Patents
Literature
40results about How to "Little stiffness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Flexible electronic skin with tactile and proximity dual-mode sensing function
InactiveCN109163824AReduce loadReduce volumeForce measurementUsing electrical meansCapacitanceDual mode
The invention discloses a flexible electronic skin with a tactile and proximity dual-mode sensing function. The flexible electronic skin is of a multi-layer structure, which comprises an upper polar plate layer, an intermediate medium layer and a lower polar plate layer in sequence, and the three layers of structures form a sensing unit; the upper polar plate layer, the intermediate medium layer and the lower polar plate layer form a tactile sensing unit to sense the size of a force, and the upper polar plate layer forms a proximity sensing unit to sense the distance; the sensing units are arranged in an array, metal films of the horizontal or vertical sensing units on the same layer are connected into a whole, perform communication by using the same channel and are connected with corresponding analog switches via leads to transmit signals; and the analog switch connects the upper and lower polar plate layers to a capacitance collection chip, and the on-off of the analog switch is controlled by a microprocessor to collect the signals and to switch a tactile sensing mode and a proximity sensing mode. The flexible electronic skin disclosed by the invention has the tactile and proximity dual-mode sensing function, is low in rigidity, is easy to be bend, and can realize the coverage of different areas by splicing.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
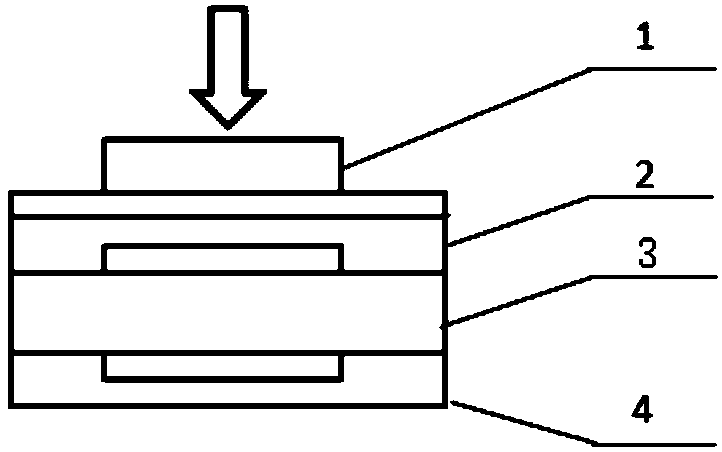
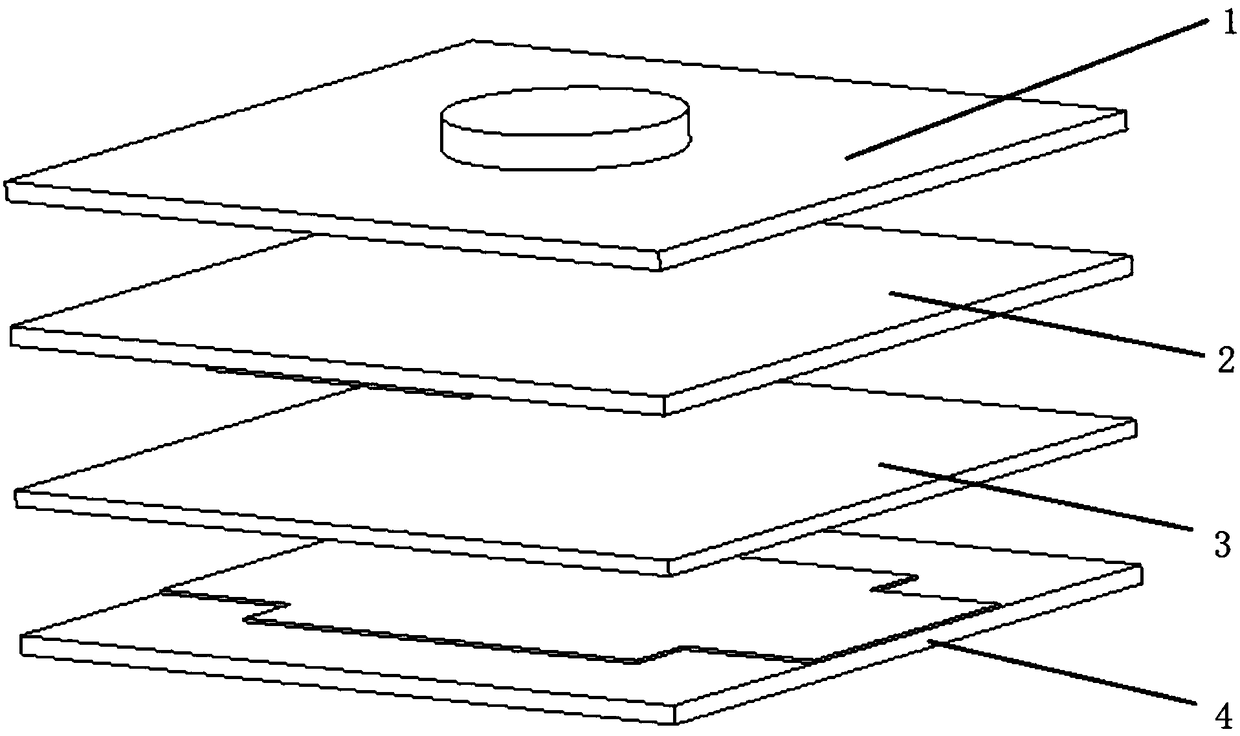
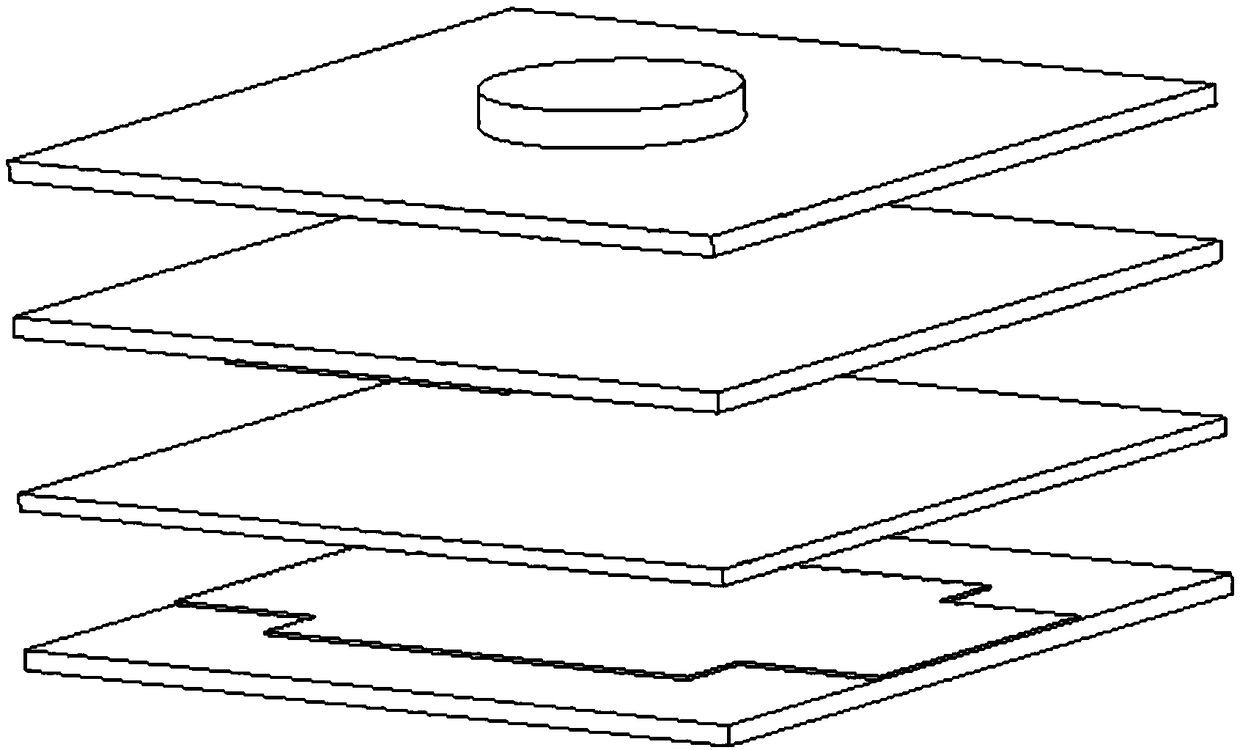
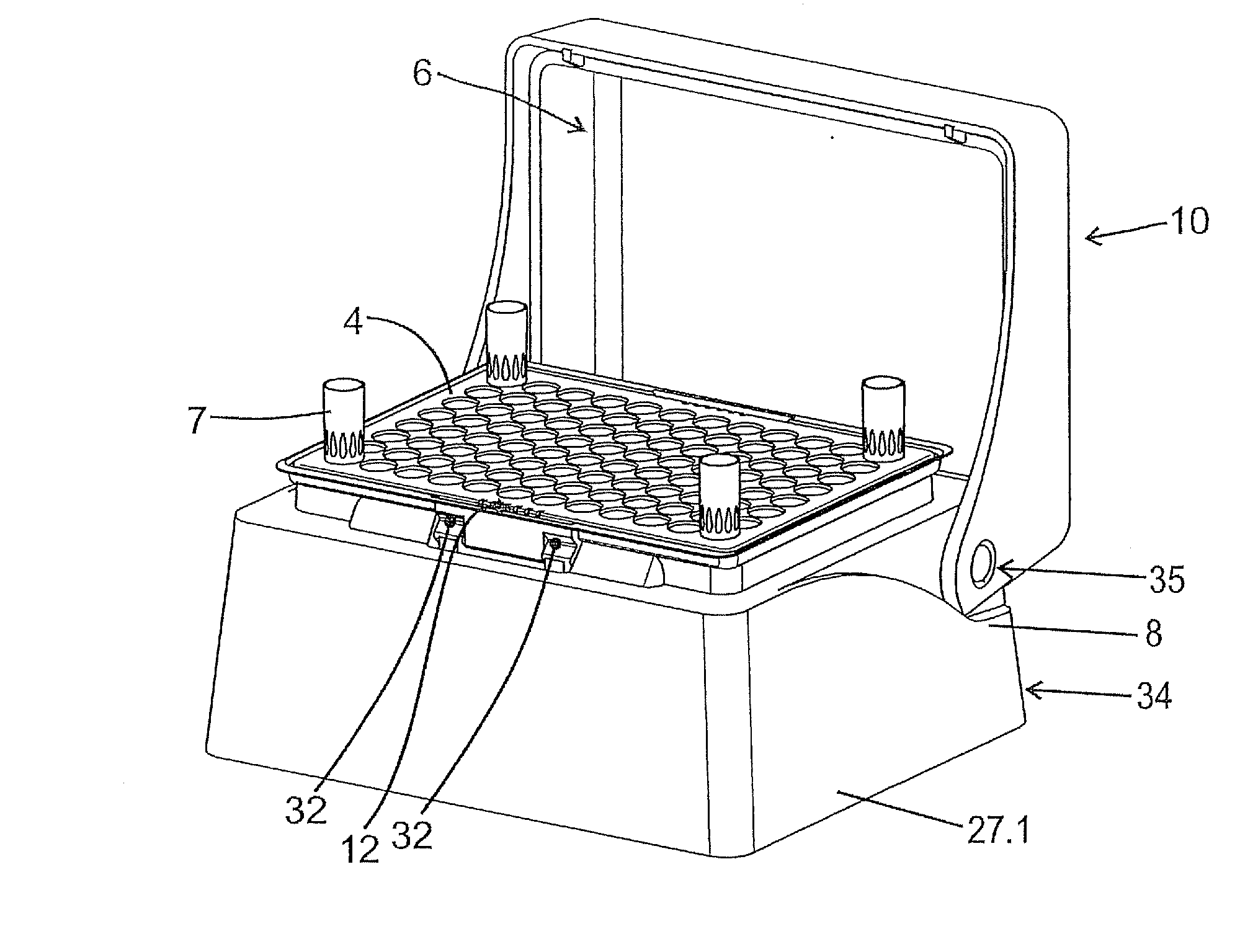
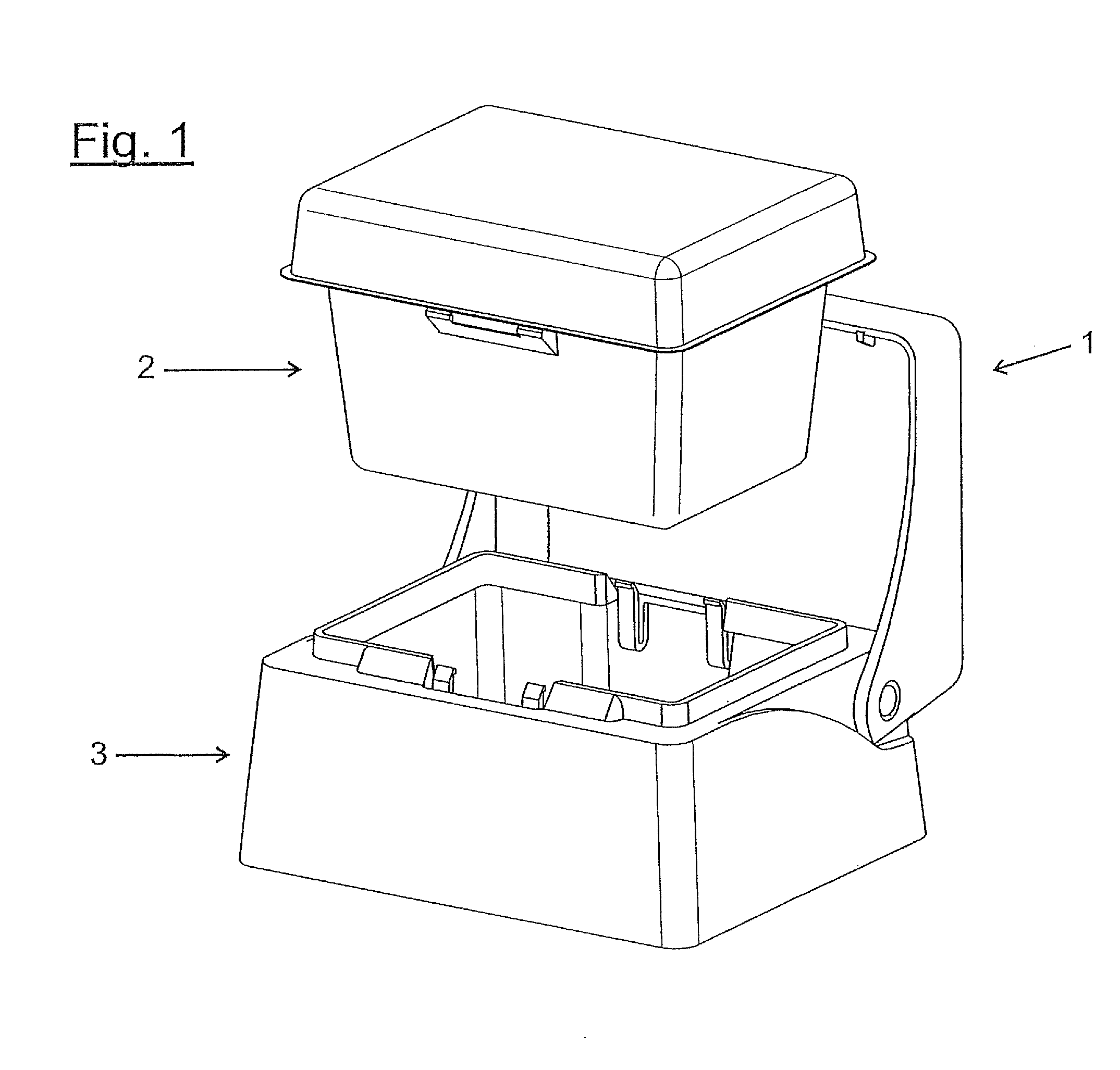
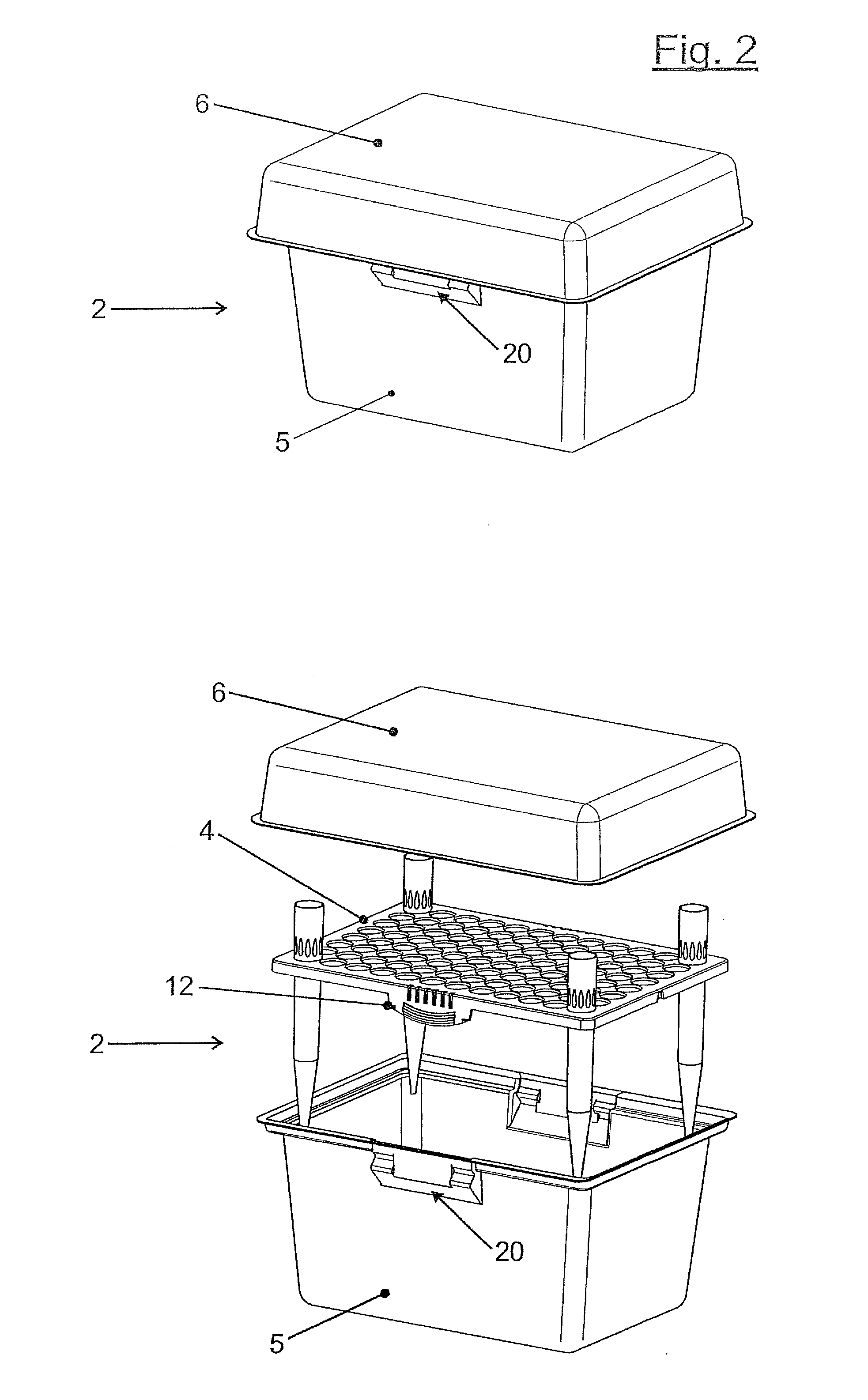
