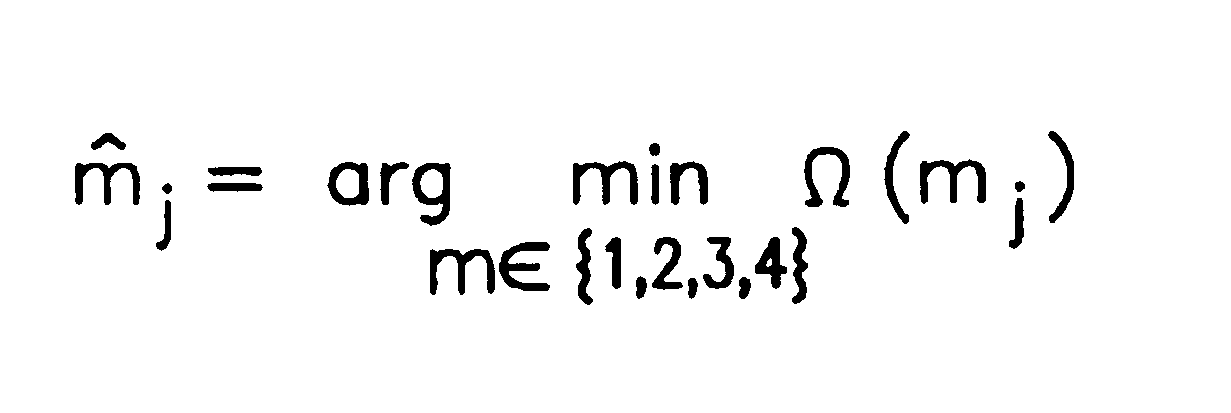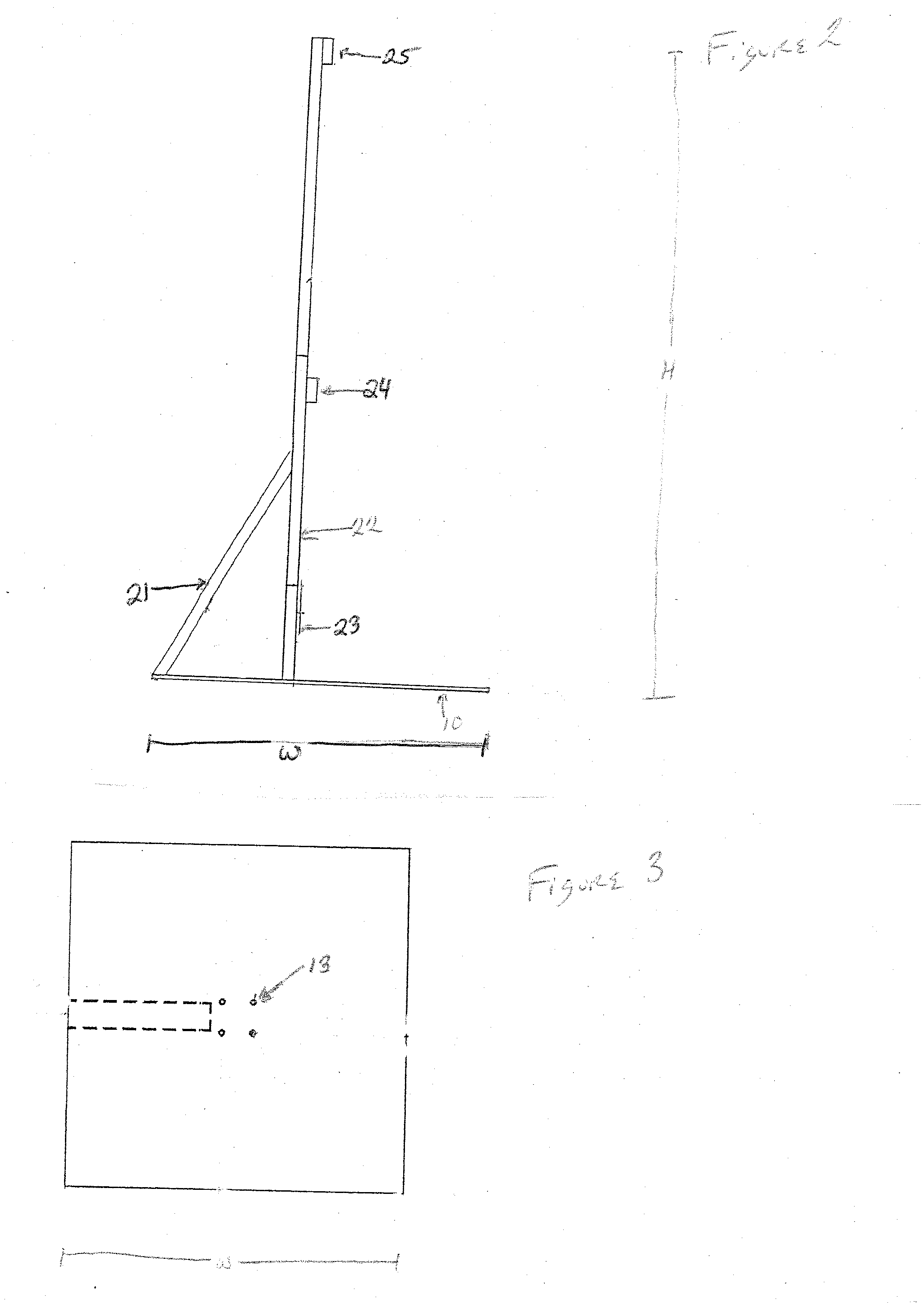Patents
Literature
50results about How to "Improve technique" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
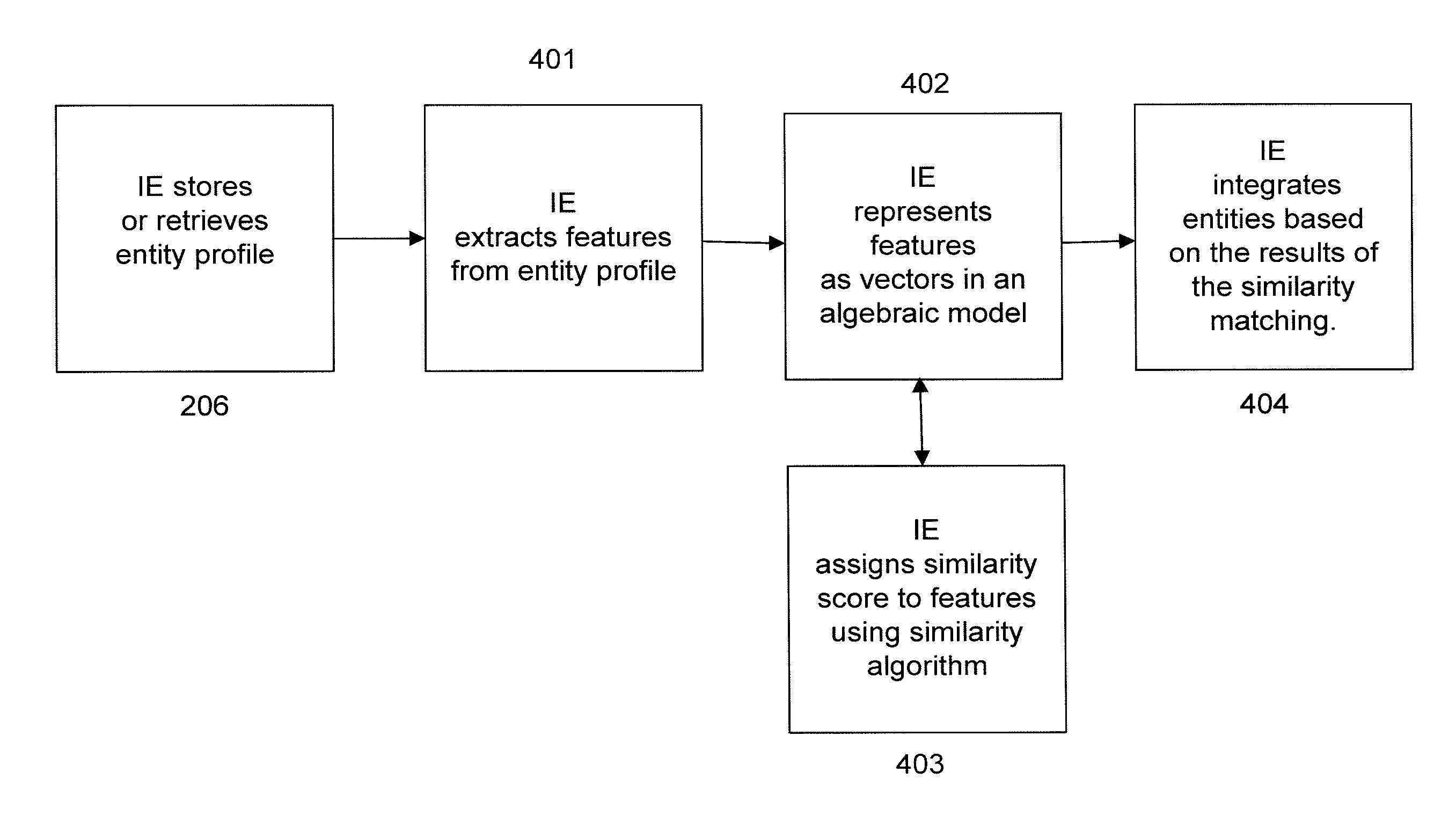
Systems and methods for information integration through context-based entity disambiguation
InactiveUS20110106807A1Improve characteristicImprove techniqueDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesEntity typeContext based
Described within are systems and methods for disambiguating entities, by generating entity profiles and extracting information from multiple documents to generate a set of entity profiles, determining equivalence within the set of entity profiles using similarity matching algorithms, and integrating the information in the correlated entity profiles. Additionally, described within are systems and methods for representing entities in a document in a Resource Description Framework and leveraging the features to determine the similarity between a plurality of entities. An entity may include a person, place, location, or other entity type.
Owner:JANYA
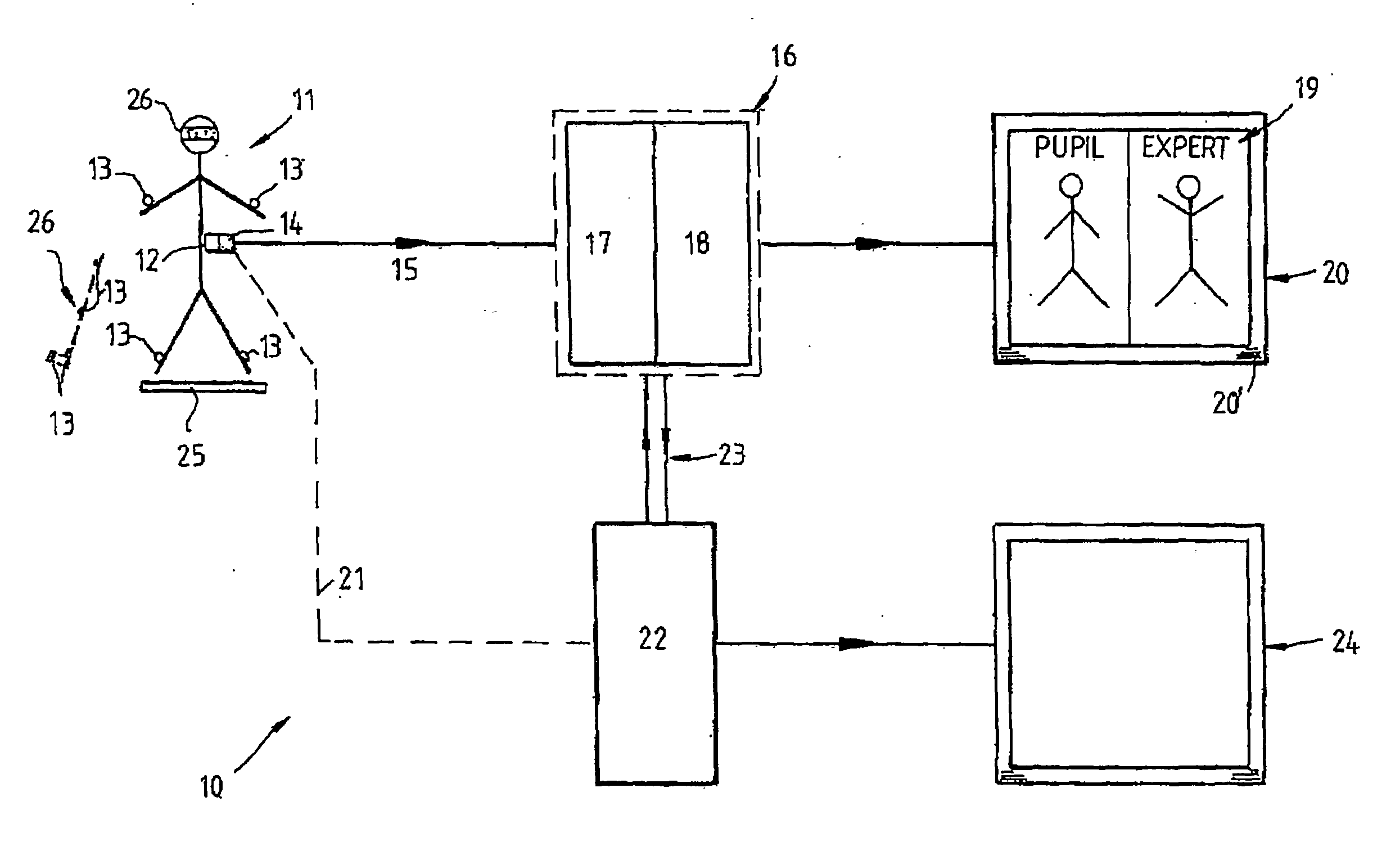
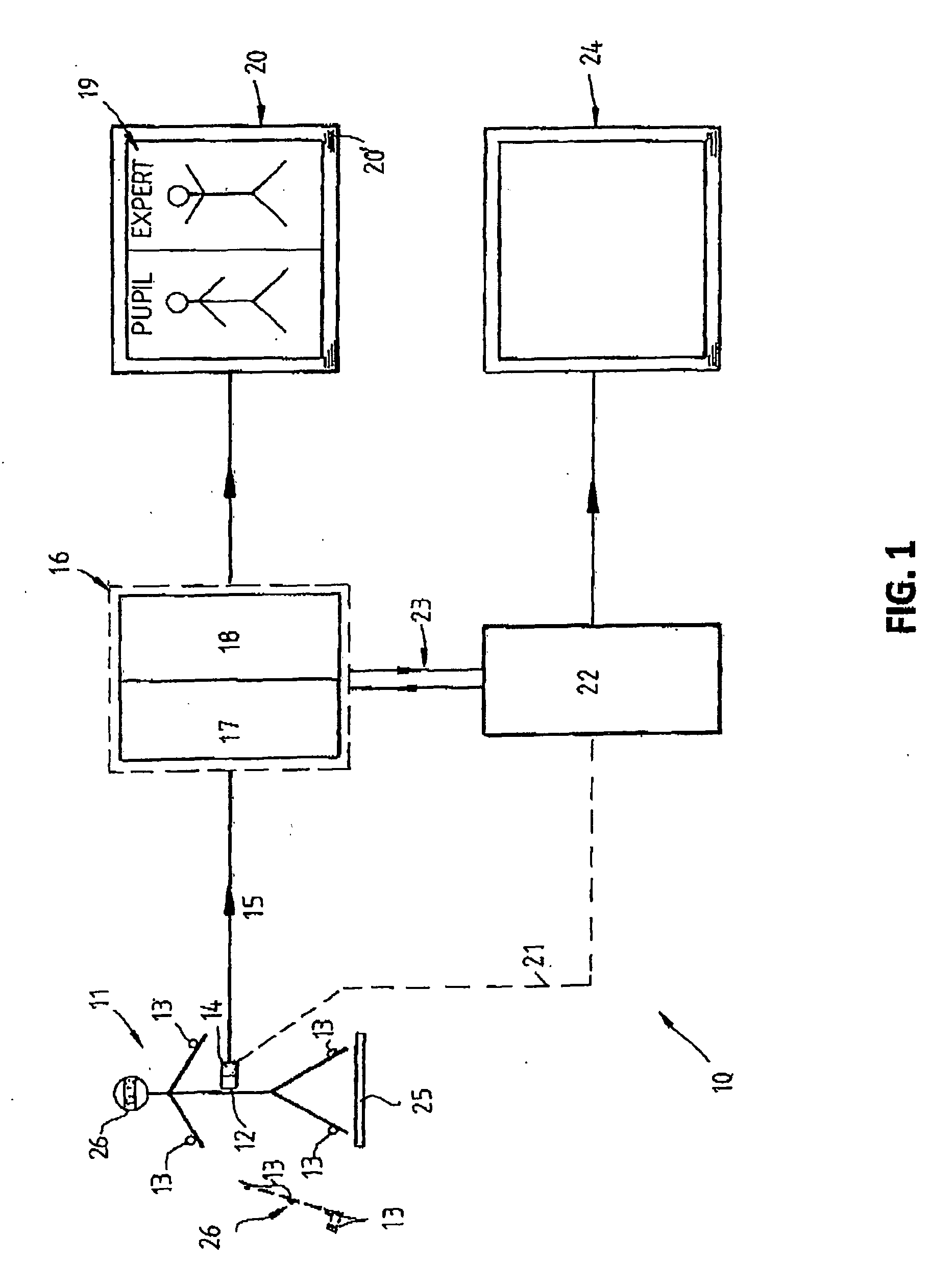
Method and apparatus for providing personalised audio-visual instruction
InactiveUS20100015585A1Improve techniqueCosmonautic condition simulationsGymnastic exercisingPersonalizationMems sensors
A method of and apparatus (10) for providing a personalized audio-visual instructional aid for assisting a person (11) to emulate preferred positions and / or movements in undertaking an activity by capturing position and / or movement data of the person (11) or an object associated with and controlled by the person undertaking the activity using position and / or movement sensing devices such as MEMS sensors (13) on the person (11) or object and using a computer (16) to analyze and compare the captured data with pre-stored data relating to preferred positions and / or movement in undertaking the activity and generating a visual presentation (19) based on the differences between the captured position and / or movement of the person or object and the preferred positions and / or movement and adding to the generated visual presentation, audio instructional comments relating to the differences.
