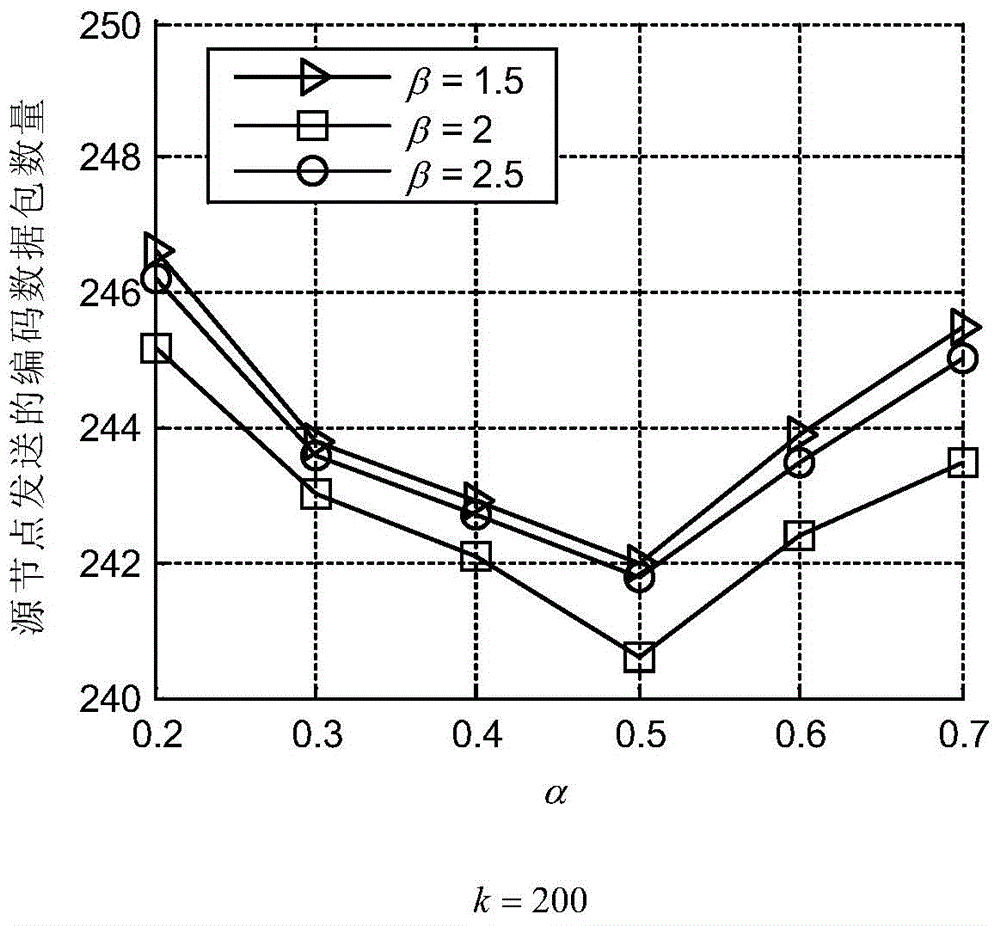
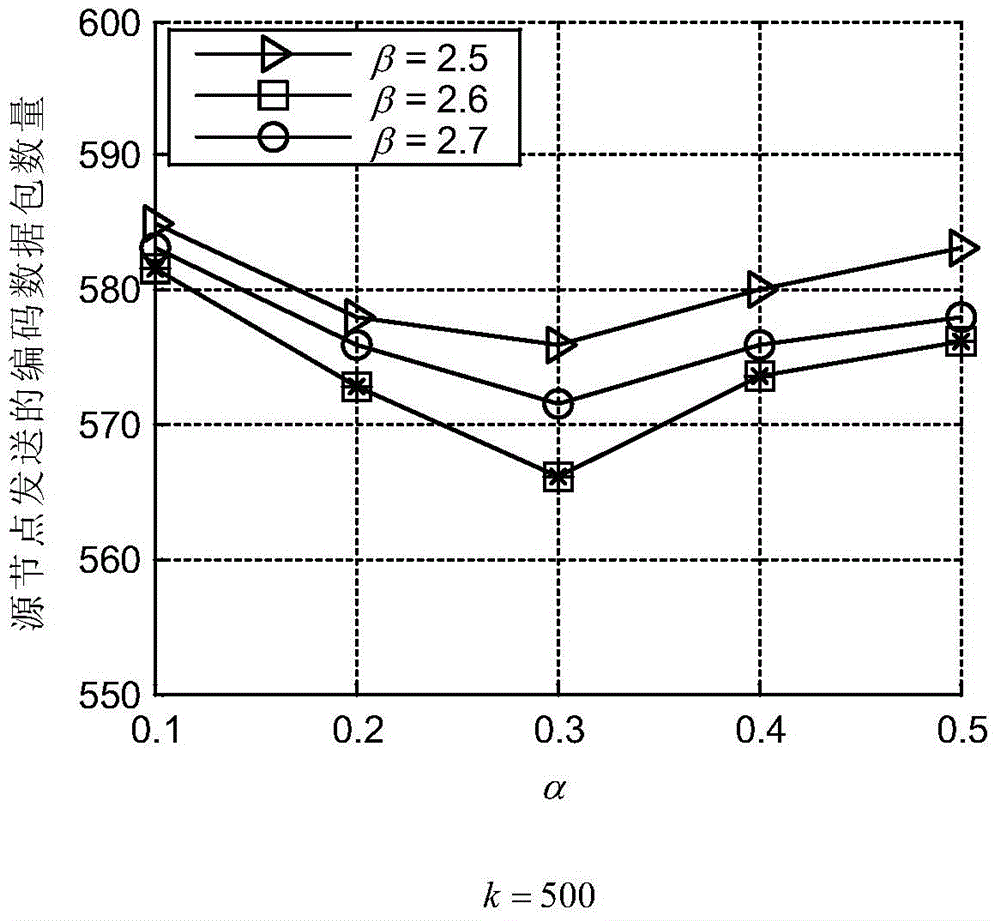
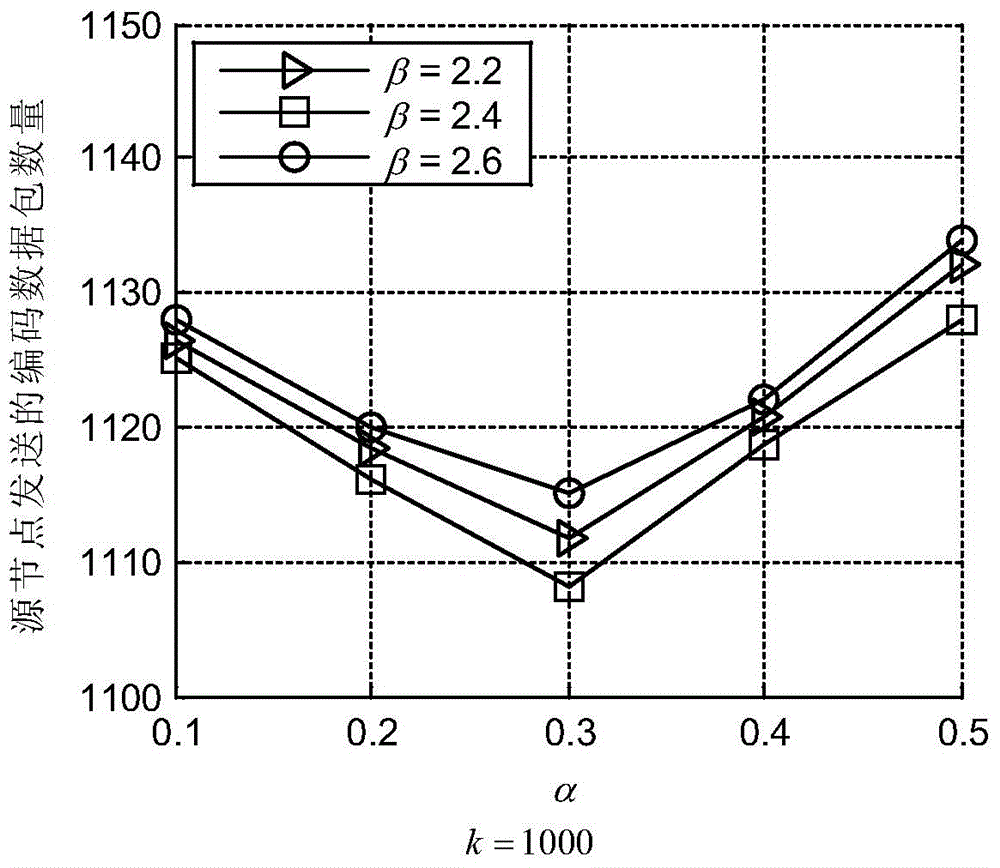
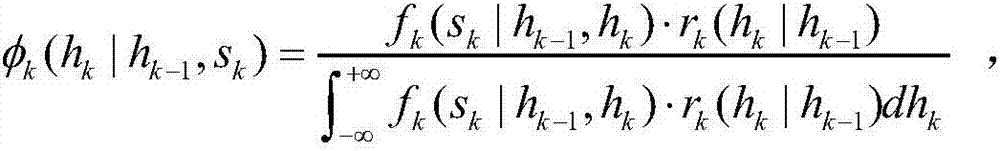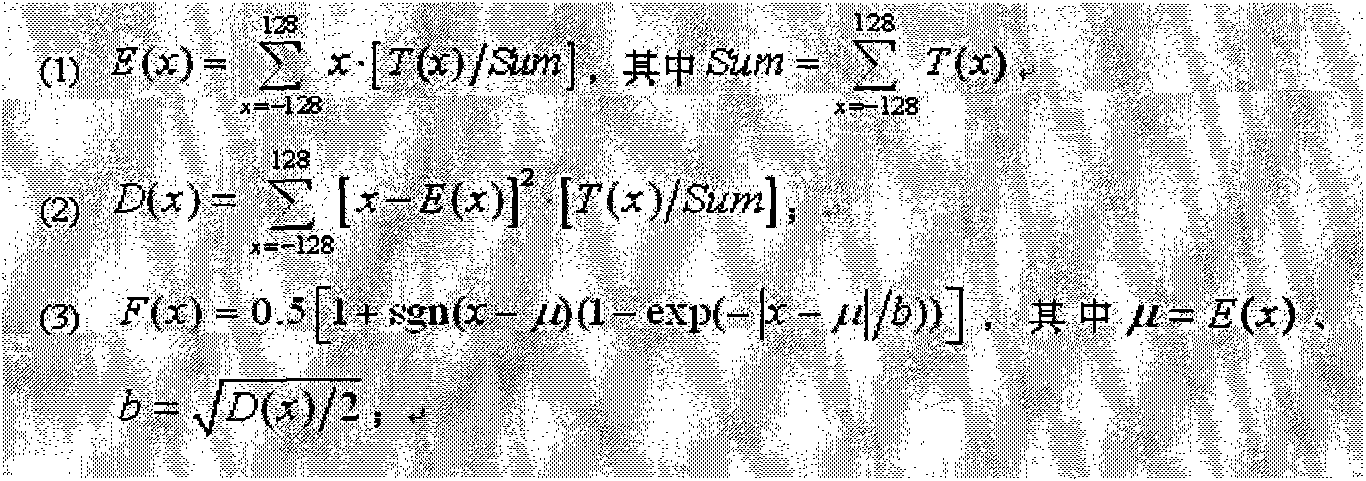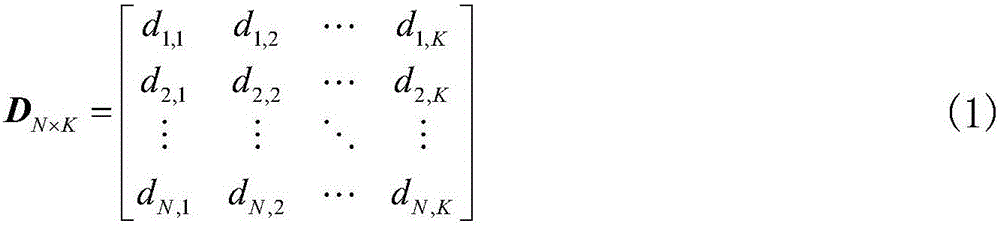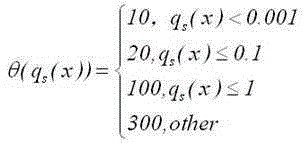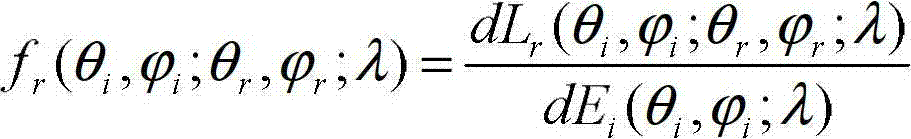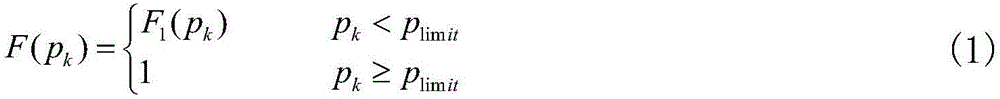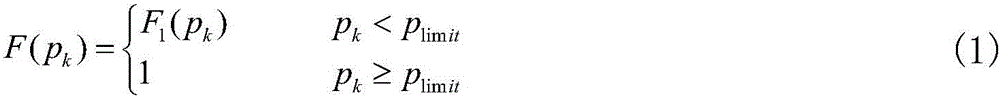Patents
Literature
157 results about "Radial distribution function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In statistical mechanics, the radial distribution function, (or pair correlation function) g(r) in a system of particles (atoms, molecules, colloids, etc.), describes how density varies as a function of distance from a reference particle. If a given particle is taken to be at the origin O, and if ρ=N/V is the average number density of particles, then the local time-averaged density at a distance r from O is ρg(r).
Condition assessment of nonlinear processes
InactiveUS6484132B1Timely, accurateReduce the amount requiredElectroencephalographyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceData setEeg data
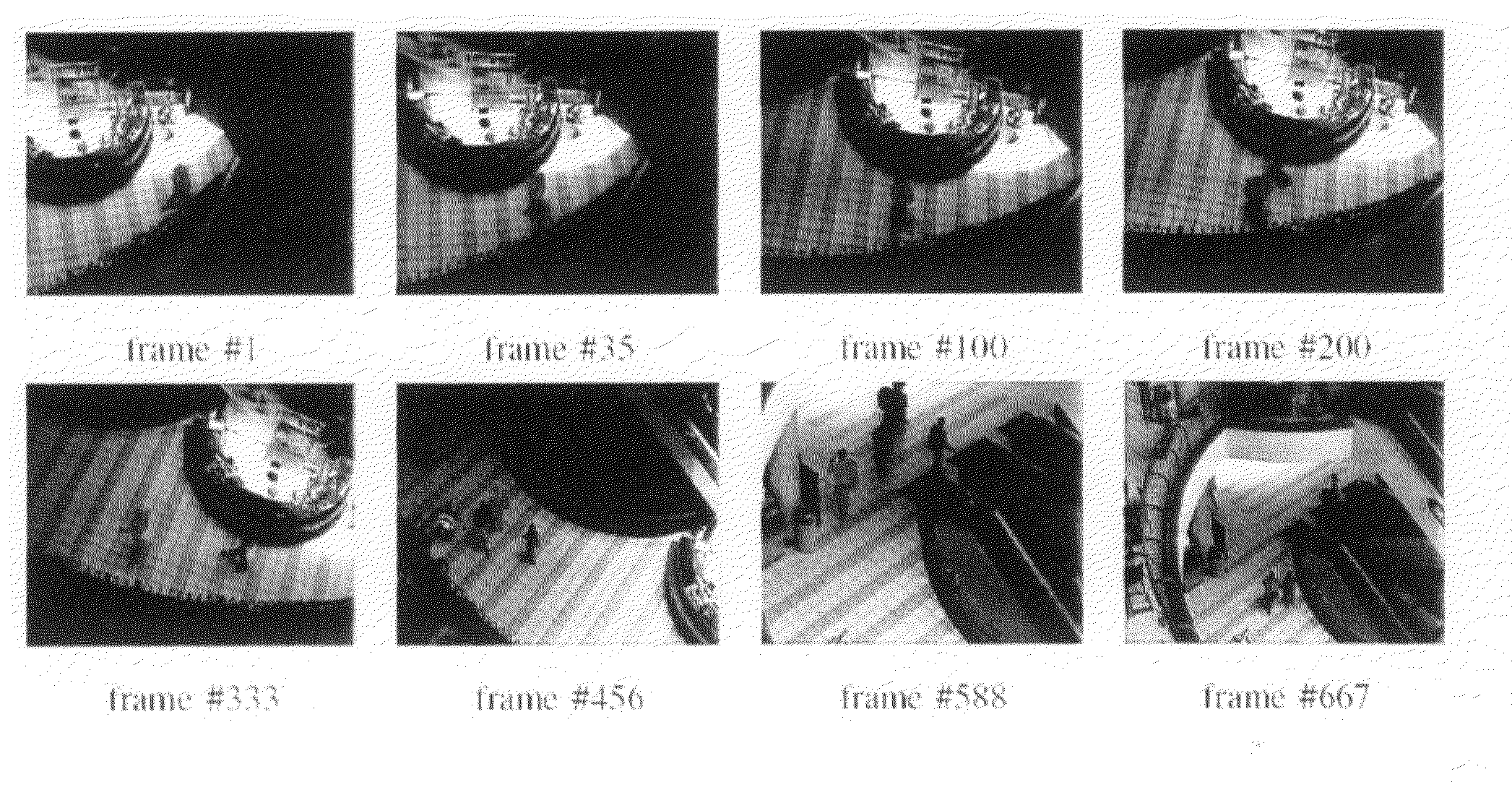
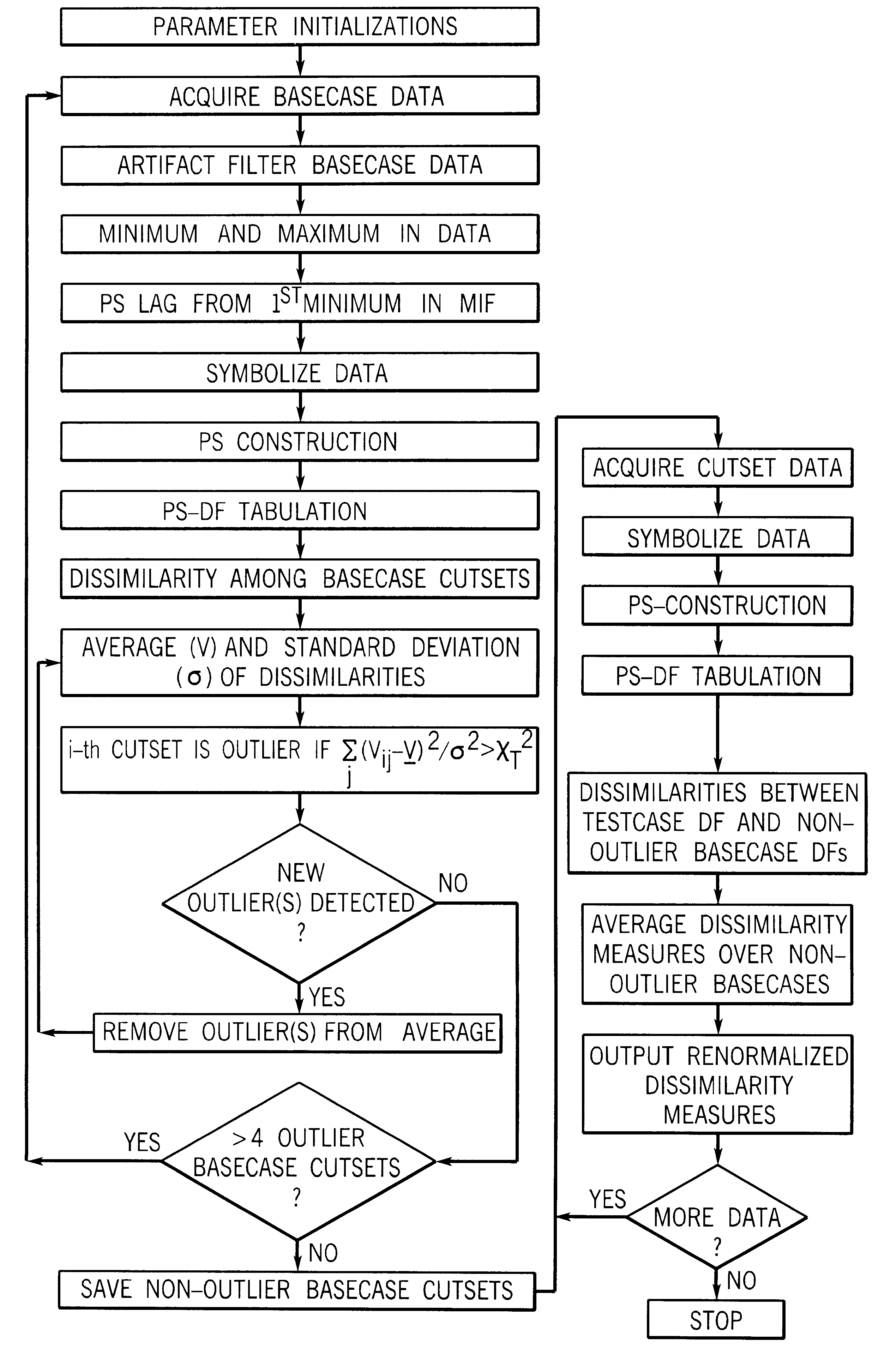
There is presented a reliable technique for measuring condition change in nonlinear data such as brain waves. The nonlinear data is filtered and discretized into windowed data sets. The system dynamics within each data set is represented by a sequence of connected phase-space points, and for each data set a distribution function is derived. New metrics are introduced that evaluate the distance between distribution functions. The metrics are properly renormalized to provide robust and sensitive relative measures of condition change. As an example, these measures can be used on EEG data, to provide timely discrimination between normal, preseizure, seizure, and post-seizure states in epileptic patients. Apparatus utilizing hardware or software to perform the method and provide an indicative output is also disclosed.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
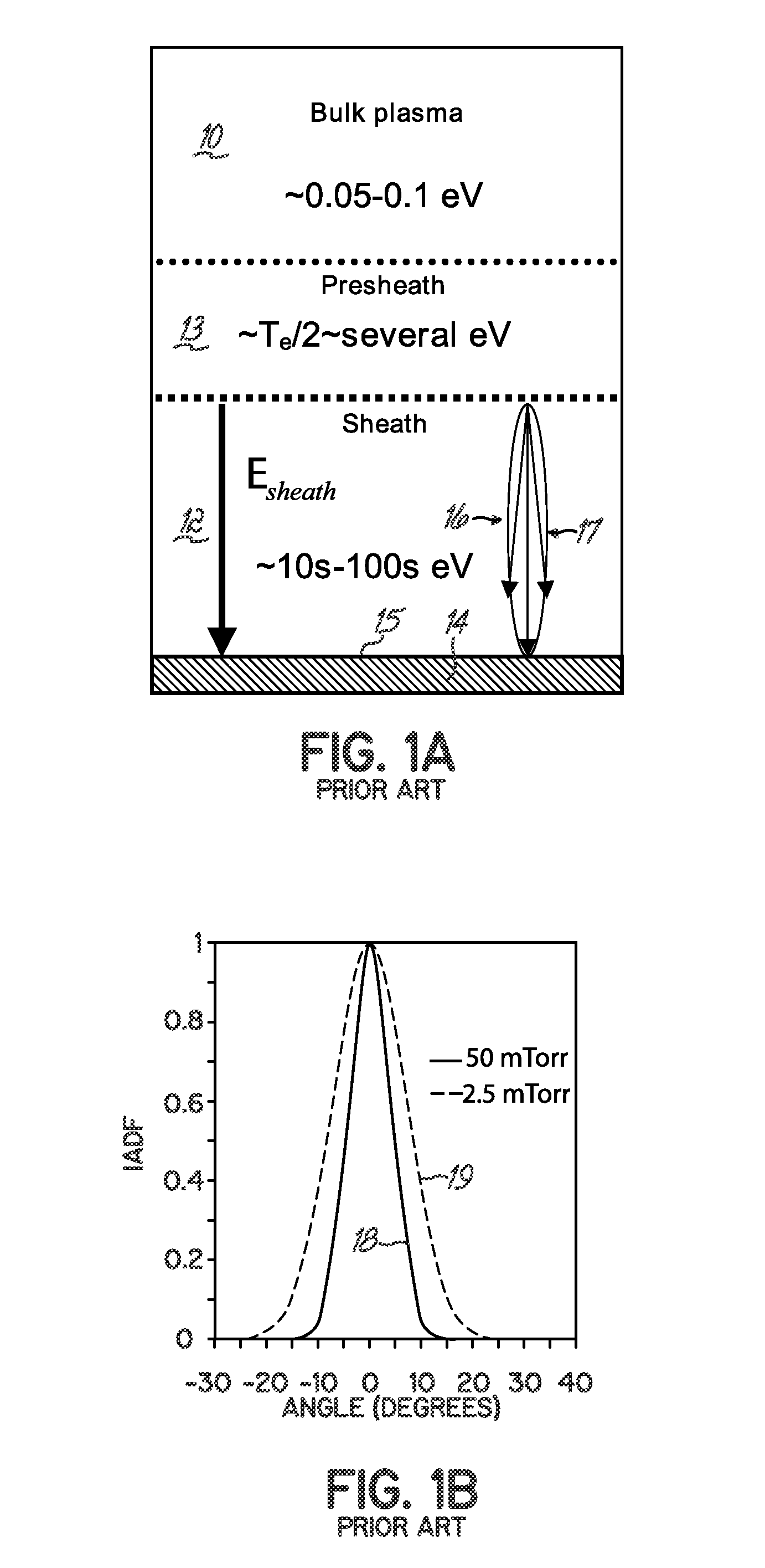
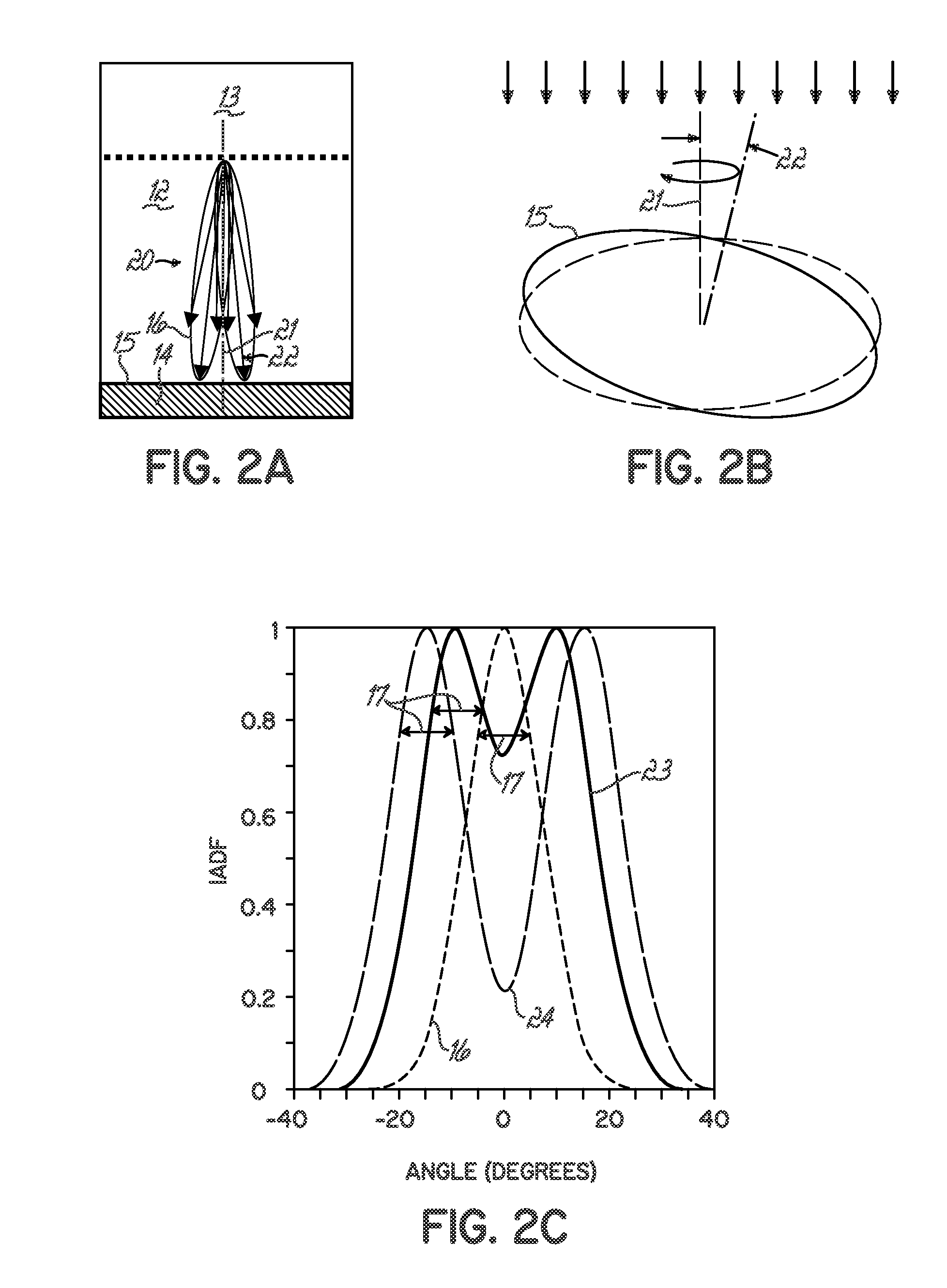
Control of ion angular distribution function at wafer surface
InactiveUS20080242065A1Suppress mutationCompensation effectElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsEtchingPower grid
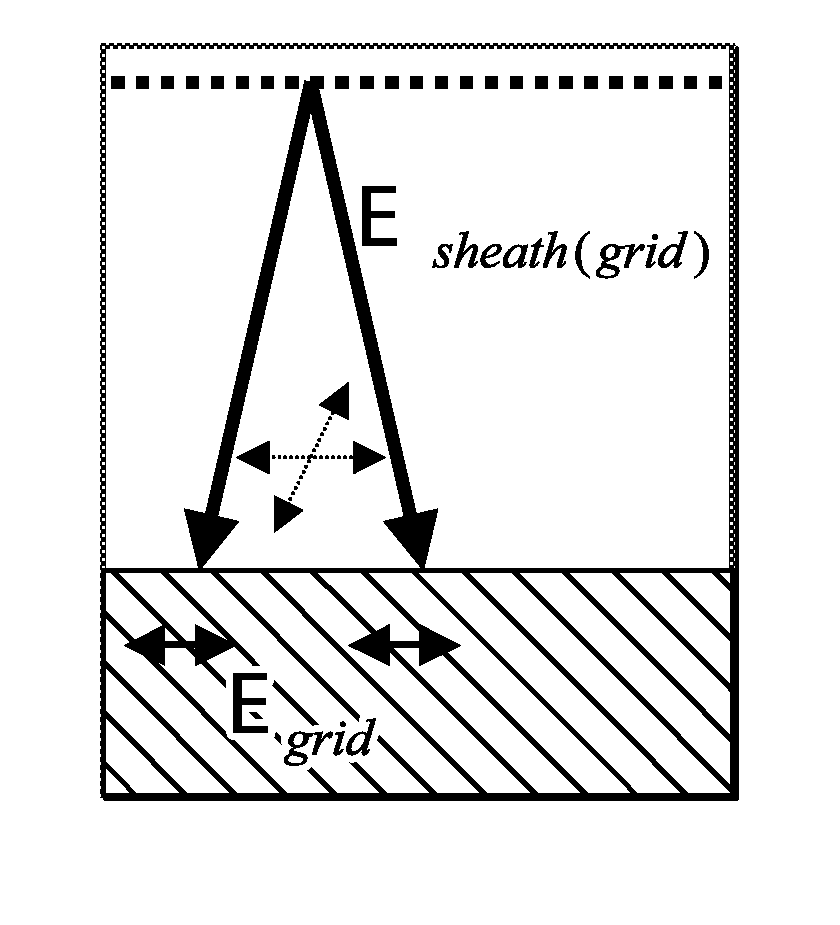
A manufacturing method and apparatus for IC fabrication controls the ion angular distribution at the surface of a wafer with electrodes in a wafer support that produce electric fields parallel to the wafer surface without disturbing plasma parameters beyond the wafer surface. The ion angular distribution function (IADF) at the wafer surface is controlled for better feature coverage or etching. Grid structure is built into the substrate holder within the coating at the top of the holder. The grid components are electrically biased to provide electric fields that combine with the sheath field to distribute the ion incidence angles from the plasma sheath onto the wafer. The grid can be dynamically biased or phased to control uniformity of the effects.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
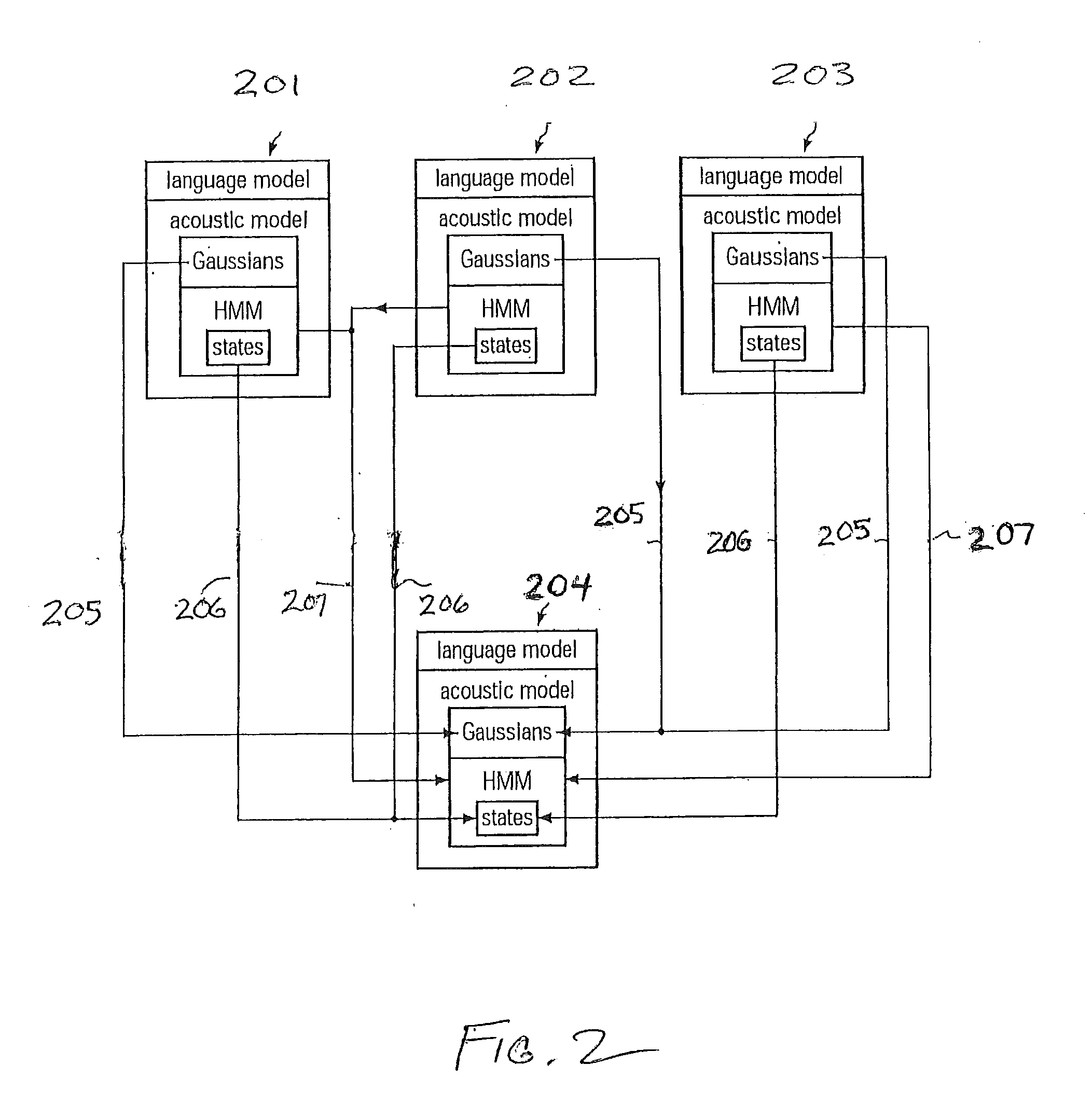
Speech Recognition Based on a Multilingual Acoustic Model
ActiveUS20100131262A1Fast and relatively reliable multilingualConvenience to workNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionSpeech identificationAcoustic model
Embodiments of the invention relate to methods for generating a multilingual acoustic model. A main acoustic model comprising a main acoustic model having probability distribution functions and a probabilistic state sequence model including first states is provided to a processor. At least one second acoustic model including probability distribution functions and a probabilistic state sequence model including states is also provided to the processor. The processor replaces each of the probability distribution functions of the at least one second acoustic model by one of the probability distribution functions and / or each of the states of the probabilistic state sequence model of the at least one second acoustic model with the state of the probabilistic state sequence model of the main acoustic model based on a criteria set to obtain at least one modified second acoustic model. The criteria set may be a distance measurement. The processor then combines the main acoustic model and the at least one modified second acoustic model to obtain the multilingual acoustic model.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
