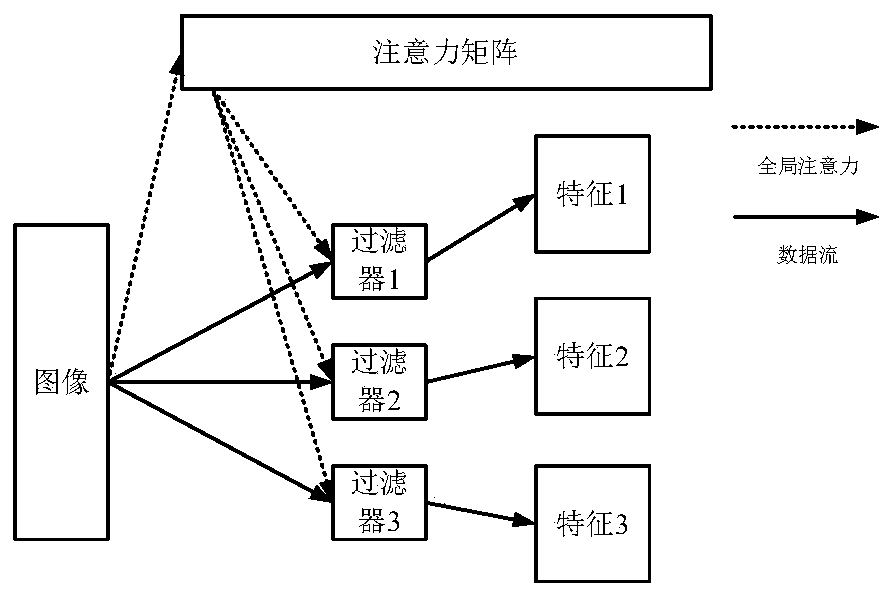
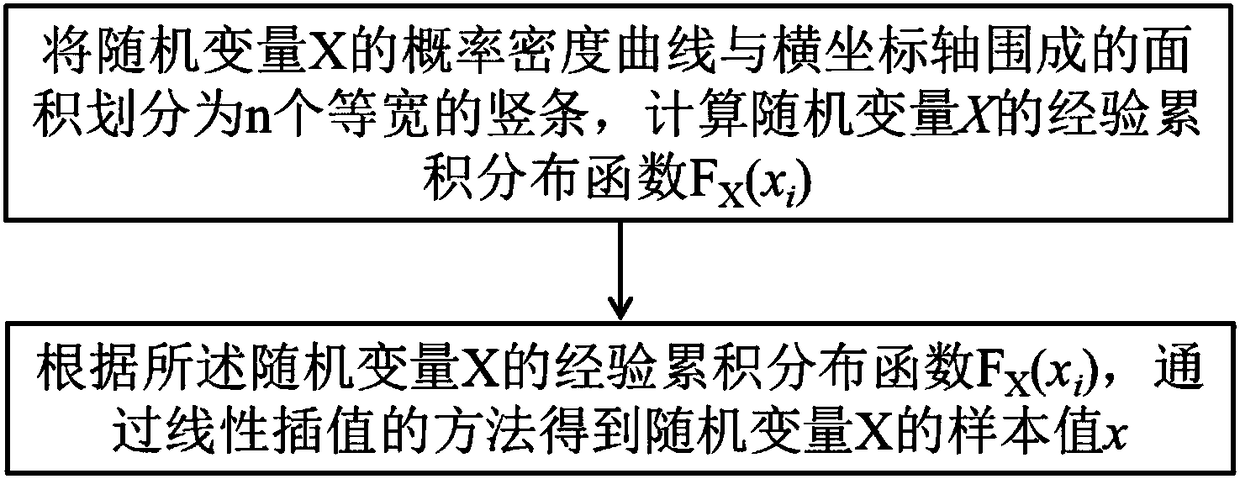
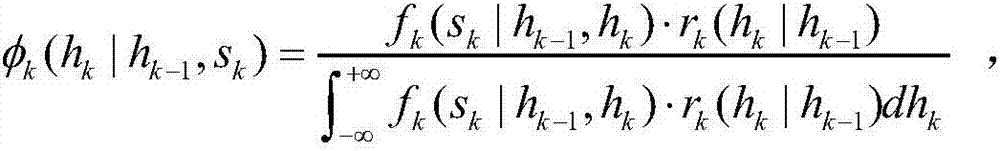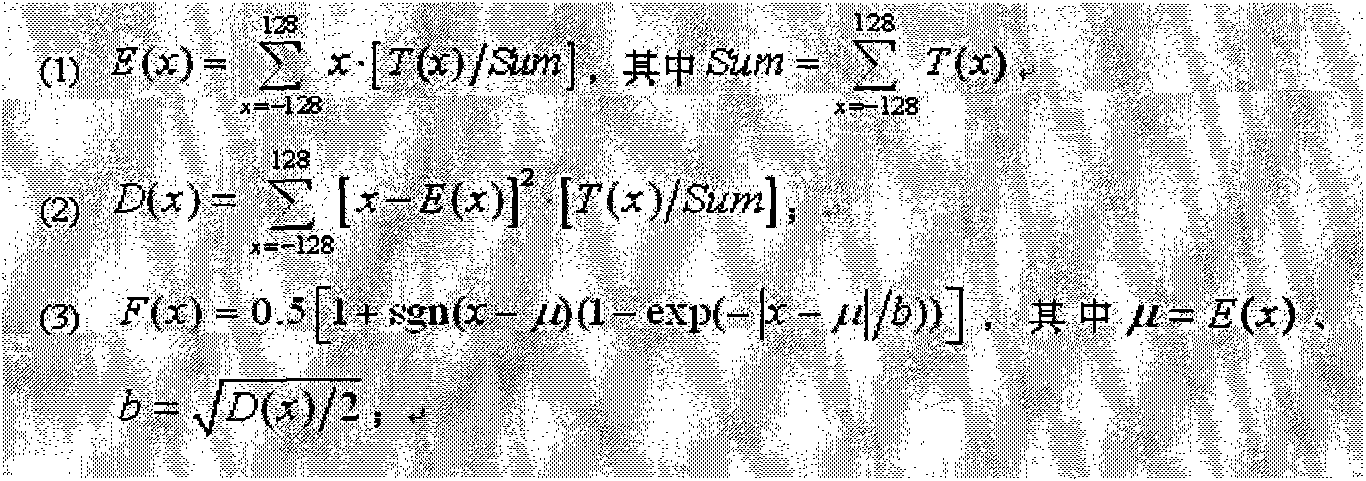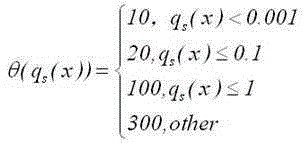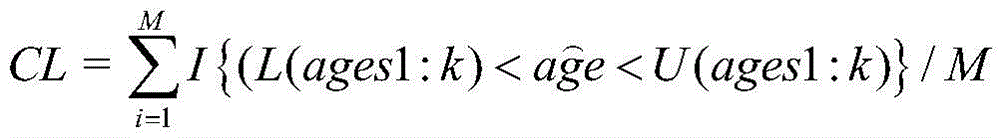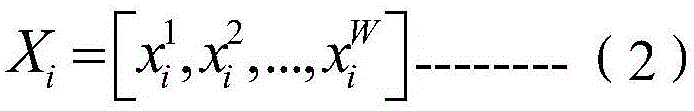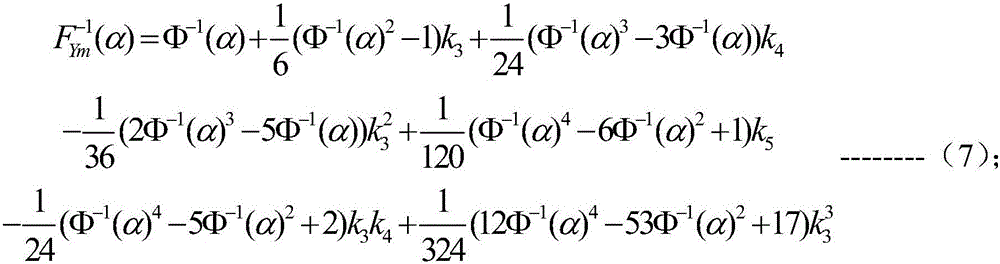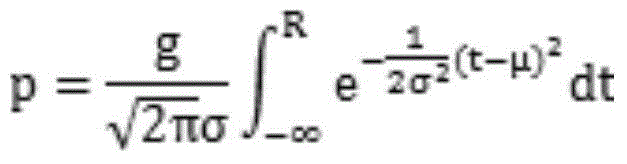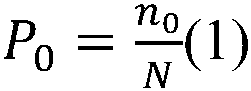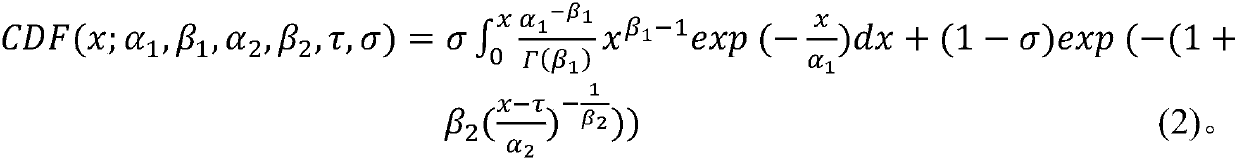Patents
Literature
66 results about "Wigner distribution function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Wigner distribution function (WDF) is used in signal processing as a transform in time-frequency analysis. The WDF was first proposed in physics to account for quantum corrections to classical statistical mechanics in 1932 by Eugene Wigner, and it is of importance in quantum mechanics in phase space (see, by way of comparison: Wigner quasi-probability distribution, also called the Wigner function or the Wigner–Ville distribution).
Condition assessment of nonlinear processes
InactiveUS6484132B1Timely, accurateReduce the amount requiredElectroencephalographyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceData setEeg data
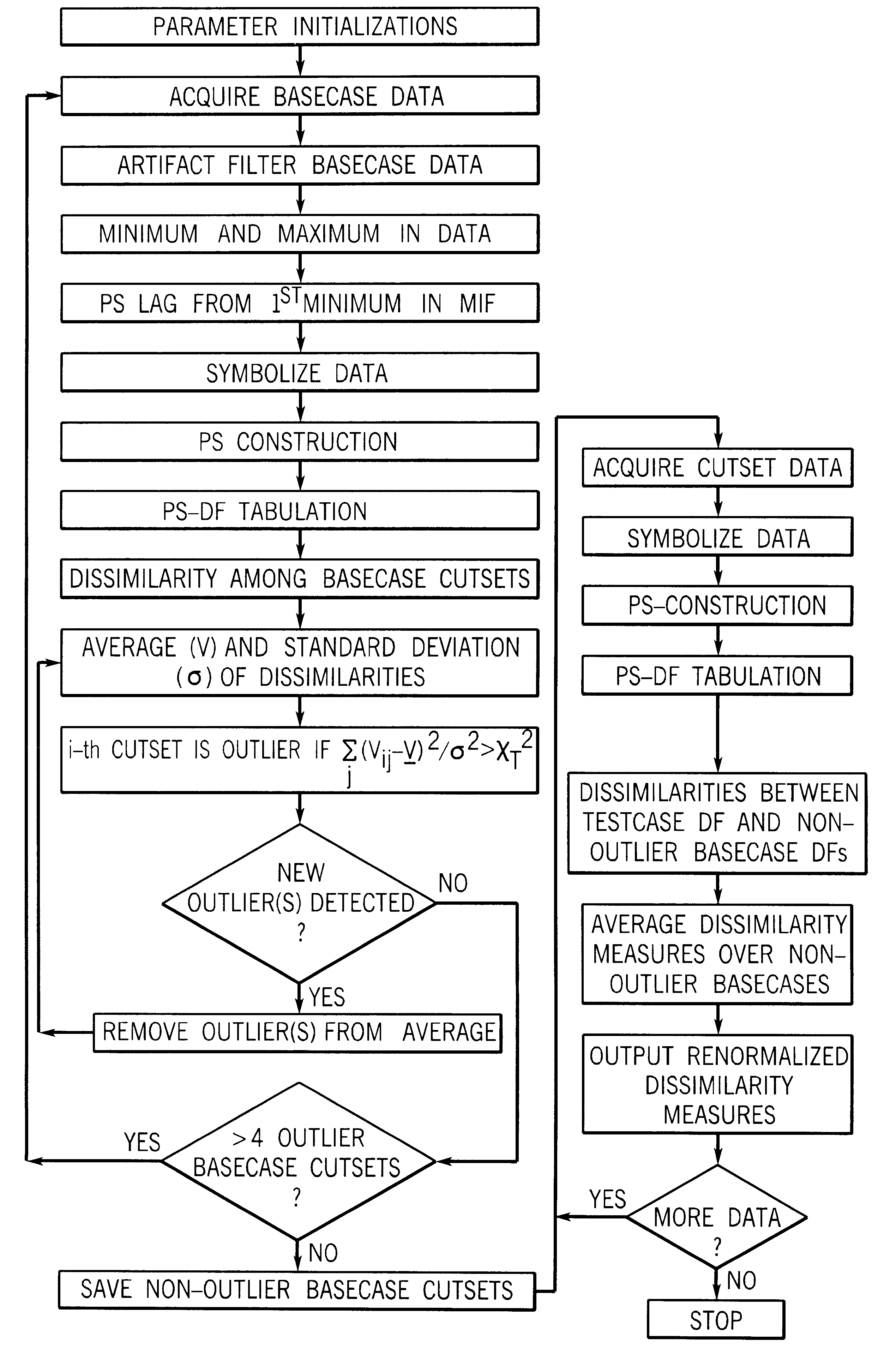
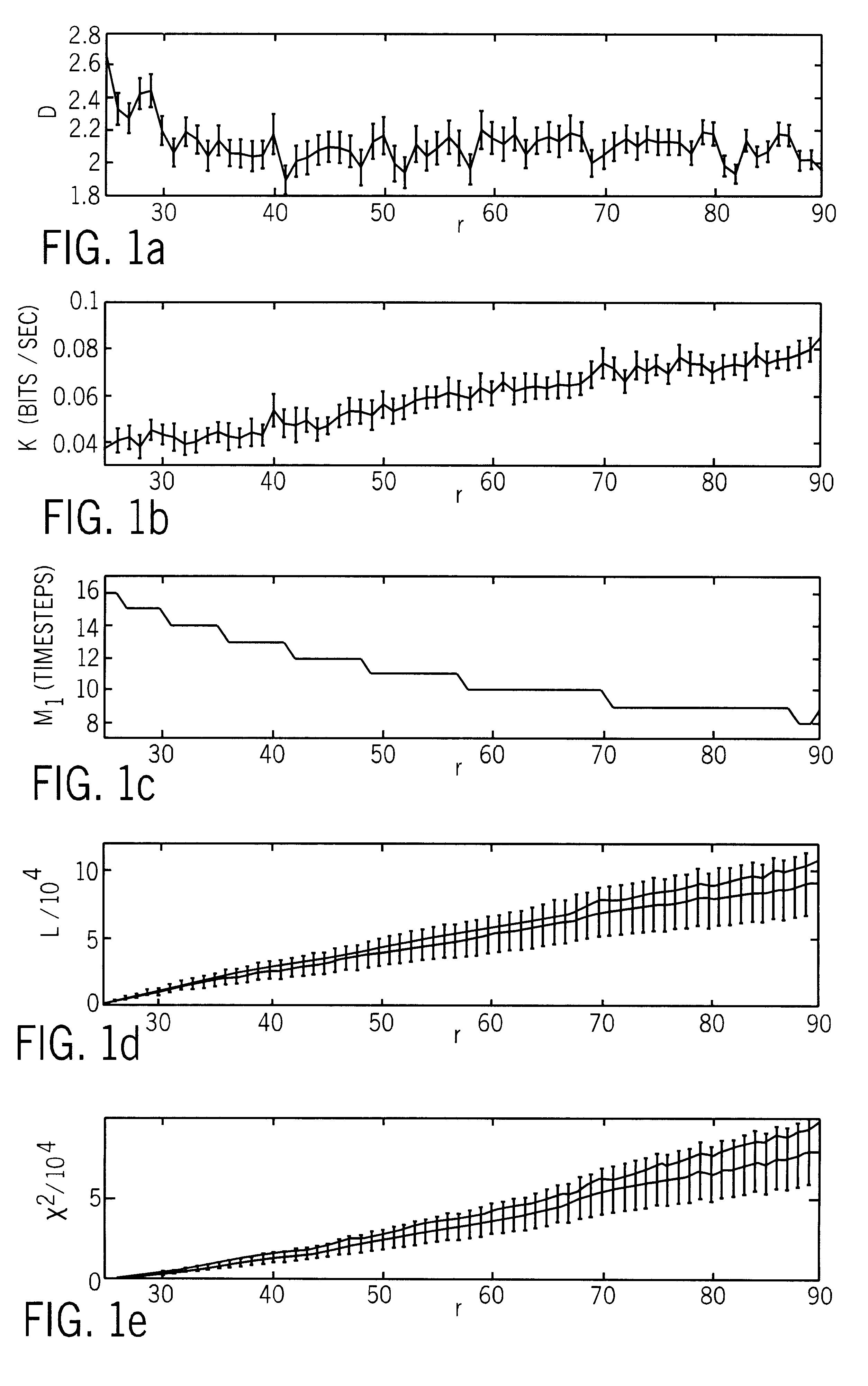
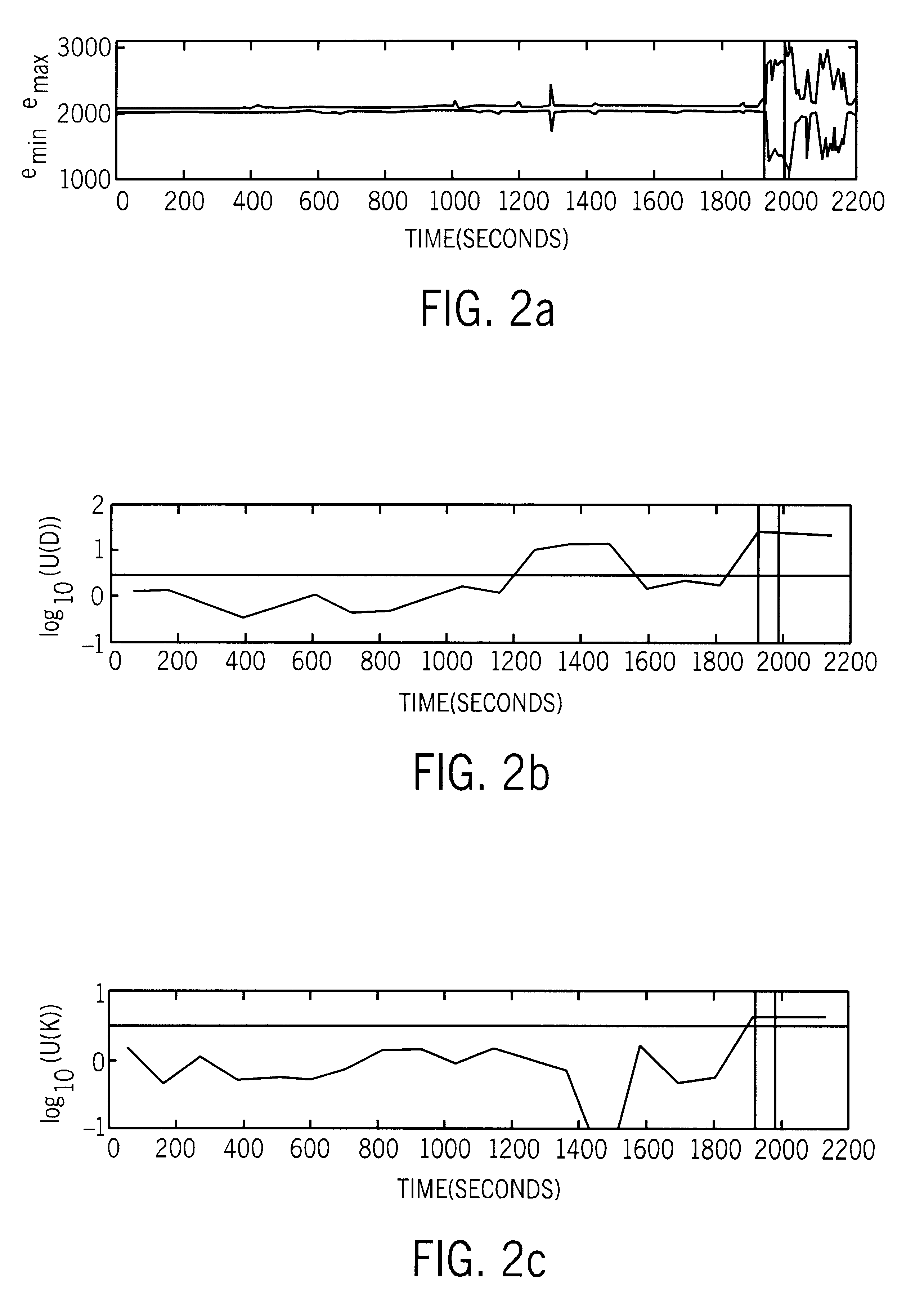
There is presented a reliable technique for measuring condition change in nonlinear data such as brain waves. The nonlinear data is filtered and discretized into windowed data sets. The system dynamics within each data set is represented by a sequence of connected phase-space points, and for each data set a distribution function is derived. New metrics are introduced that evaluate the distance between distribution functions. The metrics are properly renormalized to provide robust and sensitive relative measures of condition change. As an example, these measures can be used on EEG data, to provide timely discrimination between normal, preseizure, seizure, and post-seizure states in epileptic patients. Apparatus utilizing hardware or software to perform the method and provide an indicative output is also disclosed.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
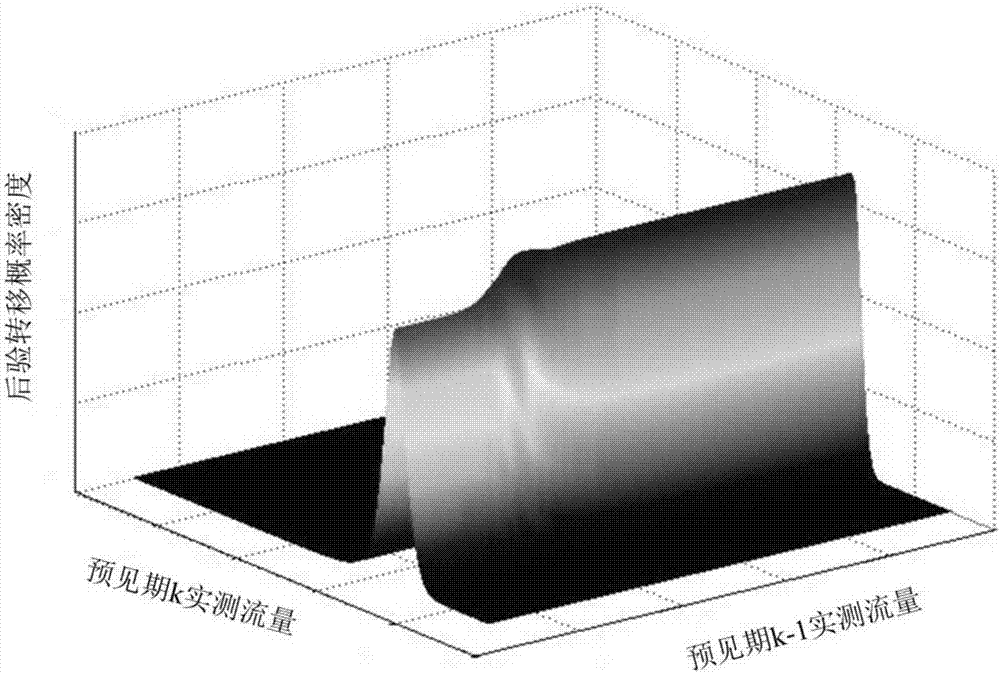
Copula function-based multivariate hydrologic uncertainty processing method
ActiveCN107423546ACapture non-linearitySnap featureSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsQuantitative precipitation forecastNormal density
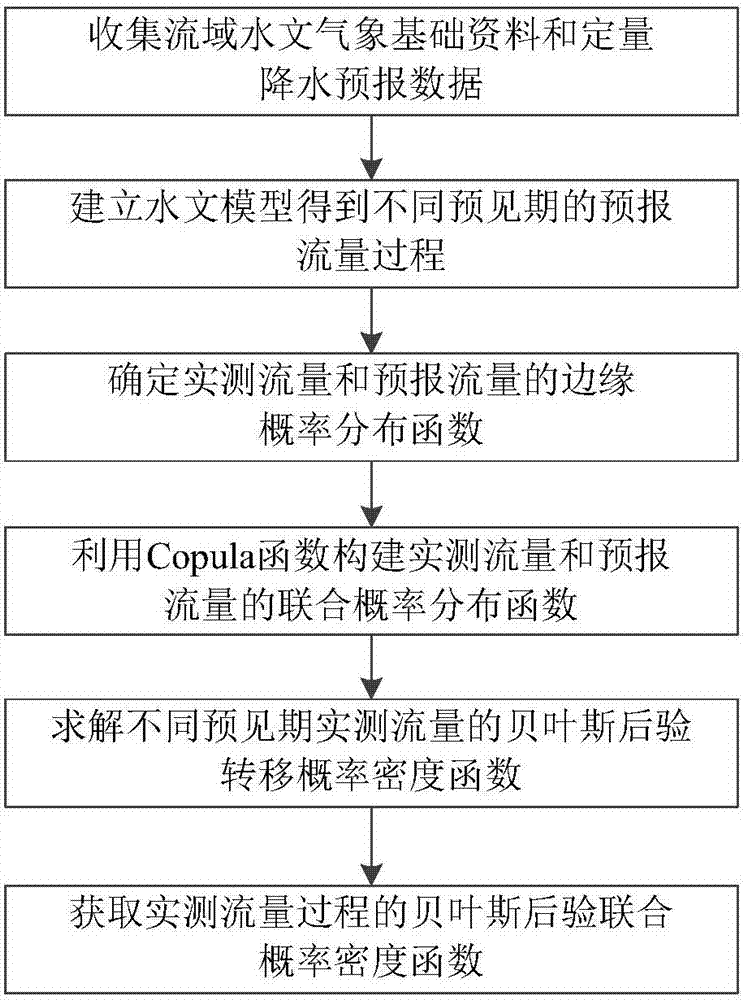
The invention provides a Copula function-based multivariate hydrologic uncertainty processing method. The method can be used for hydrologic forecasting, and is characterized by comprising the following steps: step 1, collecting hydrometeorological basic data and quantitative precipitation forecast data of a basin; step 2, establishing a hydrologic model to obtain forecast discharge processes of different forecast periods; step 3, determining marginal distribution functions of actually measured flow and forecast flow; step 4, utilizing a Copula function to construct a joint probability distribution function of the actually measured flow and the forecast flow; step 5, solving a