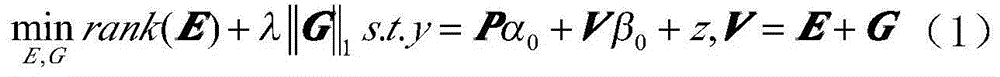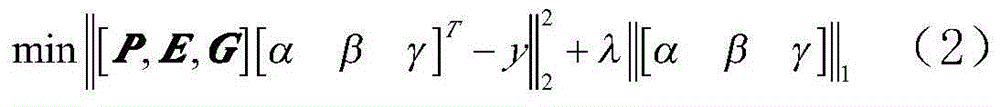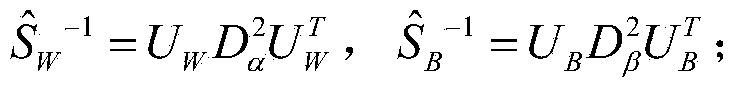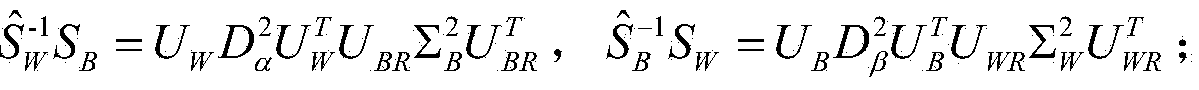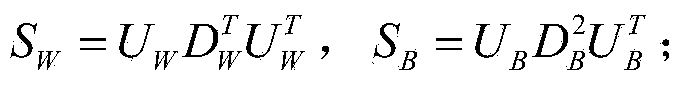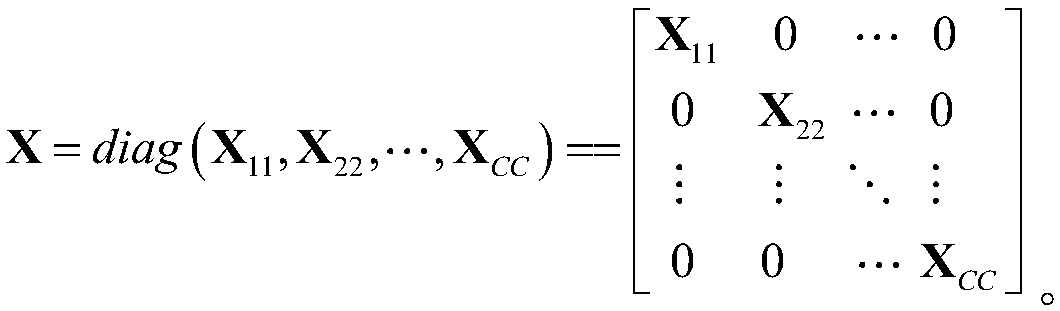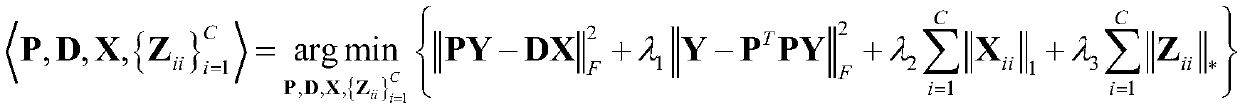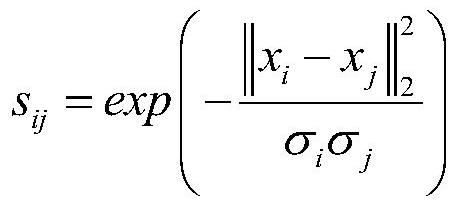Patents
Literature
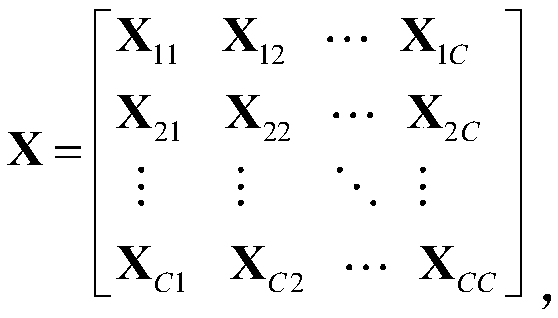
51 results about "Matrix projection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A projection matrix is an square matrix that gives a vector space projection from to a subspace . The columns of are the projections of the standard basis vectors, and is the image of . A square matrix is a projection matrix iff .
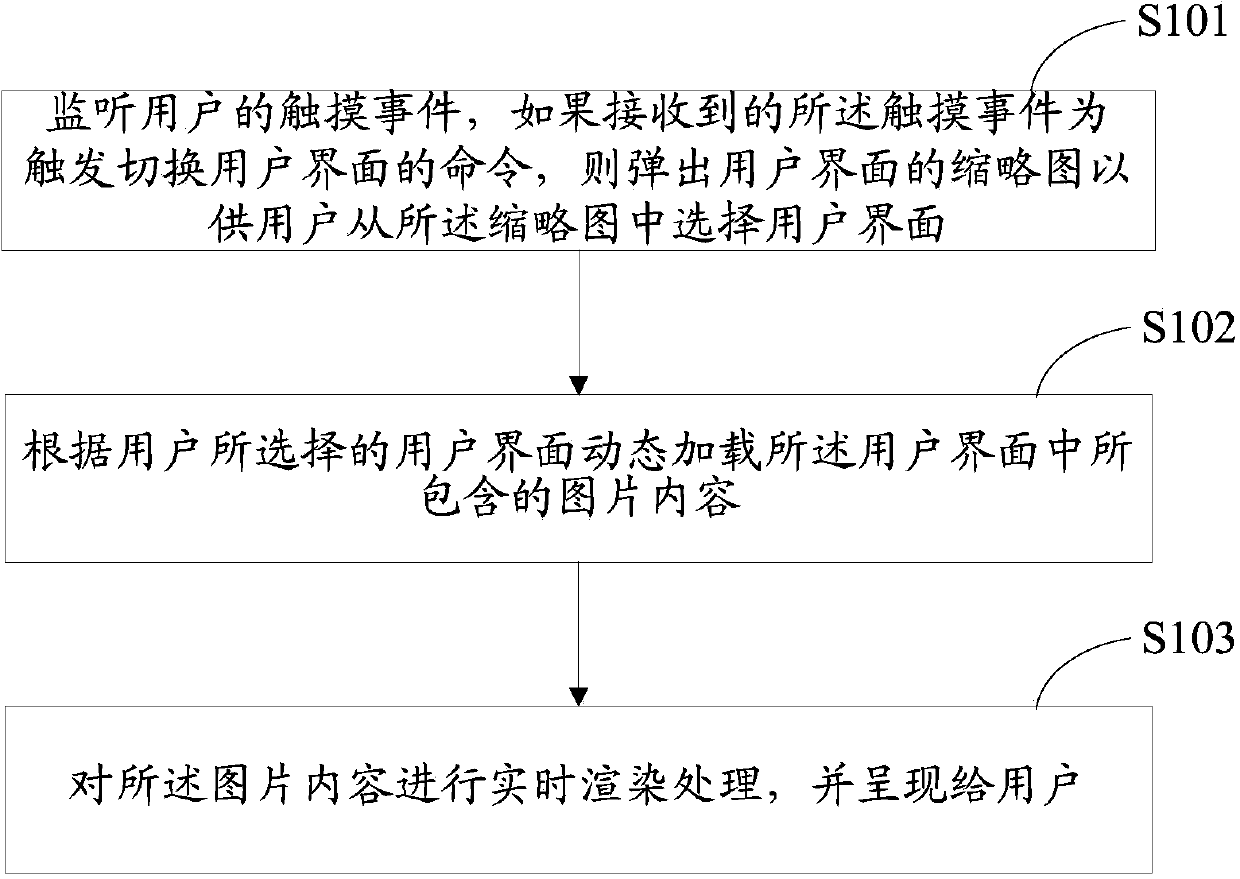
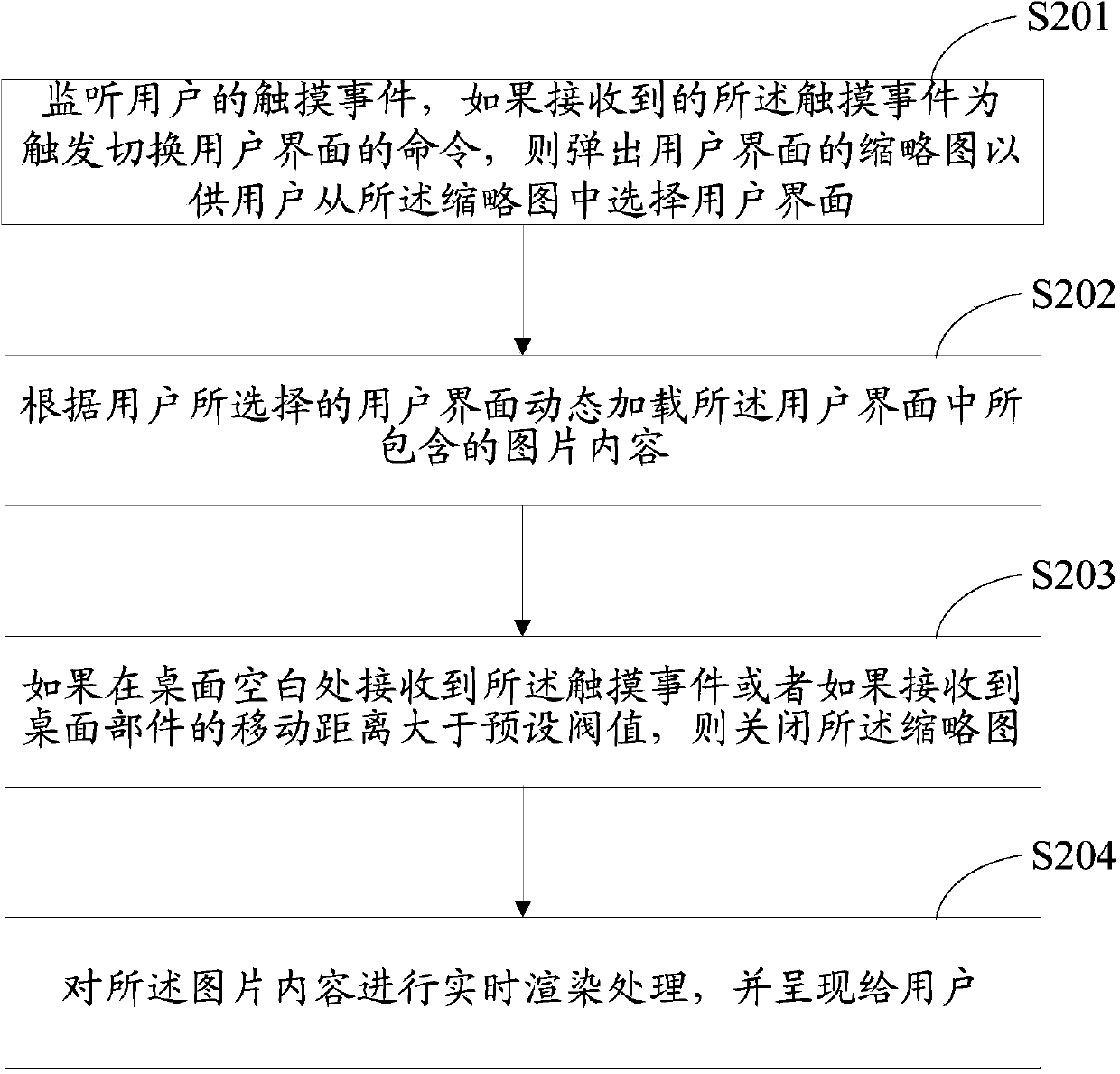
Touch screen terminal and multi-interface switching method thereof
InactiveCN103793134AReal-time rendering processing implementationInput/output processes for data processingThumbnailComputer terminal
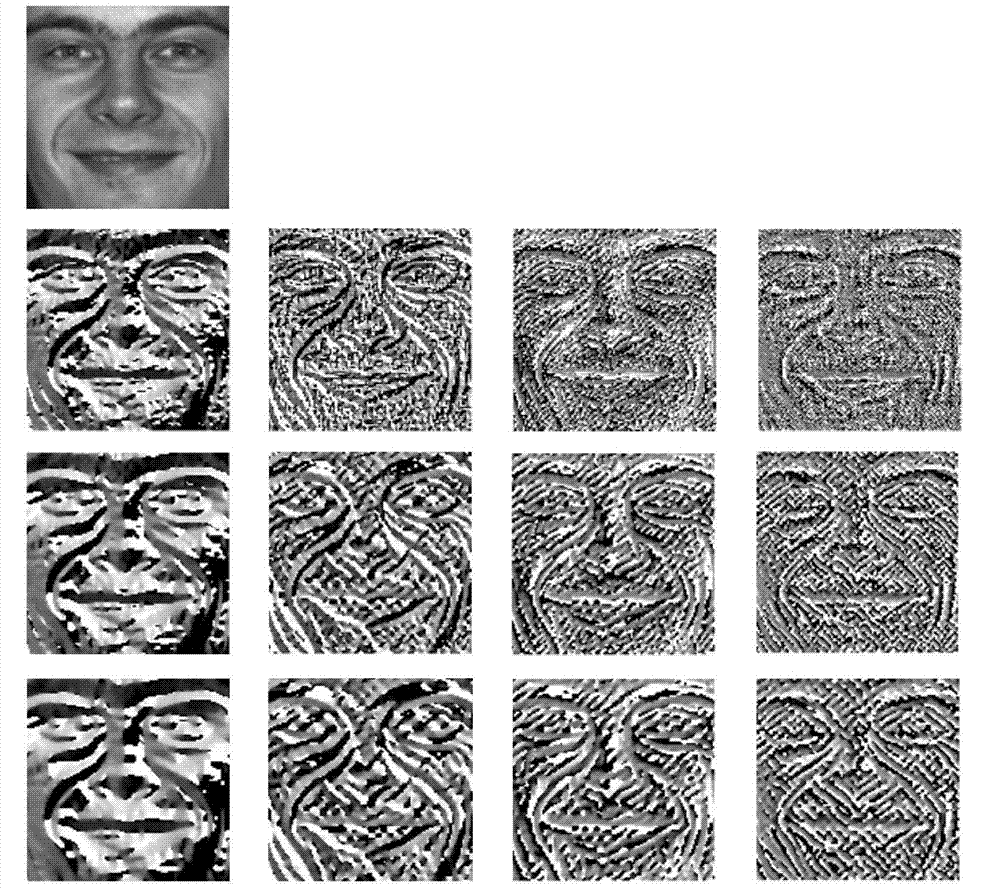
The invention discloses a touch screen terminal and a multi-interface switching method thereof. The method includes: monitoring a touch even from a user; if the touch event which triggers a command of switching a user interface is received, popping out a thumbnail of the user interface for the user to select the user interface from the thumbnail; dynamically loading image contents included by the user interface, according to the user-selected user interface; rendering the image contents in real time and displaying the contents to the user. The image contents include icons of desktop devices including a clock device and a weather device; rendering treatments include window setting, matrix projection, lighting, rotation and zooming. The touch screen terminal and the multi-interface switching method thereof have the advantages that the user interface can be rendered and displayed in real time and accordingly users can dynamically change the user interface according to needs.
Owner:SHENZHEN TINNO WIRELESS TECH
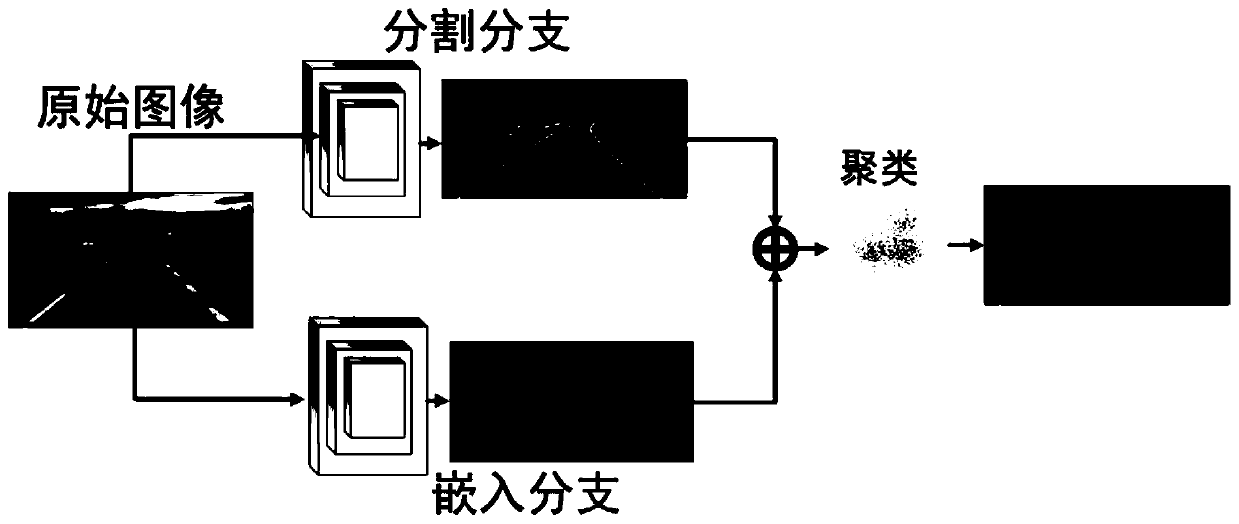
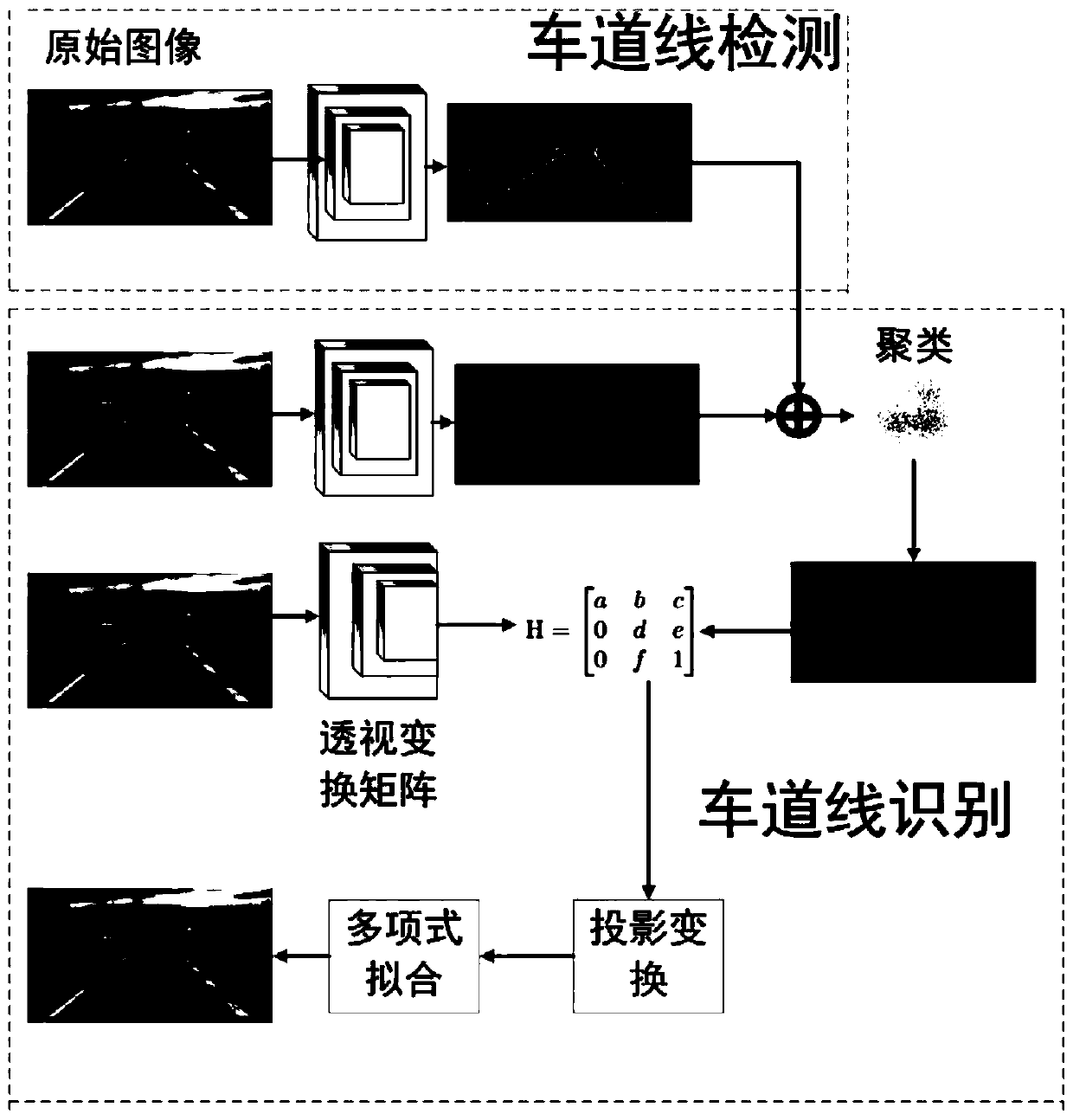
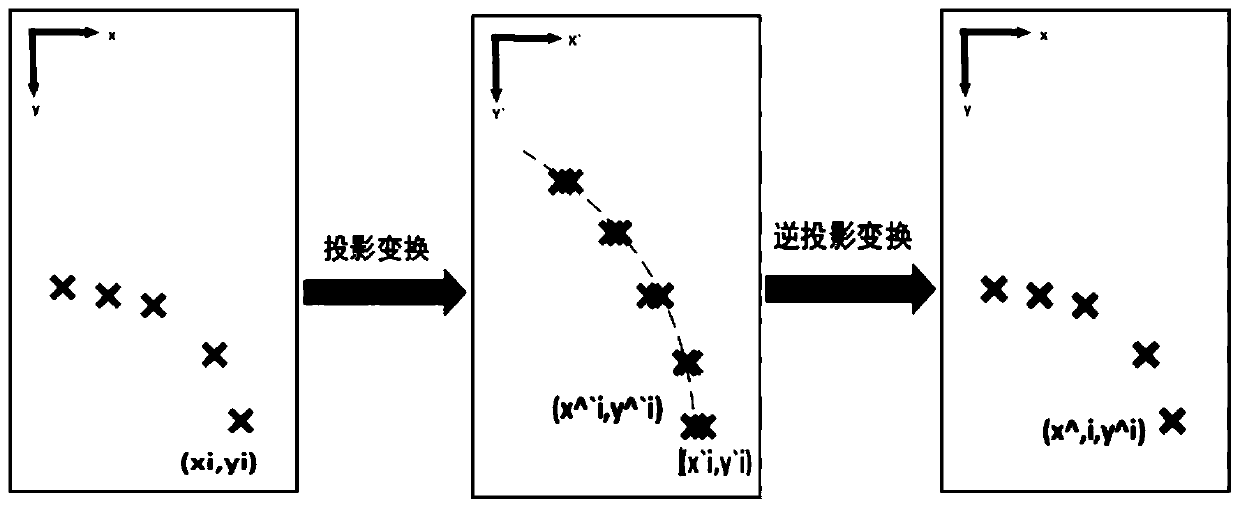
A lane line detection algorithm based on an instance segmentation neural network framework
ActiveCN109740465AImprove robustnessImprove efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionNerve networkAlgorithm
The invention discloses a lane line detection algorithm based on an instance segmentation neural network framework. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing an instance segmentation model for lane line detection, wherein the instance segmentation model comprises a binary segmentation module branch and an embedded module branch; loading the original image information into a binary segmentation module branch, and segmenting lane line pixels from background pixels; Loading the original image information into an embedding module branch to obtain a pixel embedding vector of alane line; Then clustering the lane line pixels and the pixel embedding vectors; Transforming the original image by using a transformation matrix network module, outputting a projection transformation matrix of the aerial view, and projecting lane line pixels into the aerial view through the projection transformation matrix; and finally, performing lane line fitting on the pixel points projectedinto the aerial view, and outputting a lane line fitting result. According to the method, the calculated amount is reduced, and meanwhile the influence of environment change on the lane line detectioneffect is eliminated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
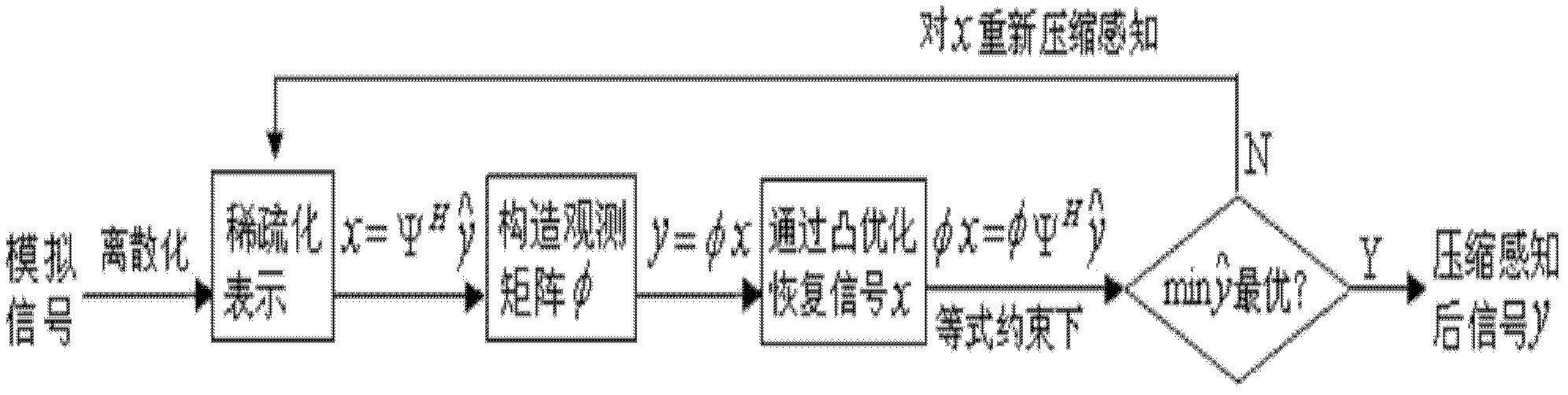
Random sampling analog circuit compressed sensing measurement and signal reconstruction method
InactiveCN102435934AReduce In-Circuit Test CostsImplement fault diagnosisAnalog circuit testingElectronic systemsDistribution characteristic
The invention relates to a random sampling analog circuit compressed sensing measurement and signal reconstruction method, which belongs to the field of electronic system test and fault diagnosis. Aiming at a fault signal having a sparsity distribution characteristic per se or in an orthogonal space in an output response of an analog circuit, a test node is selected according to a circuit topology structure, circuit output responses are randomly sampled under a distributed sensor test network, response signals are expressed in a sparse way on a transform domain by utilizing discrete orthonormal basis, compressed sensing measurement of the sparse signals is completed under observability matrix projection, and when the recovery rate of signal reconstruction by randomly compressed sampling points reaches more than 80 percent, the compressed measurement values of the circuit output responses are effective, can form a characteristic set and can be used for analog circuit fault diagnosis. The method solves the problems that the traditional analog signal sampling occupies a large number of hardware resources, large signal reconstruction calculated amount and the like; and the random sampling compressed sensing measurement method is utilized to improve the efficiency of electronic system testing.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
