Patents
Literature
150 results about "Memory span" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In psychology and neuroscience, memory span is the longest list of items that a person can repeat back in correct order immediately after presentation on 50% of all trials. Items may include words, numbers, or letters. The task is known as digit span when numbers are used. Memory span is a common measure of short-term memory. It is also a component of cognitive ability tests such as the WAIS. Backward memory span is a more challenging variation which involves recalling items in reverse order.
Reducing write amplification in a flash memory
ActiveUS20130232290A1Reducing write amplificationMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsMemory addressWrite amplification
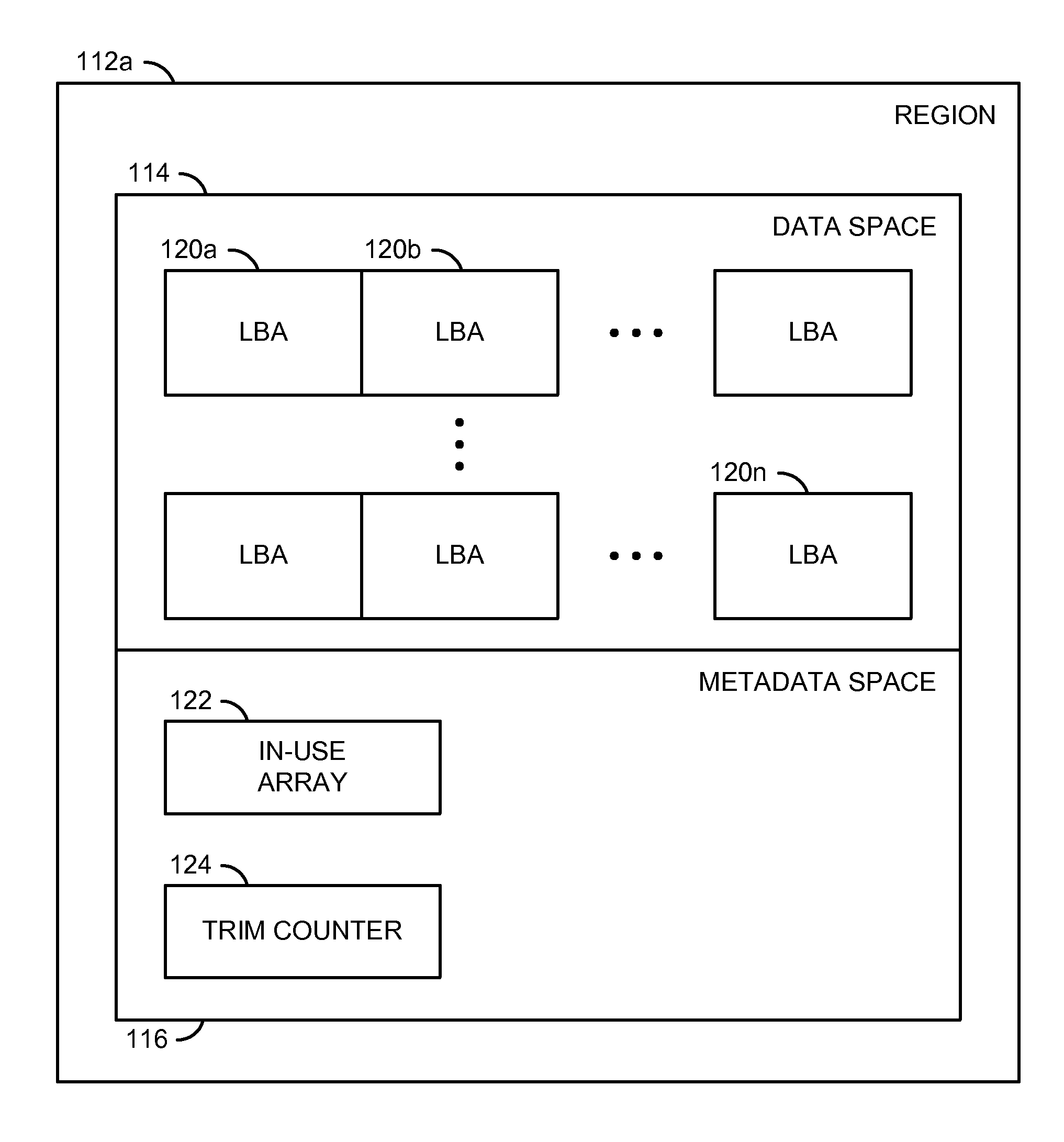
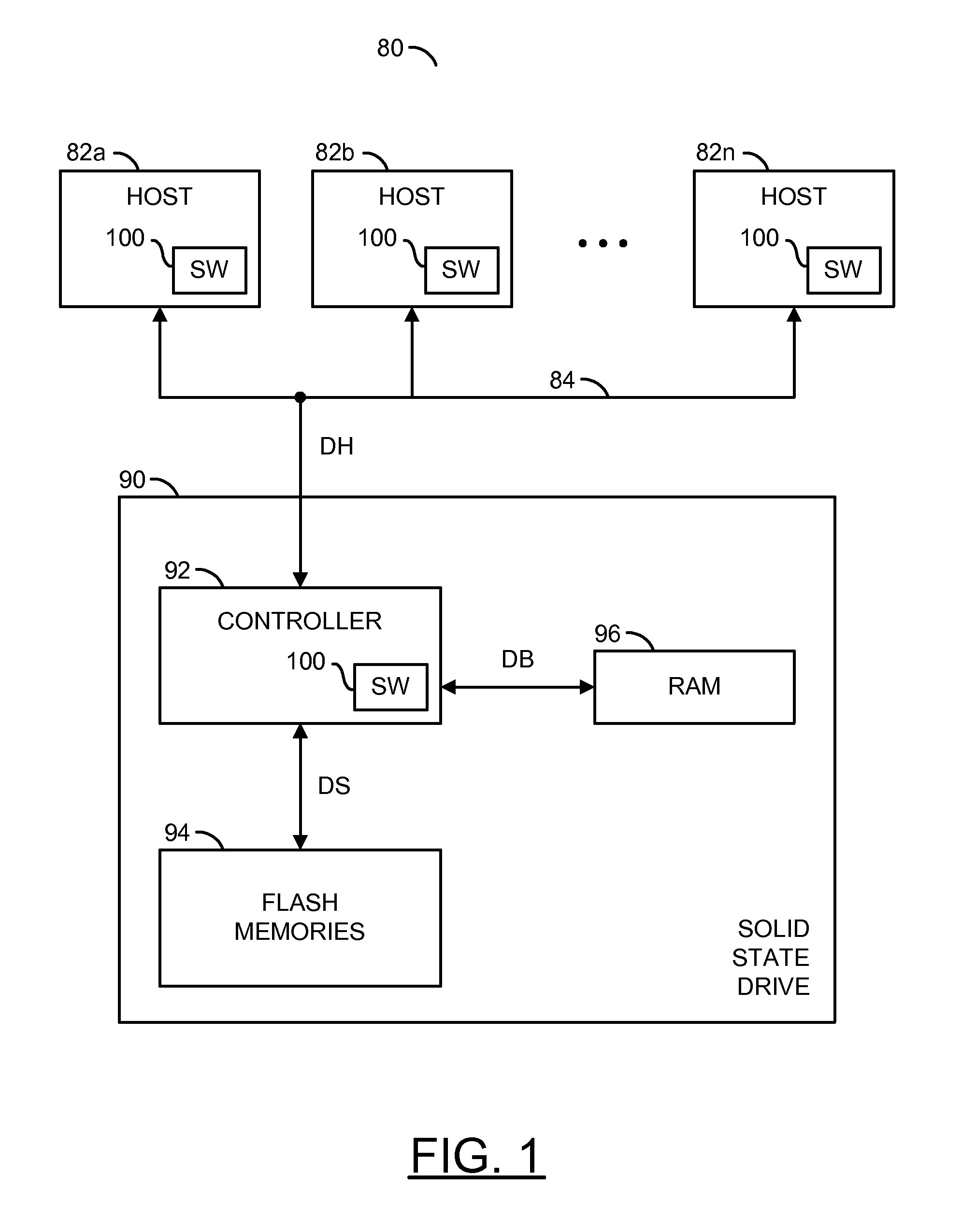
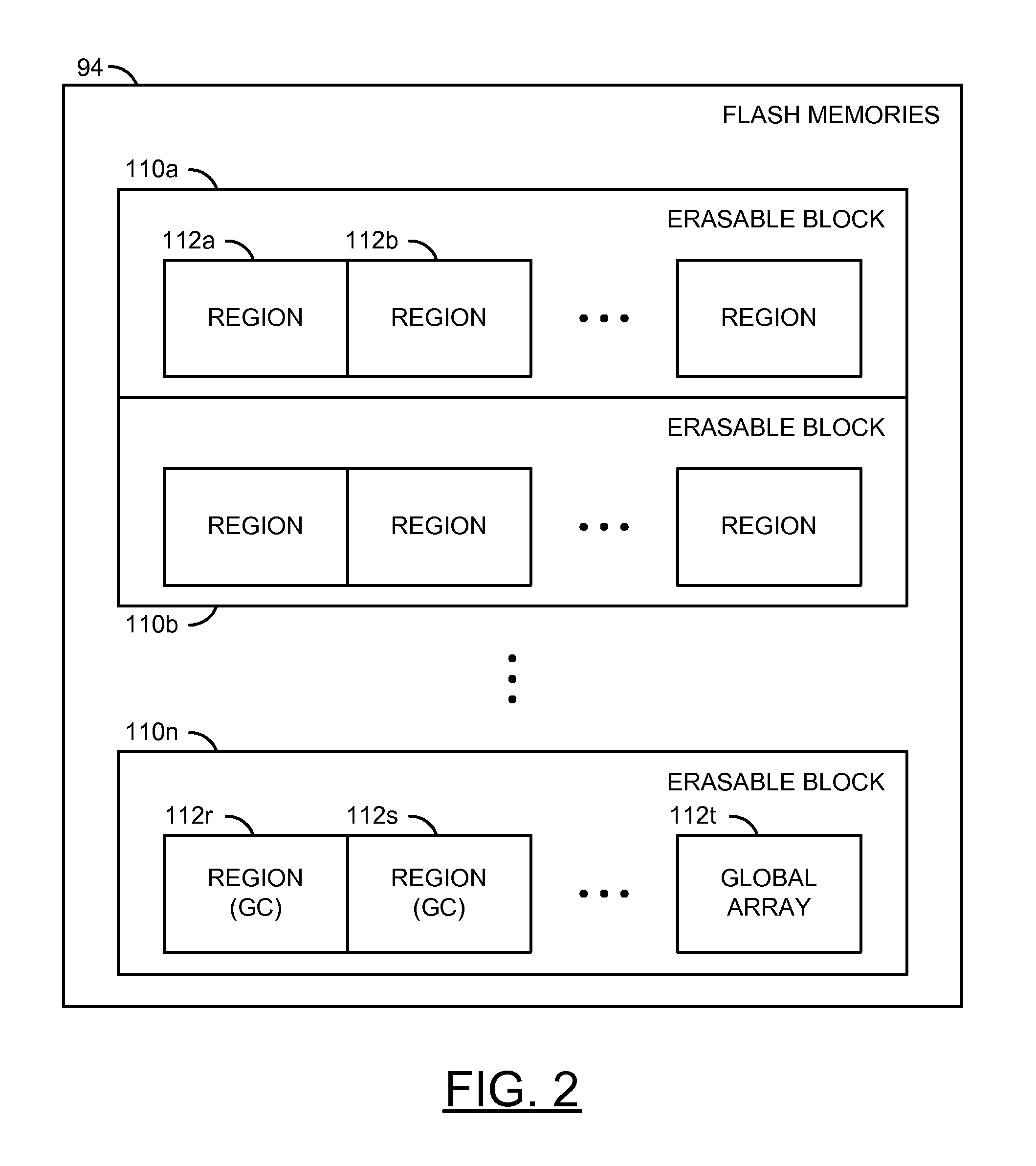
An apparatus having a memory circuit and a manager is disclosed. The memory circuit generally has (i) one or more Flash memories and (ii) a memory space that spans a plurality of memory addresses. The manager may be configured to (i) receive data items in a random order from one or more applications, (ii) write the data items in an active one of a plurality of regions in a memory circuit and (iii) mark the memory addresses in the active region that store the data items as used. Each data item generally has a respective host address. The applications may be executed in one or more computers. The memory addresses in the active region may be accessed in a sequential order while writing the data items to minimize a write amplification. The random order is generally preserved between the data items while writing in the active region.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Universal single level object memory address space
InactiveUS20160210078A1Improve efficiencyImprove performanceInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressMemory object
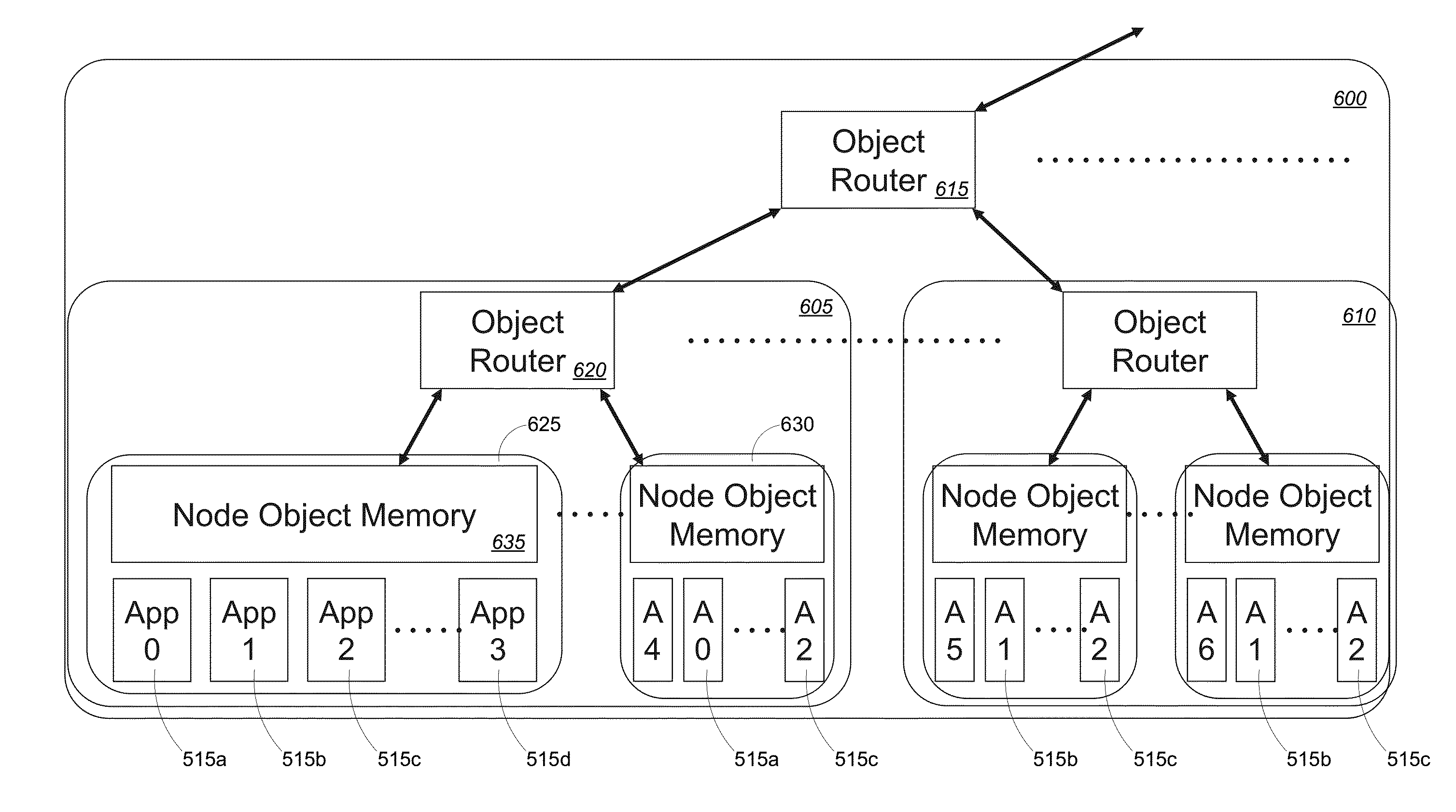
Embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for managing processing, memory, storage, network, and cloud computing to significantly improve the efficiency and performance of processing nodes. Embodiments described herein can eliminate typical size constraints on memory space of commodity servers and other commodity hardware imposed by address sizes. Rather, physical addressing can be managed within the memory objects themselves and the objects can be in turn accessed and managed through the object name space.
Owner:ULTRATA LLC
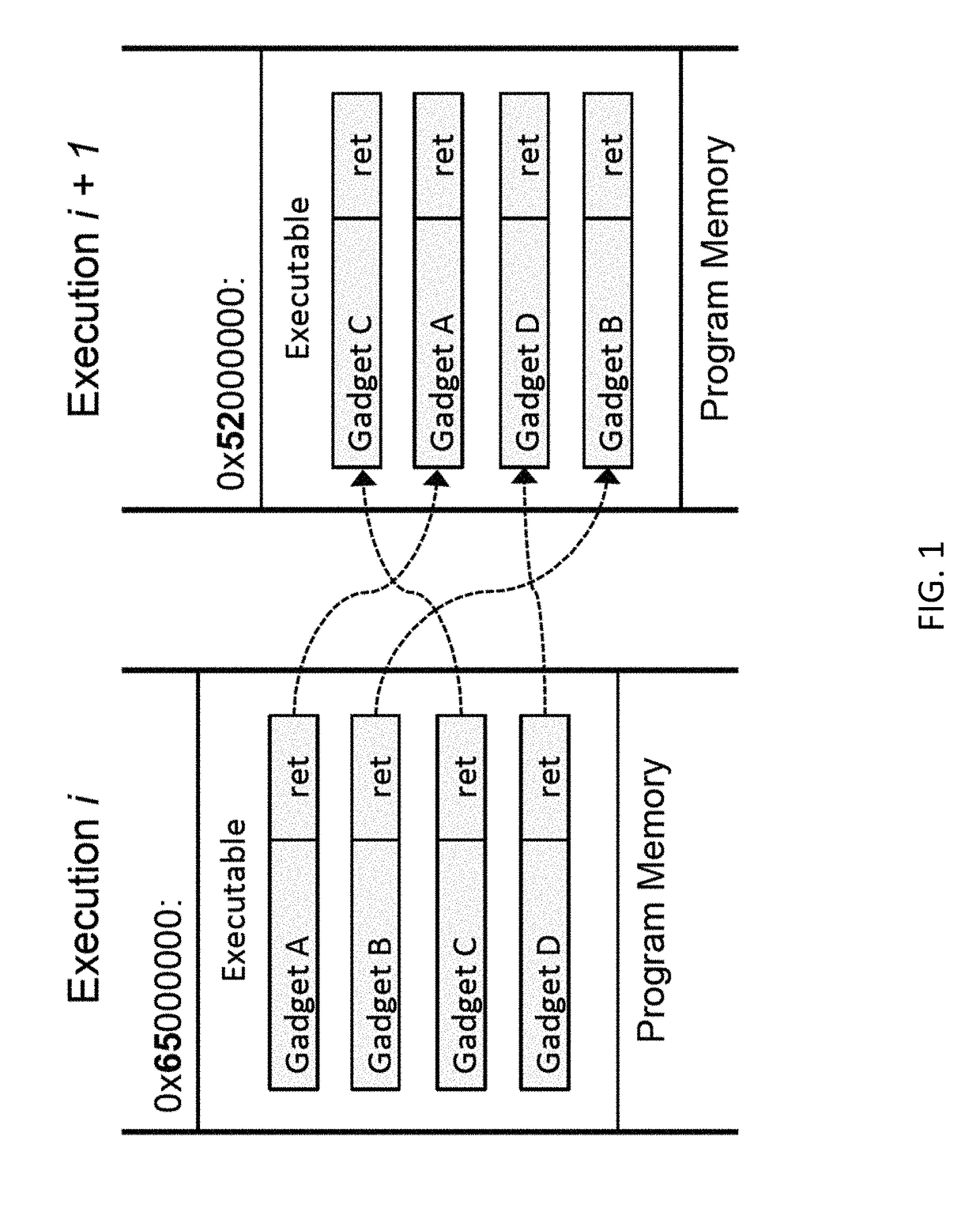
Fine-grained address space layout randomization
ActiveUS20160092675A1Reduce vulnerabilityMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionObfuscationParallel computing
A data processing system can use a method of fine-grained address space layout randomization to mitigate the system's vulnerability to return oriented programming security exploits. The randomization can occur at the sub-segment level by randomizing clumps of virtual memory pages. The randomized virtual memory can be presented to processes executing on the system. The mapping between memory spaces can be obfuscated using several obfuscation techniques to prevent the reverse engineering of the shuffled virtual memory mapping.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method for multi-code-rate coding based on grouped Markov superposition coding
ActiveCN103888151AImprove error correction performanceError correction/detection using convolutional codesError detection onlySuperposition codingBinary information
The invention belongs to the field of digital communication and digital storage, and particularly relates to a method for multi-code-rate coding based on grouped Markov superposition coding. The method is used for coding a binary information sequence shown in a specification to a codon shown in the specification, wherein the length of the binary information sequence conforms to the formula: K=kBL, the length of the codon is nB(L+m[k]), n is larger than 1, k ranges from 1 to n-1, namely, a code rate set is {1 / n, 2 / n,..., (n-1) / n}, L is the number of kB sequence groups of the same length, and mk is the memory span of each sub code with the code rate being k / n. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, the information sequence is divided into L groups shown in the specification with the equal length and a sequence shown in the specification with the length of nB is initiated when t is equal to -1, -2,...,-(mk-1), -mk; then, when t is equal to 0, 1, ...L-1, a sequence shown in the specification with the length being kB is divided into B groups and the B groups are sent to conversion defined by an n-dimensional matrix H for coding, so that a coding sequence shown in the specification with the length of nB is obtained and combined with elements shown in the specification, and the tth sub sequence shown in the specification of the codon shown in the specification is calculated. The method for multi-code-rate coding is simple in design, wide in code rate range and superior in performance.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Java card system and space distribution processing method thereof
ActiveCN102521145AImprove access speedRealize distributionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFragment processingElectricity
The invention provides a Java card system, which comprises an electrically erasable and programmable read-only memory space. The invention further provides a memory space distribution processing method of the Java card system, which includes a space distribution method, a trash recycling method and a stacked fragment processing method. The Java card system and the space distribution processing method thereof can efficiently achieve system space distribution, and lead application programs supplying to providers to be distributed in a continuous electrically erasable and programmable read-only memory (EEPROM) so as to increase access speed of application entities. By means of the trash recycling method, space in the Java card system occupied by trashes is tidied efficiently, a limited memory space of a Java card is led to be reasonably used, and sufficient space is provided for downloading of the application programs.
Owner:EASTCOMPEACE TECH
Memory fabric software implementation
ActiveUS20170199815A1Improve efficiencyImprove performanceInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationObject basedComputer module
A hardware-based processing node of an object memory fabric can comprise a memory module storing and managing one or more memory objects within an object-based memory space. Each memory object can be created natively within the memory module, accessed using a single memory reference instruction without Input / Output (I / O) instructions, and managed by the memory module at a single memory layer. The memory module can provide an interface layer below an application layer of a software stack. The interface layer can comprise one or more storage managers managing hardware of a processor and controlling portions of the object-based memory space visible to a virtual address space and physical address space of the processor. The storage managers can further provide an interface between the object-based memory space and an operating system executed by the processor and an alternate object memory based storage transparent to software using the interface layer.
