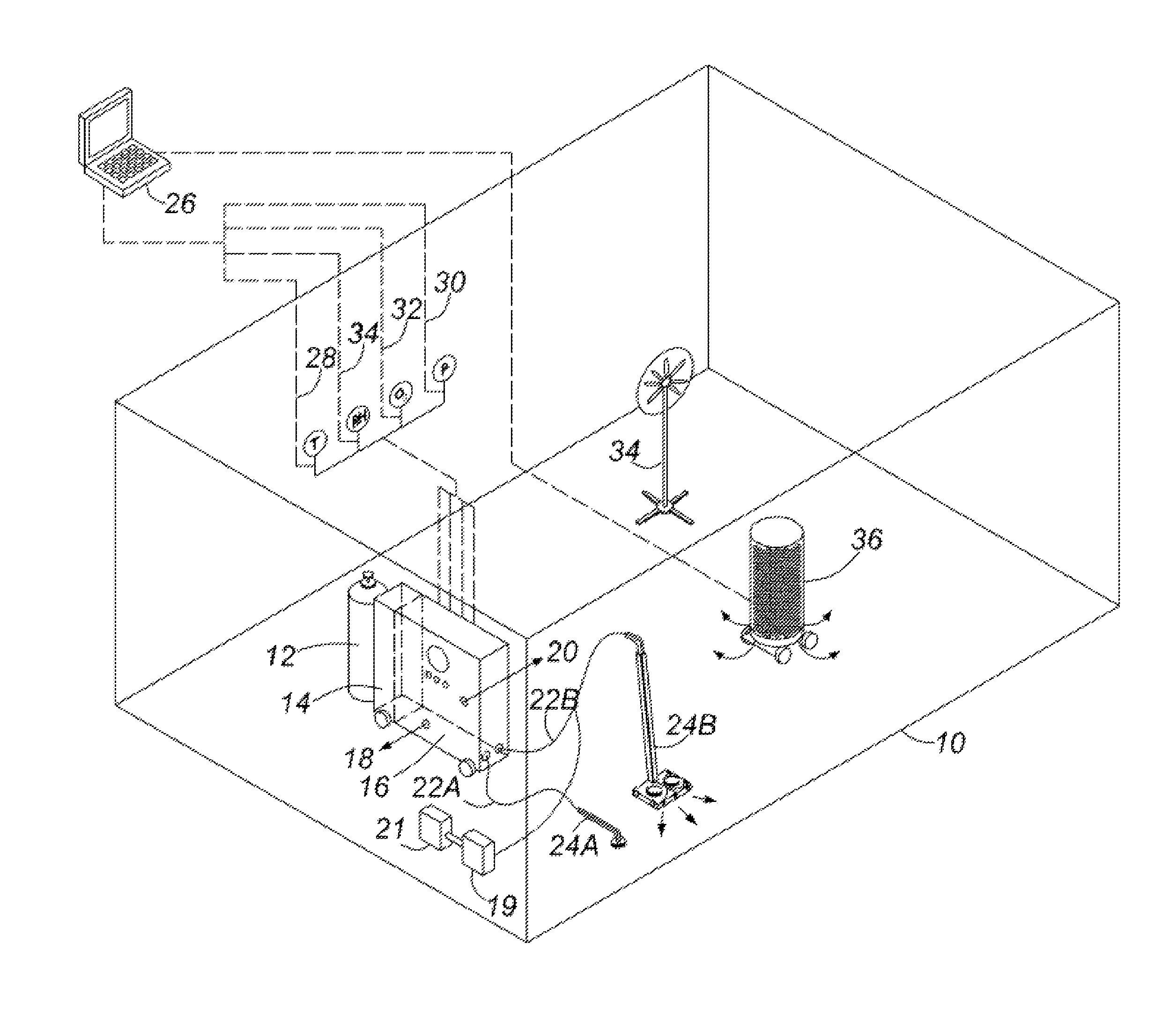
Healthcare facility disinfecting system
ActiveUS8551399B2Effectively eliminating aerosolized pathogensLavatory sanitoryDeodrantsEscherichia coliClostridium difficile toxin B
A system and process for disinfecting rooms such as health care facility rooms with an oxygen / ozone mixture is described, which is effective to combat “superbugs” such as Clostridium difficile (C. difficile); E. coli; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA); and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE). In preferred embodiments, hydrogen peroxide is additionally used. The system and process is effective to destroy bacteria deposited on surfaces as biofilm, and, accompanied by physical agitation such as jet nozzle outlets, is effective to disinfect carpet, drapery and similar absorbent and porous surfaces.
Owner:DD STEROZONE LLC +1
Macrolide polymorphs, compositions comprising such polymorphs, and methods of use and manufacture thereof
The invention relates to novel forms of compounds displaying broad spectrum antibiotic activity, especially crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, compositions comprising such crystalline polymorphic forms and amorphous forms of such compounds, processes for manufacture and use thereof. The compounds and compositions of the invention are useful in the pharmaceutical industry, for example, in the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with the use of antibiotics, chemotherapies, or antiviral therapies, including, but not limited to, colitis, for example, pseudo-membranous colitis; antibiotic associated diarrhea; and infections due to Clostridium difficile (“C. difficile”), Clostridium perfringens (“C. perfringens”), Staphylococcus species, for example, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus, or Enterococcus including Vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Methods for preventing or treating infectious diseases caused by extracellular microorganisms, including antimicrobial-resistant strains thereof, using gallium compounds
InactiveUS20080241275A1Effect be exertReduce in quantityAntibacterial agentsBiocidePresent methodInfectious Disorder
The present invention relates to methods for preventing or treating infectious diseases caused by extracellular microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, by systemically administering to a patient a compound containing gallium. The extracellular microorganisms targeted by the present methods include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE), E. coli O157:H7, fluoroquinolone-resistant Salmonella typhi, and the like. Furthermore, in the present methods, gallium compounds can be co-administered with one or more conventional antimicrobial agents to treat infectious diseases with reduced risks of creating multi-drug resistant pathogens. The methods of the present invention is also applicable to those microorganisms, such as ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, complete eradication of which so far has been difficult to achieve.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
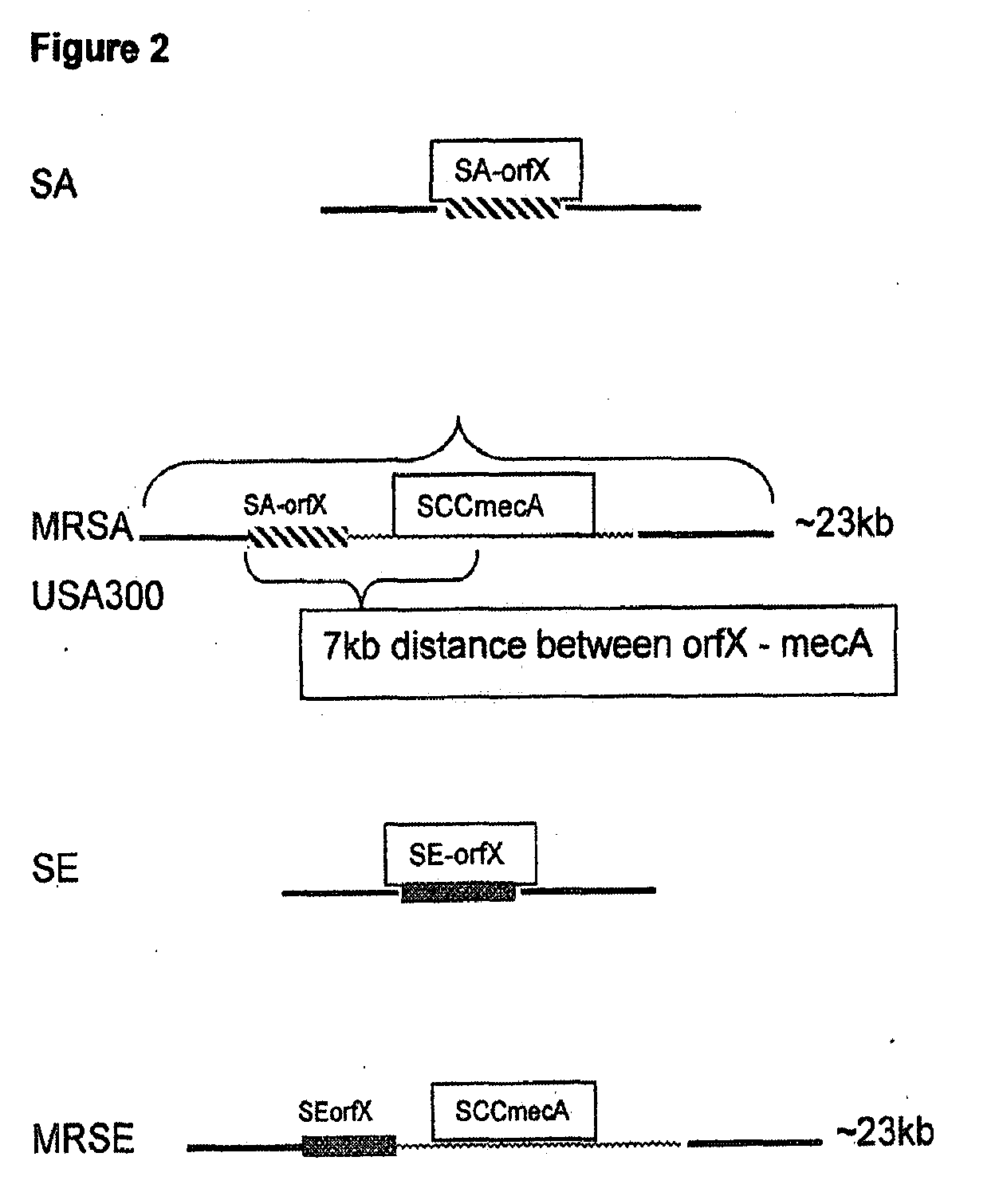
Methods and Compositions Including Diagnostic Kits For The Detection In Samples Of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
InactiveUS20120077684A1Cost-effective management and controlMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSCCmecStaphylococcus saprophyticus
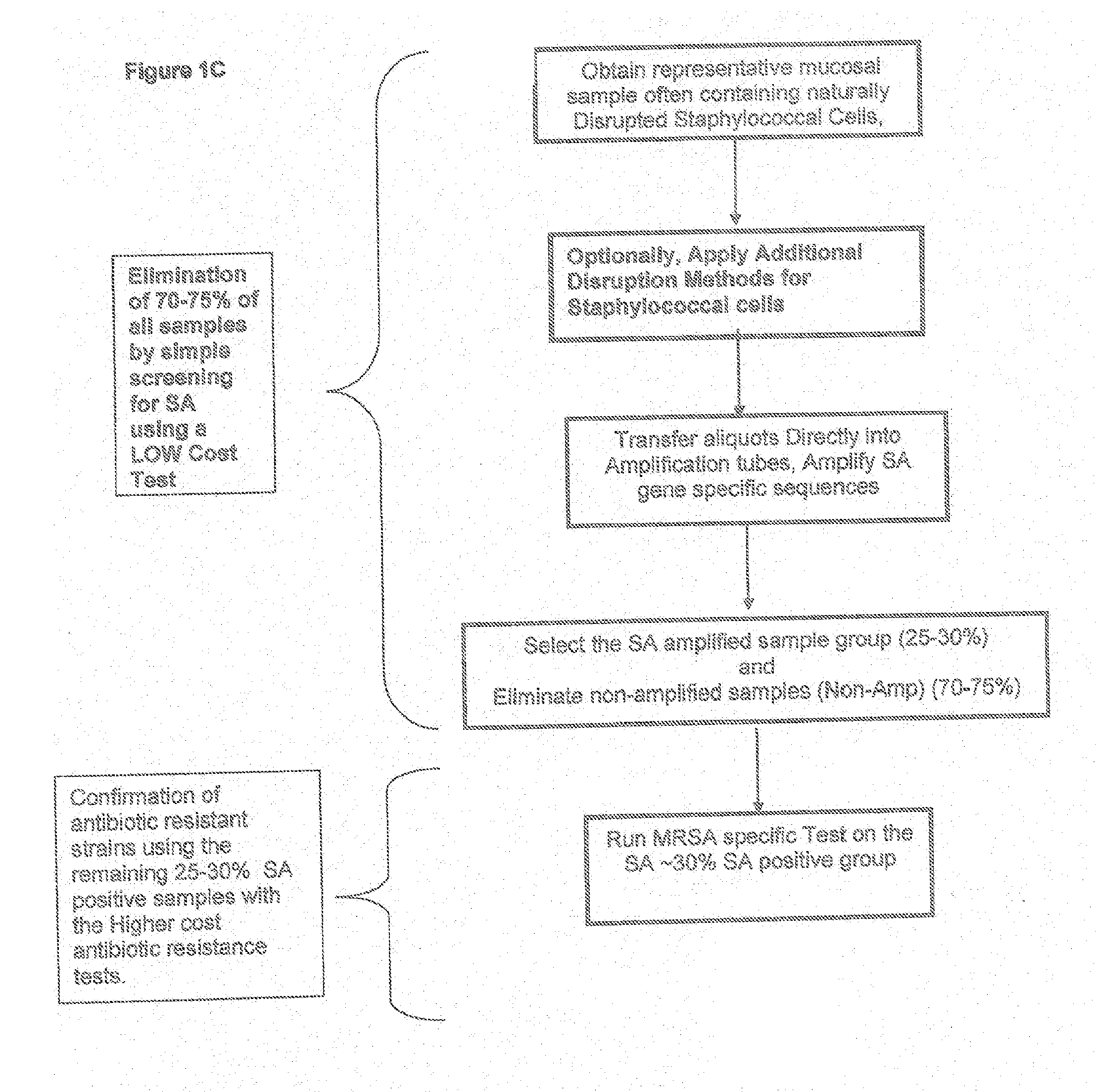
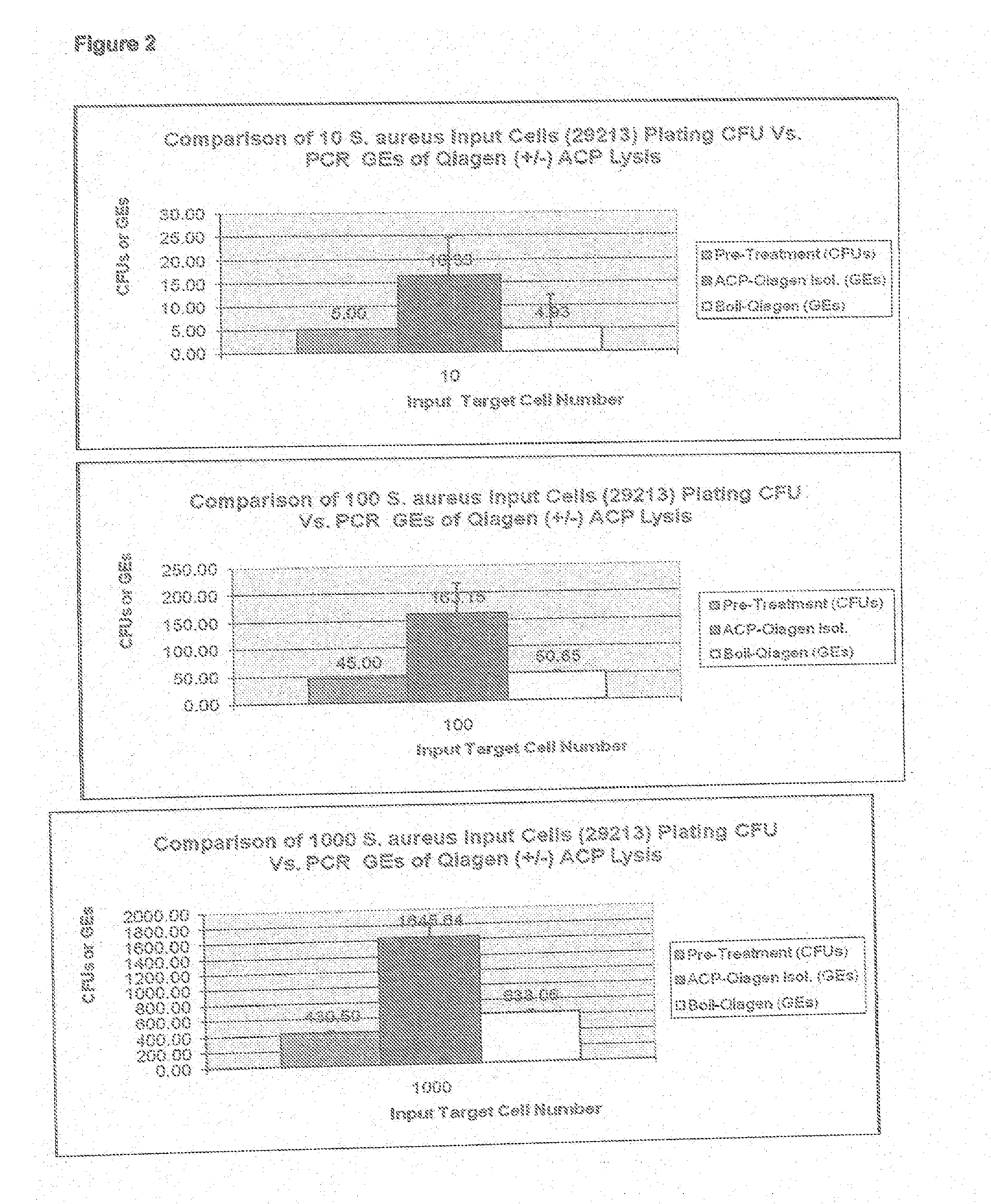
The present invention provides methods, compositions and diagnostic kits for the detection of Staphylococcus Aureus (SA) and antibiotic resistant forms and variants thereof, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA), mupirocin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (mupSA), and the like, in a sample population. The invention preferably involves the improvements of bacterial sampling by means of SA enrichment, followed by SA cell disruption and amplification procedures incorporating the use of multiplex assays for SA specific genes, such as mecA and coagulase negative Staphylococci (CONS) specific genes such as tufA, for SA identification and identification of its known species. This provides means for controlling for the thirty or more known CONS species in assessing SA samples, especially those CONS species that may carry antibiotic resistance genes, such as SCCmec.
Owner:ZEUS SCI
Healthcare facility disinfecting system
ActiveUS20120100037A1Effective but inexpensive systemReduce the amount requiredLavatory sanitoryDeodrantsEscherichia coliClostridium difficile toxin B
A system and process for disinfecting rooms such as health care facility rooms with an oxygen / ozone mixture is described, which is effective to combat “superbugs” such as Clostridium difficile (C. difficile); E. coli; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA); and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE). In preferred embodiments, hydrogen peroxide is additionally used. The system and process is effective to destroy bacteria deposited on surfaces as biofilm, and, accompanied by physical agitation such as jet nozzle outlets, is effective to disinfect carpet, drapery and similar absorbent and porous surfaces.
Owner:DD STEROZONE LLC +1
Healthcare facility disinfecting system
ActiveUS20140037499A1Safe and effective but inexpensive systemReduce the amount requiredLavatory sanitoryDeodrantsEscherichia coliClostridium difficile toxin B
A system and process for disinfecting rooms such as health care facility rooms with an oxygen / ozone mixture is described, which is effective to combat “superbugs” such as Clostridium difficile (C. difficile); E. coli; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA); and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE). In preferred embodiments, hydrogen peroxide is additionally used. The system and process is effective to destroy bacteria deposited on surfaces as biofilm, and, accompanied by physical agitation such as jet nozzle outlets, is effective to disinfect carpet, drapery and similar absorbent and porous surfaces.
Owner:STERILIZ3 CANADA INC +1
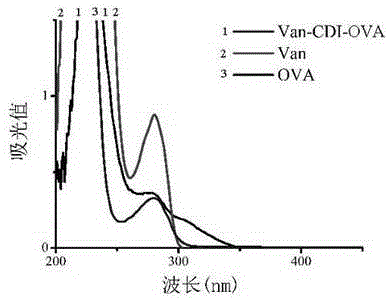
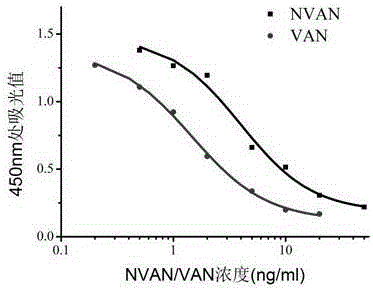
Vancomycin-resistant monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain and application thereof
ActiveCN105200013AHigh detection sensitivityImmunoglobulins against bacteriaTissue cultureIc50 valuesMicroorganism
