Patents
Literature
380results about "Movable microstructural devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
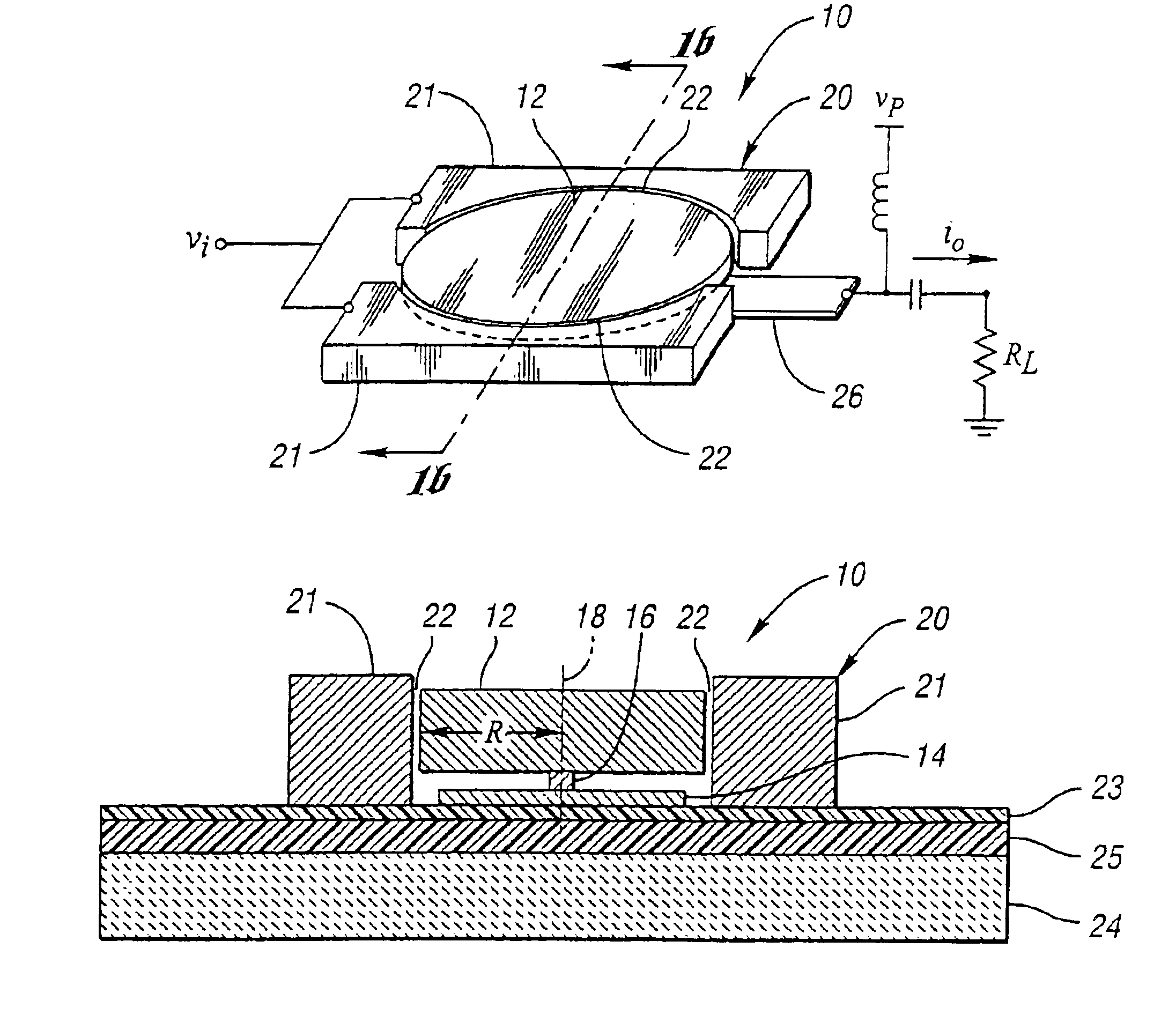
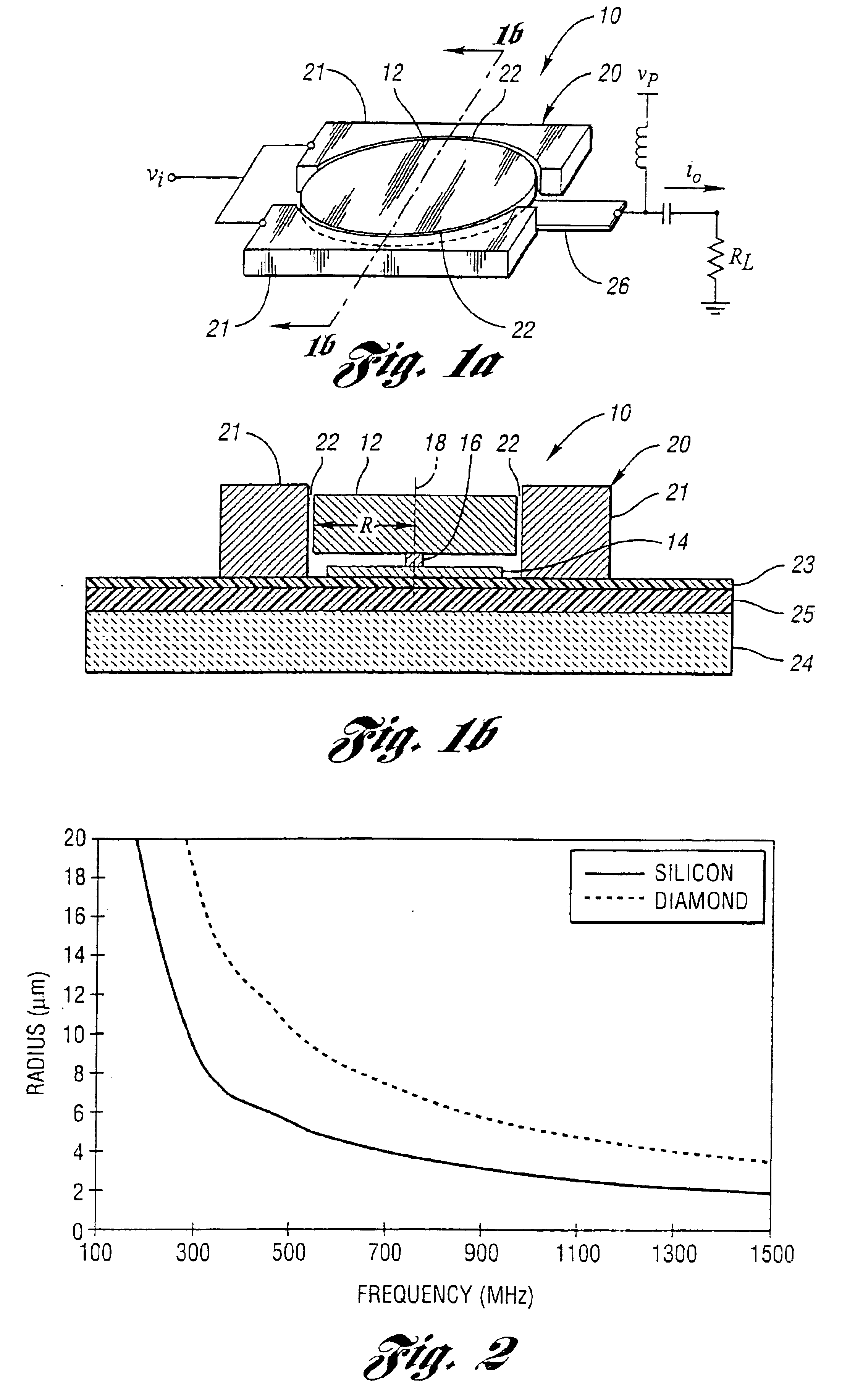
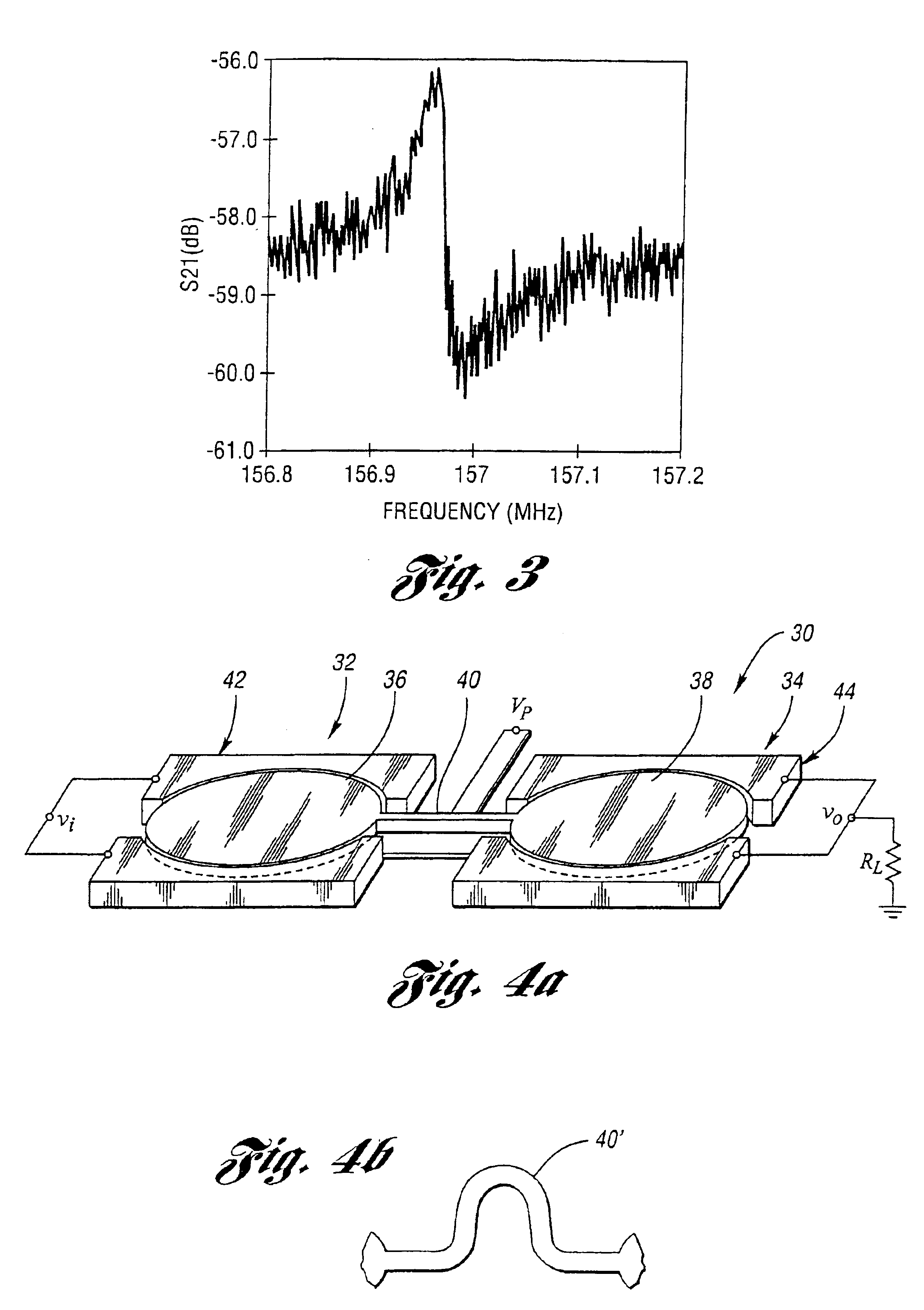
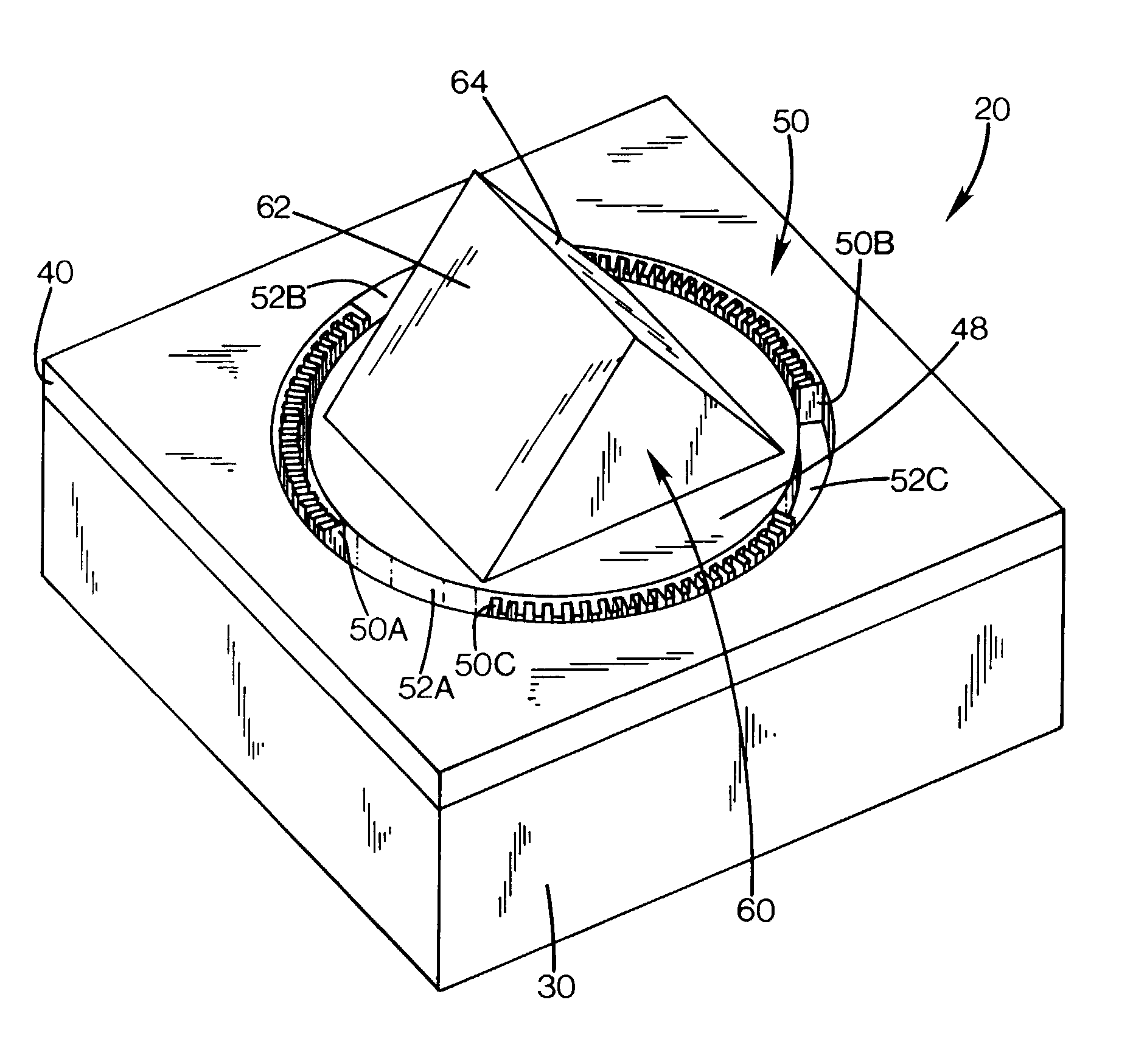
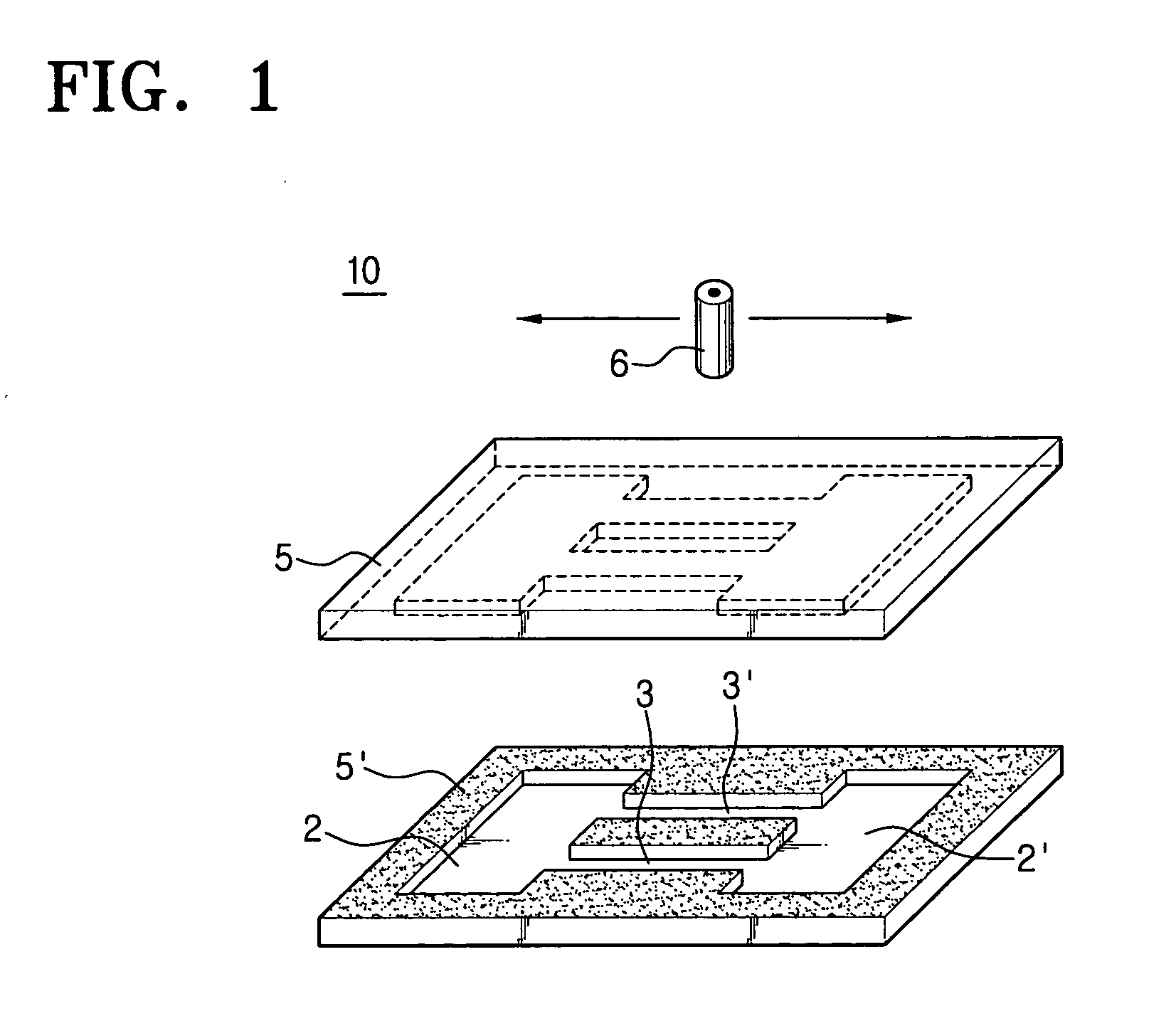
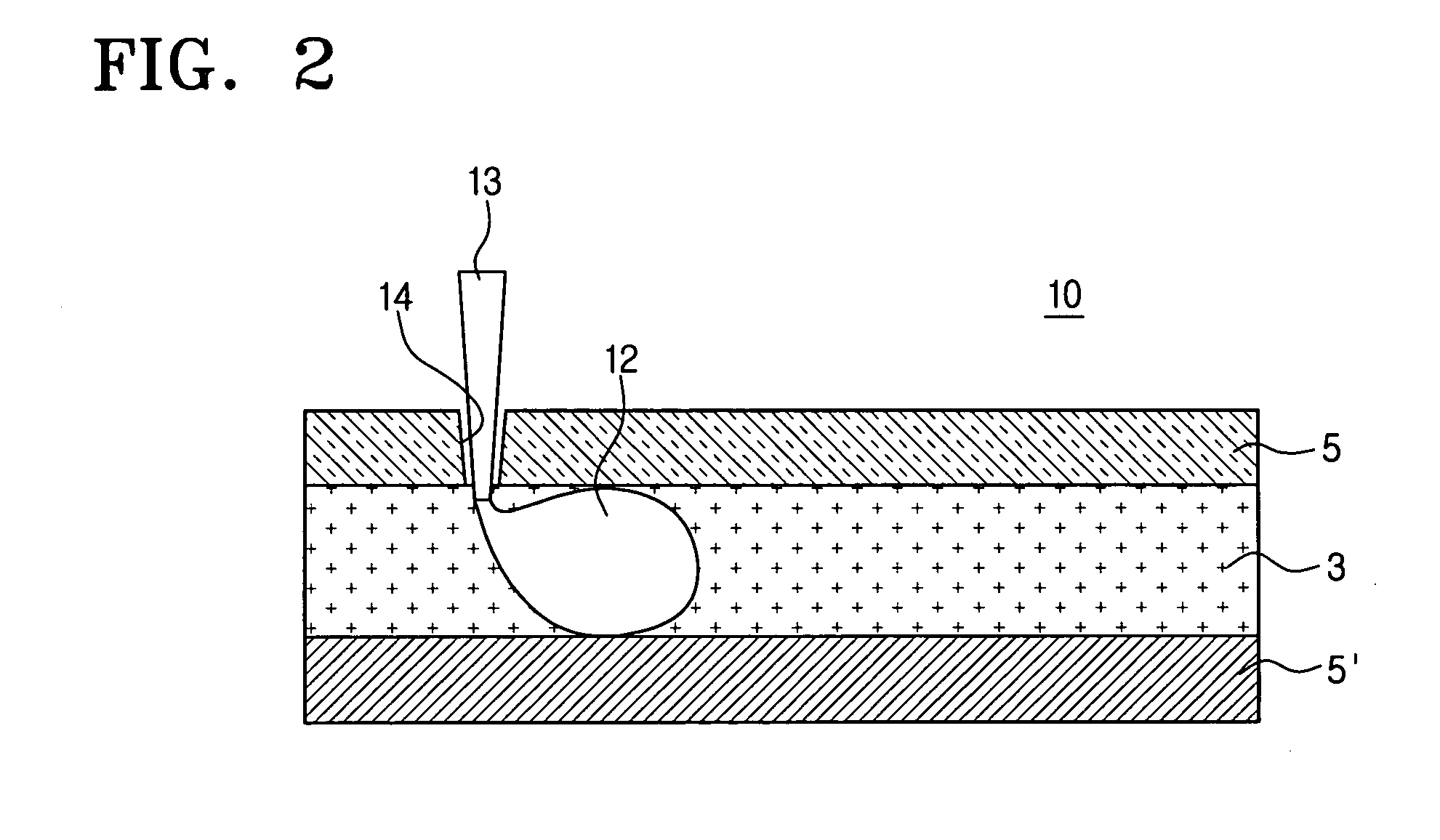
Micromechanical resonator device and micromechanical device utilizing same
InactiveUS6856217B1Improving QHigh Power Handling CapabilityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksWireless transceiverTransceiver
A micromechanical resonator device and a micromechanical device utilizing same are disclosed based upon a radially or laterally vibrating disk structure and capable of vibrating at frequencies well past the GHz range. The center of the disk is a nodal point, so when the disk resonator is supported at its center, anchor dissipation to the substrate is minimized, allowing this design to retain high-Q at high frequency. In addition, this design retains high stiffness at high frequencies and so maximizes dynamic range. Furthermore, the sidewall surface area of this disk resonator is often larger than that attainable in previous flexural-mode resonator designs, allowing this disk design to achieve a smaller series motional resistance than its counterparts when using capacitive (or electrostatic) transduction at a given frequency. Capacitive detection is not required in this design, and piezoelectric, magnetostrictive, etc. detection are also possible. The frequency and dynamic range attainable by this resonator makes it applicable to high-Q RF filtering and oscillator applications in a wide variety of communication systems. Its size also makes it particularly suited for portable, wireless applications, where, if used in large numbers, such a resonator can greatly lower the power consumption, increase robustness, and extend the range of application of high performance wireless transceivers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Micro-mirror with rotor structure
InactiveUS20040017599A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesStatic indicating devicesMirror mountMicro mirror
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
MEMS tunable capacitor based on angular vertical comb drives
InactiveUS7085122B2Appreciates the drawbacks inherent in lateral drive MEMS capacitorsIncrease tuning rangeMultiple-port networksMechanically variable capacitor detailsCapacitanceComb finger
A MEMS tunable capacitor with angular vertical comb-drive (AVC) actuators is described where high capacitances and a wide continuous tuning range is achieved in a compact space. The comb fingers rotate through a small vertical angle which allows a wider tuning range than in conventional lateral comb drive devices. Fabrication of the device is straightforward, and involves a single deep reactive ion etching step followed by release and out-of-plane assembly of the angular combs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Anchorless electrostatically activated micro electromechanical system switch
