Patents
Literature
121results about "Magnetic immunoreagent carriers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
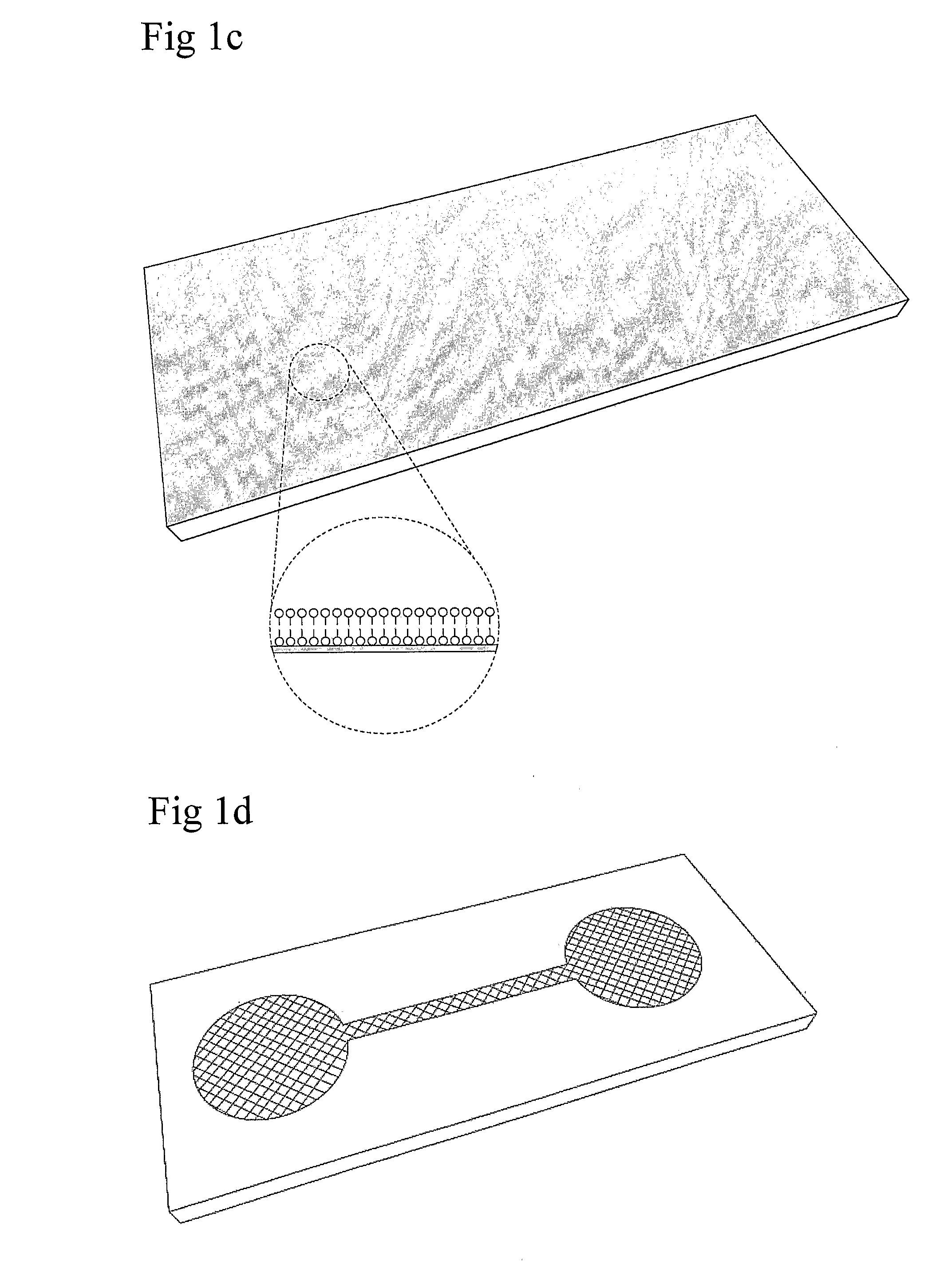
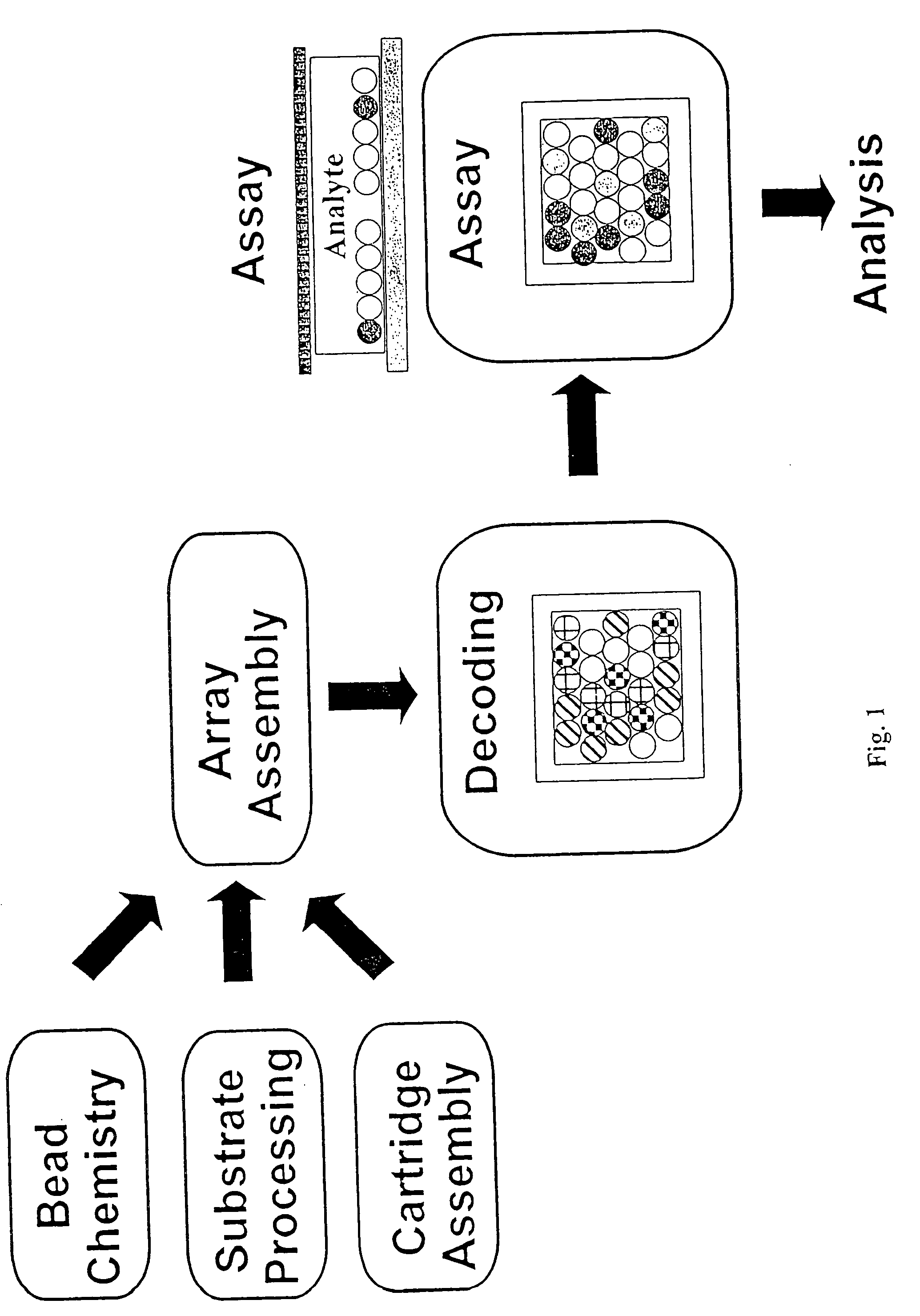
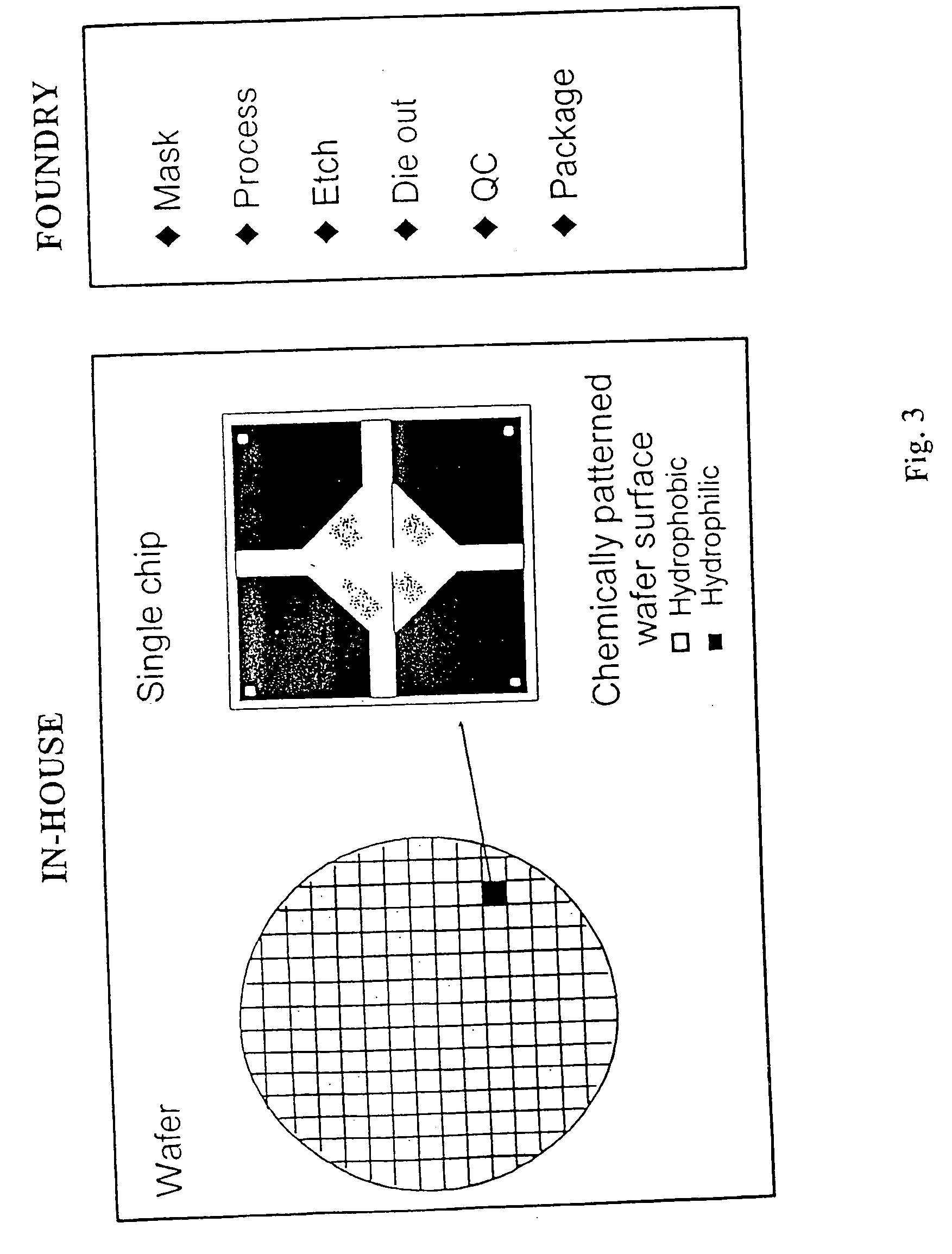
Assembly of arrays on chips segmented from wafers
InactiveUS20050244850A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsMagnetite NanoparticlesAnalyte molecule
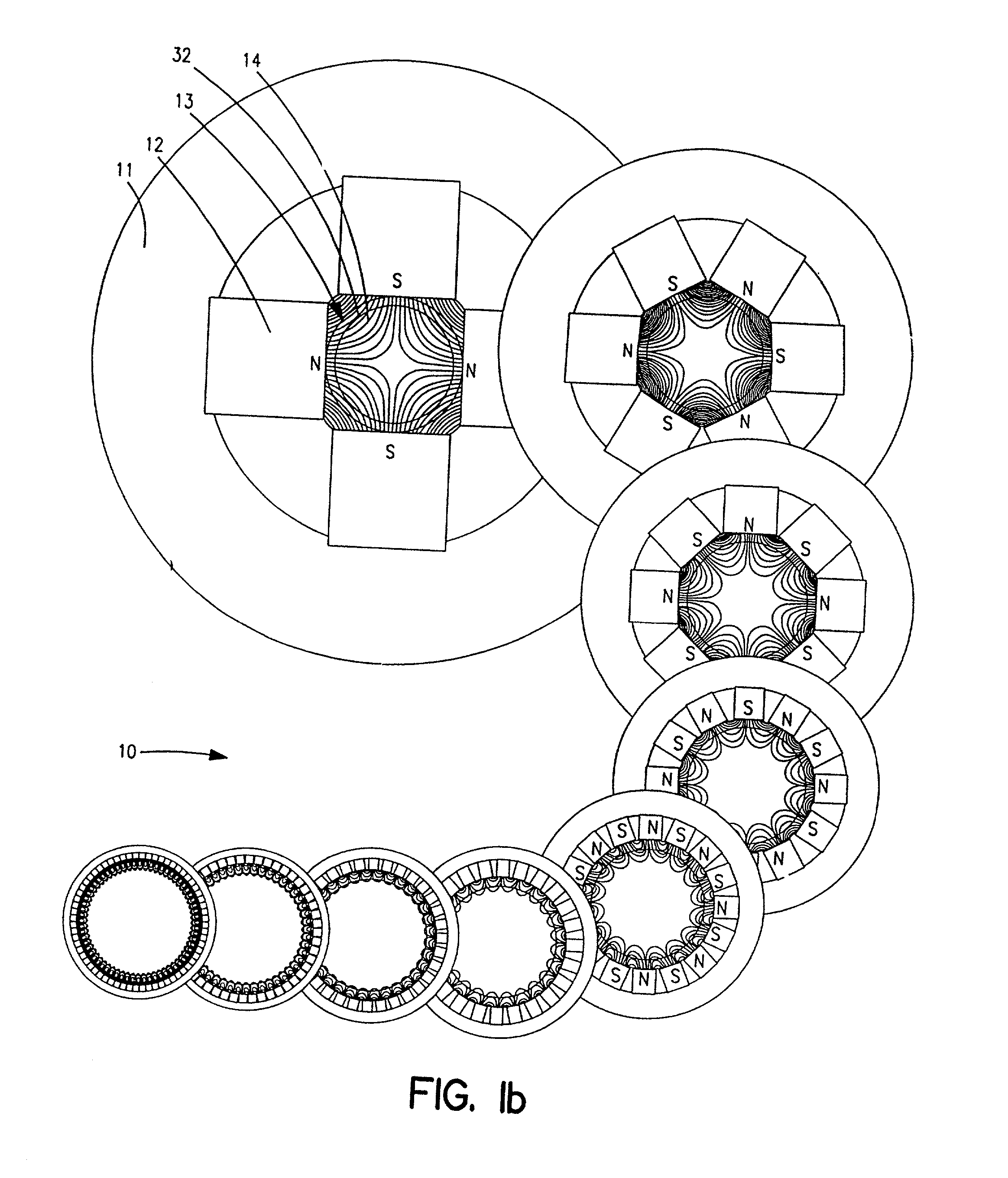
The present invention provides a method for the generation of novel libraries of encoded magnetic particles from sub-libraries of by the generation of novel sub-libraries of magnetic nanoparticles and encoded particles. The sub-libraries are functionalized on demand are useful in the formation of arrays. The present invention is especially useful for performing multiplexed (parallel) assays for qualitative and / or quantitative analysis of binding interactions of a number of analyte molecules in a sample.
Owner:HUANG HIU +1
Method of making nanoparticles
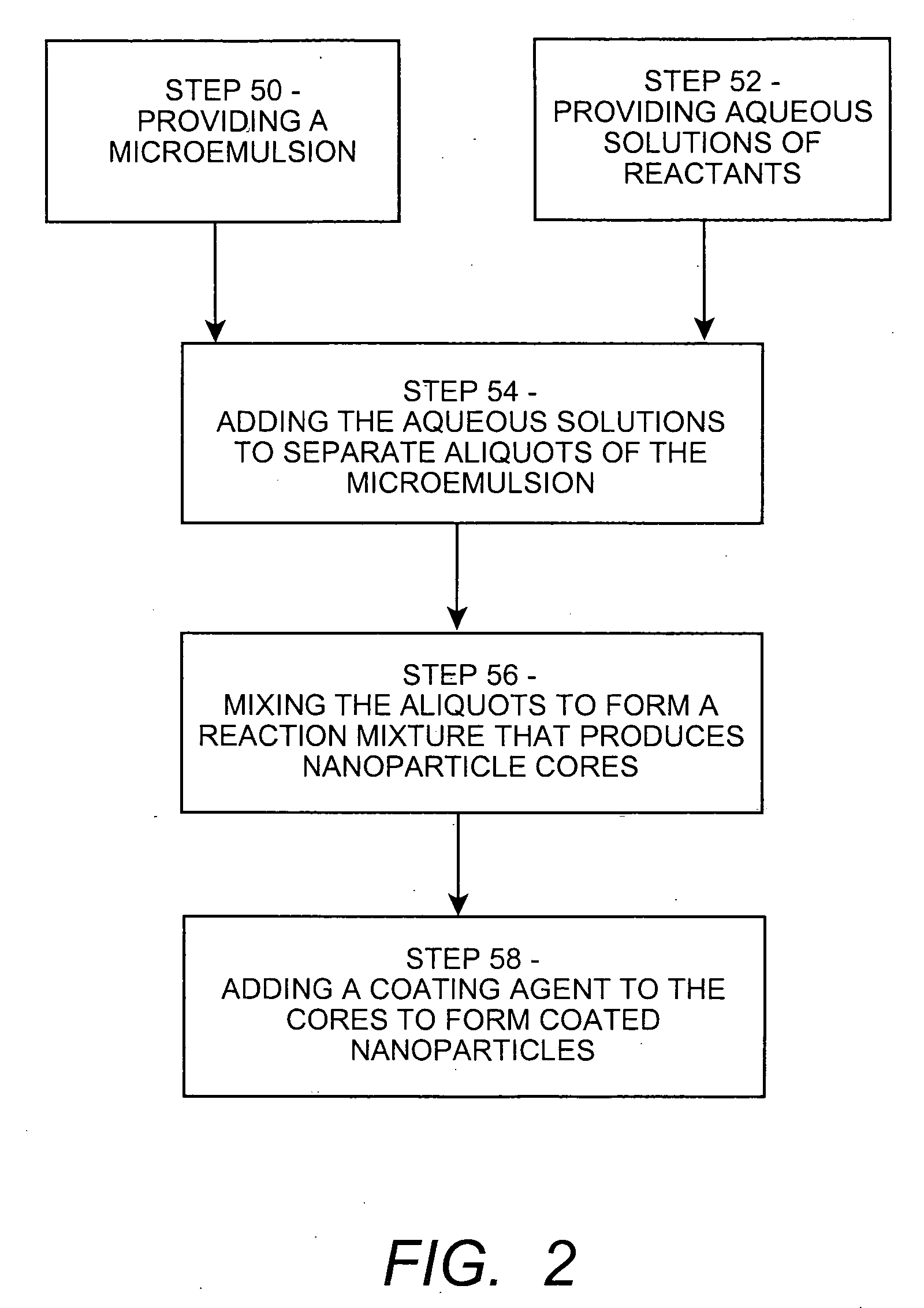
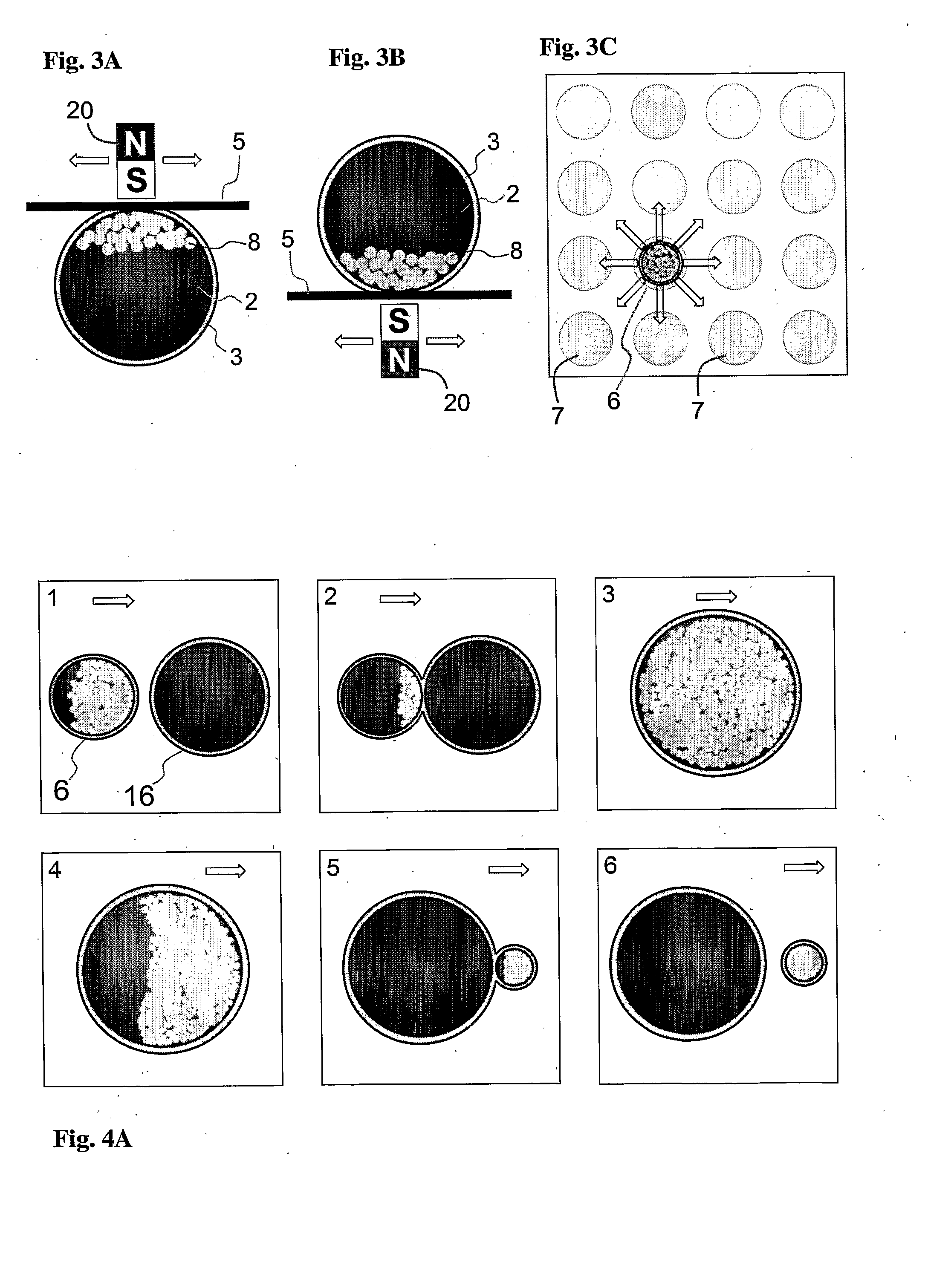
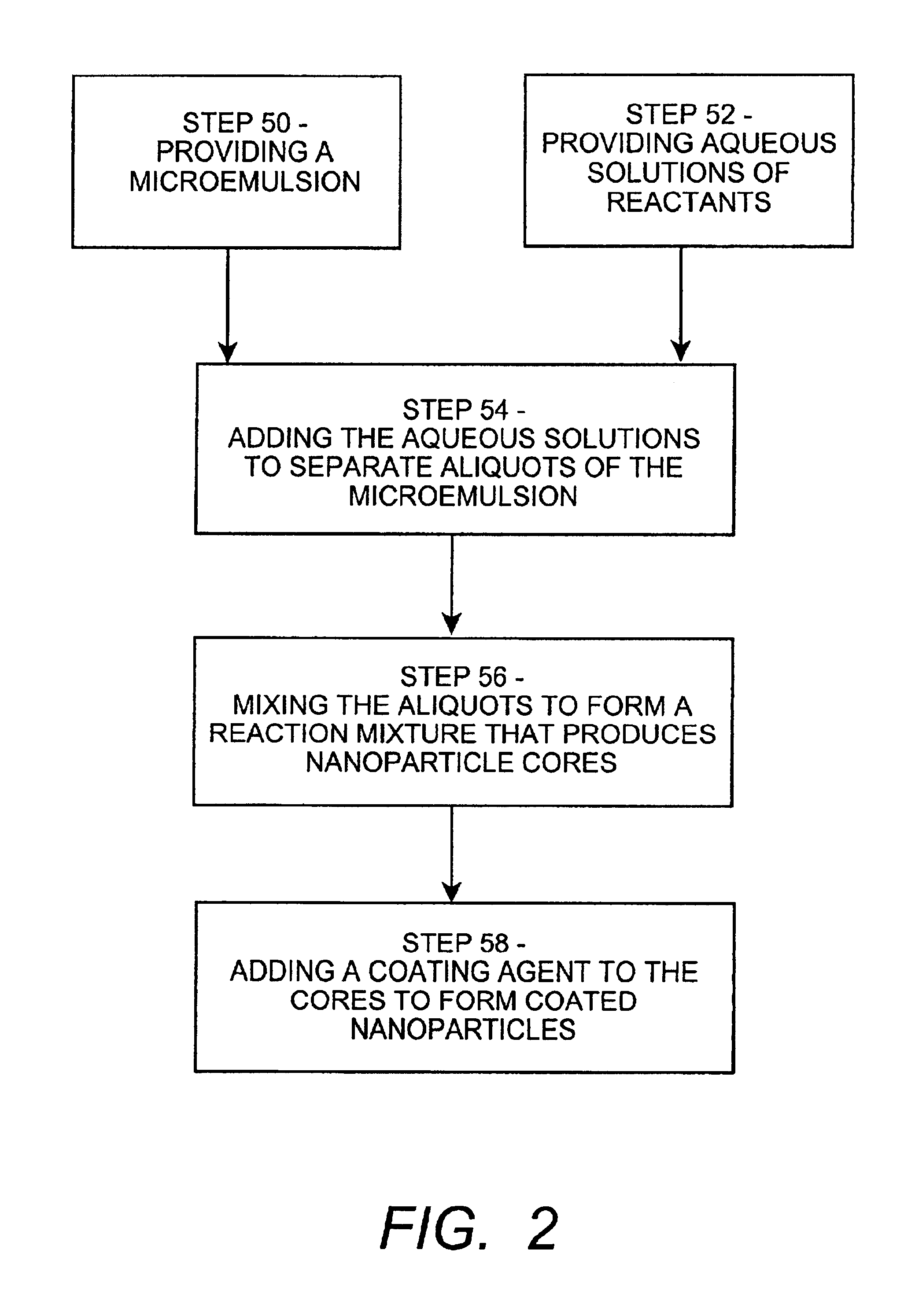
Disclosed are silica-coated nanoparticles and a process for producing silica-coated nanoparticles. Silica-coated nanoparticles are prepared by precipitating nano-sized cores from reagents dissolved in the aqueous compartment of a water-in-oil microemulsion. A reactive silicate is added to coat the cores with silica. Also disclosed are methods for functionalizing silica-coated nanoparticles for use in a variety of applications.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Apparatus and methods for magnetic separation
InactiveUS7056657B2Easy to separateHigh gradientMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh gradient magnetic separatorsSprayerMagnetic poles
Separation apparatus and method for separating magnetic and / or magnetically-labeled particles from a test medium.Test medium within a reaction chamber is caused to flow past a collecting surface, and a high-gradient magnetic field is applied to the surface to capture magnetically responsive particles in the test medium. The particles are deflected toward the collection surface by baffles, a spinner, or a sprayer, or are funneled past the surface by a plunger operable to be displaced into close proximity to the surface to provide a narrow flow path for the particle-laden test medium. The particles normally suspended in the medium are separated out of suspension by adhesion to the collection surface. The particles may be resuspended by removal of the surface from the high-gradient field, or removal of the high-gradient field from the surface. The collection surface is a thin-walled non-magnetic material having a plurality of magnetic pole faces positioned therearound.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Process for (A) separating biological/ligands from dilute solutions and (B) conducting an immunochromatographic assay thereof employing superparamagnetic particles throughtout
