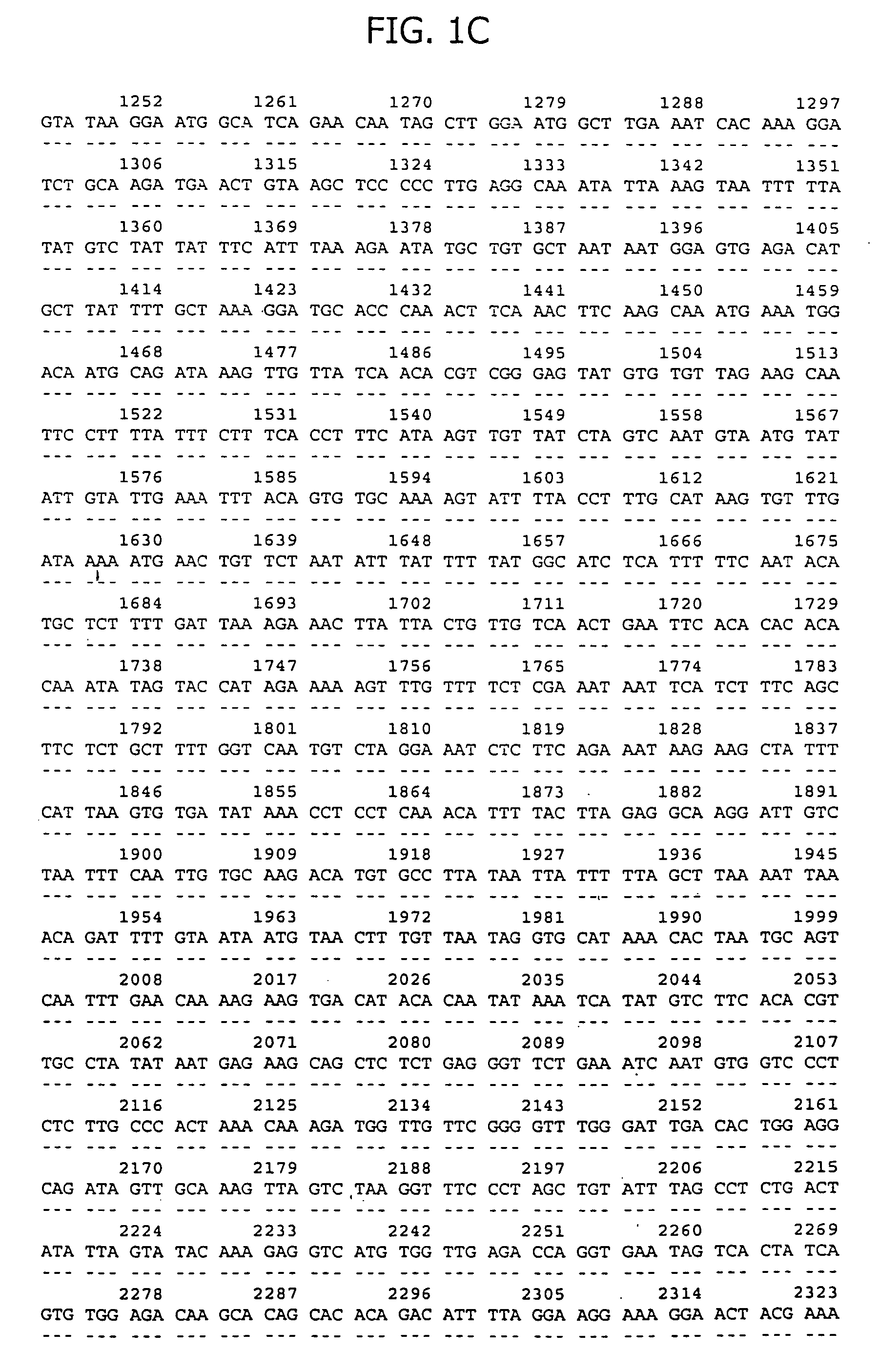Patents
Literature
66 results about "C-type lectin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
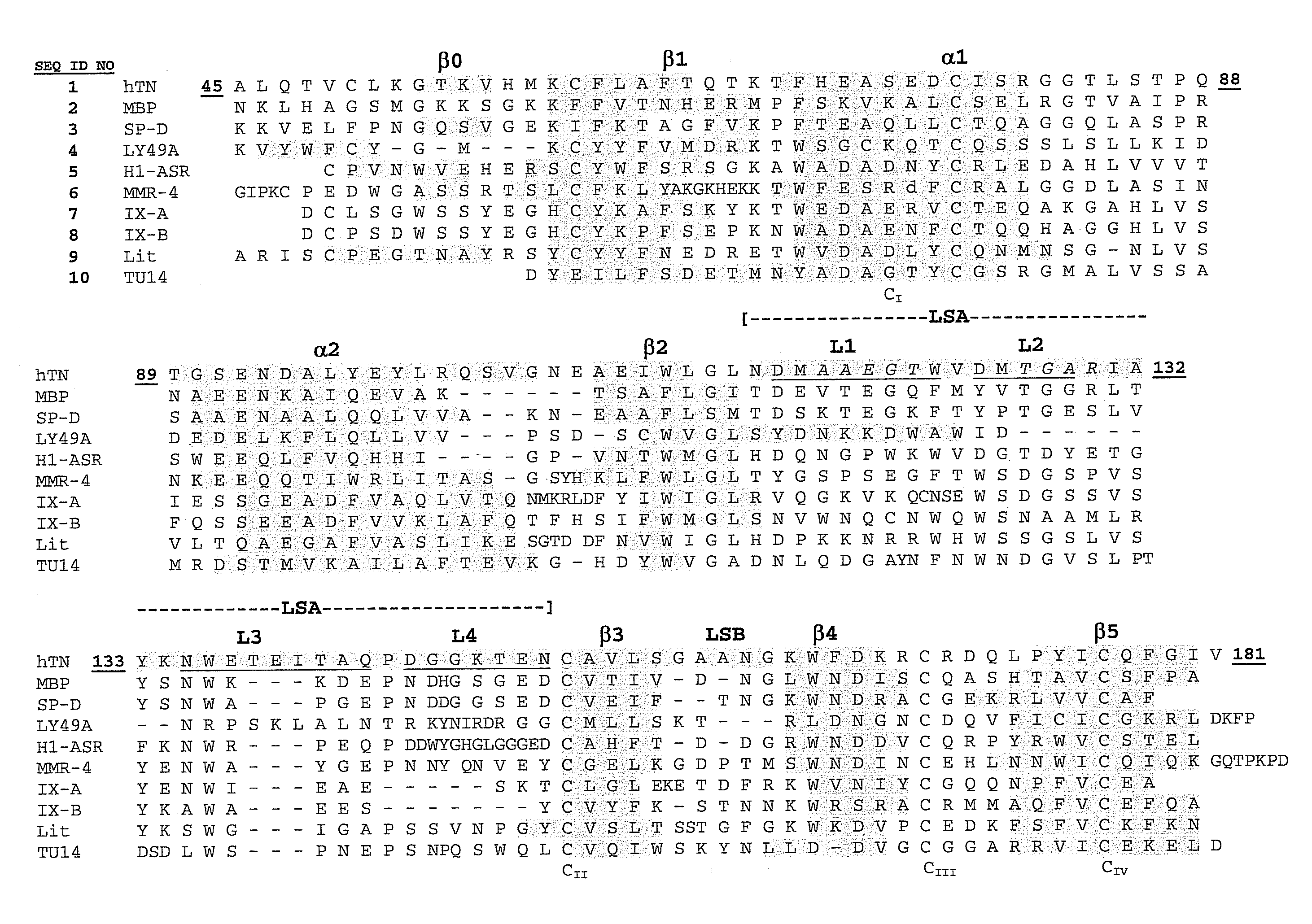
A C-type lectin (CLEC) is a type of carbohydrate-binding protein domain known as a lectin. The C-type designation is from their requirement for calcium for binding. Proteins that contain C-type lectin domains have a diverse range of functions including cell-cell adhesion, immune response to pathogens and apoptosis.
Bivalent IgY antibody constructs for diagnostic and therapeutic applications
InactiveUS20070141049A1Improve the immunityIncrease contentImmunoglobulins against virusesAntibody ingredientsHeavy chainMammal
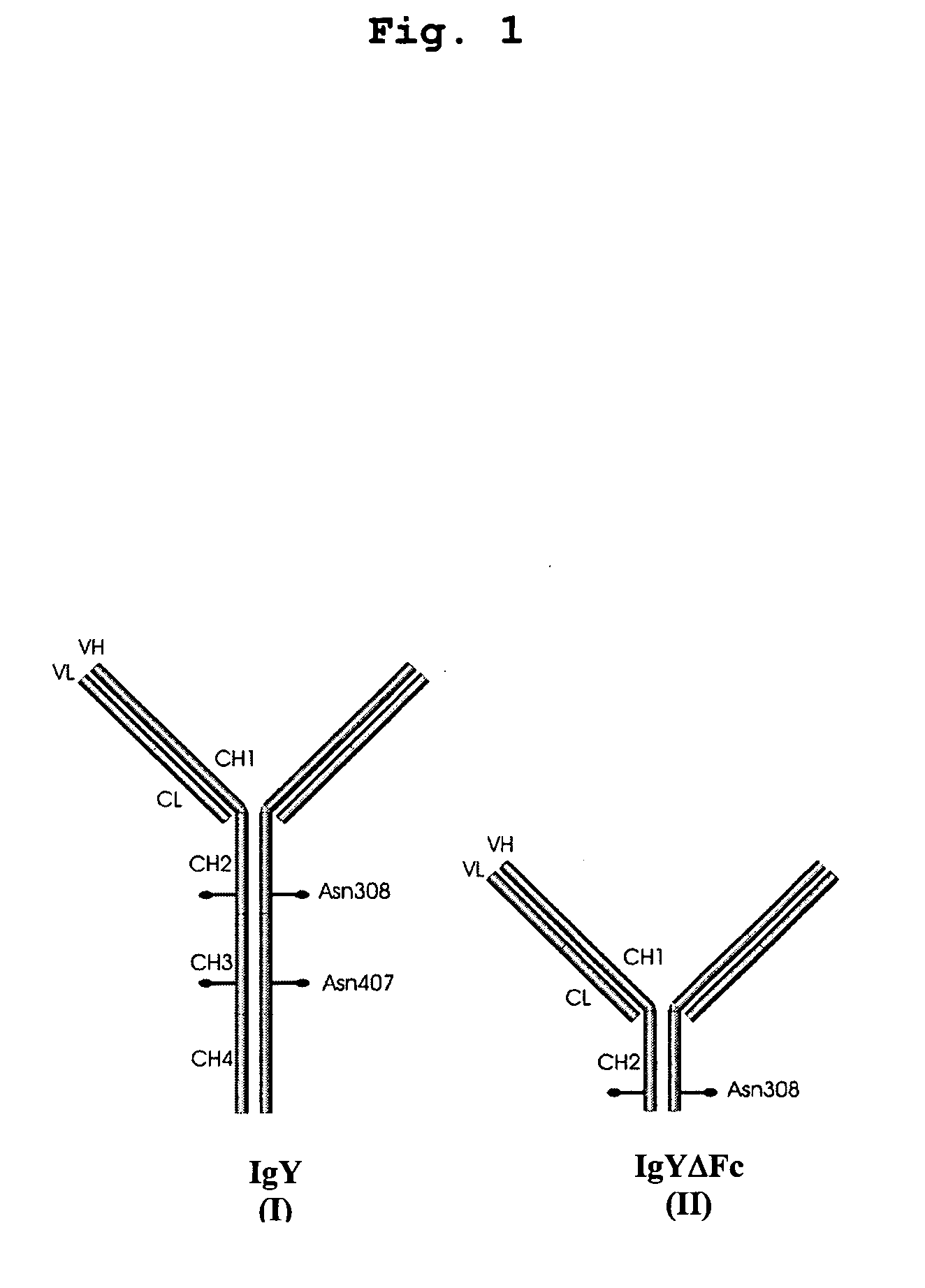
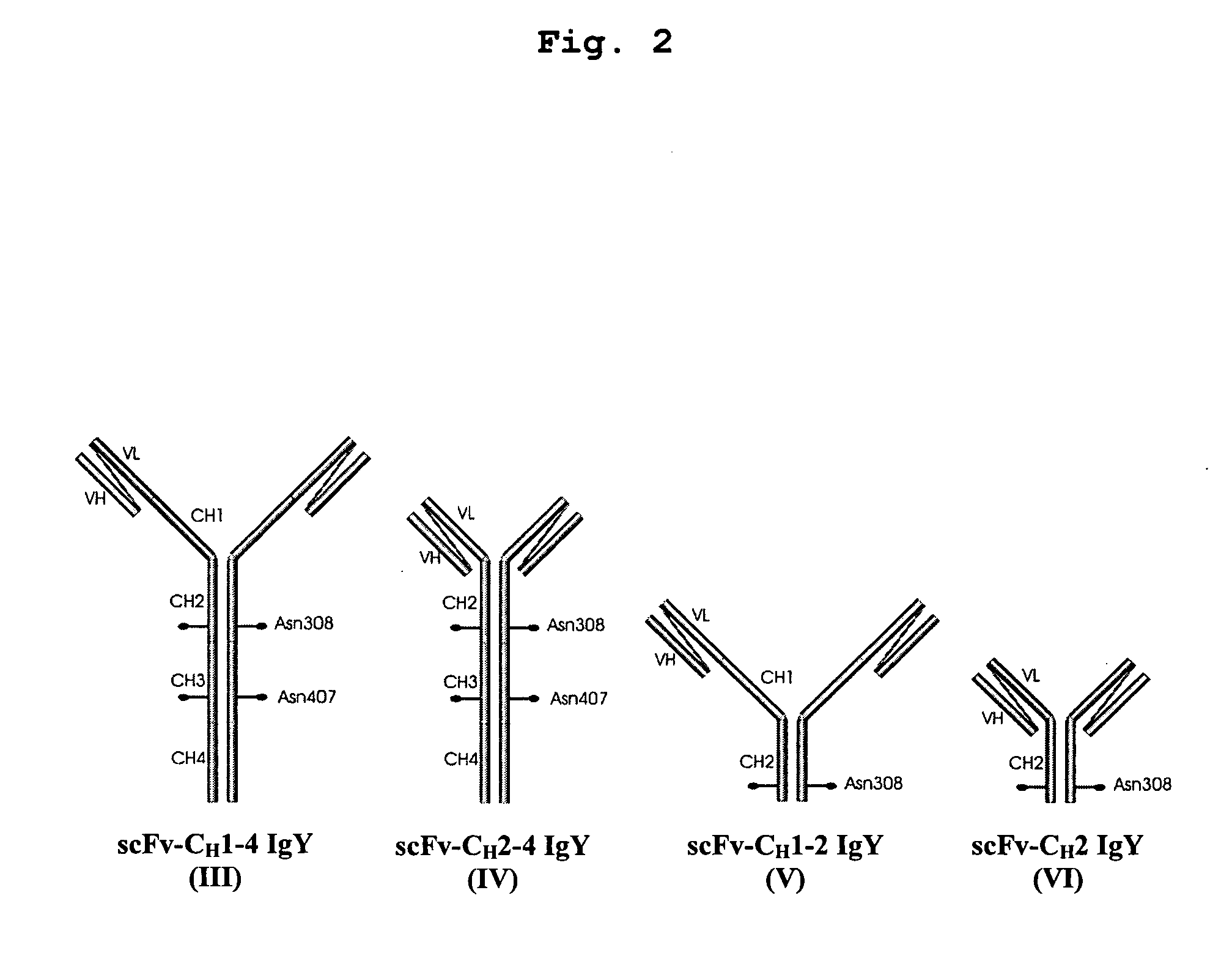
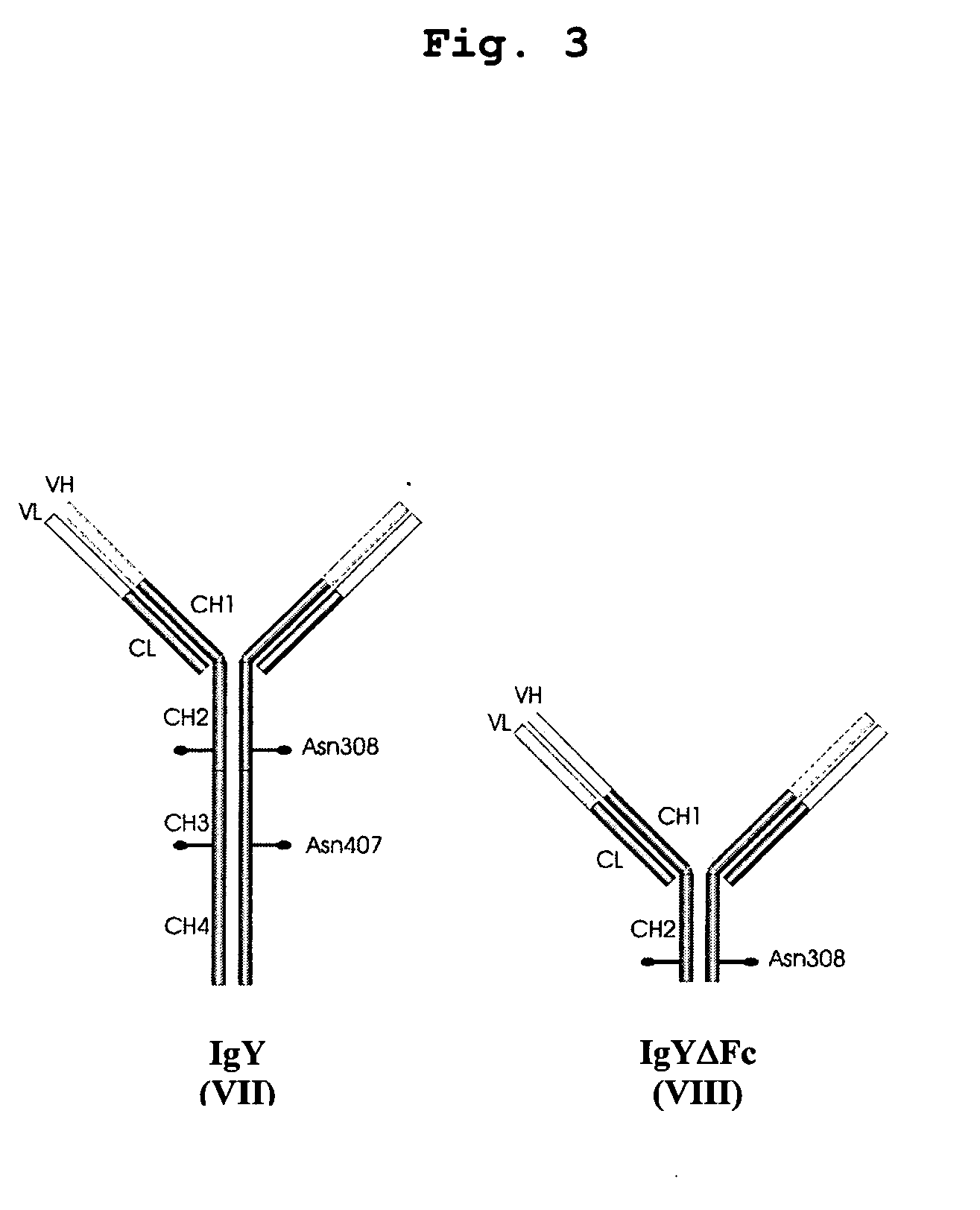
This invention relates to the field of recombinant antibody technology. It provides novel recombinant IgY antibody constructs for diagnostic and therapeutical applications. The bivalent antibody constructs display a heterotetrameric or homodimeric format stabilized by disulfide bonds. The constant heavy chain domains CH2-CH4 are partly or completely of avian origin, whereas the VH, VL, CL, and CH1 domains as well as the hinge region may be of avian origin or derived from any other species. The invention allows to combine the advantages of IgY antibodies with those of established mammalian monoclonal antibodies. IgY antibody constructs comprising nonglycosylated IgY constant heavy chain domains allow to reduce unwanted interactions with C-type lectins, e.g., in human sera. Furthermore, chimeric IgY antibody containing mammalian VH, VL, CL, and CH1 domains as well as a mammalian hinge region provide a higher molecular stability than IgY antibodies in acidic conditions and, thereby, are especially suited for peroral therapeutic applications.
