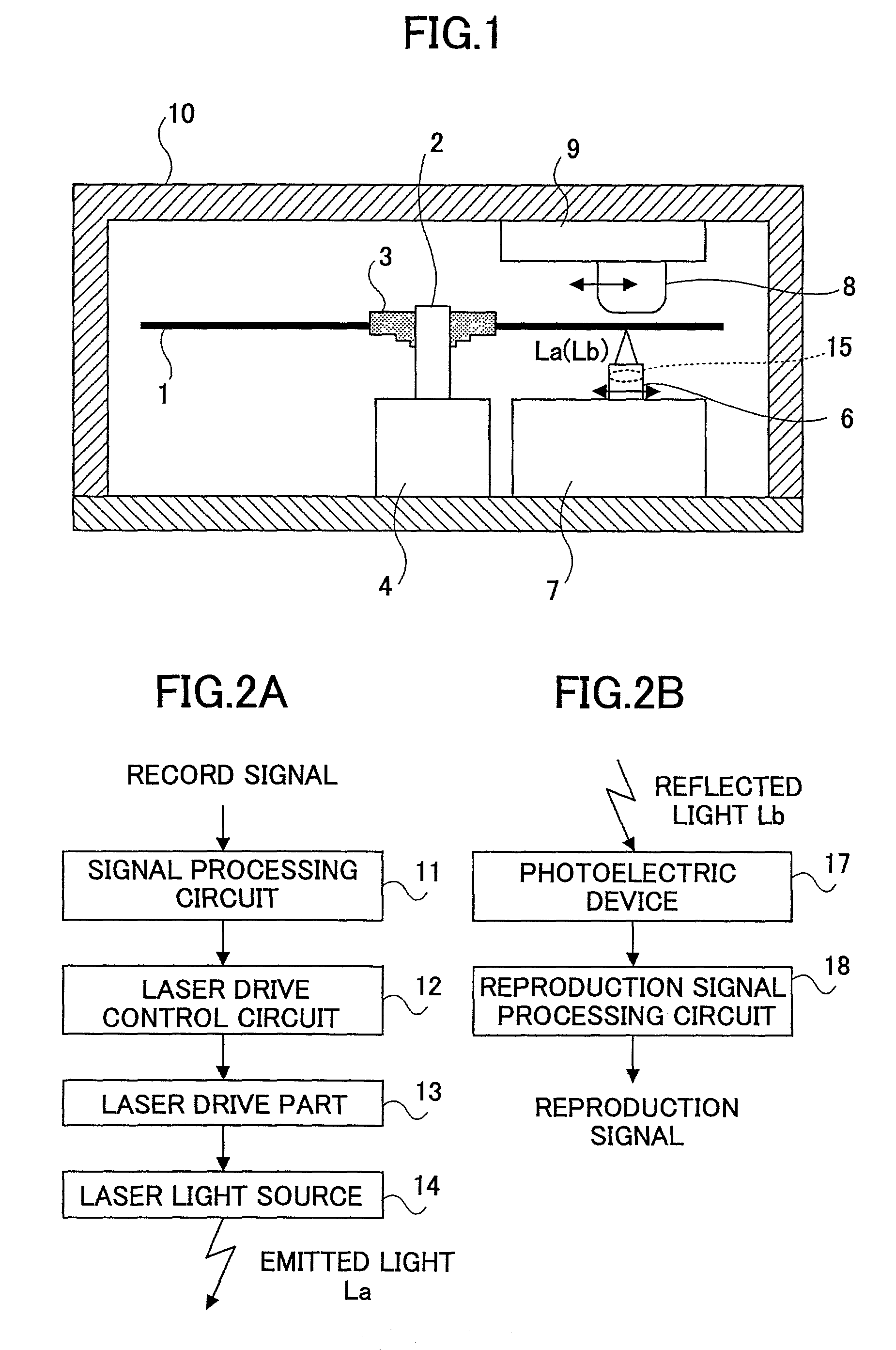
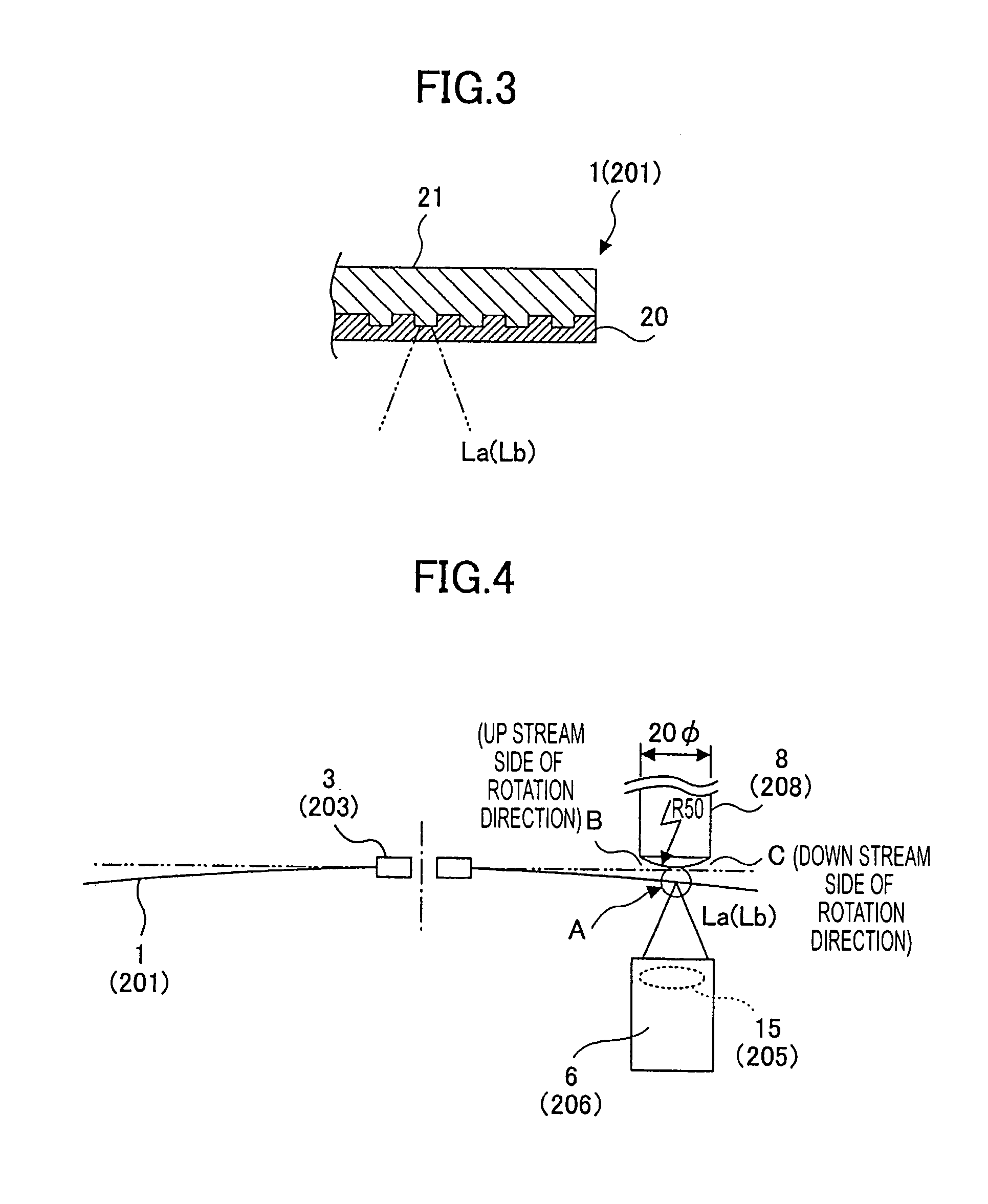
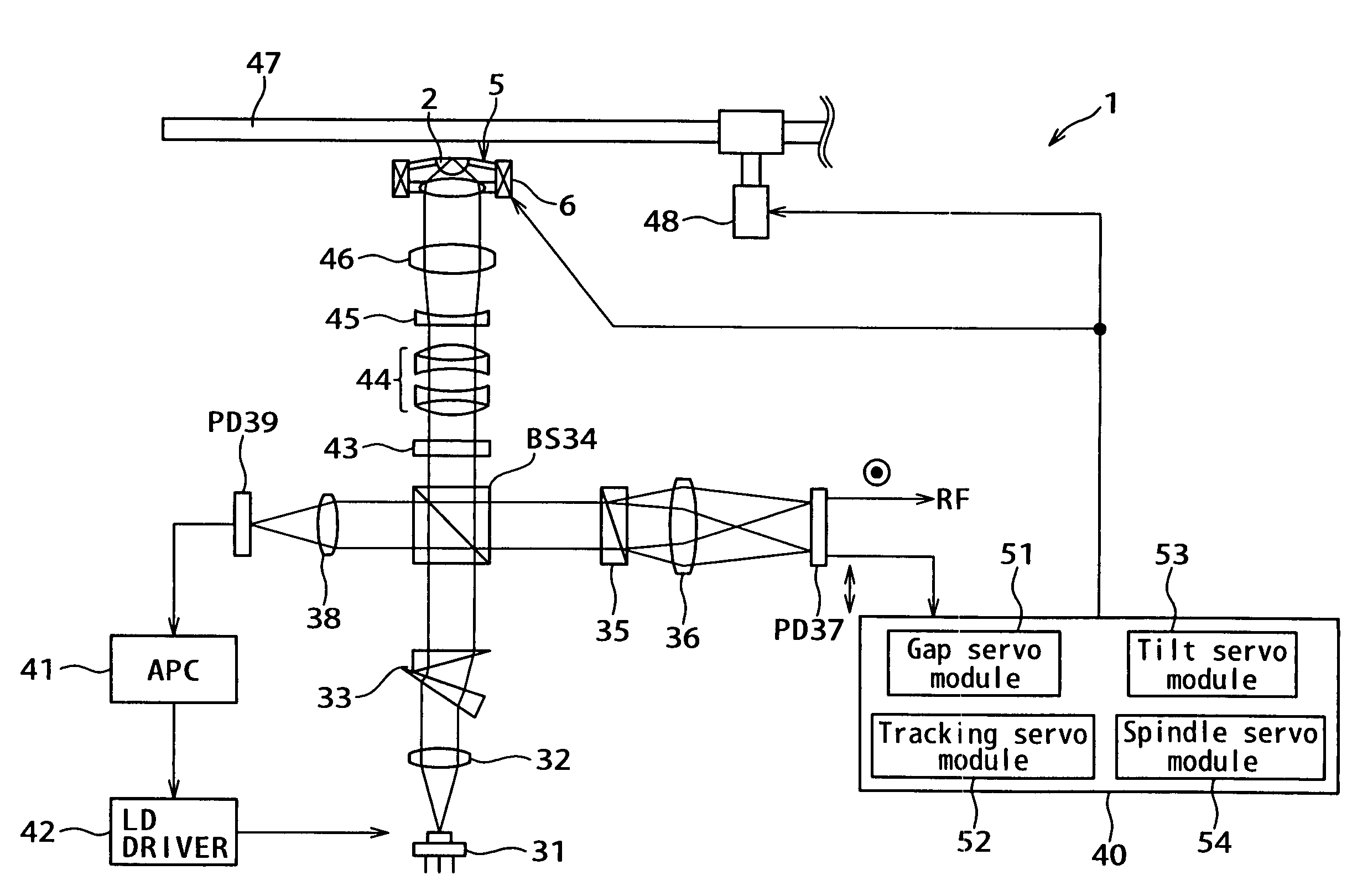
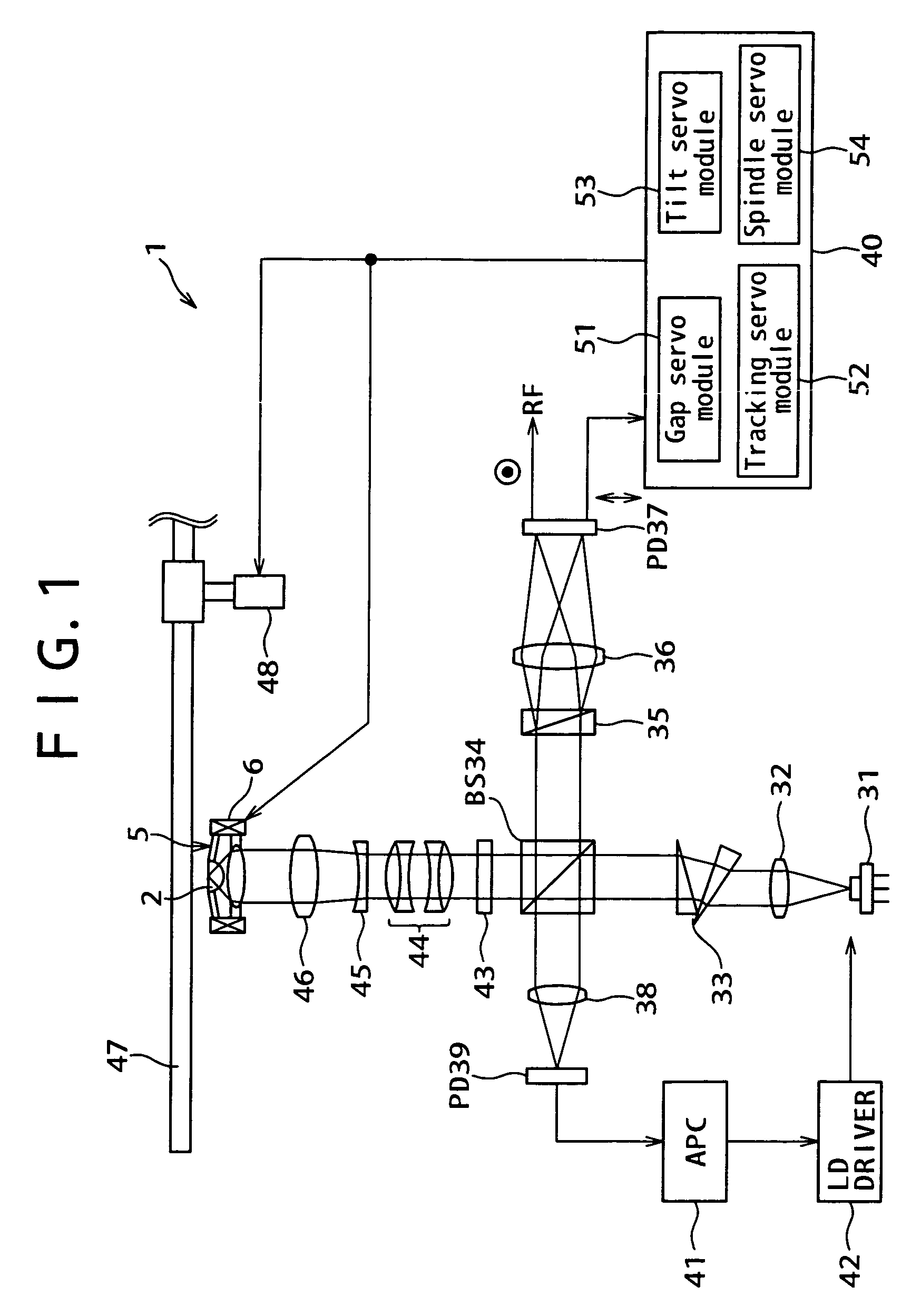
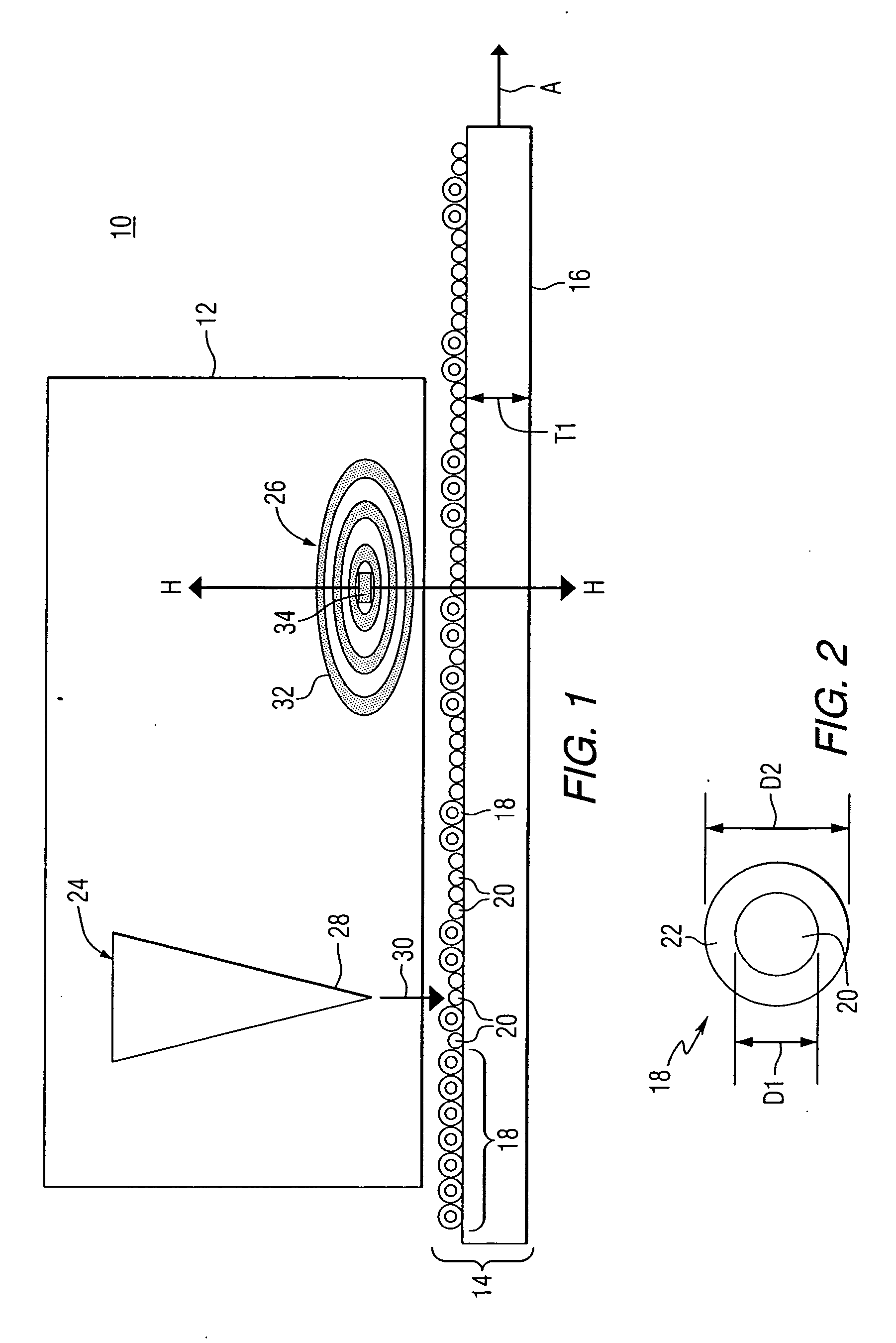
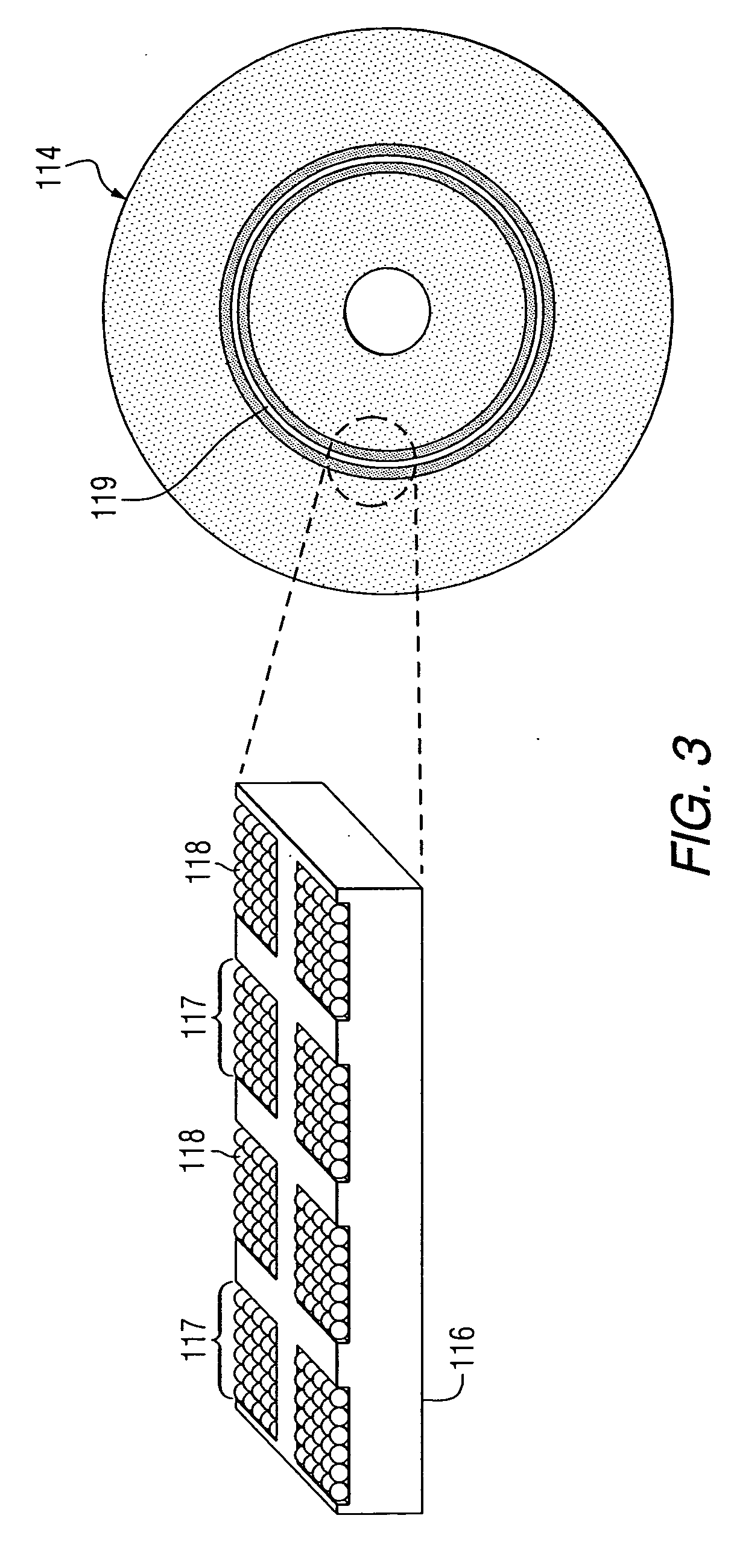
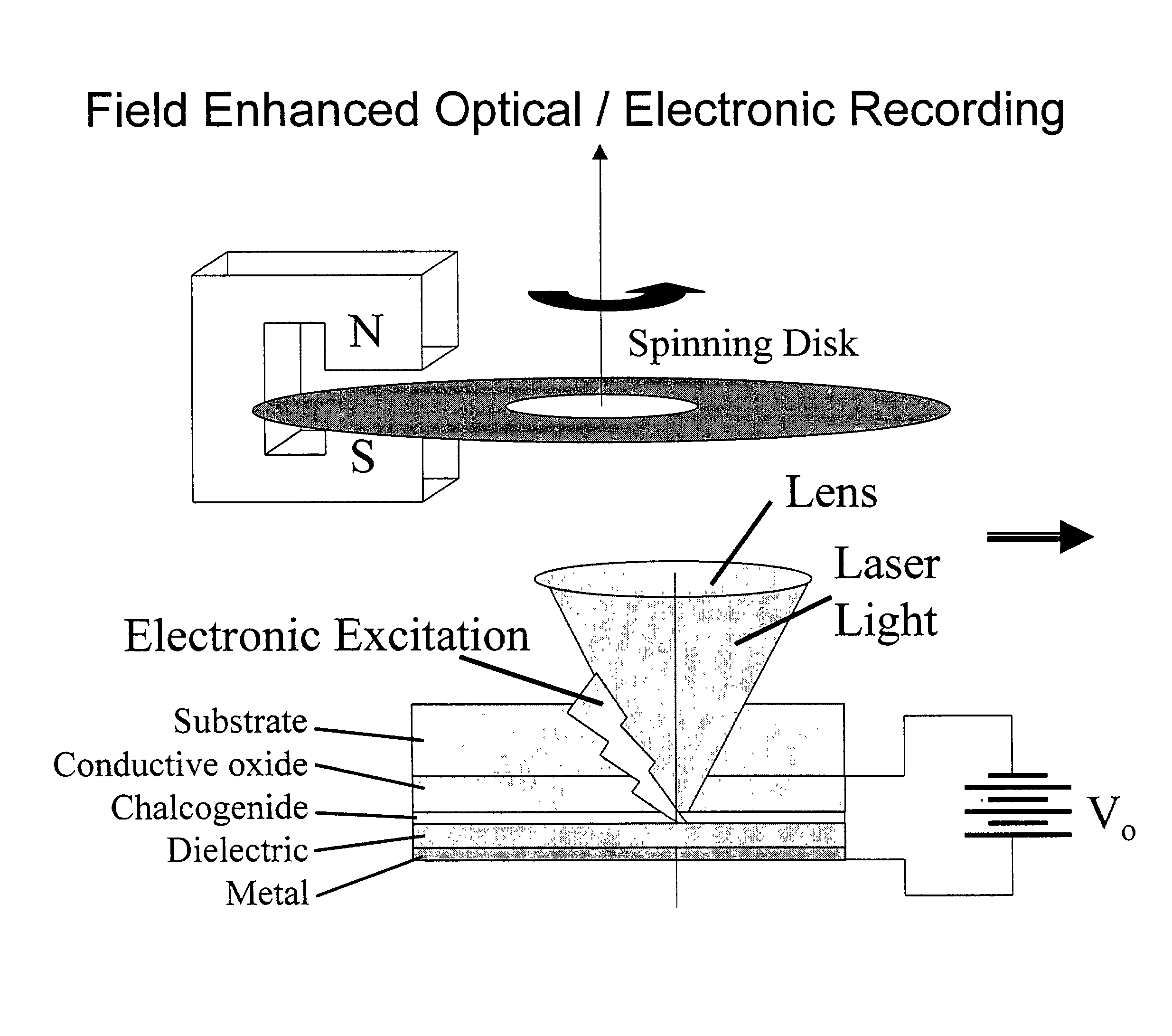
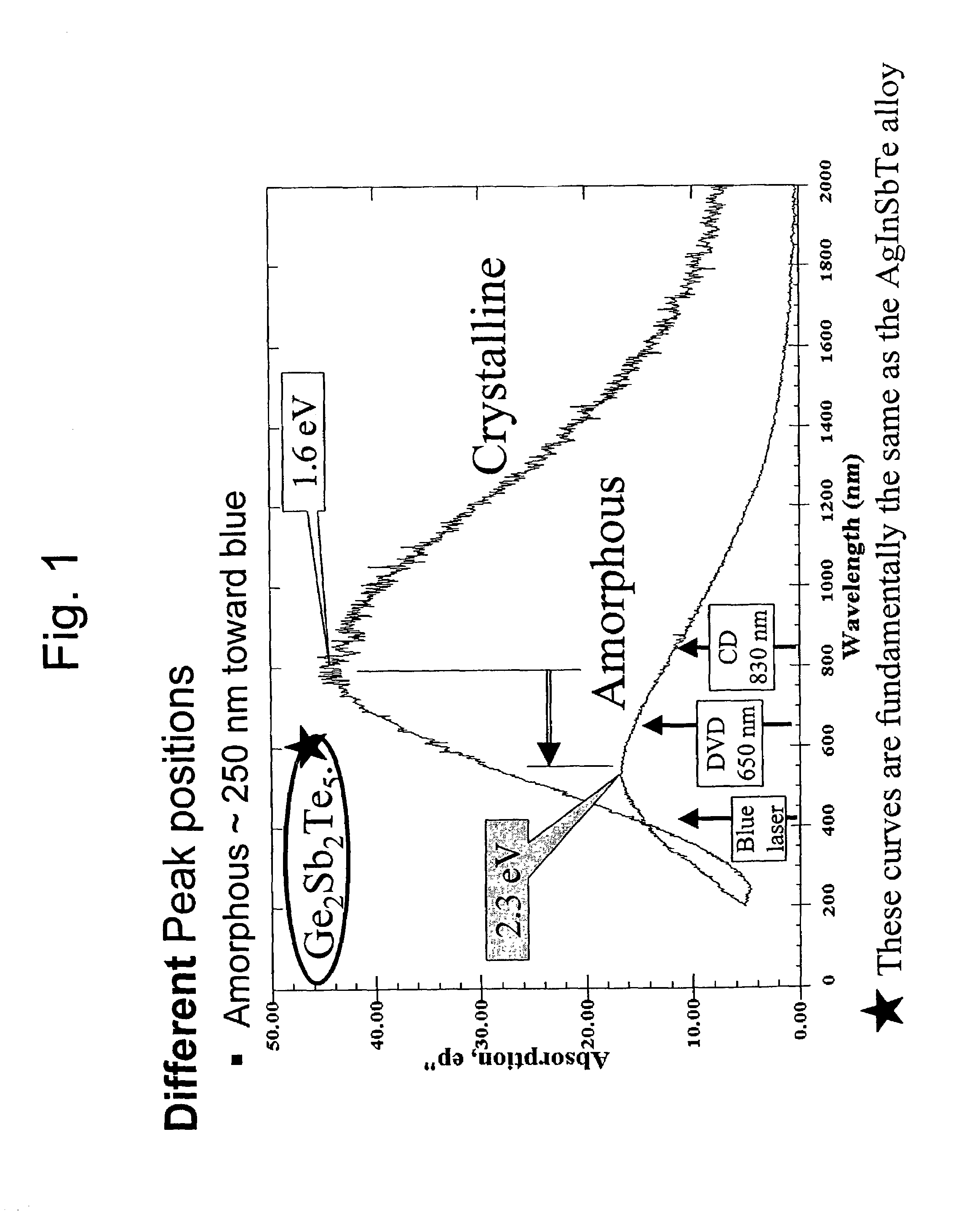
Patents
Literature
60results about "Recording by non-mechanical deformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
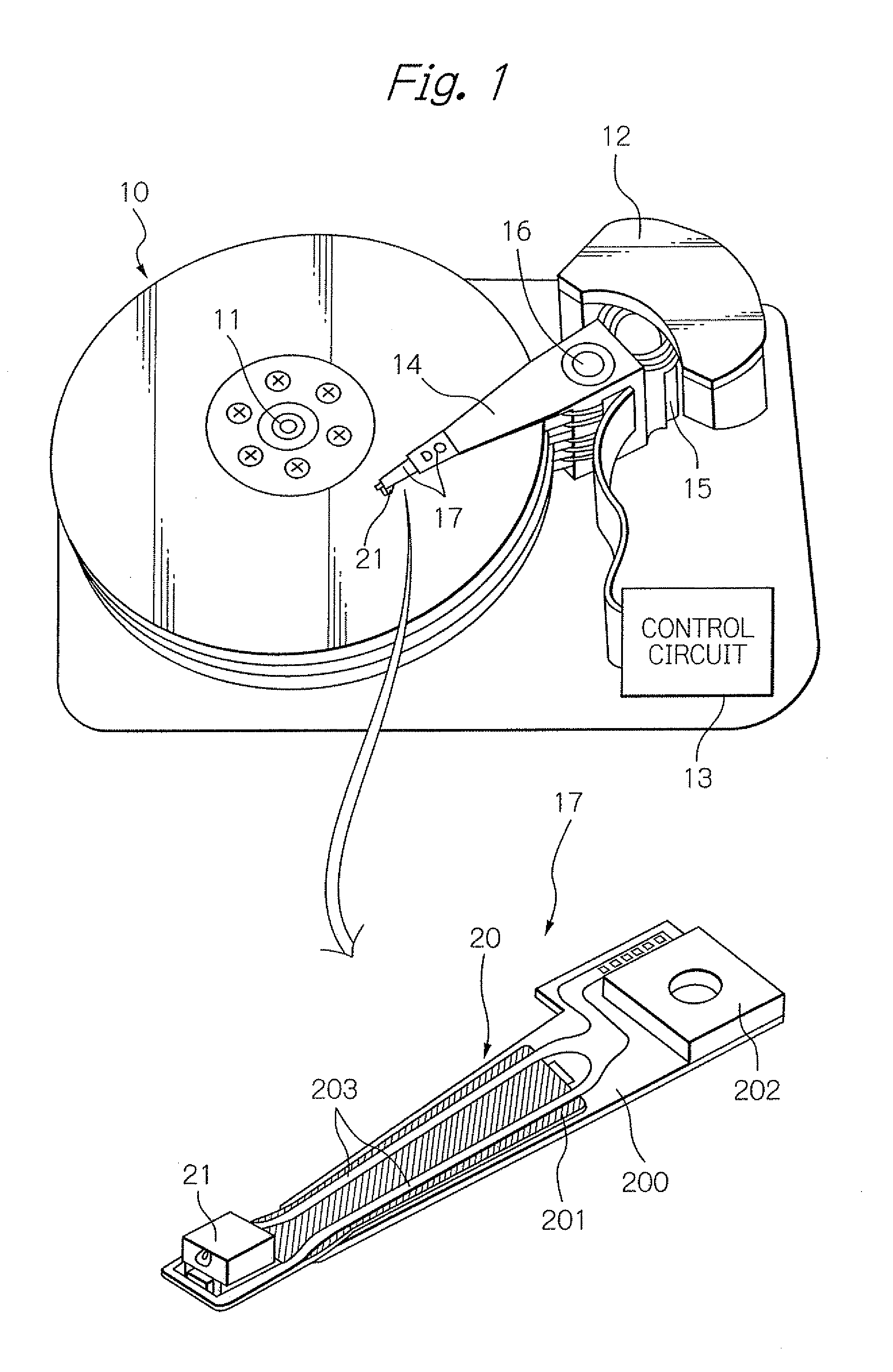
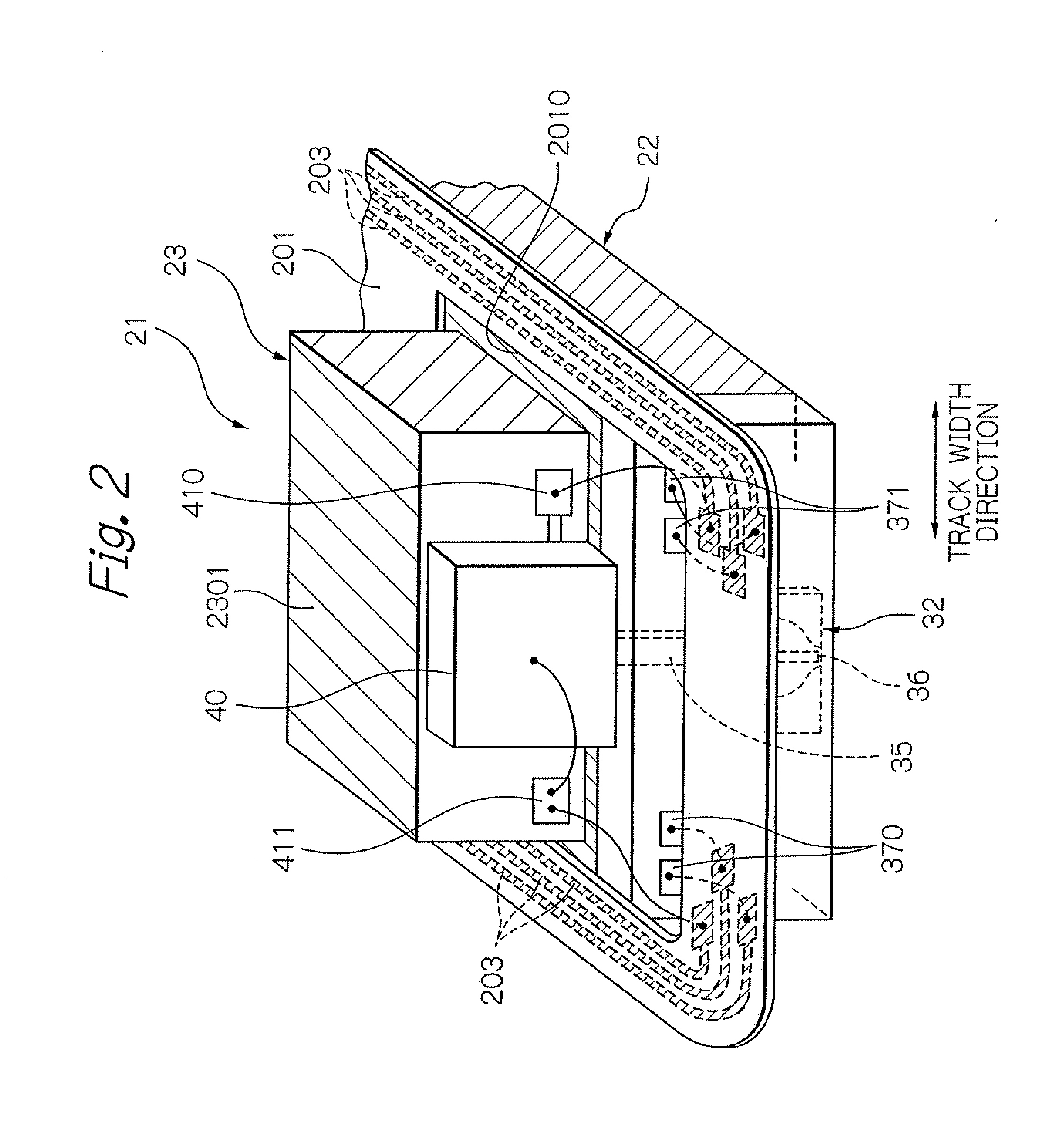
Virtual file system
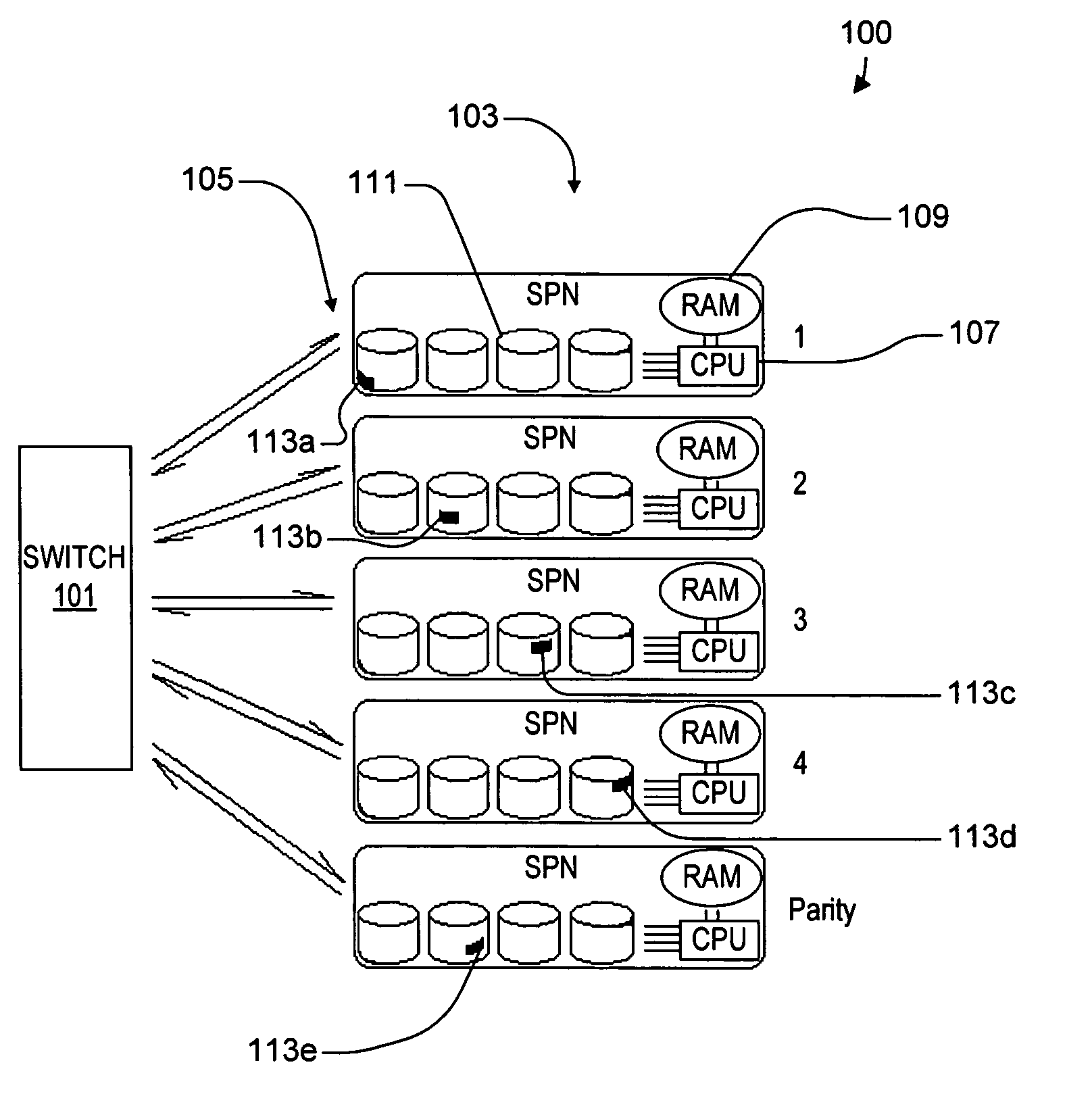
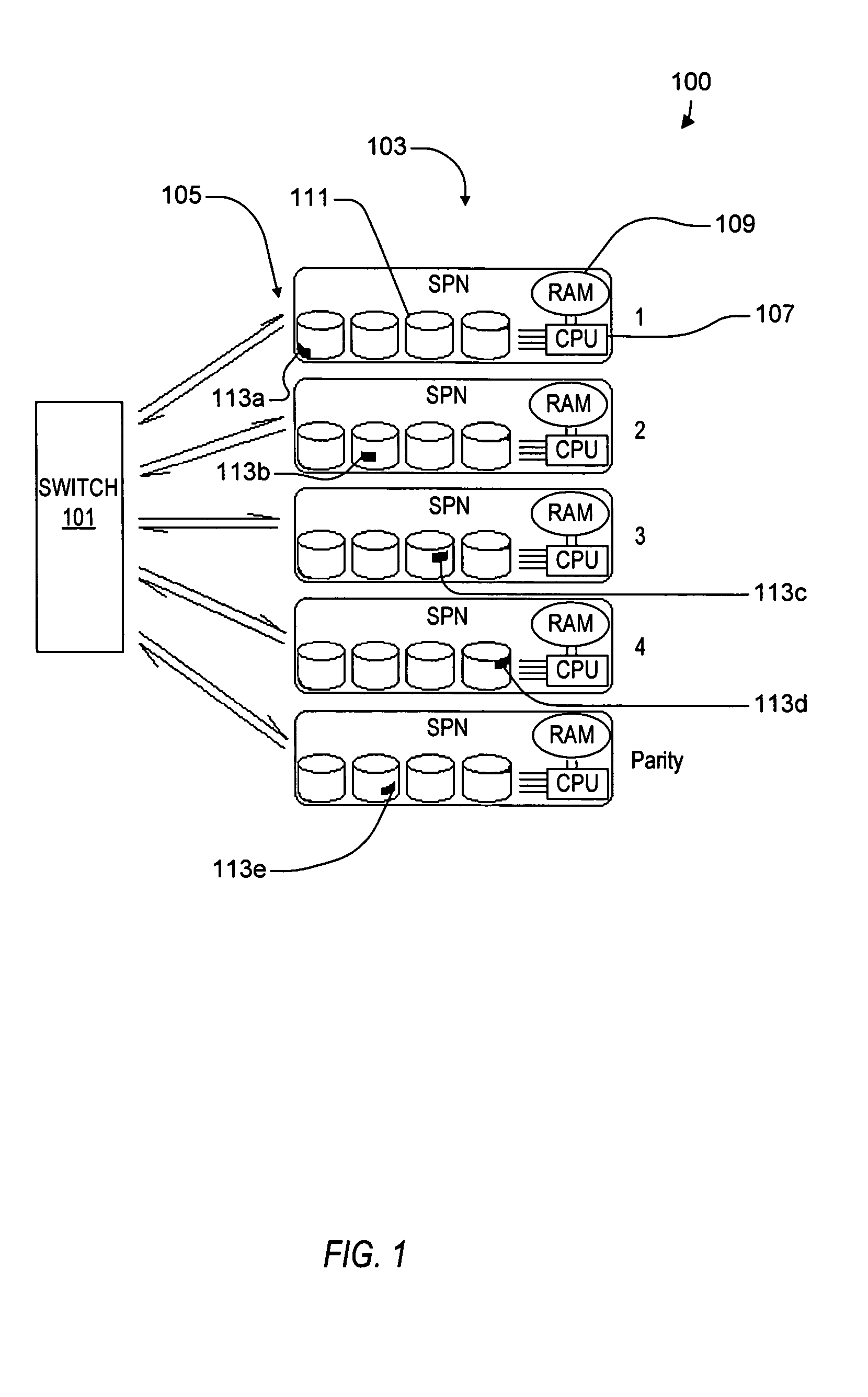
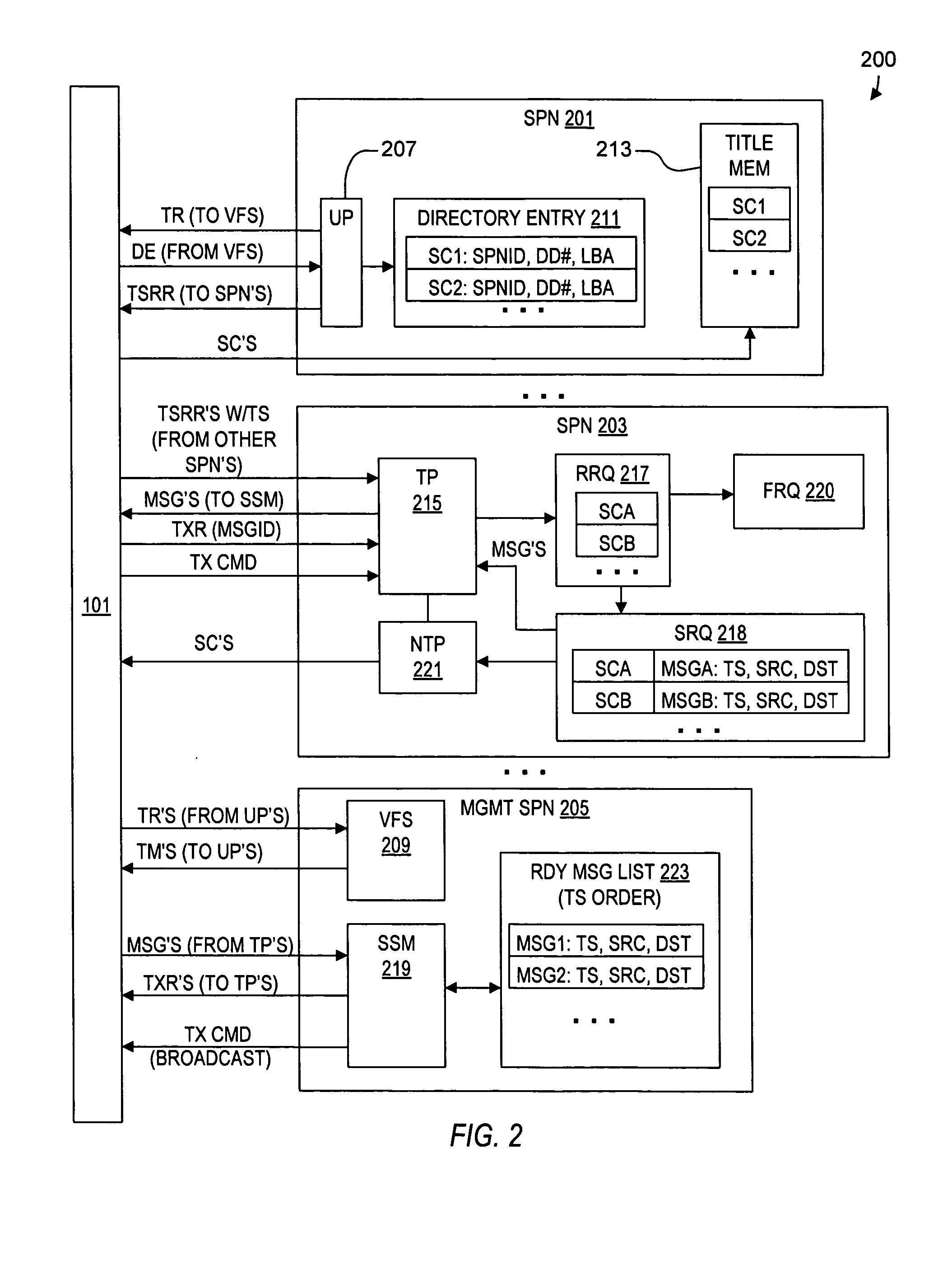
ActiveUS20050114350A1Input/output to record carriersRecording by optical meansVirtual file systemProcessor node
A virtual file system including multiple storage processor nodes including a management node, a backbone switch, a disk drive array, and a virtual file manager executing on the management node. The backbone switch enables communication between the storage processor nodes. The disk drive array is coupled to and distributed across the storage processor nodes and stores multiple titles. Each title is divided into data subchunks which are distributed across the disk drive array in which each subchunk is stored on a disk drive of the disk drive array. The virtual file manager manages storage and access of each subchunk, and manages multiple directory entries including a directory entry for each title. Each directory entry is a list of subchunk location entries in which each subchunk location entry includes a storage processor node identifier, a disk drive identifier, and a logical address for locating and accessing each subchunk of each title.
Owner:INTERACTIVE CONTENT ENGINES LLC
Heat-assisted magnetic recording head constituted of slider and light source unit, and manufacturing method of the head
ActiveUS20100085846A1High precision alignmentImprove manufacturing yieldElectrical transducersArm with optical waveguideHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
Provided is a method for manufacturing a heat-assisted magnetic recording head, capable of joining a light source unit and a slider with a sufficiently high alignment accuracy. In the method, the unit including a light source is joined to the slider including a head part. First, at least one marker provided on the head-part end surface is set so that the distance from the waveguide incident center to the marker end is substantially equal to the distance from the light-emission center of the light source to the end surface of the light source. After that, the unit and slider are relatively moved while keeping the unit in surface contact with the slider, and the relative positions are set so that the end of the marker coincides with, or is at a distance within an acceptable range from, the edge of the surface of the light source.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Heat emitting probe and heat emitting probe apparatus
InactiveUS7073937B2Improve recording densityReduce the overall diameterMaterial thermal conductivityRecording by optical meansControl circuitNanotube
