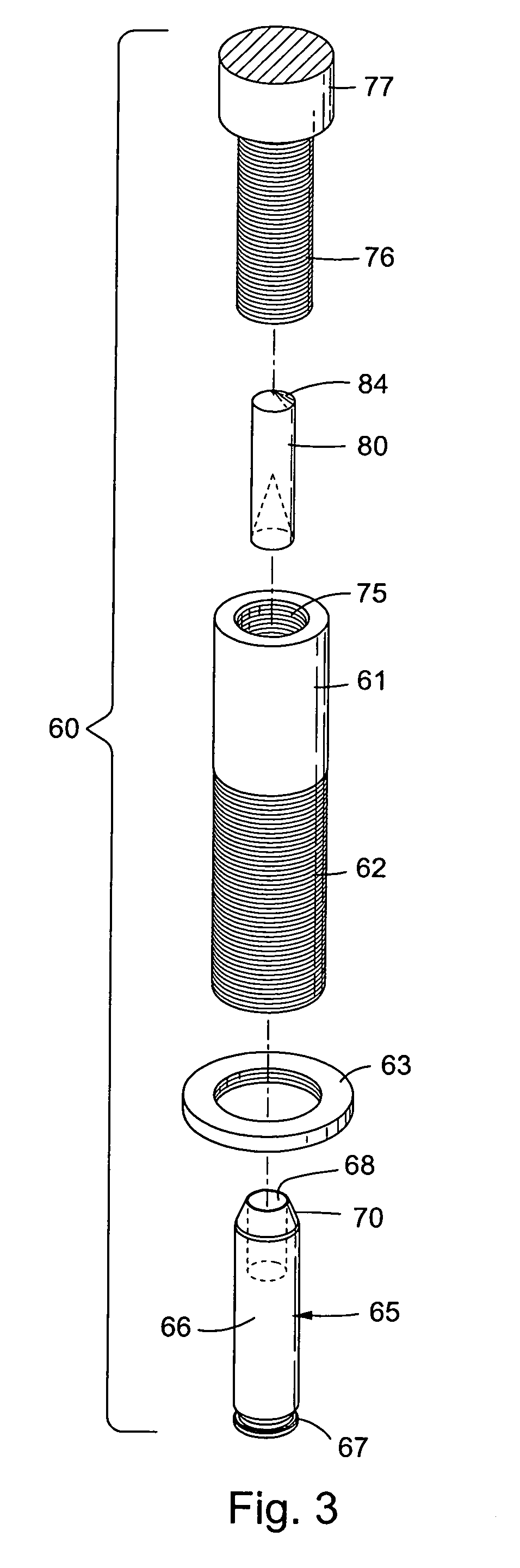
Patents
Literature
39results about How to "Improved aerodynamic stability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
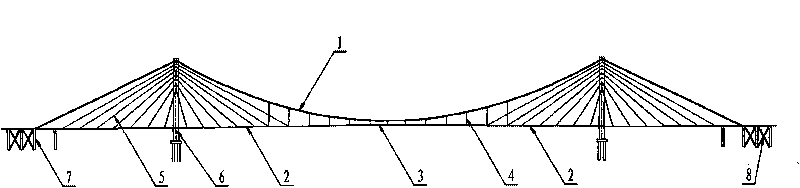
Self-anchored hybrid beam cable-stayed suspension cooperative system bridge
InactiveCN101736686AReduce construction difficultyImprove performanceCable-stayed bridgeSuspension bridgeBridge engineeringCable stayed
The invention discloses a self-anchored hybrid beam cable-stayed suspension cooperative system bridge, belongs to the technical field of constructional engineering, and particularly relates to a design for a large-span bridge in the bridge engineering. The bridge is characterized in that after a cable tower and side hole piers are manufactured, a cantilever is assembled to a concrete main bridge of the cable-stayed bridge; after the cantilever is assembled to a side hole, a main cable is hung, two ends of the main cable are anchored on an anchor block at the outer end of a concrete beam respectively, and the anchor block is pulled to a temporary anchor structure by a temporary anchor cable; a hanging rod is hoisted to span each section of steel main beam by a cable crane; after folding, the temporary anchor cables are detached in batch, and the main cables are completely anchored at two ends of the concrete main beam so as to finish the system conversion from temporary ground anchorage to self anchorage; and deck paving and rail construction are finished, the cable force of the whole bridge is adjusted, and the bridge is formed. The self-anchored hybrid beam cable-stayed suspension cooperative system bridge has the effects and advantages of solving the problems of the large-span bridge in design and construction, reducing the height of the tower, fully playing a role of materials, reducing the construction cost, shortening the construction period and reducing the risk in the construction process.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
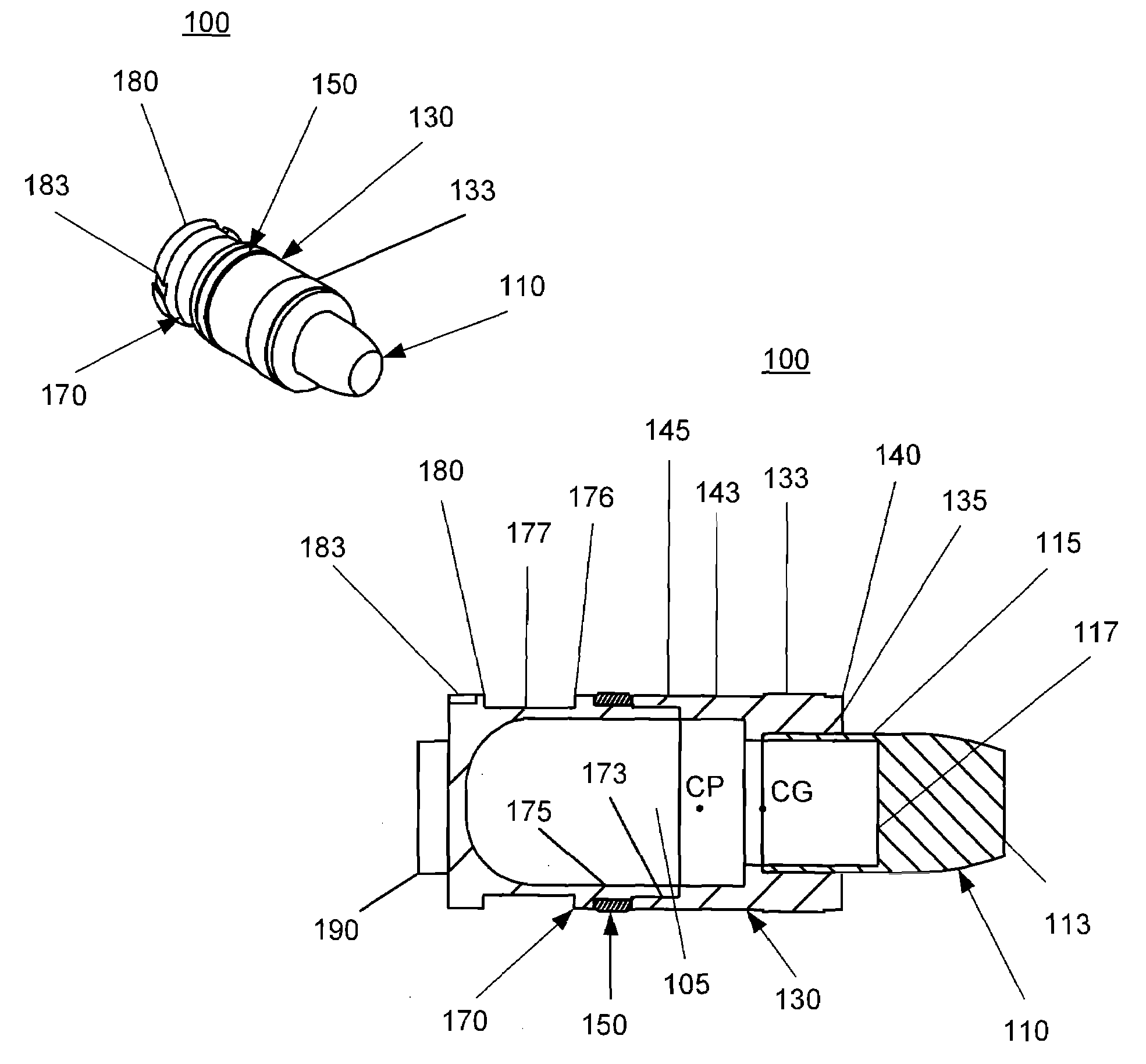
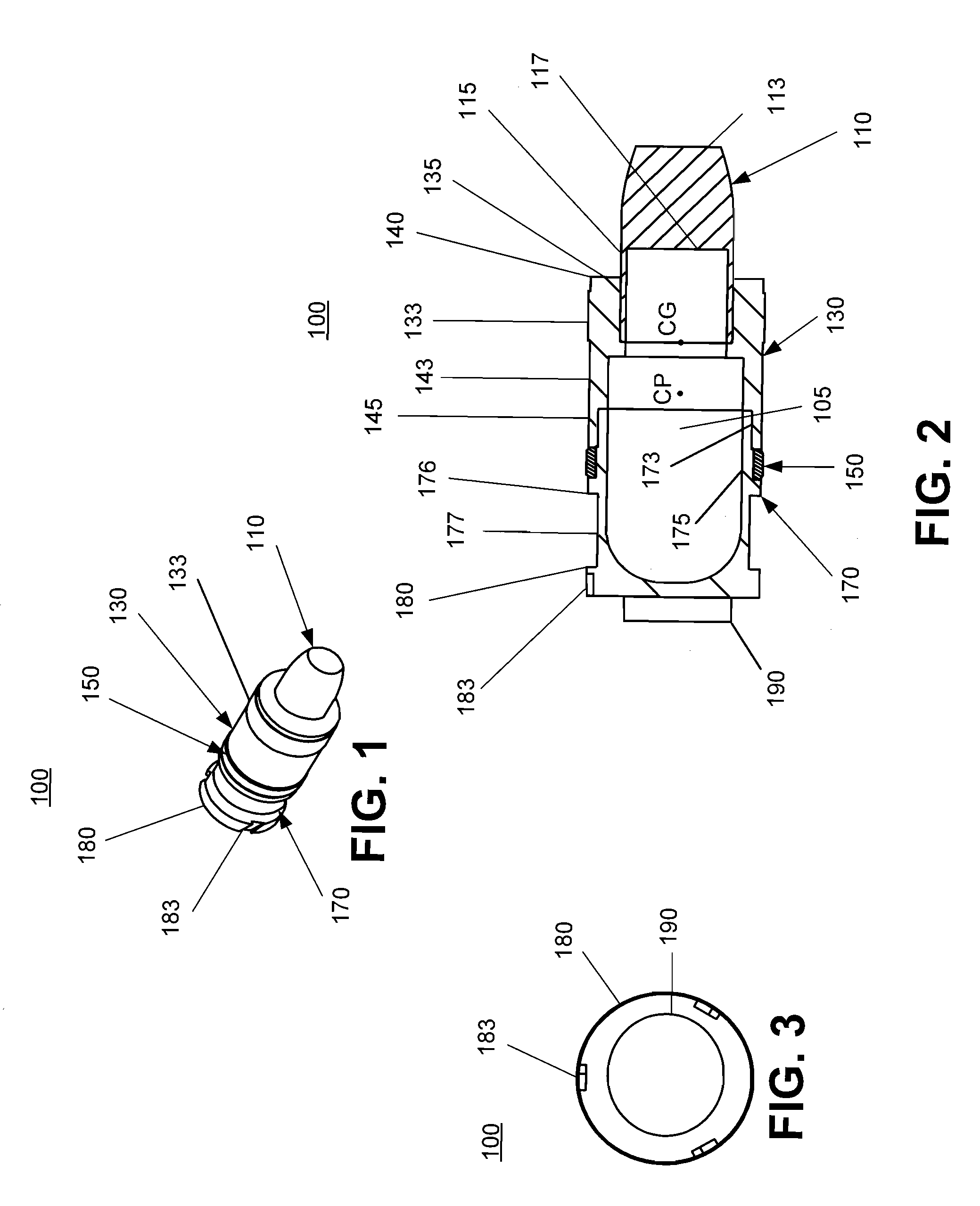
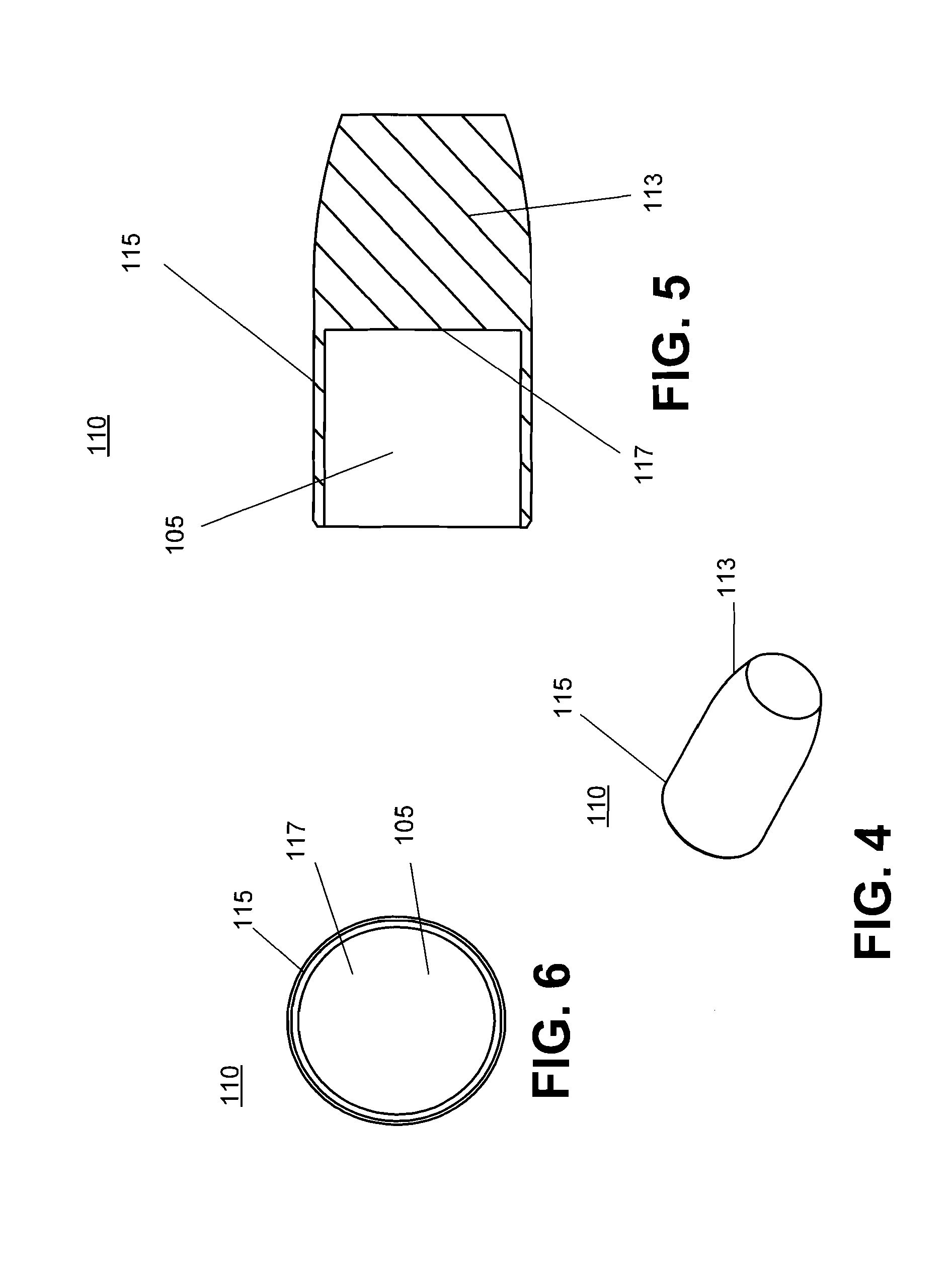
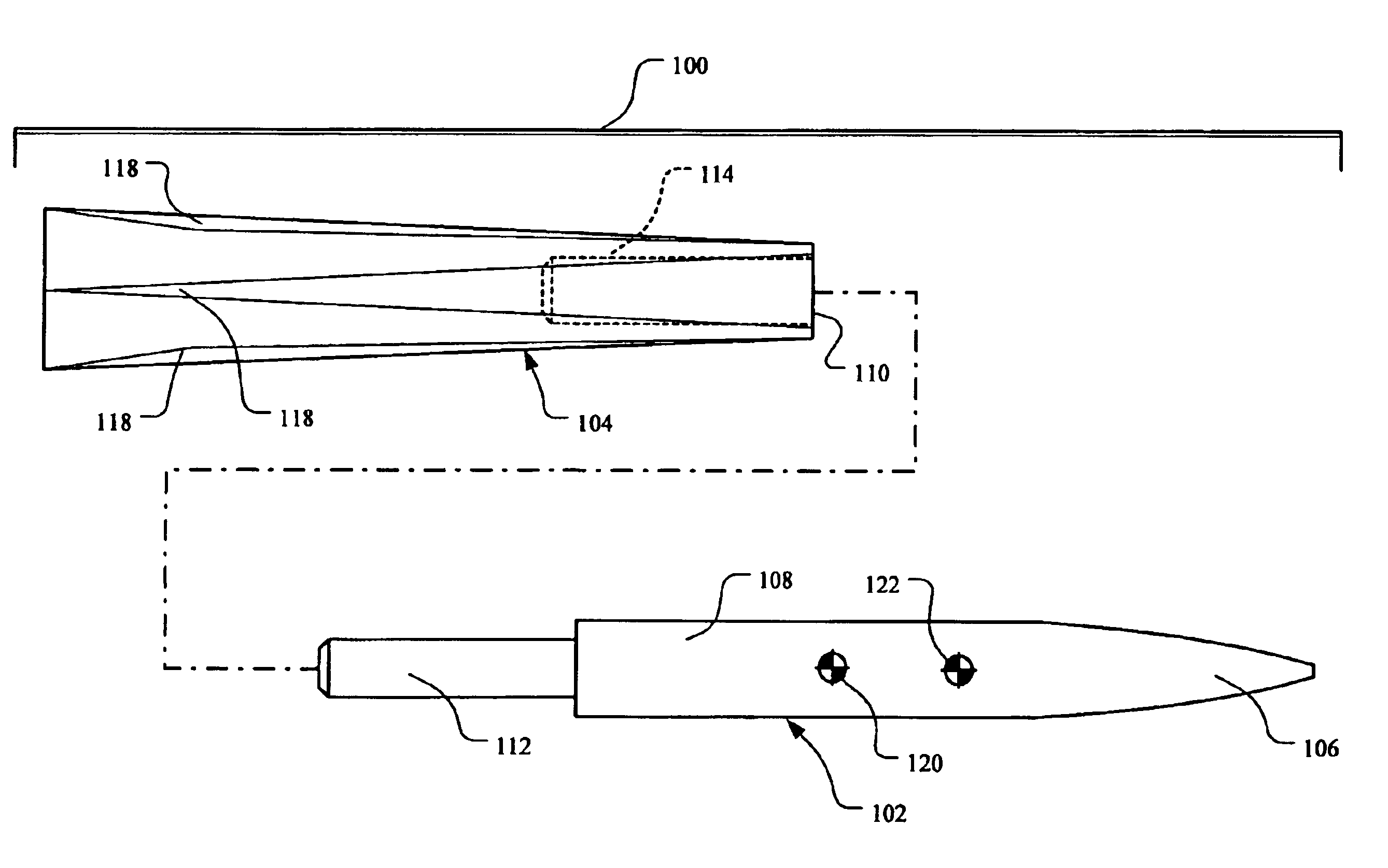
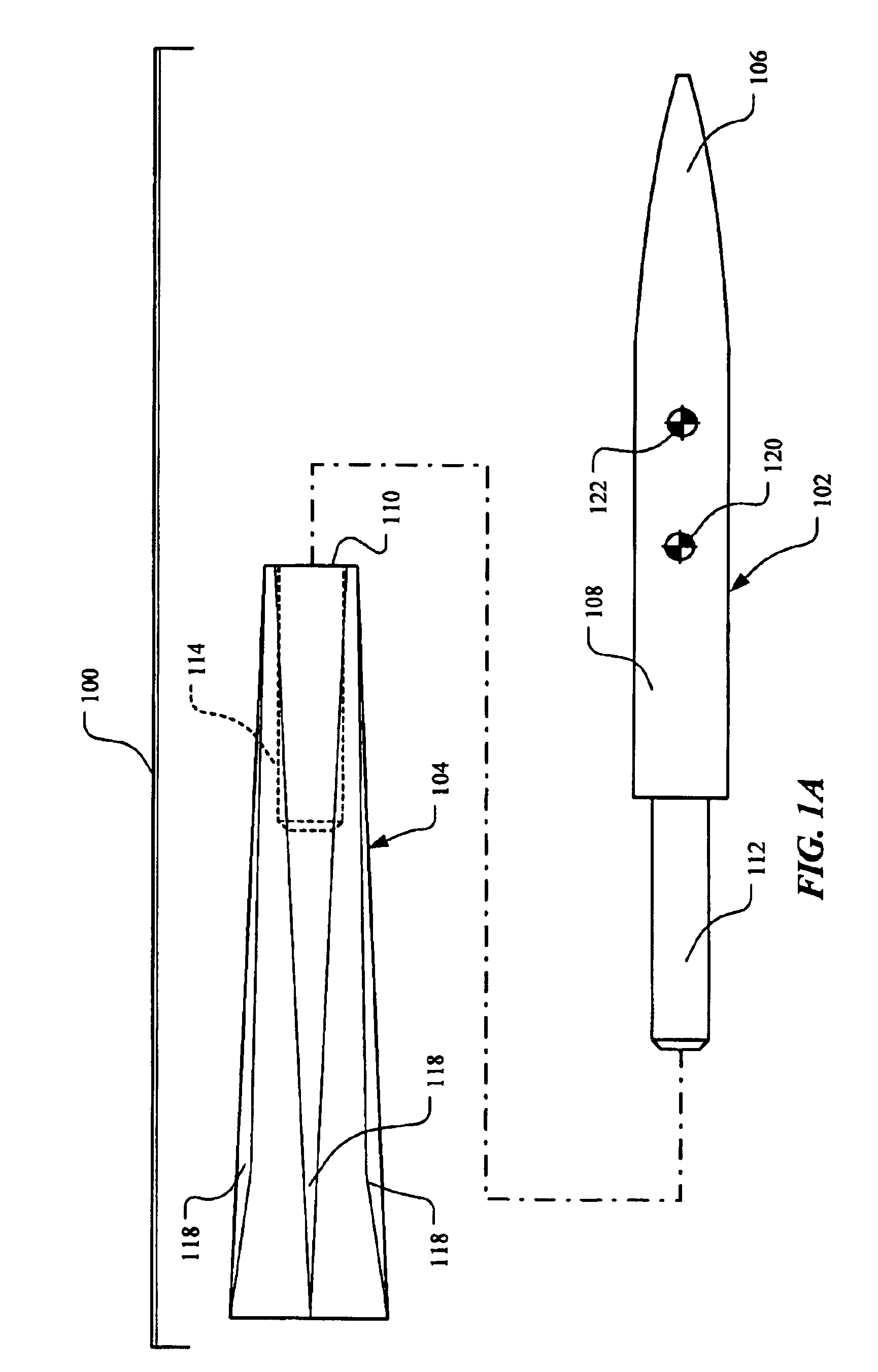
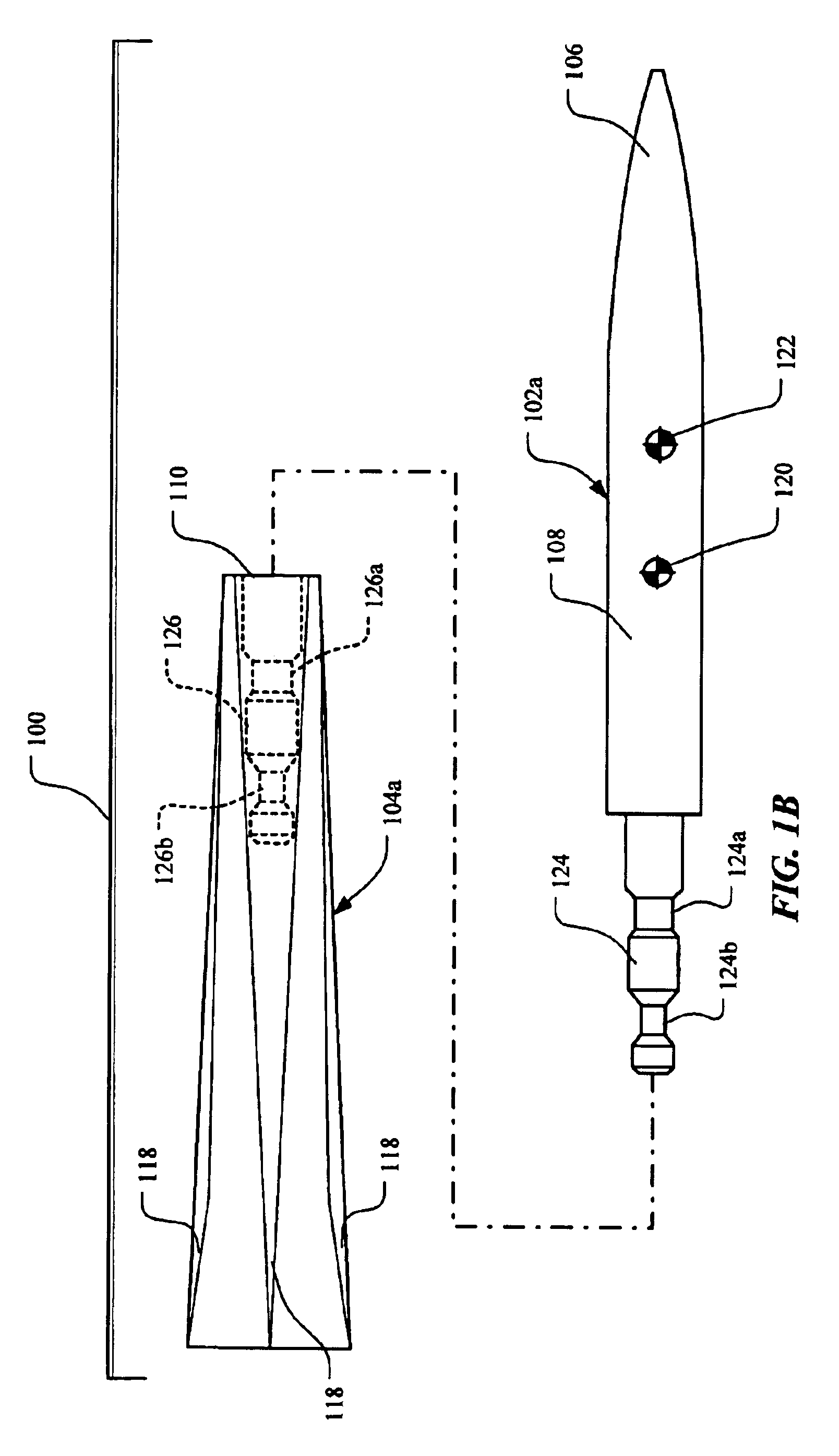
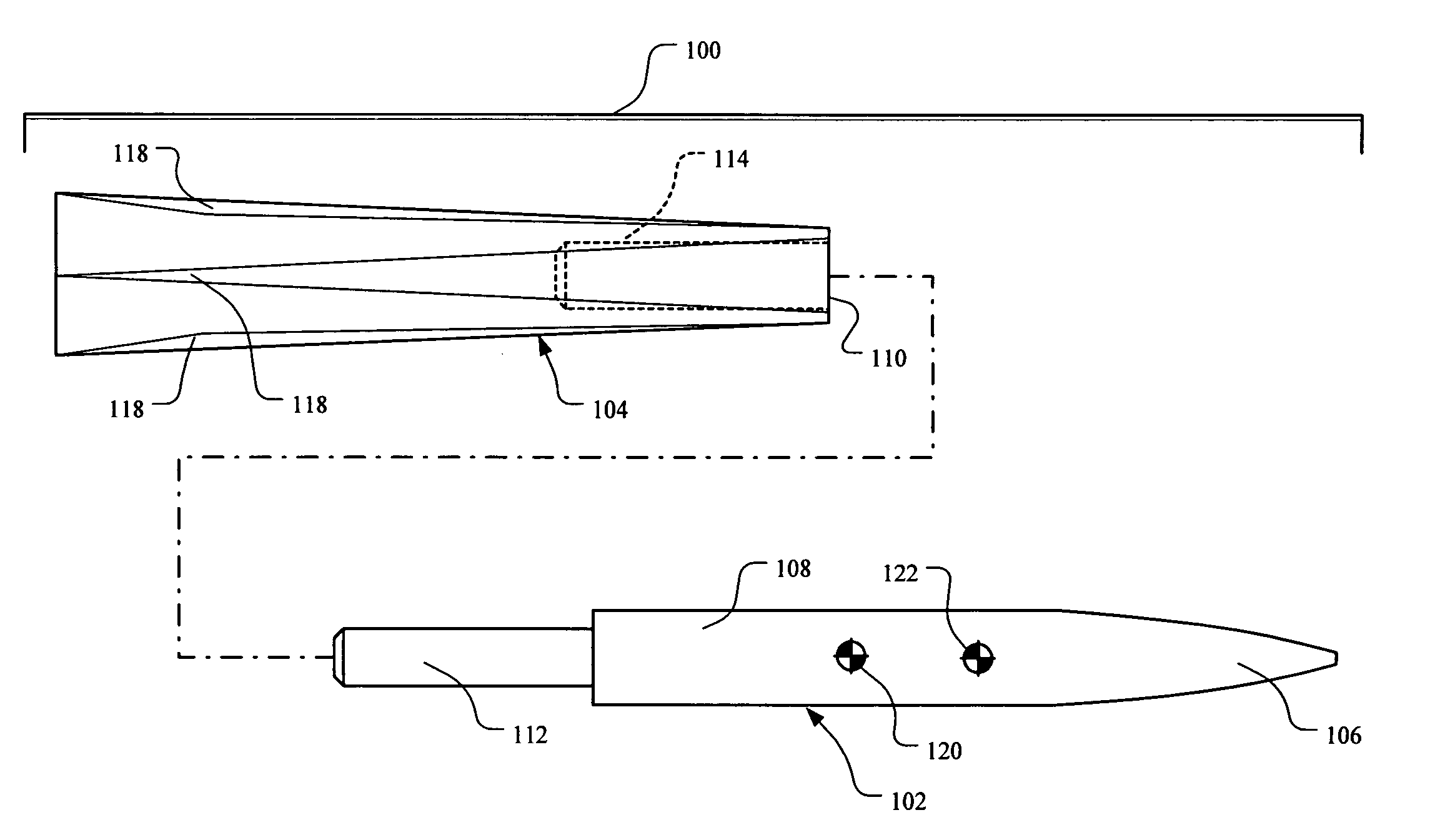
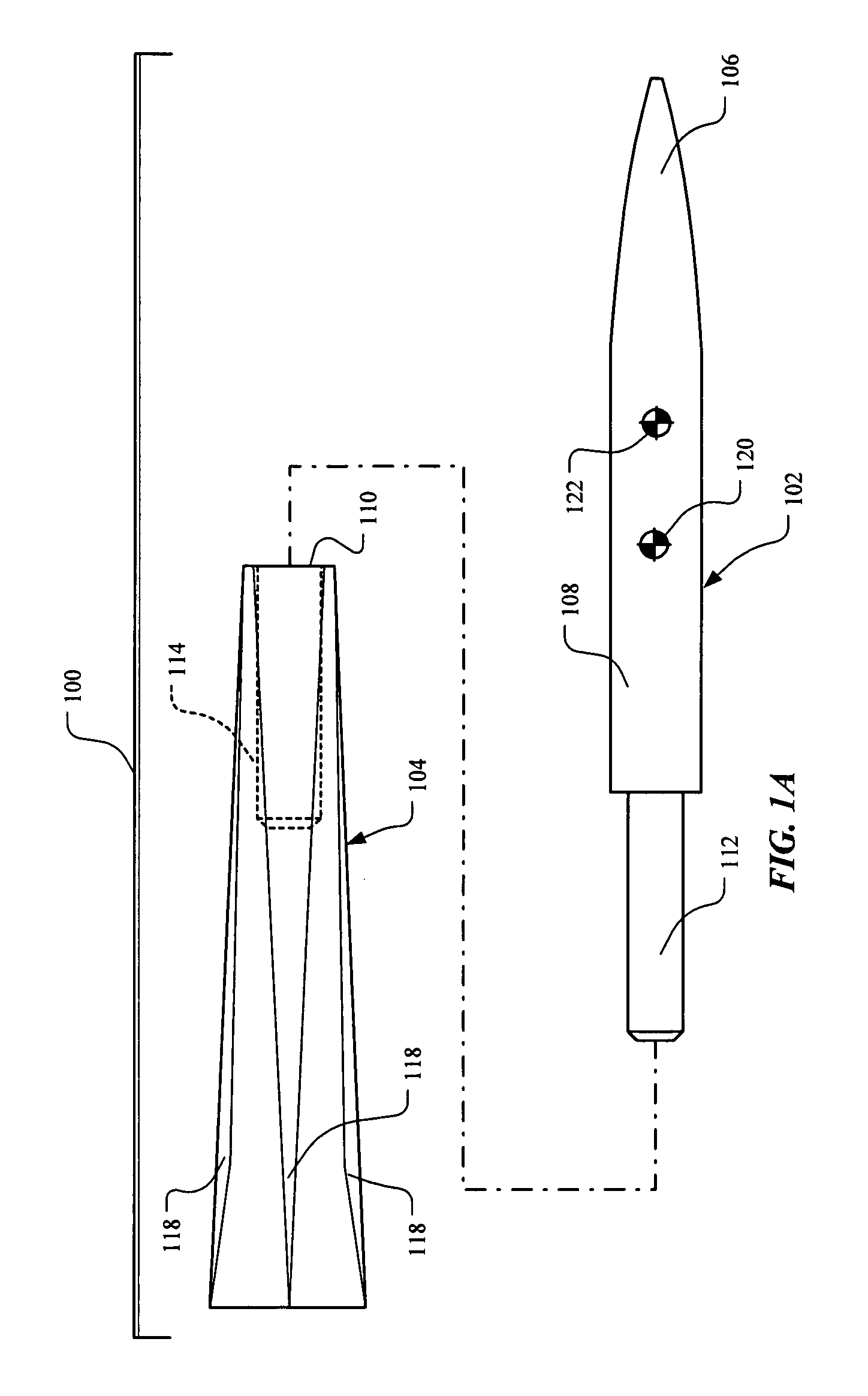
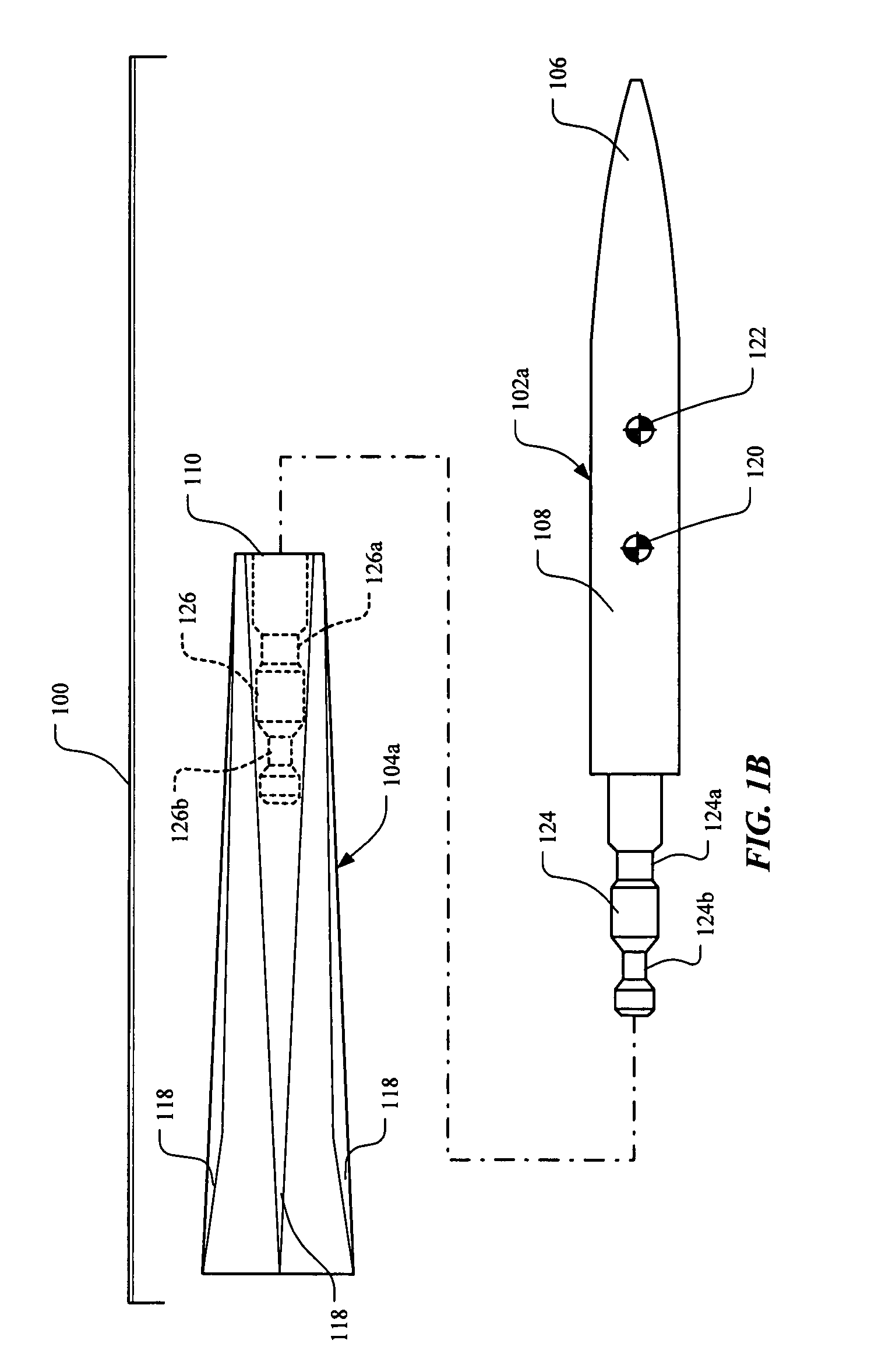
Aerodynamically stable finless projectile