Owner:ULTRATA LLC
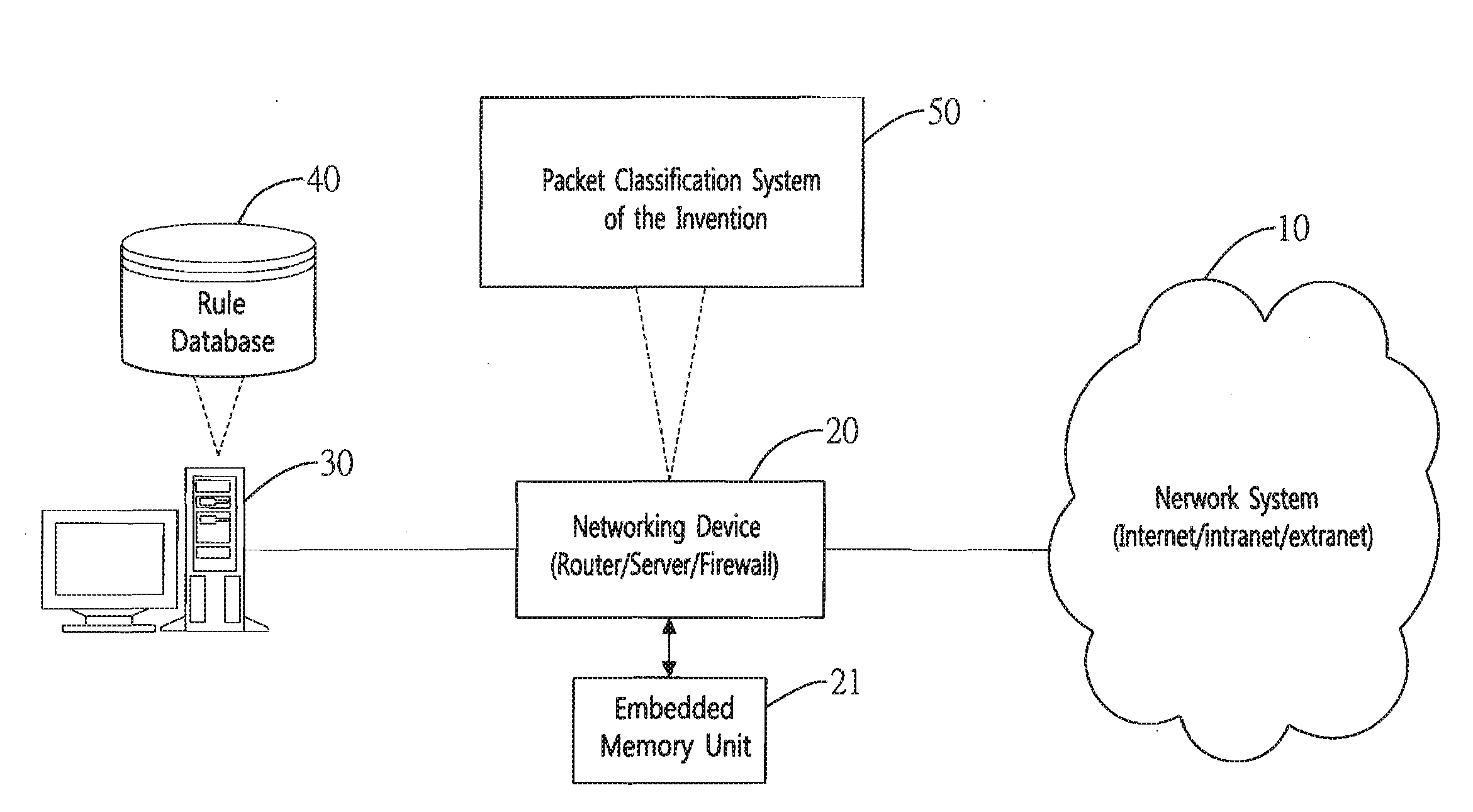
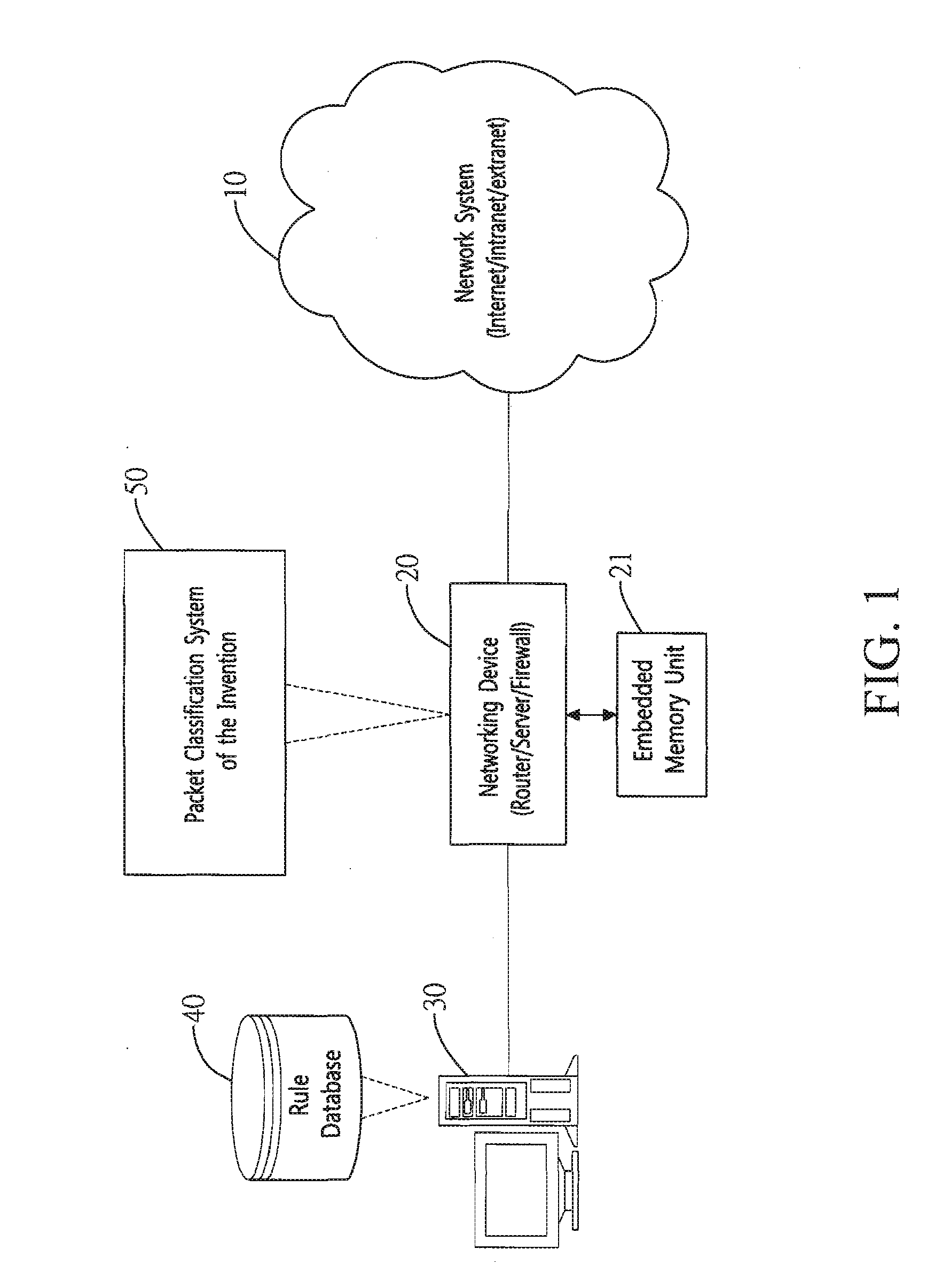
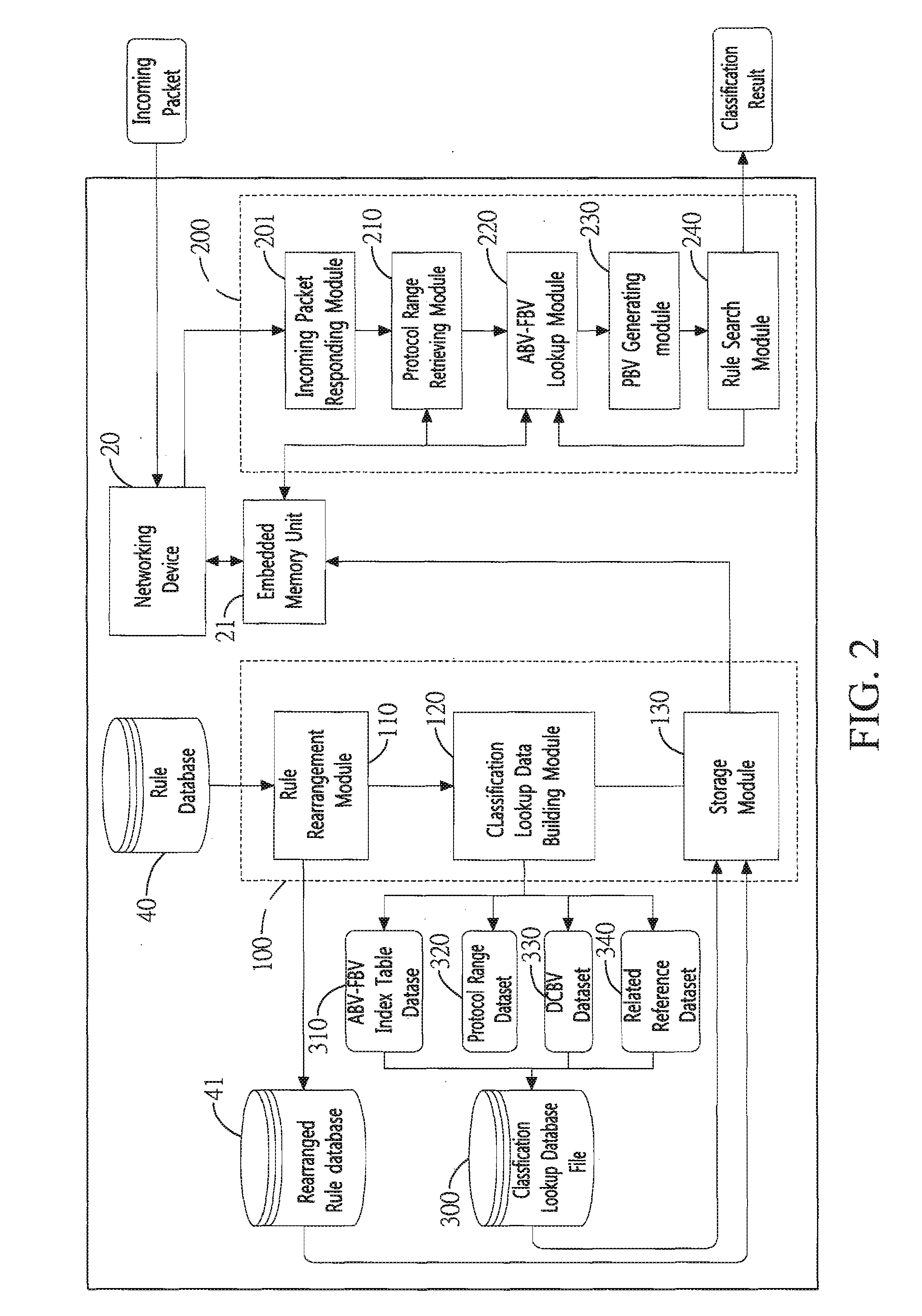
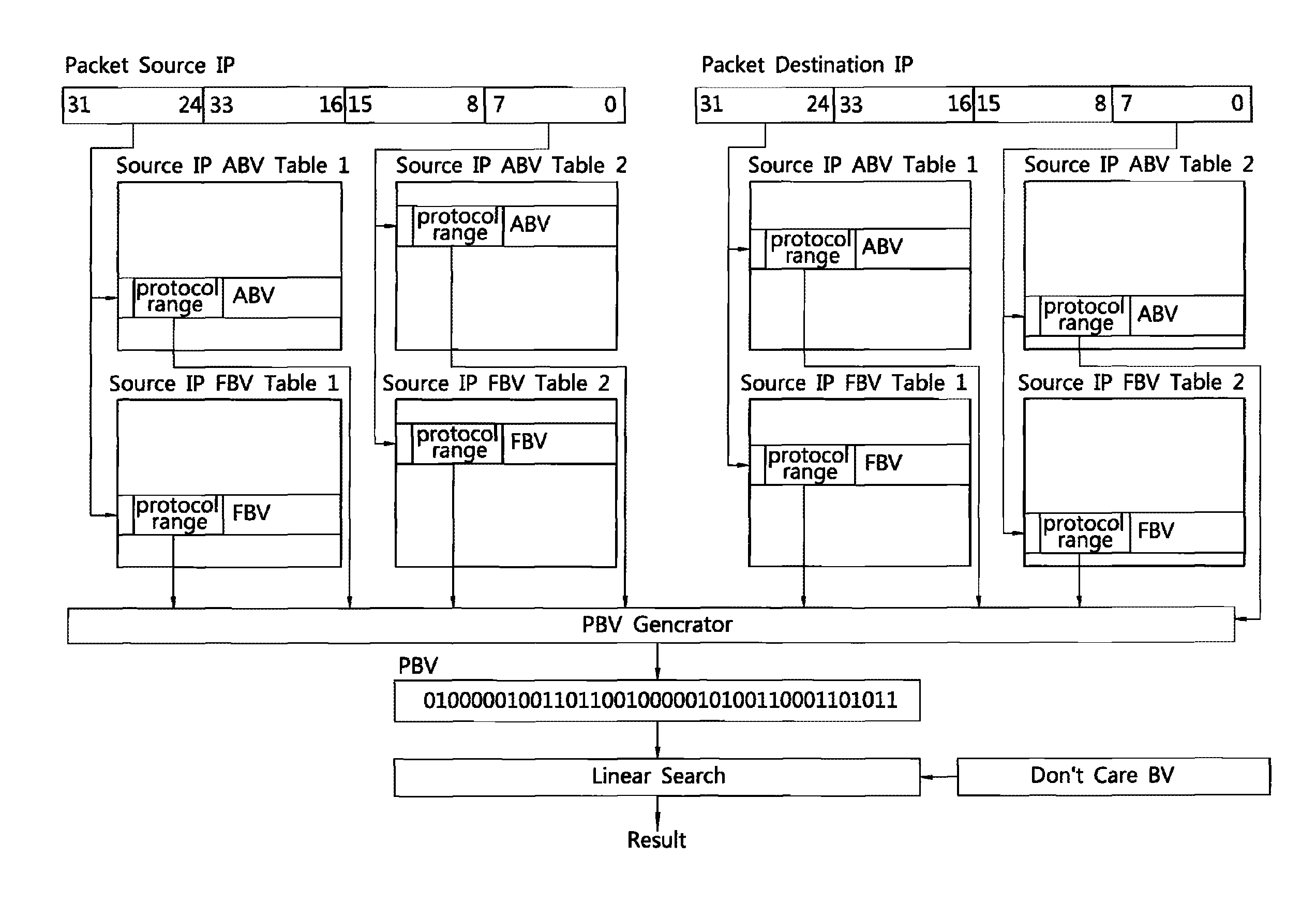
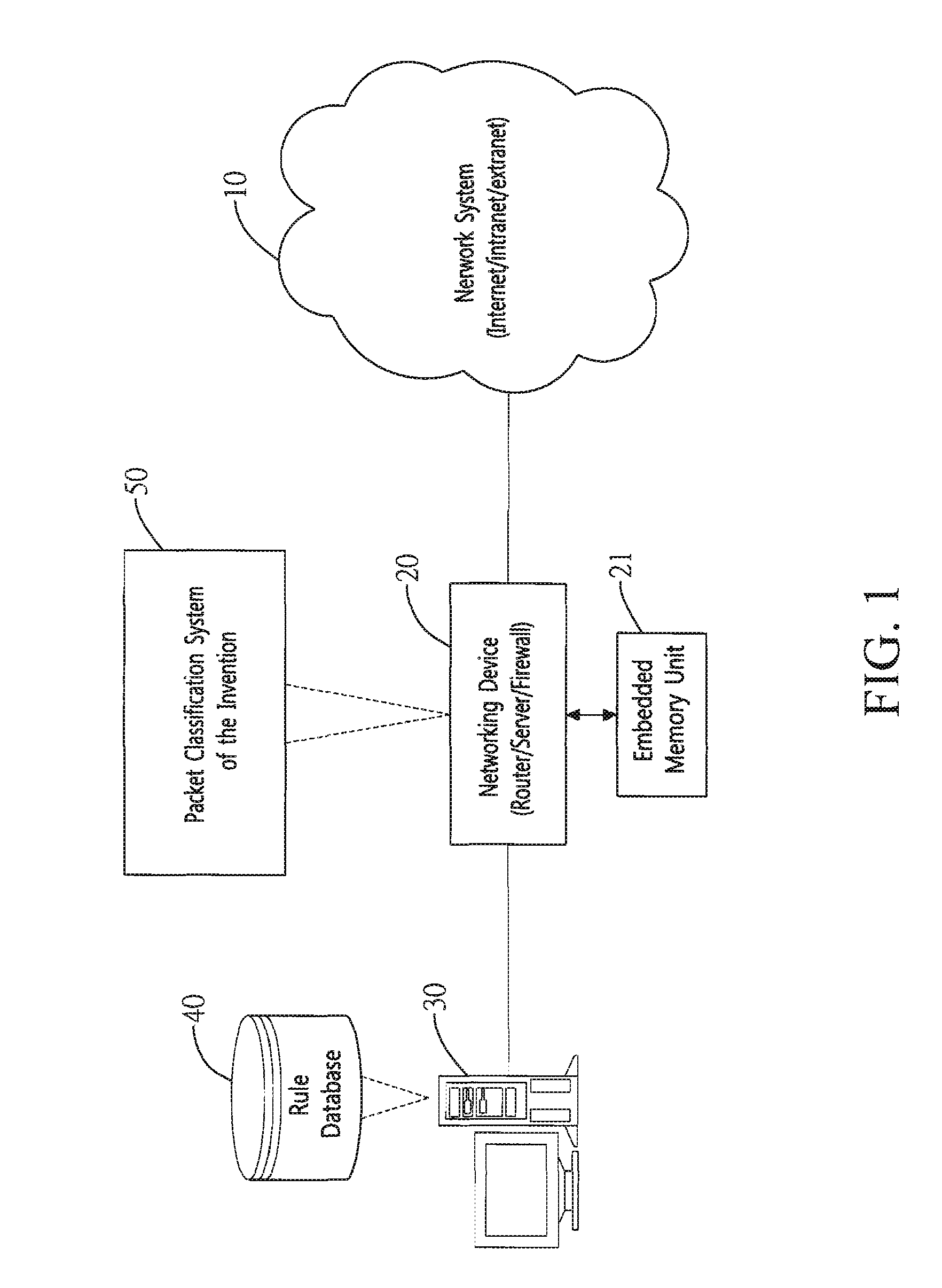
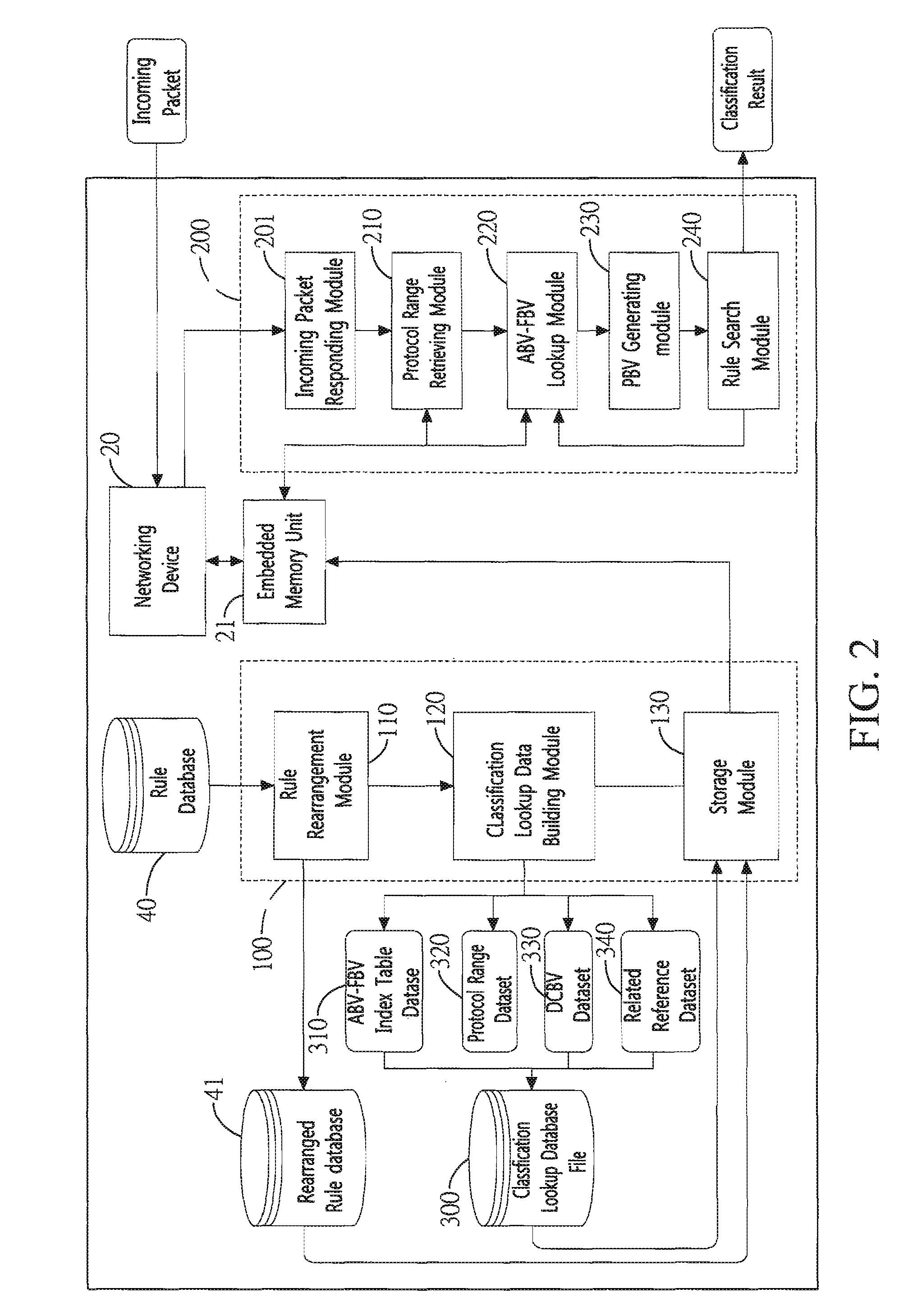
Method and system for packet classification with reduced memory space and enhanced access speed
InactiveUS20090185568A1Reduced amount of accessReduce access operationsData switching by path configurationData setAccess time
A method and system for packet classification is proposed for applications such as firewalls, intrusion detection, policy-based routing, and network service differentiations, within network systems such as Internet or intranet / extranet systems. The proposed method and system is characterized by the use of protocol-oriented rule rearrangement, the probable bit vector (PBV) based on the aggregated bit vectors (ABV) and folded bit vectors (FBV), an ABV-FBV index table dataset whose data structure is based on a featured split full-tree schema, and a DCBV (Don't-Care Bit Vector) dataset for packet classification. The combination of these features allows the packet classification to be implemented with a reduced amount of memory and access time during operation.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Method and terminal for improving utilization ratio of memory space
ActiveCN103218224AShorten the timeEasy to operateSpecific program execution arrangementsFile systemComputer terminal
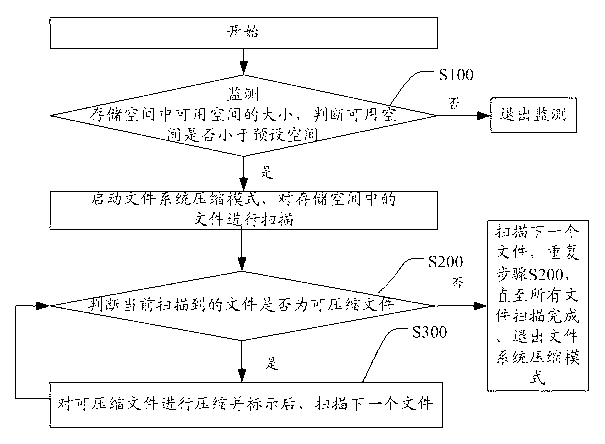
The invention discloses a method and a terminal for improving the utilization ratio of a memory space. The method comprises steps of A, monitoring the available space in the memory space, judging whether the available space is smaller than a preset space or not; if yes, starting a file system compression mode, and scanning files in the memory space; if not, stopping monitoring; B1, judging whether the currently scanned file is a compressible file or not; if yes, executing step C1; if not, scanning the next file, repeating step B1 until all the files are completely scanned, and exiting from the file system compression mode; and C1, compressing and marking the compressible file, scanning the next file, and returning to step B1. All the files in the memory space are appropriately and selectively compressed through the method, the utilization ratio of the memory space is improved, and a user does not need to select the files to perform a plurality of times of compression, so that the use by users is facilitated, and a user experience effect is improved.
