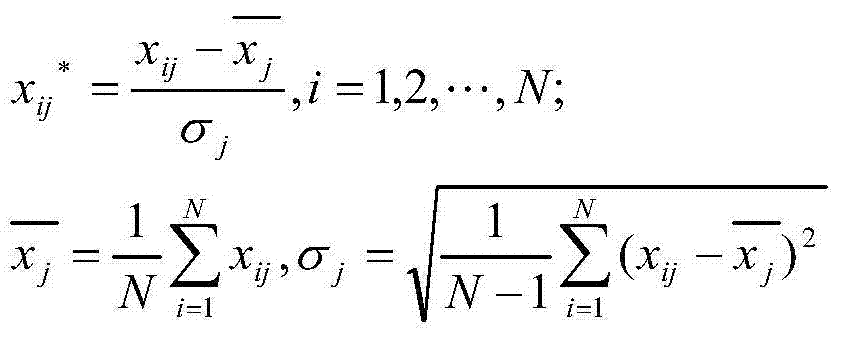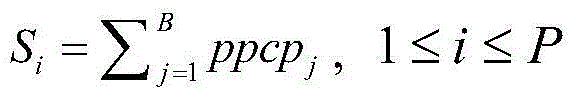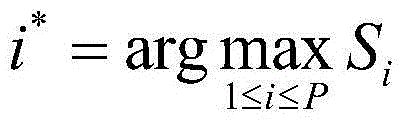Patents
Literature
123results about How to "Improve the speed of prediction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
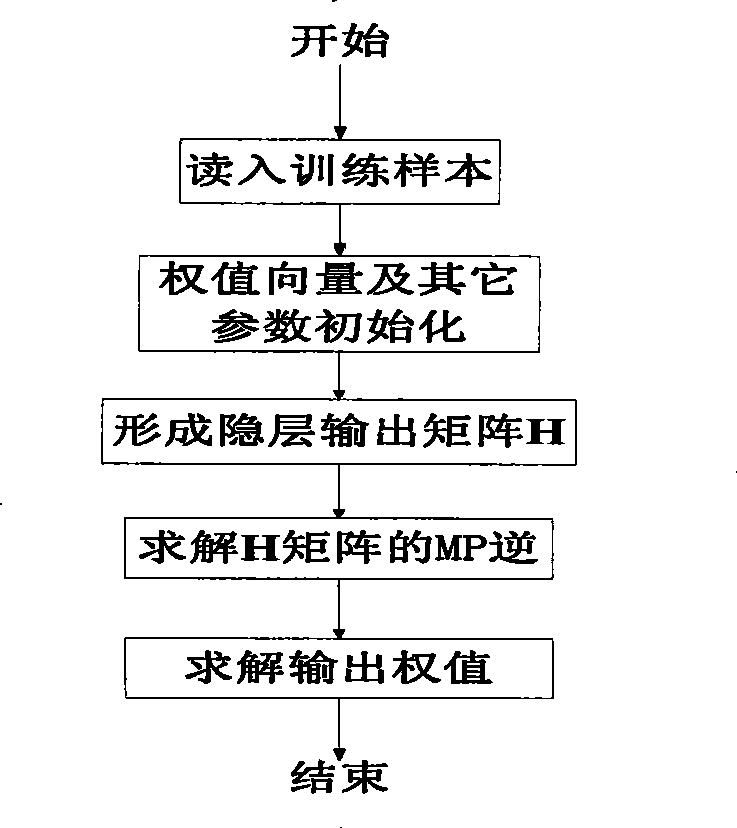
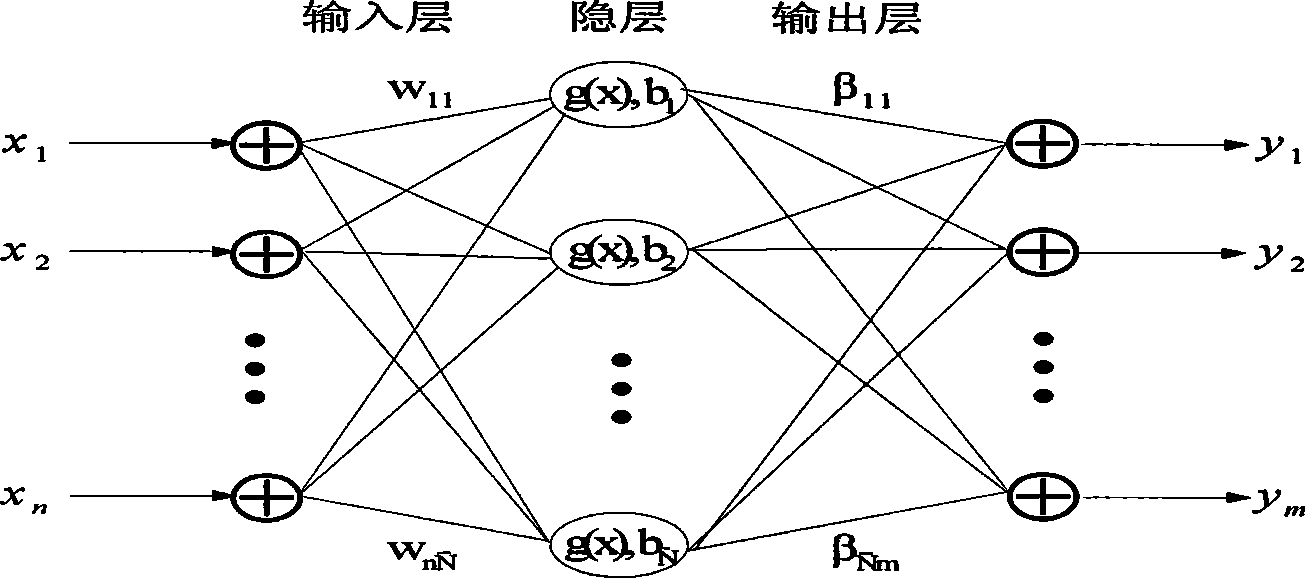
Wind power generation short-term load forecast method of least squares support vector machine
InactiveCN103488869AImprove forecast accuracyImprove the speed of predictionData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityMathematical model
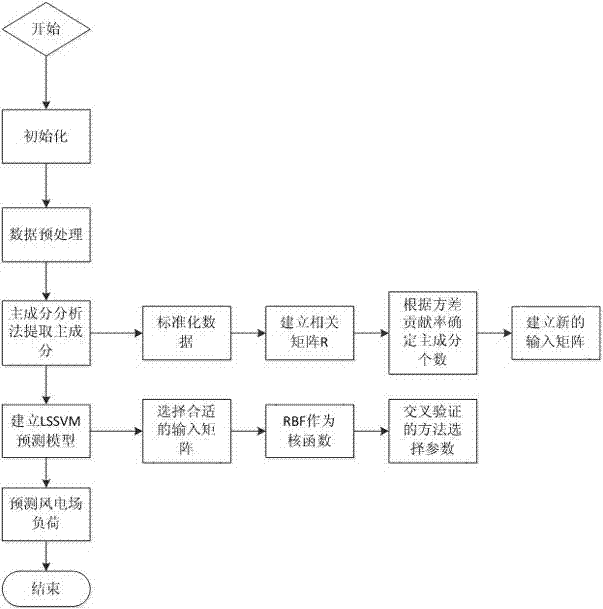
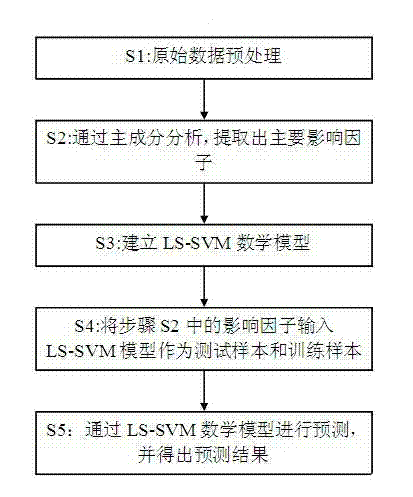
The invention discloses a wind power generation short-term load forecast method of a least squares support vector machine. The method comprises the following steps of 1, preprocessing original data; 2, carrying out principal component analysis on an original data sequence which is input to the least squares support vector machine by a principal component analysis method, and analyzing and extracting a key impacting indicator of wind power loads; 3, building a mathematical model of the least squares support vector machine; 4, inputting the analyzed and extracted key impacting indicator to the mathematical model of the least squares support vector machine to be used as a training sample and a testing sample; 5, carrying out forecast on testing sample data by the mathematical model of the least squares support vector machine to obtain a forecast result. According to the wind power generation short-term load forecast method of the least squares support vector machine, the principal component analysis method and the mathematical model of the least squares support vector machine are combined, the calculated amount is reduced, the operability is increased, and the whole forecast performance and the whole forecast accuracy are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +2
Method for forecasting electric power system short-term load based on method for improving uttermost learning machine
InactiveCN101414366AImprove forecast accuracyImprove the speed of predictionNeural learning methodsNODALLearning machine
The invention discloses a power system short-term load forecasting method based on improving extreme learning machine (IELM) methods, which adopts an extreme learning machine (ELM) as the basic structure of a forecasting model and is an iteration-analysis learning algorithm which puts forward BFGS (Broyden, Fletcher, Goldfarb, Shanno) simulated Newton's method to give optimization, training and adjustment to network left metrics and analyze to get right metric parameters. The invention establishes the short-term load forecasting model based on improving extreme learning machine (IELM) method, puts forward extreme learning machine network reference hidden node concepts, trains the equidimensional extreme learning machine networks which have the same numbers of hidden nodes and samples, orderly clusters module values of equidimensional network right metrics vector, finds out a plurality of corresponding module value break points, and regards the break points as the reference hidden nodes of predicting networks. The method of the invention is also greatly improved in the aspect of prediction precision and speed.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
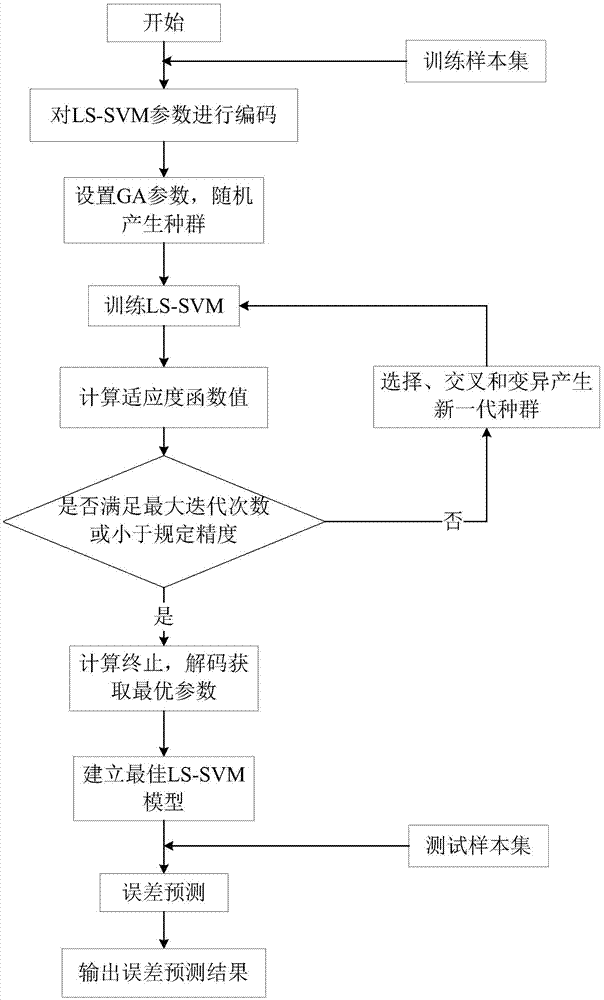
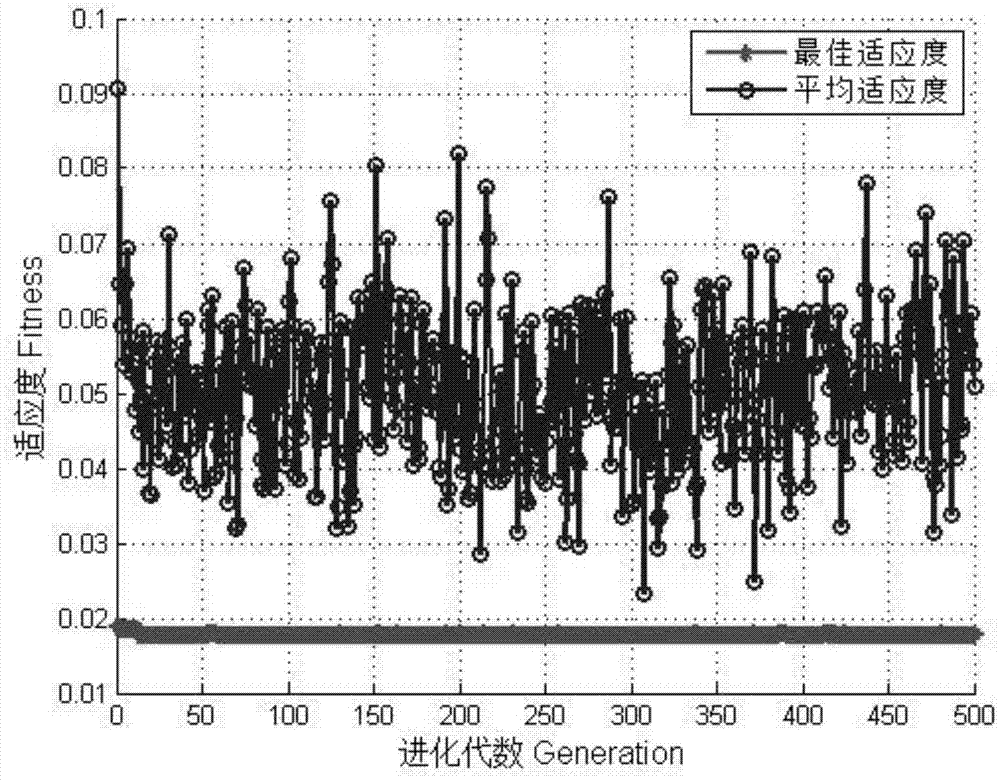
Mechanical temperature instrument error prediction method based on genetic-algorithm optimized least square support vector machine
ActiveCN105444923ASimplified Quadratic Programming ProblemReduce computing timeThermometer testing/calibrationData setAlgorithm
A mechanical temperature instrument error prediction method based on a genetic-algorithm optimized least square support vector machine is disclosed. The method comprises the following steps of (1) taking a tested characteristic parameter of a mechanical temperature instrument as model input, and taking an instrument error value and an error change rate acquired through sampling as model output; (2) carrying out pretreatment on original temperature error data; (3) selecting a Gauss radial kernel function as a kernel function of a least square support vector machine model; (4) using a genetic algorithm to optimize a parameter combination of the least square support vector machine; (5) constructing a mechanical temperature instrument error prediction model based on the genetic-algorithm optimized least square support vector machine; (6) inputting a data set and using a model obtained through training to carry out prediction; (7) comparing a temperature instrument error prediction result with an actual temperature error and analyzing a temperature error value and a change trend of a temperature error change rate. By using the method, precision is high; calculating is simple and engineering practicality is high.
Owner:邳州市润宏实业有限公司
Expressway traffic flow forecasting method based on time series
InactiveCN104269055AMeeting forecast needsMeet engineering needsDetection of traffic movementForecastingTraffic flowBusiness forecasting
The invention discloses an expressway traffic flow forecasting method based on time series. The expressway traffic flow forecasting method includes the steps of selecting one time scale, and carrying out statistics to build the traffic flow time series Q=(x); setting the value range of the number p of autoregression items and the number q of moving average items according to the selected time scale; solving the number p of the autoregression items and the number q of the moving average items; fitting the optimal number p of the autoregression items and the optimal number q of the moving average items through the maximum likelihood estimation in cooperation with the traffic flow time series Q to obtain an optimal ARMA model, and obtaining weight parameters of historical measured values and weight parameters of historical error values; solving the traffic flow forecasting series (please see the specifications) under the different time scales. By means of the expressway traffic flow forecasting method, an obtained time series model can better meet the requirement for forecasting various kinds of flow of an expressway, and the forecasting universality is improved; operation is simple, the forecasting efficiency is improved, the forecasting speed is increased, and the engineering requirement of traffic forecasting of the expressway is met.
Owner:四川省交通科学研究所
Geological disaster liability judgment method and device
ActiveCN104021267AImprove forecast accuracyImprove the speed of predictionAlarmsSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceGeological disaster
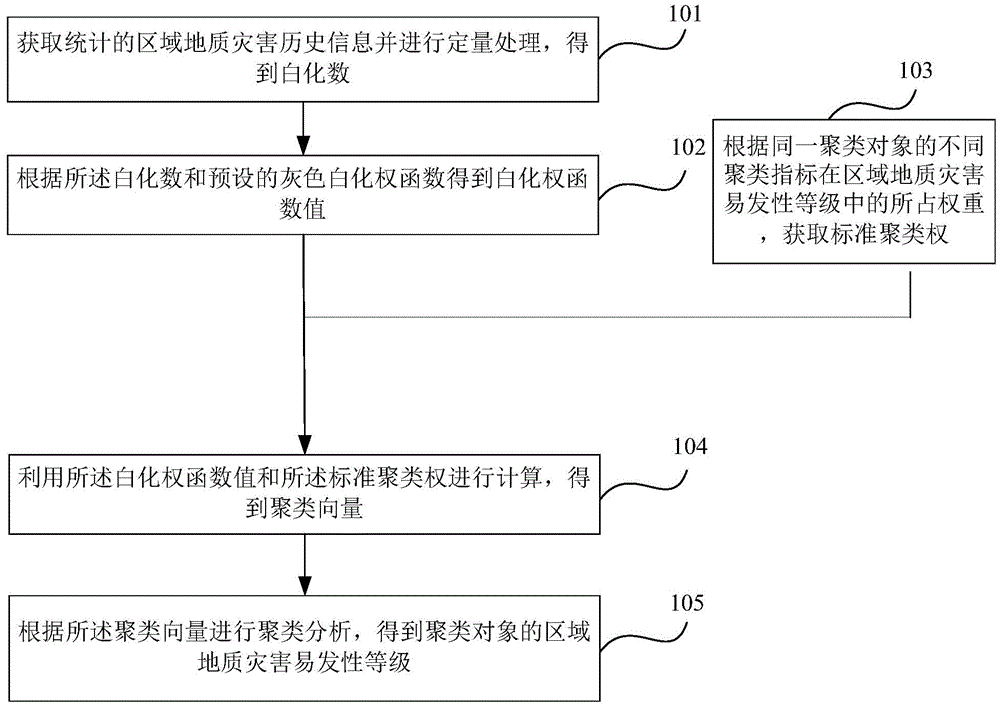
The embodiment of the invention provides a geological disaster liability judgment method and device. The geological disaster liability judgment method includes the steps of obtaining collected regional geological disaster historic information and carrying out quantitative processing to obtain an ablation function; obtaining a white function value according to the ablation function and a preset grey white function; obtaining a standard cluster weight according to weight of different cluster indexes of the same cluster object in regional geological disaster liability grades; calculating according to the white function value and the standard cluster weight to obtain a cluster vector; carrying out cluster analysis according to the cluster vector to obtain the regional geological disaster liability grade of the cluster object. Prediction accuracy and speed of regional geological disaster liability can be improved, and accordingly prediction accuracy and efficiency of regional geological disaster liability can be improved.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Multi-basin real-time intelligent water quality predication method and system
ActiveCN104318325AImprove accuracyImprove speed and precisionGeneral water supply conservationForecastingTraffic volumeRiver pollution
The invention discloses a multi-basin real-time intelligent water quality predication method and system. According to the multi-basin real-time intelligent water quality predication method and system, an NARX model is optimized through a genetic algorithm and a problem that earlier stage parameters of the NARX model are uncertain; a GA-NARX model is stored or called through a model storage module to predicate the multi-basin water quality condition in real time; essential data, recent data and history emergency data are performed on three-section training and accordingly an optimized GA-NARX model can basically comprise river pollution characteristics and the predication accuracy is improved; weather data replaces hydrological data and is performed on obfuscation processing and accordingly influences to the model from flow data missing are effectively solved; matching of similar pollution time sequence templates is performed through an improved DTW algorithm, a similar pollution process in the basin history is rapidly found out, experience is referred and learned, and sudden emergency accidents are accurately predicted. The multi-basin real-time intelligent water quality predication method and system can be widely applied to the water quality predication field.