Owner:BAKER RICHARD JOHN
Method and apparatus for distributed indexing
InactiveUS20070079004A1Improve techniqueDigital computer detailsProgram controlDistributed computingGrid computing
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for providing range based queries over distributed network nodes. Each of a plurality of distributed network nodes stores at least a portion of a logical index tree. The nodes of the logical index tree are mapped to the network nodes based on a hash function. Load balancing is addressed by replicating the logical index tree nodes in the distributed physical nodes in the network. In one embodiment the logical index tree comprises a plurality of logical nodes for indexing available resources in a grid computing system. The distributed network nodes are broker nodes for assigning grid computing resources to requesting users. Each of the distributed broker nodes stores at least a portion of the logical index tree.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
Fiber optic cable spool
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
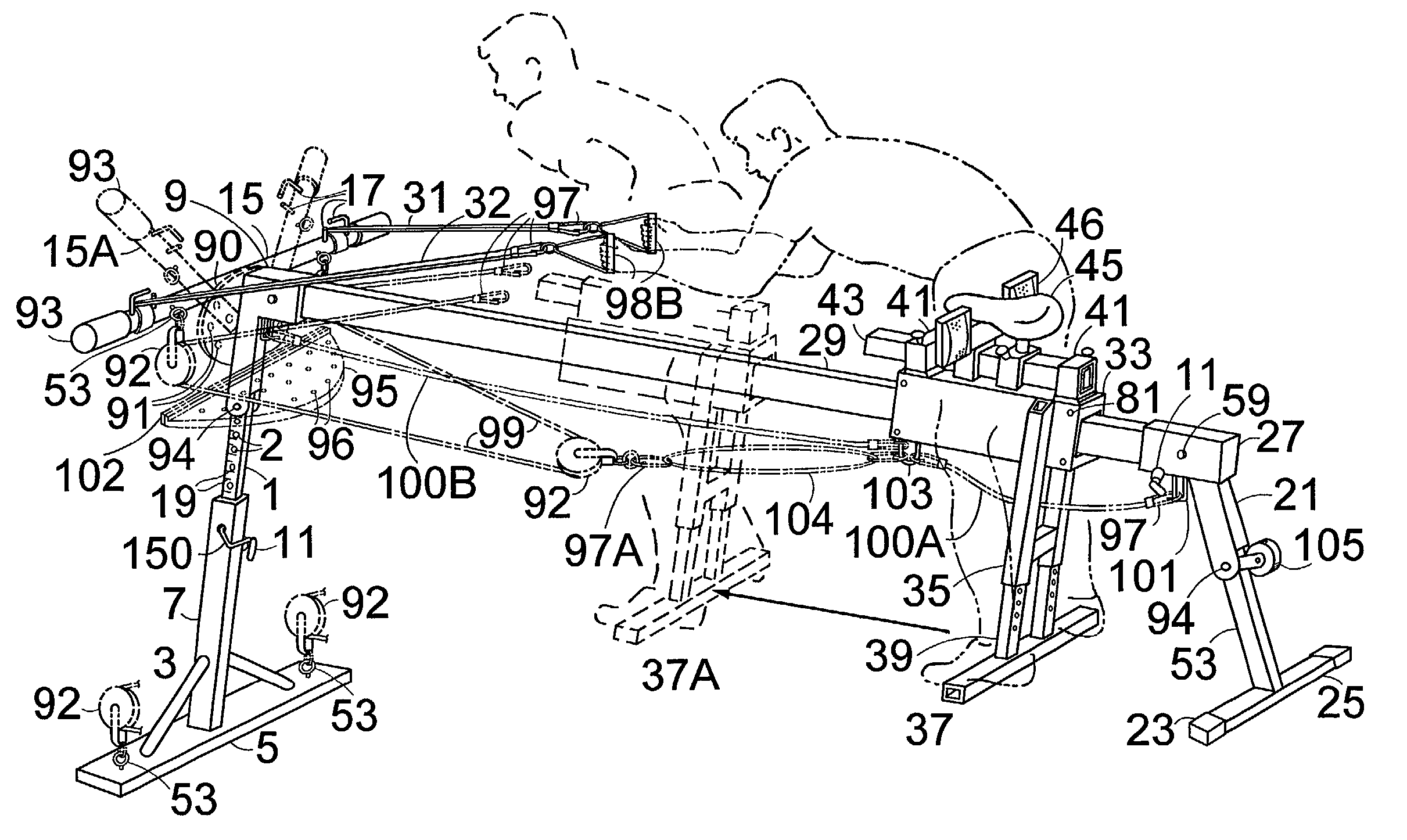
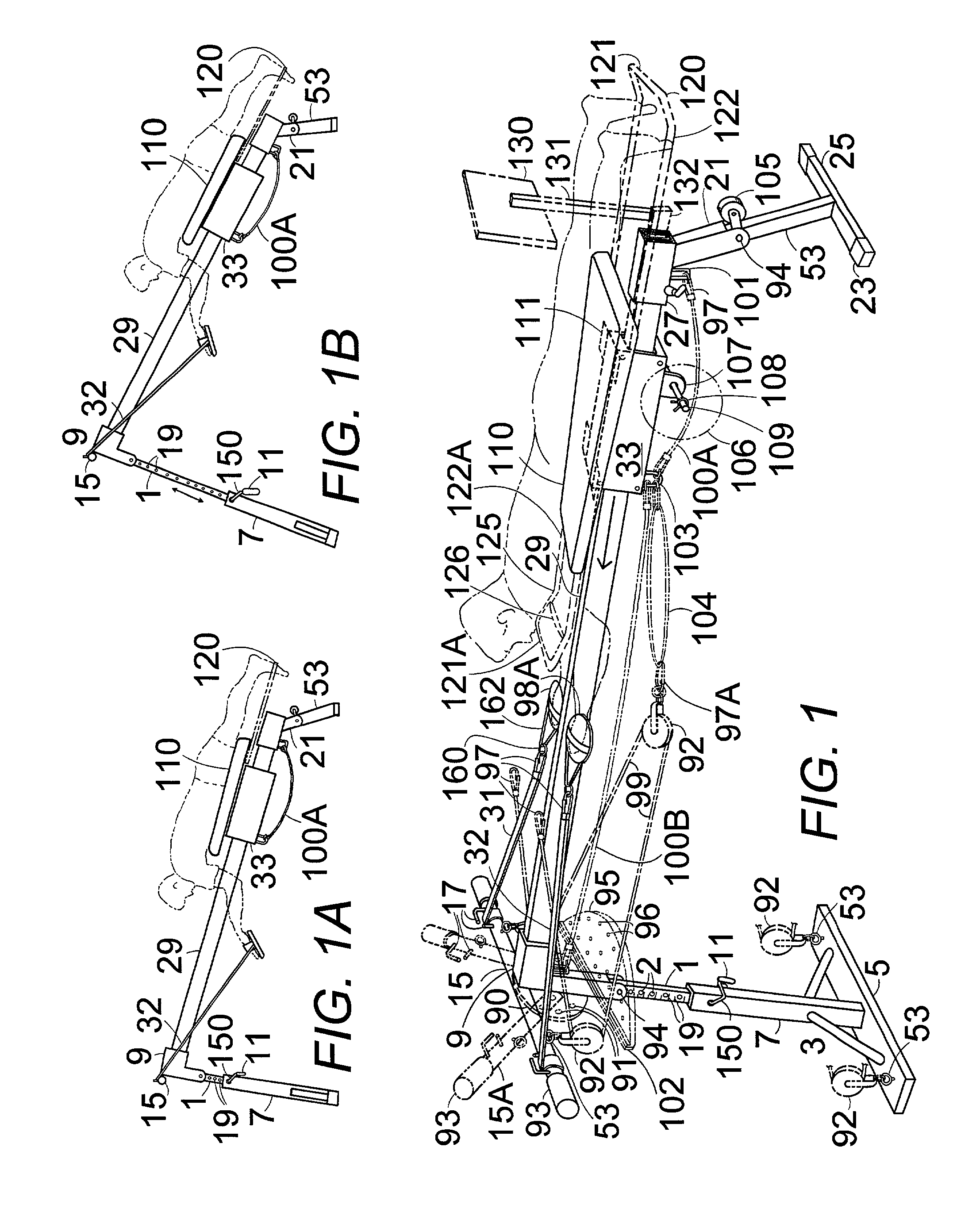
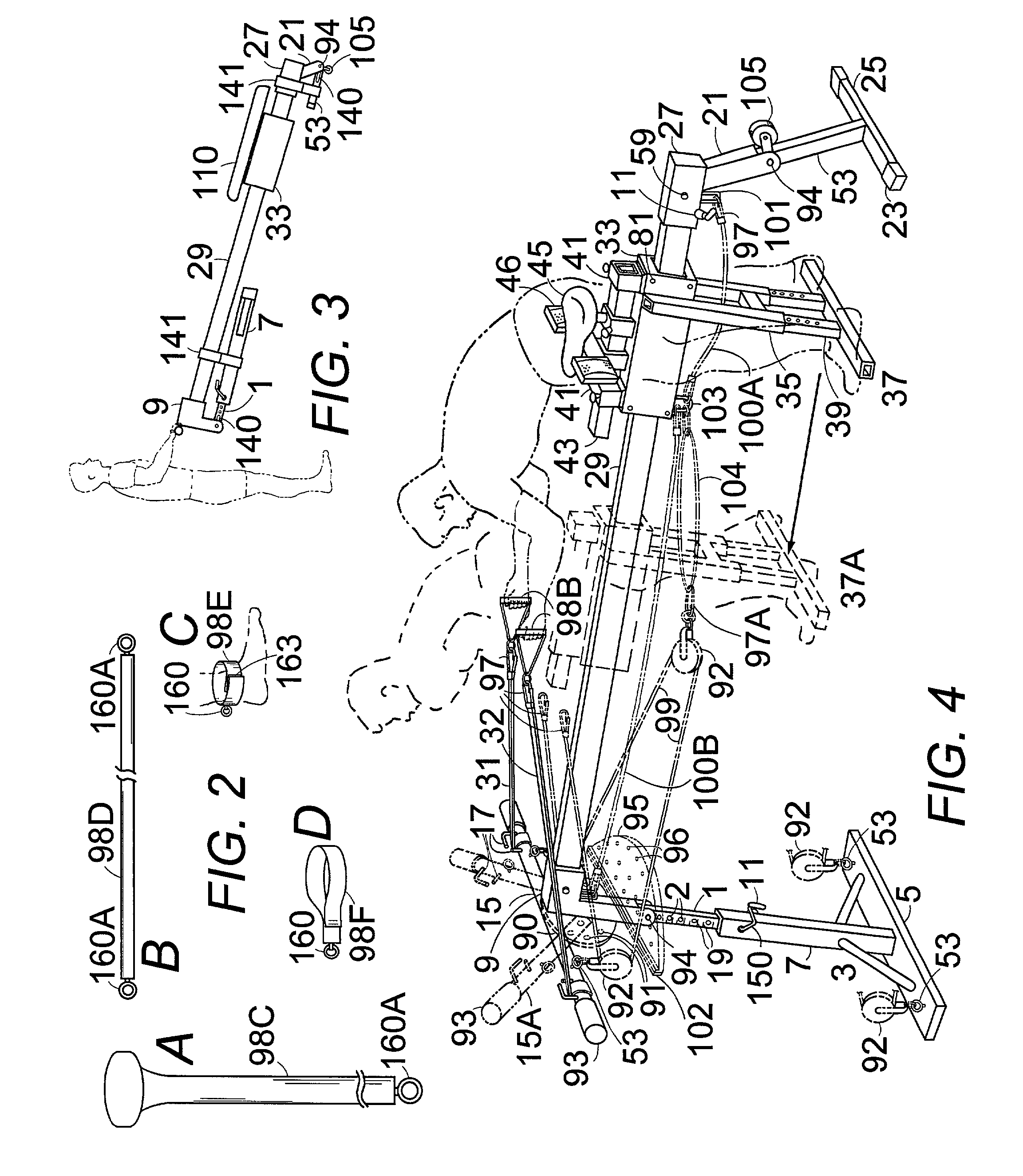
Multi-sport training machine with inclined monorail and roller carriage
ActiveUS7204790B2Improve technique and efficiencyGreat or less resistanceStiltsWeightsEngineeringSport training
An inclined monorail mounts between an adjustable front stanchion and lower rear stanchion. A roller carriage, having a padded bench or seat and spool-shaped rollers, rolls on the monorail. Elasticized tension straps attach between the roller carriage and the front or the rear stanchion to assist or resist the movement of the roller carriage. The user pulls on interchangeable handles either on pull straps on a front bar or a cable pulley system attached to the front stanchion and to the roller carriage to exercise and simulate various sports movements while moving the roller carriage. The stanchions pivot flat onto the monorail to transport the apparatus on a stanchion wheel or mount it vertically on a wall bracket and the cable pulley system lifts the roller carriage vertically with weights on the roller carriage. A detachable foot platform attaches to the rear stanchion for performing leg exercises.
Owner:SLEAMAKER ROBERT H
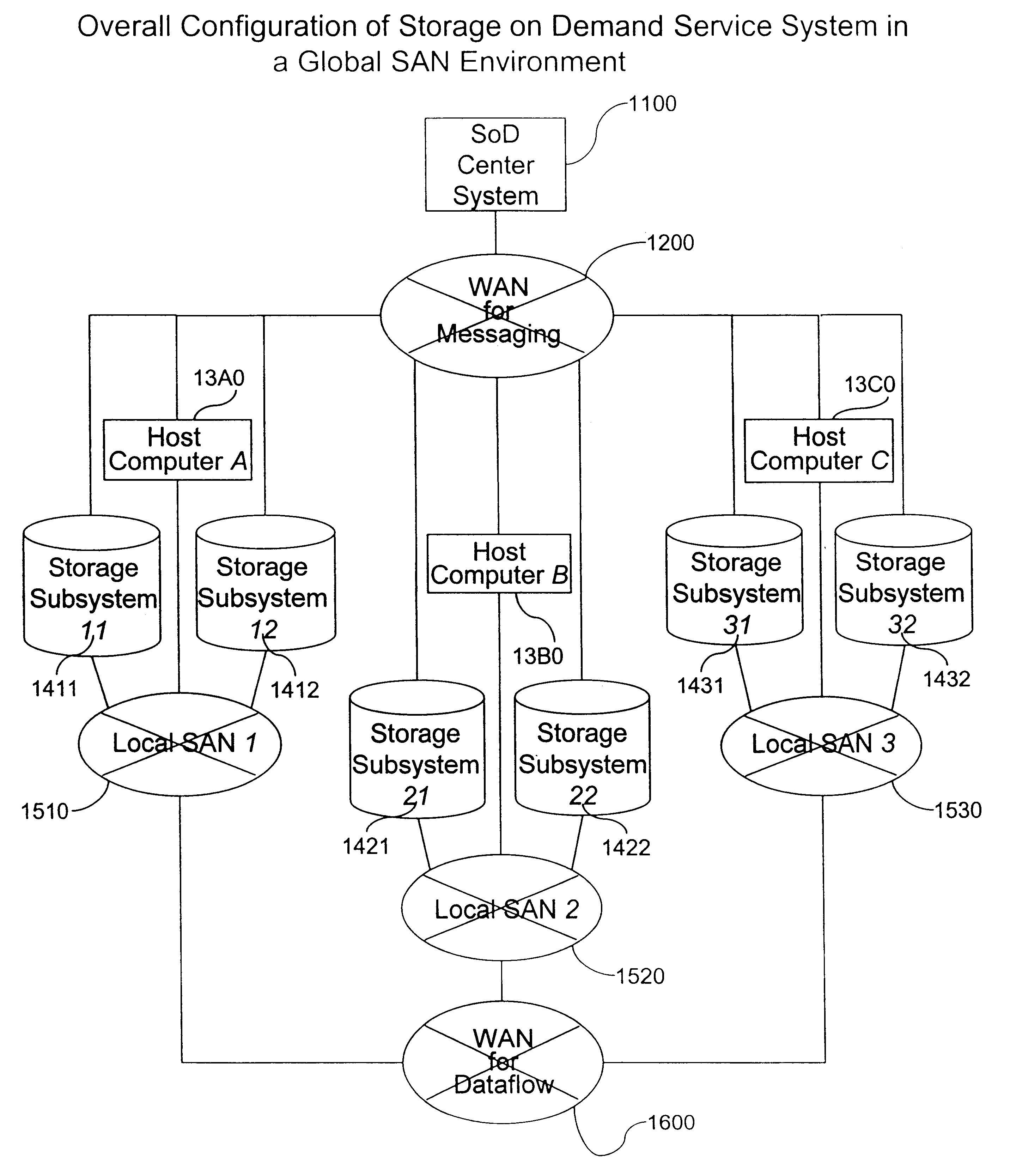
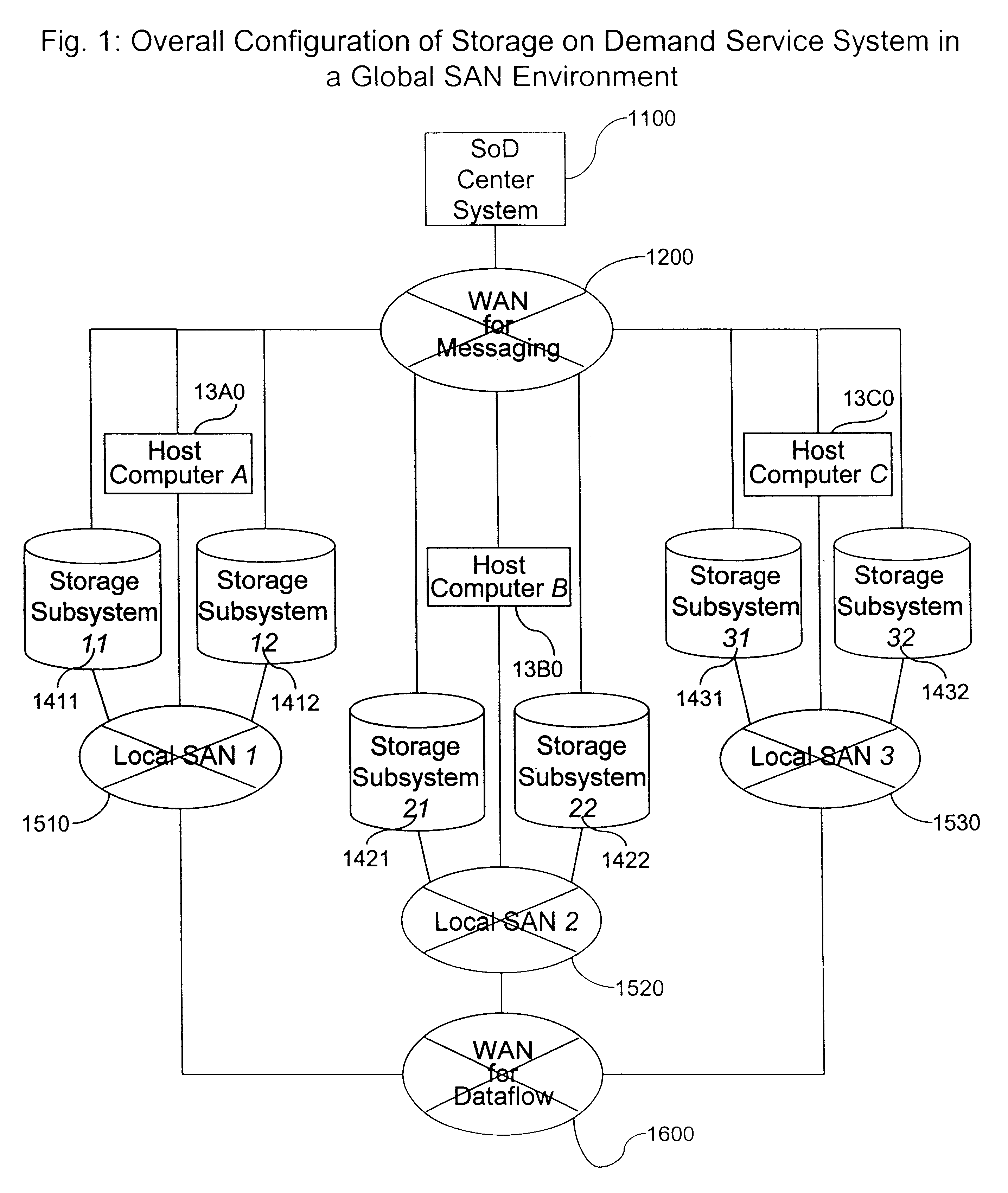
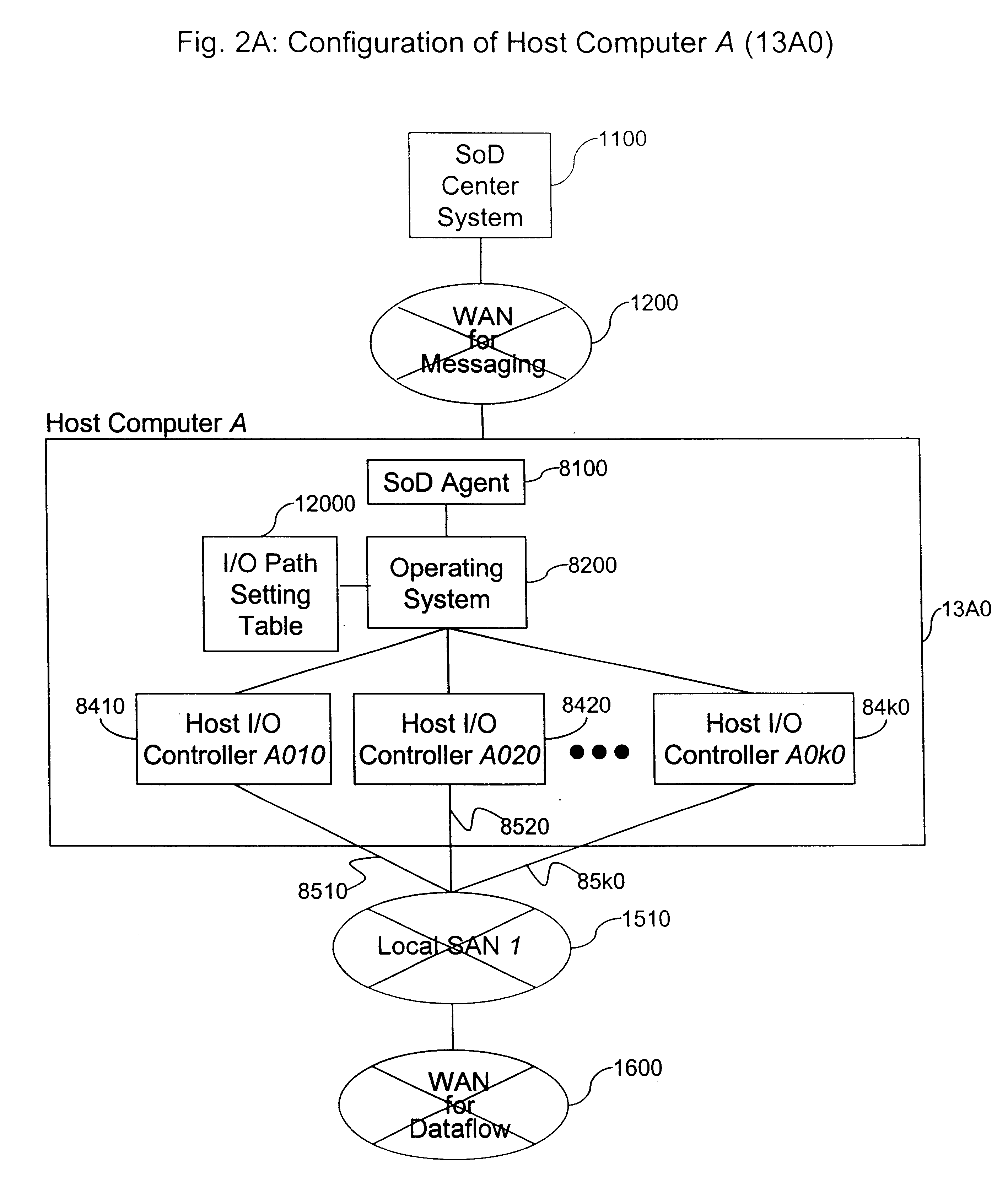
System and method for storage on demand service in a global SAN environment
InactiveUS6839815B2Improve techniqueSimple technologyData processing applicationsInput/output to record carriersOn demandDistributed computing
The present invention provides improved techniques for managing storage resources, such as disk drives, I / O ports, and the like distributed among a plurality of sites according to user demand for these storage resources. Specific embodiments provide users the capability to bring new resources on line, define pathways between resources, and the like. Embodiments can obviate the need for system programmers to manually configure storage resources at a user's site.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
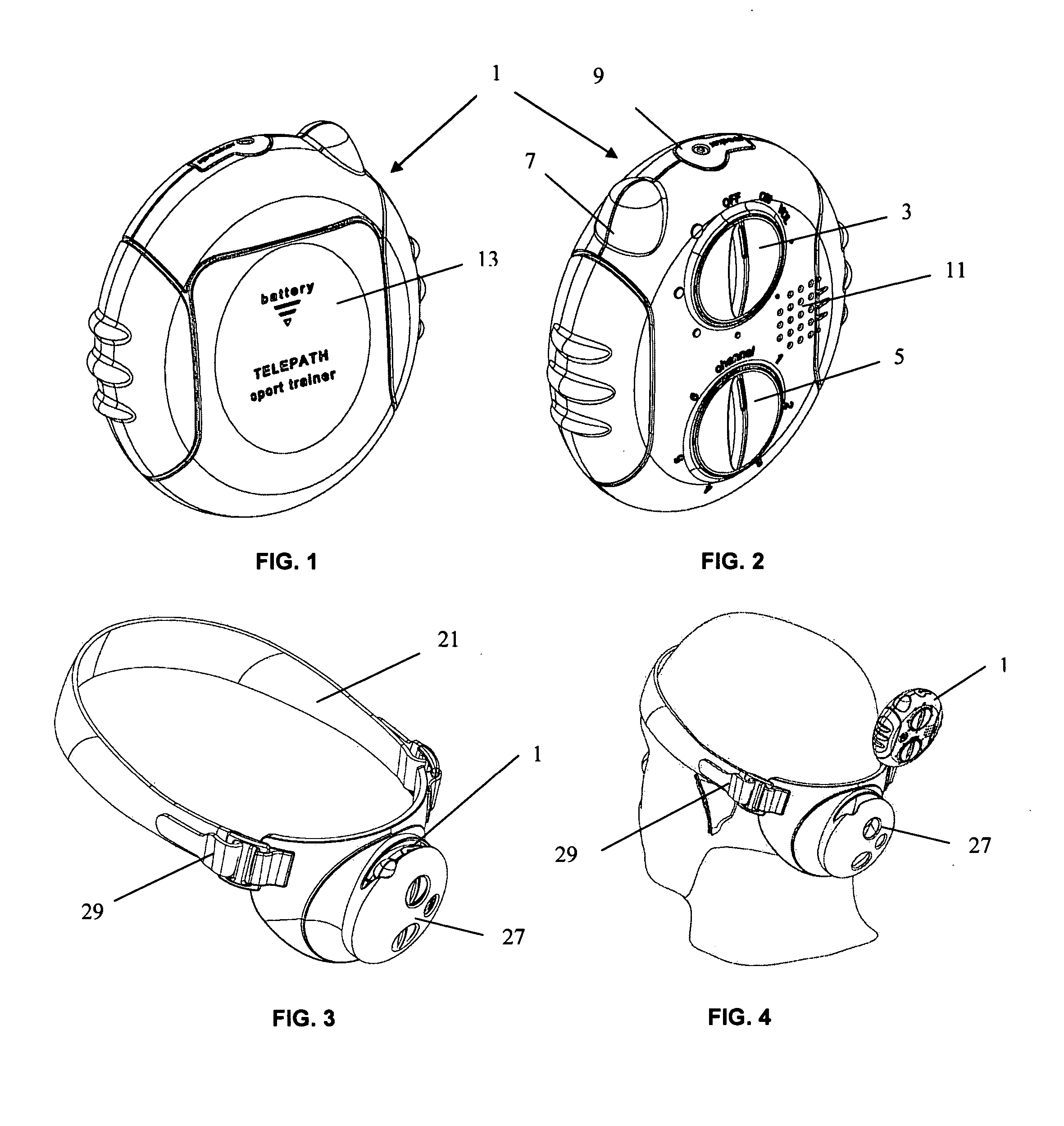
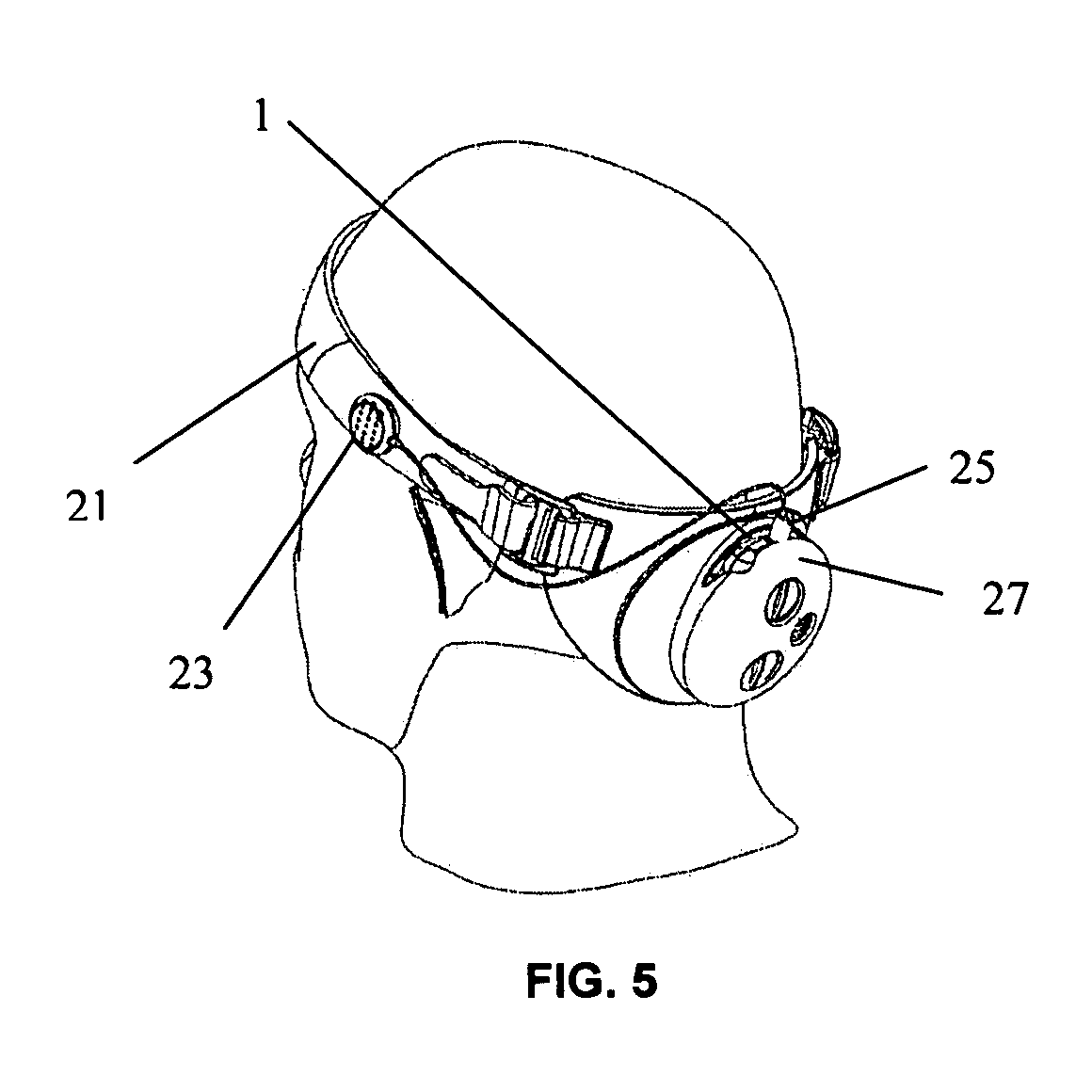
Telepath sports training system
InactiveUS20050212202A1Learn curve be greatly improveImprove techniqueSport apparatusPhysical trainerLoudspeaker
A system of communication for providing instruction, information, and verbal commands between a teacher and a student. An exemplary embodiment of the invention is particularly suited for use between a sports coach and the players on his or her team. The system of the present invention is preferably comprised of a microphone for the coach, a transmitter, at least one receiver, and at least one speaker for at least one player.