Owner:DONGGUAN YULONG COMM TECH +1
Method and apparatus for interrupting memory bank refresh
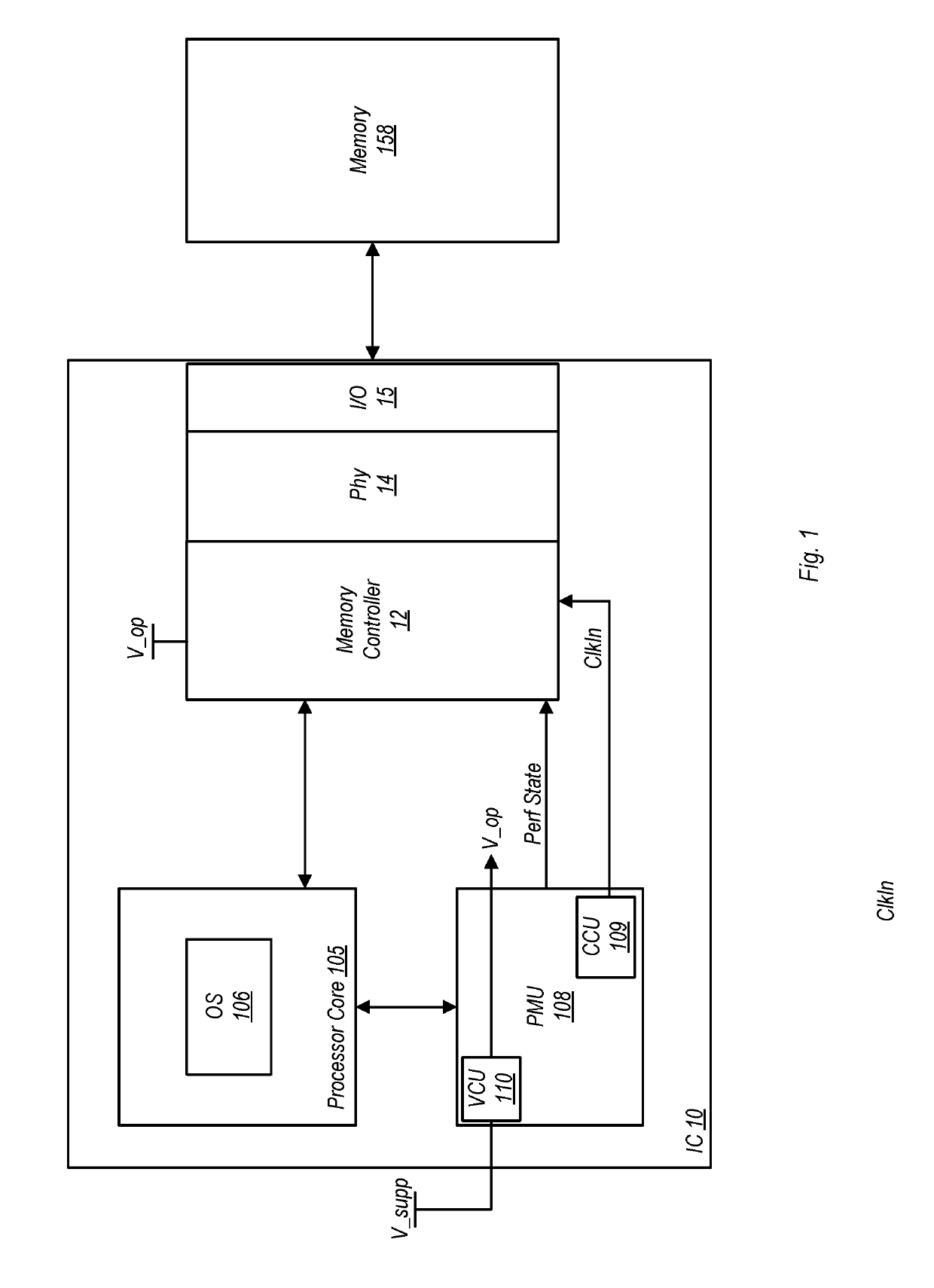
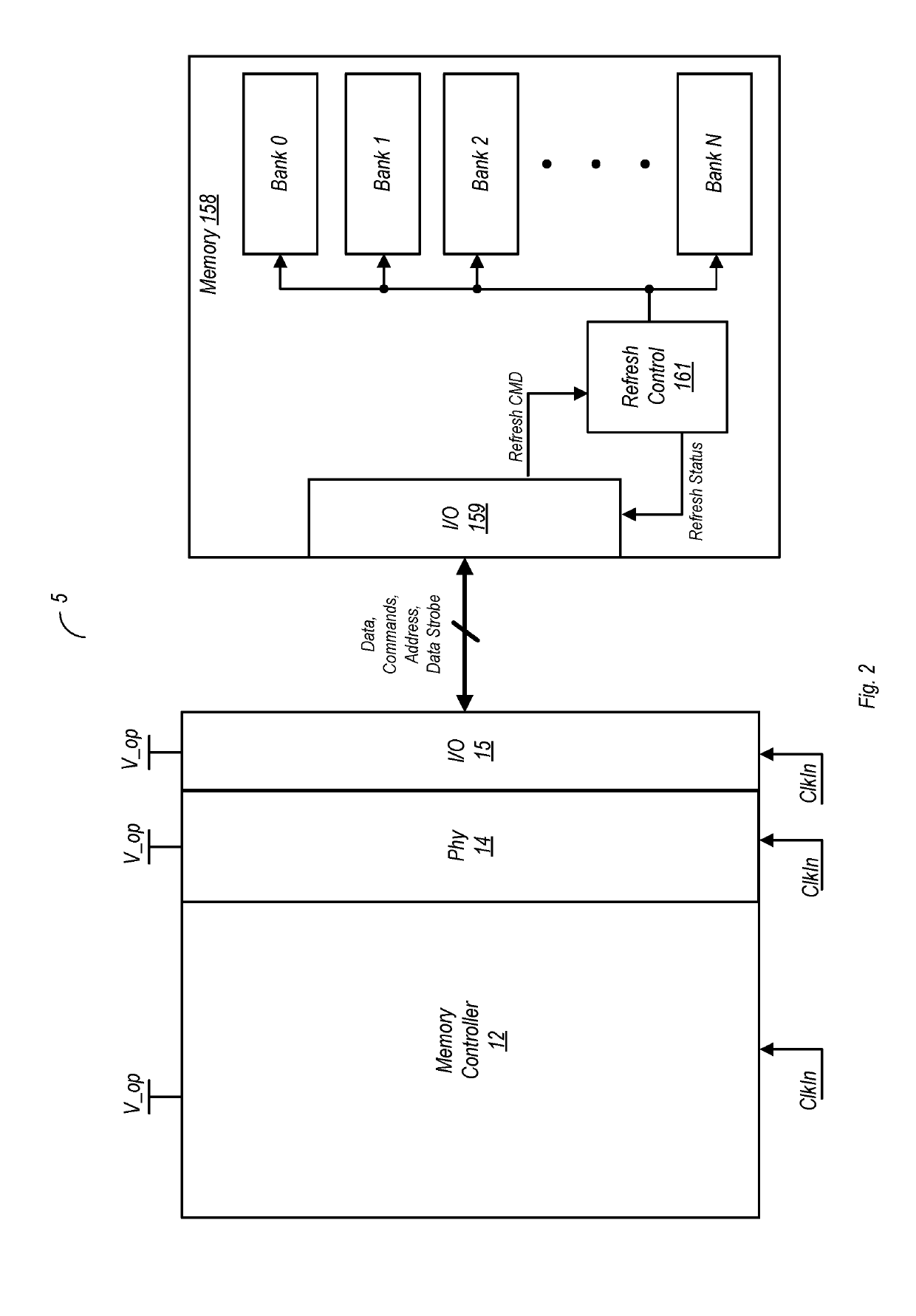
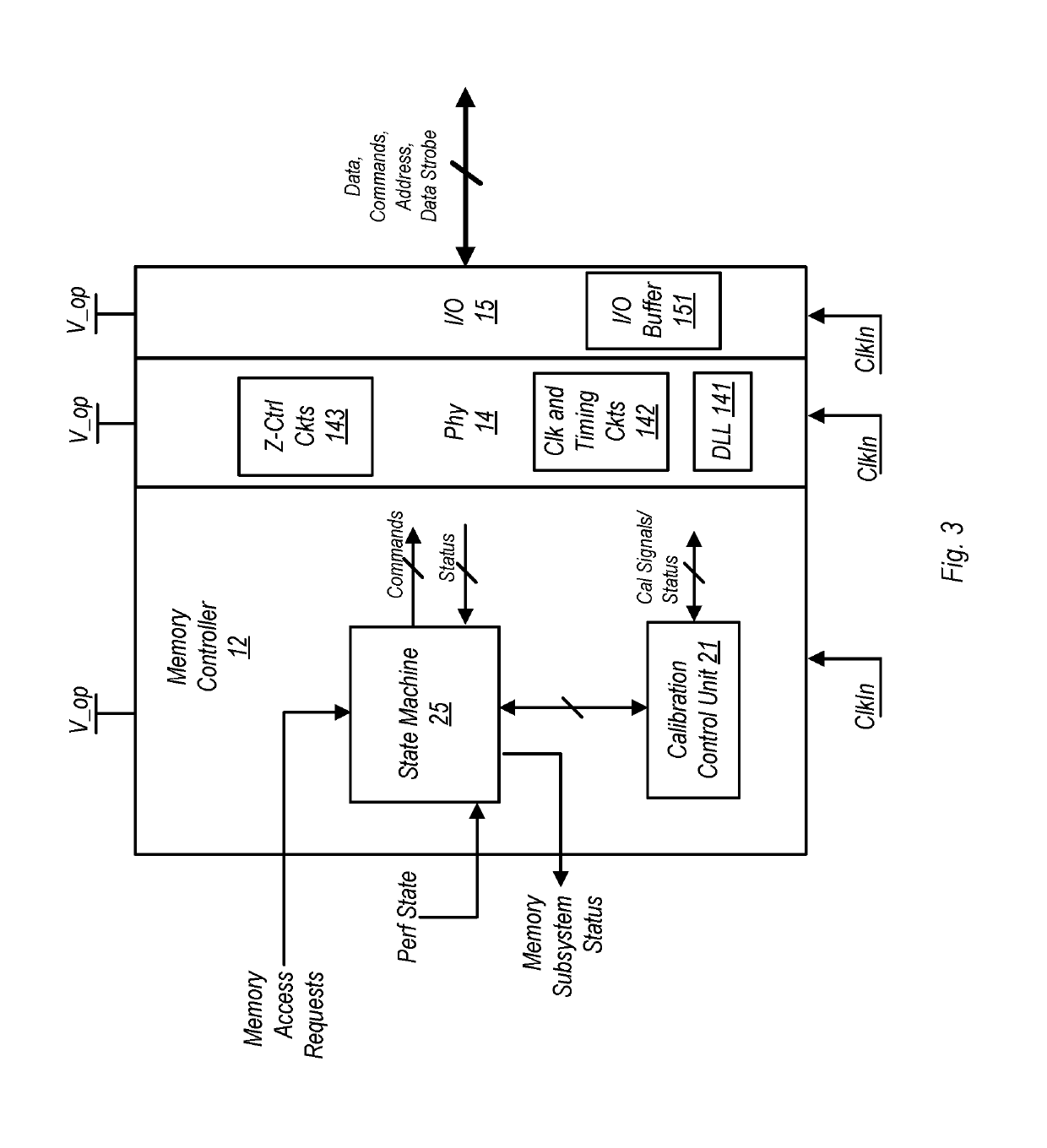
ActiveUS10510396B1Timely controlDigital storageEnergy efficient computingMemory bankMemory controller
A memory controller includes a state machine that initiates a memory refresh of a DRAM (having a number of banks) by sending thereto a refresh command. Responsive to receiving the command, the DRAM may perform a per-bank refresh in which individual ones of the banks are refreshed in succession, one at a time. Upon receiving a high priority transaction, a determination is made as to the number of memory banks that have currently been refreshed in the per-bank refresh. If the number of banks refreshed is less than a threshold value, the per-bank refresh is aborted.
Owner:APPLE INC
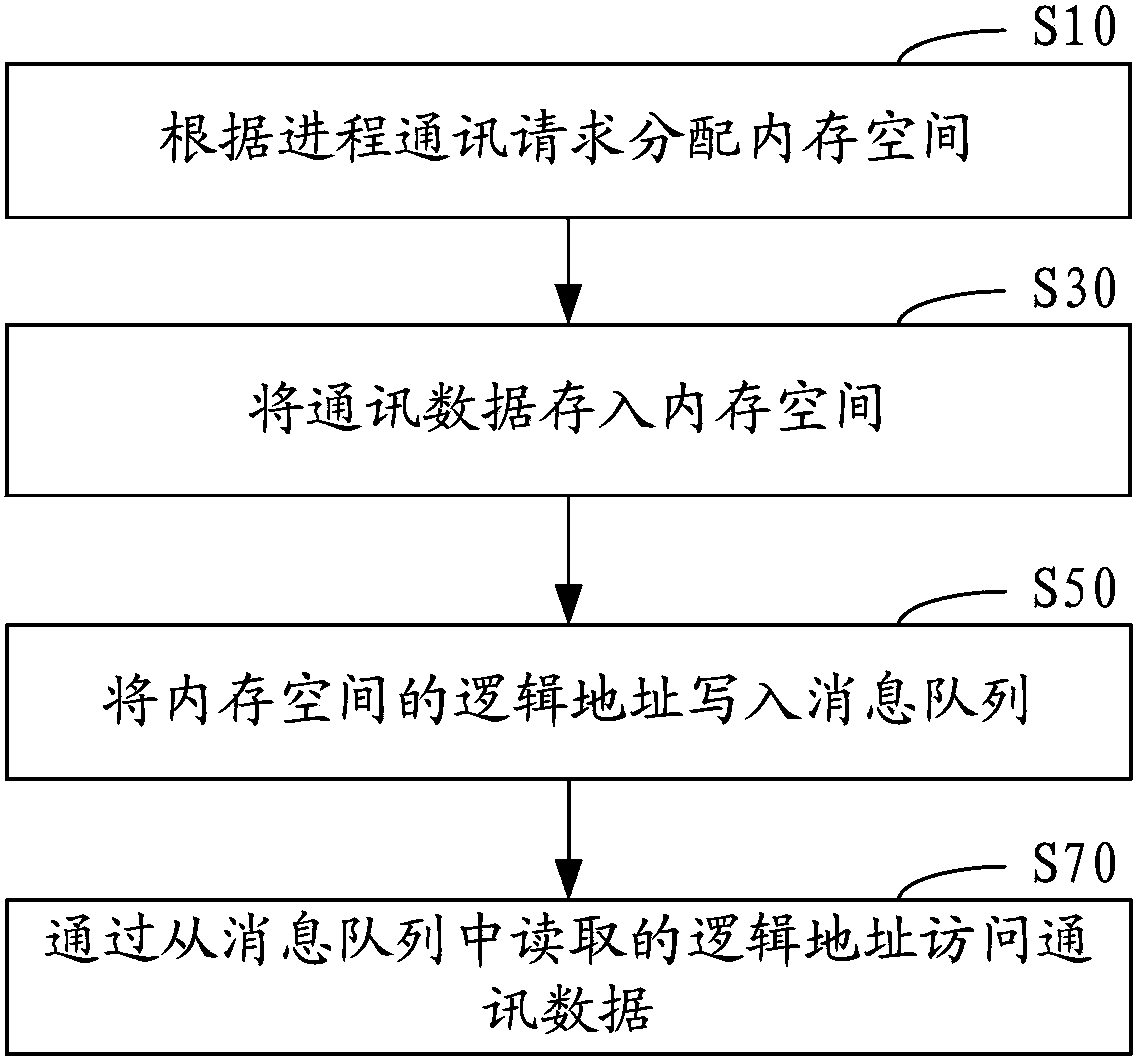
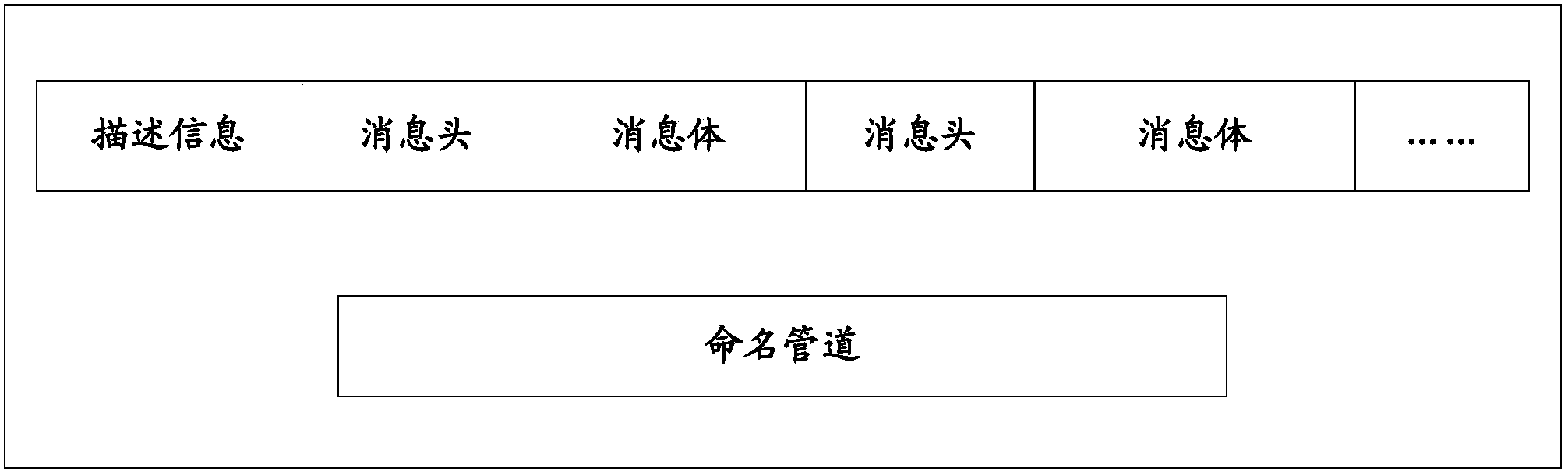
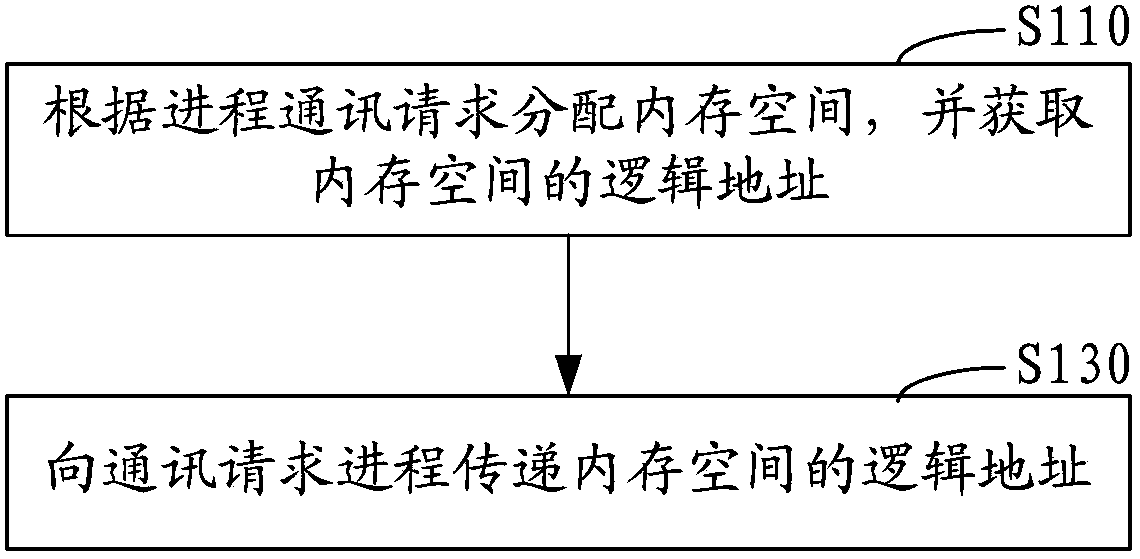
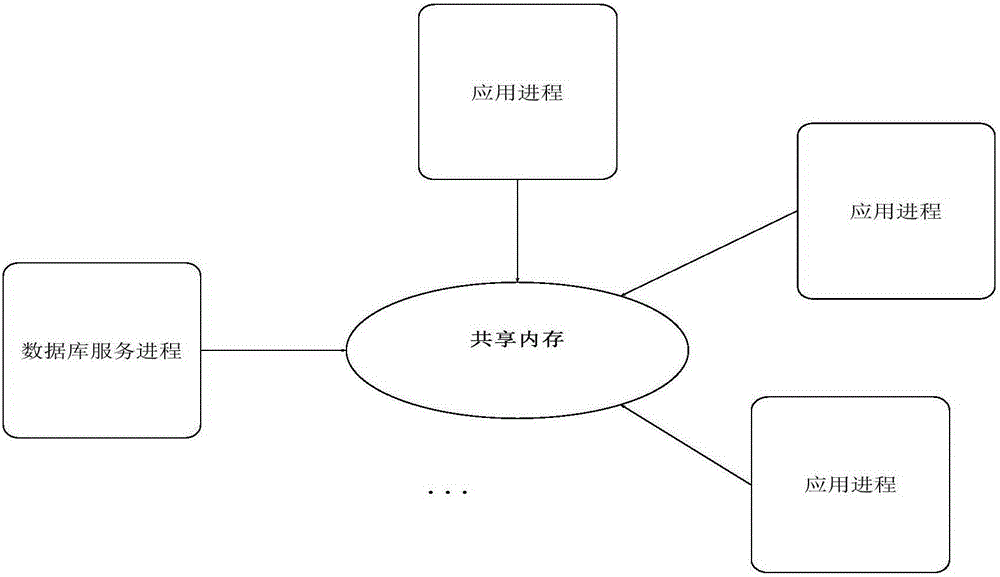
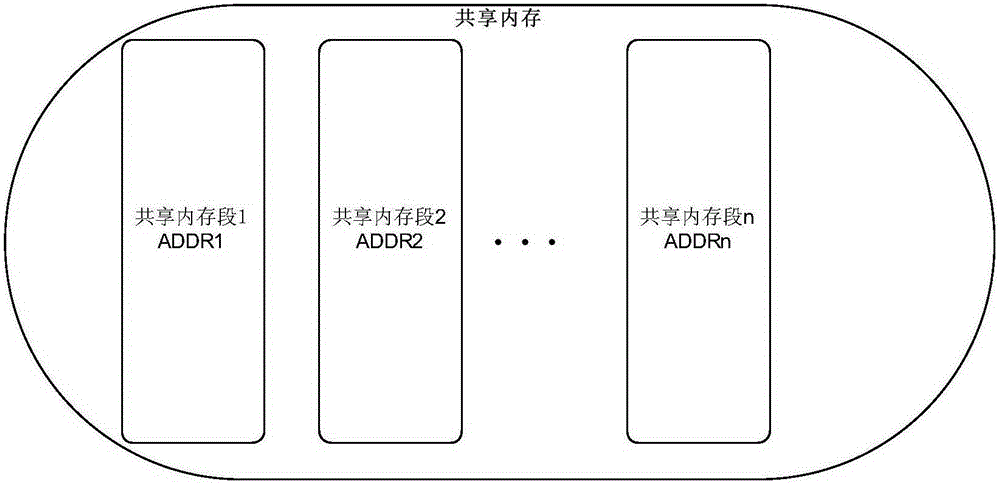
Process communication method and process communication system
ActiveCN103425538AIncrease flexibilityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInterprogram communicationComputer hardwareMessage queue
The invention discloses a process communication method. The process communication method includes steps of distributing memory spaces according to process communication requests; storing communication data into the memory spaces; writing logic addresses of the memory spaces into a message queue; reading the logic addresses in the message queue to access the communication data. The process communication method and a process communication system have the advantages that the memory spaces used for storing the communication data are distributed when the process communication requests are received, and accordingly storage spaces for the communication data are not required to be divided in advance; the logic addresses of the memory spaces are written into the message queue and can be read to access the communication data, so that the logic addresses in the message queue can be read one by one to orderly access the communication data in data access processes under the effect of the message queue, the communication data do not need to be copied in communication procedures among the multiple processes, and the data sharing flexibility is greatly improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN TENCENT COMP SYST CO LTD
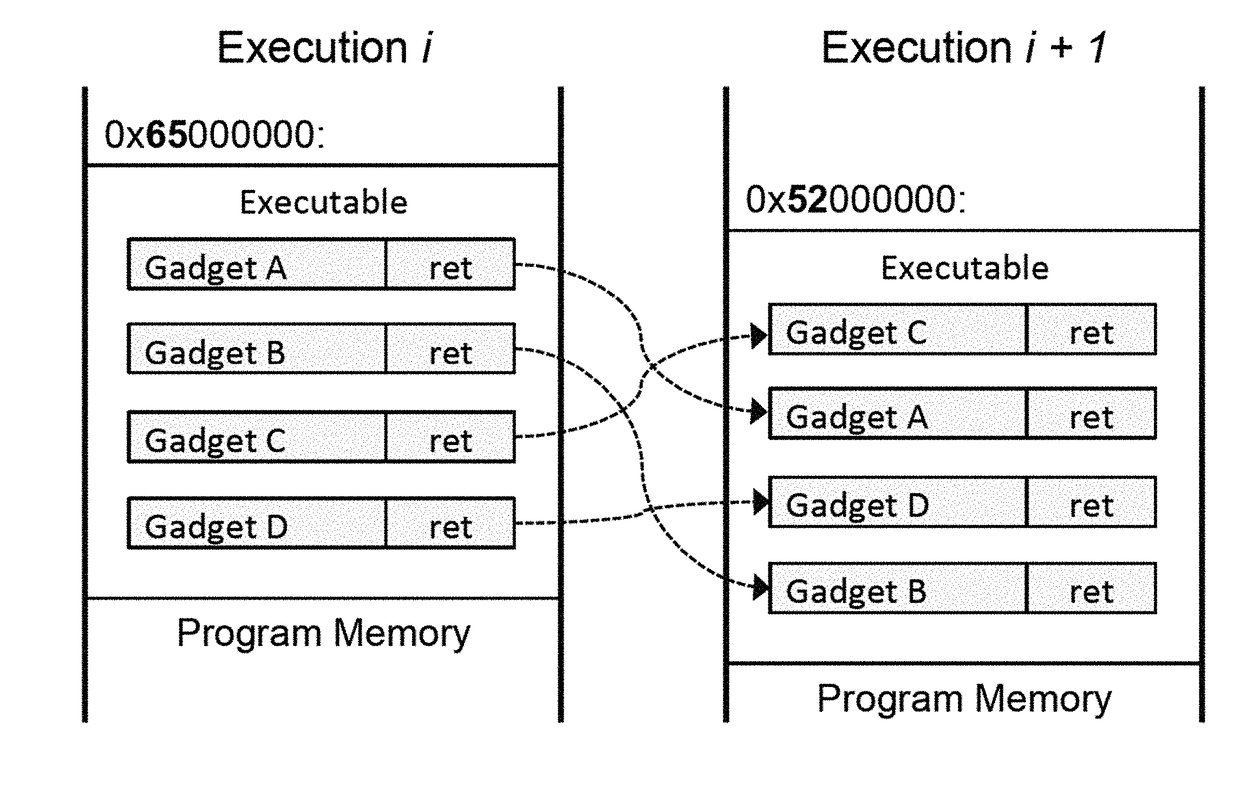
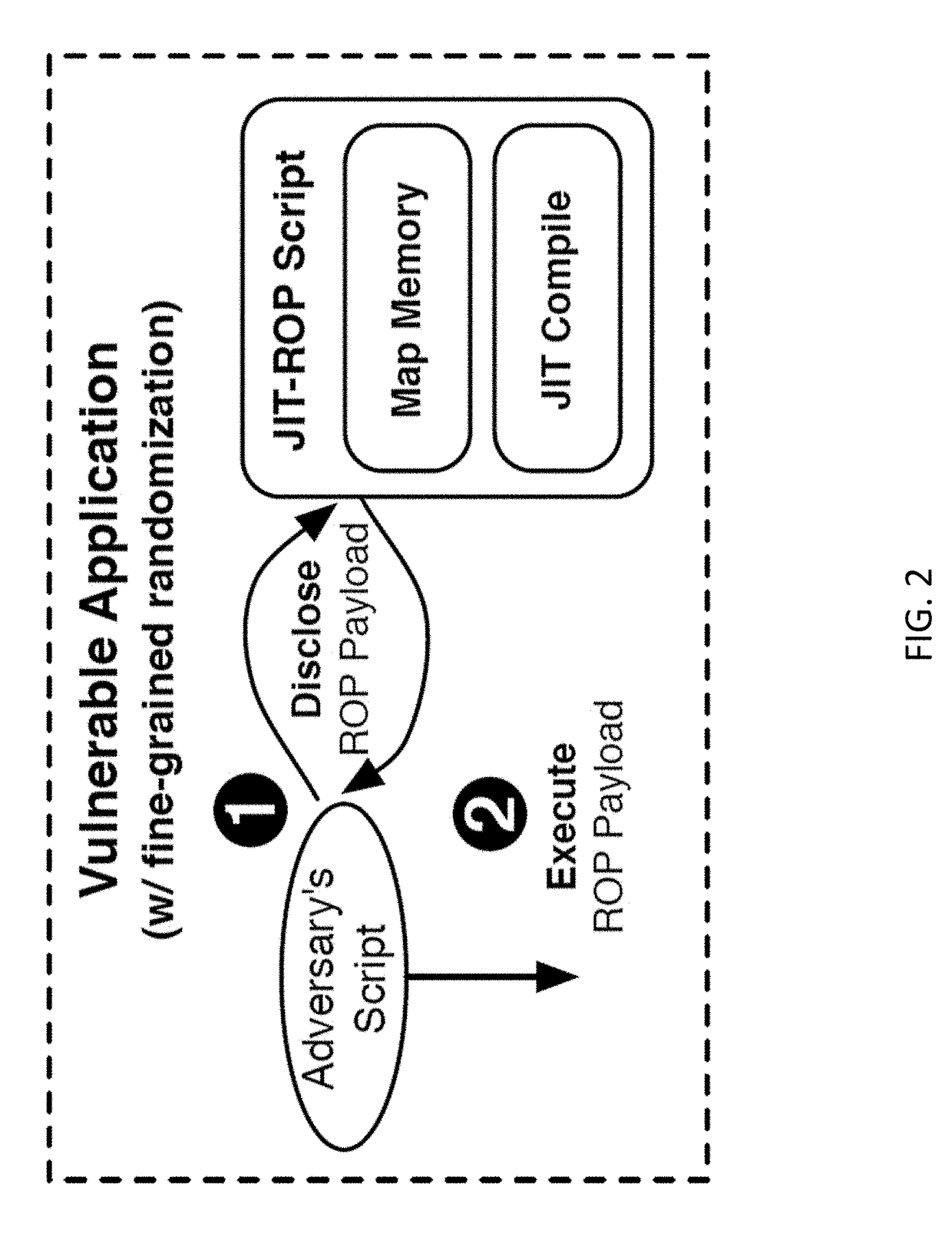
Methods, systems, and computer readable media for preventing code reuse attacks
ActiveUS20170213039A1Avoid attackMemory architecture accessing/allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer hardwareCode reuse
Methods, systems, and computer readable media for preventing code reuse attacks are disclosed. According to one method, the method includes executing, on a processor, code in a memory page related to an application, wherein the memory page is protected. The method also includes detecting a read request associated with the code. The method further includes after detecting the read request, modifying, without using a hypervisor, at least one memory permission associated with the memory page such that the code is no longer executable after the code is read.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