Owner:广东省环境监测中心
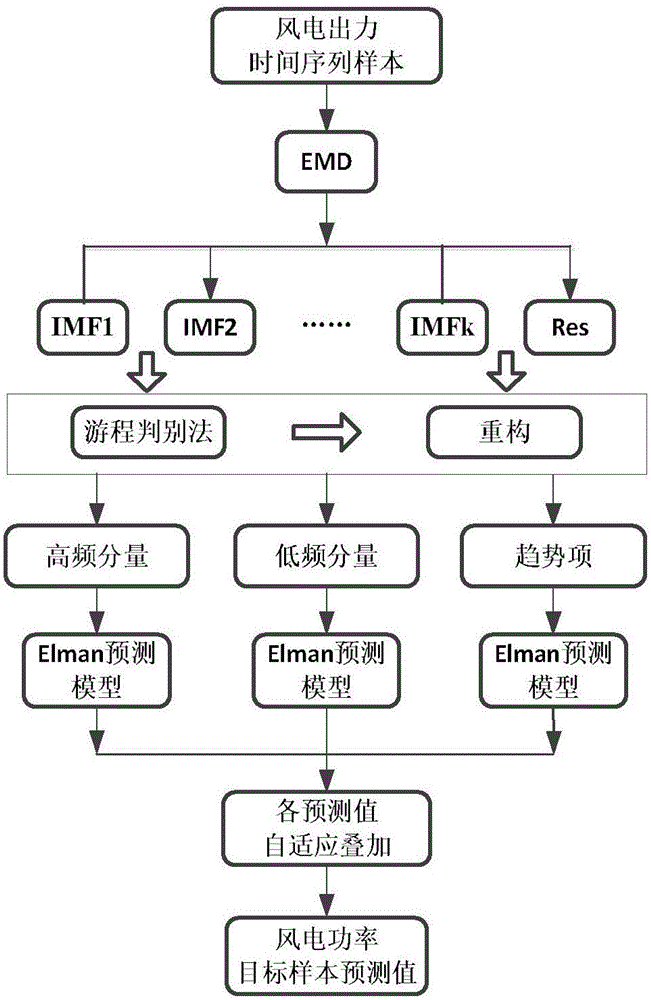
Empirical mode decomposition and Elman neural network combined wind power forecasting method
InactiveCN106295798AReduce distractionsImprove forecast accuracyNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsDecompositionNetwork model
The invention discloses an empirical mode decomposition and Elman neural network combined wind power forecasting method, comprising the following steps: screening samples which are used for forecasting a wind power field, and selecting wind power outputs of forecasting periods within fluctuation months to implement forecasting; implementing empirical mode decomposition on multiple groups of output time sequence sample data of the wind power field, and ensuring that each group can obtain multiple intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) and trend components Res according to decomposition termination conditions; implementing fluctuation degree classification on decomposed IMFs according to a run distinguishing method, and reconstructing the IMFs according to a similar fluctuation frequency principle to obtain total high-frequency components and total low-frequency components; establishing an Elman neural network model, and implementing data normalization on the total high-frequency components, the total low-frequency components and the trend components to obtain training and test data of a neural network; and implementing day-ahead power forecasting for 72h by adopting an Elman improved learning algorithm to obtain a day-ahead forecasting power value of 72h of target wind power outputs. By adopting the empirical mode decomposition and Elman neural network combined wind power forecasting method disclosed by the invention, the number of forecasting components can be reduced, and the forecasting accuracy and forecasting speed can be increased.
Owner:JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
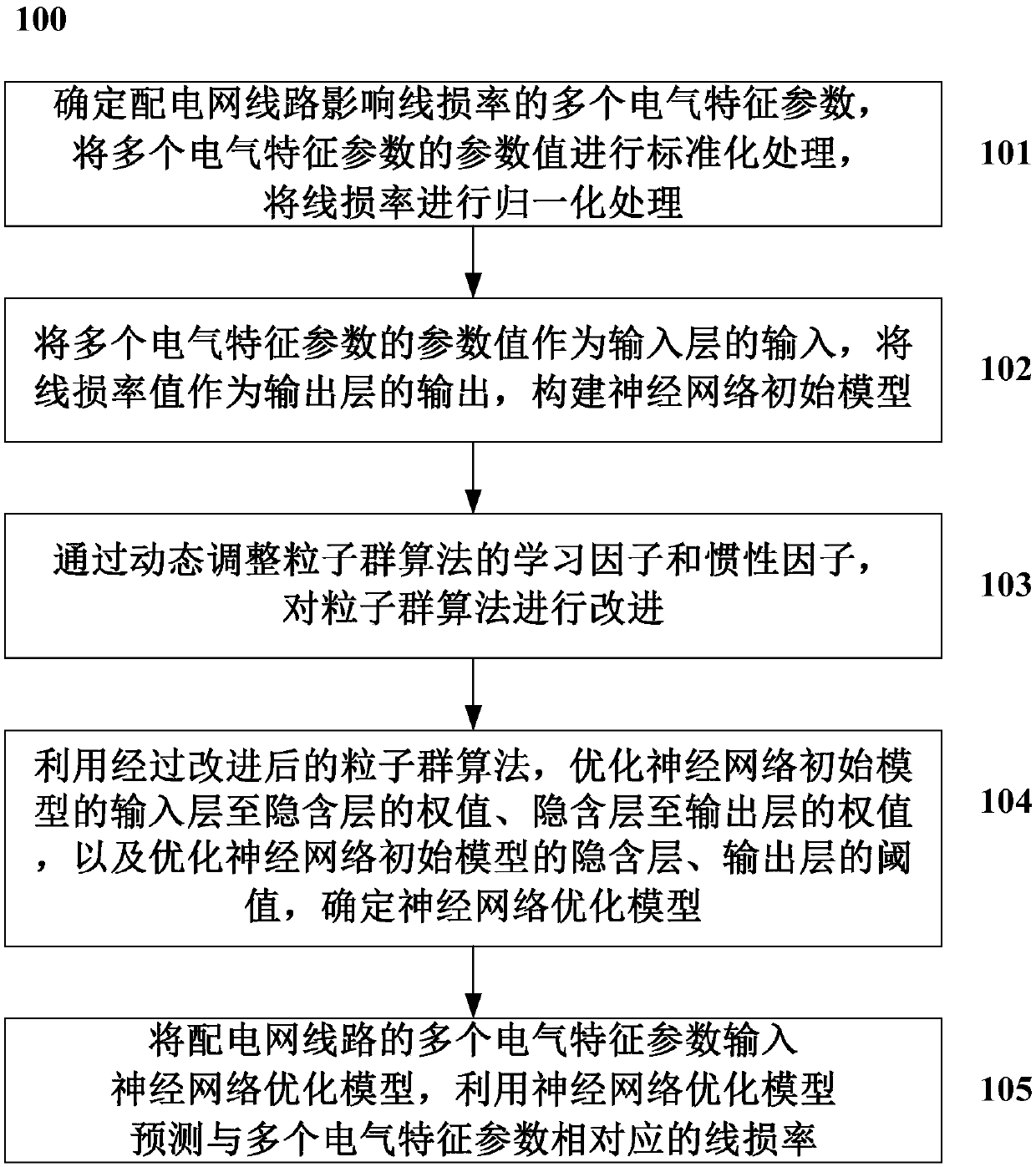
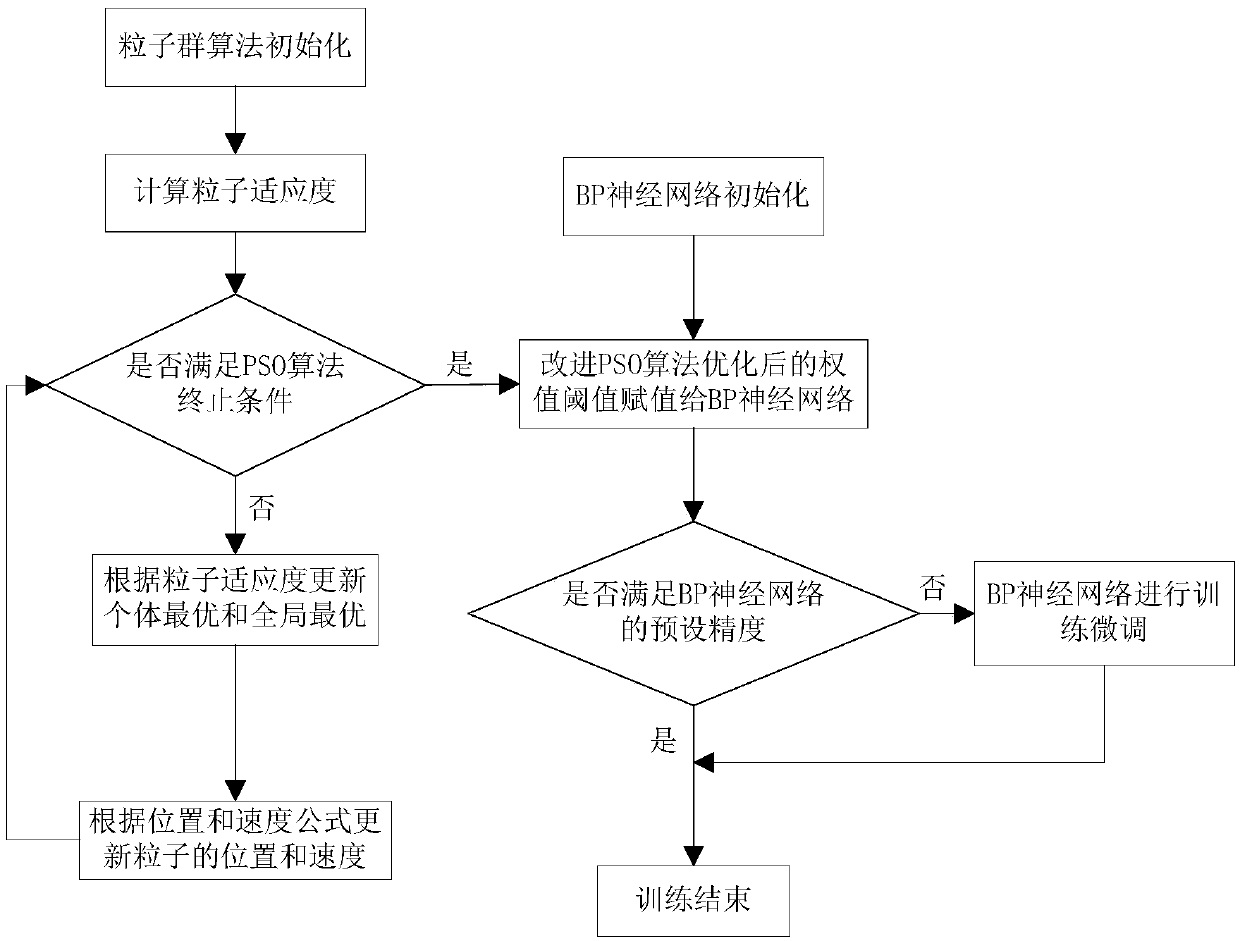
Method and system for predicting line loss rate of power distribution network
ActiveCN108694467AAchieve economical operationImprove forecast accuracyForecastingInformation technology support systemHidden layerLearning factor
The invention discloses a method for predicting a line loss rate of a power distribution network. The method comprises the steps of determining multiple electrical characteristic parameters, influencing the line loss rate, of the power distribution network, performing standardization processing on parameter values of the electrical characteristic parameters, and performing normalization processingon the line loss rate; by taking the parameter values of the electrical characteristic parameters as inputs of an input layer, and taking the value of the line loss rate as an output of an output layer, building an initial neural network model, wherein the initial neural network model comprises at least one hidden layer; determining the number of hidden layer nodes; by dynamically adjusting an inertial factor and a learning factor of a particle swarm algorithm, improving the particle swarm algorithm; by utilizing the improved particle swarm algorithm, optimizing a weight value and a thresholdvalue of the initial neural network model to determine an optimized neural network model; and inputting the electrical characteristic parameters of a power distribution network line to the optimizedneural network model, and predicting the line loss rate corresponding to the electrical characteristic parameters by utilizing the optimized neural network model.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +6
Forest fire detection method based on deep convolutional model with convolution kernels of multiple sizes
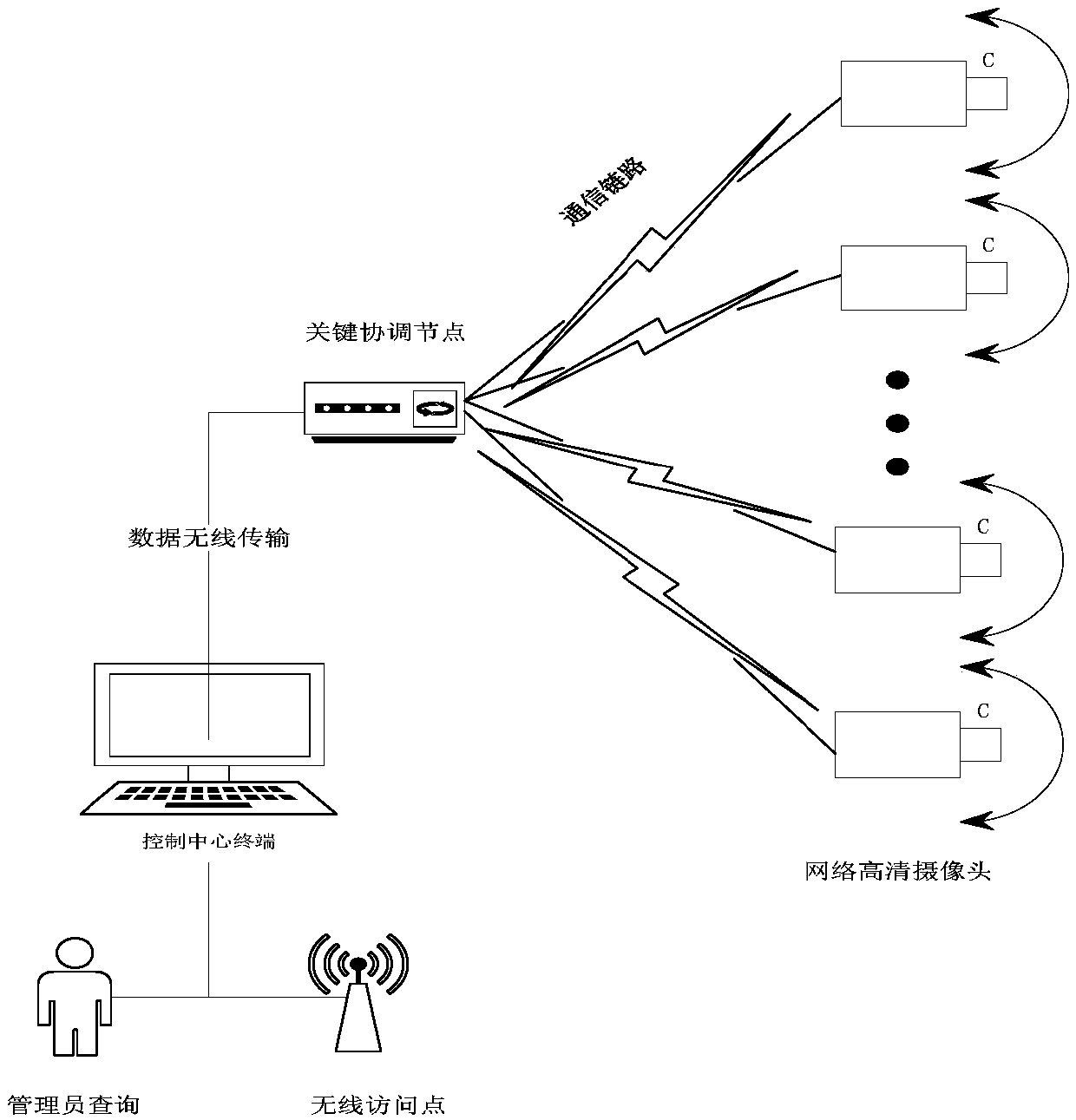
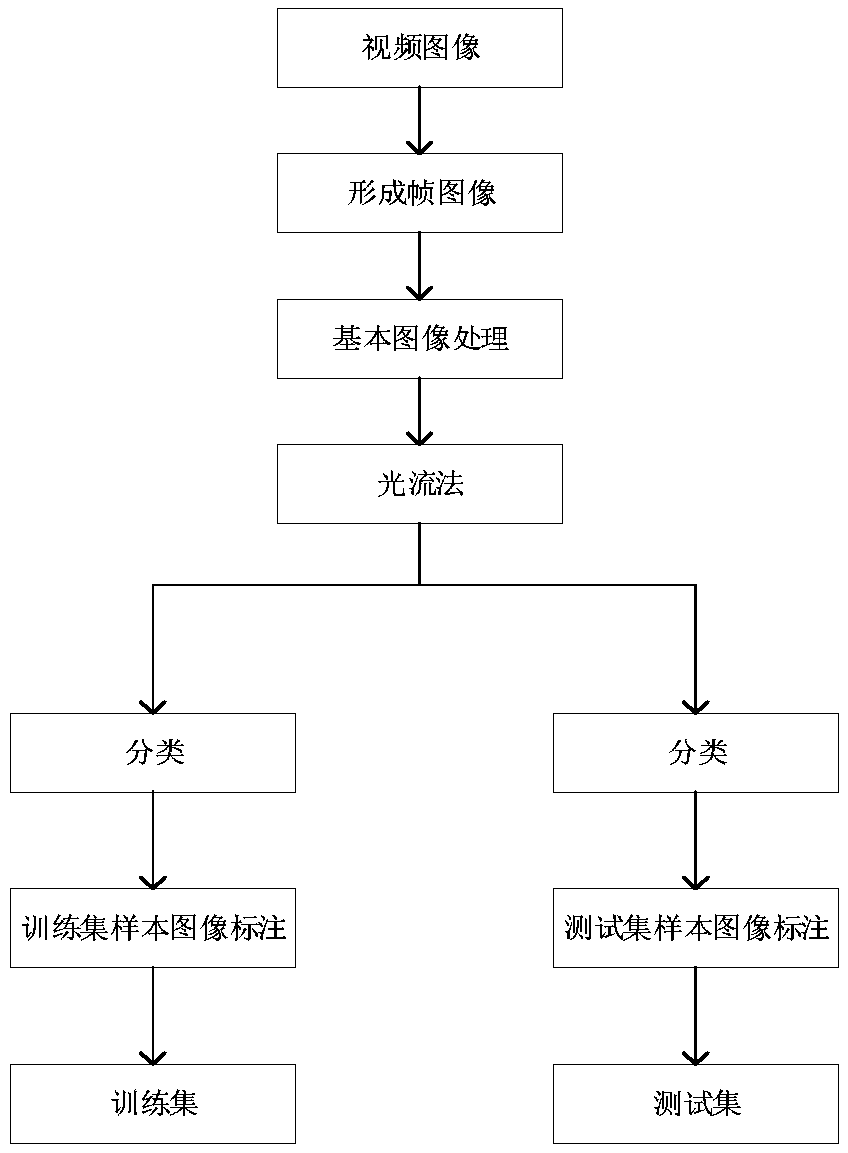
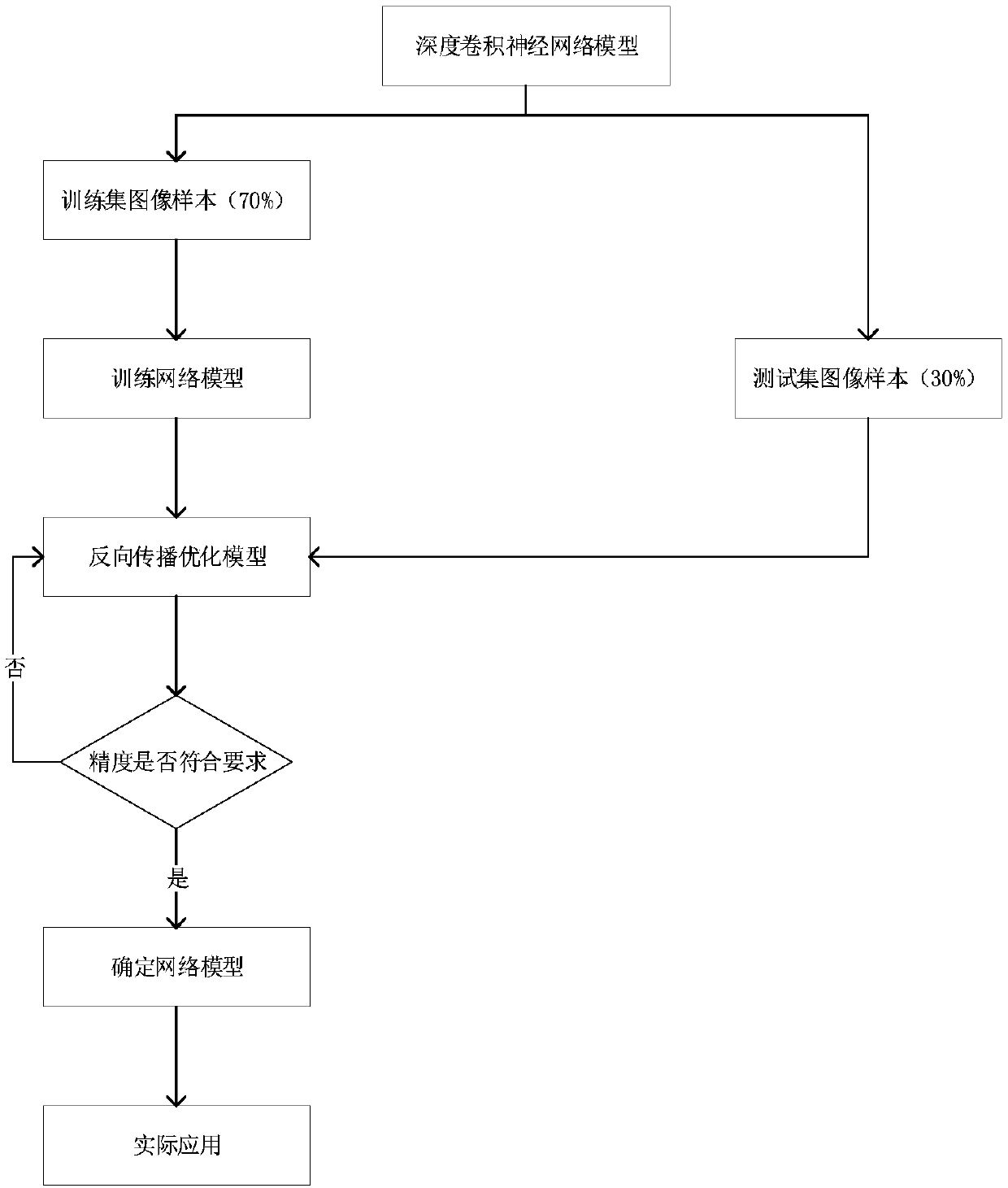
InactiveCN108921039AEfficient collectionImprove accuracyForest fire alarmsCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical flowConvolution theorem
The invention discloses a forest fire detection method based on a deep convolutional model with convolution kernels of multiple sizes, and relates to the technical field of deep learning video recognition. The method comprises the steps of collecting video image information; wirelessly transmitting data; forming an optical flow field; building a convolutional neural network model in deep learning;predicting a result; and the like. By training the deep convolutional neural network model with the convolution kernels of different sizes, an existing algorithm is improved; and in combination withexisting hardware conditions, the forest fire judgment speed is increased, the prediction precision of the whole model is improved, and the problems that an existing forest fire is not timely discovered and the economic loss is relatively serious can be effectively solved; and therefore, the method has a certain practical value.
