Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Reduce spectral width" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
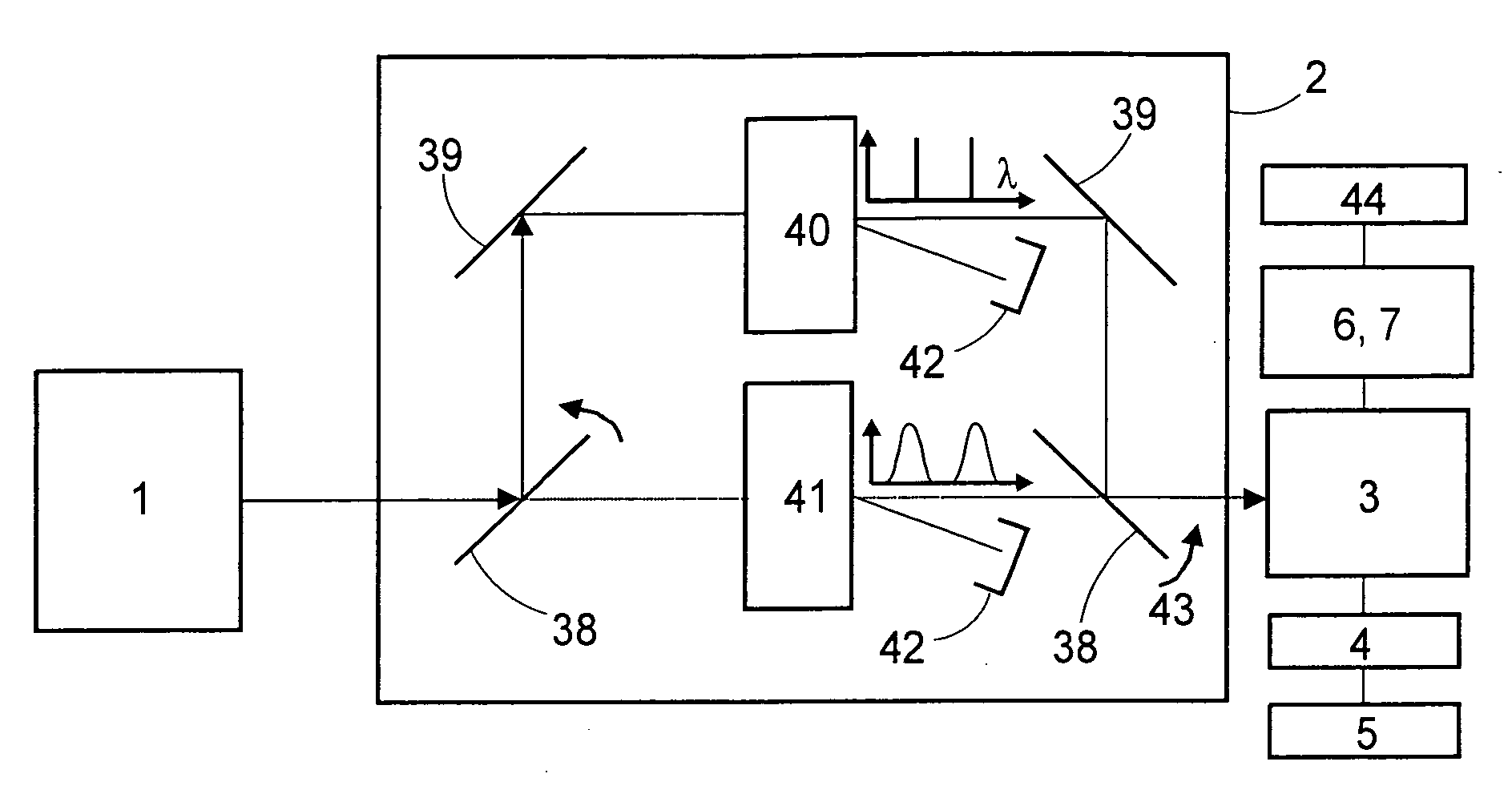
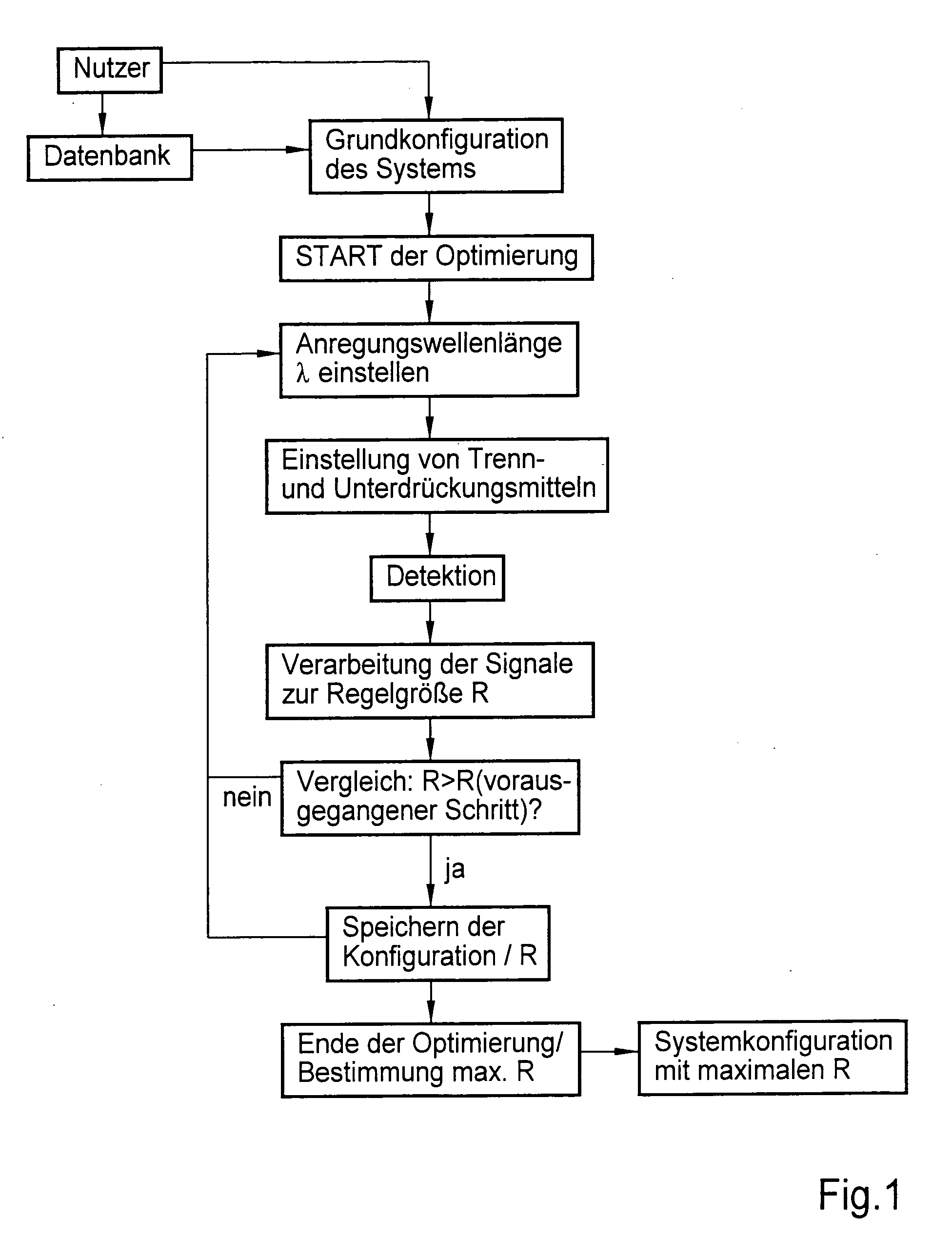
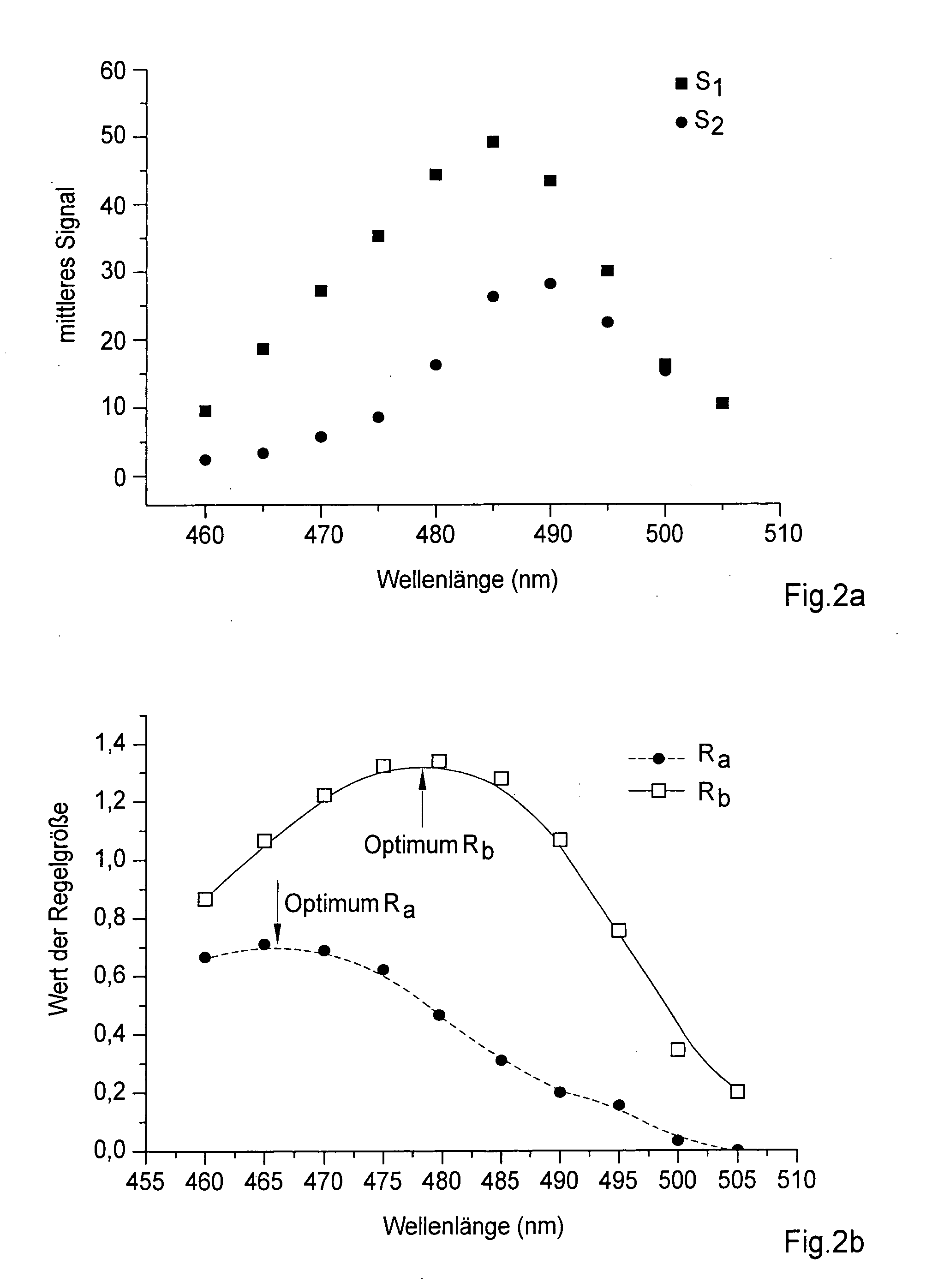
Method and apparatus for the examination of probes
InactiveUS20070133086A1Effective lightingInfluence of lightPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamLength wave
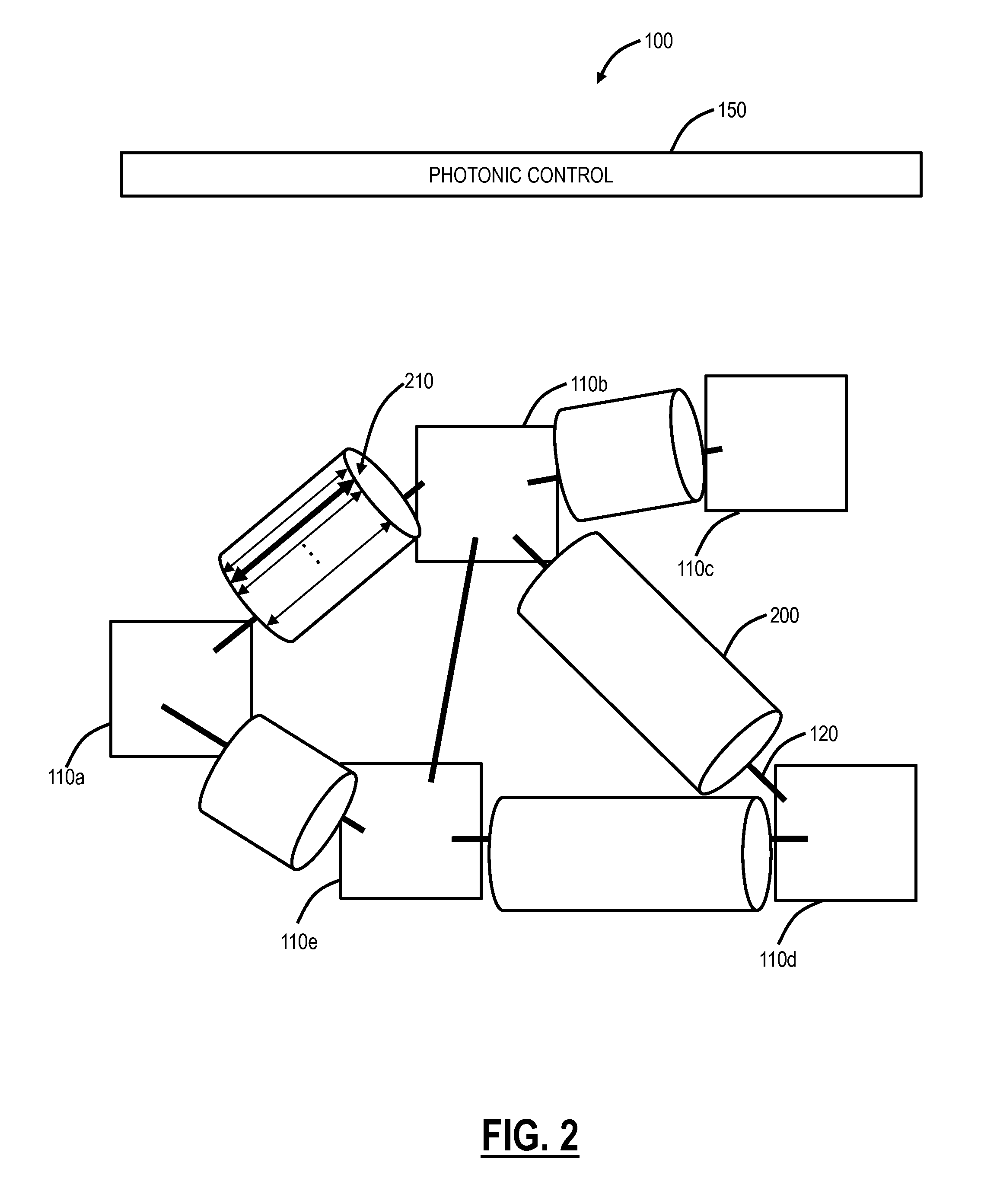
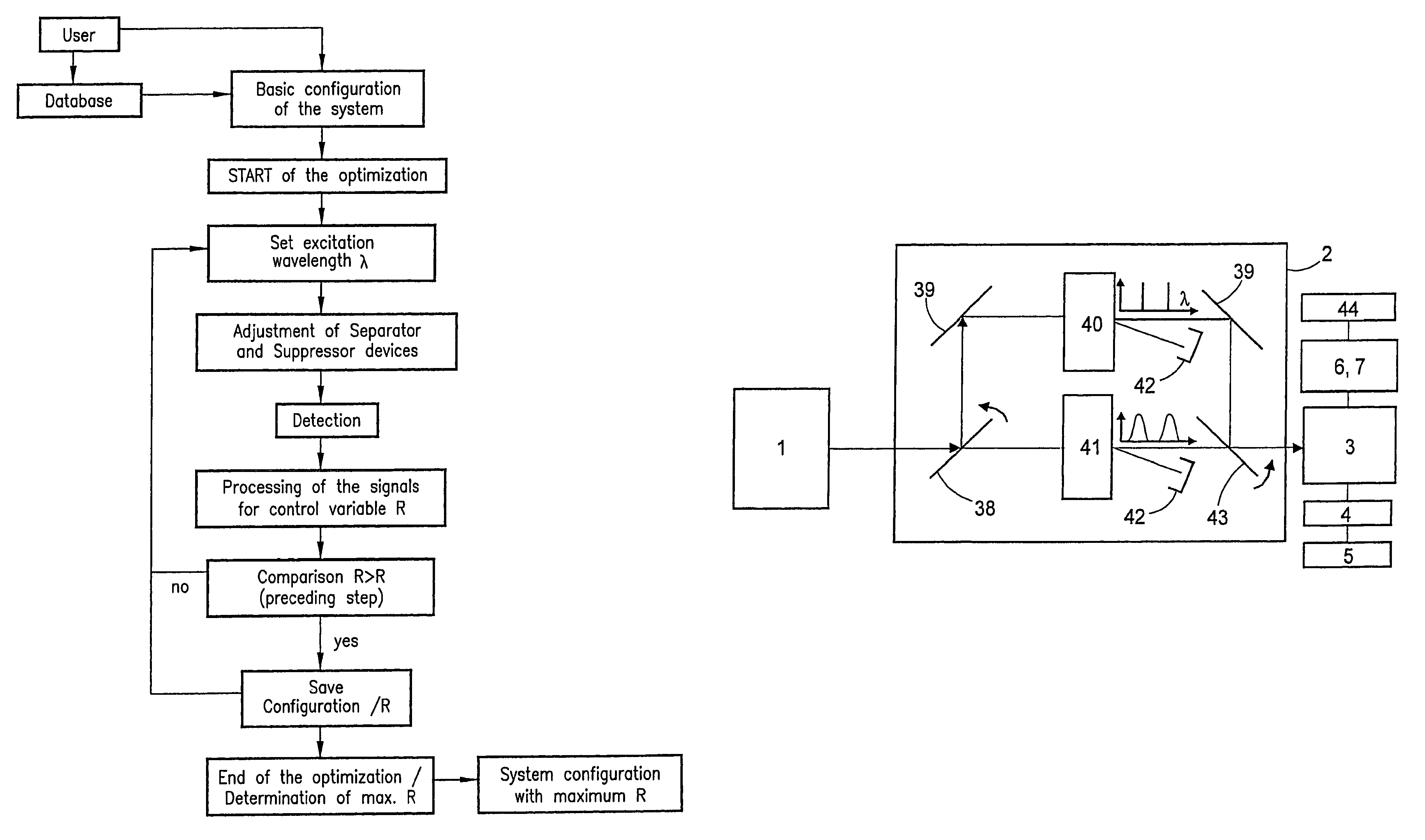
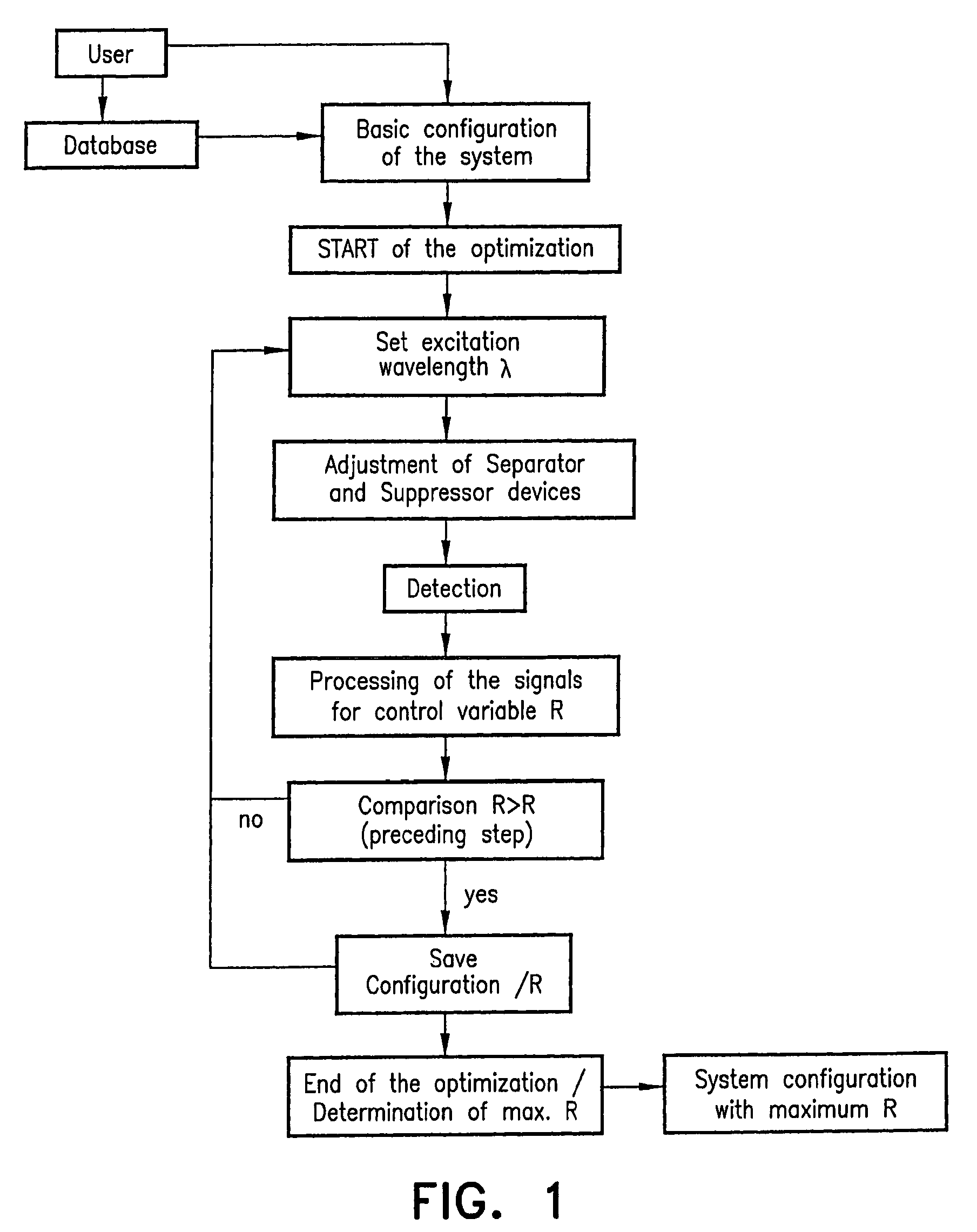
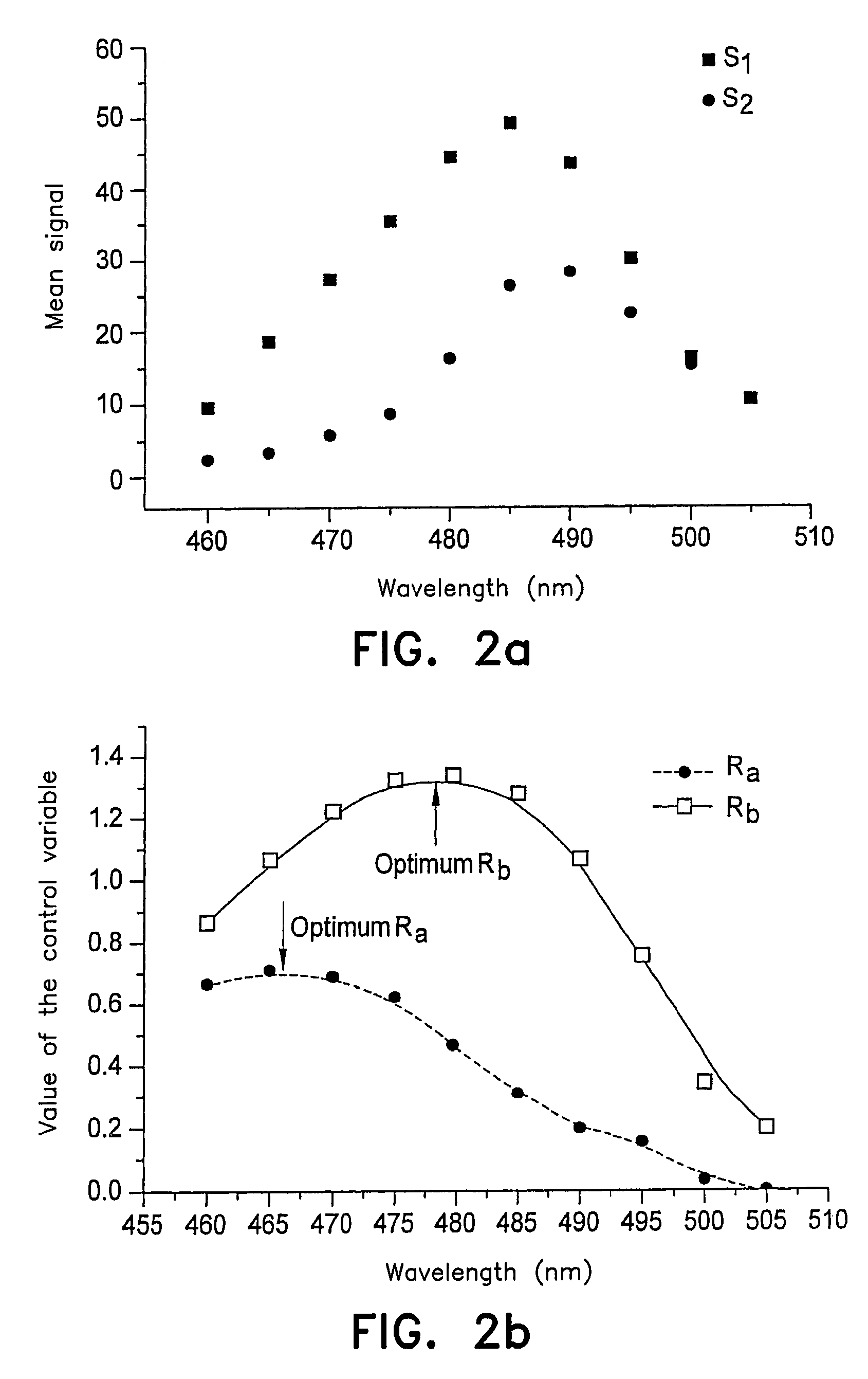
A method in which probes are examined by means a microscope. For an illuminated sample, spatially coherent light with at least one continuous wavelength range or a continuously tunable wavelength range is generated, and one or more wavelengths or wavelength ranges in the illumination light are selected in dependence on the prespecified method of examination. The probe is then illuminated with the illumination light with the selected wavelengths or wavelength ranges, the illumination light and the emission light coming from the probe are then subsequently separated, whereby the back radiated illumination light is suppressed in the detection beam before the detection and the emission light is detected. In such a method, the selection of the wavelengths or the wavelength ranges of the illumination light is tuned by means of the separation of the detection light and the illumination light and the suppression of the illumination light in such a manner that a prespecified control variable (R) is optimized.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
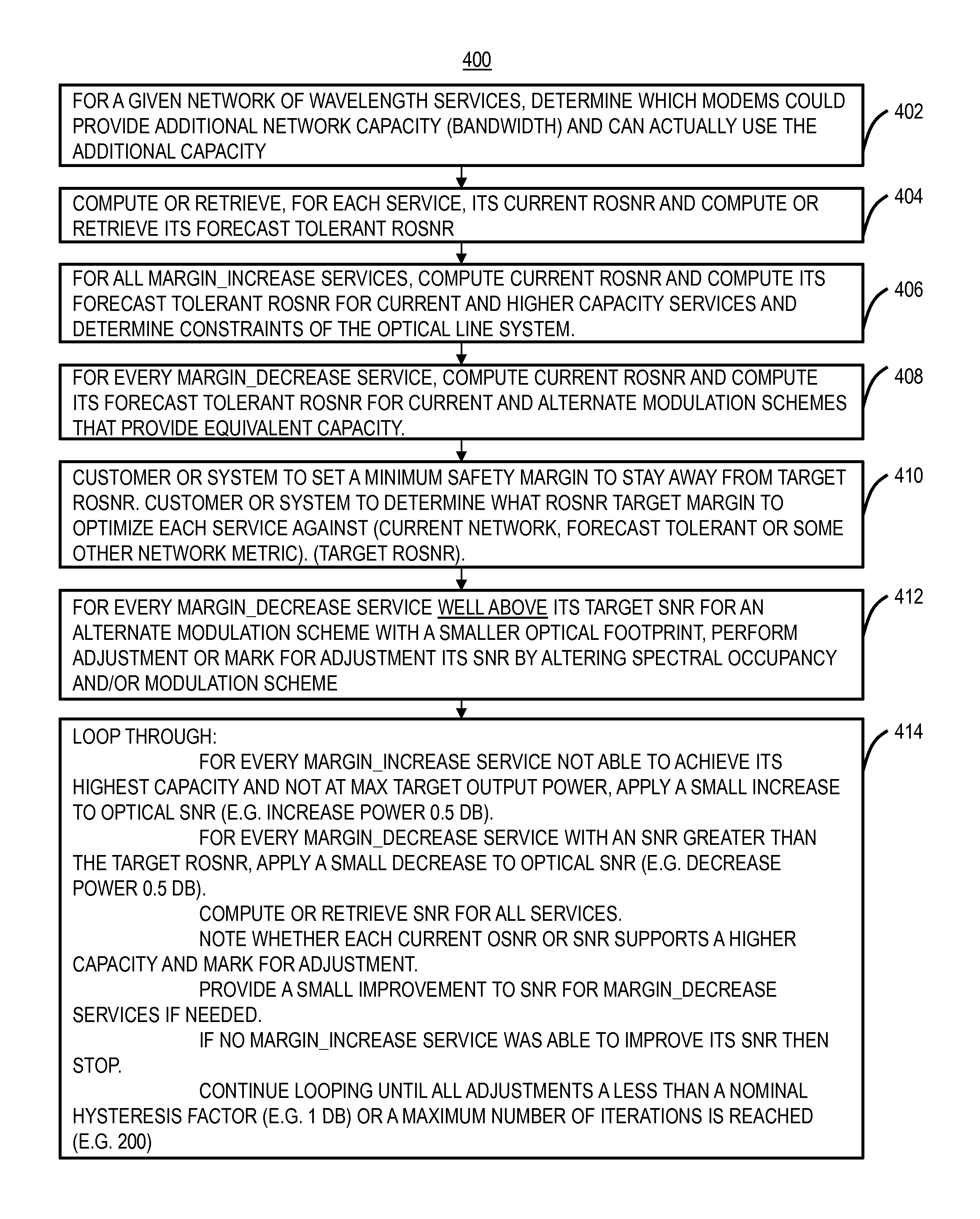
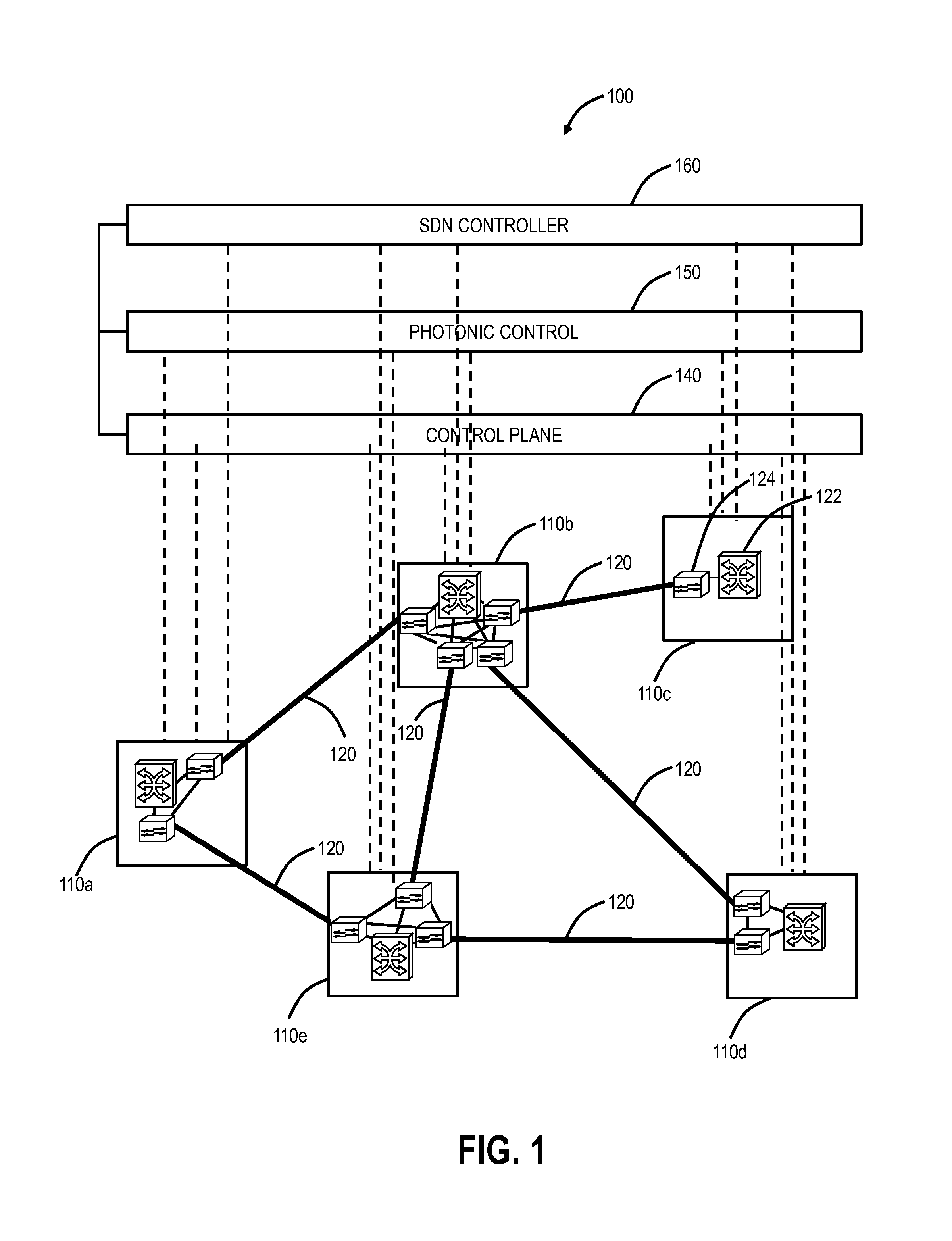
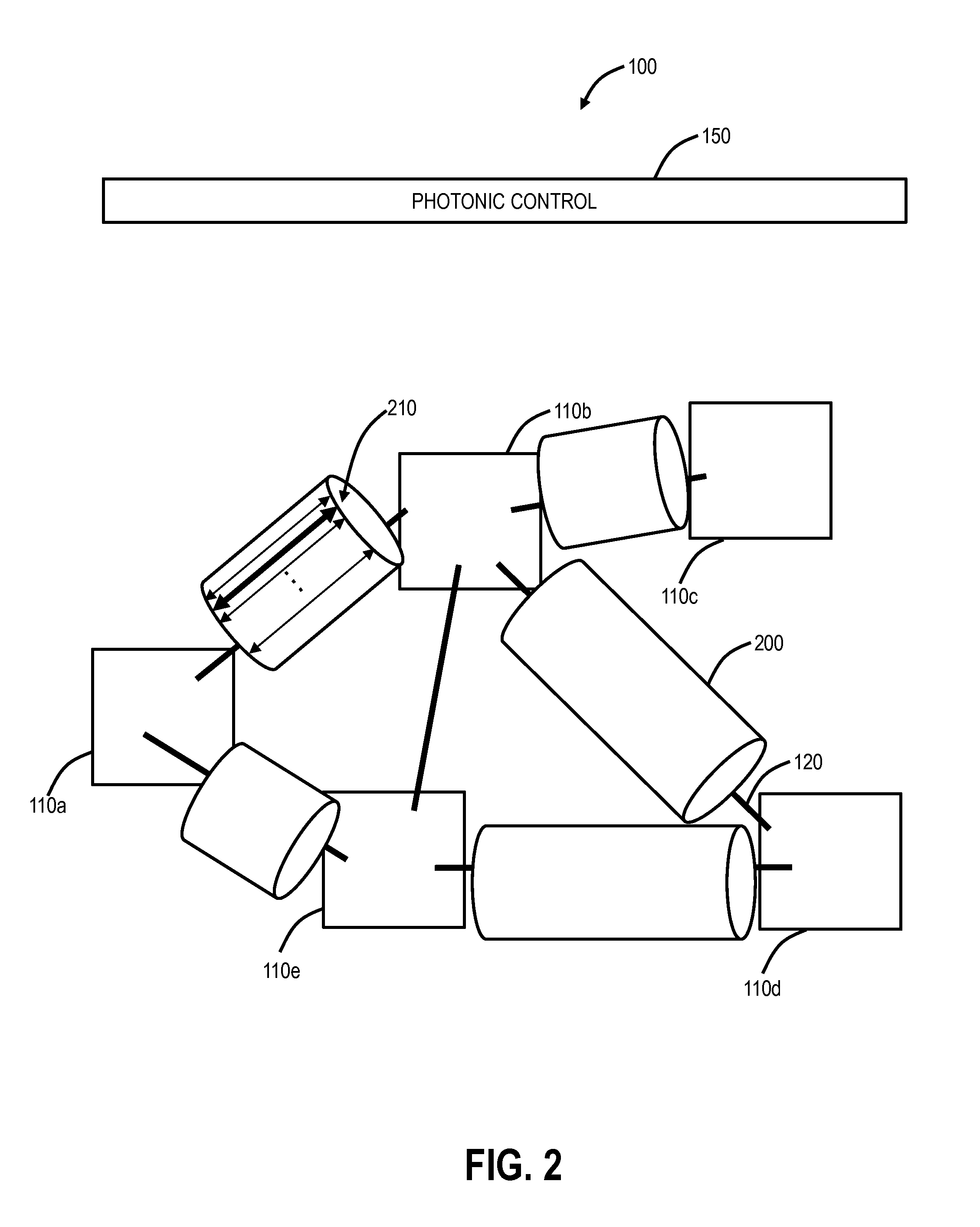
Margin-based optimization systems and methods in optical networks for capacity boosting
ActiveUS20150333824A1Increase capacityReduce marginTransmission monitoringOptical multiplexLength waveOptimization system
