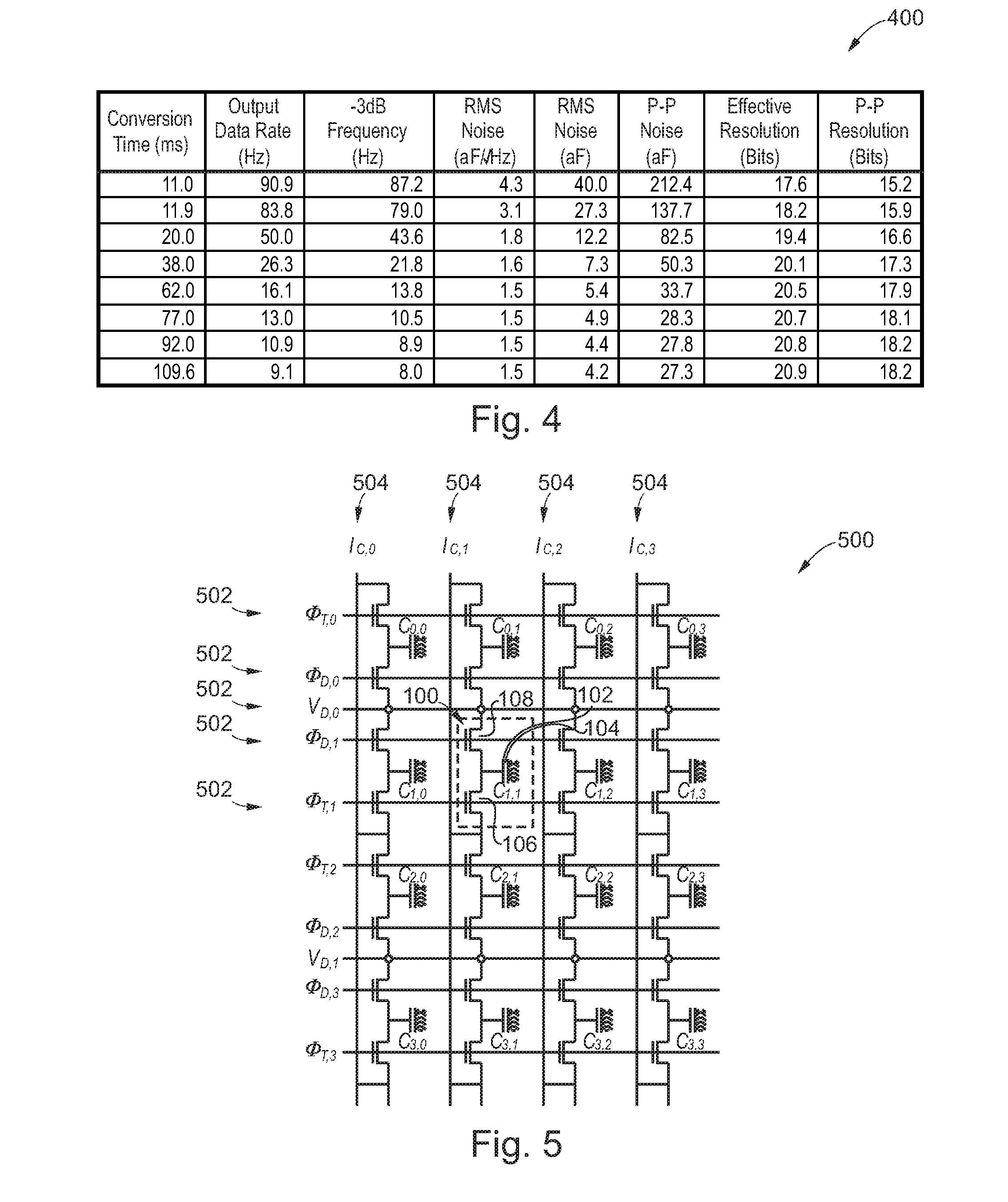
Patents
Literature
62results about How to "Manufactured small" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
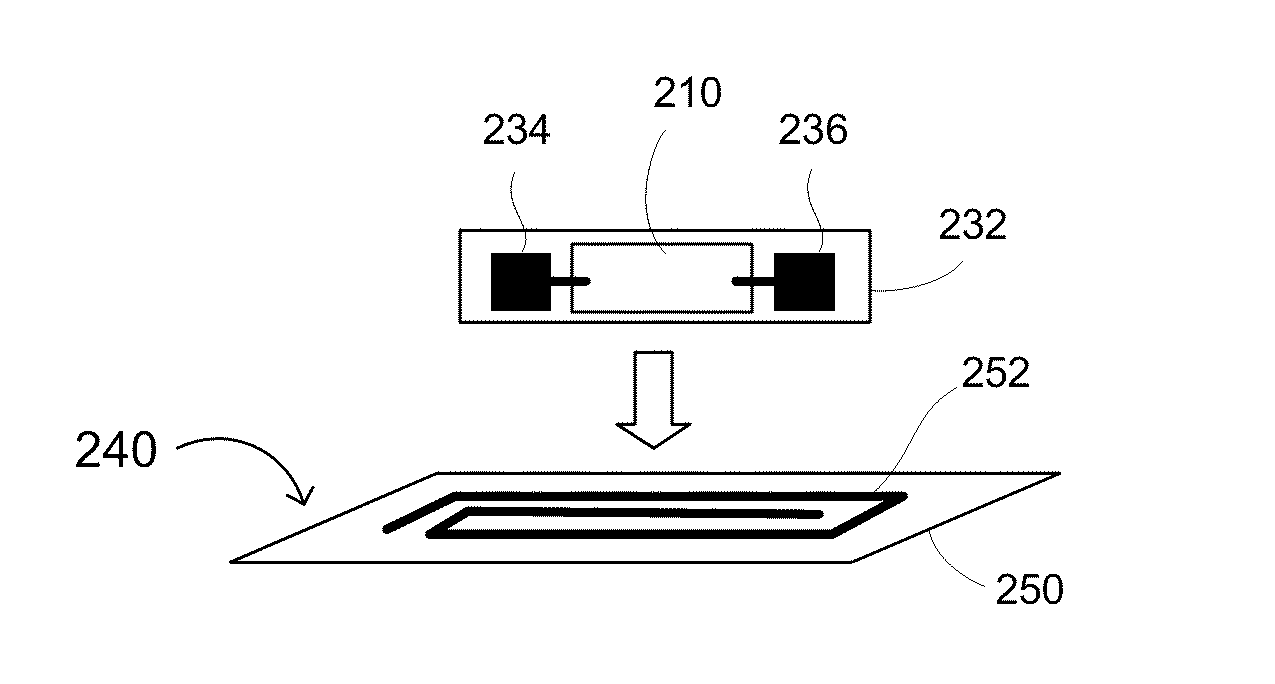
Wireless Devices Including Printed Integrated Circuitry and Methods for Manufacturing and Using the Same
InactiveUS20090095818A1Leverage low capital expenditure and operating costLow costPrinted circuit manufactureSubscribers indirect connectionElectricityElectrical devices
Printed integrated circuitry and attached antenna and / or inductor for sensors, electronic article surveillance (EAS), radio frequency (RF) and / or RF identification (RFID) tags and devices, and methods for its manufacture. The tag generally includes printed integrated circuitry on one carrier and an antenna and / or inductor on another carrier, the integrated circuitry being electrically coupled to the antenna and / or inductor. The method of manufacture generally includes of printing an integrated circuit having a plurality of first pads on a carrier, forming an antenna and / or inductor having a plurality of second pads on a substrate, and attaching at least two of the first pads of the printed integrated circuit to corresponding second pads of the antenna and / or inductor. The present invention advantageously provides a low cost RFID tag capable of operating at MHz frequencies that can be manufactured in a shorter time period than conventional RFID tags that manufacture all active electrical devices on a conventional wafer.
Owner:ENSURGE MICROPOWER ASA
Sealed rectangular battery
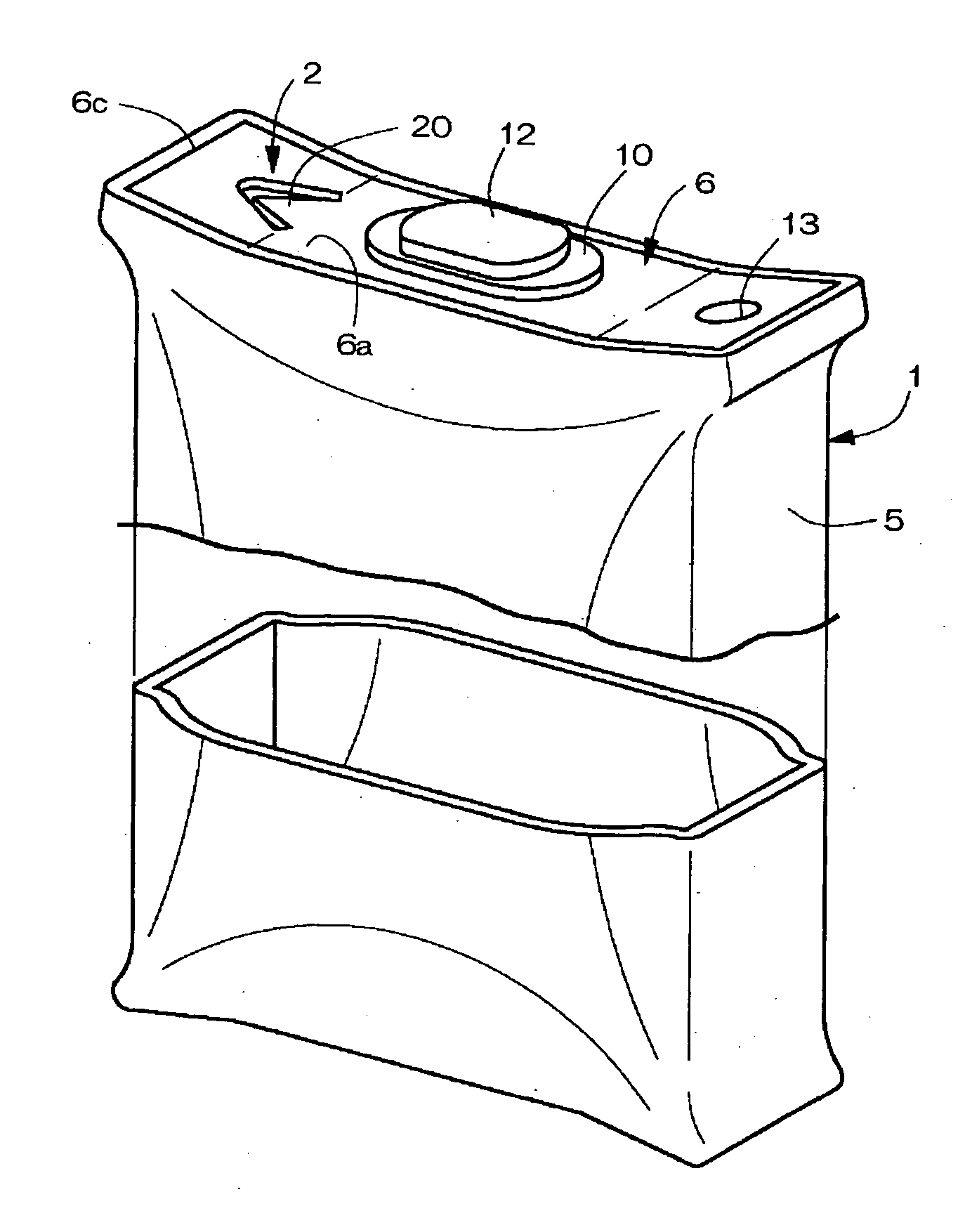
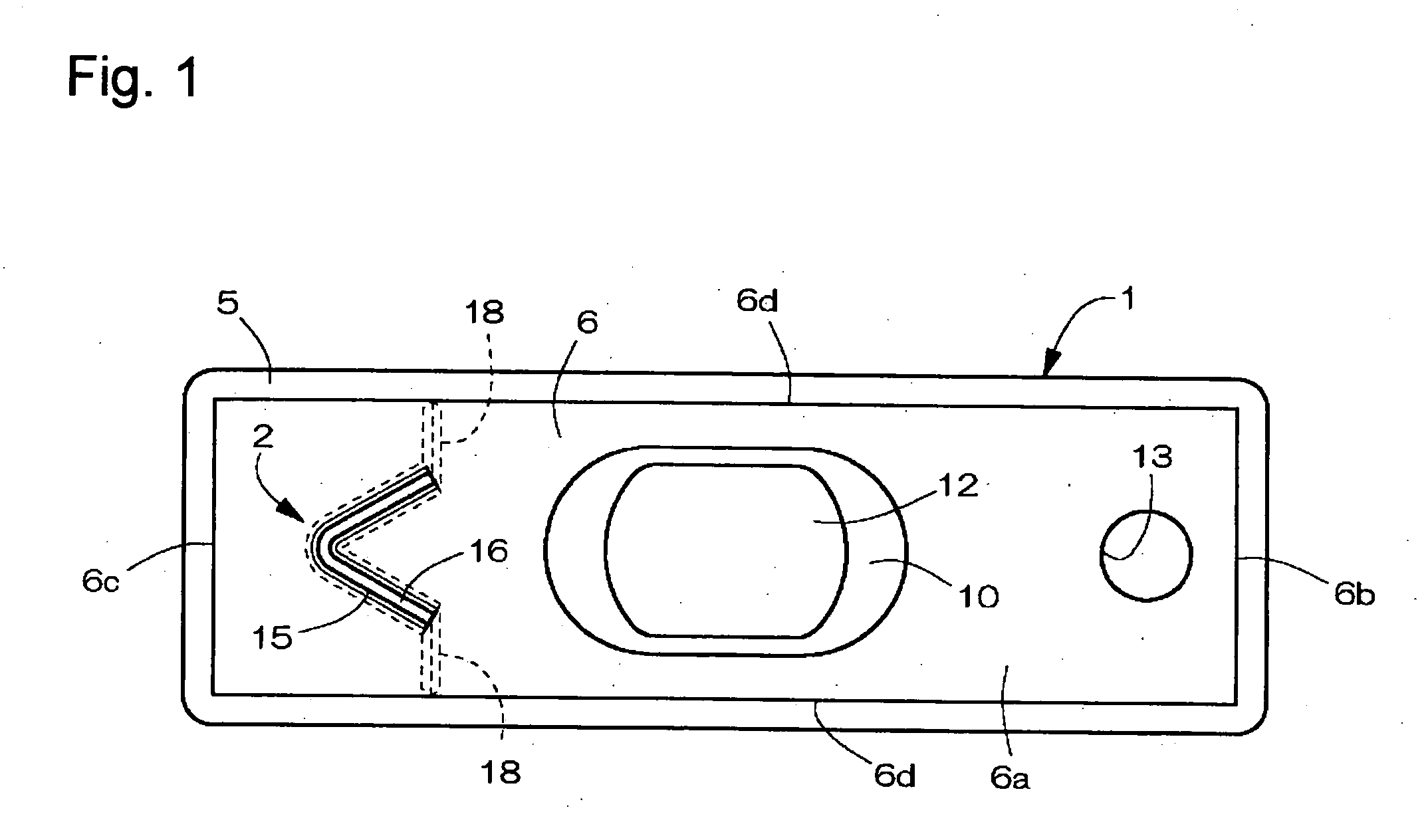
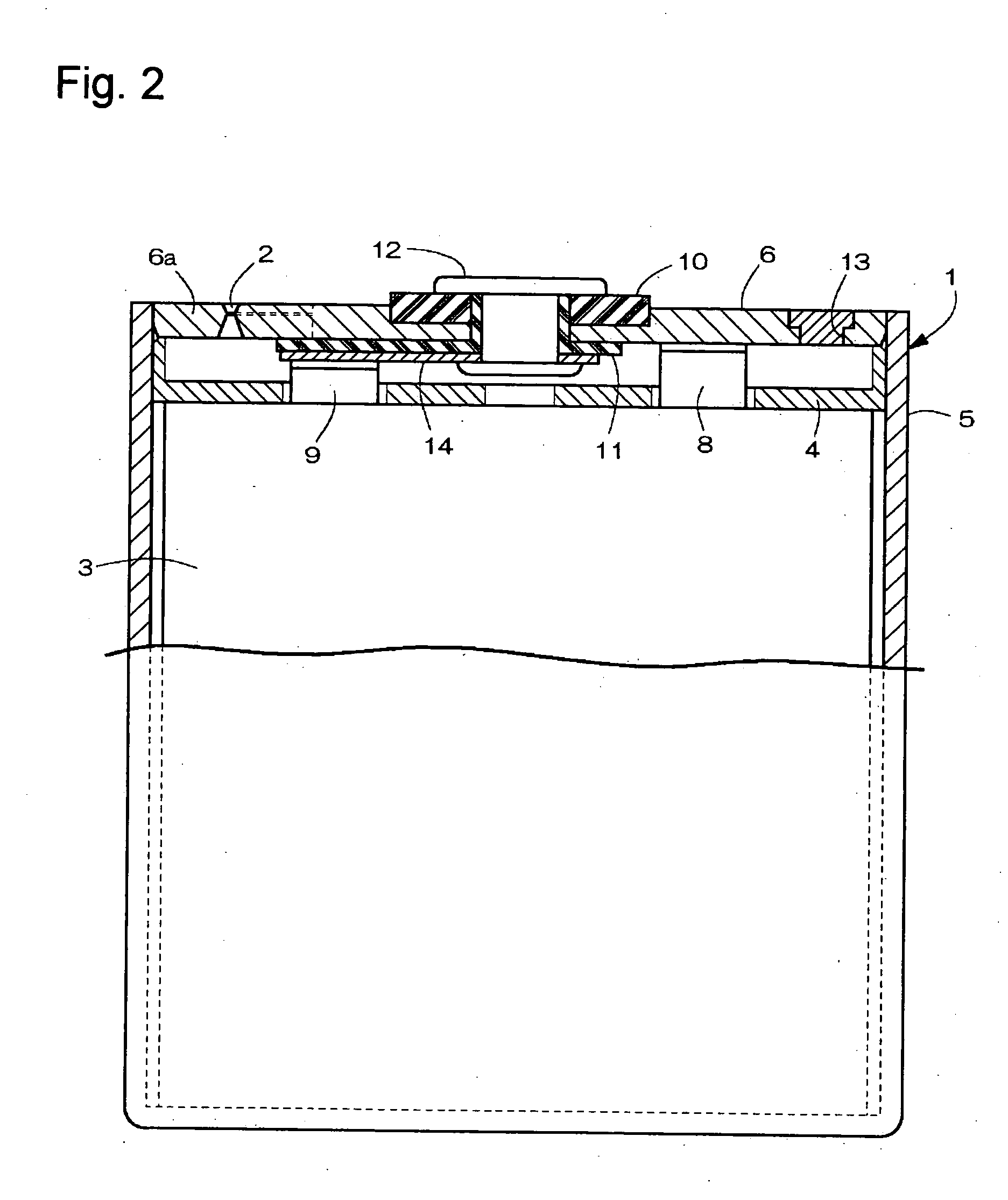
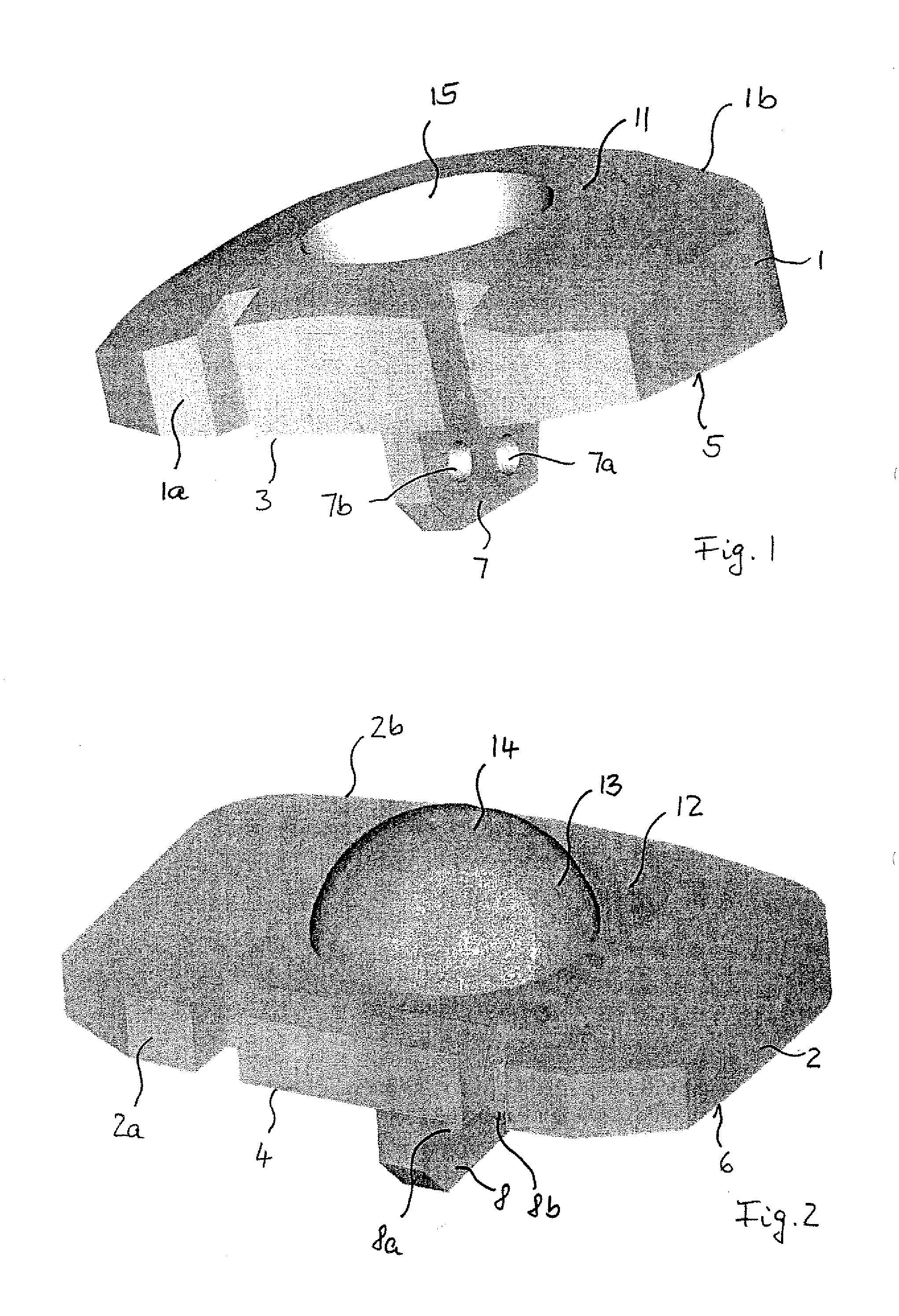
InactiveUS20050069760A1Improve reliabilityManufactured smallVent arrangementsSecondary cellsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A sealed rectangular battery having a reliably operative explosion-proof valve is provided. A rectangular battery case 1 which is long in the horizontal direction includes a square tube shaped case body 5 with a bottom in which the upper surface opens, and a lid 6 closing the opened upper surface of the case body 5 in a sealing manner. An explosion-proof valve 2 is arranged near a reference short side 6c of a installation surface wall 6a of the lid 6. The explosion-proof valve 2 includes a V-shaped groove 15 concavely formed in V-shaped or U-shaped in which a central bent part 15a is positioned at a central location in the front-back direction of the installation surface wall 6a and expanding in the front-back direction, and a thin wall 16 formed by the V-shaped groove 15. A cut groove 18 connecting the front-back end of the V-shaped groove 15 and the long side 6d in the front-back direction of the installation surface wall 6a is cut and formed in the installation surface wall 6a.
Owner:HITACHI MAXELL ENERGY LTD
Musical instrument tuner
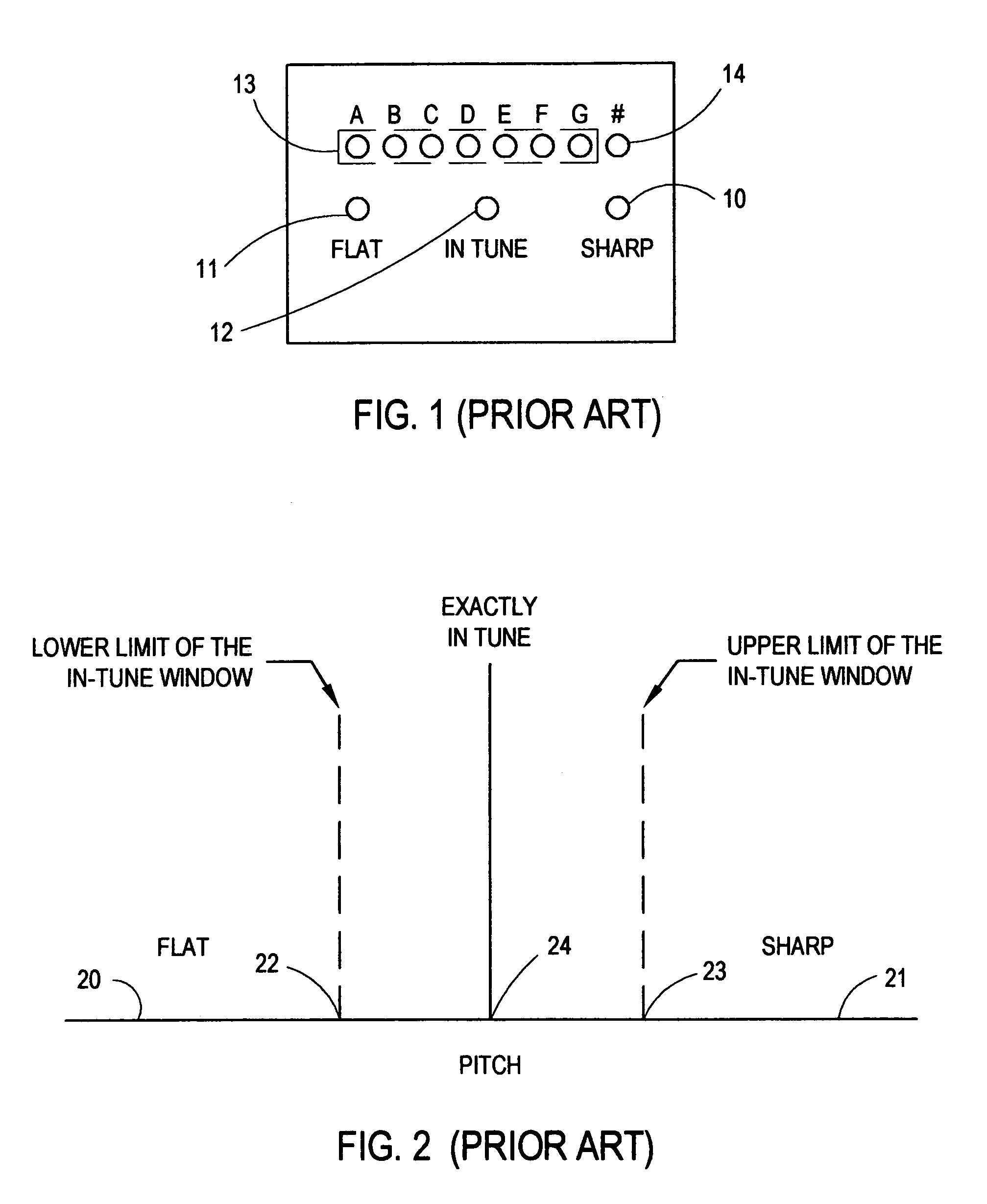
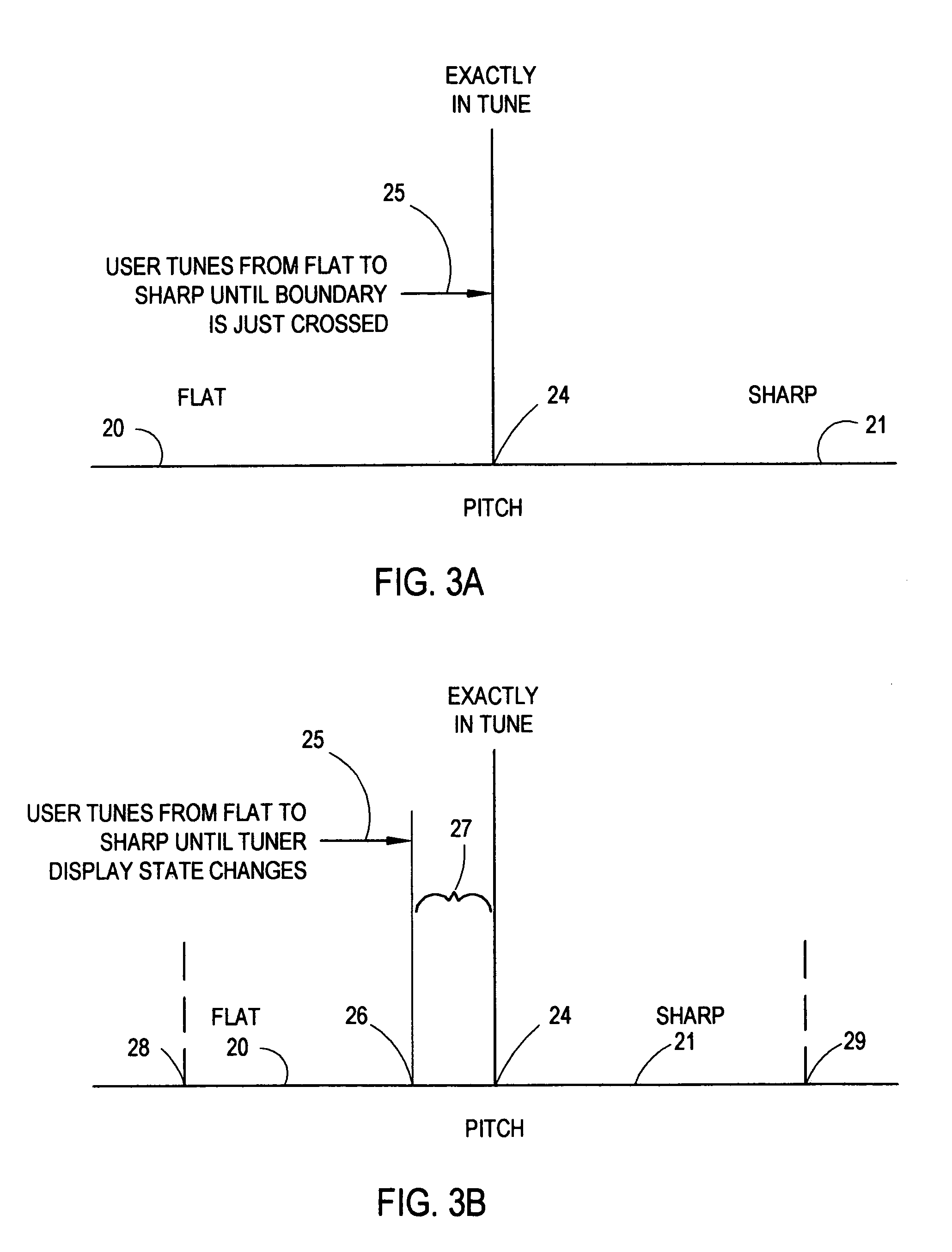
InactiveUS7285710B1Minimize impactDisplay of the tuner is very minimalMusic aidsEngineeringMusical instrument tuner
A musical instrument tuner includes a means for measuring the frequency of a note played on an instrument, a minimal display means, a means for powering and depowering the tuner, and a means for collecting the signal to be measured. The tuner displays sharp and flat indications to the user, eliminating the ambiguous finite width “in-tune” window.