Owner:RPM SPORTS
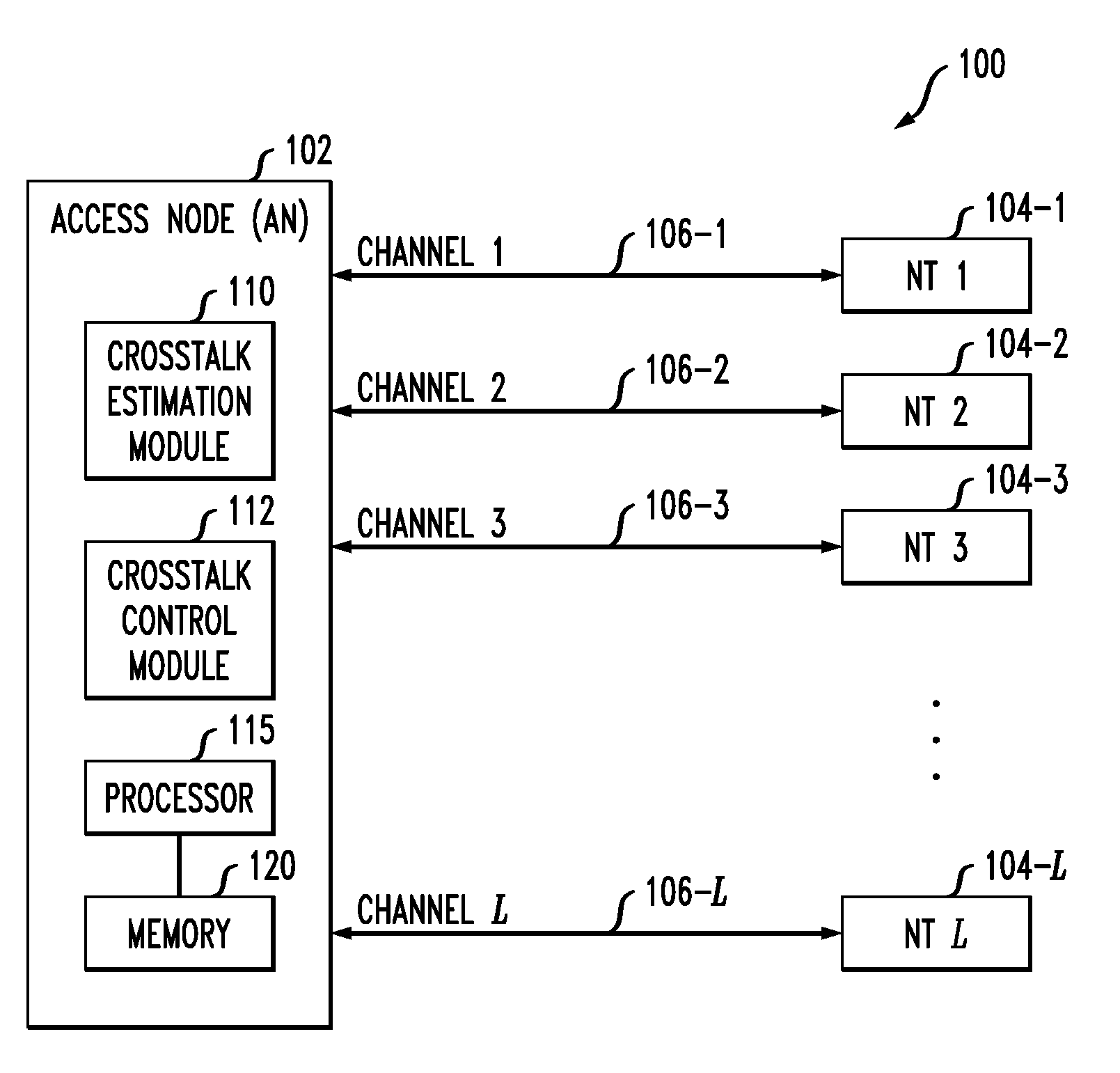
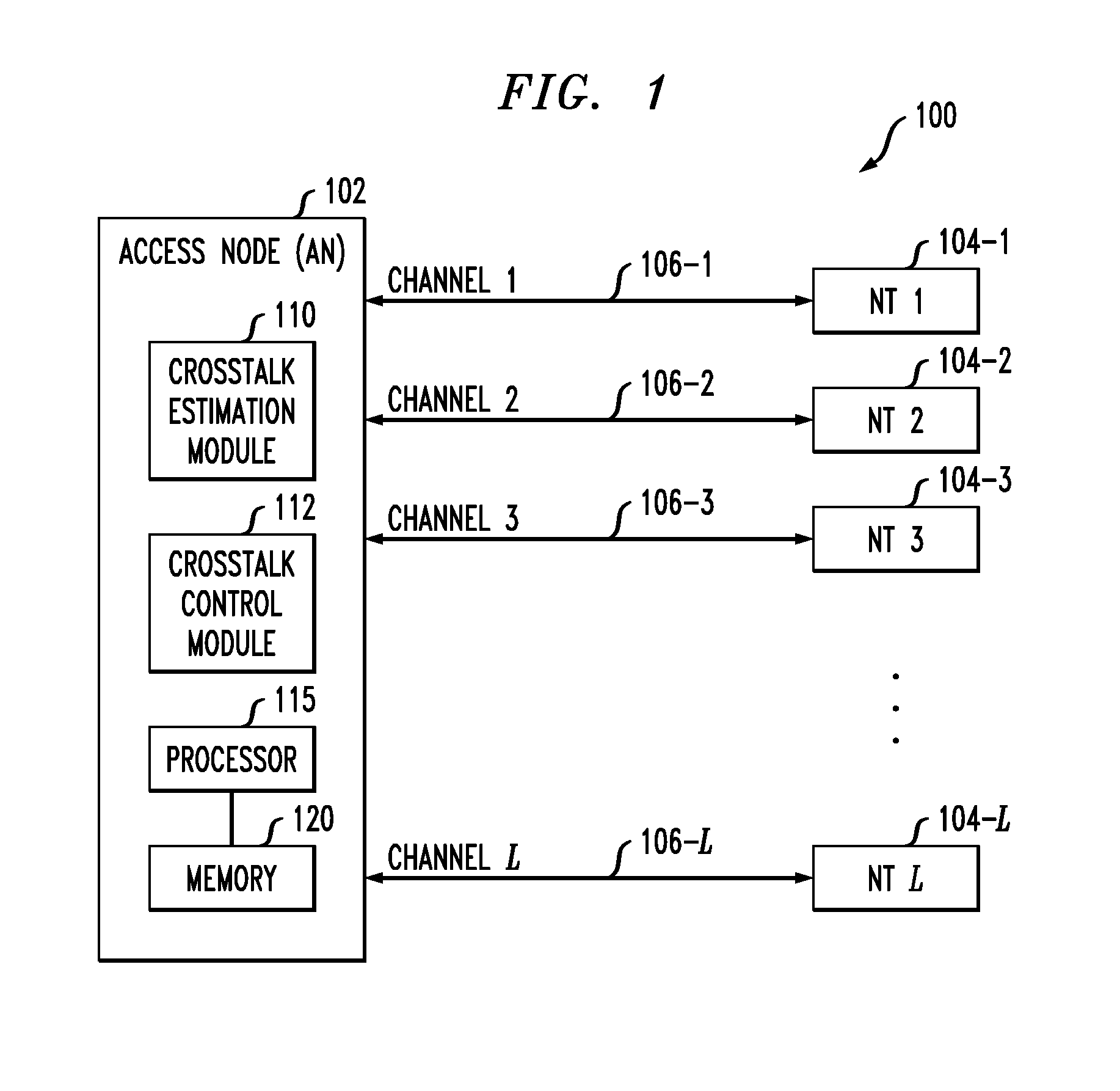
Channel estimation utilizing control signals transmitted by an activating line during initialization
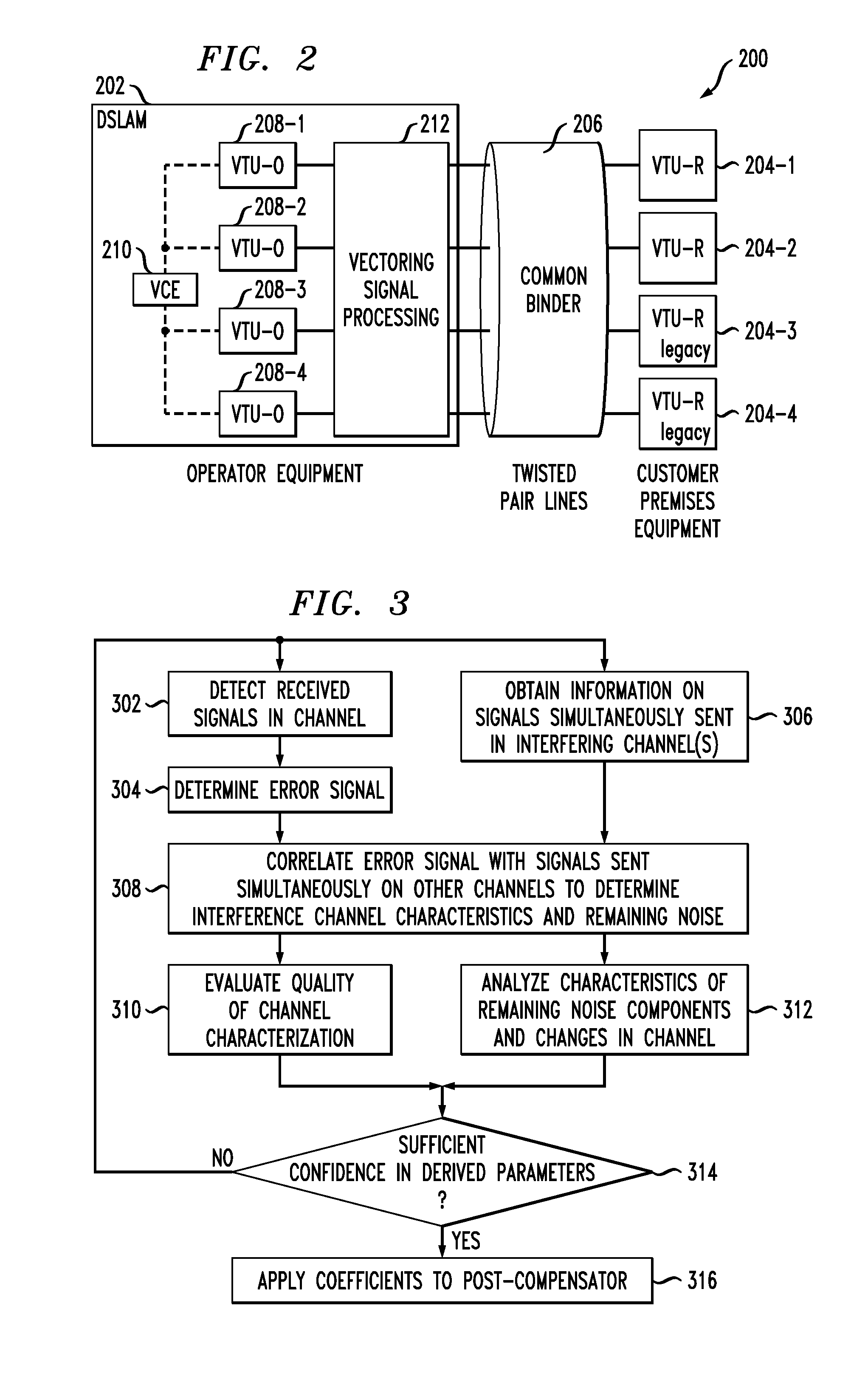
ActiveUS20120082258A1Improve techniqueSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsSignal processingError signal
An access node of a communication system is configured to control crosstalk between an activating channel associated with a first network terminal of a communication system and active channels associated with respective other network terminals of the system. The access node detects a control signal sent by the first network terminal over the activating channel in a designated phase of an initialization process of the first network terminal, determines an error signal from the detected control signal, correlates the error signal with one or more corresponding signals sent by respective ones of the other network terminals over the active channels, estimates crosstalk from the active channels into the activating channel based on the correlation, and configures a vectoring signal processing module to control the estimated crosstalk. The control signal sent by the first network terminal comprises a value that is selected by the first network terminal from a set of two or more values and prior to its detection the particular selected value is unknown to the access node.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
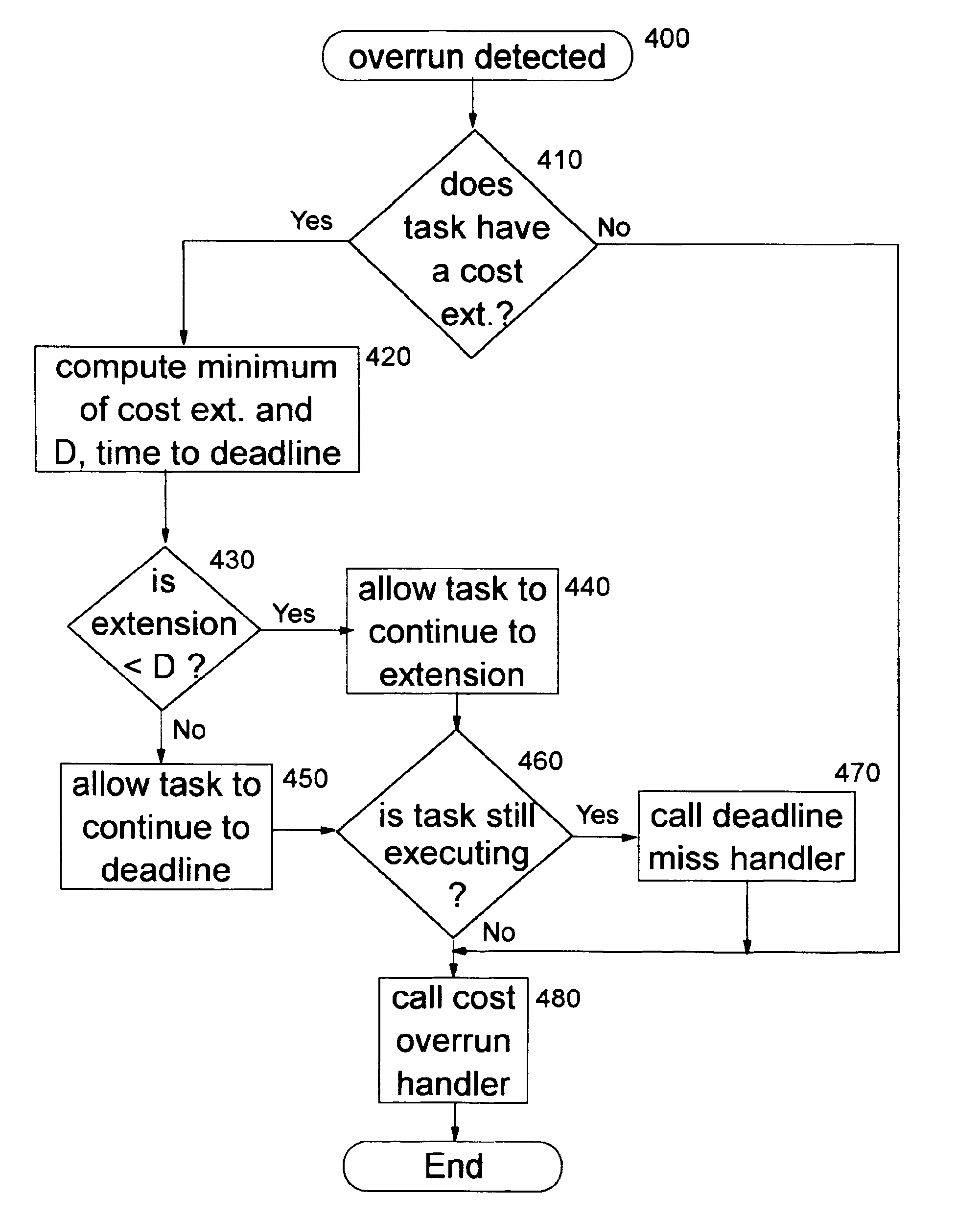
System for incrementally computing the maximum cost extension allowable for subsequent execution of each task using fixed percentage of the associated cost
InactiveUS6957431B2Improve techniqueSimple technologyProgram initiation/switchingMemory systemsRelevant costComputer program
The present invention provides a method, system, and computer program product for improving scheduling of tasks in systems that accumulate execution time. An upper bound is computed on the amount of additional time each schedulable task in the system may continue to execute after exceeding its predetermined cost, without adversely affecting overall operation of the system (that is, ensuring that the continued execution will not cause invocations of subsequent tasks to fail to meet their execution deadlines). By allowing tasks to run longer, the potential that the task will successfully end is increased, thereby yielding a more efficient overall system. In the preferred embodiment, the extensions are iteratively computed as a fixed percentage of the cost of each task until reaching an amount of time where the system is no longer feasible. The extension values resulting from the iteration before the cost-extended system becomes infeasible are then used at run-time when a particular task encounters an overrun condition. This technique is advantageous in systems where execution of non-schedulable entities (such as occurrence of hardware interrupts) occurs during execution of one or more of the scheduled tasks.