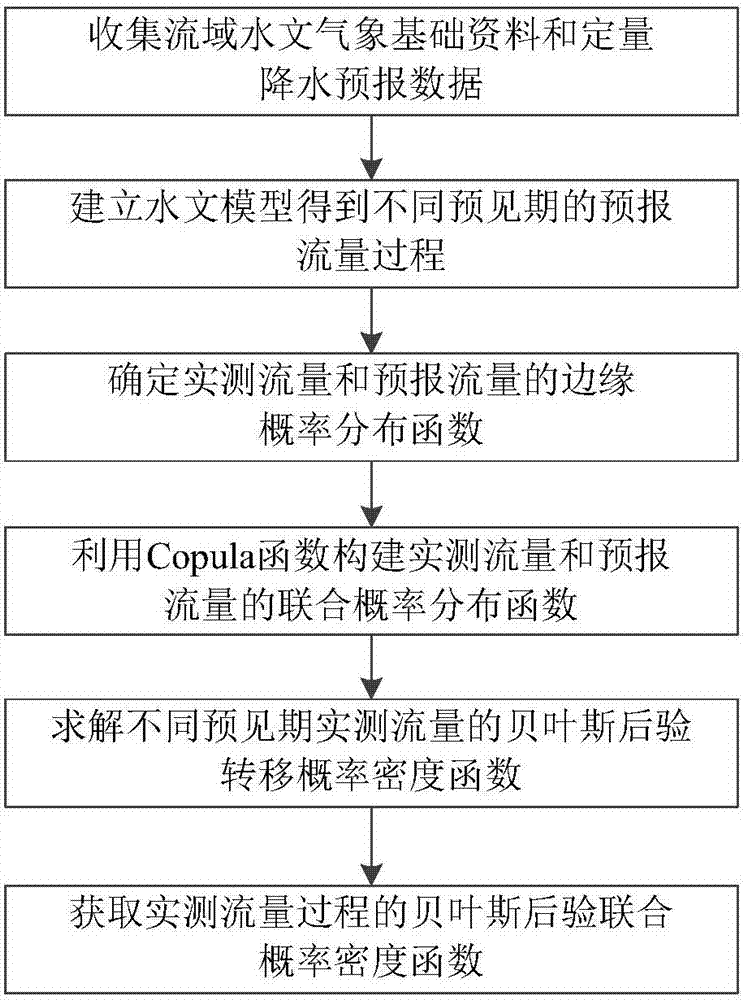
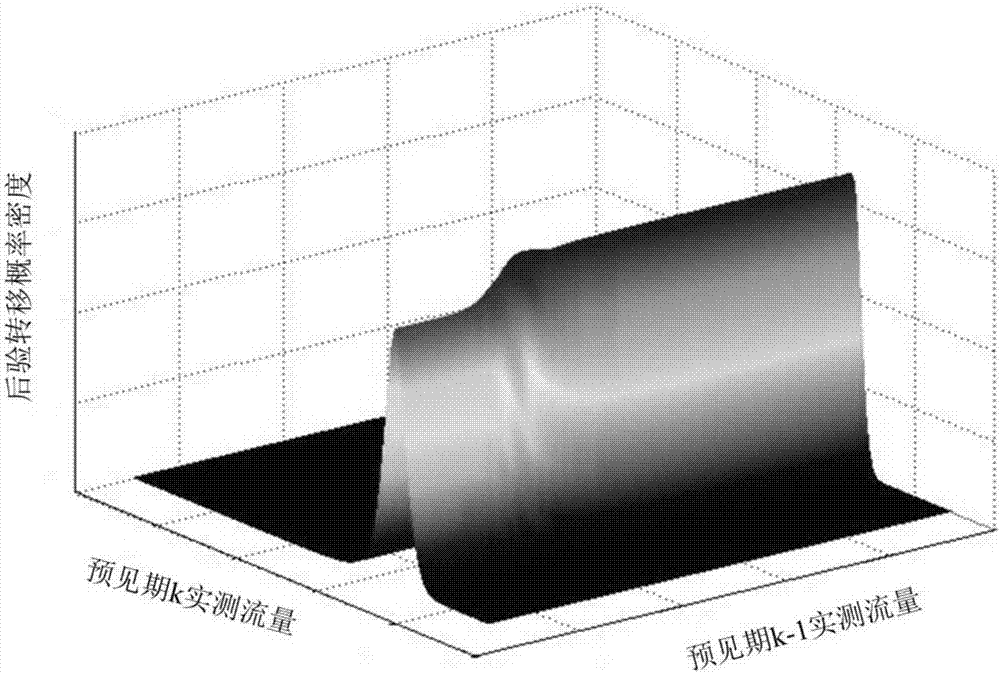
Copula function-based multivariate hydrologic uncertainty processing method
ActiveCN107423546ACapture non-linearitySnap featureSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsQuantitative precipitation forecastNormal density
The invention provides a Copula function-based multivariate hydrologic uncertainty processing method. The method can be used for hydrologic forecasting, and is characterized by comprising the following steps: step 1, collecting hydrometeorological basic data and quantitative precipitation forecast data of a basin; step 2, establishing a hydrologic model to obtain forecast discharge processes of different forecast periods; step 3, determining marginal distribution functions of actually measured flow and forecast flow; step 4, utilizing a Copula function to construct a joint probability distribution function of the actually measured flow and the forecast flow; step 5, solving a Bayesian posterior transition probability density function of the actually measured flow of the different forecast periods according to the marginal distribution functions estimated in the step 3 and the joint probability distribution function constructed in the step 4; and step 6, acquiring a Bayesian posterior joint probability density function of the actually measured discharge processes through a total probability formula according to the Bayesian posterior transition probability density function, obtained in the step 5, of the actually measured flow of the different forecast periods.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Displaying device and lighting device employing organic electroluminescence element
InactiveUS20090236962A1Shape is not particularly restrictedInhibition is effectiveControl electrodesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEffect light
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Highly effective slurry phase bed reactor
InactiveCN1593740AEasy to operateAvoid easy cloggingChemical/physical processesNuclear engineeringSpray nozzle
The invention relates to a kind of efficient reactor with paddle bed, which belongs to the chemical machinery field. It is composed mainly with the solid and liquid separator, the inner tube that the track is changeable, the reactor cover, the heat exchanger with an internal component, the riser with the spray nozzle, the inner-tube tank that has the heating and gas distribution function, the spray nozzle for protecting from choking, the mounting plate of the spray nozzle, the heat exchanger, the outlet of the heating coil, the quadratic distribution plate, the heating coil and so on. The beneficial effictiveness of the invention can be described as follows: the reactor and the distributor can't block up easily; the gas and the liquid can be mixed evenly; the reactive efficiency is high; the carrying amount of the catalyst and the solvent is so bit that it can not occur the bias current, channeling and dead bed; the size running quickly, and the viscosity of the size in the reactor is identical generally; the reactor can be shifted out in time, and especially in the stage of the catalytic, reducing and intensifying, it can realize to operate the reactor steadily; otherwise, the distribution of the virgin gas in the reactor along the axle is in agreement on the concentration of the catalyst, so that can make the catalyst have the most activity, and then it can be make the full use of the reactor space.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
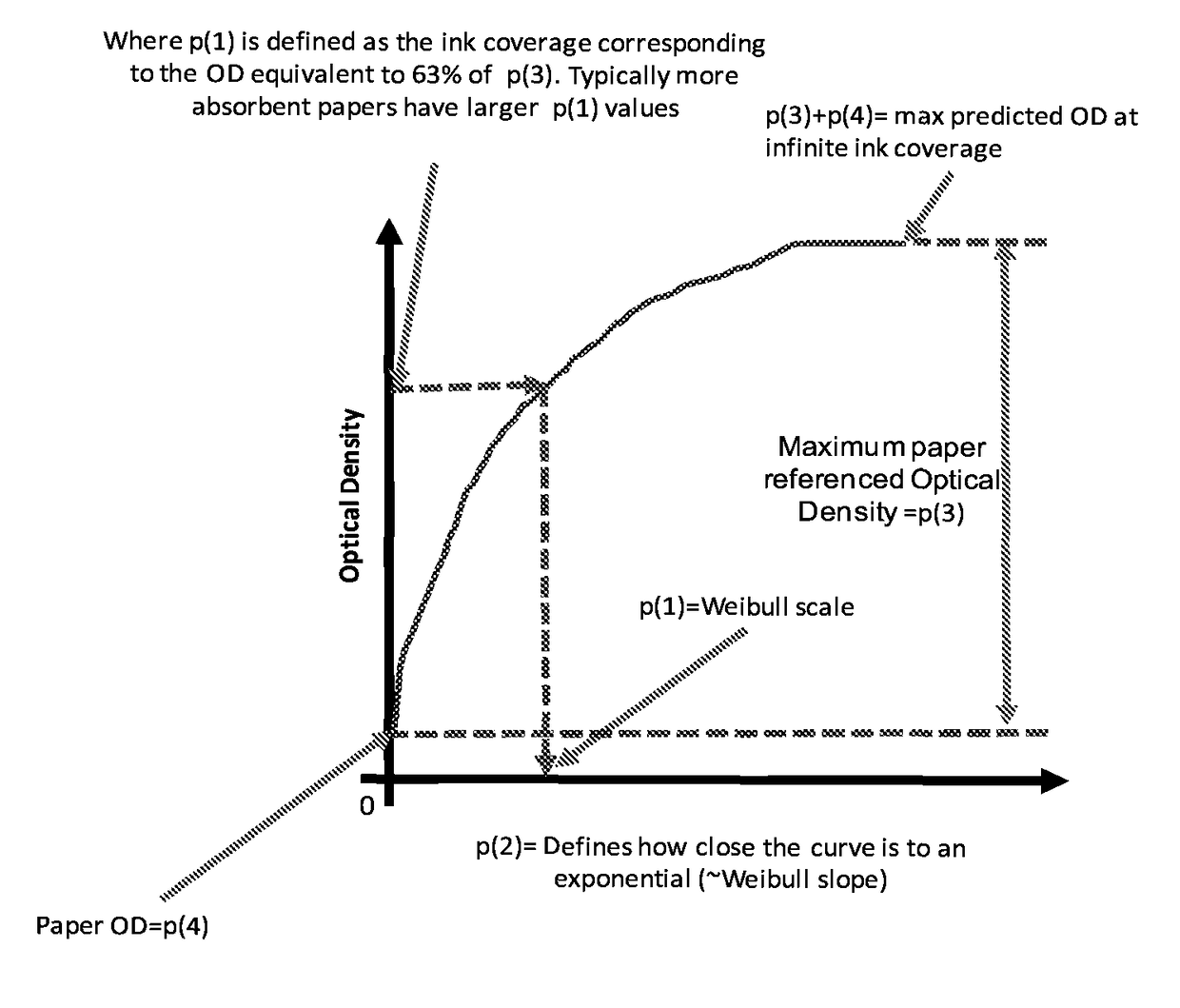
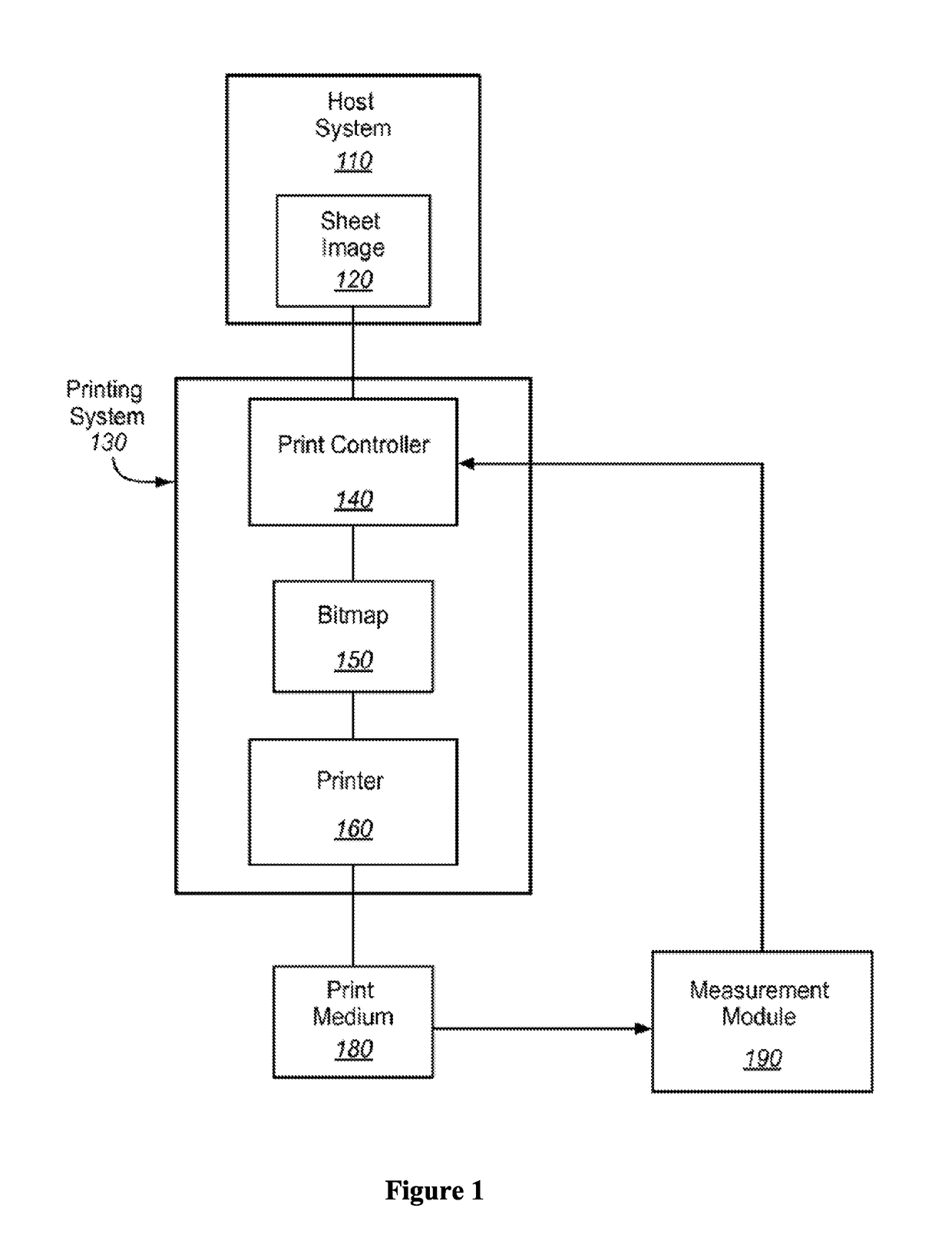
Ink model derivation mechanism using Weibull distribution function
A printing system is disclosed. The printing system includes a printer controller to receive optical density (OD) measurement data corresponding to application of a halftone pattern using ink on a medium in a printing system and calculate a predicted OD versus normalized ink coverage relationship for the printing system based on the received OD measurement data.