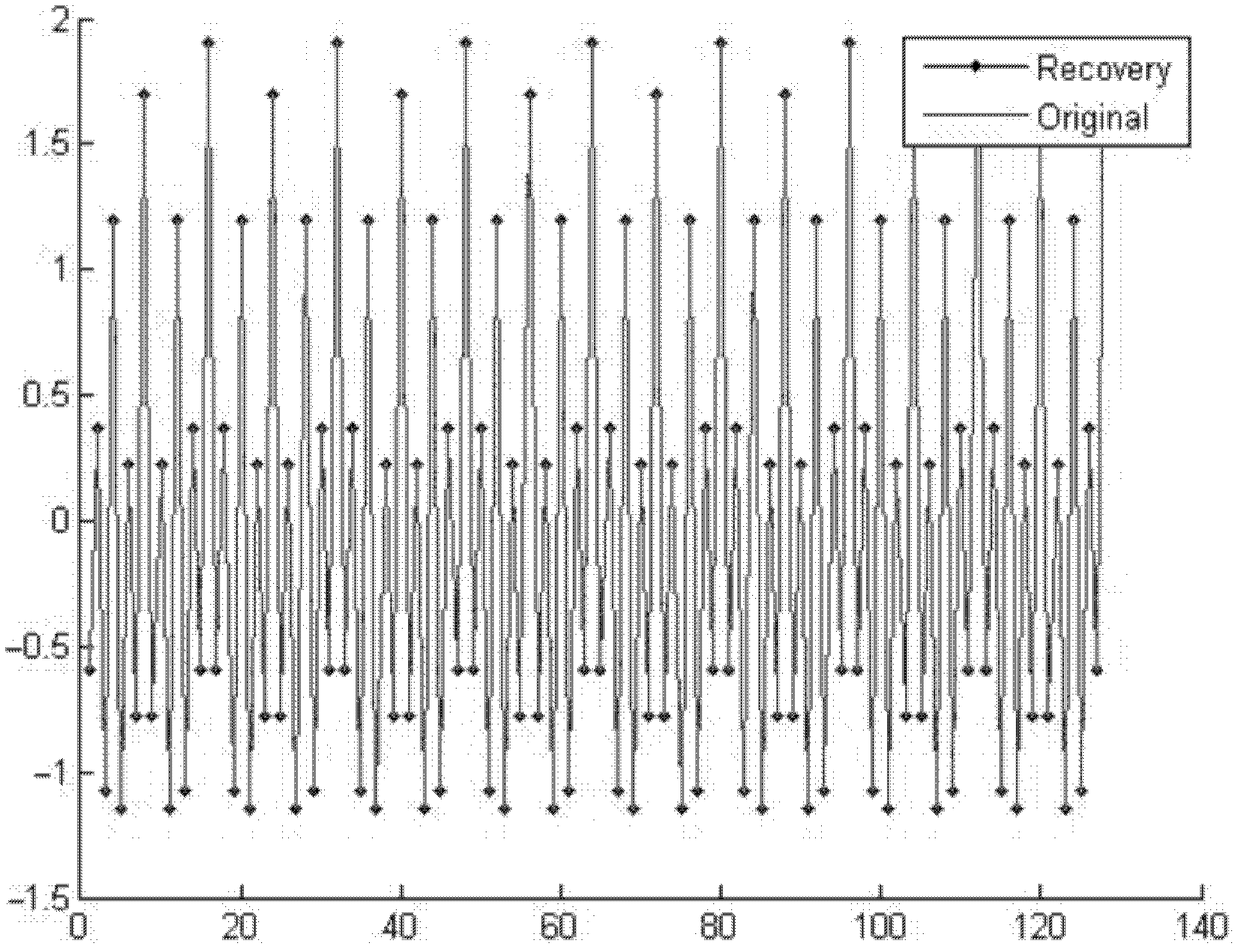
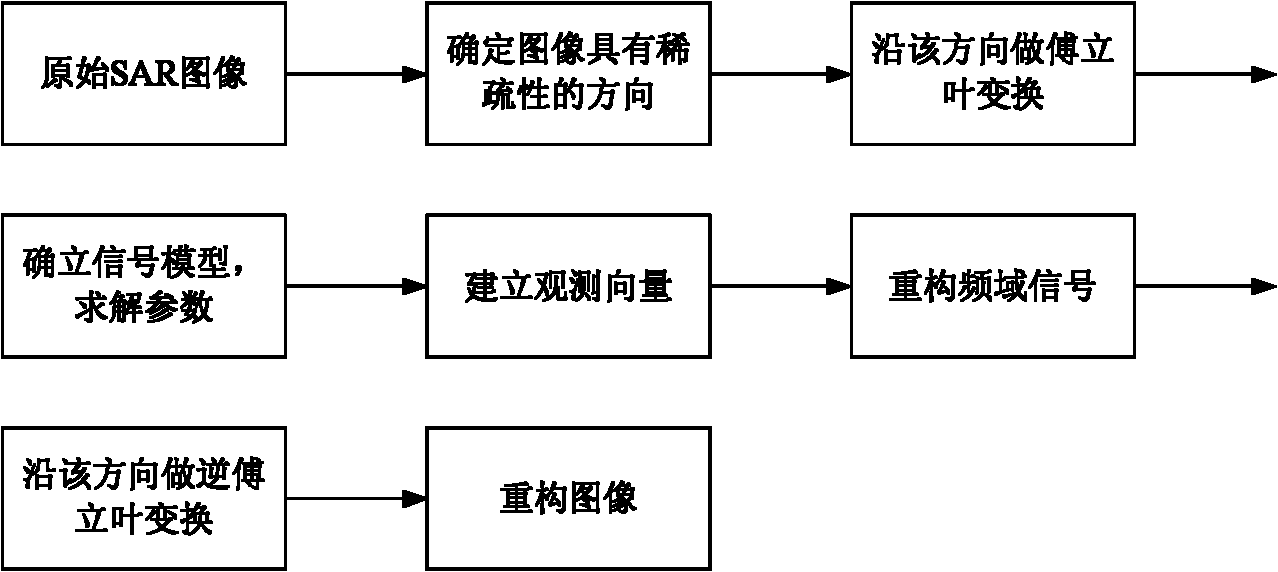
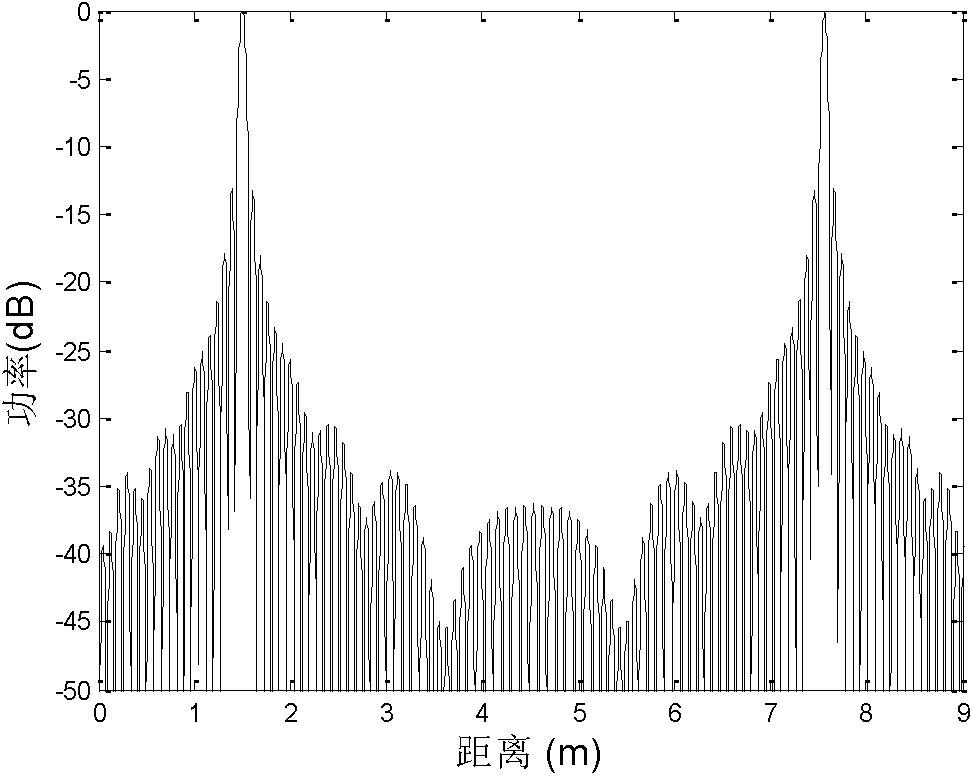
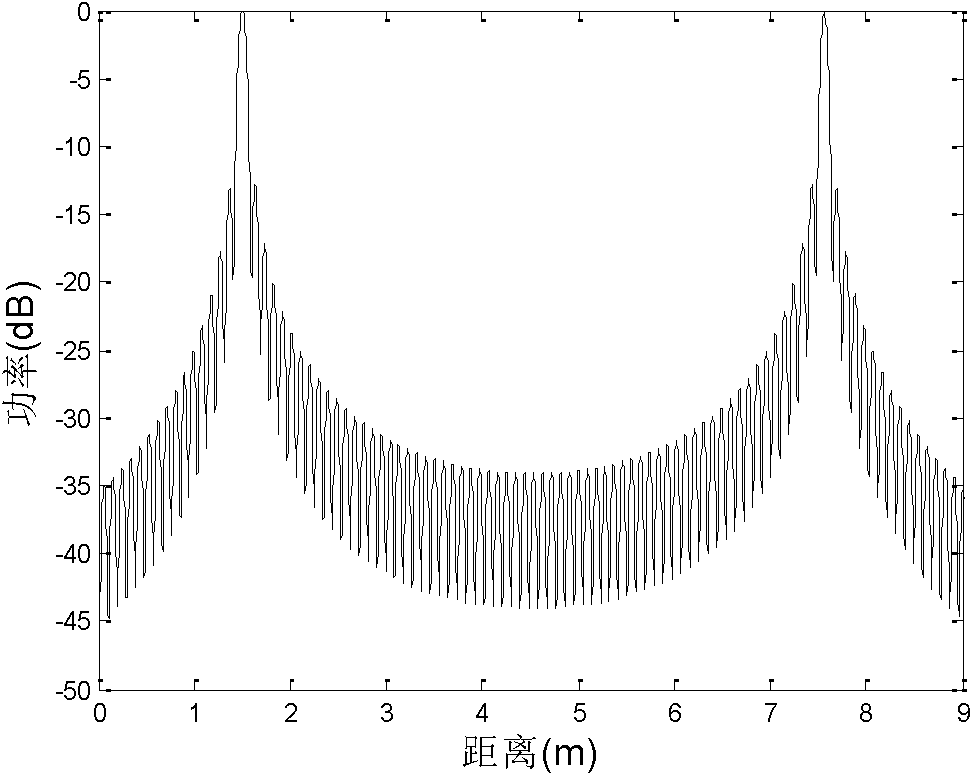
Frequency domain compressive sensing method aiming at sparse SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) images in airspace
InactiveCN102135618AAccurate solutionReduce data rateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPattern recognitionSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a frequency domain compressive sensing method aiming at sparse SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) images in airspace and belonging to the technical field of signal processing. The frequency domain compressive sensing method particularly comprises the following steps of: step 1: determining the directions of original SAR images, with sparsity; step 2: carrying out Fourier transform on the original SAR images along the directions with the sparsity to obtain frequency domain images of the directions; step 3: building frequency domain sparse reconstructed models, solving model parameters, establishing observation vectors, and reconstructing frequency domain signals so as to form reconstructed frequency domain images; and step 4: carrying out the Fourier transform on the reconstructed frequency domain images along the directions to obtain reconstructed images. In the invention, by analyzing the sparsity of the SAR images in the airspace, the frequency domain sparse reconstructed models are built by aiming at the frequency domain signals, the model parameters are estimated, projection is carried out on the basis of an appropriate observation matrix and the frequency domain signals are reconstructed by utilizing a small quantity of observed values.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
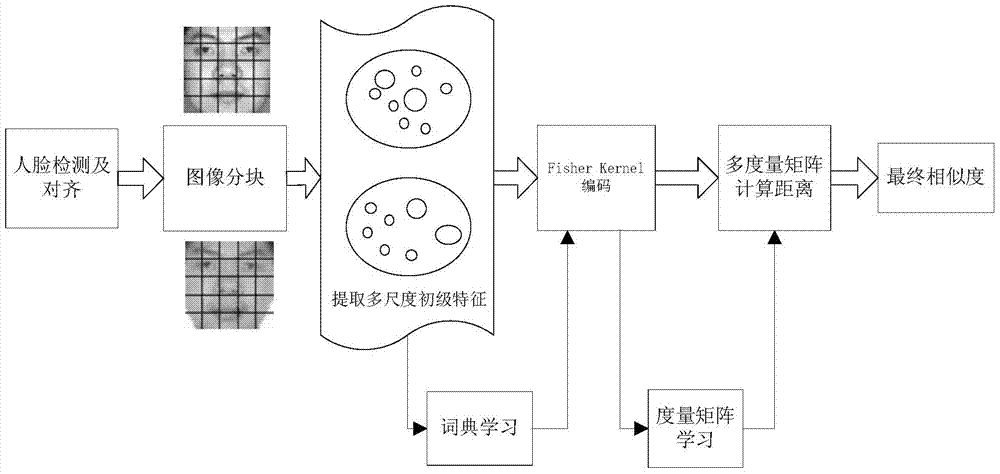
Phase encoding characteristic and multi-metric learning based vague facial image verification method
ActiveCN104123560AImprove classification accuracyExtract compactCharacter and pattern recognitionPositive sampleDictionary learning
The invention discloses a phase encoding characteristic and multi-metric learning based vague facial image verification method. The phase encoding characteristic and multi-metric learning based vague facial image verification method comprises (1) a training phase, namely, partitioning sampling images and extracting multi-scale primary characteristics of every image block, performing fisher kernel dictionary learning through the above characteristics to generate into partitioning fisher kernel coding characteristics, performing multi-metric matrix learning on the above coding characteristics to generate a plurality of metric matrixes and obtain the metric distance after training samples are performed on multi-metric matrix projection, calculating the average metric distance and variance of positive samples and negative samples to a set and confirming a final classification threshold through a probability calculation formula of Gaussian distribution and (2) a verification phase, namely, partitioning input facial images and extracting multi-scale primary characteristics, generating partitioning fisher kernel coding characteristics, obtaining the final metric distance through the multi-metric matrix and comparing the distance and the threshold to obtain a facial image verification result. The phase encoding characteristic and multi-metric learning based vague facial image verification method has the advantages that the identification rate is high and the universality is strong.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Inter-class inner-class face change dictionary based single-sample face identification method