Owner:IBM CORP
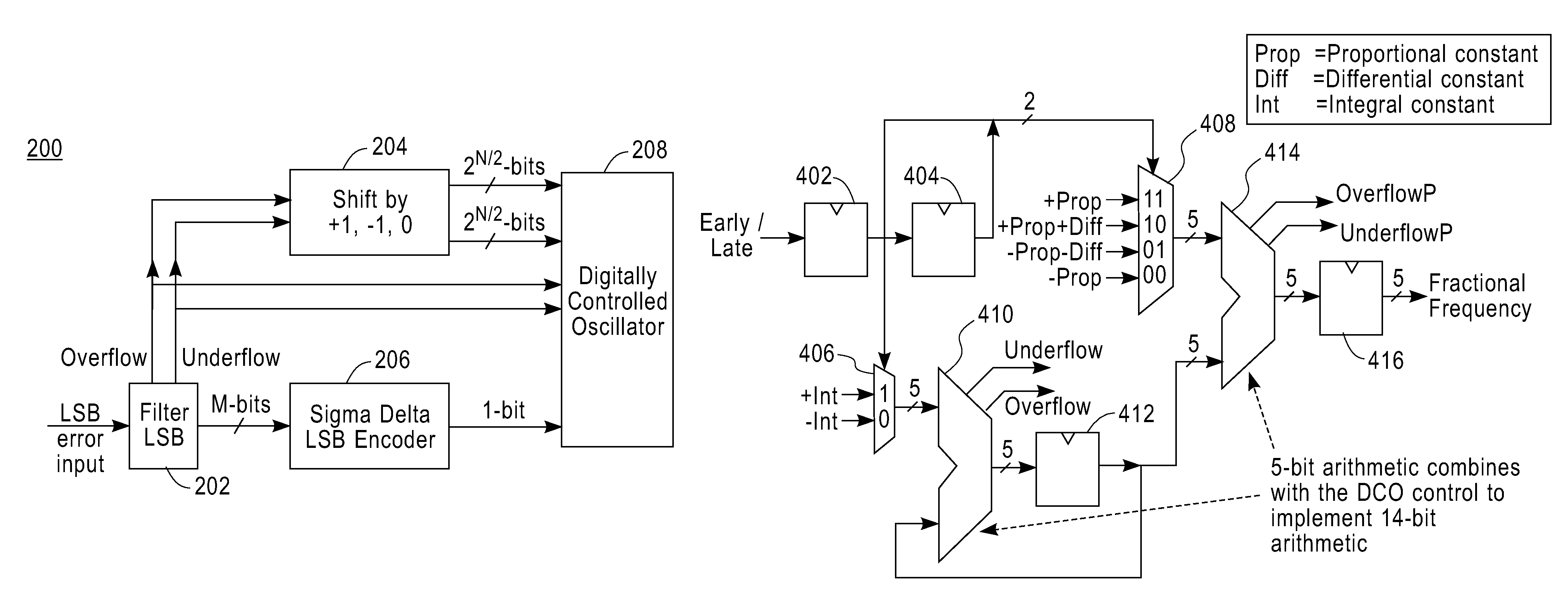
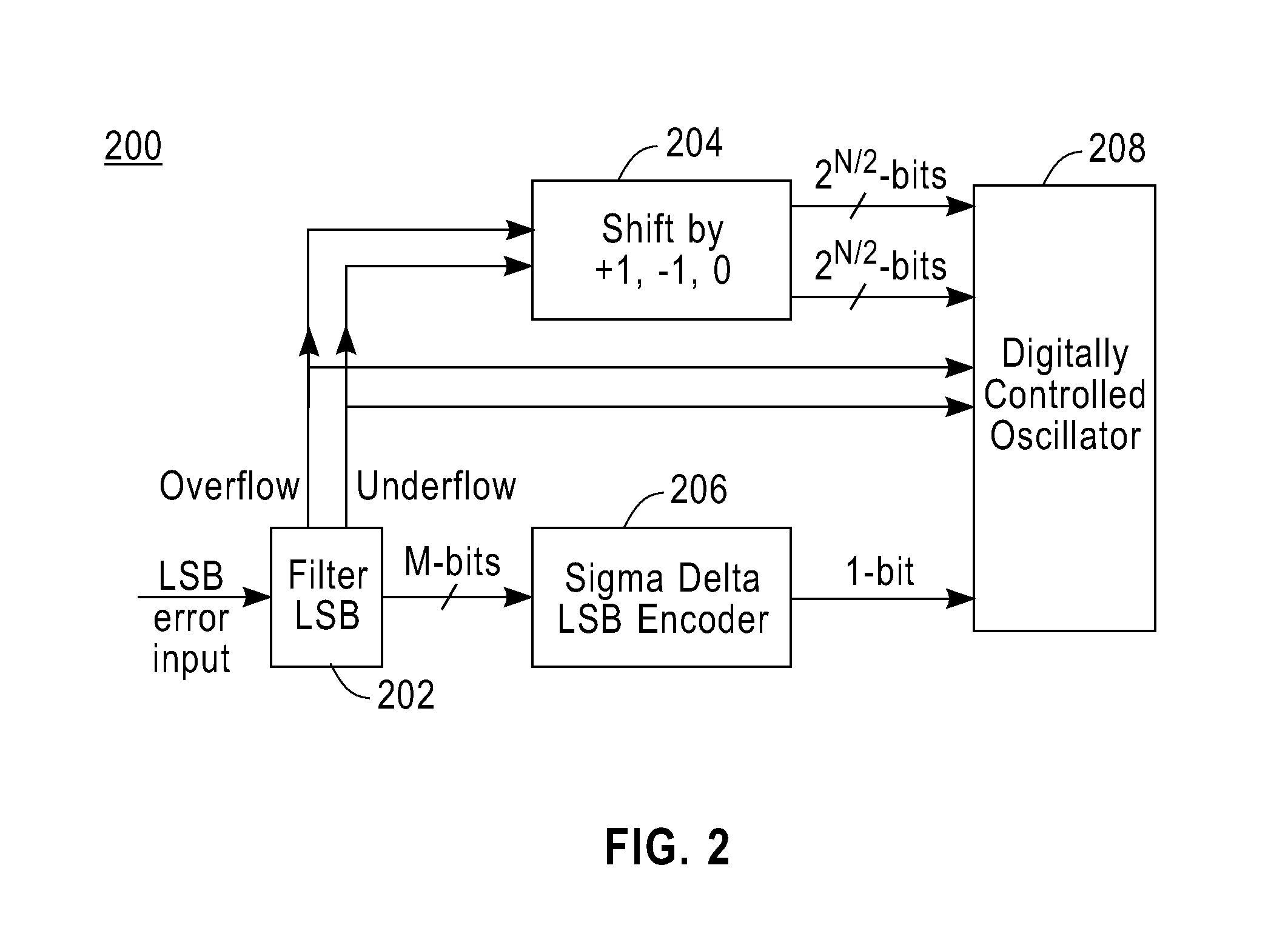
Method and apparatus for efficient implementation of digital filter with thermometer-code-like output
InactiveUS7352297B1Improve techniqueReduce complexityPulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsThermometerSign extension
A technique is disclosed for processing a binary coded signal to generate a thermometer coded signal. Such technique includes the following steps. A binary coded input signal is obtained. A binary arithmetic operation is performed on a least significant bit (LSB) portion of the binary coded input signal. At least one signal representative of an occurrence of one of an overflow condition and an underflow condition is generated, in response to the binary arithmetic operation performed on the LSB portion. A thermometer coded signal is shifted in response to the signal representative of the occurrence of one of the overflow condition and the underflow condition, wherein shifting of the thermometer coded signal represents one of incrementing and decrementing a most significant bit (MSB) portion of the binary coded input signal. The thermometer coded signal is outputted. Performance of the binary arithmetic operation on the LSB portion of the binary coded input signal and shifting of the thermometer coded signal in response to one of the overflow condition and the underflow condition results in elimination of a sign extension into the MSB portion of the binary coded input signal.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
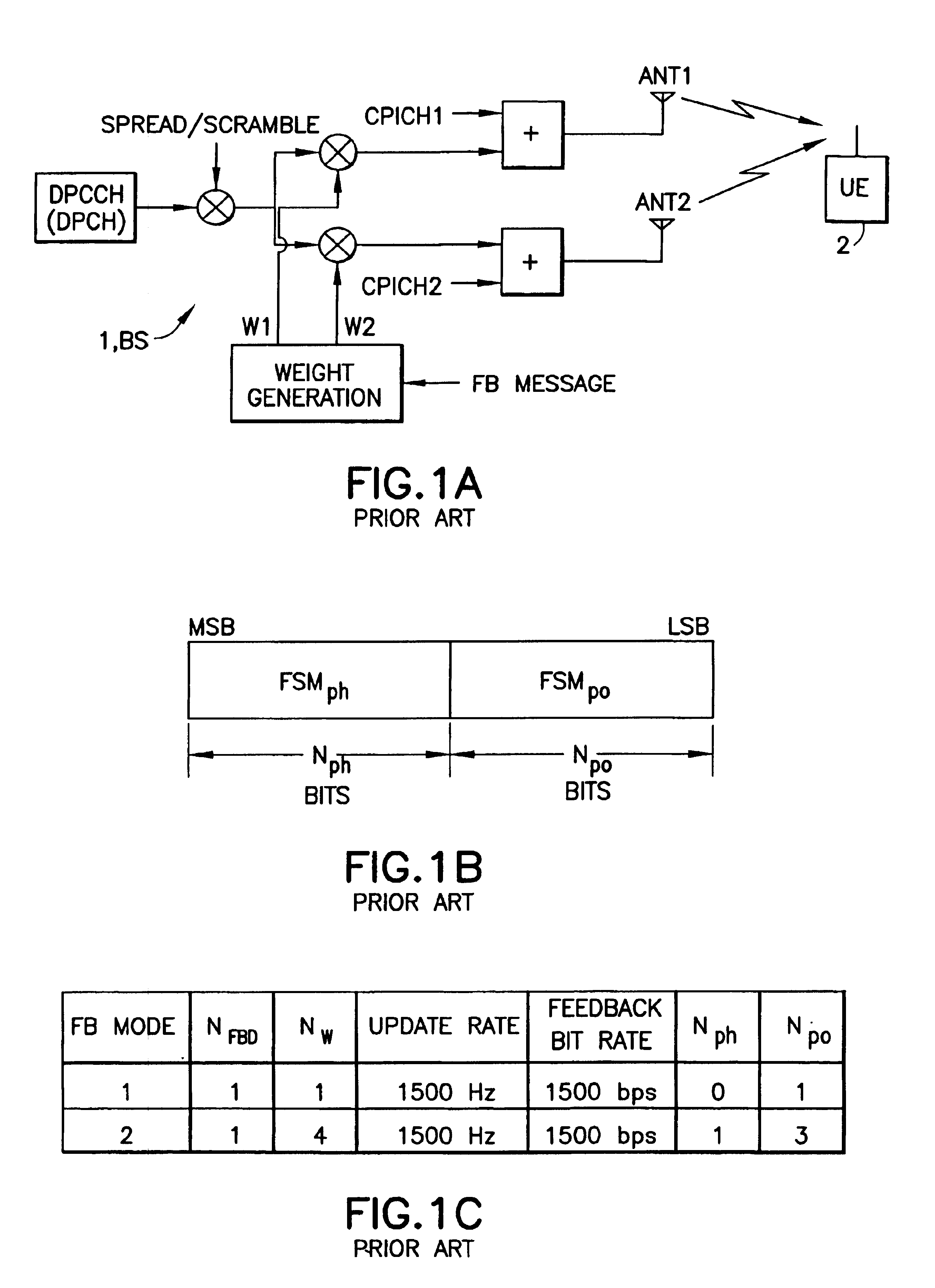
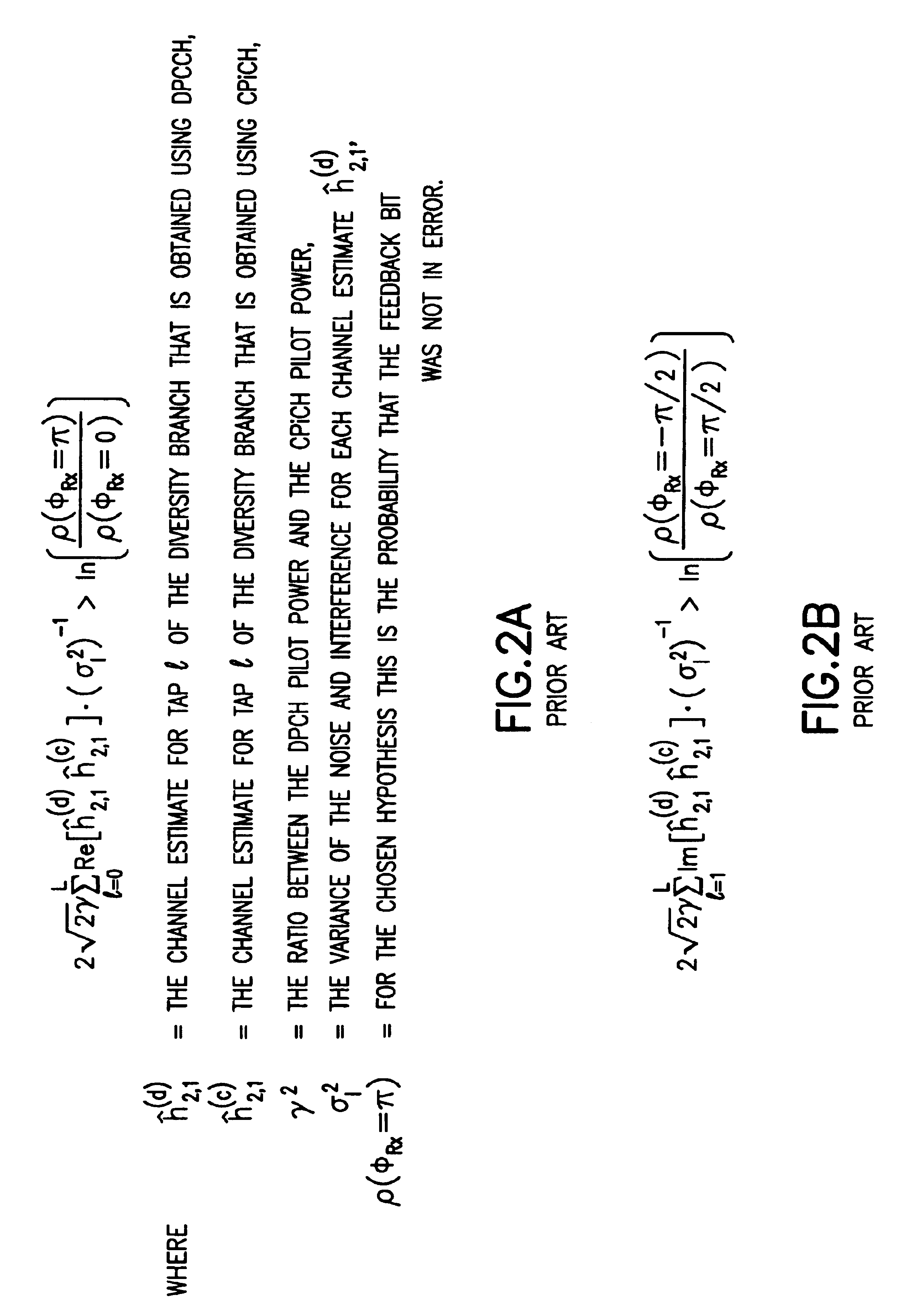
Antenna phase estimation algorithm for WCDMA closed loop transmitter antenna diversity system
InactiveUS6839326B1Improve techniqueSimple techniqueSpatial transmit diversityError preventionPhase shiftedW-CDMA
This invention teaches a method for use in a wideband CDMA telecommunications system wherein the base station (BS) utilizes transmit antenna diversity. The method enables the user equipment (UE) to perform a channel estimate for channels received from two antennas of the base station (BS), and includes steps of: (a) computing an estimated phase difference between a common pilot channel and a dedicated pilot channel received from one antenna of the two antennas; and (b) determining the channel estimate by rotating a common pilot channel estimate according to the estimated phase difference, where the phase difference is computed as a complex coefficient between the common pilot channel and the dedicated pilot channel. In a second aspect this invention teaches a method for use in a transmit antenna diversity system for enabling the UE to verify an antenna phase shift previously signaled by the UE to the BS. This method includes a first step of: (a) exploiting prior knowledge of BS rotation angle by considering a vector x that includes all hypotheses for complex rotation coefficients of the BS with respect to all possible rotation angles, in accordance with a decision rule for an estimation of a complex rotation coefficient. A second step of the method evaluates a cost function of a hypothesis m by considering the prior knowledge.
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
Composite Ceramic Substrate For Micro-Fluid Ejection Head
InactiveUS20080299361A1Improve flatnessEasy to packInking apparatusCeramic layered productsElectrical conductorComposite ceramic
A composite ceramic substrate for receiving an ejection head chip for a micro-fluid ejection head and a method for making the composite ceramic substrate. The substrate includes a high temperature previously fired ceramic base having a substantially planarized first surface and at least one fluid supply slot therethrough. A low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) tape layer bundle having at least two LTCC tape layers is attached to the ceramic base at an interface between the LTCC tape layer bundle and the first surface of the ceramic base. The LTTC tape layer bundle has at least one chip pocket therein and at least one of the LTCC tape layers includes a plurality of conductors.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Hypotube based support catheter
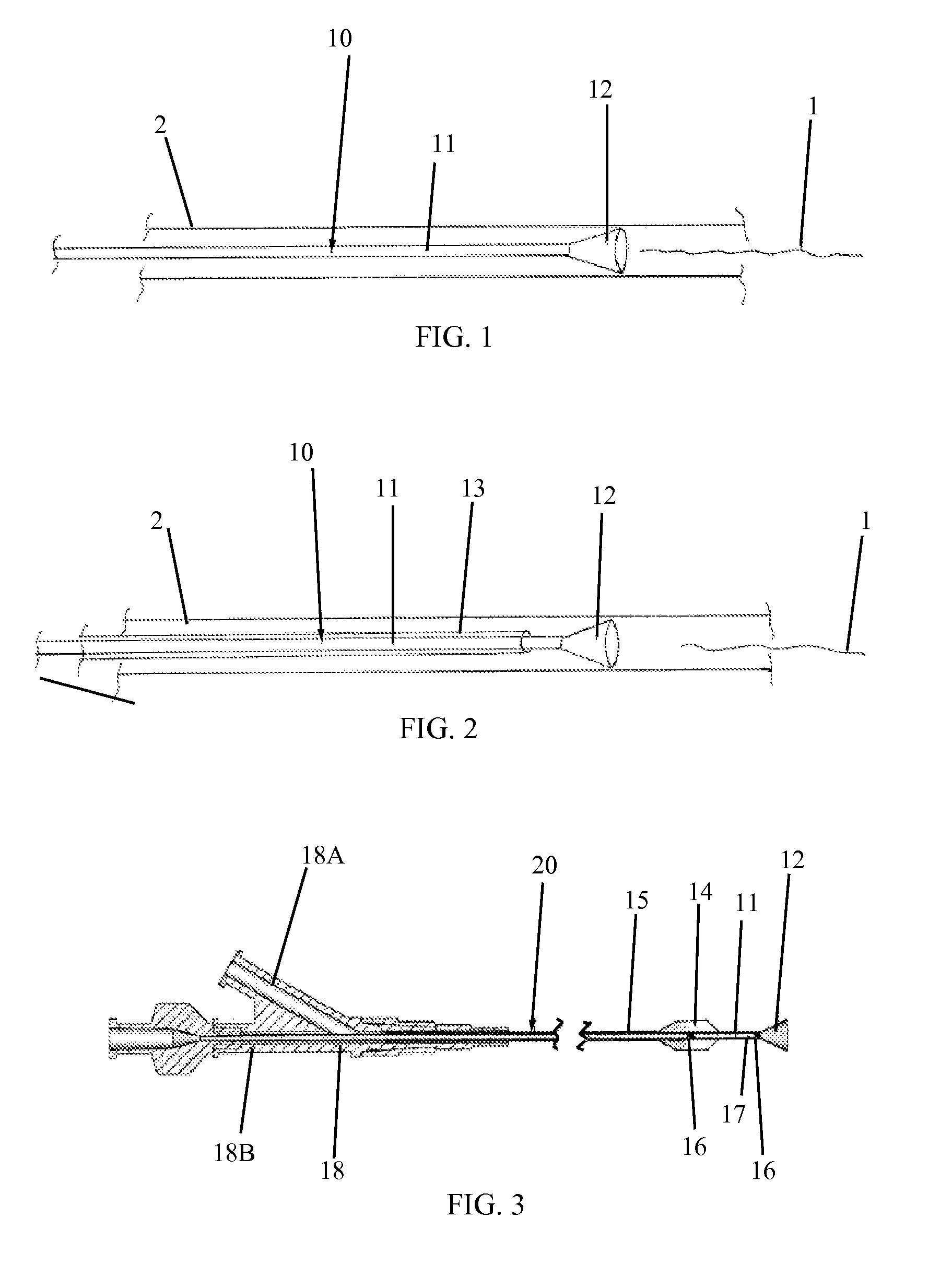
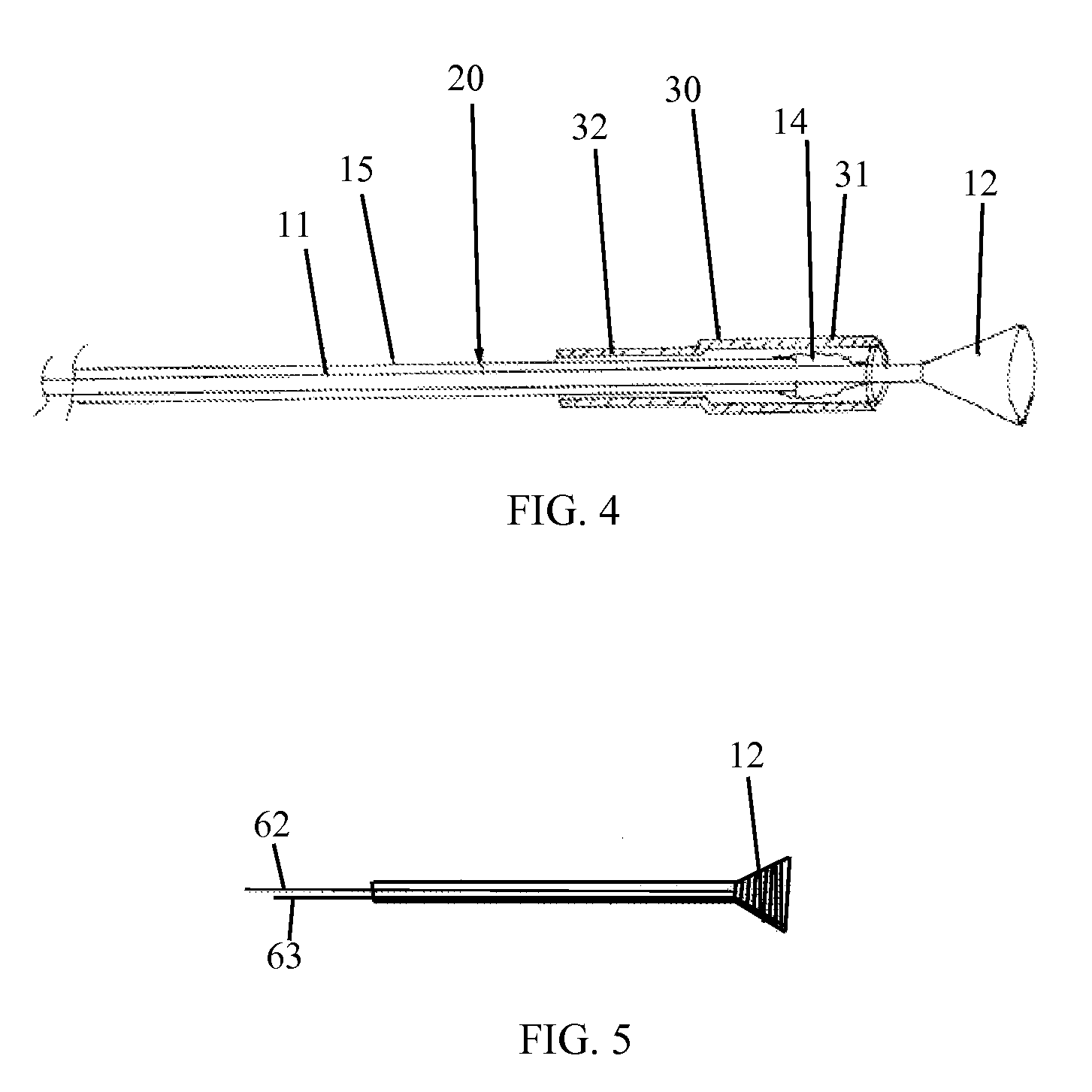
ActiveUS20140031843A1Increase successImprove techniqueCannulasGuide wiresPercutaneous angioplastyBlood vessel
Hypo-tube based support catheter (1) for treating blood vessels, such as below the knee (BTK) blood vessels and other blood vessels (e.g., coronary, pediatric), which are partially or totally occluded. The tip of the support catheter (1) of the invention is shapeable to any desired shape before the insertion of the device into the blood vessel. The disclosed device enables improved angioplasty treatment of blood vessels, especially with a retrograde approach.