Owner:RICOH KK
Copper alloy having excellent stress relaxation property
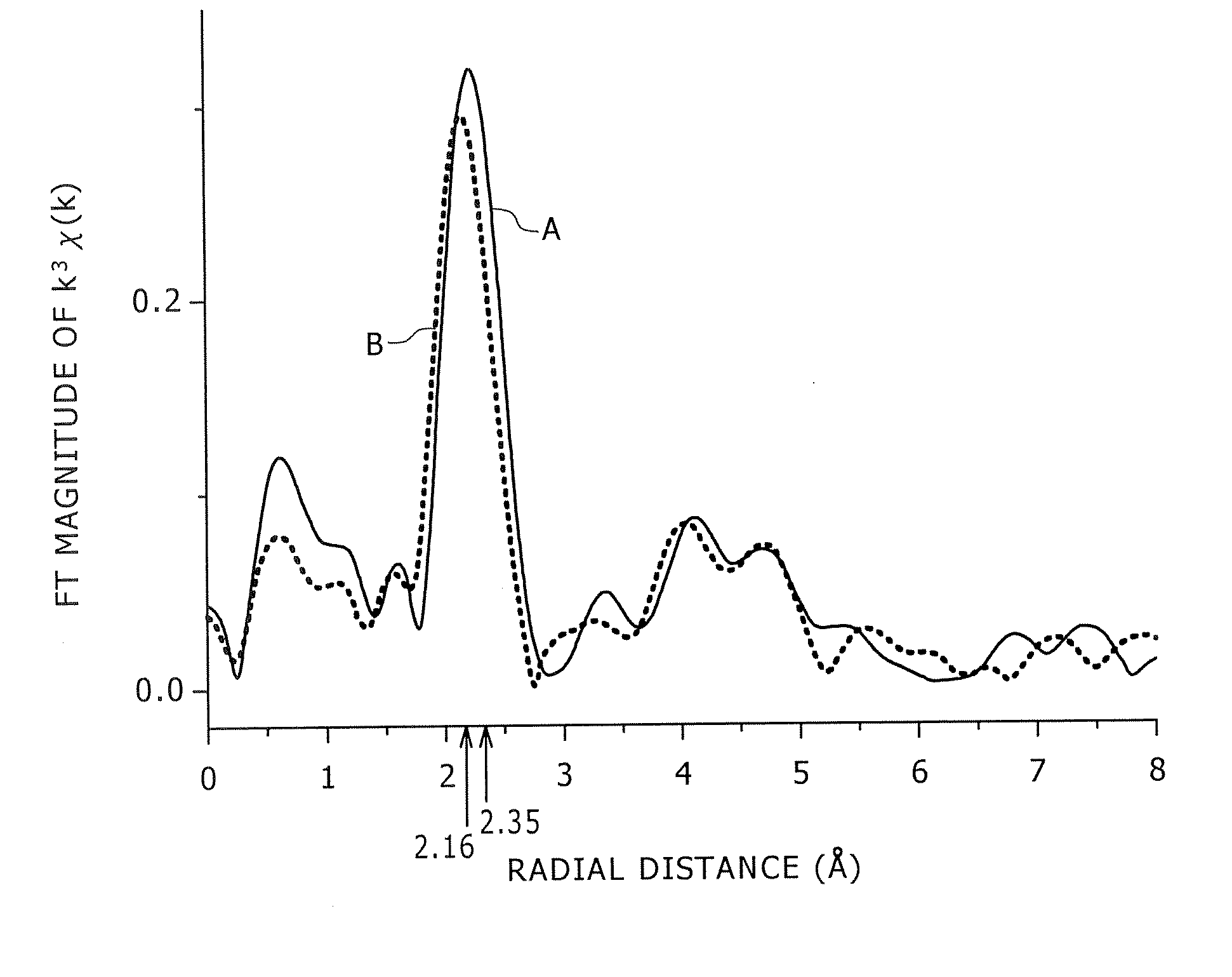
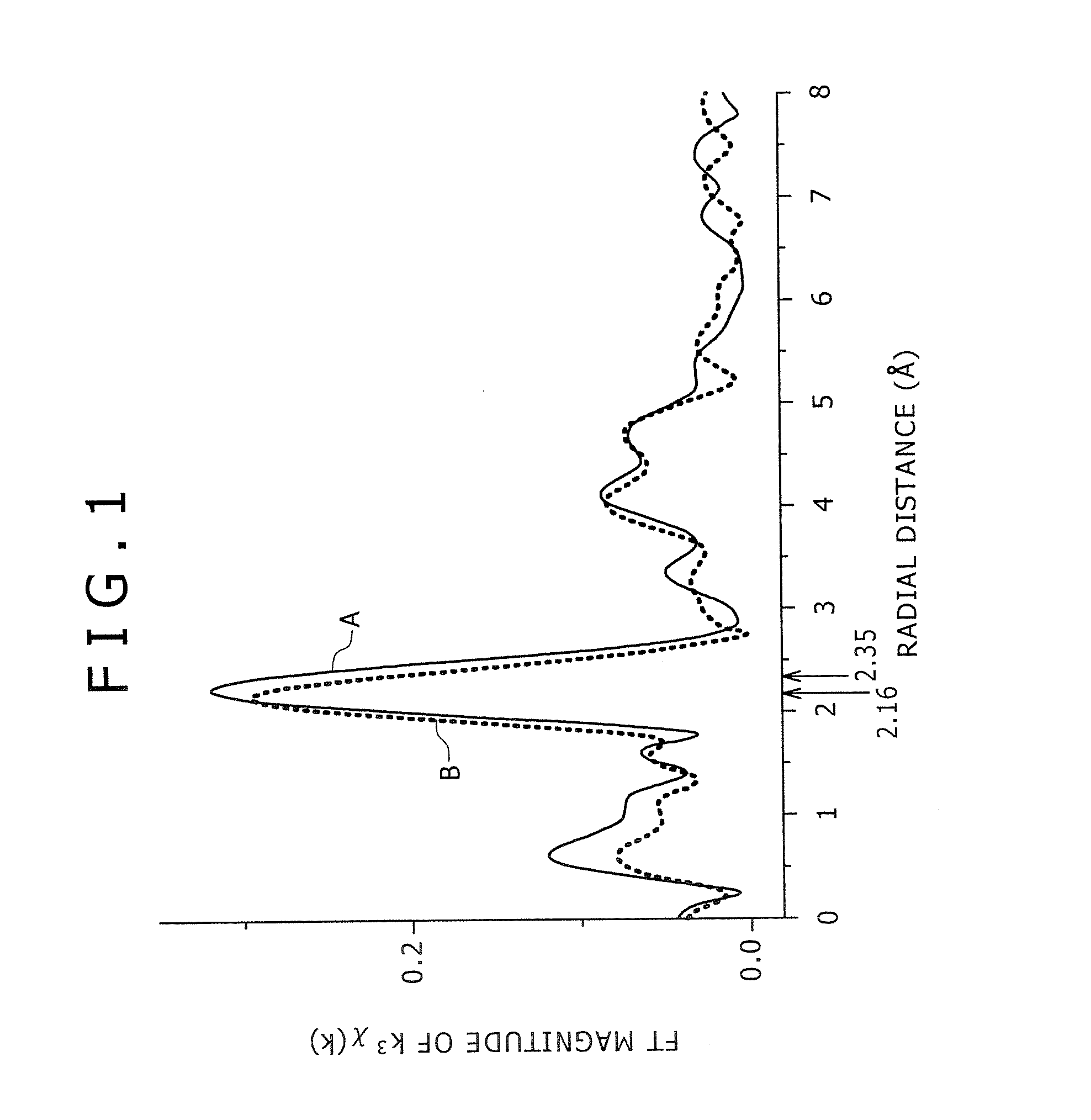
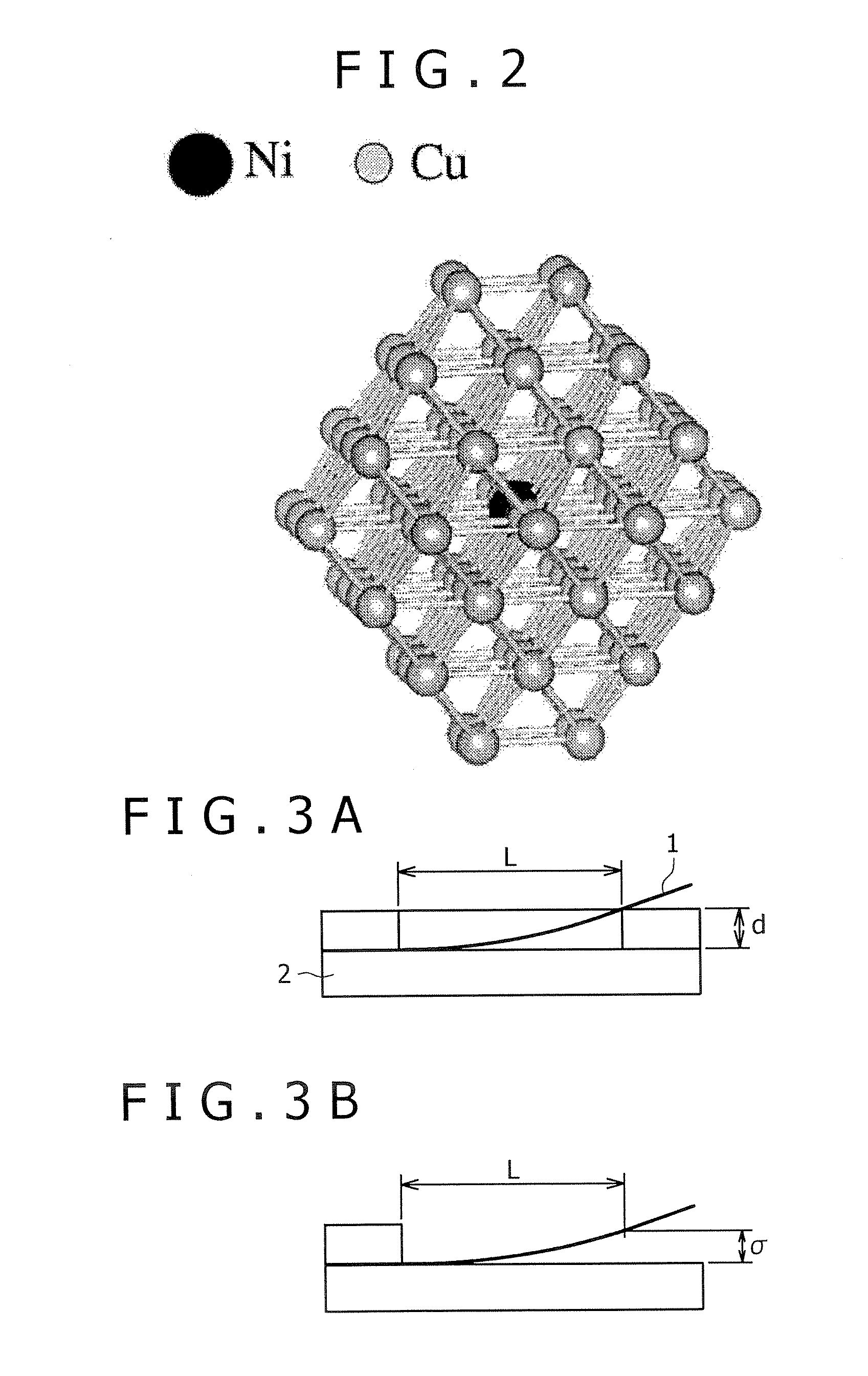
A Cu—Ni—Sn—P alloy is provided, which is excellent in stress relaxation property in a direction perpendicular to a rolling direction, and has any of high strength, high conductivity, and excellent bendability. A copper alloy contains 0.1 to 3.0% of Ni, 0.1 to 3.0% of Sn, and 0.01 to 0.3% of P in mass percent respectively, and includes copper and inevitable impurities as the remainder; wherein in a radial distribution function around a Ni atom according to a XAFS analysis method, a first peak position is within a range of 2.16 to 2.35 Å, the position indicating a distance between a Ni atom in Cu and an atom nearest to the Ni atom. Thus, distances to atoms around the Ni atom in Cu are comparatively increased, so that the stress relaxation property in a direction perpendicular to the rolling direction of the copper alloy is improved.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Holbach magnet shim coil and design method thereof
InactiveCN105548925ARapid designImprove the uniformity of the magnetic fieldMagnetic measurementsPermanent magnetsCurrent distributionBiot–Savart law
The invention discloses a Holbach magnet shim coil and a design method thereof. Aimed at the structural characteristic of a Holbach magnet and the direction of a main magnetic field, a current density function is designed flexibly according to the structural feature of the magnetic field, the relation between the current density and the main magnetic field is derived by utilizing the Biot-Savart Law, a current distribution function is inverted, and the coil structure is optimized by considering requirements for parameters including the power loss function and the linearity of the shim coil. Coils of two different structures are provided for the Halbach magnet, each coil structure has advantages and disadvantages in the aspects of structural complexity and performance, and the coils can be selected flexibly according to practical requirements.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Lithium mixed metal oxide
ActiveUS20110059363A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationAlkali metal oxidesLithiumXANES Spectroscopy
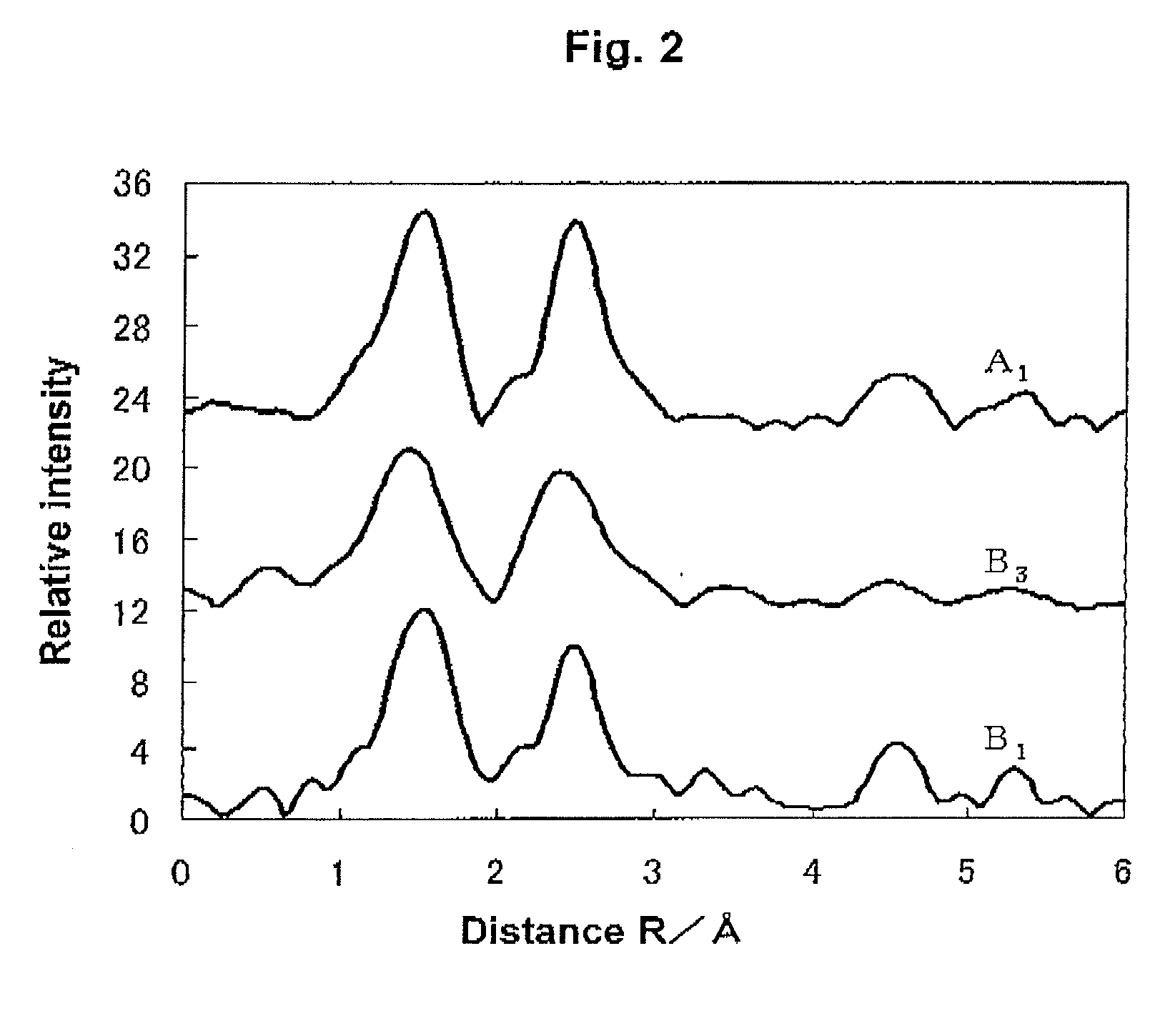
A lithium mixed metal oxide containing Li, Mn and M (M represents at least one metal element, and is free from Li or Mn), and having a peak around 1.5 Å (peak A), a peak around 2.5 Å (peak B), and the value of IB / IA is not less than 0.15 and not more than 0.9 in a radial distribution function obtained by subjecting an extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectrum at K absorption edge of Mn in the oxide to the Fourier transformation, wherein IA is the intensity of peak A and IB is the intensity of peak B.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
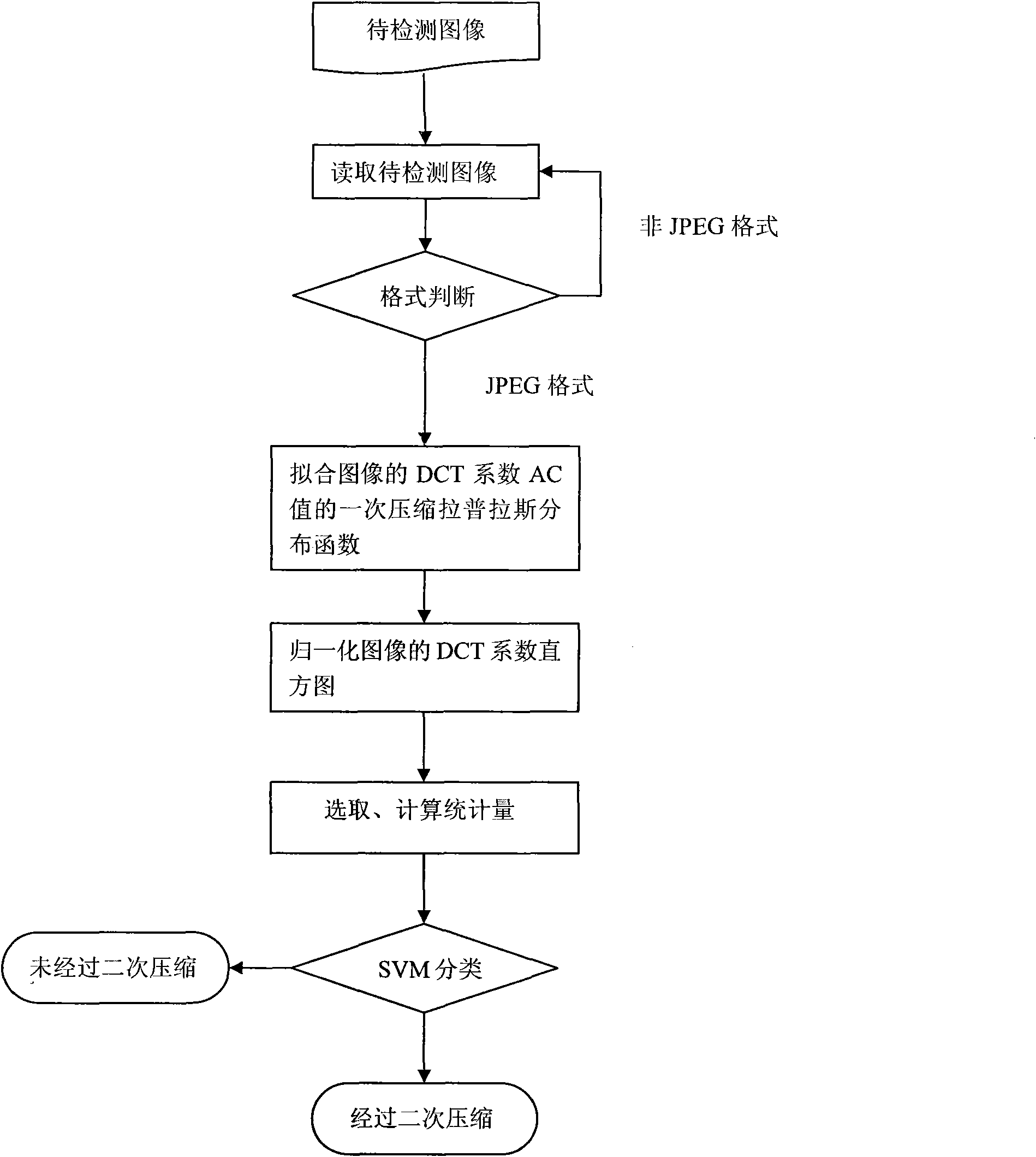
Detection method for secondary compression of JPEG image
The invention provides a detection method for secondary compression of a JPEG image. By using the characteristic that an AC coefficient histogram in a DCT coefficient of primary JPEG compression accords with Laplace distribution, a Laplace distribution function of the AC coefficient of the primary JPEG compression of an image to be detected is estimated in a fit mode according to the AC coefficient distribution of the JPEG image to be detected; the statistic is detected through a difference structure of normalized histogram distribution of the fit distribution function and an actual AC coefficient; and whether the JPEG image is subjected to the secondary compression is judged by using SVM classification. The method has high detection accuracy and wide applicability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Small current earth fault line selection method for radial distribution network
InactiveCN103308822ASmall amount of calculationEigenvalue increaseFault locationUltrasound attenuationTransient state
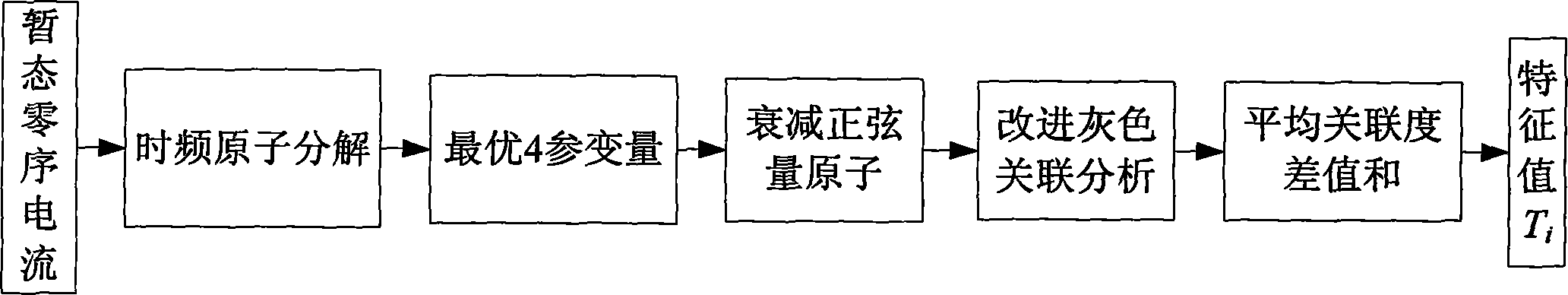
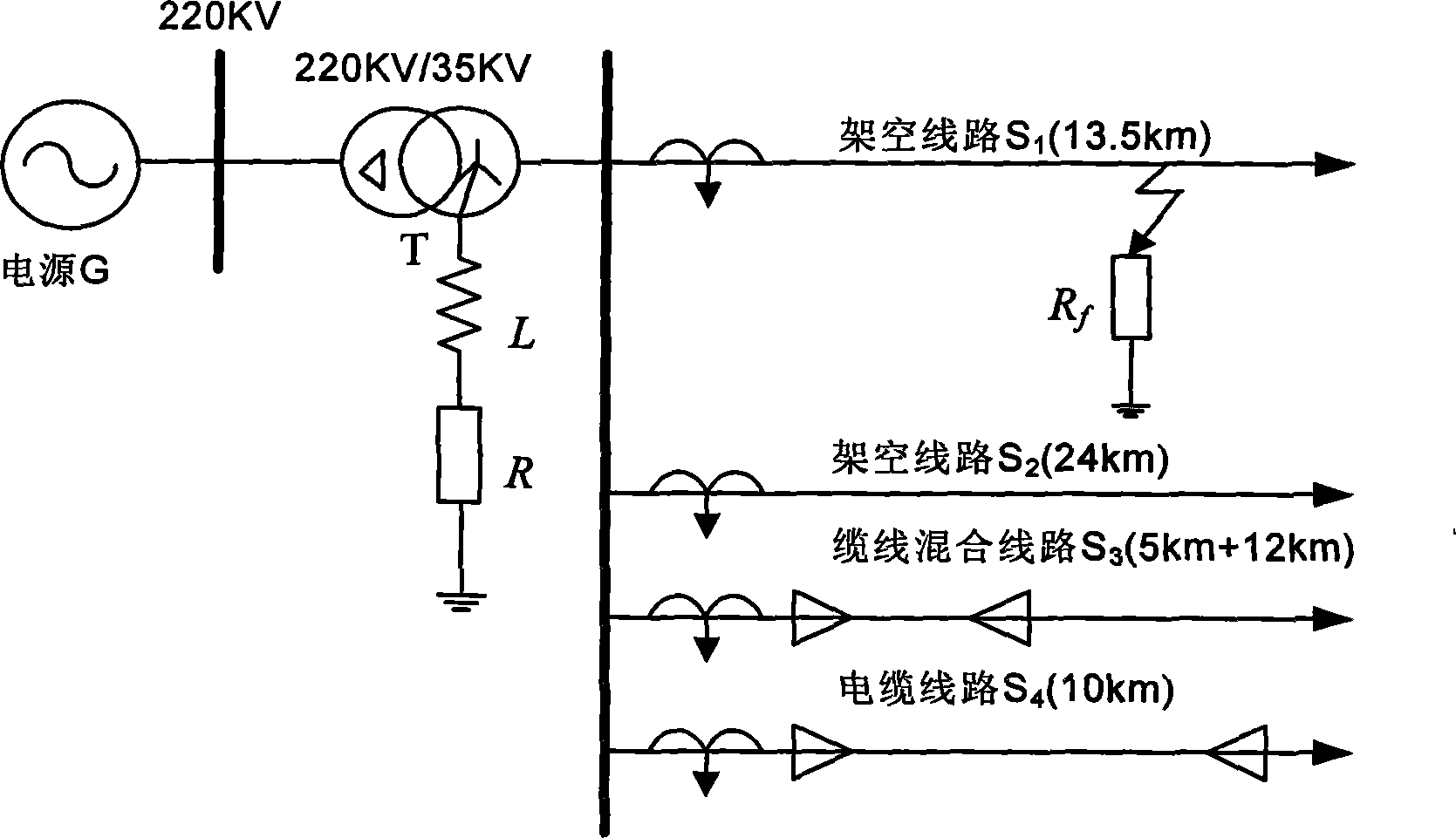
The invention relates to a small current earth fault line selection method for a radial distribution network. The small current earth fault line selection method for the radial distribution network comprises the steps that firstly, the line reference values of fault lines and non-fault lines are calculated according to the number of branch lines of a current radial distribution network system; secondarily, taking a Gabor atom dictionary as the index, a matching tracing algorithm is utilized to carry out time frequency atomic decomposition on transient zero-sequence current of each fault branch line within the first one quarter cycle, and attenuation sinusoidal quantity atoms representing the fault feature information of branch lines are further obtained; thirdly, an improved gray correlation analytic method is adopted to carry out correlation degree analysis on the attenuation sinusoidal quantity atom of each branch line, so that the feature value of each branch line is obtained; and finally, Euclidean distance is obtained by using the feature value of each branch line and the reference values of the fault lines and the non-fault lines, the Euclidean distances are compared, so that the accurate line selection is realized through the comparison of the Euclidean distances. The small current earth fault line selection method for the radial distribution network realizes low calculated amount and high line selection accuracy and is particularly applicable to radial distribution network systems with multiple branch lines.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Region extracting method for medical image
