Patents
Literature
68results about How to "Fast and efficient drying" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
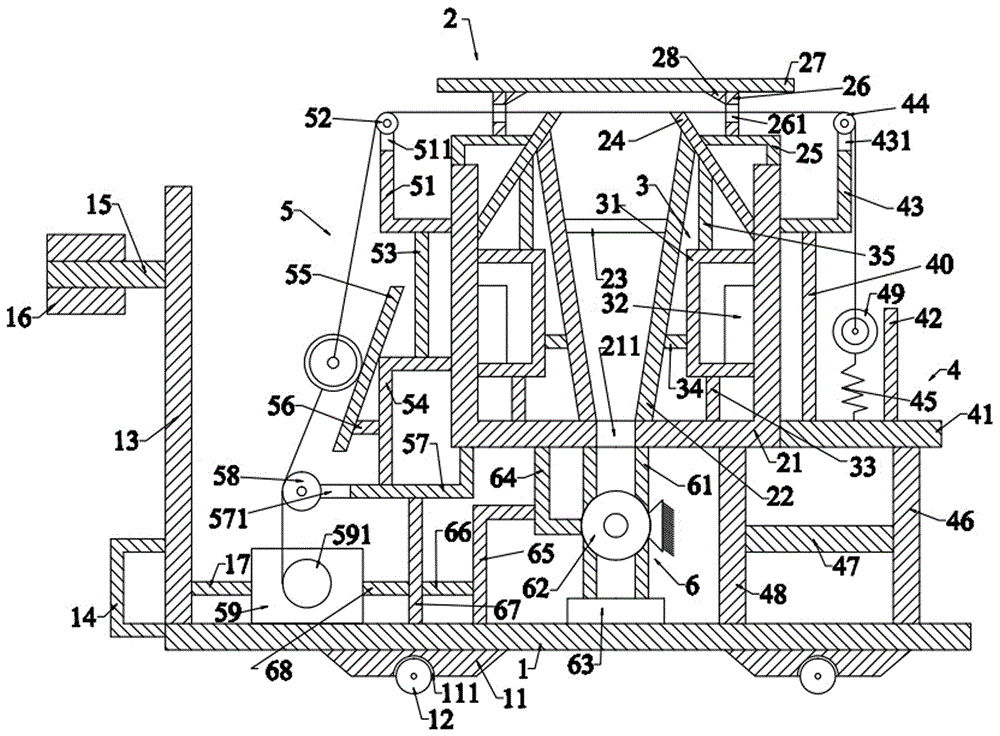
Automatic processing robot special for traditional Chinese medicine of achyranthes aspera
InactiveCN107511345AEasy to operateReduce labor intensityDrying gas arrangementsCleaning using toolsAchyranthes asperaEngineering
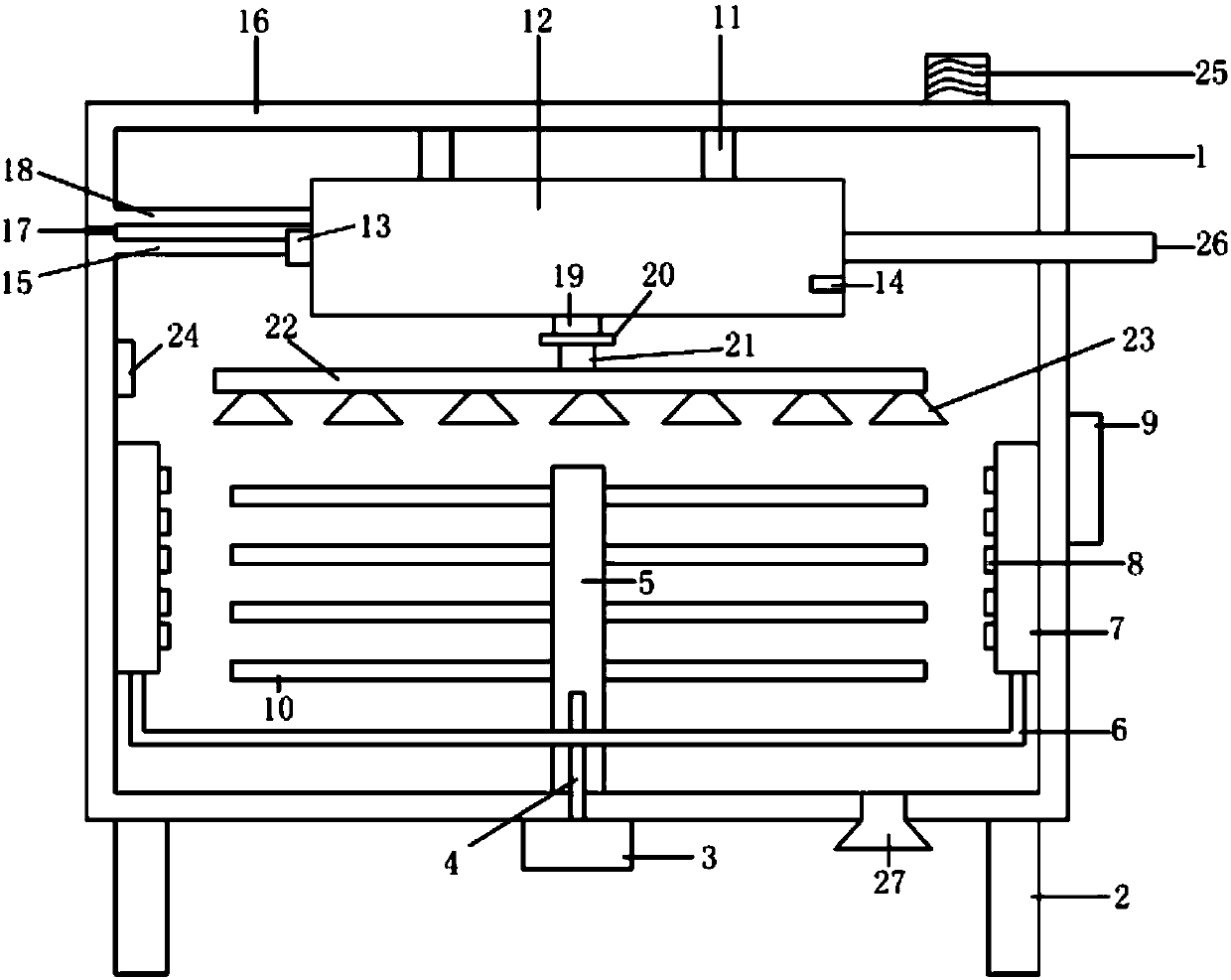
The invention relates to an automatic processing robot special for traditional Chinese medicine of achyranthes aspera. The automatic processing robot special for the traditional Chinese medicine of achyranthes aspera comprises a bottom plate, wherein the bottom plate is sequentially provided with a slicing processing device and a drying device from front to back, and the drying device is located on the lower side of the rear end of the slicing processing device. By means of the automatic processing robot for the traditional Chinese medicine of achyranthes aspera, the problems that in the process of processing achyranthes aspera fruits in existing individual workshops, workers need a tool to carry out slicing processing on the achyranthes aspera fruits, when slitting processing needs to be carried out, the processed achyranthes aspera fruits need to be naturally air-dried, the consumed time is long, potential safety hazards exist when the workers process the achyranthes aspera fruits with the tool, the workers are hurt easily, the sliced fruits need to be collected, the working procedures are tedious, repeated work is needed, the labor intensity is large, and the working efficiency is low are solved, and integrated achyranthes aspera fruit slicing and drying function is achieved.
