Patents
Literature
84 results about "Quantum well laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
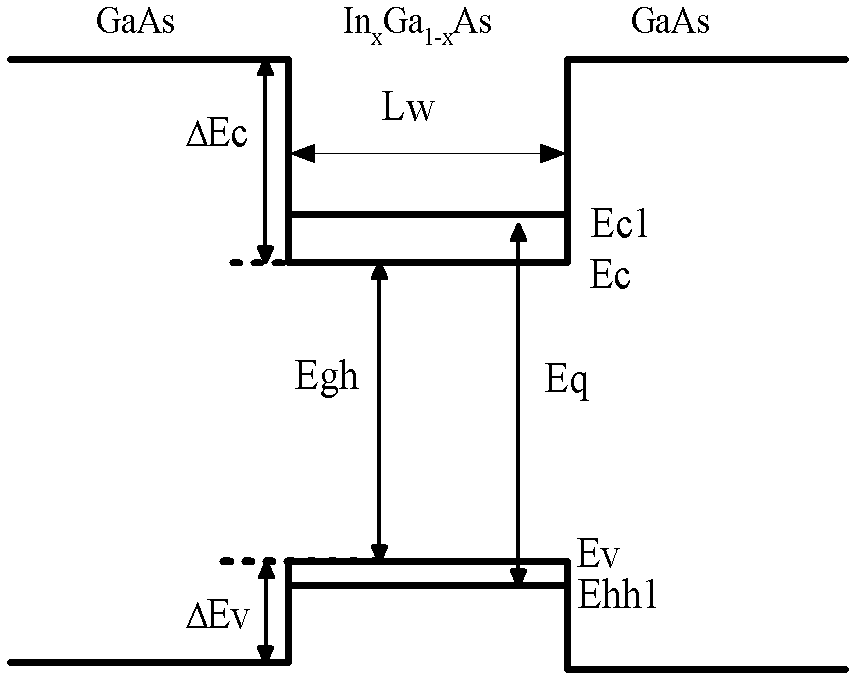
A quantum well laser is a laser diode in which the active region of the device is so narrow that quantum confinement occurs. Laser diodes are formed in compound semiconductor materials that (quite unlike silicon) are able to emit light efficiently. The wavelength of the light emitted by a quantum well laser is determined by the width of the active region rather than just the bandgap of the material from which it is constructed. This means that much longer wavelengths can be obtained from quantum well lasers than from conventional laser diodes using a particular semiconductor material. The efficiency of a quantum well laser is also greater than a conventional laser diode due to the stepwise form of its density of states function.
Ultraviolet group III-nitride-based quantum well laser diodes
InactiveUS20050224781A1Sufficient carrier confinementAvoid structural degradationOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsUltravioletGallium
A pair of undoped spacer layers are provided adjacent to, or near to, a single quantum well aluminum gallium nitride active region. In various exemplary embodiments, the undoped spacer layers are provided between the single quantum well aluminum gallium nitride active region and carrier confinement layers. The undoped spacer layers reduce the threshold current for the laser device and improve the output characteristics.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Ultraviolet group III-nitride-based quantum well laser diodes
InactiveUS7138648B2Sufficient carrier confinementAvoid structural degradationOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsUltravioletGallium
A pair of undoped spacer layers are provided adjacent to, or near to, a single quantum well aluminum gallium nitride active region. In various exemplary embodiments, the undoped spacer layers are provided between the single quantum well aluminum gallium nitride active region and carrier confinement layers. The undoped spacer layers reduce the threshold current for the laser device and improve the output characteristics.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Quantum well lasers with strained quantum wells and dilute nitride barriers
ActiveUS7457338B2Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionIndiumNitrogen
In accordance with the present invention, GaAs-based optoelectronic devices have an active region that includes a well layer composed of a compressively-strained semiconductor that is free, or substantially free, of nitrogen disposed between two barrier layers composed of a nitrogen- and indium-containing semiconductor.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Epitaxial structure of high-brightness light emitting diode and implementation method thereof
ActiveCN102832306AQuality improvementImprove luminous efficiencySemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyRecombination rate
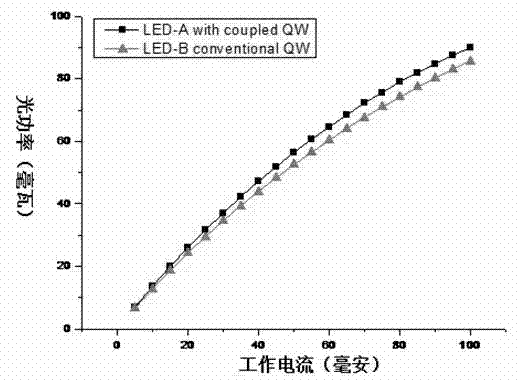
An epitaxial structure of a high-brightness light emitting diode and an implementation method thereof belong to the technical field of semiconductor production. At least three pairs of coupled quantum wells grow. When each pair of coupled quantum wells grow, firstly, quantum well layers low in In content grow; and secondly, luminous quantum well layers grow, In content of each quantum well layer low in In content gradually increases along the growth direction, and a thin GaN barrier layer grows between each adjacent quantum well layer low in In content and luminous quantum well layer. A coupled quantum well structure which is low in In content and gradually increases in composition grows before a luminous quantum well by a variable temperature and variable precursor flow method, and accordingly a quantum well low in In content cannot adsorb photons emitted by the quantum well again, built-in electric field can be lowered, localization of carriers is enhanced to increase radiative recombination rate, and internal quantum efficiency of the light emitting diode is improved greatly.
Owner:YANGZHOU ZHONGKE SEMICON LIGHTING
Laser source with broadband spectrum emission
ActiveUS20070189348A1Easy to manufactureEmission spectrumOptical resonator shape and constructionNanoopticsFrequency spectrumLaser source
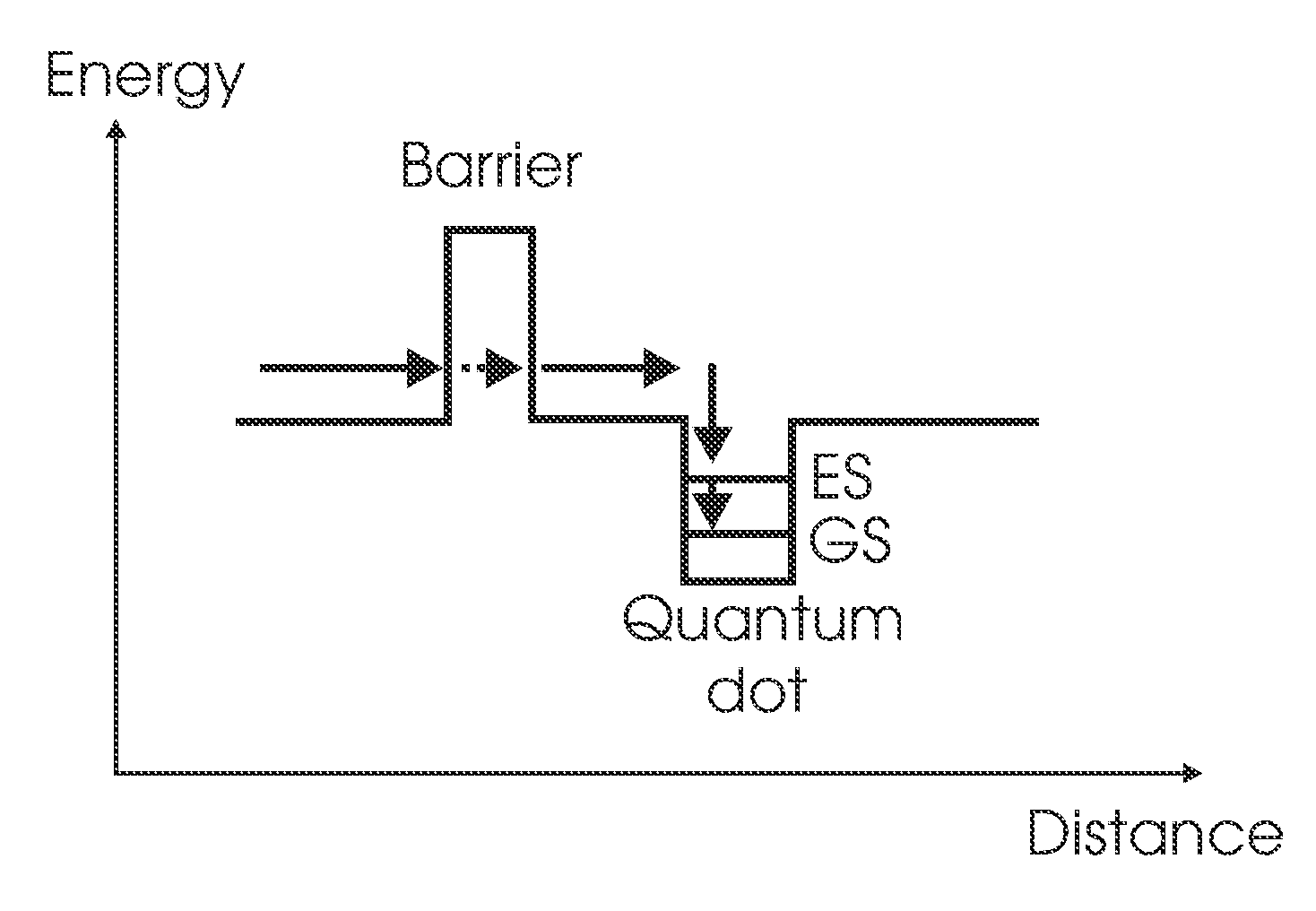
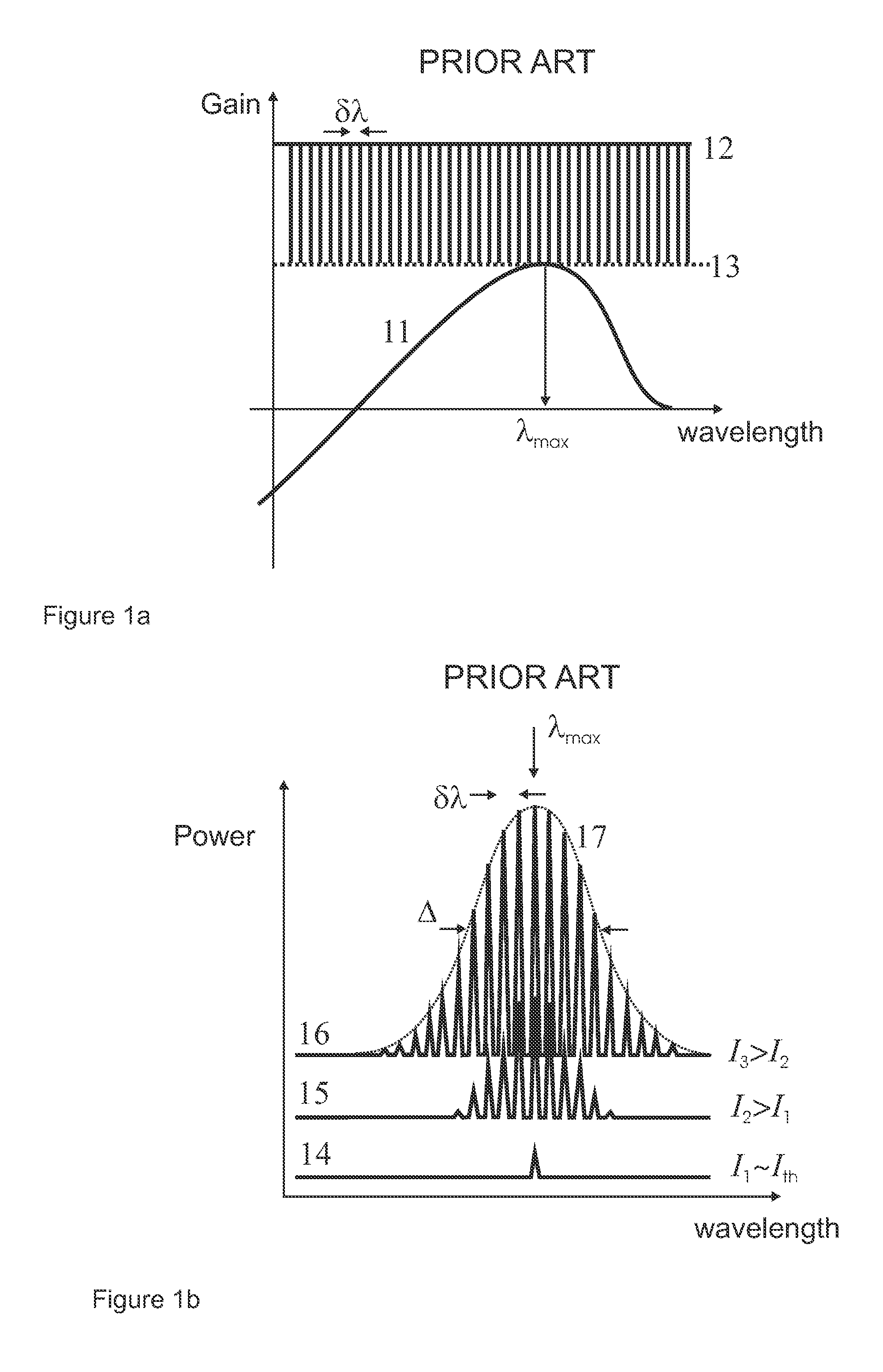
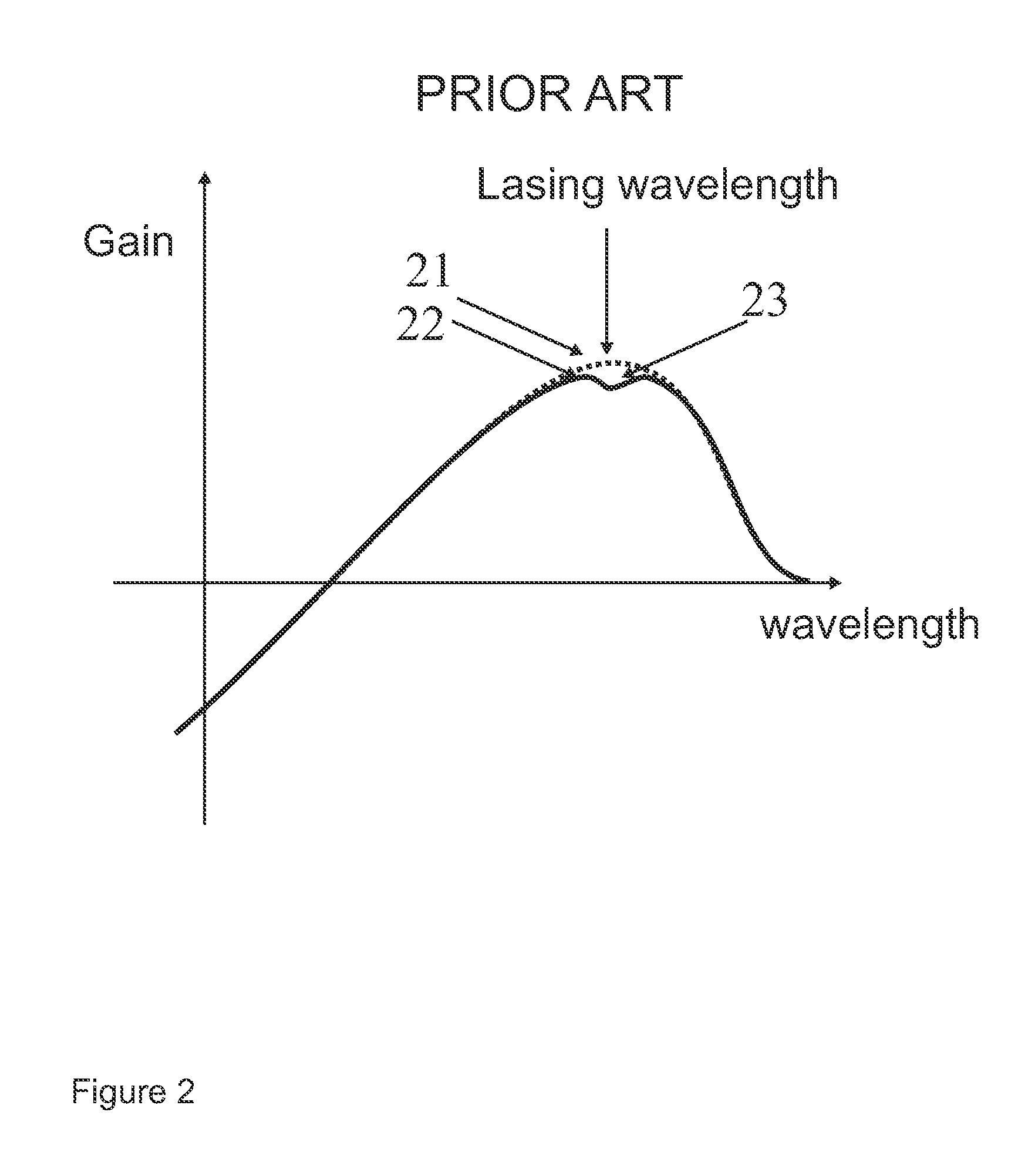
A quantum dot laser operates on a quantum dot ground-state optical transition. The laser has a broadband (preferably ≧15 nm) spectrum of emission and a high output power (preferably ≧100 mW). Special measures control the maximum useful pump level, the total number of quantum dots in the laser active region, the carrier relaxation to the quantum dot ground states, and the carrier excitation from the quantum dot ground states. In one embodiment, a spectrally-selective loss is introduced into the laser resonator in order to suppress lasing on a quantum dot excited-state optical transition, thereby increasing the bandwidth of the emission spectrum.