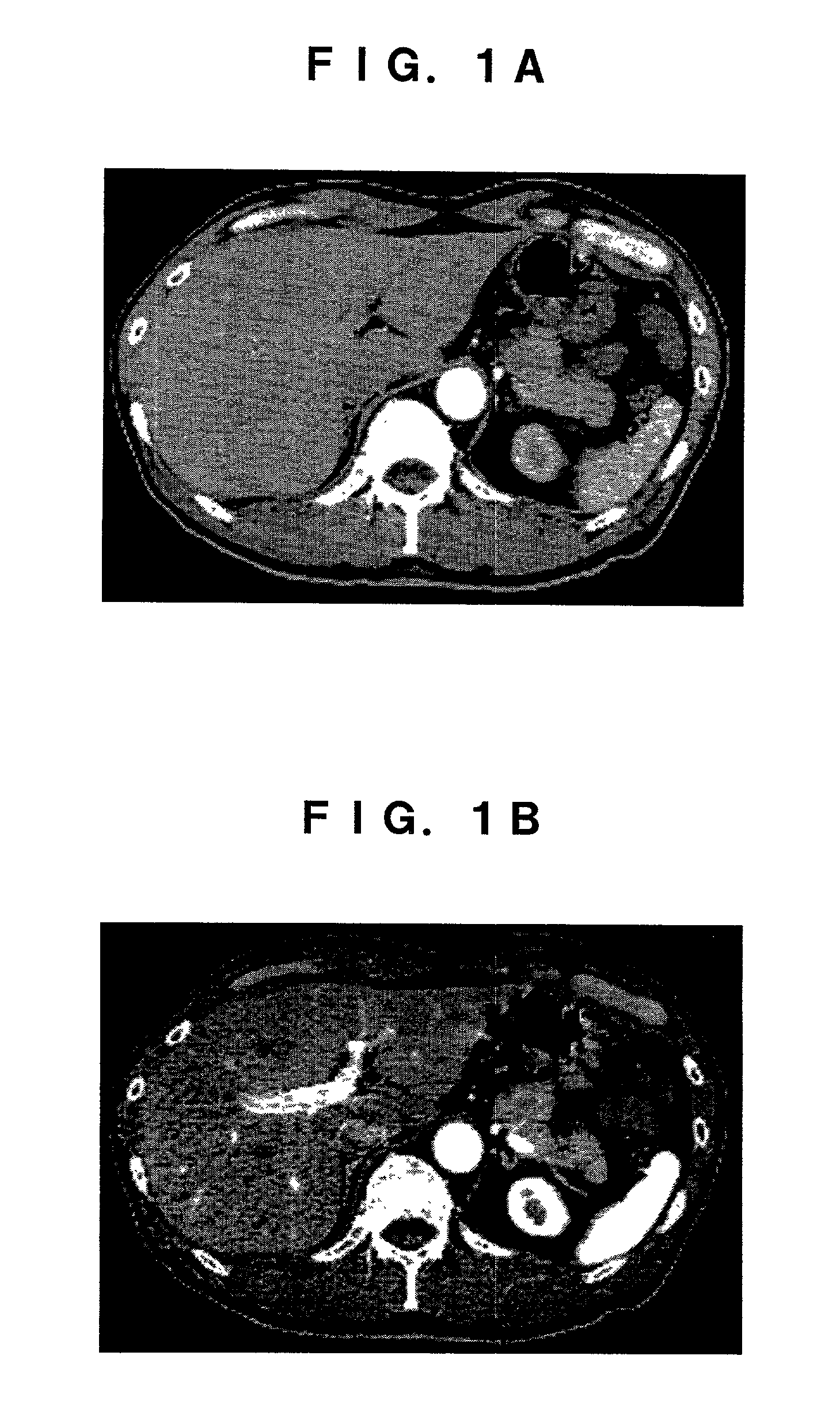
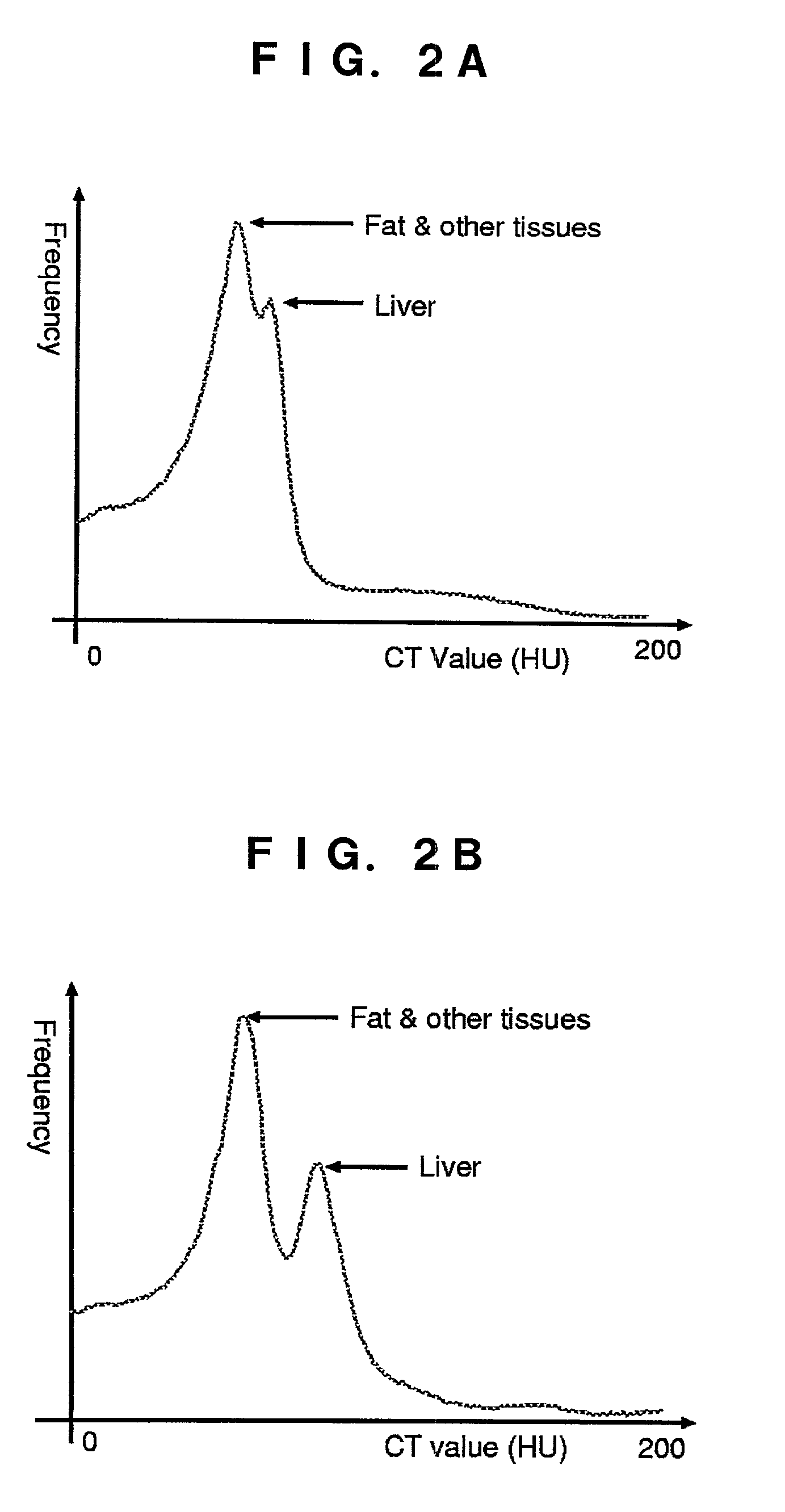
InactiveUS7046833B2Easy to operateImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisCharacteristic spaceWhole liver
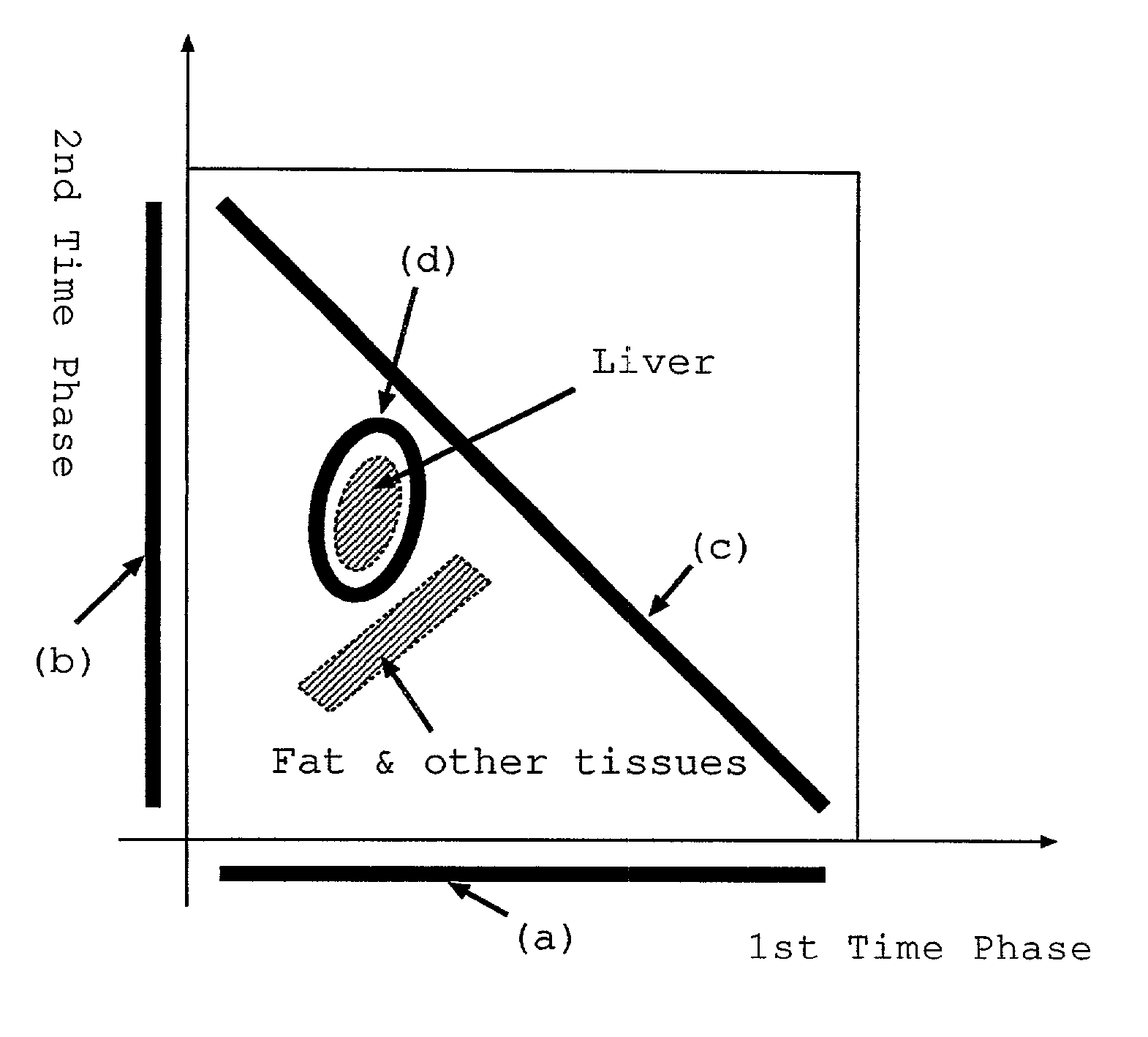
From CT images having captured an abdomen, a two-dimensional characteristic space is assumed, in which X and Y axes indicate CT values of image data taken in first and second time phases different from each other. In this space, a two-dimensional histogram concerning respective pixels located at the same position in the two time phases is taken as a sample distribution of pixels. A two-variable distribution function is applied to this sample distribution, so as to estimate a matrix distribution of pixels corresponding to the whole liver region. According to this matrix distribution, a range of CT value of pixels corresponding to the liver region is estimated.
Owner:AZE
Time domain self-correlation Nakagami-m fading complex channel simulation method
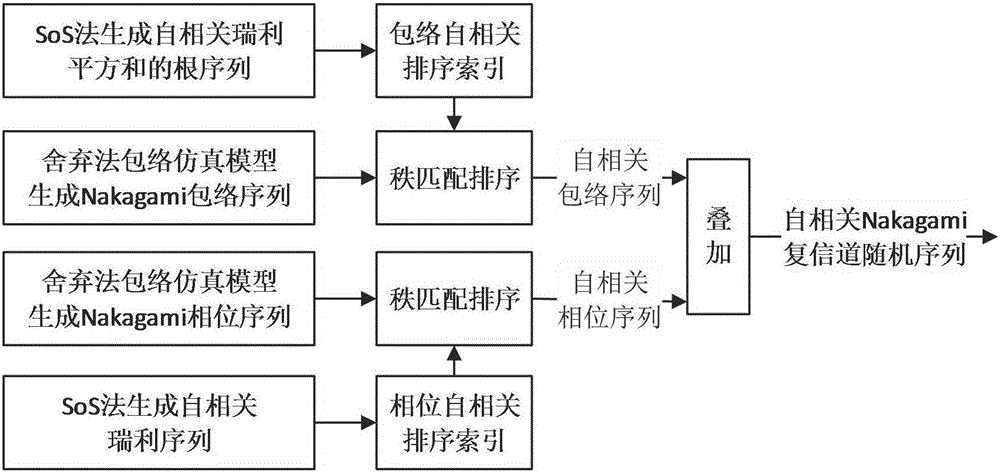
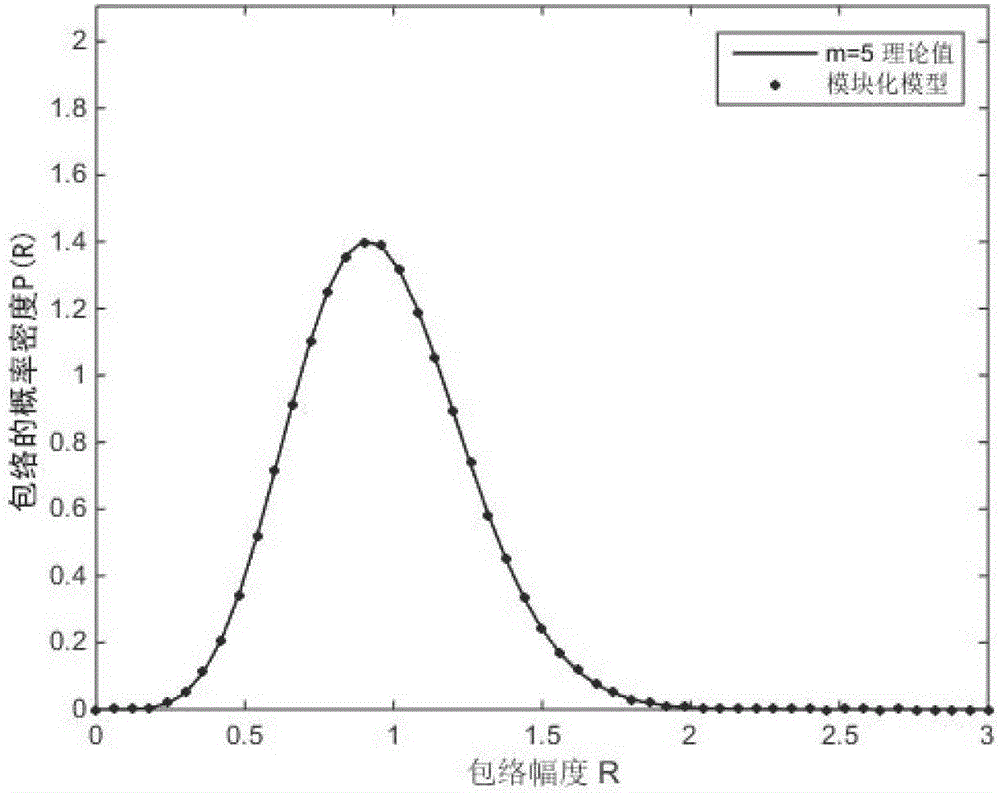
ActiveCN105846926AReduce complexityAccurate Level Pass RateTransmission monitoringExtensibilitySelf correlation
The invention discloses a time domain self-correlation Nakagami-m fading complex channel simulation method, which comprises the steps of: firstly, carrying out independent simulation on envelope distribution, so that a probability density function and a cumulative distribution function of envelopes are consistent with theoretical values; secondly, carrying out independent simulation on phase distribution, so that statistical indexes of a probability density function and a cumulative distribution function of phases are consistent with theoretical values; then ranking an envelope sequence and a phase sequence, so that a self-correlation function and a power spectral density are consistent with theoretical values; and finally, superposing the ranked envelope sequence and phase sequence to obtain a time domain self-correlation Nakagami-m fading complex channel random sequence satisfying all simulation performance evaluation statistics. The time domain self-correlation Nakagami-m fading complex channel simulation method realizes good self-correlation characteristic fading simulation and fast fading simulation of a time domain self-correlation Nakagami-m fading complex channel, has good extensibility, and brings convenience for subsequent adoption of a more efficient module simulation algorithm.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Optimization construction algorithm for aggregate grading of resin concrete
InactiveCN103514370AImprove grading accuracyImprove mechanical propertiesSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmManufactured material
The invention discloses an optimization construction algorithm for aggregate grading of resin concrete. The optimization construction algorithm comprises the following steps that (1) particle diameter intervals are chosen according to an actual aggregate situation; (2) grading orders are chosen according to needs, and particle diameter ranges of the intervals are determined according to the grading orders; (3) according to the selected grading basic parameters, an actual distribution function FF(D) of aggregate grading is established; (4) according to the established actual distribution function and a theoretical distribution function, a target optimization function of the aggregate grading is established; (6) a modern optimization algorithm is adopted to carry out iteration solving on a target, and distribution results of the intervals are obtained. The optimization construction algorithm can be suitable for different aggregate grading orders, grading precision of the aggregate of resin concrete is improved, mechanical performance of produced resin concrete materials is improved, and the manufactured materials can serve as an excellent machine tool structural component.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
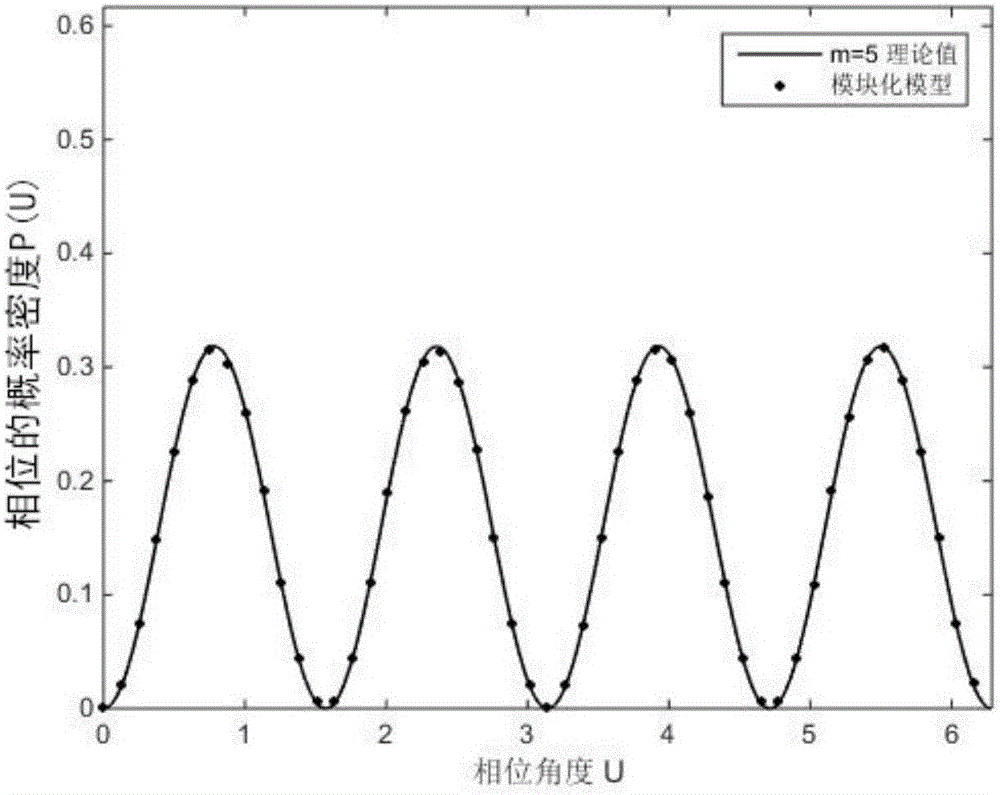
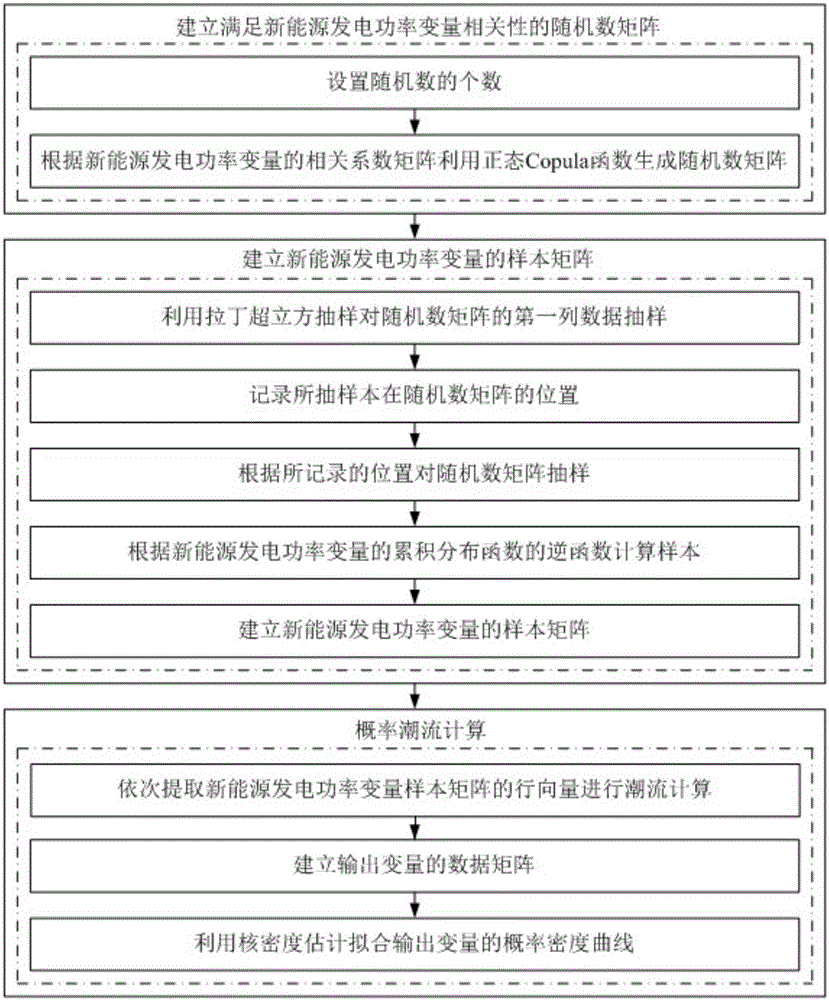
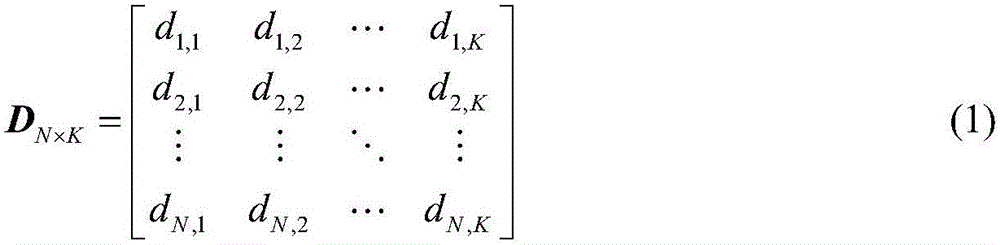
Latin hypercube sampling method probabilistic power flow calculation method based on normal Copula function
ActiveCN105790258AImprove calculation accuracyCalculation speedAc networks with different sources same frequencyCorrelation coefficientNormal density