Owner:王辉
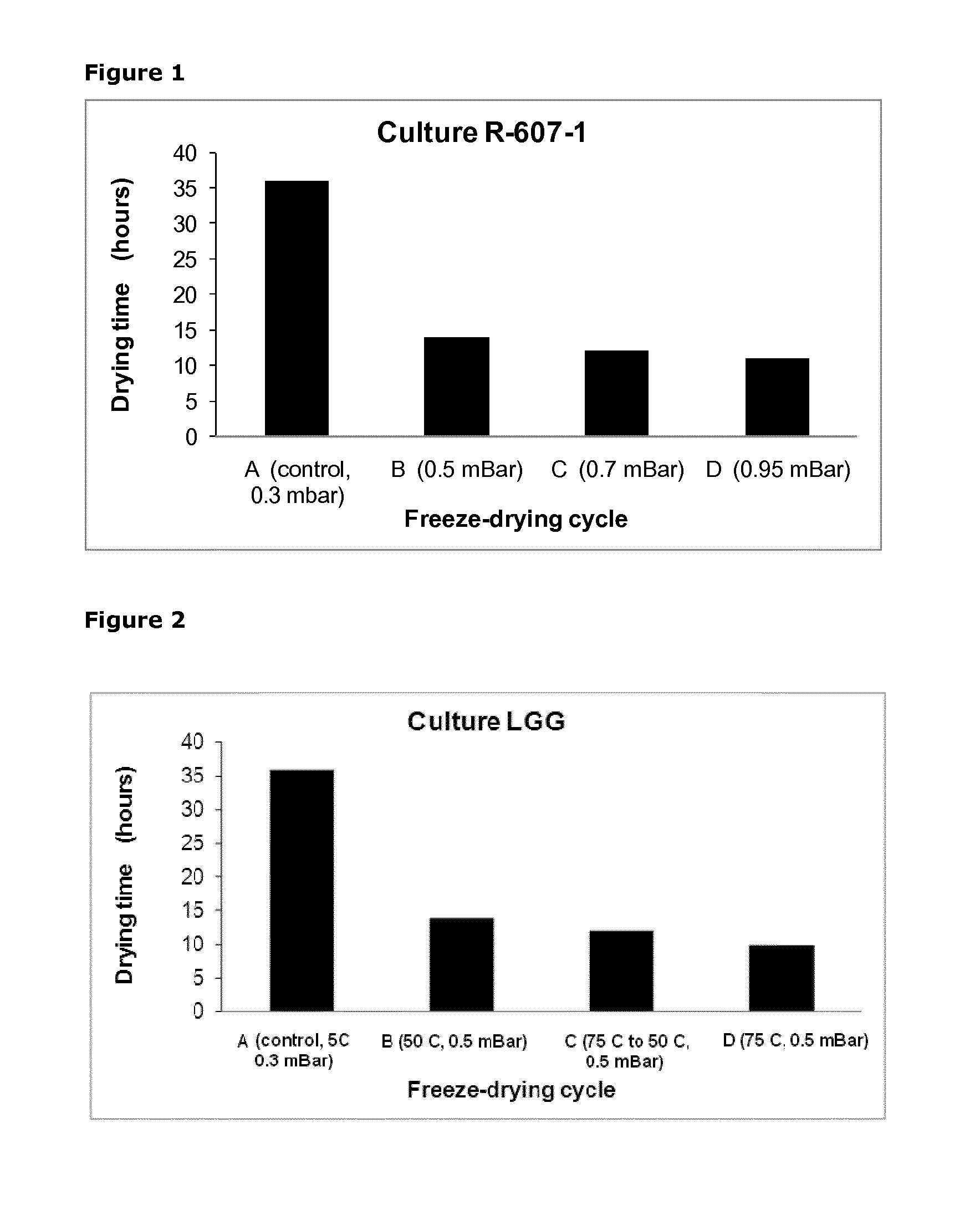
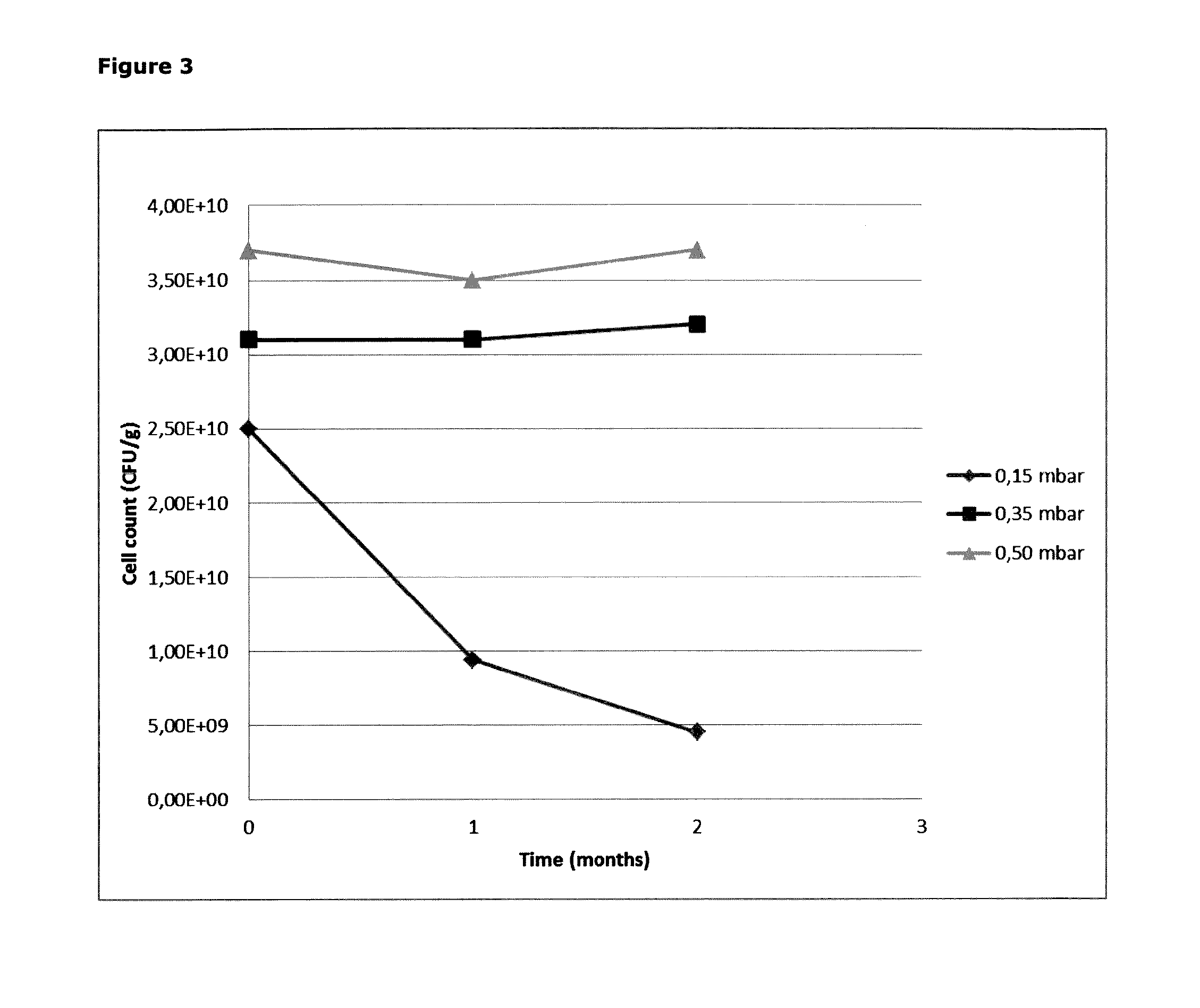
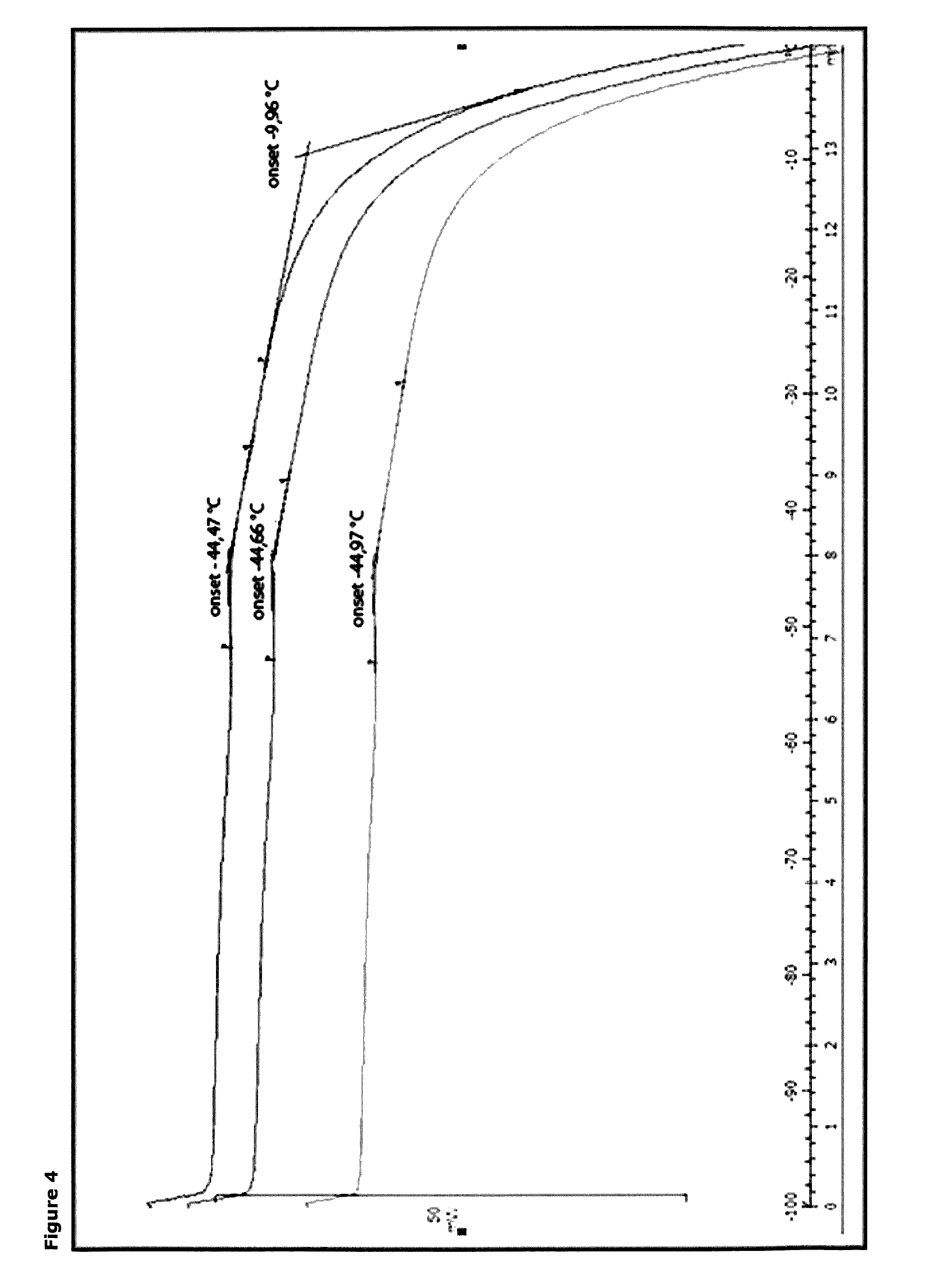
Method for optimizing a process for freeze drying a bacteria-containing concentrate
ActiveUS20150232801A1Good storage stabilityDrying stabilityMilk preparationBacteriaFreeze-dryingFreeze dry
The present invention relates to a process for optimizing the storage stability of a freeze dried bacteria-containing product obtained from a bacteria-containing concentrate, wherein the process is carried out at a pressure which will provide a sublimation temperature which is at least 10° C. above the melting point of the frozen bacteria-containing concentrate. Further, the present invention relates to the freeze dried concentrates per se.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Method for freeze drying a bacteria-containing concentrate
ActiveUS20150218507A1Storage stability be improveImprove viabilityMilk preparationBacteriaChemistryFreeze dry
The present invention relates to a process for freeze drying a bacteria-containing concentrate. Further, the present invention relates to the freeze dried concentrates per se.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Methods and apparatus for the production of viral vaccines
ActiveUS20090087452A1Fast and efficient dryingLarge batchViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementLiquid stateViral Vaccine
A viral vaccine in the dried state is described. Methods for drying viral vaccine in the liquid state into viral vaccine in the dried state are presented. The methods may include introducing the viral vaccine in the liquid state into a gas stream and recovering viral vaccine in the dried state from the gas stream.