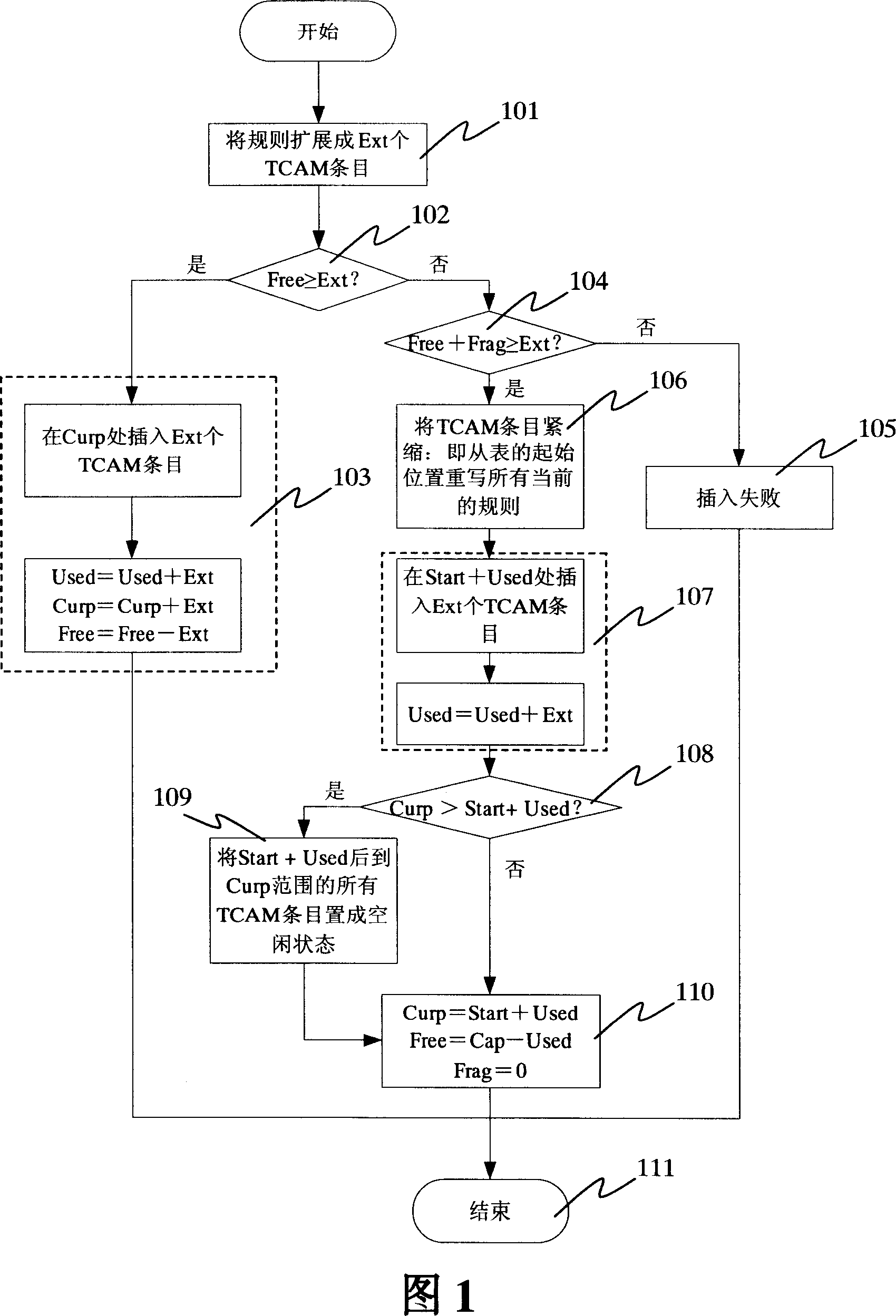
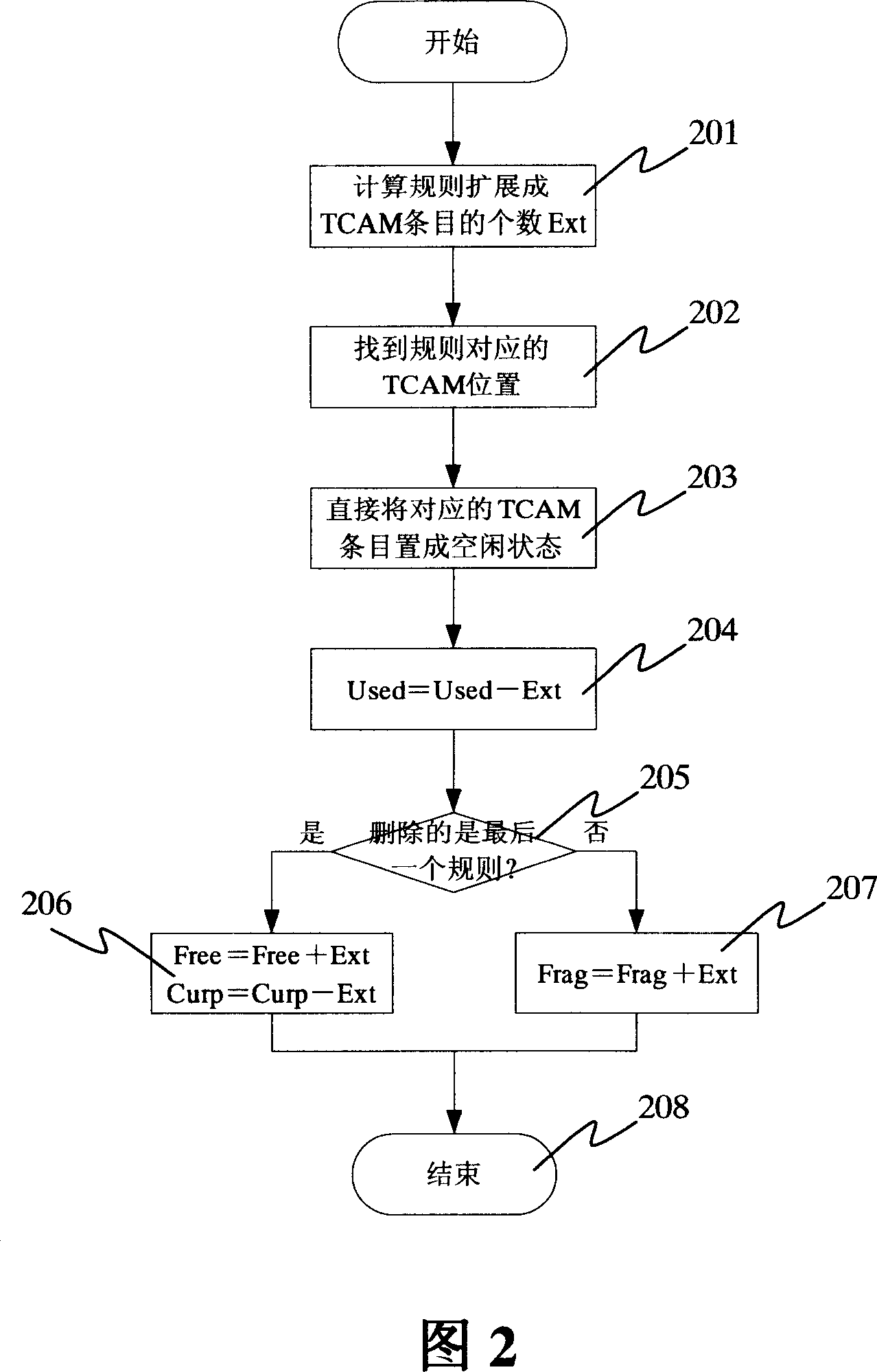
Rule update method for three-folded content addressable memory message classification
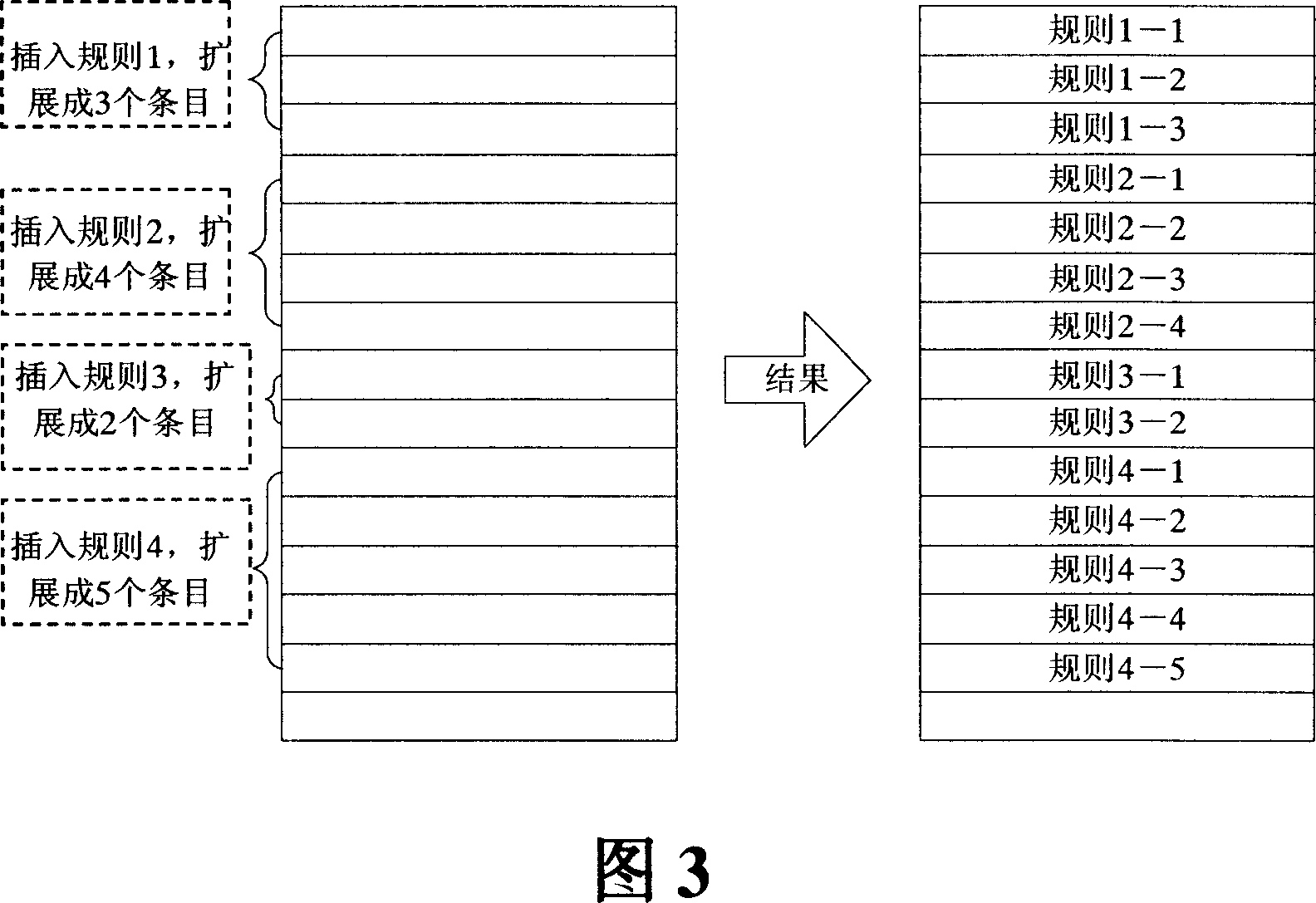
InactiveCN101035062ATroubleshoot rule updates for ACL/QoSSimple methodData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsDirect entryClassification methods
This invention discloses a rules update text classification methods for triple content addressable memory , characterized lies in the fact that the rules will expand the rules of entry into several entries stored in the memory space, adding new rules, a final judgment of the rules described in storage there and the number of entries after the entry space of the idle Head space is to be added to accommodate the new rules are described in the final accounts for direct entry after storage space referred to the new rules, or they would be referred to a memory crunch to remove already described in the last entry before the free space entry space and then referred to the new storage rules; delete rules direct store will be deleted with the rules, the number of entries space for free entry into space.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Log management method for embedded system
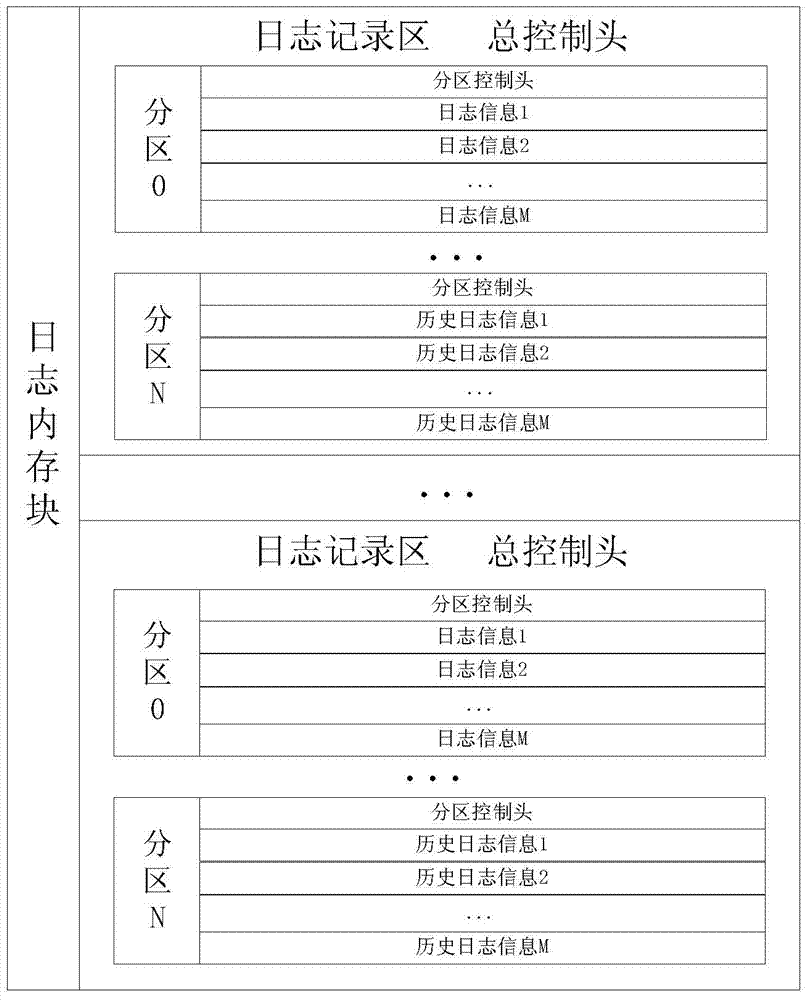
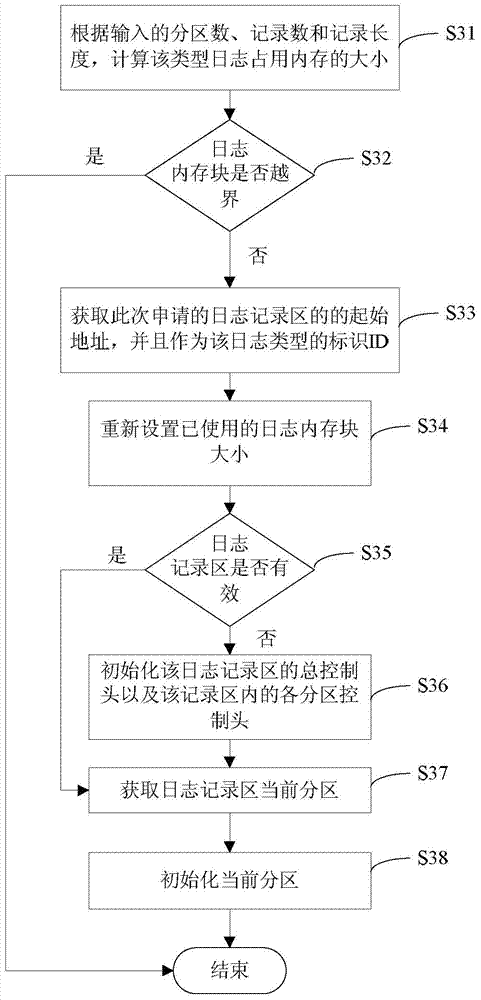
ActiveCN103927251AImprove memory allocation efficiencyReduce wasteHardware monitoringMemory addressLog management
The invention discloses a log management method for an embedded system and relates to the technical field of debugging diagnosis of the embedded system. The log management method includes the steps of S1, acquiring a log memory block from a system memory and recording an initial address of the log memory block and the total size of occupied memory space; S2, dividing the log memory block into equal and continuous logging areas, wherein each logging area is divided into different partitions and comprises a total control head, and each partition further comprises a partition control head; S3, allocating the logging areas for all types of logs according to the above steps; S4, acquiring the initial memory address used for logging information in the current partition of the logging areas according to the initial address of the logging areas and logging portion of the current log and writing the log information to be recorded into the area where the initial memory address is located. By the log management method, reading and writing on storage medium are reduced, efficient management of the logging information is improved, and the system can be diagnosed and positioned rapidly and accurately.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Allocation method and device for memory space of smart card
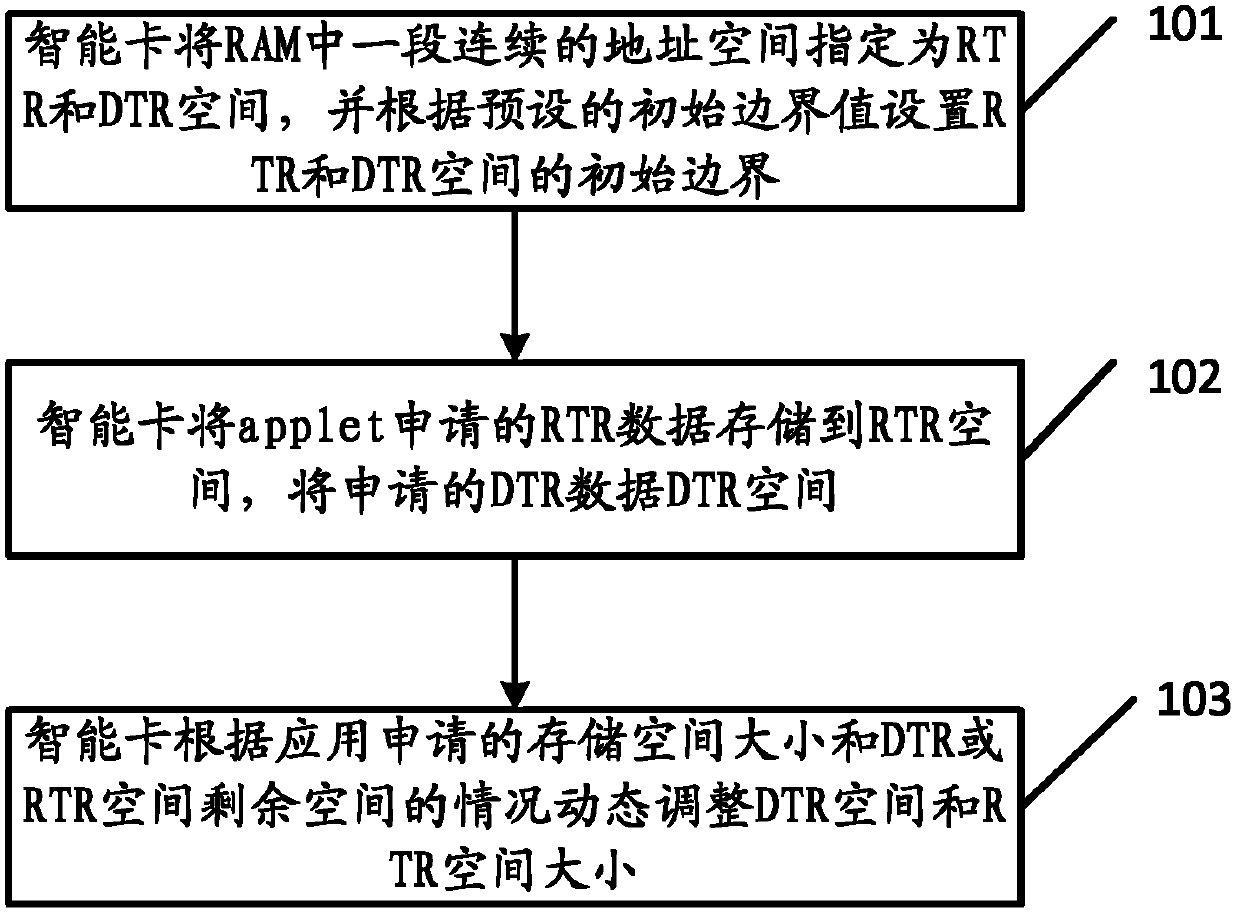
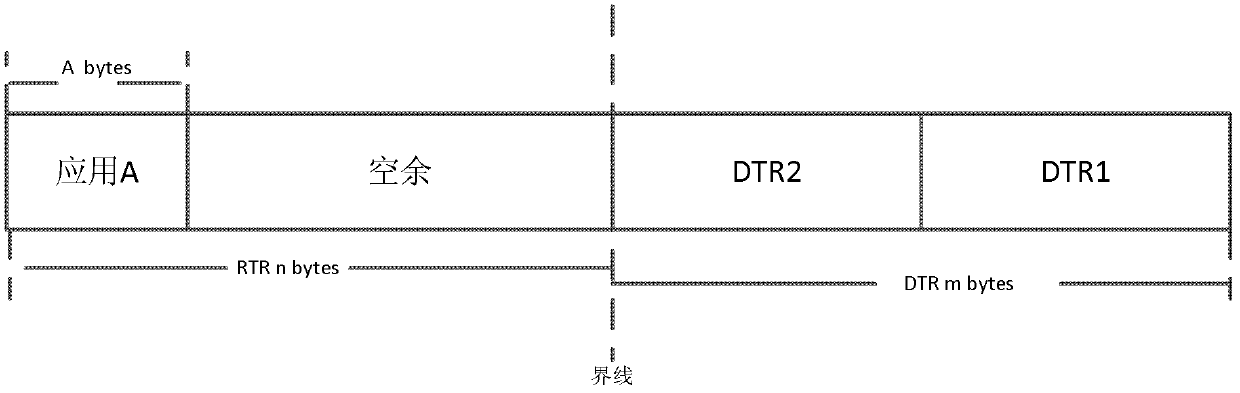
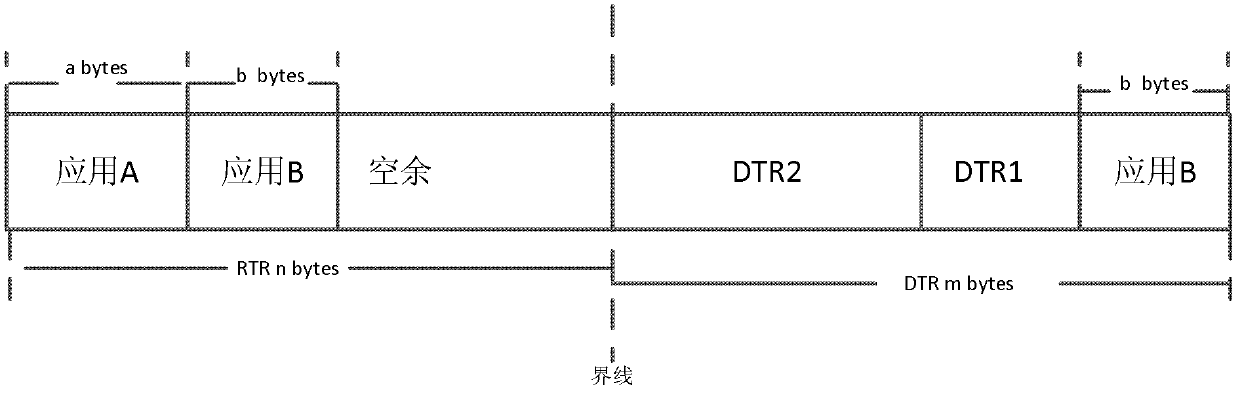
ActiveCN103309812AReasonable distributionIncrease profitMemory adressing/allocation/relocationBoundary valuesRandom access memory