InactiveUS7018849B2Highly effectiveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMean diameterSuperparamagnetism
Superparamagnetic (“SPM”) subunits of 1–30 nm average mean diameter (e.g. ferro fluid) subparticles are treated with a magnetically noninterfering substance capable of coating and covering them (e.g, BSA) and they spontaneously form agglomerates of about 100 nm to about 450 nm or higher average mean diameter and are then used to form complexes with target biological ligands such as viruses, contained in large volumes of liquid. The complexes are subjected to the gradient intensity of a strong magnetic field, and excess liquid is removed, where upon an immunochromatographic assay is conducted to determine the identity and / or amount of target ligand present, in which operation SPM particles that bonded to the ligand function as tags for ligand detection.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
Method of processing a biological and/or chemical sample
The invention provides a method of processing a biological and / or chemical sample. The method includes providing a fluid droplet, which includes an inner phase and an outer phase. The outer phase is immiscible with the inner phase, and the outer phase is surrounding the inner phase. The inner phase includes the biological and / or chemical sample. The fluid droplet furthermore comprises magnetically attractable matter. The method also includes providing at least one surface, which is of such a texture and such a wettability for the fluid of the inner phase of the fluid droplet, that the fluid droplet remains intact upon being contacted therewith. The method further includes disposing the fluid droplet onto the at least one surface. The method also includes performing a process on the biological and / or chemical sample in the fluid droplet.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for identifying cells
Disclosed are silica-coated nanoparticles and a process for producing silica-coated nanoparticles. Silica-coated nanoparticles are prepared by precipitating nano-sized cores from reagents dissolved in the aqueous compartment of a water-in-oil microemulsion. A reactive silicate is added to coat the cores with silica. Also disclosed are methods for functionalizing silica-coated nanoparticles for use in a variety of applications.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA
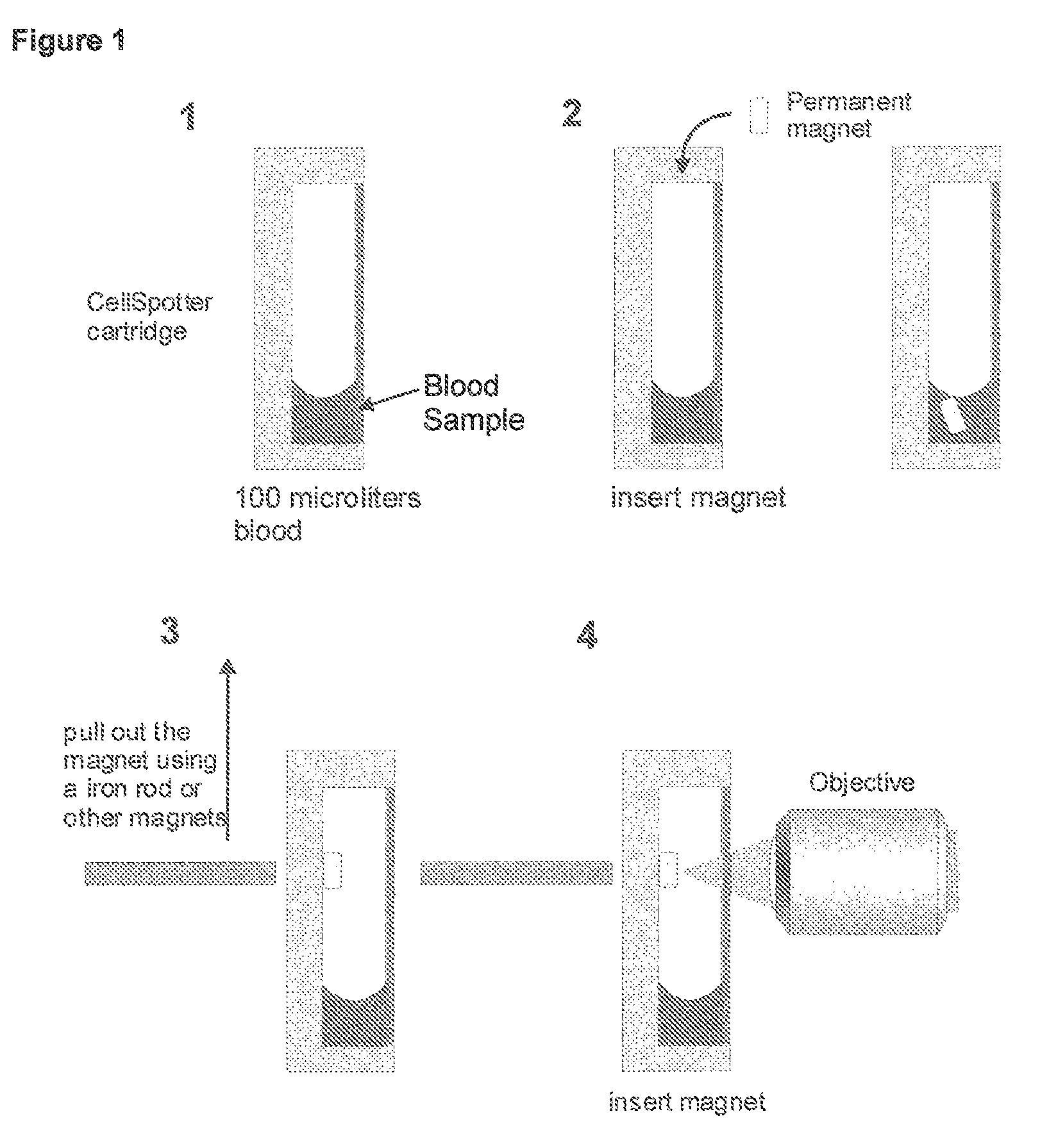
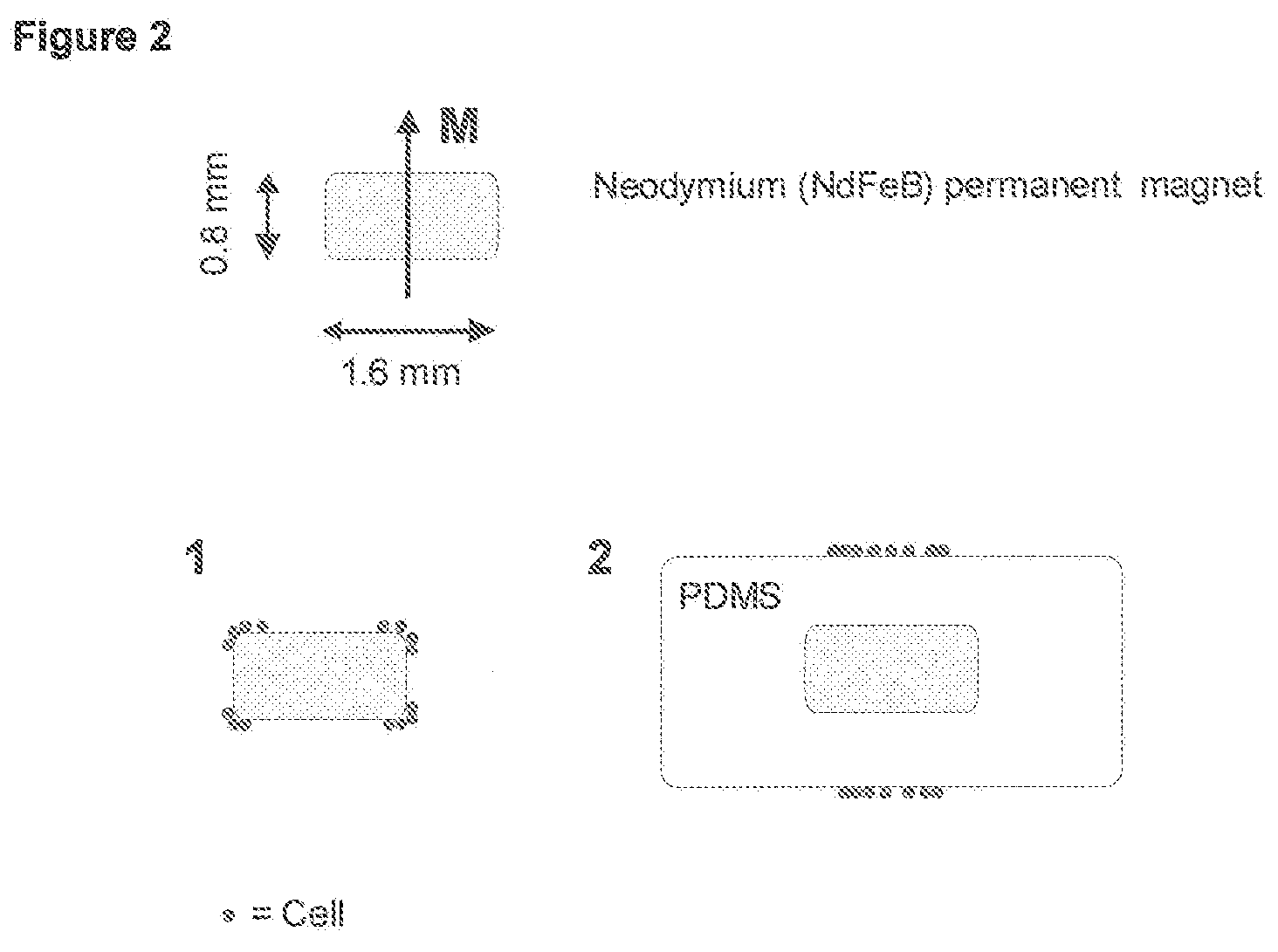
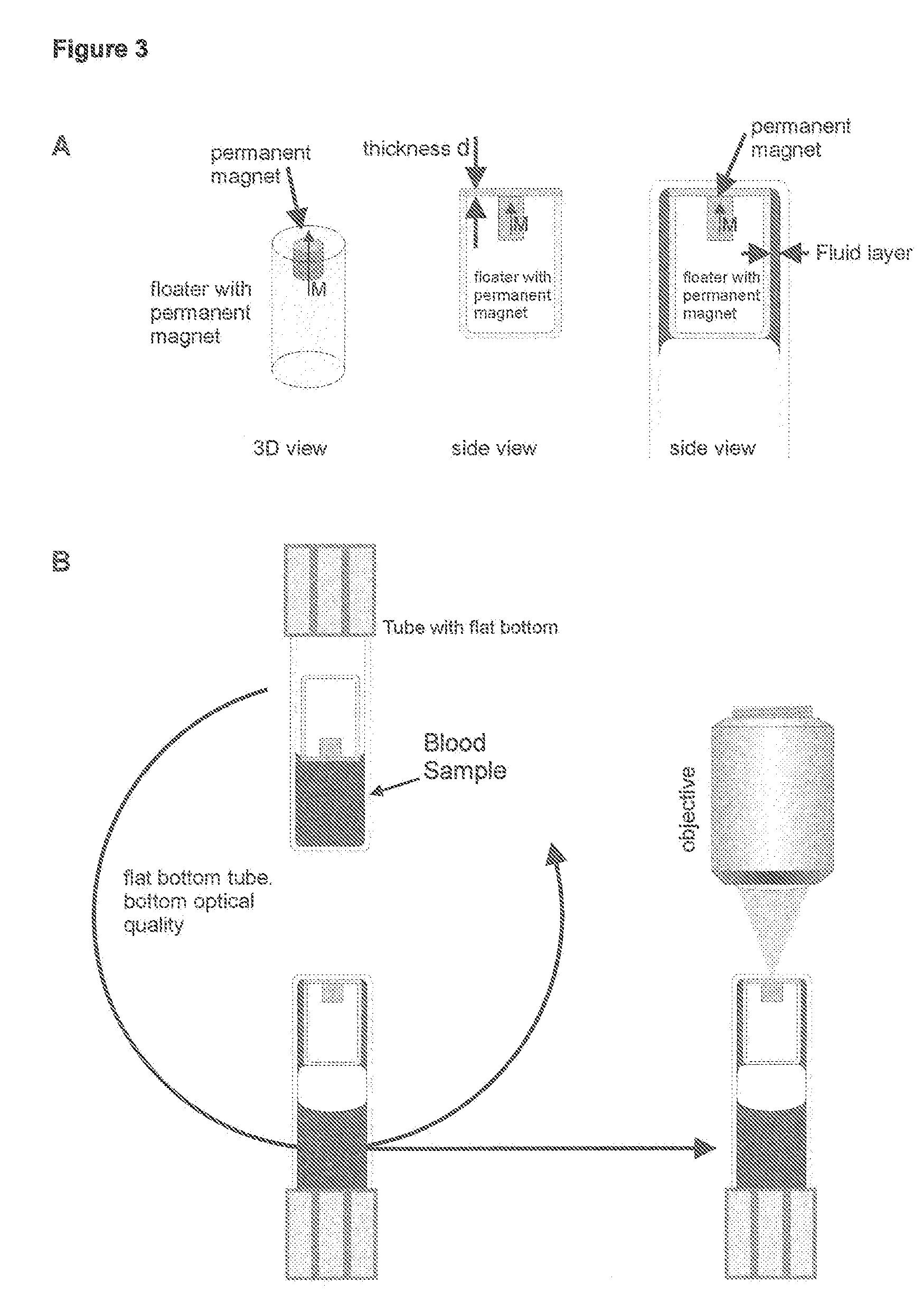
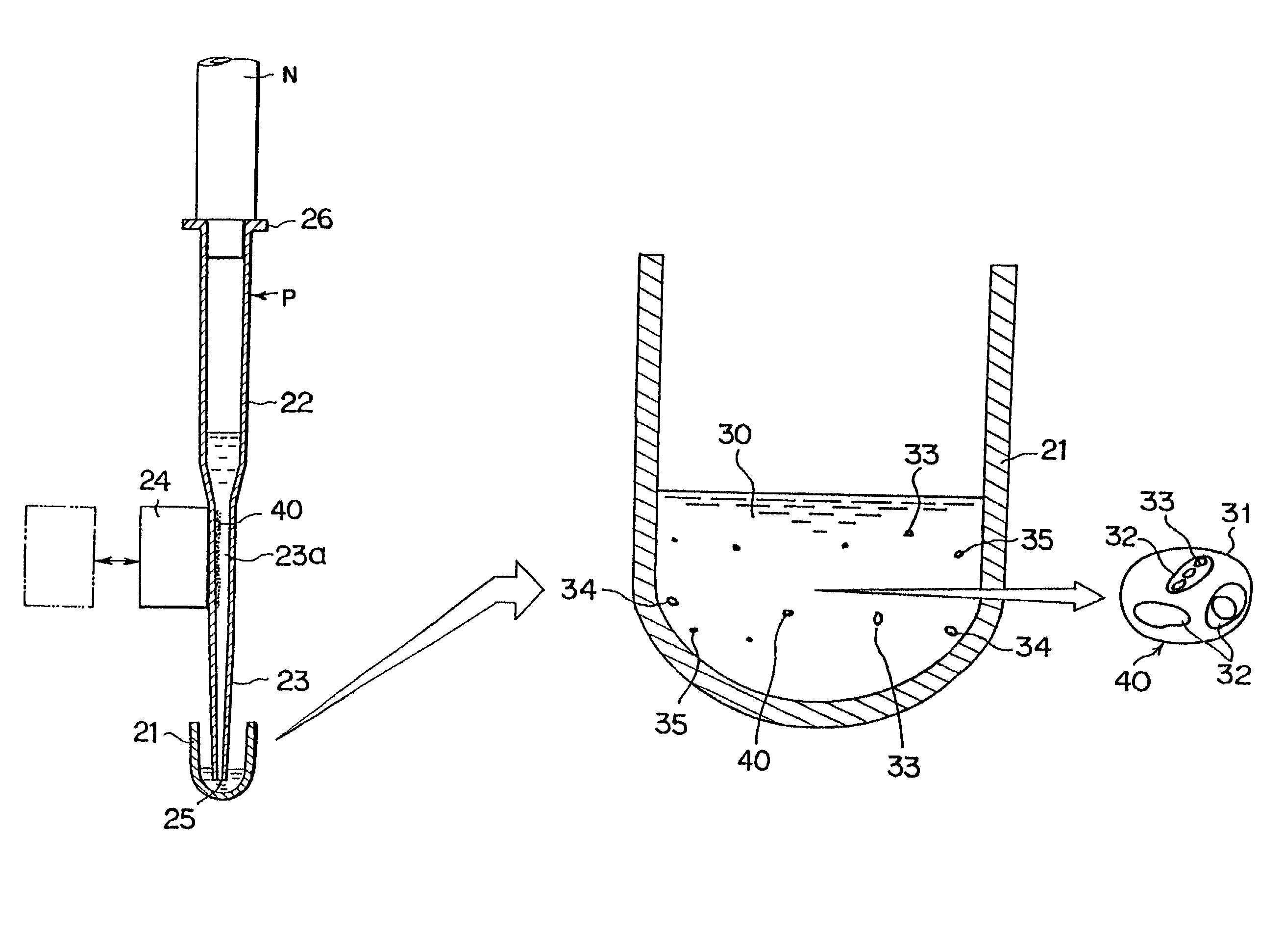
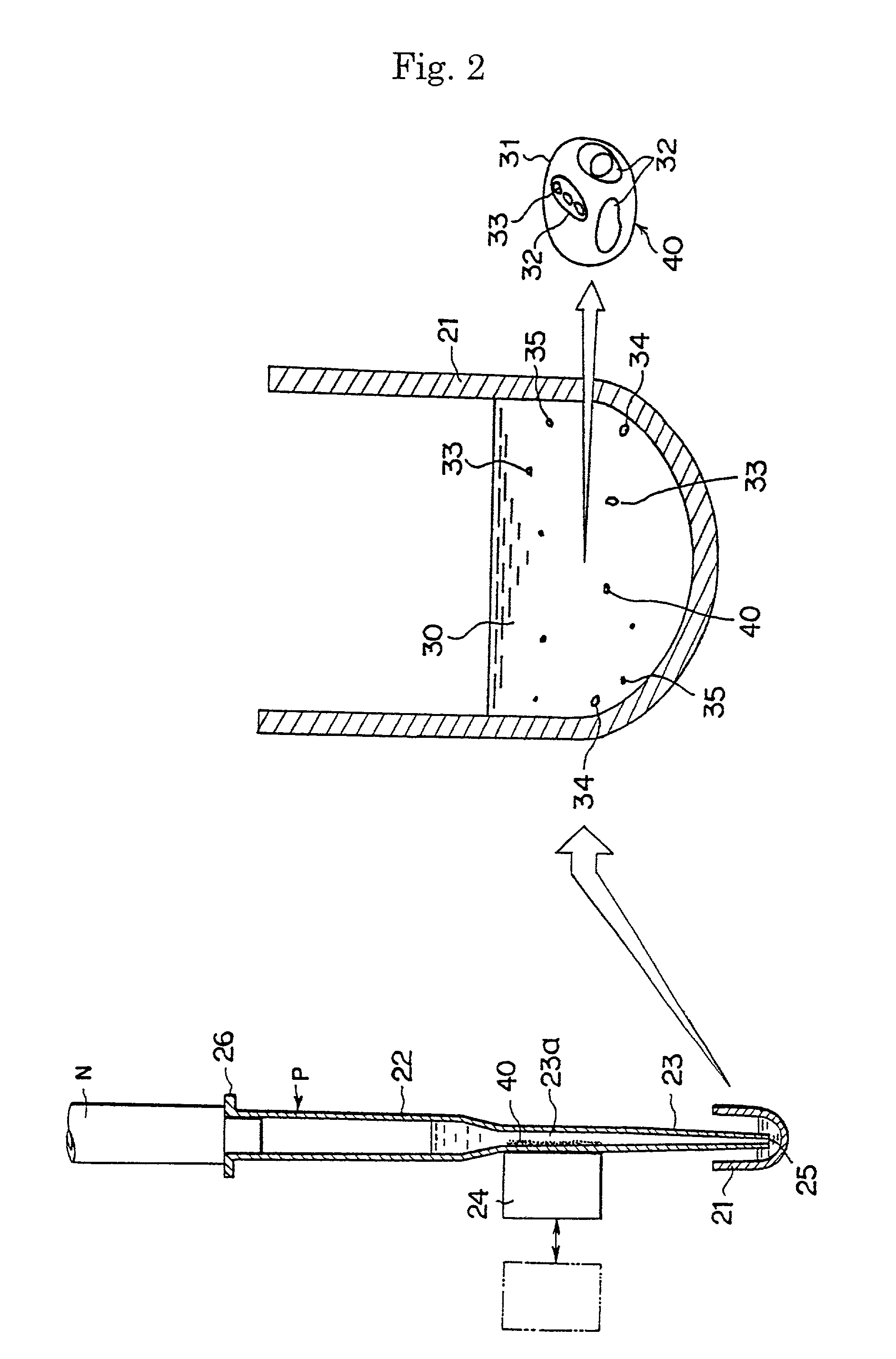
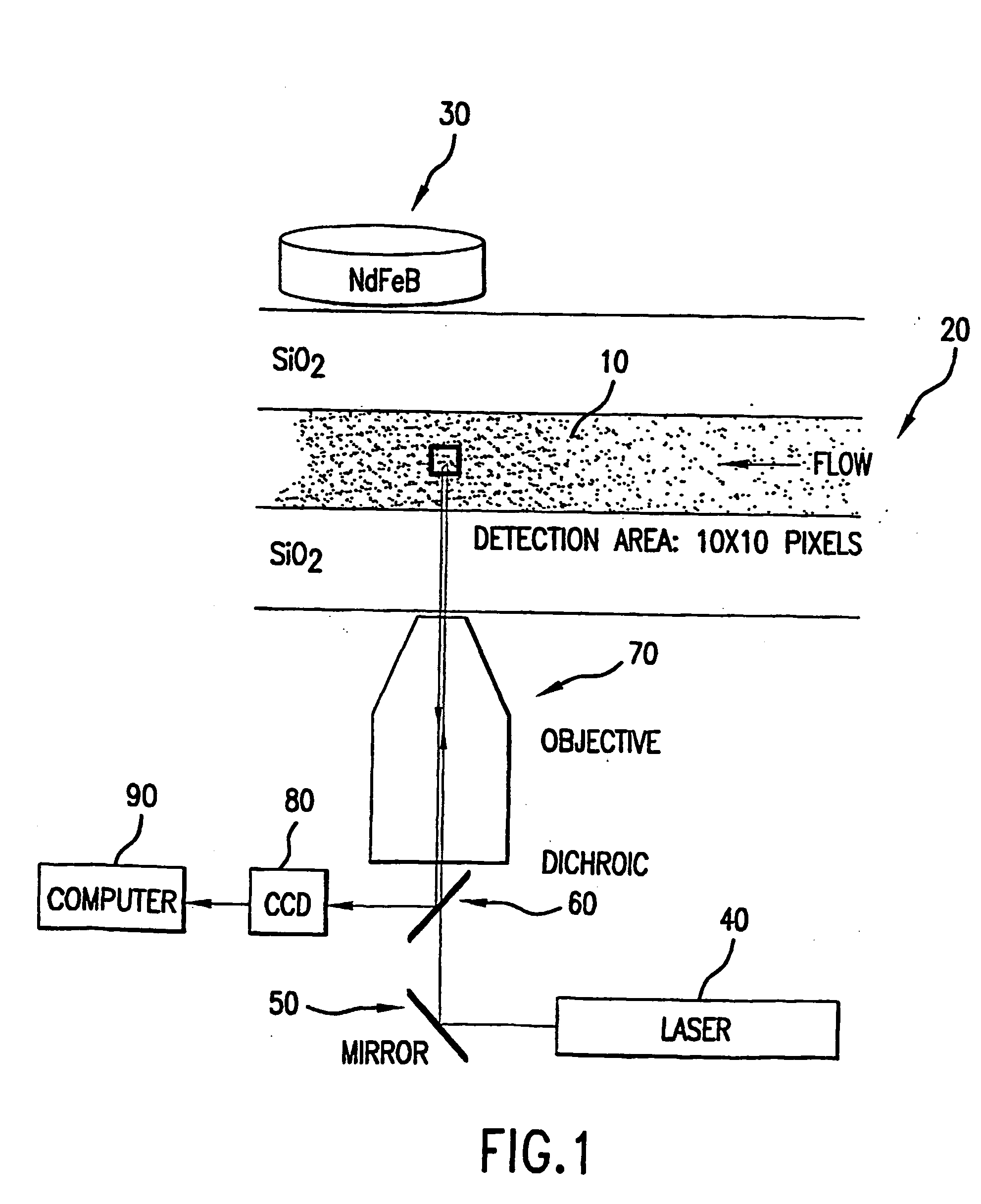
Method and apparatus for imaging target components in a biological sample using permanent magnets
ActiveUS20090061477A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhite blood cellFluorescence
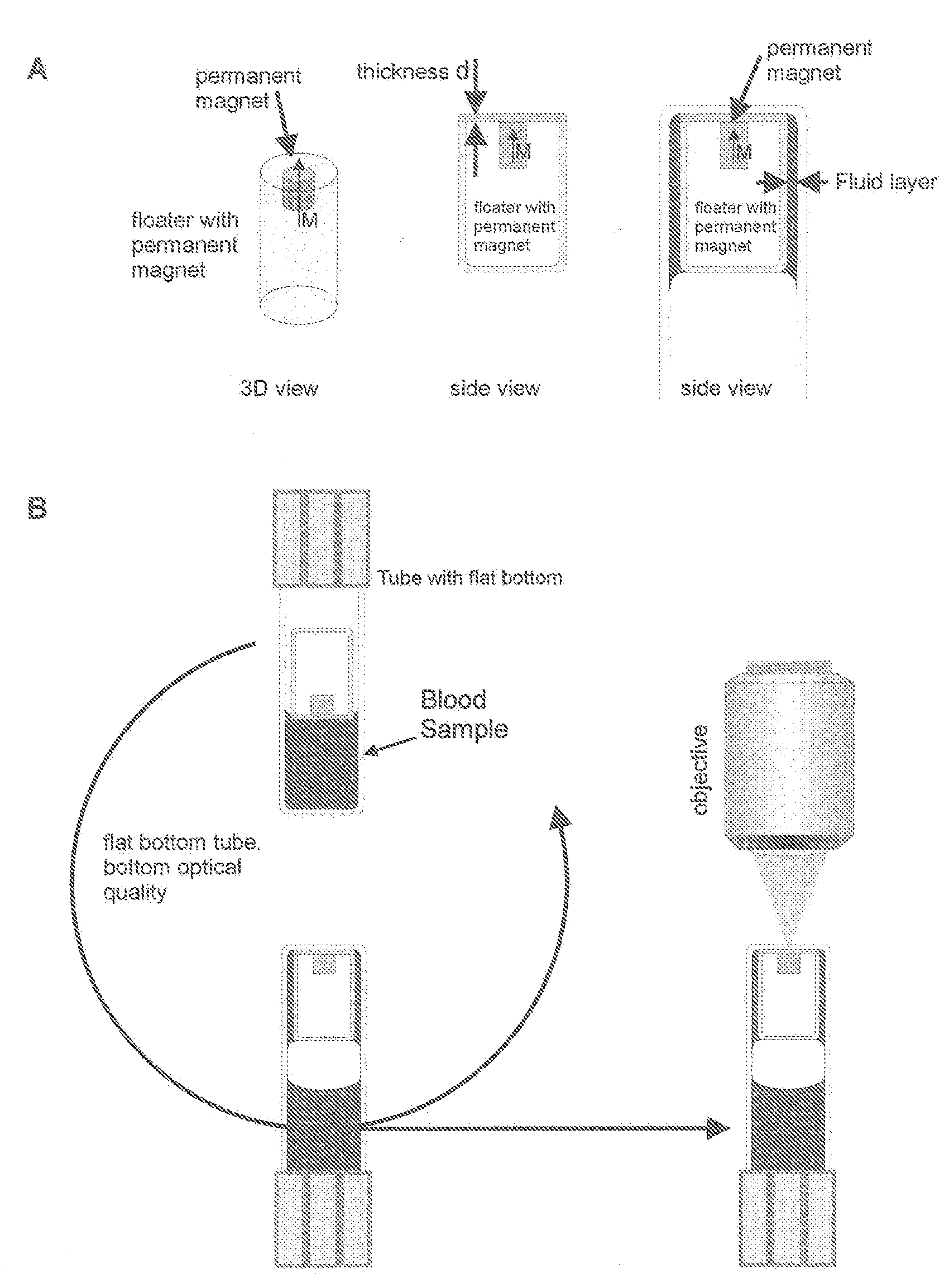
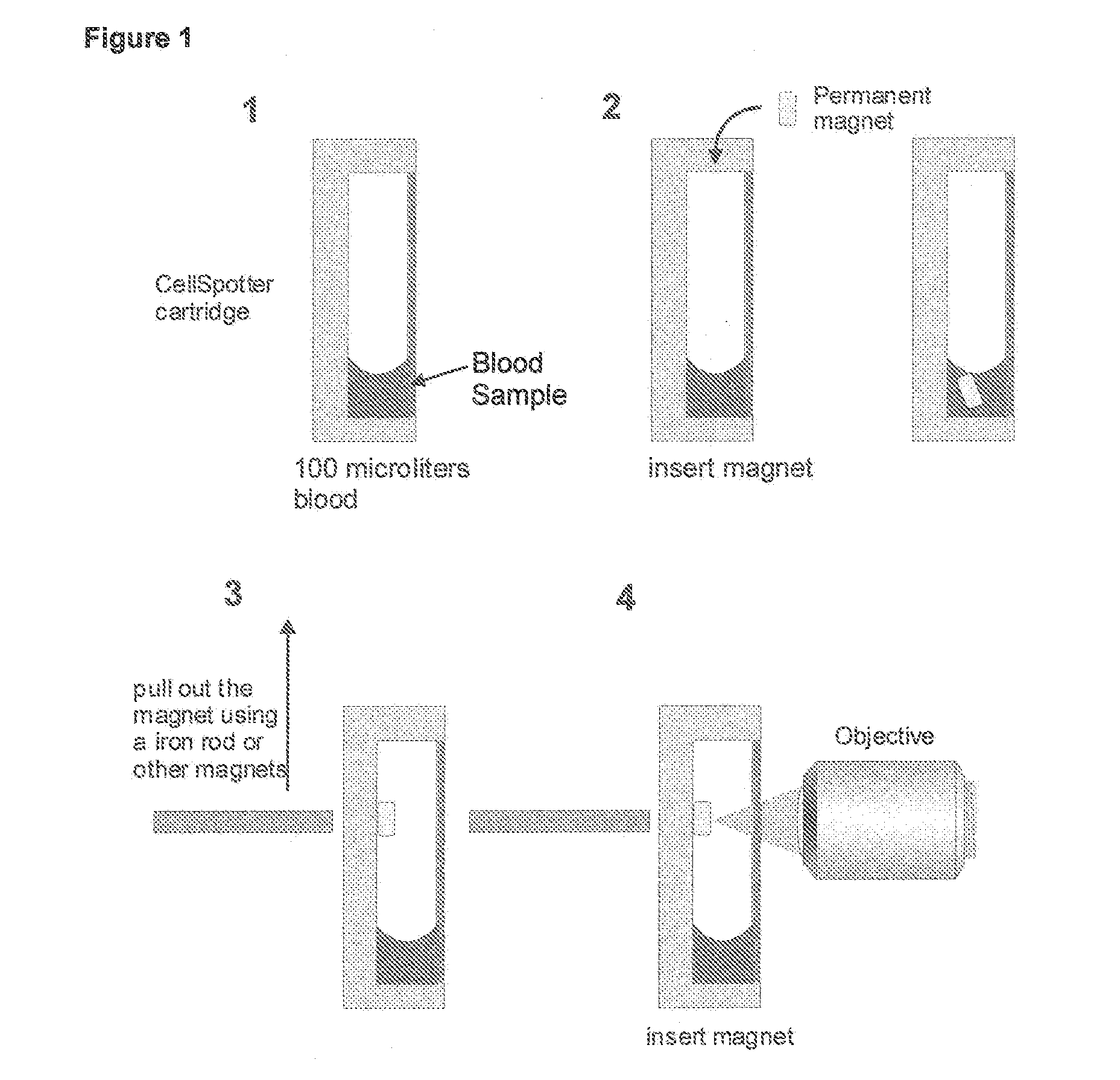
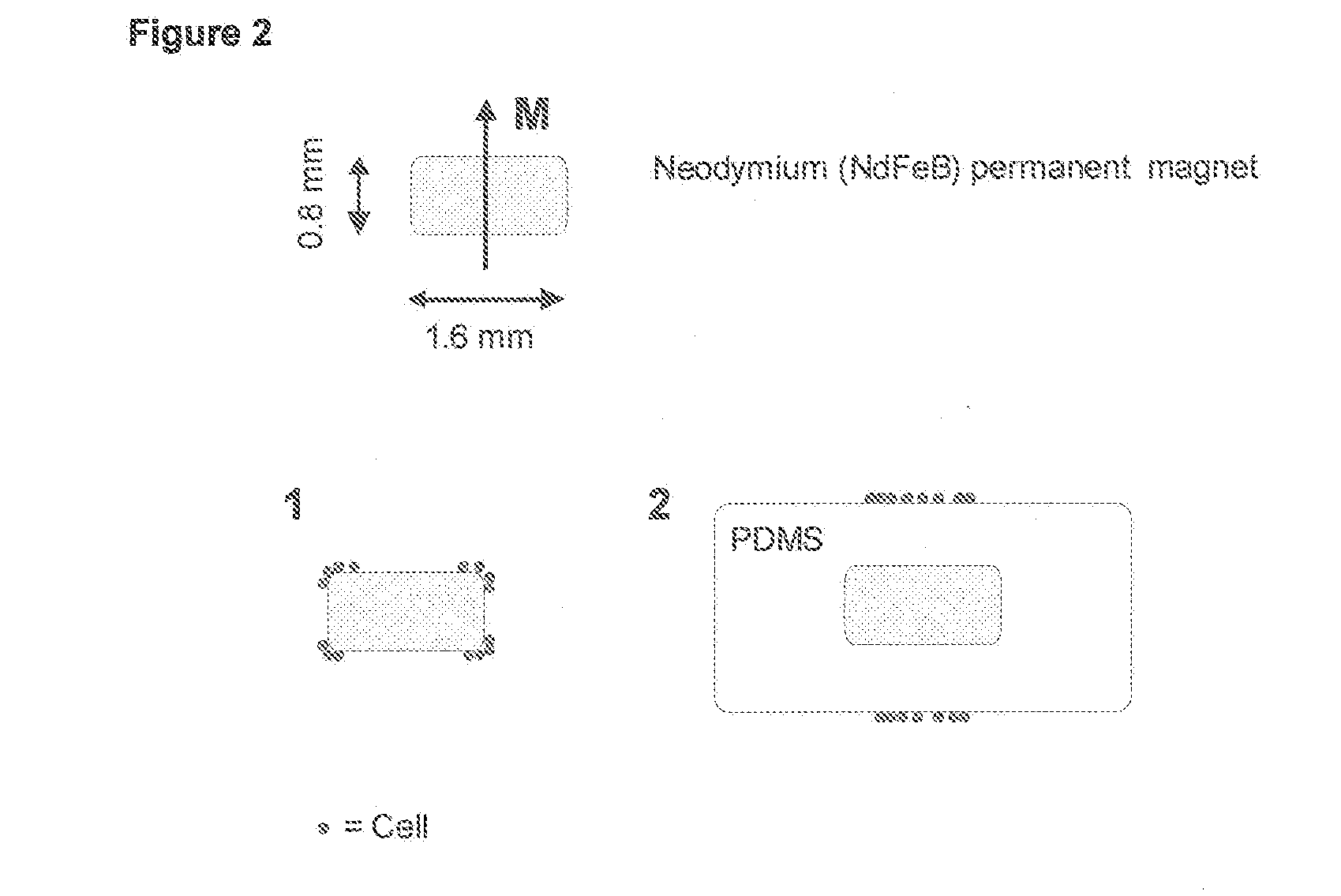