Owner:INNOLUME
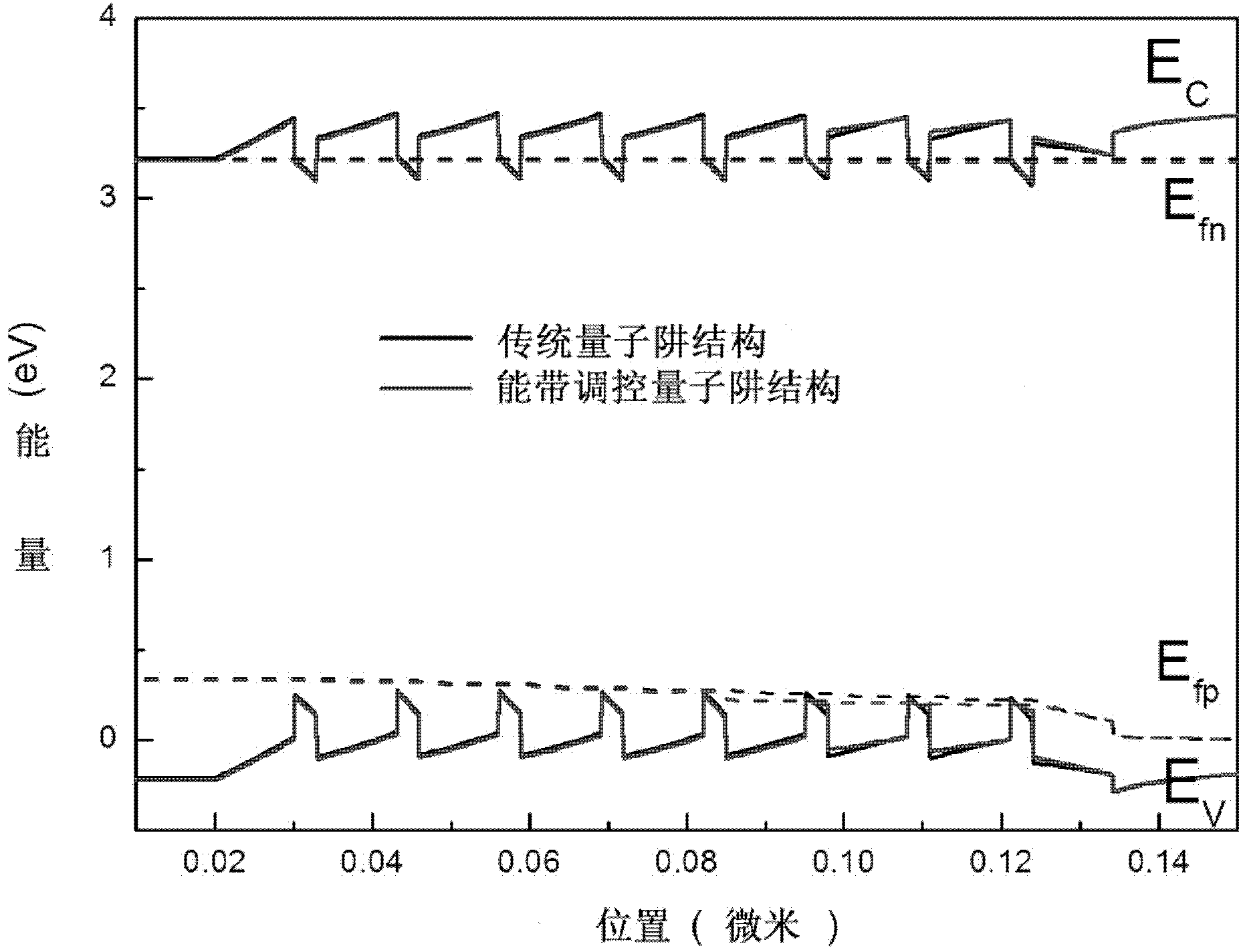
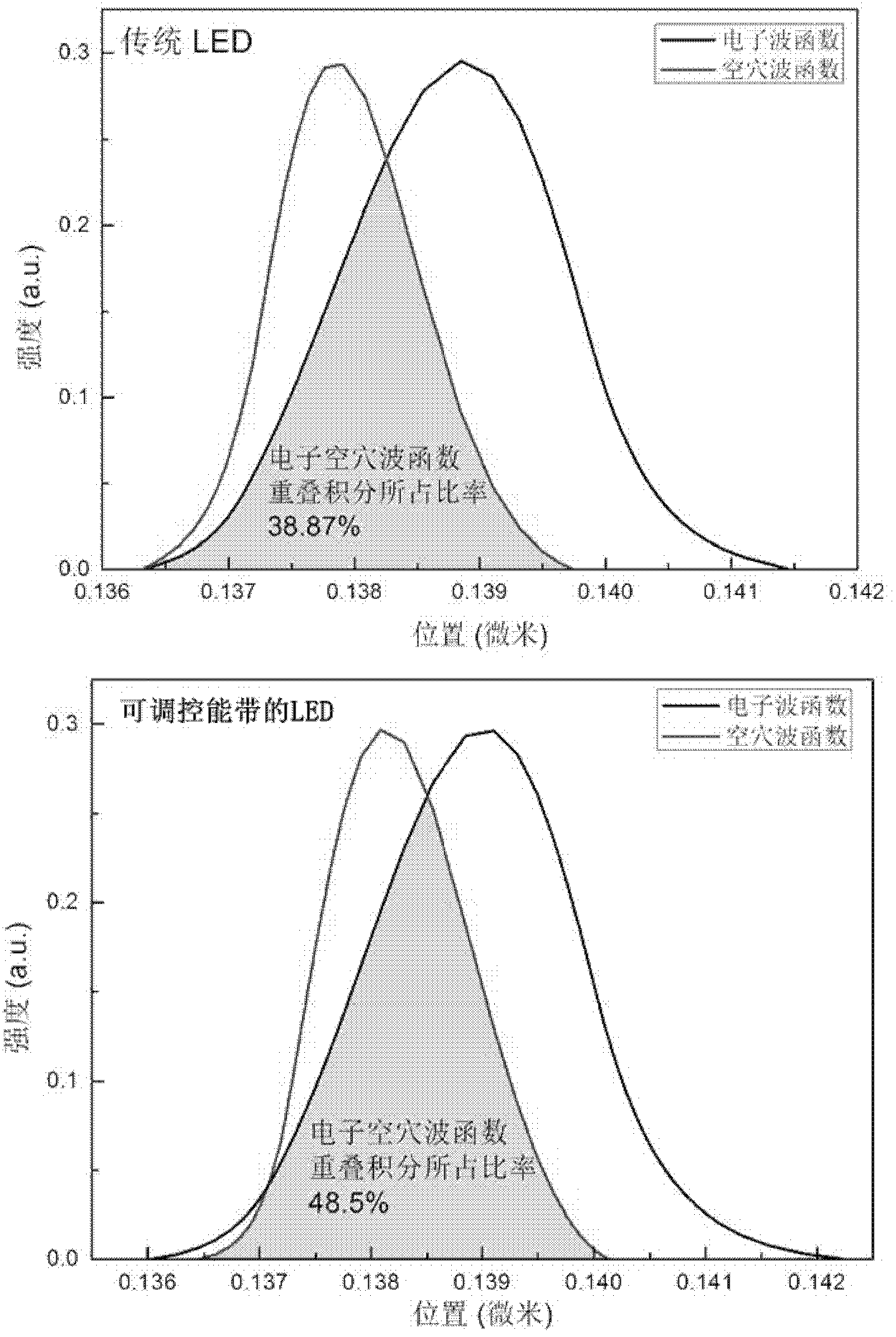
Energy band adjustable light-emitting diode (LED) quantum well structure
The invention discloses an energy band adjustable light-emitting diode (LED) quantum well structure and an epitaxial growth method thereof, wherein the energy band adjustable LED quantum well structure can improve radiative recombination efficiency in multiple quantum wells of an active area of an LED. The energy band adjustable LED quantum well structure comprises at least one quantum well potential well layer with component changing gradually, energy band control of a quantum well area can be achieved, electron hole wave function superposition in the active area of the quantum well can be improved, and radiative recombination efficiency of the LED quantum well area can be improved. The multiple quantum well structure can be applied to InGaN-based blue or green LEDs, improves internal quantum efficiency of active areas of the InGaN-based blue or green LEDs and further improves LED power and efficiency.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
MQW Laser Structure Comprising Plural MQW Regions
InactiveUS20100150193A1Promote disseminationHigh refractive indexOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsOptical pumpingStimulated emission
Multi-quantum well laser structures are provided comprising active and / or passive MQW regions. Each of the MQW regions comprises a plurality of quantum wells and intervening barrier layers. Adjacent MQW regions are separated by a spacer layer that is thicker than the intervening barrier layers. The bandgap of the quantum wells is lower than the bandgap of the intervening barrier layers and the spacer layer. The active region may comprise active and passive MQWs and be configured for electrically-pumped stimulated emission of photons or it may comprises active MQW regions configured for optically-pumped stimulated emission of photons.
Owner:THORLABS QUANTUM ELECTRONICS
Pulsed quantum dot laser system with low jitter
InactiveUS7103079B2Low and reducedReduce phase noiseLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsDriver circuitPulse sequence
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
TM-polarization GaAsP/GaInP active-region 808nm quantum-well laser
InactiveCN103457158AReduce oxidationReduce internal lossOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsLower limitOhmic contact
The invention provides a TM-polarization GaAsP / GaInP active-region 808nm quantum-well laser. The laser structurally comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, a type-N lower limit layer, a lower waveguide layer, a quantum well layer, an upper waveguide layer, a type-P upper limit layer, and an ohmic contact layer sequentially from bottom to top. The upper waveguide layer and the lower waveguide layer are made of aluminum-free material GaInP. The quantum well layer is made of GaAsP material. The waveguide layer and the quantum well layer form a wide-waveguide aluminum-free active region. The laser has the advantages that the influence of Al oxidization, growth interface roughness and accessory electric field at cavity surface upon the reliability in high power output, long service life and the like of the laser can be reduced effectively, the waveguide layer and the limit layers are optimally designed into wide-waveguide asymmetric structures, and internal loss can be reduced effectively, and maximum output power and reliability can be improved.
Owner:Shandong Huaguang Optoelectronics Co. Ltd.
Tunable infrared lasers for gas-phase spectroscopy
ActiveUS7656912B2Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingGas phase
Owner:STC UNM
Optimization method of response ratio of one-dimensional T-Hz quantum well photoelectric detector
InactiveCN101834227AImprove work performanceImprove response rateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesGratingMechanical property
The invention relates to an optimization method of response ratio of a one-dimensional T-Hz quantum well photoelectric detector, which comprises the following steps of: 1, simulating light field distribution of having the diffraction by T-Hz light normally entering the surface of an element when entering the element after passing through an optical grating, and computing a wavelength Lambda of a primary diffraction die vertical to the surface direction of the element; and 2, thinning a substrate of the element within a range allowed by mechanical properties of the element to ensure that the total thickness of the element is integer multiples of the wavelength Lambda. The method realizes the optimal distribution of a light field in the element by grinding, polishing and corroding the substrate of the element, and can ensure a plurality of quantum wells are in a region with stronger light field by reasonably designing the thickness of an upper electrode layer and properly adding the layer number of the quantum wells, thereby improving the performance of the element, optimizing the response rate, and having important meaning on the research and the implementation of THz real-time imaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
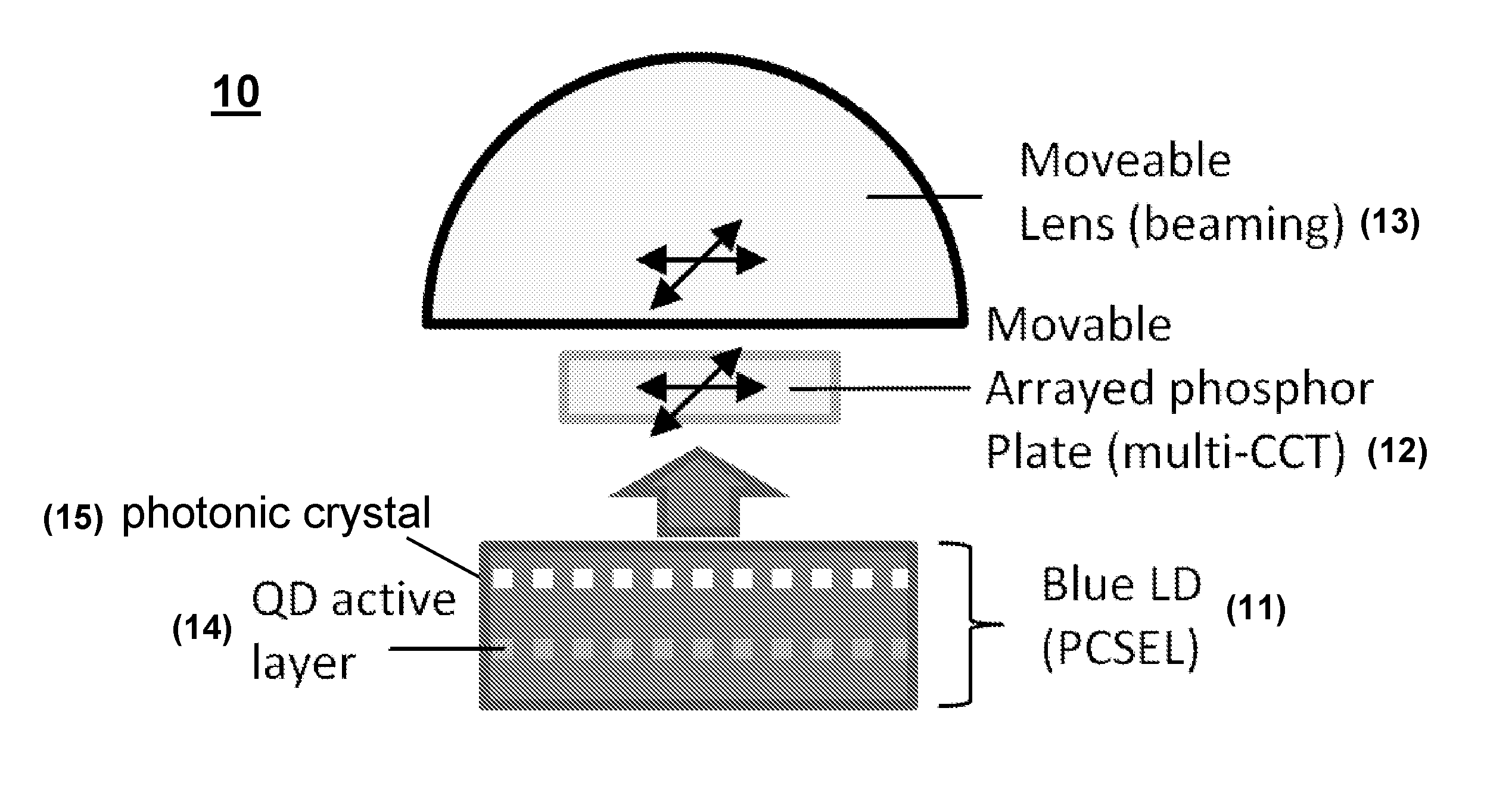
White light illuminant comprising quantum dot lasers and phosphors
InactiveUS20160087406A1Novel and more compact luminairesHigh current density operationLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersLine widthLaser light
A laser-based white light illuminant comprises a III-nitride quantum dot laser diode and phosphors that convert the emitted laser light into white light. The laser light is emitted from an active region comprised of small quantum dots having a narrow size distribution, thereby providing narrower linewidths, decreased operating current density and increased peak efficiency. The white light illuminant has a number of advantages of LED-based solid state lighting, including higher power conversion efficiency, higher achievable luminous efficacy, and new and improved functionality.
Owner:SANDIA
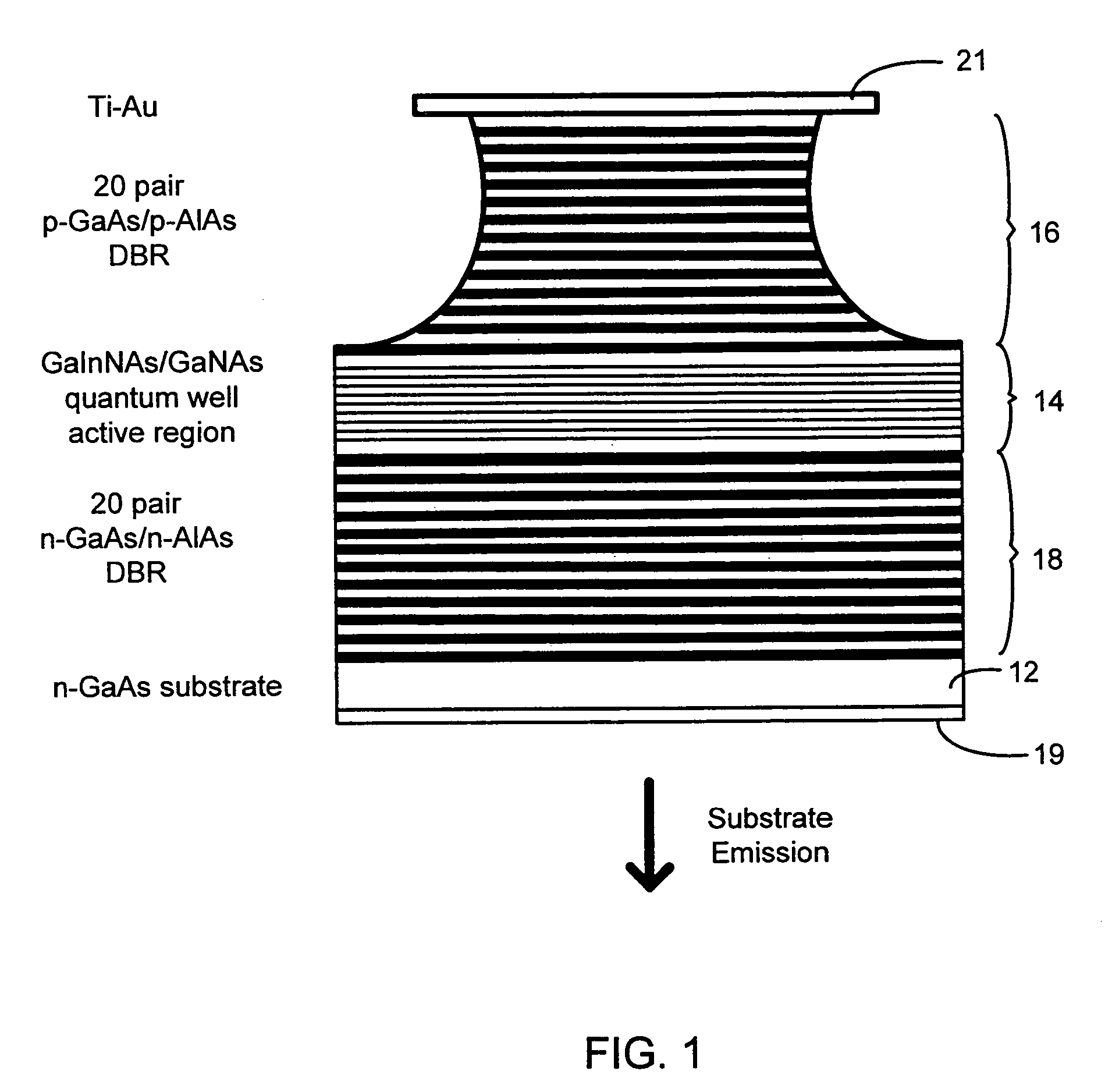
Enhanced surface-emitting photonic device
ActiveUS20090147818A1Improve performanceLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor quantum wellsDistributed Bragg reflector
A surface-emitting photonic device including a structure disposed therein to enhance a performance thereof. The structure includes a two dimensionally periodic second order distributed feedback device (DFB) to emit diffraction limited outcoupled laser light having a predetermined wavelength along a propagation direction that is substantially normal to a plane of the DFB, and a first order distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) coplanar with, adjacent to and surrounding the DFB, a geometry of the DBR being selected such that a bandgap of the DBR is maximized and centered around the predetermined wavelength of the emitted light, a substrate, and either an optical gain layer, or a semi-conductor quantum well laser disposed within the substrate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
808nm large-power quantum well laser in non-aluminum active region of asymmetric structure
ActiveCN101340060AIncreased light confinement factorReduce leakageOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsIndium arsenideWaveguide
The invention provides an aluminum-free active region 808nm high-power quantum-well laser with asymmetric structure. From the bottom to the top, the structure of the laser sequentially comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, an N-type lower limiting layer, a lower waveguide layer, a quantum-well layer, an upper waveguide layer, a potential barrier limiting layer, a P-type upper limiting layer, a transition layer and an ohmic contact layer, wherein, the upper waveguide layer and the lower waveguide layer are made of aluminum-free material Indium gallium phosphide, the quantum-well layer made of gallium indium arsenide phosphide material, the waveguide layer and the quantum-well layer form the aluminum-free active region, and one layer potential barrier limiting layer which is made of P-type aluminum gallium indium phosphide material and 50nm-150nm thick and has a band gap wider than that of the upper limiting layer is arranged between the upper limiting layer and the upper waveguide layer. The laser of the invention can increase the optical limiting factor of the P-type material region, reduce the optical leakage towards the P-type material region, reduce optical absorption loss of a current carrier at the highly doped area, and improve the work efficiency of the laser; the structure of the invention also improves the limiting effect of the active region on the carrier, reduce the leakage of the carrier and is favorable to the decrease of the threshold current.
Owner:Shandong Huaguang Optoelectronics Co. Ltd.
