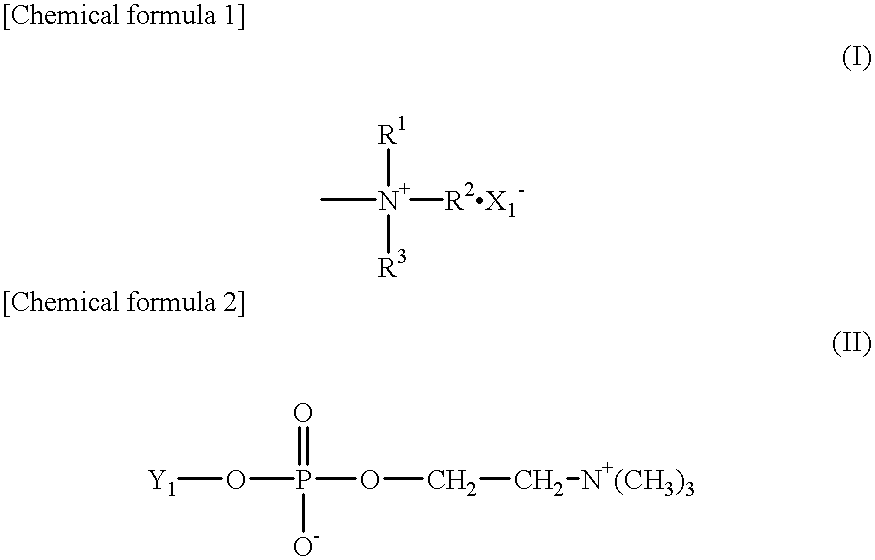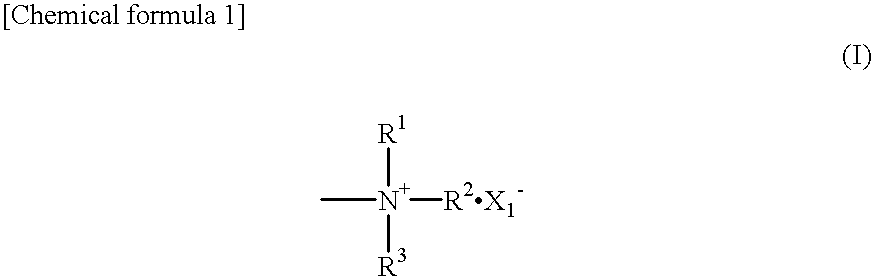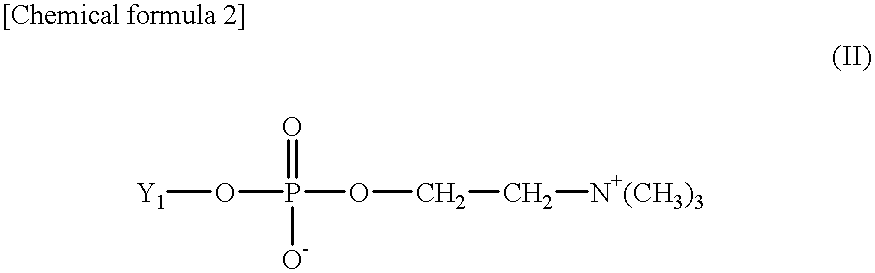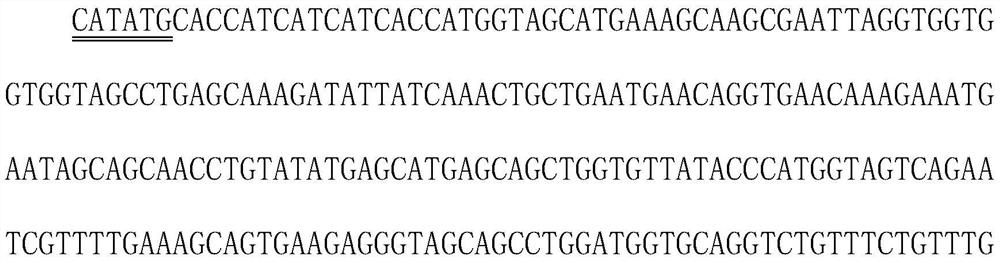Patents
Literature
31results about "C-reactive protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
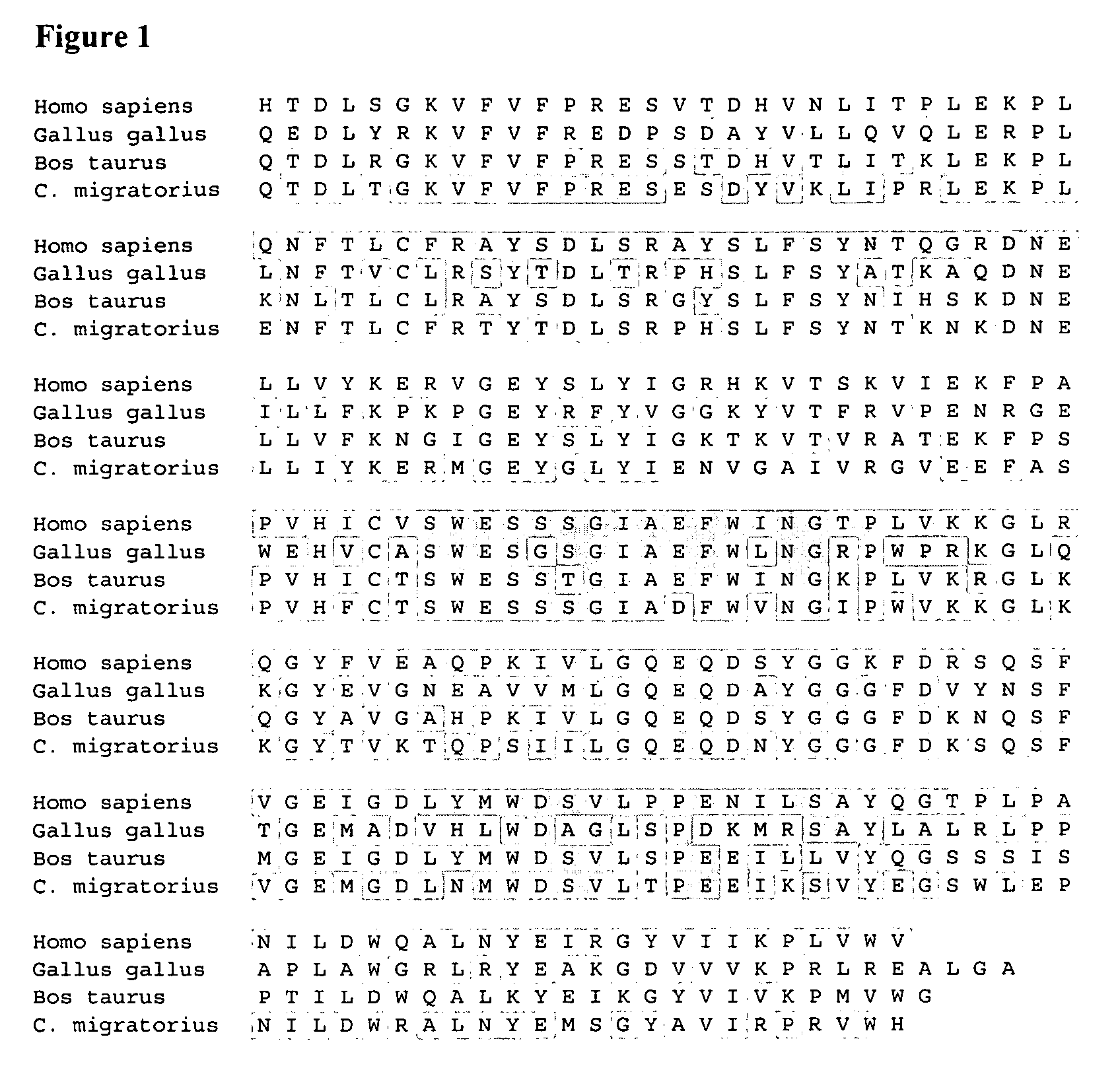
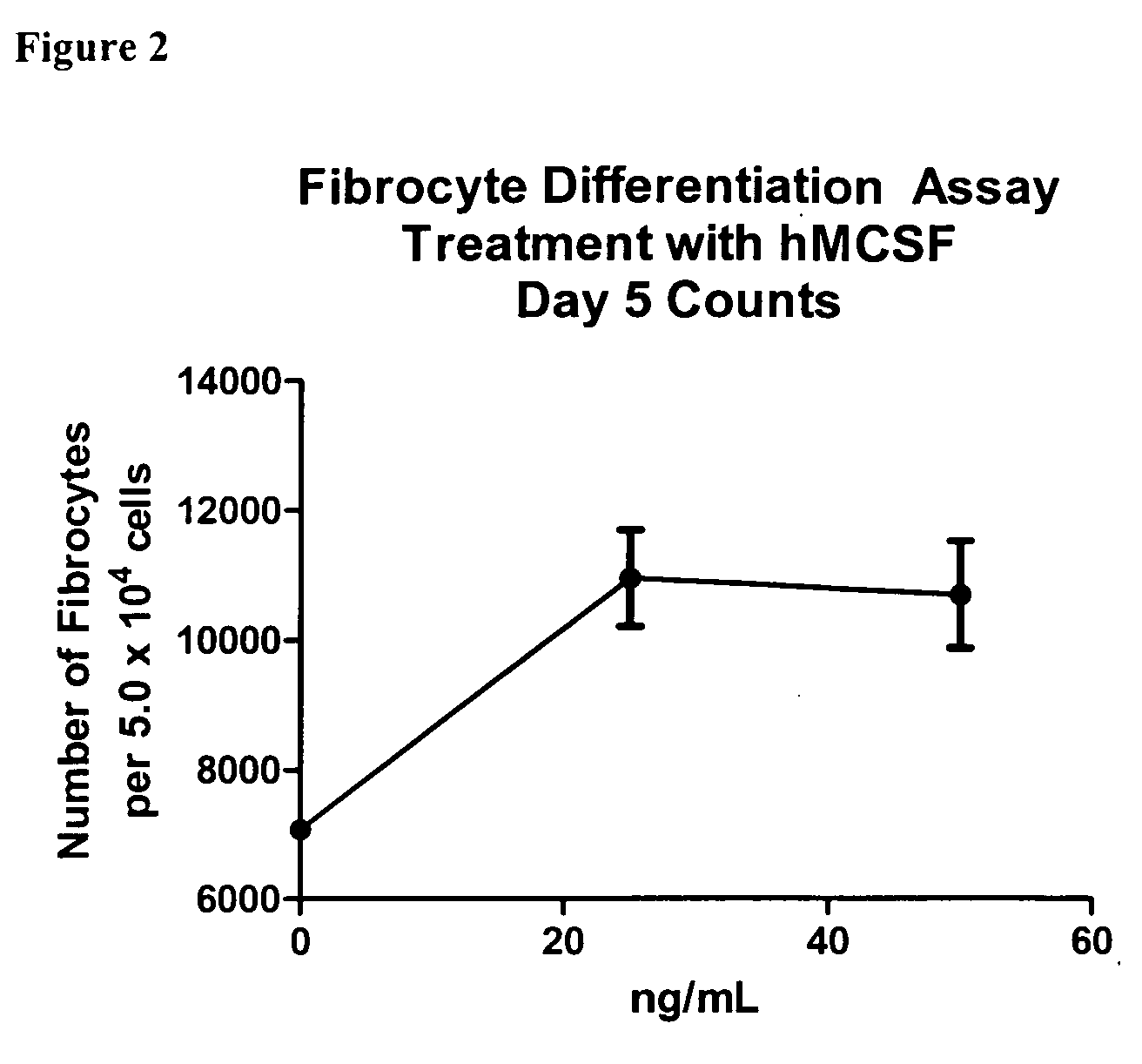
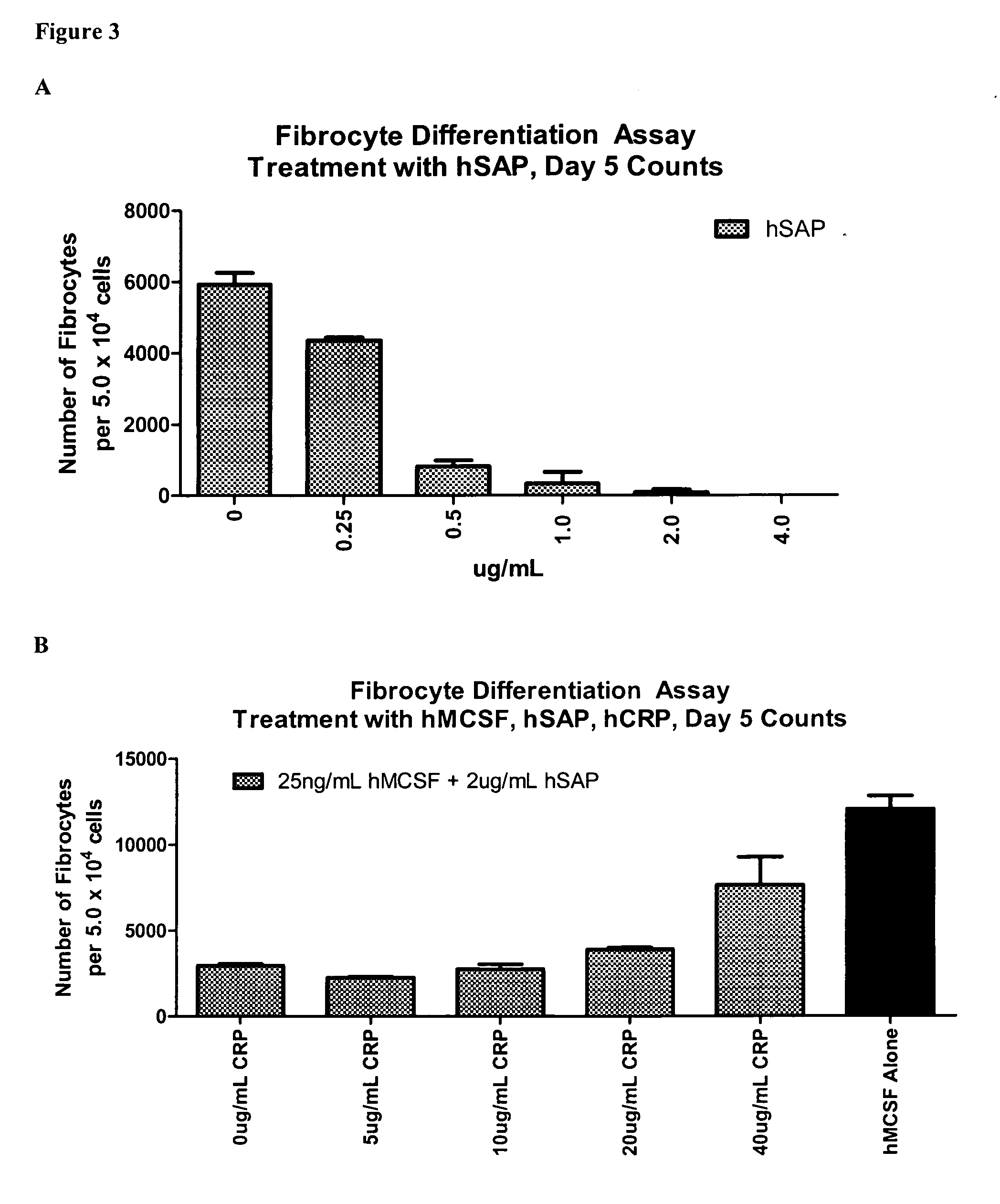
Treatment and diagnostic methods for fibrosis related disorders
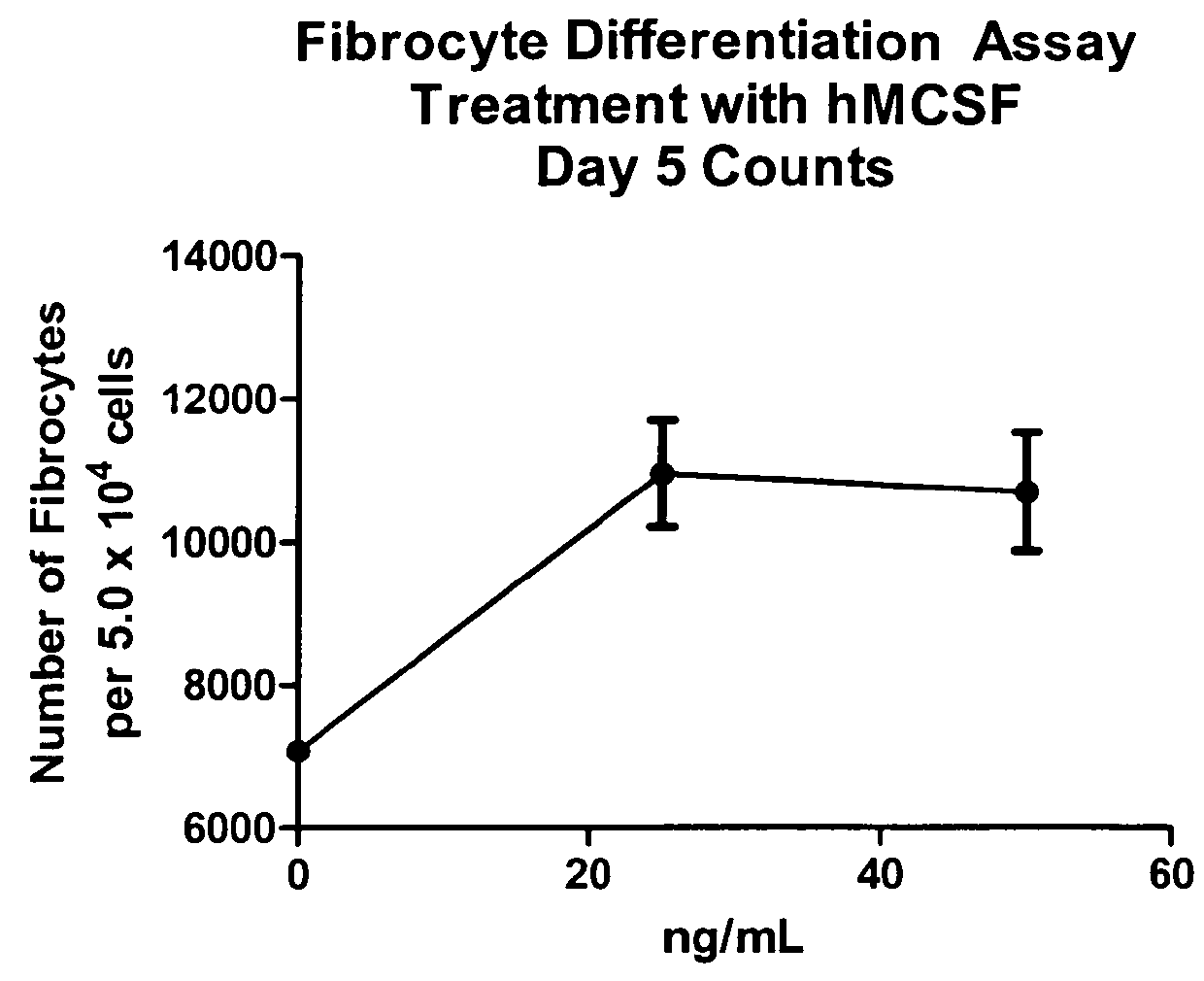
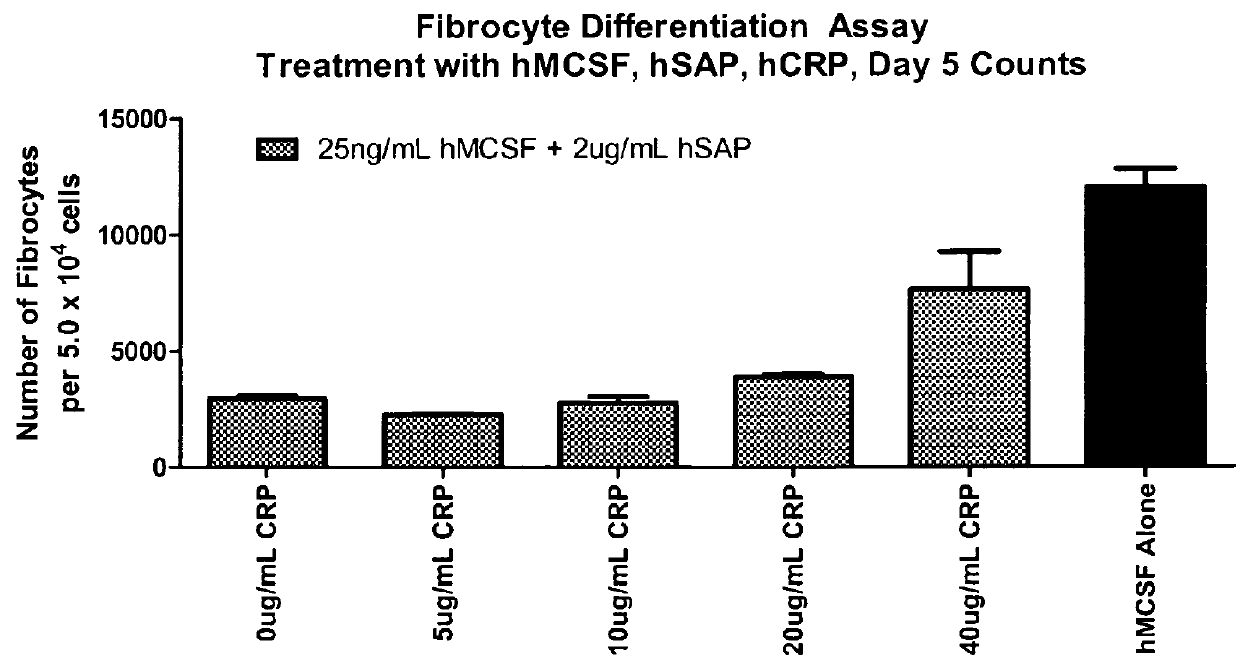
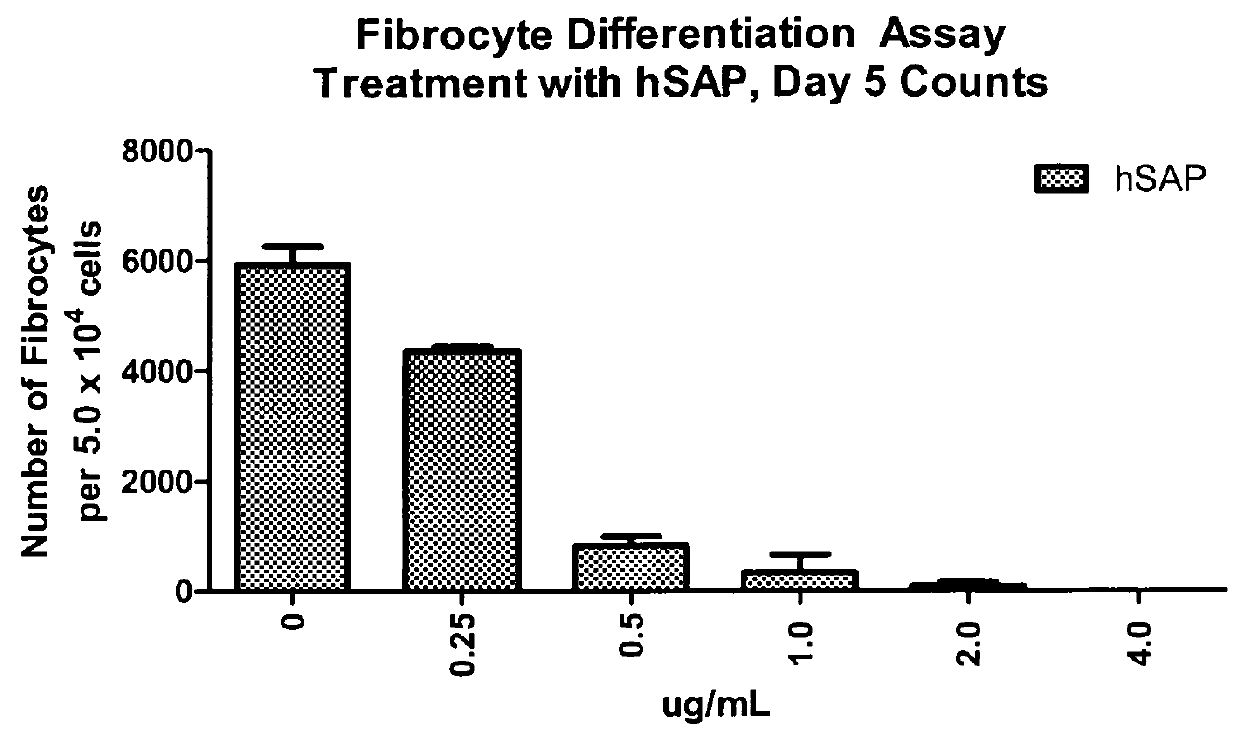
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment of fibrosis related disorders utilizing the ratio of the concentration of serum amyloid P(SAP) to C-reactive protein (CRP) in a patient. The methods may further comprise determining the R131 / H131 polymorphism of FcγRIIA. Diagnostic methods are also provided.
Owner:PROMEDIOR
Measuring method and measuring reagent of C-reactive protein
InactiveUS20010026927A1Biological material analysisBiological testingHigh concentrationHydrogen atom
An object of the present invention is to provide a method and a reagent for measuring the subject substances containing high concentration of C-reactive protein without dilution while avoiding prozone phenomenon. C-reactive protein is measured with a compound having a phosphrylcholine group and a cationic group shown by the general formula (I) [in the formula (I), where R1, R2 and R3 stand for a hydrogen atom, substituted or non-substituted alkyl, or substituted or non-substituted alkenyl, and X- stands for an inorganic anion or an organic anion) and an antibody to C-reactive protein. Or, C-reactive protein is measured with a surface active agent having a phosphorylcholine group, a surface active agent having a cationic group shown by the formula (II) [Y1 stands for a hydrophobic group, and R1, R2 