A heat emitting probe including a conductive nanotube probe needle with its base end fastened to a holder and its tip end protruded, a heat emitting body formed on the probe needle, a conductive nanotube lead wire fastened to the heat emitting body, and an electric current supply that causes an electric current to pass through the conductive nanotube lead wire and both ends of the probe needle. The tip end of the probe needle is thus heated by an electric current flowing through the heat emitting body. A heat emitting probe apparatus includes the above-described heat emitting probe, a scanning mechanism that allows the heat emitting probe to scan over a thermal recording medium, and a control circuit that causes the tip end of the probe needle to emit heat, thus recording extremely small hole patterns in the surface of a thermal recording medium.
Owner:NAKAYAMA YOSHIKAZU +1
Method and system for magnetic recording using self-organized magnetic nanoparticles
A method and system for magnetic recording using self-organized magnetic nanoparticles is disclosed. The method may include depositing surfactant coated nanoparticles on a substrate, wherein the surfactant coated nanoparticles represent first bits of recorded information. The surfactant coating is then removed from selected of the surfactant coated nanoparticles. The selected nanoparticles with their surfactant coating removed may then be designated to represent second bits of recorded information. The surfactant coated nanoparticles have a first saturation magnetic moment and the selected nanoparticles with the surfactant coating removed have a second saturation magnetic moment. Therefore, by selectively removing the surfactant coating from certain nanoparticles, a write operation for recording the first and second bits of information may be performed. A read operation may be carried out by detecting the different magnetic moments of the surfactant coated nanoparticles and the non-surfactant coated nanoparticles.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
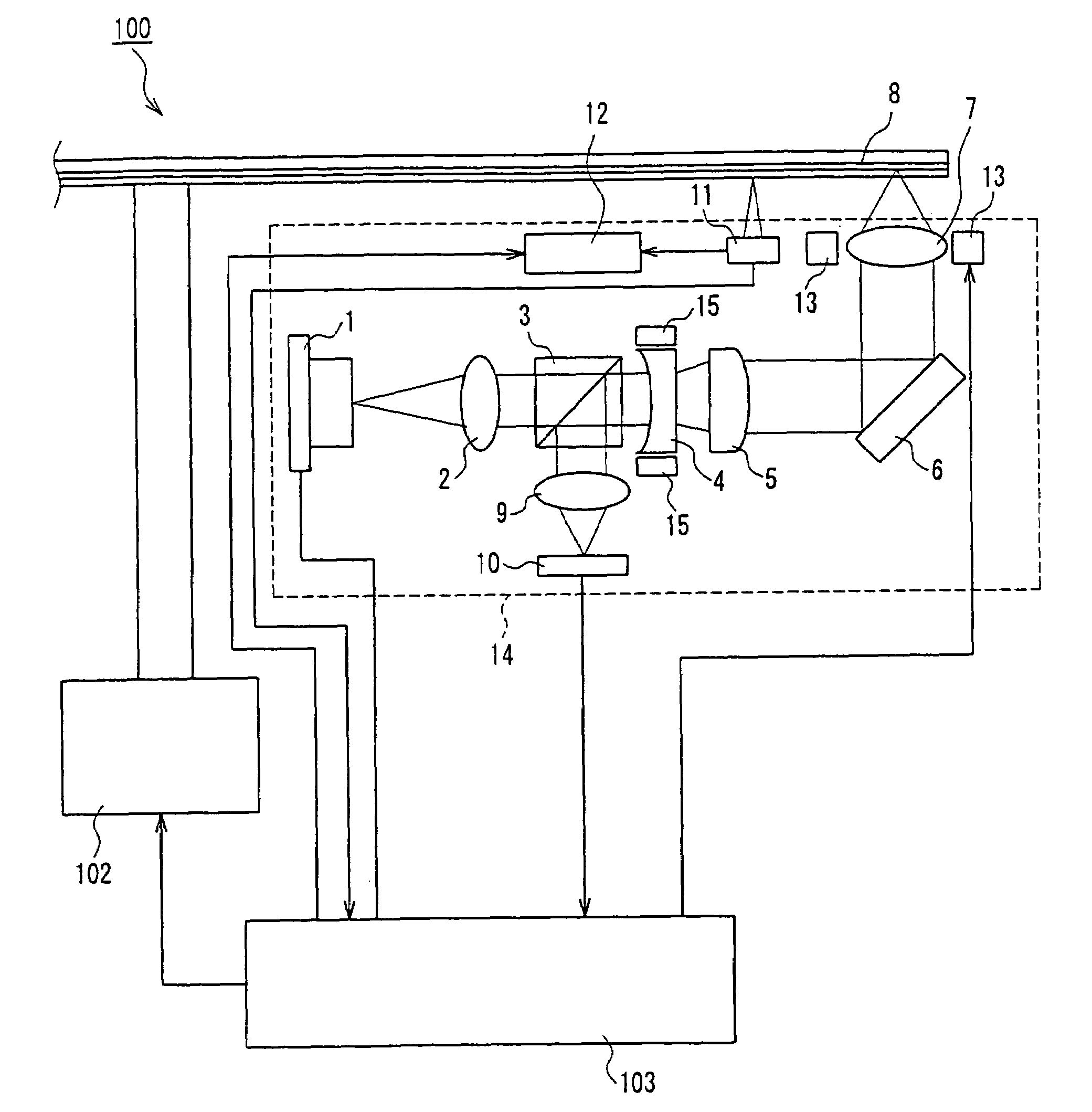
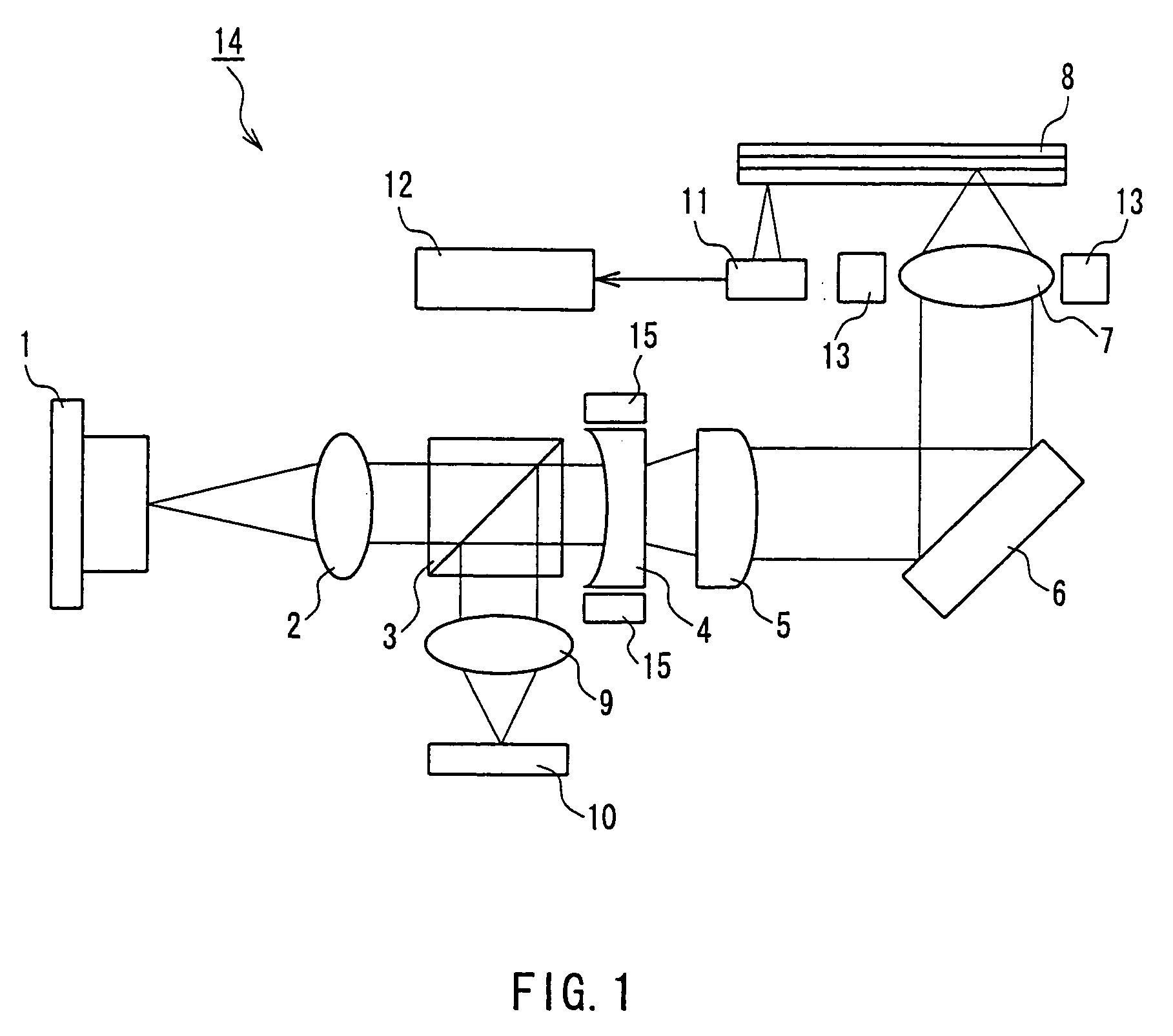
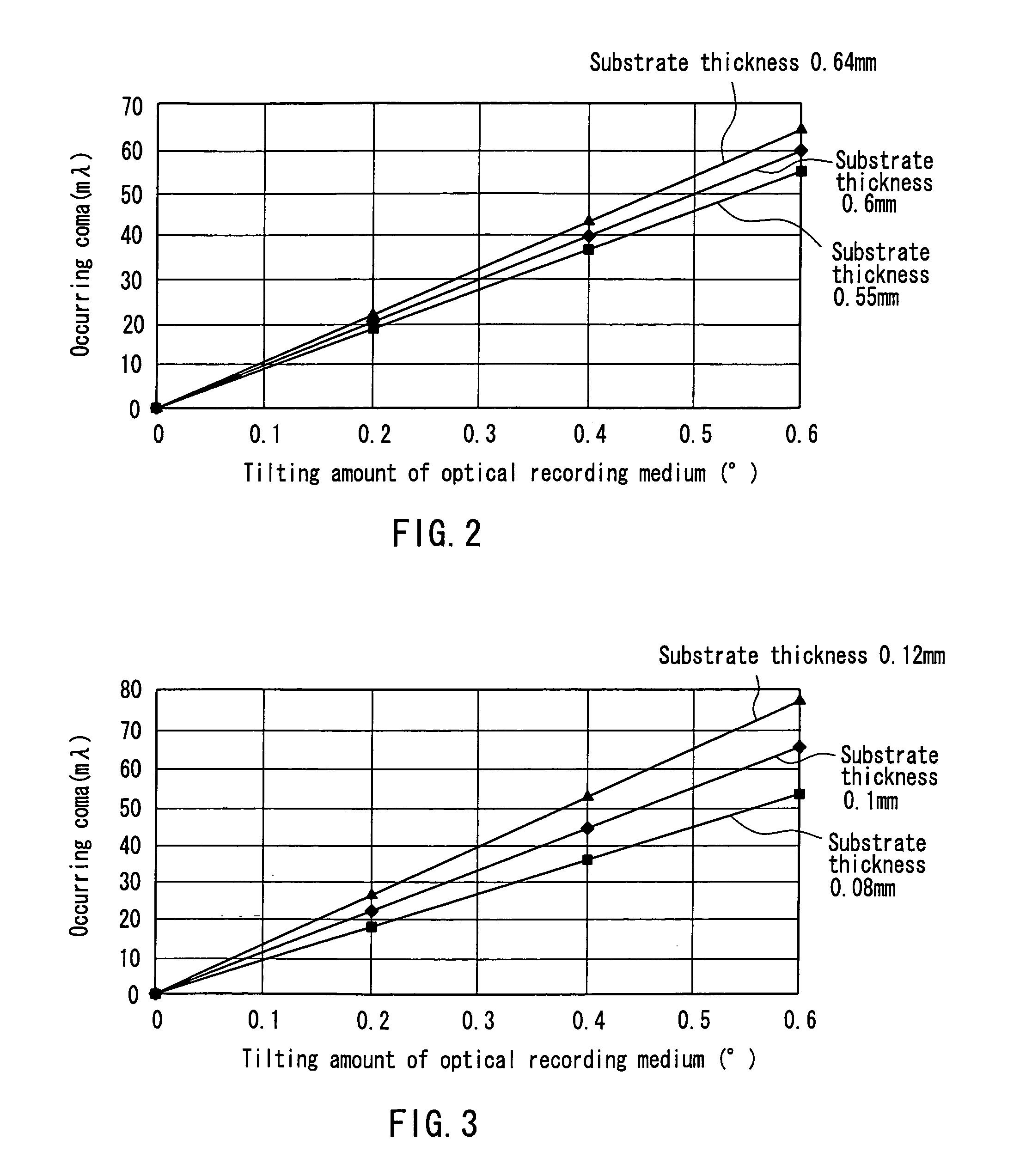
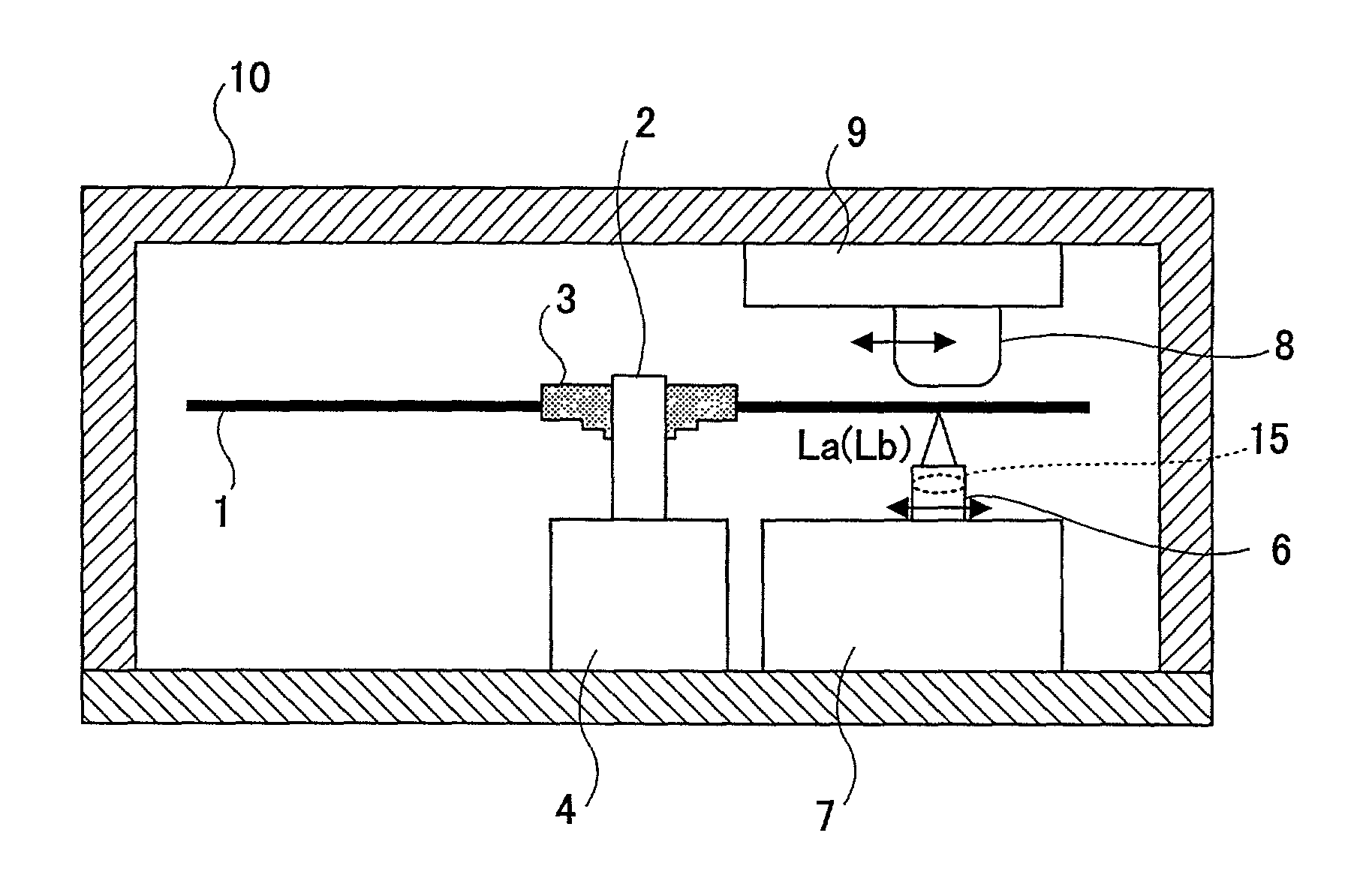
Optical head and optical recording/reproducing device using it and aberration correction method
InactiveUS7164638B2Stable recordControl signal stableRecording by optical meansRecord information storageHigh densityOptical recording
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Disk drive system employing effective disk surface stabilization mechanism
InactiveUS7233554B2Eliminate vibrationAvoid it happening againRecording by optical meansOptical beam sourcesBernoulli's principlePressure difference
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical disk apparatus and control method for controlling distance between a head and a disk
InactiveUS7406016B2Prevent speedingShorten the timeDisposition/mounting of recording headsRecording by optical meansEngineeringLight source
An optical apparatus includes: a light source outputting light; a head disposed so as to face a disk on which a signal is recordable, the head being capable of condensing a light from the light source onto the disk as near-field light; an distance adjusting mechanism adjusting a distance between the head and the disk; first control means for causing the head to approach the disk and controlling the head to nearly stop at a position where a distance from the disk is a first distance at which the light is condensed on the disk by the head as the near-field light; detection means for detecting if the distance is the first distance; and second control means for controlling the distance adjusting mechanism based on the detected signal so as that the distance is a second distance under near-field light condition.
