Patents
Literature
108results about How to "Small bandwidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
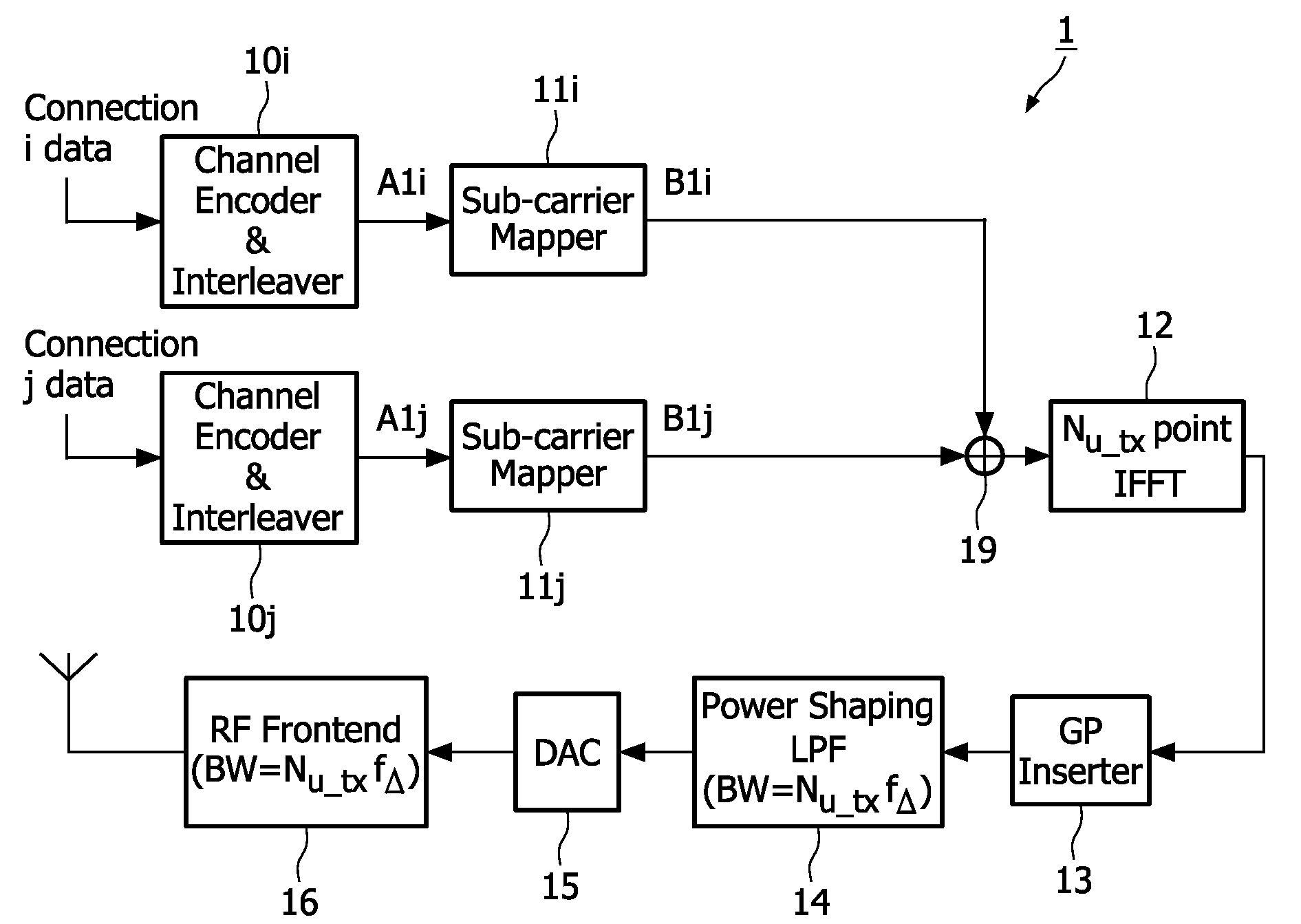
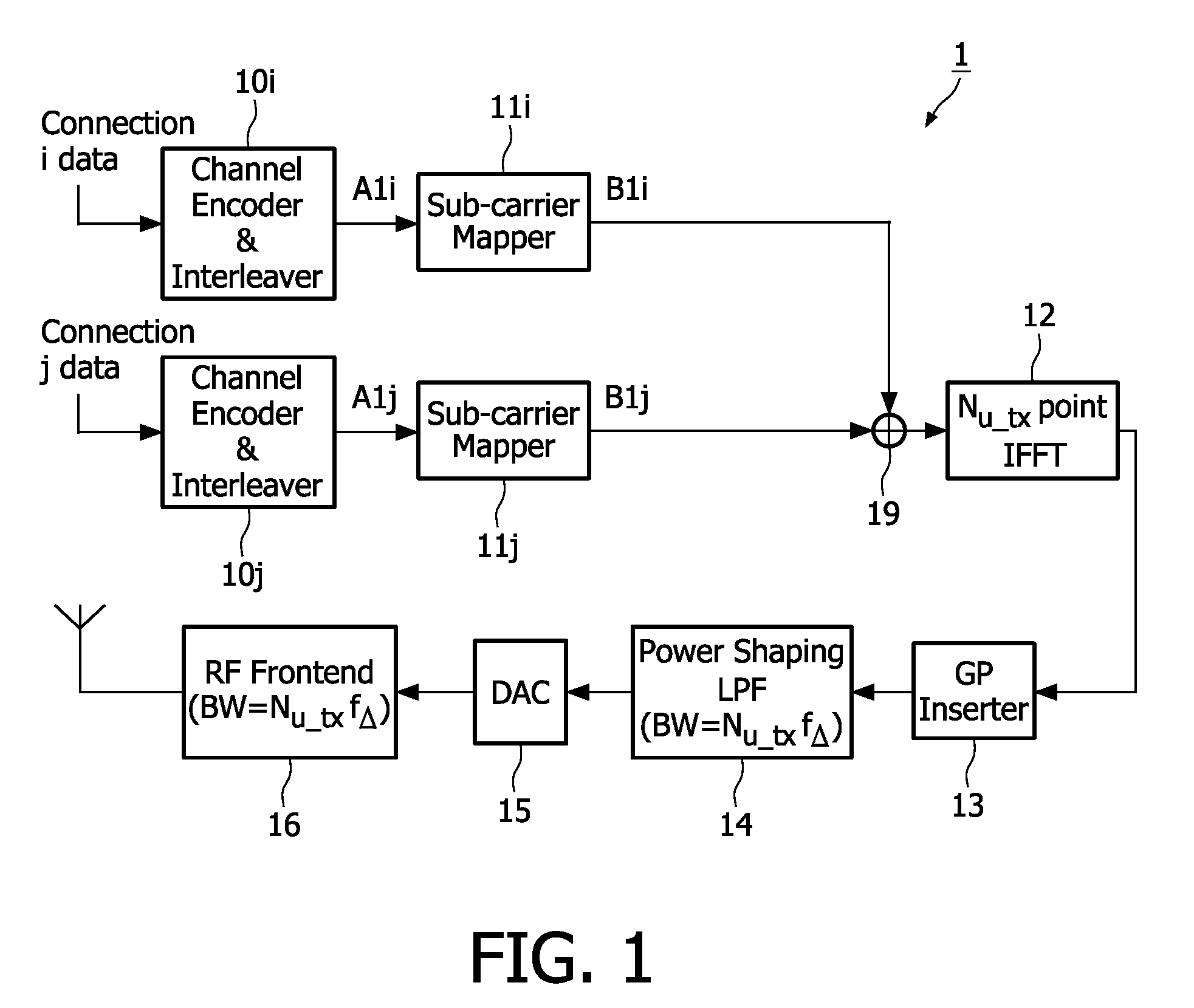
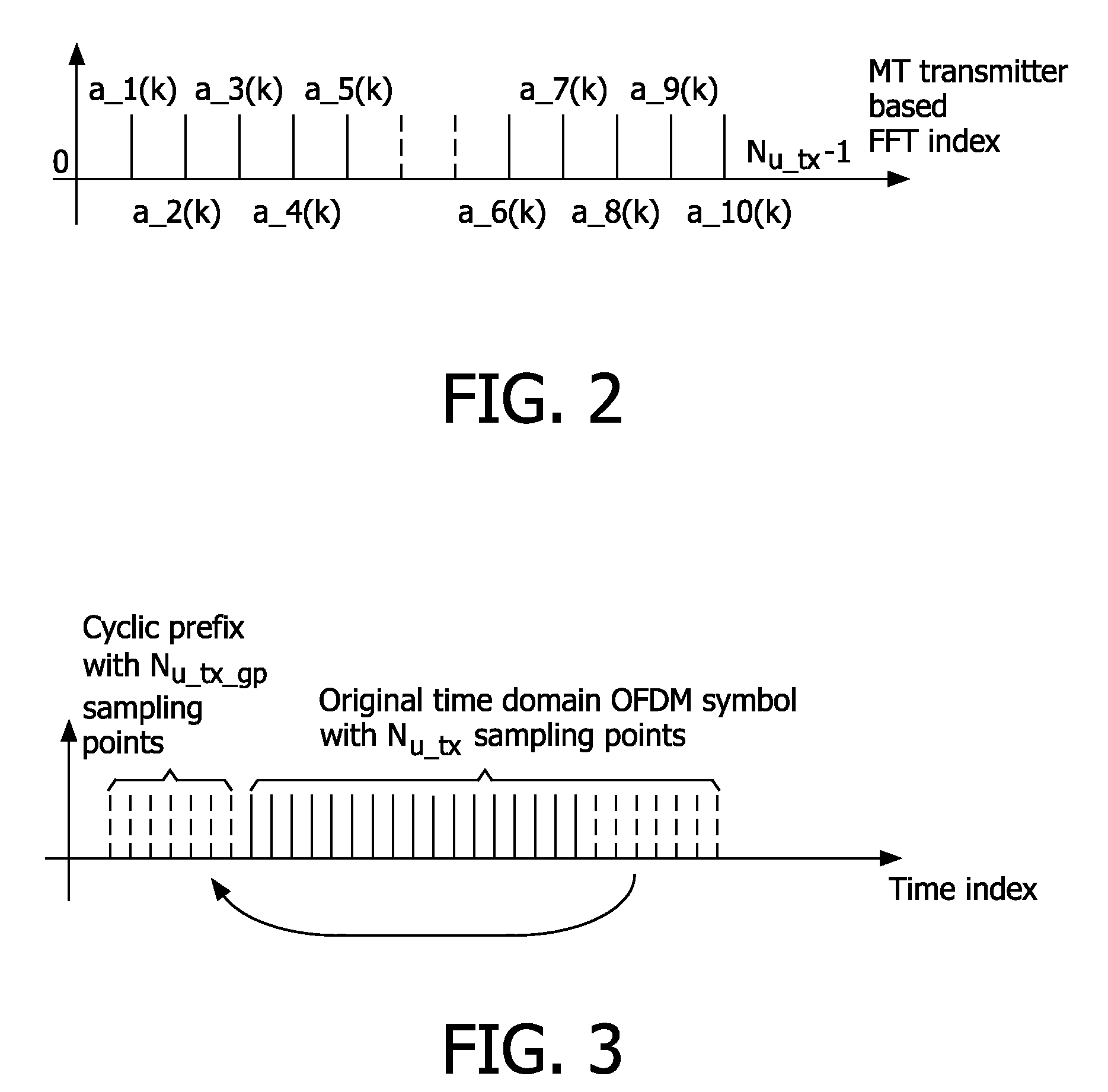
Bandwidth asymmetric communication system based on OFDM and TDMA
InactiveUS20090196163A1Reduce complexityCutting synchronizationTransmission path divisionSecret communicationCommunications systemUplink transmission
The present invention relates to a communication system comprising a plurality of terminals each having an uplink transmission unit (1) for transmitting radio frequency OFDM signals at a radio frequency and an access point having an uplink receiving unit (4) for concurrently receiving said radio frequency OFDM signals from at least two terminals, said OFDM signals being Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex (OFDM) modulated, wherein the bandwidth of said uplink transmission units and of the transmitted radio frequency OFDM signals is smaller than the bandwidth of said uplink receiving unit, that the bandwidth of at least two uplink transmission units and of their transmitted radio frequency OFDM signals is different and that the uplink transmission unit is adapted to assign different connections for concurrently transmitting radio frequency OFDM signals to different sub-carriers in the same time slots or to the same or different sub-carriers in different time slots.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
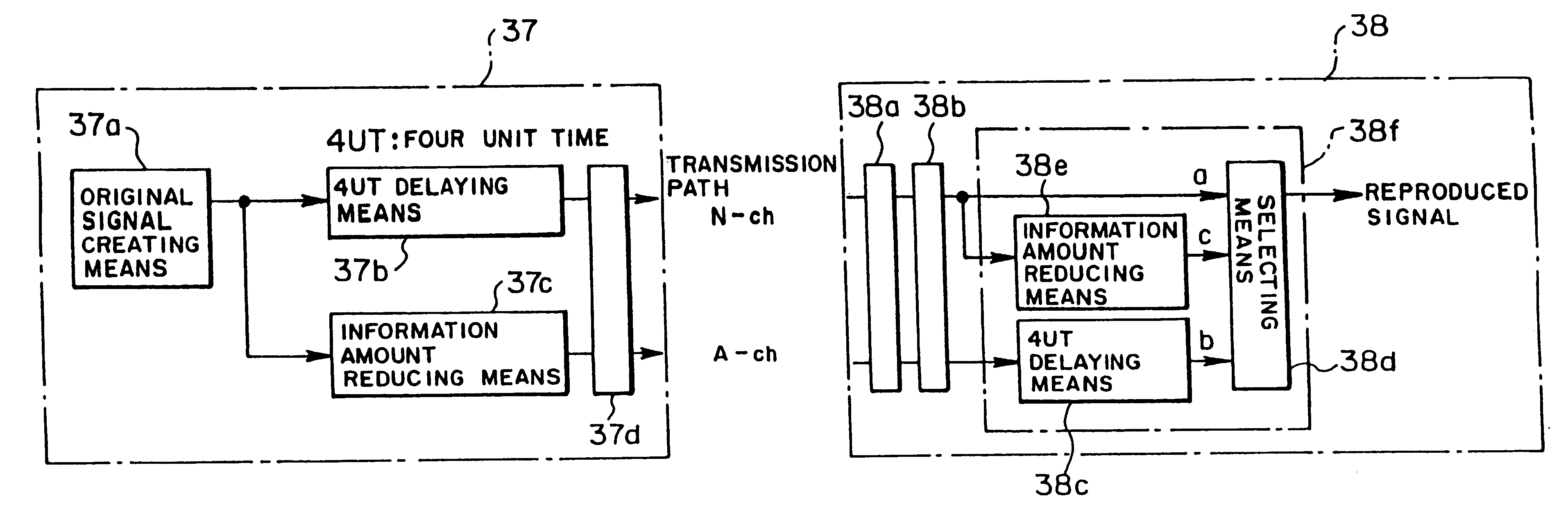
Method, system and apparatus for transmitting, receiving, and reproducing a digital broadcast signal
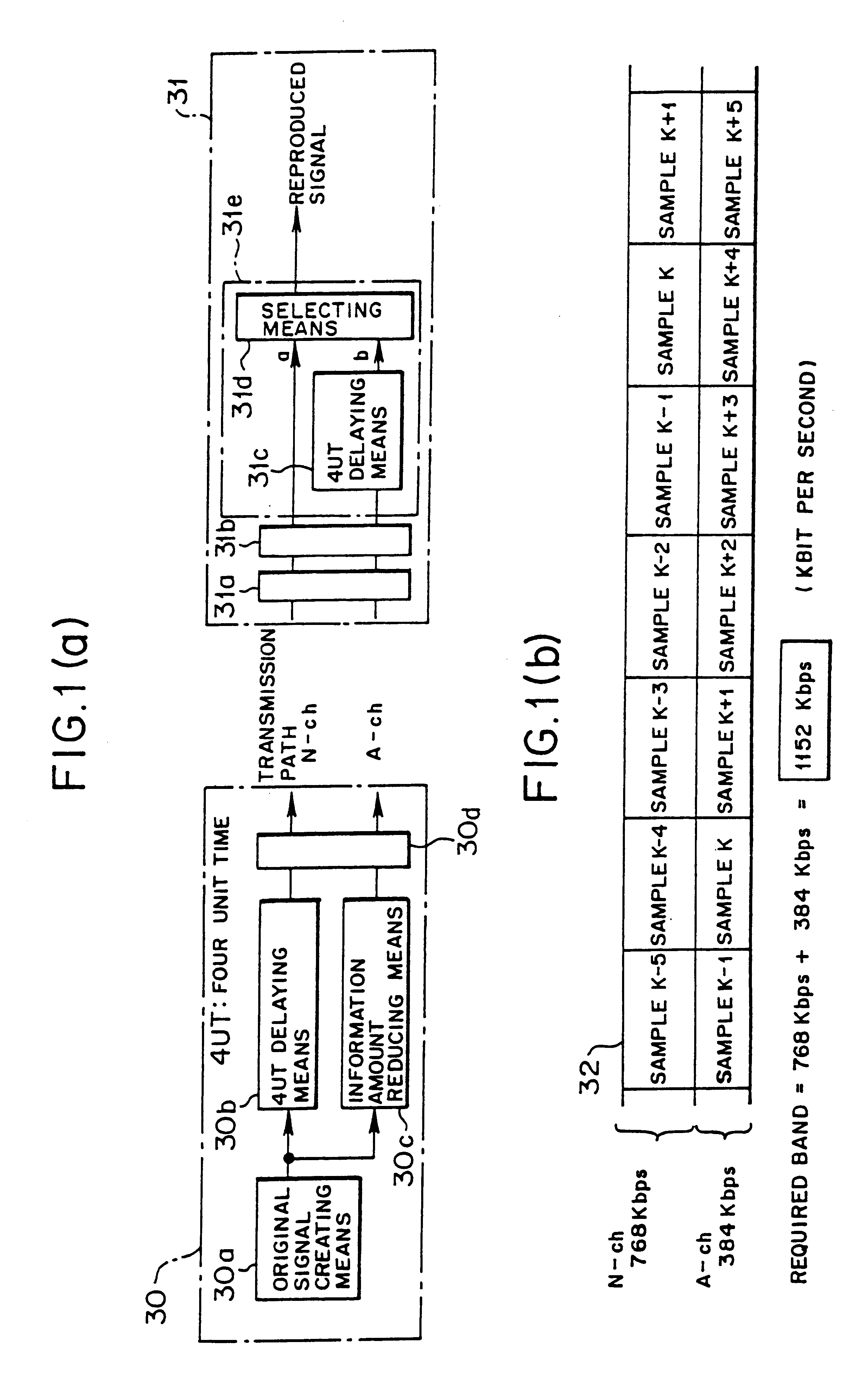
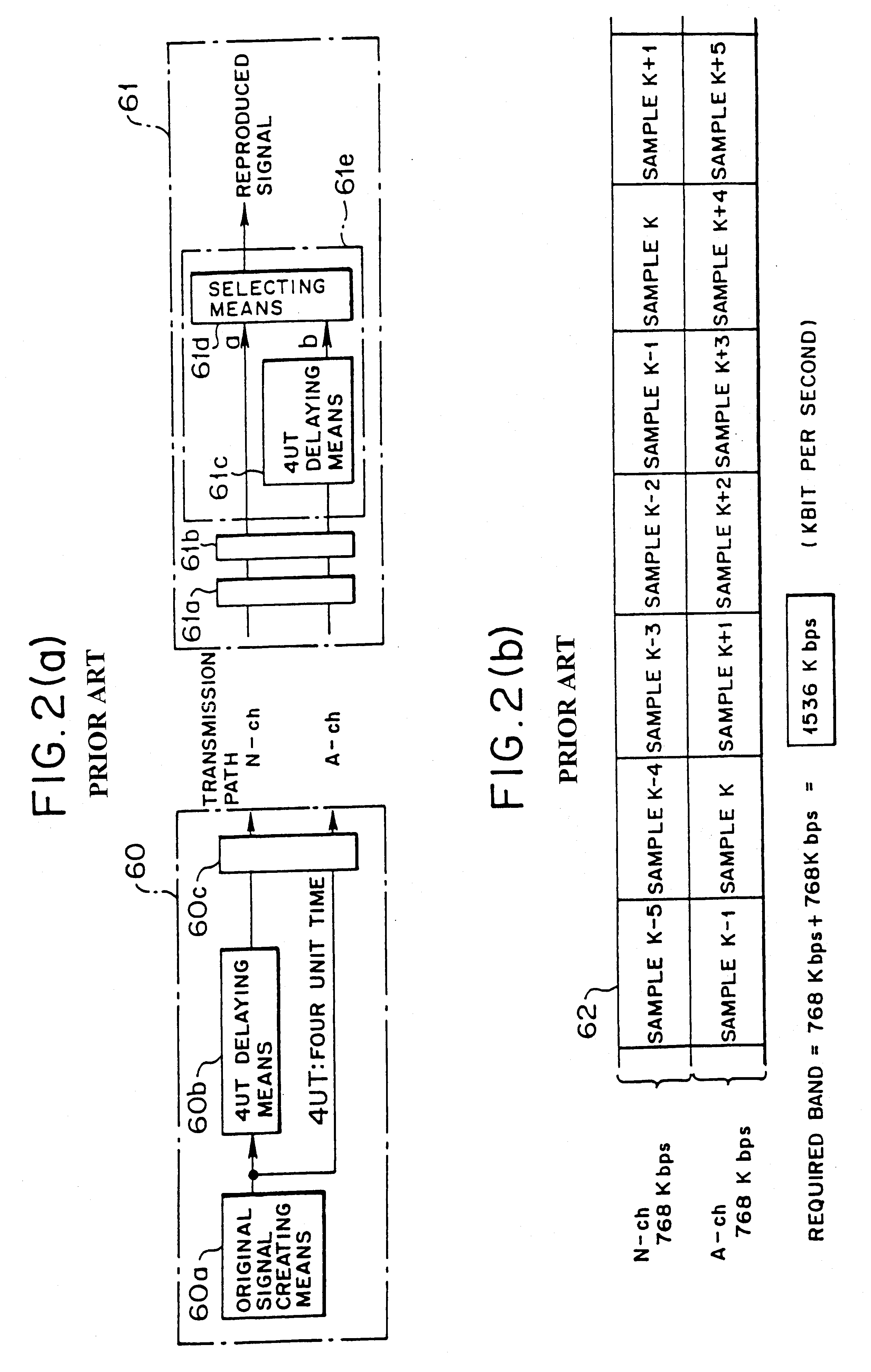
InactiveUS6535717B1Small bandwidthIncrease the number ofPulse modulation television signal transmissionBroadcast transmission systemsEngineeringDigital broadcasting
The present system comprises a transmitting apparatus for digital broadcast which includes an original signal generating section, delaying section, information amount reducing section, and transmitting section. A receiving and reproducing apparatus for digital broadcast includes a signal reception front stage unit for receiving a high quality signal and a low quality signal, mode determining section and reproducing section composed of a delaying section and selecting section for selectively reproducing the high quality signal and the low quality signal. By employing time diversity, the transmitting apparatus sends the low quality signal having a smaller bandwidth and the high quality signal so that the low quality signal has a preceding time lag relative to the high quality signal, and the receiving apparatus reproduces broadcasting programs. Utilizing the frequency band for broadcast effectively, many broadcasting programs can be increased, and the investment for providing a gap filler can be minimized.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Narrow spectrum light source
ActiveUS7835417B2Low costAvoid disadvantagesLaser detailsCoupling light guidesVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserVertical-external-cavity surface-emitting-laser
An apparatus and method are disclosed for decreasing the spectral bandwidth of a semiconductor laser, such as a vertical cavity surface emitting laser.