Systems and methods of optimizing capacity of an optical network include identifying a first wavelength with an associated target capacity; determining that the first wavelength has insufficient capability to operate at the associated target capacity; and adjusting one or more wavelengths to increase capability of the first wavelength such that the first wavelength can operate at the associated target capacity.
Owner:CIENA
Chemical sensor element, sensing apparatus, and sensing method
InactiveUS20100233825A1Reduce widthEasy to changeComponent separationPhase-affecting property measurementsFine structureResonance wavelength
A chemical sensor element contains a resonator having a first reflector in which particles of a fine metal structure are arranged two-dimensionally and periodically is counterposed with interposition of a dielectric layer to a second reflector, wherein the resonance wavelength of a resonator in which the entire of the first reflector is replaced by a metal thin film having the same thickness as the metal fine structure is different from the surface plasmon resonance wavelength induced in the metal fine structure; and the mode of the surface plasmon resonance excited in the metal fine structure is coupled with the mode of the resonator in which the entire of the first reflector is replaced by the metal thin film.
Owner:CANON KK
Margin-based optimization systems and methods in optical networks by intentionally reducing margin
ActiveUS20150333862A1Increase capacityReduce marginWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignalling characterisationEdge basedEngineering
Systems and methods of optimizing capacity of an optical network, through intentionally reducing margin on one or more wavelengths, include identifying a first wavelength capable of using excess capacity; determining the one or more wavelengths that have extra margin; adjusting at least one of the one or more wavelengths to reduce associated margin to a nominal margin so as to increase supportable capacity of the first wavelength; and increasing capacity of the first wavelength based on the supportable capacity.