Owner:SONY CORP
Electron beam recording apparatus
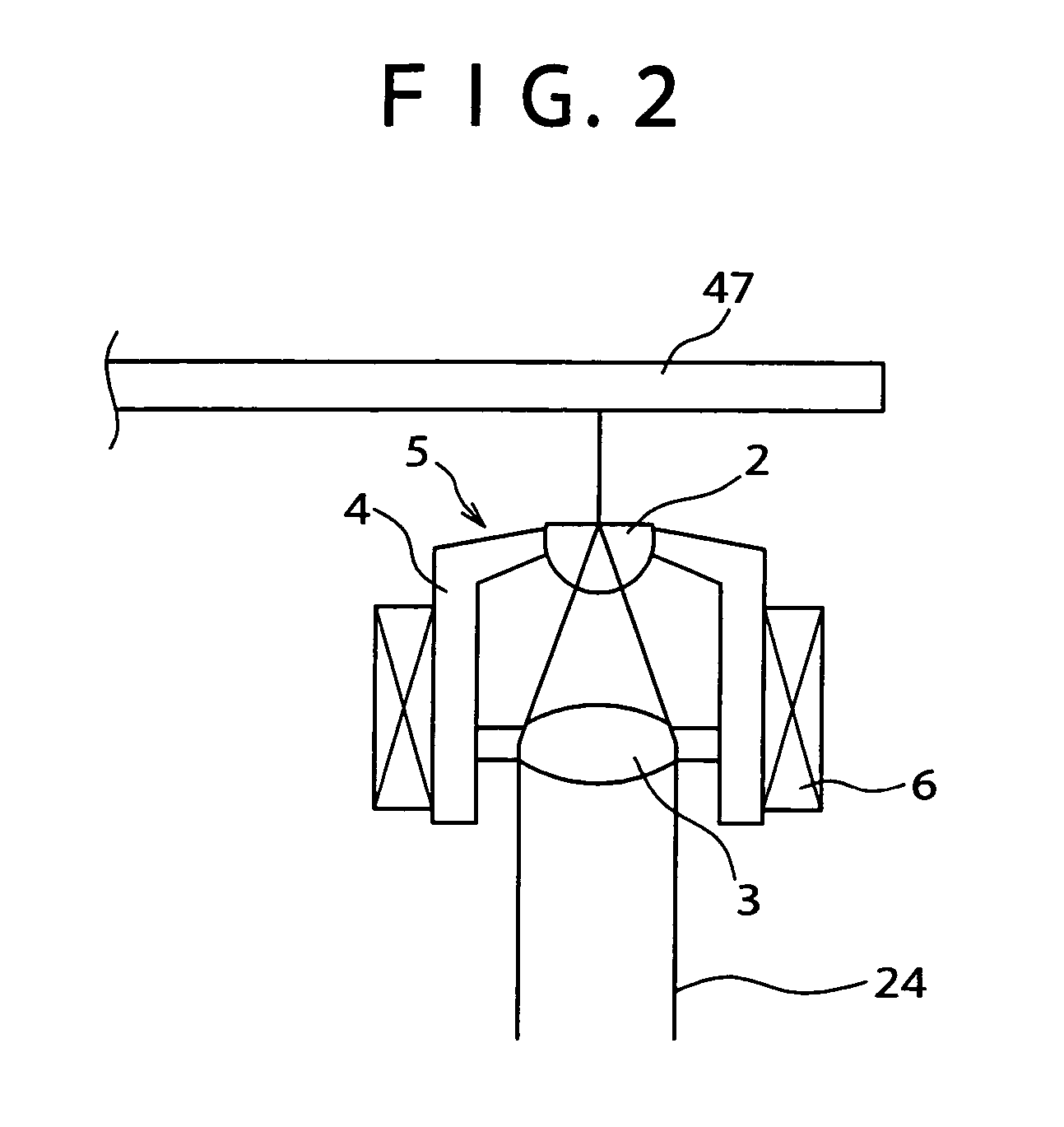
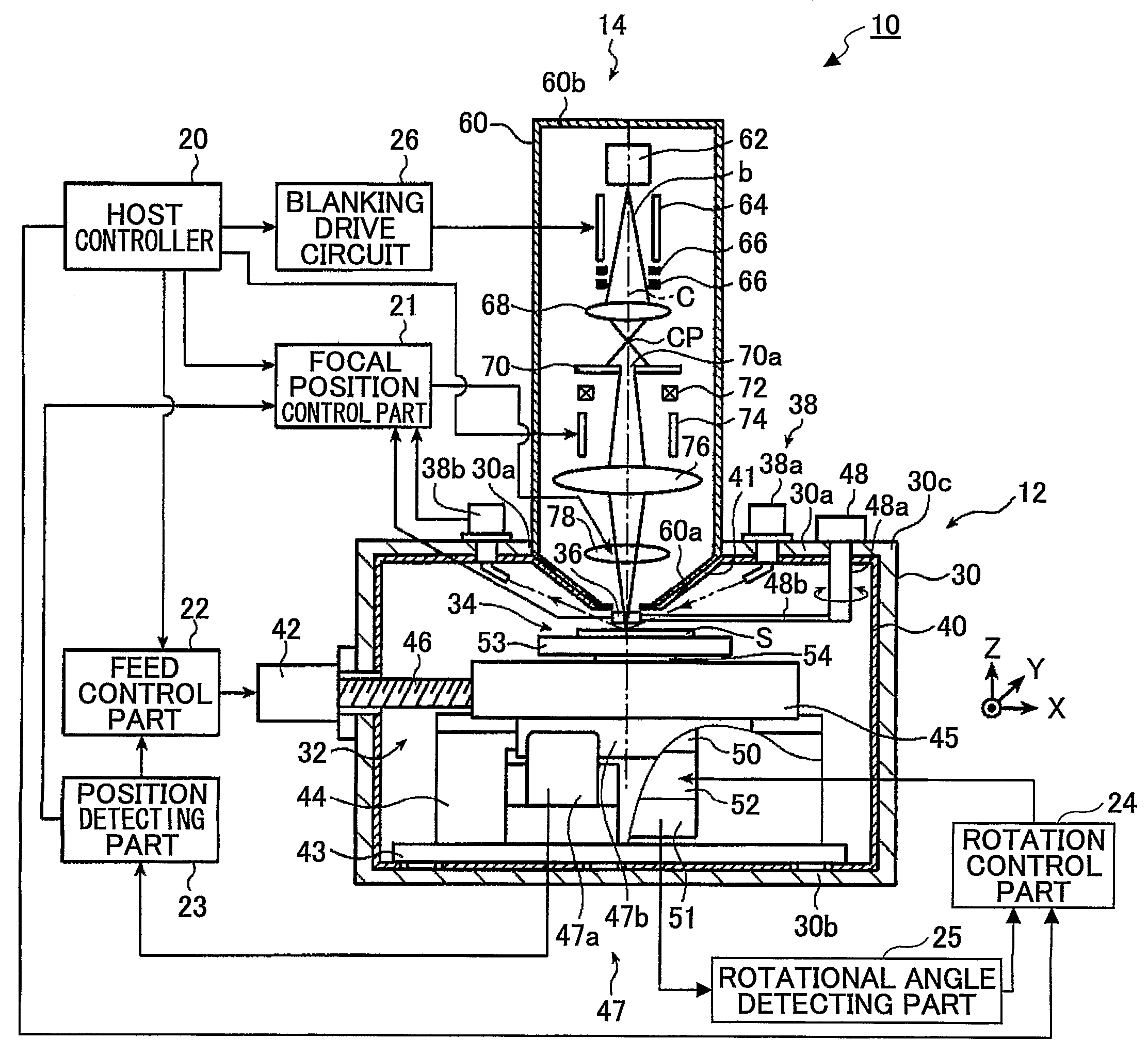
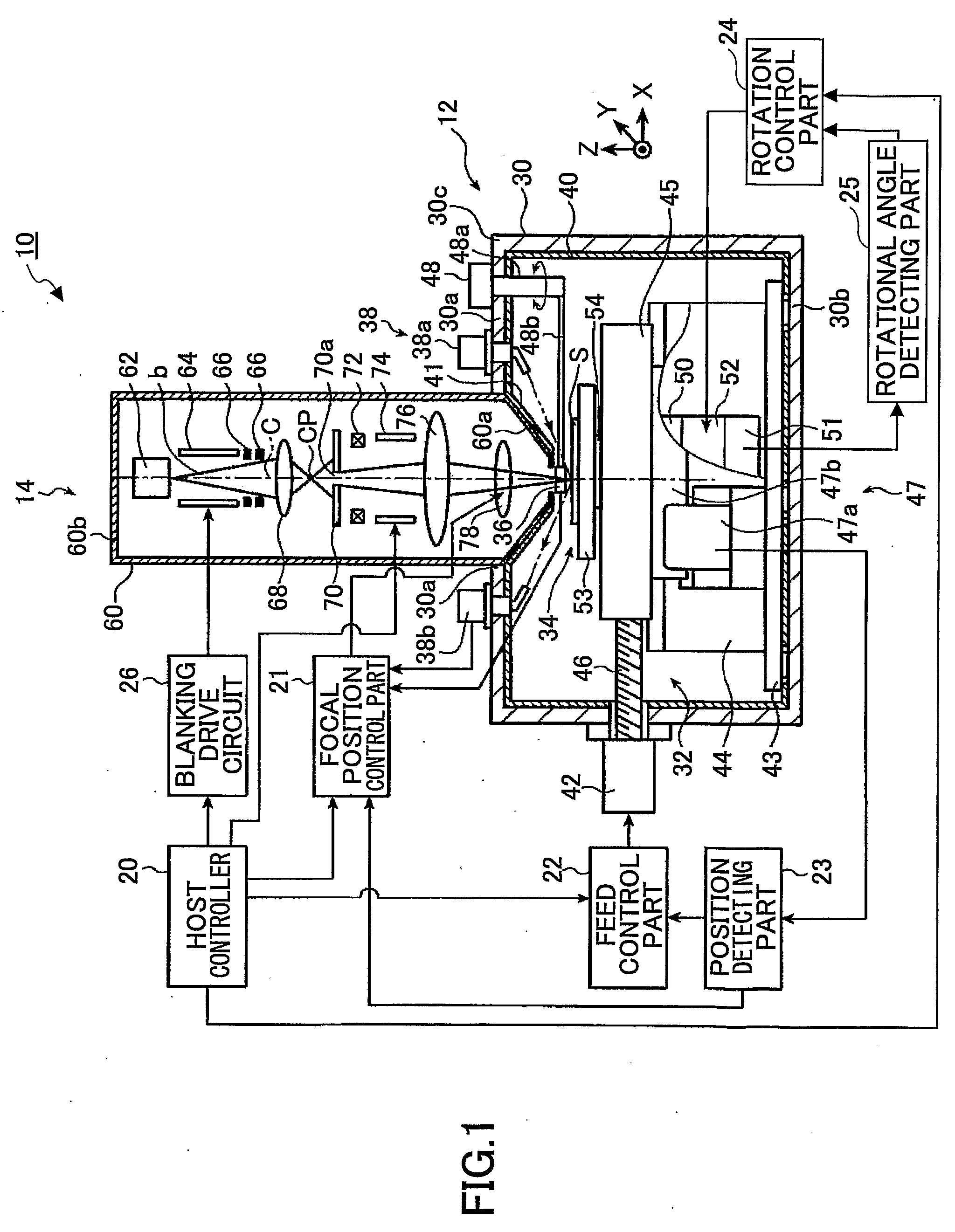
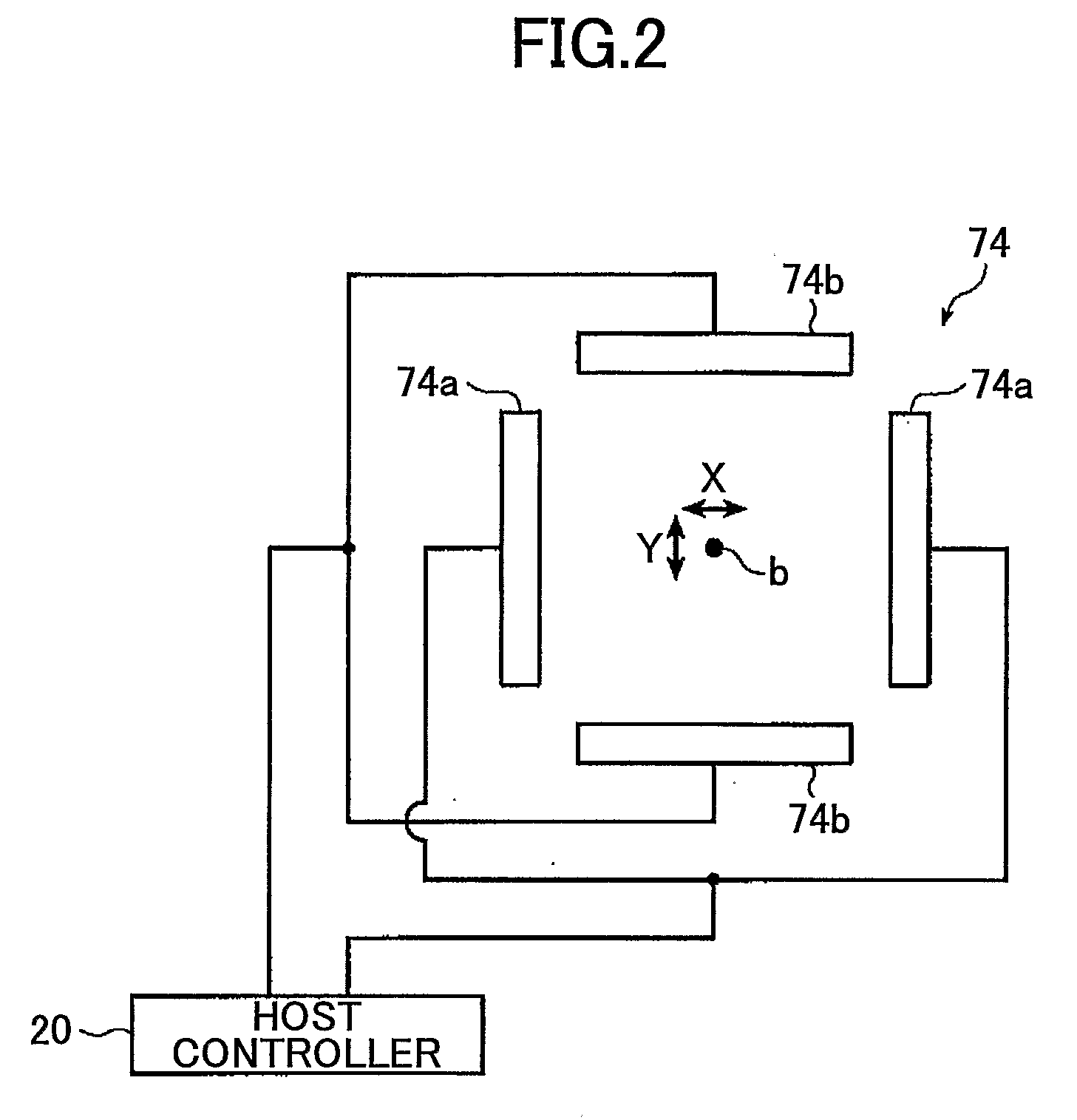
InactiveUS20090059773A1High positioning accuracyImprove accuracyElectron beam carrier recordingElectric discharge tubesElectron sourceIrradiation
An electron beam recording apparatus is disclosed that records information onto the surface of a sample by using an electron beam. The electron beam recording apparatus includes an electron source that irradiates the electron beam, a magnetic detector that is configured to move onto and out of an irradiation axis and acquires magnetic information on the irradiation axis, a convergence position control part that calculates a convergence position correction amount for correcting a convergence position of the electron beam with respect to the surface of the sample based on the magnetic information, and a convergence position adjusting part that adjusts the convergence position of the electron beam with respect to the surface of the sample. The convergence position control part causes the convergence position adjusting part to adjust the convergence position of the electron beam with respect to the surface of the sample based on the convergence position correction amount.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
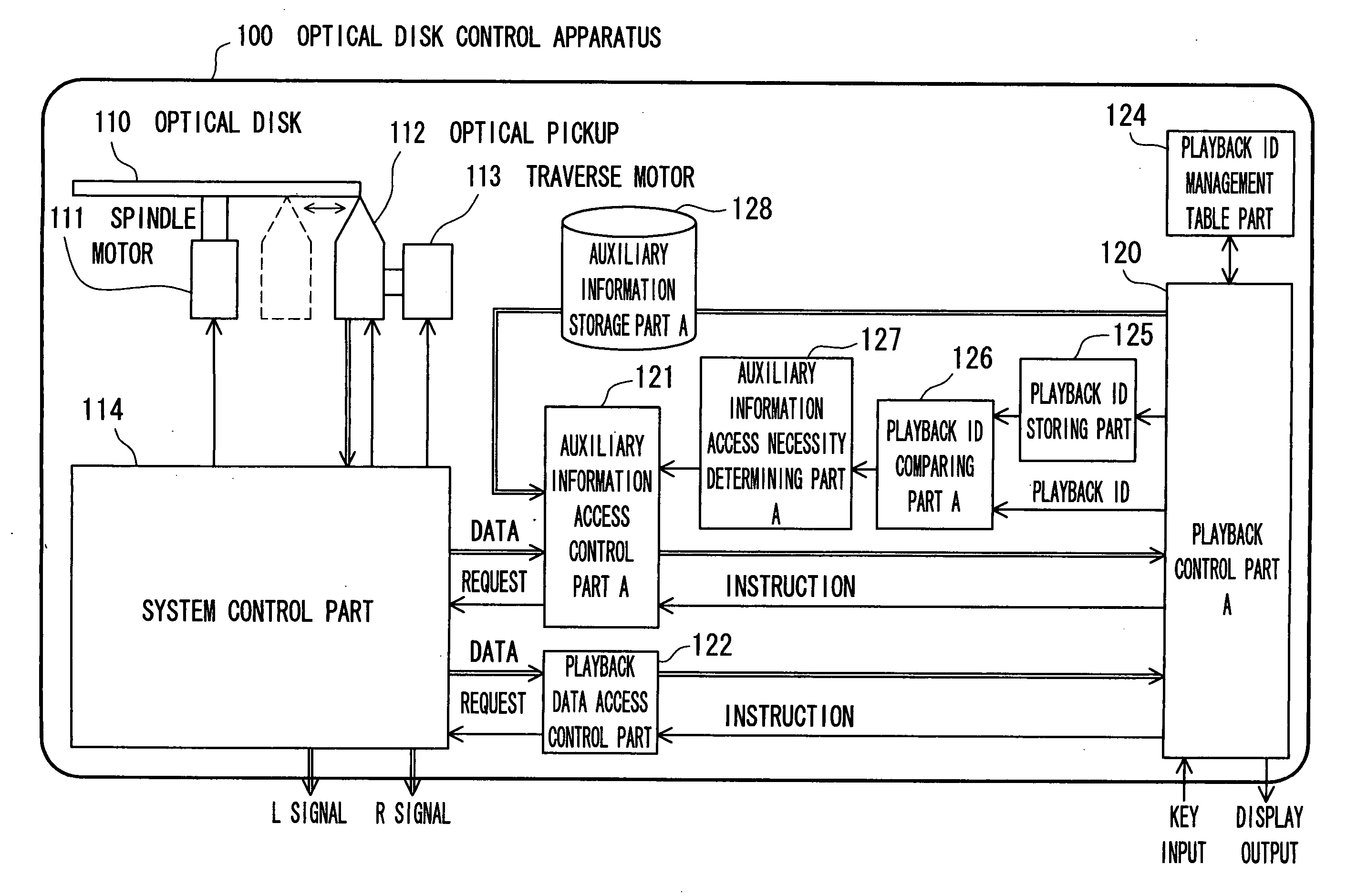
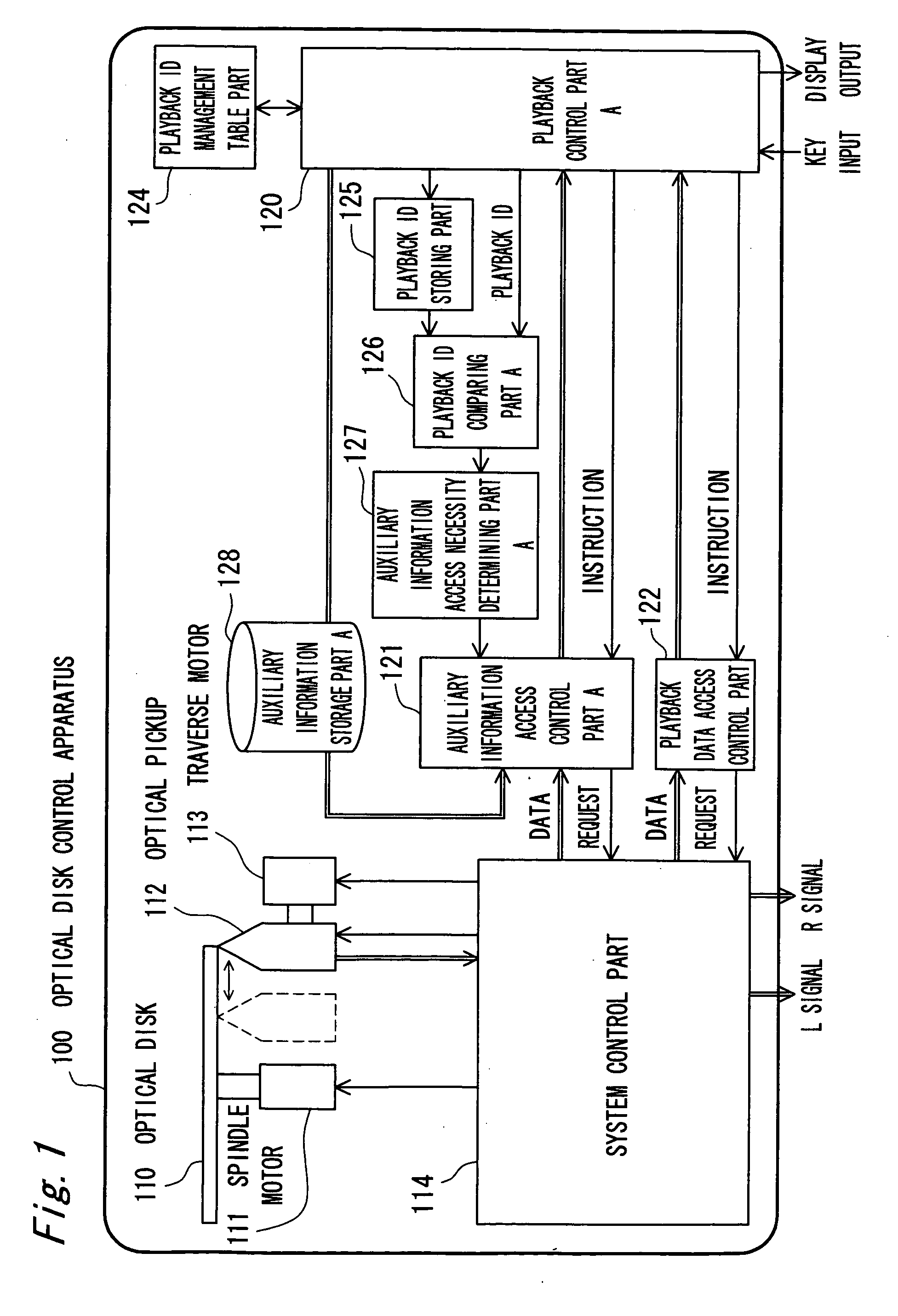
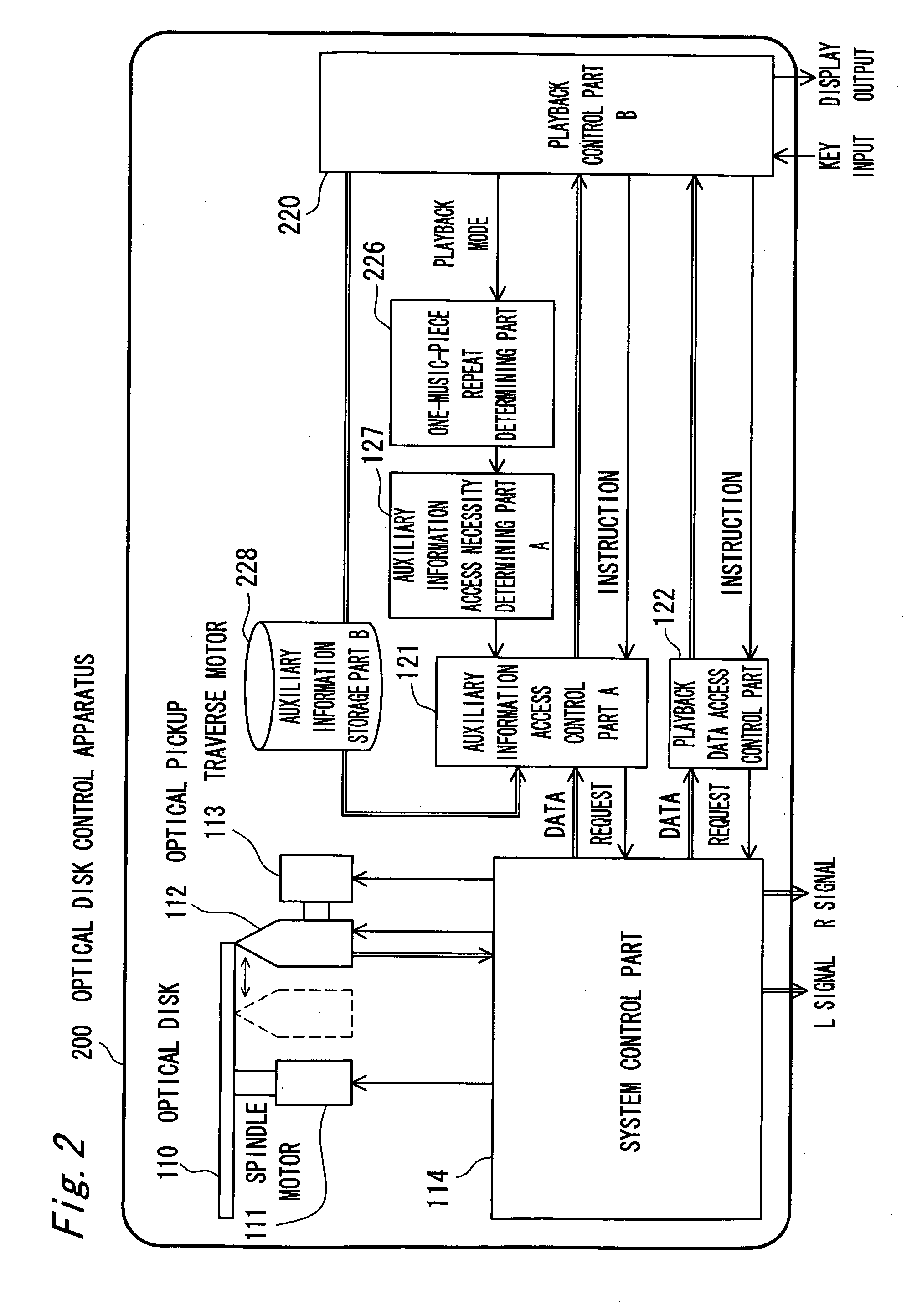
Recording medium controller and recording medium controlling method
InactiveUS20060153036A1Avoid spendingReduce exerciseRecording by optical meansUsing non-detectable carrier informationOptical pickupInformation access
A battery-operated recording medium controller monitors the ID of a replayed melody and when a replay ID comparing section (A126) makes a decision that a melody of the same ID as the previous one is replayed, a section (A127) for judging necessity of auxiliary information designates an auxiliary information access control section not to acquire auxiliary information (ID3 tag) again from a disc but to reuse auxiliary information stored in an auxiliary information storing section A. Consequently, the number of times of accessing the recording medium is decreased, and when the auxiliary information added to reproduction data like the ID3 tag of an MP3 is acquired, moving distance of an optical pickup is decreased and current consumption can be reduced.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Plasmon head with hydrostatic gas bearing for near field photolithography
InactiveUS20110159446A1Low costAccurate locationRecording by optical meansNanoinformaticsResistSurface plasmon
A low-cost approach to near field nano-scale photolithography using a plasmonic head with hydrostatic gas bearings. The hydrostatic gas bearing flies the plasmonic head at less than 100 nm, and more preferably less than 50 nm, above the photo-resist without the need to spin the substrate. The plasmonic head concentrates short-wavelength surface plasmons into about sub-100 nm regions on the photo-resist and can pattern features of about 80 nm or less.