Owner:PLS DESIGN
Chimeric NK receptor and methods for treating cancer
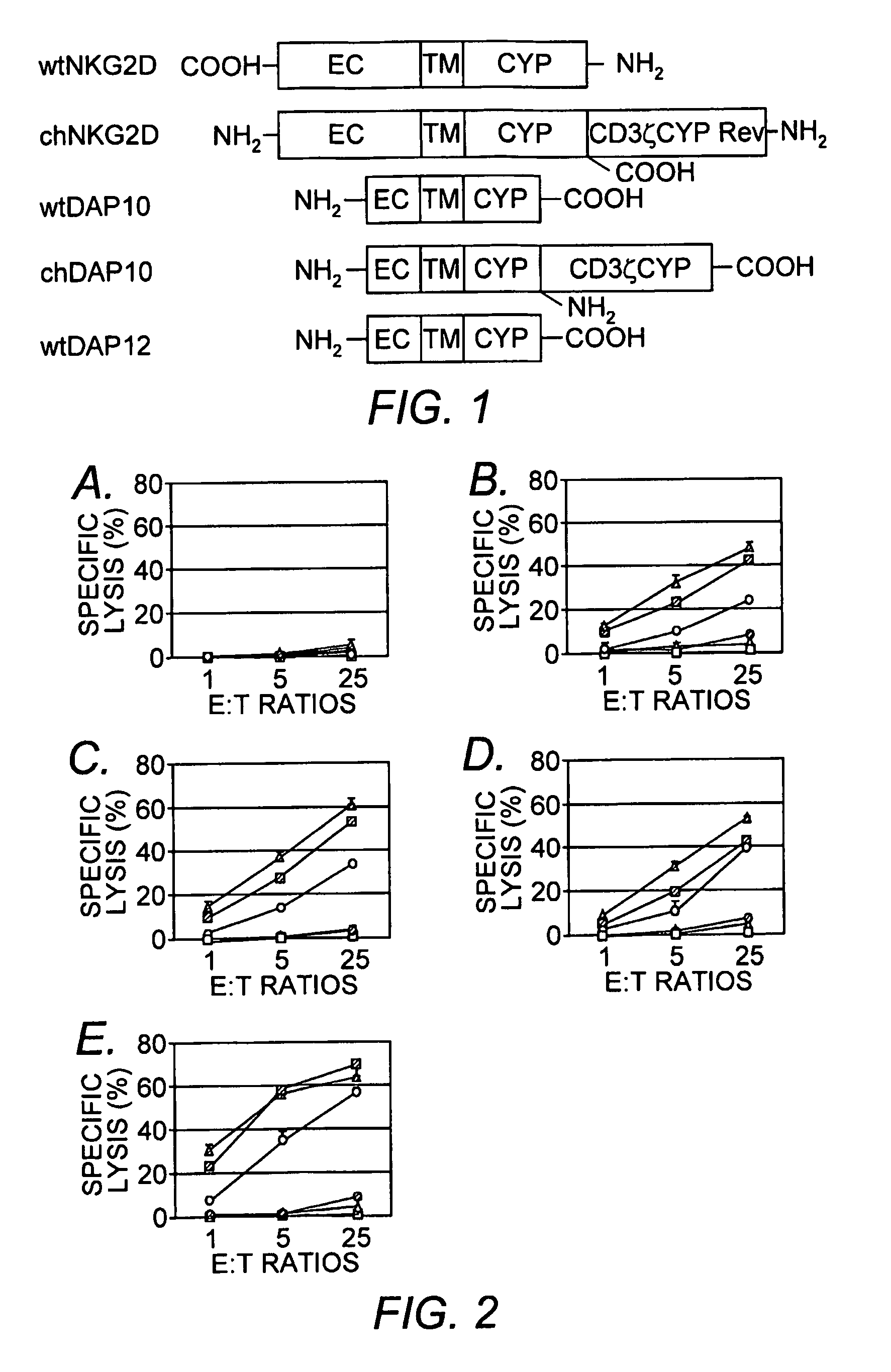
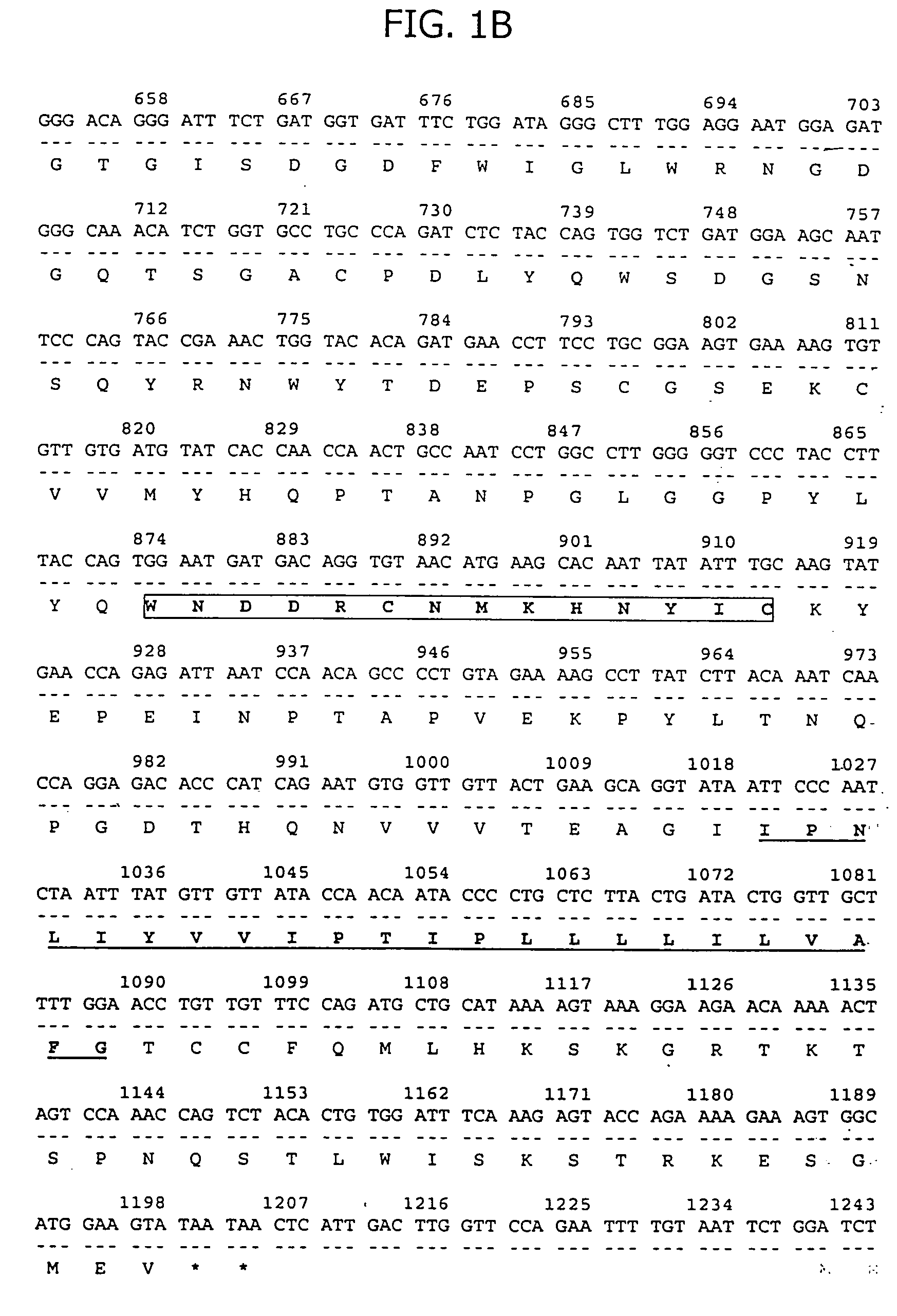
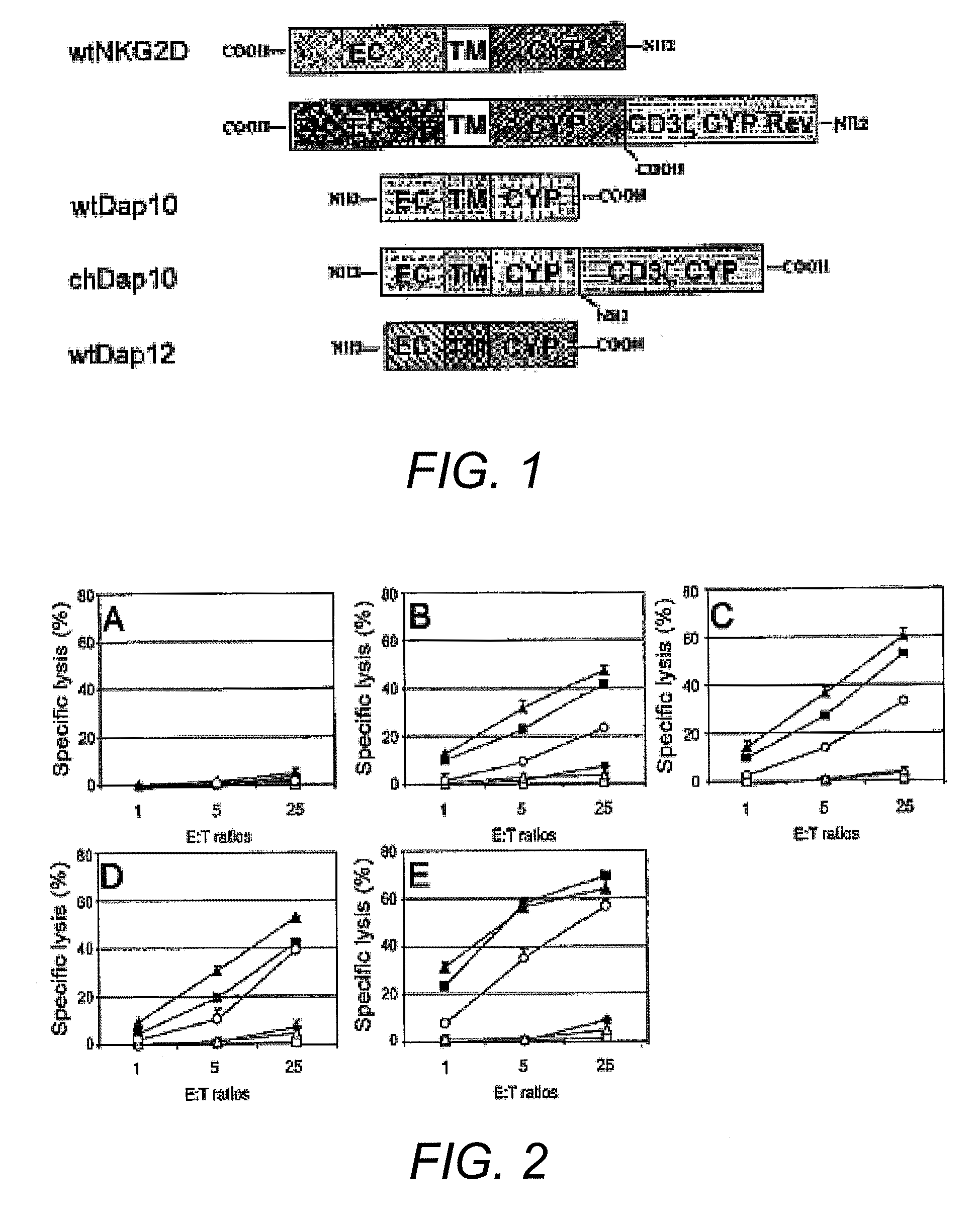
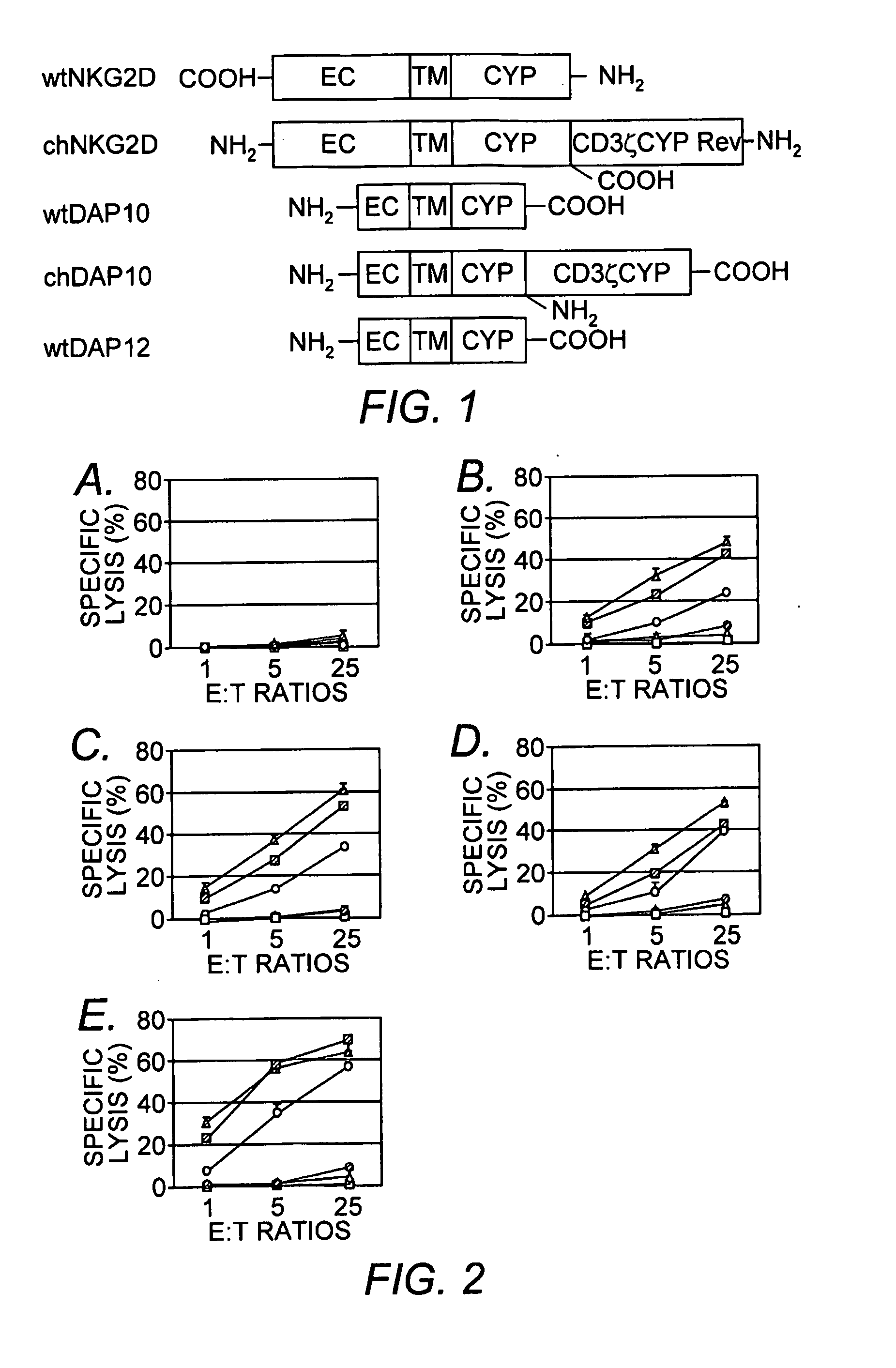
The present invention relates to chimeric immune receptor molecules for reducing or eliminating tumors. The chimeric receptors are composed a C-type lectin-like natural killer cell receptor, or a protein associated therewith, fused to an immune signaling receptor containing an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif. Methods for using the chimeric receptors are further provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Binding molecules for the treatment of myeloid cell malignancies
InactiveUS20060177451A1Suitable diagnosisSuitable preventionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMalignancyDisease cause
The present invention provides a human C-type lectin, binding molecules that specifically bind to the human C-type lectin, nucleic acid molecules encoding the binding molecules or the human C-type lectin, compositions comprising the binding molecules or the human C-type lectin and methods of identifying or producing the binding molecules. The human C-type lectin is specifically expressed on myeloid cells and binding molecules capable of specifically binding to the human C-type lectin can be used in the diagnosis, prevention and / or treatment of neoplastic disorders and diseases.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
C-type lectin transmembrane antigen expressed in human prostate cancer and uses thereof
A novel gene (designated PC-LECTIN) that is highly overexpressed in prostate cancer and its encoded protein is described. PC-LECTIN in normal human tissues is restricted to testis, but is highly expressed in prostate cancer. Consequently, PC-LECTIN provides a diagnostic and / or therapeutic target for prostate cancer.
Owner:AGENSYS
Chimeric NK receptor and methods for treating cancer
The present invention relates to chimeric immune receptor molecules for reducing or eliminating tumors. The chimeric receptors are composed a C-type lectin-like natural killer cell receptor, or a protein associated therewith, fused to an immune signaling receptor containing an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif. Methods for using the chimeric receptors are further provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Chimeric NK Receptor and Methods for Treating Cancer
The present invention relates to chimeric immune receptor molecules for reducing or eliminating tumors. The chimeric receptors are composed a C-type lectin-like natural killer cell receptor, or a protein associated therewith, fused to an immune signaling receptor containing an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif. Methods for using the chimeric receptors are further provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
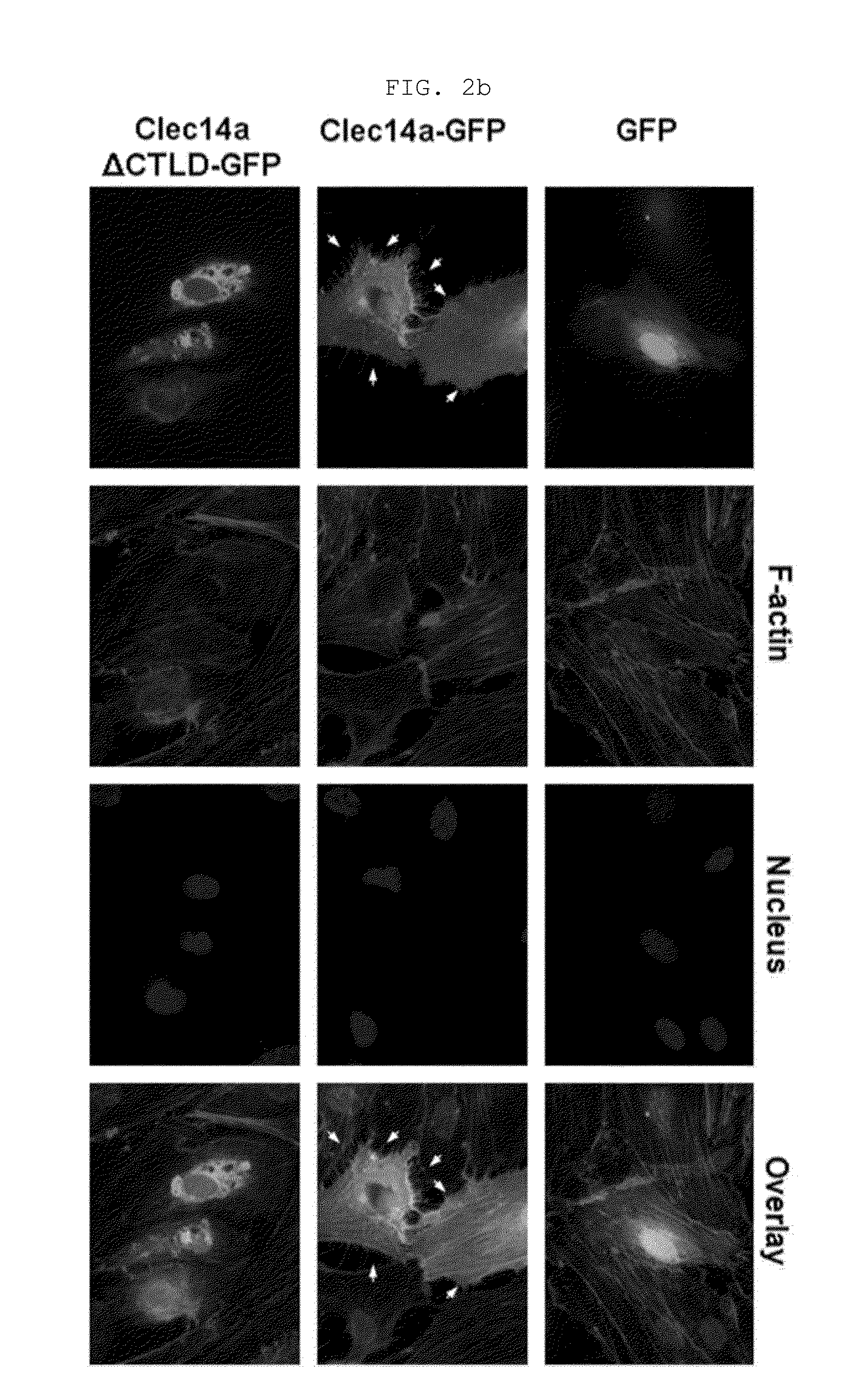
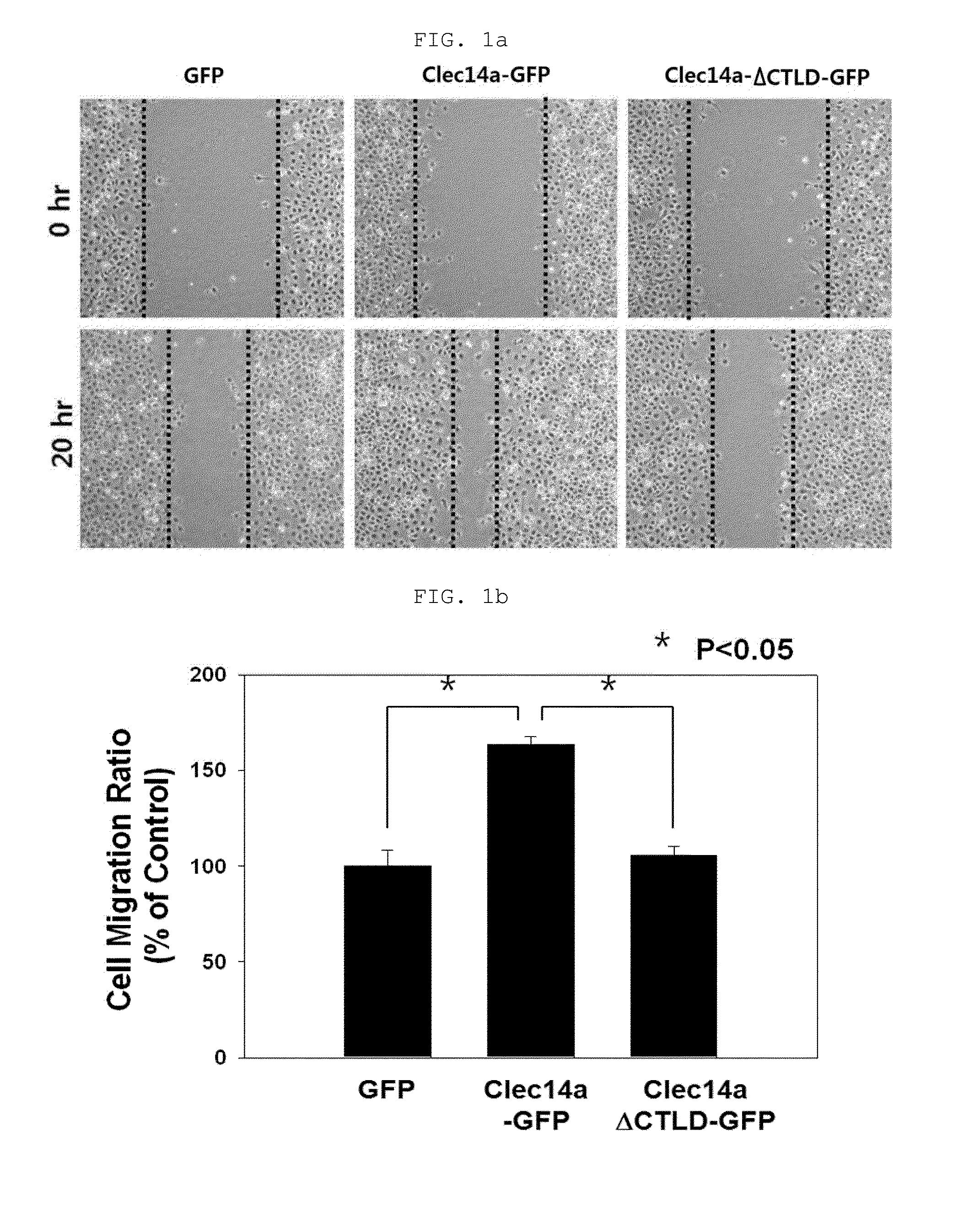
Novel antibody specific for clec14a and uses thereof
Provided is an antibody specifically binding to the CTLD (C-type lectin like domain) of clecl4a (C-type lectin domain family 14, member A), a method for preparing the antibody, a composition for suppressing angiogenesis comprising the antibody, a method for suppressing angiogenesis by administering the antibody or the composition, a composition for preventing or treating cancer comprising the antibody, a method for treating cancer by administering the antibody or the composition, a composition for diagnosing cancer comprising the antibody, a kit for diagnosing cancer comprising the composition, a method for diagnosing cancer using the composition, a composition for suppressing angiogenesis comprising a material for inhibiting expression of clecl4a, a kit for angiogenesis comprising the composition, a method for suppressing angiogenesis or treating cancer using the composition, and the use of the CTLD of clecl4a as an epitope for an antibody suppressive of angiogenesis.