A system for enumeration of cells in fluids by image cytometry is described for assessment of target populations such as leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. Briefly, fluorescently labeled target cells are linked to magnetic particles or beads. In one embodiment, a small, permanent magnet is inserted directly into the chamber containing the labeled cells. The magnets are coated with PDMS silicone rubber to provide a smooth and even surface which allows imaging on a single focal plane. The magnet is removed from the sample and illuminated with fluorescent light emitted by the target cells captured by a CCD camera. In another embodiment, a floater having a permanent magnet allows the target cells to line up along a single imaging plane within the sample solution. Image analysis can be performed with a novel algorithm to provide a count of the cells on the surface, reflecting the target cell concentration of the original sample.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Nanoparticle biosensor, method of preparing same and uses thereof
InactiveUS20130040292A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyNanoparticleSilicon dioxide
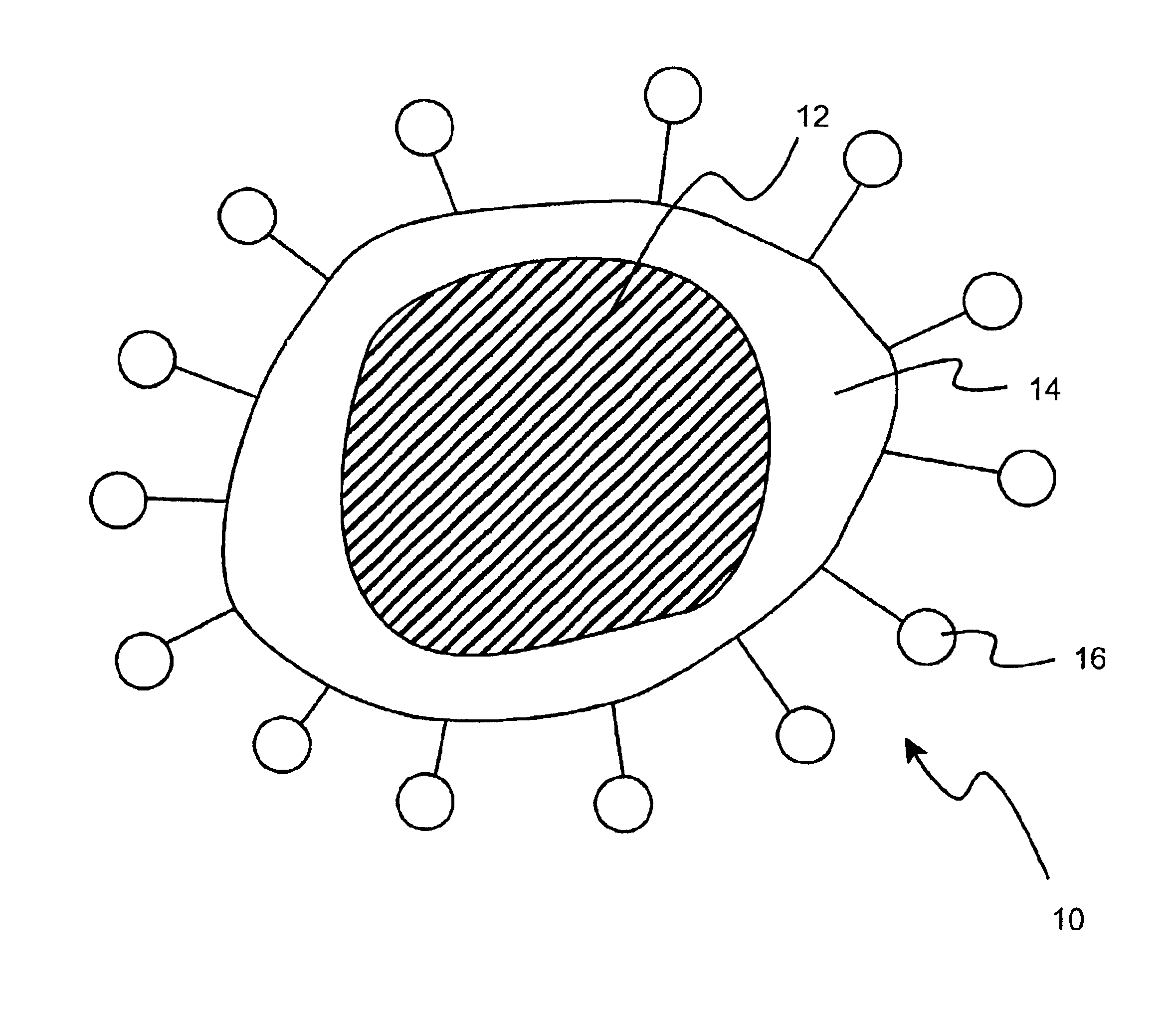
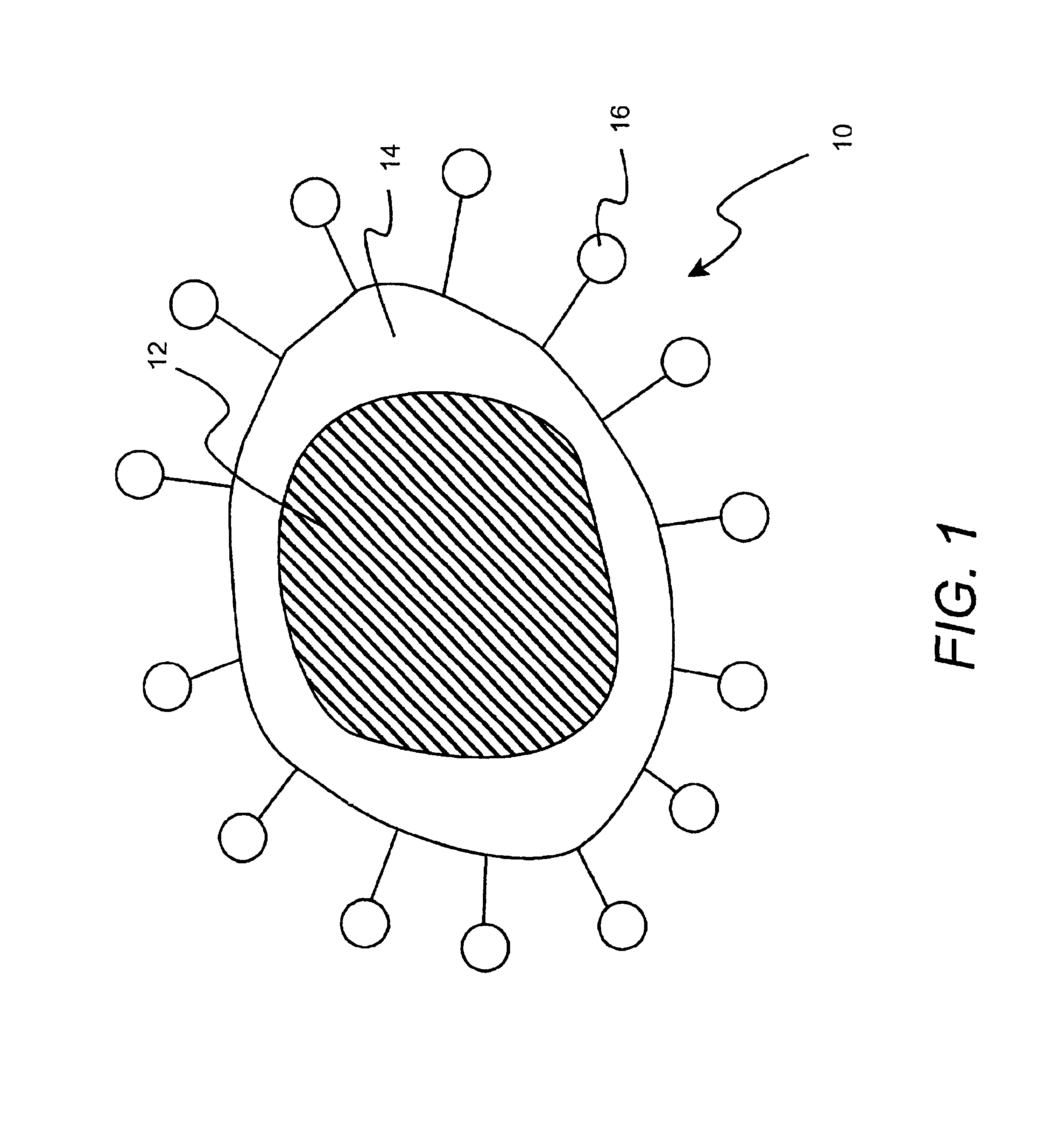
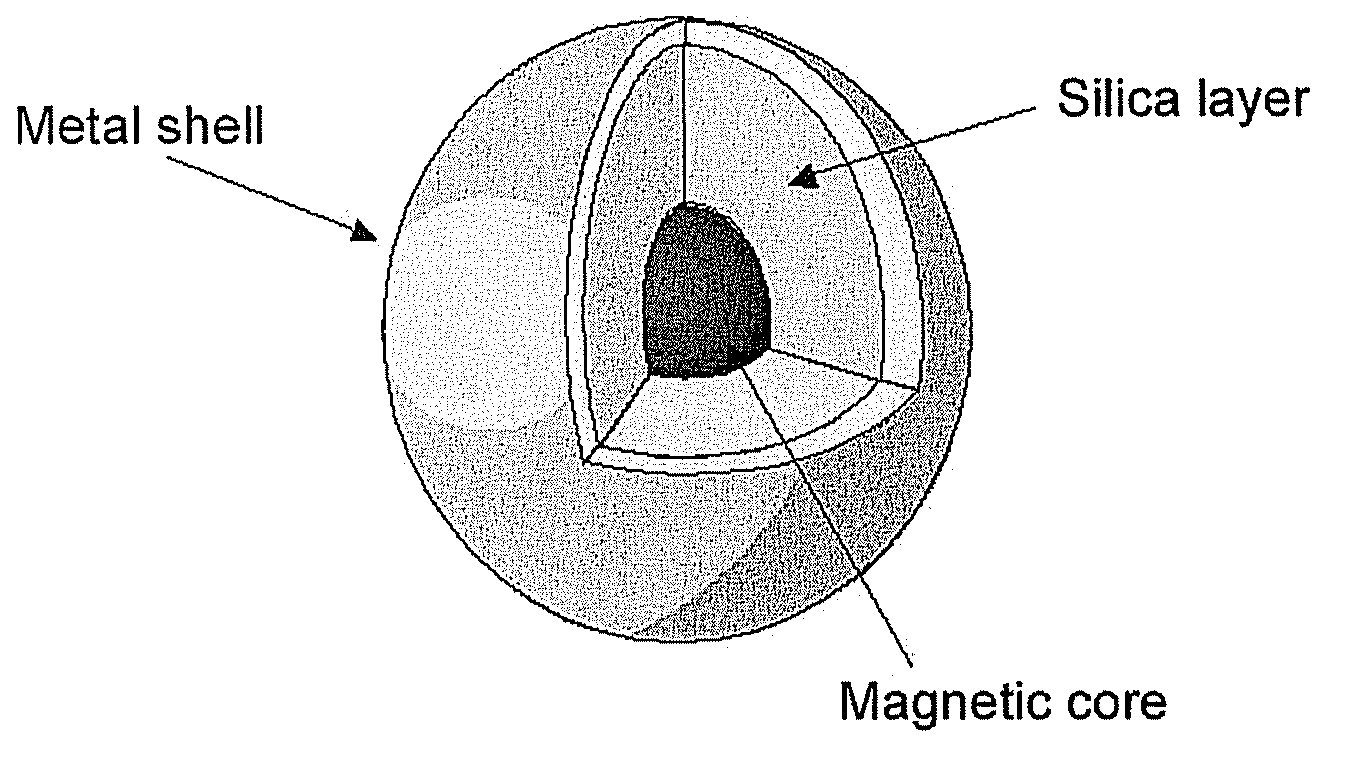
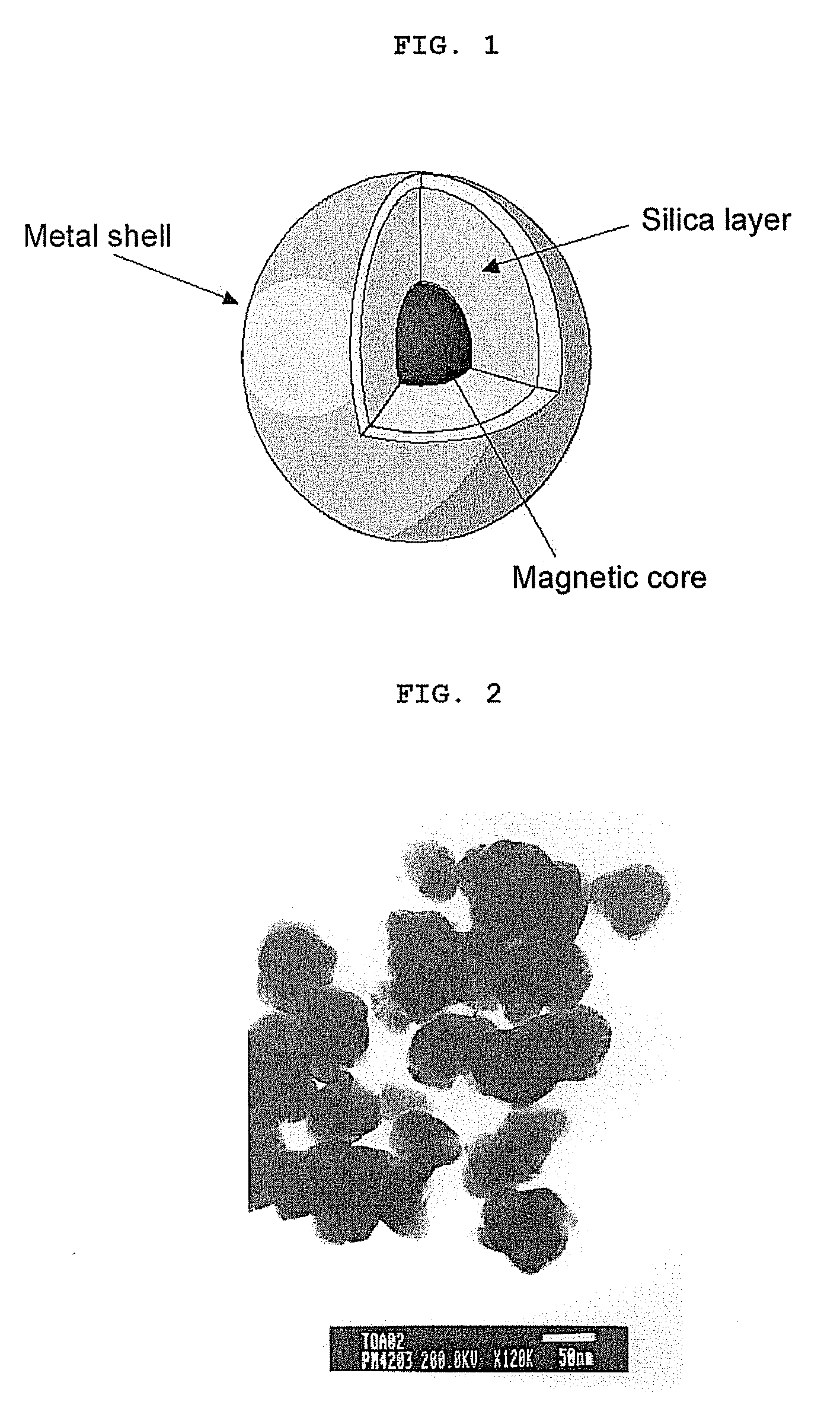
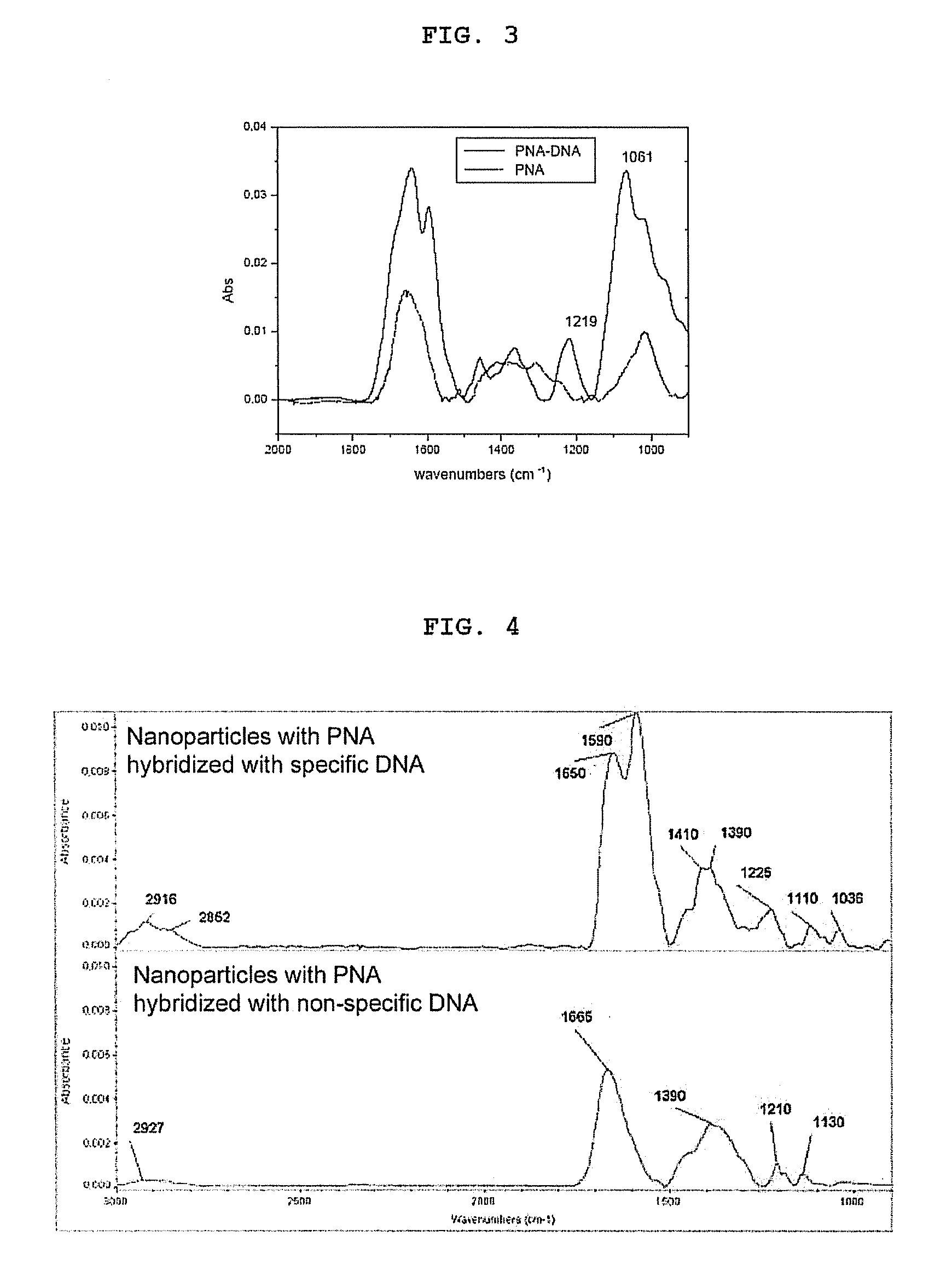
The invention relates to the field of biosensors and, more specifically, to nanoparticle biosensors comprising: a magnetic core, a silica layer, one or more outer metal layers which can be of different types and deposited in an alternating manner and immobilized on the outer surface, and a layer of synthetic or natural organic or inorganic biosensor molecules that can bind to biomolecules. The invention also relates to a method of obtaining the nanoparticle biosensors as well as to the different uses thereof.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
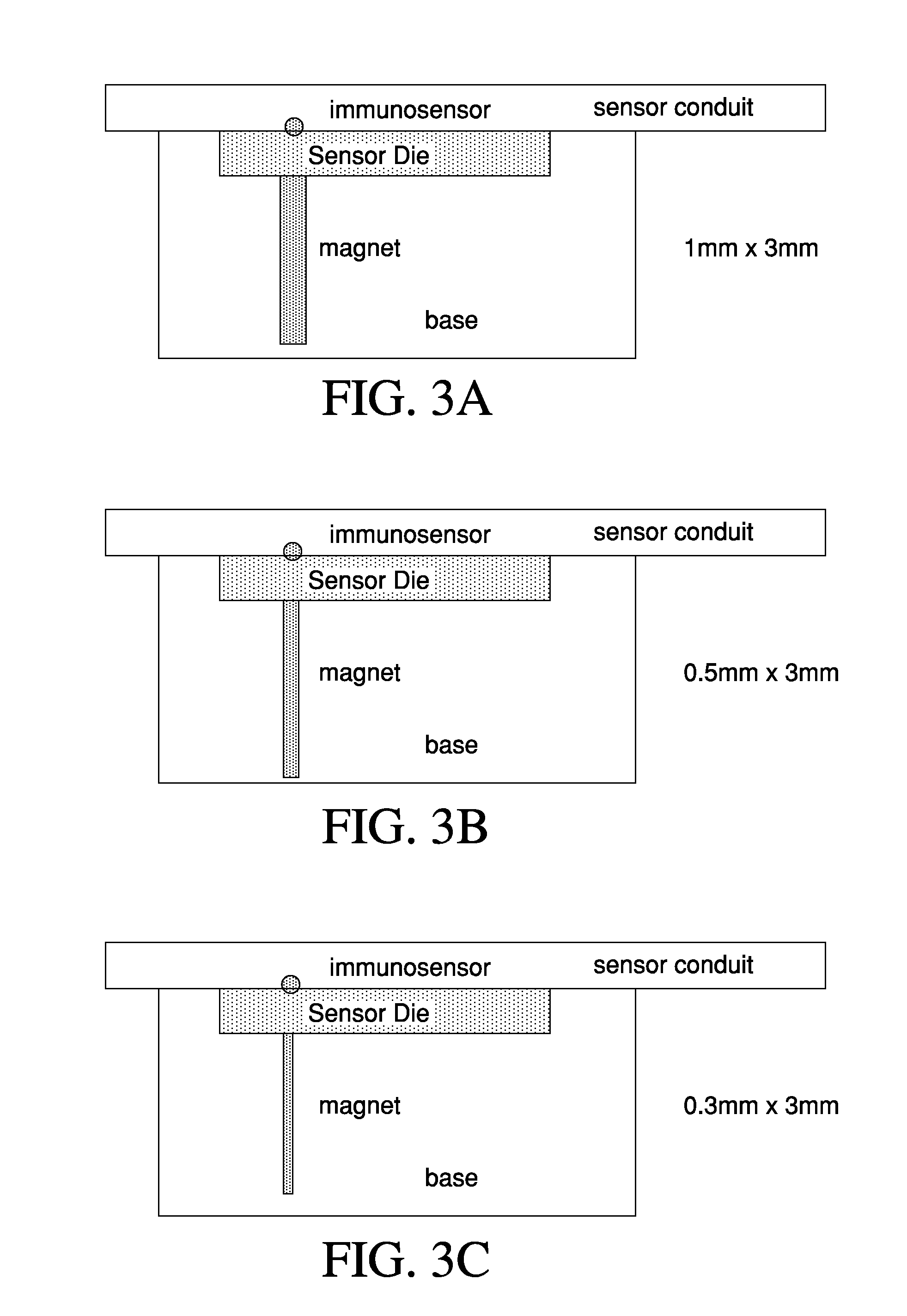
Magnetic immunosensor with trench configuration and method of use
ActiveUS20120034684A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careAnalyte
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Method and apparatus for imaging target components in a biological sample using permanent magnets
ActiveUS7828968B2Water/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsBiological testingWhite blood cellFluorescence
A system for enumeration of cells in fluids by image cytometry is described for assessment of target populations such as leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. Briefly, fluorescently labeled target cells are linked to magnetic particles or beads. In one embodiment, a small, permanent magnet is inserted directly into the chamber containing the labeled cells. The magnets are coated with PDMS silicone rubber to provide a smooth and even surface which allows imaging on a single focal plane. The magnet is removed from the sample and illuminated with fluorescent light emitted by the target cells captured by a CCD camera. In another embodiment, a floater having a permanent magnet allows the target cells to line up along a single imaging plane within the sample solution. Image analysis can be performed with a novel algorithm to provide a count of the cells on the surface, reflecting the target cell concentration of the original sample.