Pulsed quantum dot laser system with low jitter
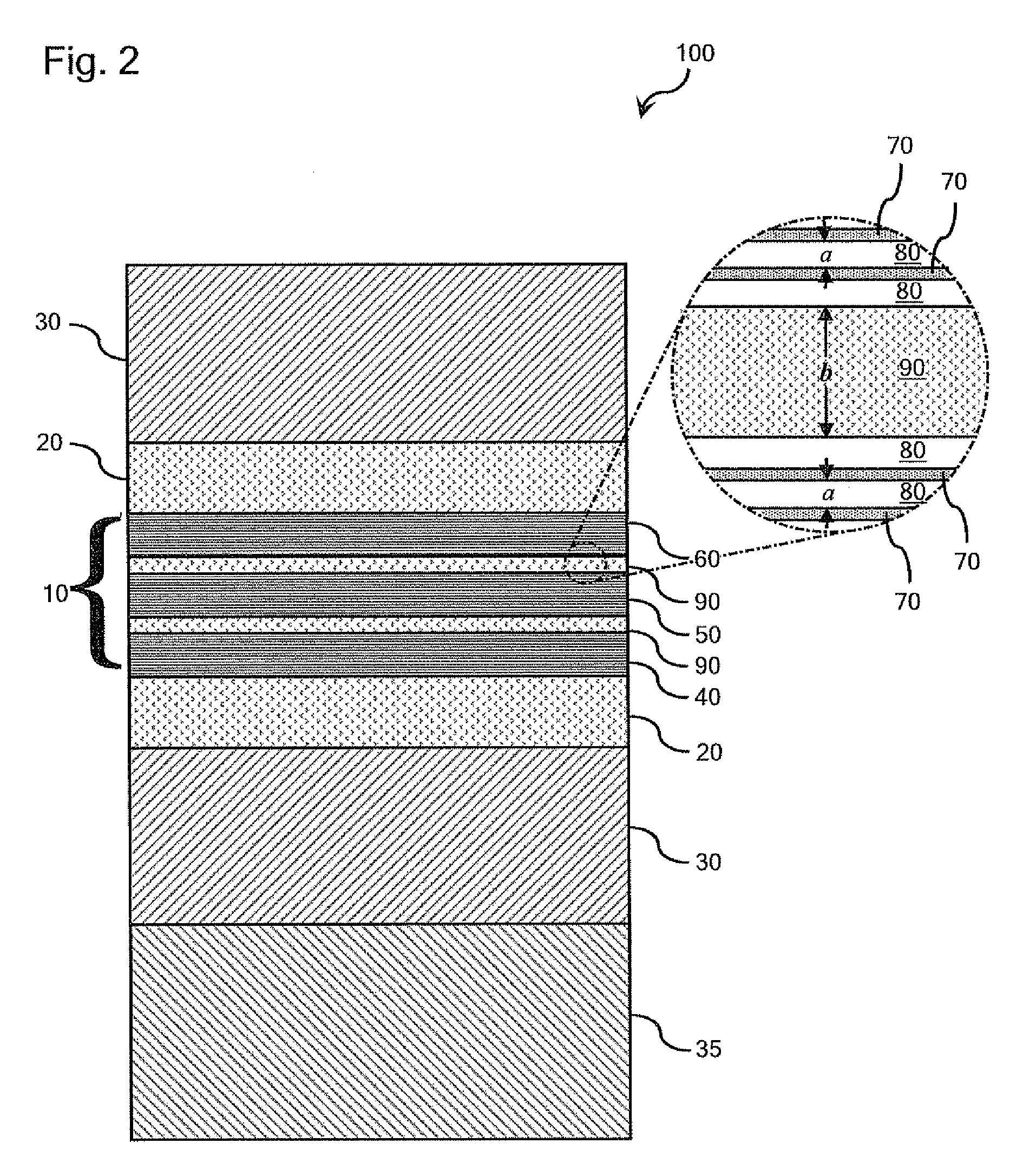
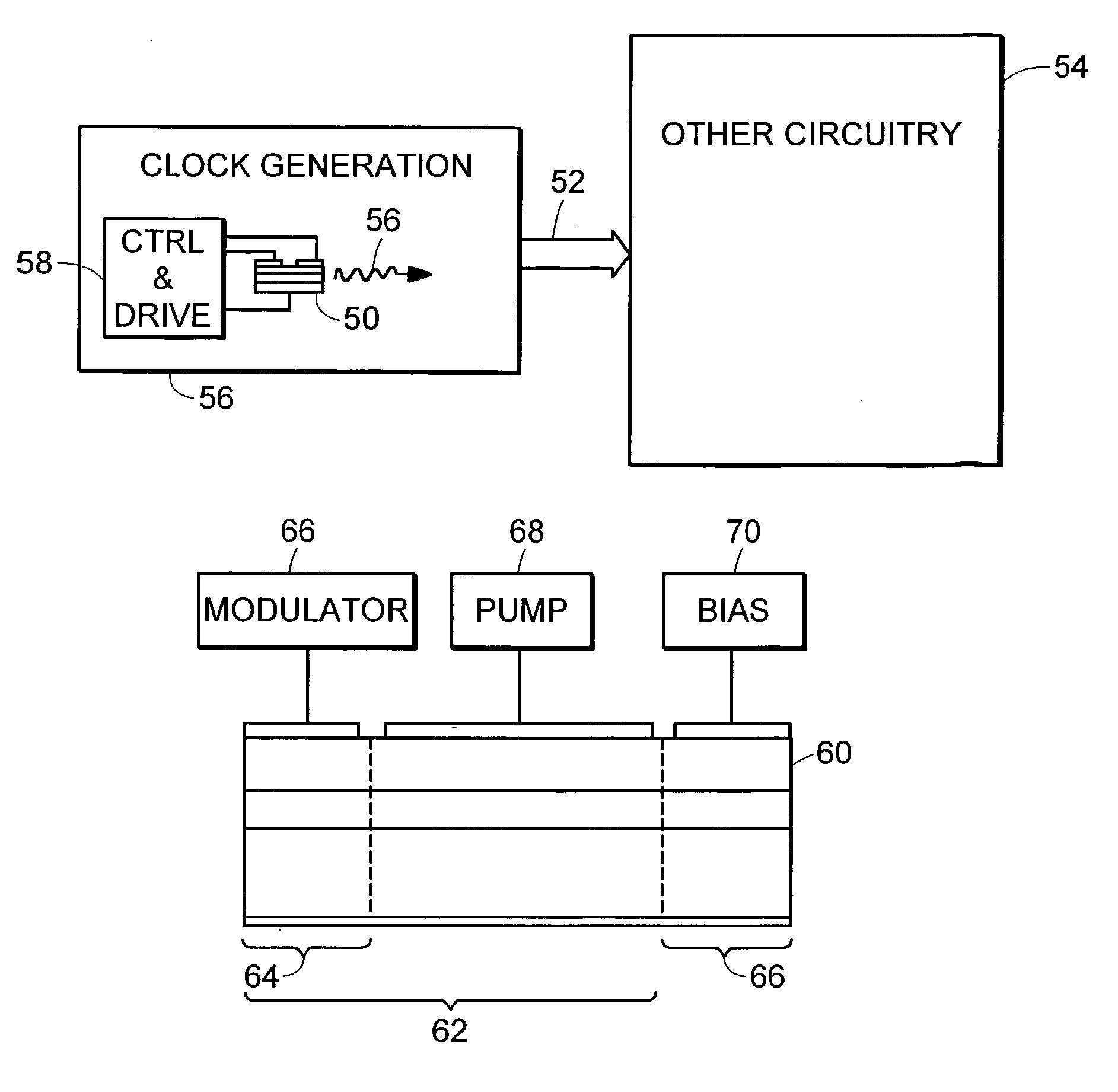
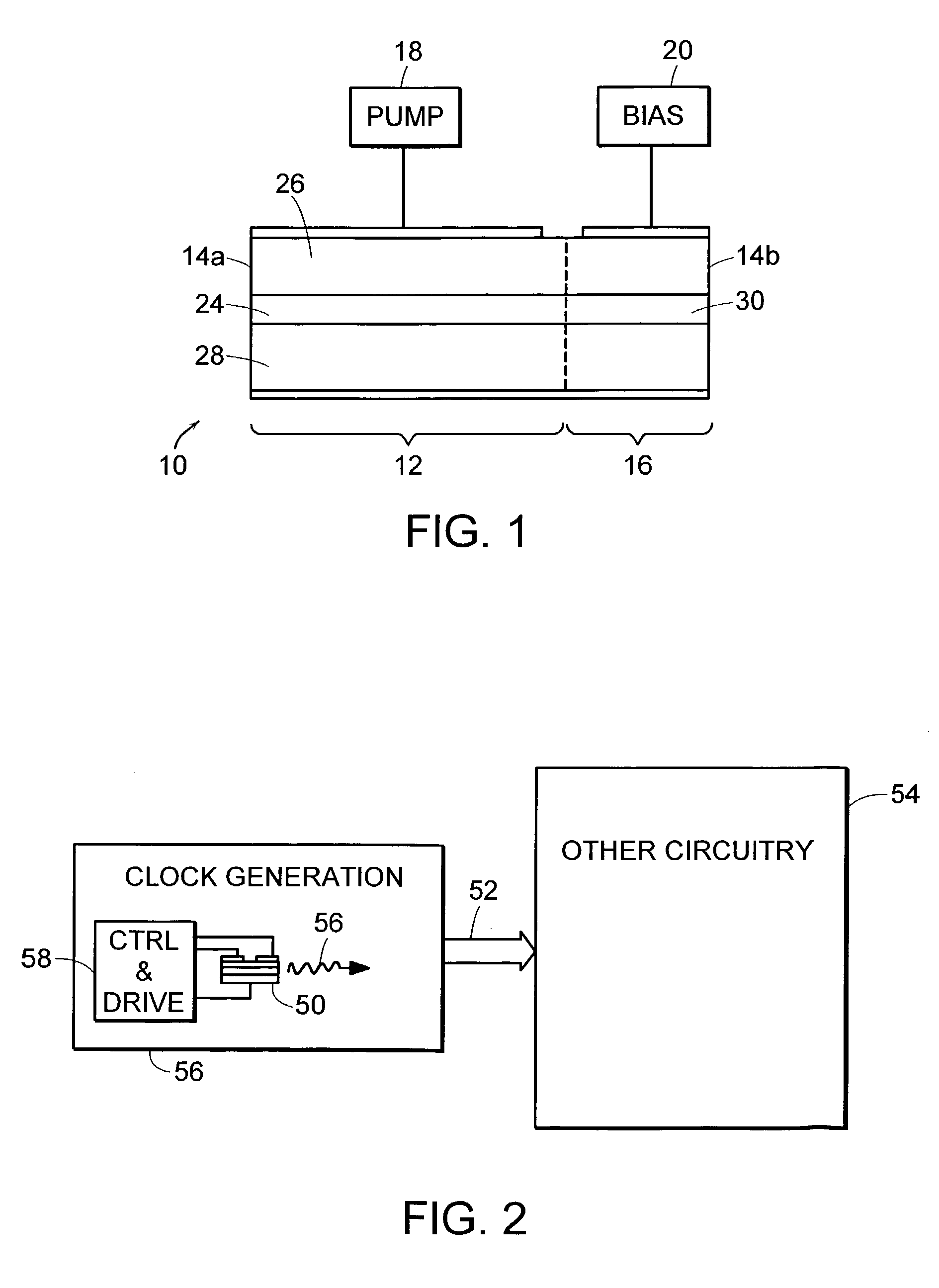
InactiveUS20050008048A1Low and reducedReduce phase noiseLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsDriver circuitLow jitter
A circuit for generating a clock or sampling signal, the circuit including: a semiconductor quantum dot laser element including a region of quantum dots, wherein the region of quantum dots is characterized by an emission distribution having a half-width of at least about 10 meV; and drive circuitry connected to the quantum dot laser element for operating the quantum dot laser element as a mode-locked laser that outputs a periodic, uniformly spaced sequence of pulses, wherein the clock or sampling signal is derived from the sequence of pulses.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
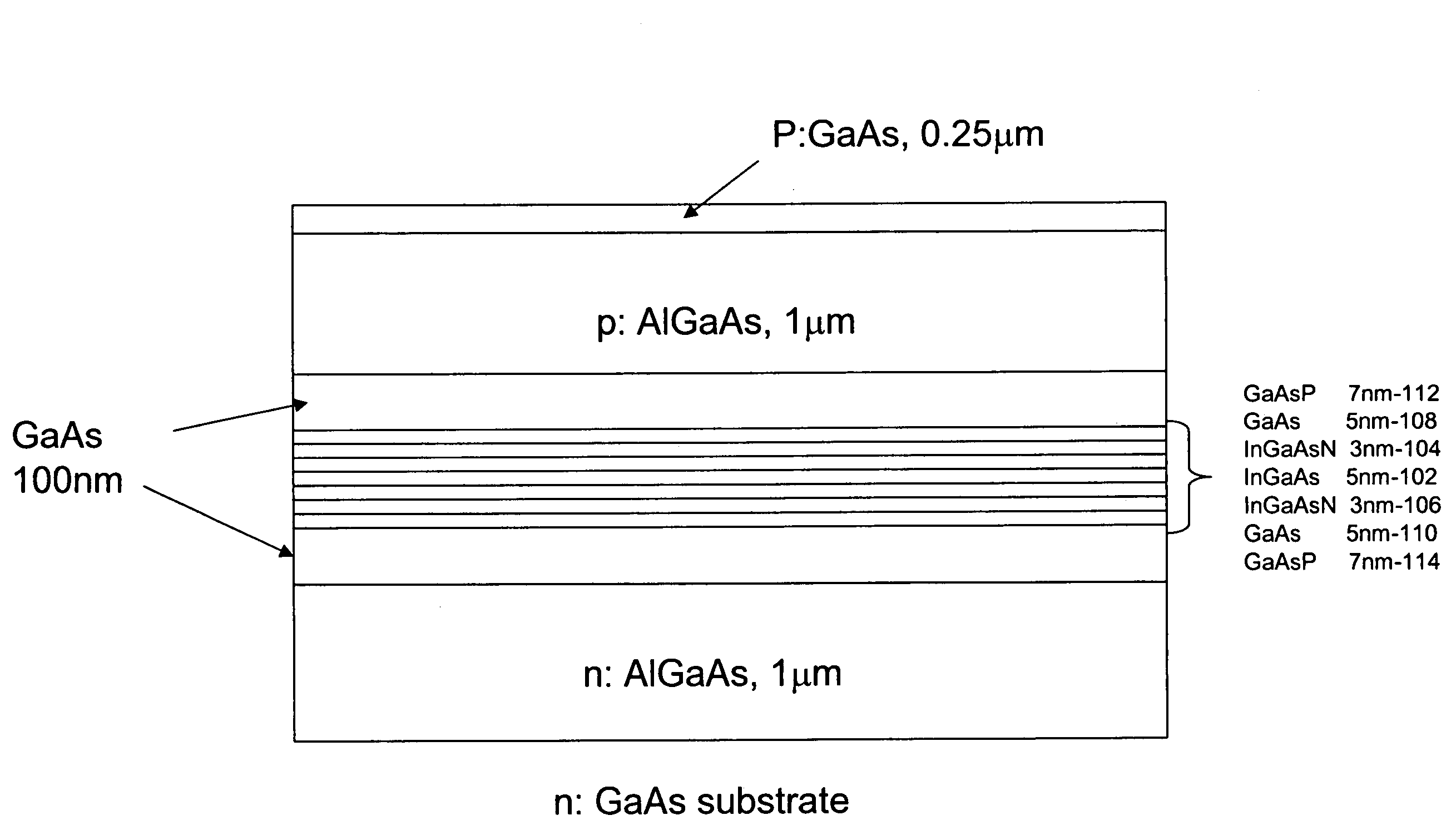
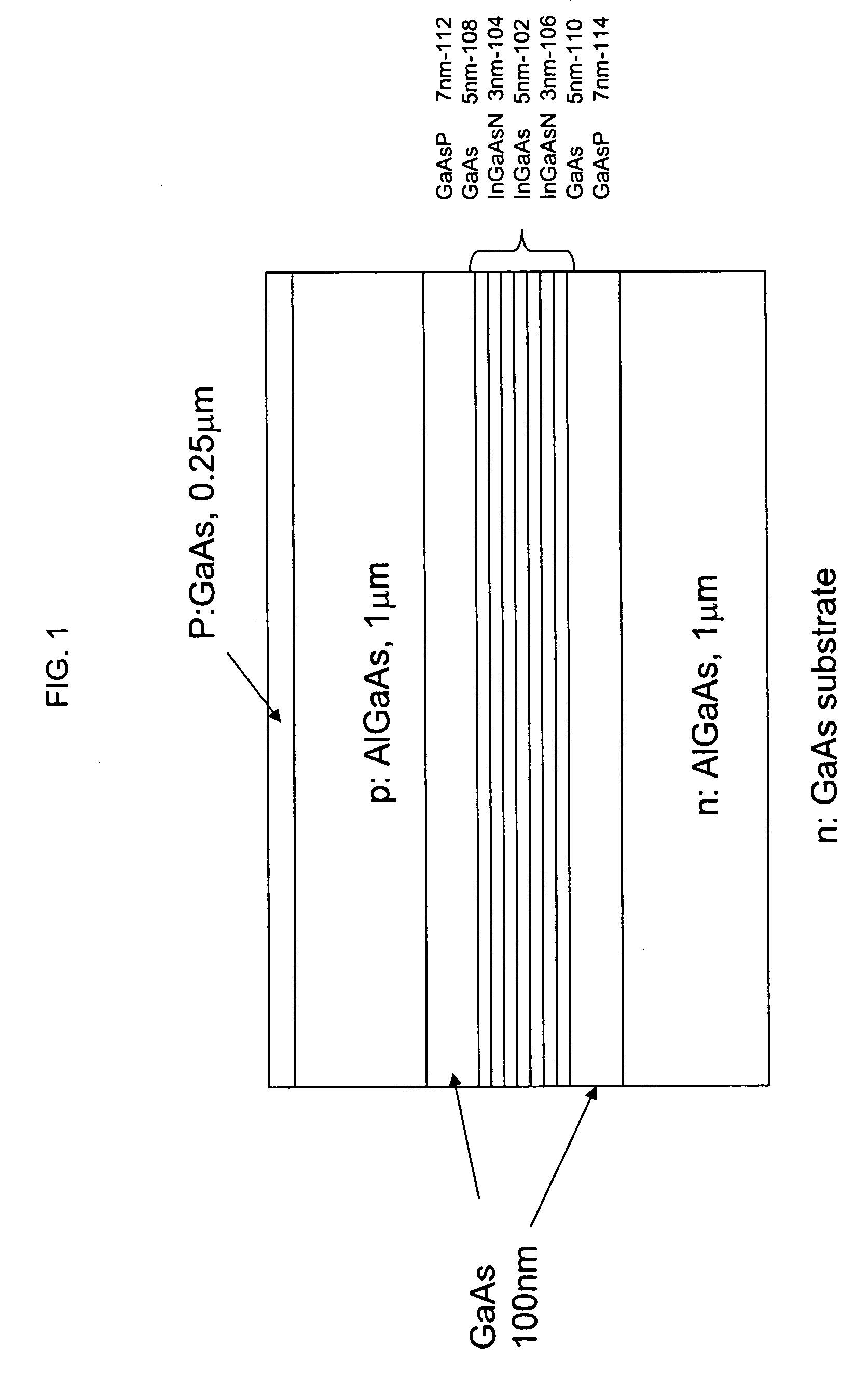
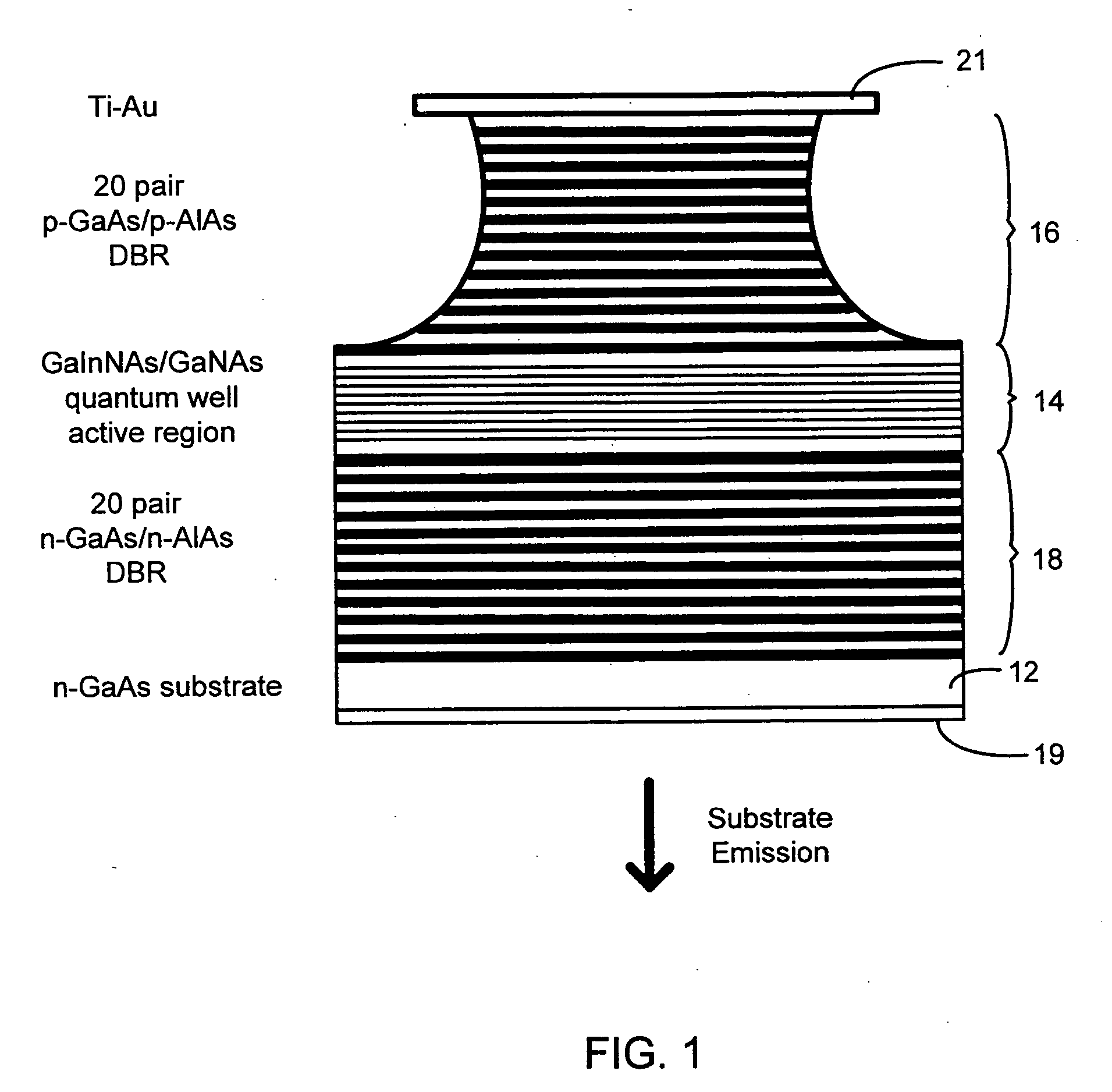
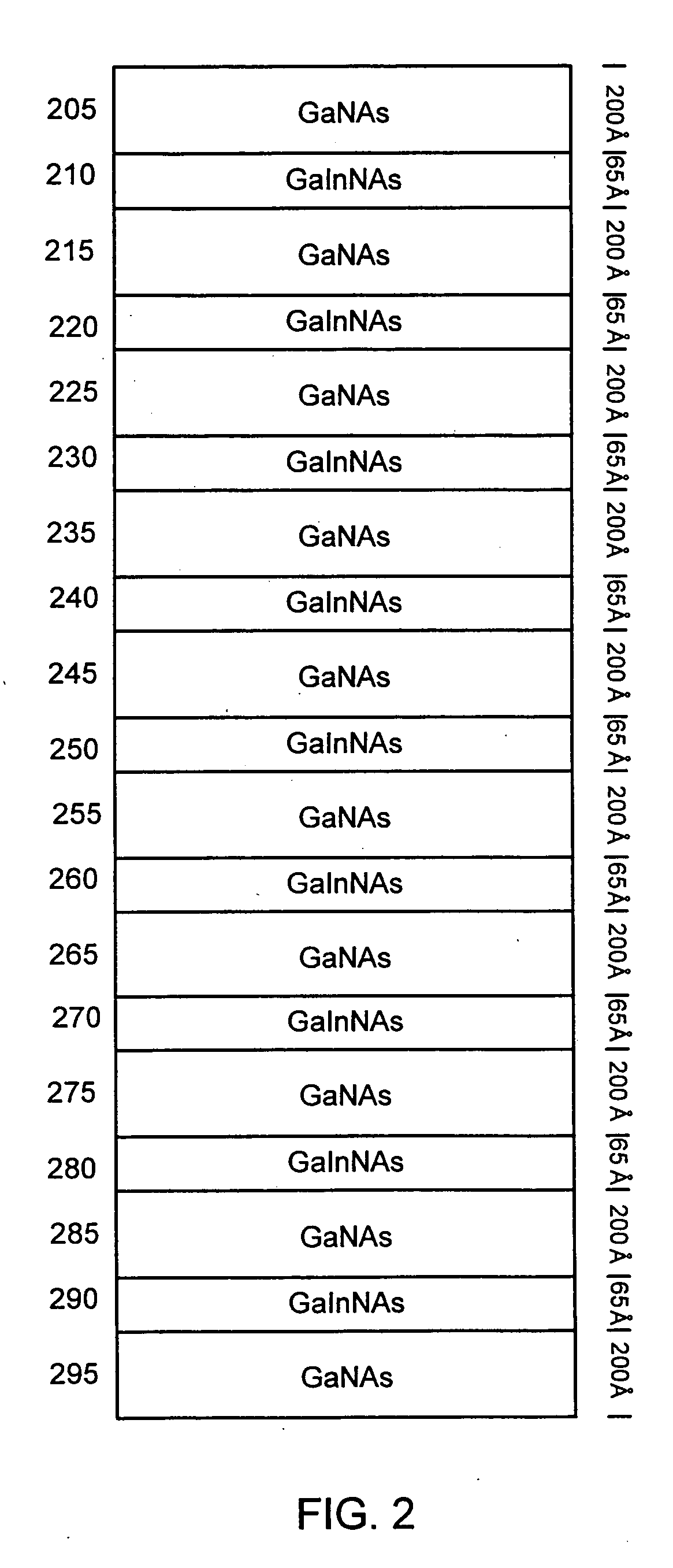
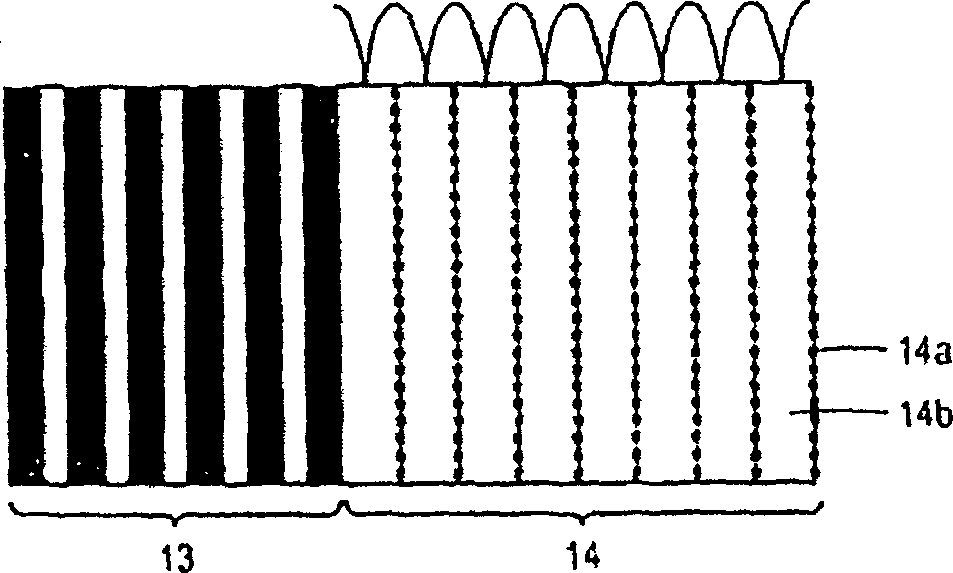
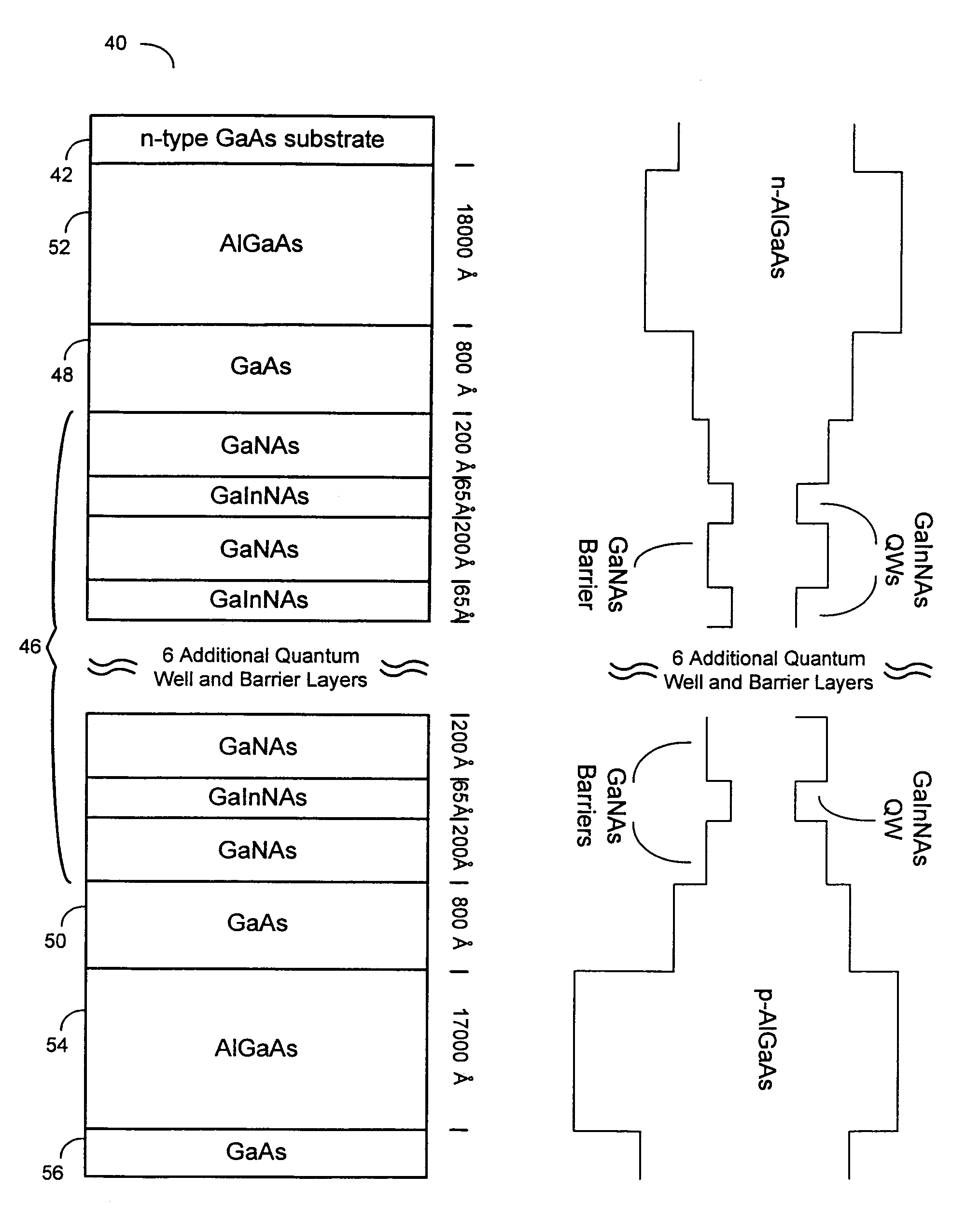
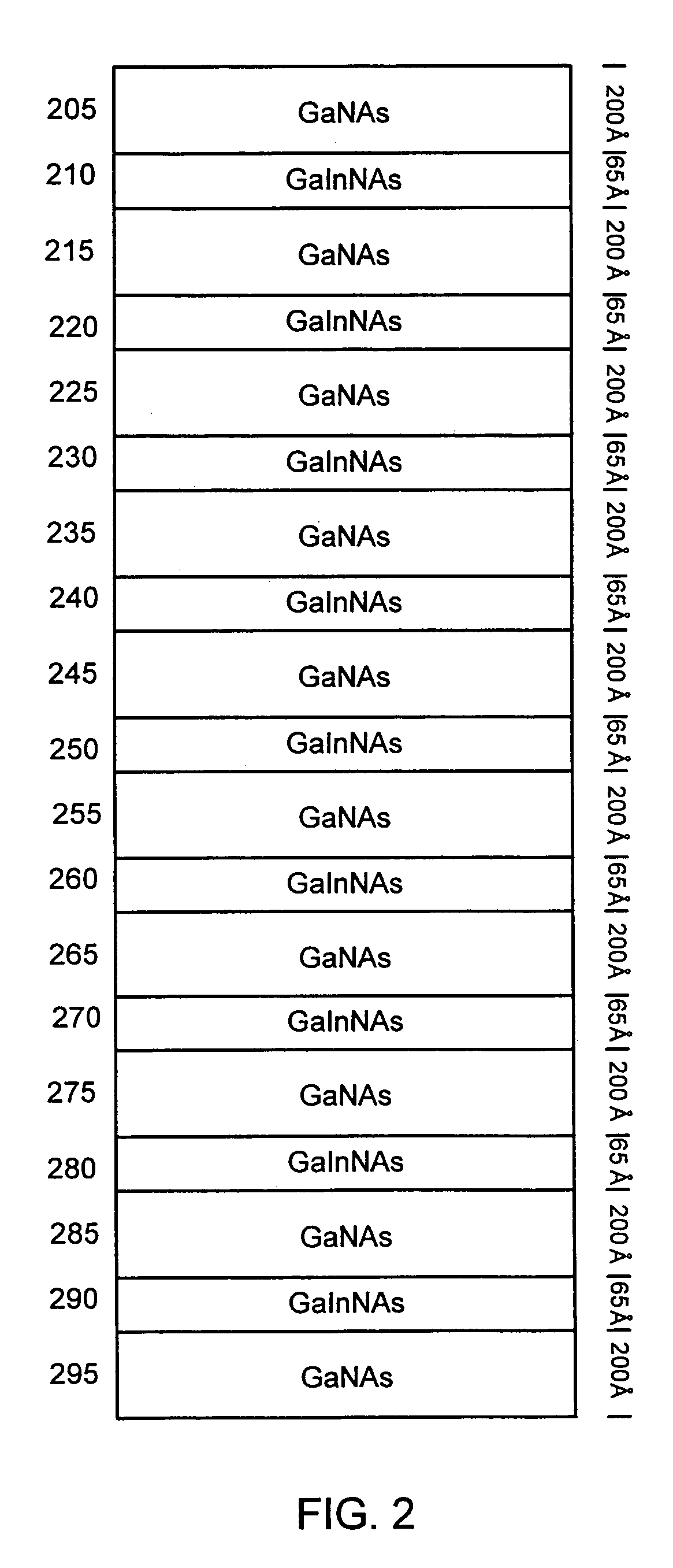
Multiple GaInNAs quantum wells for high power applications
InactiveUS20060039432A1High power outputOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserPhotoluminescence
In connection with an optical-electronic semiconductor device, improved photoluminescent output is provided at wavelengths approaching and beyond 1.3 μm. According to one aspect, a multiple quantum well strain compensated structure is formed using a GaInNAs-based quantum well laser diode with GaNAs-based barrier layers. By growing tensile-strained GaNAs barrier layers, a larger active region with multiple quantum wells can be formed increasing the optical gain of the device. In example implementations, both edge emitting laser devices and vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) devices can be grown with at least several quantum wells, for example, nine quantum wells, and with room temperature emission approaching and beyond 1.3 μm.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Electric pump micro cavity laser with integrated straight wave guide output
InactiveCN101150242AMeet research needsSimple structureLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersSemiconductor quantum wellsOhmic contact