Owner:WALLACE HENRY BURNETT
Label having transparent and opaque areas
InactiveUS20060057313A1Manufactured smallImplemented cost-effectivelyStampsEnvelopes/bags making machineryPunchingEngineering
A strip-shaped label has a transparent plastic film layer partially covered by an opaque film layer. A window area not covered by the opaque film layer remains. The film layers are bonded to one another using an adhesive layer. Before attachment, the label is positioned on a carrier. A bow-shaped suspension tab is produced through punching, on whose bottom non-adhesive areas are provided, which allow a suspension tab to be pulled out of the label plane easily for suspension of the container. Two printed voucher sections are implemented in the opaque label film. The transparent film layer has an adhesive-repellent coating, which is also transparent, below the voucher sections. In the stuck-on state, the label area in which the voucher sections are positioned overlap the transparent window area. After removal of one of the voucher sections, the window area is visible and the container contents may be viewed.
Owner:SCHREINER GRP GMBH & CO KG
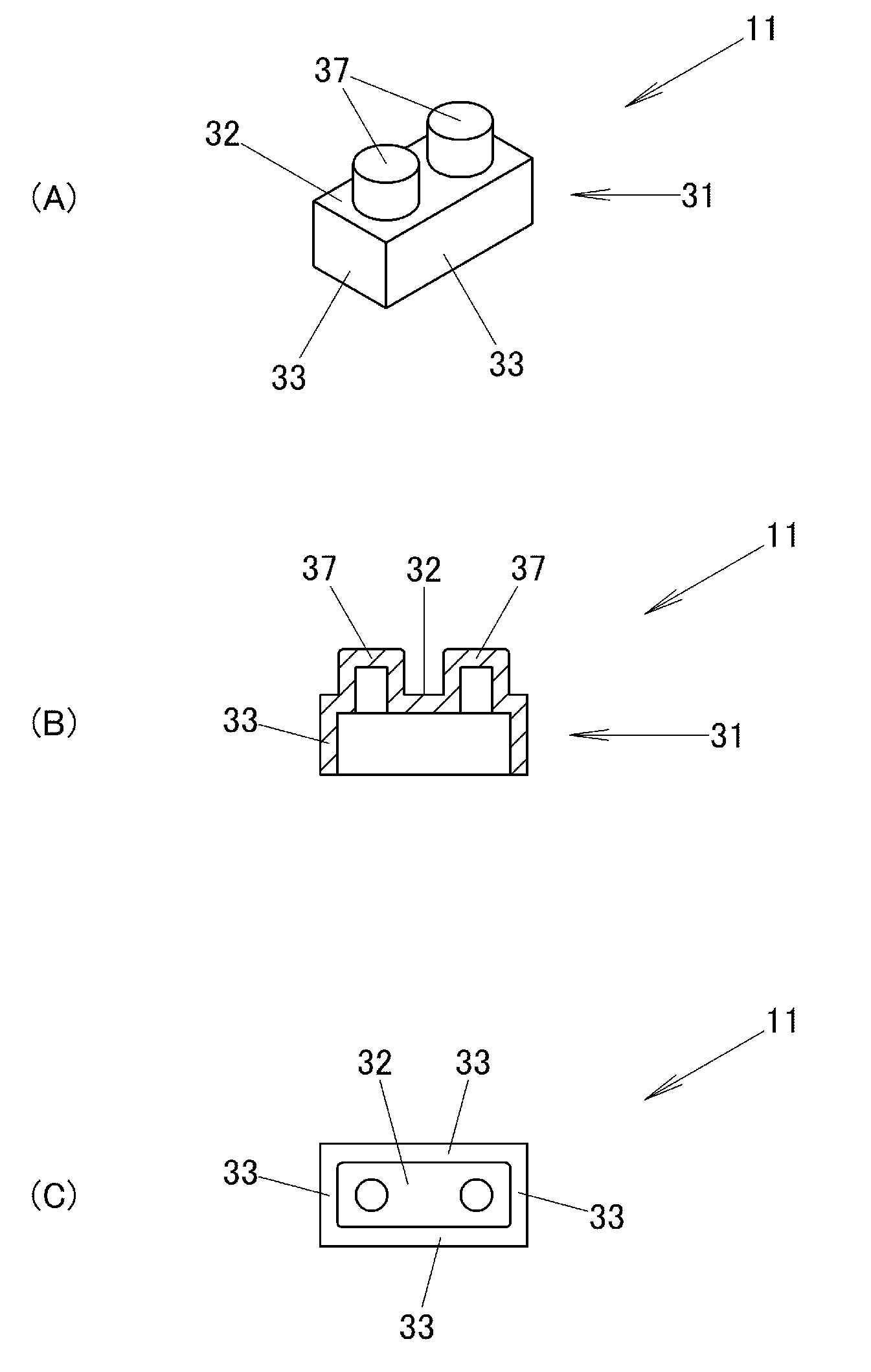
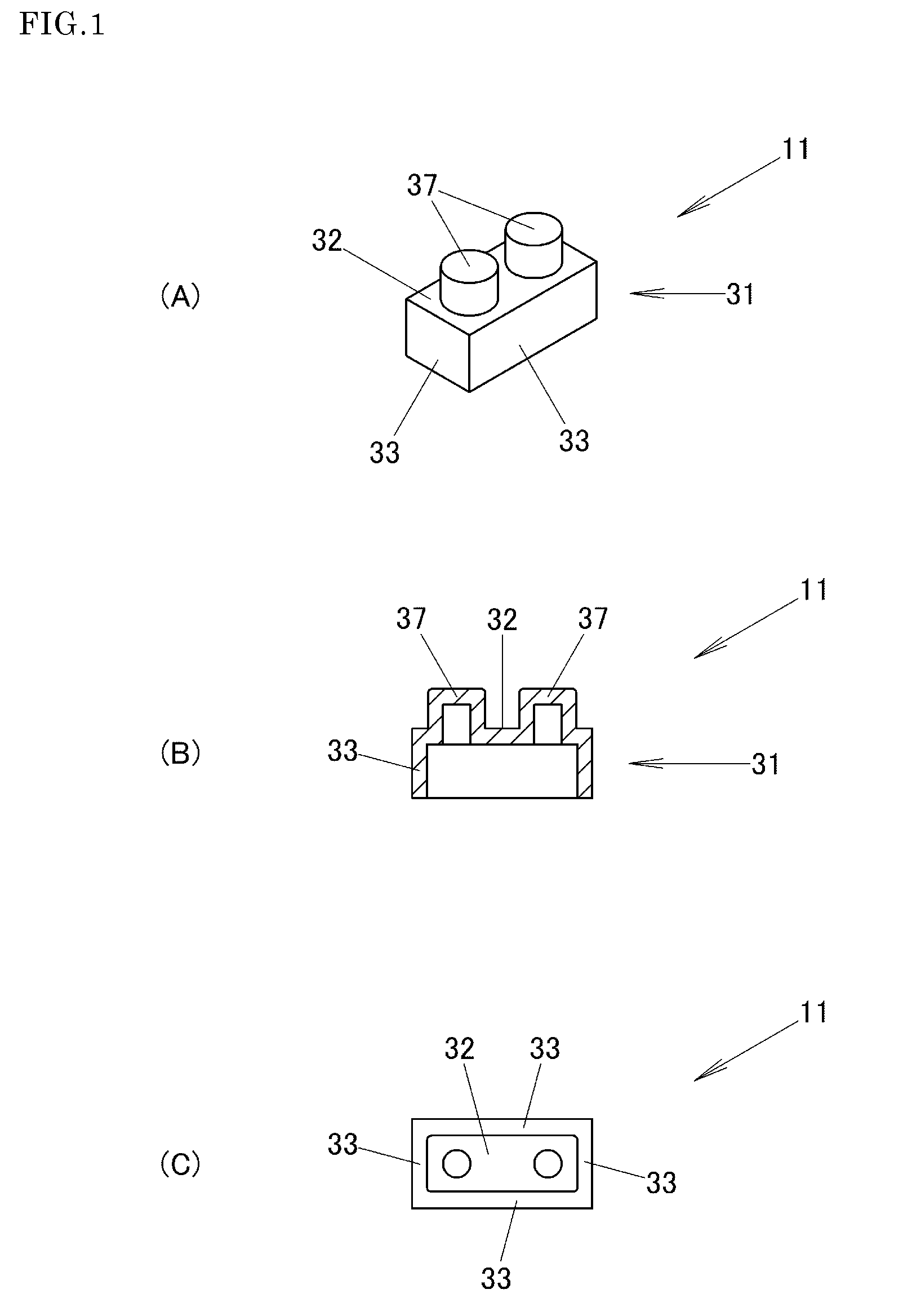
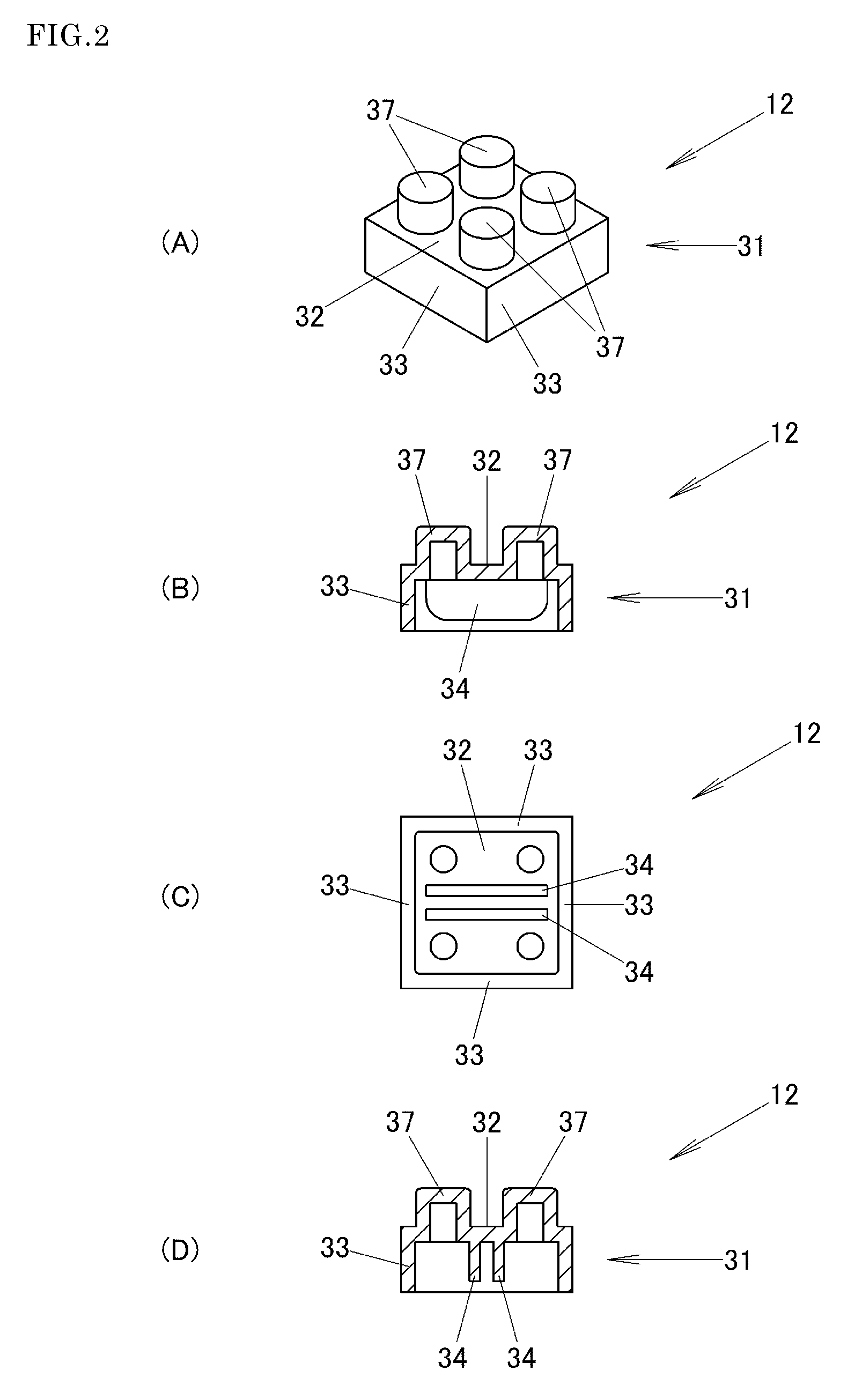
Block Toy
By a combination of a plurality of blocks 11 in which a plurality of projecting portions 37 which are formed into the same cylindrical shape are provided on an upper surface of a rectangular parallelepiped base portion 31 at intervals of several millimeters, the base portion 31 has a rectangular parallelepiped interior space which is made to open downwards so as to enable the accommodation of projecting portions 37 of other blocks, and the cylindrical projecting portions 37 of the other blocks are made to be held by side wall panels 33 of the base portion 31, a drawback that the change in shape of a shaped structure becomes less conspicuous is eliminated irrespective of a reduction in the number of types of blocks with respect to their shapes.
Owner:KAWADA KK
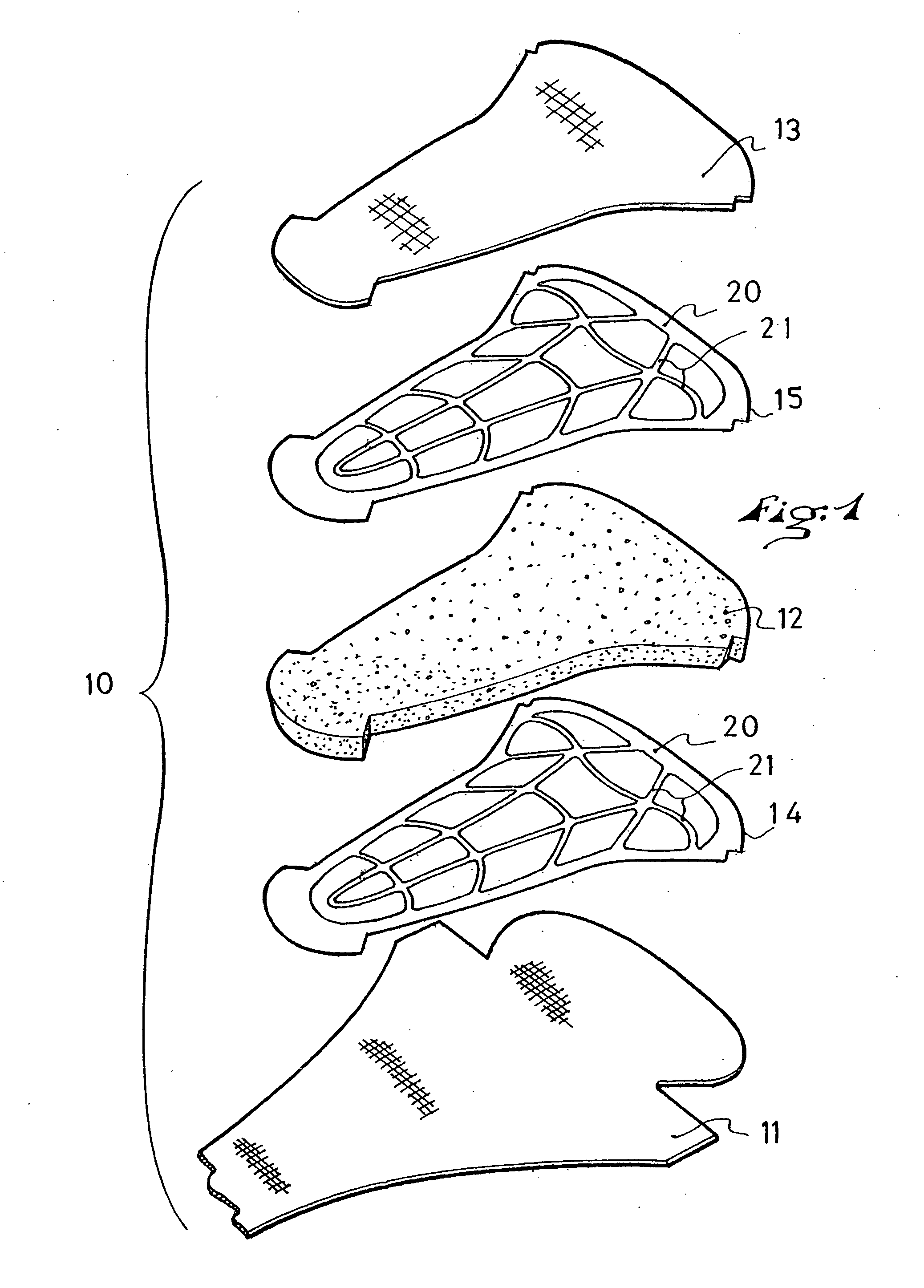
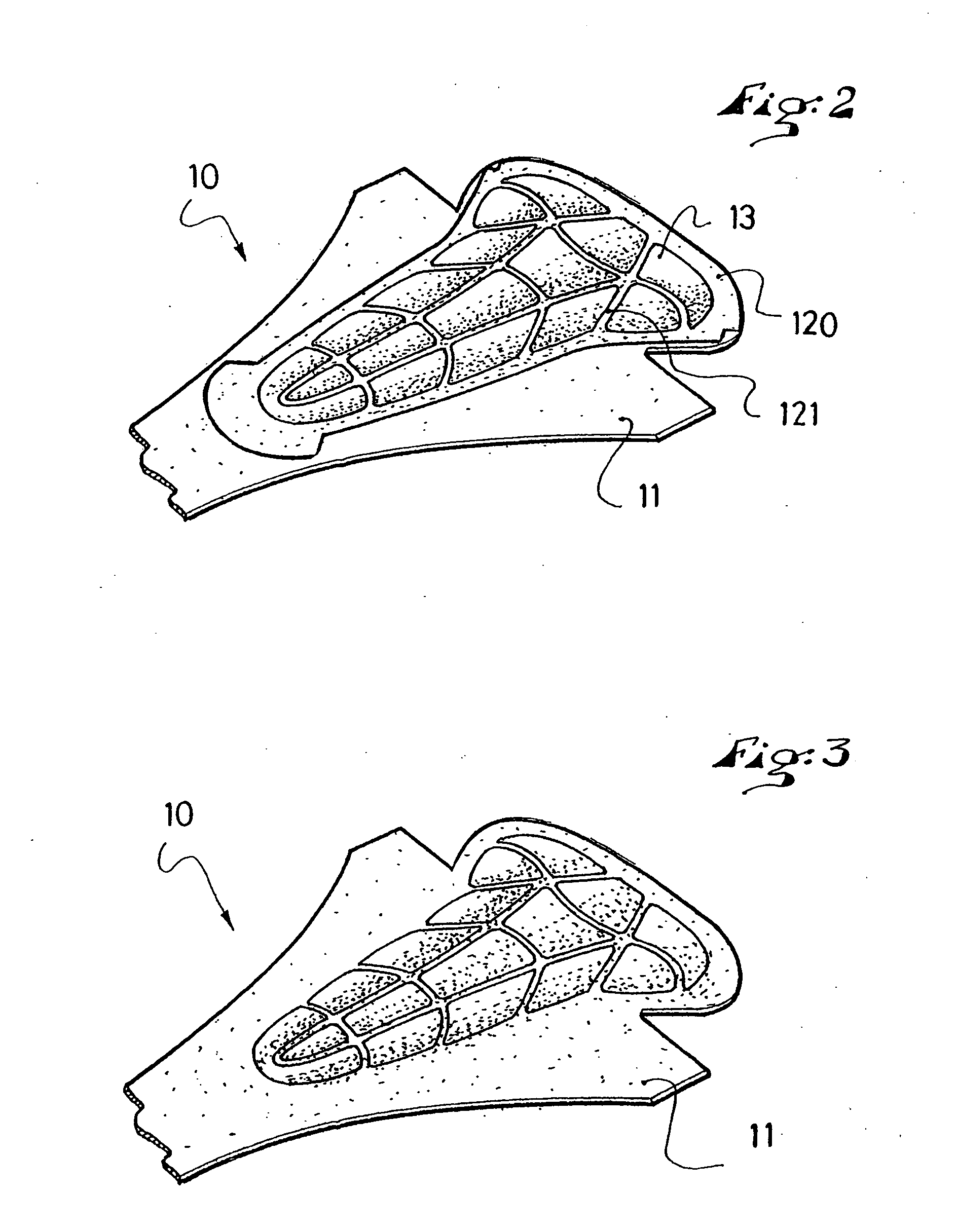
Comfort element for clothing or an article of footwear, a method of manufacturing, and an article having such an element
A comfort element for an article of footwear or an article of clothing, a method of manufacturing same, and an article of footwear or clothing that includes such element. The comfort element is manufactured by superimposing a first layer of material having a melting temperature θ1, a layer of foam material having a melting temperature θ2, a second layer of material having a melting temperature θ3, the temperature θ2 being lower than θ1 and θ3, and assembling by welding the three layers to one another along predetermined welding lines, whereby the layer of foam material is brought to a temperature θ4 comprised between θ2 and θ1, θ3 along the welding lines. At least one film of heat-meltable glue, precut along the predetermined welding lines and having a melting temperature θ5 on the order of θ2, is inserted between one of the material layers and the foam material layer.