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Carrier holding micro-substances, system suspending such carriers apparatus for manipulating such carriers and method of controlling positions of such carriers
InactiveUS7071006B2Less pollutionLess laborBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrostatic separationEngineering
Carriers hold remote-acting bodies which can be manipulated by a remote force, and also hold a micro-substance which is a target substance of an assay. The remote-acting bodies are manipulated in order to control the positions of the micro-substances, so as to execute assays for various target substances efficiently, at low cost, easily, and reliably. Various aspects of interest include the carriers which hold the micro-substances, a system suspending the carriers, an apparatus for manipulating the carriers, and a method of controlling the position of the carriers.
Owner:PRECISION SYST SCI
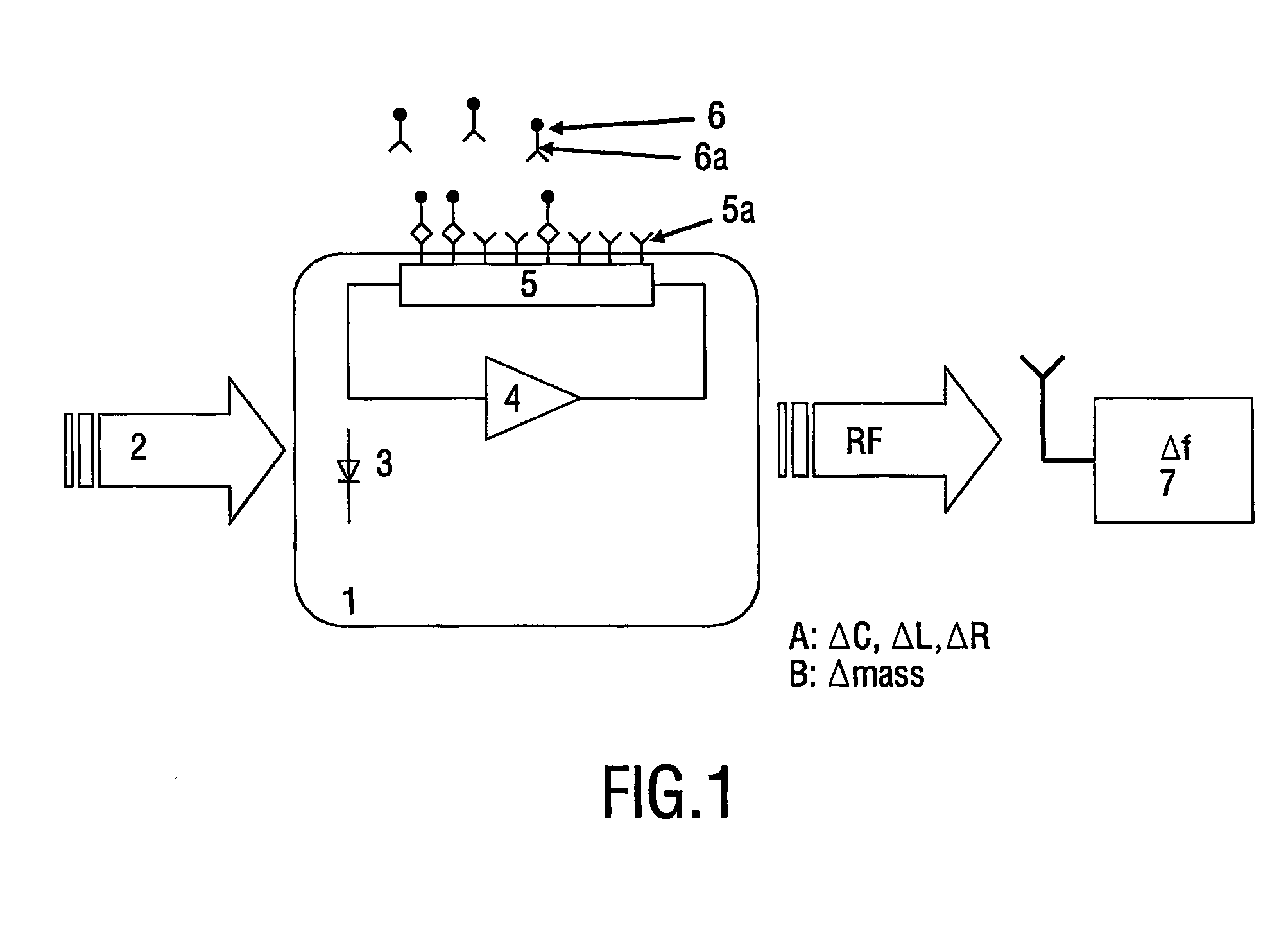
Biosensor with rf signal transmission
InactiveUS20060019373A1High sensitivityReduce complexityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesBinding siteCoupling
A device (1) and method for measuring and or detecting the presence of biomolecules. The device comprises a resonance circuit arranged to operate and emit a resonance frequency (f). The resonance circuit comprises or is coupled to a sensor element (5) for detecting the binding of biomolecules (6a) to binding sites (5a). The binding of the biomolecules changes a physical property (R, L, C. mass) of the sensor element (5), which in it's turn, either directly when the sensor element forms part of the resonance circuit, or via a coupling of the sensor element to the resonance circuit, the resonance frequency. The change in the resonance frequency is detected. The device comprises a remote power transmission element, such as a photodiode or coil, for providing power to the resonance circuit using light or RF radiation respectively.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Device And Use Thereof
InactiveUS20110091864A1Disadvantageous effectCompound screeningMaterial nanotechnologyLipid formationEmulsion
Disclosed herein is a device comprising at least one supporting solid surface comprising at least one membraneophilic region; a covering layer that is at least partially immobilized to the membraneophilic region, said covering layer consisting of (i) a surfactant membrane, (ii) a lipid mimicking polymer, (iii) a surfactant or emulsion system or (iv) a liquid crystal; and a substance included in or bound to, connected to or associated with the covering layer. Also disclosed are methods wherein the device is used and use of the device.