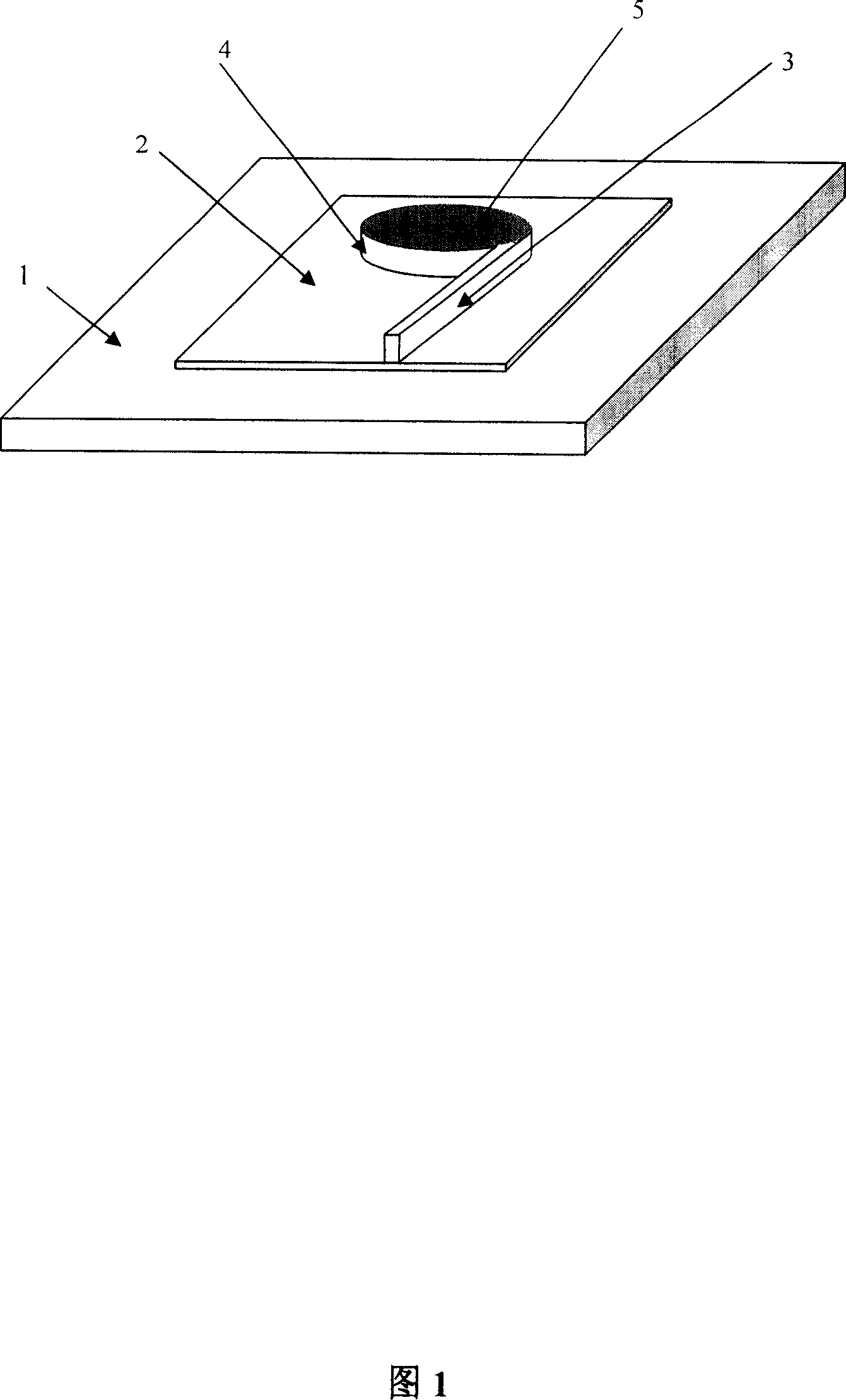
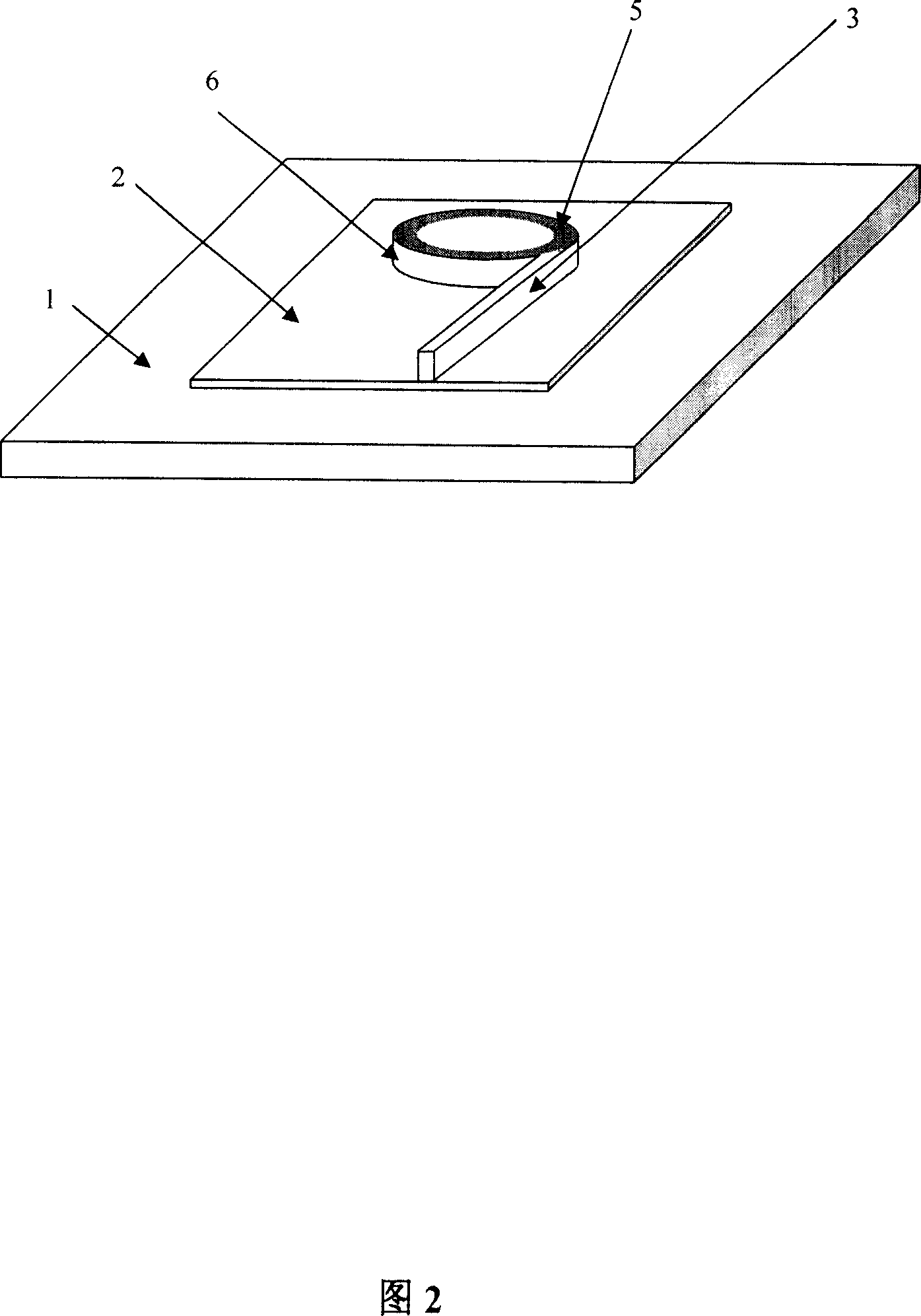
This invention discloses an electric pump micro-cavity laser outputting laser from a port of an integrated straight waveguide based on a whisper cloister mode theory and composed of a die and heat sink, in which, the die is a chip processed in complecated processes of photoetch, corrosion, oxidation and evaporation of electronic beams on the epitaxial chip of a semiconductor quantum well laser, and the center of which is a micro-disk or a micro-loop, a straight waveguide of several mum wide, several decades-several hundreds long and same thick to the disk or the loop is integrated along the tangent of the edge of the disk or loop, in which, an ohmic contact metal film is prepared on the surface of the disk or the loop and a sloder is applied to weld the die and the heat sink.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Single-chip white light LED device without fluorescent powder and with adjustable color rendering index and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108389941AAvoid defectsImprove luminous efficiencySemiconductor devicesColor rendering indexGreen-light
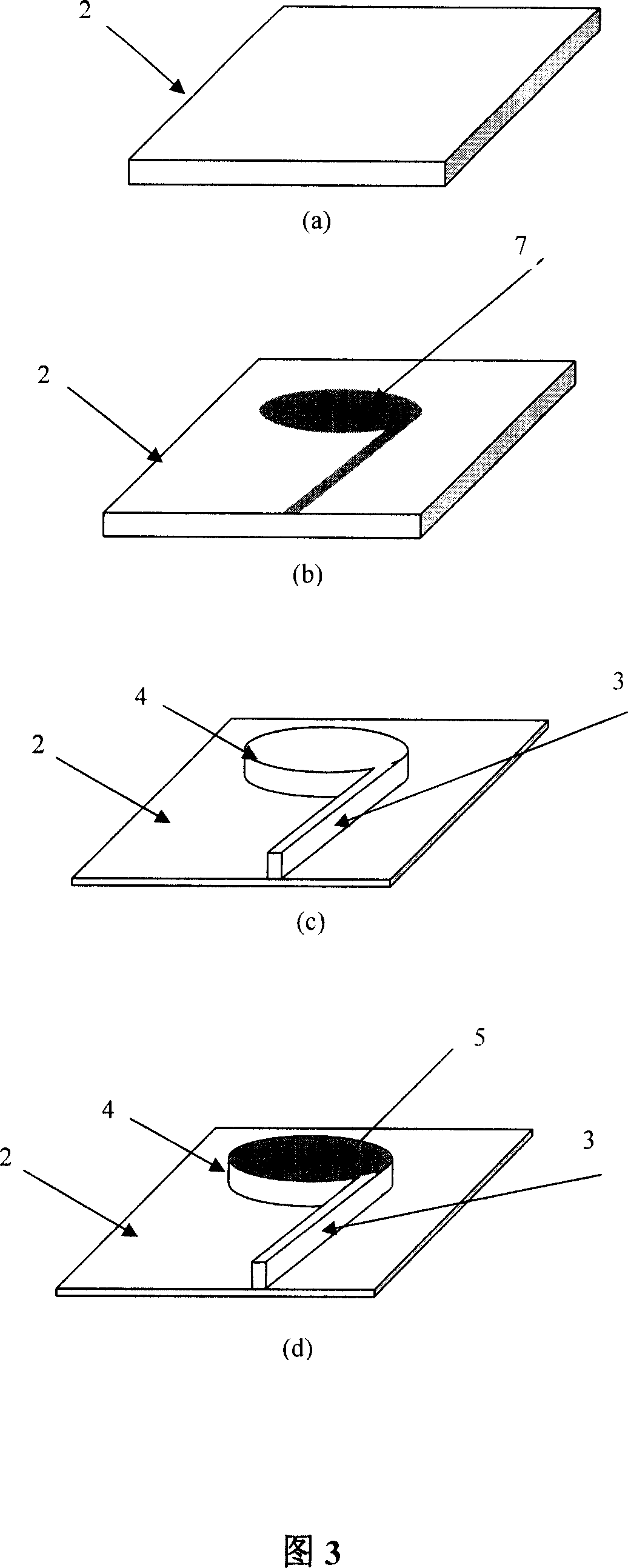
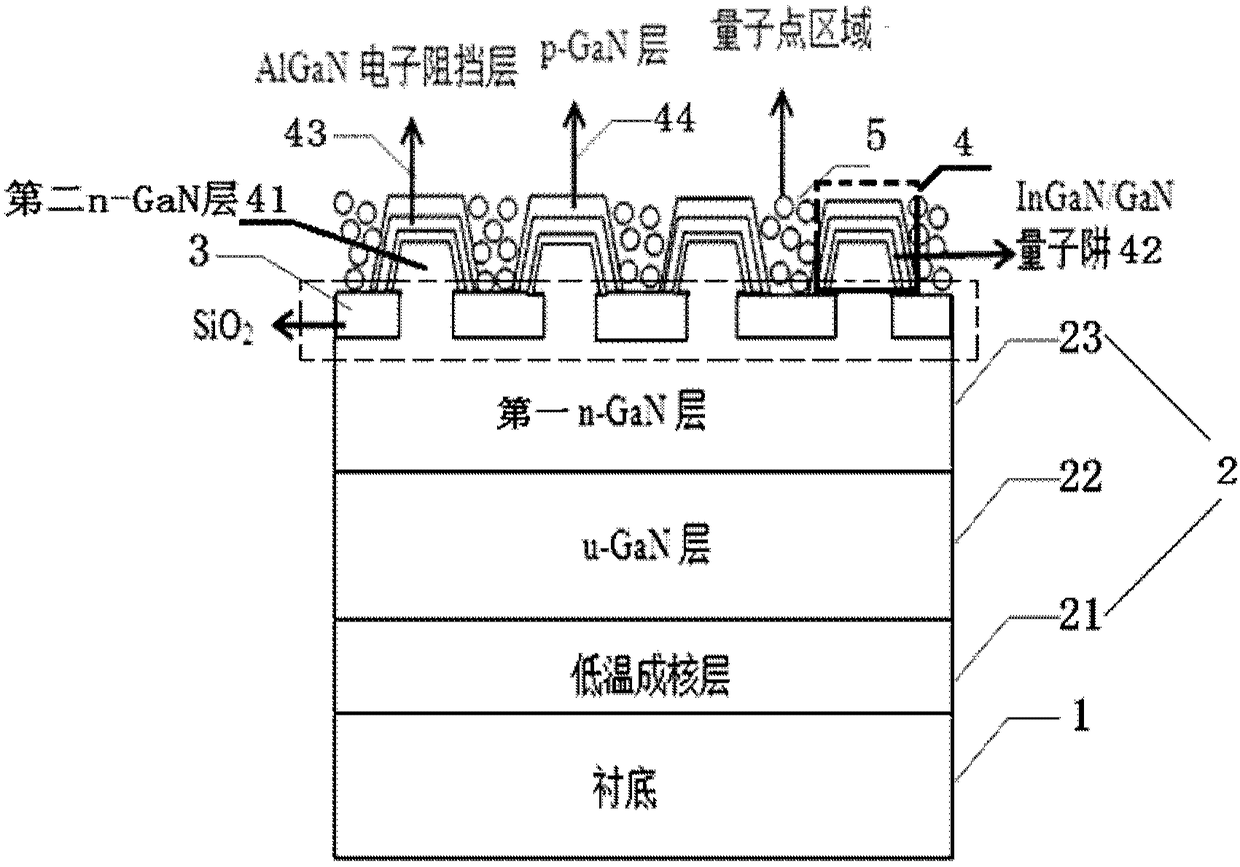
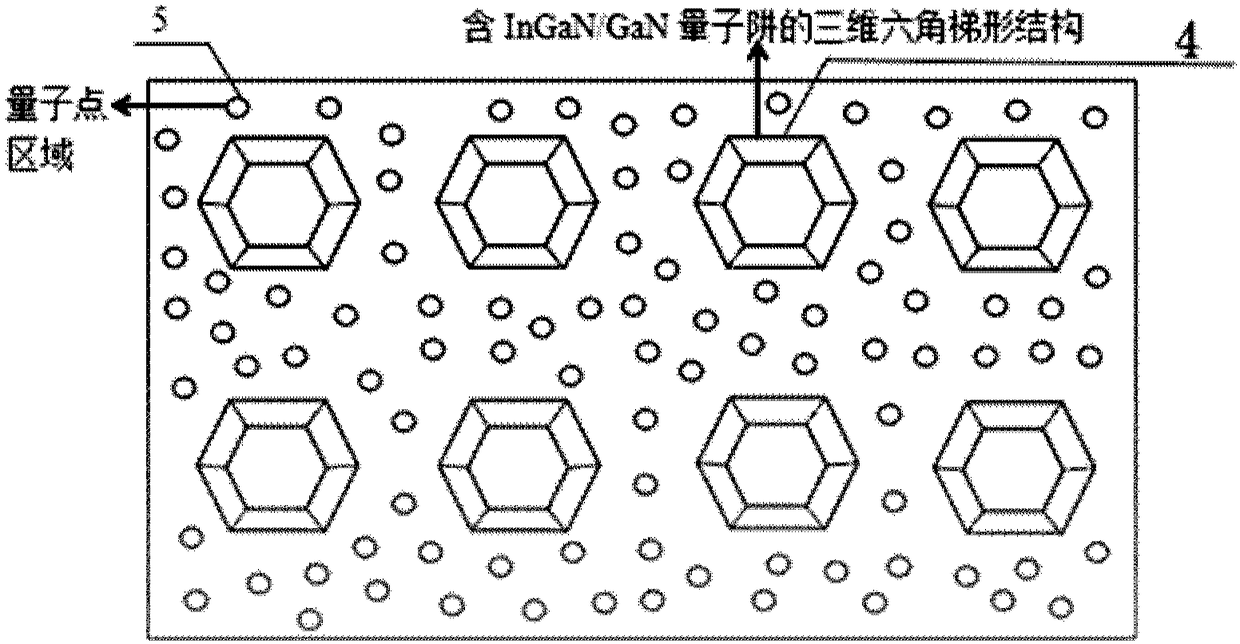
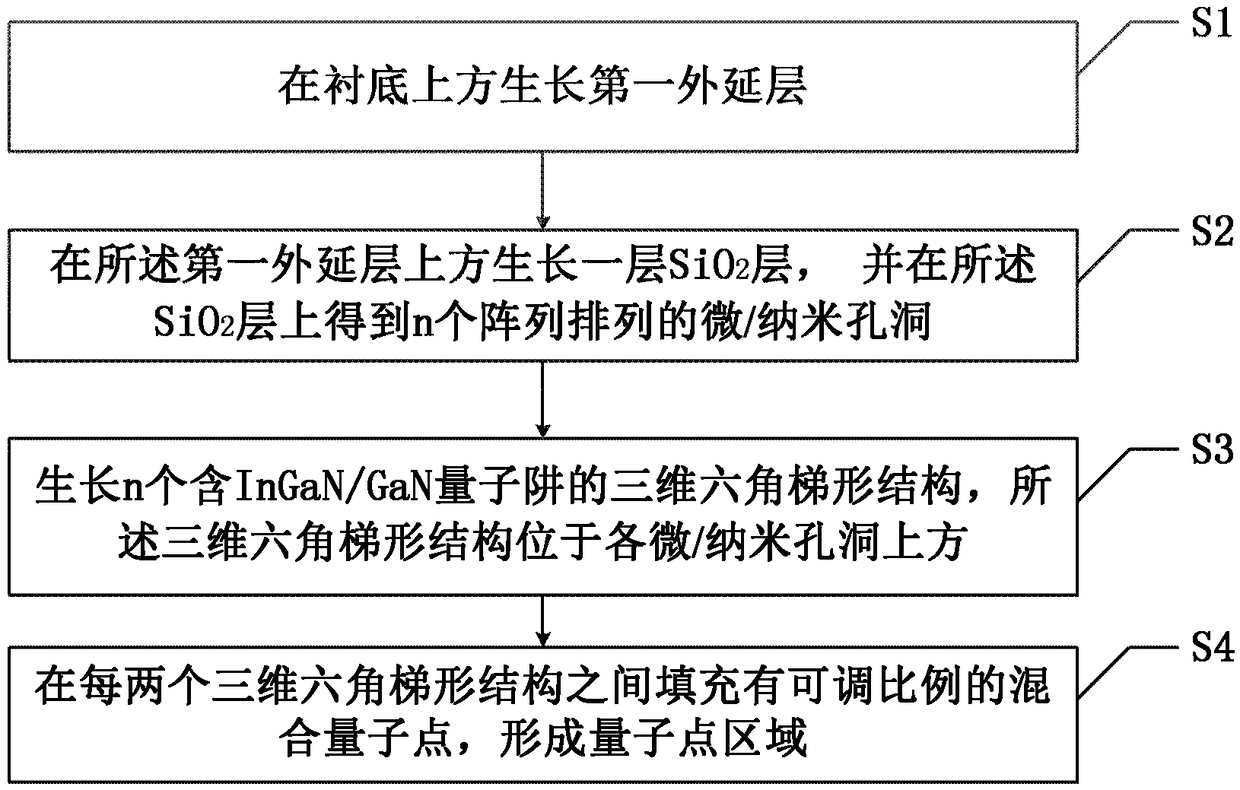
The present invention provides a single-chip white light LED device without fluorescent powder and with an adjustable color rendering index and a preparation method thereof. The device comprises: a substrate; a first epitaxial layer; n SiO2 layers with micro / nano holes in an array arrangement mode and arranged at the upper portion of the first epitaxial layer; n three-dimensional hexagonal trapezoid structures including InGaN / GaN quantum wells and located at the upper portions of the micro / nano holes; and quantum dot areas, each being located between each two three-dimensional hexagonal trapezoid structures. Through combination of luminous sources of quantum wells and quantum dots, the defects caused by fluorescent powder can be avoided, the advantages of combination of the quantum wells and the quantum dots can be fully utilized, and the luminous efficiency is improved. The components of In in the quantum wells