Owner:南京启德电子科技有限公司
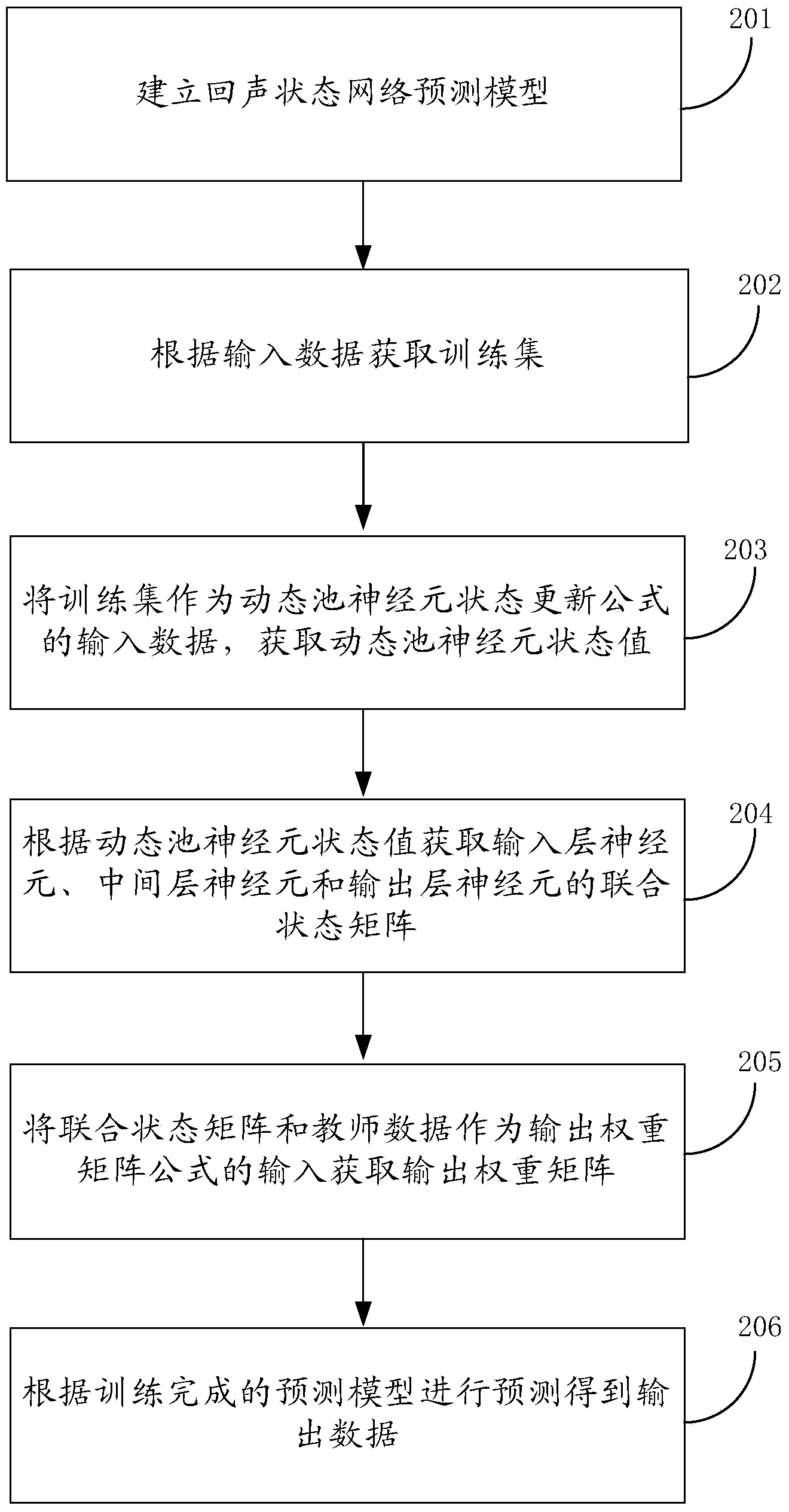
Echo state network based prediction method and prediction device
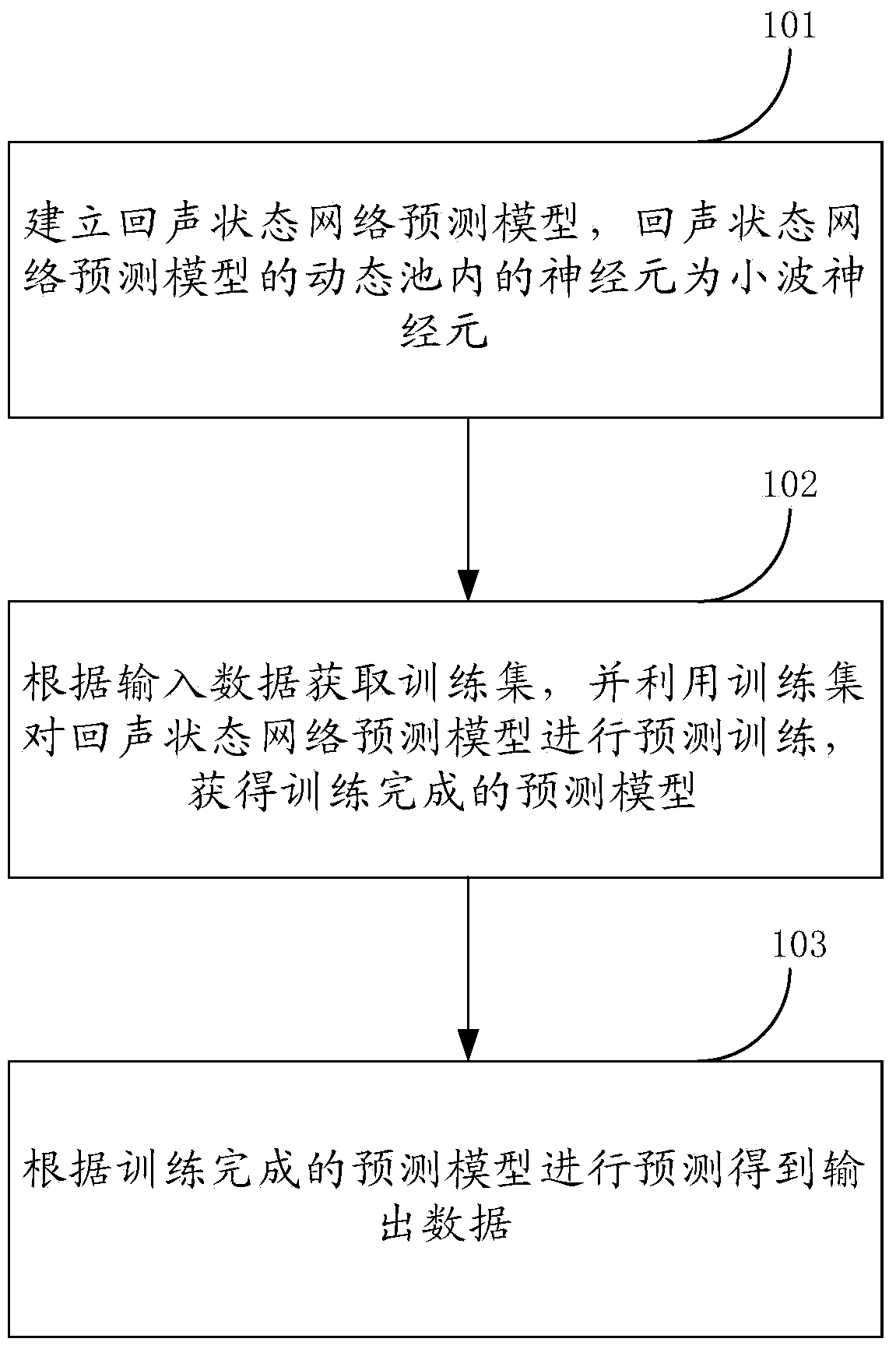
InactiveCN104346517AImprove predictive performanceImprove the speed of predictionBiological neural network modelsSpecial data processing applicationsPredictive methodsAlgorithm
The embodiment of the invention provides an echo state network based prediction method and a prediction device, and relates to the field of computers. The prediction method and prediction device can effectively improve the prediction performance of the ESN (Echo State Network), and increase the speed and the accuracy of prediction. The prediction method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing an echo state network prediction model, wherein nerve cells in a dynamic pool of the echo state network prediction model serves as wavelet nerve cells; acquiring a training set according to the input data, utilizing the training set to carry out prediction training on the echo state network prediction model, and obtaining the trained prediction model; predicting according to the trained prediction model, so as to obtain output data. The echo state network based prediction method and the prediction device disclosed by the embodiment of the invention can be applied to prediction of nonlinear chaotic time series data.
Owner:杨凤琴
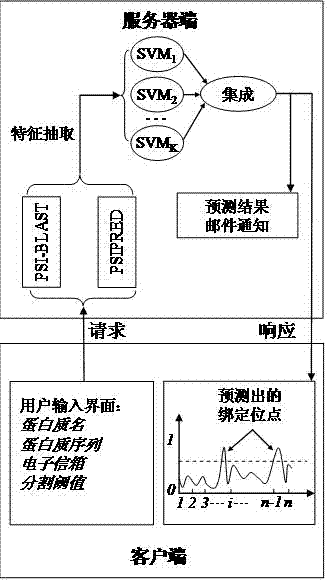
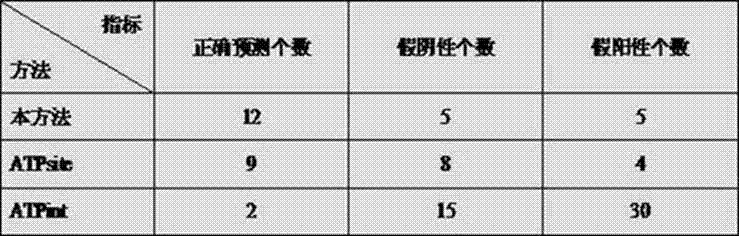
Adenosine triphosphate binding site predicting method for protein
InactiveCN102760210AImprove training and prediction speedAddress imbalancesSpecial data processing applicationsAdenosine triphosphateProtein formation
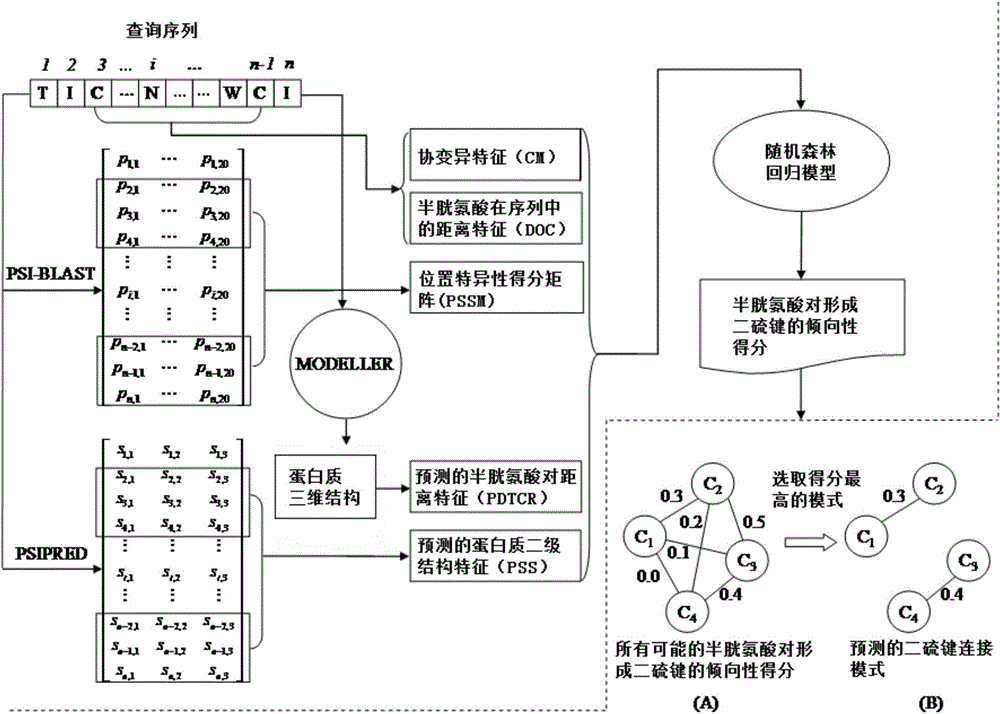
The invention discloses an adenosine triphosphate binding site predicting method for protein. The adenosine triphosphate binding site predicting method for the protein comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring evolution information and secondary structural information of the protein by using an IPSI-BLAST and PSIPRED program, and extracting characteristics of each amino acid residue by a sliding window technology; secondly, performing random downsampling on non-binding site samples for multiple times by a random downsampling technology, sample of several; thirdly, training an SVM (support vector machine) based on a non-binding site sample subset obtained in each random downsampling and a binding site sample set, and performing random downsampling on all the sample sets to obtain a plurality of SVMs; and finally, integrating the trained SVMs through Dempster-Shafer theoretic evidence. The adenosine triphosphate binding site predicting method for the protein has the advantages as follows: by a random downsampling technology, the scale of a training set can be effectively reduced and the model training speed can be effectively increased; and by an SVM integrating technology, information loss caused by downsampling can be effectively reduced and the model predicting precision can be effectively improved.