Owner:PULSE HLDG
Tea leaf drying device
InactiveCN105475528AAvoid standingAvoid getting burntPre-extraction tea treatmentAgricultural engineeringTea leaf
The invention relates to a tea leaf drying device, which comprises a bottom plate device, a frame body device, a motor device, a heating device, a moving device and a support device, wherein the bottom plate device comprises a bottom plate, a first roller and a first slanting rod, the frame body device comprises a frame body, a first lateral rod, a first pipeline, a fan, a filtering ring, a first support and a first vertical rod, the motor device comprises a motor, a first rotating shaft, a rotary disc, a first supporting rod, a first supporting block, a second support and a first fixing ring, the heating device comprises a heat radiating frame, an iron net, a heating rod, a first blocking ring and a second fixing ring, the moving device comprises a blocking column, an inner ring, a connecting plate, a second vertical rod, a first sawtooth and a first positioning rod, the support device comprises a first fixing rack, a second lateral rod, a spring, a second slanting rod, a second fixing rack, a third vertical rod, a fourth vertical rod, a third fixing rack, and a second roller, the blocking column is a column with a circular cross section, and the lower surface of the blocking column is in contact with the upper surface of the heat radiating frame. The tea drying device can be used for effectively and quickly drying tea.
Owner:刘汉佑
High-efficient cleaning and drying device for Chinese herbal medicine
InactiveCN107377503AFast and efficient cleaningFast and efficient dryingDrying gas arrangementsDrying machines with local agitationPollutionWaste management
The invention discloses a high-efficiency cleaning and drying device for Chinese herbal medicine, which comprises a fixed bottom plate, the fixed bottom plate is provided with a support plate, a cleaning bucket is arranged on the support plate, the cleaning bucket is fixed on the support plate through a support rod, and the cleaning bucket The top is provided with a material inlet, the cleaning bucket is provided with a cleaning roller, the side of the fixed bottom plate is provided with a vertical rod, the cleaning bucket is provided with a screen under the corresponding cleaning roller, and the bottom of the cleaning bucket is equipped with a screen. A vertical rotating shaft is provided, and the vertical rotating shaft is set on the bearing arranged in the middle of the bottom plate of the cleaning bucket; the invention provides a high-efficiency cleaning and drying device for Chinese herbal medicine, which has a novel structure. The invention creatively sets multiple cleaning mechanisms to realize the Fast and efficient cleaning and drying, efficient cleaning and convenient discharge and sewage discharge. In addition, the elastic support and elastic connection provide shock absorption and drive the cleaning bucket and drying bucket to swing, further improving cleaning and drying efficiency.
Owner:苏昭缄
Wood drying device capable of recycling heat energy and heat energy recycling method
InactiveCN107796188AEasy to dryFast and efficient dryingDrying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsWater flowPulp and paper industry
The invention discloses a wood drying device capable of recycling heat energy and a heat energy recycling method in the technical field of wood drying. Support legs are arranged on the left and rightsides of the bottom of a machine body; an air heater is arranged in the bottom center of the machine body, and is provided with a main air pipe; a support column is arranged at the bottom of an innercavity of the machine body; the main air pipe penetrates through the machine body, and extends into an inner cavity of the support column to connect with a M-shaped air pipe; air guide plates are arranged on the inner walls of the left and right sides of the machine body; exhaust ports are formed in the air guide plates; the left and right ends of the M-shaped air pipe communicate with the bottomsof the left and right sets of air guide plates; wood fixing pieces are arranged on the left and right sides of the support column; the air heater passes through ventilation holes in a U-shaped wood shelf and the exhaust ports in the air guide plates; the fire prevention is realized through monitoring the concentration of smoke by a smoke sensor; and water currents in a water tank pass through a water outlet to flow to a drainage plate, and are sprayed to the wood fixing pieces through a nozzle on the drainage plate to extinguish pyrophoric woods, so that the fire prevention effect is effectively achieved.
Owner:郑佳
Automatic slicing and drying integrated machine special for traditional Chinese medicinal material production of achyranthes bidentata
InactiveCN107571323AReduce labor intensityDecrease productivityDrying machines with progressive movementsMetal working apparatusEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
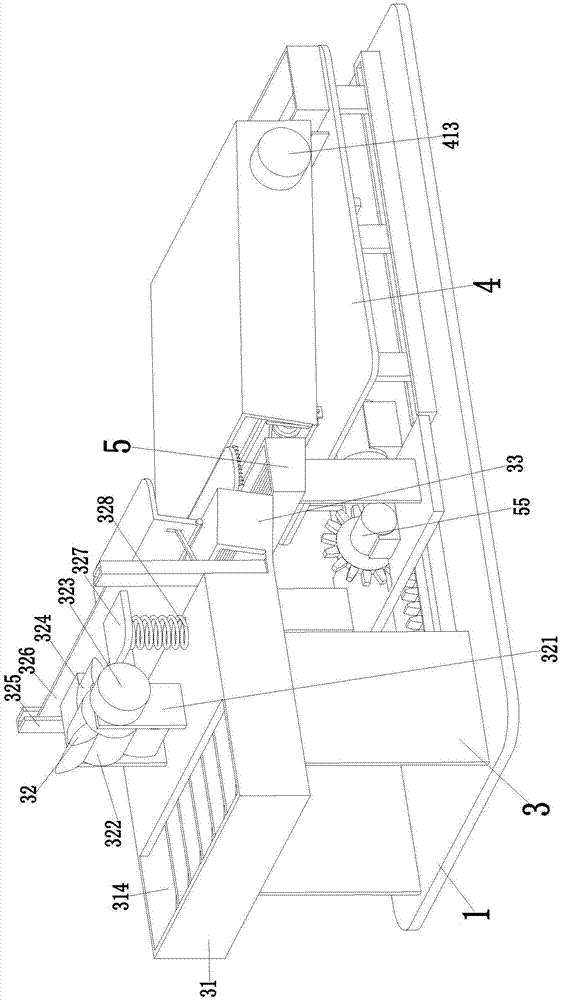
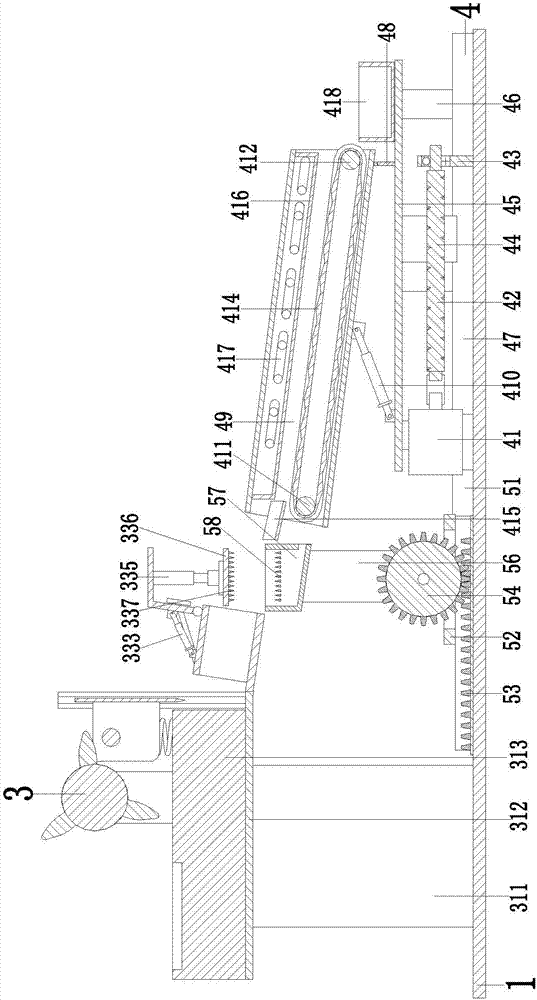
The invention relates to an automatic slicing and drying integrated machine special for traditional Chinese medicinal material production of achyranthes bidentata. The automatic slicing and drying integrated machine comprise a bottom plate. A slicing treatment device and a drying device are sequentially mounted on the bottom plate from front to rear. The drying device is located on the lower sideof the rear end of the slicing treatment device. By the adoption of the automatic slicing and drying integrated machine, the problems that during the process of processing achyranthes bidentata fruitsin an existing small workshop, artificial processing of the achyranthes bidentata fruits by using a tool is needed for slicing processing; when slicing processing is needed, the processed achyranthesbidentata fruits need to be dried naturally, the consumed time is long, and potential safety hazards exist and workers are easy to hurt during the artificial processing of the achyranthes bidentata fruits by using the tool; the sliced fruits need to be collected, the procedures are cumbersome, the repetitive work is needed, the labor intensity is large, and the working efficiency is low; and thefunctions of integrally slicing and drying the achyranthes bidentata fruits are achieved.