are regulated to allow the sides of the obtained three-dimensional hexagonal trapezoid structures to emit blue light, the upper surfaces of the three-dimensional hexagonal trapezoid structures emit green light and / or yellow light being longer than the blue light in wavelength, the ratio of the mixed quantum dots in the gaps is changed, and therefore, the luminous wavelength and the intensity of the single-chip white light LED device without fluorescent powder and with an adjustable color rendering index are regulated, and a high color rendering index performance is achieved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ingaas/gaas lasers on-silicon produced by-lepecvd and mocvd
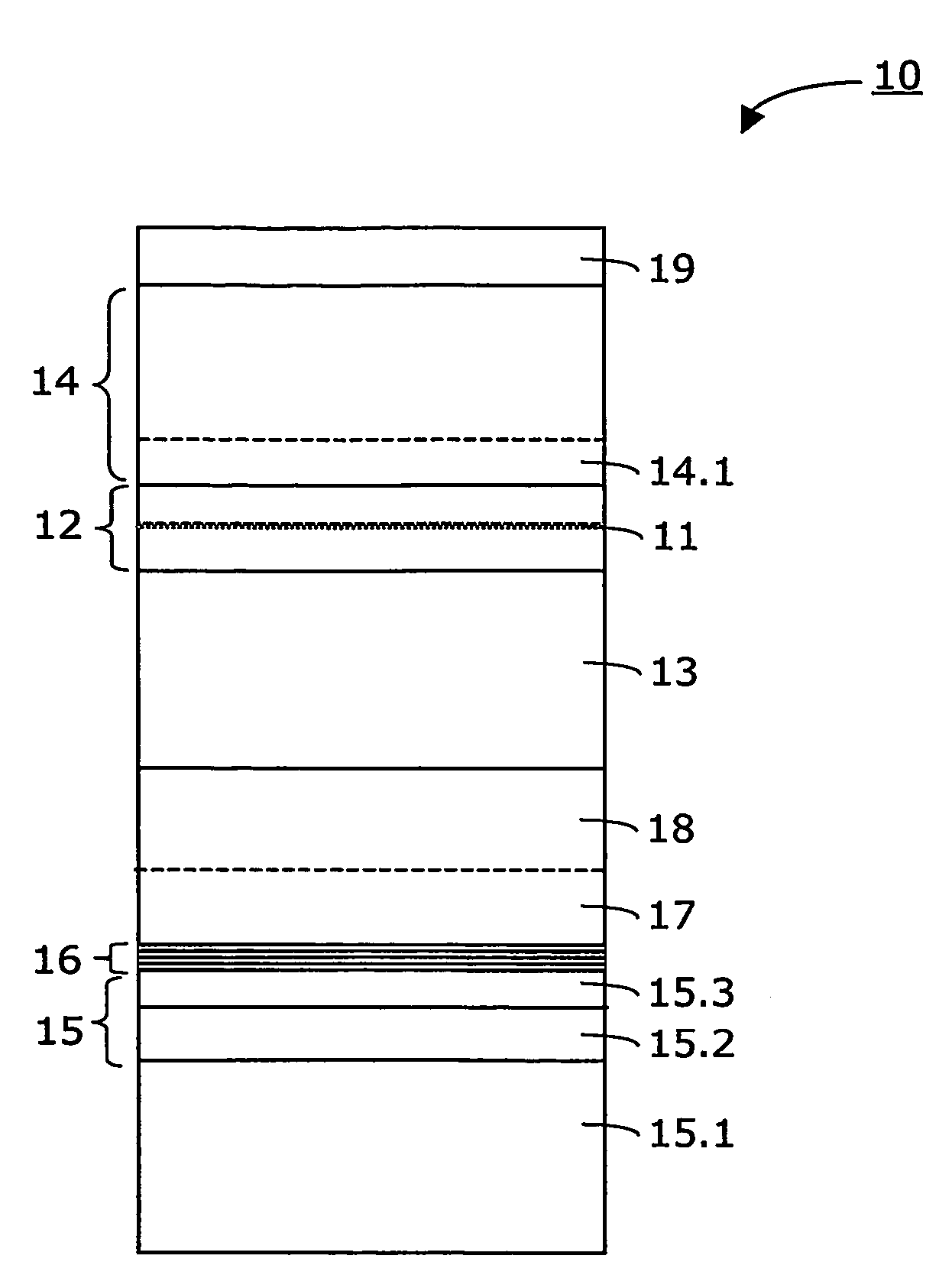
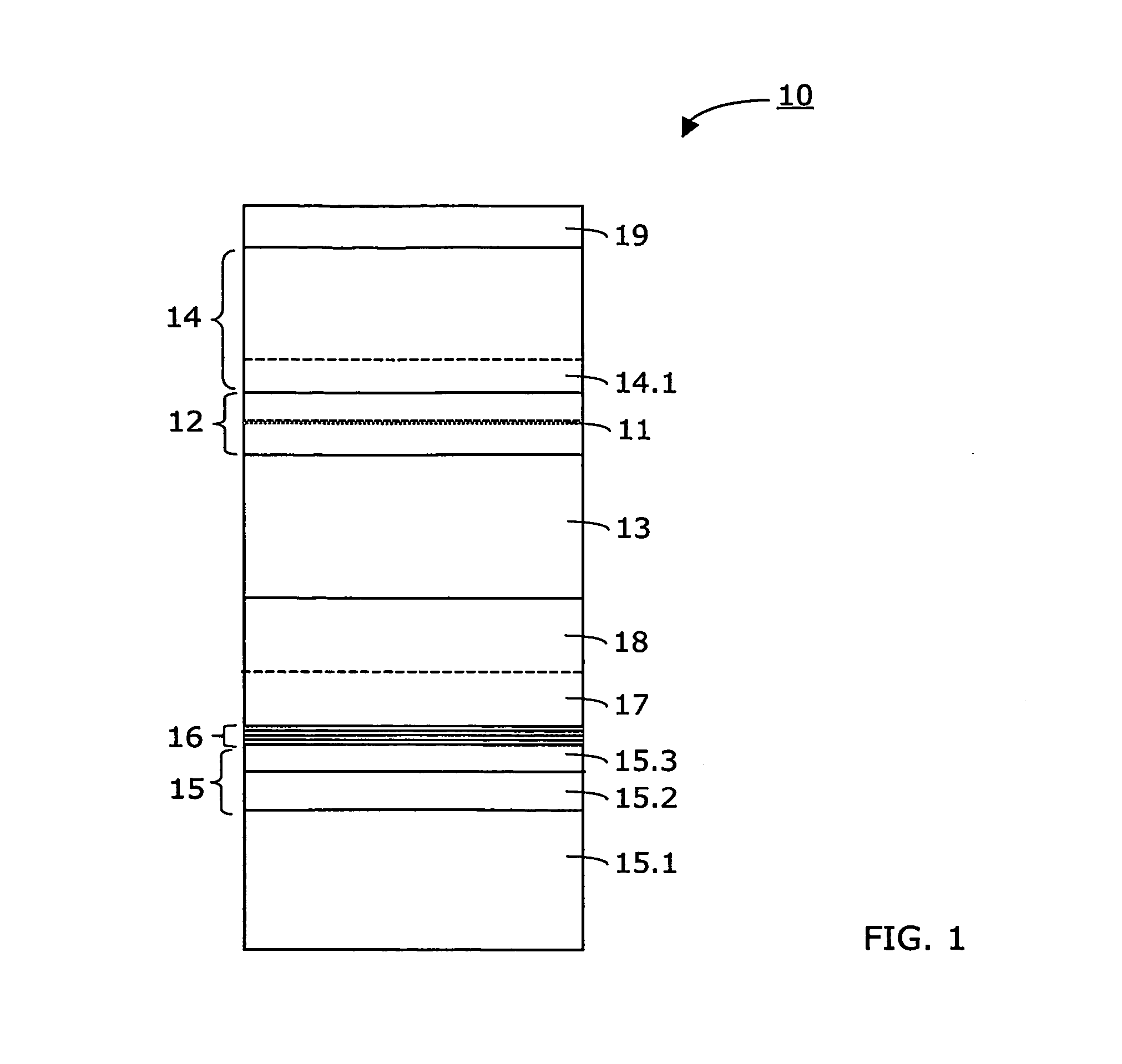
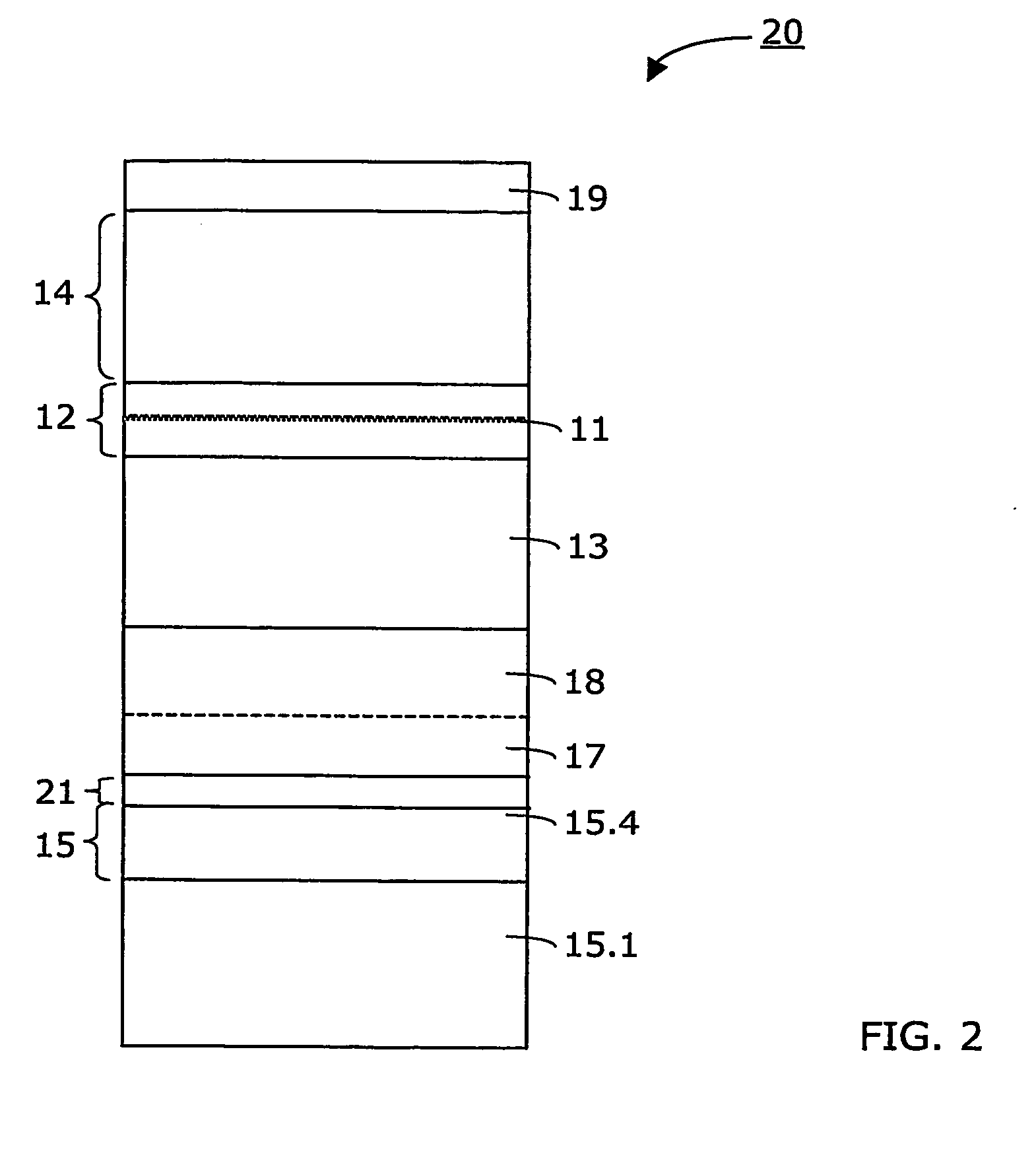
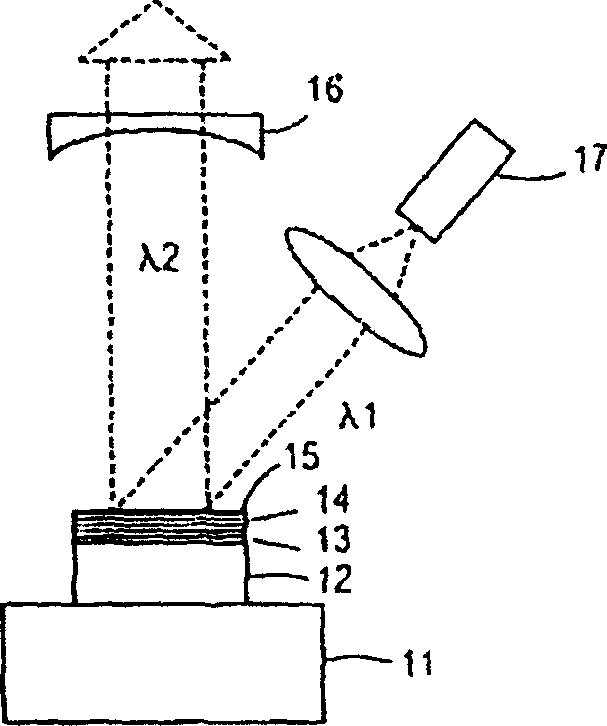
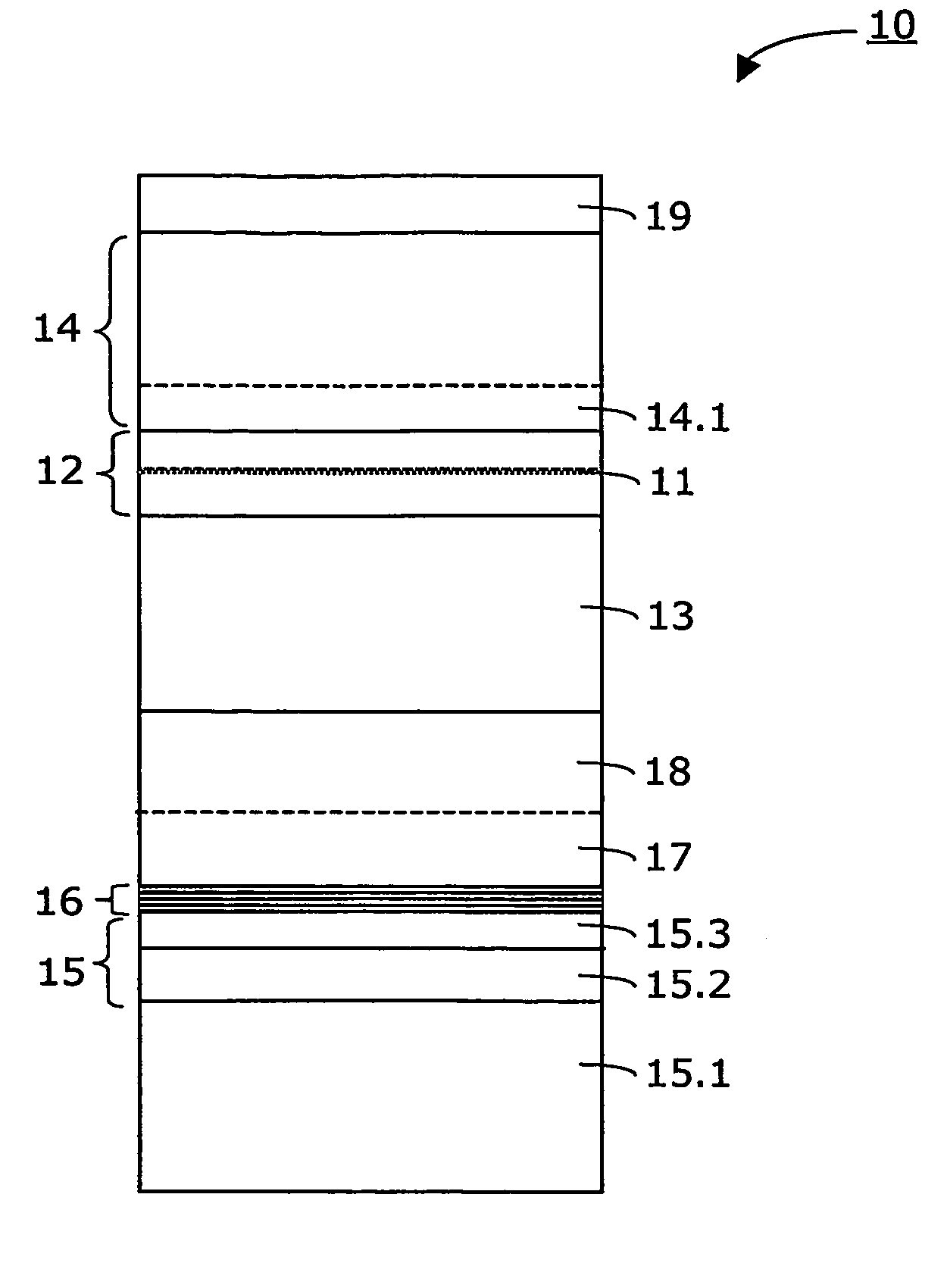
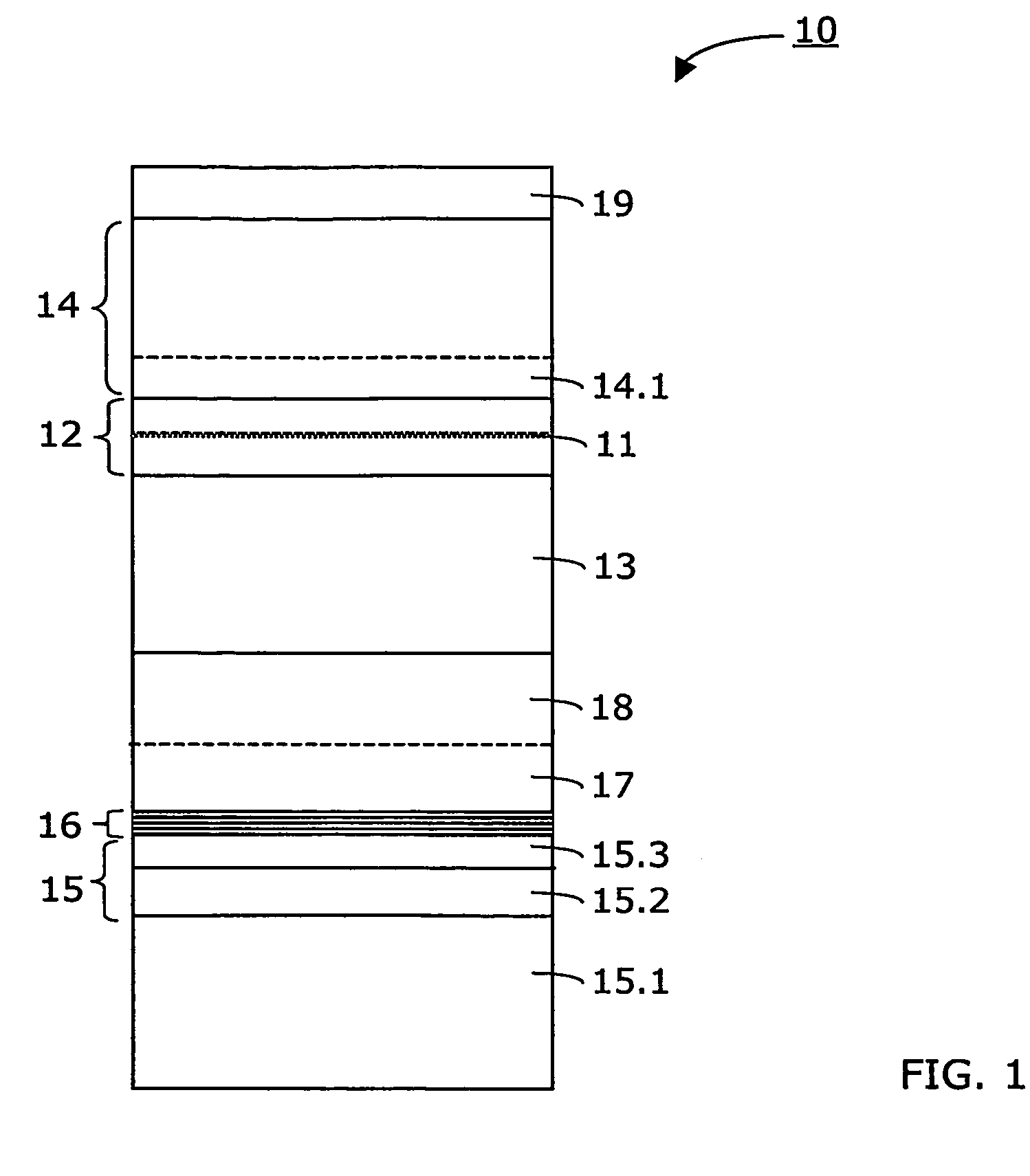
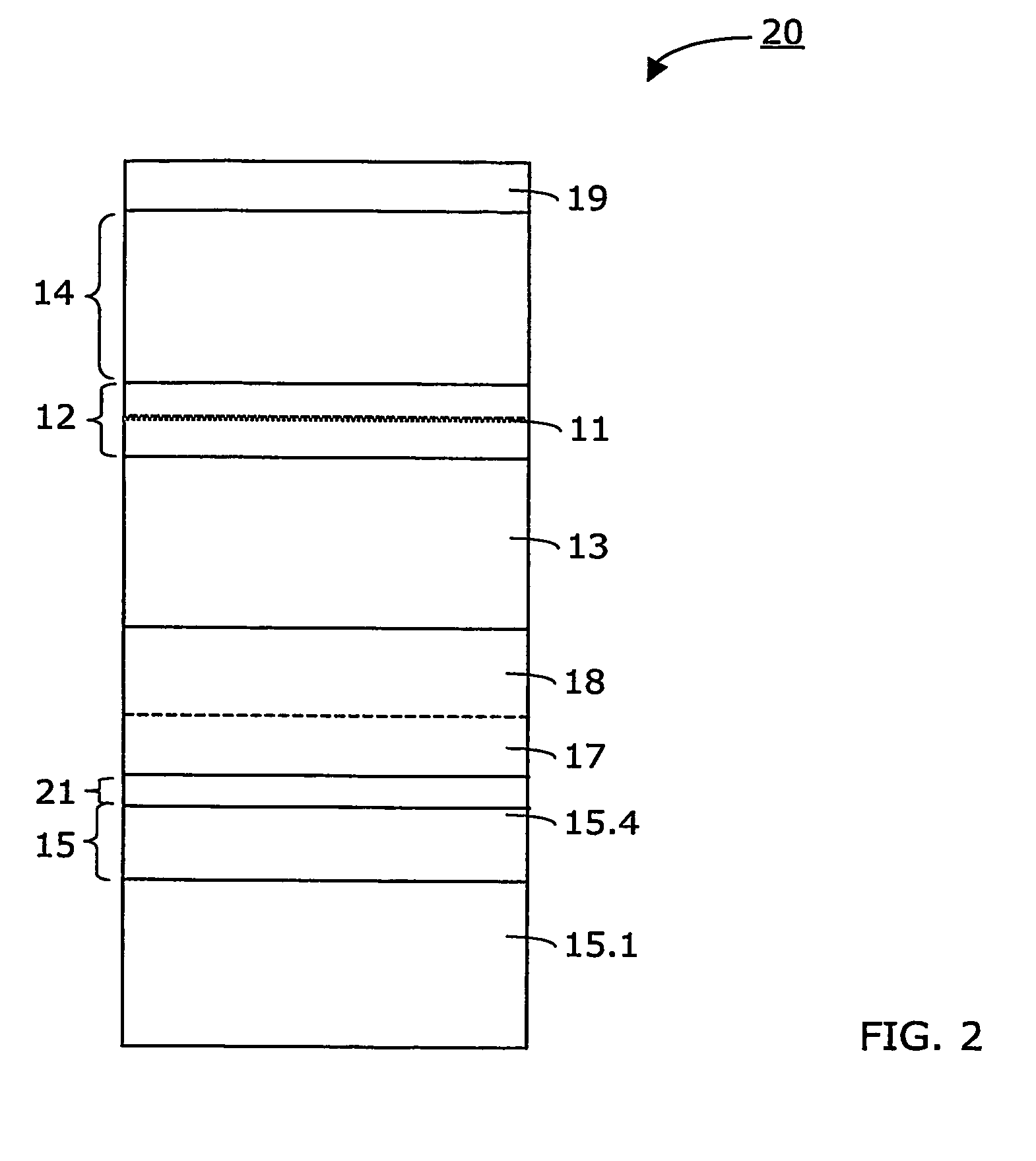
InactiveUS20070164311A1Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseWaveguide
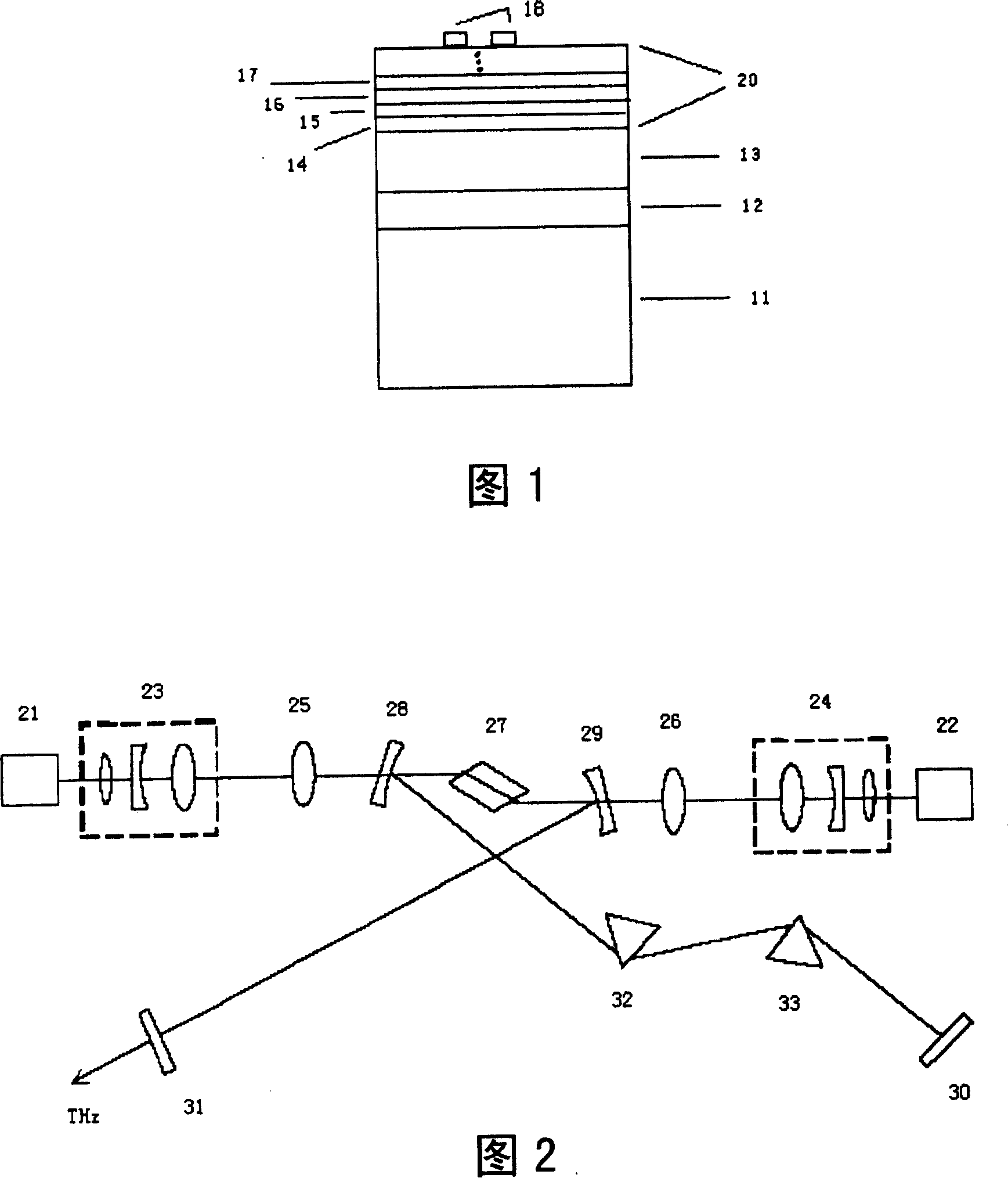
Method for making an InGaAs / GaAs quantum well laser (10) on a Silicon substrate (15.1). The method comprises the steps: Formation of a virtual Germanium substrate (15) on the Silicon substrate (15.1) by means of a low-energy plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition (LEPECVD). The virtual Germanium substrate (15) comprises a pure Germanium layer (15.3). Formation of a Gallium Arsenide structure on the virtual Germanium substrate (15) by means of a metal organic chemical vapour deposition process. The metal organic chemical vapour deposition process comprises the steps: formation of a first Gallium Arsenide layer (16) on the virtual Germanium substrate (15) at a first substrate temperature (Ts1), formation of a second Gallium Arsenide waveguide layer (17) at a second substrate temperature (Ts2), the second substrate temperature (Ts2) being higher than the first substrate temperature (Ts1) and the first Gallium Arsenide layer (16; 21) being thinner than the second Gallium Arsenide layer (17), formation of an active laser structure comprising a Gallium Arsenide waveguide layer (12) embedding a quantum well (11).
Owner:DICHROIC CELL
External cavity multiple wavelength laser system