The invention discloses an inter-class inner-class face change dictionary based single-sample face identification method to solve the problem of limitations of the current single-sample face identification algorithm. The method comprises the steps of step1, obtaining expressions of face images in the compression domain; step2, building a face image training sample matrix containing k classes; step3, building an average face matrix and an inter-class face change matrix of a face database; step4, adding low rank and sparse constraints into the inter-class face change matrix; step5, solving an inter-class similarity matrix and an inter-class difference matrix; step6, projecting the average face matrix, the inter-class similarity matrix and the inter-class difference matrix to low-dimensionality space; step7, performing normalization processing on the dimensionality reduced average face matrix, the inter-class similarity matrix and the inter-class difference matrix through a normalization method, and performing iterative solution on the face image training sample matrix based sparse coefficient vectors through a norm optimization algorithm; step8, selecting column vector face labels in the average face matrix, which are corresponding to the sparse coefficient maximum, to serve as the final face identification result.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
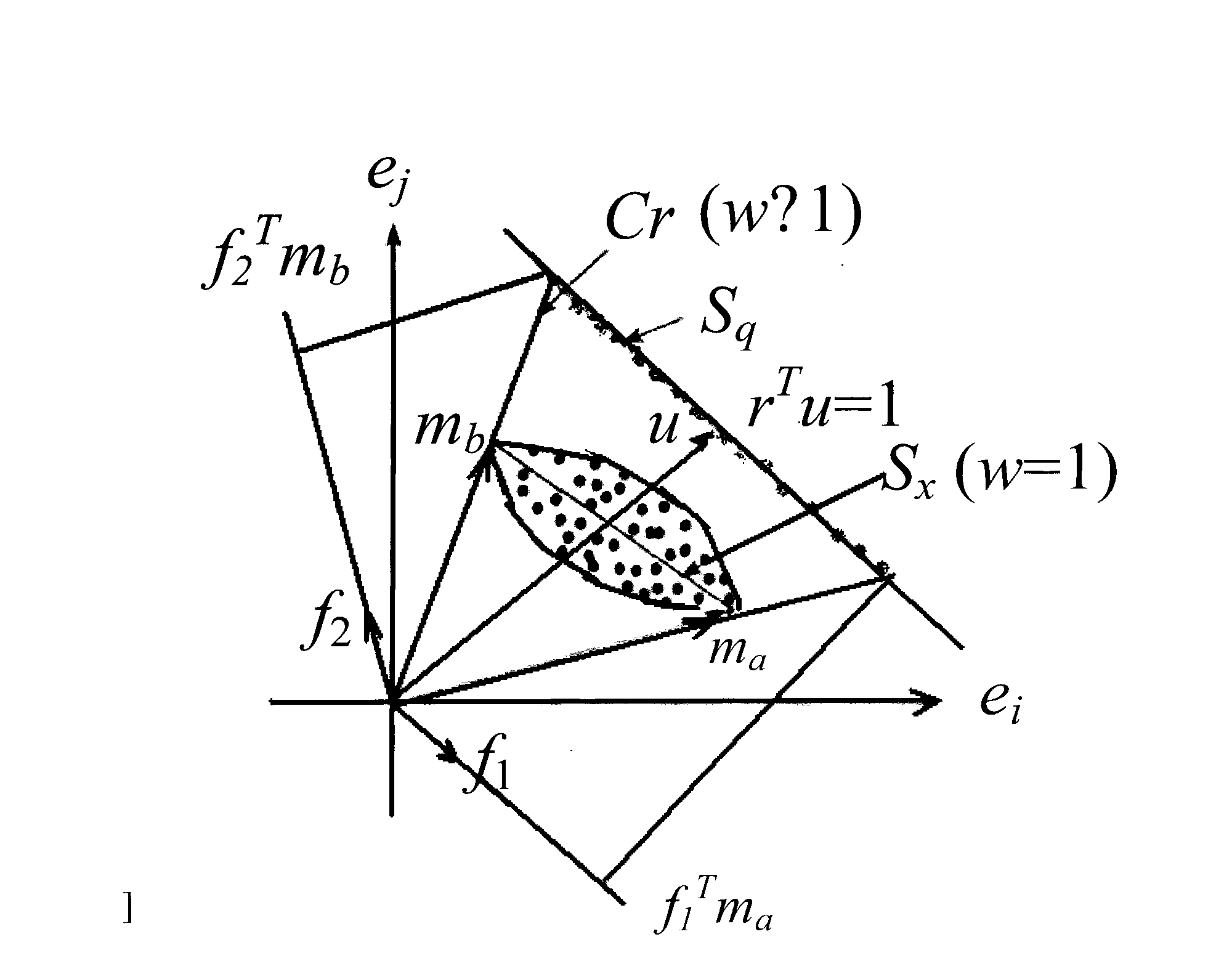
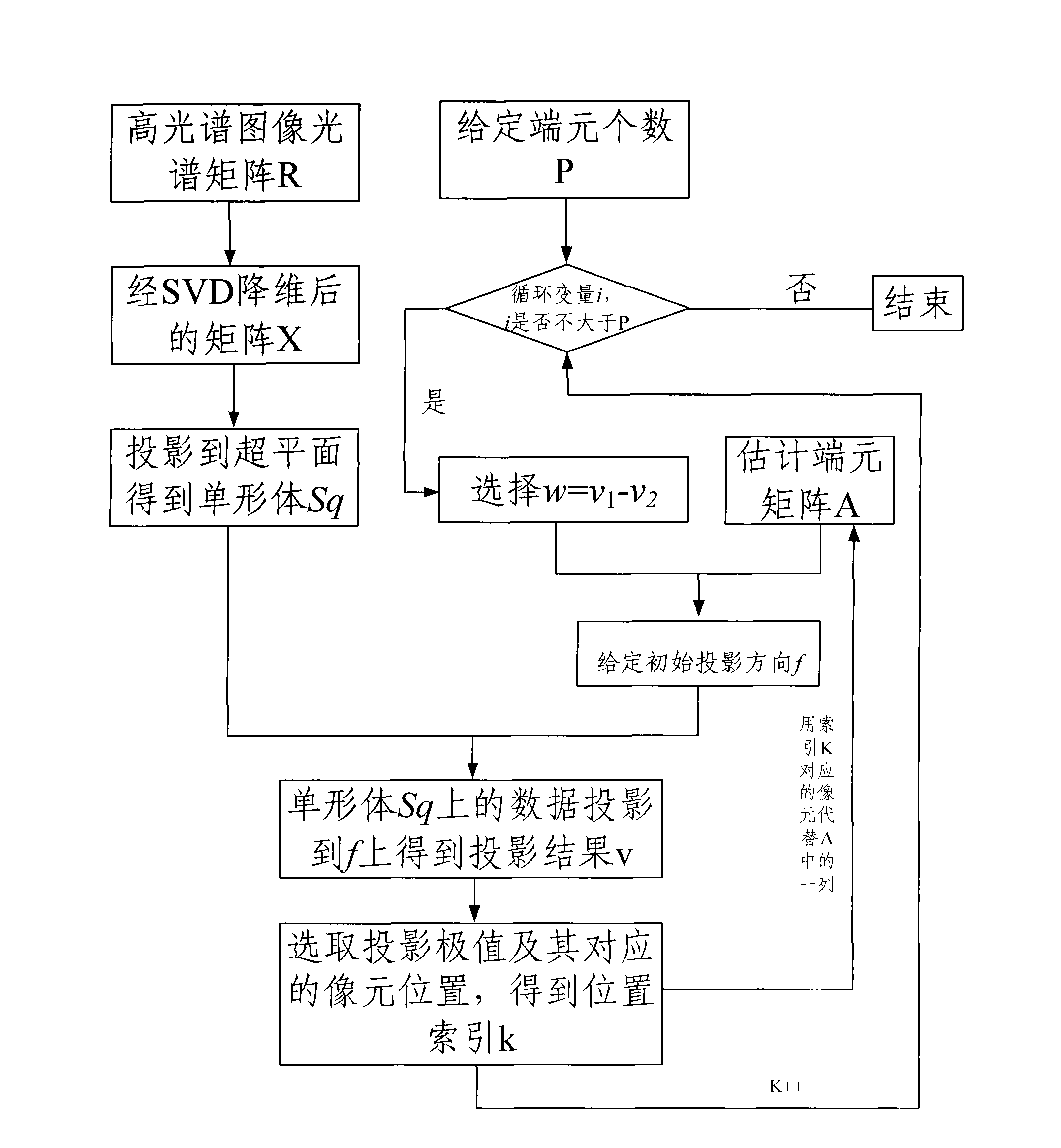
End member extract method of hyperspectral image
InactiveCN101540049AImprove extraction accuracyImprove stabilityImage analysisWave based measurement systemsComputer graphics (images)Matrix projection
Owner:中国人民解放军海军装备研究院信息工程技术研究所
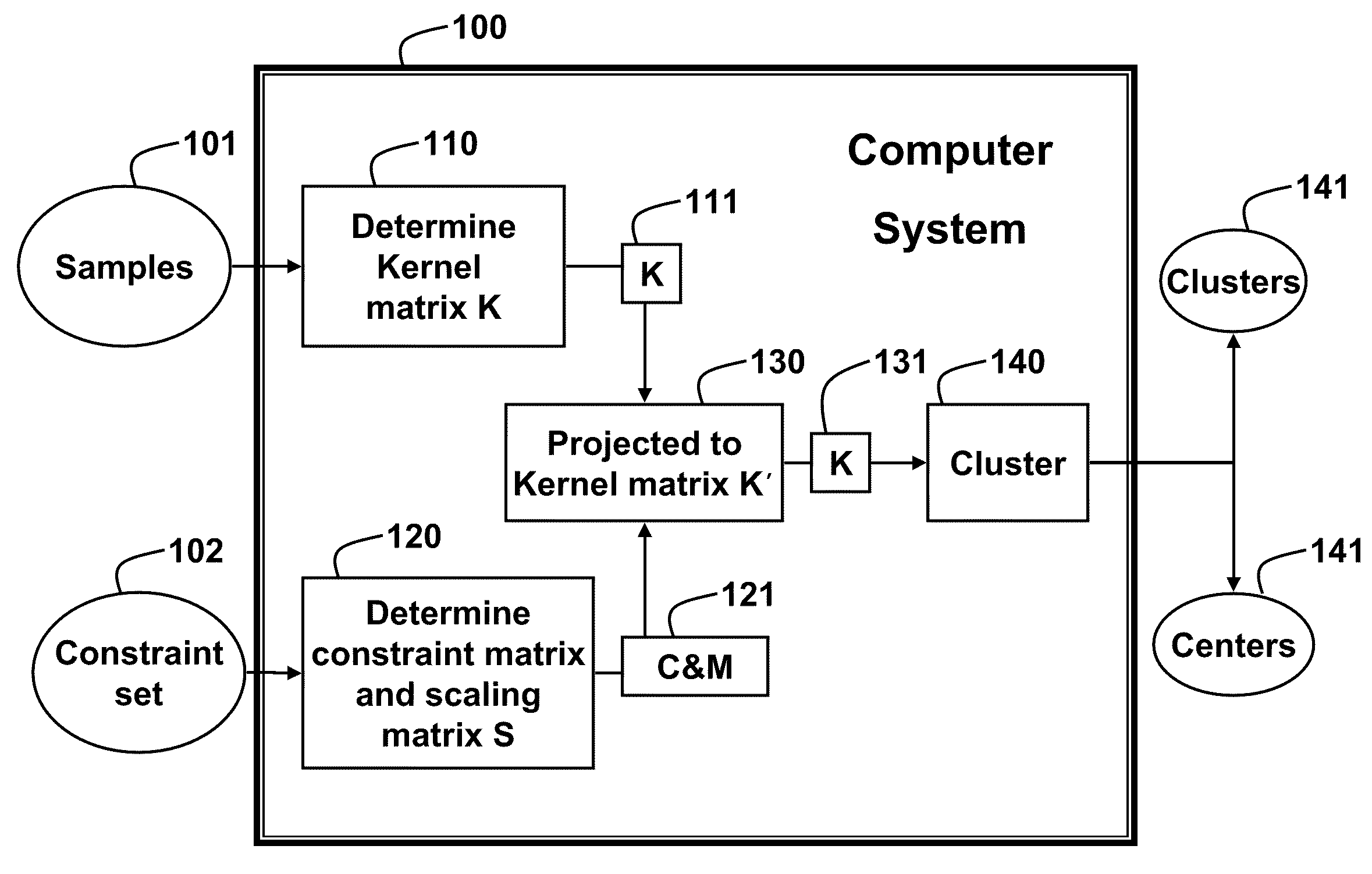
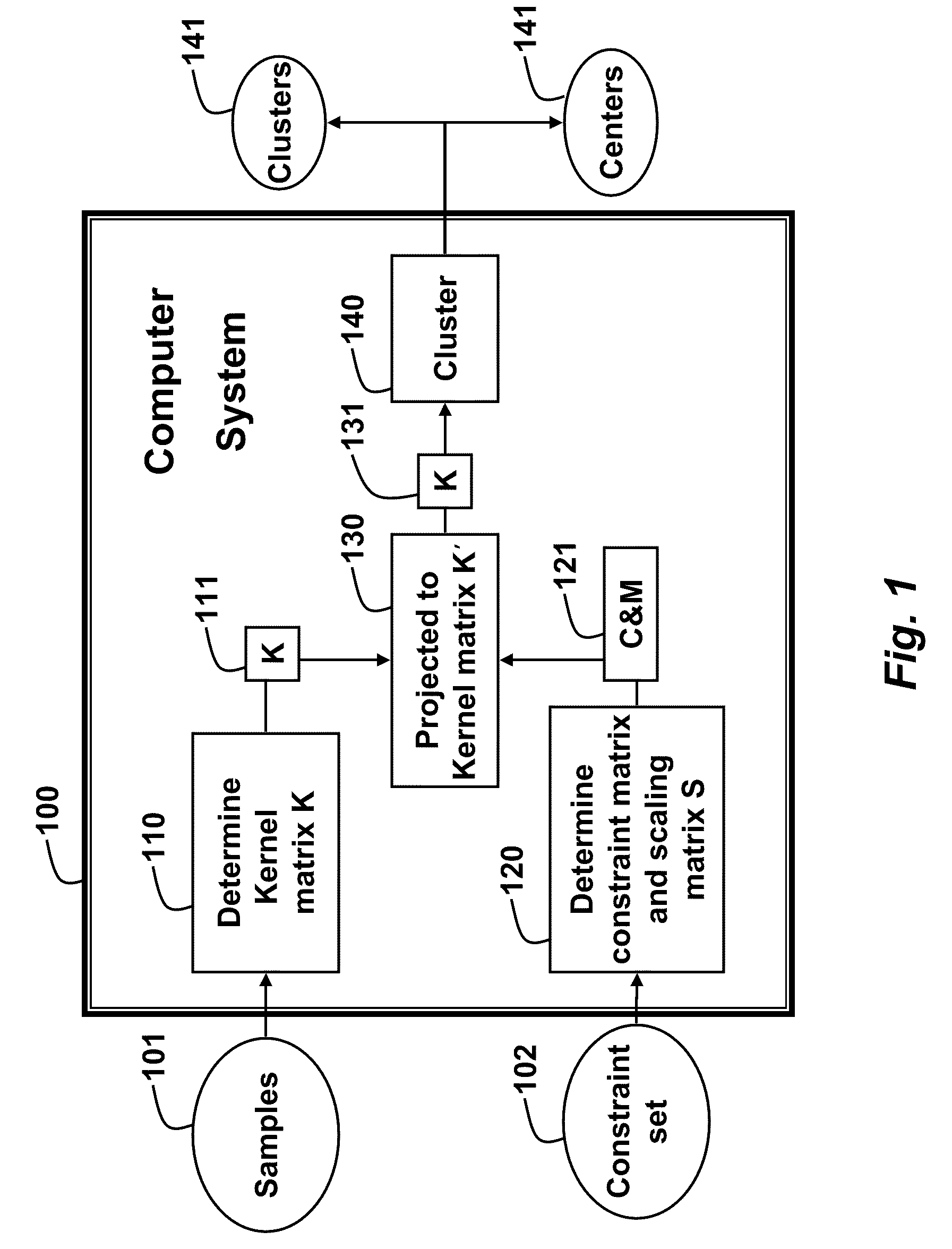
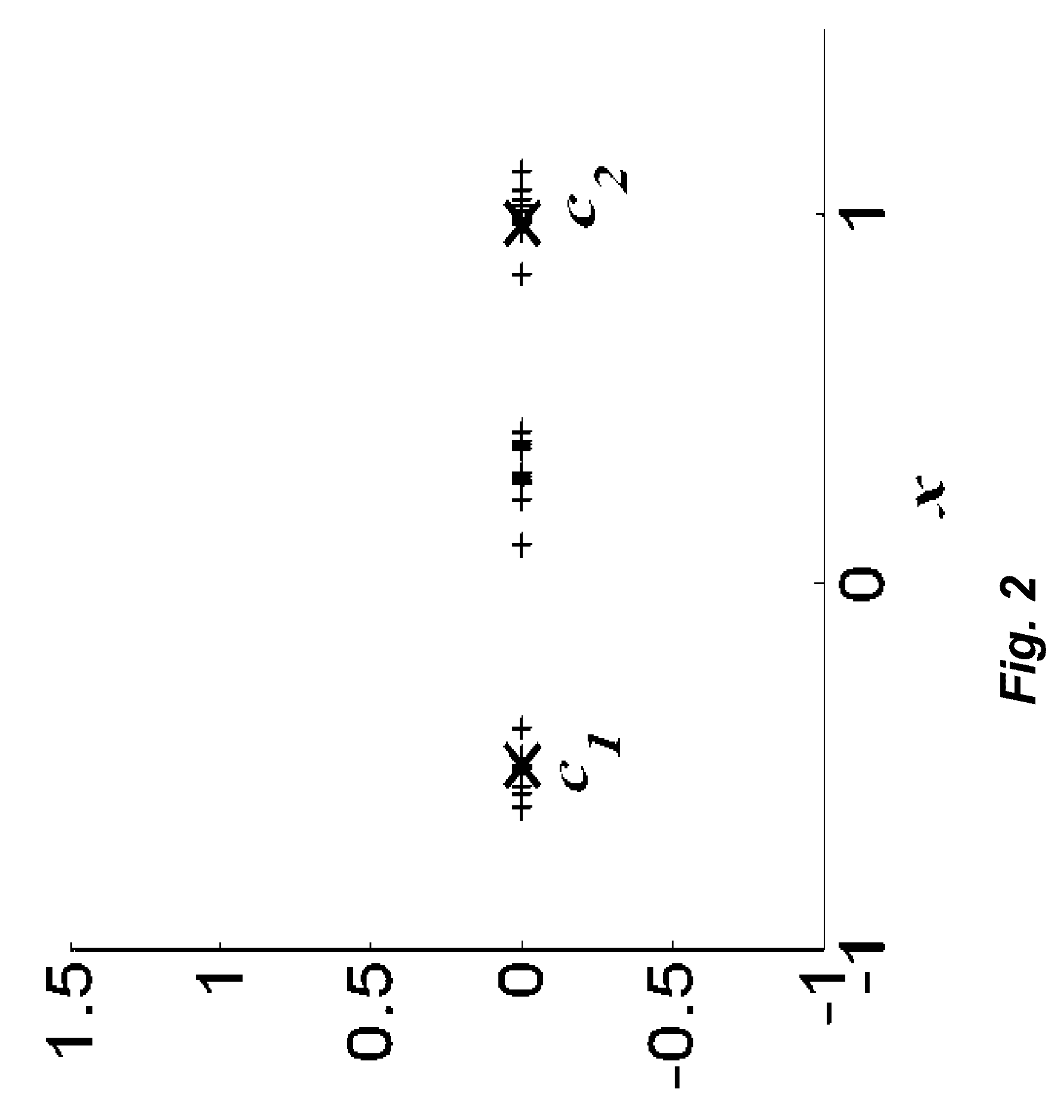
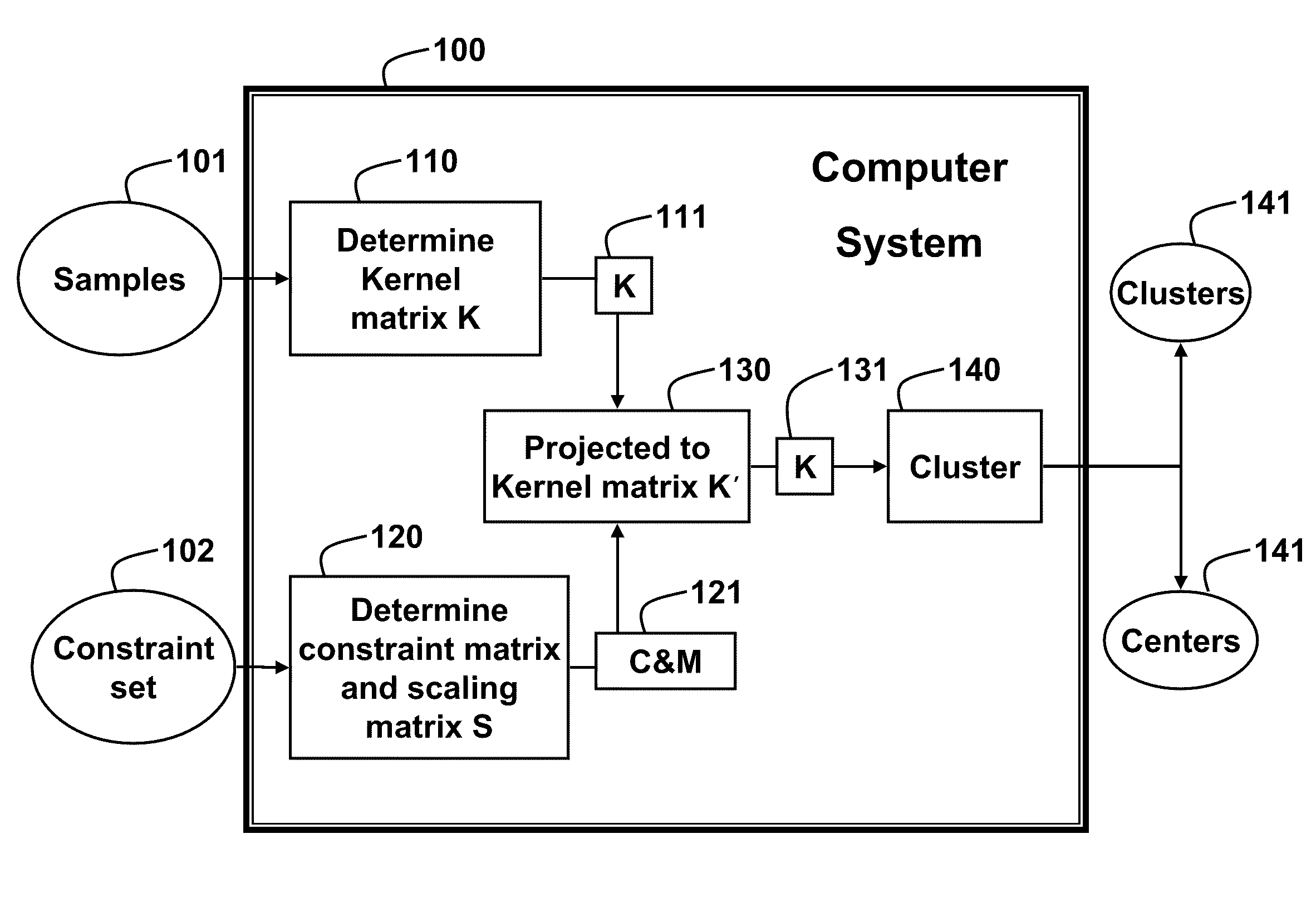
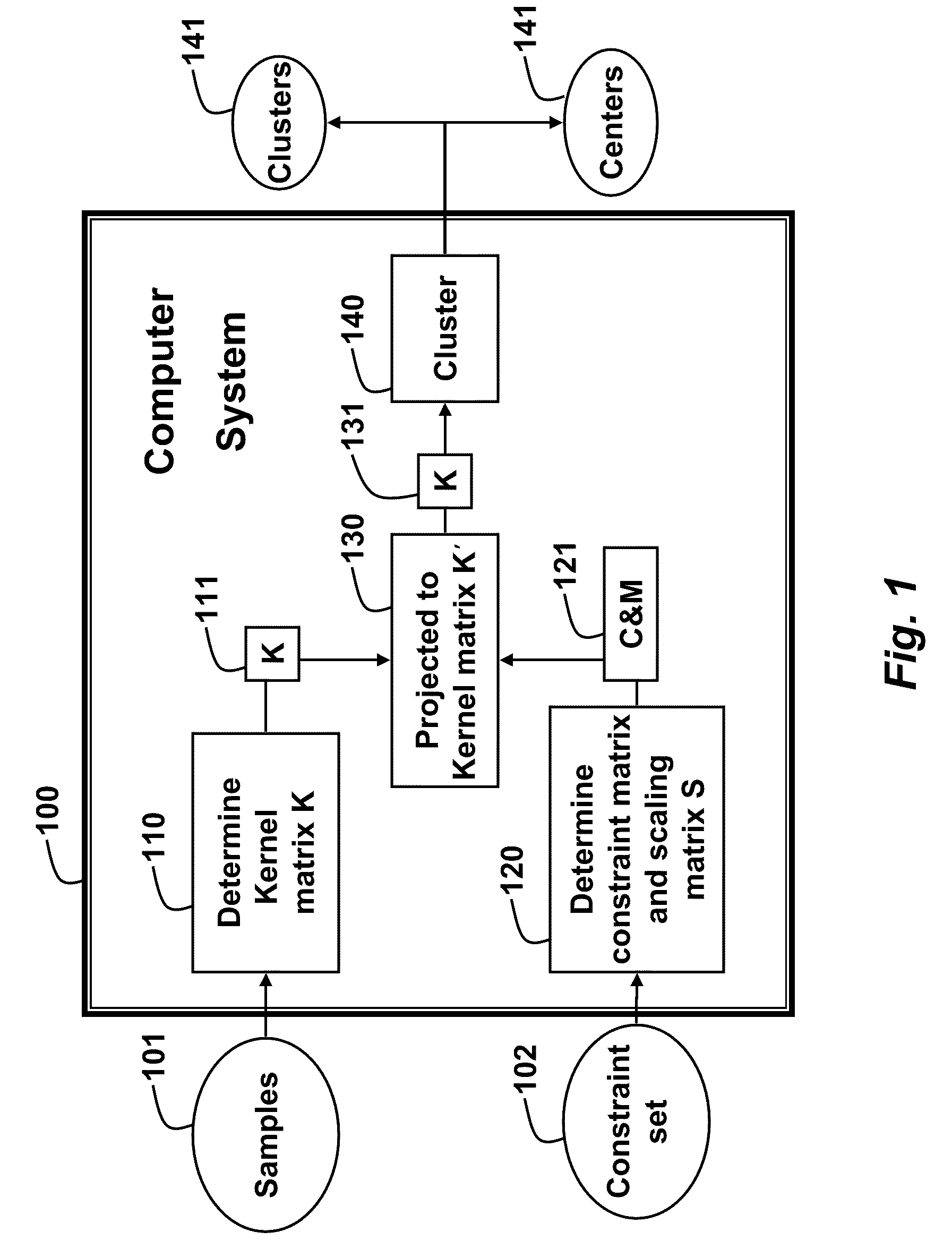
Method for Clustering Samples with Weakly Supervised Kernel Mean Shift Matrices
A method clusters samples using a mean shift procedure. A kernel matrix is determined from the samples in a first dimension. A constraint matrix and a scaling matrix are determined from a constraint set. The kernel matrix is projected to a feature space having a second dimension using the constraint matrix, wherein the second dimension is higher than the first dimension. Then, the samples are clustered according to the kernel matrix.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
License plate recognition with low-rank, shared character classifiers
A method is disclosed for performing multiple classification of an image simultaneously using multiple classifiers, where information between the classifiers is shared explicitly and is achieved with a low-rank decomposition of the classifier weights. The method includes applying an input image to classifiers and, more particularly, multiplying the extracted input image features by |Σ| embedding matrices Ŵc to generate a latent representation of d-dimensions for each of the |Σ| characters. The embedding matrices are uncorrelated with a position of the extracted character. The step of applying the extracted character to the classifiers further includes projecting the latent representation with a decoding matrix shared by all the character embedding matrices to generate scores of every character in an alphabet at every position. At least one of the multiplying the extracted input image features and the projecting the latent representation with the decoding matrix are performed with a processor.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Human face feature extraction and classification method
ActiveCN103902979AStrong characteristicEliminate weaknessesCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorFeature Dimension
The invention relates to a human face feature extraction and classification method. The method includes the following steps that feature dimension reduction is performed on human face images through a 2D-PCA method, and a high-dimensional image matrix is converted into a low-dimensional image matrix; the low-dimensional image matrix is converted into one-dimensional column vectors; according to the one-dimensional vectors of images of a training set, an intra-class divergence matrix S<W> and an inter-class divergence matrix S in the training set are solved, and eigenvalue decomposition is performed on the S<W> and the S respectively, wherein the eigenvalue decomposition formulae are as follows: and ; D<alpha> is used for estimating , D<beta> is used for estimating , and the formulae and can be obtained; the column space W<1> of and the column space W<2> of are respectively solved, and the optimum projection space W=[W<1>,W<2>] of a feature extraction algorithm with two stages of LDA based on 2D-PCA is obtained; the low-dimensional image matrix in the first step is projected into the optimum projection space W, and then feature vectors of the images are obtained; classifier training is performed on the feature vectors obtained in the sixth step through an SVM+NDA model, and a final human face classifier is obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