Bayesian posterior transition probability density function of the actually measured flow of the different forecast periods according to the marginal distribution functions estimated in the step 3 and the joint probability distribution function constructed in the step 4; and step 6, acquiring a Bayesian posterior joint probability density function of the actually measured discharge processes through a total probability formula according to the Bayesian posterior transition probability density function, obtained in the step 5, of the actually measured flow of the different forecast periods.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
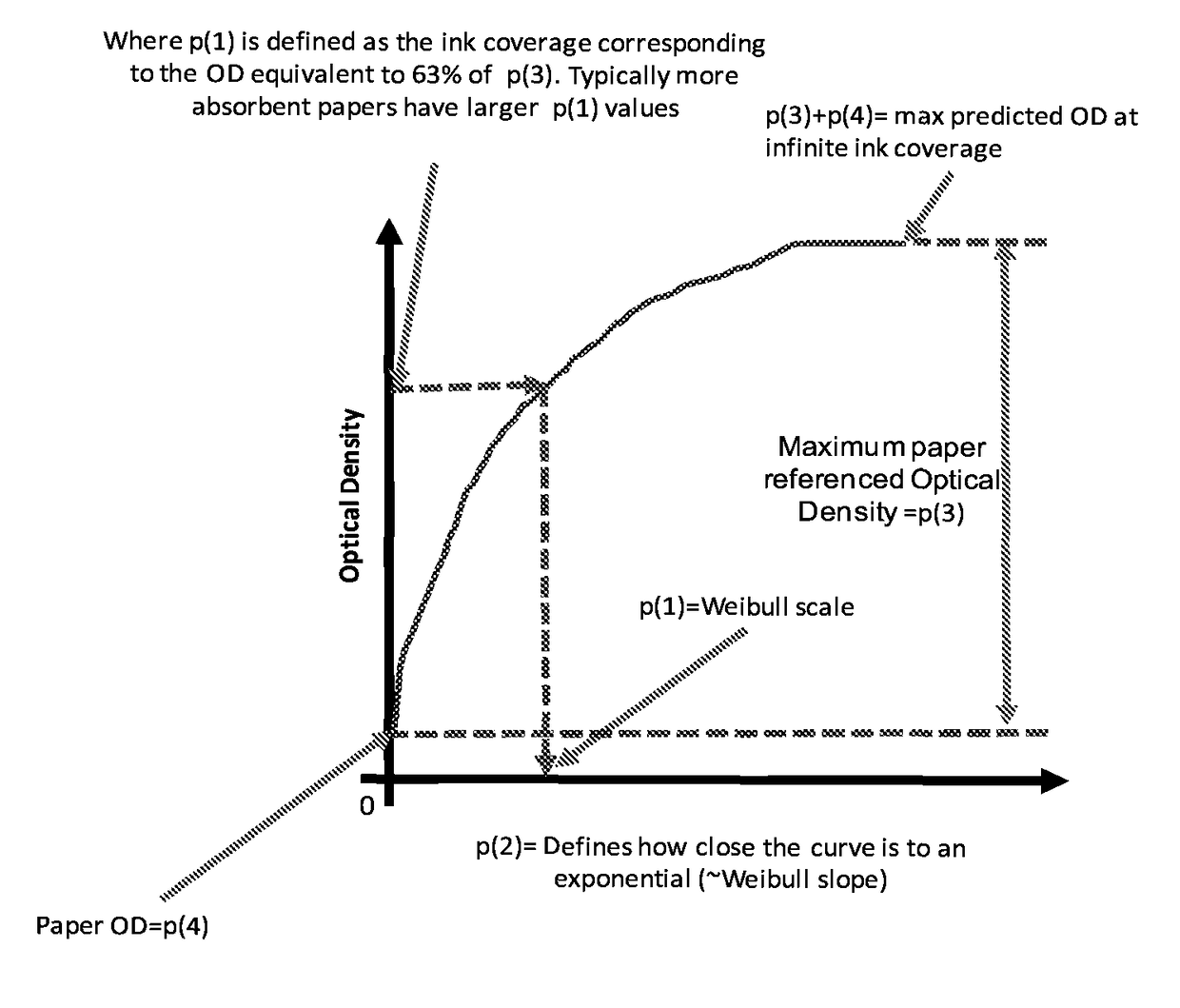
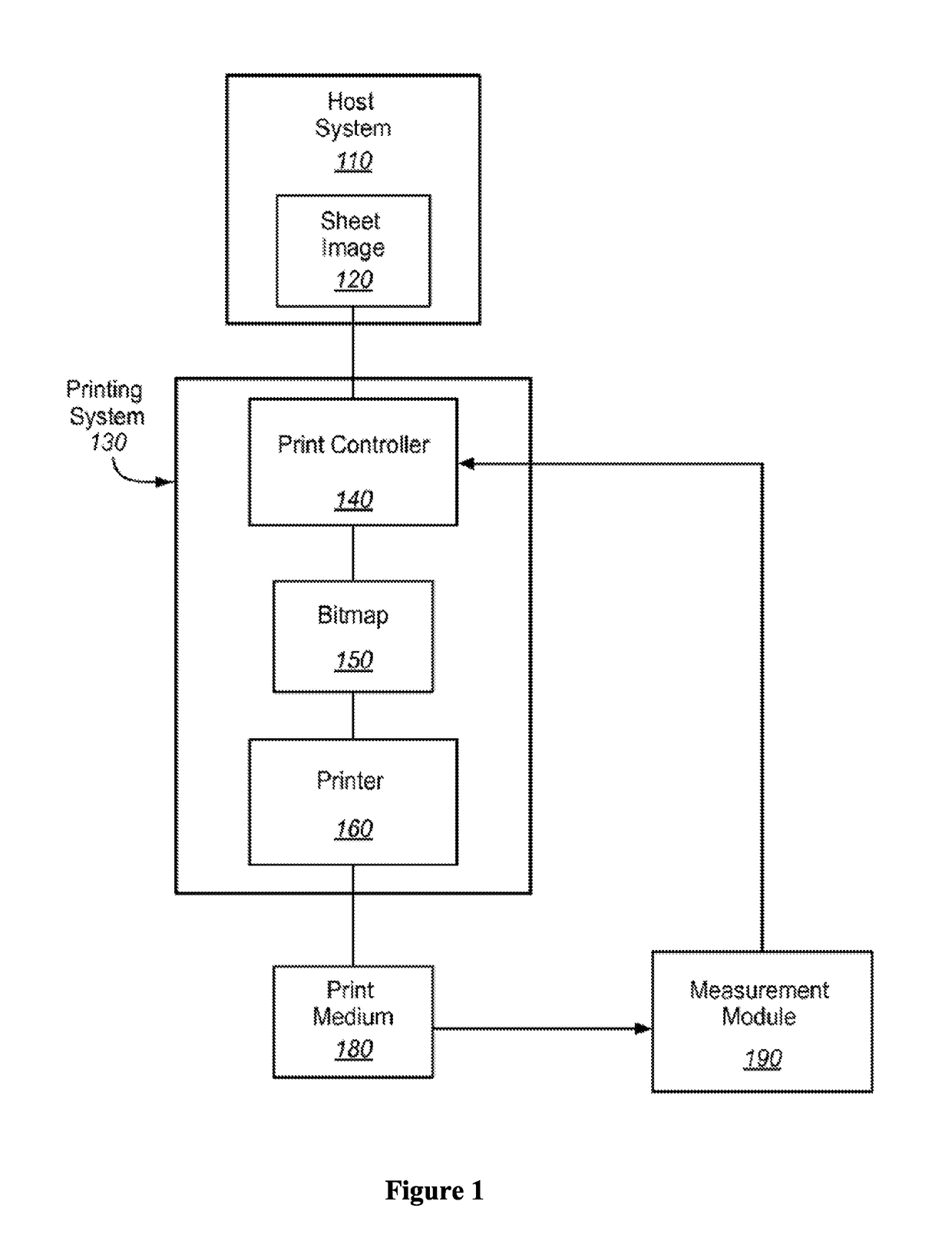
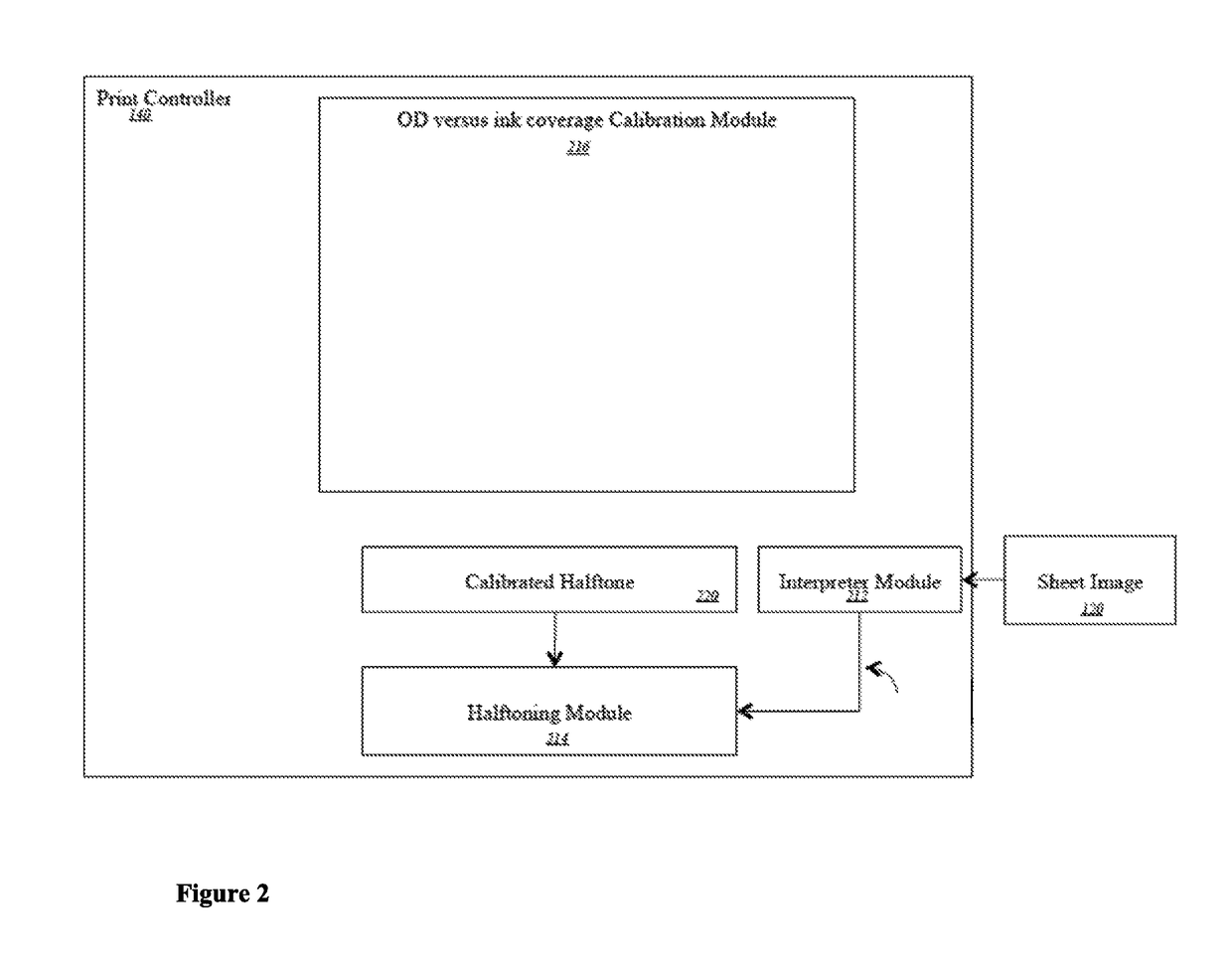
Ink model derivation mechanism using Weibull distribution function
A printing system is disclosed. The printing system includes a printer controller to receive optical density (OD) measurement data corresponding to application of a halftone pattern using ink on a medium in a printing system and calculate a predicted OD versus normalized ink coverage relationship for the printing system based on the received OD measurement data.
Owner:RICOH KK
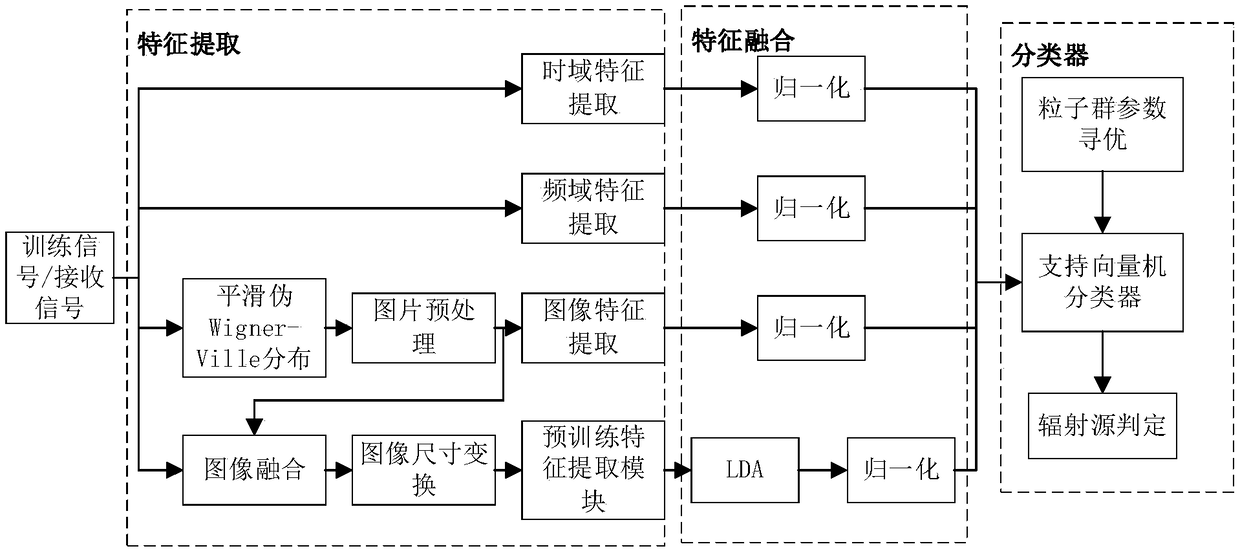
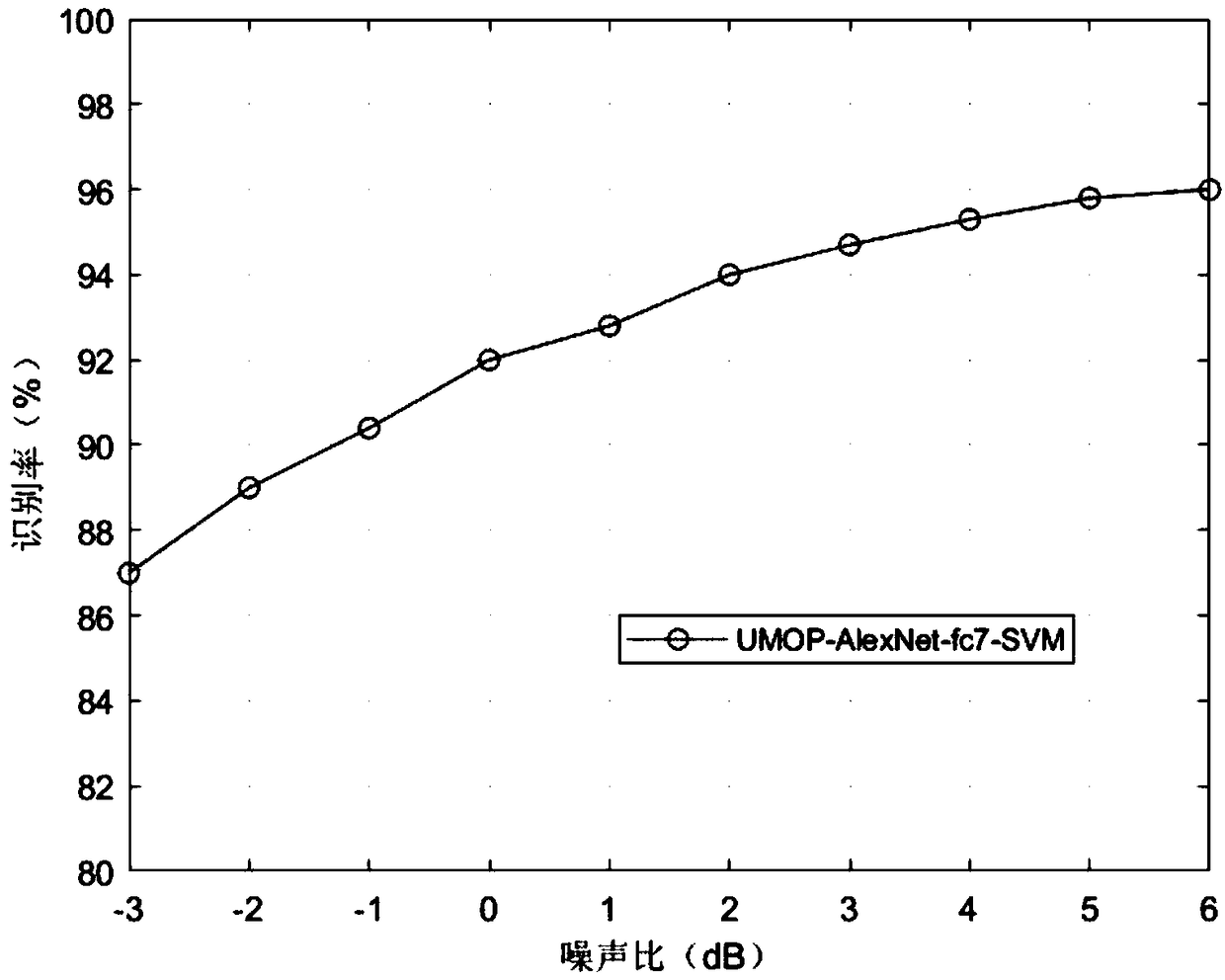
Radar radiation source identification method based on feature fusion
ActiveCN109254274AEasy to identifyImprove visibilityWave based measurement systemsRadar radiationEuclidean vector
The invention relates to a radar radiation source identification method based on feature fusion. The method comprises the steps of generating a radar radiation source unintentional modulation signal set; extracting AR model coefficients, Renyi entropy features and spectral kurtosis features; computing smoothed pseudo Wigner-Ville distribution, generating time-frequency images, and carrying out graying and adaptive binarization to obtain adaptive binarized images; extracting pseudo Zernike matrix and Hu matrix features of the images; extracting signal time-frequency image unintentional modulation features through application of an AlexNet convolutional neural network, carrying out normalization, and carrying out feature fusion to obtain fused feature vectors; and inputting the fused featurevectors into a support vector machine, training the support vector machine optimized through particle swarm optimization, and inputting the radar radiation source signal set into a system to finish identifying radar radiation sources. According to the method, the signals are analyzed from a time domain, a frequency domain and a time-frequency domain, various unintentional modulation features areextracted comprehensively, and the problems that the extracted unintentional modulation features are low applicability and reliability and the radiation sources are difficult to identify is solved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
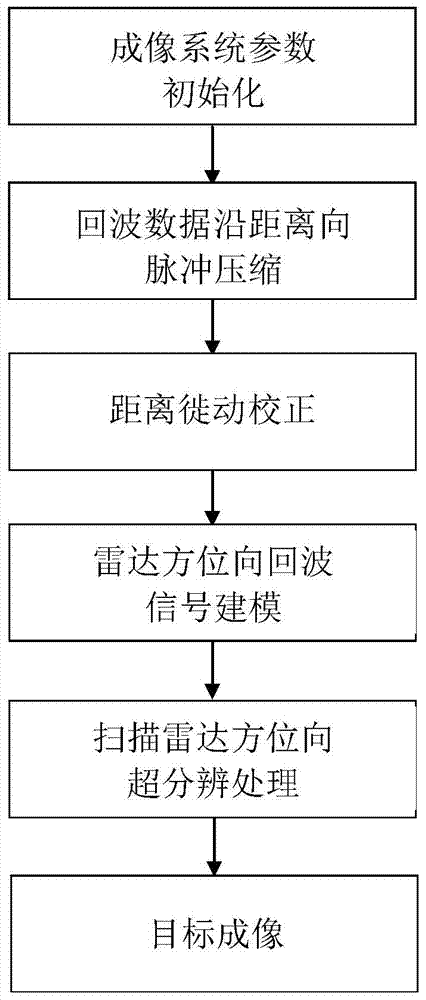
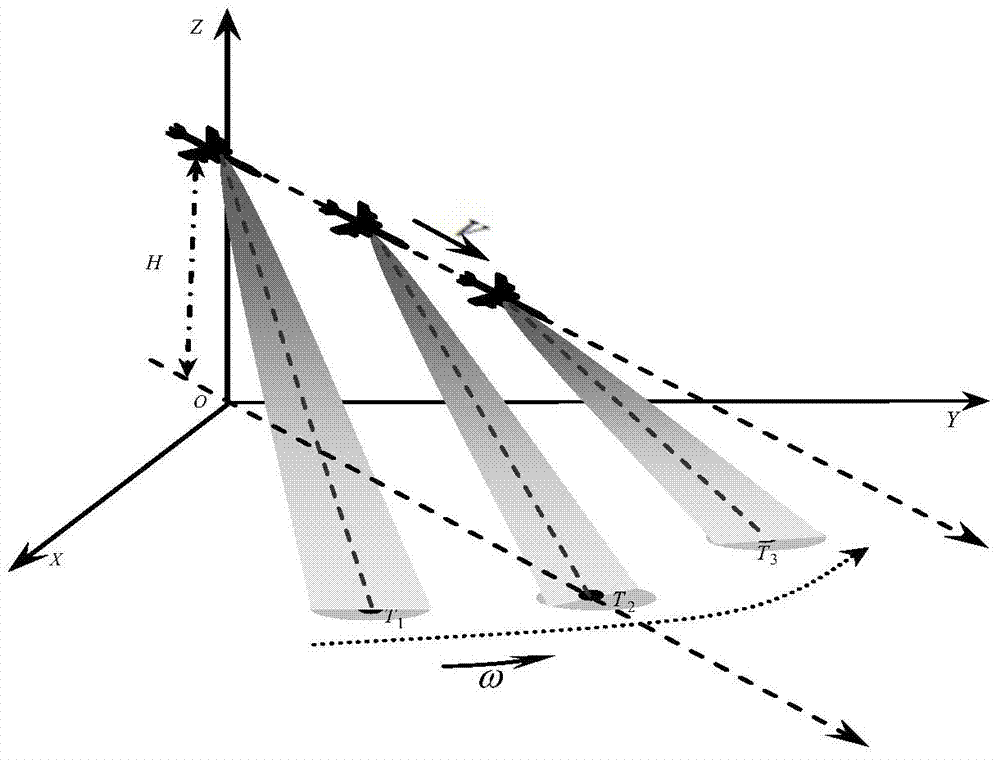
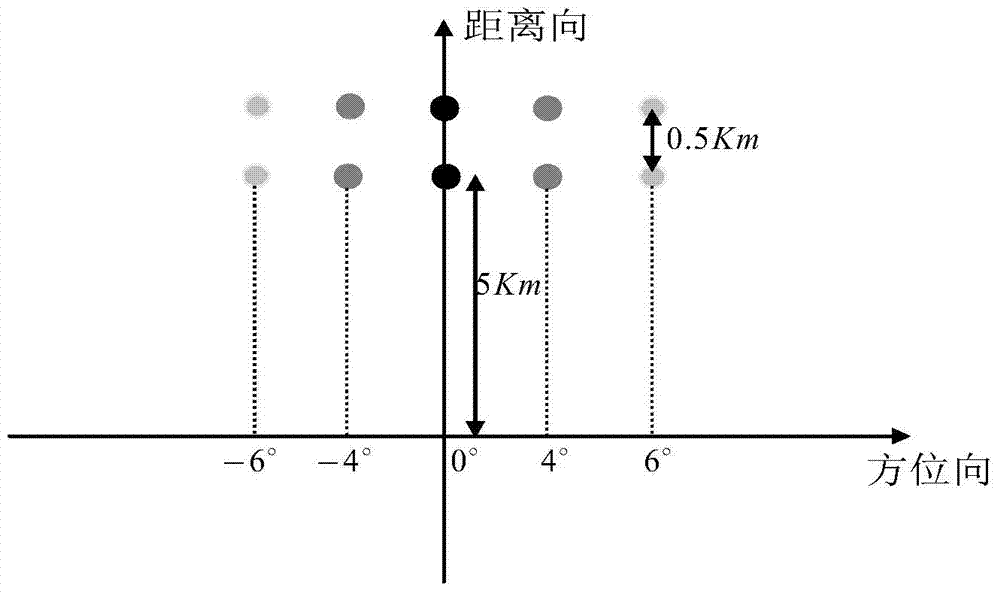
Airborne scanning radar imaging method in iteration compression mode