Owner:王辉
Experimental apparatus drying device capable of realizing rapid drying
InactiveCN106091619AFast and efficient dryingSimple structureDrying gas arrangementsDrying machines with local agitationProcess engineeringChimney
An experimental apparatus drying device capable of realizing rapid drying comprises a drying box body, wherein fans blowing air upwards are arranged at the bottom of the drying box body; an infrared heating device is arranged on one inner wall of the drying box body; one or more drying plates are horizontally arranged in the middle of the drying box body and divide the inside of the drying box body into vertically separated spaces; and multiple chimney fans standing upwards are arranged on the one or more drying plates, adopt bottom-top through structures and are used for accommodating to-be-dried experimental apparatuses. The device is simple in structure, energy-saving, environment-friendly, convenient to use and capable of drying the experimental apparatuses rapidly and effectively, drying a lot of experimental apparatuses simultaneously, keeping an experimental environment clean and improving the experimental efficiency.
Owner:无锡市三峰仪器设备有限公司
Nut cleaning equipment
PendingCN107617590APrevent flying outFast and efficient cleaningCleaning using toolsCleaning using liquidsSlide plateEngineering
The invention discloses nut cleaning equipment. The nut cleaning equipment comprises a rack, a cleaning tank, first conveying belts, a discharging hopper, arc baffles, a second conveying belt, magnets, a discharging port, a discharging plate, a material receiving box, a hot air blower, a cushion plate, a falling port, a spring and a sliding plate, wherein the cleaning tank is fixedly arranged on the rack, the multiple horizontally-arranged first conveying belts are arranged in the cleaning tank from top to bottom, the rotation directions of the vertically-adjacent first conveying belts are reverse, and the discharging hopper is arranged over the input end of the uppermost first conveying belt and fixedly connected with the rack. The output ends of the first conveying belts above the lowestfirst conveying belt are provided with the arc baffles fixedly connected with the inner side wall of the cleaning tank. Compared with the prior art, nuts can be rapidly and efficiently cleaned and dried, the nut cleaning and drying efficiency and effect are improved, the labor intensity of workers is relieved, and great convenience is brought to nut machining.
Owner:海盐晋悦五金制品有限公司
Grain drying device
InactiveCN103689078AAvoid grain leakageAvoid impactSeed preservation by dryingPhysicsElectric heating
The invention relates to a drying device, and in particular relates to a grain drying device which comprises a preheating chamber, a drying chamber and an electro thermal chamber which are arranged in sequence from top to bottom, wherein the electric thermal chamber is capable of generating hot air; a feeding hole in a funnel shape is formed in the top of the preheating chamber; baffles in a closing mode are arranged inside the preheating chamber below the feeding hole; a plurality of material ejection holes with shrunk holes are arranged at the lower part of the preheating chamber; the drying chamber is internally provided with a plurality of ventilation tubes with through holes; the top parts of the ventilation tubes are communicated with the preheating chamber; the bottoms of the ventilation tubes are communicated with the electric thermal chamber below; the electric thermal chamber is internally provided with a graphite electric thermal plate. By adopting the grain drying device with the technical scheme, grains can be sufficiently preheated without crack caused by sharp temperature raising, and the quality of the grains is ensured.
Owner:CHONGQING YUNSEN FOOD & BEVERAGE
Oxygen-enriched blast furnace blow-in method
ActiveCN114427011AFast and efficient dryingIncrease temperatureBlast furnace detailsProcess efficiency improvementHearthNitrogen gas
The blowing-in method comprises the following steps: filling furnace charge after the furnace is dried, blowing and heating nitrogen at a tuyere for preheating, then feeding hot coal gas and oxygen at the tuyere, controlling the theoretical combustion temperature at 2350-2400 DEG C, and tapping when the theoretical iron amount in a hearth reaches 60% of the normal safe iron capacity; then, the in-furnace load is gradually increased, the in-furnace reduction gas amount and oxygen amount are increased, normal tapping and in-furnace load adjustment are organized, and the theoretical combustion temperature in the stage is 2400-2500 DEG C; according to the invention, heated nitrogen is used for purging materials, quickly and effectively drying and increasing the temperature of the materials, a blast furnace gas system is inerted, heated reducing gas and high-temperature and high-reducibility gas are injected into a tuyere, enter the furnace, immediately undergo a reduction reaction with upper furnace charge, and are combusted with injected oxygen to release a large amount of heat, so that the temperature of a hearth can be quickly increased; blow-in time is shortened, and raw fuel consumption is effectively reduced.
Owner:XINJIANG BAYI IRON & STEEL
Experimental apparatus drying device
InactiveCN106052327AFast and efficient dryingSimple structureDrying gas arrangementsDrying chambers/containersEngineeringProcess engineering
An experimental apparatus drying device comprises a drying box body. Fans blowing air upwards are arranged at the bottom of the drying box body. Electric heating wires are arranged on the upper portions of the fans and used for generating hot air. One or more drying plates are horizontally arranged in the middle of the drying box body. The interior of the drying box body is divided into vertically-isolated spaces by the drying plate. Multiple upwards-upright air outlet barrels are arranged on the drying plate. Each air outlet barrel is of a bottom-top through structure and is used for containing experimental apparatus to be dried. The experimental apparatus drying device is simple in structure, achieves energy saving and environment protection and is convenient to use, and the experimental apparatus can be dried fast and effectively; a large quantity of experimental apparatus can be dried at the same time; the experimental environment can keep clean and sanitary easily; and the experimental efficiency is improved.