Owner:FIRST PRINCIPALS
Electron beam recording apparatus
InactiveCN101443847AElectron beam carrier recordingElectric discharge tubesElectron sourceIrradiation
An electron beam recording apparatus is disclosed that records information onto the surface of a sample by using an electron beam. The electron beam recording apparatus includes an electron source that irradiates the electron beam, a magnetic detector that is configured to move onto and out of an irradiation axis and acquires magnetic information on the irradiation axis, a convergence position control part that calculates a convergence position correction amount for correcting a convergence position of the electron beam with respect to the surface of the sample based on the magnetic information, and a convergence position adjusting part that adjusts the convergence position of the electron beam with respect to the surface of the sample. The convergence position control part causes the convergence position adjusting part to adjust the convergence position of the electron beam with respect to the surface of the sample based on the convergence position correction amount.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
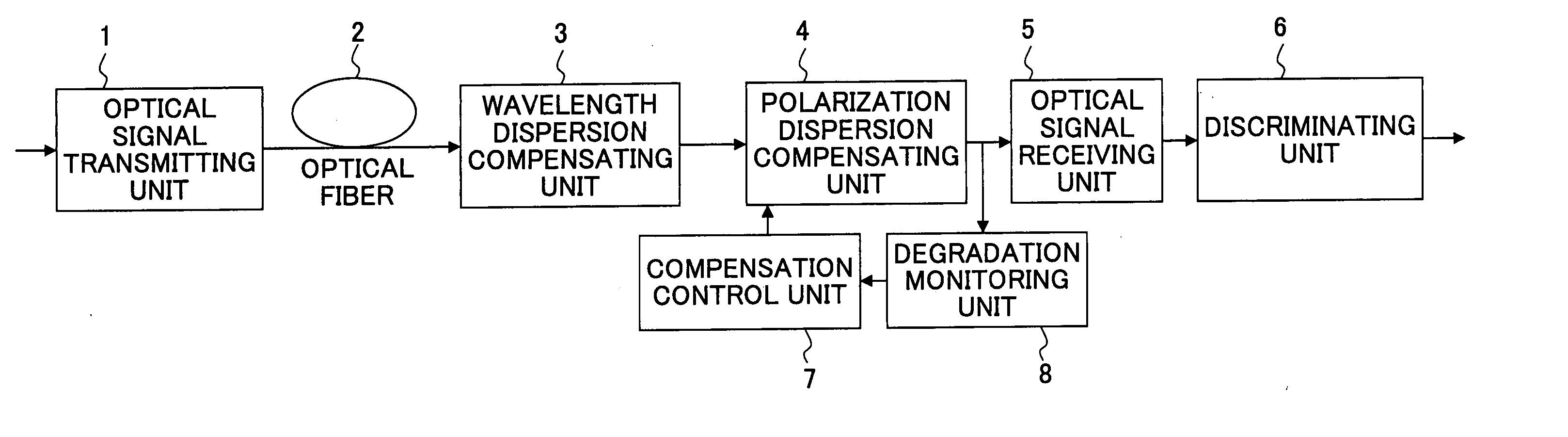
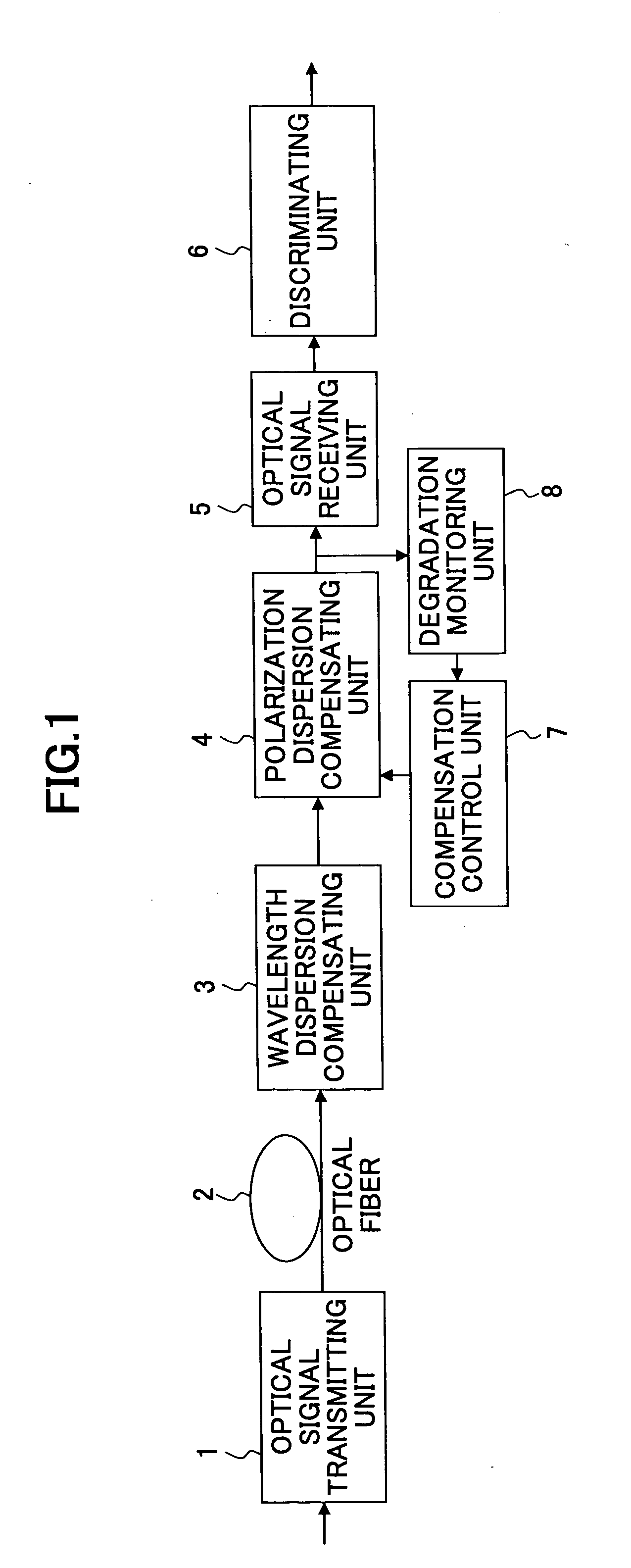
Digital signal receiving apparatus, an optical transmission apparatus therewith, and a discriminating point control method
InactiveUS20050149791A1Made smallModification of read/write signalsElectronic circuit testingEngineeringDigital signal
A digital signal receiving apparatus is disclosed. The digital signal receiving apparatus includes a main signal discriminating unit configured to discriminate a main signal of a received signal, a monitor signal discriminating unit configured to discriminate a monitor signal of the received signal, an error monitoring unit configured to monitor a discriminating error of the monitor signal discriminating unit, and a discriminating point control unit configured to control the discriminating points of the main signal discriminating unit and the monitor signal discriminating unit. The discriminating point control unit monitors an output of the error monitoring unit, moves the discriminating point of the monitor signal discriminating unit in the amplitude directions and the phase directions such that a discriminating error occurs, detects a center of discriminating points where errors are generated, and sets the detected center of the discriminating points as the discriminating point of the main signal discriminating unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for reproducing recording mark below diffraction limit of light from optical recording medium
InactiveUS7289408B2Alleviate level jitterGood error characteristicTelevision system detailsModification of read/write signalsLower limitElectrical polarity
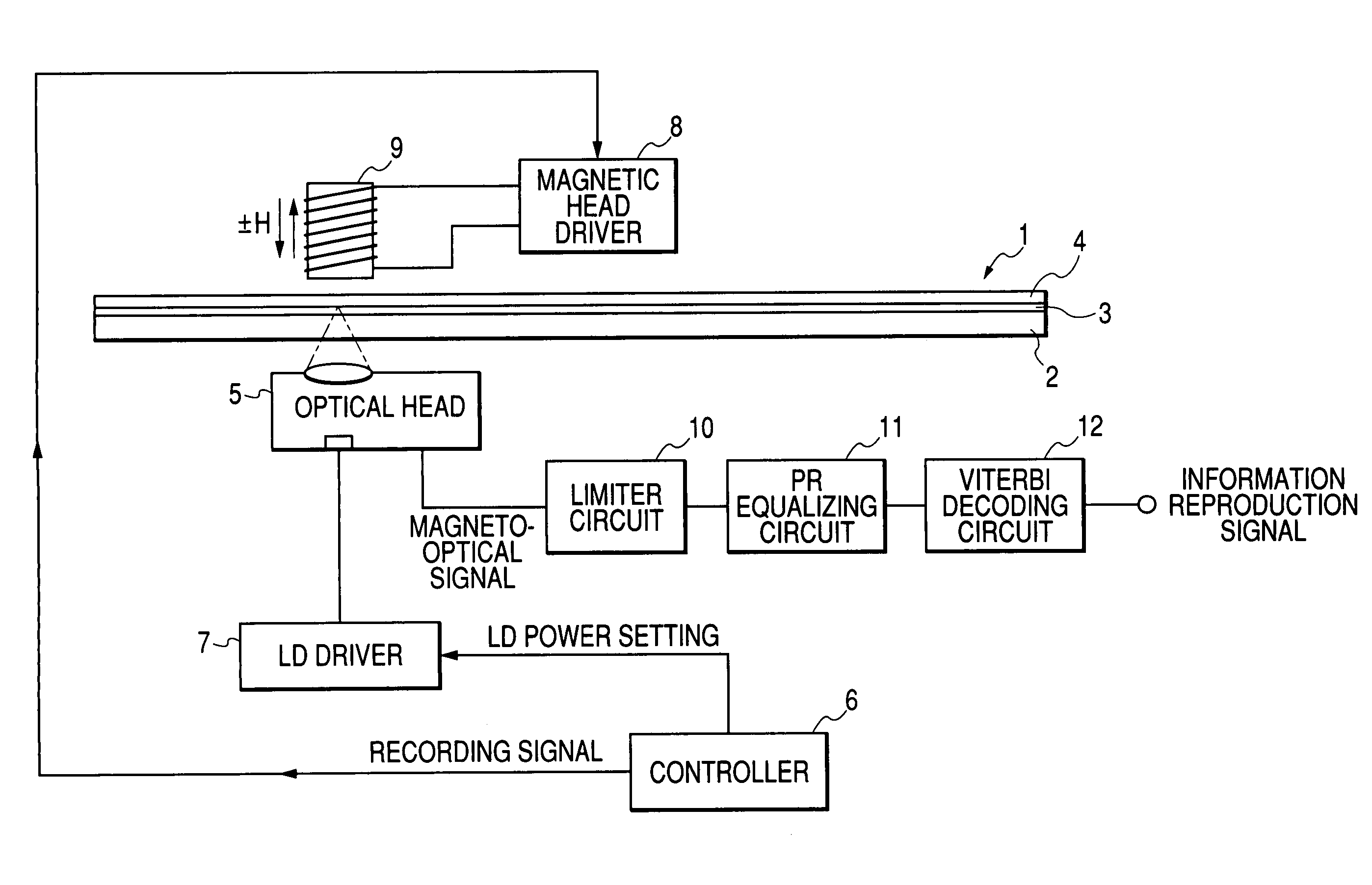
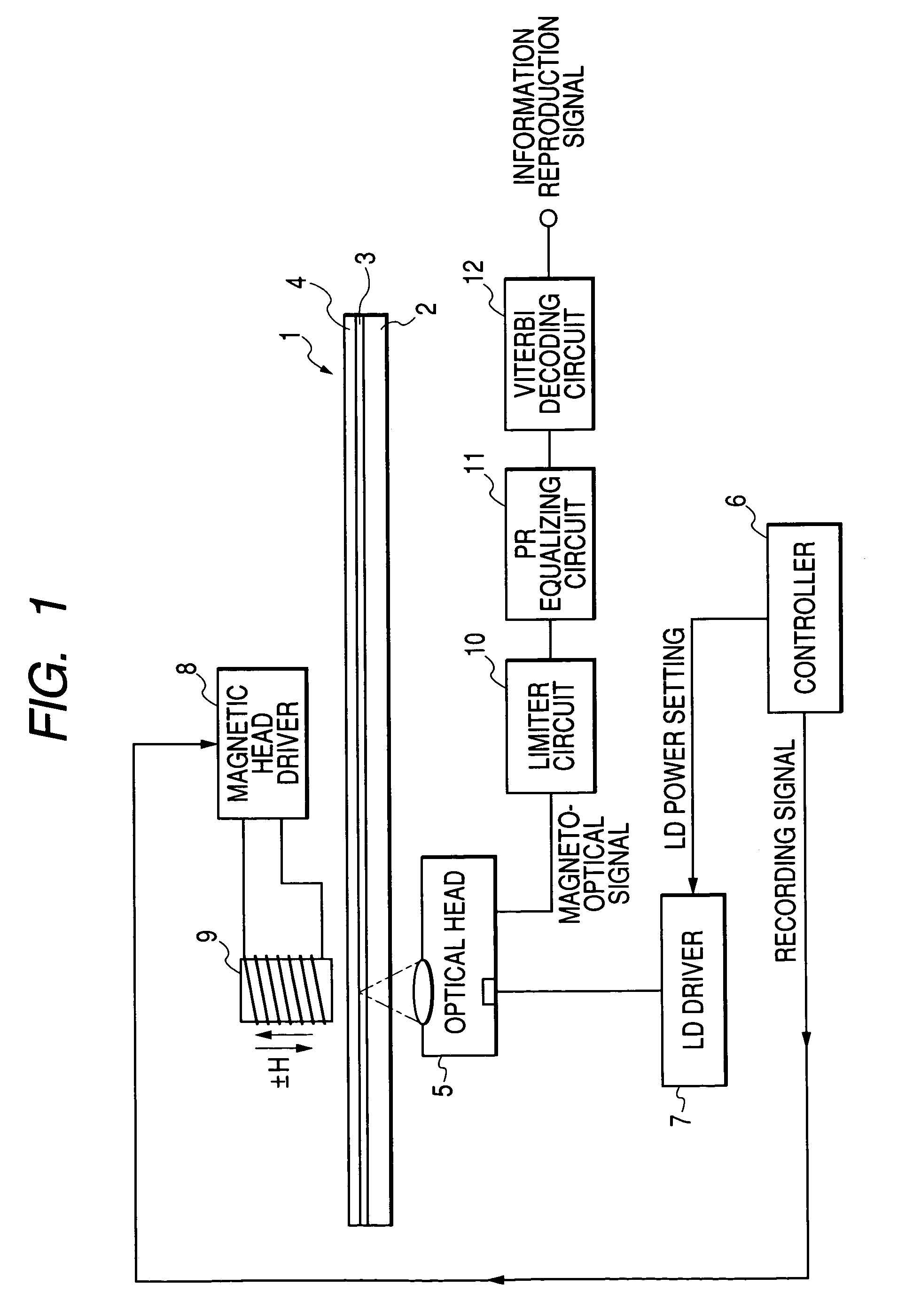
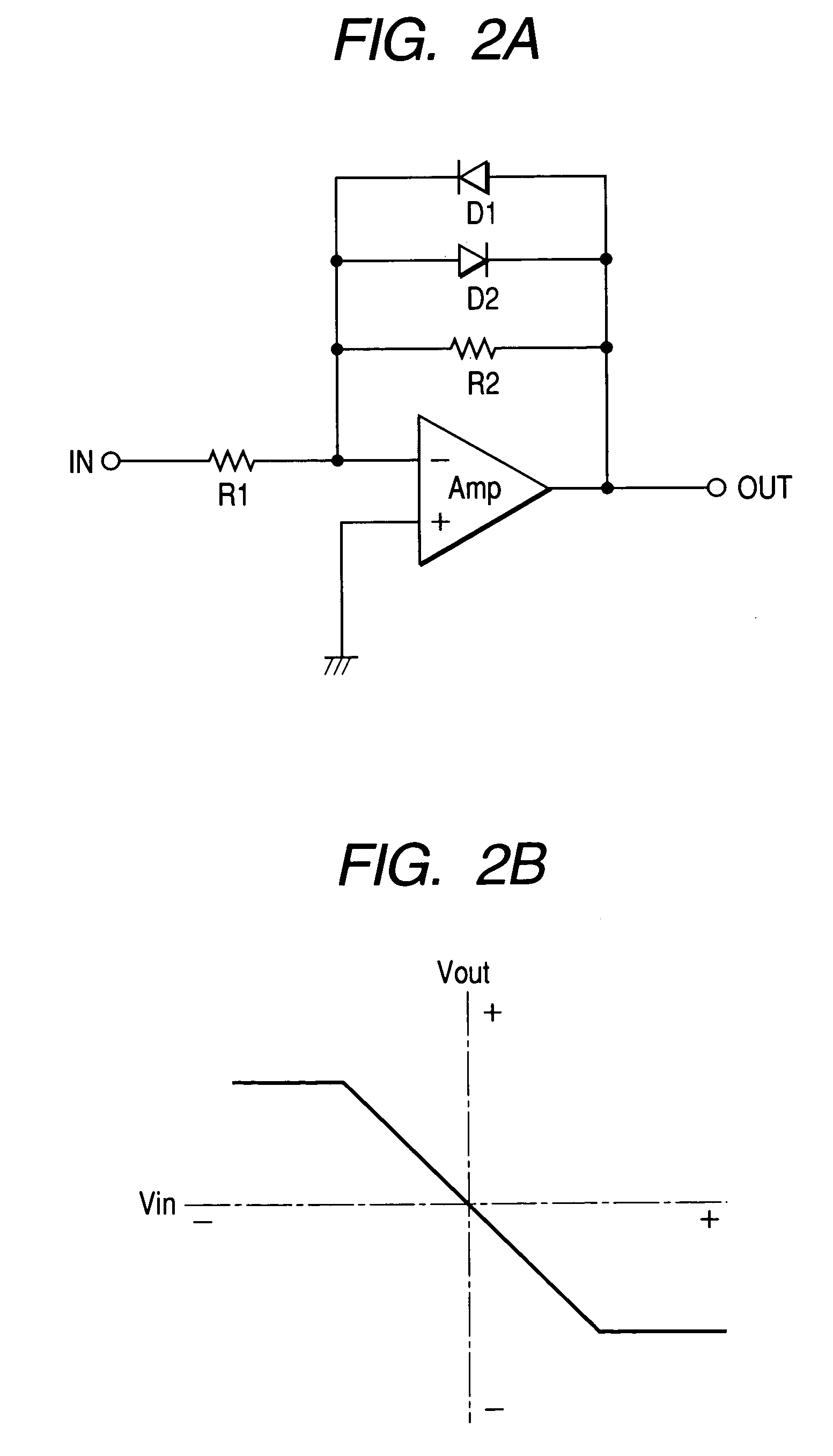
The object of the present invention is to realize reduction of the level jitter generated from a noise component at a signal saturation level or a waveform distortion in a portion except for signal polarity portions (rising edge and falling edge), and good error characteristics. In the present invention, a predetermined upper or lower limit value is set to reproduction signals, the reproduction signals are subjected to a limiter processing for correcting reproduction signals of the upper limit value or more, or the lower limit value or less to the level of the upper limit value or the lower limit value, respectively, the signal subjected to the limiter processing is subjected to a partial response equalizing (PR equalizing) processing, and PR reproduction is performed to improve the level jitter at PR detection time and the error rate at information reproduction time.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and system for magnetic recording using self-organized magnetic nanoparticles
InactiveUS20050078397A1NanomagnetismRecording by optical meansMagnetite NanoparticlesSURFACTANT BLEND
A method and system for magnetic recording using self-organized magnetic nanoparticles is disclosed. The method may include depositing surfactant coated nanoparticles on a substrate, wherein the surfactant coated nanoparticles represent first bits of recorded information. The surfactant coating is then removed from selected of the surfactant coated nanoparticles. The selected nanoparticles with their surfactant coating removed may then be designated to represent second bits of recorded information. The surfactant coated nanoparticles have a first saturation magnetic moment and the selected nanoparticles with the surfactant coating removed have a second saturation magnetic moment. Therefore, by selectively removing the surfactant coating from certain nanoparticles, a write operation for recording the first and second bits of information may be performed. A read operation may be carried out by detecting the different magnetic moments of the surfactant coated nanoparticles and the non-surfactant coated nanoparticles.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
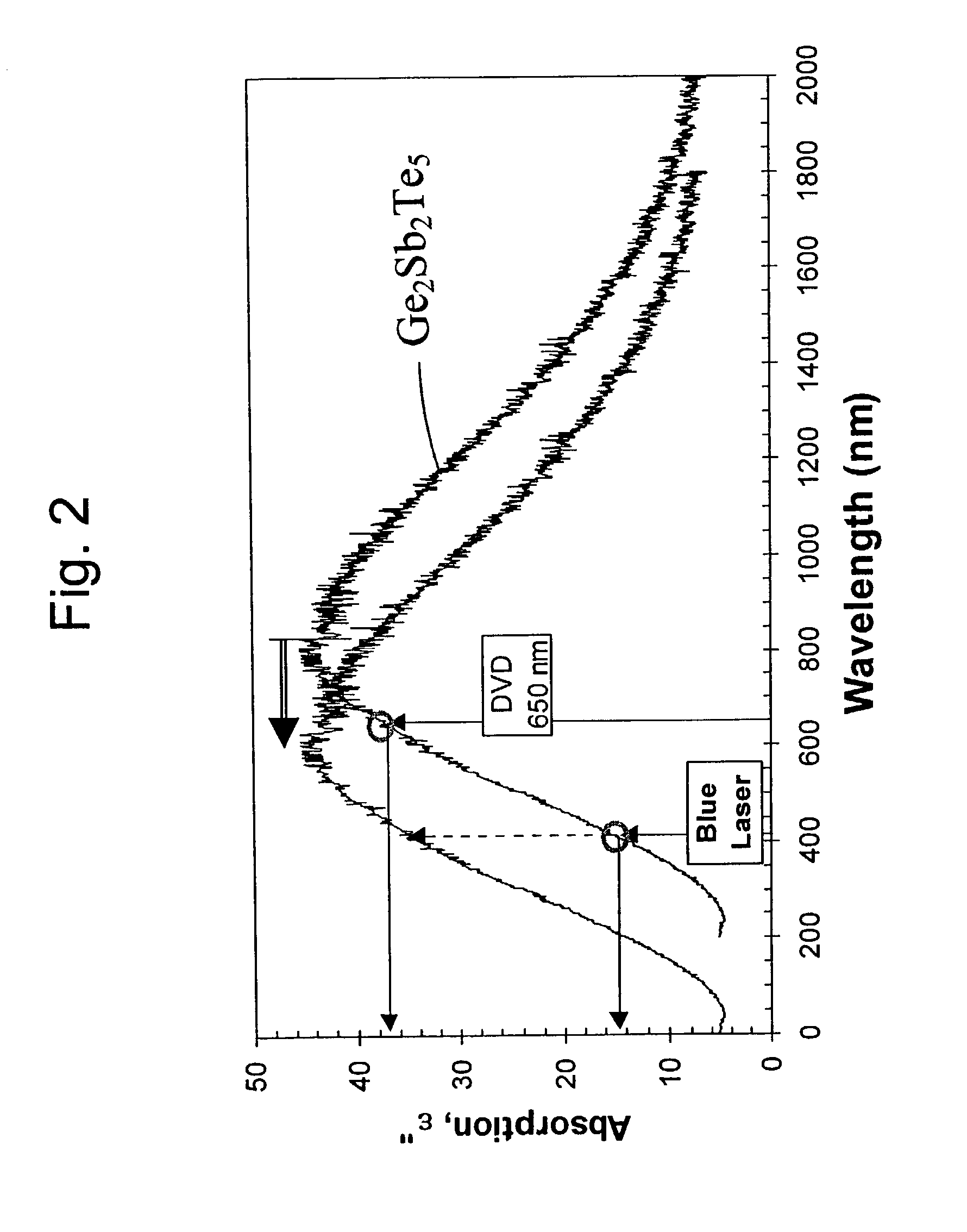
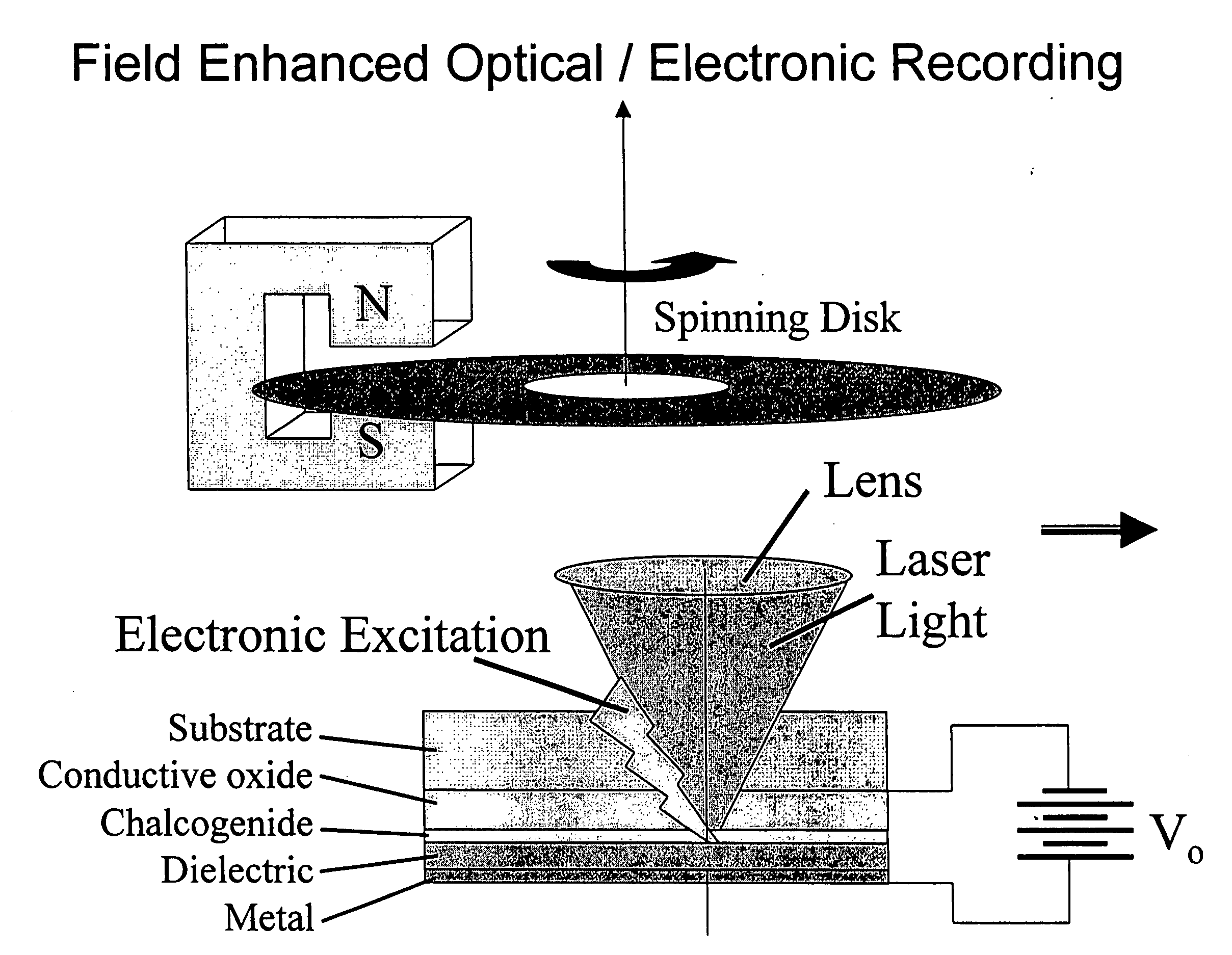
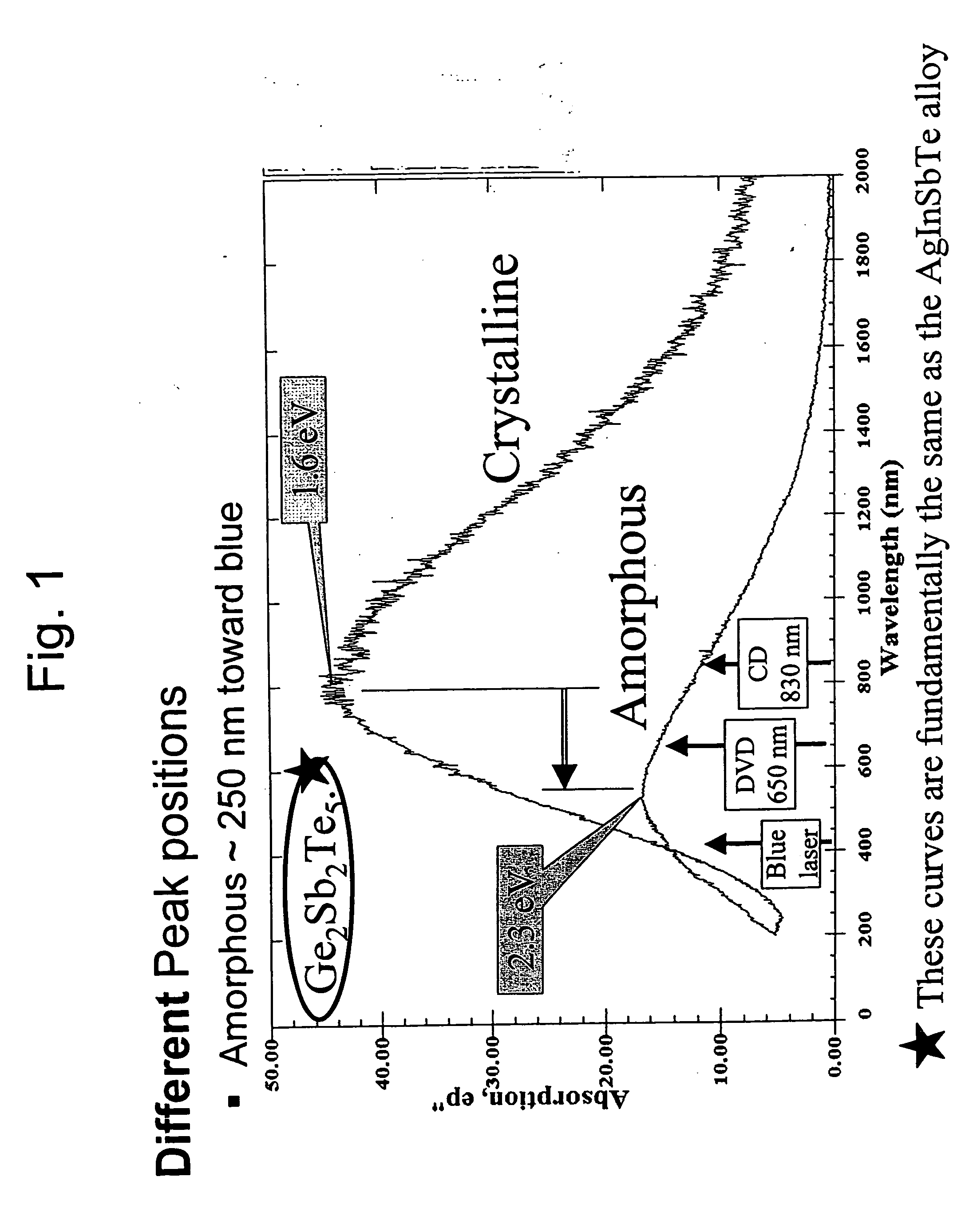
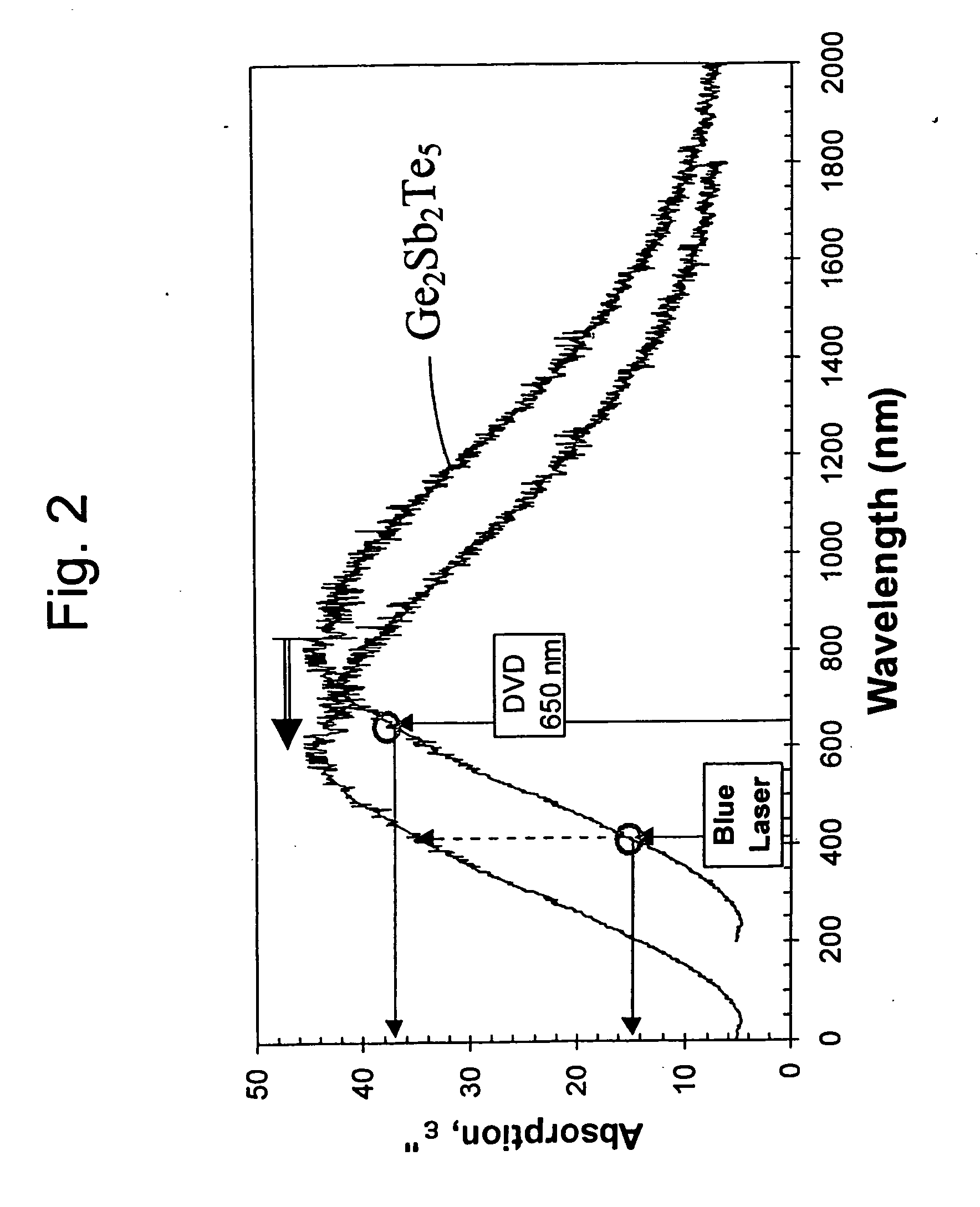
Increased data storage in optical data storage and retrieval systems using blue lasers and/or plasmon lenses
InactiveUS7113474B2Improve recordImprove erase efficiencyRecording by optical meansNanoinformaticsPhase-change memoryPlasmonic coupling
An optical recording medium includes a crystallizing layer for enhancing the crystallization of a phase change memory layer, an energy storage layer for aiding the state transformations of a phase change memory layer, and / or a modifying element for increasing absorption and contrast at short wavelengths. An optical data storage and retrieval system containing same. Also a light-plasmon coupling lens including an optically transparent substrate having a light incident surface and a light-plasmon coupling surface opposite the light incident surface. The light-plasmon coupling surface including at least a set of circular concentric peaks / valleys which form a Fourier sinusoidal pattern in the radial direction of the circular concentric peaks / valleys. A conformal layer of metal is deposited on the light-plasmon coupling surface of the substrate and has aperture at the center of thereof through which plasmons are transmitted.