Owner:WOORI TECH CORP
Binding molecules for the treatment of myeloid cell malignancies
InactiveUS7741443B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMalignancyDisease cause
The present invention provides a human C-type lectin, binding molecules that specifically bind to the human C-type lectin, nucleic acid molecules encoding the binding molecules or the human C-type lectin, compositions comprising the binding molecules or the human C-type lectin and methods of identifying or producing the binding molecules. The human C-type lectin is specifically expressed on myeloid cells and binding molecules capable of specifically binding to the human C-type lectin can be used in the diagnosis, prevention and / or treatment of neoplastic disorders and diseases.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
C-type agglutinin gene of procambarus clarkia as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN102321628AHas agglutinating effectPromote phagocytosisAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsEscherichia coliTotal rna
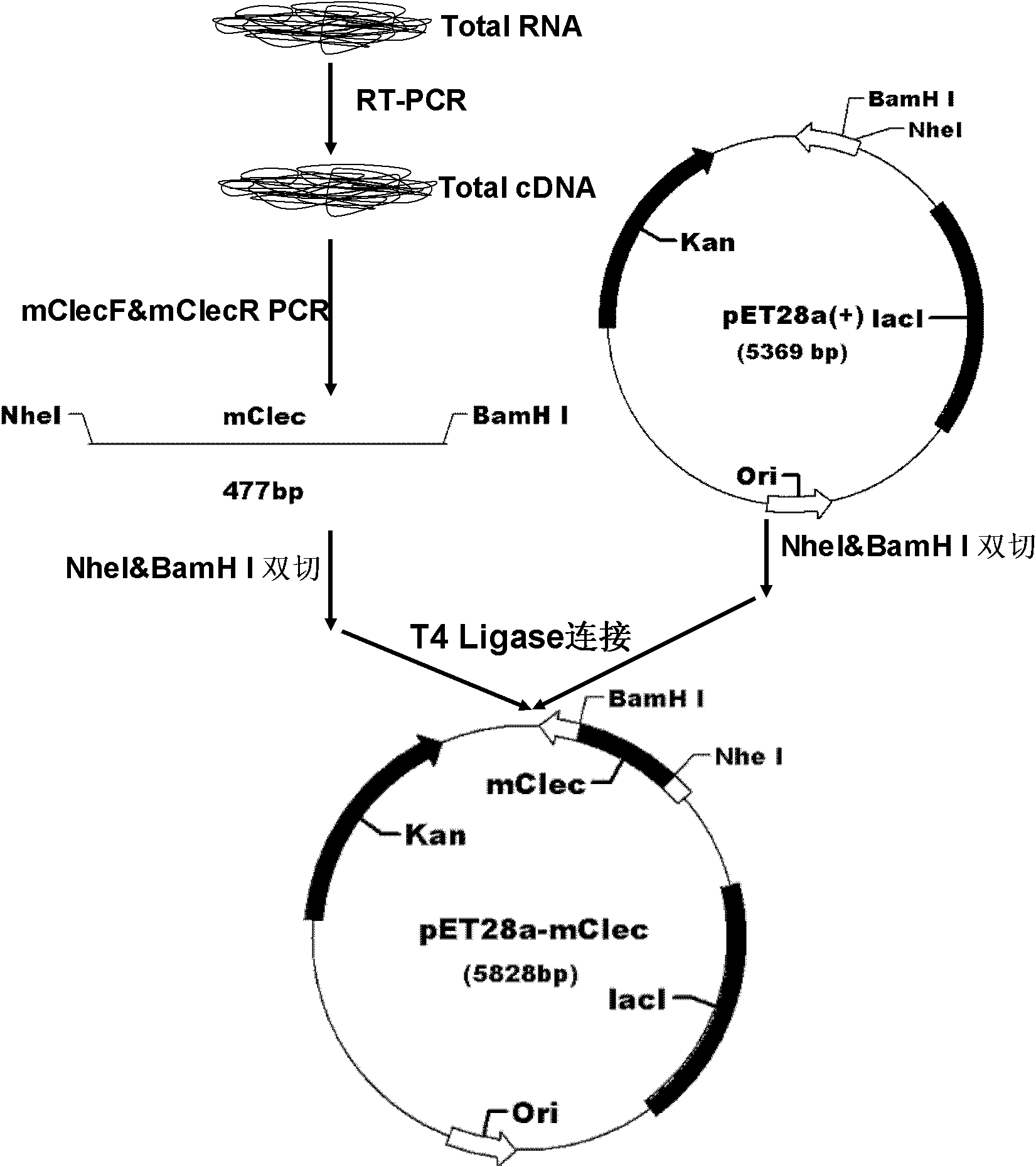
The invention discloses a C-type agglutinin gene of procambarus clarkia as well as a preparation method and applications thereof. The method comprises the following steps: A. extracting total RNA (ribose nucleic acid); B. synthetizing a first chain cDNA; C. acquiring partial nucleotide sequences; D. acquiring the nucleotide sequences at 3'-RACE: 3' end; E. acquiring the nucleotide sequences at 5'-RACE: 5' end; F. acquiring the complete nucleotide sequences of the gene; and G. coding an amino acid sequence of protein by the C-type agglutinin gene. From the cloning in procambarus clarkia to theC-type agglutinin gene, the gene is cloned to a PET-28a carrier, recombinant protein mClec is expressed in colon bacillus BL21 (DE3), and the purified mClec expresses agglutination effect to multiplebacteria and rabbit red blood cells; and the protein mClec or recombinant agglutinin obtained from cloning prokaryotic expression vector on the agglutinin gene can be used for producing shrimp and fish antivirus and antibacterial medicaments.
Owner:HUBEI TAIYANGHONG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Combinatorial Libraries Based on C-type Lectin-like Domain
This invention relates to polypeptide libraries comprising polypeptides having a C-type lectin domain (CTLD) with a randomized loop region, as well as nucleic acid libraries comprising nucleic acid molecules encoding such polypeptides. The invention also relates to methods for generating the randomized polypeptides and the polypeptide libraries. The invention further relates to methods of screening the polypeptide and nucleic acid libraries based on the specific binding of the modified CTLDs to a target molecule of interest. The invention also relates to polypeptides derived from such libraries that bind to target molecules of interest.
Owner:ANAPHORE INC
C-Type Lectin Fold as a Scaffold for Massive Sequence Variation
InactiveUS20100069300A1Reduced viabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticSequence variationBiology