InactiveUS7568433B1Improves terminal effectivenessMinimize energyAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionHollow coreAerodynamics
A finless projectile provides improved ease of use, aerodynamics, muzzle velocity, drag, target, and excursion accuracy, structural integrity, terminal effectiveness and safety, at lower cost. The finless projectile includes a slug, a forward projectile body, an aft projectile body, an obturator, and a pad. The finless projectile is a full bore projectile that defines a hollow core, but does not include a sabot nor does it carry explosives. The finless projectile functions by kinetic energy transfer from the projectile to the target by deforming the target. The center of gravity of the finless projectile is forward of the center of pressure to provide static stability to the finless projectile.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
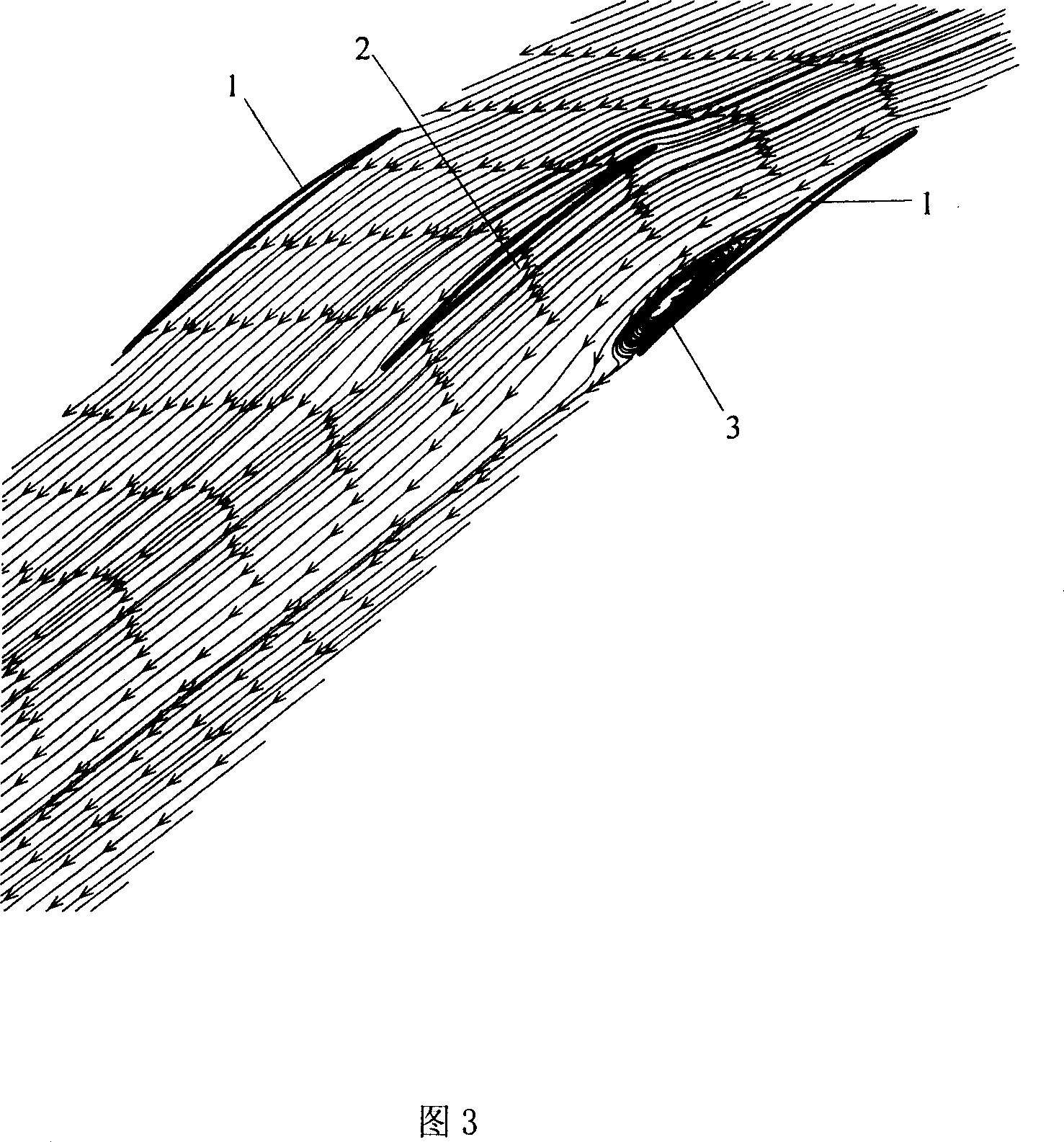
Louver distribution of raising pneumatic stability
InactiveCN1955492AImproved aerodynamic stabilityAvoid spreadingPump componentsPumpsLeading edgeEngineering
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Penetrator and method for using same
InactiveUS6843179B2Improved aerodynamic stabilityAmmunition projectilesSelf-propelled projectilesEngineeringGravity center
A penetrator includes a fore body comprising a pin and having a center of aerodynamic pressure forward of a center of gravity and a stabilizing portion comprising a material of lower density than that of the fore body and a plurality of outwardly extending fins for improving an aerodynamic stability of the projectile and defining a bore in which the pin is received for removably attaching the fore body thereto such that, when attached to the fore body, a center of gravity for the penetrator is forward of a center of aerodynamic pressure for the penetrator.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Umbrella device
InactiveUS6941958B1Mechanically simpleIncrease the areaWalking sticksUmbrellasCentrifugal forceBiomedical engineering
An umbrella device which has a shank, an umbrella-like cap formed as a membrane and a driver. The membrane is connected to the shank and is caused by the driver to move from a position of rest where it droops limply around the shank to an open position where it is essentially horizontal due to the centrifugal forces of the membrane produced by the rotation of the membrane by the driver.