The invention discloses a Latin hypercube sampling method probabilistic power flow calculation method based on a normal Copula function. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) according to the correlation coefficient matrix of a new energy generated output variable, utilizing the normal Copula function to generate a random number matrix which meets the correlation of the new energy generated output variable; 2) utilizing the Latin hypercube sampling method to sample the random number matrix generated in the 1), and establishing a sample matrix of the new energy generated output variable according to the inverse function of the cumulative distribution function of the new energy generated output variable; and 3) taking the sample matrix, which is established in the 2), of the new energy generated output variable as an input quantity to carry out probabilistic power flow calculation, obtaining a discrete result of an output variable, and utilizing nuclear density estimation to fit the discrete result of the output variable to obtain the probability density function of the output variable. Calculation time is shortened while calculation precision is improved.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +2
Construction method of LT fountain code codability distribution
ActiveCN105490771AReduce decoding overheadImprove performanceError preventionSoliton distributionFountain code
The invention provides a construction method of degree distribution of LT codes. The method first adjusts a binary system degree distribution, then organically combines the binary system degree distribution with robust soliton distribution, and further optimizes a degree distribution function through optimization of a translatable set value, thereby obtaining degree distribution which also has relatively good performance when code length of source data is short, i.e., binary system-robust soliton distribution is corrected. The corrected binary system-robust soliton distribution is utilizes to perform LT fountain coding on the source data, decoding spending can be reduced, decoding efficiency can be improved, and fountain codes can be well applied to the communication fields.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Bitmap tracker for visual tracking under very general conditions
InactiveUS8027513B2Improve matchMarking can be removedTelevision system detailsImage analysisMotion cuesPseudo-Boolean function
System and method for visually tracking a target object silhouette in a plurality of video frames under very general conditions. The tracker does not make any assumption about the object or the scene. The tracker works by approximating, in each frame, a PDF (probability distribution function) of the target's bitmap and then estimating the maximum a posteriori bitmap. The PDF is marginalized over all possible motions per pixel, thus avoiding the stage in which optical flow is determined. This is an advantage over other general-context trackers that do not use the motion cue at all or rely on the error-prone calculation of optical flow. Using a Gibbs distribution with a first order neighborhood system yields a bitmap PDF whose maximization may be transformed into that of a quadratic pseudo-Boolean function, the maximum of which is approximated via a reduction to a maximum-flow problem.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
A normal interface rigidity prediction method considering three-dimensional fractal
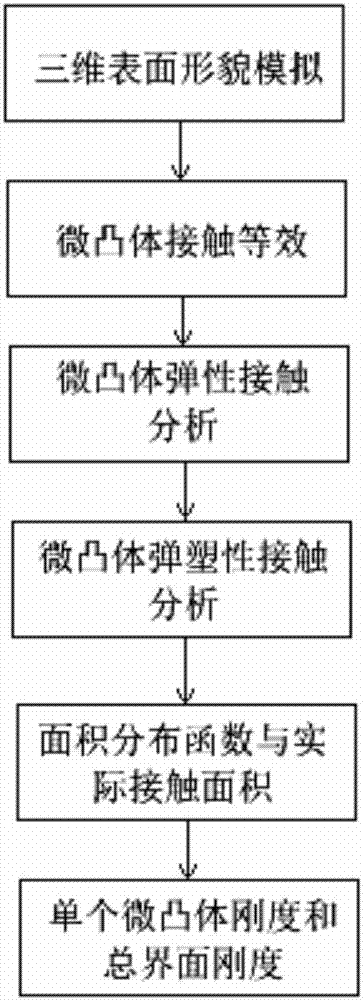
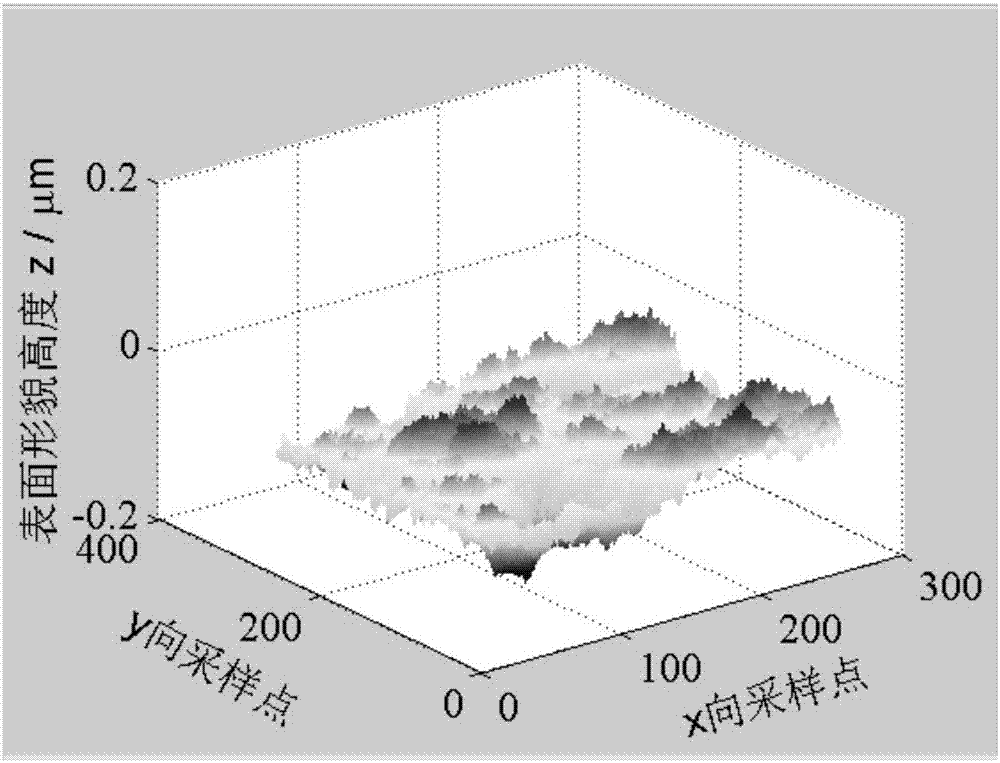
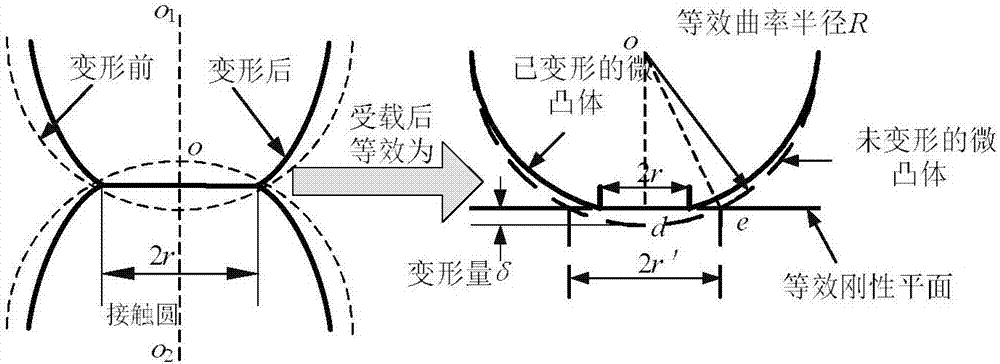
InactiveCN106991219AControl Surface DynamicsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationComputer scienceTopography
The invention relates to a normal interface rigidity prediction method considering three-dimensional fractal, the method comprising the steps of: improving a curvilinear function describing two-dimensional fractal into a correction function simulating three-dimensional fractal topography and expressing amplitudes of peaks and troughs described by the function as contact deformation quantities; making contact between two rough micro-bulges equivalent to contact between a rigid plane and an equivalent micro-bulge, wherein the actual contact area between the equivalent micro-bulge and the rigid plane meets a=pi R delta; separately calculating the deformation quantities of an elastic deformation stage and an elastoplastic deformation stage; calculating an area distribution function and the actual contact area; calculating the rigidity of a single micro-bulge and total interface rigidity; calculating the rigidity kn1 of the elastic stage, the rigidity kn2 of the elastoplastic stage and the total interface rigidity. The prediction method for acquiring the between-interface rigidity of precision machinery is simple and easy to implement. The method takes into consideration elastoplastic deformation of micro-bulges, contact friction factors and three-dimensional fractal distribution and obtained results can provide technical reference for prediction and control of dynamic characteristics of interfaces.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
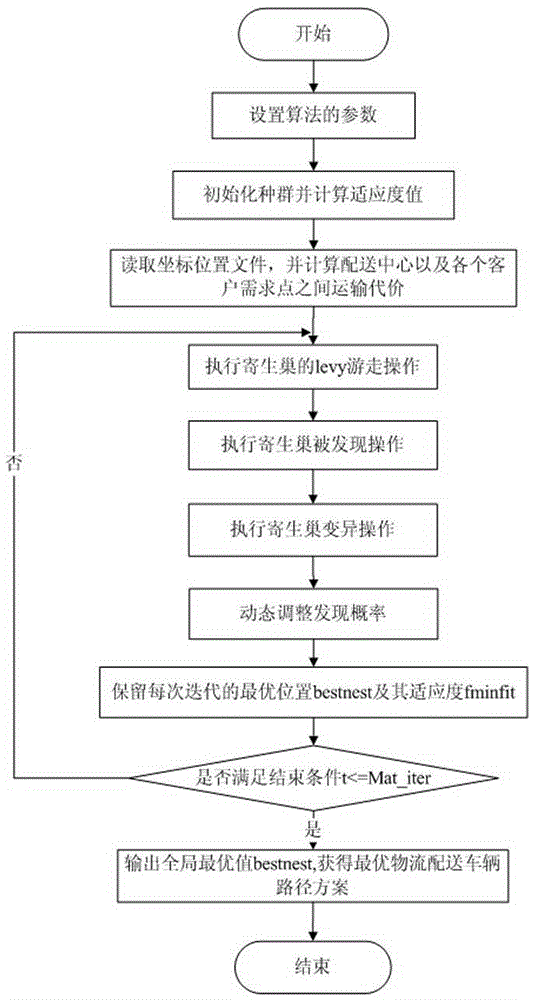
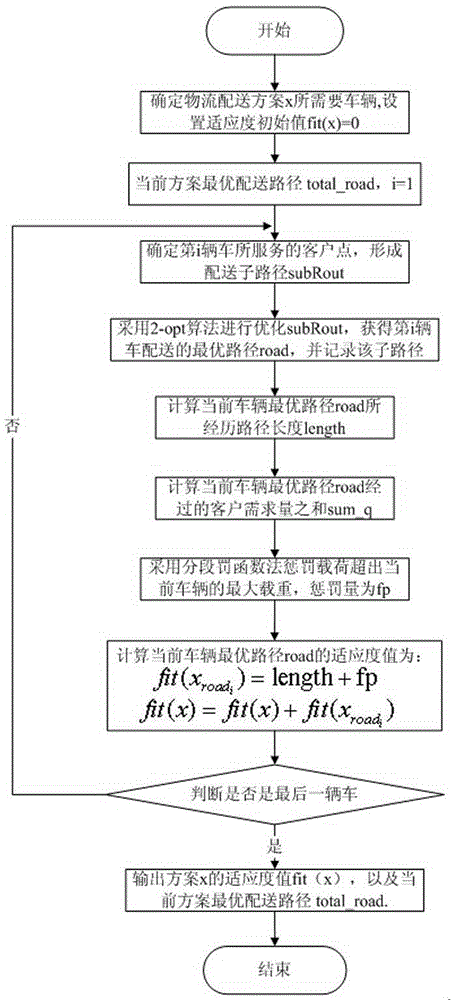
Logistic distribution vehicle path optimizing method based on improved Cuckoo algorithm
ActiveCN105260785ASolving Shipping Optimization ProblemsEnrich the method of solving logistics distribution route optimization problemForecastingEffective solutionAlgorithm
