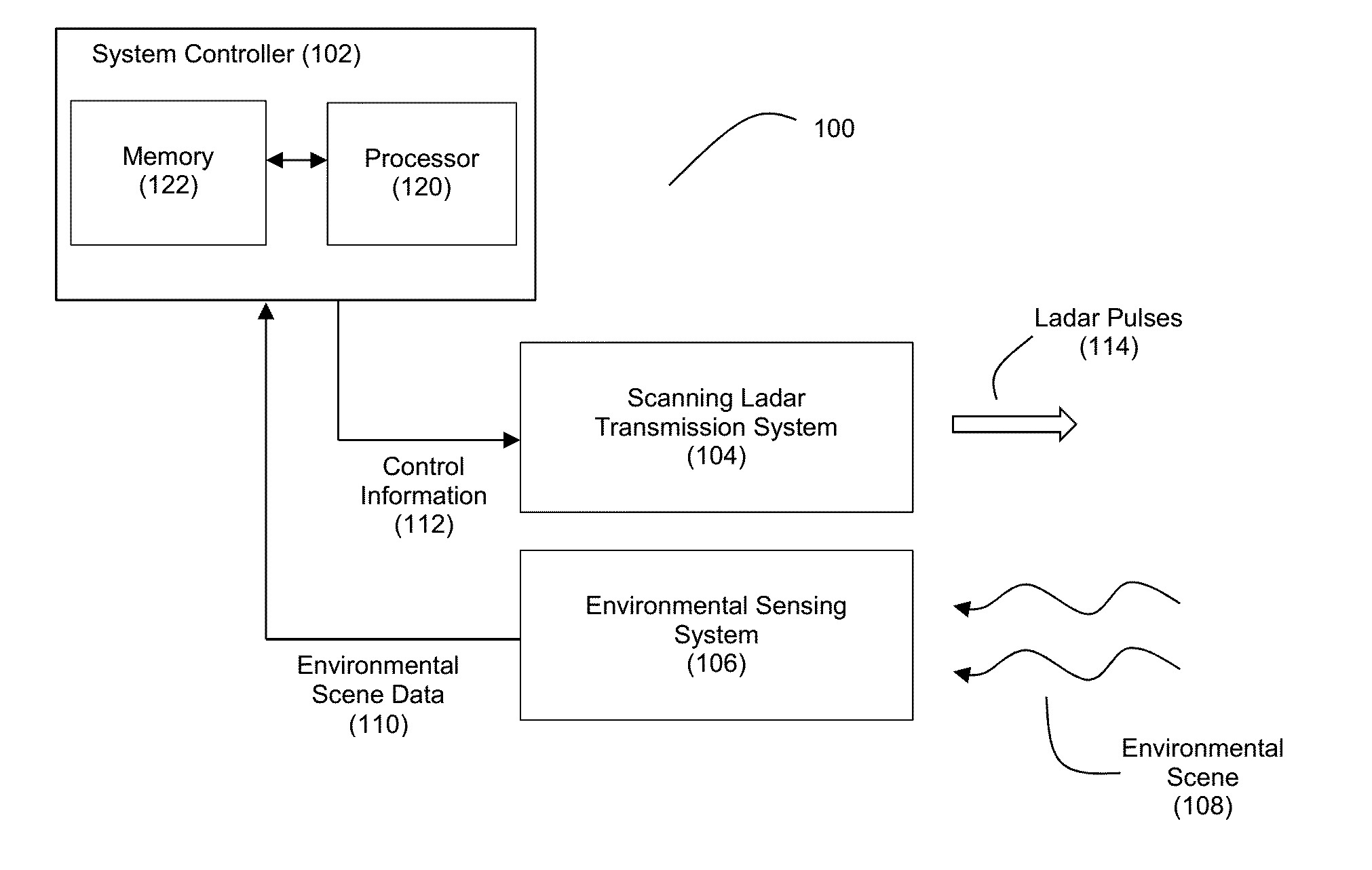
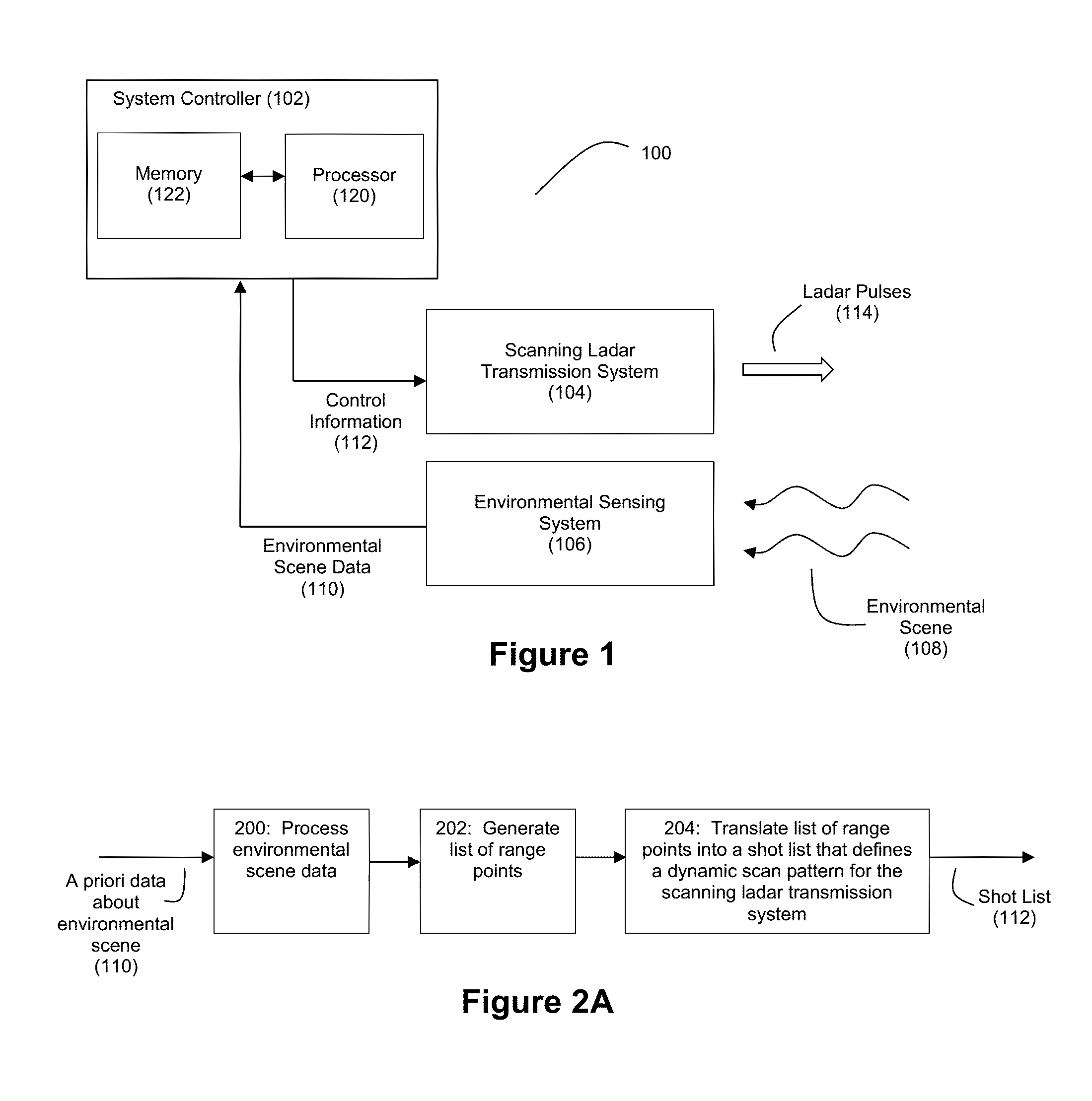
Patents
Literature
143 results about "Dynamic Scan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
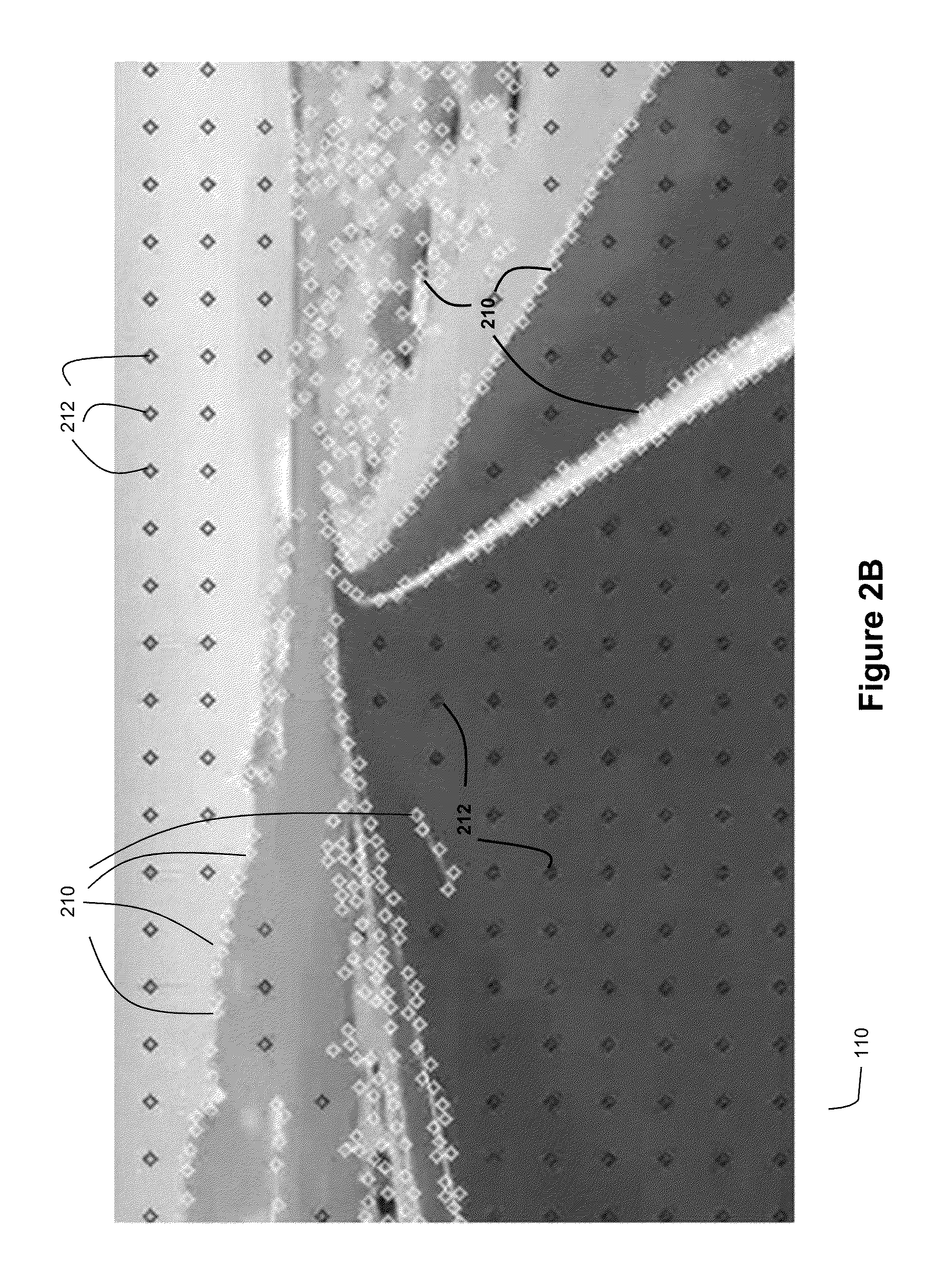
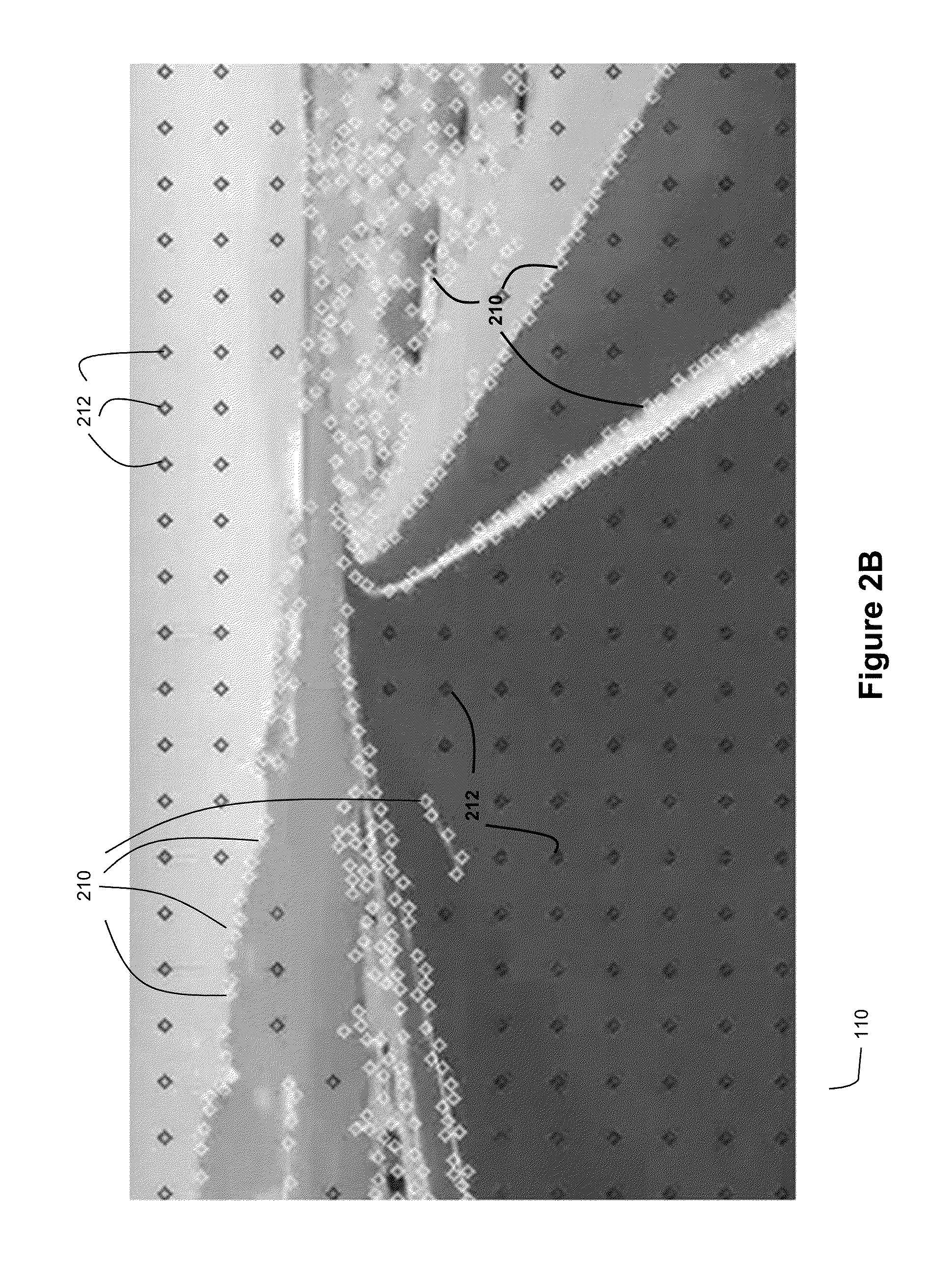
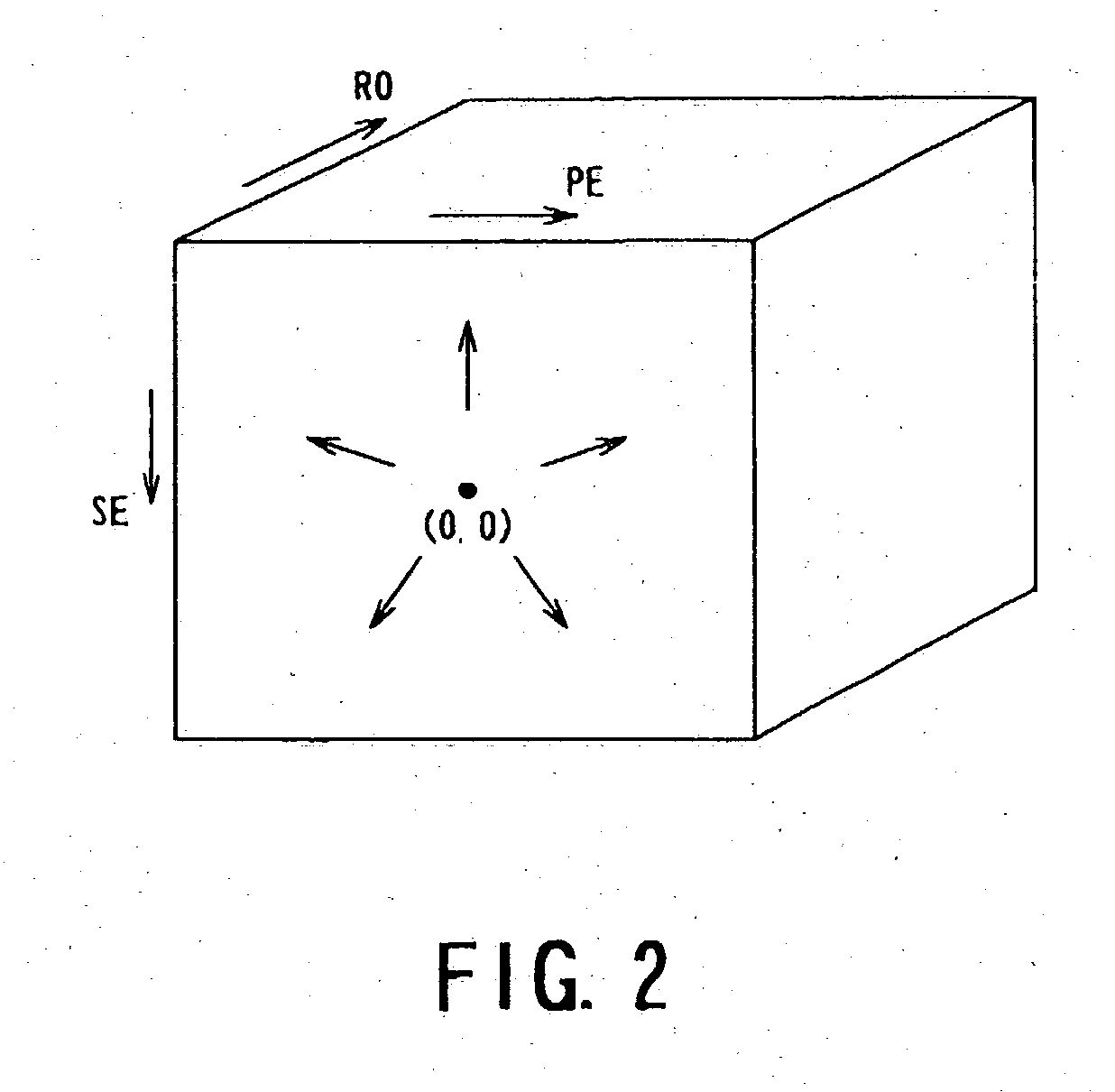
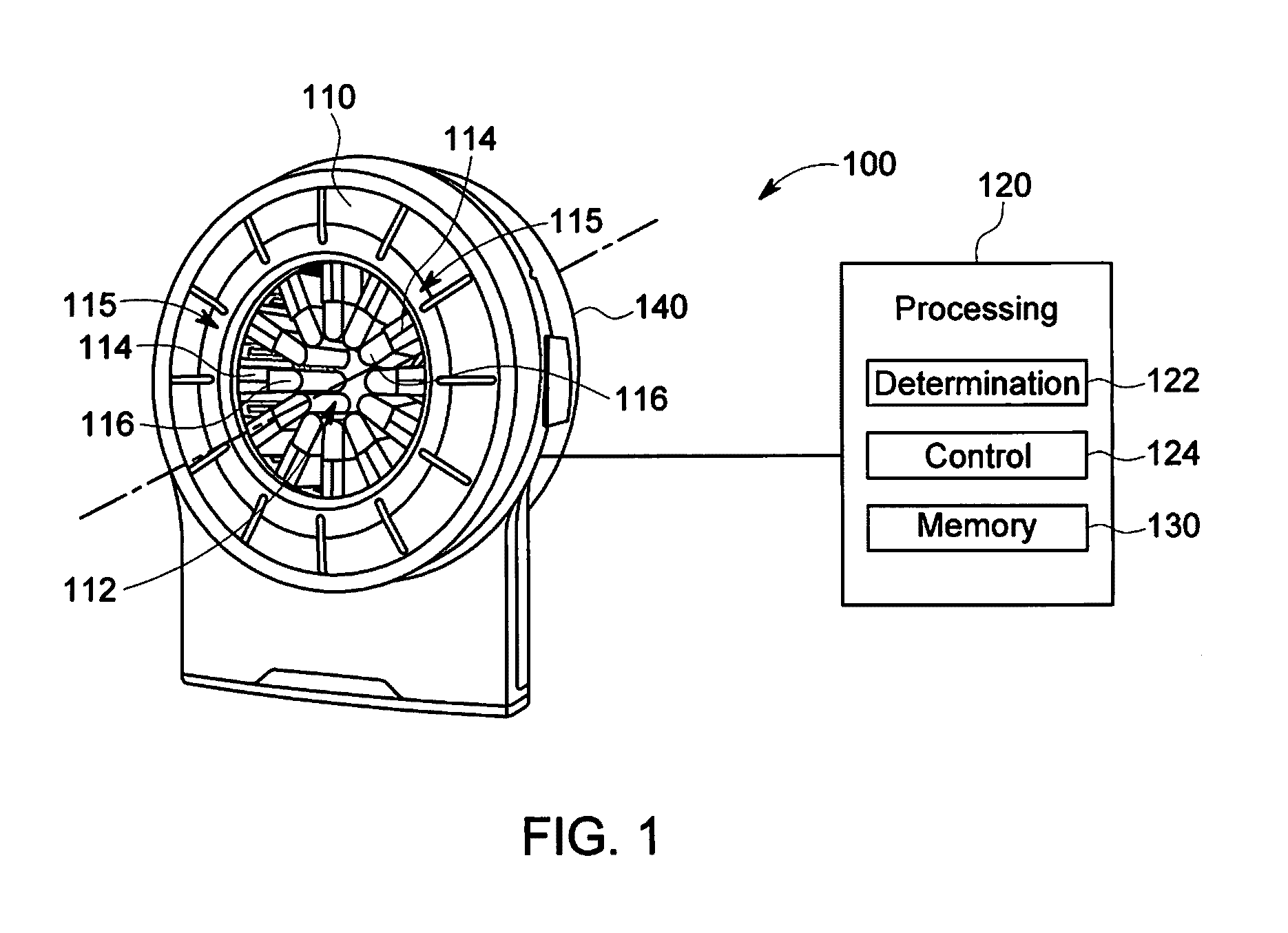
Scan having a number of sequential frames.
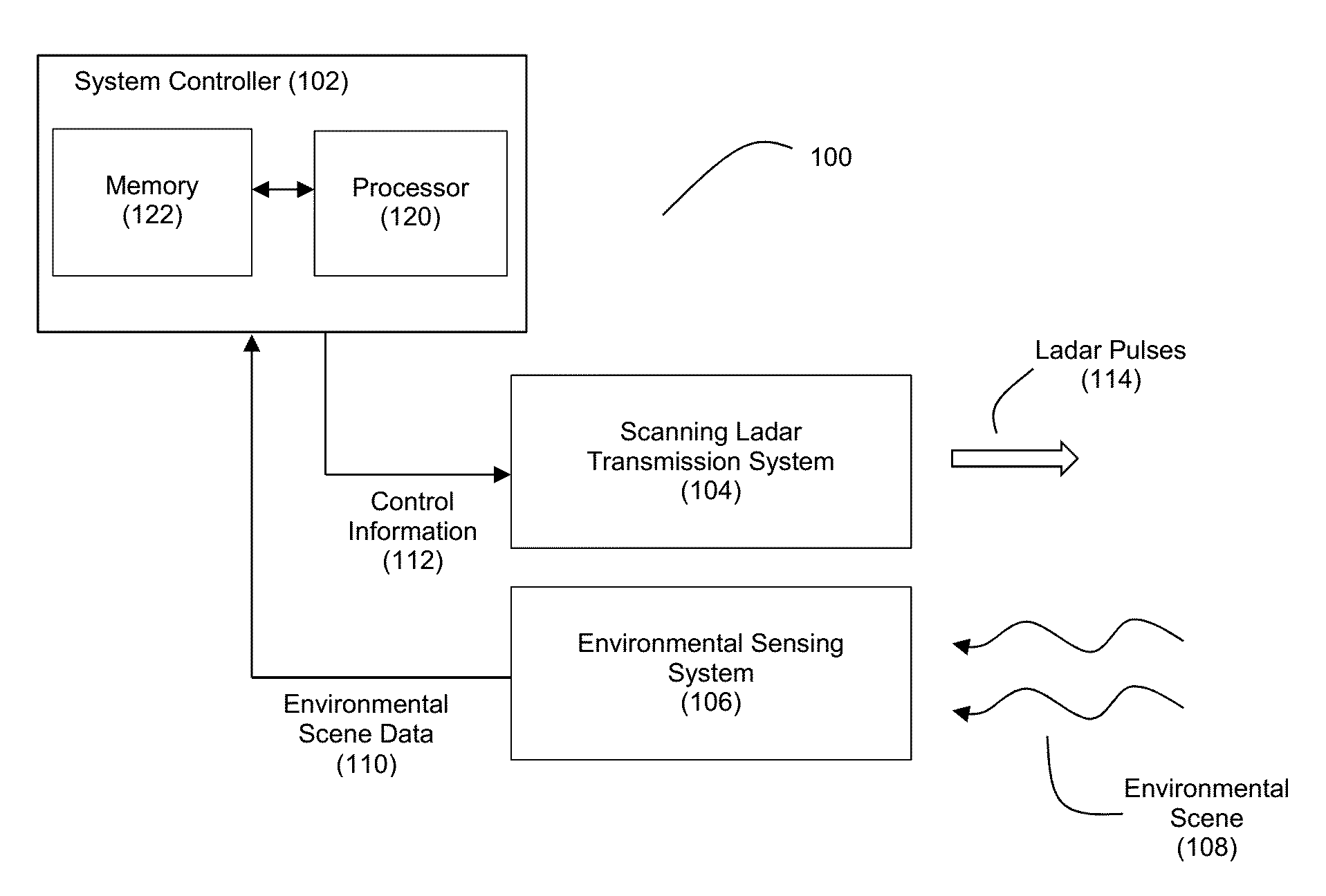
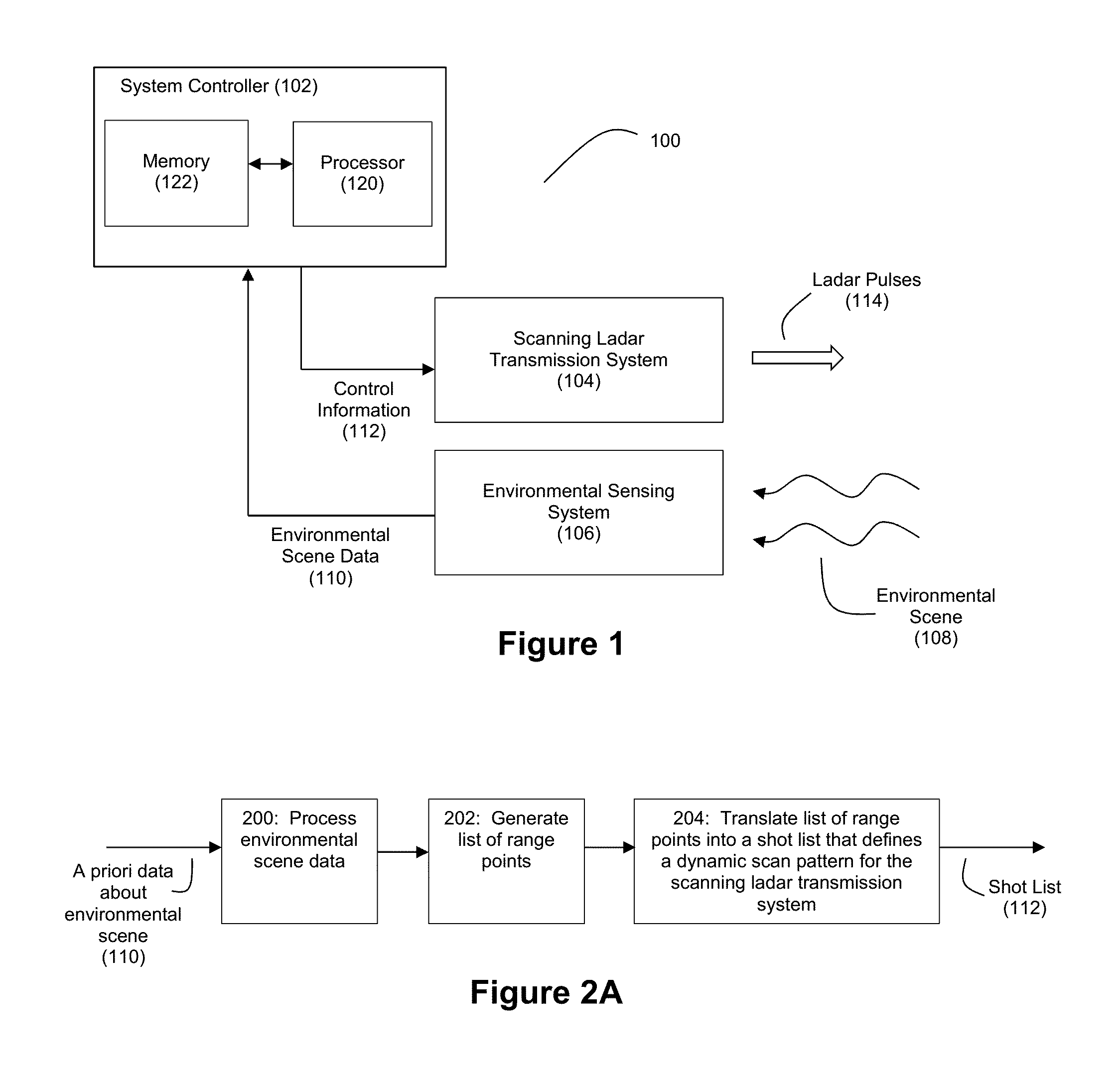
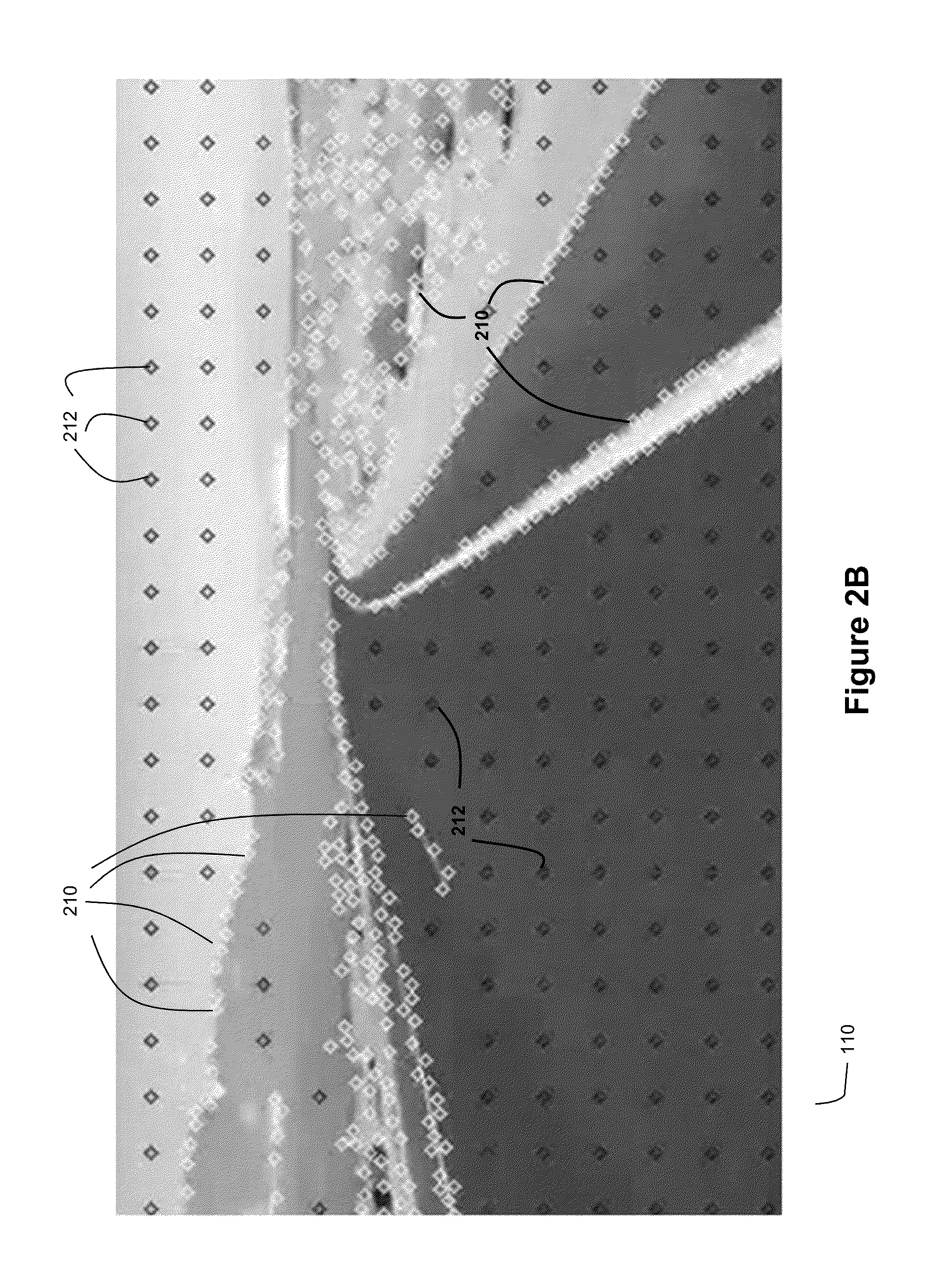
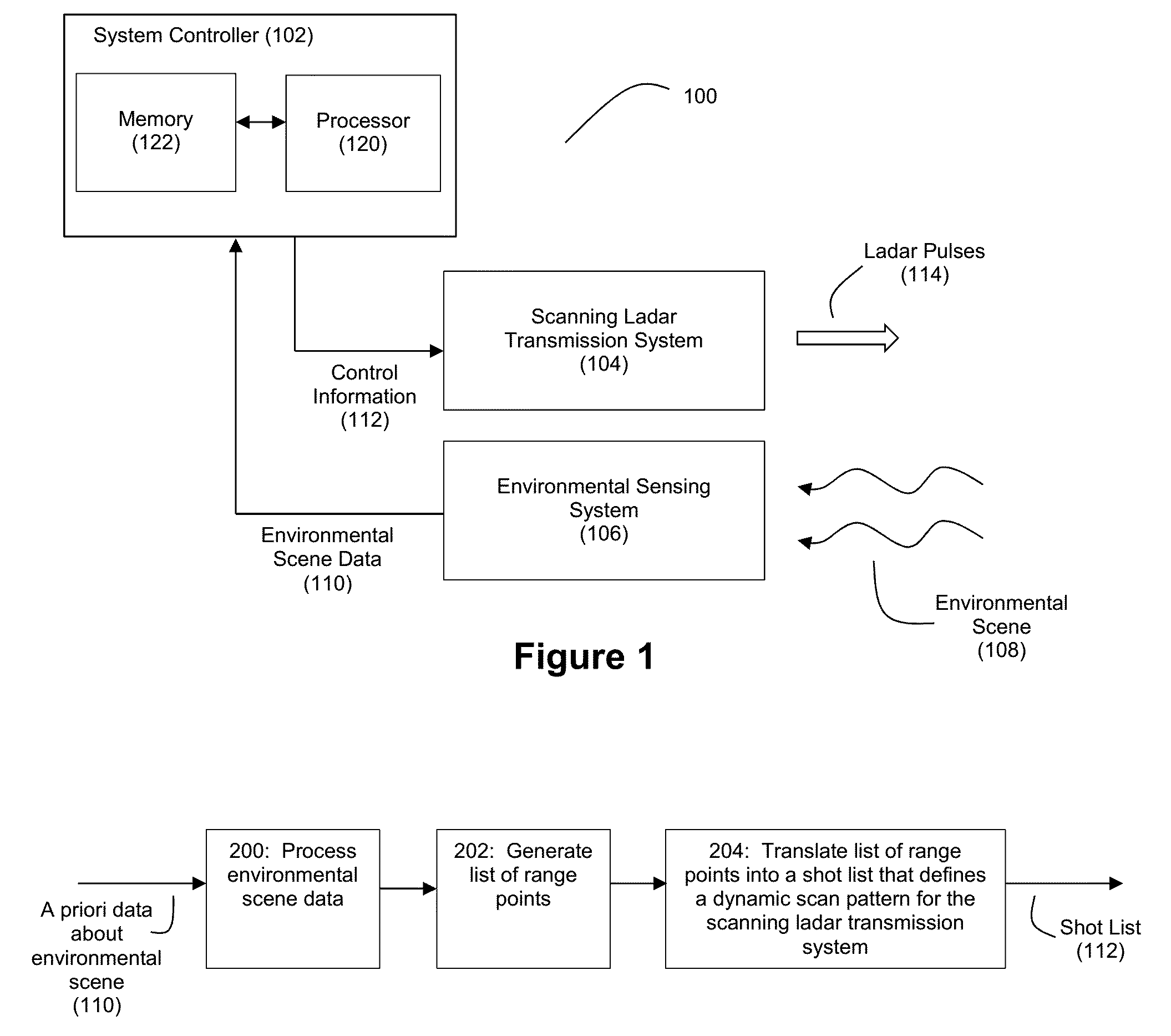
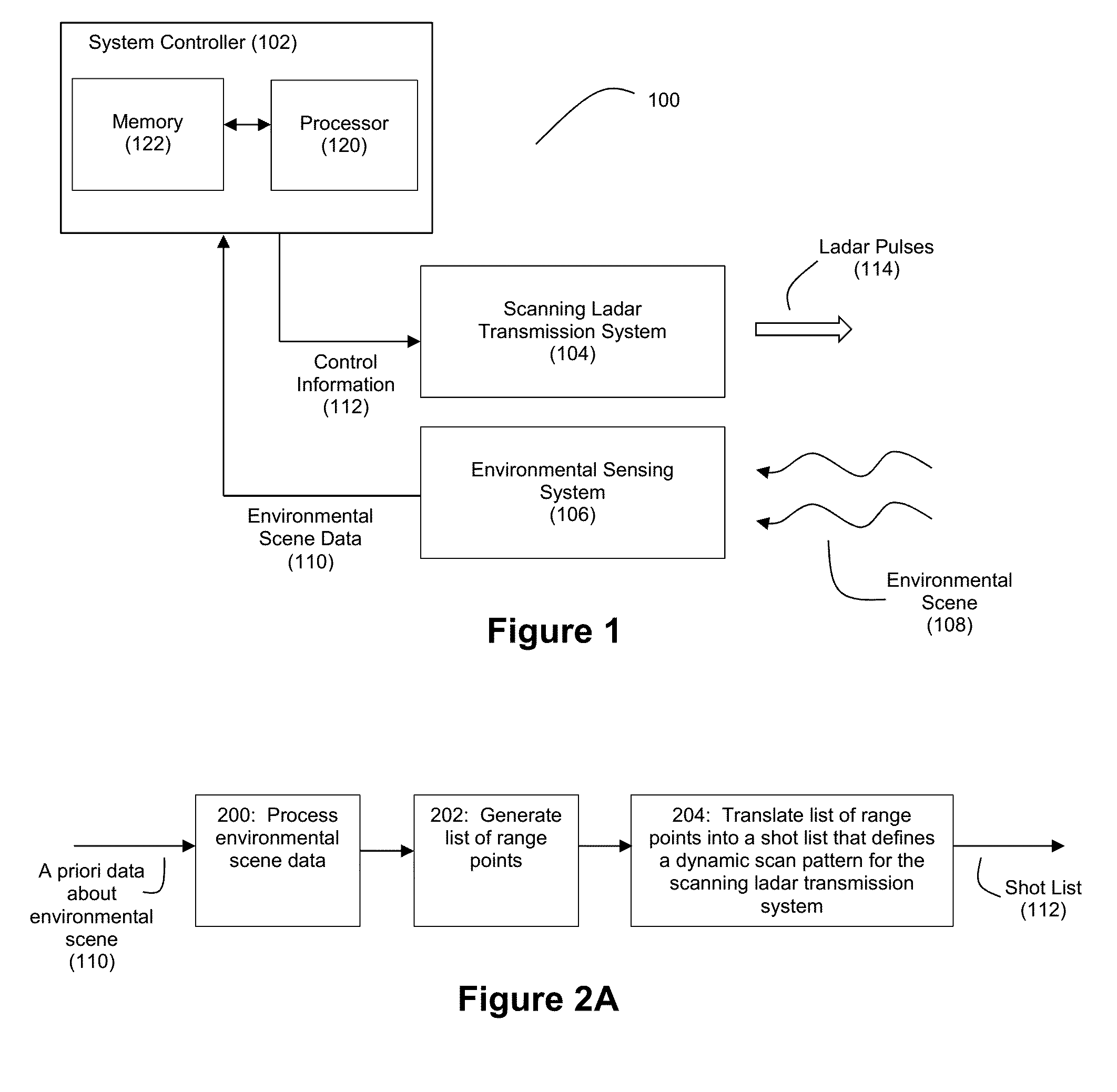
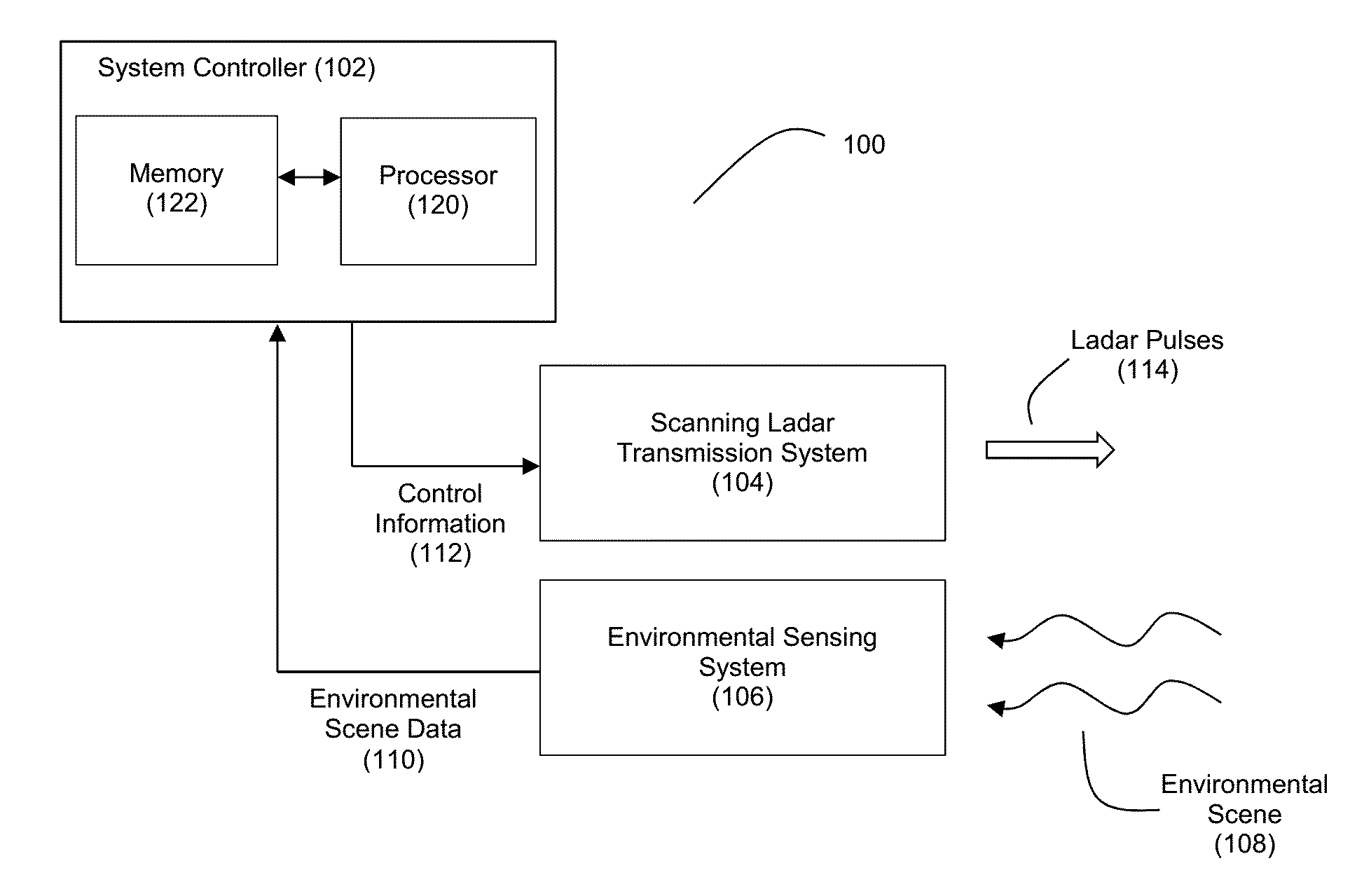
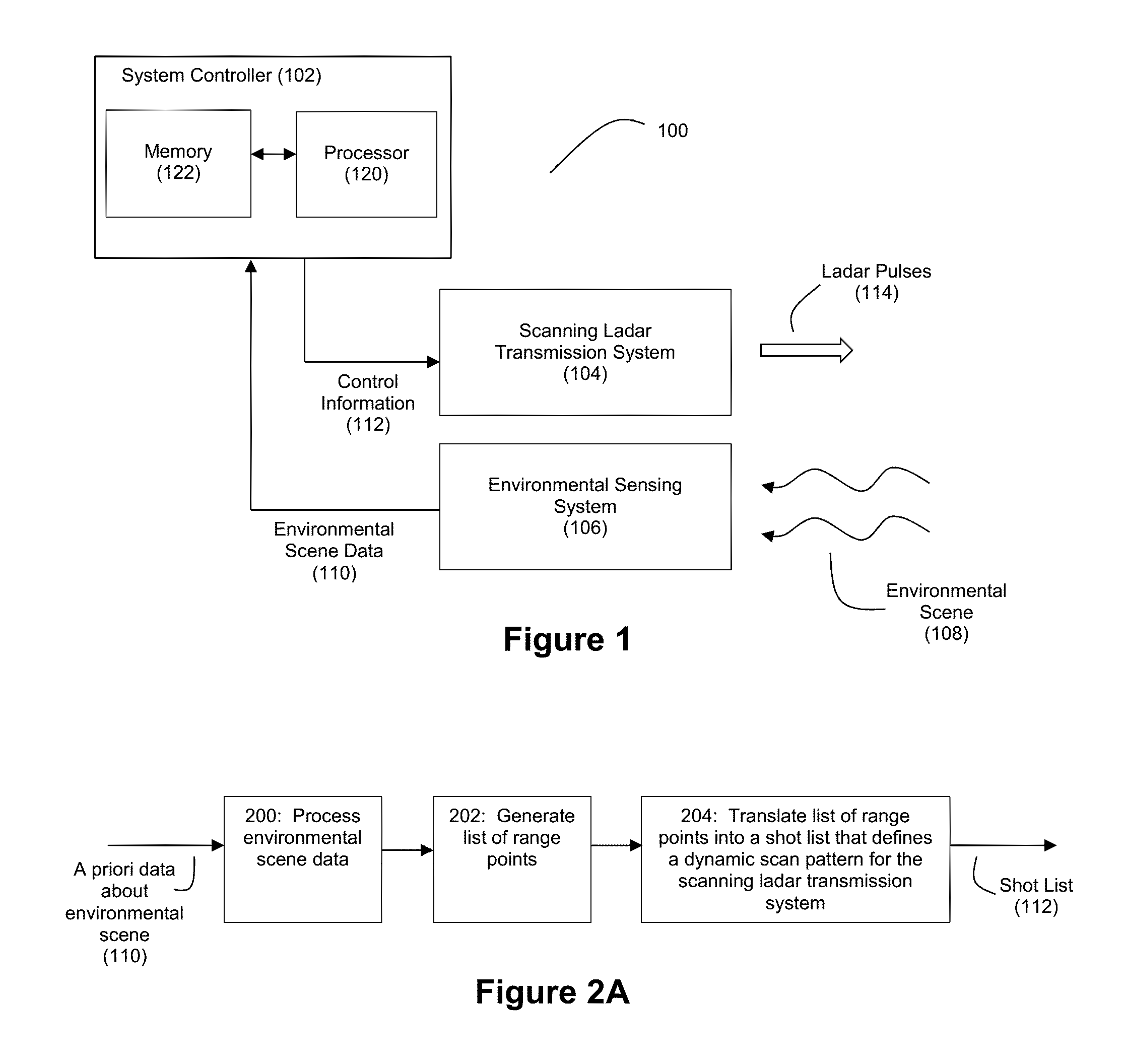
Method and System for Ladar Transmission with Spinning Polygon Mirror for Dynamic Scan Patterns
Various embodiments are disclosed for improved scanning ladar transmission, including but not limited to an example embodiment where the scanning ladar transmission system includes a spinning polygon mirror for targeting range points according to a dynamic scan pattern.
Owner:AEYE INC
Method and System for Ladar Transmission Employing Dynamic Scan Patterns with Macro Patterns and Base Patterns
ActiveUS20160047899A1Optical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationComputational physicsComputer vision
Various embodiments are disclosed for improved scanning ladar transmission, including but not limited to an example embodiment where a dynamic scan pattern for a scanning ladar transmission system includes a macro pattern having a base pattern embedded therein.
Owner:AEYE INC
Method and System for Ladar Transmission with Interline Skipping for Dynamic Scan Patterns
Various embodiments are disclosed for improved scanning ladar transmission, including but not limited to an example embodiment where a dynamic scan pattern for a scanning ladar transmission system includes interline skipping and detouring.
Owner:AEYE INC
Method and System for Ladar Transmission with Spiral Dynamic Scan Patterns
Various embodiments are disclosed for improved scanning ladar transmission, including but not limited to an example embodiment where a scanning ladar transmission system employs a spiral dynamic scan pattern.