Owner:TRANSSOLAR ENERGIETECHN +1
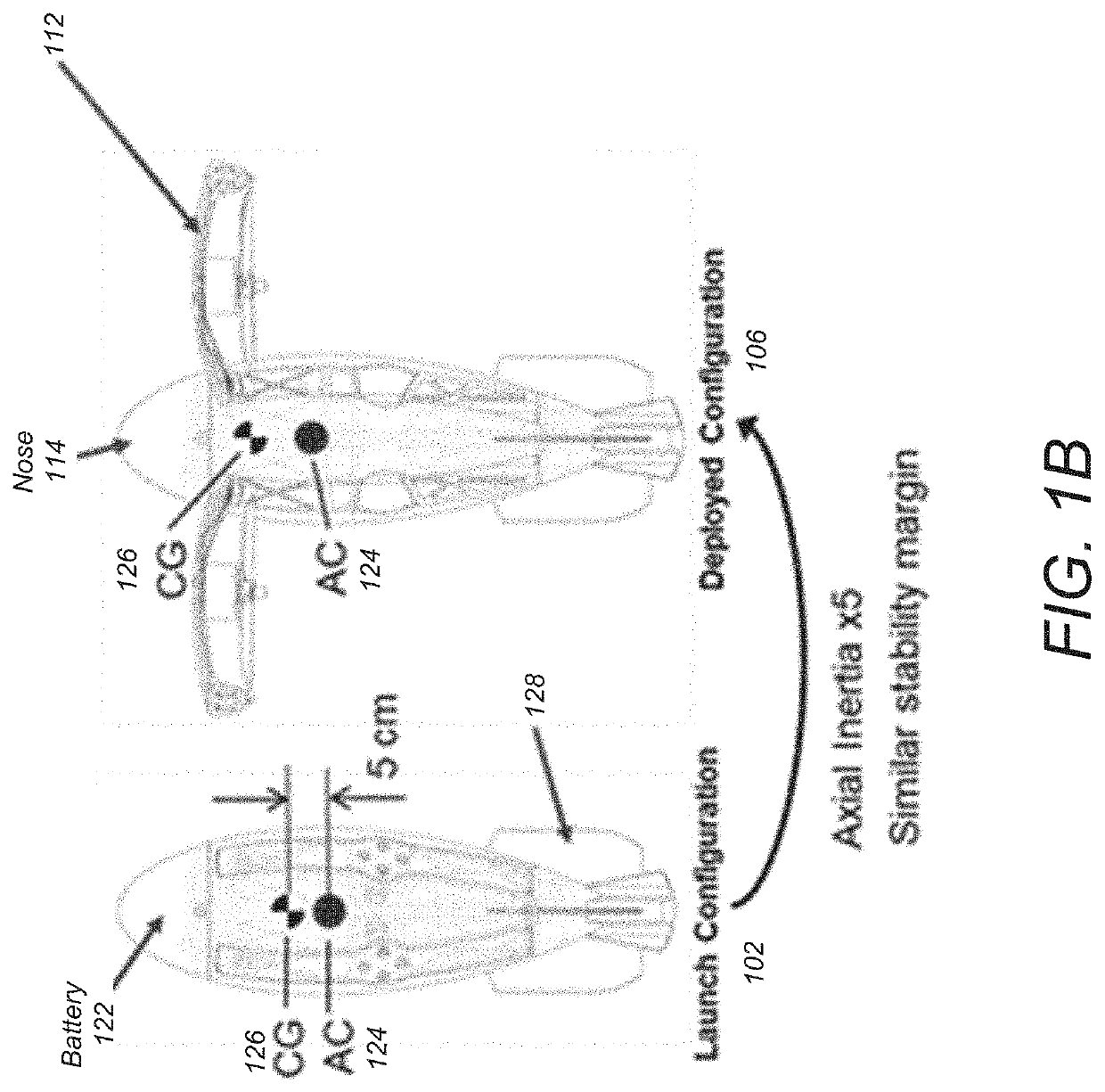
Passive and active stability systems for ballistically launched multirotors
PendingUS20210107645A1Efficient irrigationQuick coverFuselage framesRocket launchersFlight vehicleClassical mechanics
A ballistically launched foldable multirotor vehicle has a central body frame. A battery is located in an upper vertical location of the vehicle and positions a center of mass of the vehicle to provide aerodynamic stability during a launch. Fins are attached to the central body frame such that aerodynamic forces on the fins shift an aerodynamic center (AC) of the vehicle downward below the center of mass of the vehicle. Three or more foldable arms are attached to the central body frame via a hinge and exist in two states—a closed state where the foldable arms are parallel to a central body axis, and an open state (after launch) where the foldable arms extend radially outward perpendicular to the central body axis. Rotors mounted to each foldable arm are controlled by a motor to enable flight.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Ammunition projectile having improved aerodynamic profile and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20180038673A1Improve aerodynamic efficiencyEnhanced external ballisticsAmmunition projectilesProjectilesEngineeringBearing surface
A solid projectile for a firearm having a central cylindrical section defining a bearing surface and an integral, coaxial leading section tapered into a uniform conical surface, the apex at the distal end thereof projecting to a point or apex. The apex angle of the conical surface of the leading section of the projectile is within the range of 20°-40° of arc.
Owner:FRIDLUND JASON
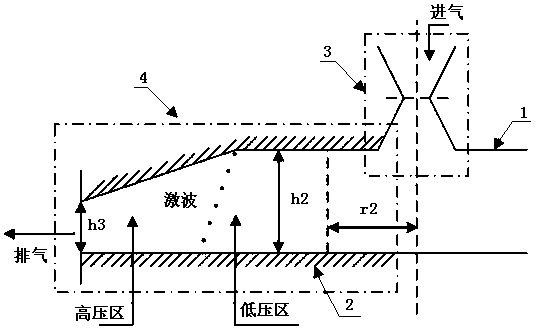
Method for increasing the aerodynamic stability of a working fluid flow of a compressor
InactiveUS20080168761A1Disadvantage be reduce and avoidIncrease aerodynamic stabilityPump componentsGas turbine plantsGas turbinesWorking fluid
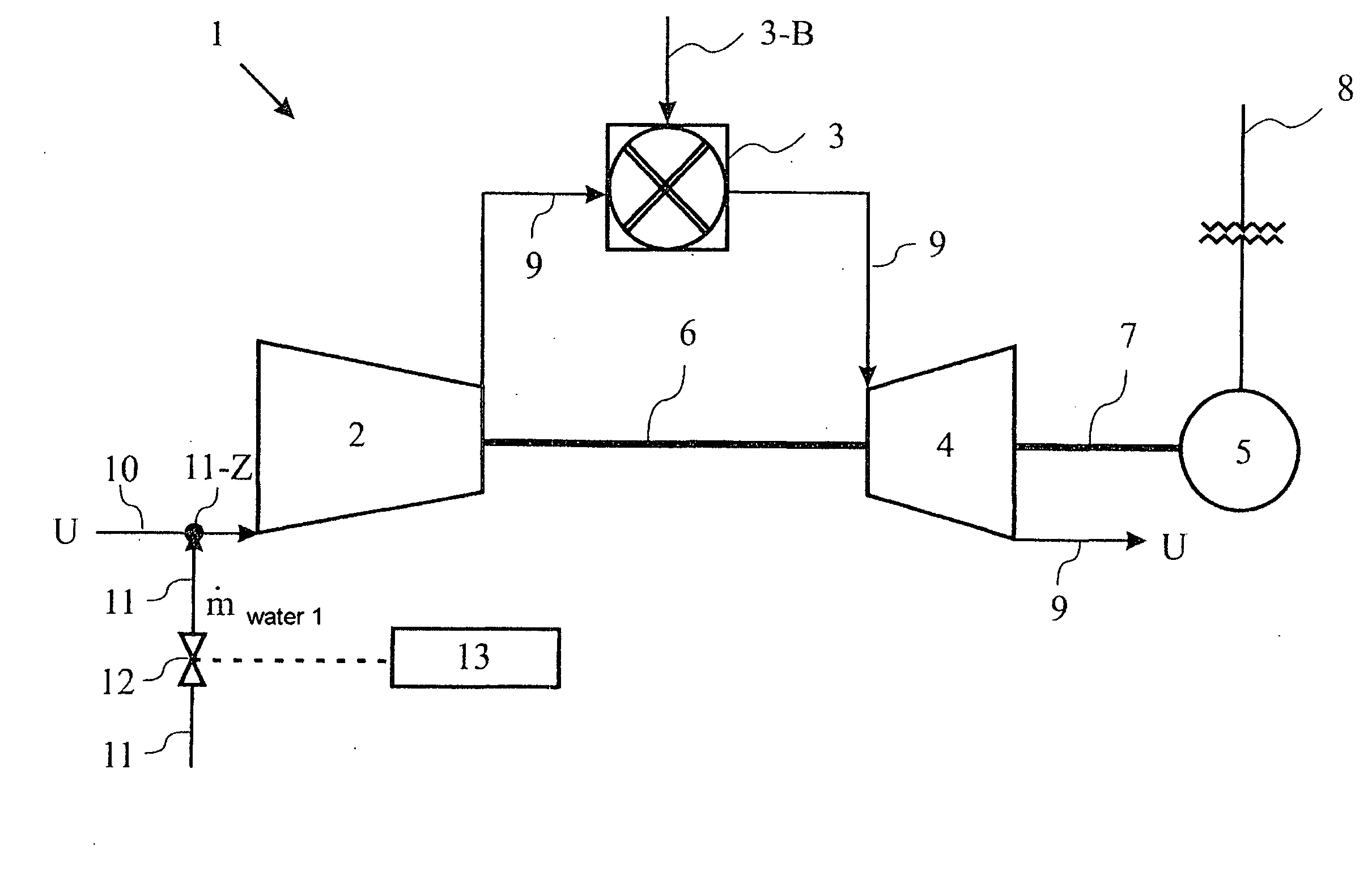
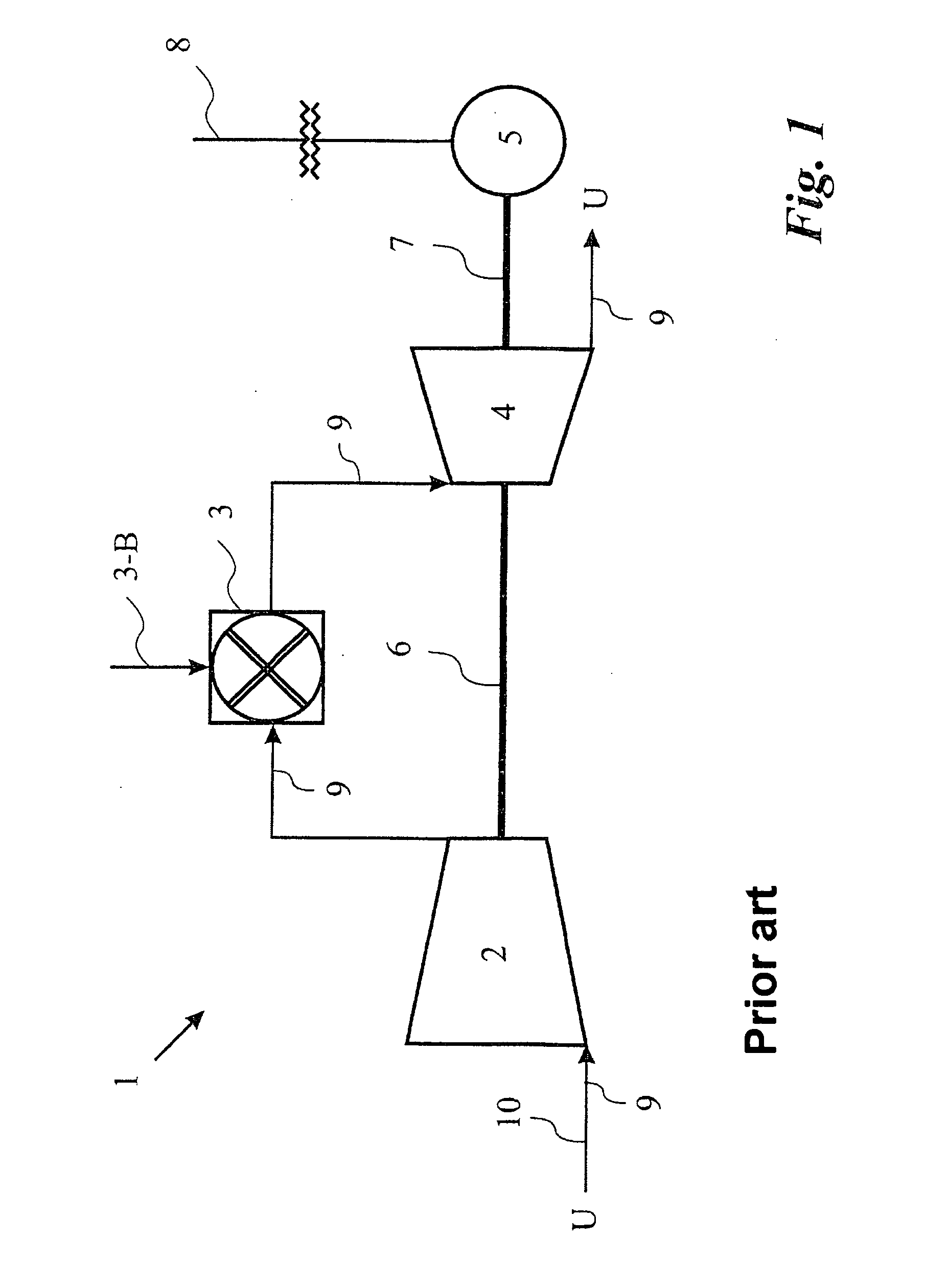
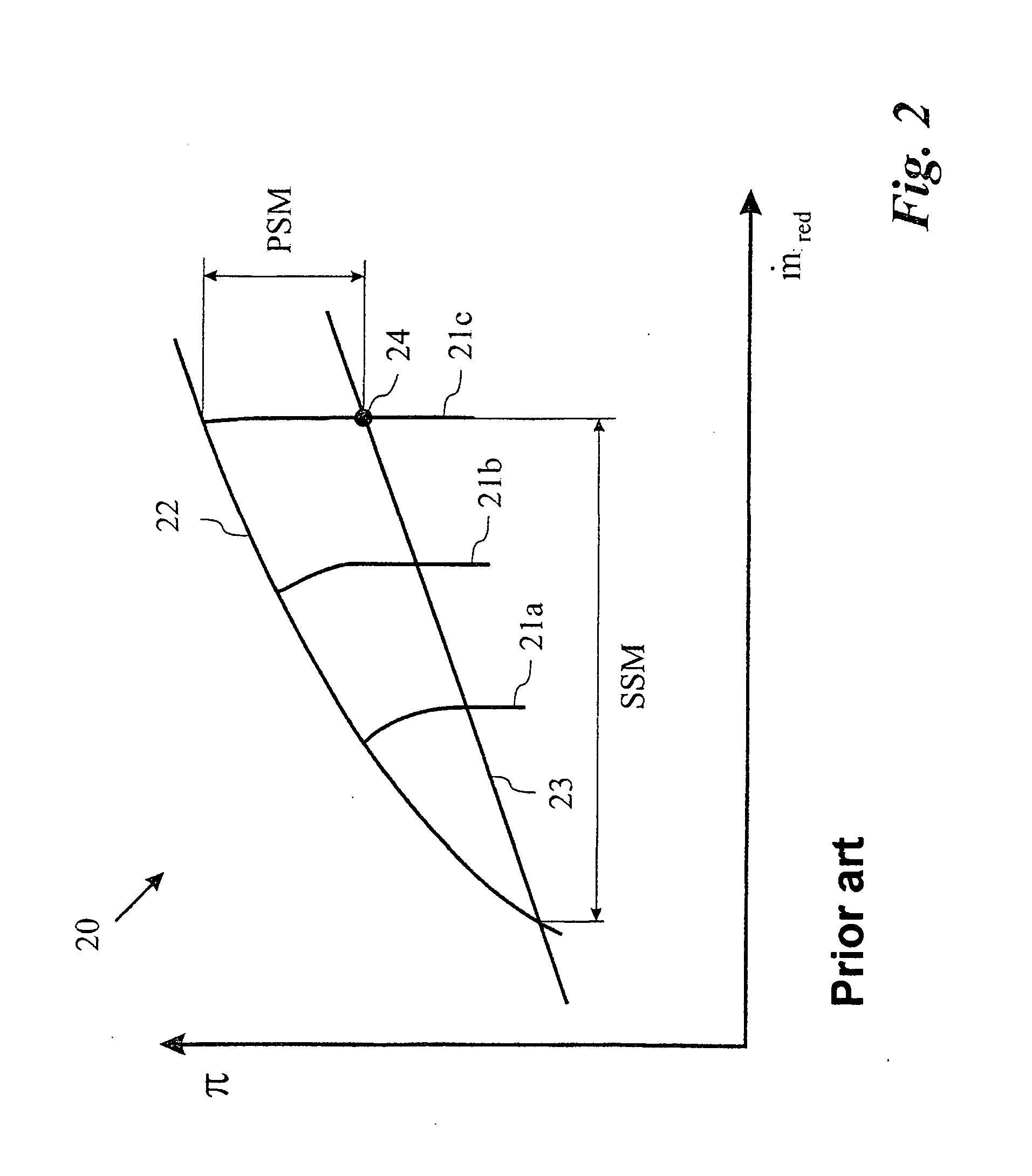
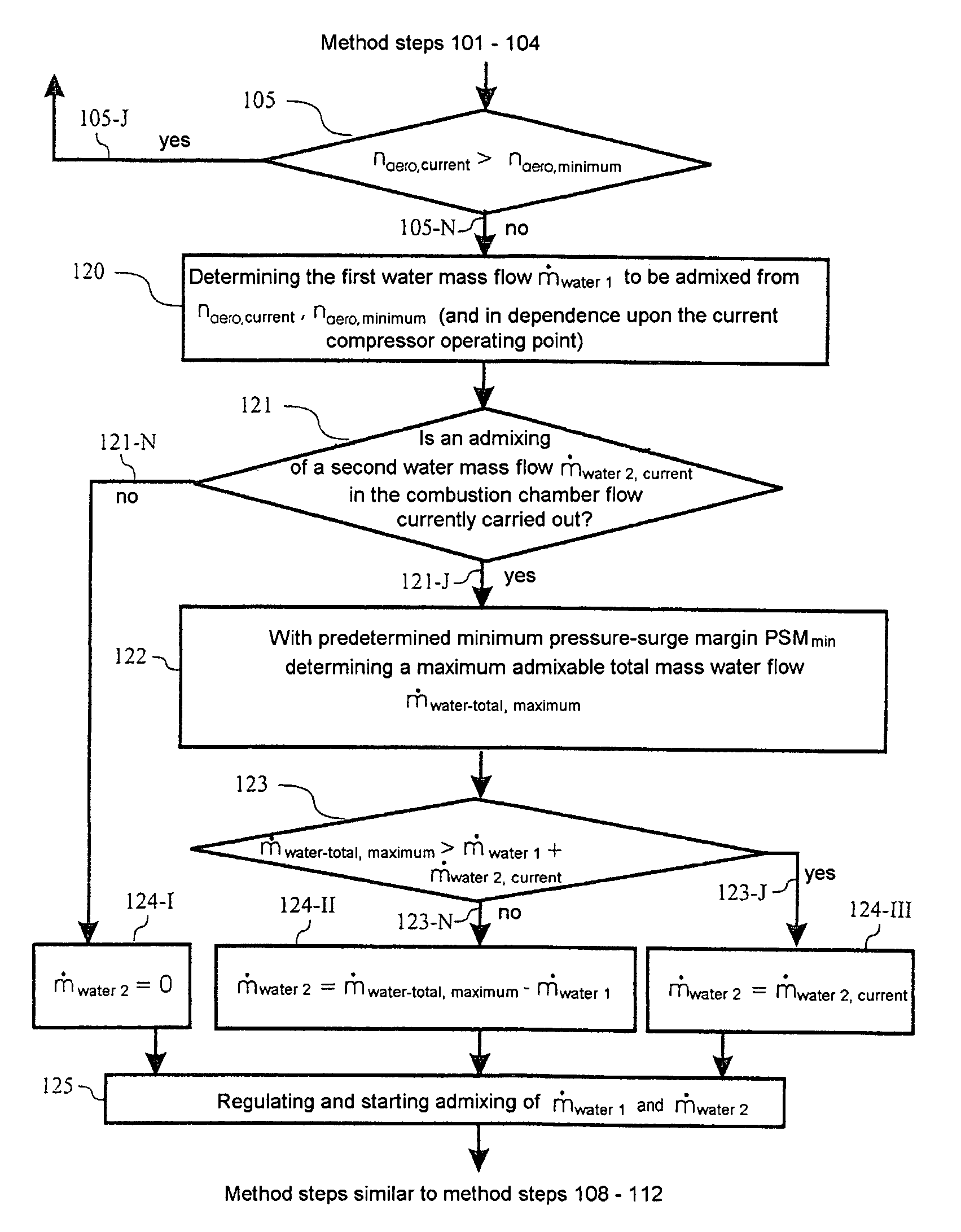
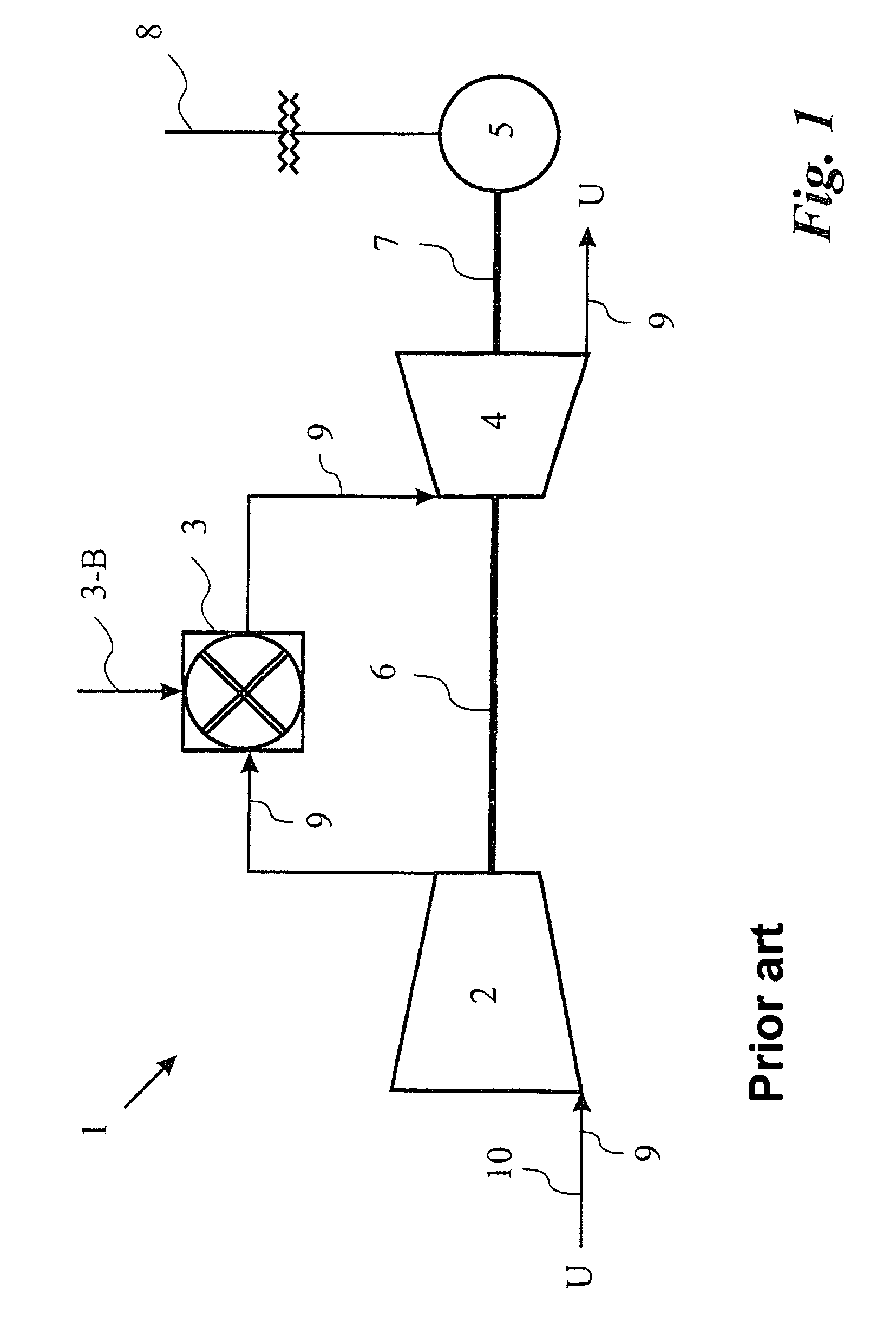
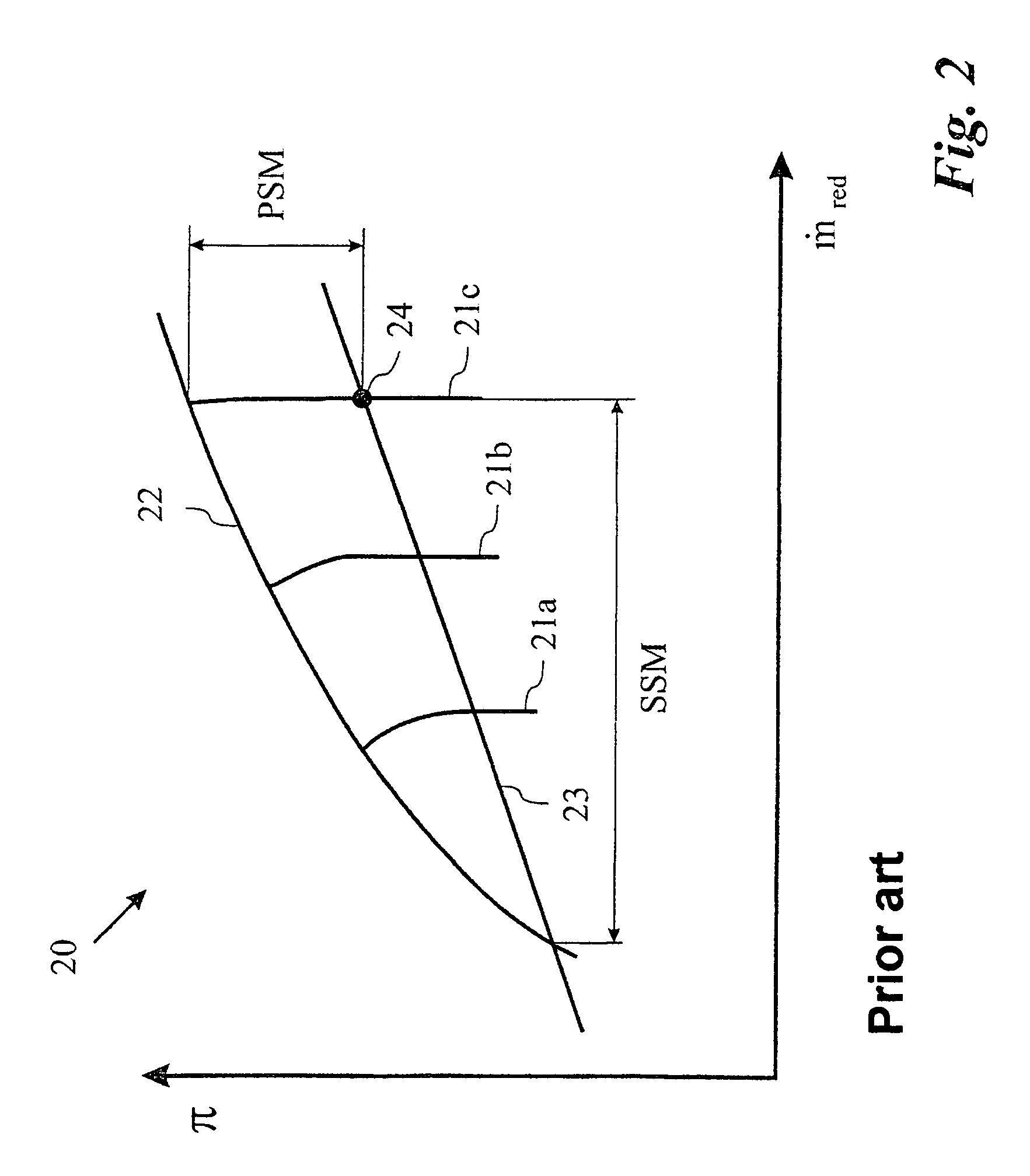
The present disclosure relates to a method for improving aerdynamic stability of a working fluid flow through a compressor of a turbomachine, in particular through a compressor of gas turbine used for power production, particularly against rapidly changing aero speed of the compressor. The method comprises to introduce a first water mass flow to the working fluid flow of the compressor. Furthermore, the disclosure relates to a turbomachine, in particular a gas turbine, which can be driven according to the above method.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
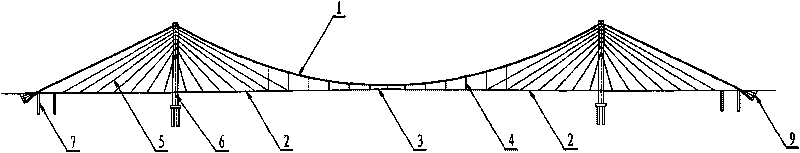
Ground-anchored-self-anchored suspension combined system bridge
InactiveCN101736685AEconomically reasonableLow costBridge erection/assemblyBridge engineeringCable stayed
The invention relates to a ground-anchored-self-anchored suspension combined system bridge which belongs to the technical field of constructional engineering and particularly relates to a design of a long-span bridge under a complex geologic condition in bridge engineering. The ground-anchored-self-anchored suspension combined system bridge is characterized in that after a tower and a lateral hole pier are constructed, a concrete main girder of a cable-stayed bridge begins to be assembled through a cantilever; after the cantilever is assembled to a lateral hole, a main cable is suspended, one end thereof is anchored on a permanent anchor block, the other end thereof is anchored on a concrete girder external anchor block, and the anchor blocks are pulled on a temporary anchor through temporary anchor cables; the end of a main girder provided with the permanent anchor block is