Owner:OCTROLIX
Bandwidth asymmetric communication system
InactiveUS20090232234A1Reduce complexityCutting synchronizationSignal allocationSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlCommunications systemUplink transmission
The present invention relates to a communication system comprising a plurality of terminals each having an uplink transmission unit (1) for transmitting radio frequency OFDM signals at a radio frequency and an access point having an uplink receiving unit (4) for concurrently receiving said radio frequency OFDM signals from at least two terminals, said OFDM signals being Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex (OFDM) modulated, wherein the bandwidth of said uplink transmission units and of the transmitted radio frequency OFDM signals is smaller than the bandwidth of said uplink receiving unit and that the bandwidth of at least two uplink transmission units and of their transmitted radio frequency OFDM signals is different. The present invention relates further to a communication system wherein the access point has a downlink transmission unit (7) for transmitting radio frequency OFDM signals at a radio frequency and that the at least two terminals each have a downlink receiving unit (11) for receiving said radio frequency OFDM signals, wherein the bandwidth of said downlink transmission unit is larger than the bandwidth of said downlink receiving units and that the downlink transmission unit is adapted to generate and transmit radio frequency OFDM signals having a bandwidth that is smaller than or equal to the bandwidth of the downlink transmission unit and that is equal to the bandwidth of the downlink receiving unit by which the radio frequency OFDM signals shall be received. Still further, the present invention relates to a communication method, to a terminal and to an access point for use in such a communication system.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
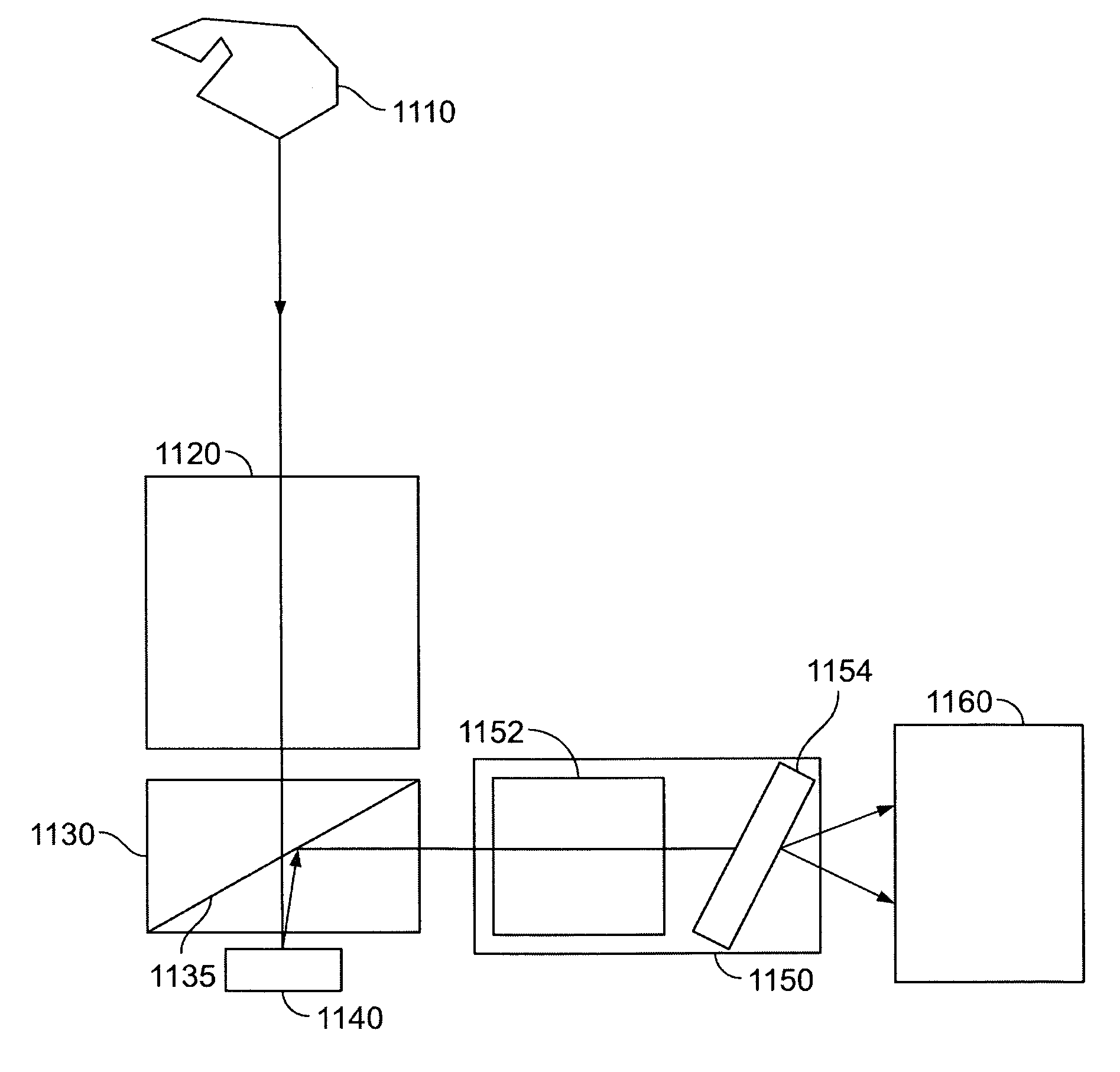
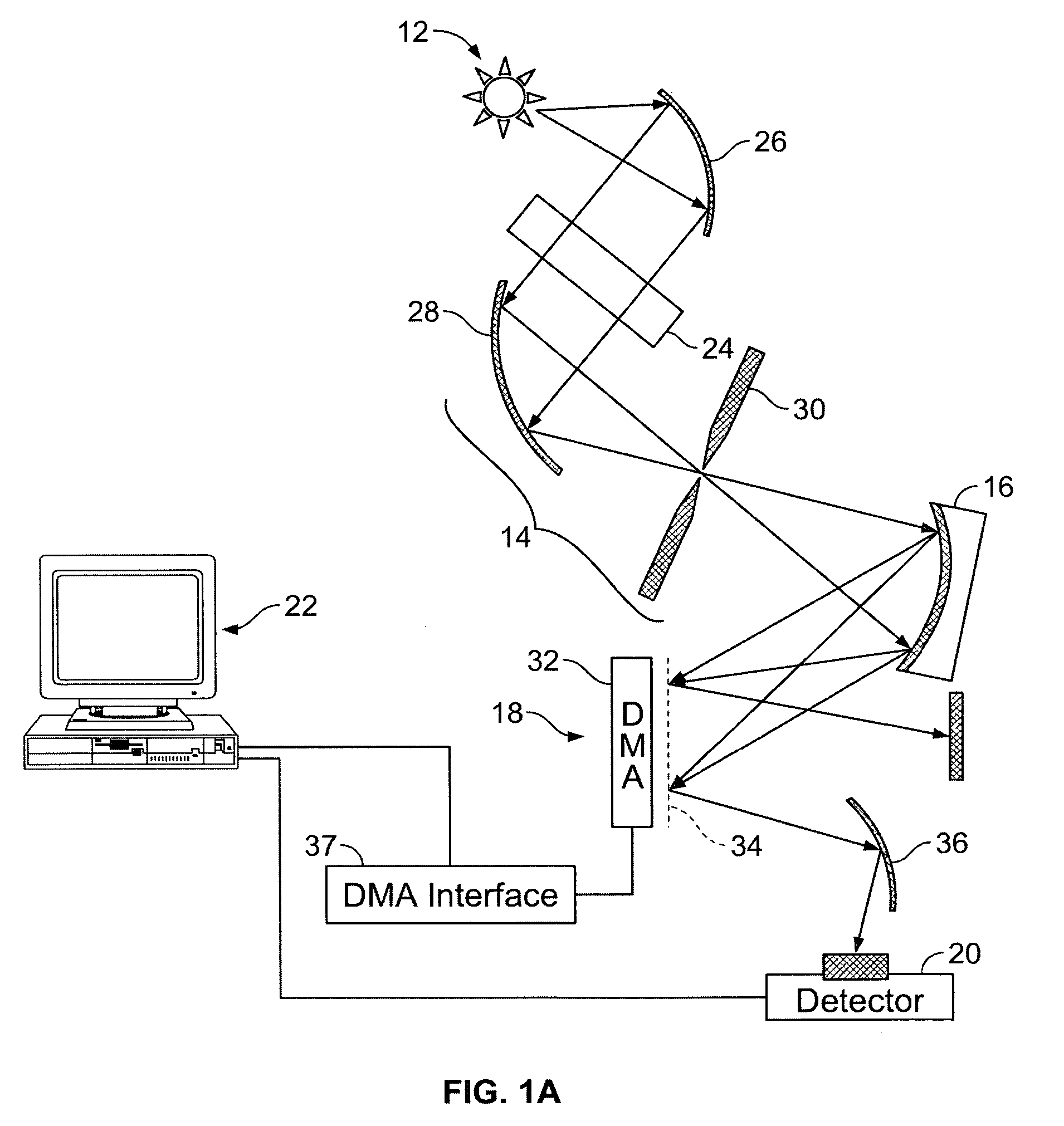
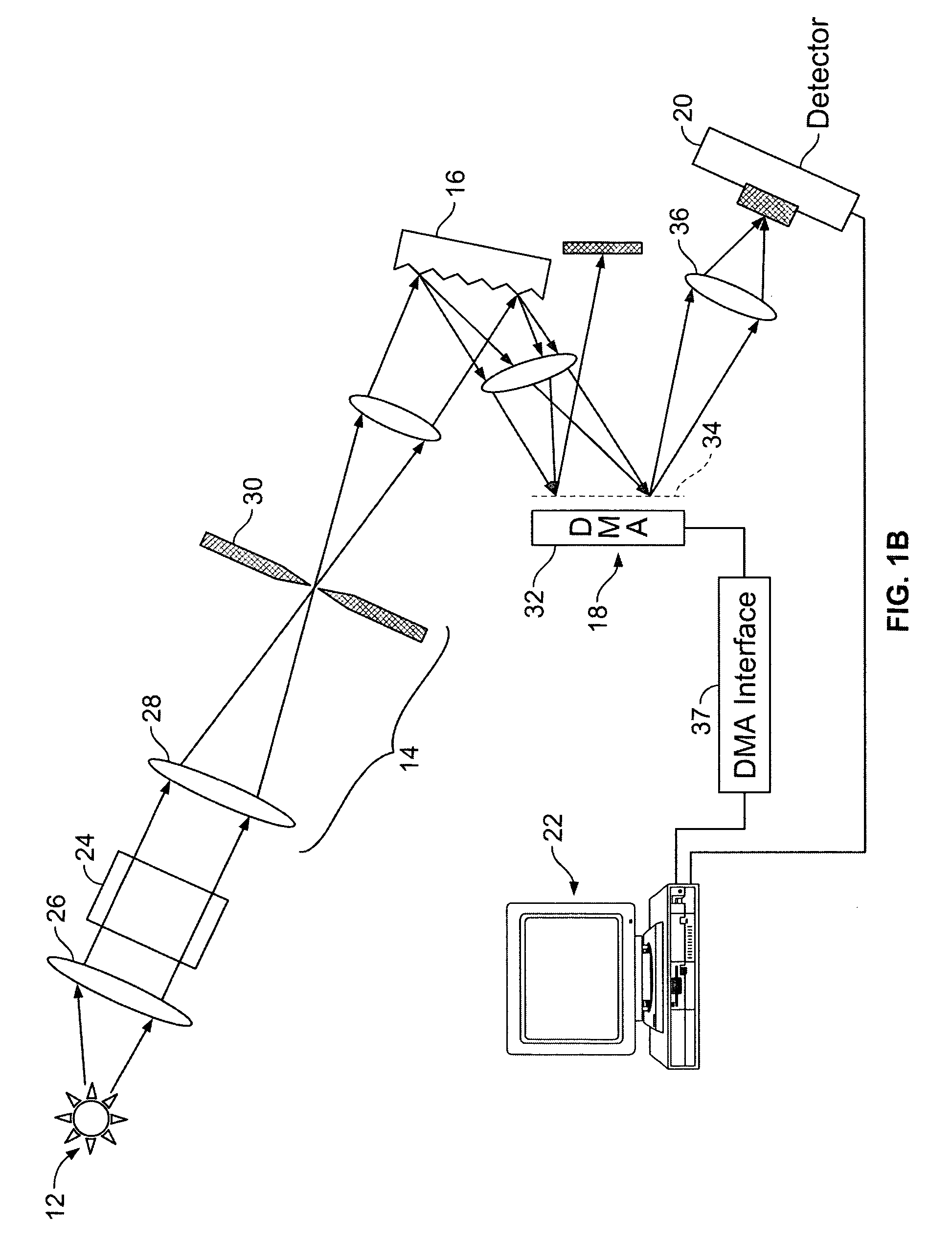
Hyper-spectral imaging methods and devices
InactiveUS20050270528A1Improve signal to noise ratioSmall bandwidthRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsSpectral imagingLight spectrum
A hyper-spectral imaging system comprises imaging foreoptics to focus on a scene or object of interest and transfer the image of said scene or object onto the focal plane of a spatial light modulator, a spatial light modulator placed at a focal plane of said imaging foreoptics, an imaging dispersion device disposed to receive an output image of said spatial light modulator, and an image collecting device disposed to receive the output of said imaging dispersion device.
Owner:PLAIN SIGHT SYST
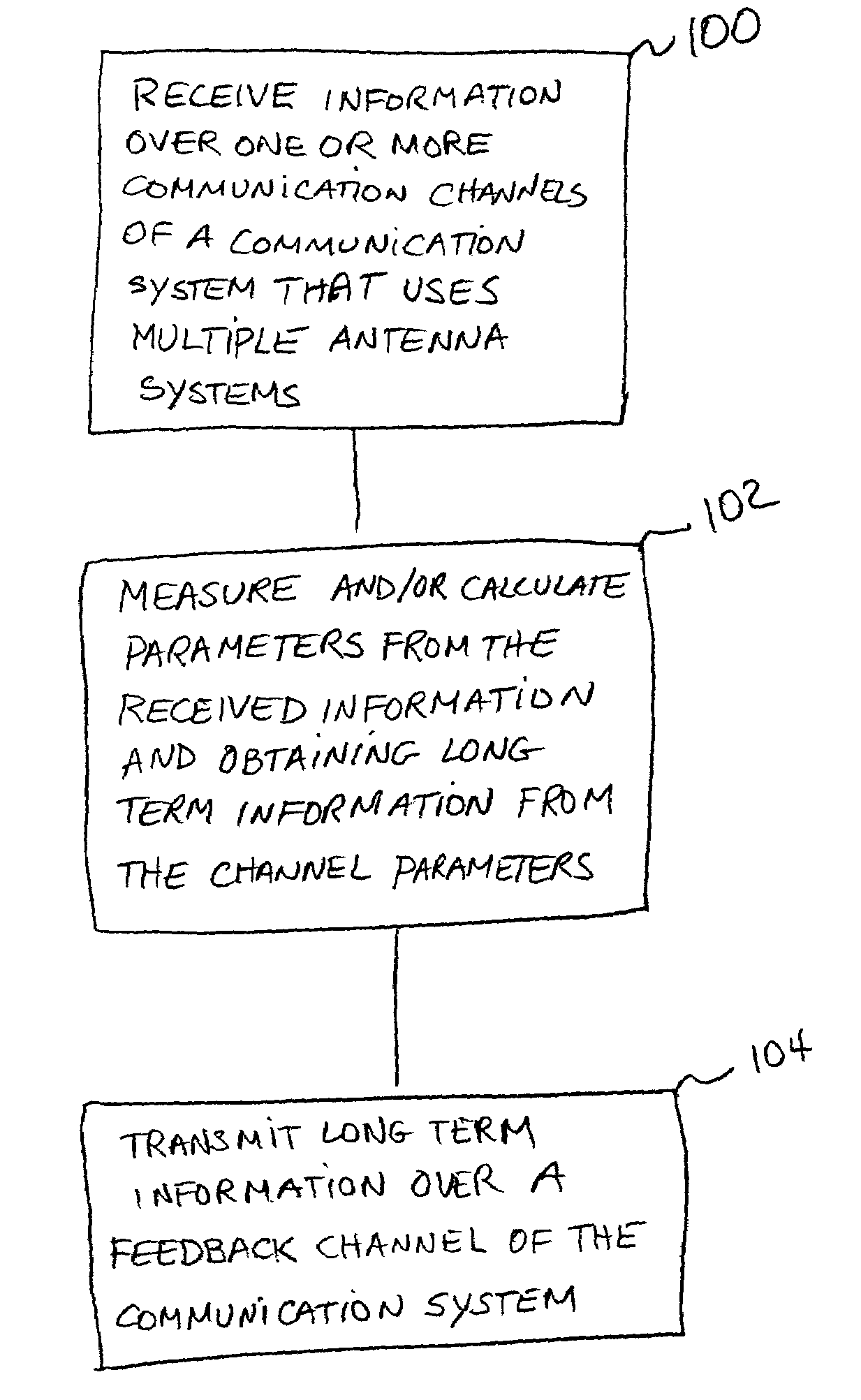
Method for improved performance and reduced bandwidth channel state information feedback in communication systems
ActiveUS7433661B2Reduce throughputUse amountSubstation equipmentTransmission monitoringCommunications systemTime segment
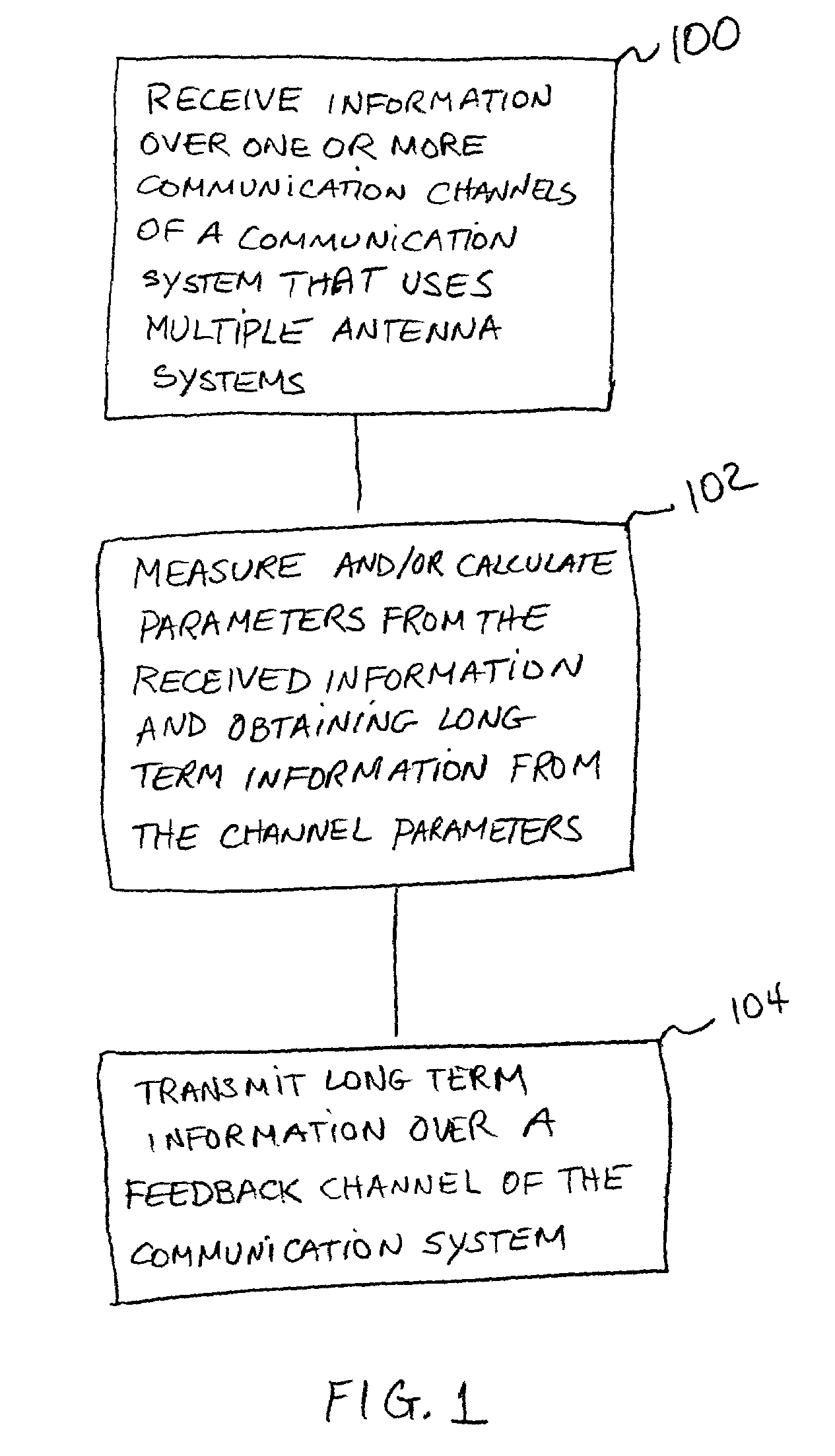
A method of transmitting information over a feed back channel of a communication system that has multiple antenna systems is provided. Long term channel condition information is obtained from received measured and / or calculated channel parameter values. The obtained long term channel condition information is arranged in a particular manner and transmitted over a defined time period during which the long term channel condition information varies relatively slowly. Because the long term information remains relatively constant for one or more defined time periods, the amount of bandwidth needed to communicate this value is small because it need only be communicated occasionally. Thus only a small bandwidth needs to be allocated for transmitting this long term information.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