and R3 stand for a hydrogen atom, substituted or non-substituted alkyl, or substituted or non-substituted alkenyl], and an antibody to C-reactive protein. As an antibody to C-reactive protein, an antibody carried by a water-insoluble carrier such as latex made from polystyrene is preferable.
Owner:KYOWA MEDEX CO LTD
Medicament comprising inhibitors of long pentraxin ptx3
InactiveUS20070098722A1Inhibitory activitySenses disorderNervous disorderAutoimmune conditionPentraxins
The use of inhibitors of long pentraxin PTX3 for the preparation of a medicament for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases and of degenerative diseases of bone and cartilage is described.
Owner:DEFIANTE FARM
Aptamer and detection method for C-reactive protein
InactiveUS20110318846A1High sensitivitySugar derivativesBiological material analysisAptamerNucleotide
An aptamer specifically binding to C-reactive protein (CRP) is provided. The aptamer includes a following nucleotide sequence: 5′-angngggngnntgnnt-3′, wherein n is a nucleotide selected from a, t, c and g.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
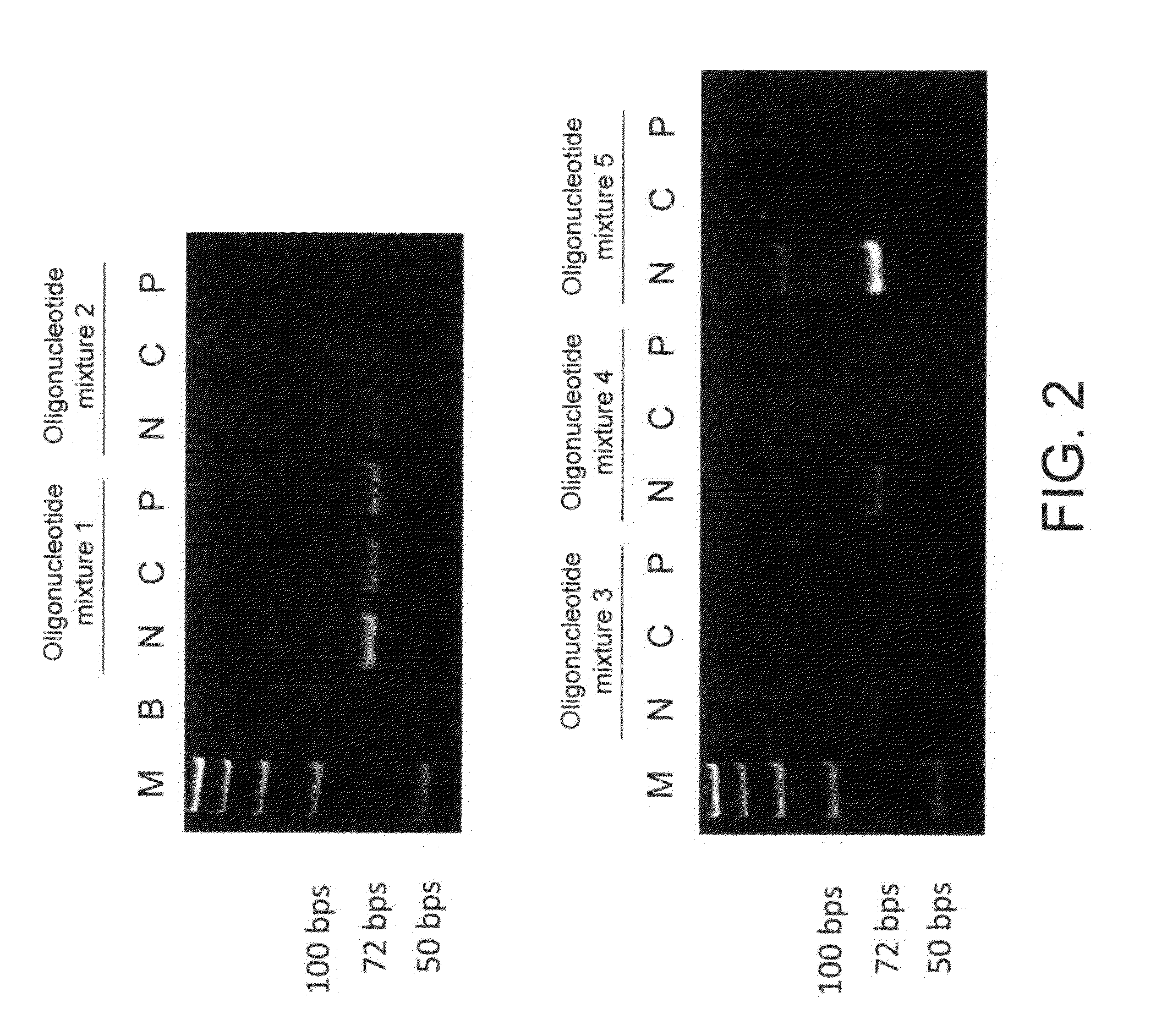
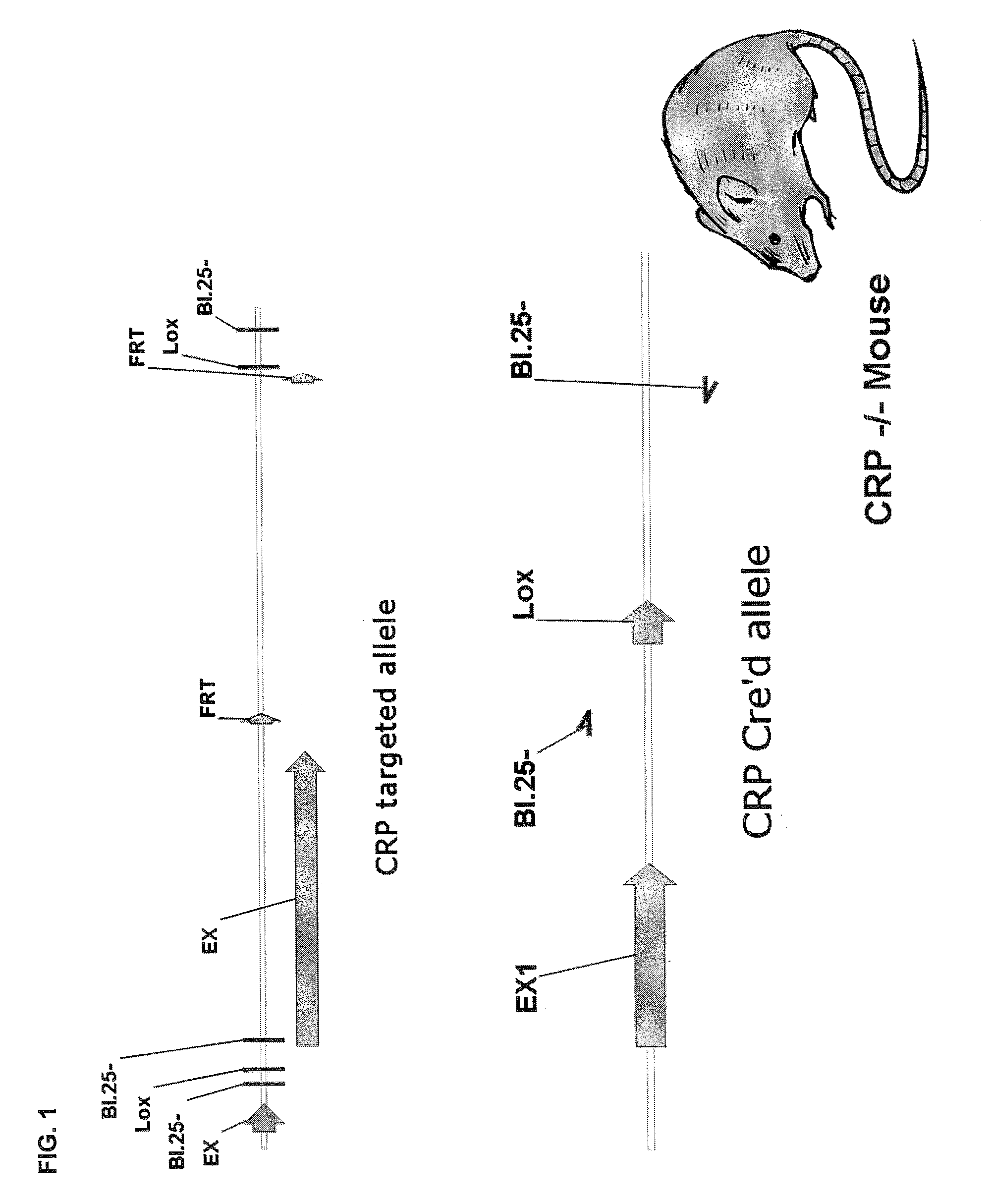
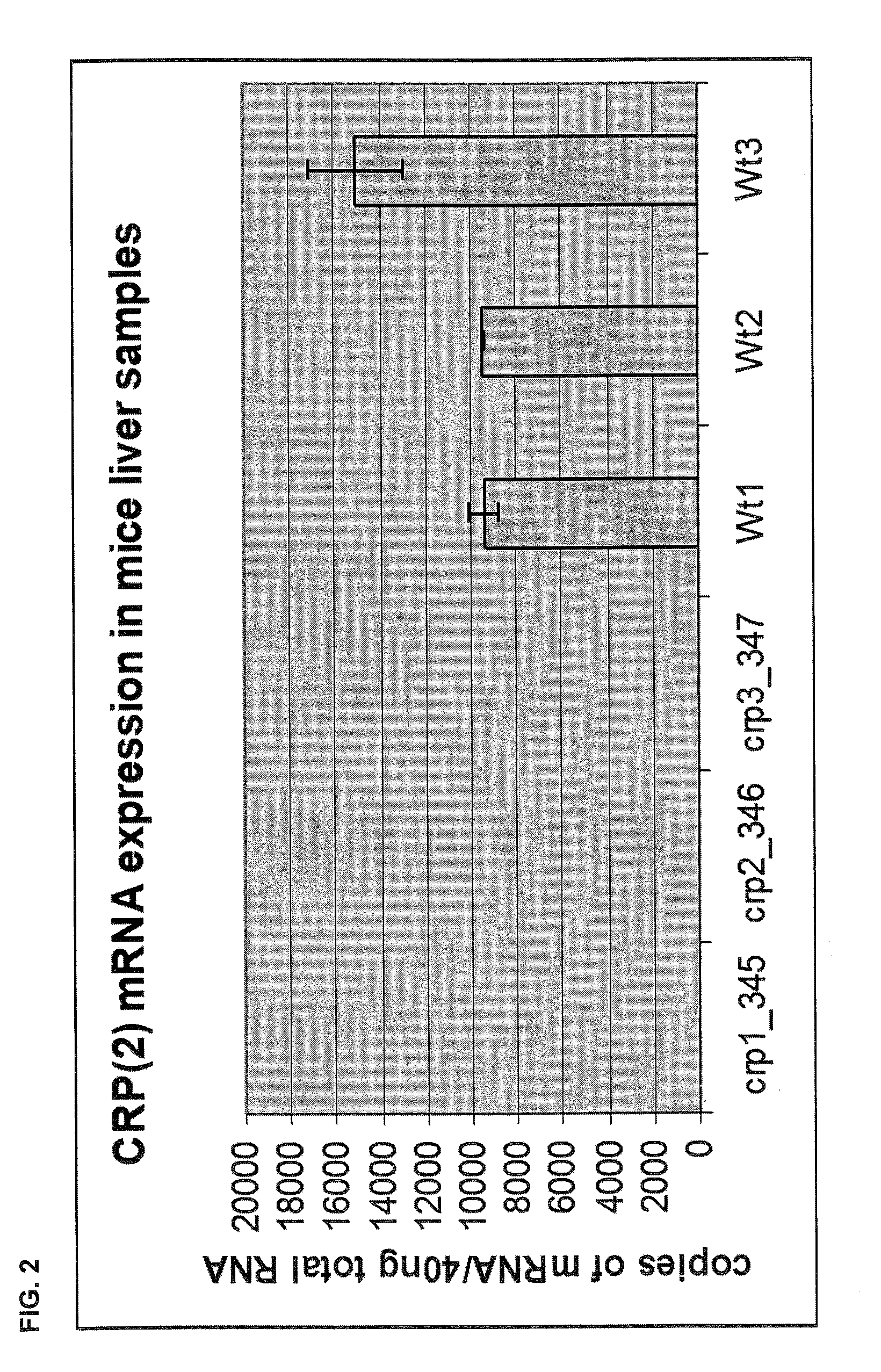
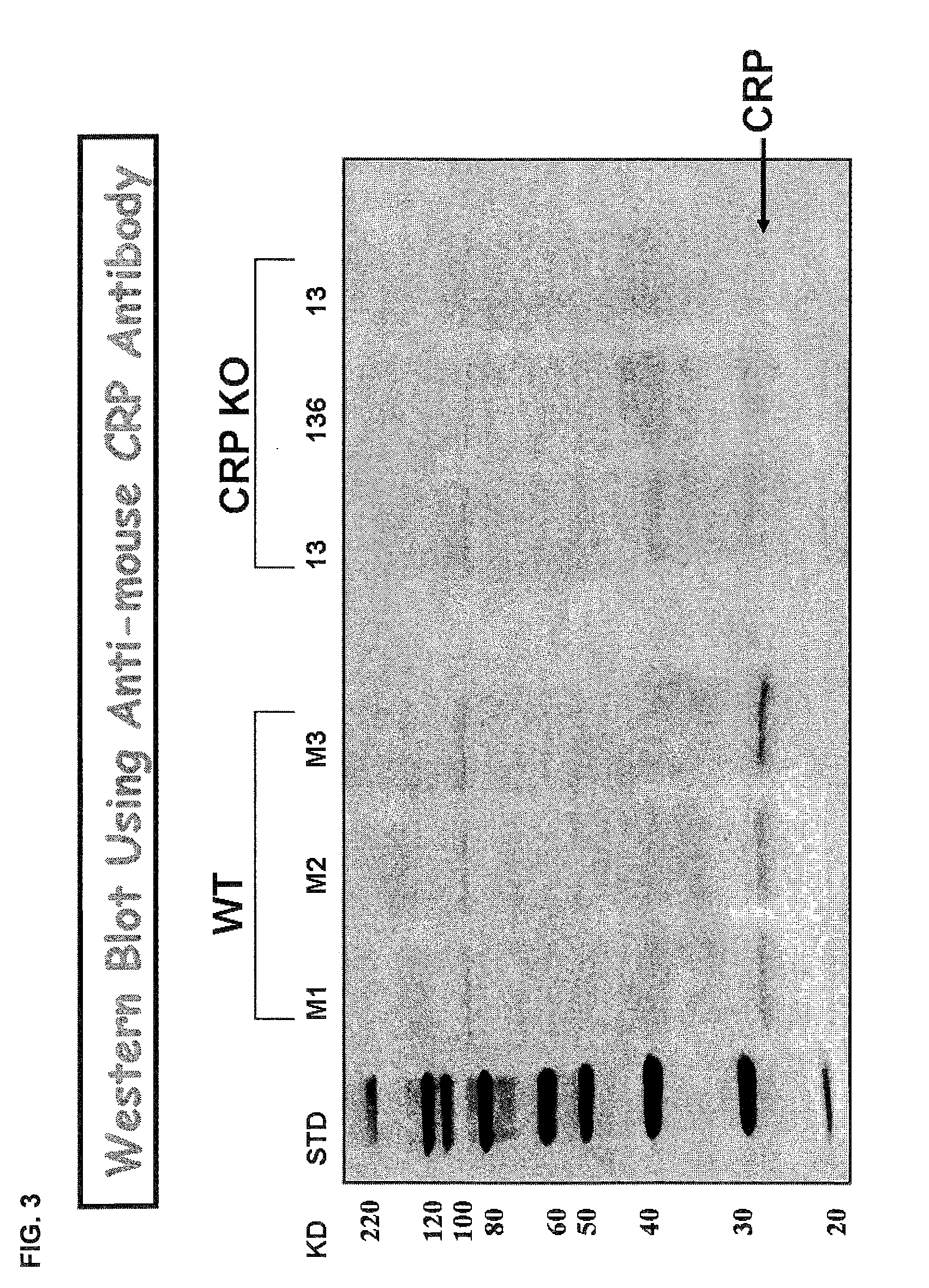
C-reactive protein (CRP) knockout mouse
InactiveUS20100107263A1Microbiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationKnockout animalDeficient mouse
The instant invention relates to a transgenic, non-human animal that carries a mutation in the gene encoding C-reactive protein (CRP). Preferably, the invention relates to an animal comprising a homozygous CRP-deficient mouse and techniques for producing such animals. The invention also relates to organs, tissues, cells, cell lines and sub-cellular fractions derived from such animals. Techniques for generating total or tissue-specific CRP knockout animals are also described. The invention further relates to the use of such knockout animals for the study of the role of CRP proteins in vivo or ex vivo, particularly in relation to its role in inflammatory pathway and in the etiology human diseases.