The embodiment of the invention discloses an allocation method and an allocation device for the memory space of a smart card, relates to the technical field of smart cards and solves the technical problem in the prior art that RTR (CLEAR_ON_RESET RAM) and DTR (CLEAR_ON_DESELECT RAM) space of the RAM of a smart card are difficult to allocate and determine. The allocation method mainly comprises the steps that a section of continuous address space in the RAM (random access memory) is allocated as the RTR and DTR space, and the initial boundaries of the RTR and DTR space in the continuous address space are set according to preset initial boundary values; when the free memory capacity of the RTR space is smaller than the capacity requested by RTR data, or when the free memory capacity of the DTR space is smaller than the capacity requested by DTR data, the boundaries are dynamically adjusted in the continuous address space to change the size of the RTR space or the DTR space.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
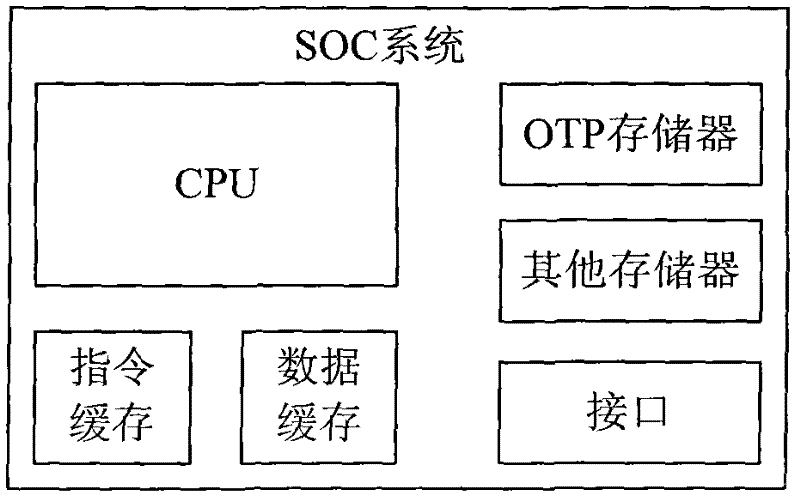
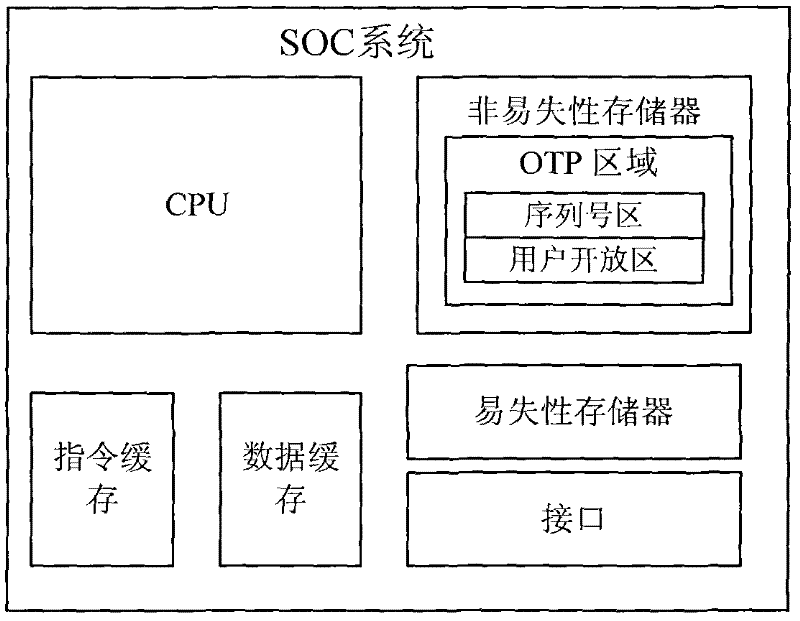
Novel OTP implementation method
InactiveCN102129486AReduce complexityLow costSpecial data processing applicationsThird partyElectricity
The invention relates to a novel OTP (One Time Programmable) implementation method. A part of memory area of a SOC (System On Chip) integrated nonvolatile memory module and a method for combining hardware with system software are adopted to implement two functions below: 1, a memory space for serial numbers is set aside in the memory area of the nonvolatile memory module, and a user cannot write, but only read in the memory space, and unique serial numbers are written in the memory space during chip test; and 2, a special area is partially set aside in the memory area of the nonvolatile memory module, the method for combining hardware with system software is adopted to ensure that the user completes write lock through user configuration parameters when completing write operation for the special area, and once the write operation is locked, the chip cannot modify the write operation-locked area after being re-electrified. The method has the advantages that: the integration of a third-party OTP memory is not required, the chip design complexity is reduced, and the cost is lowered since independent test for OTP is not required during chip test.
Owner:HANGZHOU SYNOCHIP DATA SECURITY TECH CO LTD
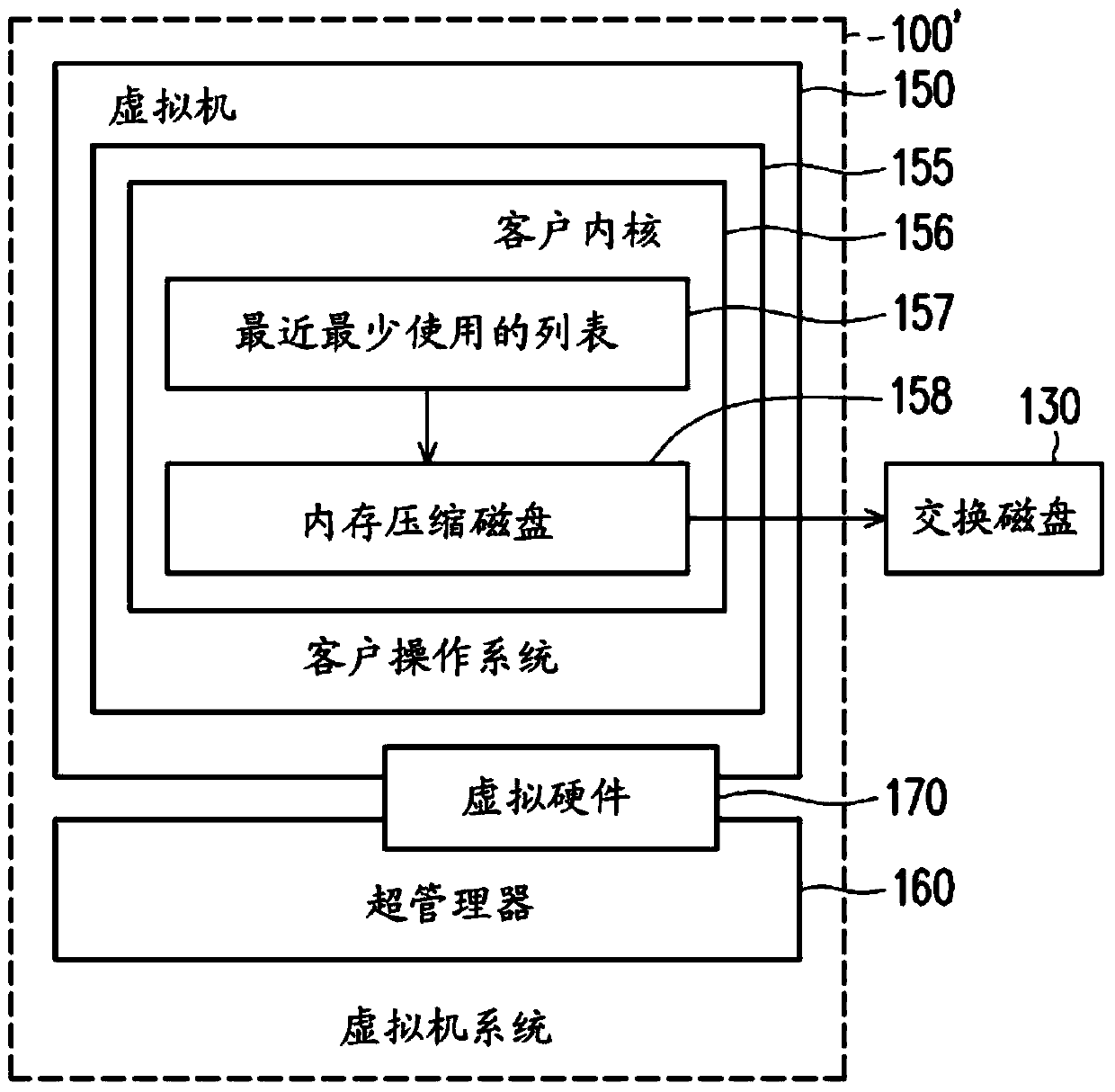
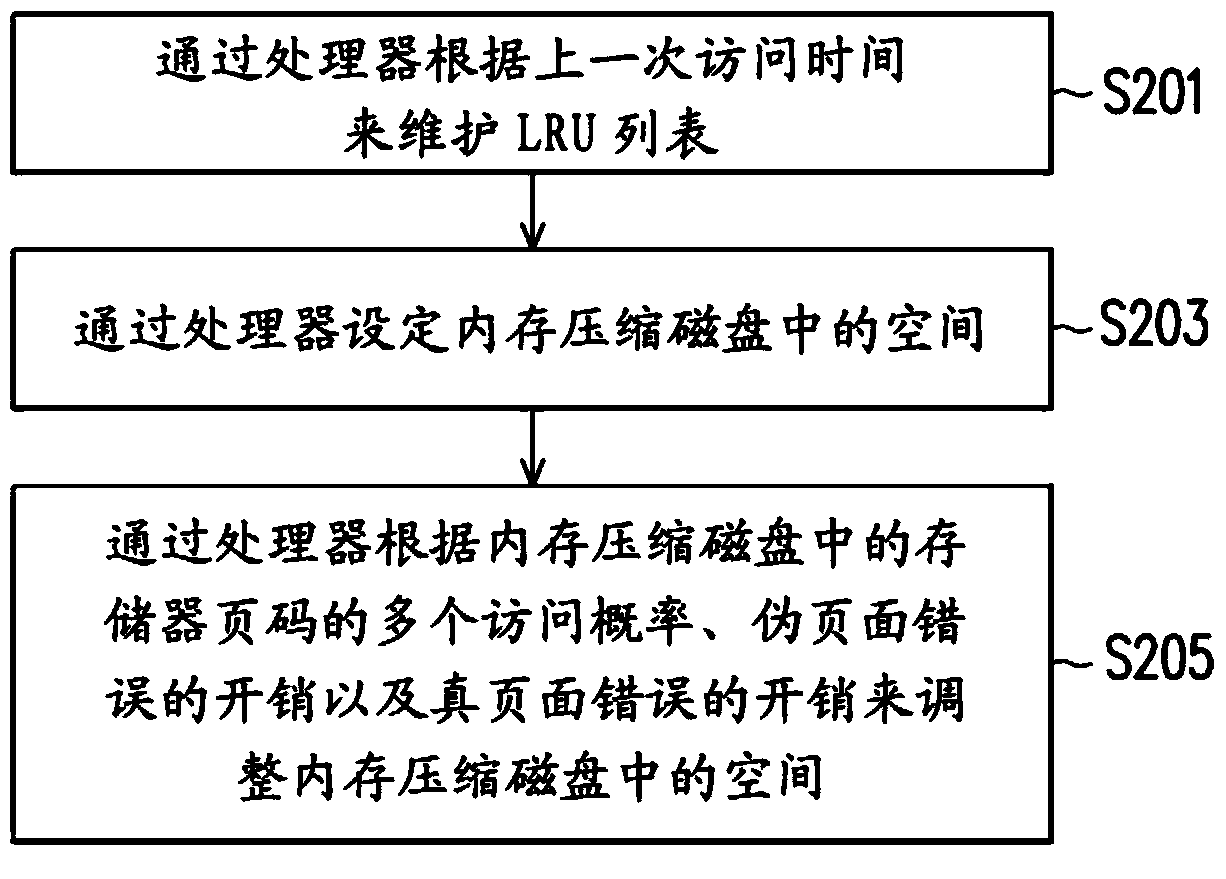
Method and computer system for memory management on virtual machine system
ActiveCN103729305AMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAccess timeComputerized system
A method and a computer system for memory management on a virtual machine system are provided. The memory management method includes the following steps. A least recently used (LRU) list is maintained by at least one processor according to a last access time, wherein the LRU list includes a plurality of memory pages. A first portion of the memory pages are stored in a virtual memory, a second portion of the memory pages are stored in a zram driver, and a third portion of the memory pages are stored in at least one swap disk. A space in the zram driver is set by the at least one processor. The space in the zram driver is adjusted by the processor according to a plurality of access probabilities of the memory pages in the zram driver, an overhead of a pseudo page fault, and an overhead of a true page fault.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Virtual cluster-oriented shared memory system