Owner:CHANGSHU RES INSTITUE OF NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
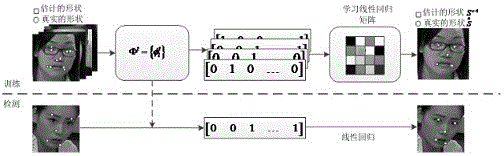
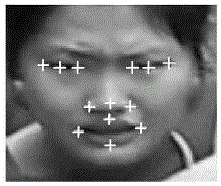
Face alignment method
InactiveCN106096560AImprove recognition ratePrecise positioningCharacter and pattern recognitionCrucial pointLinear regression
The invention discloses a face alignment method comprising the steps as follows: collecting a certain number of face images as training samples and predicting samples, enhancing the images, and for the training samples, calibrating face key points and storing the location information of the key points; learning the training samples calibrated in S1 through a random forest algorithm to get the feature mapping functions Phi<t> of the calibrated key points and to further get the local binary features of the calibrated key points; and combining the local binary features of the calibrated key points obtained in S2 into a global binary feature, getting a global linear regression model Wt based on the feature and through global linear regression learning, and thus locating the face key points of a sample to be tested.
Owner:广州高新兴机器人有限公司
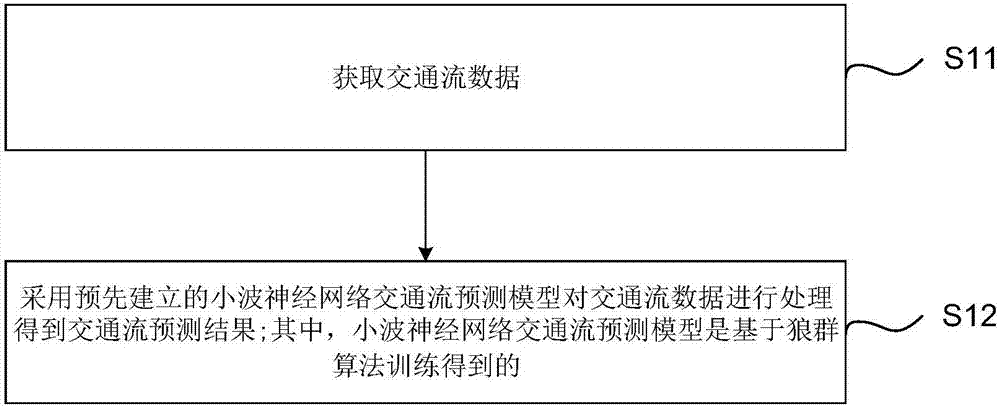
Traffic-flow forecasting method, device and system based on wolf-pack algorithm
ActiveCN107085942AImprove search abilityWide range of searchDetection of traffic movementBiological neural network modelsTraffic flowBusiness forecasting
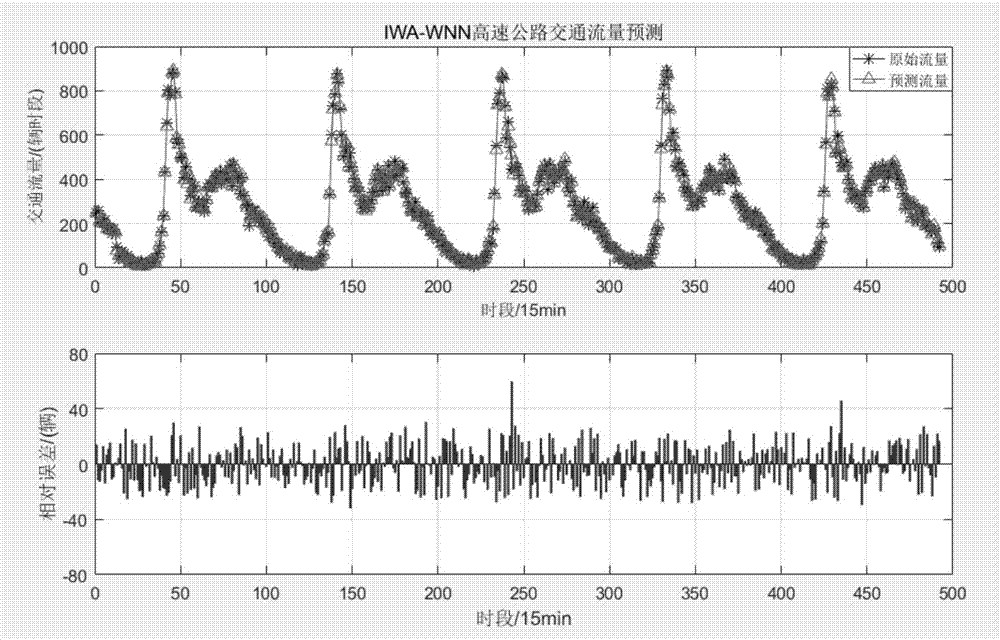
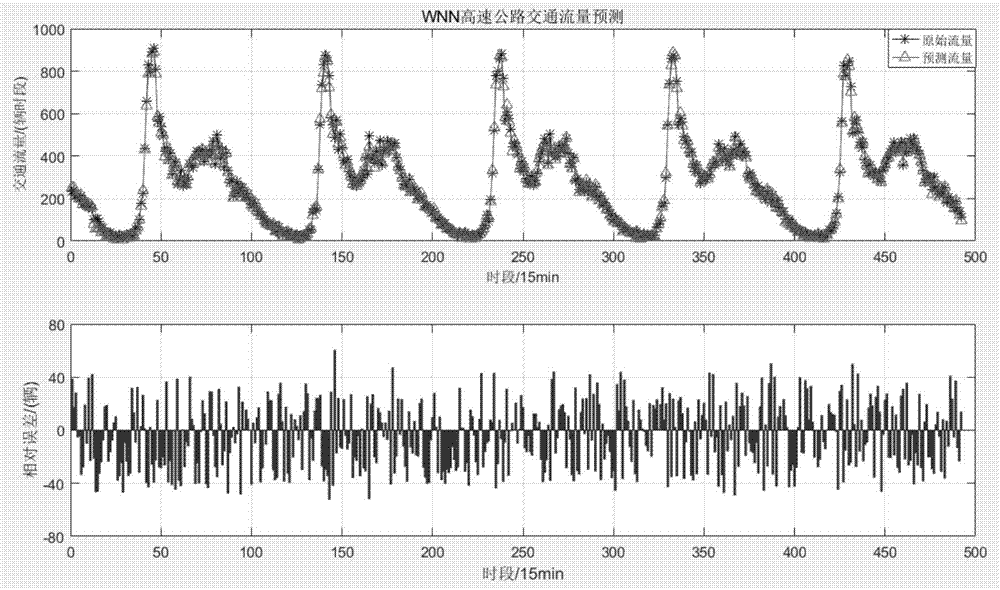
The embodiment of the invention discloses a traffic-flow forecasting method, device and system based on the wolf-pack algorithm. The traffic-flow forecasting method includes the steps that traffic-flow data is obtained; the traffic-flow data is processed through a pre-established wavelet-neural-network traffic-flow forecasting model to obtain the traffic-flow forecasting result, wherein the wavelet-neural-network traffic-flow forecasting model is trained based on the wolf-pack algorithm, and the training process of the pre-established wavelet-neural-network traffic-flow forecasting model is that an initialized wavelet-neural-network parameter is calculated according to historical data and the wolf-pack algorithm; the initialized wavelet-neural-network parameter is trained through a wavelet neural network and the historical data to obtain the wavelet-neural-network traffic-flow forecasting model. According to the traffic-flow forecasting method, device and system based on the wolf-pack algorithm in the embodiment, when traffic flow is forecasted through the wavelet-neural-network traffic-flow forecasting model trained through the initialized wavelet-neural-network parameter obtained based on the wolf-pack algorithm, the forecasting speed and the forecasting accuracy are increased to a certain degree.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
System and method for on-line multi-view video compression
InactiveUS20060023787A1Computer processing power becomes strongSolve narrow bandwidthColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputation complexityRound complexity
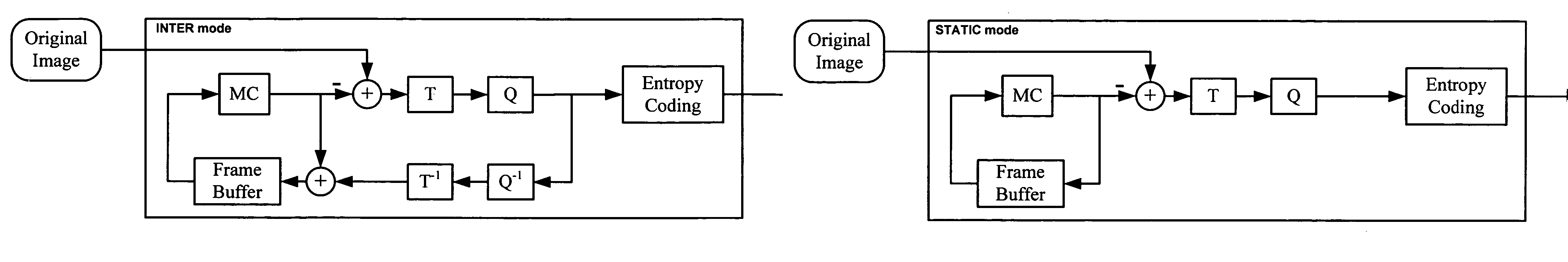
Interactive multi-view video presents new types of video capture systems, video formats, video compression algorithms, and services. Many video cameras are allocated to capture an event from various related locations and directions. The captured videos are compressed and are sent to a server in real-time. A big difference from the conventional schemes and the on-line compression of the interactive multi-view video system of the invention lies in a unique “STATIC” mode that is introduced to speed up the predictive coding. To find the STATIC mode, it is necessary to calculate the difference between the original image and a reference image. To further reduce the computing complexity, the decision of whether to use this STATIC mode or not is determined jointly among all views. In the STATIC mode, the involved macroblock (MB) will be coded like the traditional INTER mode, while its corresponding reference image, which will be used by the next frame for temporal prediction, is simply copied from its previous reconstructed image. As a result, none of de-quantization, inverse DCT and motion compensation is required for creating the reference image of this MB. In addition to the new coding mode, joint motion estimation (ME) is also applied to reduce the complexity of ME.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
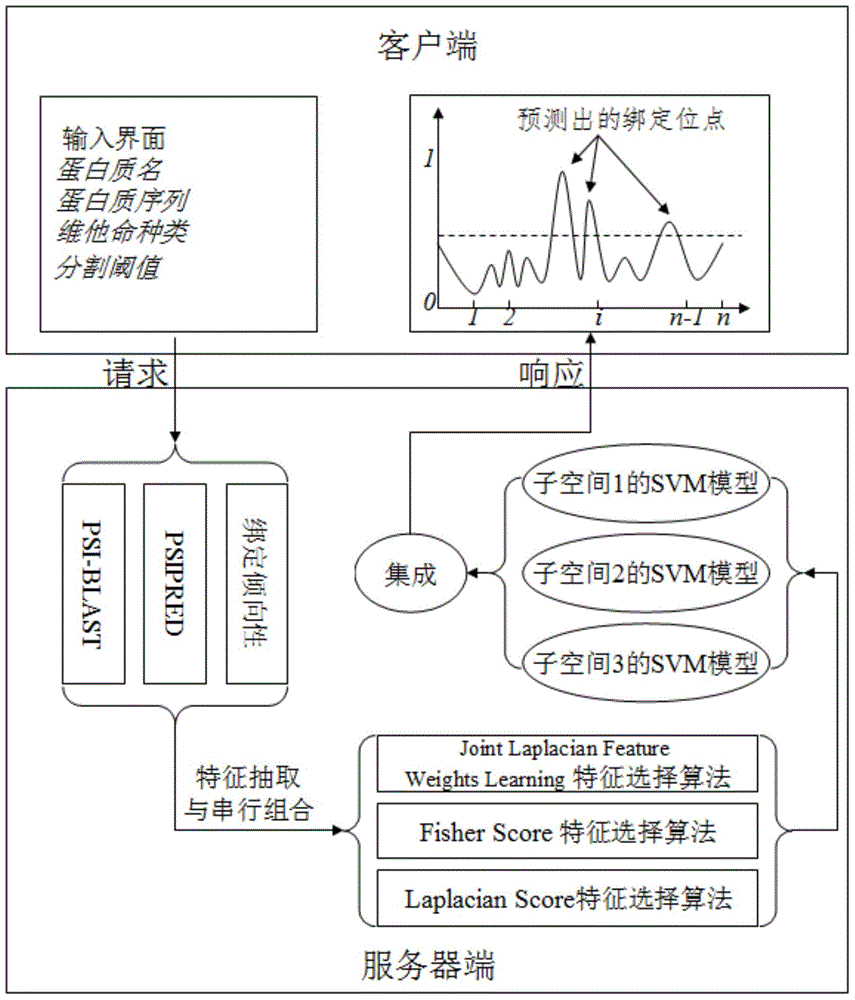
Subspace fusion-based protein-vitamin binding location point predicting method
InactiveCN103955628ASolve the phenomenon of mutual exclusionReduce dimensionalitySpecial data processing applicationsEuclidean vectorProtein
The invention provides a subspace fusion-based protein-vitamin binding location point predicting method. The method comprises the steps of feature extracting and feature combining: extracting evolution information, secondary-level structural information the binding tendency information of a protein by respectively using a PSI-BLAST, a PSIPRED and a protein-vitamin binding location point tendency table, and converting amino acid residues in a protein sequence into a vector presentation mode by a sliding window and serial combination; using a multi-feature selection algorithm to perform feature selection on an original feature space for multiple times; forming a feature subspace by feature subsets obtained from feature selection every time and establishing multiple feature subspaces; training one SVM (support vector machine) classifier for each obtained feature subspace; fusing multiple SVM classifiers which are trained by a weighted average classifier fusing mode; performing protein-vitamin binding location prediction on the protein to be predicted based on a fused SVM predictor. The prediction method is fast in prediction sped and high in prediction precision.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
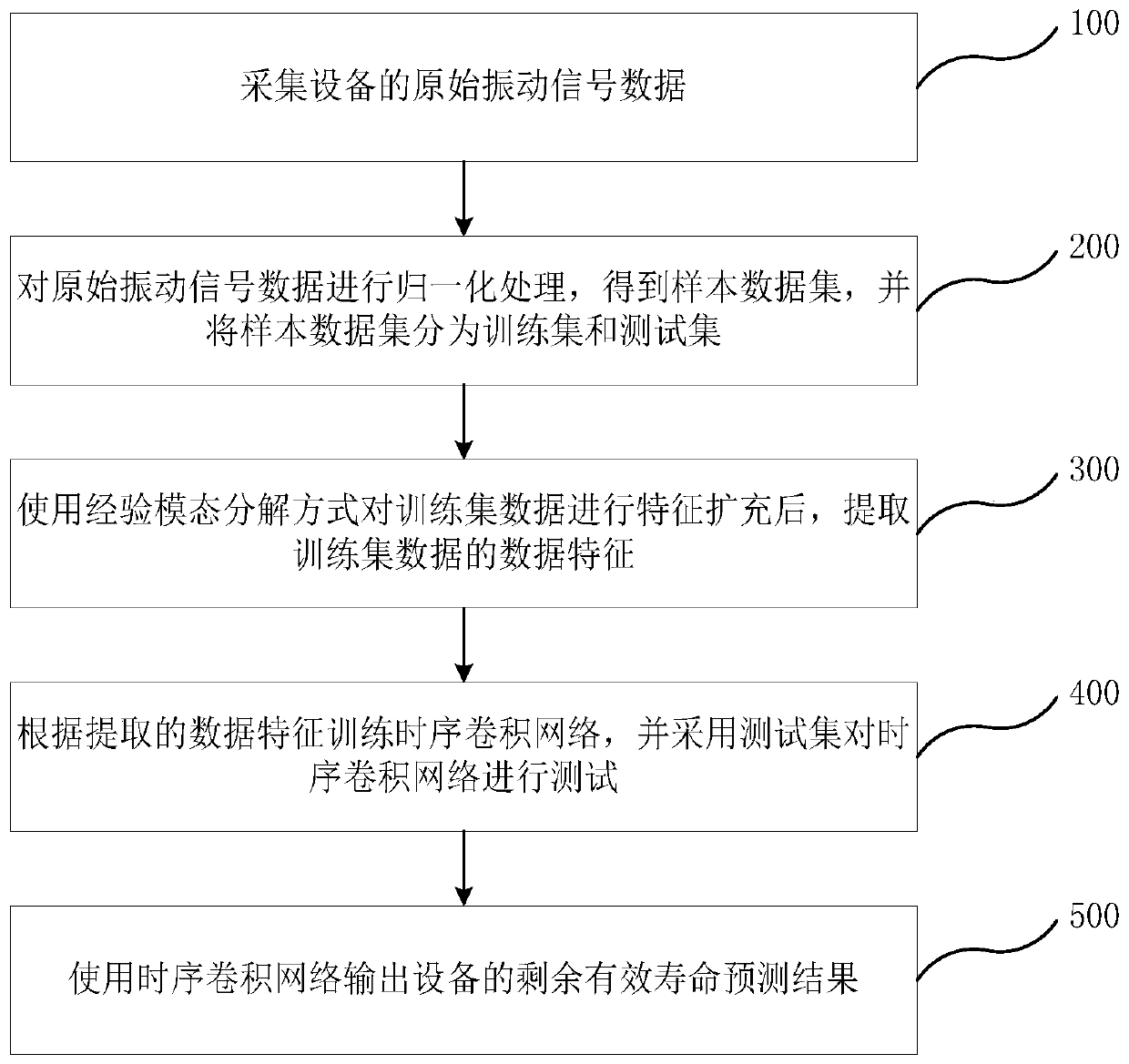
