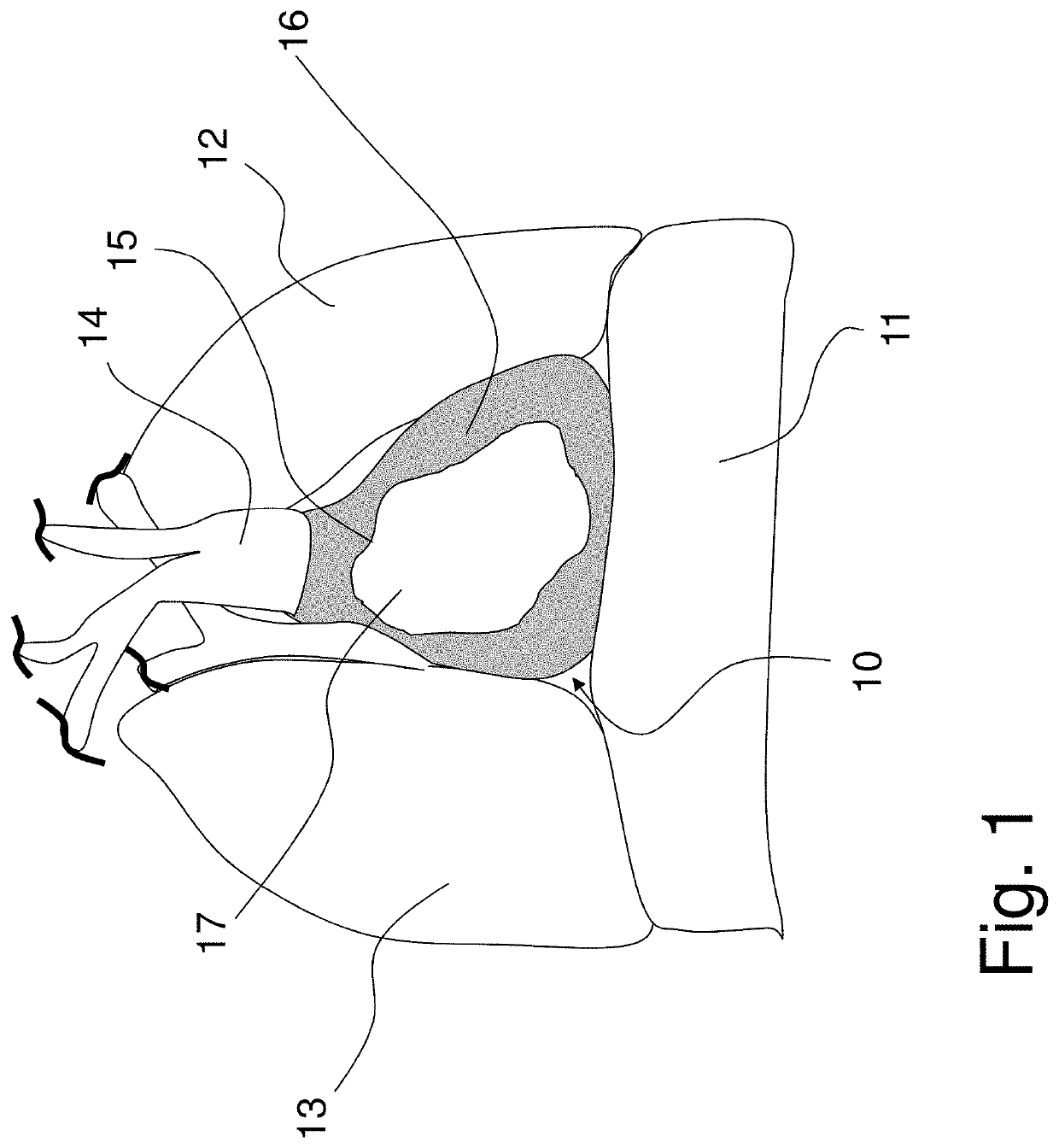
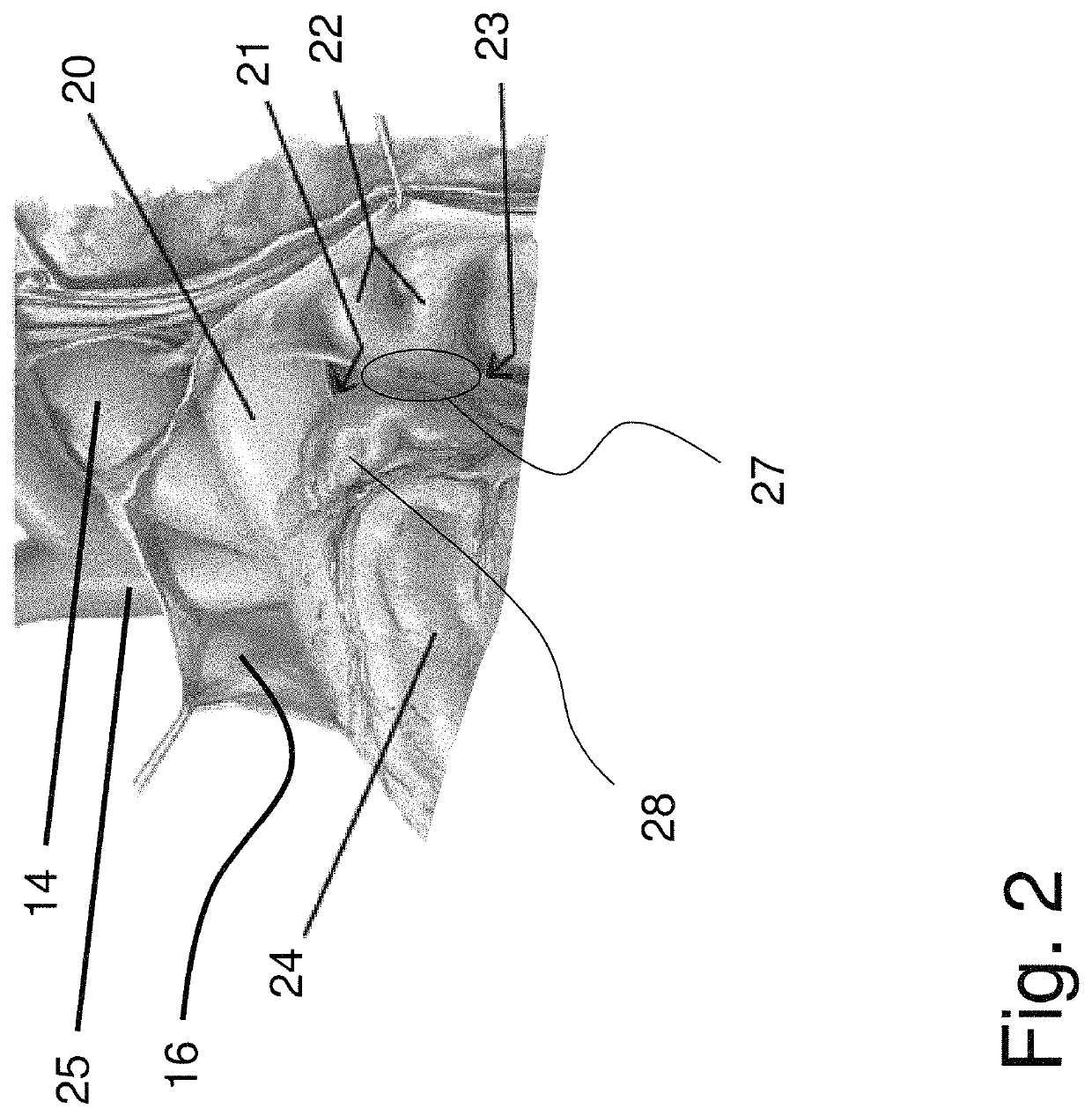
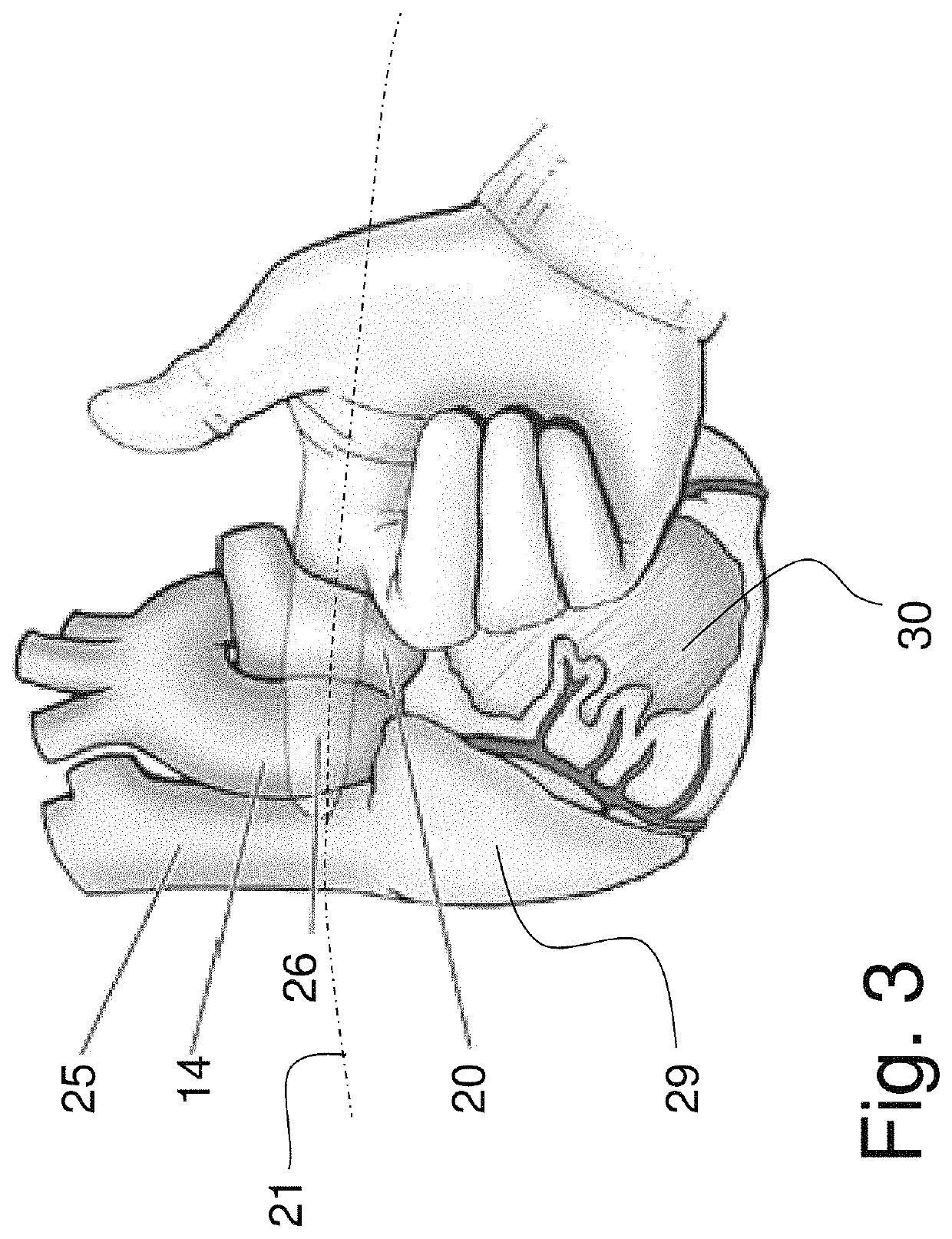
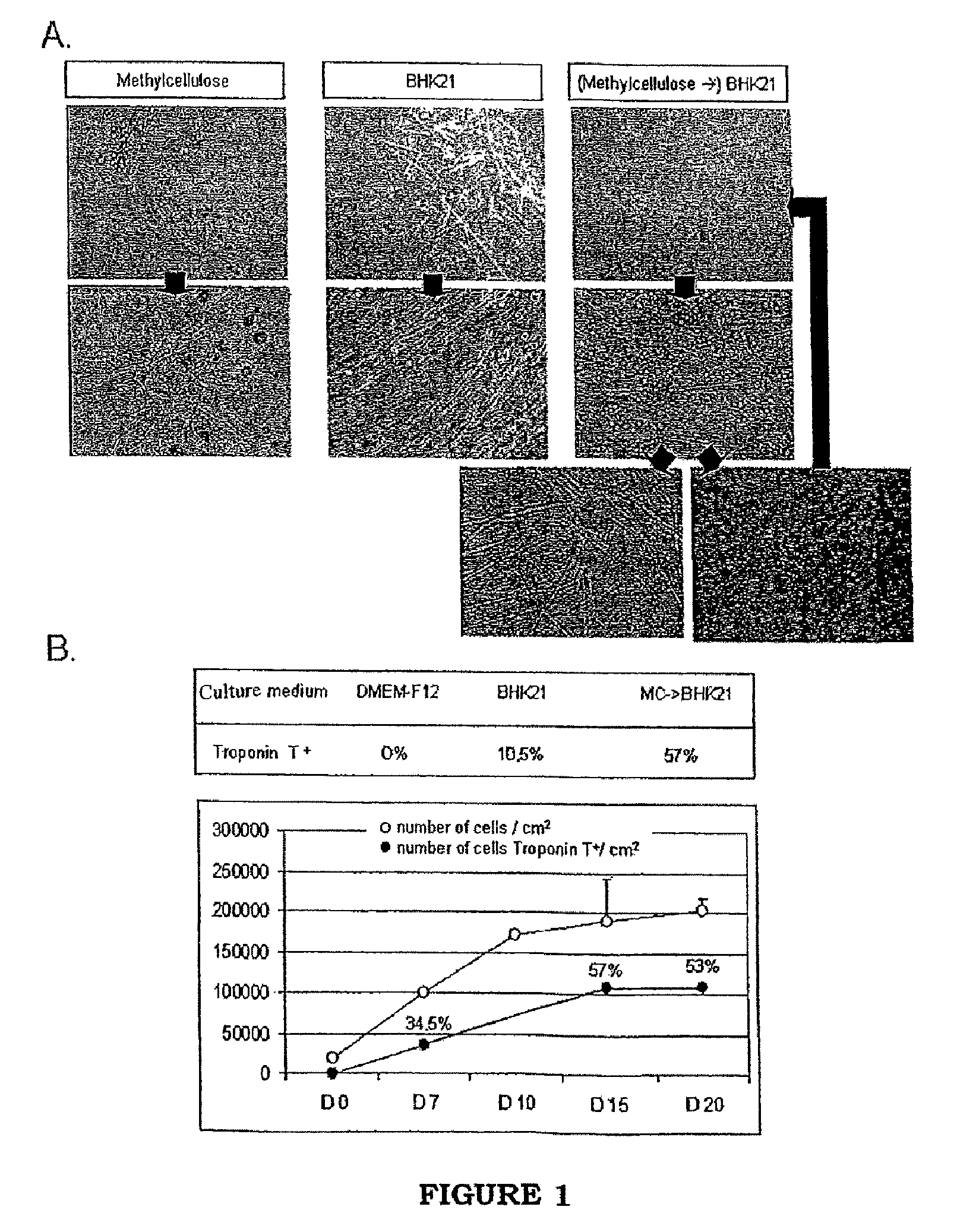
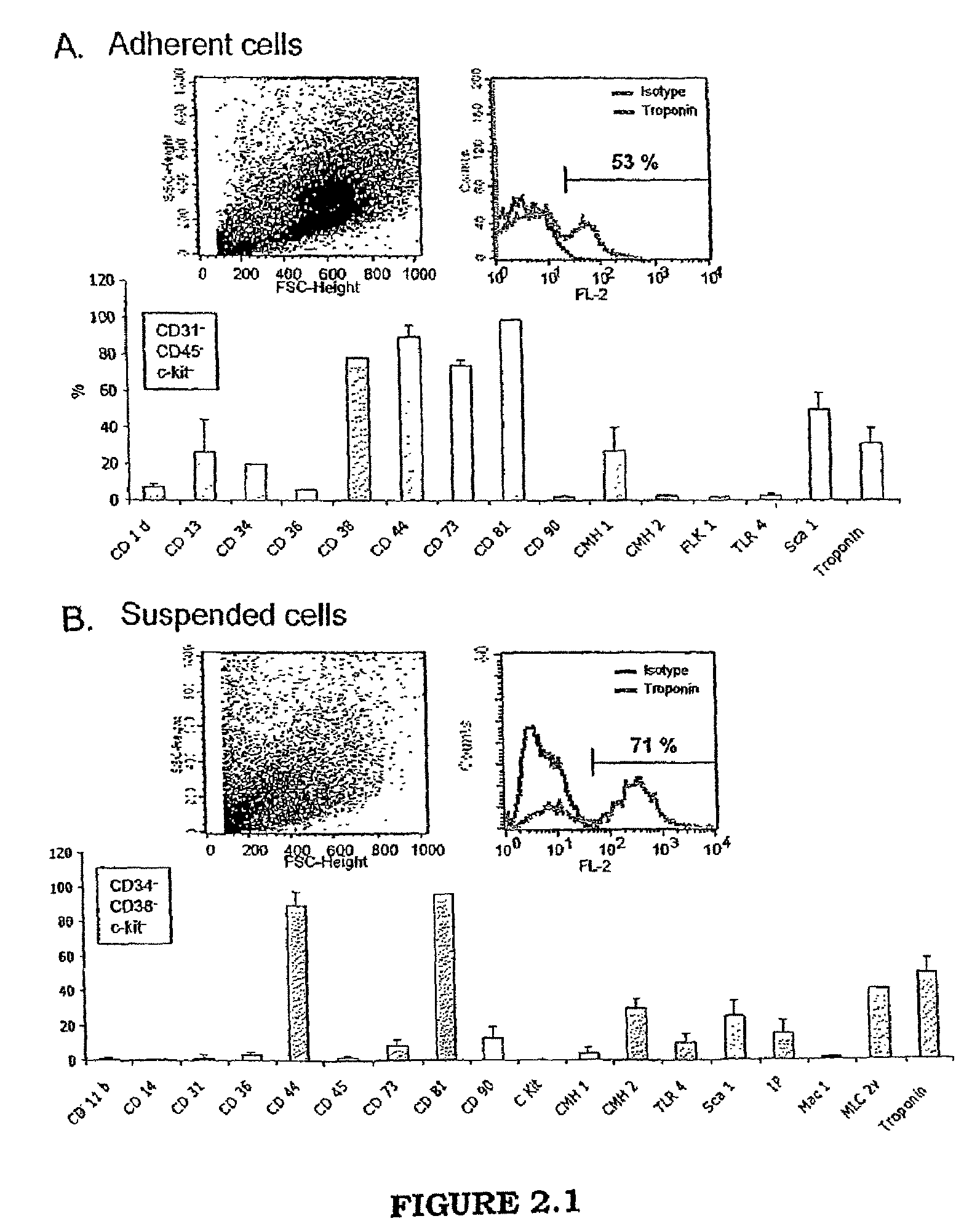