ActiveCN105242872ATake advantage ofAchieve efficiencyInput/output to record carriersApplication softwareMemory module
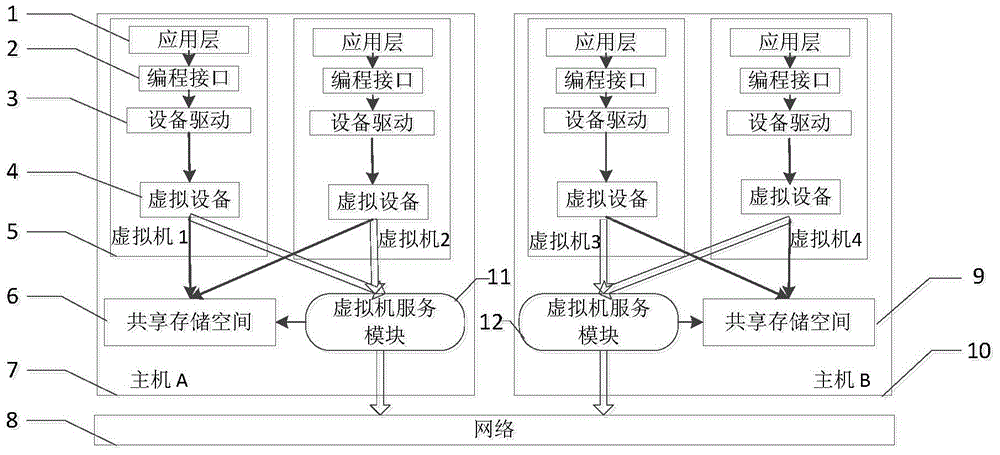
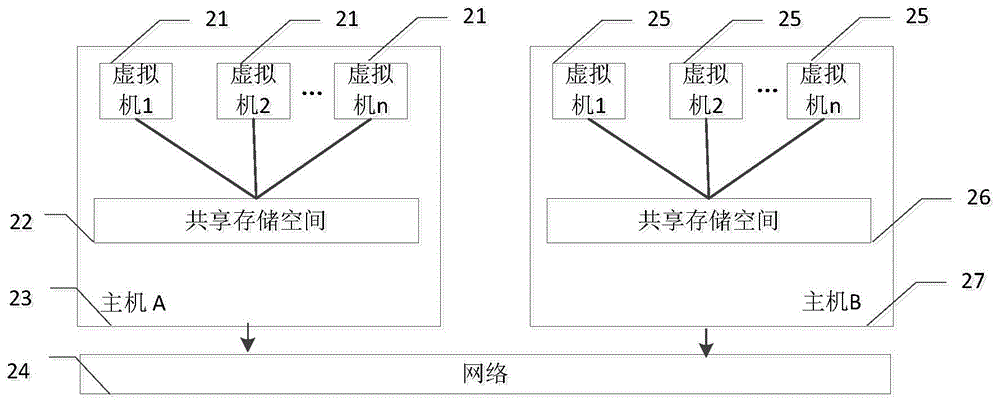
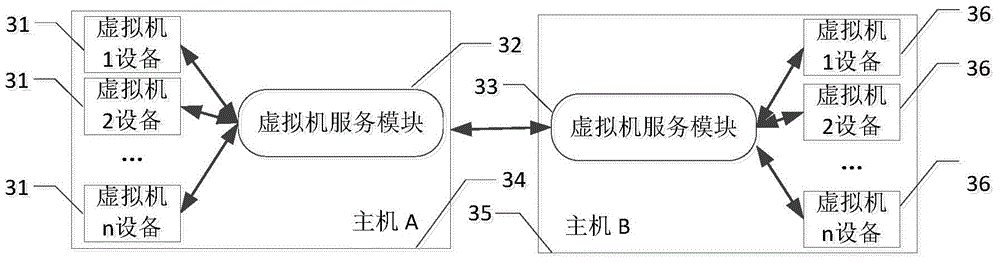
The invention provides a virtual cluster-oriented shared memory system, which belongs to the technical field of computer memory. A system main body part consists of two hosts which are in interconnection through a network. Each host mainly comprises shared memory modules used for forming a shared memory space, a plurality of virtual machines, and virtual machine service modules which provide relevant services for the virtual machines; and each virtual machine mainly comprises one virtual machine, an equipment driving module in a kernel space, and an access interface module for an application program to be called. The invention provides the novel distributed shared memory system and has the features that a mechanism is provided for the information transfer of the virtual machines on different physical machines so as to realize shared memory programming semantics in a cloud virtual cluster. The invention provides the user-mode programmable shared memory space for a user layer, shared memory read-write efficiency is guaranteed and intervention on a client kernel layer and a virtual machine monitoring layer is prevented.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
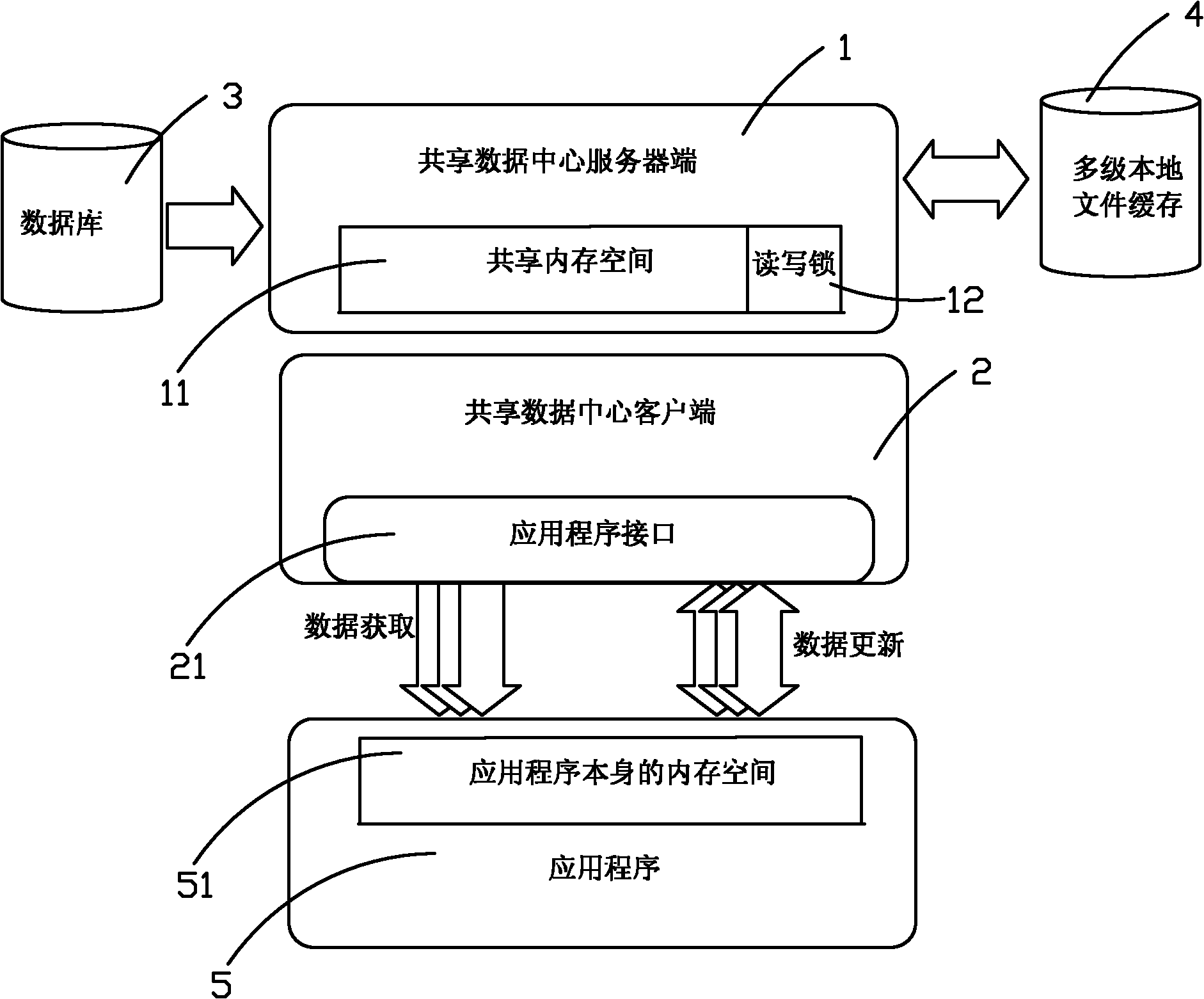
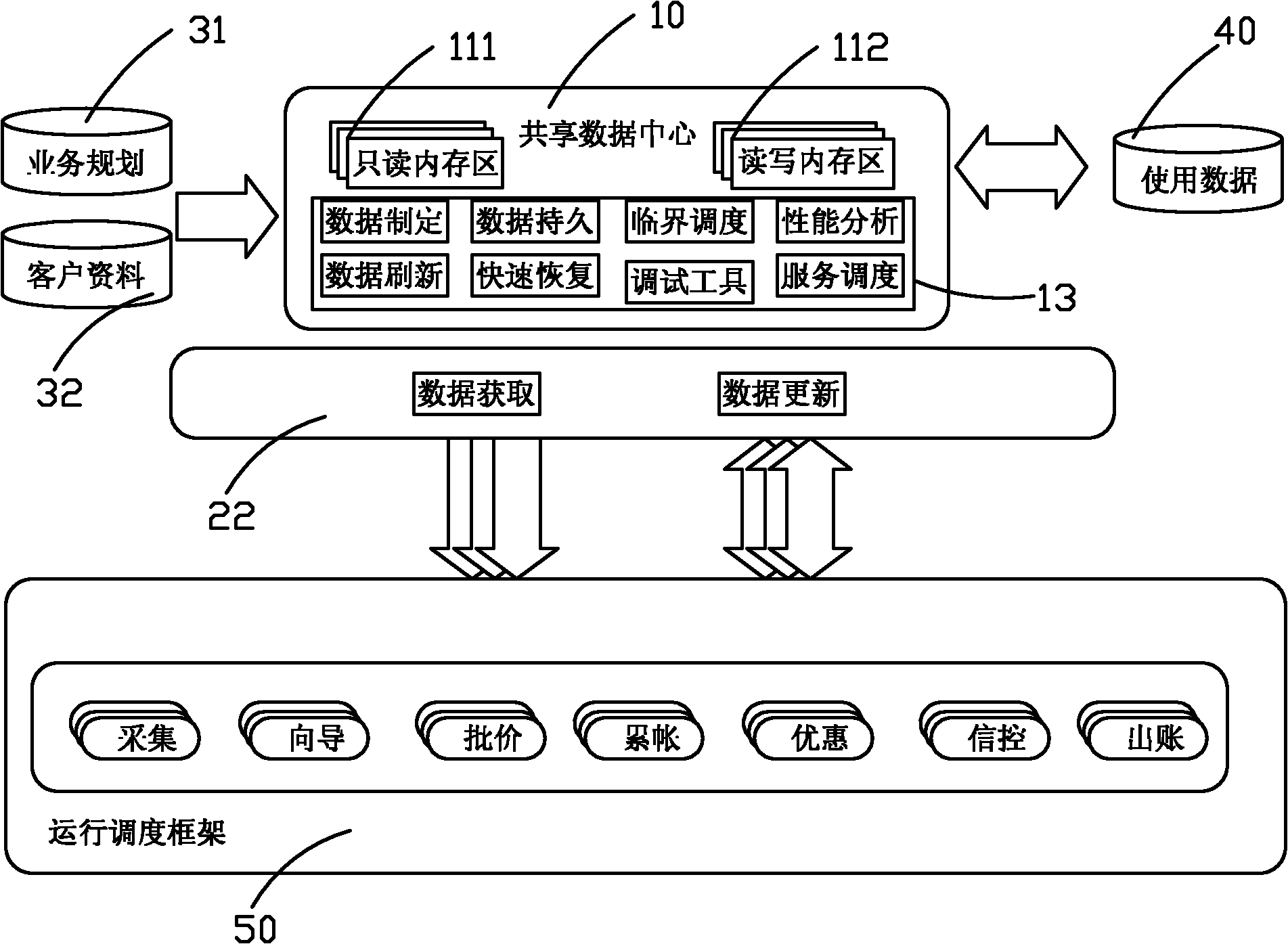
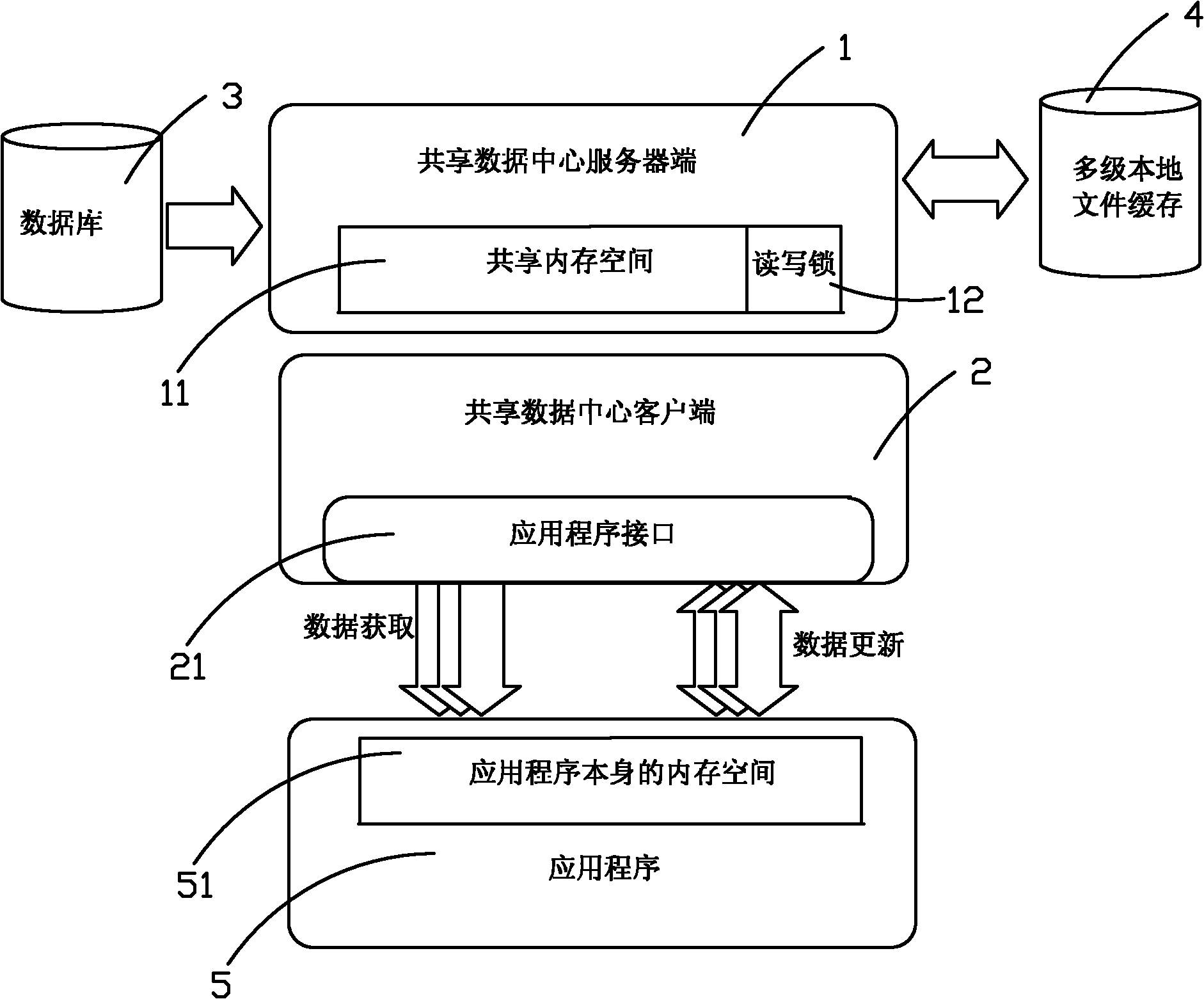
Shared data center used in telecommunication industry billing system
ActiveCN101986649AEfficient queryReduce memory consumptionMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsClient-sideData library
Owner:SHENZHEN TIANYUAN DIC INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
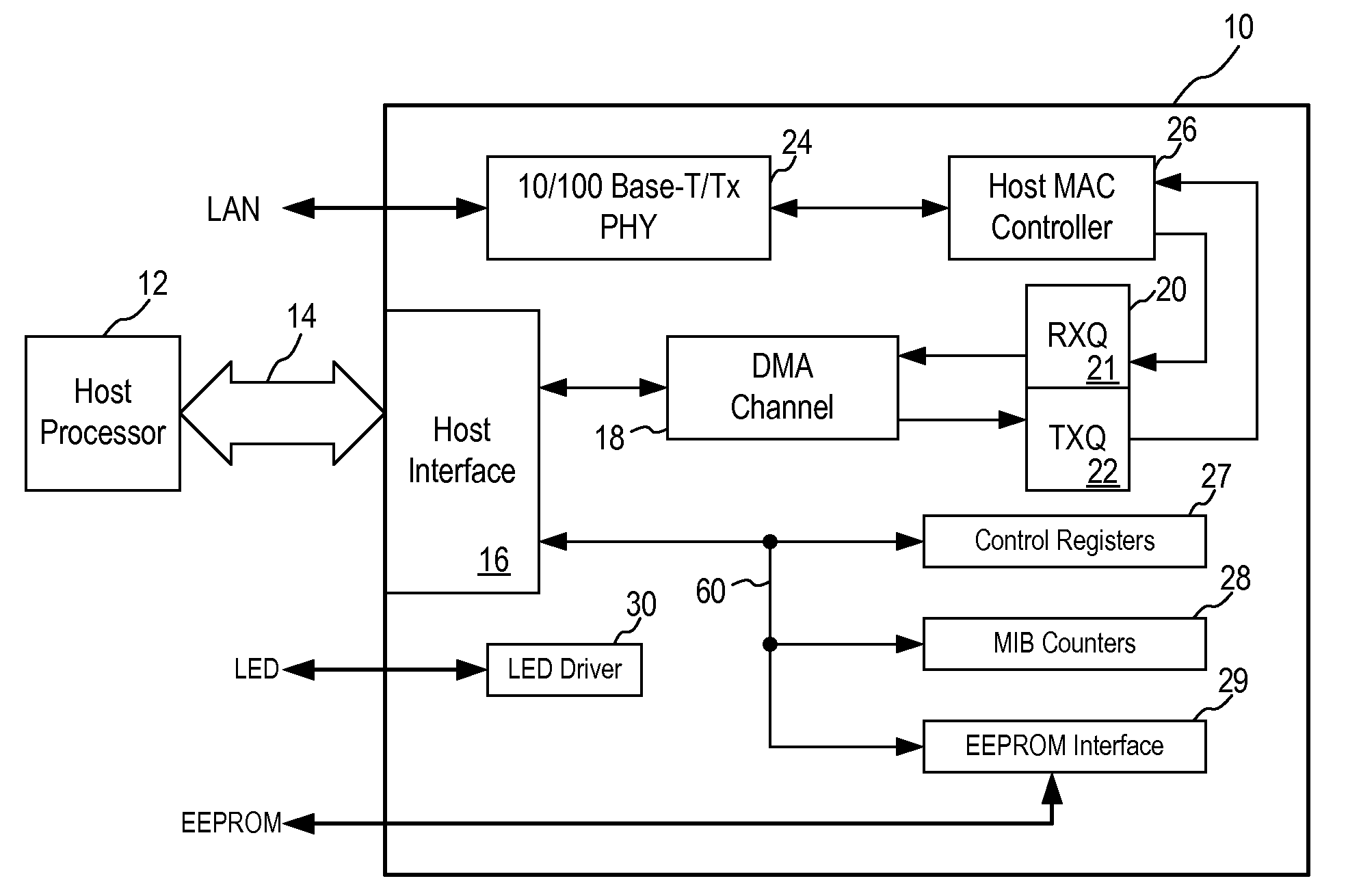
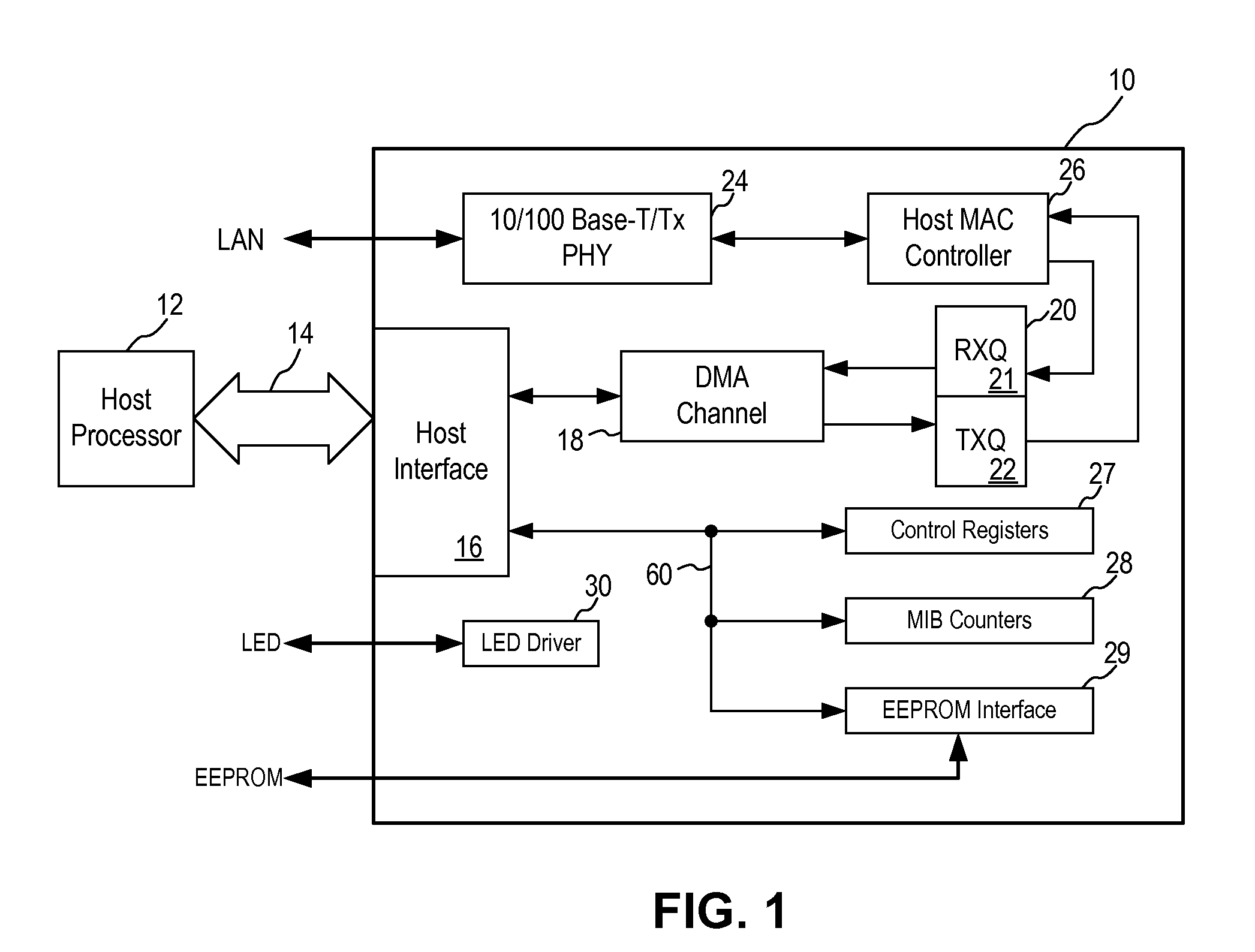
Dynamic Queue Memory Allocation With Flow Control
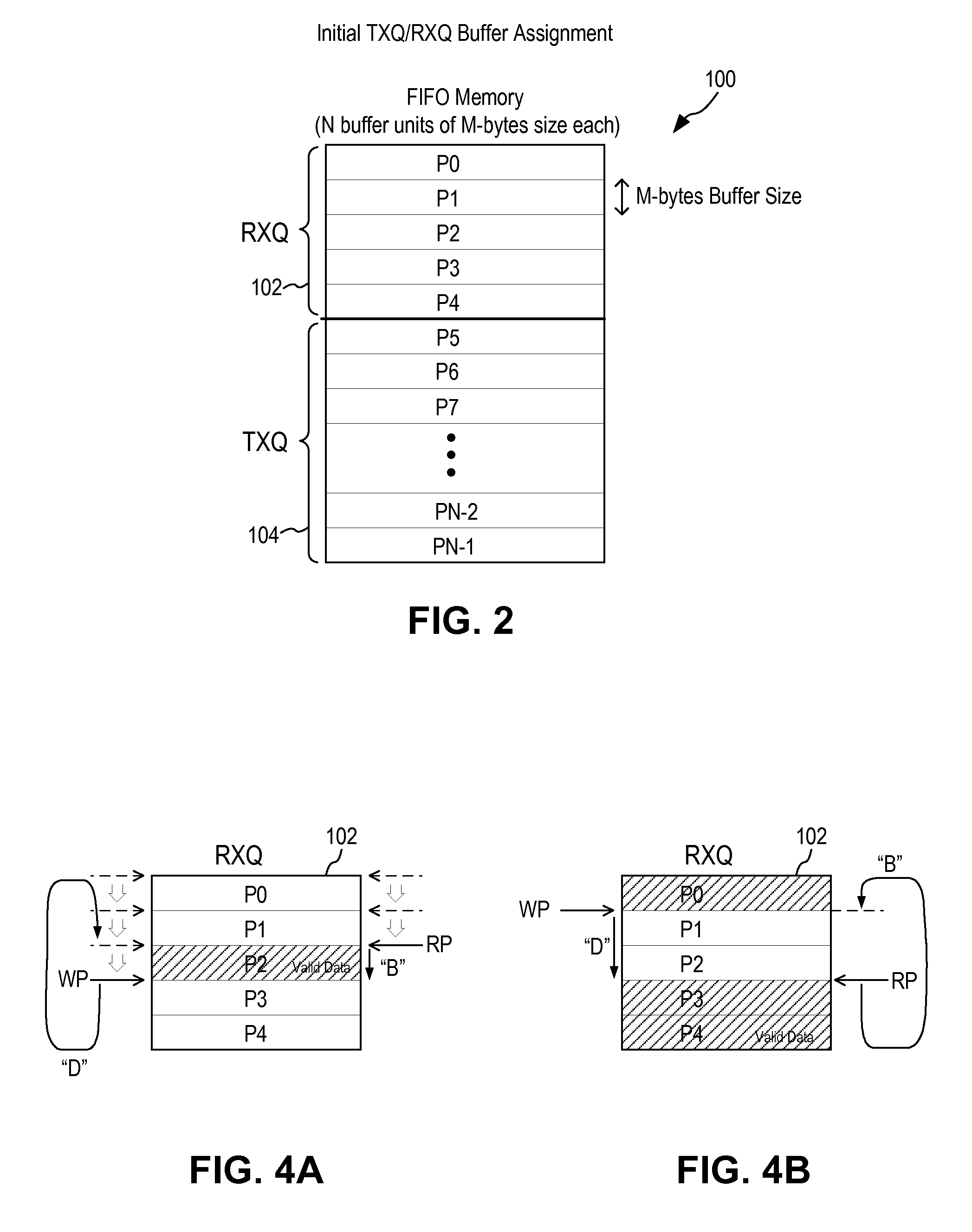
InactiveUS20100202470A1Improve memory usageSolve high memory usageData switching by path configurationSpatial allocationComputer science
A method in an Ethernet controller for allocating memory space in a buffer memory between a transmit queue (TXQ) and a receive queue (RXQ) includes allocating initial memory space in the buffer memory to the RXQ and the TXQ; defining a RXQ high watermark and a RXQ low watermark; receiving an ingress data frame; determining if a memory usage in the RXQ exceeds the RXQ high watermark; if the RXQ high watermark is not exceeded, storing the ingress data frame in the RXQ; if the RXQ high watermark is exceeded, determining if there are unused memory space in the TXQ; if there are no unused memory space in the TXQ, transmitting a pause frame to halt further ingress data frame; if there are unused memory space in the TXQ, allocating unused memory space in the TXQ to the RXQ; and storing the ingress data frame in the RXQ.