ActiveCN103487803AAchieving super-resolution imagingEfficient integrationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPrior informationMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention discloses an airborne scanning radar imaging method in an iteration compression mode. The airborne scanning radar imaging method is characterized in that an azimuth-direction super-resolution imaging back model is built under the Bayesian theory framework, and the model built under the Bayesian theory can effectively fuse prior information of a target. When the super-resolution imaging back model is built, the assumption of a radar imaging basic idea on the noise statistical property is followed, and the Gaussian distribution function is adopted in the model to describe the noise statistical property. Due to the fact that target scattering has sparsity relative to an imaging background, the prior information of target scattering is described through the Laplace distribution function, radar super-resolution imaging is precisely converted into the maximum posterior probability problem in mathematics, corresponding target information when the posterior probability is maximum is solved, then the target information is reconstituted, and therefore the radar super-resolution imaging is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
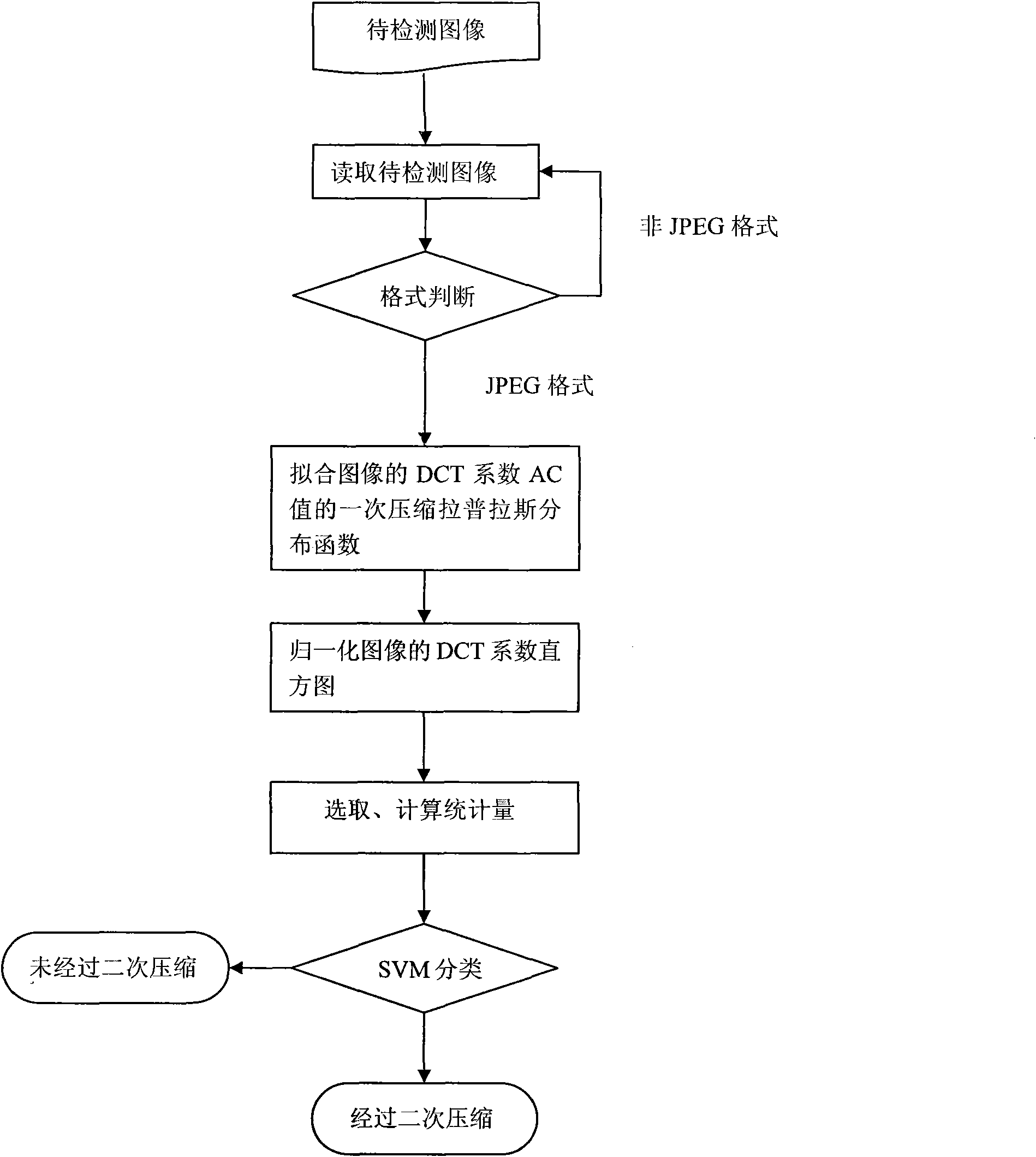
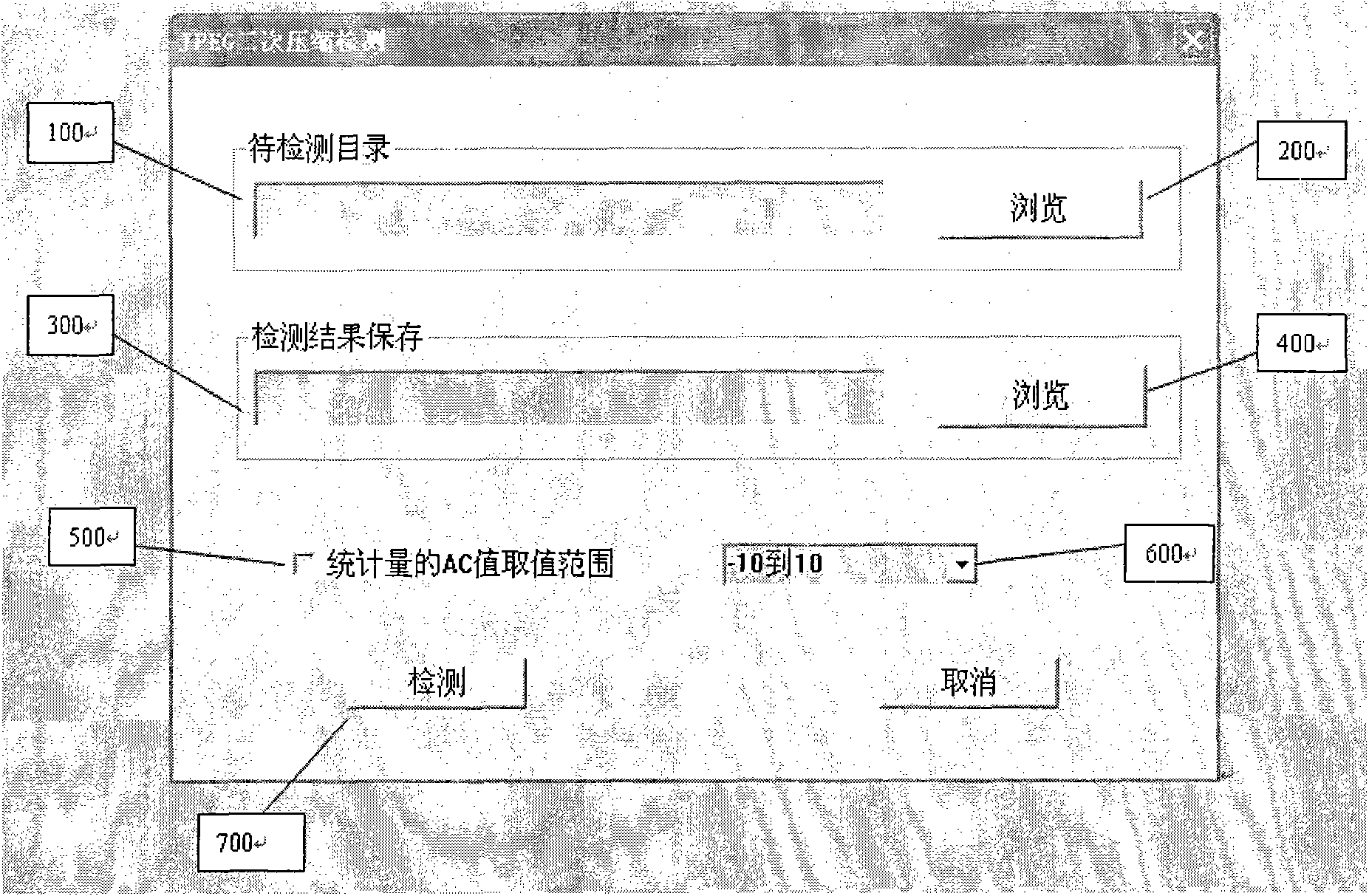
Detection method for secondary compression of JPEG image
The invention provides a detection method for secondary compression of a JPEG image. By using the characteristic that an AC coefficient histogram in a DCT coefficient of primary JPEG compression accords with Laplace distribution, a Laplace distribution function of the AC coefficient of the primary JPEG compression of an image to be detected is estimated in a fit mode according to the AC coefficient distribution of the JPEG image to be detected; the statistic is detected through a difference structure of normalized histogram distribution of the fit distribution function and an actual AC coefficient; and whether the JPEG image is subjected to the secondary compression is judged by using SVM classification. The method has high detection accuracy and wide applicability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Region extracting method for medical image
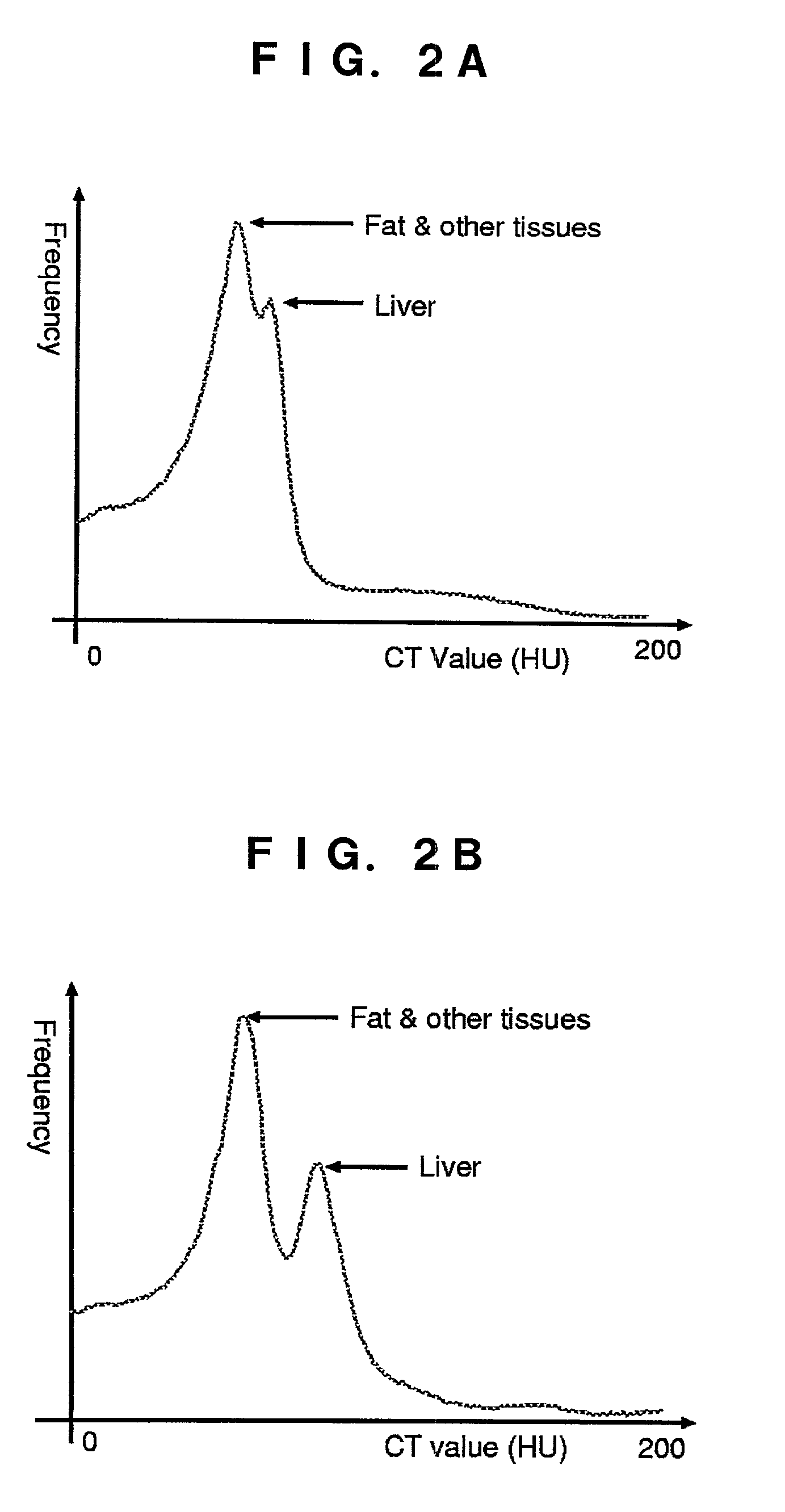
InactiveUS7046833B2Easy to operateImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisCharacteristic spaceWhole liver
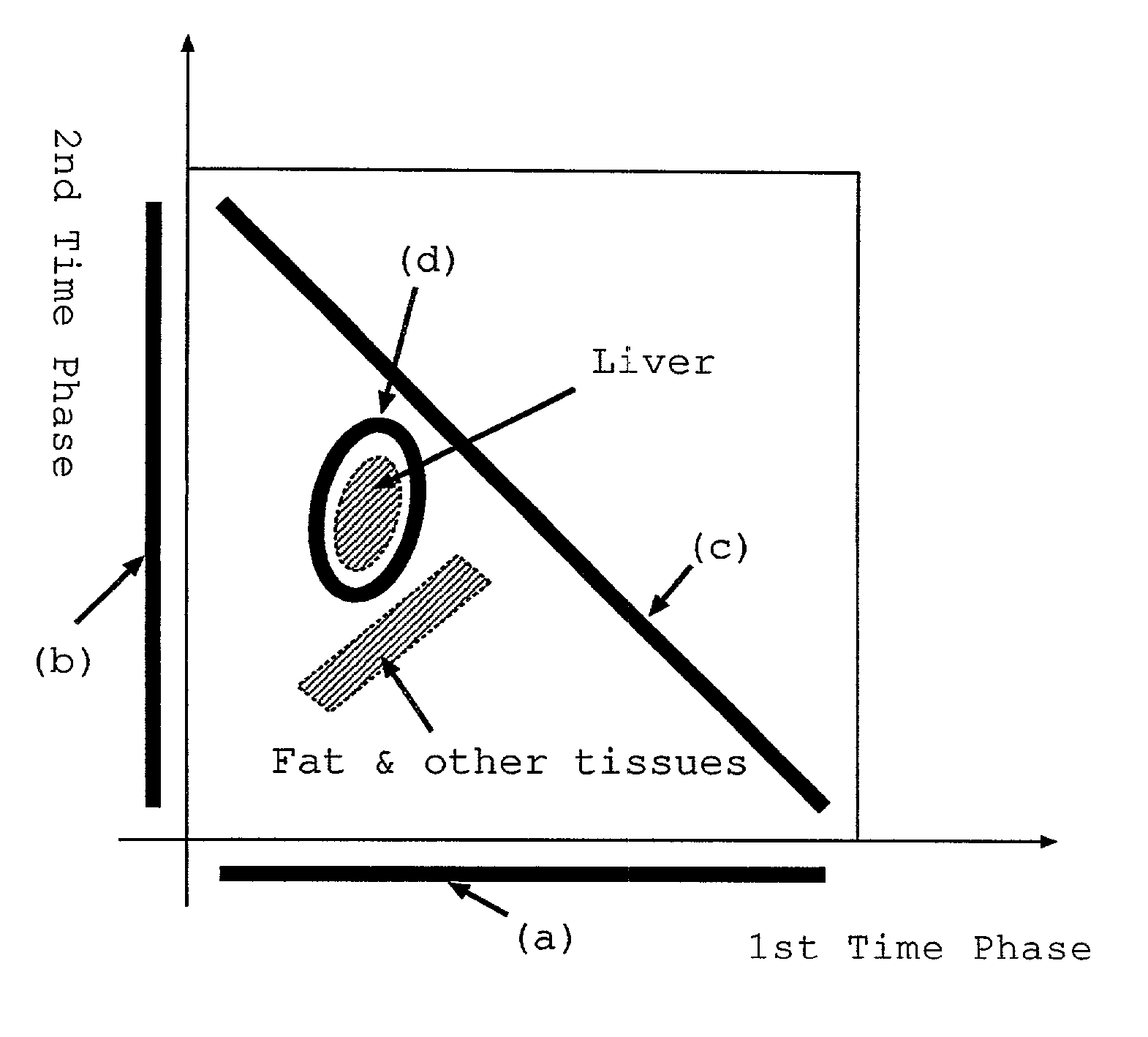
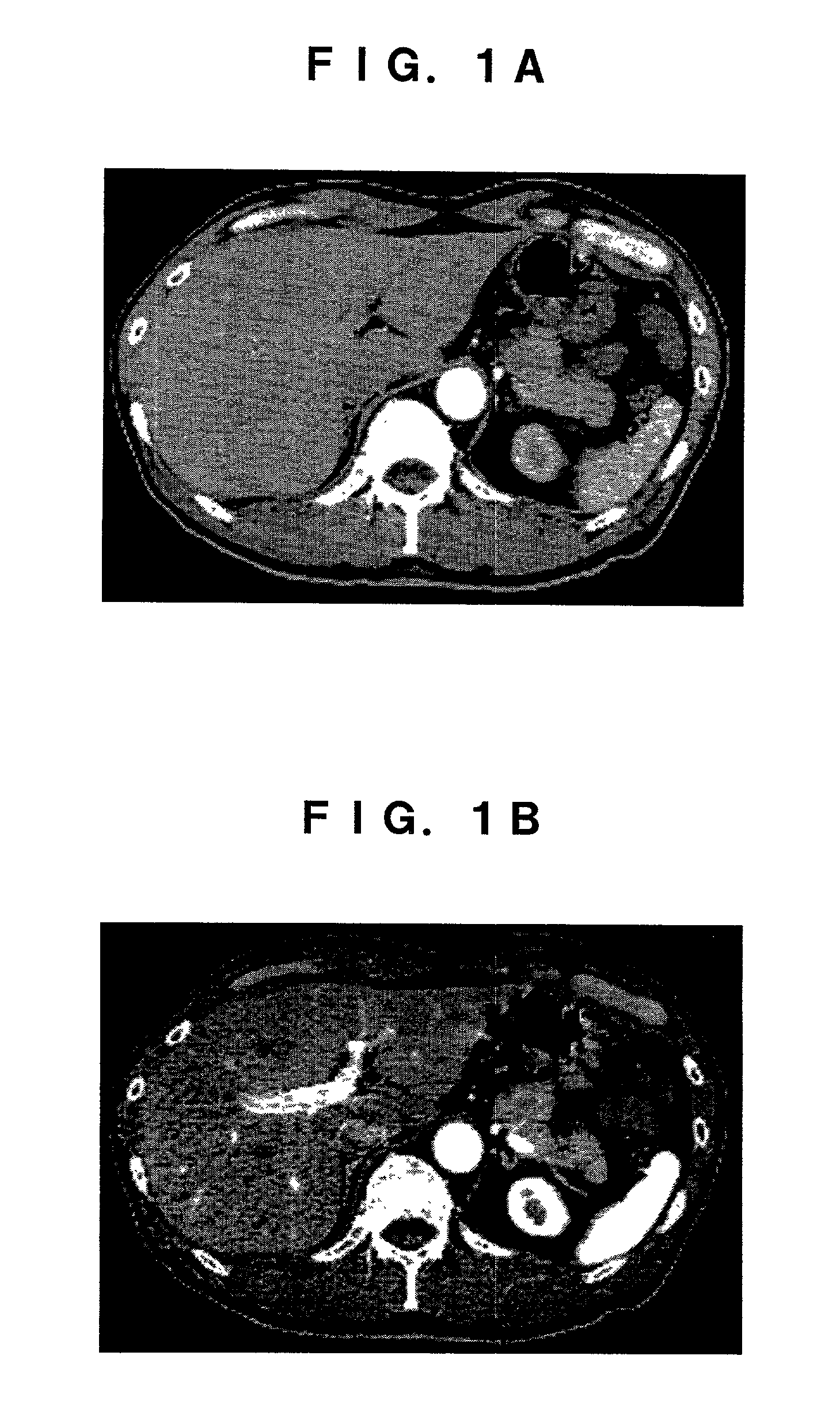
From CT images having captured an abdomen, a two-dimensional characteristic space is assumed, in which X and Y axes indicate CT values of image data taken in first and second time phases different from each other. In this space, a two-dimensional histogram concerning respective pixels located at the same position in the two time phases is taken as a sample distribution of pixels. A two-variable distribution function is applied to this sample distribution, so as to estimate a matrix distribution of pixels corresponding to the whole liver region. According to this matrix distribution, a range of CT value of pixels corresponding to the liver region is estimated.