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Cardiac zone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
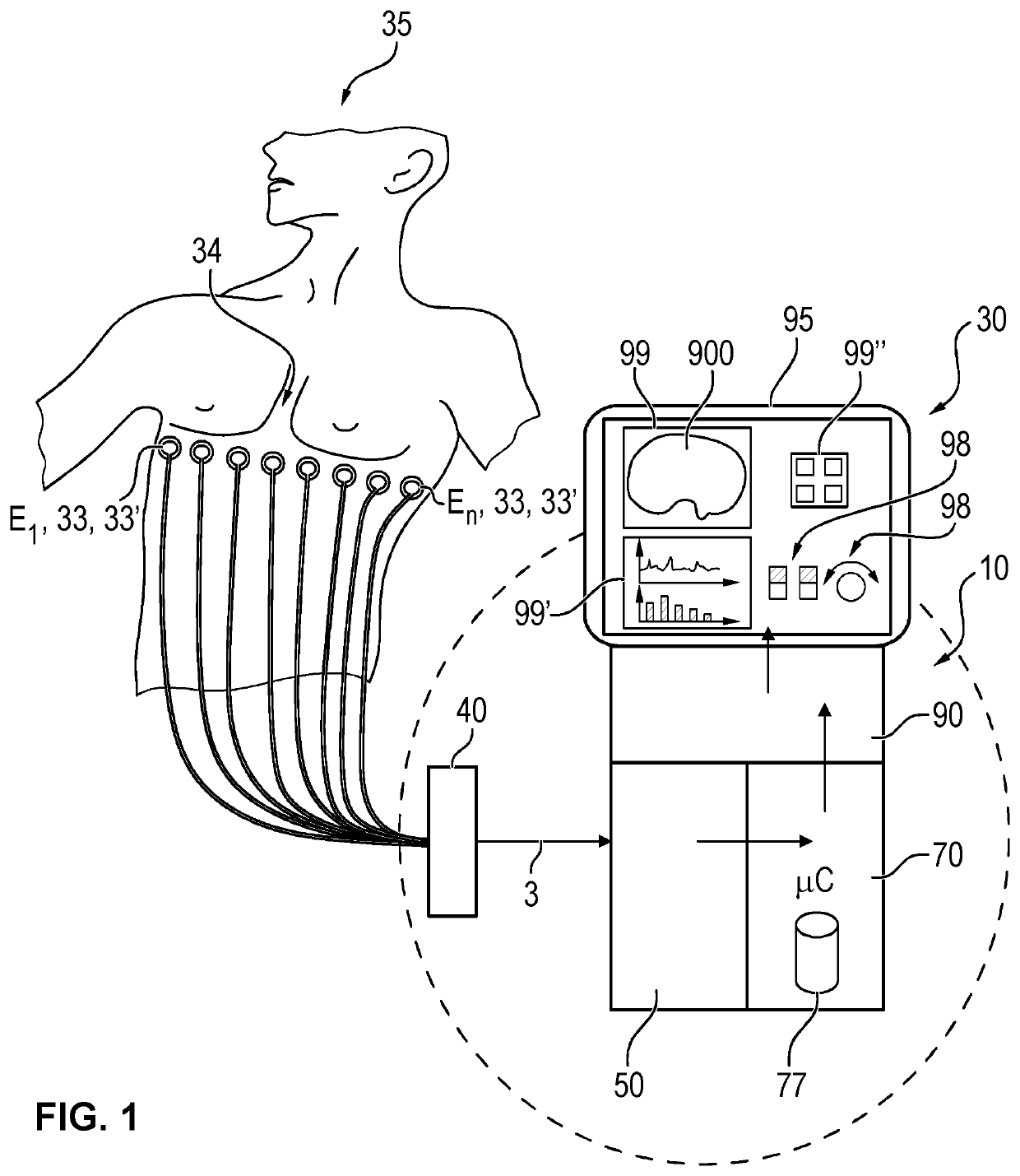
Method and apparatus for obtaining an electrocardiograph