InactiveCN1710764ALaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusOptoelectronicsLength wave
Controlling the number and type of quantum wells in a multilayer gain member of an external cavity surface emitting laser can provide output of light at more than one coherent optical wavelength. The number and type of layers in the multilayer mirror structure can provide a dual wavelength reflector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multiple GaInNAs quantum wells for high power applications
InactiveUS7645626B2Laser detailsLaser active region structureVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserPhotoluminescence
In connection with an optical-electronic semiconductor device, improved photoluminescent output is provided at wavelengths approaching and beyond 1.3 μm. According to one aspect, a multiple quantum well strain compensated structure is formed using a GaInNAs-based quantum well laser diode with GaNAs-based barrier layers. By growing tensile-strained GaNAs barrier layers, a larger active region with multiple quantum wells can be formed increasing the optical gain of the device. In example implementations, both edge emitting laser devices and vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) devices can be grown with at least several quantum wells, for example, nine quantum wells, and with room temperature emission approaching and beyond 1.3 μm.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
InGaAs/GaAs lasers on silicon produced by LEPECVD and MOCVD
Owner:DICHROIC CELL
Laser source with broadband spectrum emission
ActiveUS7555027B2Easy to manufactureOptical resonator shape and constructionNanoopticsFrequency spectrumLaser source
A quantum dot laser operates on a quantum dot ground-state optical transition. The laser has a broadband (preferably ≧15 nm) spectrum of emission and a high output power (preferably ≧100 mW). Special measures control the maximum useful pump level, the total number of quantum dots in the laser active region, the carrier relaxation to the quantum dot ground states, and the carrier excitation from the quantum dot ground states. In one embodiment, a spectrally-selective loss is introduced into the laser resonator in order to suppress lasing on a quantum dot excited-state optical transition, thereby increasing the bandwidth of the emission spectrum.