Owner:SALOMON SA
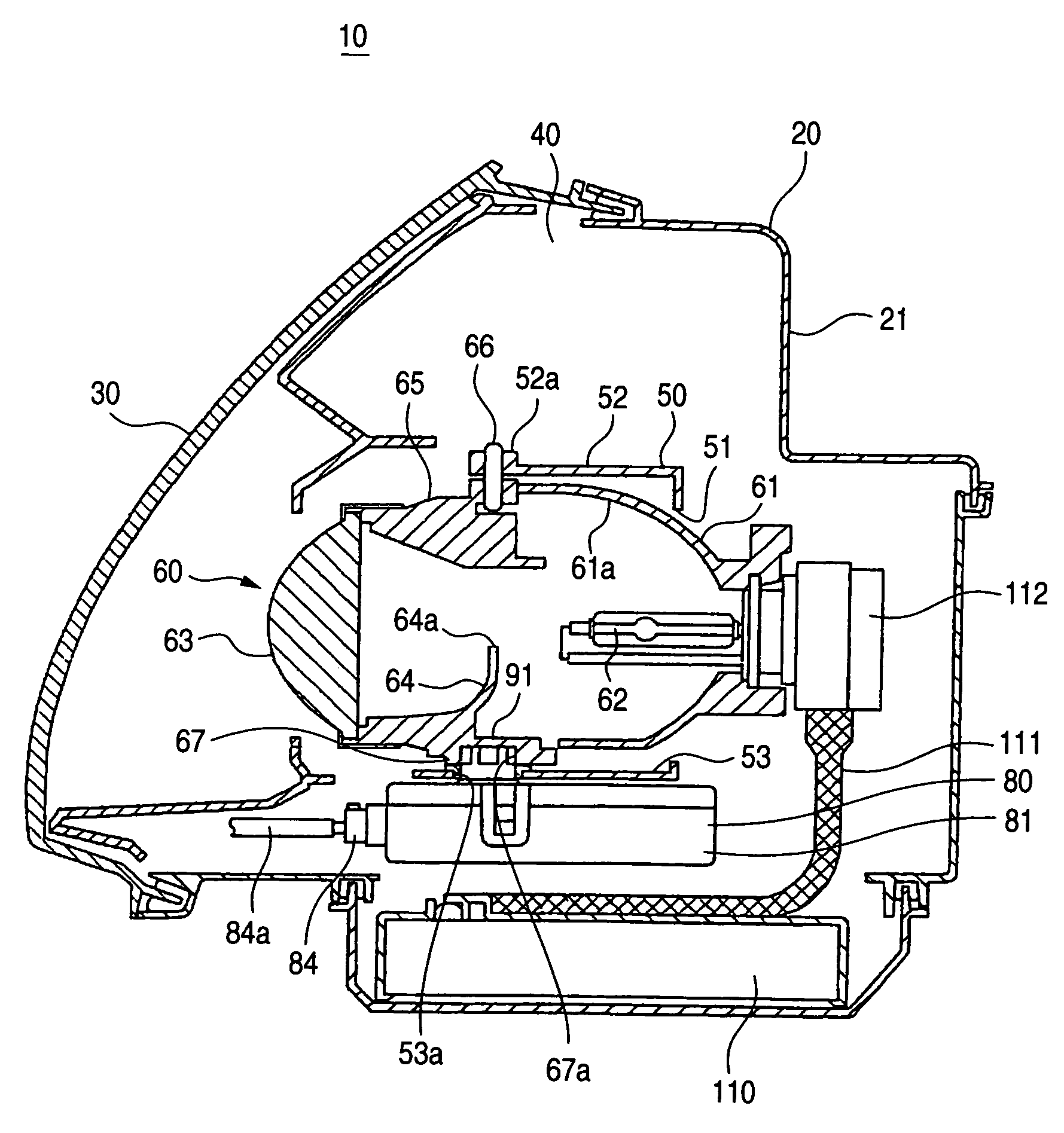
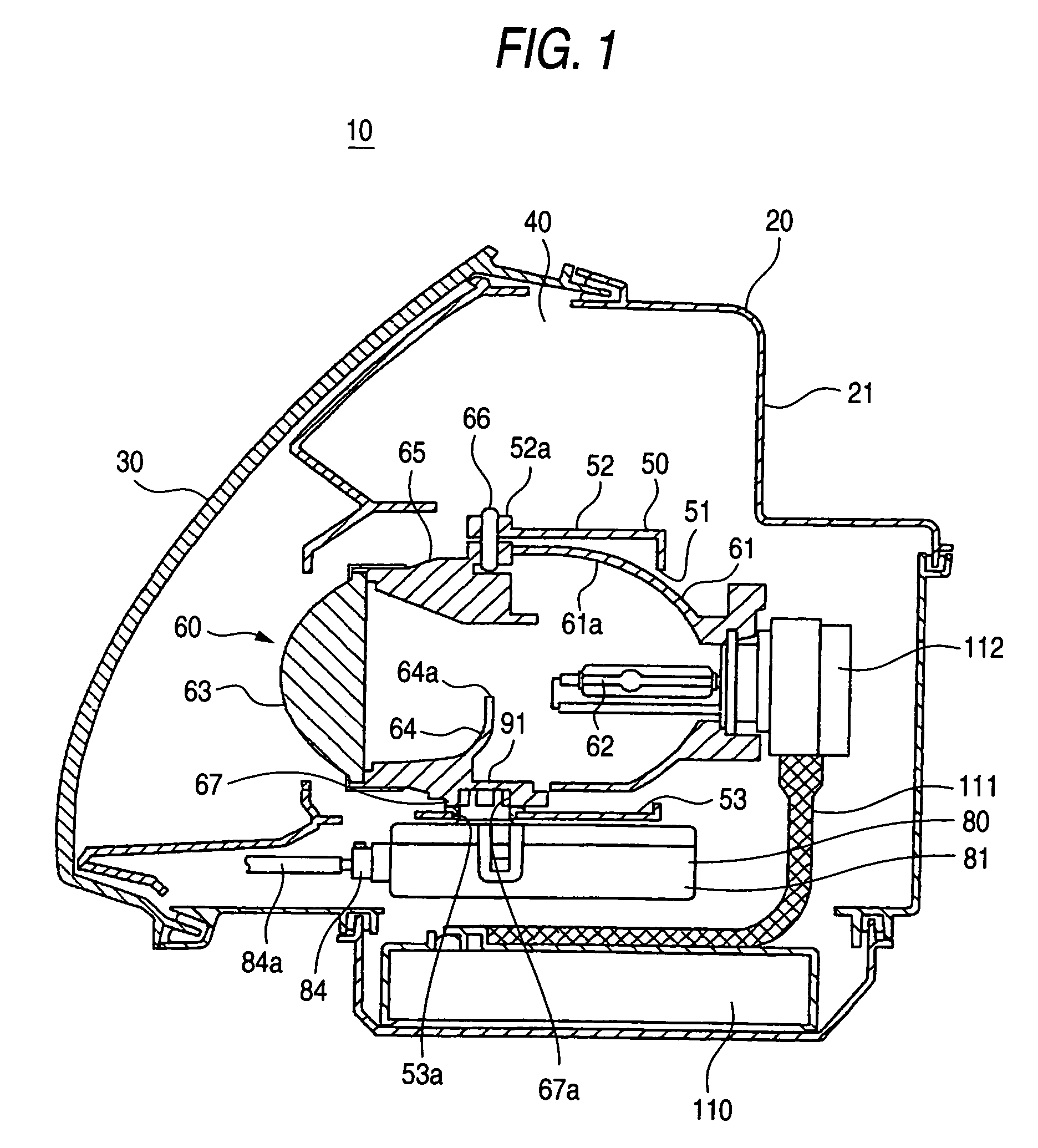
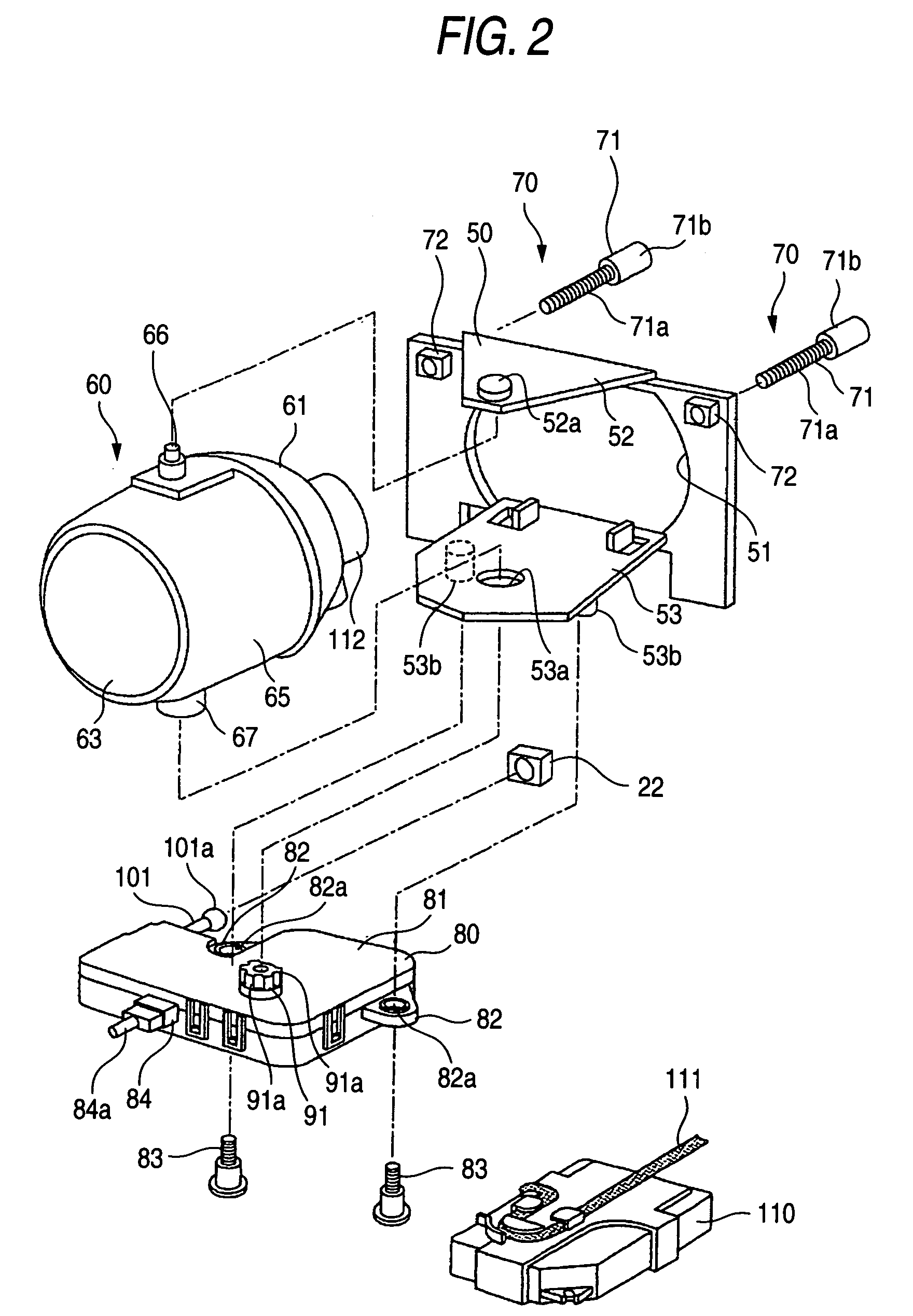
Vehicle lighting apparatus
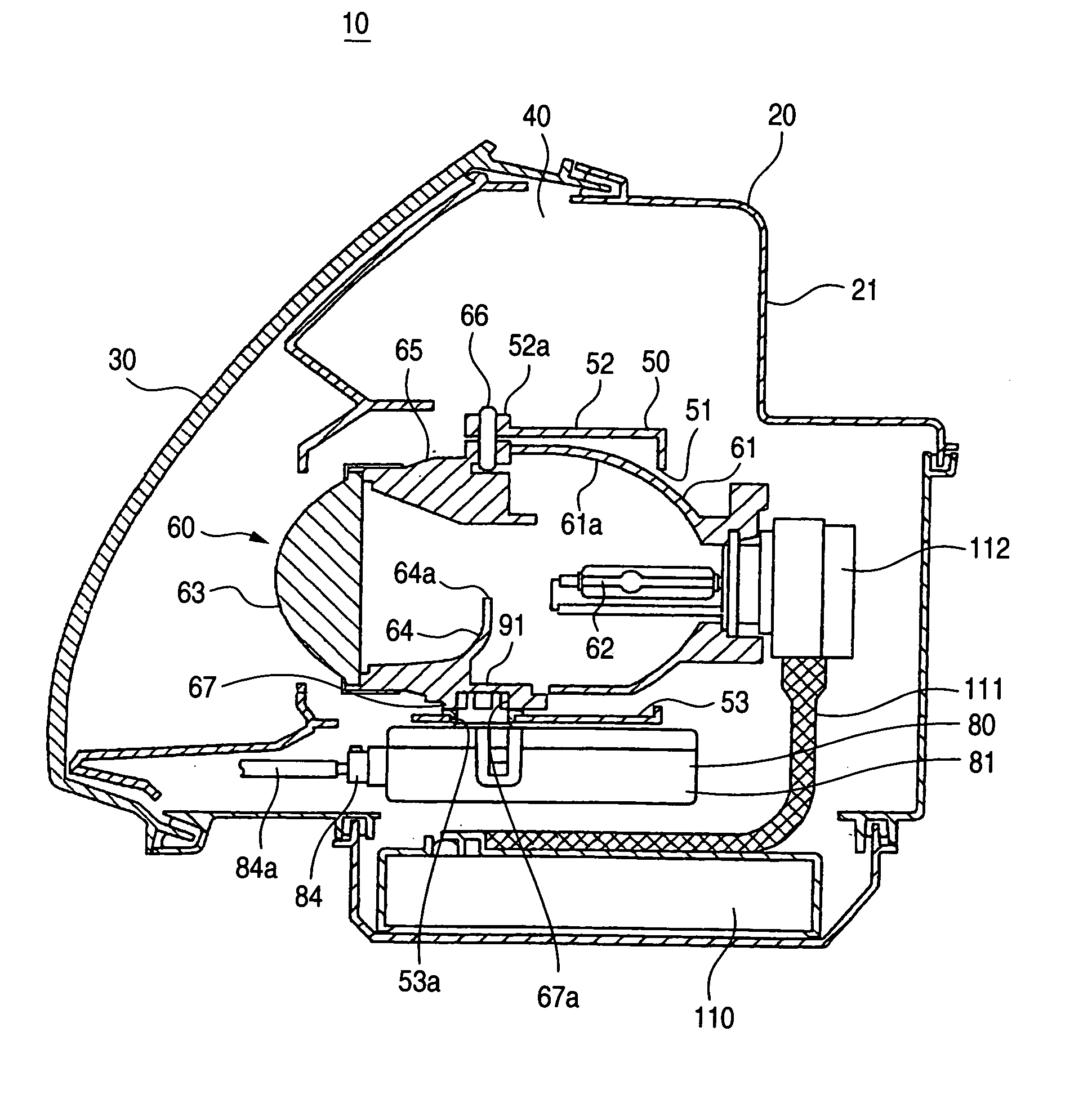
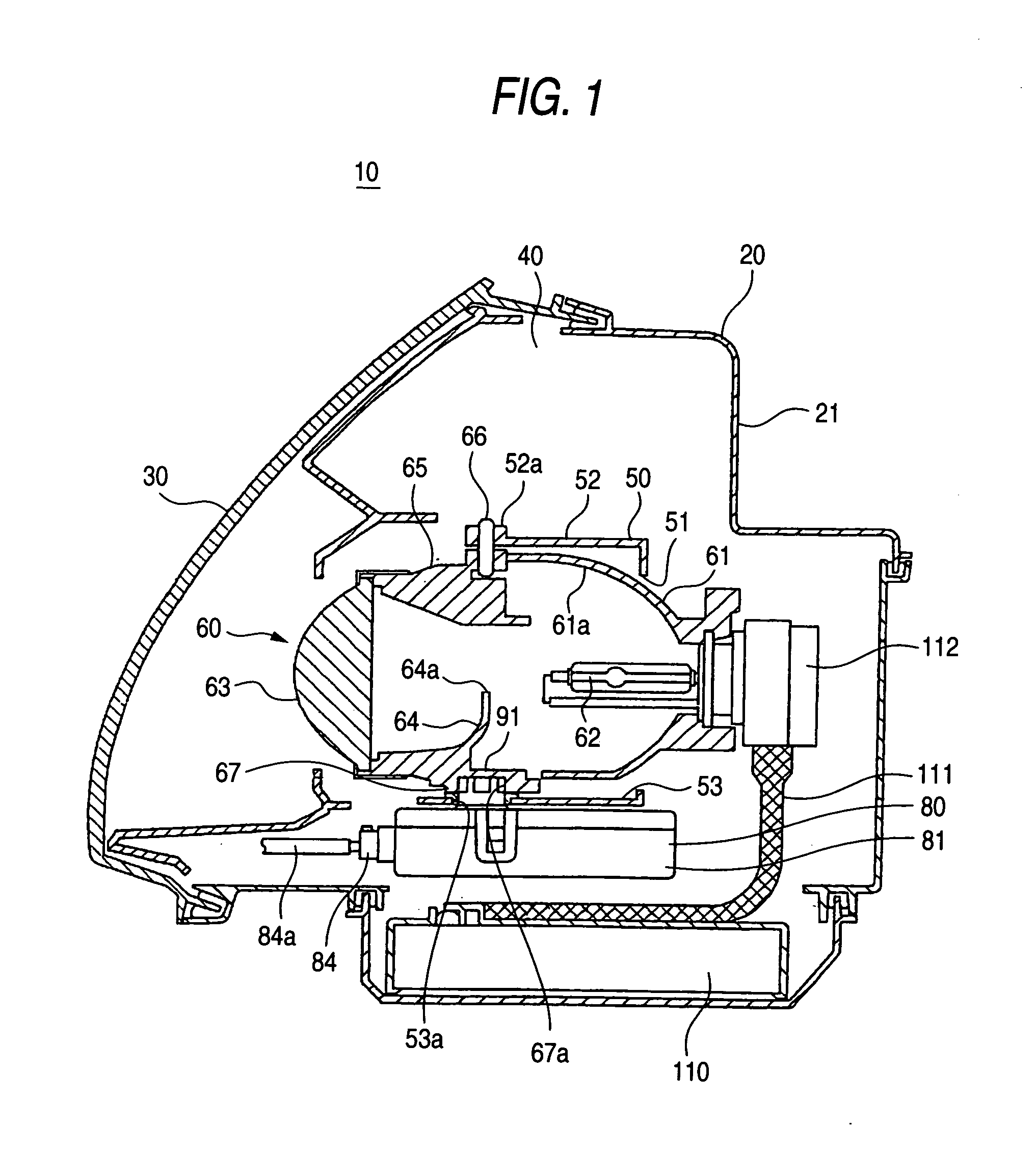
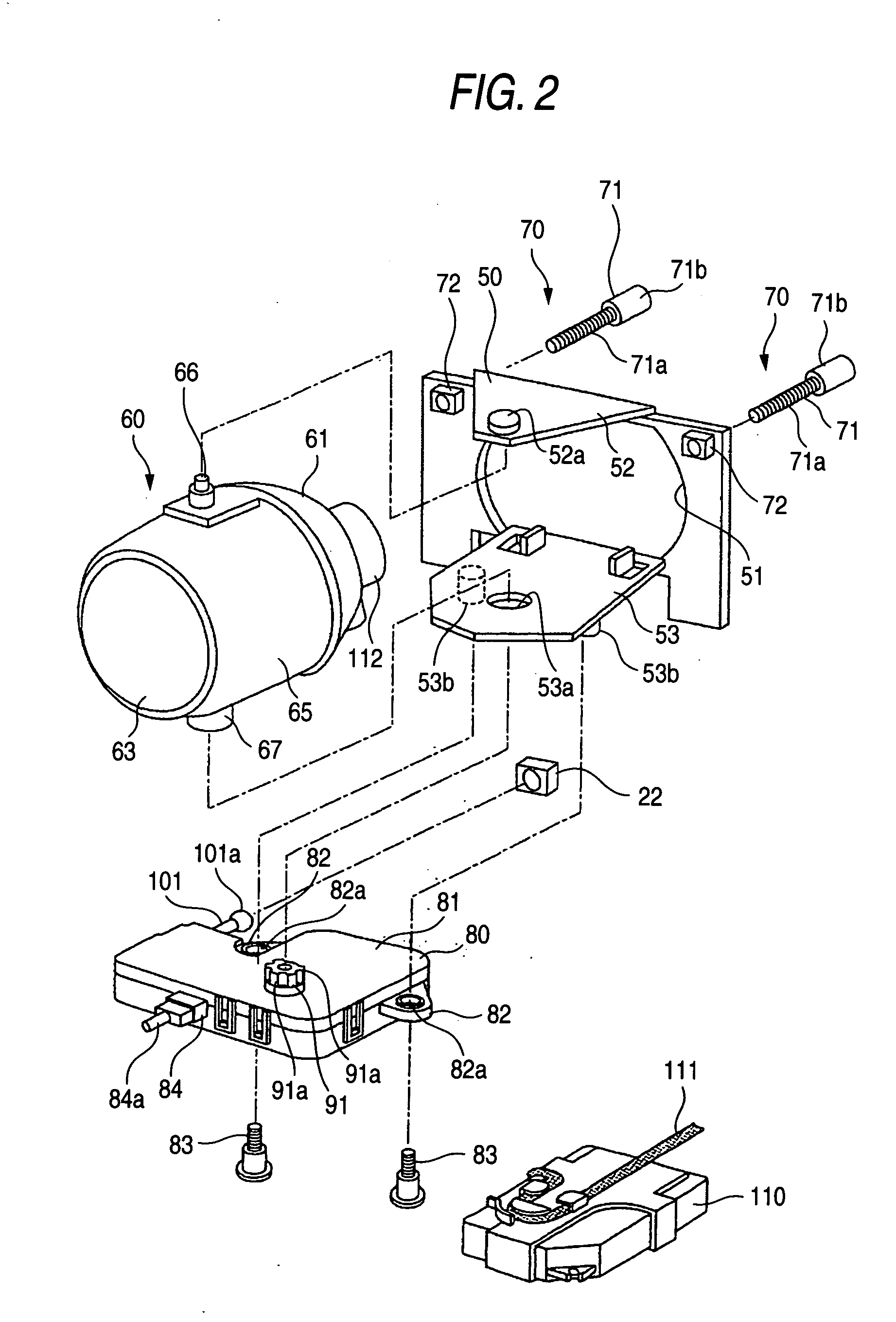
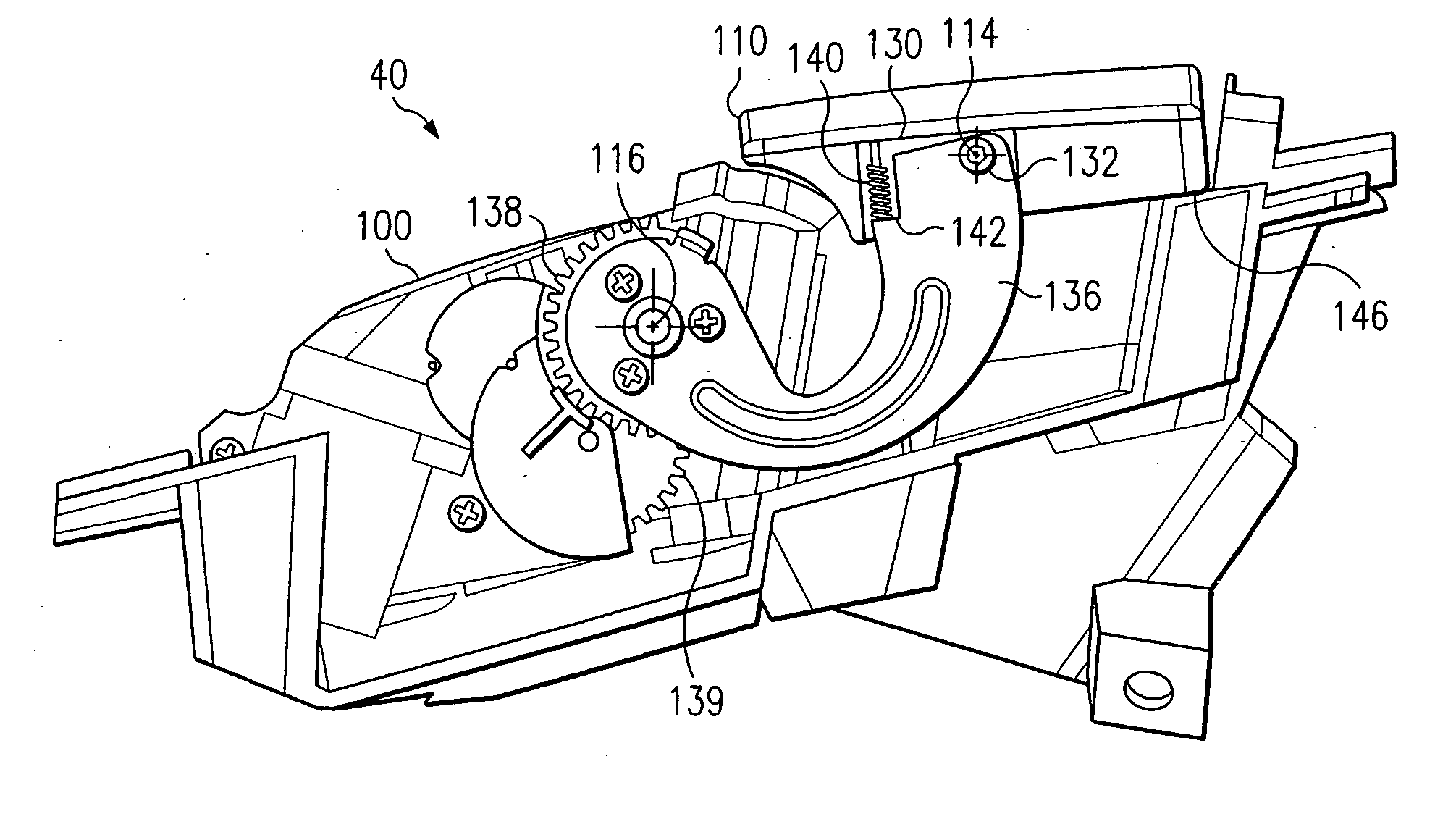
ActiveUS7175319B2Reduce the numberSimple structureVehicle headlampsLighting support devicesLight equipmentMan-hour
A lamp body 20 includes a lamp unit 60 whose irradiation direction is changed according to a running state of a vehicle, a horizontal driving mechanism 90 for horizontally changing the irradiation direction, and a vertical driving mechanism 100 for vertically changing the irradiation direction. The horizontal driving mechanism and the vertical driving mechanism are integrated with each other, so that a lighting apparatus 10 can be mounted in a vehicle by using only a small mounting space. Moreover, the lighting apparatus 10 needs only small numbers of components and mounting man-hours.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
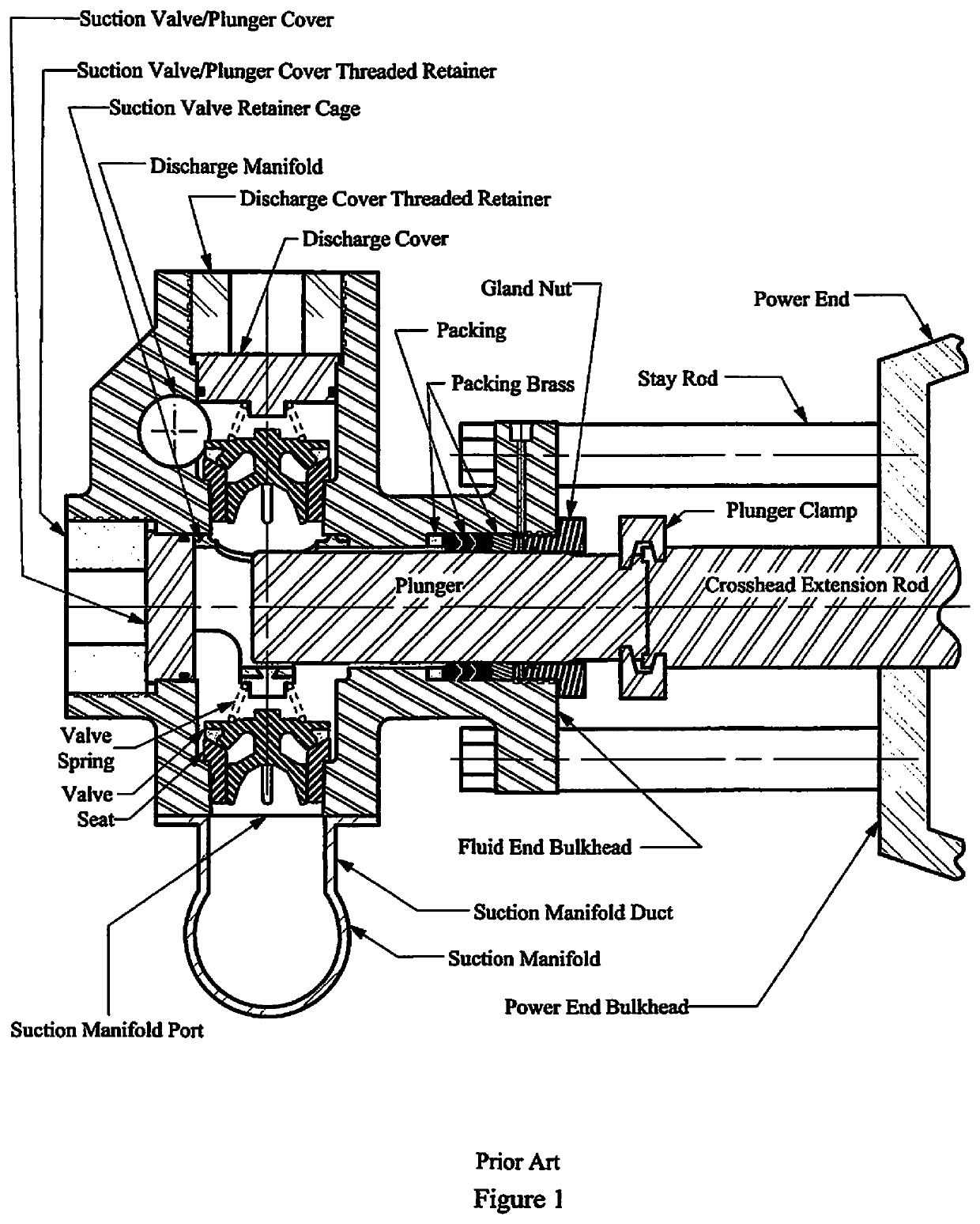
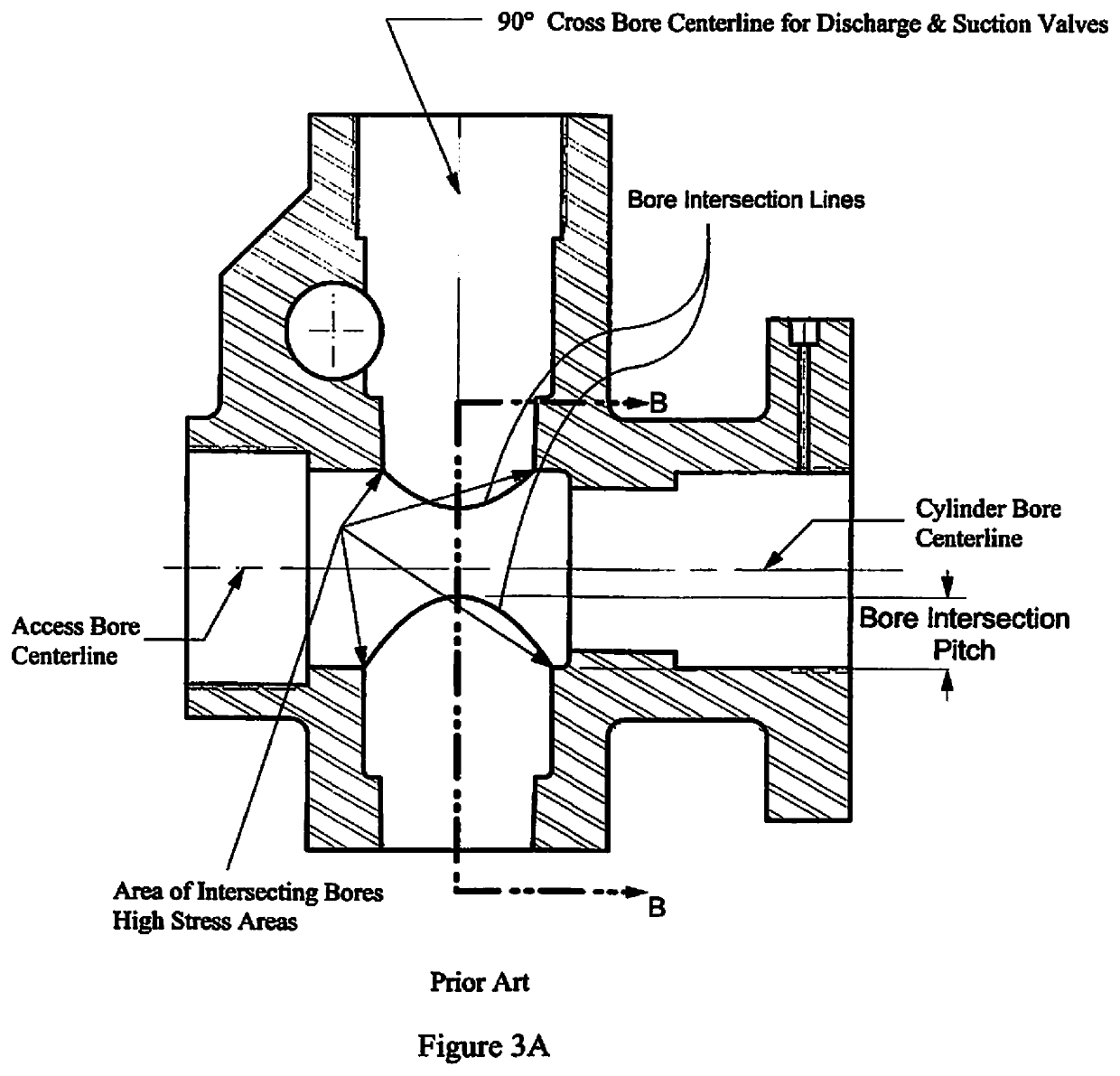
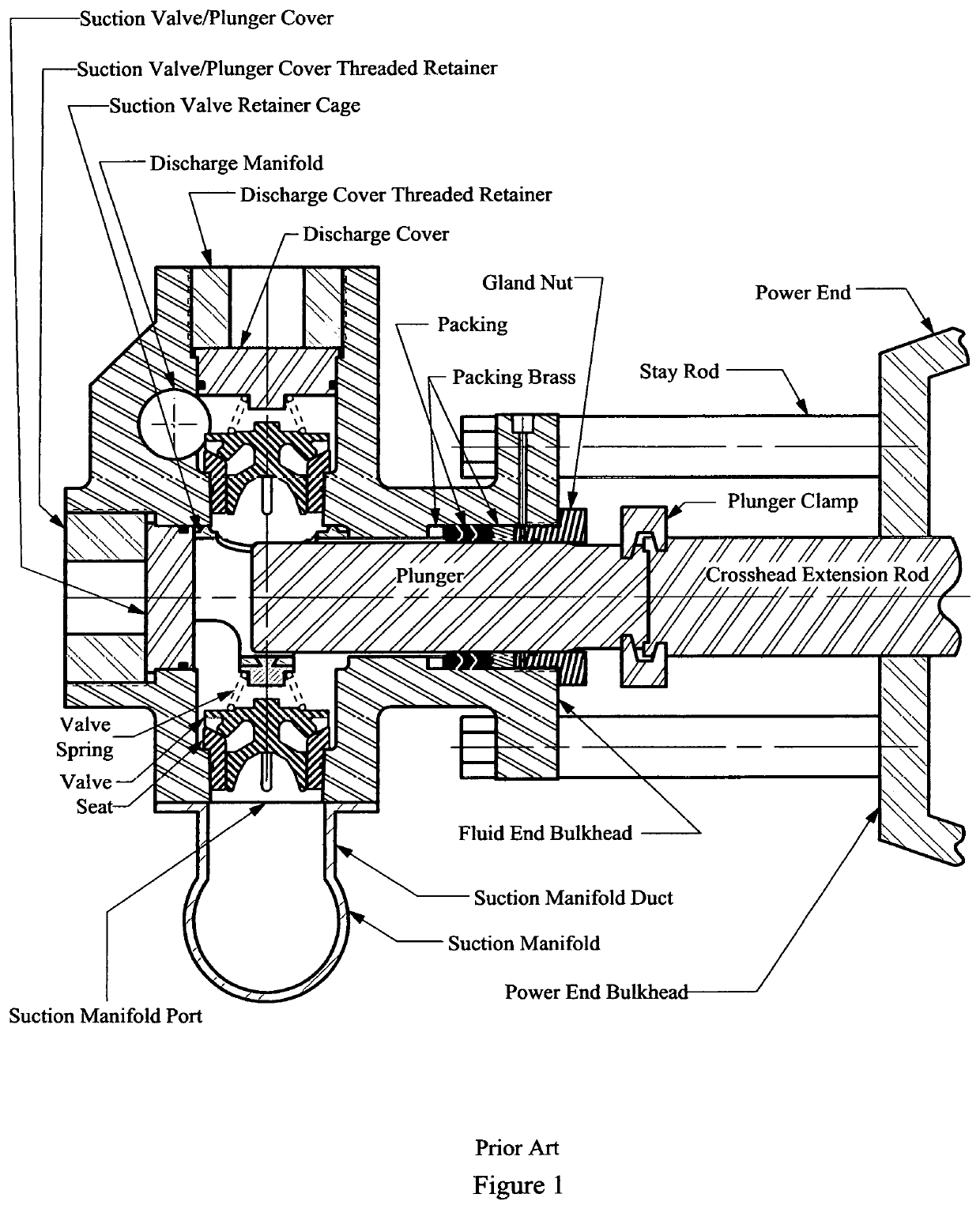
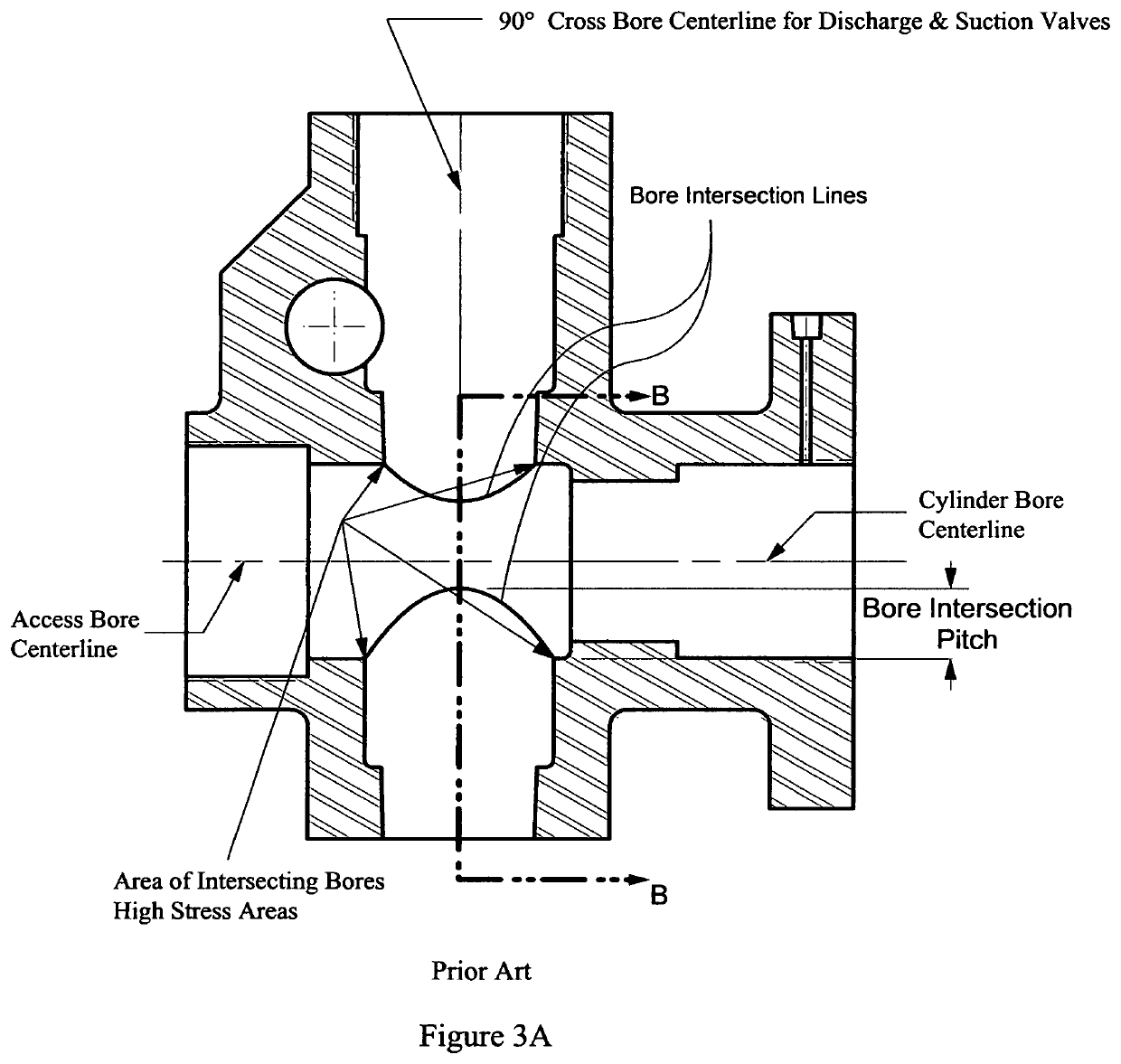
Pump With Segmented Fluid End Housing and In-Line Suction Valve
InactiveUS20200232455A1Improve advancedEasy accessPositive displacement pump componentsPositive-displacement liquid enginesMechanicsPlunger pump
Owner:ALTIS INVESTMENTS LLC
Vehicle lighting apparatus
ActiveUS20050141234A1Manufactured smallNumber of mounting is smallVehicle headlampsLighting support devicesLight equipmentEffect light
A lamp body 20 includes a lamp unit 60 whose irradiation direction is changed according to a running state of a vehicle, a horizontal driving mechanism 90 for horizontally changing the irradiation direction, and a vertical driving mechanism 100 for vertically changing the irradiation direction. The horizontal driving mechanism and the vertical driving mechanism are integrated with each other, so that a lighting apparatus 10 can be mounted in a vehicle by using only a small mounting space. Moreover, the lighting apparatus 10 needs only small numbers of components and mounting man-hours.