Owner:CIENA
System and Method For Increasing Spectral Efficiency, Capacity and/or Dispersion-Limited Reach of Modulated Signals in Communication Links
ActiveUS20080226301A1Reduce signal bandwidthImprove spectral efficiencyElectromagnetic transmissionTelecommunications linkFrequency spectrum
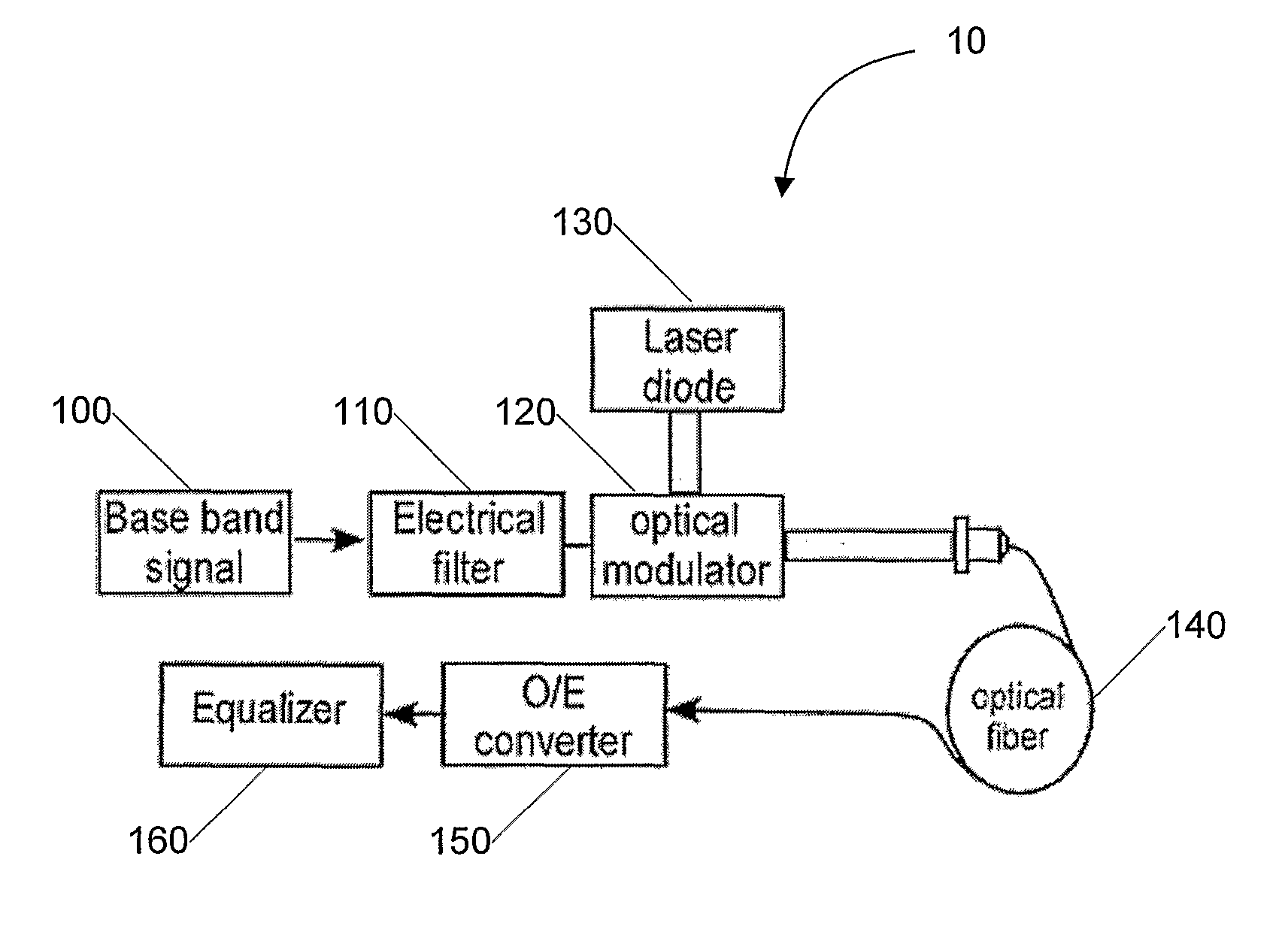
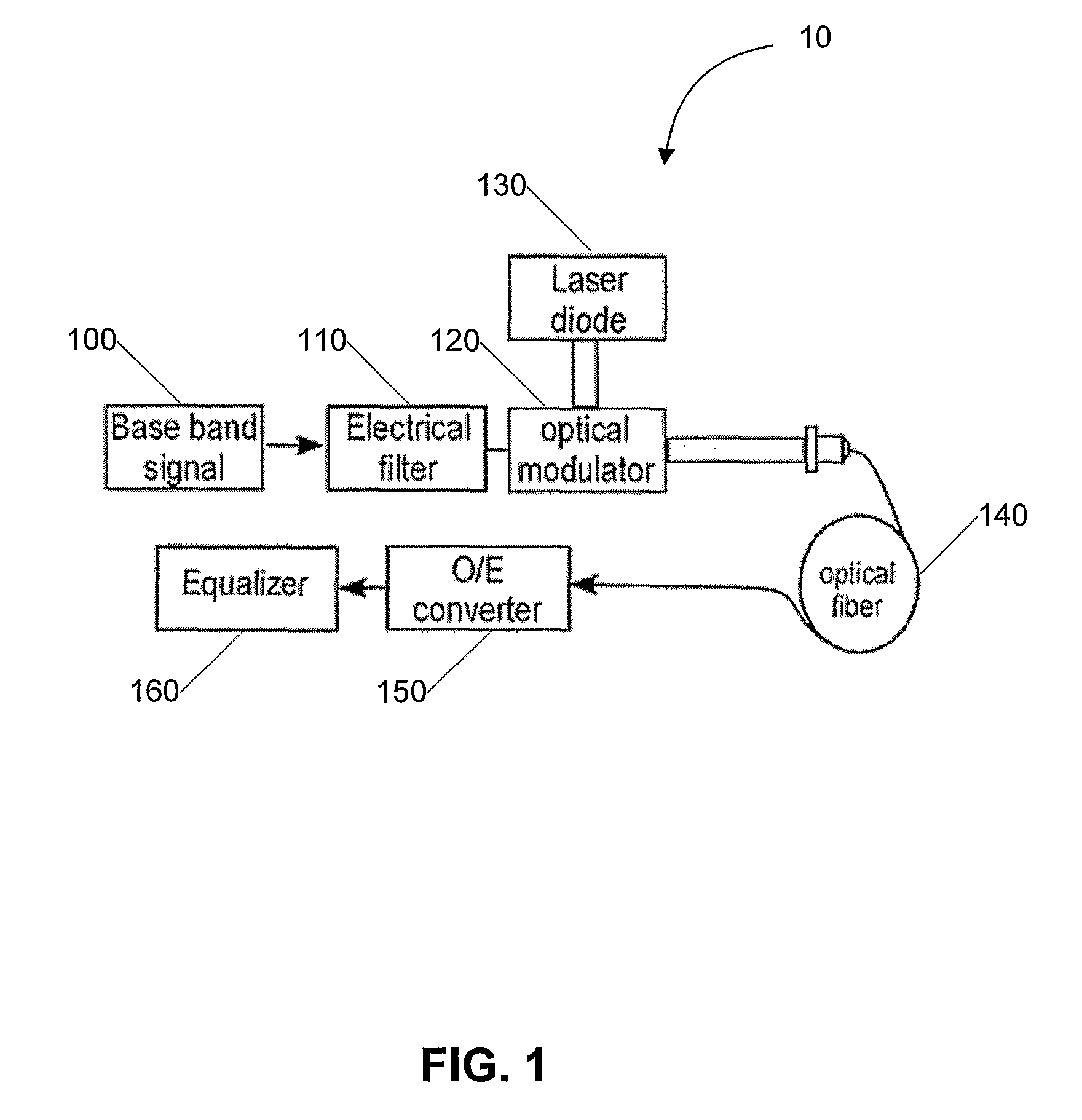
A system and method for increasing spectral efficiency, capacity and / or extending dispersion-limited reach in a communication link employs narrow filtering of a baseband signal to reduce the original bandwidth to a substantially smaller bandwidth for transmission across a transmission medium such as an optical fiber. By restricting the bandwidth, the rate of spreading is reduced significantly. The receiver at the other end of the transmission medium includes an equalizer for returning the received signal to its original bandwidth for retrieval of information contained in the signal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
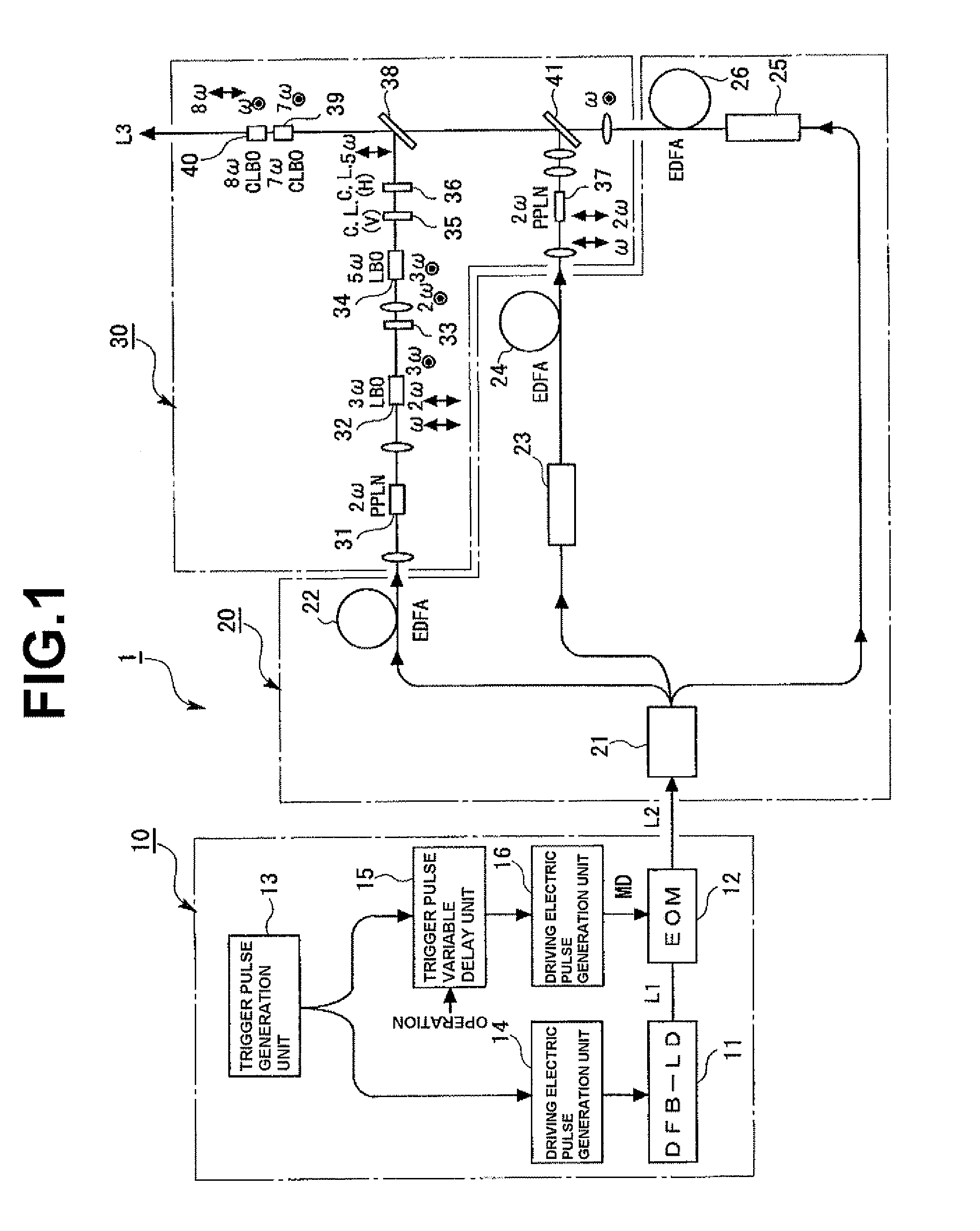
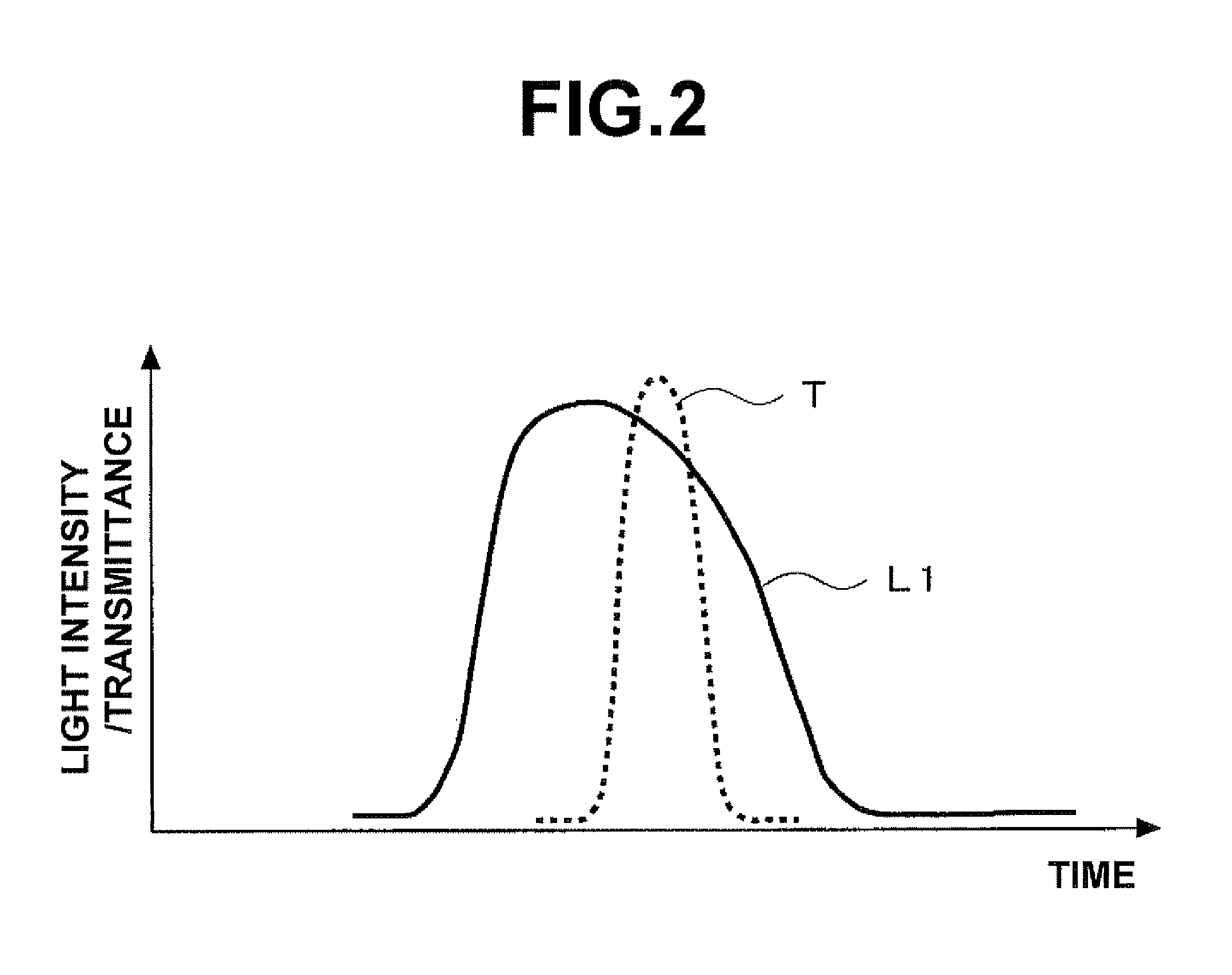
Seed light generation device, light source device, adjustment method thereof, light irradiation device, exposure device, and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20110211184A1Broaden the spectral widthLight leakageRadiation pyrometryLaser detailsLight irradiationLength wave
A light source device including a seed light generation device, a light amplification unit which optically amplifies seed light generated by the seed light generation device, and a wavelength conversion unit which converts the wavelength of the light optically amplified by the light amplification unit. The seed light generation device includes a pulsed light generation unit which generates pulsed light having a single wavelength, a pulse modulation unit which selectively passes and extracts a part of the pulsed light, and a timing adjustment unit which relatively adjusts the extracting timing of the pulsed light by the pulse modulation unit during the generation period of the pulsed light by the pulse generation unit, according to an operation.
Owner:NIKON CORP
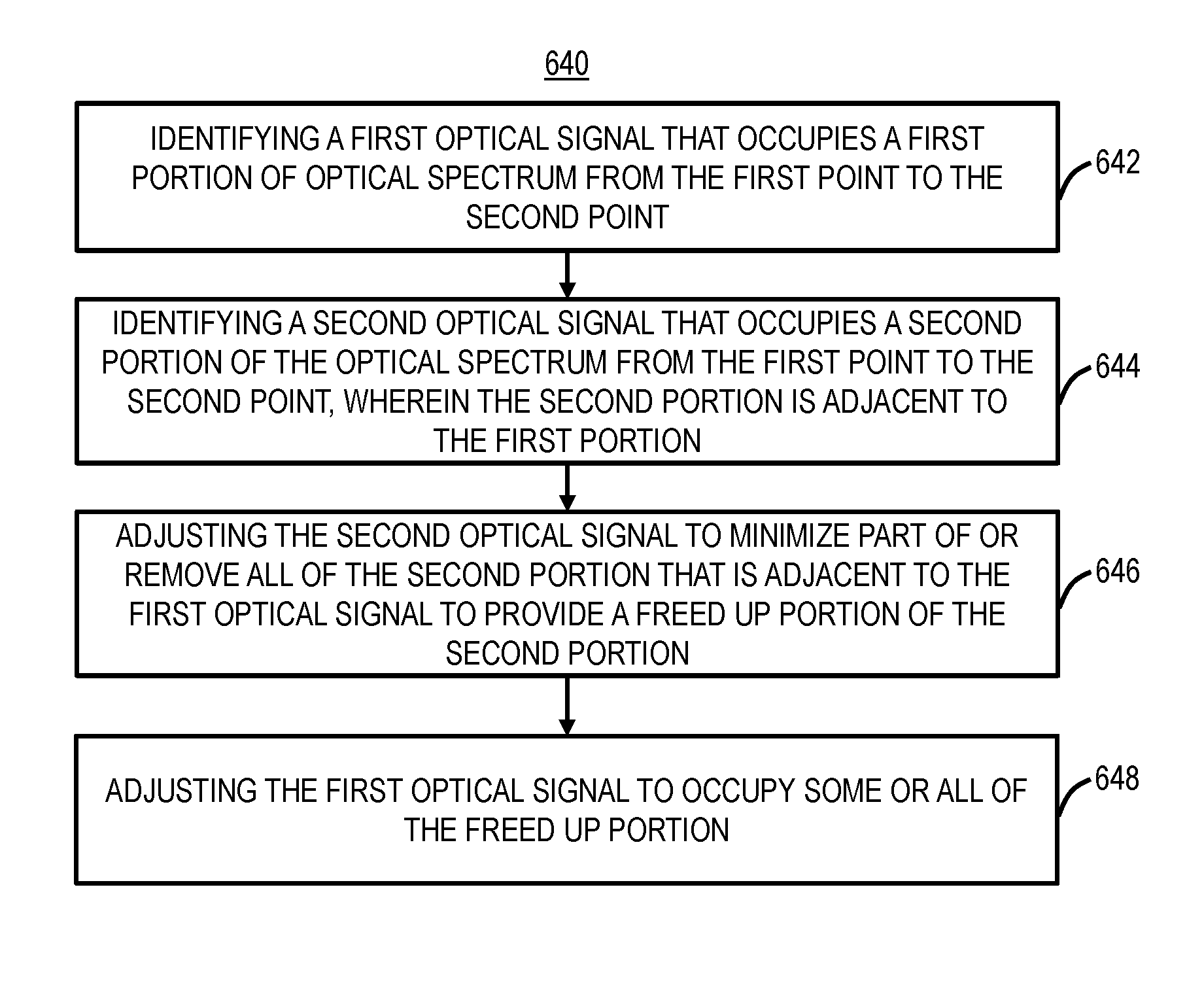
Margin-based optimization systems and methods in optical networks to unblock superchannels
ActiveUS20150333864A1Reduce marginOptimize capacityWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignalling characterisationOptimization systemEdge based
Systems and methods of increasing the supportable capacity from a first point to a second point in an optical network, include identifying a first optical signal that occupies a first portion of optical spectrum from the first point to the second point; identifying a second optical signal that occupies a second portion of the optical spectrum from the first point to the second point, wherein the second portion is adjacent to the first portion; adjusting the second optical signal to minimize part of or remove all of the second portion that is adjacent to the first optical signal to provide a freed up portion of the second portion; and adjusting the first optical signal to occupy some or all of the freed up portion.
Owner:CIENA
Method and apparatus for the examination of specimens
InactiveUS7593158B2Improve powerGood flexibilityPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamMicroscopic exam
A method in which specimens are examined using a microscope. For an illuminated specimen, spatially coherent light with at least one continuous wavelength range or a continuously tunable wavelength range is generated, and one or more wavelengths or wavelength ranges in the illumination light are selected in dependence on the prespecified method of examination. The specimen is then illuminated with the illumination light with the selected wavelengths or wavelength ranges, the illumination light and the emission light coming from the specimen are then subsequently separated, whereby the back radiated illumination light is suppressed in the detection beam before the detection and the emission light is detected. In such a method, the selection of the wavelengths or the wavelength ranges of the illumination light is tuned by means of the separation of the detection light and the illumination light and the suppression of the illumination light in such a manner that a prespecified control variable (R) is optimized.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Margin-based optimization systems and methods in optical networks for capacity boosting
ActiveUS9438369B2Increase capacityReduce marginWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignalling characterisationLength waveOptimization system
Systems and methods of optimizing capacity of an optical network include identifying a first wavelength with an associated target capacity; determining that the first wavelength has insufficient capability to operate at the associated target capacity; and adjusting one or more wavelengths to increase capability of the first wavelength such that the first wavelength can operate at the associated target capacity.
Owner:CIENA
Low time jitter fiber femtosecond laser based on narrowband spectrum filtering
InactiveCN107785769AStable Spectral ComponentsReduce widthActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionFiberTime domain
The invention provides a low time jitter fiber femtosecond laser based on narrowband spectrum filtering, uses the intracavity narrowband spectrum filtering process to effectively stabilize the spectrum components of the pulse in the intracavity evolution process, thus obviously suppressing the pulse center wavelength drift, and greatly eliminating the time jitter components coupled by the intracavity dispersion of the center wavelength drift. The pulse with mass chirps passes the narrowband spectrum filter, the time domain width and spectrum width can be reduced in the same time, thus keepingthe average width of the pulse in a ytterbium-doped single-mode fiber to be at a low state, and limiting the pulse time jitter components directly coupled in the time domain at a low level. The femtosecond laser does not need to repeatedly optimize the intracavity pour dispersion measure and the mode locked state, thus realizing low time jitter operation under different pour dispersion conditions;the femtosecond laser is simple in structure, easy to operate, good in repeatability and long-term stability, thus obtaining a practical low time jitter ultrashort pulse sequence.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Optical combiner and applications thereof
ActiveUS20200096767A1Increase and decrease outcoupling efficiencyReduce spectral widthInput/output for user-computer interactionMechanical apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
An optical combiner including an array of pairs of resonating waveguide gratings. The waveguiding layer of the array, which includes the resonating waveguide gratings, is configured to guide at most ten guided light modes in the visible wavelength range. At least a portion of the resonating waveguide grating array is configured to incouple a portion of incident light on the array and to outcouple a fraction of that incident light. The outcoupled fraction has a predetermined wavelength λ in the visible and near-infrared wavelength range and has a predetermined spectral width Δλ. The optical combiner is preferably configured to be used in a near-eye display apparatus. The invention is also achieved by a near-eye display apparatus that is adapted to combine projected images provided by a light emitter with light provided by a scene observed by an observer looking through the optical combiner.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
Margin-based optimization systems and methods in optical networks to unblock superchannels
ActiveUS9438370B2Increase capacityReduce marginWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignalling characterisationComputer scienceOptimization system
Systems and methods of increasing the supportable capacity from a first point to a second point in an optical network, include identifying a first optical signal that occupies a first portion of optical spectrum from the first point to the second point; identifying a second optical signal that occupies a second portion of the optical spectrum from the first point to the second point, wherein the second portion is adjacent to the first portion; adjusting the second optical signal to minimize part of or remove all of the second portion that is adjacent to the first optical signal to provide a freed up portion of the second portion; and adjusting the first optical signal to occupy some or all of the freed up portion.