Owner:AZE
Time-interval-adaptation-based power line power frequency communication system and method
InactiveCN101980451AAutomatically adapt to the connection methodImprove power frequency communication performanceCurrent/voltage measurementPower distribution line transmissionAnti jammingLow voltage
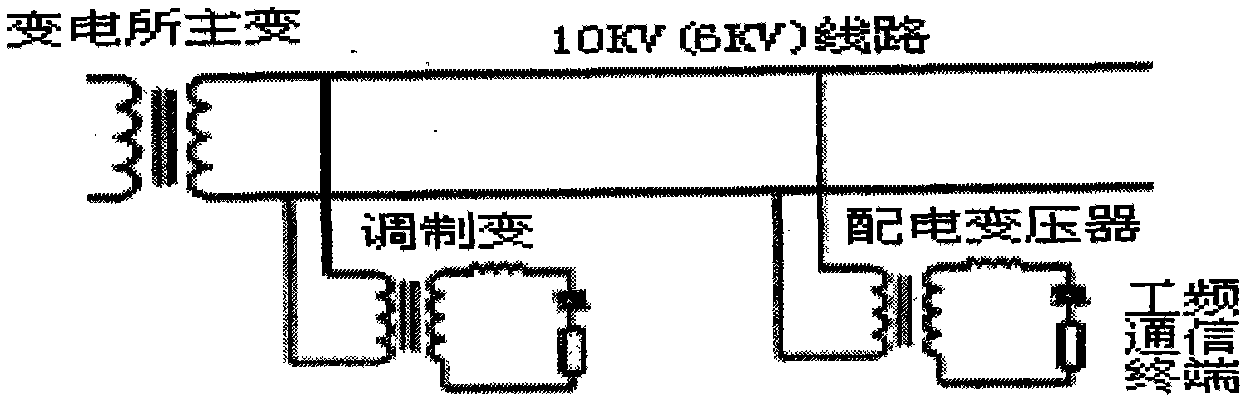
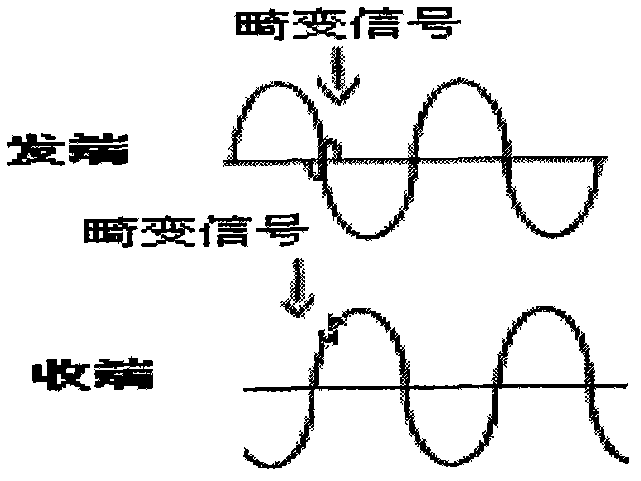
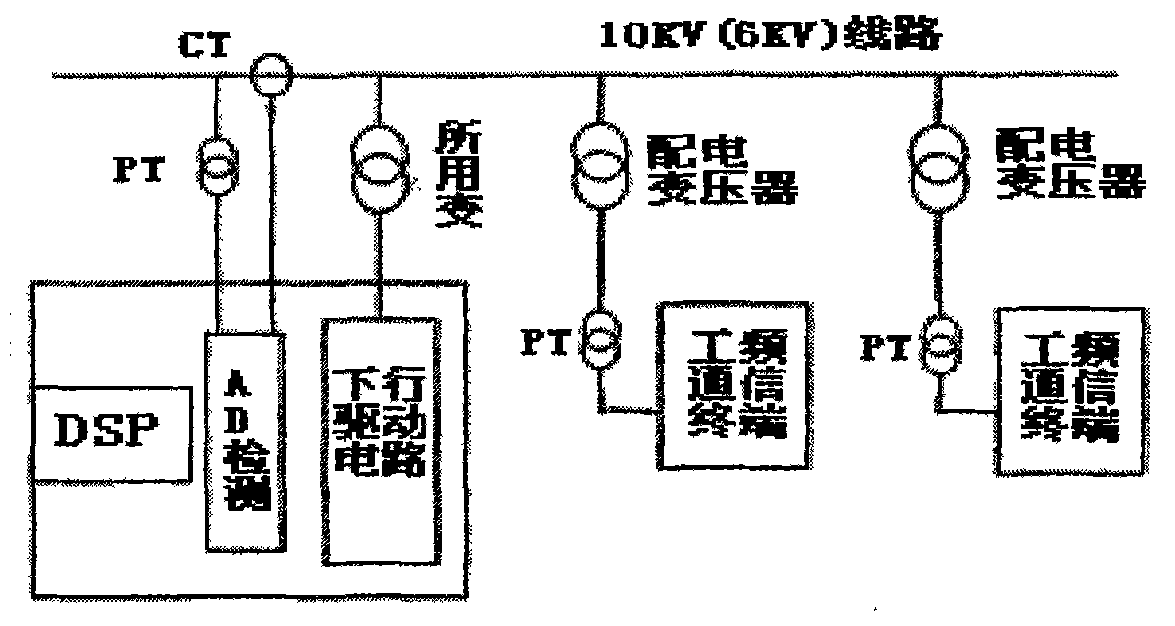
The invention discloses a time-interval-adaptation-based power line power frequency communication system and a time-interval-adaptation-based power line power frequency communication method, which relate to the network structure and signal processing of a power system and belong to technical field of power line power frequency communication. The power line power frequency communication system consists of master station equipment which is positioned in a substation and a remote communication terminal which is positioned on a low-voltage side of a distribution transformer, wherein the master station equipment also comprises a downlink signal driving device and an uplink signal demodulation device. In the method, leading information is adopted in the specified power frequency cycle during power frequency signal modulation; during demodulation, the signal-to-noise ratio of a power frequency distortion signal is improved by accumulating a sampling signal in multiple cycles in a time period of the leading information; the time domain of a modulating signal is determined by performing time frequency analysis on the basis of Wigner distribution; and data demodulation is performed in the time domain through a related detection mode. Because an accurate receiving time period and an optimal judgment moment can be obtained for demodulation, the anti-jamming capacity of the power frequency communication is greatly improved, and the system can adapt to various connection modes of the distribution transformers.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Construction method of LT fountain code codability distribution
ActiveCN105490771AReduce decoding overheadImprove performanceError preventionSoliton distributionFountain code
The invention provides a construction method of degree distribution of LT codes. The method first adjusts a binary system degree distribution, then organically combines the binary system degree distribution with robust soliton distribution, and further optimizes a degree distribution function through optimization of a translatable set value, thereby obtaining degree distribution which also has relatively good performance when code length of source data is short, i.e., binary system-robust soliton distribution is corrected. The corrected binary system-robust soliton distribution is utilizes to perform LT fountain coding on the source data, decoding spending can be reduced, decoding efficiency can be improved, and fountain codes can be well applied to the communication fields.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A normal interface rigidity prediction method considering three-dimensional fractal
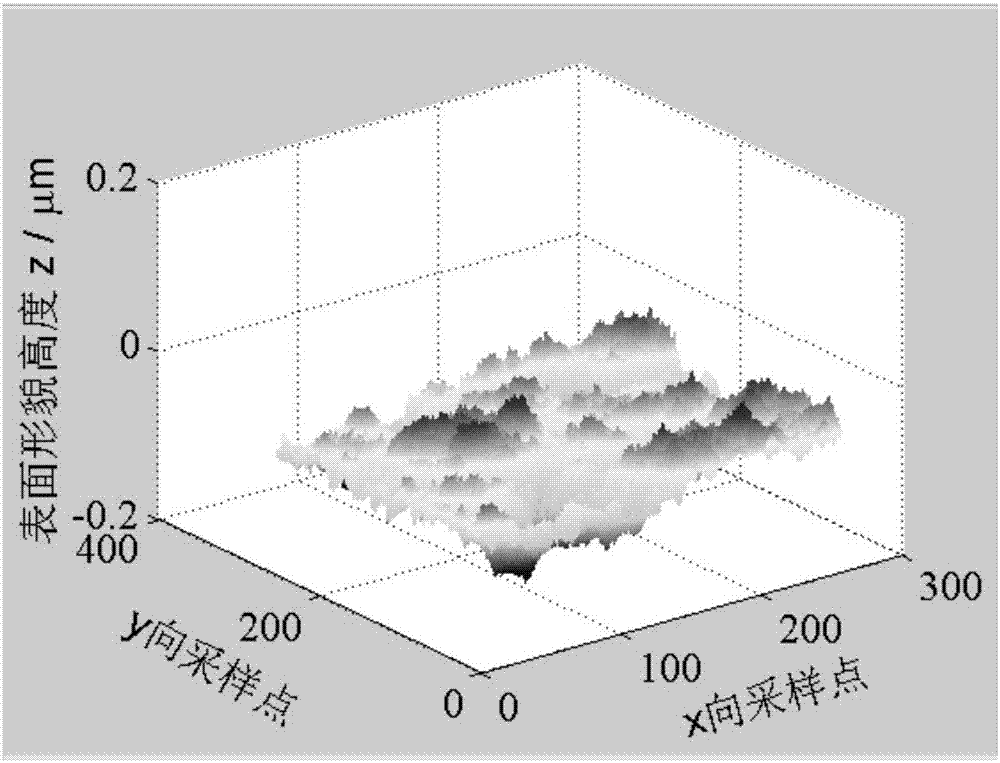
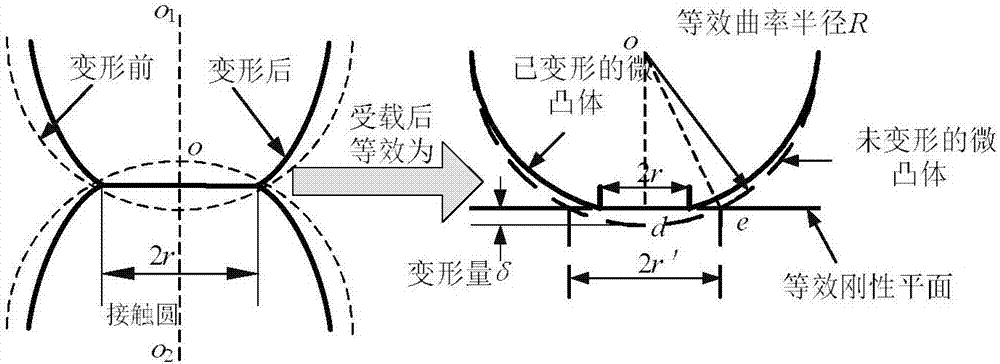
InactiveCN106991219AControl Surface DynamicsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationComputer scienceTopography
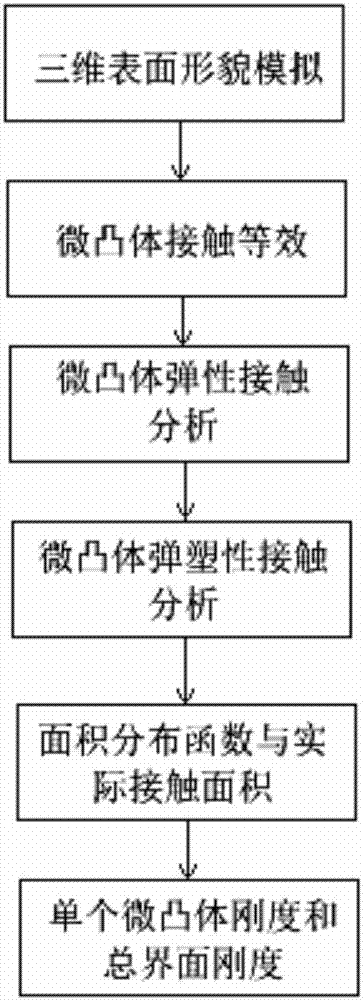
The invention relates to a normal interface rigidity prediction method considering three-dimensional fractal, the method comprising the steps of: improving a curvilinear function describing two-dimensional fractal into a correction function simulating three-dimensional fractal topography and expressing amplitudes of peaks and troughs described by the function as contact deformation quantities; making contact between two rough micro-bulges equivalent to contact between a rigid plane and an equivalent micro-bulge, wherein the actual contact area between the equivalent micro-bulge and the rigid plane meets a=pi R delta; separately calculating the deformation quantities of an elastic deformation stage and an elastoplastic deformation stage; calculating an area distribution function and the actual contact area; calculating the rigidity of a single micro-bulge and total interface rigidity; calculating the rigidity kn1 of the elastic stage, the rigidity kn2 of the elastoplastic stage and the total interface rigidity. The prediction method for acquiring the between-interface rigidity of precision machinery is simple and easy to implement. The method takes into consideration elastoplastic deformation of micro-bulges, contact friction factors and three-dimensional fractal distribution and obtained results can provide technical reference for prediction and control of dynamic characteristics of interfaces.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Logistic distribution vehicle path optimizing method based on improved Cuckoo algorithm
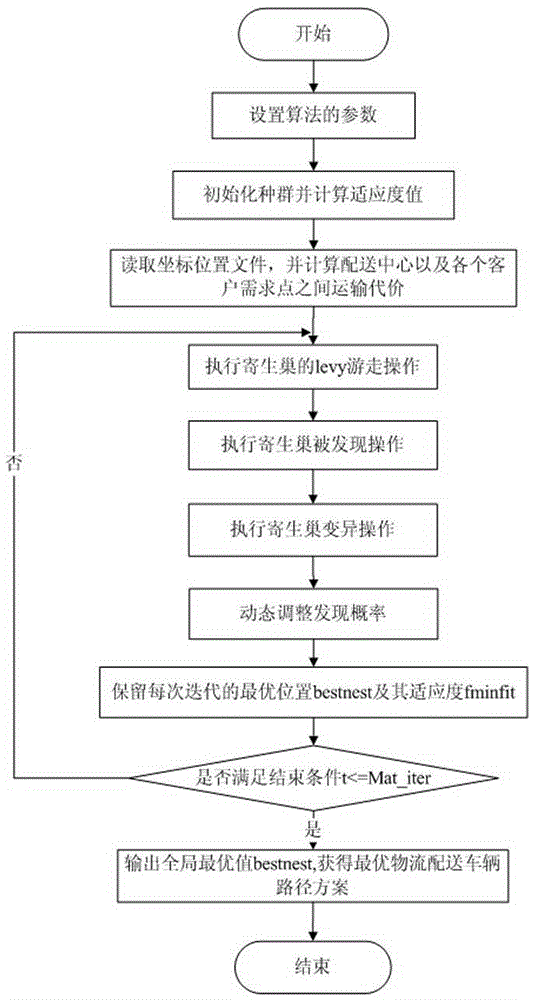
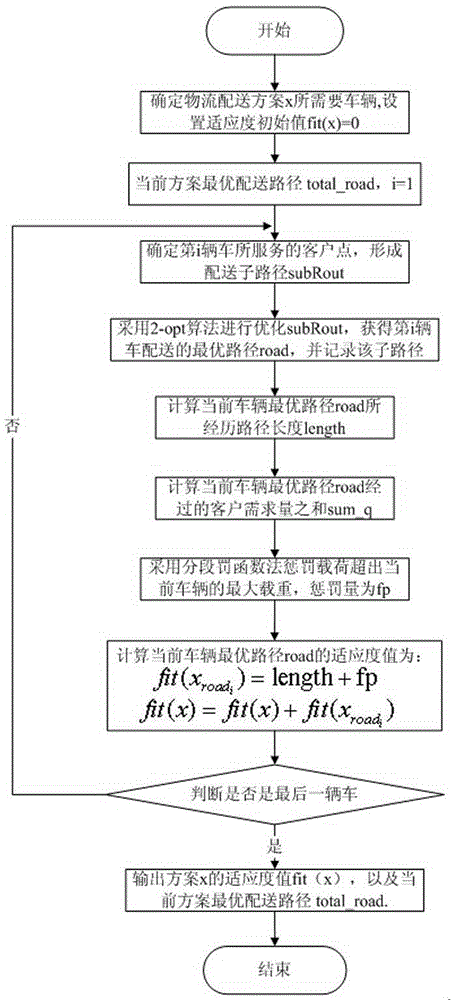
ActiveCN105260785ASolving Shipping Optimization ProblemsEnrich the method of solving logistics distribution route optimization problemForecastingEffective solutionAlgorithm
The invention relates to a logistic distribution vehicle path optimizing method based on an improved Cuckoo algorithm, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of 1, setting the parameters of the improved Cuckoo algorithm; 2, initializing population and calculating a fitness value, wherein the population adopts a uniform distribution function to generate size parasitic nests with an nd-dimensional searching space range of [1, carnumber], calculation of the fitness value comprises firstly adopting a 2-opt algorithm to locally optimize the path in each route and solving the path value of each optimized route by a segmented penalty function; 3, executing the levy migration operation of the parasitic nests; 4, executing the operation that the parasitic nests are detected; 5, executing the mutation operation of the parasitic nests; and 6, dynamically adjusting detection probabilities. According to the logistic distribution vehicle path optimizing method based on the improved Cuckoo algorithm, combination of the improved Cuckoo algorithm and the 2-opt algorithm is applied to solving the problem about the logistic distribution vehicle path, a novel available and effective solution is provided for solving the problem about the optimization of logistic vehicle distribution, and methods for solving the problem about optimizing the logistic distribution path are enriched.
Owner:屈迟文
Frequency hopping (FH) signal identification method
InactiveCN105991492ARealize identificationImprove recognition rateModulation type identificationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Frequency spectrum