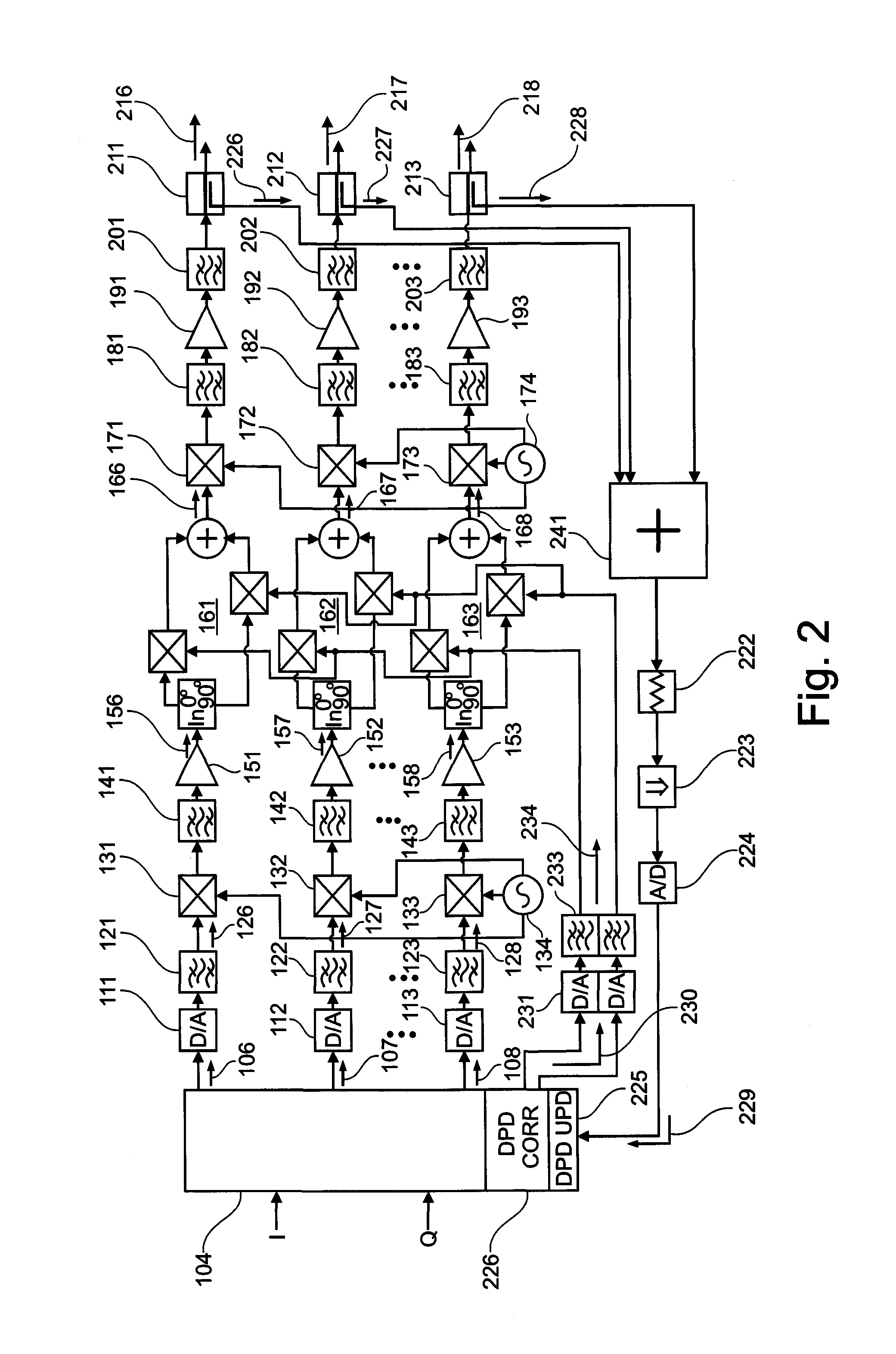
Active antenna array with modulator-based pre-distortion
ActiveUS20110150130A1Low costSmall bandwidthPolarisation/directional diversityPower amplifiersSignal generatorSignal modulation
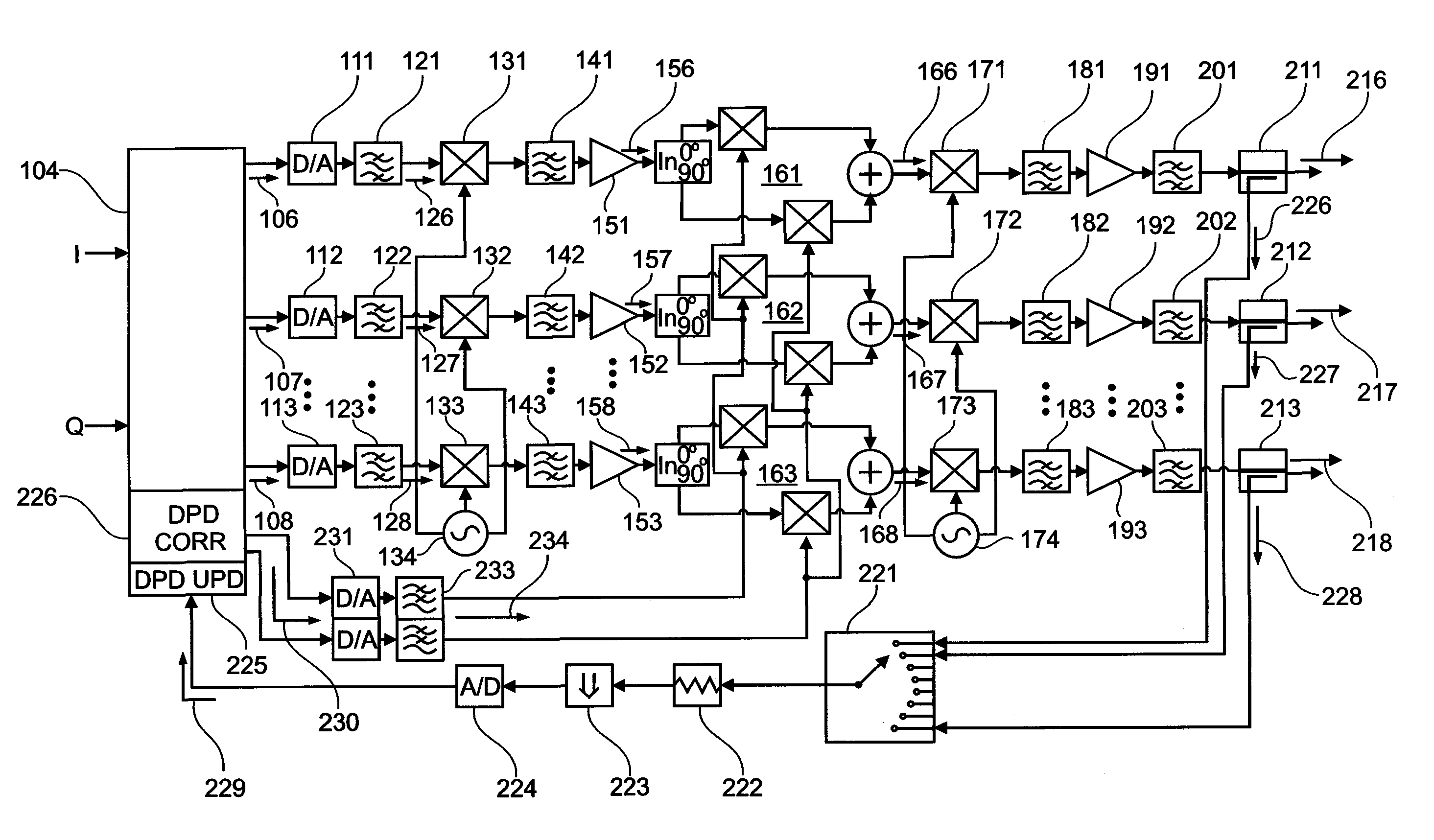
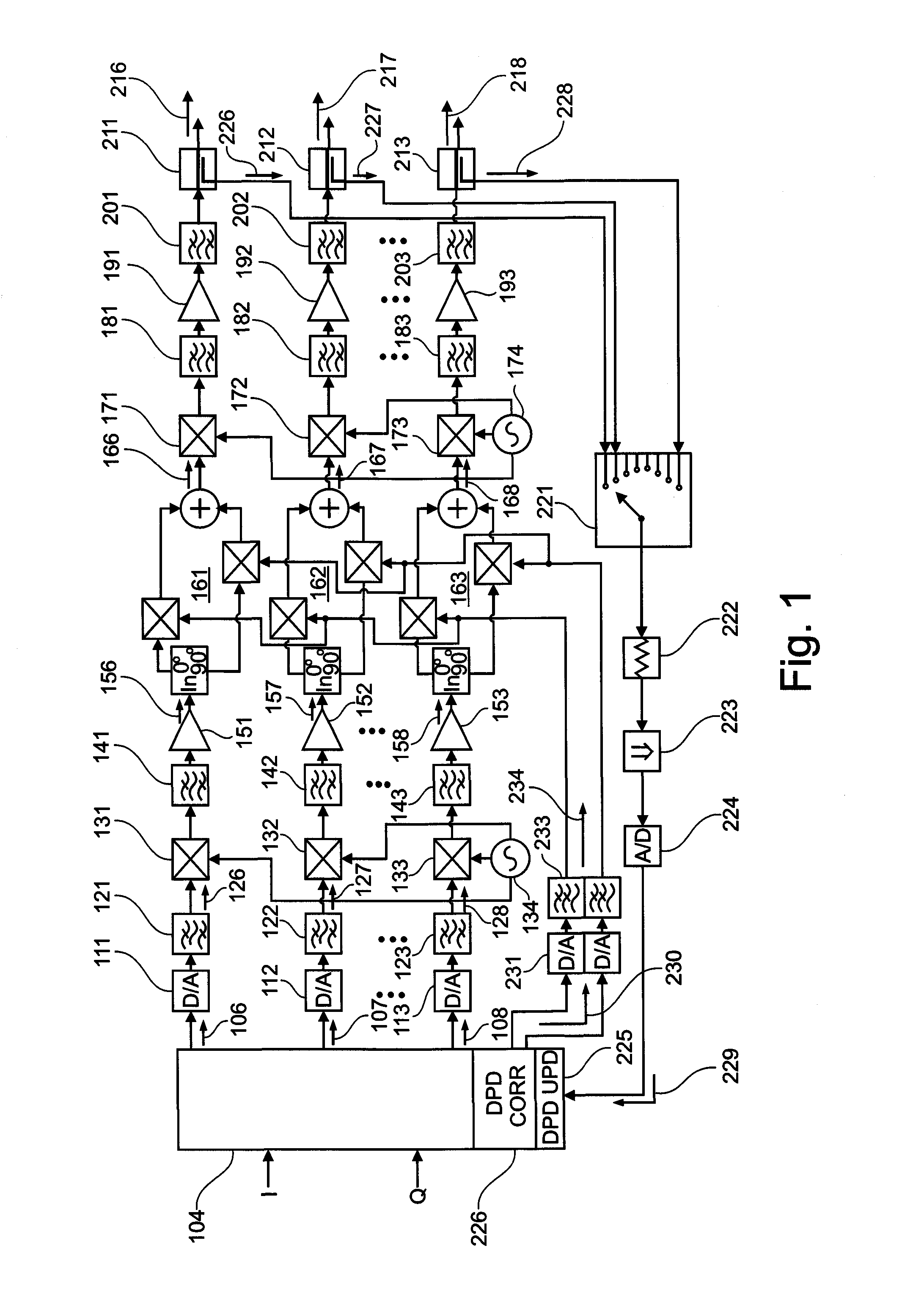
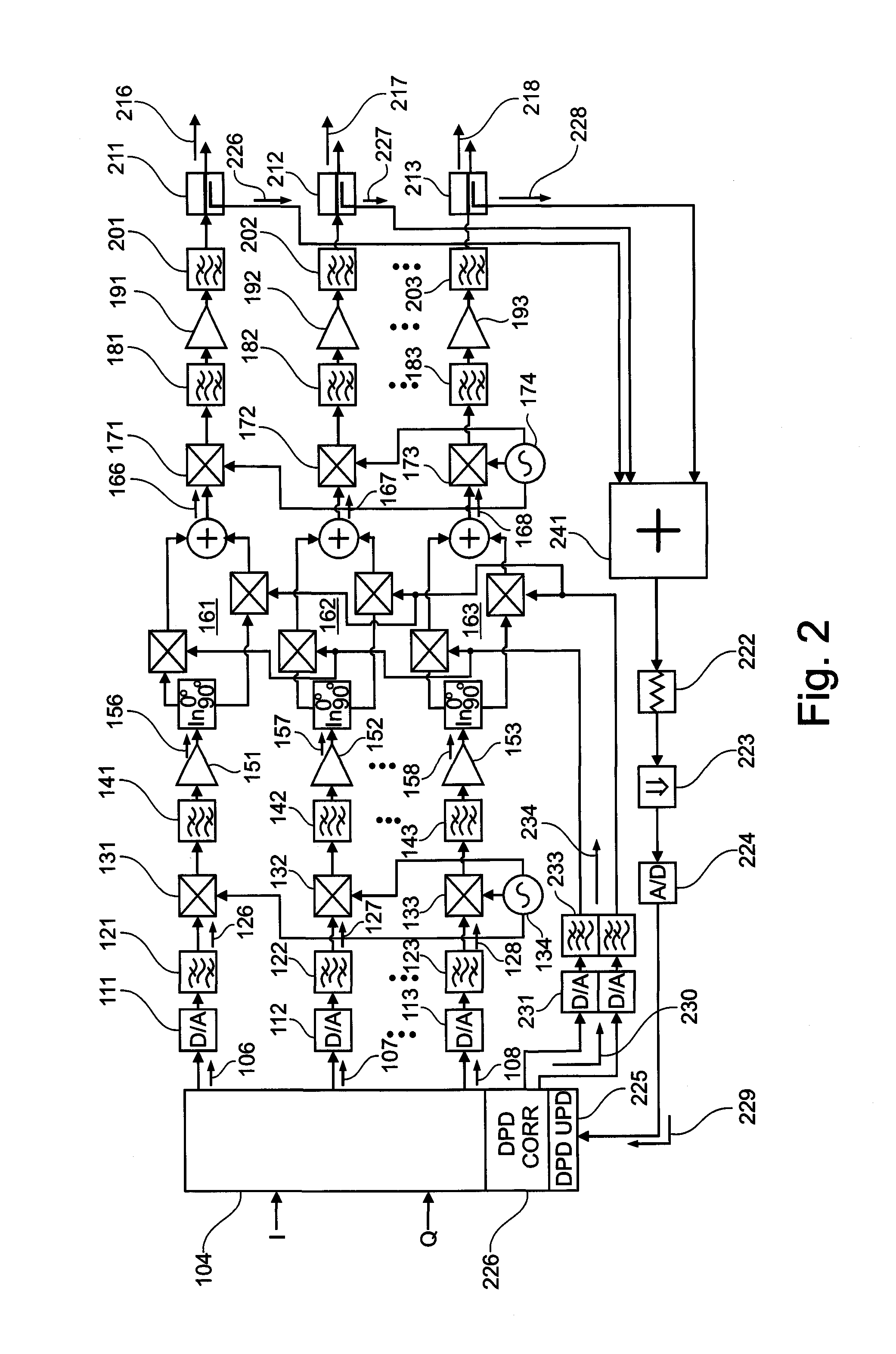
An active antenna array comprises a plurality of transmission paths, a predistortion modulation signal generator, and a predistortion modulation signal distribution structure. At least two of the plurality of transmission paths comprise a predistortion modulator for modulating a transmission path signal with a predistortion modulation signal generated by the predistortion modulation signal generator and distributed by predistortion modulation signal distribution structure to the at least two of the plurality of transmission paths. A method for predistorting at least two of a plurality of transmission path signals in an active antenna array and computer program products for manufacture and method execution are also claimed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
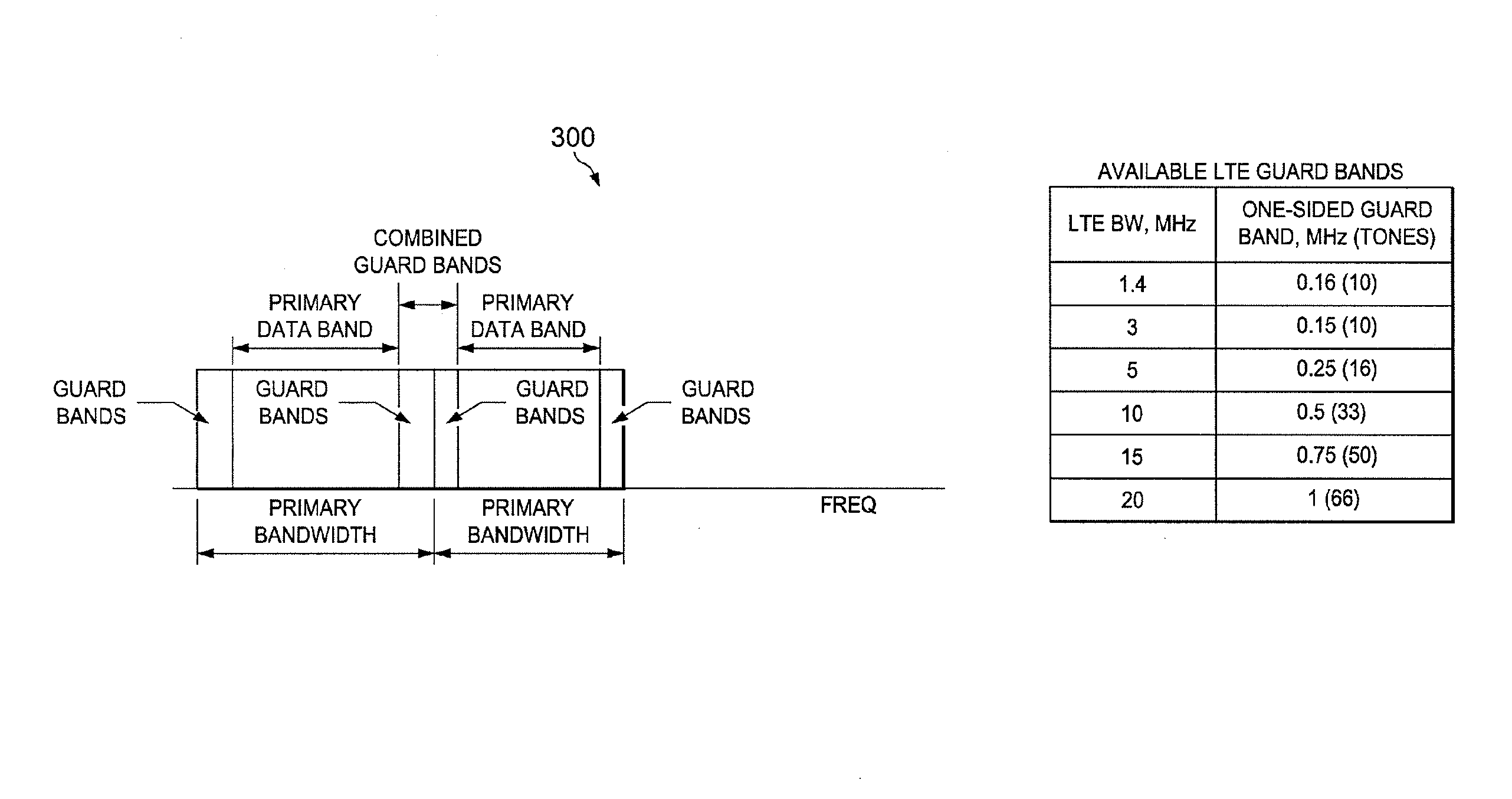
System and Method for Guard Band Utilization for Synchronous and Asynchronous Communications
ActiveUS20160269212A1Improve frequency band utilizationSmall bandwidthTransmission path divisionMulti-frequency code systemsAsynchronous communicationFrequency spectrum
Embodiments are provided for guard band utilization for synchronous and asynchronous communications in wireless networks. A user equipment (UE) or a network component transmits symbols on data bands assigned for primary communications. The data bands are separated by a guard band having smaller bandwidth than the data bands. The UE or network component further modulates symbols for secondary communications with a spectrally contained wave form, which has a smaller bandwidth than the guard band. The spectrally contained wave form is achieved with orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation or with joint OFDM and Offset Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (OQAM) modulation. The modulated symbols for the secondary communications are transmitted within the guard band.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
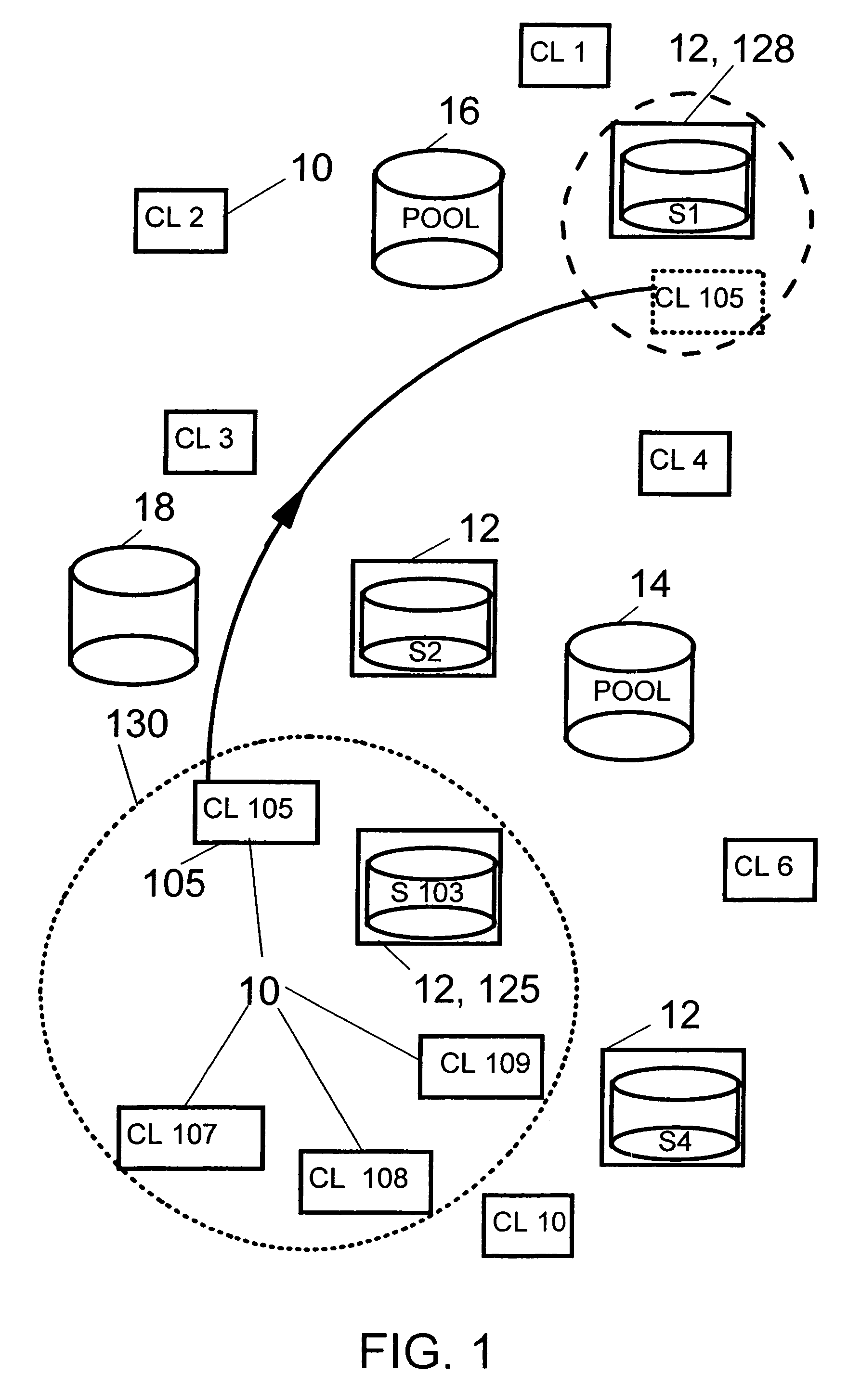
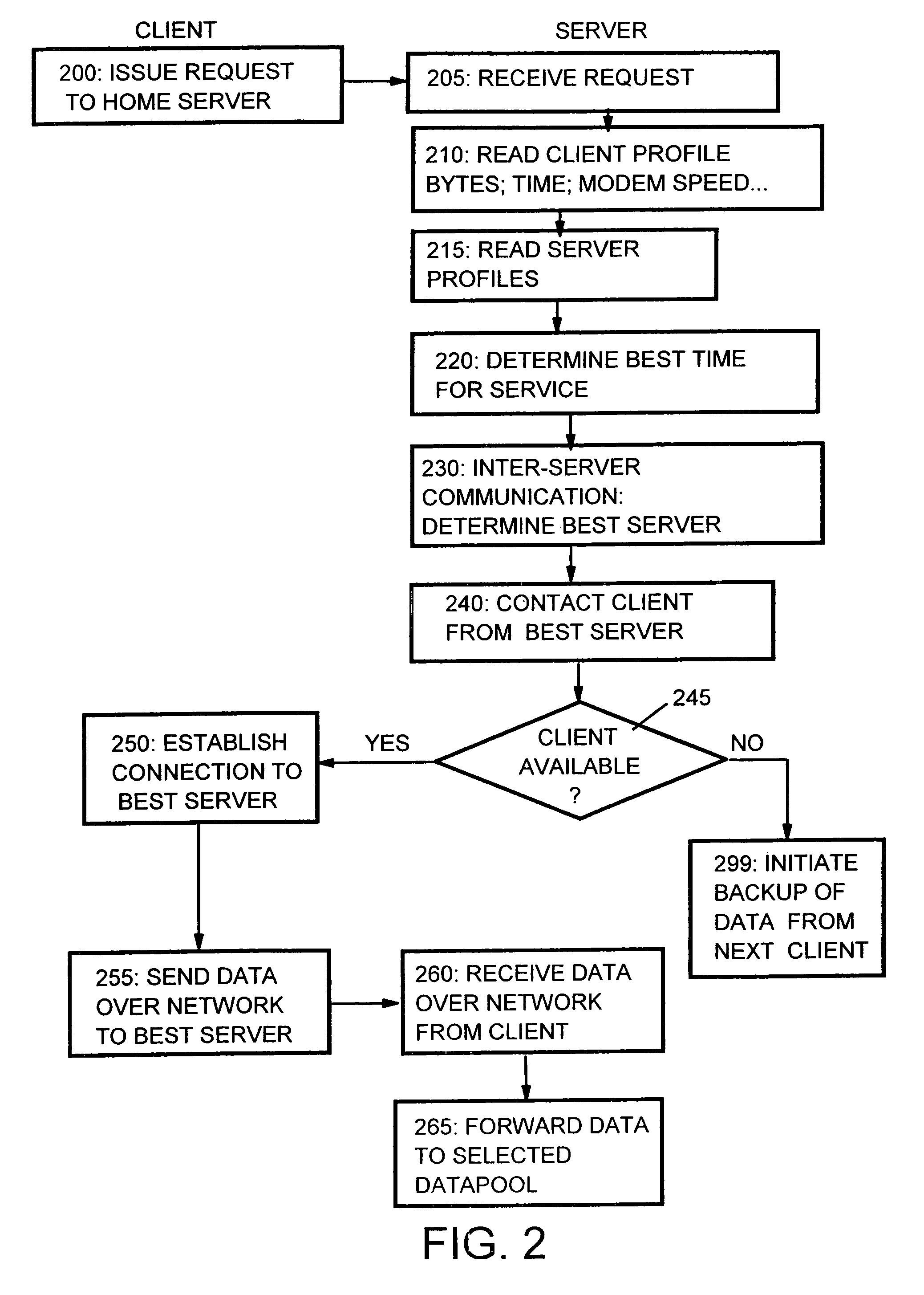
Location independent backup of data from mobile and stationary computers in wide regions regarding network and server activities
InactiveUS8230066B2Small bandwidthGreat network loadingDigital computer detailsTransmissionClient-sideService provision
The present invention relates to a computerized method and respective system for servicing a request for a networked data transfer from a client system, which is able to be serviced on a particular server system being a member of a plurality of server systems dedicated to service said client requests, in which the server systems are connected via a network and share information about a plurality of client systems, and in which the service is known to consume some non-negligible network bandwidth. In order to balance required bandwidth peaks and to improve user comfort, it is proposed to establish an inter-server communication, which determines the best suited server for providing the service, reflecting pre-collected client history data, favorite service provision times, etc. The method can be applied primarily for backup of data from distributed client systems, or for improving print services.