InactiveUS20050068128A1Control displacementPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysEngineeringStress free
A micro electromechanical system (MEMS) switch (10) includes a substrate (12) and a stress free beam (14) disposed above the substrate (12). The stress free beam (14) is provided within first and second platforms (16, 18) to limit displacement of the stress free beam (14) in directions that are not substantially parallel to the substrate (12). A set of one or more control pads (20) is disposed in a vicinity of a first lengthwise side (22) of the stress free beam (14) for creating a potential on the first lengthwise side (22) of the stress free beam (14). The stress free beam (14) is displaceable in directions substantially parallel to the substrate (12) in accordance with the potential for providing a signal path.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Adjustable nanopore, nanotome, and nanotweezer
InactiveUS20030080042A1Material nanotechnologyPaper/cardboard articlesRotational axisPlanar substrate
An adjustable nanopore is fabricated by placing the surfaces of two planar substrates in contact, wherein each substrate contains a hole having sharp corners and edges. A corner is brought into proximity with an edge to define a triangular aperture of variable area. Ionic current in a liquid solution and through the aperture is monitored as the area of the aperture is adjusted by moving one planar substrate with respect to the other along two directional axes and a rotational axis. Piezoelectric positioners can provide subnanometer repeatability in the adjustment process. The invention is useful for characterizing, cleaving, and capturing molecules, molecular complexes, and supramolecular complexes which pass through the nanopore, and provides an improvement over previous devices in which the hole size of nanopores fabricated by etching and / or redeposition is fixed after fabrication.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
MEMS tunable capacitor based on angular vertical comb drives
InactiveUS20050013087A1Increase tuning rangeAppreciates the drawbacks inherent in lateral drive MEMS capacitorsMultiple-port networksMechanically variable capacitor detailsCapacitanceComb finger
A MEMS tunable capacitor with angular vertical comb-drive (AVC) actuators is described where high capacitances and a wide continuous tuning range is achieved in a compact space. The comb fingers rotate through a small vertical angle which allows a wider tuning range than in conventional lateral comb drive devices. Fabrication of the device is straightforward, and involves a single deep reactive ion etching step followed by release and out-of-plane assembly of the angular combs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Adjustable nanopore, nanotome, and nanotweezer