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Image quality enhancement with histogram diffusion
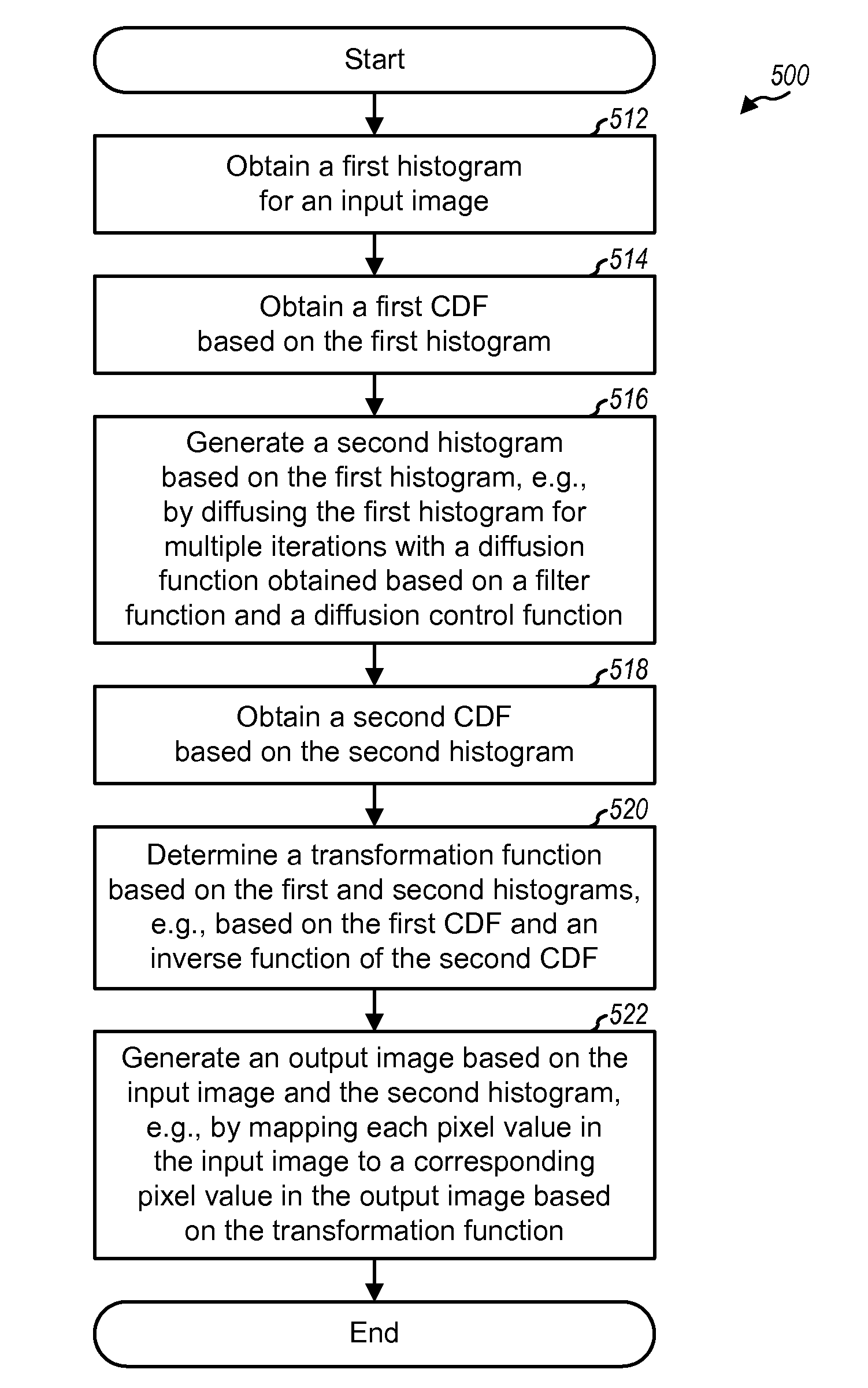
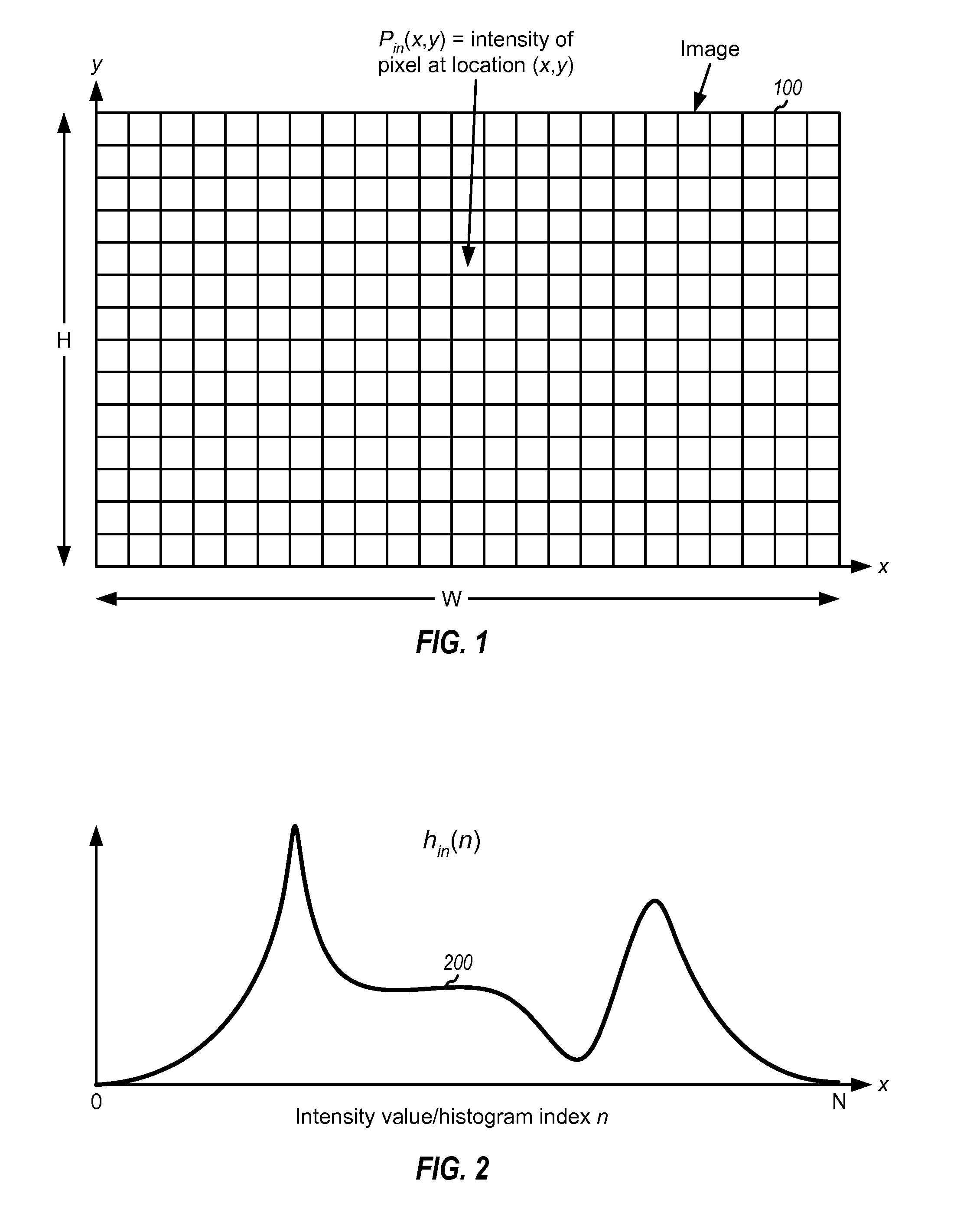
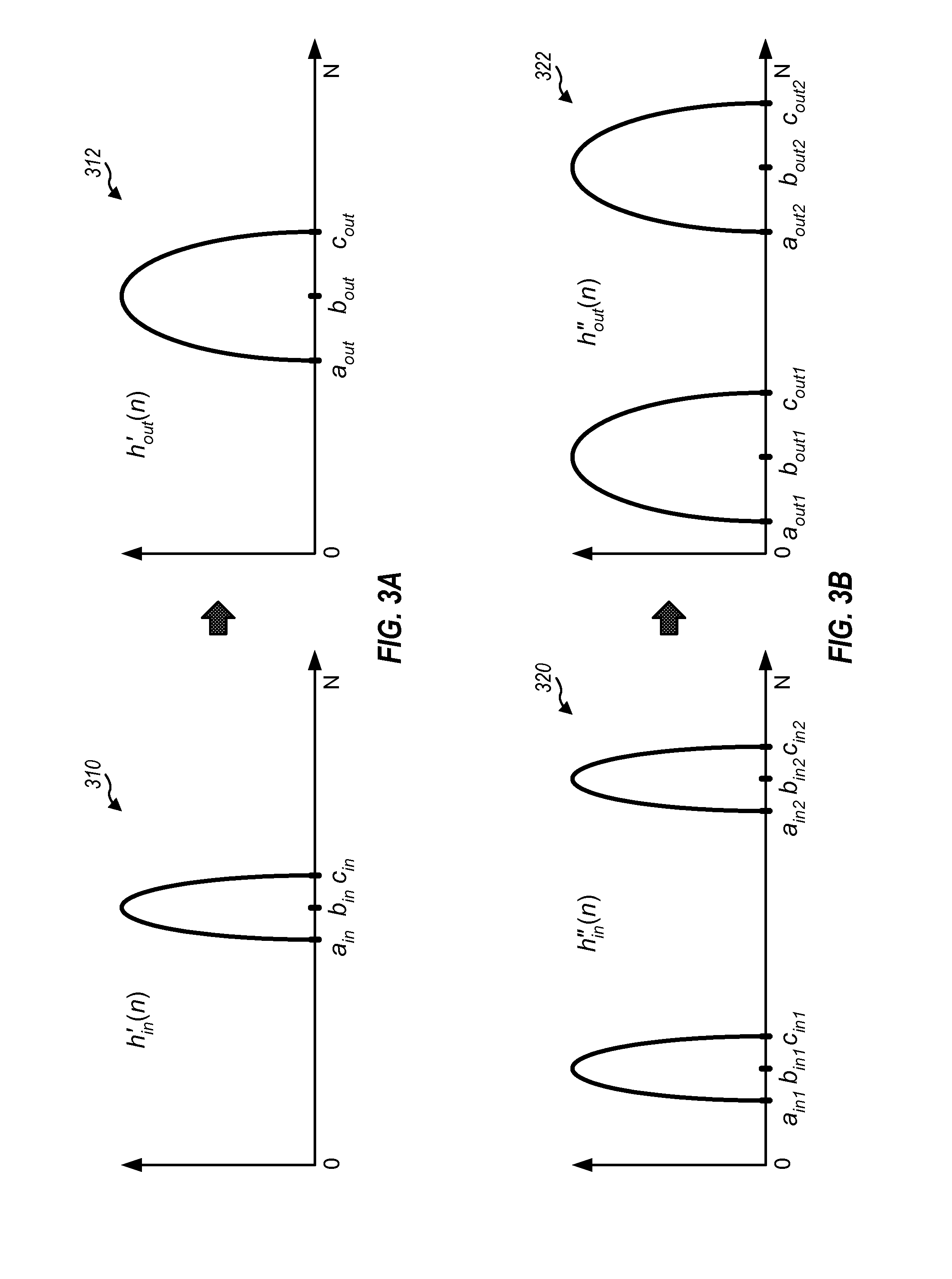
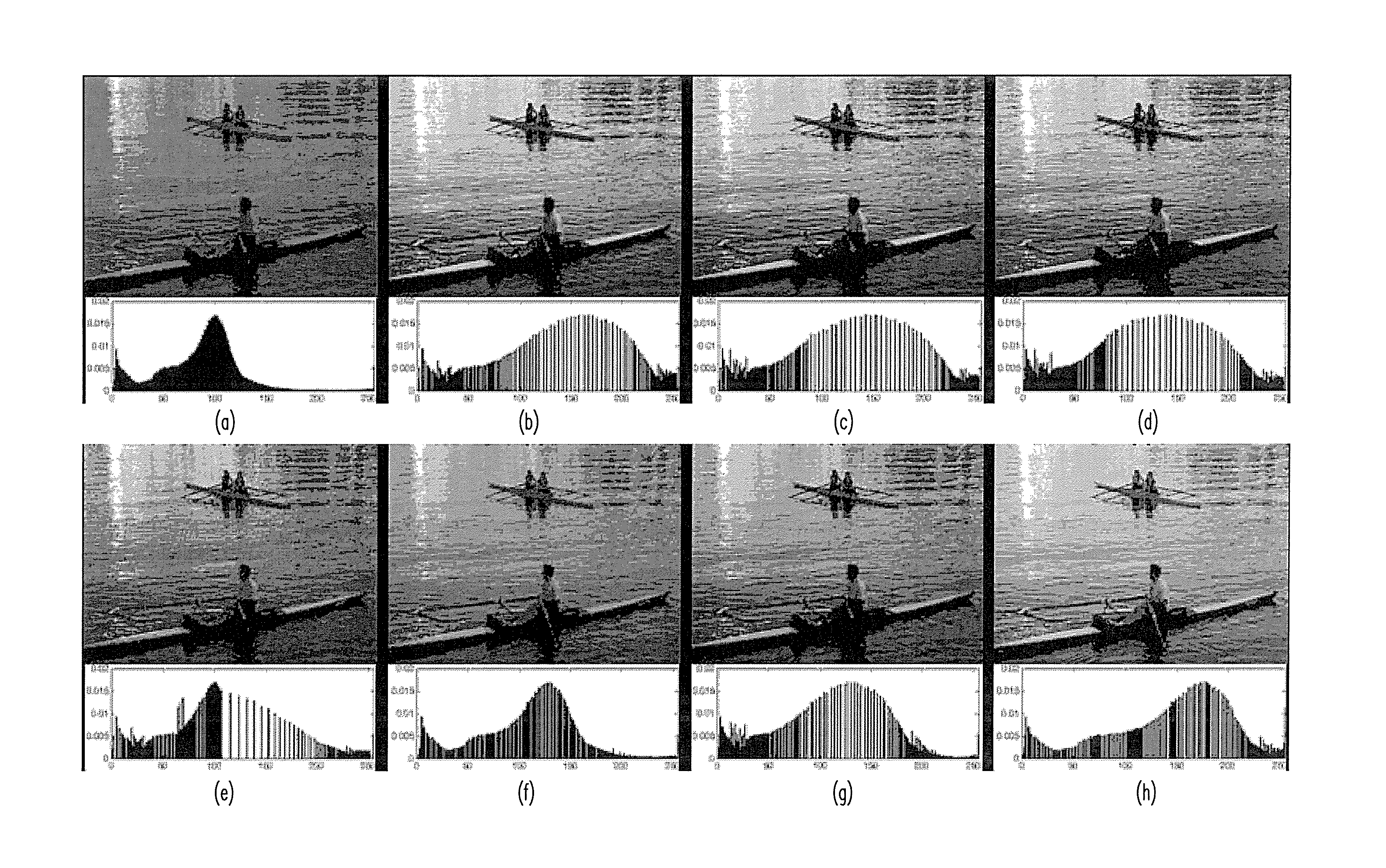
InactiveUS20090110274A1Quality improvementIncrease coverageImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusionImaging quality
Techniques for improving the quality of images are described. A first histogram of intensity values may be obtained for an input image and diffused to obtain a second histogram with better intensity coverage. The diffusion may be achieved by filtering the first histogram for multiple iterations with a diffusion function obtained based on a filter function and a diffusion control function. The filter function may control the rate and / or characteristics of the diffusion. The diffusion control function may control shifts in positions of lobes in the first histogram. A transformation function may be determined based on a first cumulative distribution function (CDF) for the first histogram and an inverse function for a second CDF for the second histogram. An output image may be generated by mapping each pixel value in the input image to a corresponding pixel value in the output image based on the transformation function.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Image processing apparatus
InactiveUS20130287299A1High image processing efficiencyImprove image qualityImage enhancementImage codingImaging processingNormal density
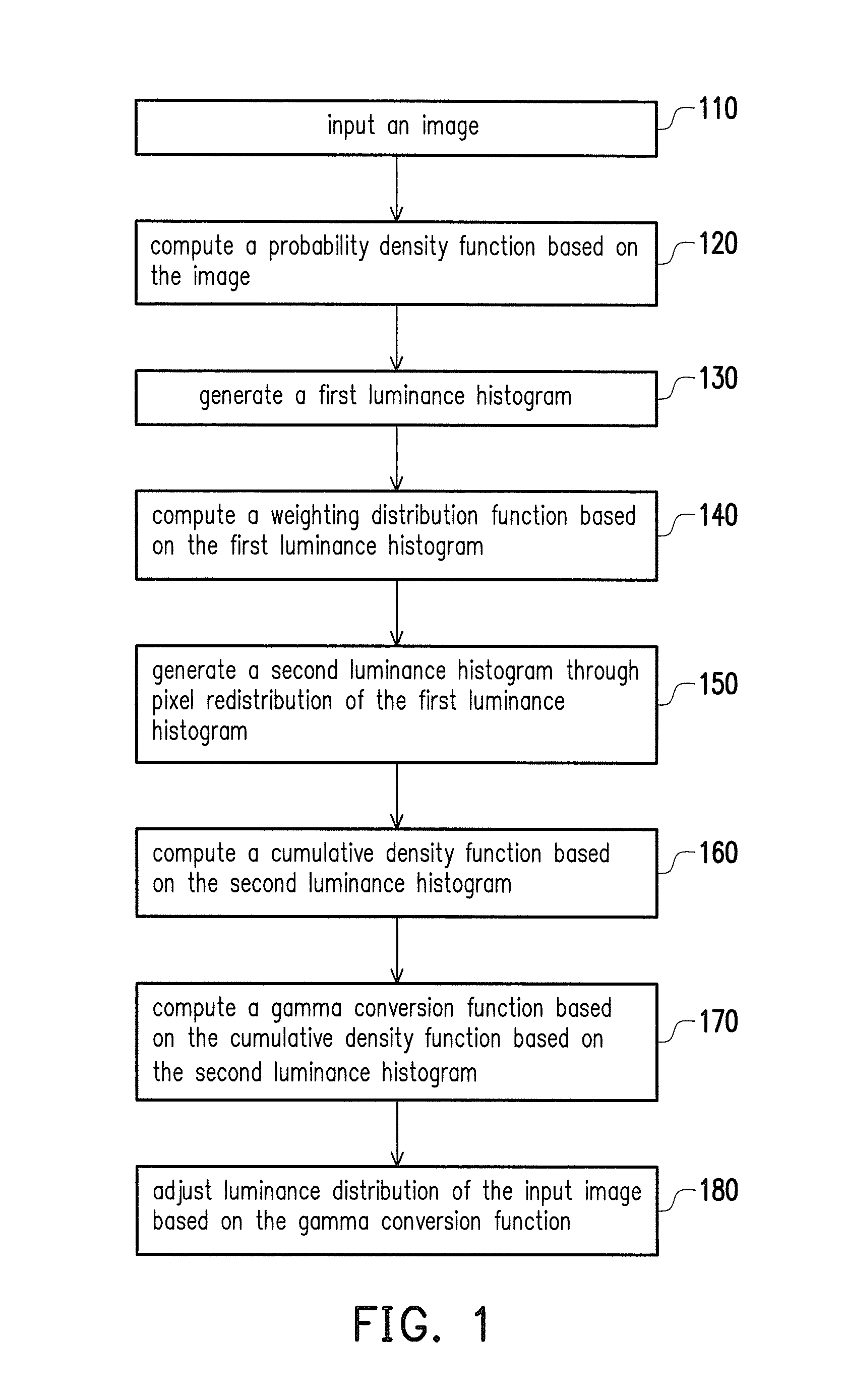
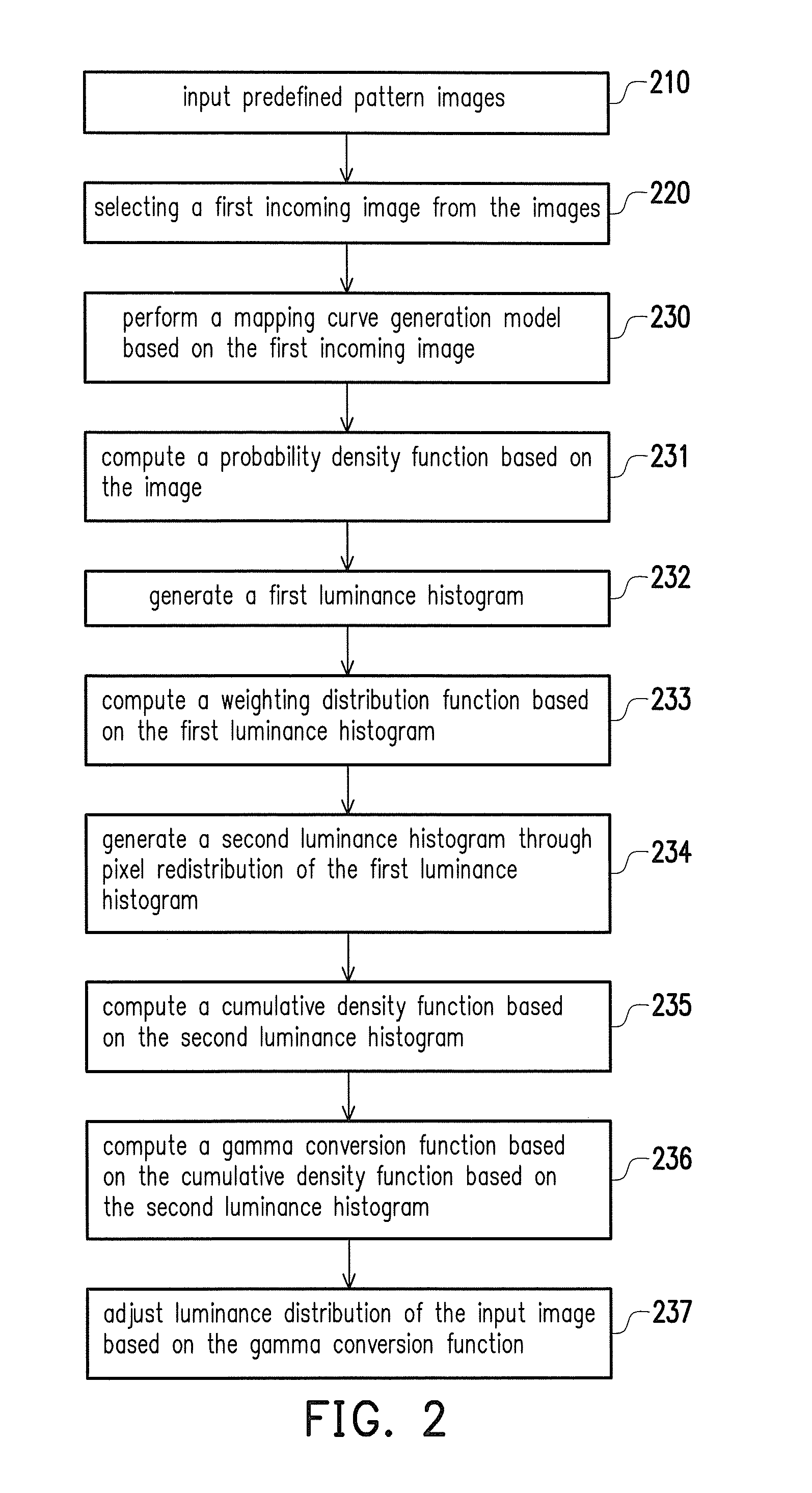
The invention discloses an image processing apparatus. The image processing apparatus includes an image statistic computation circuitry, a reconfigurable circuitry and a luminance transformation circuitry. The image statistic computation circuitry computes a probability density function corresponding to an inputted image; generates a first luminance histogram by subsampling a luminance histogram related to the probability density function in a first period. The reconfigurable circuitry computes a weighting distribution function according to the first luminance histogram in a second period after the first period; computes a smoothed cumulative density function according to the weighting distribution function in a third period after the second period; computes a gamma transform function in a fourth period after the third period. The luminance transformation circuitry generates a resulted image by adjusting a luminance distribution of the inputted image based on the gamma transform function in a fifth period after the fourth period.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
A network structure optimization method based on an attention mechanism
InactiveCN109948783AHigh precisionImprove training effectNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsNetwork structureMachine learning
The invention provides a network structure optimization method based on an attention mechanism, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the reasonable weight distribution of each module of aneural network, emphasizing or weakening the contribution of certain input data to the next processing, carrying out the design in a differentiable mode, and completing an end-to-end neural network. According to the specific method, a multi-layer neural network is used for learning a weight distribution function. The learning mode is different from a common neural network training mode, firstly, only one target network is trained and then a weight distribution network is added to the network, then parameters of the target network are fixed, the weight distribution network is trained, and the target network and the weight distribution network are trained in an iteration mode until the effect is optimal.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
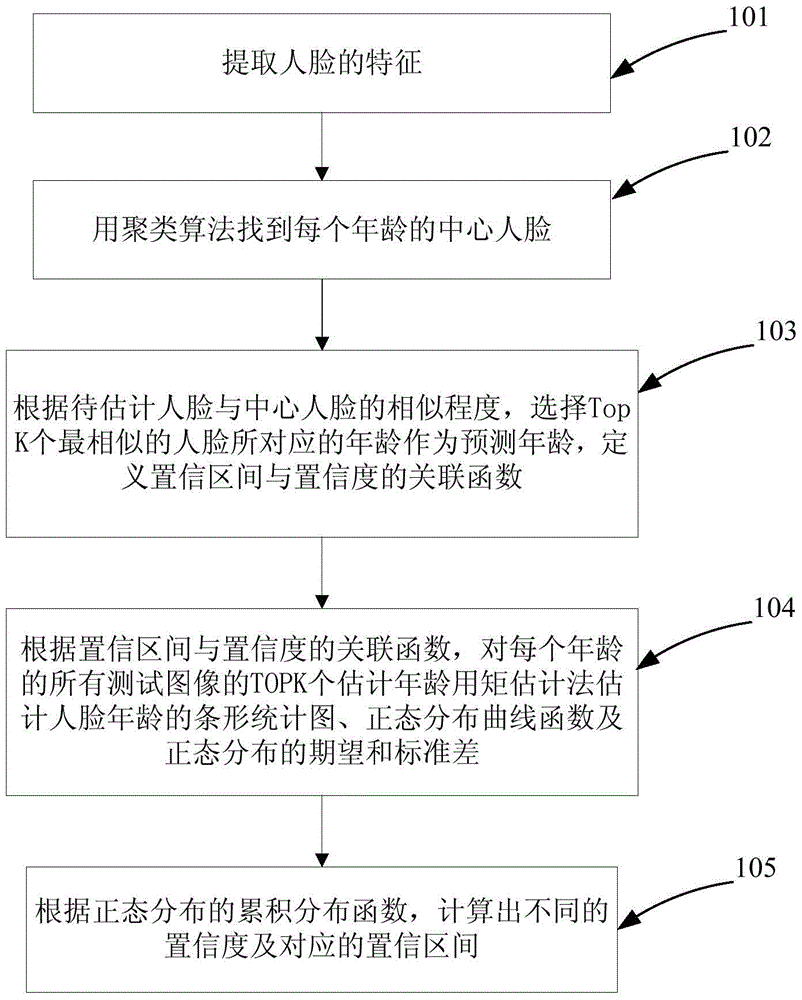
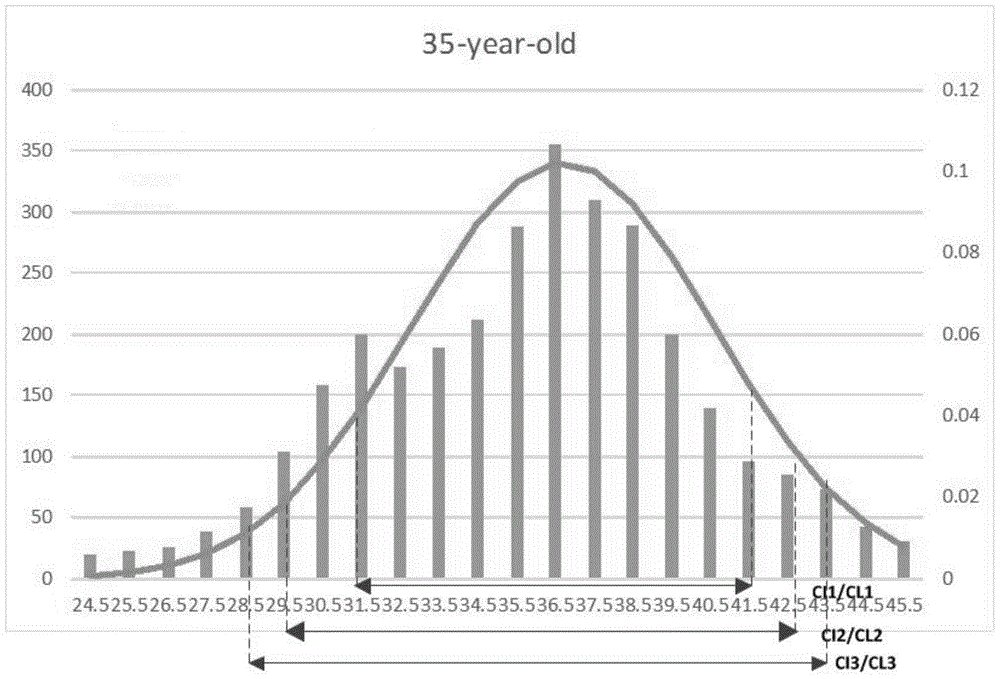
Dynamic interval-based face age estimation method
InactiveCN105678269AThe solution accuracy is not highCharacter and pattern recognitionCluster algorithmAlgorithm
The present invention discloses a dynamic interval-based face age estimation method. The method comprises the steps of extracting the features of a face; finding a central face at each age based on the clustering algorithm; according to the similarity degree between a to-be-estimated face and the central face, selecting top K ages corresponding to a most similar face as prediction ages and defining a correlation function between the confidence interval and the confidence coefficient; according to the correlation function between the confidence interval and the confidence coefficient, estimating the bar graph, the normal distribution curve, the normal distribution expected value and the standard deviation of a face age according to the square estimation method by utilizing the top K ages of all test images at each age; calculating different confidence coefficients and the corresponding confidence intervals thereof according to the cumulative distribution function of the normal distribution. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the problem in the prior art that the traditional single-age estimation method is not high in accuracy can be effectively solved.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Method and system for image processing for structured light profiling of a part
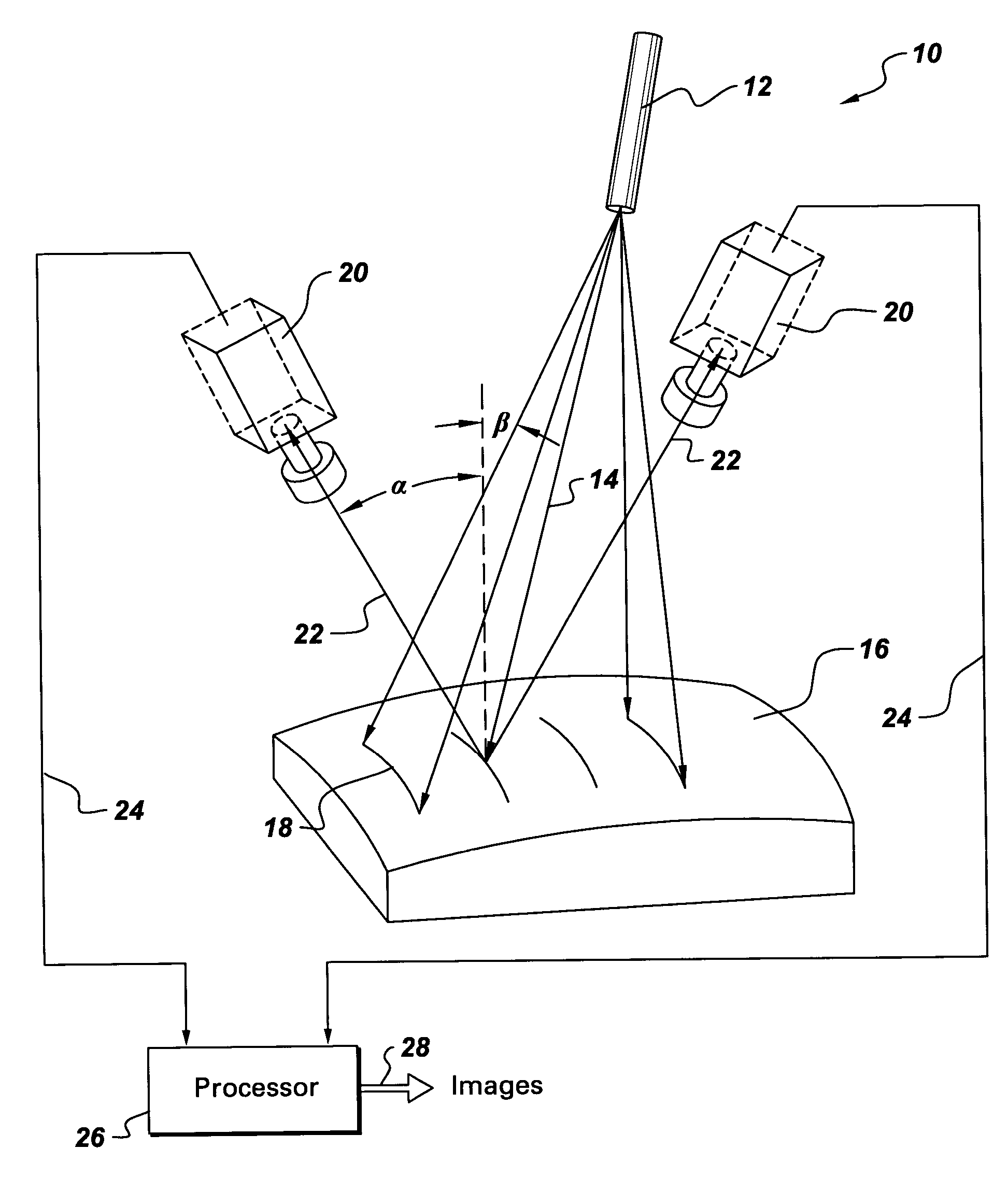
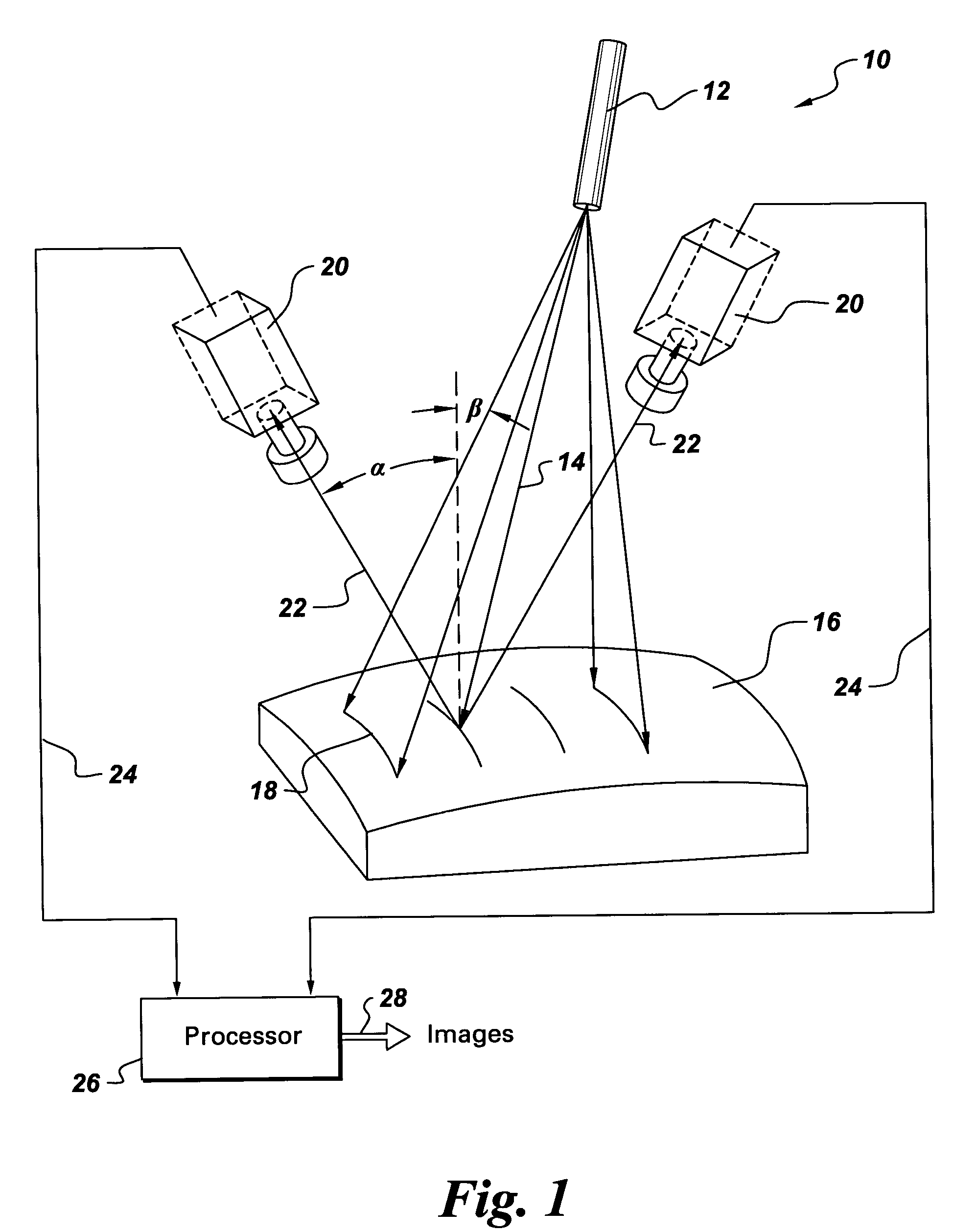
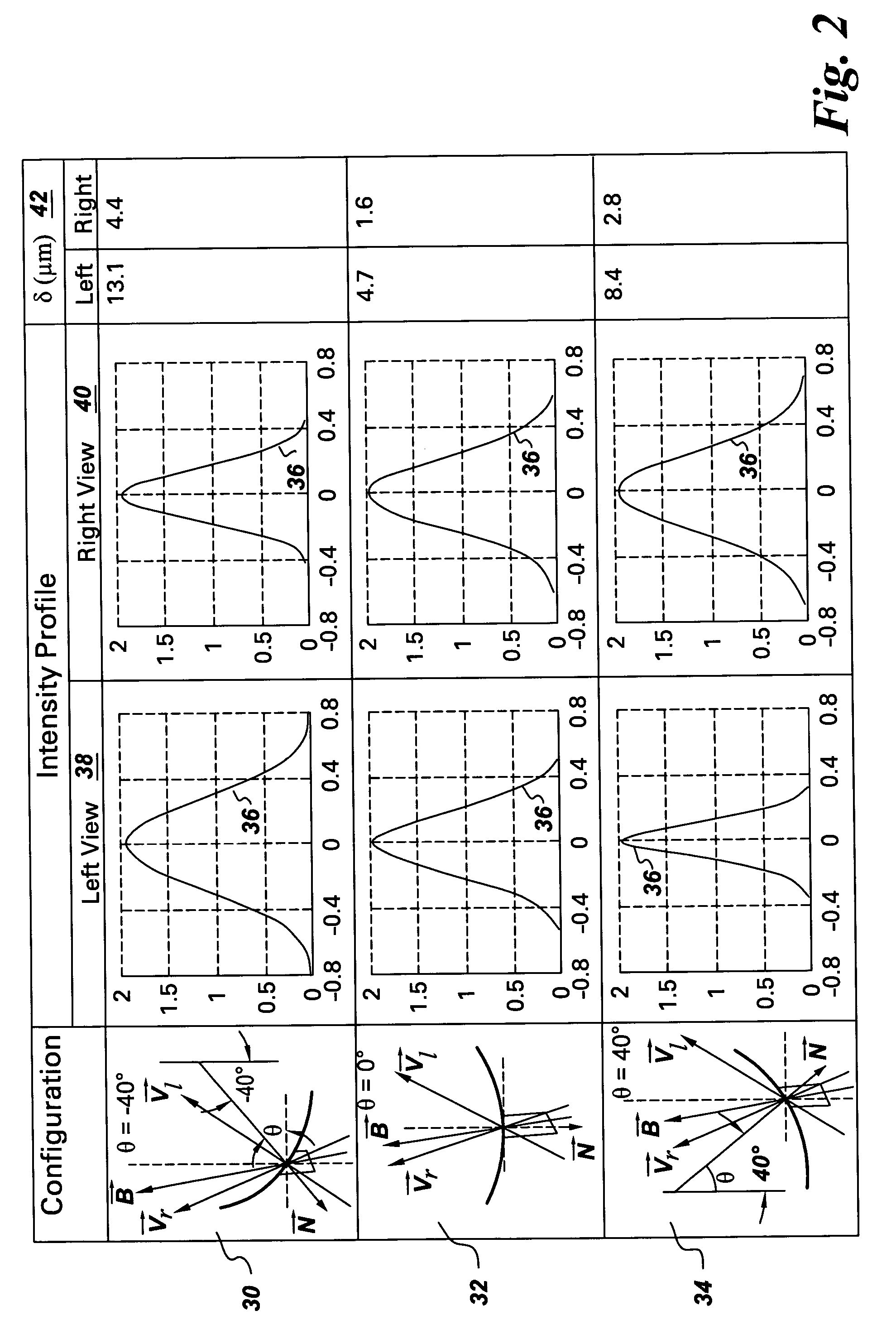
InactiveUS7302109B2Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPair distribution functionImaging processing
An image processing method for structured light profiling includes sampling an image of a structured light pattern to obtain an intensity distribution, selecting a number of sets of sampled points from the intensity distribution. Each of the respective sets includes a number of sampled points. The image processing method further includes fitting each of the sets of sampled points to a respective distribution function and filtering the distribution functions to select a representative distribution function for the intensity distribution.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
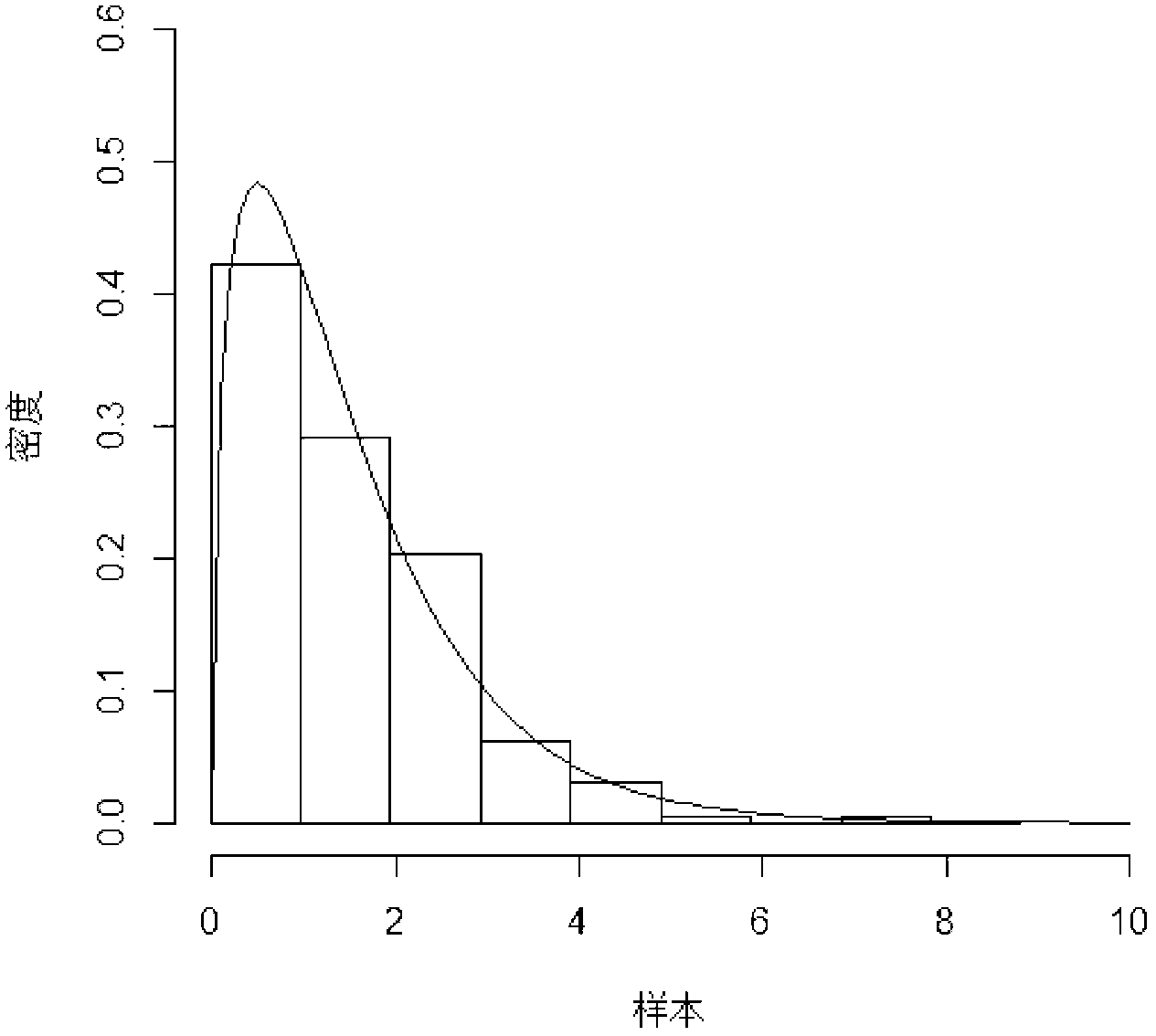
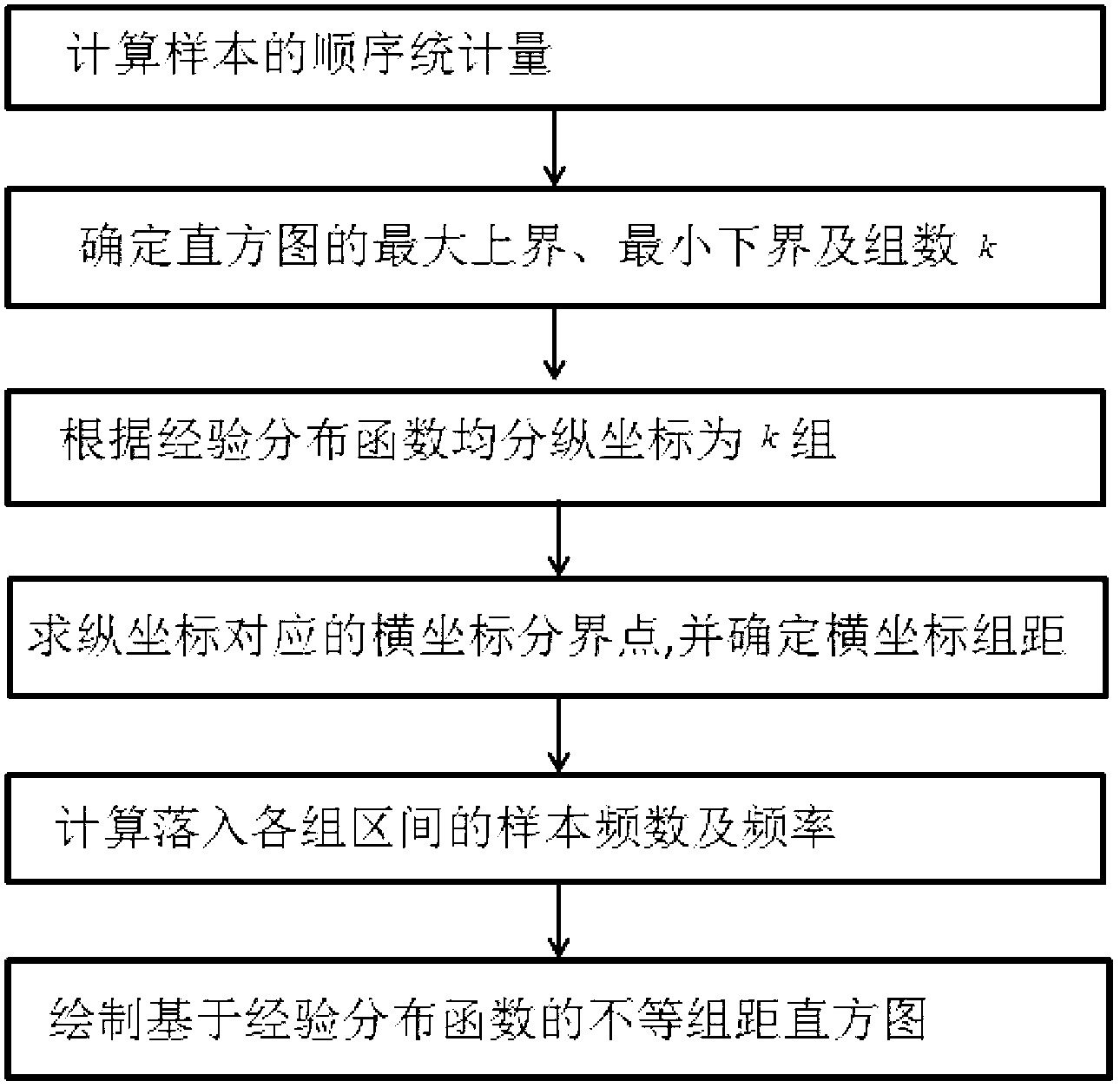
Unequal class interval histogram rendering method based on empirical distribution function