Owner:OPTICAL MEMORY STORAGE
Method for Long-Term Storage of Information and Storage Medium Therefor
ActiveUS20210046588A1Cheap and efficient information storage systems has been acuteEasy to degradeElectron beam carrier recordingVacuum evaporation coatingParticle beamCeramic substrate
The present invention relates to an information storage medium and a method for long-term storage of information comprising the steps of: providing a ceramic substrate; coating the ceramic substrate with a layer of a second material different from the material of the ceramic substrate, the layer having a thickness no greater than 10 μm; tempering the coated ceramic substrate to form a writable plate or disc; encoding information on the writable plate or disc by using a laser and / or a focused particle beam to manipulate localized areas of the writable plate or disc.
Owner:CERAMIC DATA SOLUTIONS GMBH
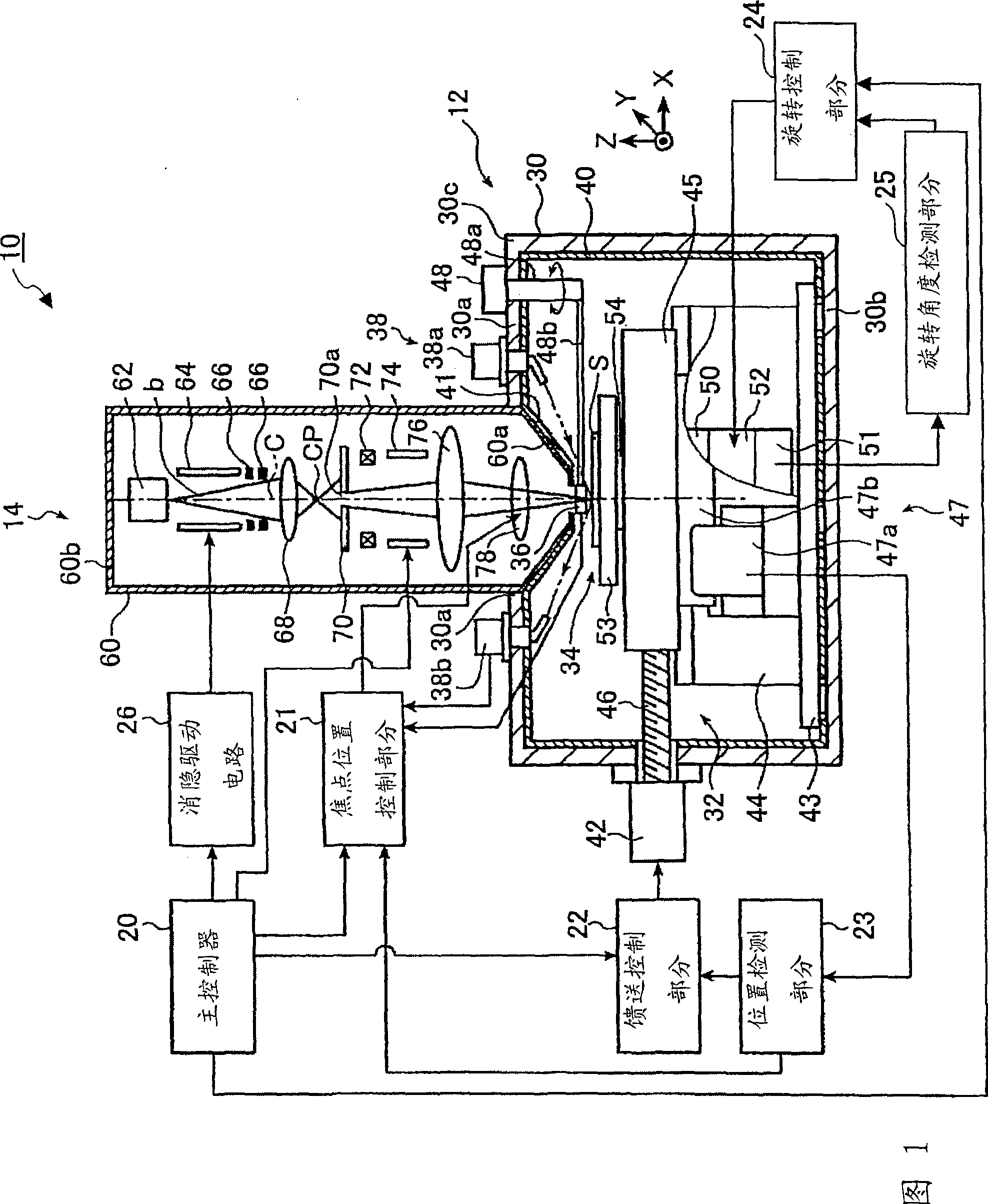
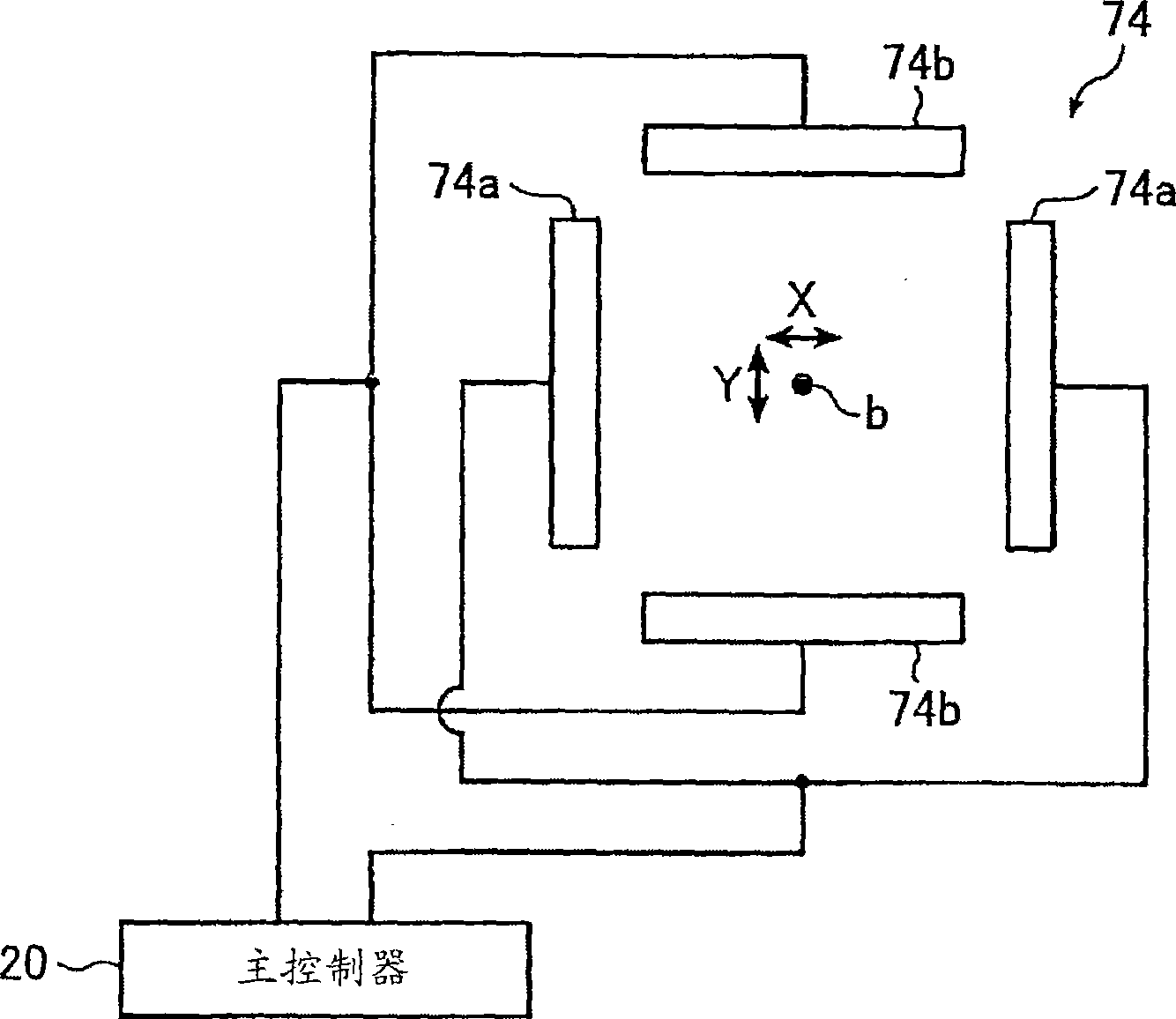
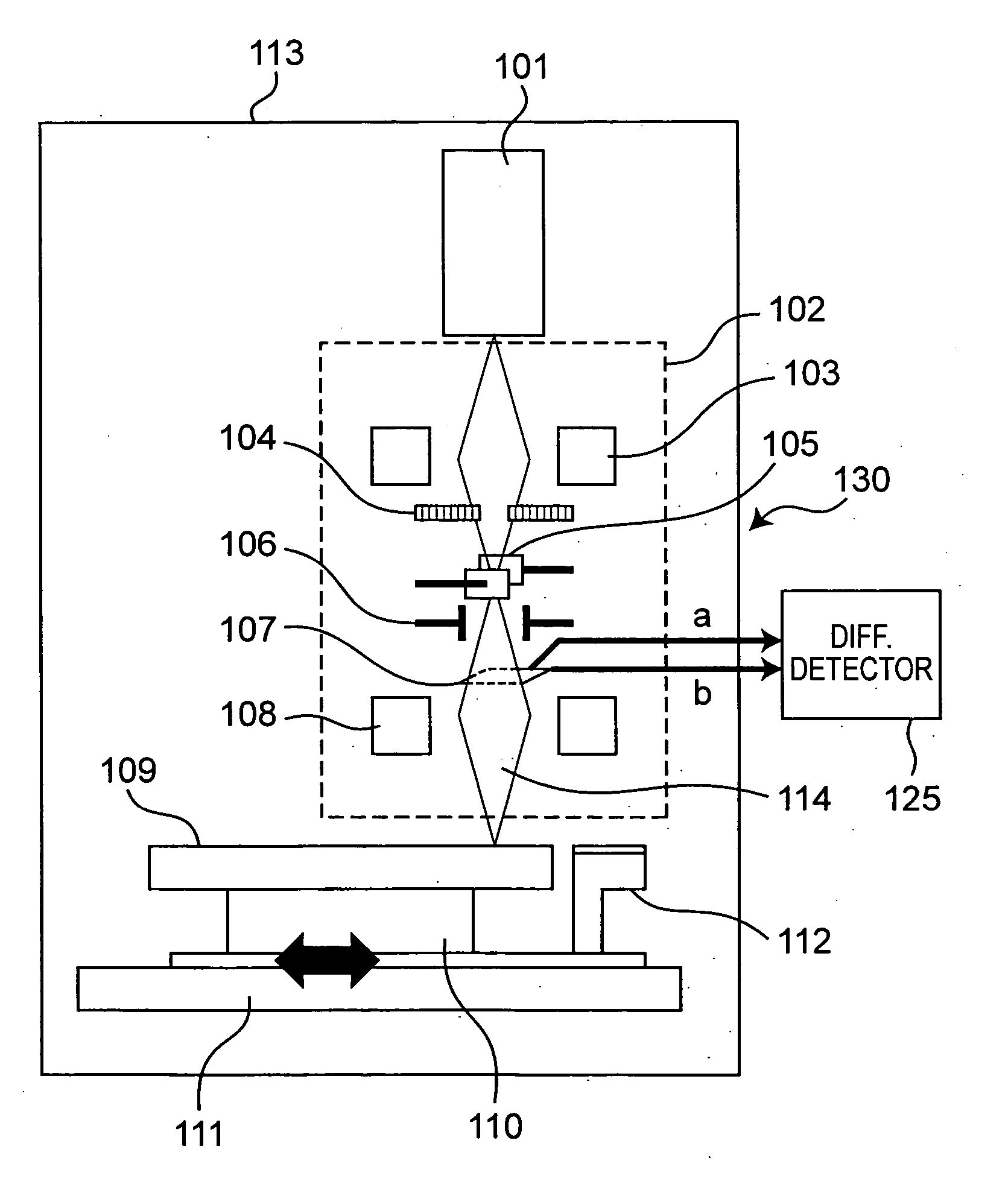
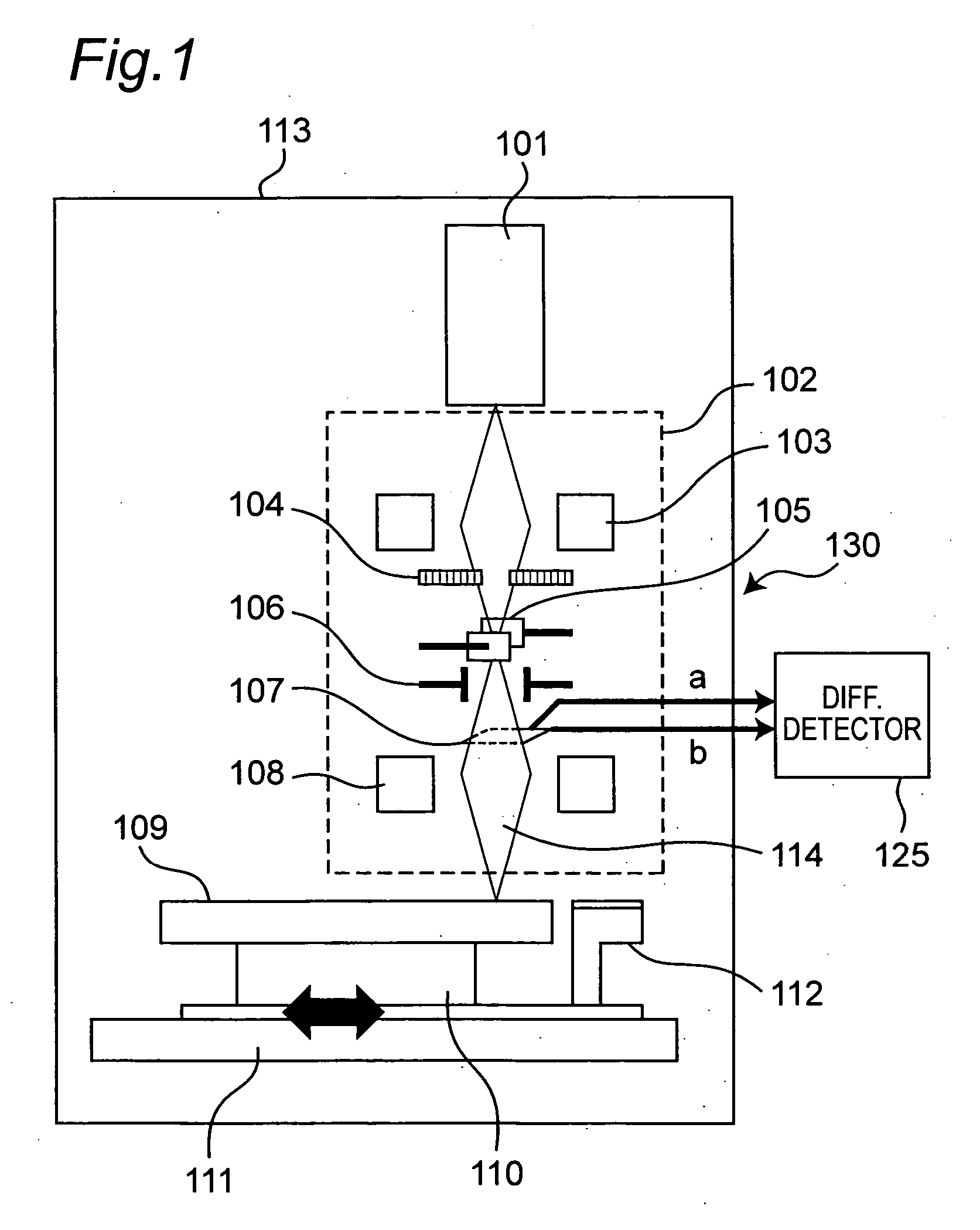
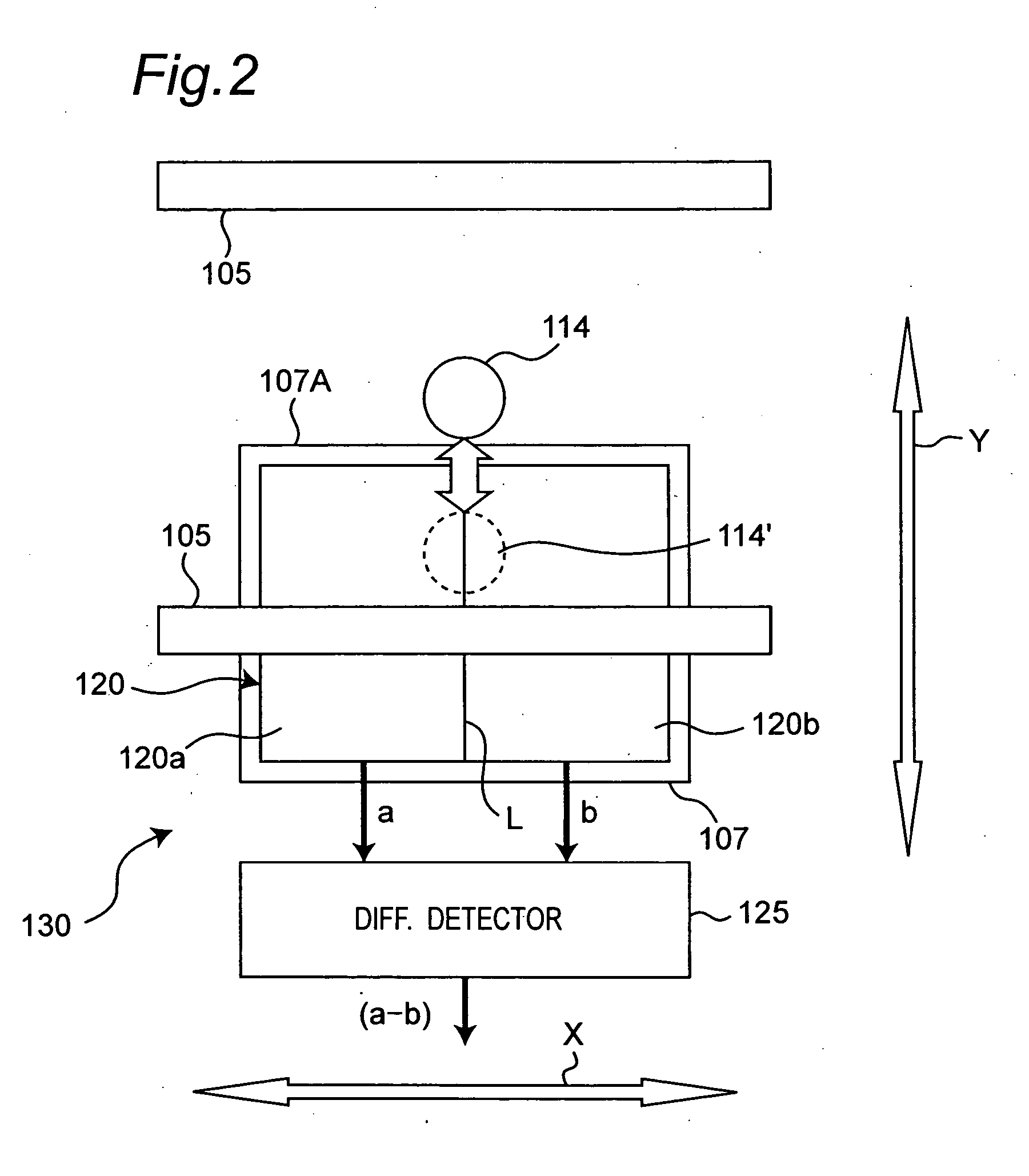
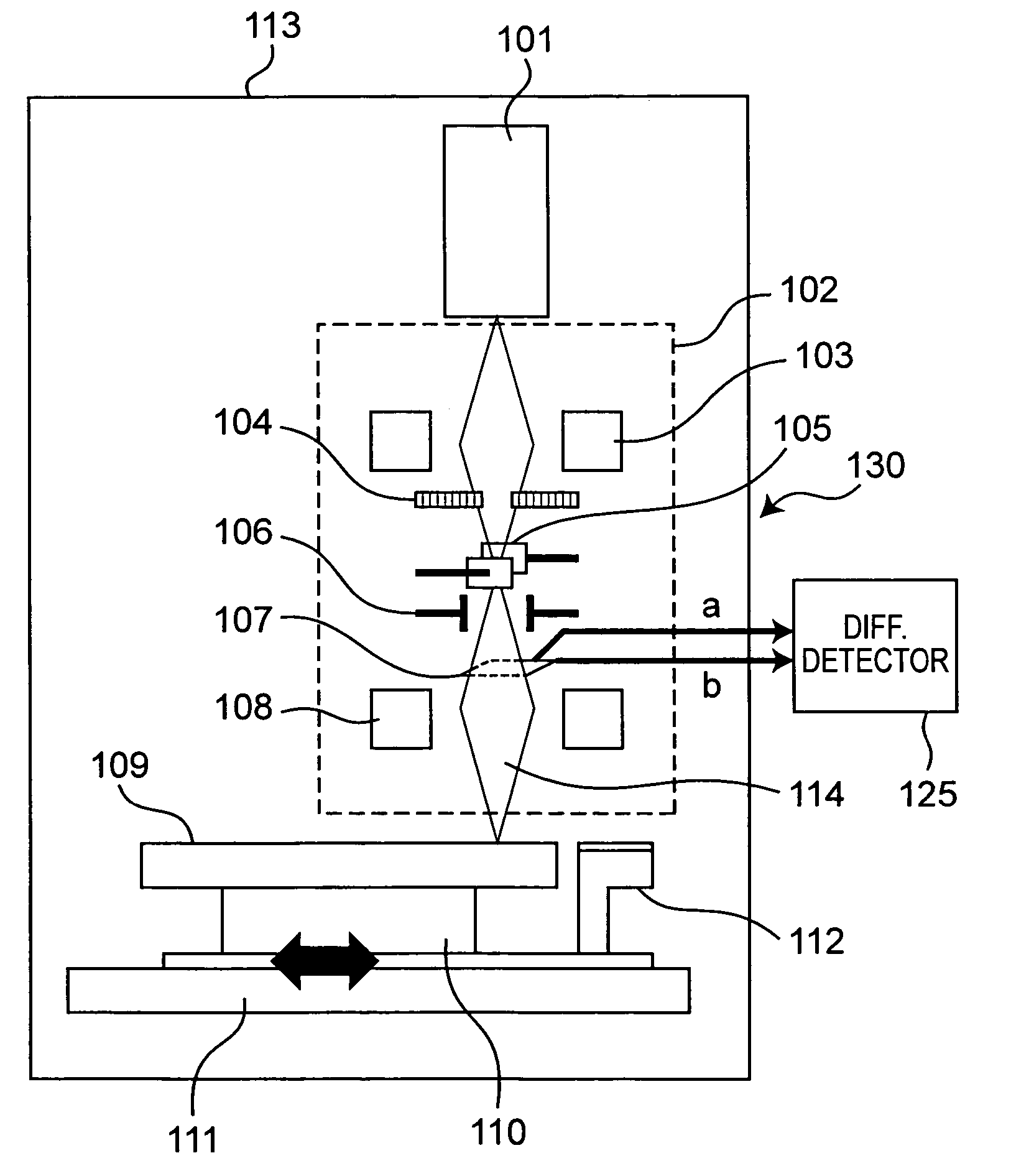
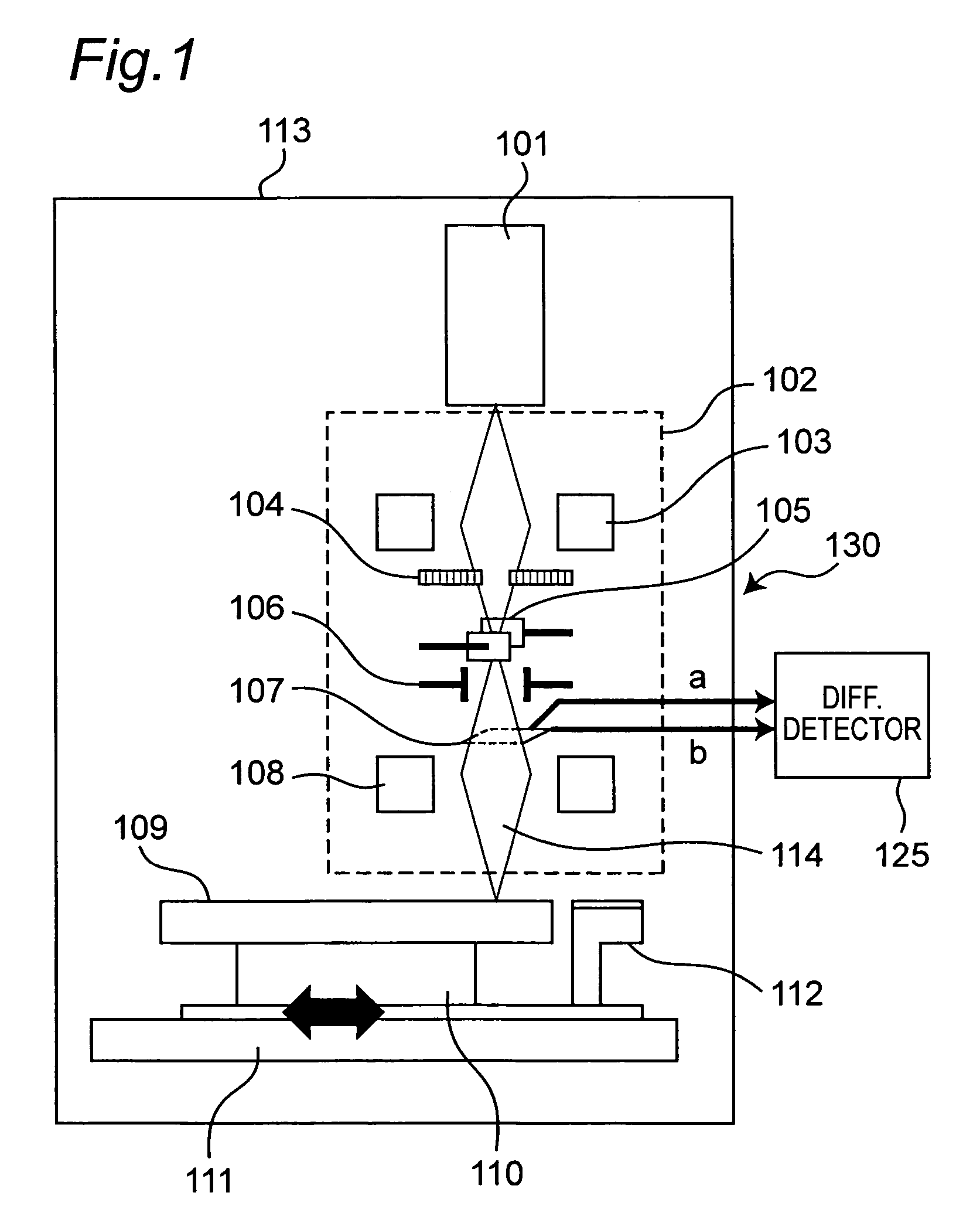
Electron beam recorder, electron beam irradiation position detecting method and electron beam irradiation position controlling method
InactiveUS20050232114A1Improve accuracyCorrection for variationElectron beam carrier recordingElectric discharge tubesElectron bunchesAtomic physics
An electron beam recorder includes an electron optical system for irradiating the electron beam on a master of an information recording medium and a shielding plate for shielding the electron beam. An electron beam irradiation quantity detector is provided on the shielding plate and is divided into first and second electron beam detecting portions along an information recording direction on the master. A difference detector calculates a difference between a first quantity of the electron beam irradiated on the first electron beam detecting portion and a second quantity of the electron beam irradiated on the second electron beam detecting portion such that a position of the electron beam in a direction substantially perpendicular to the information recording direction is detected from the difference.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Fabrication of digital media using ion beam technology and digital media created using ion beam technology
InactiveCN101432812ARecord information storageRecording involving reflectivity/absorption/color-changeControl mannerIon beam
A method for writing data to an optical medium includes directing intermittent pulses of a beam of ions from an ion source onto an optical medium in a controlled pattern for creating surface features on the optical medium, the surface features representing data. A system for performing this method, according to one embodiment, includes a medium receiving portion for holding an optical medium, an ion source for emitting a beam of ions at the optical medium on the medium receiving portion, and a steering mechanism for directing the ion beam onto the optical medium in a controlled manner. The beam of ions strikes the optical medium in intermittent pulses for creating surface features on the optical medium, the surface features representing data.