Owner:AEYE INC
Fast scaning based on magnetic resonance history
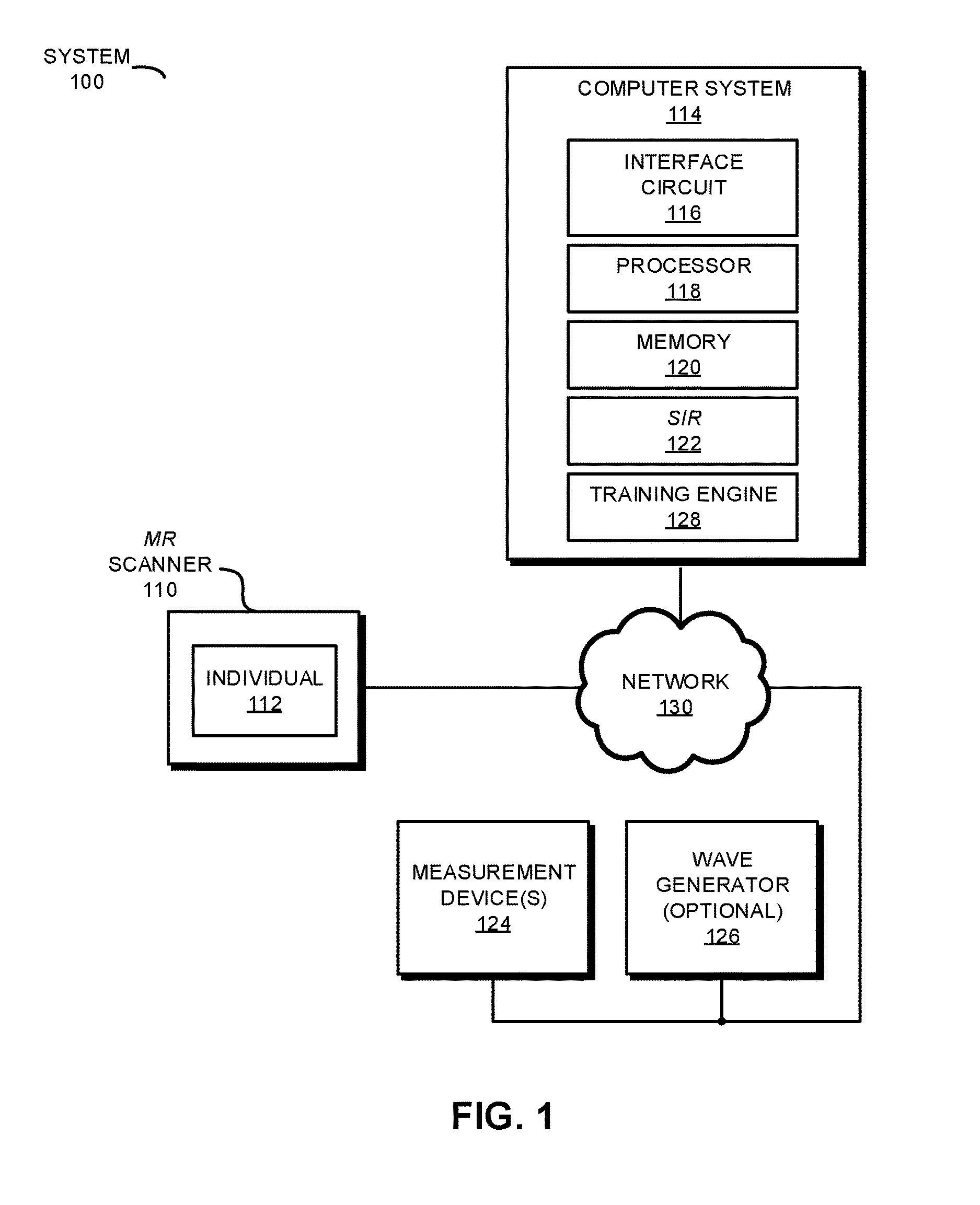
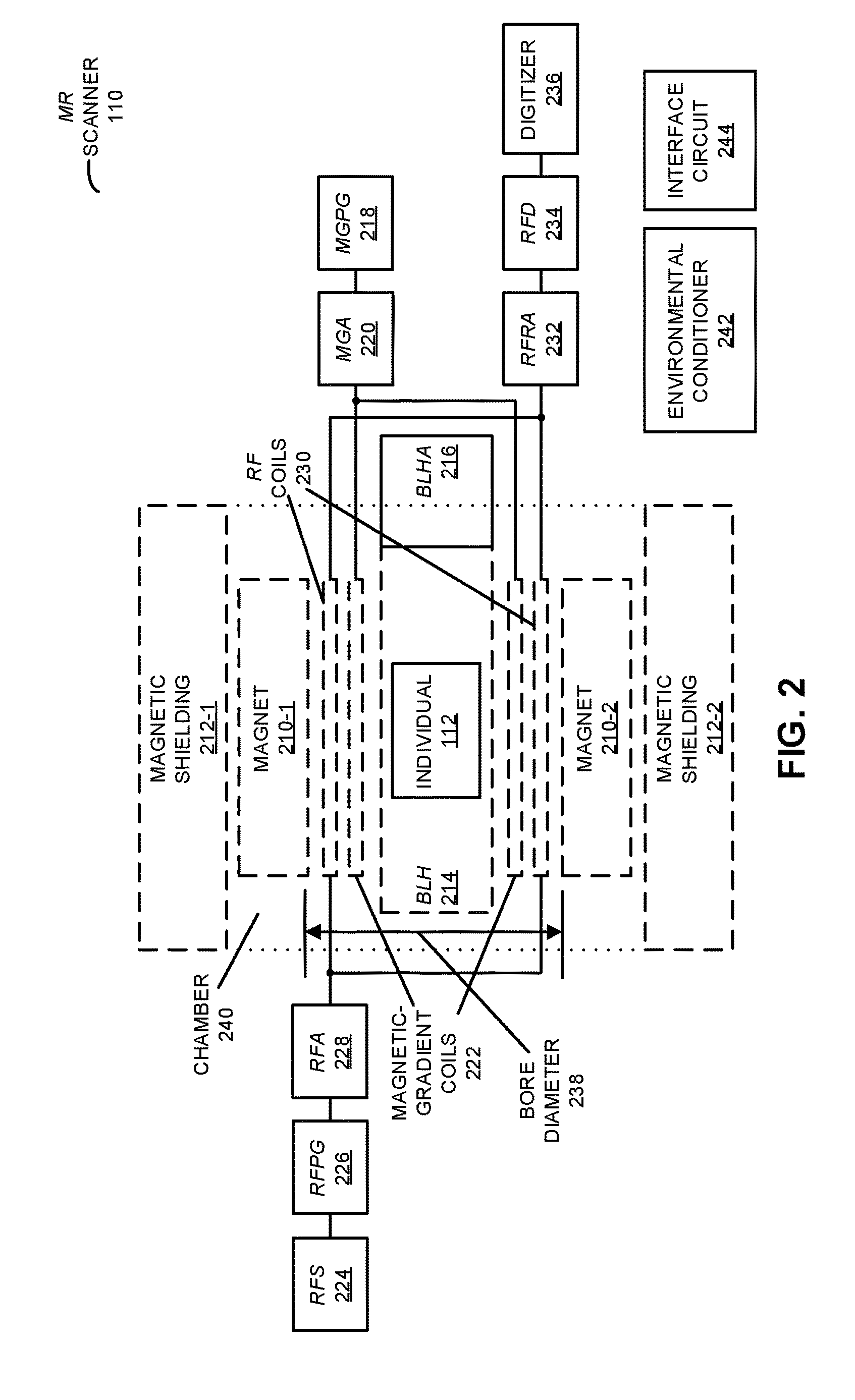
During operation, a system iteratively captures MR signals of one or more types of nuclei in one or more portions of a biological lifeform based on scanning instructions that correspond to a dynamic scan plan. The MR signals in a given iteration may be associated with voxels having associated sizes at three-dimensional (3D) positions in at least a corresponding portion of the biological lifeform. If the system detects a potential anomaly when analyzing the MR signals from the given iteration, the system dynamically modifies the scan plan based on the detected potential anomaly, a medical history and / or an MR-scan history. Subsequent measurements of MR signals may be associated with the same or different: types of nuclei, portions of the biological lifeform, voxels sizes and / or 3D positions.
Owner:Q BIO INC
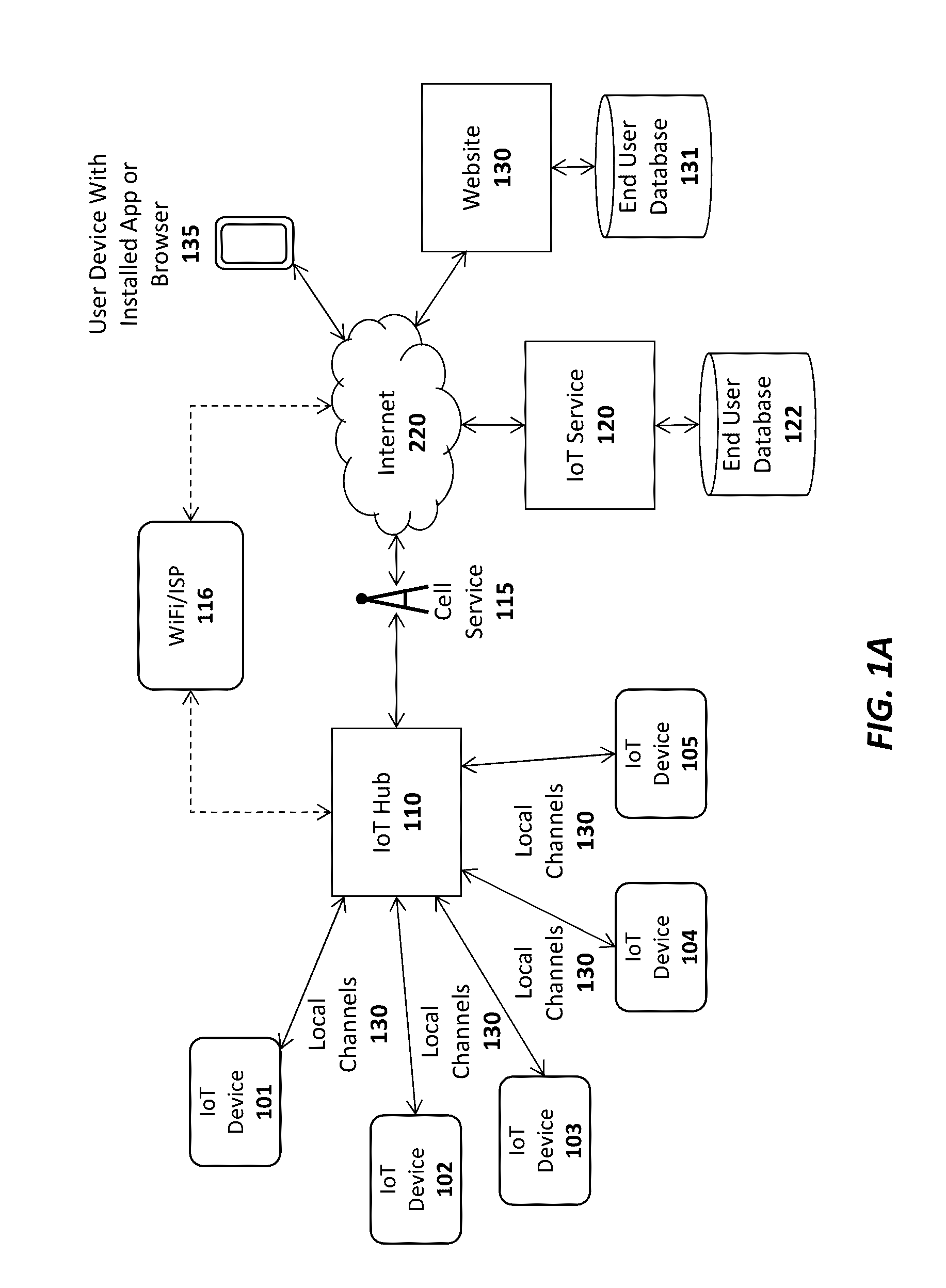
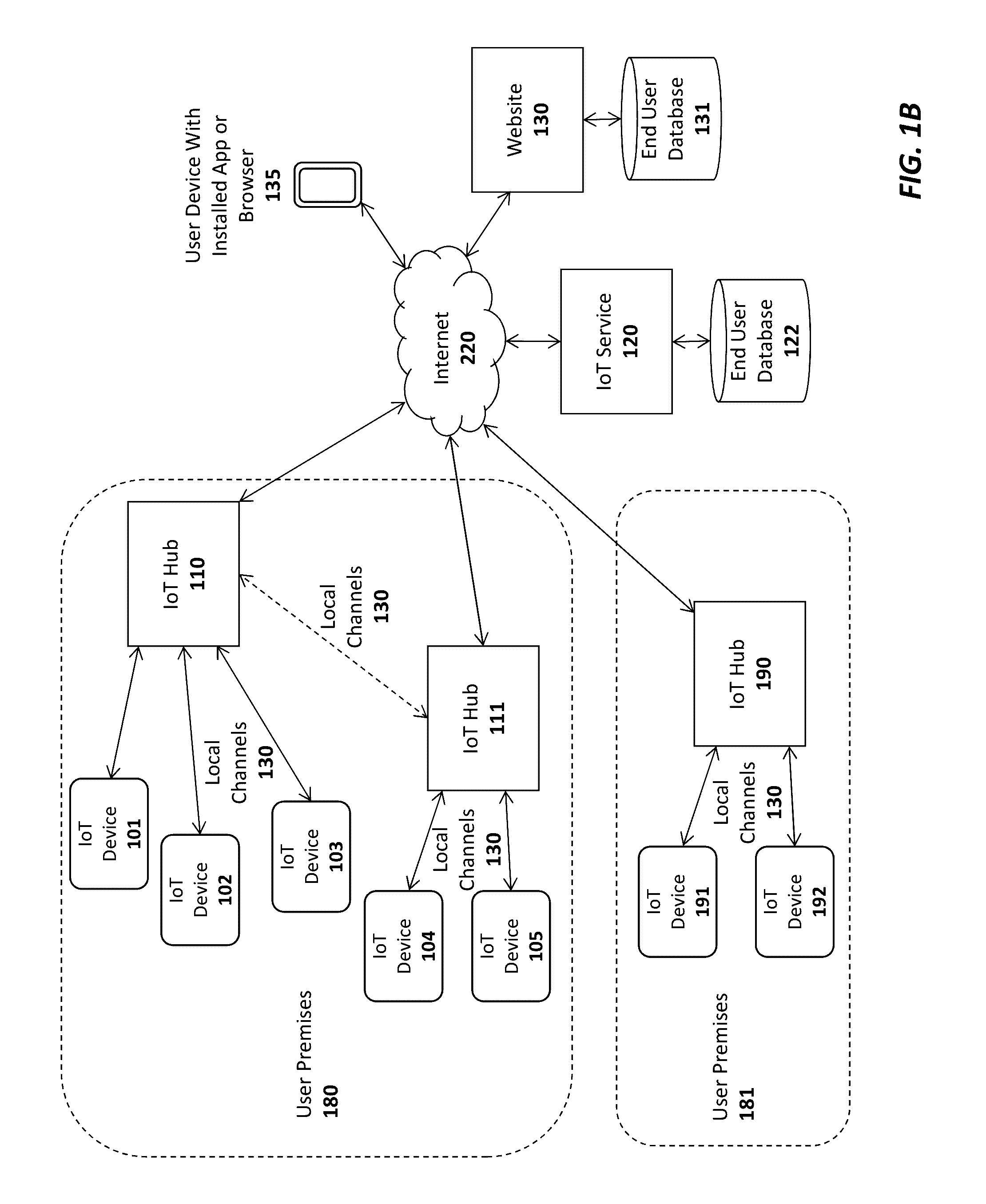
Apparatus and method for a dynamic scan interval for a wireless device
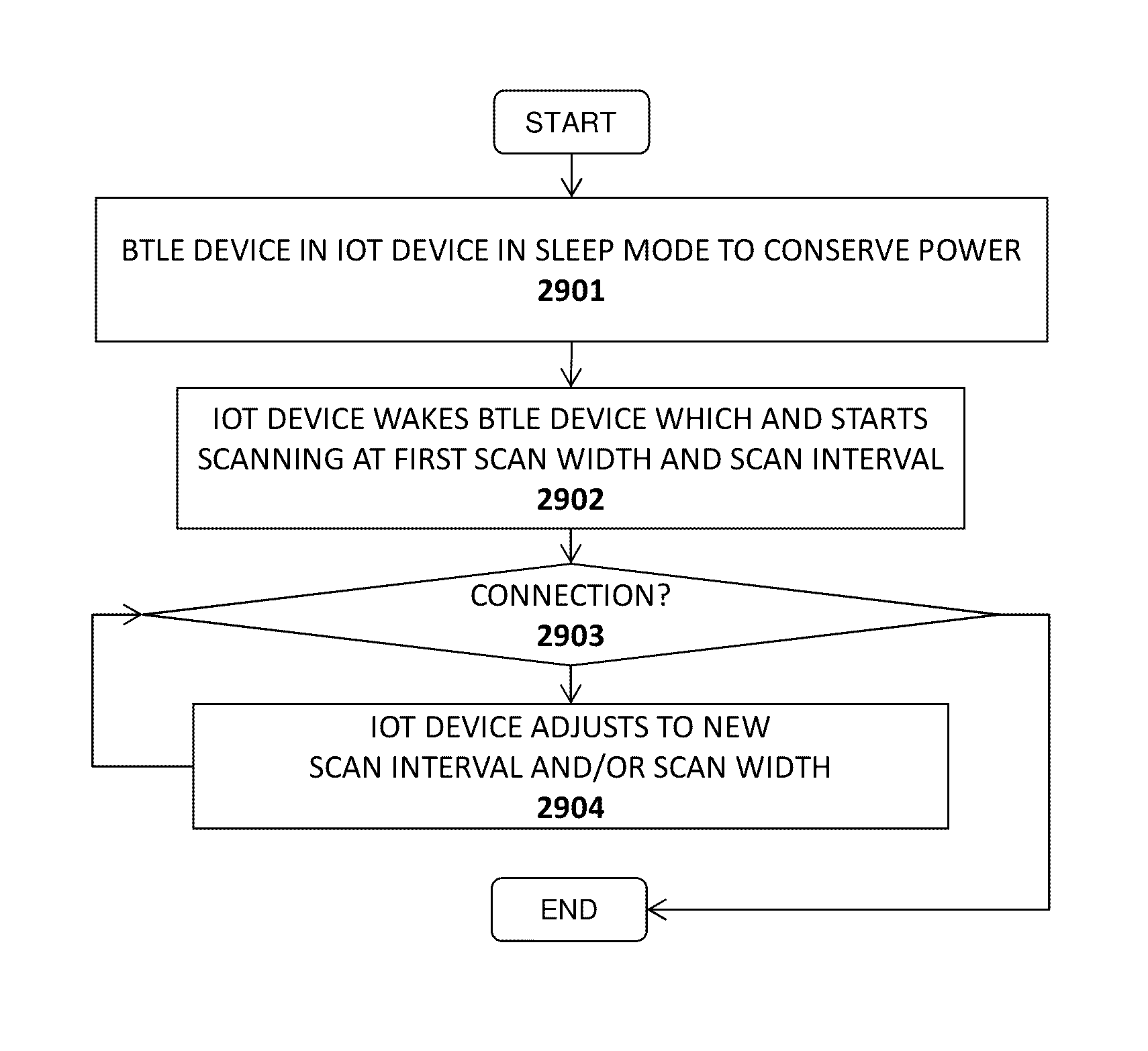
An apparatus and method are described for adjusting a scan interval or scan width of a BTLE device. For example, one embodiment of a method comprises: placing a Bluetooth Low Energy (BTLE) device of an IoT device into a low power or sleep state; waking the BTLE device from the low power or sleep state in response to a specified schedule or set of conditions; attempting to establish a connection between the BTLE device and a BTLE device of an IoT hub using a first scan width and / or scan interval; dynamically adjusting the first scan width and / or scan interval to a second scan width and / or scan interval, respectively, based on a randomly-selected value if a connection is not established after a specified time period; and reattempting to establish a connection between the BTLE device of the IoT device and the BTLE device of the IoT hub using the second scan width and / or scan interval.