The invention relates to a vancomycin-resistant monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain and application thereof, and belongs to the field of food safety immunodetection. The vancomycin-resistant monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell strain 2A1 is preserved in the General Microbiological Center of China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the preservation number of CGMCC No.10869; the vancomycin-resistant monoclonal antibody is produced by the hybridoma cell strain 2A1 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.10869 through secretion. The monoclonal antibody produced by the hybridoma cell strain through secretion has an IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration) value of 1.45 ng / mL to vancomycin, has an IC50 value of 3.98 ng / mL to demethylvancomycin, and further can be used for simultaneous detection of vancomycin and demethylvancomycin in food.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Methods And Compositions Including Diagnostic Kits For The Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus
InactiveUS20110111399A1Cost-effectiveFaster and methodMicrobiological testing/measurementStaphylococcus cohniiContamination
Methods and compositions, including diagnostic kits, for the detection of Staphylococcus Aureus (SA) and clinically important antibiotic resistant forms thereof, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA), mupirocin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (mupSA), and the like, from individuals in a sample population are disclosed Also disclosed are cost effective methods and kits for bacterial sampling and analysis via inherent and expeditious SA cell disruption methods followed by Direct PCR, circumventing the need, expense and contamination πsks associated with DNA isolation methods These improved methods in conjunction with SA prevalence analysis are applied so as to eliminate the approximately 70% of samples in the human population which do not carry SA (SA negative), followed by a second more costly test for antibiotic resistant forms thereof, such as amplification to confirm for presence of MRSA or other target disease
Owner:OHARA SHAWN MARK +1
Method for detecting the presence or absence of pathogenic Staphylococci in a test sample, including test mixture with micro particles
InactiveUS8546103B2Favorable source of coagulase substrateImprove performance consistencyMicrobiological testing/measurementStaphylococcus cohniiFirst generation
Owner:PILOTS POINT LLC
Mediucm for detecting Van A and Van B vancomycin-resistant entercocci and method of using the same
InactiveUS7364874B2Reduce detectionEasy to useBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementSodium lactateMicroorganism
Owner:TOKYO WOMENS MEDICAL UNIV
Mediucm for detecting vana and vanb vancomycin-resistant enterocci and method of using the same
Van A and Van B vancomycin resistant enterococci detection media as well as a method of selectively detecting Van A and Van B vancomycin resistant enterococci clinically important in vancomycin resistant enterococci from testing microorganisms or specimens using the media. The media for selectively detecting Van A and Van B VRE from testing microorganisms and specimens are media where enterococci can grow where vancomycin, D-cycloserine and D-lactate are added. Preferably 32-256 mug / ml of vancomycin, 1-64 mug / ml of D-cycloserine, and 0.025-0.8 mol / l of sodium lactate are added to culture medium where enterococci can grow.
Owner:TOKYO WOMENS MEDICAL UNIV
Vancomycin-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and application thereof
ActiveCN107435034ABacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementVancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus aureus bacteria
The invention relates to a vancomycin-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of biomedical technology. The above strain is Staphylococcus aureus and is named as vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus 0630 (VRSA); and the strain is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center (CDMCC) with the preservation number of GDMCC NO.60082. The vancomycin-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus can be used for screening medicines, and has a very good application prospect.
Owner:中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九二0医院
Method of re-sensitizing vancomycin resistant bacteria which selectively cleave a cell wall depsipeptide
The present invention relates to pyrrolidine compounds of the general structure: where n is an integer 1-6 and R is hydrogen or a C1 to C6 straight chain or branched alkyl group, and wherein when n=1, R=CH3 or H, useful for re-sensitizing vancomycin resistant Gram-positive bacteria in which resistance results from the conversion of an amide bond to an ester bond on the cell wall peptide precursors of the bacteria.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Method and reagents for detecting the presence or absence of staphylococcus aureus in a test sample
InactiveUS20110027823A1Small amountFavorable source of coagulase substrateMicrobiological testing/measurementStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
A presence / absence test for Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) involves placing a first generation test sample in a solution that will clot in the presence of S. aureus. The solution contains components that will selectively grow S. aureus and also contains clotting factors that will react with S. aureus, if S. aureus is present in the sample, to clot the solution. Examples of specimen samples that can be tested include nasal swabs and lesion swabs, among others. The test can also be modified to detect the presence or absence of methicillin resistant S. Aureus (MRSA). The addition of micro particles having a size in the range of about 0.1 micron to about 1.0 mm provides localities where the bacteria agglomerate, thereby significantly decreasing the clotting time, and providing a significantly stronger clot. The micro particles can be used in other bacteria tests to accelerate the production of an end result. Such other tests can include a vancomycin-resistant enterococcus test; a Group B Streptococcus test; a test for hemolytic E. coli; and a test for Listeria monocytogenes, to name a few. These tests are all performed in a liquid broth-type reagent mixture and do not necessarily involve clotting of the broth.