An adjustable nanopore is fabricated by placing the surfaces of two planar substrates in contact, wherein each substrate contains a hole having sharp corners and edges. A corner is brought into proximity with an edge to define a triangular aperture of variable area. Ionic current in a liquid solution and through the aperture is monitored as the area of the aperture is adjusted by moving one planar substrate with respect to the other along two directional axes and a rotational axis. Piezoelectric positioners can provide subnanometer repeatability in the adjustment process. The invention is useful for characterizing, cleaving, and capturing molecules, molecular complexes, and supramolecular complexes which pass through the nanopore, and provides an improvement over previous devices in which the hole size of nanopores fabricated by etching and / or redeposition is fixed after fabrication.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
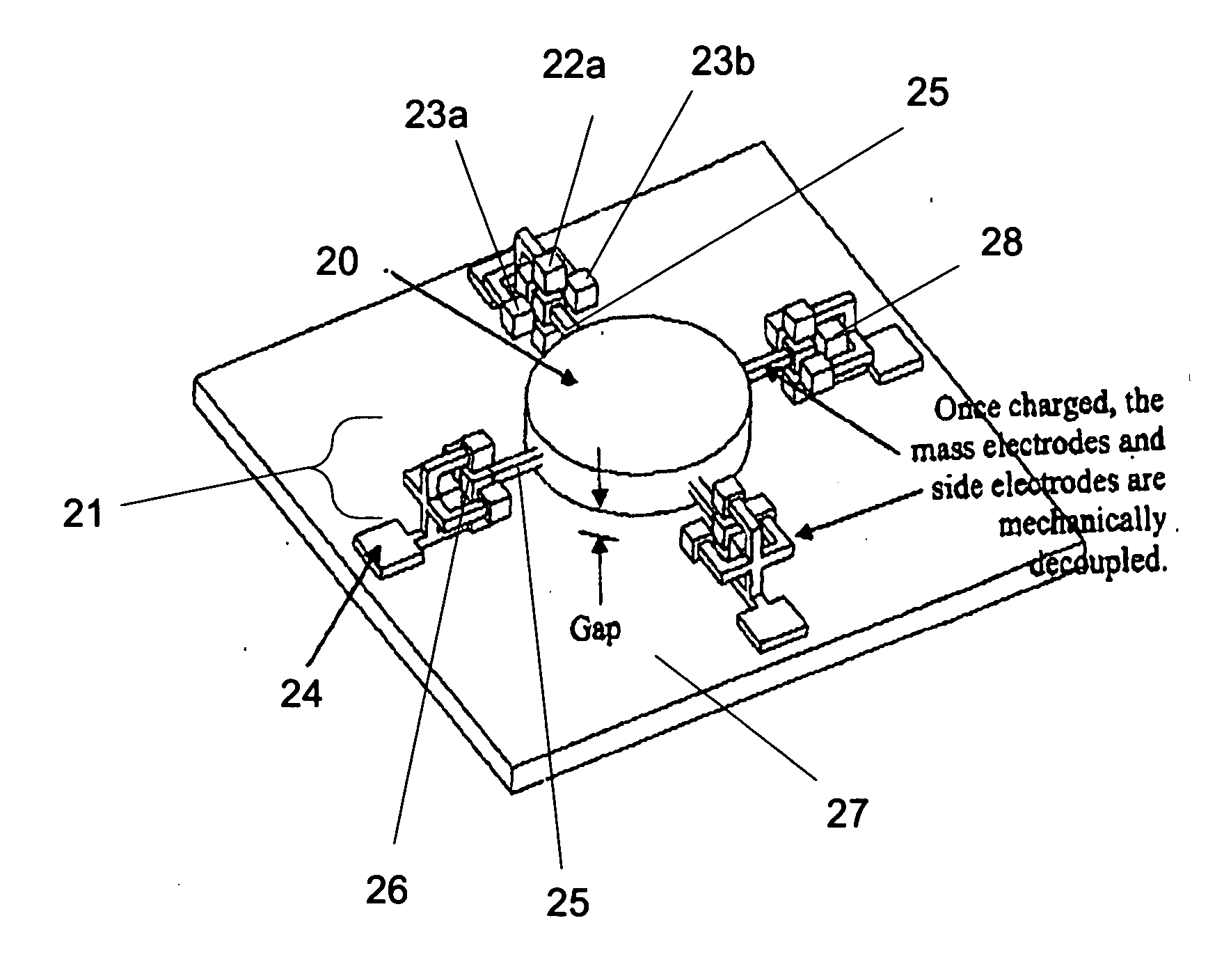
Capacitive micro-acceleration sensor with symmetrically combined elastic beam structure and production method thereof
ActiveCN101858929AReduce sensitivityGreat lateral sensitivityPrecision positioning equipmentPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCross sensitivityShaped beam
The invention relates to a capacitive micro-acceleration sensor with a symmetrically combined elastic beam structure and a production method thereof. The acceleration sensor comprises a symmetric center mass block, an external support frame, eight symmetric straight beams, two symmetric frame beams, a combined elastic beam structure, an upper cover plate and a lower cover plate, wherein the eight symmetric straight beams are used for connecting the center mass block with the external support frame, and the combined elastic beam structure is formed by connecting eight symmetric L-shaped beams together; and the other end of each straight elastic beam connected with the frame beams is connected to the middle or a vertex angle at the top end and the bottom end of the lateral face of the center mass block, and the other end of each L-shaped beam connected with the frame beams is connected to the inner side face of the external support frame. The acceleration sensor adopts the combined elastic beam structure which is formed by connecting the symmetric straight beams, the frame beams and the L-shaped beams together, has high symmetry and can remarkably reduce the cross-sensitivity of the sensor; and the sensor is produced by adopting a microelectronic mechanical system technology and is the capacitive micro-acceleration sensor with high sensitivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Self-stabilizing, floating microelectromechanical device
InactiveUS7225674B2Eliminate mechanical wearMechanical parasitic effects are sharply reduced or eliminatedAcceleration measurement using interia forcesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityCommunication device
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Process for fabricating micromechanical devices
InactiveUS6300156B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDecorative surface effectsDissolutionSemiconductor