Owner:AFERO
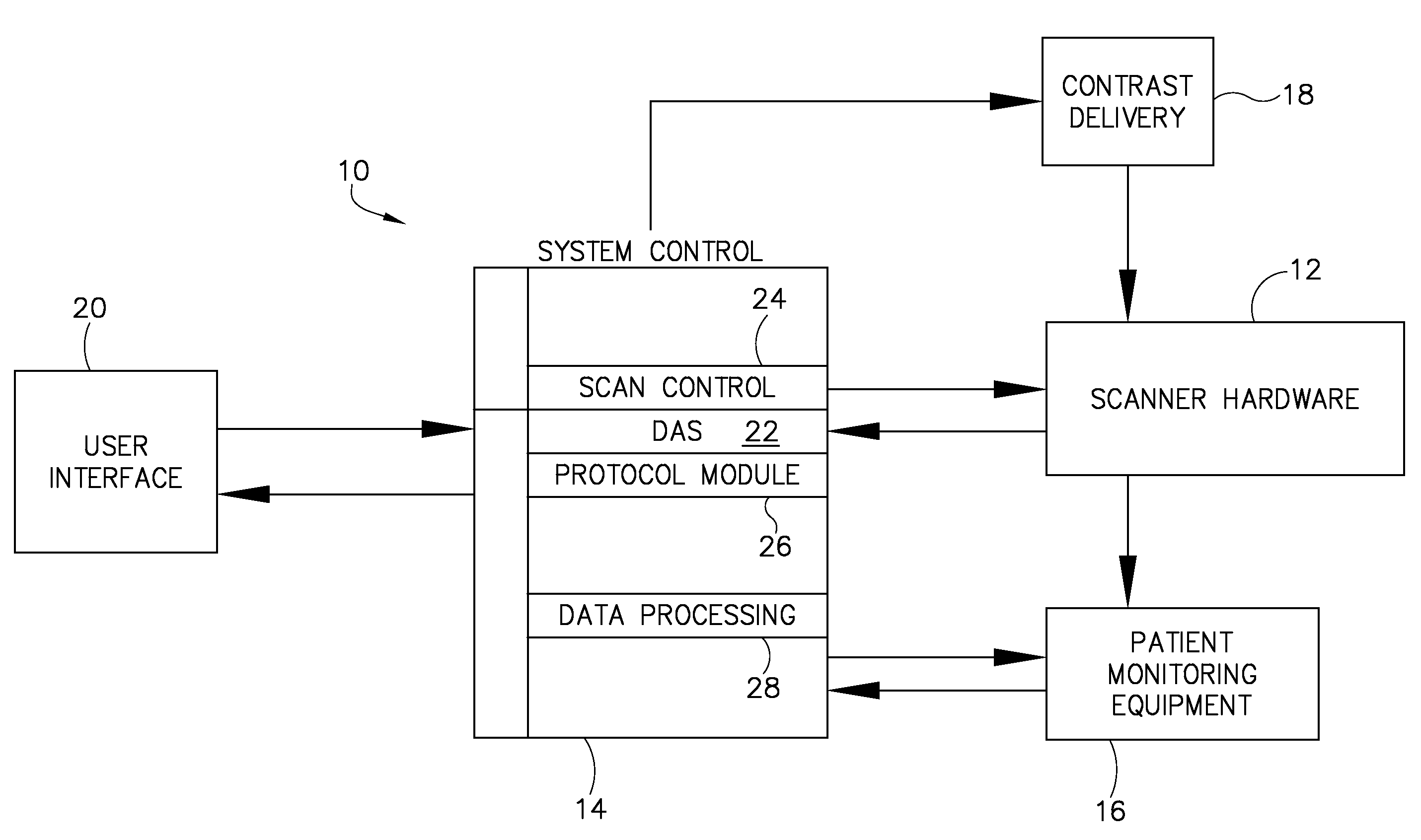
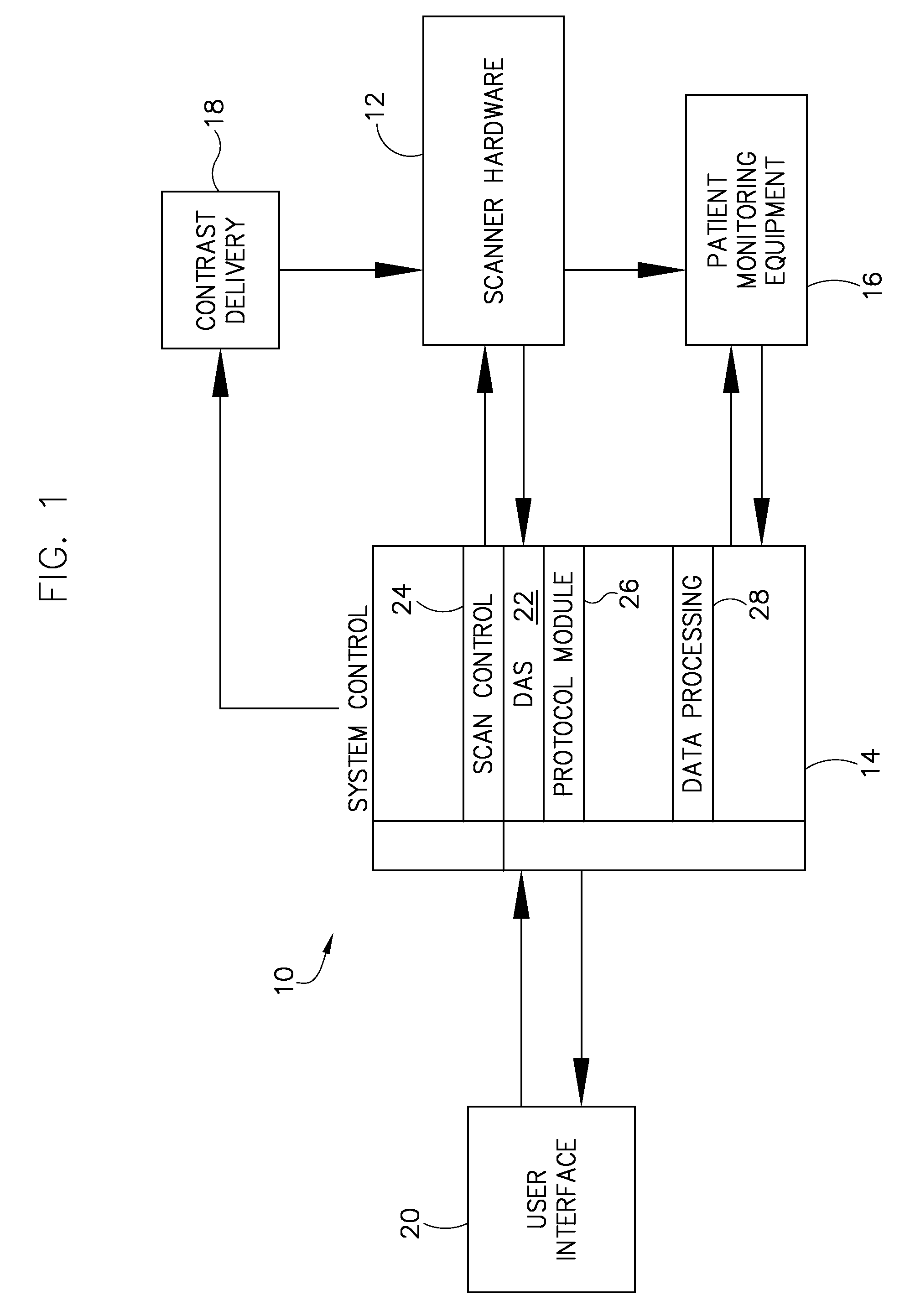
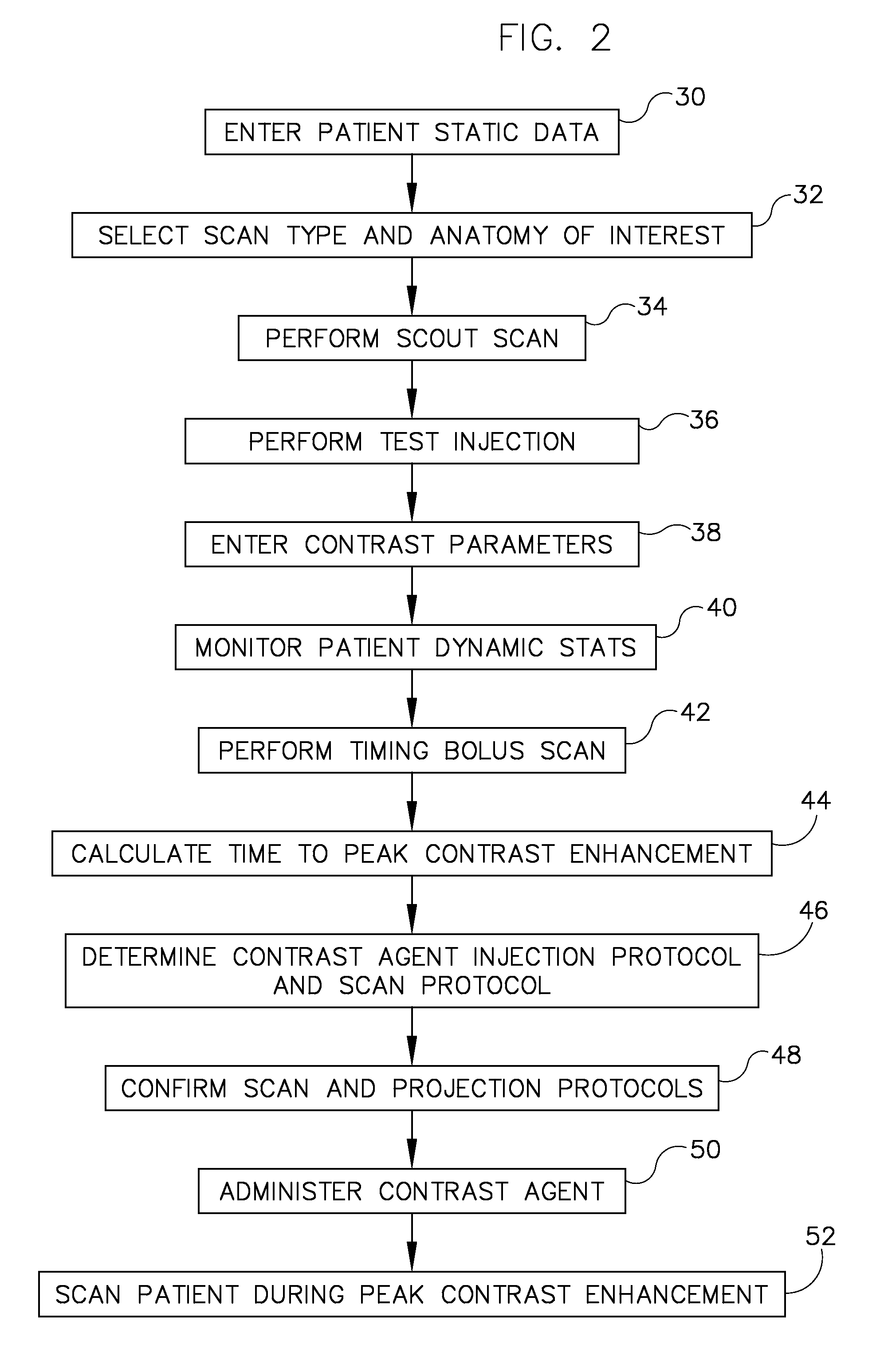
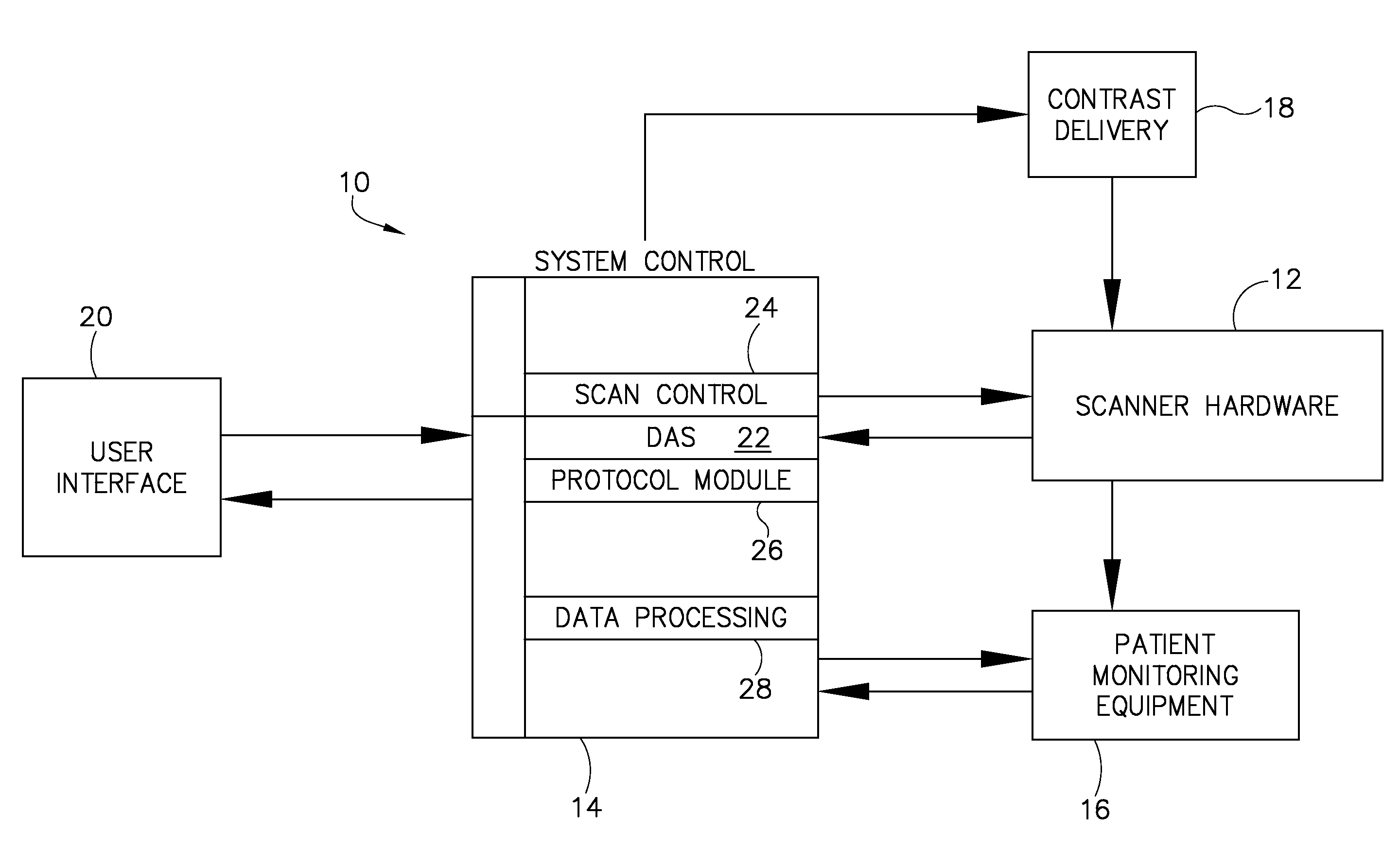
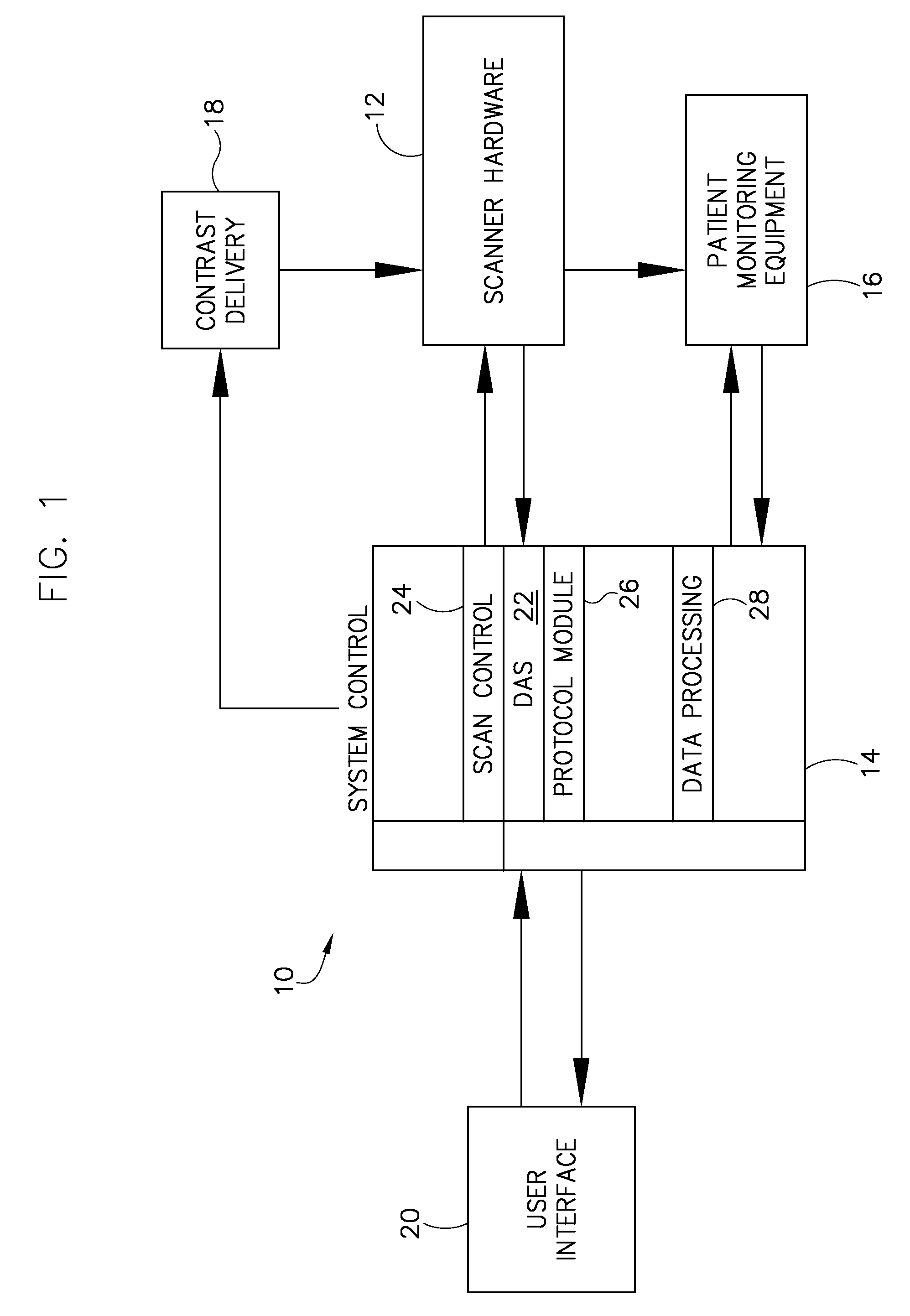
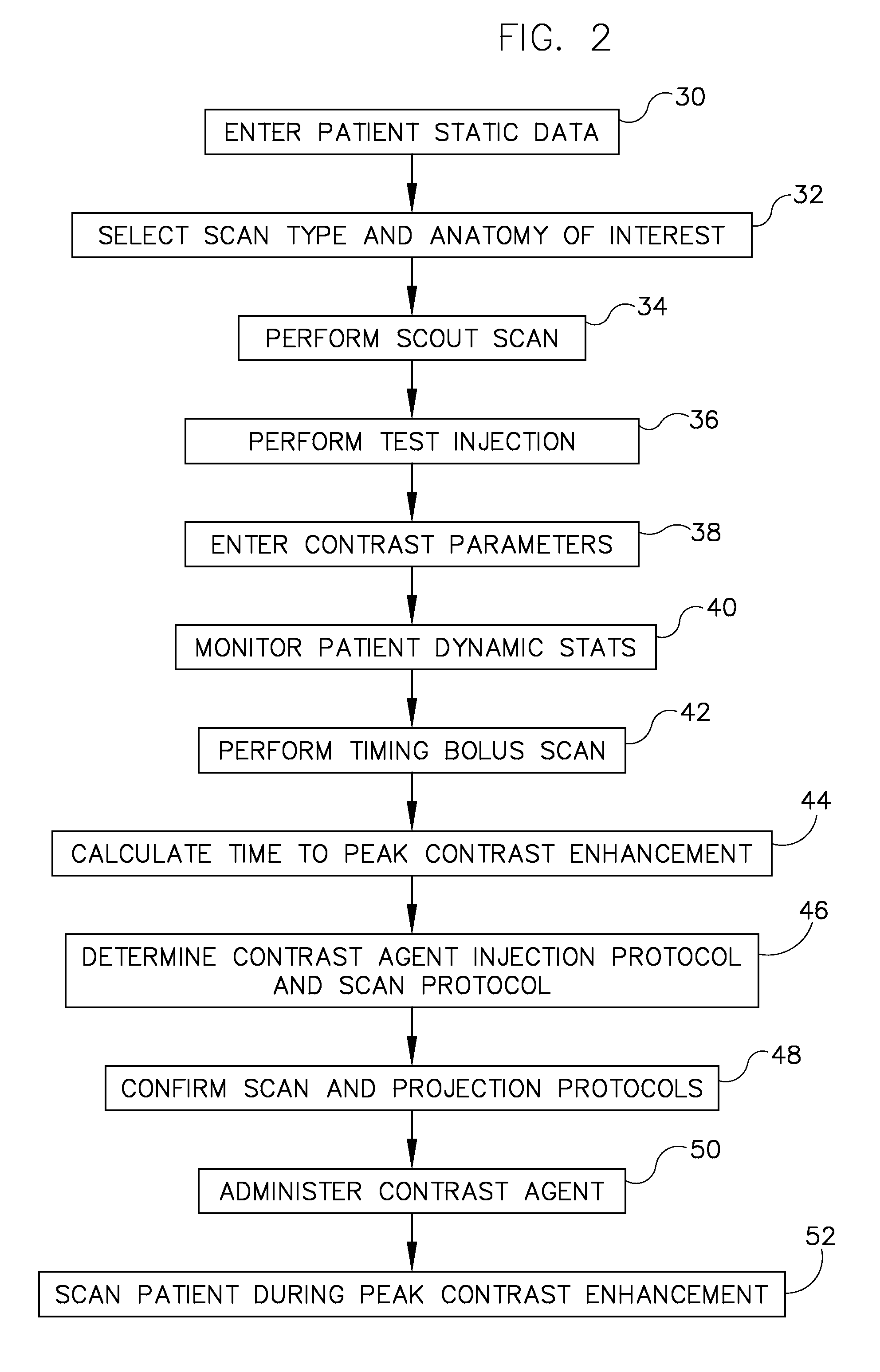
System and method to adaptively control contrast-enhanced diagnostic imaging procedure
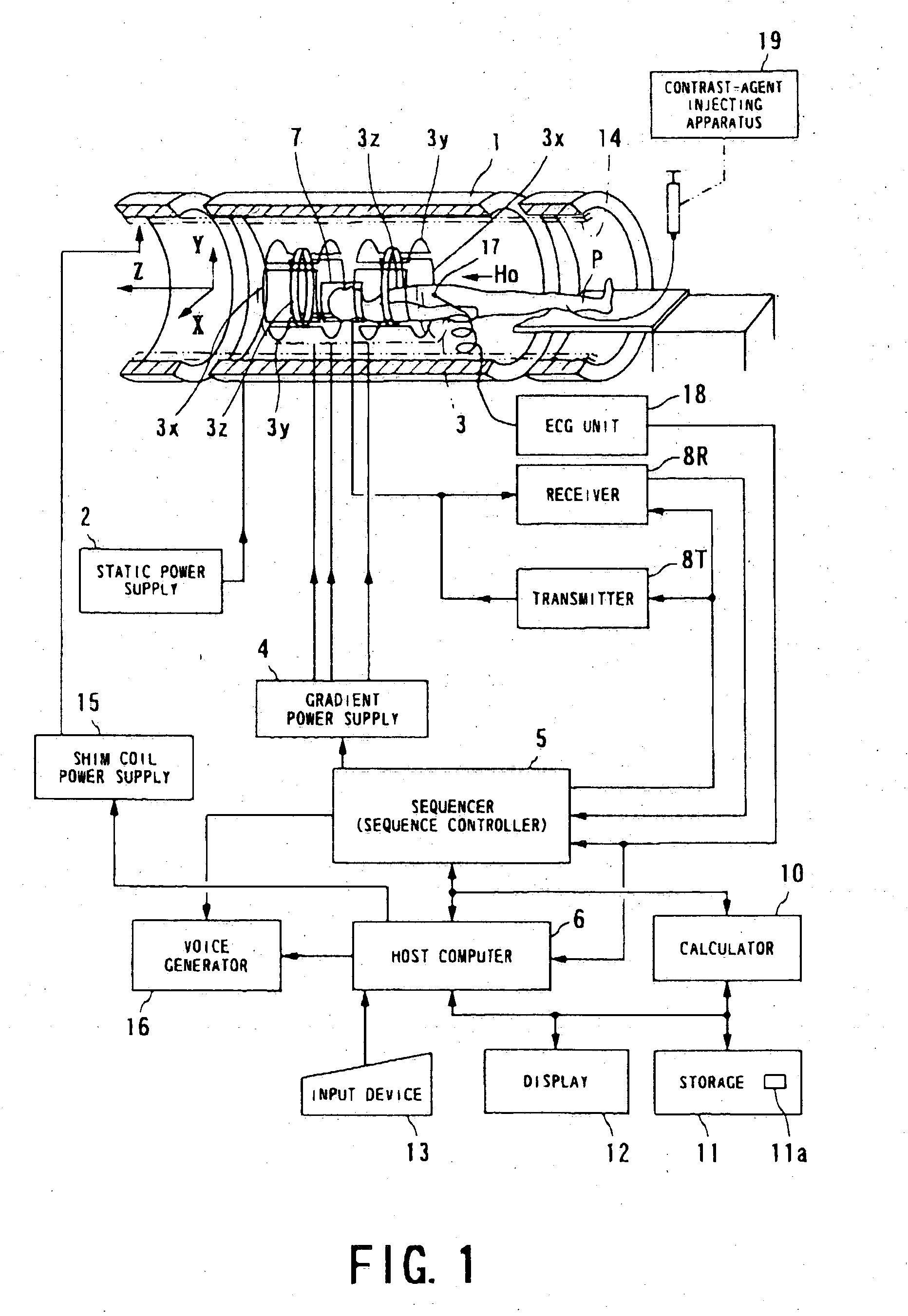
A system and method are provided for determining individualized scan and injection protocols for contrast-enhanced diagnostic imaging. Taking into account parameters specific to the scan subject, injection-related parameters, and scan parameters, the system and method can determine an optimal timing for a scan sequence to begin, to ensure that the scan sequence coincides with a desired contrast enhancement. Some embodiments further provide for real-time triggering of the scan commencement based on bolus tracking, and can adapt the scan and injection protocols in real-time based on monitored dynamic scan subject parameters and / or actual enhancement values determined from image data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
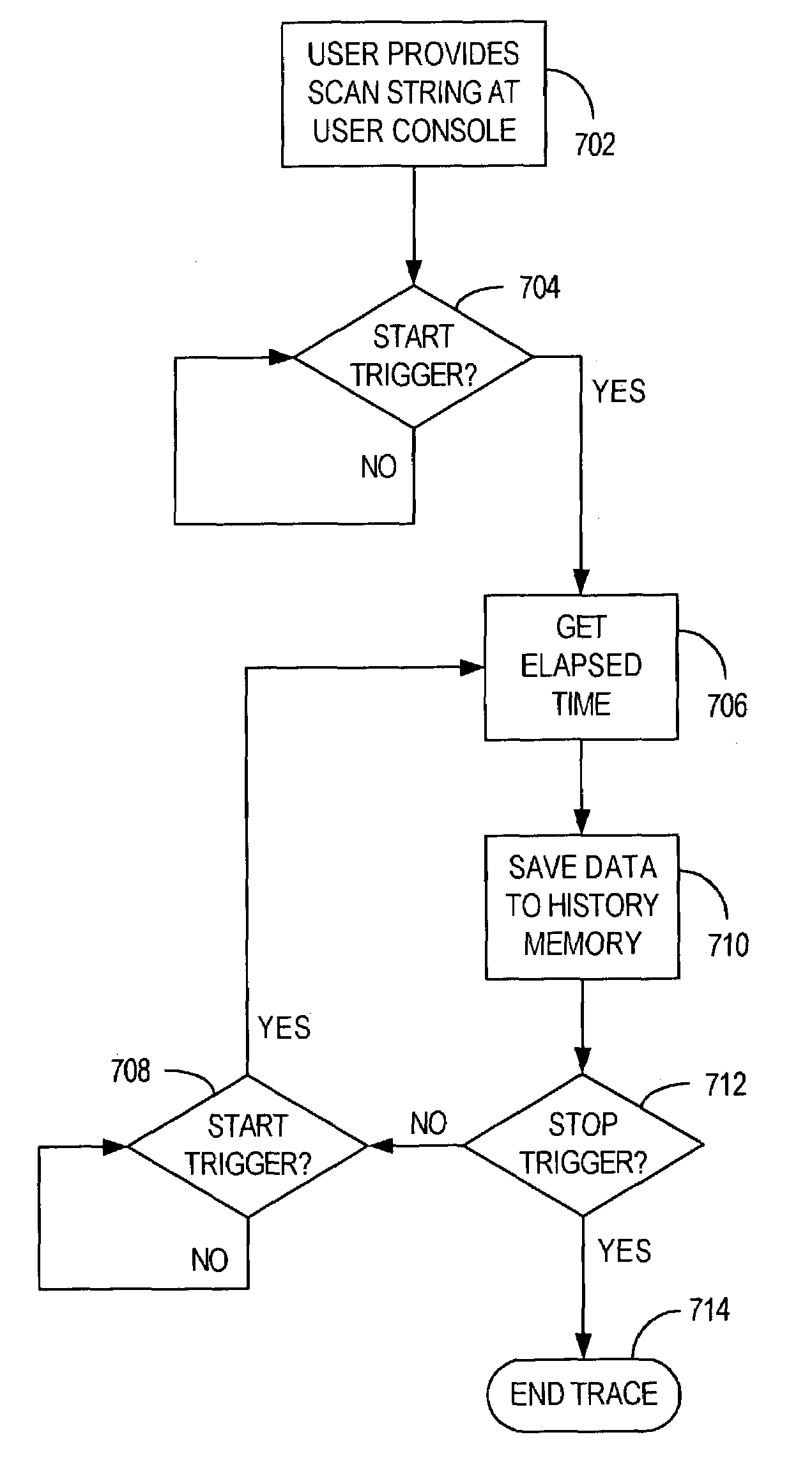
Method and apparatus for recording and monitoring bus activity in a multi-processor environment
ActiveUS7051131B1Error detection/correctionInput/output processes for data processingMulti processorProcessor register
A method and apparatus to facilitate a history trace of system bus activity in a Symmetric Multi-Processor (SMP) environment. A dynamic scan capability is provided to User (516) via Computer (504) that allows dynamic configuration of History Control Register (518), thus providing a maskable history stack of system bus activity to be obtained from History Memory (508) for subsequent analysis.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
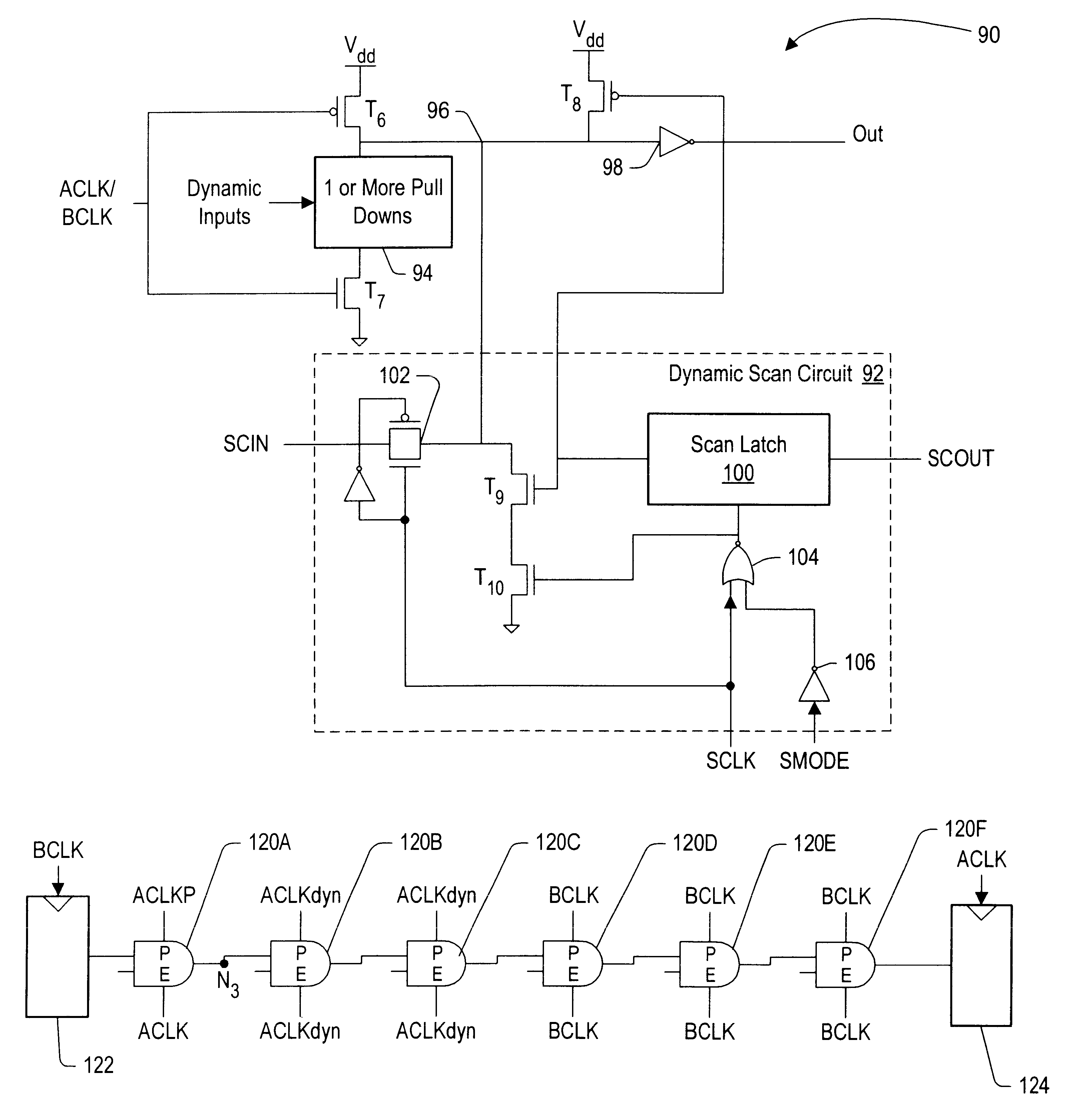
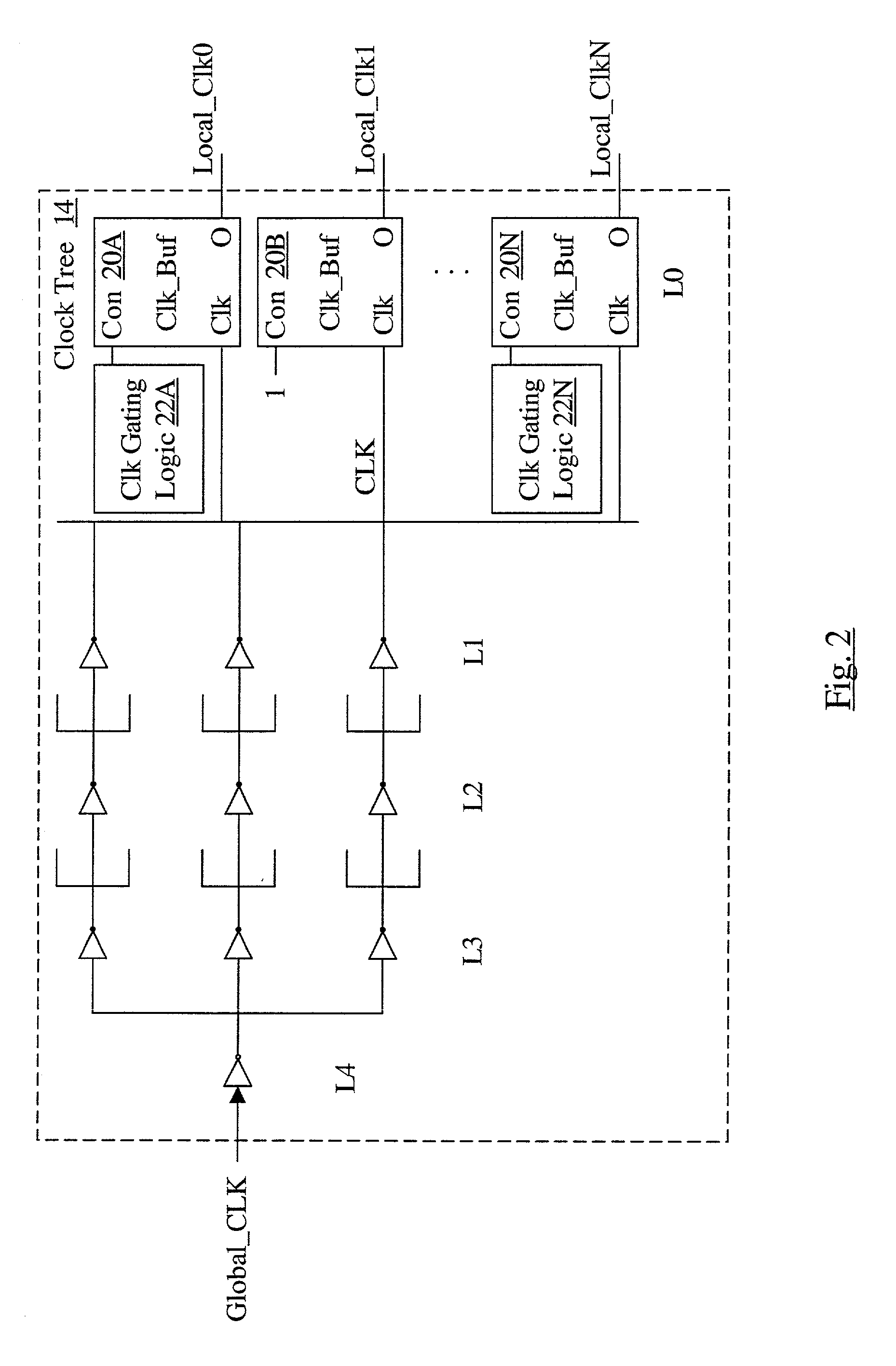
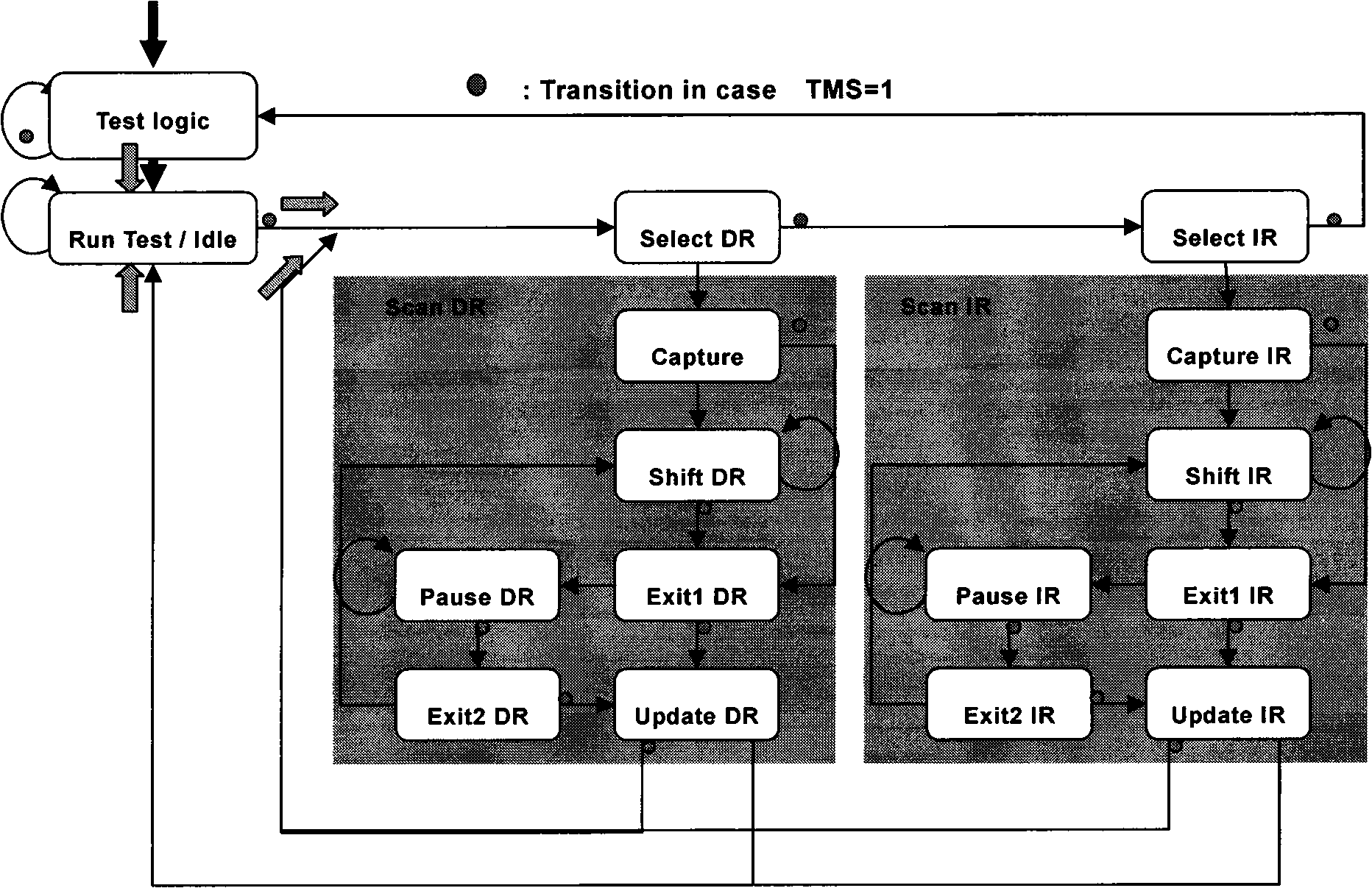
Dynamic scan circuitry for B-phase
A first dynamic logic circuit has an output node on which a scan value is provided during scan. One of one or more second dynamic logic circuits has an input coupled to the output node of the first dynamic logic circuit, and an output of the second dynamic logic circuits is sampled in response to the scan value during scan. In one embodiment, clock generation circuitry may be included which generates a first clock, a second clock, and a third clock. At least one evaluate pulse on the first clock prior is generated prior to sampling the output of the second dynamic logic circuits, the first clock controlling at least the evaluation of the second dynamic logic circuits. The second and third clocks are generated to isolate the output node from inputs to the first dynamic logic circuit responsive to the scan mode signal indicating that scan is active.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Hand-held dual spherical antenna system
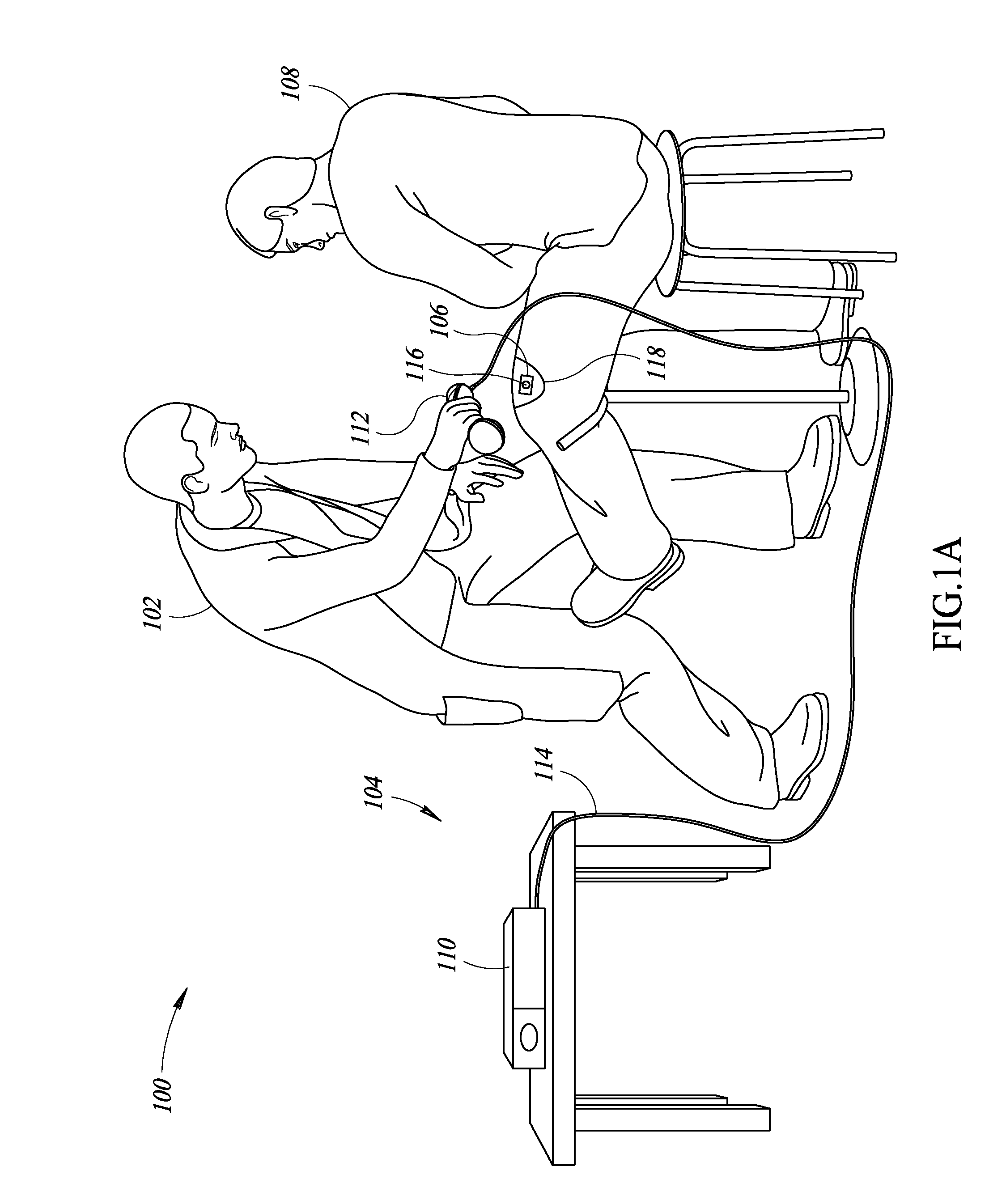
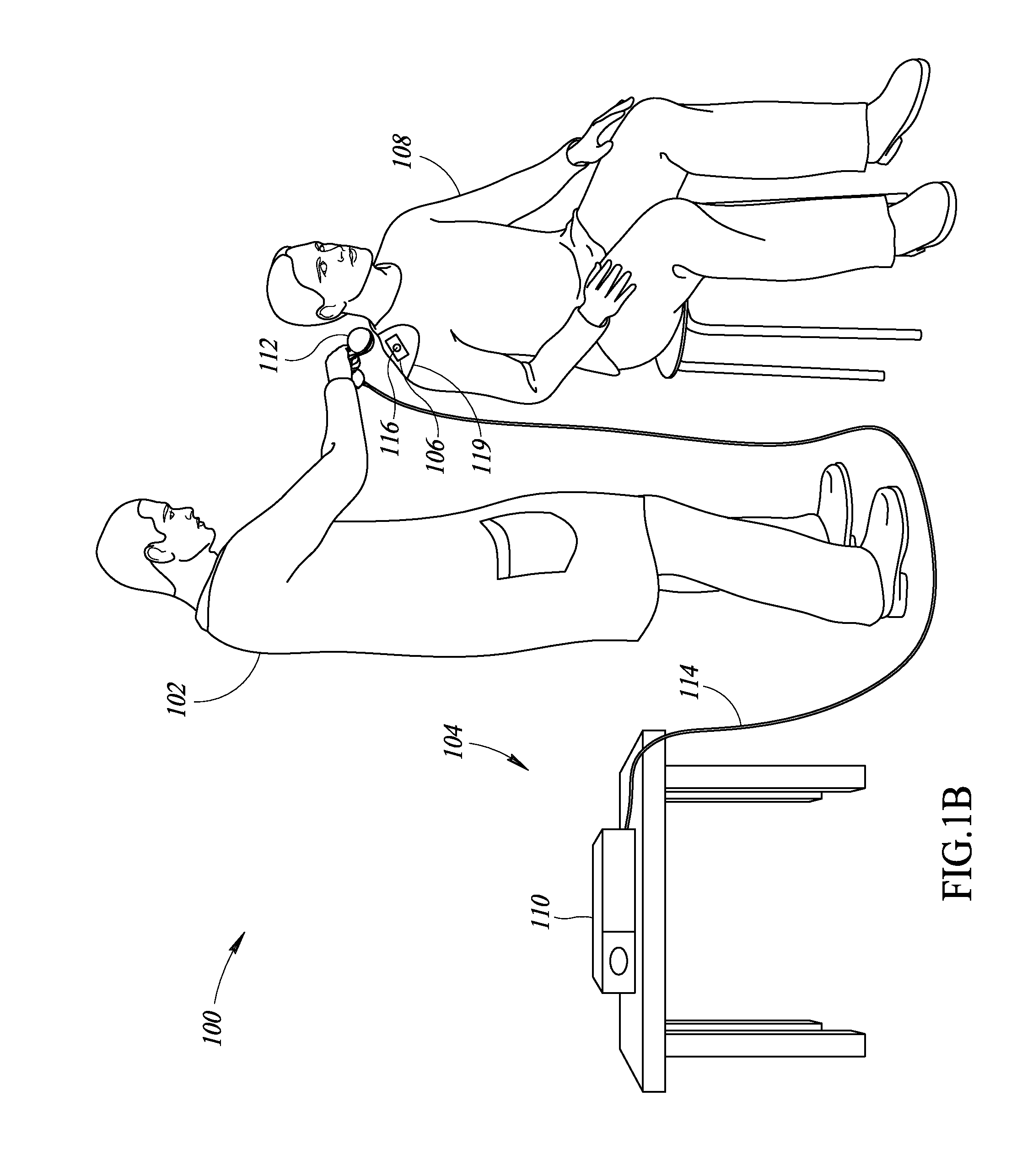