Owner:KOITO MANUFACTUARING
Physical quantity sensor having multiple through holes
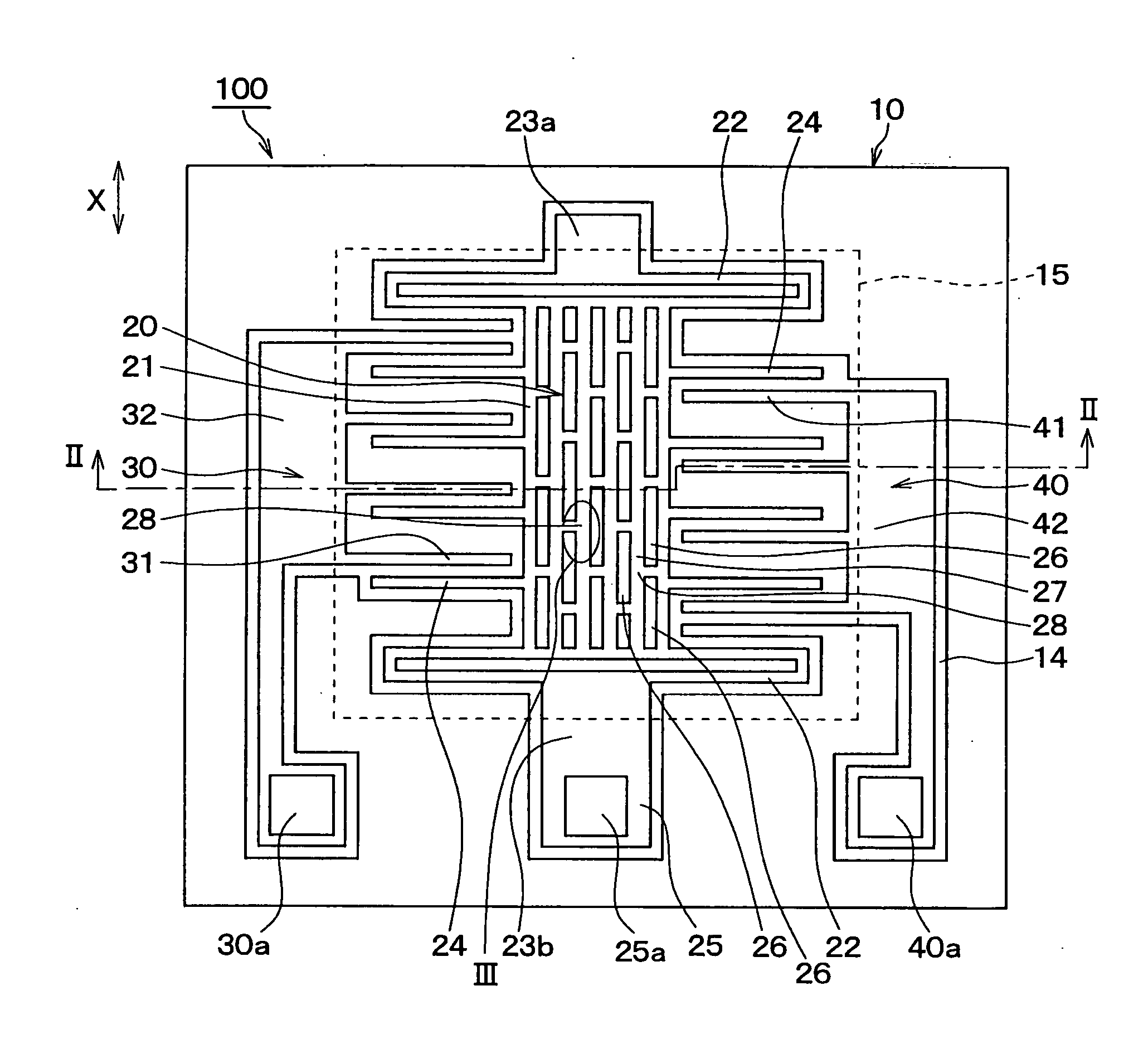
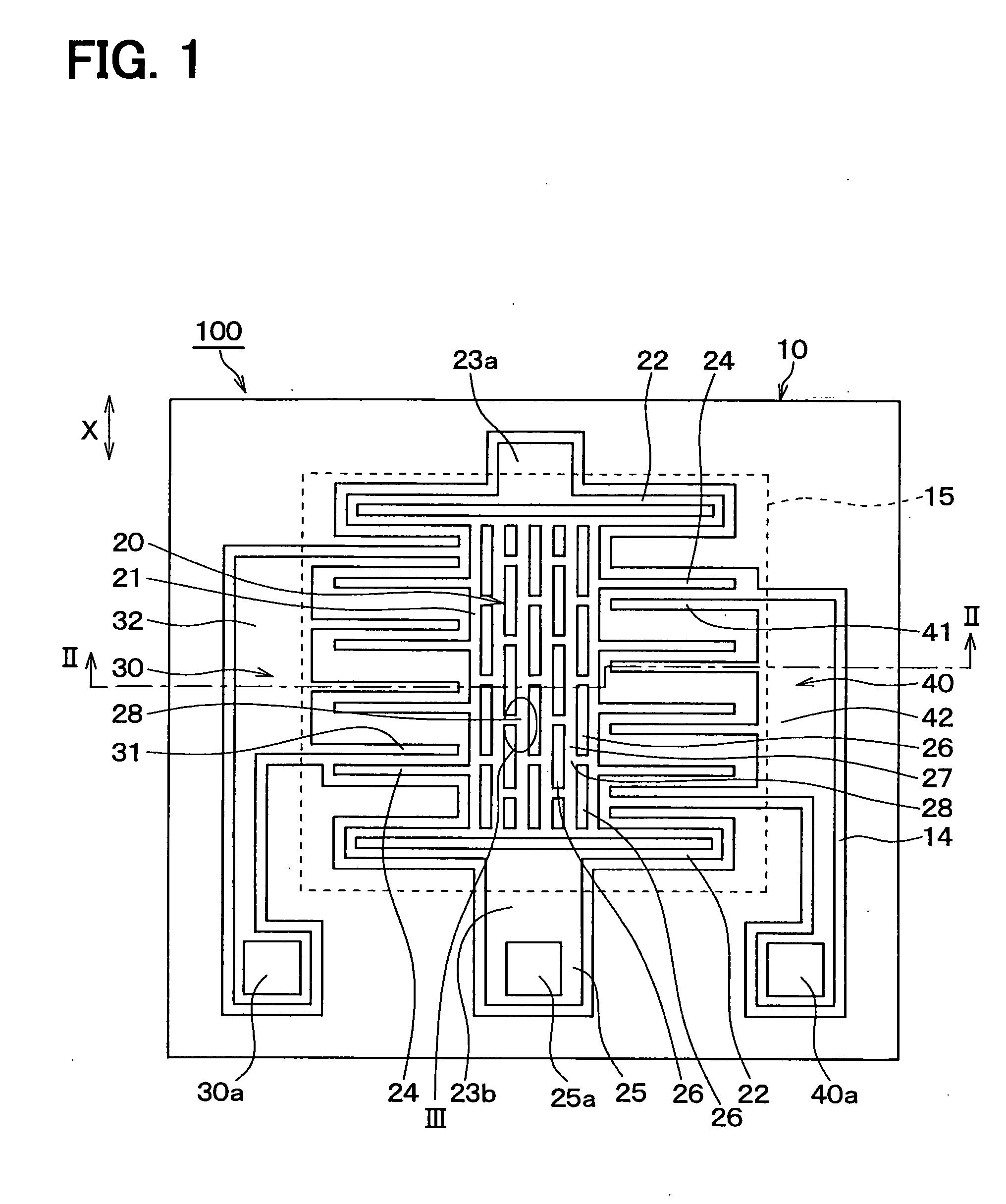
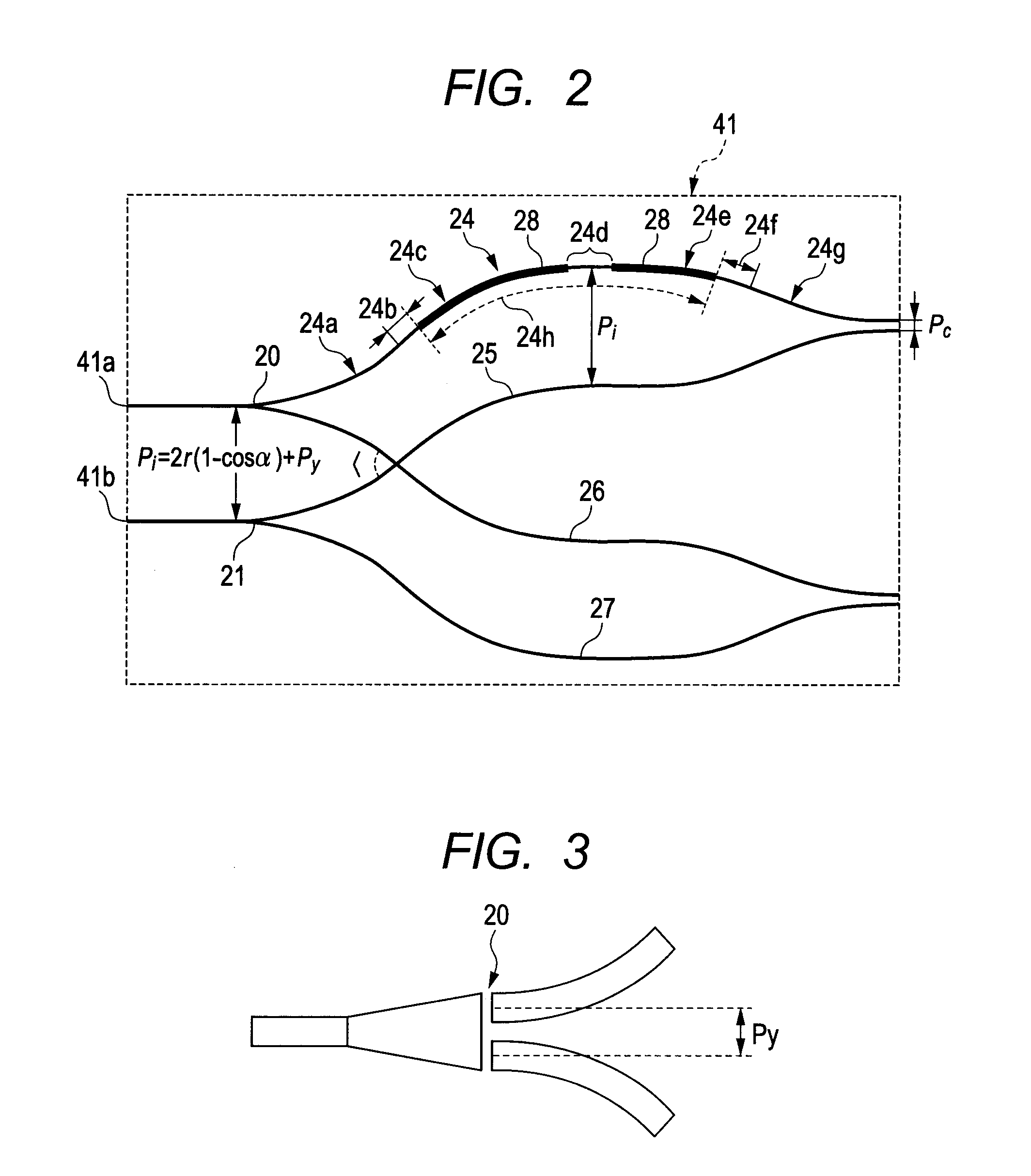
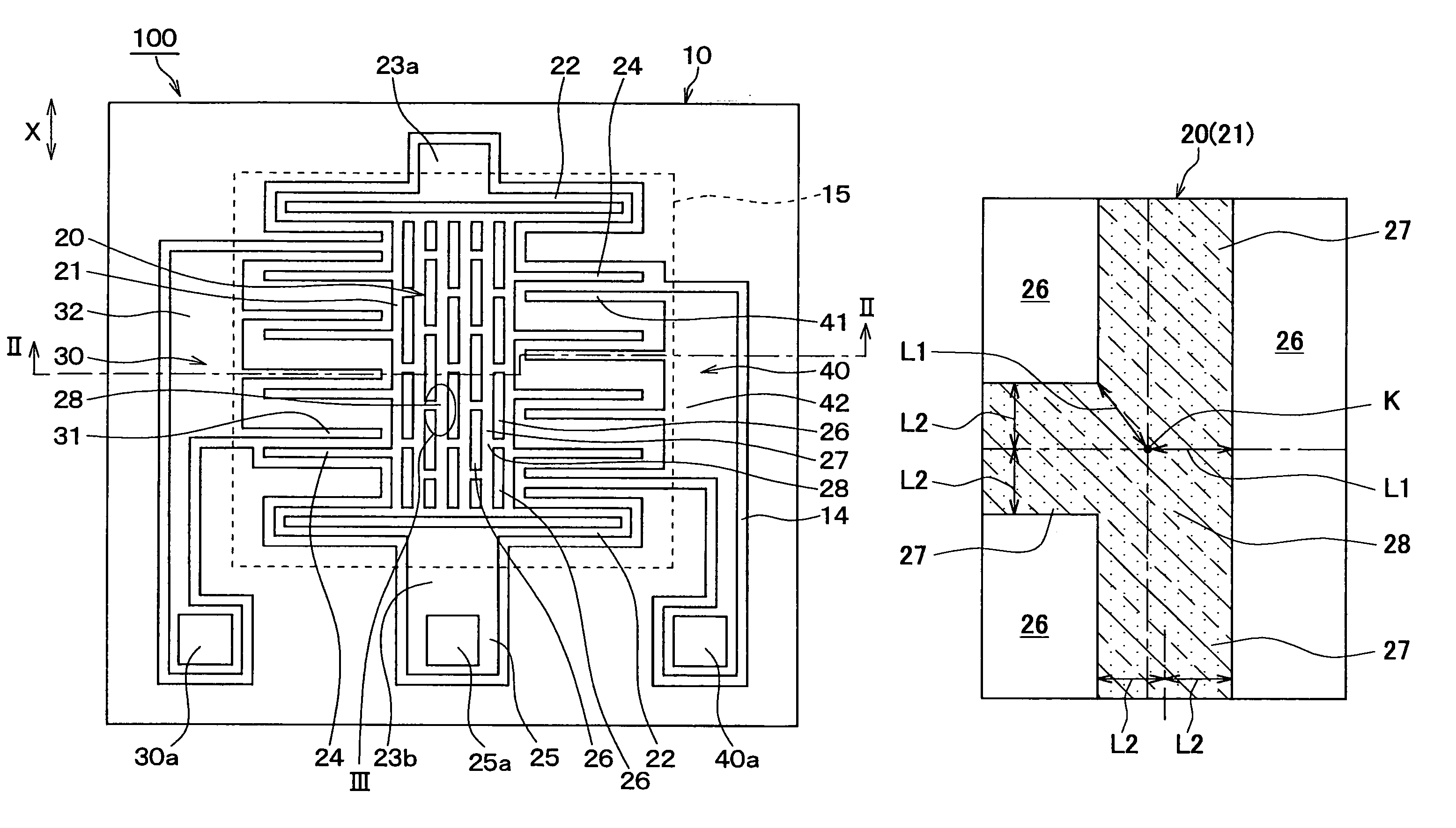
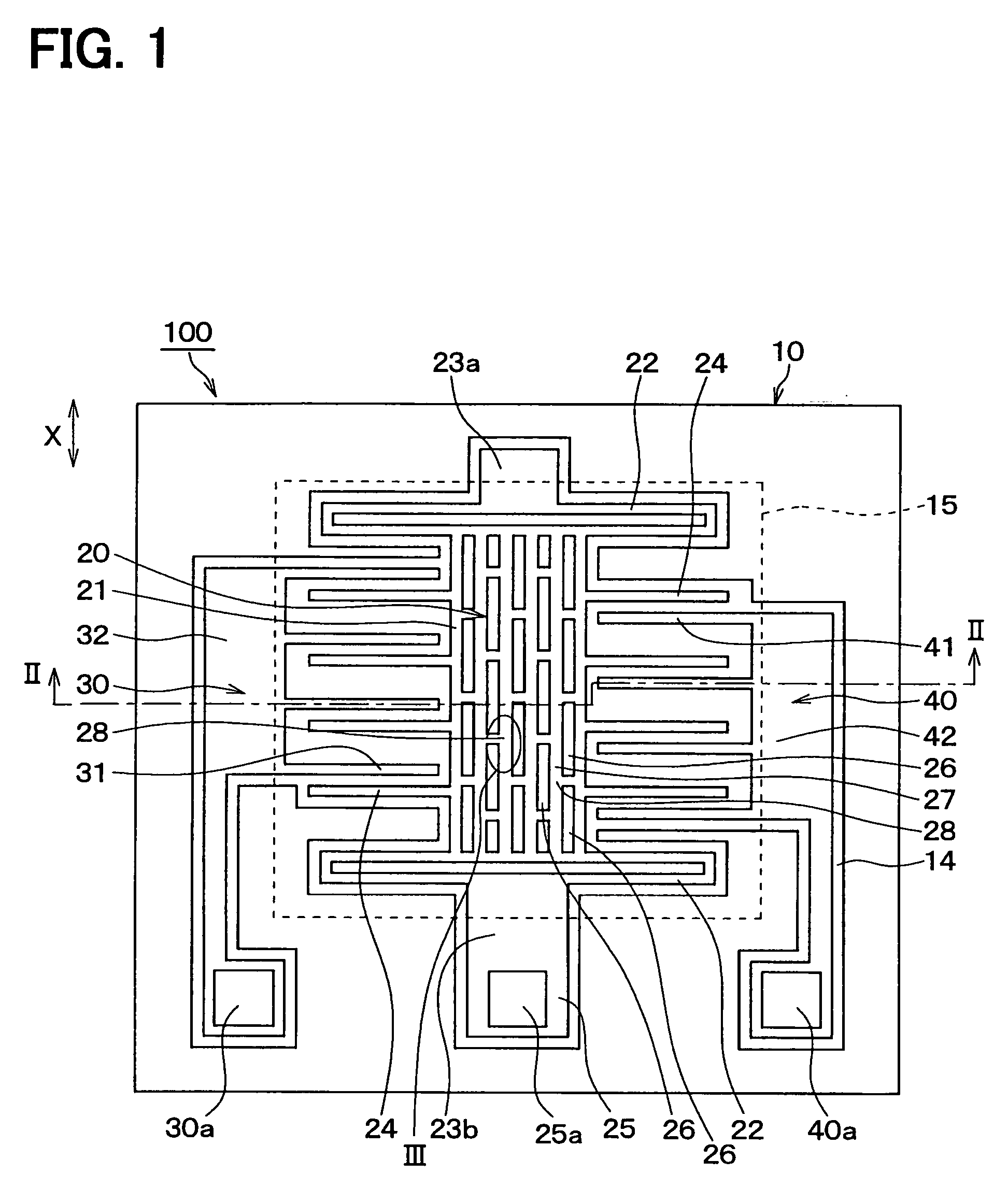
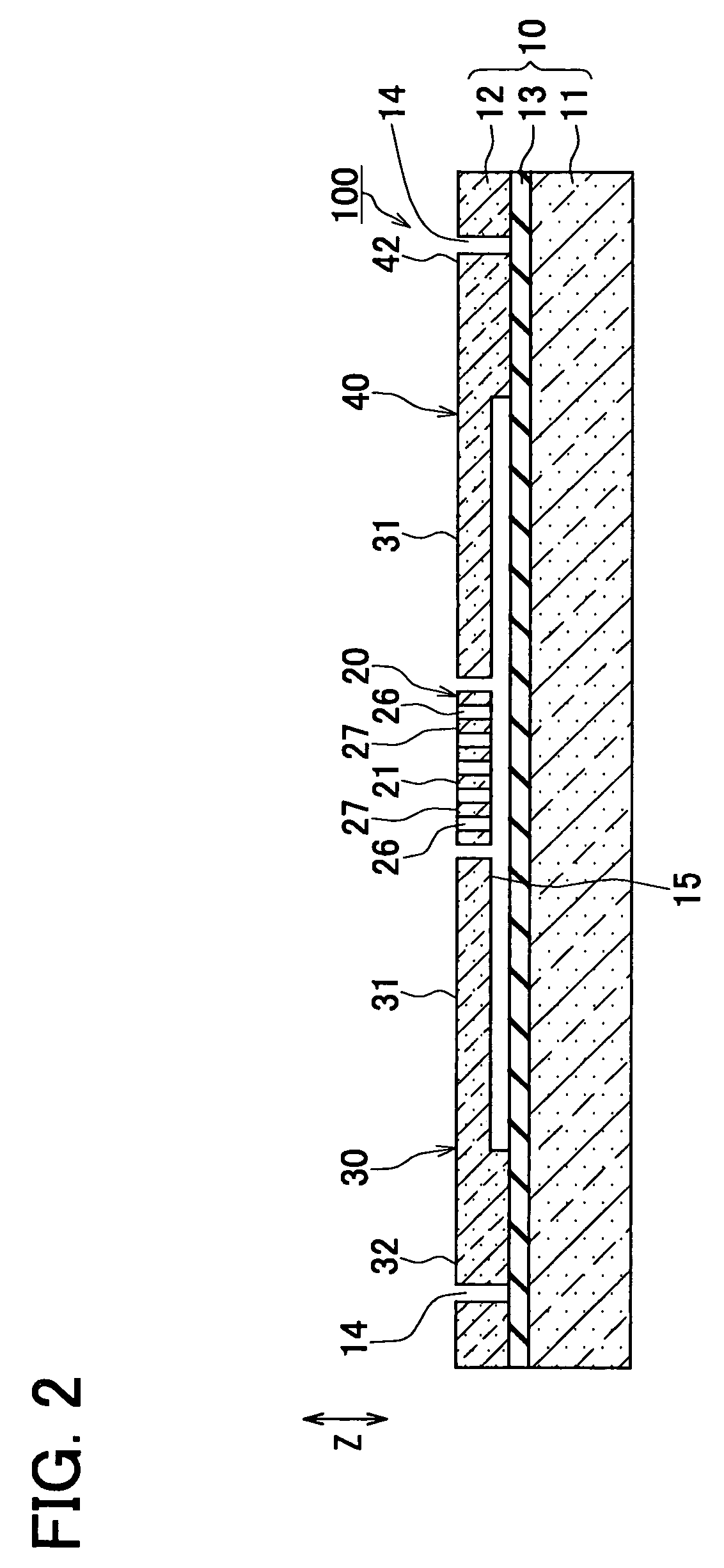
ActiveUS20050229704A1Small manufacturing errorShort processing timeAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTurn-sensitive devicesSemiconductorPhysical quantity
A semiconductor physical quantity sensor includes: a substrate; a semiconductor layer supported on the substrate; a trench disposed in the semiconductor layer; and a movable portion disposed in the semiconductor layer and separated from the substrate by the trench. The movable portion includes a plurality of through-holes, each of which penetrates the semiconductor layer in a thickness direction. The movable portion is capable of displacing on the basis of a physical quantity applied to the movable portion so that the physical quantity is detected by a displacement of the movable portion. The movable portion has a junction disposed among the through-holes. The junction has a trifurcate shape.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Sensor, a sensor array, and a method of operating a sensor
InactiveUS20100221846A1Improve accuracyAccurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSensor arrayEngineering
In an example embodiment, there is a sensor for detecting particles. The sensor comprises an electrode, a sensor active region covering the electrode and the sensor active region is sensitive-for the particles. A first switch element is operable to bring the electrode to a first electric potential when the first switch element is closed, and a second switch element is operable to bring the electrode to a second electric potential when the second switch element is closed. A detector is adapted to detect the particles based on a change of the electric properties of the sensor in an operation mode in which the electrode is brought to the first electric potential and an operation mode in which the electrode is brought to the second electric potential.