Owner:无锡市三峰仪器设备有限公司
Efficient textile drying device
InactiveCN105841459ASimple structureEasy to useDrying gas arrangementsDrying machines with progressive movementsEngineeringIdler-wheel
An efficient textile drying device comprises a bottom plate, a frame device, heating devices, a support device, a motor device and an air inlet device. The bottom plate is provided with first supporting blocks, first idler wheels, a first supporting rod, a first support, a first transverse rod, a friction ring and a second transverse rod. The frame device comprises a frame, first inclined plates, a first filter screen, second inclined plates, second supports, second supporting rods, a first transverse plate and first triangular blocks. Each heating device comprises a heat dissipation frame, a heating bar, a third supporting rod, a third transverse rod and a fourth supporting rod. The support device comprises a fourth transverse rod, a first vertical rod, a second vertical rod, a third support, a second idler wheel, a first spring, a first buckle ring, a fifth supporting rod, a fifth transverse rod and a sixth supporting rod. The motor device comprises a fourth support, a fourth idler wheel, a seventh supporting rod, a fifth support, a third inclined plate, a sixth transverse rod, a sixth support, a third idler wheel and a motor. The efficient textile drying device can rapidly and efficiently dry cloth and is high in drying efficiency.
Owner:陈文华
Jujube cleaning and screening machine
InactiveCN111822360AFast and efficient dryingSmall footprintFood treatmentGradingEngineeringSmall footprint
The invention relates to the field of fruit screening, and particularly relates to a jujube cleaning and screening machine. The jujube cleaning and screening machine comprises a workbench, a cleaningmechanism, a drying mechanism, a heating mechanism and a screening mechanism, wherein the cleaning mechanism is vertically and fixedly arranged on one side of the top of the workbench; the drying mechanism is obliquely arranged in the middle of the top end of the workbench; the heating mechanism is fixedly arranged on one side, far away from the cleaning mechanism, of the drying mechanism; the drying mechanism comprises a turning and lifting mechanism; the screening mechanism is fixedly arranged at the bottom of the workbench; a discharging connecting pipe is fixedly arranged at the bottom ofthe cleaning mechanism; the output end of the discharging connecting pipe communicates with the interior of the drying mechanism; the drying mechanism comprises a drying cylinder; a discharging channel is vertically and downwards formed in the bottom of the lower end of the drying cylinder; and the discharging channel is positioned right above the starting end of the screening mechanism. The jujube cleaning and screening machine is simple in structure, convenient to operate and small in occupied area, jujubes are screened according to the sizes of the jujubes, water drops attached to the peelsof the cleaned jujubes can be dried, and the market requirements are met.
Owner:诸暨市金家坪水果专业合作社
Garbage incineration system
The invention discloses a garbage incineration system which comprises an incineration furnace and a scattering and drying integral device, wherein the scattering and drying integral device comprises ashell and a conveying machine; a plurality of air blowers and scattering machines are mounted at the top of the shell; the air blowers and the scattering machines are arranged at intervals; the distance between both sides of a conveyer belt of the conveying machine and a shell wall of an inlet section is 0-5mm; the distance between both sides of the conveyer belt of the conveying machine and theshell wall of an outlet section is 20cm or above; the incineration furnace comprises a furnace body; a garbage feeding hole is formed in the right side of the furnace body; an ash outlet is formed inthe bottom of the furnace body; an exhaust hole is formed in the top of the furnace body; a gas feeding hole is formed in the right side of the furnace body; a hot air inlet is connected with the exhaust hole in the incineration furnace; the garbage feeding hole of the incineration furnace is connected with the discharge hole through a pipeline; an air blower is mounted on the right side of the discharge hole. When garbage is incinerated by using the garbage incineration system, the garbage is scattered when being incinerated, so that not only is a good scattering and incineration function achieved, but also a floor space is reduced, the cost is reduced, heat can be circulated and recycled, and the energy consumption can be reduced.
Owner:湖州高盛环保科技有限公司
Straw granule drying device
PendingCN107883734AFast and efficient dryingReduce the temperatureGranular material dryingDrying gas arrangementsElectric machineryProcess engineering
The invention discloses a straw granule drying device. A feeding spiral conveying shaft is arranged below a dehydrator, one end of the feeding spiral conveying shaft is connected with a motor, the other end of the feeing spiral conveying shaft is connected with an air drying furnace, an air drying sliding plate is arranged in the air drying furnace, a primary conveying belt is arranged below the air drying sliding plate, the end, away from the feeding spiral conveying shaft, of the air drying furnace is connected with a drying machine, electric heating wires are arranged on the periphery inside the drying machine, a drying support is arranged in the middle inside the drying machine, a drying table is fixedly connected to the top of the drying support, an electric heating net is arranged inside the drying table, and one side of the drying table is provided with a secondary conveying belt. By arranging the drying machine and the cooling box, rapid and effective drying can be carried outon the premise of not damping the structure, the straw granules can be cooled in the cooling box after completion, the temperature is rapidly reduced, materials discharge from a discharge outlet can be immediately packaged, and operation is rapid and efficient and saves time and labor.
Owner:巴东隆生生物科技有限公司
Coating device for building artworks, having automatic adjusting function
InactiveCN109663692AWith automatic adjustment functionCoating is fast and effectiveSpraying apparatusPretreated surfacesSemi automaticEngineering
The invention discloses a coating device for building artworks, having an automatic adjusting function. The coating device comprises a base, artworks, a bearing plate and a crossbeam, wherein the artworks are placed on the upper wall surface of the base; the bearing plate is mounted on the upper wall surface of the base and located behind the artworks; the crossbeam is placed on the upper wall surface of the bearing plate; a core unit is arranged on the lower wall surface of the crossbeam; and an auxiliary unit is mounted on the lower wall surface of the crossbeam and the side wall surface ofthe base. The coating device has the beneficial effects that the coating device is compact in structure and low in cost; through massive semi-automatic design, the working procedure of coating on artworks can be quickly and effectively completed, after the first building artworks are coated, a lifting spraying mechanism performs coating on the next building artworks, a drying mechanism can quicklydry the previous building artworks, and the working efficiency is improved effectively.