Owner:PILOTS POINT LLC
Anti-infective hydroxy-phenyl-benzoates and methods of use
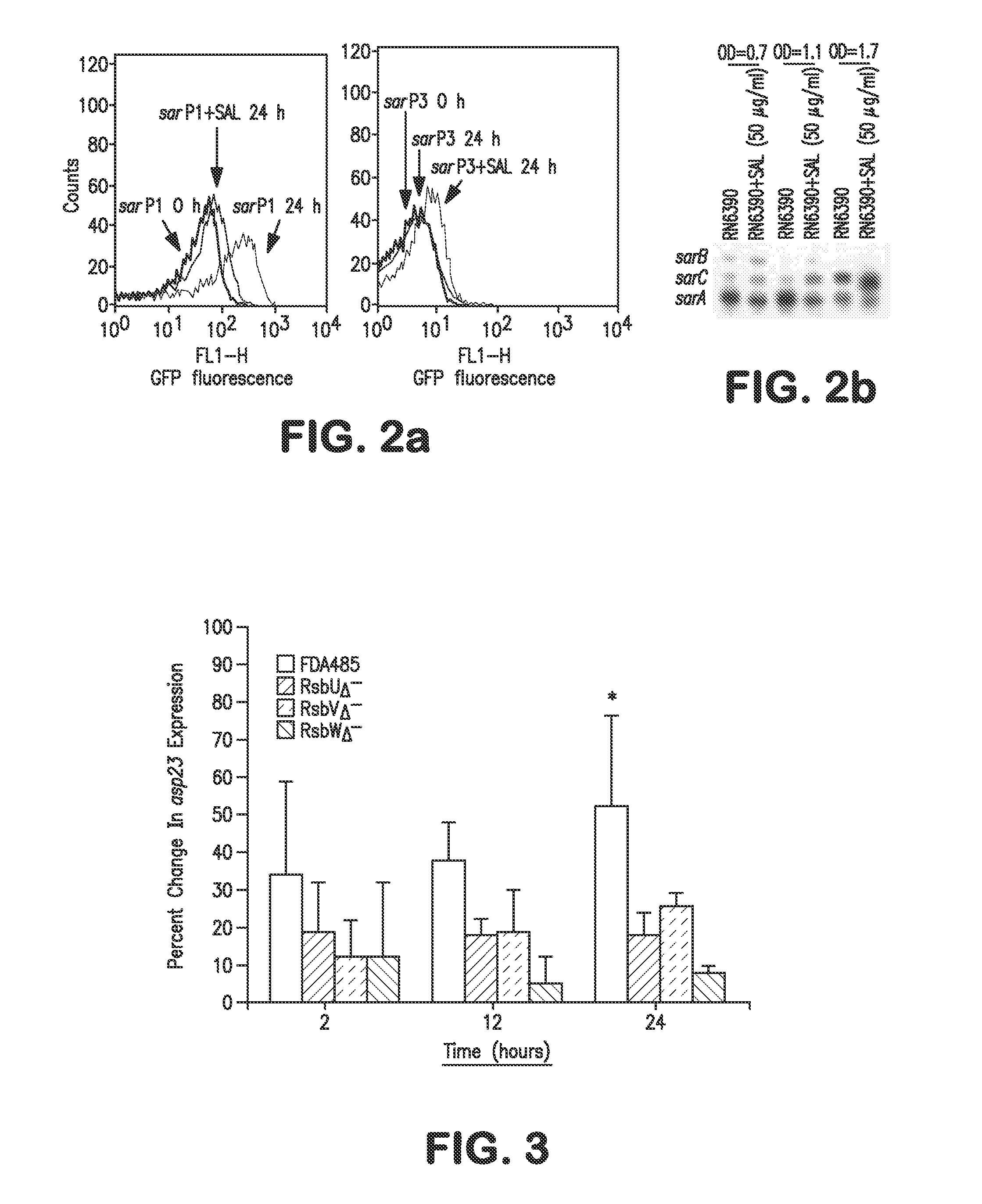
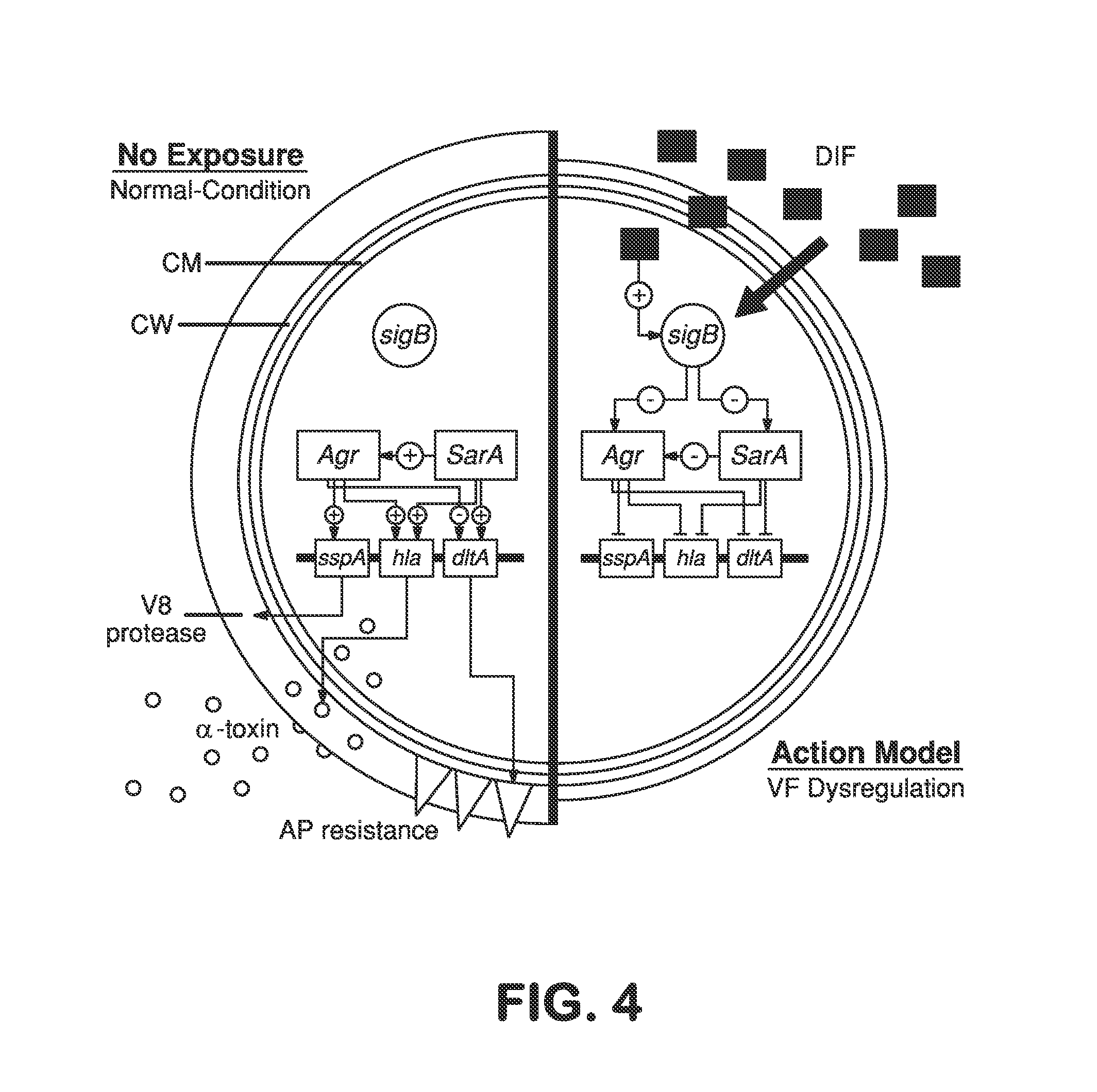
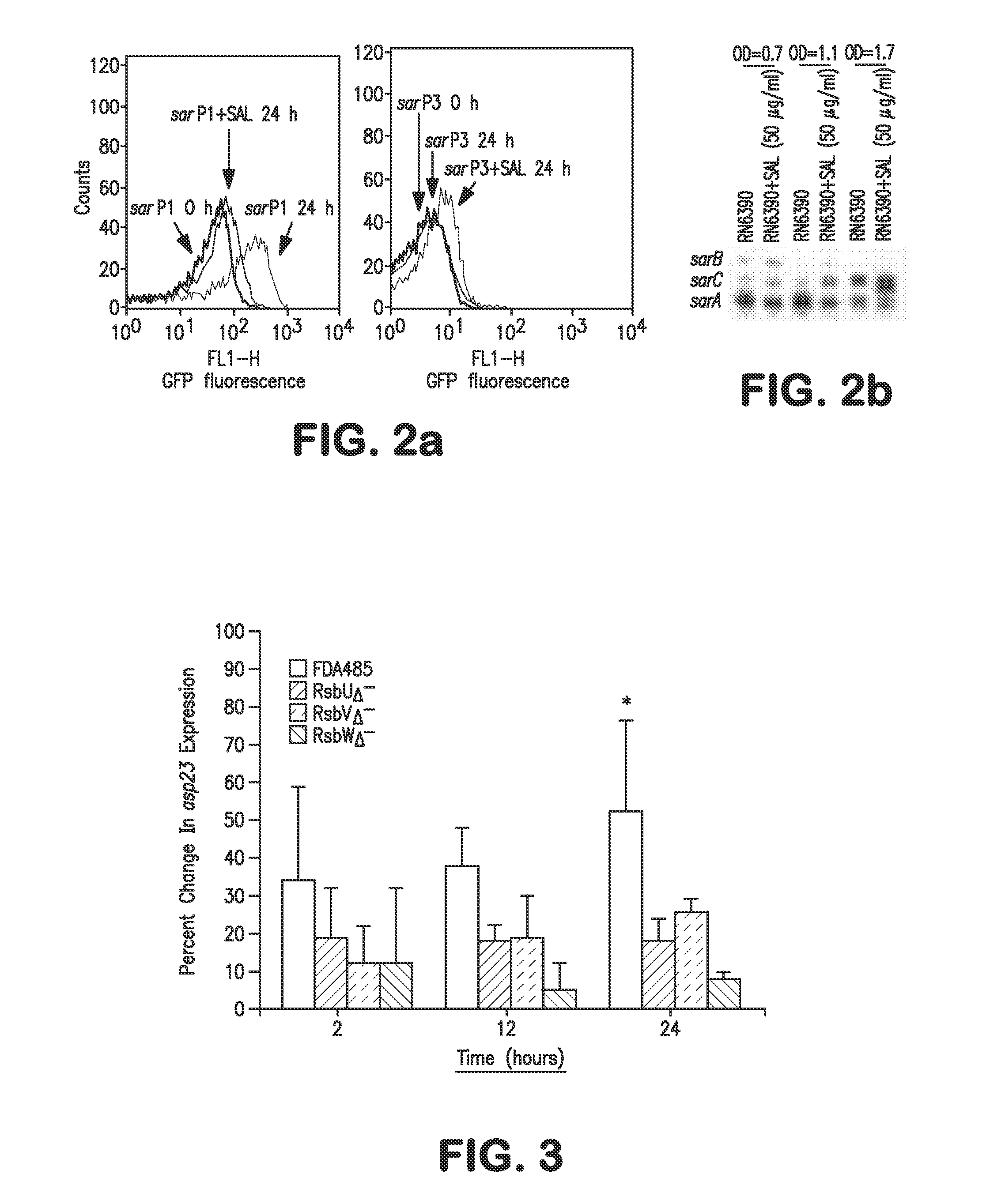
The invention provides a method for preventing or treating a disease caused by an extracellular microorganism, said method comprising systemically administering to a subject in need thereof a prophylactically or therapeutically effective amount of a salicylic acid (SAL) or a SAL analogue. The extracellular microorganism can be of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus, for example, Staphylococcus aureus. The extracellular microorganism can be a strain that is resistant to at least one antibiotic. The strain can be selected from the group consisting of methycillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA) and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA). The invention also provides a method for preventing or treating an infectious disease caused by of methycillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA) or vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA), comprising systemically coadministering in a synergistic combination to a subject in need thereof prophylactically or therapeutically effective amounts, individually or collectively, of a salicylic acid (SAL) or a SAL analogue and at least one additional antimicrobial agent, for example, vancomycin and / or linezolid.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Methods for preventing or treating infectious diseases caused by extracellular microorganisms, including antimicrobial-resistant strains thereof, using gallium compounds
InactiveUS8895077B2Reduce in quantityGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsHeavy metal active ingredientsBacteroidesSalmonella wien
The present invention relates to methods for preventing or treating infectious diseases caused by extracellular microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, by systemically administering to a patient a compound containing gallium. The extracellular microorganisms targeted by the present methods include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE), E. coli O157:H7, fluoroquinolone-resistant Salmonella typhi, and the like. Furthermore, in the present methods, gallium compounds can be co-administered with one or more conventional antimicrobial agents to treat infectious diseases with reduced risks of creating multi-drug resistant pathogens. The methods of the present invention is also applicable to those microorganisms, such as ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, complete eradication of which so far has been difficult to achieve.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Anti-infective hydroxy-phenyl-benzoates and methods of use
The invention provides a method for preventing or treating a disease caused by an extracellular microorganism, said method comprising systemically administering to a subject in need thereof a prophylactically or therapeutically effective amount of a salicylic acid (SAL) or a SAL analogue. The extracellular microorganism can be of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus, for example, Staphylococcus aureus. The extracellular microorganism can be a strain that is resistant to at least one antibiotic. The strain can be selected from the