horizontally supported on a bridge abutment; each segment of a main steel girder in a span is hoisted through a cable crane; after folding, the temporary anchor cables are dismantled in batches, and the main cable is completely anchored at the end part of the main girder to finish the system switching from the temporary anchor to a self-anchor. The invention has the effects and advantages that material performance is fully exerted, and by aiming at the complex geologic condition, the huge anchor is saved, the construction cost is lowered, the construction period is shortened, and the risk in the construction process is reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
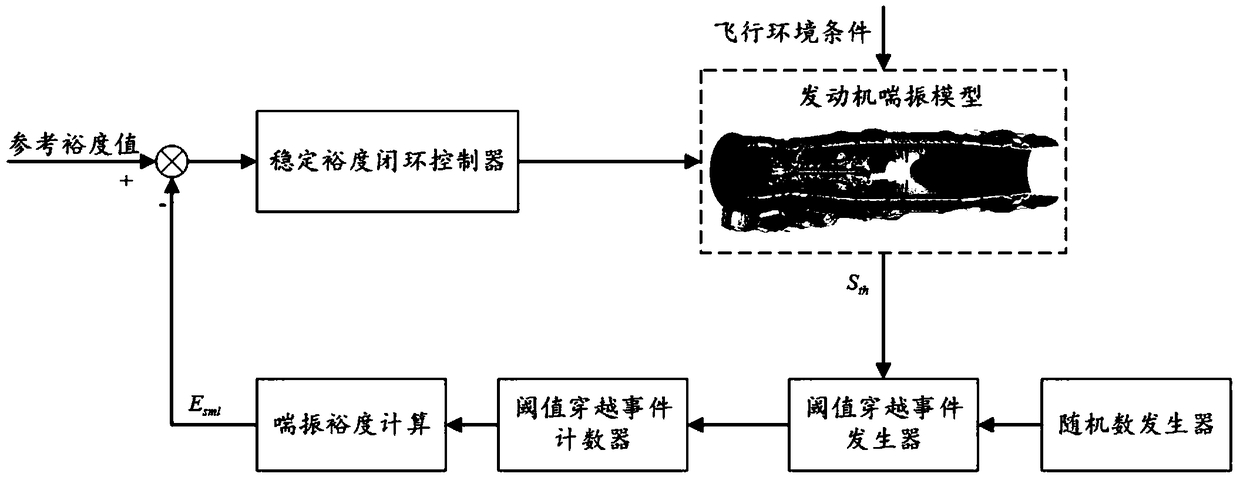
An active stability control method based on aero-engine stability margin estimation is proposed
PendingCN109344510AImproved aerodynamic stabilityMaximize dynamic performanceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAviationTransient state
The invention discloses an active stability control method based on an aero-engine stability margin estimation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) an aero-engine surge real-time model; (2)surge margin estimation algorithm and simulation; (3) Active stability control law of aeroengine. As to that problem of aerodynamic stability of an aero engine, By utilizing the residual stability margin to improve the aerodynamic stability of the engine, The real-time model of engine surge and the estimation model of engine stability margin are established. The active stability control law is designed by robust control method, and the closed-loop control loop of engine stability margin is constructed, which ensures that the dynamic performance brought by the residual stability margin can be brought into full play under the condition of stable operation of the engine in transient state. In addition, this scheme can make the engine work at the high performance point with small surge marginduring acceleration, improve the acceleration performance of the engine and enhance the maneuverability of the aircraft.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Integrated marine performance system
InactiveUS20050247251A1Easy to optimizeCharacteristic can be alteredWatercraft hull designFloating buildingsMarine engineeringStream flow
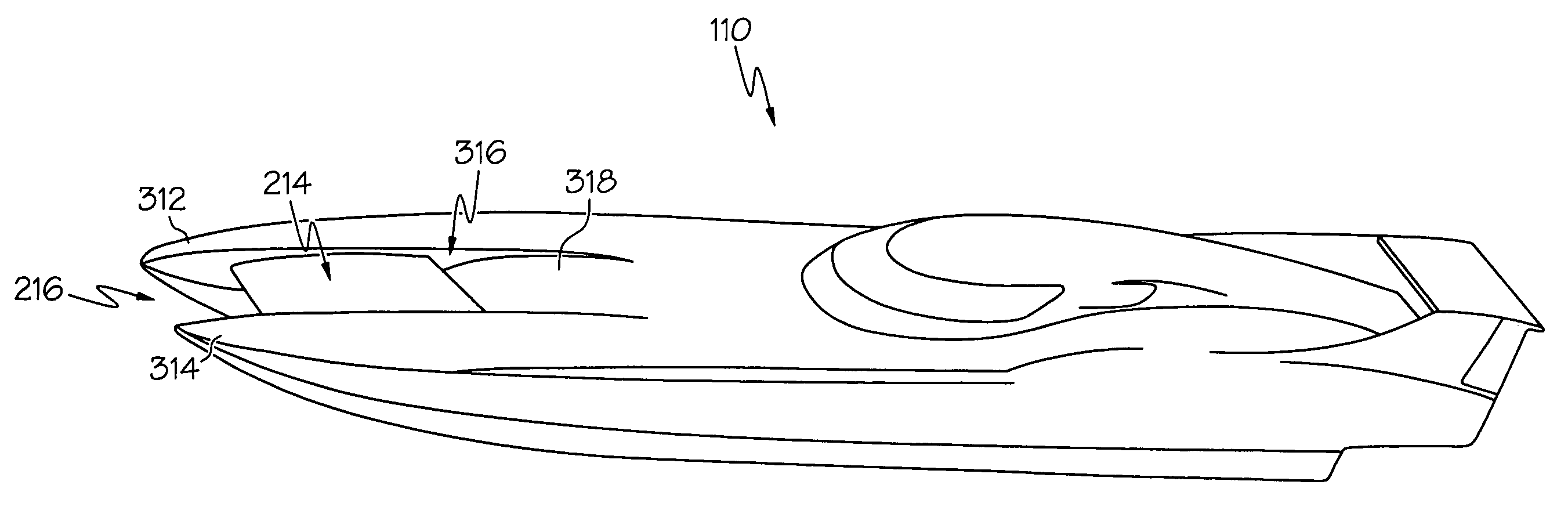
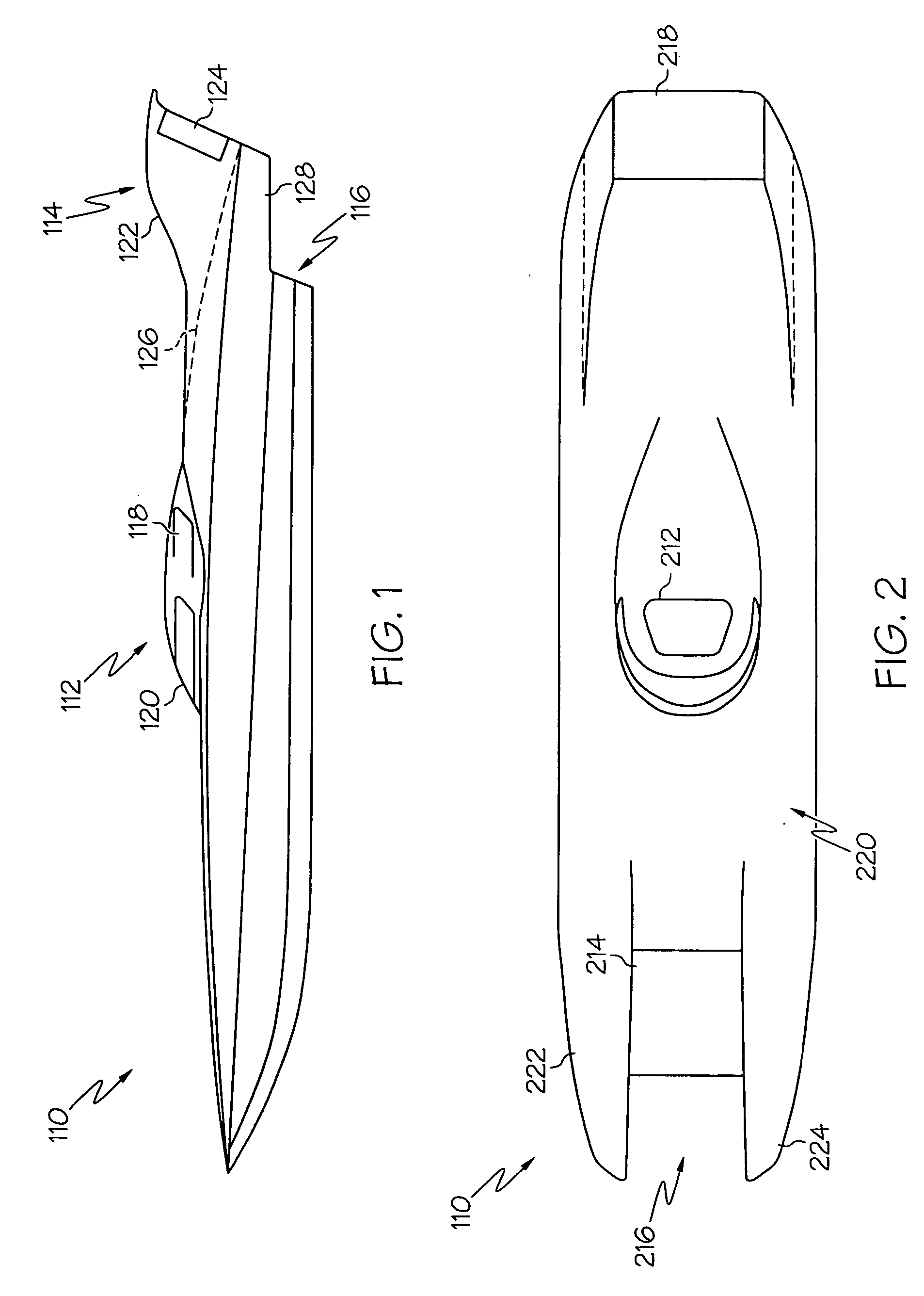
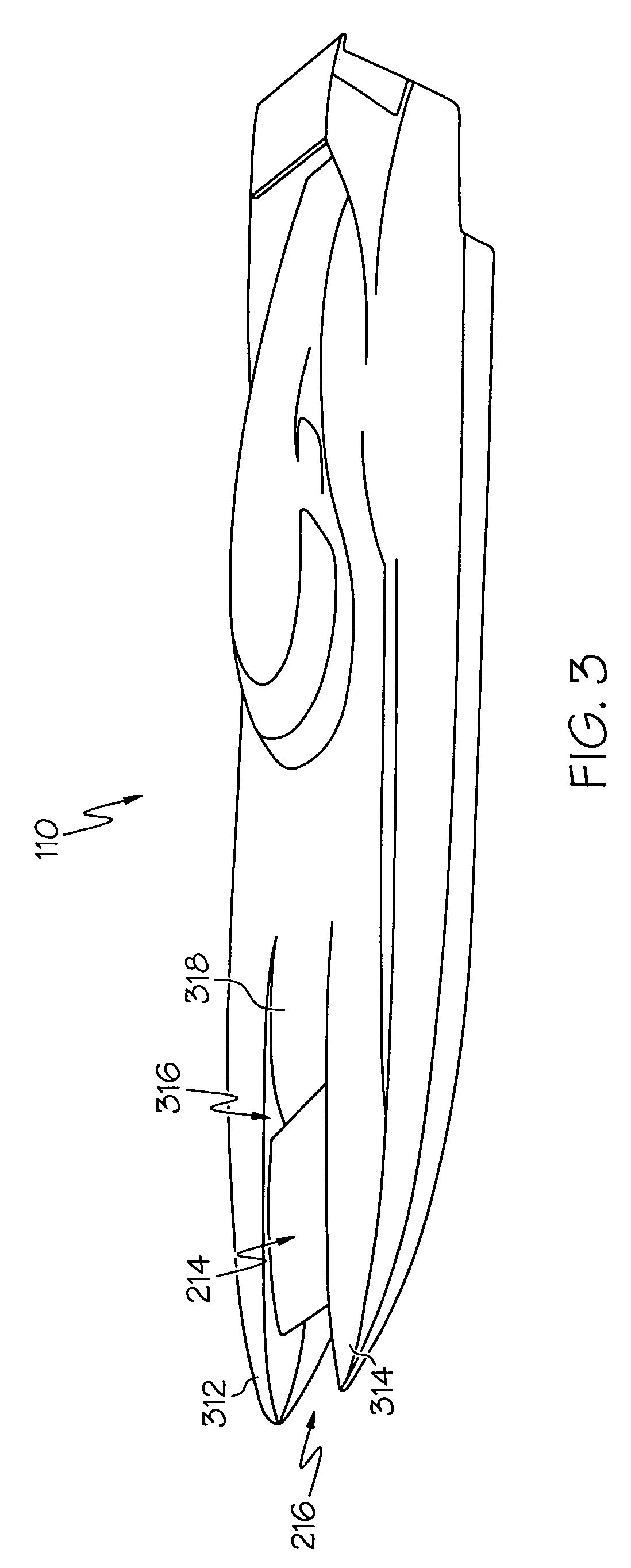
A system for improving the performance of a powered boat that includes both methods and apparatuses that provide a powered boat means to stabilize, control, and optimize the powered boat's performance when the powered boat is in powered motion. The system provides capabilities of enhancing the powered boat's performance by responding to both aerodynamic and hydrodynamic effects upon the powered boat when the powered boat is in motion. Some embodiments of the system are capable of altering its means of response to aerodynamic effects while the powered boat is in powered motion, other embodiments are capable of altering the powered boat's response to hydrodynamic effects while the powered boat is in powered motion, and still other embodiments are capable of altering the powered boat's response to both aerodynamic and hydrodynamic effects while the powered boat is in powered motion. Certain embodiments of the system are capable of utilizing aerodynamic elements that operate on the air stream flowing within a tunnel formed within a multihull of a powered boat, while other embodiments are capable of mitigating the effects of water impacts upon the roof of a tunnel formed within a multihull powered boat. Still other embodiments are capable of responding to aerodynamic effects by interacting with portions of the air stream that passes above the boat while mitigating the potential for negative effects due to cross-winds impacting the structure which rises above a deck of the powered boat.