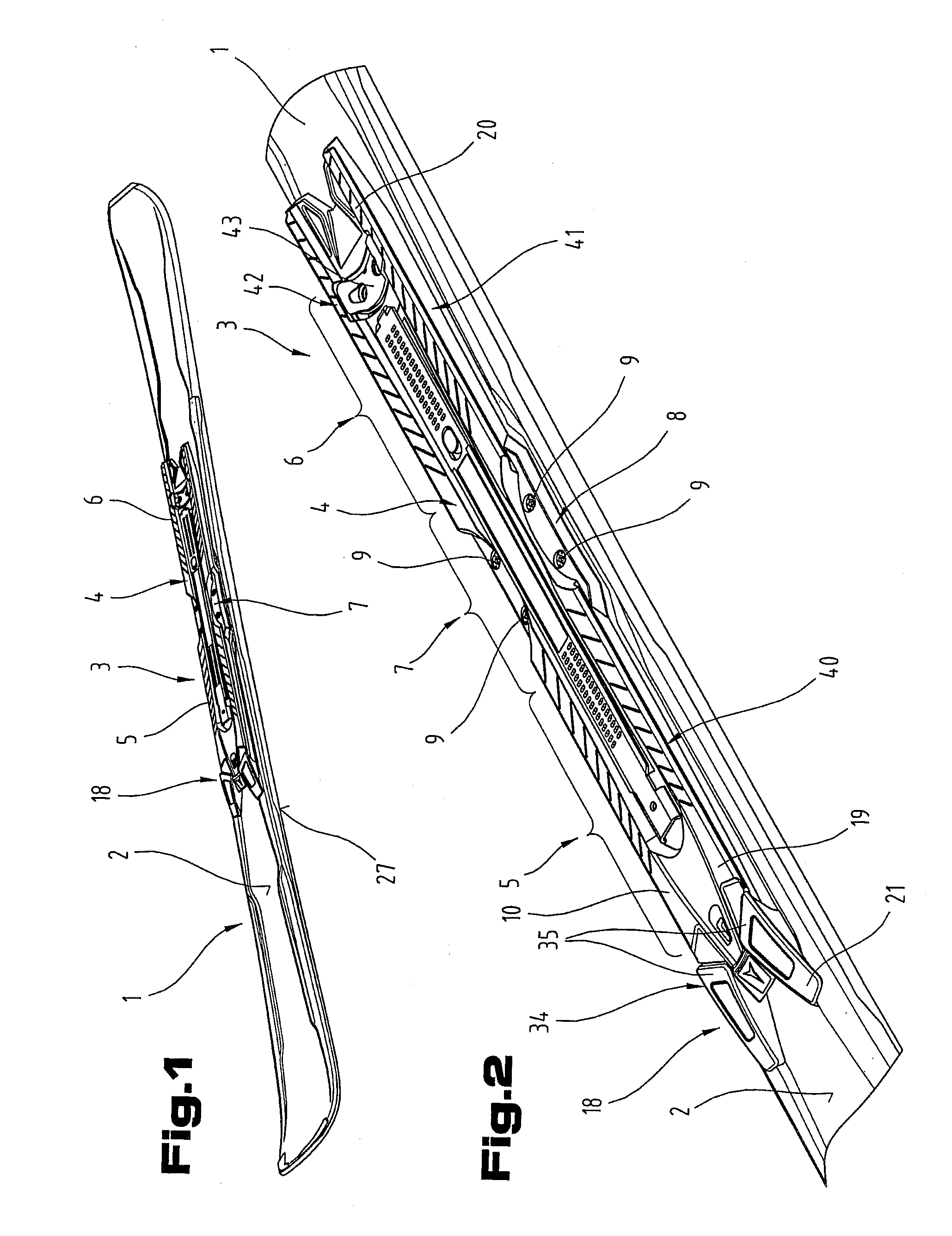
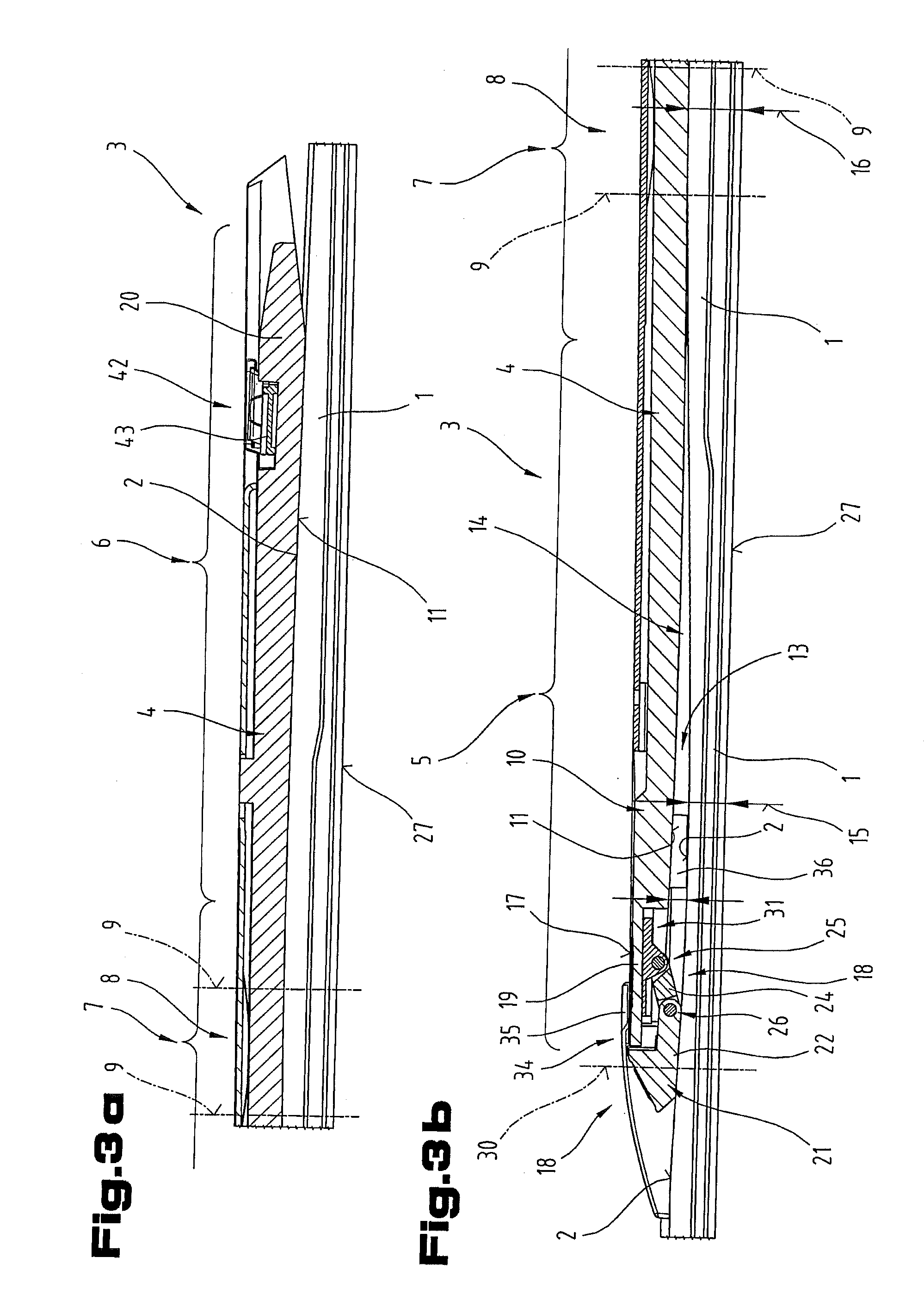
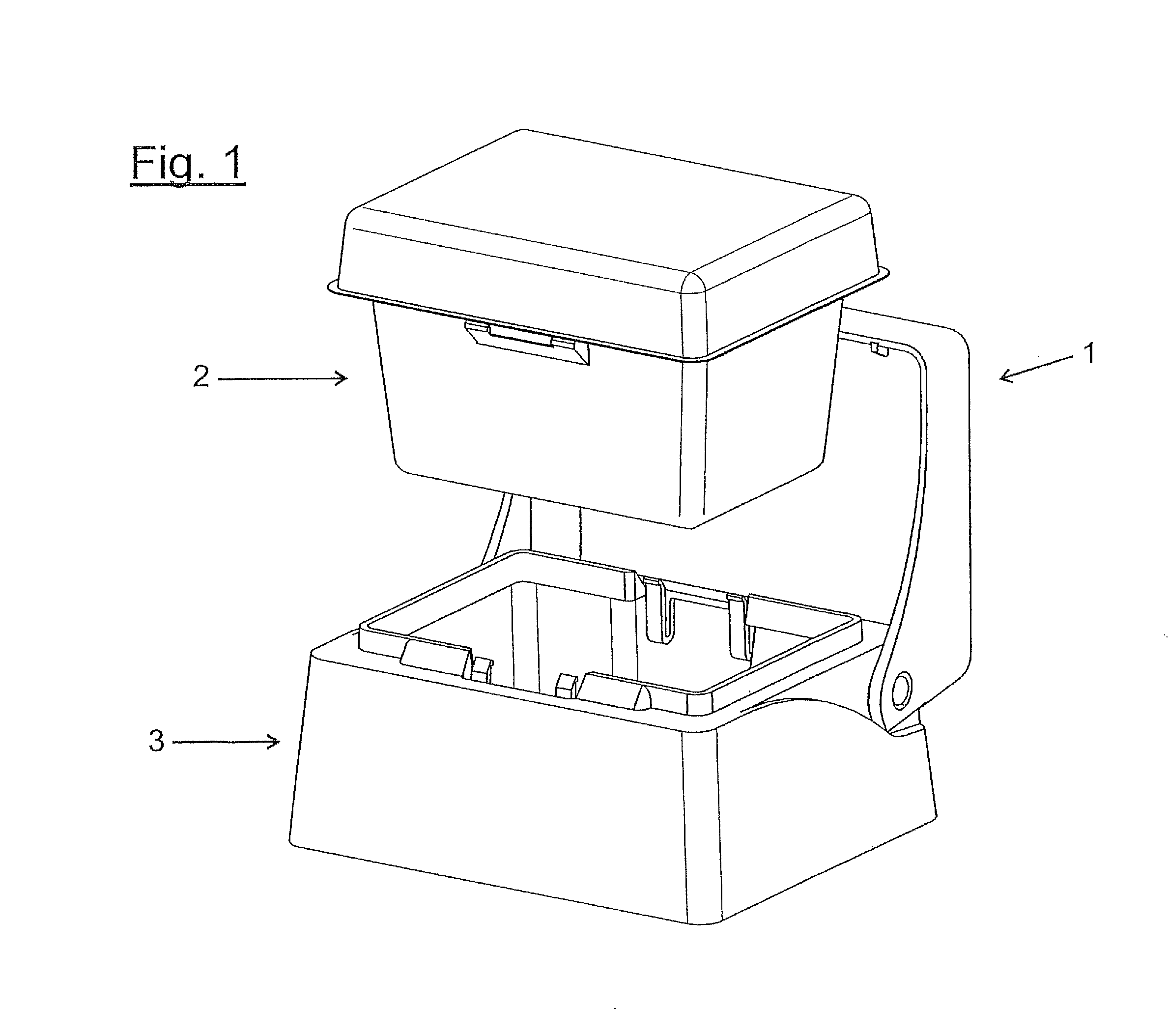
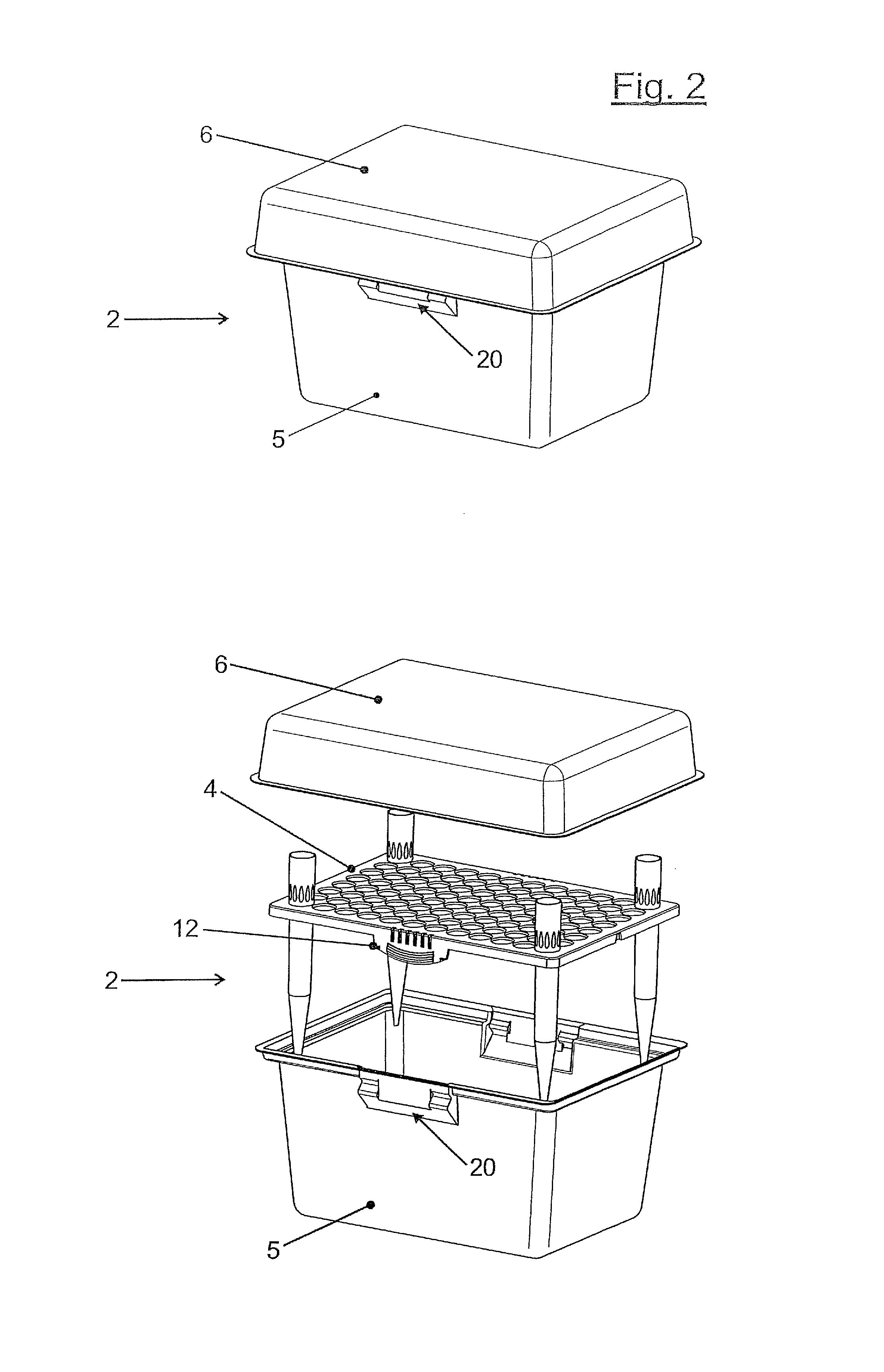
Device for providing pipette tips
ActiveUS20120328489A1Avoid pollutionLittle stiffnessSolid materialBurettes/pipettesPipetteSoftware engineering
Device for providing pipette tips comprisinga refill pack which comprisesa perforated plate with a plurality of holes,pipette tips inserted into the holes,a container covering the pipette tips at the bottom with a stiffness of up to 300 N / mm anda removable cover, covering the pipette tips from the top anda holder with a receiver for inserting the refill pack,means being present between the refill pack and holder for supporting the refill pack when said refill pack is inserted into the receiver.
Owner:EPPENDORF SE
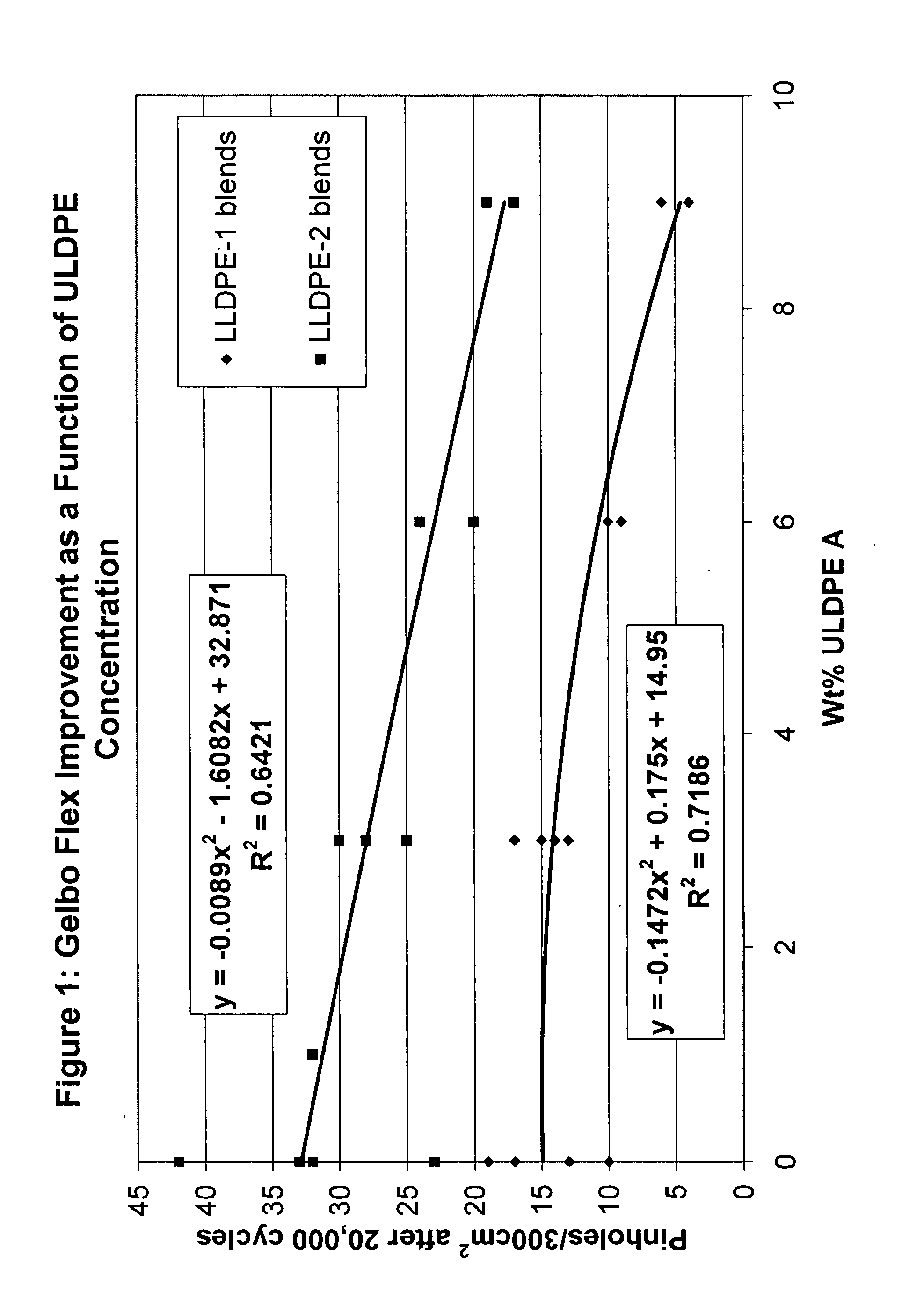
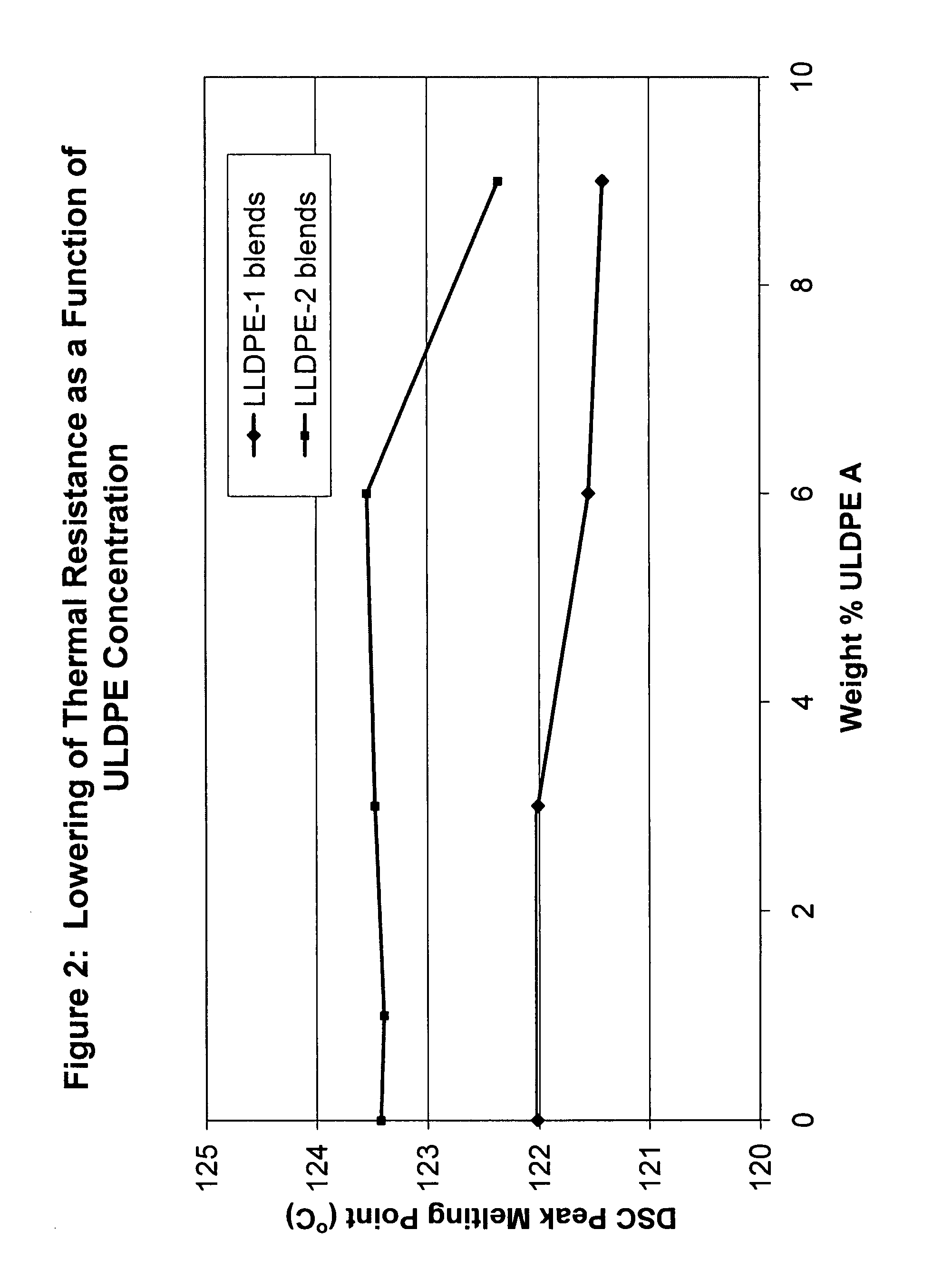
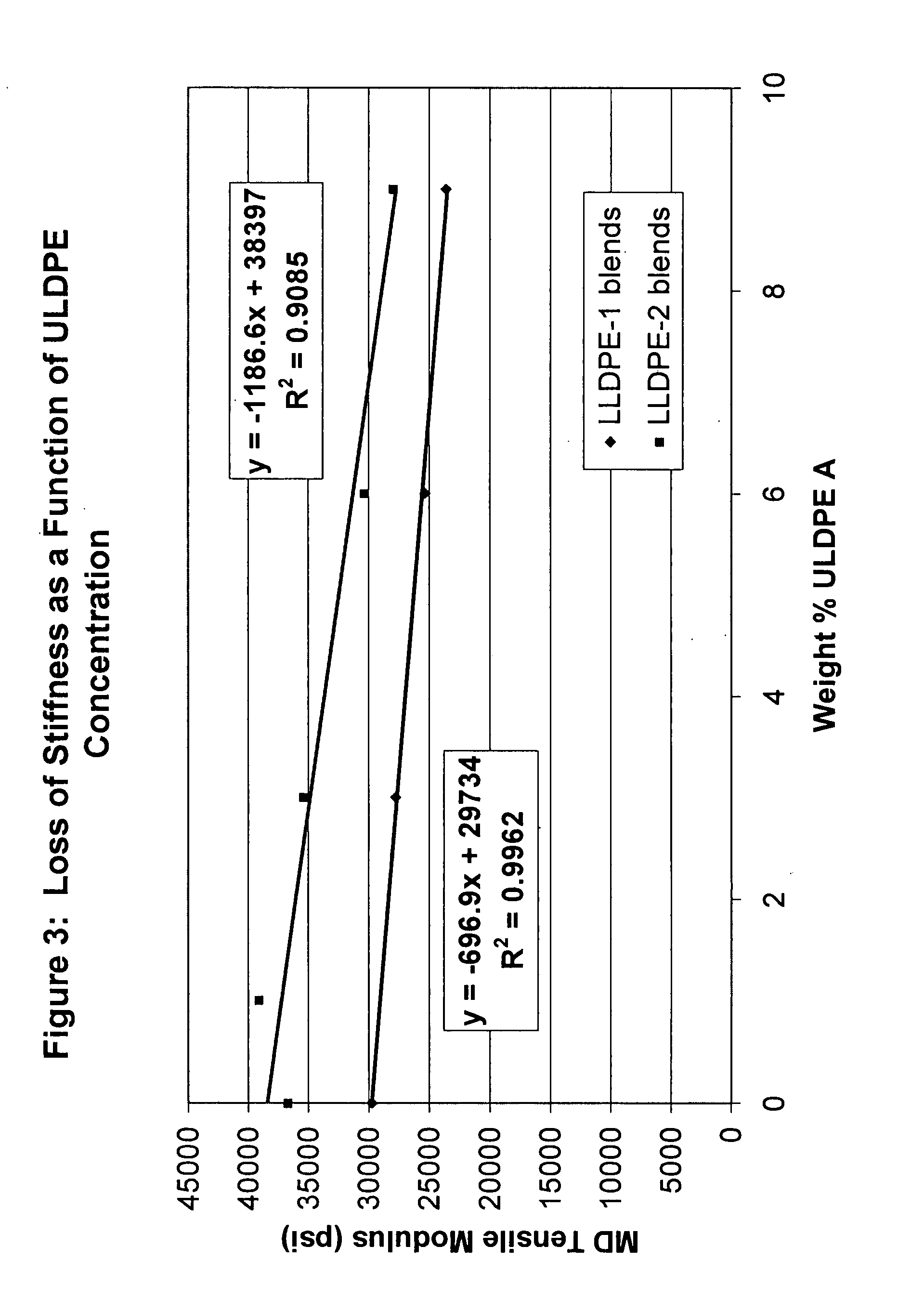
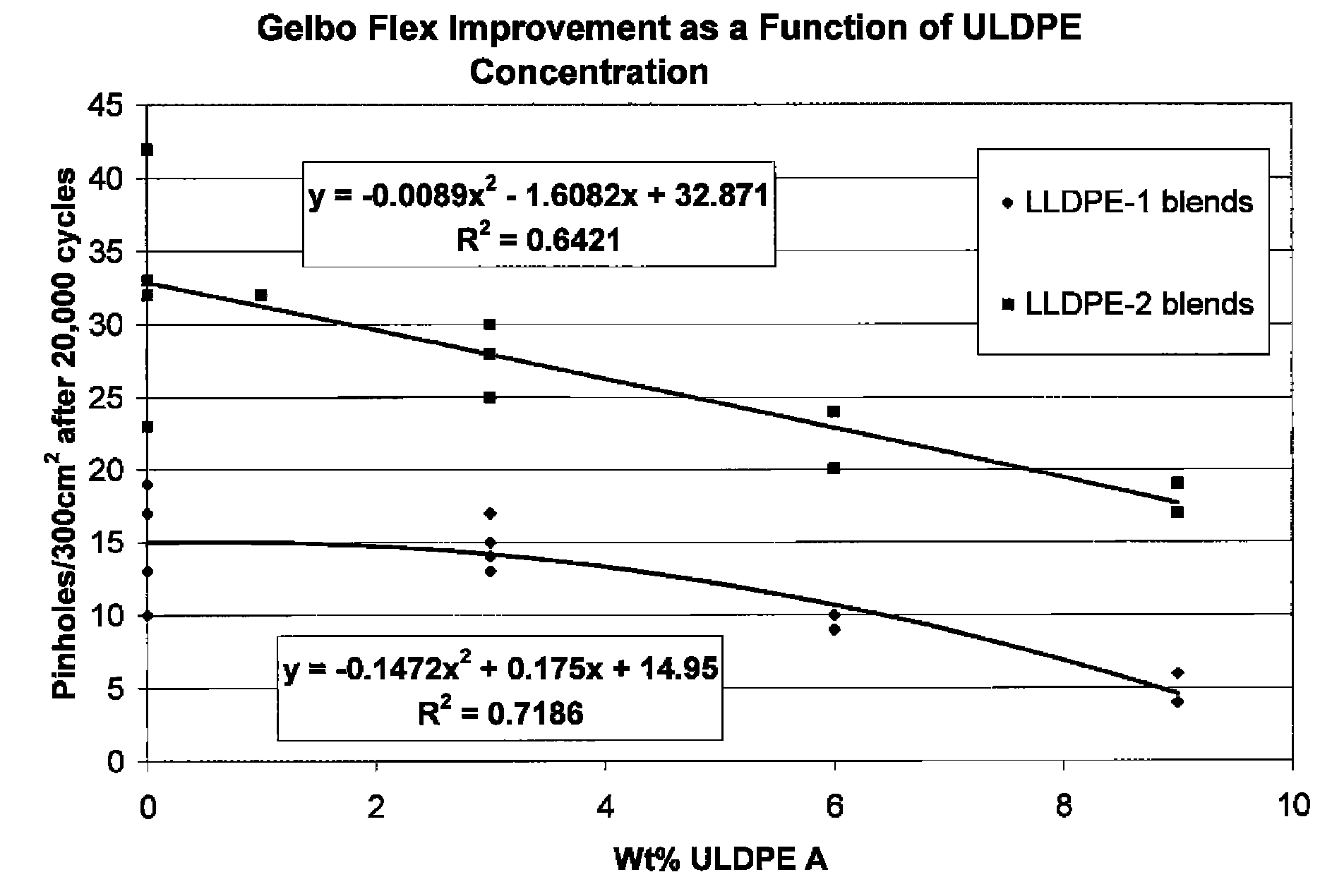
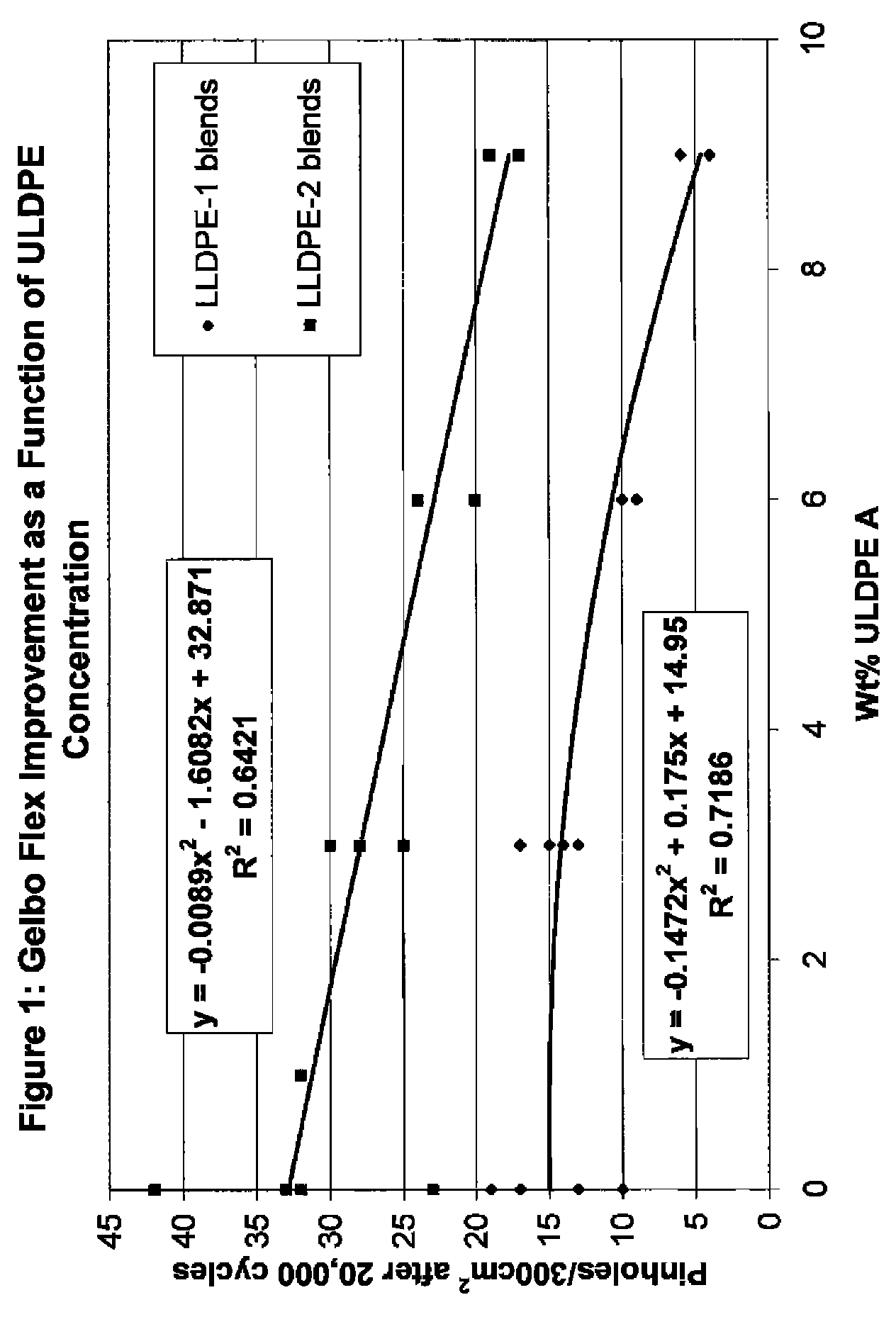
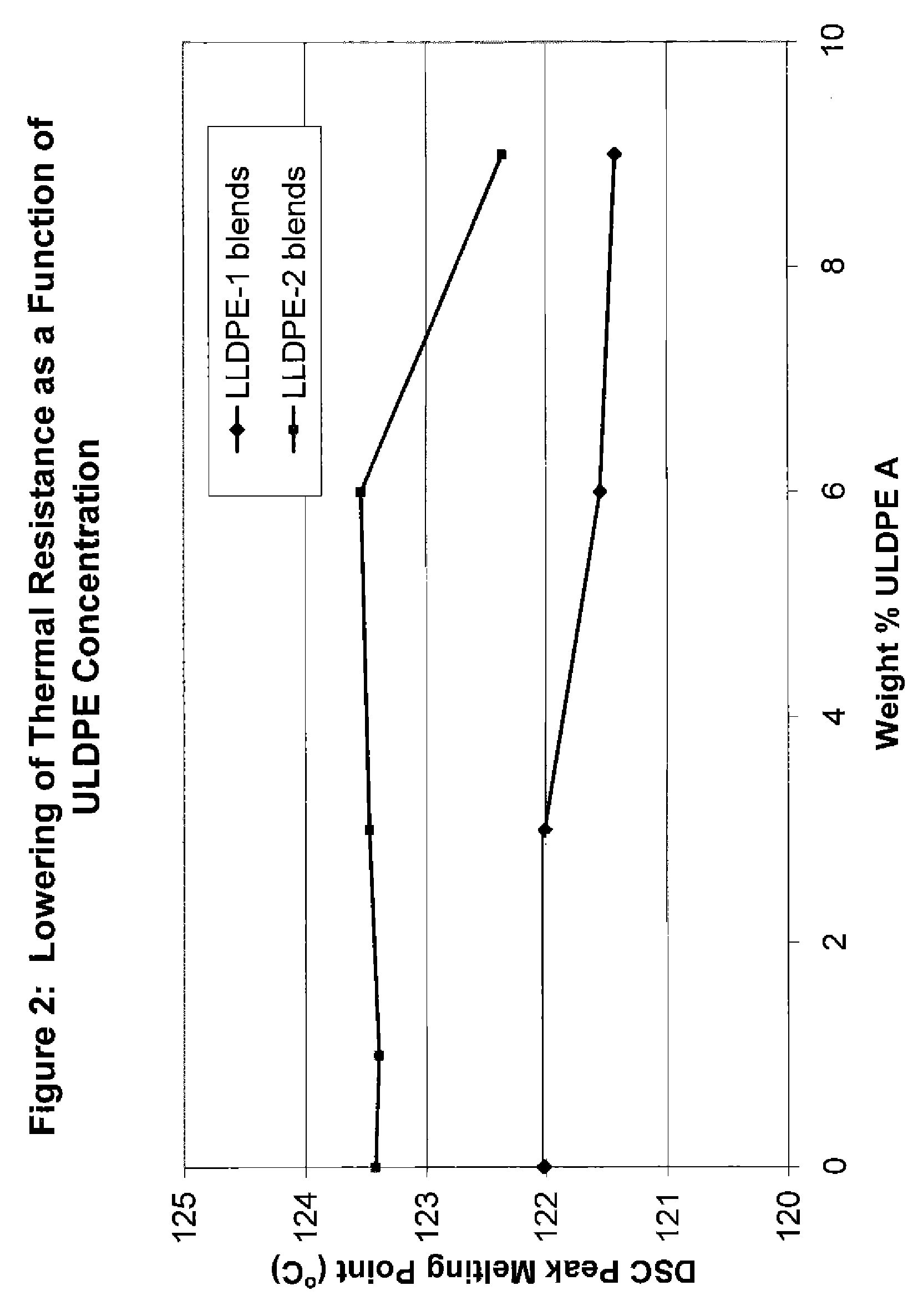
Flex crack resistant low density polyethylene films
ActiveUS20070269623A1Good flex crack performanceSmall resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsBagsLow-density polyethylenePolymer science
A sealant film for use in a film structure for the manufacture of pouches and bags for containing flowable materials, the sealant film comprising: (1) from about 2.0 to about 9.5 wt %, based on 100 wt % total composition, of an ethylene C4-C10-alpha-olefin interpolymer having a density of from 0.850 to 0.890 g / cc and a melt index of 0.3 to 5 g / 10 min, the interpolymer being present in an amount that optimizes flex crack resistance as measured using a Gelbo Flex tester set up to test in accordance with ASTM F392, and minimizes reduction of thermal resistance, as measured using DSC (ASTM E794 / E793) Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) which determines temperature and heat flow associated with material transitions as a function of time and temperature, and stiffness of the sealant film layer as measured using Tensile Modulus of the polyethylene films measured in accordance with ASTM Method D882; (2) from about 70.5 wt % to about 98.0 wt %, based on 100 wt % total composition, of one or more polymers selected from ethylene homopolymers and ethylene C4-C10-alpha-olefin interpolymers, having a density between 0.915 g / cc and 0.935 g / cc and a melt index of 0.2 to 2 g / 10 min; and (3) from about 0 wt % to about 20.0 wt %, based on 100 wt % total composition, of processing additives selected from slip agents, antiblock agents, colorants and processing aids; and wherein the sealant film has a thickness of from about 2 to about 60 μm.
Owner:LIQUI BOX
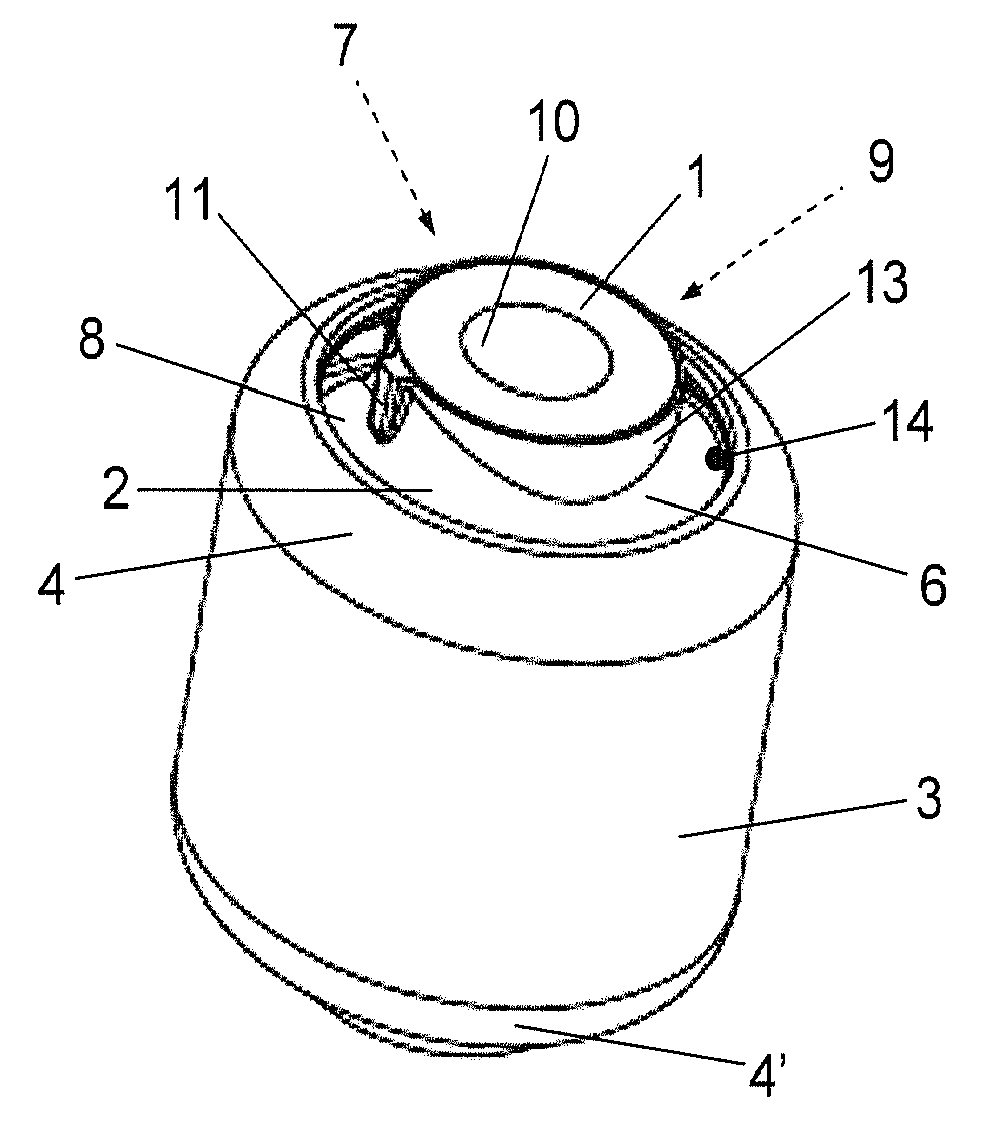
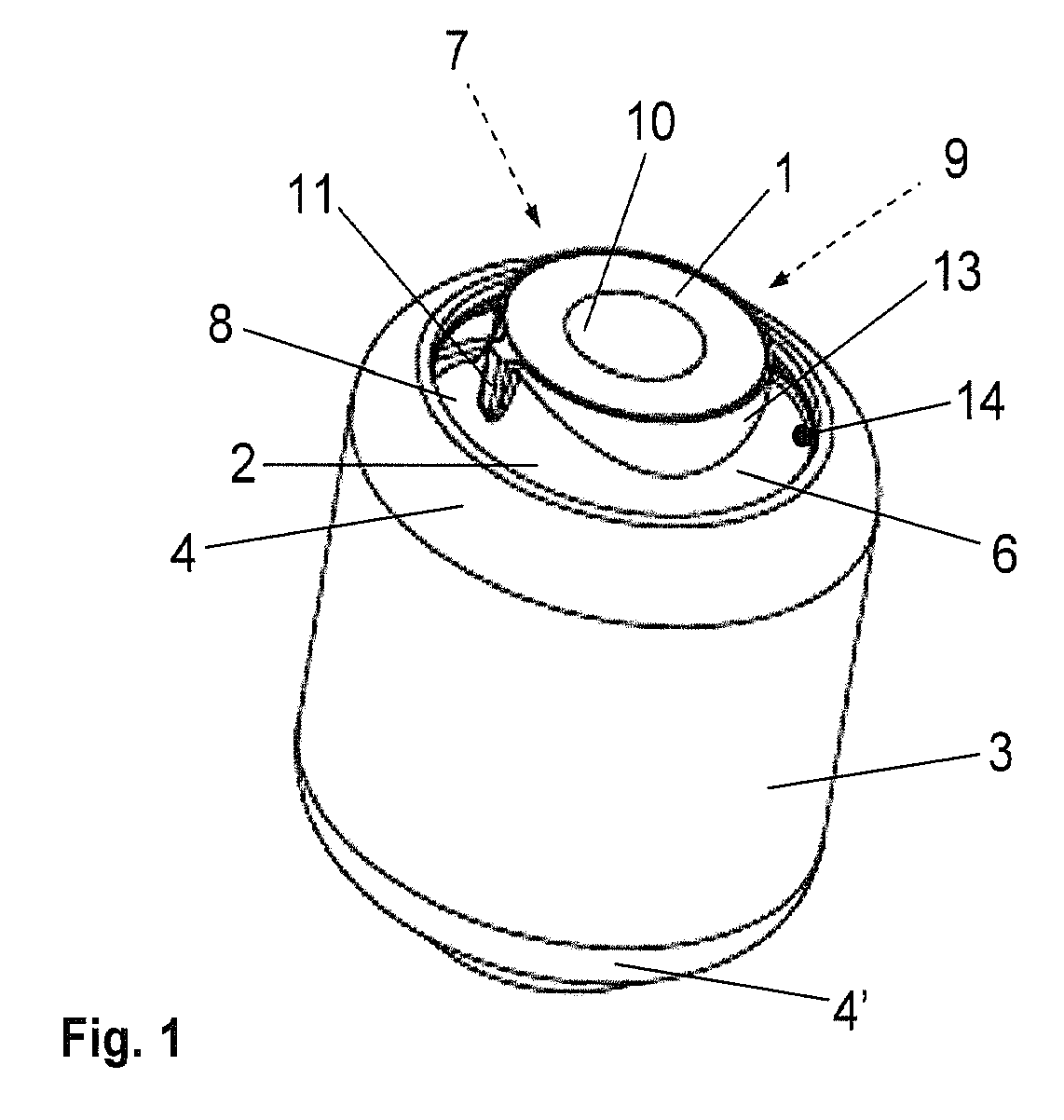
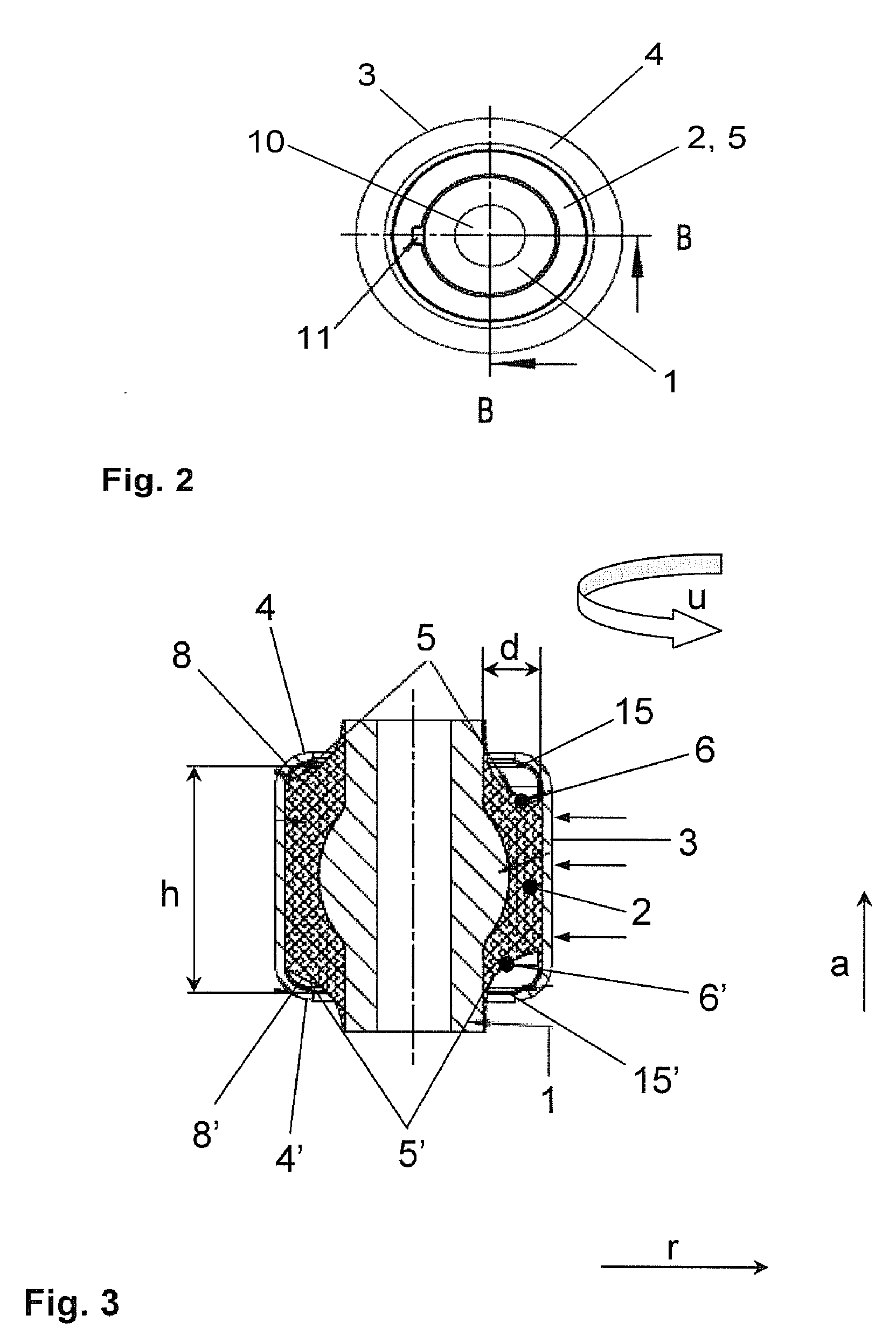
Bush bearing with bearing body having an axial profile
InactiveUS20070258671A1Lift radial loadAffecting service lifeResilient suspensionsRubber-like material springsElastomerEngineering
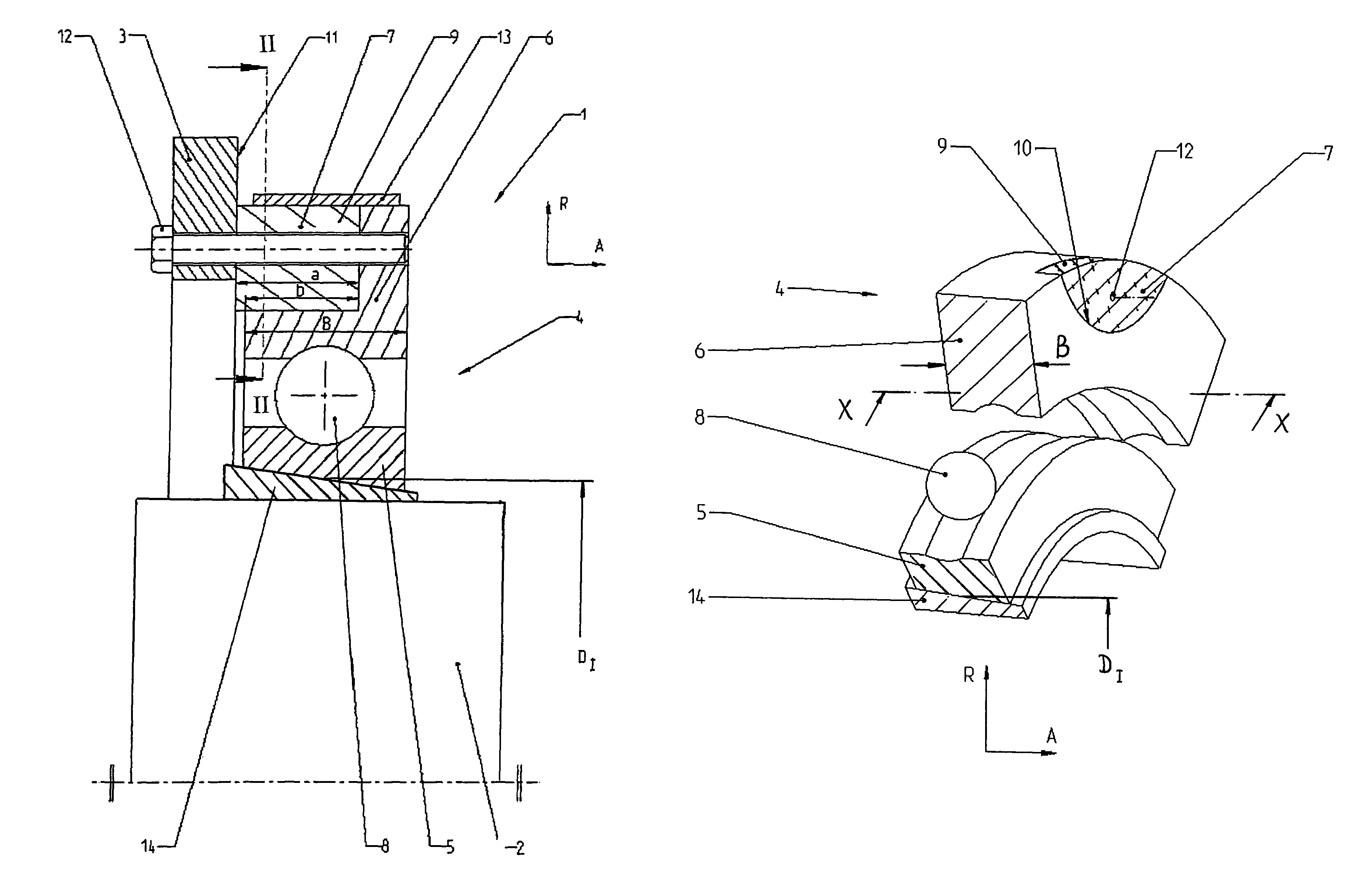
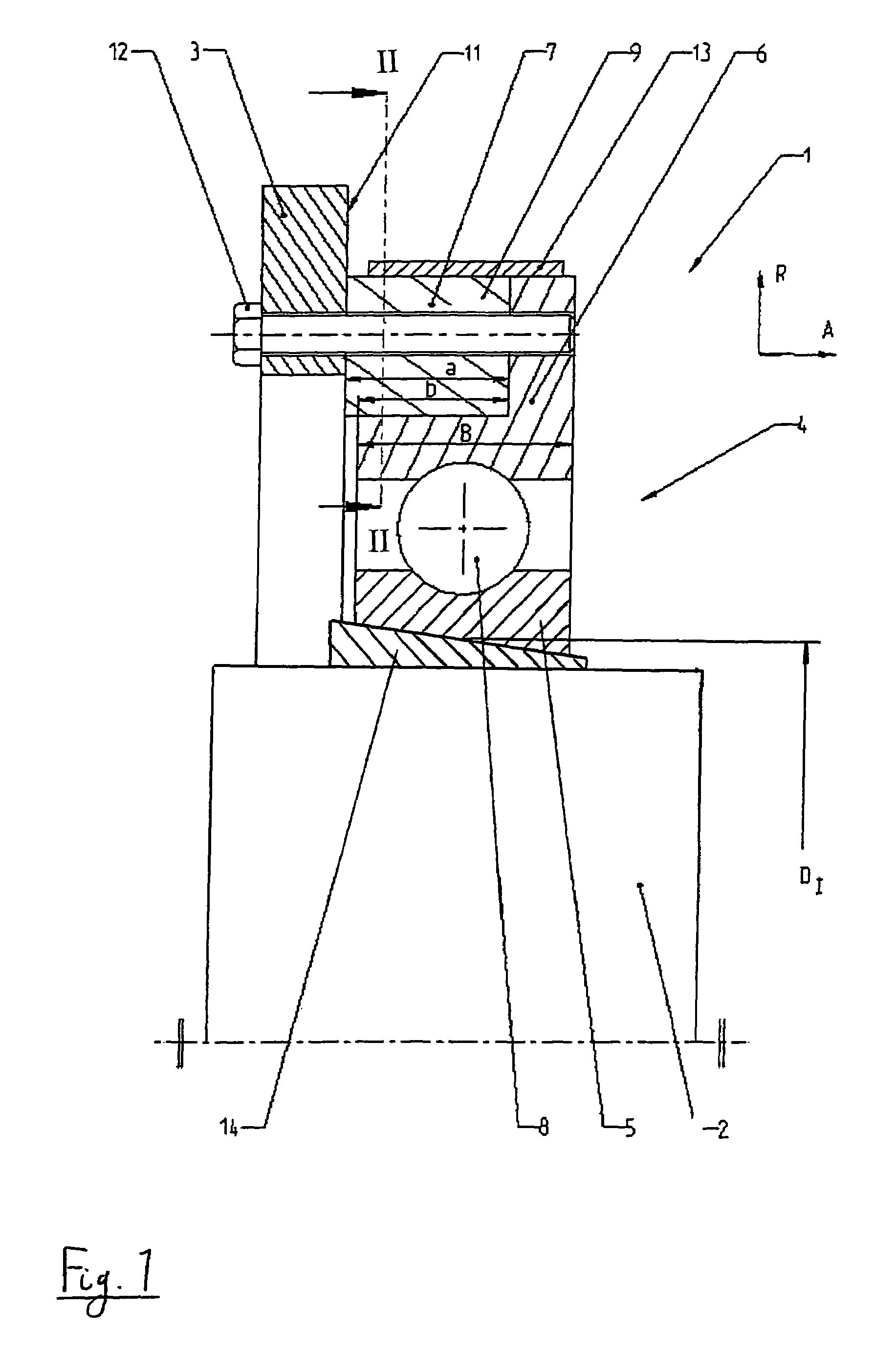
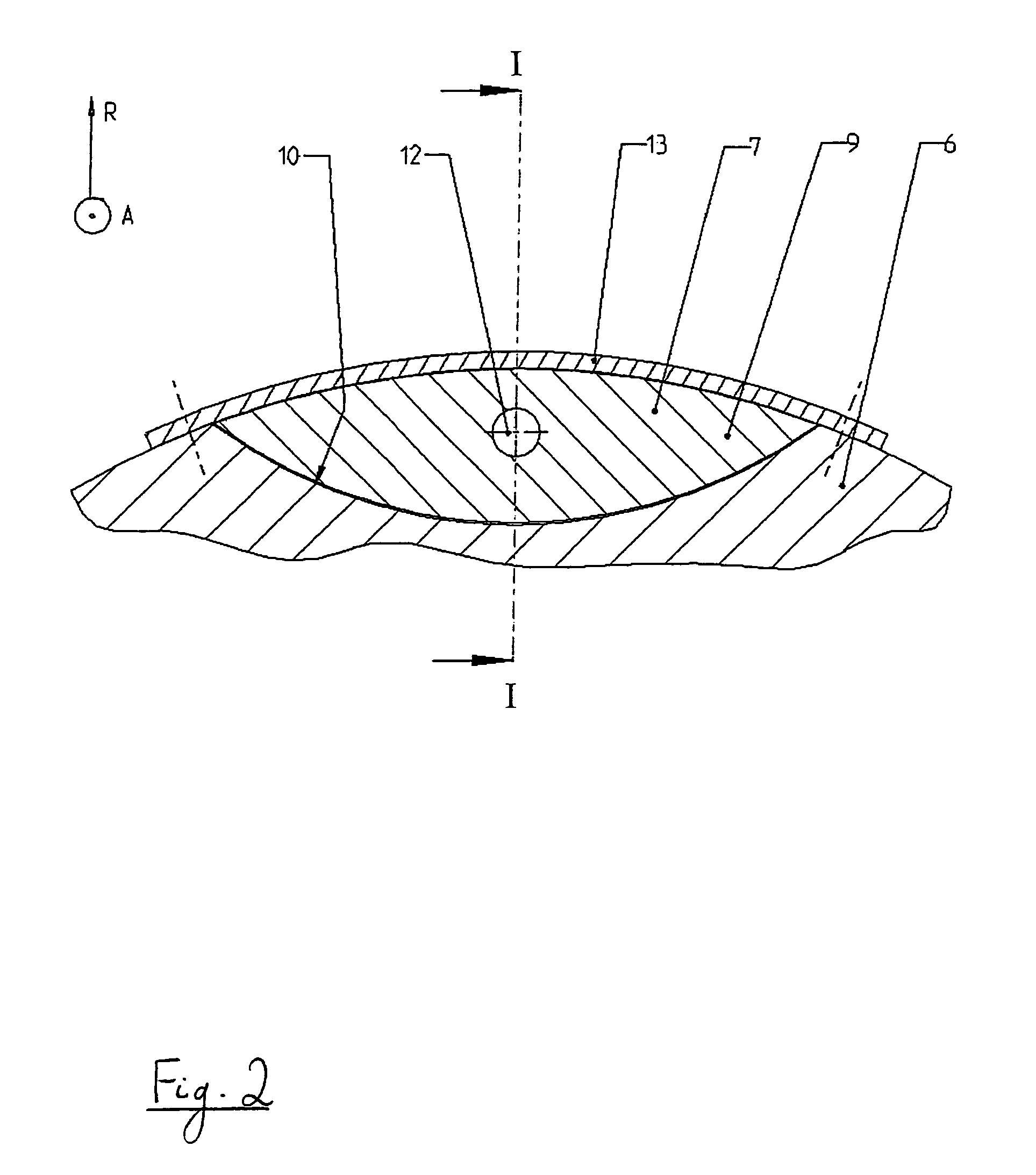
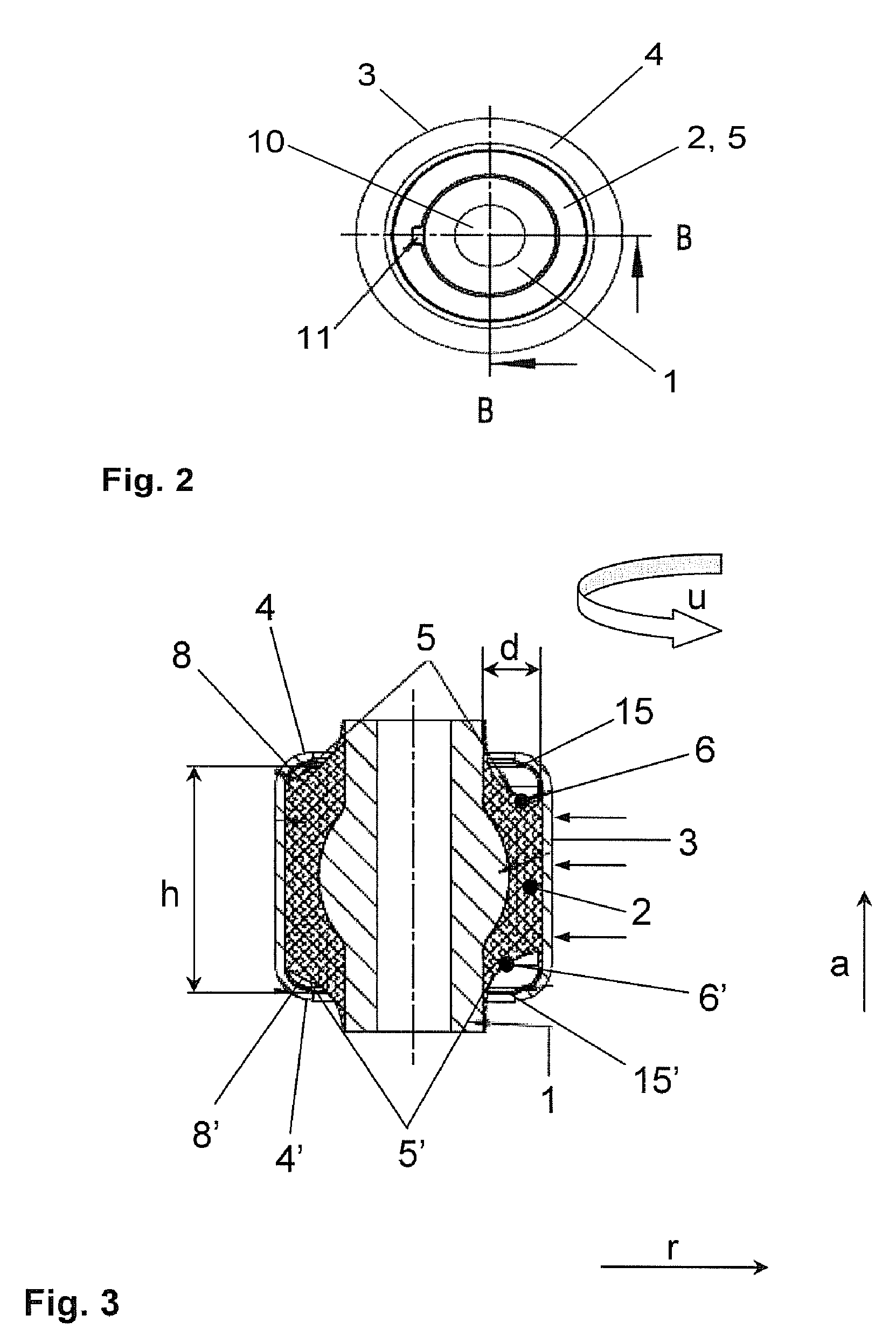
An elastomer bush bearing, wherein the bearing body (2) is encapsulated through axial flanges (4, 4′) of the outer bearing sleeve (3), with the bush bearing having an elastomer bearing body (2) with a special profile in the axial direction. The bearing body (2) is employed in constructing the bush bearing of the invention, which is capable of supporting high radial loads even with low radial stiffness and without adversely affecting its stability and service life. The two axial end faces (5, 5′) of the bearing body (1) each have undulated contours which extend in the