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
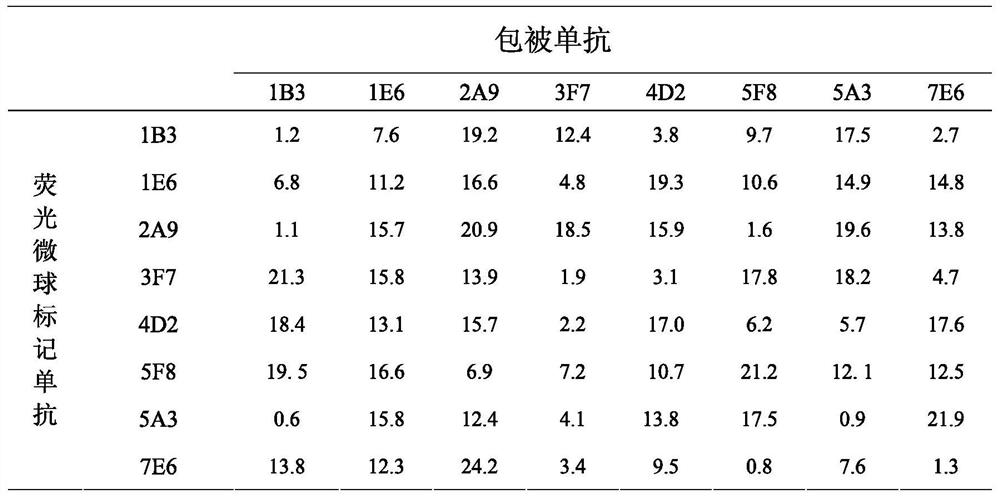
Recombinant canine C-reactive protein and preparation of mono-clone antibody
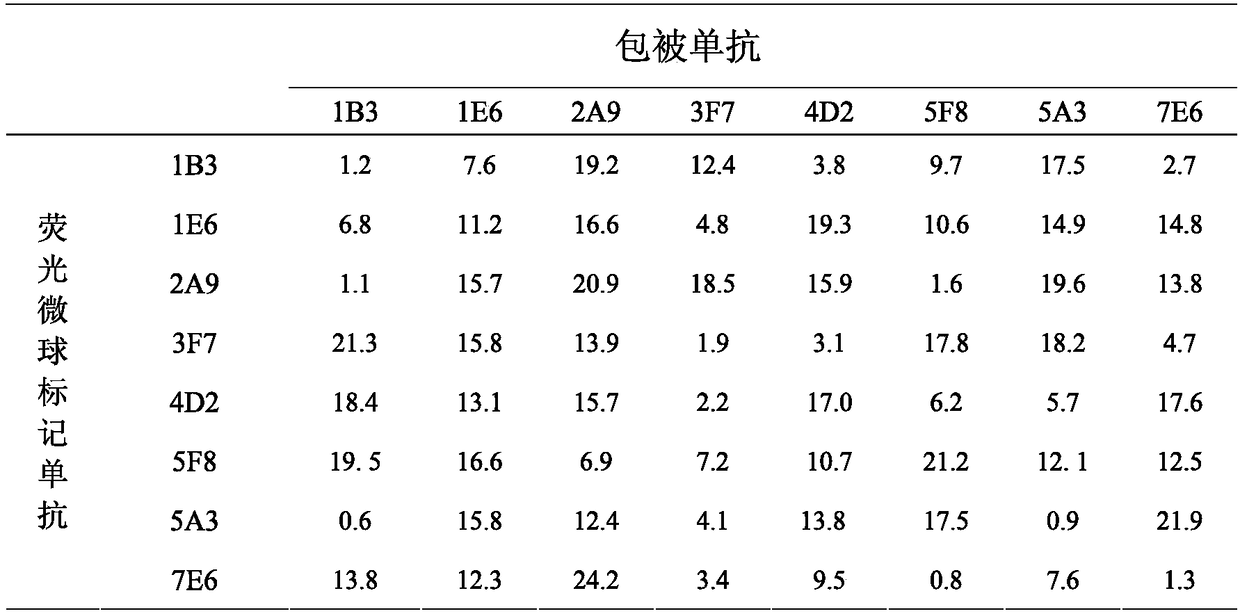
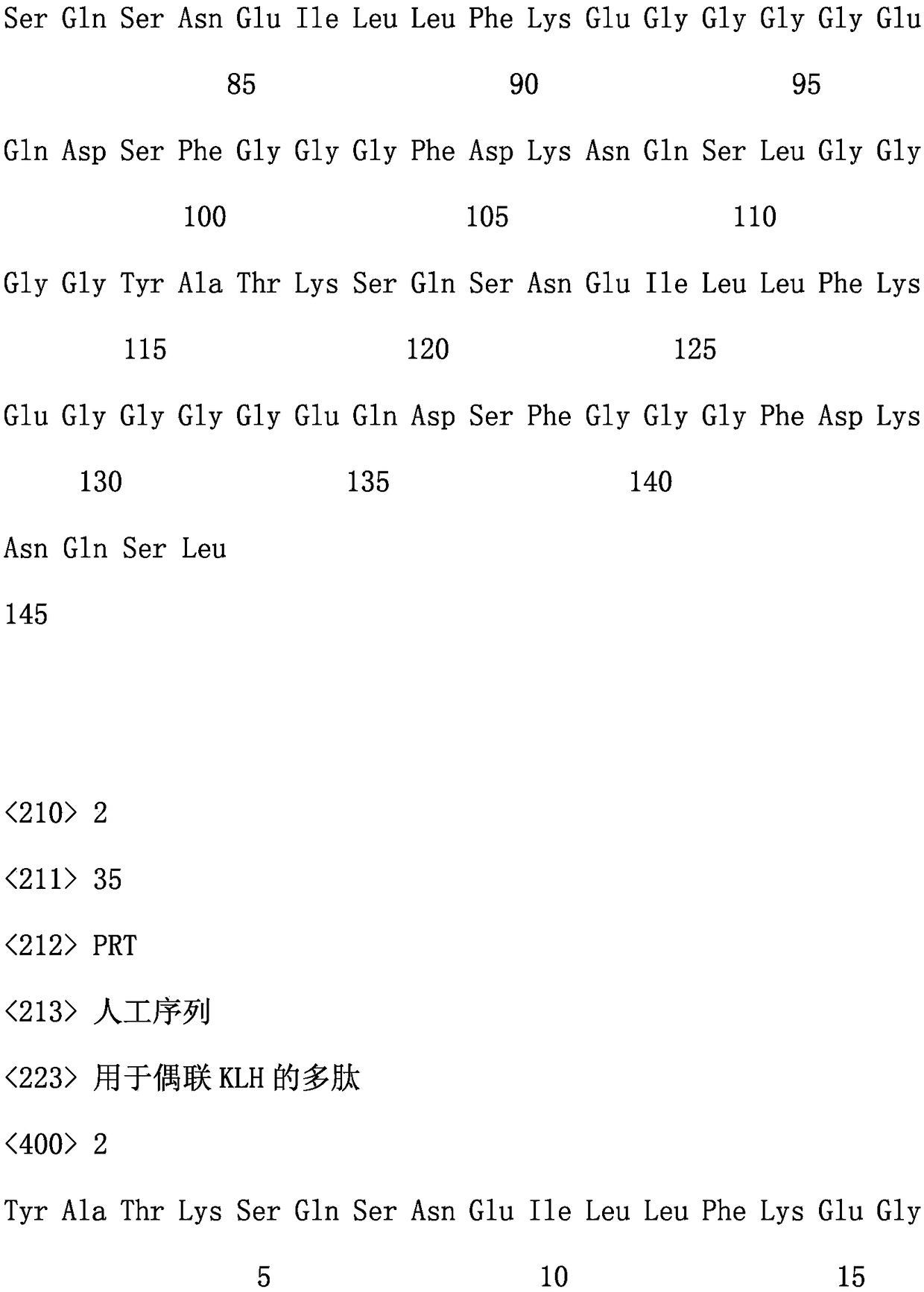
ActiveCN108084255AImprove expression levelHigh detection sensitivityBacteriaImmunoglobulins against animals/humansChemical synthesisBiotechnology
The invention belongs to the biotechnological field, and provides a polypeptide. The polypeptide includes two dominant antigen epitopes of the recombinant canine C-reactive protein (CRP). The polypeptide is coupled with the KLH protein for enhancing the immune effect. The invention provides a canine CRP recombinant protein. The canine CRP recombinant protein mainly includes the two dominant antigen epitopes. Specific to the aim of increasing the yield of the recombinant protein in a prokaryotic expression system, the recombinant protein amino acid sequence is converted into a corresponding nucleotide sequence by using an escherichia coli preferred codons, the nucleotide sequence is subjected to chemical synthesis, and the recombinant protein expression vector is built. The invention further relates to the preparation of the recombinant protein mono-clone antibody, the mono-clone antibody is prepared by antigen immunization, cell fusion and a plurality of screening, the mono-clone antibody is purified, the fluorescent microsphere is marked respectively, the best mono-clone pair determined through orthogonal experiment, the recombinant canine C-reactive protein can be applied to diagnosis of inflammation.