Owner:CIENA
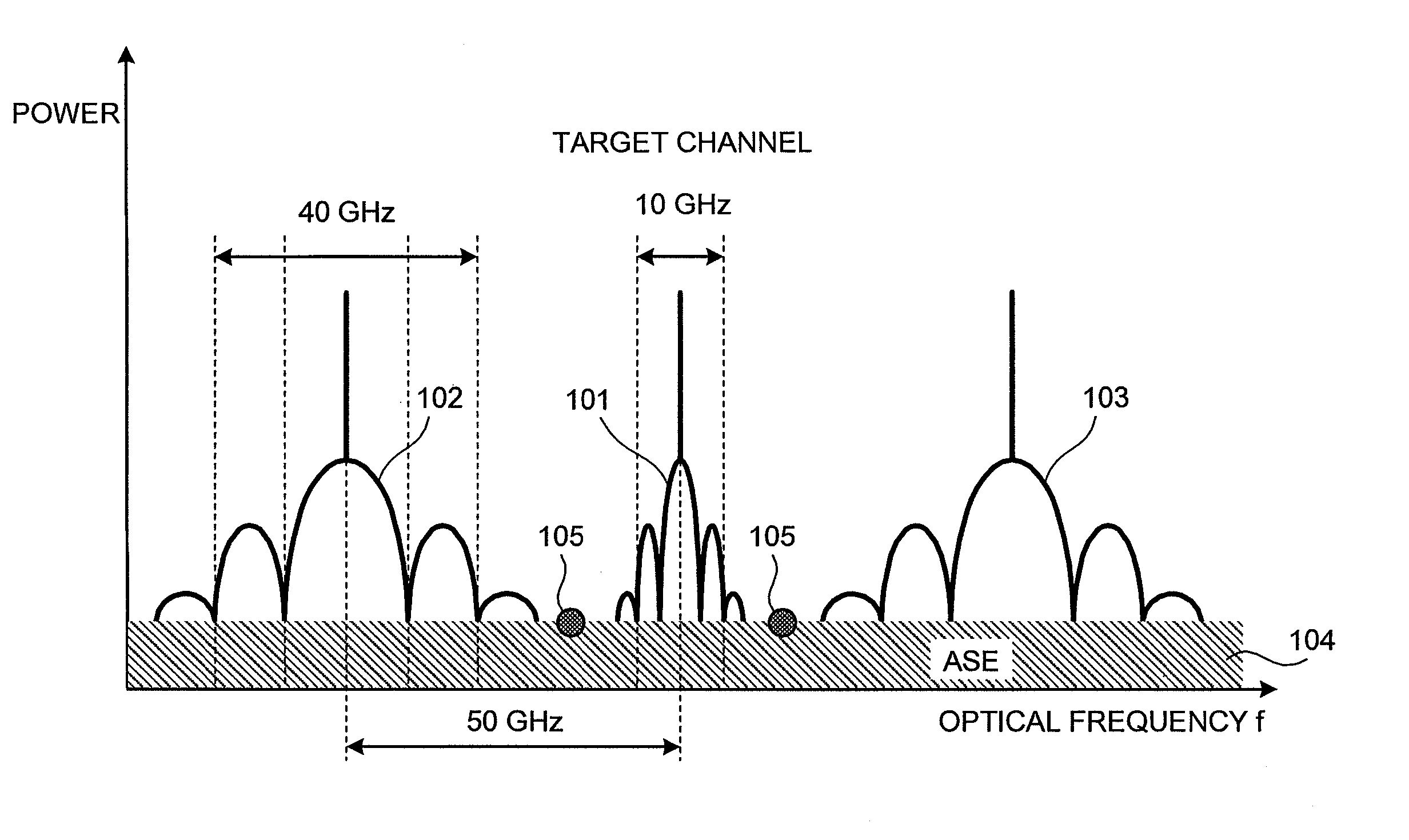
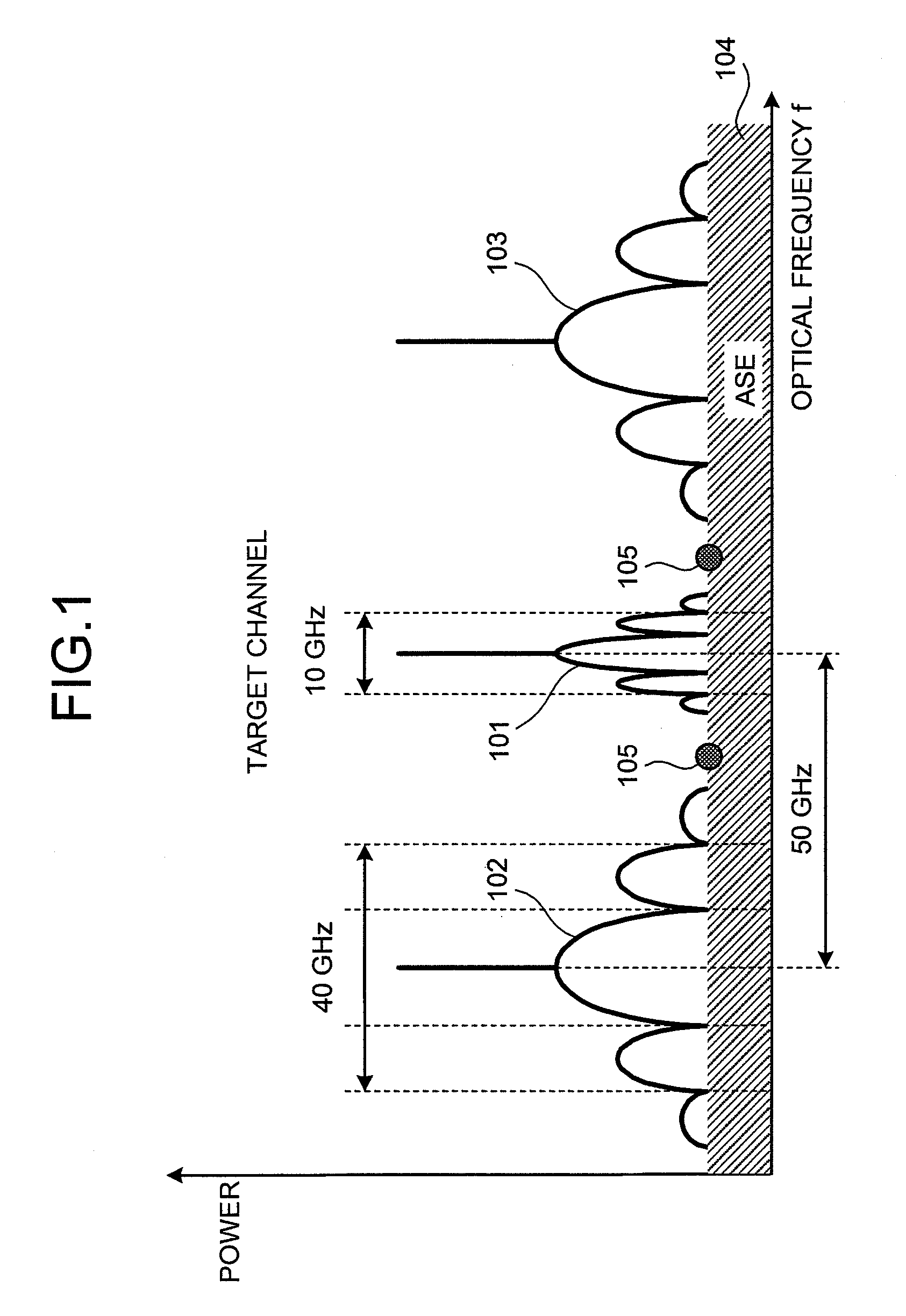
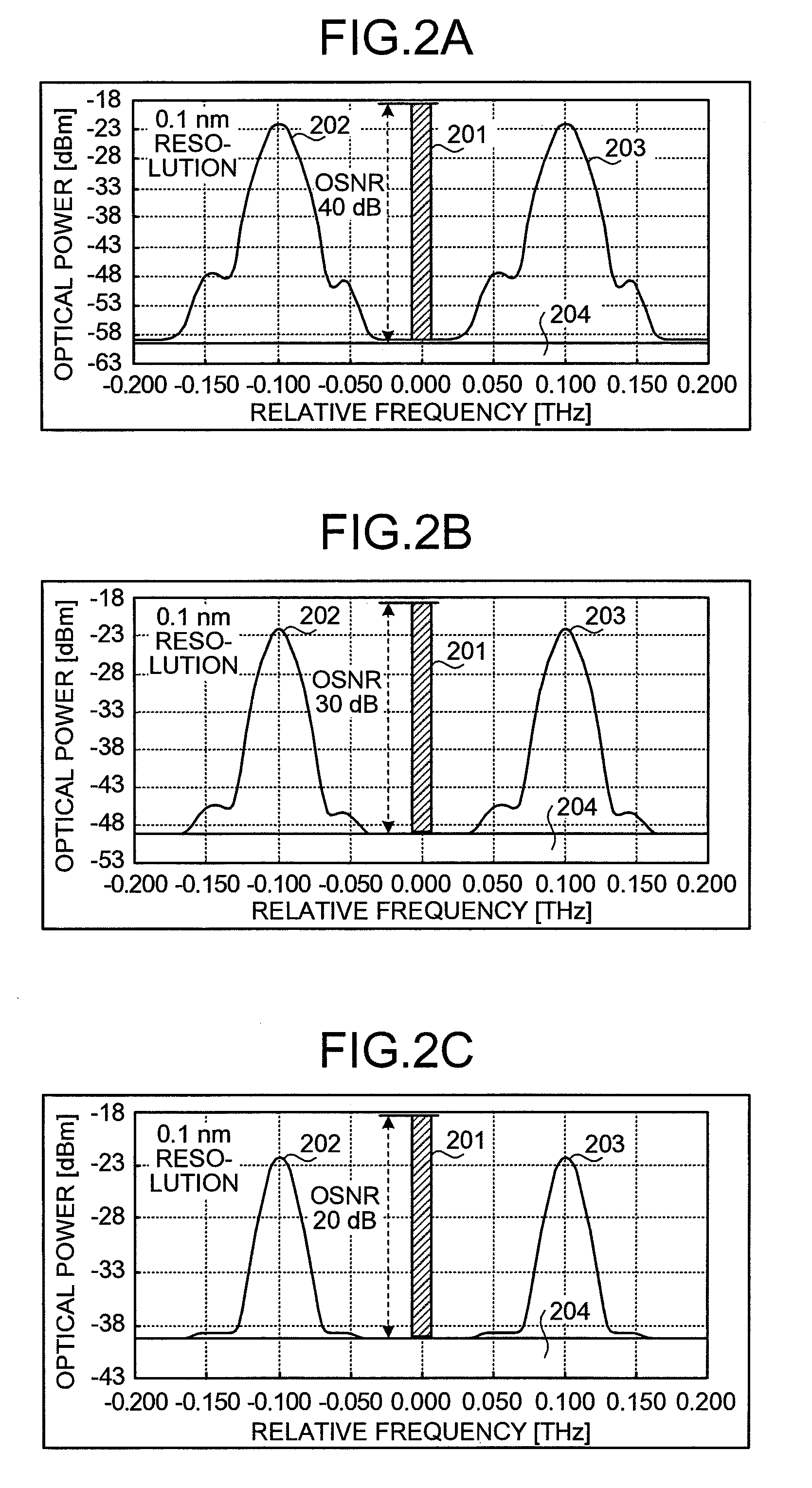
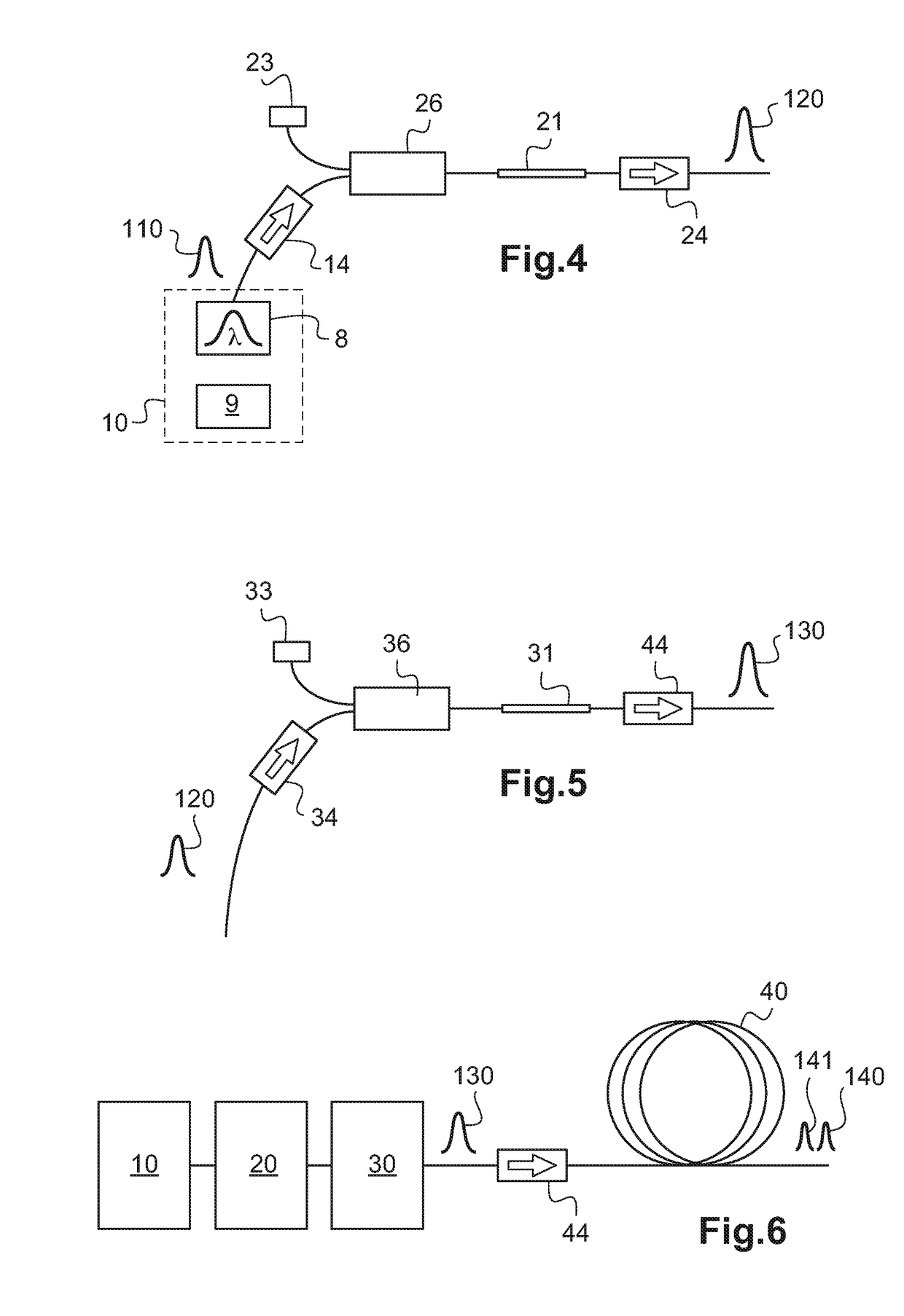
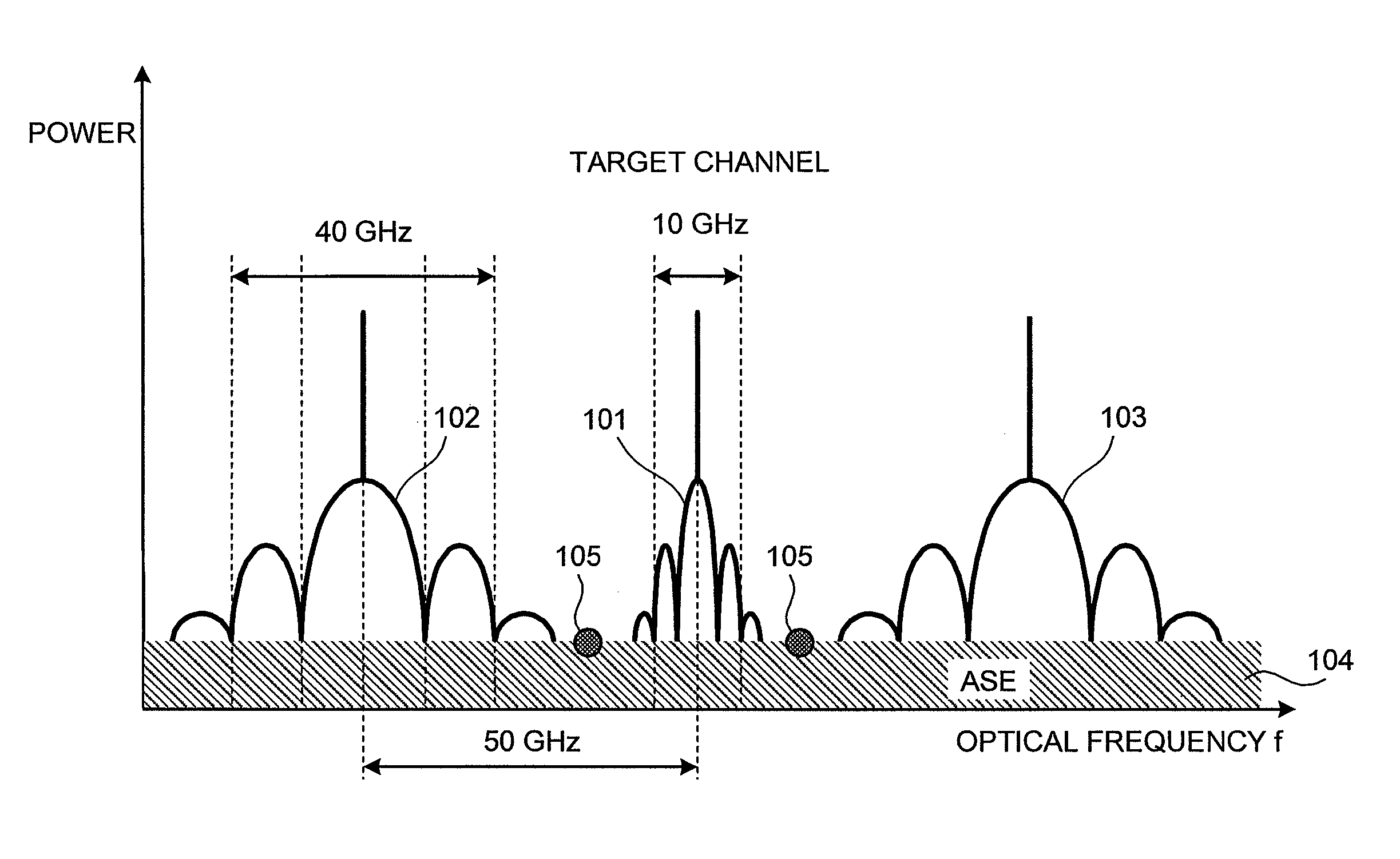
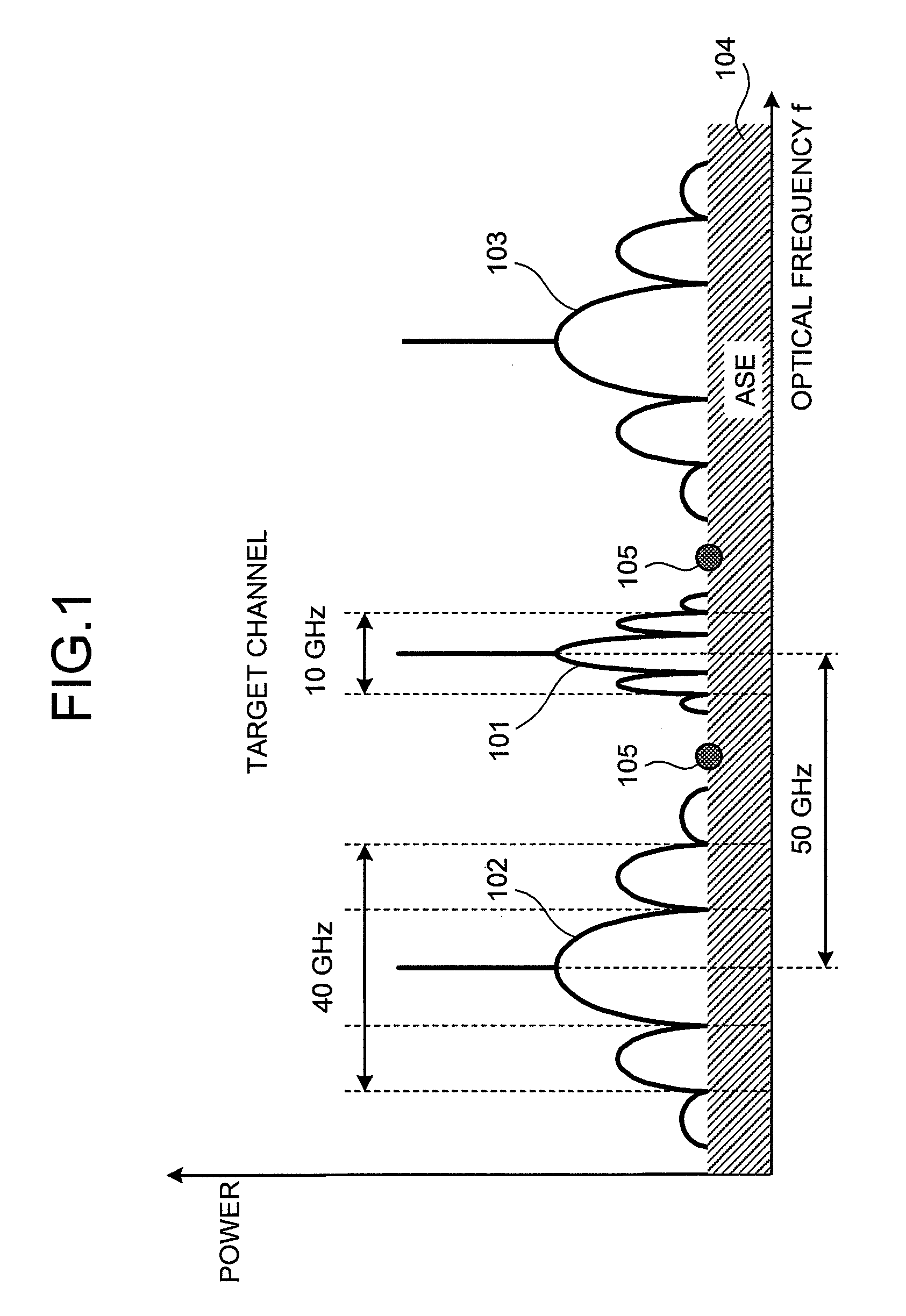
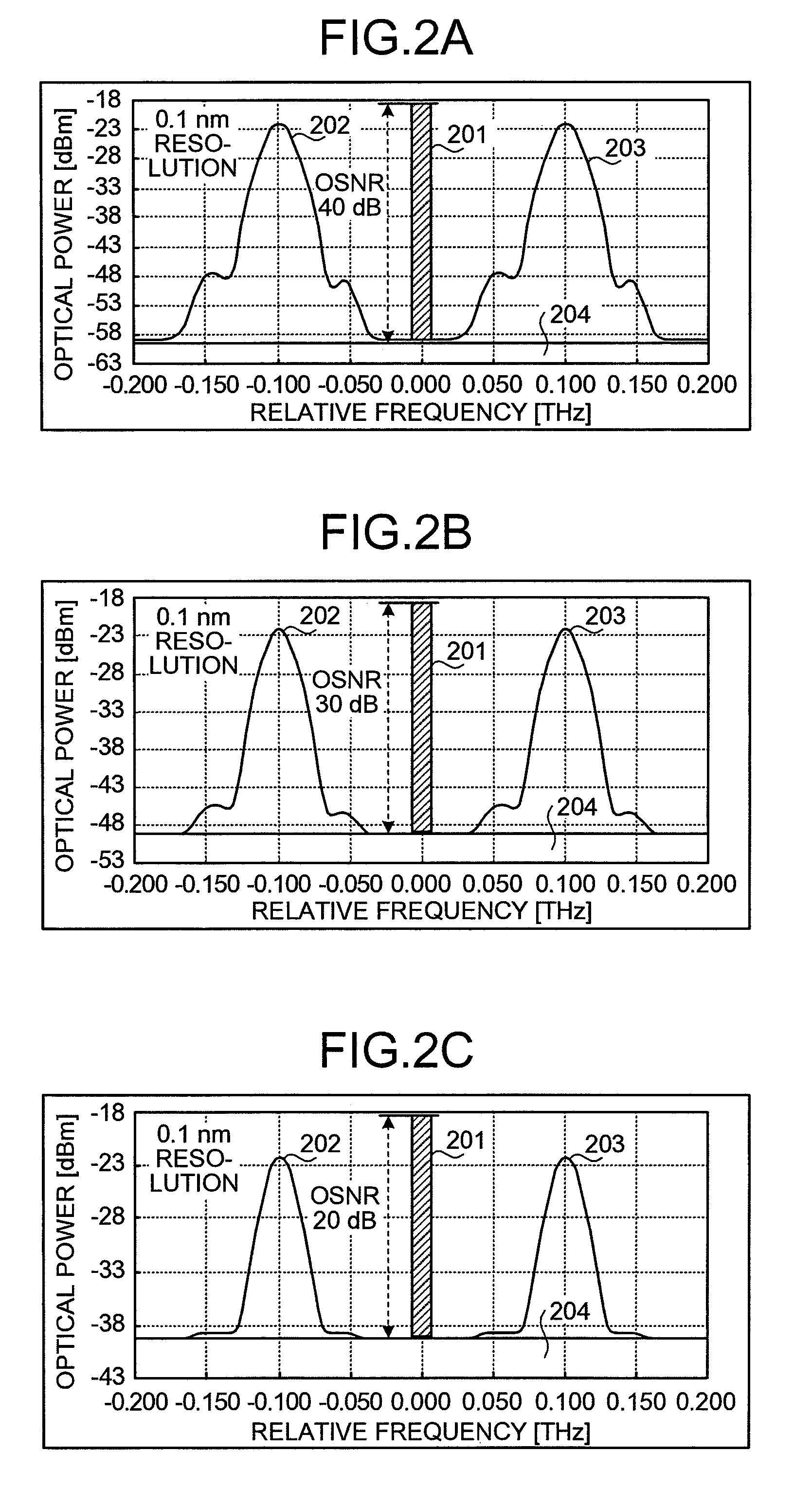
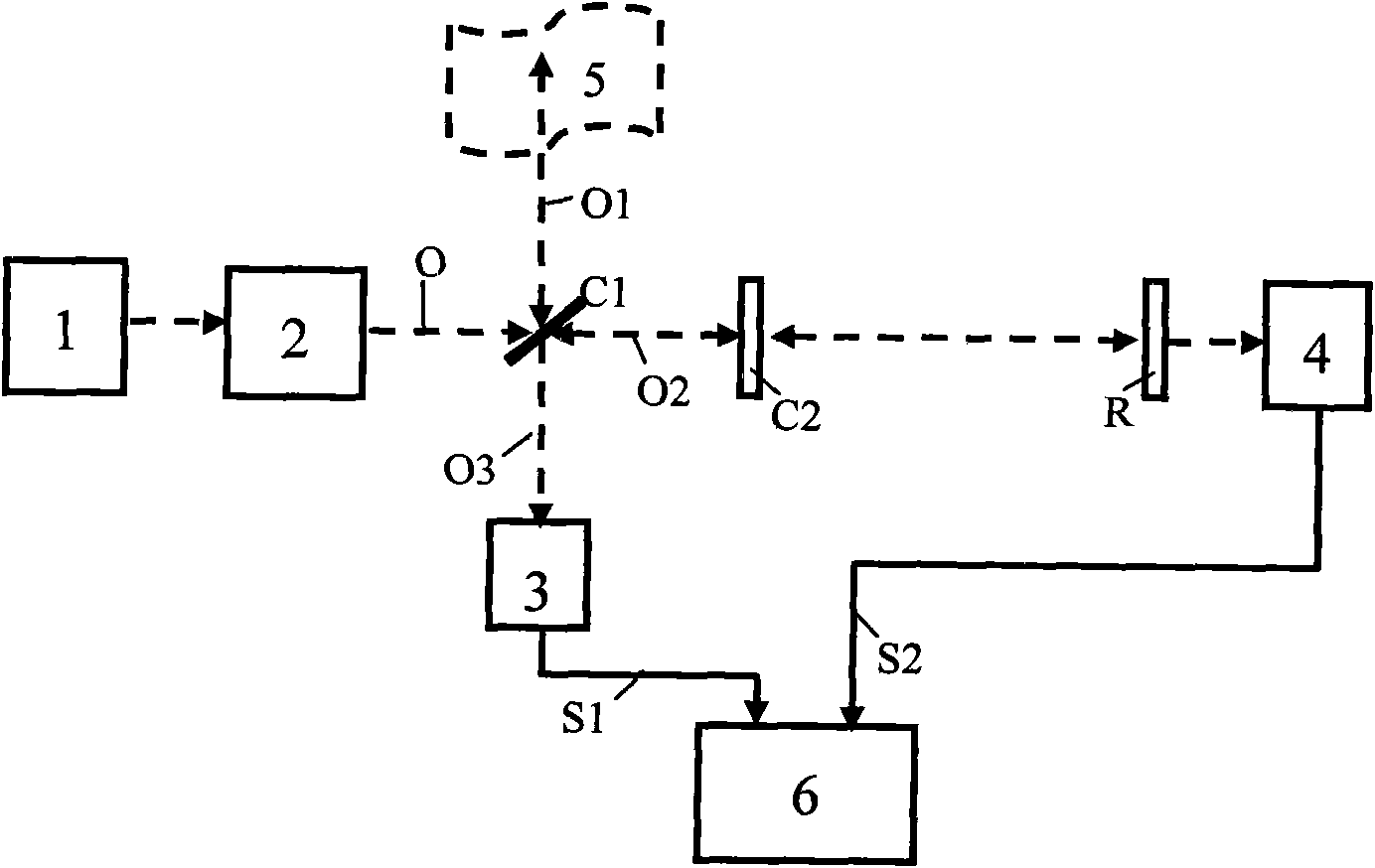
OSNR measuring apparatus and OSNR measuring method
InactiveUS20080080857A1Reduce spectral widthWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
An apparatus for measuring an OSNR for a communication channel in a WDM optical communications system includes a signal control unit, a receiving unit, and a measuring unit. The signal control unit controls spectral width reduction for an optical signal sent through a target channel. The receiving unit receives spectral data measured from the optical signal received by the target channel under control of the control unit. The measuring unit, based on the spectral data received by the receiving unit, measures the OSNR of the target channel.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
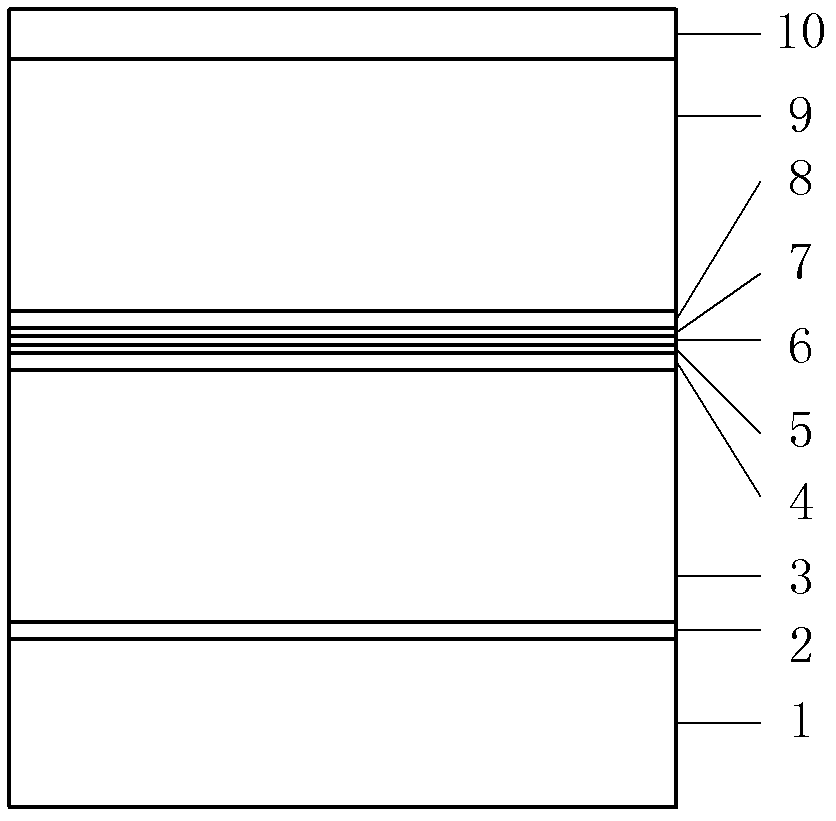
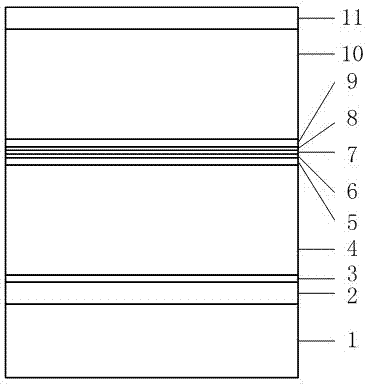
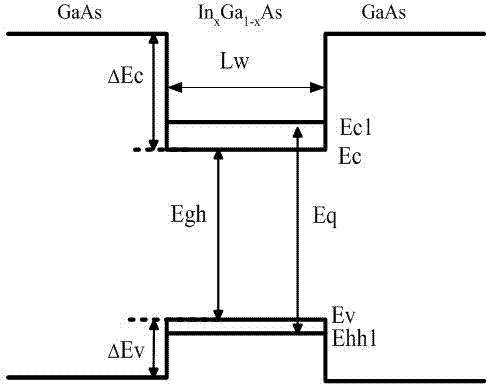
F-P (Fabry-Perot) cavity strained quantum well laser with low linewidth
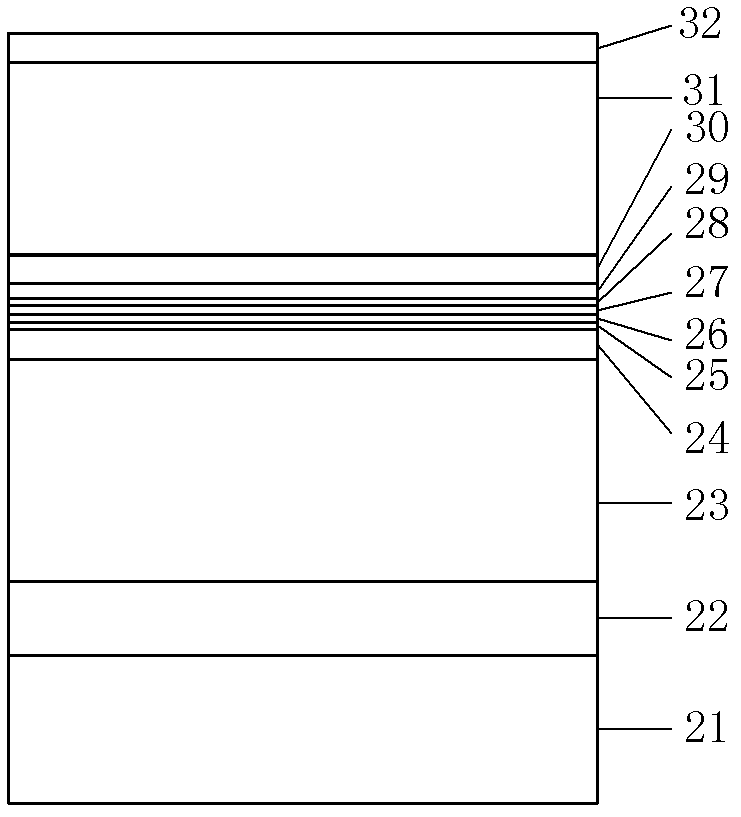
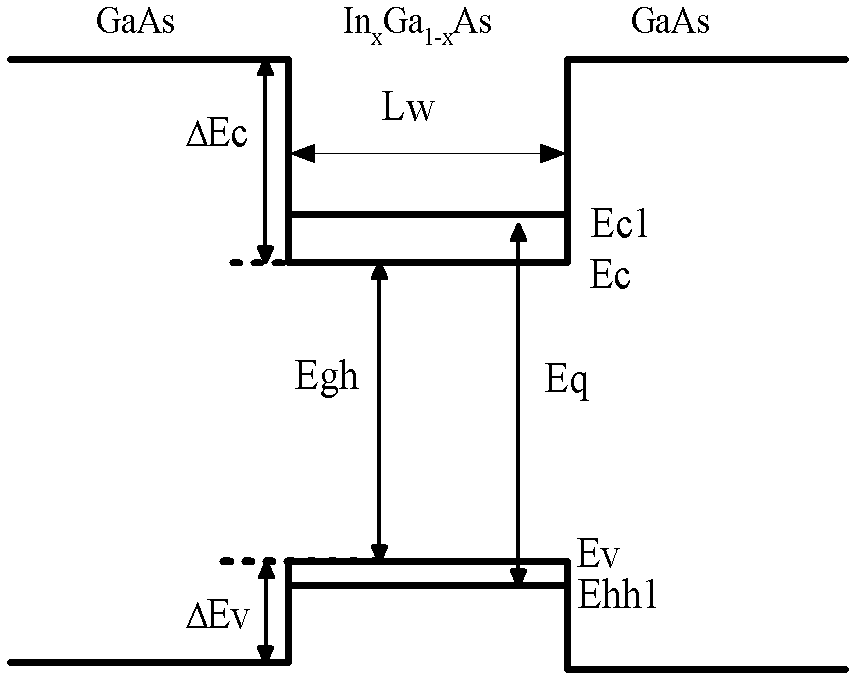
InactiveCN102332681AReduce spectral widthQuality improvementLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionSpectroscopyOptical measurements
The invention provides an F-P (Fabry-Perot) cavity strained quantum well laser with low linewidth. The F-P cavity strained quantum well laser comprises a substrate (1), a buffer layer (2), an n type lower limiting layer (3), a lower waveguide layer (4), a lower barrier layer (5), an active layer (6), an upper barrier layer (7), an upper waveguide layer (8), a p type upper limiting layer (9) and an ohmic contact layer (10) which are sequentially connected. Through the optimal design of the active layer (6), a linewidth enhancement factor generated