Owner:IBM CORP
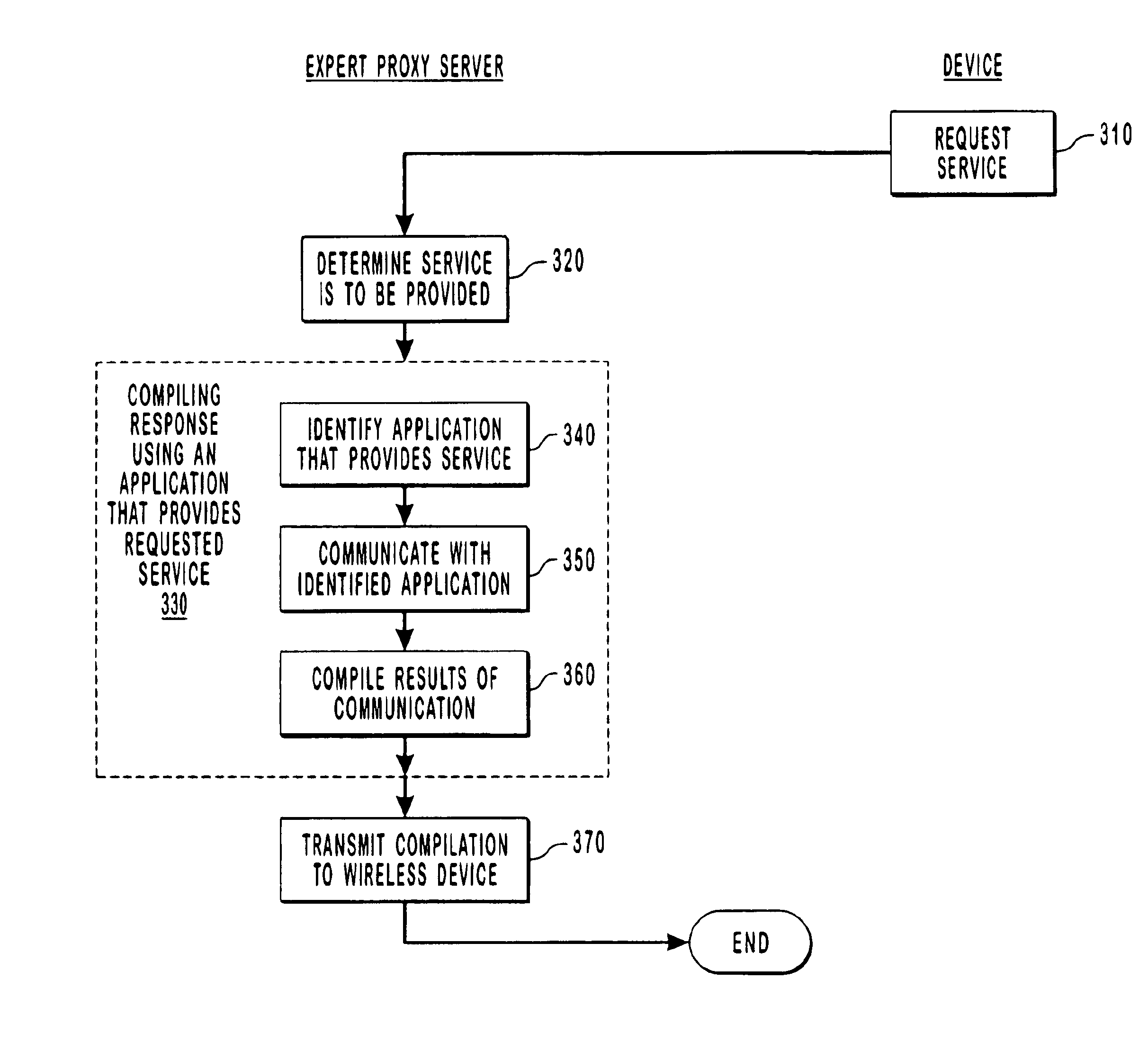
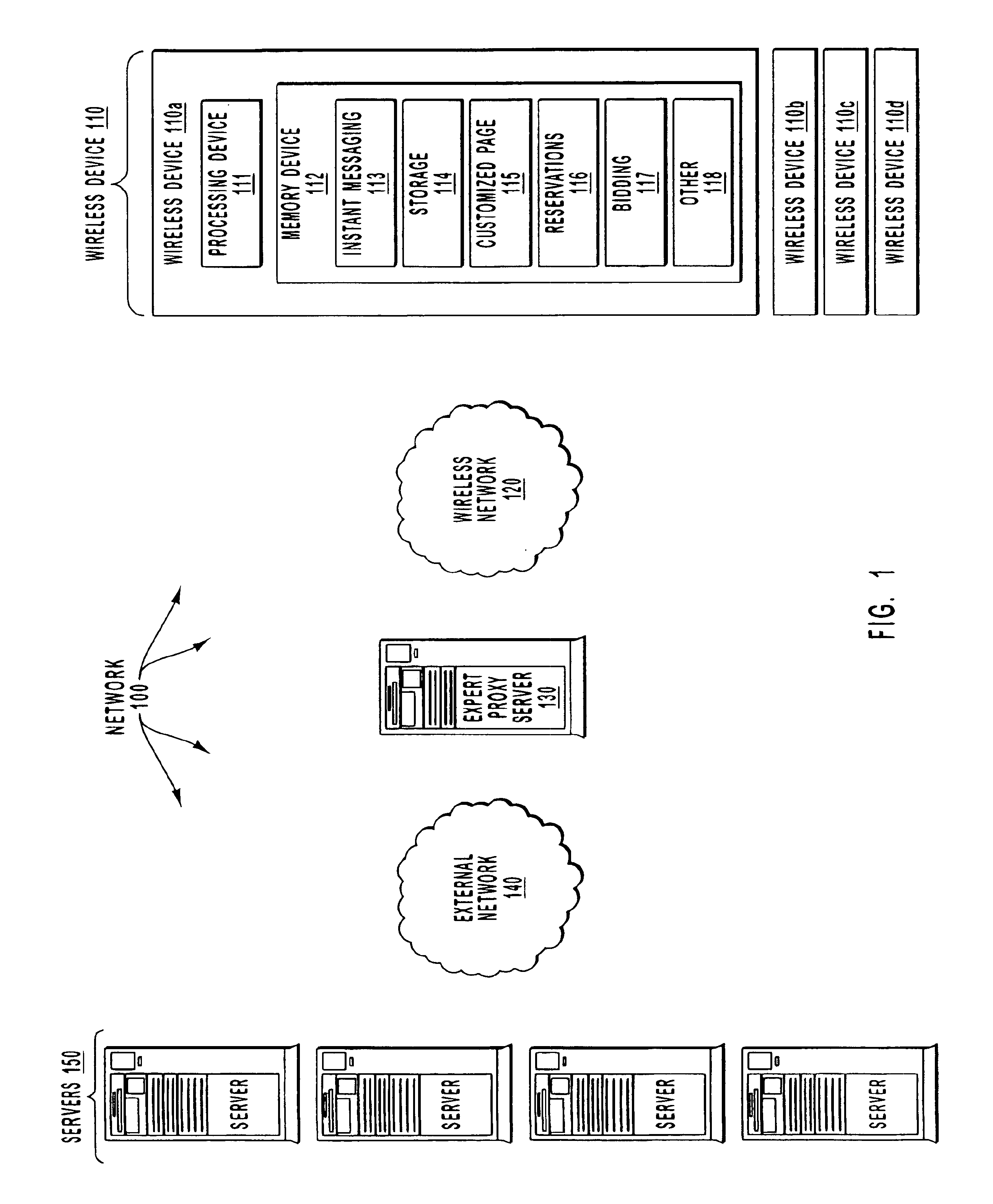
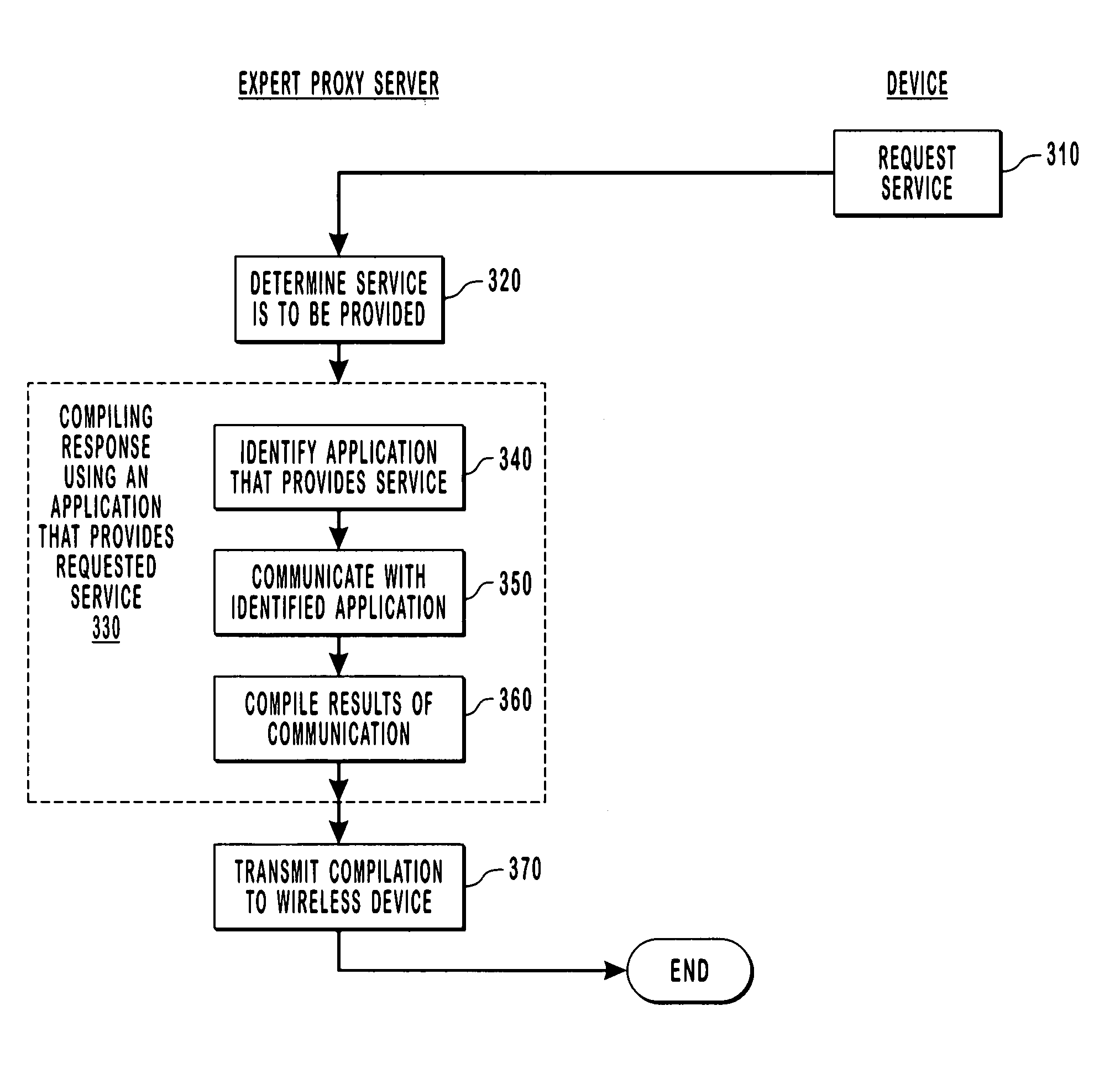
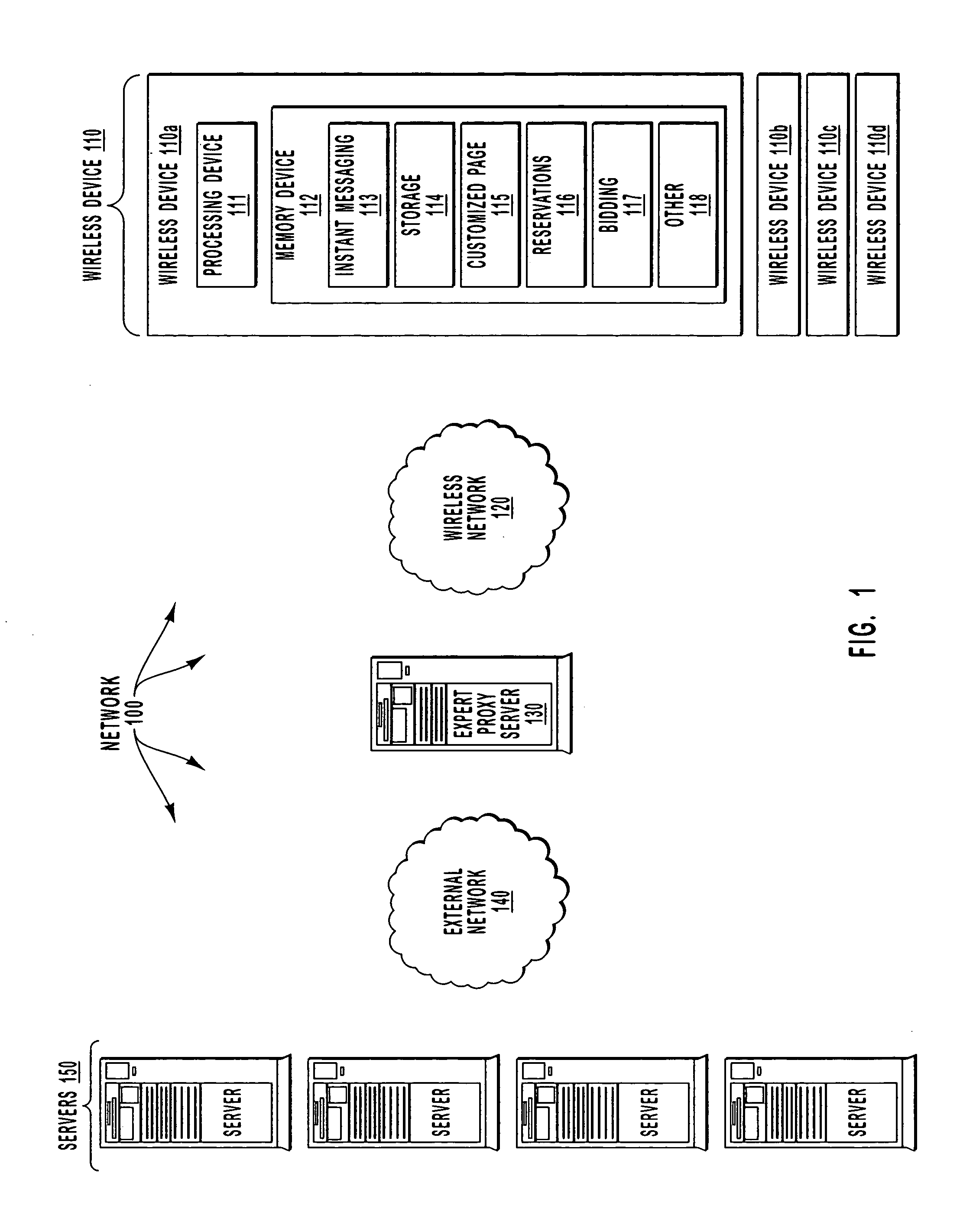
Using an expert proxy server as an agent for wireless devices
InactiveUS6895425B1Small bandwidthExtensive communicationNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationHigh bandwidthThe Internet
An expert proxy server is described that is coupled to a number of wireless devices through a wireless network, and to a number of server computer systems through an external network such as, for example, the Internet. The expert proxy server acts as an agent for a wireless device by providing a service for the wireless device. Specifically, the expert proxy server determines that a service is to be provided to the wireless device. Next, the expert proxy server identifies an application that provides the service and then communicates with the identified application that provides the service. The expert proxy server compiles the results of the communication with the application and then transmits the compilation to the wireless device over the wireless network. Thus, the relatively smaller bandwidth of the wireless network is preserved by transmitting a minimal amount of information over the wireless network while leaving more extensive communications to occur over higher bandwidth external networks. Also, since the extensive processing occurs at the expert proxy server rather than at the wireless device, the application on the wireless device may be simplified and smaller as compared to the supporting applications on the expert proxy server thereby preserving the limited memory and processing capability of the wireless device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Use of separate control channel to mitigate interference problems in wireless networking
InactiveUS7440728B2Small bandwidthAvoids and reduces problemData switching by path configurationRadio transmissionControl dataInterference problem
Described is a system and method for transporting interference-related control data and other information between nodes in a wireless network, using a control channel that is distinct from a content channel used to transport content. The control channel may be a different channel in the same unlicensed band as the content channel, a channel in a different unlicensed band, or a channel in a licensed band, and thereby not subject to the same interference-related problems that the unlicensed content channel may experience. As a result, management information for adjusting the content channel's communication parameters may still be communicated between the nodes, whereby mitigation actions may occur. For example, the content channel may be changed to another frequency, compression may be implemented or varied, and / or the data transfer rate may be varied. The control data can also be used to change the control channel's communication parameters.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
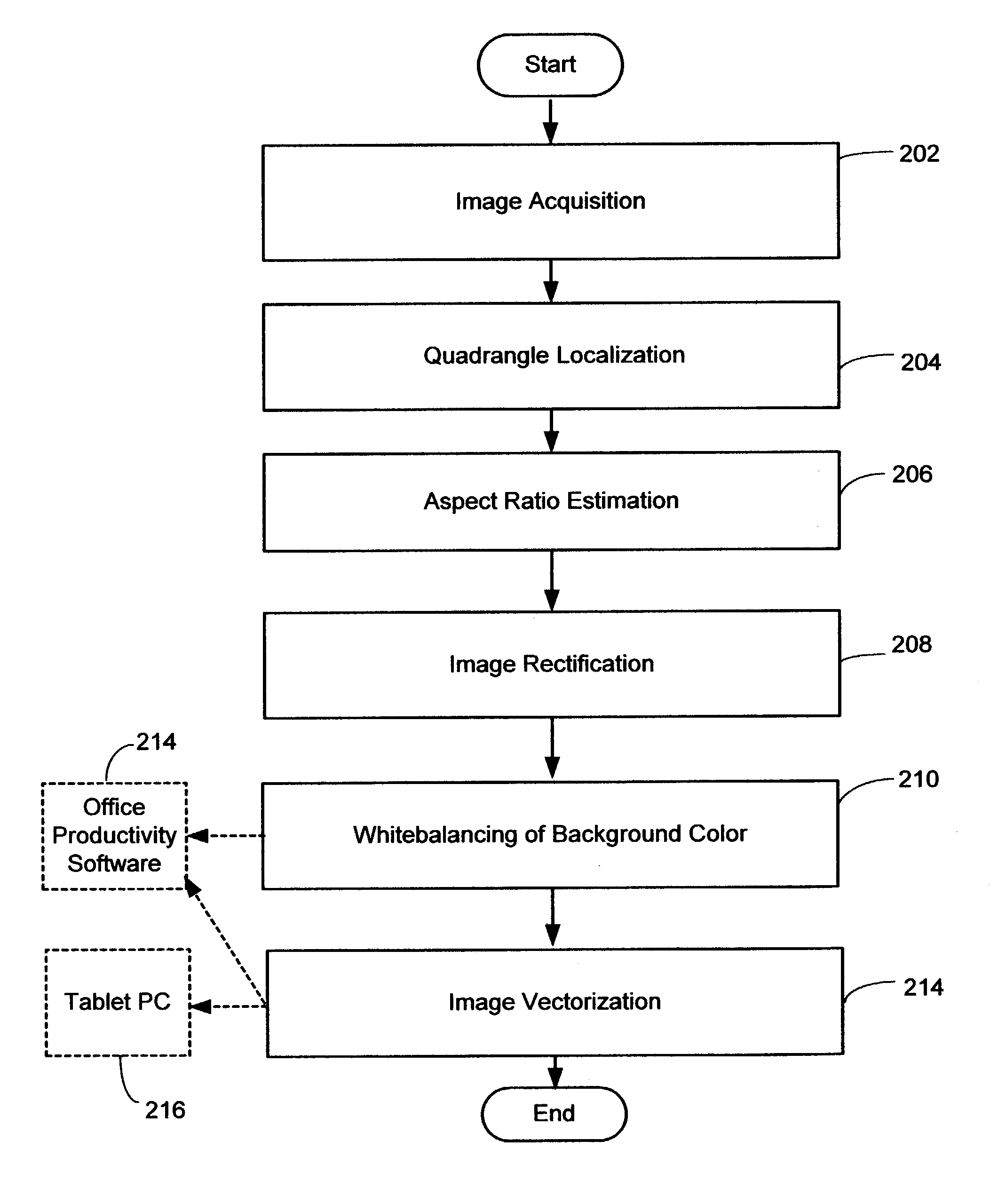
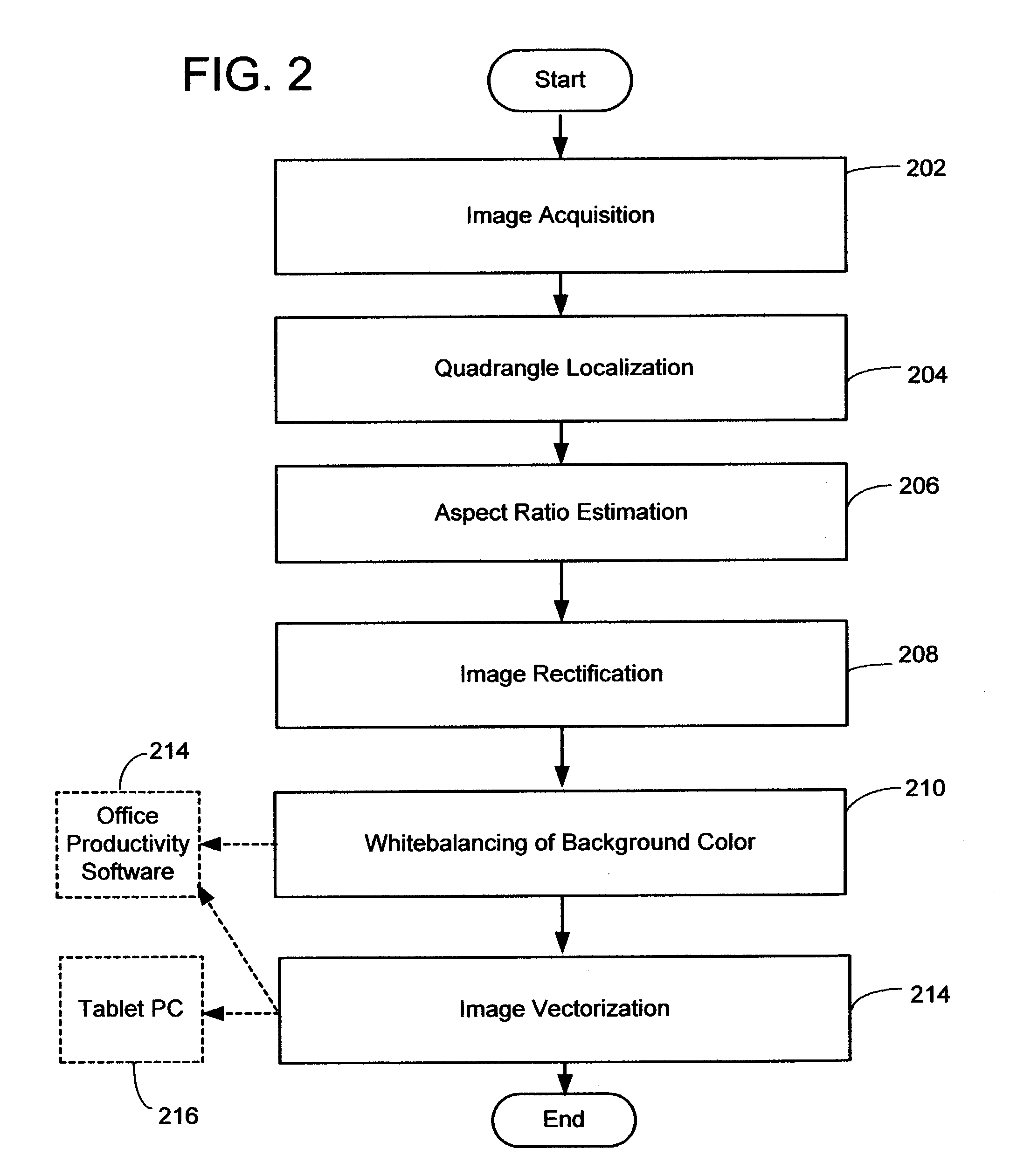
System and method for converting whiteboard content into an electronic document
ActiveUS7171056B2Improve legibilityGuaranteed economic efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisElectronic documentWhiteboard
A system and method of converting the content of a regular whiteboard into an electronic document. This system and method provides an effective, economical and easy to use way to convert whiteboard content as an enhanced and easily editable electronic document though the use of a still or video camera. It uses a series of image processing steps to clip borders, rectify the whiteboard image and correct colors.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Location, identification and telemetry system using strobed signals at predetermined intervals
InactiveUS6222440B1Save powerAvailable bandwidthElectric signal transmission systemsDirection finders using radio wavesEngineeringWireless transmitter
A tracking system is implemented according to the invention in which the identification data of a wireless transmitter is divided into multiple bursts. Instead of transmitting the entire identification in a single burst, the identification is split among bursts, so that it takes a period of time to uniquely identify a particular transmitter. However, the time between bursts falls under tight tolerance, so once a transmitter is identified, it can be further identified based on when it transmits as opposed to what it transmits. In this way, high tractability can be maintained without repeatedly transmitting the entire identification code of the transmitter.
Owner:FRESHLOC TECH
Interactive video
InactiveUS20060206581A1Quality improvementEasy to control dataMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsVideo playerUser device
An interactive video platform, interactive video player and computer implemented methods are described, for providing interactive video on a user device, such as a mobile phone. An item of video content to be displayed is identified and a control file associated with the item of video content is determined. A control command is received from the user device while the video content is being displayed. The control file is read to determine an action to be carried out based on the control command received and the action is carried out. The action can control the item of video content being displayed and / or can cause user interface entities to be displayed allowing the user to interact with the displayed video.
Owner:VEMOTION
Use of separate control channel to mitigate interference problems in wireless networking
InactiveUS20060121854A1Small bandwidthAvoid and reduce communication problemData switching by path configurationRadio transmissionInterference problemControl data
Described is a system and method for transporting interference-related control data and other information between nodes in a wireless network, using a control channel that is distinct from a content channel used to transport content. The control channel may be a different channel in the same unlicensed band as the content channel, a channel in a different unlicensed band, or a channel in a licensed band, and thereby not subject to the same interference-related problems that the unlicensed content channel may experience. As a result, management information for adjusting the content channel's communication parameters may still be communicated between the nodes, whereby mitigation actions may occur. For example, the content channel may be changed to another frequency, compression may be implemented or varied, and / or the data transfer rate may be varied. The control data can also be used to change the control channel's communication parameters.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multiband antenna system and methods
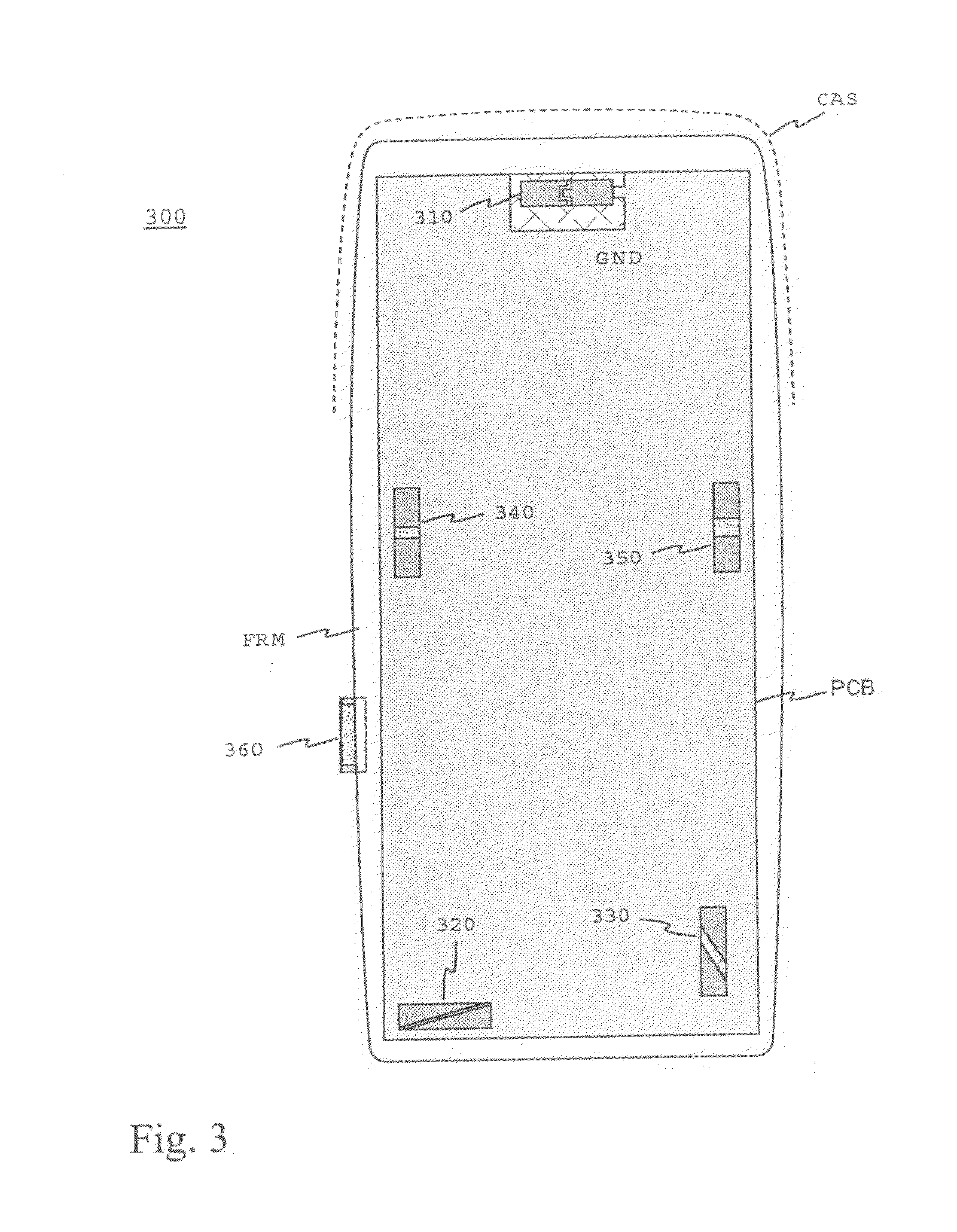
InactiveUS20080303729A1Improve matchConvenient ArrangementSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsRadio equipmentEngineering
An antenna system internal to a radio device, the system comprising separate antennas and having separate operating bands. The system is implemented as decentralized in a way that each antenna is typically based on a small-sized chip component (310; 320; 330; 340; 350; 360; 610), which are located at suitable places on the circuit board (PCB) and possibly on also another internal surface in the device. The chip component comprises a ceramic substrate and at least one radiating element. The operating band of an individual antenna covers e.g. the frequency range used by a radio system or only the transmitting or receiving band in that range. At least one antenna is connected to an adjusting circuit with a switch, by which the antenna's operating band can be displaced in a desired way. In this case the operating band covers at a time a part of the frequency range used by one or two radio systems. The antennas can be made small-sized, because a relatively small bandwidth is sufficient for an individual antenna, when there is a plurality of antennas. When the bandwidth is small, a material with higher permittivity can be chosen for the antenna than for an antenna having a wider band, in which case the antenna dimensions can be made correspondingly smaller. In addition, a good matching of the antenna is achieved on the whole width of each radio system, because the matching of a separate antenna having a relatively narrow band is easier to arrange than that of a combined multiband antenna.