Industrial equipment remaining useful life prediction method and system and electronic equipment
ActiveCN110377984AImprove the speed of predictionImprove forecast accuracyForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionDecompositionIndustrial equipment
The invention relates to an industrial equipment remaining useful life prediction method and system and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: a, performing normalization processing on original vibration signal data of equipment; b, after feature expansion is conducted on the normalized vibration signal data in an empirical mode decomposition mode, extracting data featuresof the vibration signal data; c, constructing a time sequence convolution network according to the extracted data features; and d, outputting a residual effective life prediction result of the equipment by using the time sequence convolution network. According to the method, the data characteristics of the original signals are decomposed, extracted and enriched through the empirical model, and then the sequential convolutional neural network is used for training and predicting to obtain the residual effective service life prediction model, so that the prediction speed and prediction precisionof the residual life of the industrial equipment can be greatly improved, and the method has realizability in the actual manufacturing process.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
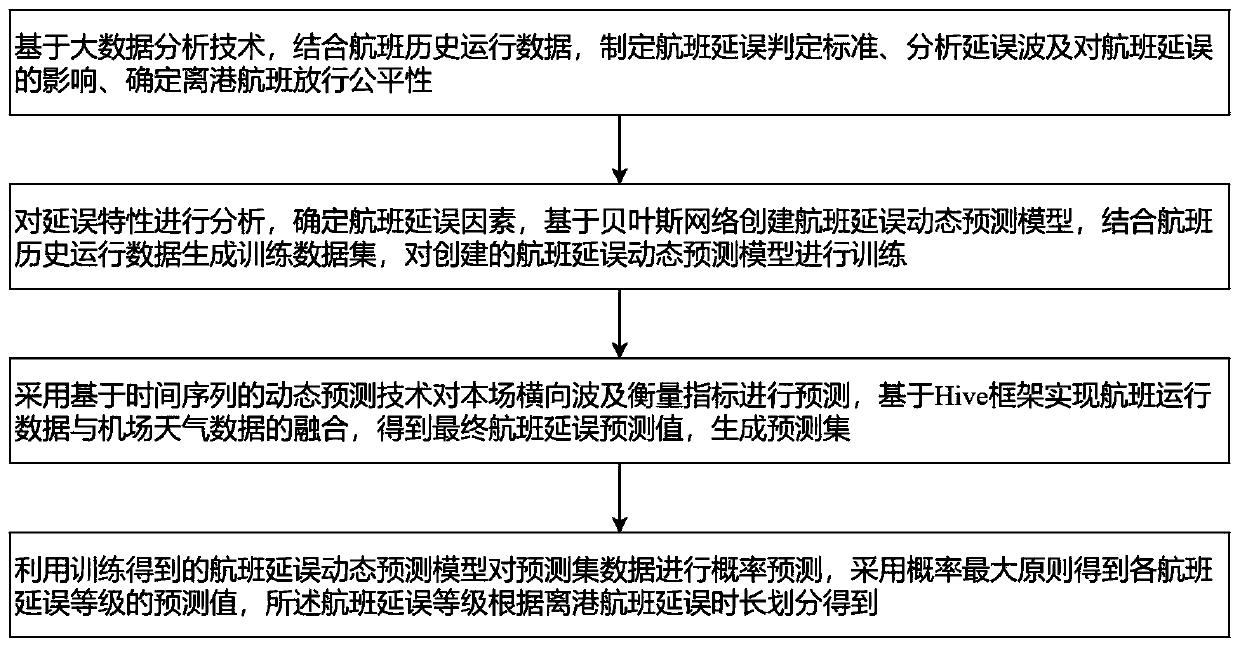
Flight delay real-time probability prediction method based on Bayesian network algorithm
ActiveCN111144631AImprove forecast accuracyEnables real-time forecastingForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmEngineering
The invention discloses a flight delay real-time probability prediction method based on a Bayesian network algorithm, and the method comprises the steps: formulating a flight delay judgment standard,analyzing a delay wave and the impact on flight delay, and determining the release fairness of departure flights; analyzing the delay characteristics, determining flight delay factors, and creating aflight delay dynamic prediction model based on a Bayesian network; adopting a dynamic prediction technology based on a time sequence to predict the present transverse wave and measurement index to obtain a final flight delay prediction value, and generating a prediction set; and carrying out probability prediction on prediction set data by utilizing the flight delay dynamic prediction model obtained by training, and obtaining a prediction value of each flight delay level by adopting a probability maximum principle. According to the invention, real-time probability prediction can be carried outon the departure delay level of a single flight of an airport every day, the flight delay prediction precision is improved, a delay early warning notice is issued to passengers in time, an operationstrategy is adjusted in time, and various adverse effects caused by flight delay are reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
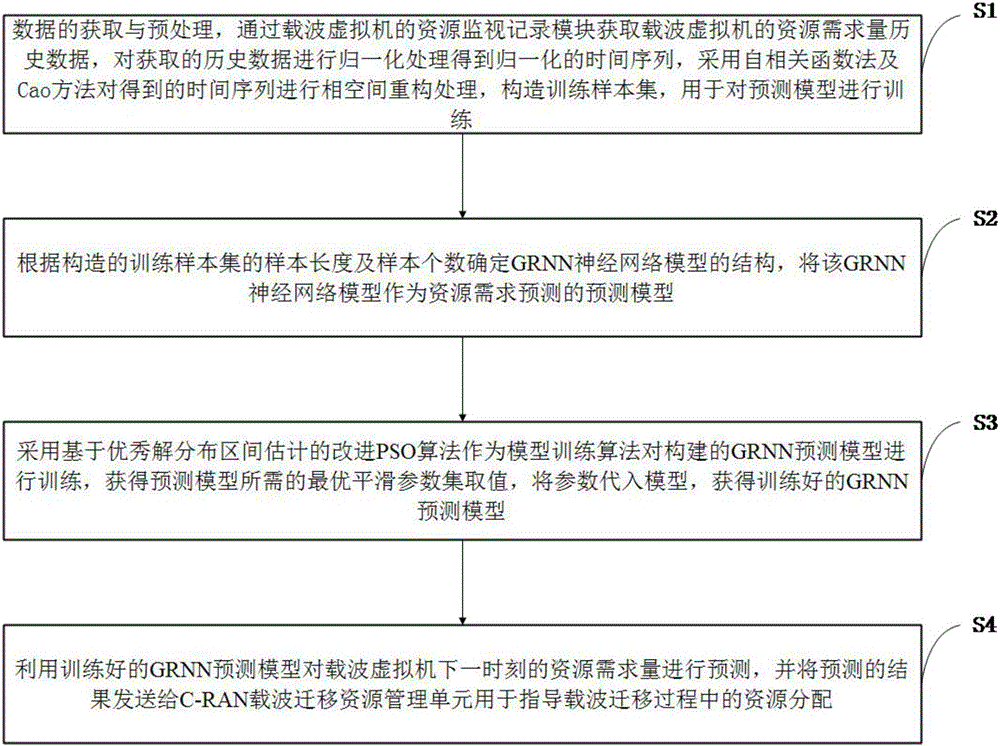
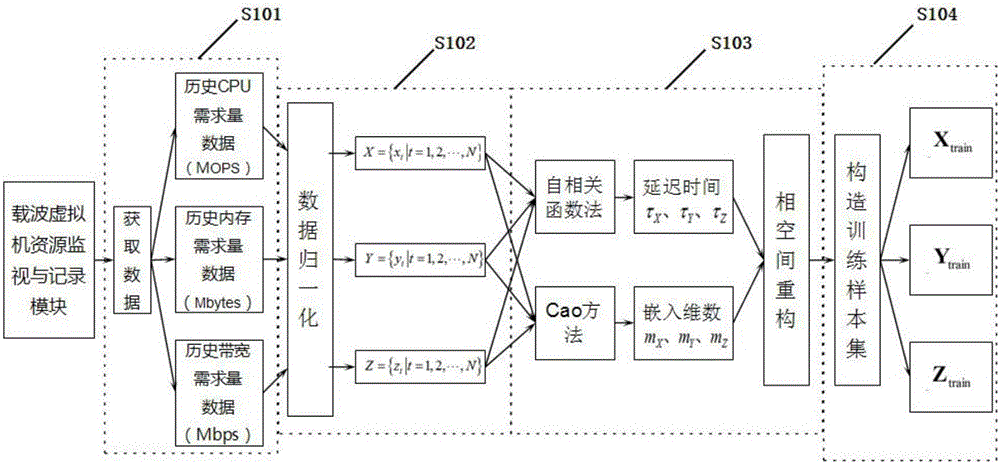
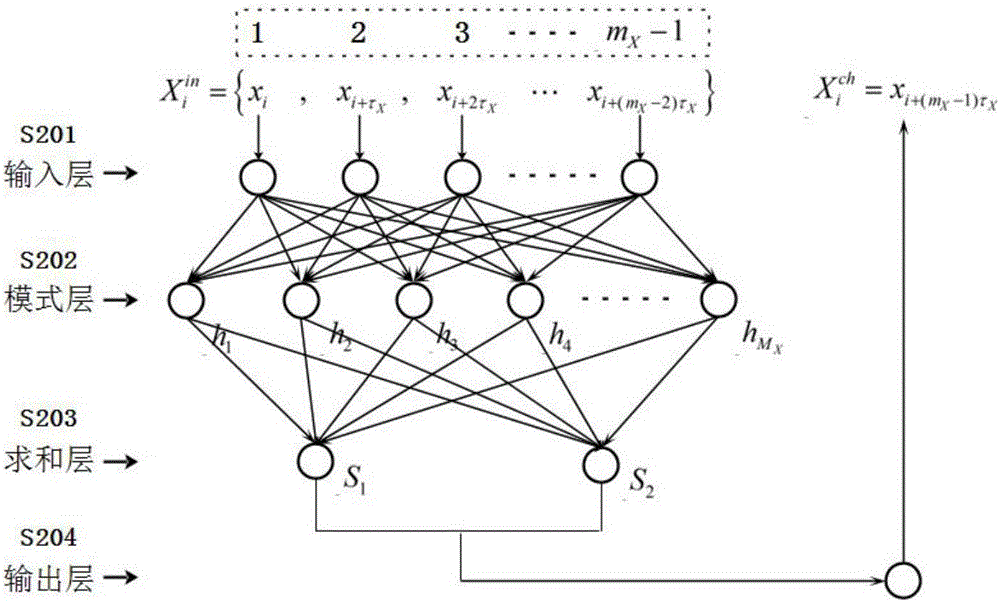
C-RAN carrier migration resource demand prediction method based on improved PSO
ActiveCN106102079AFast convergenceNot easy to fall into local extremumNetwork planningAlgorithmCarrier signal
The invention discloses a C-RAN carrier migration resource demand prediction method based on improved PSO. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring and preprocessing data, and generating a training sample set of a prediction model; determining the structure of a GRNN prediction model according to the generated training sample set; training the GRNN prediction model by using an improved PSO algorithm; and prediction the resource demand of a carrier virtual machine at a next moment by employing the trained GRNN prediction model. The problem in the existing carrier migration technology that resource allocation is carried out only depending on the load condition of the carrier virtual machine at the current moment, resulting in resource waste or resource shortage to cause short-term secondary migration is effectively solved; and in view of the defect that the existing prediction method cannot be applicable to the C-RAN scene with high instantaneity due to an overlong prediction time, the improved PSO algorithm is proposed to train the prediction model, so as to effectively improve the prediction accuracy and the prediction speed in resource demand prediction.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
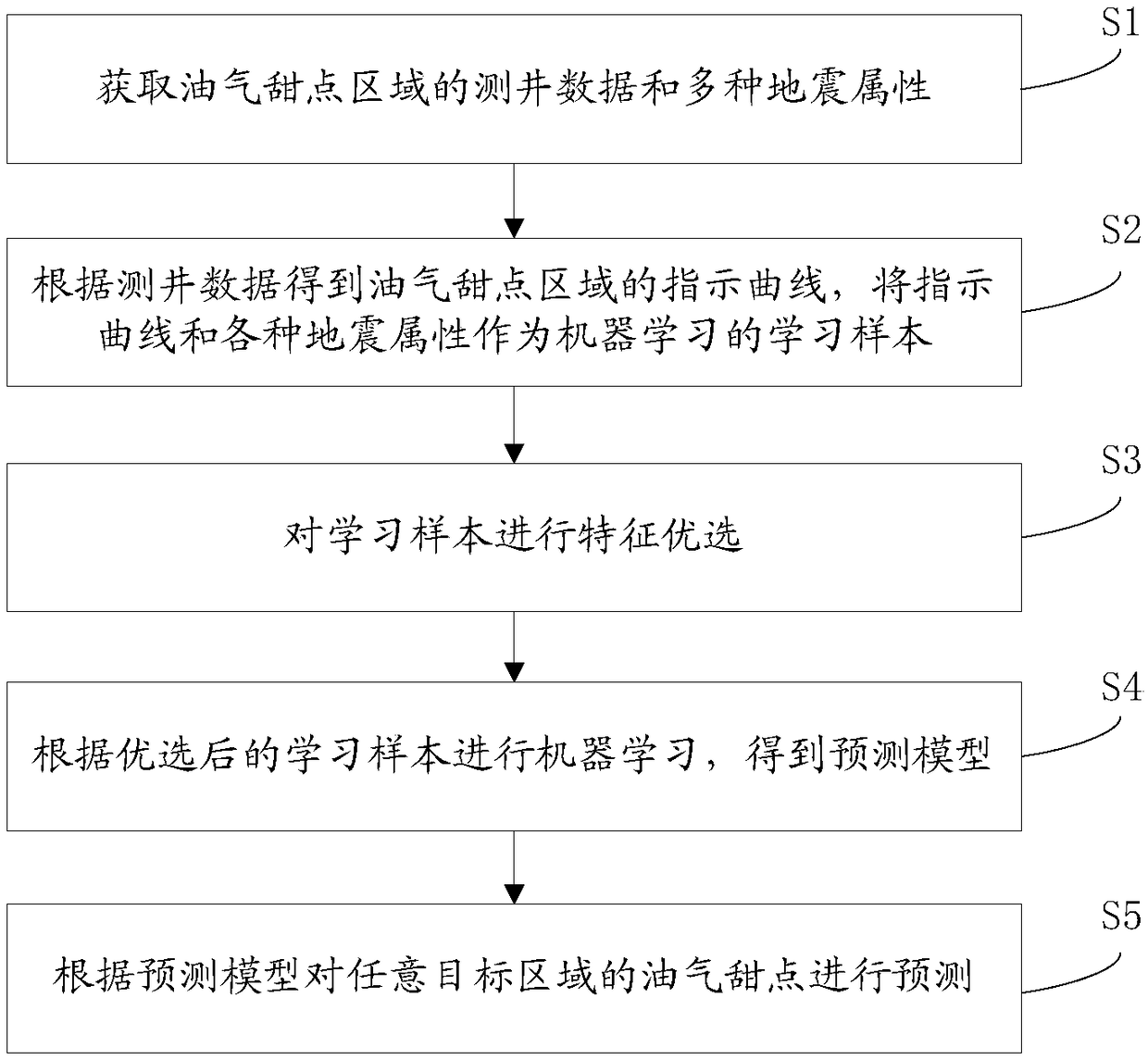
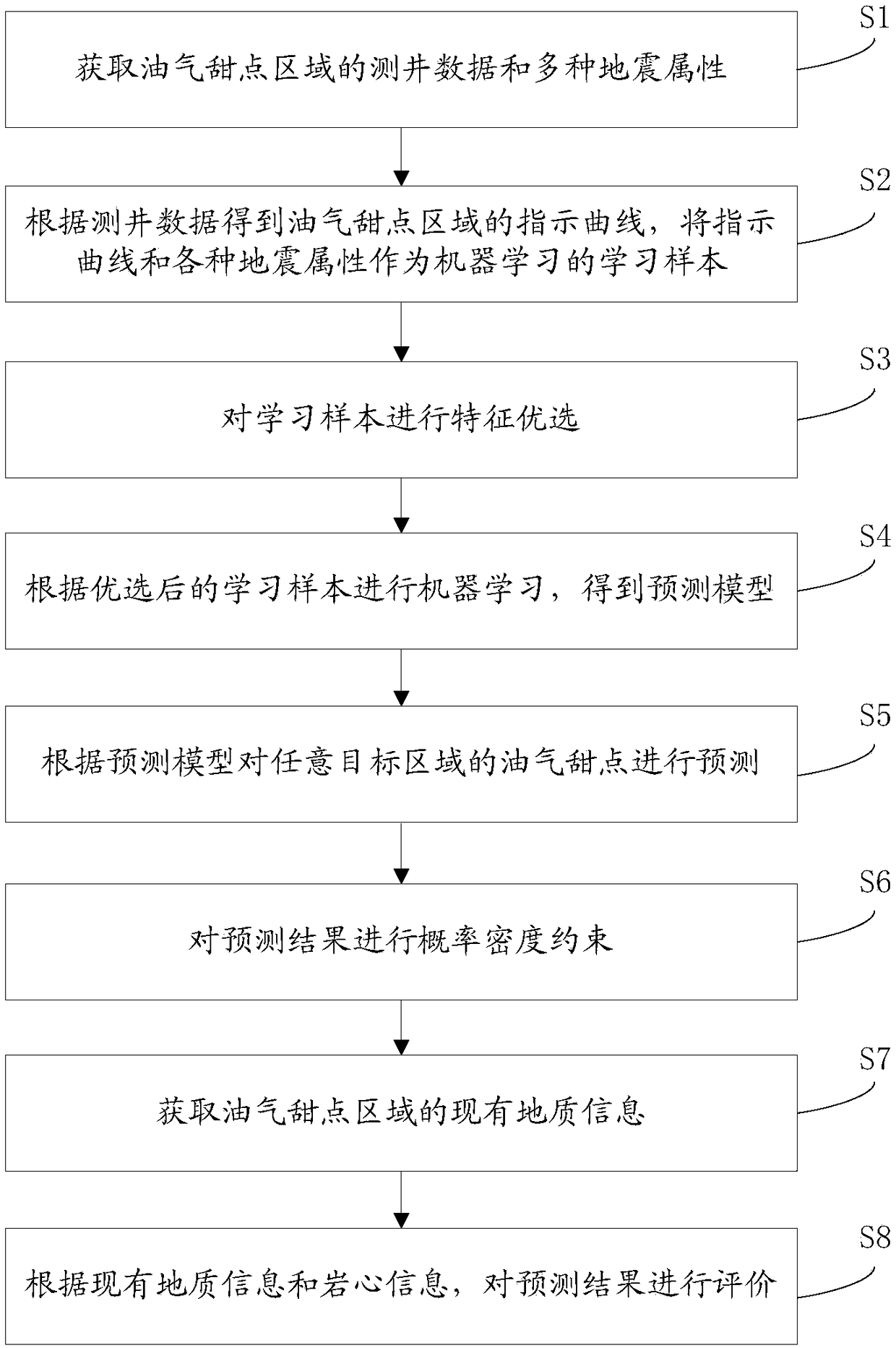
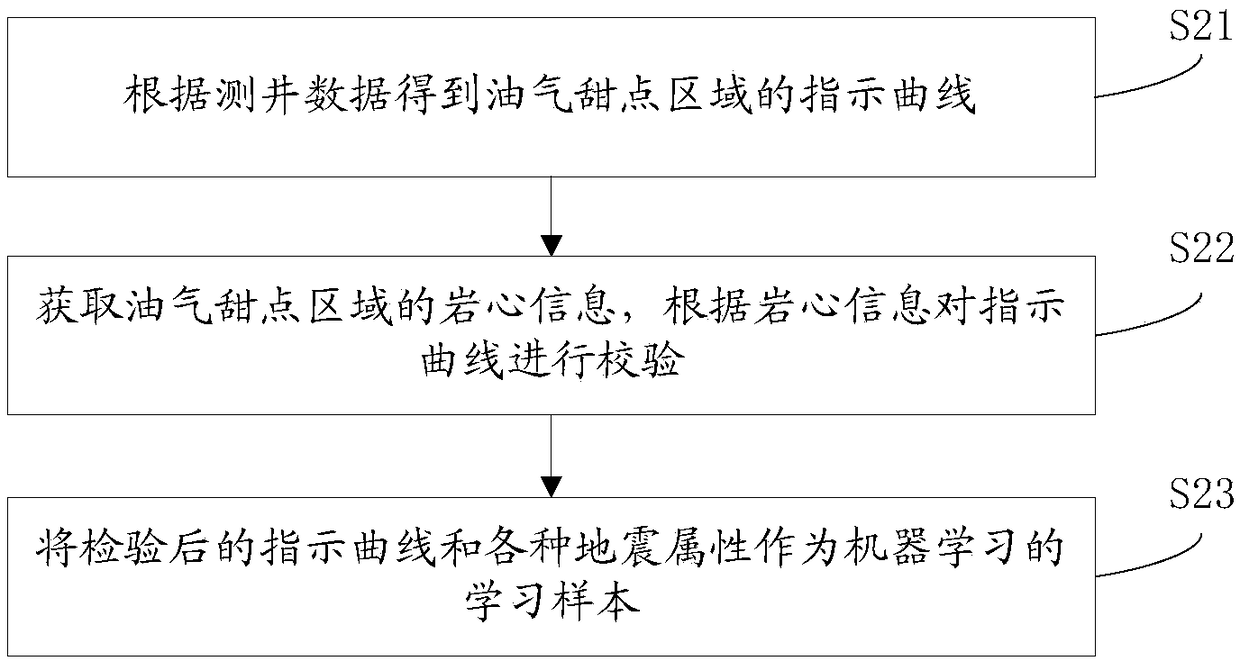
Oil and gas dessert prediction method and storage medium
ActiveCN108376295AHigh-resolutionRealize Quantitative PredictionForecastingMachine learningImage resolutionSeismic attribute
The invention discloses an oil and gas dessert prediction method and a storage medium, and relates to the oil gas exploration field. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining logging data and various earthquake attributes of an oil gas dessert area; obtaining an oil and gas dessert area indication curve according to the logging data, and using the indication curve and various earthquakeattributes as machine learning samples; optimizing features of the learning samples; carrying out machine learning according to optimized learning samples, thus obtaining a prediction model; predicting oil gas desserts in a random target area according to the prediction model. The invention provides the oil and gas dessert prediction method and the storage medium, aims to improve the prediction accuracy, and can improve the prediction resolution, thus quantitatively predicting oil gas desserts, preventing artificial factor influences, and simplifying a calculation process; the method can obtain high resolution and high precision prediction results without making complex redundant calculations.