by interband transition of a quantum well and a linewidth enhancement factor generated by free carrier absorption and band-gap shrinkage can offset mutually, thereby realizing the low linewidth and improving the quality of a light beam of the quantum well laser. The active layer of the laser provided by the invention is made of InxGa1-xAs materials, wherein x is equal to 0.33, the width thickness of the well is 3-5nm, the center wavelength lambda is equal to 980nm-1036nm, and the linewidth of the F-P cavity strained quantum well laser can be reduced by three orders of magnitude in comparison with a quantum well laser. The F-P cavity strained quantum well laser can be used for optical measurement, solid-state laser pumping, laser spectroscopy research and other fields.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for generating wavelength-tunable, ultra-short light pulses having high power spectral density
ActiveUS20170352999A1Reduce spectral widthIncrease power spectral densityActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionLighting spectrumSpectral density
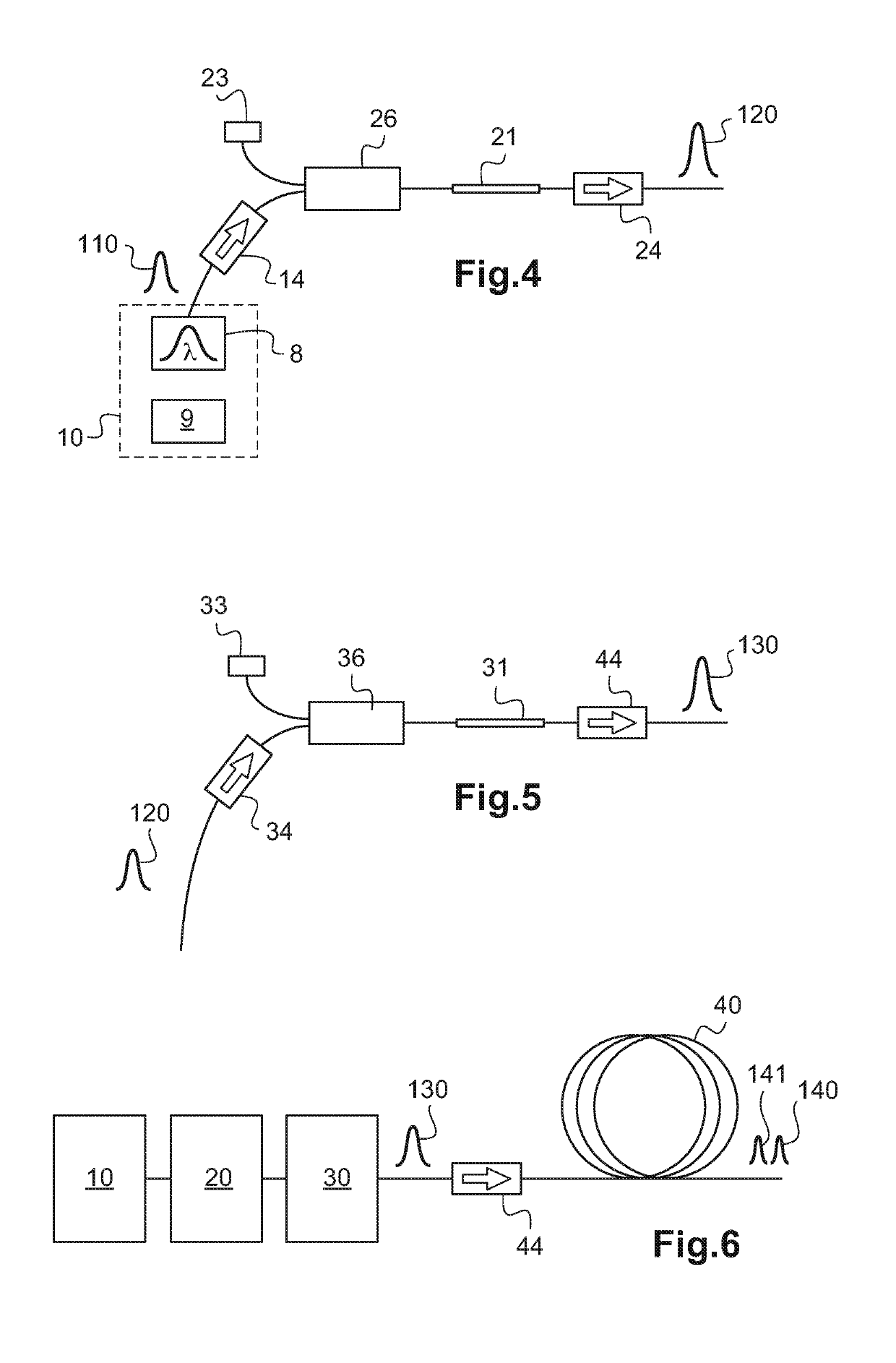
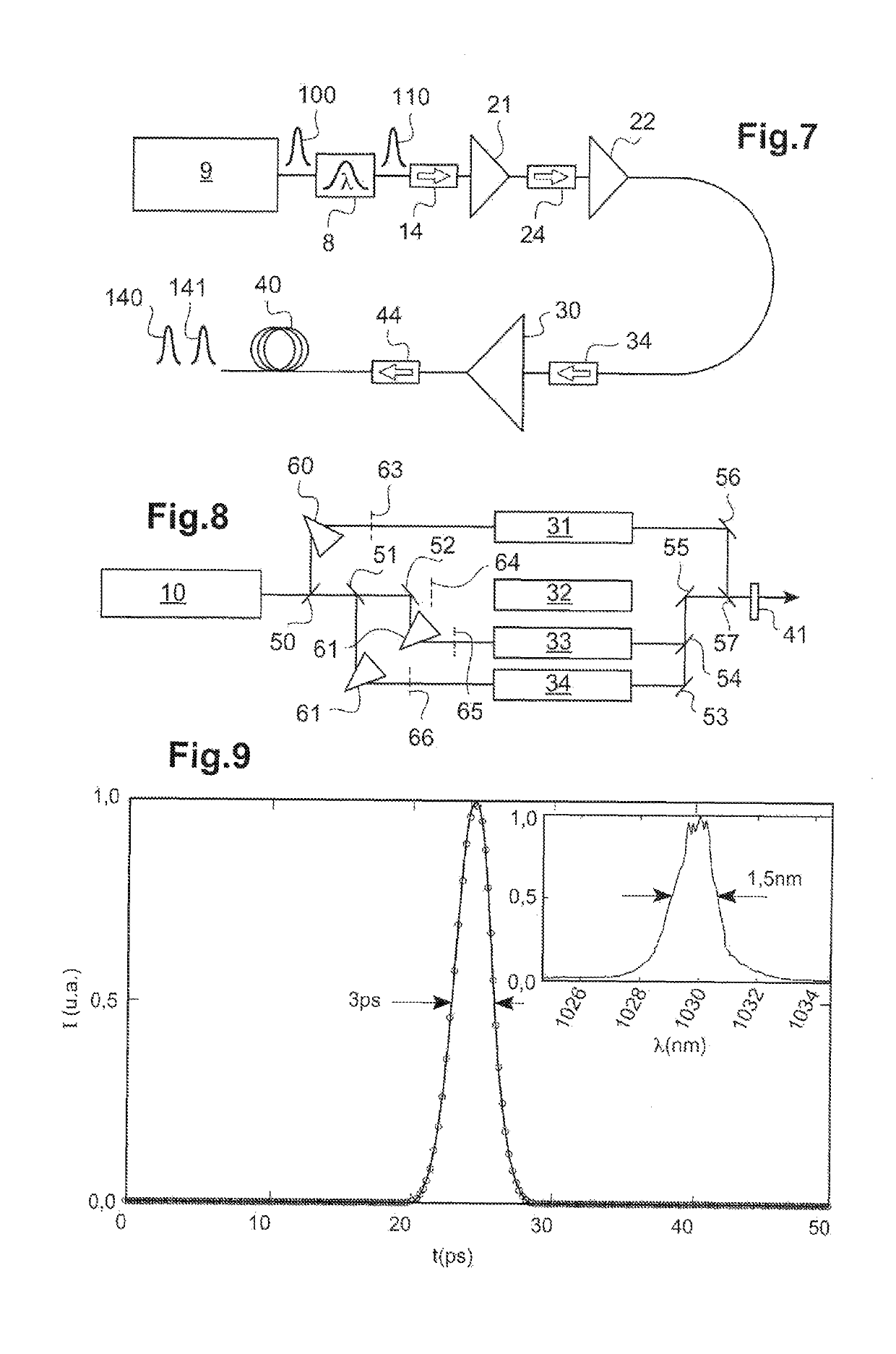
Disclosed is a system for generating wavelength-tunable, ultra-short light pulses within the visible or infrared light spectrum. The system includes an injection module including a light source and a wavelength-tunable spectral filter. The light source is suitable for generating short light pulses, having a duration measured in nanoseconds, within an emission spectrum having a spectral width of several tens of nanometers to several hundred nanometers. The spectral filter has a spectral width between 250 pm and 3 nm and is suitable for spectrally and temporally filtering the short light pulses such that the injection module generates wavelength-tunable, spectrally filtered, ultra-short light pulses. The system also includes at least one optical amplifier suitable for generating wavelength-tunable, ultra-short, amplified pulses based on the wavelength of the spectral filter.