Owner:SCISM RANDY MARK +1
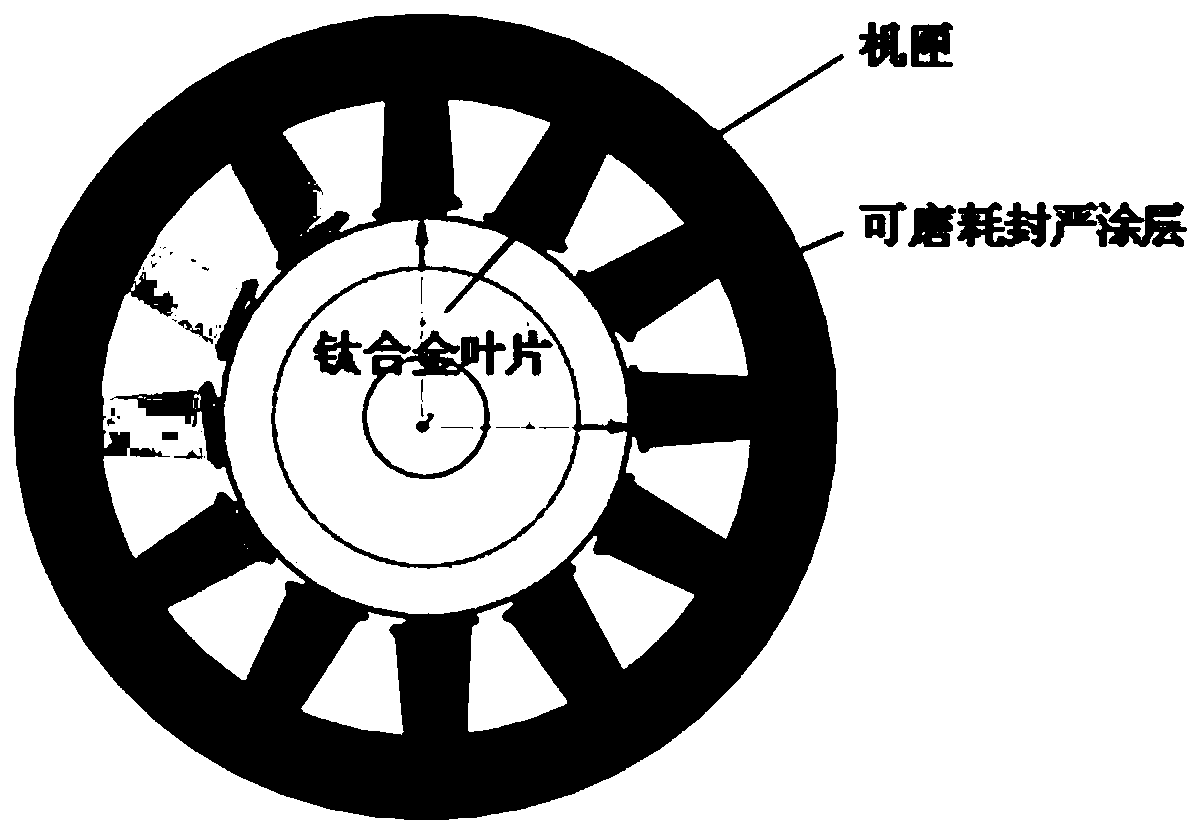
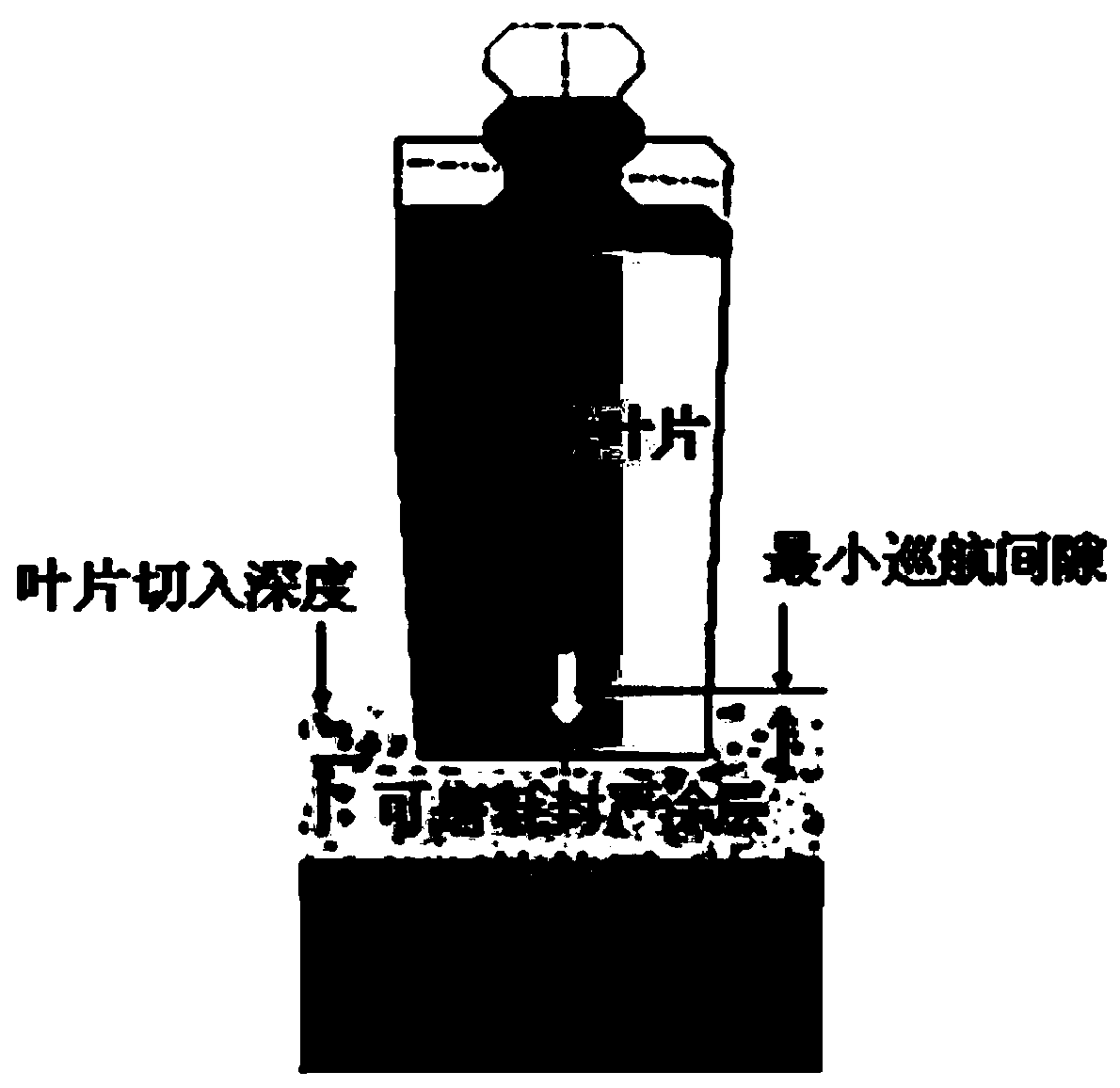
Control method of titanium alloy compressor tip clearance
InactiveCN110905607AReduce gas leakage rateImprove surge marginLeakage preventionMachines/enginesAviationTitanium alloy
The invention aims to provide a control method of a titanium alloy compressor tip clearance. The control method is characterized in that an abradable sealing coating is sprayed on the inner wall of acasing; tips of rotor blades are compositely electroplated with a Ni / c-BN coating; and the abradable sealing coating and the Ni / c-BN coating are used as a pair of abradable sealing friction pair, thereby forming a novel gas circuit sealing coating structure. In the operation process of an engine, the tips of the rotor blades can cut into the abradable sealing coating on the inner wall of the casing, thus grooves capable of improving the sealing effect are reserved, ideal radial airflow gaps are formed, and the maximum pressure difference is obtained, so that the power of the engine is remarkably improved, the consumption of aviation kerosene is reduced, and the one-time test run percent of pass of the whole engine is improved.
Owner:SHENYANG LIMING AERO-ENGINE GROUP CORPORATION
Roof edge structure for securing roofing materials
InactiveUS10077558B2Fast dryingIncrease air circulationRoof covering using tiles/slatesRoof drainageEavesWater flow
A ridge structure at a roof edge, having a base panel lying on a roof surface and a hollow ridge structure over the base panel. The hollow ridge structure is constructed in a flat spring form along the eaves, and therefore one slope of the ridge faces the roof and the other slope the opposite direction. The slope facing the roof can be lifted to receive and secure roofing materials between the slope and the base panel. When water flows down the roof surface, most water flows over the ridge structure and the rest flows into the hollow space inside the ridge structure and drains through drain holes on the base panel.
Owner:HEO BAL
Wind Turbine Blade Vibration Control Method Using Composite Damping Structure
ActiveCN103321853BAchieving tremor suppressionSuppress chatterMachines/enginesWind energy generationGlass fiberCarbon fibers
The invention is specifically a method for suppressing flutter of wind turbine blades using a composite damping structure, which solves the problem that large flexible blades are prone to flutter and lack effective prevention and control methods. The vibration suppression method of wind turbine blades using a composite damping structure is specifically to set a co-cured constrained damping layer on the surface of the blade, and set a free damping layer on the outer surface of the main beam; the free damping layer is composed of a single layer of damping material, and the damping viscoelastic material or Damping alloy or damping composite material; the co-cured constrained damping layer is co-cured and formed by the interstitial arrangement of the composite material layer and the damping material layer. Choose damping viscoelastic material. Compared with the prior art, the present invention has universal applicability, effective tremor suppression, economy and designability.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
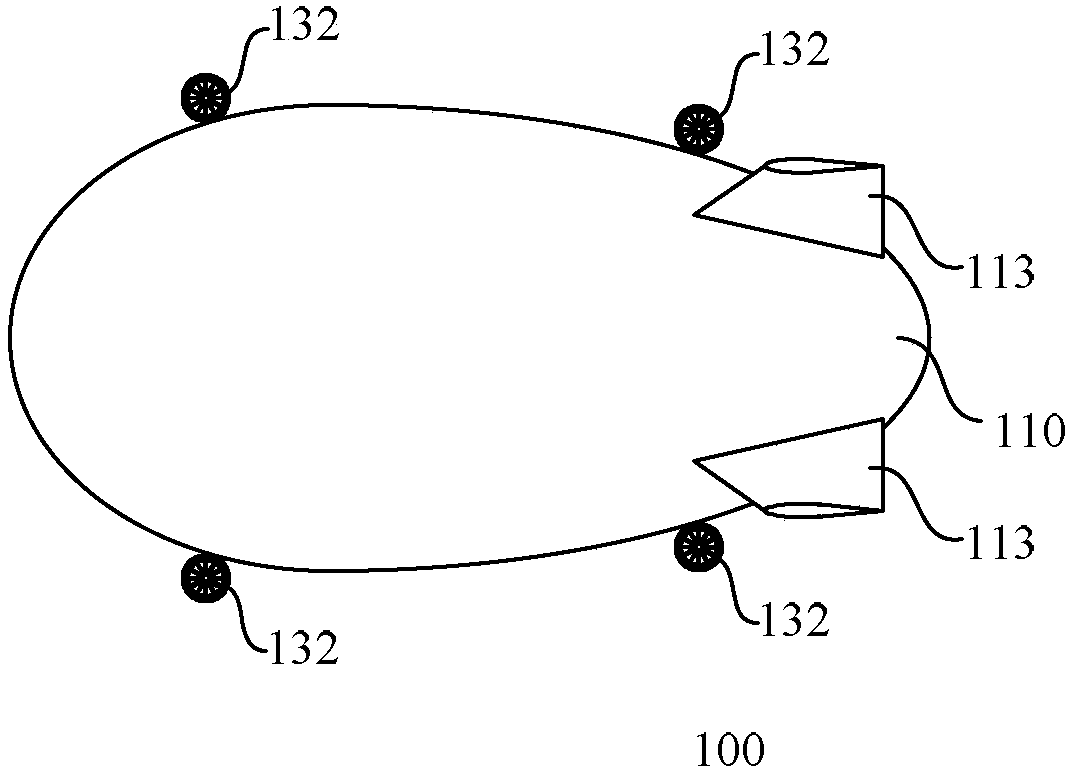
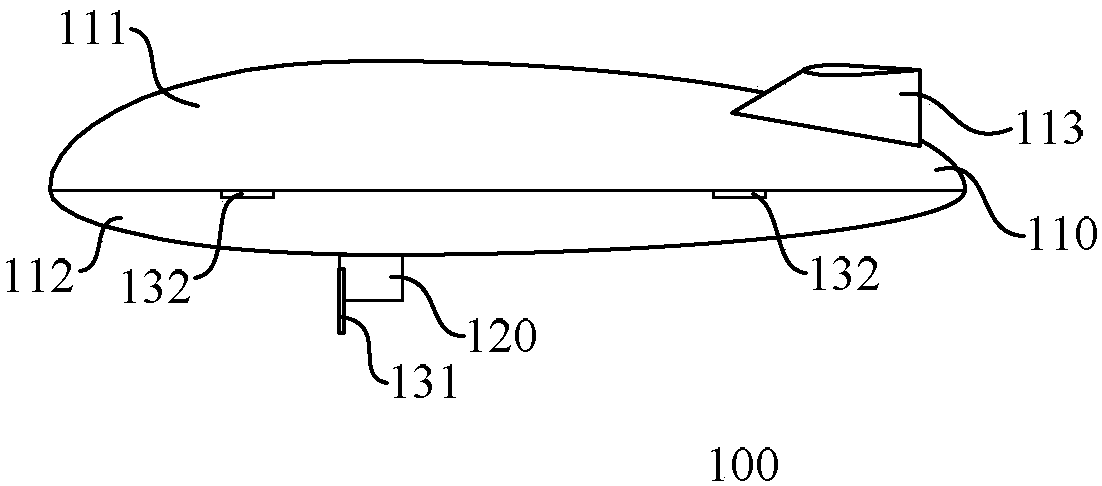
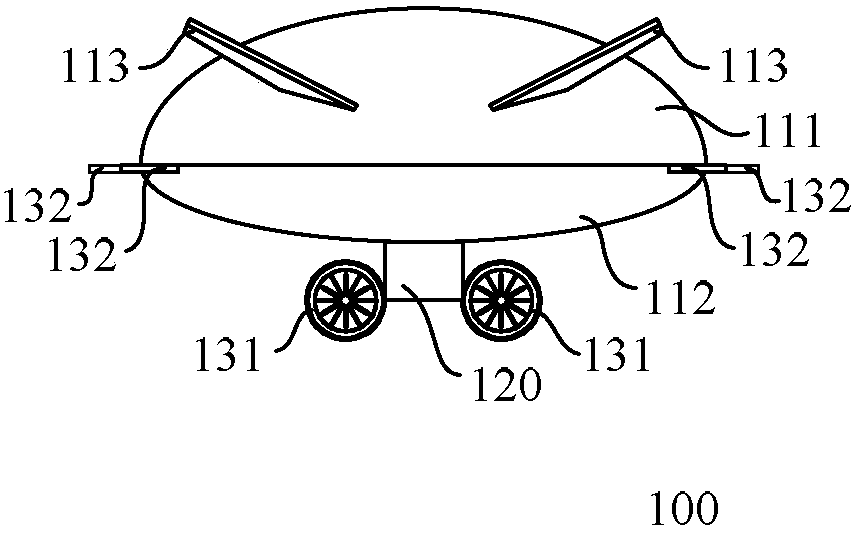
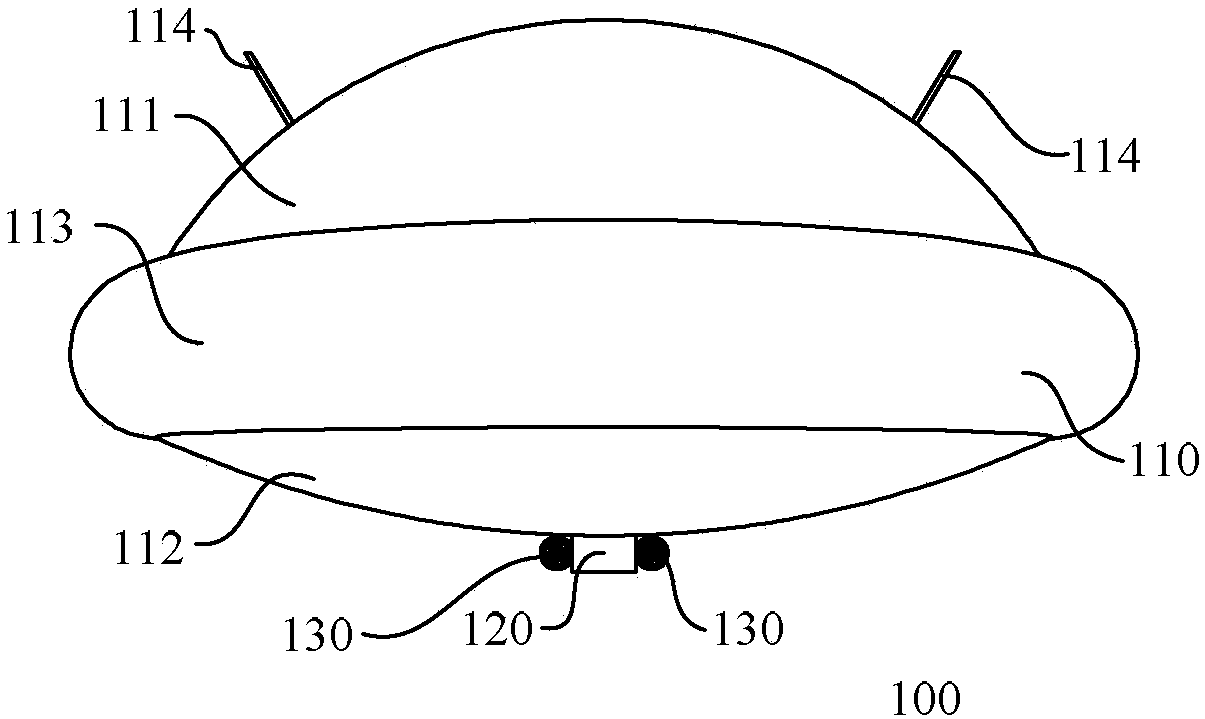
Airship
InactiveCN107618647AIncrease profile liftSolve the problem of a single source of take-off and landing powerRigid airshipsEngineeringPower consumption
The invention discloses an airship comprising an airship body; the airship body comprises an upper half part and a lower half part; the upper half part and the lower half part both comprise arc projections, wherein eh arc projection of the upper half part is higher than that of the lower half part. The airship is spindle-shaped; the interface contours of the upper half part and the lower half partare oval. The design of the airship's surface increases the lift of the airship's surface, thus saving the power consumption of the airship.