Owner:CANTOR FITZGERALD SECURITIES
Teleconferencing arrangement
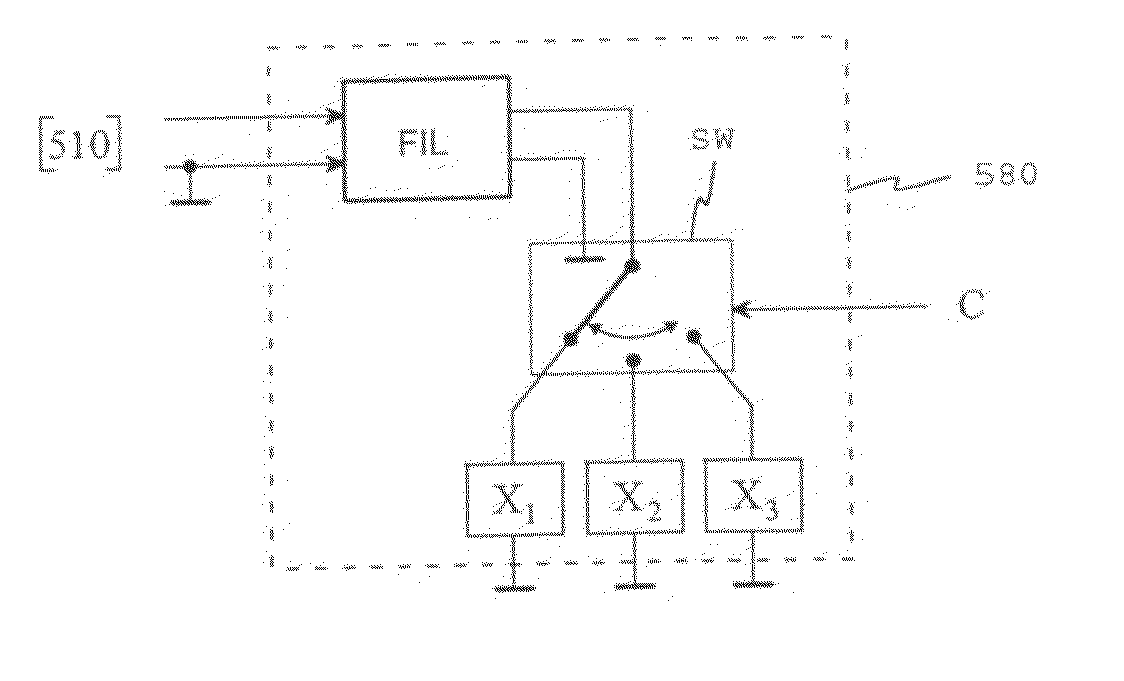
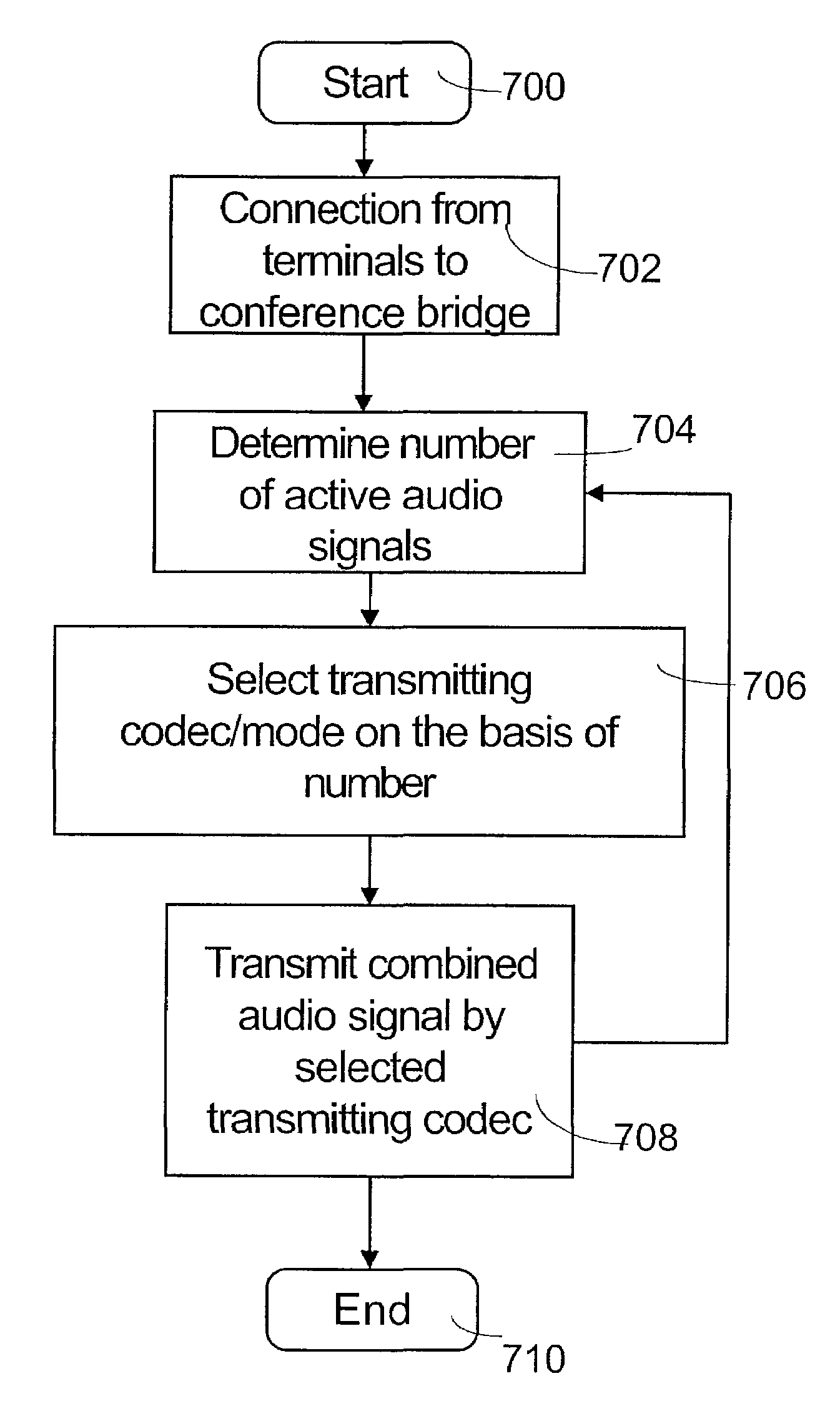
InactiveUS7420935B2Improve sound qualitySmall bandwidthSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsConference callAudio signal flow
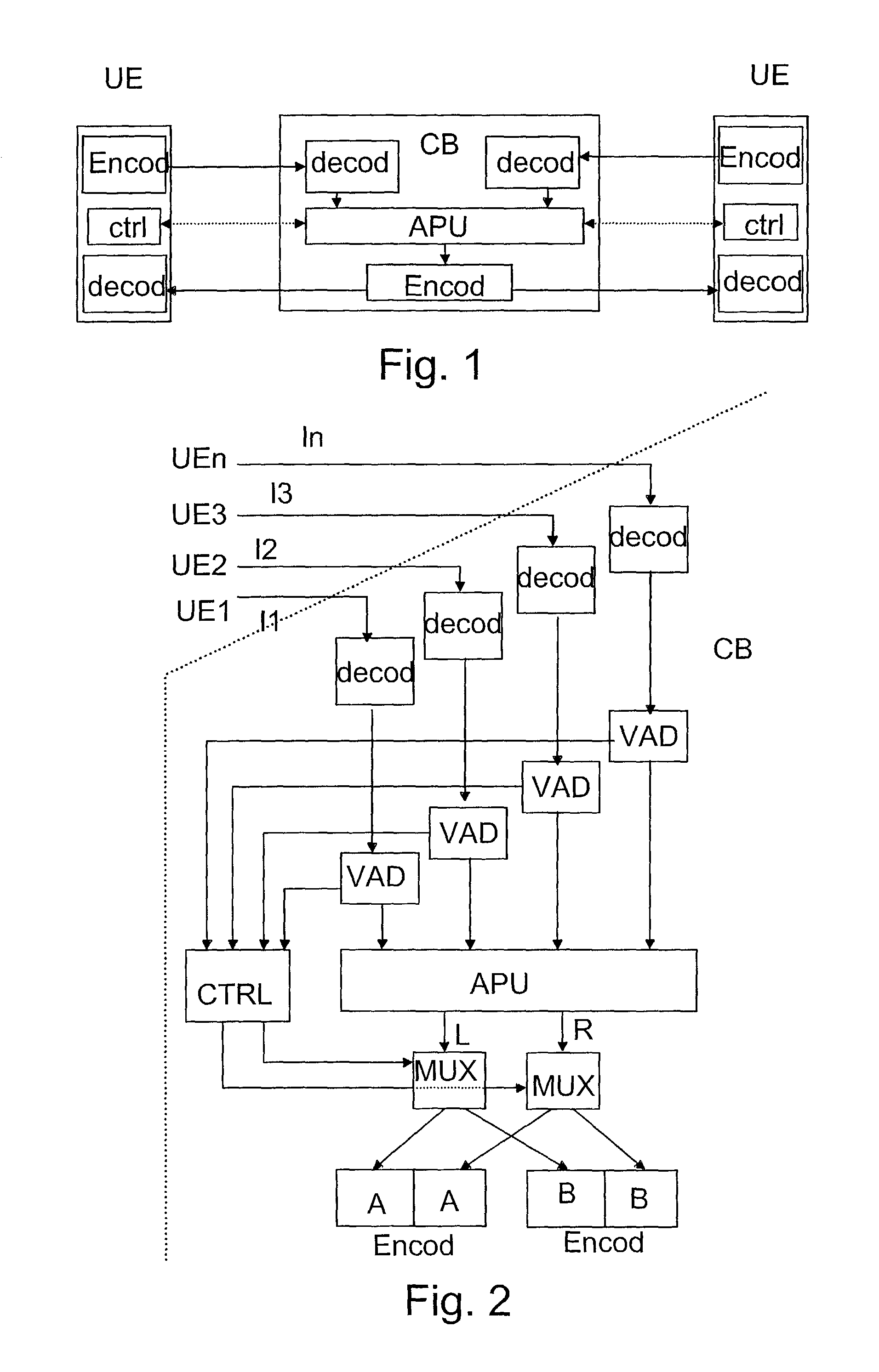
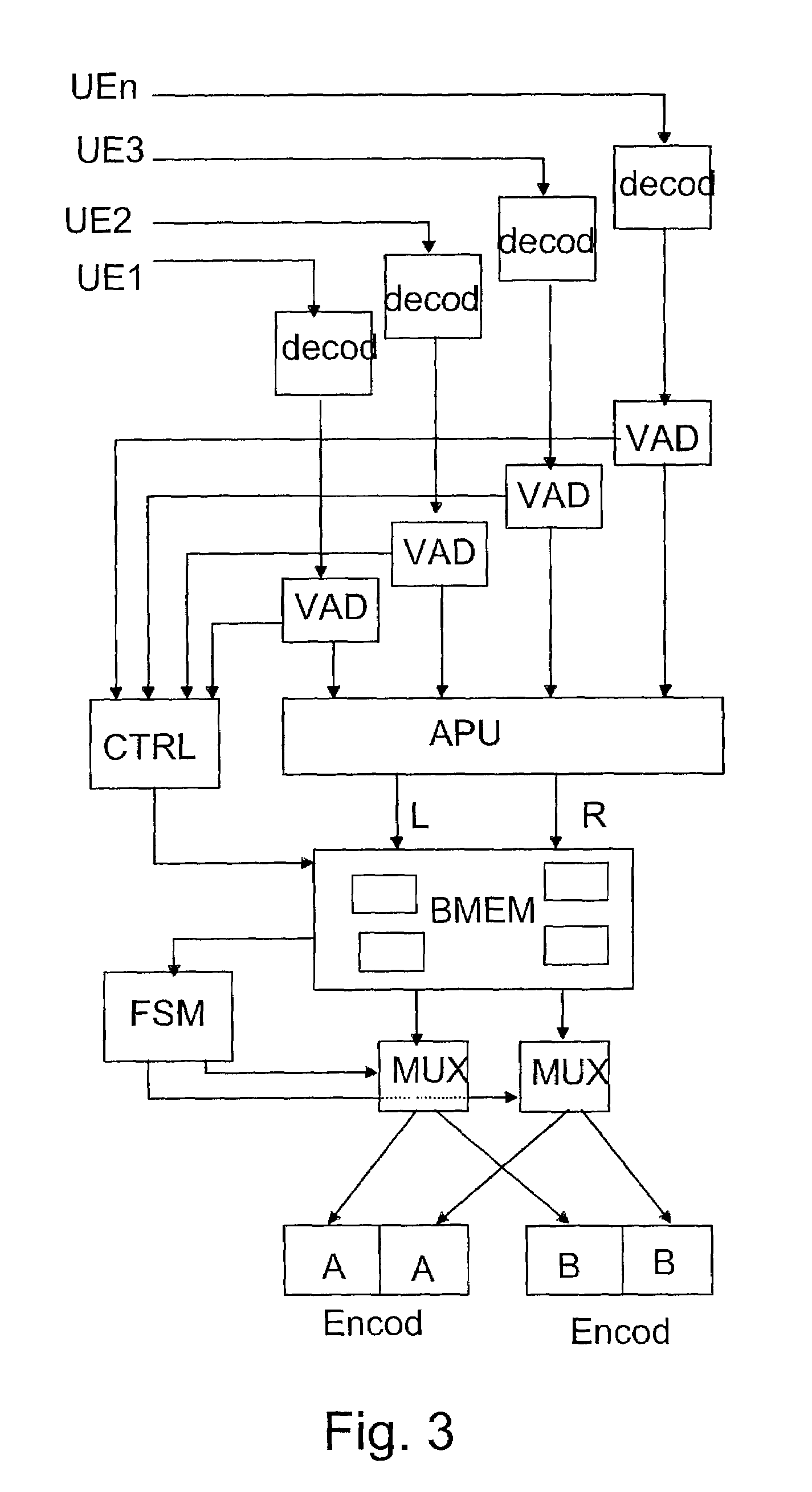
A method and an apparatus for controlling a conference call is a system which comprises a conference bridge for combining several audio signals arriving from terminals and for transmitting the combined signal further to at least one of the terminals using at least one transmitting codec. The conference bridge comprises a spatialization unit for creating a spatial effect. The number of simultaneously active audio components, such as speech signals, is determined from the audio signals of the conference bridge inputs. At least one transmitting codec is selected for use on the basis of the number of simultaneously active audio components and the combined signal is transmitted to at least one terminal using the selected transmitting codec.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and supply line structure for transmitting data between electrical automotive components
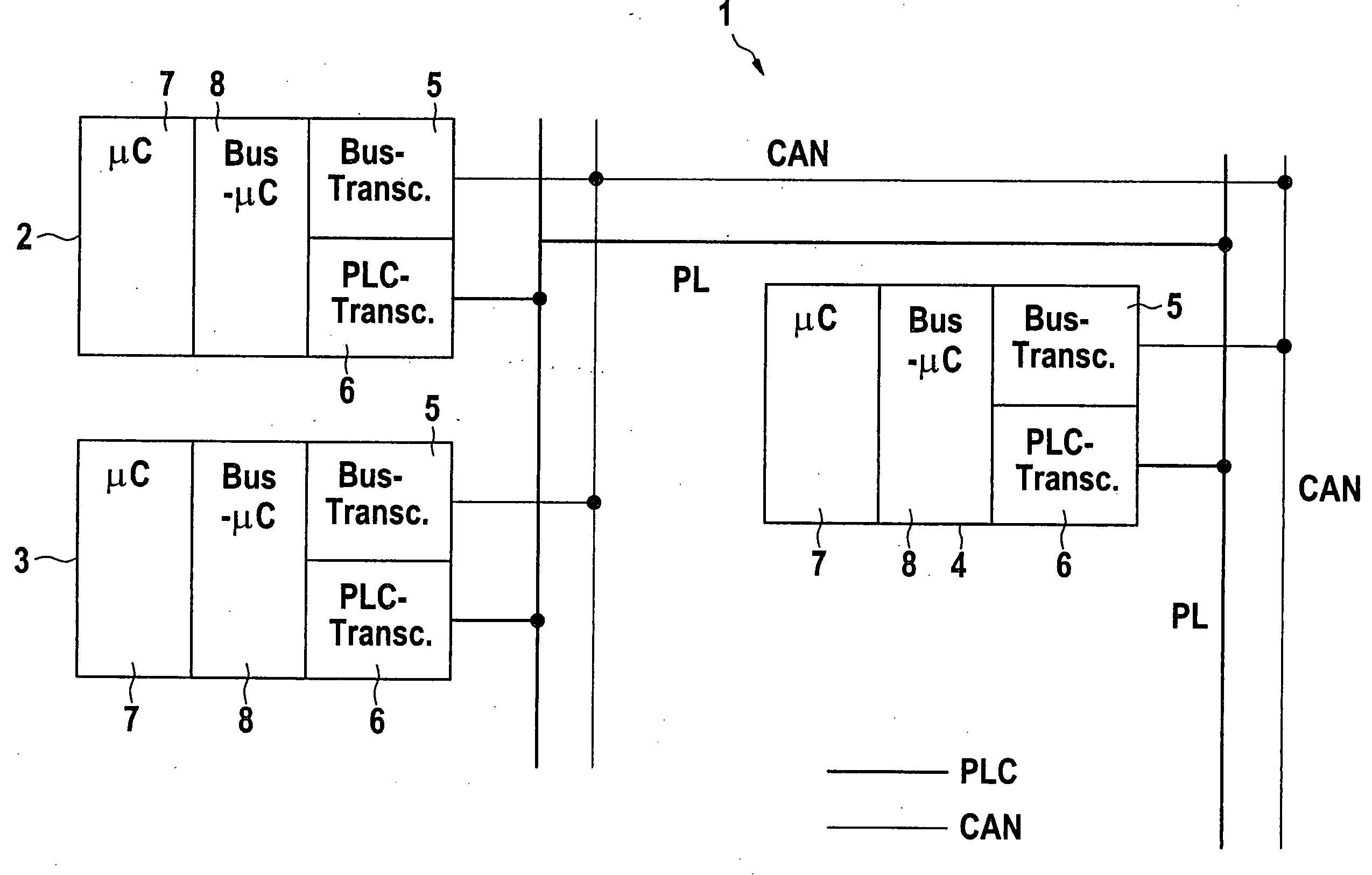
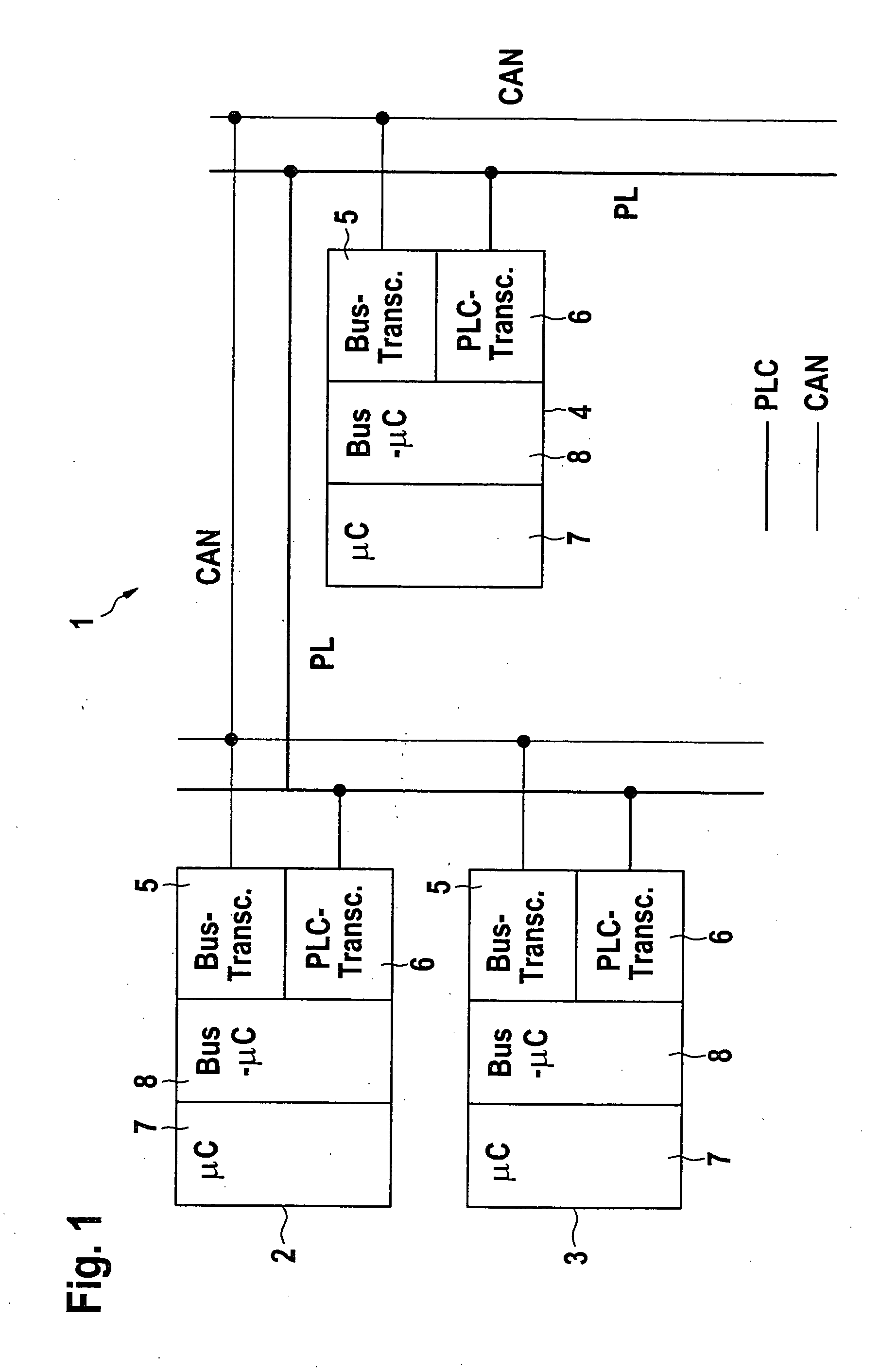
InactiveUS20050040709A1Add featureLow costElectric signal transmission systemsError preventionMobile vehicleEngineering
A method and a supply line structure for transmitting information between electrical components in a motor vehicle is described. The information is transmitted over a data bus. At least some of the components are powered via a supply line structure. To make the transmission of information between the components fail-safe, the information is also transmitted over the supply line structure in addition to over the data bus at least after a failure of the data bus.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