Owner:杭州贤至生物科技有限公司
Medicament comprising inhibitors of long pentraxin ptx3
The use of inhibitors of long pentraxin PTX3 for the preparation of a medicament for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases and of degenerative diseases of bone and cartilage is described.
Owner:DEFIANTE FARM
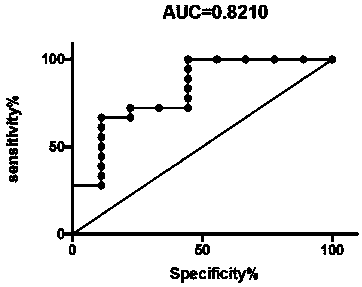
Specific protein marker for ovarian cancer diagnosis and preparation method of protein marker
ActiveCN110596403AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresBiological testingFermentationSolute transportersOvarian cancer
The invention relates to a specific protein marker for ovarian cancer diagnosis and a preparation method of the protein marker. The specific protein marker comprises the components including C reactive protein in serum exosome, solute transport protein family 11 member 2, ubiquitin-like PHD and ring finger domain protein 1. The preparation method comprises the following steps of protein extraction, pancreatin enzymolysis, TMT labeling, HPLC grading, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis, database search, protein identification, protein differential expression analysis, protein annotation and bioprotein marker screening. The protein marker has the advantages that (1) the marker has relatively high sensitivity and specificity; (2) ovarian malignant tumors can be distinguished frombenign tumors / healthy people; and (3) the preparation process is clear, the operability is high, and the repeatability is high.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Phospholipid organic polymer whole material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108456280AHigh densityImprove permeabilityPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesSorbentBiocompatibility Testing
The invention belongs to the technical field of protein purification, and discloses a phospholipid organic polymer whole material and a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprisesthe steps that phospholipid monomeric compound, crosslinking agent, porogen and initiator are mixed and then poured into a container after ultrasonic dissolving and deaeration are conducted, aggregation reaction is conducted under the temperature of 40-70 DEG C or under ultraviolet irradiation, and the phospholipid organic polymer whole material is obtained. The phospholipid organic polymer wholematerial has the advantages of high reproducibility, good biocompatibility and protein nonspecific adsorption resistance, and the existing defects of a traditional CRP purified material are effectively overcome. According to the material, by taking the phospholipid organic polymer whole material as an absorbent purifying standard protein mixed sample or an actual sample, CRP proteins with high purity can be obtained simply by one purifying strategy, the operation is easy, and the recovery rate is close to 100%.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Methods of detecting inflammatory markers and treating inflammatory conditions in humans
The present invention provides methods and systems to accurately detect and measure in a biological sample from a patient, endogenous antibodies, e.g., IgA, to inflammatory proteins, which antibodies are useful as diagnostic markers for inflammatory conditions, including bowel disease (IBD), in patients. Such methods and systems identify whether a sample from the patient is associated with an inflammatory condition, by using non-invasive means, thus conveniently providing information useful for guiding treatment decisions.
Owner:VETICA LABS INC