Owner:MICREL
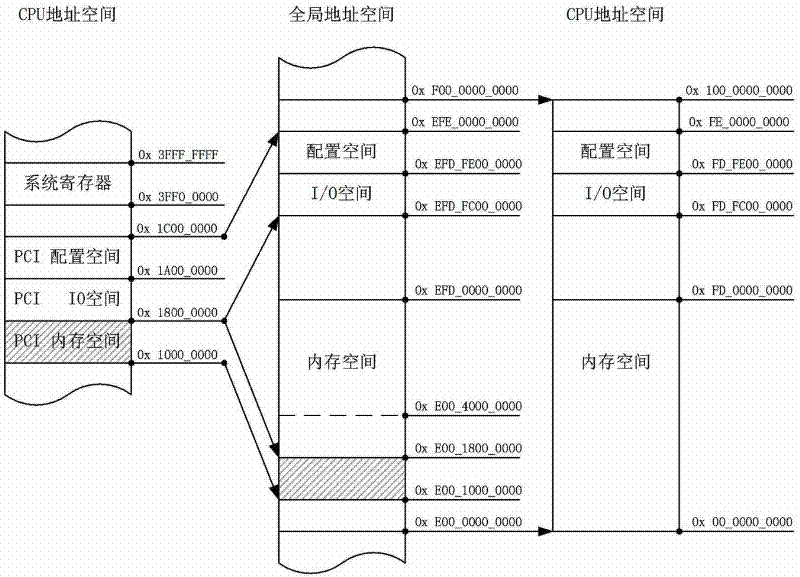
Address mapping method for large memory devices of Loongson 3A platforms
ActiveCN102646074AImplementation supportTake advantage ofMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGlobal address spaceAddress mapping
The invention discloses an address mapping method for large memory devices of Loongson 3A platforms, which comprises the implementation steps: 1) aiming at each CPU (central processing unit) core of a Loongson 3A processor, moving a PCI (peripheral component interconnect) memory space in a CPU address space out of an address range of a system register, and adjusting the size of the PCI memory space; 2) establishing a mapping relation between the PCI memory space being moved in the CPU address space and a memory space in a global address space, and establishing a mapping relation between the memory space in the global address space and a memory space in an HT (hyper transport) address space; and 3) according to the PCI memory space being moved in the CPU address space, updating a PCI memory resource structure body of an operating system. According to the invention, the large memory PCI / PCIE (peripheral component interconnect express) device support of a Loongson 3A platform can be realized, the popularization and application of the Loongson 3A platform can be promoted, and the method has the advantages of good compatibility and wide application range.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
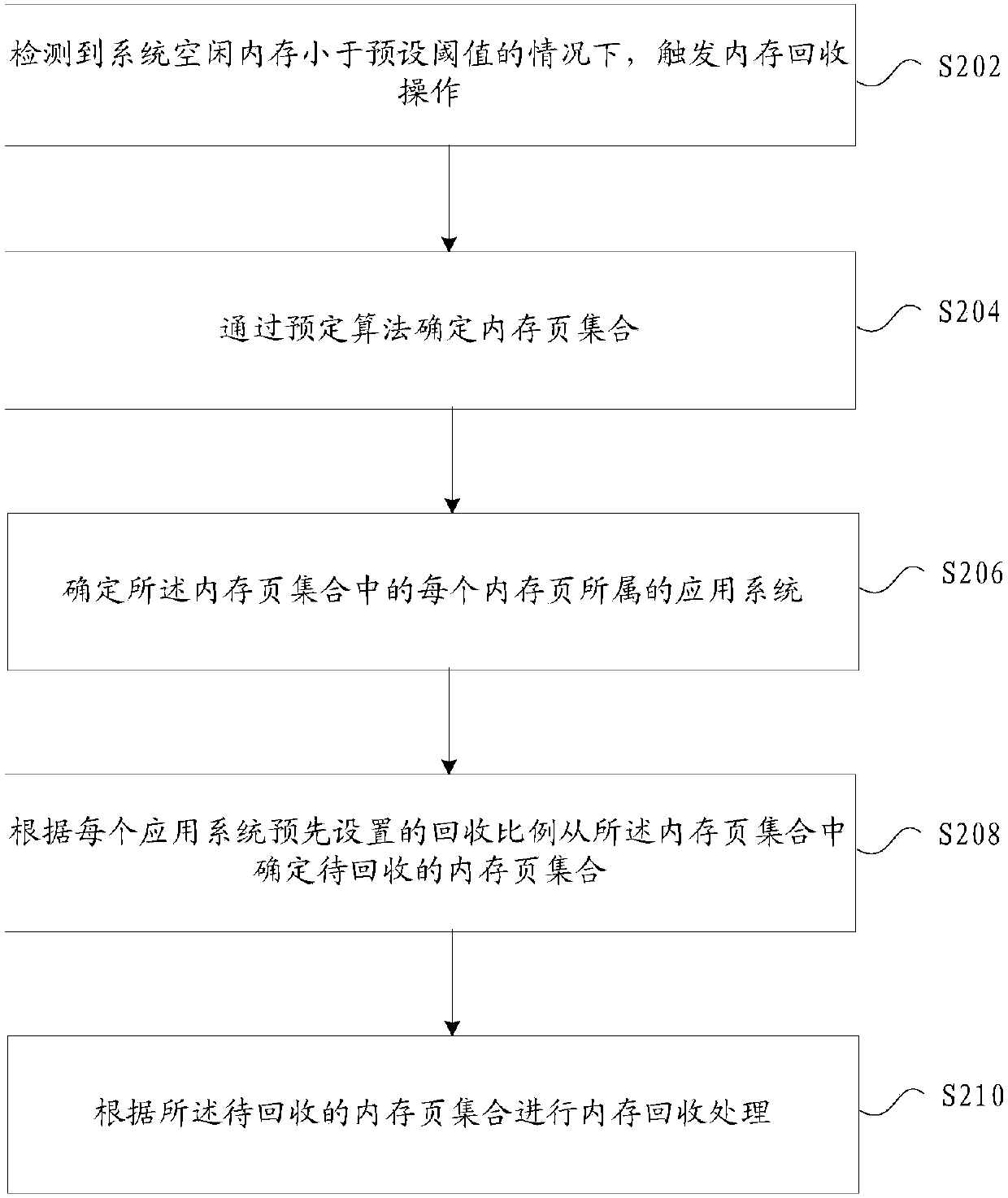
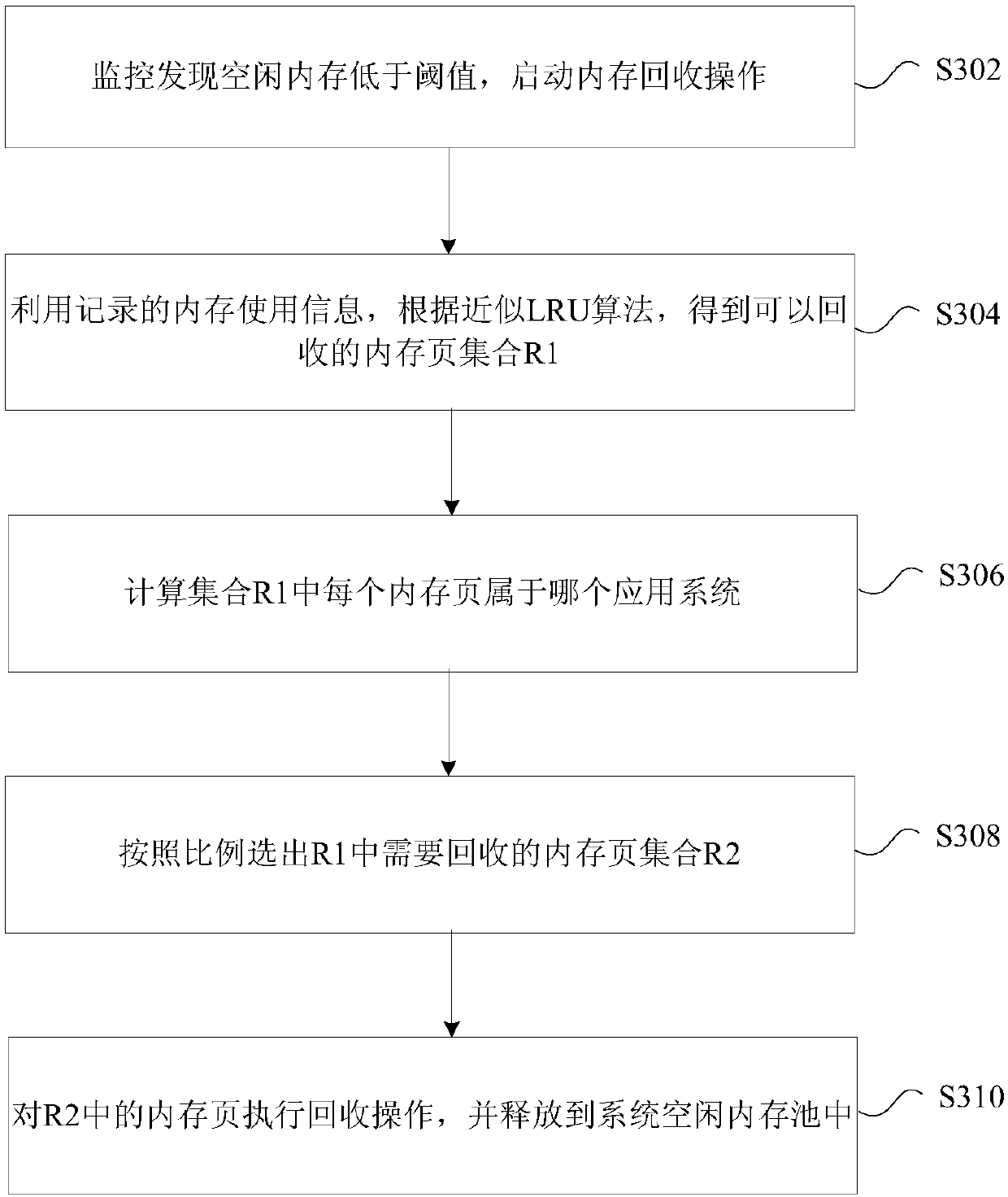
A terminal memory recovery processing method and device
InactiveCN109697119AExperience does not affectThe experience is not affected or reducedResource allocationComputer hardwareHeavy load
The invention provides a terminal memory recovery processing method and device, and the method comprises the steps: triggering a memory recovery operation when detecting that a system idle memory is smaller than a preset threshold value; determining a memory page set through a predetermined algorithm; determining an application system to which each memory page in the memory page set belongs; determining a to-be-recovered memory page set from the memory page set according to a preset recovery ratio of each application system; and performing memory recovery processing according to the memory page set to be recovered, according to the method and the device, the problem that different influences of the same management operation on the system are not considered for the same memory recovery mechanism under multiple systems in the prior art is solved, and the effects of ensuring that all system functions are not influenced and simultaneously not influencing or reducing the user experience canbe achieved under the condition of heavy load of the system memory.
Owner:ZTE CORP
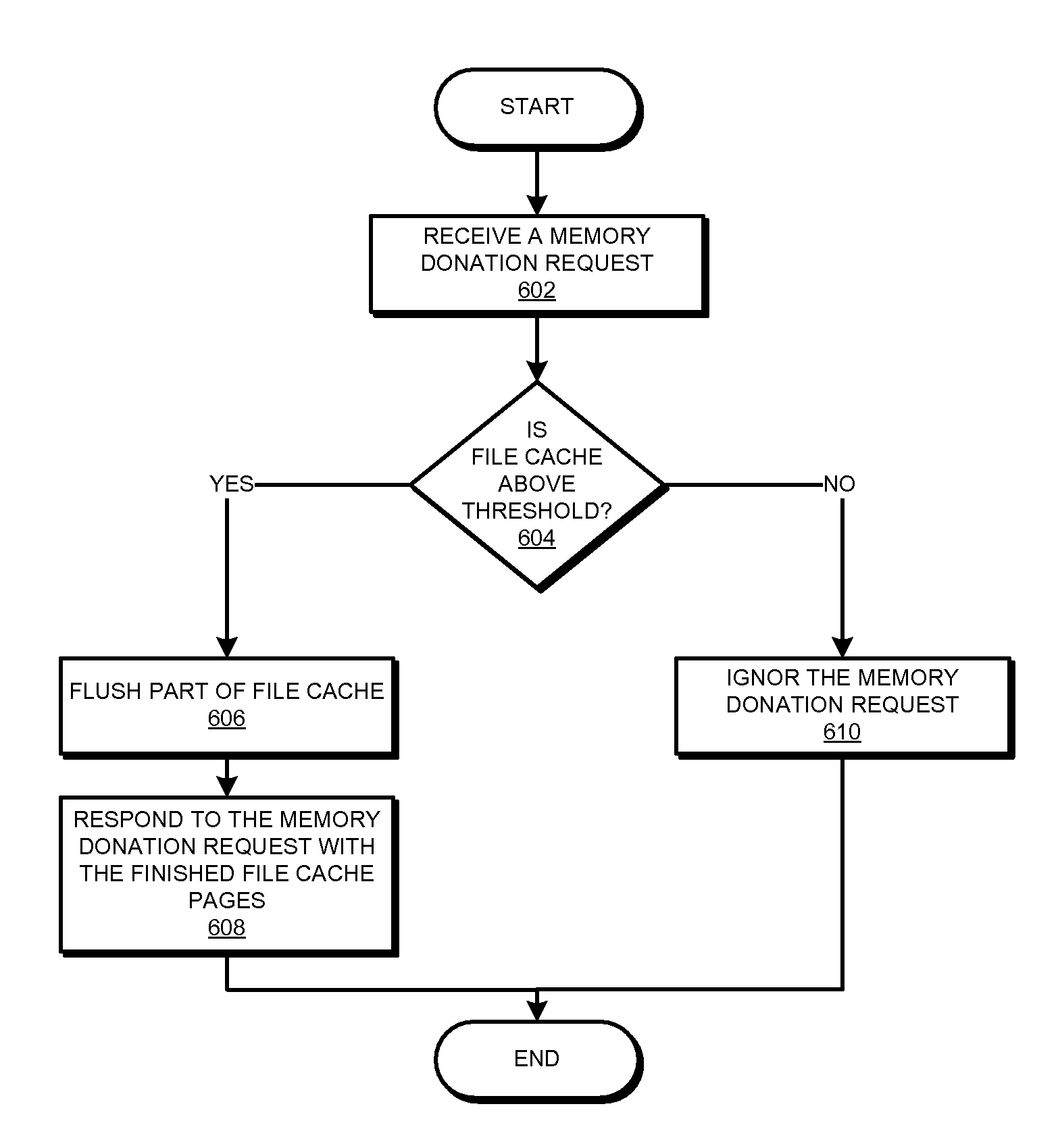
Selective memory donation in virtual real memory environment
InactiveUS8799892B2Multiprogramming arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtual machineFile caching
A method, system, and computer usable program product for selective memory donation in a virtual real memory environment are provided in the illustrative embodiments. A virtual machine receives a request for memory donation. A component of the virtual machine determines whether a portion of a memory space being used for file caching exceeds a threshold. The determining forms a threshold determination, and the portion of the memory space being used for file caching forms a file cache. If the threshold determination is false, the component ignores the request. If the threshold determination is true, a component of the virtual machine releases a part of the file cache that exceeds the threshold. The part of the file cache forms a released file cache. In response to the request, the virtual machine makes the released file cache available to a requester of the request.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Memory management method and memory management device of image data
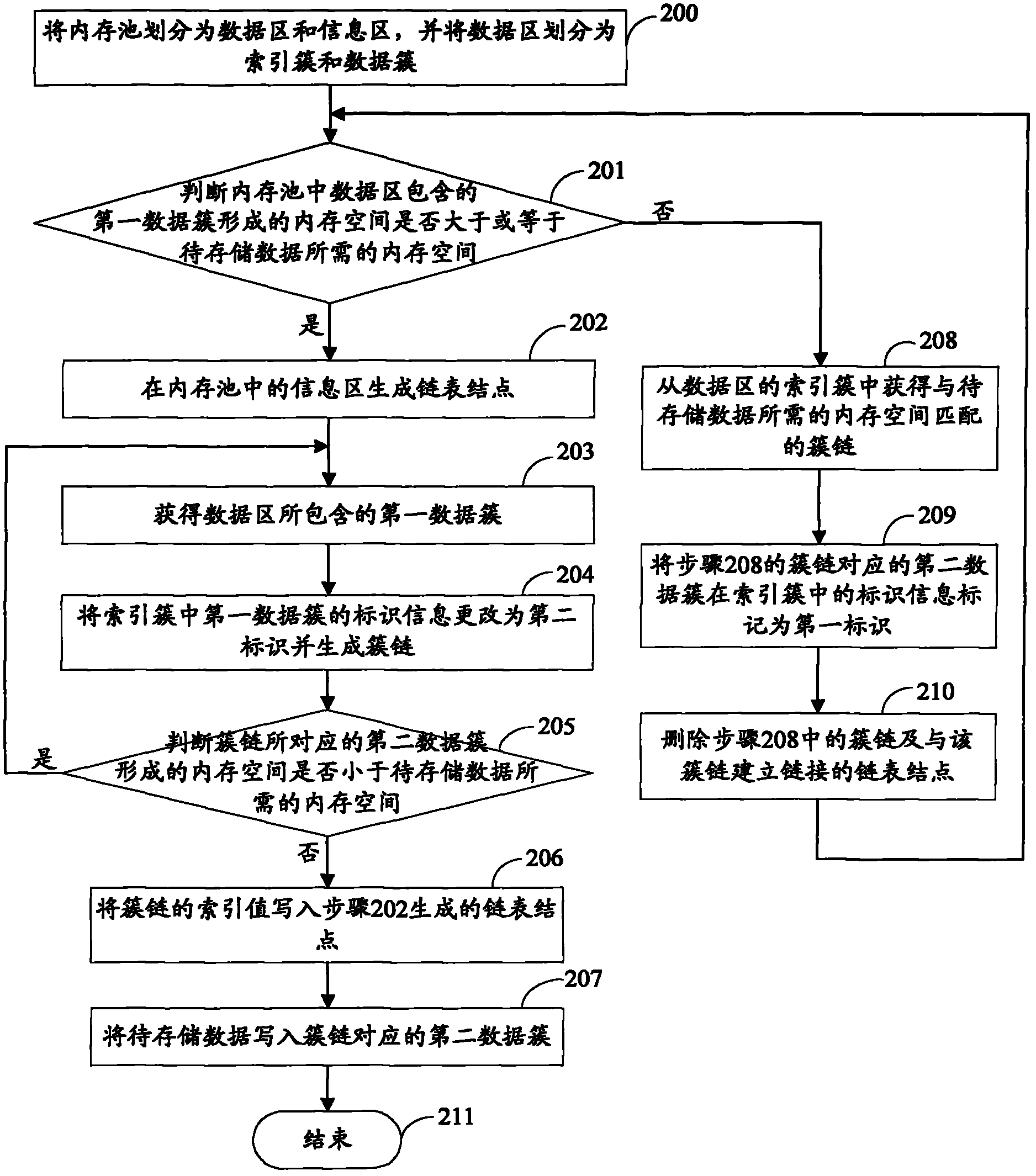
ActiveCN102253898ARealize multi-channel forwardingAvoid it happening againMemory adressing/allocation/relocationImage memory managementMemory management unitImaging data
The invention provides a memory management method and a memory management device of image data. The method comprises the following steps of: A, dividing a memory pool into a data area and an information area, and dividing the data area into data clusters and index clusters; B, judging whether a memory space, which is formed by a first data cluster, in the data area is greater than or equal to the memory space required by data to be stored, if so, executing the step C, otherwise, executing the step D; C, generating linked list nodes in the information area, generating a cluster link in the index clusters of the data area, and executing the step E; D, obtaining the cluster link which is matched with the memory space required by the data to be stored from the index clusters, marking a second data cluster which corresponds to the cluster link as a first identifier in the index clusters, deleting the cluster link and the linked list nodes which are linked with the cluster link, and executing the step B; and E, writing the data to be stored into the second data cluster in the data area. By adoption of the method and the device provided by the invention, generation of fragments can be avoided, and the utilization rate of the memory space and the storage efficiency of the image data are improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION DIGITAL TECH
Memory fabric software implementation
ActiveUS20190171361A1Improve performance and efficiencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersObject basedComputer module
A hardware-based processing node of an object memory fabric can comprise a memory module storing and managing one or more memory objects within an object-based memory space. Each memory object can be created natively within the memory module, accessed using a single memory reference instruction without Input / Output (I / O) instructions, and managed by the memory module at a single memory layer. The memory module can provide an interface layer below an application layer of a software stack. The interface layer can comprise one or more storage managers managing hardware of a processor and controlling portions of the object-based memory space visible to a virtual address space and physical address space of the processor. The storage managers can further provide an interface between the object-based memory space and an operating system executed by the processor and an alternate object memory based storage transparent to software using the interface layer.