A hand-held antenna system allows medical personnel to ascertain the presence or absence of objects (e.g., medical supplies) tagged with transponders in an environment in which medical procedures are performed. In use, the hand-held antenna system may be positioned proximate a patient at a time after a medical procedure, such as after childbirth, so the system can scan the patient's body to determine the presence of objects tagged with transponders. The antenna system includes two sets of three antenna elements arranged mutually orthogonal to each other to transmit and receive signals in at least three coordinate directions. A controller is coupled to the antenna elements to transmit signals to the transponders and to receive response signals. The antenna system may operate in a static scan mode wherein the antenna system is held in a fixed position by a user and a dynamic scan mode wherein the antenna system is moved by a user.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
MR imaging under control of both the number of data acquisition times and the number or pre-pulse application times in the same k-space
InactiveUS20040061496A1Significant timeReduce application rateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsK-spaceData acquisition
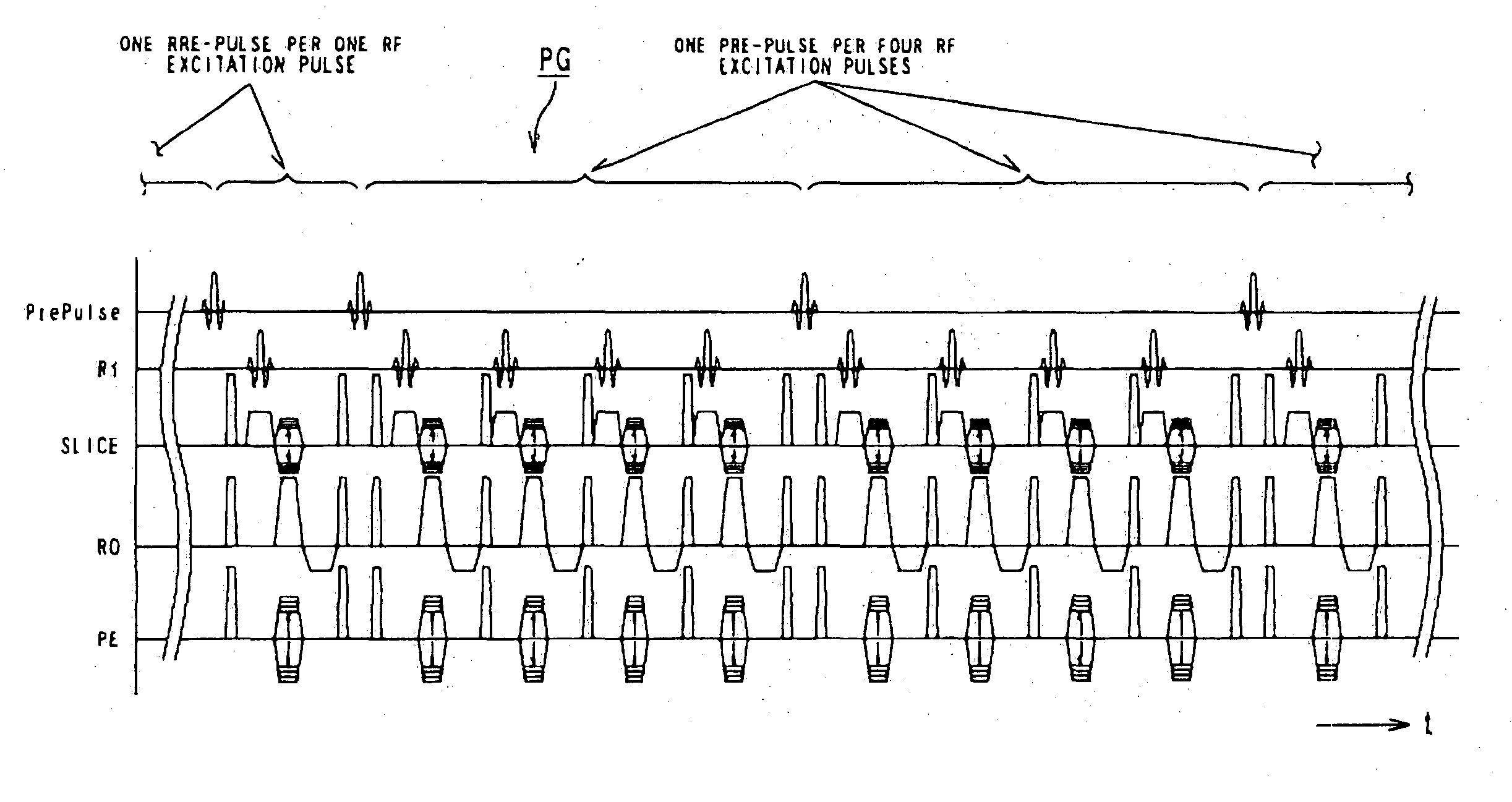
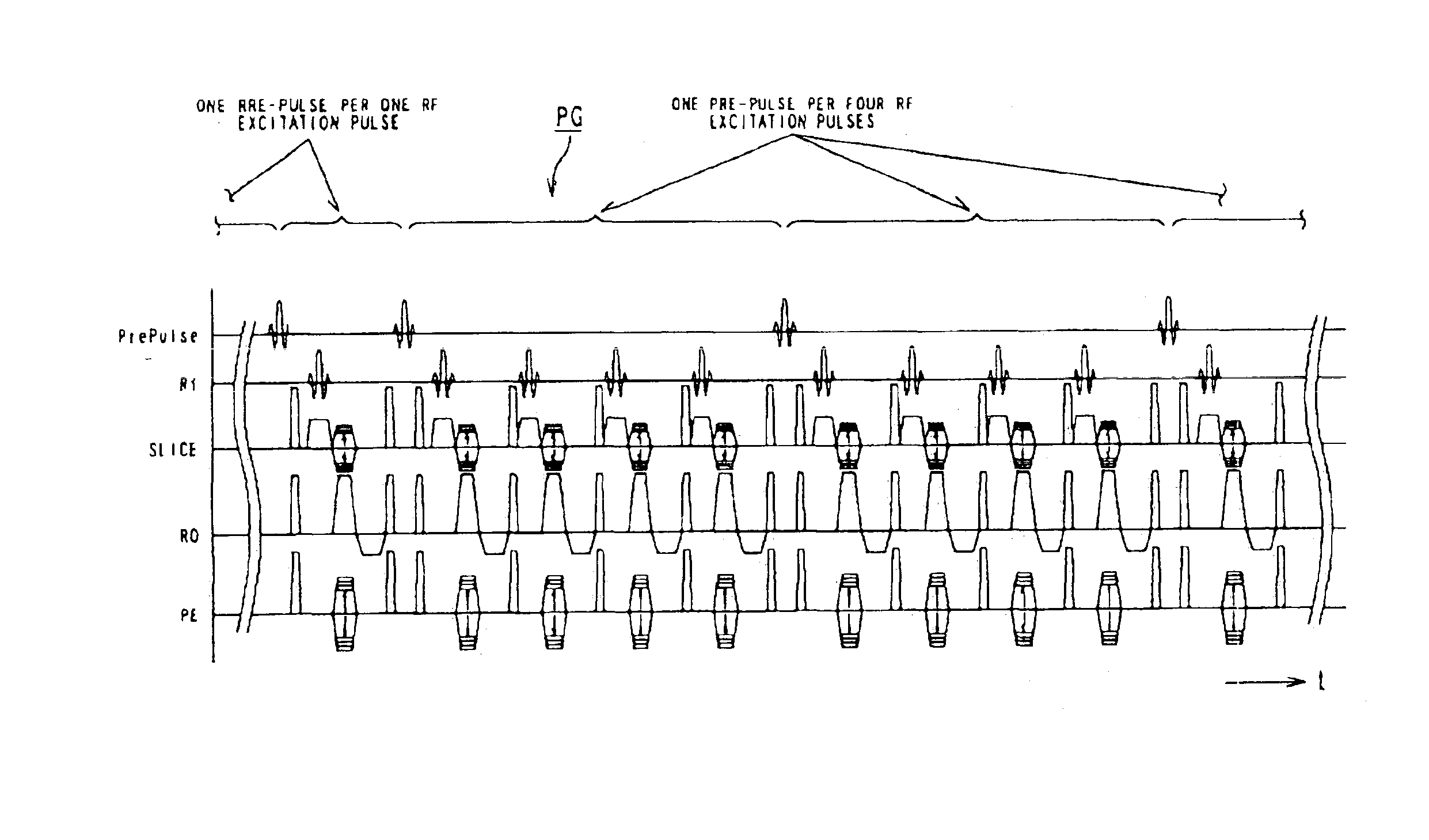
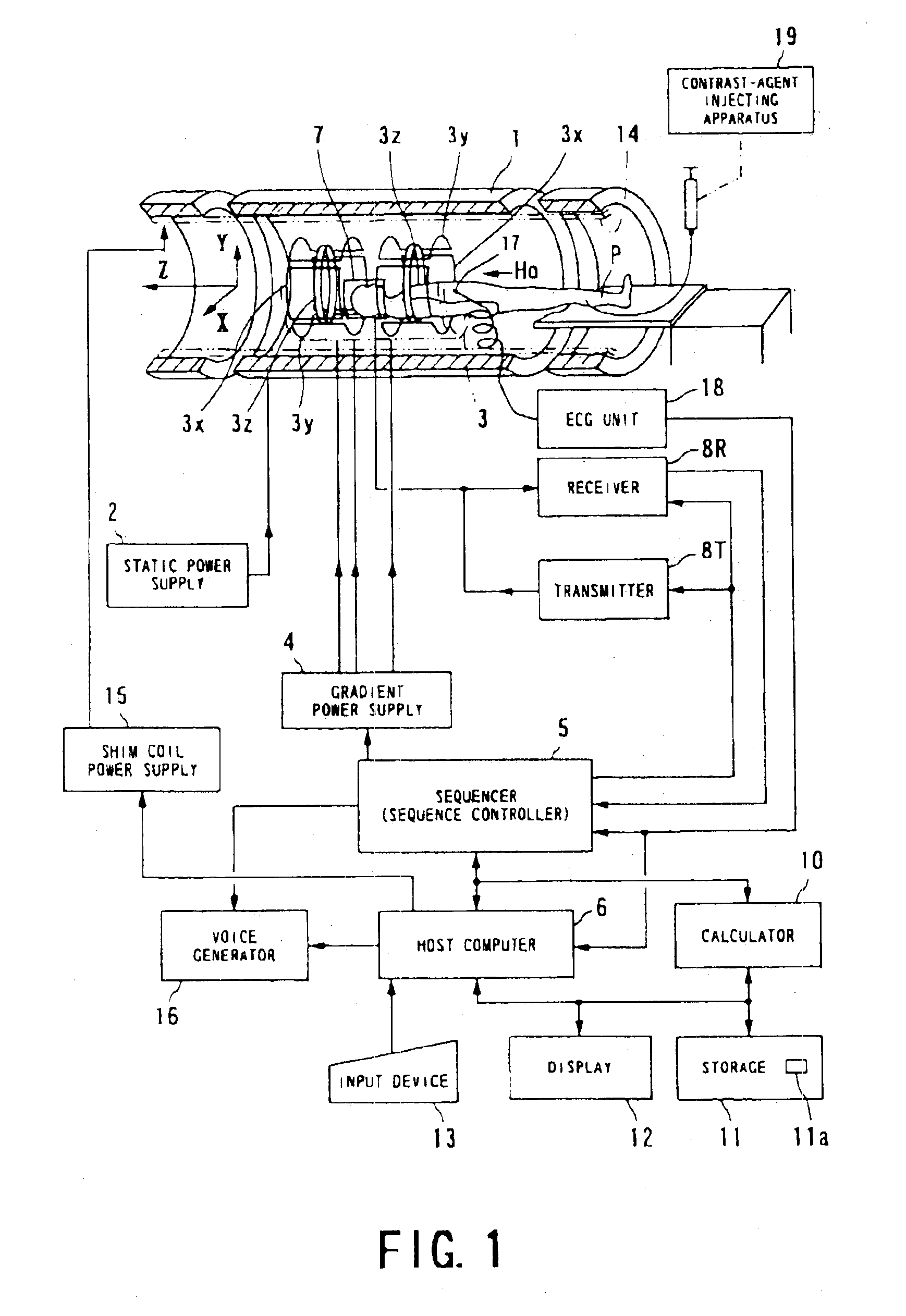
Magnetic resonance imaging uses a pulse sequence formed to include a pre-pulse, an RF excitation pulse, an encoding gradient pulse, and a reading gradient pulse. The encoding gradient pulse has an encoding amount determined to allow a data acquisition position in a k-space to be directed outward from a center of the k-space. A train of pulses including the RF excitation pulse, the encoding gradient pulse, and the reading gradient pulse is repeated to allow the number of times of data acquisition in the k-space to become larger as approaching to a central region of the k-space. The pre-pulse is formed to be reduced in an application rate to the RF excitation pulse as approaching to an outward position in the k-space. By way of example, this pulse sequence is used for contrast enhanced MRA carried out under a dynamic scan.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
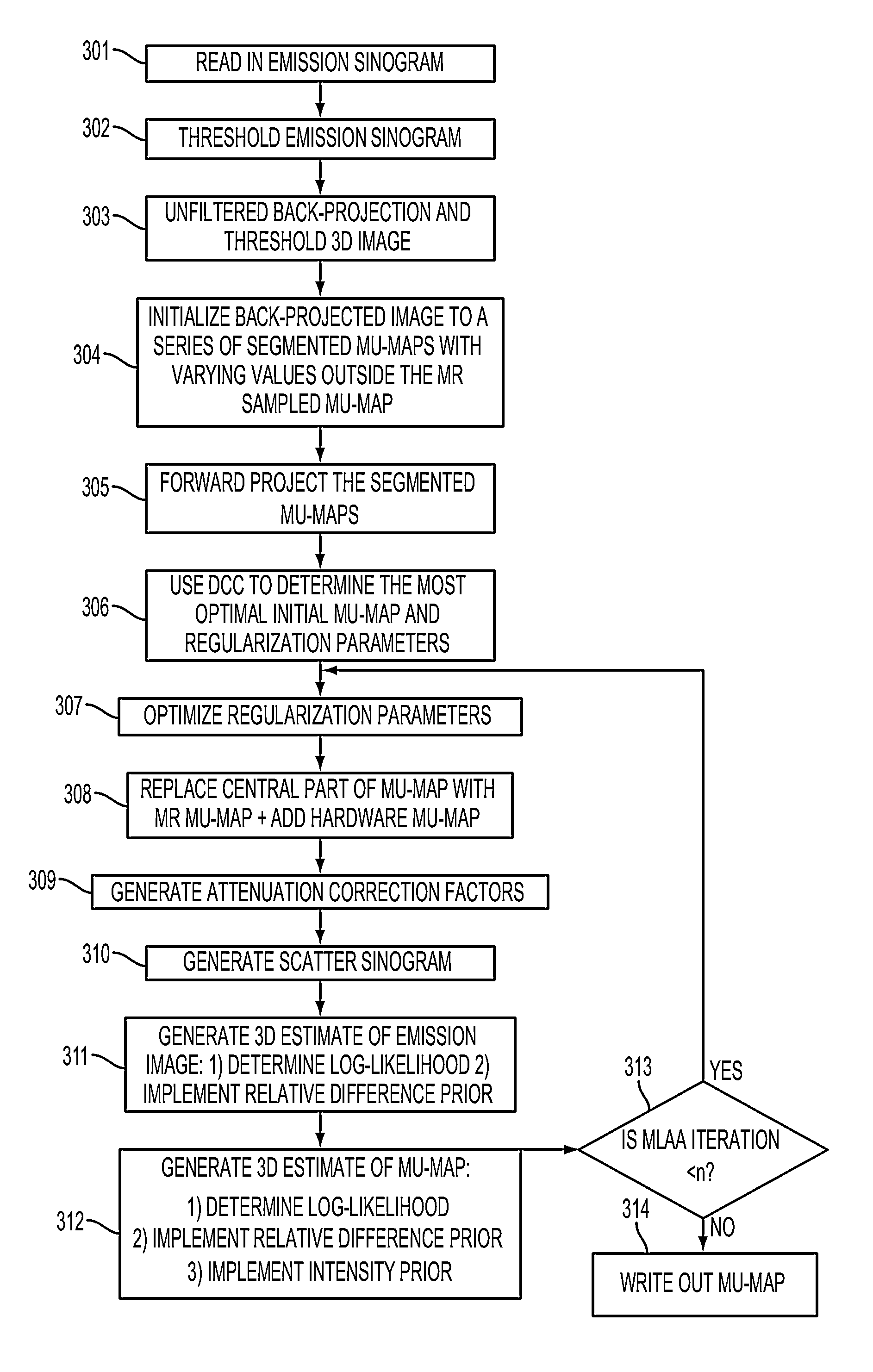
Generating Attenuation Correction Maps for Combined Modality Imaging Studies and Improving Generated Attenuation Correction Maps Using MLAA and DCC Algorithms
ActiveUS20140056500A1Reduce noiseReduce the numberReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionWhole bodyCompanion animal
The DCC (Data Consistency Condition) algorithm is used in combination with MLAA (Maximum Likelihood reconstruction of Attenuation and Activity) to generate extended attenuation correction maps for nuclear medicine imaging studies. MLAA and DCC are complementary algorithms that can be used to determine the accuracy of the mu-map based on PET data. MLAA helps to estimate the mu-values based on the biodistribution of the tracer while DCC checks if the consistency