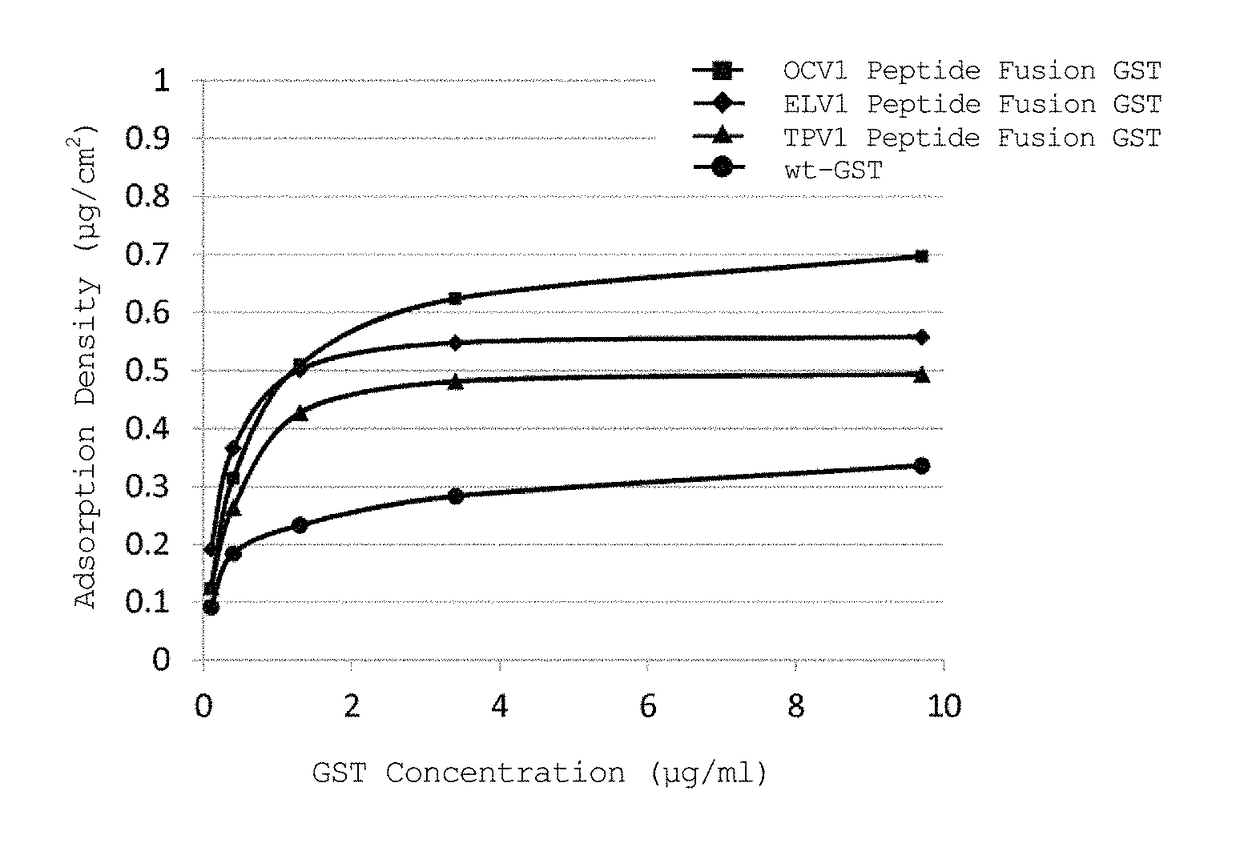
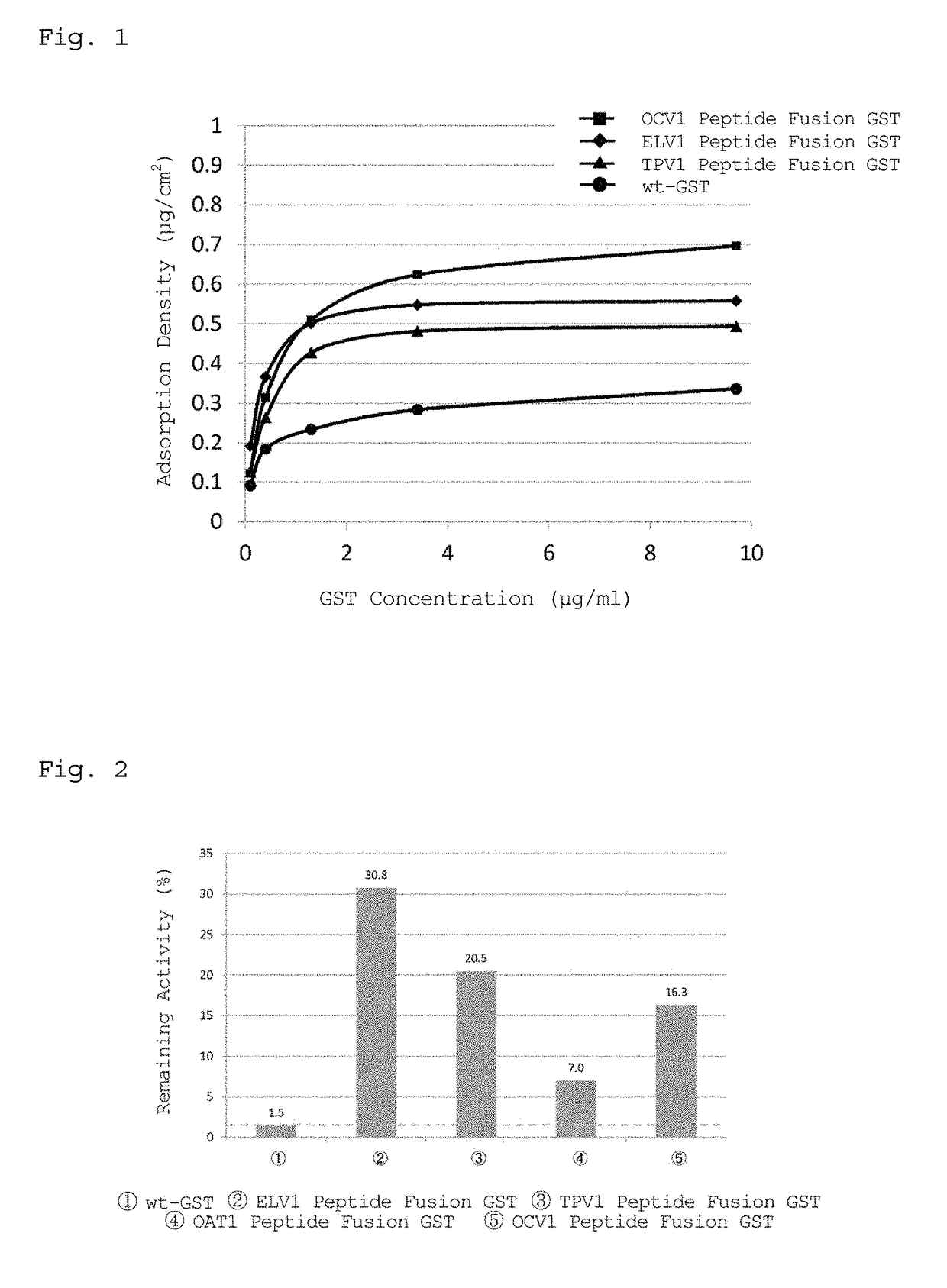
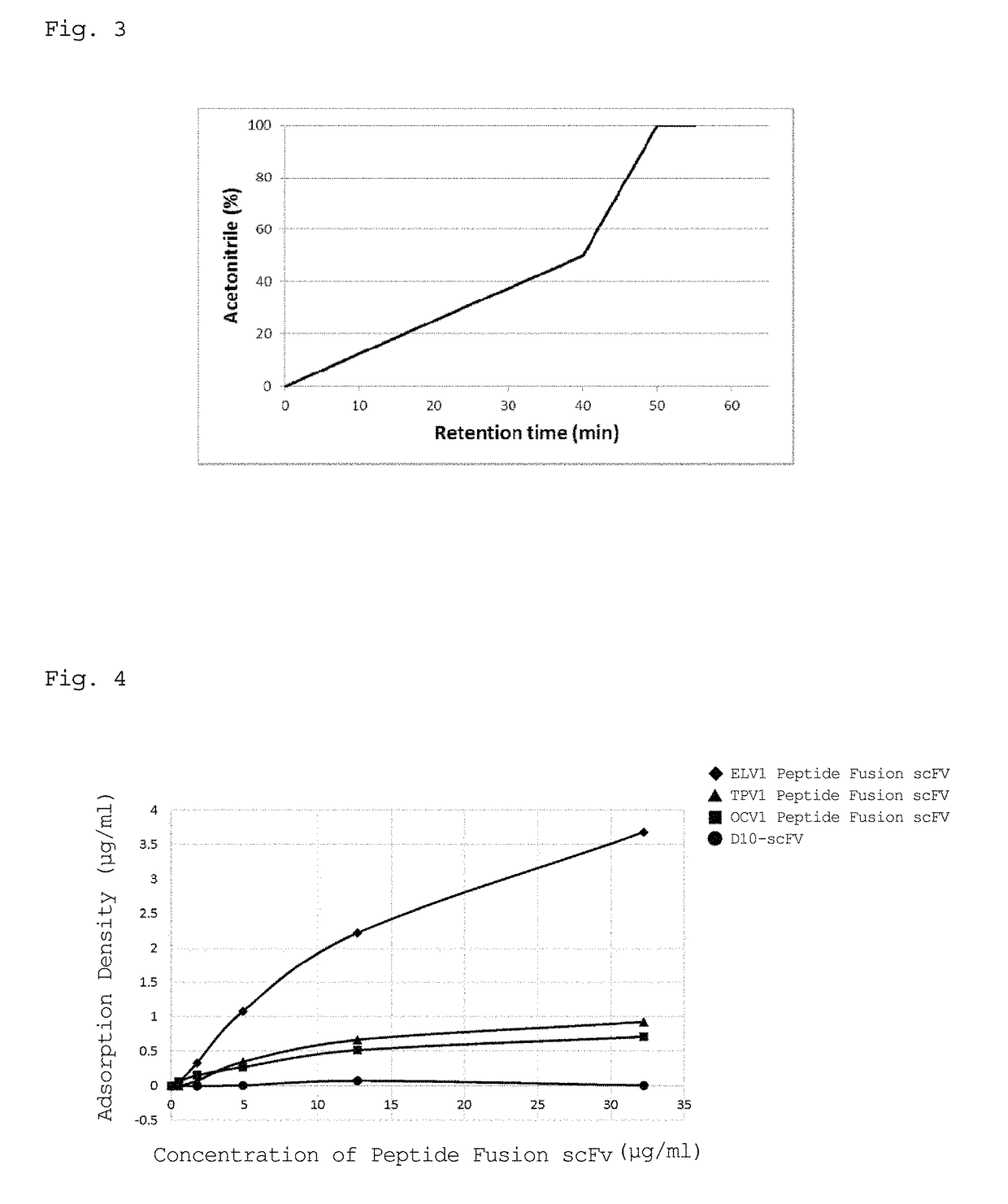
Protein production method, fusion protein, and antiserum
InactiveUS20110223686A1Improve isolationPromote recoveryImmunoglobulins against bacteriaPeptide preparation methodsMicroorganismSerum ige
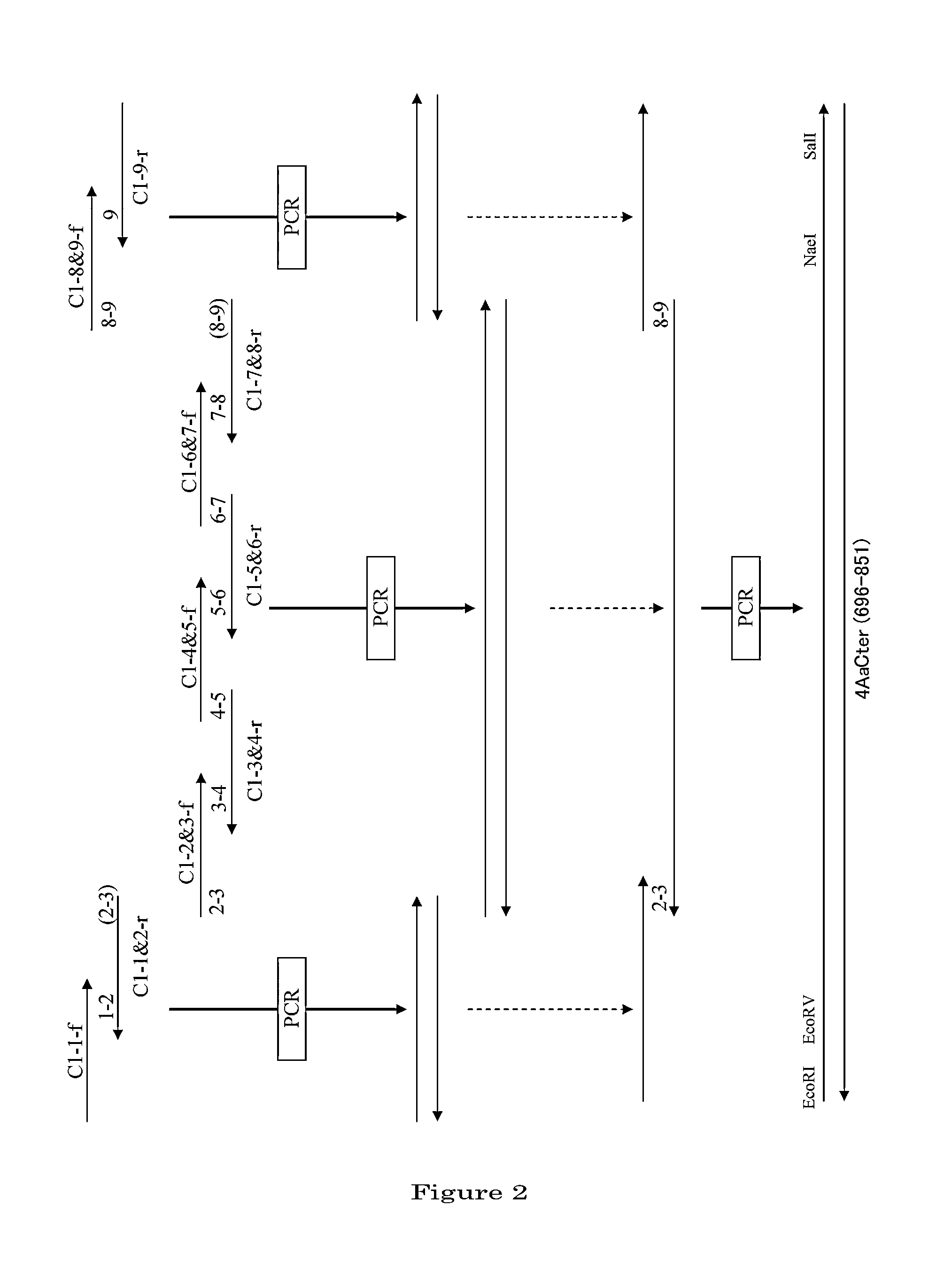
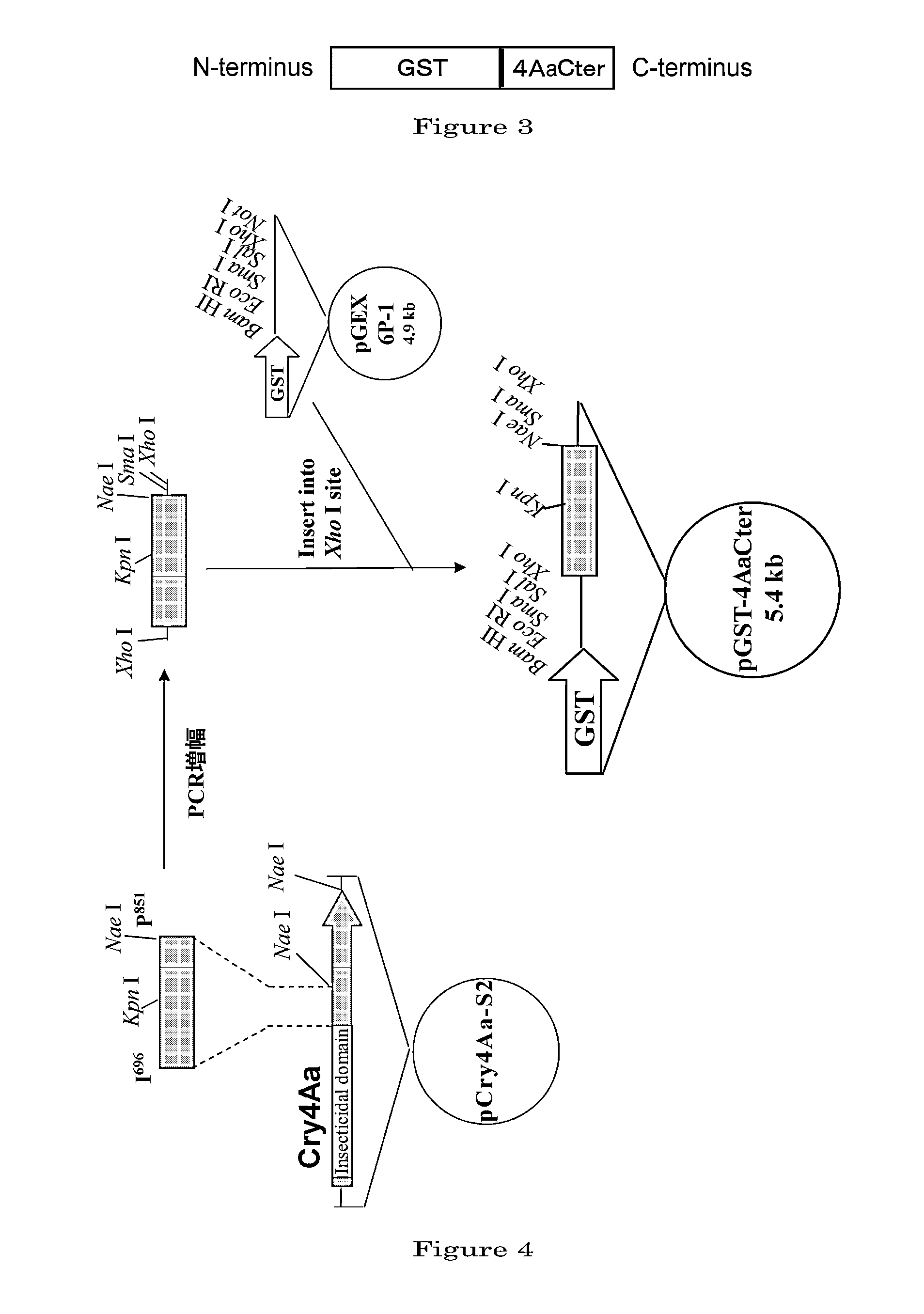
Disclosed are a highly efficient method for production of heterologous proteins performed by utilizing microorganisms, as well as fusion proteins, and an antiserum. The method includes a method for production of a protein (A) in the form of a fusion protein, comprising the steps of (a) preparing a DNA which codes for a fusion protein comprising the peptide chain forming the protein (A) and the C-terminal peptide or its fragment (B) of the Cry proteins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis, and (b) introducing the DNA into a host bacterium to transform the same, and (c) allowing the fusion protein to be expressed in the transformed host bacterium, as well as a method for production of the protein (A) itself comprising a further step of removing the peptide chain (B) from the fusion protein obtained.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA +1
Aptamer and detection method for C-reactive protein
An aptamer specifically binding to C-reactive protein (CRP) is provided. The aptamer includes a following nucleotide sequence: 5′-angngggngnntgnnt-3′, wherein n is a nucleotide selected from a, t, c and g.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Biomarker for human eyes and method thereof
InactiveUS20160305951A1High sensitivityDisease diagnosisBiological testingHyperhomocysteinemiaOrganism
The present invention provides a biomarker for detecting and diagnosing polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV) of human eyes, including levels of hyperhomocysteinemia that are identified, wherein elevated levels of hyperhomocysteinemia are highly associated with PCV of the human eyes. In addition, the present invention further provides a method for detecting and diagnosing PCV of the human eyes.
Owner:DELL SOFTWARE +2
Polynucleotides that home to atherosclerotic plaque
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV +1
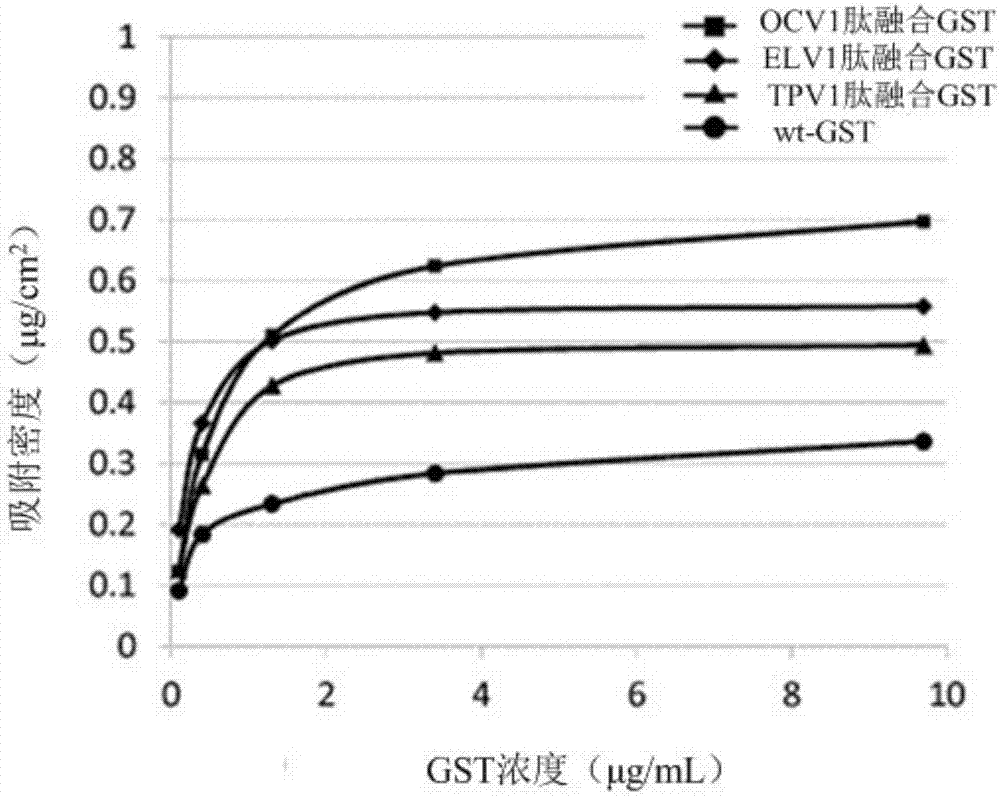
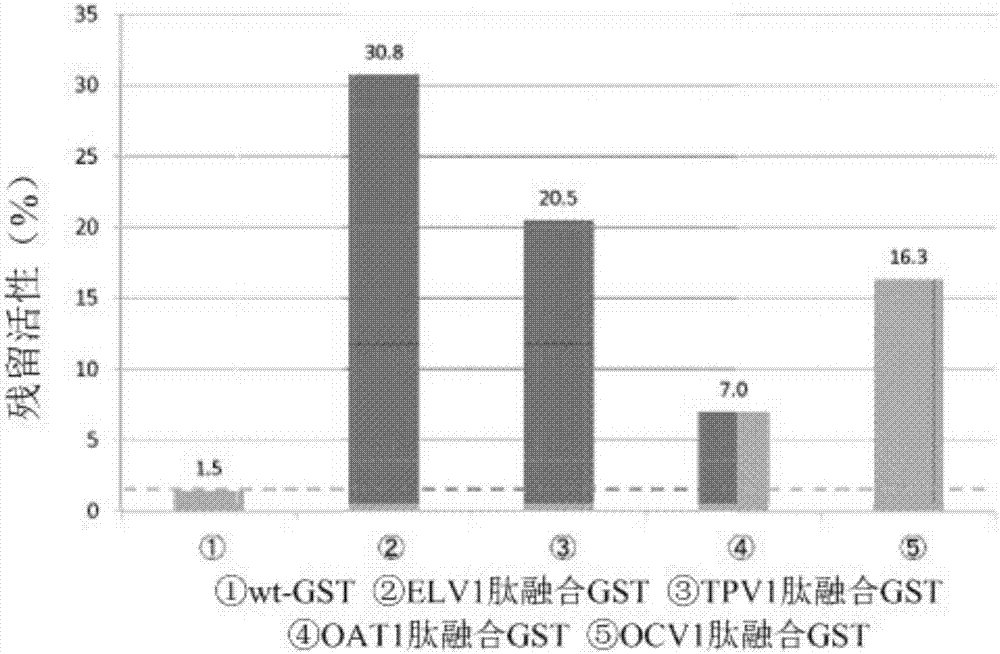
Peptides having affinity for polydimethylsiloxane, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20180022830A1Easy to fixHighly accurately and highly efficiently immobilizedAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsInactivation/attenuationProtein targetNucleotide
An object of the present invention is to provide a polydimethylsiloxane substrate to which a peptide having an affinity for polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is bound; a method for immobilizing a target protein on a polydimethylsiloxane substrate; a peptide having an affinity for PDMS; a polynucleotide encoding a peptide having an affinity for PDMS; and a vector using thereof. A polydimethylsiloxane substrate to which a peptide having an affinity for polydimethylsiloxane is bound, the peptide comprising the following peptide (1a) or (1b), or a fragment thereof: (1a) a peptide comprising an amino acid sequence represented by at least one member selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 9; and (1b) a peptide comprising the amino acid sequence of (1a) in which one or more amino acids are deleted, substituted, and / or added, the peptide having an affinity for polydimethylsiloxane.