Owner:SHANDONG LABOR VOCATIONAL & TECHN COLLEGE
Efficient drying equipment for ore processing
InactiveCN106871595AGuaranteed production efficiencyEasy to useDrying gas arrangementsDrying machines with local agitationEngineeringCam
The invention relates to efficient drying equipment for ore processing. The equipment comprises a bottom plate, a heating device, a pipeline device, a filter device, a frame body device, a cam device, a bracket device and a swinging device. A first bracket, a first supporting rod and a first transverse rod are arranged on the bottom plate; the heating device comprises a heating frame, a heat dissipating frame, a heating rod and a first spring; the pipeline device comprises a first pipeline, a fan, a first connecting rod, a second supporting rod, a second transverse rod, a first oblique rod and a third transverse rod; the filter device comprises a housing, a third supporting rod, a second bracket, a first filter screen, a first sponge block, a second sponge block, a second spring, a third bracket and a fourth supporting rod; the frame body device comprises a first frame body and a first transverse plate; the cam device comprises a fourth bracket, a first bent rod, a fourth transverse rod, a first vertical rod, a second oblique rod, a fifth bracket, a cam and a third oblique rod. The equipment provided by the invention can quickly and effectively dry ores and is relatively uniform and fast to dry.
Owner:王杨
Melt-blown fabric production device with automatic winding function
PendingCN112678577AWith automatic winding functionImprove filtering effectMechanical cleaningPressure cleaningWinding functionComposite material
The invention discloses a melt-blown fabric production device with an automatic winding function. The melt-blown fabric production device comprises a bottom plate, wherein a production device body is fixedly arranged at the top of the bottom plate; a treatment box is fixedly arranged at one side of the production device body; four stand columns are fixedly arranged at the bottom of the treatment box; the four stand columns are arranged at equal intervals; the bottom ends of the four stand columns are fixedly connected to the top of the bottom plate; a drying cavity and a cleaning cavity are arranged in the treatment box; and a feeding port is arranged in the inner wall of the side, close to the production device body, of the drying cavity. The melt-blown fabric production device is reasonable in design and good in practicability, produced melt-blown fabric can be automatically wound, in the melt-blown fabric winding process, the melt-blown fabric can be rapidly and effectively dried, and the surface of the melt-blown fabric is effectively subjected to dust collection and cleaning, so that the production quality of the melt-blown fabric is improved; and a winding shaft is rapidly disassembled and assembled, so that the winding shaft is convenient to replace, time and labor are saved, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:ANHUI HONGSHI ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Silicon wafer drying tank
InactiveCN107478007ASolution to short lifeSmall sizeDrying gas arrangementsDrying chambers/containersEngineeringCentrifugal fan
The invention discloses a silicon wafer drying tank. The silicon wafer drying tank comprises an inner box and an outer box; the inner box is located inside the outer box; a separating space is formed between the inner box and the outer box, and the inner box and the outer box are each provided with an upward opening, and the openings are the same in size; a tank body for containing a silicon wafer basket is formed inside the inner box, and first air holes are uniformly distributed in at least one side face of the inner box; heating pipes are installed in the separating space and right face the first air holes; second air holes are uniformly distributed in the bottom face of the inner box; and at least one centrifugal fan is installed in the separating space and is axially perpendicular to the bottom face of the inner box. The silicon wafer drying tank has the advantages that silicon wafers are dried in the tank, the equipment size is decreased, the cost is low, power consumption is also low, the power consumption of the silicon wafer drying tank is about 1 / 3 of that of a previous silicon wafer drying tank, and the service life of a silicon wafer carrier is prolonged.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG ULTRASONIC & ELECTRIC
PET bottle flake or thin film drying device
The invention discloses a PET bottle flake or thin film drying device with low energy consumption, quick drying and small size; the drying device includes that at least two drying box units are arranged between a feeding box and a discharging box on a rack; the structure of each drying box unit includes a shell body having an inner cavity divided into a drying chamber and a heating chamber, each heating chamber is internally provided with a heater, the top of each heating chamber is provided with a draught fan, each drying chamber is internally provided with a circular arc separating plate having the bottom protruding downwards and having a plurality of through holes, each drying chamber is separated into a drying upper chamber and a drying lower chamber by the circular arc separating plate, and a shell body of the top of each drying upper chamber is provided with a plurality of wet discharge holes; the drying chambers are communicated with the heating chambers respectively; a stirring shaft with spiral blades successively passes through the feeding box, the drying upper chambers of the drying box units, and the discharging box which are successively communicated with one another, and the stirring shaft is rotated under driving of a stirring driving device, so as to make a material in the feeding box continuously go forwards to be successively outputted from a discharge port of the discharging box through the drying upper chambers.
Owner:JIANGSU ASG PACKAGING MACHINERY GRP
Dust-removing dryer for grain
InactiveCN106804699AFast and efficient dryingImprove qualityUsing liquid separation agentSeed preservation by dryingPulp and paper industryAir blower
The invention relates to a dust-removing dryer for grain and belongs to the field of agricultural drying machinery. The dryer comprises a box, an air heater and a purification tank, wherein water is contained in the purification tank, an air blower is arranged at the top of the box, an air outlet of the air blower is connected with an air inlet of the box, and an air inlet of the air blower is connected with the air heater through a pipeline; drying pipes are arranged in the box, a plurality of through holes are formed in the side wall of each drying pipe, and exhaust ports are formed in one side wall of the box and extend into the liquid level of the purification tank. The dust-removing dryer for the grain dries the grain in an up-ventilation and down-exhaust manner, the grain is ensured to be dried quickly and effectively, and the workload of farmers can be reduced; moisture in the grain is fully diffused, the quality of the dried grain is higher, the exhaust ports are placed in water, impurities and dust in exhaust air are adsorbed by water, pollution can be prevented, the exhaust air is purified, and the dryer is simple in structure and has very high practicability.
Owner:CHENGDU 90 DEGREE IND PROD DESIGN CO LTD
Plant for drying pretreated flexible sheet products
ActiveCN111417733ALow costEasy to controlDrying solid materials with heatDrying machines with progressive movementsPlantAgricultural engineering
A drying plant (1) for drying pretreated flexible sheet products, having at least one side on which a layer of a chemical compound has previously been deposited, said system (1) comprising feeding means (2) for feeding the sheet products in a direction (L), drying means (3) for drying the products as they are being fed, which have at least open operating unit (5) with a chamber (6) through which the feeding means (2) are designed to pass, and with at least one applicator (10) connected to a respective generator (11) for application of an alternating electromagnetic field in the RF range and acontrol unit (1 6), for controlling the generator (11) and / or the applicator (10). The field has an oscillation frequency that ranges from 300 kHz to 300MHz and is preferably 27.12 MHz at least one air blowing means (18) (18) for delivering hot air and / or at least one suction means (19) are provided. The control unit (16) is configured to change the speed of the feeding means (2) or to change theelectromagnetic field application time. Sensor means are further provided, for detecting one or more physical and / or thermodynamic parameters of the operating unit (5) and the temperature of the sheetand for controlling the means (2, 18, 19) separately from or in combination with each other and carry out complete drying of the chemical compound layer.