A process for fabricating a MEMS device is disclosed. The device has at least one hinged element. The MEMS device including the hinged element is delineated and defined on a semiconductor substrate. The substrate is placed device side down in a chamber. The MEMS device is then exposed to a release expedient for sufficient amount of time for the release expedient to dissolve a sacrificial material connecting the element to the substrate. Upon the dissolution of the sacrificial material, the element is released from the substrate and pivots away from the surface.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
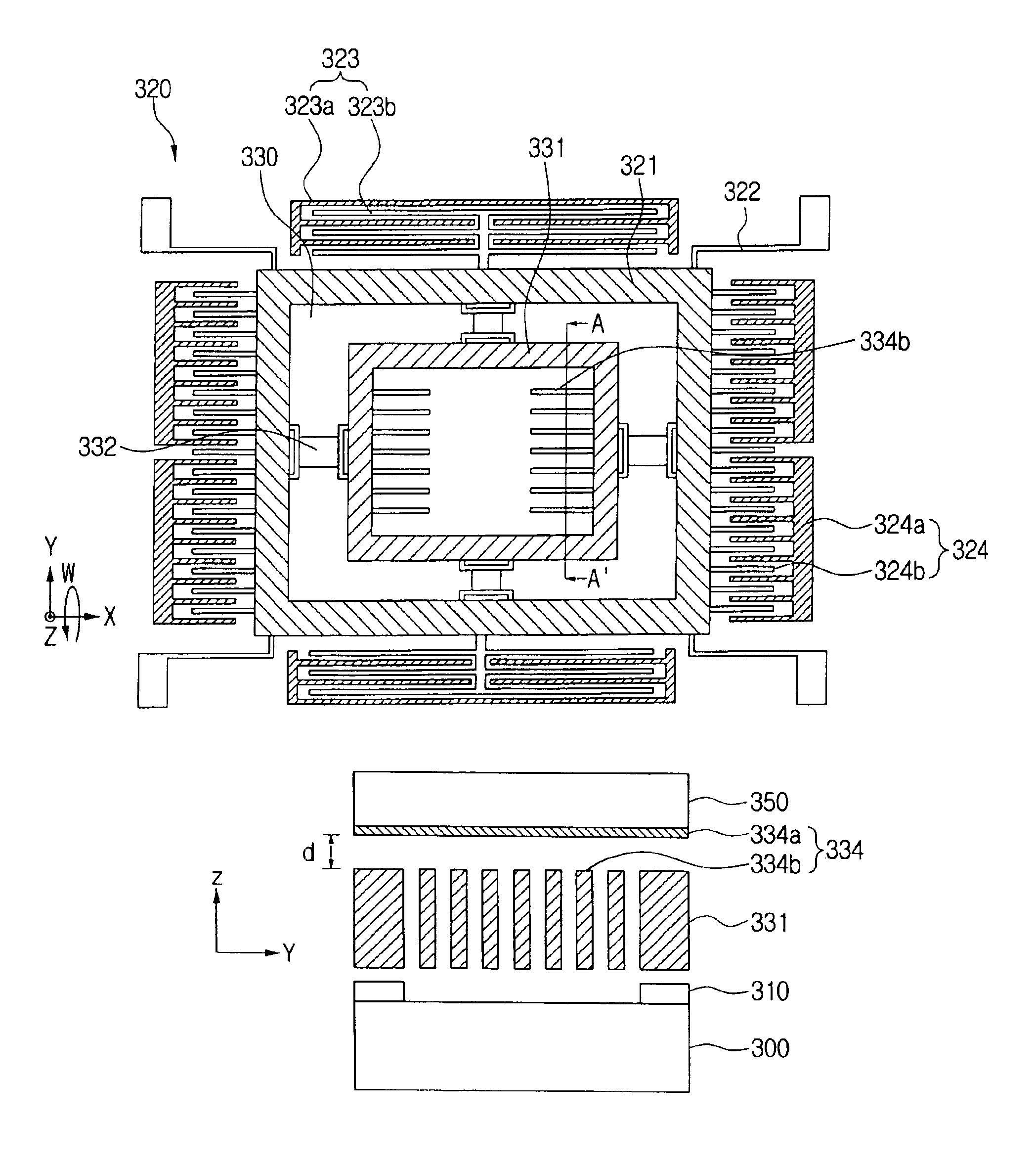
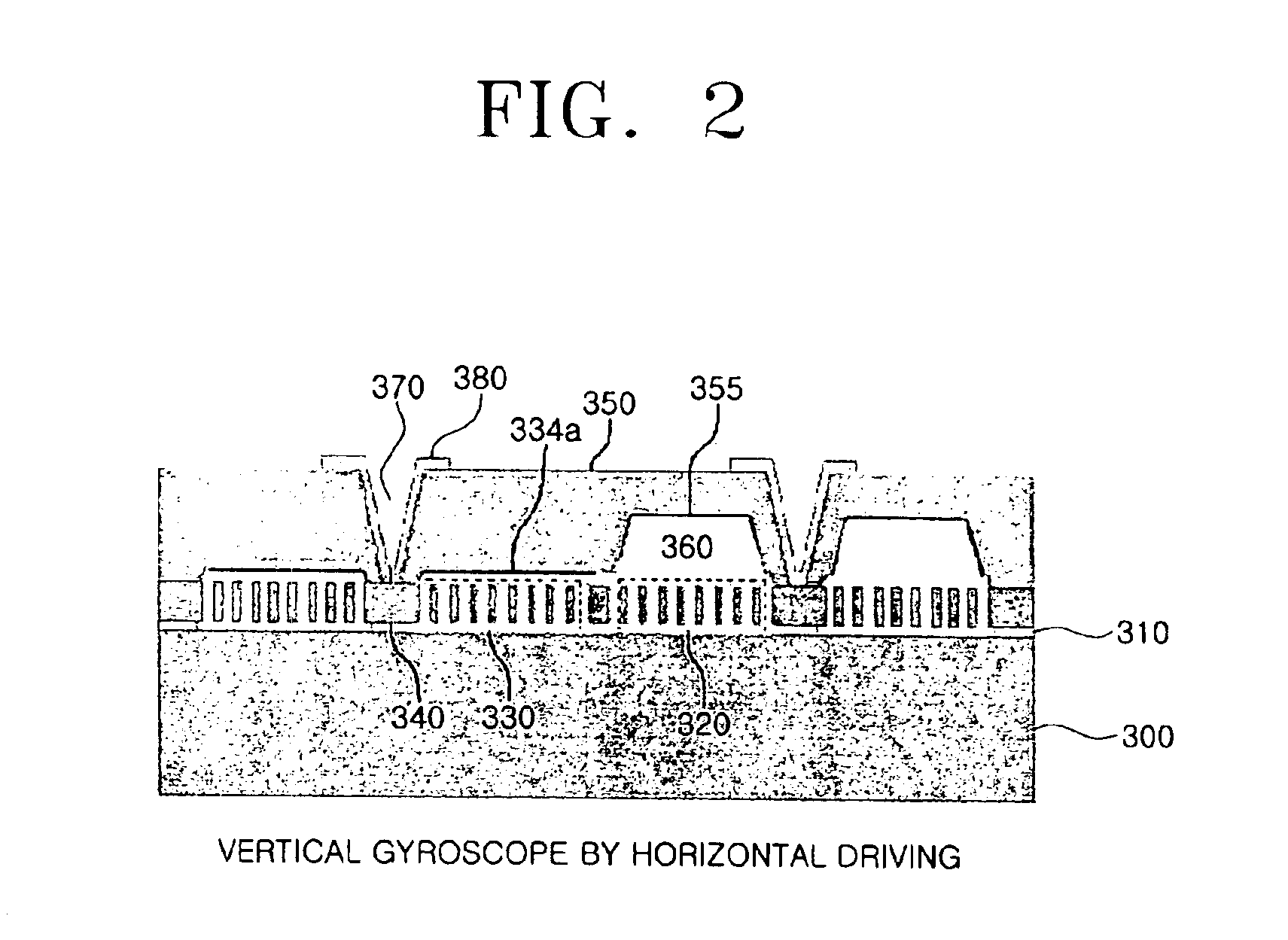
Vertical MEMS gyroscope by horizontal driving
ActiveUS6952965B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesGyroscopeEngineering
A vertical MEMS gyroscope by horizontal driving includes a substrate, a support layer fixed on an upper surface of an area of the substrate, a driving structure floating above the substrate and having a portion fixed to an upper surface of the support layer and another portion in parallel with the fixed portion, the driving structure having a predetermined area capable of vibrating in a predetermined direction parallel to the substrate, a detecting structure fixed to the driving structure on a same plane as the driving structure, and having a predetermined area capable of vibrating in a vertical direction with respect to the substrate, a cap wafer bonded with the substrate positioned above the driving structure and the detecting structure, and a fixed vertical displacement detection electrode formed at a predetermined location of an underside of the cap wafer, for detecting displacement of the detecting structure in the vertical direction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electrostatic actuator
InactiveUS20050219017A1Prolong lifePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysConductive materialsEngineering
A switch with an actuator has two supporting columns on a substrate, and a rocking plate on the supporting columns. The rocking plate is pivoted by (pivotally mounted on) the two supporting columns. The rocking plate is made of conductive material, so that it can be subjected to electrostatic force of an adsorption electrode. In the switch, it is not necessary to provide a narrow beam to support the rocking plate, because the rocking plate is pivoted by the supporting columns. Therefore, the switch is a long-life microswitch.
Owner:SHARP KK
Self-stabilizing, floating microelectromechanical device
InactiveUS20050241394A1Eliminate mechanical wearReduce parasitic effectsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityGyroscope
The present invention relates to MicroElectroMechanical Systems (MEMS), devices and applications thereof in which a proof mass is caused to levitate by electrostatic repulsion. Configurations of electrodes are described that result in self-stabilized floating of the proof mass. The electrical properties of the electrodes causing floating, such as currents and / or voltages, typically change in response to environmental perturbations affecting the proof mass. Measuring such currents and / or