circumferential direction (u) in the same direction, both with respect to one another and also over the entire region of the material thickness (d) of the bearing body (2). The end faces (5, 5′) of the bearing body (2) thus have wave troughs (6, 6′, 7, 7′) and wave crests (8, 8′, 9, 9′), whereby the corresponding wave troughs (6, 6′, 7, 7′) of both end faces (5, 5′) and their wave crests (8, 8′, 9, 9′) are formed so as to face one another, and each extend radially over the entire material thickness (d) of the bearing body (2) in the respective circumferential segment.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Flex crack resistant low density polyethylene films
ActiveUS8252397B2Good flex crack performanceSmall resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsBagsLow-density polyethyleneCrack resistance
This invention relates to film used to manufacture pouches and bags for containing flowable material. The film is made of low density polyethylene and can be formed into a monofilm or a multi-layer film that can be used to produce packages that exhibit improved flex crack resistance.
Owner:LIQUI BOX
Power tool with a slip clutch
A power tool includes an output member (8) projecting from the tool housing (4), a drive (6) located in the housing for rotating the output member (8), and a slip clutch (22) for transmitting torque from the drive (6) to the output member (8) and including a plurality of clutch elements (24) retained against rotation relative to the housing (4), a plurality of separate spring elements (28) for adjustable preloading the clutch elements (24) against the counter-clutch elements (51) of the control element (18) for retaining the control element (18) against rotation upon application of the torque thereto until threshold of the torque is reached, and a common support element for supporting the spring elements and movable relative to the housing (4).