conditions are met for a given mu-map. These methods are combined to get a better estimation of the mu-values. In gated MR / PET cardiac studies, the PET data is framed into multiple gates and a series of MR based mu-maps corresponding to each gate is generated. The PET data from all gates is combined. Once the extended mu-map is generated the central region is replaced with the MR based mu-map corresponding to that particular gate. On the other hand, in dynamic PET studies the uptake in the patient's arms reaches a steady state only after the tracer distributes throughout the body. Hence, for dynamic scans, the projection data of all frames is summed and used to generate the MLAA based extended mu-map for all frames.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Dynamic PET image denoising method based on combined image guiding
InactiveCN103955899AQuality improvementReduce noiseImage enhancementComputerised tomographsPattern recognitionImage denoising
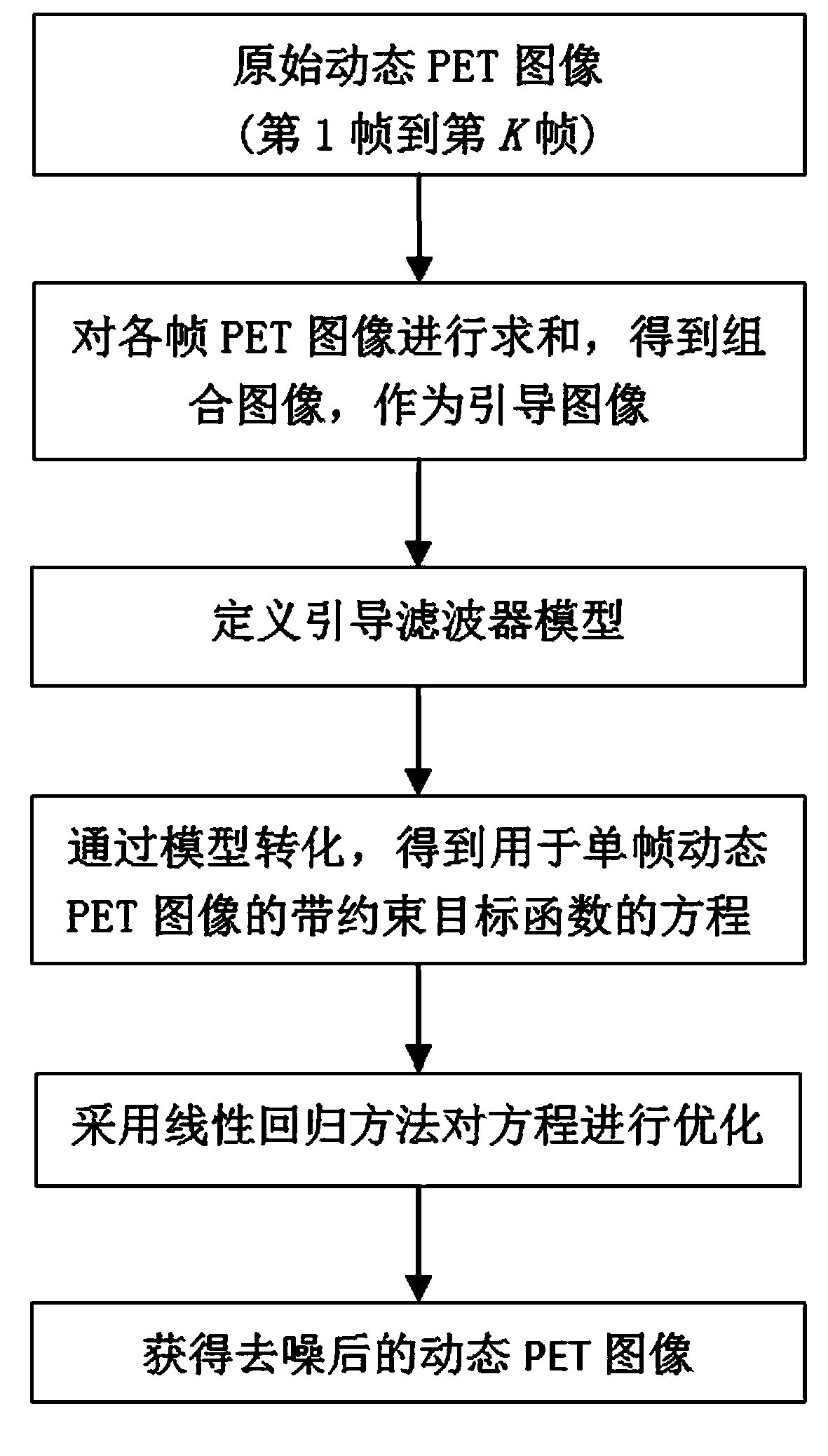
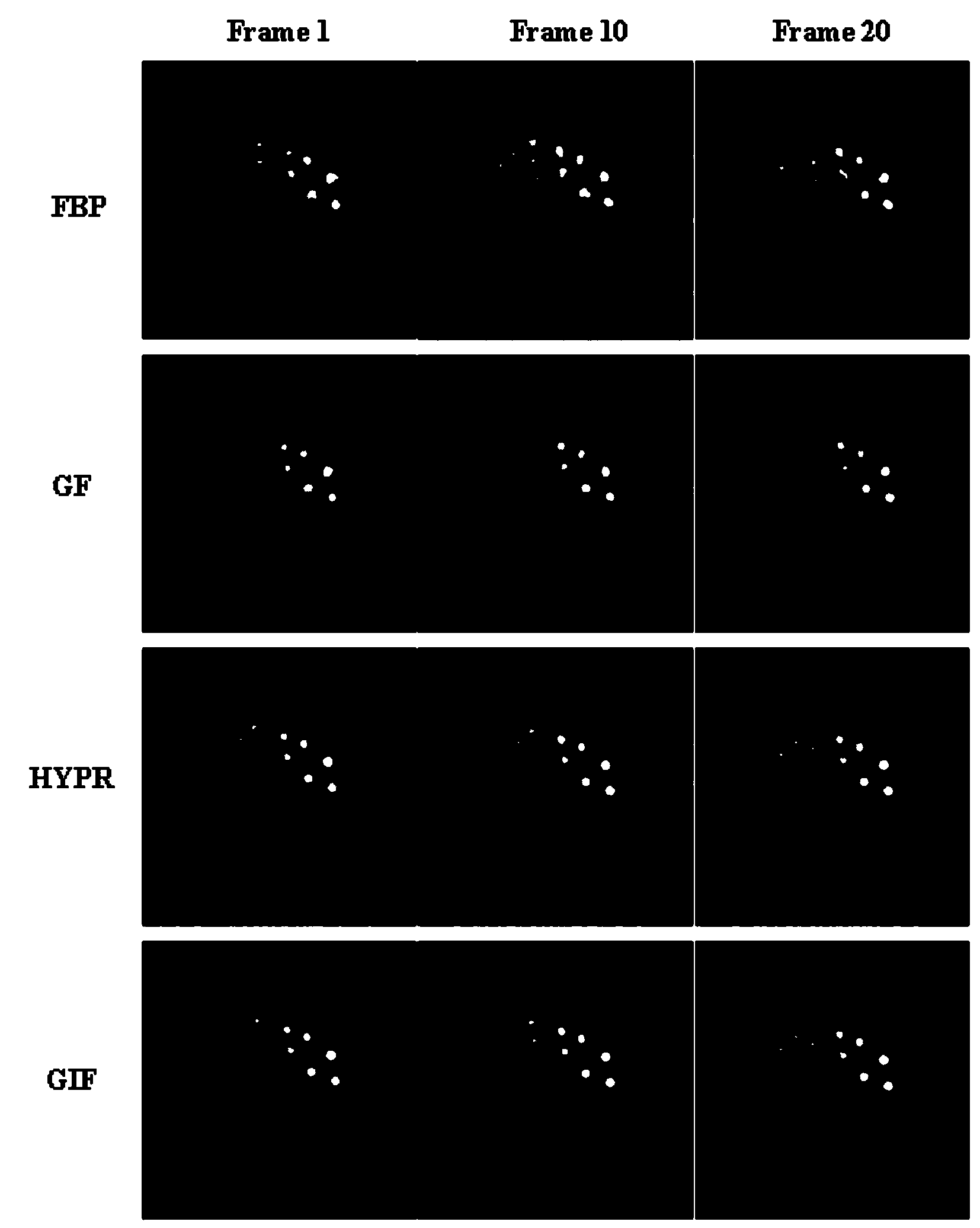
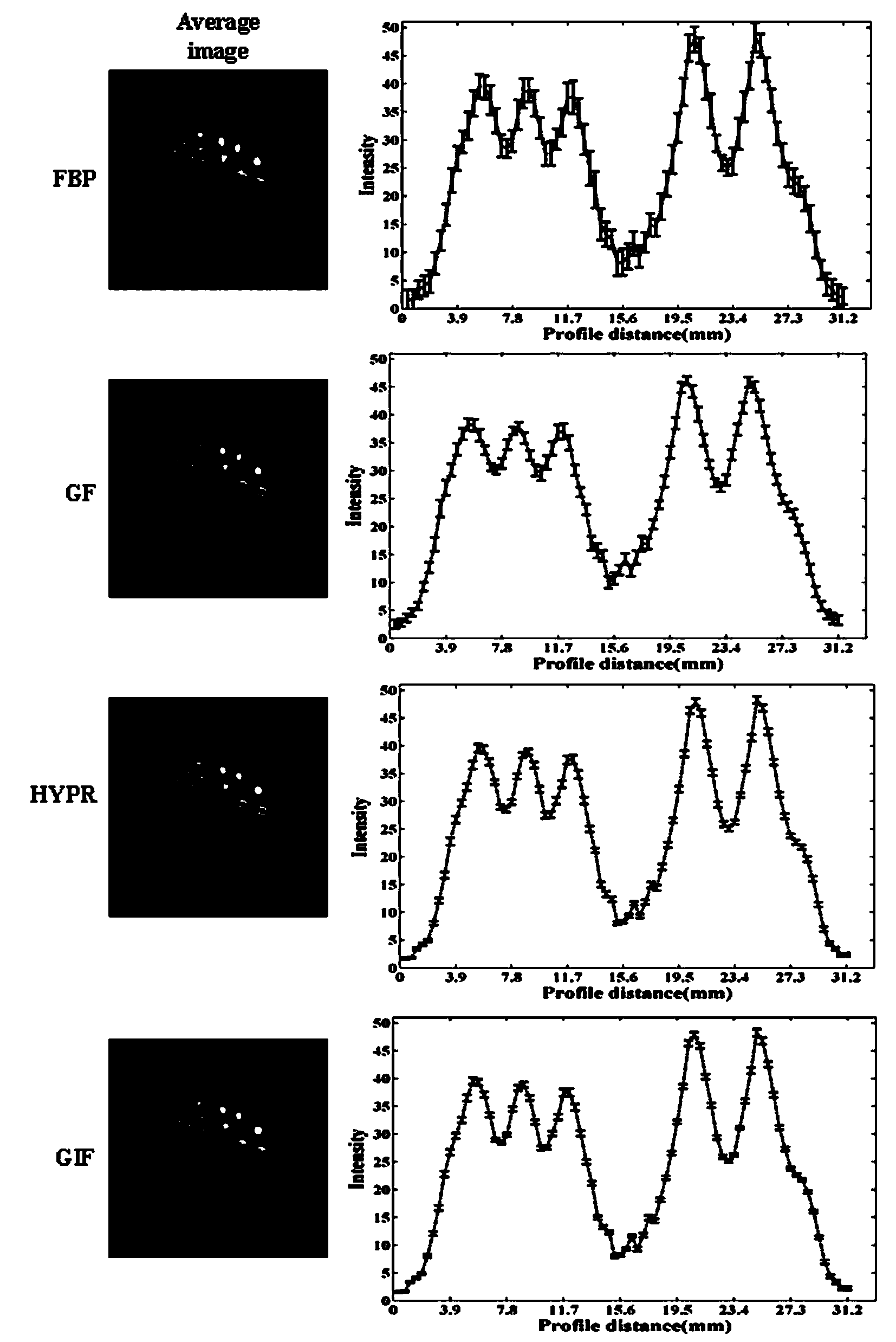
The invention discloses a dynamic PET image denoising method based on combined image guiding. The method comprises the first step of utilizing a PET imaging device to carry out dynamic scanning and reestablishing a dynamic PET image, the second step of calculating and obtaining a combined image according to the reestablished PET image obtained in the first step, the third step of defining a guiding filter model and a kernel function of the guiding filter model, the fourth step of regarding the combined image obtained in the second step as a guiding image, and converting the model obtained in the third step to obtain an equation with a constraint target function for the single-frame dynamic PET image, and the fifth step of carrying out calculation to obtain the denoised dynamic PET image based on the linear regression method and overall parameter selection on the equation according to the result obtained in the fourth step. According to the method, the combined image serves as the guiding image, the noise of the single-frame dynamic PET image can be effectively reduced, and the quality of the dynamic PET image can be greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Detecting device integrated with light sound ultrasonic excitation and sensor
InactiveCN101301201AImprove excitationImprove efficiencyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationSonificationCell sensitivity
The invention provides an optical acoustic ultrasound excitation and induction integrated detection device. An acoustic insulating layer, a sound absorption pad, a miniaturized semiconductor laser tube, a Fourier lens, a cylinder lens, a protection film and an annular multi-ring array sensor are all arranged in casing of the detection device and at same axle wire to form an integrated coaxial confocal structure. The multi-ring array sensor can generate ultrasonic signal, receive ultrasonic echo signal and receive optical acoustic signal by