The invention provides an unequal class interval histogram rendering method based on an empirical distribution function. Aiming at the fact that an equal class interval histogram can not reflect distribution characteristics of a sample adequately, the distribution characteristics of the sample reflected by the equal class interval histogram is inconsistent with an actual situation, and the unequal class interval histogram rendering method based on the empirical distribution function is brought out by means of the property that the empirical distribution function is effective fitting of a distribution function. The rendering method includes the specific steps: 1, computing order statistic of the sample; 2, confirming maximum upper bond, minimum lower bond and class count k of a histogram; 3, dividing a vertical coordinate into k classes equally according to the empirical distribution function; 4, calculating demarcation points, corresponding to k classes of vertical coordinates, of a horizontal coordinate, confirming class intervals of k classes of horizontal coordinates; 5, computing frequency number and frequency of the sample dropping in each class interval; and 6, rendering the unequal class interval histogram based on the empirical distribution function. By means of a graphic method and comparative mean integrated square error (MISE), the histogram rendered through the unequal class interval histogram rendering method based on the empirical distribution function is testified to have an accurate fitting effect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Assessment method considering voltage probabilities of multiple electric power systems with wind power output randomness
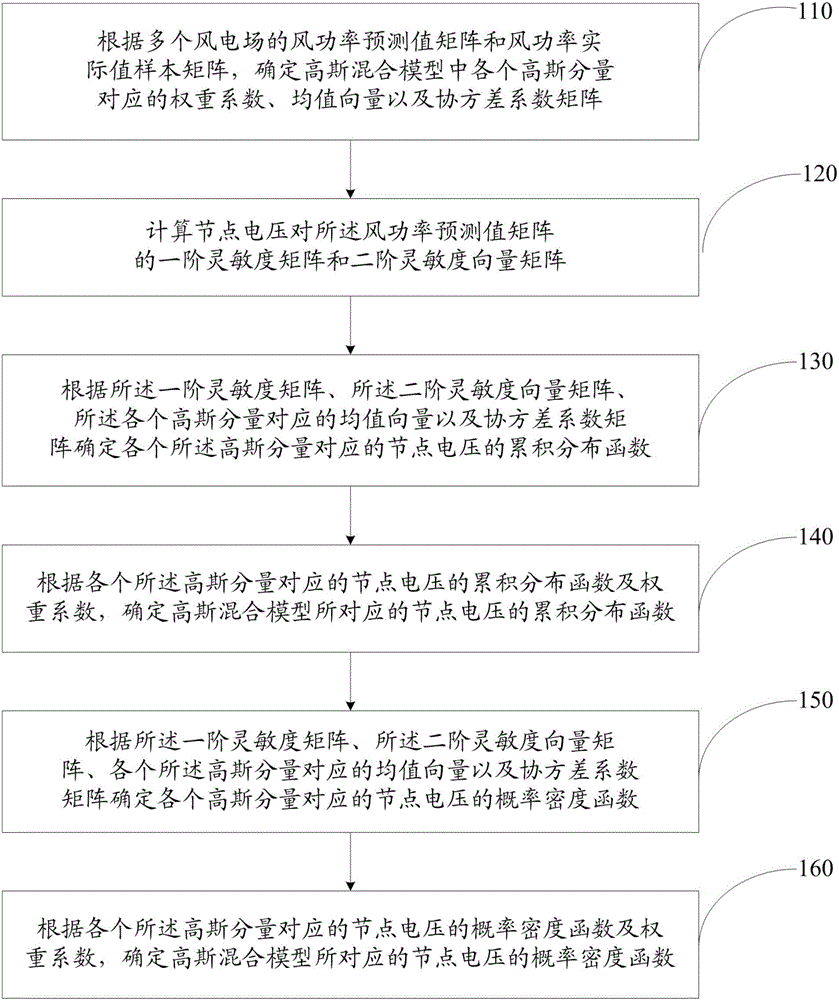
InactiveCN105808962AImprove accuracyEasy to calculateSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsWeight coefficientElectric power system
The invention discloses an assessment method considering voltage probabilities of multiple electric power systems with wind power output randomness. The assessment method comprises the following steps: determining a weight coefficient, a mean vector and a covariance coefficient matrix according to a wind power predicted value matrix and a wind power actual value sample matrix of a plurality of wind power plants; calculating first-order and second-order sensitivity vector matrixes from node voltages to the wind power predicted value matrix; determining cumulative distribution functions of the node voltage corresponding to each Gaussian component according to the first-order and second-order sensitivity vector matrixes, the mean vector and the covariance coefficient matrix; determining cumulative distribution functions of the node voltage corresponding to a Gaussian hybrid model according to each cumulative distribution function and the weight coefficient. According to the assessment method, the cumulative distribution functions of the node voltages can be determined through extracting the wind power predicted value matrix and the wind power actual value sample matrix of the plurality of wind power plants, so that the used time is short; the first-order and second-order sensitivity vector matrixes are calculated, so that the nonlinear relationship between the node voltages and the wind power is fully considered and the correctness is high.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID NINGXIA ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
Truncated versatile distribution model representing renewable energy power probability distribution
The invention discloses a truncated versatile distribution model representing renewable energy power probability distribution. Compared with common normal, beta and versatile distribution in current renewable energy power representation, truncated versatile distribution has a bounded truncation characteristic that other distribution does not have. In the aspect of representing the renewable energy power distribution, the model has higher fitting precision on one hand and ensures the boundedness of a distribution function on the other hand, and a CDF (Cumulative Distribution Function) and an inverse function of the distribution function both have closed analytical expressions, so that the model is more suitable for economic dispatching of a power system using renewable energy including wind, power and the like. By comparison with fitting effects of other common distribution on actual wind power distribution of a wind power plant and actual photovoltaic power distribution of a photovoltaic power station, the advantages of a mentioned probability distribution model are verified. A method has high promotion values and good application prospects.
Owner:武汉龙德控制科技有限公司
Backlight image micron-order edge detection method
ActiveCN105005985AHigh accuracy of surface fittingHigh precisionImage analysisDiffusion functionPoint spread function
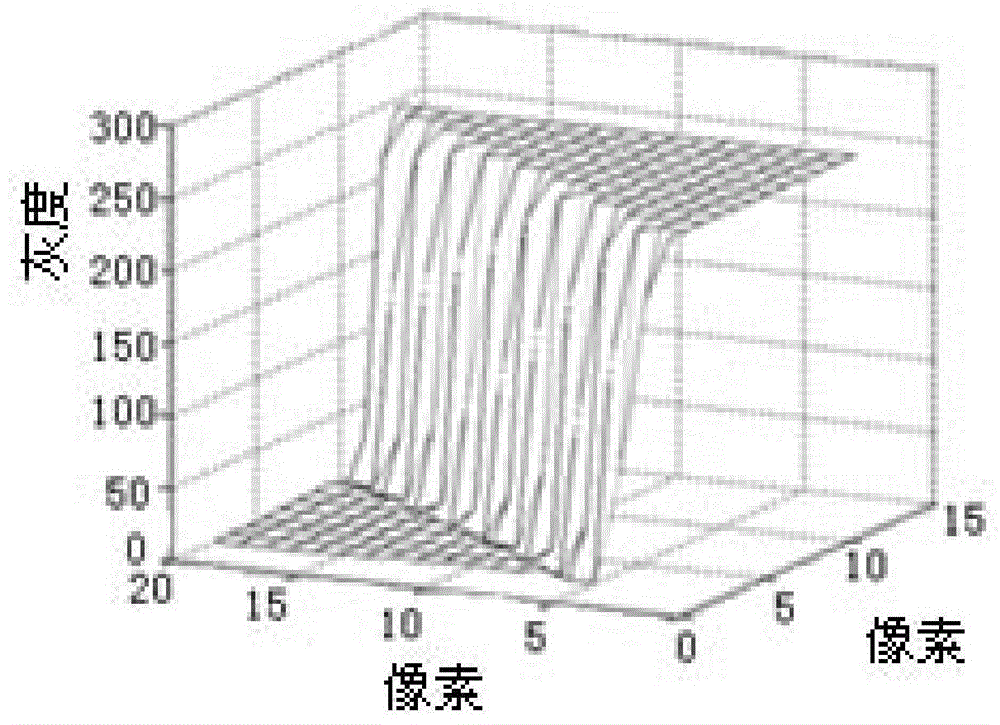
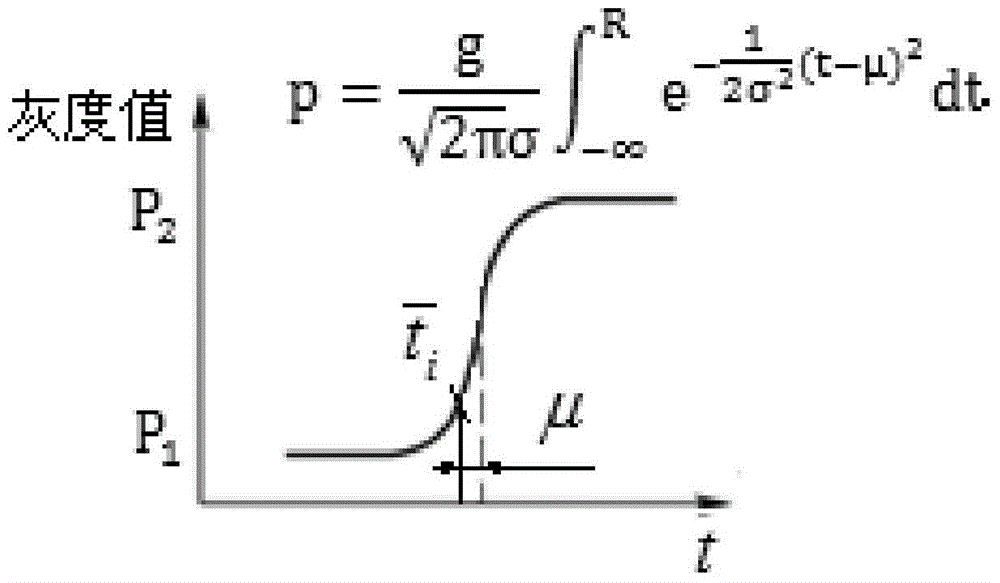
The invention belongs to the technical field of high-precision detection and especially relates to a backlight image micron-order edge detection method with high curved surface fitting precision and a good anti-interference effect. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) in combination with a point spread function and a unilateral step model, constructing a backlight image step edge normal plane transversal normal distribution function model, wherein the foreground and the background of a backlight edge detection image are constants P1 and P2, the gray difference of the foreground and the background is g=P2-P1, a transversal of the gray curved surface passing through the edge normal plane is a normal distribution function (gauss integration) curve is described in the specifications, then a formula described in the specifications is satisfied, and the projection of image edge points passing the central point of the curve in an image place is described in the specifications or satisfies t- [mu]=0.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Improved versatile distribution and versatile mixture distribution models characterizing wind power probability distribution
ActiveCN105930671AFit closelyReduce orderSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsElectricityGaussian mixture distribution
The present invention discloses improved versatile distribution and versatile mixture distribution models characterizing wind power probability distribution. By selecting an appropriate shape parameter and order, a versatile mixture distribution model is capable of fitting wind power distribution or error distribution in any shape under a precision requirement. A CDF of a distribution function of the model has a closed analytic expression, and an inverse function of the CDF is an implicit function expression, which is applicable to economic dispatch in a wind power integrated system. Compared with fitting performed on actual wind power distribution of an actual wind farm by a Gaussian mixture distribution model, an advantage of a probability distribution model is verified. The method has great promotion value and an excellent application prospect.