This invention provides a class of binding proteins with a range of binding specificities and affinities based upon variation at select amino acid positions within a scaffold. The variable positions may be readily modified to produce a library of binding proteins with different binding specificities and affinities. The library may be screened to identify one or more as binding a ligand of interest. Compositions comprising the binding proteins, as well as methods of using the binding proteins are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
LLT uses thereof in immune system modulation
InactiveUS20060002892A1Reduce rejectionReducing natural killer cell mediated rejectionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthENCODE
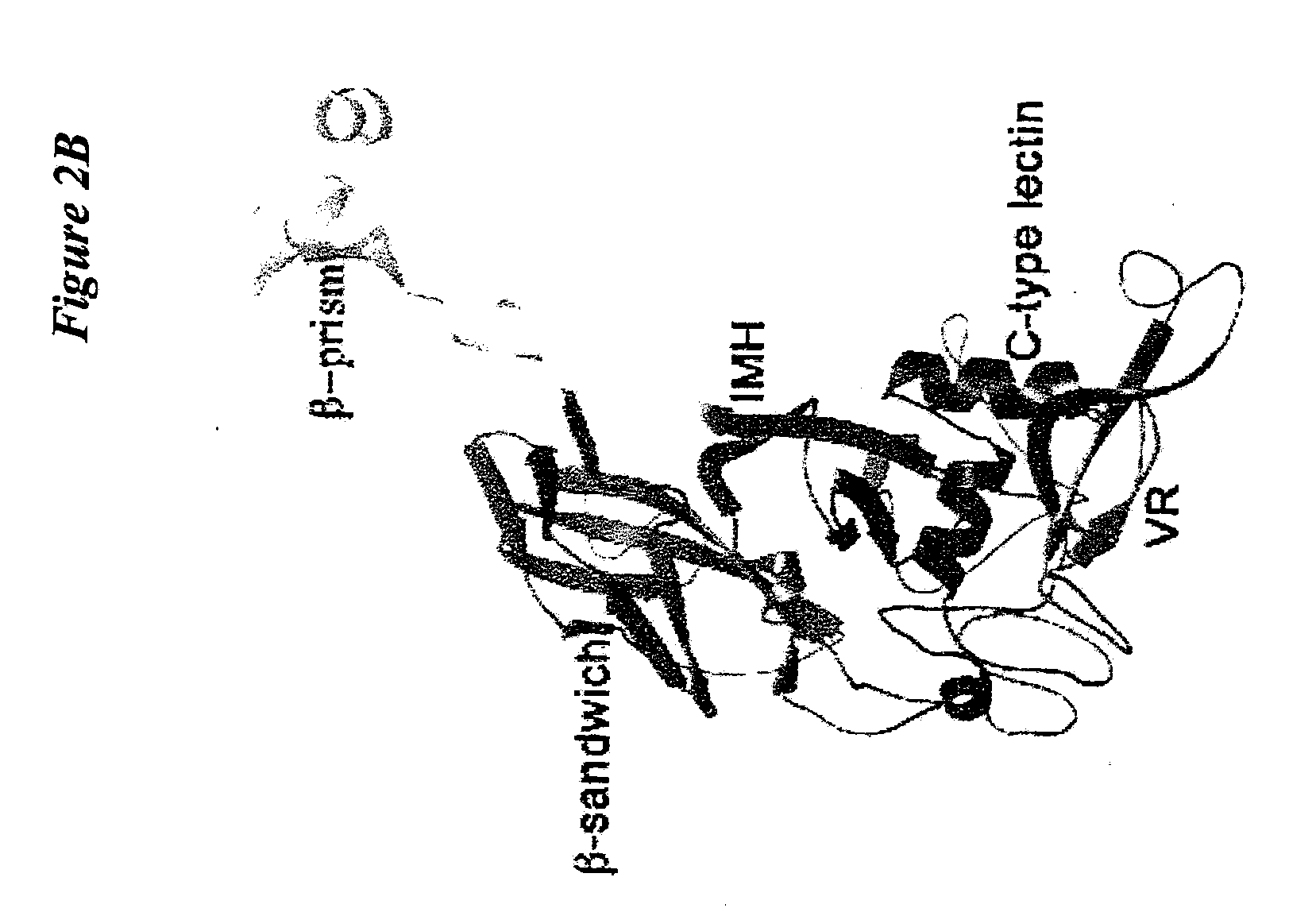
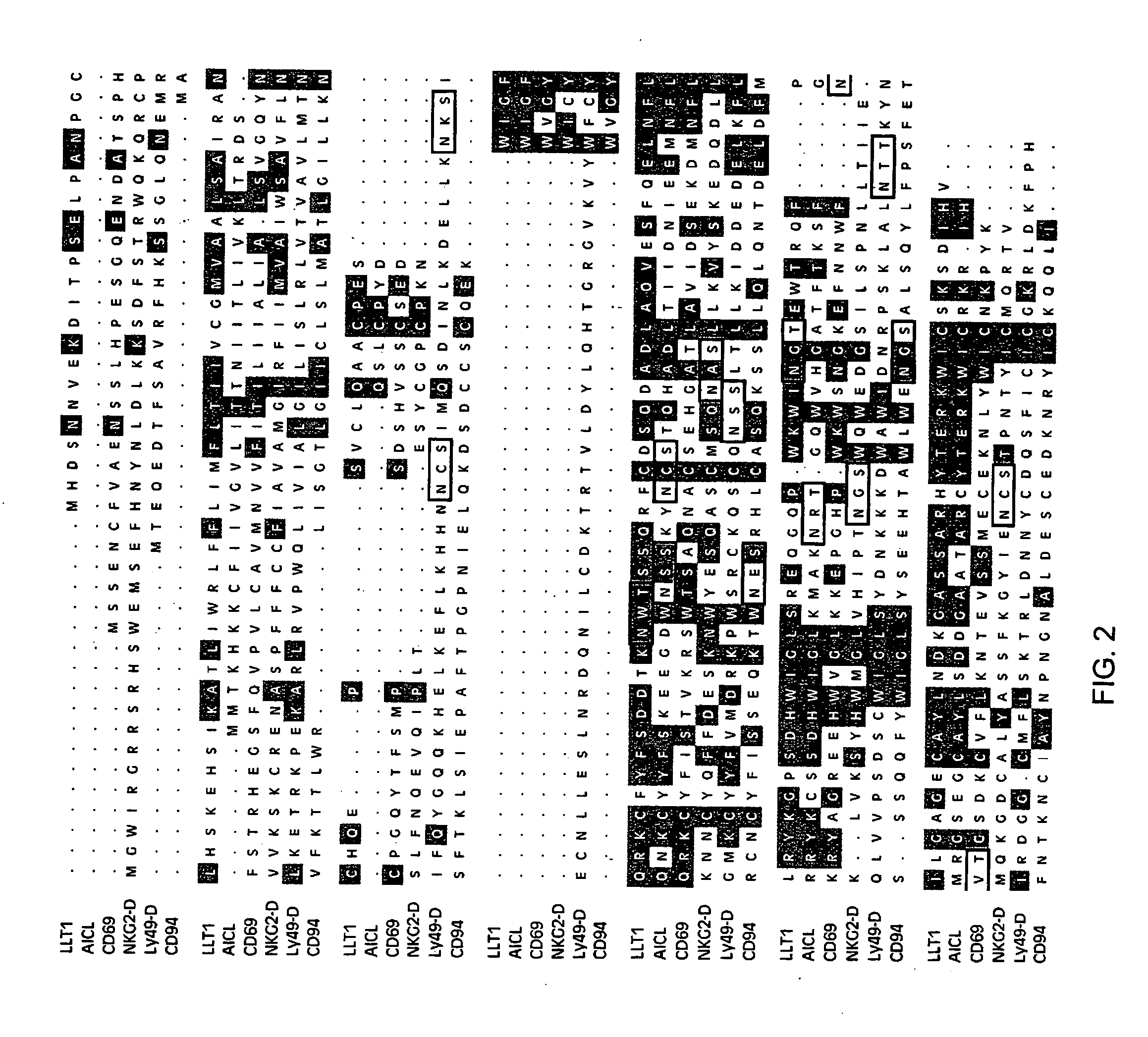
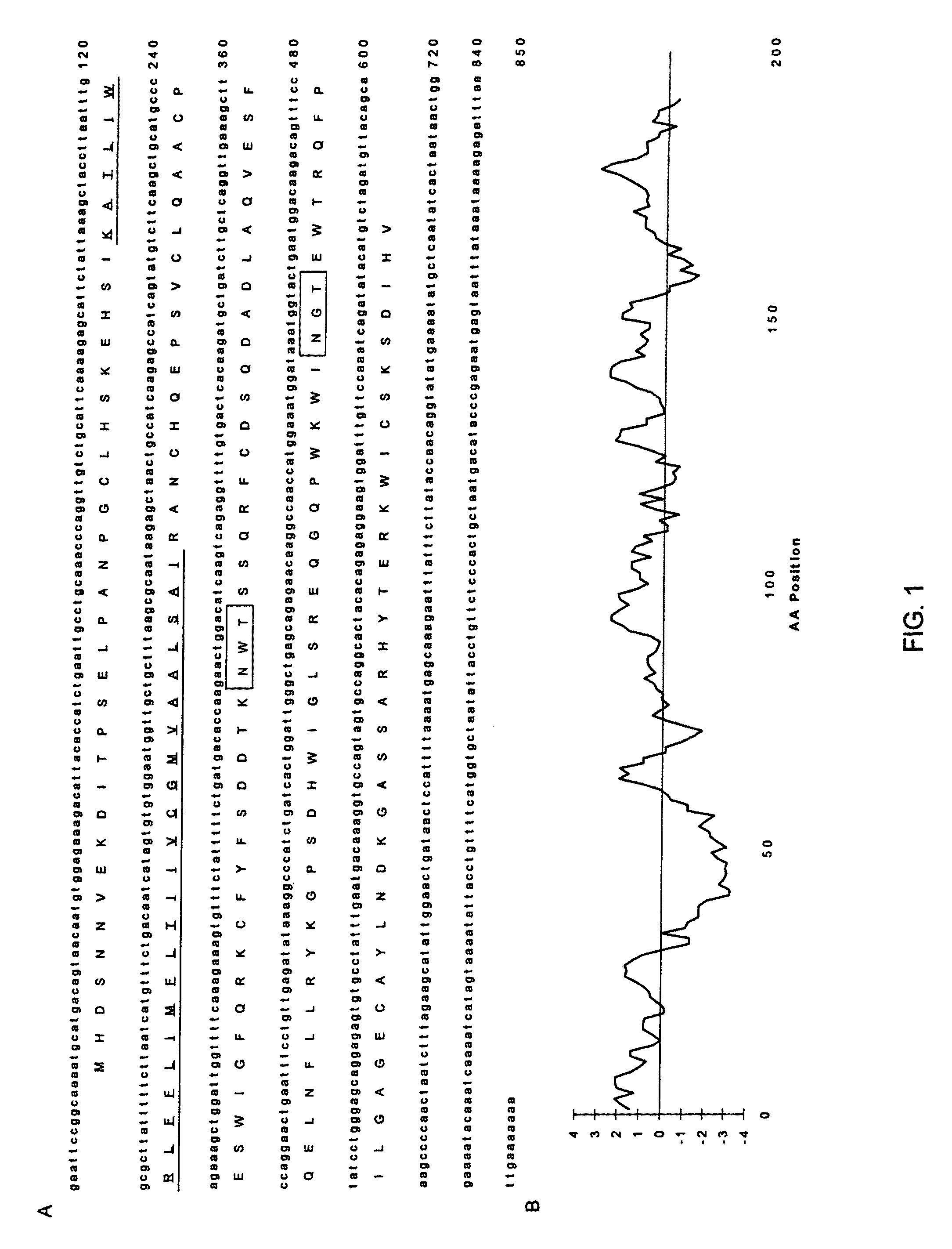
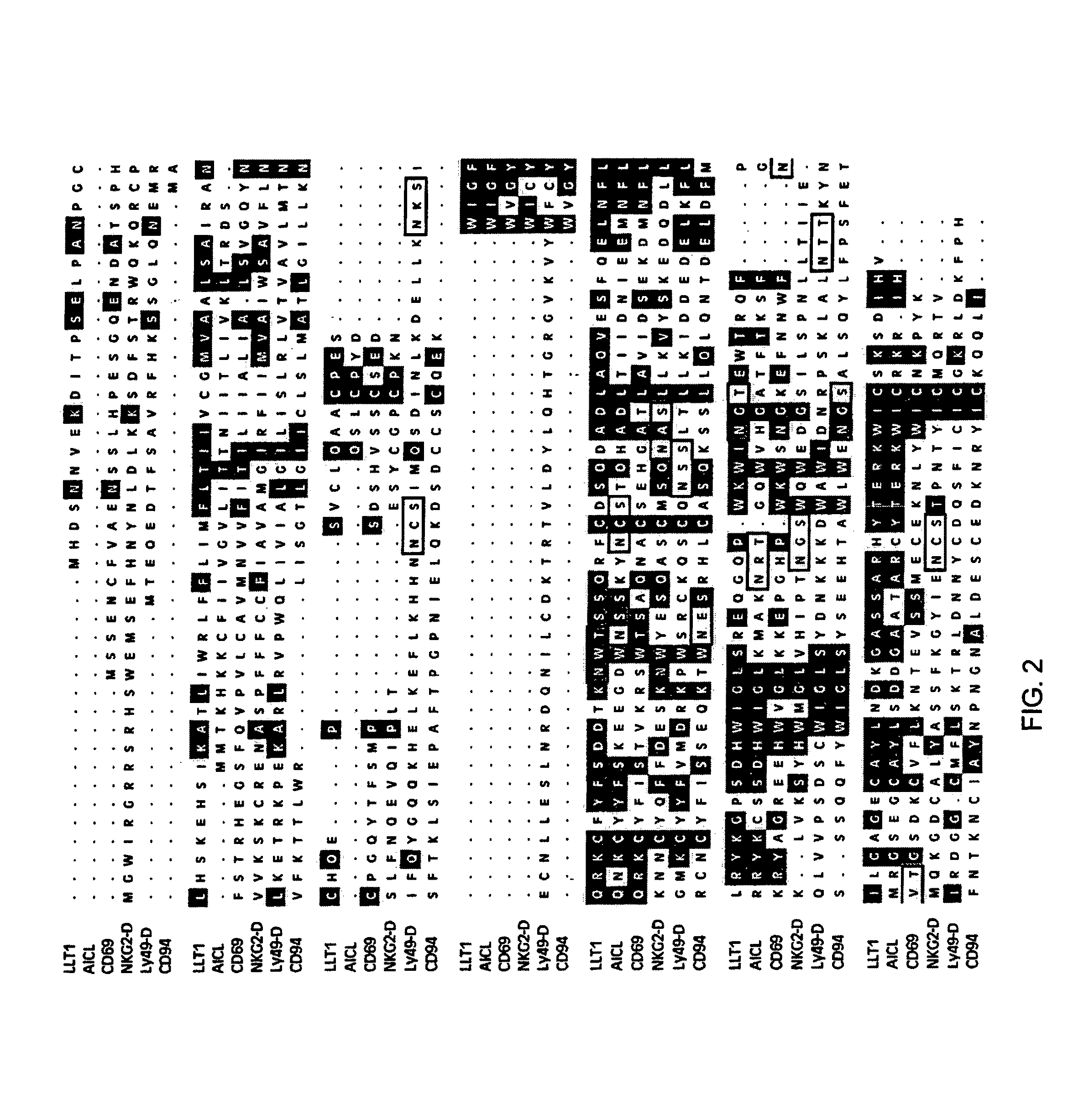
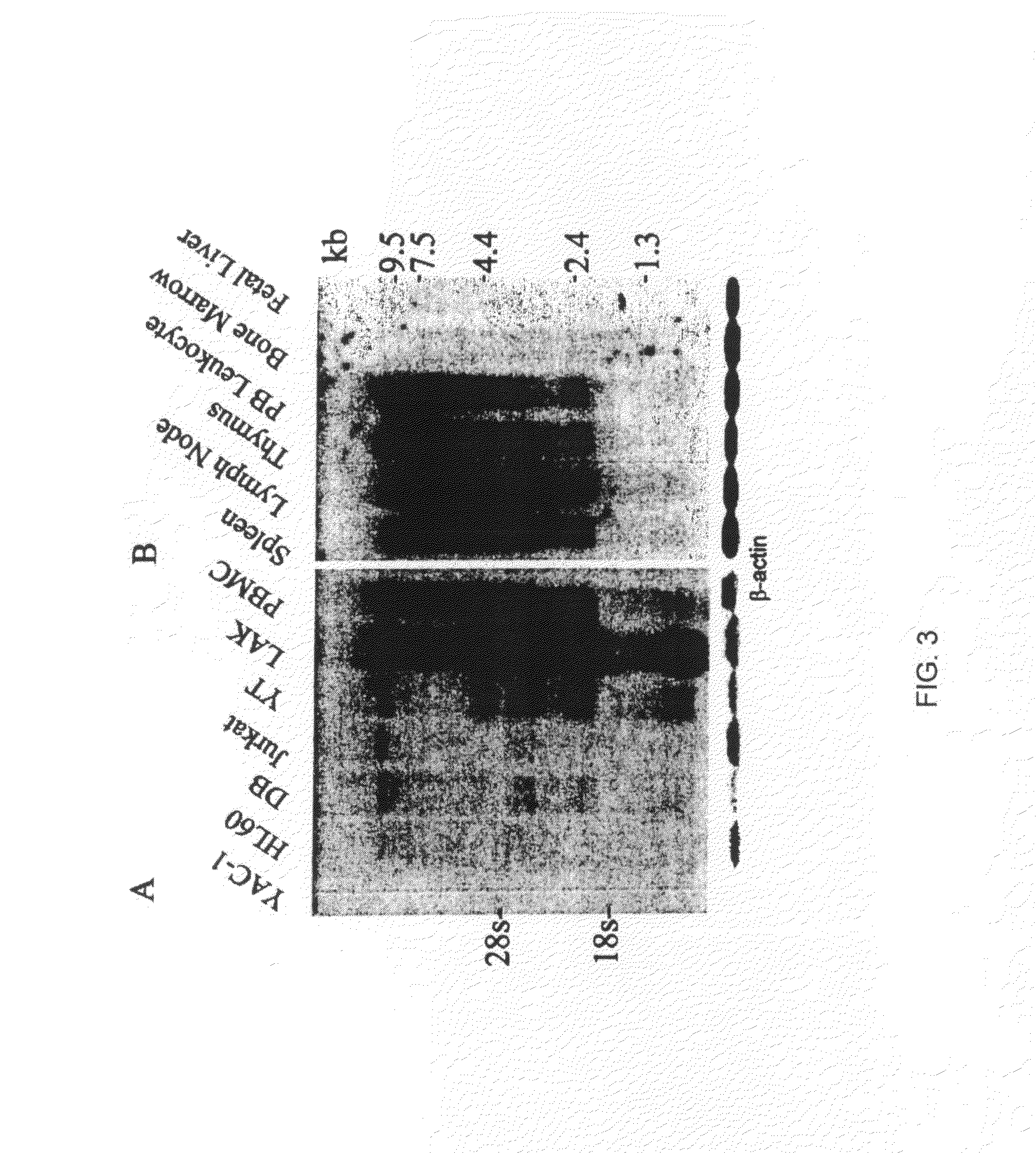
Natural killer (NK) cells possess the inherent capacity to kill various tumor and virally infected cells and mediate the rejection of bone-marrow grafts in lethally irradiated animals. A large family of NK cell receptors belong to the C-type lectin super-family. Genes in the NK gene complex encode type II receptors and examples include the families of NKR-P1, Ly-49, and NKG2 receptors. Examples of other C-type lectin-like NK cell receptors that occur as individual genes are CD94, CD69, and AICL. The invention includes a cDNA that encodes a predicted protein of 191 amino acid residues having similarity to the carbohydrate recognition domain of C-type lectins. The predicted protein of LLT1 shows 59 and 56% similarity to AICL and CD69, respectively. The predicted protein does not contain any intracellular ITIM motifs indicating the LLT1 protein may be involved in mediating activation signals.
Owner:UNIV OF NORTH TEXAS HEALTH SCI CENT
Molecule and chimeric molecules thereof
InactiveUS20090155267A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEGF-like domainProtein molecules
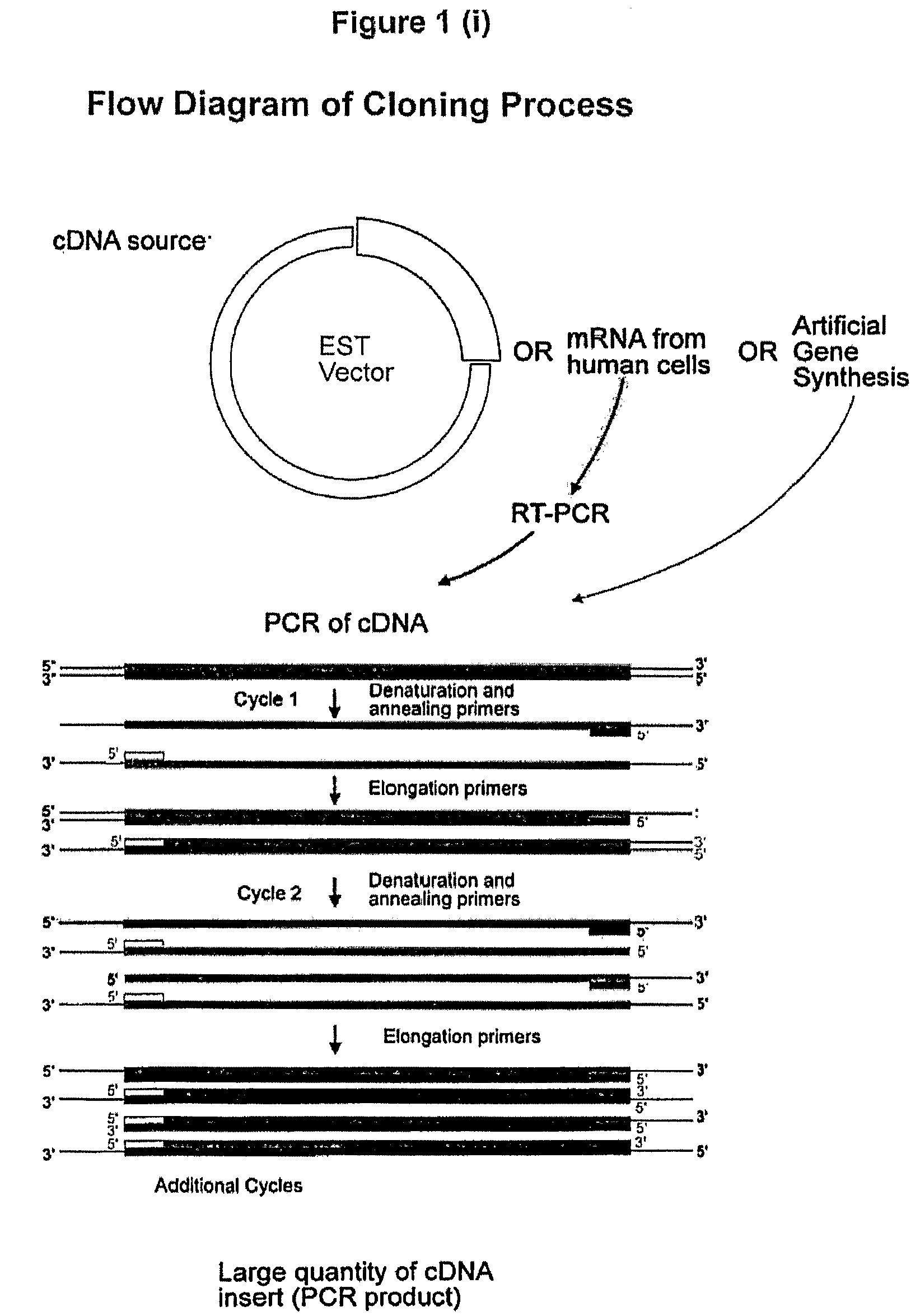
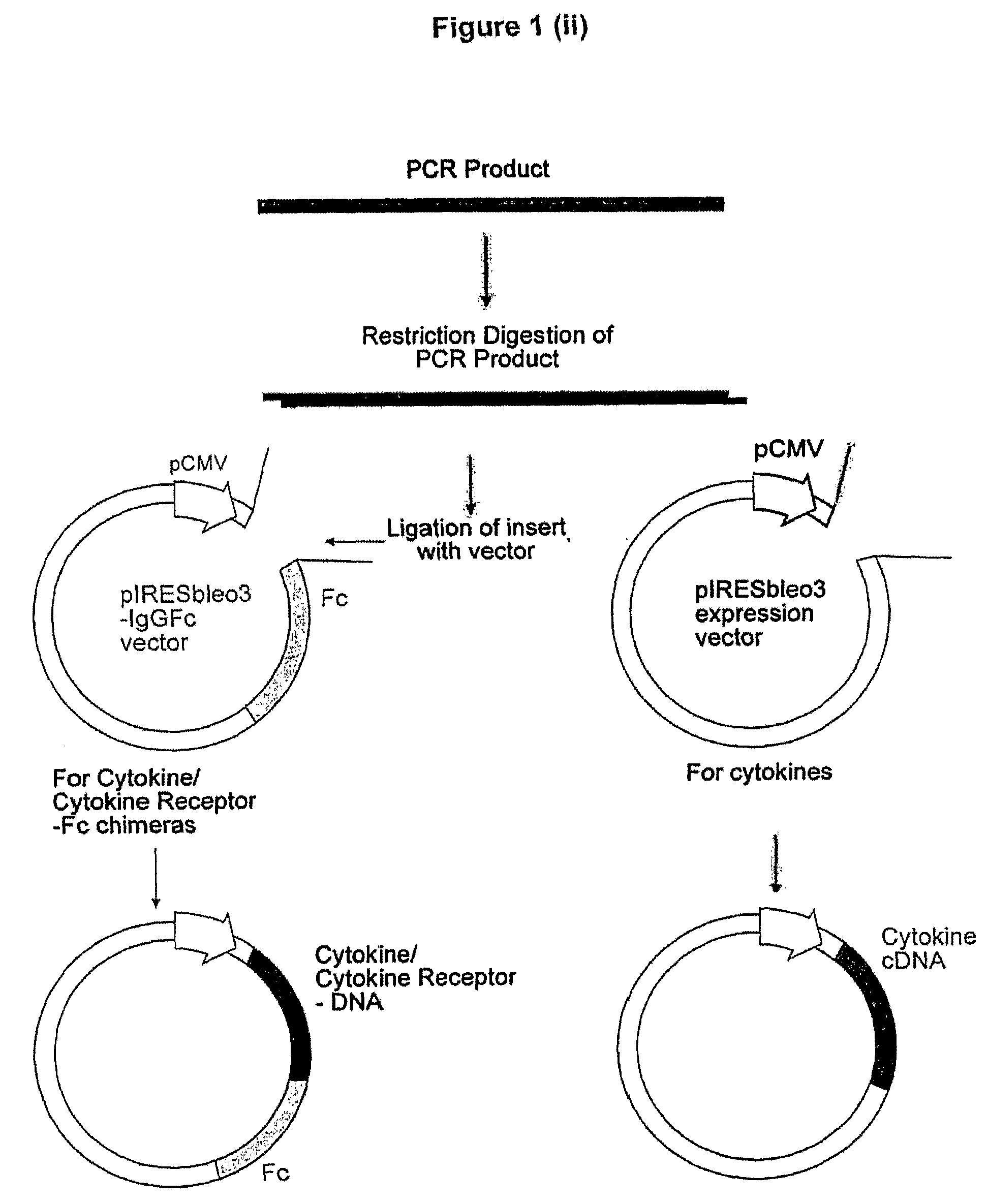
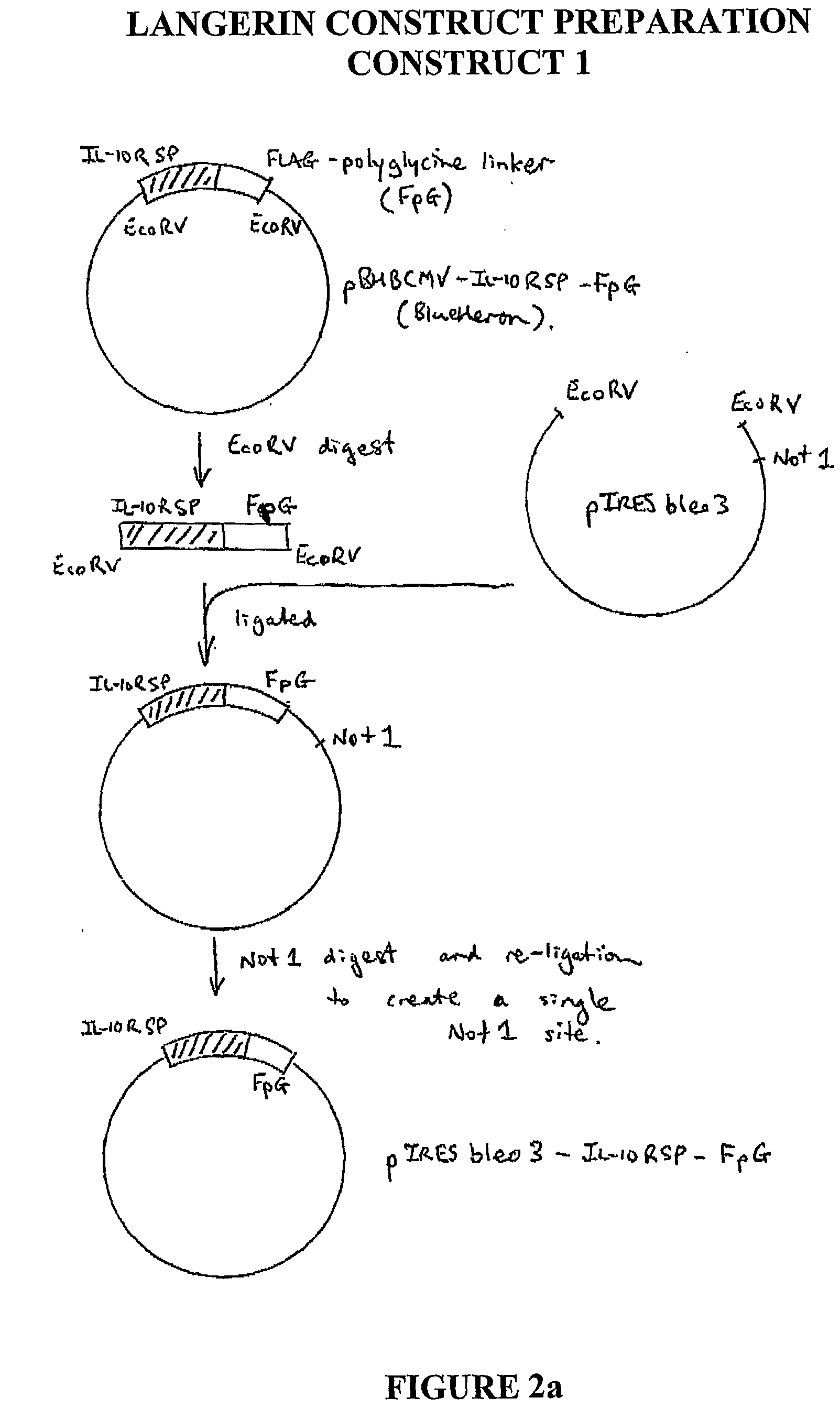
The present invention relates generally to the fields of proteins, diagnostics, therapeutics and nutrition. More particularly, the present invention provides an isolated protein molecule which comprises a C-type lectin or an EGF-like domain such as amphiregulin, CD209L, Langerin, L-selectin or chimeric molecules thereof comprising at least a portion of the protein molecule, such as amphiregulin-Fc, CD209L-Fc, Langerin S, Langerin L, Langerin L-FLAG, Langerin-Fc, L-selectin-Fc wherein the protein or chimeric molecule thereof has a profile of measurable physiochemical parameters, wherein the profile is indicative of, associated with or forms the basis of one or more pharmacological traits. The present invention further contemplates the use of the isolated protein or chimeric molecule thereof in a range of diagnostic, prophylactic, therapeutic, nutritional and / or research applications.