time-sharing excitation to realize optical acoustic ultrasound single or combined detection of A-type dynamic scan. The detection device has advantages of integrating excitation and induction of optical acoustic ultrasound, greatly increasing excitation and induction efficiency optical acoustic ultrasound, effectively reducing laser energy demand, increasing detection depth, and having high measurement sensitivity, simple operation and low cost. The detection device can be widely applied in fields of blood oxygen detection, blood sugar detection, HIFU therapy and effect monitoring, industrial crack detection and so on.
Owner:刘国栋
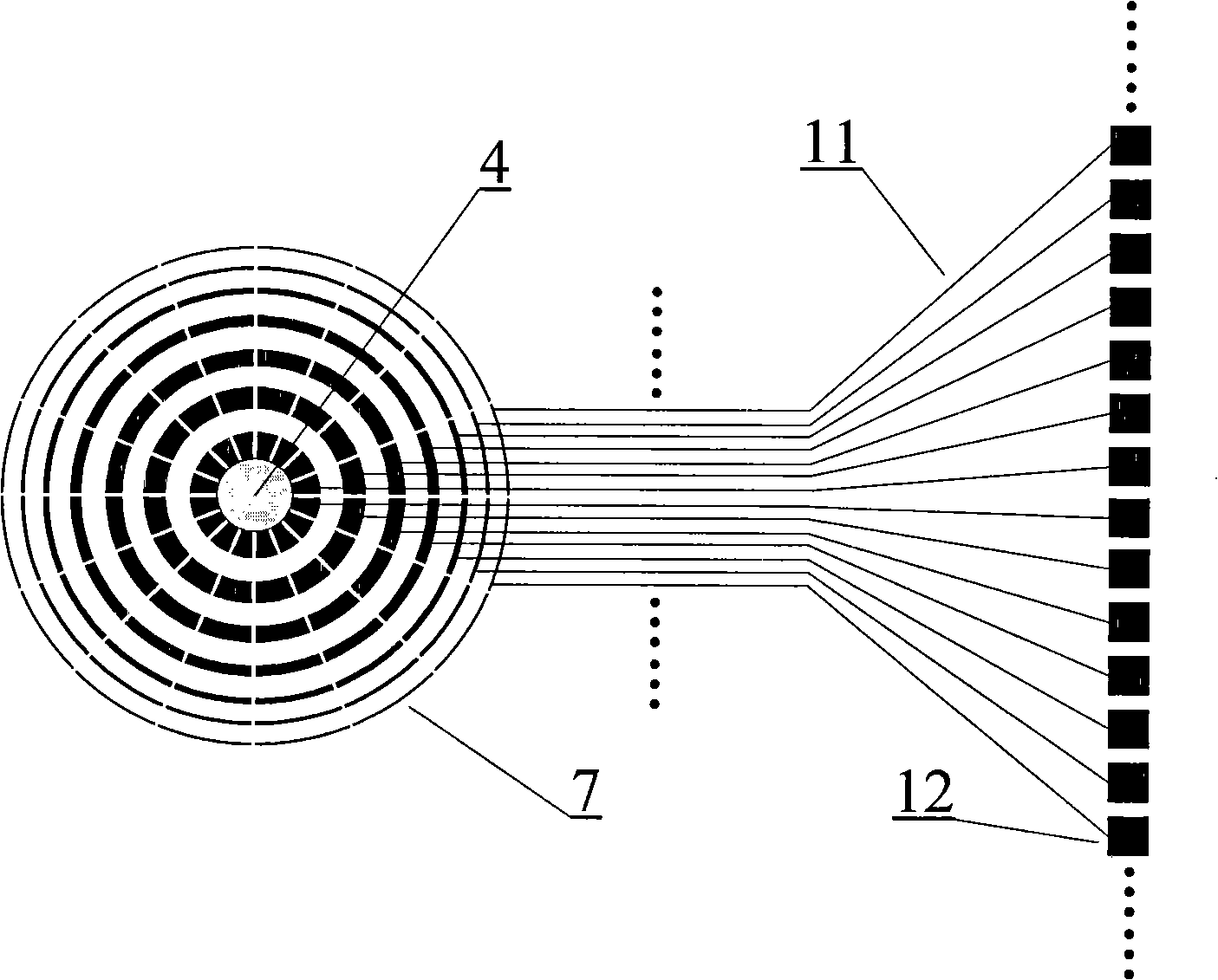
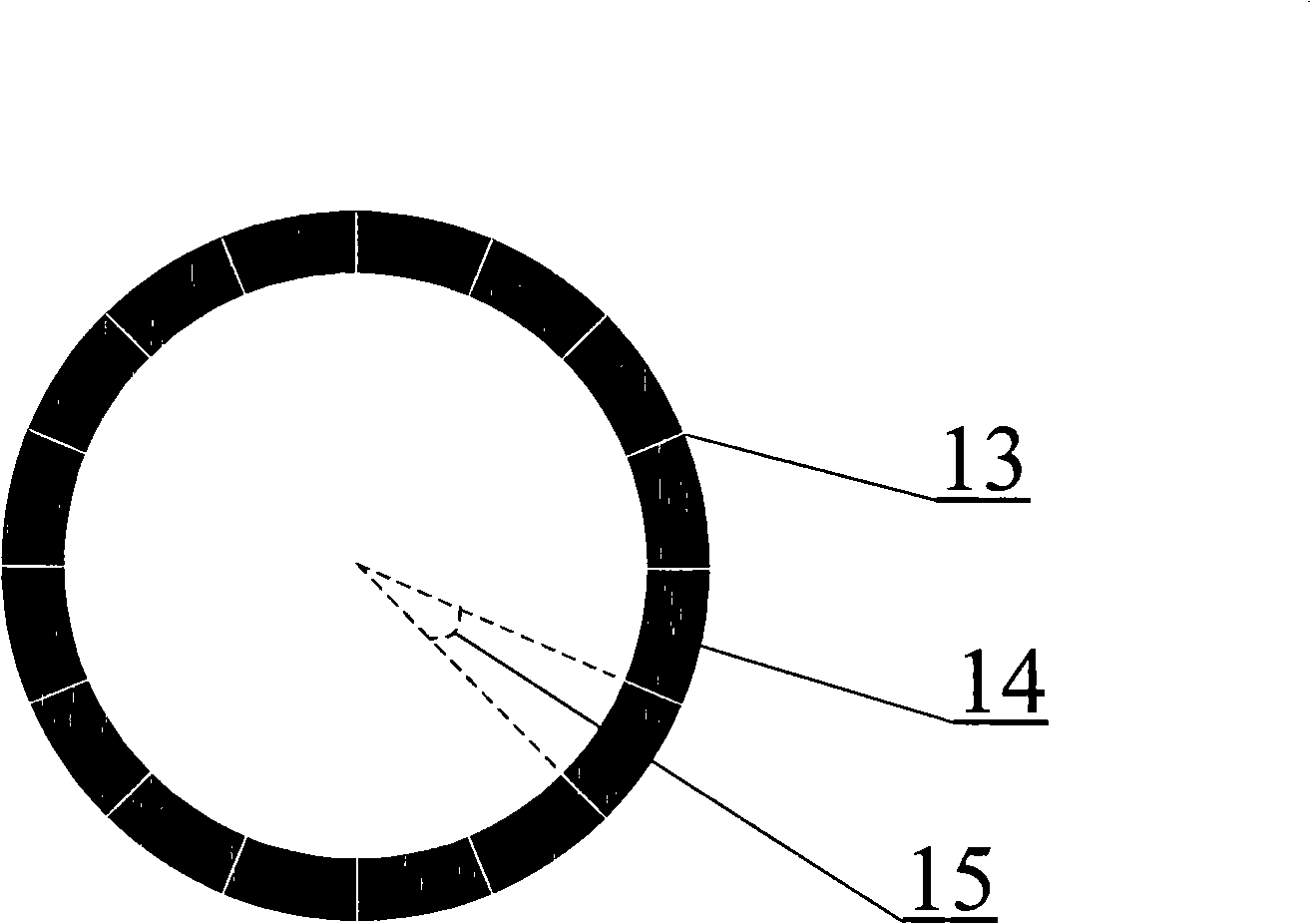
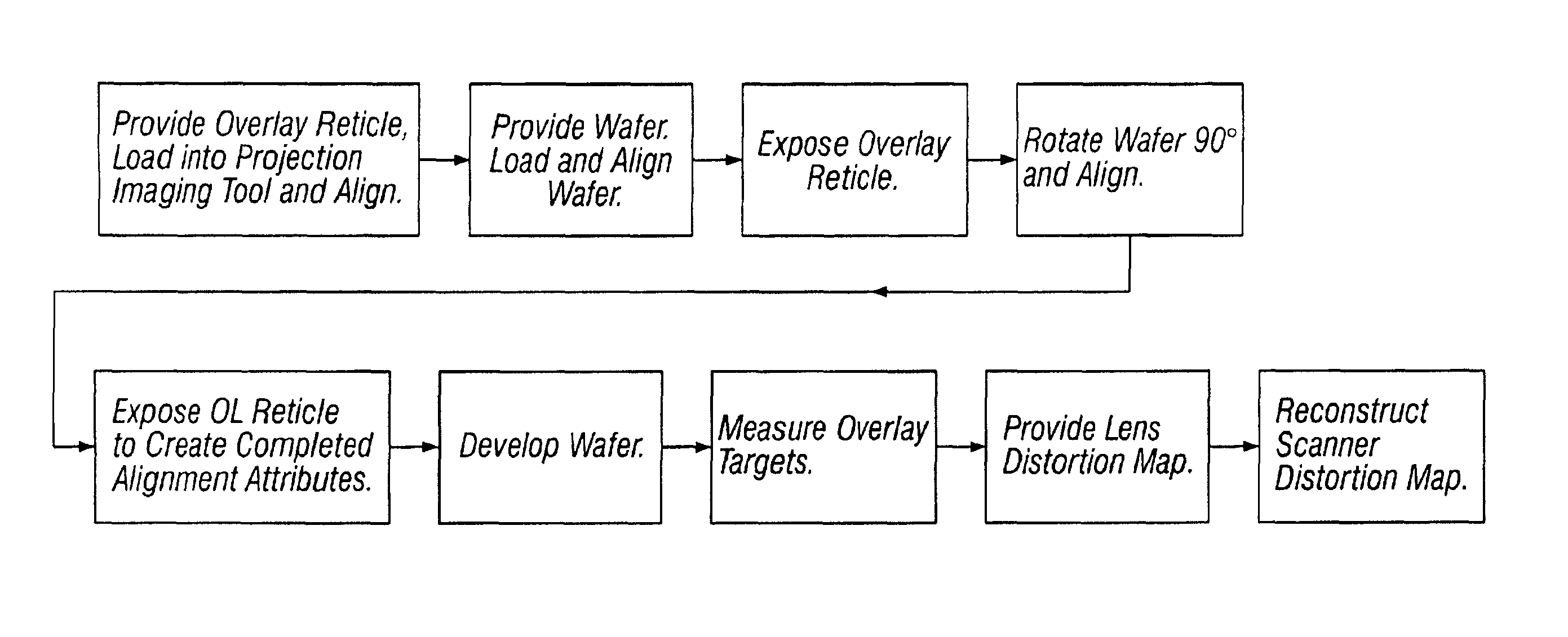
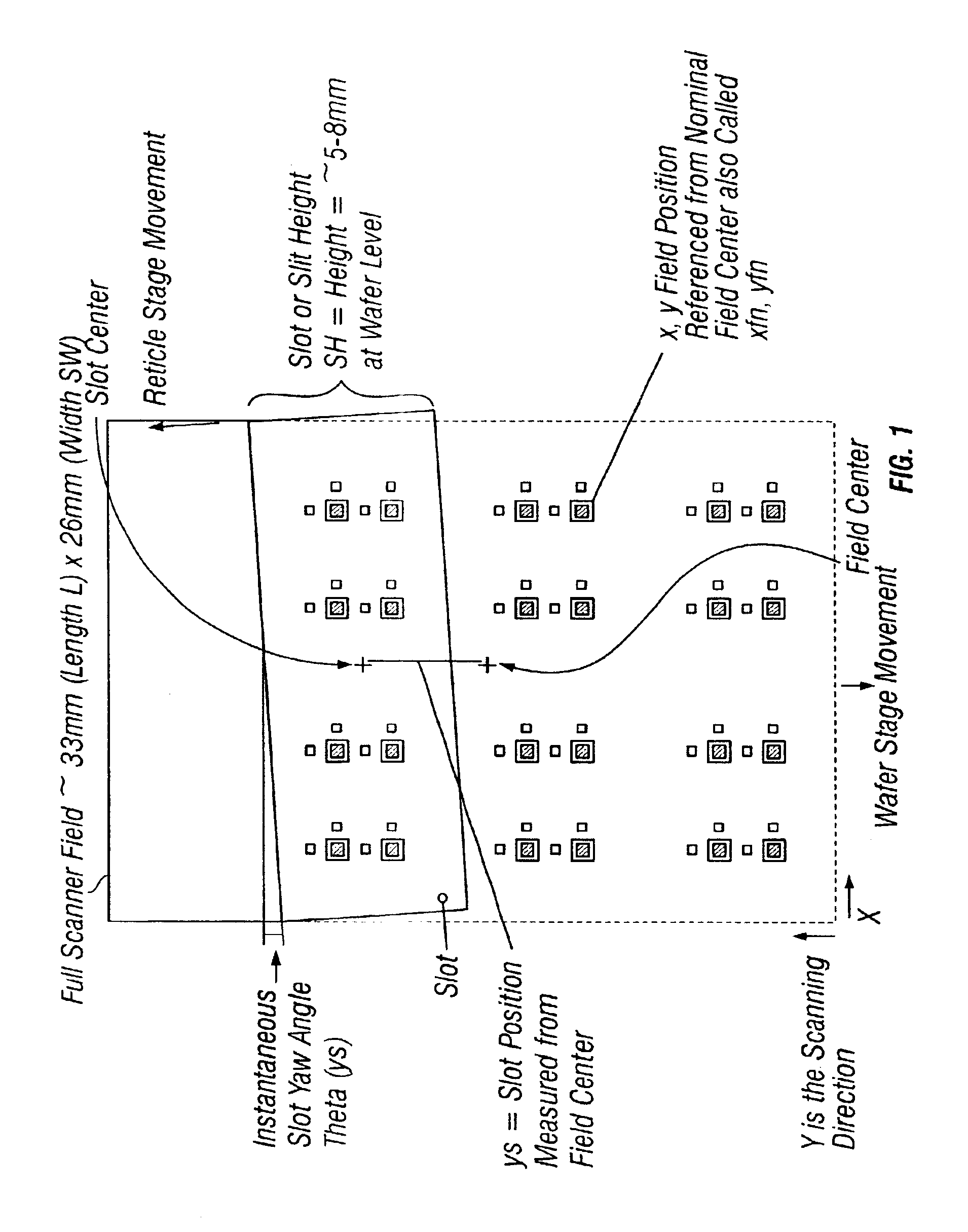
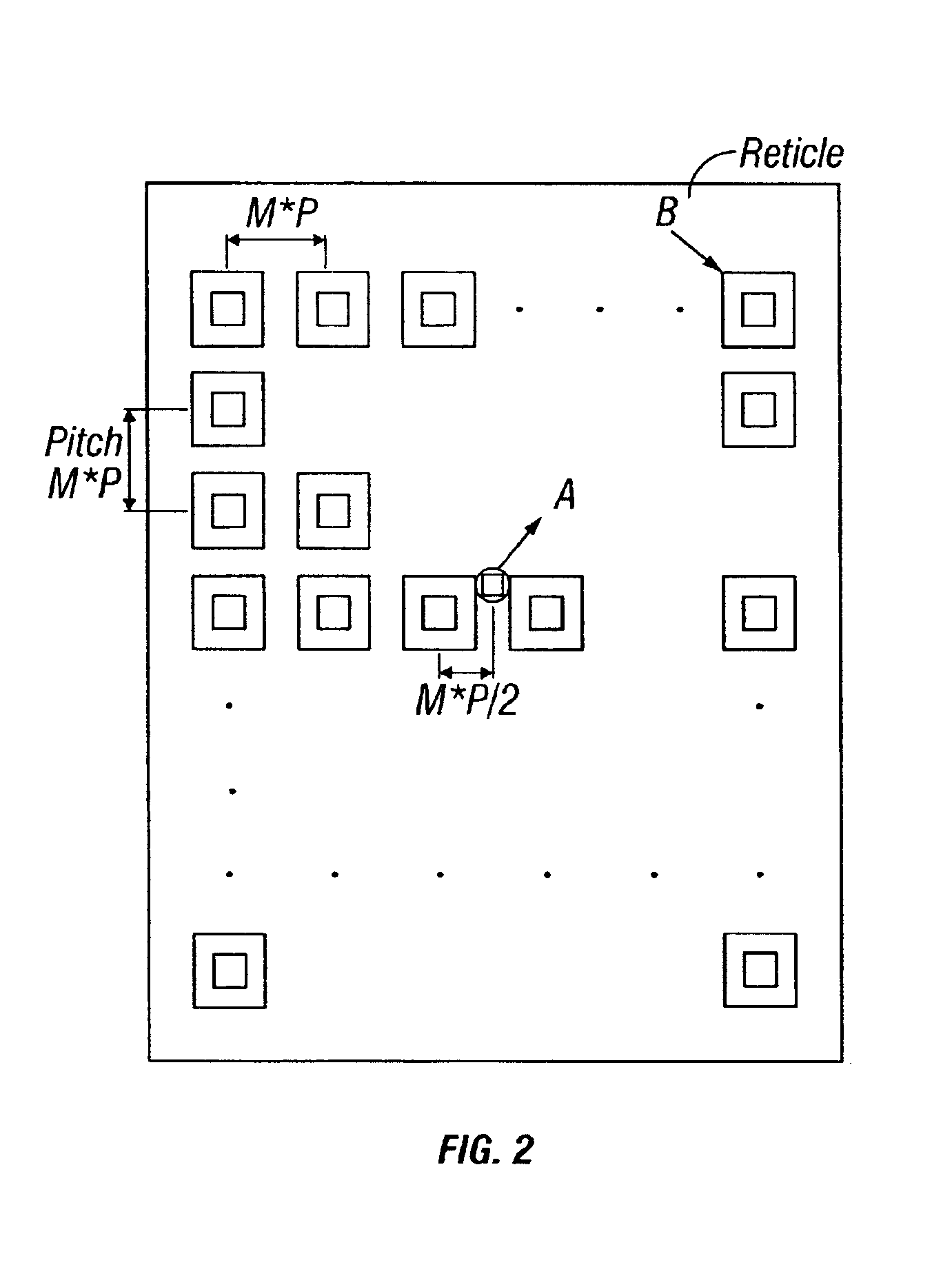
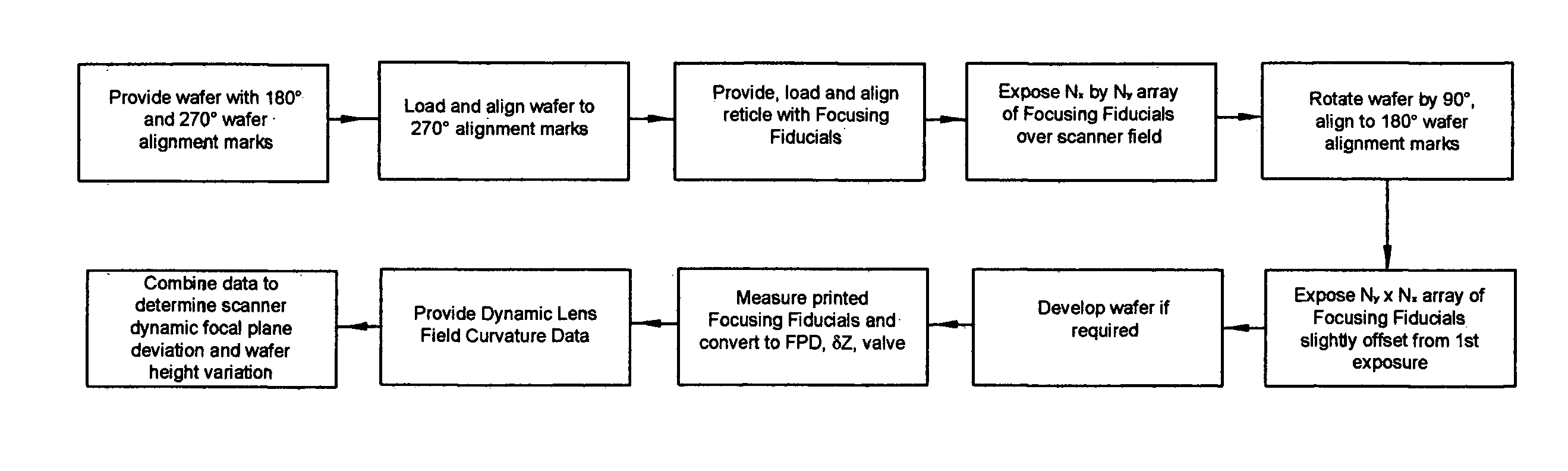
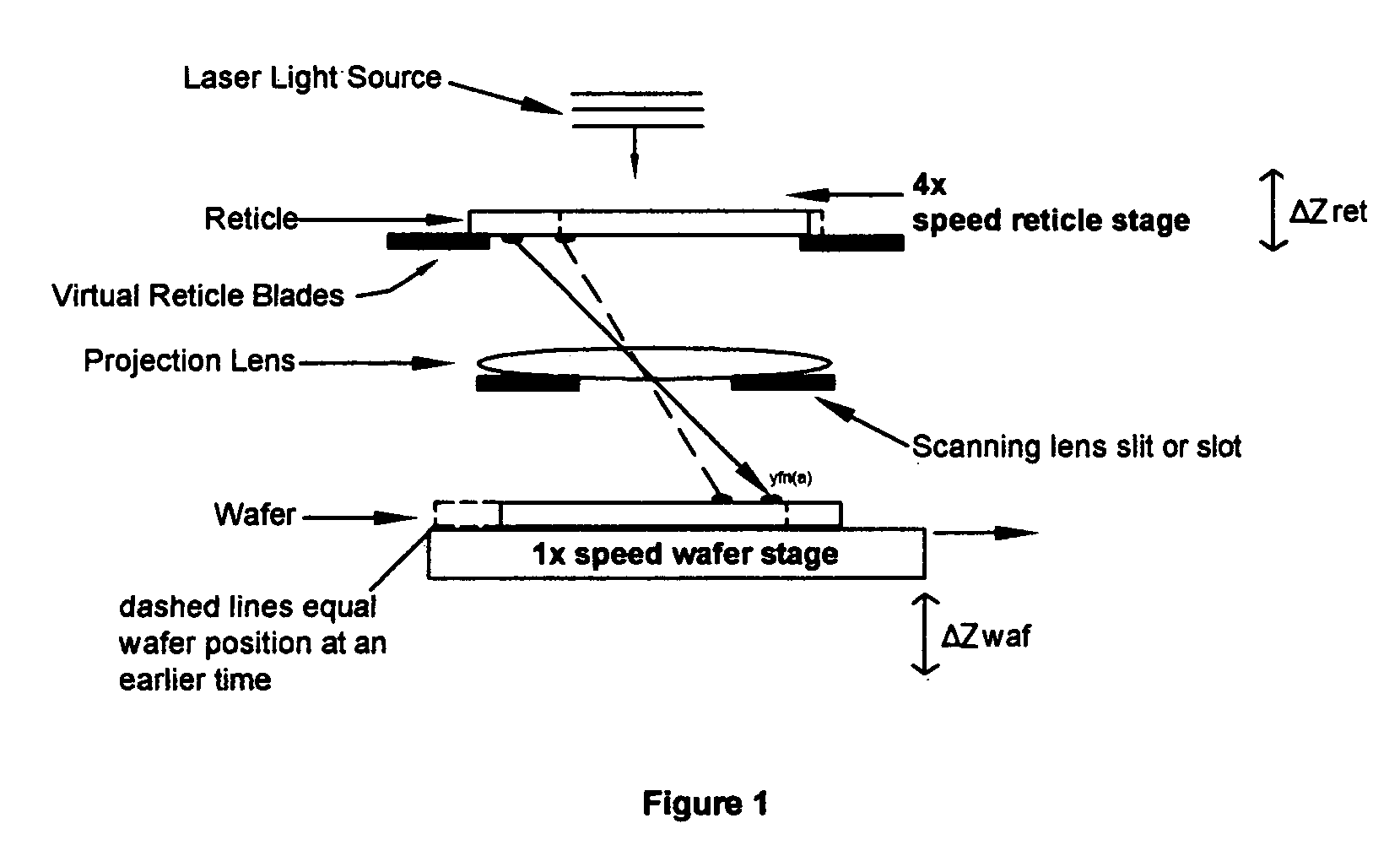
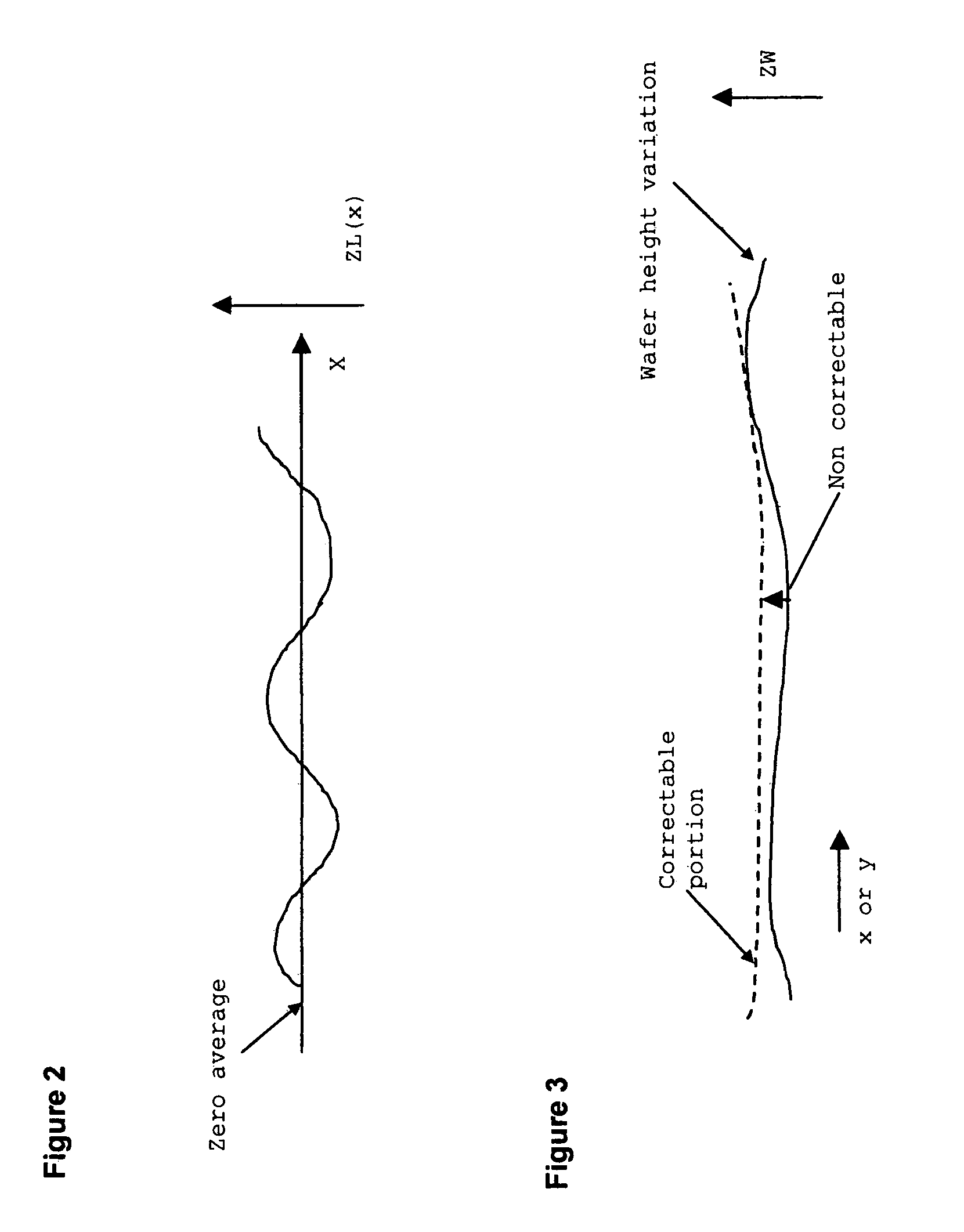
Method and apparatus for self-referenced dynamic step and scan intra-field scanning distortion
A method and apparatus for determining the dynamic scanning distortion present in lithographic scanners. A special reticle pattern is exposed over the full field that is to be characterized. The wafer is then rotated 90 degrees and one or more exposures over the same field are made. Interlocking alignment structures on the resulting developed wafer are then measured and used to reconstruct the dynamic scanner distortion to within a translation, rotation, and scan skew. Alternative embodiments describe techniques for extracting the repeatable part of the dynamic scan error.
Owner:LITEL INSTR
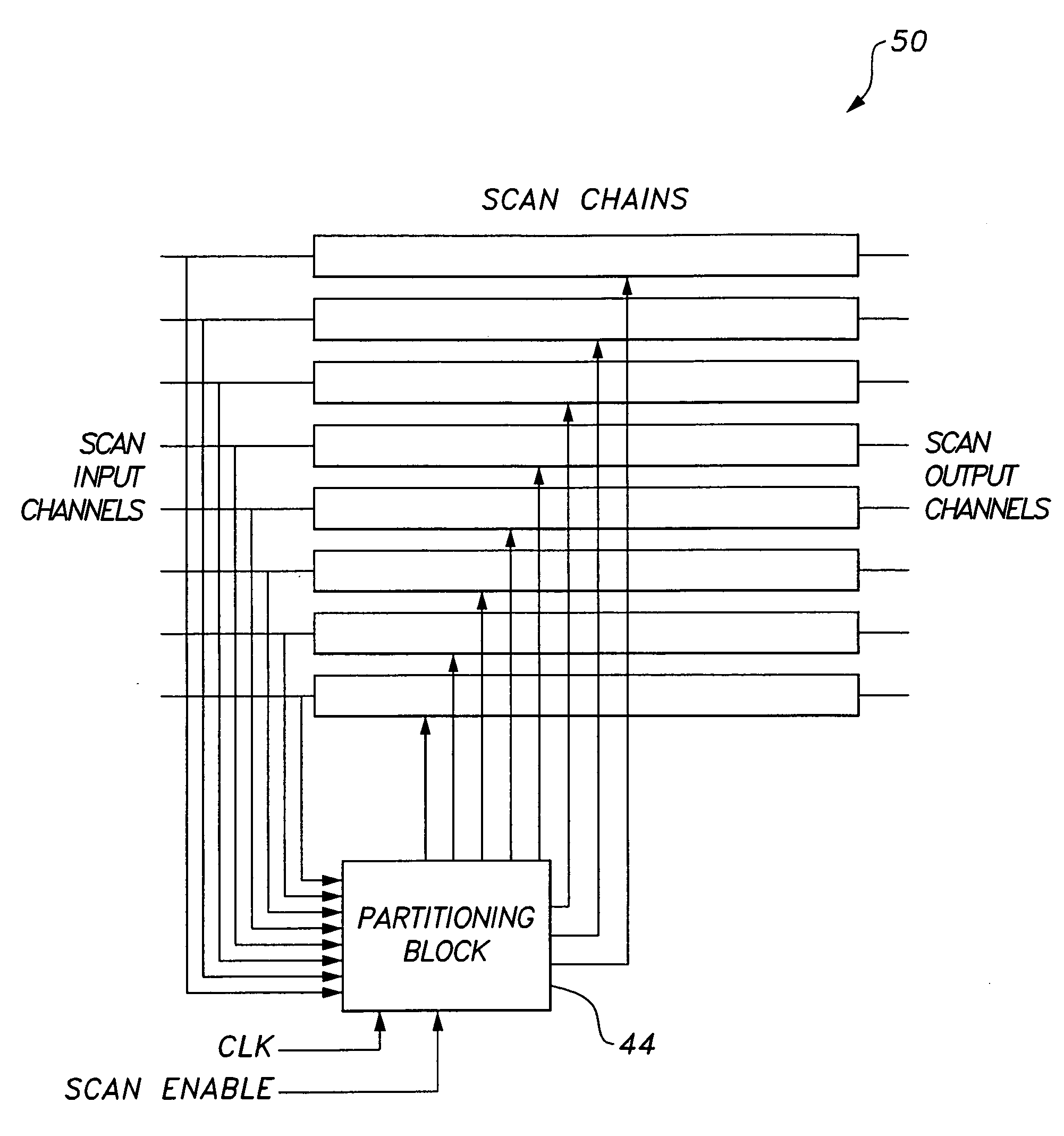
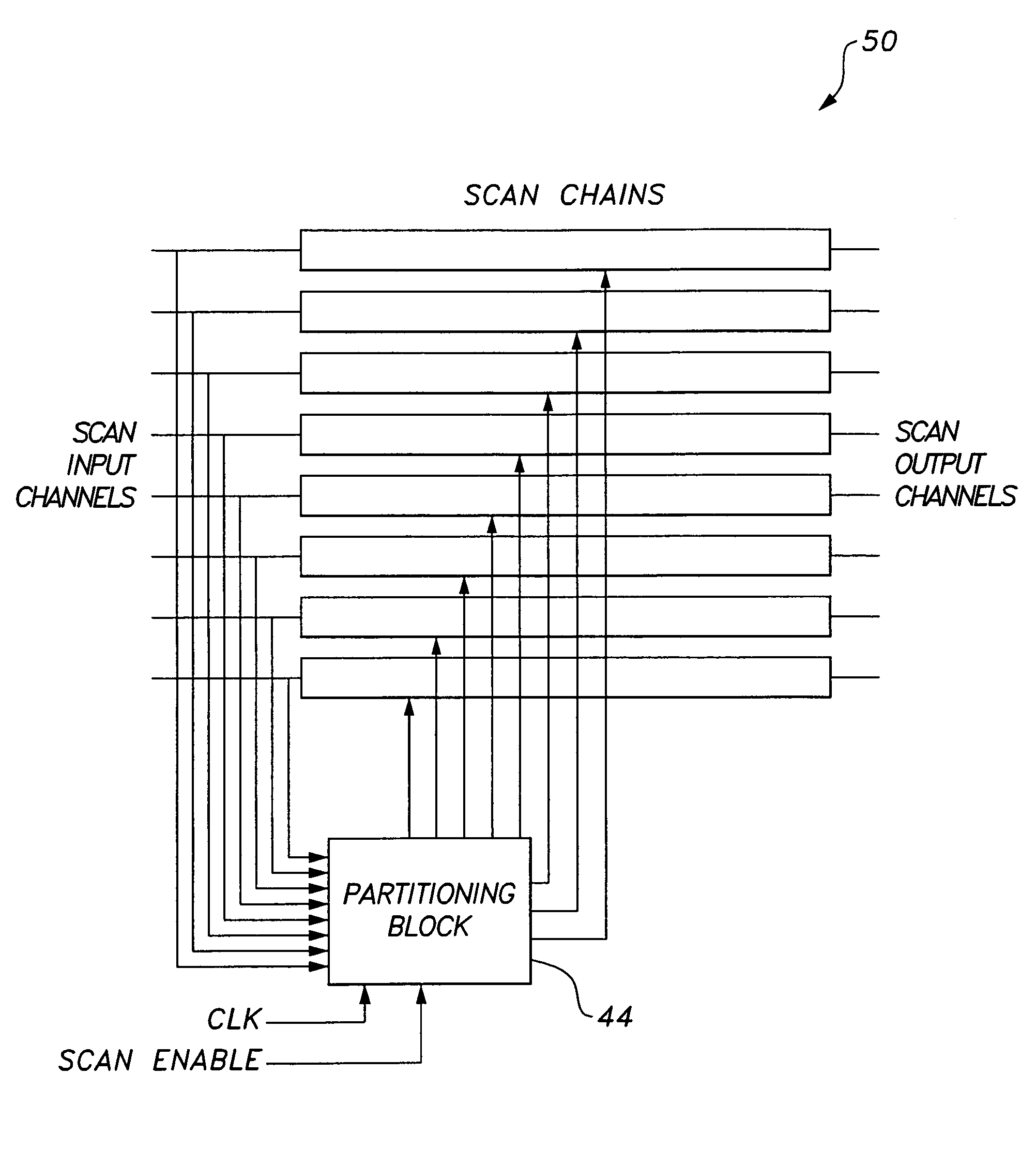
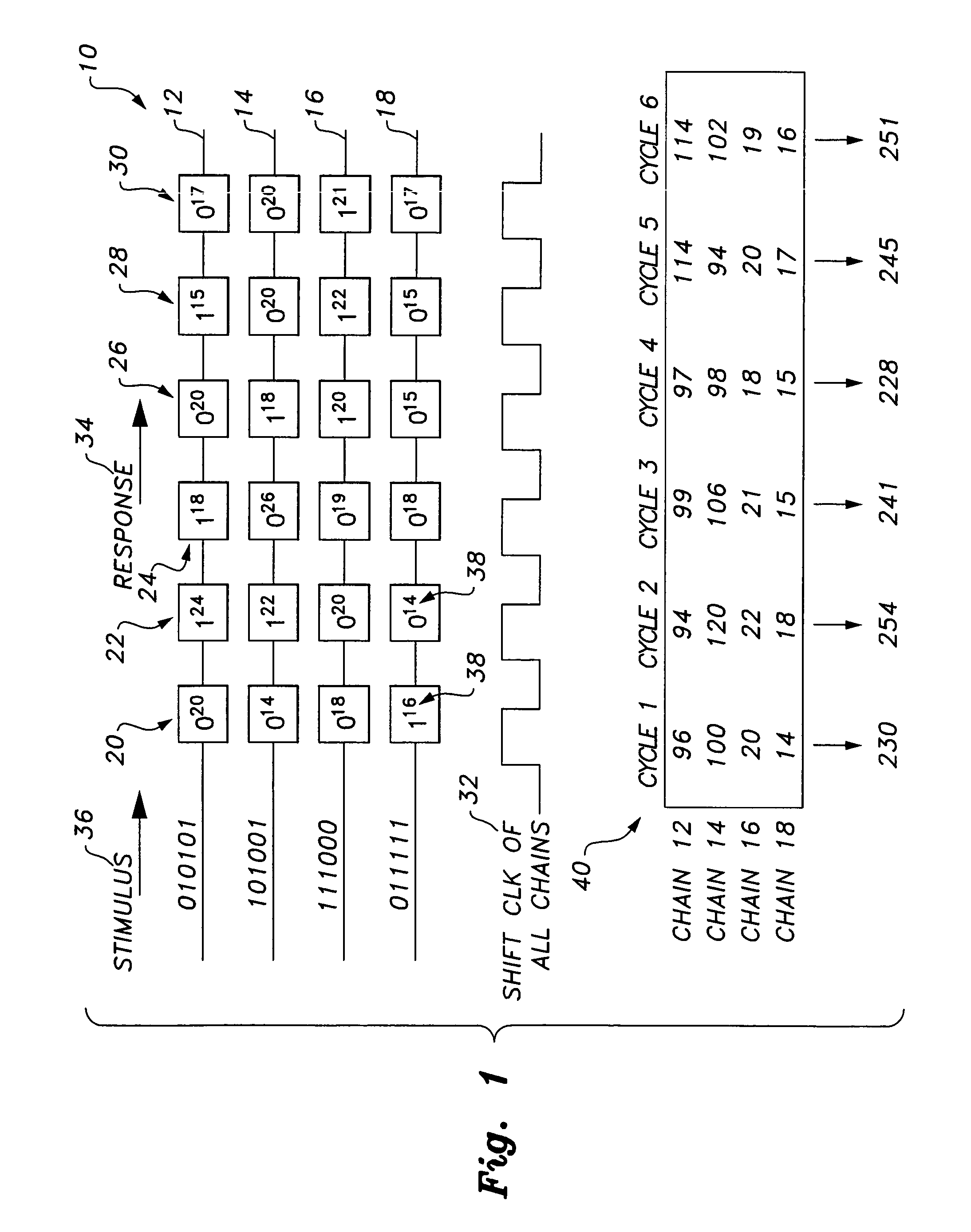
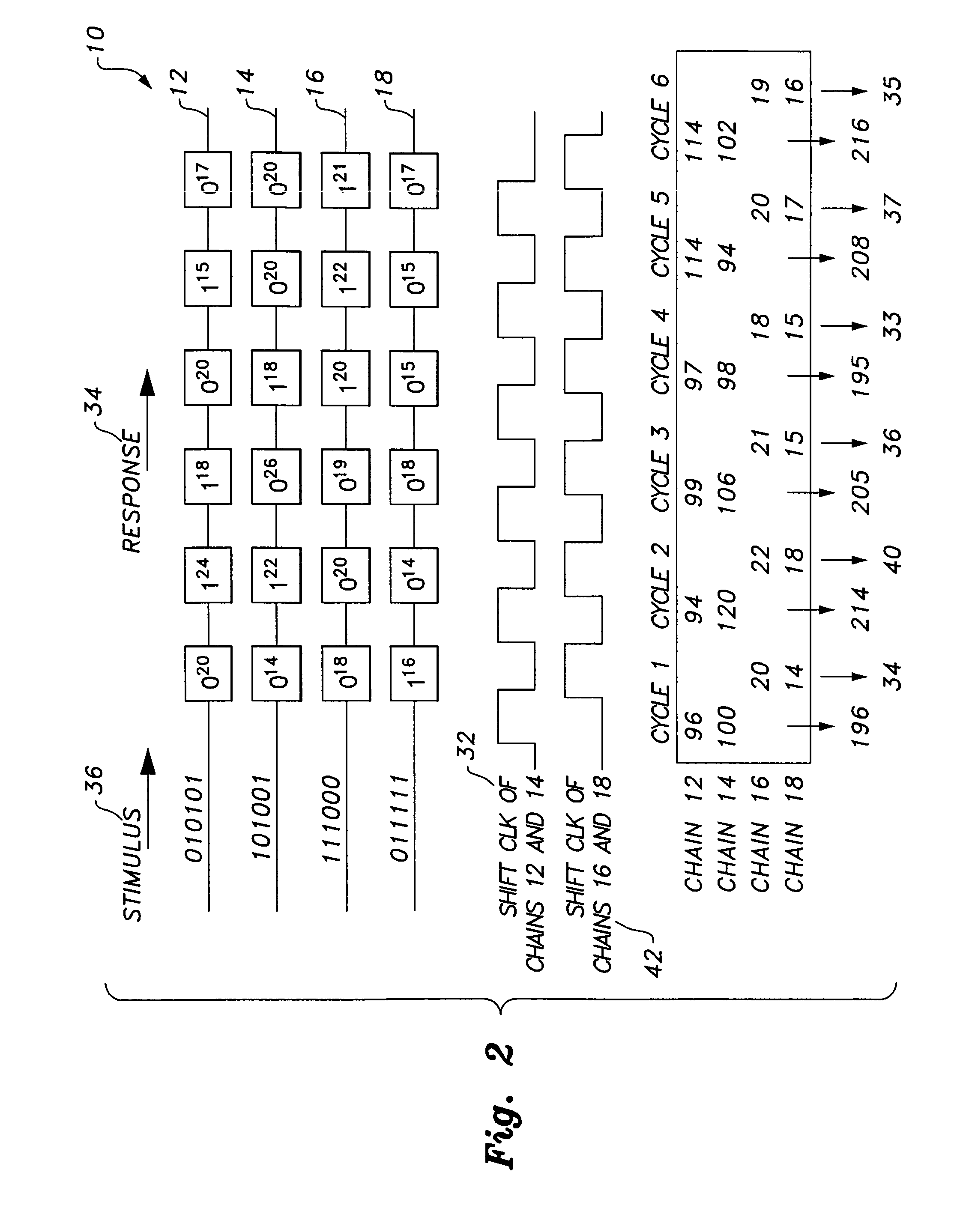
Circuit and method providing dynamic scan chain partitioning
InactiveUS20100211839A1Minimize powerElectronic circuit testingLogical operation testingReconfigurabilityPeak value
The circuit and method providing dynamic scan chain partitioning delivers peak power reduction by dynamically partitioning scan chains into multiple groups, wherein transitions are equally distributed among these multiple groups. For each test pattern, a particular partitioning that leads to the even partitioning of the transitions is computed by analyzing the transition distribution of the pattern. The scan chain partitioning is formulated using an Integer Linear Programming (ILP) and an efficient greedy heuristic. The computed information is loaded into the reconfigurable scan chain partitioning hardware during the capture window. The partitioning hardware is composed of controllable clock gating logic, which is reconfigured on a per pattern basis, wherein the reconfiguration is effected by only utilizing the existing scan channels. The reconfigurability delivers a solution that is test set independent. The results confirm the superiority of dynamic scan chain partitioning over static partitioning techniques in terms of peak power reduction.