Owner:NANOXIS
Rapid flow-based immunoassay microchip
InactiveUS20050032051A1Quick analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSmall sampleParamagnetic particles
A microimmunoassay arrangement including paramagnetic particles having labeled antibody held in a microchannel by an external magnetic field provides rapid analysis using small sample volumes.
Owner:HAYES MARK A +4
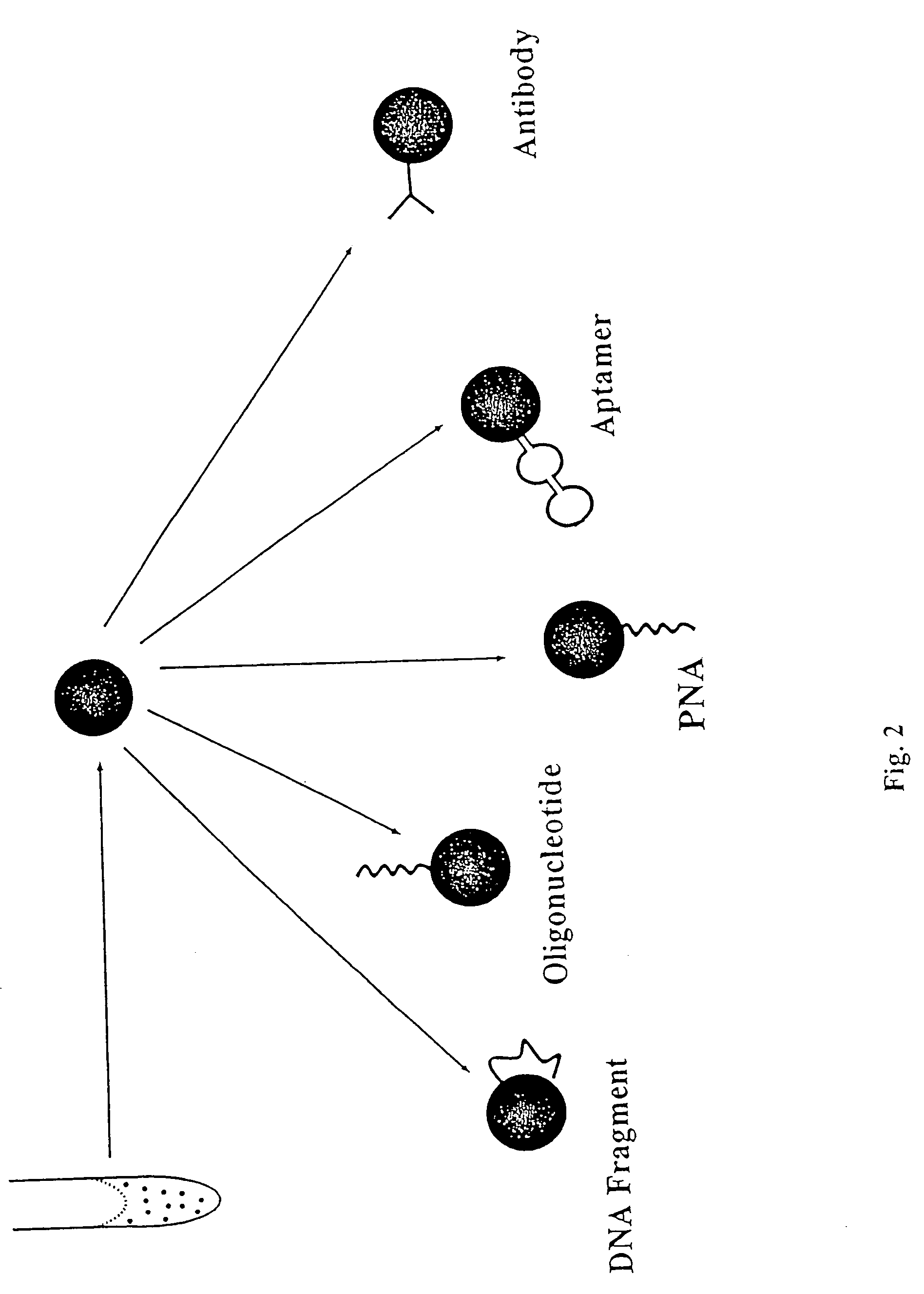
Arrays of magnetic particles
ActiveUS20050272049A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsMagnetite NanoparticlesAnalyte molecule
The present invention provides a method for the generation of novel libraries of encoded magnetic particles from sub-libraries of by the generation of novel sub-libraries of magnetic nanoparticles and encoded particles. The sub-libraries are functionalized on demand are useful in the formation of arrays. The present invention is especially useful for performing multiplexed (parallel) assays for qualitative and / or quantitative analysis of binding interactions of a number of analyte molecules in a sample.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
Magnetic particles and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20090017518A1Uniform diameter distributionHigh magnetizationNanomagnetismMetal-working apparatusMagnetizationBiological materials
A magnetic particle and fabrication method thereof. The magnetic particle comprises a polymer core, a magnetic material layer covering the polymer core, and a silicon containing layer covering the magnetic material layer. In addition, the magnetic particle may further comprise a coupling agent on the silicon containing layer, and an active molecule connected to the coupling agent. The magnetic particles provide controllable size, uniform diameter distribution, high magnetization, improved storage stability, and modified surface for targeting biomolecules for biomaterial separation and environmental analysis.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
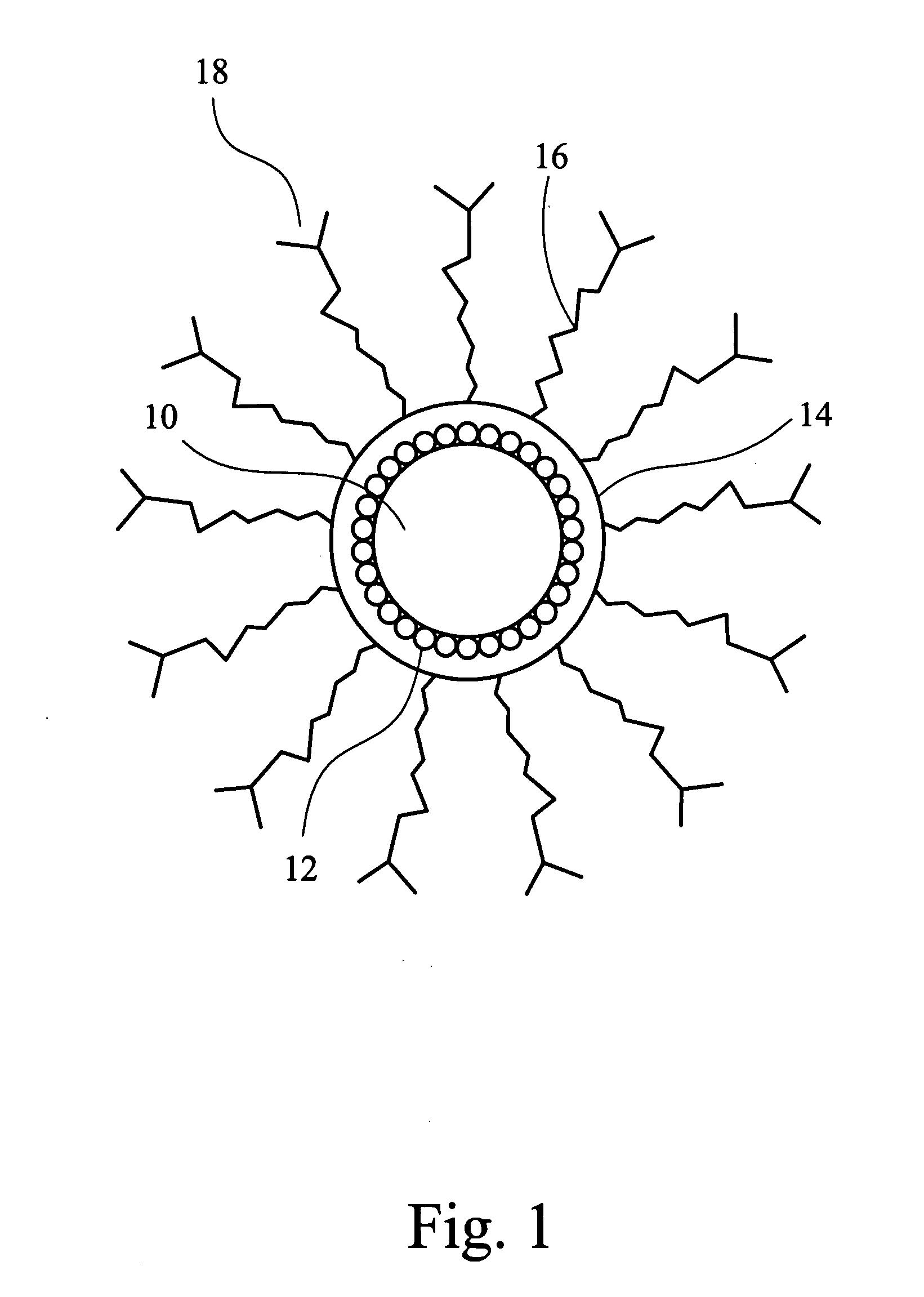
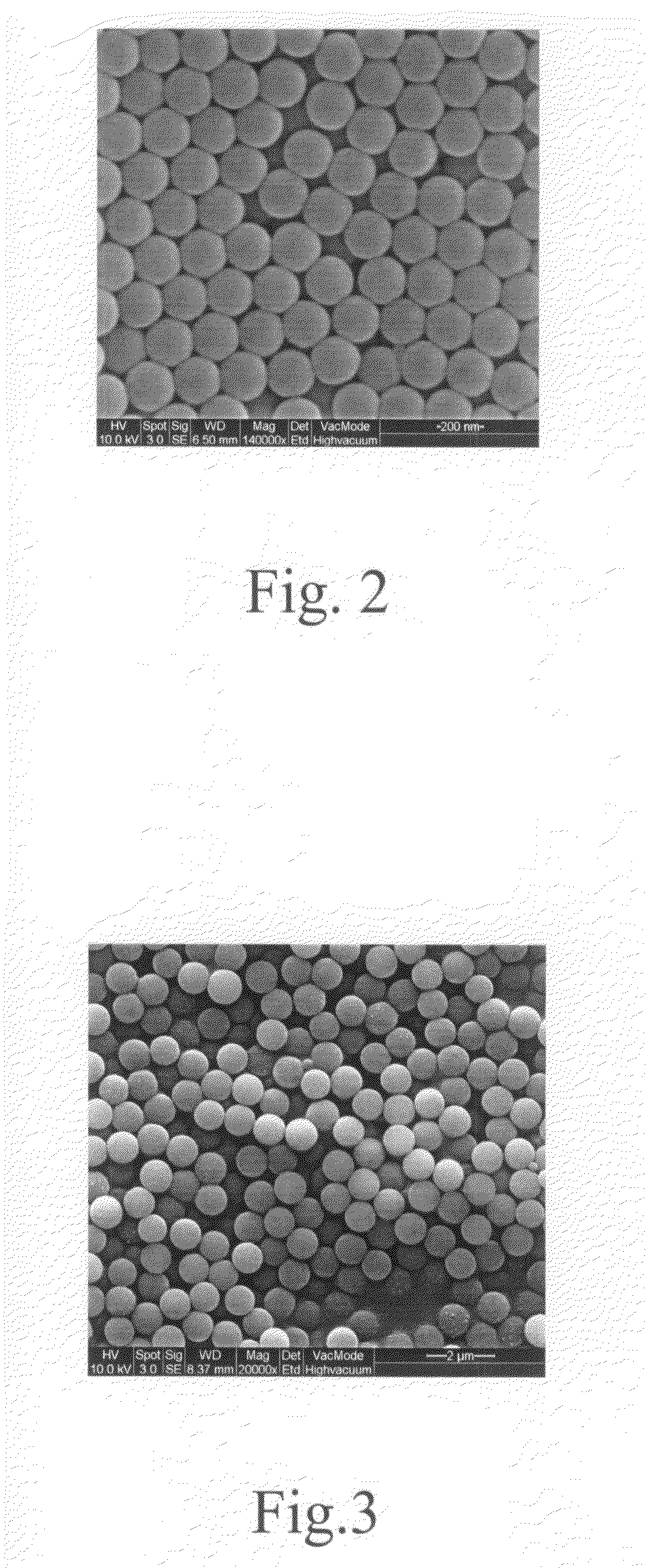
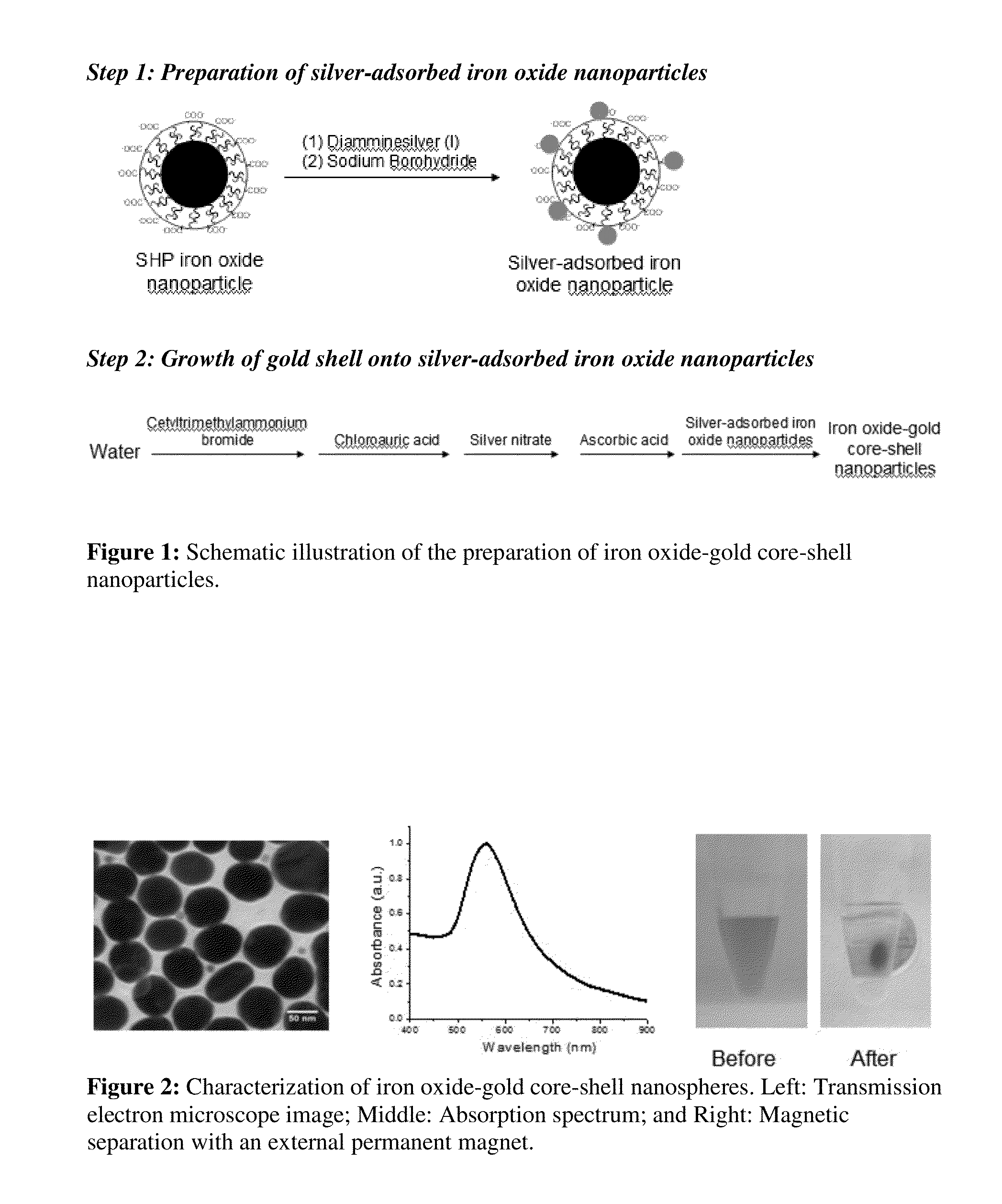
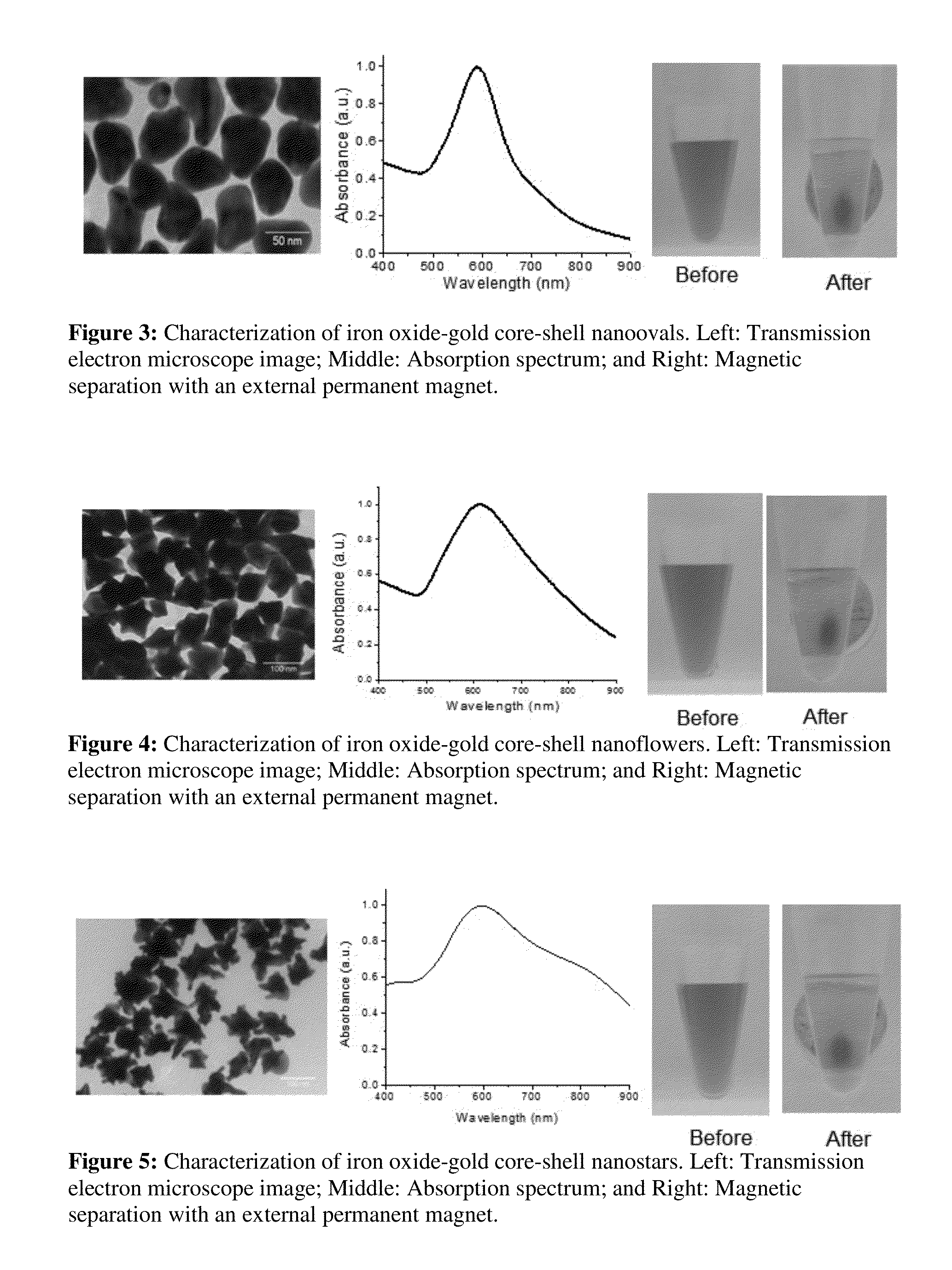
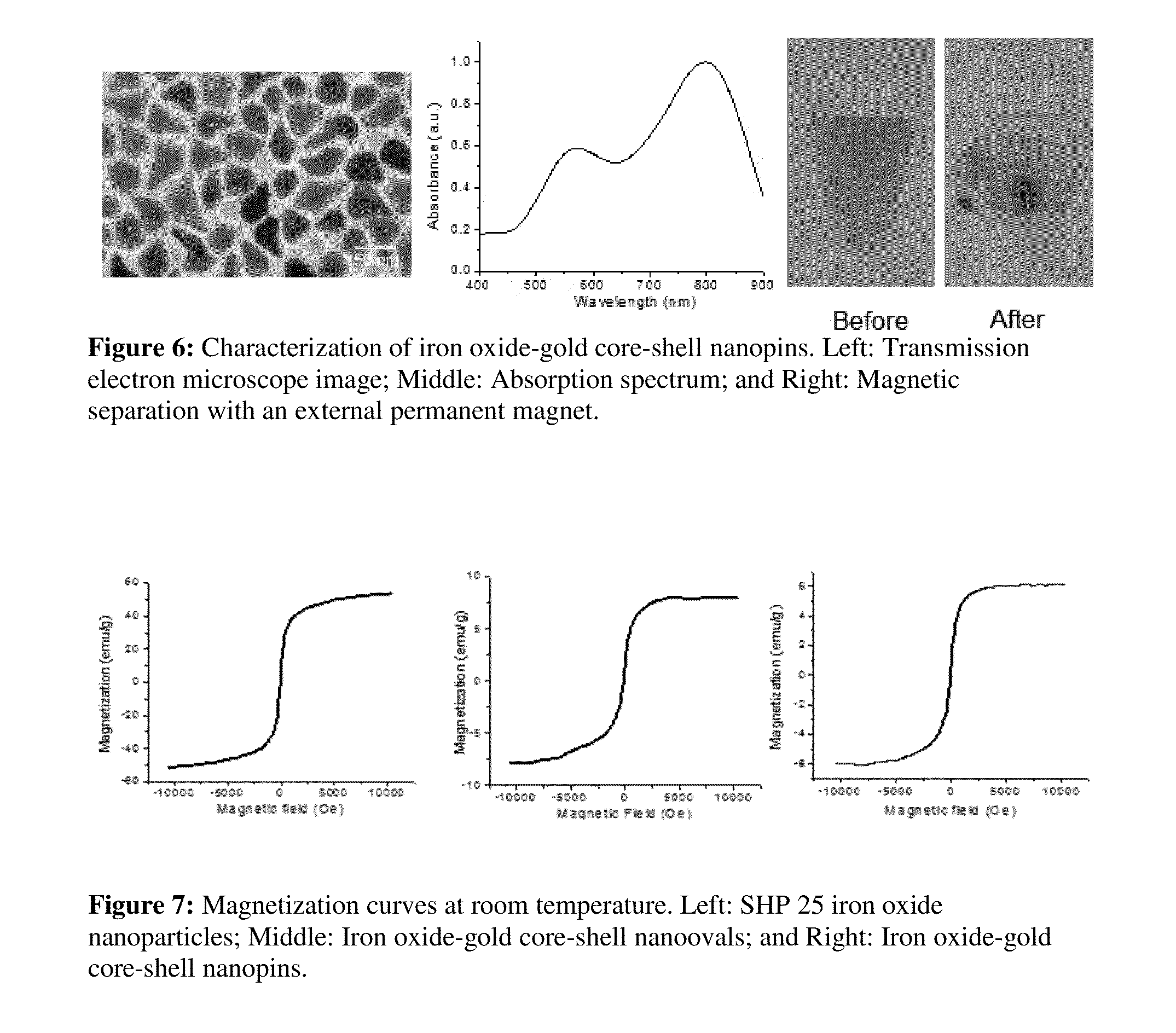
Iron oxide-gold core-shell nanoparticles and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150037818A1Transportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusCore shell nanoparticlesNanometre
Magnetic-optical iron oxide-gold core-shell nanoparticles are disclosed. Methods for making and using the nanoparticles are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MEMPHIS RESEARCH FOUNDATION
Preparation method of immune-magnetic bead
ActiveCN103926398AHigh sensitivityLow background valueMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsMagnetic beadFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a preparation method of an immune-magnetic bead. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, dispersing freeze-dried silicon-based magnetic beads in a polar organic solvent, treating with ultrasonic wave, subsequently adding a dispersant dissolved in the polar organic solvent, stirring, dripping organic small molecules which are dissolved in the polar organic solvent and contain double-end carboxyl, and then reacting for 6-18 hours after the dripping is ended; magnetically separating out carboxyl magnetic beads after the reaction ends, sequentially and repeatedly washing precipitates for a plurality of times by use of absolute ethyl alcohol and deionized water until the pH value of a washing liquid is 6-7, performing ultrasonic treatment for 15-30 minutes, and dispersing into 0.02% of NaN3 water to obtain the carboxyl magnetic beads; washing the carboxyl magnetic beads by use of an MES (Methyl Ester Sulfonate) buffer solution at least once, re-suspending the carboxyl magnetic beads in the MES buffer solution, activating the magnetic beads by using an activating agent carbodiimide, and then coupling an antibody in the environment of the MES buffer solution. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple in technological process, simple and convenient to operate and suitable for batch production.