Owner:APOLLO LIFE SCI
Immune modulation via C-type lectin
The invention relates to the regulation of the immune system, and in particular to the finding that the CLEC9a molecule is a marker for dendritic cells which are capable of cross-presenting extracellular antigens via the MHC class I pathway. This makes them particularly suitable for generation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. Materials and methods are provided both for the induction of immune responses against target antigens, and for the inhibition or suppression of undesirable immune responses in which these cells are involved.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
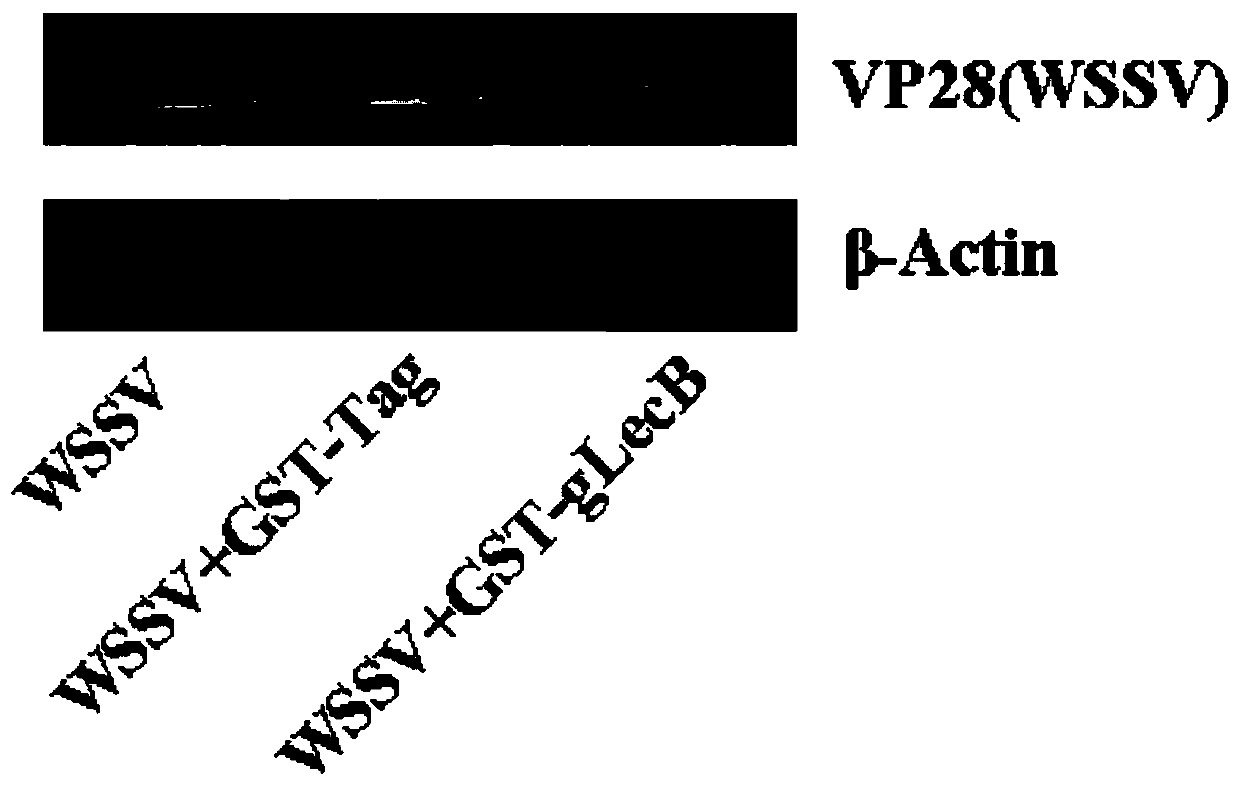
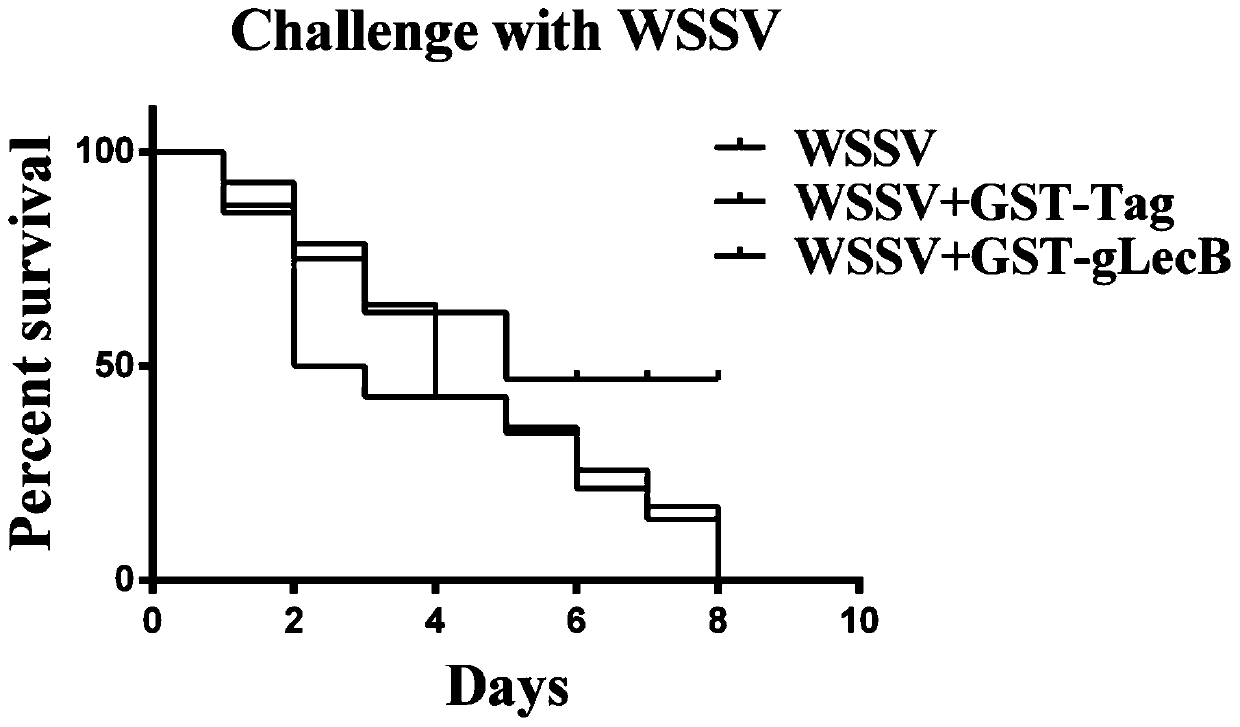
Procambarus clarkii C-type lectin gLecB gene and encoded gLecB protein thereof
InactiveCN110041421ALevel of inhibition of replicationAntiviralsPeptide preparation methodsProcambarus clarkiiGenetic engineering
The present invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and discloses a procambarus clarkii C-type lectin gLecB gene and an encoded gLecB protein thereof. A sequence of the procambarus clarkii C-type lectin gLecB gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1; an amino acid sequence of the gLecB protein is shown in SEQ ID NO:2; and an expression vector is pGEX-5X-1-B-Lectin. The new C-type lectin gLecB is isolated from procambarus clarkii and has an antiviral effect.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
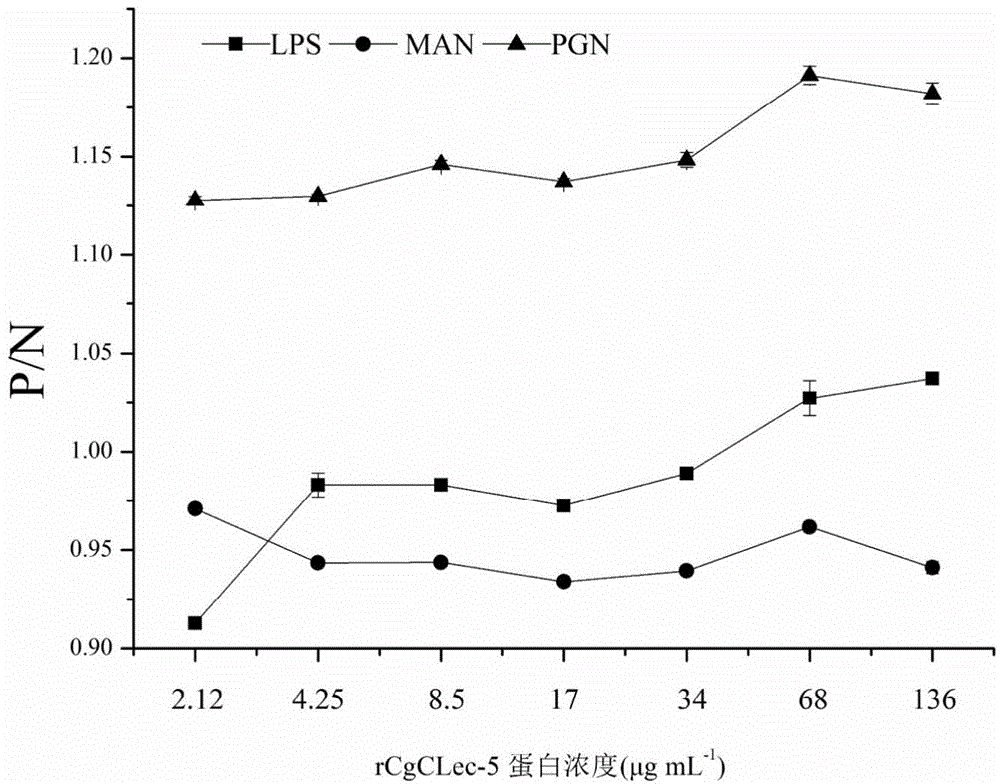
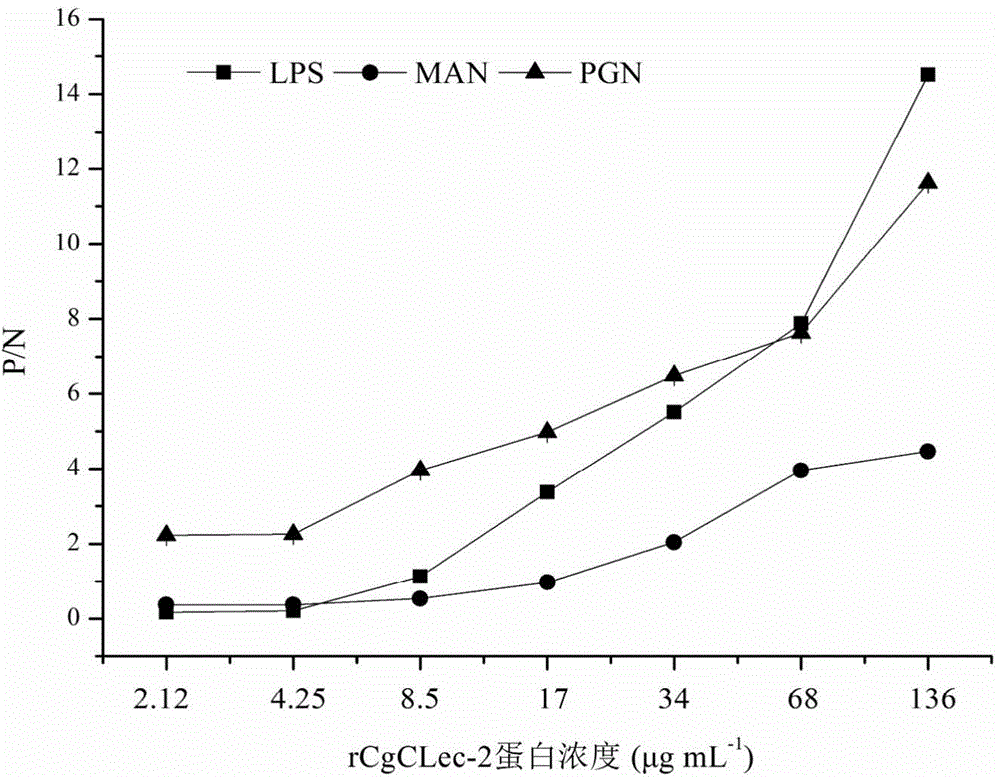
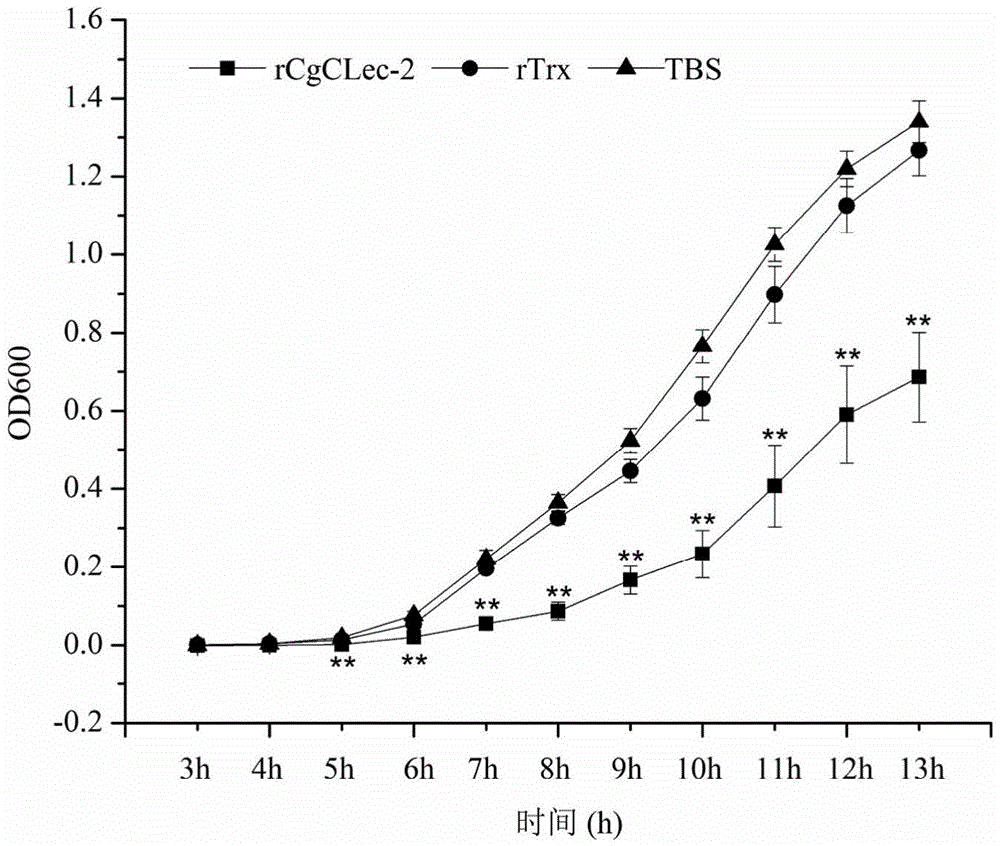
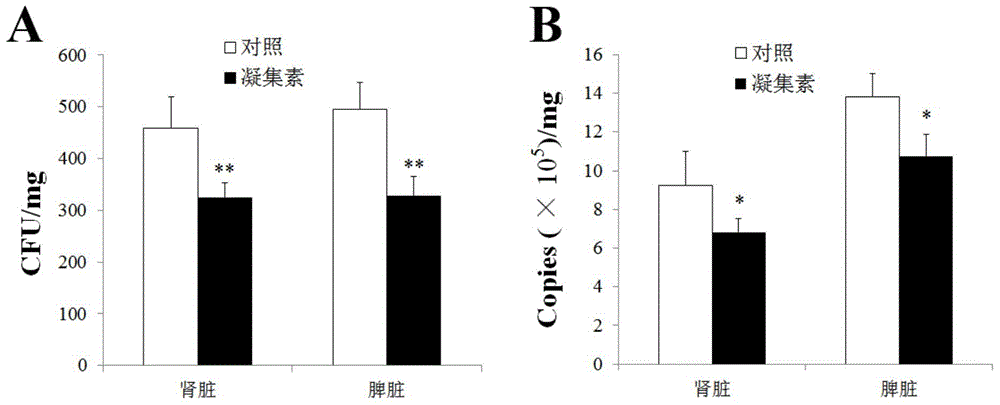
Application of Pacific oyster C-type lectin-2(CgCLec-2) recombinant protein with antibacterial activity
InactiveCN104474557AAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyStaphylococcus aureus
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of C-type lectin
InactiveCN104623631AImprove infection abilityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesViral infection
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and particularly relates to application of C-type lectin. The C-type lectin is used for preparing inhibitors for inhibiting bacterial and viral infection. The recombinant C-type lectin is used for preparing preparations for inhibiting bacterial and viral infection of fishes and is capable of enhancing the bacterium and virus resistance of fishes significantly.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
C-type lectin PtCLec1 gene of portunus trituberculatus and encoded protein and application thereof
ActiveCN110343703AGood effectEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPichia pastorisAgglutination
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and particularly relates to a C-type lectin PtCLec1 gene of portunus trituberculatus and an encoded protein and application thereof.Through unigene obtained by transcriptome sequencing and the RAC technology, amplification is conducted in the portunus trituberculatus to obtain PtCLec1 gene cDNA, and the recombinant protein PtCLec1has obvious bacteriostasis, bacterium binding and bacterium agglutination activity. The recombinant protein PtCLec1 has an obvious inhibition effect on gram negative bacteria and gram-positive bacteria. The recombinant protein PtCLec1 has obvious binding activity to vibrio alginolyticus, vibrio parahaemolyticus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, micrococcus luteus and pichia pastoris. In the presence of Ca<2+>, the recombinant protein PtCLec1 has an obvious agglutination effect on vibrio alginolyticus, vibrio parahaemolyticus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcus aureus, micrococcus luteus and pichiapastoris.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Deep sea shrimp C-type lectin and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, and concretely relates to a deep sea shrimp C-type lectin and an application thereof. The deep sea shrimp C-type lectin is amino acids in a sequence table represented by SEQ ID No.1. The agglutinin can be applied to the production of a bacterium agglutination preparation. The agglutinin is a recombinant protein expressed by agglutinin in Escherichia coli. The recombinant agglutinin is used for combining and agglutinating pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant expression method of insect C-type lectin and use
InactiveCN101434955AReduce fatalityReduce the number of survivorsPeptide/protein ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffVital activityEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and provides a biological medicament that has recombinant gene expression of helicoverpa armigera C-type lectin and two carbohydrate recognizing structural domains of Ha-CRD1 and Ha-CRD2 of the gene. The helicoverpa armigera C-type lectin gene and the two carbohydrate recognizing structural domains of Ha-CRD1 and Ha-CRD2 of the gene have recombinant expression in Escherichia coli. The invention further provides a recombinant gene expression method of the helicoverpa armigera C-type lectin and the two carbohydrate recognizing structural domains of Ha-CRD1 and Ha-CRD2 of the gene. The lectin can reduce the insect fatal rate of pathogenic organisms, improve the pathogenic organism phagocytizing efficiency of blood corpuscle, and reduce the survival number of pathogenic organisms in insect bodies. The biological medicament does not generate drug-fast bacteria, does not have adverse effect to the normal vital activity of insects, can reduce the usage of antibiotic, and can reduce the drug-fast bacteria generation in environments.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Portunus trituberculatus C-type lectin PtCLec2 gene and encoded protein thereof and application of encoded protein
ActiveCN110317813ACohesive activityGood effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAgglutinationPortunus trituberculatus
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and particularly discloses a portunus trituberculatus C-type lectin PtCLec2 gene and an encoded protein thereof and application of the encoded protein. A RACE technology and a unigene obtained by adopting transcriptome sequencing are adopted to acquire cDNA of the PtCLec2 gene from portunus trituberculatus through amplification, and it is found that a recombinant PtCLec2 gene has significant activity of bacterium inhibition, somatic agglutination and bacterium removal. The recombinant PtCLec2 gene has significant inhibiting effects on Gram-negative bacteria (vibrio alginolyticus and pseudomonas aeruginosa) and Gram-positive bacteria (staphylococcus aureus and micrococcus luteus). In the presence of Ca<2+>, the recombinant PtCLec2 gene has significant agglutination effects on vibrio alginolyticus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcus aureus and micrococcus luteus. Meanwhile, the recombinant PtCLec2 gene has a removal effect on vibrio alginolyticus.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method and application of HLA-A0201-restrictive anti-Sox2 specific CTL
InactiveCN105031631AEffective targeted killingIt has the nature of "curing the root cause"Blood/immune system cellsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDendritic cellSOX2
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and particularly relates to a preparation method and an application of HLA-A0201-restrictive anti-Sox2 specific CTL. In the preparation method, with a cationic liposome of a C-typed agglutinin receptor on a targeted dendritic cell as an antigen supporter, a tumor stem cell antigen Sox2 is coated. The dendritic cell is quickly matured in 72 h and meanwhile positive antigen intake efficiency and MHC-I approach antigen presentation efficiency of the dendritic cell are improved. The method, compared with a conventional method in which the matured dentritic cells are obtained in 7-8 days, is greatly reduced in best therapeutic time window of tumor patients, so that the method is beneficial to generation of the signal-inductive antigen-specific CTL by stimulating initial T cells with abundant matured dendritic cells. With combination of engineering cells and cell factors, the antigen-specific T cells and Tcm are amplified in a large scale, thereby producing the Tcm being stronger in killing capability and being higher in ratio and further improving the anti-tumor immunity effect. The method can be used for quickly and effectively preparing the tumor stem cell antigen-specific CTL and has great economic value and market prospect.