Owner:ULTRATA LLC
Dynamically managing memory lifespan in hybrid storage configurations
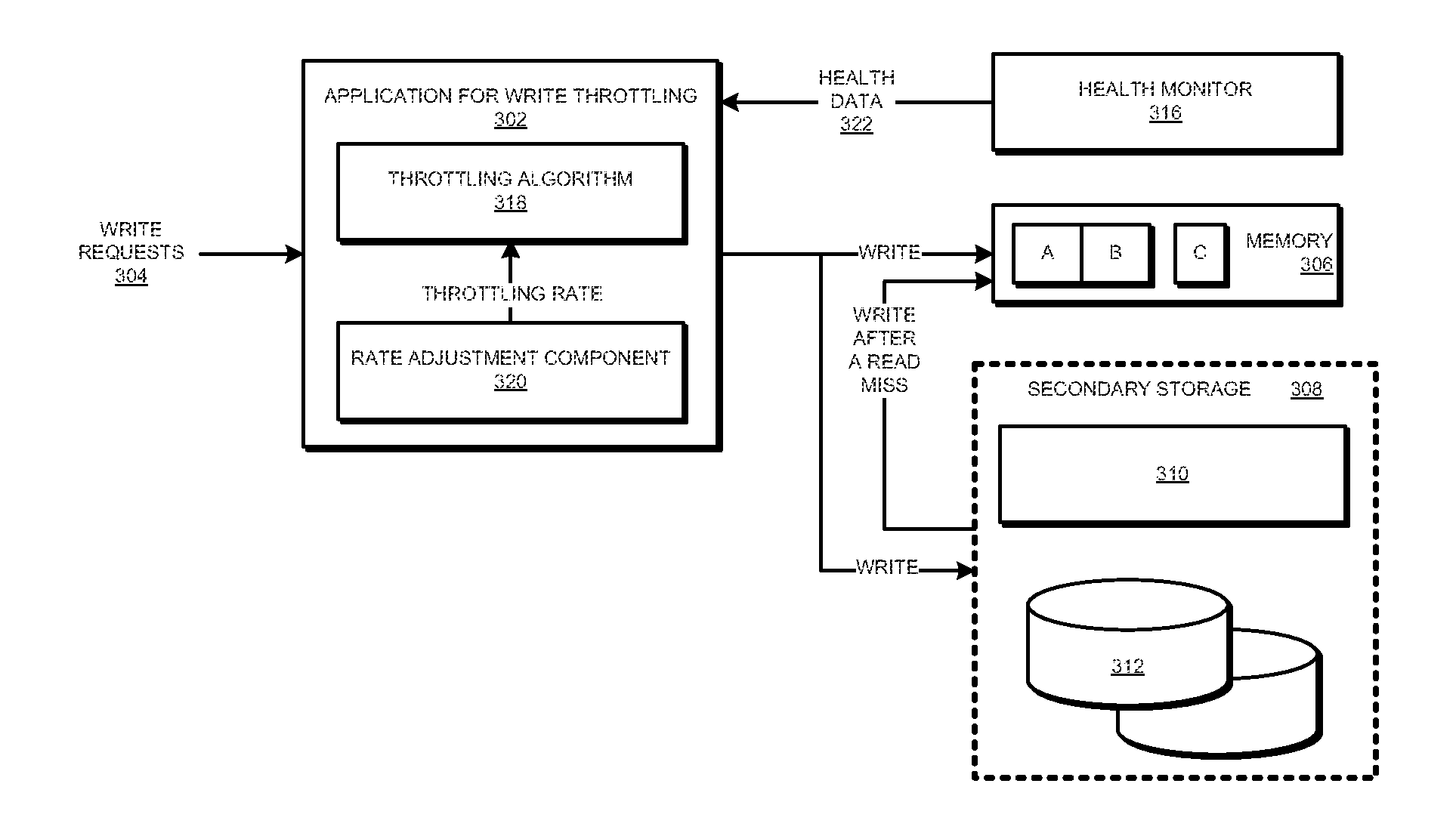
InactiveUS20130145075A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationReliability/availability analysisProcess memoryParallel computing
A system, and computer program product for managing the lifespan of a memory using a hybrid storage configuration are provided in the illustrative embodiments. A throttling rate is set to a first value for processing memory operations in the memory device. The first value is set using a health data of the memory device for determining the first value. A determination is made whether a memory operation can be performed on the memory device within the first value of the throttling rate, the first value of the throttling rate allowing a first number of memory operations using the memory device per time period. In response to the determining being negative, the memory operation is performed using a secondary storage device.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data writing method, memory storage device and memory controller
ActiveCN104182293AImprove securityImprove efficiencyInput/output to record carriersRedundant data error correctionError checkMemory chip
The invention provides a data writing method, a memory storage device and a memory controller for controlling a rewritable non-volatile memory module. The rewritable non-volatile memory module comprises at least one memory chip, wherein each memory chip comprises a plurality of entity erasing units. The data writing method comprises the following steps: writing data into at least one first entity erasing unit; generating a first error check code and a second error check code according to the data, wherein the number of bits which can be checked by the second error check code is greater than the number of bits which can be checked by the first error check code; writing the second error check code into a second entity erasing unit, wherein the first entity erasing units and the second entity erasing unit belong to the same memory chip. Thus, a memory space can be more efficiently used.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
Securing portable data elements between containers in insecure shared memory space
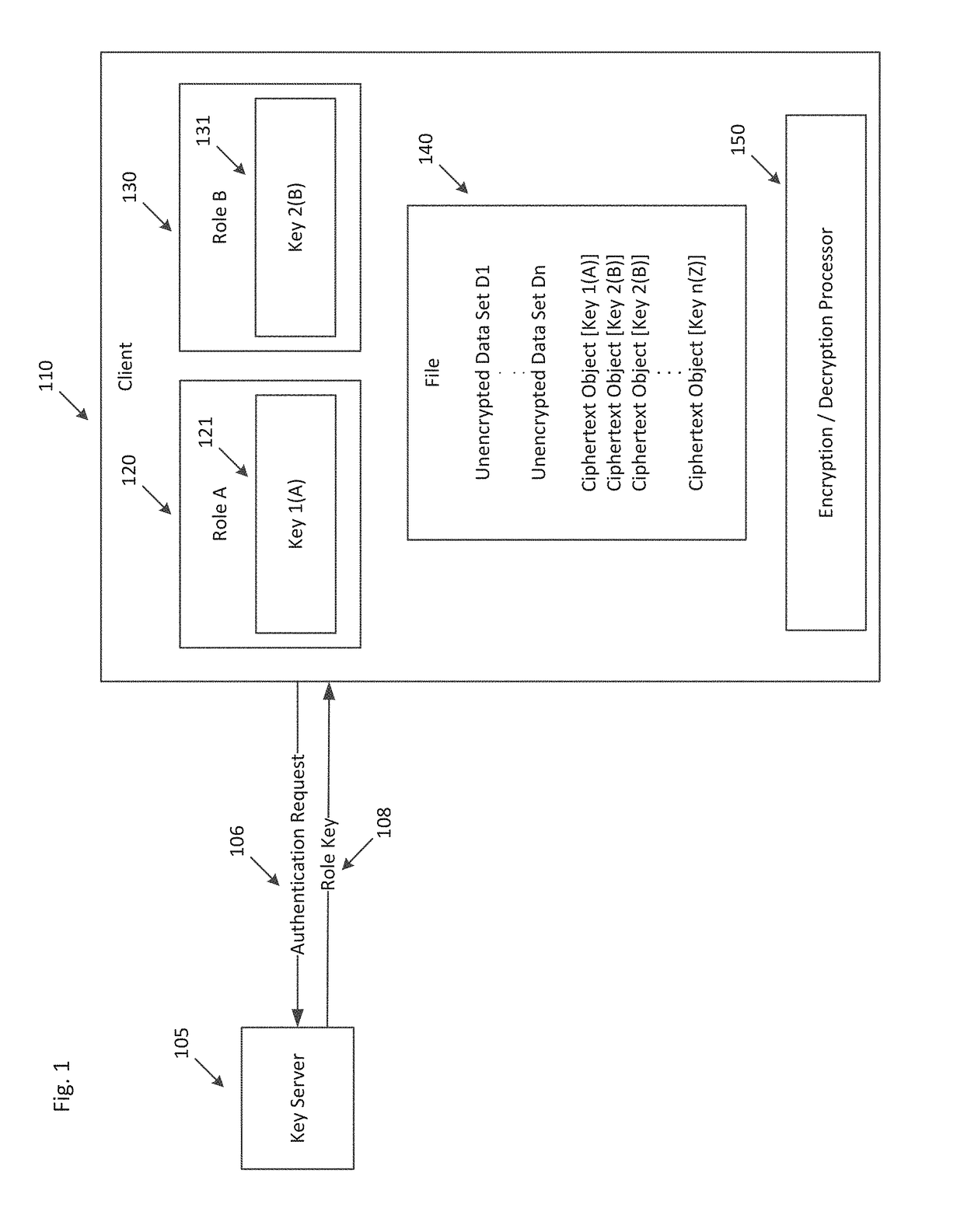
ActiveUS10061932B1Multiple keys/algorithms usageEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesData setMultiple applications
Systems and methods for encrypting an unencrypted data set within a file are provided. The disclosed systems and methods can be configured to create a ciphertext object within the existing data structures of a native file format. The systems and methods enable the secure copying data between multiple applications while displaying a revealed form of the data to a user.
Owner:WINDTALKER LLC
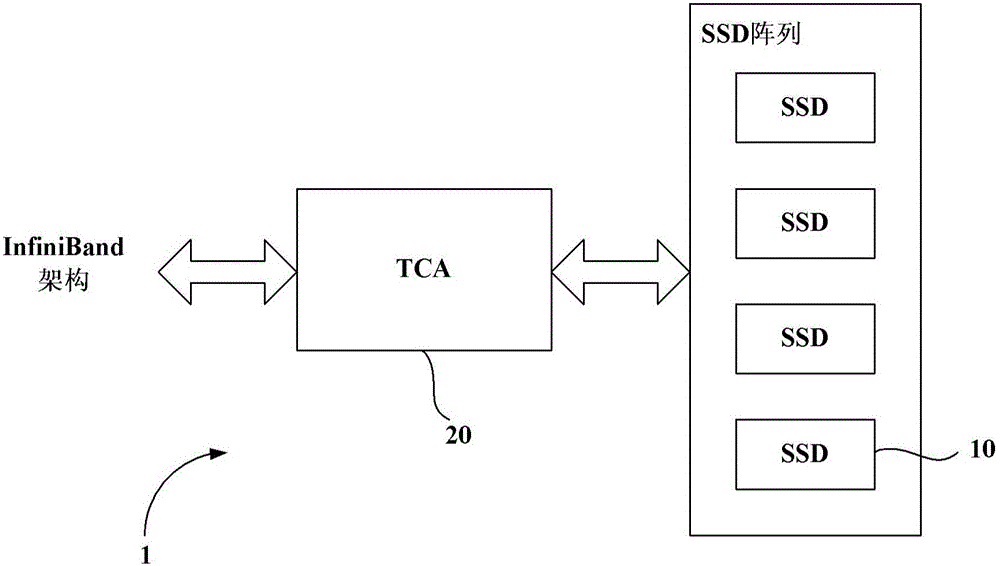
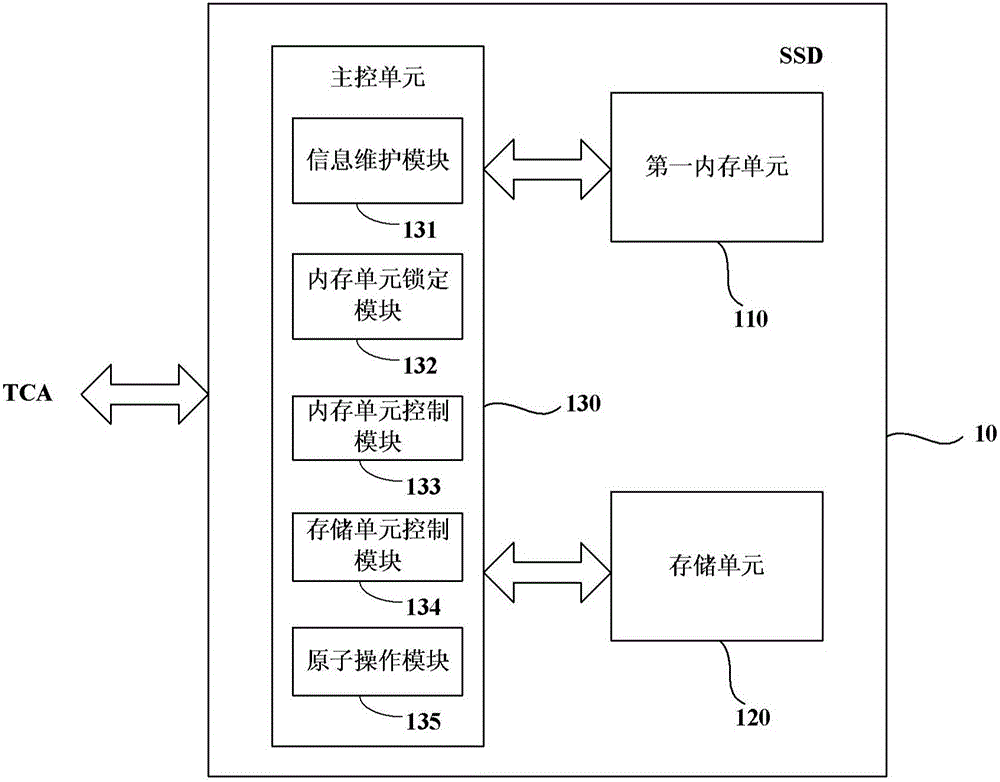
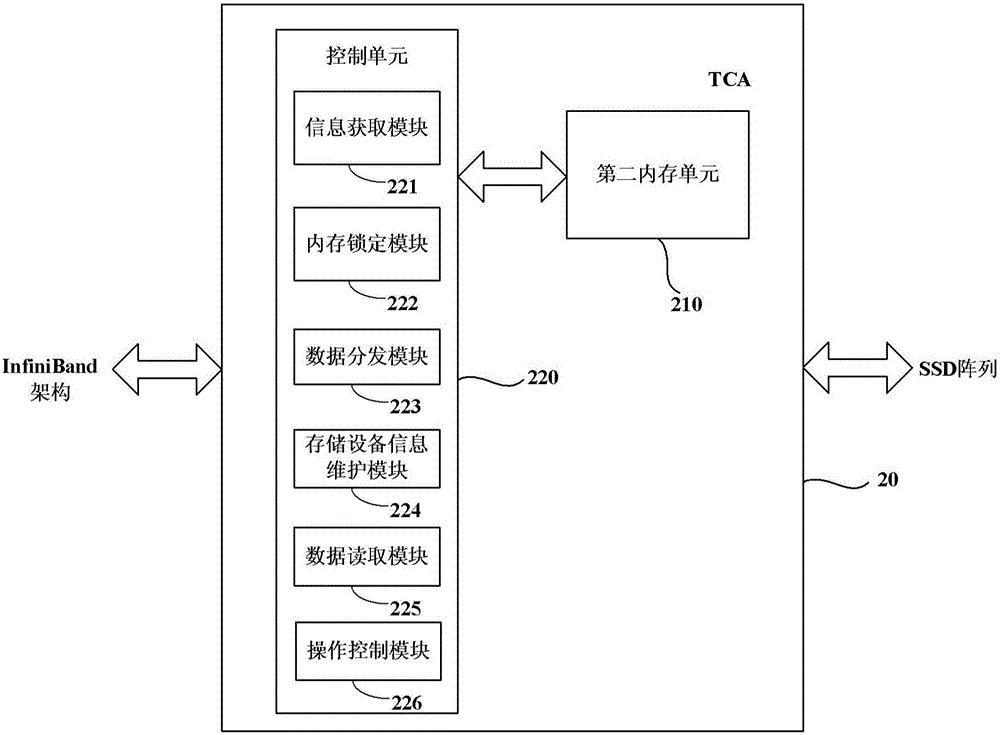
Storage device, storage device array and network adapter
The invention discloses a storage device which comprises a first memory unit, a storage unit and a master control unit. The first memory unit temporarily stores read-in data from an external device; the storage unit stores the read-in data; the master control unit locks a memory space in the first memory unit according to a memory locking command received from the external device and is used for storing the read-in data and storing the read-in data stored in the first memory unit into the storage unit, wherein locking means that the memory space is allocated to be used for storing the read-in data, and the space cannot be used for storing other data. The invention further discloses a network adapter. The network adapter comprises a second memory unit and a control unit. The second memory unit temporarily stores read-in data from a far-end device. The control unit comprises an information obtaining module, a memory locking module and a data distribution module, wherein the information obtaining module obtains address information of to-be-stored read-in data and the size of the read-in data from a data storage request of the read-in data, and a memory space is required to be locked, and the data distribution module sends the read-in data to the locked memory space.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
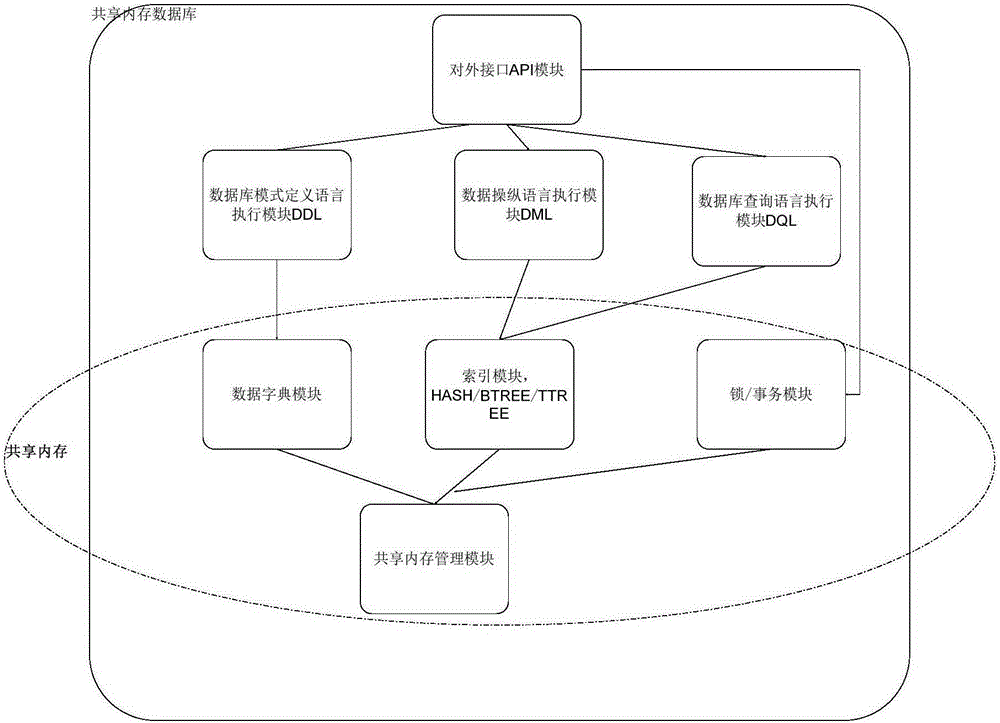
Memory management method and device for shared memory database
ActiveCN106557427ALarge memory capacityImprove access efficiencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSpecial data processing applicationsIn-memory databaseMemory management unit
The invention provides a memory management method and device of a shared memory database. The method comprises the following steps of: in a space for creating the database, according to the preset maximum value of database capacity, distributing a virtual memory space to the database; distributing a first physical memory to the database, setting the beginning address of the first physical memory as the beginning address of the virtual memory space so as to bring convenience for inserting or revising data in the first physical memory; judging whether the idle memory of the database is smaller than a preset threshold value or not so as to obtain a first judgment result; when the first judgment result shows that the idle memory of the database is smaller than the preset threshold value, adding a second physical memory with a preset dilatation step size into the virtual memory space of the database, and setting the beginning address of the second physical memory as the tail address of the previous physical memory; and expanding the available memory space of the database. By use of the method, the problem that the address of a multistage shared memory database is discontinuous can be solved, and management complexity caused in a way that the shared memory needs to be remapped when the multistage shared memory database is subjected to dilatation is simplified.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and system for packet classification with reduced memory space and enhanced access speed
InactiveUS7953082B2Improve performanceReduce the amount requiredData switching by path configurationData setAccess time
A method and system for packet classification is proposed for applications such as firewalls, intrusion detection, policy-based routing, and network service differentiations, within network systems such as Internet or intranet / extranet systems. The proposed method and system is characterized by the use of protocol-oriented rule rearrangement, the probable bit vector (PBV) based on the aggregated bit vectors (ABV) and folded bit vectors (FBV), an ABV-FBV index table dataset whose data structure is based on a featured split full-tree schema, and a DCBV (Don't-Care Bit Vector) dataset for packet classification. The combination of these features allows the packet classification to be implemented with a reduced amount of memory and access time during operation.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com