Owner:HILTI AG
Device comprising at least a body and a bumper, and robot cleaner comprising such a device
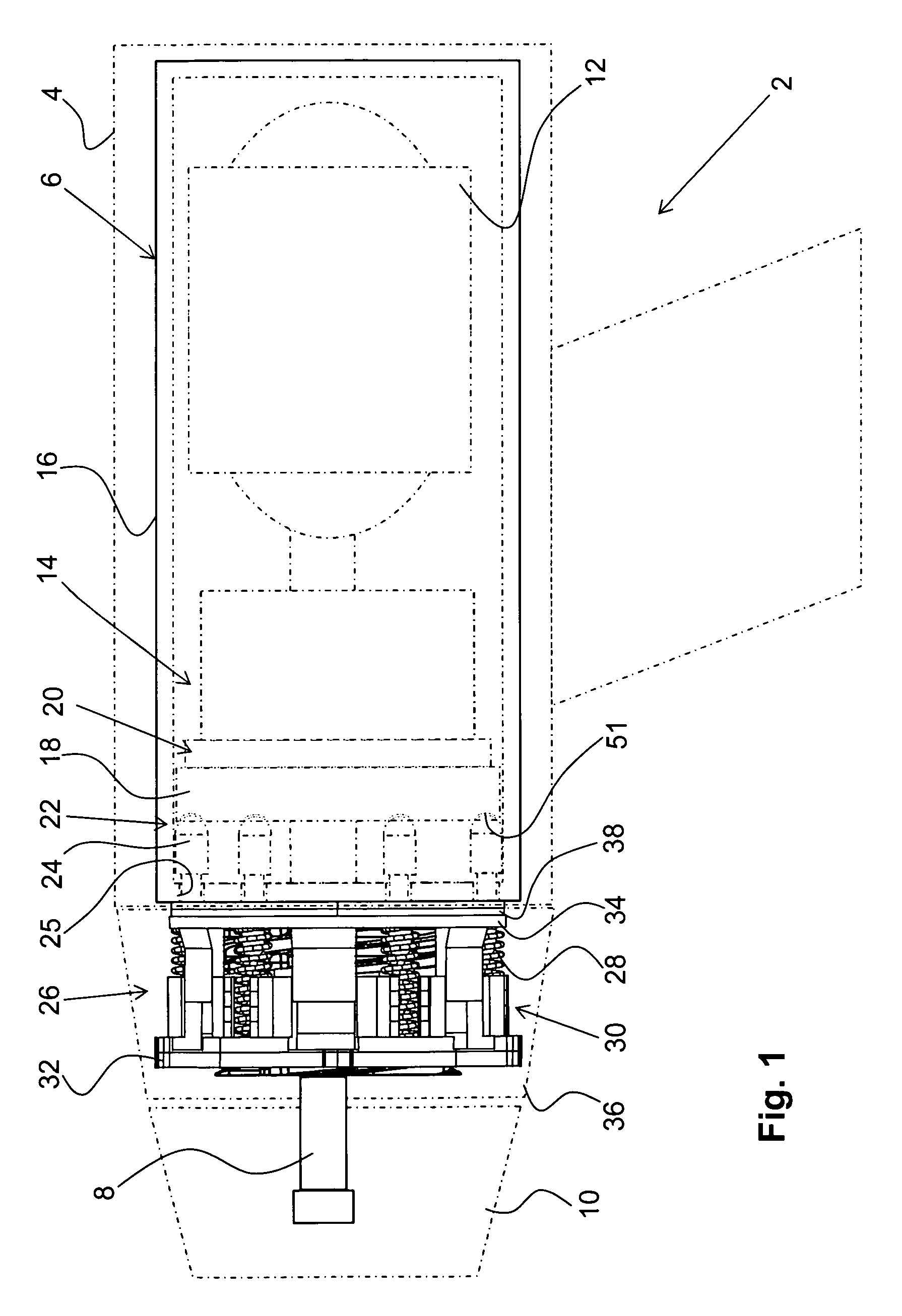
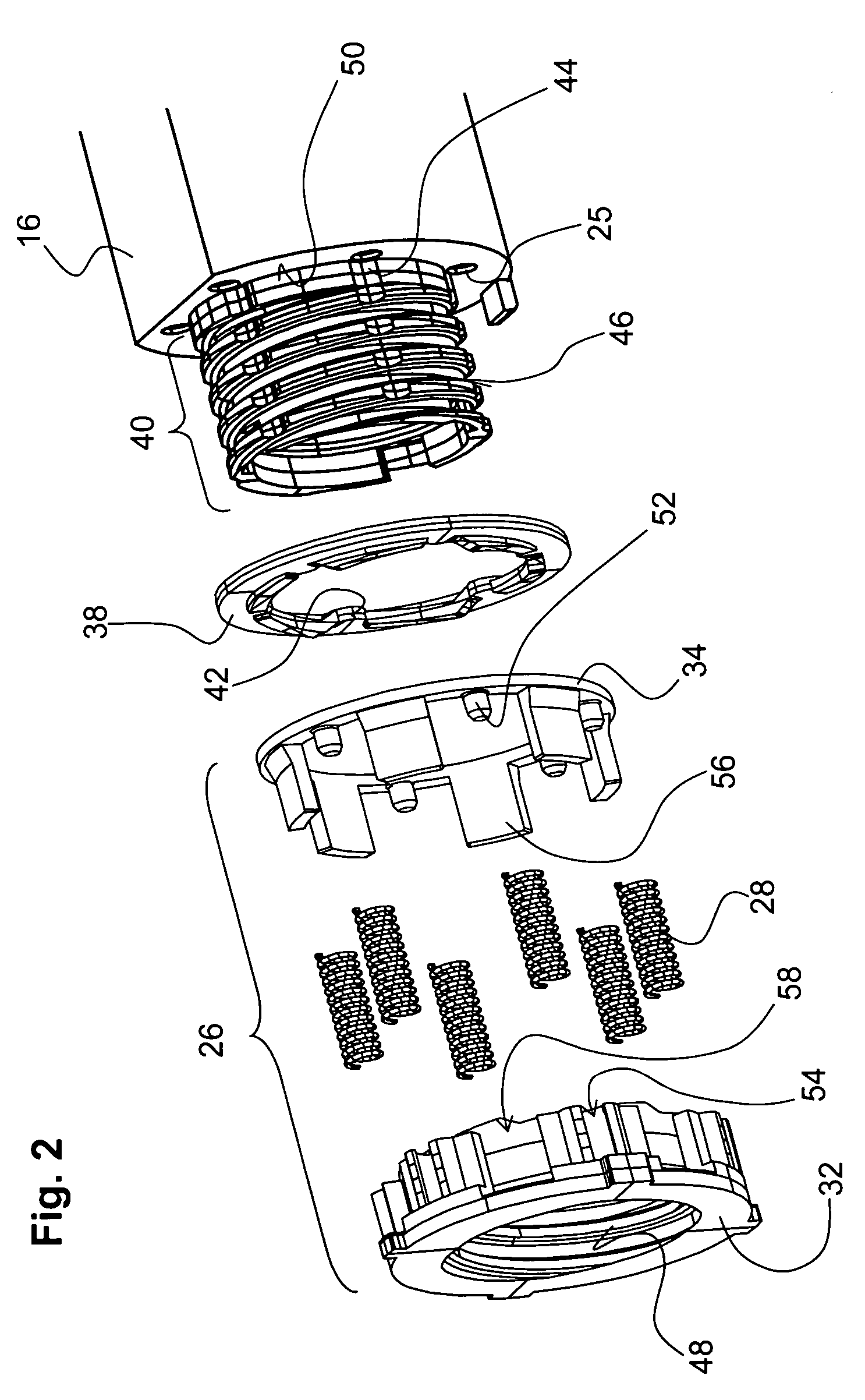
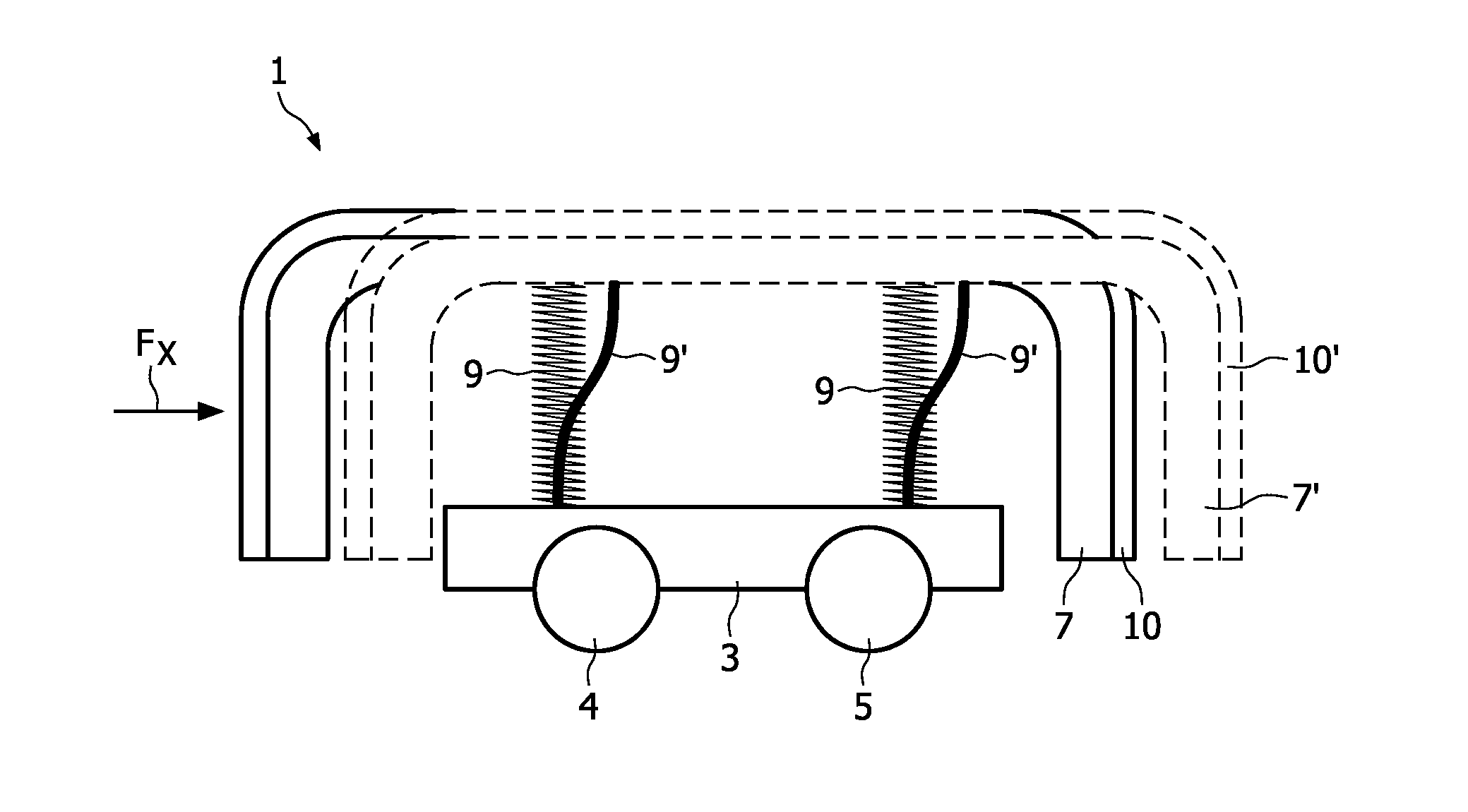
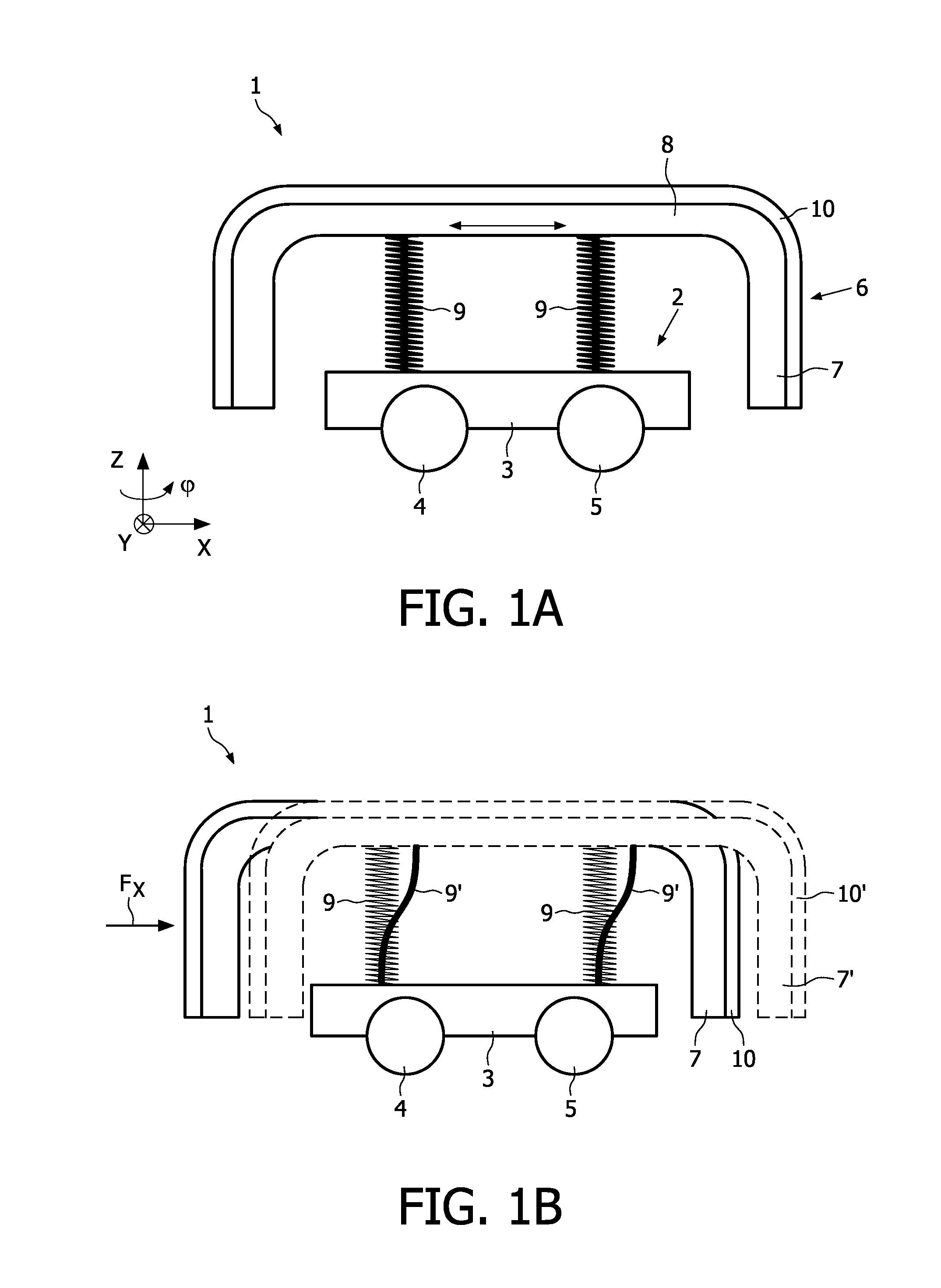
InactiveUS20100306932A1Simple wayLittle stiffnessCarpet cleanersFloor cleanersStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
A device (1) comprises at least a body (2) and a bumper (6) which is movably attached to the body so as to protect the body from shock caused by collision with an obstacle during movement of the device across a surface. The bumper is attached to the body by means of at least one spring (9) extending in a direction which is at least substantially perpendicular to the direction into which the bumper is movable with respect to the body. Furthermore,a robot cleaner comprising such a device is provided.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
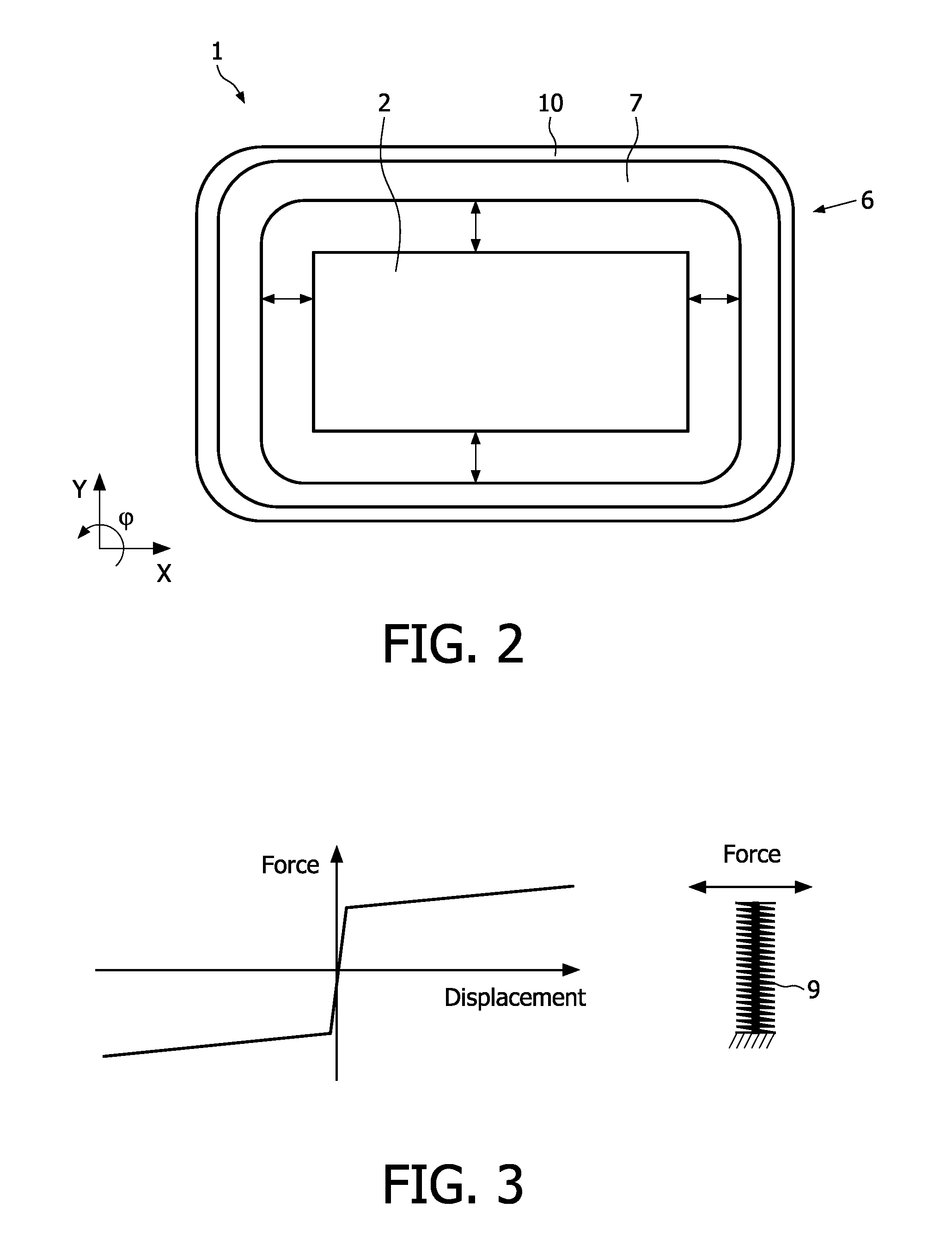
Torsional Vibration Damper Comprising A Damping System, A Damping Device And A Ground Device
ActiveUS20170023096A1Reduce stiffnessLittle stiffnessRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingTorsional vibrationControl theory
A torsional vibration damper (70) with a damping device which has an input (67) and an output (72) which is operatively connected to a driven side (73). The output is connected to a mass damper system (1) and also to a mass arrangement (100). One of the two subassemblies—i.e., mass damper system (1) and mass arrangement (100)—which are connected to the output (72) of the damping device (70) engages at the respective other subassembly comprising mass damper system or mass arrangement which is in turn connected to the output by a connection arrangement (77).
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Compact inertial sensor
InactiveUS6904803B2Small sizeLittle stiffnessAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsMechanical engineeringInertia
Owner:SAGEM DEFENSE SECURITE SA
Tire for an aircraft and method for producing the same
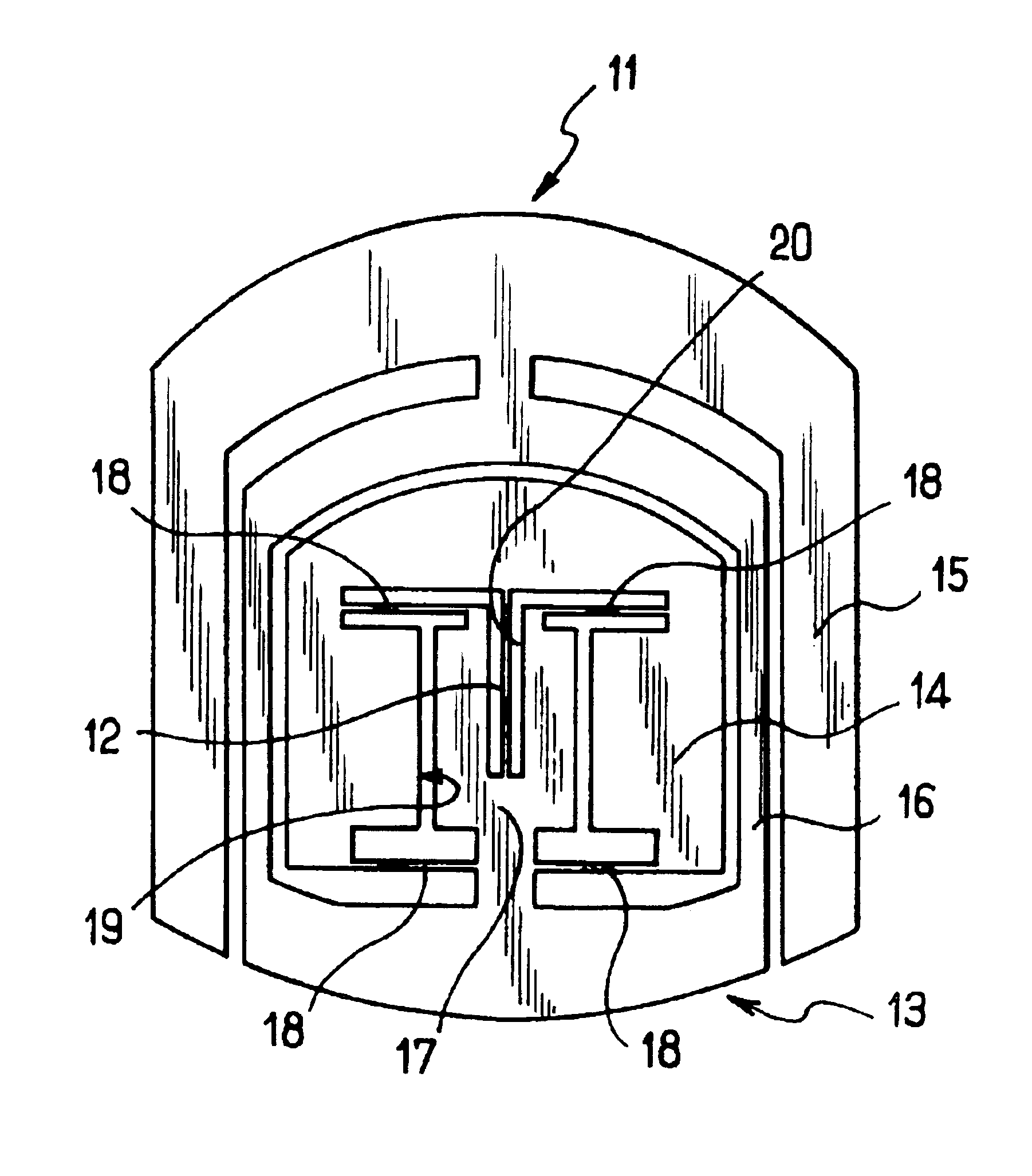
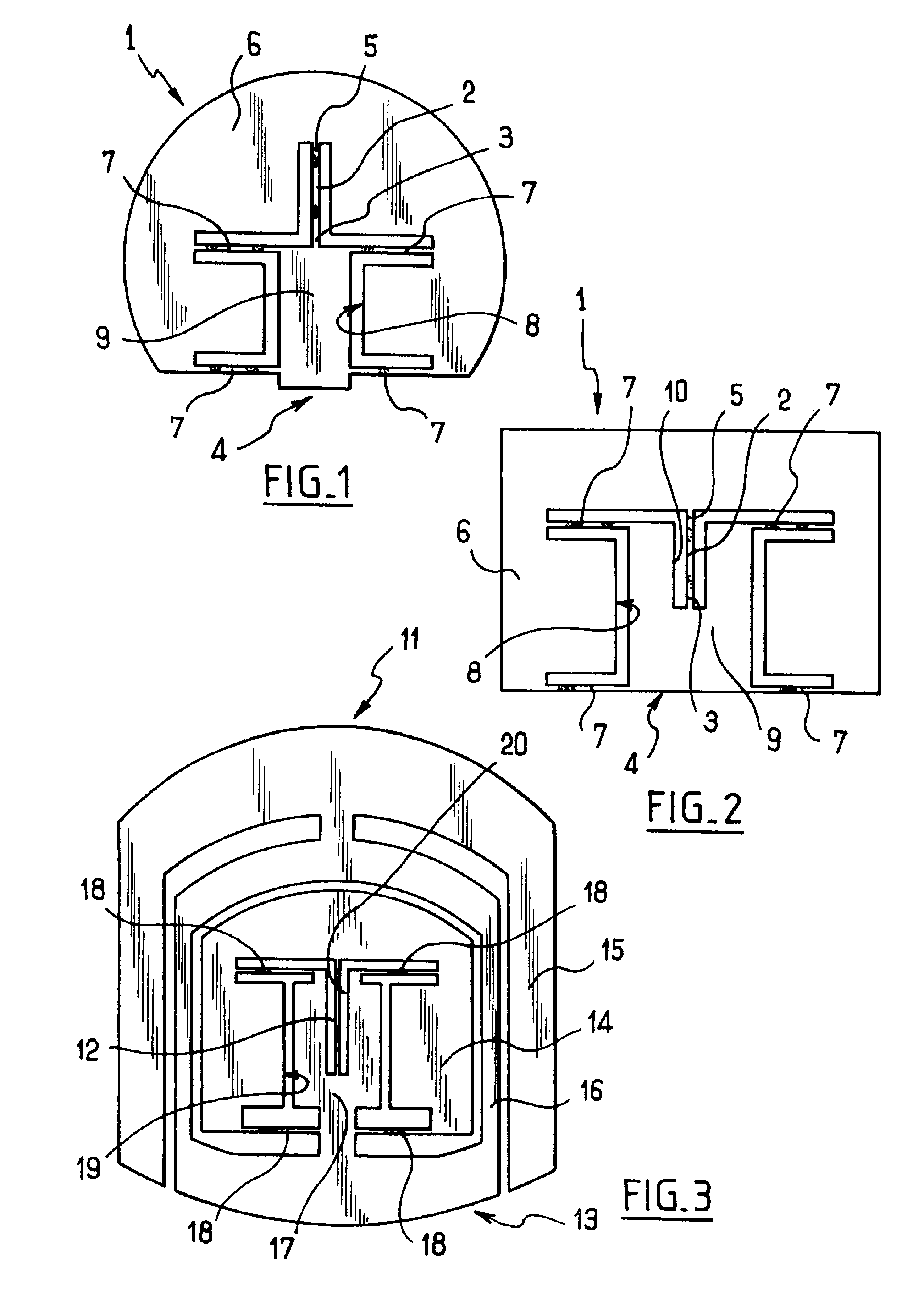
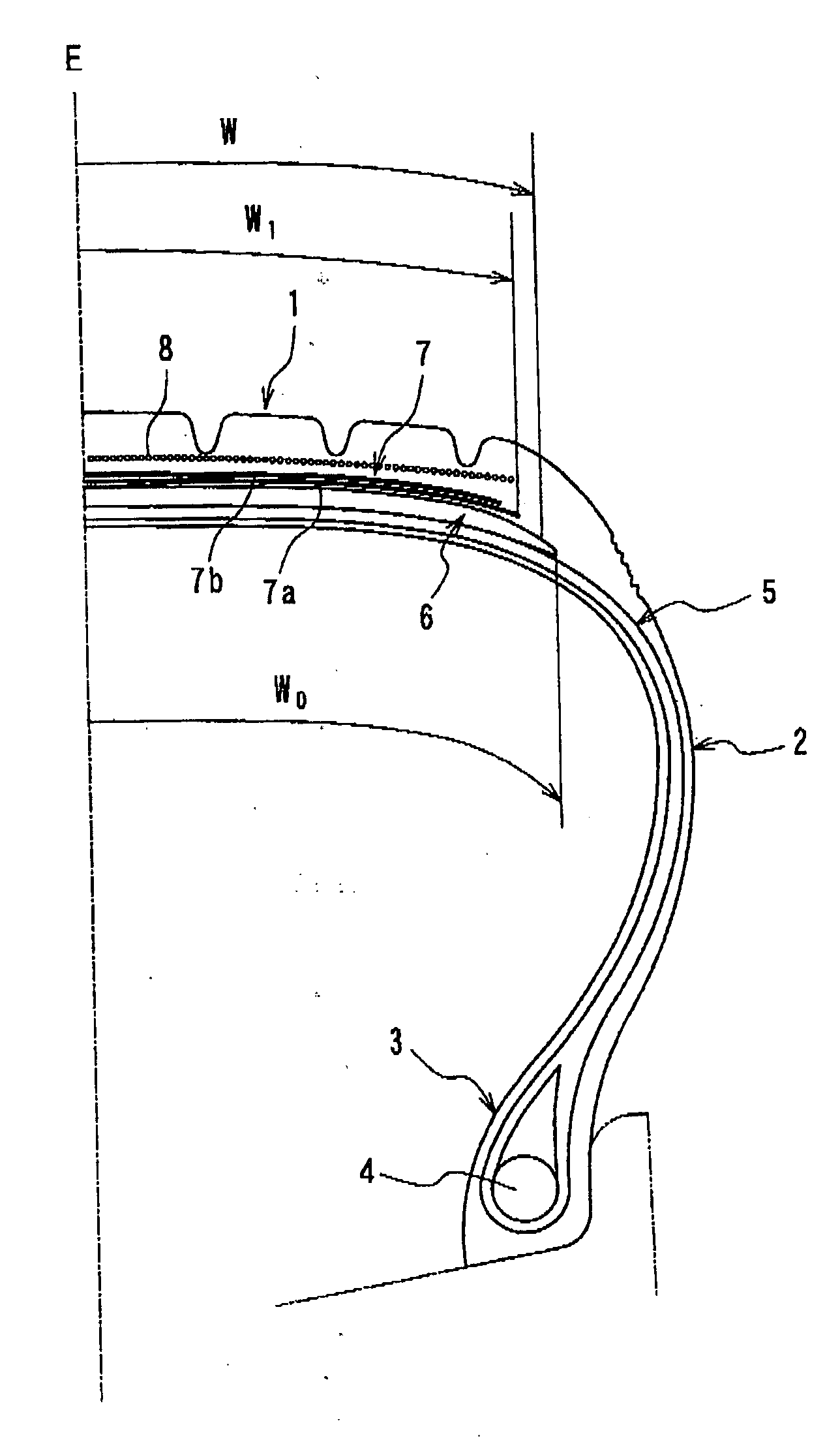
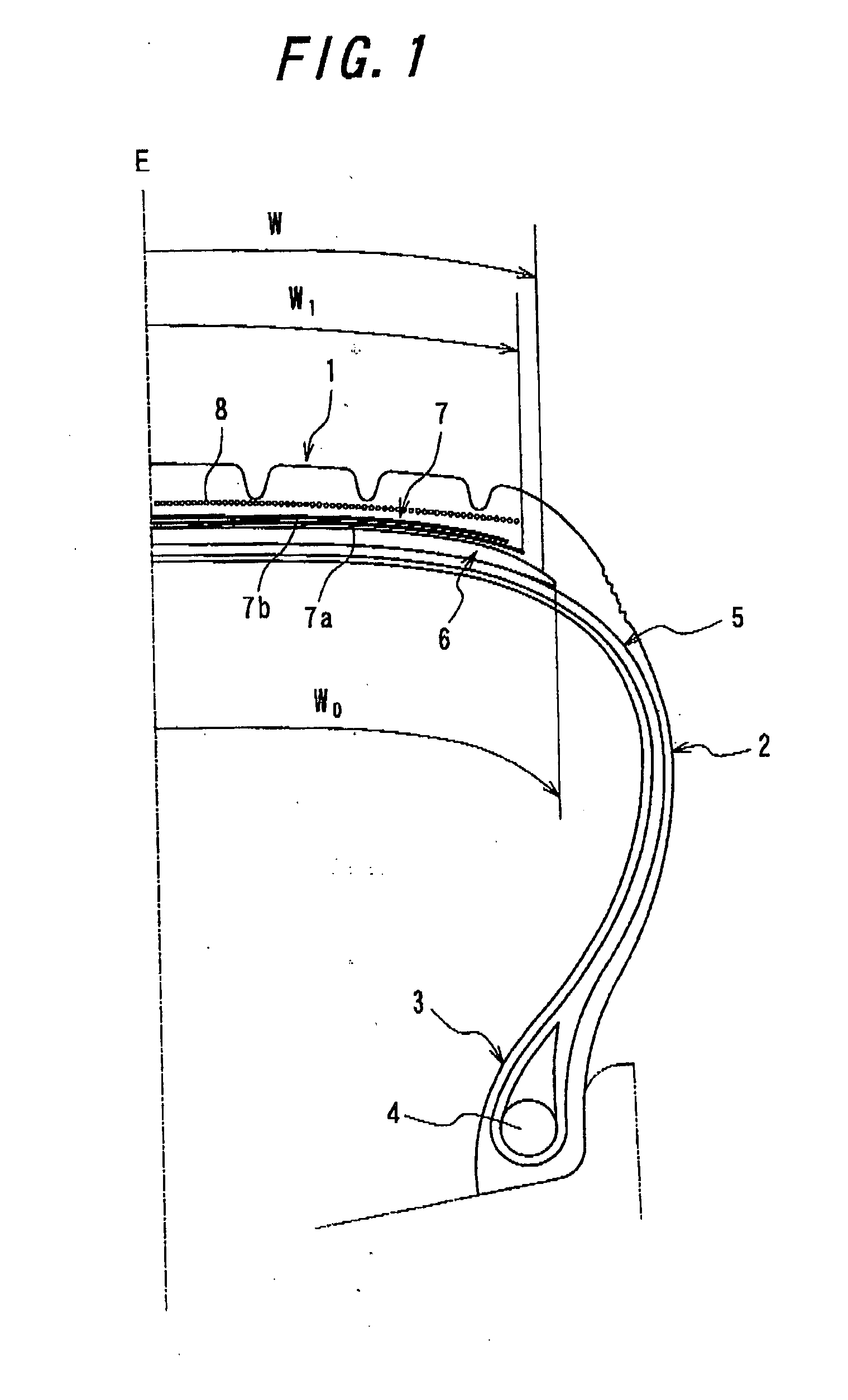
There is provided a tire for an aircraft capable of enhancing abrasion resistance and effectively preventing a progress of peeling of the non-extensible cords of the main belt layers even when the tire suffers external injury reaching the main belt layers. A tire comprises a pair of bead cores 4, a carcass 5 toroidaly extending between the bead cores, a main belt 6 disposed on an outer peripheral side of a crown area of the carcass 5 and consisting of main belt layers having a spirally-wound structure of a non-extensible cord, and a sub belt 7 disposed on the outer peripheral side of the main belt 6 and consisting of sub belt layers 7a, 7b having an organic fiber cord extending in a circumferential direction of the tire in a zigzag pattern, wherein the sub belt layers 7a, 7b are formed in such a manner that the organic fiber cord in a zigzag pattern is wound several times in the circumferential direction of the tire, and that a crossing angle of the organic fiber cord with respect to an equatorial plane of the tire is within a range between 45 degrees and 90 degrees.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Bearing arrangement for a medical device
InactiveUS7441960B2Low inherent stiffnessQuiet operationRolling contact bearingsBearing assemblyEngineeringMedical device
Owner:AB SKF
Printing head
ActiveUS20090309923A1Small amount of deformationLittle stiffnessPrintingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
There is provided a printing head, enabling to suppress the occurrence of cracks in a printing element substrate, even if the printing head is erroneously fallen. The printing head comprises: a printing element substrate, an ink flow passage and a sheet-shaped portion comprising a rectangular major surface. A rear surface side of the major surface of the sheet-shaped portion is provided with a space formed separately from the ink flow passage. A surface adjacent to the major surface is provided with an opening of the space formed therein, and wherein the sheet-shaped portion is provided with a concave portion formed on the rear surface side of two regions between the printing element substrate and two corner portions arranged proximate to the opening in the major surface.
Owner:CANON KK
Method of controlling vibration damping in a helicopter, and apparatus implementing the method