Owner:KUWAIT UNIV
MR imaging system and data acquisition method
InactiveUS6914429B2Significant timeReduce application rateDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData acquisitionContrast enhancement
Magnetic resonance imaging uses a pulse sequence formed to include a pre-pulse, an RF excitation pulse, an encoding gradient pulse, and a reading gradient pulse. The encoding gradient pulse has an encoding amount determined to allow a data acquisition position in a k-space to be directed outward from a center of the k-space. A train of pulses including the RF excitation pulse, the encoding gradient pulse, and the reading gradient pulse is repeated to allow the number of times of data acquisition in the k-space to become larger as approaching to a central region of the k-space. The pre-pulse is formed to be reduced in an application rate to the RF excitation pulse as approaching to an outward position in the k-space. By way of example, this pulse sequence is used for contrast enhanced MRA carried out under a dynamic scan.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
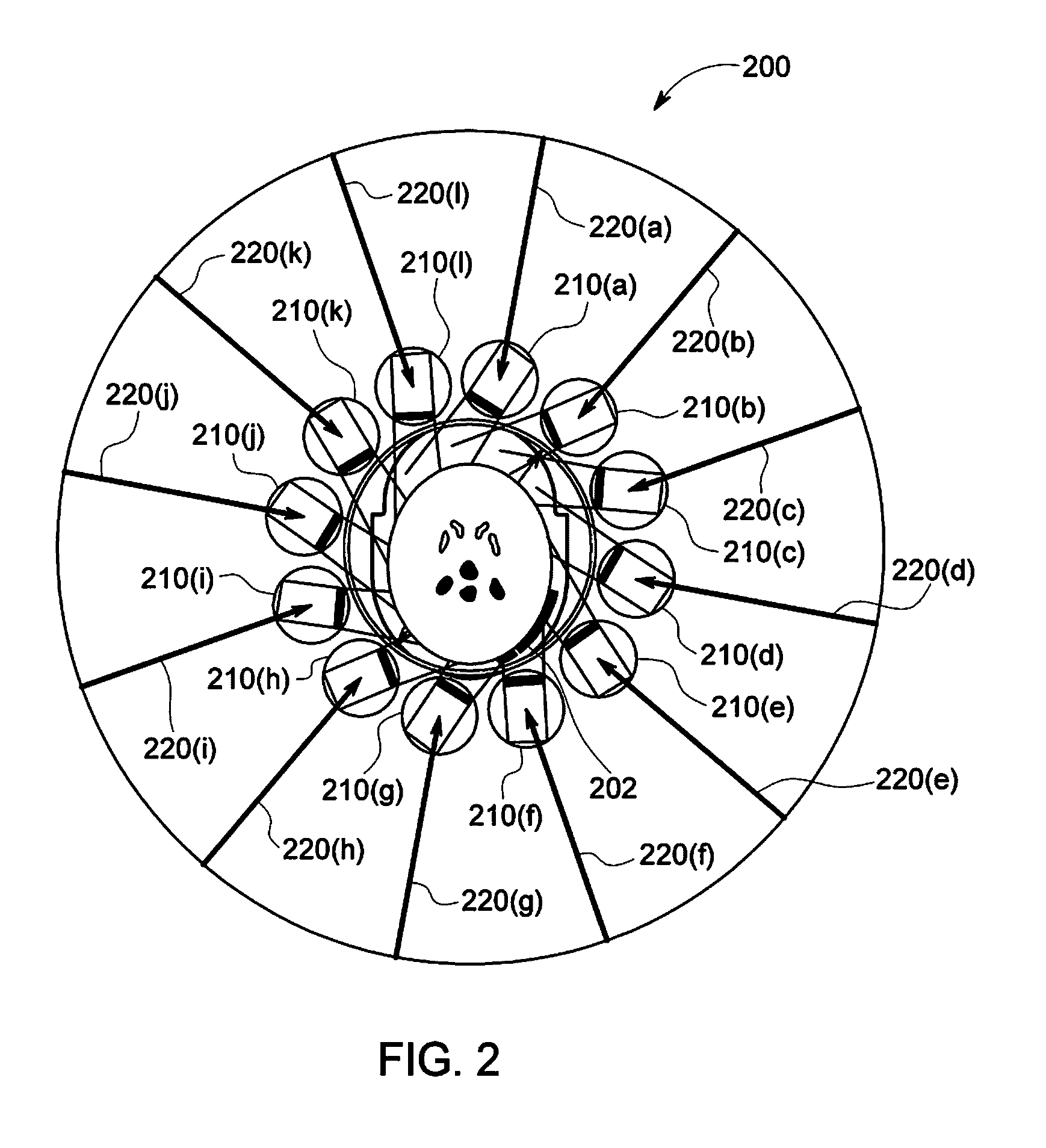
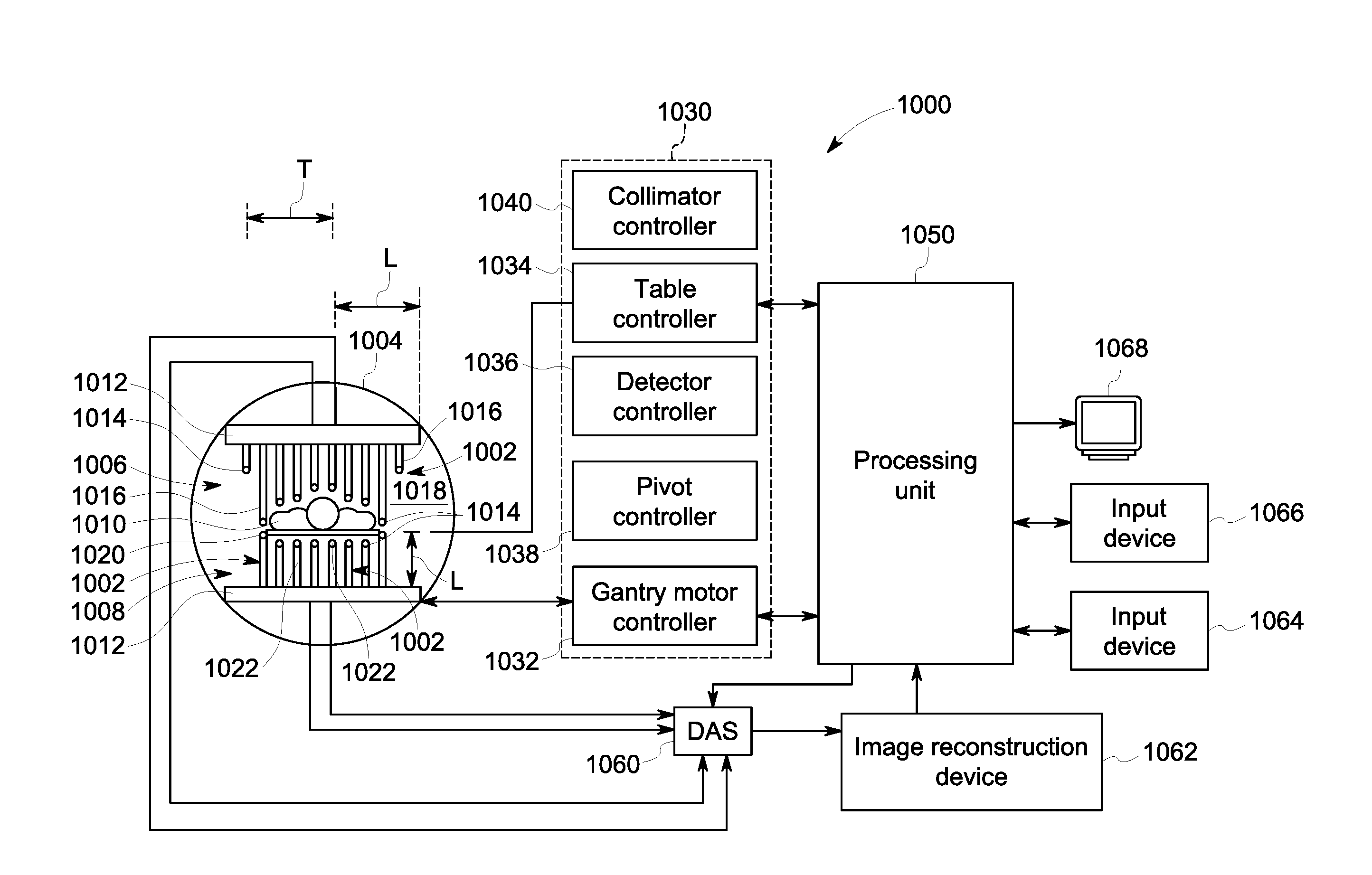
Systems and methods for dynamic scanning with multi-head camera
A nuclear medicine (NM) multi-head imaging system is provided that includes a gantry, plural detector units mounted to the gantry, and at least one processor operably coupled to at least one of the detector units. The detector units are mounted to the gantry. Each detector unit defines a detector unit position and corresponding view oriented toward a center of the bore. Each detector unit is configured to acquire imaging information over a sweep range corresponding to the corresponding view. The at least one processor is configured to, for each detector unit, determine plural angular positions along the sweep range corresponding to boundaries of the object to be imaged, generate a representation of each angular position for each detector unit position, generate a model based on the angular positions using the representation, and determine scan parameters to be used to image the object using the model.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
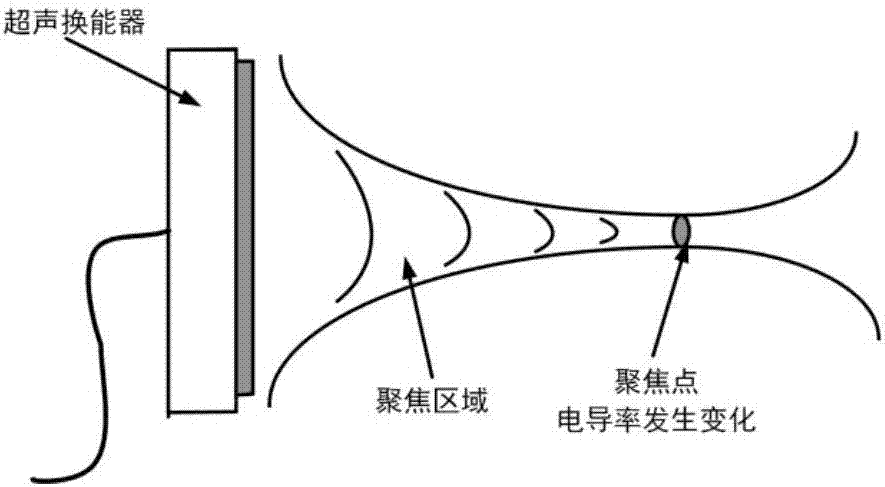
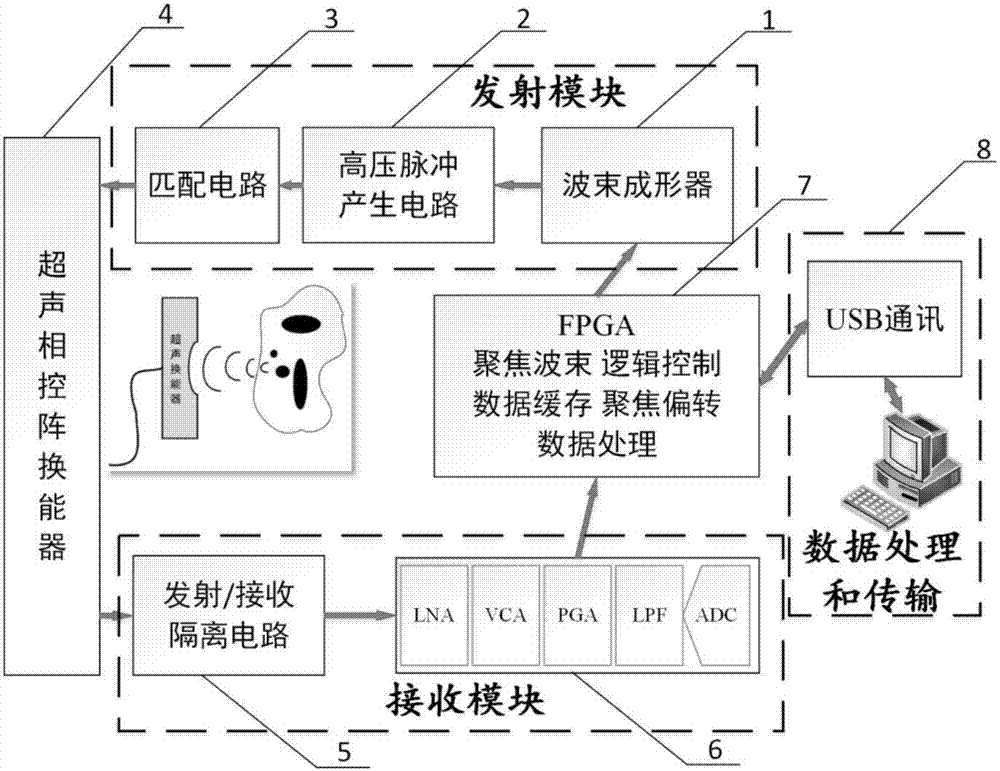
Phased array ultrasonic focusing system for acoustic and resistivity imaging
InactiveCN107280707ASmall sizeImprove bindingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationArray element
The invention relates to a phased array ultrasonic focusing system for acoustic and resistivity imaging. The phased array ultrasonic focusing system comprises an upper computer, a transmitting module, a receiving module and a digital control and data processing module, delay time and pulse width of array elements of a phased-array transducer are calculated through a PC terminal by the upper computer according to position and depth of focus points, the delay time and the pulse width are transmitted to FPGA (field programmable gate array), transceiving control and emission focusing, deflection and dynamic scanning of a multi-channel phased array probe are achieved by the aid of programming of the FPGA, and delay information and pulse width information of the energy converter are transmitted to a beam former in real time.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Circuit and method providing dynamic scan chain partitioning
InactiveUS7937634B2Minimize powerElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionReconfigurabilityPeak value
The circuit and method providing dynamic scan chain partitioning delivers peak power reduction by dynamically partitioning scan chains into multiple groups, wherein transitions are equally distributed among these multiple groups. For each test pattern, a particular partitioning that leads to the even partitioning of the transitions is computed by analyzing the transition distribution of the pattern. The scan chain partitioning is formulated using an Integer Linear Programming (ILP) and an efficient greedy heuristic. The computed information is loaded into the reconfigurable scan chain partitioning hardware during the capture window. The partitioning hardware is composed of controllable clock gating logic, which is reconfigured on a per pattern basis, wherein the reconfiguration is effected by only utilizing the existing scan channels. The reconfigurability delivers a solution that is test set independent. The results confirm the superiority of dynamic scan chain partitioning over static partitioning techniques in terms of peak power reduction.
Owner:KUWAIT UNIV
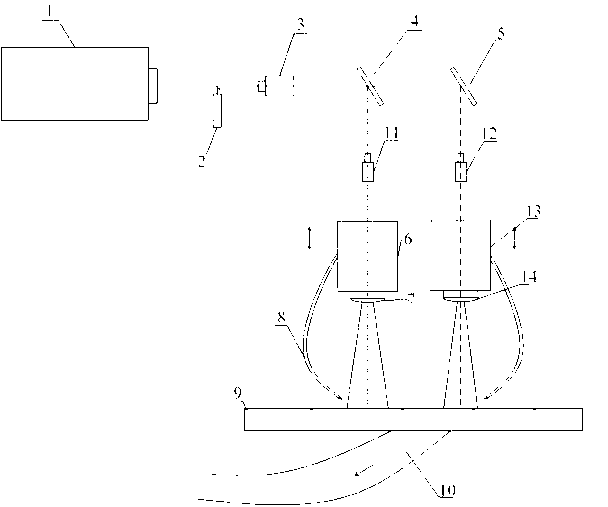
Apparatus and process for determination of dynamic scan field curvature
InactiveUS7126668B2Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusResistSilicon
Owner:LITEL INSTR
Device and method for processing one glass solution (OGS) touch screens
InactiveCN103056530AImprove efficiencyEasy to processGlass severing apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusEngineeringTouchscreen
The invention relates to a device and a method for processing OGS touch screens. Lasers emitted by a green ultra-short pulse laser are subjected to coaxial beam expansion through a beam expander, light beams after being expanded through the beam expander pass through a 45-degree transflective mirror, and the light path direction is changed; one path of light beams is focused on the lower surface of a work-piece through a first 3D dynamic scanning galvanometer and a first focusing mirror, and the other path of the light beams penetrates through the 45-degree transflective mirror, a second 3D dynamic scanning galvanometer and a second focusing mirror to be focused on the lower surface of the work-piece; a first coaxial charge coupled device (CCD) and a second CCD position the work-piece accurately, capture a positioning mark on the work-piece and calculate a compensation value; and the 3D dynamic scanning galvanometers lift the focus automatically during processing and the work-piece is processed from bottom to top. The two light paths perform optical focusing on the green ultra-short pulse lasers which penetrate through the work-piece to be focused on the lower surface of the work-piece, and energy of the laser is applied optimally and efficiently, and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU DELPHI LASER
System and method to adaptively control contrast-enhanced diagnostic imaging procedure
ActiveUS7974682B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsComputerised tomographsContrast enhancementSelf adaptive
A system and method are provided for determining individualized scan and injection protocols for contrast-enhanced diagnostic imaging. Taking into account parameters specific to the scan subject, injection-related parameters, and scan parameters, the system and method can determine an optimal timing for a scan sequence to begin, to ensure that the scan sequence coincides with a desired contrast enhancement. Some embodiments further provide for real-time triggering of the scan commencement based on bolus tracking, and can adapt the scan and injection protocols in real-time based on monitored dynamic scan subject parameters and / or actual enhancement values determined from image data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
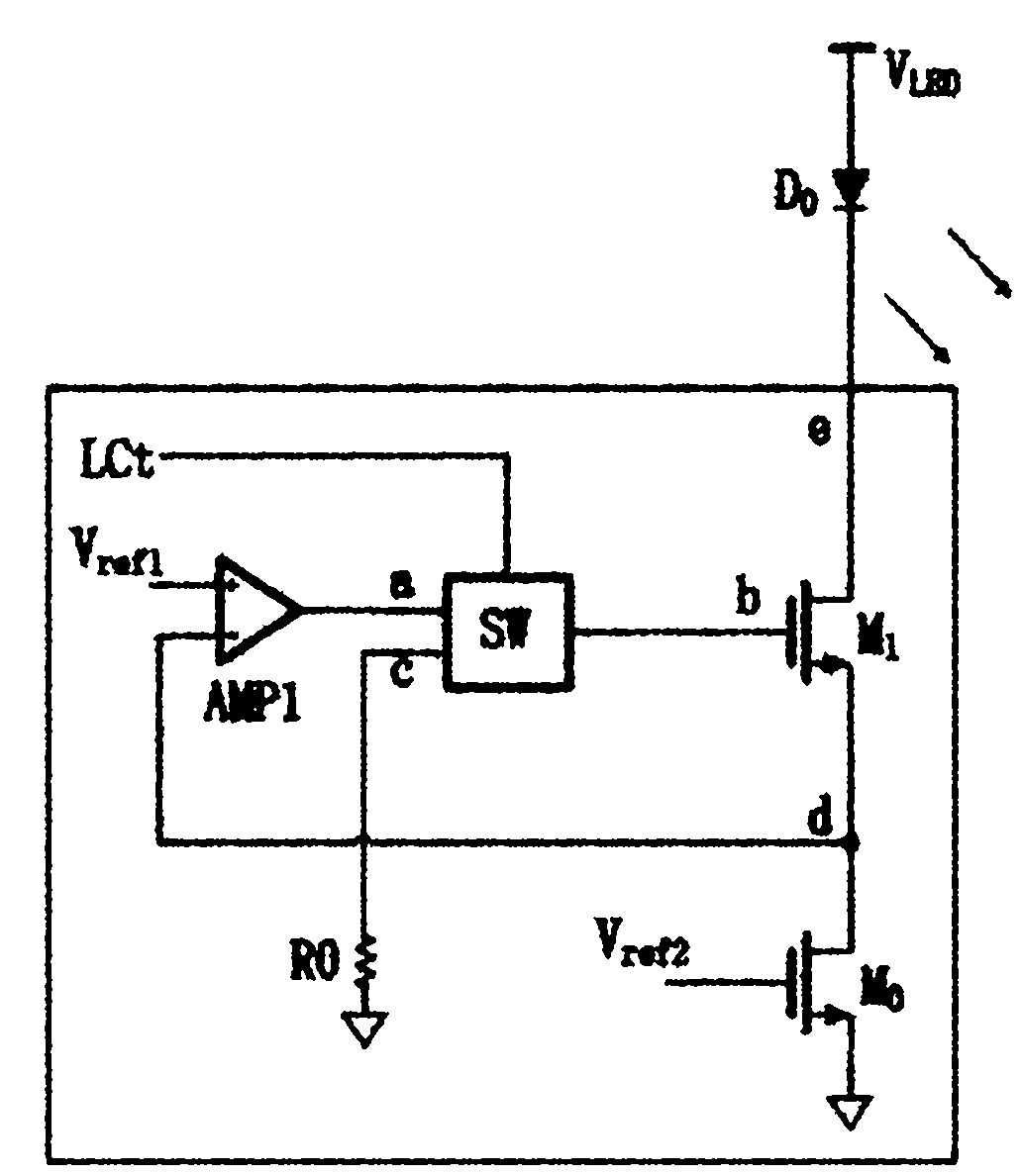
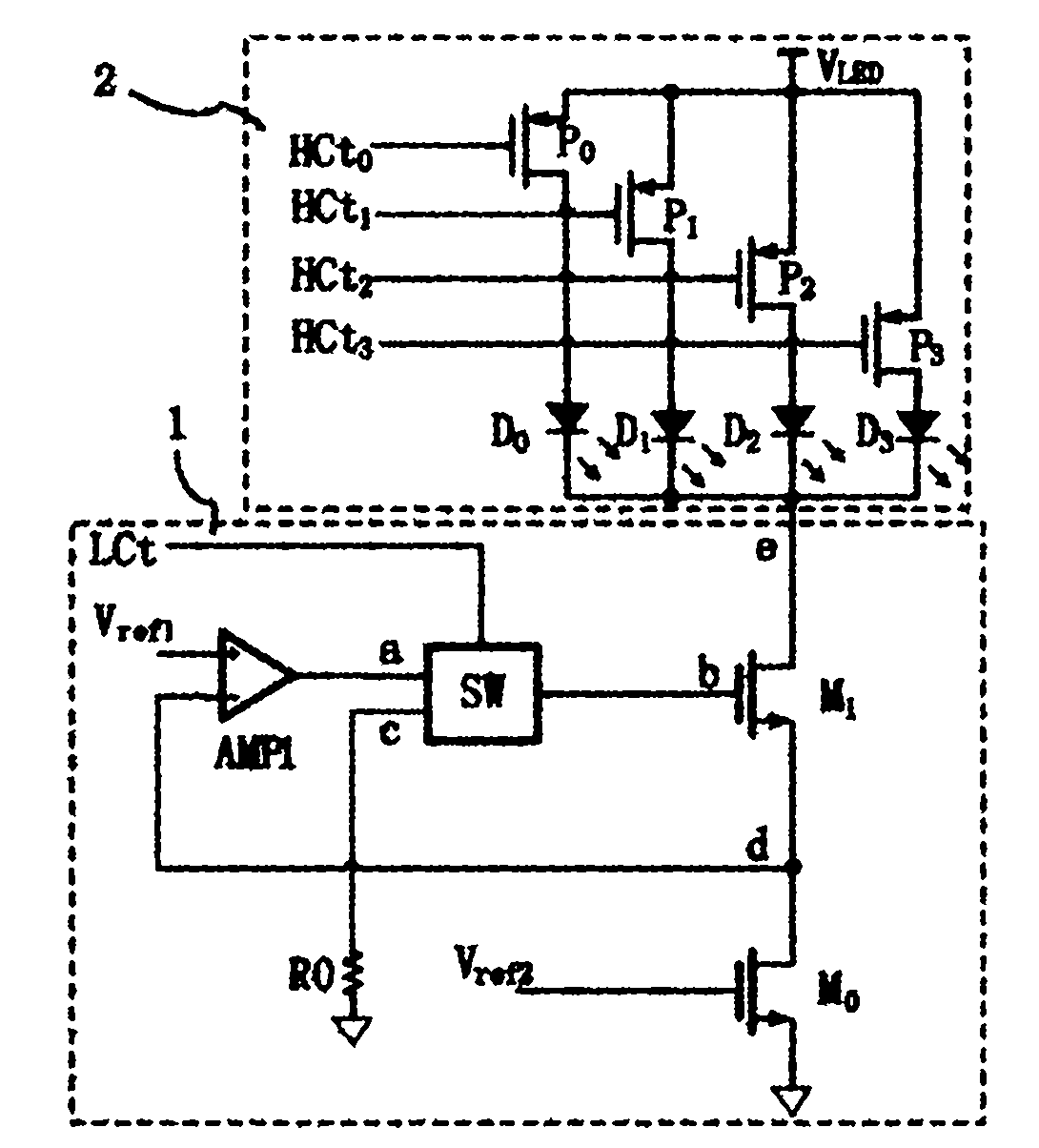
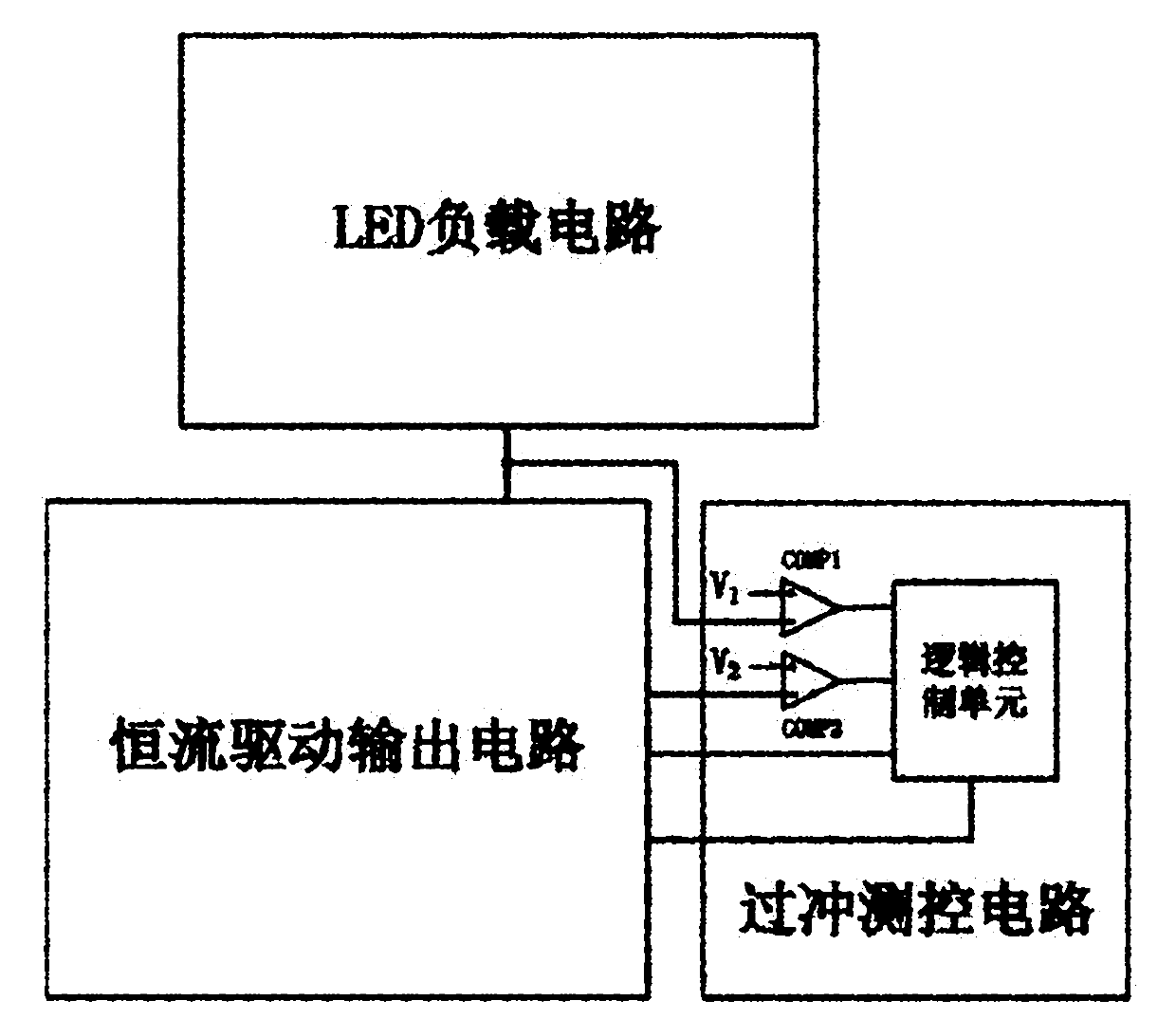
Light-emitting diode (LED) dynamic scan driving circuit capable of preventing current from overshooting
ActiveCN102170727AEffective protectionSolve the problem of severe current overshootElectric light circuit arrangementEnergy saving control techniquesLoad circuitHigh resistance