Owner:NAT UNIV KYOTO INST OF TECH +1
Preparation method of recombinant human C-reactive protein
ActiveCN110964096AIncrease productionSolve the acquisition problemMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid vectorEscherichia coliGene
The invention discloses a preparation method of recombinant human C-reactive protein. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a protein sequence of the human C-reactive protein from NCBI;artificially optimizing and synthesizing a C-reactive protein encoding gene according to codon bias characteristics of escherichia coli; further constructing an expression vector of the human C-reactive protein; converting the expression vector into the escherichia coli for induced expression; and purifying an expression product to obtain pure recombinant protein. ELISA detection results show thatthe immunological characteristics of the expressed and purified recombinant human C-reactive protein are very similar to those of natural human C-reactive protein, and the detection requirements canbe met. In addition, the purification process of the recombinant human C-reactive protein is beneficial to quality control and the requirement of industrial production are met.
Owner:润方(长春)生物科技有限公司 +1
Biomarker for human eyes and method thereof
The present invention provides a biomarker for detecting and diagnosing polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV) of human eyes, including levels of hyperhomocysteinemia that are identified, wherein elevated levels of hyperhomocysteinemia are highly associated with PCV of the human eyes. In addition, the present invention further provides a method for detecting and diagnosing PCV of the human eyes.
Owner:LIN PO KANG
Methods for treating fibrosis using CRP antagonists
The application provides methods for determining a patient's risk for developing fibrosis or a fibrosis-related disorder. Concentrations of C reactive protein (CRP) and serum amyloid protein (SAP) are measured from a biological sample to determine the SAP-to-CRP ratio. This ratio can then be compared with one or more SAP-to-CRP reference ratios to determine a patient's risk for developing a fibrosis related disorder. The diagnostic methods can also be used to determine the severity of fibrosis in a patient afflicted with such a disease. Furthermore, methods for treating patients having a fibrosis-related disorder are provided. For example, a patient that has a lower SAP-to-CRP ratio than one or more reference values may be treated with an SAP agonist and / or CRP antagonist to treat or prevent a fibrosis disorder. The methods may further comprise determining the R131 / H131 polymorphism of FcγRIIA as a risk factor for developing fibrosis or a fibrosis-related disorder.
Owner:PROMEDIOR
Means and methods for determining the arteriosclerotic stenosis using inflammatory biomarkers
InactiveUS20110082349A1Disease diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringInflammatory biomarkersBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing the degree of arteriosclerotic stenosis in a subject including determining the amount of CRP or LPa in a sample of the subject and comparing the determined amount to a reference whereby the degree of arteriosclerotic stenosis is determined. The present invention also contemplates a method for identifying a subject in need of prevention or therapy of arteriosclerosis. Further, devices and kits are encompassed for carrying out the methods.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Preparation of a recombinant canine c-reactive protein and its monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN108084255BImprove expression levelHigh detection sensitivityBacteriaImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntigen epitopeEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the biotechnological field, and provides a polypeptide. The polypeptide includes two dominant antigen epitopes of the recombinant canine C-reactive protein (CRP). The polypeptide is coupled with the KLH protein for enhancing the immune effect. The invention provides a canine CRP recombinant protein. The canine CRP recombinant protein mainly includes the two dominant antigen epitopes. Specific to the aim of increasing the yield of the recombinant protein in a prokaryotic expression system, the recombinant protein amino acid sequence is converted into a corresponding nucleotide sequence by using an escherichia coli preferred codons, the nucleotide sequence is subjected to chemical synthesis, and the recombinant protein expression vector is built. The invention further relates to the preparation of the recombinant protein mono-clone antibody, the mono-clone antibody is prepared by antigen immunization, cell fusion and a plurality of screening, the mono-clone antibody is purified, the fluorescent microsphere is marked respectively, the best mono-clone pair determined through orthogonal experiment, the recombinant canine C-reactive protein can be applied to diagnosis of inflammation.
Owner:杭州贤至生物科技有限公司
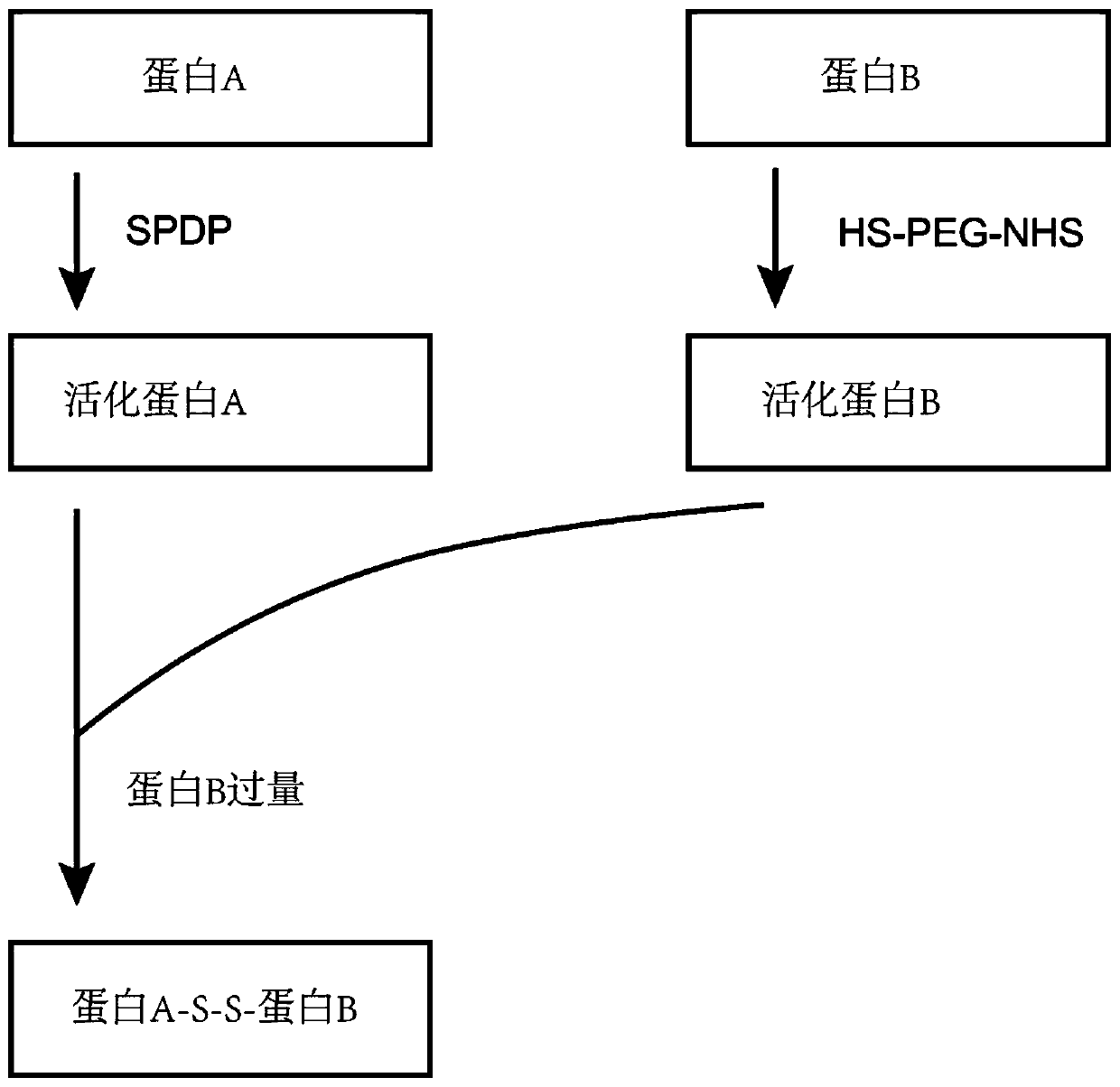
Method for preparing heterodimer protein
PendingCN111454369ASmall molecular weightGood repeatabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide preparation methodsOligomerProtein
The present invention discloses a method for preparing heterodimer protein. The specific steps are as follows: firstly activating proteins: taking SPDP (3-(2-pyridinedimercapto) propionate N-hydroxysuccinimide ester) to be mixed with a protein 1 in a buffer and taking HS-PEG-NHS (sulfhydryl PEG-N-hydroxysuccinimide) to be mixed with a protein 2 in a buffer to separately obtain an activated protein1 and an activated protein 2; and mixing the activated protein 1 and the activated protein 2, purifying the obtained product and conducting preservation at low temperature. The protein product prepared by the method is an oligomer with low molecular weight, the product is mostly heterodimers, all used reagents can stably exist in a water phase, and the method has good repeatability, stability andreliability.
Owner:润方(长春)生物科技有限公司 +1
Protein production method, fusion protein, and antiserum
InactiveUS8865428B2Improve isolationPromote recoveryBacterial antigen ingredientsDepsipeptidesAureobasidium sp.Bacillus thuringiensis
Disclosed are a highly efficient method for production of heterologous proteins performed by utilizing microorganisms, as well as fusion proteins, and an antiserum. The method includes a method for production of a protein (A) in the form of a fusion protein, comprising the steps of (a) preparing a DNA which codes for a fusion protein comprising the peptide chain forming the protein (A) and the C-terminal peptide or its fragment (B) of the Cry proteins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis, and (b) introducing the DNA into a host bacterium to transform the same, and (c) allowing the fusion protein to be expressed in the transformed host bacterium, as well as a method for production of the protein (A) itself comprising a further step of removing the peptide chain (B) from the fusion protein obtained.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA +1
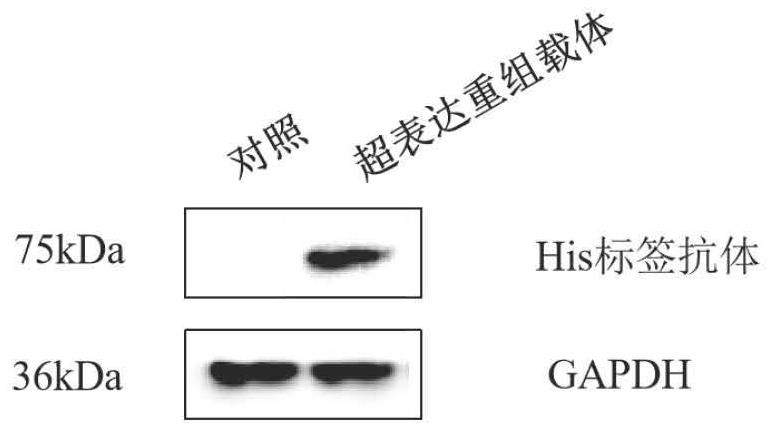
Recombinant C-reactive proteins
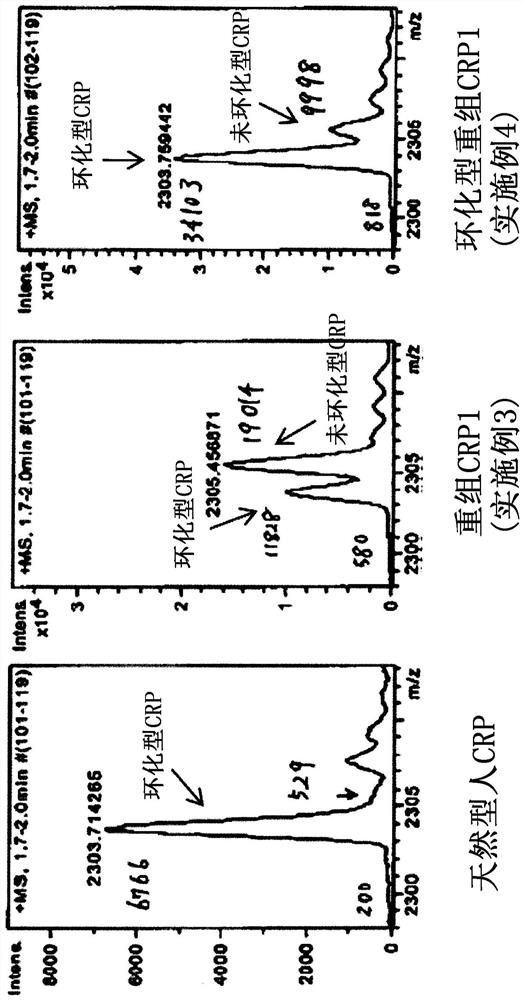
PendingCN114761561AImprove accuracyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBiological material analysisGENE RE-ARRANGEMENTSAminoacylation
In immunoassay using a latex reagent, the correctness of immunoassay in a CRP high-concentration range is improved. The recombinant C-reactive protein is a C-reactive protein produced by gene recombination, and 55% or more of the N-terminus of the C-reactive protein is pyroglutaminated.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Peptides having affinity for polydimethylsiloxane, and uses thereof
InactiveCN107207612AEasy to fixEffectively fixedAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsInactivation/attenuationCrystallographyProtein target
The purpose of the present invention is to provide: a polydimethylsiloxane substrate obtained through the bonding of peptides having an affinity for polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS); a method for immobilizing a target protein on the polydimethylsiloxane substrate; peptides having an affinity for PDMS; polynucleotides for coding the peptides having an affinity for PDMS; and vectors and the like that use the polynucleotides. A polydimethylsiloxane substrate obtained through the bonding of peptides having an affinity for polydimethylsiloxane, said peptides comprising (1a) or (1b) below or fragments thereof. (1a) A peptide comprising an amino acid sequence represented by at least one sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID Nos. 1 to 9. (1b) A peptide having an affinity for polydimethylsiloxane, and comprising an amino acid sequence in which one or a plurality of amino acids have been deleted, substituted and / or added in the amino acid sequence of (1a).