Owner:OFFICINE DI CARTIGLIANO SPA
Rapid furnace opening method
ActiveCN114134263AShort timeImprove efficiencyBlast furnace detailsProcess efficiency improvementHot blastChemistry
A rapid blow-in method comprises the following steps that (1) an air supply pipeline is pre-buried in an iron notch; (2) the main channel is filled with ramming mass and coke powder; (3) baking the furnace; (4) selecting a furnace opening material; (5) nitrogen cooling; (6) charging with wind; (7) hot air ignition; and (8) quickly introducing coal gas. The method has the beneficial effects that the consumed time is short, the efficiency is high, and the environmental protection and safety problems are reduced; the oven adopts a helical blade hot air shunting table for uniformly shunting hot air, so that the oven baking time is greatly shortened; coke and firewood mixed loading facilitates air supply, facilitates rapid ignition and combustion, makes space for descending of the upper furnace burden, and facilitates rapid loosening of the stock column. Charging with wind has a remarkable effect on drying coke and moisture of a charging material, the blow-in total coke ratio can be reduced by 200-300kg / t, and the phenomenon of material collapse and suspension in the blow-in process of the blast furnace is reduced; and clay gun tapping is omitted during tapping of the iron notch embedded air supply pipeline, so that the tapping time is shortened, and the tapping efficiency is improved. Compared with the conventional technology, the method provided by the invention can shorten the blow-in time by 8-12 hours.
Owner:德龙钢铁有限公司 +1
Sesame seed peeling equipment capable of performing drying
InactiveCN107865450AFast and efficient dryingImprove peeling efficiencyGas current separationVegetable peelingSesamum orientaleVertical tube
The invention discloses a sesame peeling device with drying, which includes a peeling device and a drying device. The peeling device includes a vertical cylinder and an inner cylinder. The turntable and the outer disk have the same center of circle, and the rotation direction of the turntable is opposite to that of the outer disk. The drying device includes a drying barrel, an air supply device, a collection chamber and an impurity chamber. Through the sesame peeling device with drying of the present invention, the sesame is thoroughly peeled, the efficiency of sesame peeling is improved, and the damage rate in the process of sesame peeling is reduced at the same time, the sesame is quickly and effectively dried, and the color and luster of the sesame are guaranteed. degree, to ensure the quality of the finished product.
Owner:黄林海
Integrated drying equipment for polyester staple fiber production
PendingCN113532058AEasy to dry and handleEasy to operateDrying gas arrangementsDrying chambers/containersPolyesterManufacturing engineering
The invention discloses integrated drying equipment for polyester staple fiber production. The integrated drying equipment comprises a machine body, a mounting cavity is formed in the middle of the machine body, a drawing head is arranged in the mounting cavity, clamping heads are connected to the two sides of the drawing head in a rotating mode, a roller is arranged between the two clamping heads and is connected between the two clamping heads in a clamped mode, a motor is arranged in one side of the machine body, and the output end of the motor is inserted into the mounting cavity and is connected to the clamping heads in a clamped mode. The integrated drying equipment has the advantages that the problems that existing roller drying equipment is mostly large in size, PET slices are inconvenient to dry, in addition, feeding and discharging of the PET slices are inconvenient through the existing roller drying equipment, and the PET slices are inconvenient to dry effectively can be solved, the structure of the roller drying equipment is improved and optimized, so that a roller of the roller drying equipment can be flexibly disassembled, the PET slices in the roller can be conveniently and smoothly discharged and fed, and then workers can conveniently and rapidly dry the PET slices.
Owner:ANHUI XINDE CHEM FIBER
Domestic appliance for clothes drying
InactiveCN108085944AFast and efficient dryingDry evenlyTextiles and paperLaundry driersEngineeringScrew thread
The invention discloses a domestic appliance for clothes drying, comprising a fixing base. A motor seat is fixedly connected to the left top of the fixing base, a motor is fixedly connected to the topof the motor seat, a driving conical gear is fixedly connected to the output end of the motor, a fixed rotary shaft is rotationally connected to the top center of the fixing base, a driven conical gear is fixedly connected to the outer side of the top of the fixed rotary shaft, the driven conical gear is engaged with the driving conical gear, an outer sleeve is in threaded connection with the topof the fixed rotary shaft, a telescopic rod is slidably connected to the top of the outer sleeve, a fixing bolt is in threaded connection with the outer side of the outer sleeve, the fixing bolt is passed through the outer sleeve and mates with a telescopic rod, and a cavity is arranged in the fixing base. Compared with the prior art, the domestic appliance for clothes drying is simple in structure and convenient to use, can quickly and efficiently dry clothes during use, allows clothes to be dried more evenly by continuously changing the flowing direction of a drying flow, and is particularly suitable for use on snowy and rainy days.
Owner:李建武
Water washing equipment for vehicle speed sensor production
InactiveCN112044839ATroubleshoot poor job performanceEfficient washing treatmentCleaning using liquidsStationary filtering element filtersWater storageEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses water washing equipment for vehicle speed sensor production, and relates to the technical field of vehicle speed sensor machining equipment. The water washing equipment aims tosolve the problem that existing water washing equipment is poor in working performance, and comprises a water washing box body, and a water washing cavity, a treatment cavity and a water storage cavity are formed in the water washing box body. A vertically-arranged water pump is fixed to one side of the outer portion of the washing box body through screws, the input end of the water pump is connected with a water conveying pipe, the end, away from the water pump, of the water conveying pipe extends into the water storage cavity, the output end of the water pump is connected with a water outlet pipe, and the end, away from the water pump, of the water outlet pipe extends into the water washing cavity and is closed. According to the water washing equipment, circumferential washing treatmentcan be efficiently carried out on vehicle speed sensor raw materials, redundant water of the water washing equipment can be recycled, bearing parts of the water washing equipment can be simply and conveniently disassembled, assembled and replaced, the washing efficiency is high, and use is convenient.
Owner:安徽博昕远智能科技有限公司
Integrated screen printing device capable of realizing fully-automatic drying
PendingCN112060753AFast and efficient dryingIncrease air circulationScreen printersPrinting press partsScreen printingElectric machinery
The invention discloses an integrated screen printing device capable of realizing fully-automatic drying. A circulating drying device comprises a first drying box, a second drying box, a third dryingbox, a first box door hinged to one side of the first drying box through a first hinge, a second box door hinged to one side of the second drying box through a second hinge, and a third box door hinged to one side of the third drying box through a third hinge; a back plate is fixedly arranged on the sides, away from the third box door, of the first drying box, the second drying box and the third drying box, and a first motor is fixedly arranged at the center of the side, away from the third drying box, of the back plate; and the printing device comprises a plurality of groups of first extension plates fixedly connected to one side of the first drying box, a base, and a side plate fixedly arranged at the top end of one side of the base. The integrated screen printing device capable of realizing fully-automatic drying is high in automation degree, reduces the labor cost while increasing the production efficiency, and is capable of rapdily and effectively drying printed materials, time-saving and labor-saving, and high in practicability.
Owner:雅致精密工业(深圳)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com