Owner:UNIV DE BORDEAUX +1
OSNR measuring apparatus and OSNR measuring method
InactiveUS8073325B2Reduce spectral widthWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringCommunications systemSpectral width
An apparatus for measuring an OSNR for a communication channel in a WDM optical communications system includes a signal control unit, a receiving unit, and a measuring unit. The signal control unit controls spectral width reduction for an optical signal sent through a target channel. The receiving unit receives spectral data measured from the optical signal received by the target channel under control of the control unit. The measuring unit, based on the spectral data received by the receiving unit, measures the OSNR of the target channel.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
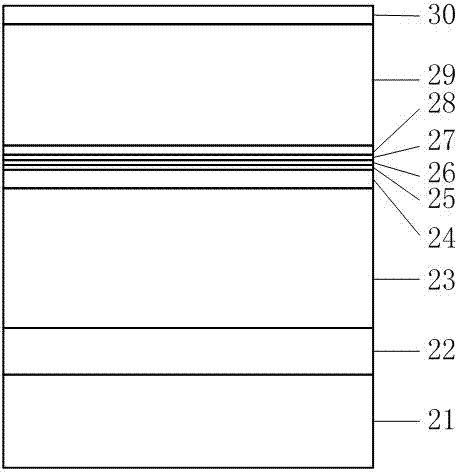
Epitaxial wafer for 980nm F-P cavity strained quantum well laser with narrow line width and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102780159AReduce spectral widthQuality improvementLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionLine widthSpectroscopy
The invention discloses an epitaxial wafer for a 980nm F-P cavity strained quantum well laser with a narrow line width and a preparation method of the epitaxial wafer for the 980nm F-P cavity strained quantum well laser with the narrow line width, and relates to the field of a semiconductor laser. A growth buffer layer, a transition layer, a n-type lower restriction layer, a lower waveguide layer, a lower potential barrier layer, an active layer, an upper potential barrier layer, an upper waveguide layer, a p-type upper restriction layer and an ohmic contact layer are grown on a GaAs substrate layer in sequence so as to be processed into the 980nm F-P cavity strained quantum well laser with the narrow line width. The epitaxial wafer for the 980nm F-P cavity strained quantum well laser with the narrow line width can be applied to the fields, such as optical measurement, solid laser pumping, laser spectroscopy, medical research and the like.
Owner:YANGZHOU CHANGELIGHT
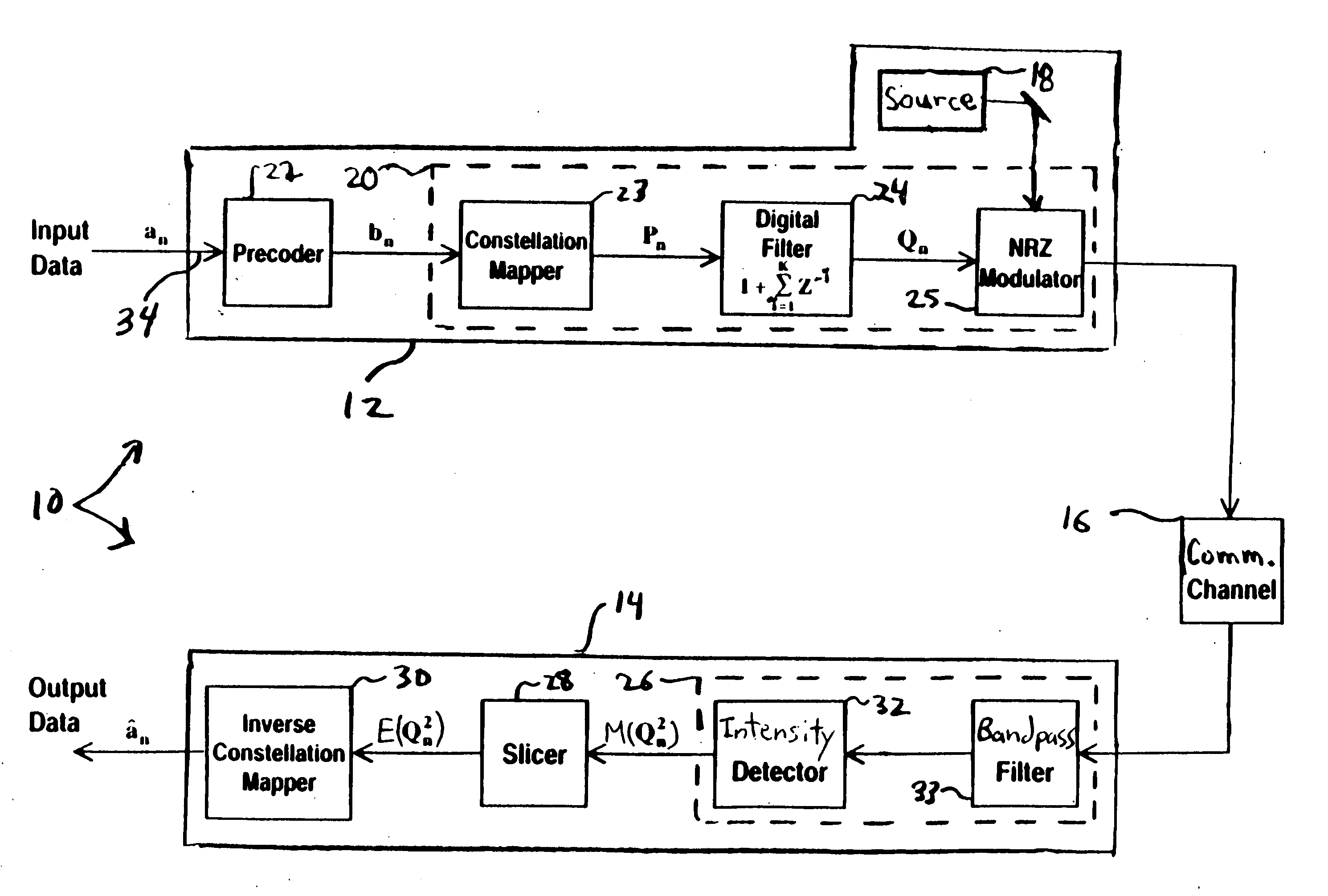
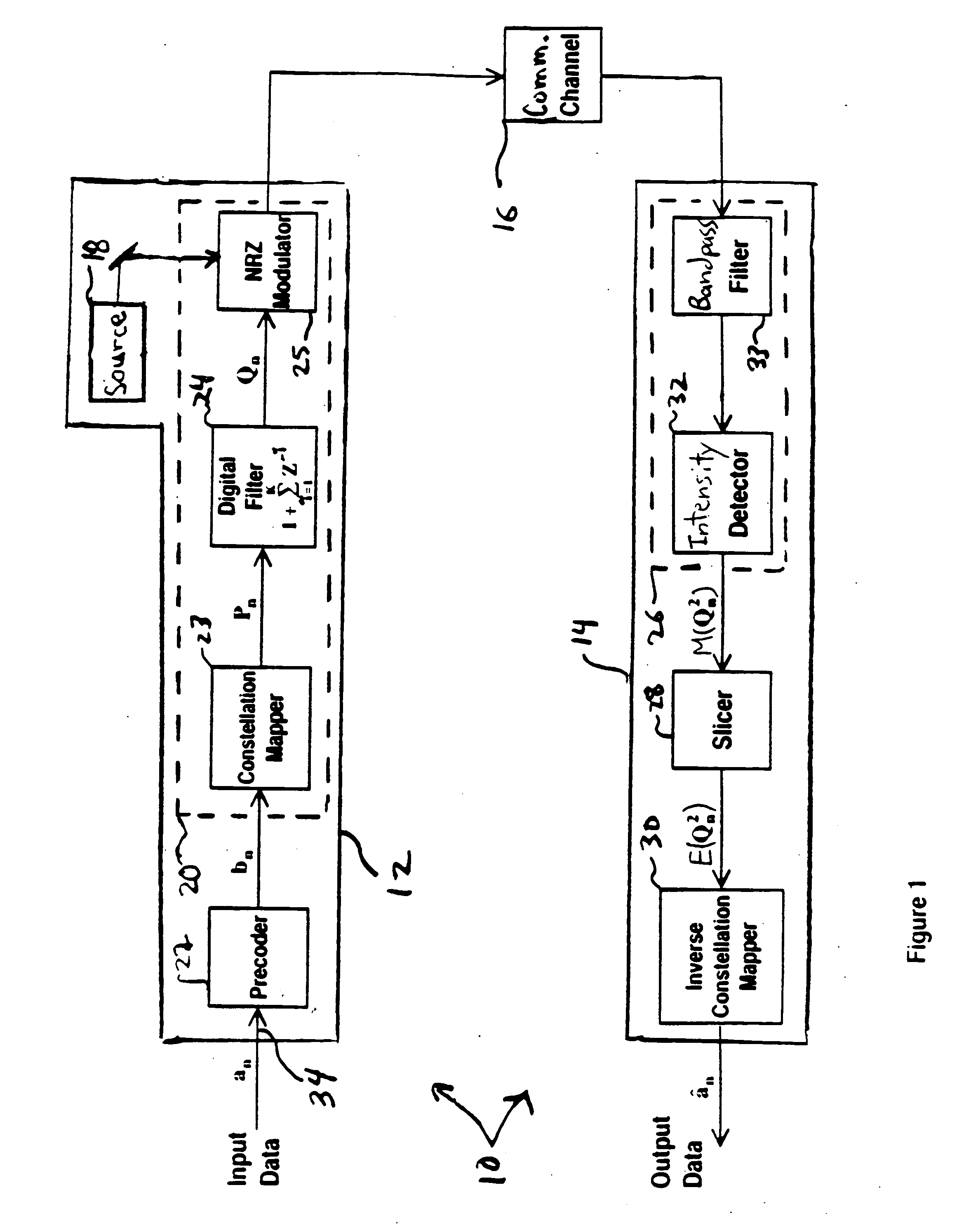
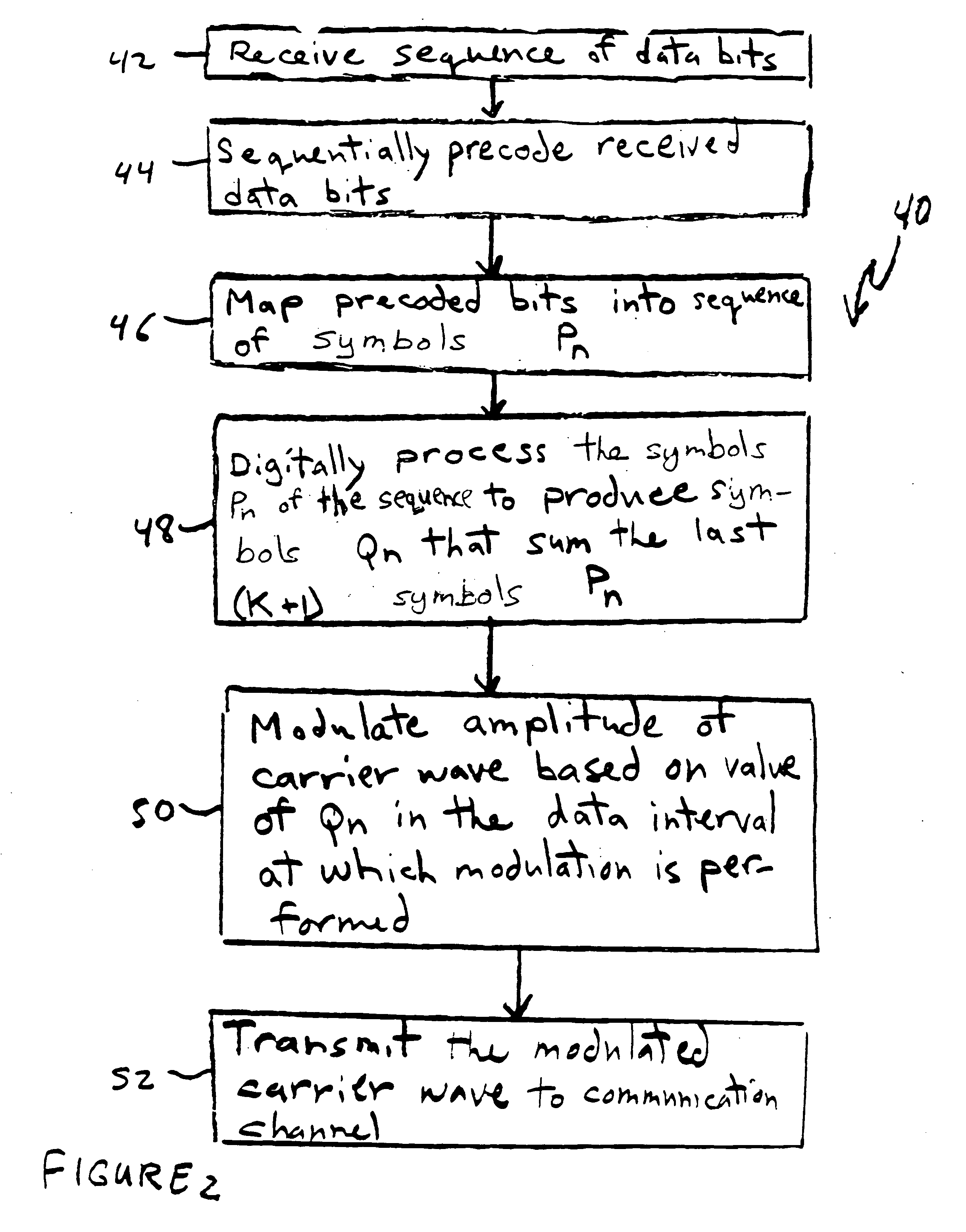
Bandwidth-efficient modulation in communication systems
InactiveUS20050213675A1Reduce spectral widthImprove interferencePulse conversionMultiple carrier systemsDigital dataCommunications system
A transmitter of digital data includes a modulator with an input for a carrier signal and an input for a first stream of control symbols. The modulator modulates the carrier signal with a second stream of symbols produced by the modulator. Each symbol of the second stream has a value that corresponds to a sum of the present control symbol and the last K first symbols of the first stream. The integer K is greater than one.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
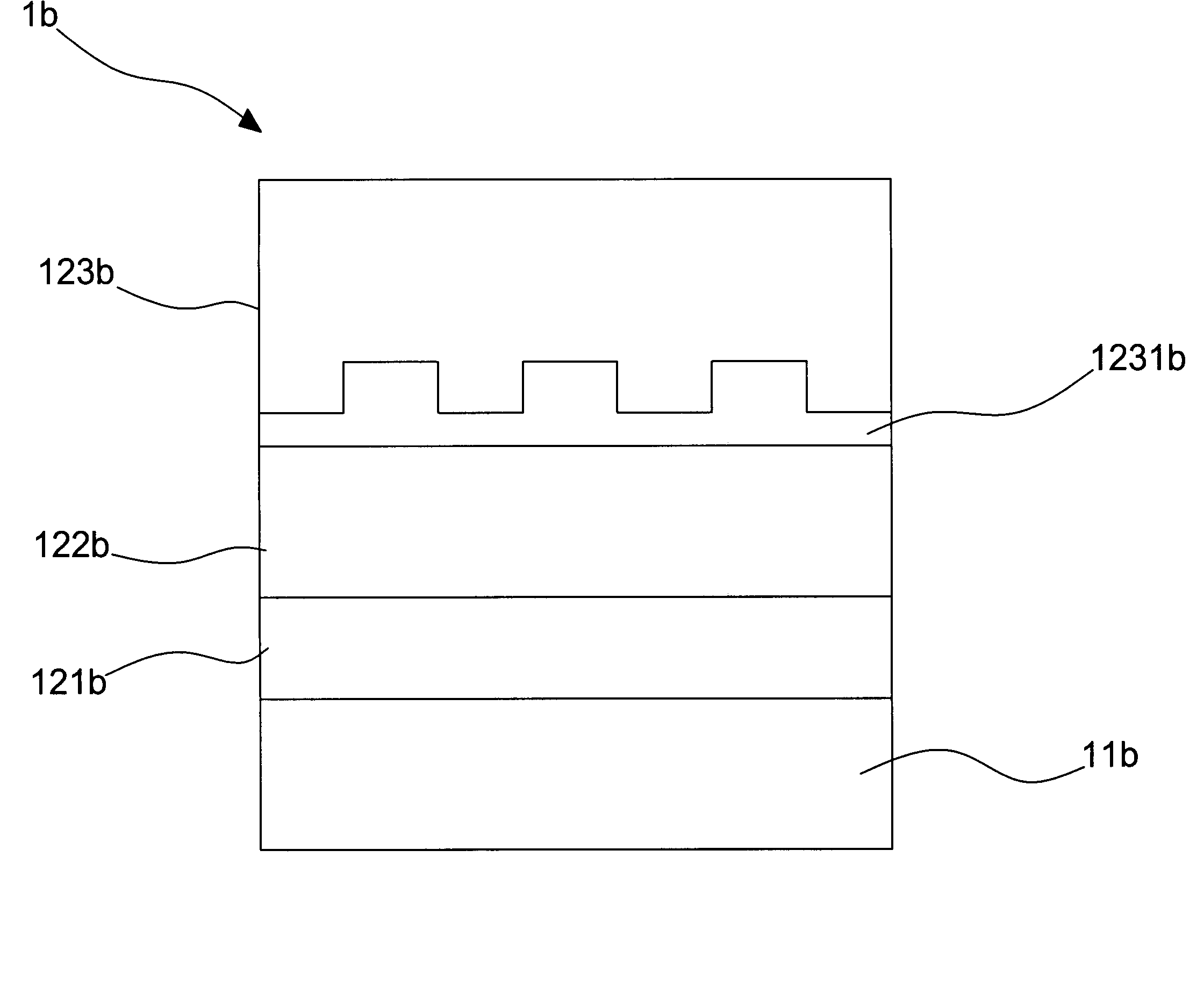
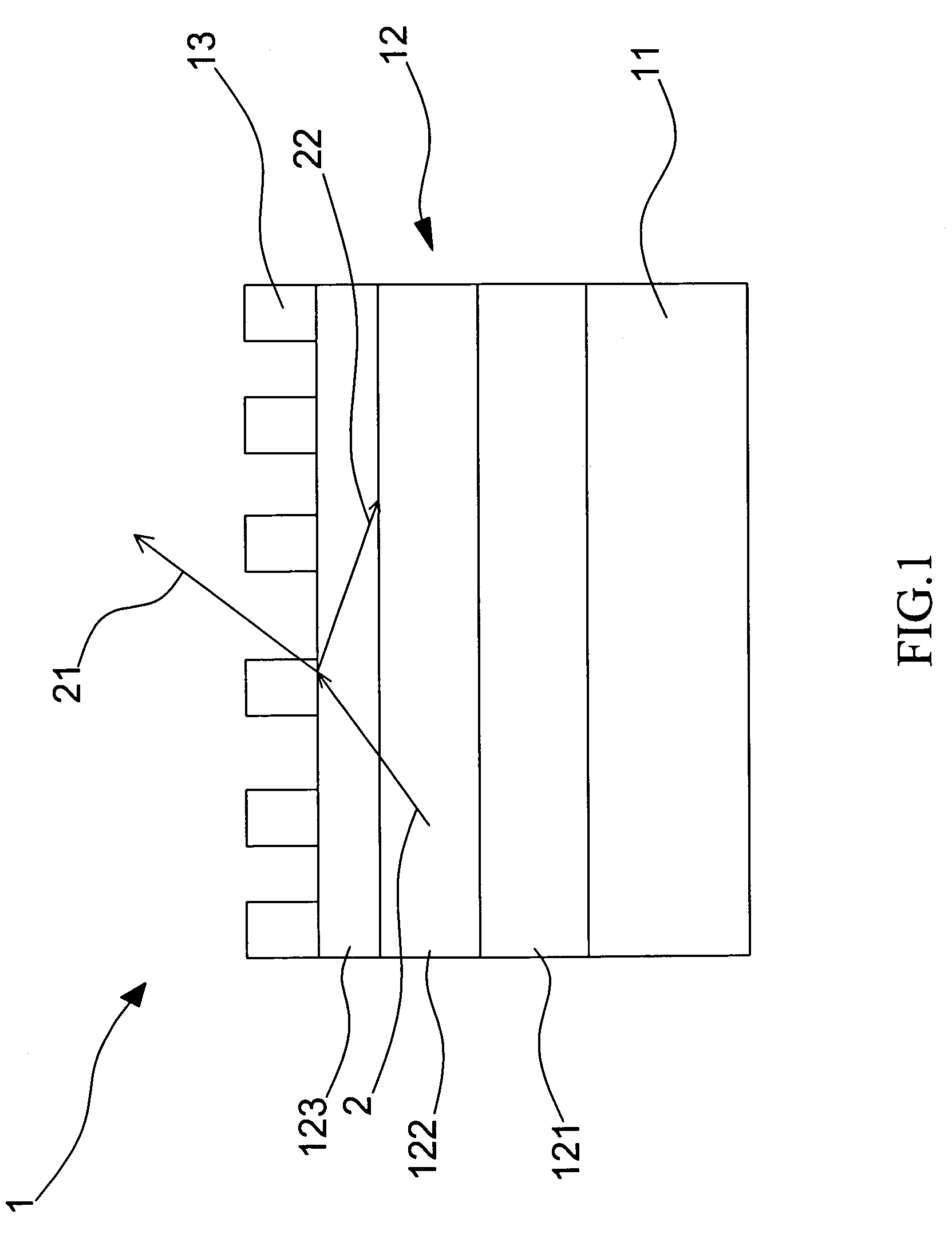
LED device having reduced spectrum
InactiveUS7456436B2Reduce spectral widthSimple methodSolid-state devicesDisplay meansGratingSpectral width
A structure of light emitting diode (LED) effectively reduces its spectral width. The LED structure is applied in a three color mixing of a backlight module to broaden a color space and to improve a saturation of a color display. A grating structure is used as a waveguide layer to coordinate with the LED structure. The present invention does not affect the original thermo and electrical characteristics of the LED structure and has a simple fabrication method.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Pulse grid coherent chromatography method