voltages allow immediate and accurate measurements to be performed related to those perturbations affecting the location and / or the orientation of the proof mass. Additional sensing electrodes can be included to further enhance sensing capabilities. Drive electrodes can also be included that allow forces to be applied to the charged proof mass resulting in a floating, electrically controllable MEMS device. Several applications are described including accelerometers, inertial sensors, resonators and filters for communication devices, gyros, one and two axis mirrors and scanners, among other devices. Several fabrication methods are also described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
MEMS having a three-wafer structure
InactiveUS6930368B2Television system detailsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesWaferingMicroelectromechanical systems
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Miniature manipulate with piezoelectric-type flexible drive and adjustable range
InactiveCN1376631AReduce nonlinear errorHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsMicromanipulatorSpatial structureMicro robotics
A piezoelectric clamping micromanipulator with flexible drive and amplification and adjustable range is composed of microactuator, flexible multiplying mechanism, size pre-regulator, and clamping micromanipulator. Its advantages are compact structure, high reliability, and low non-linear error.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Artificial hollow micro-nano motor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102556935AGood load functionImprove transportation effectPrecision positioning equipmentPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCationic polyelectrolytesEngineering
The invention provides an artificial hollow micro-nano motor and a preparation method thereof, relating to artificial motors and preparation methods thereof and solving the problem that the existing solid spherical motor, tubular motor and linear motor are poor in loading performance. The artificial hollow micro-nano motor is made from a polyelectrolyte double-layer skeleton and a catalyst or is made from a cationic polyelectrolyte skeleton and the catalyst; and the preparation method of the artificial hollow micro-nano motor comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing micro-nano catalyst particles; (2) synthesizing a core substrate; (3) synthesizing an artificial hollow micro-nano motor skeleton; and (4) removing the core substrate by using a template solvent so as to obtain the artificial hollow micro-nano motor. The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity and feasibility, stable process, good repeatability and convenience in mass production, and the prepared artificial hollow micro-nano motor is good in transportability and loading function, has a wide application prospect in a plurality of aspects, such as drug release control, blood purification, clinical diagnosis, and is simple in operation. The artificial hollow micro-nano motor prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention is applicable to the medical field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