Owner:NXP BV
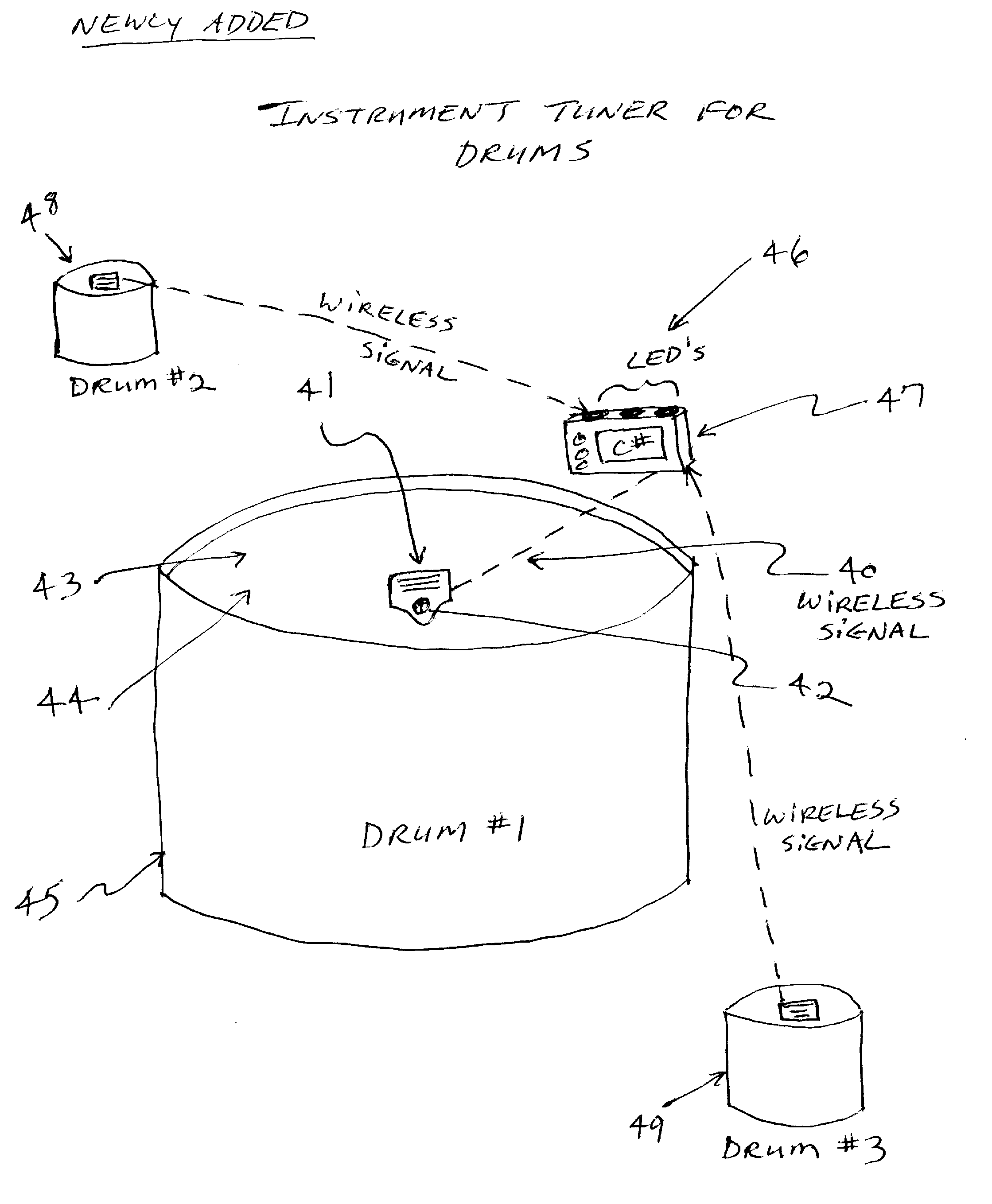
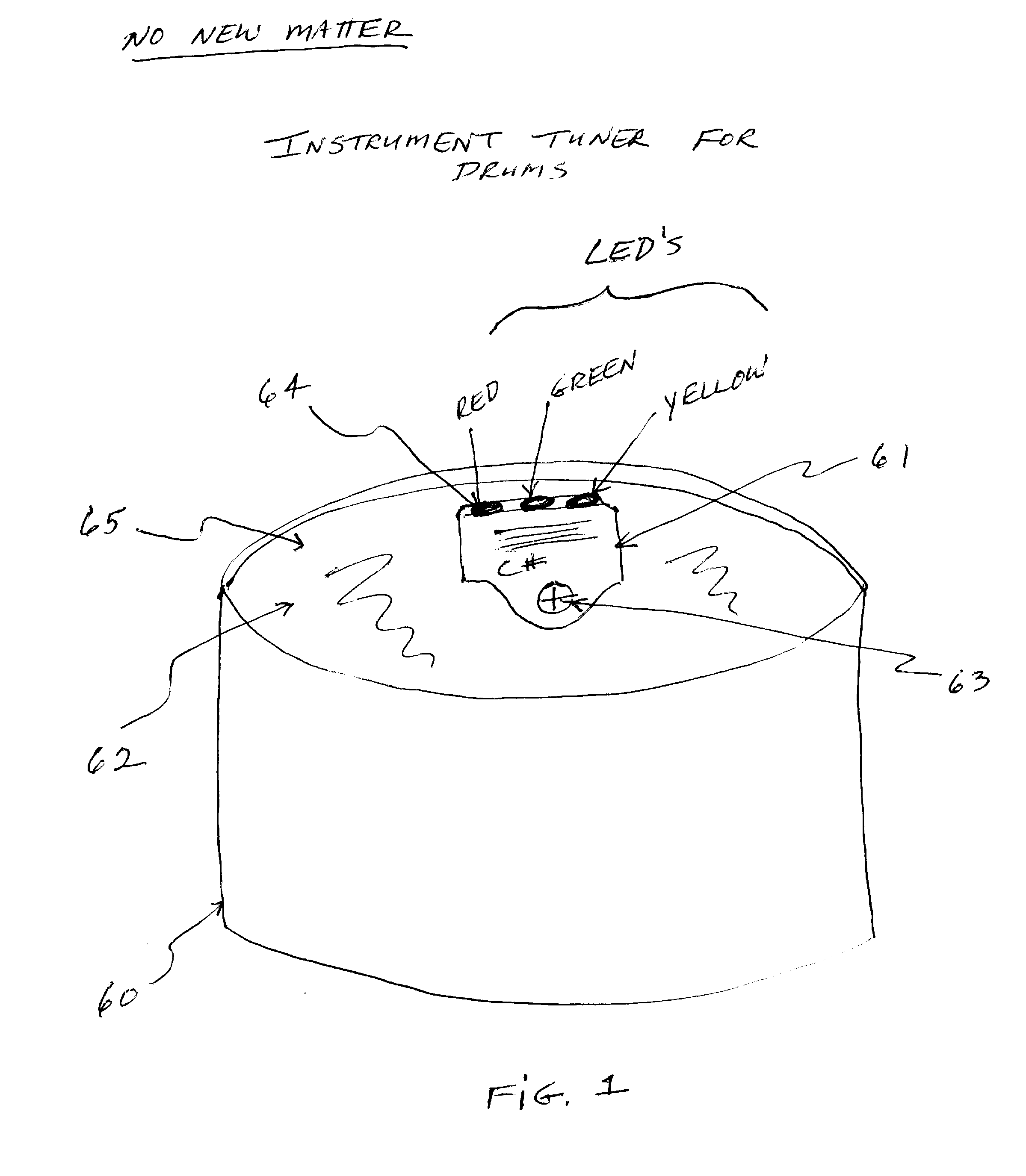
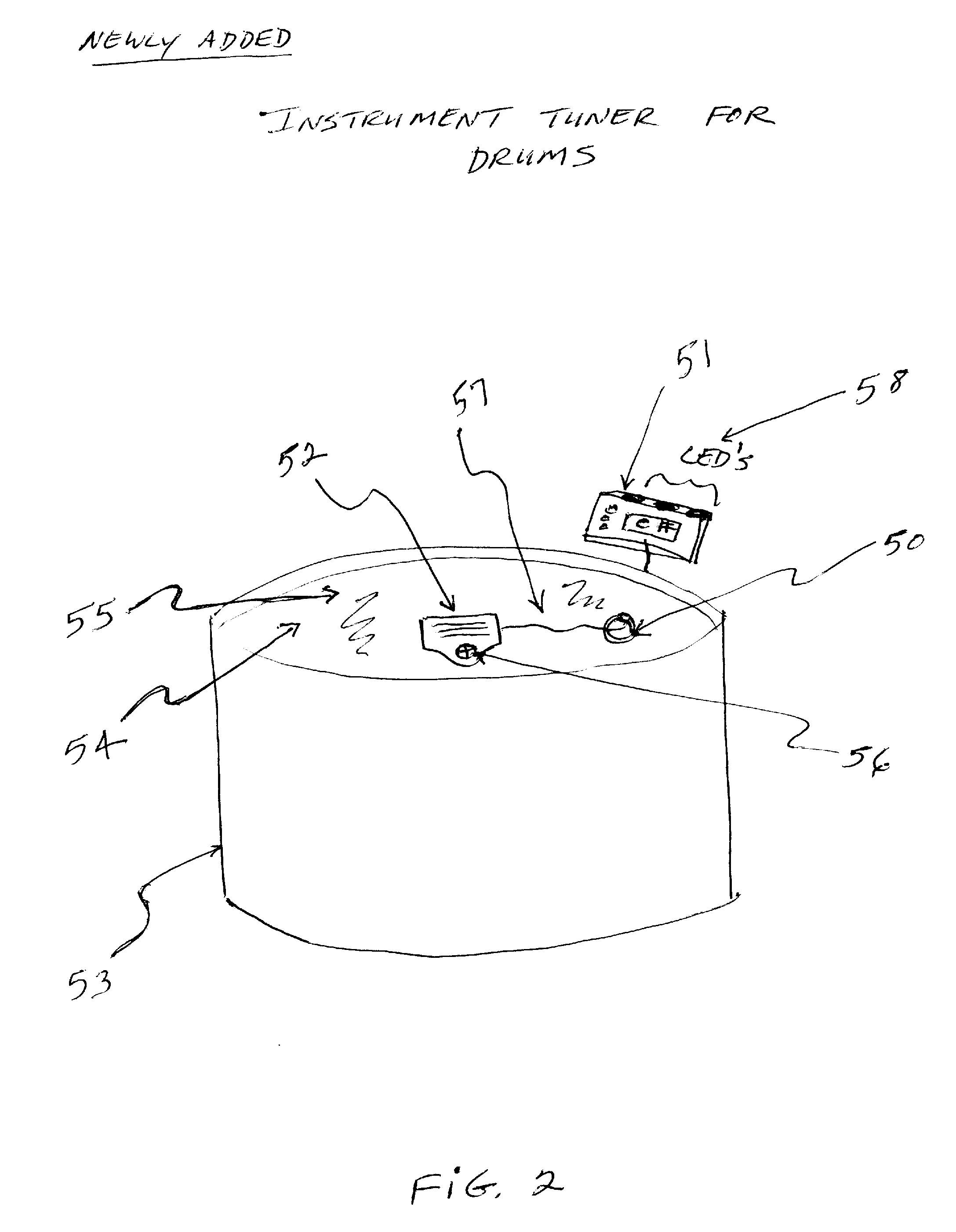
Instrument Tuner for Drums
InactiveUS20120240749A1Faster and more accuratelySmall display formatPercussion musical instrumentsMusic aidsResonanceDisplay device
An instrument tuner for drums that has a sensing means for sensing the combined fundamental resonance and pitch from inside the drum; a measurement means for measuring a frequency of said combined fundamental resonance and pitch; and a selection means to then compare the frequency measured to a corresponding musical note of the instrument tuner. Eventhough the sensing means will be internal to the drum, the tuner or display could be external to the drum and / or separate from the sensing means; a wireless device or system is specified also that could be used with this method. A single-note tuner is specified, as well as a tuner designed to recognize more than a single-note, if a wireless device or system is used, as one example, for a complete drumset.
Owner:OVERTONE LABS
Manufacturing method of expanded graphite products
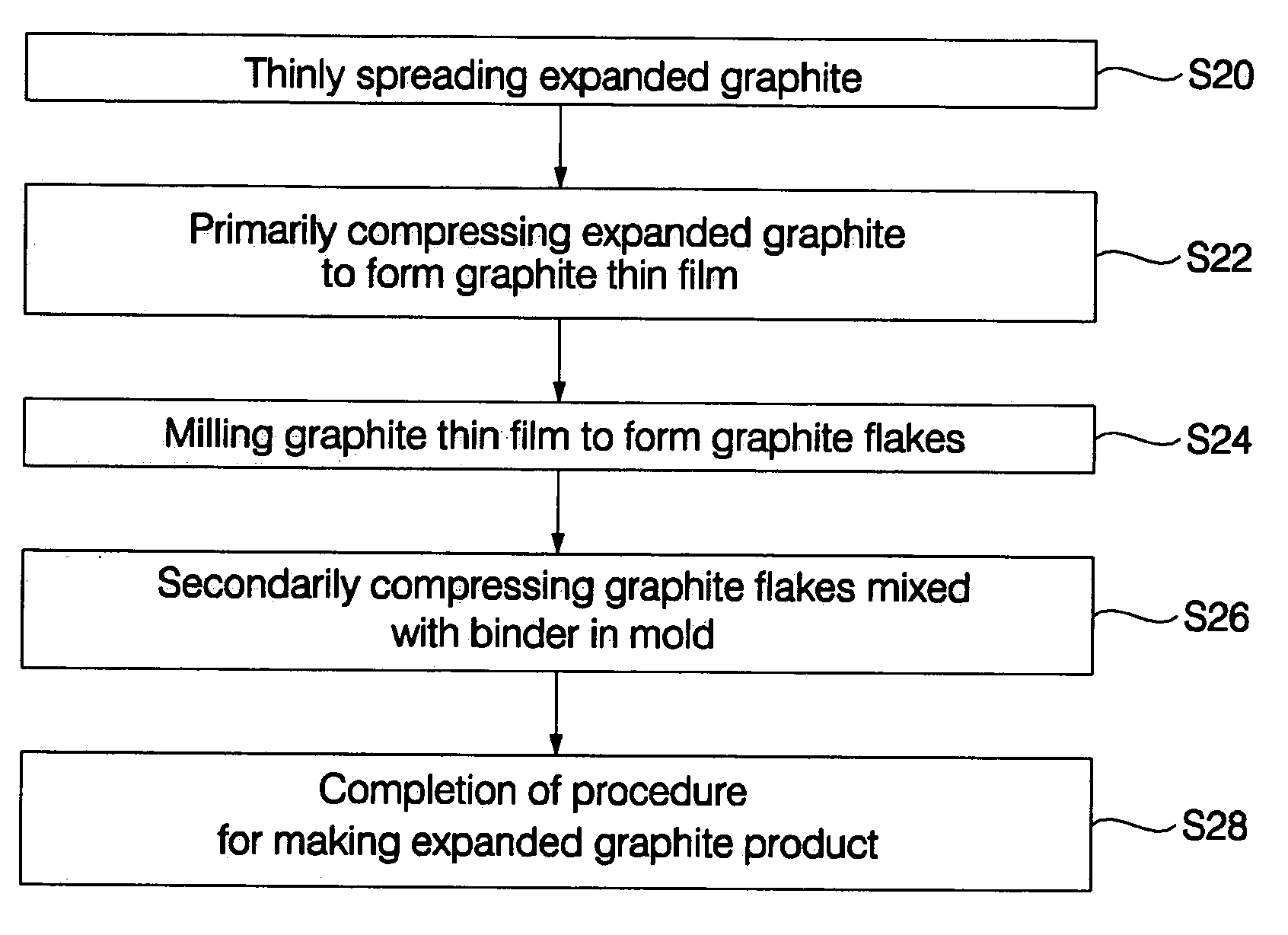
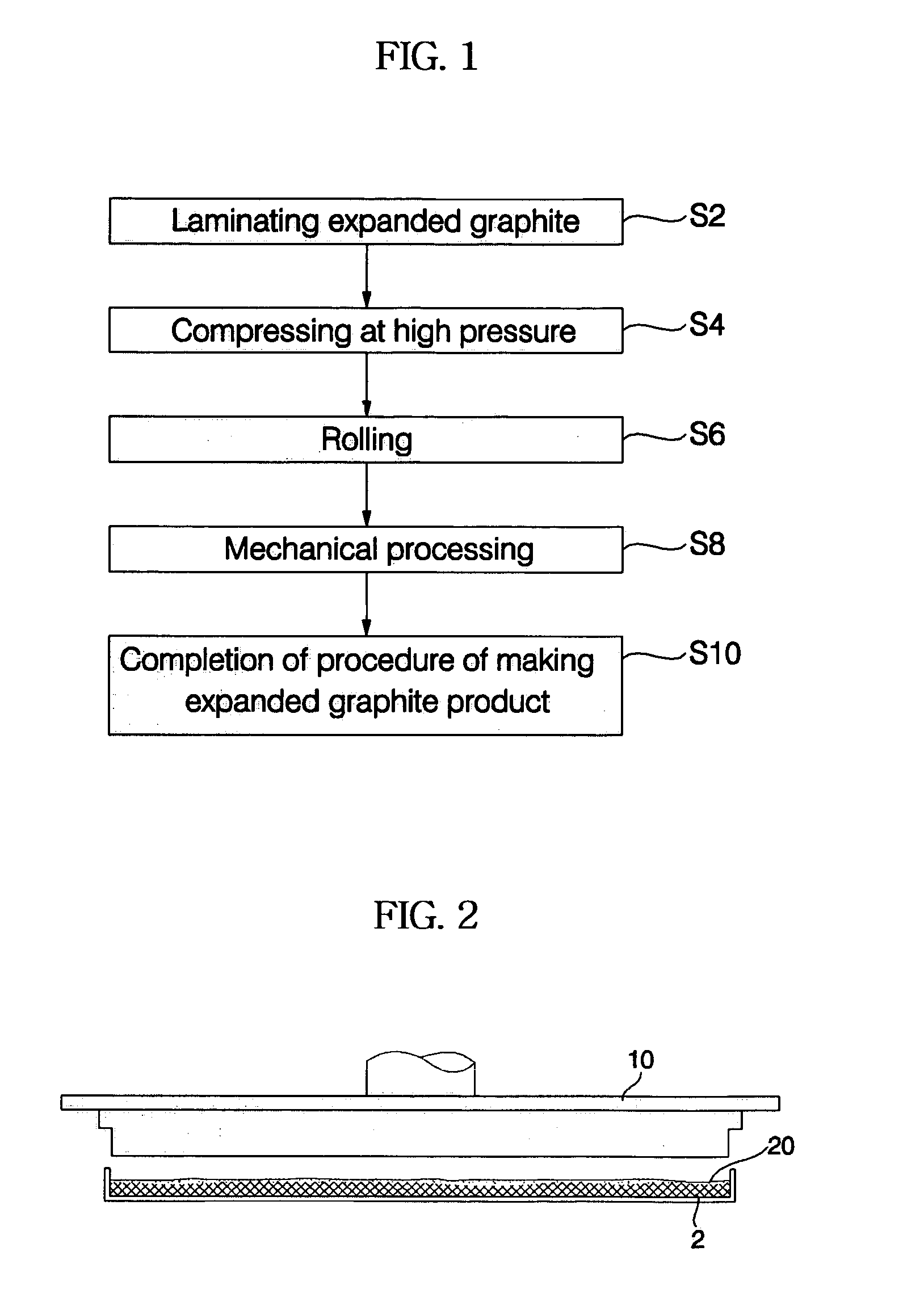
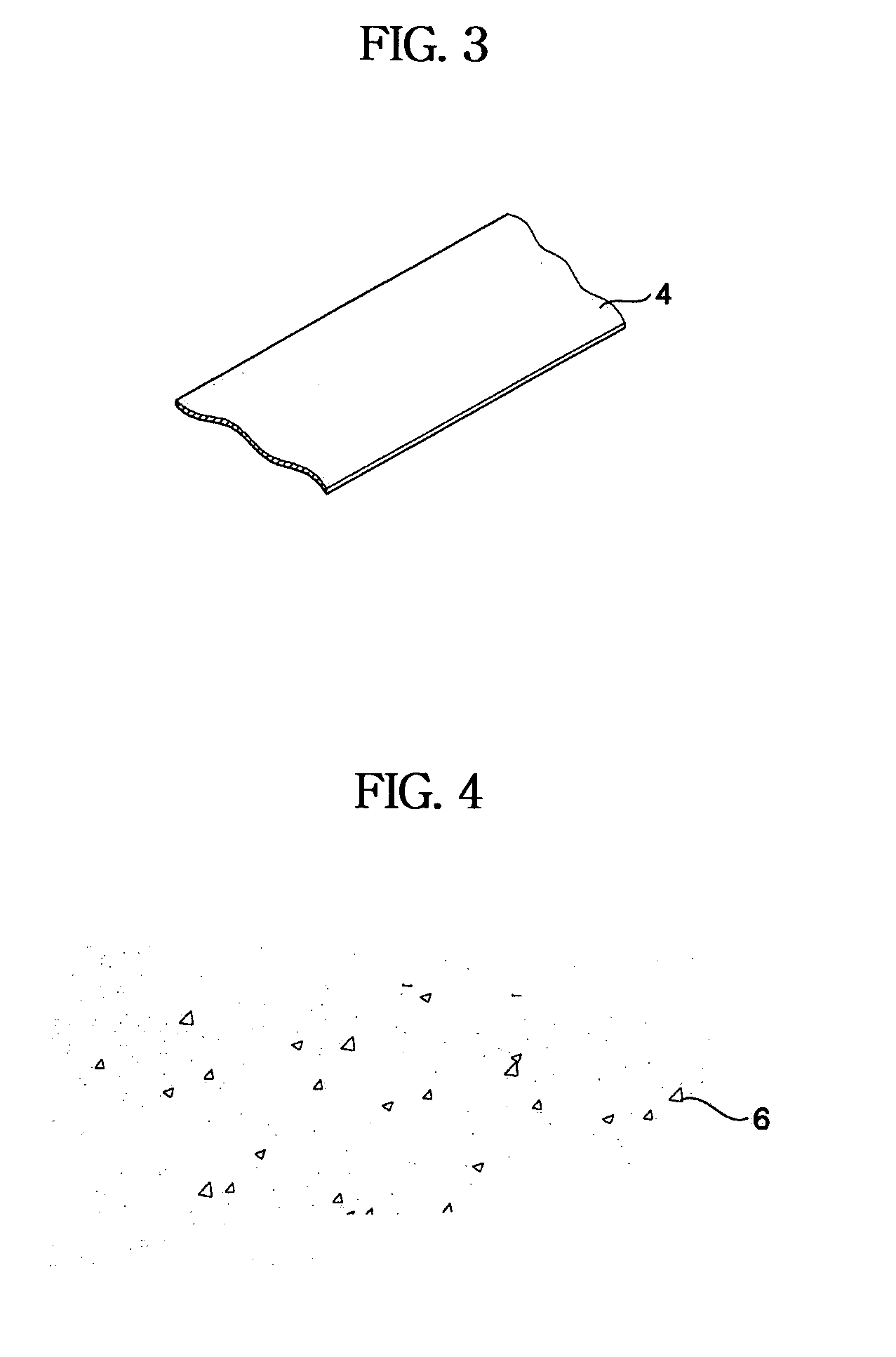
ActiveUS7105115B2Manufactured smallInitial equipment costDomestic sealsCarbon compoundsMetallurgyGraphite
Disclosed herein is a method of manufacturing expanded graphite products. The method comprises the steps of a) compressing expanded graphite to form a graphite thin film, b) milling the graphite thin film to form graphite flakes, and c) placing the graphite flakes in a mold and compressing the graphite flakes to form a predetermined shape, wherein during at least any one of the steps a), b) and c), a binder is mixed with the expanded graphite. There are provided advantageous effects that as the density of the expanded graphite product increases through respective manufacturing steps, not only are initial equipment costs reduced due to minimized equipment, but also an expanded graphite product having a uniform density and a closely packed structure is provided. Additionally, since the expanded graphite product is finally compressed in the mold, the expanded graphite product does not have directional preference and can be formed into various shapes.
Owner:TAKUMISPIRIT CORP
Parts Assembly and Part for a Prosthesis
InactiveUS20090043390A1Manufactured smallCost-effectiveJoint implantsSpinal implantsIntervertebral discProsthesis
The invention relates to a parts assembly for a prosthesis, particularly a cervical spine intervertebral disc prosthesis, comprising two base parts (1, 2), which are coupled to one another in an articulated manner by means of coupling parts (11, 12) formed on said base parts. These base parts, together with an associated coupling part, are provided as a single piece. The base parts and the coupling parts are made of one material, which is selected from the following group of materials: polyetherketone (PEK) polyetheretherketone (PEEK), polyacryletherketone (PAEK), polyetherketoneketone (PEKK), polyetherketoneetherketoneketone (PEKEKK) and polyetherketoneetherketone (PEKEK).