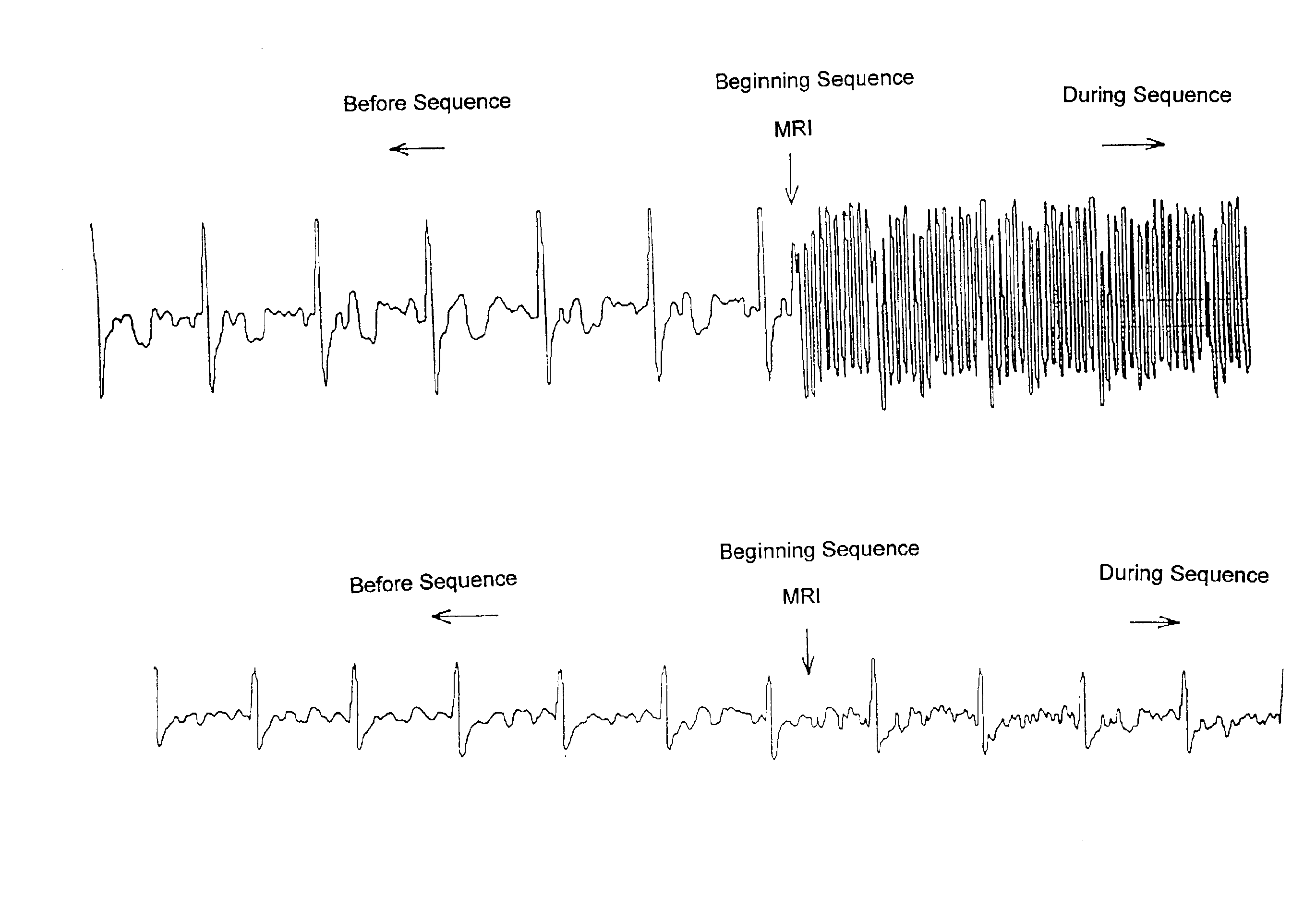
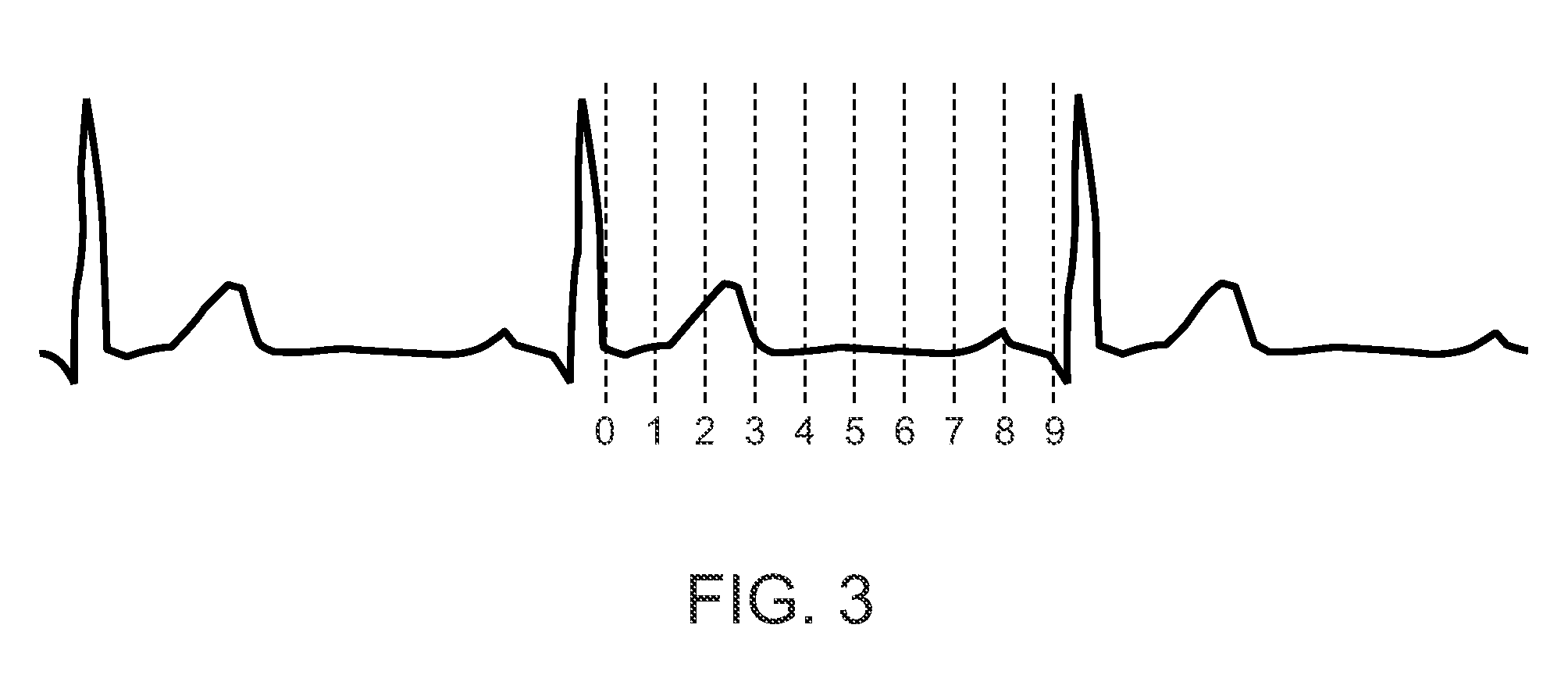
A method of obtaining an electrocardiograph (ECG) of a patient located in a turbulent electromagnetic environment. The method includes recovering an ECG