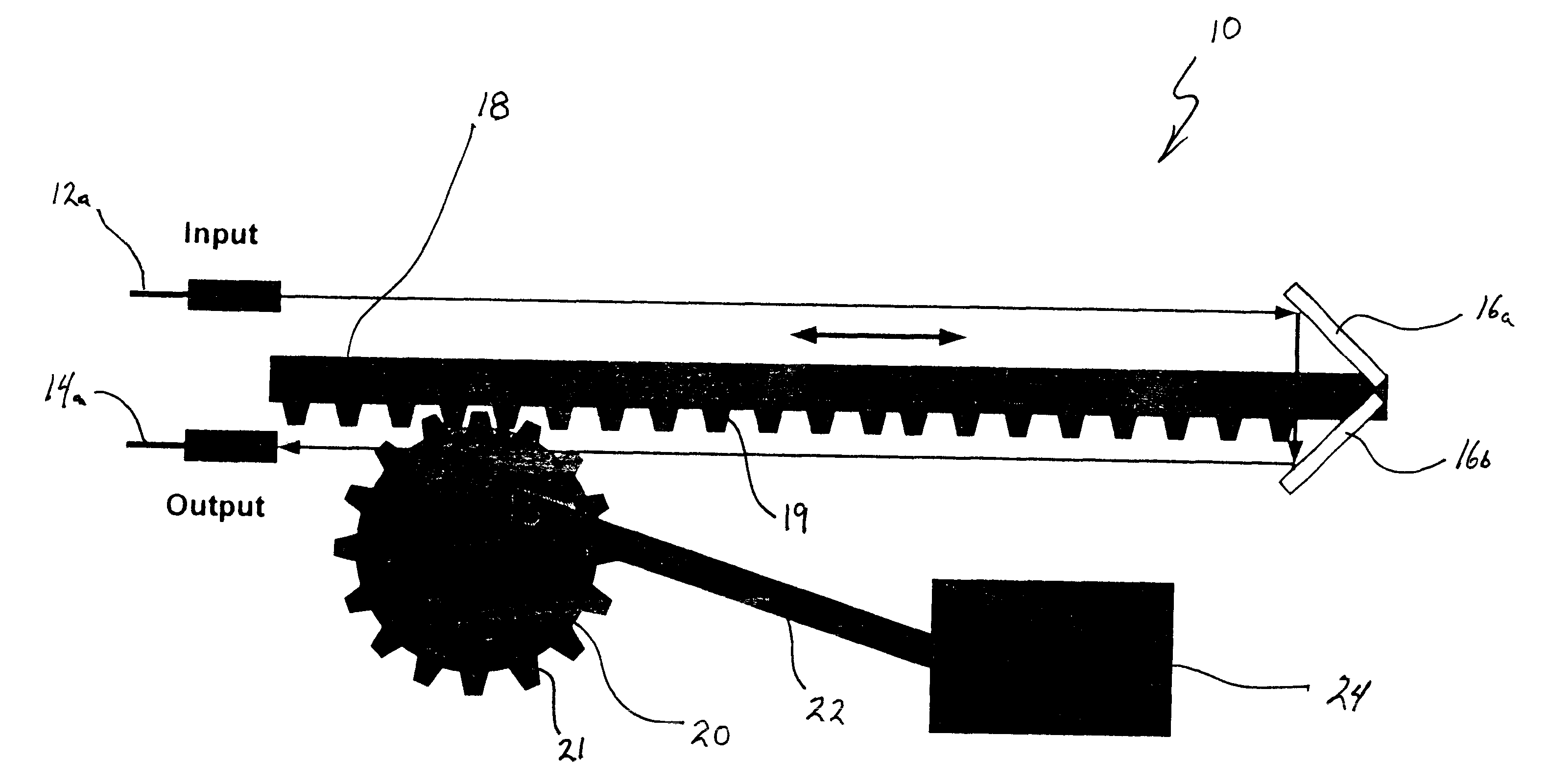
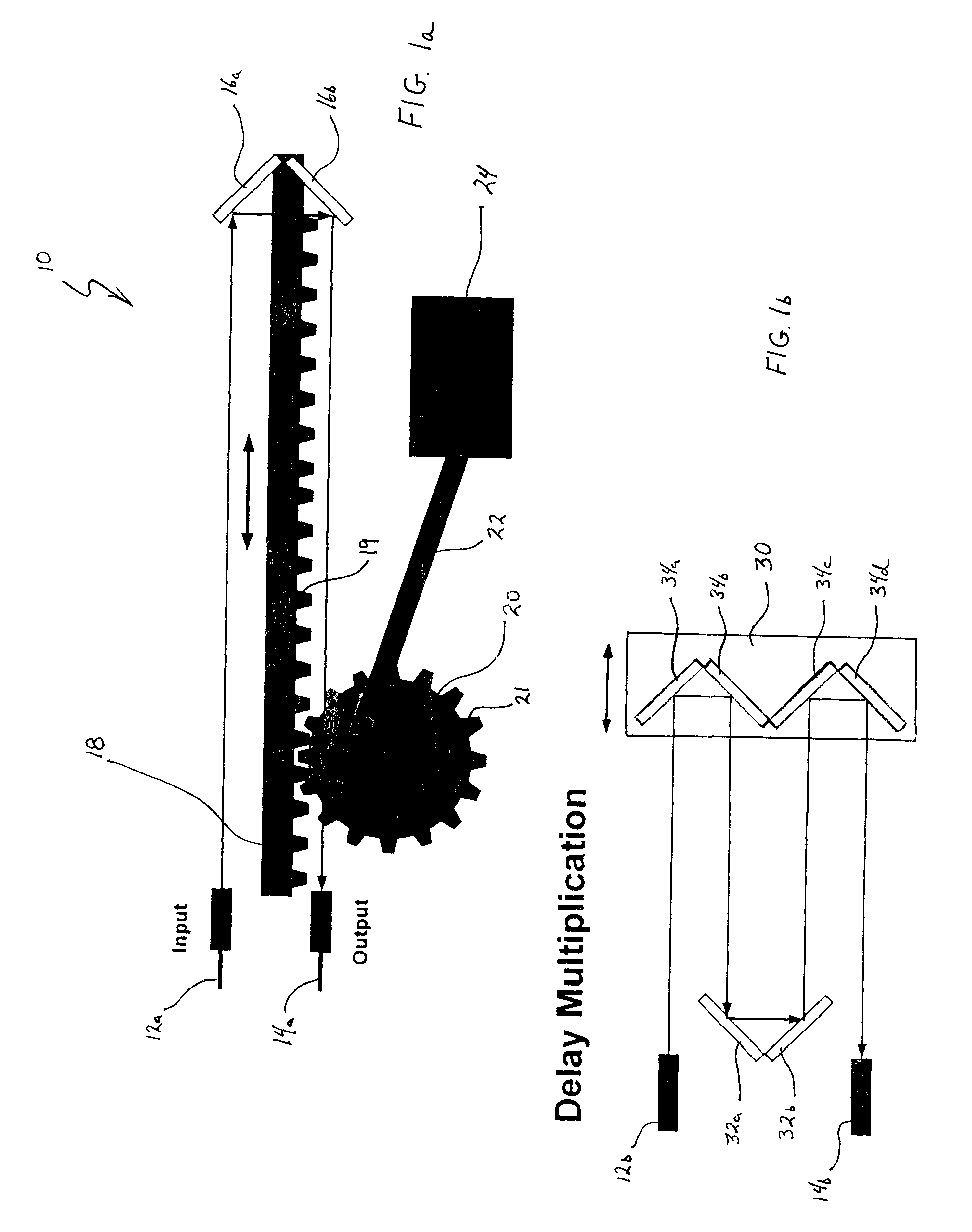
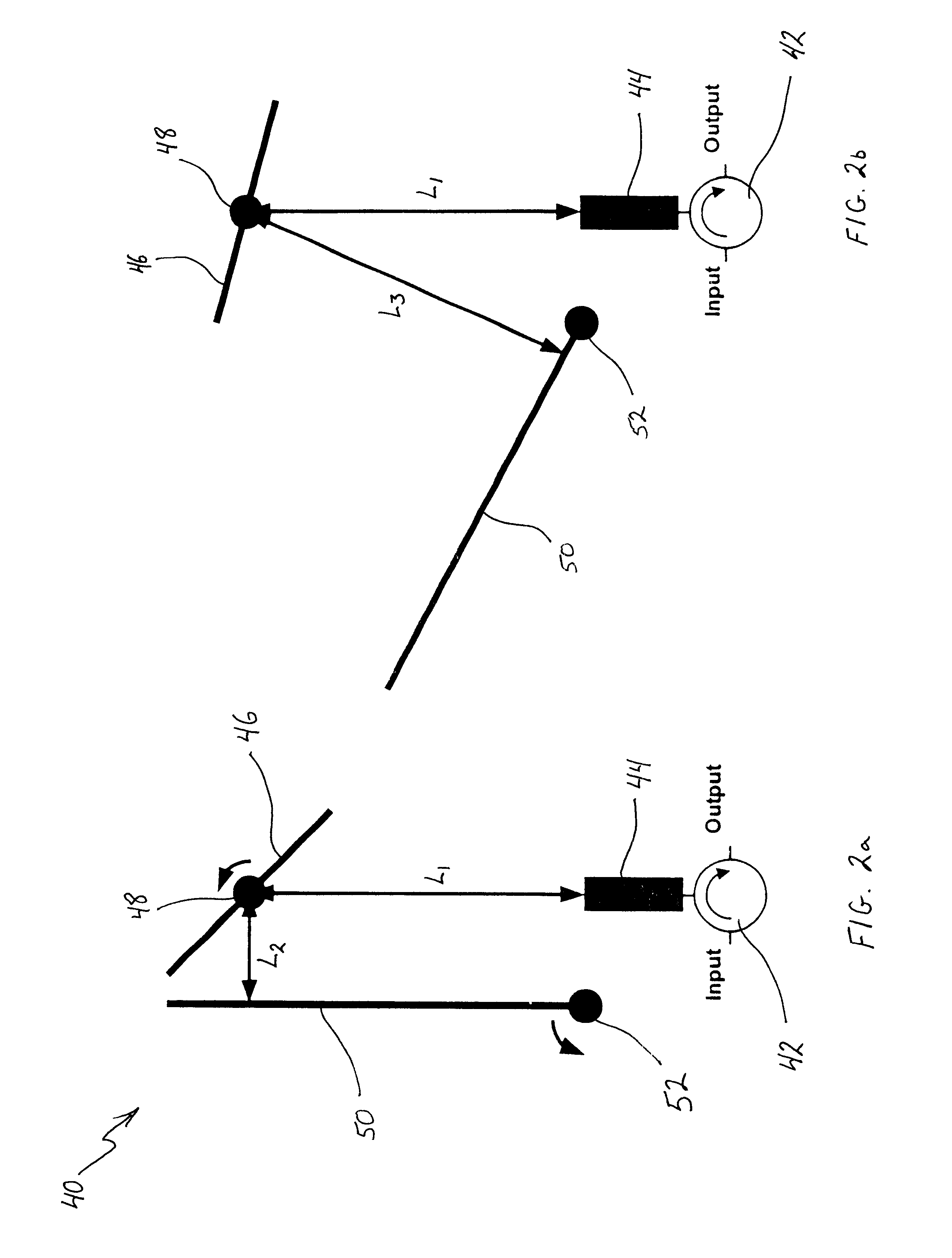
Mems variable optical delay lines
InactiveUS6356377B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSnap-action arrangementsEngineeringOptical delay line
A variable optical delay line using MEMS devices. A reflector on a micro machine linear rack is positioned and spaced from an input source and / or an output to receive and reflect input light waves toward the output. The distance between the reflector and the input and output is variable and thereby enables selective path delay compensation of the input light wave signals. Other disclosed embodiments utilize pivoting MEMS mirrors and selective adjustment of the mirror pivot angles to provide the selective path delay compensation required in a light wave system.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
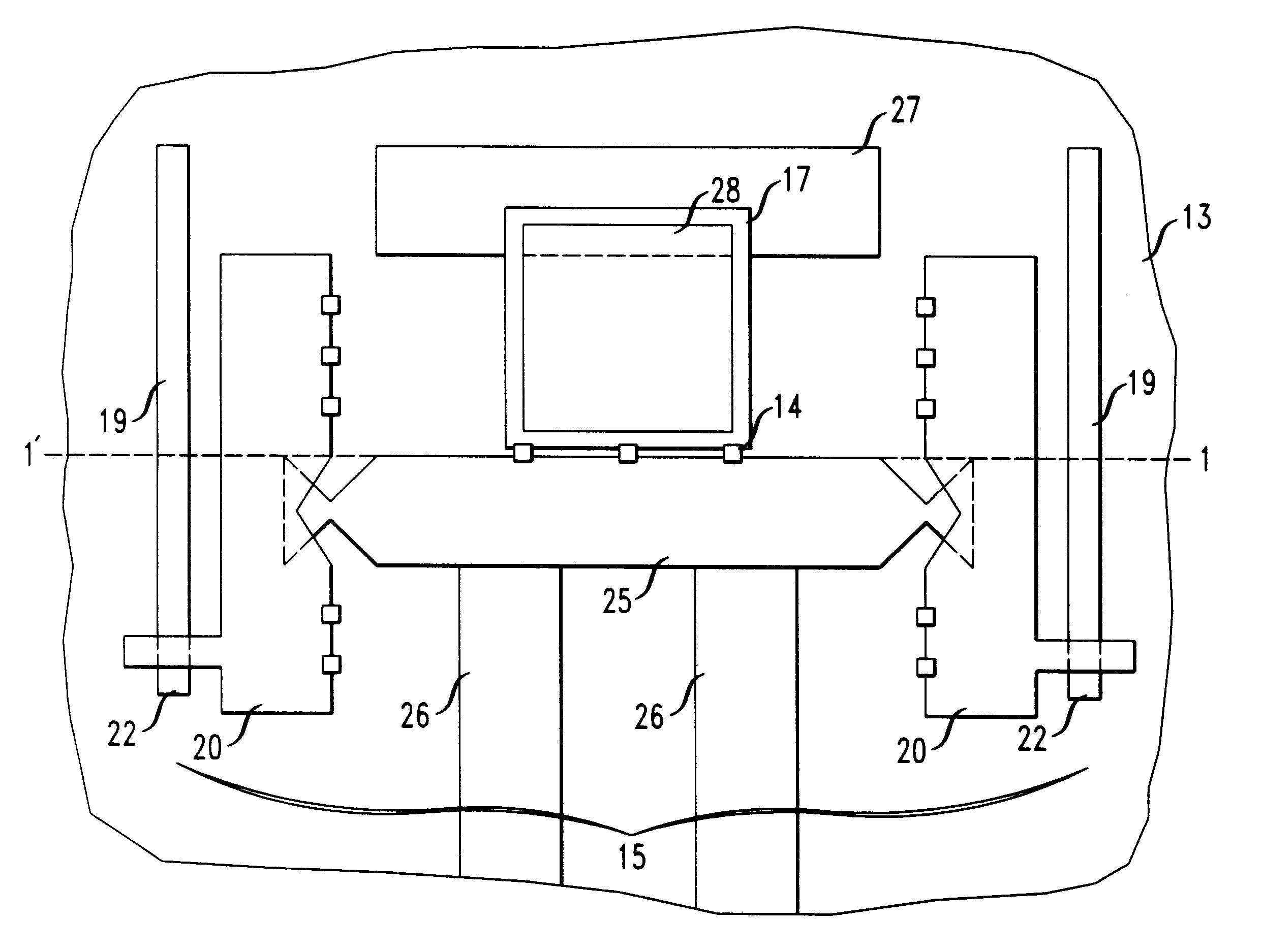
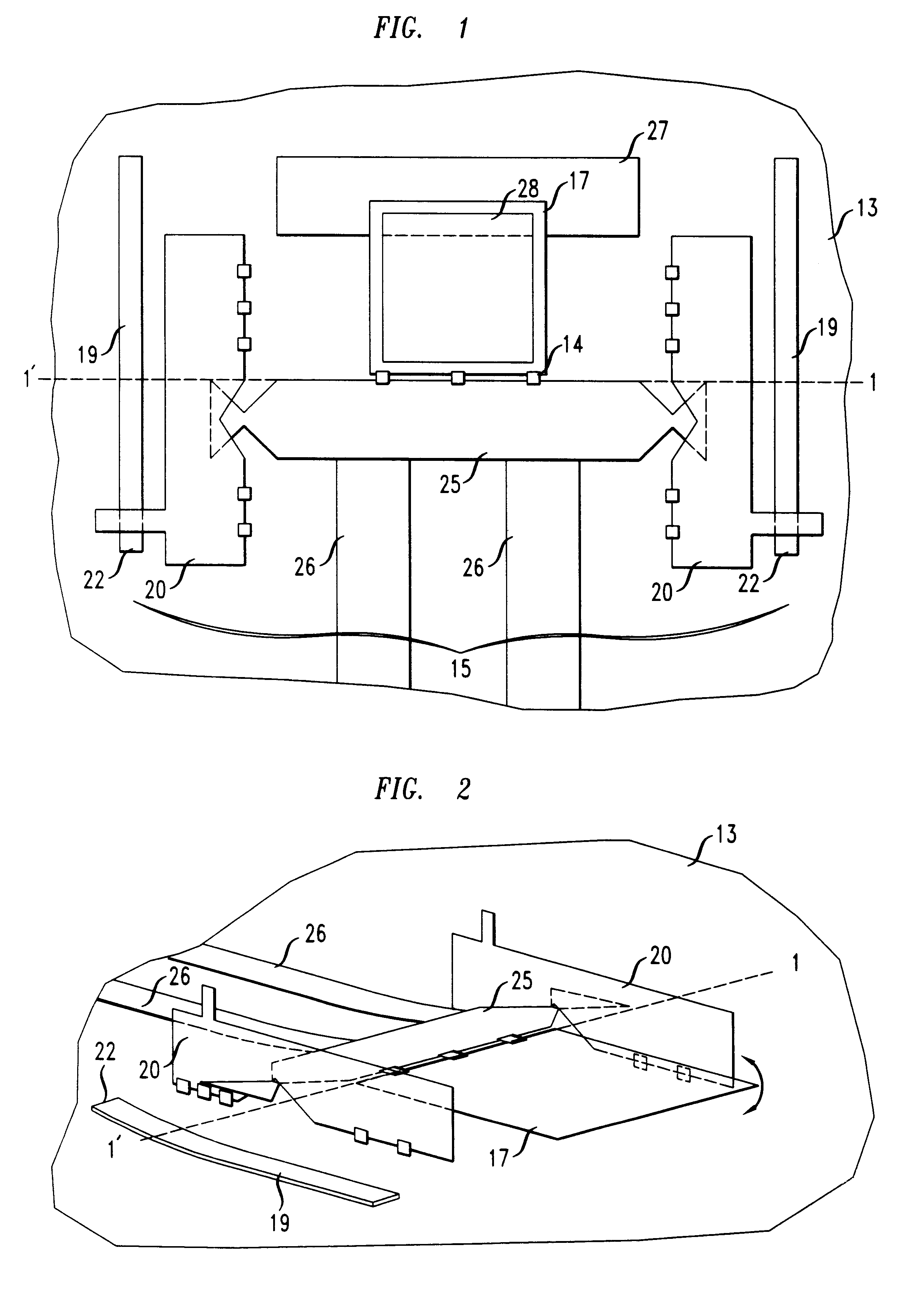
Multi-stable micro electromechanical switches and methods of fabricating same
InactiveUS7190245B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysMedical deviceMedical treatment
A micro electromechanical (MEMS) switch suitable for use in medical devices is provided, along with methods of producing and using MEMS switches. In one aspect, a micro electromechanical switch including a moveable member configured to electrically cooperate with a receiving terminal is formed on a substrate. The moveable member and the receiving terminal each include an insulating layer proximate to the substrate and a conducting layer proximate to the insulating layer opposite the substrate. In various embodiments, the conducting layers of the moveable member and / or receiving terminal include a protruding region that extends outward from the substrate to switchably couple the conducting layers of the moveable member and the receiving terminal to thereby form a switch. The switch may be actuated using, for example, electrostatic energy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Micro-oscillating element provided with torsion bar
InactiveUS7031041B2Reduce the possibilityLarge twisting anglePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSnap-action arrangementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
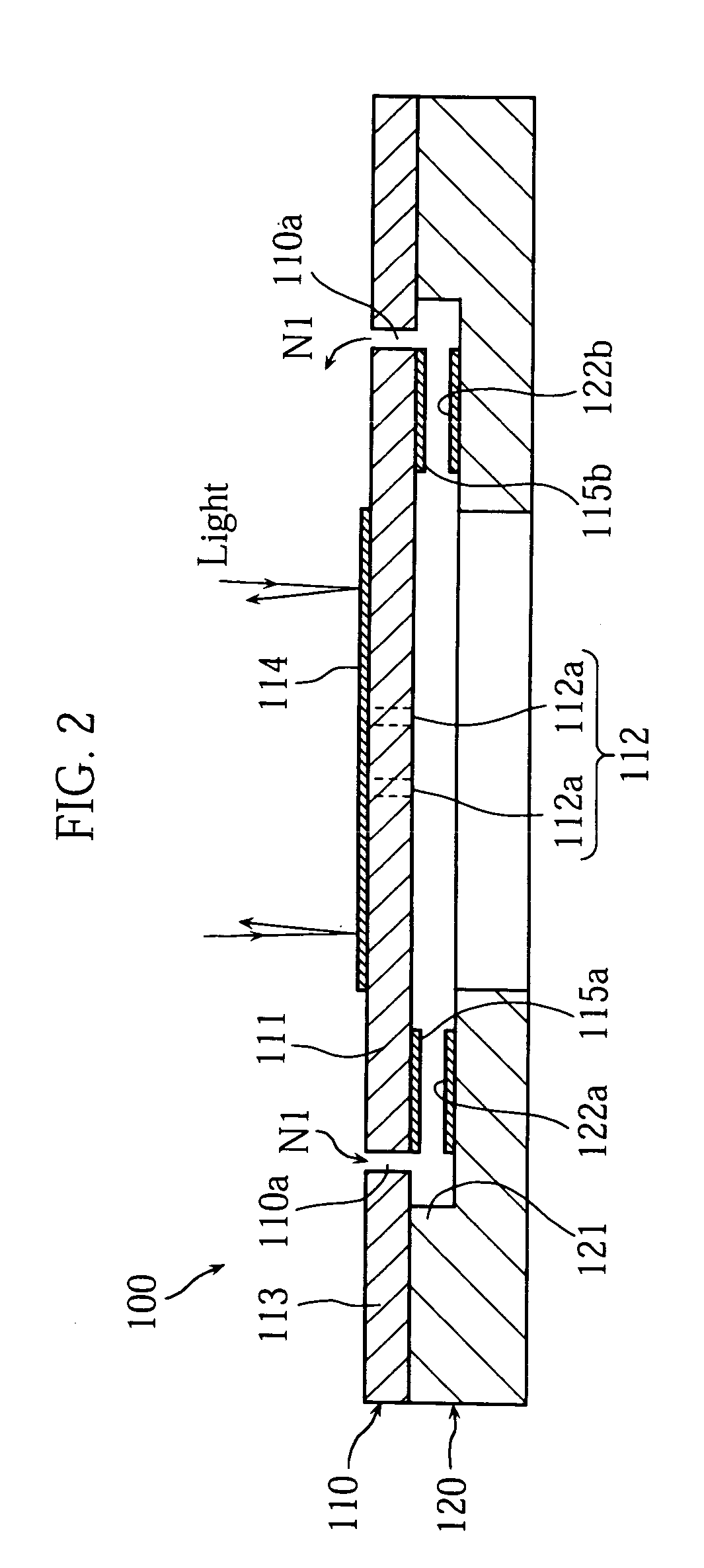
Fabrication of a reflective spatial light modulator
InactiveUS7022245B2Improve fill rateSoldering apparatusSnap-action arrangementsSpatial light modulatorSingle crystal
Fabrication of a reflective spatial light modulator including a micro-mirror array. In one embodiment, the micro mirror array is fabricated from a substrate that is a single crystal material by only two main etching steps. A first etch forms cavities in a first side of the material. A second etch forms support posts, a vertical hinge, and a mirror plate. Between the first and second etches, the substrate can be bonded to addressing and control circuitry.