Owner:MEISEL HANS JORG
Liquid crystal display device
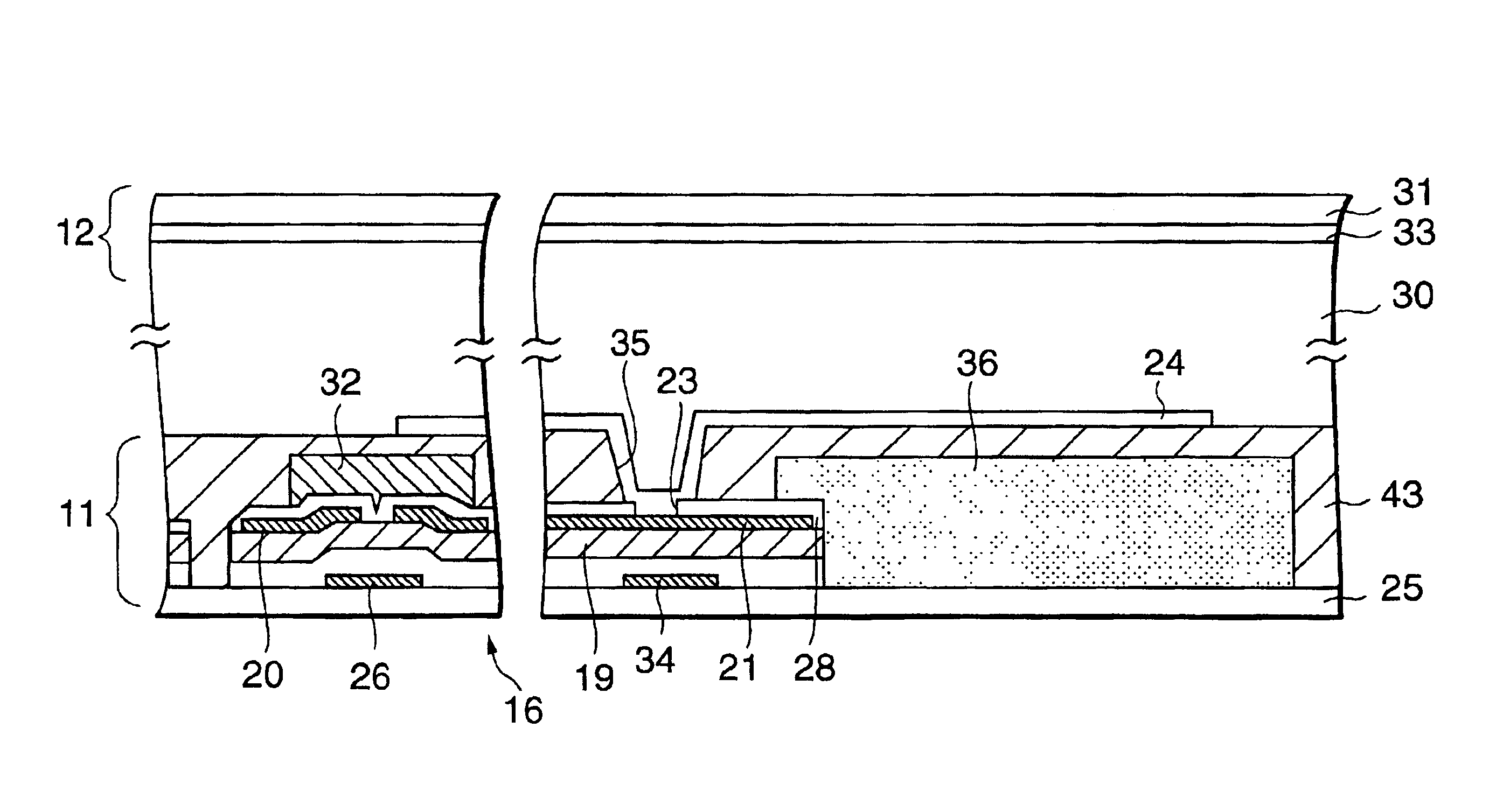
InactiveUS6917393B2Improve performanceManufactured with small manufacturing stepTransistorFencingLiquid-crystal displaySemiconductor
There is provided a liquid crystal display device comprising a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix form, each of the pixels including a pixel electrode formation area wherein a pixel electrode is formed and a thin film transistor formation area wherein a thin film transistor is formed and connected to the pixel electrode. The thin film transistor having a semiconductor layer serving as a channel, a terminal formed to be connected to the pixel electrode, a passivation layer formed to cover the thin film transistor and an organic insulating layer covering the passivation layer. The semiconductor layer is extended from a channel toward the pixel electrode formation area beyond the terminal and terminated in the pixel electrode formation area to form a termination end that is aligned with a termination end of the passivation layer. The organic insulating layer is elongated to cover the termination ends of the semiconductor layer and the passivation layer.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
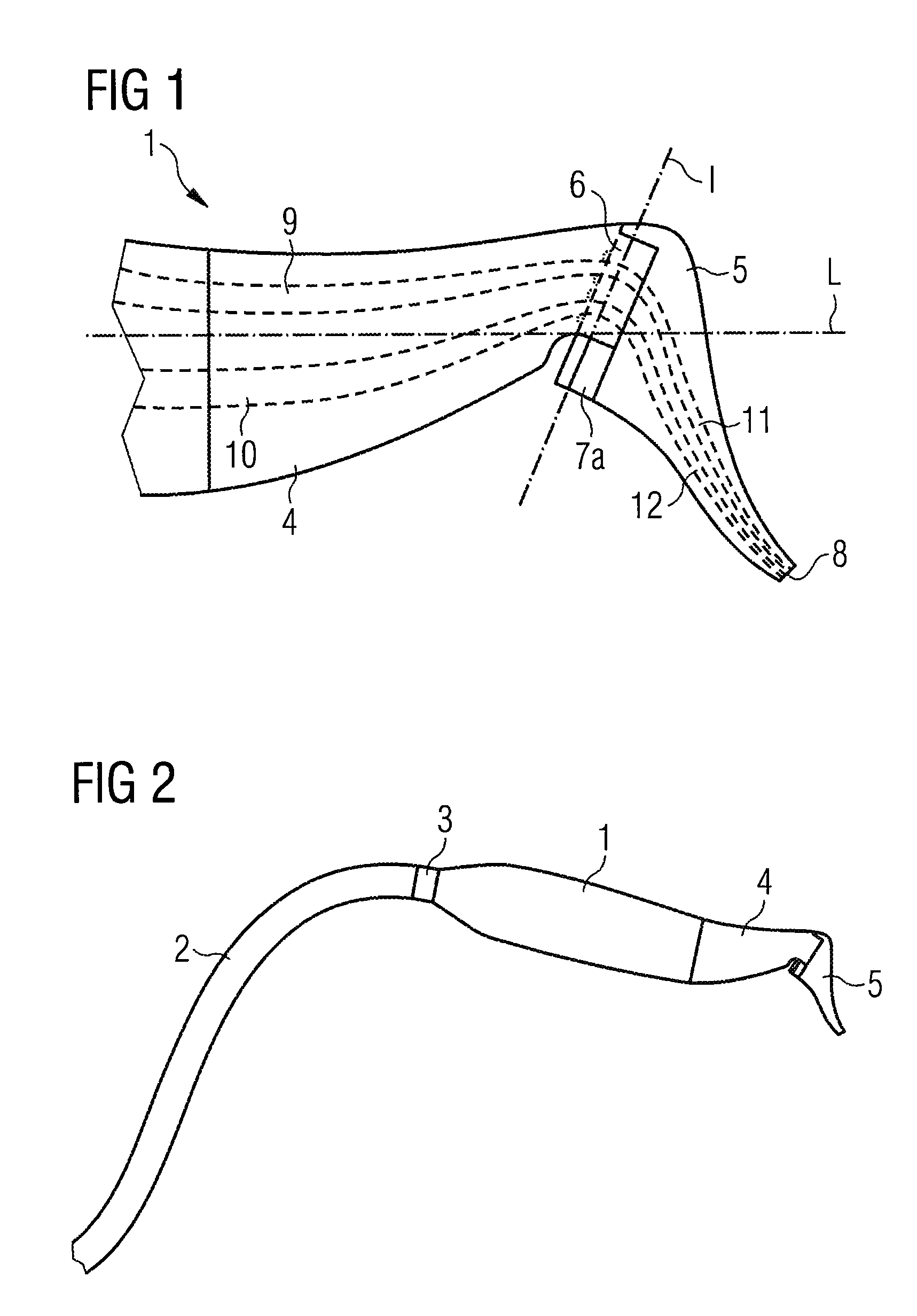
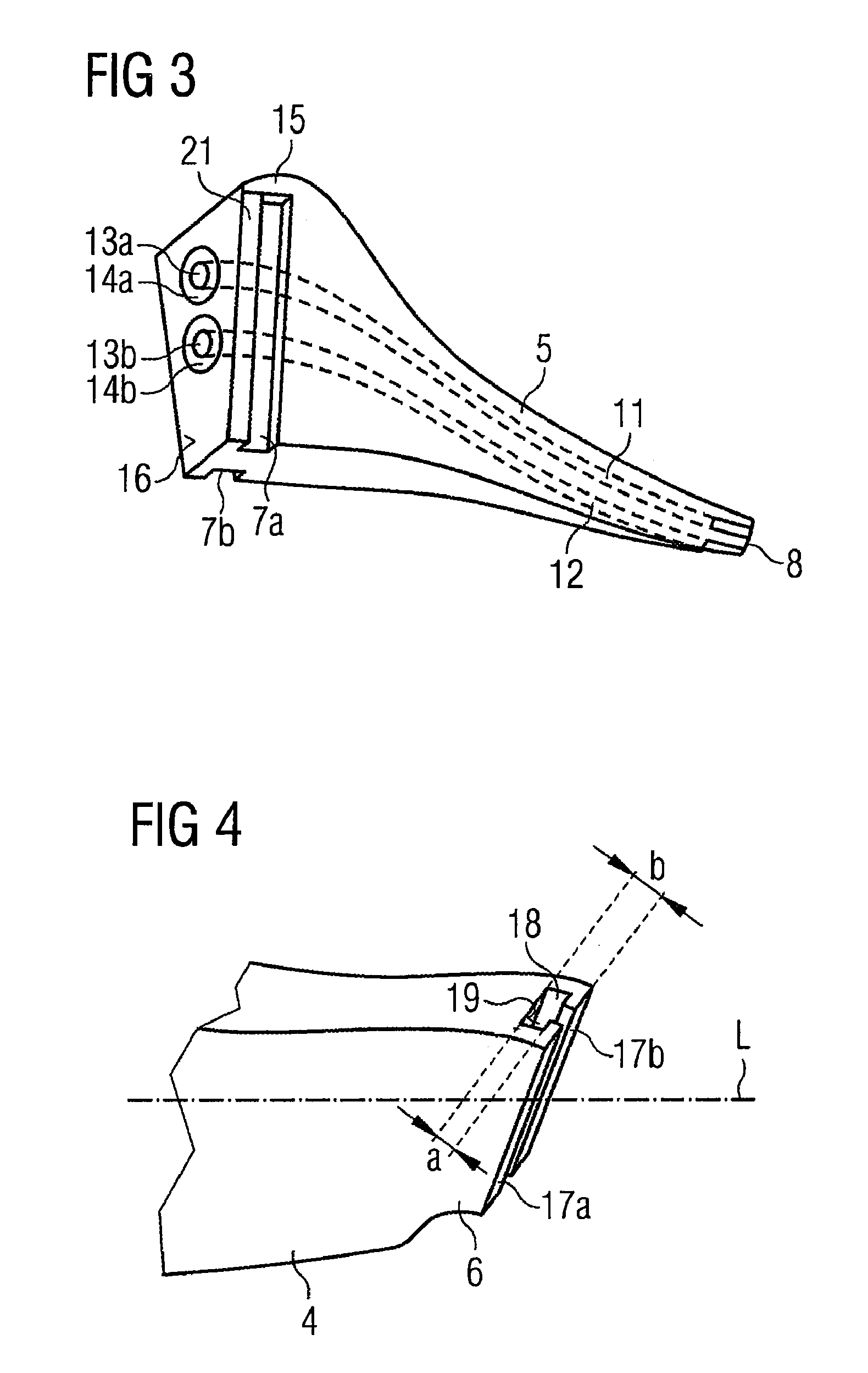
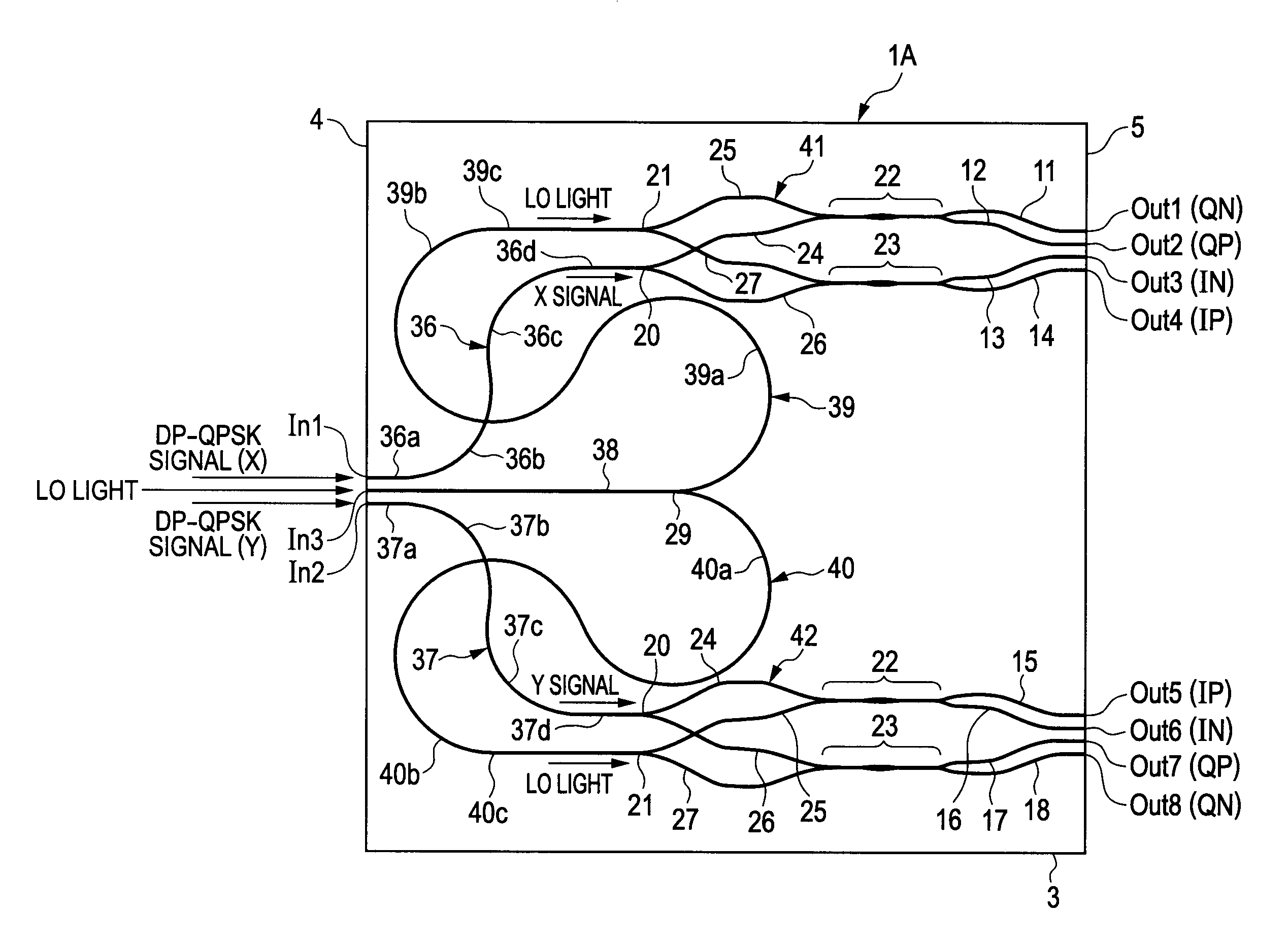
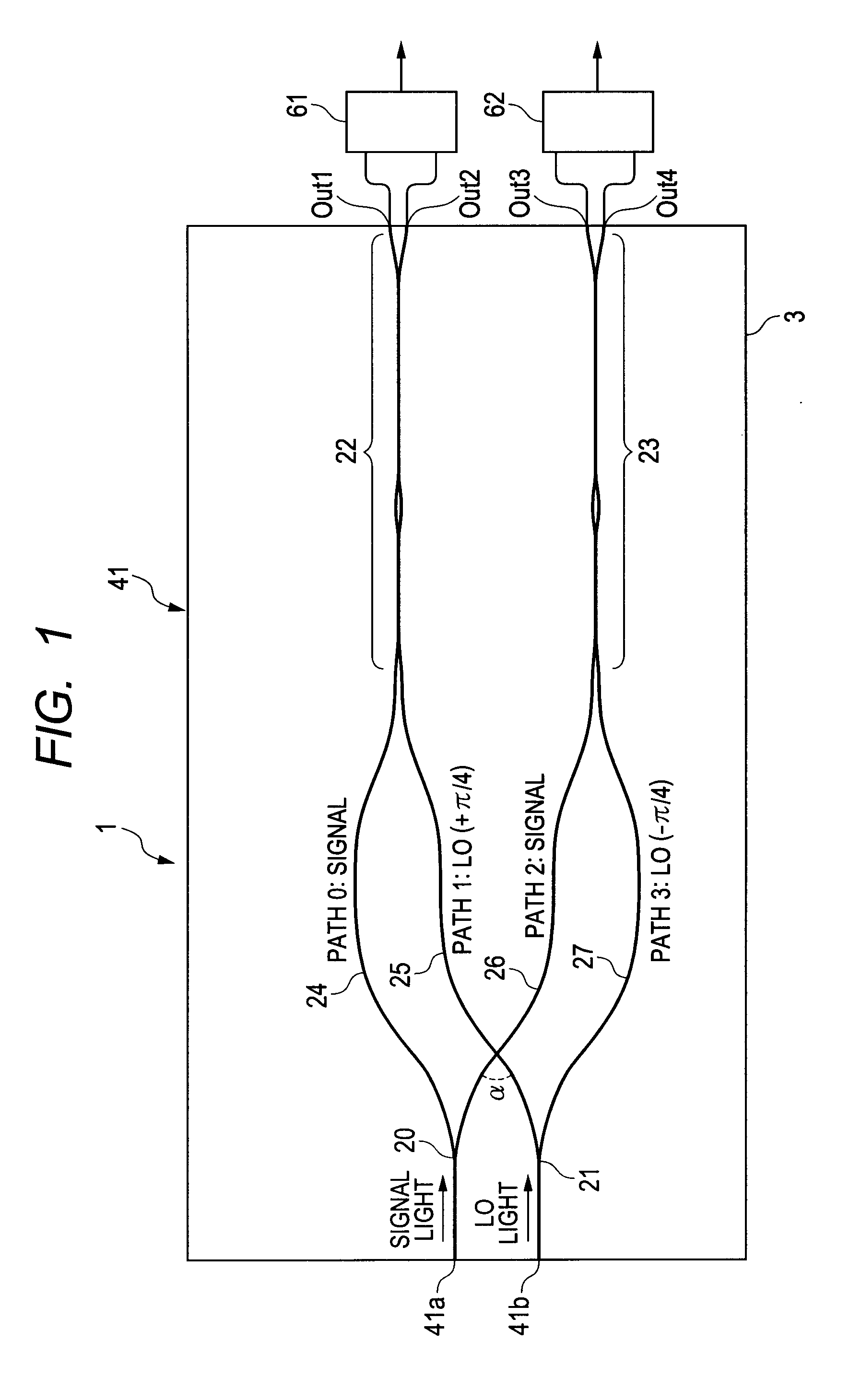
90-degree hybrid
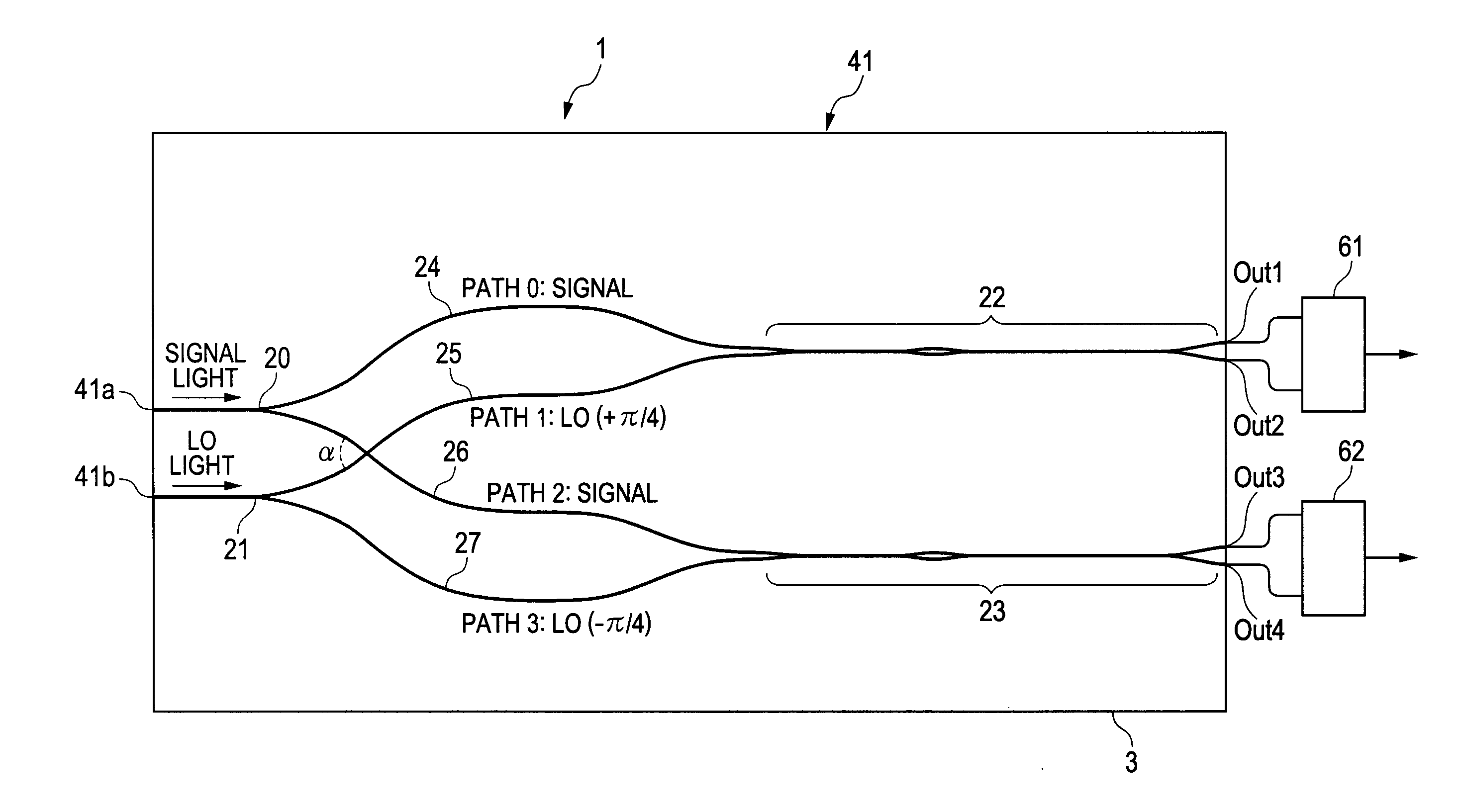
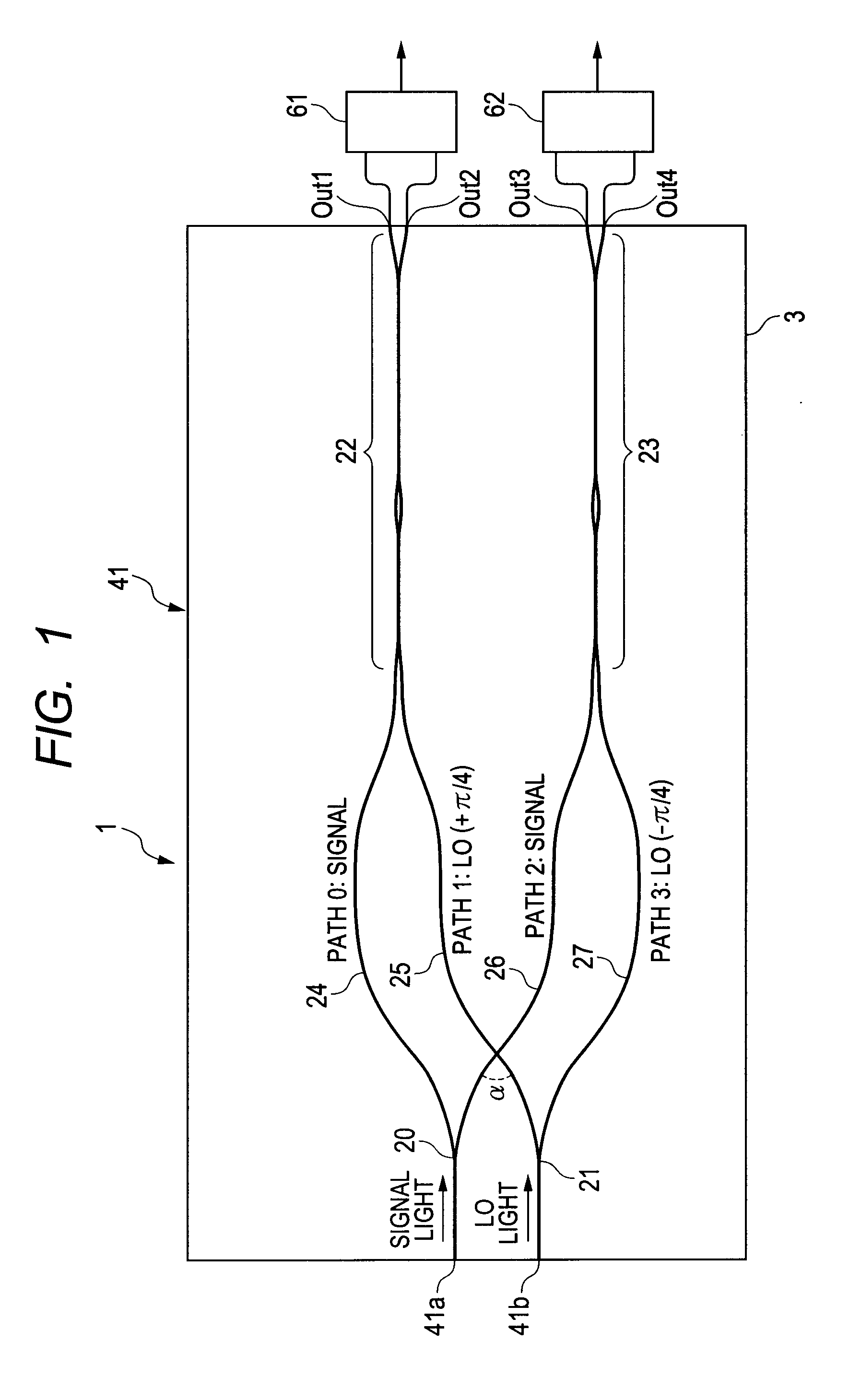
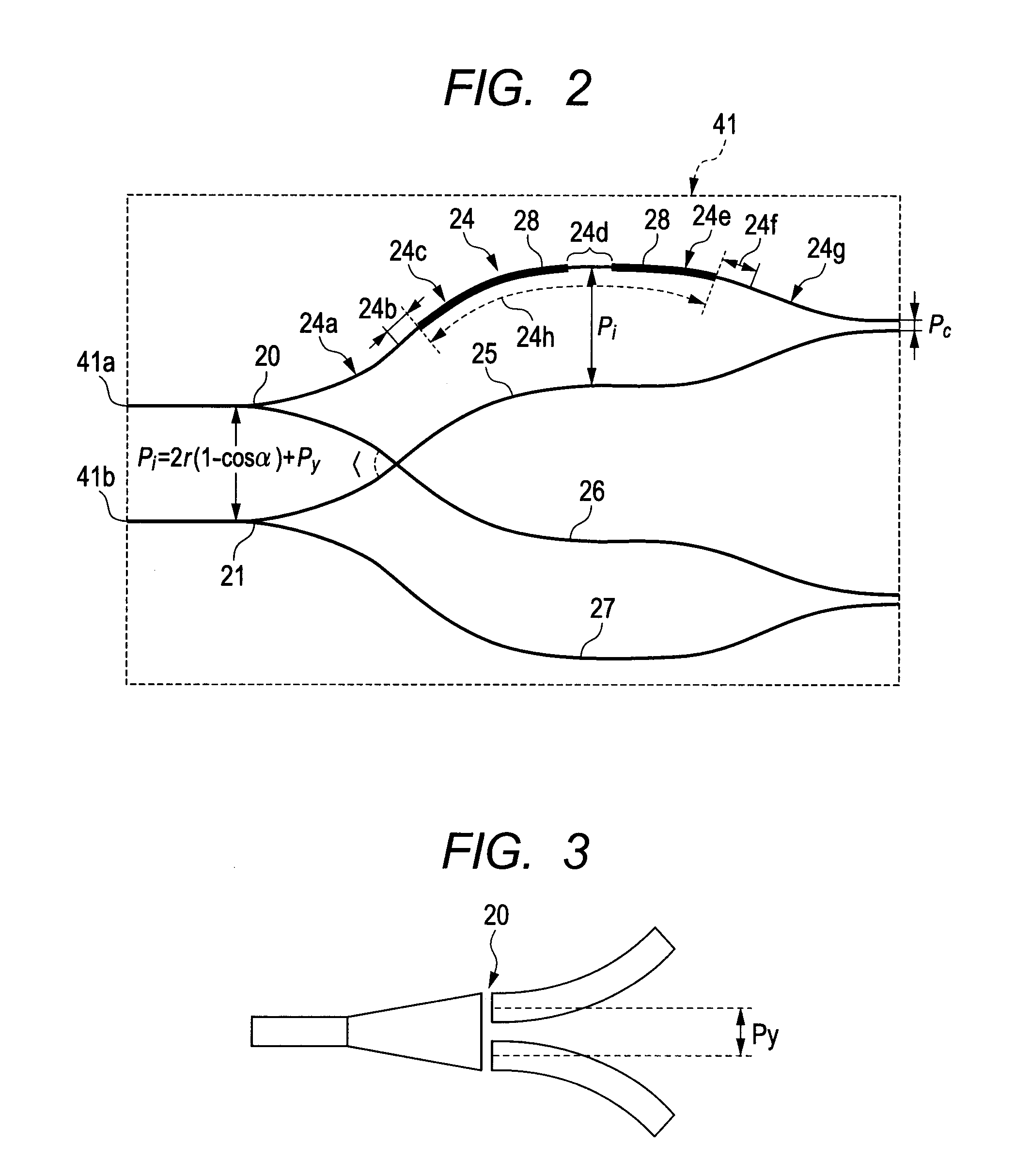
ActiveUS20120224812A1Guaranteed uptimeWide bandModulated-carrier systemsCoupling light guidesMiniaturizationSignal light
The present invention provides a 90-degree hybrid capable of miniaturization and also capable of a stable operation in a wide band. According to an embodiment of the present invention, a PLC-type 90-degree hybrid comprises: a PLC chip having a planar lightwave circuit formed therein; and a 90-degree hybrid circuit formed in the planar lightwave circuit, mixing a modulated signal light and an LO light to separate the signal light into quadrature components I and Q, and outputting the same. The 90-degree hybrid circuit includes: two Y-branch couplers each branching the signal light and the LO light; and two wavelength-independent directional couplers which cause LO lights passing through two paths and signal lights passing through two paths to interfere with each other, respectively. The above-described paths include waveguides having mutually inverted shapes and waveguides having an identical shape, and have a shape substantially symmetrical with respect to the signal light.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
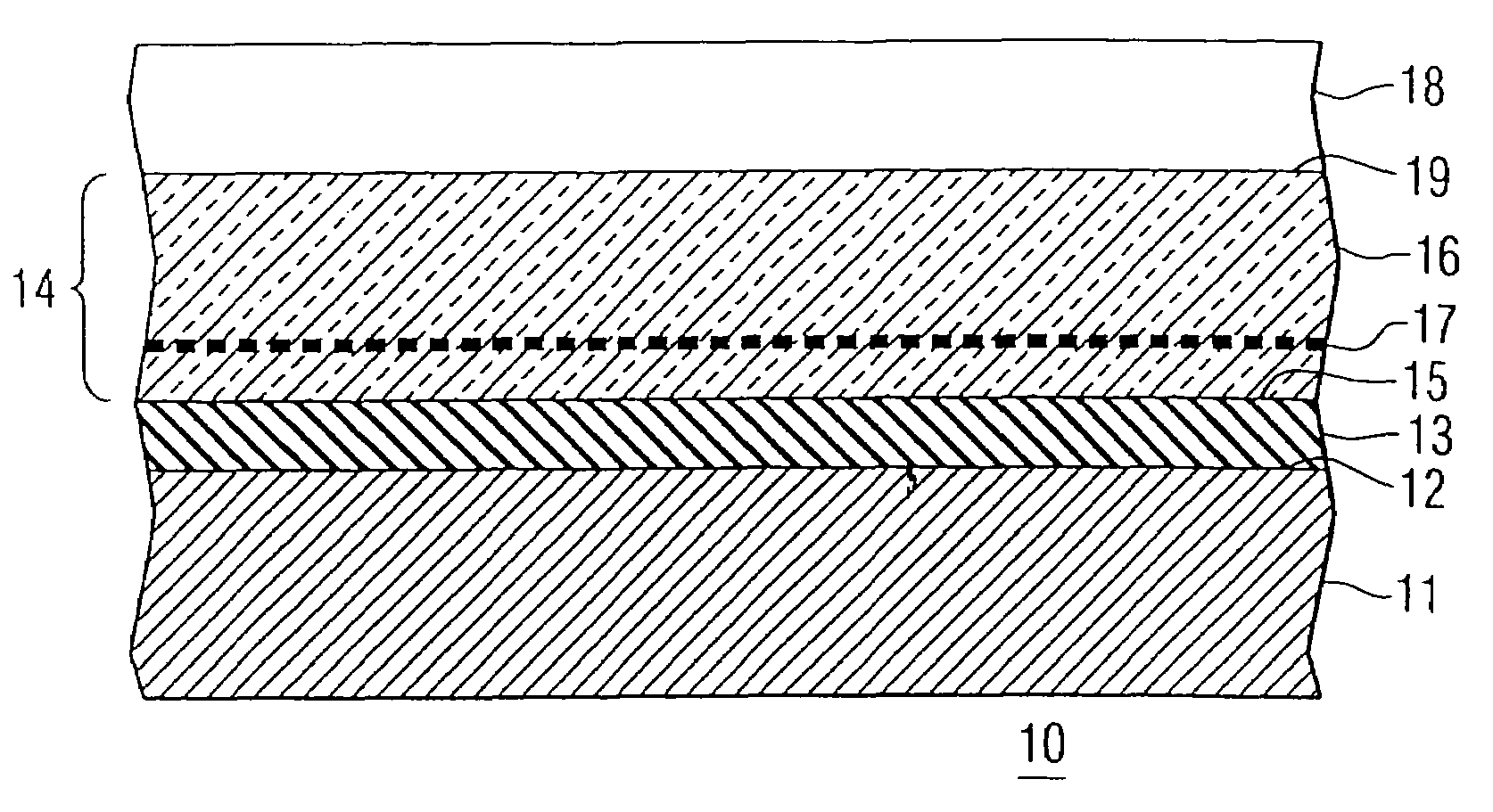
Method for forming a bonded substrate containing a planar intrinsic gettering zone and substrate formed by said method
InactiveUS20010016399A1Improve efficiencyFacilitates small geometry manufactureTransistorSolid-state devicesLattice defectsSemiconductor materials
In a method for forming a bonded semiconductor-on-insulator substrate for the fabrication of semiconductor devices and integrated circuits, a surface of a wafer of a monocrystalline semiconductor material is implanted with ions of the semiconductor material a to a selected depth in the wafer to form, adjacent to the surface, an amorphous layer of the semiconductor material. The layer of amorphous semiconductor material extends to a substantially planar zone disposed at substantially the selected depth and comprising the monocrystalline semiconductor material damaged by lattice defects, i.e., end-of-range implant damage. Undamaged material below the selected depth comprises a first layer of the monocrystalline semiconductor material. The wafer is heated under conditions effective to convert the amorphous layer to a second layer of the monocrystalline semiconductor material and to coalesce the zone of damaged monocrystalline semiconductor material, thereby forming a substantially planar intrinsic gettering zone of substantially pure semiconductor material that includes active gettering sites disposed at substantially the selected depth. An insulating bond layer on one surface of a handle wafer is bonded to the surface of the wafer to form a bonded semiconductor-on-insulator substrate comprising a handle wafer, an insulating bond layer, and a device wafer of monocrystalline semiconductor material. The device wafer includes a substantially planar intrinsic gettering zone comprising substantially pure semiconductor material and including active gettering sites. The described bonded substrate is employed in the fabrication of semiconductor devices and integrated circuits.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Medical handset and exchangeable nozzle for the same
ActiveUS7762812B2Down timePatients can be treated more quicklyTeeth fillingDental toolsInterference fitPowder mixture
The present invention relates to a medical handset with a nozzle having at least one nozzle line for supplying a medically active medium, such as for example an air-powder mixture and / or a fluid, in particular for the prophylactic treatment of teeth, wherein the handset has a head part with a connecting part on the head for the exchangeable connection of the handset to the nozzle, wherein at least one supply line of the handset is connected to the at least one nozzle line of the nozzle by producing a sealing-tight interference fit of a sealing face on the nozzle with a sealing face on the handle, in particular in that a tongue-and-groove connection is produced between the nozzle and the connecting part, e.g. in that a T-groove on the nozzle is inserted into a T-tongue on the handle, the axis of insertion lying roughly at right angles to the longitudinal axis of the handset.