The invention discloses a light-emitting diode (LED) dynamic scan driving circuit capable of preventing current from overshooting. The driving circuit provided by the invention comprises an LED load circuit, a constant-current driving output circuit connected with the LED load circuit and an overshooting measurement and a control circuit connected with the constant-current driving output circuit. According to the invention, the overshooting measurement and control circuit is utilized to detect a state of the LED load circuit when the closure of all row selection pipes and the opening of constant-current output channels are carried out simultaneously; the constant-current output channels are closed or enter into a high-resistance conducting state before the row selection pipes are conducted; and the constant-current output channels are turned back to a normal constant-current output state after the row selection pipes are conducted, thus the problem of serious current overshooting occurred when the row selection pipes are changed into the conducting state from the closed state is effectively eliminated, the driving circuit is effectively protected, the display effect of LED dynamic scan driving application is improved, the gradation of grey is greatly enhanced, and the cost and power consumption of LED products are reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU YONGJIAN PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
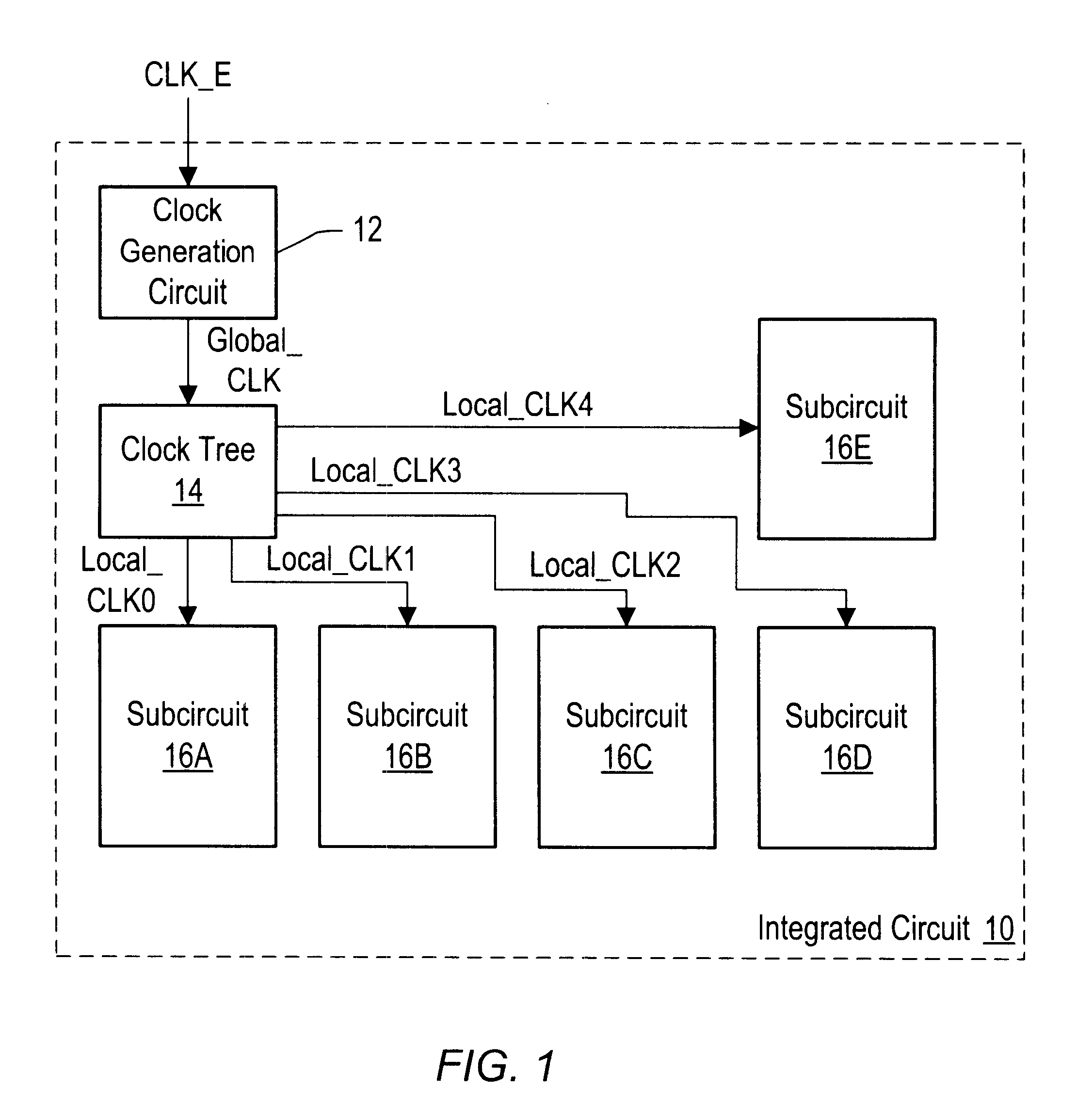
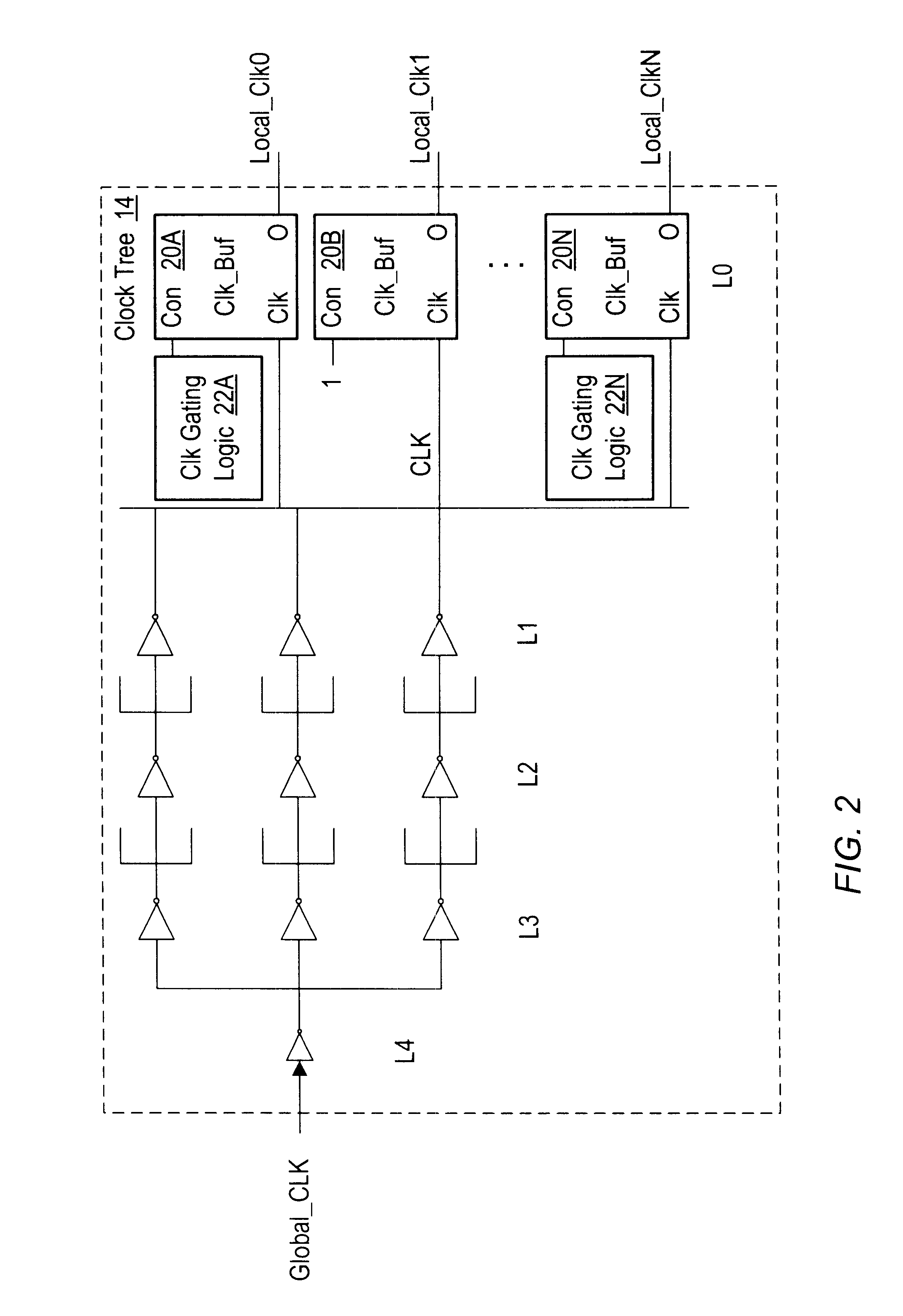
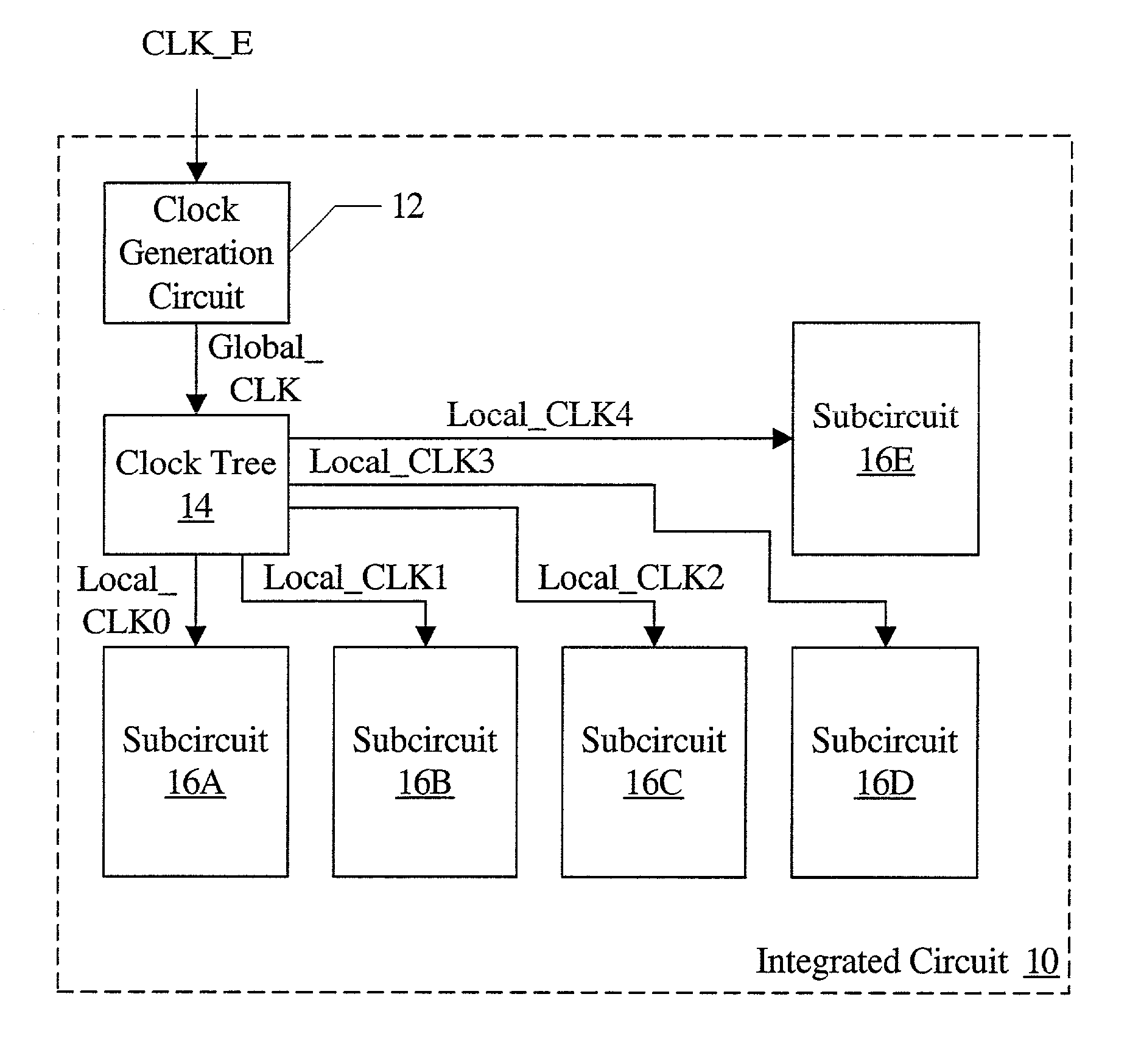
Scan Interface
A scan interface for an integrated circuit includes a scan clock and a scan mode signal. The scan mode signal is indicative of whether or not scan is active, and may be used by dedicated scan circuitry in integrated circuit. Such circuitry may be inactive if the scan mode indicates that scan is inactive, and active if the scan mode indicates that scan is active. For example, the scan circuitry may not toggle is scan is inactive. The scan circuitry may present a reduced load to functional circuitry if scan is inactive. In some embodiments, static and dynamic scan circuits are included for use with static and dynamic logic circuits, respectively.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Systems and methods for dynamic scanning with multi-head camera
ActiveUS20170000448A1Radiation diagnostic image/data processingTomographyComputer scienceDynamic Scan
A nuclear medicine (NM) multi-head imaging system is provided that includes a gantry, plural detector units, and at least one processor. The gantry defines a bore configured to accept an object to be imaged. The plural detector units are mounted to the gantry. Each detector unit defines a corresponding view oriented toward a center of the bore, and is configured to acquire imaging information over a sweep range. The at least one processor is configured to dynamically determine at least one boundary of an acquisition range corresponding to an uptake value of the object to be imaged for at least one of the detector units. The acquisition range is smaller than sweep range. The at least one processor is also configured to control the at least one detector unit to acquire imaging information over the acquisition range.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
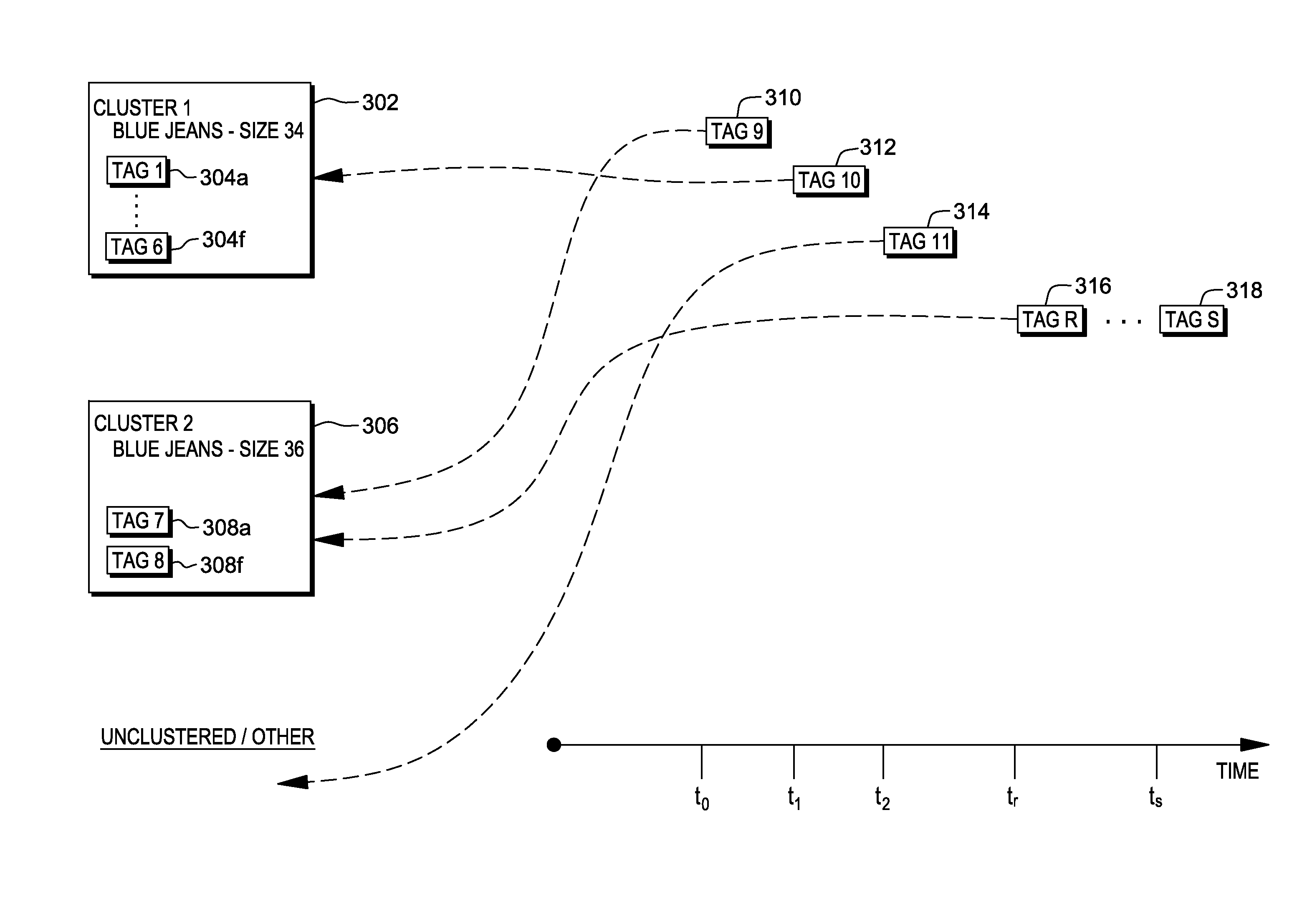
Dynamic scan context determination for asset reconciliation
ActiveUS20130293352A1Facilitating reconciliationOvercomes shortcomingSensing detailsNear-field in RFIDDatabaseDynamic Scan
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Dynamic scan driving method for smectic phase LCD (liquid crystal display)
ActiveCN102831865AExtended service lifeReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesVoltage amplitudeLiquid-crystal display
The invention discloses a dynamic scan driving method for a smectic phase LCD (liquid crystal display). The method comprises the following steps of: scanning and driving all lines of a display screen; applying a corresponding line pulse to the scanned and driven line when each line is scanned and driven, wherein the line pulse is a high-frequency high-voltage positive and negative pulse with a duty ratio of 50%; applying zero-volt voltages to other lines free from scanning and driving; and meanwhile, applying a corresponding column pulse to each column, wherein voltage amplitudes of the line pulse applied on each line and the column pulse applied on each column can be controlled according to amount of required voltage energy caused by each display state on pixels, different distances of leading-out terminals of line distance column electrode and the different distances of the leading-out terminals of column distance line electrode. According to the dynamic scan driving method disclosed by the invention, the voltage amplitudes of the line pulse and the column pulse can be dynamically adjusted in the whole scanning and driving period, therefore, a phenomenon that the pixels with no need of being driven by high-voltage energy are driven by excessively high voltage energy can be avoided to a great degree, and power consumption is dramatically reduced.
Owner:HALATION PHOTONICS CORP
Dynamic boundary scanning chain test method based on programmable devices
InactiveCN101515019AReduce overheadLow costDigital circuit testingProgrammable logic deviceProcessor register
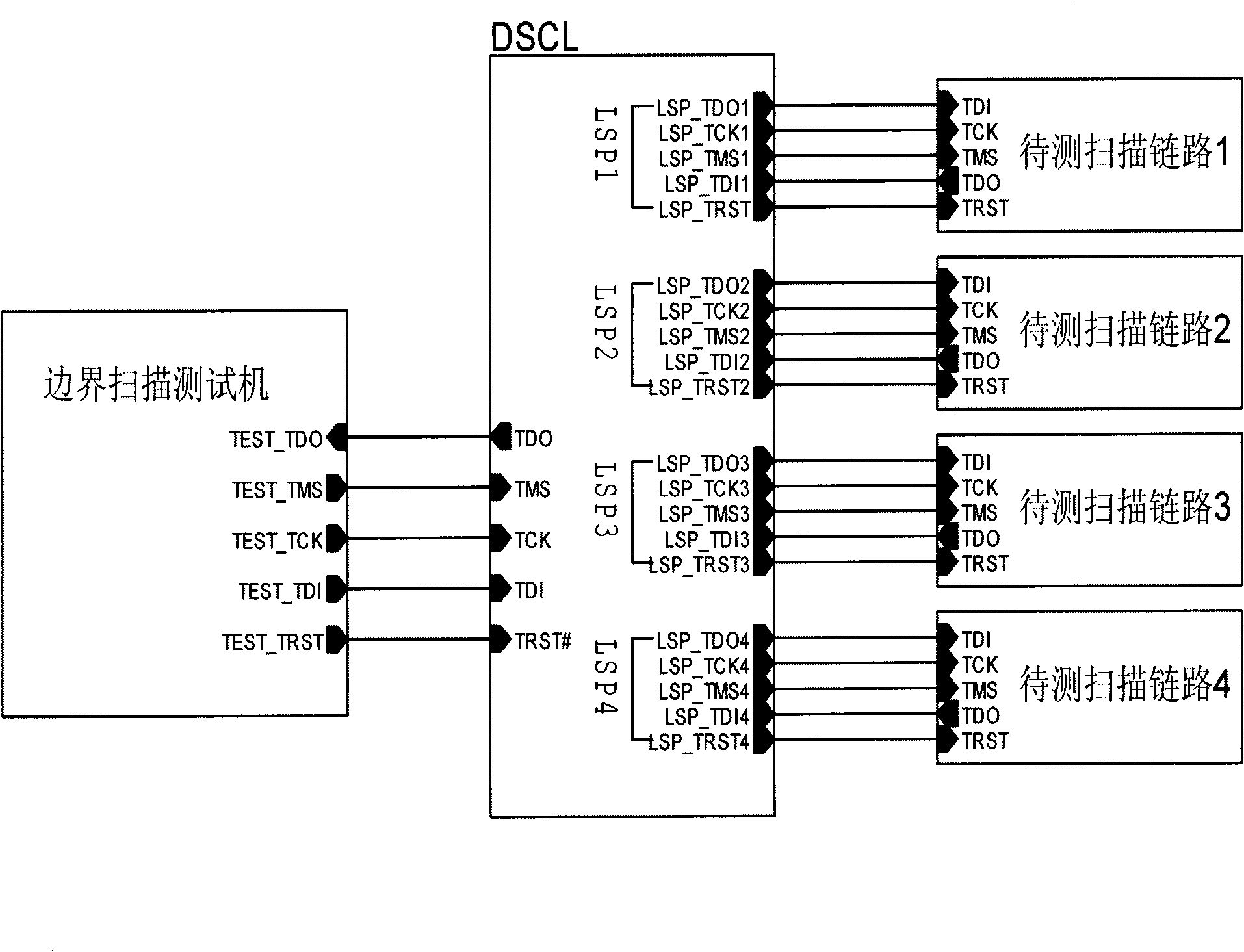
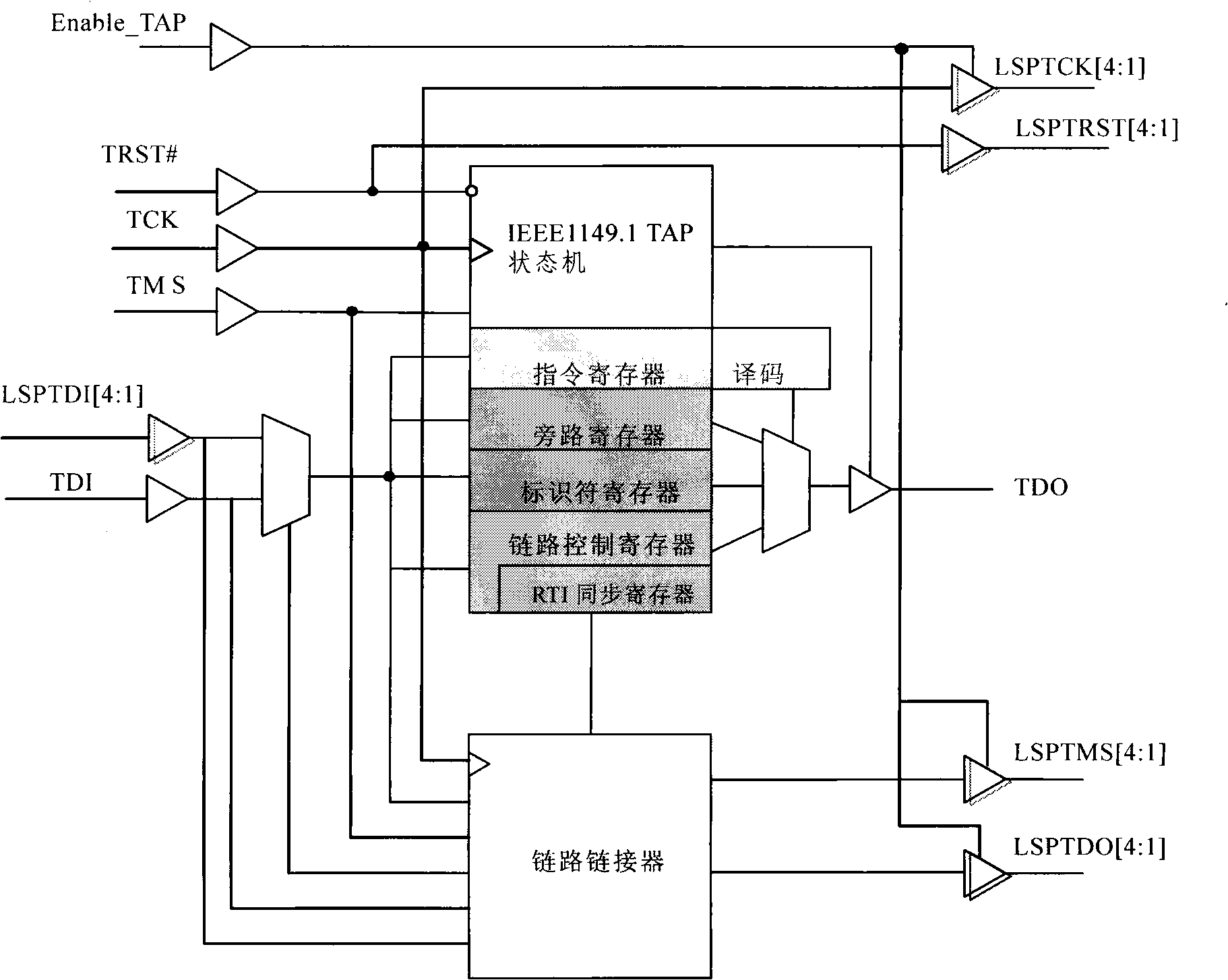
The invention provides a dynamic boundary scanning chain test method based on PLD and FPGA devices. A dynamic scan chain linker (DSCL) is specialized in a programming device by adopting HDL RIL codes for realizing the dynamic loading and unloading of a plurality of scanning chains, thus limberly testing boundary scanning circuits. The DSCL comprises an IEEE 1149.1 TAP state machine, an instruction order register, an identifier register, a chain control register, a RTI synchronous register, a bypass register and a chain linker so that a test machine can control the chain control register by a testing access port TAP, and the chain linker links the scanning chains hooked on a link scanning port (LSP) according to the value of the chain control register.
Owner:UTSTARCOM TELECOM CO LTD
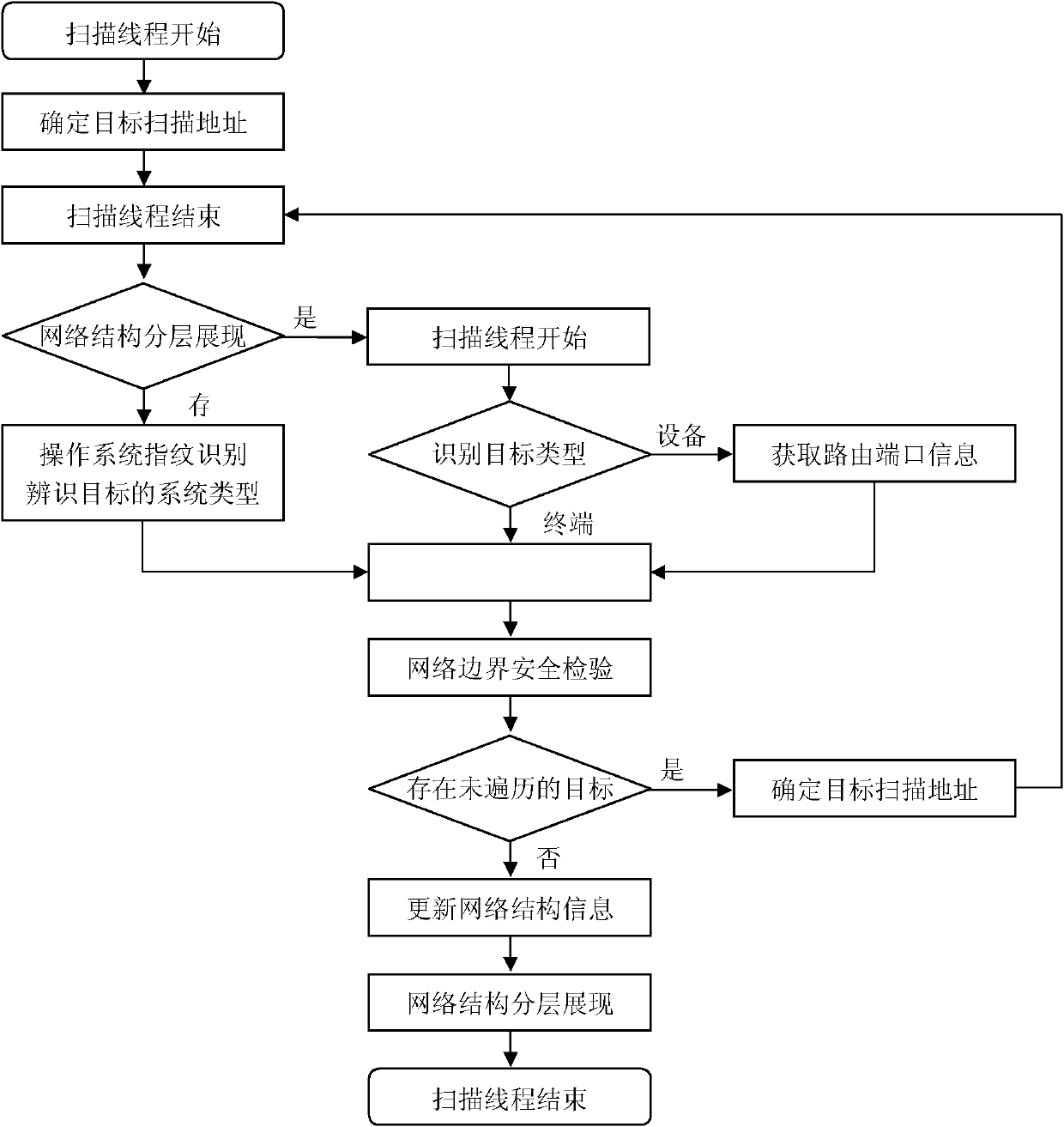
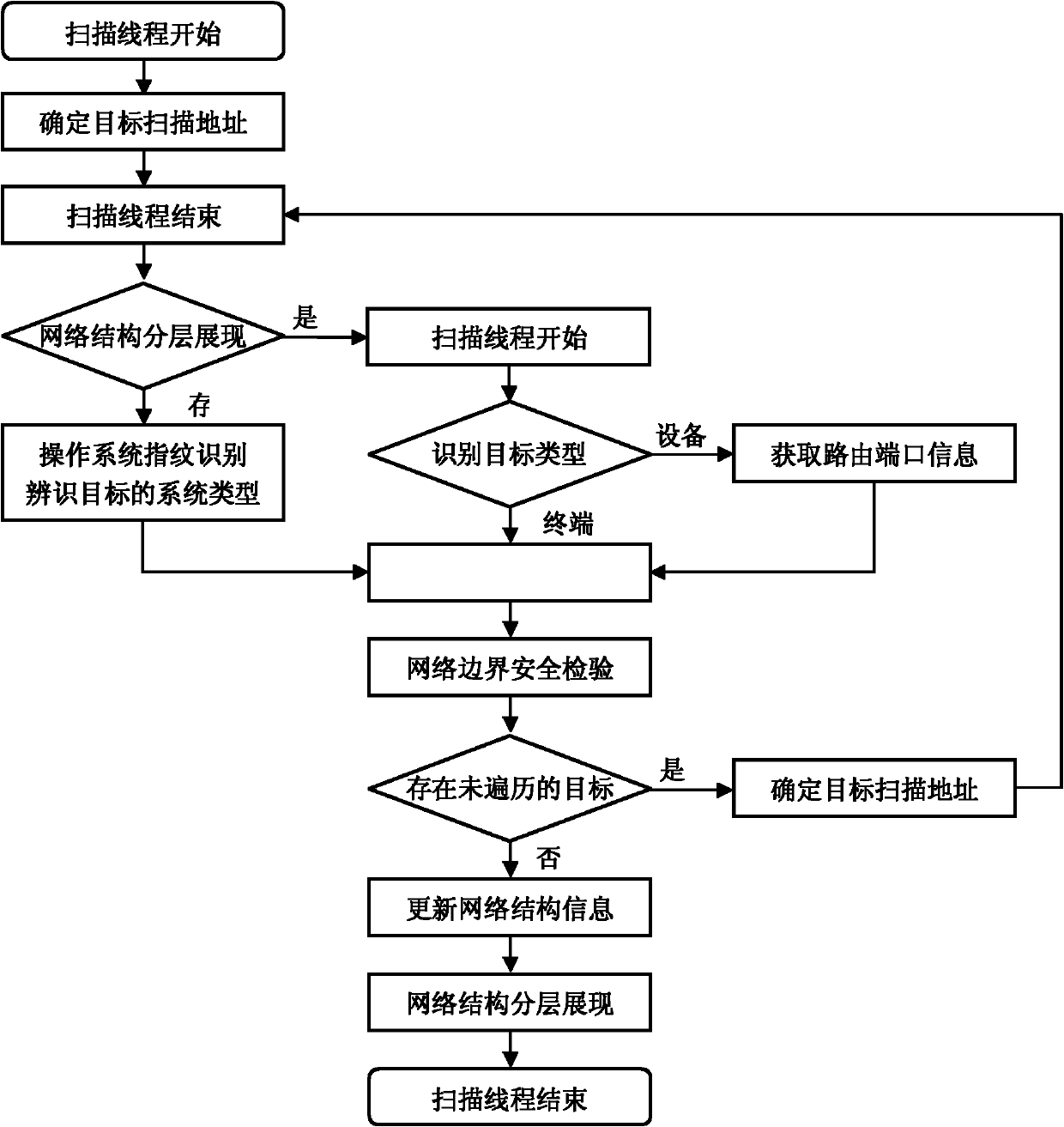
Method for network structure monitoring and boundary inspection
InactiveCN102170372ATimely discovery of illegal private connection to dual networksReal-time grasp of operation statusData switching networksDual networkNetwork structure
The prior art has the problems of being incapable of monitoring the running state of a network comprehensively and accurately, understanding the change of the network structurization, and grasping the access condition on the network boundary. A method for network structure monitoring and boundary inspection provided by the invention mainly solves the problems of the prior art. The specific method for network structure monitoring and boundary inspection is carried out by the following steps of network structure dynamic scan; network boundary safety inspection; network structure updating and storage, and network structure hierarchical revelation. The method for network structure monitoring and boundary inspection collectively reveals the basic information of a network device, can carry out a real-time network scan, collects the state data and makes a hierarchically revelation on a network structure view; completes the identity type identification of a network device and an access terminal in order to confirm the network boundary; emphatically monitors a boundary device so as to timely find a violated private dual network connection happened on the network boundary, and monitors the access state of the terminal under the static norm.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com