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
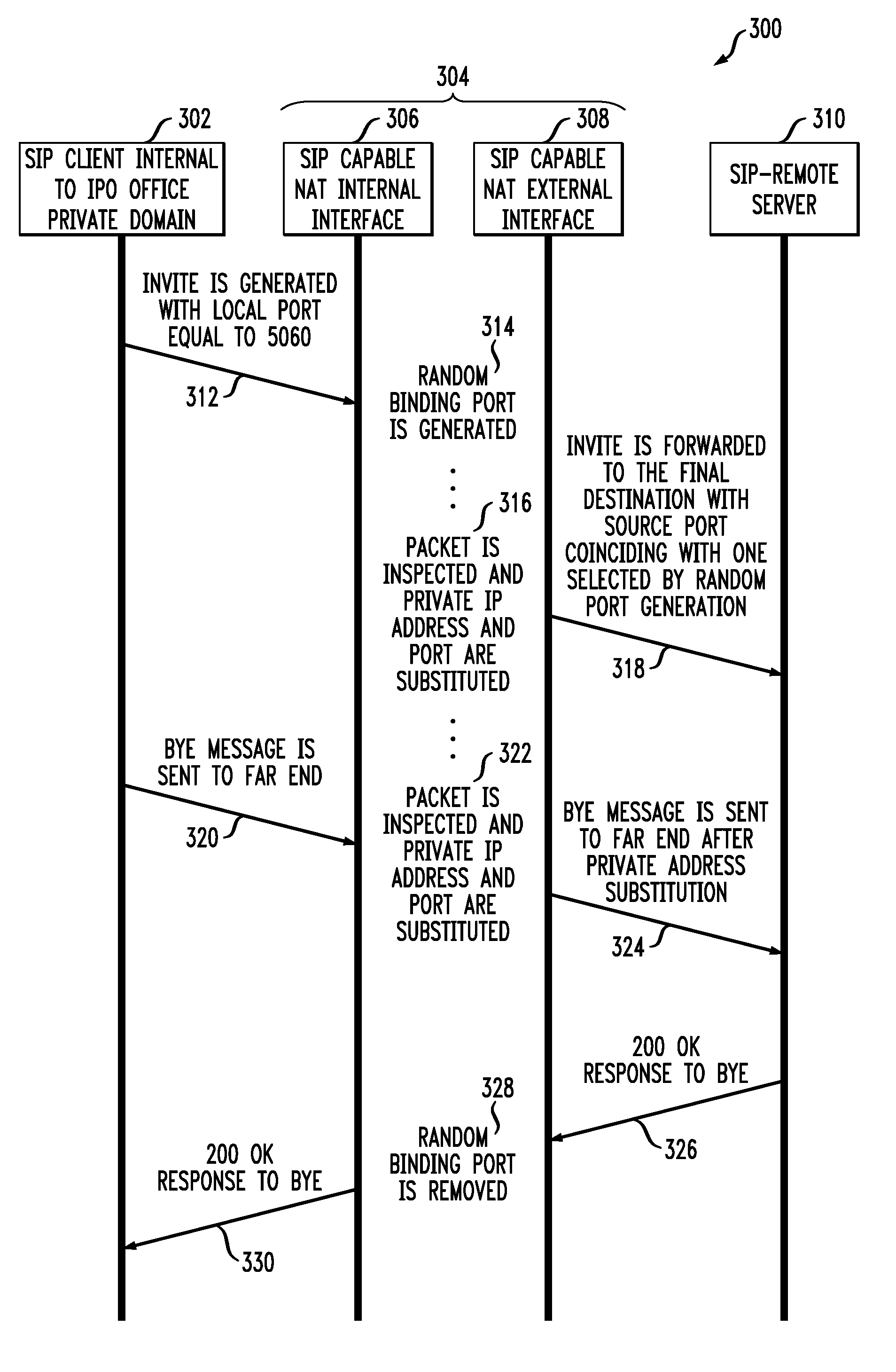
Network address translation in session initiation protocol based application
ActiveUS20080080510A1Improve techniqueTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationLogical addressUnique identifier
Improved techniques are disclosed for providing network address translation (NAT) in a session initiation protocol (SIP) based application. For example, a method for use in a router for performing NAT on a SIP message associated with a session being initiated between a first device and at least a second device, wherein the first device is part of a first network and the second device is part of a second network, includes the following steps. A SIP message is obtained from the first device, wherein a header field of the SIP message includes a local address and local port number usable by the first device on the first network. A port number to be associated with the session being initiated is randomly selected. The randomly selected port number is usable on the second network. An association (e.g., a binding) is generated between the randomly selected port number and a global address usable on the second network, the local address and the local port number. The local address and the local port number are substituted in the header field of the SIP message with the global address and the randomly selected port number thereby generating an address-translated SIP message. The address-translated SIP message is sent to the second device on the second network. The randomly selected port number may serve as a unique identifier for the session being initiated.
Owner:AVAYA ECS
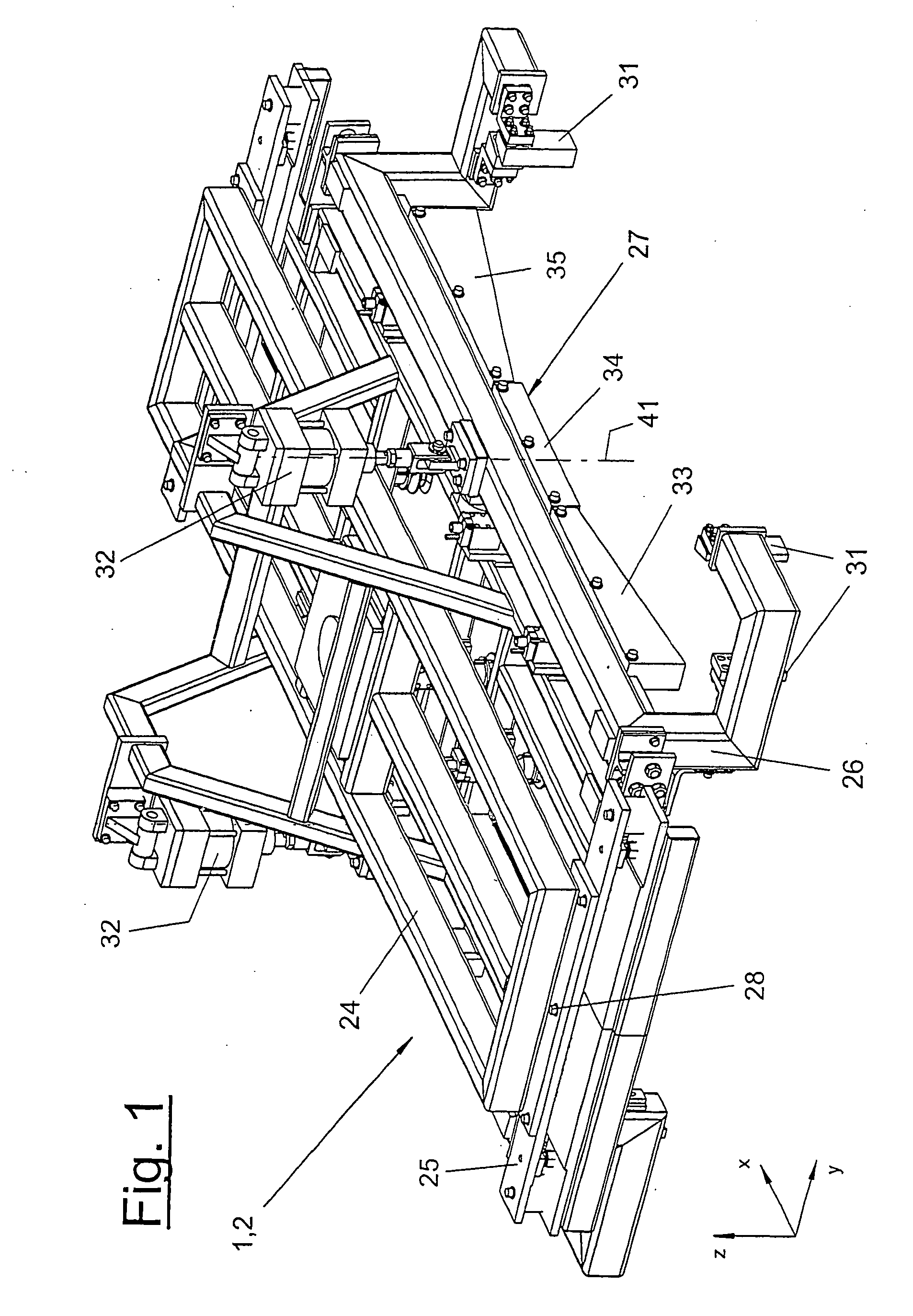
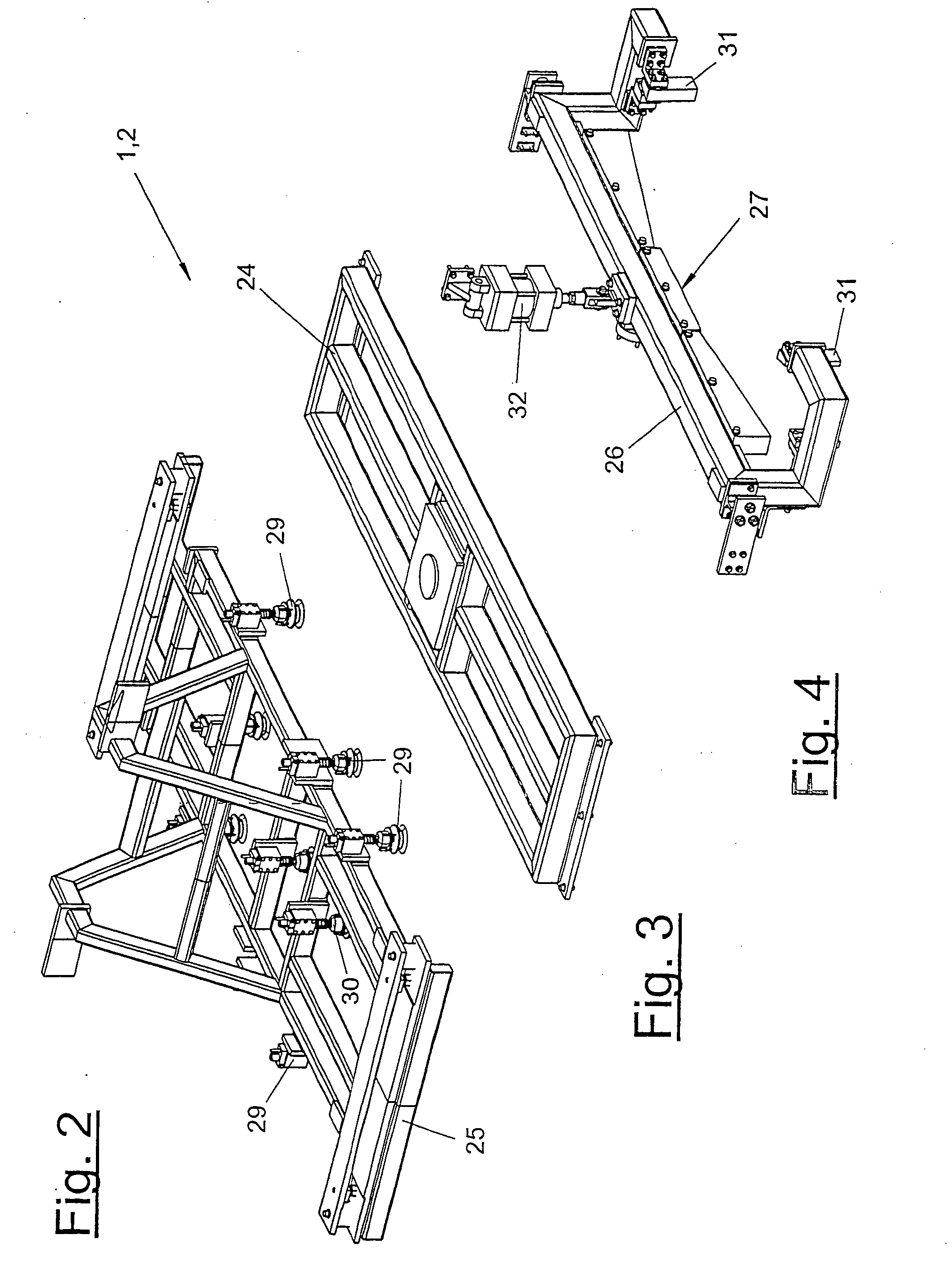
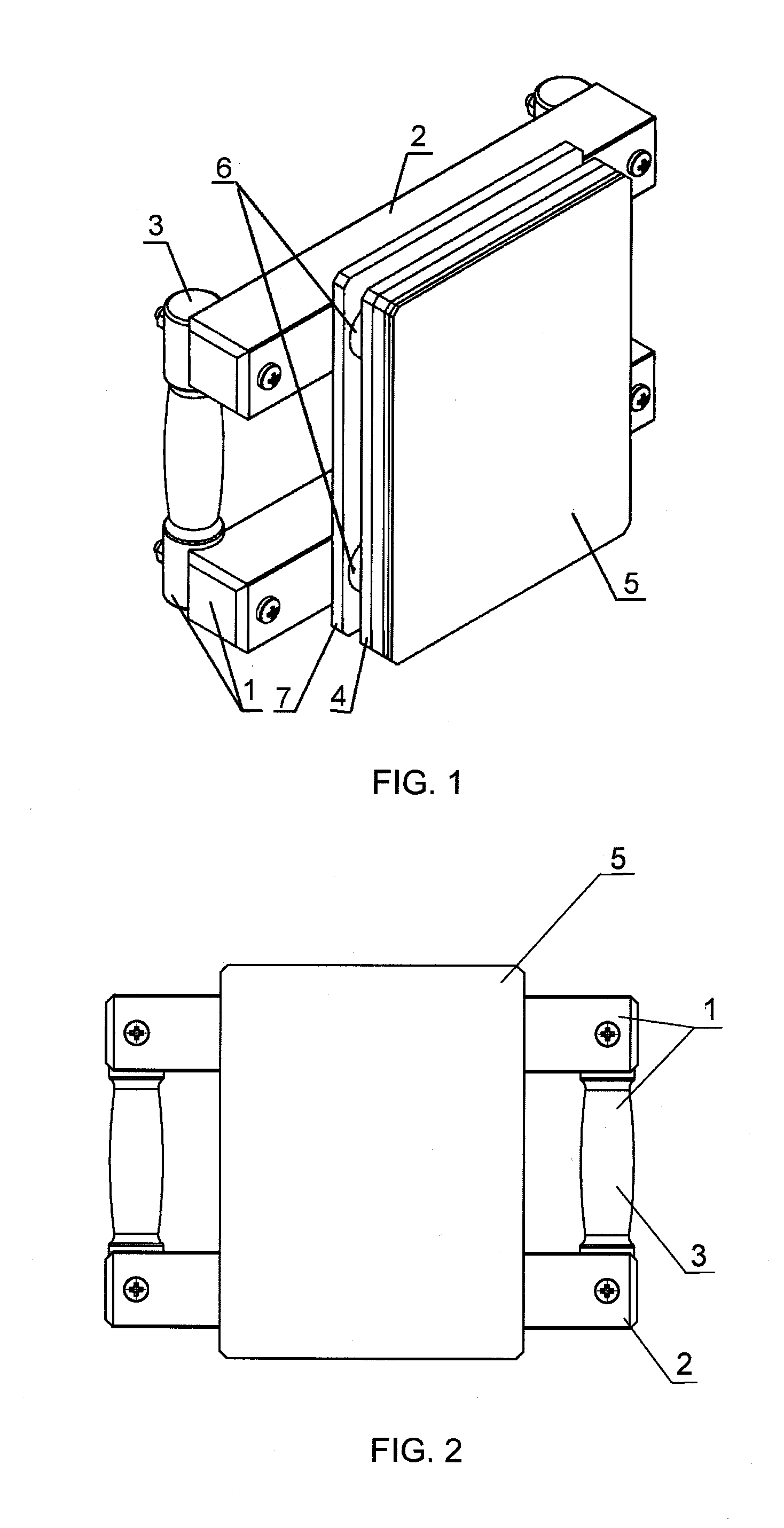
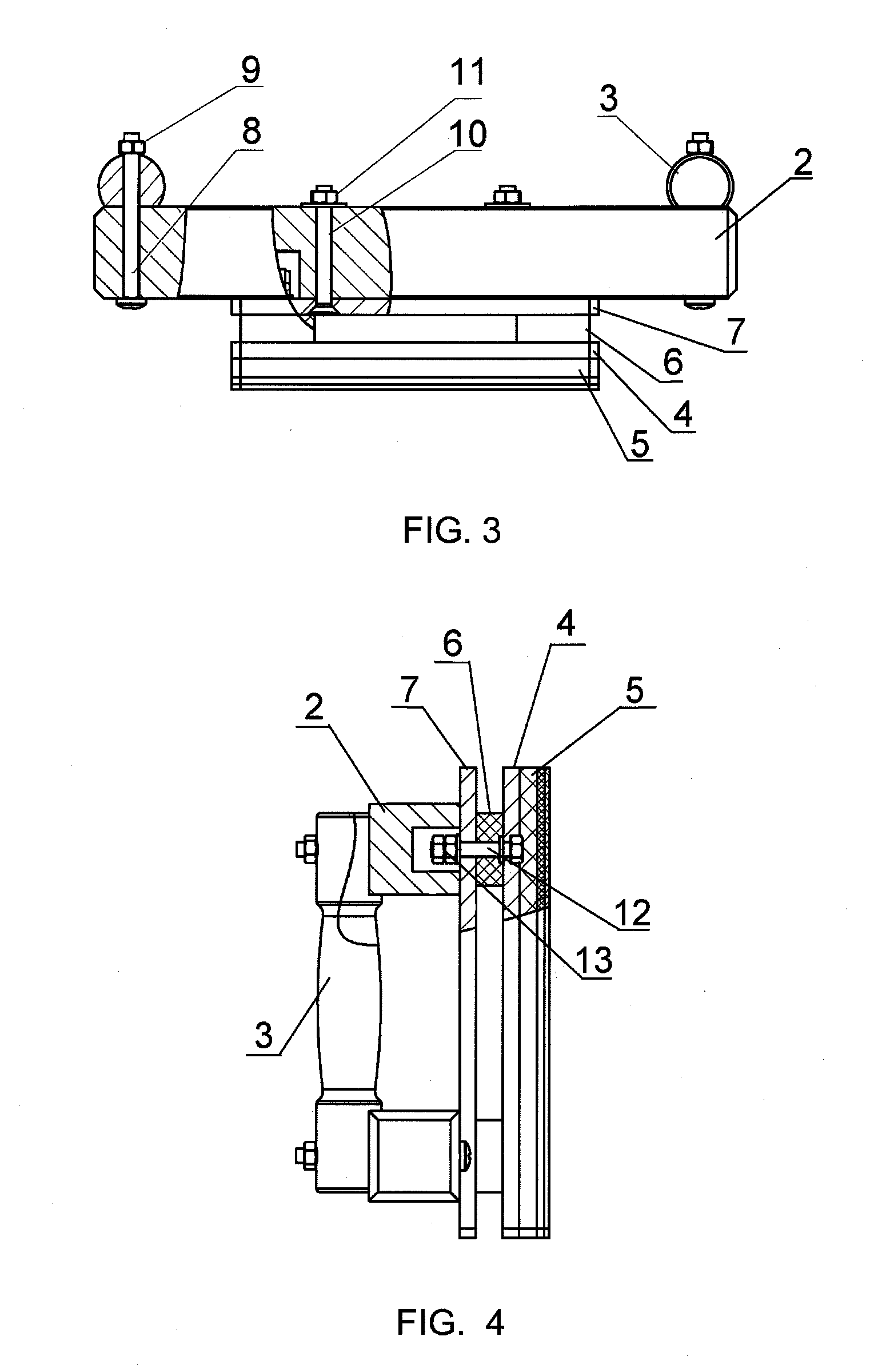
Joining device and joining process
InactiveUS20060179628A1Improve techniqueJoining is strengthenedWelding/cutting auxillary devicesSuperstructure subunitsMarine engineering
A joining method and to a joining device (1) for joining roof skins (11) to parts (4) of vehicle bodies (3) is provided. The joining device (1) includes one or more joining grippers (2), which are comprised of at least one frame (24), of a number of gripping elements (29, 30), of at least one pressing strip (27), which acts upon the roof skin (11), and of an associated adjusting device (32). The pressing strip (27) is adapted to the joining contour (6) of the part (4) and has one or more dimensionally stable strip segments (33, 34, 35, 36, 37) that, independent of one another, are mounted on a strip support (26) with a limited flexibility in the direction of adjustment (41). The roof skin (11) with the joining part edge (13) thereof, is pressed against and fixed to the contact area (7) of the part (4) by means of the strip segments (33, 34, 35, 36, 37) and, optionally, is permanently deformed.