InactiveUS7360994B2Reduce vibrationAvoid premature wearPropellersPump componentsReal time analysisControl theory
The present invention relates to a method of controlling a drag damper for a helicopter blade under all operating configurations of the helicopter, the method consisting in:a) measuring the elongation of the damper;b) amplifying the measured signal and filtering out noise;c) isolating the natural response of the blade corresponding to the drag movement of the blade from the forced response imposed by a rotor driving the blades; andd) analyzing in real time the natural response and adjusting the damping as a function of the analysis.
Owner:EUROCOPTER
Power tool with a slip clutch
ActiveUS7806200B2Simple methodEasy to adjustConstructionsPortable power-driven toolsPower toolClutch
A power tool includes an output member (8) projecting from the tool housing (4), a drive (6) located in the housing for rotating the output member (8), and a slip clutch (22) for transmitting torque from the drive (6) to the output member (8) and including a plurality of clutch elements (24) retained against rotation relative to the housing (4), a plurality of separate spring elements (28) for adjustable preloading the clutch elements (24) against the counter-clutch elements (51) of the control element (18) for retaining the control element (18) against rotation upon application of the torque thereto until threshold of the torque is reached, and a common support element for supporting the spring elements and movable relative to the housing (4).
Owner:HILTI AG
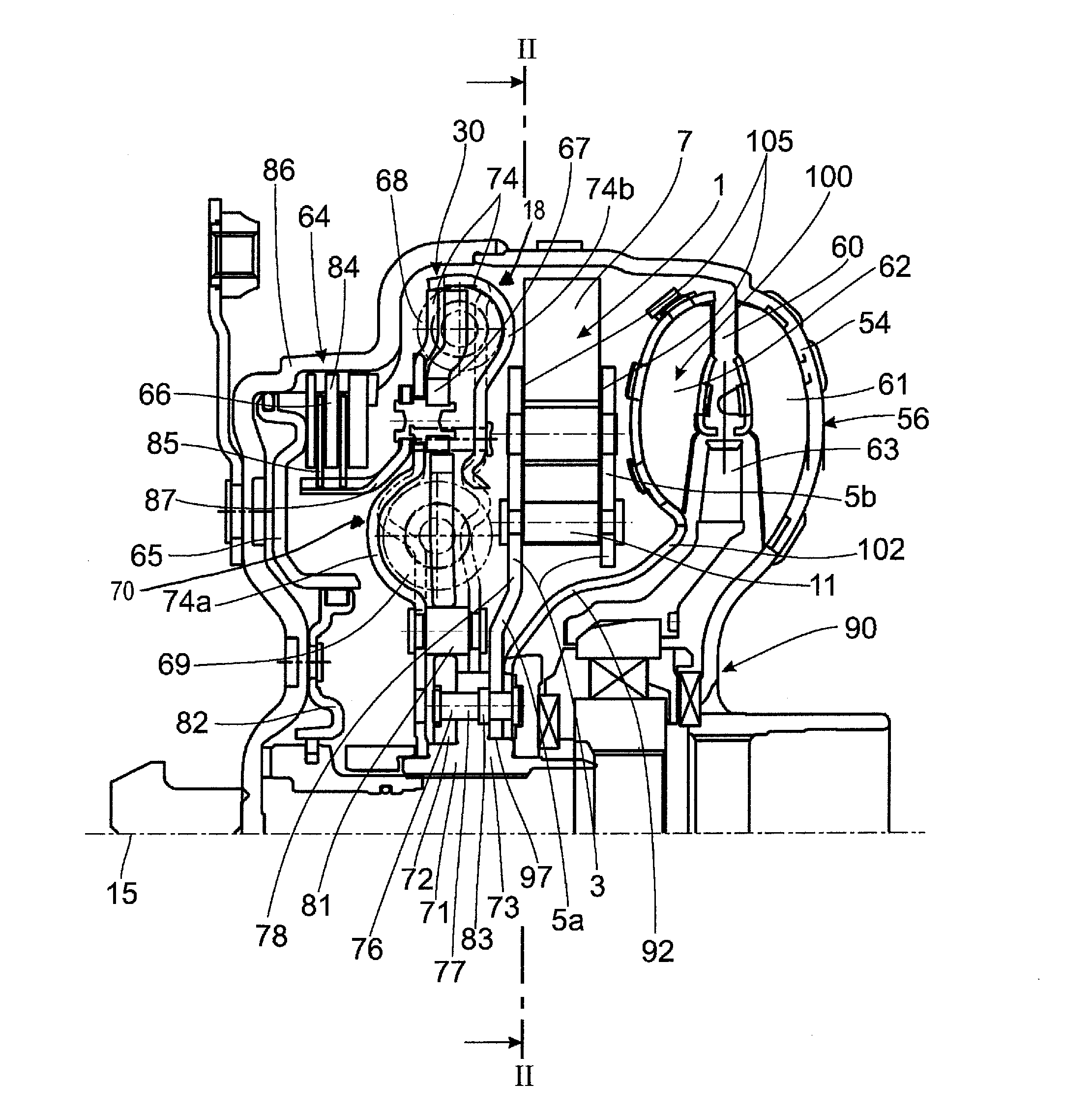
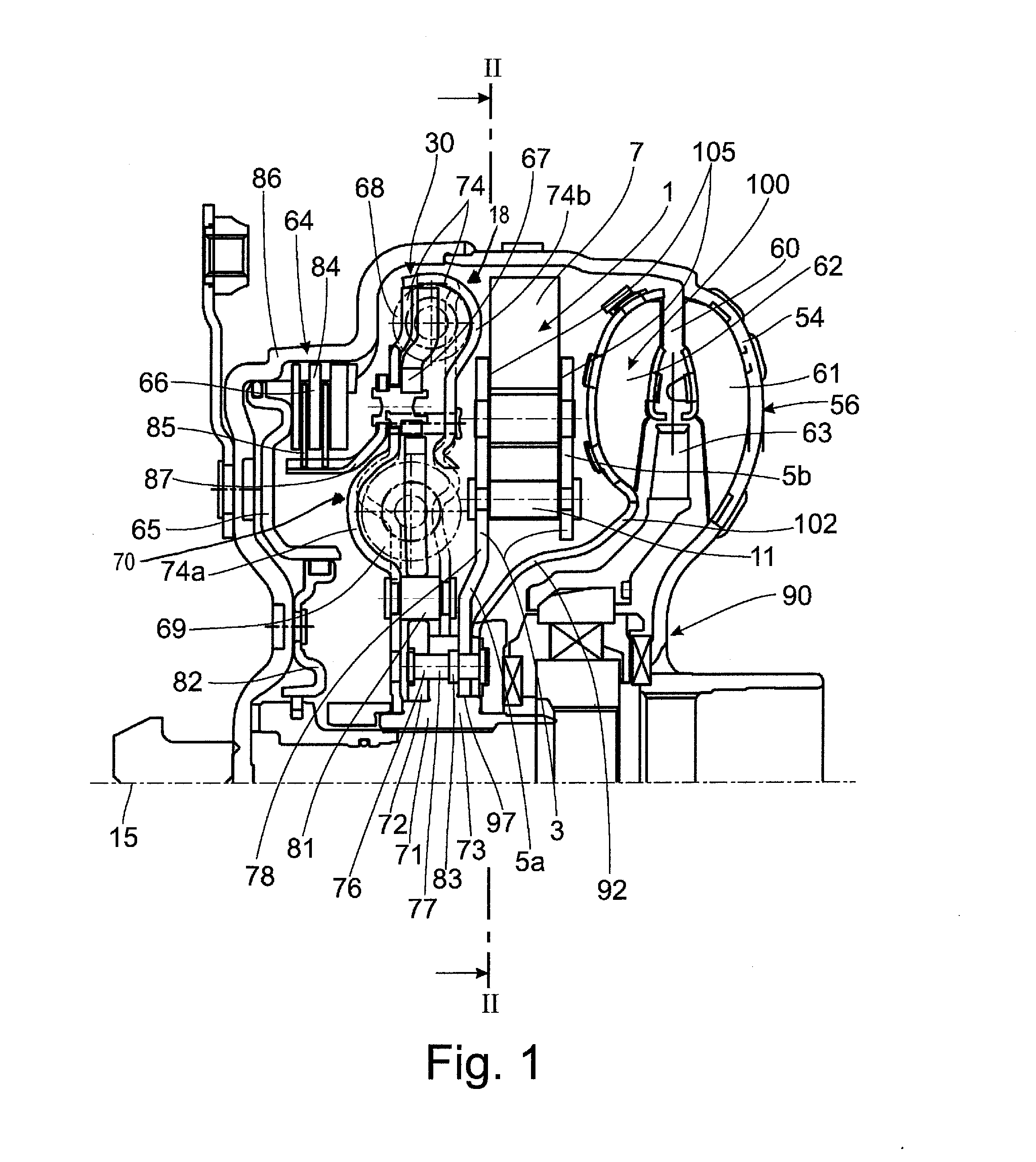
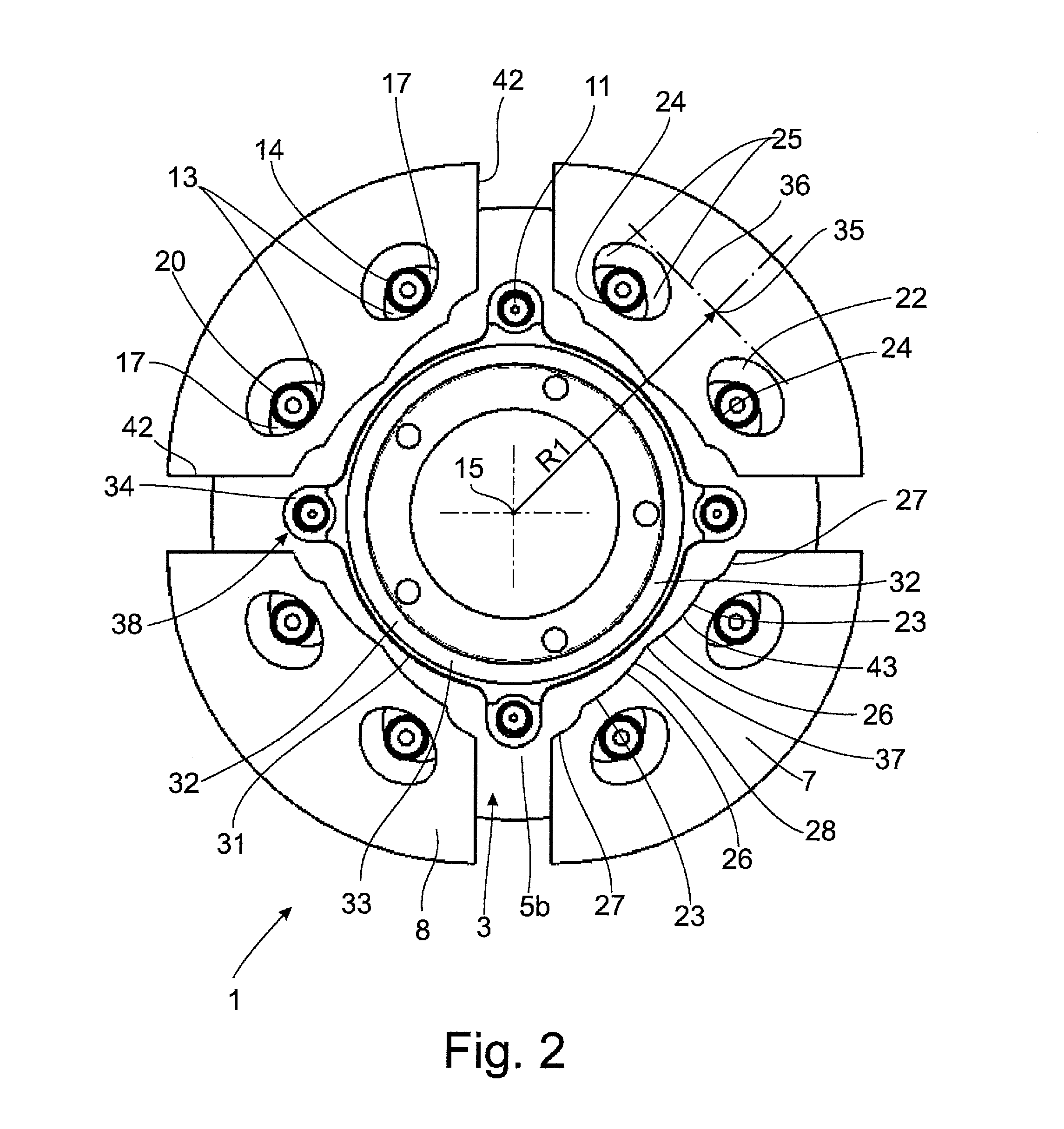
Bearing and gear unit for wind turbines
InactiveUS20160153426A1Little stiffnessFacilitate the many poles relatively inexpensivelyEngine fuctionsMachines/enginesNacelleFree rotation
The economic efficiency of wind turbines improves by upscaling but the weight to strength ratio deteriorates. This is especially true for the large shaft and bearing of the rotor, the gearbox and the generator. Solutions to this was the gearless generator, getting heavy because the amount of magnetic material is inversely proportional to speed, or several smaller generators adapted to the wind on a distribution gear as shown in references (1), (2) and (3). The large roller bearing of the rotor has relatively large bearing clearance so only the top or lower rollers bear the entire weight of the rotor and thus must be dimensioned relatively large. The present invention spreads the load on the support bearing to more rollers and to smaller faster running and thereby lighter generators. It has the rotor attached to the outer ring, each roller rotatably mounted to the nacelle and the inner ring free wheeling. The outer and inner rings are relatively stiffer than the rotatable fixation of the upper rollers to the nacelle, so that the upper rollers flex slightly down under the weight of the rotor allowing some of the force of gravity to be transferred to the inner ring and on to the bottom relatively stiff journalled rollers. Gear teeth can be used to transfer torque to all rollers, or the inner ring pressed against the side rollers, or the conical rollers can be pressed dynamically in between the outer and inner ring with relatively constant force. This is shown in FIGS. 1 and 6 in perspective and FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, in radial section. The relatively small roller shafts can now be used as PTO with gear ratio bearing diameter to roller diameter. The cost of the extra bearings for each roller is offset by savings in the usual center shaft and gear. Also, the friction from the edge of the outer or inner ring to keep the large rollers in place is missing. These benefits are especially important for wind turbines with heavy hub, axle and gear on a tall tower, and large wing rotor bearing clearance causing inappropriate vibrations of the long components. With no central hub shaft, gear and generator in the nacelle center there is space for force carrying structures as strong as the top of the tower to a point on the centre line of the rotor in front of it. To this a bearing for sustaining the varying moments of the wind can be affixed so the weight carrying bearing and gear unit can be designed cylindrical; or stays can be continued to other tower elements achieving a tower structure with significantly lower weight and higher natural frequency than usual wind moment influenced single column towers.