The invention relates to a logistic distribution vehicle path optimizing method based on an improved Cuckoo algorithm, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of 1, setting the parameters of the improved Cuckoo algorithm; 2, initializing population and calculating a fitness value, wherein the population adopts a uniform distribution function to generate size parasitic nests with an nd-dimensional searching space range of [1, carnumber], calculation of the fitness value comprises firstly adopting a 2-opt algorithm to locally optimize the path in each route and solving the path value of each optimized route by a segmented penalty function; 3, executing the levy migration operation of the parasitic nests; 4, executing the operation that the parasitic nests are detected; 5, executing the mutation operation of the parasitic nests; and 6, dynamically adjusting detection probabilities. According to the logistic distribution vehicle path optimizing method based on the improved Cuckoo algorithm, combination of the improved Cuckoo algorithm and the 2-opt algorithm is applied to solving the problem about the logistic distribution vehicle path, a novel available and effective solution is provided for solving the problem about the optimization of logistic vehicle distribution, and methods for solving the problem about optimizing the logistic distribution path are enriched.
Owner:屈迟文
Bitmap tracker for visual tracking under very general conditions
InactiveUS20080232643A1Improve matchMarking can be removedTelevision system detailsImage analysisMotion cuesPseudo-Boolean function
System and method for visually tracking a target object silhouette in a plurality of video frames under very general conditions. The tracker does not make any assumption about the object or the scene. The tracker works by approximating, in each frame, a PDF (probability distribution function) of the target's bitmap and then estimating the maximum a posteriori bitmap. The PDF is marginalized over all possible motions per pixel, thus avoiding the stage in which optical flow is determined. This is an advantage over other general-context trackers that do not use the motion cue at all or rely on the error-prone calculation of optical flow. Using a Gibbs distribution with a first order neighborhood system yields a bitmap PDF whose maximization may be transformed into that of a quadratic pseudo-Boolean function, the maximum of which is approximated via a reduction to a maximum-flow problem.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Probability Distribution Function Mapping Method
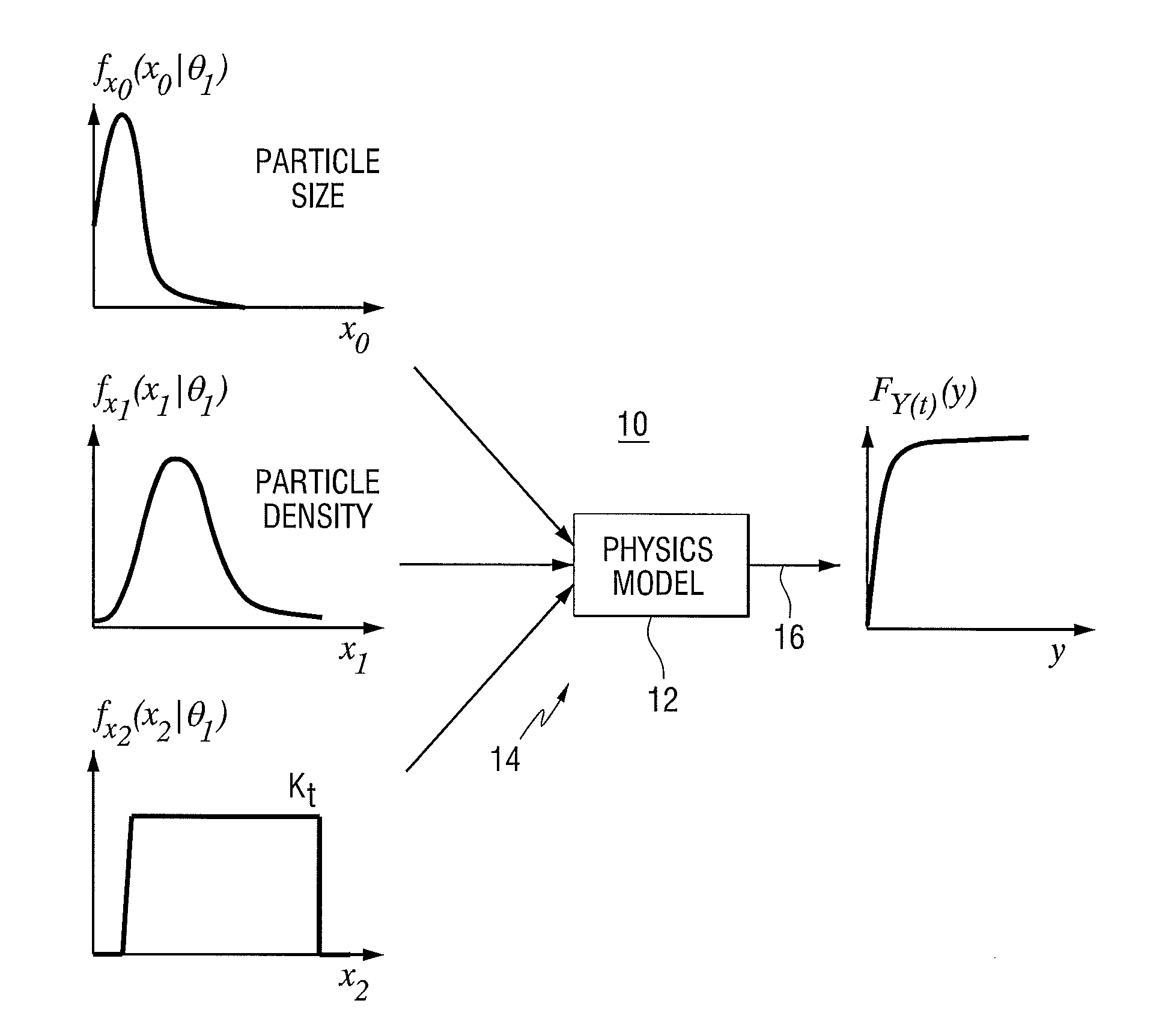
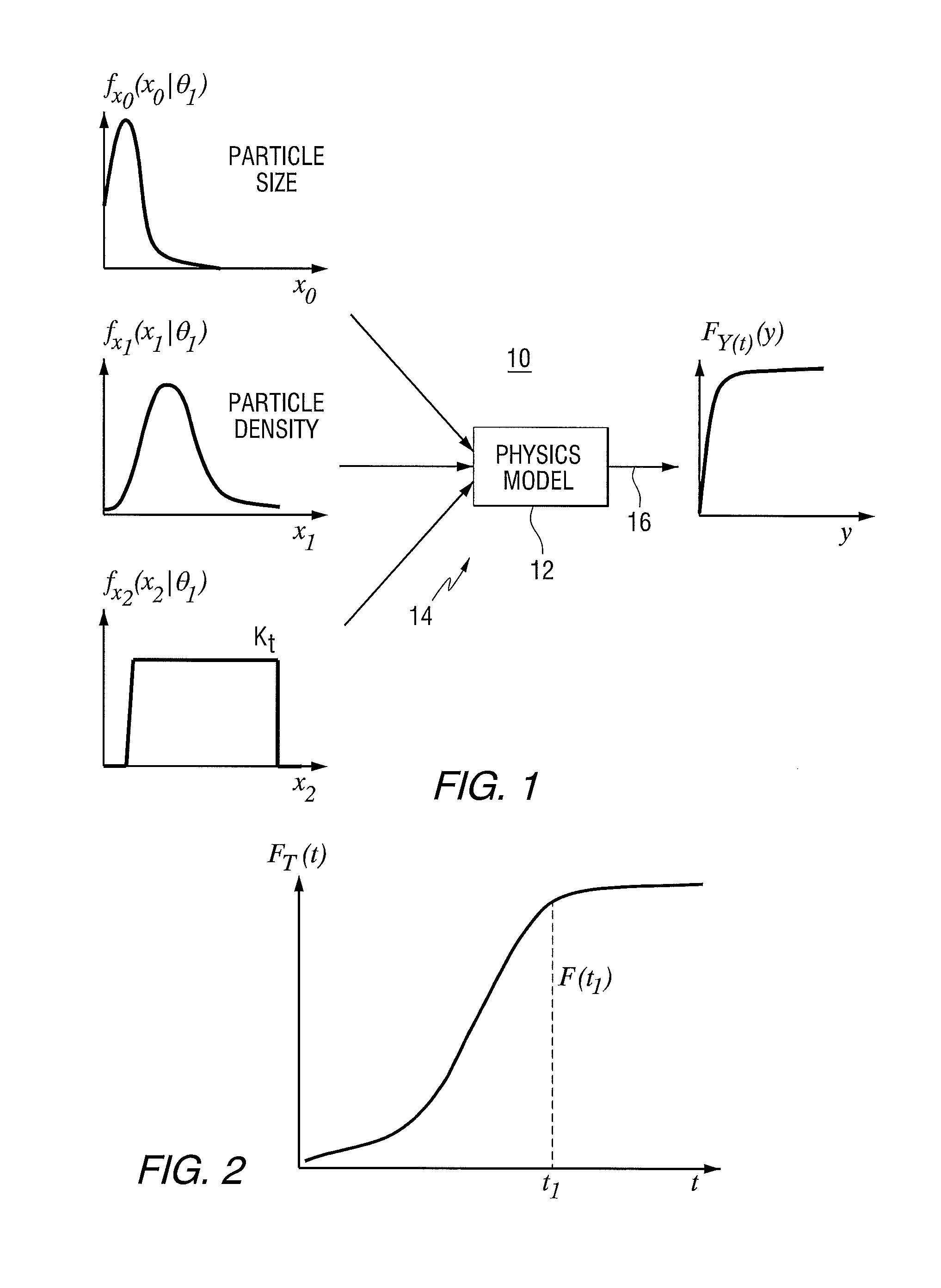
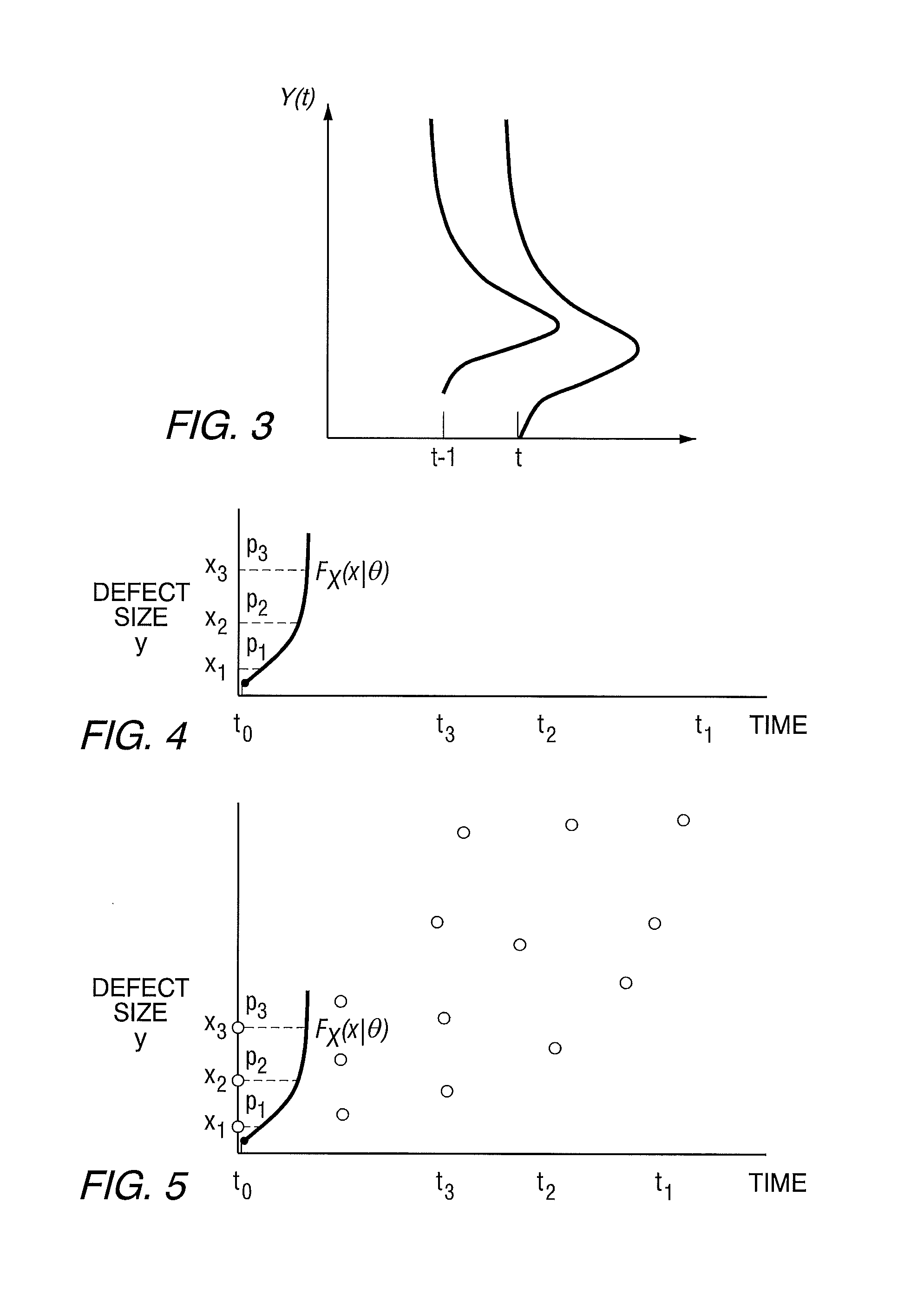
InactiveUS20110010140A1Computation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsFunction mappingComputer science
A method includes: receiving a plurality of values of an input variable representative of a physical characteristic of a component or system, using a physics model to produce an estimate of an output for each of the input values, mapping the output estimates to the input values to produce an output probability density or cumulative distribution function for the physical characteristic at a future time, and outputting the probability density or cumulative distribution function. An apparatus that implements the method is also provided.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
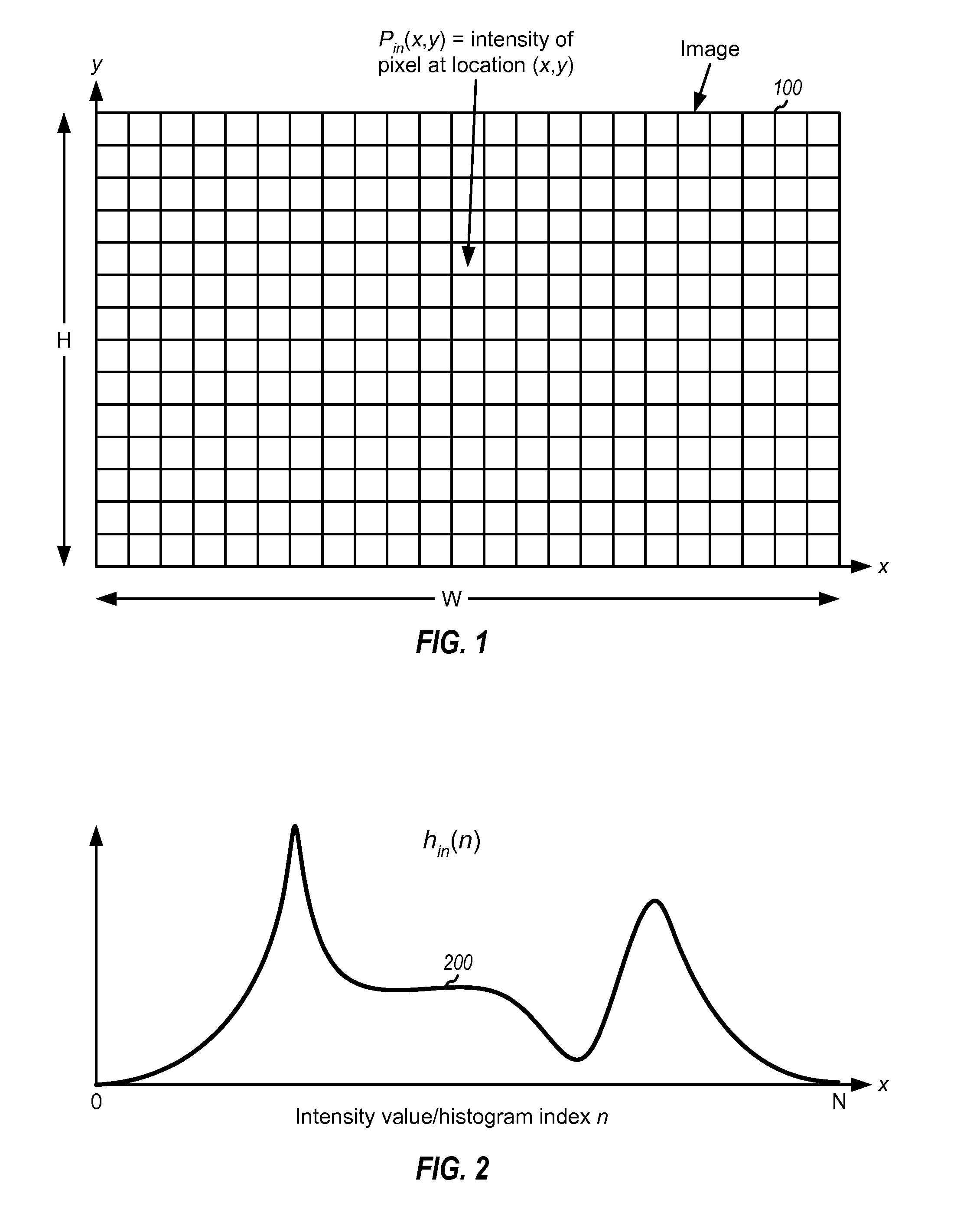
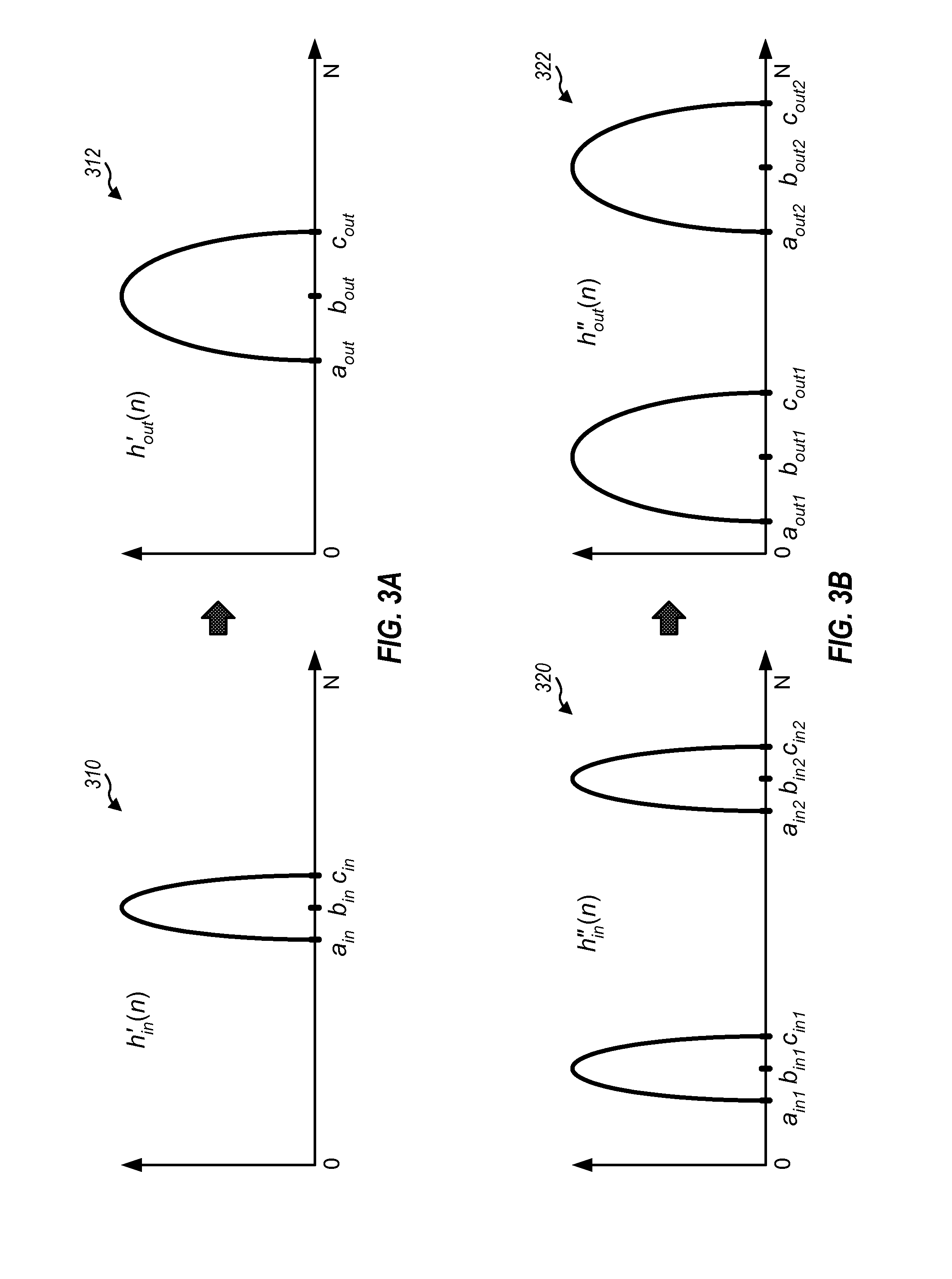
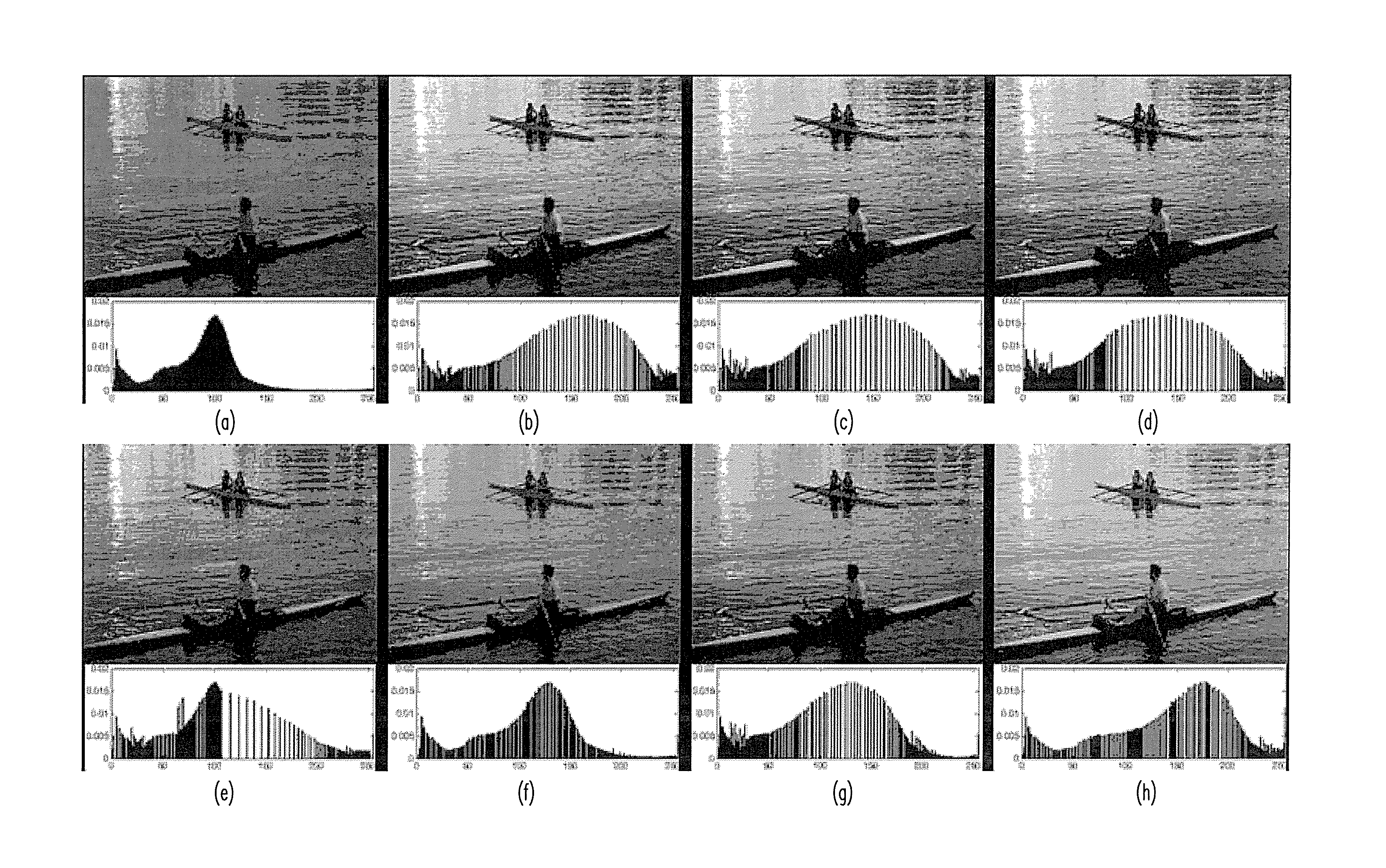
Image quality enhancement with histogram diffusion
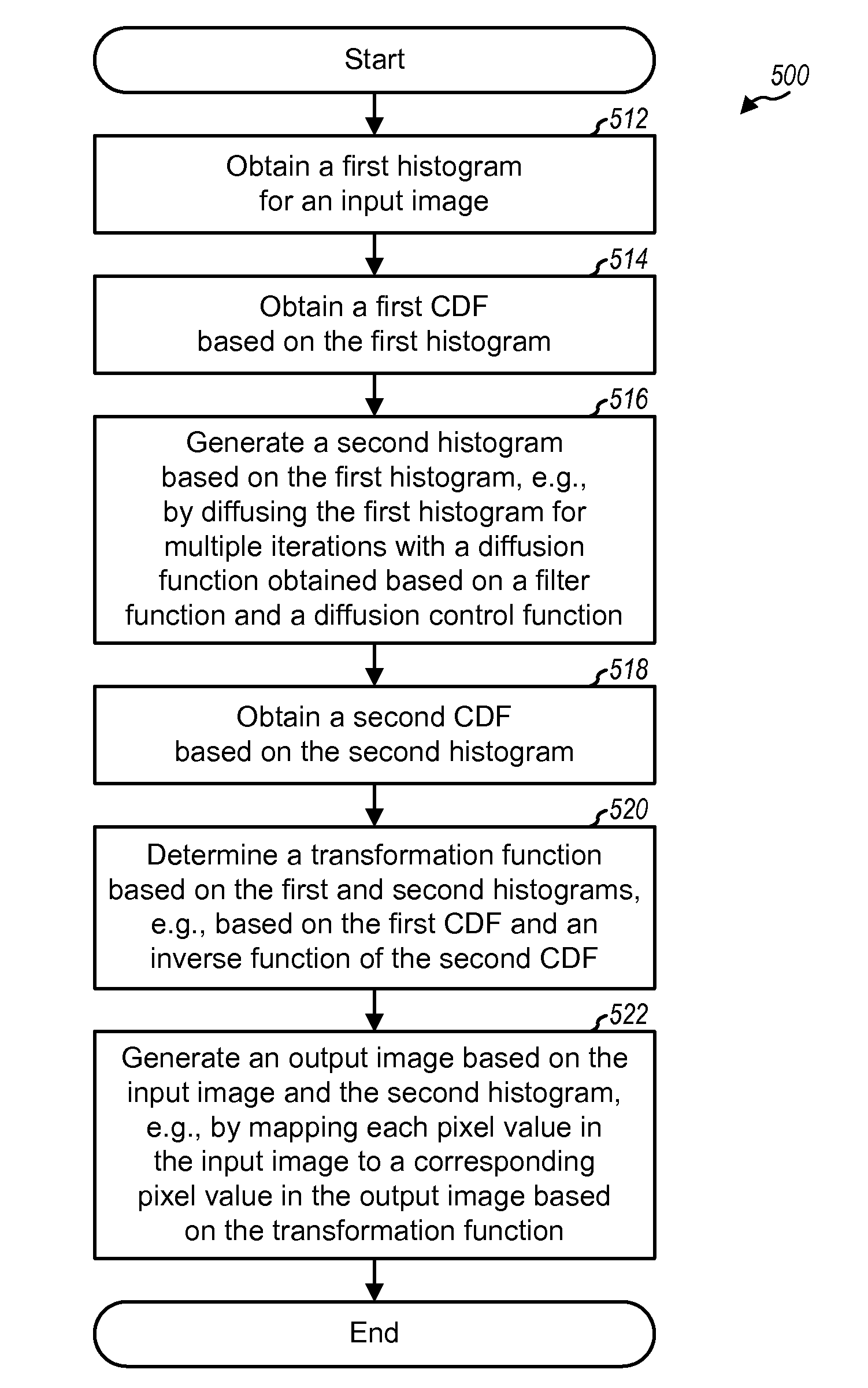
InactiveUS20090110274A1Quality improvementIncrease coverageImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusionImaging quality
Techniques for improving the quality of images are described. A first histogram of intensity values may be obtained for an input image and diffused to obtain a second histogram with better intensity coverage. The diffusion may be achieved by filtering the first histogram for multiple iterations with a diffusion function obtained based on a filter function and a diffusion control function. The filter function may control the rate and / or characteristics of the diffusion. The diffusion control function may control shifts in positions of lobes in the first histogram. A transformation function may be determined based on a first cumulative distribution function (CDF) for the first histogram and an inverse function for a second CDF for the second histogram. An output image may be generated by mapping each pixel value in the input image to a corresponding pixel value in the output image based on the transformation function.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Measuring apparatus for continuous spectrum bidirectional scattering distribution function
InactiveCN102854149AReal physical propertiesReal structureColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberMeasurement device