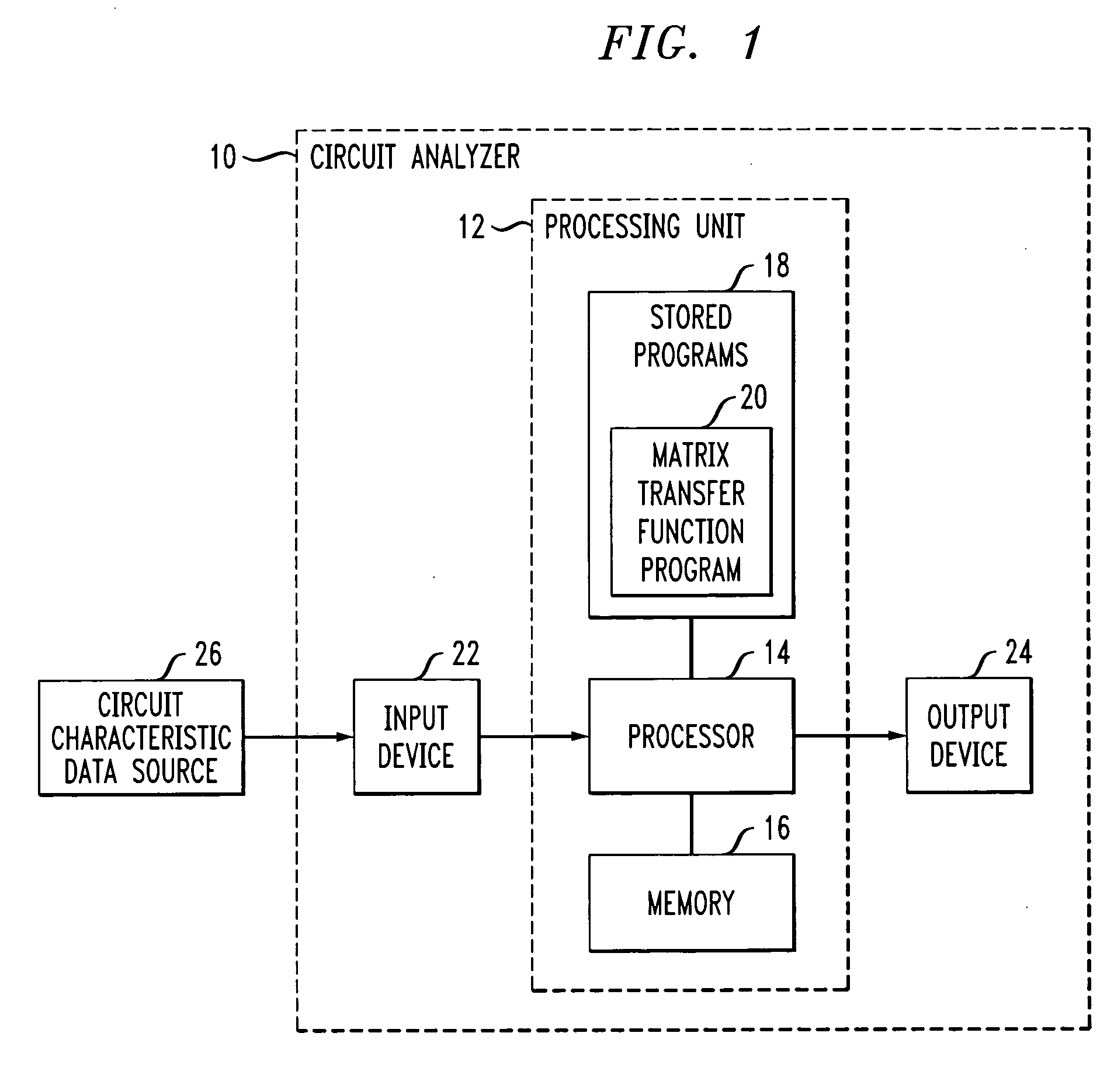
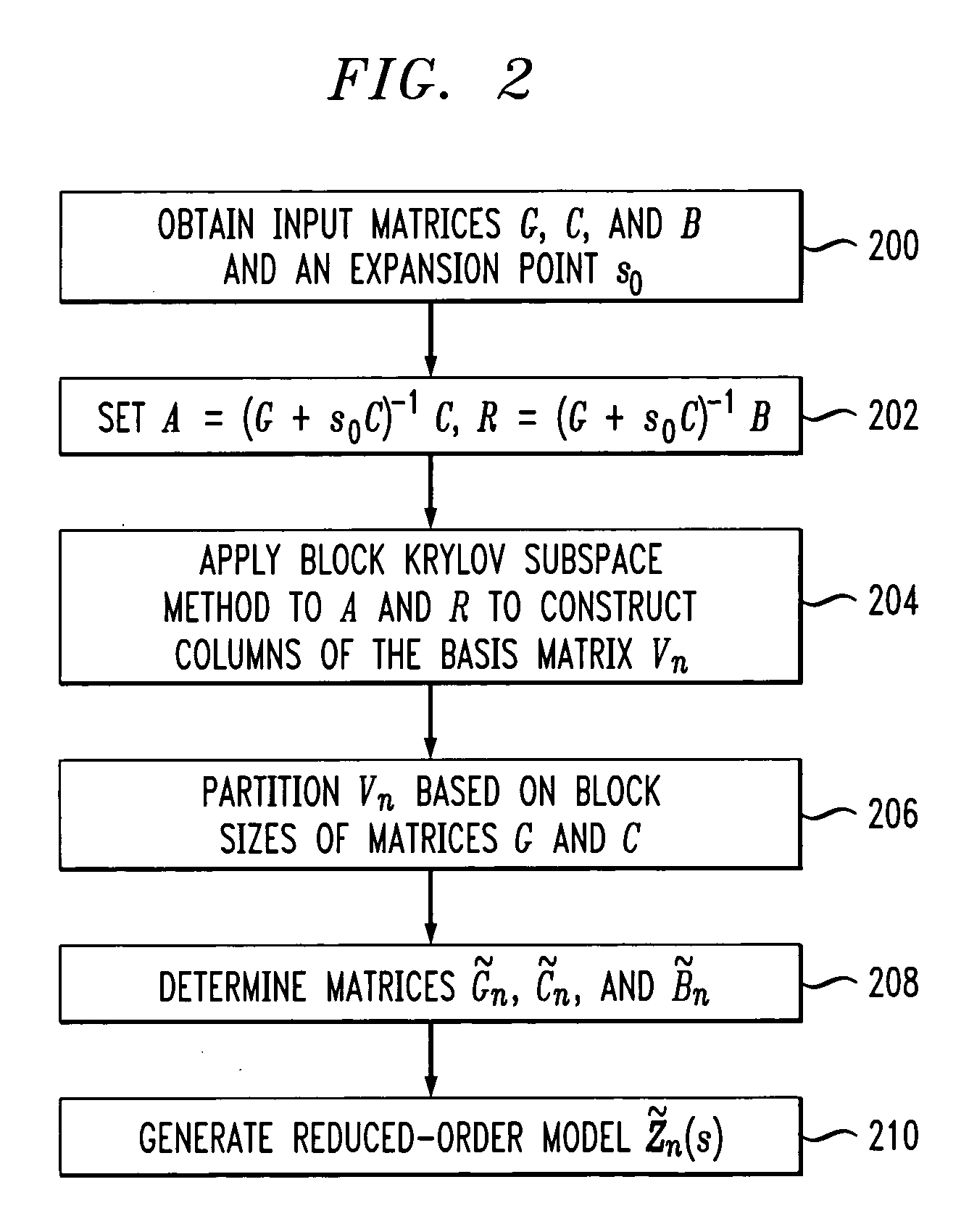
Method and apparatus for structure-preserving reduced-order modeling
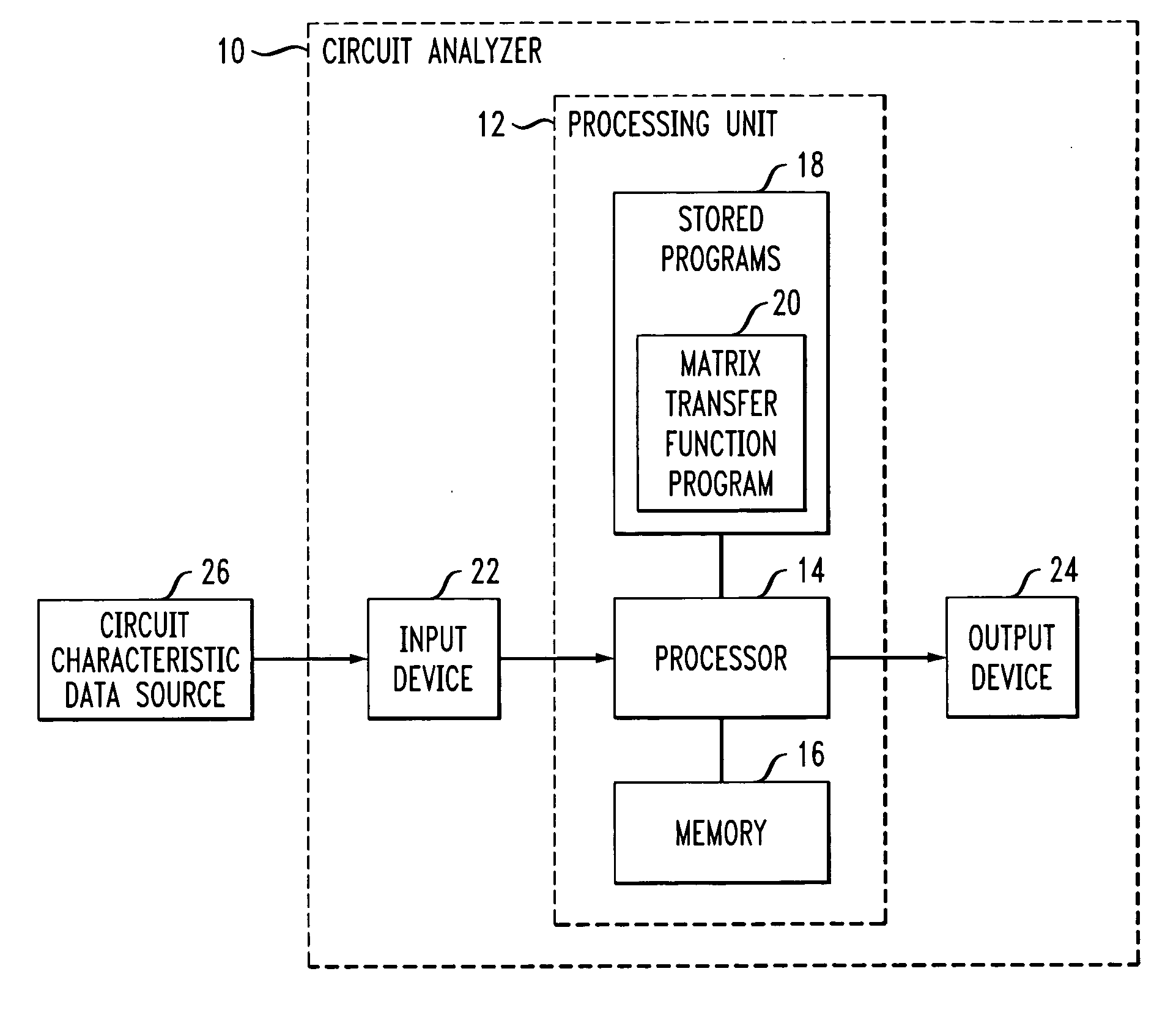
InactiveUS20060004551A1Improve approximationAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationAlgorithmProcessing element
A processing unit of an analysis system comprises a processor coupled to a memory, and is configured to generate a structure-preserving reduced-order model of a circuit, device or system. The reduced-order model in one embodiment is generated by projection of input matrices characterizing the circuit, device or system onto at least one block Krylov subspace, the block Krylov subspace having a corresponding basis matrix. The projection utilizes at least one matrix that has a column range which includes a corresponding portion of the block Krylov subspace but is not itself the basis matrix of the block Krylov subspace. The processing unit generates a frequency response or other signal characterizing the circuit, device or system, based at least in part on the reduced-order model, and an associated output unit presents the generated signal in a user-perceptible format.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
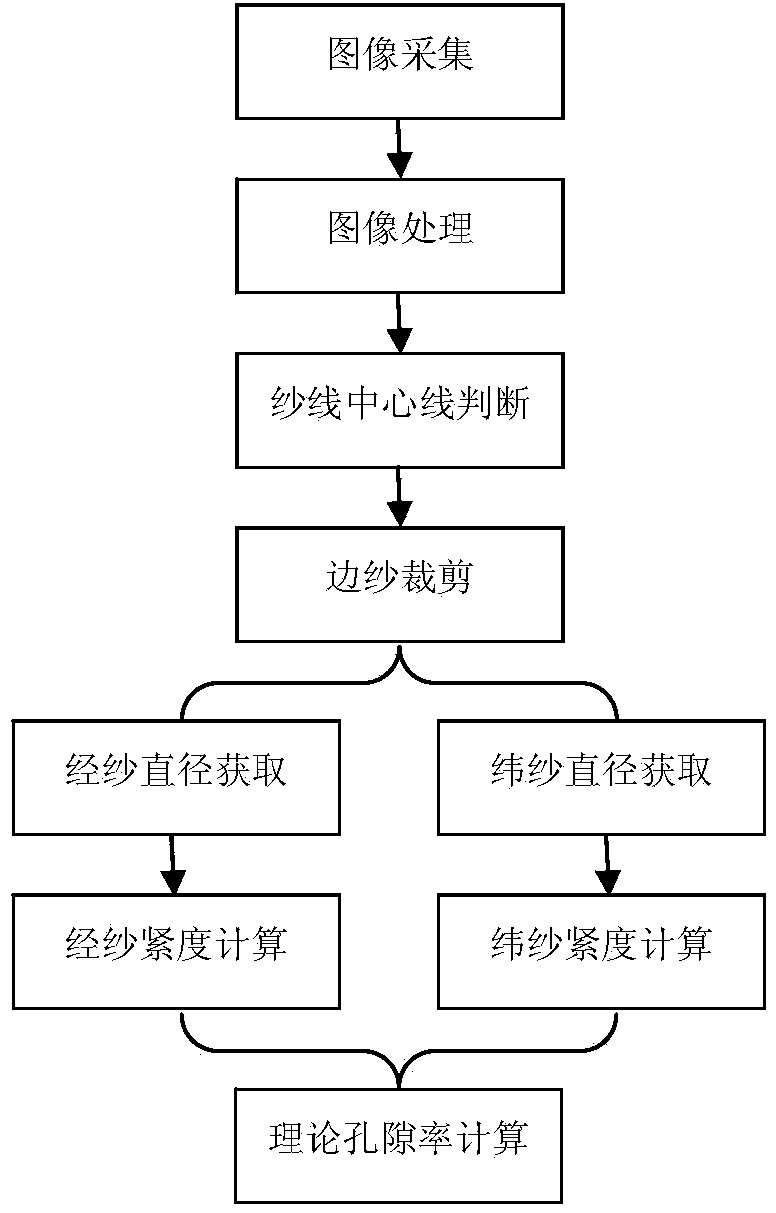
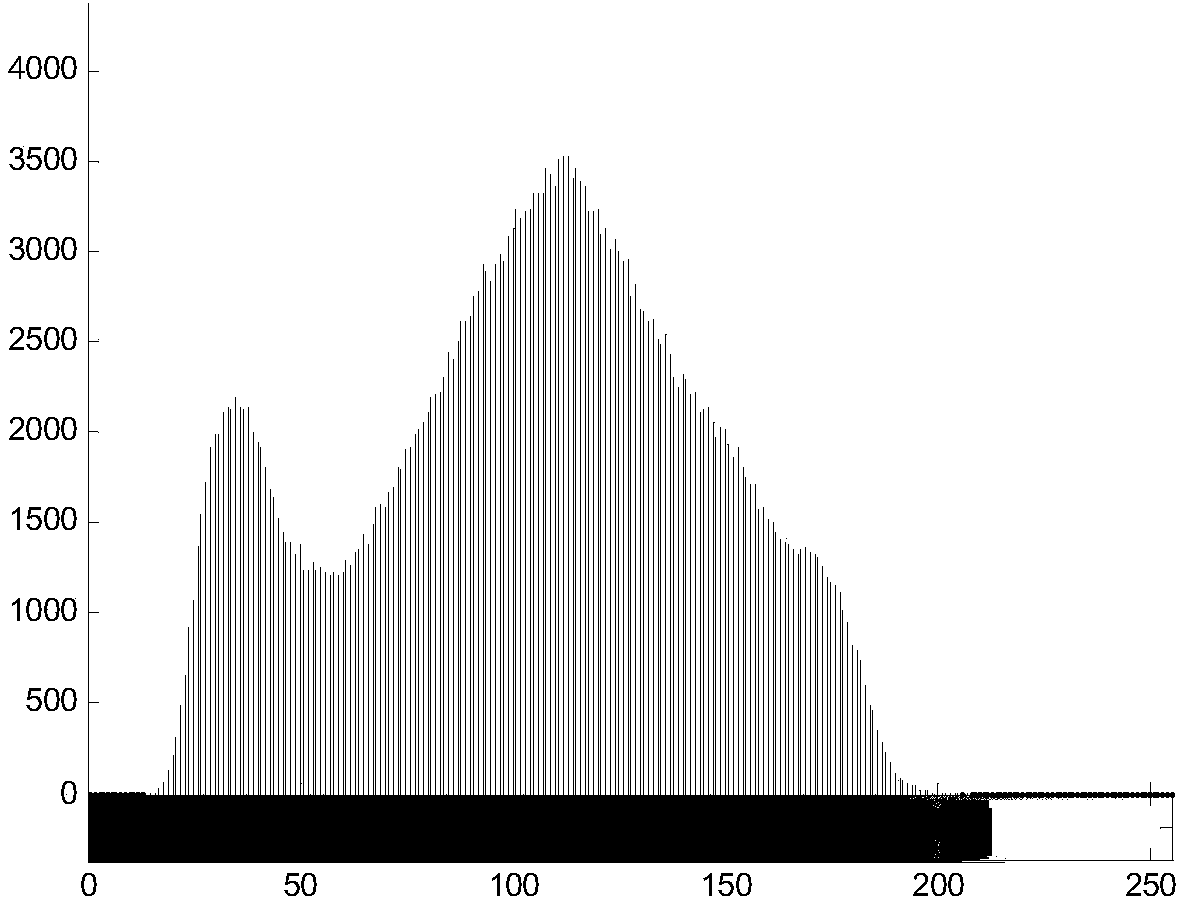
Method for determining theoretic porosity of fabric through image method
InactiveCN103471974ATightness is objective and accurateQuick calculationPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityCentral line placement
The invention relates to a method for determining the theoretic porosity of a fabric through an image method, and in particular relates to a method for determining the theoretic porosity of a latticed sparse fabric through an image method. The method comprises the following steps of analyzing and processing a sparse fabric image through a digital image processing technology to obtain a theoretic porosity index; converting a gray image into a binary image according to a gray histogram two-peak method threshold of the fabric image, setting the pixel of a yarn region in a binary matrix corresponding to the binary image as 1, respectively projecting the binary matrix in the warp yarn direction and the weft yarn direction, and analyzing the central line positions of warp yarns and weft yarns; analyzing a cut image peripheral region according to the central positions of side yarns, wherein the quantity of the warp yarns and the quantity of the weft yarns in a new image are integers; acquiring the diameters of the yarns according to analysis on a wavy curve formed by projection of the binary matrix; calculating warp tightness and weft tightness so as to obtain the theoretic porosity index. By the adoption of the method, the theoretic porosity index can be objectively, accurately and quickly calculated.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Material mark discrimination method and device
InactiveCN105373811ARapid identificationLow costCharacter and pattern recognitionTest sampleCharacteristic space
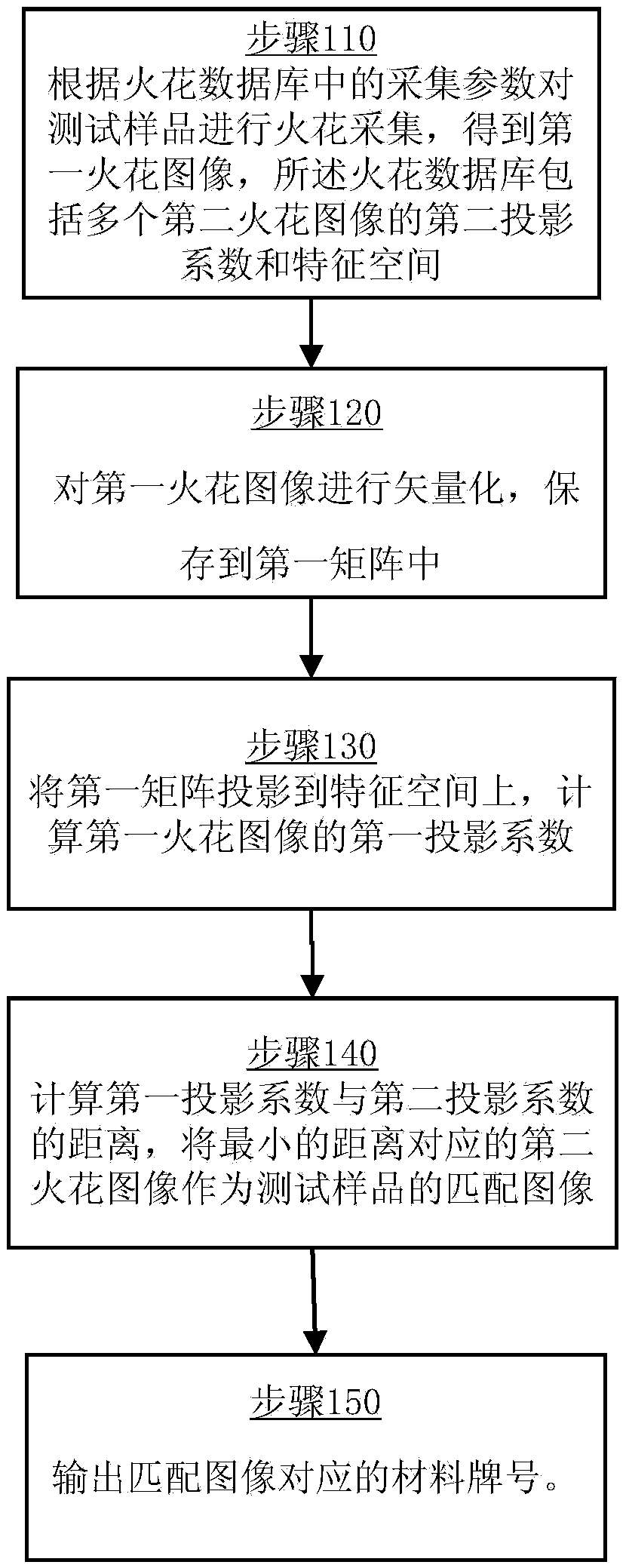
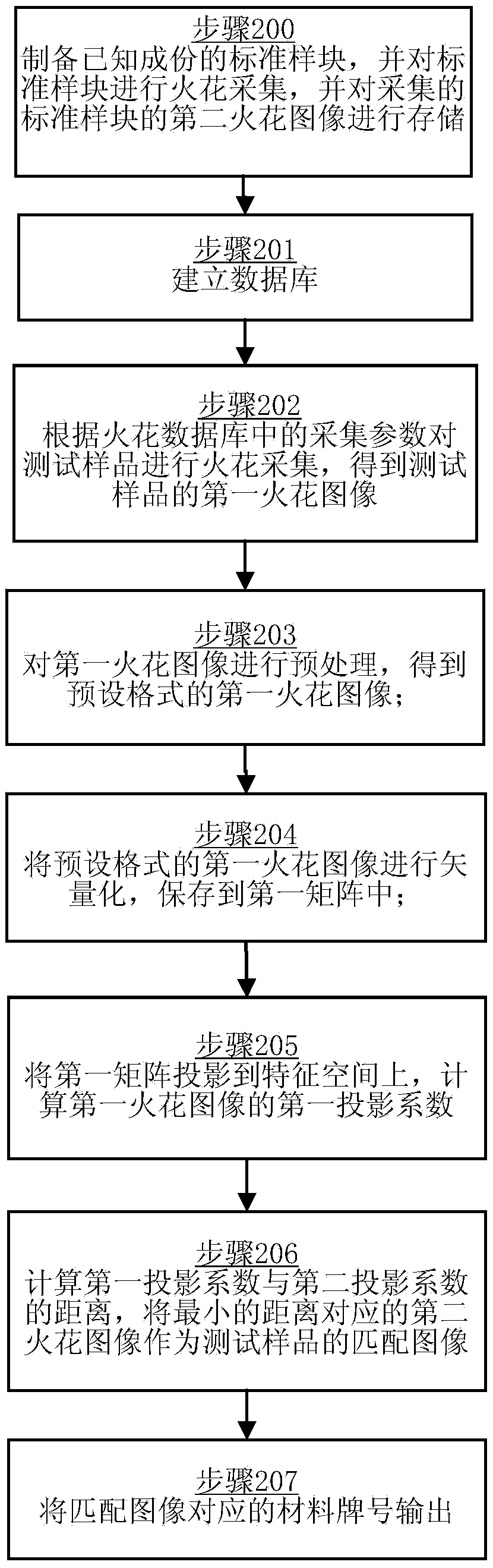
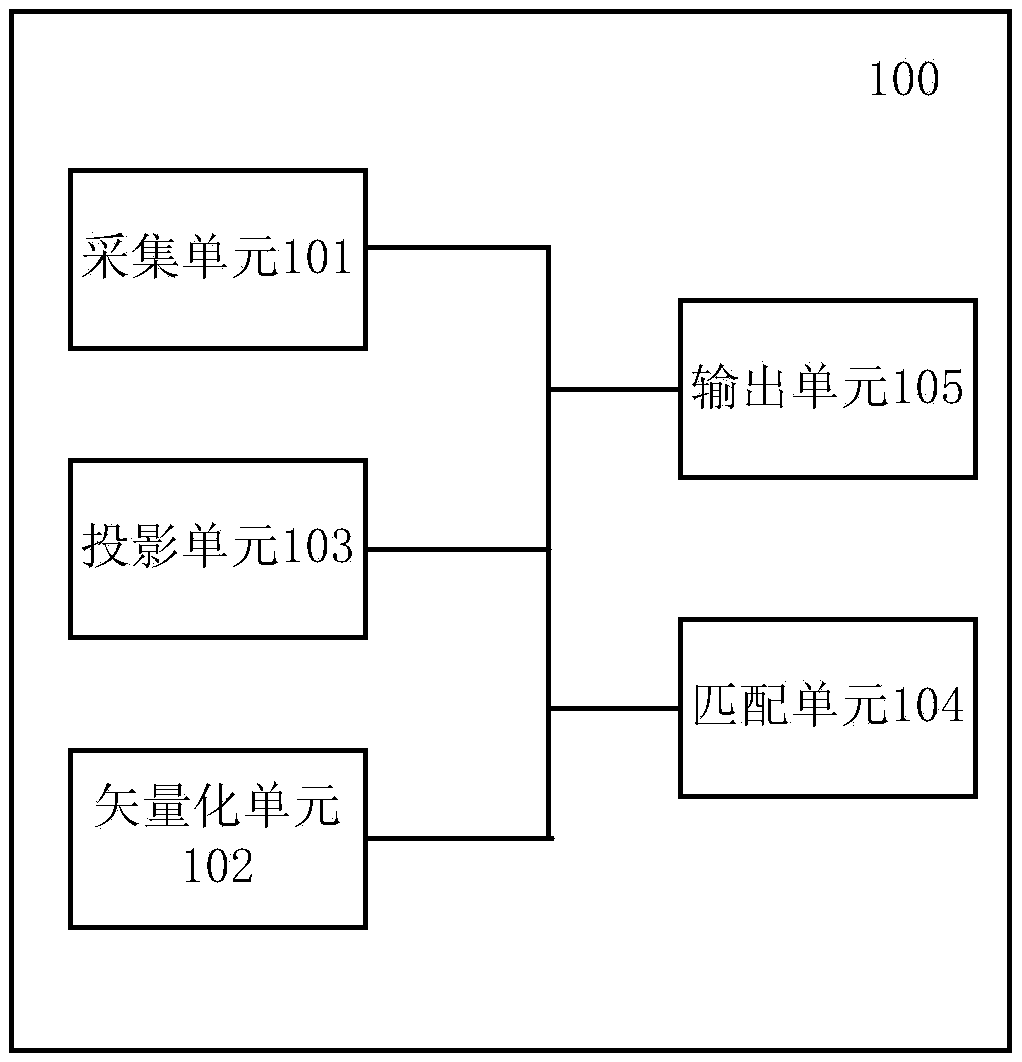
The invention discloses a material mark discrimination method comprising the steps that spark acquisition is performed on a test sample according to acquisition parameters in a spark database so that first spark images are obtained, and the spark database includes second projection coefficients of multiple second spark images and characteristic space; the first spark images are vectorized and saved in a first matrix; the first matrix is projected to the characteristic space of the spark database, and the first projection coefficients of the first spark images are calculated; distance between the first projection coefficients and the second projection coefficients is calculated, and the second spark image corresponding to the minimum distance acts as a matching image of the test sample; and a material mark corresponding to the matching image is outputted. The invention also discloses a material mark discrimination device comprising an acquisition unit, a vectorization unit, a projection unit, a matching unit and an output unit. With application of the method and device, material marks and components can be rapidly identified by comparison of the spark images so that the method and the device are suitable for identification of any material marks capable of generating sparks.