Owner:GROENAGER JENS
Pitch system for a wind turbine rotor
ActiveUS20140003944A1Simpler and cheap provideIncrease stiffnessPropellersPump componentsBlade pitchWind force
A pitch system for a wind turbine rotor, comprising a first bearing and a second bearing, each provided with an outer race, an inner race, and at least one row of rolling elements, the first and second bearings being adapted to be arranged between a hub and a blade root portion or extender, to allow rotation of the blade with respect to the hub, wherein the first bearing is adapted to be arranged nearer to the hub than the second bearing in the axial direction, the pitch system further comprising an intermediate body arranged between the first bearing and the second bearing in the axial direction, said intermediate body comprising at least a blade-side part extending between the race of the first bearing that is associated with the blade and the race of the second bearing that is associated with the blade.
Owner:GE RENEWABLE TECH WIND BV
Structure system composed of special-shaped cross section column frame and corrugated sheet steel wall
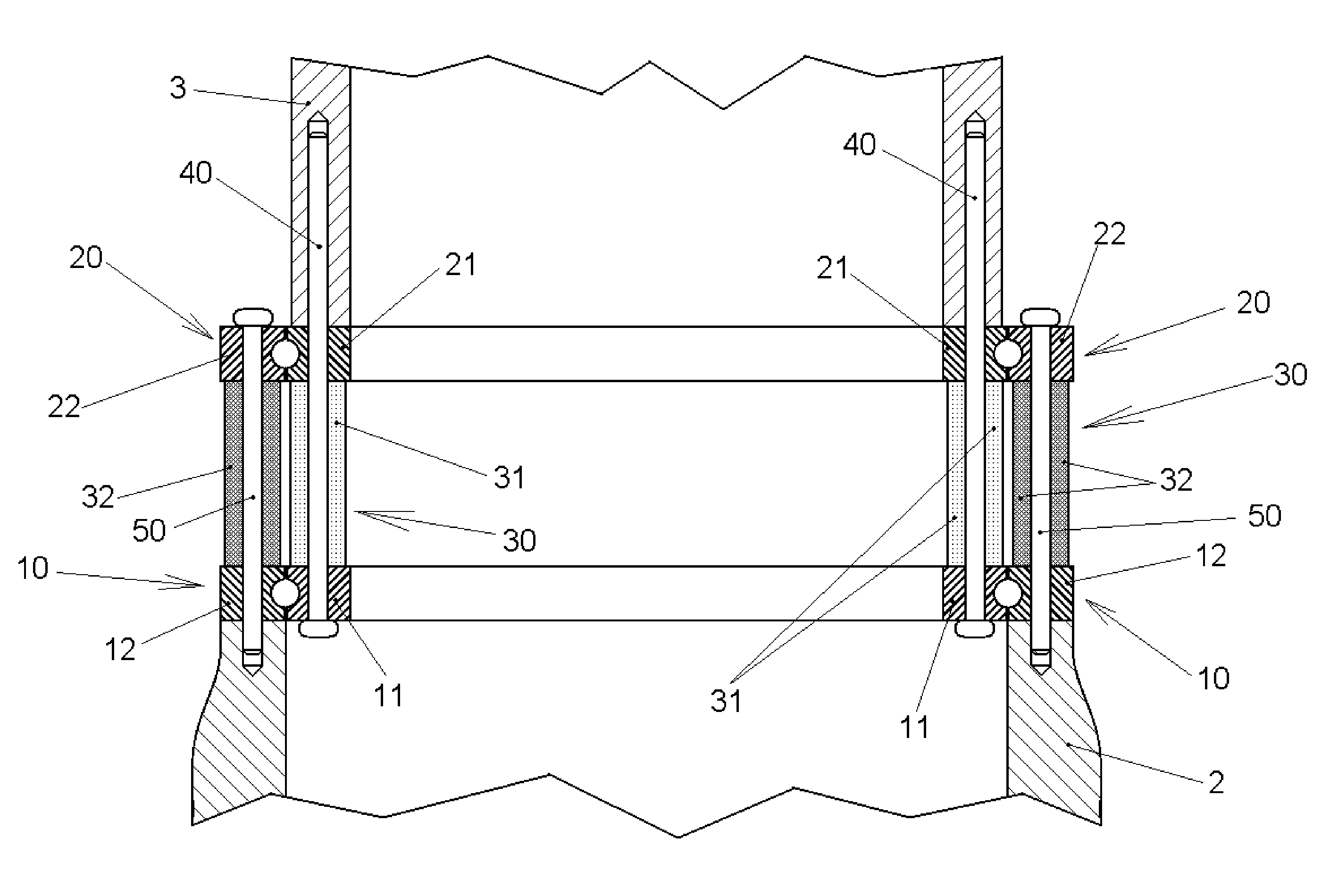
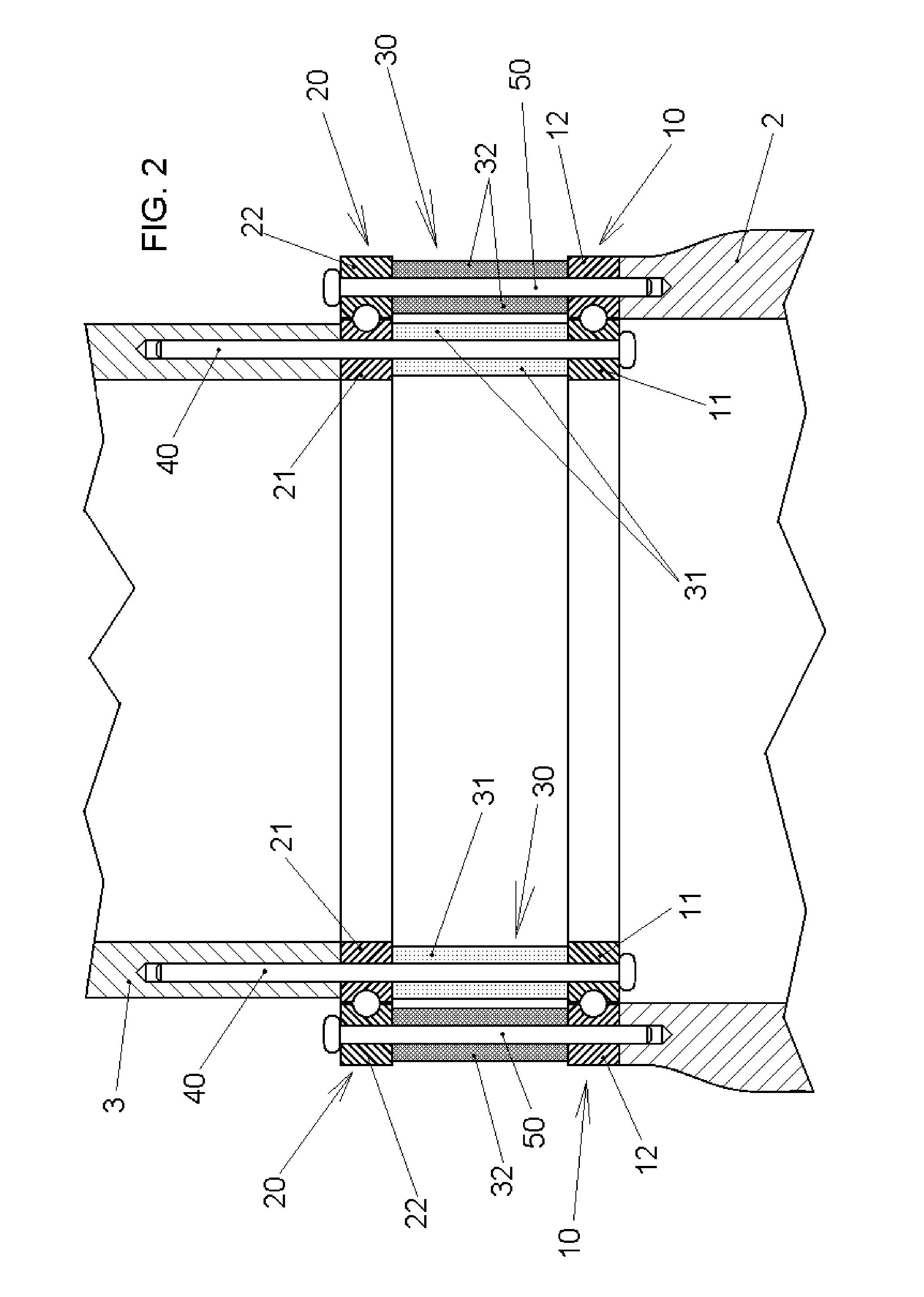
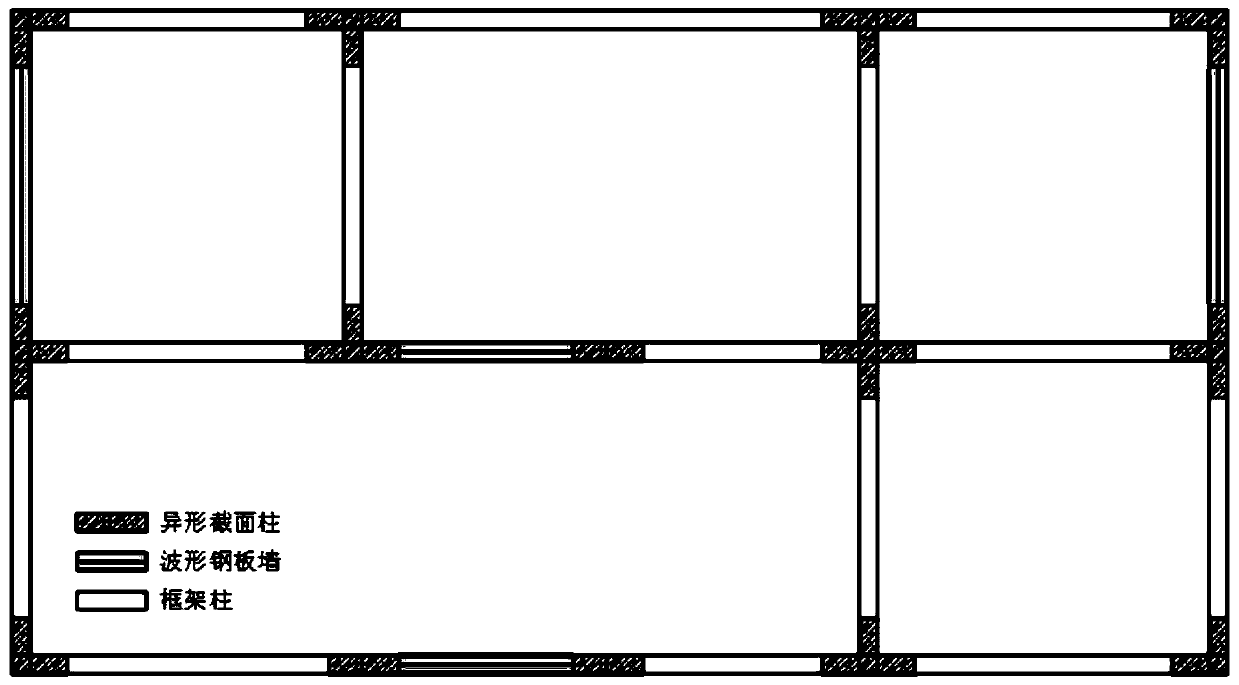
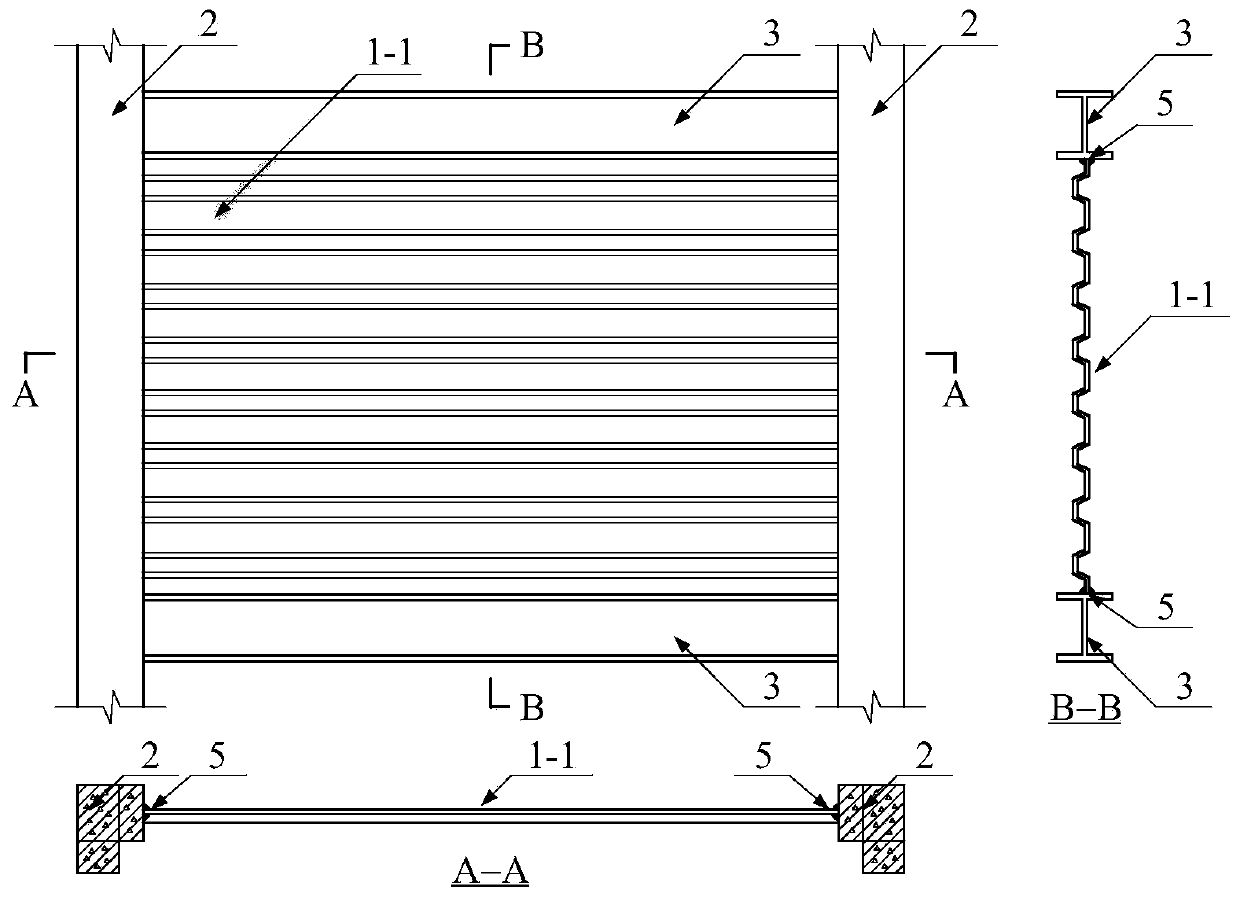
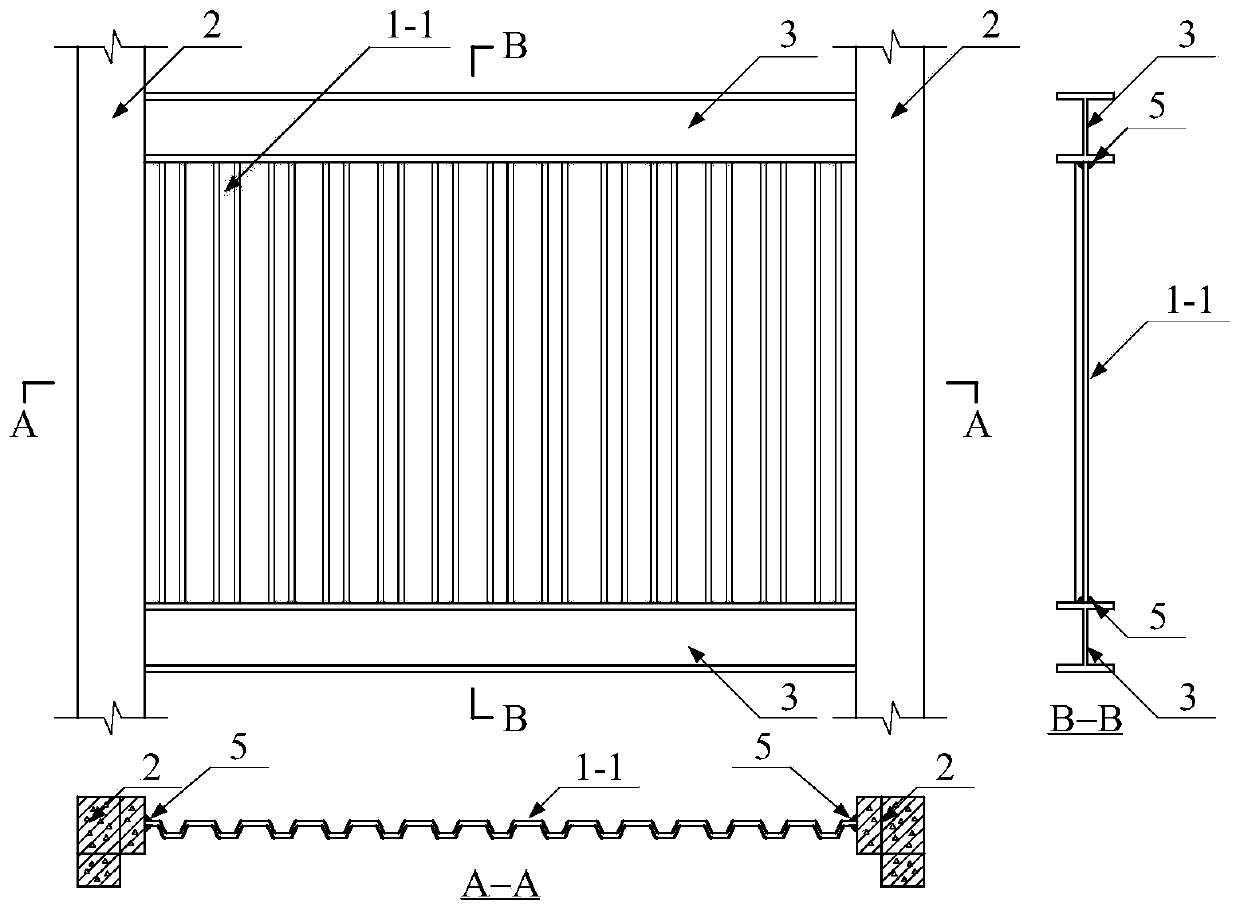
PendingCN111188433AMeet the requirements of flexible layoutOvercome the problem of exposed beams and exposed pillarsConstruction materialWallsSheet steelSteel columns
The invention relates to a structure system composed of a special-shaped cross section column frame and a corrugated sheet steel wall, and belongs to the technical field of structure engineering. Thespecial-shaped cross section column frame-corrugated sheet steel wall structure system is composed of the special-shaped cross section column frame and the corrugated sheet steel wall embedded in theframe. The special-shaped cross section column frame adopts L-shaped, T-shaped and cross-shaped special-shaped cross section steel columns and special-shaped cross section steel pipe concrete columns.The corrugated sheet steel wall adopts a single corrugated sheet steel wall, a stiffening corrugated sheet steel wall, a double corrugated sheet steel wall in a parallel buckle connection mode, and adouble corrugated sheet steel wall in an orthogonal buckle connection mode. The stiffening corrugated sheet steel wall is formed by arranging stiffening ribs such as angle steel or U-steel on a corrugated sheet steel. The structure system provided by the invention has the characteristics of being flexible in plane arrangement, good in building impression, small in steel use amount, good in bearing performance, convenient to transport and install and capable of achieving corrugated sheet steel bolt connection, and has great economic benefits by being applied to residential structures.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Compact inertial sensor
InactiveUS20040226371A1Little stiffnessEasy to assembleAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsMechanical engineeringInertia
The inertial sensor comprises at least one vibrating element having one end connected to a support element and an opposite end connected to a test mass which is hinged to the support element by at least two link elements and which includes a cavity in which the vibrating element and a portion of the support element adjacent to the vibrating element are received. The link elements are housed in the cavity surrounding a portion of the support element to which the link elements are connected.
Owner:SAGEM DEFENSE SECURITE SA
Vehicle Hood and a Method of Fabricating Such a Hood
InactiveUS20090167060A1Creep resistanceReducing damage and orientationVehicle seatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementMechanical propertyBiomedical engineering
The hood comprises an outer skin and an inner lining made of SMC, the lining extending essentially at a distance from the skin. This structure enables the hood to present satisfactory mechanical behavior in terms of protecting the head of a pedestrian striking the hood: because of the SMC, the hood then deforms essentially elastically without breakage, with predetermined uniform behavior.
Owner:INOPLAST +1
Apparatus for determining and/or monitoring a process variable
InactiveUS7886602B2Assure maximum effectivenessWide temperature rangeVibration measurement in solidsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesResonanceEngineering
An apparatus for determining and / or monitoring at least one physical or chemical, process variable of medium having at least one oscillatable unit, which produces, and / or receives, mechanical oscillations. Included is at least one tuning unit, whose stiffness is changeable and which is embodied in such a manner and connected in such a manner with the oscillatable unit, or is a part of the oscillatable unit in such a manner, that at least the resonance frequency of the oscillatable unit is changeable via the tuning unit. A corresponding method is also noted.