Owner:PST SERVICE CORP
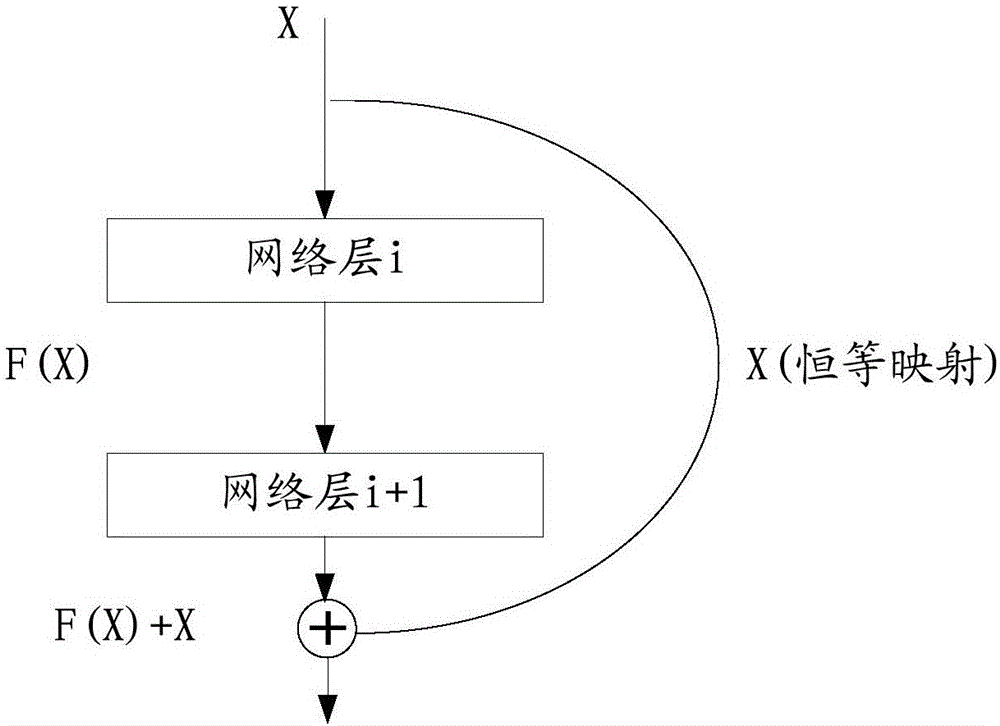
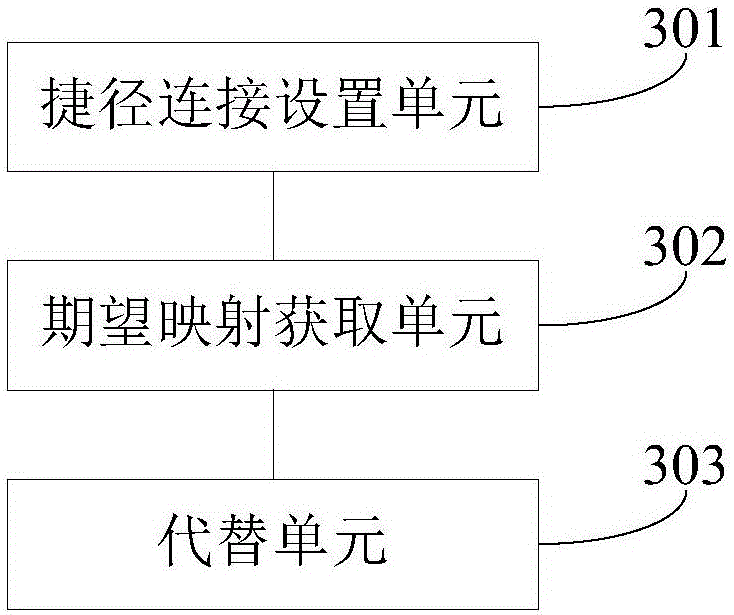
Optimization method and optimization device of convolution neural network
InactiveCN106779050AFew parametersImprove forecast accuracyNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsAlgorithmNetwork model
The invention provides an optimization method of a convolution neural network. The optimization method comprises steps of setting a shortcut connection on an added layer of the convolution neural network and acquiring residual error mapping corresponding to the shortcut connection; according to the residual error mapping, determining expectation mapping corresponding to the shortcut connection; and replacing a layer corresponding to the shortcut connection with the expectation mapping, and carrying out convolution neural network model prediction. According to the invention, parameters of the added layer can be effectively reduced; data circulation between networks is allowed to be quite smooth; and improvement of prediction precision and prediction speed of the model is facilitated.
Owner:厦门熵基科技有限公司
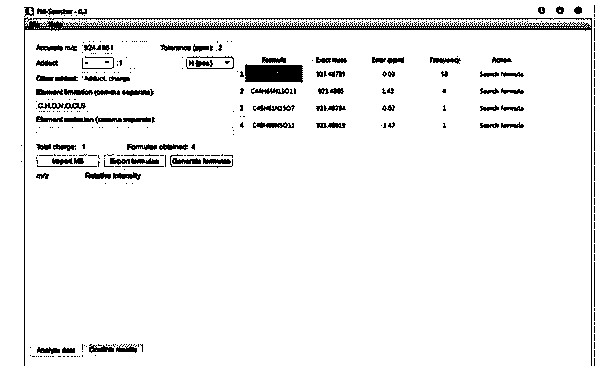
High-resolution mass spectrum accurate molecular formula forecasting method
InactiveCN103792275AImprove rankingReduce in quantityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansScreening algorithmCompound structure
The invention discloses a high-resolution mass spectrum accurate molecular formula forecasting method. According to the method, candidate molecular formulas are graded and ranked by mainly adding a condition of a probability that the molecular formula exists in practice so as to improve the rank of the accurate molecular formula. Through actual tests, no matter the speed or accuracy of the method is better than that of a common method. In addition, due to the combination of the method and a common candidate molecular formula screening algorithm, the universality and accuracy of the forecast of the molecular formula can be greatly improved; through the method, accurate molecular formula forecasting can be conveniently carried out on high-resolution mass spectrum data; extremely valuable reference results are provided for operations of analyzing compound structure, and screening known substances or unknown substances.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Prediction method and prediction device of echo state network
ActiveCN104424507AImprove predictive performanceImprove the speed of predictionBiological neural network modelsPredictive methodsEcho state network
The embodiment of the invention provides a prediction method and a prediction device of an echo state network (ESN) and relates to the technical field of a communication service network so that the prediction performance of the ESN can be improved effectively and the prediction speed and the prediction precision can be improved. The method is as follows: through establishment of a prediction model of the ESN, wherein a dynamic pool of the prediction model is a mixed neuron dynamic pool which includes wavelet neurons, a training set is obtained from input data and prediction training is carried out on the prediction model according to the training set and then the prediction model which completes training is obtained; and through prediction input data, the prediction model which completes training is predicted and then prediction output data in a prediction process is obtained. The prediction method and the prediction device are used for prediction of nonlinear chaotic time sequence data.
Owner:杨凤琴
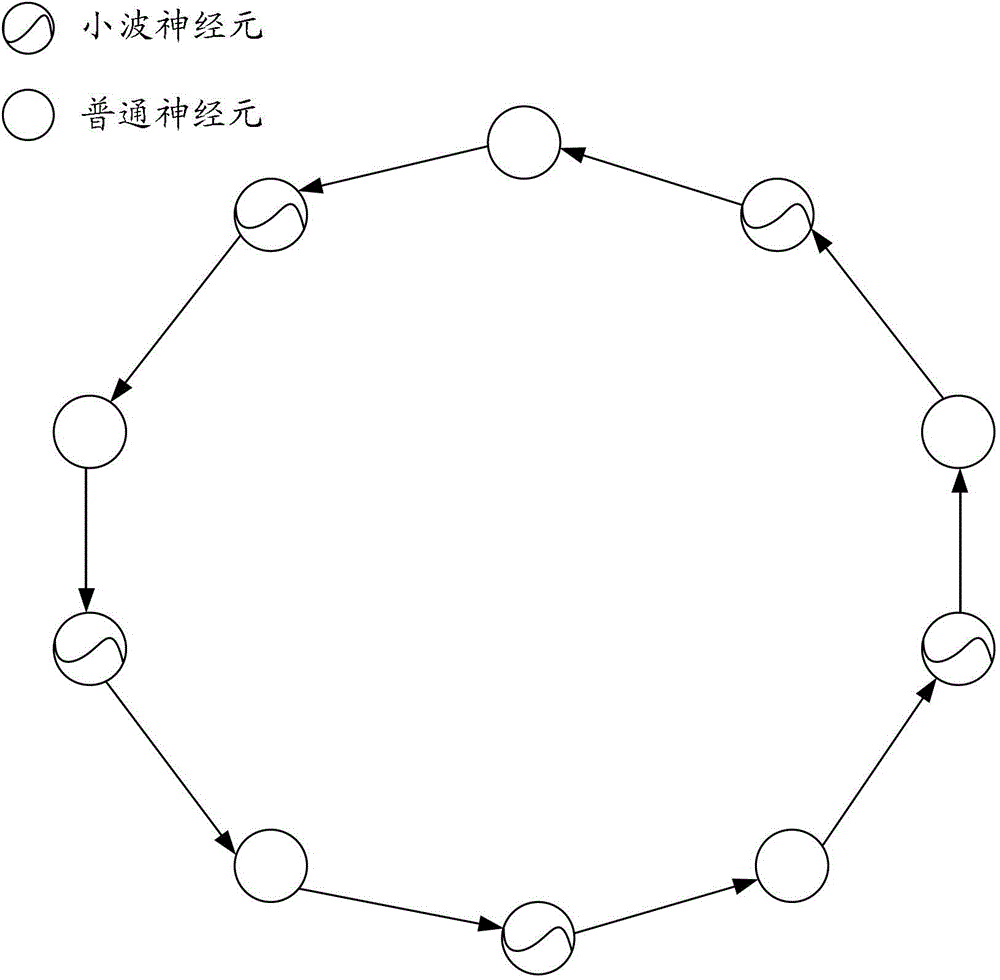
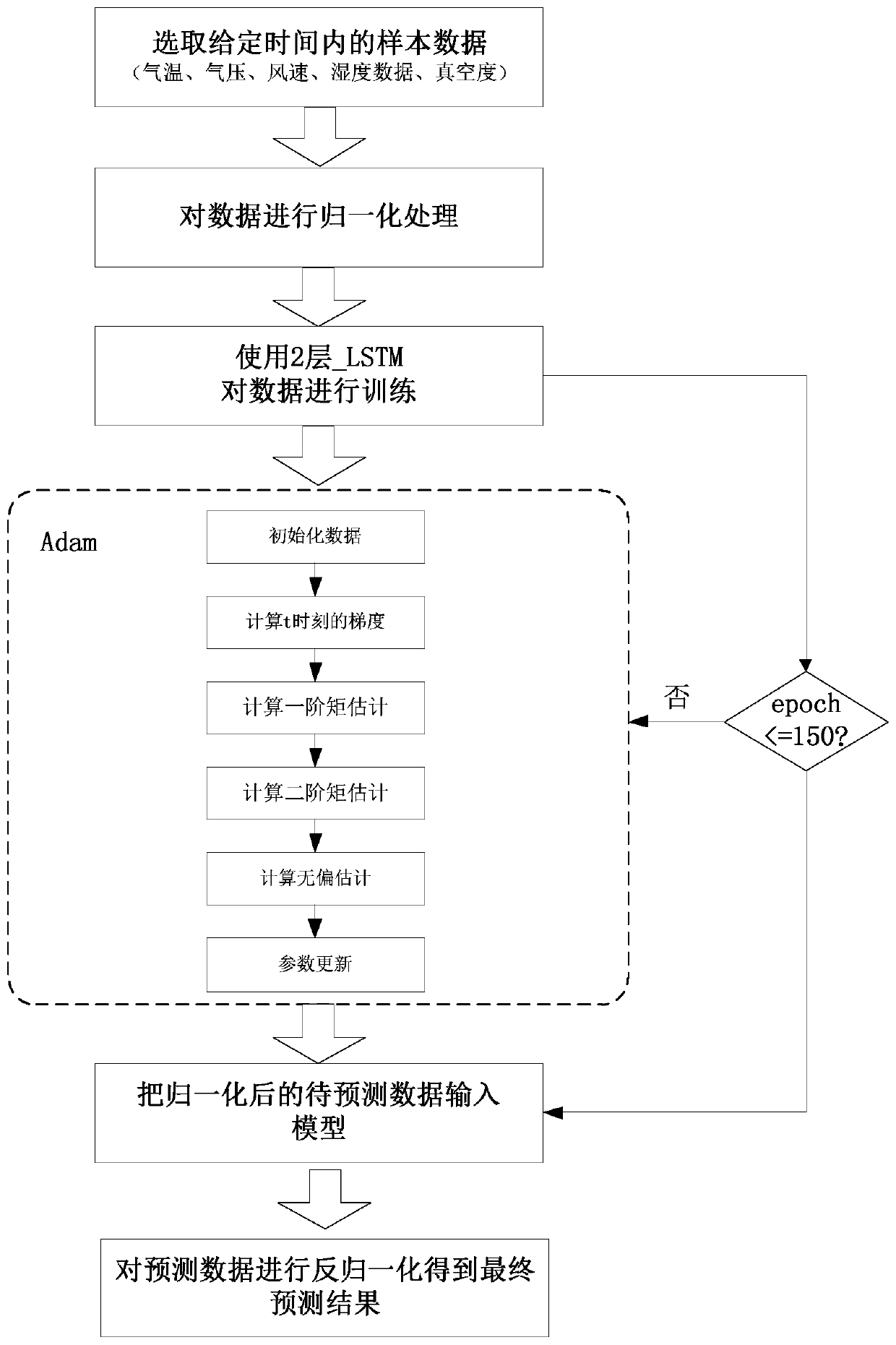
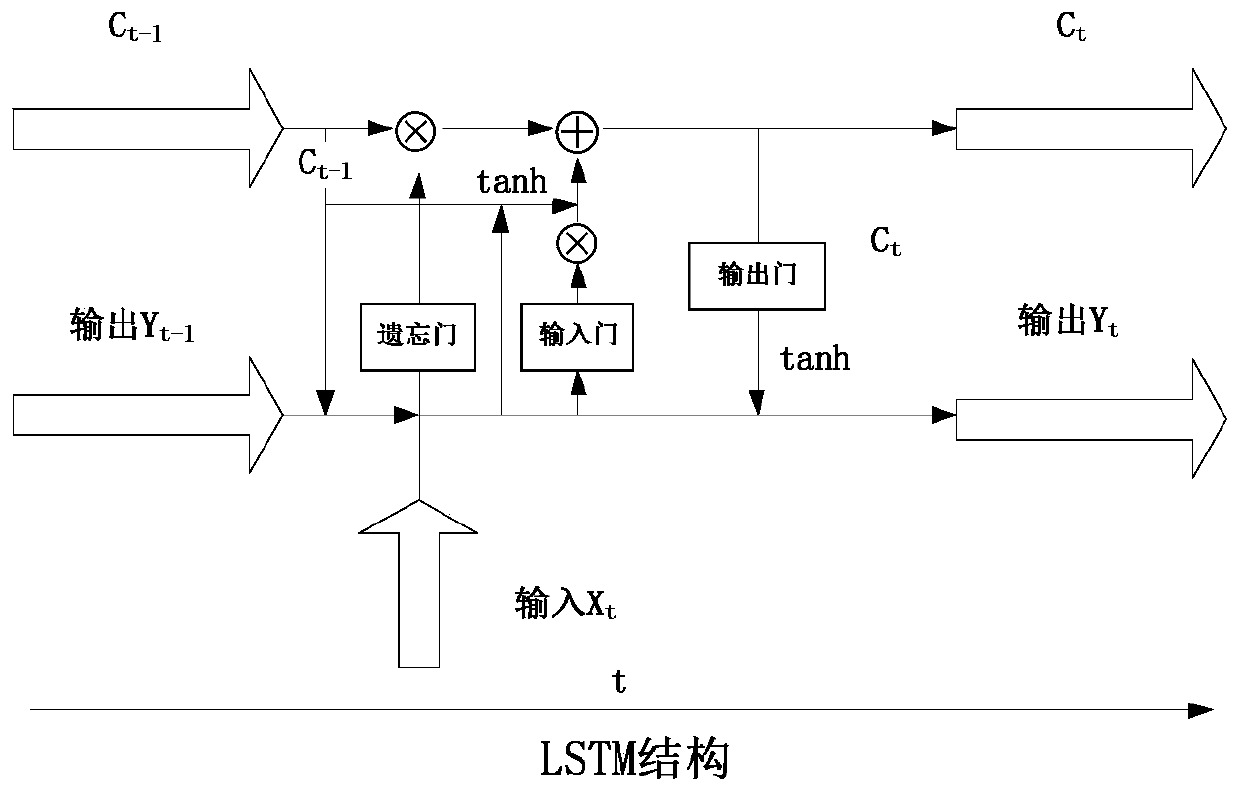
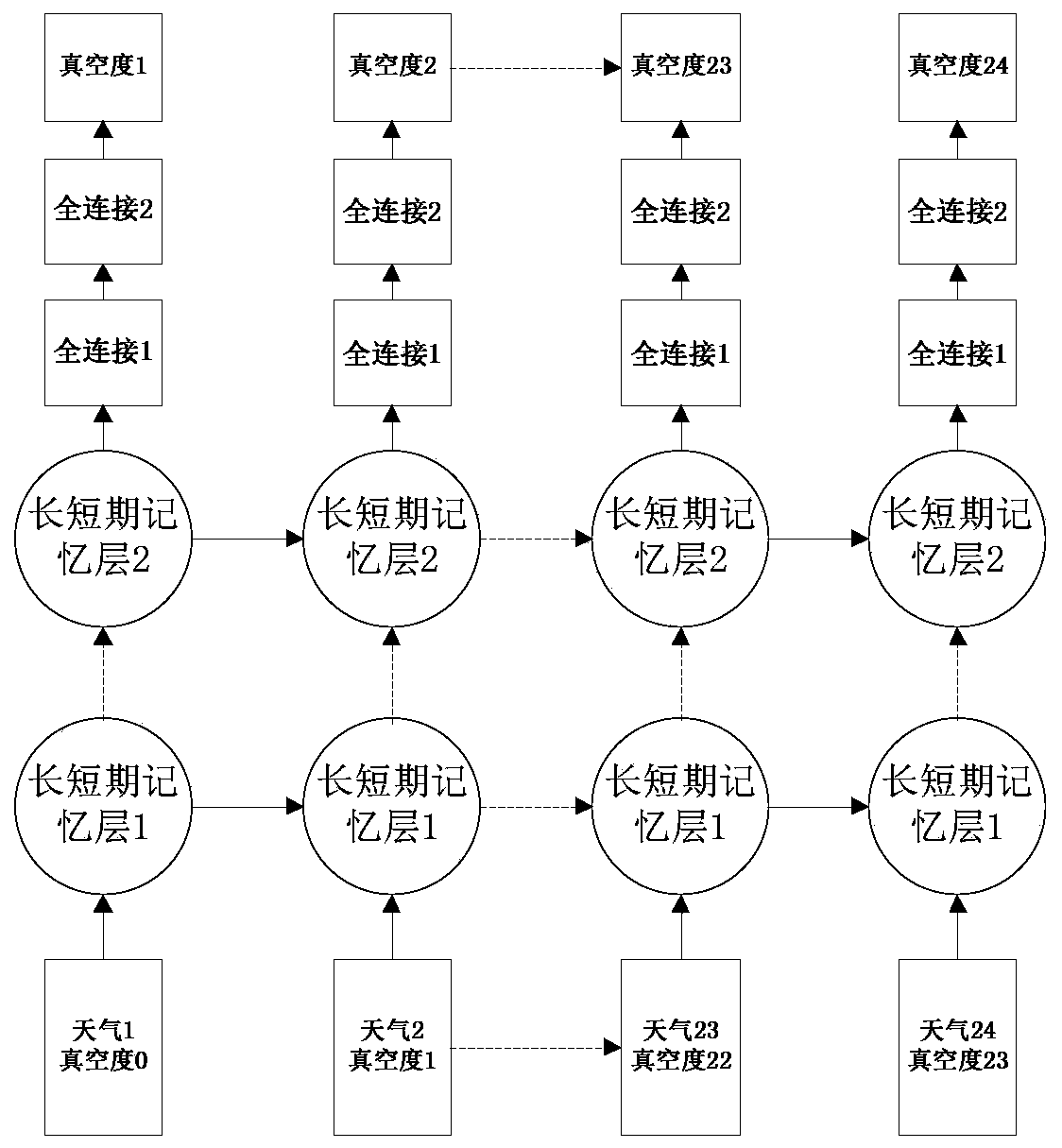
Thermal power plant condenser vacuum degree prediction method based on multi-layer LSTM
PendingCN111353631ARealize deep miningFast convergenceForecastingNeural architecturesData setAlgorithm
The invention provides a thermal power plant condenser vacuum degree prediction method based on multilayer LSTM. Firstly, a sample data set is constructed, input data and output data in a sample are subjected to standardization processing respectively, then the input data sequentially enter a multi-layer long-short-term memory neural network, and model training is performed by using an adaptive moment estimation algorithm; and finally, to-be-predicted data is input into the trained prediction model, and the vacuum degree of the condenser is predicted. According to the method, the long-term andshort-term memory neural network structure is applied to condenser vacuum degree analysis, deep mining of big data is achieved, the accuracy and speed of data prediction are improved, and use of system resources is optimized. According to the two-layer LSTM structure designed by the invention, the model depth can be increased, the model capacity can be increased, the prediction precision can be improved, and meanwhile, the adaptive moment estimation algorithm is used for optimizing the traditional gradient descent algorithm, so that the problem of gradient explosion is avoided.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
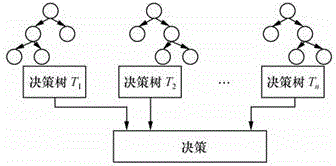
Prediction method for protein sequence disulfide bond connection mode based on forest regression model