Owner:王少鲲
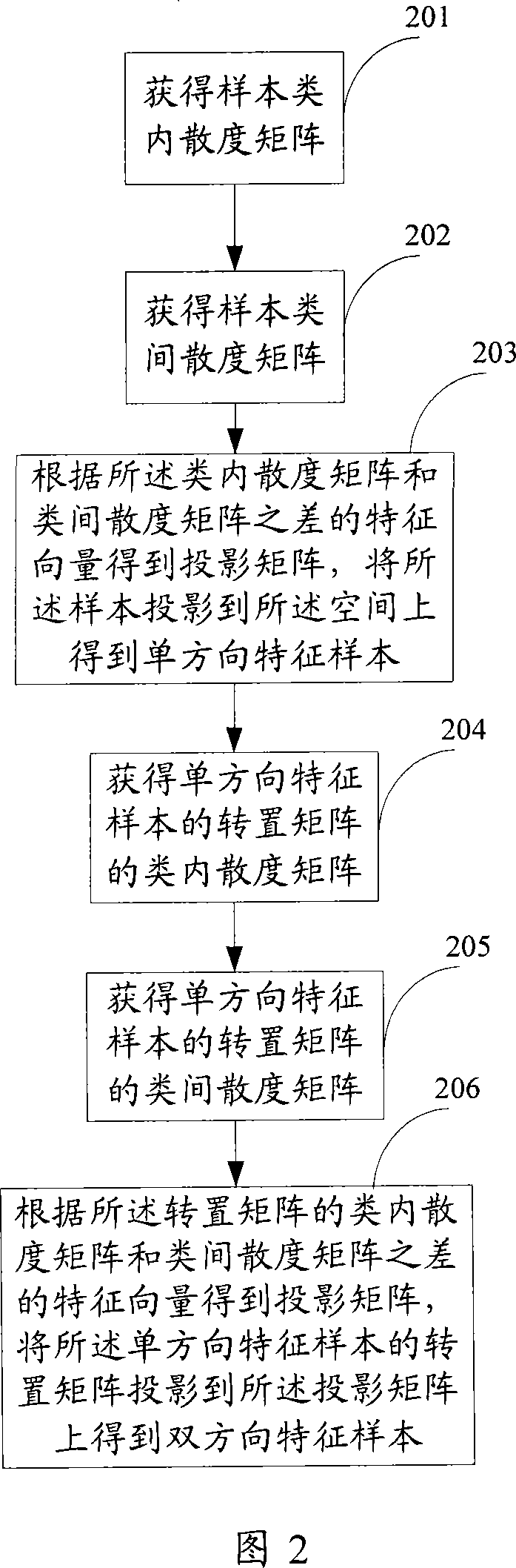
Feature extracting method, device and pattern recognition method and device
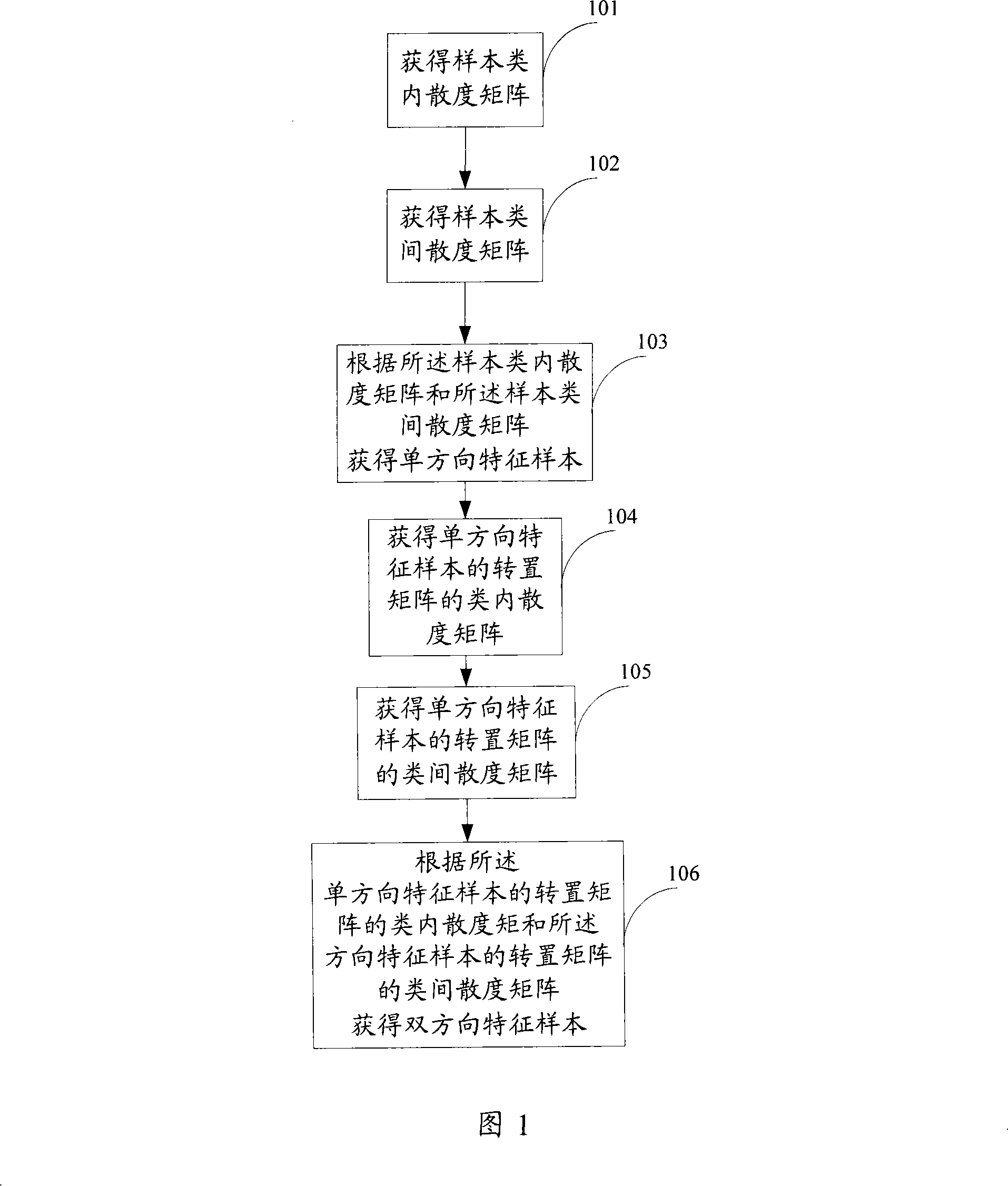
The invention discloses a feature extraction method. The method includes steps: acquiring a unidirectional projection matrix formed by a first determined number of eigenvectors corresponding to the maximum eigenvalues of the difference matrix of a first inter-class scatter matrix and a first intra-class scatter matrix of a sample matrix including more than one class of samples, and projecting the sample matrix onto the unidirectional projection matrix to obtain a unidirectional characteristic sample matrix; and acquiring a bidirectional projection matrix formed by a second determined number of eigenvectors corresponding to the maximum eigenvalues of the difference matrix of a second inter-class scatter matrix and a second intra-class scatter matrix of the transposed matrix of the unidirectional characteristic sample matrix, and projecting the transposed matrix of the unidirectional characteristic matrix to the bidirectional projection matrix to obtain bidirectional characteristic samples. The invention also discloses a feature extraction device and a pattern recognition method and a device. Applying the inventive method and the device can improve stability and speed for feature extraction and pattern recognition.
Owner:北京中星天视科技有限公司
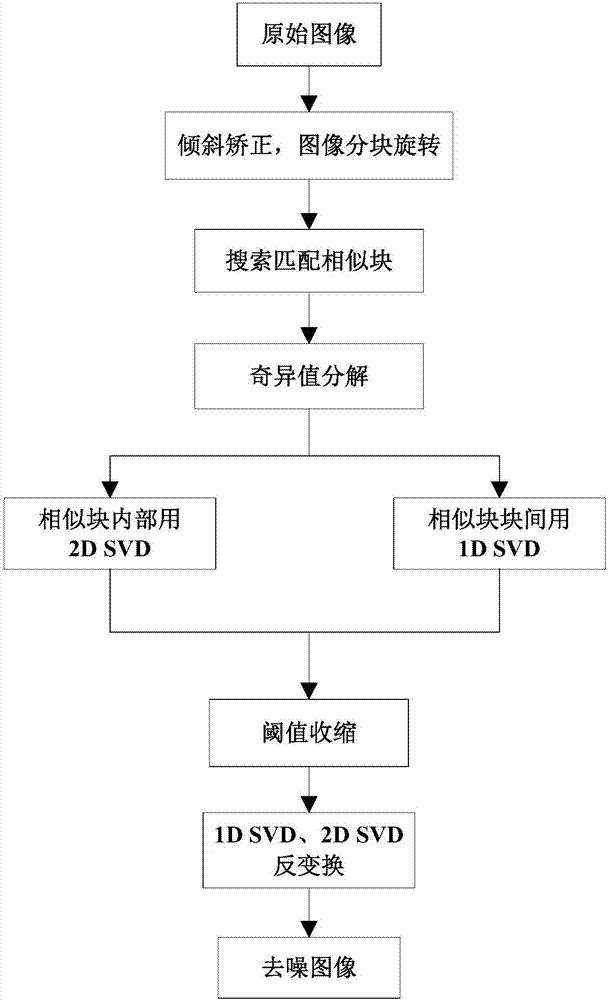
Image denoising method based on image rotation and partitioning singular value decomposition
InactiveCN107085834AReduce lossesImprove constant errorImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionSingular value decompositionImage denoising
The invention discloses an image denoising method based on image rotation and partitioning singular value decomposition. Firstly partitioning rotation is performed on an original input image; then the rotated image blocks are searched, and similarity matching is performed according to the image blocks; and finally two-dimensional and one-dimensional singular value decomposition is performed inside and outside the successfully matched similar blocks, and 1D SVD inverse transformation and 2D SVD inverse transformation are performed on the contracted projection coefficient by using the soft and hard compromise threshold contraction matrix projection coefficient so that final image denoising can be realized. According to the method, partitioning rotation is performed on the image before denoising so that image information attenuation in the block can be eliminated, the processing time can be shortened, different dimensions of singular value decomposition can be performed inside and outside the image and the anti-noise performance can be enhanced based on the conventional SVD algorithm.
Owner:XI'AN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Projection system
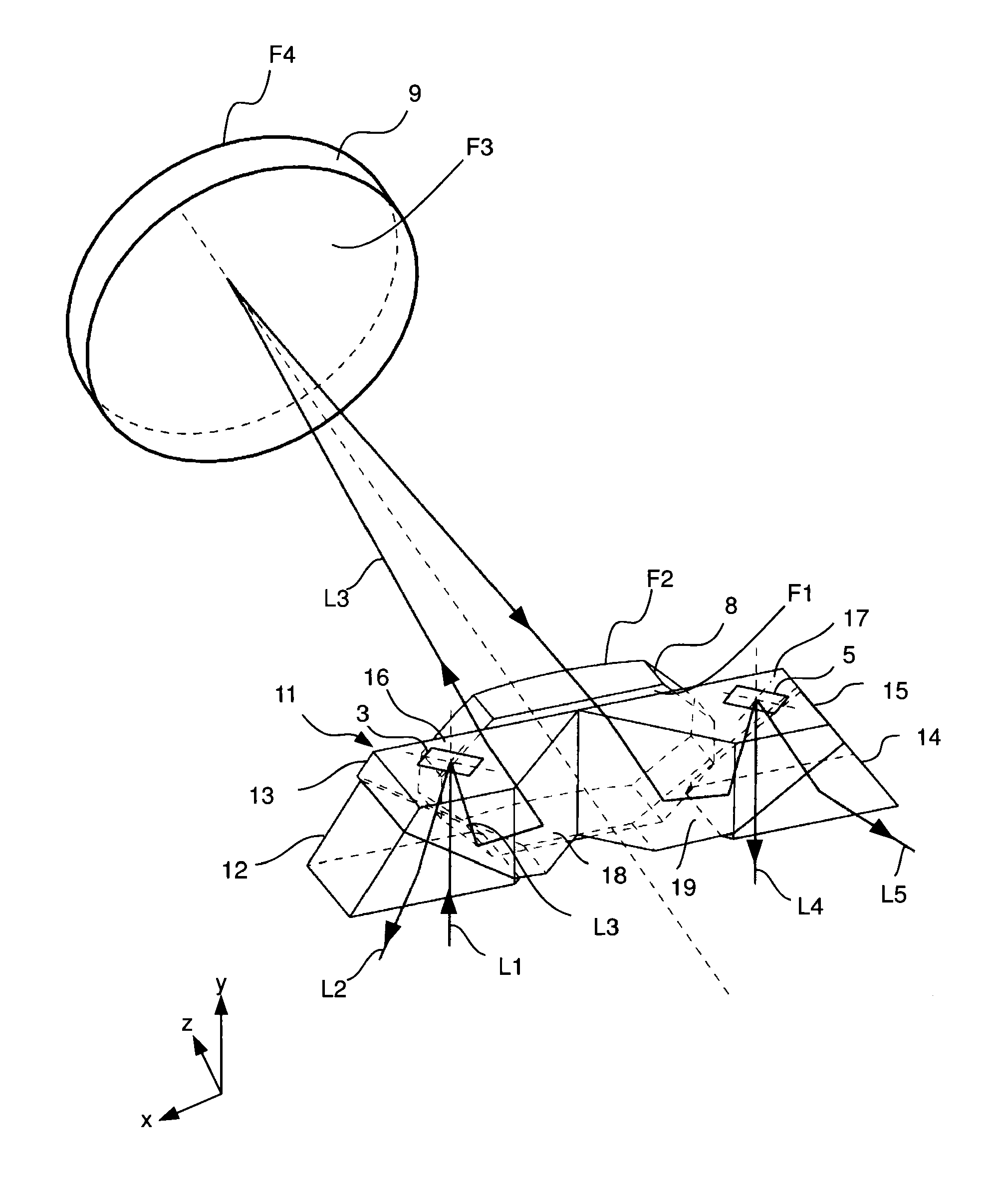
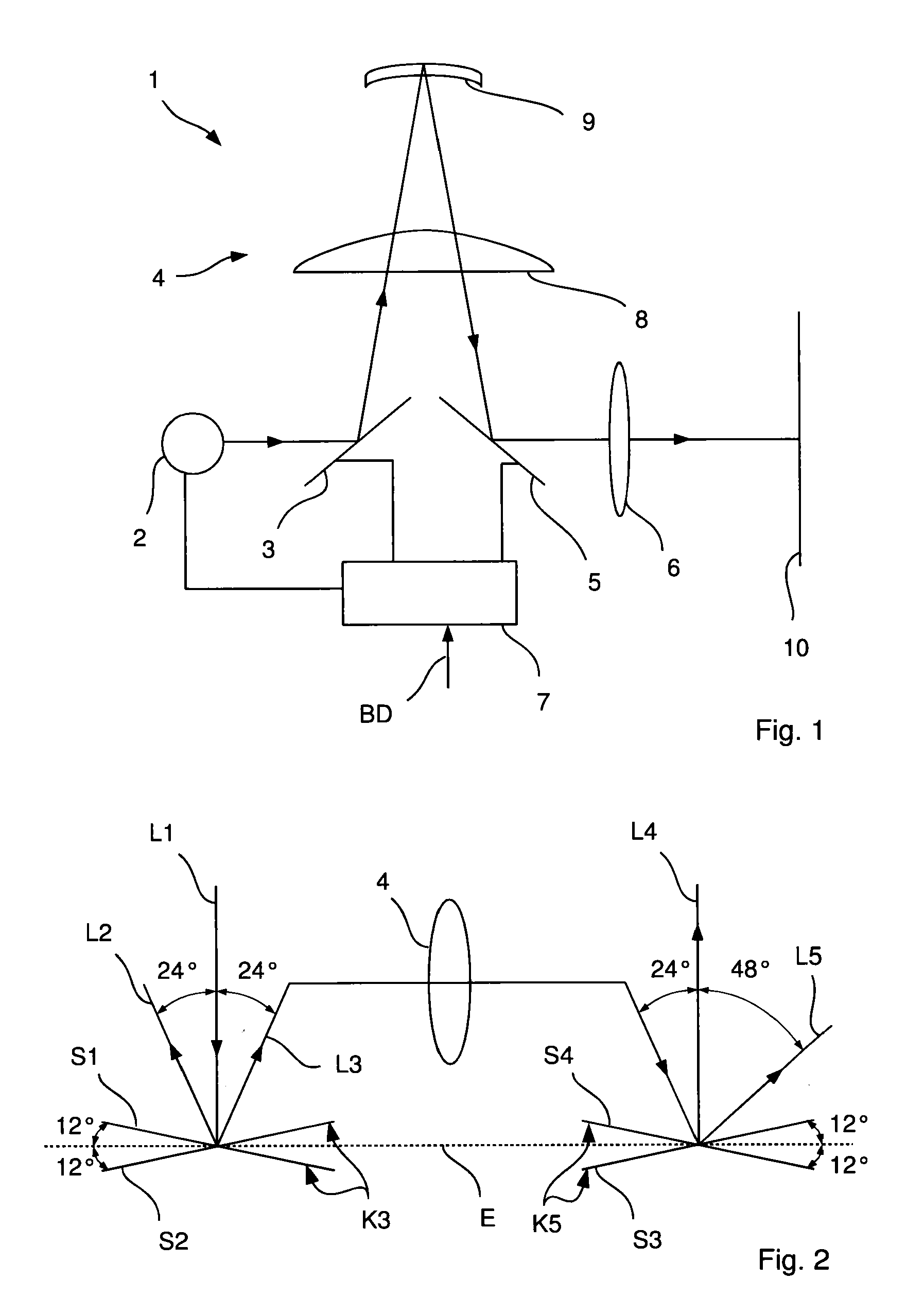
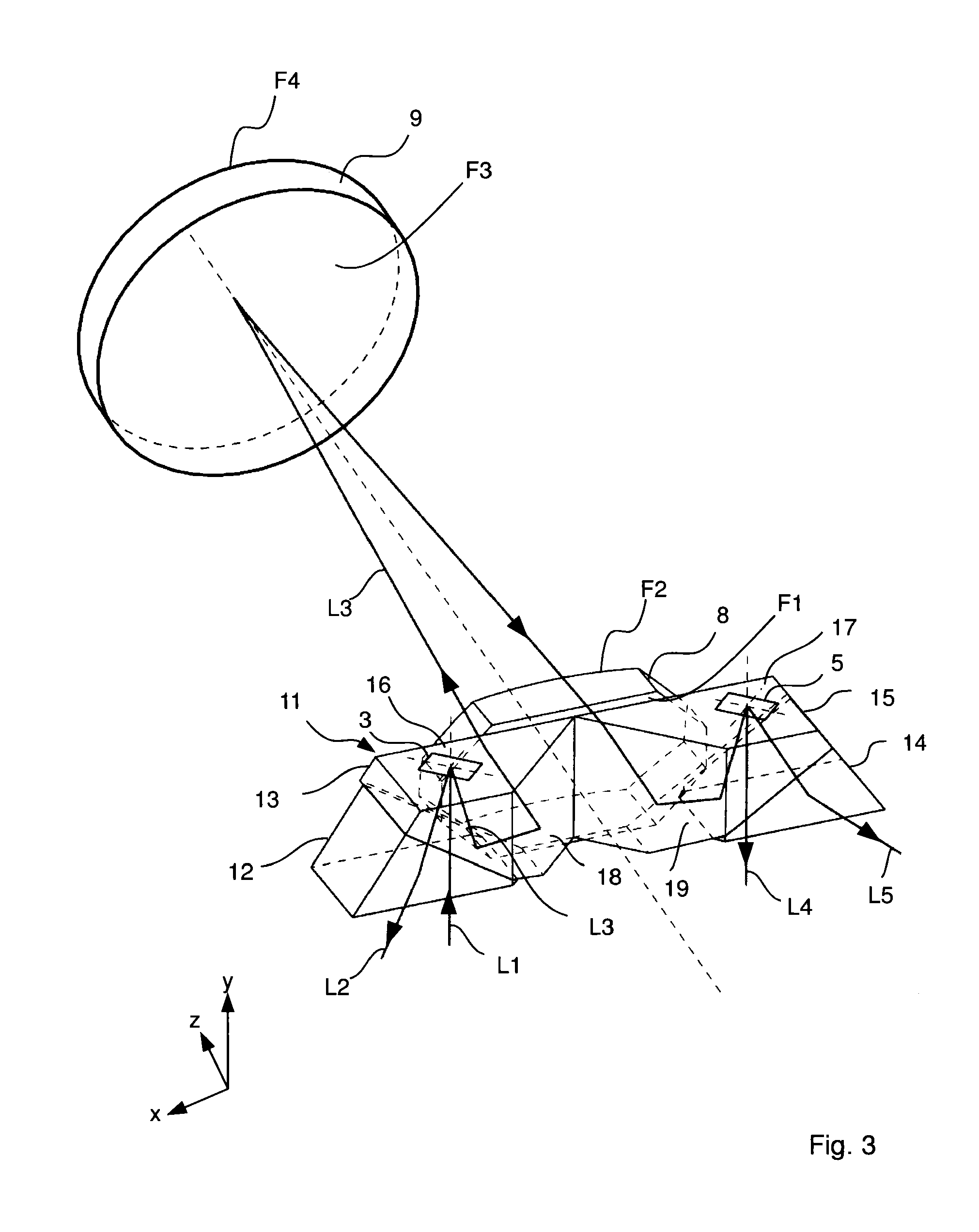
ActiveUS8500290B2Optically compactImprove image qualityProjectorsColor television detailsCamera lensImaging lens
A projection system having a first tilting mirror matrix, a second tilting mirror matrix, and an imaging lens, which projects the first tilting mirror matrix onto the second tilting mirror matrix, wherein each tilting mirror matrix has multiple tilting mirrors, the tilting axes of which are positioned in a modulator surface plane. The imaging lens includes a first lens and an imaging mirror, and the imaging mirror forms an aperture stop of the imaging lens, wherein the aperture diaphragm includes an uneven angle of 90° together with the normal of the modulator surface of the first tilting mirror matrix without taking into account any optical path folds.