Owner:山东辛丁技术有限公司
Method of separating unattached Raman-active tag from bioassay or other reaction mixture
InactiveUS20060216835A1Radiation pyrometryMagnetic materialsSuperparamagnetismCombinatorial chemistry
A superparamagnetic Raman-active complex that includes a Raman-active tag, a target, and a superparamagnetic particle is disclosed. A method of applying a magnetic field to a mixture is also disclosed. The mixture includes a Raman-active tag unattached to a target and a superparamagnetic Raman-active complex. Also disclosed is a method of separating a Raman-active tag unattached to a target from a Raman-active complex. The Raman-active complex includes a Raman-active tag attached to a target.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
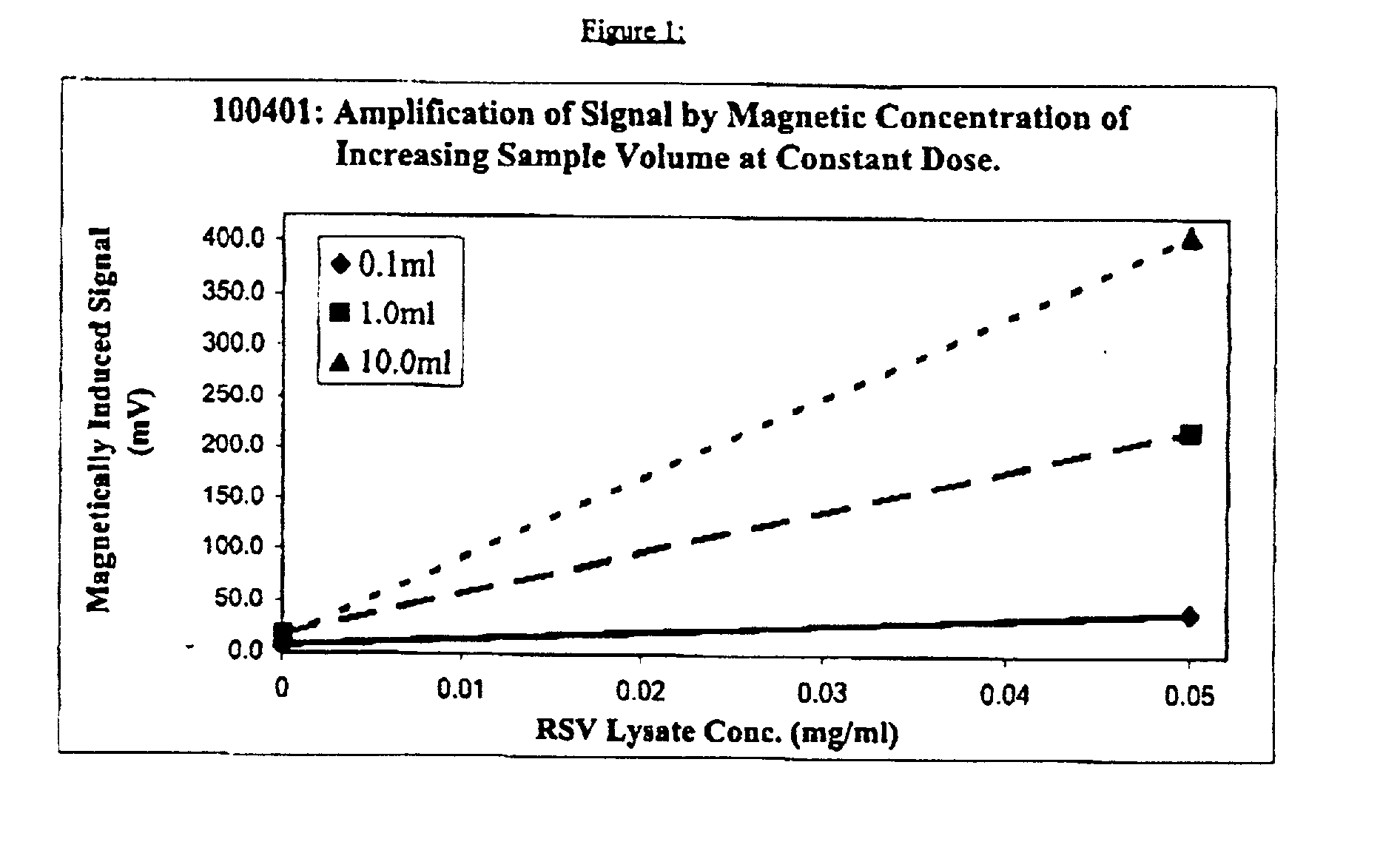
Magnetic particle tagged blood bank reagents and techniques
InactiveUS20070059782A1Effect separationBiological testingMagnetic immunoreagent carriersMagnetic markerIsotope
Magnets and magnetic particle-labeled reagents are used to capture and / or release magnetic particle-tagged entities for immunohematology diagnostic testing purposes, especially tests performed in blood banking. The magnetic tagged entities may be tagged antibodies, tagged blood cells, tagged universal binding partners, especially tagged lectins and tagged Coombs reagent, and other binding agents such as biotin-avidin, Protein A or G, ligands and their receptors and the like. Separation of unbound material from bound material is effected through the use of one or both the magnetic field effect on the magnetic labeled reactants and the density gradients of layers of an assay construct. Constructs such as chromatographic strip lateral flow format, and liquid phase reactions in suitable vessels with end point determinations that do not require centrifugation to detect reacted entities. Readable labels such as enzymes, fluorophors, chemiluminescent materials, radioactive isotopes, and other labels may be attached to Coombs reagent to provide a readable product of the Coombs reagent with any antibody participating in the assay.
Owner:CHROME RED TECH
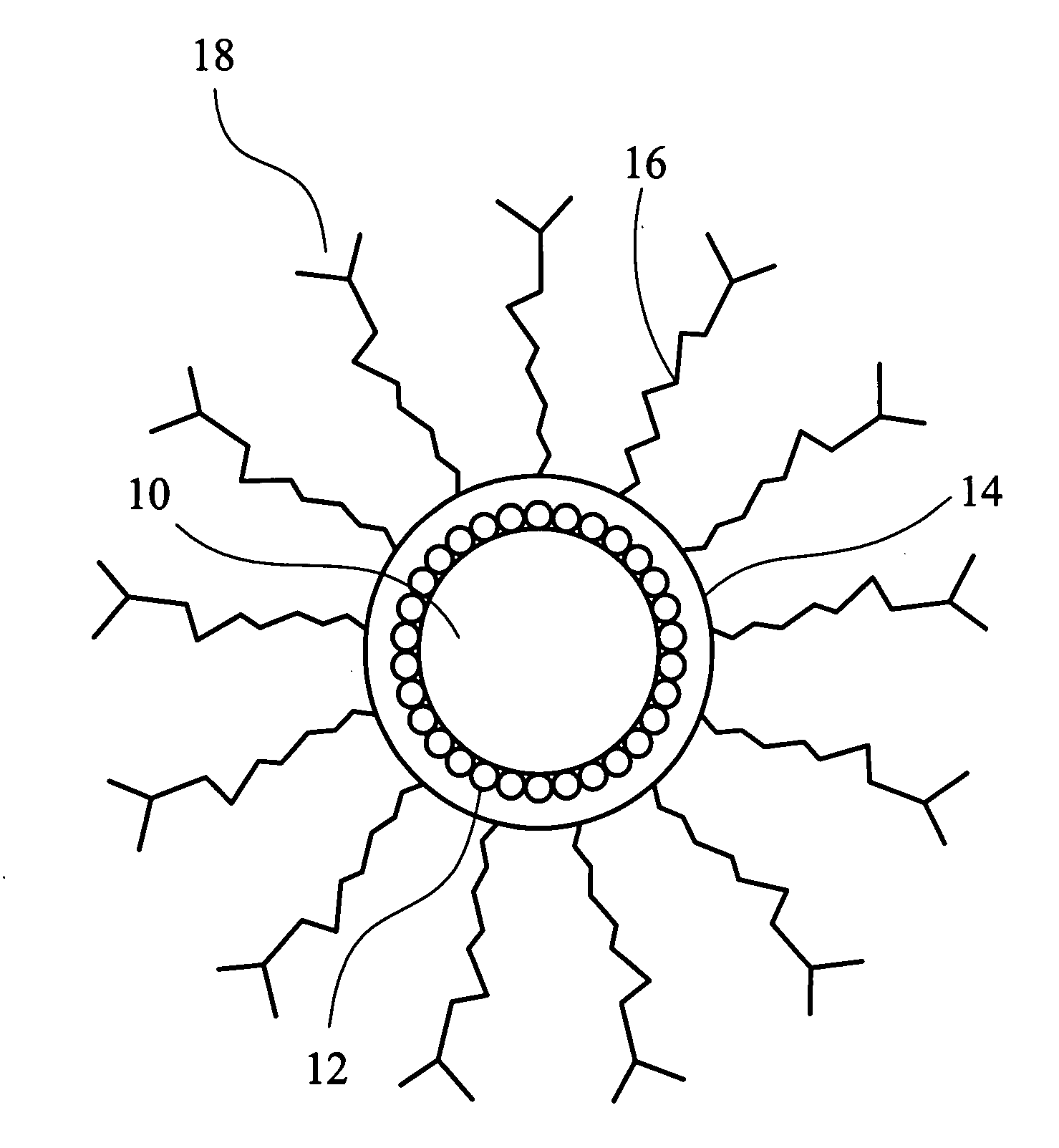
Multifunctional nanoparticles for molecular and cellular separation, detection and quantification
ActiveUS20150051102A1Easily respond to external magnetic field controlElectrostatic separationMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteMultifunctional nanoparticles
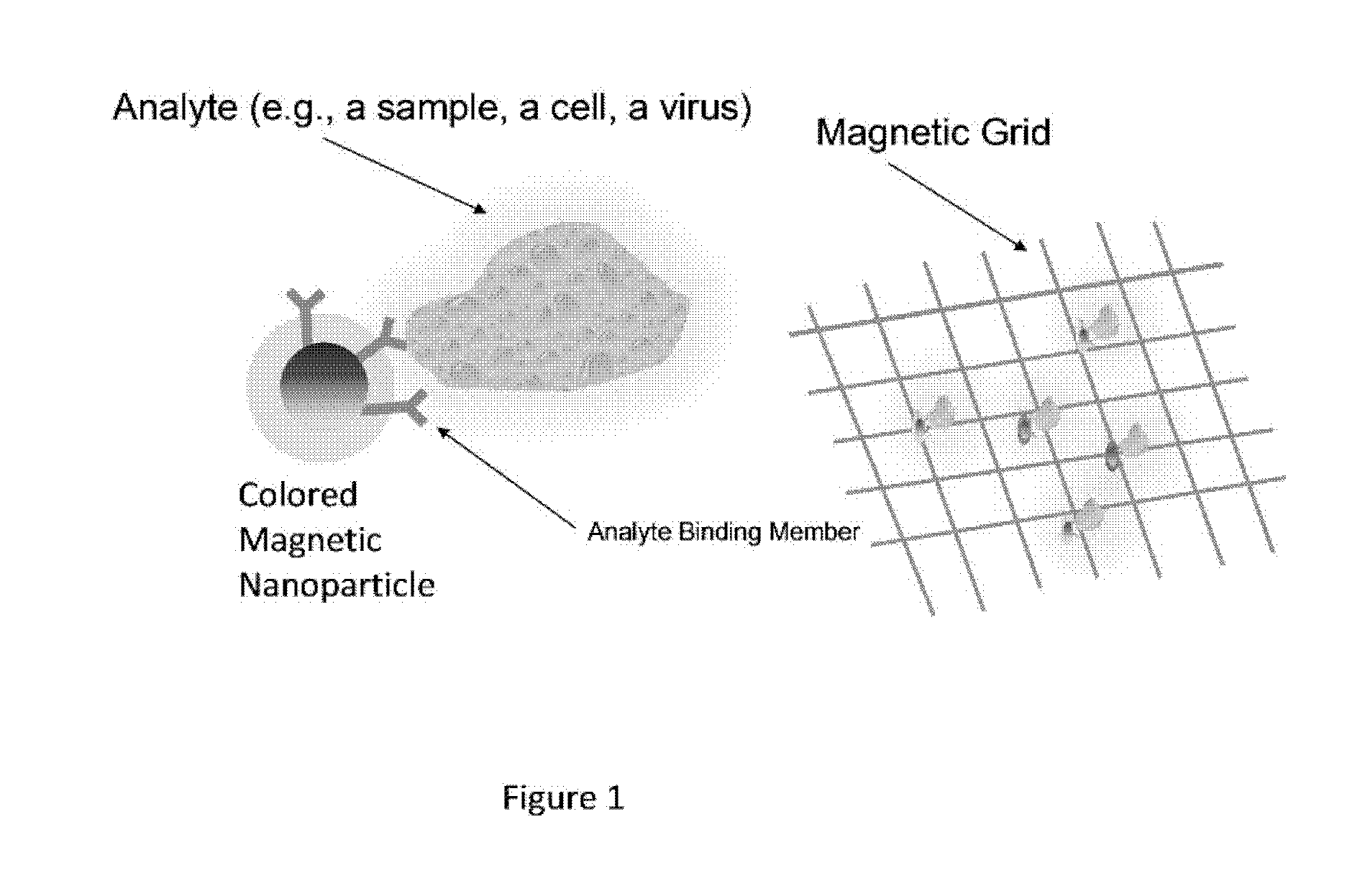
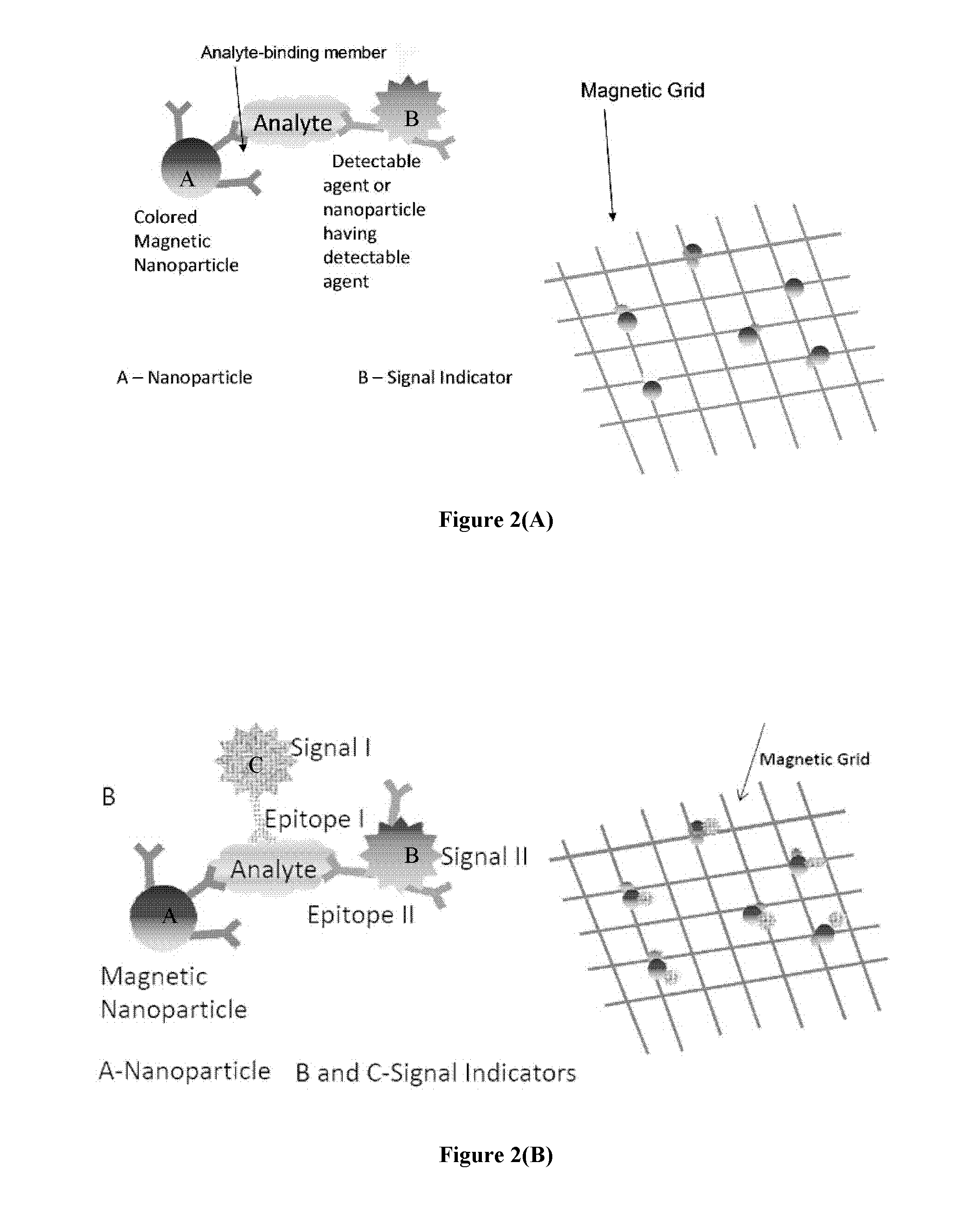
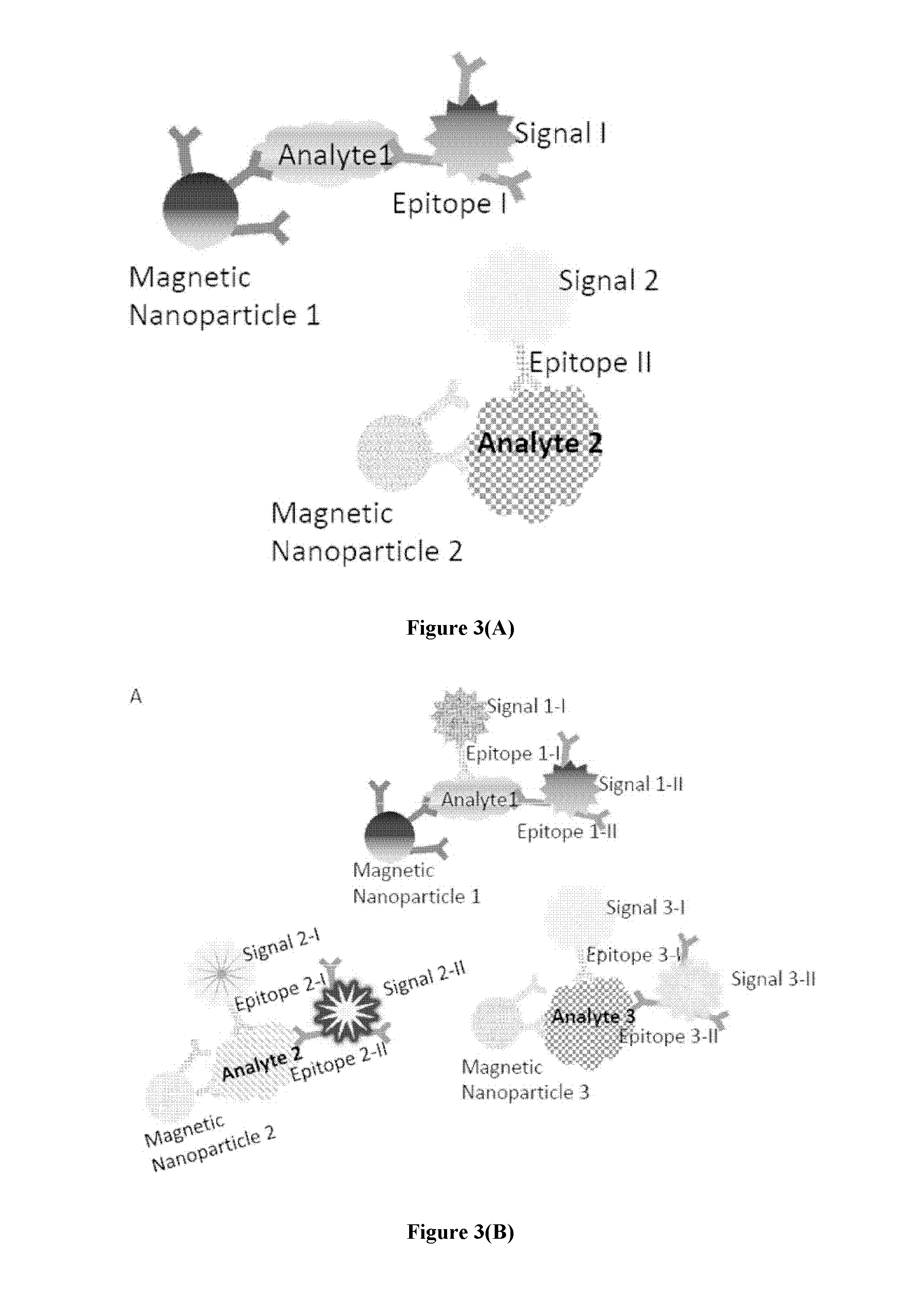
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods useful for molecular and cellular separation, detection and quantification. The compositions provided herein comprise a nanostructure having magnetic property operably linked to an analyte-binding member.
Owner:NVIGEN
Magnetically-responsive microparticles with improved response times
ActiveUS7989065B2Faster magnetic response timeSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsGramMicroparticle
Magnetically responsive particles can include two or more magnetically responsive layers (“MRL”). As such, the particles can have the following: a polymeric core; a first magnetically responsive layer (“MRL”) on the core; a first polymeric layer bound to the first MRL; a second MRL layer bound to the first polymeric layer; and a second polymeric layer bound to the second MRL. The particles can have a faster magnetic response time compared to a similar particle having only a single MRL, which can be at least 25% faster. Also, the particle can have a magnetic squareness of less than about 0.1. Preferably, the particle can have negligible residual magnetism after being exposed to a magnetic field sufficient for the particle to respond thereto. Further, the particle can be colloidally stable in water at concentrations from about 0.1 to 10 grams of particle per 100 milliliters of water.
Owner:HYCLONE LAB INC
Magnetic particles and methods of producing coated magnetic particles
An improved method for separating materials is provided, using colloidal, magnetizable aggregates, optionally silanized, and coated with a one or more layers of novel polysaccharide derivatives. Materials separated by the aggregates of the invention include inorganic and organic molecules, viruses, organelles, and cells. The invention also relates to a kit for separating such materials. The separated materials are useful in analytical and preparative or in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques.