The invention provides a measuring apparatus for a continuous spectrum bidirectional scattering distribution function (BSDF), which relates to optical measurement equipment. The invention aims to overcome the problems of incapable measurement of the continuous spectrum BSDF, a narrow measurement spectral band, a small measurement angle and a low measuring speed. The rotating shaft of a rotating table board is connected with the motor shaft of a stepping motor; a sample ring is fixedly arranged at a through hole in the center of the rotating table board; a lighting source probe is fixedly arranged above the sample ring; a collimation amplifier assembly is fixedly arranged at a ray emitting lens of the lighting source probe; a reflection ray reception probe is installed above the sample ring, and a ray reception lens of the reflection ray reception probe faces the sample ring; a transmitted ray reception probe is fixedly arranged below the sample ring; a ray reception lens of the transmitted ray reception probe faces the sample ring; a ray signal input end of a control and data processor is connected with a ray signal output end of a two-channel fiber spectrometer. The measuring apparatus provided by the invention can be extensively used for measuring optical scattering characteristics of a material.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Image processing apparatus
InactiveUS20130287299A1High image processing efficiencyImprove image qualityImage enhancementImage codingImaging processingNormal density
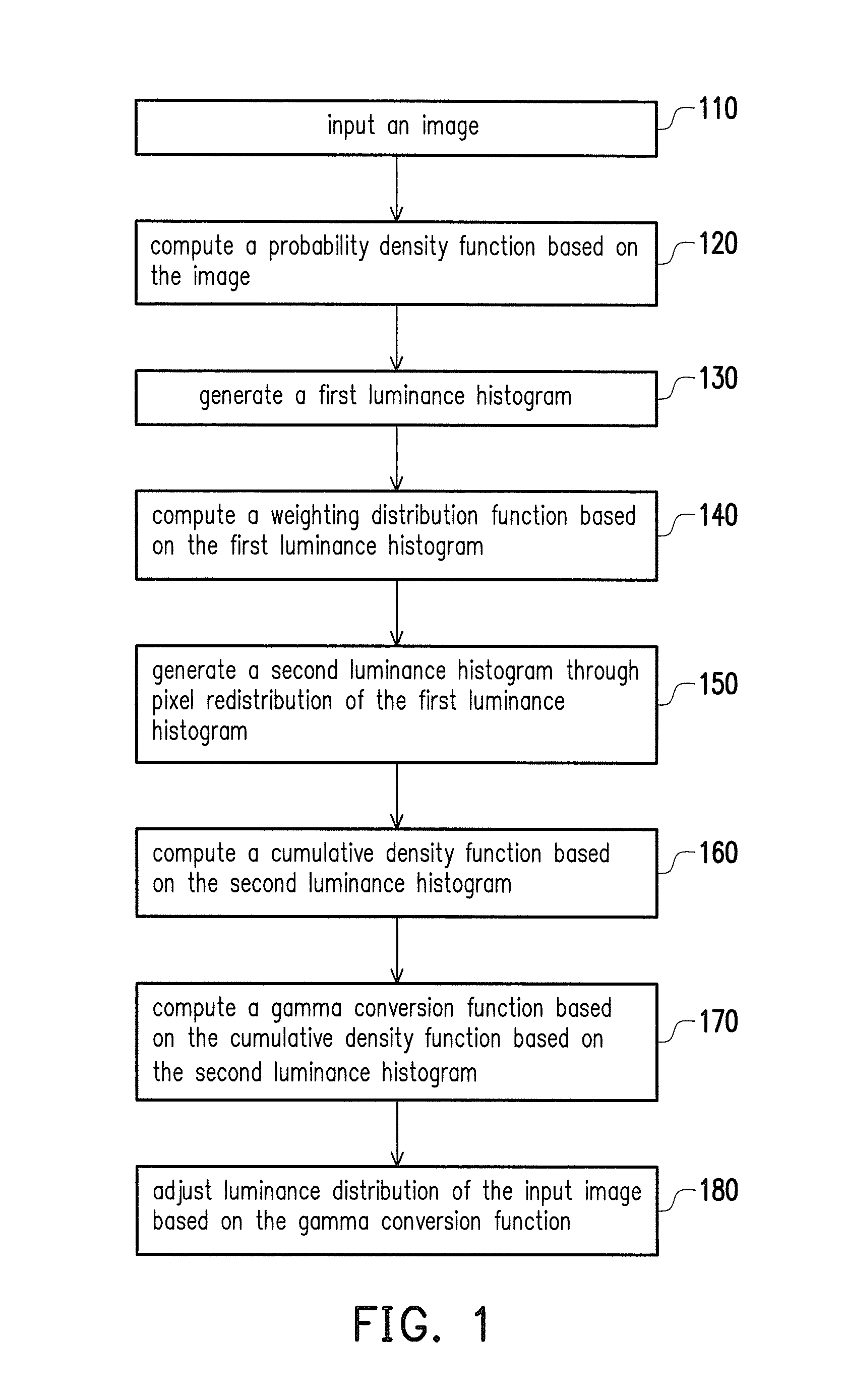
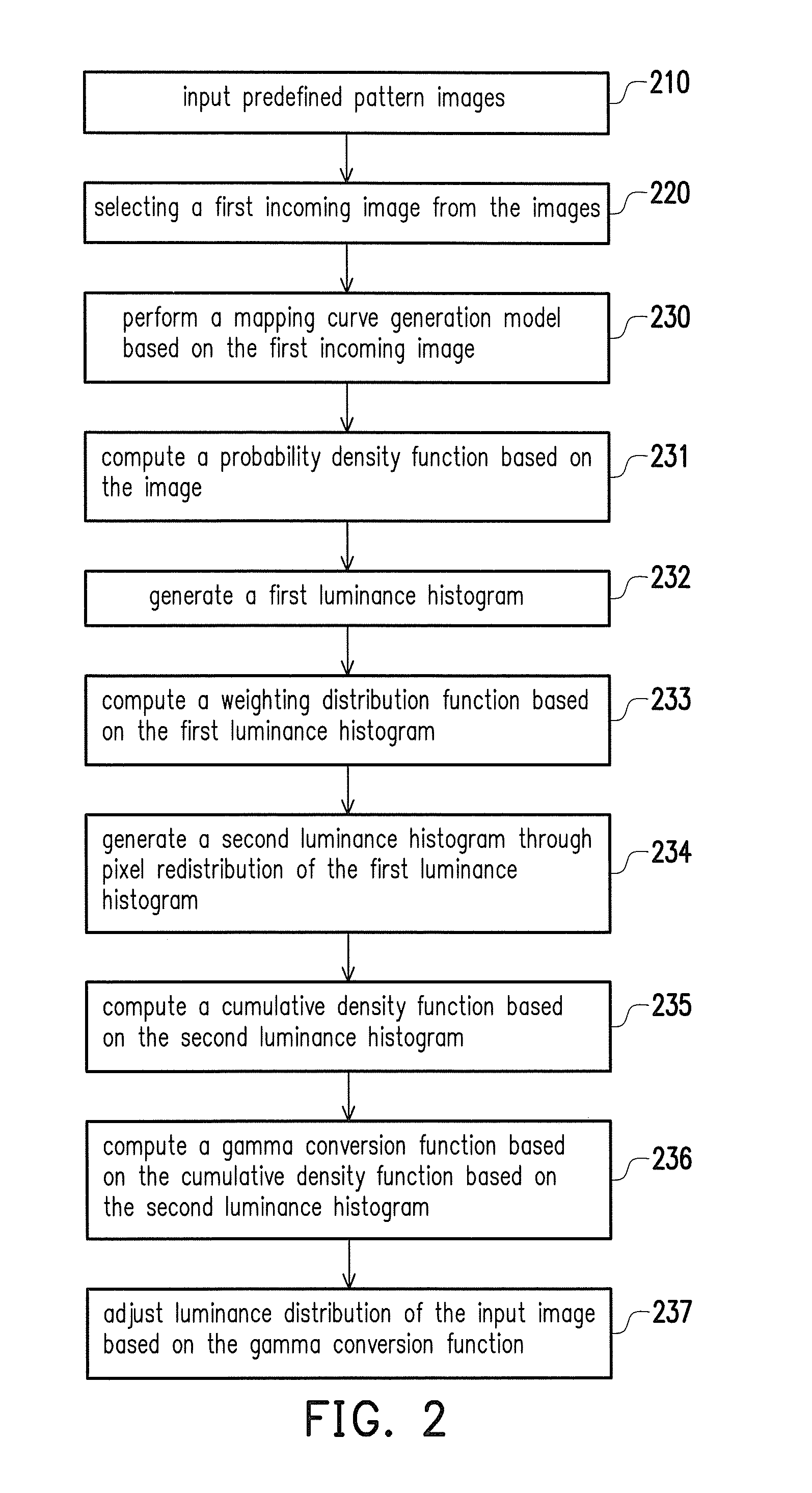
The invention discloses an image processing apparatus. The image processing apparatus includes an image statistic computation circuitry, a reconfigurable circuitry and a luminance transformation circuitry. The image statistic computation circuitry computes a probability density function corresponding to an inputted image; generates a first luminance histogram by subsampling a luminance histogram related to the probability density function in a first period. The reconfigurable circuitry computes a weighting distribution function according to the first luminance histogram in a second period after the first period; computes a smoothed cumulative density function according to the weighting distribution function in a third period after the second period; computes a gamma transform function in a fourth period after the third period. The luminance transformation circuitry generates a resulted image by adjusting a luminance distribution of the inputted image based on the gamma transform function in a fifth period after the fourth period.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
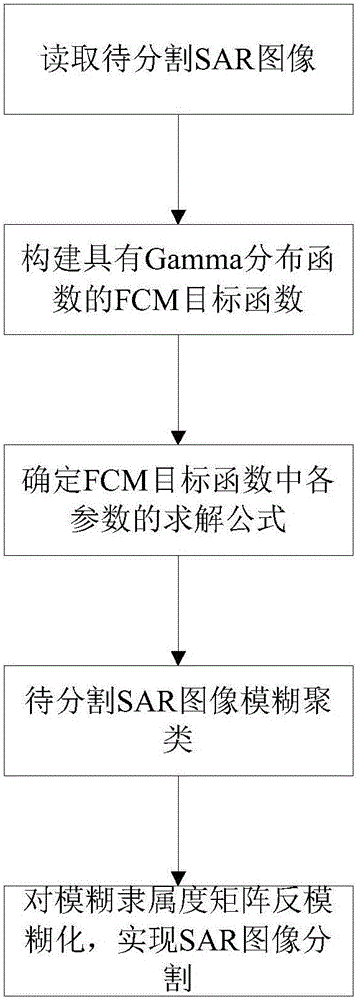
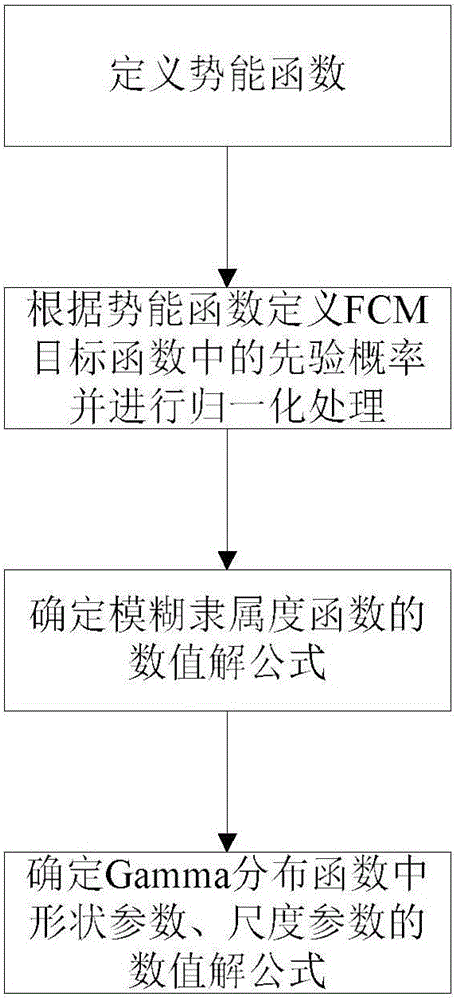
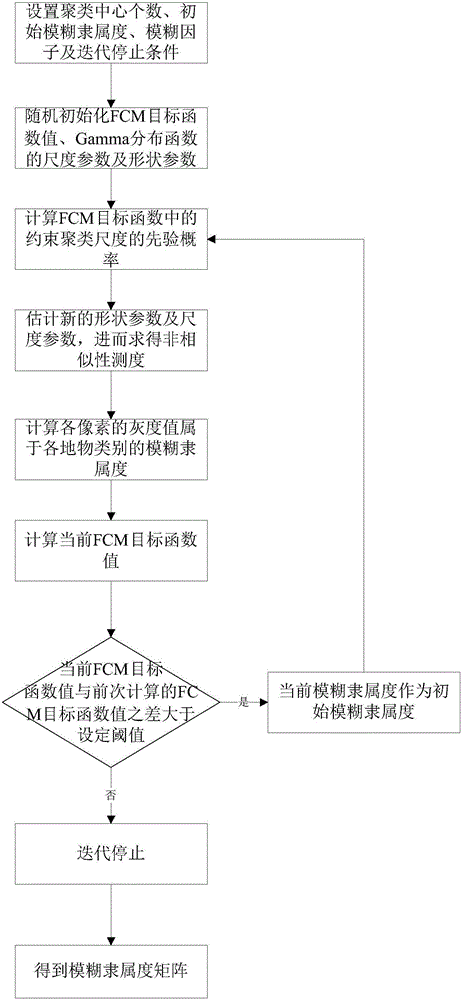
Fuzzy cluster SAR image segmentation method based on Gamma distribution
InactiveCN105787935AImprove fitting accuracyImprove Segmentation AccuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionNormal density
The invention provides a fuzzy cluster SAR image segmentation method based on Gamma distribution. The method comprises the following steps: taking ray values of pixels of an SAR image to be segmented as sampling points, and constructing an FCM object function with a Gamma distribution function; determining solution formulas of parameters in the FCM object function; carrying out fuzzy clustering on the SAR image to be segmented by use of the FCM object function with the Gamma distribution function to obtain fuzzy membership degree matrixes when the gray value of each pixel of the SAR image to be segmented belongs to each ground object type; and performing defuzzification on the fuzzy membership degree matrixes according to a maximum membership degree principle so as to realize SAR image segmentation. According to the invention, a dissimilarity measure from pixel points to clusters is described by use of negative logarithms of a Gamma distribution probability density function, through accurate fitting of SAR image distribution features, the influence exerted by noise in the SAR image on a segmentation result is further overcome, the segmentation precision is improved, and the fitting and segmentation precision of the SAR image is effectively improved.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
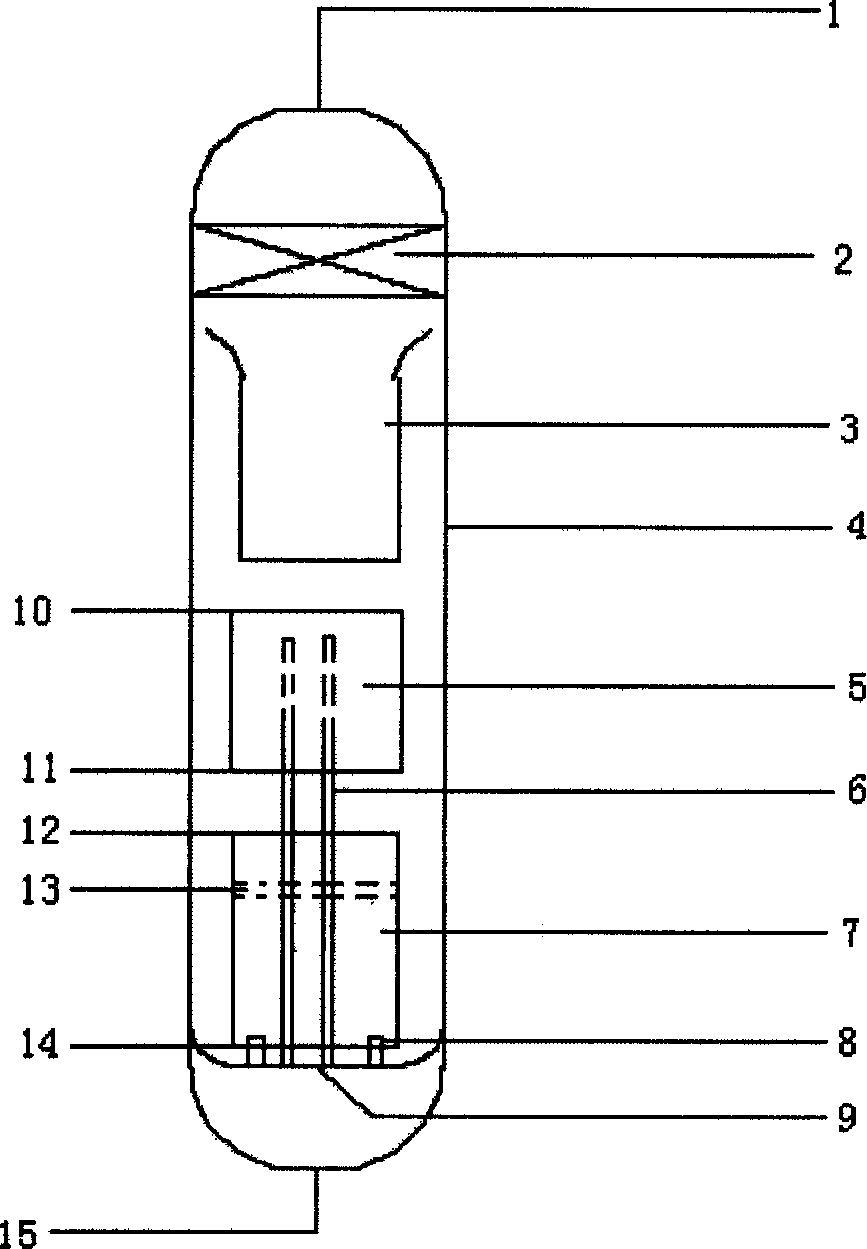
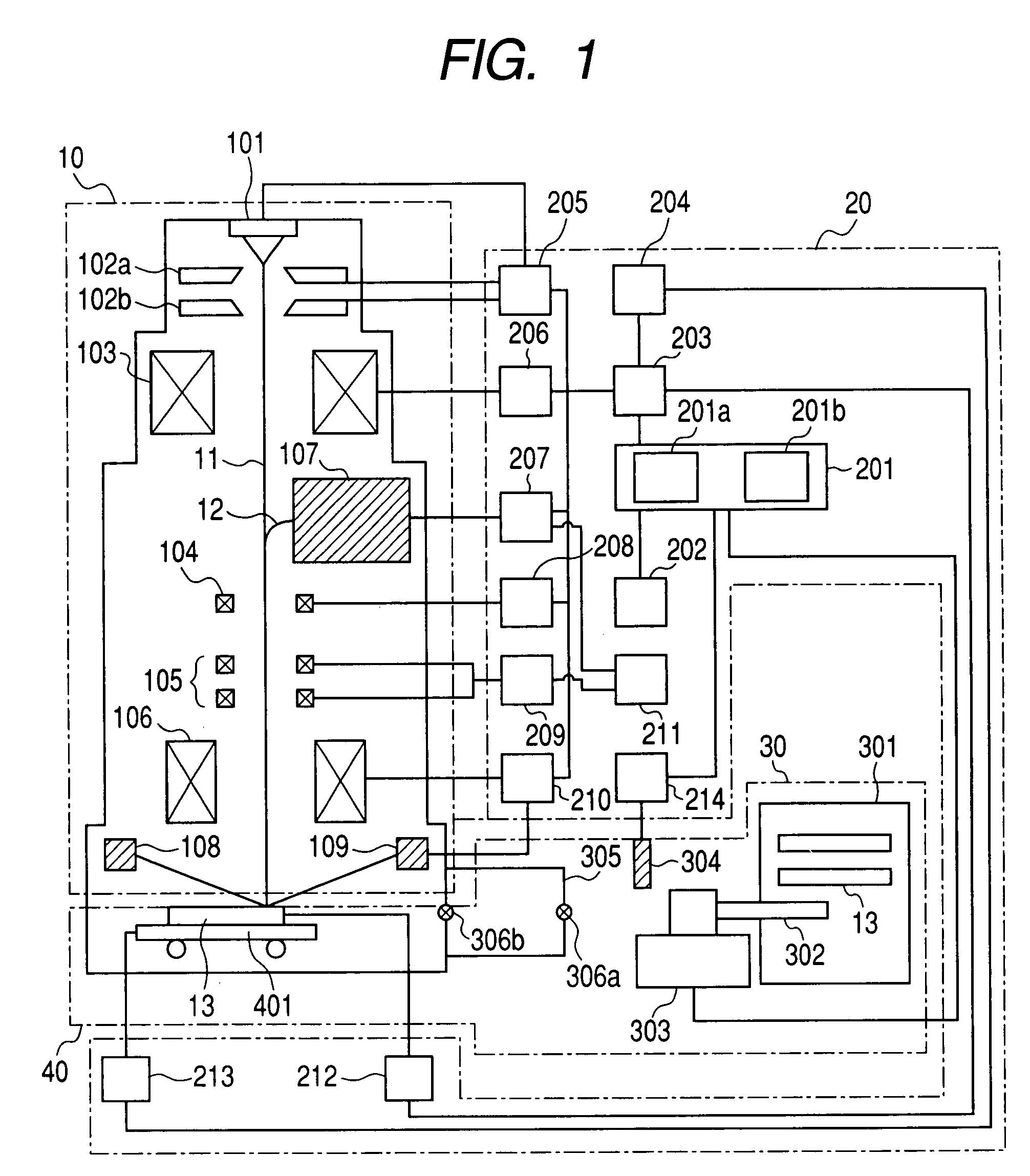
Charged particle beam apparatus and pattern measuring method
ActiveUS7655907B2Easy to handleImprove the accuracy of the approximate function representing the surface potential distributionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesMeasurement pointParticle beam
It is to provide a technology that can quickly process many measurement points on a substrate by a primary charged particle beam. In a control system, with respect to each measurement point (irradiation position of the primary charged particle beam) on a wafer, a calculator obtains a probability of a surface potential at a relevant measurement point that is obtained from a surface potential distribution function of the wafer and is stored in a data storage unit. Based on the probability, the calculator determines an amplitude of a set parameter (for example, retarding voltage) of charged particle optics at the relevant measurement point. Then the calculator checks the focus state of the primary charged particle beam by changing the set parameter in the range of the determined amplitude, and determines the set parameter to be used for measurement.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