Owner:深圳市中美康士生物科技有限公司
Identification of therapeutic agents for HIV infection
InactiveUS20100061991A1Prone to infectionEfficient transferOrganic active ingredientsCompound screeningImmature MonocyteDENDRITIC CELL IMMUNORECEPTOR
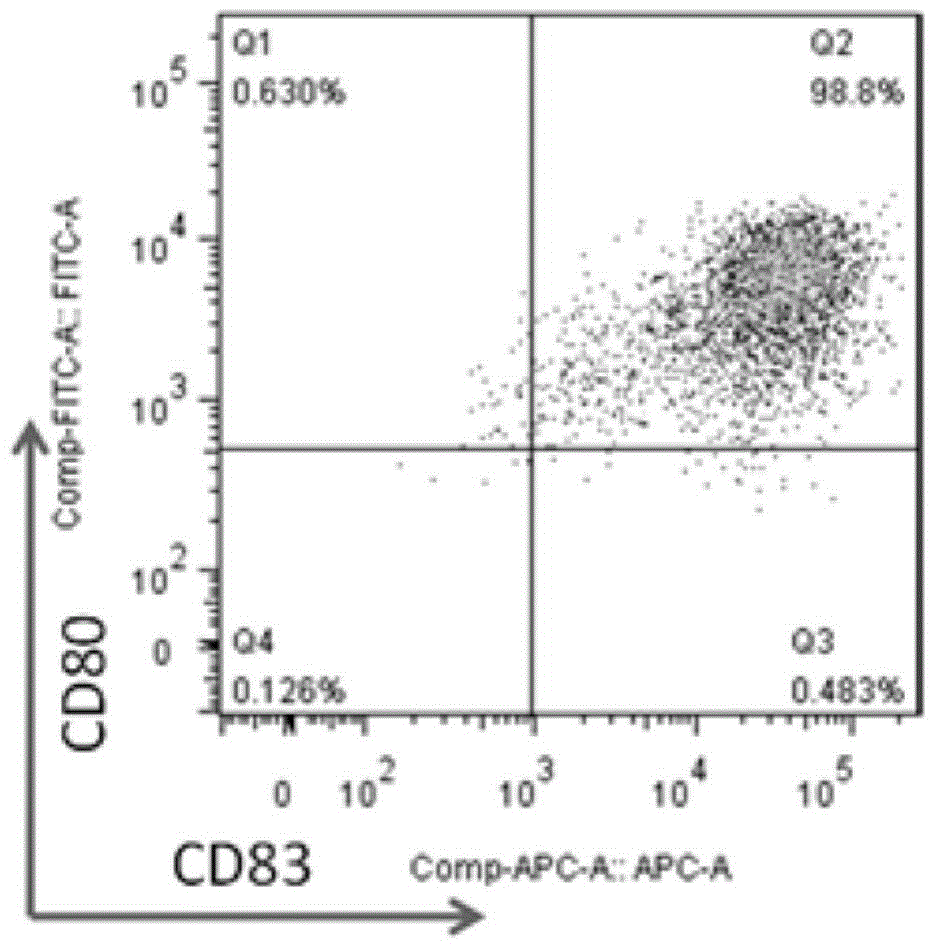
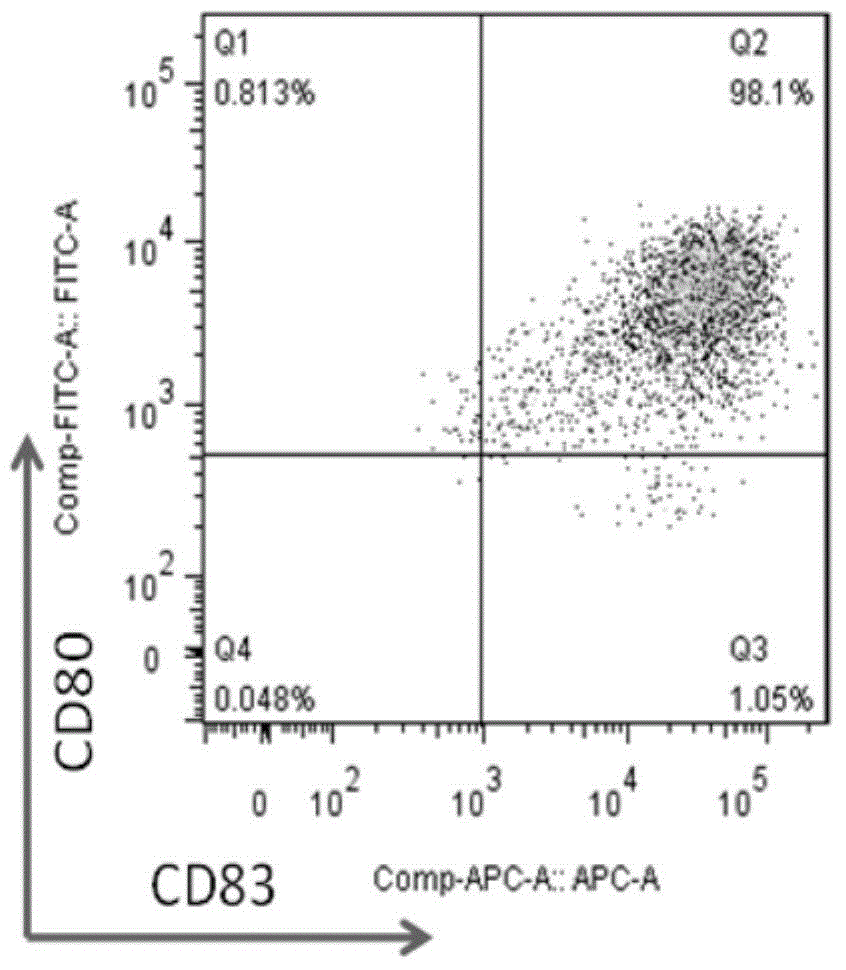
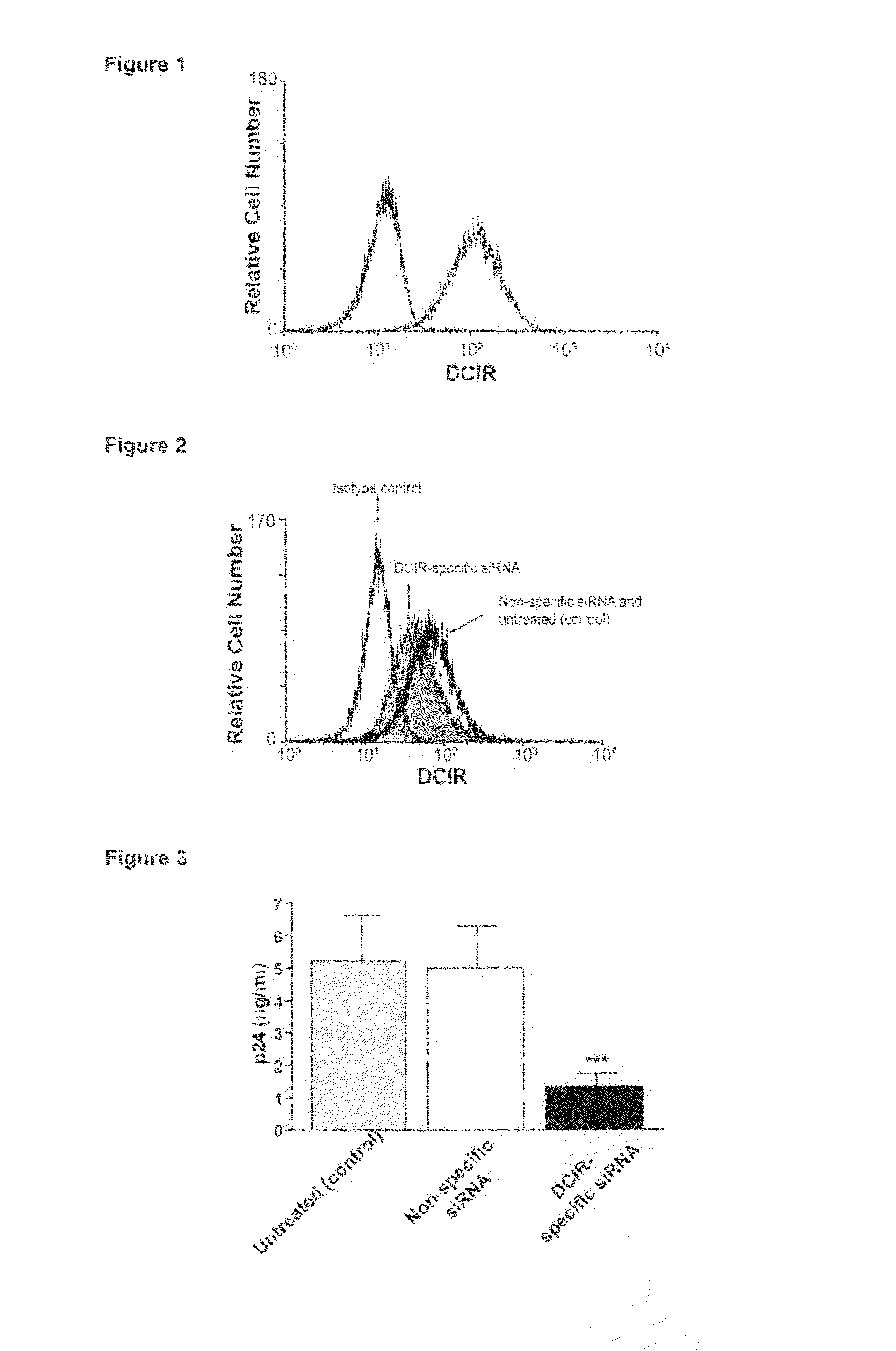
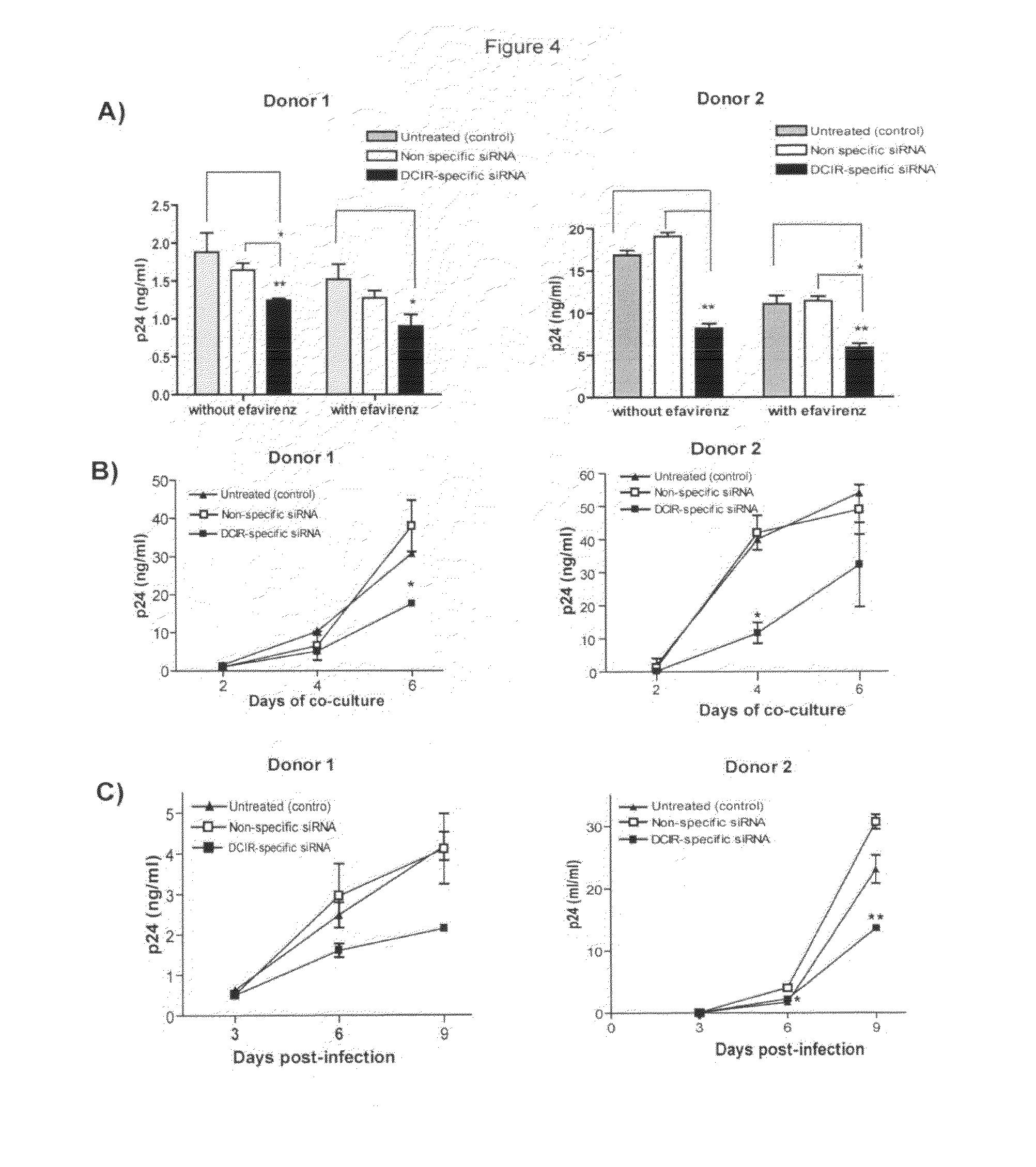
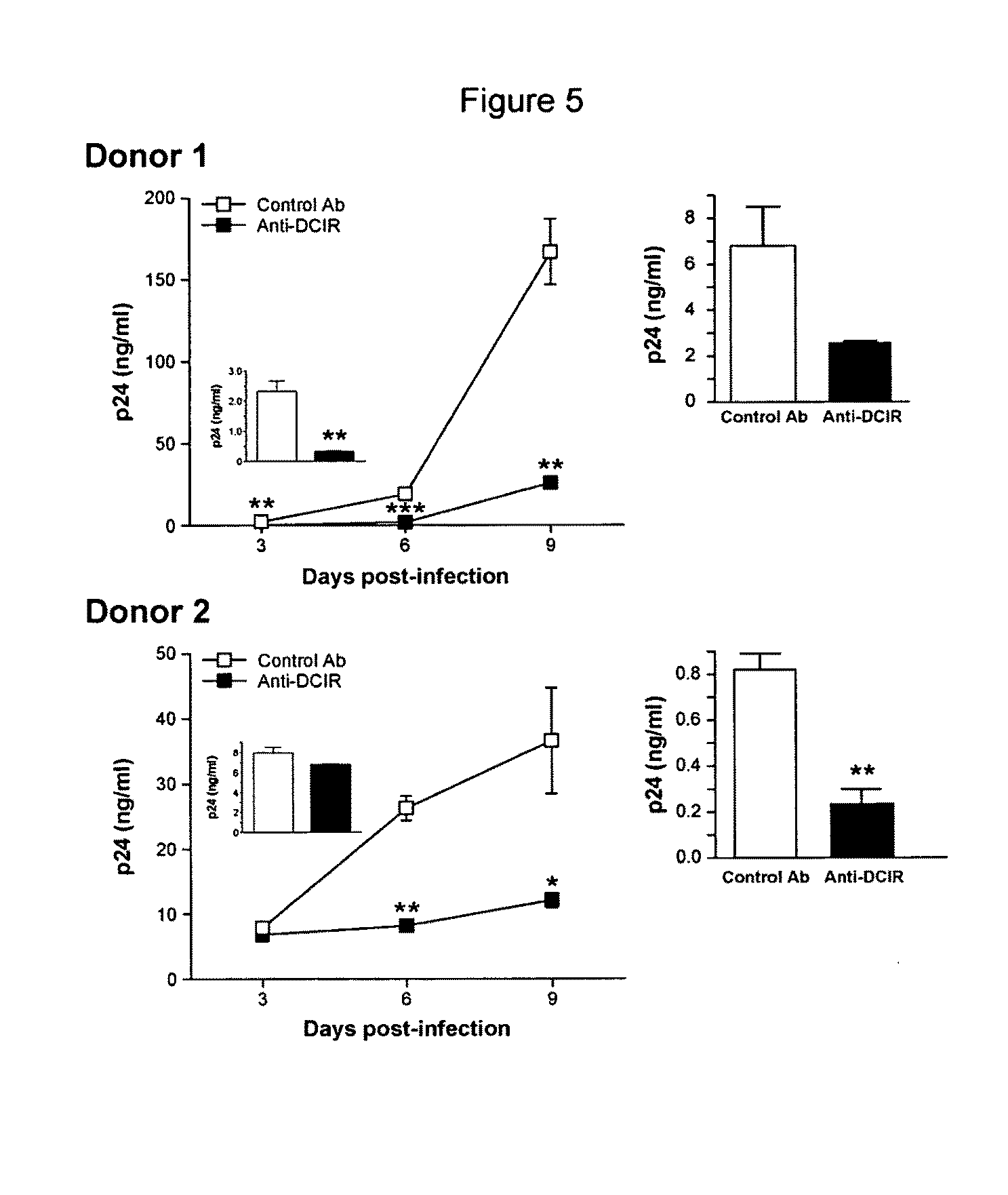
A cell surface molecule designated DCIR (for dendritic cells ImmunoReceptor), a member of a recently described family of DC-expressing C-type lectin receptors, has been shown to participate to the capture of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and promote infection in trans and in cis of autologous CD4(+) T cells from human immature monocyte-derived DC. The contribution of DCIR to these processes was revealed using DCIR-specific siRNAs and a polyclonal antibody specific for the carbohydrate recognition domain of DCIR. Therapeutic agents for HIV infection are therefore provided herein. These therapeutic agents are useful for impairing the interaction between DCIR and HIV and as such may be useful for treatment or prevention of HIV infection. Also provided are assays for identifying additional therapeutics agents for treatment or prevention HIV infection.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
L-type lectin of litopenaeus vannamei as well as coding gene and application of L-type lectin
The invention discloses an L-type lectin of litopenaeus vannamei as well as a coding gene and the application of the L-type lectin. According to the invention, an L-type lectin gene lecV of litopenaeus vannamei is cloned from gill tissues of litopenaeus vannamei and has a nucleotide sequence as shown by 18th-1007th bases of SEQ ID NO. 1; the L-type lectin lecV of litopenaeus vannamei has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The L-type lectin lecV of litopenaeus vannamei provided by the invention has functions of agglutinating bacteria and rapidly removing bacteria in shrimps, which indicates that the L-type lectin lecV of litopenaeus vannamei is involved in an immune regulation mechanism of shrimps, thereby promoting the research of immune regulation mechanism of the shrimps, providing a reliable genetic marker for breeding shrimp varieties with disease resistance and stress resistance, and also providing a novel target site for genetic improvement of the shrimps.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for increasing production of IFN-gamma in natural killer cells expressing LLT1 receptor
InactiveUS7524622B2Reducing natural killer cell mediated rejectionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsADAMTS Proteins
Natural killer (NK) cells possess the inherent capacity to kill various tumor and virally infected cells. A large family of NK cell receptors belongs to the C-type lectin super-family. Genes in the NK gene complex encode type II receptors and examples include the families of NKR-P1, Ly-49, and NKG2 receptors. Examples of other C-type lectin-like receptors that occur as individual genes are CD94, CD69 and AICL. The invention includes a cDNA that encodes a predicted protein of 191 amino acid residues having similarity to the carbohydrate recognition domain of C-type lectins. The predicted protein of LLT1 shows 59 and 56% similarity to AICL and CD69, respectively. A monoclonal antibody (L9.7) against LLT1 receptor was generated. Binding of mAb L9.7 to surface LLT1 induced interferon gamma production in YT, a human NK cell line, as well as in resting and IL-2 activated NK cells, without modulating cytotoxicity.