Owner:SKOLD TECH
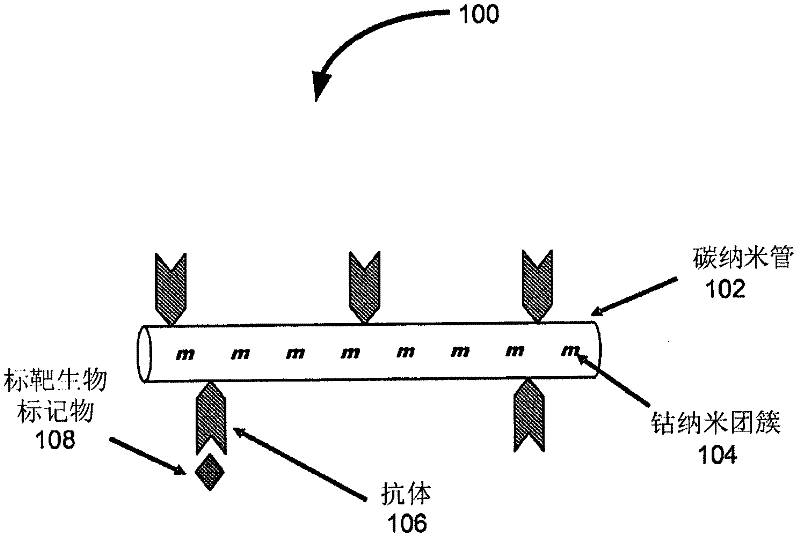
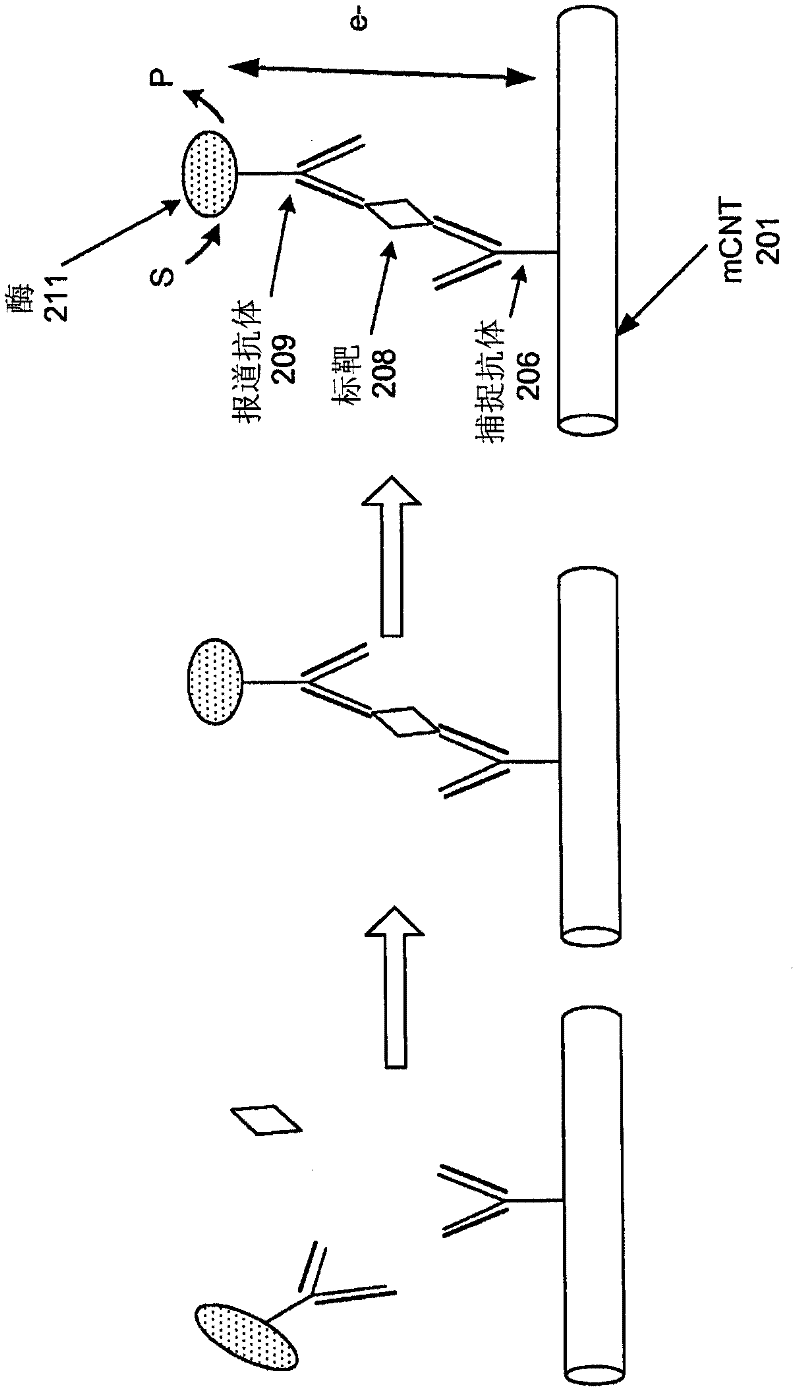
Magnetic carbon nanotube based biodetection
InactiveCN102471051AMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufacturePerformance enhancementMagnetic carbon
Provided herein is a new hybrid material system, mCNT, including magnetic carbon nanotubes for biological and medical sensing applications. In certain embodiments, the systems include magnetic material on the interior of carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The amount of magnetic particles inside CNTs may be such that mCNT can respond to small, low cost, portable magnet. The exterior CNT surface is kept intact for biomolecular attachments or other functionalizations. Performance enhancement with this novel material includes improved sensitivity, reduced response time, and reduced sample volume. According to various embodiments, the mCNTs are substrates for the adherence of molecules participating in these assays or as active sensing elements. Also provided are methods of fabricating two-dimensional mCNT and CNT networks on printed electrodes.
Owner:NANOMIX
Magnetic particles, method for producing same, and probe-bonded particles
ActiveUS20080026222A1High sensitivityReduce noiseSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsSulfurGlycylxylidide
A method for producing magnetic particles includes forming a hydrophobic first polymer layer on the surface of a mother particle containing superparamagnetic particles, forming a second polymer layer having glycidyl groups at least on its surface on the first polymer layer, and introducing a polar group containing one or more of at least one atom selected from the group consisting of an oxygen atom, a nitrogen atom, and a sulfur atom by chemically modifying the glycidyl groups.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
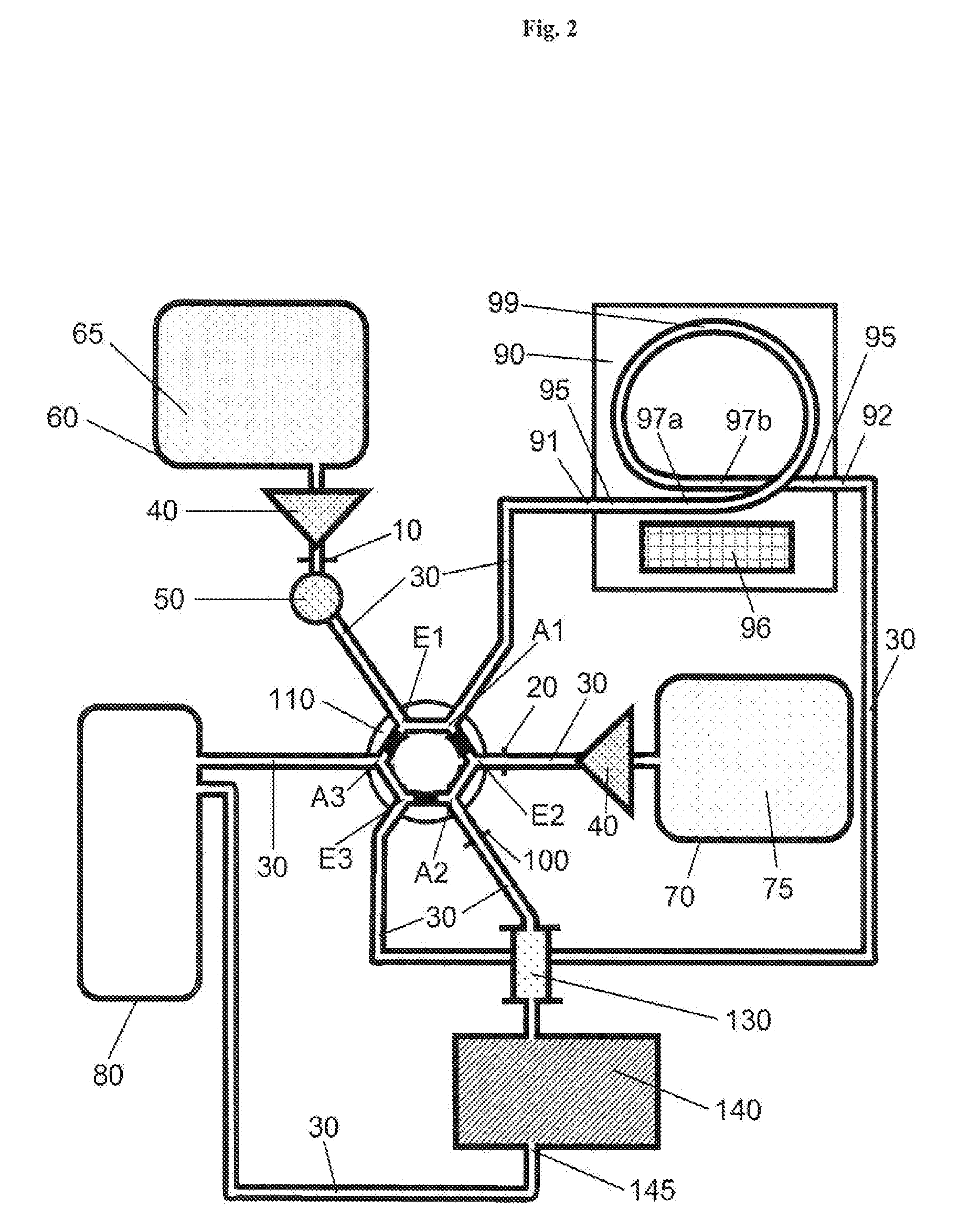
Manipulation of magnetic microparticles in a high pressure liquid system and extraction process
ActiveUS20100326909A1Component separationIon-exchanger regenerationChromatographic separationAnalyte
Described are a device and a method for the manipulation of a liquid sample material in which magnetic microparticles are suspended whereby the microparticles have a functionalized surface and an analyte is bound to the surface. The sample material is introduced into a device with a liquid system through an injection device (50) and in a first mobile phase the sample material is carried to an extractor (90). In a section (97) of the extractor (90) the microparticles are immobilized by means of a magnetic field of a controllable means (96) and separated from the remaining sample material. By switching over of a switching unit (110) a second mobile phase (75) is carried to the extractor (90) and the second mobile phase (75) detaches the adsorbed analyte from the surface of the microparticles. The second mobile phase (75) with the dissolved analyte(s) can be analyzed by way of chromatographic separation (130) and subsequent detection (140).
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Polymer-coated magnetic particles comprising a 2,3-hydroxypropyl group, and probe-bonded particles
ActiveUS7732051B2High sensitivityReduce noiseSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsSulfurSuperparamagnetism