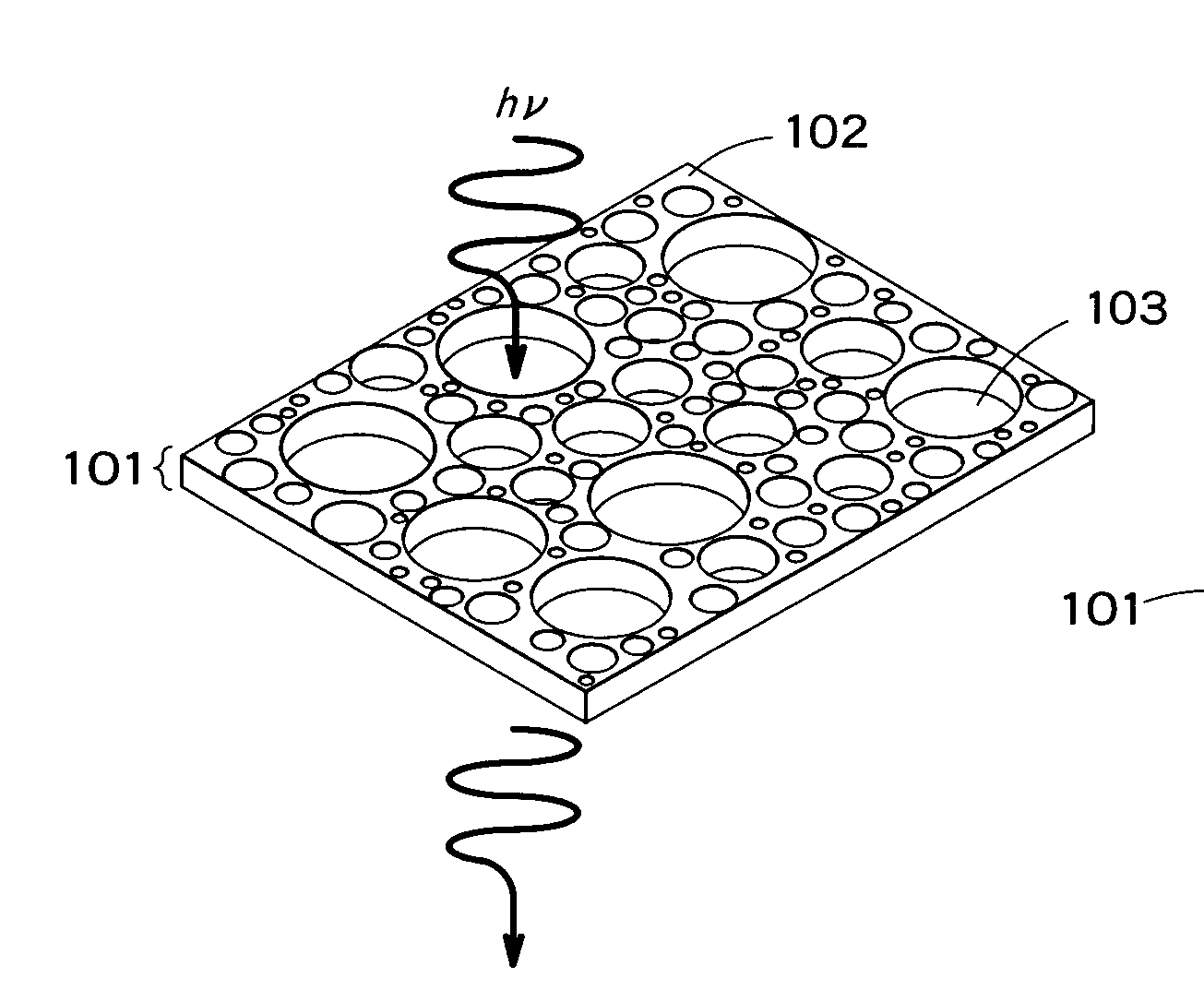
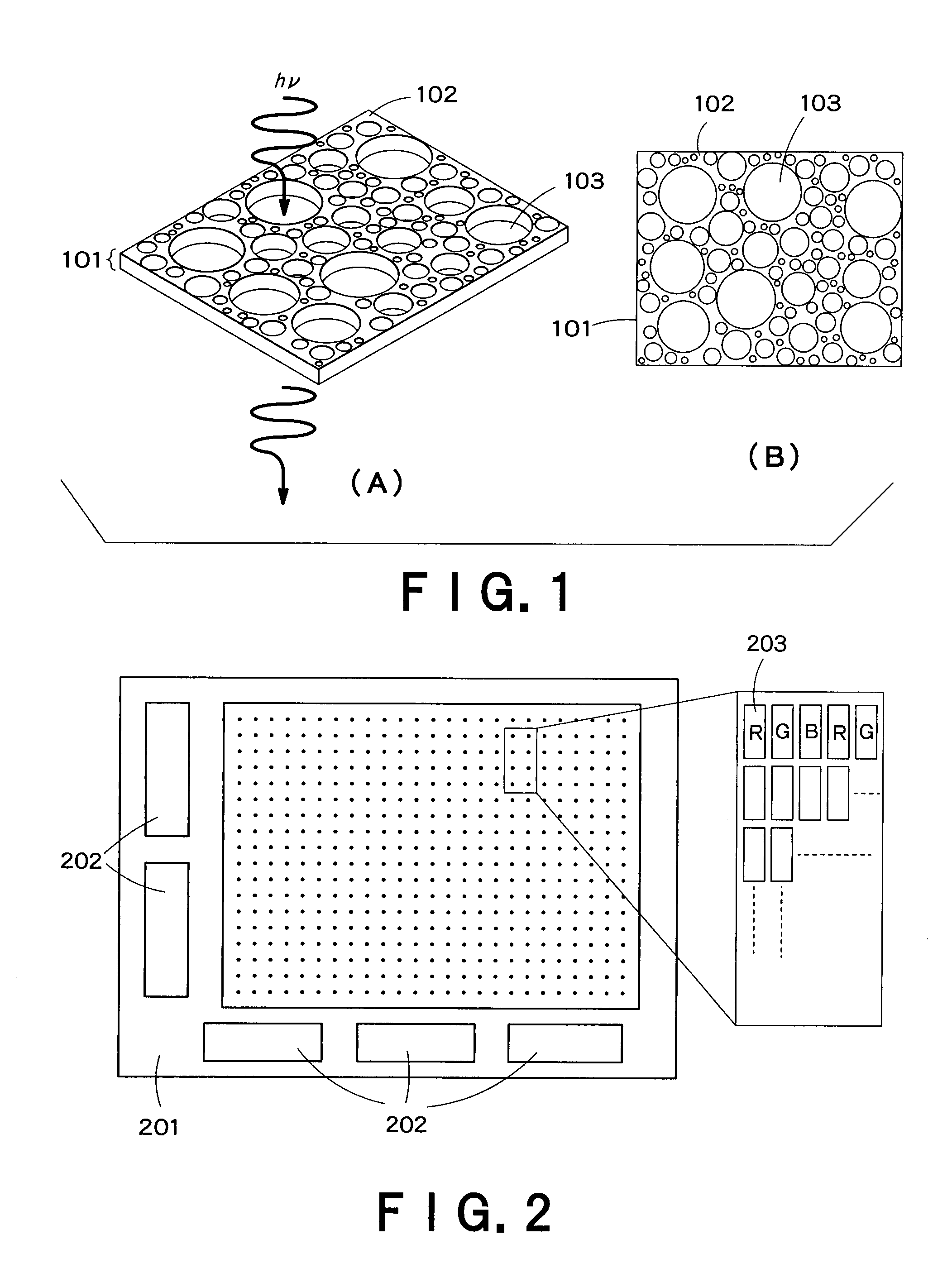
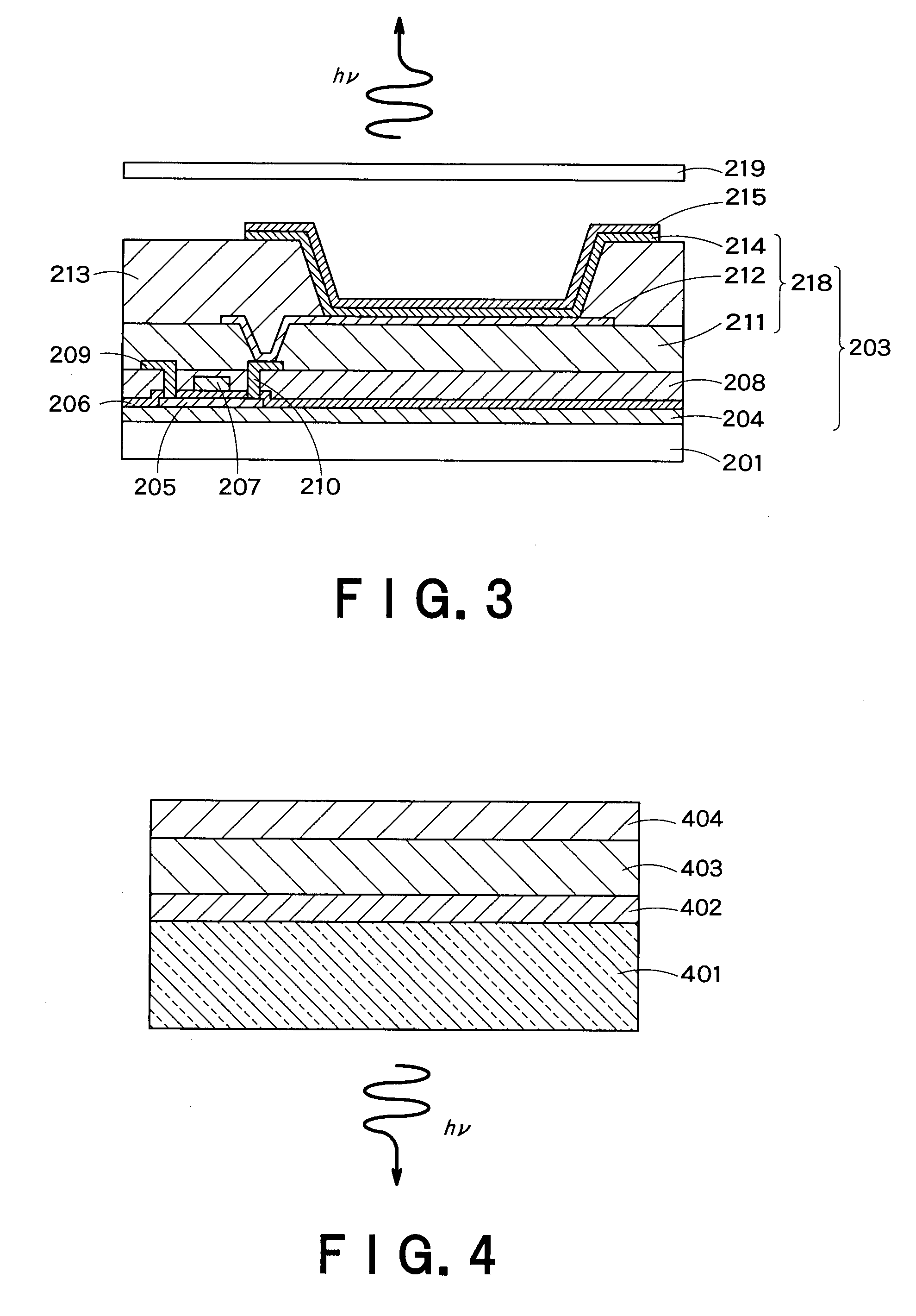
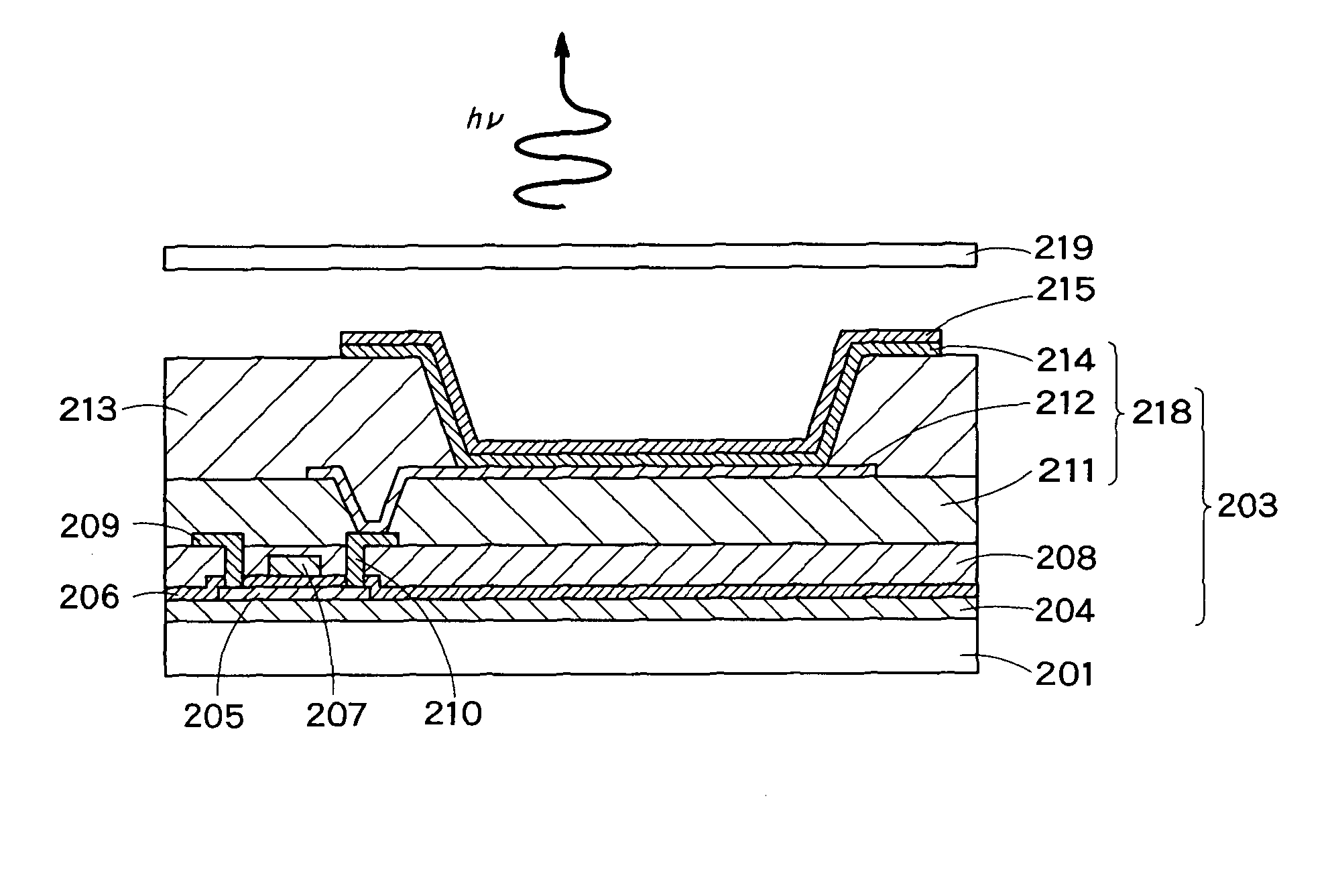
Displaying device and lighting device employing organic electroluminescence element
InactiveUS7928353B2Improve efficiencyReduced scattering effectControl electrodesDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic layerDisplay device
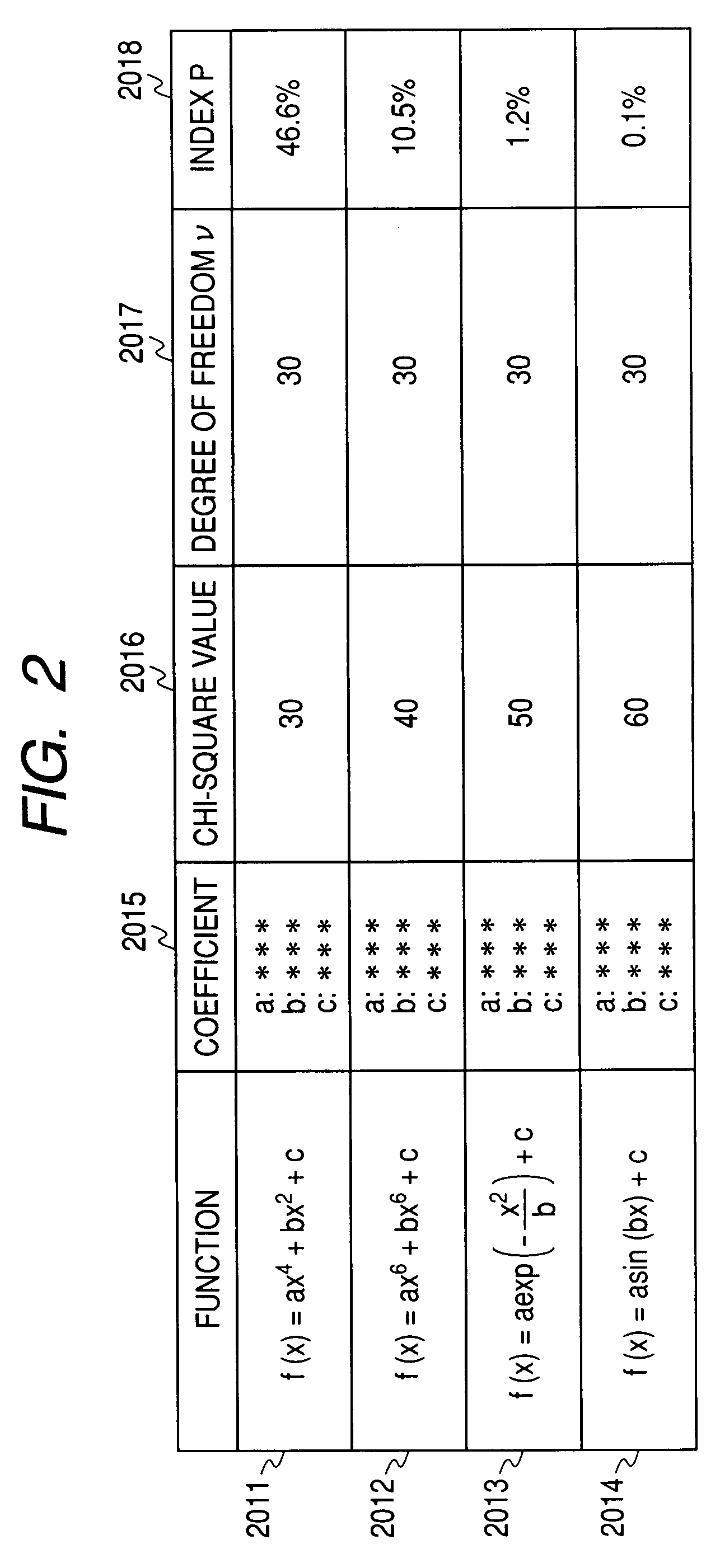
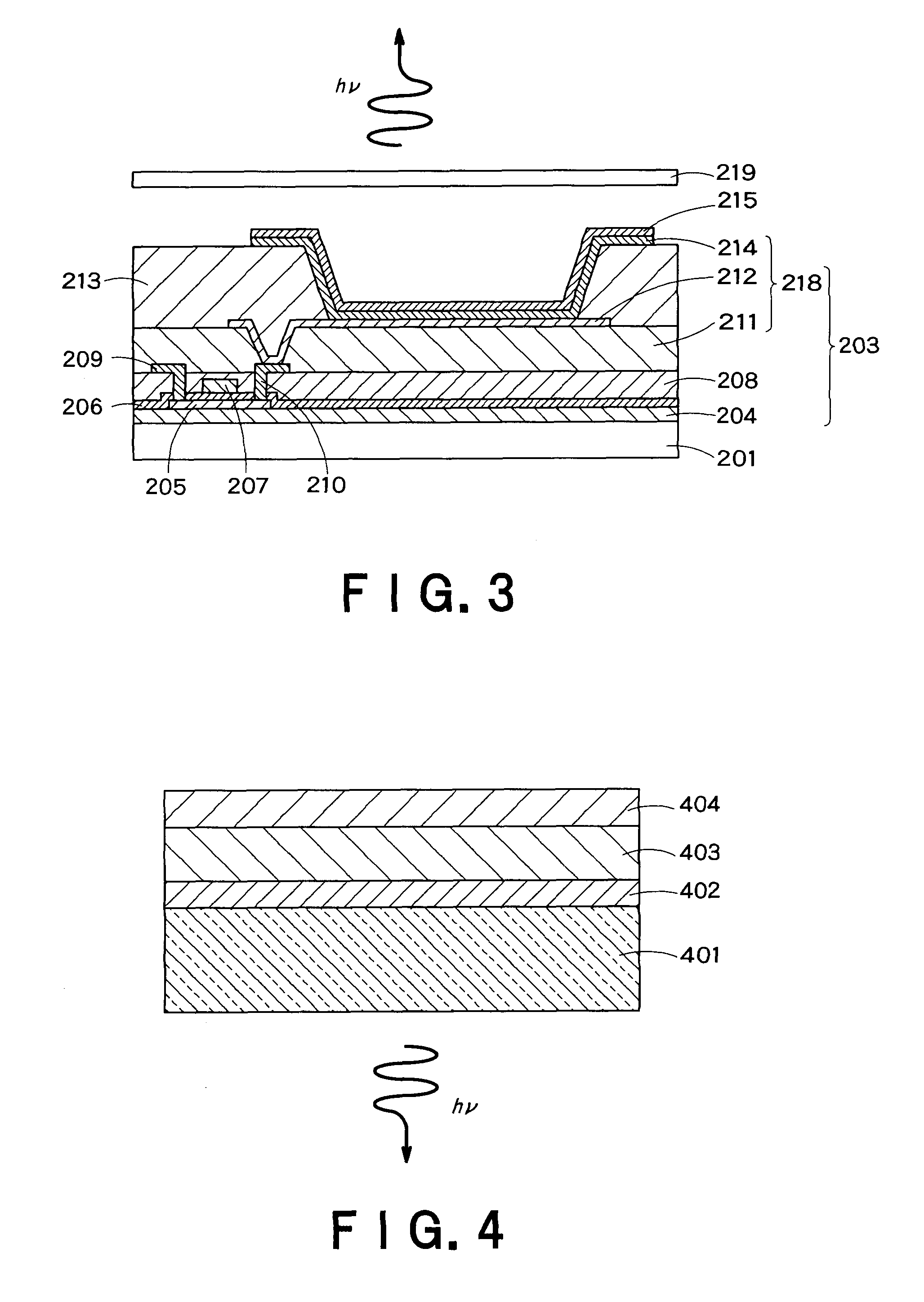
The Present invention provides an organic EL display and a lighting device having high efficiency. The organic EL display comprises a substrate, a pixel-driving circuit unit, and pixels arranged in the form of a matrix on the substrate. The pixel comprises a light-emitting part, and the light-emitting part is composed of a first electrode placed near to the substrate, a second electrode placed far from the substrate, and at least one organic layer placed between the first and second electrodes. The second electrode has a metal electrode layer having a thickness of 10 nm to 200 nm, and the metal electrode layer comprises a metal part and plural openings penetrating through the layer. The metal part is seamless and formed of metal continuously connected without breaks between any points therein. The openings have an average opening diameter of 10 nm to 780 nm, and are arranged so periodically that the distribution of the arrangement is represented by a radial distribution function curve having a half-width of 5 nm to 300 nm.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
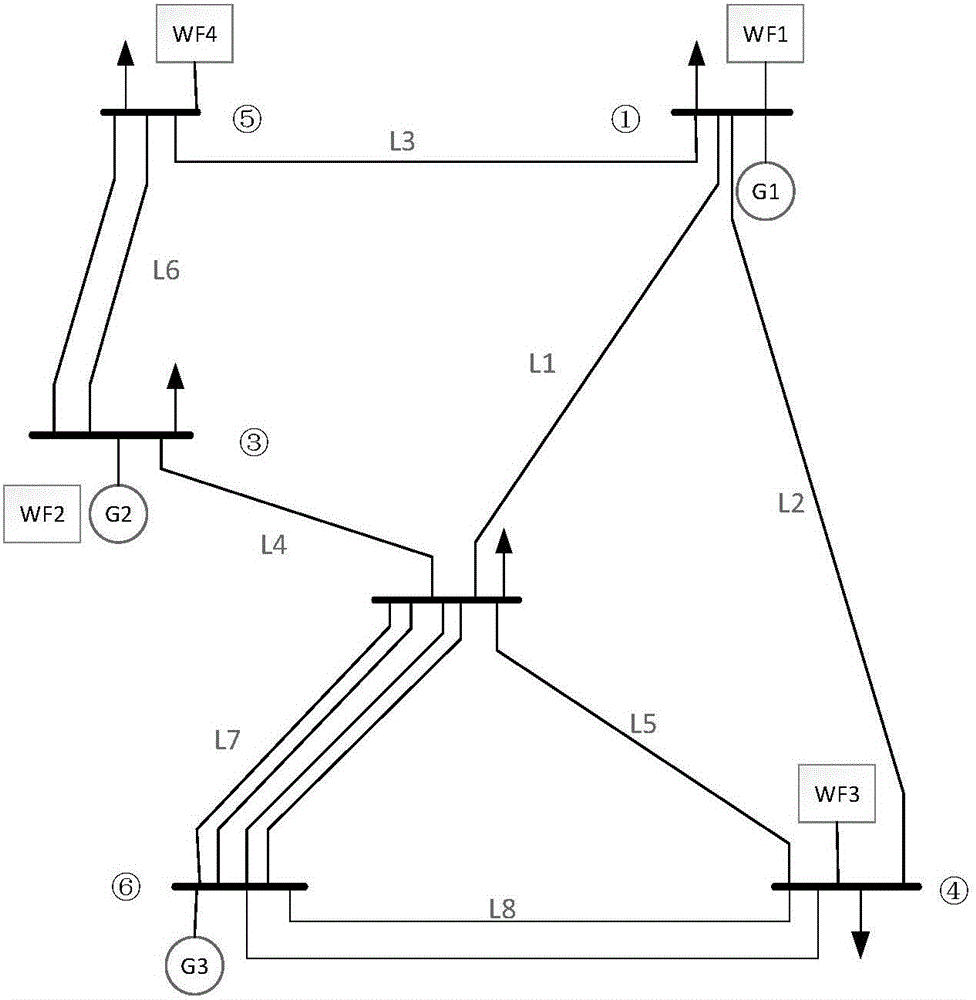
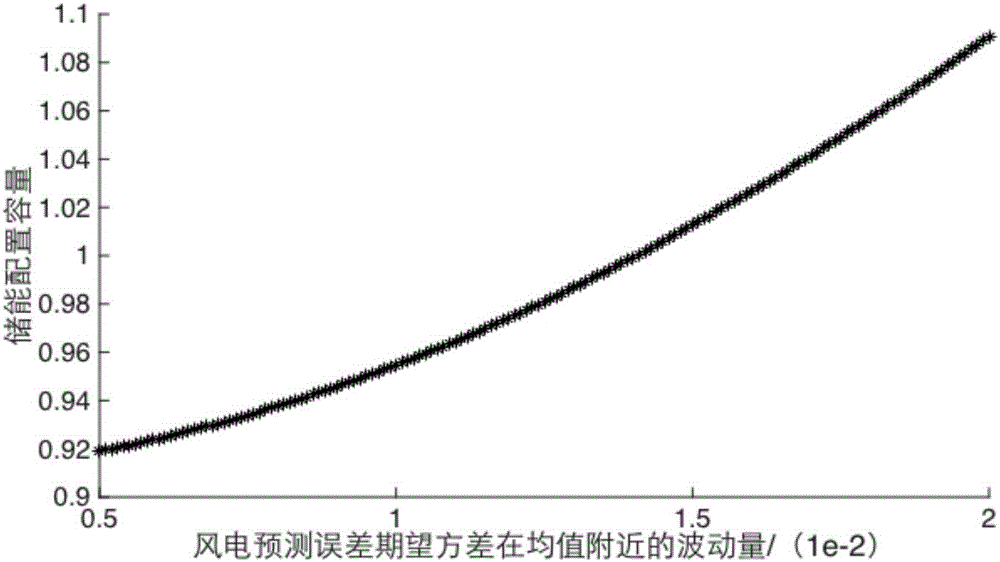
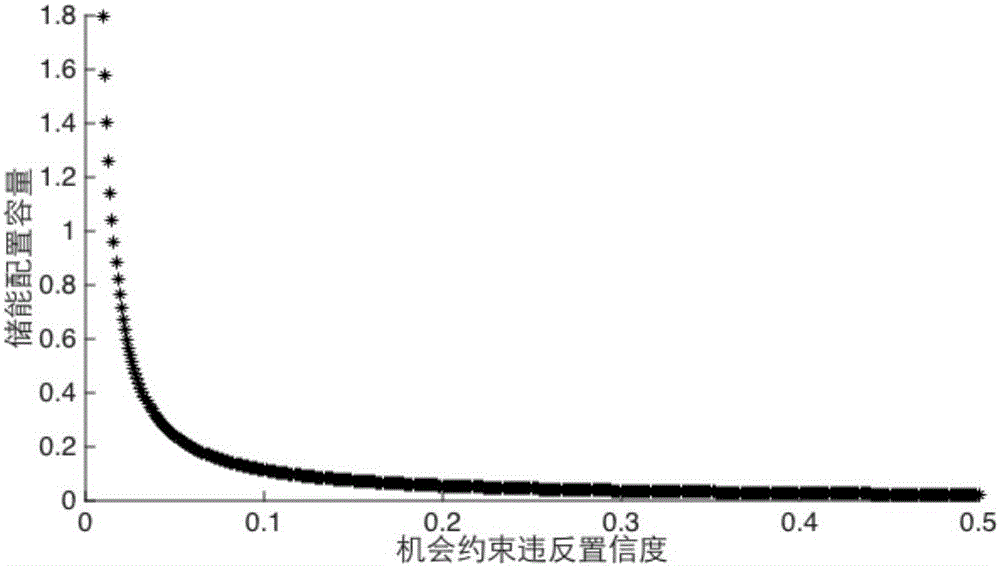
Stochastic robust optimization-based energy storage allocation method of wind field system
ActiveCN106786735AGuaranteed Economic AllocationReduce diversitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationLinear matrixSecond order moments
The invention discloses a stochastic robust optimization-based energy storage allocation method of a wind field system. A scenario method, stochastic programming, interval programming and an artificial intelligence method are widely used for energy storage planning of a renewable energy-containing system at present. These methods are based on accurate renewable energy output or accurate probability distribution and have certain limitations. The method comprises the steps of describing a wind power prediction error as a random variable meeting given second-order moment and fluctuation quantity; describing an energy storage allocation problem containing the wind field system by a probability distribution function set meeting the second-order moment characteristics of the random variable by adopting a probability distribution robust joint opportunity constraint optimization model; converting the probability distribution robust joint opportunity constraint optimization model into definitive linear matrix inequalities; and finally solving the definitive linear matrix inequalities by adopting a convex optimization algorithm. According to the stochastic robust optimization-based energy storage allocation method, an economical and optimal energy storage allocation scheme meeting the safe operation requirements of a power system under the worst distribution of wind power can be obtained.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER +1
Probability load flow calculation method considering admitting ability of power grid
ActiveCN105656038ASampling implementationGuaranteed calculation accuracyData processing applicationsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsNew energyProbabilistic load flow
The invention discloses a probability load flow calculation method considering the admitting ability of a power grid. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a cumulative distribution function of a new energy power generation power variable is built according to the admitting ability of the power grid to new energy power generation power, wherein the cumulative distribution function is described in the form of a piecewise function; 2, the sampling frequency between all sections of the new energy power generation variable is calculated according to the cumulative distribution function F(pk) of the built new energy power generation power variable based on the proportional distribution principle, then a Latin hypercube sampling method is utilized for sampling all the sections of the new energy power generation power variable, and a sample matrix of the new energy power generation power variable is built; 3, the sample matrix of the new energy power generation power variable is adopted as an input variable for probability load flow calculation, a disperse result of an output variable is obtained, an empirical distribution function is utilized for fitting, and a probability distribution function of the output variable is obtained. The application range of the Latin hypercube sampling method is widened, and calculating precision is guaranteed.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com