Owner:NAT UNIV KYOTO INST OF TECH +1
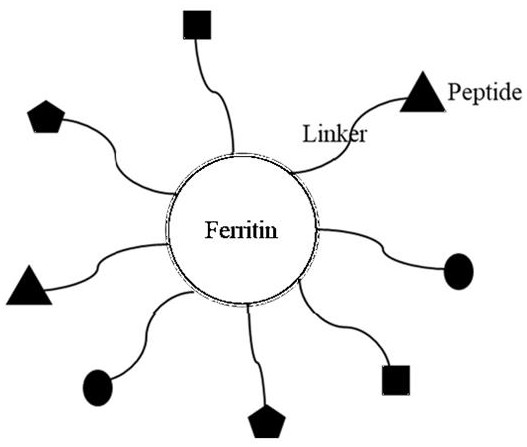
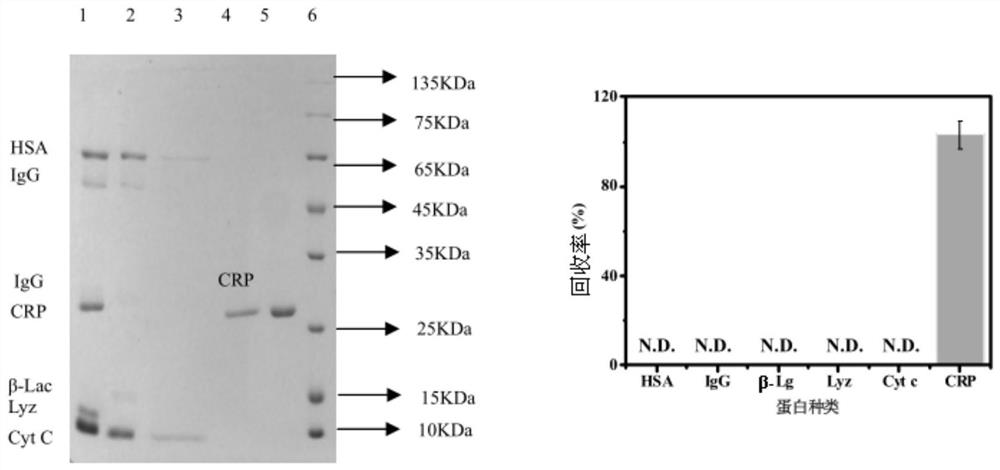
A composite quality control product for clinical diagnosis and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112094355BEasy to useAvoid duplicationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHaemoglobins/myoglobinsAntiendomysial antibodiesLarge intestine
The invention discloses a composite quality control product based on multiple diagnostic marker-specific epitope polypeptide molecules linked by ferritin nanoparticle carriers and a preparation method thereof. Through antibody detection and epitope analysis techniques, most of the The dominant epitope of the diagnostic marker protein is located, and then linked to the ferritin molecule by connecting esters to form a "Fer-Linker-Epitope Peptide" complex, and the synthetic gene sequence of the complex is transferred into the prokaryotic large intestine through a specific vector Bacillus recombinant expression, so that the composite antigen (quality control product) containing the dominant epitope polypeptide molecules of multiple diagnostic markers can be detected by multiple diagnostic reagents at the same time. The quality control product of the invention has high detection efficiency, low cost and excellent stability, and can be stored stably for a long time under the condition of 2-8°C.
Owner:南京佰抗生物科技有限公司
A kind of monolithic material of phospholipid organic polymer and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108456280BHigh densityImprove permeabilityPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesChemical compoundPhospholipid
The invention belongs to the technical field of protein purification, and discloses a phospholipid organic polymer whole material and a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprisesthe steps that phospholipid monomeric compound, crosslinking agent, porogen and initiator are mixed and then poured into a container after ultrasonic dissolving and deaeration are conducted, aggregation reaction is conducted under the temperature of 40-70 DEG C or under ultraviolet irradiation, and the phospholipid organic polymer whole material is obtained. The phospholipid organic polymer wholematerial has the advantages of high reproducibility, good biocompatibility and protein nonspecific adsorption resistance, and the existing defects of a traditional CRP purified material are effectively overcome. According to the material, by taking the phospholipid organic polymer whole material as an absorbent purifying standard protein mixed sample or an actual sample, CRP proteins with high purity can be obtained simply by one purifying strategy, the operation is easy, and the recovery rate is close to 100%.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
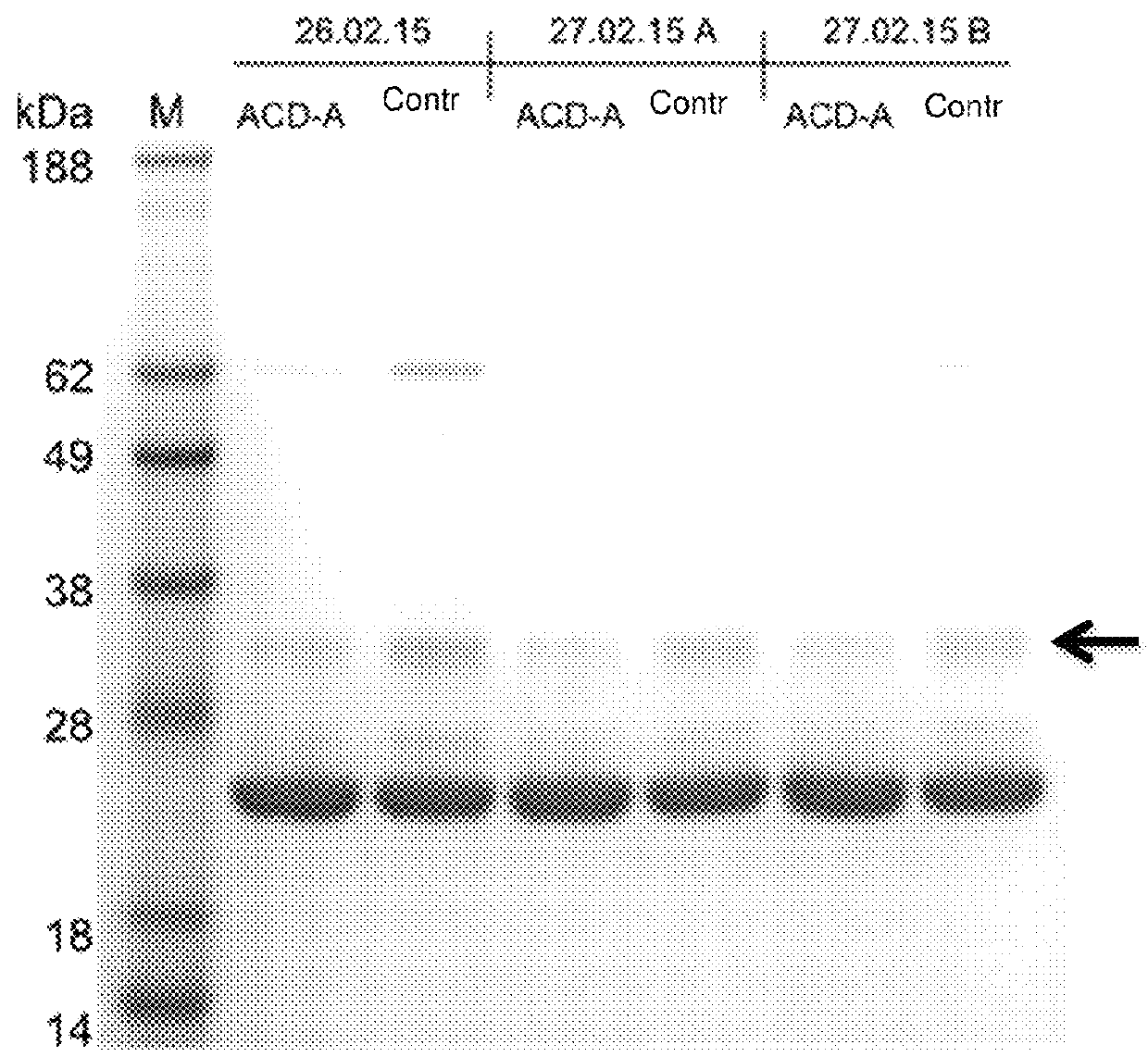
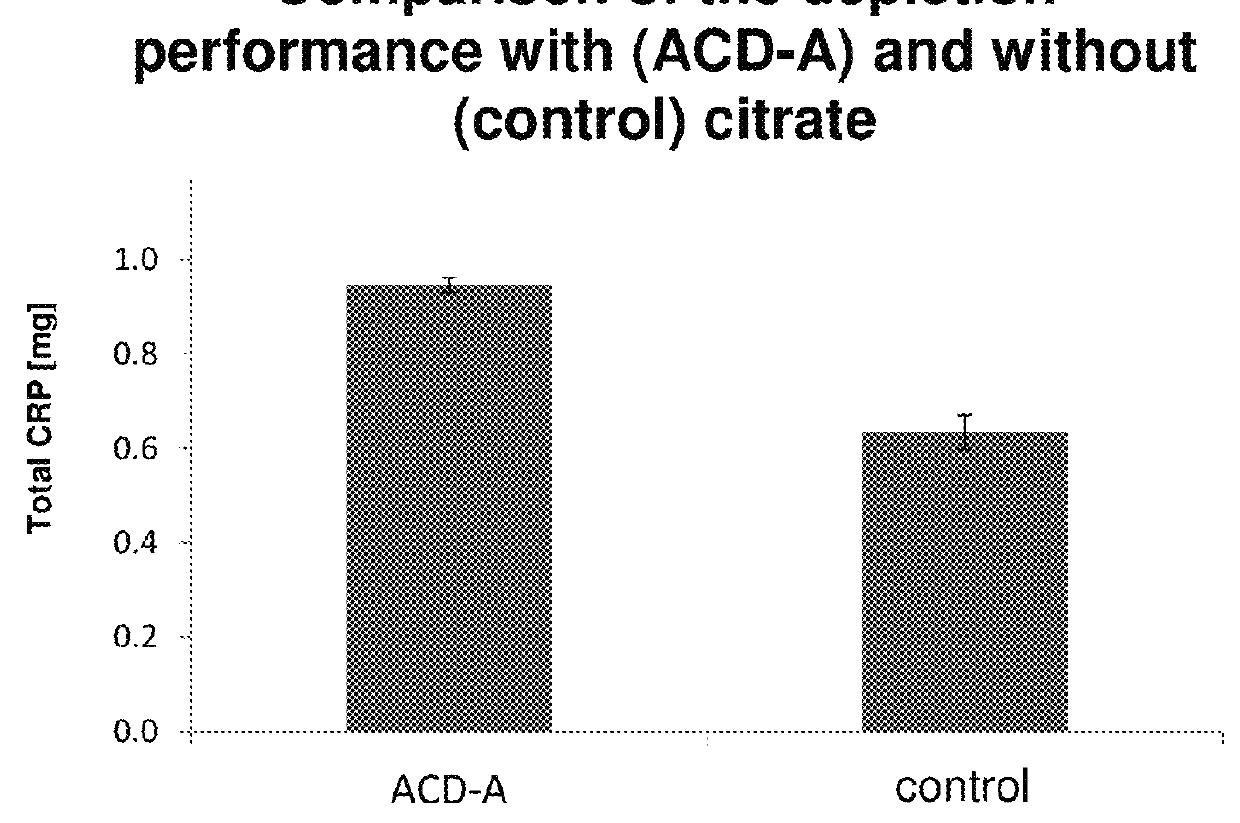
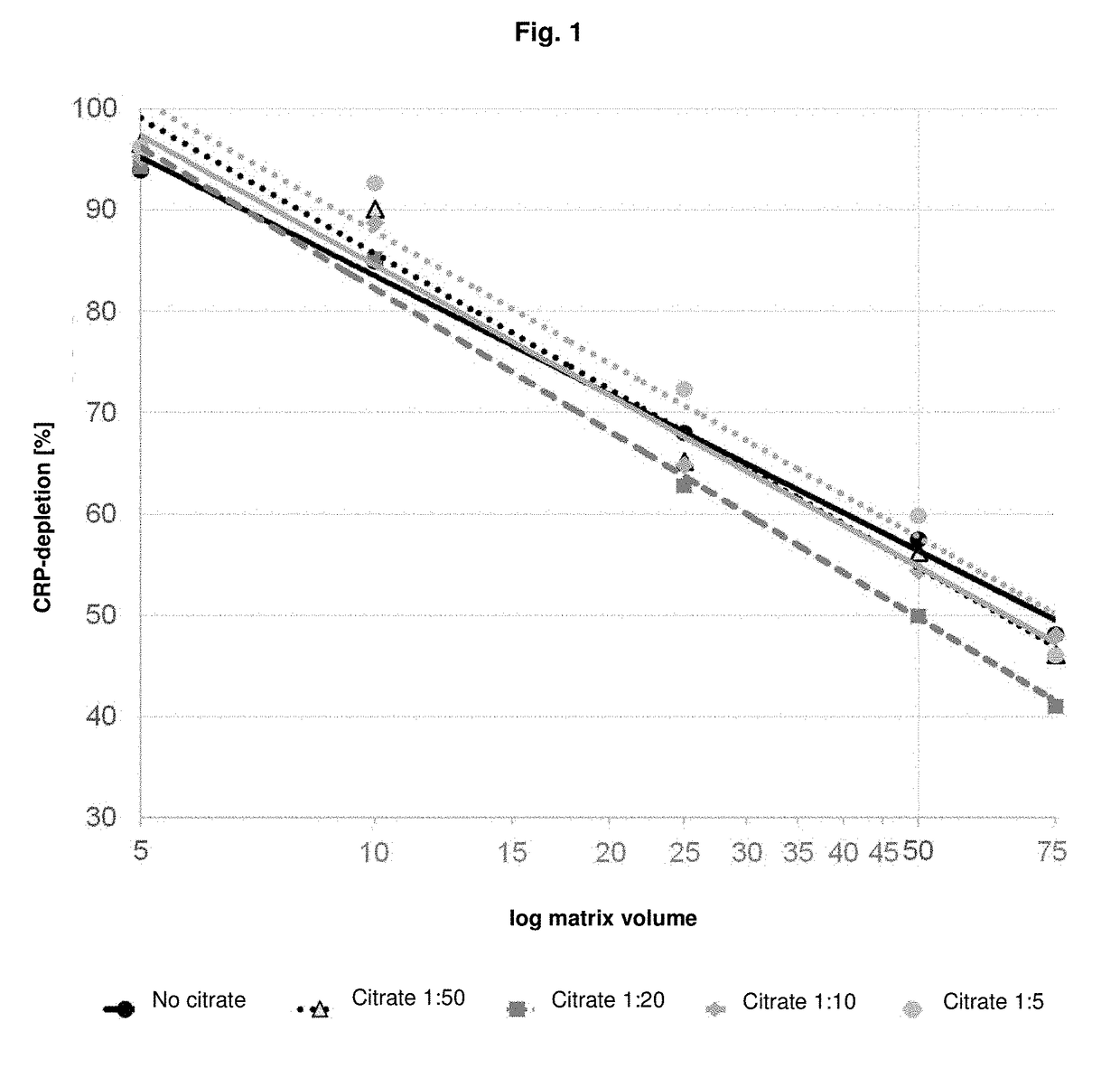
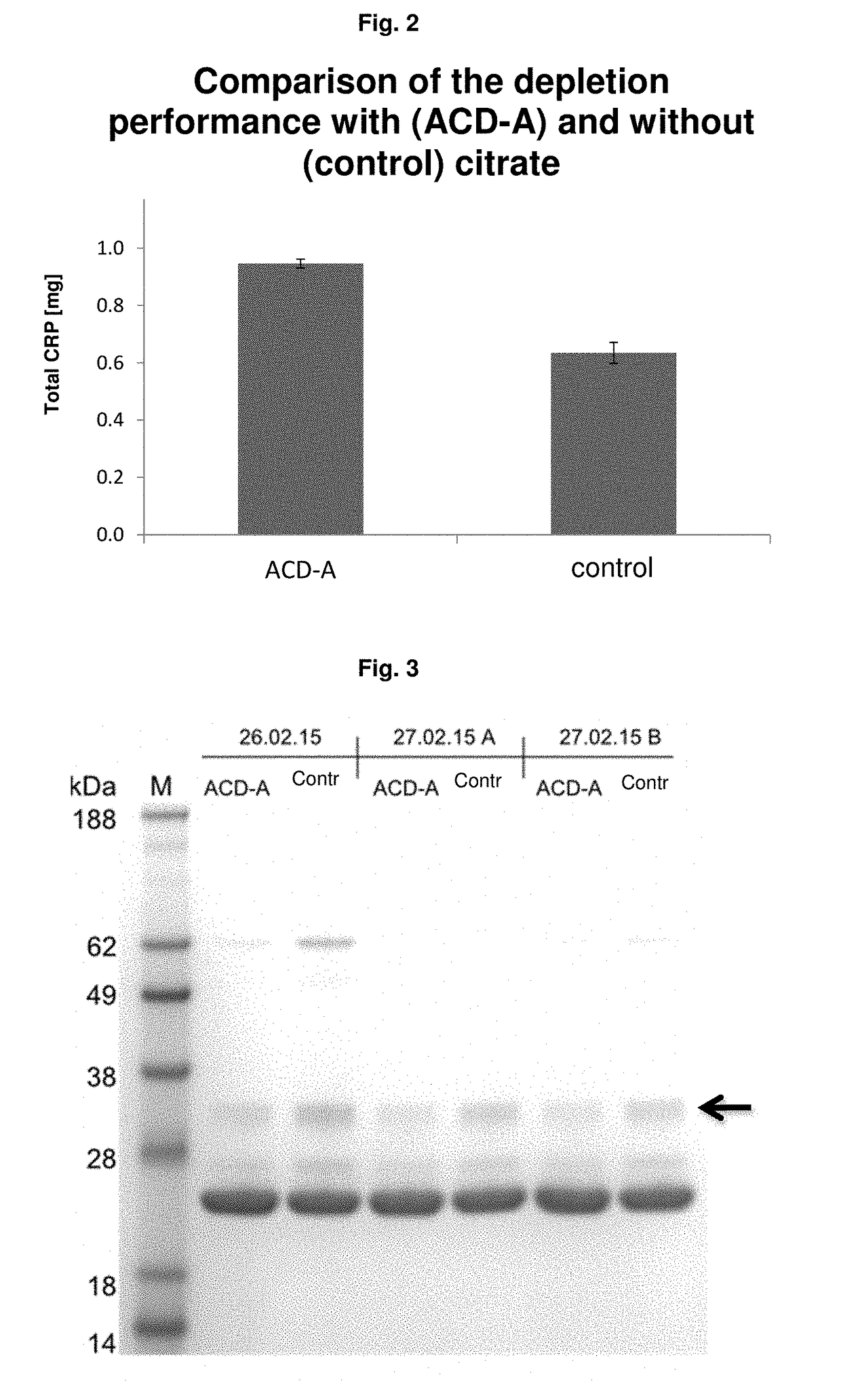
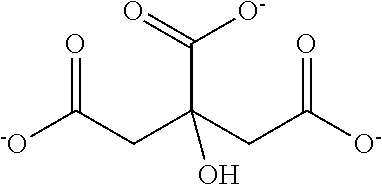
Use of citrate solution for affinity chromatographic purification of CRP using phosphocholine and derivatives thereof
ActiveUS9962628B2Inhibit aggregationEasily realizedOther chemical processesComponent separationPhosphocholineBiological fluids
Owner:PENTRACOR GMBH
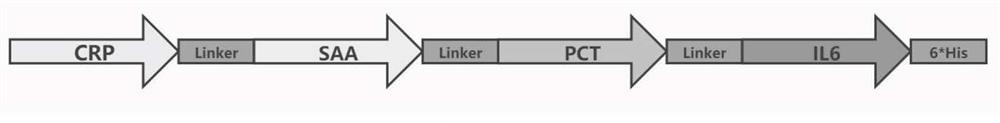
Fusion expression protein as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114350708AGuarantee structureGuaranteed biological functionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCalcitoninsBiotechnologyQuality control
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to a fusion expression protein as well as a preparation method and application thereof. An inflammation item quality control product adopted during existing inflammation diagnosis and detection is either a single-item quality control product and is inconvenient to operate, or a composite quality control product preparation method is complex and high in cost, aiming at the problems, the invention provides a fusion expression protein, four inflammation marker proteins of RP, SAA, PCT and IL6 are creatively subjected to fusion expression, and the fusion expression protein is used for preparing the inflammation marker protein. The obtained fusion protein can be used for respectively preparing PCT and IL6 project composite quality control and CRP and SAA project composite quality control according to the proportion, not only has good stability and accuracy, but also can effectively reduce the cost of quality control products, improve the convenience of in-vitro diagnosis and detection and well control the batch-to-batch difference of the quality control products.