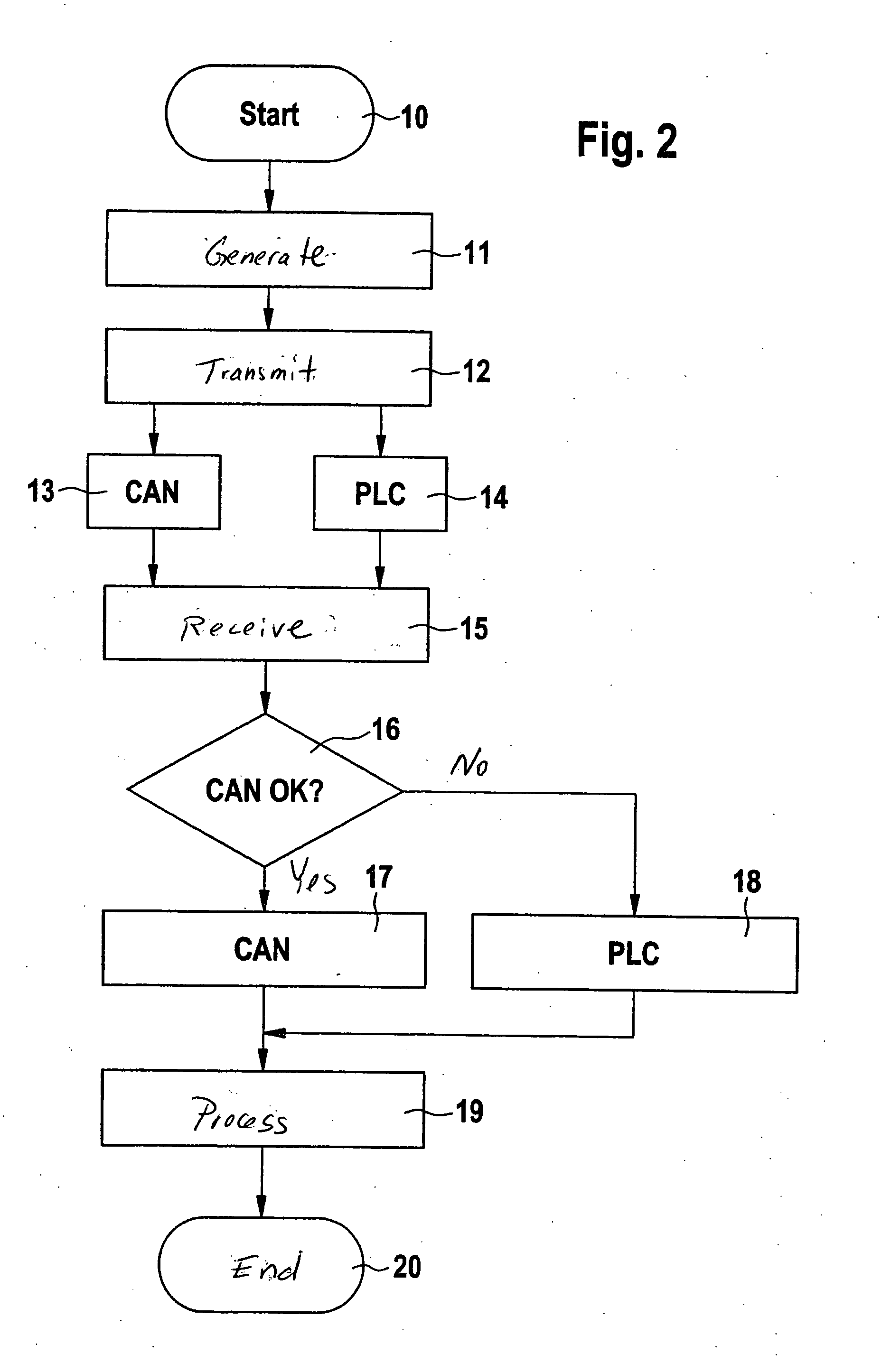
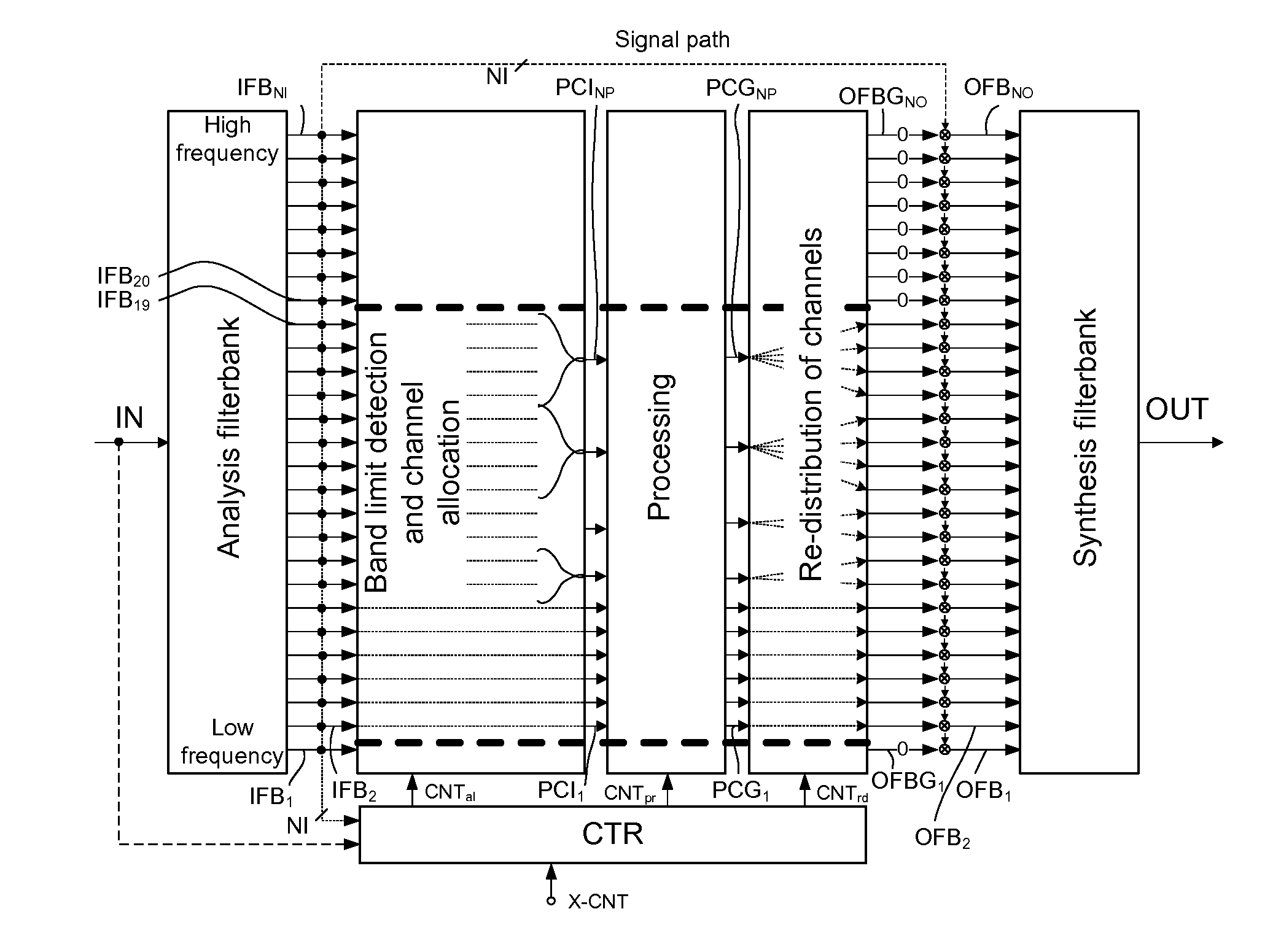
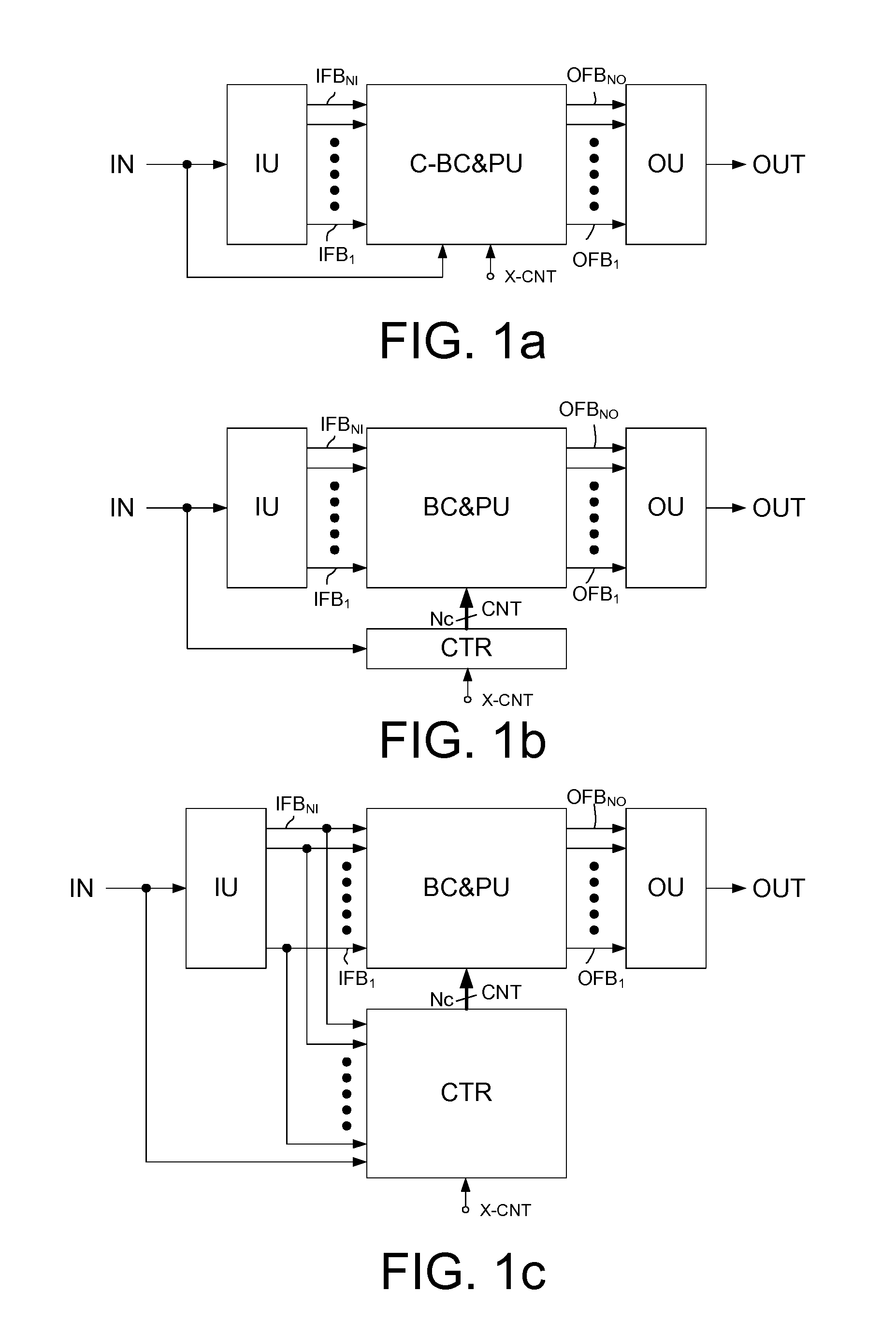
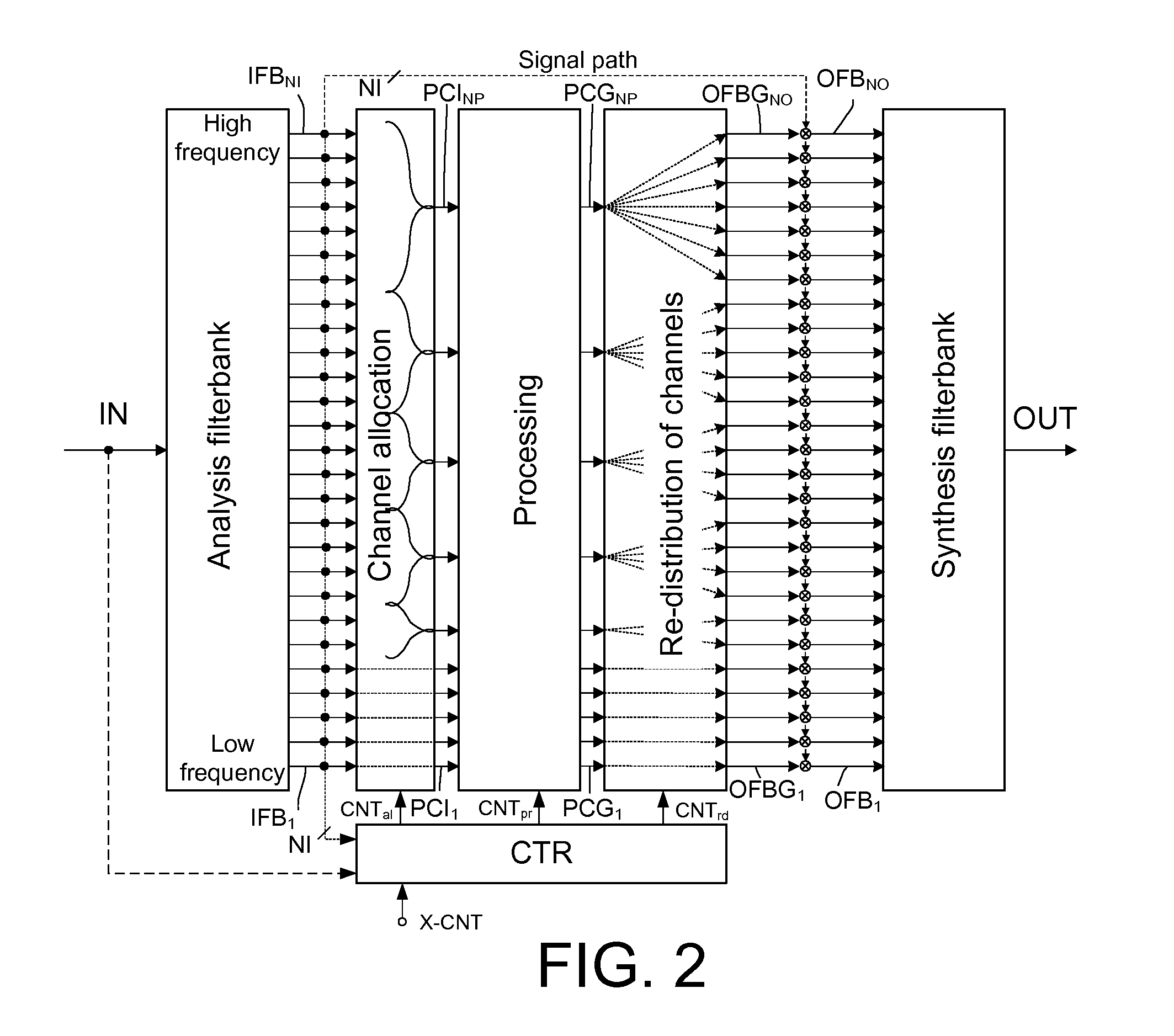
Audio processing device, system, use and method
ActiveUS20120243715A1Attenuation bandwidthMaintain bandwidthSignal processingHearing device energy consumption reductionTime domainComputer science
An audio processing device includes a) an input unit for converting a time domain input signal to a number NI of input frequency bands and b) an output unit for converting a number NO of output frequency bands to a time domain output signal. A signal processing unit processes the input signal in a number NP of processing channels, smaller than the number NI of input frequency bands. A frequency band allocation unit allocates input frequency bands to processing channels. A frequency band redistribution unit redistributes processing channels to output frequency bands, and a control unit dynamically controls the allocation of input frequency bands to processing channels and the redistribution of processing channels to output frequency bands.
Owner:OTICON
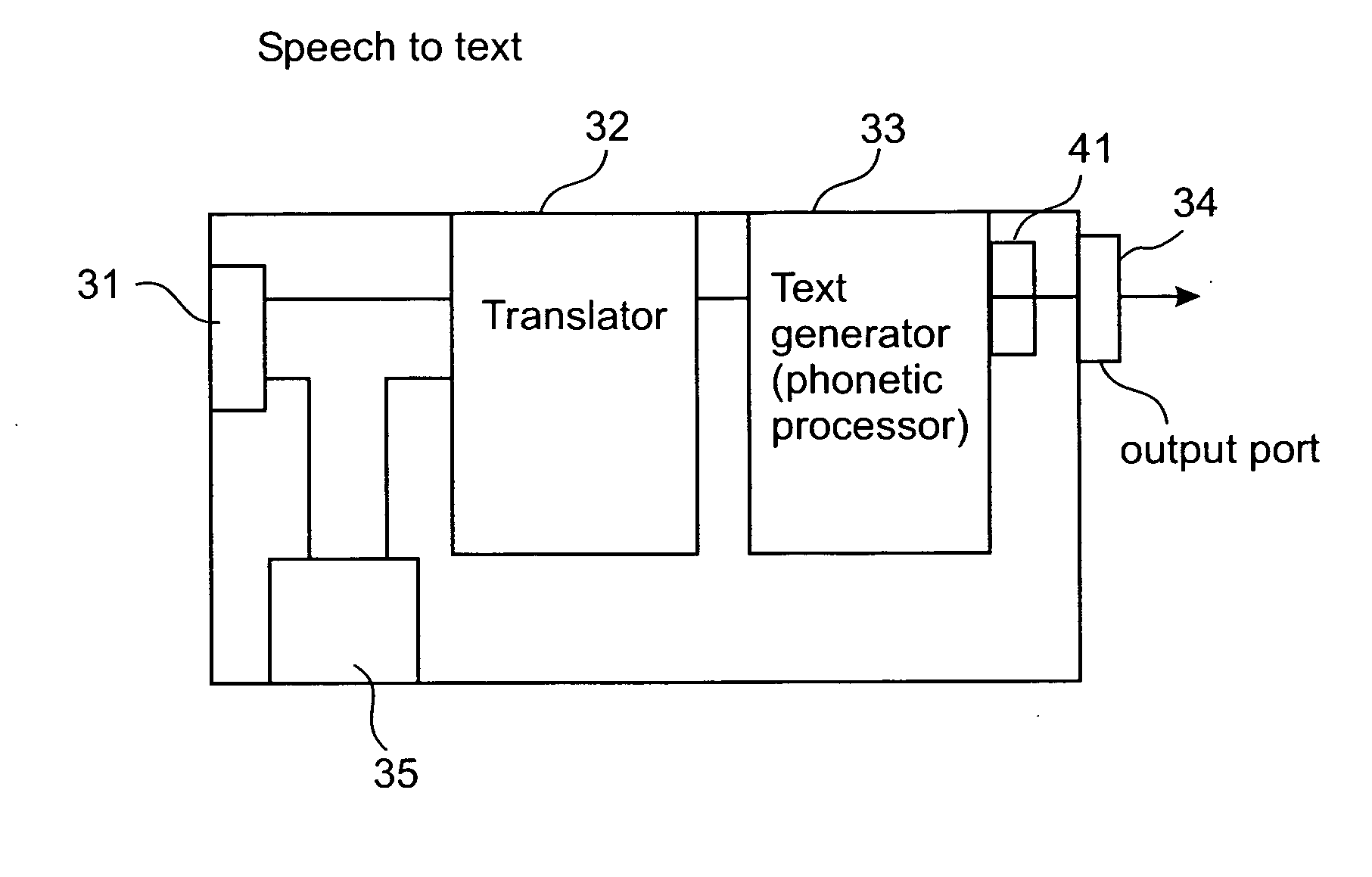
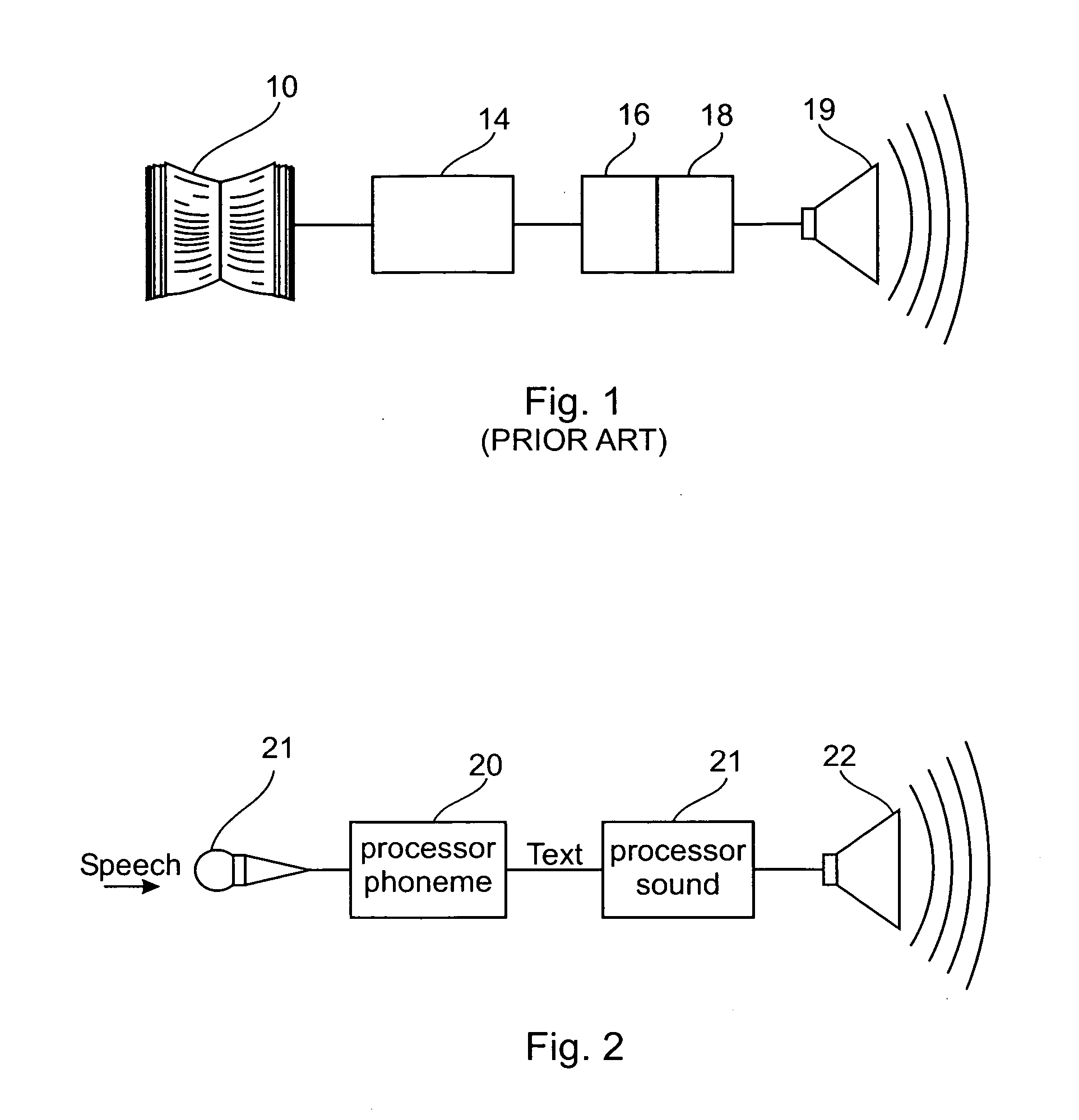
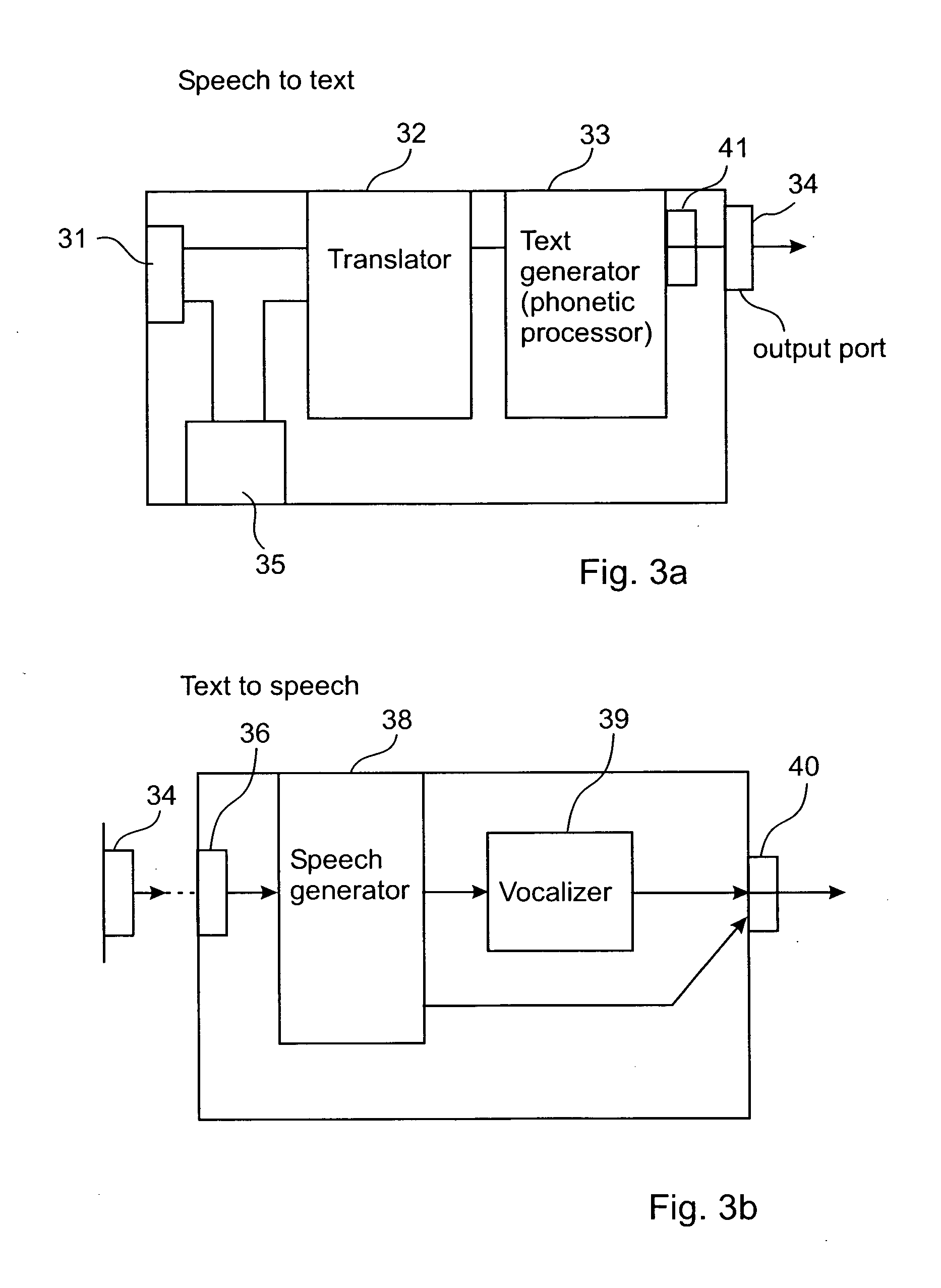
Phonetic speech-to-text-to-speech system and method
InactiveUS20070088547A1Small bandwidthSpeech recognitionSpeech synthesisCommunications systemVoice transformation
A speech-to-text-to-speech for use with on-line and real time transmission of speech with a small bandwidth from a source to a destination. A speech is received and broken down to speechlets, which are encoded into series of symbols compatible with communication systems and other than a known symbolic representation of the speech in a known language for being transmitted through communication networks. When received, the series of symbols is decoded to restore the speechlets and for reconstituting a speech according to the speechlets prior to being communicated to a listening party.