Owner:INNOLUME
InGaN/GaN quantum well laser and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN106785919AEvenly distributedQuality improvementLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersOhmic contactLayer thickness
The invention discloses an InGaN / GaN quantum well laser, comprising a substrate and the following components sequentially arranged on the substrate: a low temperature GaN buffer layer, a high temperature n-type GaN layer and an n-type AlGaN light confinement layer; an n-type InGaN lower waveguide layer on the n-type AlGaN light confinement layer; an InGaN / GaN quantum well active region on the n-type InGaN lower waveguide layer; a u-type InGaN upper waveguide layer on the InGaN / GaN quantum well active region; a p-type AlGaN electron barrier layer on the u-type InGaN upper waveguide layer; a p-type AlGaN / GaN light confinement layer on the p-type AlGaN electron barrier layer; and a p-type GaN ohmic contact layer on the p-type AlGaN / GaN light confinement layer. The invention also discloses a manufacturing method for the InGaN / GaN quantum well laser. The invention adopts the InxGa1-XN of 1 to 2 single-atom layer thickness to be inserted into the cap layer so that the two-dimensional island-like surface of the InGaN quantum well surface becomes smooth, that the distribution of the In group becomes more uniform and that the subsequently formed GaN cap layer has a better quality in which the InGaN quantum well is not decomposed during the temperature rise and does not undergo thermal degradation during the subsequent high temperature growth of the p-type AlGaN / GaN light confinement layer.
Owner:杭州增益光电科技有限公司
A micron wave length THz radiation transmission chip and its making method
InactiveCN101150153AReduce strainEasy to useLaser detailsLaser active region structureThz radiationWavelength
This invention relates to a THz radiation chip of one micron wave length including: a substrate, a buffer layer prepared on the substrate, a Bragg reflection mirror set on the buffer layer to form a reflection mirror of high reflection rate and multiple quantum wells including multiple pairs of stranied compensated mono-quantum wells, in which, a low temperature growing technology is applied to process the multiple pairs of strained compensated quantum wells on the Bragg reflection mirror to absorb light and relax photocarriers, a pair of strip Ti-Au electrodes is made on the multiple quantum wells to play the role of offsetting current and strengthening the THz radiation.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
F-P (Fabry-Perot) cavity strained quantum well laser with low linewidth
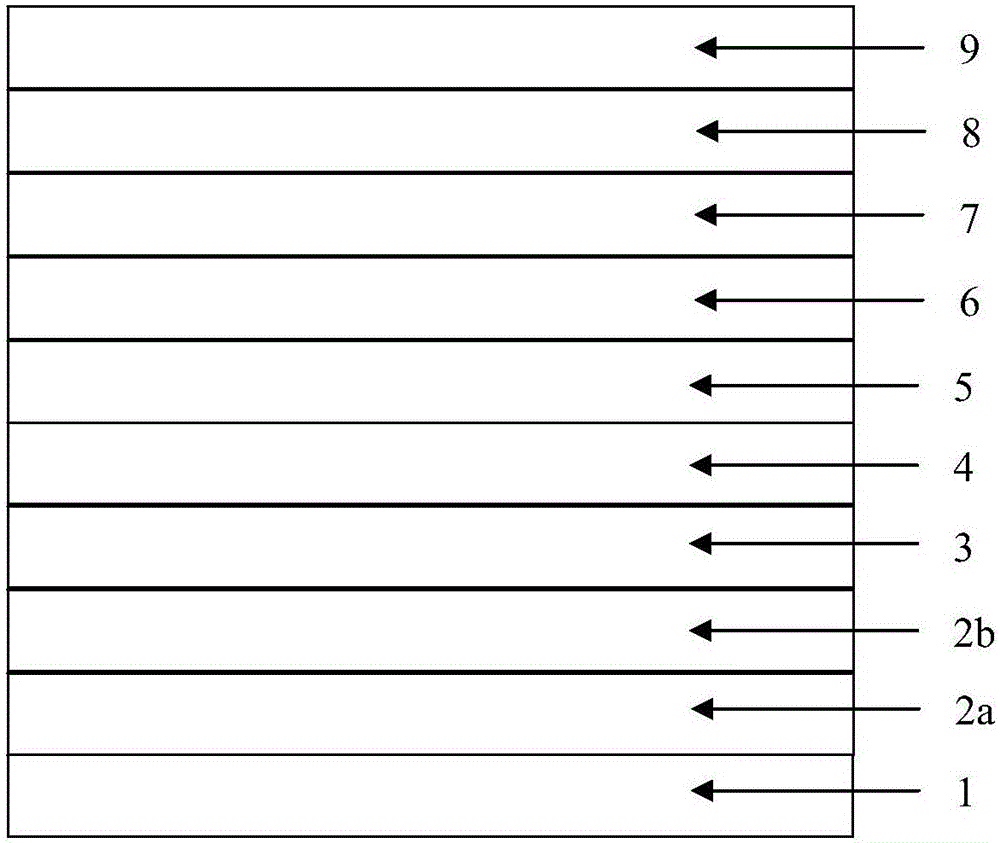
InactiveCN102332681AReduce spectral widthQuality improvementLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionSpectroscopyOptical measurements
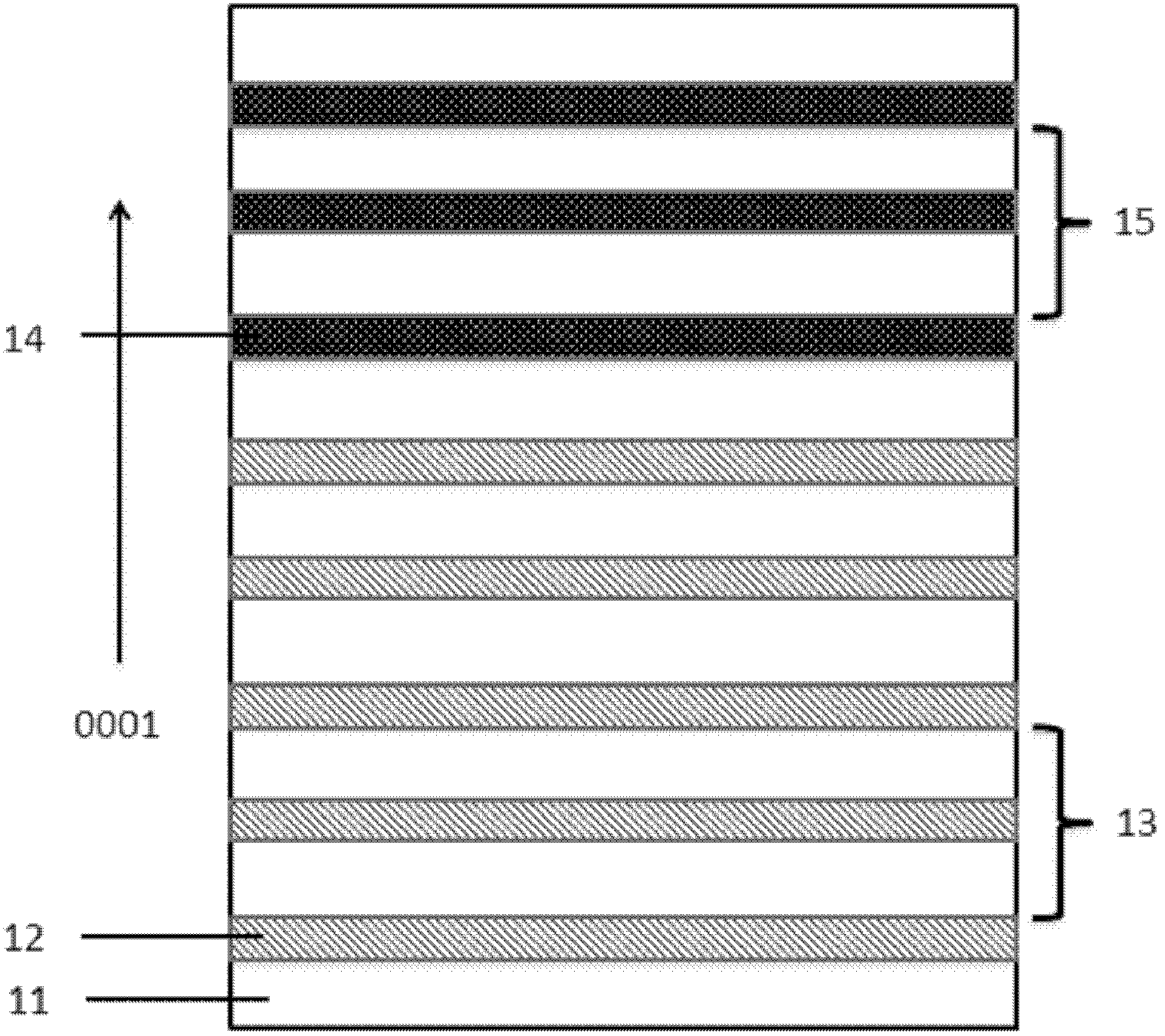
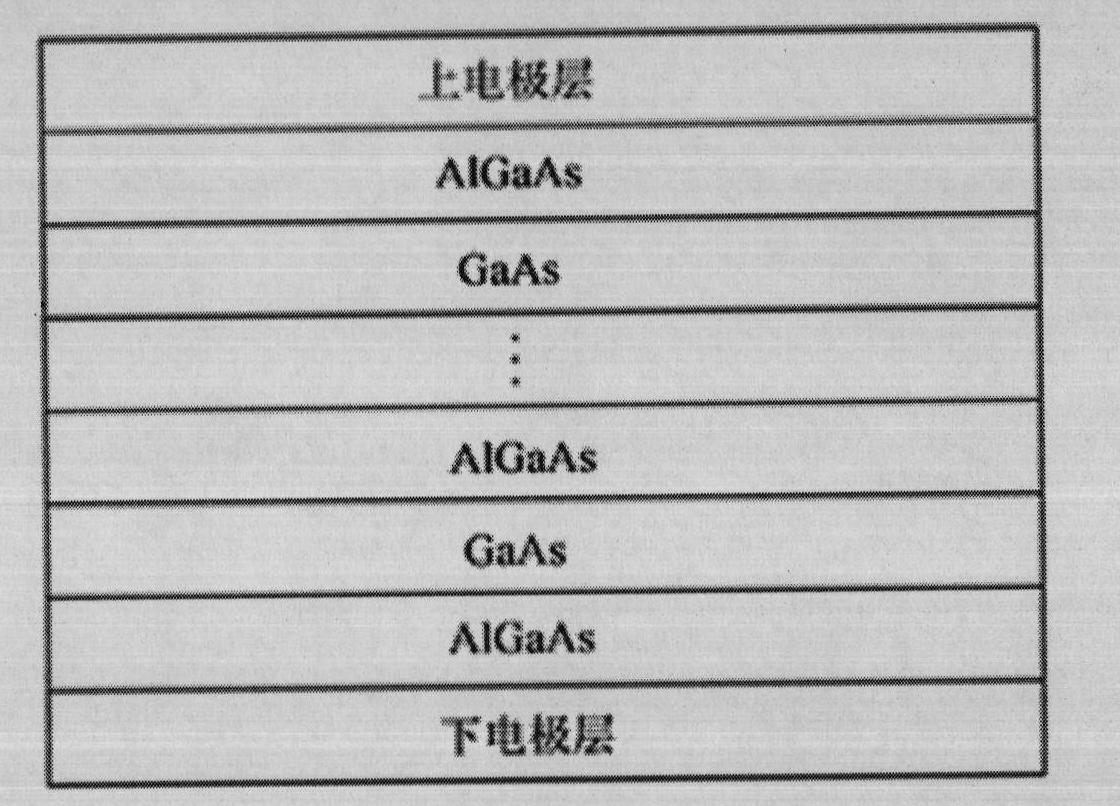
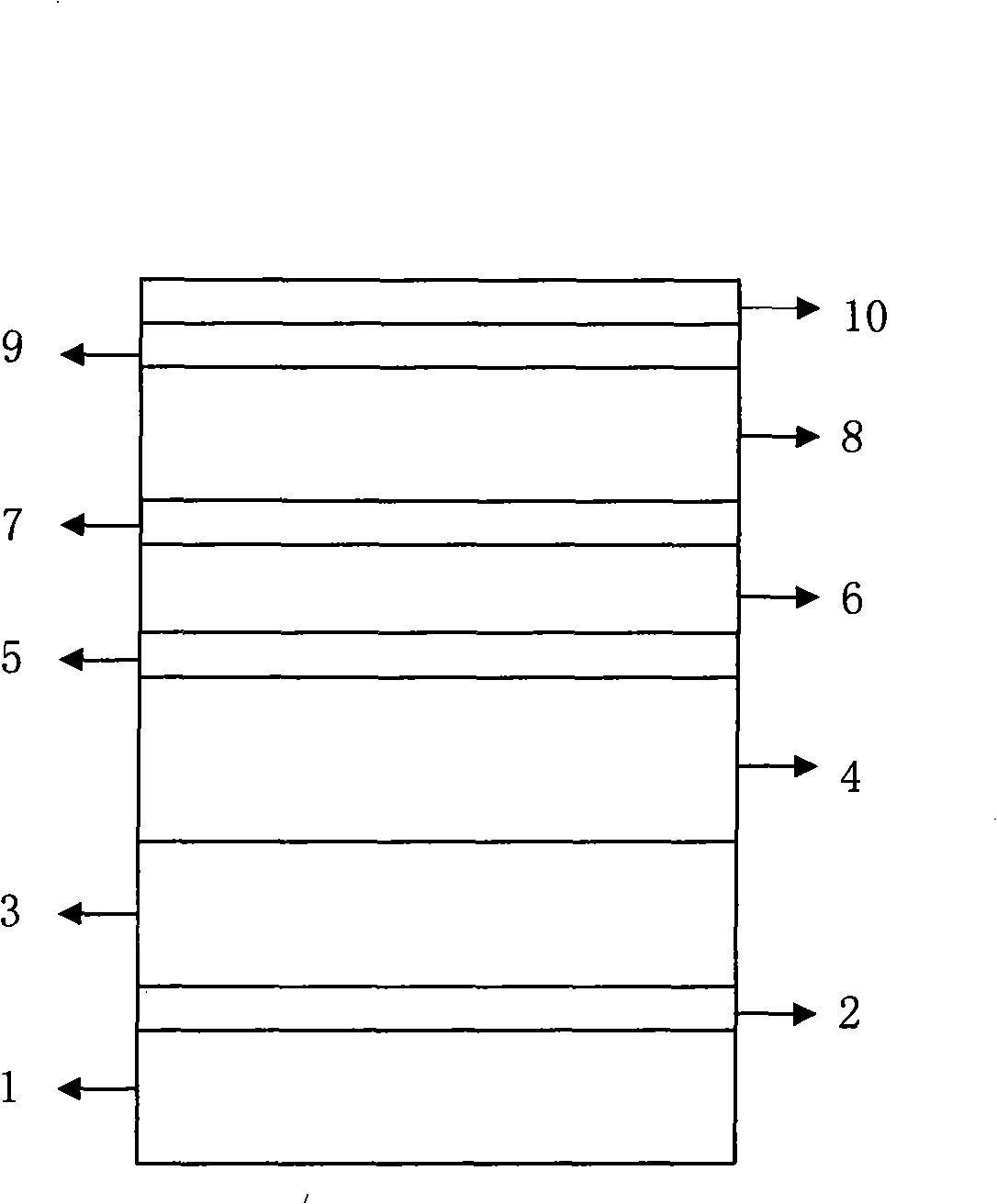
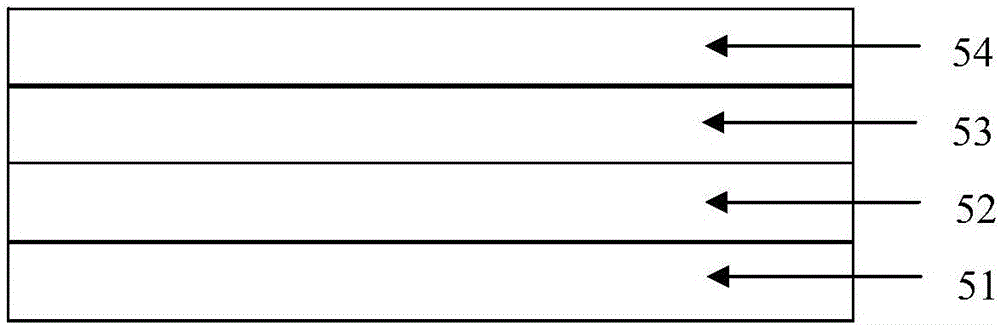
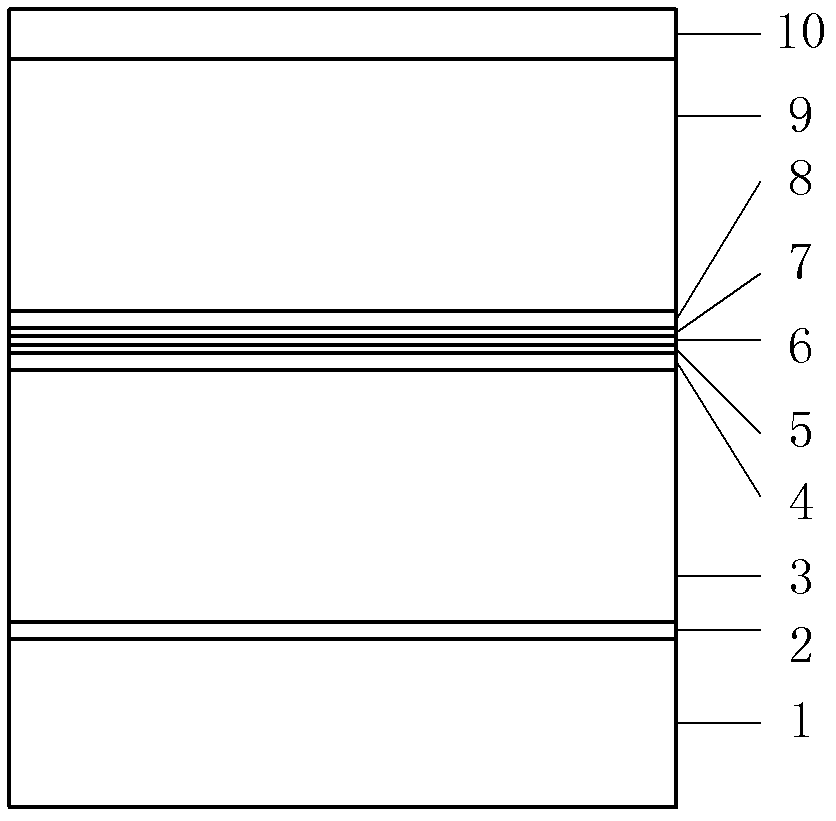
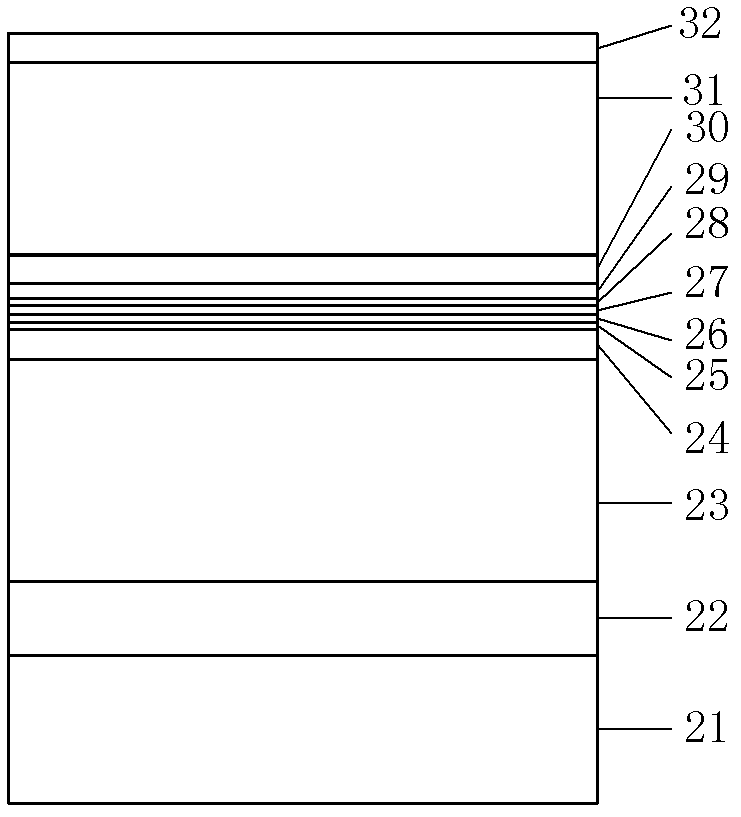
The invention provides an F-P (Fabry-Perot) cavity strained quantum well laser with low linewidth. The F-P cavity strained quantum well laser comprises a substrate (1), a buffer layer (2), an n type lower limiting layer (3), a lower waveguide layer (4), a lower barrier layer (5), an active layer (6), an upper barrier layer (7), an upper waveguide layer (8), a p type upper limiting layer (9) and an ohmic contact layer (10) which are sequentially connected. Through the optimal design of the active layer (6), a linewidth enhancement factor generated by interband transition of a quantum well and a linewidth enhancement factor generated by free carrier absorption and band-gap shrinkage can offset mutually, thereby realizing the low linewidth and improving the quality of a light beam of the quantum well laser. The active layer of the laser provided by the invention is made of InxGa1-xAs materials, wherein x is equal to 0.33, the width thickness of the well is 3-5nm, the center wavelength lambda is equal to 980nm-1036nm, and the linewidth of the F-P cavity strained quantum well laser can be reduced by three orders of magnitude in comparison with a quantum well laser. The F-P cavity strained quantum well laser can be used for optical measurement, solid-state laser pumping, laser spectroscopy research and other fields.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Epitaxial method for preparing AlGaAsSb/InGaAsSb multi-quantum wells by using AlSb buffer layer
InactiveCN101645577AQuality improvementImprove material performanceLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersFree energiesHigh surface