Owner:巴迪泰(广西)生物科技有限公司
Use of a citrate solution for affinity chromatographic purification of crp using phosphocholine and derivatives thereof
ActiveUS20170319982A1Inhibit aggregationEasily realizedSolid sorbent liquid separationPeptide preparation methodsBiological fluidsAntibody Affinity Chromatography
The invention relates to the use of a citrate solution for affinity-chromatographic removal of C-reactive protein (CRP) from biological fluids, wherein the CRP is affinity-chromatographically removed using (Ca2+-dependent) binding of CRP to a column material functionalized with ω-phosphonooxyalkyl ammonium groups and / or with ω-ammoniumalkoxy-hydroxy-phosphoryloxy groups.
Owner:PENTRACOR GMBH
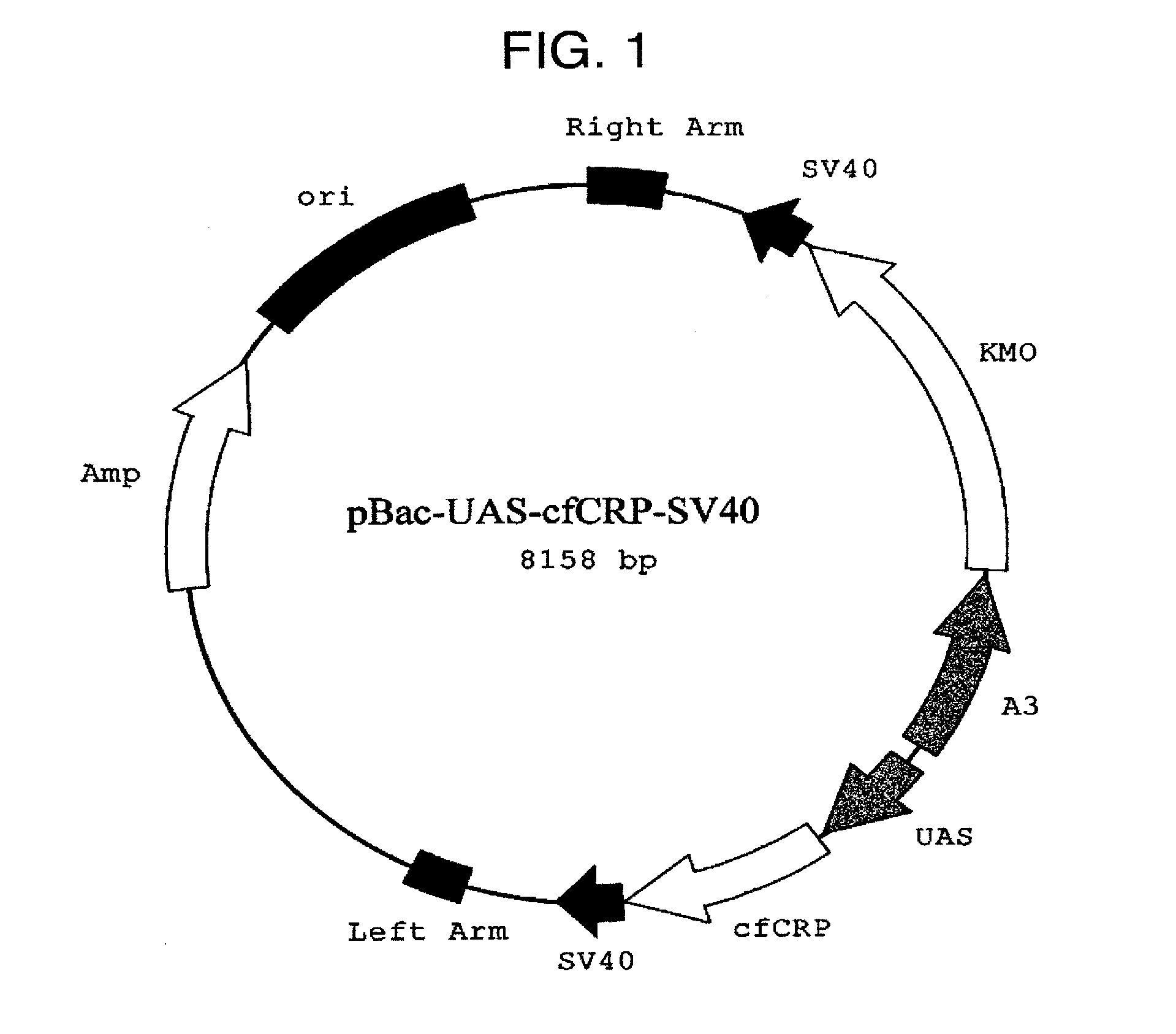
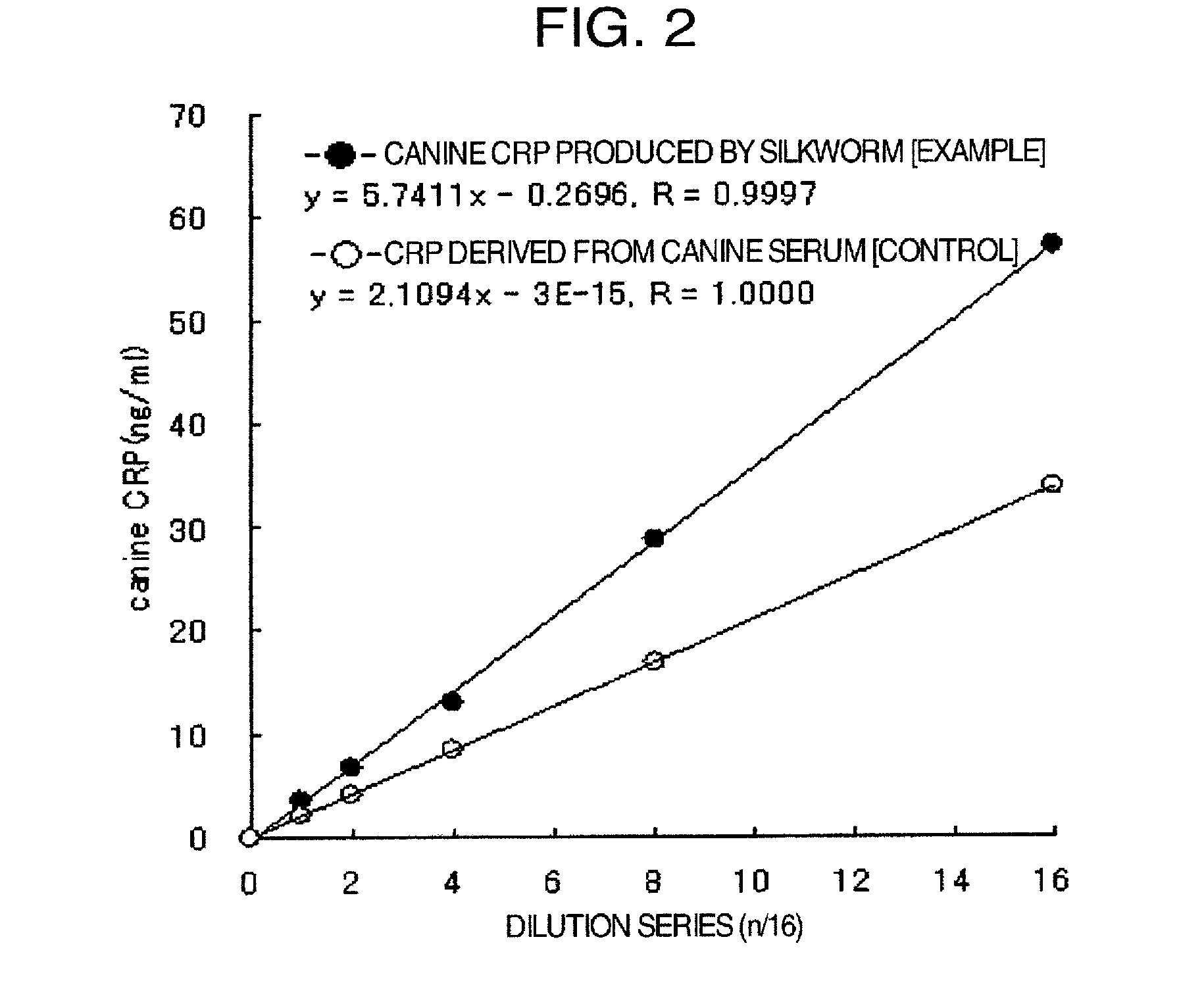
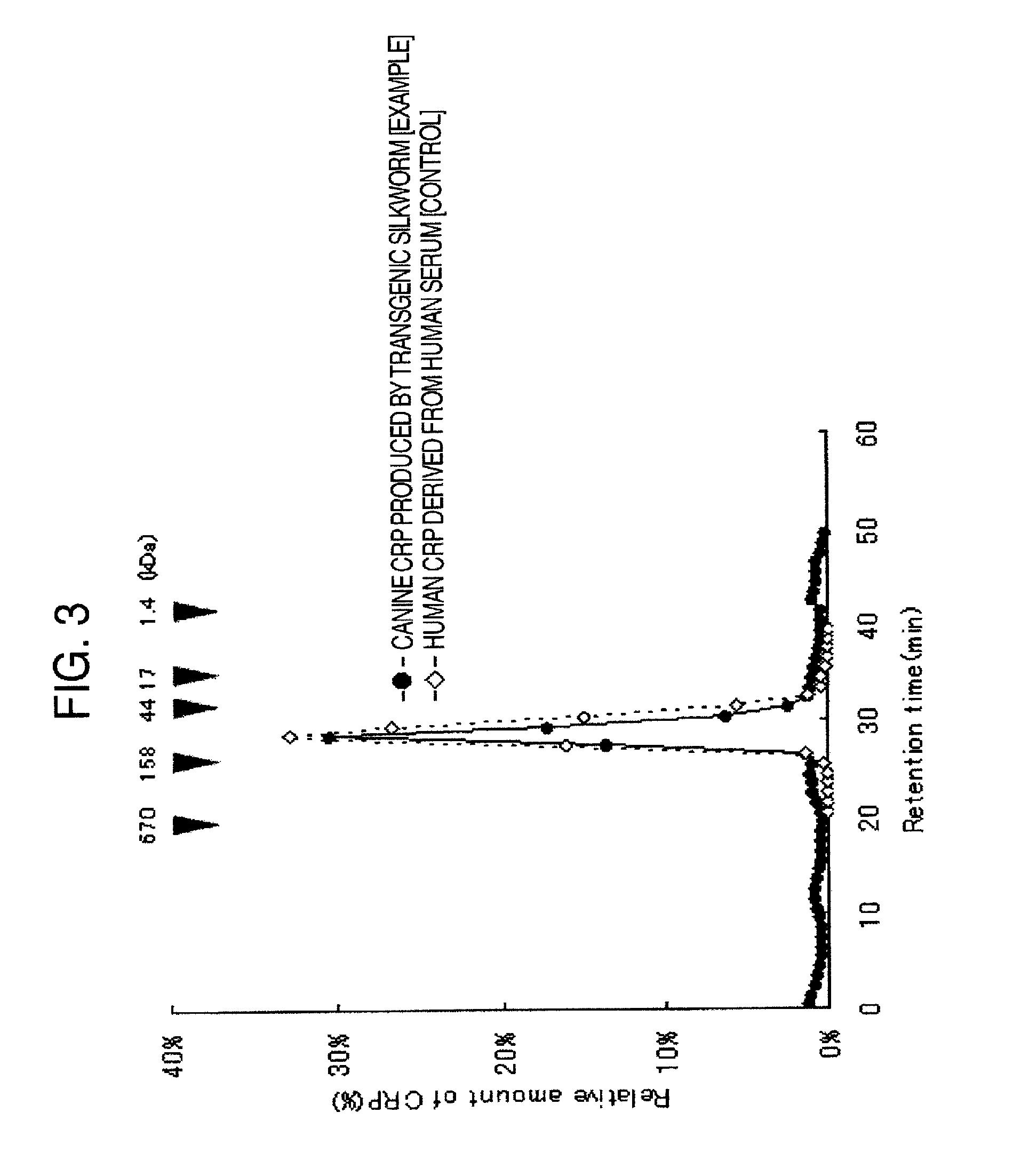
DNA encoding canine monomeric CRP and expression vector containing the DNA
ActiveUS20150037880A1Improve efficiencyEasy to collectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesDna encodingDNA
Pentameric CRP is produced at a high efficiency by transferring DNA, which encodes monomeric CRP, into a silkworm to thereby construct a transgenic silkworm and then collecting and purifying pentameric CRP that is produced by the transgenic silkworm constructed above.
Owner:NITTO BOSEIKI CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com