InactiveCN101639440AHigh sensitivityImprove anti-interference abilityPhase-affecting property measurementsLight beamSignal light
The invention discloses a pulse grid coherent chromatography method comprising the following steps: dividing low coherent pulse light into at least two beams, wherein one light beam enters chromatography matters, and distribution reflected light is signal light; the other light seam is magnified by cyclic repeating split light or split light combined light to generate a pulse grid, the pulse gridand the signal light generate interference and form a signal light pulse string, and the signal light pulse string comprises the reflected light distribution of the chromatography matters to representchromatography information. The pulse grid coherent chromatography method has large chromatography range, high sensitivity as well as simple and quick reconstitution of the chromatography information, is suitable for the chromatography imaging of the continuous scattering matters and the distribution sensing of parameters of biology, chemistry, physics, and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Optical transmission system
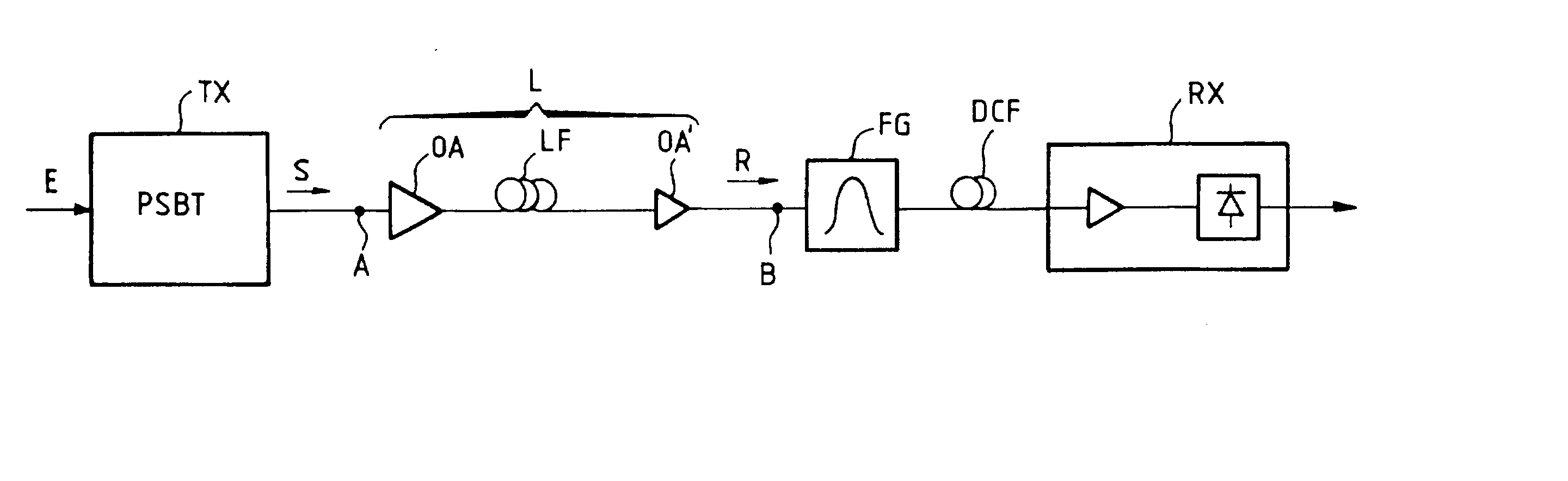
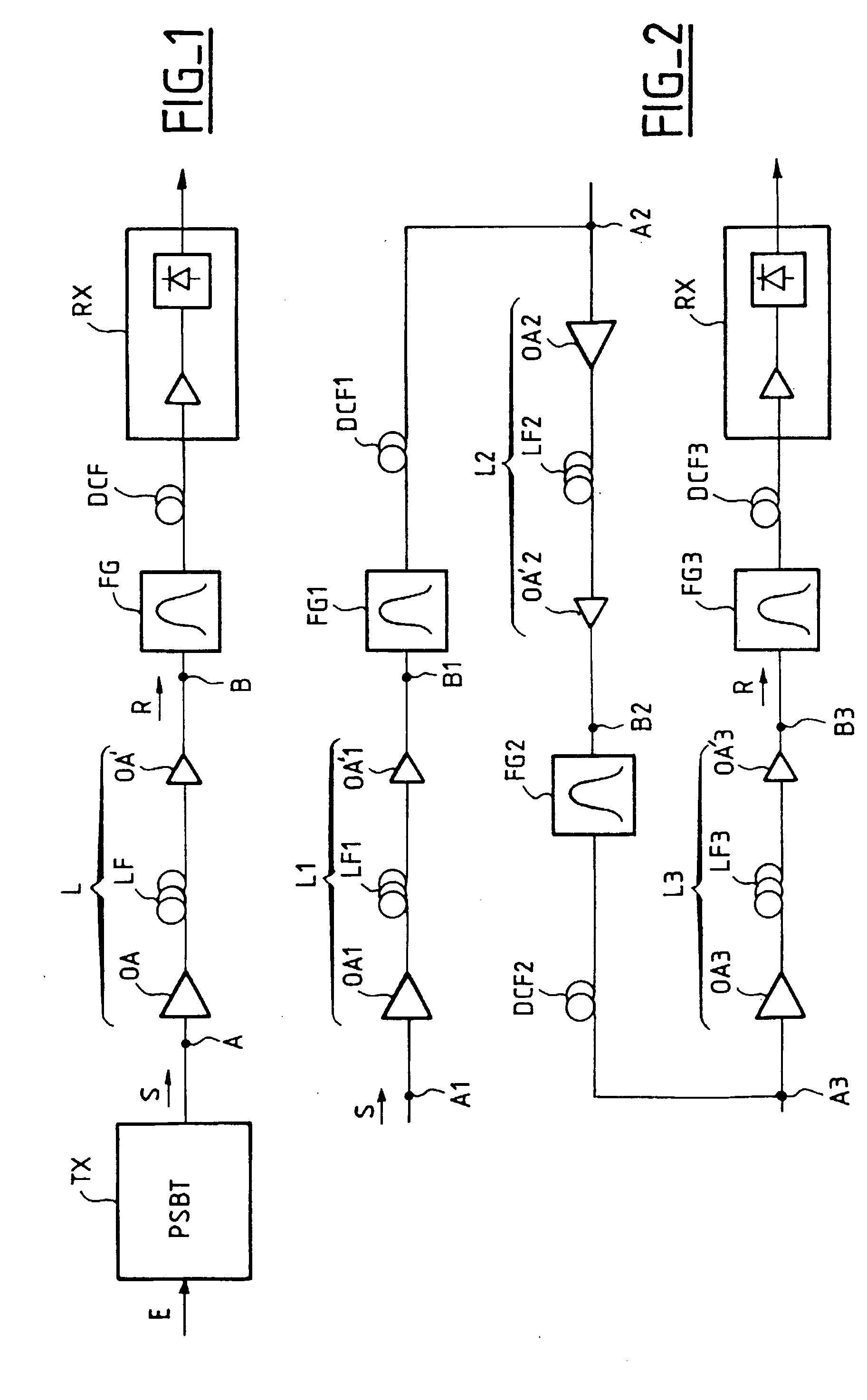
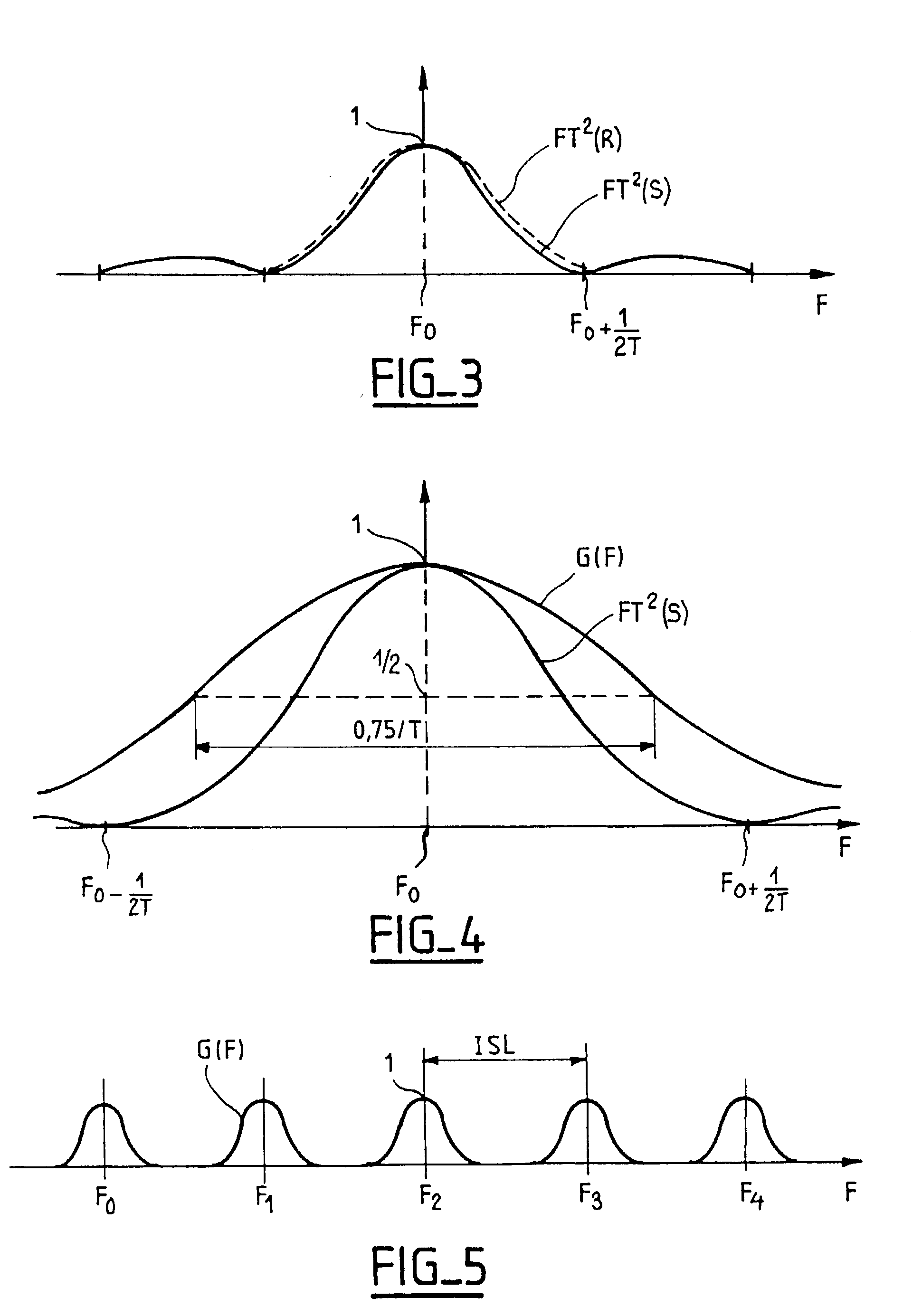
InactiveUS20030090770A1Improve signal qualityBroaden spectrumDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency spectrumOptical correction
The transmission system is suitable for amplitude modulated controlled phase optical signals (S) having an optical phase in each low level pulse that precedes or follows a high level pulse. The system includes an optical link (L) and, to allow a high transmitting power, optical corrector means (FG) are provided for applying optical filtering to the signal R at the exit (B) of the link and / or at one point or a plurality of points of the link (L), to compensate widening of its spectrum that the controlled phase signal (S) may suffer because of phase self-modulation during its transmission. Application to long-haul optical transmission.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Dislocation-based light emitter
InactiveUS20090321757A1Quantum efficiency of the light emission in the respectively optimized luminescence rangeImprove quantum efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersMicrometerElectroluminescence spectra
A light-emitting semiconductor component comprising a substrate which has a first interface between a first and a second silicon layer, whose lattice structures which are considered as ideal are rotated relative to each other through a twist angle about a first axis perpendicular to the substrate surface and are tilted through a tilt angle about a second axis parallel to the substrate surface, in such a way that a dislocation network is present in the region of the interface, wherein the twist angle and the tilt angle are so selected that an electroluminescence spectrum of the semiconductor component has an absolute maximum of the emitted light intensity at either 1.3 micrometers light wavelength or 1.55 micrometers light wavelength.