group consisting of methycillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA) and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA). The invention also provides a method for preventing or treating an infectious disease caused by of methycillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA) or vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA), comprising systemically co-administering in a synergistic combination to a subject in need thereof prophylactically or therapeutically effective amounts, individually or collectively, of a salicylic acid (SAL) or a SAL analogue and at least one additional antimicrobial agent, for example, vancomycin and / or linezolid.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Anti-infective hydroxy-phenyl-benzoates and methods of use
The invention provides a method for preventing or treating a disease caused by an extracellular microorganism, said method comprising systemically administering to a subject in need thereof a prophylactically or therapeutically effective amount of a salicylic acid (SAL) or a SAL analogue. The extracellular microorganism can be of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus, for example, Staphylococcus aureus. The extracellular microorganism can be a strain that is resistant to at least one antibiotic. The strain can be selected from the group consisting of methycillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA) and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA). The invention also provides a method for preventing or treating an infectious disease caused by of methycillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA) or vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA), comprising systemically coadministering in a synergistic combination to a subject in need thereof prophylactically or therapeutically effective amounts, individually or collectively, of a salicylic acid (SAL) or a SAL analogue and at least one additional antimicrobial agent, for example, vancomycin and / or linezolid.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Pharmaceutical composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
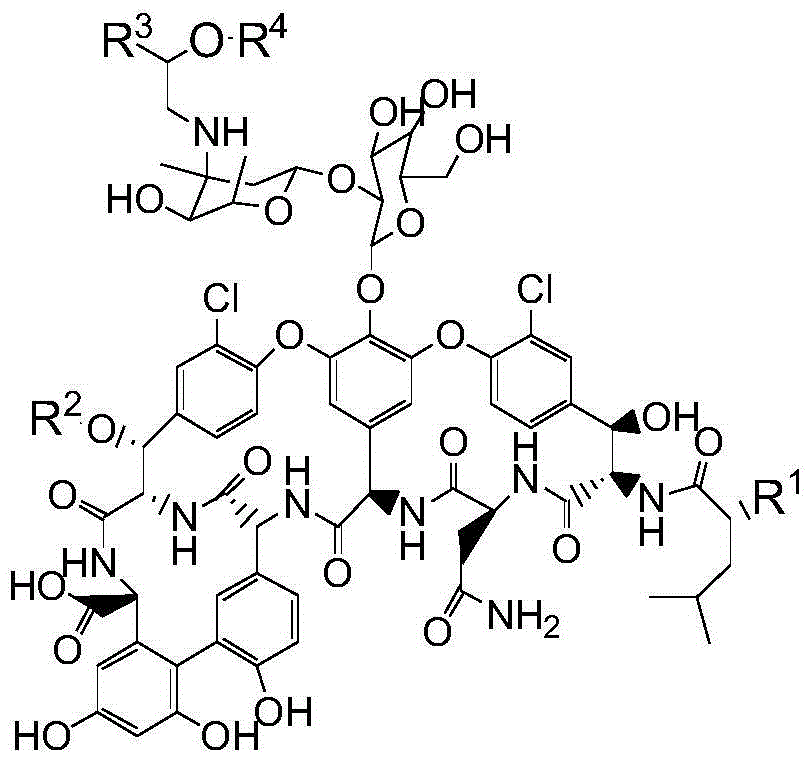
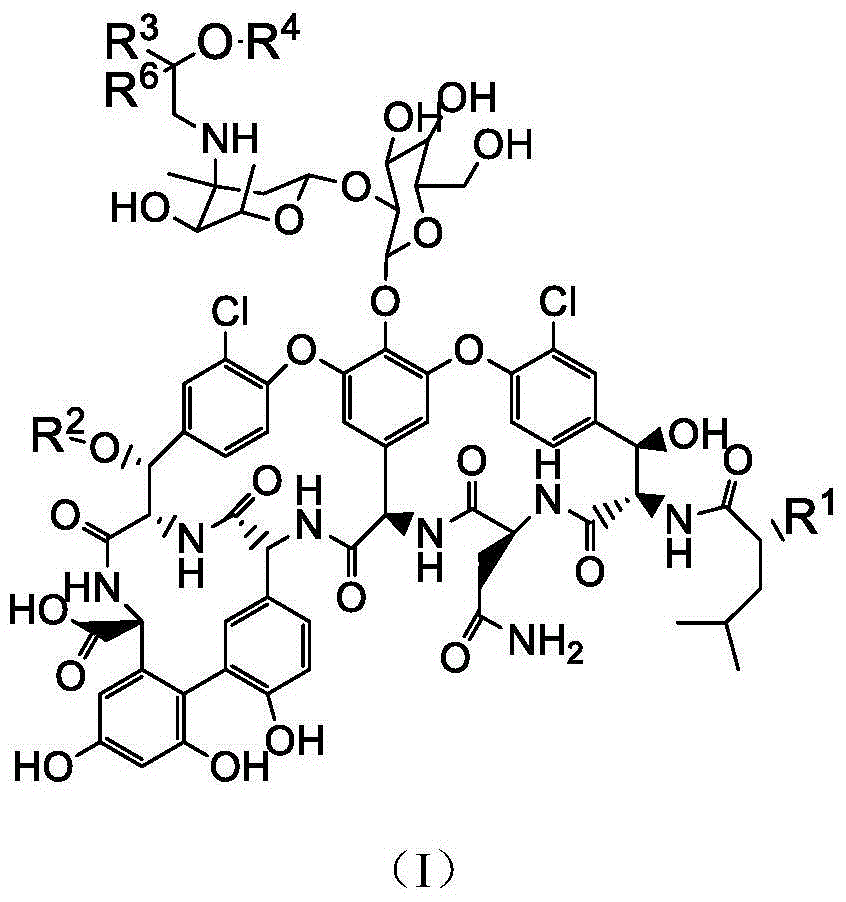
InactiveCN106673989AGive full play to medicinal valueGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseMedicine
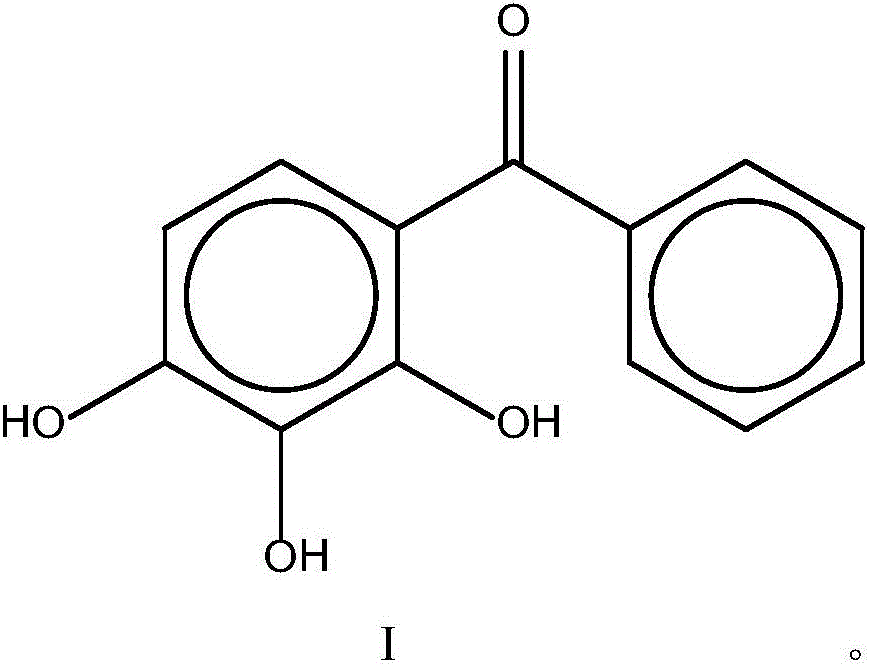
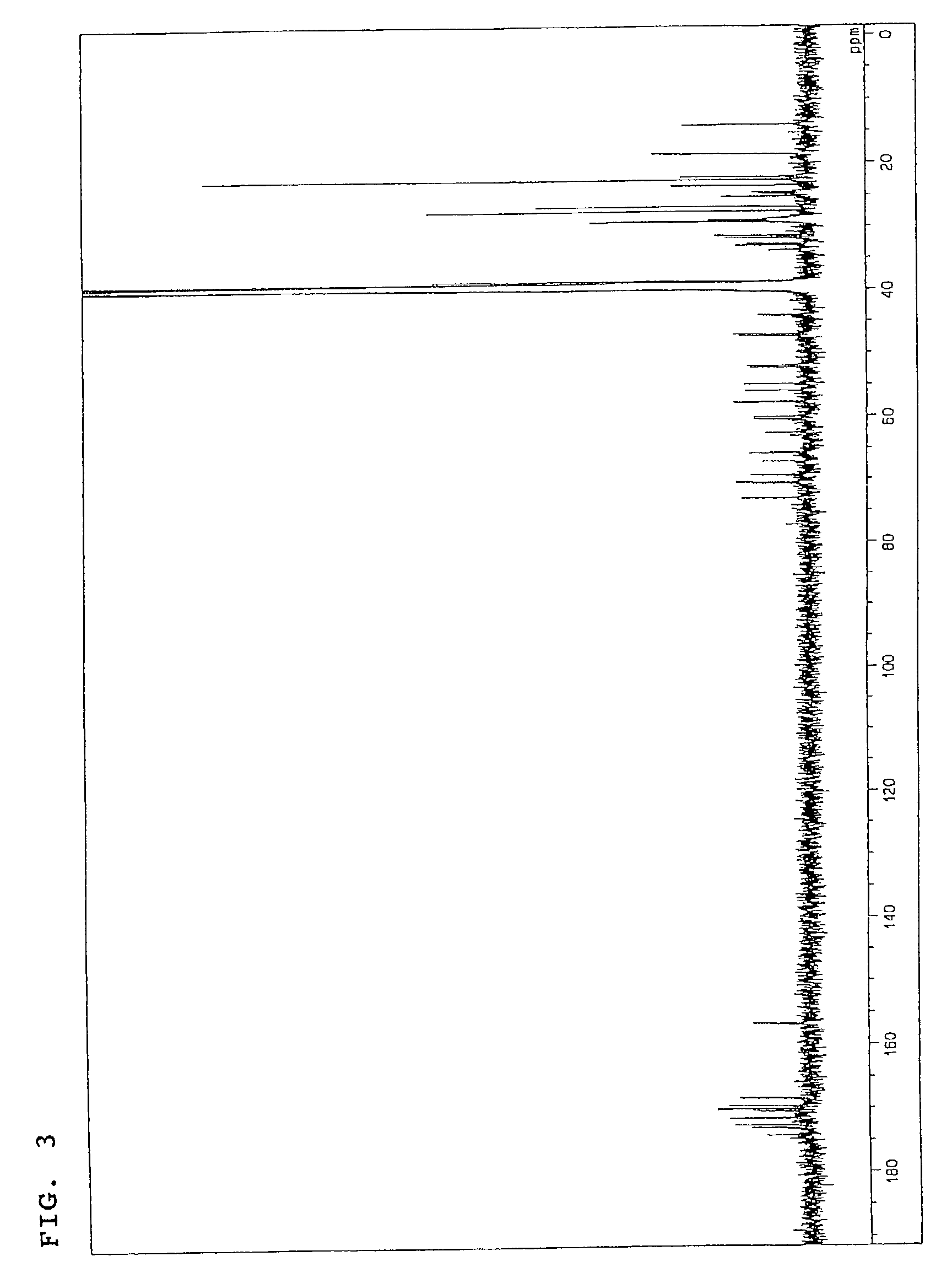
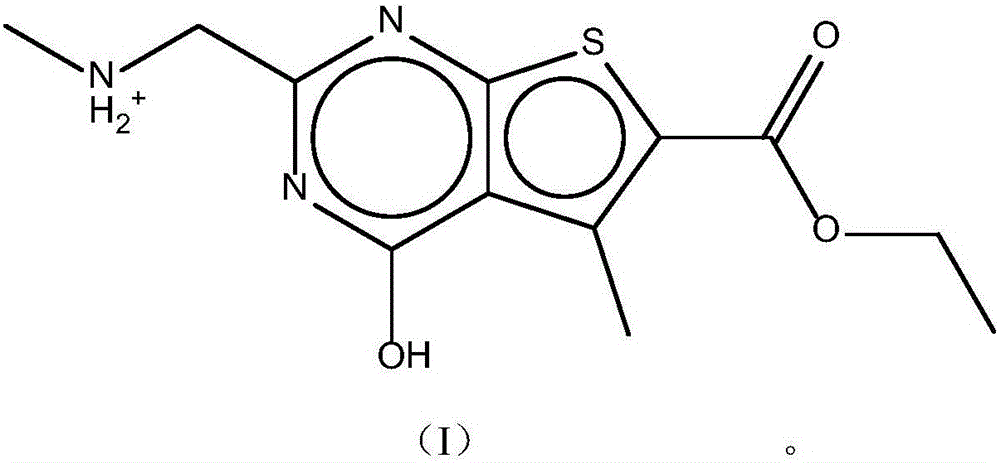
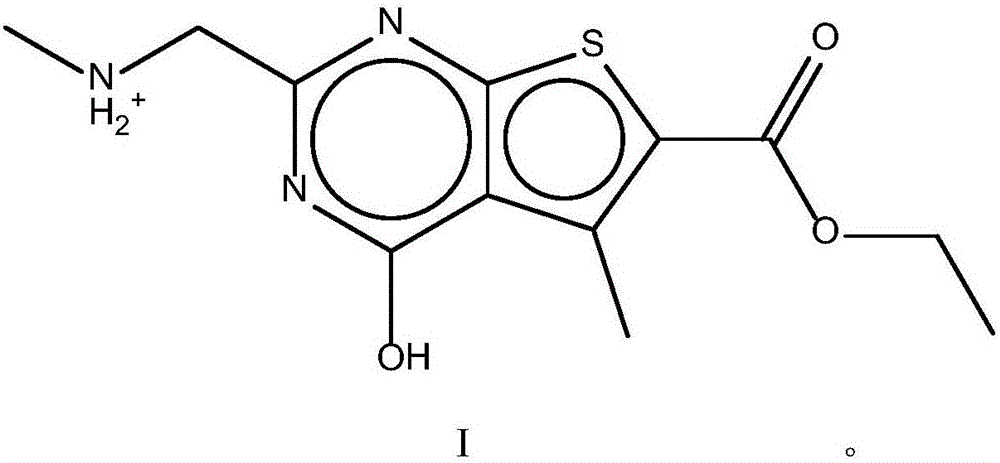
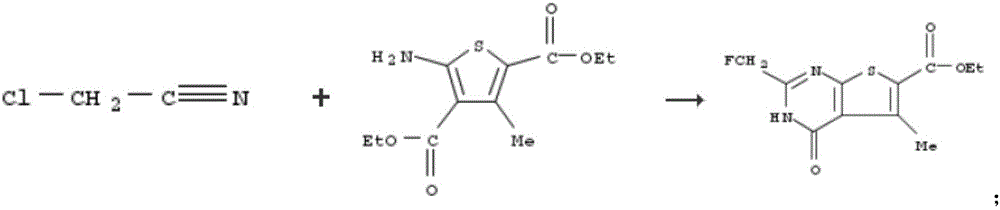
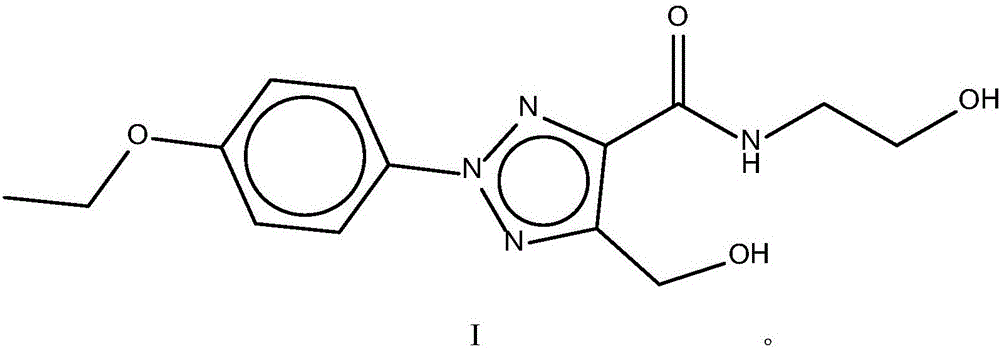
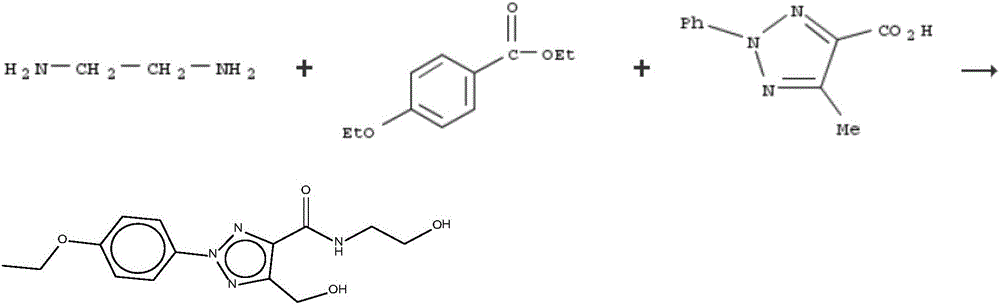
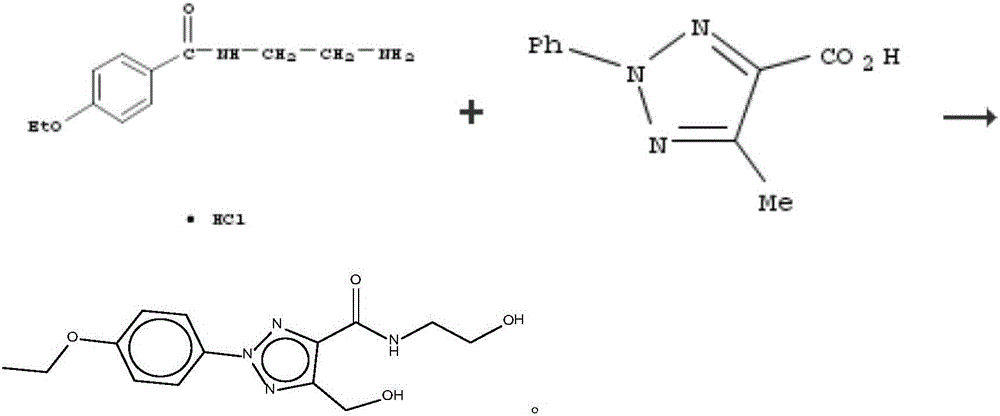
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition and application thereof. The pharmaceutical composition is a compound expressed in the formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier thereof. The formula (I) is as shown in description. The pharmaceutical composition can be used for preparing antibacterial medicines and can be especially used for preparing medicines for preventing or treating diseases infected by vancomycin-resistant bacteria. Experiment data shows that the compound can be used for effectively inhibiting the growth of vancomycin-resistant enterococcus when the compound is combined with glycopeptides antibacterial medicines.