Owner:FERTON HLDG
90-degree hybrid
ActiveUS8401351B2Small sizeStable operation in wideModulated-carrier systemsCoupling light guidesMiniaturizationEngineering
The present invention provides a 90-degree hybrid capable of miniaturization and also capable of a stable operation in a wide band. According to an embodiment of the present invention, a PLC-type 90-degree hybrid comprises: a PLC chip having a planar lightwave circuit formed therein; and a 90-degree hybrid circuit formed in the planar lightwave circuit, mixing a modulated signal light and an LO light to separate the signal light into quadrature components I and Q, and outputting the same. The 90-degree hybrid circuit includes: two Y-branch couplers each branching the signal light and the LO light; and two wavelength-independent directional couplers which cause LO lights passing through two paths and signal lights passing through two paths to interfere with each other, respectively. The above-described paths include waveguides having mutually inverted shapes and waveguides having an identical shape, and have a shape substantially symmetrical with respect to the signal light.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Physical quantity sensor having multiple through holes
ActiveUS7178400B2Small manufacturing errorShort processing timeAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTurn-sensitive devicesSemiconductorPhysical quantity
Owner:DENSO CORP
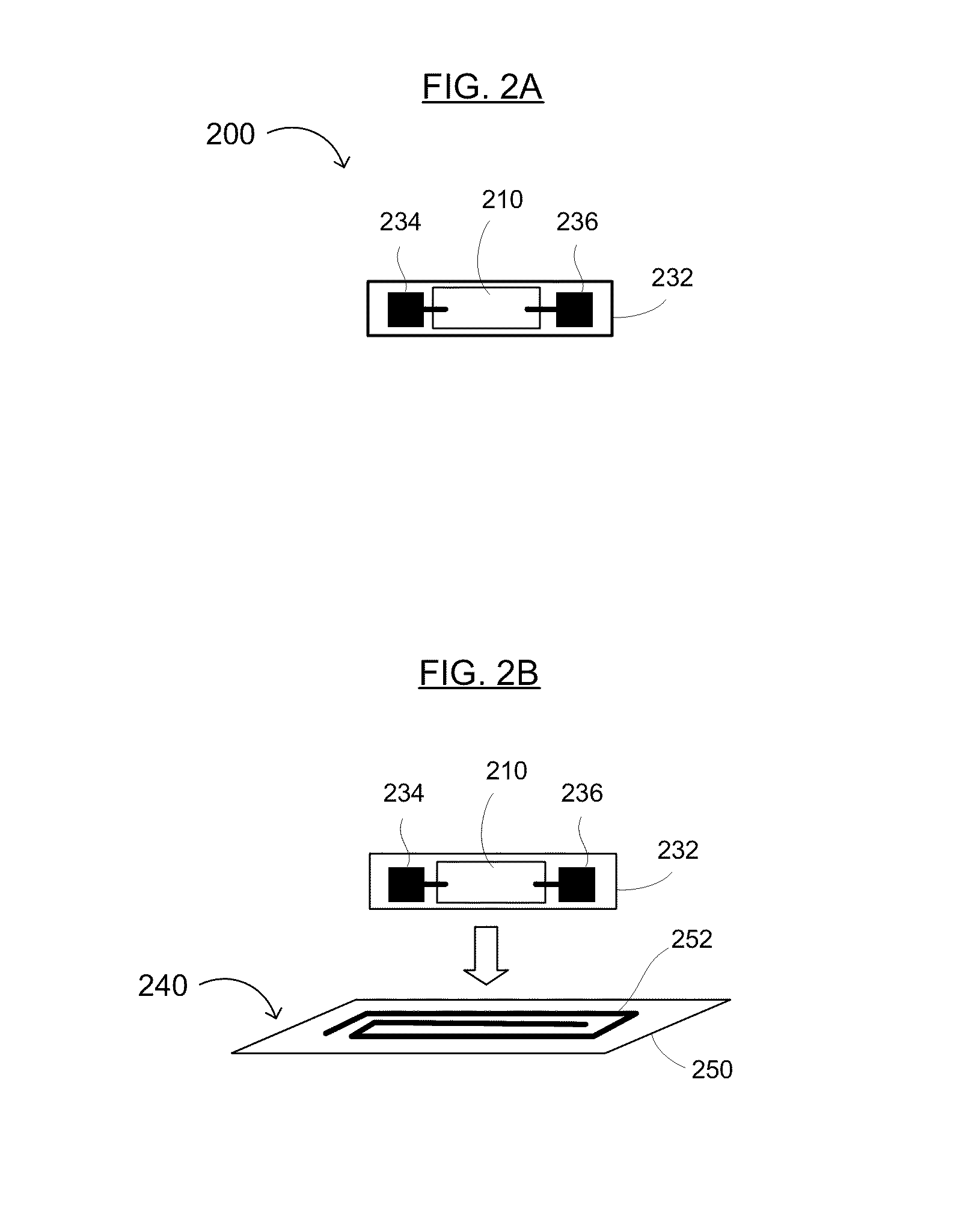
Wireless devices including printed integrated circuitry and methods for manufacturing and using the same
InactiveUS9004366B2Leverage low capital expenditure and operating costLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityElectrical devices
Printed integrated circuitry and attached antenna and / or inductor for sensors, electronic article surveillance (EAS), radio frequency (RF) and / or RF identification (RFID) tags and devices, and methods for its manufacture. The tag generally includes printed integrated circuitry on one carrier and an antenna and / or inductor on another carrier, the integrated circuitry being electrically coupled to the antenna and / or inductor. The method of manufacture generally includes of printing an integrated circuit having a plurality of first pads on a carrier, forming an antenna and / or inductor having a plurality of second pads on a substrate, and attaching at least two of the first pads of the printed integrated circuit to corresponding second pads of the antenna and / or inductor. The present invention advantageously provides a low cost RFID tag capable of operating at MHz frequencies that can be manufactured in a shorter time period than conventional RFID tags that manufacture all active electrical devices on a conventional wafer.
Owner:ENSURGE MICROPOWER ASA
Pump with segmented fluid end housing and in-line valve
ActiveUS10655623B2Improve advancedEasy accessPositive displacement pump componentsPositive-displacement liquid enginesMechanicsPlunger pump
A plunger pump fluid end assembly design in which the suction valve and seat is aligned with the plunger and the fluid end housing is constructed with multiple modules. Modules are held in a rigid assembly by staybolts that connect to the power end of the plunger pump. Said staybolts pass though bores in the central fluid module and the suction seat module and bound by a conventional threaded nut. Packing box modules are bound to the central fluid module by bolts that also pass through separate bores in the same central module. A suction valve spring retainer / plunger spacer within the plunger bore of the assembly shields the intersection of the plunger bore and the discharge bore from destructive erosion damage.
Owner:ALTIS INVESTMENTS LLC
Intake module
InactiveUS6321718B1Manufactured smallGuaranteed uptimeInternal combustion piston enginesFuel-injection pumpsCouplingRotary valve
An intake module for an internal combustion engine. The intake module including at least two intake ducts which can be opened and closed by rotatable valves. The valves are connected to one another via a coupling mechanism and to a common actuating mechanism in the form of a servomotor. In order to compensate for tolerances between the valves and the actuating mechanism, the coupling mechanism includes at least one elastic portion, formed by a weakened material portion, which allows the intake valves to be closed and opened completely. The resilience of the coupling mechanism can be brought about by a change in cross-section or a material reduction. In one embodiment of the invention, the coupling mechanism includes multi-part articulated main rods which control the valves by resiliently mounted legs. In another embodiment, the coupling mechanism includes a main rod having branch rods emerging therefrom with a resilient region extending as a relatively thin cross-section of the branch rods over their entire length.
Owner:MANN HUMMEL GMBH
Method of assembling a fuel injector
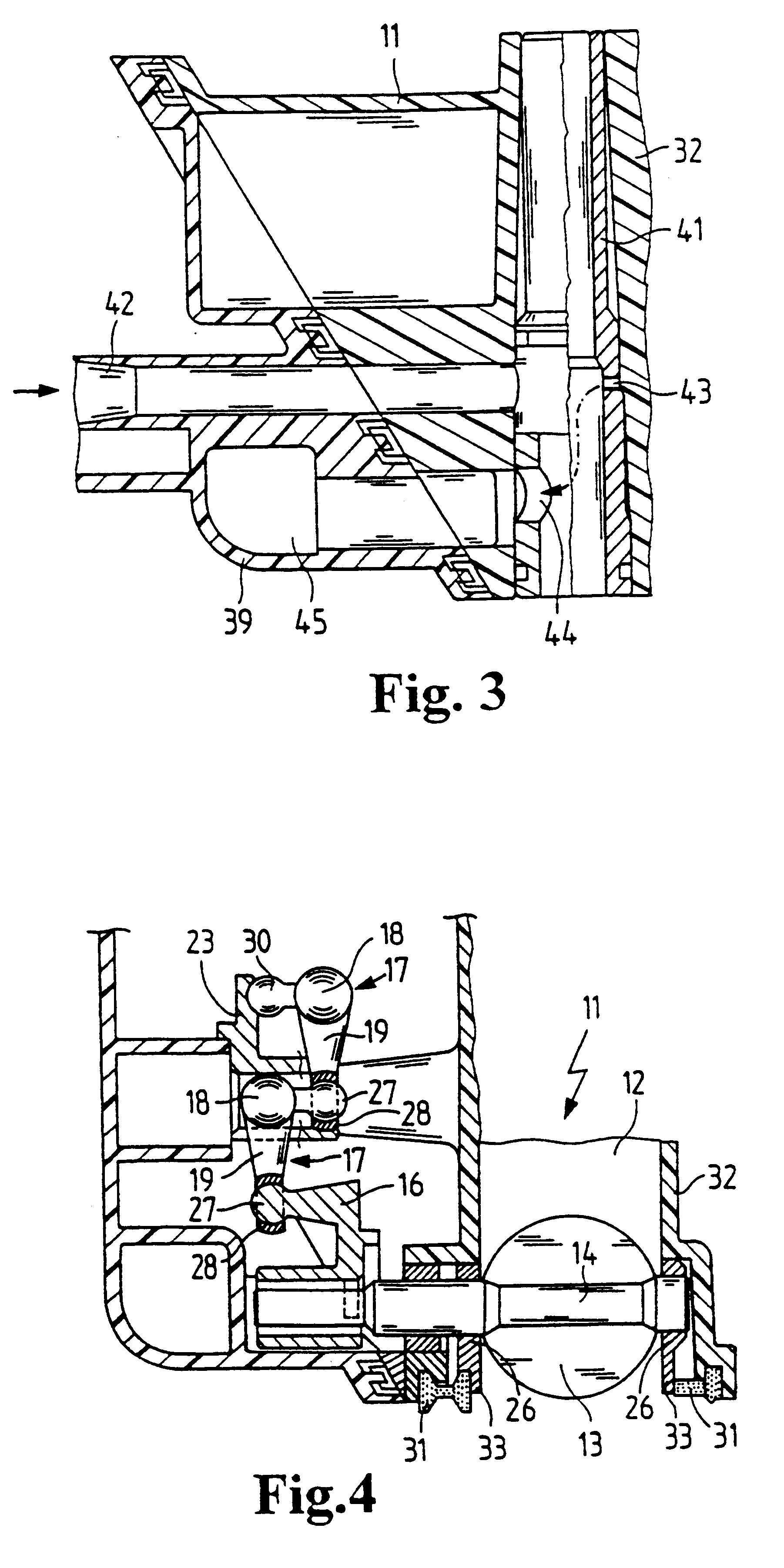
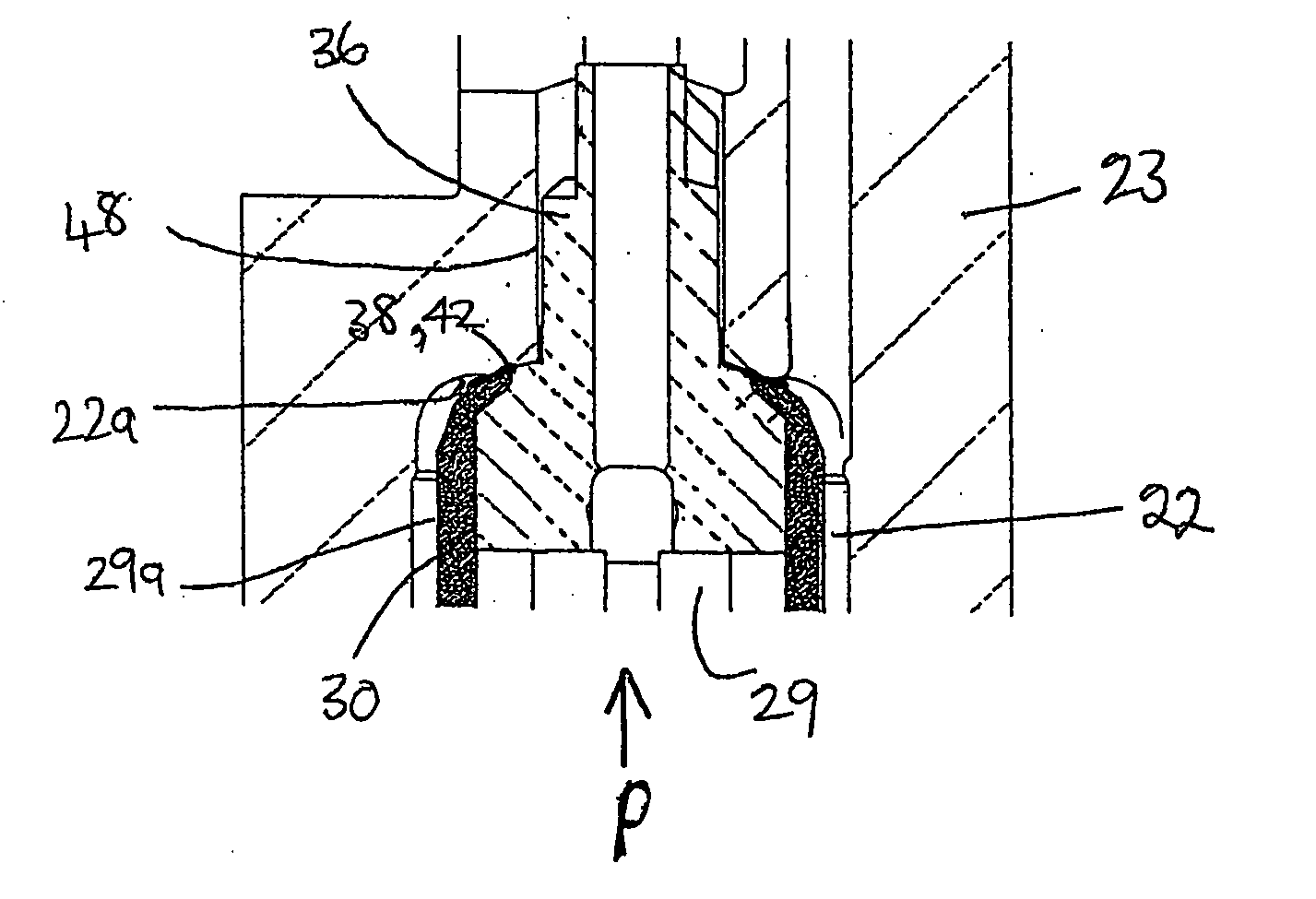
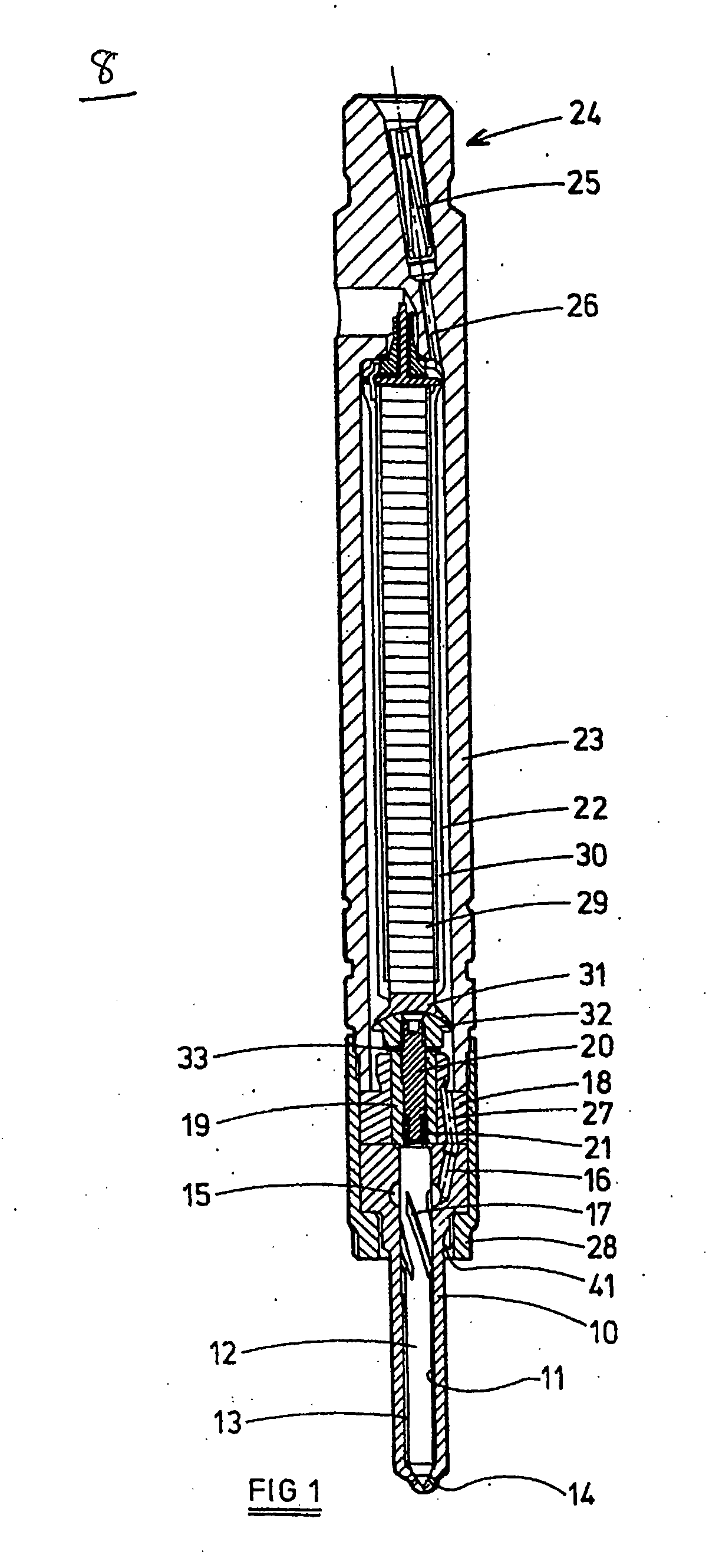
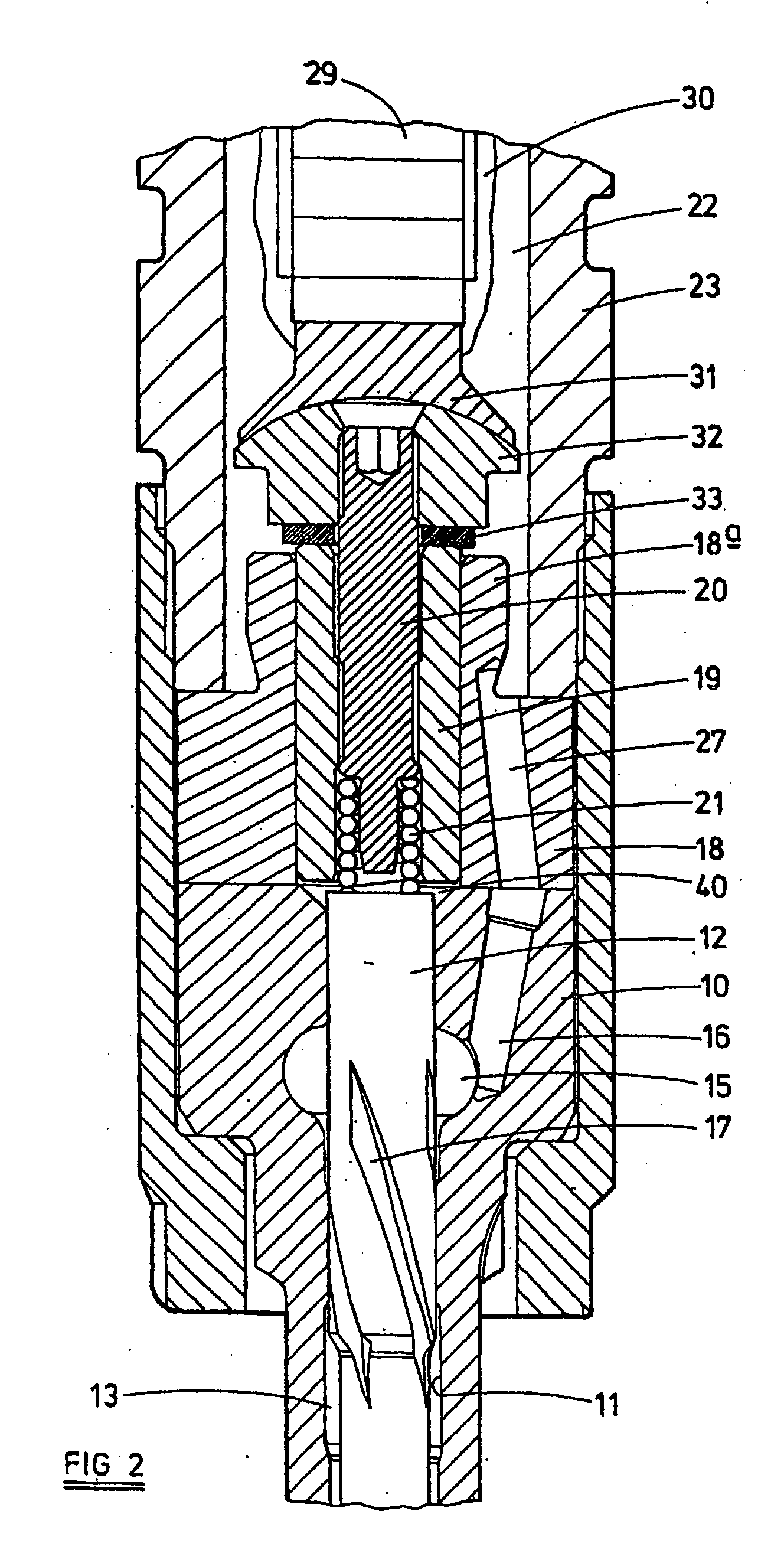
InactiveUS20050199745A1Soften the volume of sealing materialManufactured smallPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMovable spraying apparatusPiezoelectric actuatorsElectrical connector
A method of assembling a fuel injector (8) comprising a fuel injector body having an accumulator volume (22) defined therein is described. The method comprises: providing an encapsulated actuator arrangement (29a) having a piezoelectric actuator stack (29) and electrical connector means (34,36), wherein the stack (29) is encapsulated in a sleeve member (30); providing a volume of sealing material (42) in the region of the electrical connector means (34,36); locating the encapsulated actuator arrangement (29a) in the accumulator volume (22); applying heat indirectly to the volume of sealing material (42) so as to soften the volume of sealing material; and applying pressure to the encapsulated actuator arrangement (29a) such that the volume of sealing material (42) deforms to form a substantially fluid-tight seal (38) between the encapsulated actuator arrangement (29a) and the accumulator volume (22) in the region of the electrical connector means (34,36).