Owner:TWISTED INNOVATIONS
Optical measuring device for determining temperature in a cryogenic environment and winding arrangement whose temperature can be monitored
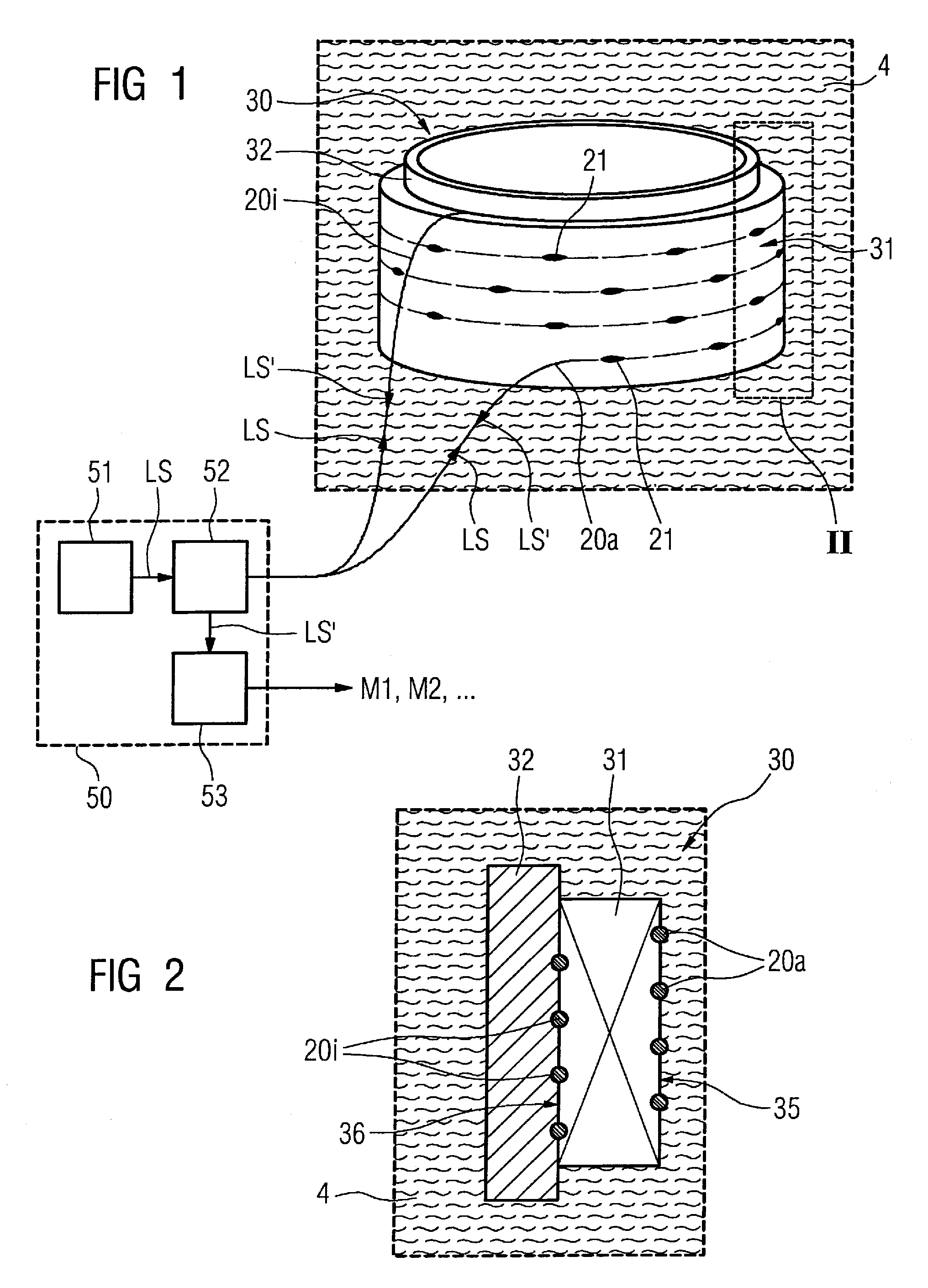
InactiveUS20090202194A1Used in environmentMinimizing heat capacityCryogenic temperature measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesGratingElectrical conductor
An optical measuring device for determining temperature in a cryogenic environment includes at least one optical waveguide provided with at least one fiber Bragg grating sensor that is interrogated by a light signal. The device includes a light injector that injects light into the at least one fiber Bragg grating sensor, and an evaluation unit that determines a temperature value from the modulated light signal emanating from the at least one fiber Bragg grating sensor. The device includes at least one jacket that non-rigidly encloses the optical waveguide, at least in the region of the at least one fiber Bragg grating sensor. The jacket has a larger coefficient of thermal expansion, at least at cryogenic temperatures, than the optical waveguide. A winding arrangement for use in a cryogenic environment is provided with such a device for temperature monitoring of a conductor of the winding arrangement.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Multi-Frequency Band Receiver
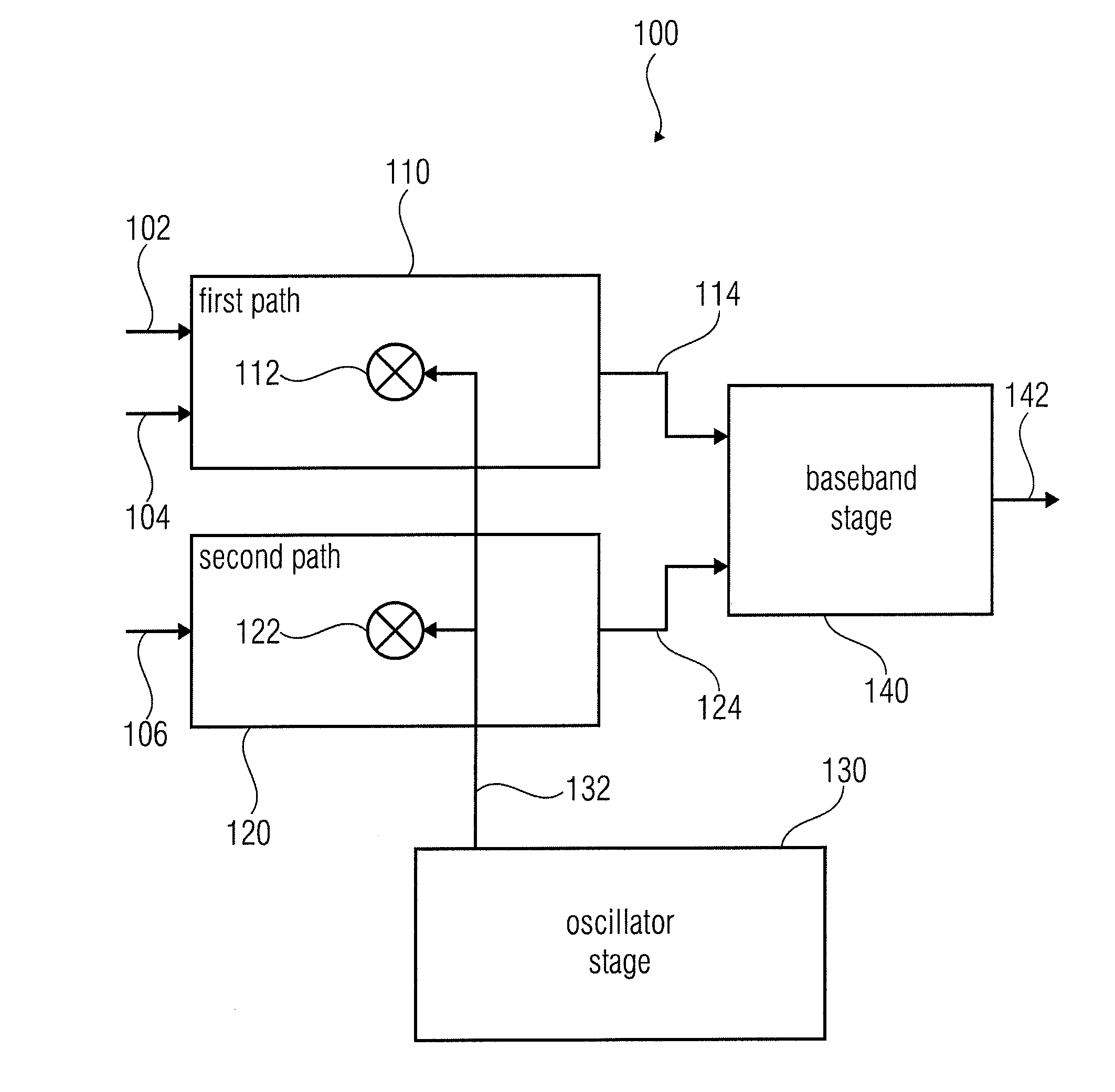
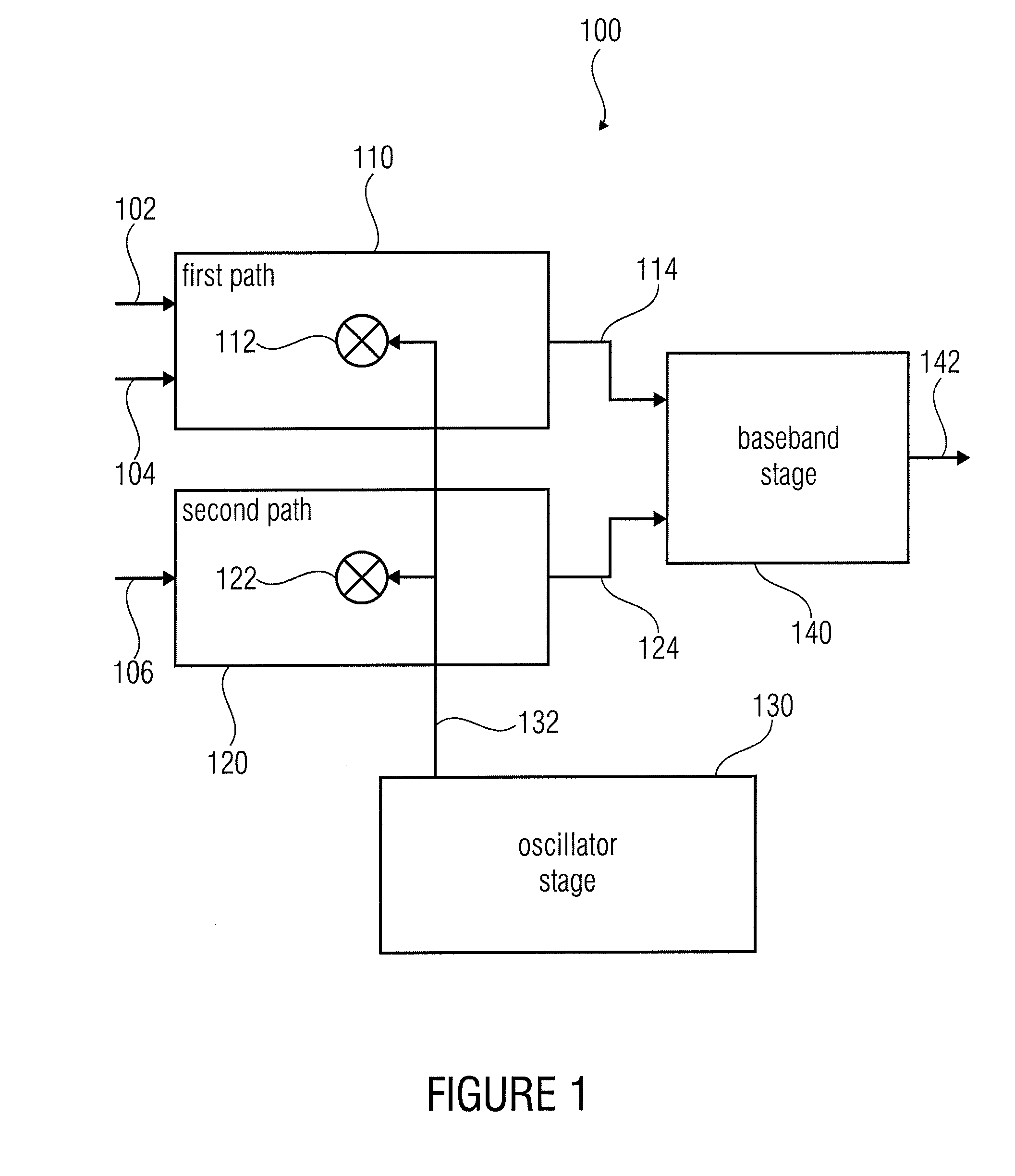
InactiveUS20110128999A1Total current dropReduce consumptionModulated-carrier systemsPosition fixationLocal oscillator signalCenter frequency
A multi-frequency band receiver has a first path configured to process first and second frequency bands, and a second path configured to process a third frequency band, the first and second frequency bands having a smaller distance than the first and third frequency bands, and having a smaller distance than the second and third frequency bands. In addition, the multi-frequency band receiver has an oscillator stage for providing a local oscillator signal having a frequency that is between the center frequencies of the first and second frequency bands, the first path having a mixer that may be supplied with the local oscillator signal, and the second path having a mixer that may also be supplied with the local oscillator signal. In addition, the multi-frequency band receiver has a baseband stage for processing output signals of the first and second paths so as to obtain a receive signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Techniques for binding scalable vector graphics to associated information
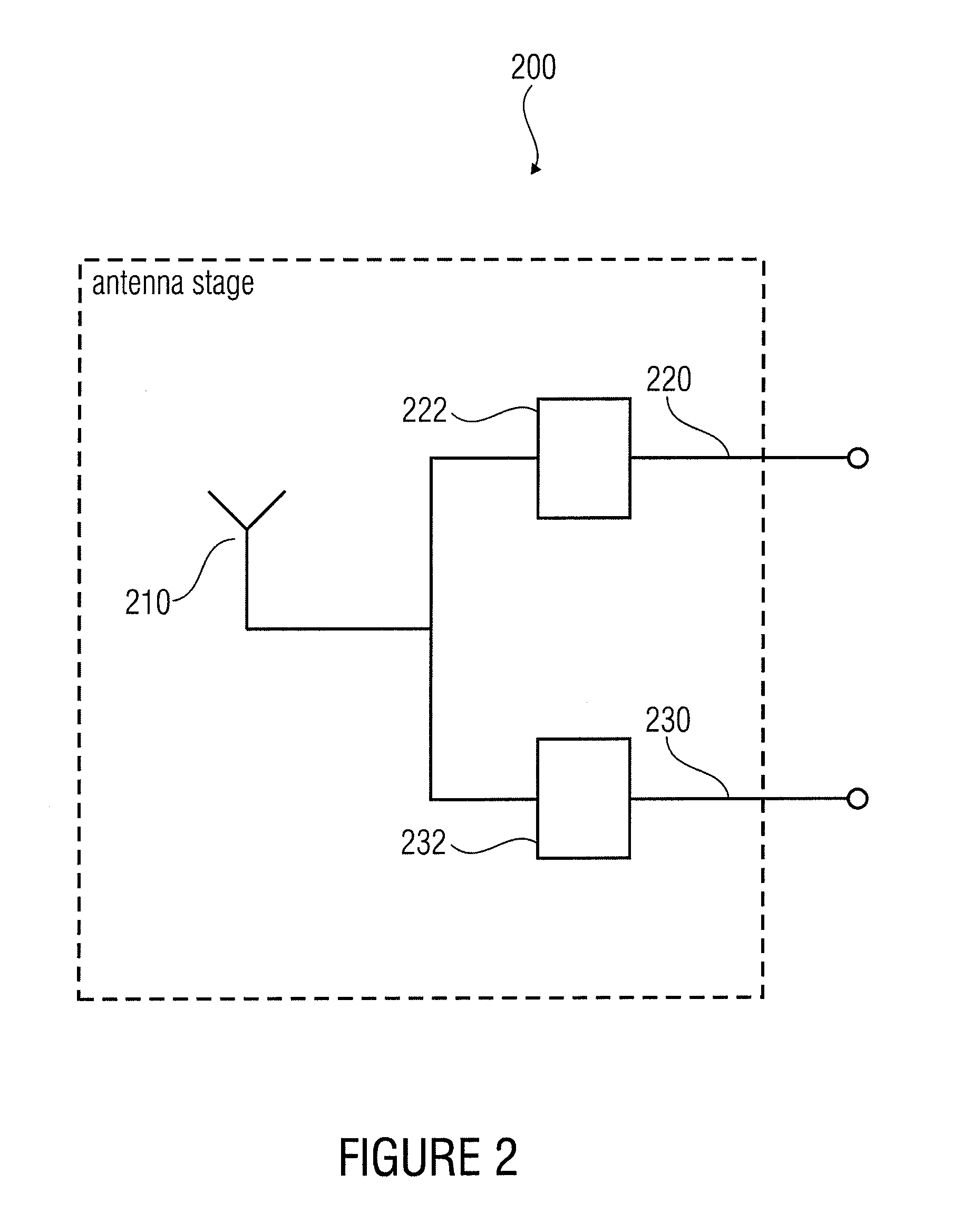
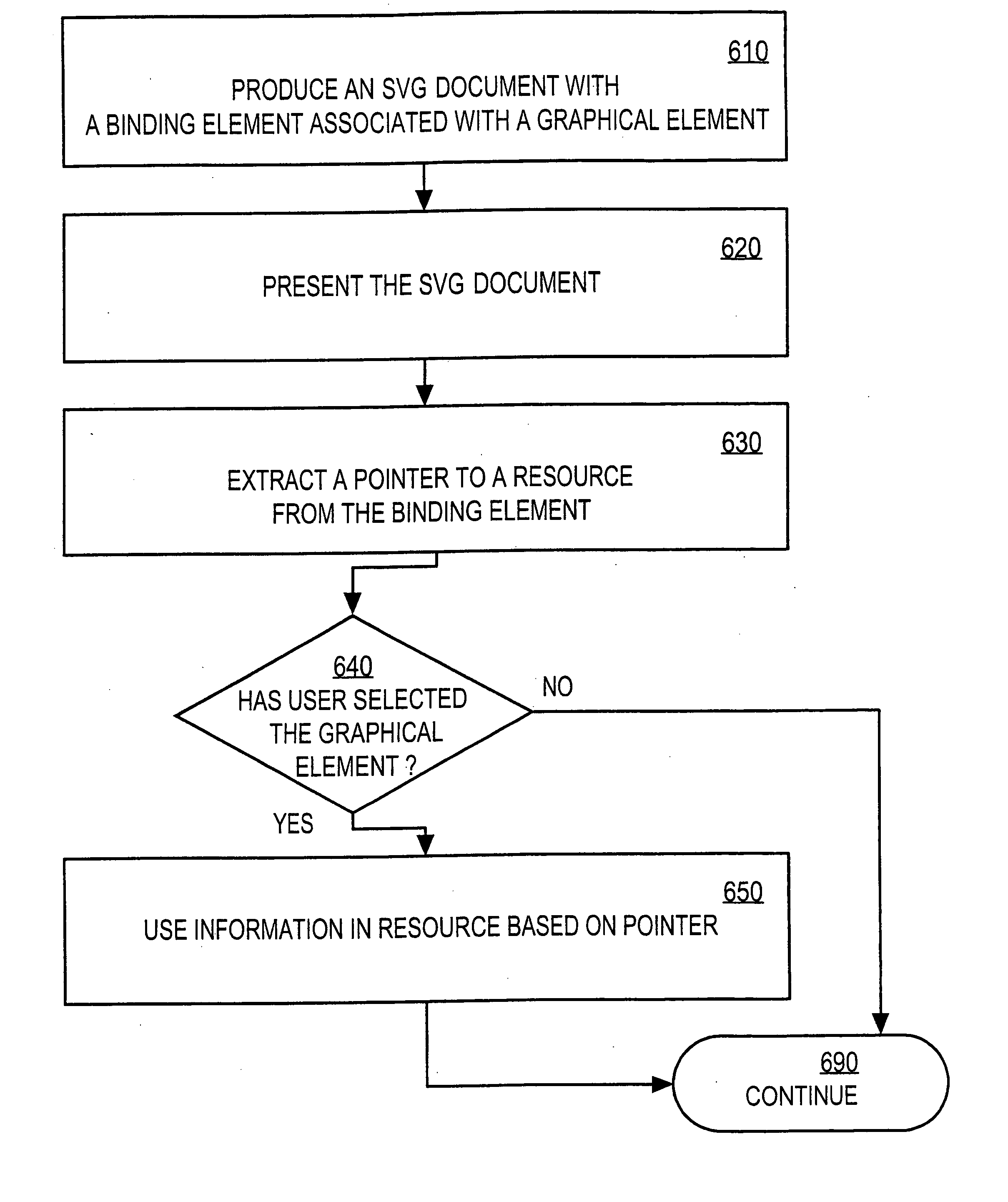
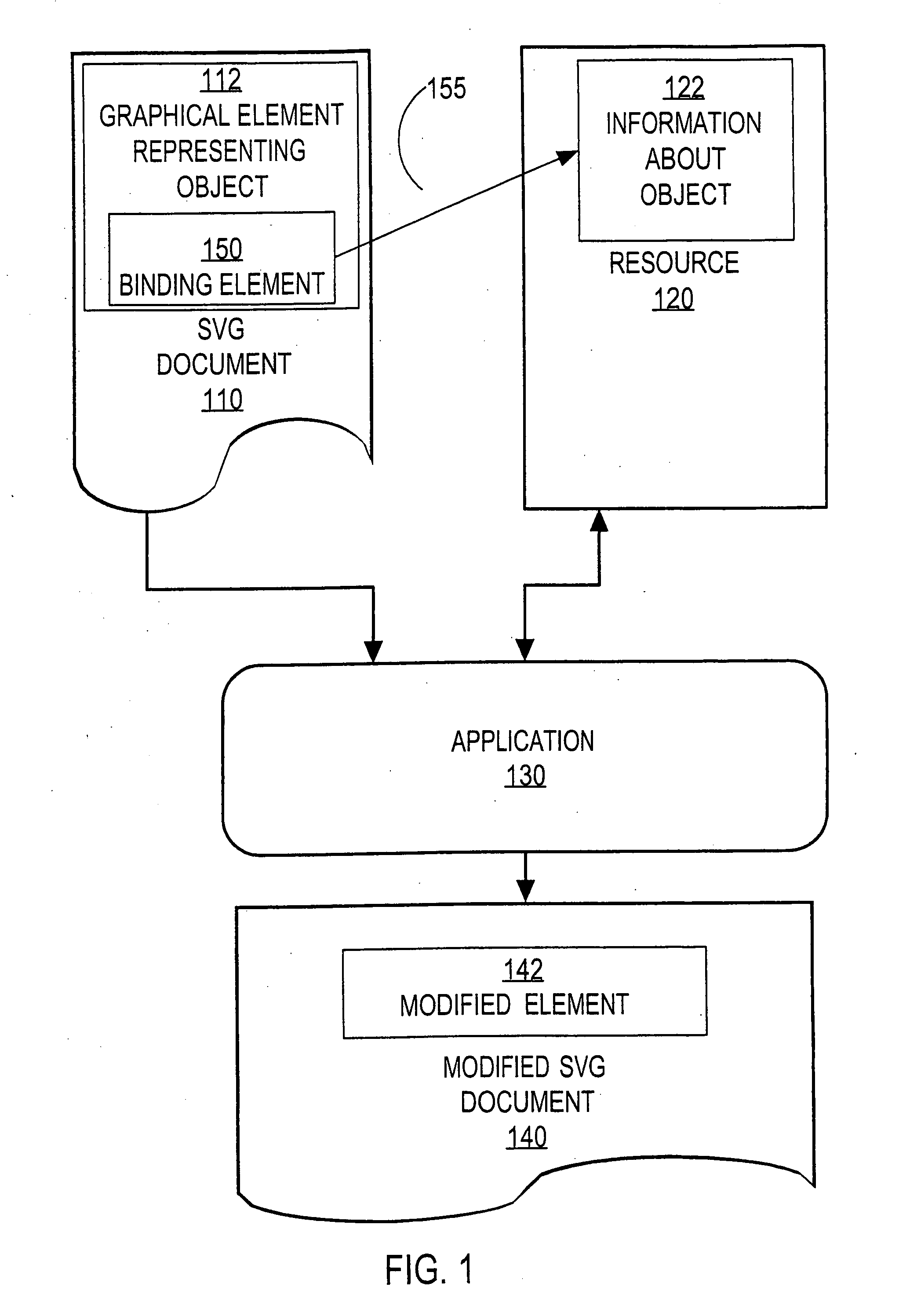
InactiveUS20070198918A1Small bandwidthSmall amount of calculationDigital computer detailsWebsite content managementGraphicsResource based
Techniques for providing information about an object through a graphical interface include providing in a document scalable vector graphics (SVG) statements associated with a graphical representation of the object. The SVG statements are bound to a pointer to a resource that includes information pertaining to the object. The pointer to the resource associated with the SVG statements may then be extracted from the document. Information is then retrieved from the resource based on the pointer. The SVG statements may then be modified based on the information. Then a second graphical representation of the object is presented based on the SVG statements after the modifying. The presentation provides information, or control, or both, for the object.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Unified cloud-based core network supporting multiple private cbrs networks of multiple operators with network slicing
ActiveUS20190166506A1Small bandwidthPoor latencyAccounting/billing servicesTelephonic communicationGPRS core networkTelecommunications network
A unified core network provides core network services to a number of telecommunications network operators. The unified core is partitioned into a number of slices with each slice being the core network for a network operator. Each network operator is then free to define services within its own partition to serve its own users. In this manner, the network operators are freed from building and maintaining a core network while simultaneously enjoying the benefit of having a core network.
Owner:NXGEN PARTNERS IP
Data broadcast method
InactiveUS7685618B1Function provideSmall bandwidthTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital dataCable television
A technique for broadcasting a broadcast data service together with broadcast digital television data as part of a broadcast signal, the broadcast data service comprising a plurality of data portions including data portions having digital data in non-real time. The technique comprising, during normal broadcasting, only broadcasting portions of the broadcast data service required to replace previous respective portions which have been changed and broadcasting television data of the broadcast data service as non-real time data.