Owner:武汉龙德控制科技有限公司
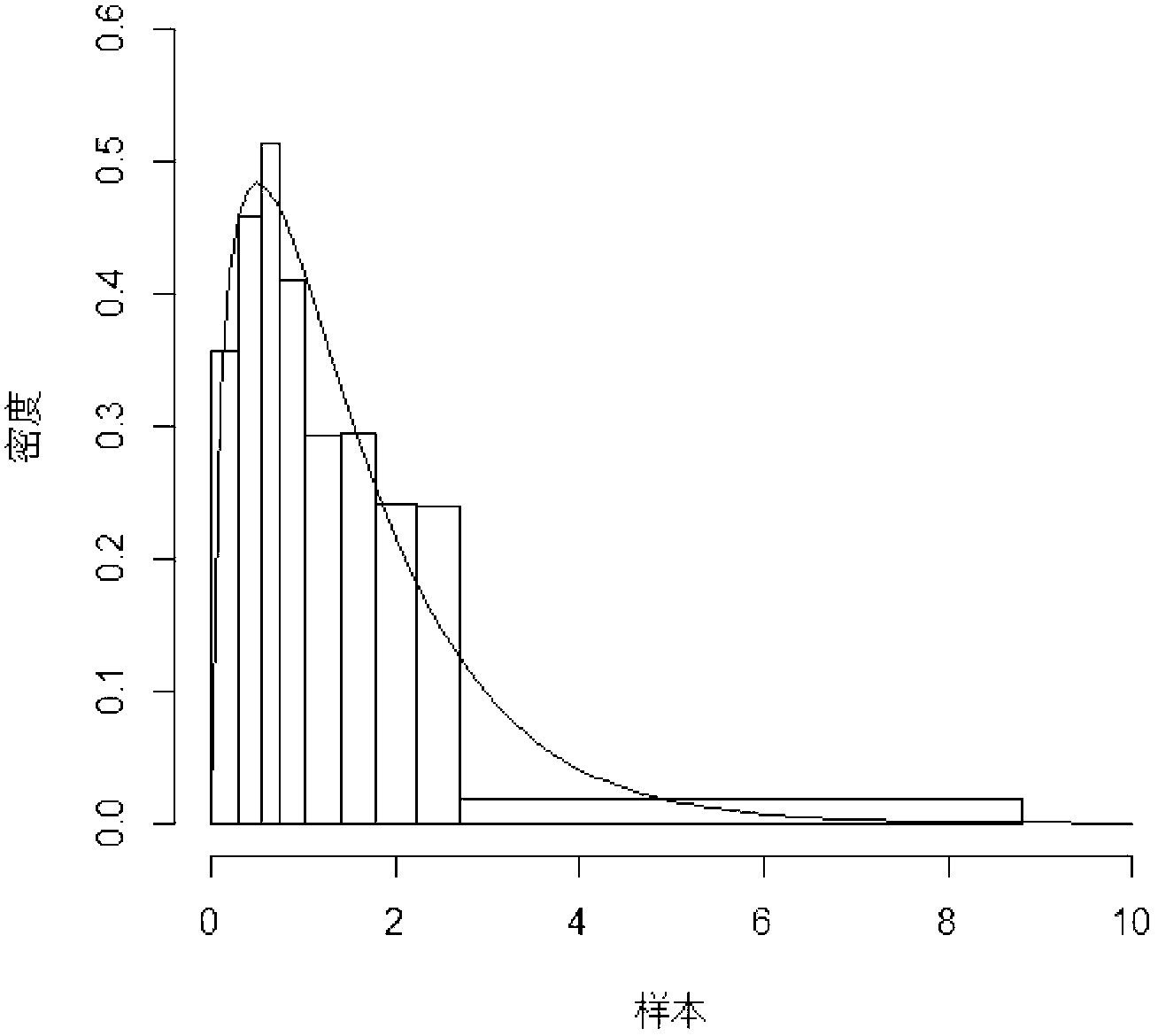
Light spot centroid calculation method for weak signal of Hartmann wavefront detector
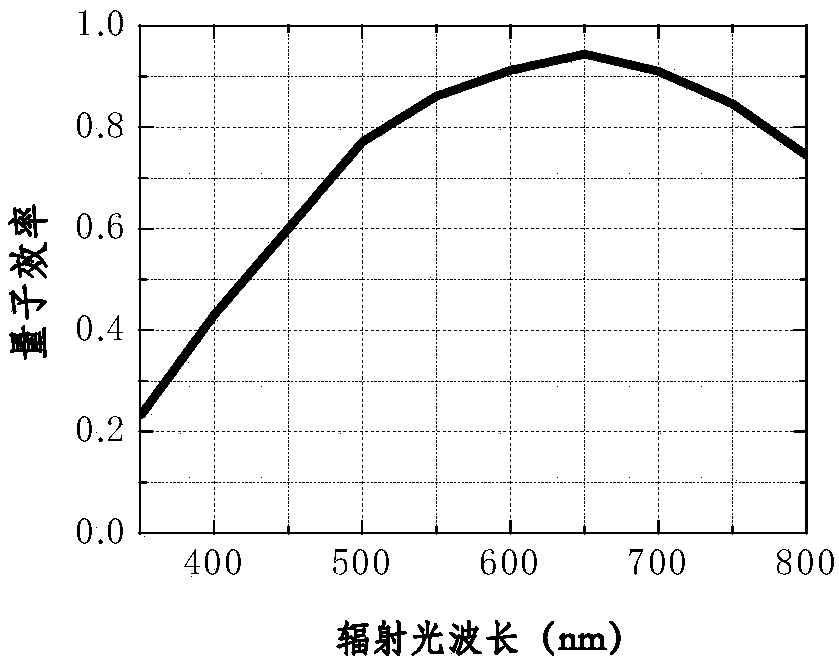
The invention belongs to the technical field of adaptive optical imaging, and proposes a filtering method for solving a problem of big wavefront detection errors caused by the low signal to noise ratio of the weak signal. The basic idea of the invention is that the intensity distribution of each light spot of a Hartmann wavefront detector should be similar to the Gaussian-like intensity distribution function shown by drawing 1; the weight of a central intensity signal of a light spot will be highlighted and the weight of the edge photon noise of a subregion will be reduced if the Gaussian-likeintensity distribution function in a 3*3 pixel region is used for the correlation calculation with an intensity distribution function of a 6*6 pixel subregion, and a regional weight filtering windowW is formed; the range of W is also located in the 6*6 pixel subregion; an effective subregion weight filtering window W is also used for the weight calculation with the intensity distribution I of the subregion, thereby obtaining the intensity distribution of the light spot of a subregion with the noise being suppressed; and the centroid of the light spot of the subregion is calculated through acommon centroid algorithm. The method can enable the wavefront detection error (the magnitude of 5.5) to be reduced by 20%.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
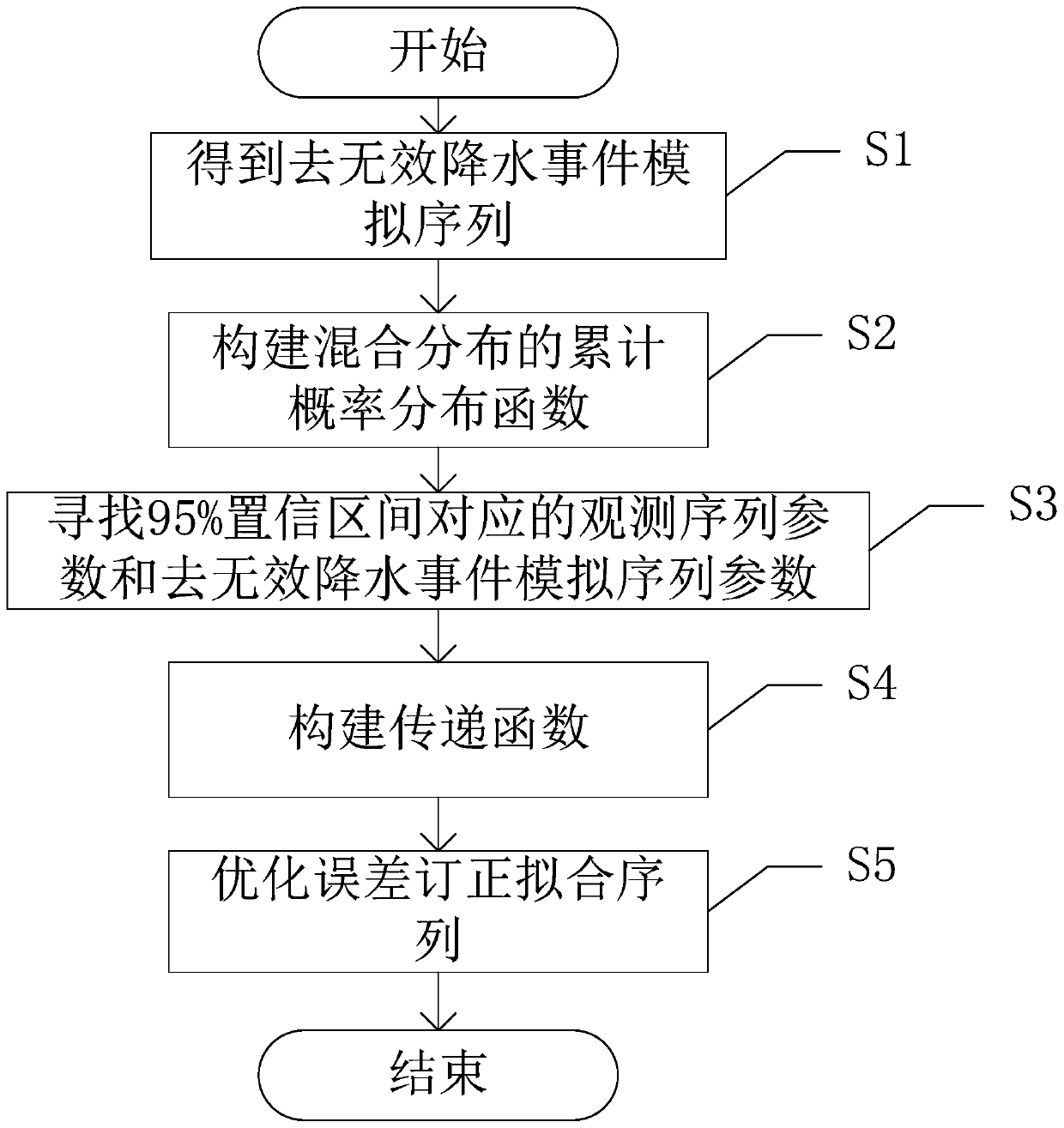
Regional climate mode dynamic downscaling factor error correction method
The invention discloses a regional climate mode dynamic downscaling factor error correction method. A mixed distribution function is constructed by using Gamma distribution and GEV distribution; multi-parameter factors are set, the problem that an existing QM quantile mapping method cannot give consideration to correction capacity of common type daily precipitation and extreme precipitation eventsin dynamic downscaling elements of a regional climate mode is solved. Parameter optimization is carried out in a 95% confidence space by using a genetic algorithm, so that error correction indexes with excellent relative error indexes MRE, correlation coefficients CORR and Nash efficiency coefficients NSE can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
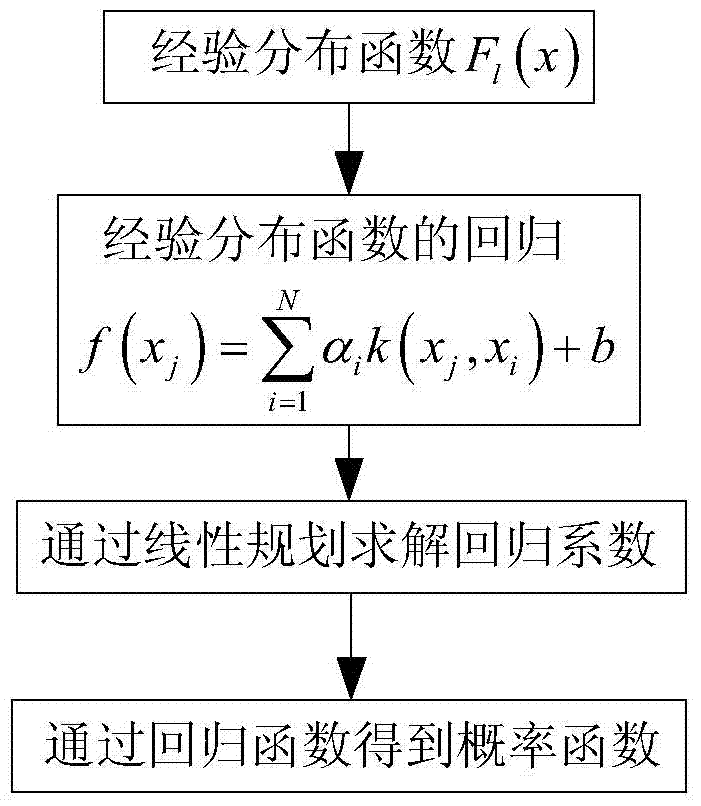
Sparse nonparametric body area channel probability representation method
InactiveCN103577690AOvercoming demanding issuesTo achieve "sparseSpecial data processing applicationsProbability representationBody area network
The invention discloses a sparse nonparametric body area channel probability representation method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, adopting an electromagnetic wave transceiver in a body area network to collect data, S2, establishing an empirical distribution function and solving the empirical distribution function through a step function, S3, adopting an empirical distribution function approximate density function and establishing a regression function, S4, solving the regression function through linear programming, S5, obtaining a corresponding probability function through derivation of the regression function, and S6, evaluating and analyzing an obtained sparse nonparametric probability model. A representation model proposed in the method is not restricted by specific propagation circumstances, and is more applicable to wireless communication in a body area network because of nonparametric property. The method overcomes the problem that the requirements on simple capacity of traditional models are rigorous, ensures that coefficients of a large amount of linear combinations are zero by controlling the quantity of support vectors during the process of regression, and realizes the sparsification of regression coefficients.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
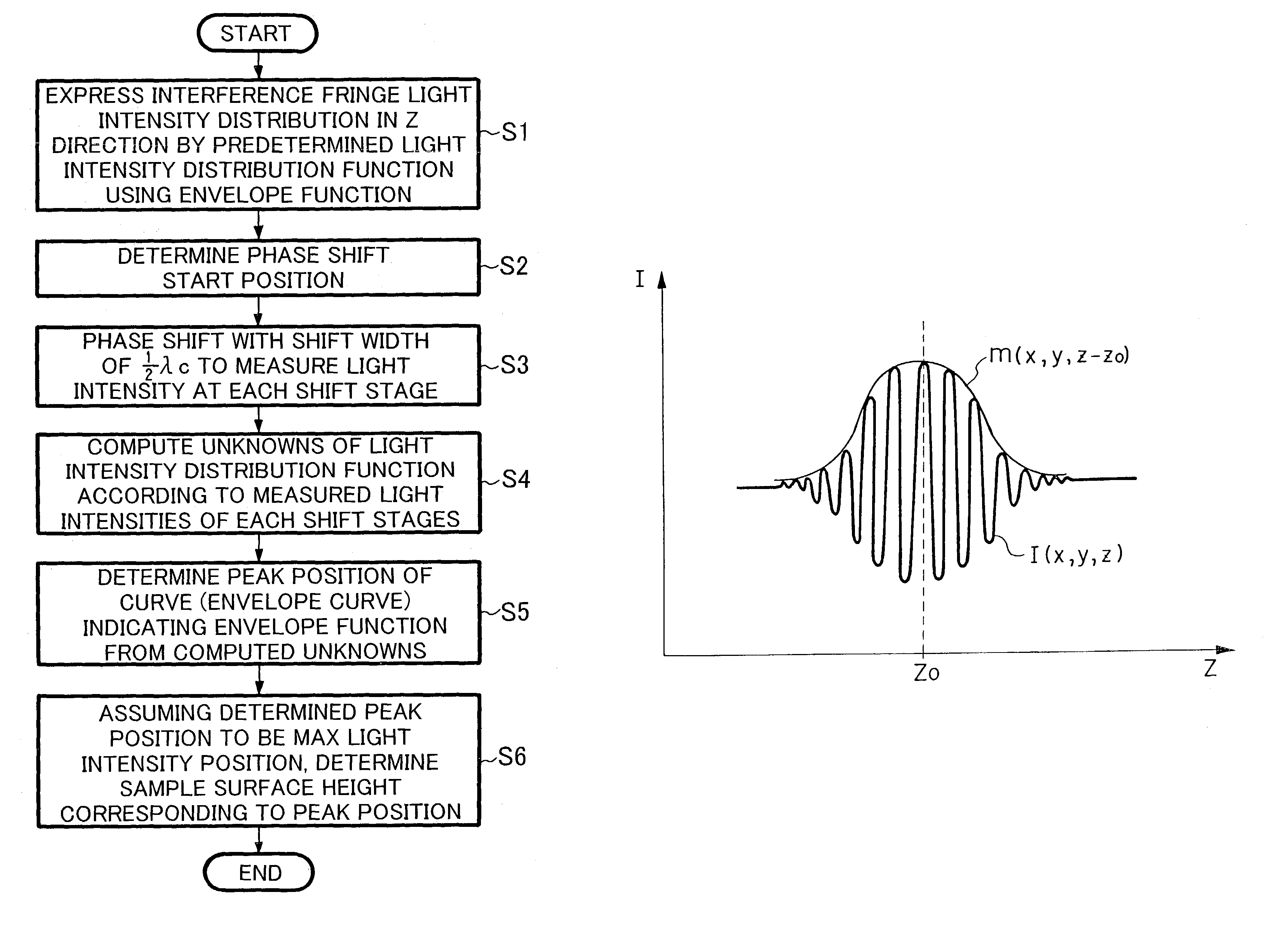
Low coherent interference fringe analysis method
InactiveUS7119907B2Increase speedSmall amountOptical measurementsPhase-affecting property measurementsPeak valueAnalysis method
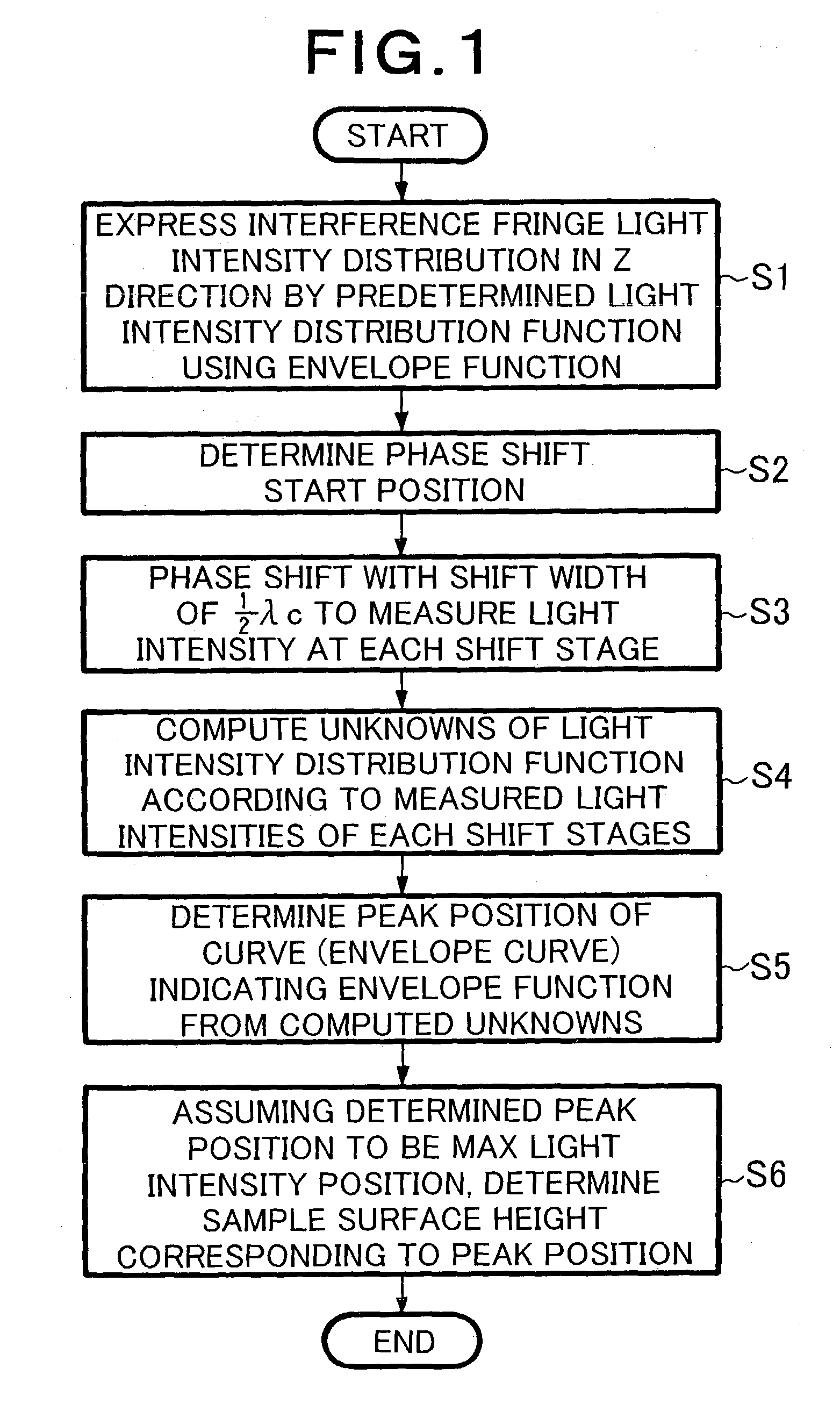
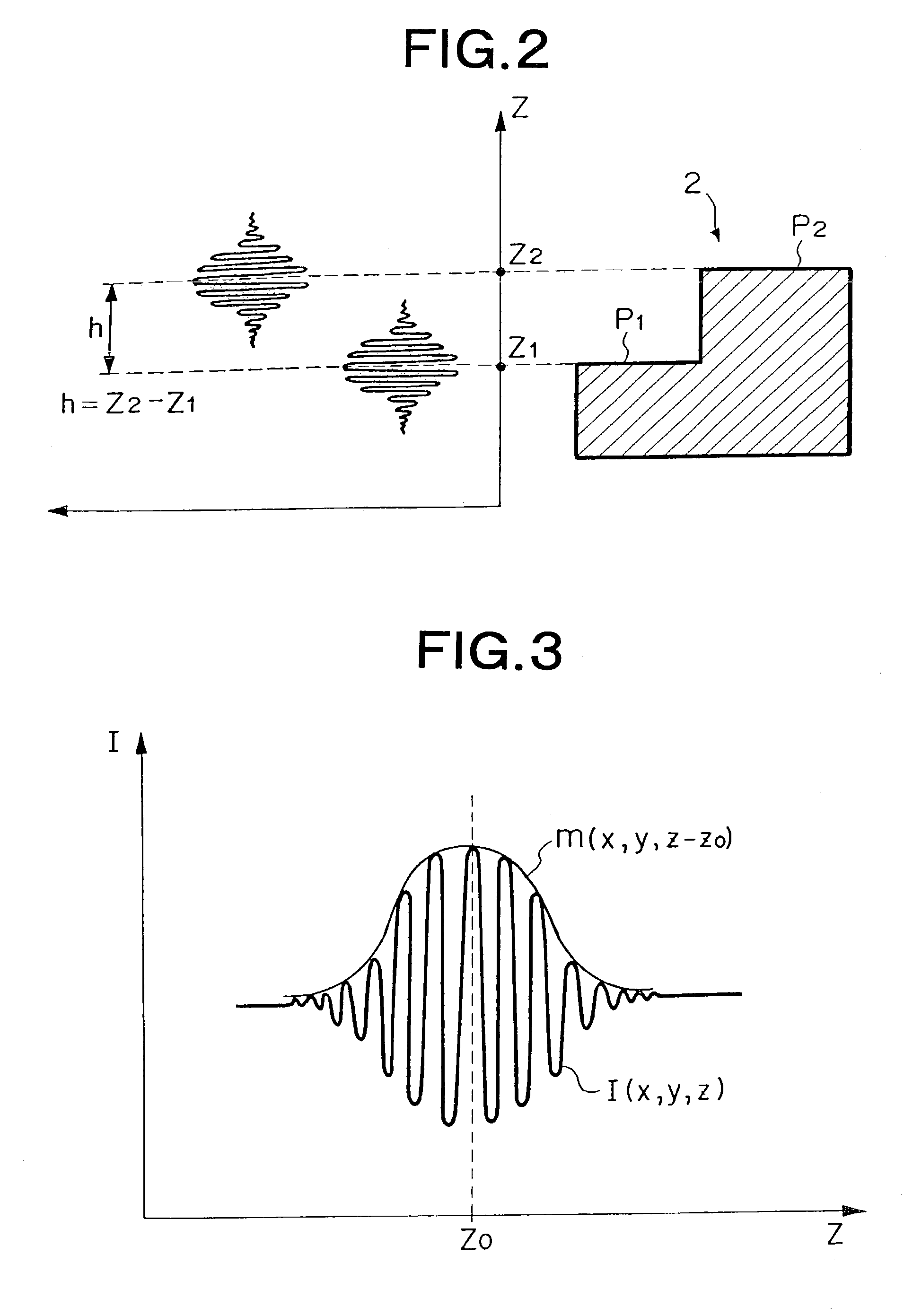
In a low coherent interference fringe analysis method, a light intensity distribution of interference fringes formed by object light and reference light in a sample is represented by a light intensity distribution function using an envelope function. Subsequently, phase shifting is carried out, so as to measure the light intensity at each shift stage. According to thus measured light intensities at respective shift stages, unknowns of the light intensity distribution function are computed. Then, according to the computed unknowns, a peak position of a curve of the envelope function is determined. According to thus determined peak position, phase information of the sample is determined.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
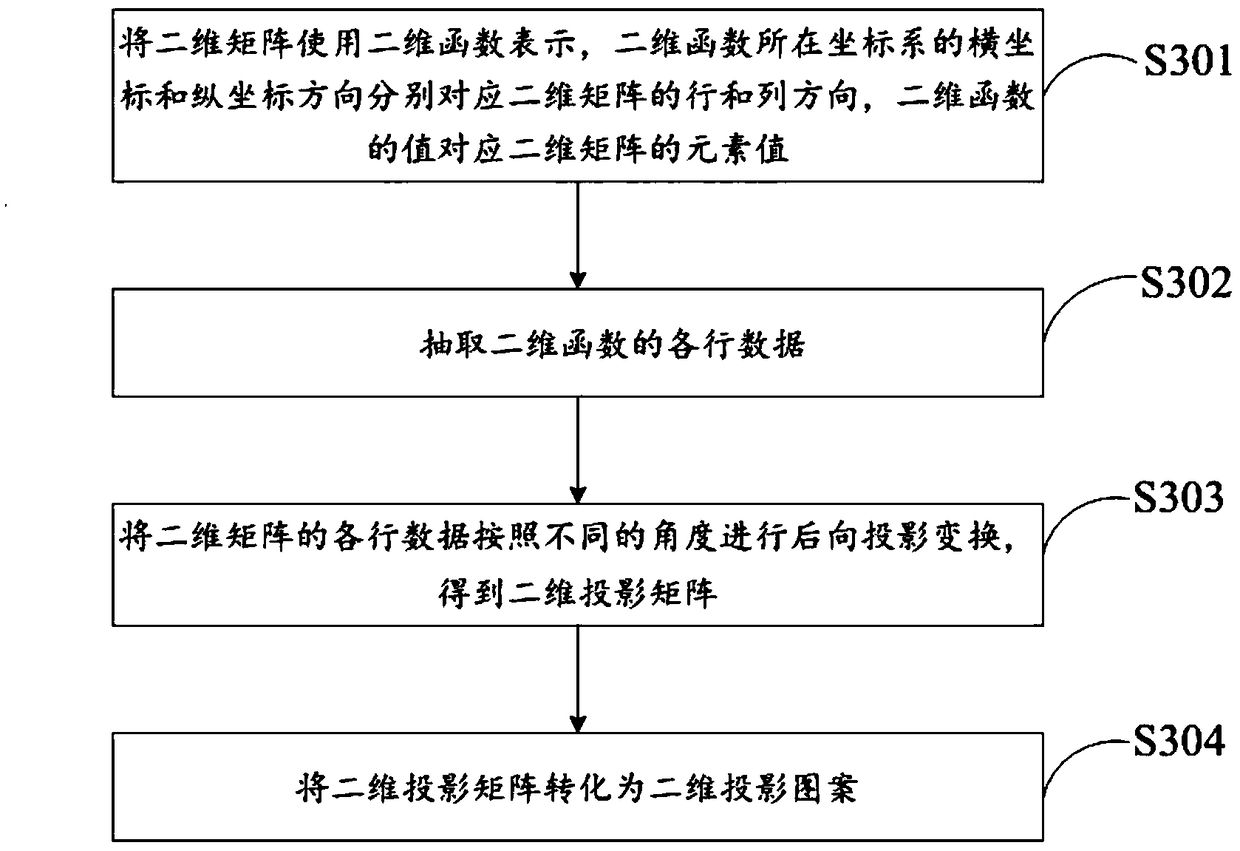
A single pixel imaging method based on Radon transform
InactiveCN109151419AImprove featuresEasy to identifyPicture reproducers using projection devicesElectromagnetic transmissionFeature extractionRadon transform
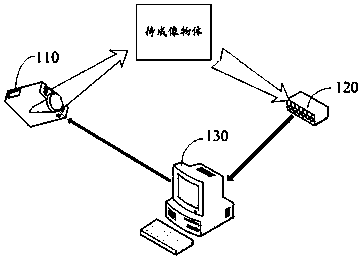
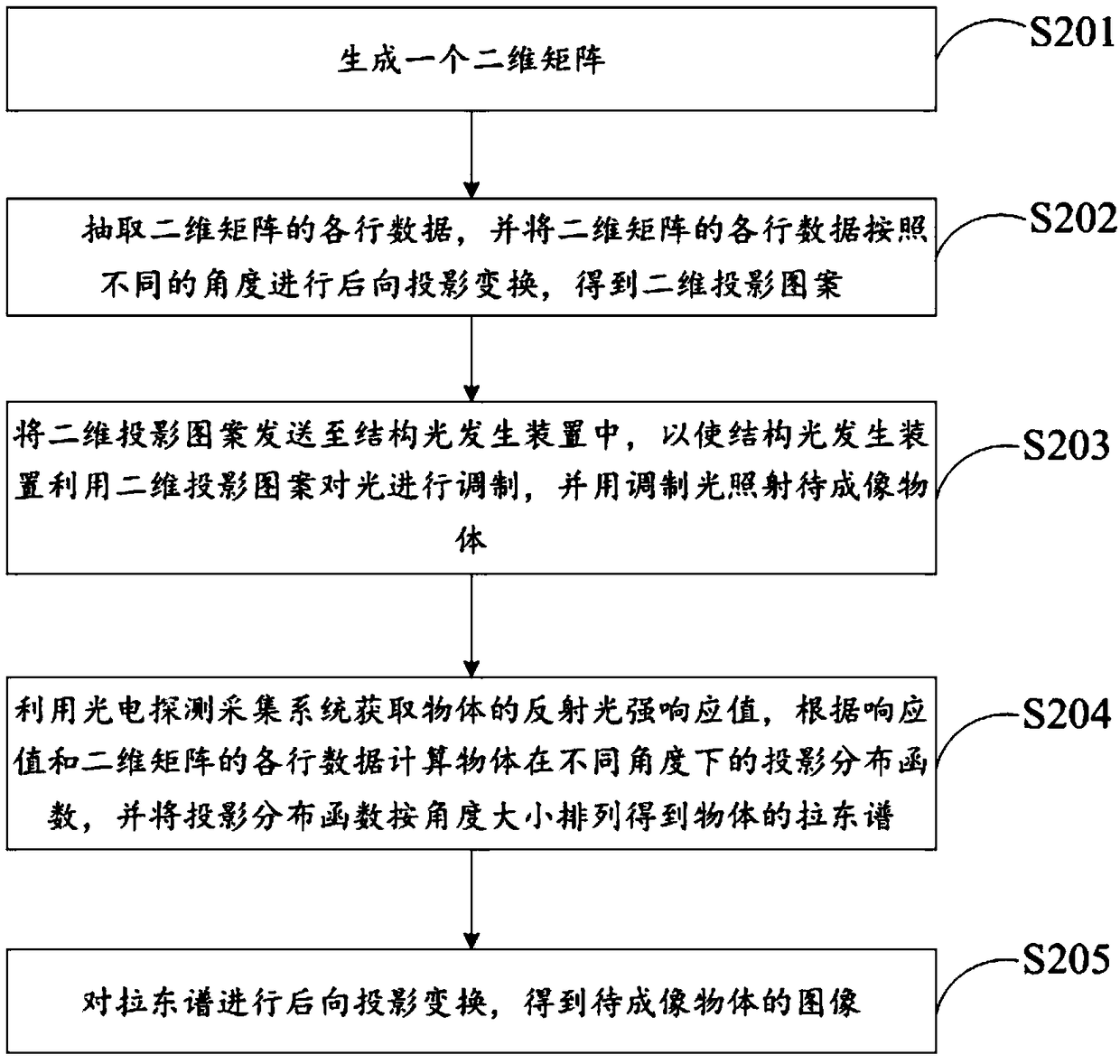