Owner:查理·马歇尔
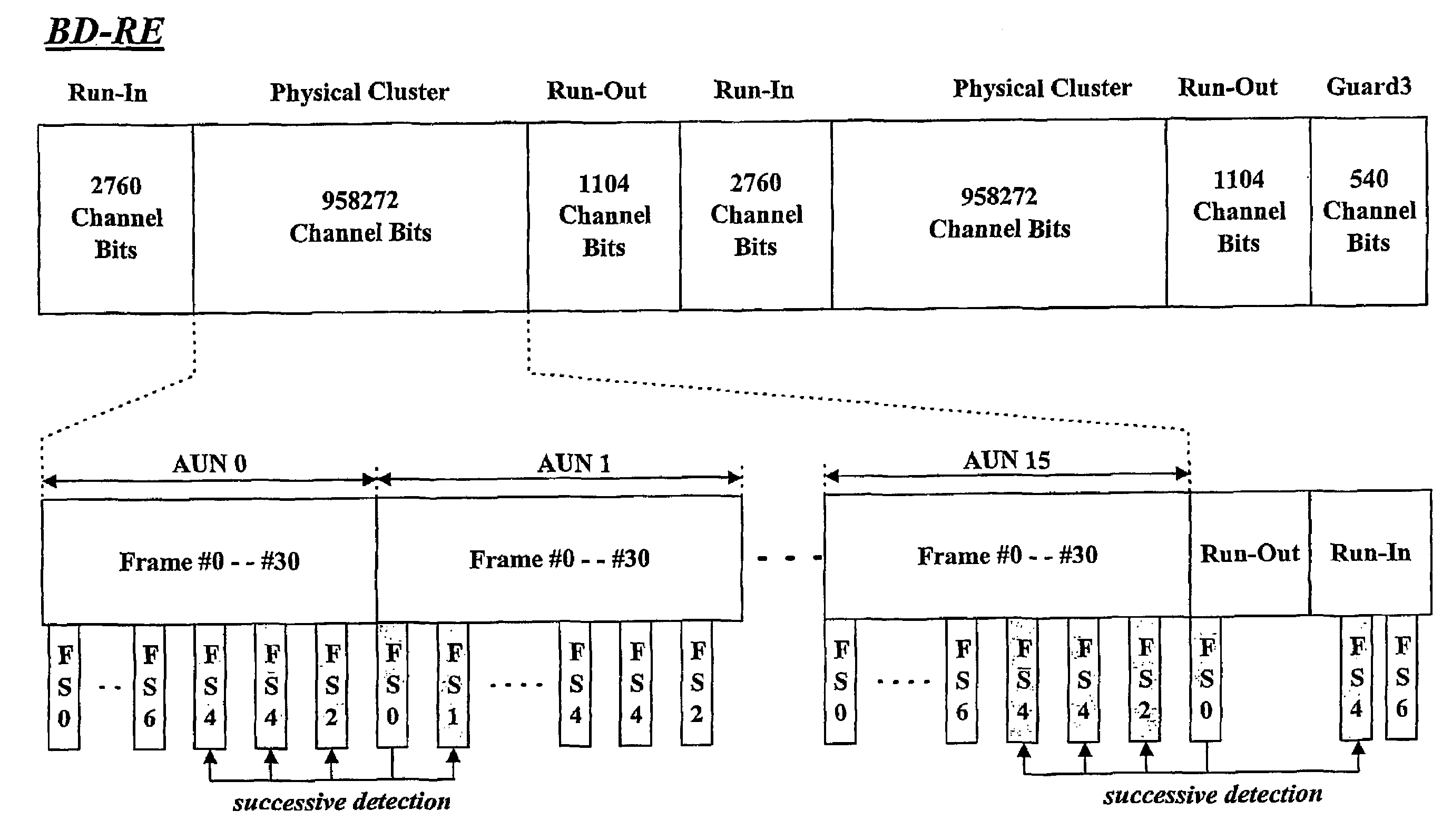
Method and apparatus of determining a recording location on a high-density recording medium
InactiveUS7215622B2Recording by optical meansRecord information storageComputer hardwareHigh density
The present invention relates to method and apparatus of determining a recording location of a high-density recording medium. The present method determines a targeted recording location on a high-density rewritable or read-only recording medium based on successively-detected frame syncs or their combination that includes at least one frame sync written after the targeted recording location.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method of Writing on an Optical Recording Medium, Optical Recording Medium, and Method of Manufacturing an Optical Recording Medium
InactiveUS20080212459A1Improve accuracyLess contrastMechanical record carriersRecord information storageLength waveOptical recording
The present invention relates to a method of writing information on an optical recording medium (10 to 38), the optical recording medium having at least one data layer (40) for storing data readable by use of an optical readout device and at least one label layer (42) for storing visible information, the method comprising the steps of: focusing a first wavelength laser beam (44 to 58) onto the at least one data layer for writing data on the data layer, and focusing a second wavelength laser beam (60 to 78) onto the at least one label layer for writing visible information on the label layer, thereby a laser spot size being usable that is also employable when using the second wavelength laser beam for writing data on a data layer for storing data readable by use of an optical readout device. The present invention further relates to an optical recording medium and to a method of manufacturing an optical recording medium.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Optical data storage and systems utilizing plasmon lenses
InactiveUS20060245333A1Improved optical recordingImprove efficiencyRecording by optical meansNanoinformaticsPlasmonic couplingOptical recording
Owner:OPTICAL MEMORY STORAGE
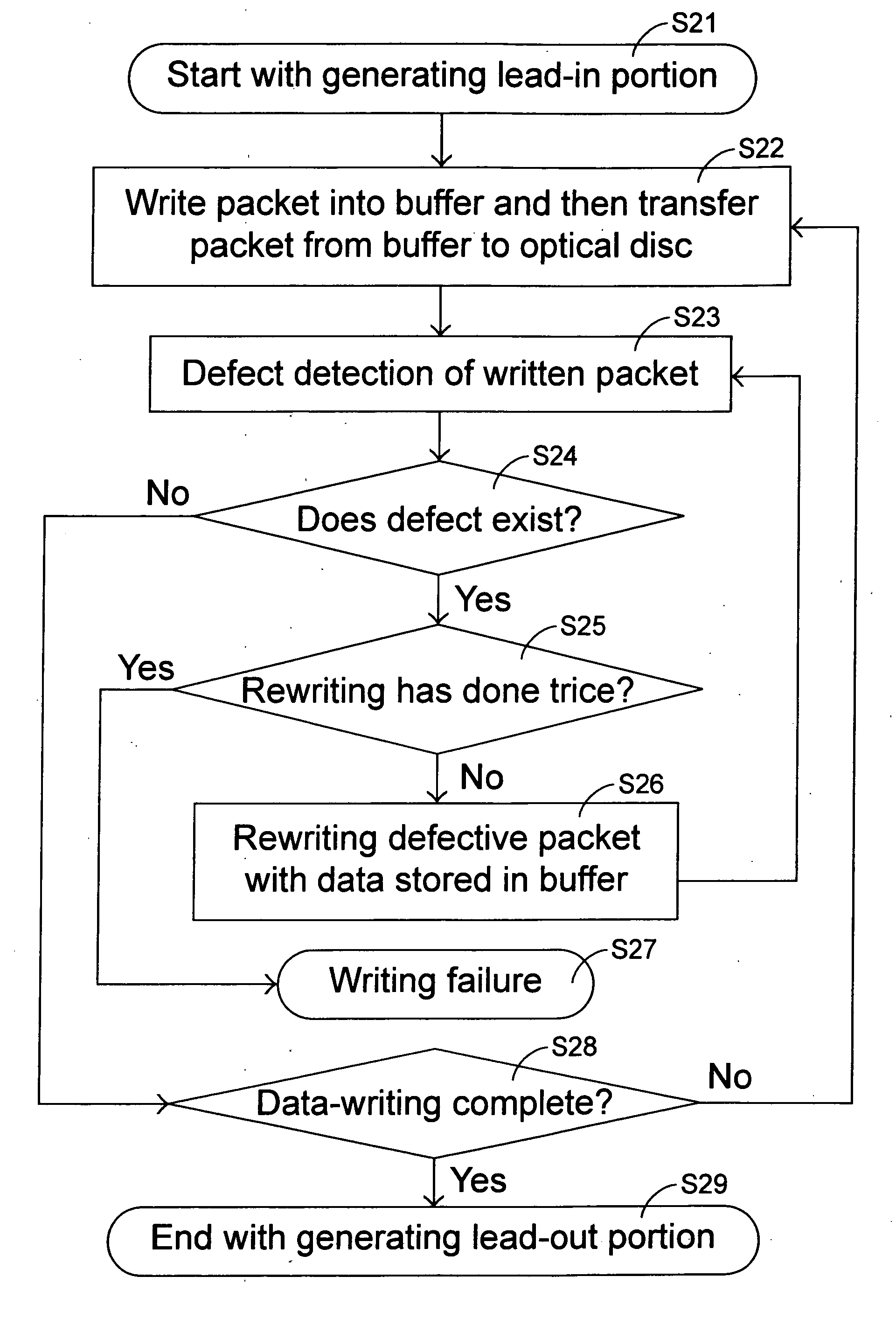
Data writing method
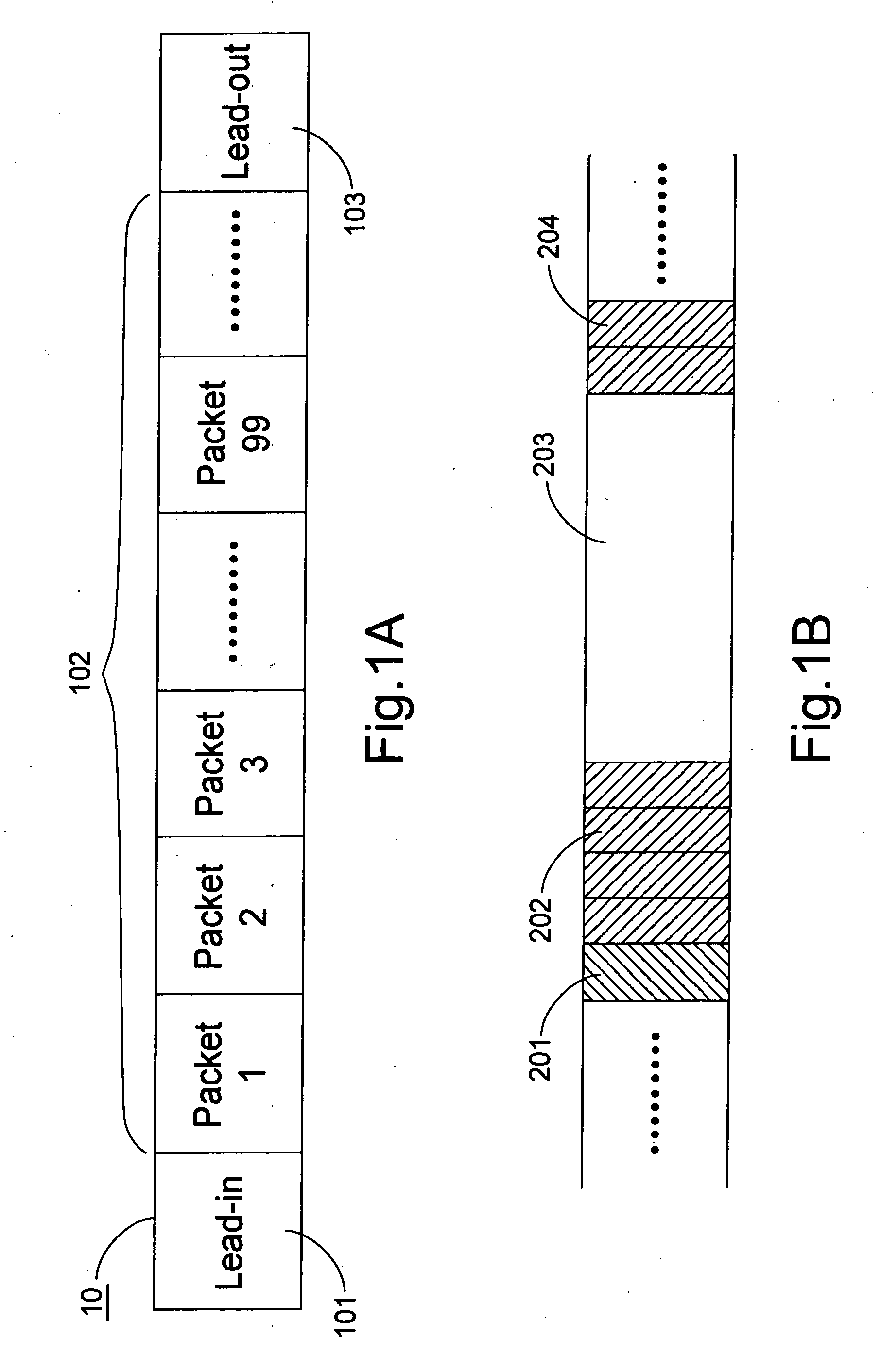
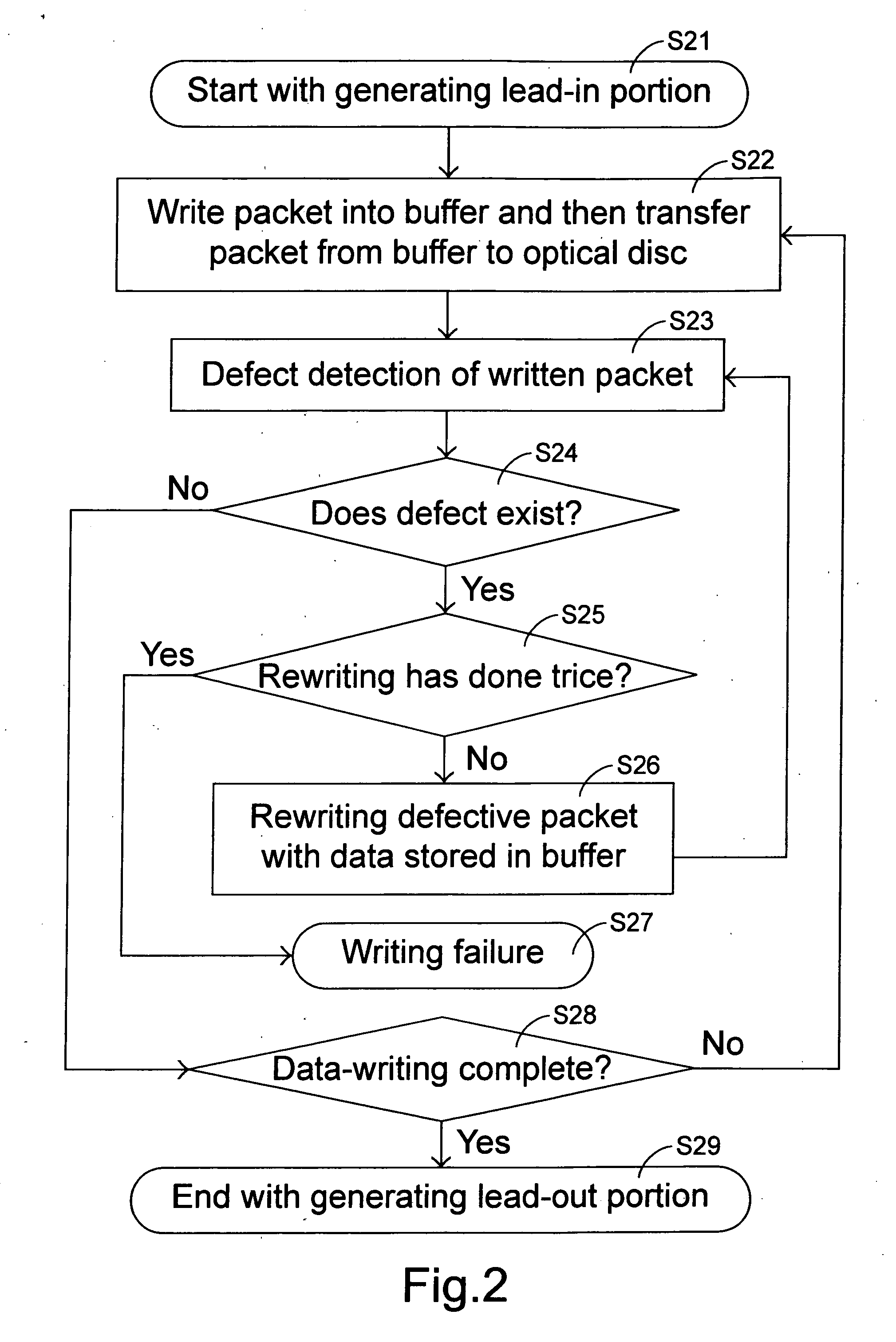
InactiveUS20050286378A1High readingHigh writing accuracyRecording verificationRecording by optical meansData packOptical recording
A data writing method is used with an optical recording apparatus to write data into a rewritable disc. For writing data, the optical recording apparatus enters a writing mode and a first packet is written into the rewritable disc. Then, the optical recording apparatus enters a detecting mode and data of the first packet written into the rewritable disc are read for defect detection. If no defect of the first packet is detected in the detecting mode, the writing mode is entered again, so a second packet can be written into the rewritable disc. On the other hand, if a defect of the first packet is detected in the detecting mode, a rewriting mode will be entered and the first packet is rewritten into the rewritable disc again.
Owner:LITE ON IT
Electron beam recorder, electron beam irradiation position detecting method and electron beam irradiation position controlling method
InactiveUS7474604B2Improve accuracyCorrection for variationElectron beam carrier recordingElectric discharge tubesElectron bunchesAtomic physics
An electron beam recorder includes an electron optical system for irradiating the electron beam on a master of an information recording medium and a shielding plate for shielding the electron beam. An electron beam irradiation quantity detector is provided on the shielding plate and is divided into first and second electron beam detecting portions along an information recording direction on the master. A difference detector calculates a difference between a first quantity of the electron beam irradiated on the first electron beam detecting portion and a second quantity of the electron beam irradiated on the second electron beam detecting portion such that a position of the electron beam in a direction substantially perpendicular to the information recording direction is detected from the difference.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Defective sector determination device and optical disk drive
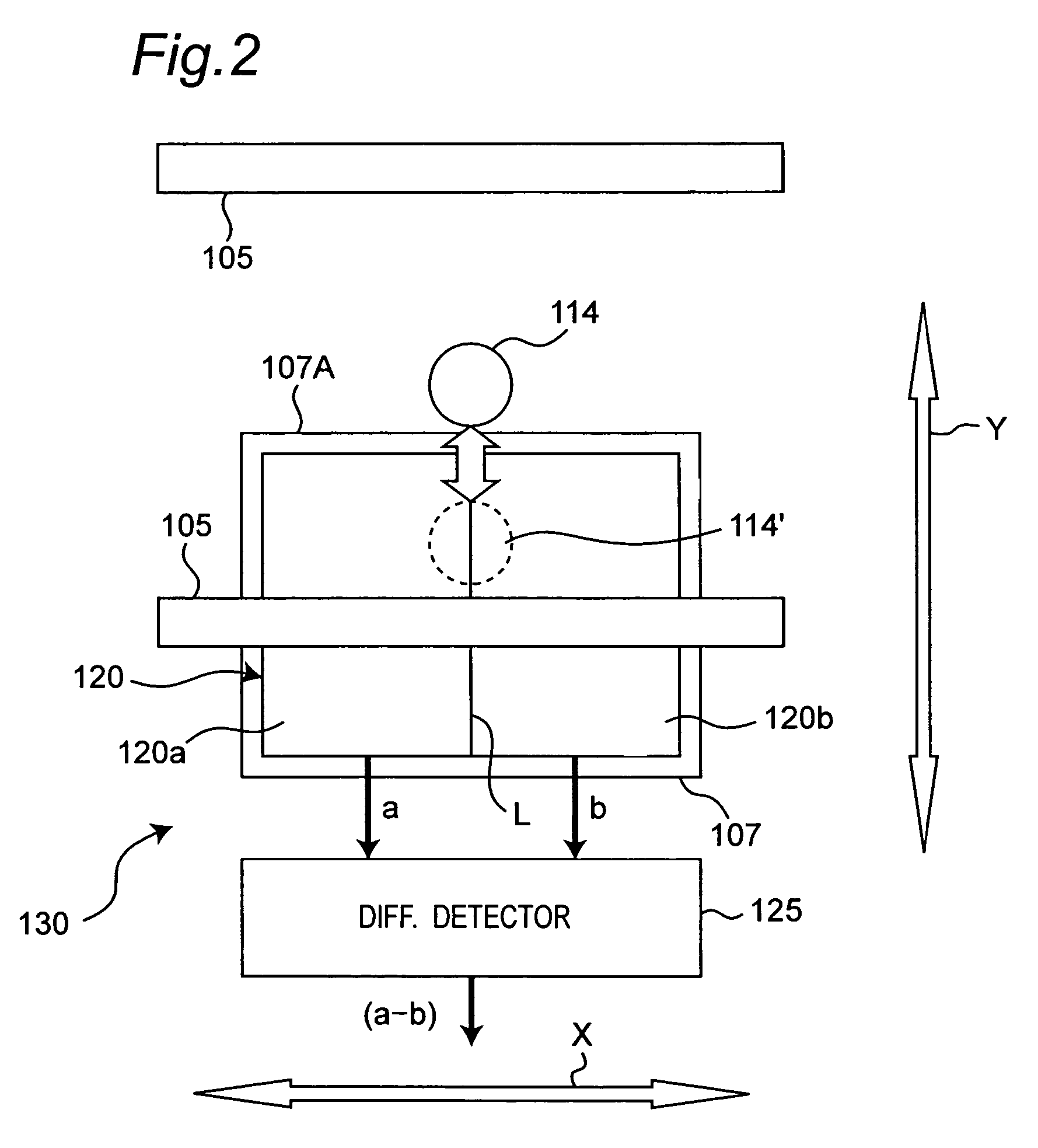