Owner:SHENZHEN KUANG CHI SPACE TECH CO LTD
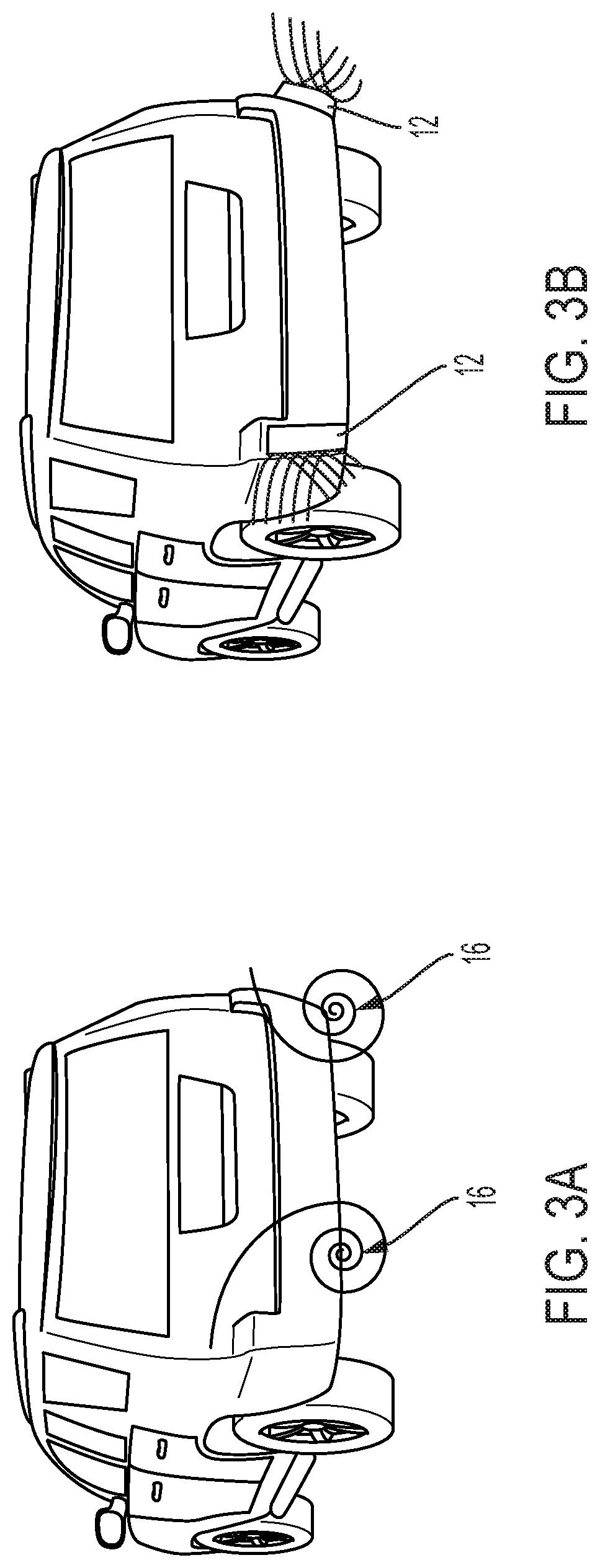
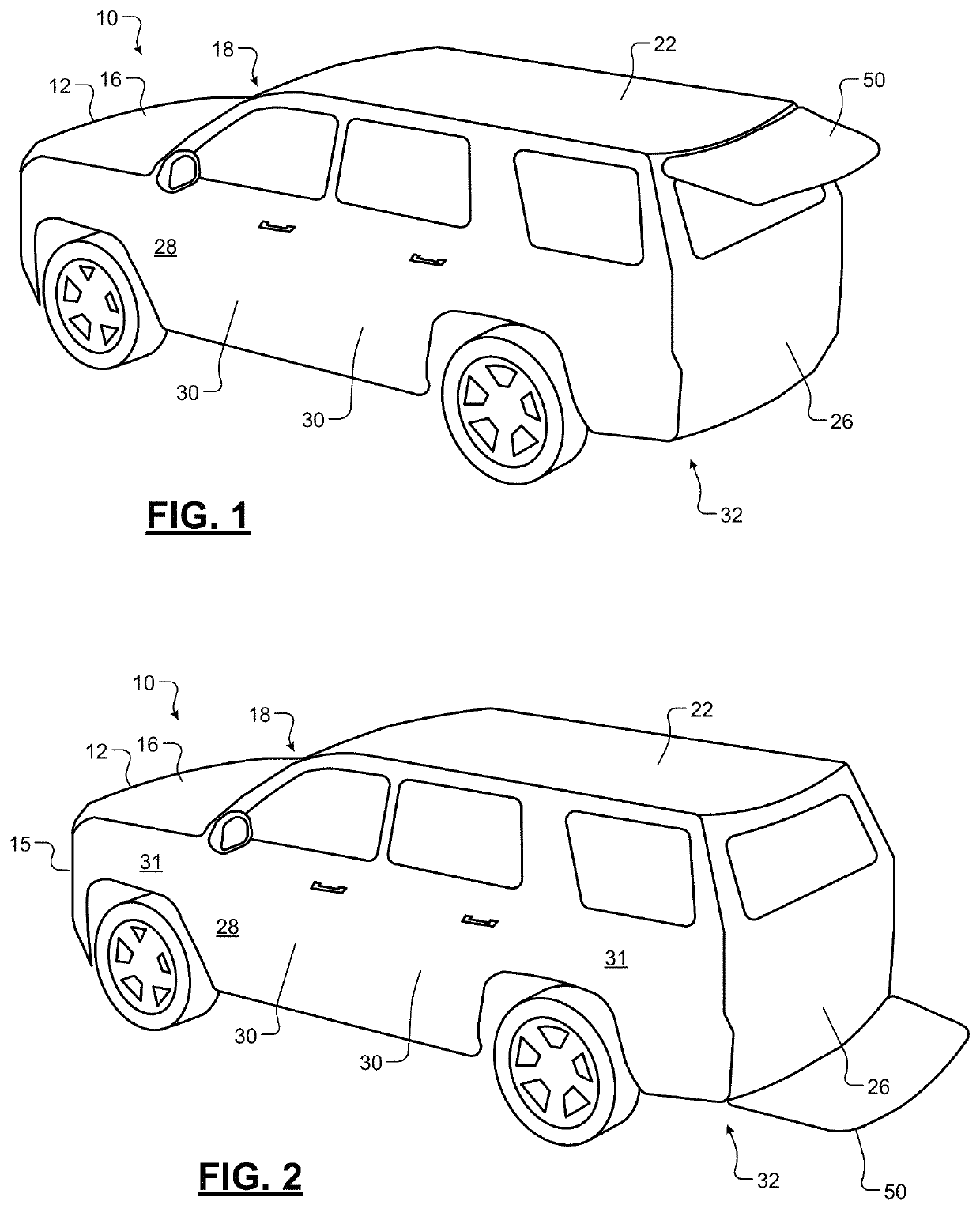
Deployable panels for drag reduction and stability
InactiveUS20200391811A1Emission reductionReduced footprintVehicle body stabilisationGearingAerodynamic dragEngineering
A deployable panel for a vehicle, the deployable panel including: a telescopically adjustable body, where, when in a retracted state, the body is configured to be enclosed within at least a portion of the vehicle, and where, when in an extended state, the body is configured to reduce aerodynamic drag generated during movement of the vehicle or increase aerodynamic stability against external forces impacting at least one side of the vehicle; and a linear actuator installed within the body, the linear actuator configured to telescopically adjust the body from the retracted state to the extended state or somewhere therebetween.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Distributed parameterized impeller self-circulation treatment casing
ActiveCN112539184AIncrease stall marginReduce efficiency lossPump componentsRadial flow pumpsImpellerInlet channel
The invention discloses a distributed parameterized impeller self-circulation treatment casing which is composed of a casing body, an air inlet channel, impeller blades, a front channel, a rear channel and air entraining bridge circuits; the air entraining bridge circuits are fixed to the outer side of an impeller casing, and air flows back in the bridge circuits through the front channel and therear channel connected to a channel front edge of the impeller casing; and the front channel and the rear channel of the impeller self-circulation treatment casing are located at the positions with different axial chord lengths away from an impeller inlet respectively, an inner wall face two-dimensional molded line is formed by fitting and optimizing a structured curve so as to ensure that jet flow is close to the wall face as much as possible, and the outer wall face molded line is a controllable contraction molded line, so that the effects of guiding and accelerating airflow are achieved. The impeller self-circulation treatment casing utilizes the airflow pressure difference in rotor channels corresponding to the self-circulation front channel and the self-circulation rear channel to perform air exhaust and air injection. According to the treatment casing structure, the blocking margin and the stall margin of the centrifugal impeller can be improved, the purpose of reducing the efficiency loss is achieved, and the impeller can operate and work at a larger margin.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Fluid-solid coupled gas shock wave adjusting bearing
ActiveCN106545576AImprove carrying capacityImproved aerodynamic stabilityBearingsShock waveCarrying capacity
The invention relates to a fluid-solid coupled gas shock wave adjusting bearing. At present, a widely used dynamic pressure foil-bearing is limited in carrying capacity and lacks of stability and the coating process requirements on the surface of a foil are high, and a static pressure-dynamic pressure mixed bearing is insufficient in carrying capacity at a slow rotating speed while is pneumatically unstable at a high rotating speed. The bearing provided by the invention comprises a bearing bush (1) which is provided with air supply throttling orifices (3), damping cavities (4) are arranged in the outlet positions of the air supply throttling orifices, one or more than one row of air supply throttling orifices and the damping cavities is uniformly distributed circumferentially on the inner surface of the bearing bush, and foil structures (7) are arranged between the outlets of the damping cavities and a rotor (2); the foil structures comprises bump foils (6) and flat foils (5). By changing the air supply pressure of the bearing, the throttling orifice structures and the damping cavity structures, the fluid-solid coupled gas shock wave adjusting bearing can be matched with a large-gap high-load bearing working condition. The invention is the fluid-solid coupled gas shock wave adjusting bearing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
Method for increasing the aerodynamic stability of a working fluid flow of a compressor
InactiveUS7726132B2Disadvantage is reduced and avoidedImproved aerodynamic stabilityPump componentsGas turbine plantsWorking fluidEngineering
The present disclosure relates to a method for improving aerdynamic stability of a working fluid flow through a compressor of a turbomachine, in particular through a compressor of gas turbine used for power production, particularly against rapidly changing aero speed of the compressor. The method comprises to introduce a first water mass flow to the working fluid flow of the compressor. Furthermore, the disclosure relates to a turbomachine, in particular a gas turbine, which can be driven according to the above method.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
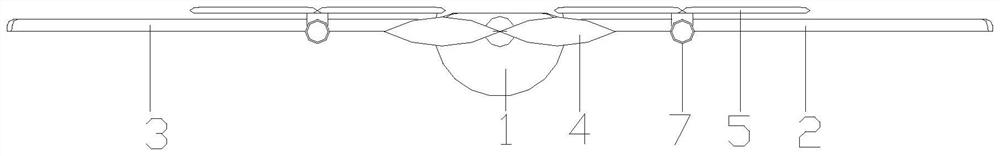
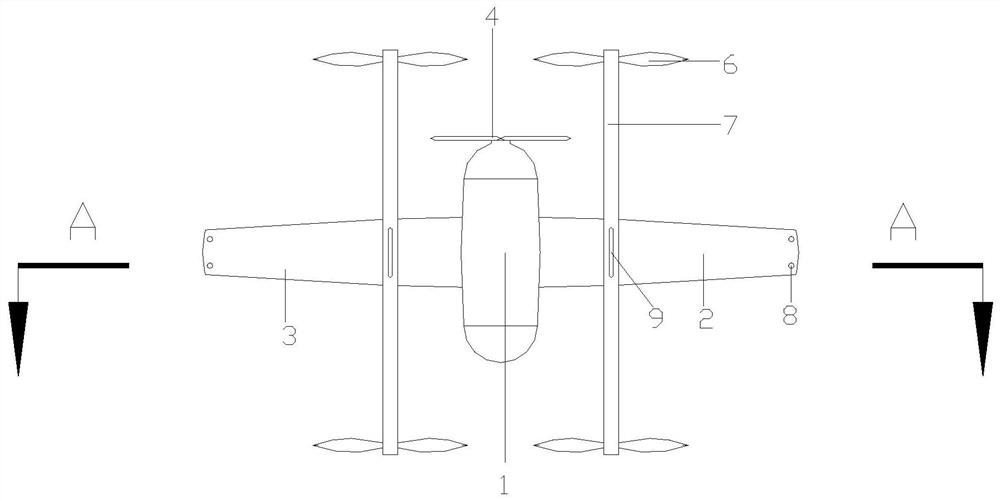
Composite wing unmanned aerial vehicle and pneumatic balance method
PendingCN114275157AExtend battery lifeImprove stabilityAircraft navigation controlRotocraftBalancing machineMarine engineering
The invention discloses a composite wing unmanned aerial vehicle and an aerodynamic balance method. The composite wing unmanned aerial vehicle comprises a fuselage, wings located on the two sides of the fuselage, a main rotor located at the front end of the fuselage and auxiliary rotors installed on the wings. The unmanned aerial vehicle further comprises a pneumatic balance mechanism, the pneumatic balance mechanism comprises an air chamber installed on the vehicle body and drainage pipes connected to the air chamber, every two drainage pipes form a group, and each group of drainage pipes comprises a left drainage pipe and a right drainage pipe which are located on wings on the two sides of the vehicle body correspondingly. The controllability of the unmanned aerial vehicle is improved, and the use safety of the unmanned aerial vehicle is improved.
Owner:重庆交通大学绿色航空技术研究院 +1
Penetrator and method of using same