Owner:SONY EUROPE BV
Active antenna array with modulator-based pre-distortion
ActiveUS8351543B2Low costSmall bandwidthPolarisation/directional diversityPower amplifiersSignal generatorPredistortion
An active antenna array comprises a plurality of transmission paths, a predistortion modulation signal generator, and a predistortion modulation signal distribution structure. At least two of the plurality of transmission paths comprise a predistortion modulator for modulating a transmission path signal with a predistortion modulation signal generated by the predistortion modulation signal generator and distributed by predistortion modulation signal distribution structure to the at least two of the plurality of transmission paths. A method for predistorting at least two of a plurality of transmission path signals in an active antenna array and computer program products for manufacture and method execution are also claimed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for arranging transmissions on a downlink carrier
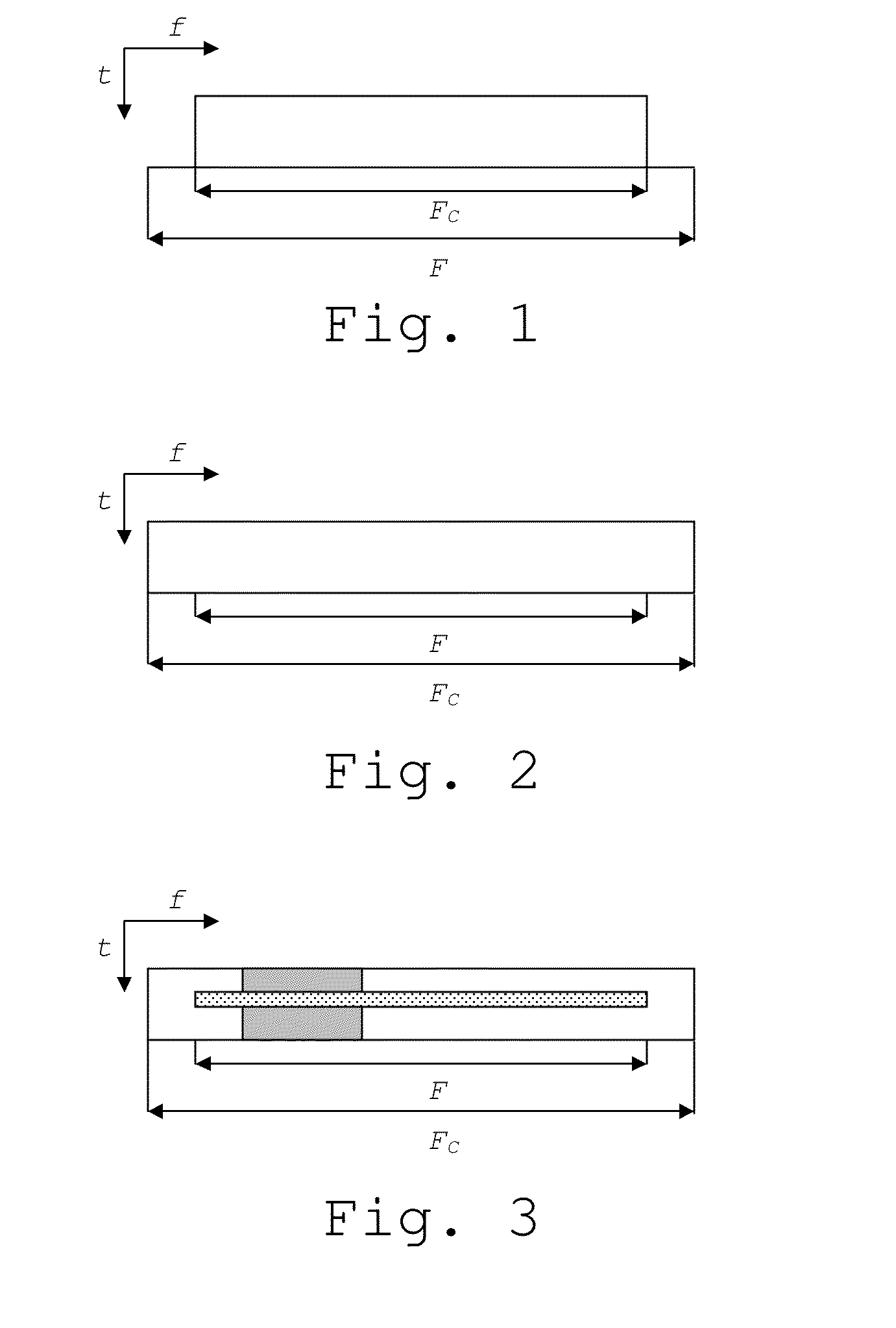
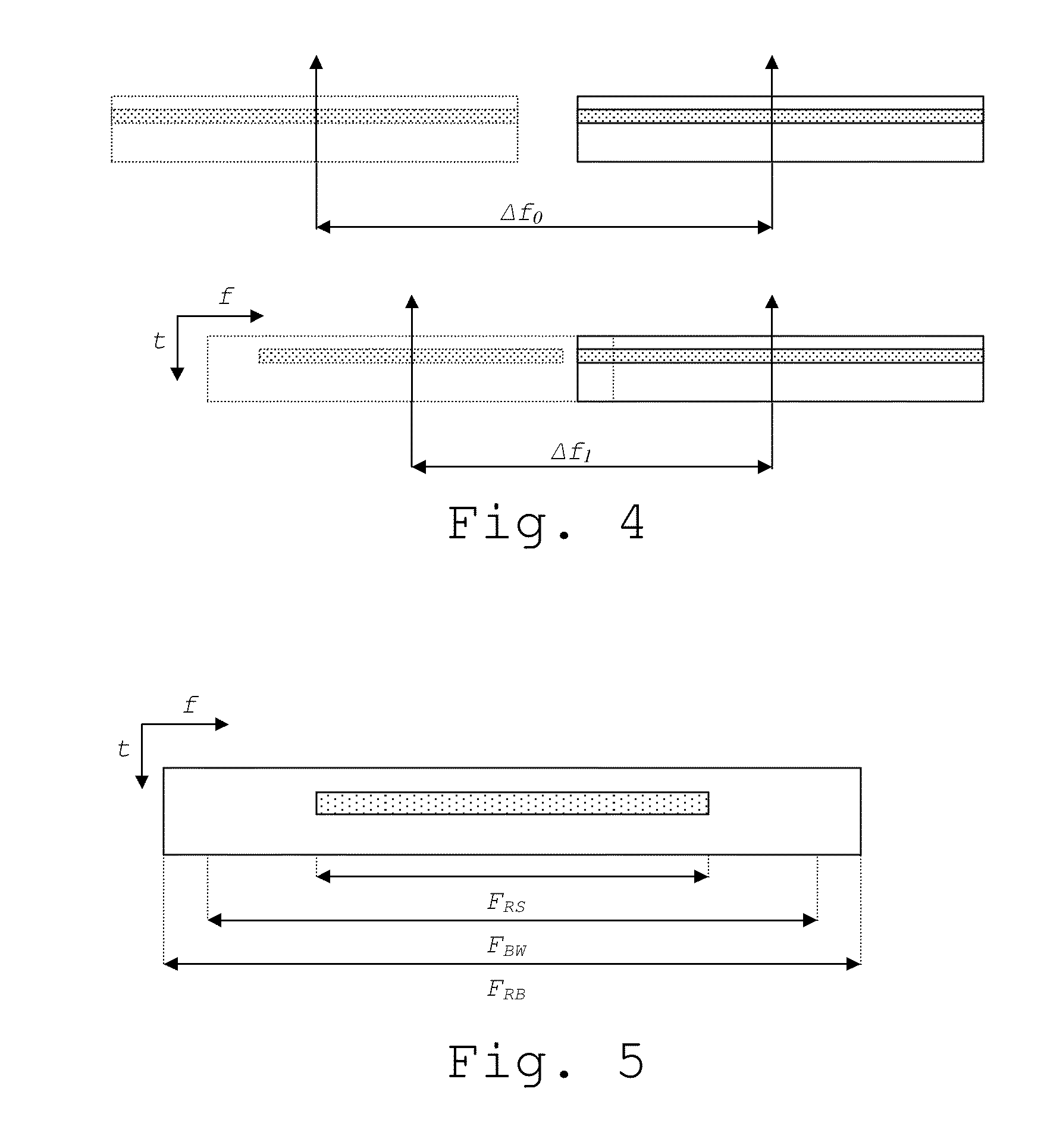
ActiveUS20140112303A1Maximize deploymentMaximize utilizationPilot signal allocationWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemCarrier signal
A method is provided for arranging transmissions on a downlink carrier c, spanning a frequency range Fc, in a mobile radio communications system, wherein a bandwidth of Fc belongs to a set of predefined channel bandwidths in the communications system, and wherein the carrier c comprises a reference signal defined in the communications system. A configurable frequency range FRS comprising a set of time-frequency resources for comprising the reference signal of the carrier c is provided. Information associated with the configuration of said frequency range FRS is signaled to a receiver in the communications system, such that c can be deployed over a frequency range F smaller than Fc when the frequency range FRS is configured within F and any other transmissions on the carrier c are arranged to be within F.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Using an expert proxy server as an agent for wireless devices
InactiveUS20050160140A1Small bandwidthExtensive communicationNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationHigh bandwidthThe Internet
An expert proxy server is described that is coupled to a number of wireless devices through a wireless network, and to a number of server computer systems through an external network such as, for example, the Internet. The expert proxy server acts as an agent for a wireless device by providing a service for the wireless device. Specifically, the expert proxy server determines that a service is to be provided to the wireless device. Next, the expert proxy server identifies an application that provides the service and then communicates with the identified application that provides the service. The expert proxy server compiles the results of the communication with the application and then transmits the compilation to the wireless device over the wireless network. Thus, the relatively smaller bandwidth of the wireless network is preserved by transmitting a minimal amount of information over the wireless network while leaving more extensive communications to occur over higher bandwidth external networks. Also, since the extensive processing occurs at the expert proxy server rather than at the wireless device, the application on the wireless device may be simplified and smaller as compared to the supporting applications on the expert proxy server thereby preserving the limited memory and processing capability of the wireless device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
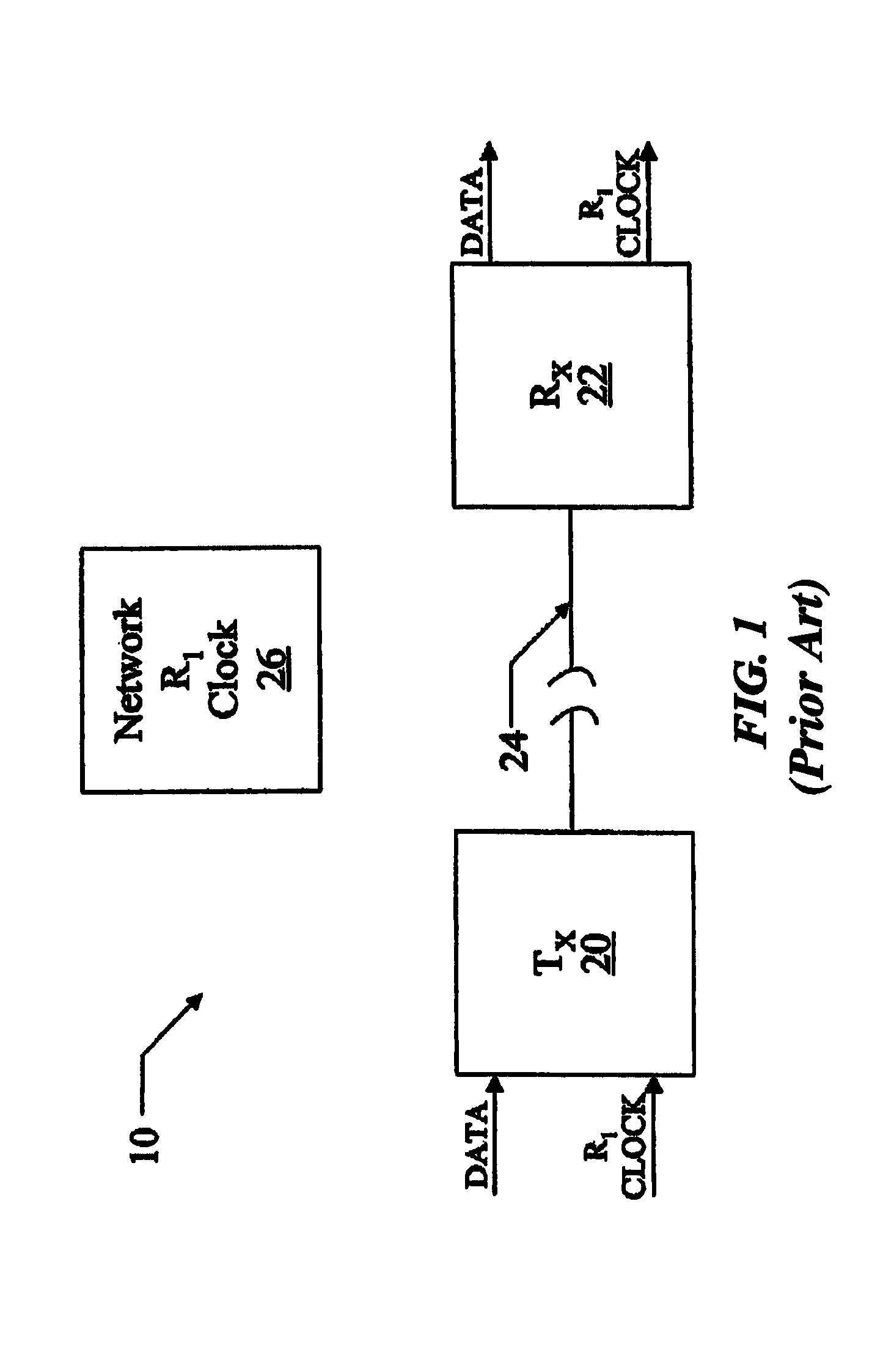
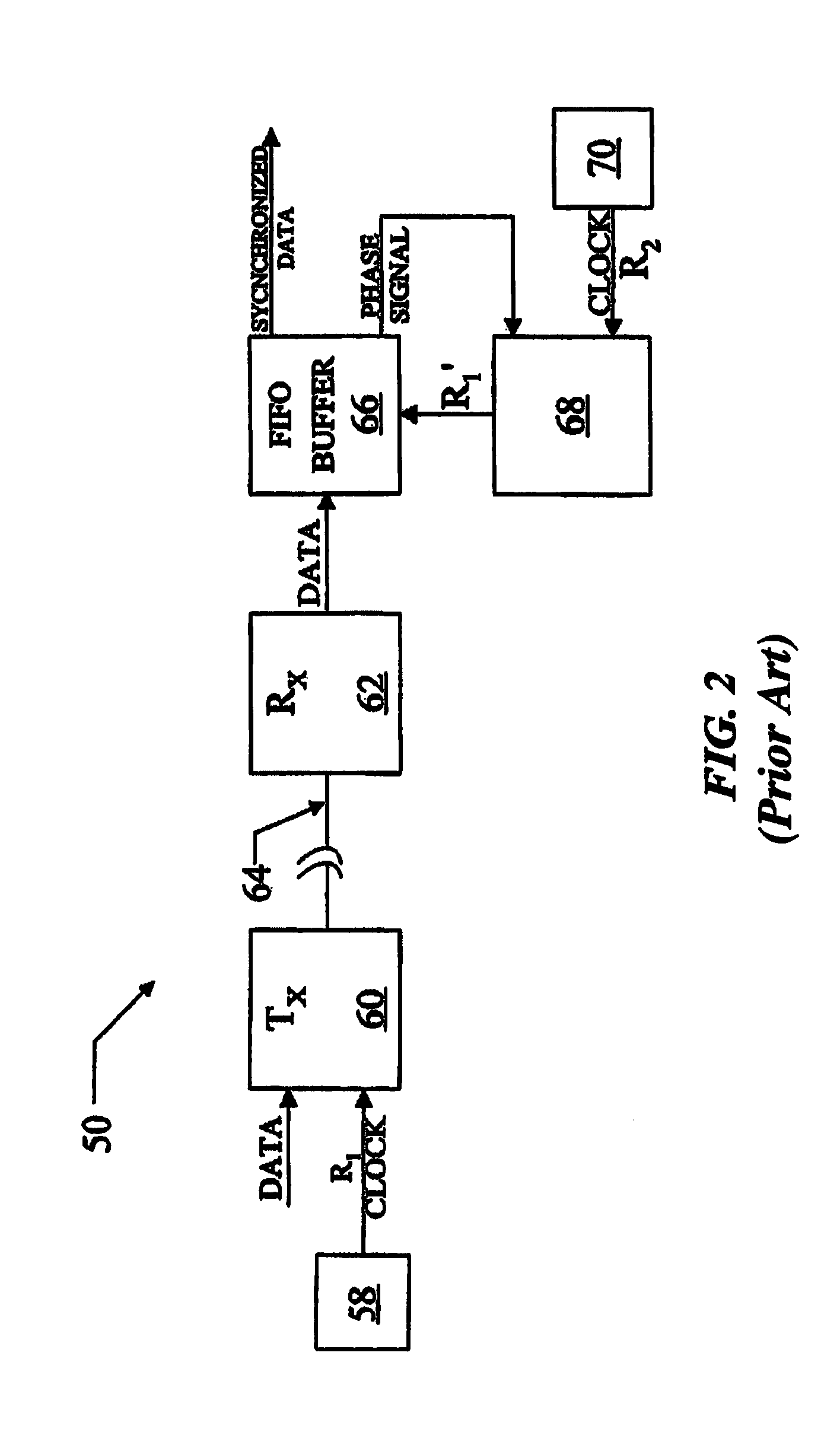
Low wander timing generation and recovery
InactiveUS7415092B2Improve accuracySmall bandwidthPulse automatic controlModulated-carrier systemsPhase detectorCommunications system
Systems, apparatuses, and methods for low wander timing generation and / or recovery are disclosed here. In one aspect, embodiments of the present disclosure include a communication system for high speed communications between a first location and a second location. The communication system, may include a transmitter module at the first location associated a first clock. The transmitter module may further include a phase detector module that is operable to generate a one or more data bits to indicate phase offset between the first clock and a second clock, the first clock can be associated with a transmission rate and the second clock can be associated with a network link rate and / or a receiver module at the second location associated with the second clock. The receiver module may be coupled to the transmitter module via a network.
Owner:POSITRON ACCESS SOLUTIONS
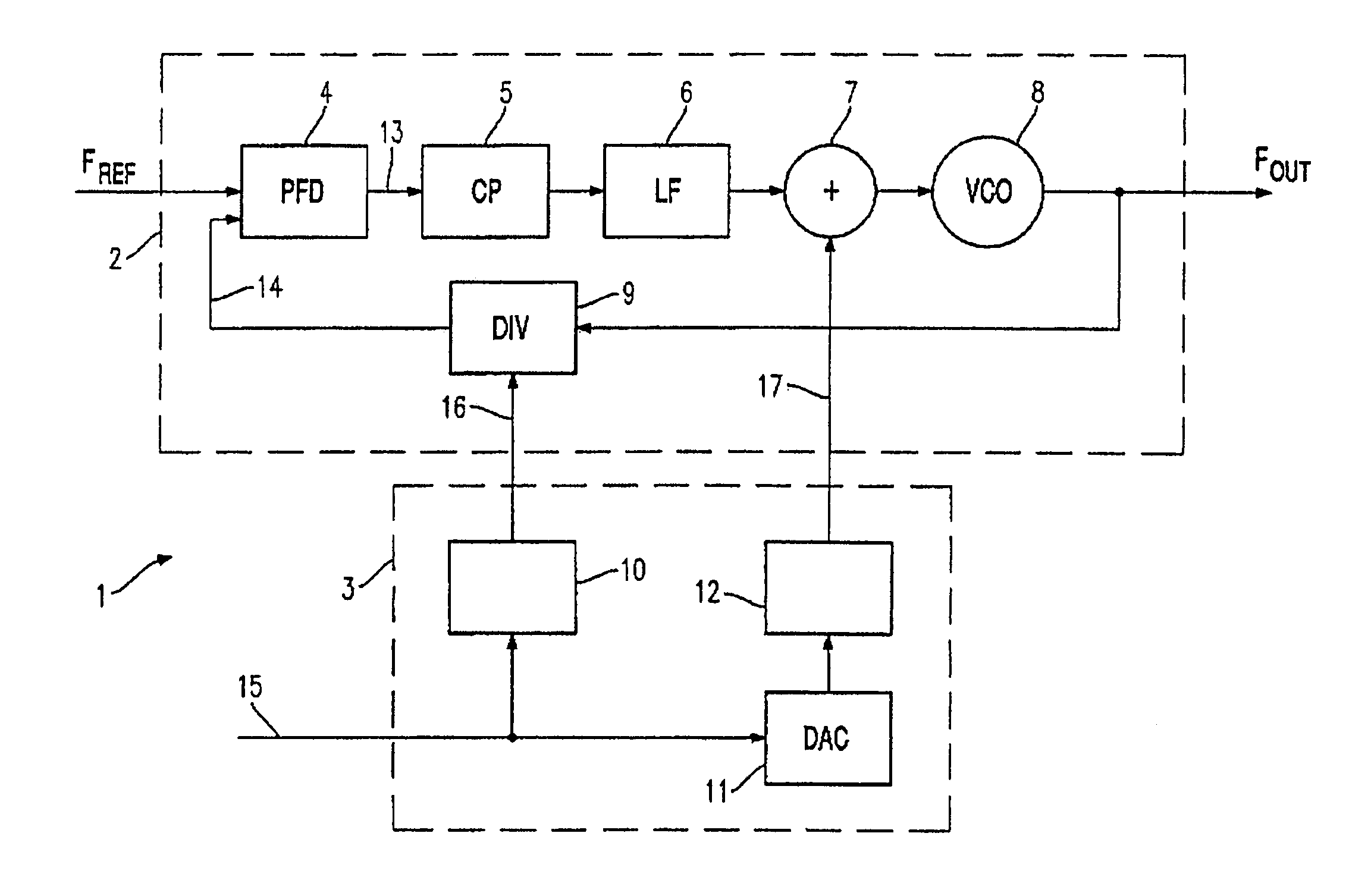
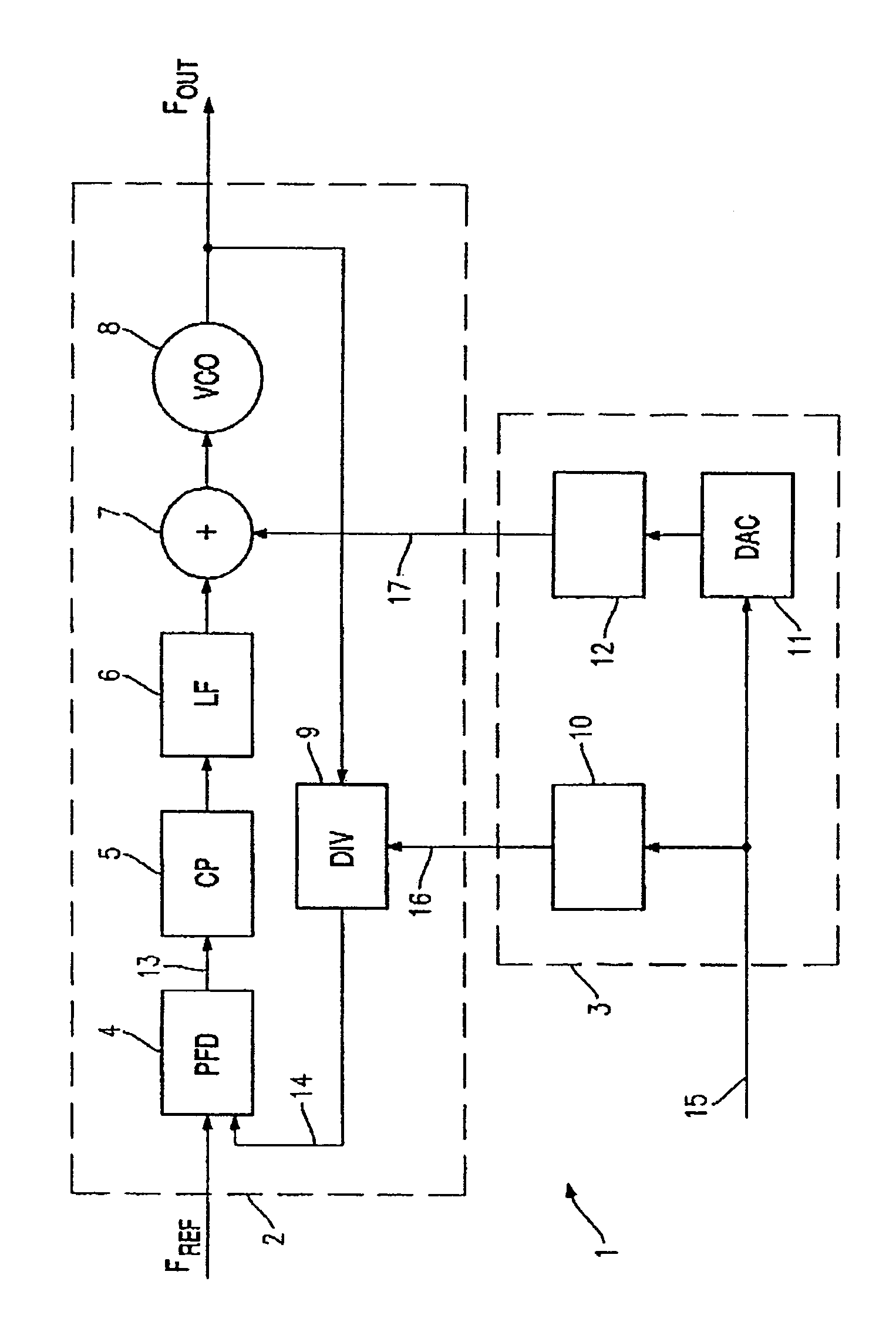
Two-point modulator comprising a PLL circuit and a simplified digital pre-filtering system
InactiveUS7142063B2Implementation complexity is lowReduce complexityPulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsSquare waveformDigital filter
A two-point modulator includes a PLL circuit and a simplified digital pre-filtering system. The two-point modulator includes a first circuit path for impressing an analog modulation signal into a first point in the PLL circuit, and a second circuit path for impressing a digital modulation signal into a second point in the PLL circuit. The second circuit path actuates a frequency divider in the feedback path in the PLL circuit and contains a digital filter which has a square-wave pulse response.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com