Owner:MIRADIA INC
Flexible microgripper through topological optimization
InactiveCN101717063ALarge output displacementNovel structure typeMicromanipulatorPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesShaped beamMicro-operation
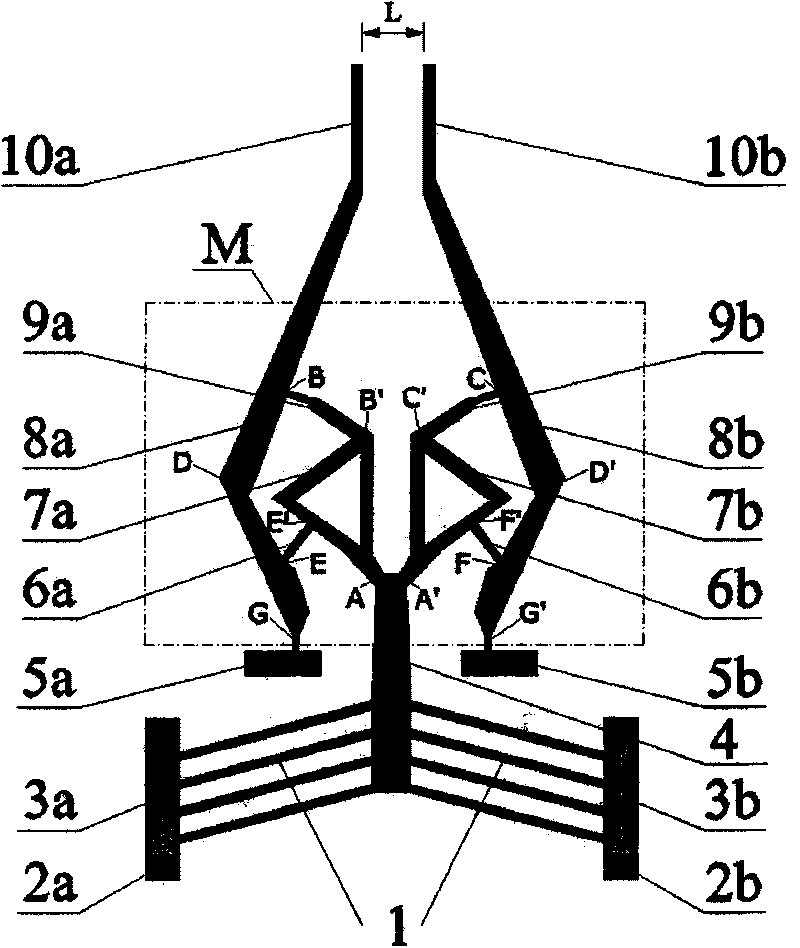
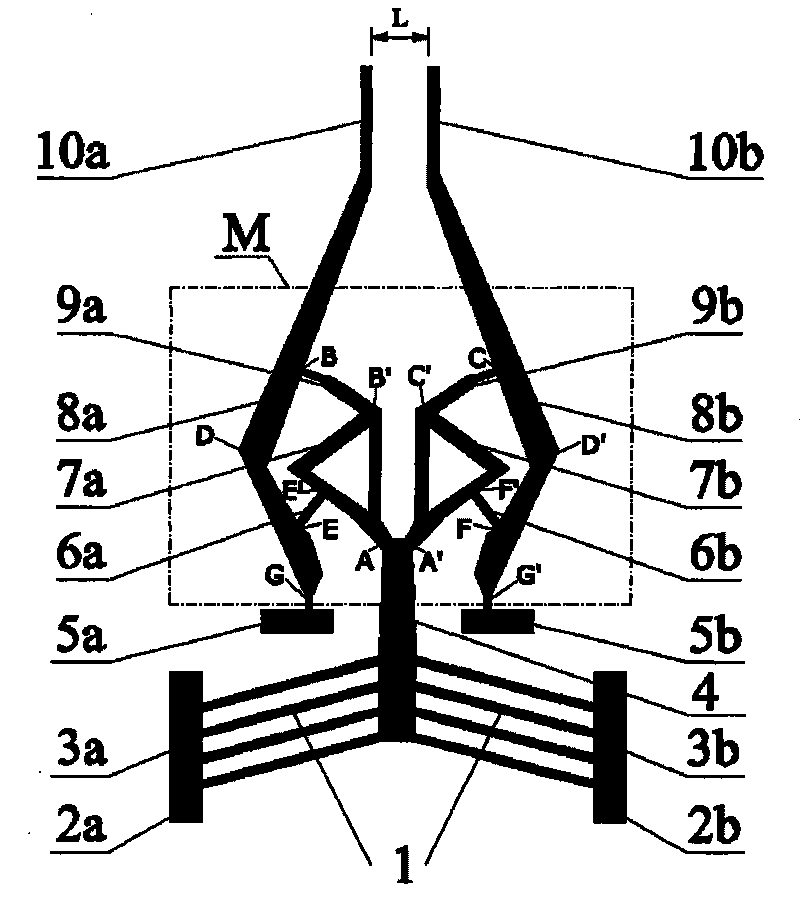
The invention relates to a flexible microgripper through topological optimization, which belongs to a microactuators in the technical field of the micro electro mechanical systems and is a flexible electrothermally driven microgripper. The flexible microgripper consists of a shift amplifying section and a driving section and is an integral structure with the eudipleural gripper body. The shift amplifying section M is designed by using the topological optimization method and comprises left and right triangular components and a flexible rod, wherein the left and right triangular components randomly hollow triangle structures. The driving section comprises a V-shaped beam array, left and right driving fixed rods and left and right electrodes. The microgripper has the advantages of unique and novel structure, large output shift, rapid response, simple control, convenient integration and is effective and energy-saving without applying drive in the process of gripping objects, thereby the microgripper is quite suitable for gripping minute objects for micro-assembly, micro-operation and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Device and method for pumping fluids employing the movement of gas bubbles in microscale
InactiveUS20050129529A1Eliminating solid frictionEliminate heat lossTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesLiquid temperatureLight beam
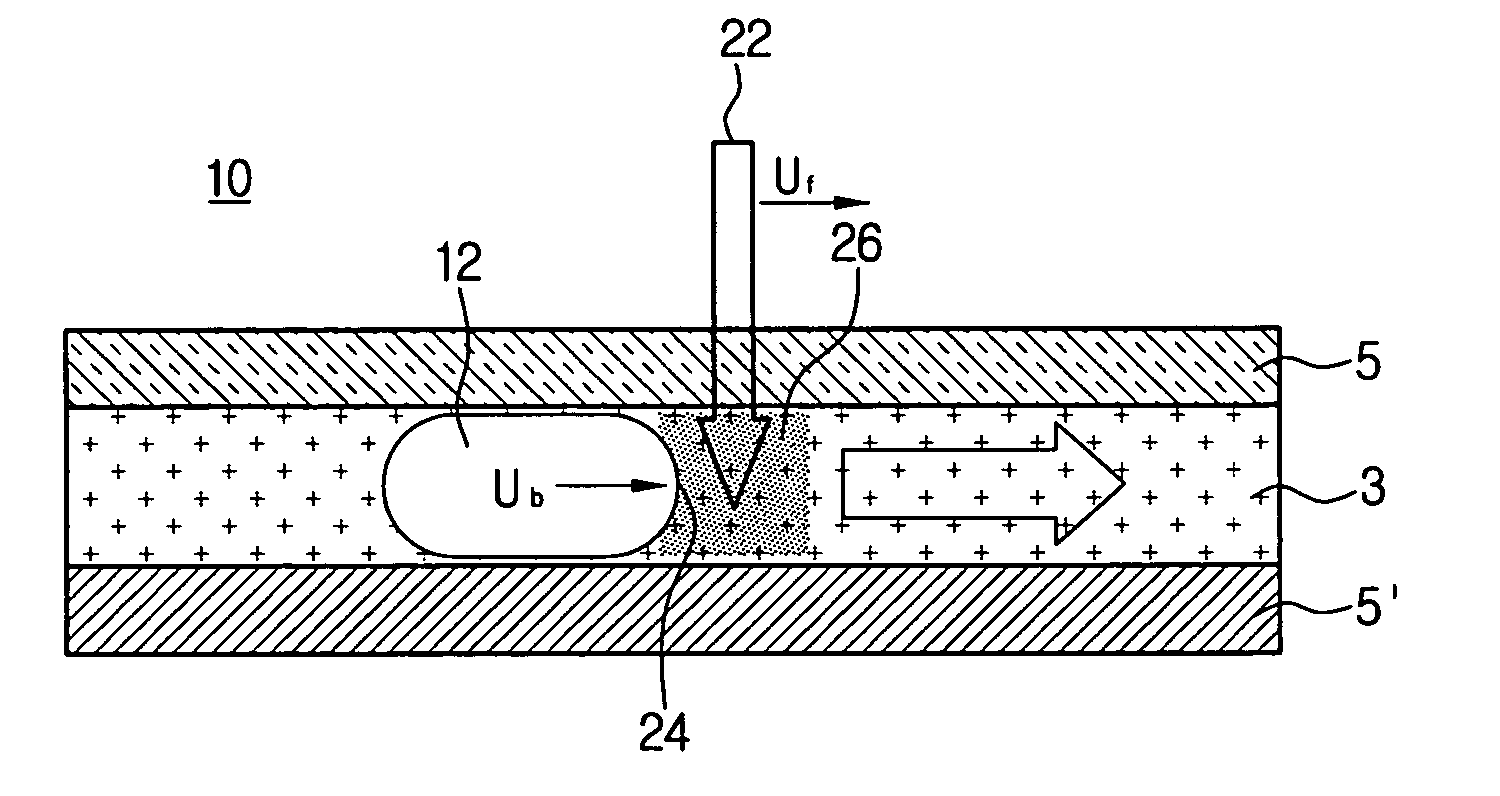
The present fluid pumping method for micro-fluidic devices uses gas bubbles to move fluid by light beams. The light beams are emitted to the fluid near the gas bubble through an optically transparent cover and correspondingly heat the fluid in the micro channels. The liquid temperature variation changes the surface tension of the gas bubble near the heated fluid side, therefore, a pressure gradient between the end portions of the gas bubble generates accordingly. By moving the light beams, the moved pressure difference will be achieved, which will drive the gas bubbles and pump the fluid. Such a fluid pumping can simplify the structure of a micro-fluidic device and eliminate heat loss because of using a controllable light beam.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Micro-electro-mechanical optical device
InactiveUS6392221B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSolid-state devicesElectricityOptoelectronics
A micro-electro-mechanical optical device is disclosed. The micro-electro-mechanical optical device includes a micro-electro-mechanical structure coupled with an optical device. Both the micro-electro-mechanical structure and the optical device are disposed on a substrate surface. The micro-electro-mechanical structure lifts the optical device a predetermined distance above the plane of the substrate surface. Thereafter, the lifted optical device is moveable relative to the plane of the substrate surface in response to an electrostatic field generated between the optical device and the substrate.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
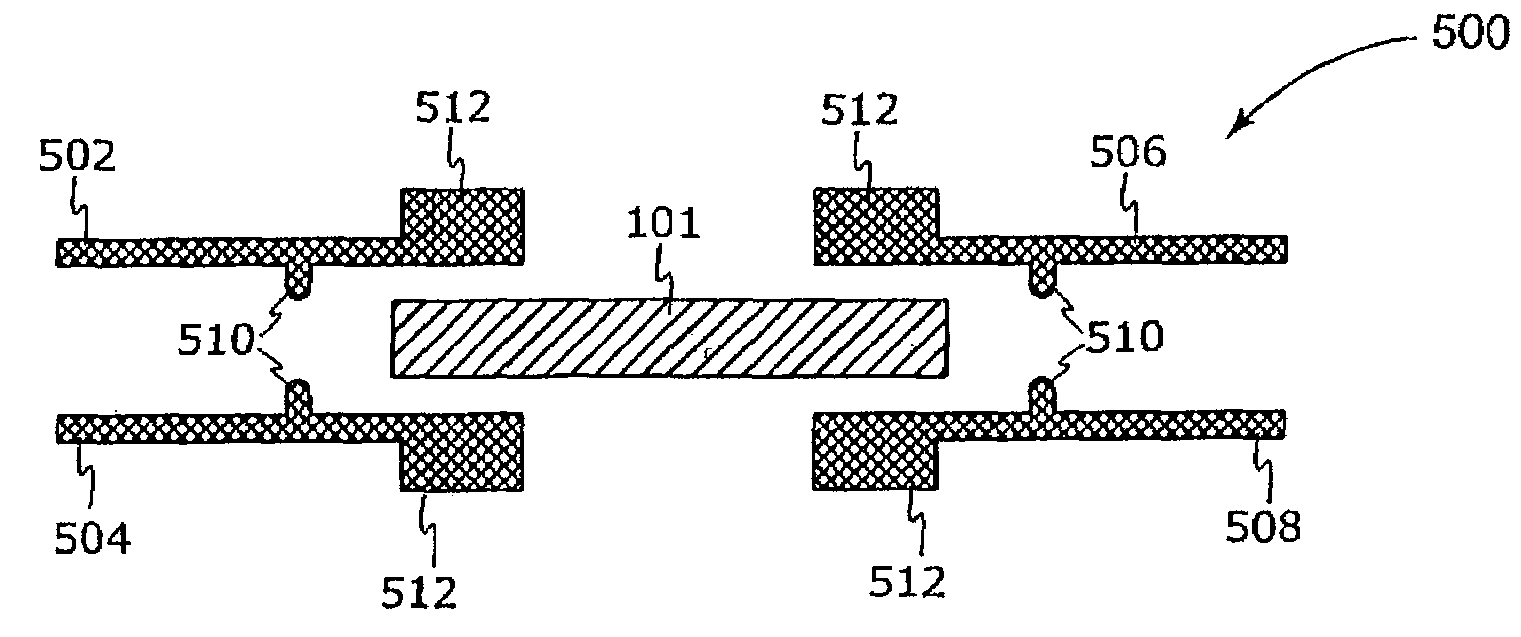
Microstructure, semiconductor device, and manufacturing method of the microstructure
InactiveCN101033057AAvoid badImprove yieldPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor deviceMicrostructure
A microstructure includes a first structural layer and a second structural layer which faces the first structural layer with a space interposed therebetween and is partially fixed to the first structural layer. At least one of the first structural layer and the second structural layer can be displaced. Further, opposed surfaces of the first structural layer and the second structural layer are different in roughness.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Nanostructured liquid bearing
InactiveUS20050211505A1Reduce frictionSmall high angular velocityRotary combination bearingsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesGyroscopeEngineering
A liquid bearing is disclosed wherein a droplet of liquid separates a first surface having a plurality of nanostructures from a second surface which may or may not be nanostructured. In one embodiment, the liquid droplet is in contact with the nanostructures on the first surface and the second surface in a way such that friction is reduced between the first and second surfaces as one or both surfaces move laterally or rotationally. In one illustrative embodiment, the first surface of the bearing is a surface of a housing in a gyroscope and the second surface is a nanostructured surface of a mass adapted to rotate within the housing. Thus situated, the rotating mass moves with very low friction thereby permitting, for example, the manufacture of very small, highly precise gyroscopes.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Light modulator and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6891654B2Low costPrecision positioning equipmentPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesBiomedical engineeringElectric potential
A method of manufacturing a light modulator in which micromirrors are tilted by an electrostatic force generated by an electrical potential difference between drive electrodes and the micromirrors. The method includes integrally forming support sections disposed at fulcrum points for tilting the micromirrors and axis portions forming axes for tilting the micromirrors.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Micro-electro-mechanical optical device
InactiveUS6265239B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSolid-state devicesElectricity
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
MEMS having a three-wafer structure
InactiveUS20050023547A1Television system detailsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesMicroelectromechanical systemsElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Bionic flexible force sensor and preparation method thereof
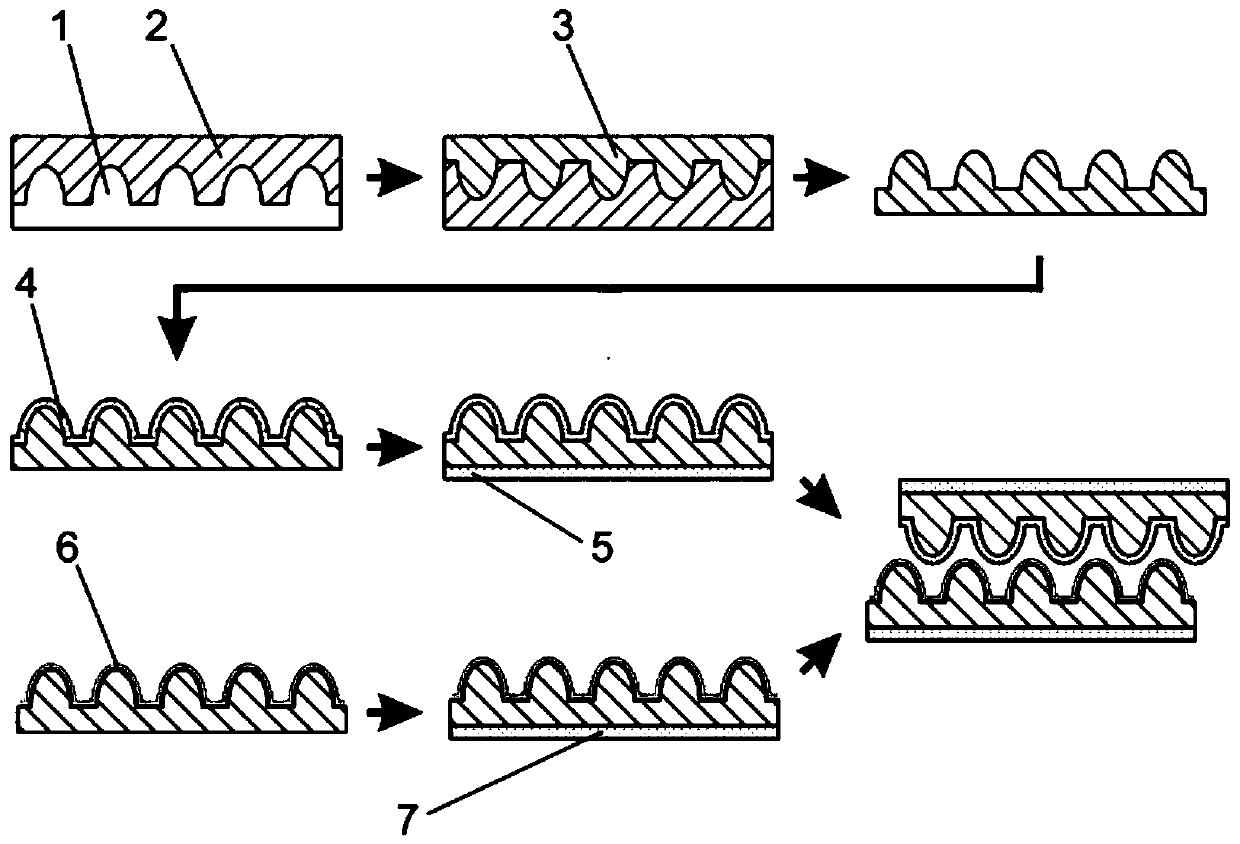
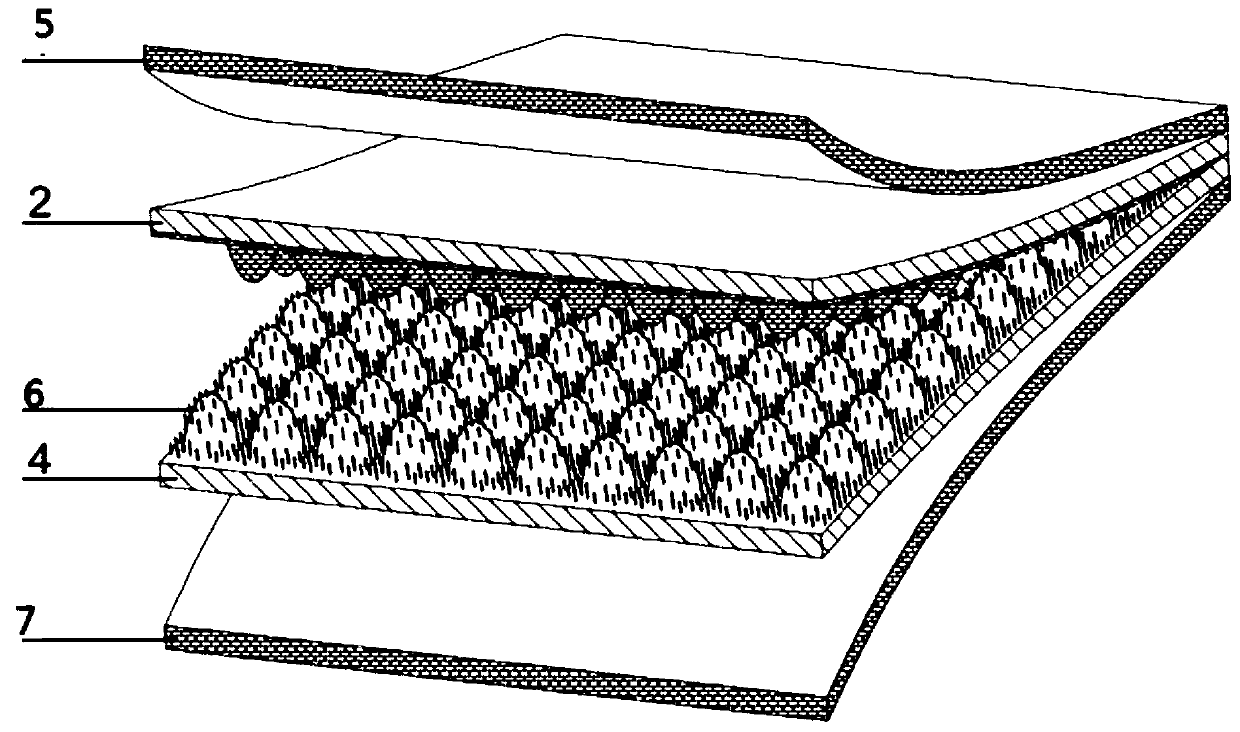
ActiveCN110329986ASimple processAvoid micro-nano fabrication processPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDecorative surface effectsMicro nanoFlexible electronics
The invention belongs to the related technical field of flexible electronics, and discloses a bionic flexible force sensor and a preparation method thereof, the method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a flexible substrate through a reverse mold technology, and forming a bionic microstructure on the surface of the flexible substrate; (2) preparing a layer of silver nanowire and a layerof micro hair on the bionic microstructures of the two flexible substrates respectively, and preparing a shielding layer and a negative friction layer back electrode on the surfaces, opposite to the surface where the bionic microjunctions are located, of the two corresponding flexible substrates respectively, so as to obtain a positive friction layer and a negative friction layer; and (3) packaging the positive friction layer and the negative friction layer to form a flexible force sensor, wherein the bionic microstructure of the positive friction layer and the bionic microstructure of the negative friction layer are interlocked to form interlocking. According to the invention, a complex micro-nano manufacturing process is avoided, the flow is simplified, the process is simple, and the implementation is easy.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
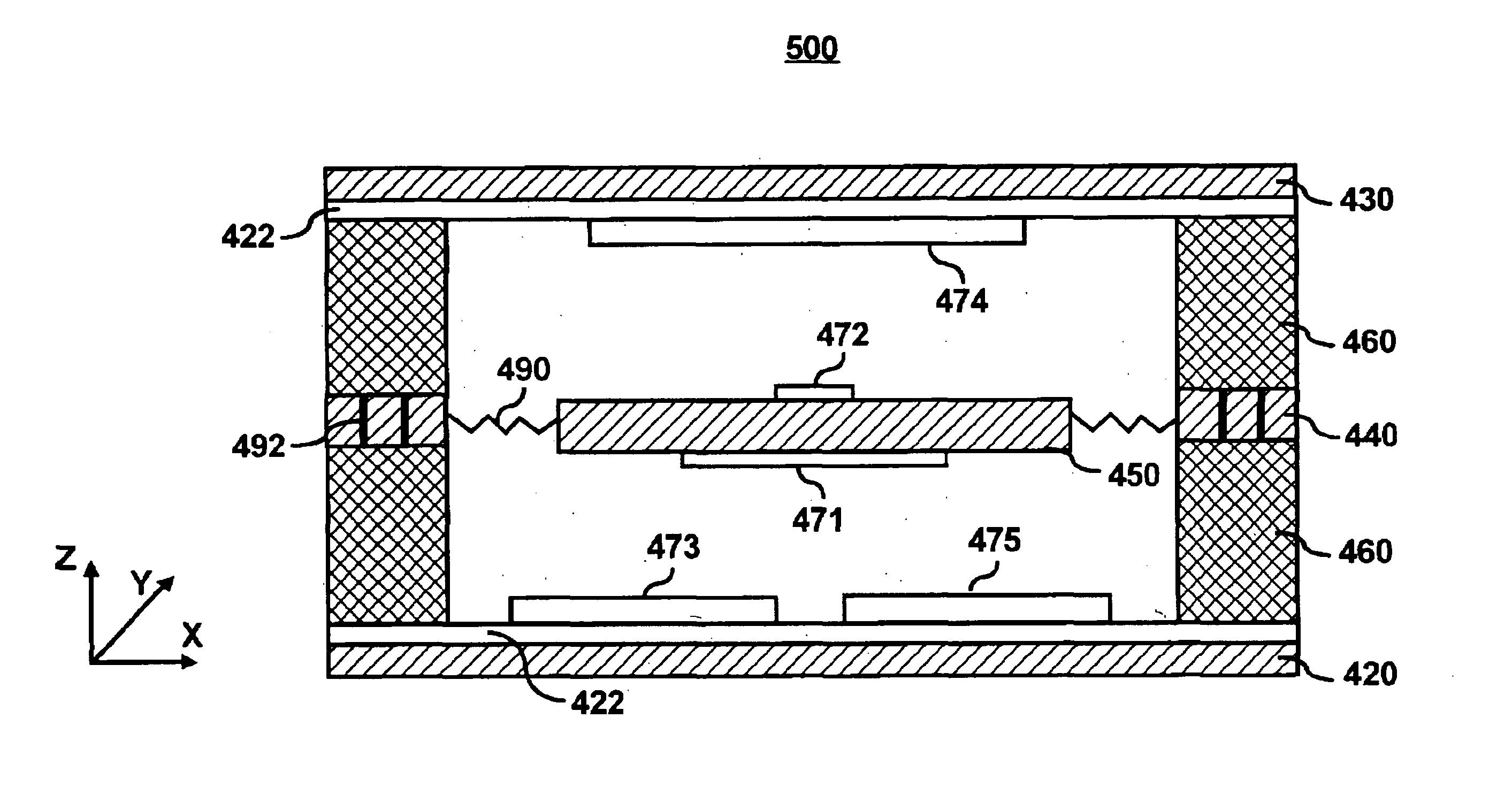
Microelectromechanical device with motion limiters
ActiveUS20150241216A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsElement spaceOut of plane motion
A microelectromechanical device that comprises a first structural layer, and a movable mass suspended to a primary out-of plane motion relative the first structural layer. A cantilever motion limiter structure is etched into the movable mass, and a first stopper element is arranged on the first structural layer, opposite to the cantilever motion limiter structure. Improved mechanical robustness is achieved with optimal use of element space.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Popular searches
Electrostatic generators/motors Electromagnetic relay details Movable microstructural devices Piezoelectric/electrostrictive devices Flexible microstructural devices Coupling light guides Microelectromechanical systems Capacitor with electrode area variation Capacitor with electrode distance variation Microstructural device manufacture
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com