ActiveCN104063632AImprove the speed of predictionImprove forecast accuracySpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorPredictive methods
The invention discloses a prediction method for protein sequence disulfide bond connection mode based on a forest regression model. The method comprises the following steps that step 1, the feature vector of each cysteine residues pair in the protein sequence is obtained through multi-view feature extraction and feature combination; step 2, for the to-be-predicated protein sequence information and training datasets, the feature vectors of all the cysteine residues pairs in the to-be-predicated protein sequence information and training datasets are generated, so that a training sample set and a to-be-predicated sample set are respectively formed; step 3, the distribution rule of cysteine samples in the feature space is studied through the random forest algorithm, so that a random forest regression model is generated; step 4, the feature vector of the to-be-predicated sample set is predicated through the random forest regression model, so that the prone value of each cysteine residues pair forming disulfide bond is obtained, and the disulfide bond connection mode with the highest score is finally-predicated the disulfide bond connection mode in the protein sequence.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Intelligent working face coal-rock interface recognition method based on geological data
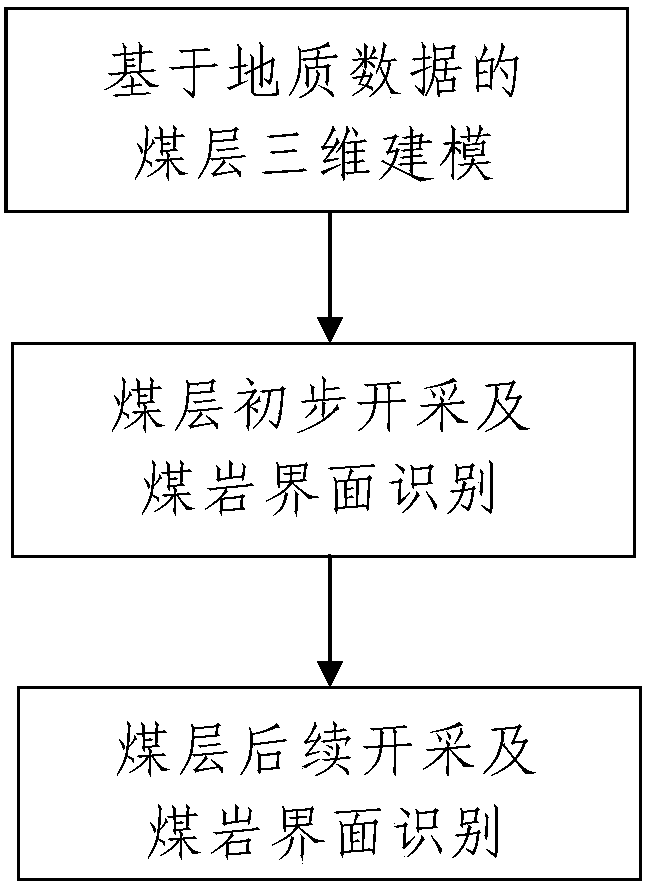
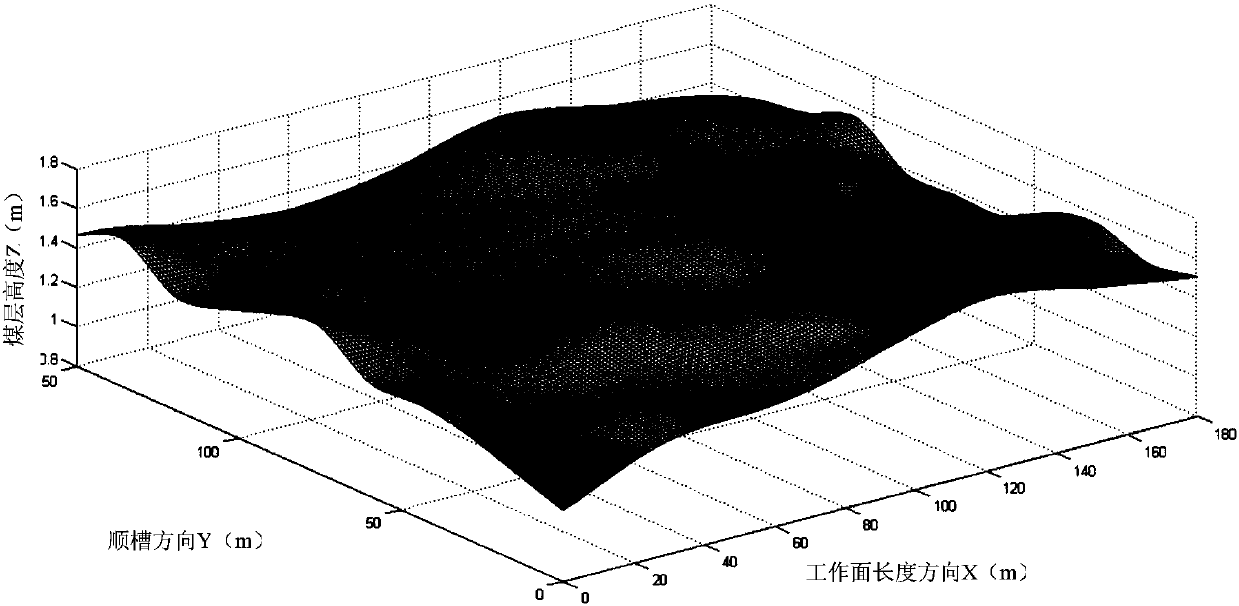
ActiveCN106194181AThe method steps are simpleReasonable designTesting machinesSlitting machinesDimensional modelingComputer science
The invention discloses an intelligent working face coal-rock interface recognition method based on geological data. The method includes the first step of coal seam three-dimensional modeling based on geological data, the second step of coal seam primary mining and coal-rock interface recognition, and the third step of coal seam subsequent mining and coal-rock interface recognition. The first step includes the substeps that 101, geological data is obtained through actual measurement, wherein actual measurement geological data of to-be-mined coal seam is obtained and includes coal seam geological data, mining roadway geological data and cut hole geological data; 102, a coal seam model is constructed, wherein data storage, interpolation operation, three-dimensional coordinate database generation and model construction are conducted. The third step includes the substeps that the to-be-mined coal seam continues to be mined by means of a coal mining machine from back to front, and a coal-rock interface of the working face is recognized before each working face is mined. The method is simple in step, reasonable in design, convenient to implement and good in use effect, and the coal-rock interface is conveniently, quickly and accurately recognized according to the actual measurement geological data and cylinder height adjustment track prediction data.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for predicting elastic cloud computing resources based on SARIMA-WNN model
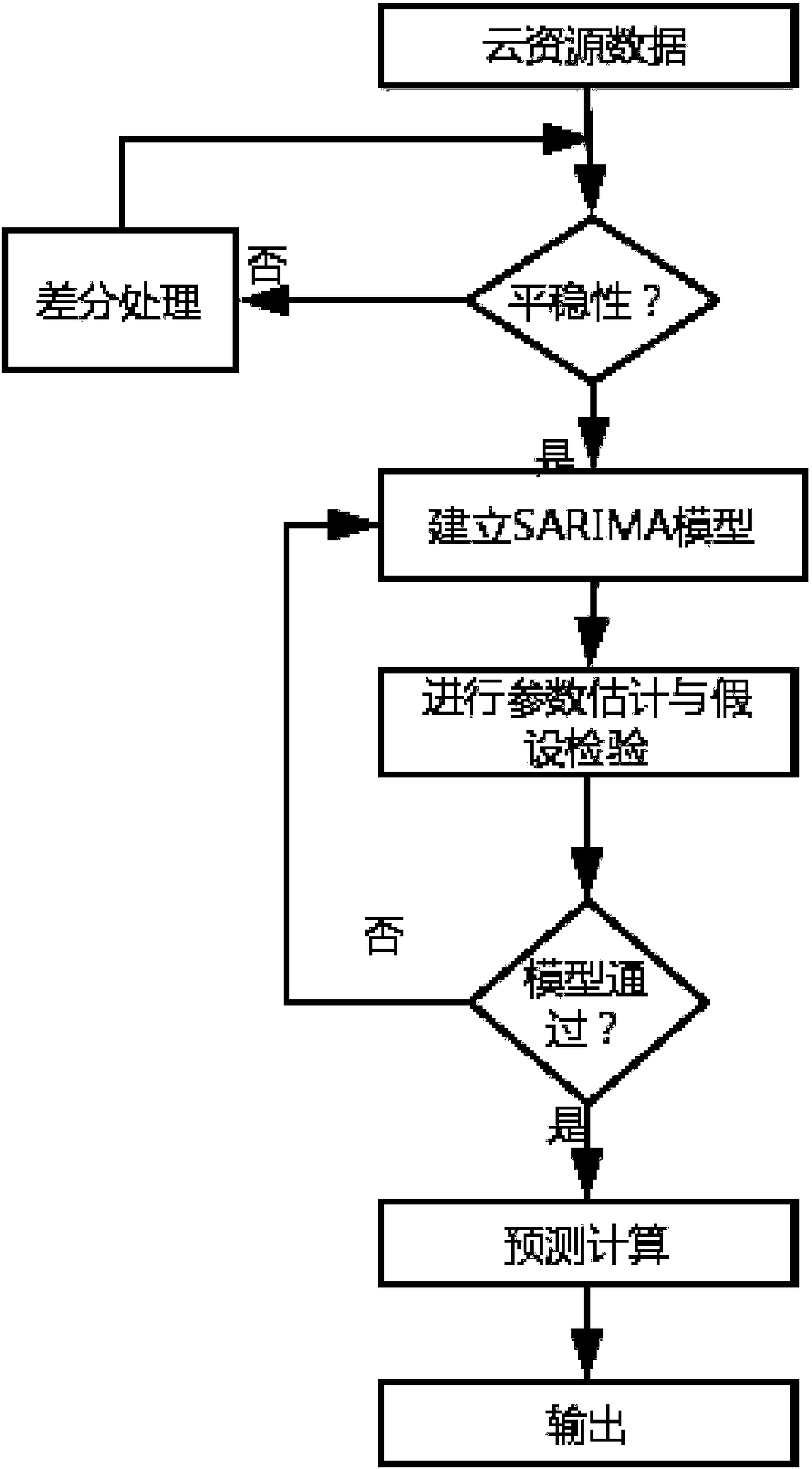
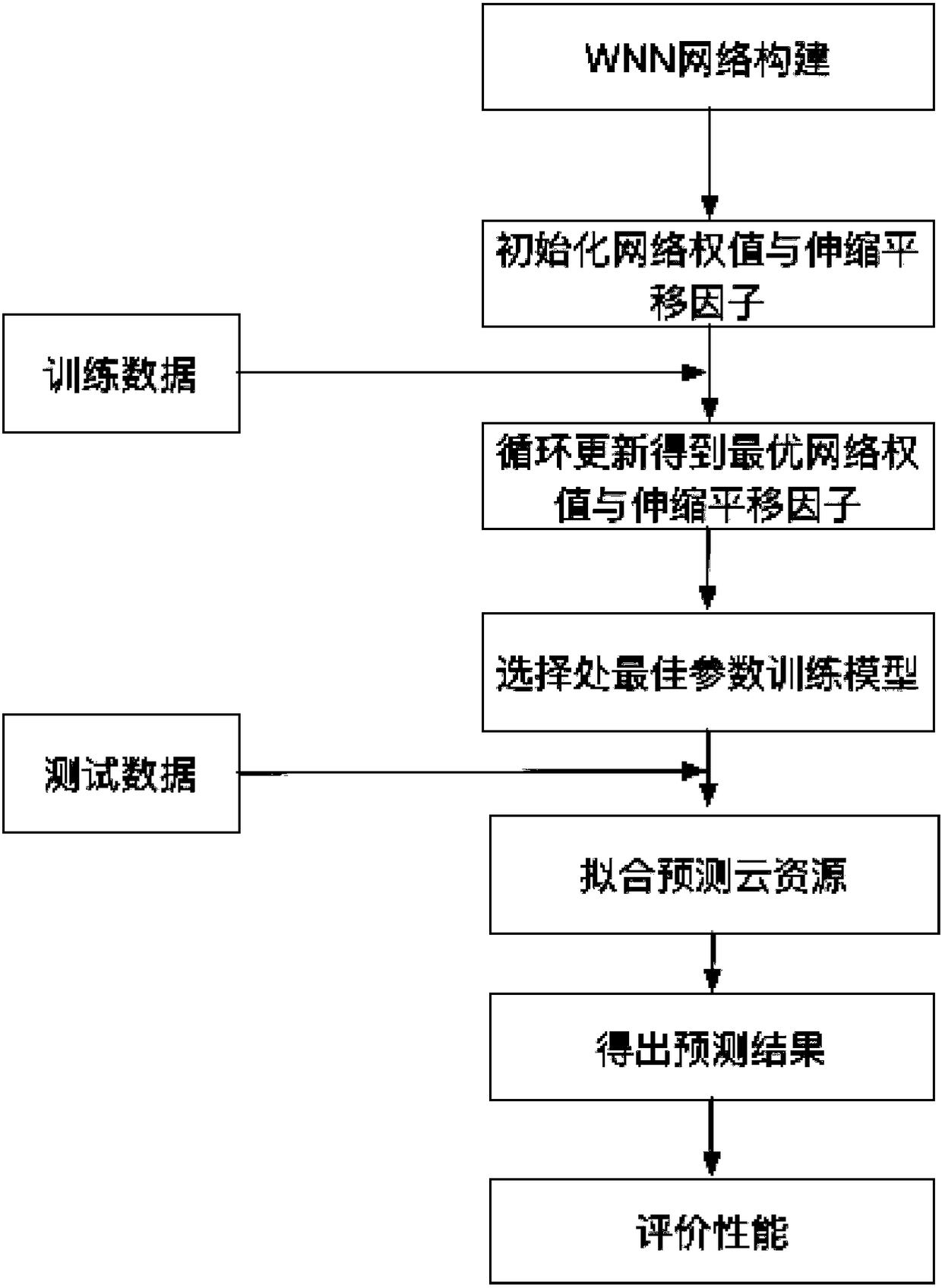
ActiveCN108304355AAvoid inaccuraciesSolve blindnessNeural architecturesData switching networksElastic cloudAutoregressive integrated moving average
The invention discloses a method for predicting elastic cloud computing resources based on an SARIMA-WNN model. The method comprises the steps that complementary advantages are achieved by using a seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average (SARIMA) model combining with a wavelet neural network (WNN) prediction model to improve the prediction accuracy; according to the SARIMA, seasonal periodic factors are added on the basis of an ARIMA model, periodic cloud resource demand data of a past section is input to a SARIMA (q, d, q)(P, D, Q) s model to obtain d, p, q, D, P and Q respectively;prediction is conducted on tranquilized and sequenced codes by using the SARIMA model, and a prediction result is marked as and an L residual value is marked as rt, wherein the prediction result andthe residual value can be obtained through the prediction; a model which conforms to elastic cloud source prediction is obtained through conducting training on the WNN network by using training samples, prediction is conducted aiming at the residual sequence rt, and the prediction result is marked as ; finally the prediction result of the SARIMA-WNN combined model is obtained. By means of the method, the problems of inaccuracy of a single model, poor effects of other combined models and the like are solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
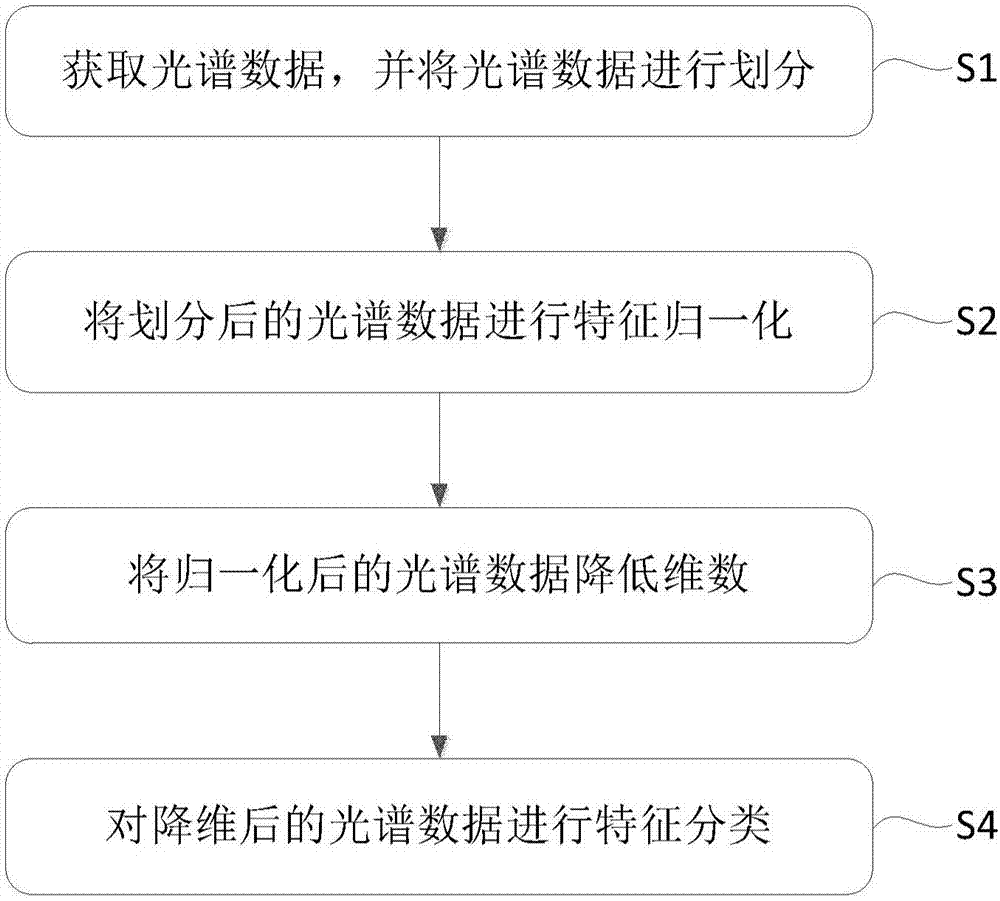
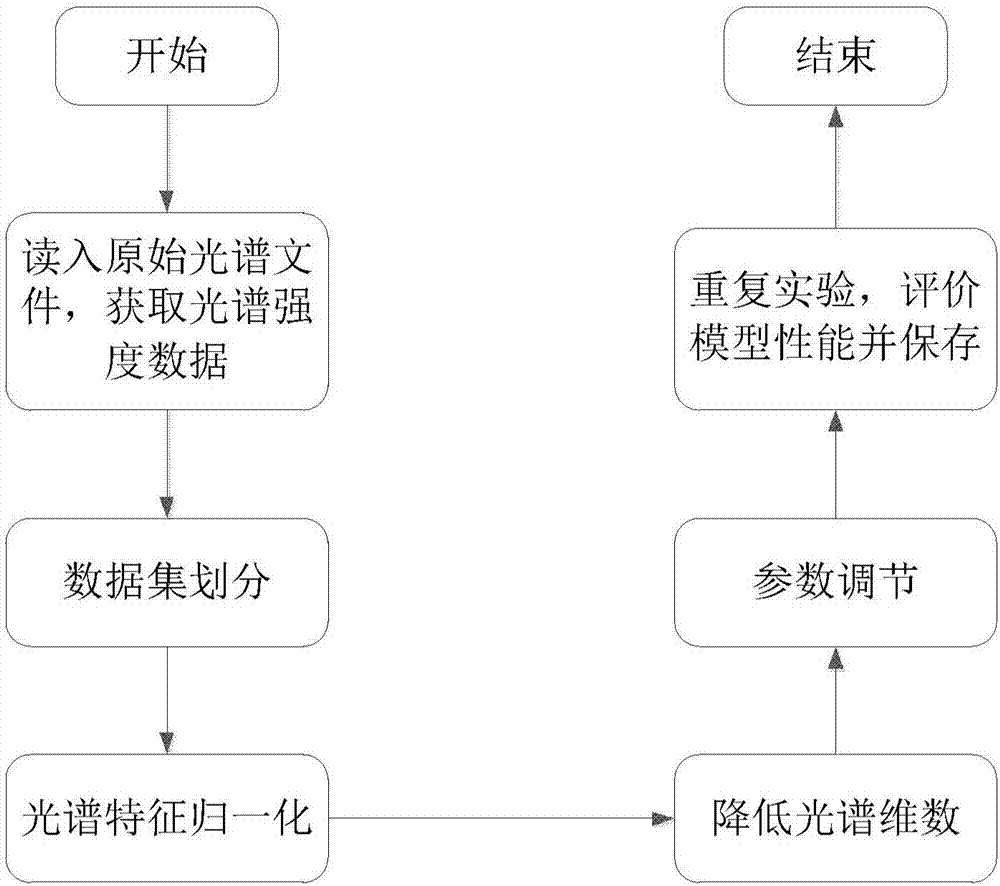
Method for discriminating corn haploid kernels based on near-infrared spectrum technology
InactiveCN107037001ARealize authenticationEasy to identifyMaterial analysis by optical meansPattern recognitionData set
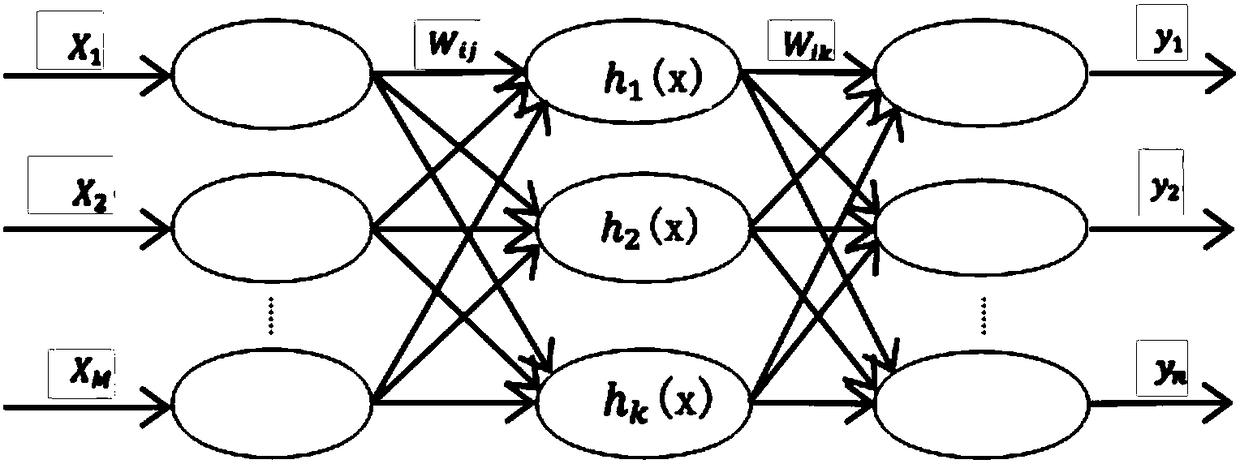