InactiveUS20050257713A1Improved aerodynamic stabilityAmmunition projectilesSelf-propelled projectilesEngineeringGravity center
A penetrator includes a fore body comprising a pin and having a center of aerodynamic pressure forward of a center of gravity and a stabilizing portion comprising a material of lower density than that of the fore body and a plurality of outwardly extending fins for improving an aerodynamic stability of the projectile and defining a bore in which the pin is received for removably attaching the fore body thereto such that, when attached to the fore body, a center of gravity for the penetrator is forward of a center of aerodynamic pressure for the penetrator.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Miniature fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle with belly adsorbed to wall surface
The invention discloses a miniature fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle with a belly adsorbed on a wall surface, which comprises a main wing, a vector power system, a pneumatic control surface, a vertical fin, an adsorption-separation system and a belly equipment bin, wherein the adsorption-separation system is mounted on the middle upper side of the belly; the adsorption-separation system comprises bionic adsorption dry glue and a separation servo mechanism; the bionic adsorption dry glue is laid on the outer side of the belly in the front-back direction of the main wing and is used for adsorbing a wall surface; two sets of separation servo mechanisms are symmetrically mounted on two sides of the belly and are used for realizing separation of the bionic adsorption dry glue from the wall surface; and the separation servo mechanism comprises a wall separation servo steering engine, a wall separation cam and a wall separation rocker arm. After the unmanned aerial vehicle flies to a preset site for a long distance, low-power-consumption long-time adsorption on a vertical wall surface can be realized, a reconnaissance task can be executed in the adsorption process, and the unmanned aerial vehicle is separated from the wall surface and returns after being completed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
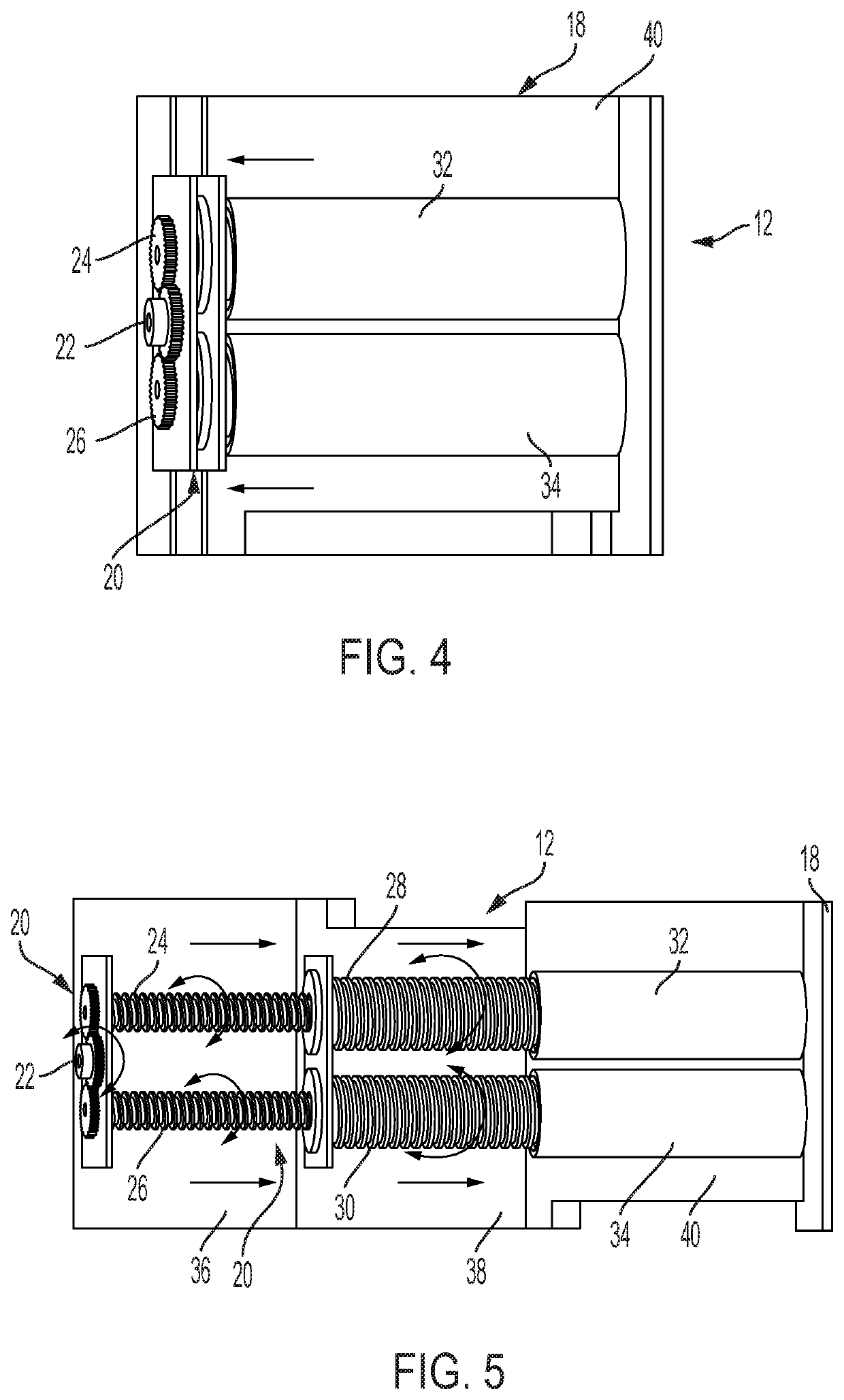
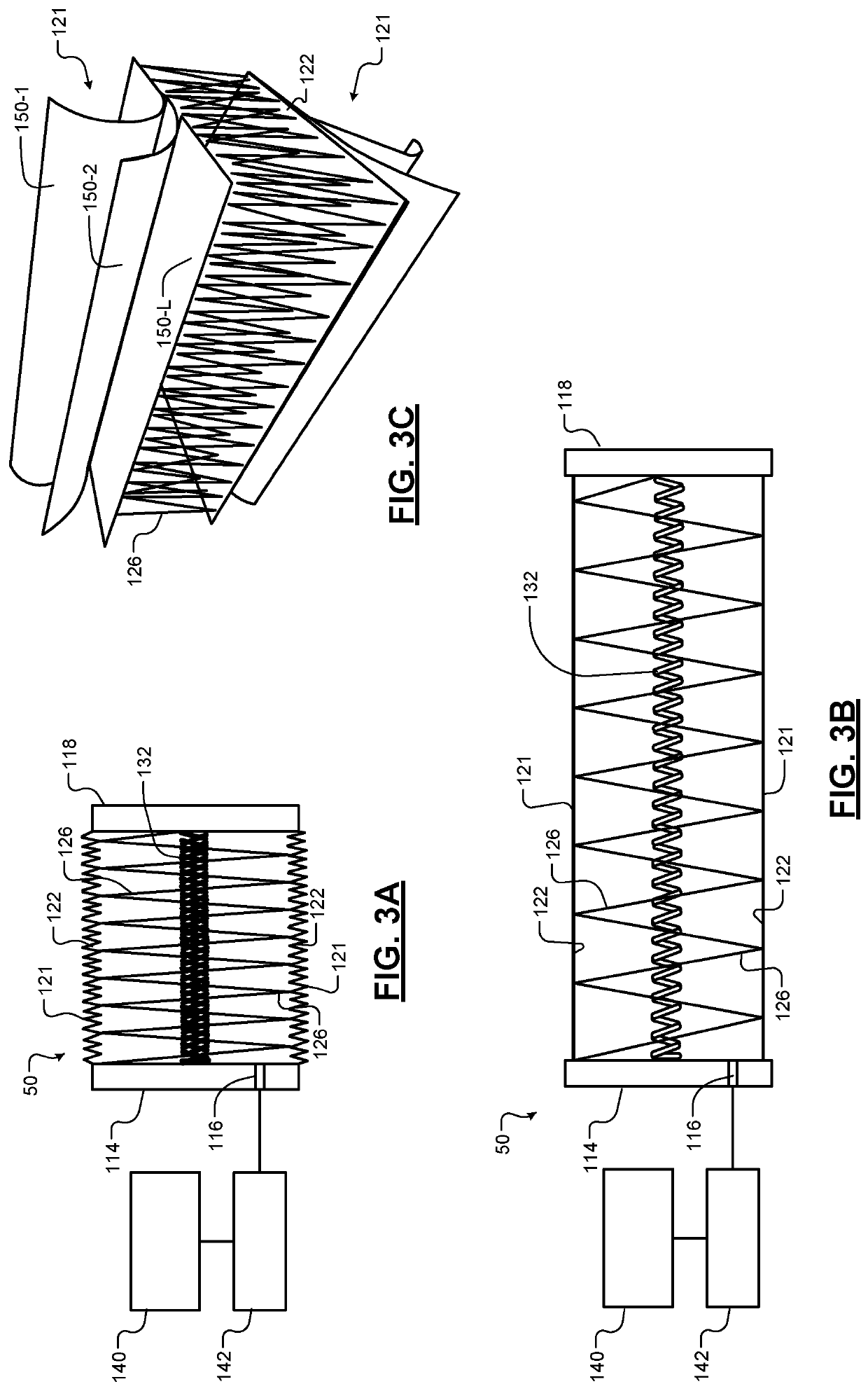
Internally-tensioned inflatable device for active flow control drag reduction or stability increase
ActiveUS11014619B2Reduce air resistanceImprove fuel economyVehicle body stabilisationDesign optimisation/simulationScrew threadMechanics
An inflatable active flow control device includes a first surface, a second surface, and a spring including one end connected to the first surface and an opposite end connected to the second surface. A flexible material is connected to both the first surface and the second surface around the spring, defines an inflatable internal volume, and includes a plurality of threads extending between opposing inner surfaces of the flexible material at spaced locations through the inflatable internal volume.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
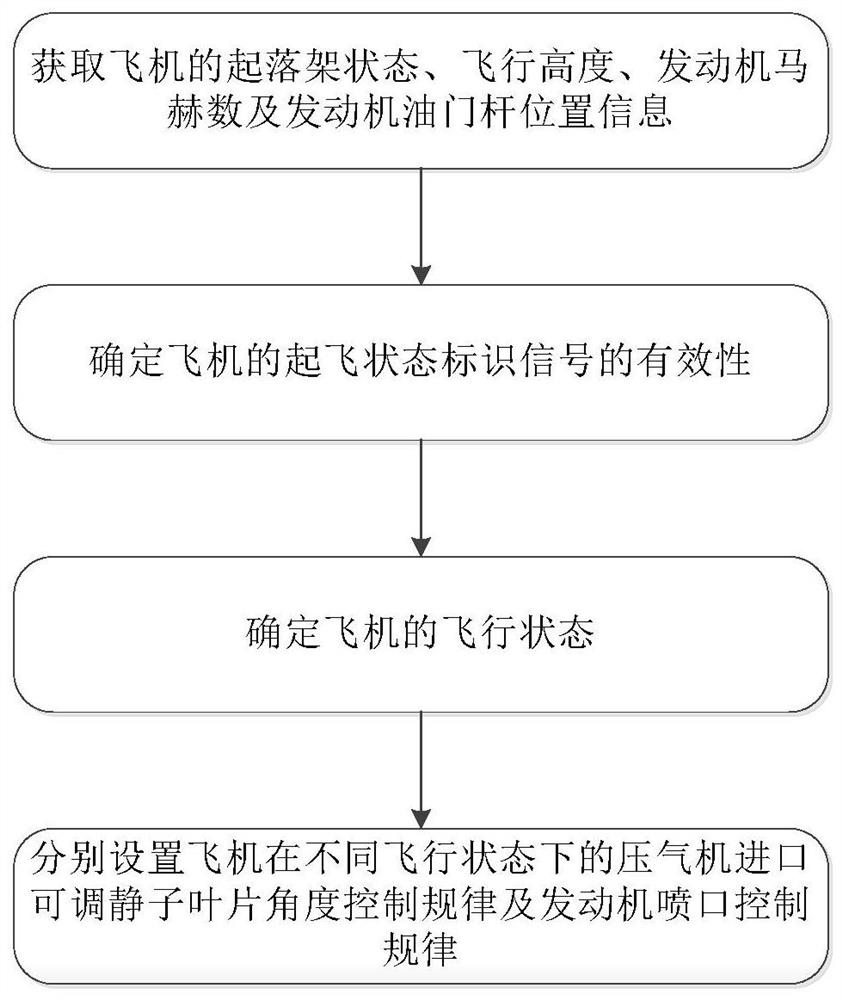
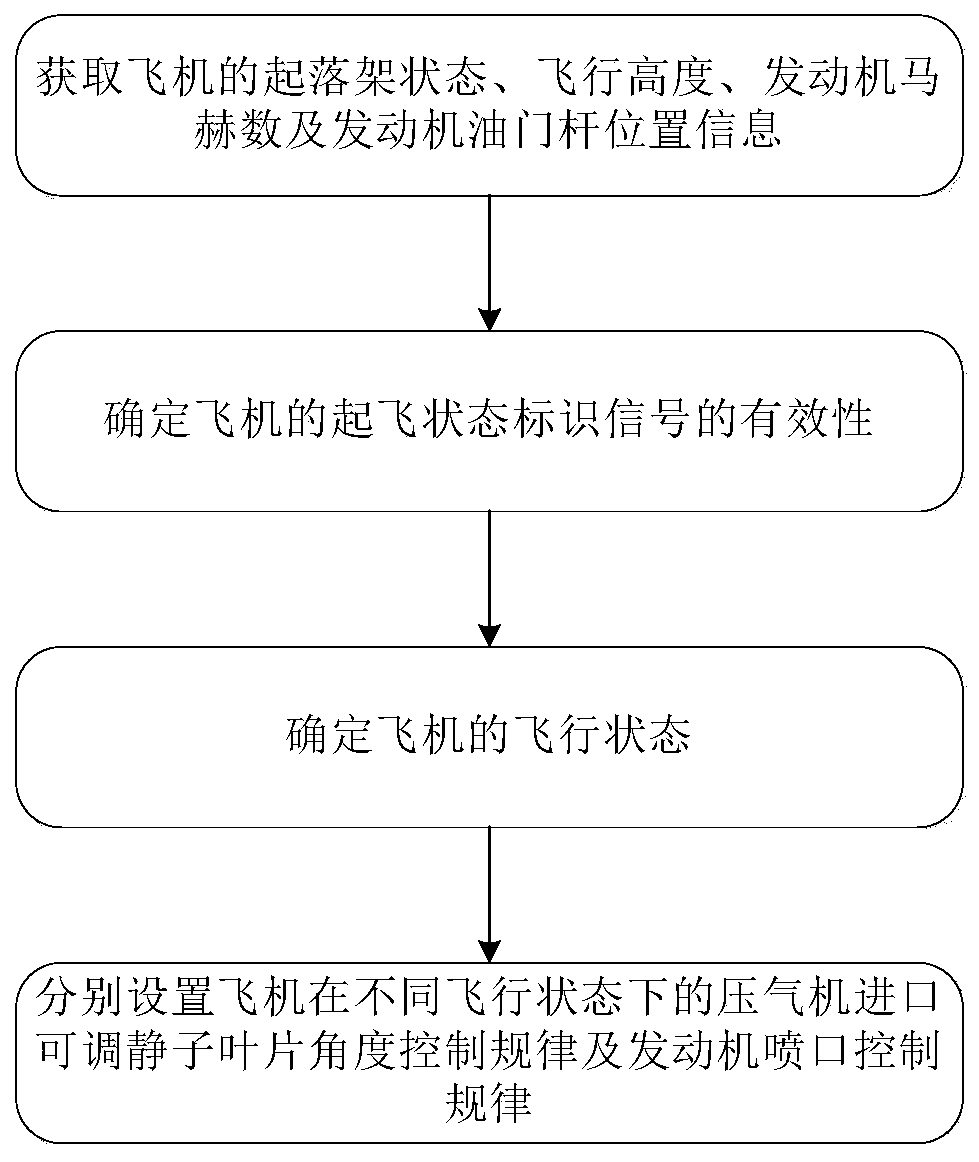
Method and device for improving aerodynamic stability of carrier-based aircraft engine based on state recognition
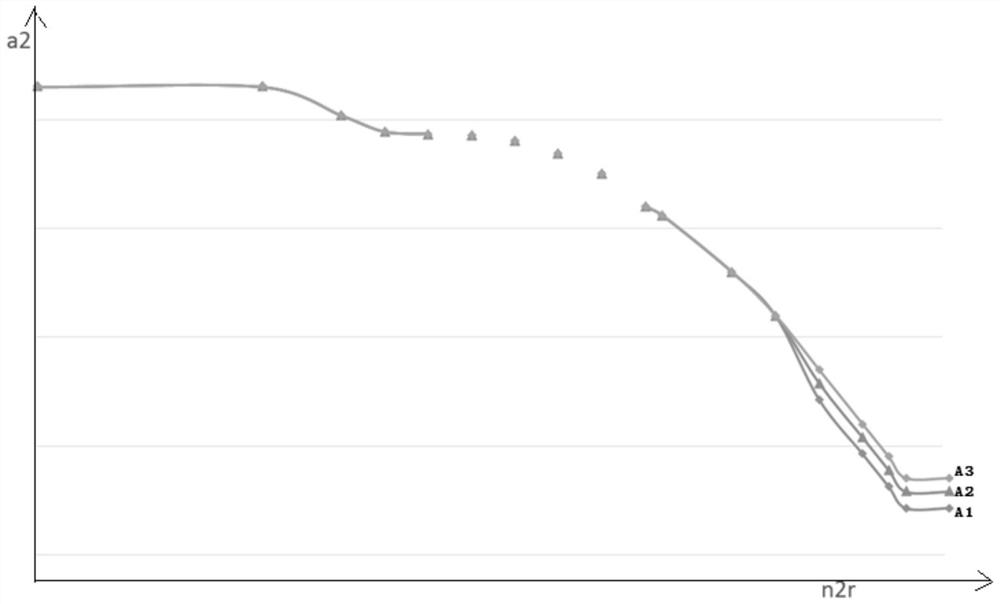
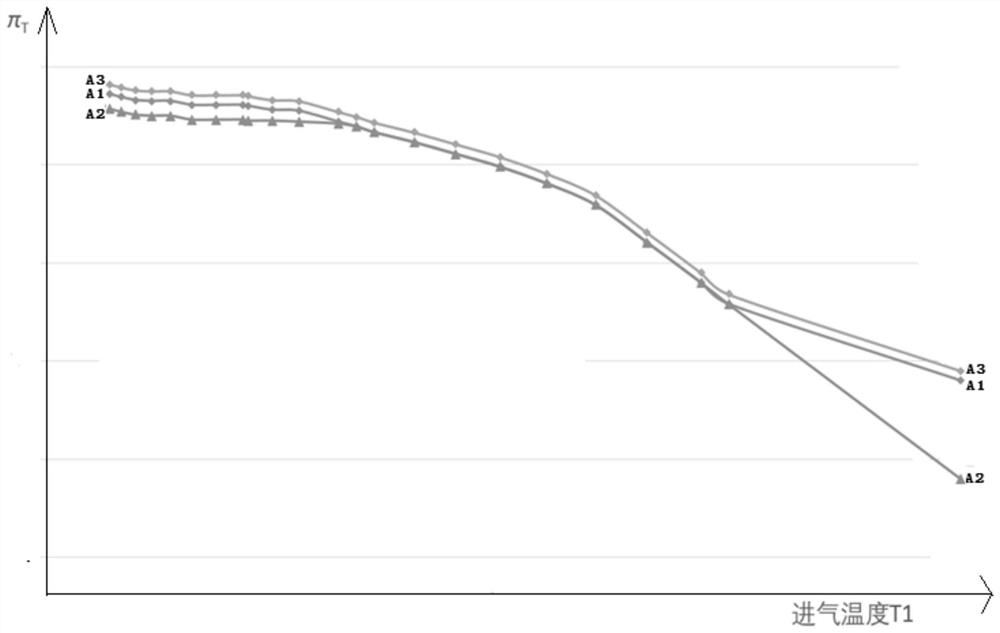
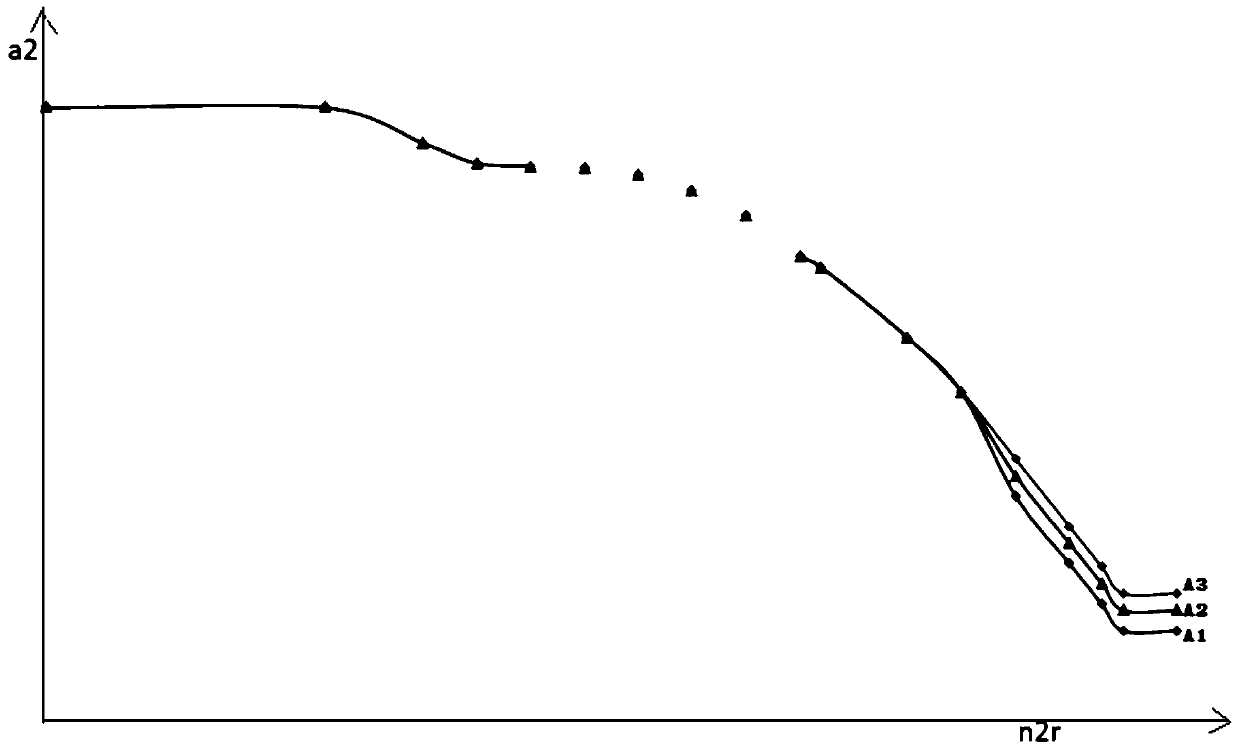
The application belongs to the technical field of carrier-based aircraft engine design, and in particular relates to a method and device for improving the aerodynamic stability of a carrier-based aircraft engine based on state identification. The method includes firstly acquiring the landing gear state, flight altitude, engine Mach number and engine throttle lever position information of the aircraft; then determining the validity of the take-off state identification signal of the aircraft; further determining the flight state of the aircraft, and finally setting the aircraft respectively The compressor inlet adjustable stator blade angle control law and the engine nozzle control law under different flight conditions improve the aerodynamic stability of the engine. Through this application, according to the environment in which the engine is used, the geometric area control methods of a2 and A8 are classified and designed in detail according to the flight state, take-off / catapult take-off state, and landing / go-around state, which can greatly improve the aerodynamic stability of the engine and greatly increase the shipboard capacity. Aircraft engine aerodynamic stability working margin.
Owner:AECC SHENYANG ENGINE RES INST
Method and device for improving aerodynamic stability of carrier-based aircraft engine based on state identification
The invention belongs to the technical field of carrier-based aircraft engine design, and particularly relates to a method and device for improving the aerodynamic stability of a carrier-based aircraft engine based on state identification. The method for improving the aerodynamic stability of the carrier-based aircraft engine based on state identification comprises the following steps that firstly, landing gear state, flight height, engine mach number and engine accelerator lever position information of an aircraft are acquired; then the validity of a takeoff status identification signal of the aircraft is determined; then the flight state of the aircraft is determined, and finally the compressor inlet adjustable stator blade angle control law and the engine nozzle control law of the aircraft under different flight states are separately arranged, so that the aerodynamic stability of the engine is improved. According to the method and device for improving the aerodynamic stability of the carrier-based aircraft engine based on state identification, a2 and A8 geometric area control methods are classified and designed in detail according to the flight state, a takeoff / ejection takeoffstate and a landing / go-around state according to the engine use environment, so that the aerodynamic stability of the engine is greatly improved, and the aerodynamic stability working margin of the carrier-based aircraft engine is greatly increased.