Owner:XIANGTAN ZHILIAN TECH MATASTASIS PROMOTE CO LTD
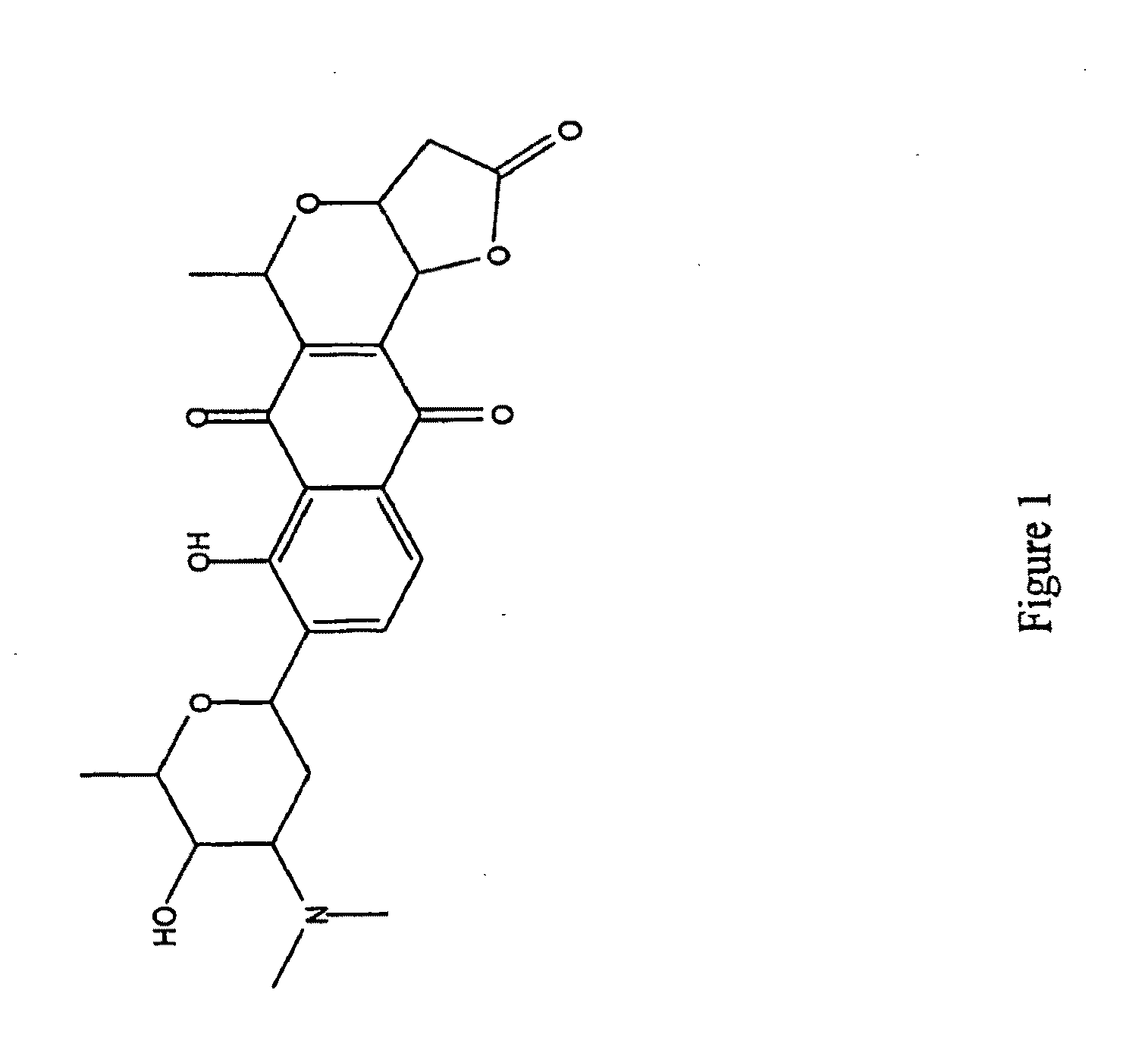
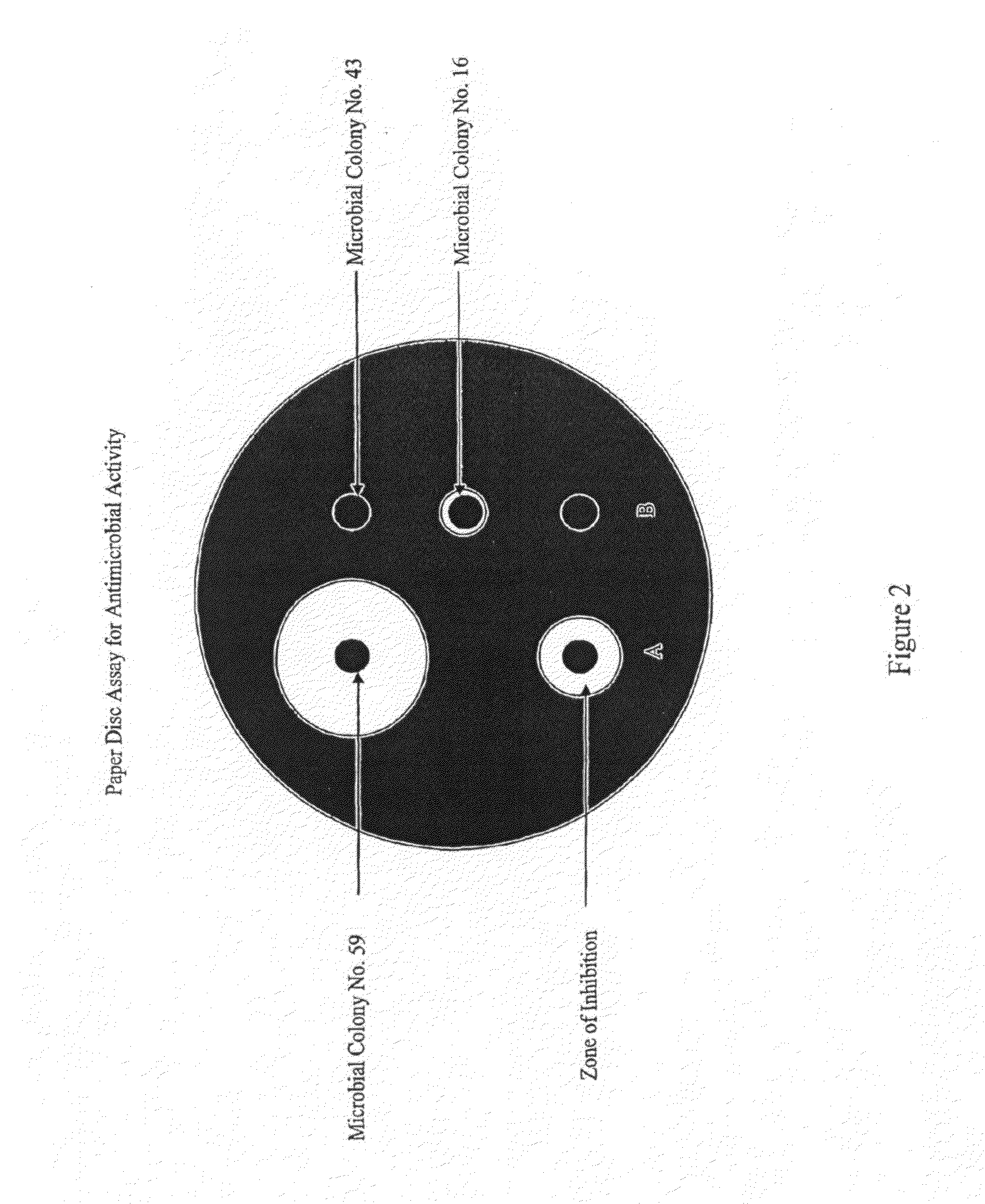
Streptomyces-derived antimicrobial compound and method of using same against antibiotic-resistant bacteria
InactiveUS20100227918A1Useful in treatmentEffective treatmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideMethicillin resistanceFermentation
The present invention relates to a novel antimicrobial compound of lactoquinomycin that is highly effective against many antibiotic-resistant gram-positive bacteria; namely, methicillin-resistant and vancomycin-resistance Staphylococcus aureus, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecilis and Mycobacteria. The present invention also relates to a fermentation process of culturing a Streptomyces strain to prepare the antimicrobial compound and its use in killing the antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Owner:TARO PHARMA INDS
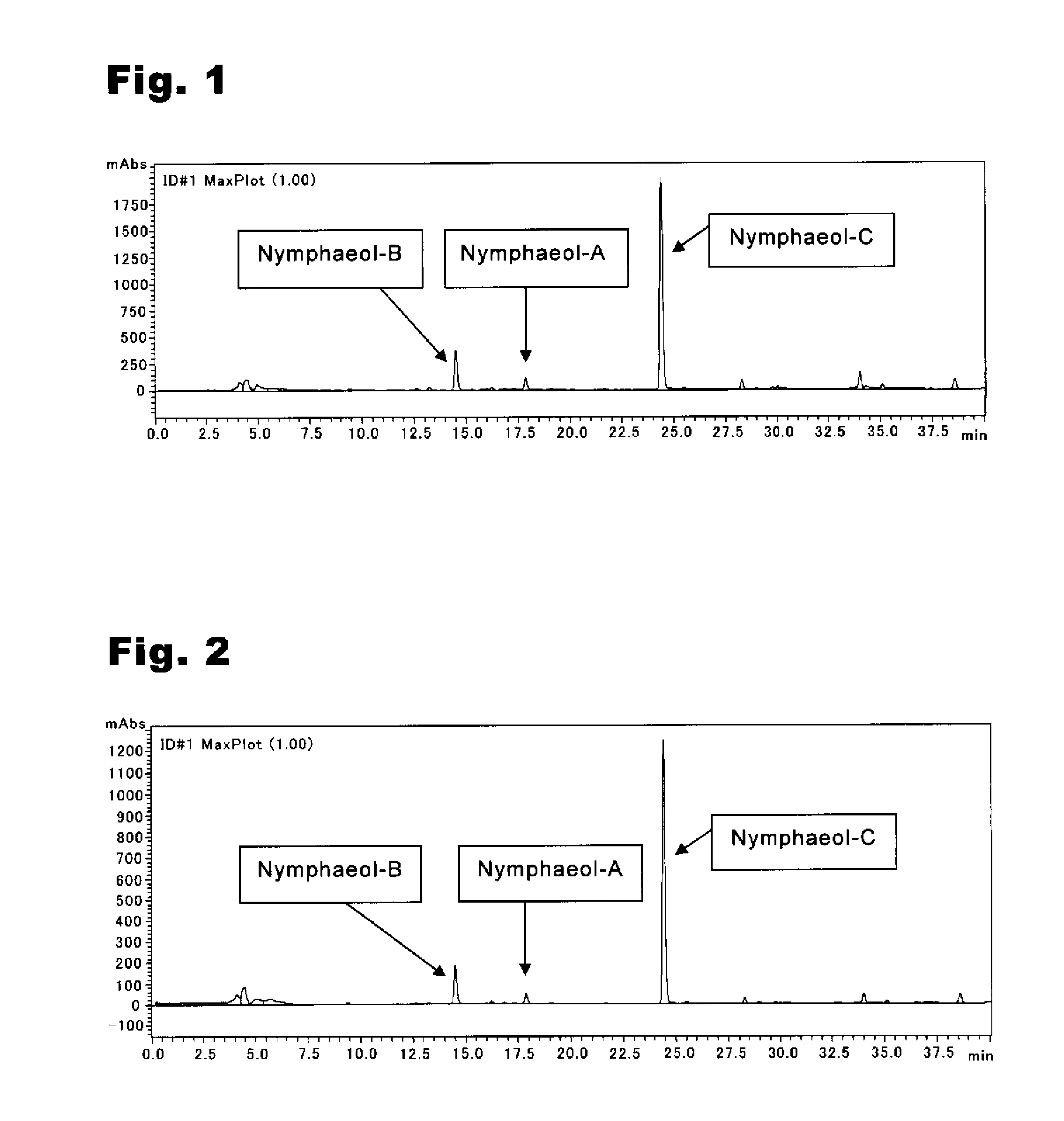
Anti-methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus agent and Anti-vancomycin-resistant enterococcus agent
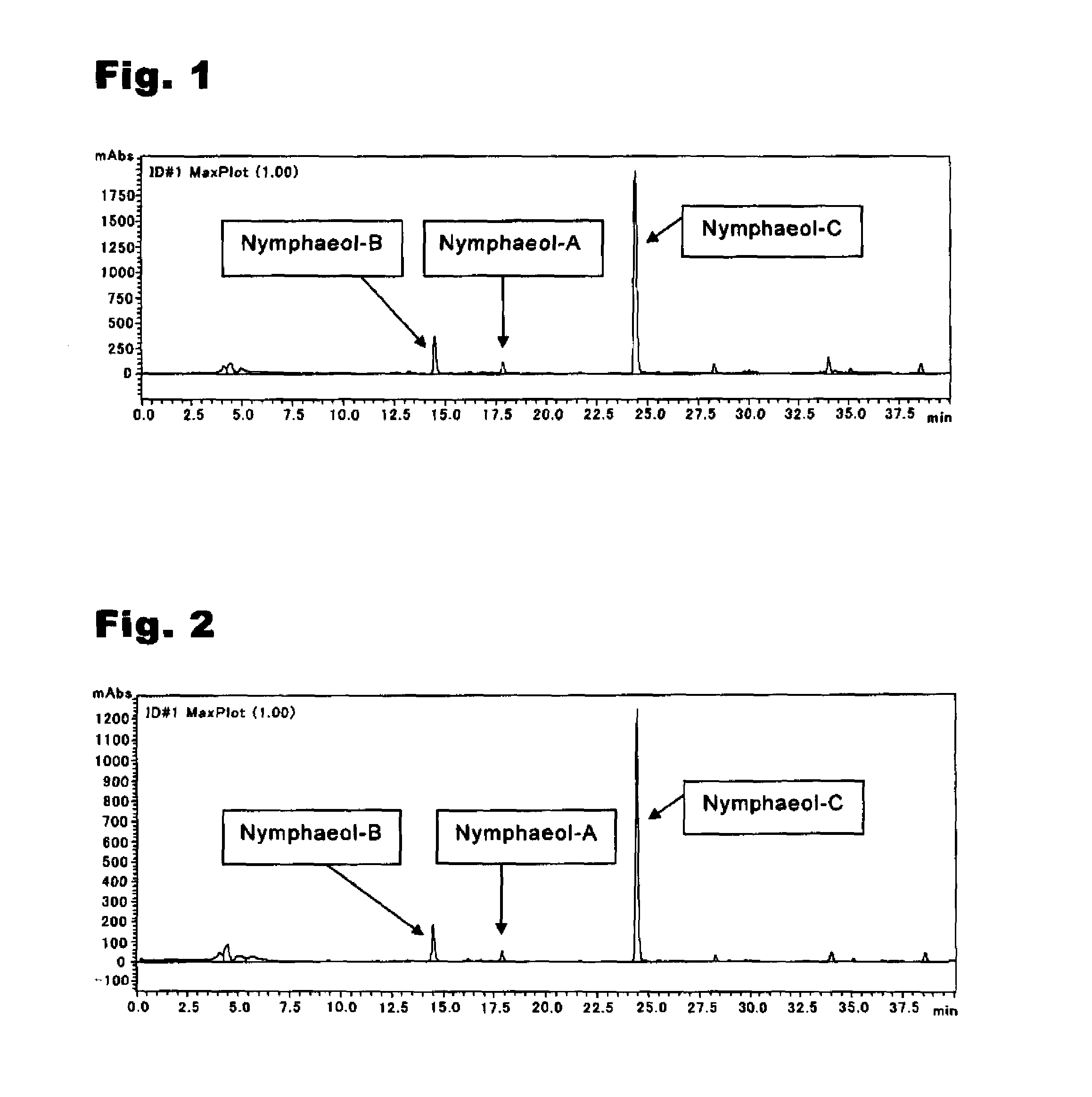
An anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus agent (anti-MRSA agent) and an anti-vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus agent (anti-VRE agent) contain as an active ingredient an Oobagi extract extracted from Oobagi with an extraction solvent including at least an organic solvent. Alternatively, the anti-MRSA agent and the anti-VRE agent contain as an active ingredient at least one selected from nymphaeol-A, nymphaeol-B, and nymphaeol-C.
Owner:POKKA SAPPORO FOOD & BEVERAGE
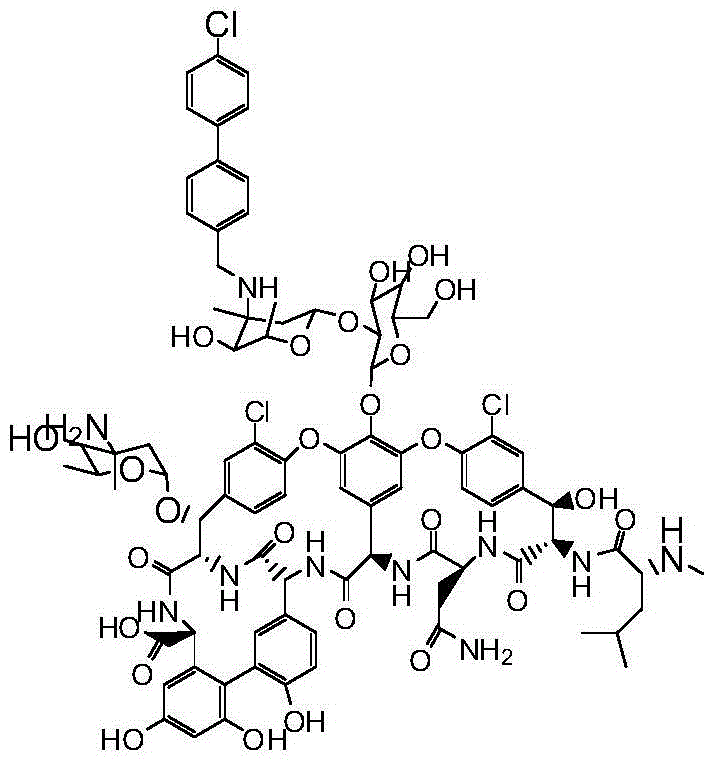
Vancomycin derivatives and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN105985412ANo reduction in biological activityImprove biological activityAntibacterial agentsSaccharide peptide ingredientsChemical synthesisGram-positive bacterium
The invention discloses a series of vancomycin derivatives as shown in a formula (I). The series of compounds can be used for treating infection of gram-positive bacteria or vancomycin-resistant bacteria and can be prepared from vancomycin through a chemical synthesis method. (Please see the description for the formula (I).).
Owner:ACESYS PHARMATECH LTD
Antibiotics, tripropeptins and process for producing the same
By culturing Lysobacter sp. BMK333-48F3 (deposit number of FERM BP-7477), an antibiotic, tripropeptin Z, tripropeptin A, tripropeptin B, tripropeptin C or tripropeptin D represented by the general formula (I):wherein R is 7-methyl-octyl group, 8-methyl-nonyl group, 9-methyl-dodecyl group, 10-methyl-undecyl group or 11-methyl-dodecyl group, is obtained as antibiotics having excellent antibacterial activities against bacteria and having a novel molecular structure. These tripropeptins each have an excellent antibacterial activity against various bacteria and drug-resistant strains thereof, such as methicillin-resistant strains and vancomycin-resistant strains.
Owner:ZH BISEIBUTSU KAGAKU KENYKU KAI
Pharmaceutical composition, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106674249AGive full play to medicinal valueGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMedicineAntimicrobial drug
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition and application thereof. The pharmaceutical composition contains compounds disclosed as chemical formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The pharmaceutical composition disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing antibacterial drugs, and especially preparing drugs for preventing or treating vancomycin-resistant bacterial infection diseases. The experimental data indicates that the compounds can effectively inhibit growth of vancomycin-resistant enterococcus when being combined with glycopeptide antibacterial drugs.