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
Structured sparse representation and low-dimension embedding combined dictionary learning method
InactiveCN108573263AEnhance expressive abilityEliminate dependenciesCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDictionary learning
The invention discloses a structured sparse representation and low-dimension embedding combined dictionary learning method. Dictionary construction and dimension-reduced matrix projection are carriedout in parallel alternatively, a sparse representation coefficient matrix forced to include a block diagonal structure in a low-dimension projection space is used to enhance inter-type incoherence ofa dictionary, intra-type coherence of the dictionary is maintained via low-rank performance of a representative coefficient in a type sub-dictionary, dictionary construction and projection learning prompt each other to main the sparse structure of data fully, and a coding coefficient with a higher type discriminating capability is coded. The problems that the coded representation coefficient is low in discriminating and distinguishing capabilities in an existing dictionary learning method in the prior art due to high maintaining characteristic of training sample data and lack of a dictionary with strictly constraint of the block diagonal structure.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for clustering samples with weakly supervised kernel mean shift matrices
A method clusters samples using a mean shift procedure. A kernel matrix is determined from the samples in a first dimension. A constraint matrix and a scaling matrix are determined from a constraint set. The kernel matrix is projected to a feature space having a second dimension using the constraint matrix, wherein the second dimension is higher than the first dimension. Then, the samples are clustered according to the kernel matrix.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
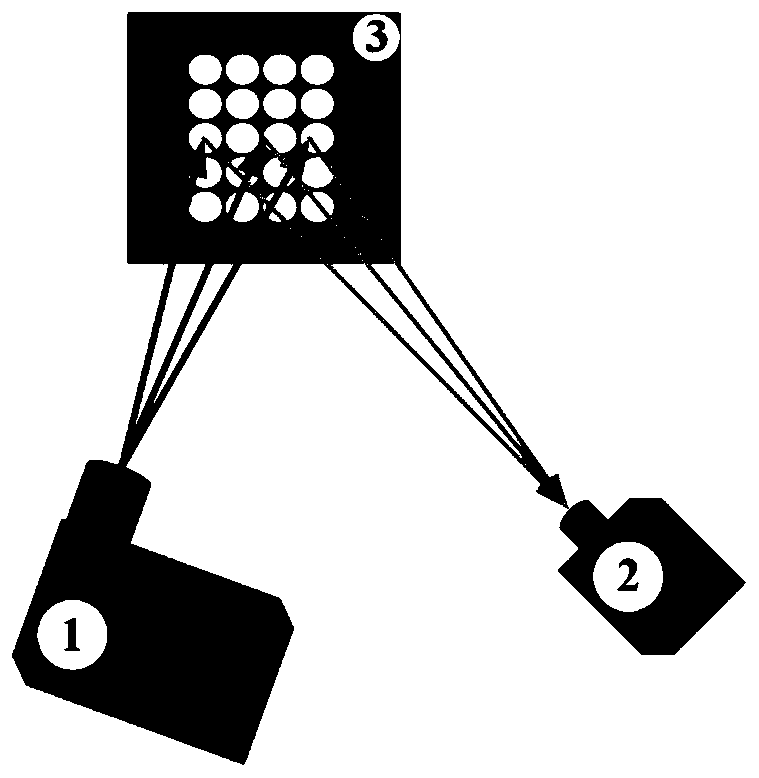
Outdoor matrix projection system
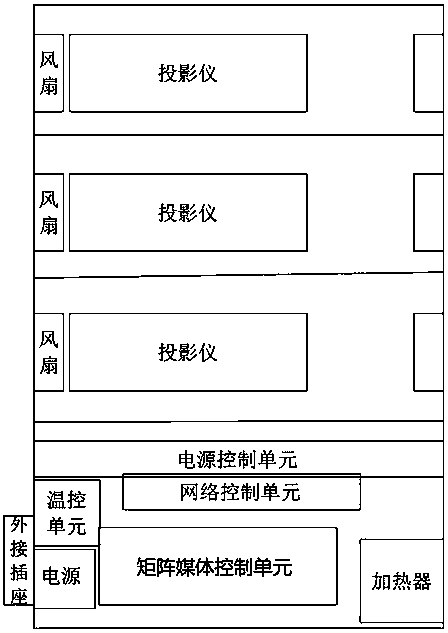
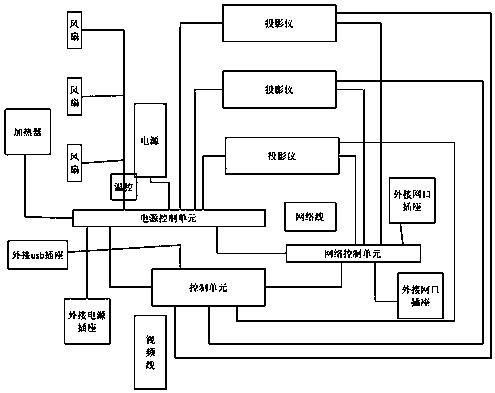
ActiveCN108761977ARealize networkingImprove performancePrintersProjectorsTemperature controlNetwork control
The invention discloses an outdoor matrix projection system, comprising: matrix projectors, wherein the plurality of matrix projectors are used by networking through a network, and comprise a casing;at least two projections and a light source are arranged in the casing; each projector is cooled by a separate fan in the manner of blowing; the power input end of each projector is electrically connected to the power output end of the digital control switch on the power control unit through the wire; the power input end of the fan is electrically connected to the power output end of another digital control switch on the power control unit through the wire; and the casing is internally provided with a temperature control unit, a control unit and a network control unit. The invention is capableof realizing networking of a plurality of matrix projectors, thereby realizing function superposition, splicing and 3dMapping, and improving overall performance. The matrix projectors of the invention have temperature sensors and may can be cooled by fans and heated by heaters to adapt to different outdoor environments.
Owner:上海煊瑾多媒体科技有限公司
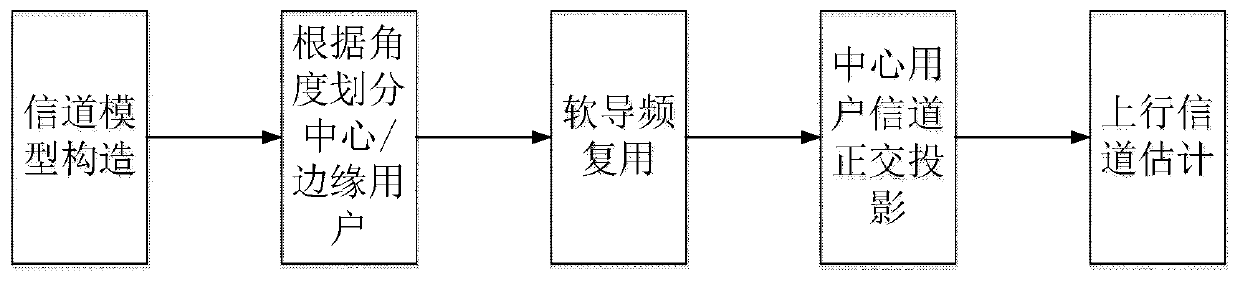
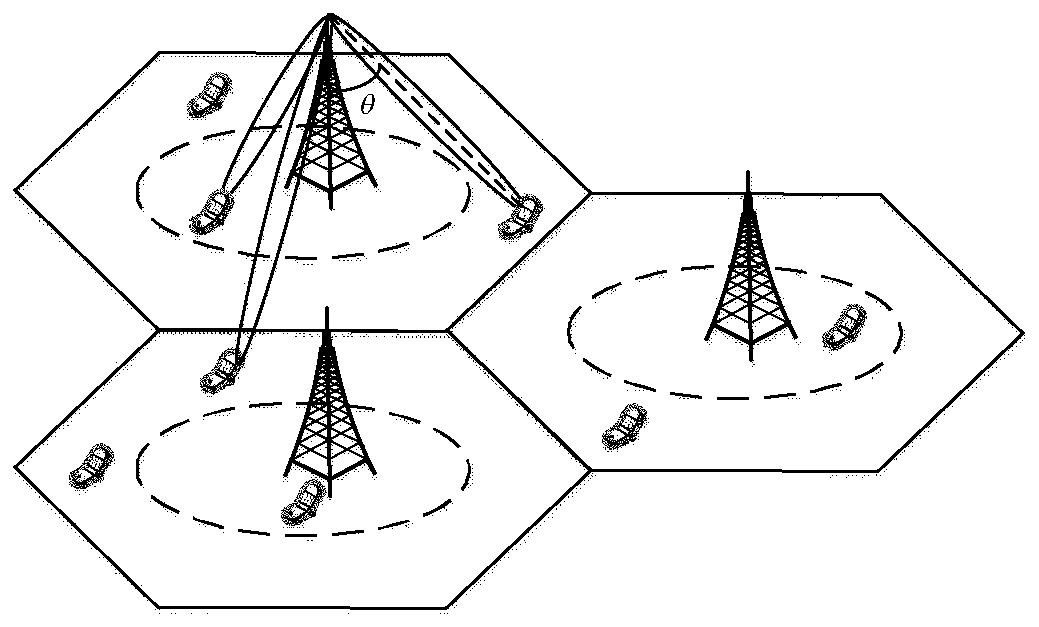
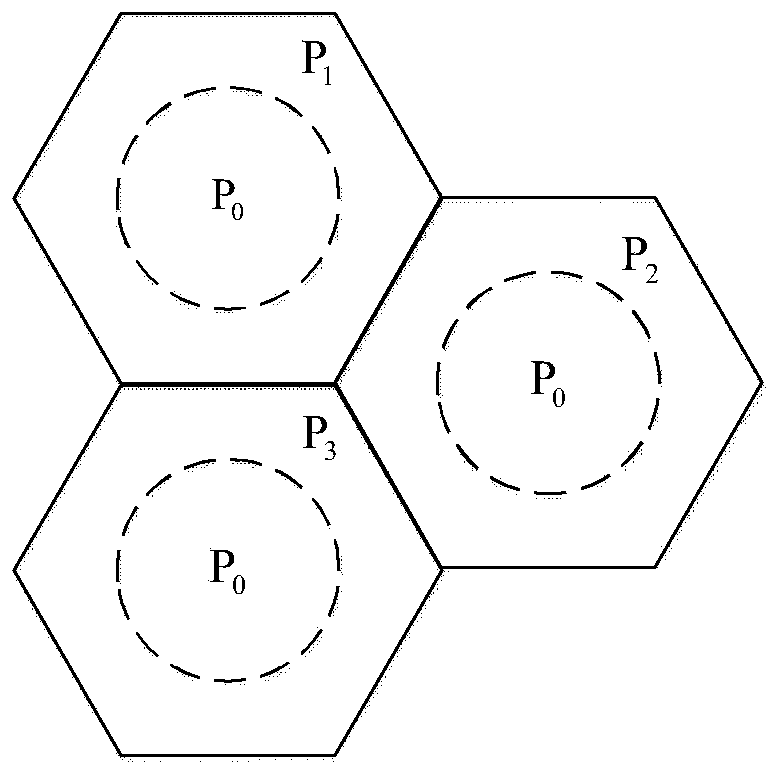
Channel estimation method based on user division under three-dimensional large-scale MIMO
ActiveCN110113083AReduce pollution impactImprove adaptabilityRadio transmissionChannel estimationMultiplexingComputation complexity
The invention provides a channel estimation method based on user division under three-dimensional large-scale MIMO, and solves the problem of low channel estimation precision caused by pilot frequencypollution in the prior art. The method comprises the following implementation steps: firstly, constructing a three-dimensional large-scale MIMO channel model; dividing the users into central users oredge users according to a given division angle; and adopting a soft pilot frequency multiplexing method for the central user and the edge users, and projecting the channel matrix of the central userto the zero space of the edge region and the adjacent cell region to complete uplink channel estimation. All users are divided into central users and edge users, and orthogonal projection is carried out on the central users on the basis of soft pilot frequency multiplexing. On the premise of low computational complexity, the accuracy of channel estimation is effectively improved, and the method can be used for pilot frequency depollution and inter-cell interference suppression of a three-dimensional large-scale MIMO multi-cell multi-user system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Projector calibration method based on Gold matrix projection
ActiveCN110796708AFast calibrationLow number of projectionsImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Computational physics
The invention discloses a projector calibration method based on Gold matrix projection. The projector calibration method mainly utilizes a Gold matrix coding structured light technology to calibrate aprojector. By projecting the specially designed Gold matrix structured light, the projector calibration method overcomes the defects of low calibration speed, poor stability and low precision of theprojector at the present stage, and has the characteristics of simplicity, quickness and high precision in calibration of the projector.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fully passive polarization quantum state chromatography method and chip
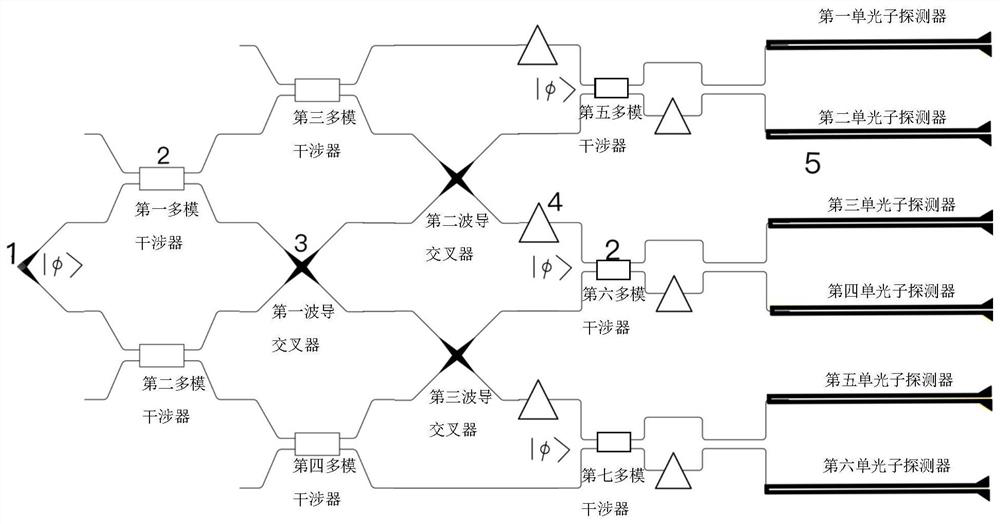
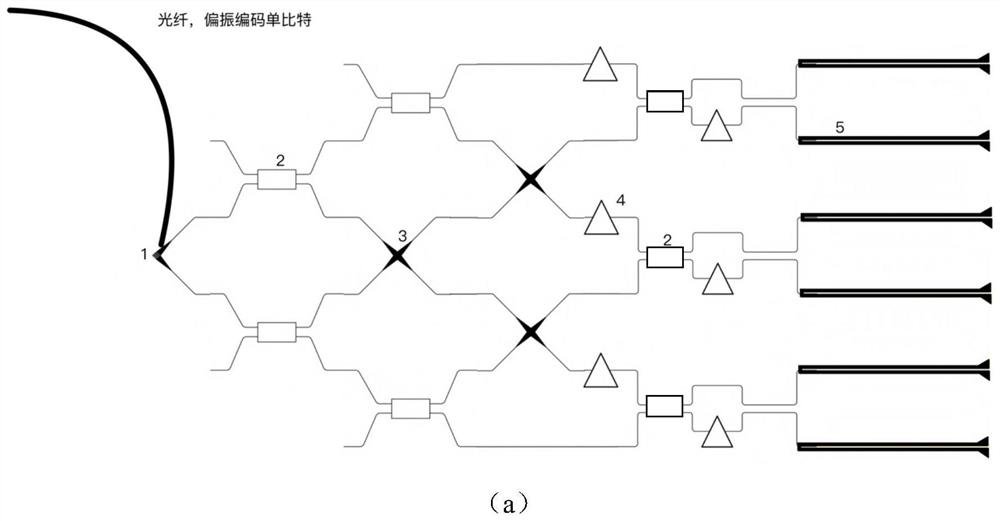
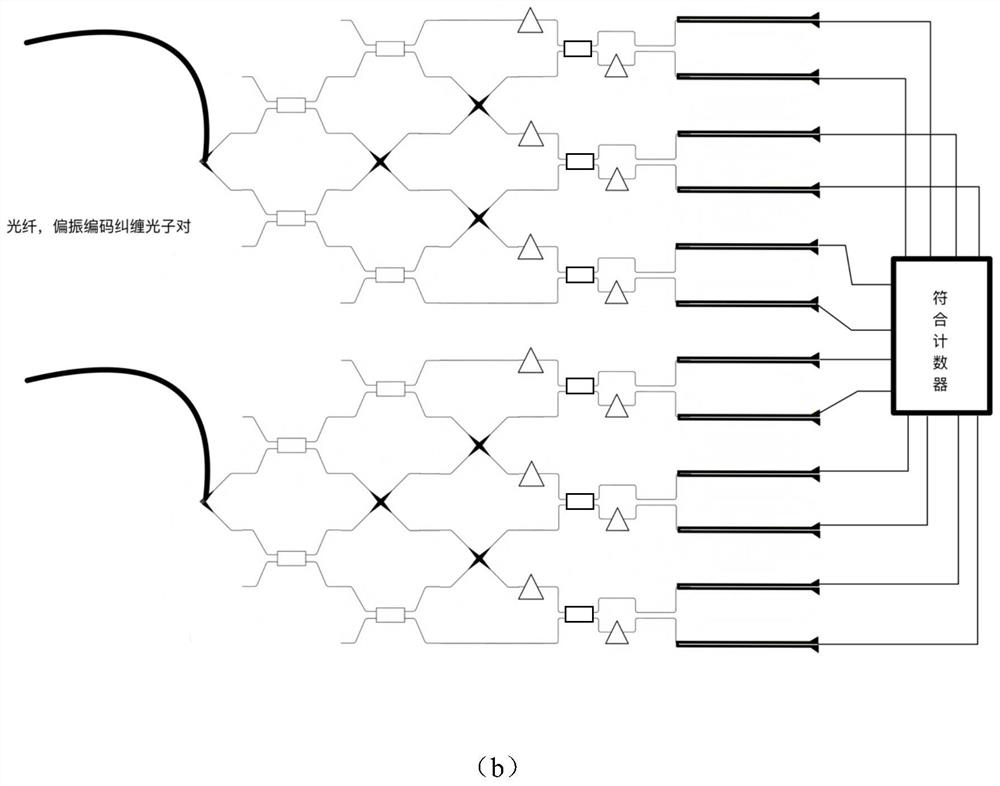
ActiveCN113589435AIncrease chromatography speedImprove adaptabilityPhotonic quantum communicationCoupling light guidesMultimode interferenceEngineering