Owner:FORD GERMANY +1
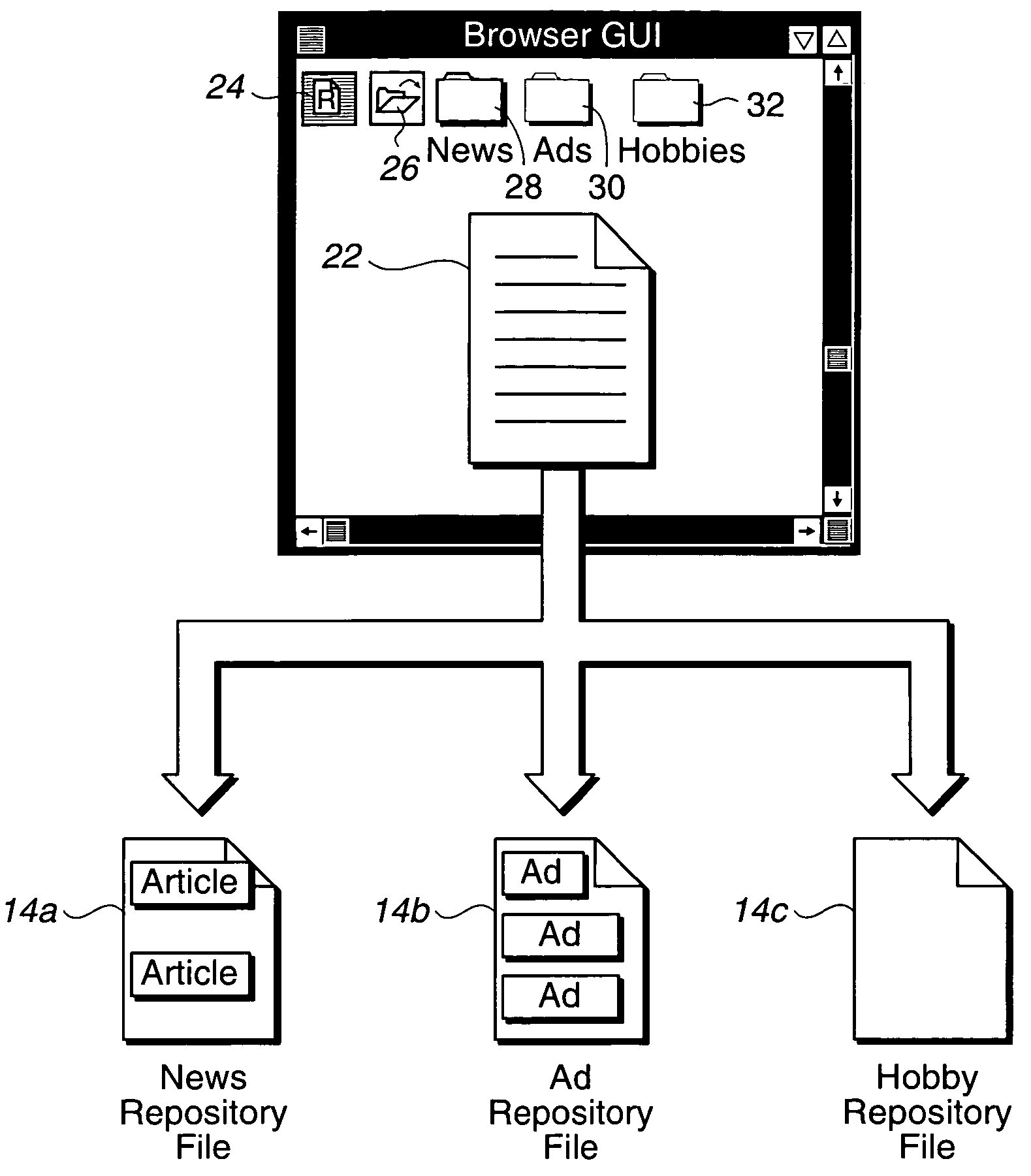
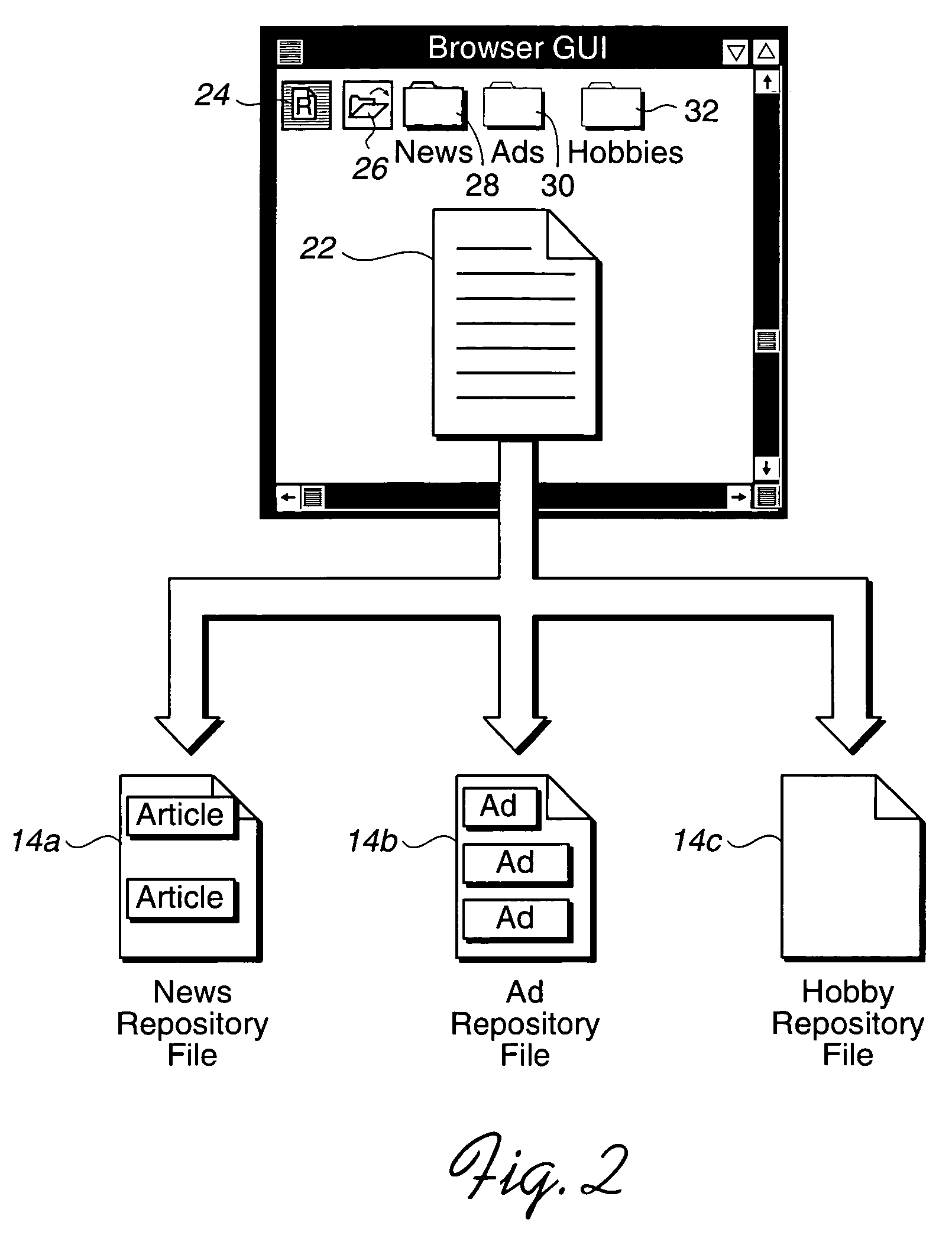
Method, system, and program for saving object content in a repository file
InactiveUS7213204B1Improve techniqueEasy to storeBiological modelsSpecial data processing applicationsMultimedia
Disclosed is a method, system, and program for saving content of electronic objects displayed in a computer viewer program. Content of an object is presented in an interface generated by the viewer program. User selection of a command is received with respect to the presented object content. In response to the user selection of the command, a determination is made of a repository file. The content of the selected object is appended to the determined repository file. The repository file is capable of including content from multiple objects appended to the repository file in response to previous user selections of the command.
Owner:IBM CORP
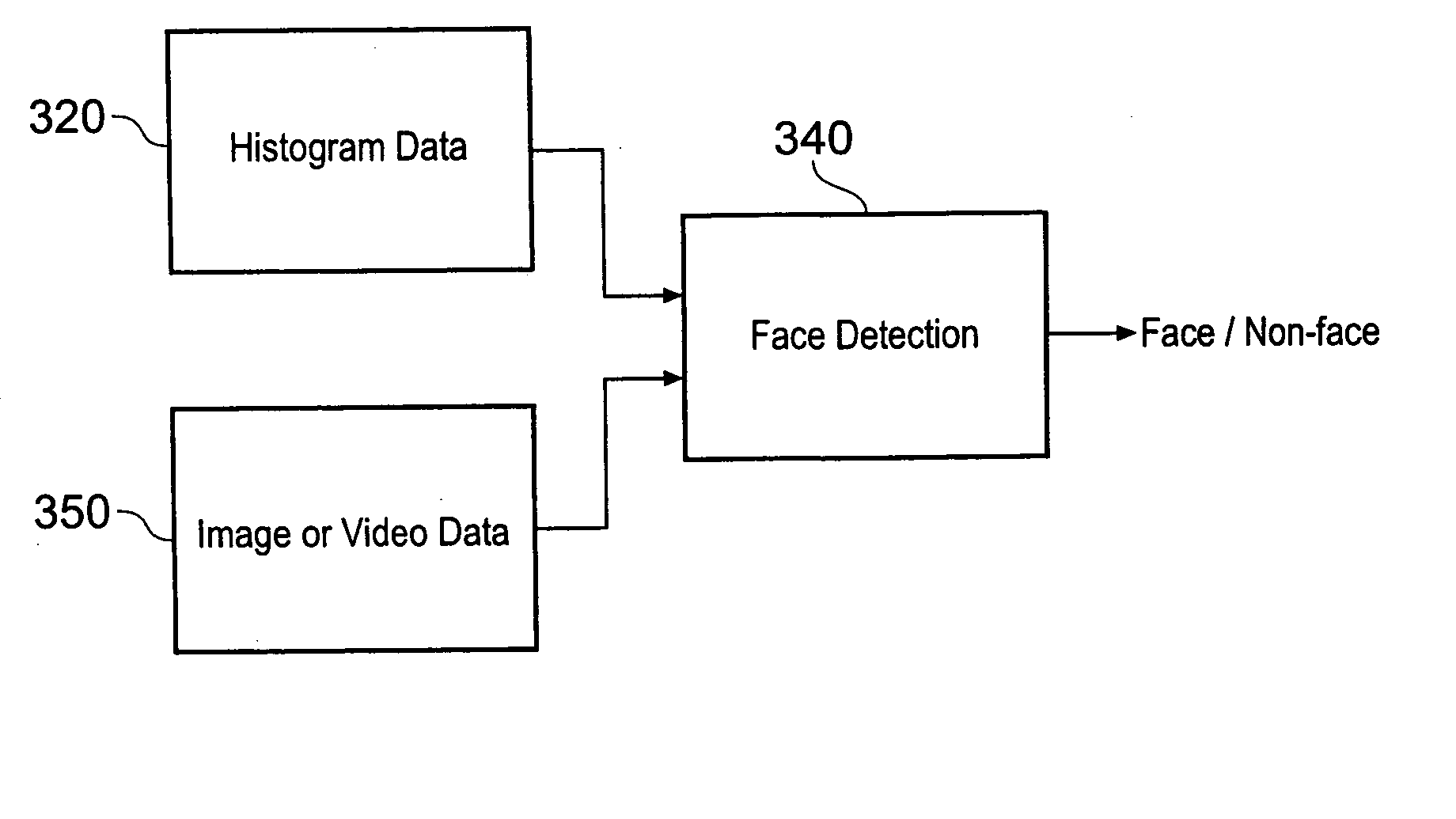
Object detection
InactiveUS20050129277A1Improve techniqueLighten the taskTelevision system detailsImage analysisObject detectionAssociated image
Object detection apparatus in which images from an ordered series of images are processed to detect objects, each image having an associated image period, the detection of objects in a whole image requiring a set of processing tasks to be carried out comprises means for executing subsets of the set of processing tasks during respective image periods associated with a group of two or more images from the ordered series; the subsets being arranged so that substantially all of the set of processing tasks are carried out in the course of the image periods associated with the group of images and that each such task is carried out with respect to at least one respective image in the group of images.
Owner:SONY UK LTD
Method and apparatus for diagnostic analyses
InactiveUS20130022962A1Improve performanceImprove techniqueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPathogenMass spectrometry
A method for diagnostic analyses, in particular to identify pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria or other micro-organisms present in a biological sample, comprises a first step of measuring and continuously monitoring the turbidity and / or the concentration of the pathogens, by means of an instrumental reading technique, of a liquid culture medium into which the sample to be analyzed has been inoculated and in which the replication of the pathogens possibly present occurs, said measuring and monitoring being carried out dynamically during the replication of the pathogens growing in the culture medium; and a second step of identifying the pathogens, carried out by taking at least an aliquot of the liquid culture medium containing the biological sample directly obtained from the first step, which has reached a desired value of turbidity according to a standardized value scale, such as the McFarland turbidity scale, and / or of concentration of the pathogens, and using said aliquot directly in mass spectrophotometric identification means (15) in order to identify the pathogens, which means are calibrated in their functioning depending on the measurement results of the first step. The desired values of turbidity and / or of concentration of the pathogens are preliminarily selected, during the first step, on the basis of the specific needs which, on each occasion, are identified in order to carry out the second identification step
Owner:ALIFAX
Dual-chamber syringe and associated connecting systems
InactiveUS20160175537A1Step be reduceImprove techniqueInfusion syringesCheck valvesQuality assuranceSyringe
A dual-chamber syringe system is disclosed. Critical system oriented elements are disclosed, including plunger valve designs for accurate measurement and true, non-canting displacement; tamper and inadvertent valve actuation indicators, as well as, valve status indicators; anti-reflux construction; novel indicia patterns for dual-chamber syringe operation;structure and method for quality assurance that no gas can be delivered from a proximal chamber of the dual-chamber syringe and a kit for single step dose transfer. In addition, a tapered fitting valve is disclosed. The tapered fitting valve comprises a single molded incompressible, but supple part and a skeletal support whereby the tapered fitting valve is opened by insertion into a tapered fitting. The preferred embodiment of an actuator portion of the valve is elliptical in shape. The valve opens by compressing a slit which is parallel to, but offset from the major elliptical axis to provide sufficient space for other valve components within a limited size, such as that of a luer fitting. A syringe barrel comprising a skeletal support structure for an affixed valve for a tapered fitting is also disclosed.
Owner:THORNE CONSULTING FOR INT PROPERTY LLC
Reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the burning of a fossil fuel
ActiveUS20090205492A1Reduce carbon dioxide emissionImprove techniqueGas treatmentEmission preventionFossil fuelCarbon dioxide
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
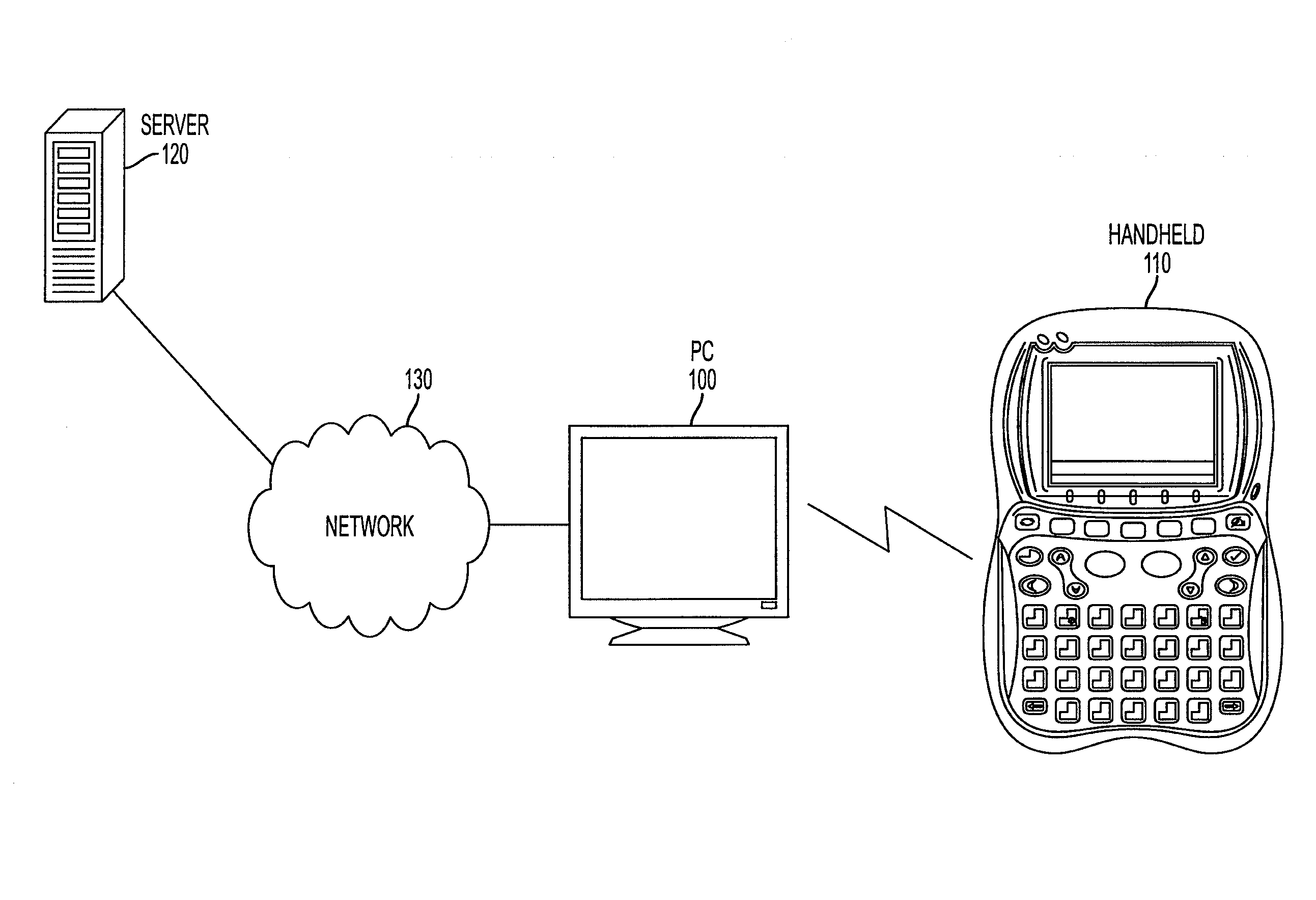
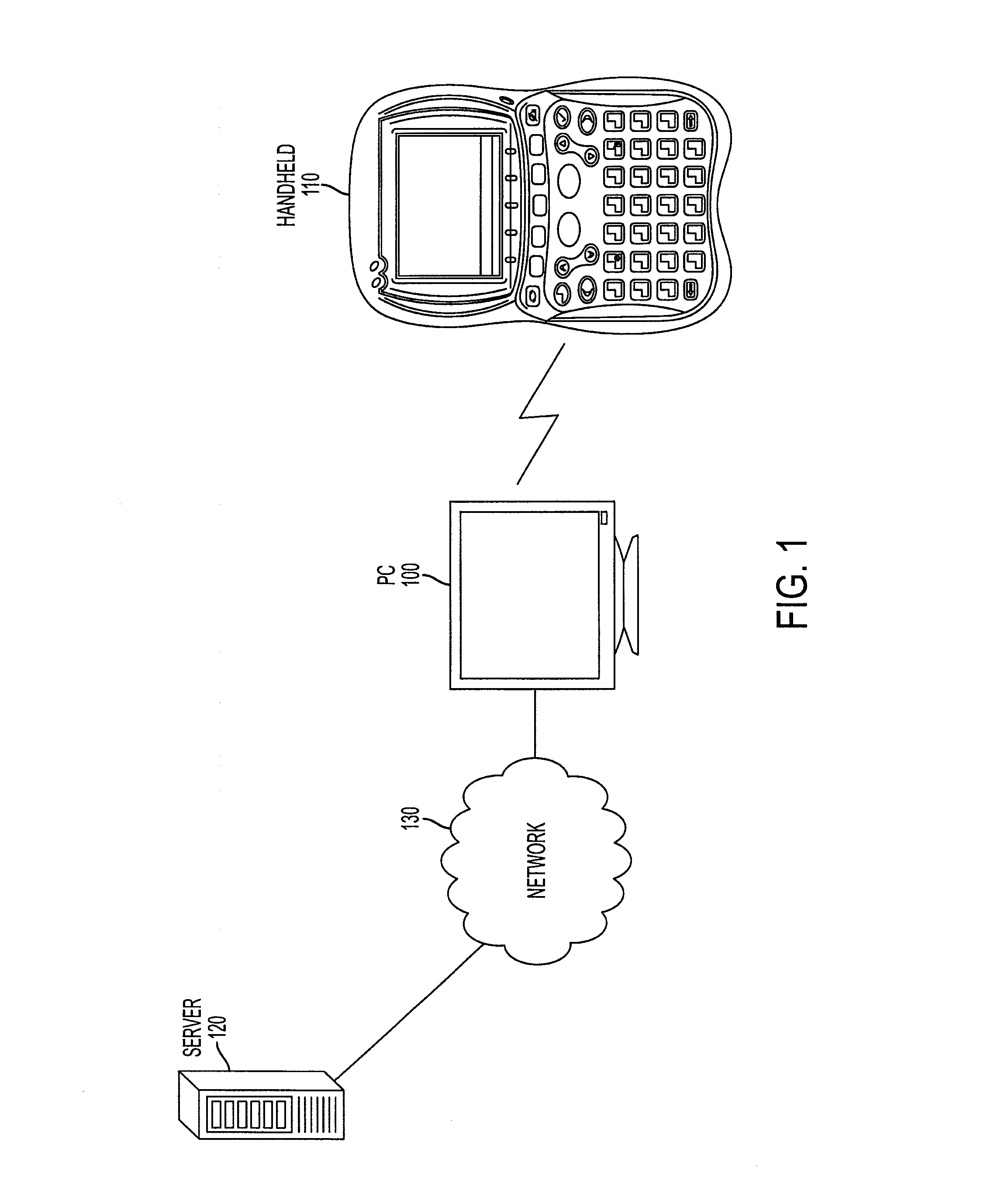
Systems and methods for improving user efficiency with handheld devices
A system, method, and computer program product are provided for training users how to operate handheld electronic devices and / or their respective applications, wherein the handheld electronic device may receive an expected input associated with an application executing on the handheld from a computing device. The handheld may then receive an actual input from a user of the handheld electronic device, compare the two inputs, and release the actual input from the user to the application if the inputs are substantially the same.