The invention discloses a method for discriminating corn haploid kernels based on a near-infrared spectrum technology. The method comprises the following steps of: reading into an original spectrum file and acquiring spectrum intensity data; dividing data sets; carrying out feature normalization on spectrum data; adopting a partial least-squares regression method to reduce the dimensionality; adjusting parameters of a neural network classifier; carrying out fine adjustment and performance evaluation on the neural network classifier; and storing the parameters of the neutral network. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the corn haploid kernels can be identified from heterozygote kernels, and simultaneously higher correct discrimination rate and model stability are ensured.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Short-term wind power combined prediction method
InactiveCN105631550AImprove forecast accuracyImprove the speed of predictionForecastingElectricityData set
The invention relates to the technical field of wind power, and particularly relates to a short-term wind power combined prediction method. The short-term wind power combined prediction method is based on a grey system and a least square support vector machine. The short-term wind power combined prediction method is characterized by comprising the following steps that original wind power data are preprocessed and grey prediction is performed so as to obtain a residual error sequence, and then the residual error sequence is predicted by using a least square support vector machine model so as to obtain a new residual error value; a kernel function is selected, and the regression parameters of the least square support vector machine are determined by using a cross validation method; after a data set is obtained, a radial basis function is selected to act as the kernel function, including width parameters and optimization parameters of quadratic programming; a combined prediction model is constructed; the data set is inputted and a prediction function is generated; and prediction error evaluation analysis is performed. Prediction accuracy and speed can be enhanced by the method.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
GPCR(G Protein-Coupled Receptor)-drug interaction prediction method based on postprocessing study
ActiveCN104239751AImprove forecast accuracyImprove the speed of predictionSpecial data processing applicationsData setMedication information
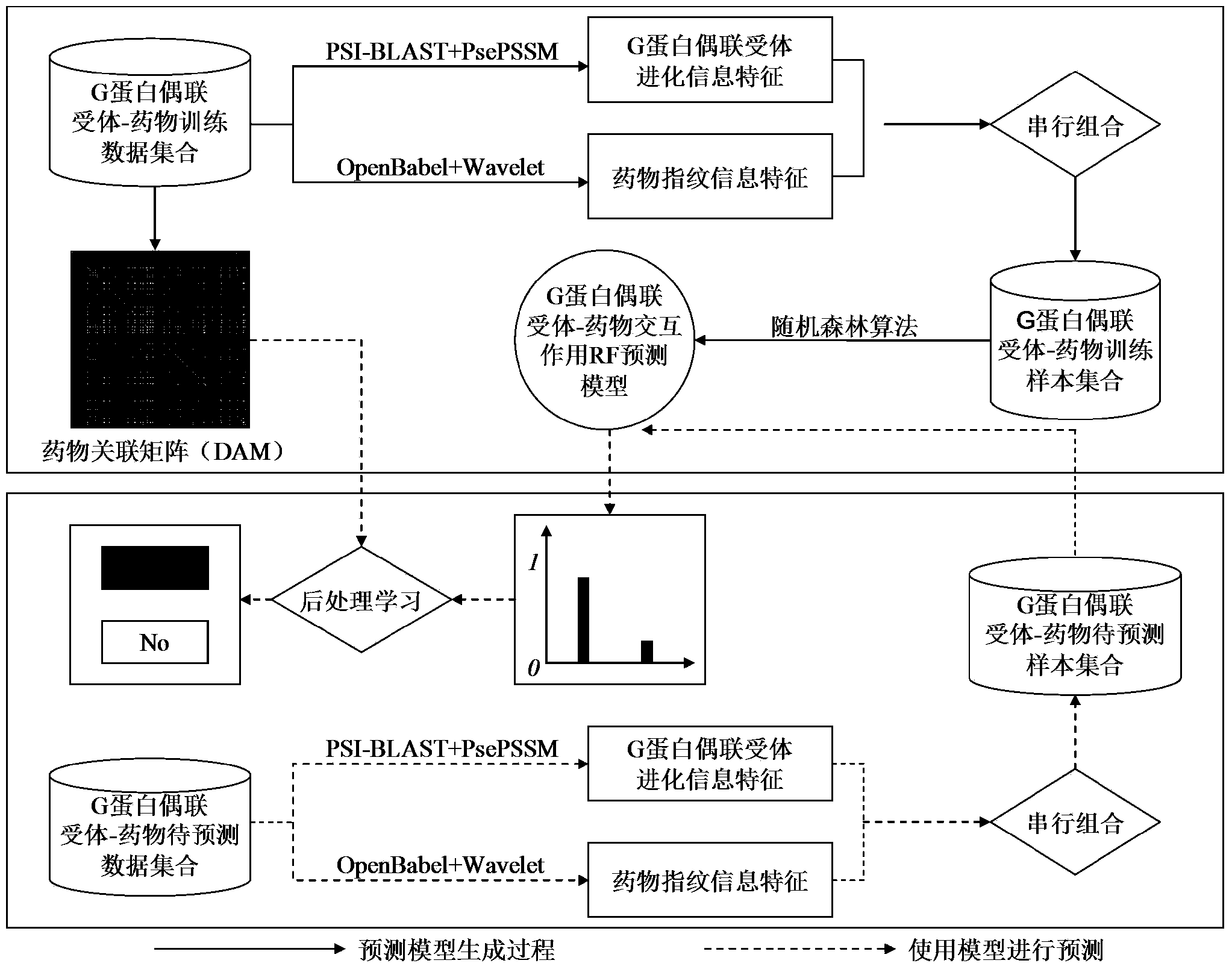
The invention provides a GPCR(G Protein-Coupled Receptors)-drug interaction prediction method based on postprocessing study. The method comprises the following steps that on the basis of all GPCR-drug information with interaction effects in a training data set, a DAM (drug associated matrix) is built; all of the GPCR-drug information in the training data set is subjected to multi-view-angle feature expression, a training sample set is formed, and then, the training sample set is trained into a GPCR-drug interaction RF (random forest) prediction model by using an RF algorithm; the multi-view-angle feature expression is carried out on each pair of GPCR-drug information with the interaction effect to be predicted, and a set of samples to be predicted is formed; then, the RF prediction model is used for carrying out interaction existence probability prediction, and finally, the prediction probability is output; the postprocessing study is carried out according to the output probability, and finally, the judgment that whether the GPCR-drug information has the interaction effect or not can be directly obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
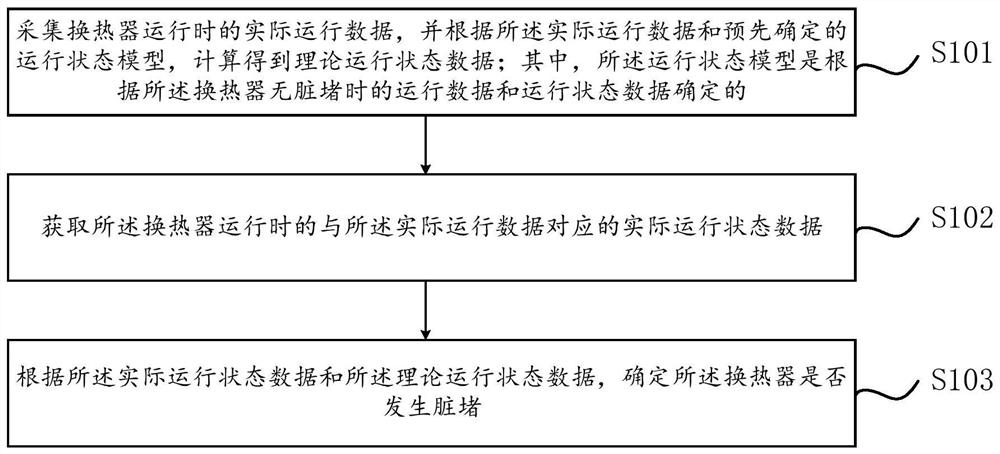
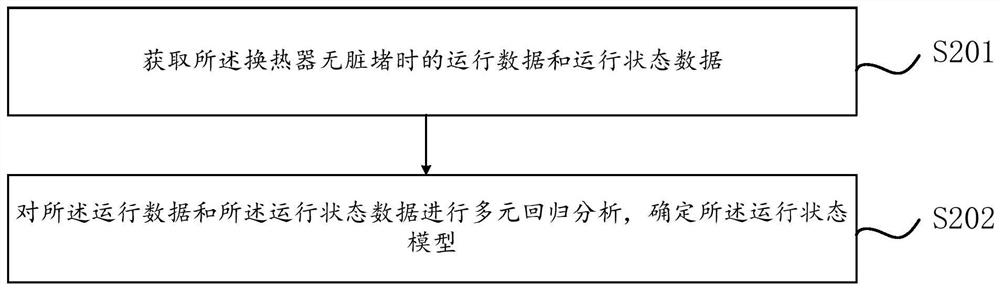
Heat exchanger filth blockage detection method and device
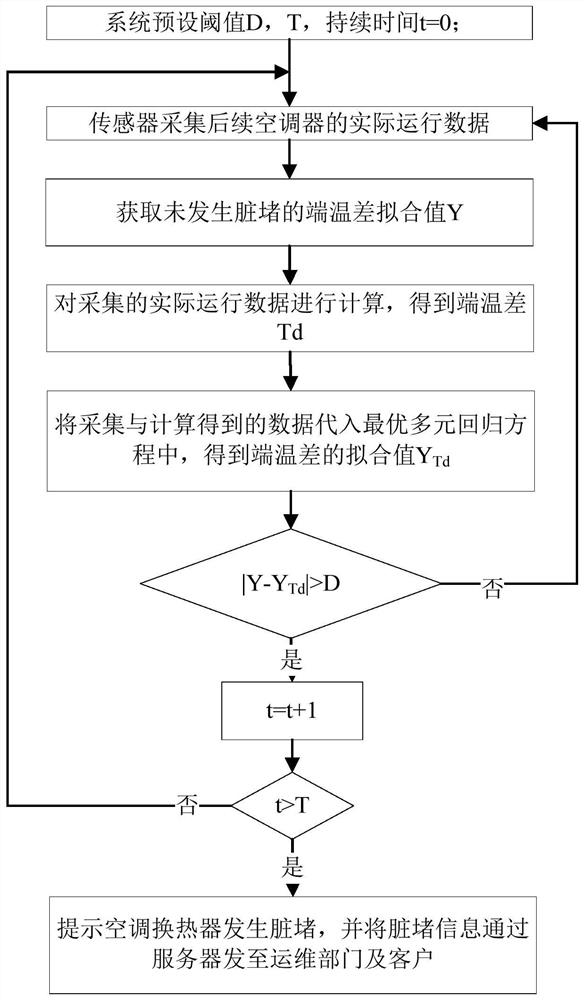
ActiveCN111811108AReduce configuration requirementsReduce time complexityMechanical apparatusProcess engineeringHeat exchanger
The invention relates to a heat exchanger filth blockage detection method and device. The method comprises the steps of collecting the actual operation data of a heat exchanger during operation, and obtaining the theoretical operation state data through calculation according to the actual operation data and a predetermined operation state model, wherein the operation state model is determined according to operation data and operation state data when the heat exchanger is not blocked by dirt; acquiring actual operation state data corresponding to the actual operation data when the heat exchanger operates; and according to the actual operation state data and the theoretical operation state data, determining whether filth blockage occurs to the heat exchanger. According to the method, the filth blockage degree of the unit heat exchanger can be judged based on historical data, the judgment effect and the detection speed are improved, the problems of too large algorithm error and insufficient stability caused by few monitored operating parameters are solved, the accuracy of filth blockage judgment of the heat exchanger is improved, and the development trend can be summarized through historical operation data and real-time operation data, so that the filth blockage condition of the heat exchanger in the future is accurately predicted.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com