Owner:UNIV OF NORTH TEXAS HEALTH SCI CENT
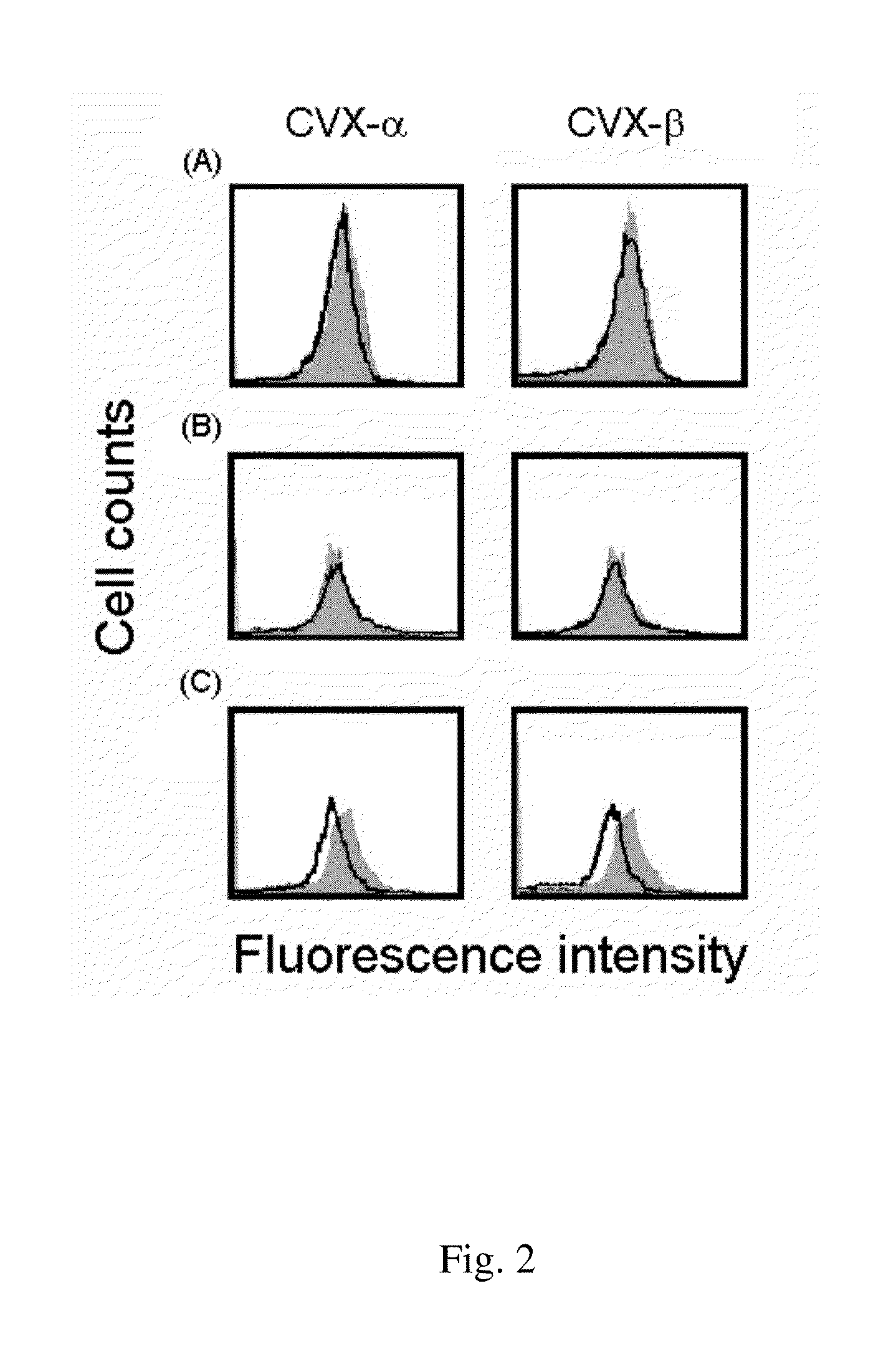
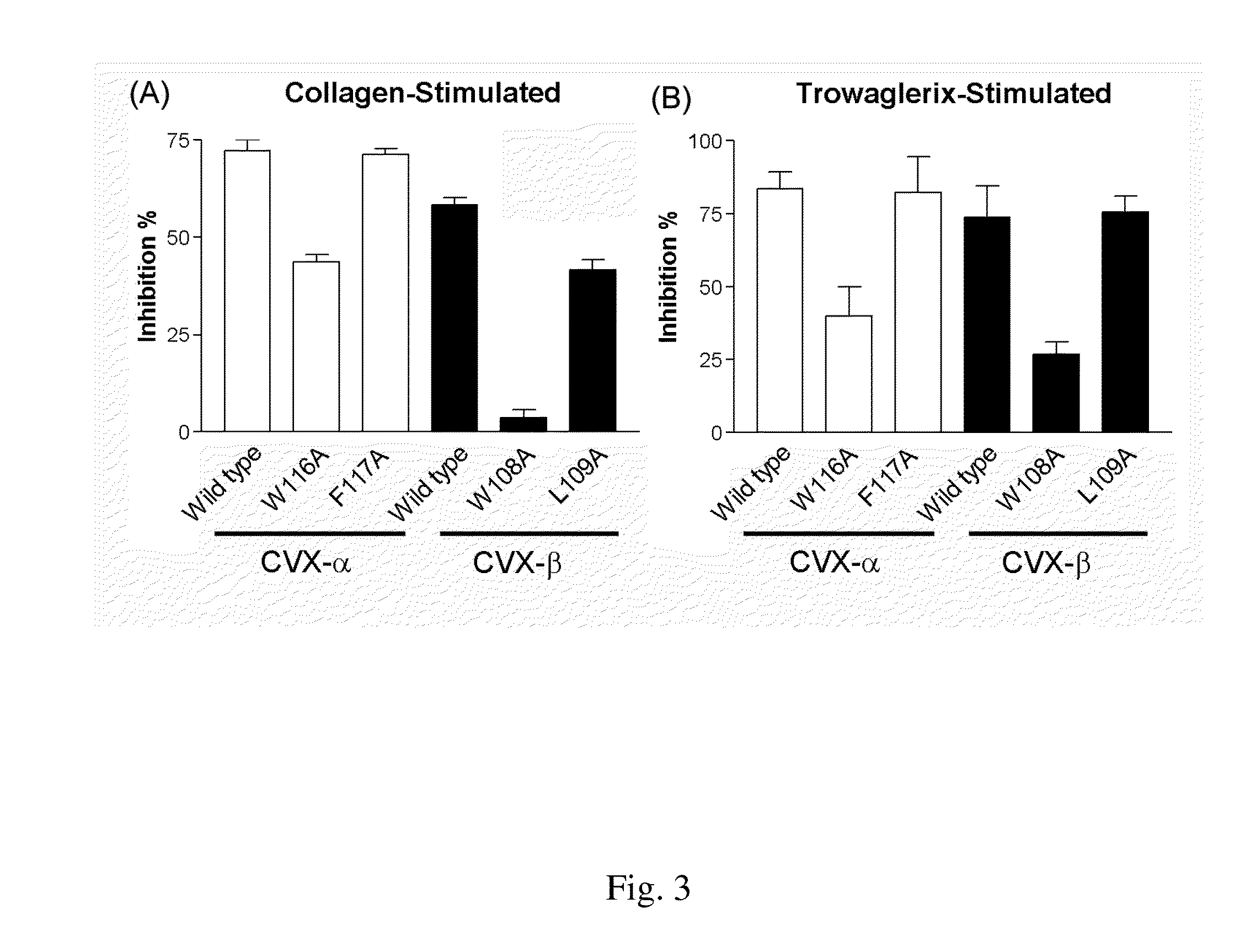
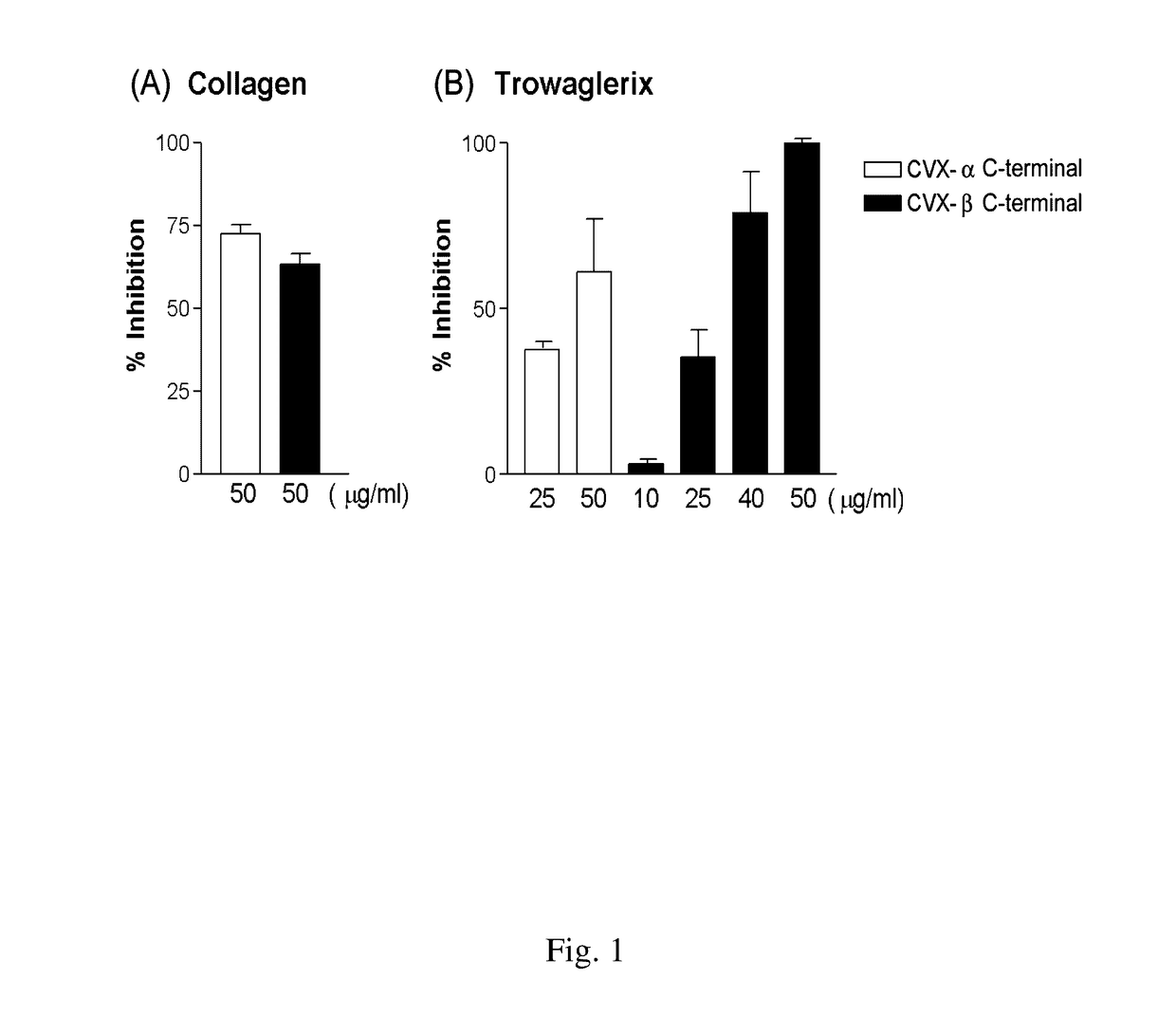
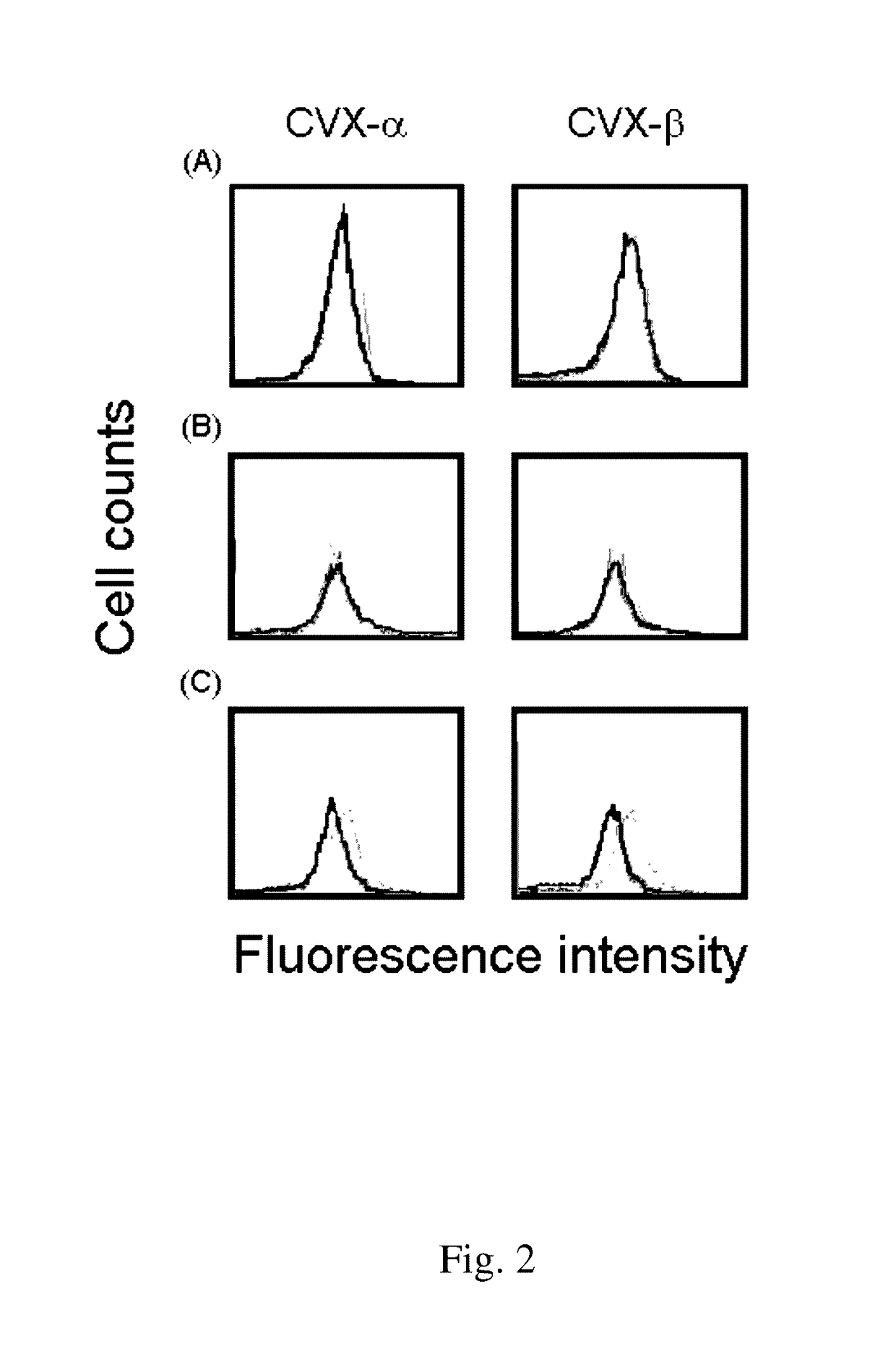
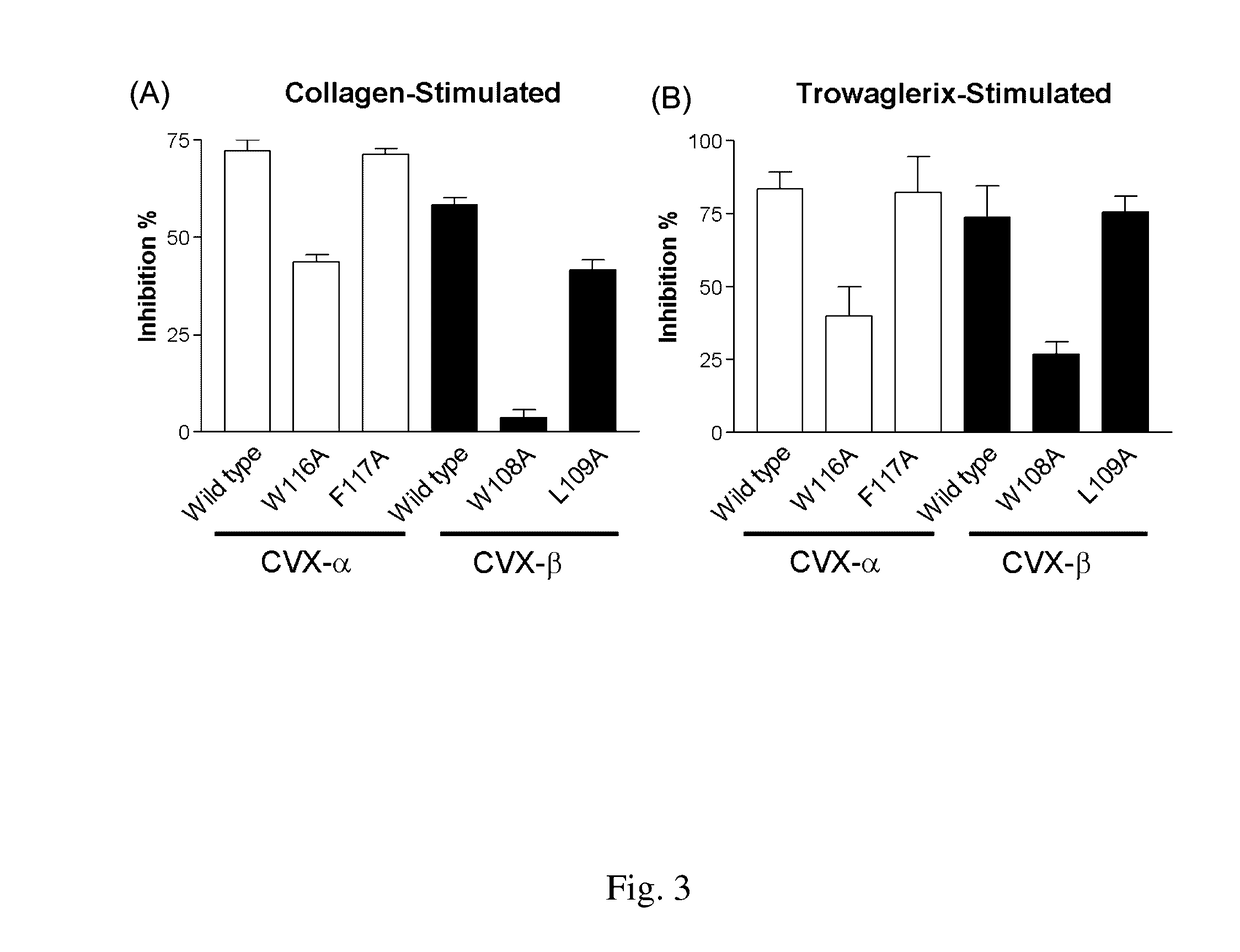
Peptide compounds for inhibition of platelet aggregation
ActiveUS20140363423A1Inhibits platelet aggregationCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseMedicine
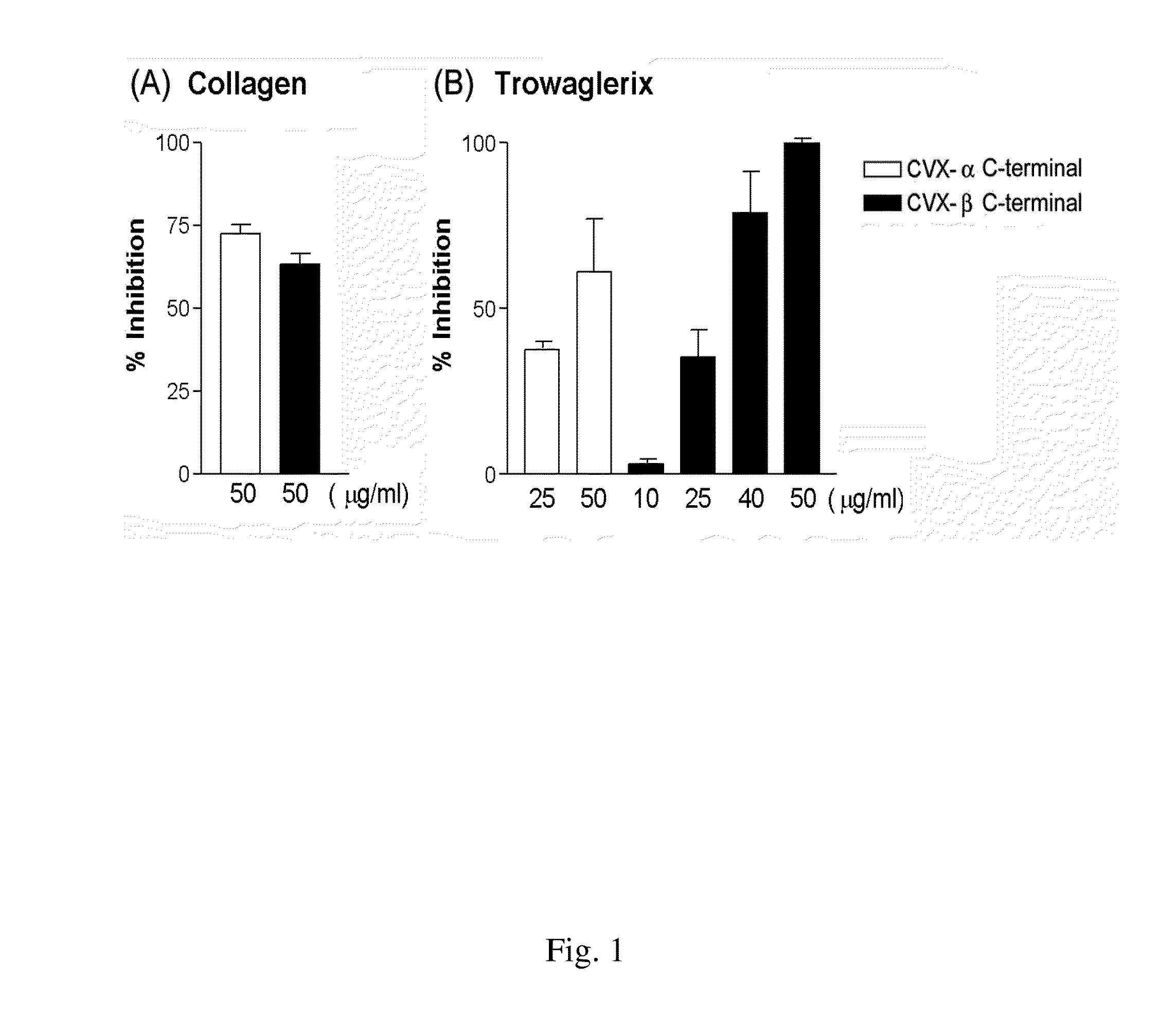
The invention relates to a peptide compound and its pharmaceutical composition for inhibiting platelet aggregation and preventing / treating thrombogenic diseases. The invention develops pentapeptides and hexapeptides derived from snake venom C-type lectin-like proteins (CLPs) fragments, which can inhibit platelet aggregation and have antithrombotic activity without hemorrhagic tendency. Accordingly, they can be used as potential agents for the prevention and therapy of thrombogenic diseases.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
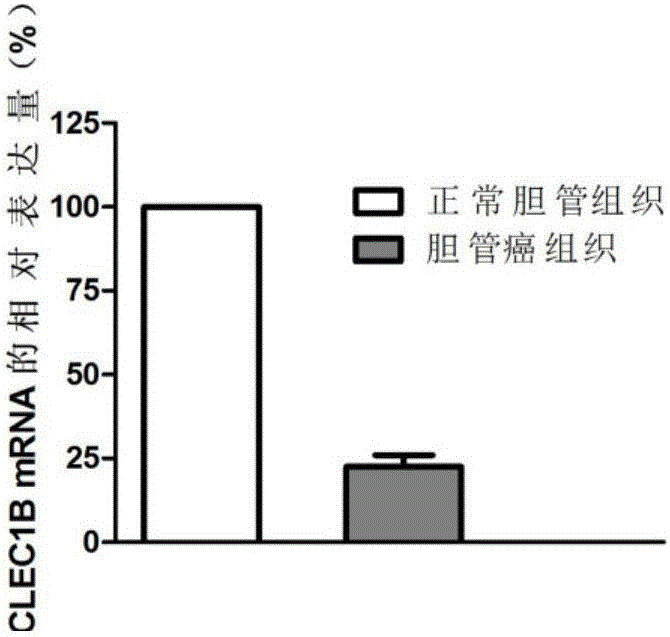
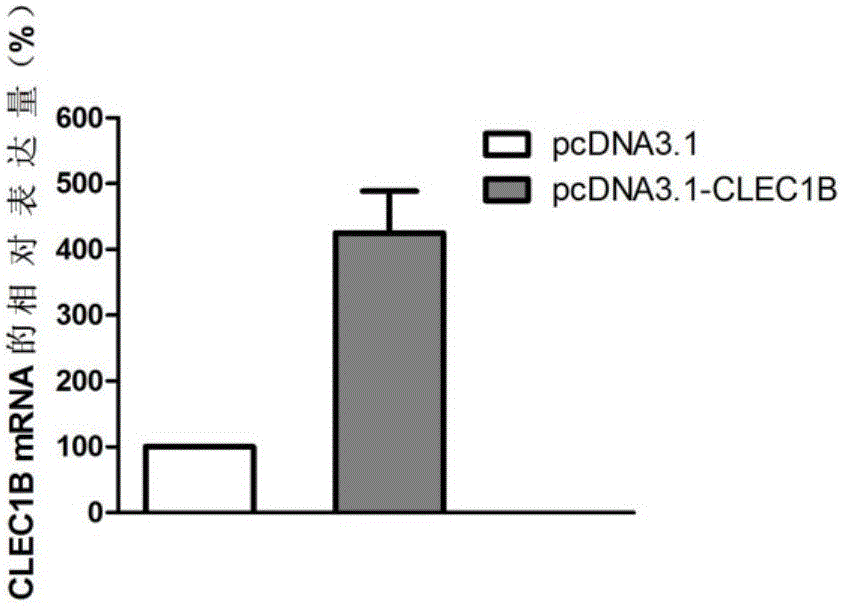
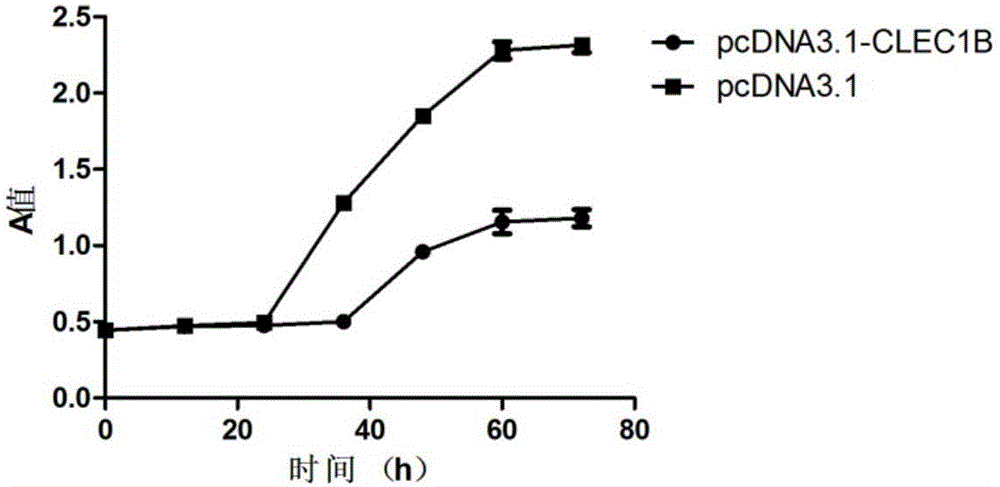
Application of CLEC1B (C-type lectin domain family 1 member B) genes on diagnosis and treatment of bile duct carcinoma
ActiveCN105112554AAchieve early diagnosisReduce mortalityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementTrue positive rateDomain family
The invention discloses application of CLEC1B (C-type lectin domain family 1 member B) genes on diagnosis and treatment of bile duct carcinoma. RNA (ribonucleic acid)-sep screening is carried out, and a large sample RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) proves that CLEC1B gene expression abnormality is related to initiation and development of the bile duct carcinoma. According to a research result, CLEC1B can also be used for preparing medicines for treating the bile duct carcinoma. By the application of the CLEC1B genes on diagnosis and treatment of the bile duct carcinoma, sensitivity and specificity of diagnosis of the bile duct carcinoma are greatly improved, and a new target spot is provided for gene therapy of the bile duct carcinoma.
Owner:BEIJING MEDINTELL BIOMED CO LTD
Peptide compounds for inhibition of platelet aggregation
ActiveUS9617302B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineThrombus
The invention relates to a peptide compound and its pharmaceutical composition for inhibiting platelet aggregation and preventing / treating thrombogenic diseases. The invention develops pentapeptides and hexapeptides derived from snake venom C-type lectin-like proteins (CLPs) fragments, which can inhibit platelet aggregation and have antithrombotic activity without hemorrhagic tendency. Accordingly, they can be used as potential agents for the prevention and therapy of thrombogenic diseases.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
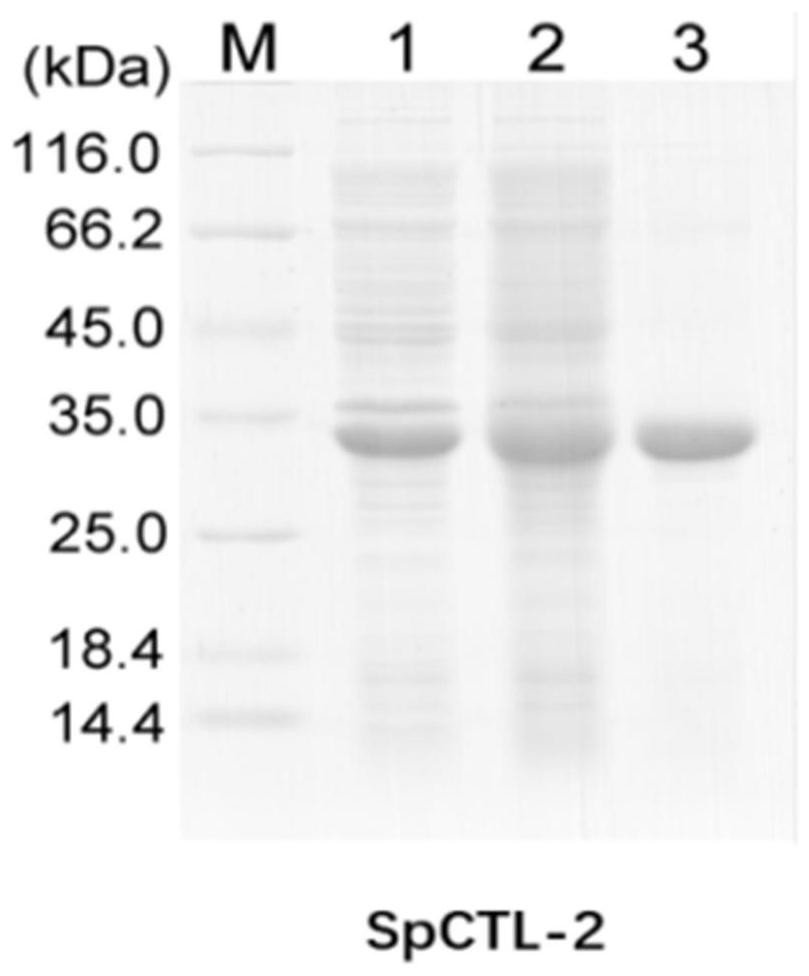
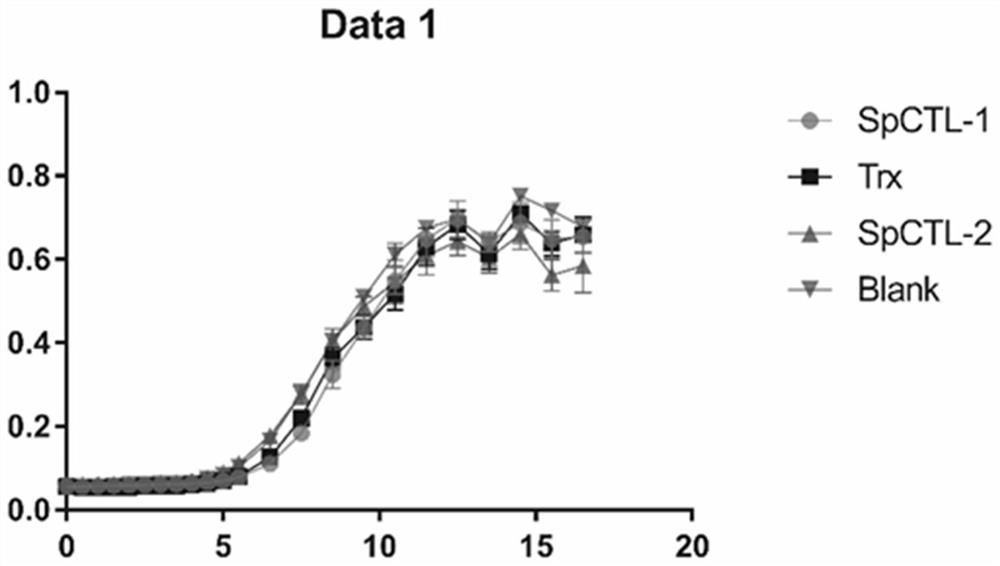
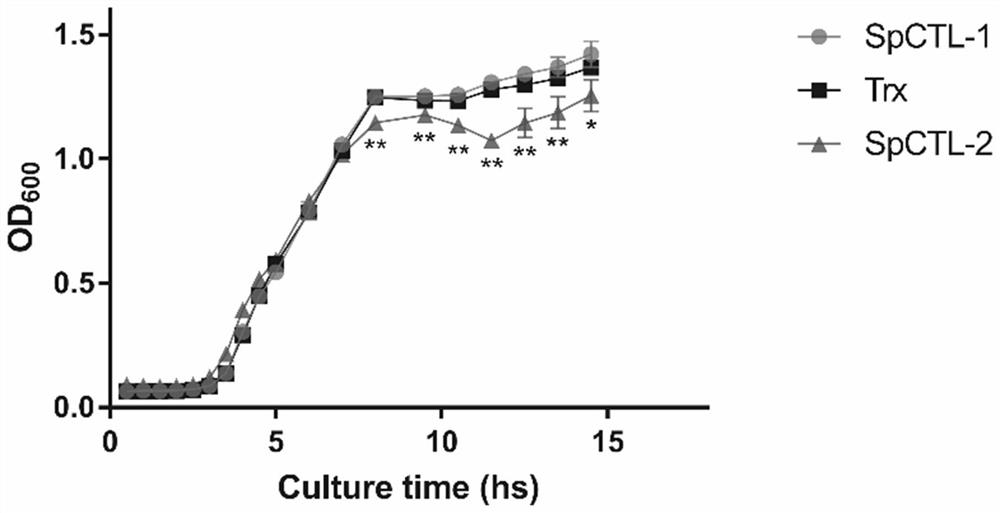
Scylla paramamosain C-type lectin as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113234132AGet stableGood antibacterial effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideScylla paramamosain
The invention discloses a scylla paramamosain C type lectin Spctl-2. The amino acid sequence of the scylla paramamosain C type lectin Spctl-2 is SEQ ID No: 1. The invention also discloses a gene for coding the scylla paramamosain C-type lectin Spctl-2. The nucleotide sequence of the antibacterial protein Spctl-2 gene is SEQ ID No: 2; the invention further discloses a recombinant antibacterial protein rSpctl-2 based on the C-type lectin Spctl-2, The invention also discloses an application of the recombinant antibacterial protein rSpctl-2 in preparation of medicines for preventing and controlling Vibrio fluvialis infection. The invention also discloses an application of the recombinant antibacterial protein rSpctl-2 in preparation of medicines for preventing and controlling micrococcus luteus. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the recombinant antibacterial protein rSpctl-2. The recombinant protein is produced by using escherichia coli, has the advantage of secretory expression, is easy to industrially produce and provides more choices for designing the dosage form of the immunopotentiator.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
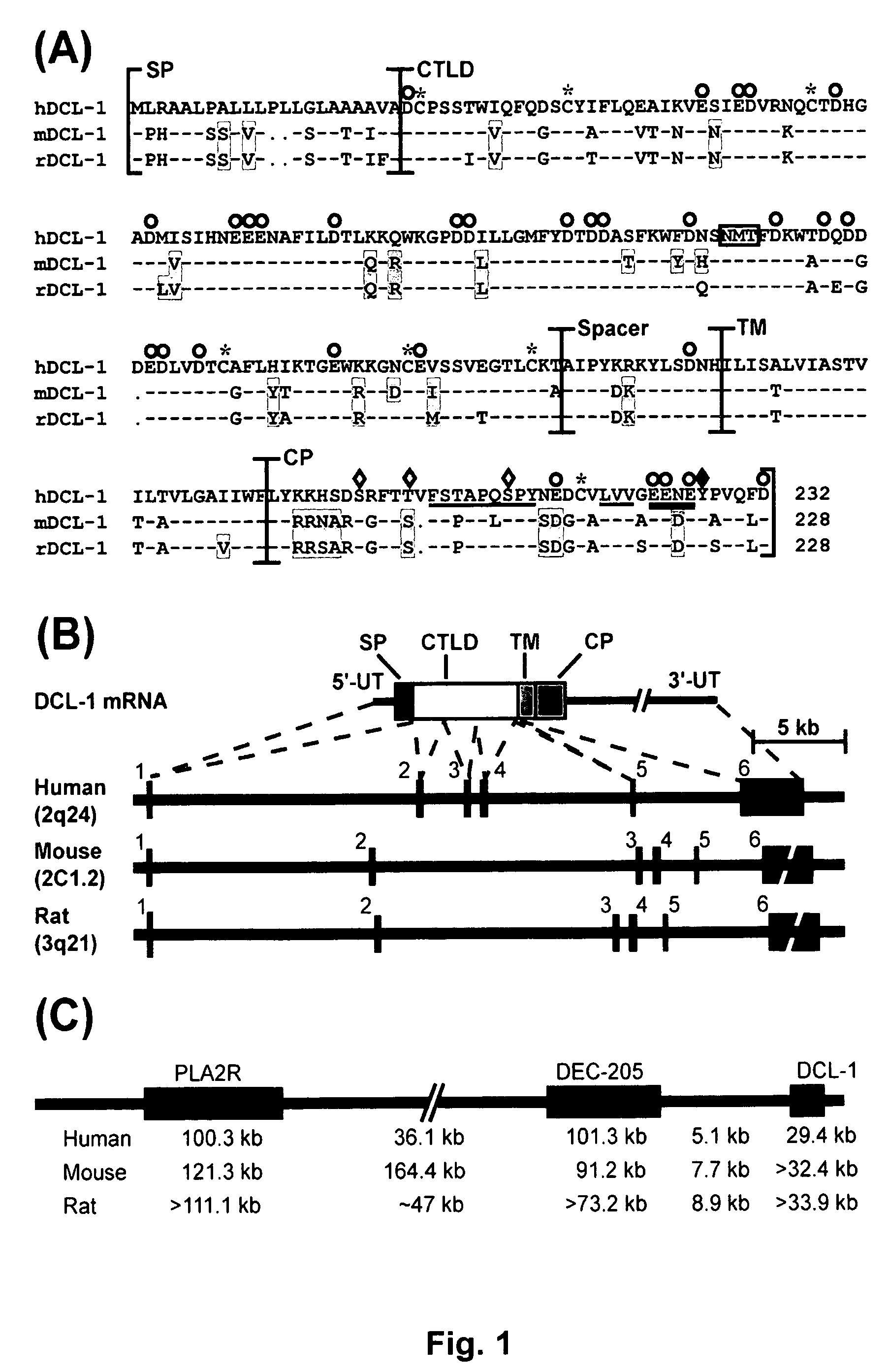
DCL-1 and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090130109A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDolichos biflorus lectinChemistry
The present invention relates generally to a novel lectin and to derivatives, homologues, analogues, chemical equivalents and mimetics thereof and, more particularly, to a novel type I C-type lectin, herein referred to as “DCL-1”. In particular, the present invention relates to the use of DCL-1 in therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic applications.
Owner:THE OF THE TRUSTEES OF THE SISTERS OF MERCY & QUEENSLAND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com