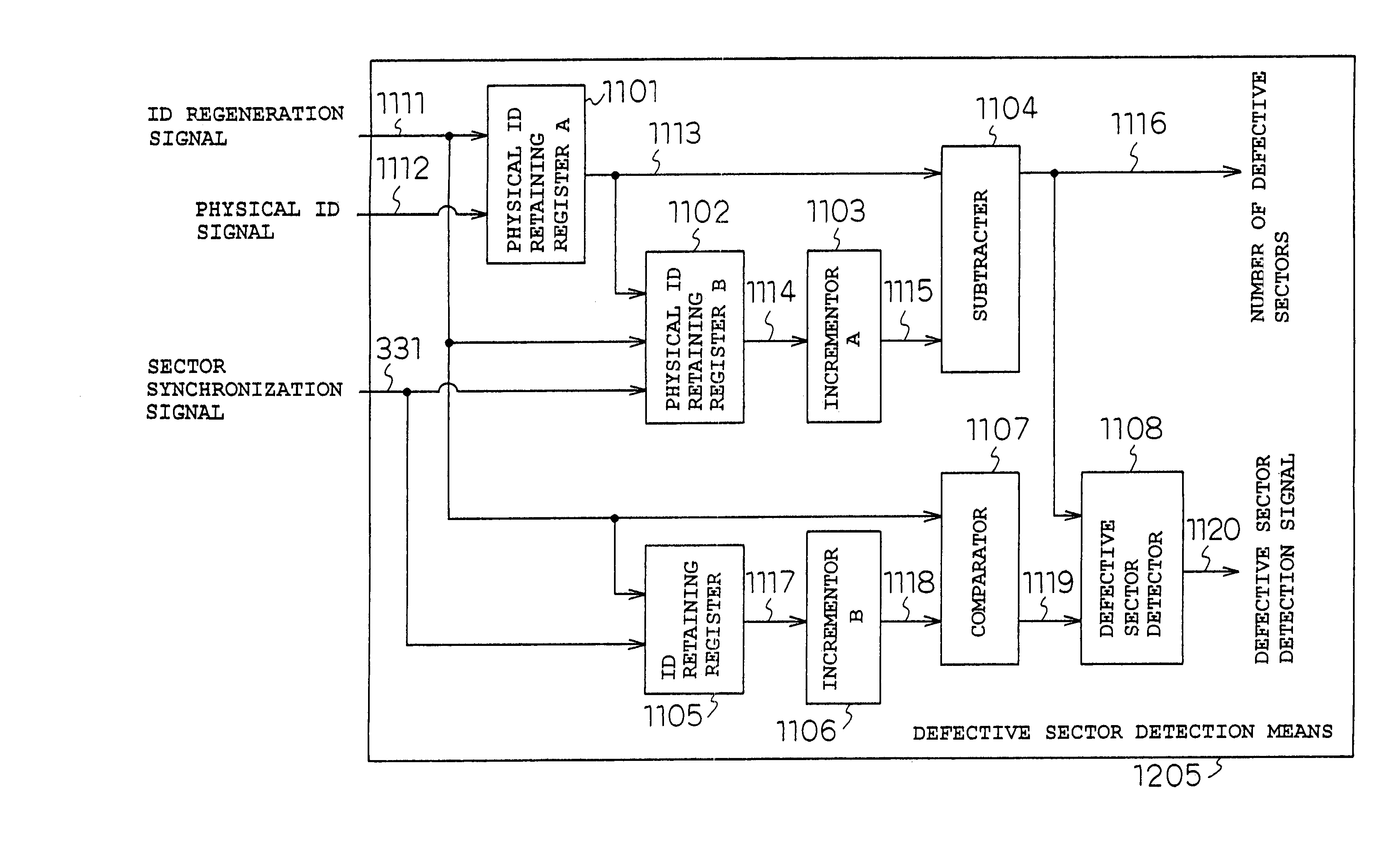
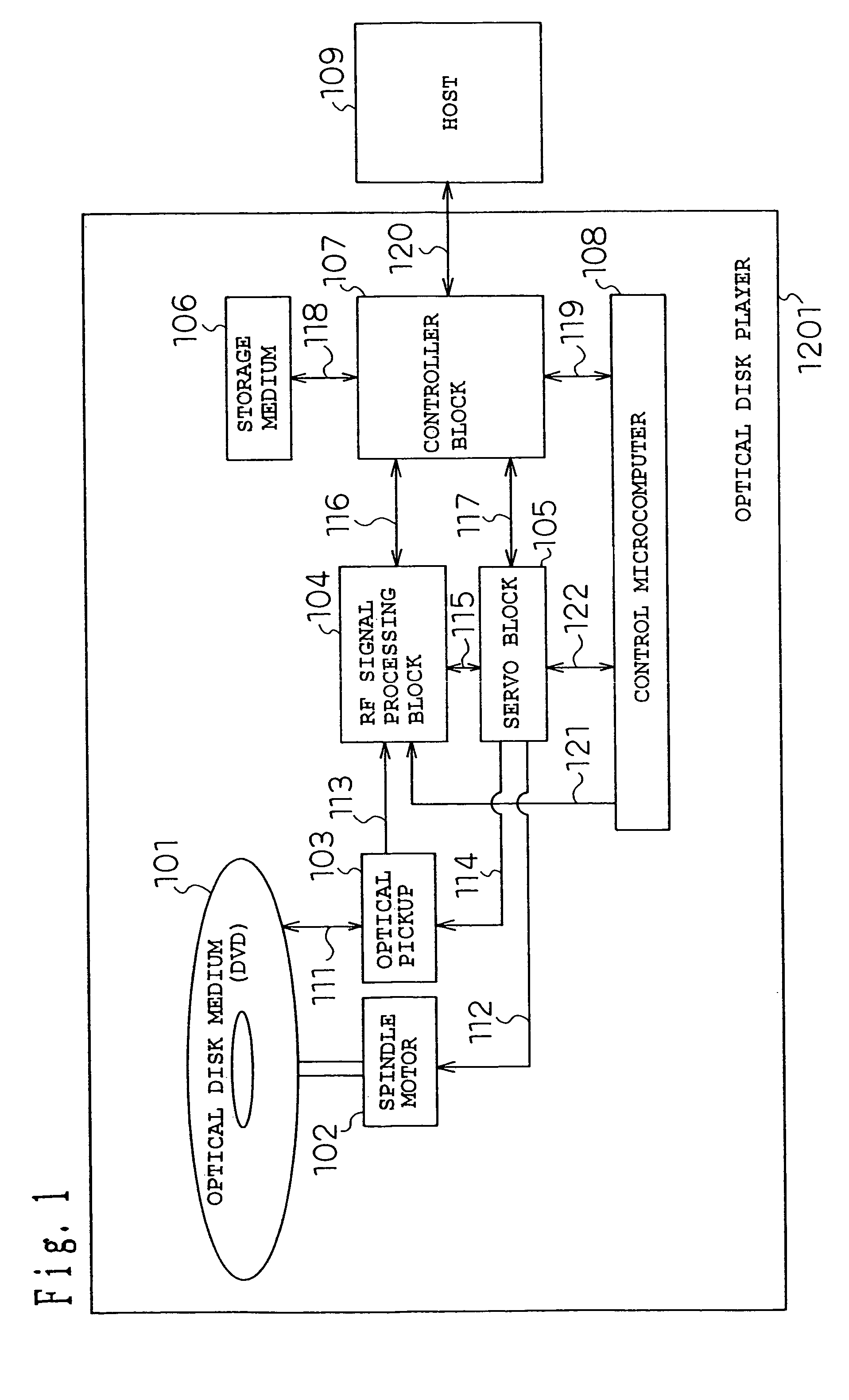
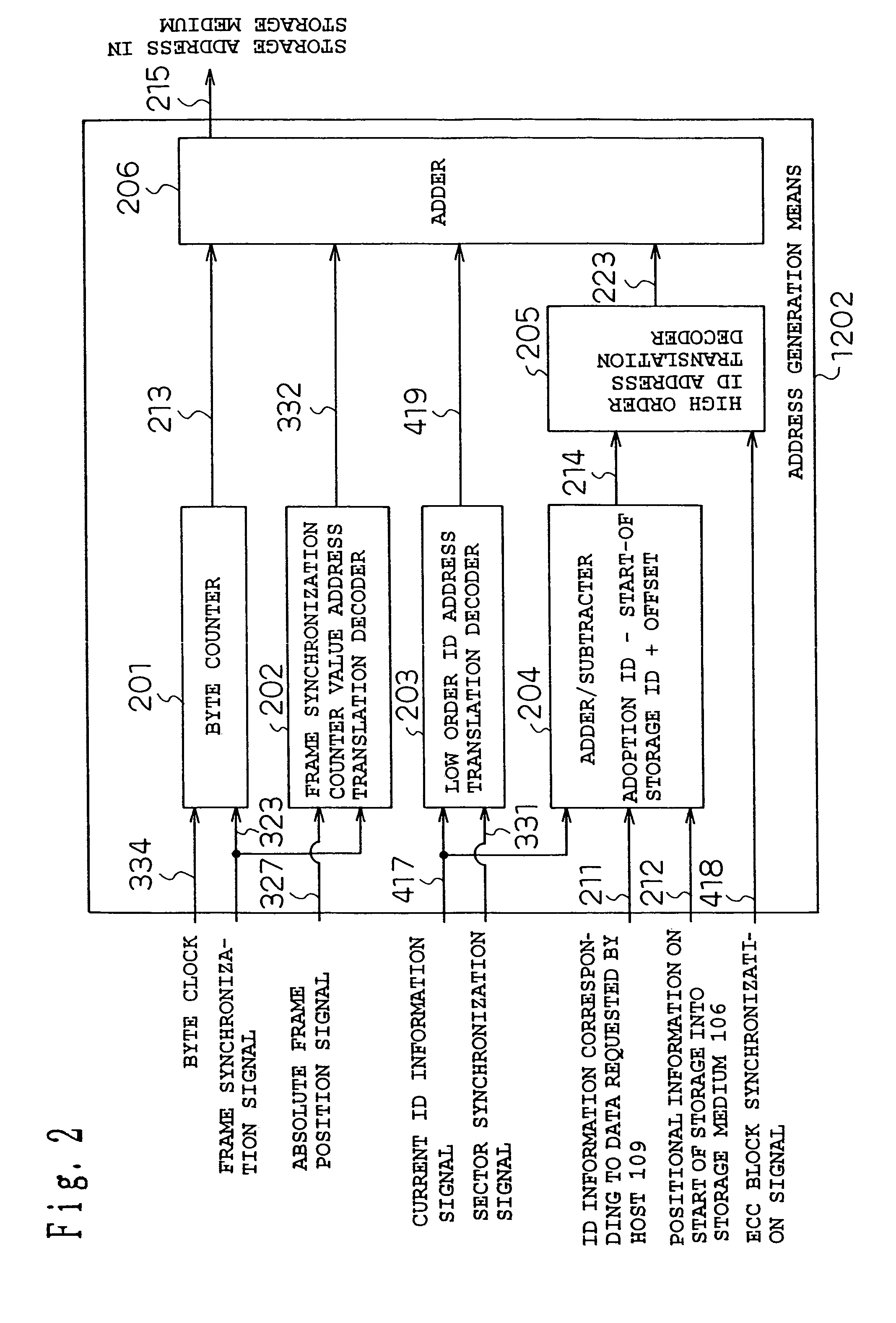
InactiveUS7116618B2Keep safeRecording by optical meansFilamentary/web record carriersOptical disc driveInformation transformation
To provide an optical disk drive having an enhanced replaying capability in case of an abnormality occurring in various kinds of synchronization of the optical disk drive or in replay of a defective sector. A frame synchronization counter value address translation decoder, low order ID address translation decoder, adder / subtracter, high order ID address translation decoder, and adder are used to translate information read from an optical disk medium into an absolute storage address in a storage medium, and thus data that is highly replayed can be stored in the storage medium.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
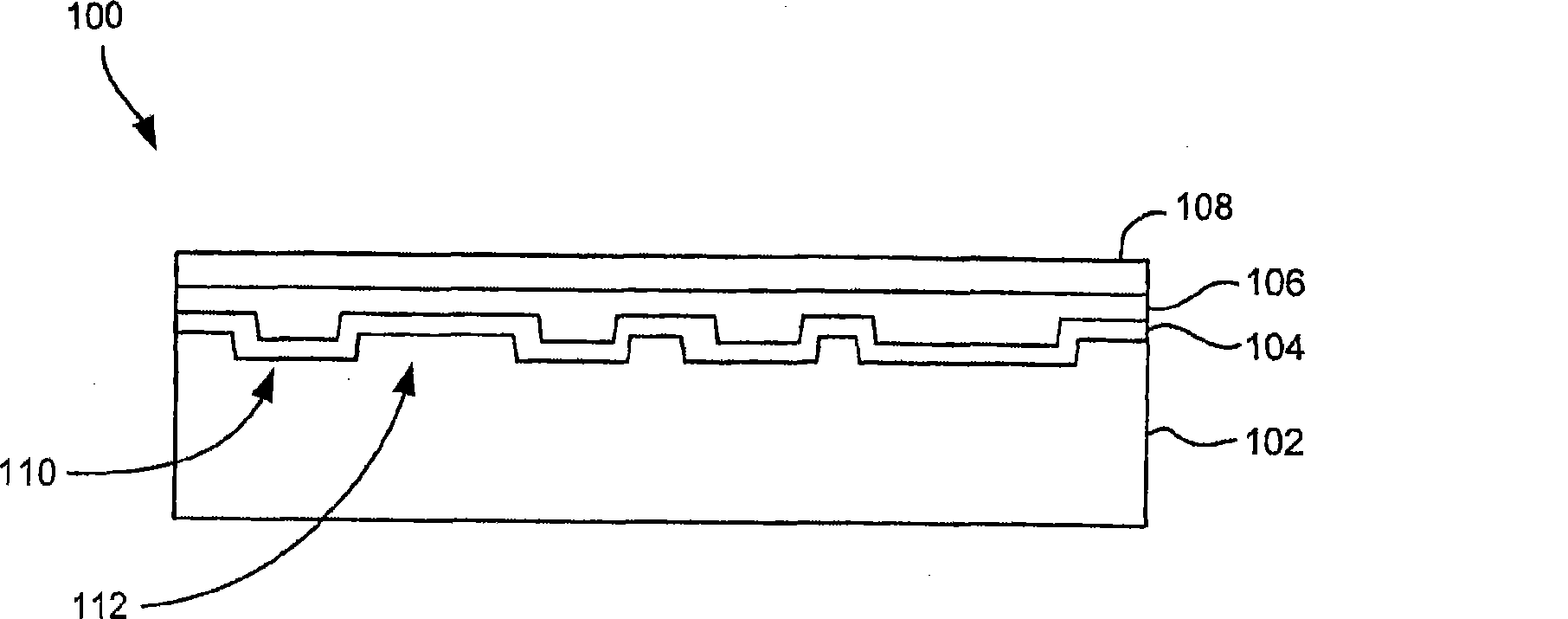
Apparatus for recording of information
InactiveUS7136337B2Avoid failureReliability can be promotedRecording by optical meansOptical beam sourcesOperating systemRecording media
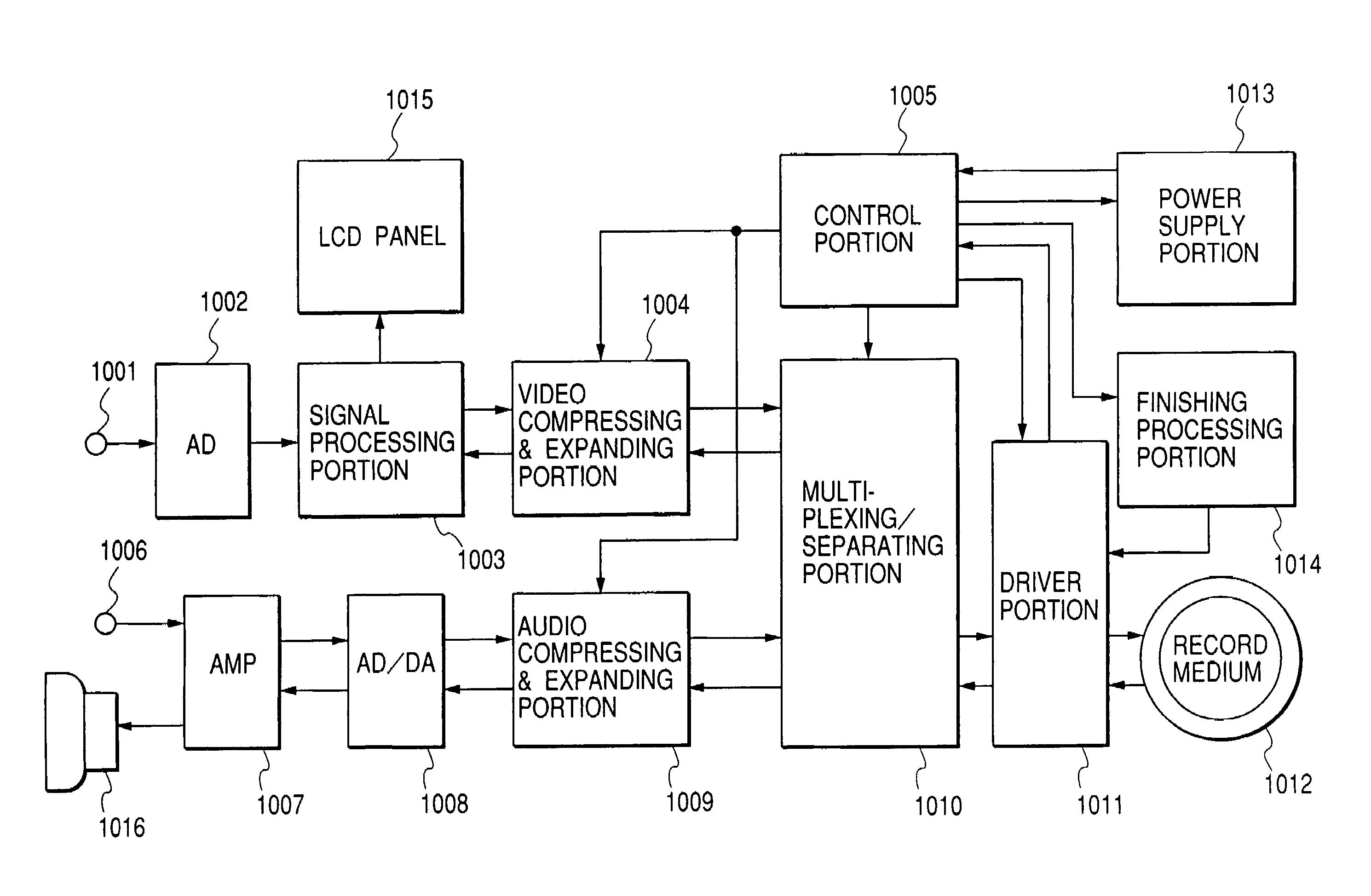
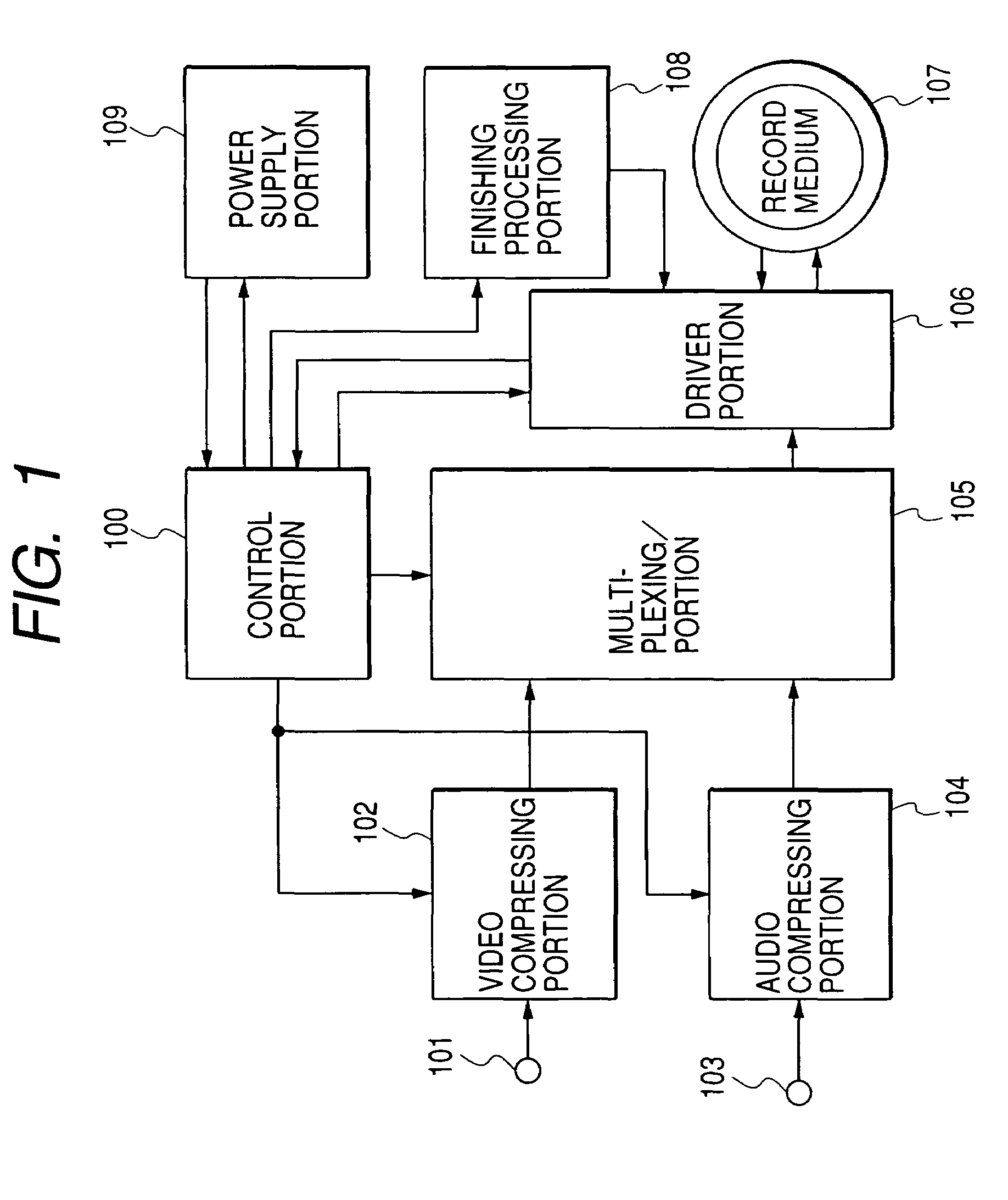
With an object of executing excellent finishing processing when information is recorded to a rewritable type record medium or a write once type record medium, the finishing processing is switched by whether a kind of a medium for recording information is the rewritable type record medium or the write once type record medium and a method of executing the finishing processing is switched based on a state of supplying power.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD +1
Method for restoring data stored on an optical disc and optical disc drive suitable therefore
InactiveUS20070242375A1Easy to readHigh precisionRecording by optical meansFilamentary/web record carriersPhysical changeEngineering
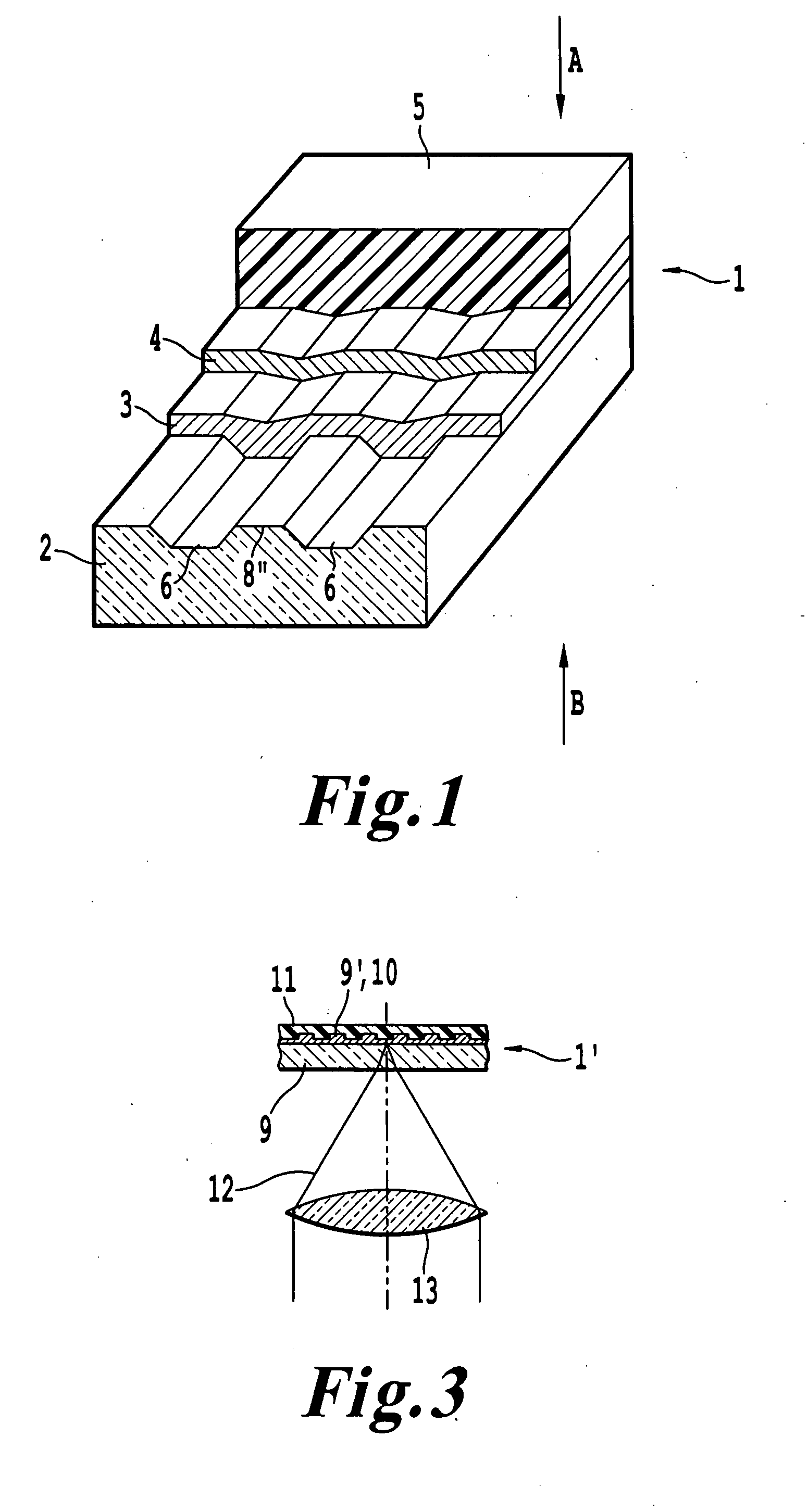
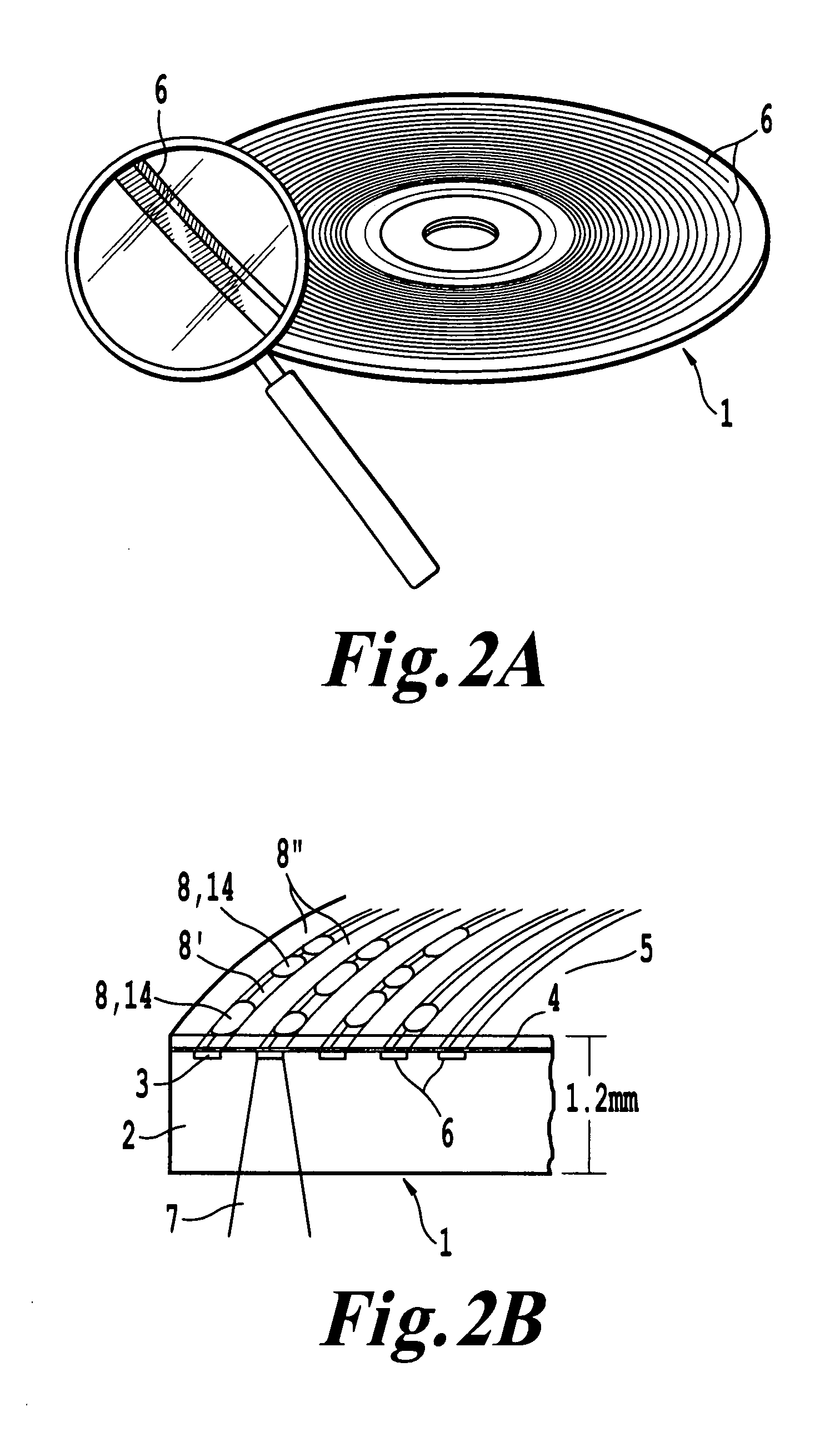
A method for restoring data stored along a data storage path on an optical disc (1) which is unreadable for conventional optical disc drives due to undesired chemical or physical changes within a recording layer (3) of the optical disc comprises the following steps: detecting deformations (14) of a groove (6) extending along the data storage path, the deformations (15) being generated by a laser beam (7) during a recording process, determining the data to be restored from the detected deformations (14) and lands (8′).
Owner:SONY DADC AUSTRIA
Method and system for realizing data access by using transparent substances as carriers
InactiveCN104332164AEasy to store and readLarge storage capacityRecording by optical meansRecording by non-mechanical deformationFractographyDot matrix
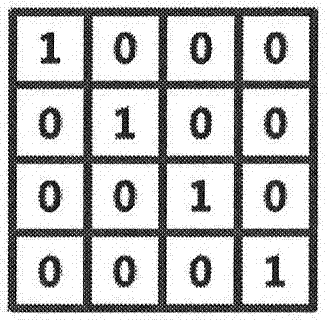
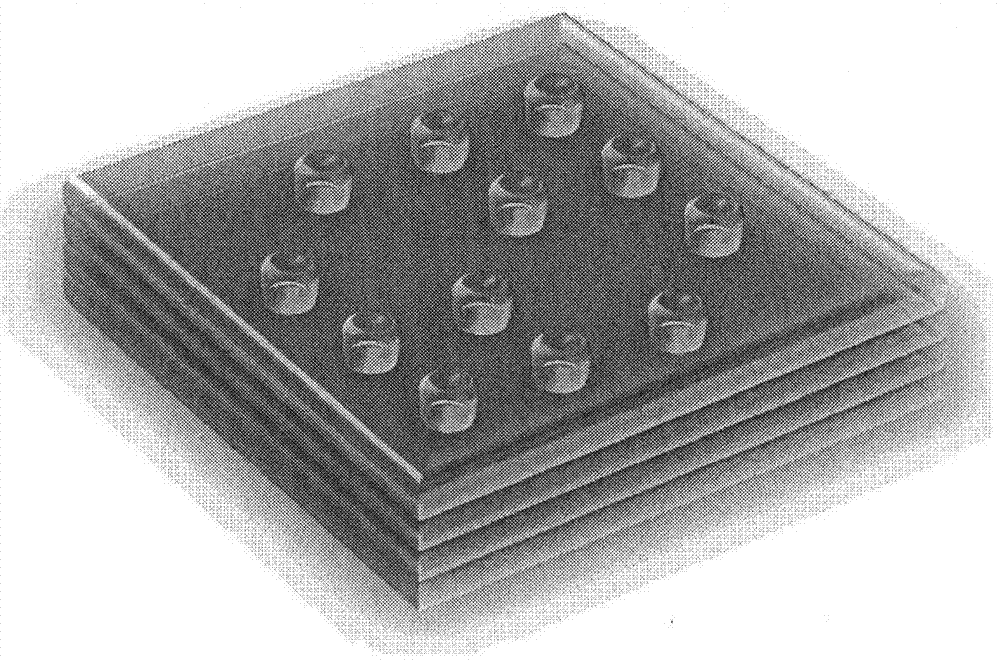
The invention relates to a method and a system for realizing data access by using transparent substances as carriers. The method and the system aim at solving the problems that in the prior art, the storage capacity is small, and the pollution and the damage can easily occur. The method comprises the following steps that: multilayer metamorphic dot matrixes are manufactured inside a transparent body through an internal manufacturing method not destroying an integral structure; and according to a dot matrix information reading method, space positions of the dot matrixes are read, and space distribution data of the dot matrixes is obtained. The internal manufacturing method not destroying the integral structure is an internal engraving method not destroying the integral structure; and the reading is the non-intrusive reading. The internal engraving method not destroying the integral structure is a laser internal engraving method; and the non-intrusive reading is perspective three-dimensional scanning. According to the laser internal engraving method, metamorphic dots including vaporization explosion dots or melting points are formed in the transparent body, and the perspective three-dimensional scanning is tomography. The manufacturing is burning; and the multilayer dot matrixes are layer-by-layer burning. The method and the system have the advantages that the storage capacity is great, the pollution resistance and the damage resistance can be realized, and the information storage and the information reading are convenient.
Owner:汤淼