Owner:XIANGTAN ZHILIAN TECH MATASTASIS PROMOTE CO LTD
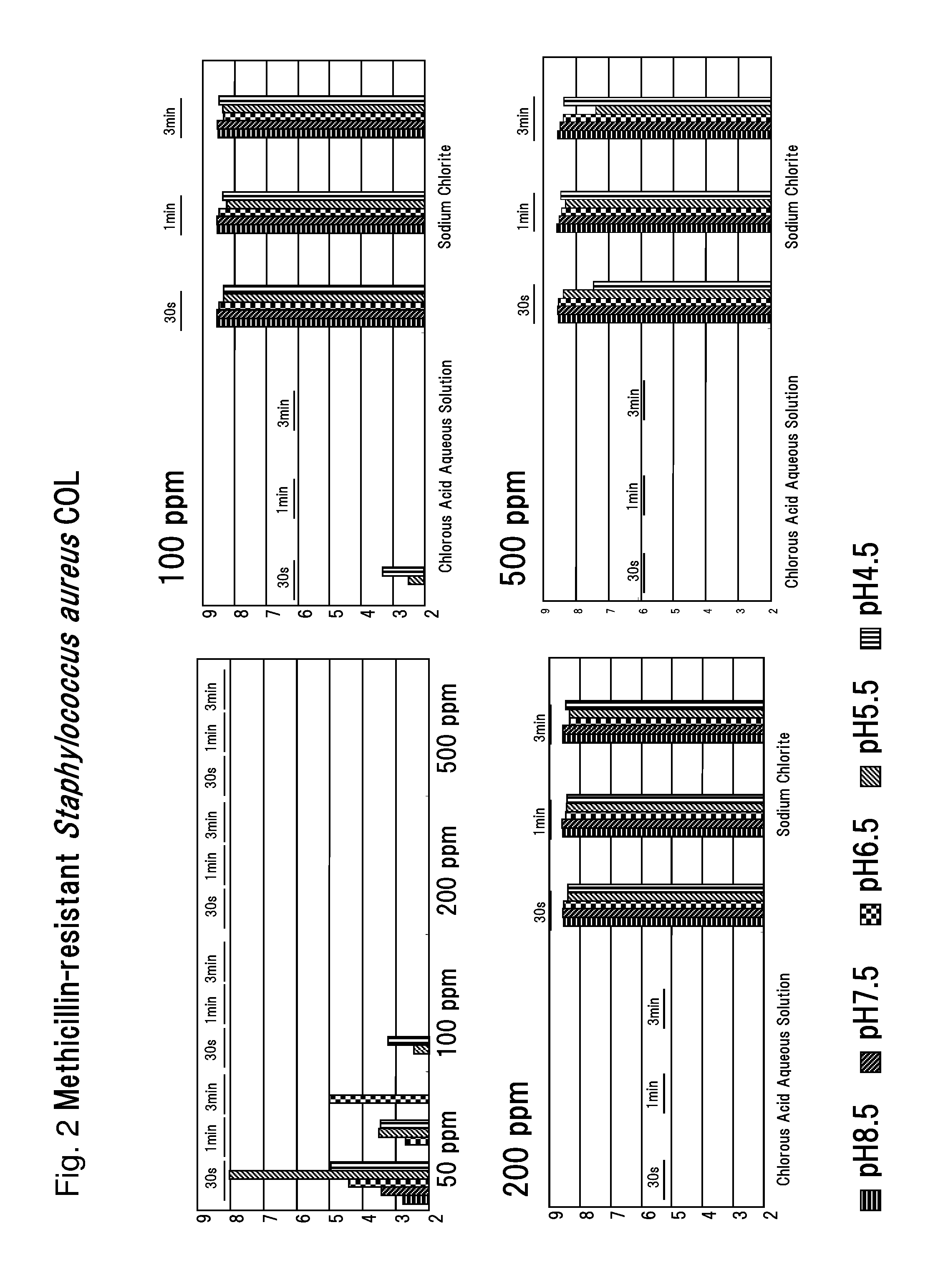
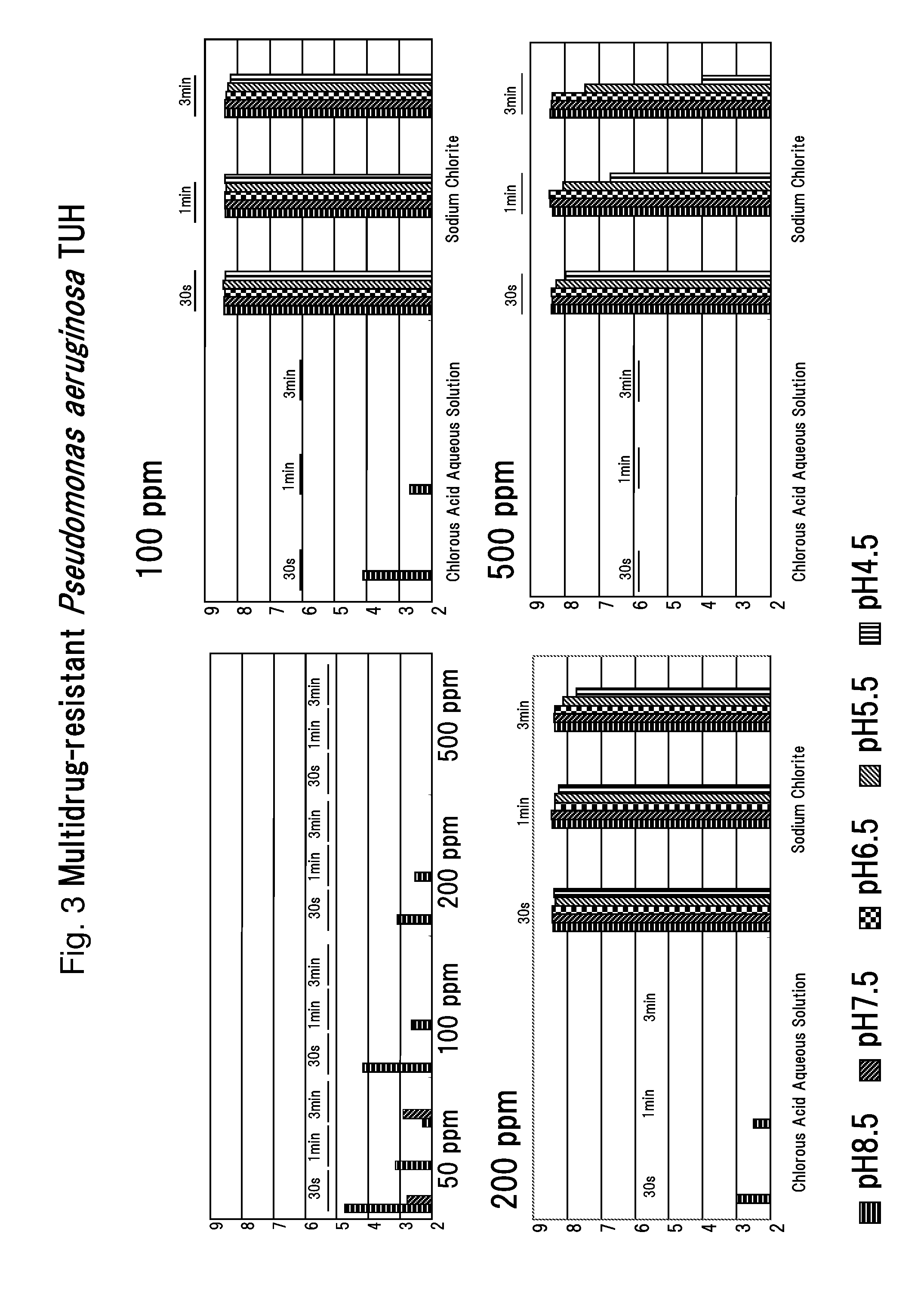
Drug-resistant microbe and variant microbe disinfectant containing chlorous acid aqueous solution
InactiveUS20160106106A1Easy to useSuppress generationBiocideCosmetic preparationsSalmonella entericaFood additive
The present invention provides microbe disinfectants, providing: Drug-resistant microbe disinfectants comprising a chlorous acid aqueous solution for inactivating microbes selected from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus; and microbe disinfectants, which are made with acidity when applied to gram-negative microbes and with alkalinity when applied to gram-positive microbes. The microbes comprise at least one species of microbes selected from the group consisting of E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, microbes of genus Bacillus, microbes of genus Paenibacillus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus, Salmonella enterica, and periodontal disease microbes. The present invention is usable as a microbe disinfectant that is safe to human body and easy to handle as a microbe disinfectant for pretreatment in food processing and produces chlorous acid that generates little chlorine dioxide. The microbe disinfectant comprising a chlorous acid aqueous solution of the present invention can be utilized as a sterilizing agent, food additive, antiseptic, quasi-drug, medicine, etc.
Owner:HONBU SANKEI
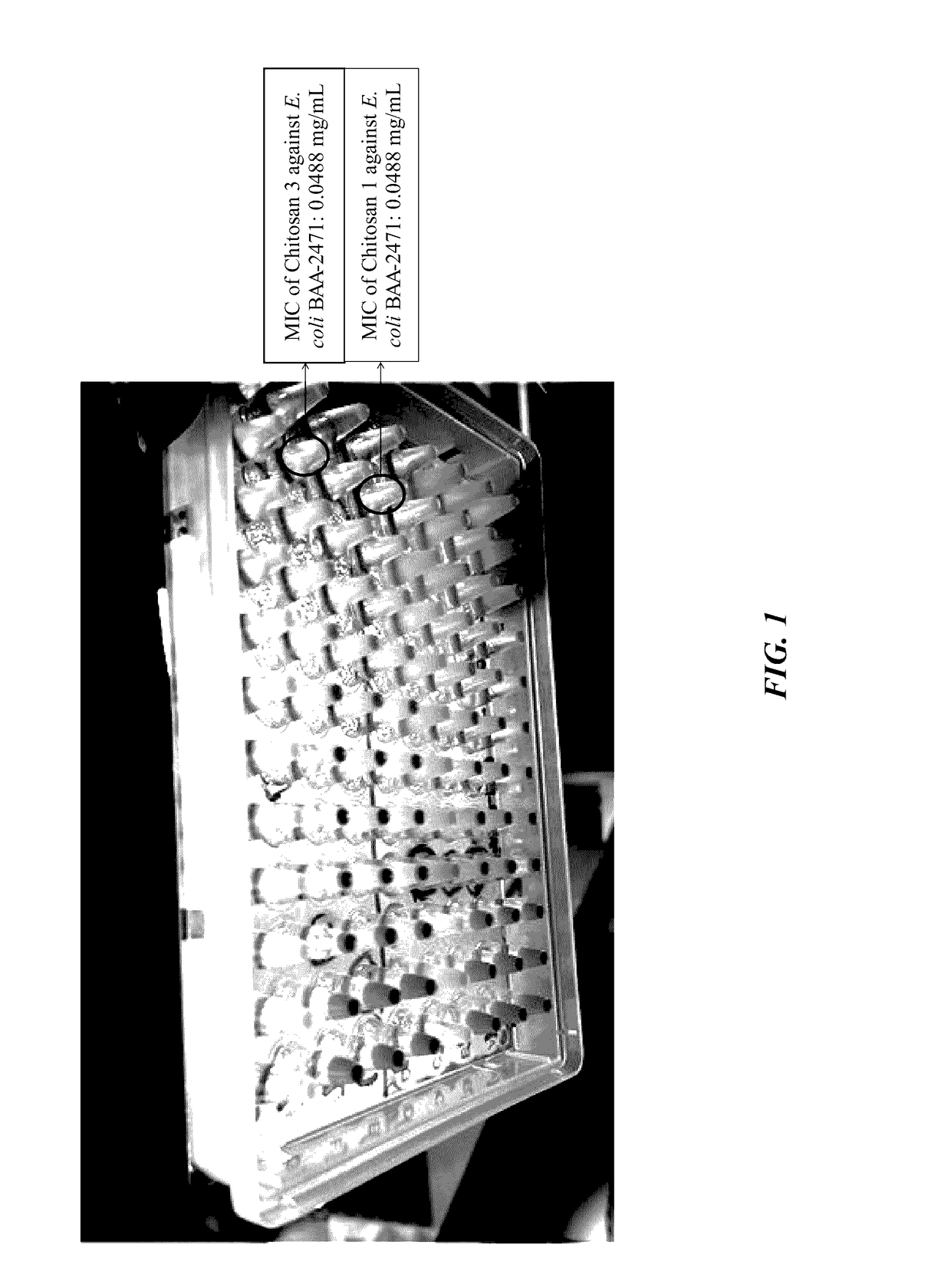
Compositions and methods for mitigating drug resistant bacteria
InactiveUS20170106019A1Problem in their usePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseBacterial strain
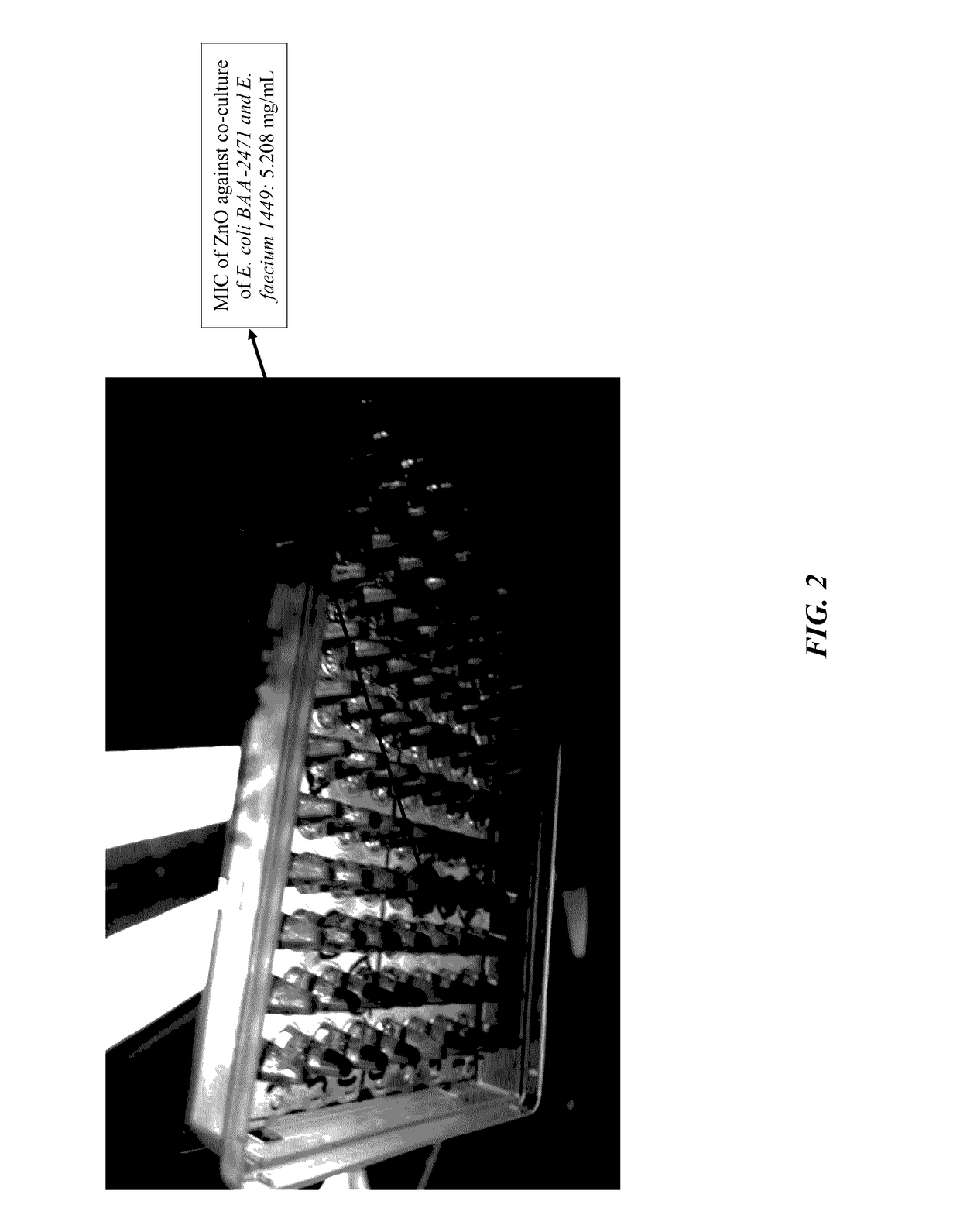
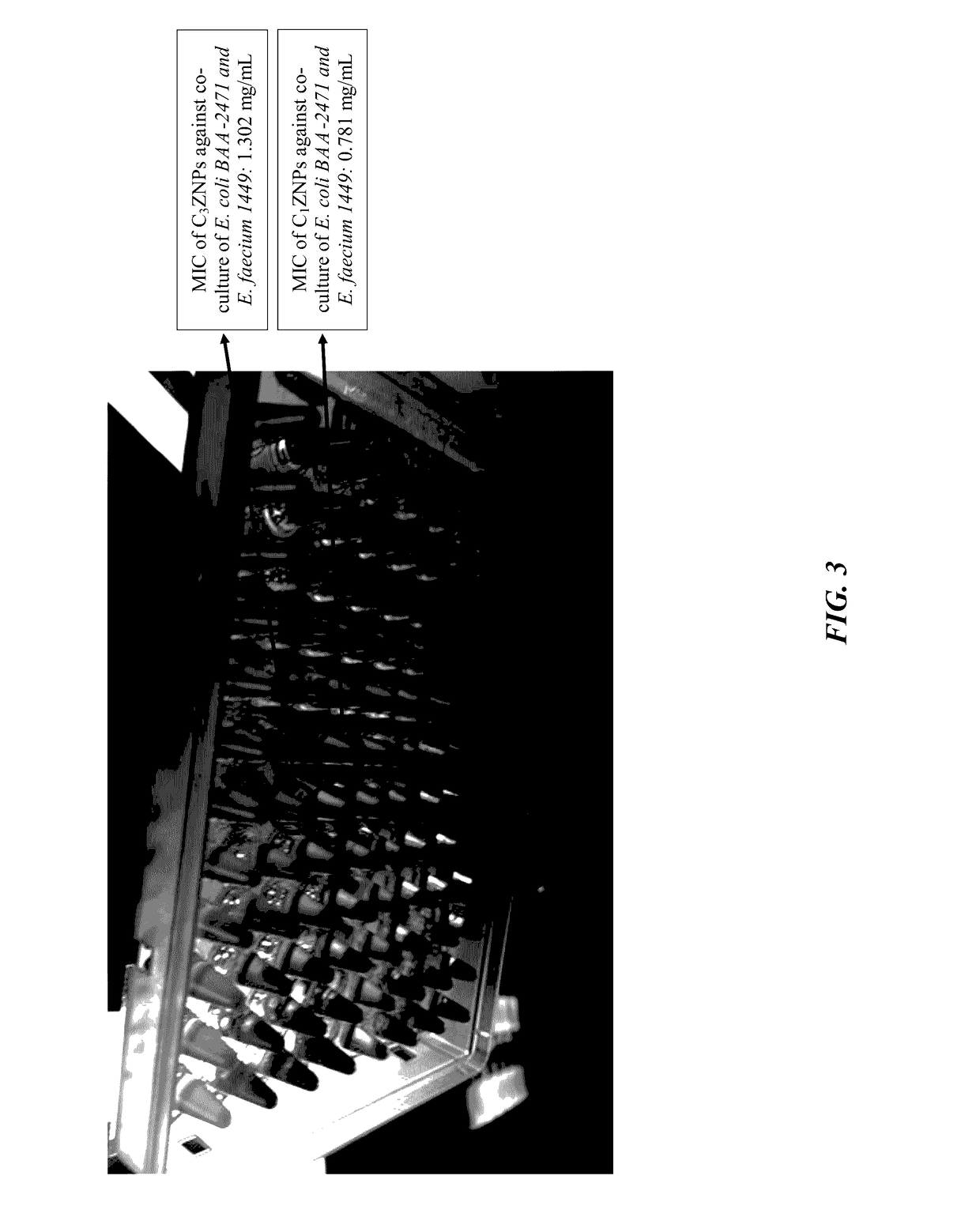