Owner:IHP GMBH INNOVATIONS FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE MICROELECTRONICS LEIBNIZ INST FUR INNOVATIVE
Chemical sensor element, sensing apparatus, and sensing method
InactiveUS8877519B2Reduce widthEasy to changeComponent separationPhase-affecting property measurementsFine structureResonance wavelength
Owner:CANON KK
Method and device for controlling output light power and optical communication system
ActiveCN102098099AReduce spectral widthHigh extinction ratioElectromagnetic transmissionCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
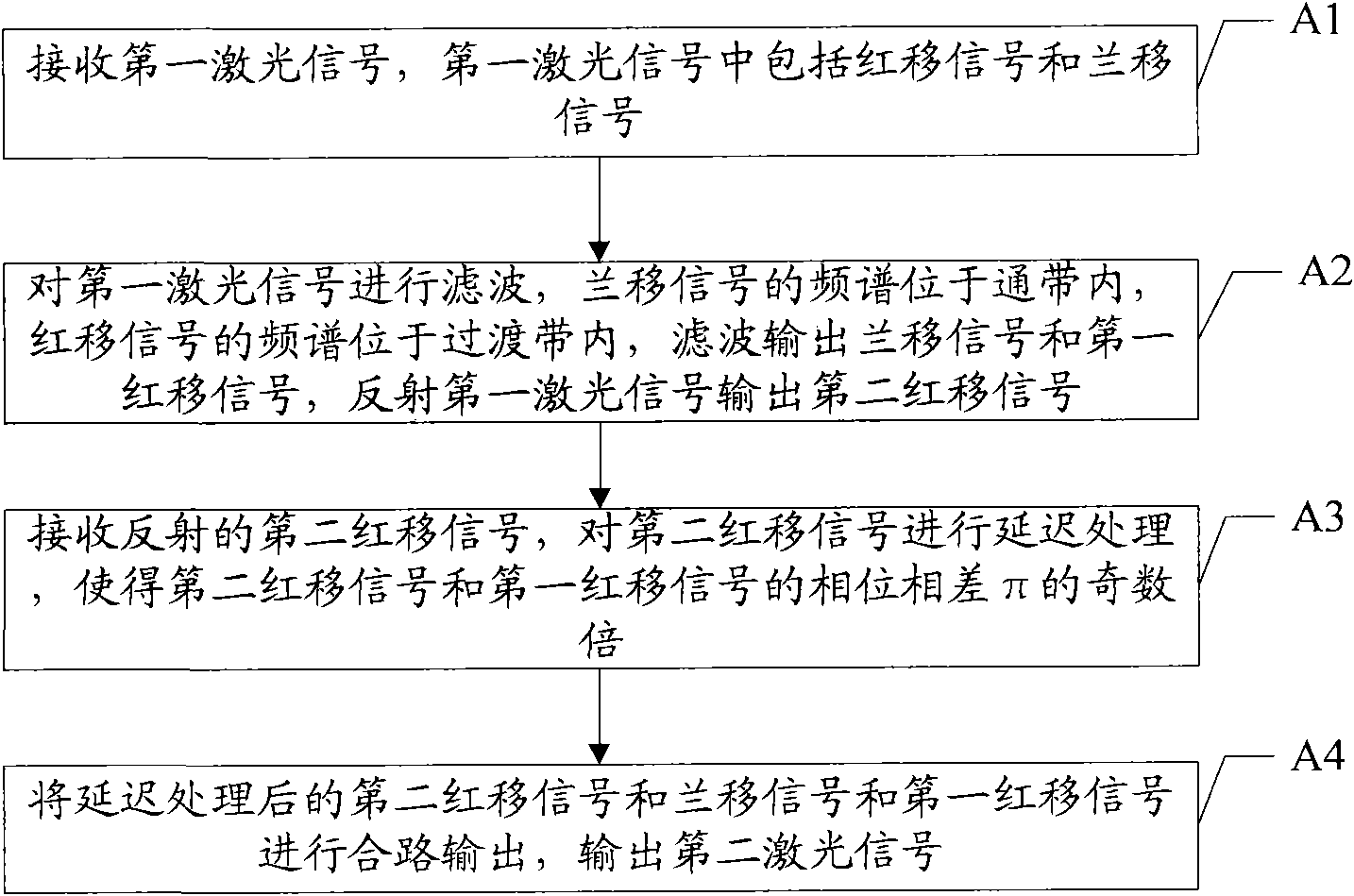
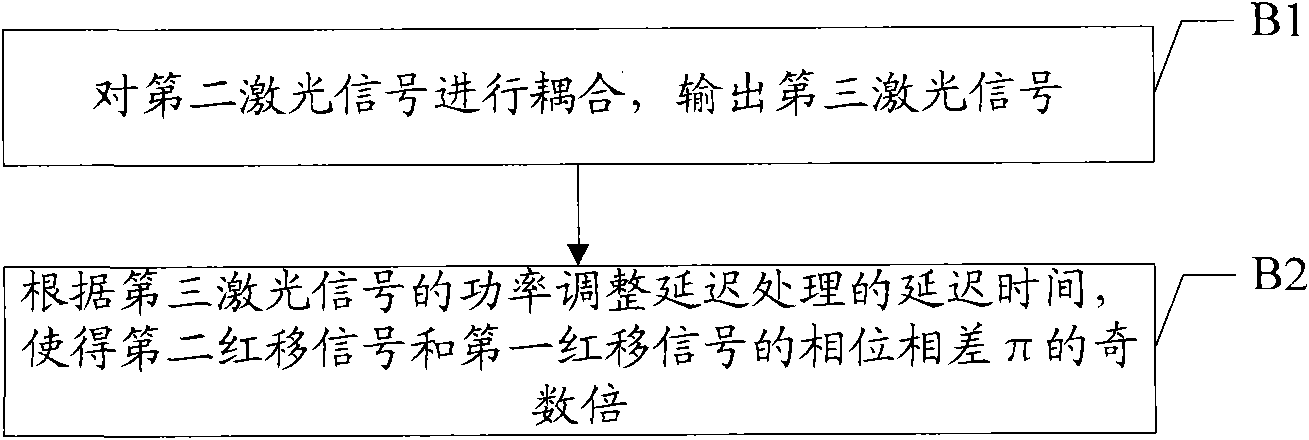
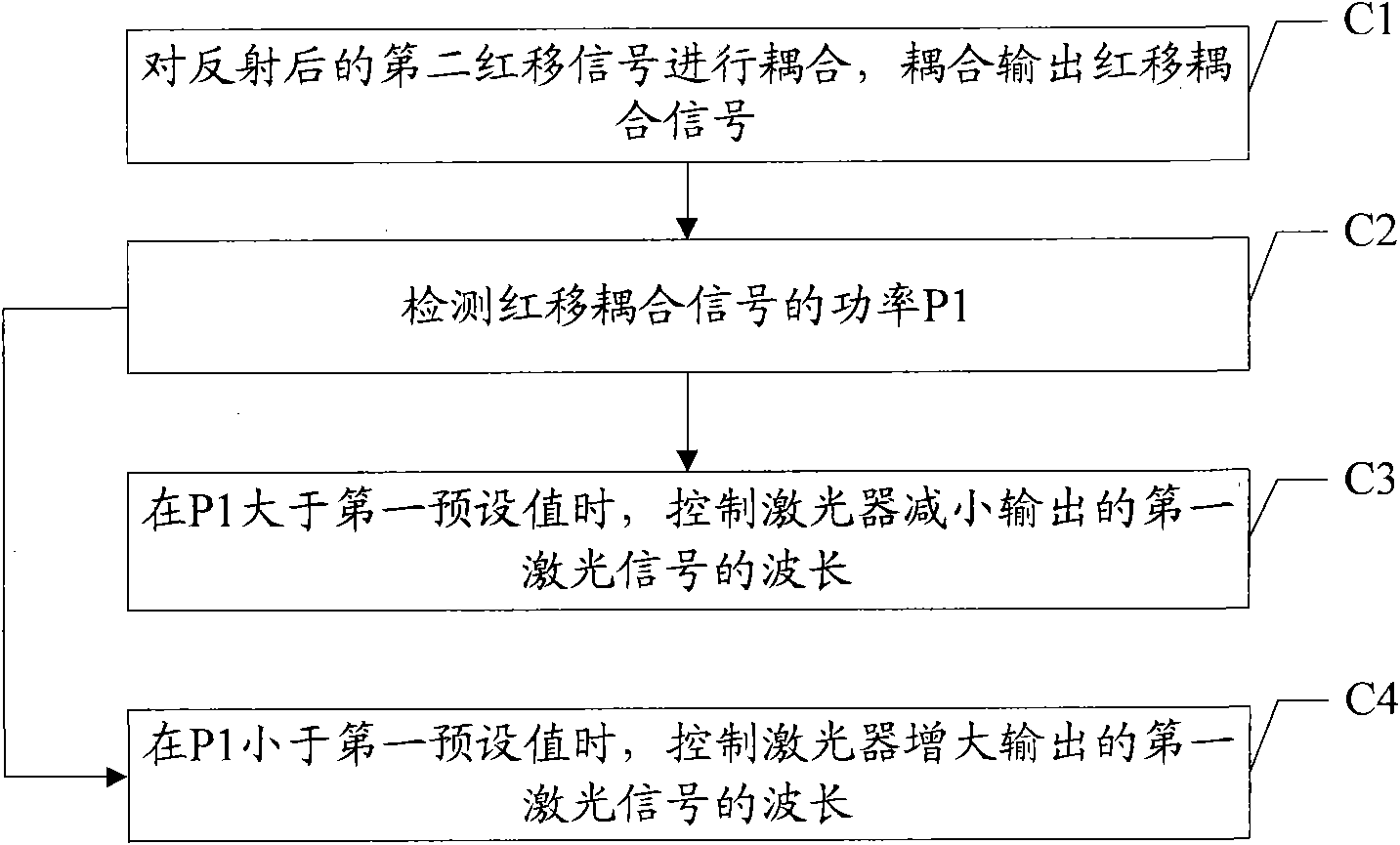
The invention discloses a method for controlling output light power, comprising the following steps: receiving a first laser signal, wherein the first laser signal comprises red shift signals and blue shift signals; filtering the first laser signal, filtering and outputting the blue shift signals and a first red shift signal, and reflecting a second red shift signal when the frequency spectrum of the blue shift signal is in a passband and the frequency spectrum of the red shift signal is in a transition zone; receiving the reflected second red shift signal, and carrying out deferred processing on the second red shift signal, so that the phase difference of the second red shift signal and the first red shift signal is odd times of pi; and combining the second red shift signal which is subjected to the deferred processing with the blue shift signals and the first red shift signal so as to output a second laser signal. According to the embodiment, the spectrum width of output signals can be decreased, the extinction ratio of the output signals is increased, the implementation difficulty of a filter can be reduced, and the implementation cost is reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Seed light generation device, light source device, adjustment method thereof, light irradiation device, exposure device, and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS8792083B2Increase widthLeakage of lightLaser detailsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLight irradiationLength wave
A light source device including a seed light generation device, a light amplification unit which optically amplifies seed light generated by the seed light generation device, and a wavelength conversion unit which converts the wavelength of the light optically amplified by the light amplification unit. The seed light generation device includes a pulsed light generation unit which generates pulsed light having a single wavelength, a pulse modulation unit which selectively passes and extracts a part of the pulsed light, and a timing adjustment unit which relatively adjusts the extracting timing of the pulsed light by the pulse modulation unit during the generation period of the pulsed light by the pulse generation unit, according to an operation.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Dislocation-based light emitter
InactiveUS7880189B2Quantum efficiency of the light emission in the respectively optimized luminescence rangeImprove quantum efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersDislocationAbsolute maximum
A light-emitting semiconductor component comprising a substrate which has a first interface between a first and a second silicon layer, whose lattice structures which are considered as ideal are rotated relative to each other through a twist angle about a first axis perpendicular to the substrate surface and are tilted through a tilt angle about a second axis parallel to the substrate surface, in such a way that a dislocation network is present in the region of the interface, wherein the twist angle and the tilt angle are so selected that an electroluminescence spectrum of the semiconductor component has an absolute maximum of the emitted light intensity at either 1.3 micrometers light wavelength or 1.55 micrometers light wavelength.
Owner:IHP GMBH INNOVATIONS FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE MICROELECTRONICS LEIBNIZ INST FUR INNOVATIVE
Method of making a distributed bragg mirror
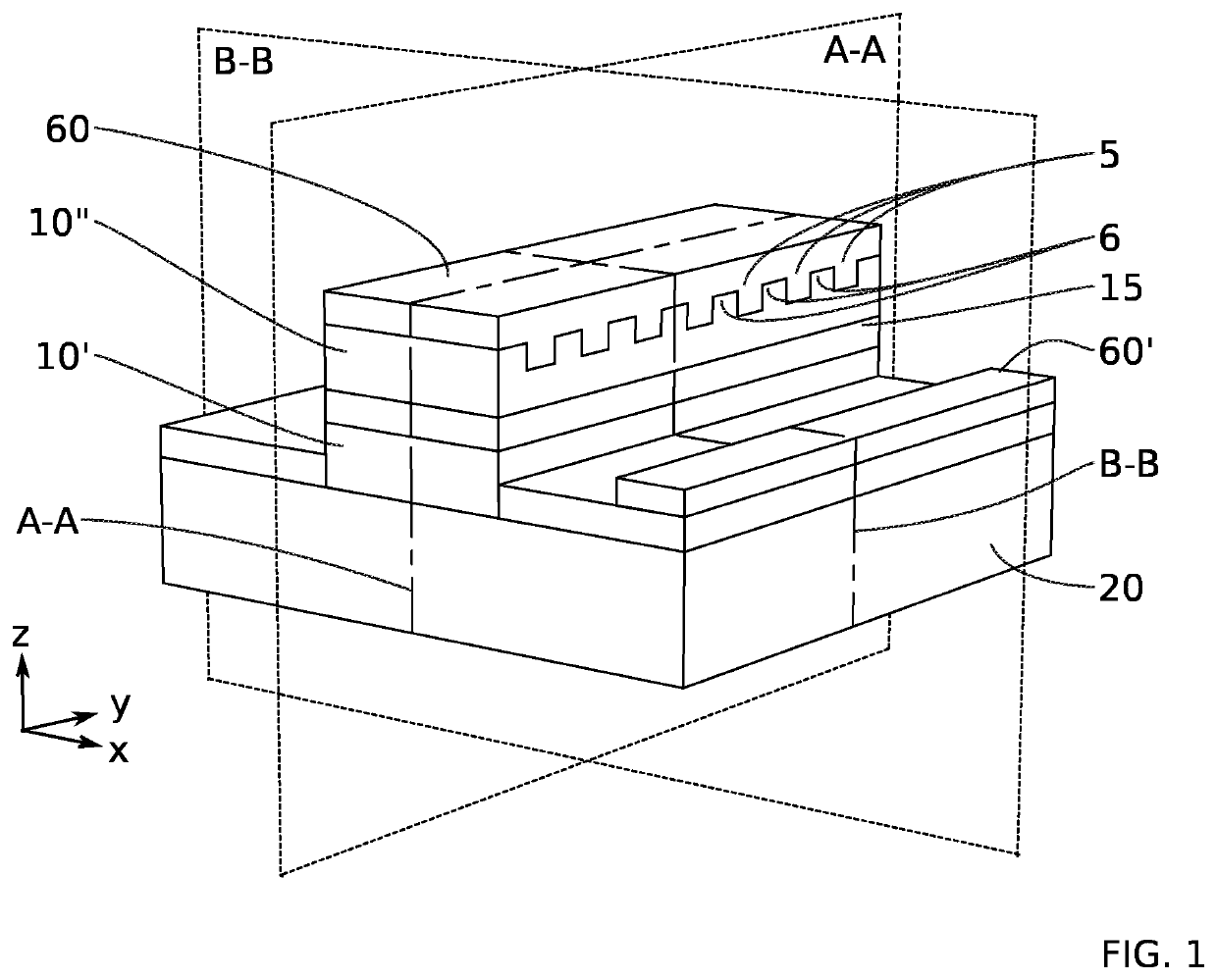
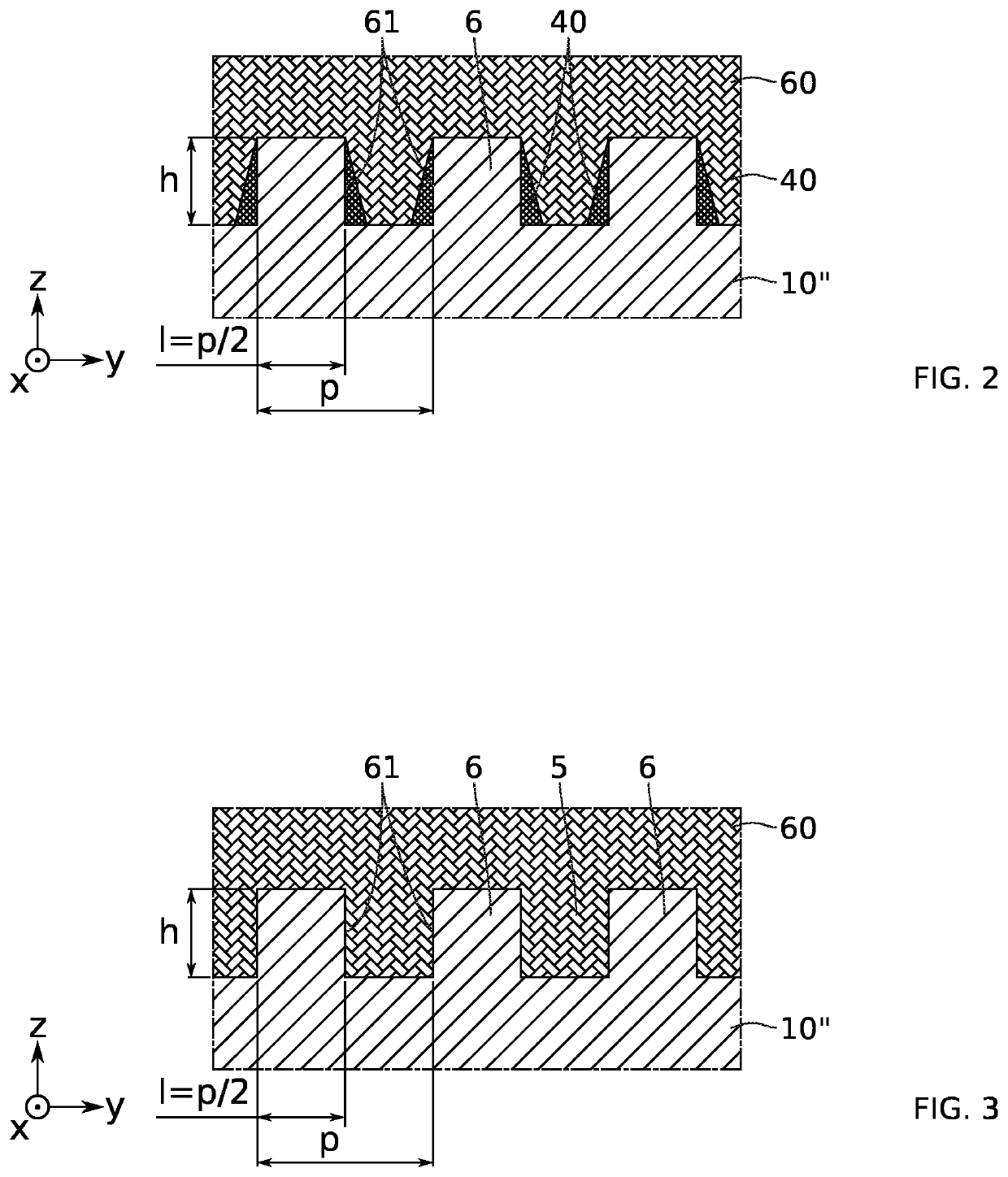
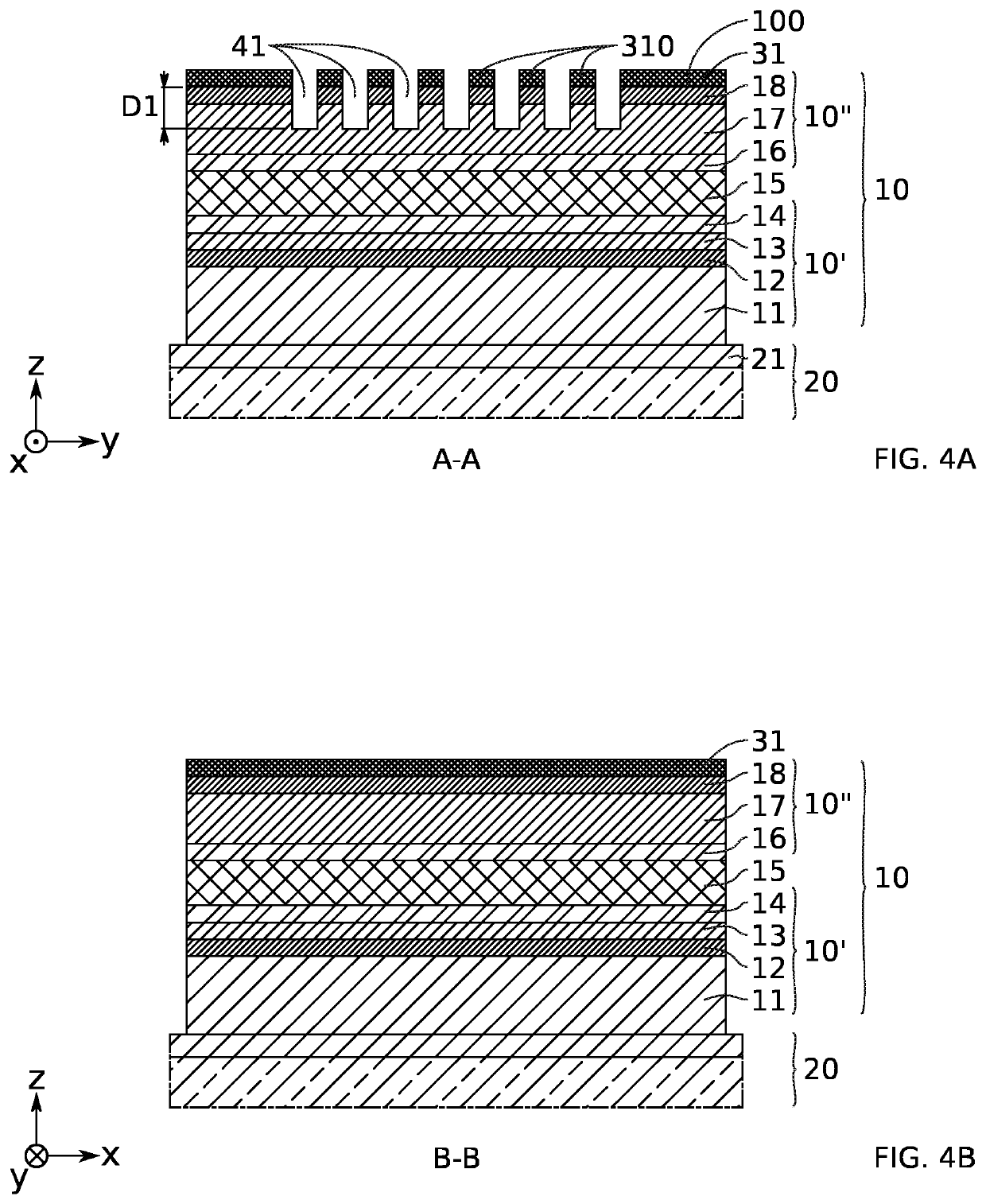
PendingUS20220181850A1Easy to eliminateIncrease contact areaOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsInter layerDistributed Bragg reflector
A method for forming a Bragg reflector includes after forming first trenches in the stack, which are intended to form structures of the distributed Bragg reflector, forming a sacrificial interlayer at least in the first trenches, depositing a second masking layer at least inside the first trenches, forming second trenches intended to form sidewalls of the laser, removing the second masking layer from inside the first trenches, removing said sacrificial interlayer so as to remove, by lift-off, residues of the second masking layer that remain inside the first trenches, and filling said first trenches with at least one metal material.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
System and method for generating wavelength-tunable, ultra-short light pulses having high power spectral density
ActiveUS10250006B2Reduce spectral widthIncrease power spectral densityOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialLighting spectrumSpectral density
Disclosed is a system for generating wavelength-tunable, ultra-short light pulses within the visible or infrared light spectrum. The system includes an injection module including a light source and a wavelength-tunable spectral filter. The light source is suitable for generating short light pulses, having a duration measured in nanoseconds, within an emission spectrum having a spectral width of several tens of nanometers to several hundred nanometers. The spectral filter has a spectral width between 250 pm and 3 nm and is suitable for spectrally and temporally filtering the short light pulses such that the injection module generates wavelength-tunable, spectrally filtered, ultra-short light pulses. The system also includes at least one optical amplifier suitable for generating wavelength-tunable, ultra-short, amplified pulses based on the wavelength of the spectral filter.
Owner:UNIV DE BORDEAUX +1
Coating determination
PendingUS20210109028A1Accurate CalibrationAccurate measurementLiquid surface applicatorsRaman scatteringOptical spectrometerPhysical chemistry
A method performed in a coating testing system for automatically determining the polymerisation of coating material includes positioning a spectrometer probe adjacent to an object (wire 10), the object comprising a polymer coating; acquiring spectra of the polymer coating using the probe; and performing chemometric analysis on the acquired spectra in order to measure the polymerisation of the polymer coating.
Owner:TAU ACT GMBH
Pulse grid coherent chromatography method
InactiveCN101639440BHigh sensitivityImprove anti-interference abilityPhase-affecting property measurementsLight beamSignal light
The invention discloses a pulse grid coherent chromatography method comprising the following steps: dividing low coherent pulse light into at least two beams, wherein one light beam enters chromatography matters, and distribution reflected light is signal light; the other light seam is magnified by cyclic repeating split light or split light combined light to generate a pulse grid, the pulse gridand the signal light generate interference and form a signal light pulse string, and the signal light pulse string comprises the reflected light distribution of the chromatography matters to represent chromatography information. The pulse grid coherent chromatography method has large chromatography range, high sensitivity as well as simple and quick reconstitution of the chromatography information, is suitable for the chromatography imaging of the continuous scattering matters and the distribution sensing of parameters of biology, chemistry, physics, and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com