Owner:UNITED PARCEL SERVICE OF AMERICAN INC
Intergrated pump laser and rare earth waveguide amplifier
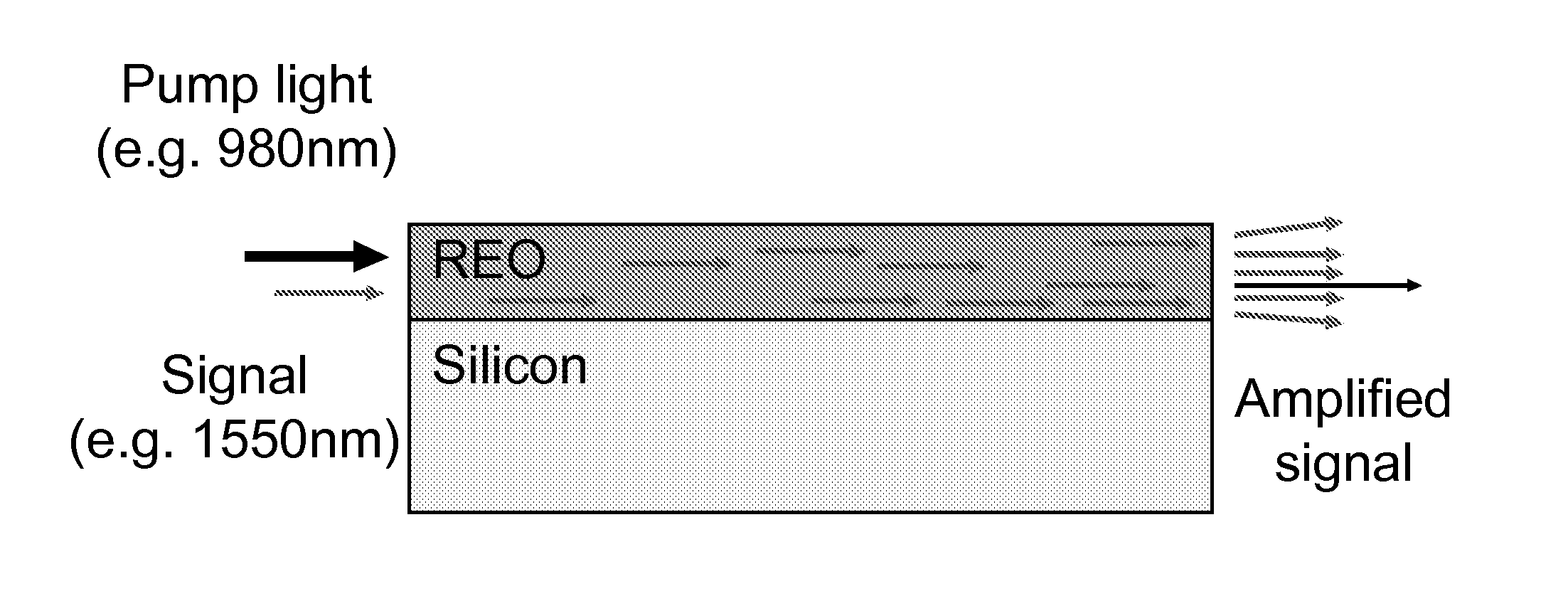
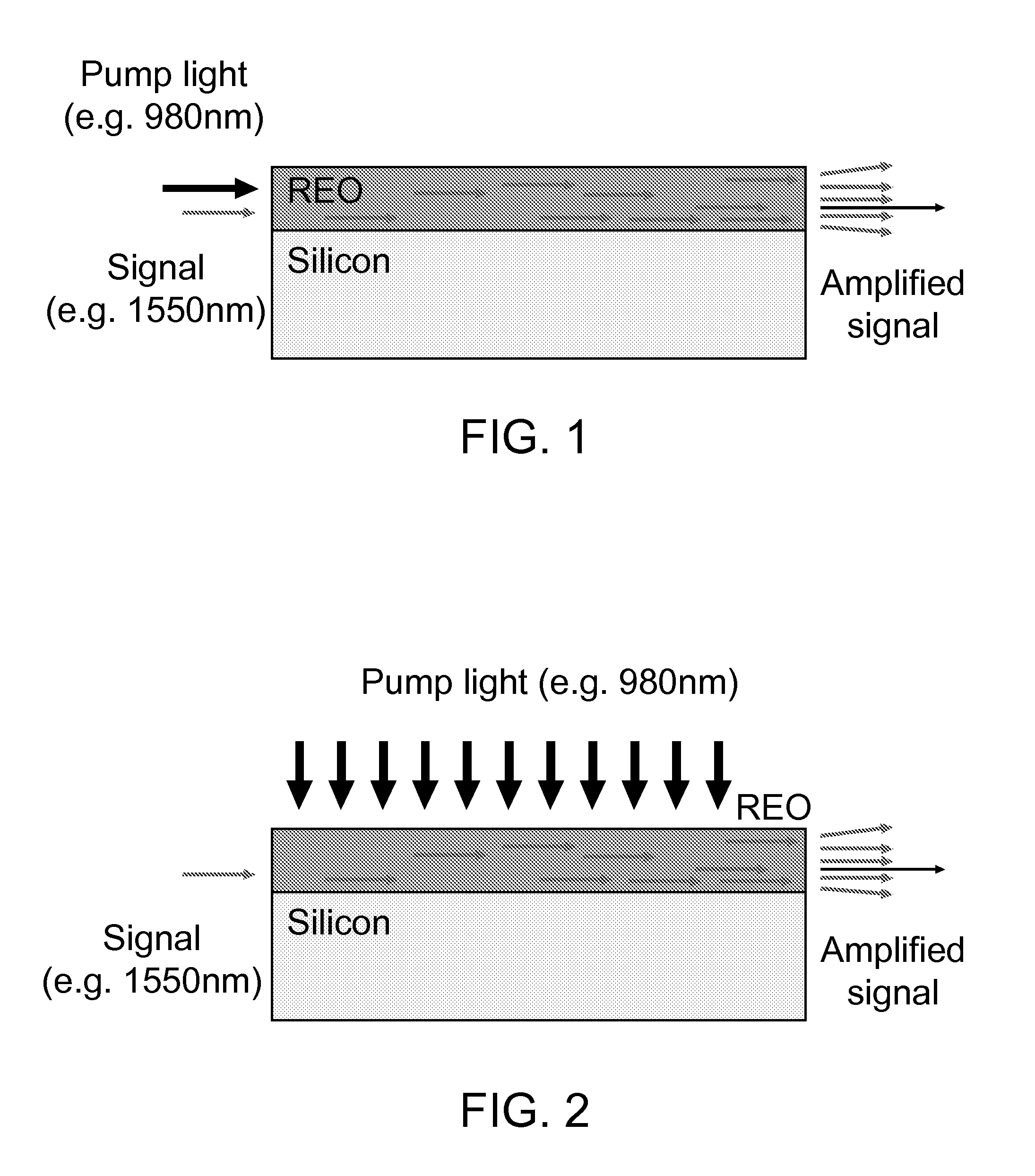
InactiveUS20120019902A1Improve fabricating techniqueStrengthen interconnectionLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaveguide amplifierRare earth
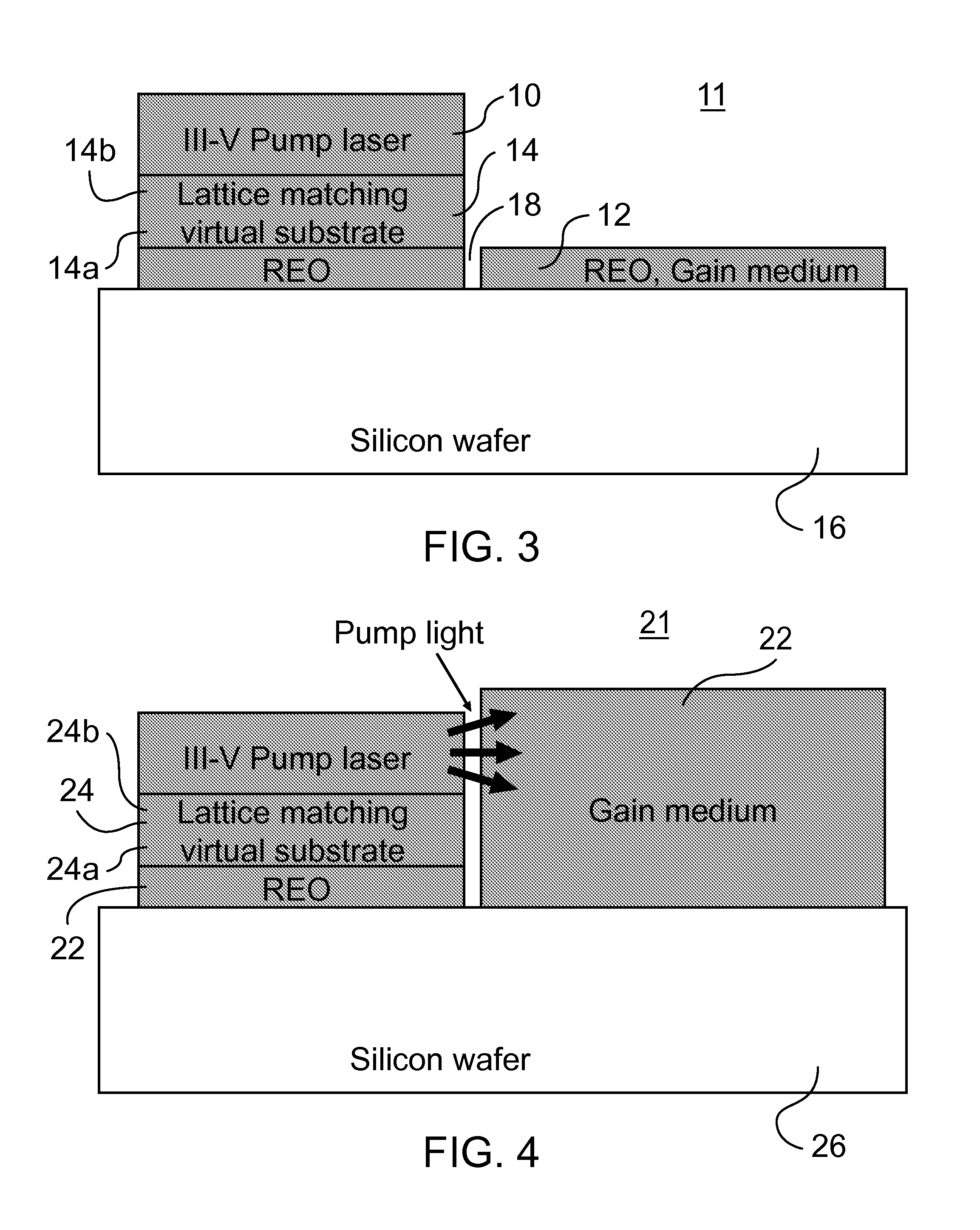
A light amplifier includes a single crystal semiconductor substrate with a rare earth oxide, light amplifying gain medium deposited on the substrate and formed into a light waveguide, and a pump laser. A lattice matching virtual substrate integrates the pump laser to the gain medium with a first opposed surface crystal lattice matched to the gain medium and second opposed surface crystal lattice matched to the pump laser. The pump laser is positioned with a light output surface coupled to a light input surface of the gain medium so as to introduce pump energy into the light waveguide. The light amplifier has a very small footprint and allows the integration of control and monitoring electronics.
Owner:IQE
MRI with dixon-type water/fat separation with estimation of the main magnetic field variations
ActiveUS20160313423A1Improve techniqueEnhance the imageMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAmount of substanceNuclear magnetic resonance
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of at least two chemical species having different MR spectra. It is an object of the invention to provide a Dixon water / fat separation technique that avoids swaps of water and fat signals in the reconstructed MR images due to large gradients of the main magnetic field B0. The method of the invention comprises the steps of: a) generating echo signals at different echo times by subjecting an object (10) positioned in a main magnetic field to a multi-echo imaging sequence of RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients; b) acquiring the echo signals; c) correcting the acquired echo signals by virtual shimming, which comprises:—reconstructing single echo images from the echo signals;—selecting a number of voxel positions;—fitting a given mathematical function, which reproduces the spatial variation of the main magnetic field, to the echo time-dependent phase evolution of the single echo image values at the selected voxel positions; demodulating the single echo images according to the spatial variation of the main magnetic field as reproduced by the mathematical function; and d) reconstructing a MR image, wherein signal contributions of the at least two chemical species are separated on the basis of the demodulated single echo images. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device and to a computer program to be nm on a MR device.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Device and method for capturing guidewires
InactiveUS20140025086A1Improve techniqueSimple technologyGuide wiresSurgeryBiomedical engineeringBlood vessel
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
Header compression optimization method during and after handovers in cellular communication network
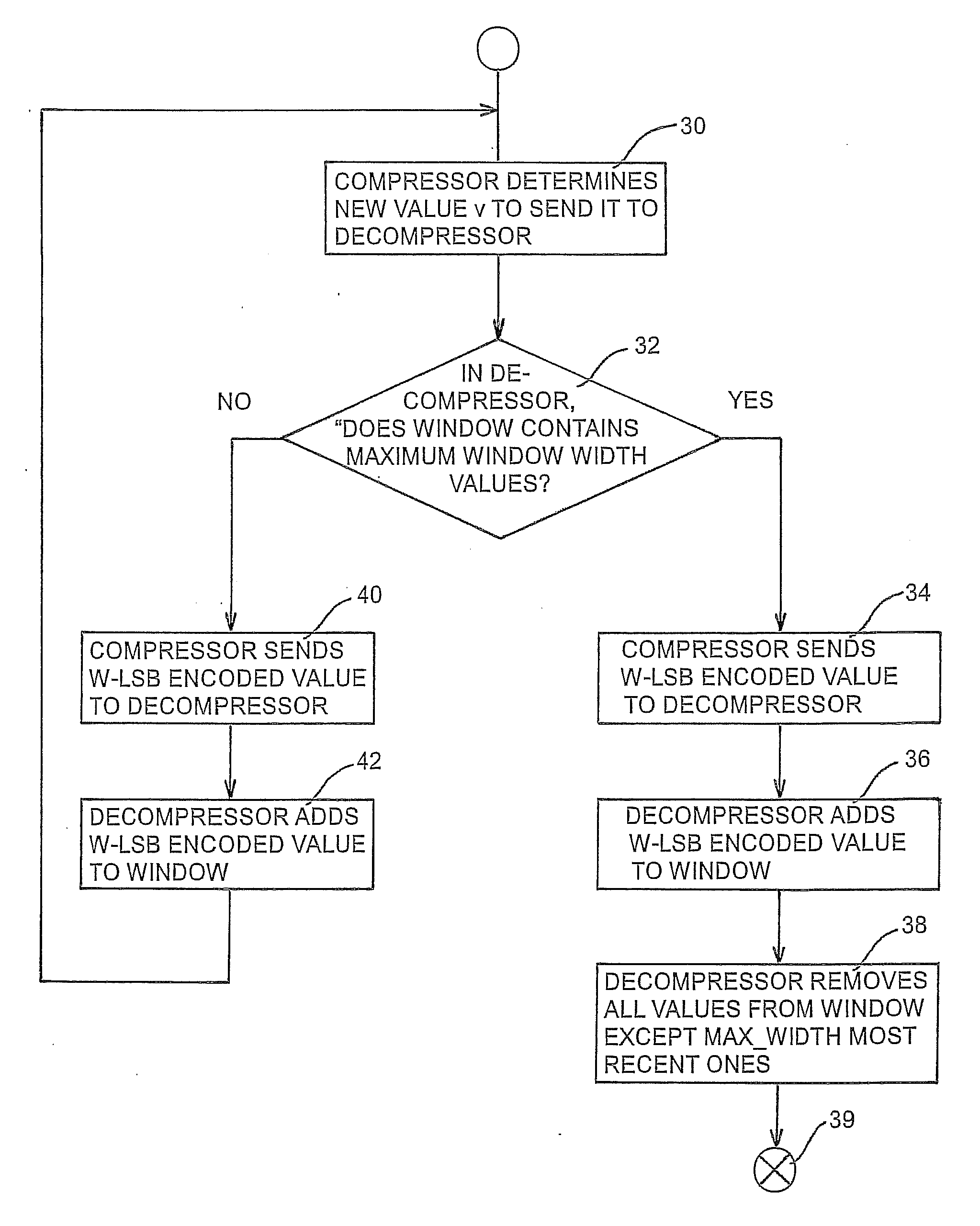
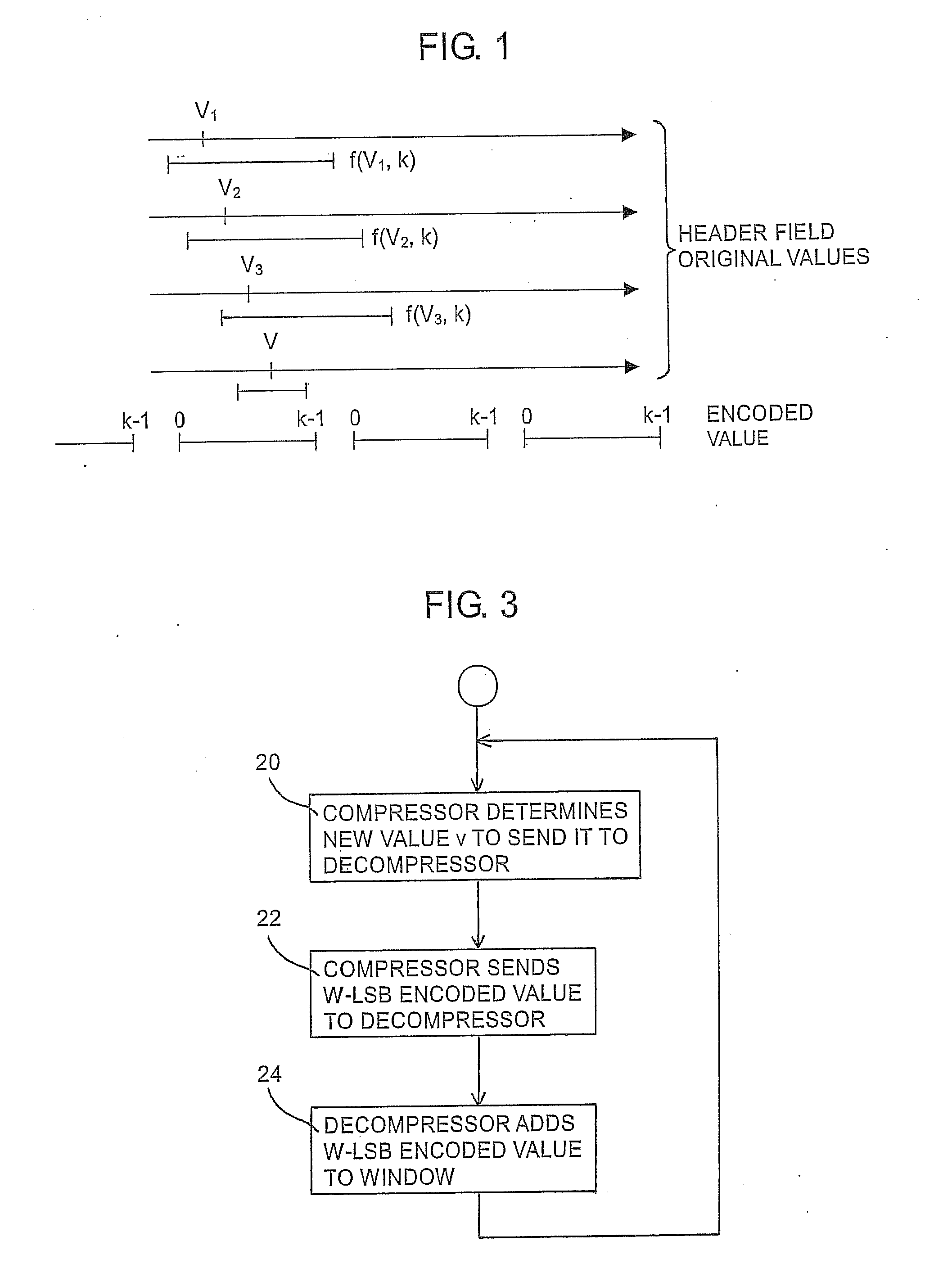
ActiveUS20090232093A1Improve techniqueSave resourcesNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesNo referenceTime Protocol
The present invention concerns a method for optimizing ROHC RTP (Robust Header Compression Real Time Protocol) compression applied to IP header of data packets stream so as to use more compact formats enable to remain in a steady state, to never discard received packet, and to serve radio resources without requiring to modify ROHC specification. In the method, when handover or mobility procedure is started, new reference values are normally added to a sliding compression window, but no reference value is removed from the window as long as the handover or mobility procedure is on going. After the handover or mobility procedure is complete, when the number of values transmitted on the new radio link are appropriate to cope against the error properties on the new link, all older values can be removed at once from the compression window, thereby reverting to normal window operation.
Owner:NEC CORP
Nanoscale infrared spectroscopy with multi-frequency atomic force microscopy
ActiveUS20150034826A1Improve techniqueRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsRegion of interestMicroscope
Described are techniques for obtaining spectroscopic information from sub-micron regions of a sample using a probe microscope. The current invention uses the response of an AFM cantilever at a plurality of frequencies to substantially reduce the impact of background absorption away from the sub-micron region of interest. This innovation substantially improves the quality of spectra for top down illumination of samples that are not suitable for bottoms up illumination of the prior art.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
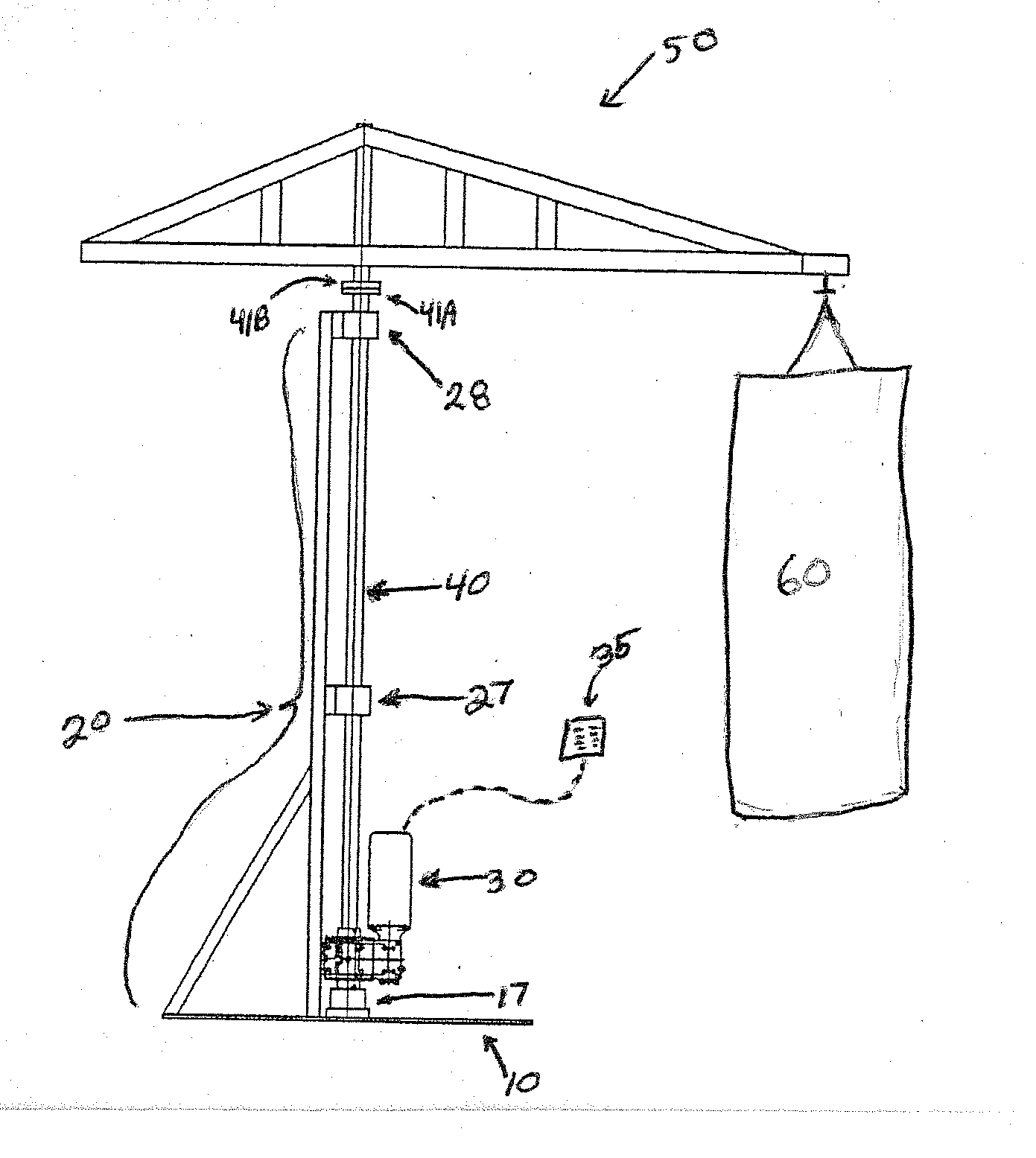
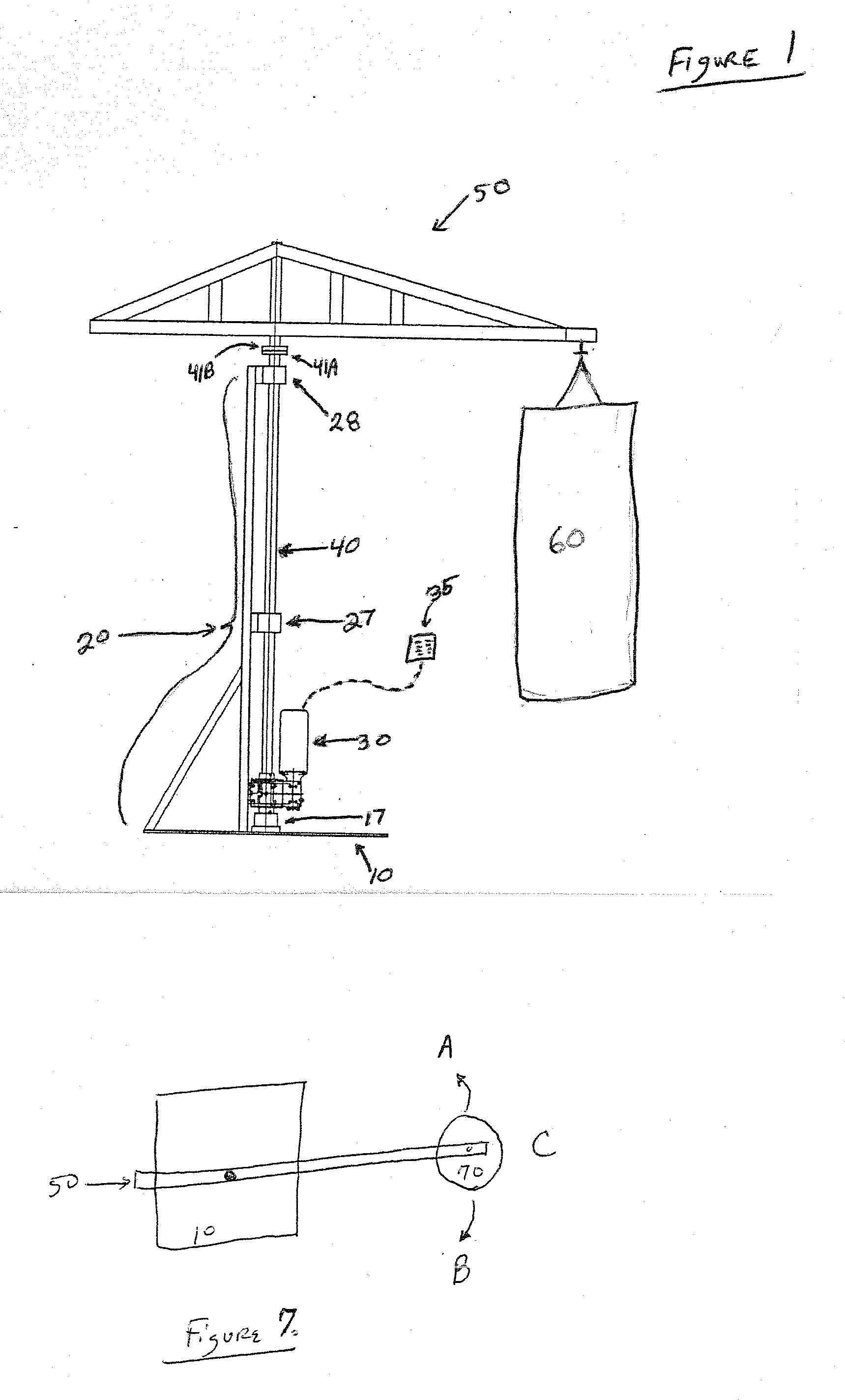
Moving punching bag and method
Apparatus and method for training a boxer, martial artist, or other competitive combatants. The apparatus can have a support base 10, a rotatable shaft 40, a transverse member 50 secured to the rotatable shaft, a drive 30 to rotate the shaft, and a training target 60 such as a punching bag, speed bag, heavy bag. The apparatus can mimic an opponent, being able to advance toward, move away from, or move to the left or right of the training combatant. The drive can be remotely controlled so as to mimic the random movements of an opponent.