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
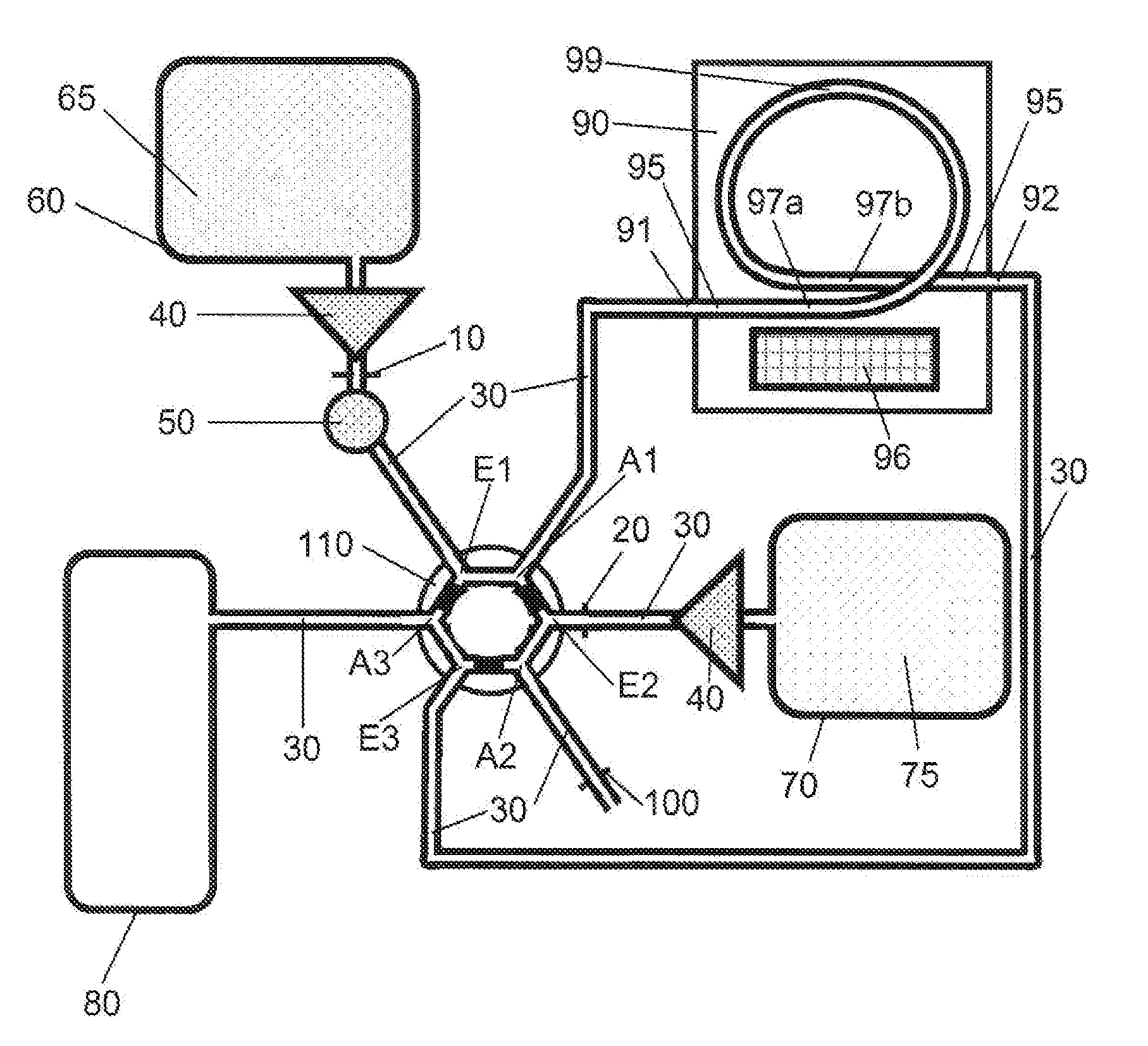
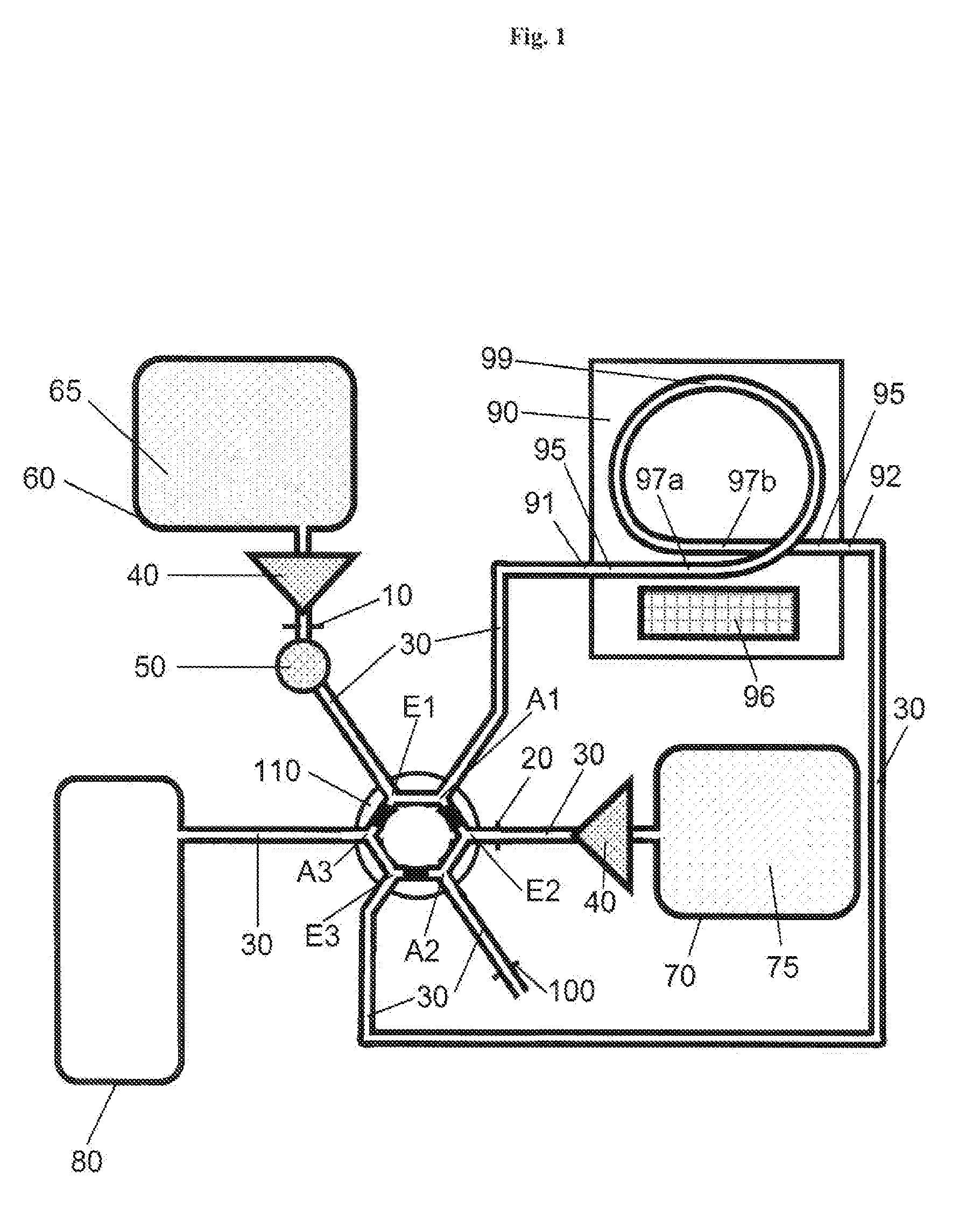
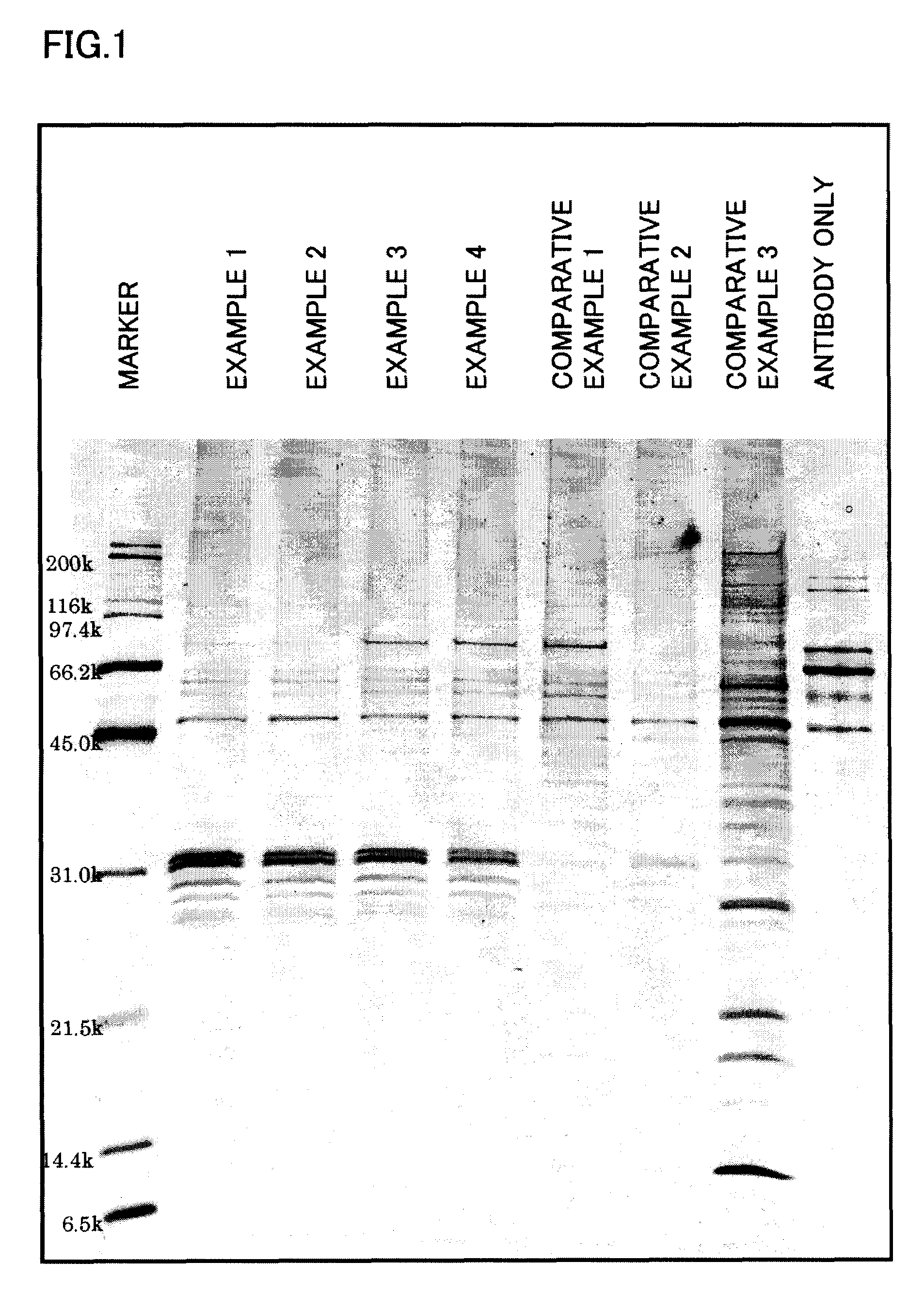
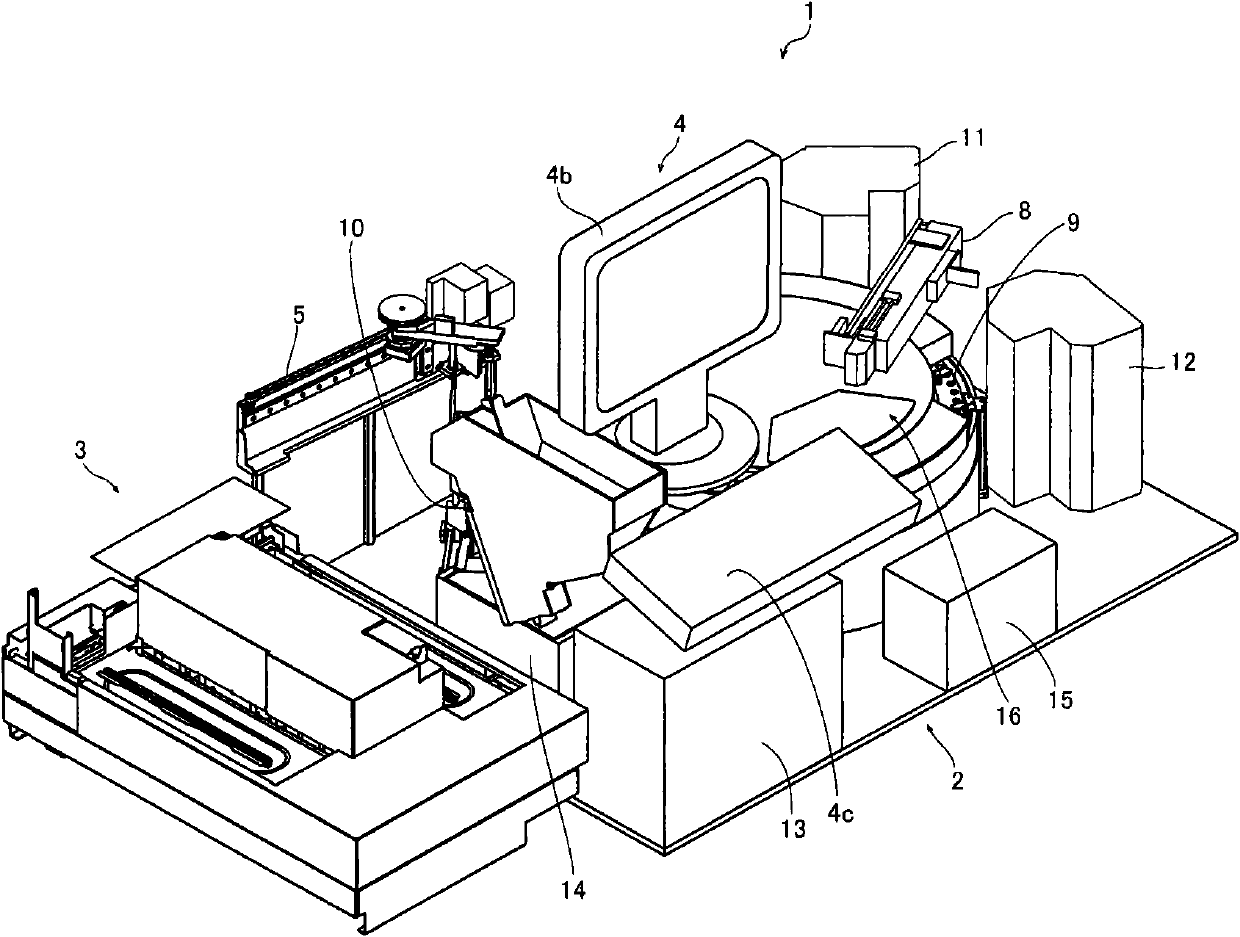
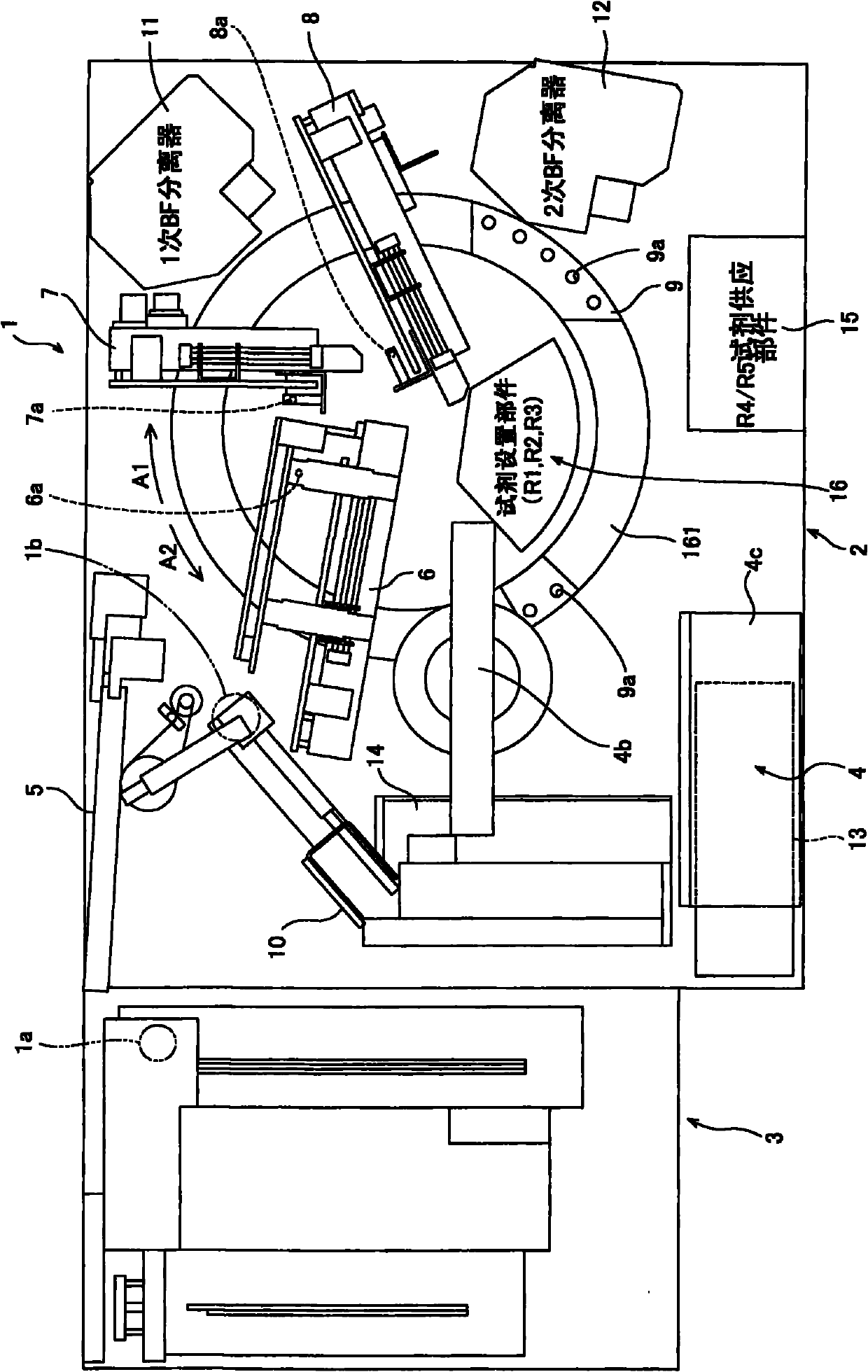
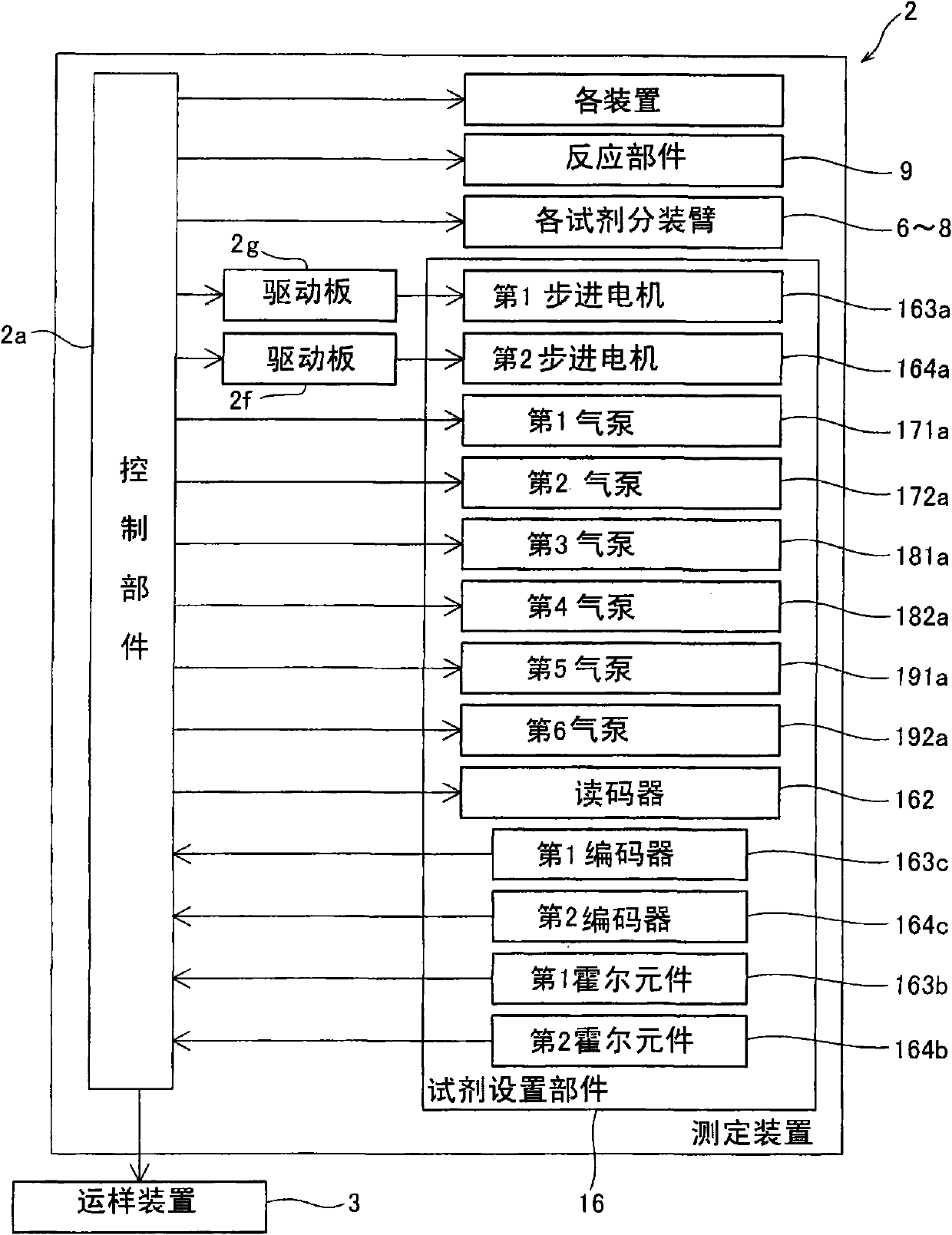
Sample analyzer and sample analyzing method
A sample analyzer comprising: a reagent container holder, configured to rotate around a rotational axis and to hold a reagent container containing a reagent; a reagent aspirator for aspirating, at a reagent aspirating position, the reagent from the reagent container held by the reagent container holder; an analysis section for analyzing a measurement sample prepared from the reagent aspirated by the reagent aspirator and a sample; and a controller for controlling: the reagent container holder to rotate and thereby transport the reagent container to the reagent aspirating position, the reagent aspirator to aspirate the reagent from the reagent container, and the reagent container holder to accelerate and decelerate alternately while being rotated is disclosed. A sample analyzing method is also disclosed.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
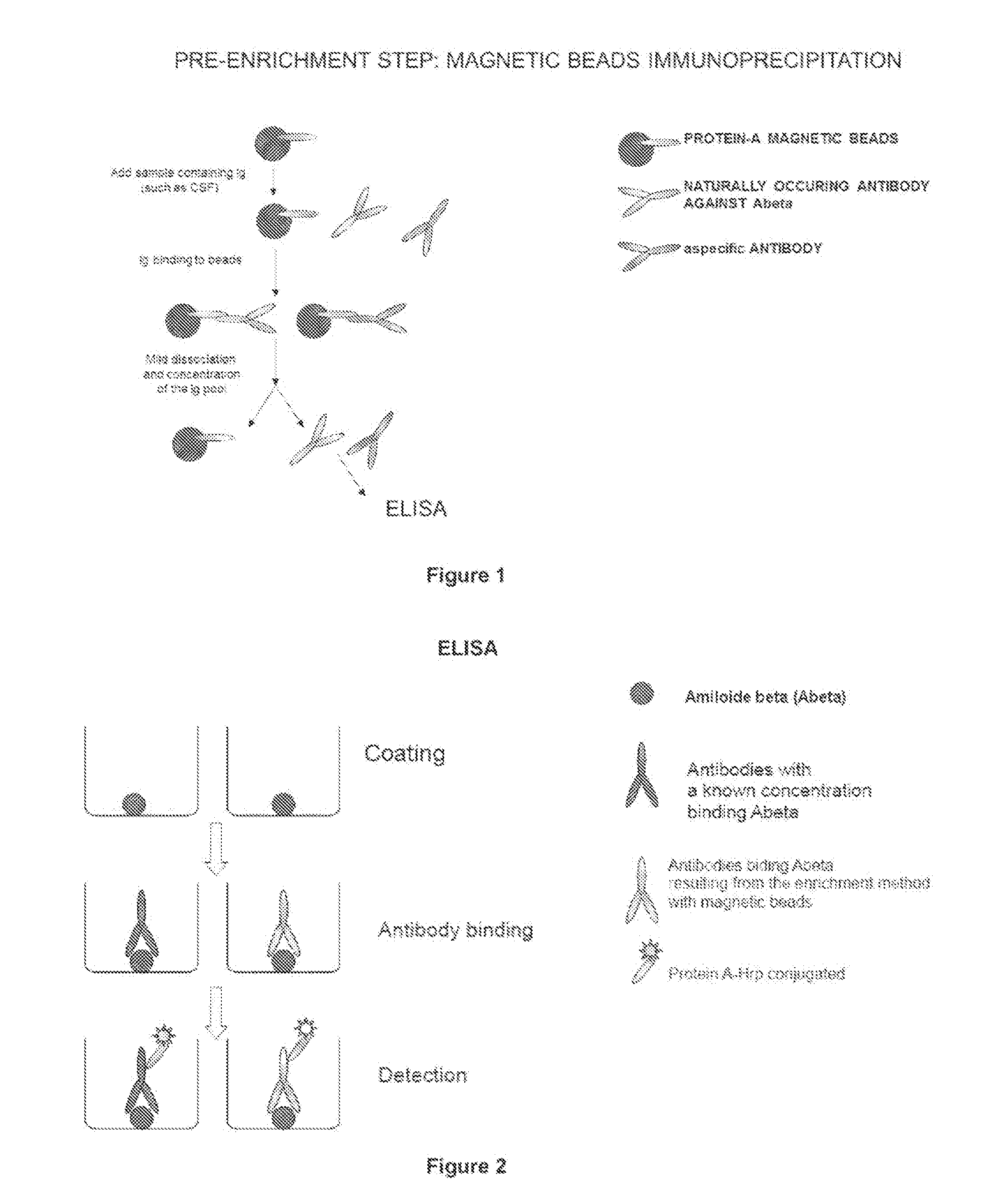
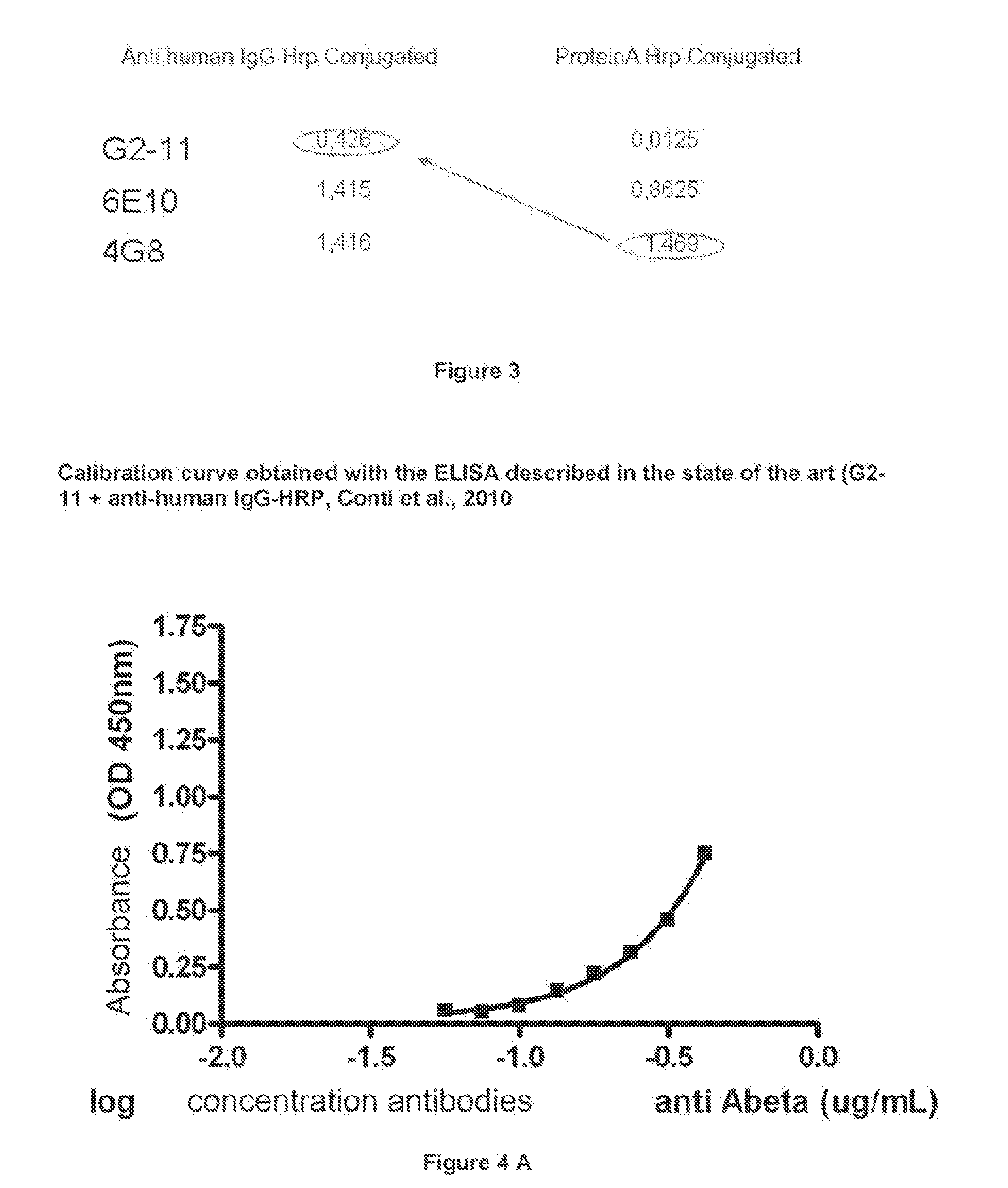
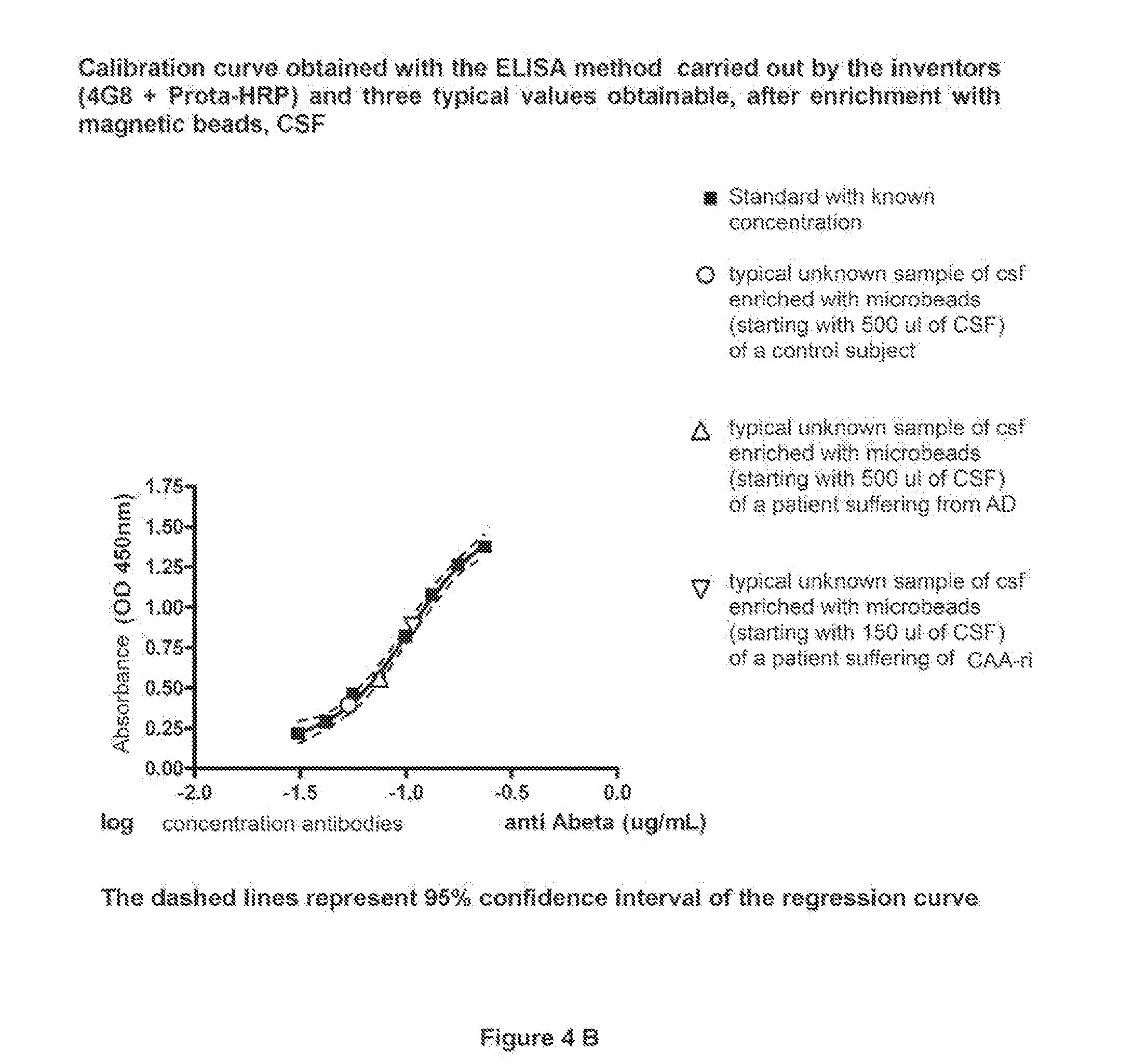
Method and kit for detection of Anti-beta amyloid antibodies
InactiveUS20150094218A1Easy to disassembleHigh sensitivityPeptide librariesLibrary screeningCrystallographyCerebrospinal fluid
An in vitro method and a kit for the quantification of antibodies anti-beta amyloid protein in a sample of cerebrospinal fluid comprising the following steps a) concentrating the quantity of said antibodies of said sample with magnetic micro beads coated with macromolecules capable of binding said antibodies b) analysing the concentrated sample obtained in step a) by immunoenzyme assay or by radioimmunoassay; c) analysing a sample comprising antibodies anti-beta amyloid protein having a known titre with the same assay used in step b) and elaborating the related calibration curve, wherein said antibody having a known titre is a murine antibody belonging to the IgG2a or IgG2b class or a human or humanized antibody belonging to the IgG2b or IgGi class.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI MILANO BICOCCA
Process for (A) separating biological/ligands from dilute solutions and (B) conducting an immunochromatographic assay thereof employing superparamagnetic particles throughout
Superparamagnetic ("SPM") subunits of 1-30 nm average mean diameter (e.g. ferro fluid) subparticles are treated with a magnetically noninterfering substance capable of coating and covering them (e.g, BSA) and they spontaneously form agglomerates of about 100 nm to about 450 nm or higher average mean diameter and are then used to form complexes with target biological ligands such as viruses, contained in large volumes of liquid. The complexes are subjected to the gradient intensity of a strong magnetic field, and excess liquid is removed, where upon an immunochromatographic assay is conducted to determine the identity and / or amount of target ligand present, in which operation SPM particles that bonded to the ligand function as tags for ligand detection.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com