An AlGaAsSb / InGaAsSb multi-quantum well laser belongs to first Class of quantum well structure, the materials and the devices are very difficult to research; large immiscible gaps exist in antimonidematerial, the material in the immiscible gaps is in the metastable state, the high-quality material is very difficult to grow, the material is one of the most complicated materials in Group III-V compounds and also one of the scientific key points mainly researched in the world. The invention provides an epitaxial method for preparing AlGaAsSb / InGaAsSb multi-quantum wells by using an AlSb buffer layer. The AlSb buffer layer can be used for obtaining high crystal quality and high surface flatness. The AlSb buffer layer can be used as a surfactant to reduce the interfacial free energy between the substrate and the epitaxial layer, and can also be used as a filter board to prevent dislocation from happening. The method is used for preparing materials of high-quality AlGaAsSb / InGaAsSb multi-quantum well laser.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
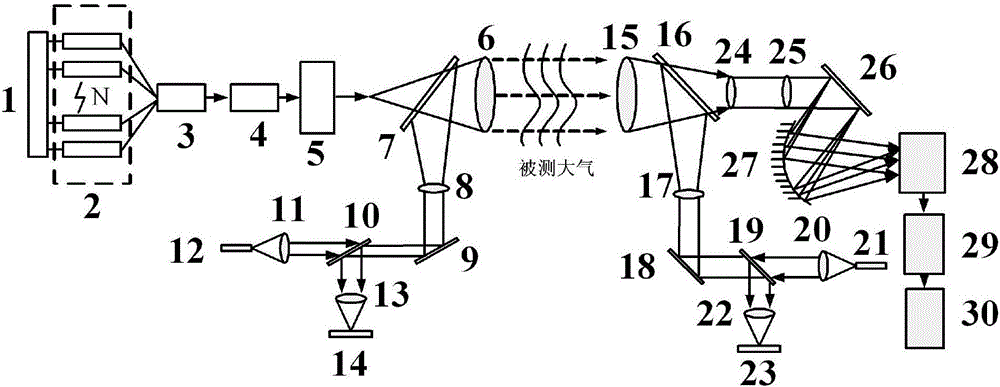
Atmosphere laser occultation signal generation and detection equipment
ActiveCN106643668AMeet the requirements of occultation detectionHigh precisionMethod using image detector and image signal processingPicture taking arrangementsSignal processing circuitsGlobal climate
The invention discloses atmosphere laser occultation signal generation and detection equipment and belongs to the technical field of atmospheric remote sensing measurement. In order to solve the problem that characteristic gas components and concentrations cannot be measured in the existing occultation signal generation system, the atmosphere laser occultation signal generation and detection equipment comprises a frequency and power stabilizing circuit, a quantum well laser array, a beam coupler, an optical fiber isolator, a power amplifier, an optical transmitting antenna, a first optical filter, a first collimating mirror, a first two-dimensional galvanometer, a second optical filter, a first coupling lens, a first beacon beam laser, a second coupling lens, a first imaging camera, an optical receiving antenna, a third optical filter, a second collimating mirror, a second two-dimensional galvanometer, a fourth optical filter, a third coupling lens, a second beacon beam laser, a fourth coupling lens, a second imaging camera, a third collimating mirror, a cylindrical mirror, a diffraction grating, an imaging reflector, an imaging CCD, a signal processing circuit and a data inversion module. The equipment has wide applications in the fields of atmospheric chemistry, global climate change, military battlefield aircraft monitoring and the like.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
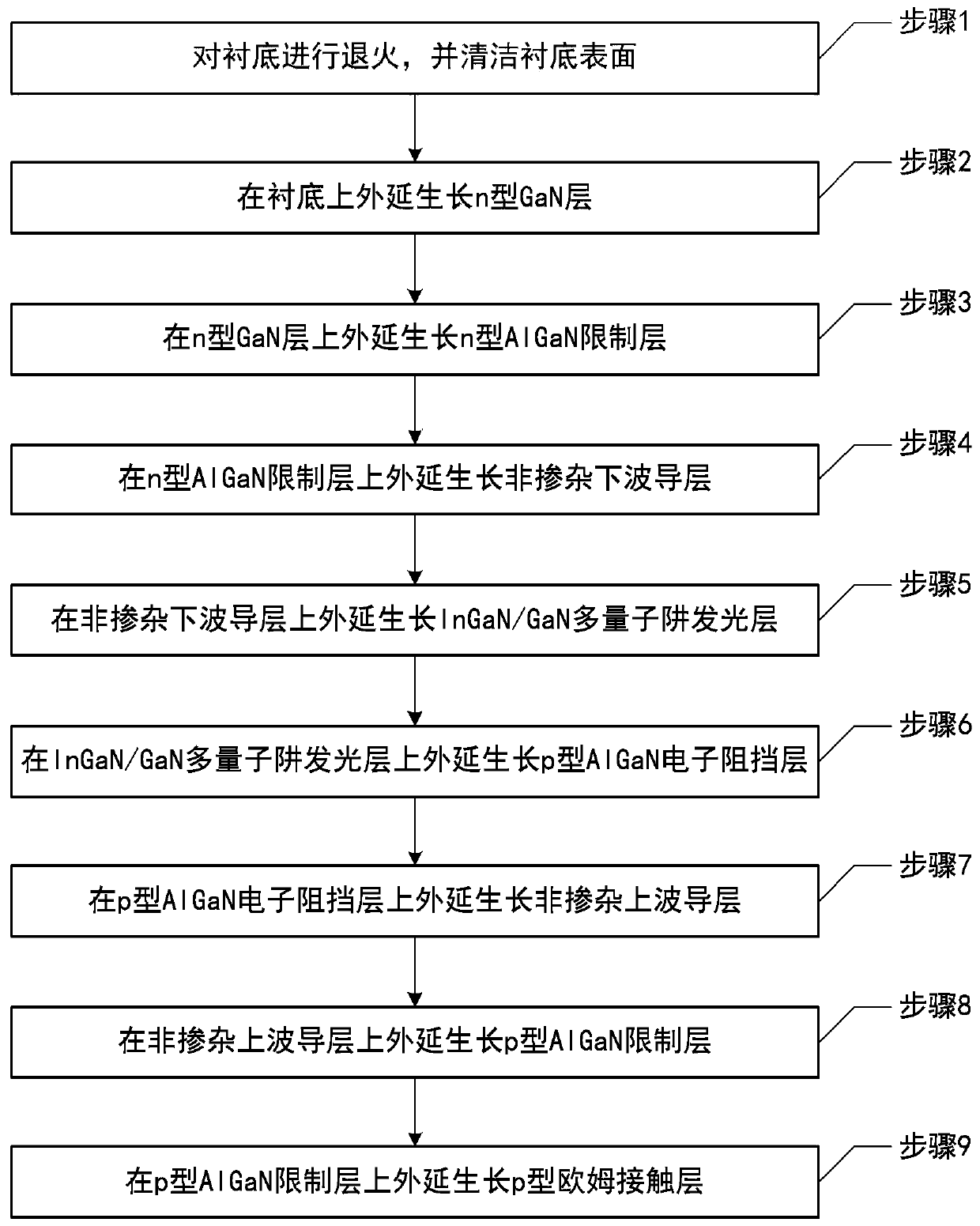
GaN-based multi-quantum-well laser epitaxial wafer with low V-type defect density and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109873299AV-shaped defect eliminationImprove thermal stabilityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersSurface cleaningOhmic contact
The invention disclose a GaN-based multi-quantum-well laser epitaxial wafer with low V-type defect density and a preparation method thereof; the preparation method comprises the steps that annealingand surface cleaning are carried out on a substrate (10), and an n-type GaN layer (11), an n-type AlGaN limiting layer (12), an unintentionally-doped lower waveguide layer (13), an InGaN / GaN multi-quantum-well light-emitting layer (14), a p-type AlGaN electron blocking layer (15), an unintentionally-doped upper waveguide layer (16), a p-type AlGaN limiting layer (17) and a p-type ohmic contact layer (18) are grown on the substrate (10) in an epitaxial mode in sequence, wherein the InGaN / GaN multi-quantum-well light-emitting layer (14) comprises an InGaN well layer and a GaN barrier layer; andin growing the GaN barrier layer a TMIn source is pumped so as to inhibit the formation of V-type defects in the GaN barrier layer and eliminate the common V-type defects in the InGaN / GaN multi-quantum wells, so that the reverse electric leakage of the device is reduced, the absorption loss of the device is lowered, and the thermal stability of the quantum well is improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
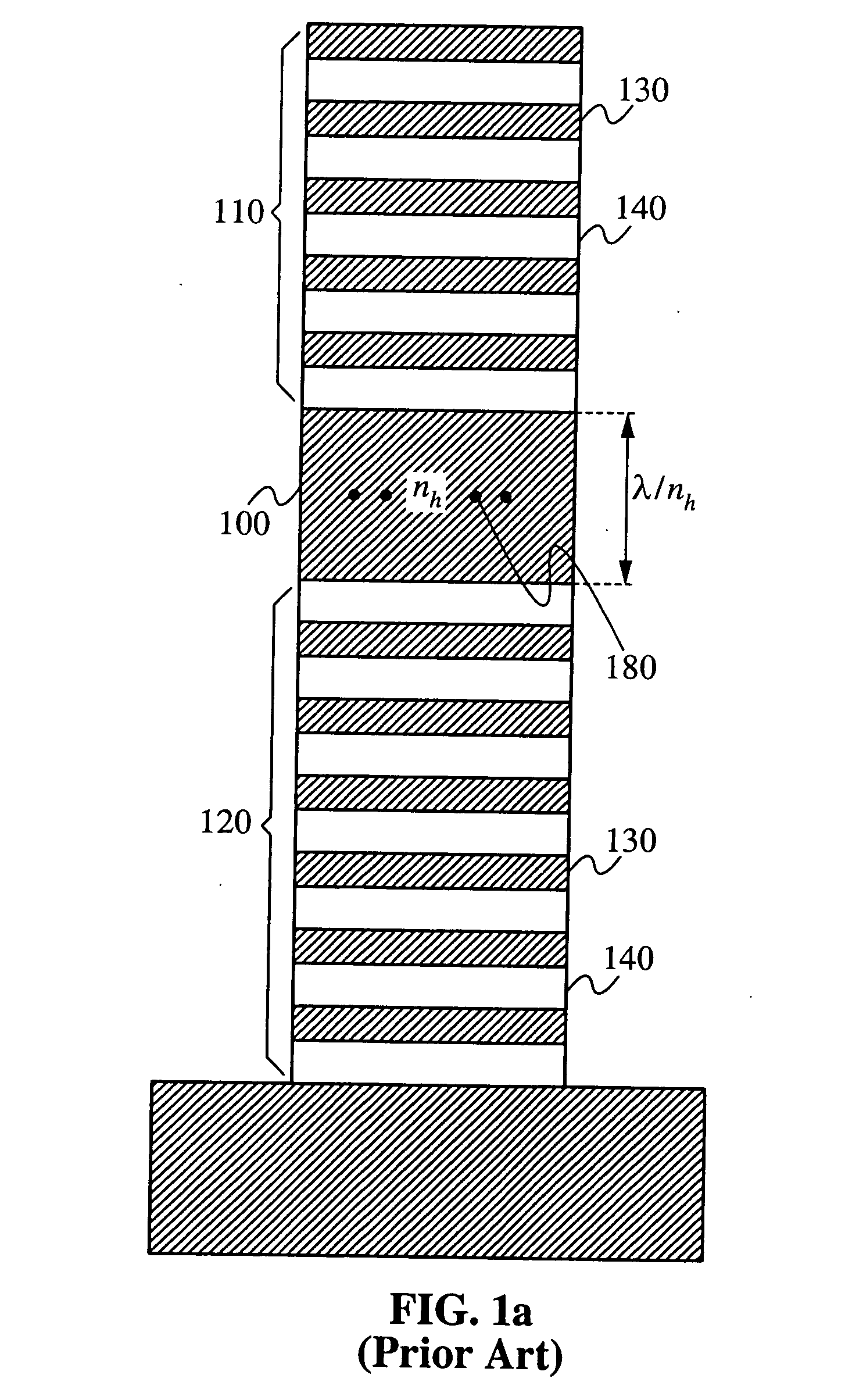
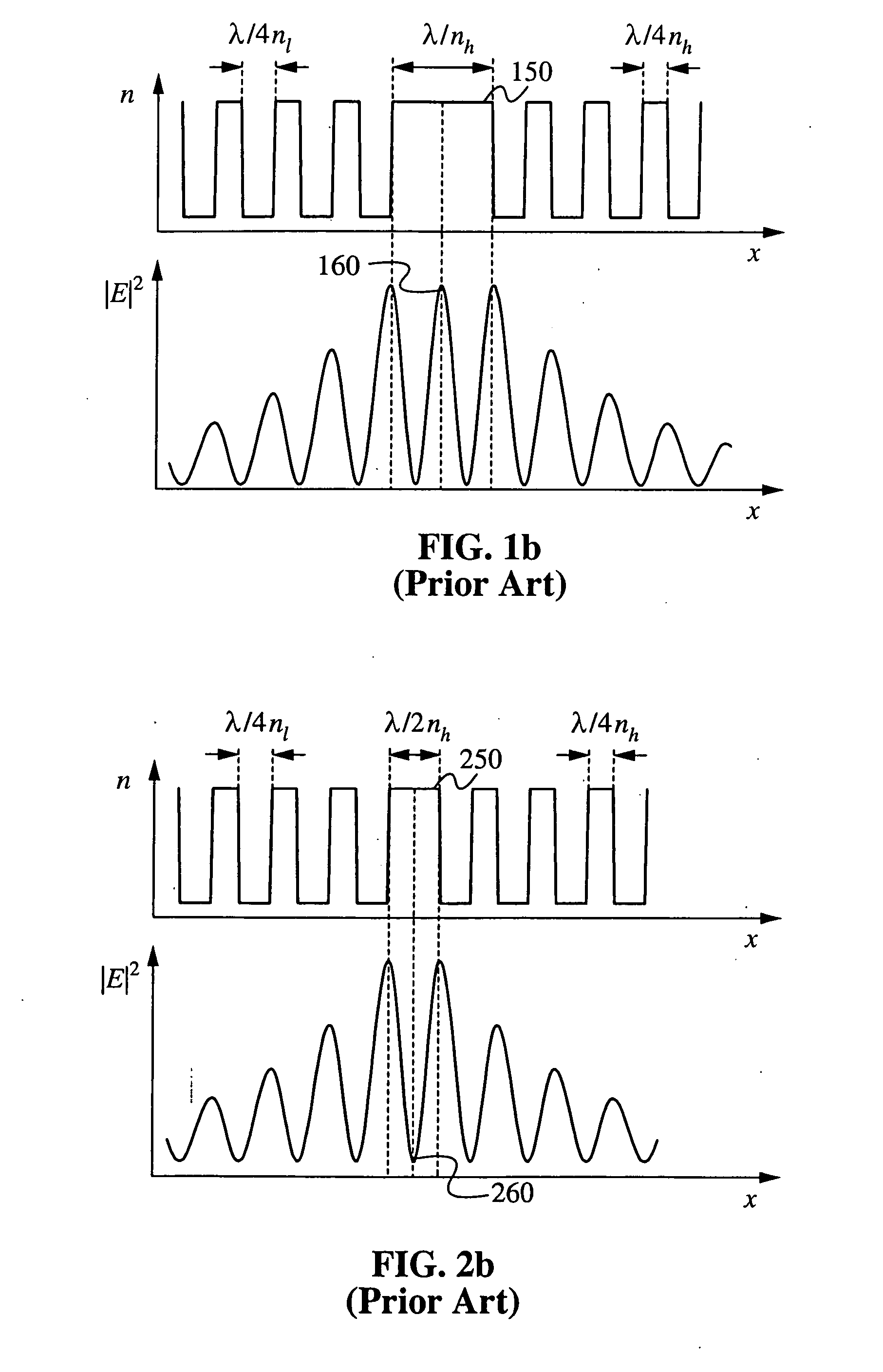
Half-wavelength micropost microcavity with electric field maximum in the high-refractive-index material
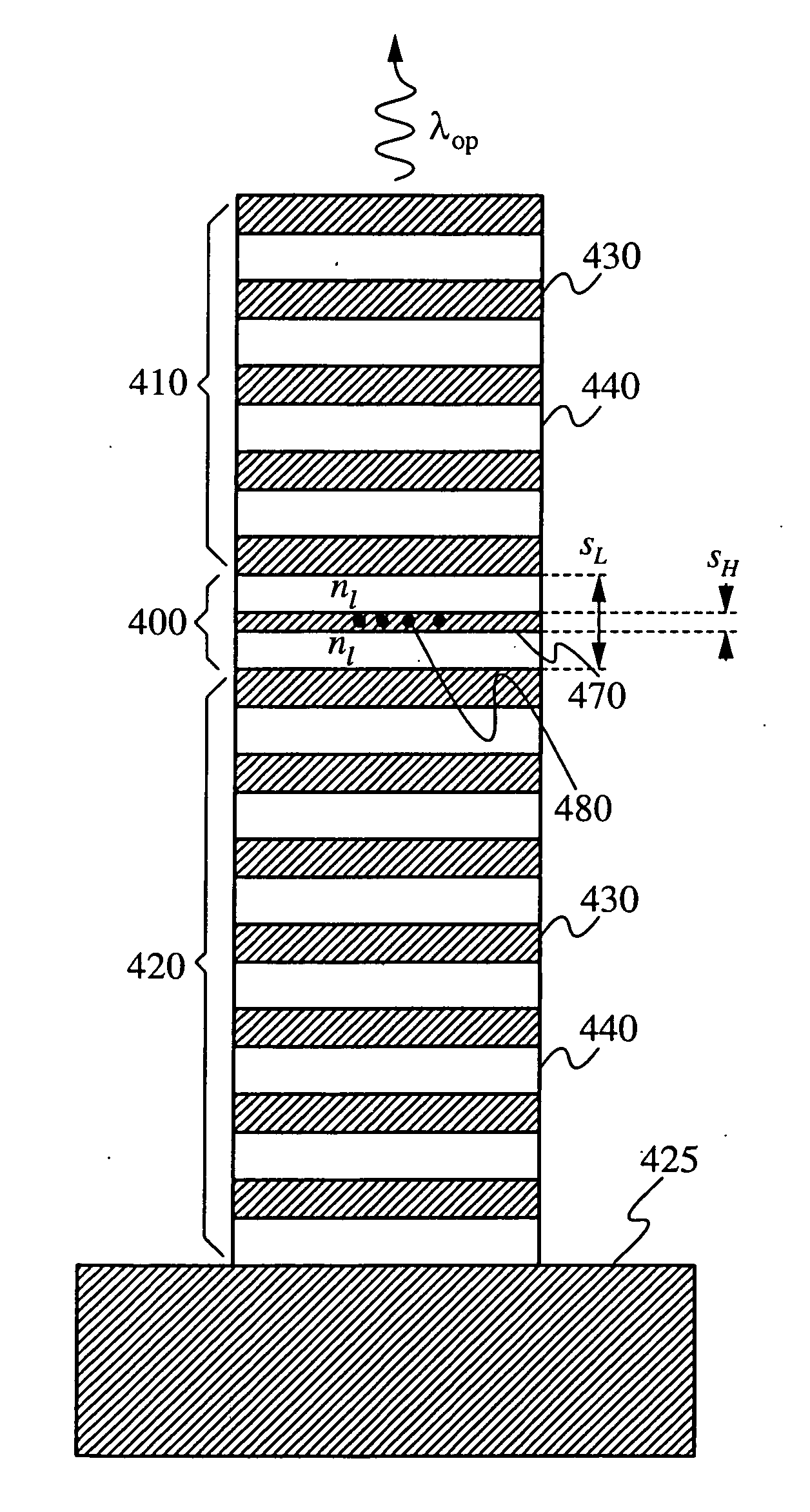
InactiveUS20070183471A1Strong interactionRaise the ratioQuantum computersLaser active region structureRefractive indexQuantum network
A micropost microcavity device has a maximum field intensity at the center of a high-index spacer as well as a small mode volume. The device has an approximately half-wavelength thick low-index spacer [400] sandwiched between two quarter wave stacks [410, 420]. The low-index spacer has a high-index subspacer layer [470] positioned at its center. The subspacer layer has a thickness smaller than a quarter wavelength. As a result, the electric field intensity remains a maximum at the center of the spacer where the high-index subspacer is positioned. A quantum dot or other active region [480] may be embedded within the subspacer [470]. The microcavity devices provide, for example, single photon sources, single dot lasers, low-threshold quantum dot or quantum well lasers, or devices for strong coupling between a single quantum dot and the cavity field which can be used as components of photonic integrated circuits, quantum computers, quantum networks, or quantum cryptographic systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com