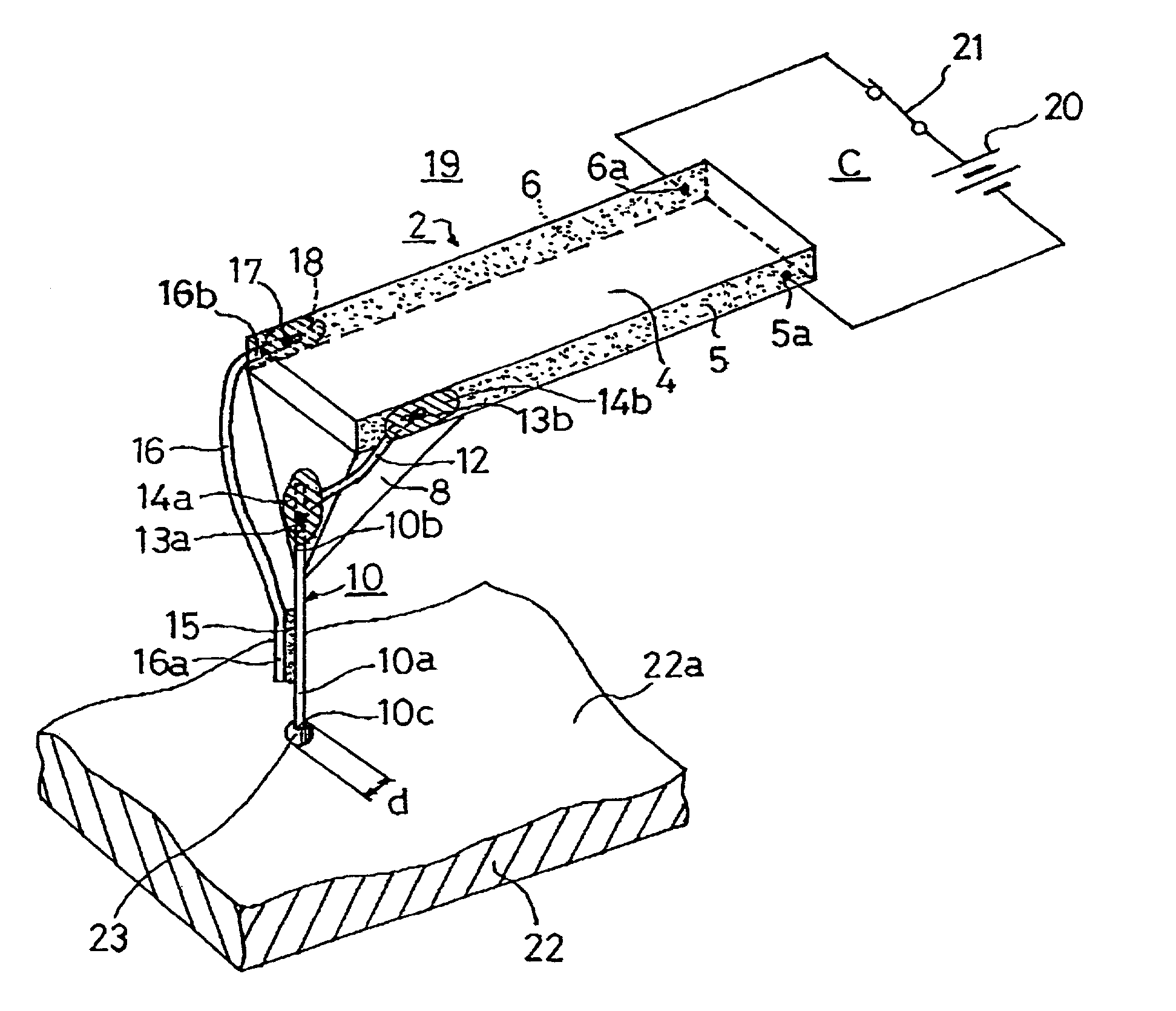
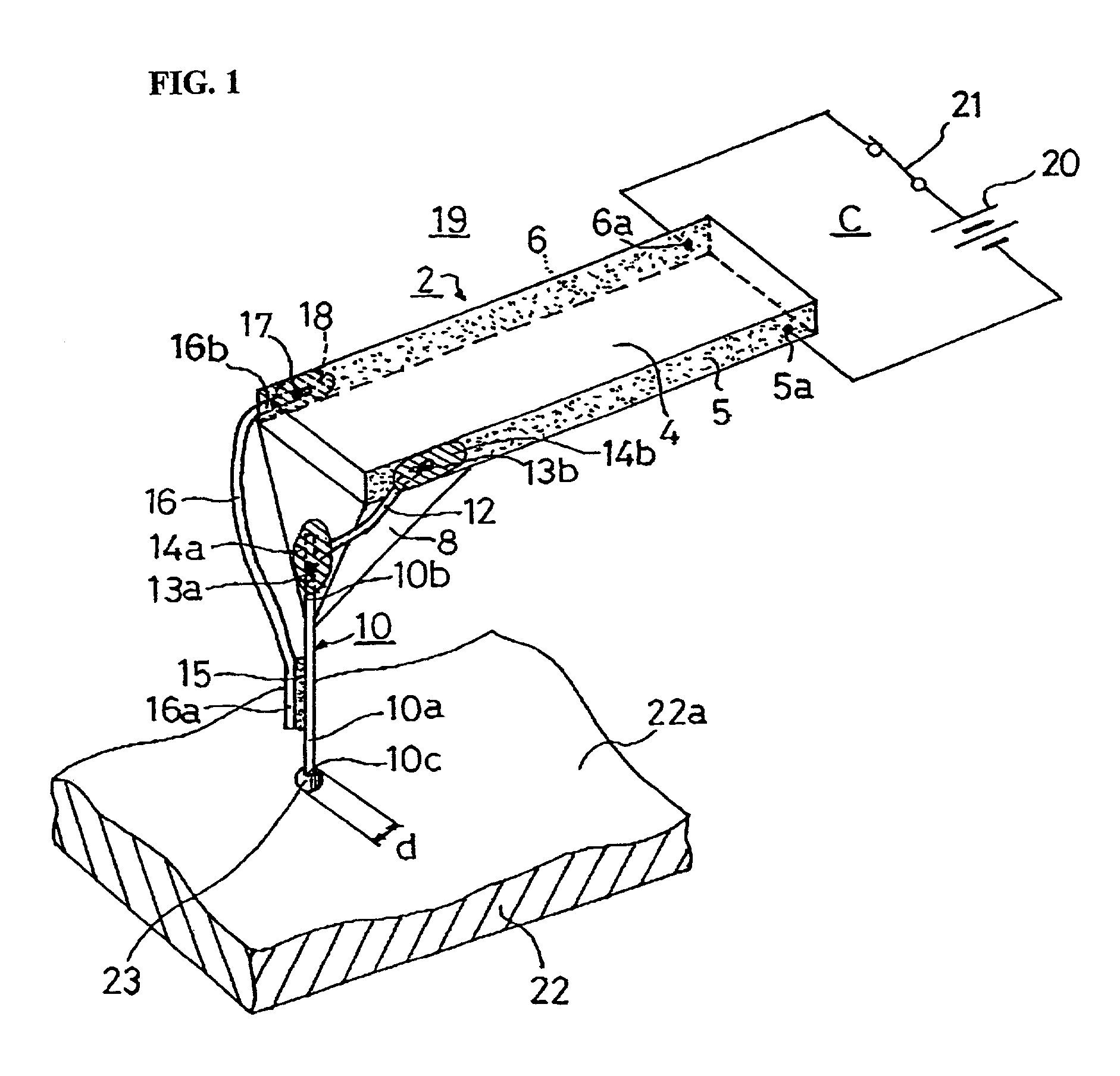
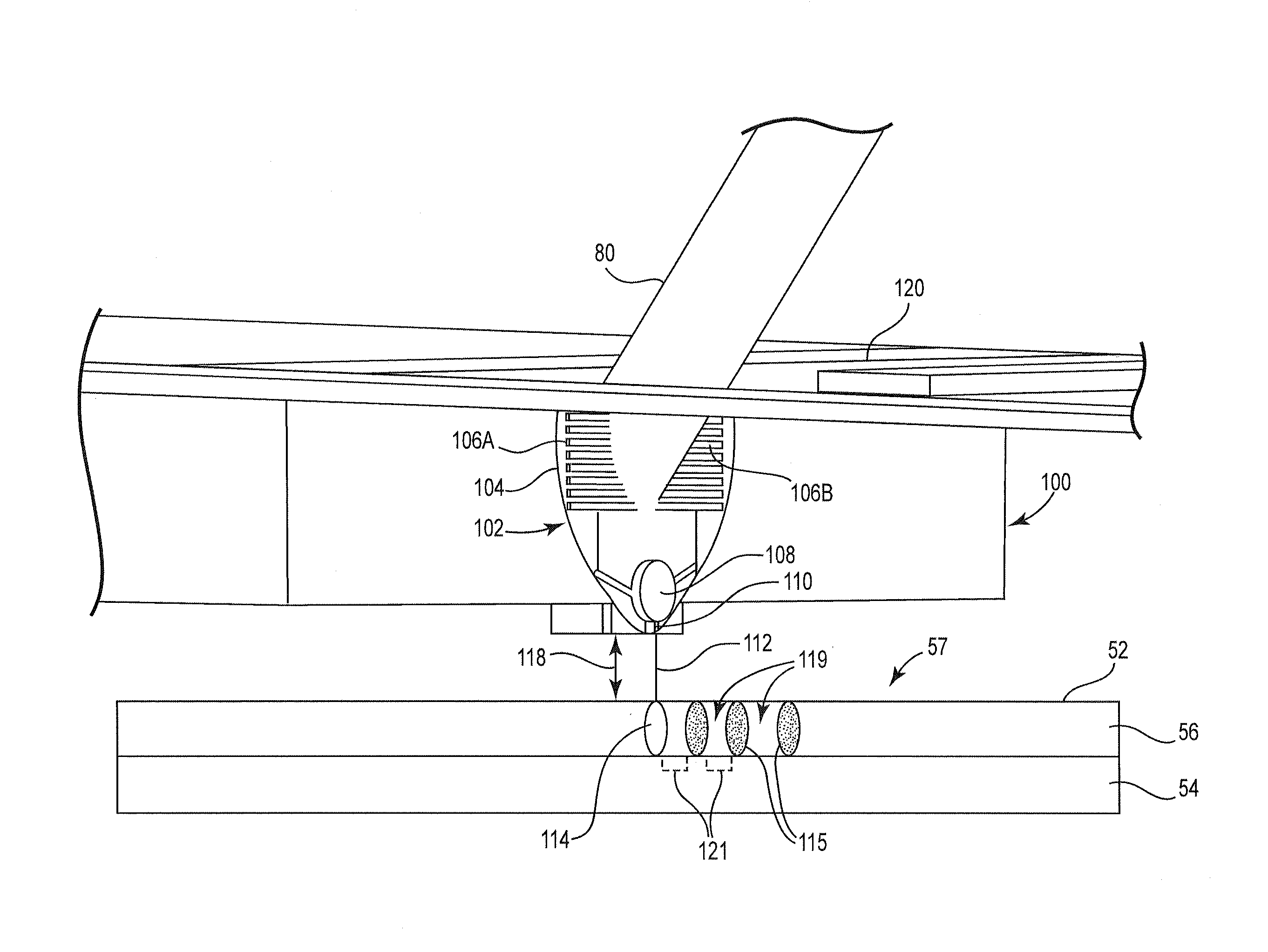
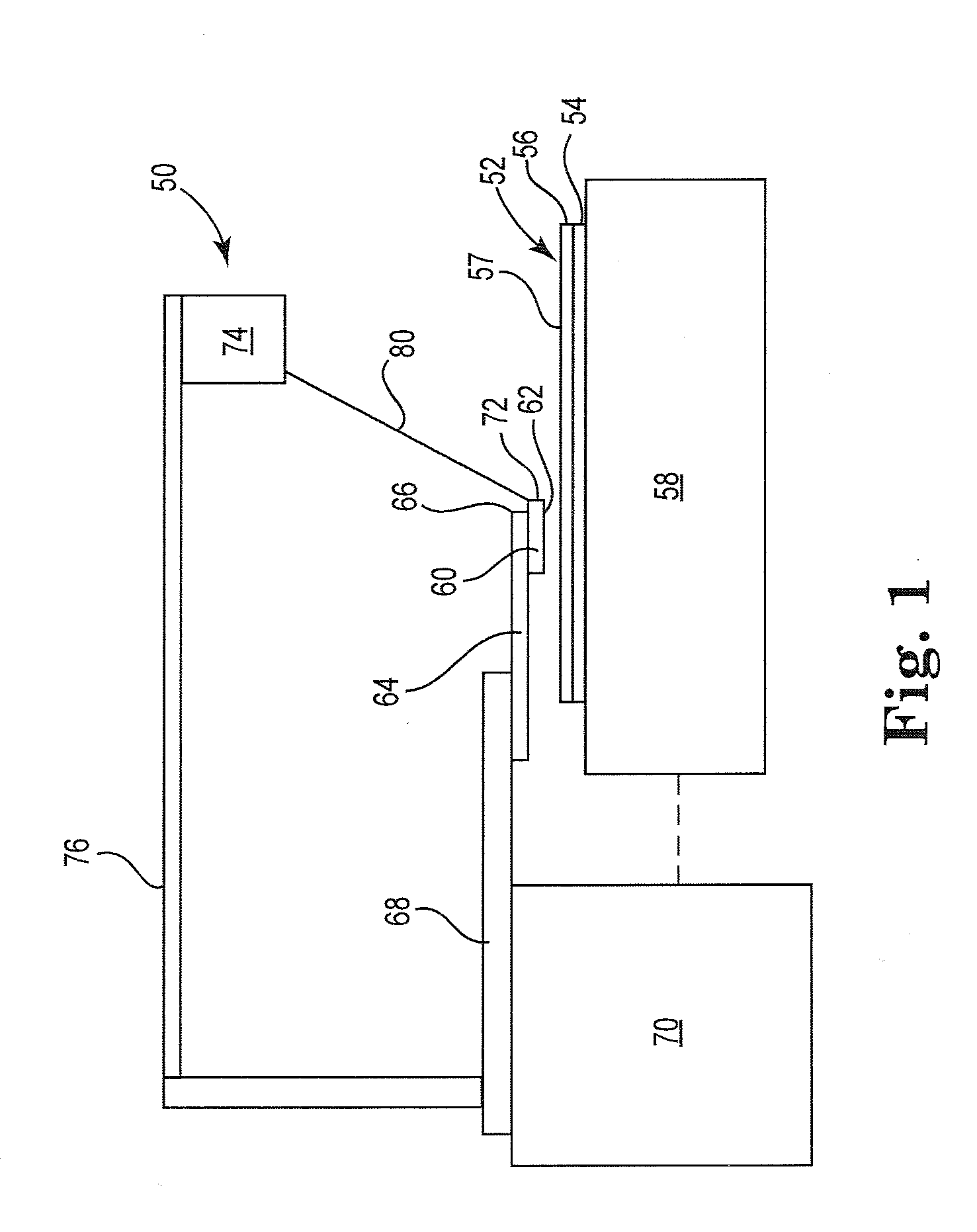
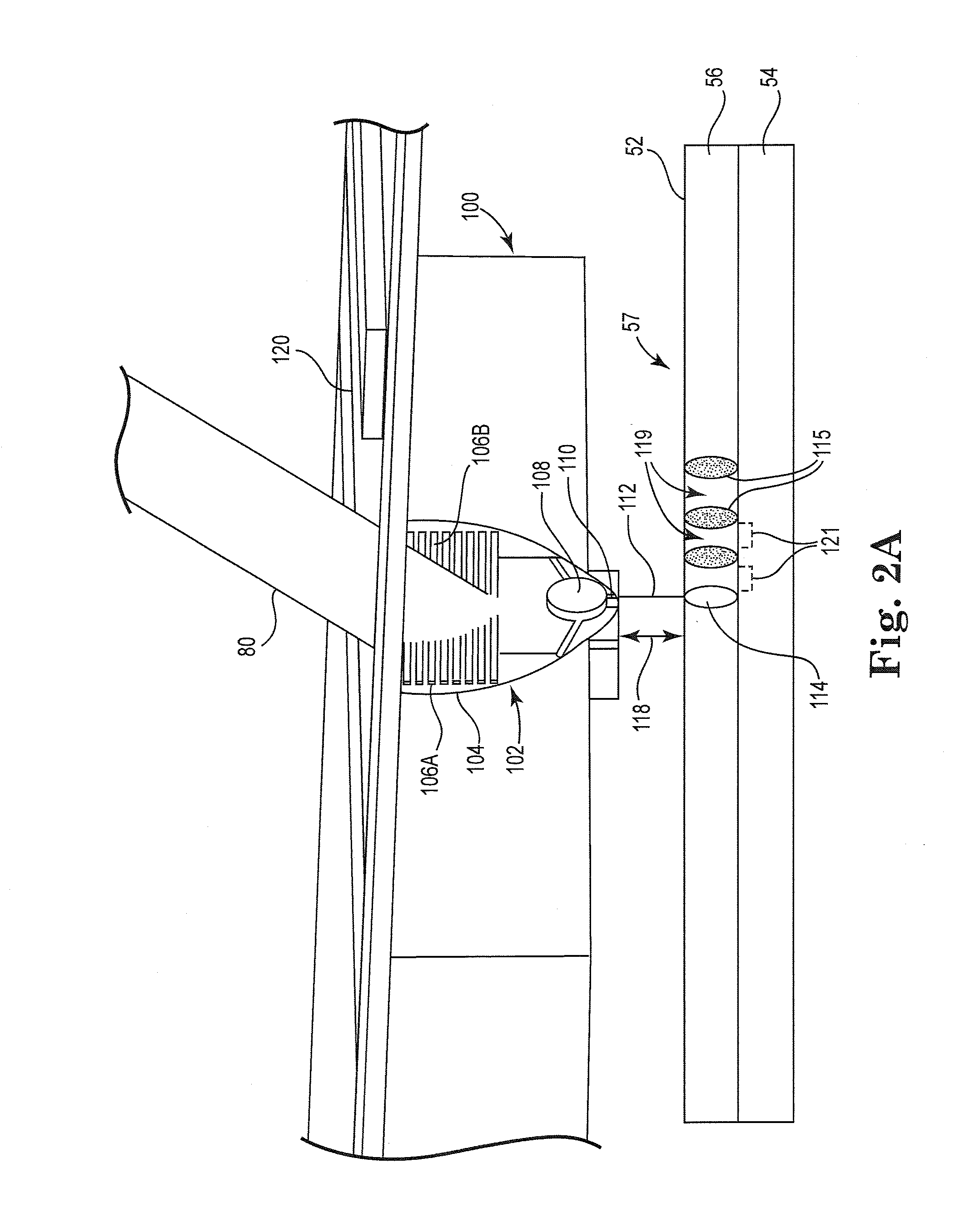
AFM-based data storage and micrascopy
Read / write components for AFM-based data storage devices are provided. In particular embodiments, a read / write component (30, 45, 50, 65, 80) comprises lever means (31, 51, 66, 82) and a support structure (32, 52, 67, 81), the lever means being connected to the support structure for substantially pivotal movement. The lever means (31, 51, 66, 82) provides first and second current paths between a pair of electrical supply lines (R, C) on the support structure via which the lever means can be connected in use to power supply means operable in a write mode and a read mode. A write-mode heater (36, 47, 56, 73) is provided on the lever means in the first current path, and a read / write tip (37, 57, 74, 84) is provided on the write-mode heater. A read-mode heater (39, 46, 58, 75, 83) is provided on the lever means in the second current path. Decoupling means (38a, 38b, 40a, 40b, 60, 61, 77a, 77b, 78a, 78b) is arranged to inhibit current flow to the write-mode heater via the first current path in use when the power supply means is operated in the read mode. The component, with separate write and read-mode heaters, can thus be addressed in both the write and read modes via a single pair of supply lines. Other embodiments provide read / write components (100) employing a thermal decoupling mechanism, and read / write components (80) where read-sensing is performed by a proximity sensing arrangement between the lever means and the support structure. Sensing apparatus (115) for atomic force microscopes is also provided where tip movement can be detected via similar proximity sensing arrangements.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus for detecting abnormal states of laser diode power in an optical disc recording/reproducing device
InactiveUS20060002268A1Effective protectionDelay the time of being blockedRecording by optical meansFilamentary/web record carriersOperation modeMode switch
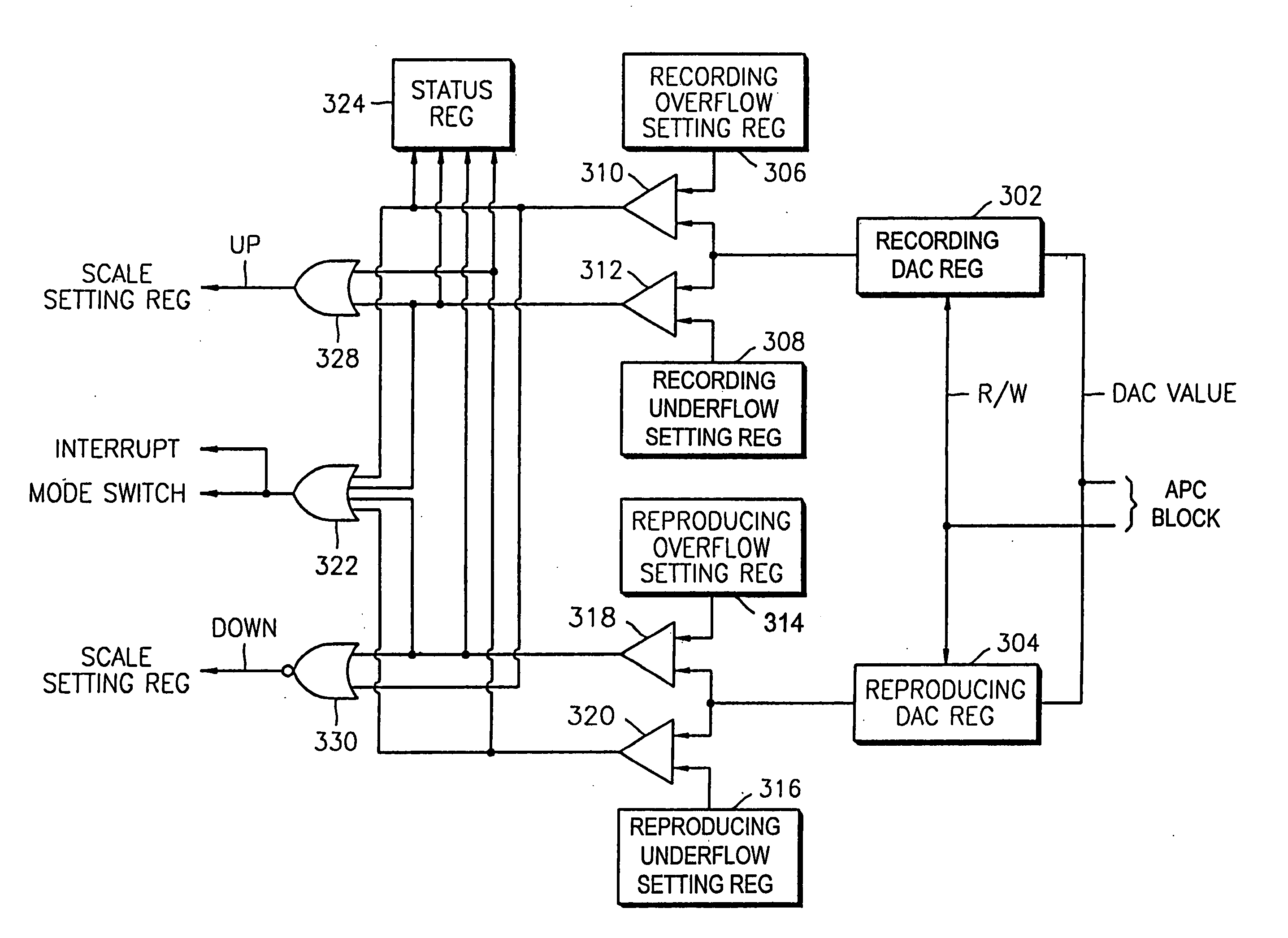
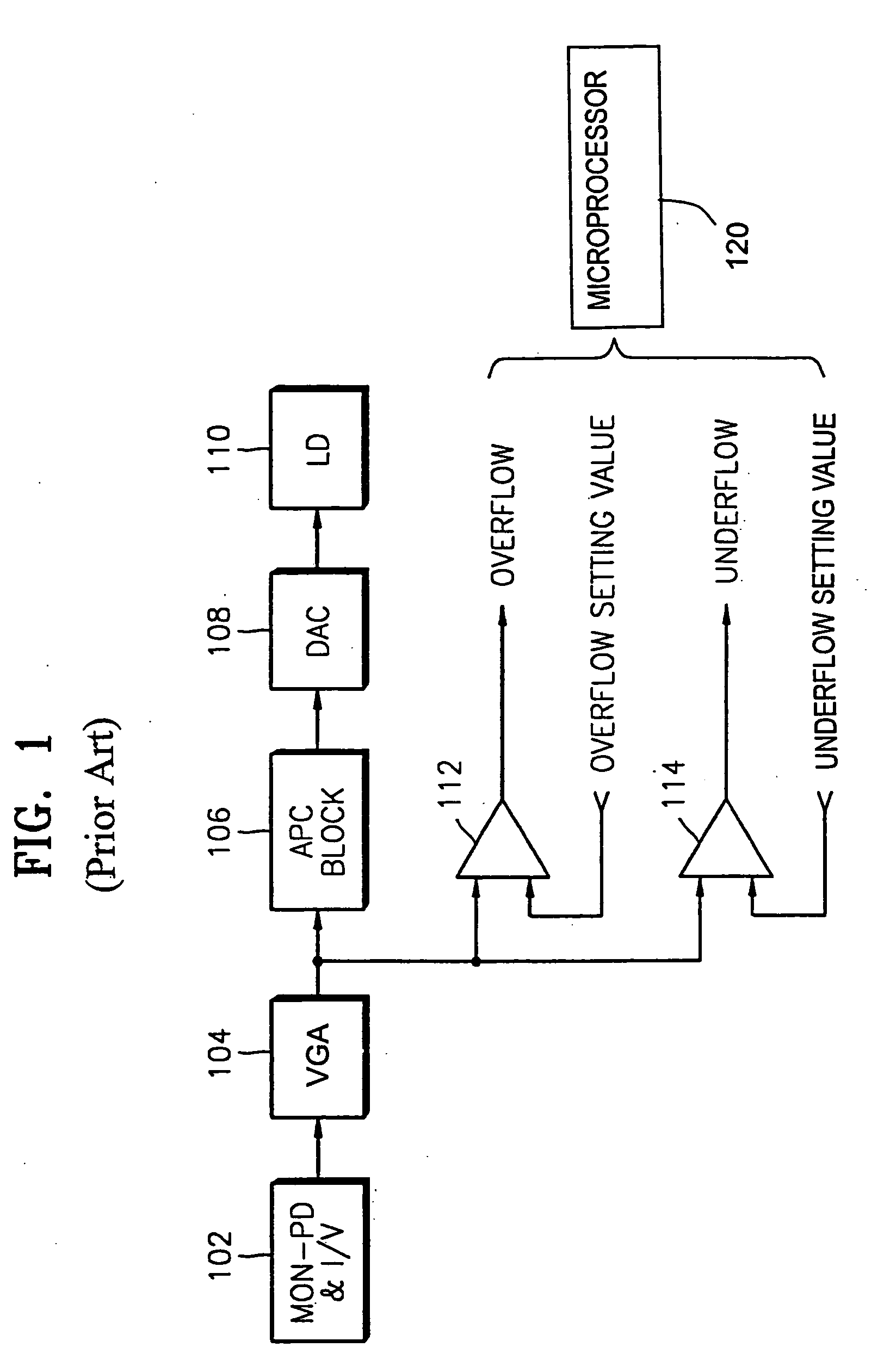
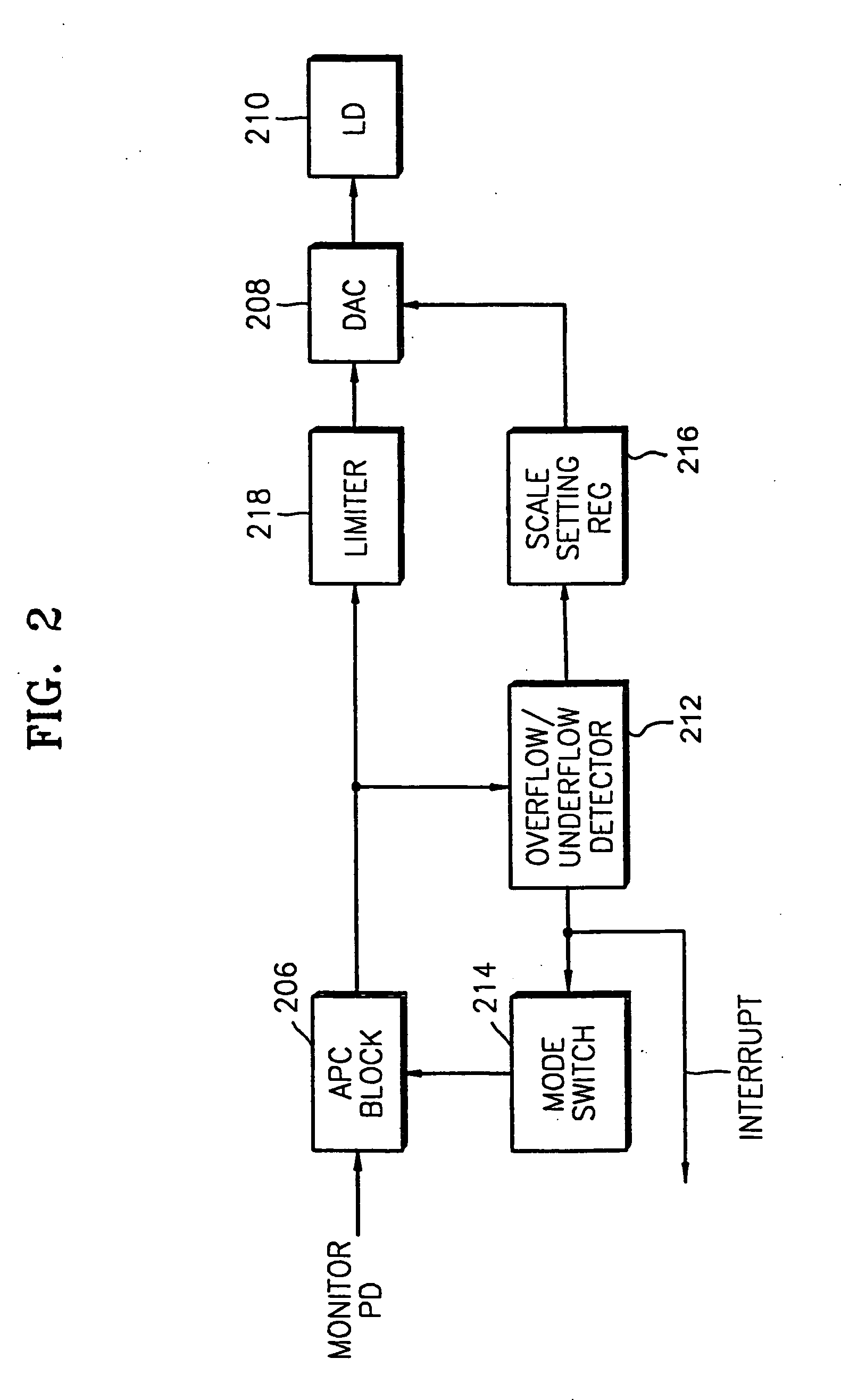
An apparatus for detecting abnormal states which prevents damage to a laser diode or data recorded on a disc and swiftly correcting the abnormal state. An overflow / underflow detector detects whether overflow or underflow of the laser diode occurs, by comparing a laser diode output power control value, which is output from the laser diode output power control circuit, with an overflow setting value and an underflow setting value. A mode switch switches an operation mode of the laser diode output power control circuit from a recording mode to a reproducing mode, in response to the detection result of the overflow / underflow detector.
Owner:TS OPTICS CORP
Optical disc cutting apparatus and method for manufacturing optical disc
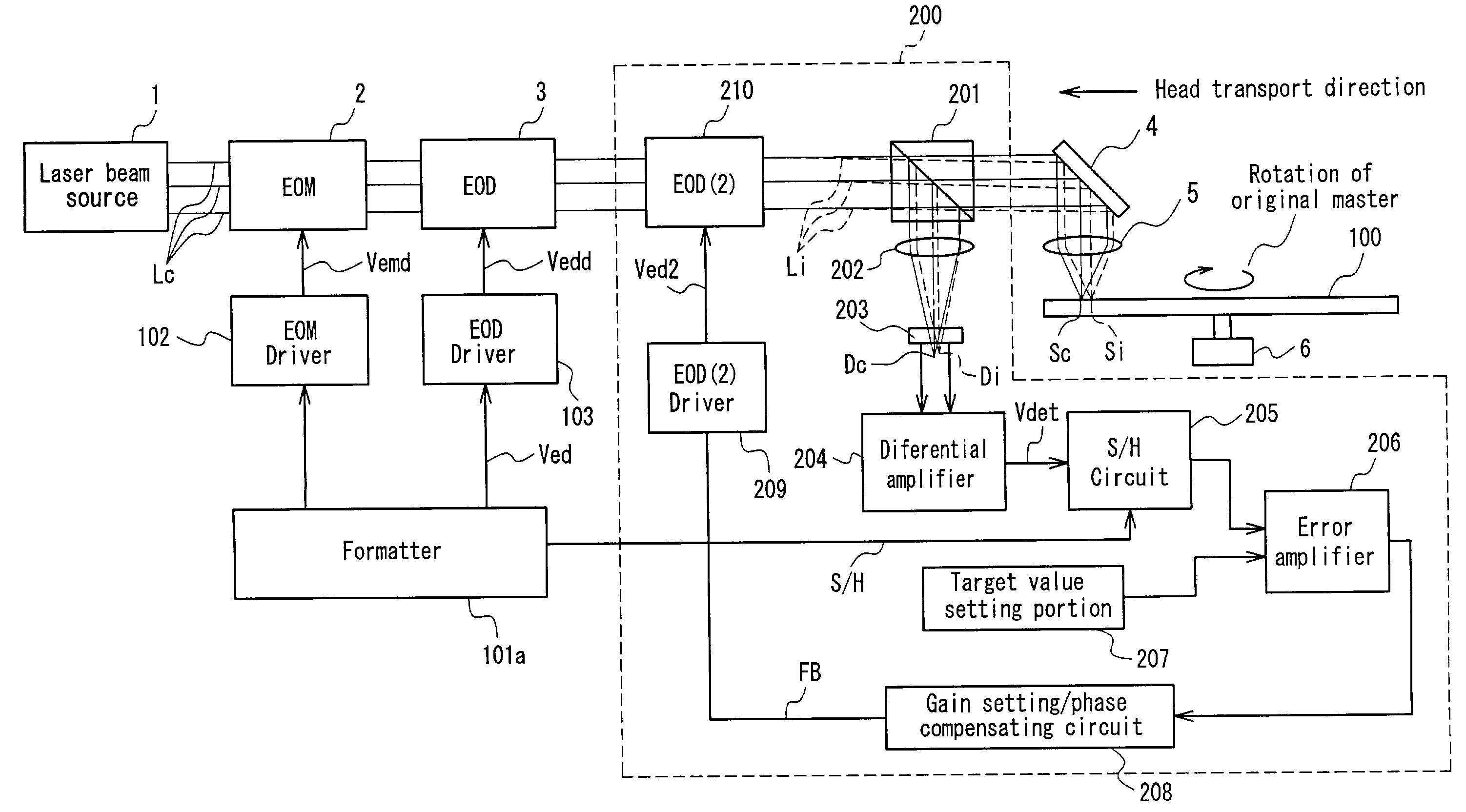
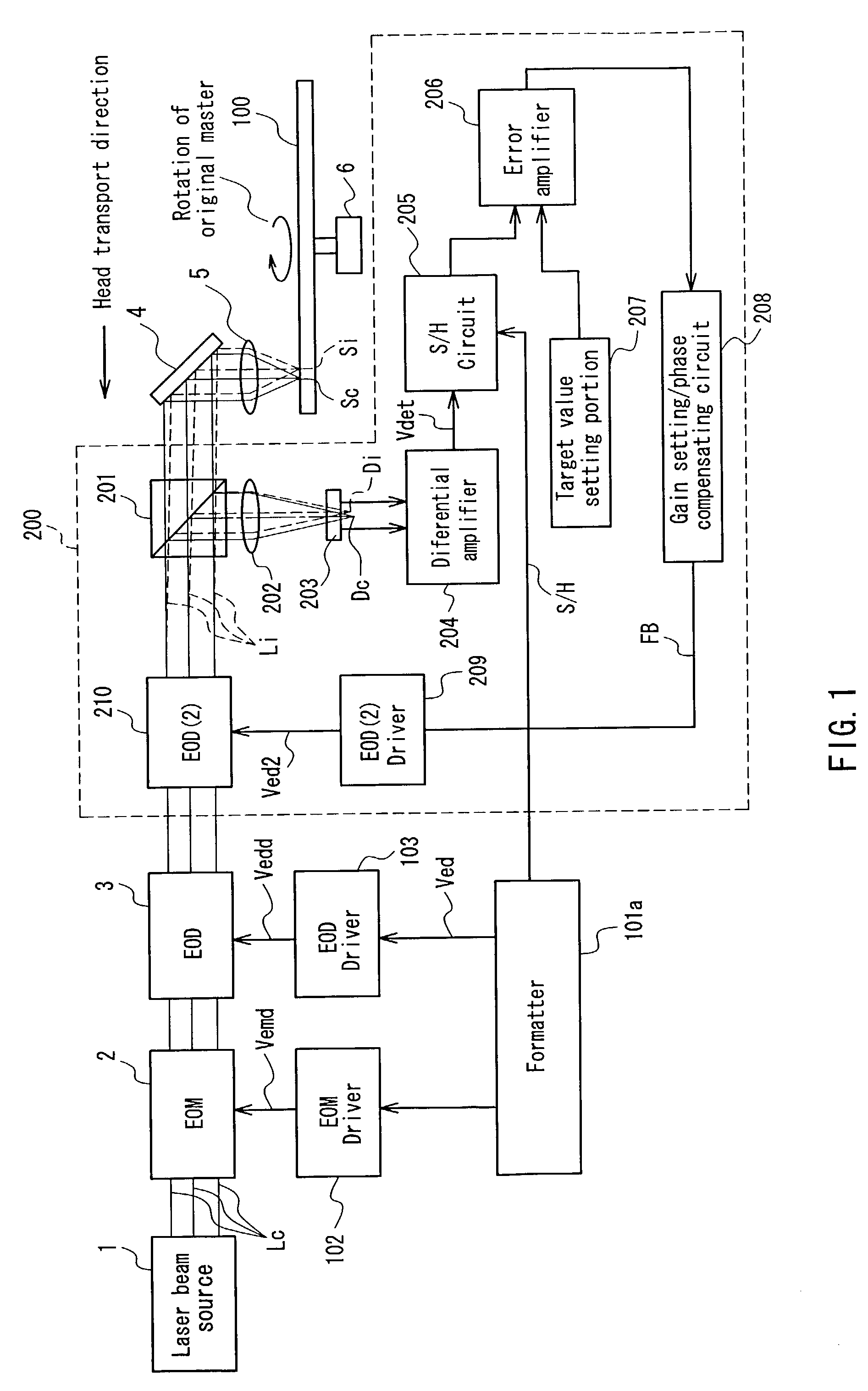
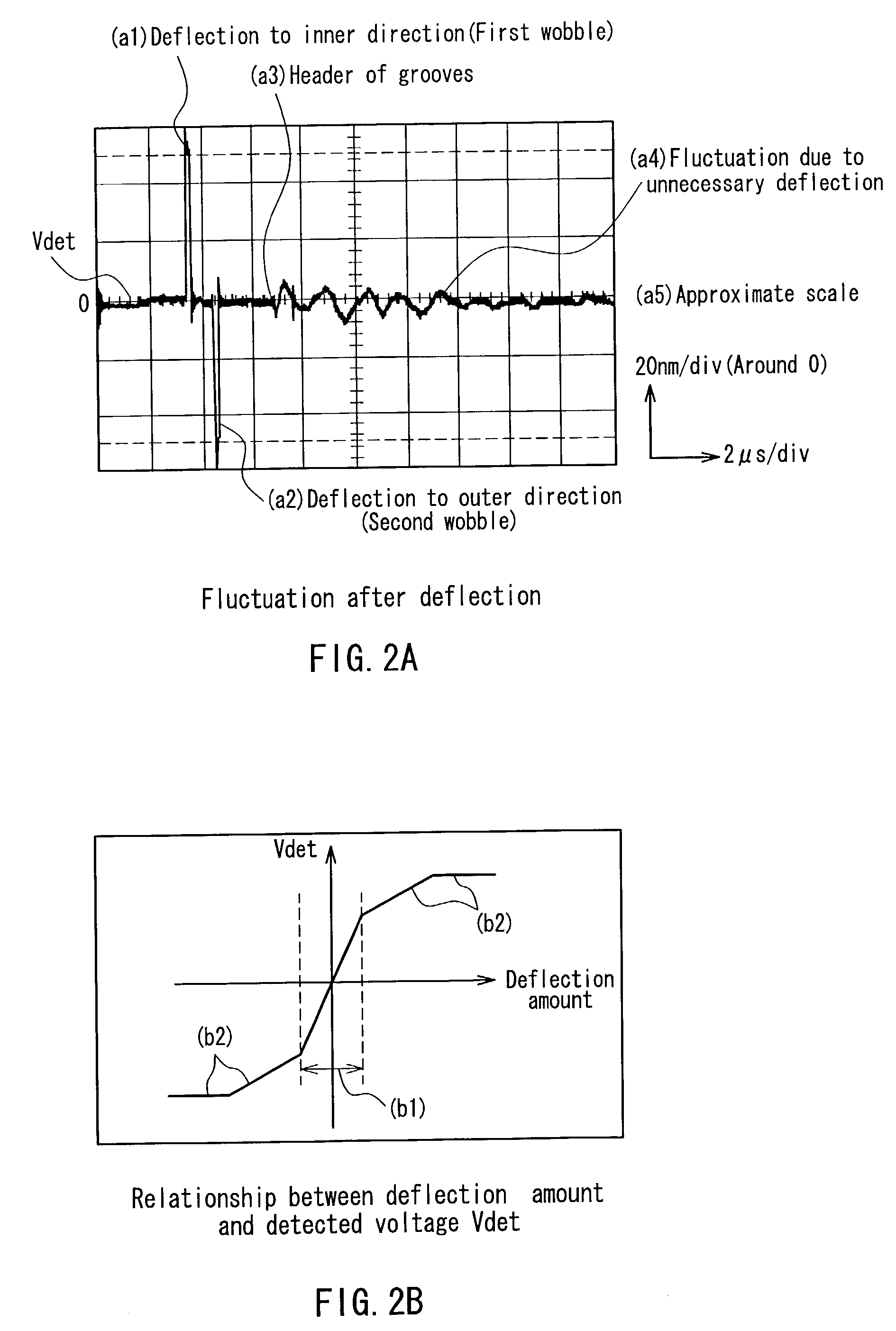
InactiveUS7180842B2Detect and suppress unnecessary deflection amountLess fluctuationDisposition/mounting of recording headsRecording by optical meansHigh densityFeedback controller
An optical disc cutting apparatus capable of suppressing an unnecessary deflection component and unnecessary light intensity variation component and manufacturing a optical disc suitable for a high definition, high precision and high density optical disc. The optical disc cutting apparatus includes a light beam controller including at least one of an optical modulator for controlling the light intensity of light beam emitted from a laser beam source and an optical deflector for controlling the deflection amount of the light beam in the radial direction on an optical disc original master, a deflection error detector for detecting a deflection error in the radial direction included in the light beams controlled by the light beam controller, a second optical deflector, which is disposed between the light beam controller and the deflection error detector, for deflecting the light beams in the radial direction, and a feedback controller for feeding back a feedback signal using the deflection error in the radial direction to the second optical deflector.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com