The current invention is a broad-based remediation mechanism against MRFs and includes nanotechnology formulations and methodologies that may be used to develop novel mitigation strategies against certain drug resistant bacterial strains. In an embodiment, the current invention relates to mitigation of drug resistant bacteria from nosocomial infections, for example in hospitals and in food animals. The invention uses hybrid nanomaterials comprising oligo-chitosan and zinc oxide formulated as nanoparticles and micelles. The inventors unexpectedly found unique properties of very small oligomers of chitosan that effectively mitigate MRFs- and Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus (VRE)-induced illnesses without compromising the balance of the beneficial flora in the abdomen. Also, the combination of chitosan with zinc oxide demonstrated synergistic and unexpected effects in remediation of important food-borne bacteria including the resistant types.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Pharmaceutical composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106632104AGive full play to medicinal valueGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseMedicine
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition and application thereof. The pharmaceutical composition is a compound shown as a chemical formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts and pharmaceutically acceptable carriers thereof: (the formula is shown in the description). The compound can be used for preparing an antibacterial drug, in particular preparing a medicine for preventing or treating vancomycin-resistant bacteria infectious diseases. Experimental data show that the compound is combined with glycopeptide antibacterial drugs, so that the growth of vancomycin-resistant enterococci can be effectively inhibited.