The invention discloses a fully passive polarization quantum state chromatography method and a chip. The method comprises the steps: 1) converting polarization information of a to-be-measured optical signal into path information by using an on-chip integrated polarization-path converter, and respectively outputting the path information through 2n paths of waveguides; 2) leading out an optical signal in each path of waveguide to 3n paths through an on-chip integrated multimode interference device and waveguide crossers, and dividing path information into 6n paths of output light; 3) combining every two output lights on the 6n paths into 3n identical input quantum states by using the waveguide crossers; 4) dividing each input quantum state into two paths of output, measuring each path of output through an on-chip integrated superconducting single-photon detector, and achieving measurement of the input quantum states under any two-dimensional unitary matrix projection basis vector; and 5) fitting a measurement result to reconstruct a density matrix of the quantum states, and realizing the chromatographic measurement of the quantum state. According to the method, the complex quantum state chromatography process is simplified, full automation is achieved, and high expansibility is achieved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Observation matrix construction method based on low-coherence unit norm tight frame
ActiveCN111475768AAvoid the problem of difficult structureRobustImage memory managementImage acquisitionComputation complexityTight frame
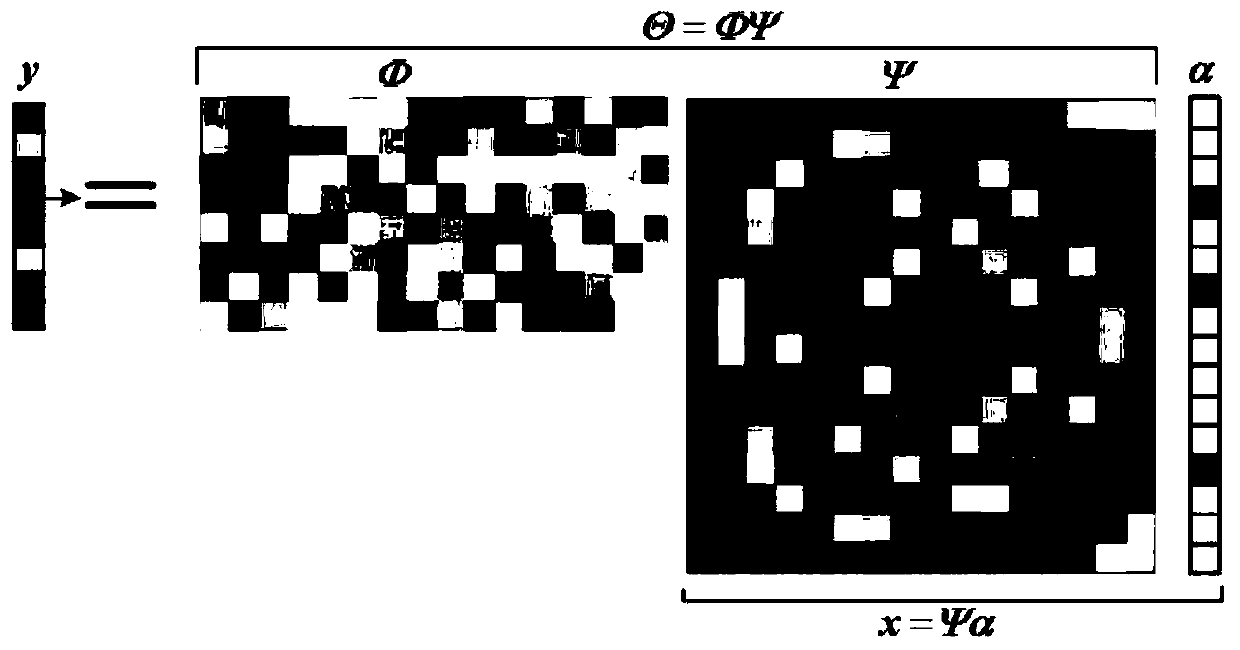
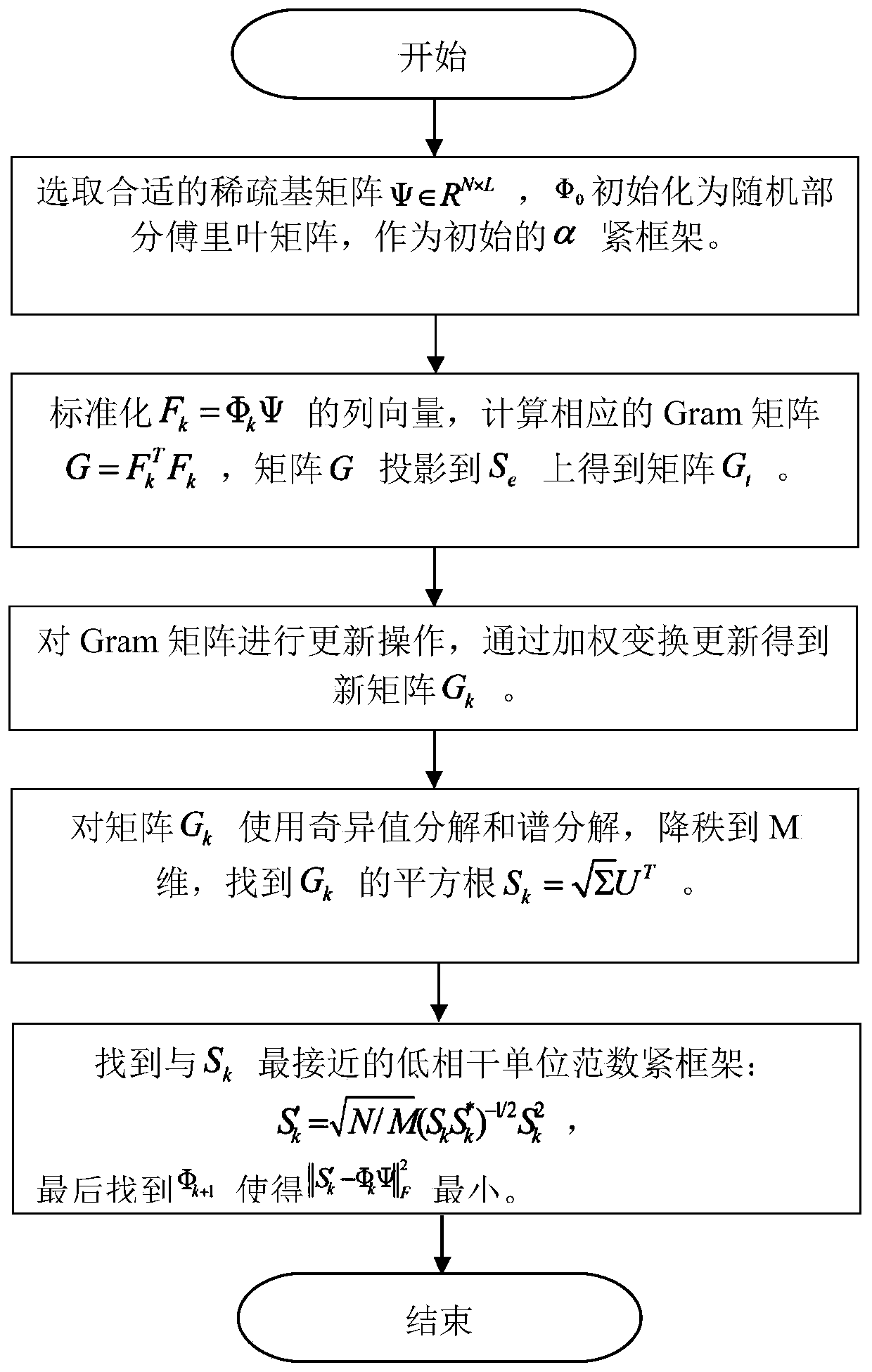
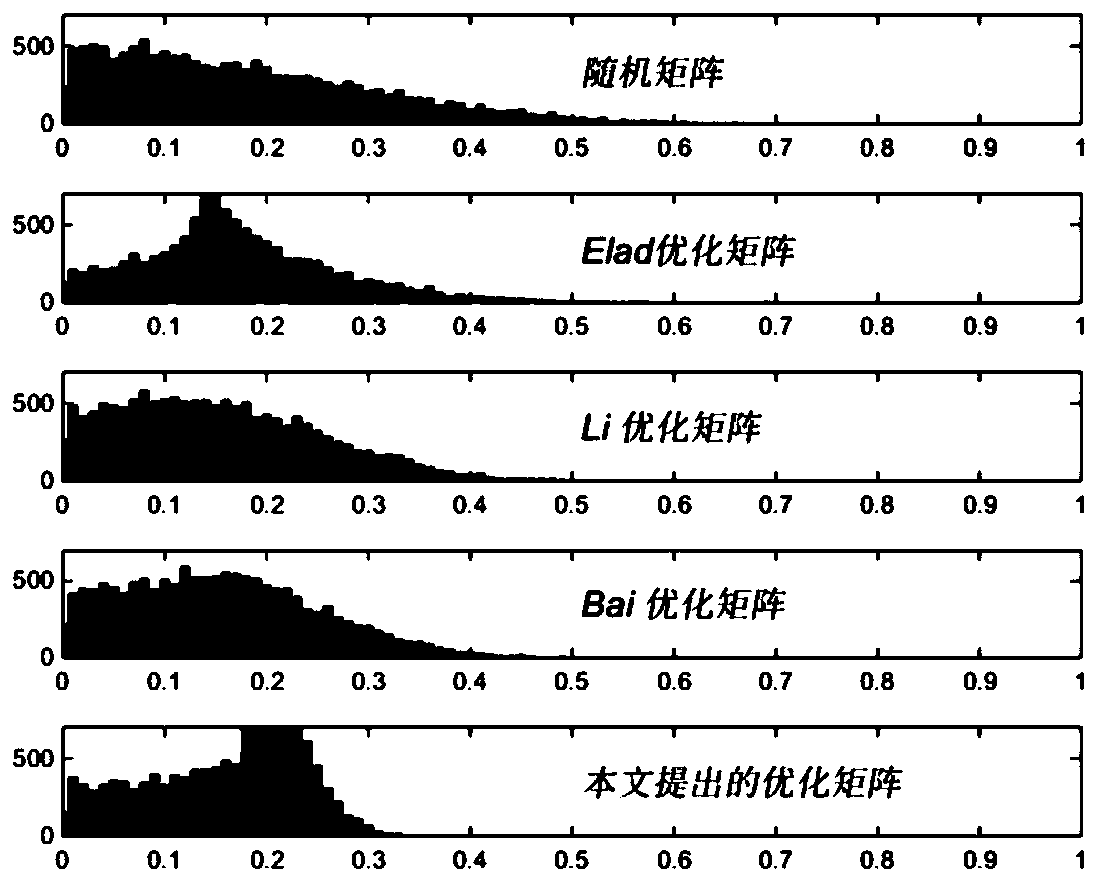
The invention relates to an observation matrix construction method based on a low-coherence unit norm tight frame, and belongs to the technical field of signal processing, and the method comprises thesteps: S1, initializing an initial observation matrix phi 0 into a random part Fourier matrix, and enabling the initial observation matrix phi 0 to serve as an initial alpha tight frame F; s2, calculating a Gram matrix corresponding to the framework F, and projecting the matrix to a structure constraint set of a tight framework by using a contraction function to generate a new Gram matrix; s3, updating the Gram matrix through a weighted iteration process; s4, reducing the rank of the new Gram matrix, calculating the square root of the new Gram matrix, and finding out a tight frame closest toa unit norm tight frame; and S5, solving the optimal target function to obtain an observation matrix. According to the method, the mutual interference coefficient between the observation matrix and the sparse basis is reduced, the dependence degree on signal sparsity is reduced, the problem that an ETF frame is difficult to construct is avoided, the initial observation matrix is initialized into apart of Fourier matrix, the calculation complexity is reduced, and the pressure of storage and processing equipment is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
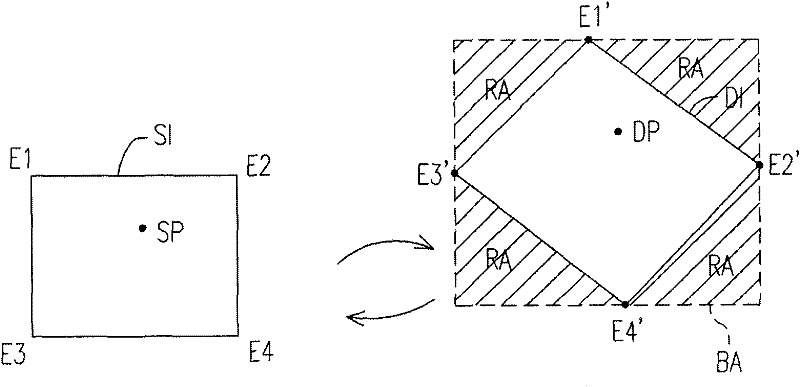
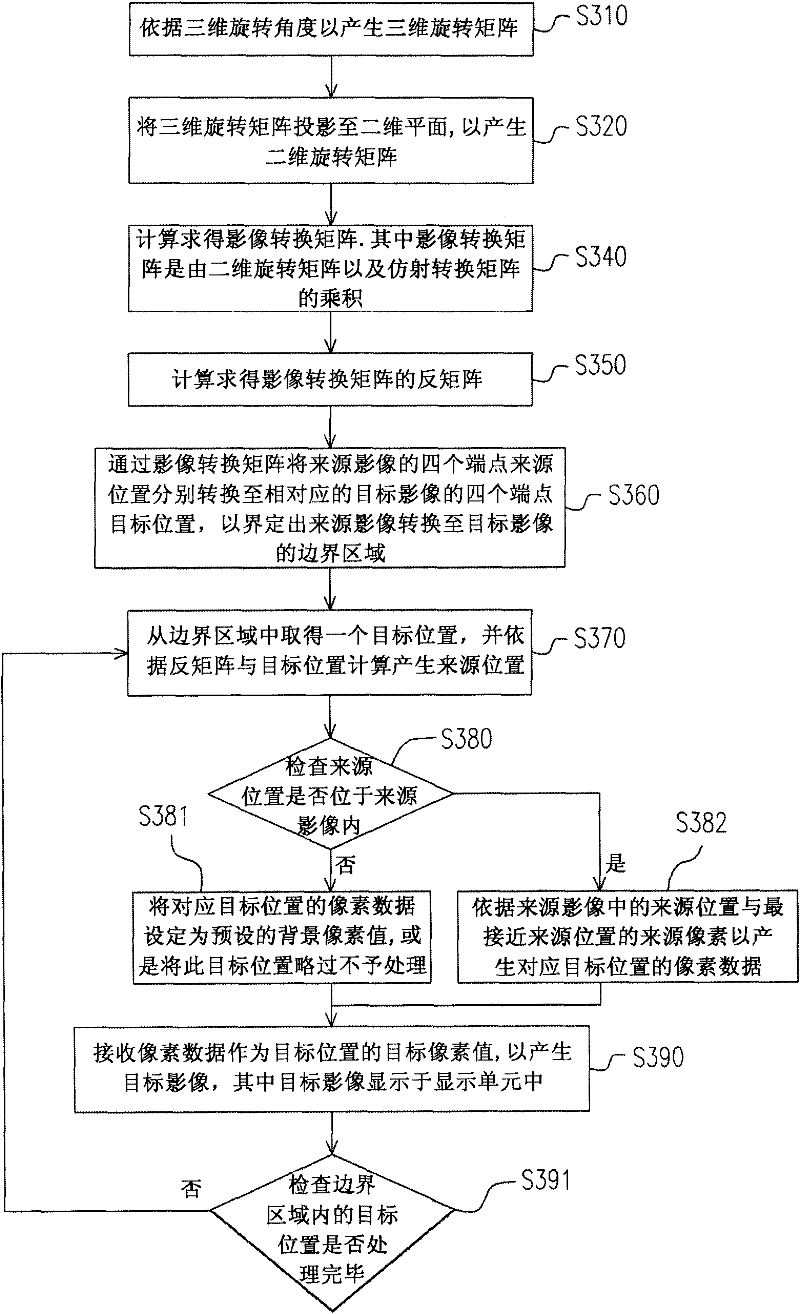
Method for generating image transformation matrix as well as image transformation method and device
InactiveCN102238313AInstant displayTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSource imageMatrix projection
The invention provides a method for generating an image transformation matrix as well as an image transformation method and device. The image transformation device can generate one three-dimensional rotation matrix in accordance with a three-dimensional rotation angle; the three-dimensional rotation matrix is projected to a two-dimensional plane to generate a two-dimensional rotation matrix; and according to the two-dimensional rotation matrix and an affine transformation matrix, a target position in a target image is calculated to generate a source position corresponding to the target position, wherein the source position is located in a source image, and the affine transformation matrix is used for carrying out displacement, zoom and rigid body deformation on the target image. The source position and a source pixel nearest to the source position are utilized to generate pixel data. The pixel data are received to be taken as a target pixel value of the target position so as to generate the target image.
Owner:ALICORP
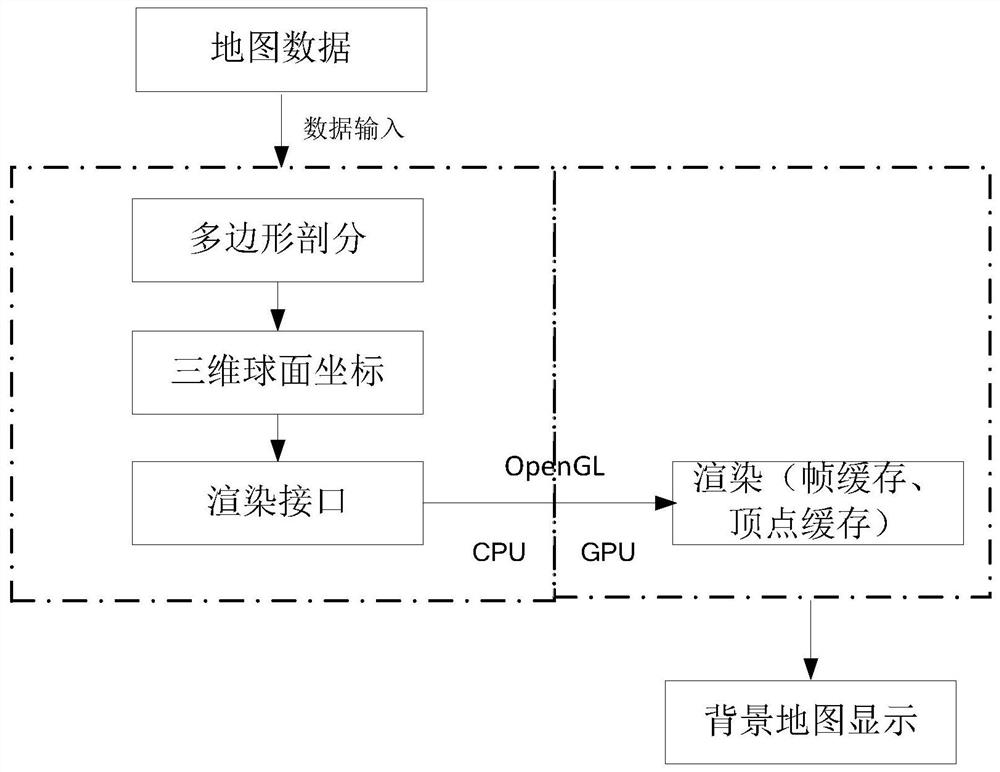
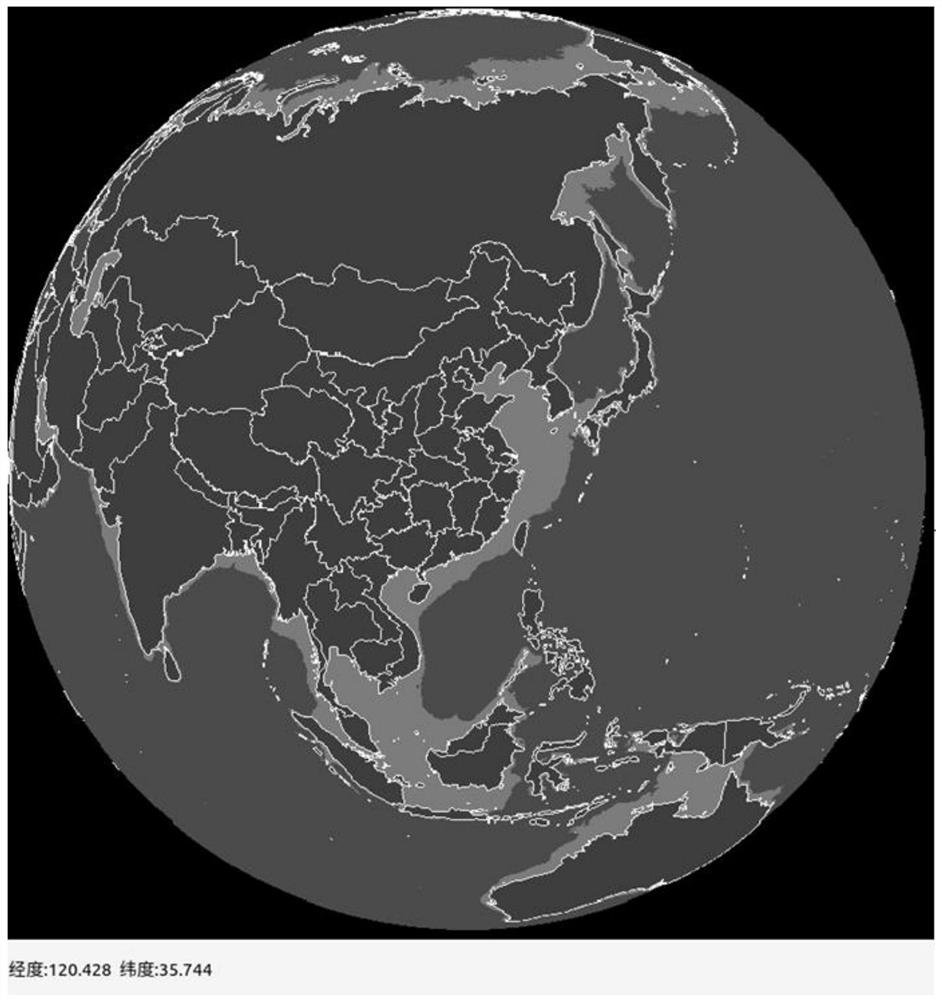
Three-dimensional background map rapid filling method based on OpenGL
PendingCN111815775ARealize stepless zoom without distortionAvoid position deviationImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsEngineering
The invention relates to the field of radar background map drawing, in particular to a method capable of displaying longitude and latitude coordinate data in real time in a three-dimensional background map form through an OpenGL graphics library, and the method can be used as a background map for radar situation display. A closed area is formed by adopting a longitude and latitude direct projection mode for geographic coordinate information, and the closed area is segmented into minimum graphic units (triangles and quadrangles) supported by OpenGL by adopting a segmentation filling algorithm.And the method further includes converting the coordinate information of the minimum graphic unit into a spherical position coordinate, and filling the minimum graphic unit in the three-dimensional model by using OpenGL. Vertex cache, a model view matrix and a projection matrix are adopted, and frequent data interaction between a CPU and a GPU is reduced. Through matrix inverse transformation, transformation from screen coordinates to world coordinates is realized, and a real-time roaming scaling function is realized.
Owner:中国船舶集团有限公司第七二四研究所
Robust beam forming method based on desired signal elimination and spatial spectrum estimation
PendingCN114647931AImprove robustnessImprove performanceDesign optimisation/simulationConstraint-based CADSignal cancellationOptimal weight
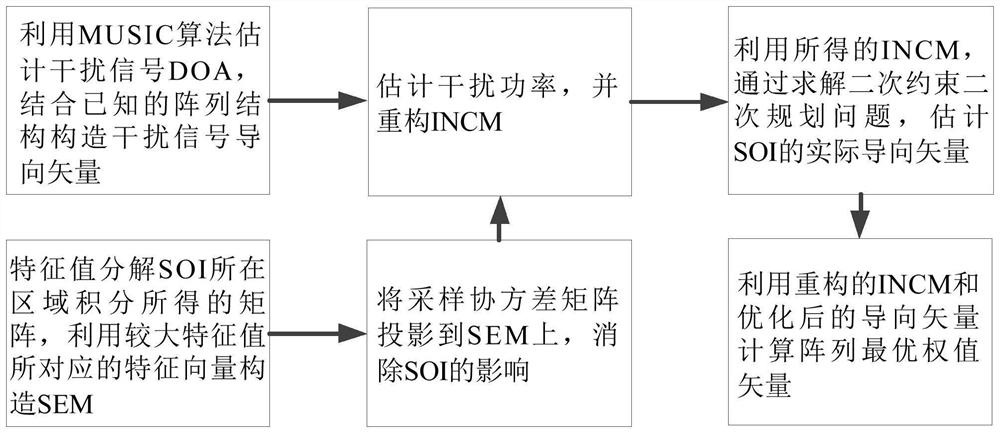
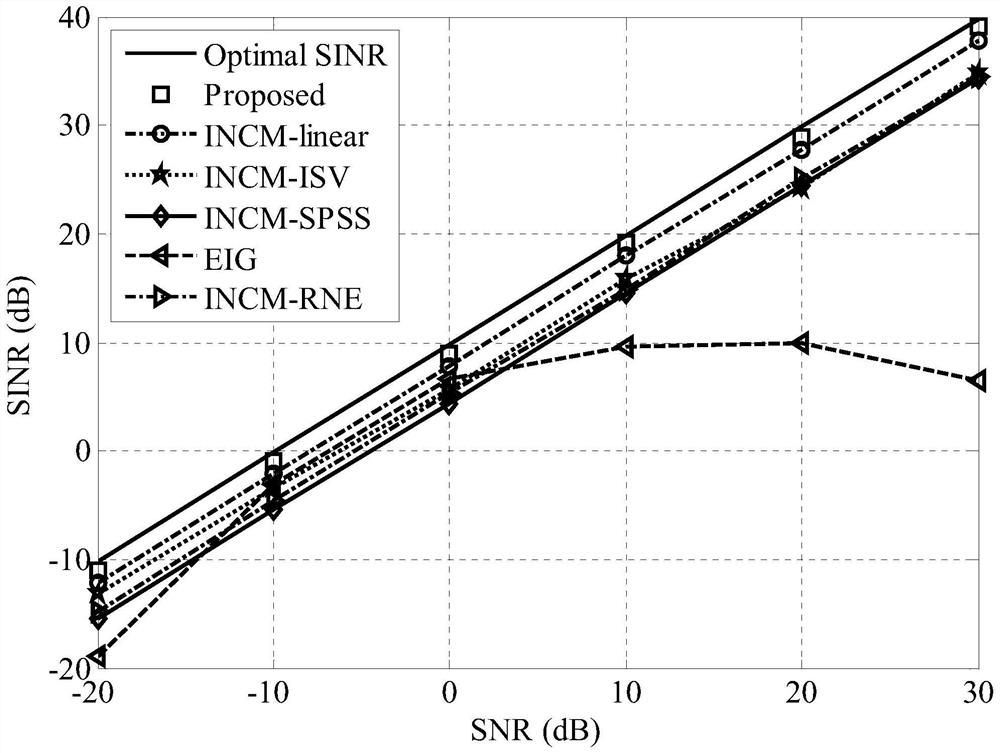
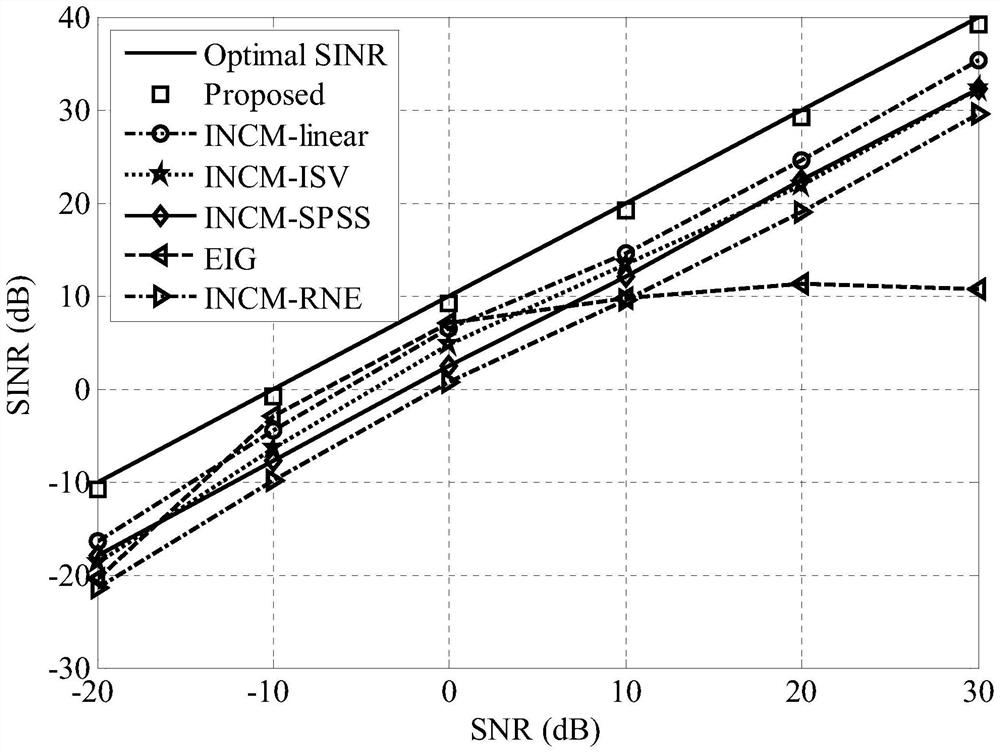
The invention provides a robust beam forming method based on desired signal elimination and spatial spectrum estimation, which comprises the following steps: firstly, estimating a DOA (Direction of Arrival) of a signal by using a MUSIC high-resolution spatial spectrum estimation algorithm; secondly, carrying out eigendecomposition on an integral matrix of an area where the SOI is located, and constructing an SEM by utilizing eigenvectors corresponding to several relatively large eigenvalues; then, the sampling covariance matrix is projected to the SEM to eliminate the influence of the SOI, and the power of an interference signal is estimated, thereby constructing the INCM. And the SOI steering vector is optimized by solving a quadratic constraint quadratic programming problem. And finally, the optimal weight vector of the array is calculated by using the reconstructed INCM and the estimated SOI steering vector. The method has good robustness for errors such as desired signal DOA errors, array element position disturbance errors and incoherent local scattering, and has better comprehensive performance than several existing typical robust beam forming methods.