Owner:CARPENTER WILLIE L +1
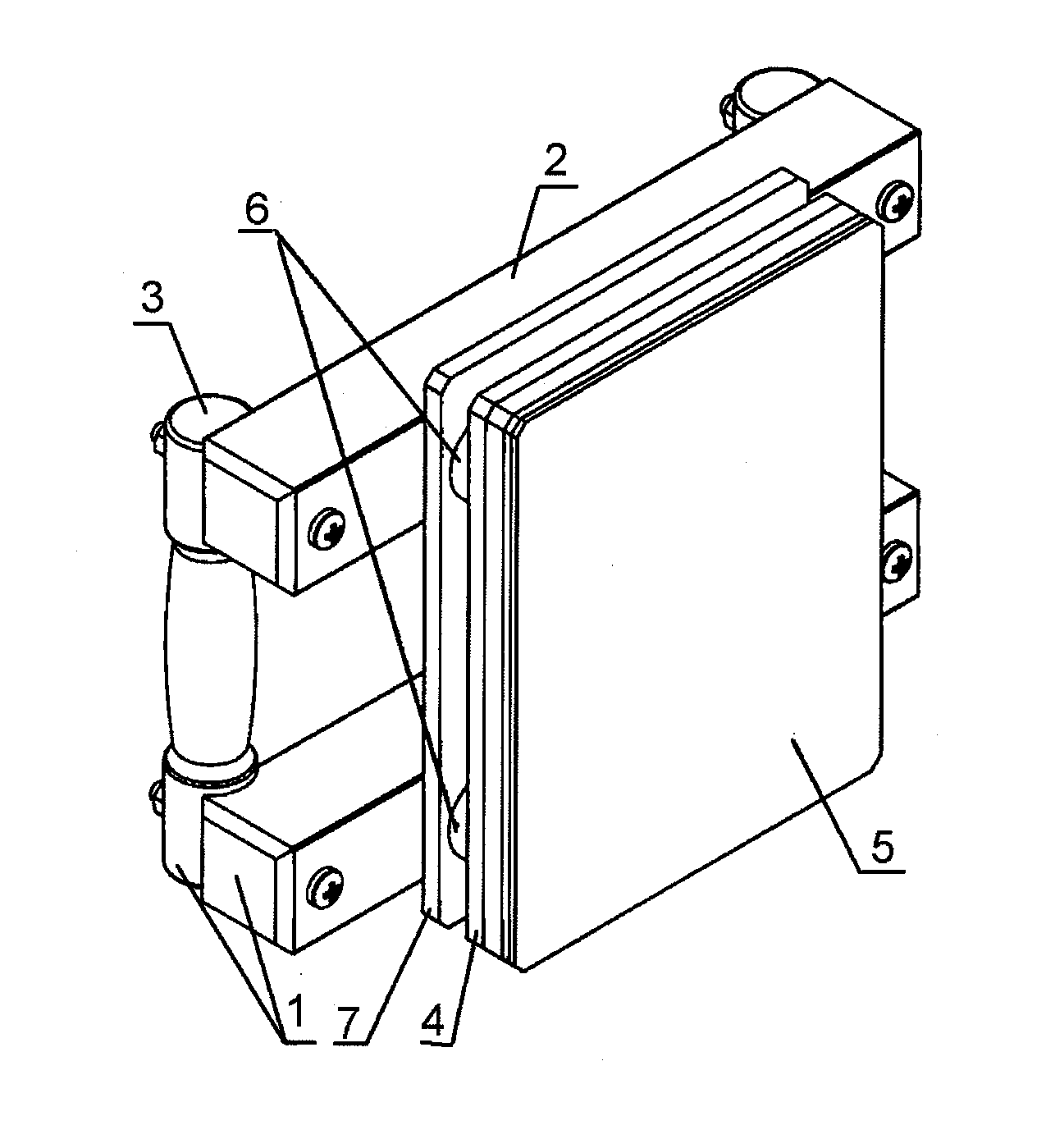
Exercise device for developing of capability to deliver knockout concentrated penetrating strikes of different types and for practicing in technique of delivery, speed and power of knockout strikes
An exercise device for developing capability to deliver knockout concentrated penetrating strikes of different kinds and for practice in technique of delivery, speed and power of knockout strikes that comprises of a base and a striking area plate with buffering coating, where the base has two parallel bars fixed to two handles and the striking area plate with buffering coating is fixed through the pads-dampers to the support plate attached to the base.
Owner:YEVGENIYOVYCH GUSIEV VALERII +1
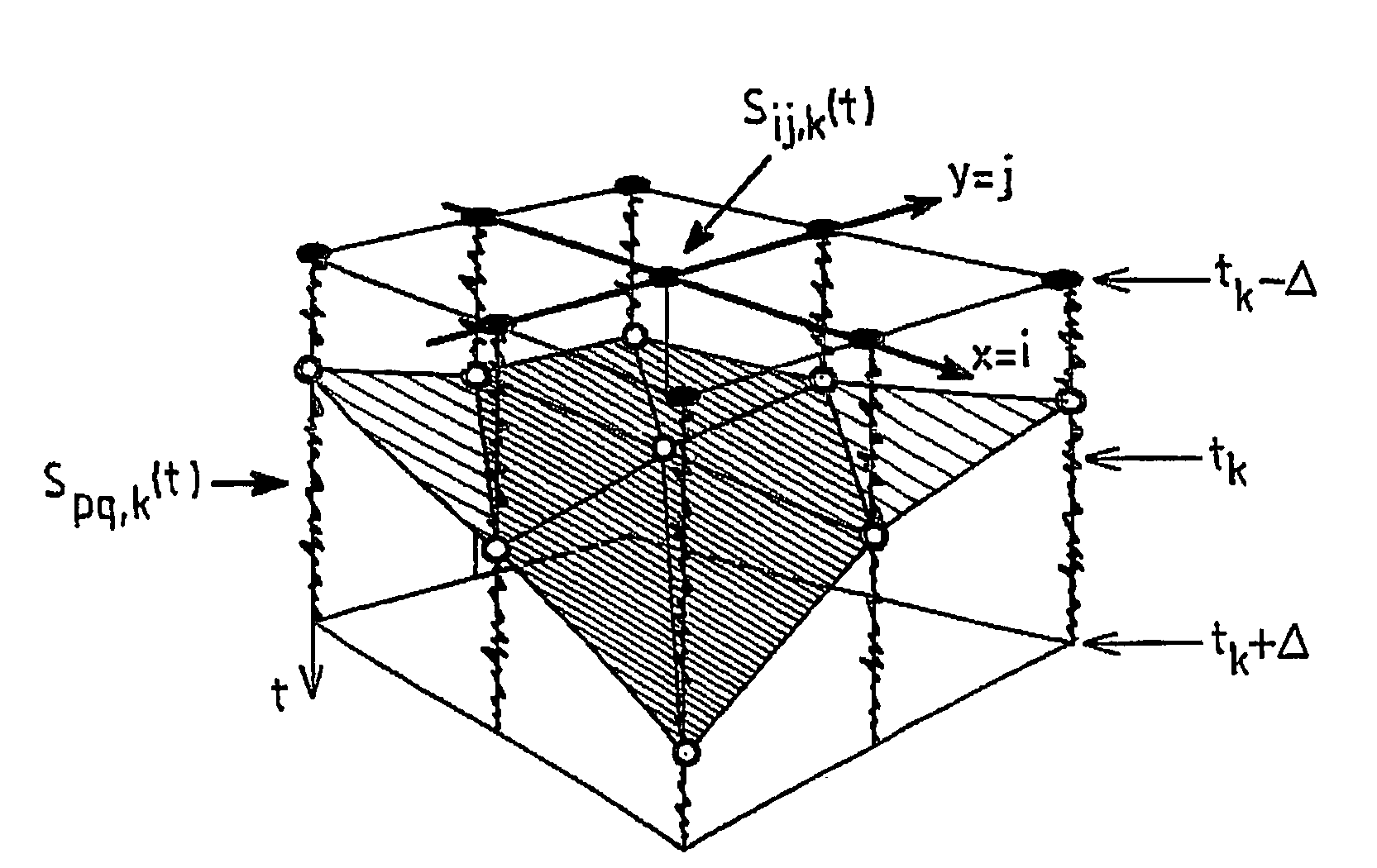
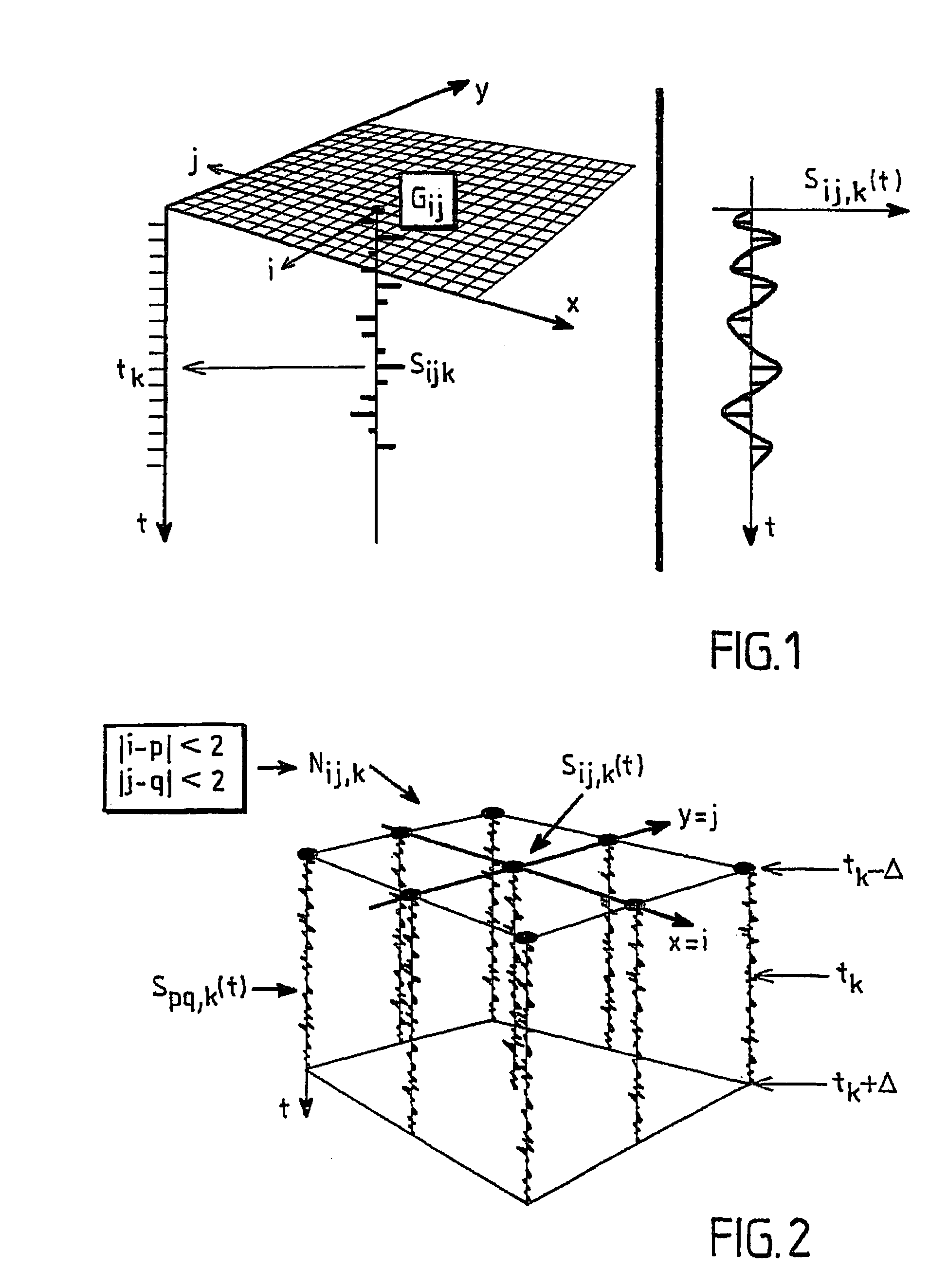
Device and software package for extracting a geological horizon and related properties
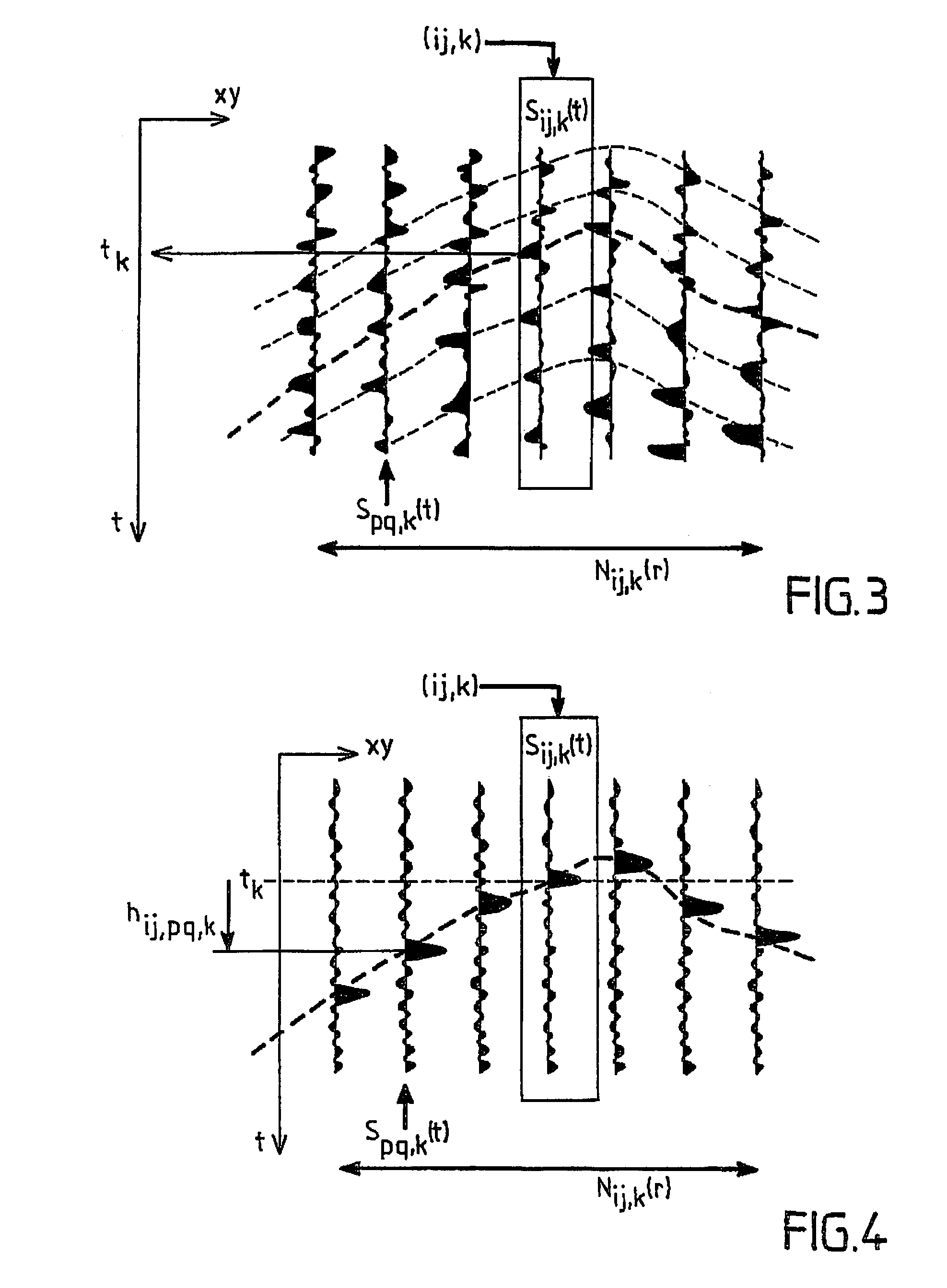
ActiveUS7328139B2Improve techniqueMinimize riskComputation using non-denominational number representationSeismic signal processingGeophoneHorizon
The invention concerns a method for extracting a geological horizon and related properties of a seismic representation, comprising a step (100) which consists in digital modeling with continuous local seismic traces, calculating the optimal offset and defining a conditional neighbourhood of a reference central continuous local seismic trace; a step (101) which consists in defining a two-dimensional matrix whereof the line and column indices correspond to the coordinates of the geophones; a third step (102) which consists in selecting a seed point; a fourth step (103) which consists in determining the point vertically closest to the seed point and a fifth step (104) which consists in assigning to the point P(p,q,t) the value P(p,q,t+hij,pq,k), where hij,pq,k is optimal offset of the neighbouring point P(i,j,k), so as to estimate the related properties of the conditional neighbourhood thereby filling the two-dimensional extraction matrix of step (101).
Owner:PARADIGM FRANCE
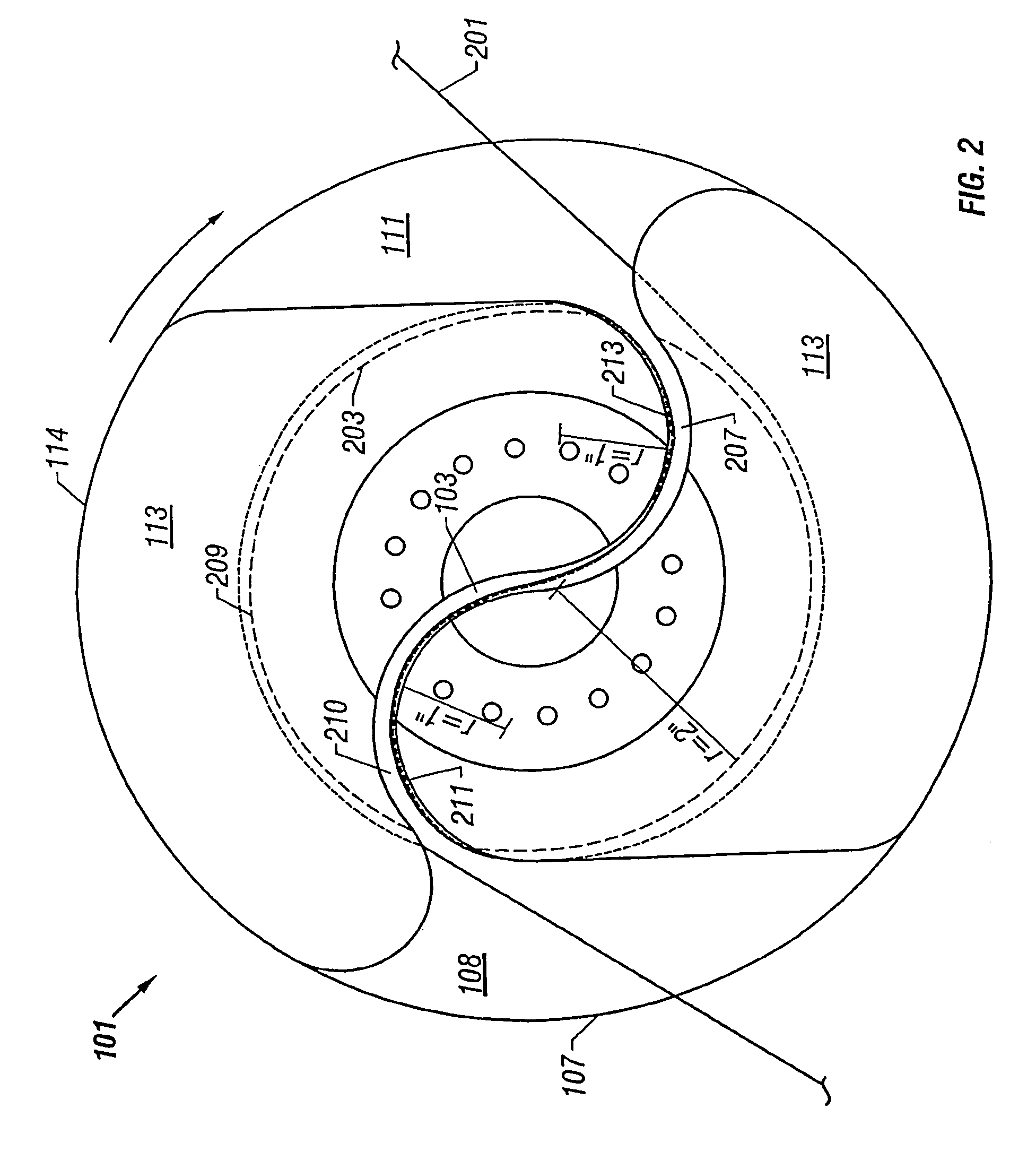
Apparatuses for improving throwing technique and methods of using same
InactiveUS20120231903A1Improve techniqueImprove throw techniqueBall sportsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:GEAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com