Owner:XIANGTAN ZHILIAN TECH MATASTASIS PROMOTE CO LTD
Method of use of an Anti-methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus agent and an Anti-vancomycin-resistant enterococcus agent
Methods of use of an anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus agent (anti-MRSA agent) and an anti-vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus agent (anti-VRE agent) contain as an active ingredient a Macaranga tanarius extract extracted from Macaranga tanarius with an extraction solvent including at least an organic solvent are disclosed. The anti-MRSA agent and the anti-VRE agent contain as an active ingredient at least one selected from nymphaeol-A, nymphaeol-B, and nymphaeol-C.
Owner:POKKA SAPPORO FOOD & BEVERAGE
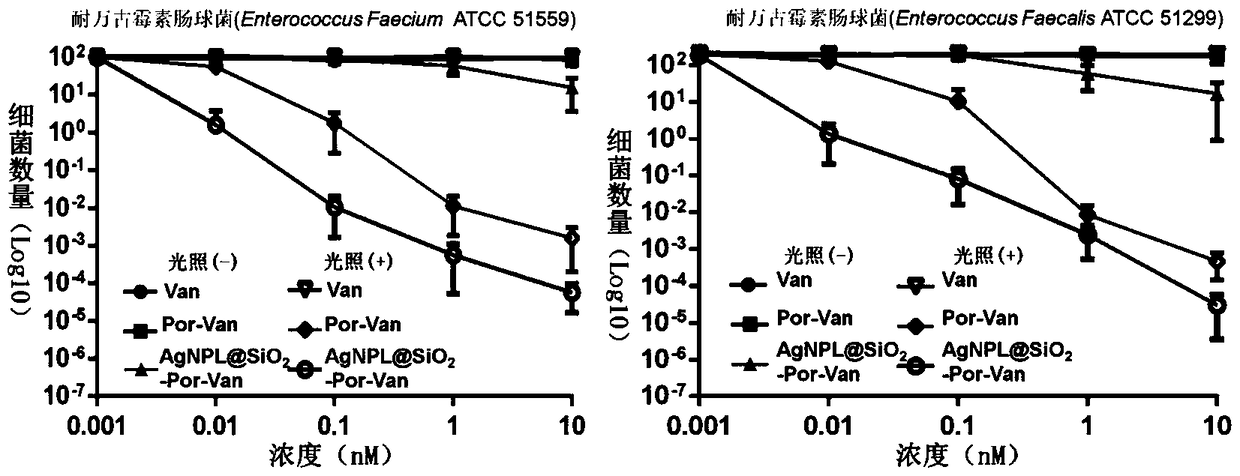
A composite nano-antibacterial material for the treatment of vancomycin-resistant pathogens
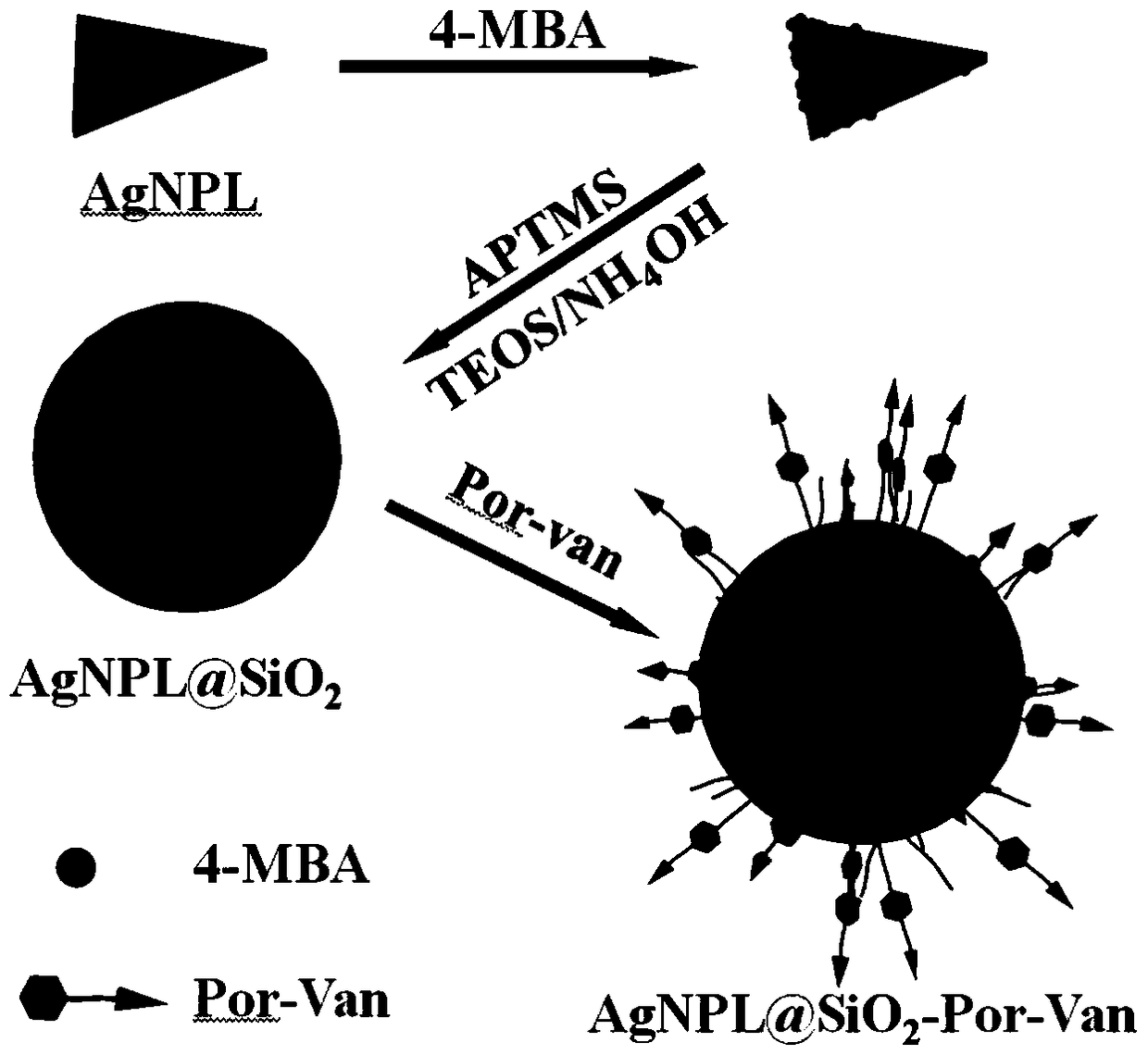
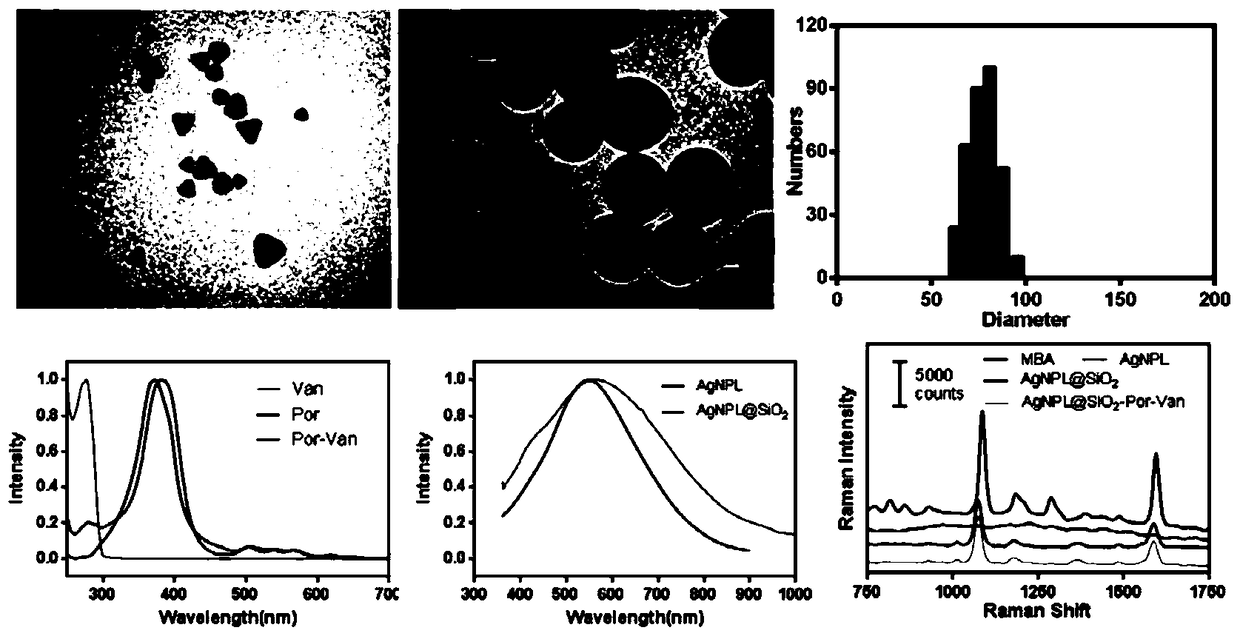
InactiveCN105412940BImprove surface affinityHigh affinityAntibacterial agentsEnergy modified materialsSilica particlePorphyrin molecule
The invention discloses a composite nanometer antibacterial material and a preparing method thereof. The composite nanometer antibacterial material is used for solving the problems that conventional target photosensitive drugs are complex to synthesize and poor in biocompatibility. The nanometer antibacterial material is formed by a triangle silver nanometer sheet of a core-shell structure, silicon dioxide particles and vancomycin-porphyrin molecules on the surface. A core of the triangle silver nanometer sheet serves as a host material to form a surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) signal, a silicon dioxide shell serves as a rigid platform to couple the vancomycin-porphyrin molecules to form a poly mode. The synthesis cost of the nanometer antibacterial material is low, the preparing method is simple, and the material has good biocompatibility and tissue permeability; in addition, the invention further discloses application to Raman images and photodynamics treatment of vancomycin drug resistant pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com