Owner:中国人民解放军火箭军工程大学
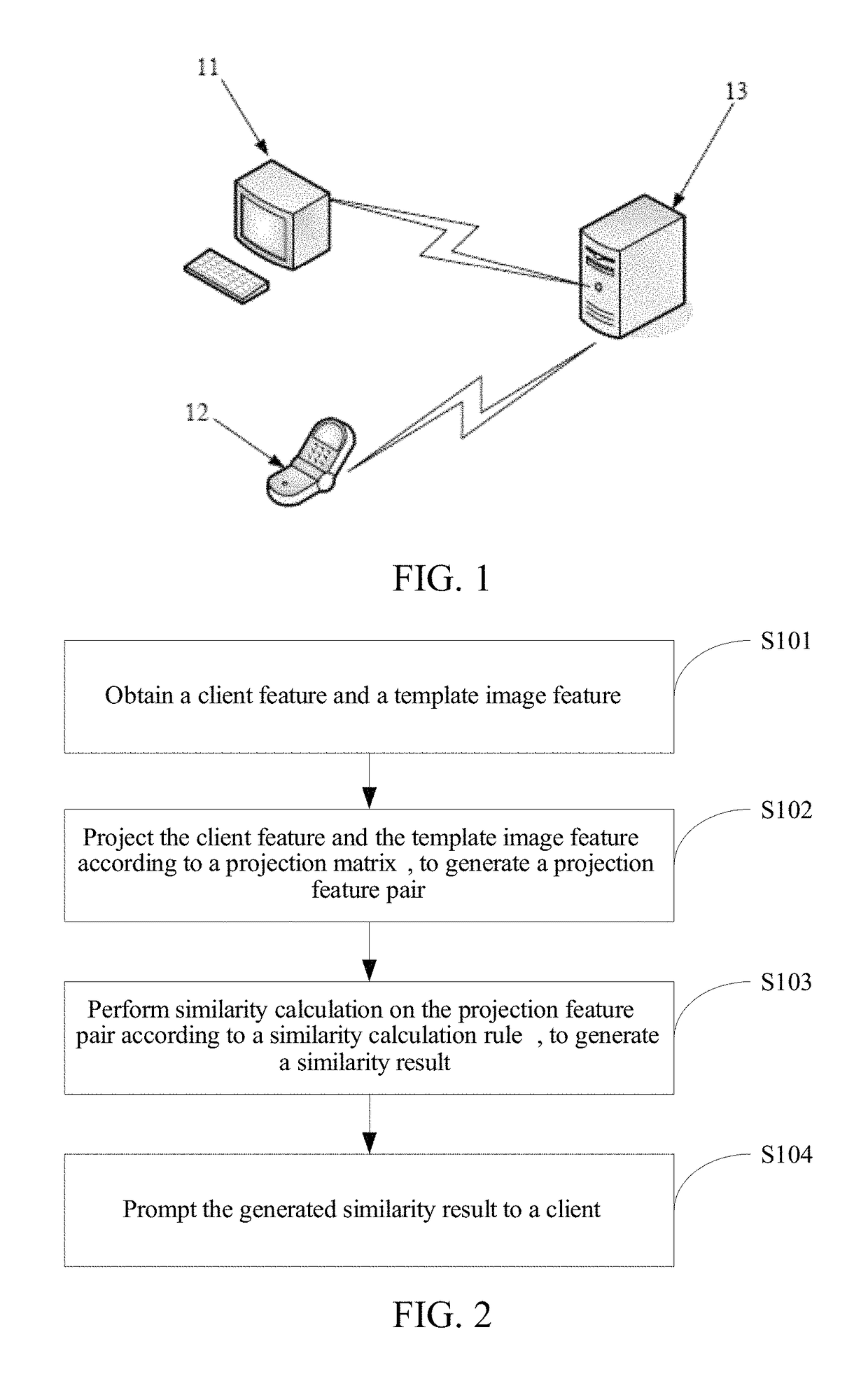
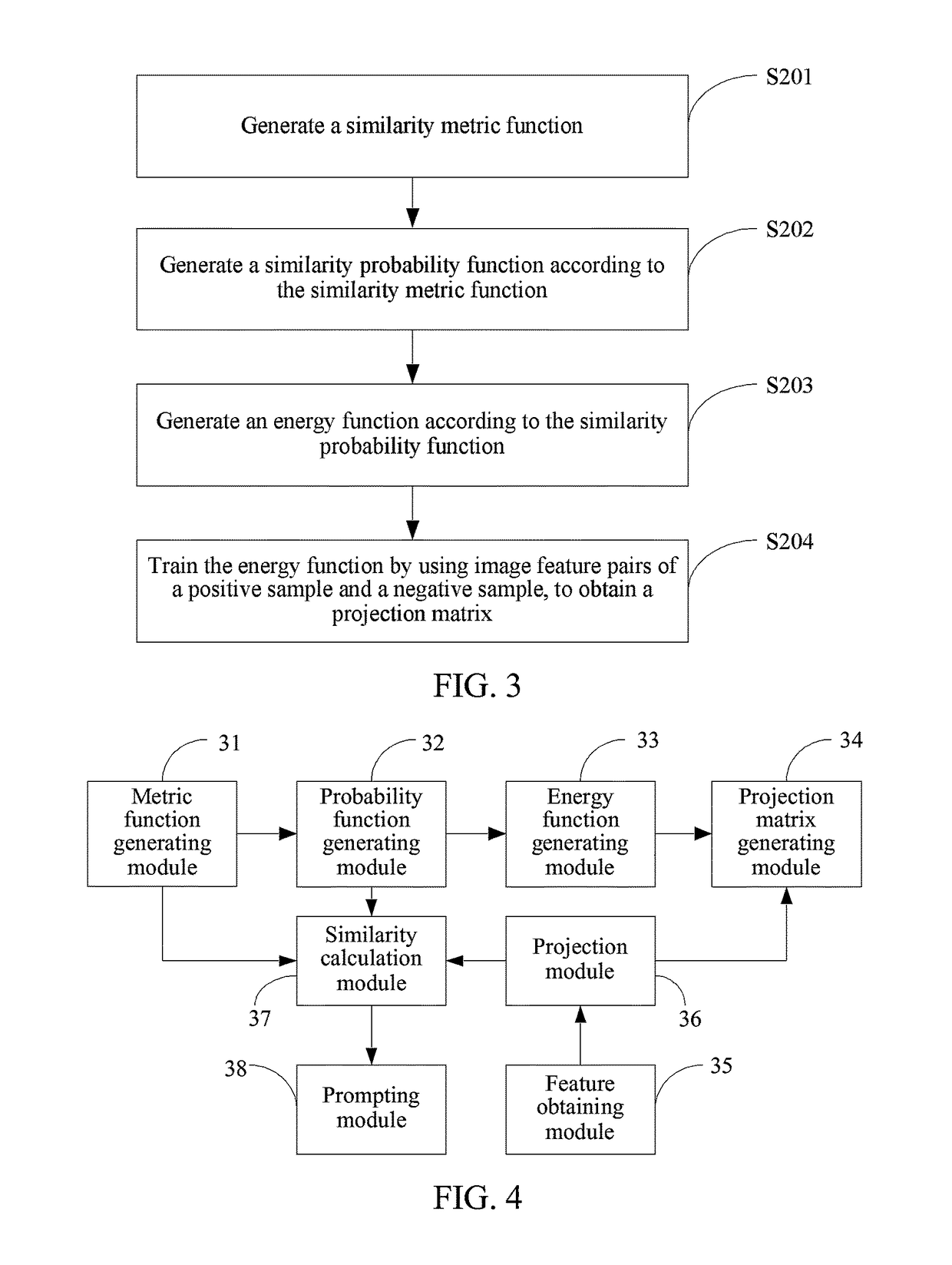
Method and apparatus for recognizing client feature, and storage medium
ActiveUS9697440B2Improve accuracyRecognition rateMatching and classificationPattern recognitionHat matrix
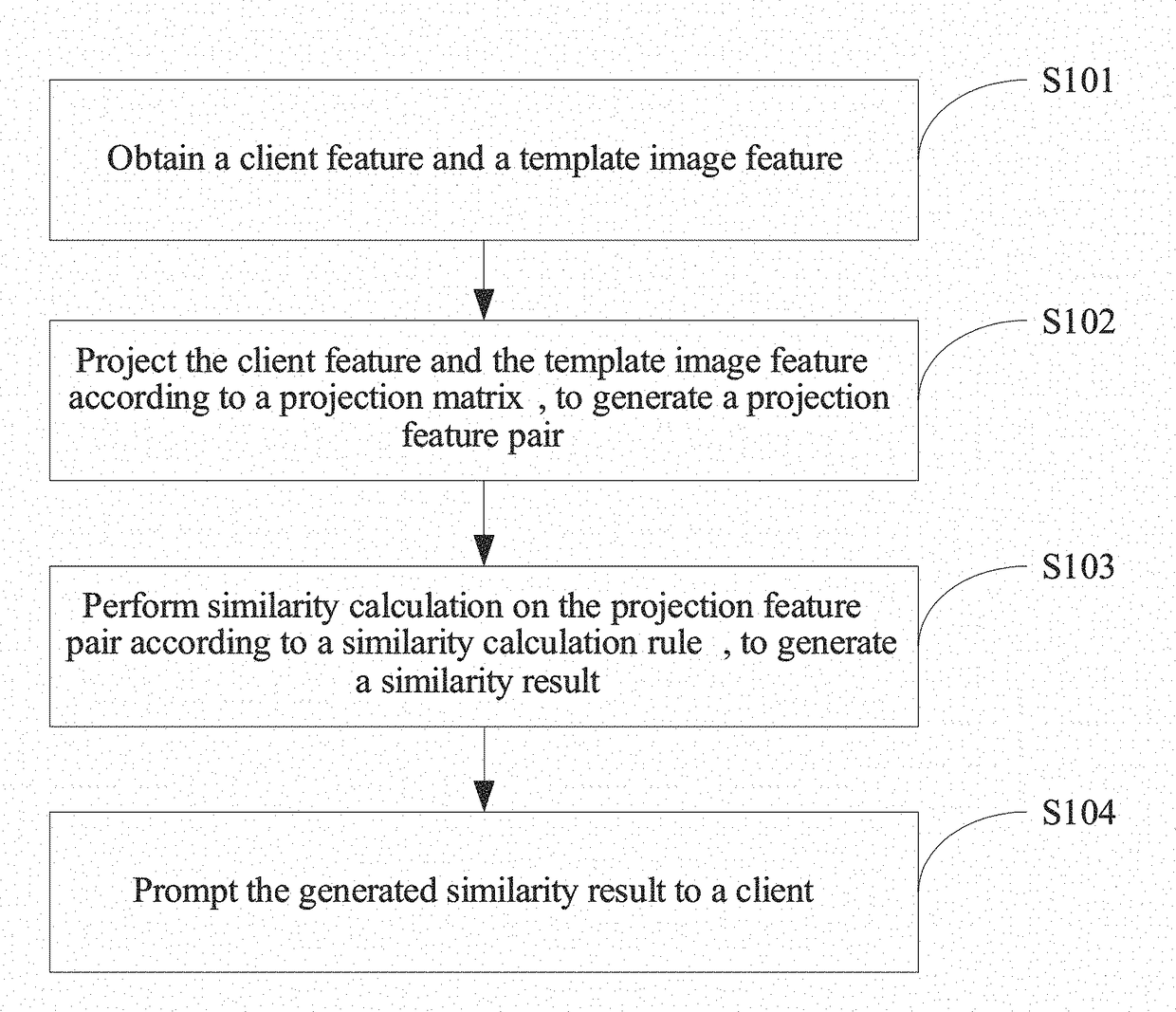
In the present disclosure, a client feature and a pre-stored template image feature are obtained; the obtained client feature and template image feature are projected according to a preset projection matrix, to generate a projection feature pair, where the projection matrix is formed by training of a first template image feature of a same object and a second template image feature of a different object; and similarity calculation is performed on the projection feature pair according to a preset similarity calculation rule, to generate a similarity result and prompt the similarity result to a client.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Model order determination method based on S-shaped function random subspace identification
ActiveCN111125626AReduce the impactSufficient smoothnessSustainable transportationComplex mathematical operationsSingular value decompositionHat matrix
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Spatial orientation measuring instrument precision evaluation method based on single-star projection
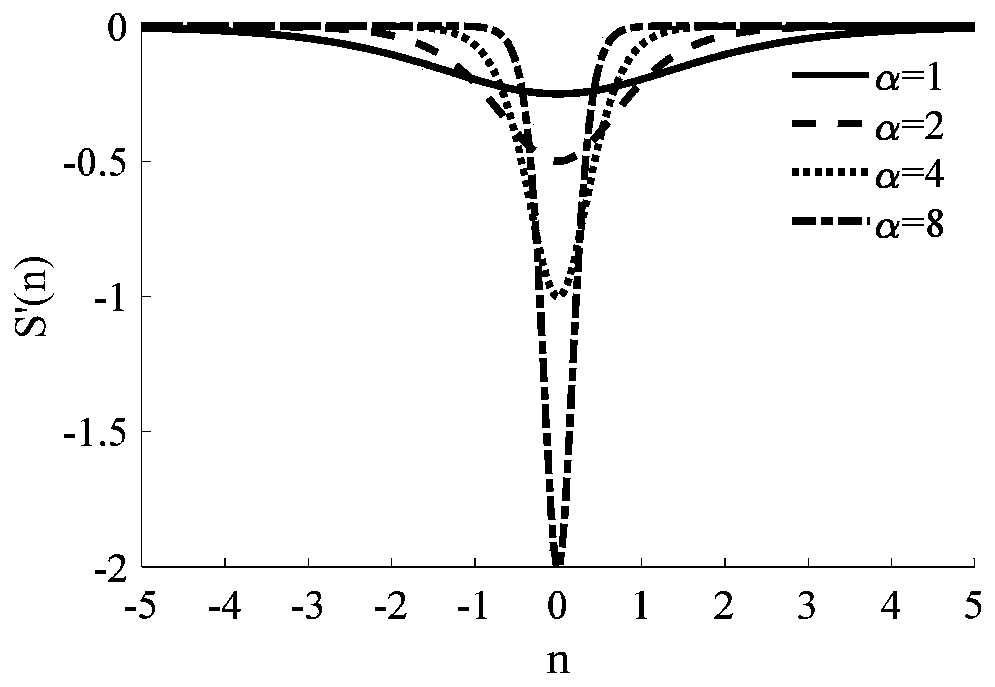
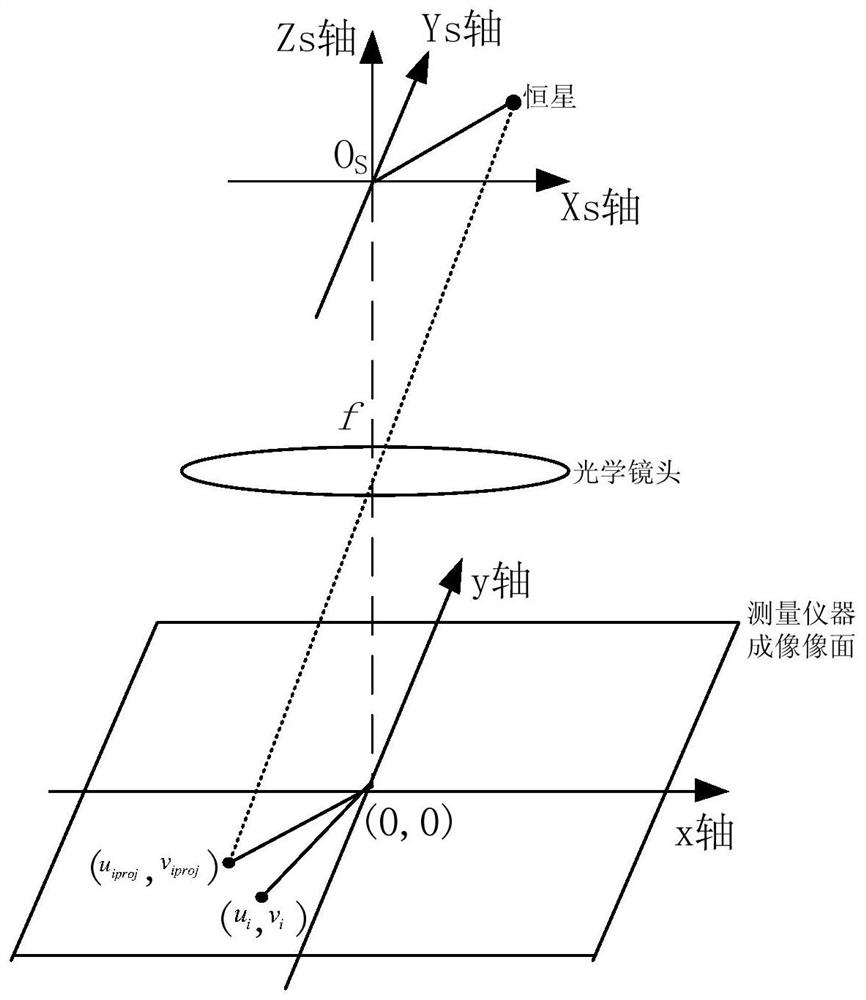
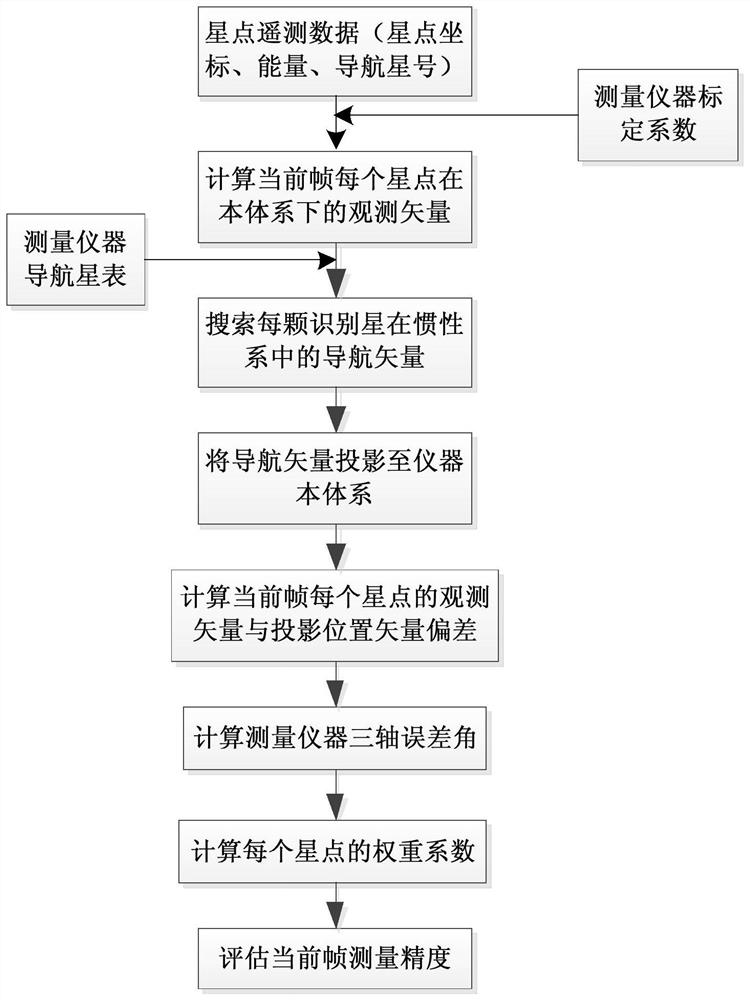
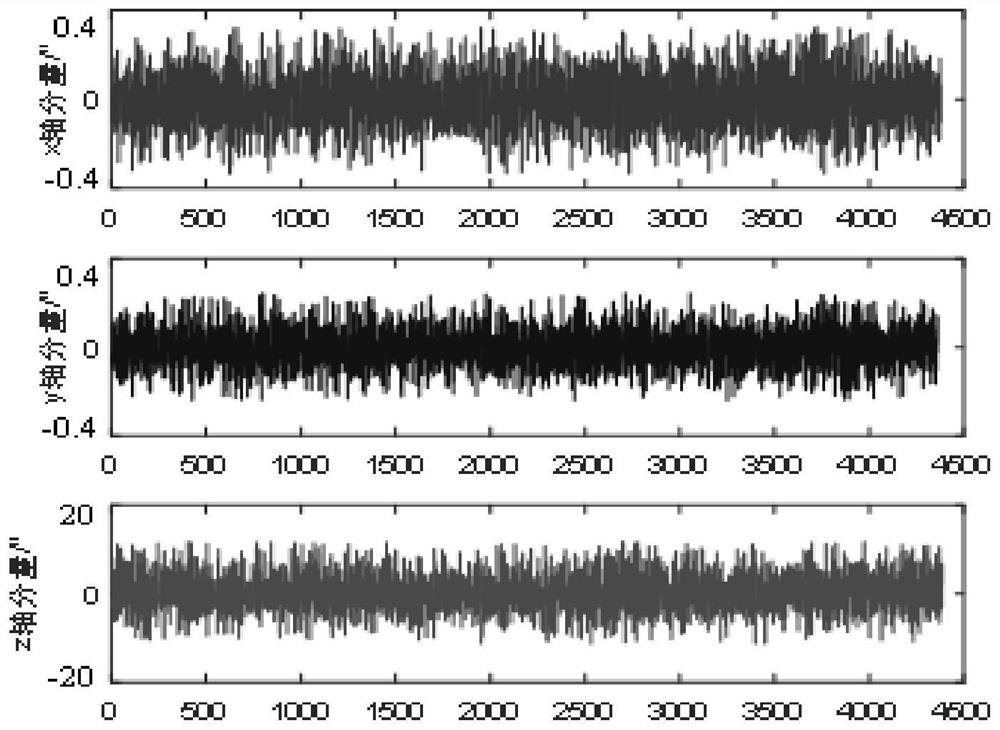
PendingCN113465627AReduce the impactScience of Assessment ResultsMeasurement devicesSpatial OrientationsSingle star
The invention discloses a spatial orientation measuring instrument precision evaluation method based on single-star projection. The method comprises the specific steps of: firstly, calculating an observation vector of each star point in a measuring instrument body system according to the position coordinates of the star points and a calibration coefficient; secondly, searching an inertial vector corresponding to the star point according to a navigation star number, and projecting the inertial vector to the instrument body system according to an attitude matrix, so as to obtain a projection position vector of the navigation star in the system; thirdly, calculating the deviation of the projection position vector relative to the observation vector, and calculating a three-axis error angle according to a measuring instrument imaging model; and finally, calculating a weight coefficient corresponding to each identified star in the frame of star map according to star magnitude, and comprehensively evaluating the measurement precision of the frame according to a multi-star attitude determination principle. Compared with a polynomial fitting method based on multi-frame analysis and a difference method based on adjacent two-frame analysis, the influence of a spacecraft platform on the method is minimum, and the evaluation result is closest to the measurement precision of an instrument.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Unsupervised data dimension reduction method based on noise suppression
PendingCN113469209AReduce the impactReduce computational complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixComputation complexity
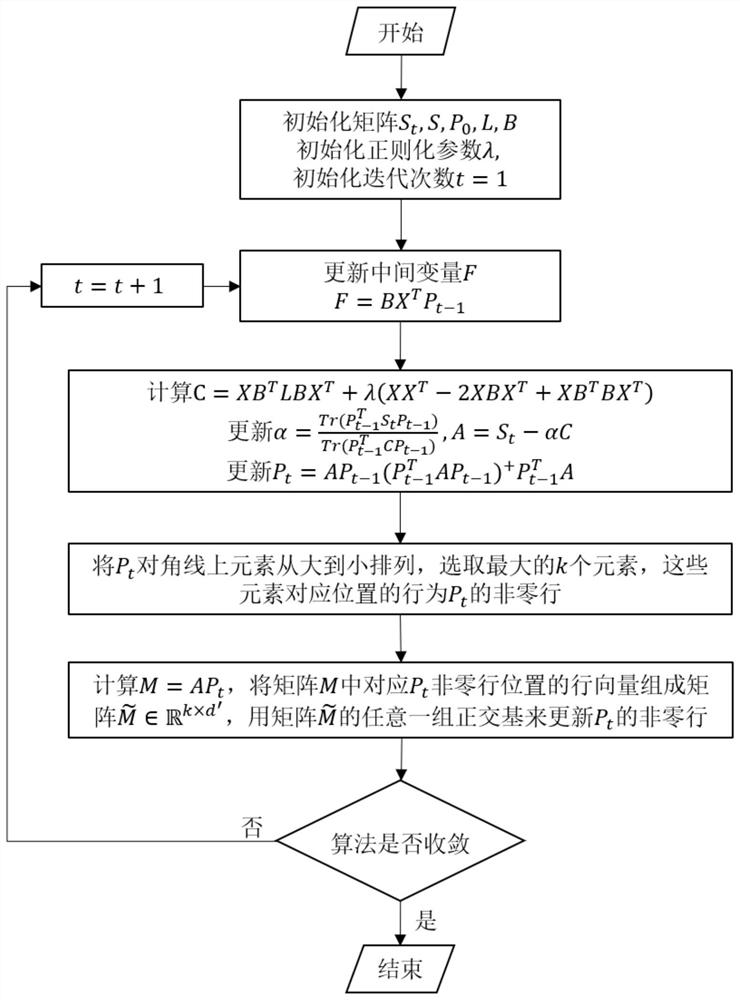
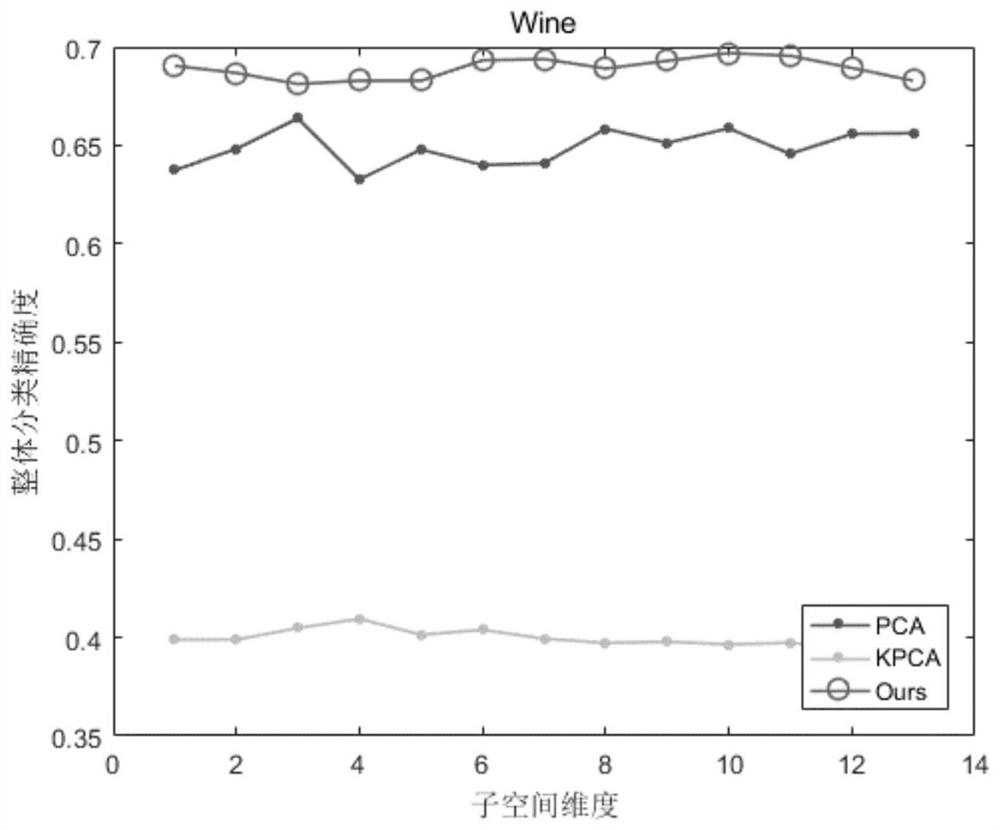
The invention discloses an unsupervised data dimension reduction method based on noise suppression, which comprises the following steps of: firstly initializing a global divergence matrix, a graph matrix, a projection matrix, a Laplacian matrix and regularization parameters, then updating a matrix F, then updating a projection matrix P, and repeatedly iterating until an objective function is converged to realize unsupervised data dimension reduction. Calculation complexity is reduced, the operation time is shortened, and quick and effective dimension reduction of high-order data can be realized.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com