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Method and system for deploying a mirror assembly from a recessed position
InactiveUS20050105196A1Eliminates and reduces disadvantageEfficient integrationMirrorsMountingsEngineeringMechanical engineering
There is disclosed a method and apparatus for deploying a mirror assembly from a recessed position that includes rotating the mirror assembly in a first direction about a first axis, the mirror assembly coupled proximate the first axis to at least one lifting arm and rotating each lifting arm in a second direction about a second axis such that the mirror assembly moves to an operational position. The first direction may be opposite from the second direction.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
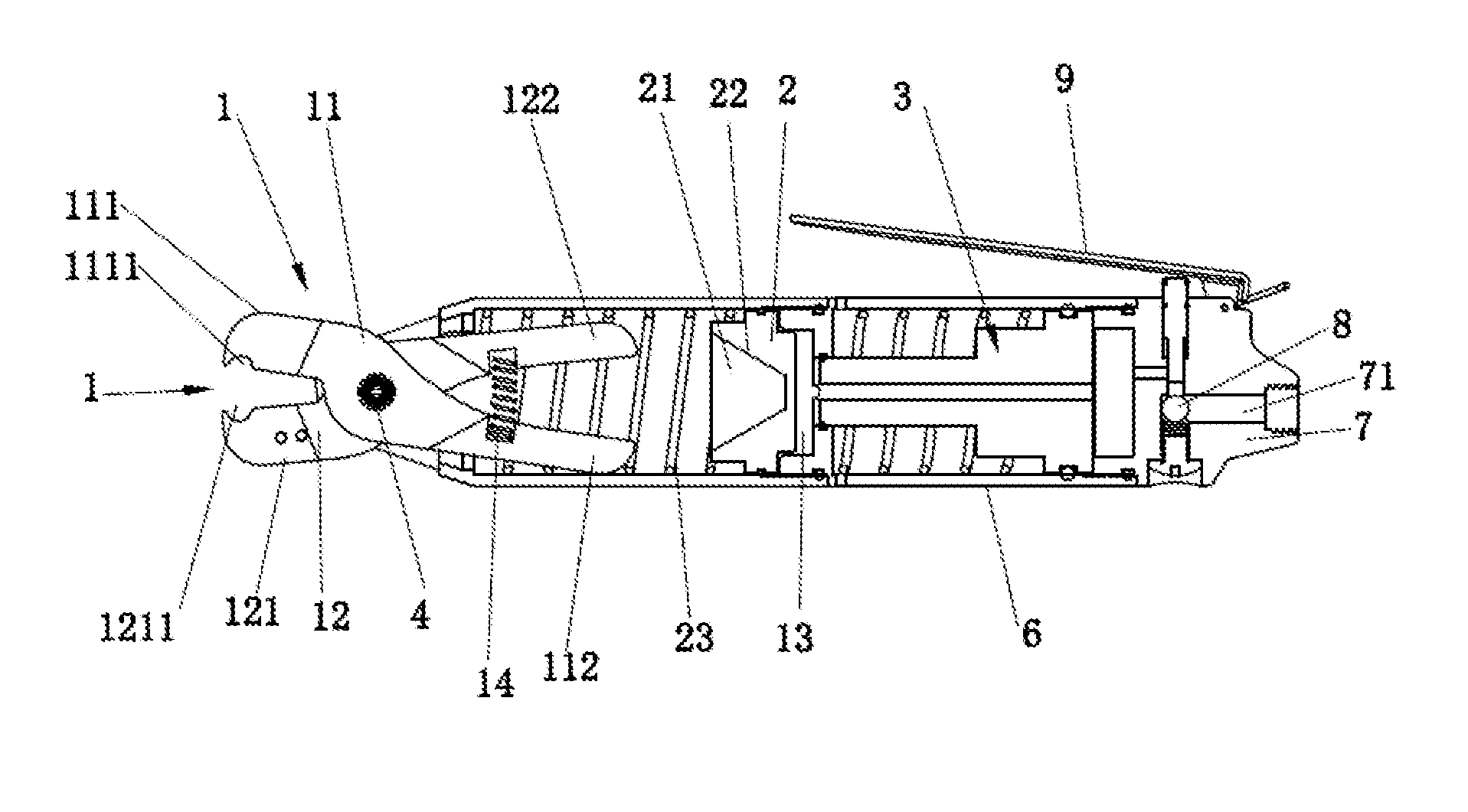
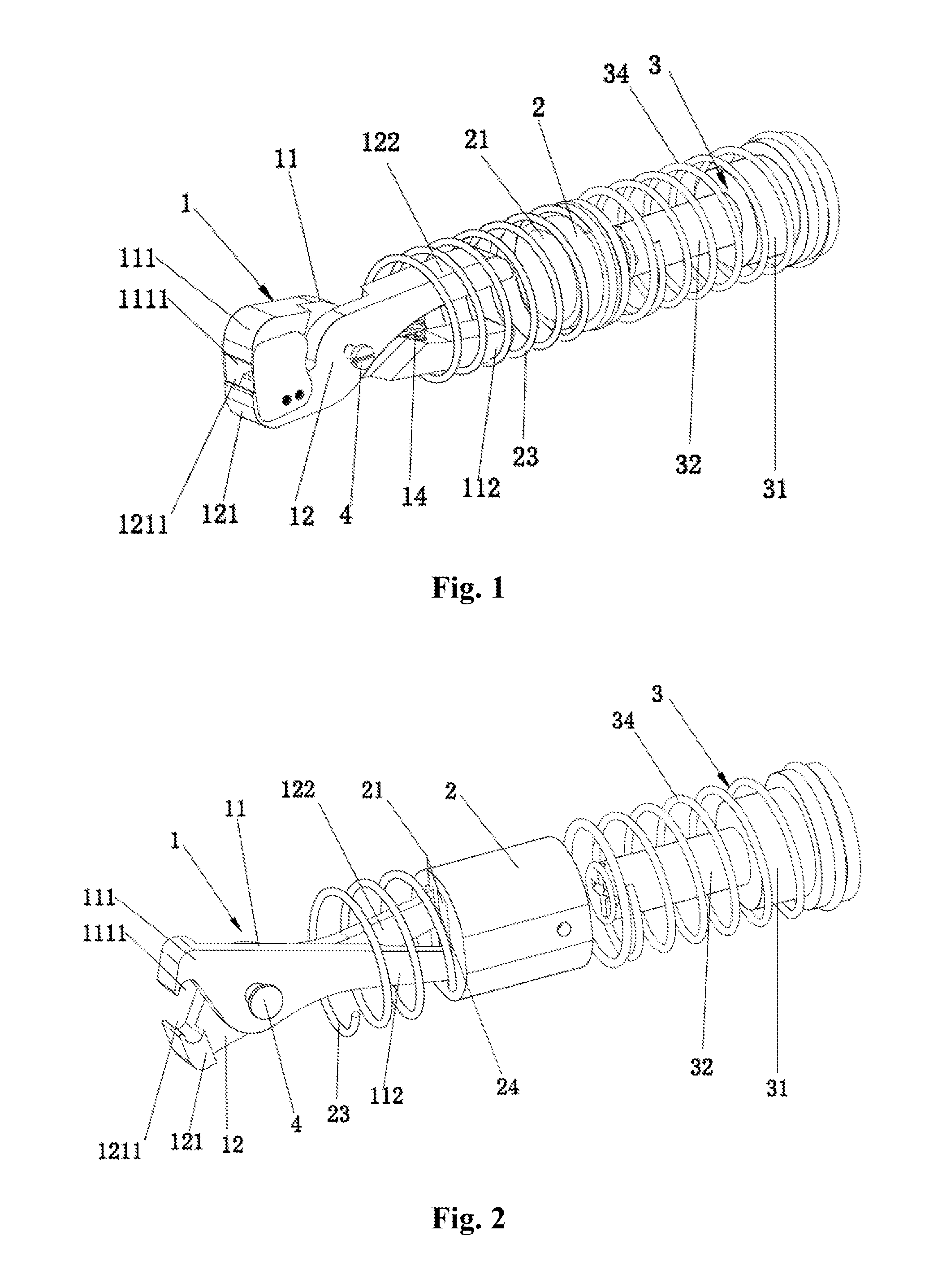
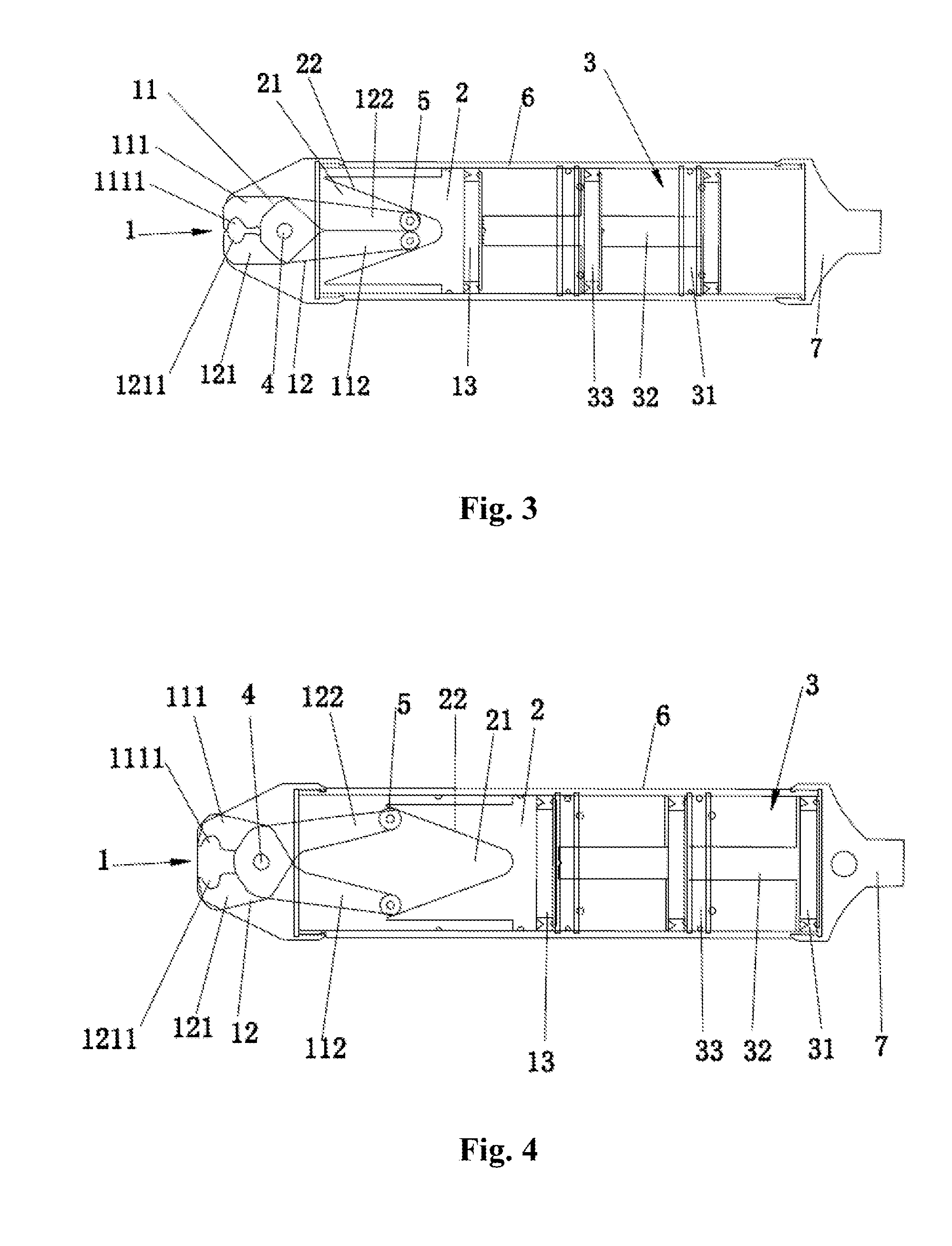
Clip clamping mechanism of pressure fixture and pneumatic caliper having the same
A clip clamping mechanism of a pressure fixture, which the clip comprises a fixedly mounted shaft, and a first clip and a second clip hinged through the fixed shaft. Two ends of the first clip and the second clip corresponding to the hinging joint form respectively a front arm, and a rear arm in linkage with a propulsion piece, wherein the propulsion piece is provided with an accommodation cavity for mounting the rear arm; and the accommodation cavity is provided with a wedge-shaped sidewall for butt junction and slip fit with the rear arm; one end of the accommodation cavity close to the front arm is a big end with opening, while the other end far away the front arm is a small end. The first clip and the second clip achieve a transmission connection through one fixed shaft only to realize butting clamp.
Owner:YUEQING DONGBO ELECTROMECHANICAL
Optical sensor having light projecting prism
An optical sensor projects light rays emanating from a light emitting element that are collimated by a lens and reflected by a mirror and then directed to a light projecting prism. The collimated light rays incident upon the prism are refracted at an incident surface and come out from the prism through a light exit surface so as thereby to be projected into the field of detection. Light rays passing through the field of detection are directed to a light receiving prism. The light rays incident upon the light receiving prism through a light incident surface are reflected by a light exit surface and then come out from the light receiving prism. The outgoing light rays are received and converted into an electric signal by a light receiving element.
Owner:KEYENCE
Electrical system, especially a microelectronic or microelectromechanical high frequency system
InactiveUS20060097388A1Manufactured smallAvoid problemsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCoplanar waveguideEngineering
An electrical component is proposed, in particular a high-frequency microelectronic or microelectromechanical component having a base element that is provided with a feedthrough, a first conductive structure extending on an upper side of the base element being connected by the feedthrough, continuously for high-frequency electromagnetic waves, to a second conductive structure extending on a lower side of the base element. The feedthrough has the form of a right prism or cylinder, and the first and / or the second conductive structure is embodied as a planar waveguide, in particular as a coplanar waveguide. Also proposed is a method for producing an electrical component having a feedthrough for high-frequency electromagnetic waves through a base element, an electrically conductive layer being applied on an upper side of the base element and an etching mask being applied on a lower side of the base element; a trench, having at least almost perpendicular sidewalls and penetrating through the base element, then being etched into the base element in a plasma etching step; an electrically conductive layer being applied on the lower side after the etching and after removal of the etching mask; and the trench lastly being filled or lined with an electrically conductive material.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
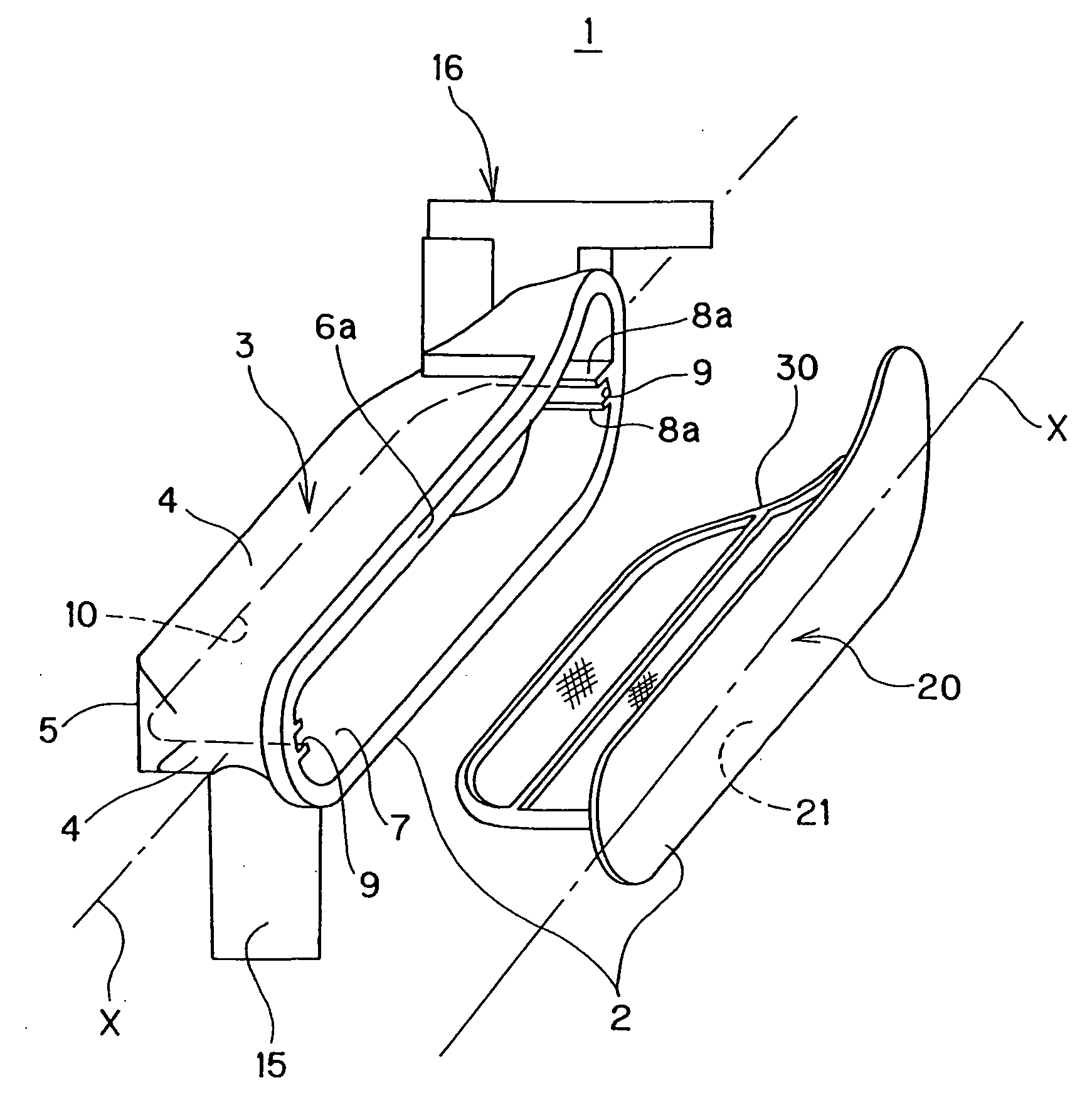
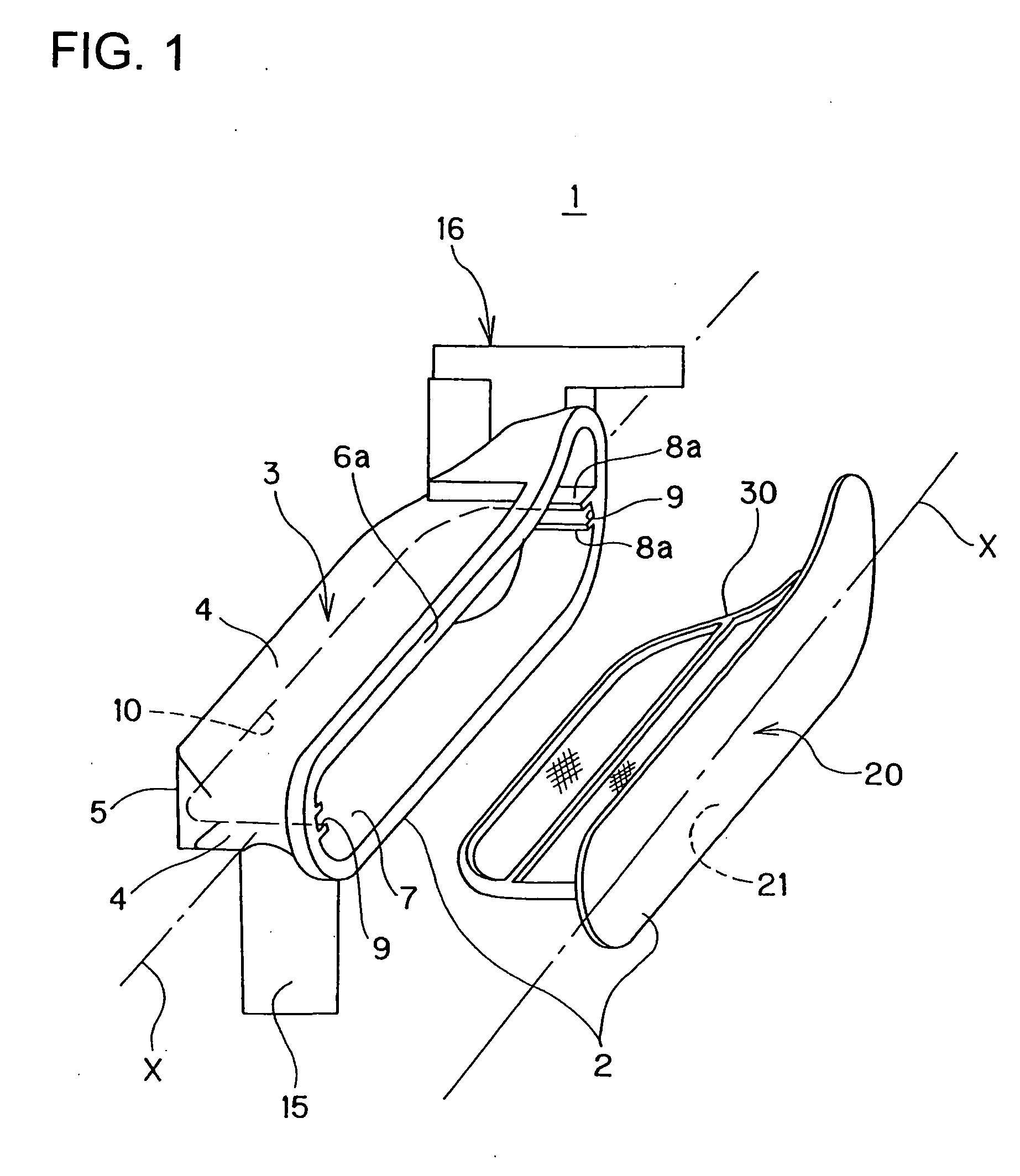
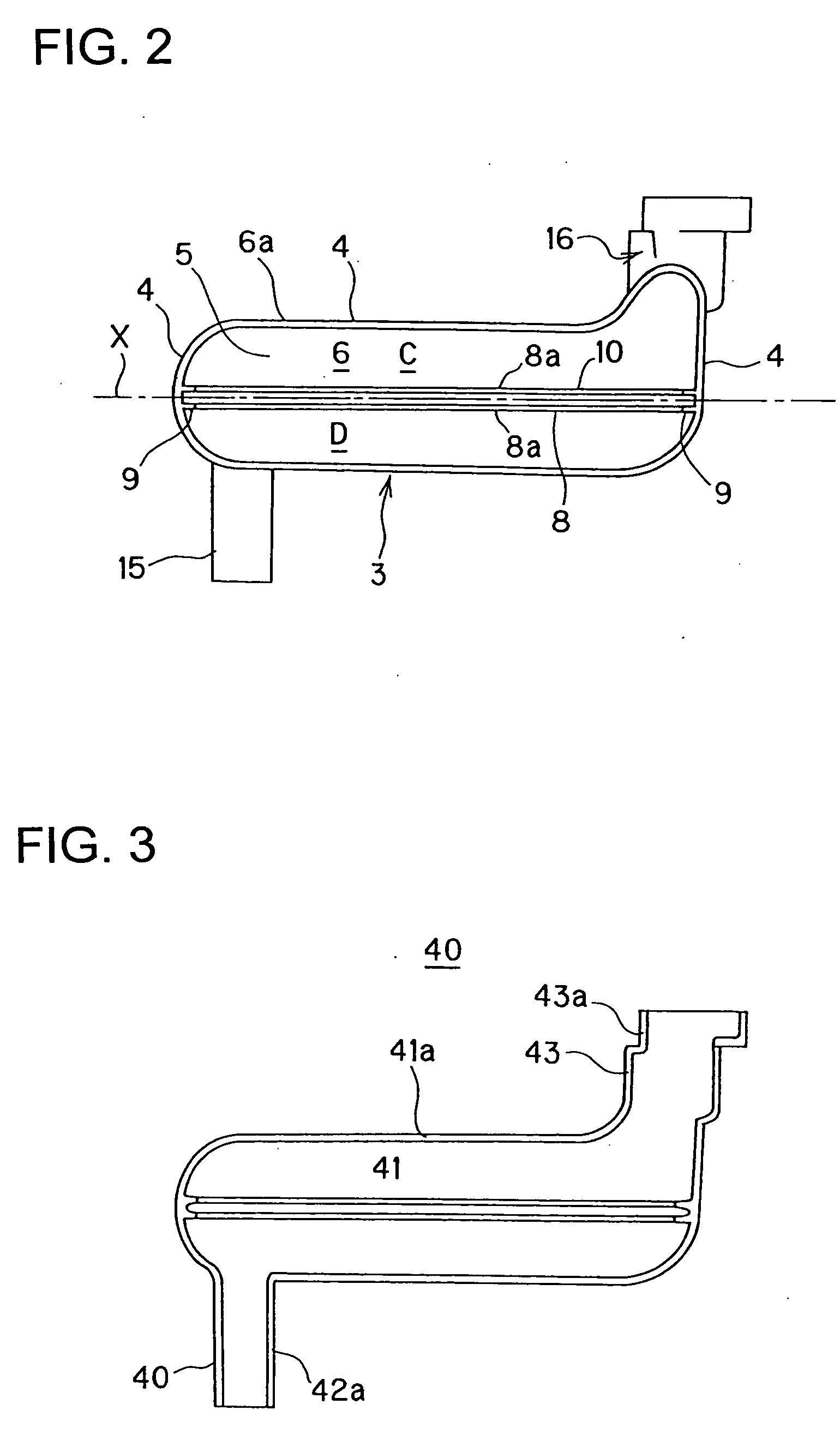
Oil strainer
InactiveUS20070163948A1Liable can be deformedImprove rigidityLoose filtering material filtersCartridge filtersEngineeringMechanical engineering
There is provided an oil strainer in which the assembling work can be performed very easily, and more over high quality can be ensured. An oil strainer 1 includes a housing 2 formed by closing an open portion 6 of a case body 3 by a cover body 20 and a filter element 30 disposed in the housing 2. In the case body 3, there is provided a groove portion 8 including a guide portion 9 for guiding the filter element 30 to the inside of the case body 3 by inserting both side edges of the filter element 30 into the inside and a locking portion 10 for locking the filter element 30 by inserting the tip end edge in the insertion direction of the filter element 30 into the inside.
Owner:TOYO ROKI MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com