Owner:EHNDRESS KHAUZER GMBKH KO KG
Front floor panel
ActiveUS20140367999A1Desired stiffnessLittle stiffnessVehicle seatsMetal-working apparatusEngineeringFlange
A front floor panel for an automotive body as a lightweight sheet can be reliably press-formed without a press forming loads becoming excessively large, can have desired stiffness, and noise and vibration characteristics for all directions since there is little stiffness anisotropy. The front floor panel includes a floor tunnel formed in a center in an automotive width direction to be oriented to a longitudinal direction, upright flanges disposed left and right formed at a left and right end portions in the automotive width direction to be joined to side sills, and a left and right plane portions formed between the upright flanges disposed left and right and a left and right longitudinal wall portions of the floor tunnel. In loop-shaped areas including outer edge portions of the plane portions, convex-concave parts in specific shapes are formed, and remaining areas excluding the loop-shaped areas are formed into flat sheet shapes.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
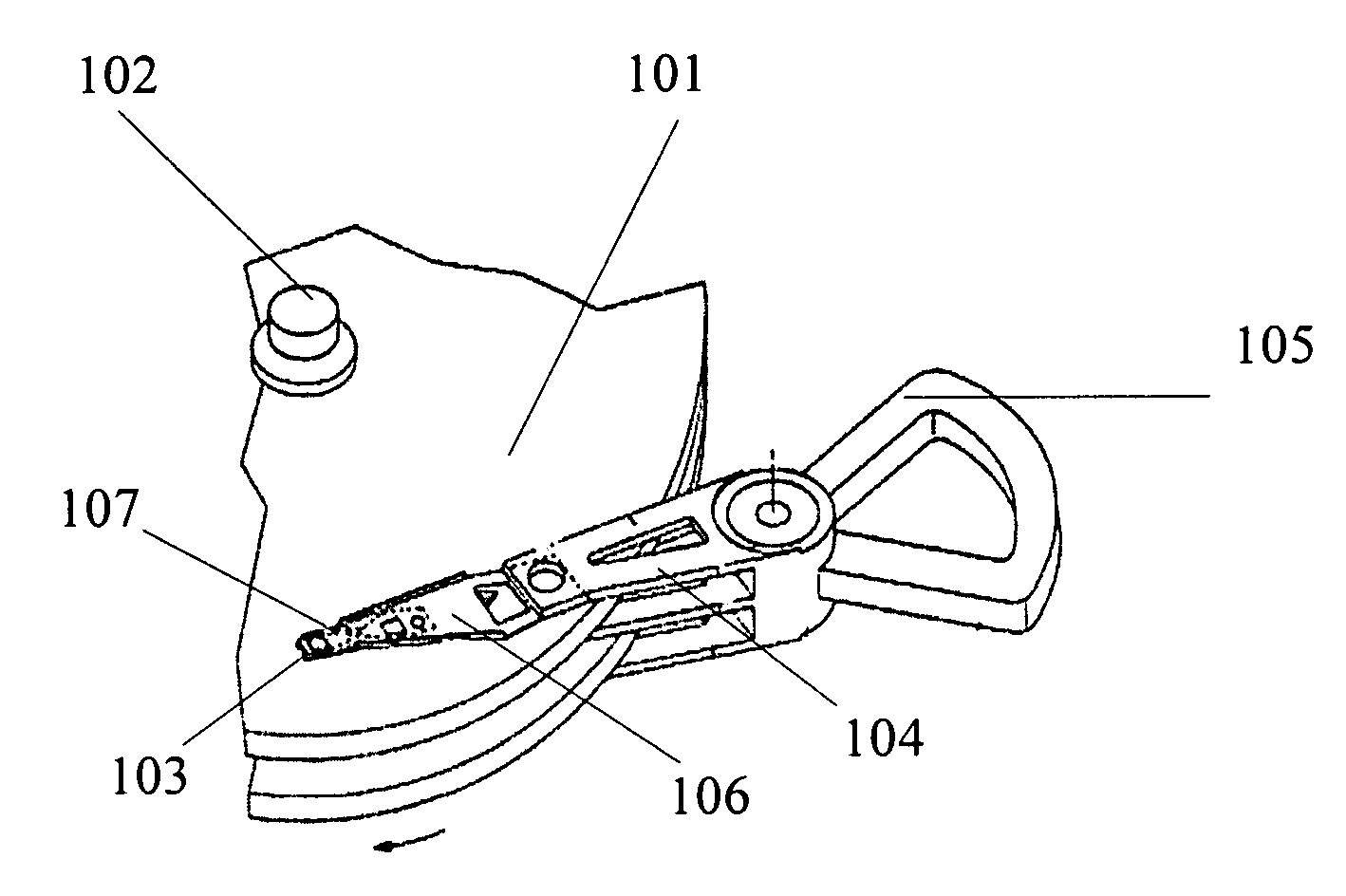
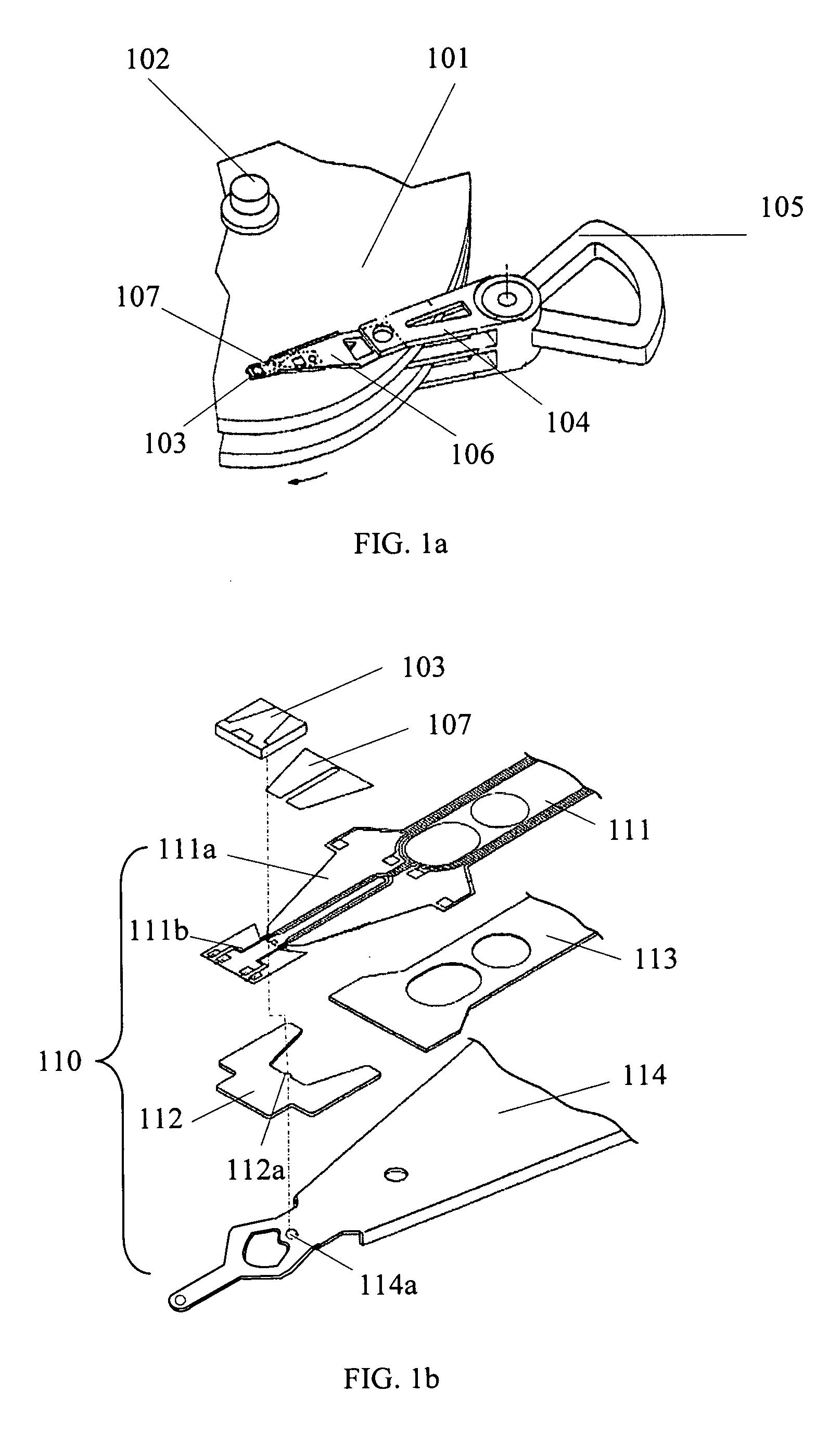
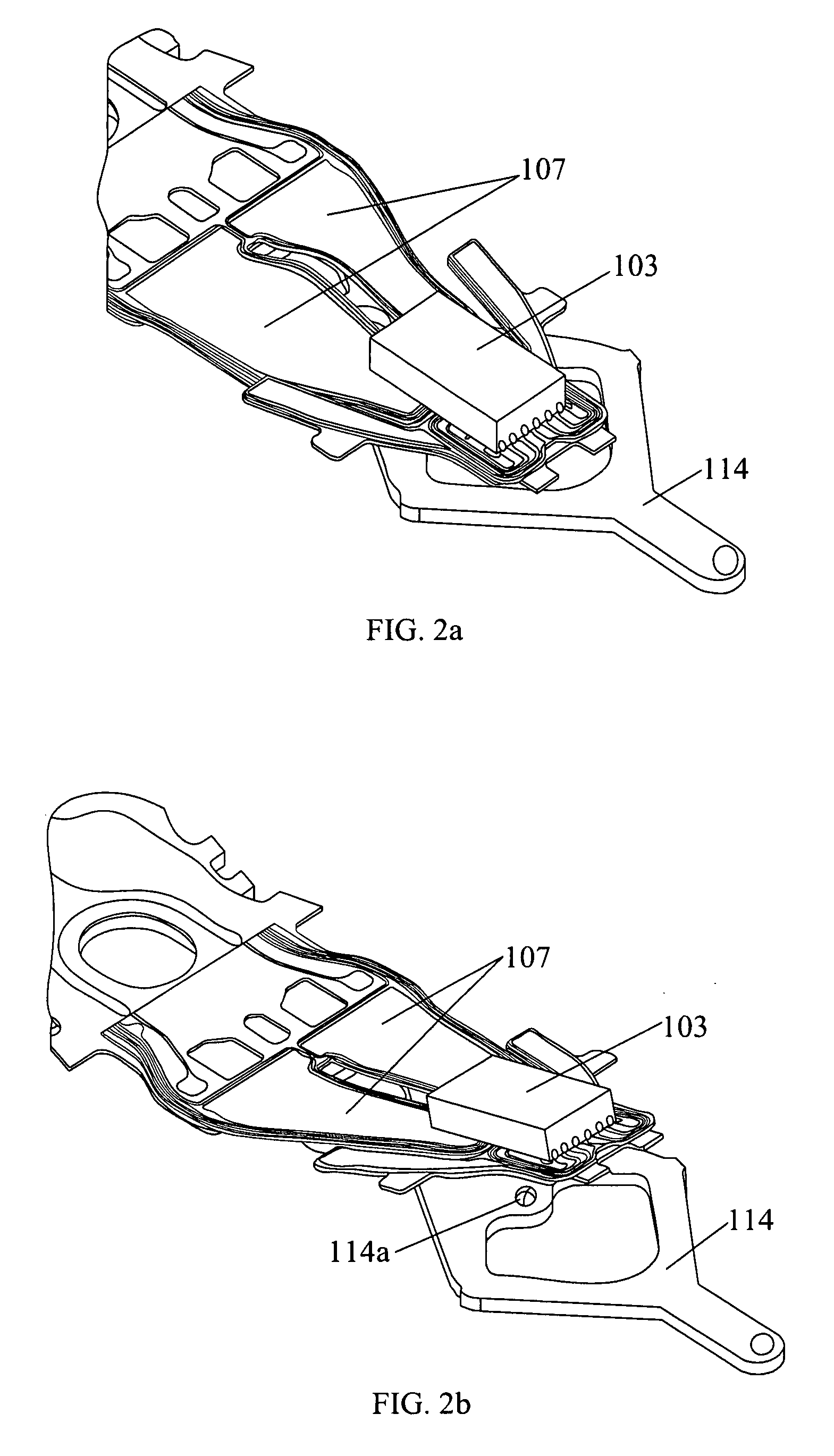
Suspension, head gimbal assembly, and disk drive unit with the same
InactiveUS20090135525A1Improve performanceReduced stabilityElectrical connection between head and armRecord information storageStructural deformationMicro actuator
A suspension includes a flexure, a load beam, and a deformation-resistant plate positioned between the flexure and the load beam. The deformation-resistant plate has a holding plate portion for holding a slider through the flexure and a pair of beam portions. The beam portions each have a bent portion bent in a direction approximately perpendicular to the holding plate portion such that the deformation-resistant plate is configured into a three-dimensional structure. The three-dimensional structure of the deformation-resistant plate advantageously resists structural deformation, thus further enables the suspension to possess stable pitch and roll stiffness as well as small yaw stiffness. This not only assists the suspension to have good static performance and improved shock performance, but also assists the slider to rotate easily and to have desirable displacement when the micro-actuator is excited. The present invention also discloses a HGA with the suspension and a drive unit with such HGA.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Pitch system for a wind turbine rotor
ActiveUS9567973B2Increase stiffnessSimple and cost-effectiveRolling contact bearingsWind motor controlBlade pitchWind force
A pitch system for a wind turbine rotor, comprising a first bearing and a second bearing, each provided with an outer race, an inner race, and at least one row of rolling elements, the first and second bearings being adapted to be arranged between a hub and a blade root portion or extender, to allow rotation of the blade with respect to the hub, wherein the first bearing is adapted to be arranged nearer to the hub than the second bearing in the axial direction, the pitch system further comprising an intermediate body arranged between the first bearing and the second bearing in the axial direction, said intermediate body comprising at least a blade-side part extending between the race of the first bearing that is associated with the blade and the race of the second bearing that is associated with the blade.
Owner:GE RENEWABLE TECH WIND BV
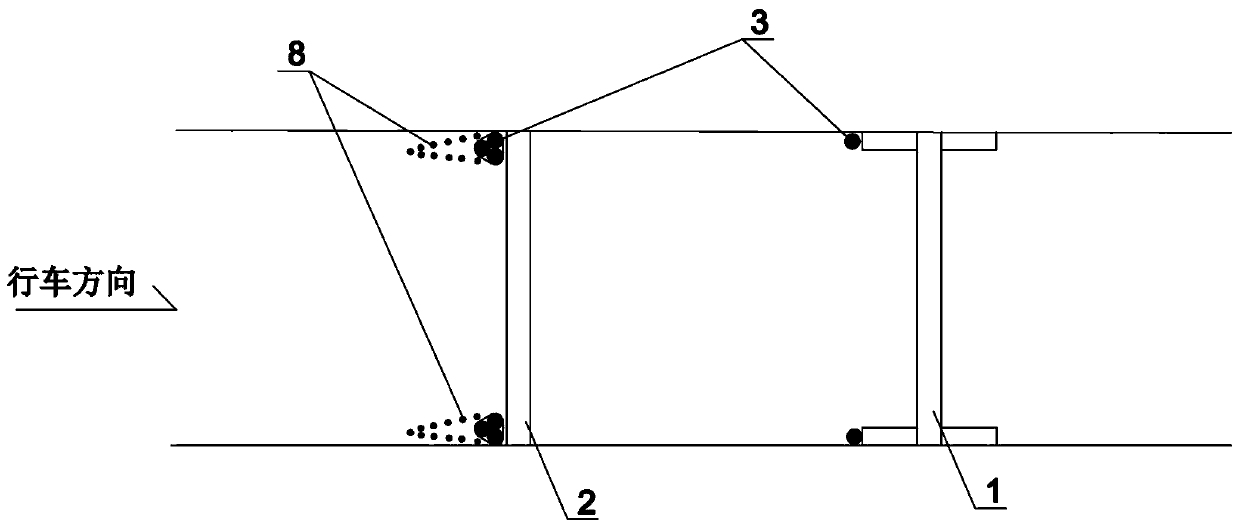
River-spanning bridge entrance ramp height limitation frame
InactiveCN109778733AWarningImprove the induction effectTraffic signalsRoad signsDriver/operatorEngineering management
The invention relates to the technical field of traffic safety, in particular to a river-spanning bridge entrance ramp height limitation frame. The frame comprises a lifting-adjustable height limitation protective frame arranged at the ramp entrance and a lifting-adjustable height limitation warning frame provided with reflective film, the height limitation protective frame and the height limitation warning frame are arranged at a distance, and the height limitation warning frame is arranged in front of the height limitation protective shelf, a height limitation sign and a variable informationboard are arranged on the upper portion of the height limitation warning frame, a height-adjustable height limitation warning frame height limitation bar is arranged on the lower portion of the height limitation warning frame, an anti-collision barrel is arranged in front of a height limitation protective frame vertical rod of the height limitation protective frame, an anti-collision barrel and awarning column are arranged in front of a height limitation warning frame vertical rod of the height limitation warning frame. By means of the height limitation warning frame provided with the reflective film, the height limitation sign and the variable information board, the good warning performance is achieved, drivers can pay more attention to the height limitation information; by means of theanti-collision barrel and the warning column which are arranged in front of the height limitation warning frame vertical rod of the height limitation warning frame, the phenomenon that vehicles directly impact the height limitation warning frame vertical rod can be avoided, and the certain sight guiding effect is achieved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Bush bearing with bearing body having an axial profile
InactiveUS7909313B2Lift radial loadAffecting service lifeResilient suspensionsRubber-like material springsElastomerEngineering
An elastomer bush bearing, wherein the bearing body (2) is encapsulated through axial flanges (4, 4′) of the outer bearing sleeve (3), with the bush bearing having an elastomer bearing body (2) with a special profile in the axial direction. The bearing body (2) is employed in constructing the bush bearing of the invention, which is capable of supporting high radial loads even with low radial stiffness and without adversely affecting its stability and service life. The two axial end faces (5, 5′) of the bearing body (1) each have undulated contours which extend in the circumferential direction (u) in the same direction, both with respect to one another and also over the entire region of the material thickness (d) of the bearing body (2). The end faces (5, 5′) of the bearing body (2) thus have wave troughs (6, 6′, 7, 7′) and wave crests (8, 8′, 9, 9′), whereby the corresponding wave troughs (6, 6′, 7, 7′) of both end faces (5, 5′) and their wave crests (8, 8′, 9, 9′) are formed so as to face one another, and each extend radially over the entire material thickness (d) of the bearing body (2) in the respective circumferential segment.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Printing head
ActiveUS8240814B2Little stiffnessAmount of deformationPrintingElectrical and Electronics engineeringEngineering
Owner:CANON KK
Device comprising at least a body and a bumper, and robot cleaner comprising such a device
InactiveUS8458854B2Little stiffnessOvercome the small stiffnessSuction cleanersVehicle position/course/altitude controlStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
A device (1) comprises at least a body (2) and a bumper (6) which is movably attached to the body so as to protect the body from shock caused by collision with an obstacle during movement of the device across a surface. The bumper is attached to the body by means of at least one spring (9) extending in a direction which is at least substantially perpendicular to the direction into which the bumper is movable with respect to the body. Furthermore, a robot cleaner comprising such a device is provided.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Ski with a connecting device for a ski binding
InactiveUS20130249193A1Improve performanceSmall hindranceSki bindingsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A ski with a connecting device for connecting a ski binding to the ski. The connecting device includes a plate-type support body which has a fixing zone in its longitudinal middle portion for providing a rigid connection to the ski. At least the front end portion of the support body forms a flexural element extending freely with respect to the fixing zone and to the ski. The freely extending flexural element is made from plastic and is coupled with the ski via a coupling device. This coupling device comprises a connecting arm, which has a first articulated connection to the flexural element in its first end portion and a second articulated connection to the ski in its second end portion.
Owner:ATOMIC AUSTRIA
Novel low-frequency inertial vibration feeding machine
InactiveCN105752614AImprove the quality of workGood vibration isolationJigging conveyorsBaghouseVibration exciter
The invention discloses a novel low-frequency inertial vibration feeding machine which comprises a rack, a driving pulley, a triangle belt, a driven pulley, a low-frequency inertial vibration exciter, an elastic connecting system, a feeding groove body, rubber damping springs and a base. Dust removal equipment is adopted for removing dust, and the clean and hygienic use environment is ensured; meanwhile, a bag-type dust remover is used and is beneficial for reutilization of accumulated dust; wheels are arranged, and therefore the feeding machine can be moved at will according to the use requirement; meanwhile, the two front wheels are universal wheels, and therefore the direction can be changed at any time; the feeding groove body arranged in the mode of inclining downwards from front to back is adopted, and fed materials are finer and purer. The technology is mainly applied to crushing and sieving combined equipment in the industry such as metallurgy, coal mine, ore dressing, building materials, chemical engineering and abrasive materials; by means of a low-frequency vibration isolating system, rigidity of the vibration isolating springs changes little, and the novel low-frequency inertial oscillation feeding machine has good vibration isolating performance and is good in conveying performance.
Owner:XIAN YIMU SOFTWARE TECH
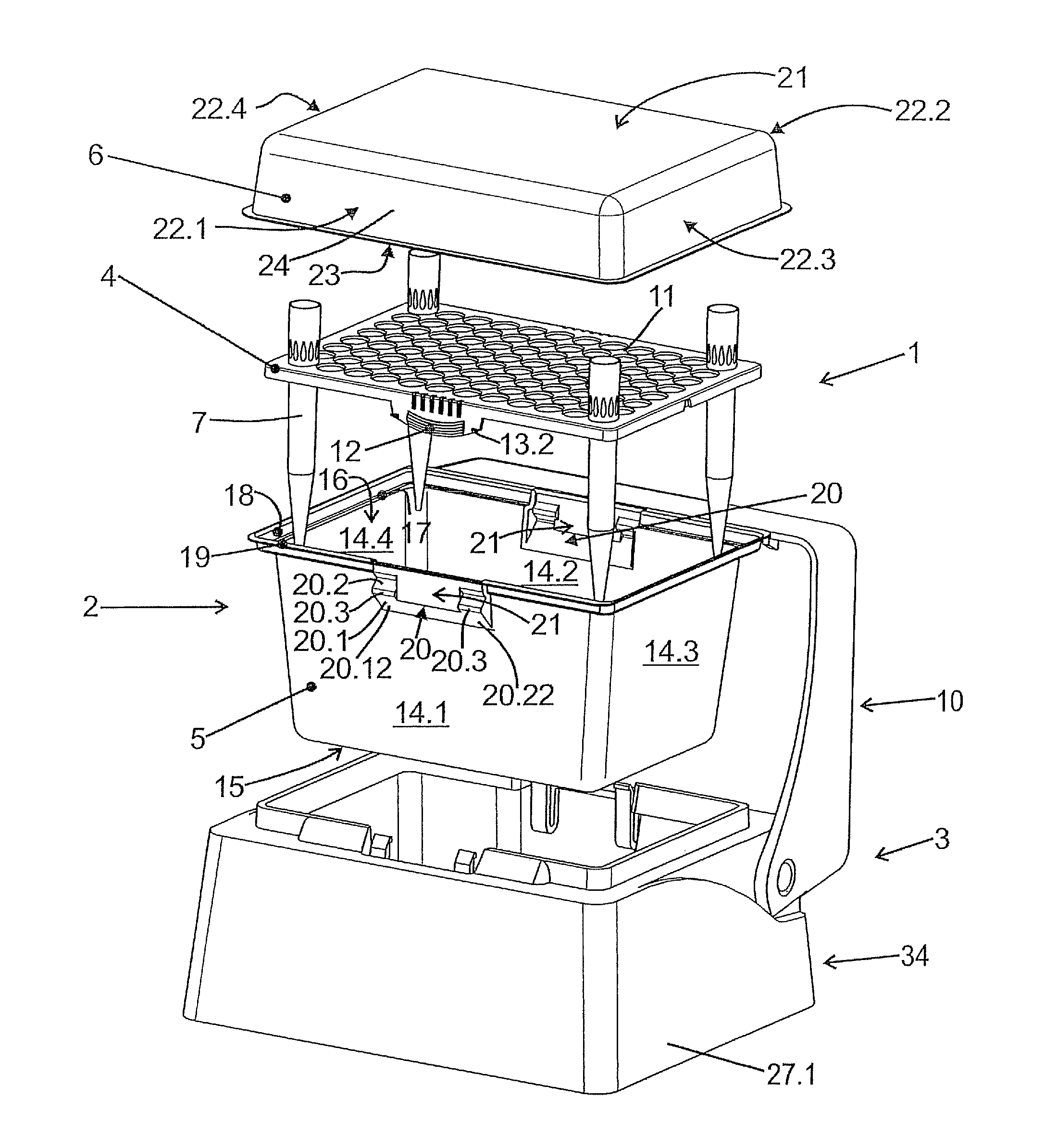
Device for providing pipette tips
Device for providing pipette tips including a refill pack which includes a perforated plate with a plurality of holes, pipette tips inserted into the holes, a container covering the pipette tips at the bottom with a stiffness of up to 300 N / mm and a removable cover, covering the pipette tips from the top and a holder with a receiver for inserting the refill pack, a laterally protruding upper bearing edge being present between the refill pack and holder for supporting the refill pack when said refill pack is inserted into the receiver.
Owner:EPPENDORF SE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com