The invention relates to the technical field of imaging, and discloses a single pixel imaging method based on Radon transform. The method comprises the following steps: generating a two-dimensional matrix; executing each row of data of the two-dimensional matrix, and performing backward projection transformation on each row of data of the two-dimensional matrix according to different angles to obtain a two-dimensional projection pattern; transmitting the two-dimensional projection pattern to a structured light generating device so that the structured light generating device modulates light using the two-dimensional projection pattern and irradiates an object to be imaged with the modulated light; obtaining the reflected light intensity response value of the object, calculating the projection distribution function of the object at different angles, and arranging the projection distribution function according to the angle magnitude to obtain the Radon spectrum of the object; The image ofthe object to be imaged is obtained by backward projection transformation of the Radon spectrum. The invention can effectively reduce the cost and complexity of the Radon spectrum acquisition systemand improve the feature extraction, classification and identification efficiency of the single pixel imaging system on the object through the combination of the single pixel imaging and the Radon transform technology.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
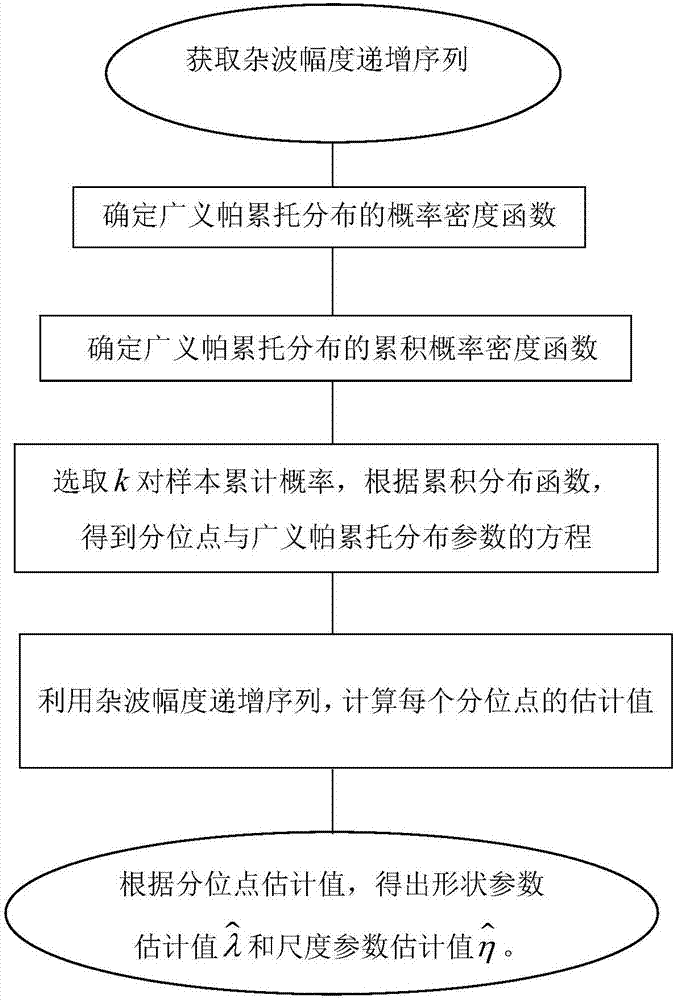
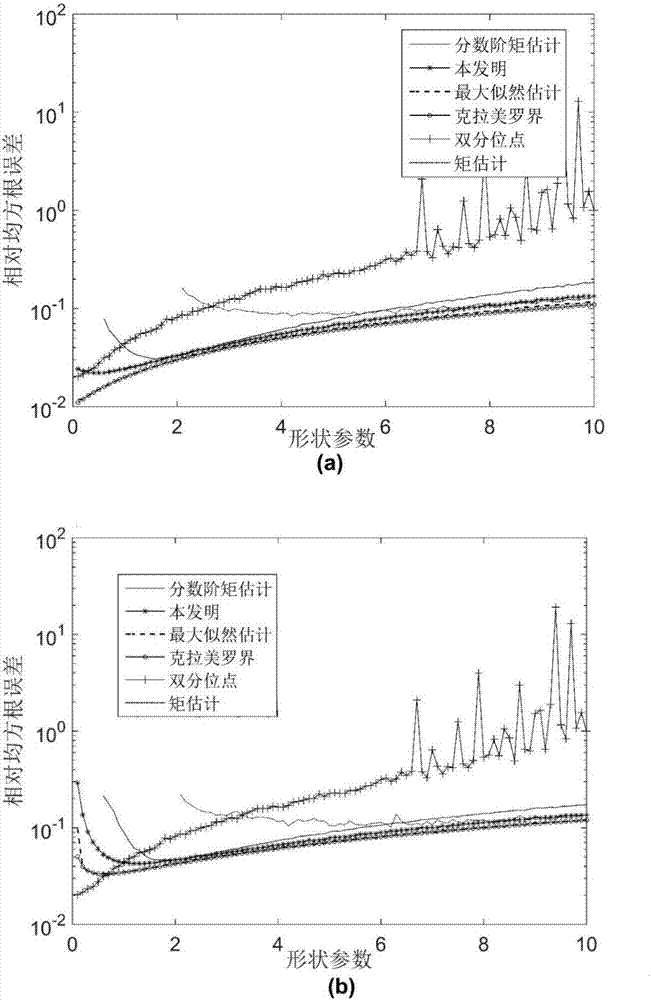
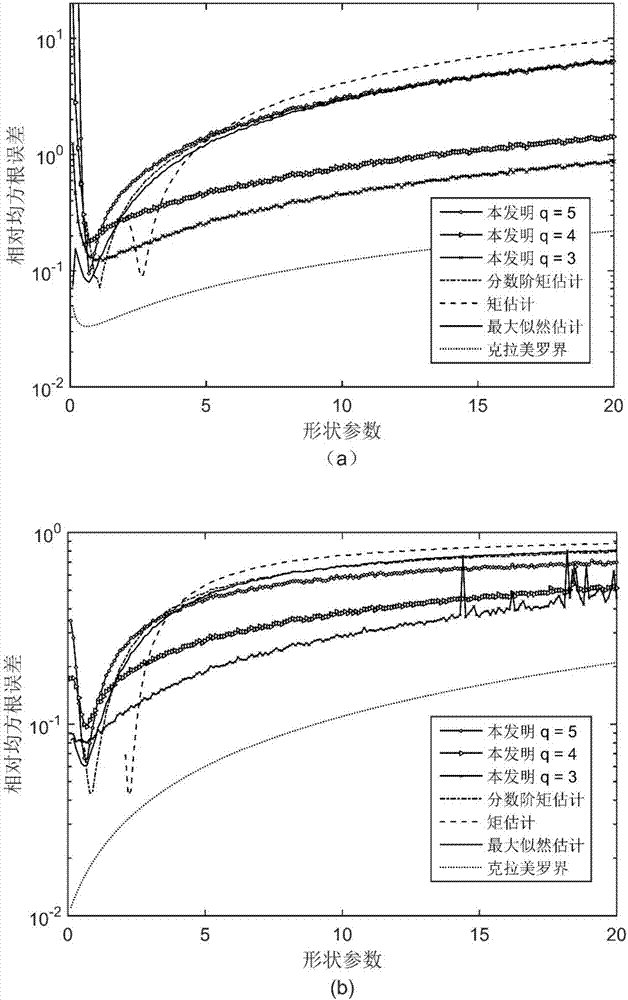
Generalized Pareto distribution parameter joint double quantile estimation method
ActiveCN107271979AHigh precisionEstimation High Precision RobustWave based measurement systemsEstimation methodsProbit
The invention discloses a generalized Pareto distribution parameter joint double quantile estimation method, so as to solve problems of poor applicability and not robustness to abnormal samples in the prior art. The method comprises steps: 1) a clutter amplitude increasing sequence is acquired; 2) according to a generalized Pareto distribution probability density function, a cumulative distribution function for generalized Pareto distribution is determined; 3) k pairs of sample cumulative probabilities are selected, and according to the cumulative distribution function, equations of quantiles and generalized Pareto distribution parameters are obtained; 4) according to the clutter amplitude increasing sequence, the estimation value of each quantile is solved; and 5) the estimation value of the quantile is used to replace a quantile in the equations of quantiles and generalized Pareto distribution parameters, and a shape parameter estimation value lambda-hat and a scale parameter estimation value eta-hat are obtained. Interference of abnormal samples on sample data is reduced, the parameter estimation performance is improved, and the method can be used for target detection in a sea clutter background.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Random variable sampling simulation method
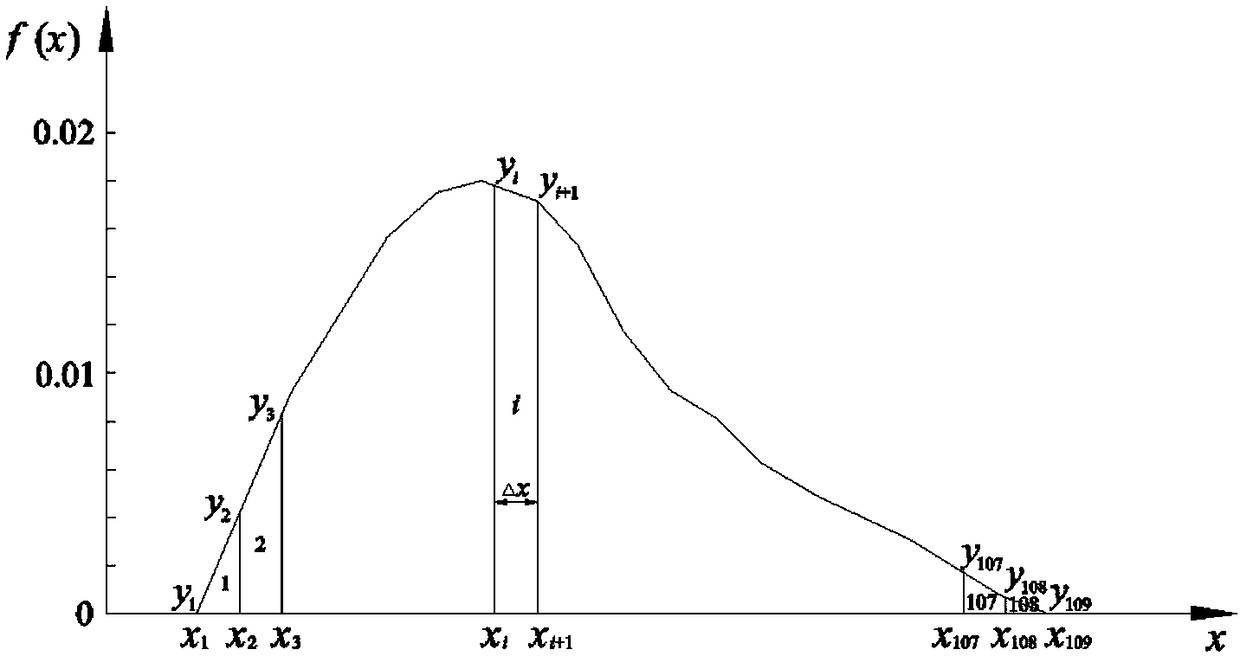
InactiveCN108563889AImprove applicabilityDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsVertical barDensity curve
The invention provides a random variable sampling simulation method, which comprises the following steps of: dividing an area, enclosed by a probability density curve of a random variable X and a horizontal coordinate axis, into n vertical bars with equal width, calculating an empirical cumulative distribution function FX (xi) of the random variable X; obtaining a sample value x of the random variable X by a linear interpolation method according to the empirical cumulative distribution function FX (xi) of the random variable X. According to the random variable sampling simulation method, the sampling simulation can be carried out only knowing the probability density curve of the random variable, the inverse function of the cumulative distribution function of random variable is not required, and the method is suitable for sampling simulation of random variable of arbitrary distribution type, and has the advantages of wider application range and stronger applicability to practical problem analysis.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Non-coherent radar image background modeling method based on normal distribution function
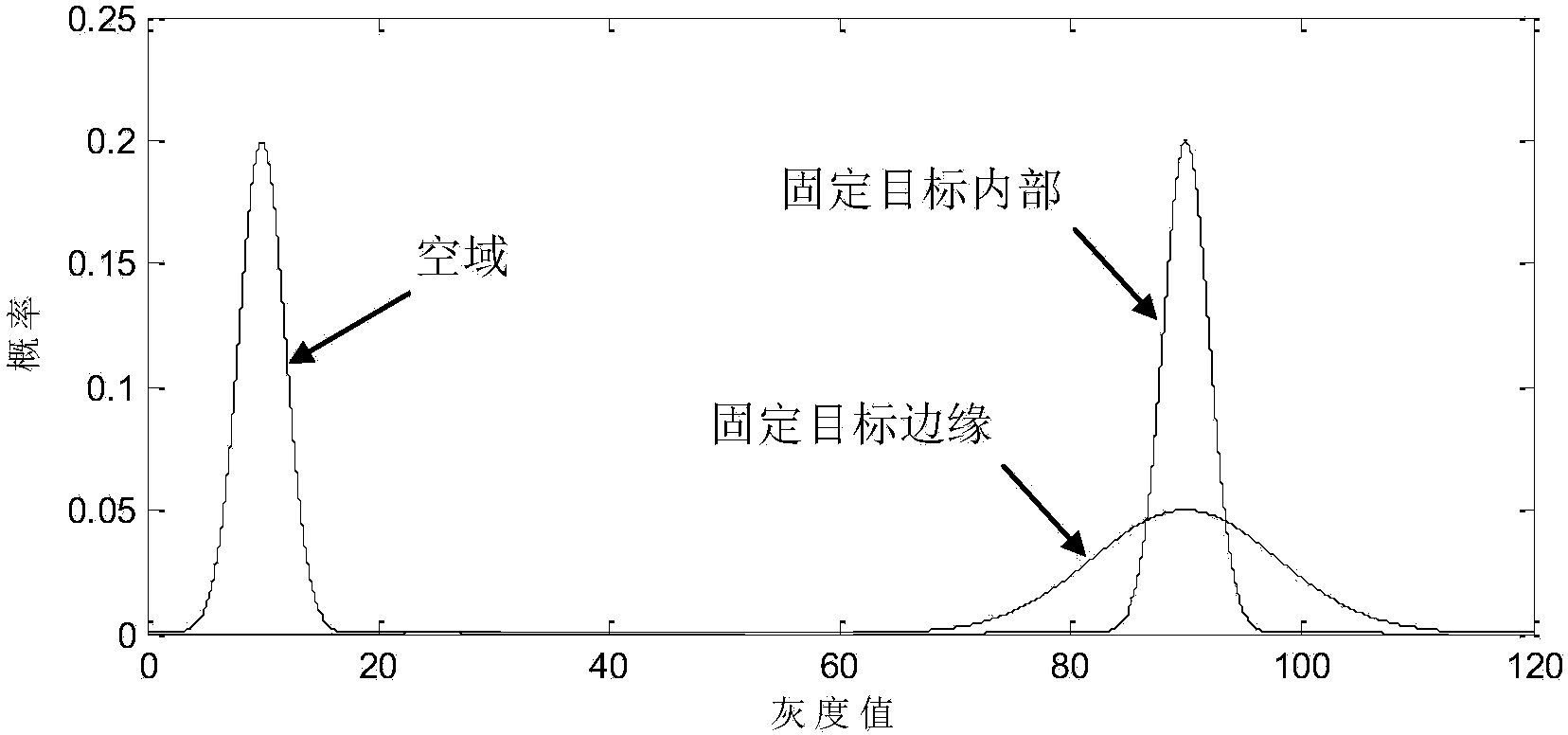
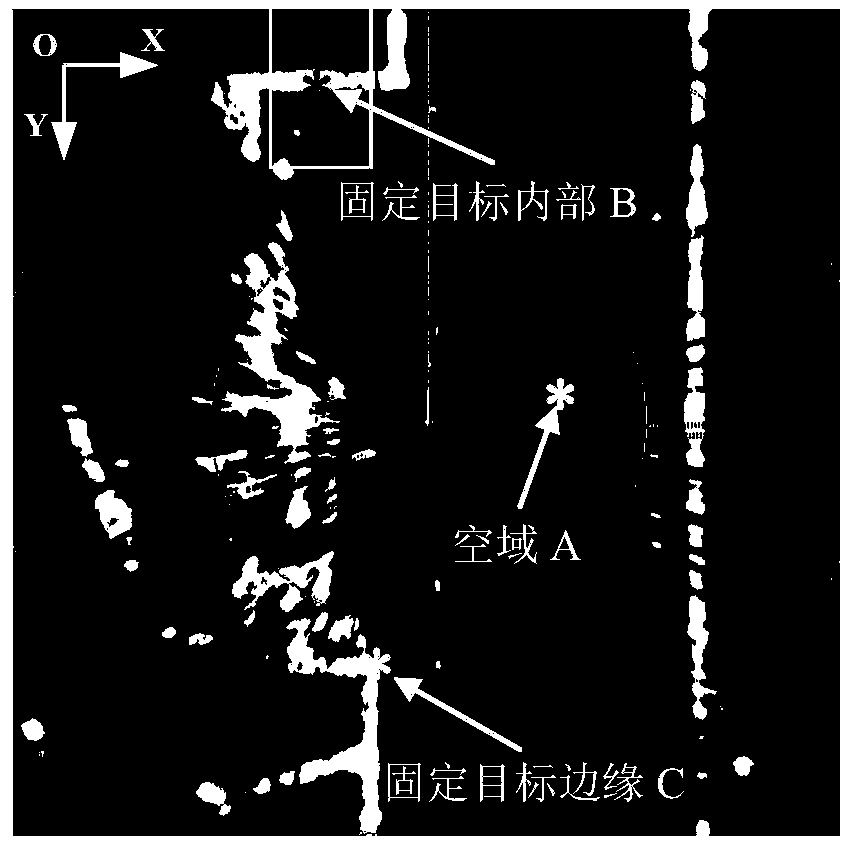
ActiveCN104268874AEasy to detectReduce the number of false alarmsImage enhancementImage analysisTime domainImaging processing
The invention discloses a non-coherent radar image background modeling method based on a normal distribution function. The method is used for radar image processing and target detecting. According to the method, a time domain background pixel sample set is built by utilizing the grey levels of pixels in a non-coherent radar image background image sequence, the probability distribution features of the grey levels of the background pixels are described with the normal distribution function, and the background pixel area is distinguished to be an airspace area, a fixing target interior area and a fixing target edge area according to the mean value and the variance. In a background model, the pixels of the airspace area are calibrated to be zero, the pixels of the fixing target interior area are one, and the pixels of the fixing target edge area are the decimals between zero and one. The background model is built based on the time domain probability distribution features of the grey levels of the pixels in non-coherent radar images and is the important foundation of low-altitude airspace radar target detection, the detection capacity for targets in the airspace area in the non-coherent radar images can be improved effectively, and meanwhile the frequency of false alarms in the fixing target edge area is reduced.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF CIVIL AVIATION SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com