Owner:AECC SHENYANG ENGINE RES INST
Premixing burner arrangement for operating a combustion chamber in addition to a method for operating a combustion chamber
InactiveUS7896646B2Improve stabilityLow pressure lossCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelBurner safety arrangementsCombustorCombustion chamber
A premixing burner is disclosed for operating a combustion chamber with a liquid and / or gaseous fuel, with a swirl generator for a combustion inflow air stream for forming a swirl flow, and with injection of fuel into the swirl flow. The swirl generator is adjacent to the combustion chamber indirectly via a mixing zone or directly, in each case via a burner outlet, a cross-sectional widening at the burner outlet being provided which, is discontinuous in the flow direction of the swirl flow and through which the swirl flow bursts open so as to form a backflow zone. A contour locally narrowing the flow cross section of the swirl generator or of the mixing zone in the flow direction can be provided upstream of the burner outlet.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
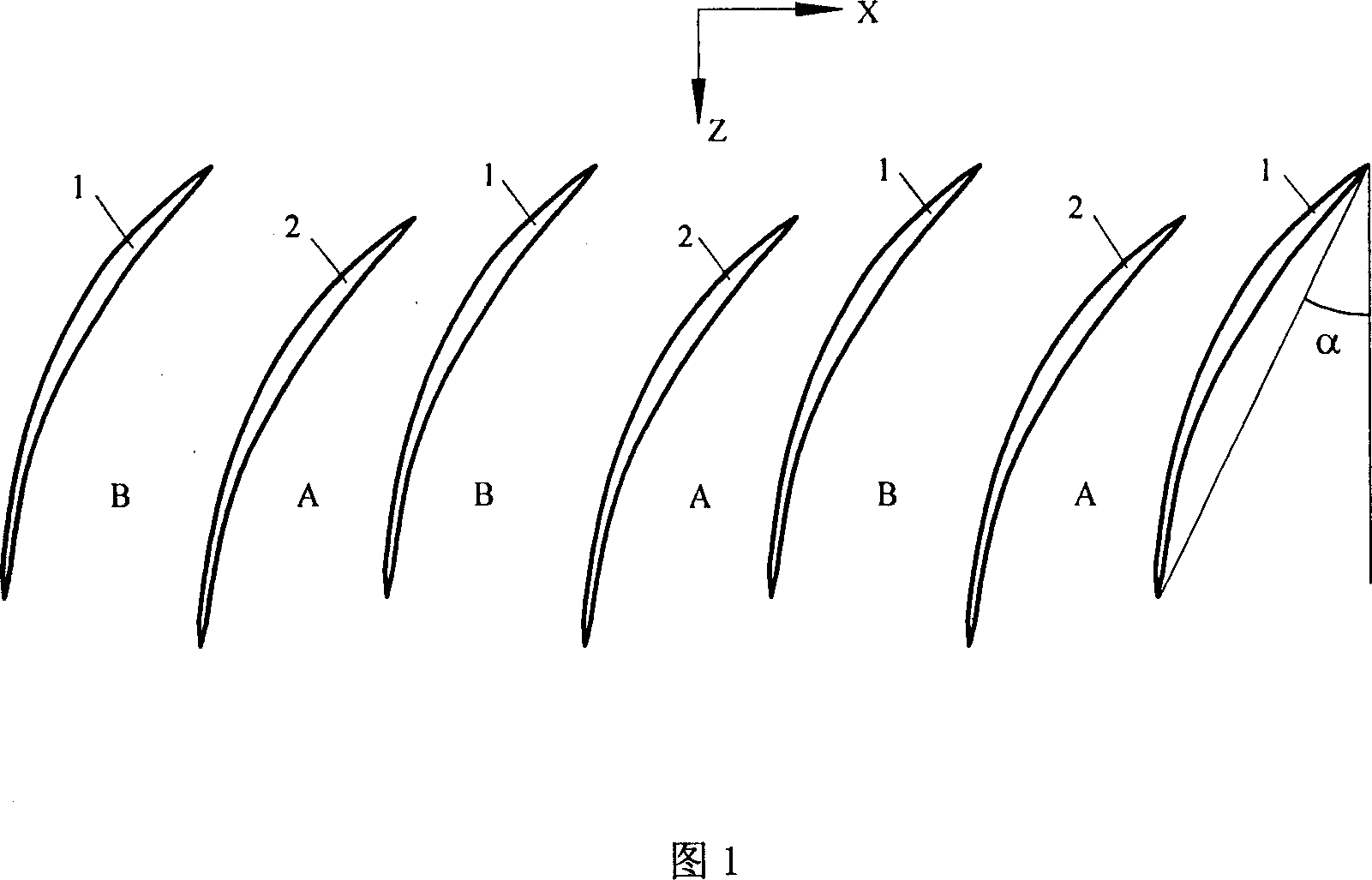
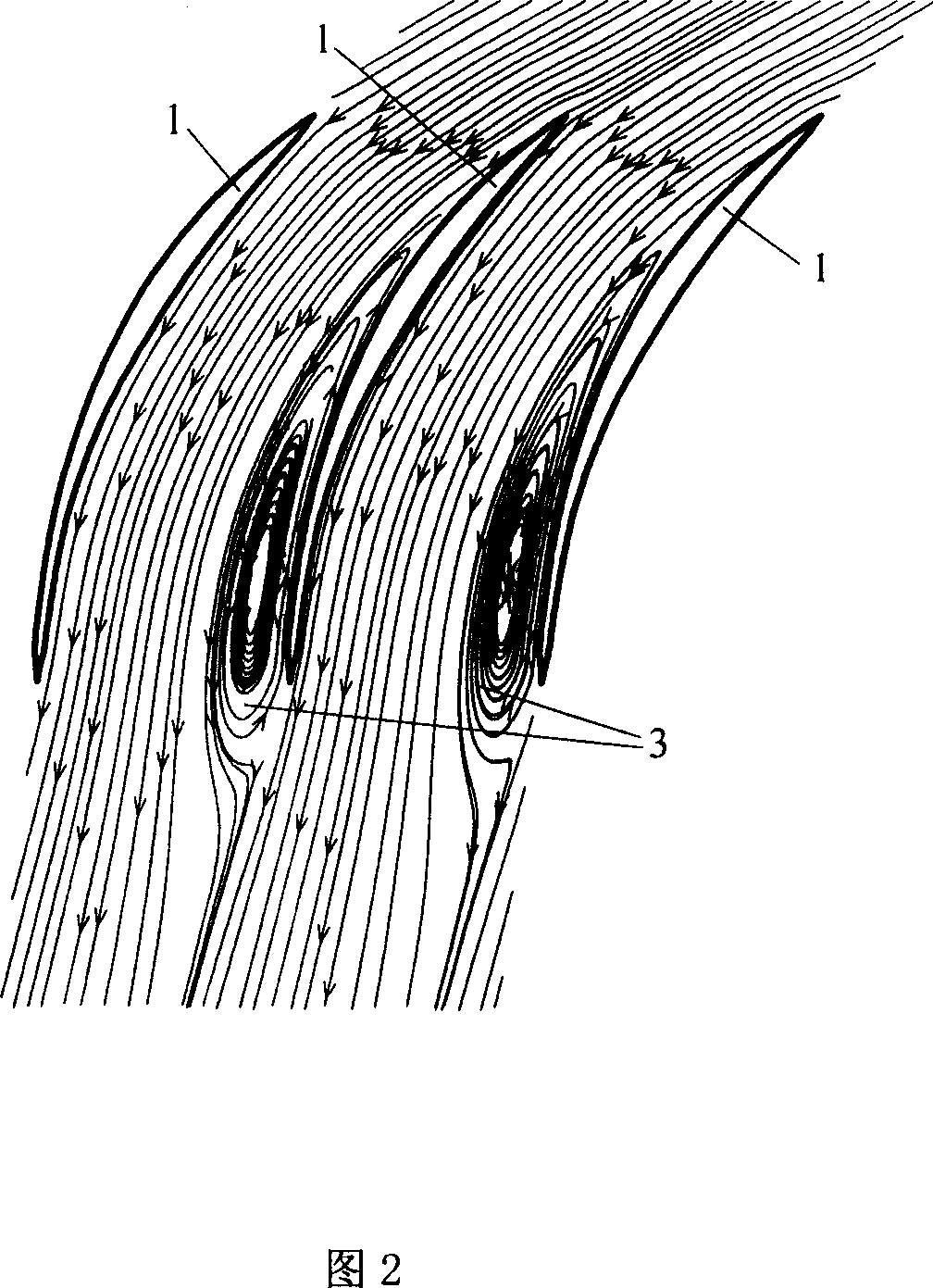
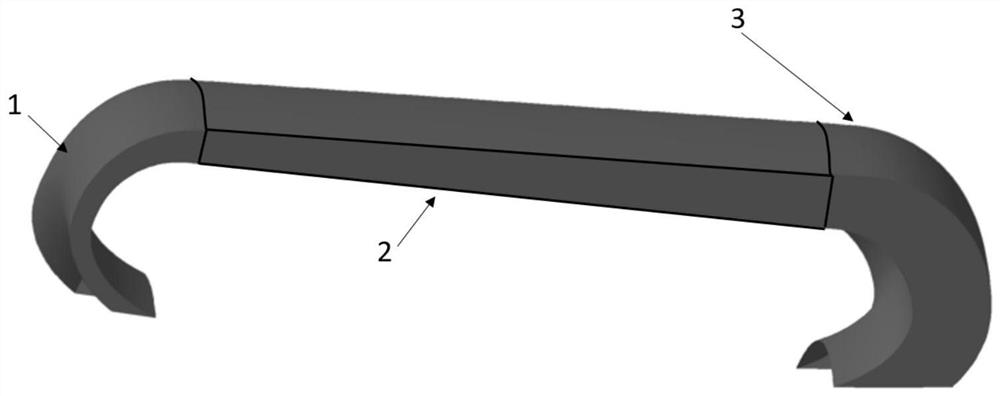
Blade arrangement mode of compressor blade row for enhancing air load and stability
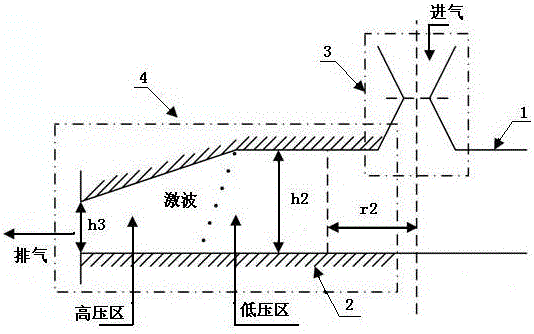
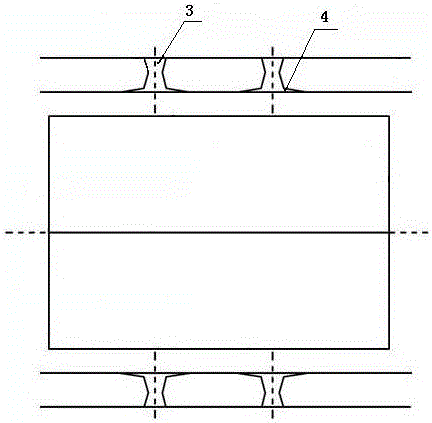
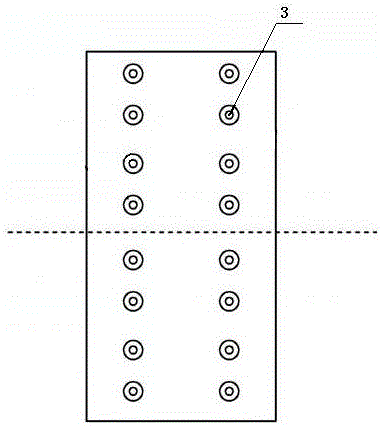
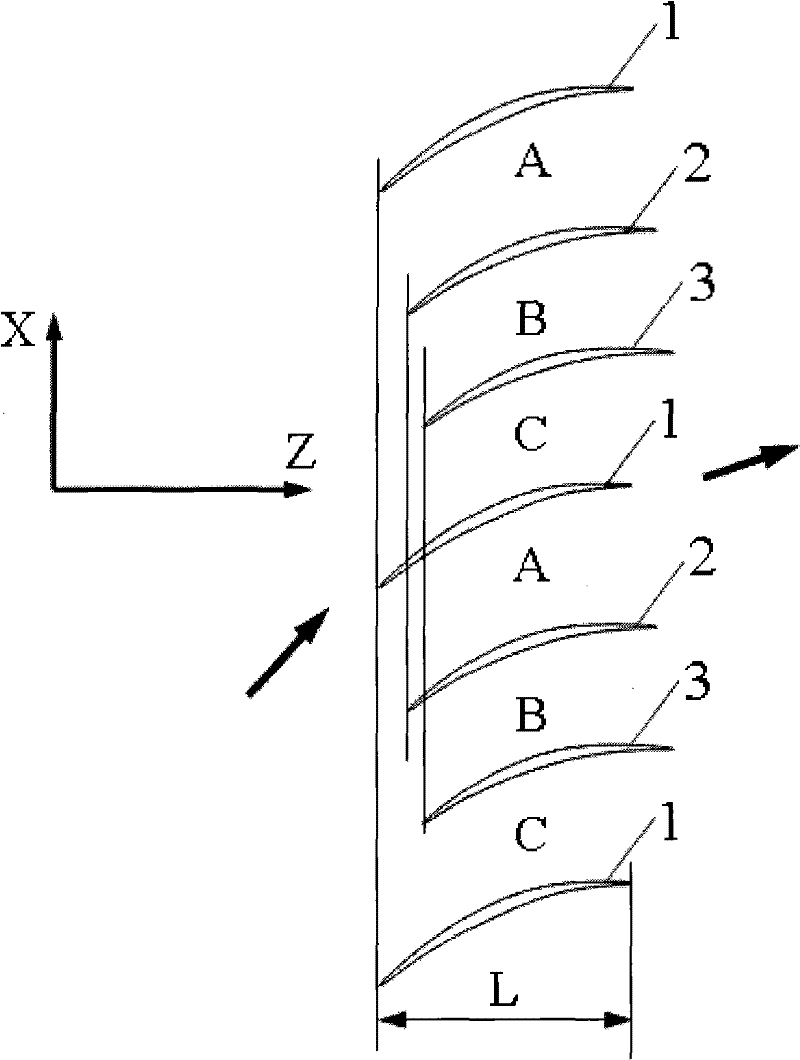
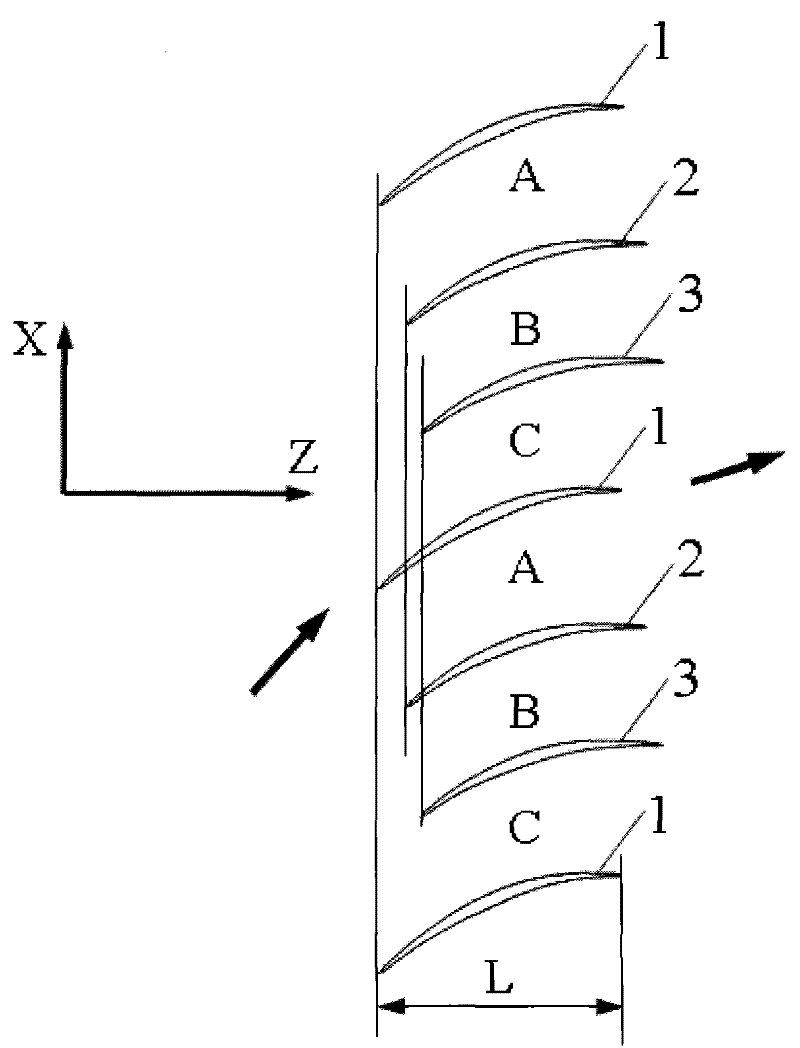
The invention discloses a blade arrangement mode of a compressor blade row for enhancing air load and stability. Every three adjacent blades in the same blade row form a group; based on the axial position of the front edge of a first blade (1), a second blade (2) adjacent to the first blade is positioned on one side of the blade basin surface of the first blade; the front edge of the second blade(2) moves backwards along the axial direction of the blade row and the movement distance accounts for 7 to 15 percent of the axial chord length L of the first blade; a third blade (3) adjacent to thesecond blade is positioned on one side of the blade basin surface of the second blade; the front edge of the third blade moves backwards relatively to the front edge of the second blade (2) along theaxial direction of the blade row and the movement distance accounts for 5 to 15 percent of the axial chord length of the first blade (1); and the third blade rotates around the front edge of the third blade by 1 to 3 degrees. Three different air flow passages are formed in one blade row, and air flow in the air flow passages can enhance the air stability of an air compressor and the air load of the blade is remarkably enhanced under the condition that the blade shape design bending deflection of each blade is not changed.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Airship
PendingCN107618648AReduce wind resistanceReduce power consumptionRigid airshipsEngineeringPower consumption
The invention discloses an airship comprising an airship body; The airship body comprises opposite upper ball crown part and a lower ball crown part, wherein the bottoms of the upper ball crown part and the lower ball crown part are sealingly connected so that the profiles of the airship is dish-like. The camber of the upper ball crown is larger than that of the lower ball crown so that the airship body has a positive curved dish profile. According to the airship of the invention, the dish-like design is adopted so as to reduce wind resistance in all directions during flight and increase the profile lift of the airship, therefore saving power consumption.
Owner:SHENZHEN KUANG CHI SPACE TECH CO LTD
Fluid-solid coupled gas shock wave adjustment bearing
ActiveCN106545576BImprove carrying capacityImproved aerodynamic stabilityBearingsShock waveEngineering
The invention relates to a fluid-solid coupled gas shock wave adjusting bearing. At present, a widely used dynamic pressure foil-bearing is limited in carrying capacity and lacks of stability and the coating process requirements on the surface of a foil are high, and a static pressure-dynamic pressure mixed bearing is insufficient in carrying capacity at a slow rotating speed while is pneumatically unstable at a high rotating speed. The bearing provided by the invention comprises a bearing bush (1) which is provided with air supply throttling orifices (3), damping cavities (4) are arranged in the outlet positions of the air supply throttling orifices, one or more than one row of air supply throttling orifices and the damping cavities is uniformly distributed circumferentially on the inner surface of the bearing bush, and foil structures (7) are arranged between the outlets of the damping cavities and a rotor (2); the foil structures comprises bump foils (6) and flat foils (5). By changing the air supply pressure of the bearing, the throttling orifice structures and the damping cavity structures, the fluid-solid coupled gas shock wave adjusting bearing can be matched with a large-gap high-load bearing working condition. The invention is the fluid-solid coupled gas shock wave adjusting bearing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
High-speed trains and maglev transportation systems used in vacuum pipeline maglev transportation systems
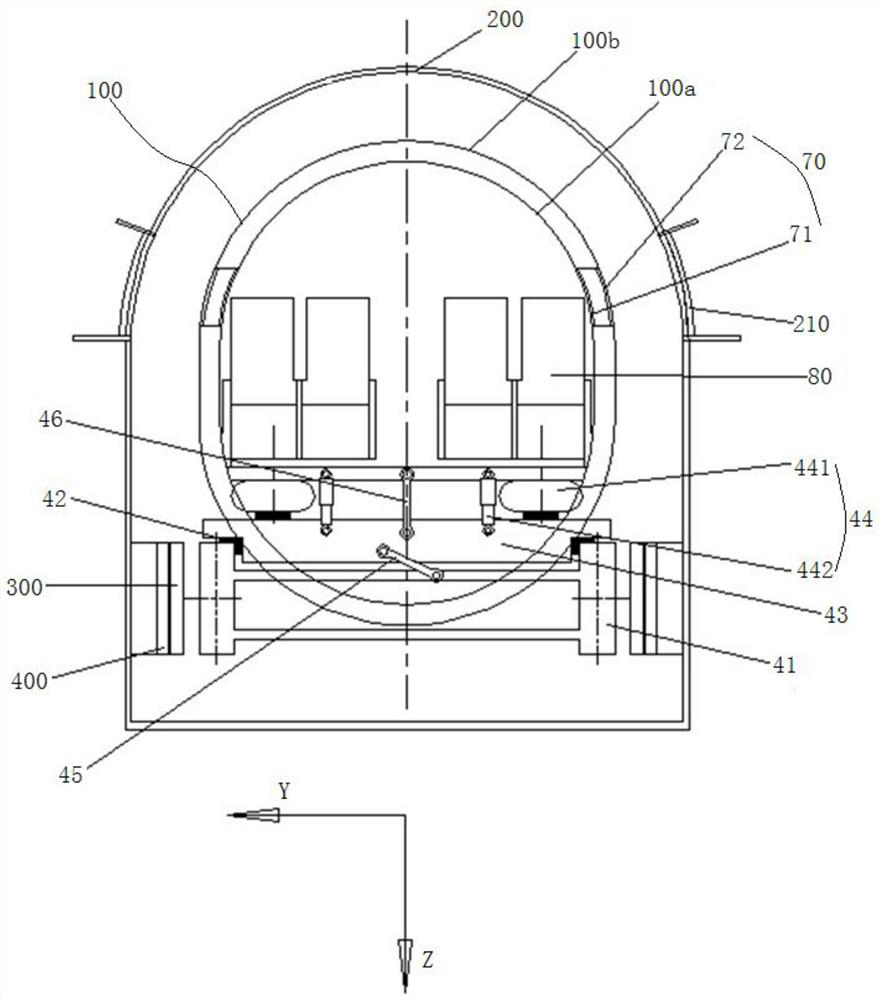
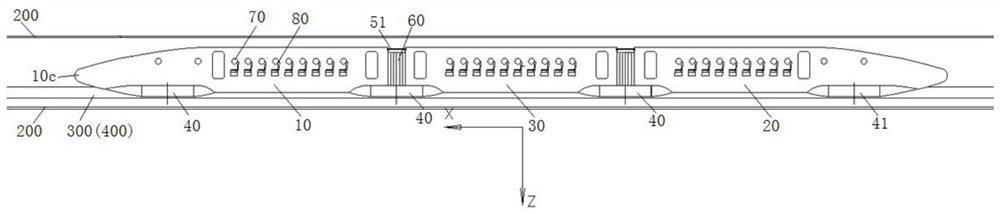
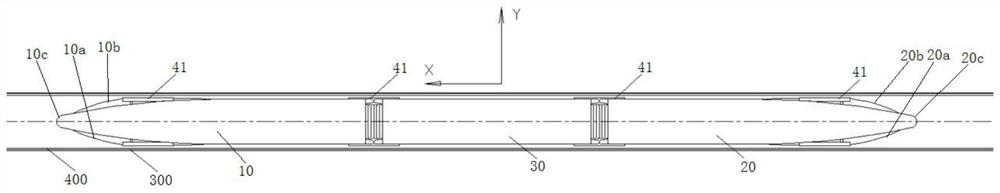
ActiveCN111845368BImproved aerodynamic stabilityReduced aerodynamic liftRailway transportAxle-box lubricationControl theoryMechanical engineering
The invention provides a high-speed train and a maglev transportation system for a vacuum pipeline maglev transportation system. The train includes a first car body, a second car body and at least one intermediate car body. The first car body has first, second The structural section and the first nose cone, the first structural section, the first nose cone and the second structural section are sequentially connected to form the first tip structure, and the second car body has the third and fourth structural sections and the second nose Cone, the vertical distances between the tip of the first nose cone and the tip of the second nose cone and the height center line of the high-speed train body are all less than or equal to 10% of the height of the high-speed train body, the third structural section , the second nose cone portion and the fourth structural segment are connected in sequence to form a second tip structure, and the two ends of at least one intermediate vehicle body are respectively connected with the first and second vehicle bodies. The technical scheme of the present invention is applied to solve the technical problems of poor safety and limited capacity of capsule trains in the prior art.
Owner:HIWING TECH ACAD OF CASIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com