signal from a patient. The signal, including added noise, is recovered near the cardiac region as the differential signal resulting from signals delivered by two electrodes forming part of a first measurement loop. The signal further consists of simultaneously recovering from the patient a second measurement signal incorporating at least the noise, as a differential signal resulting from the signals delivered by two electrodes forming part of a second measurement loop distinct from the first measurement loop. Then, the second measurement signal is added or subtracted from the first noisy ECG signal, in real time. The second measurement signal is as a function of the polarity of the noise in the second signal relative to the noise in the first noisy ECG signal. The resulting signal is processed, converted, transmitted and displayed in real time representing the ECG essentially devoid of noise.
Owner:SCHILLER MEDICAL
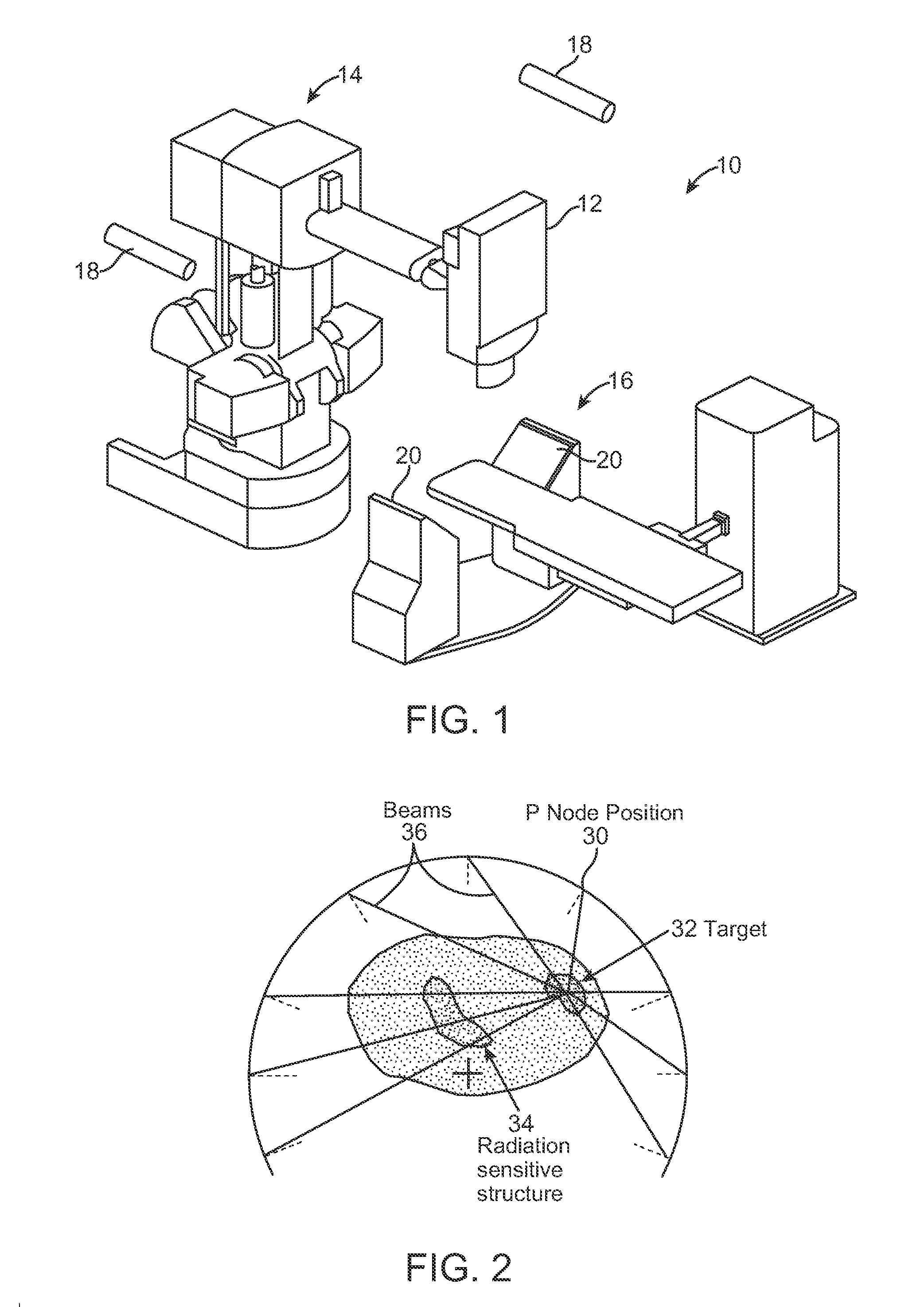
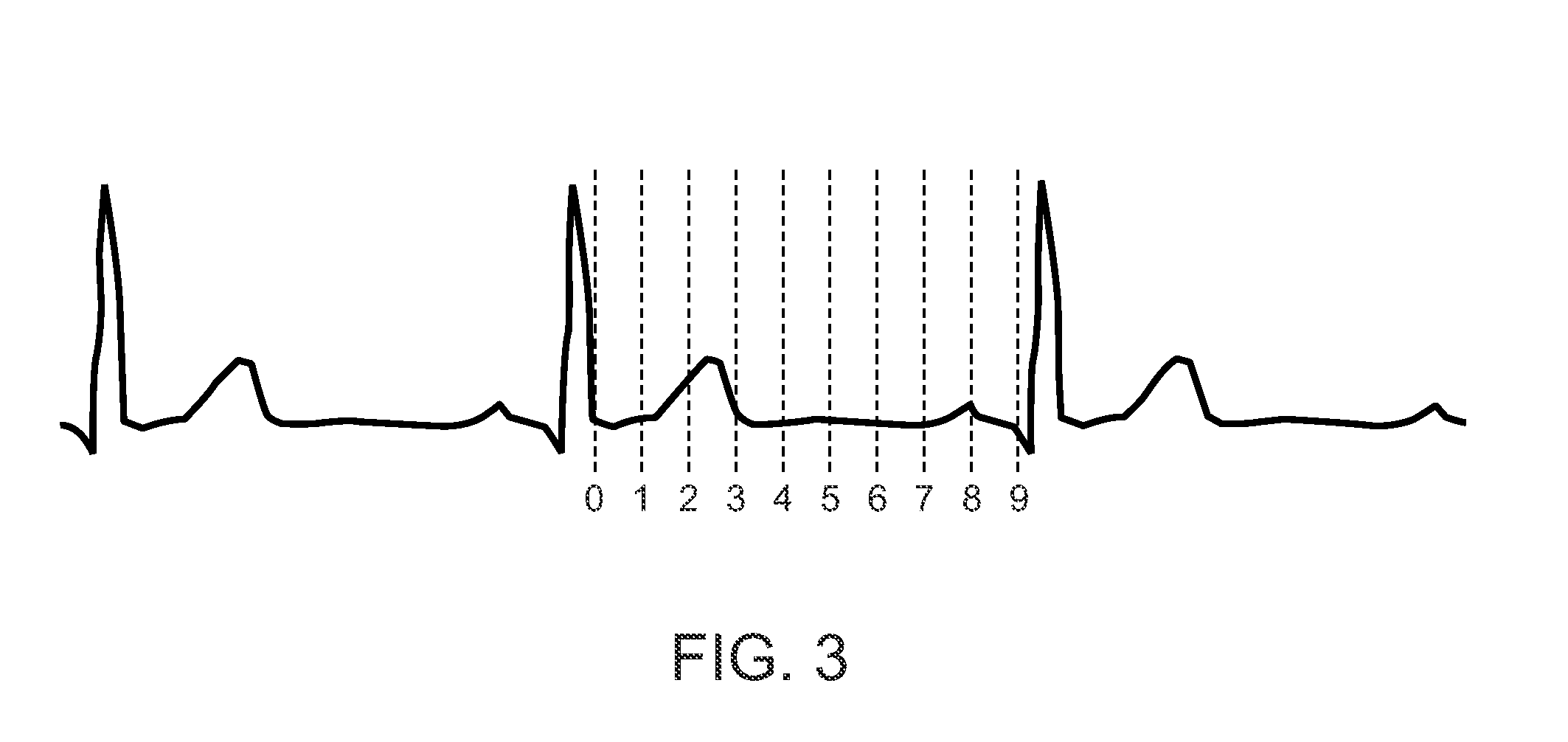
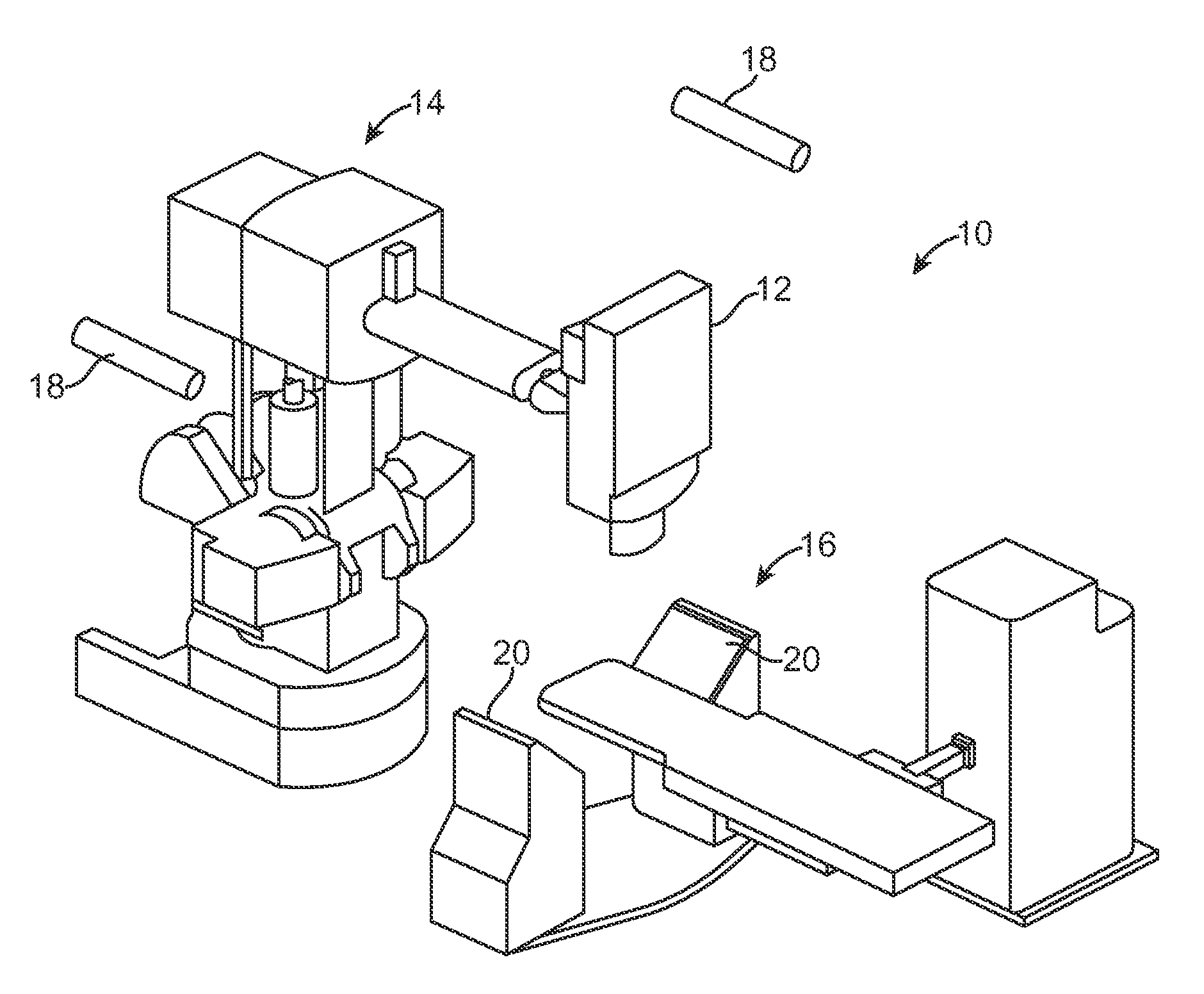
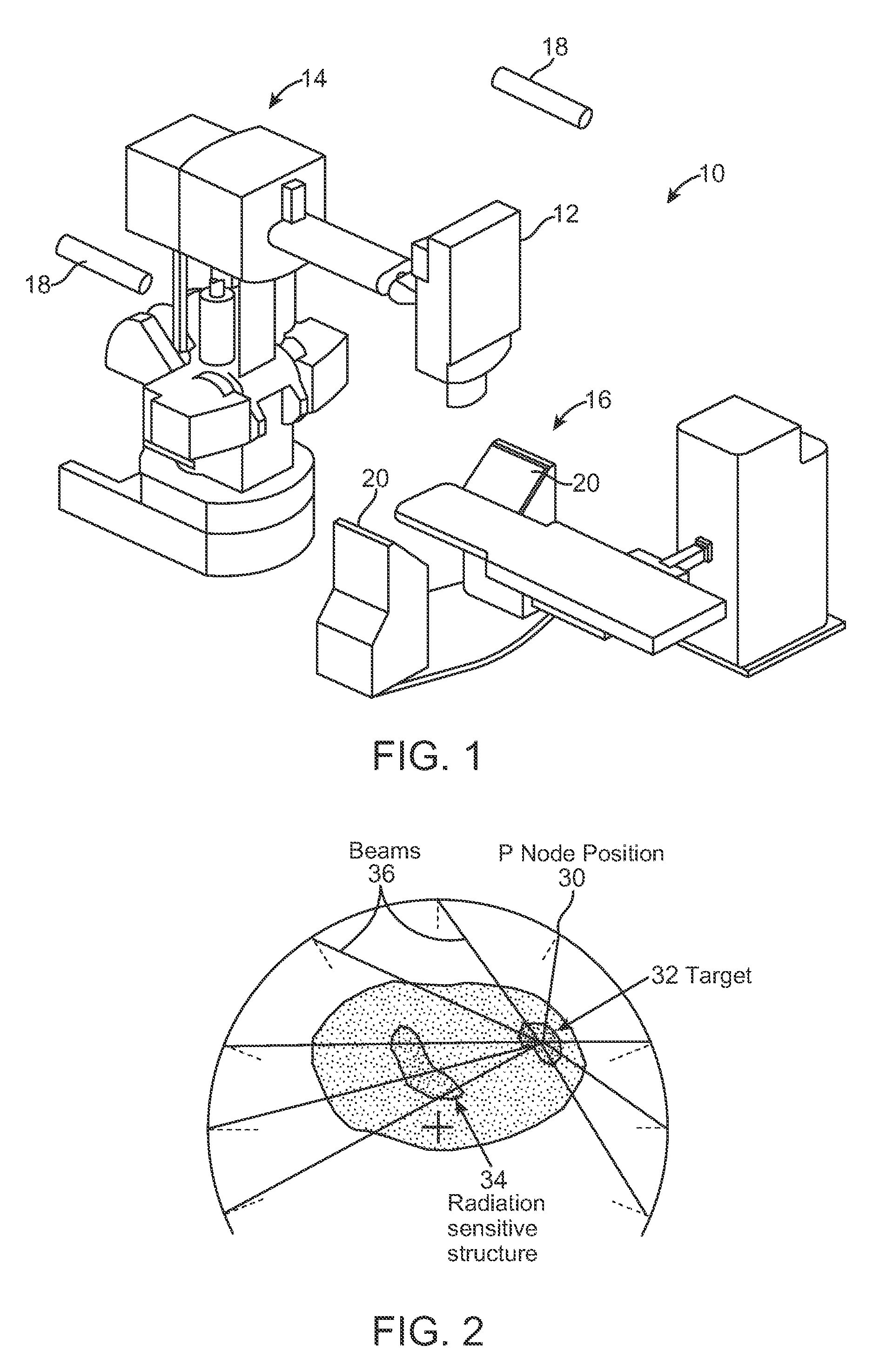
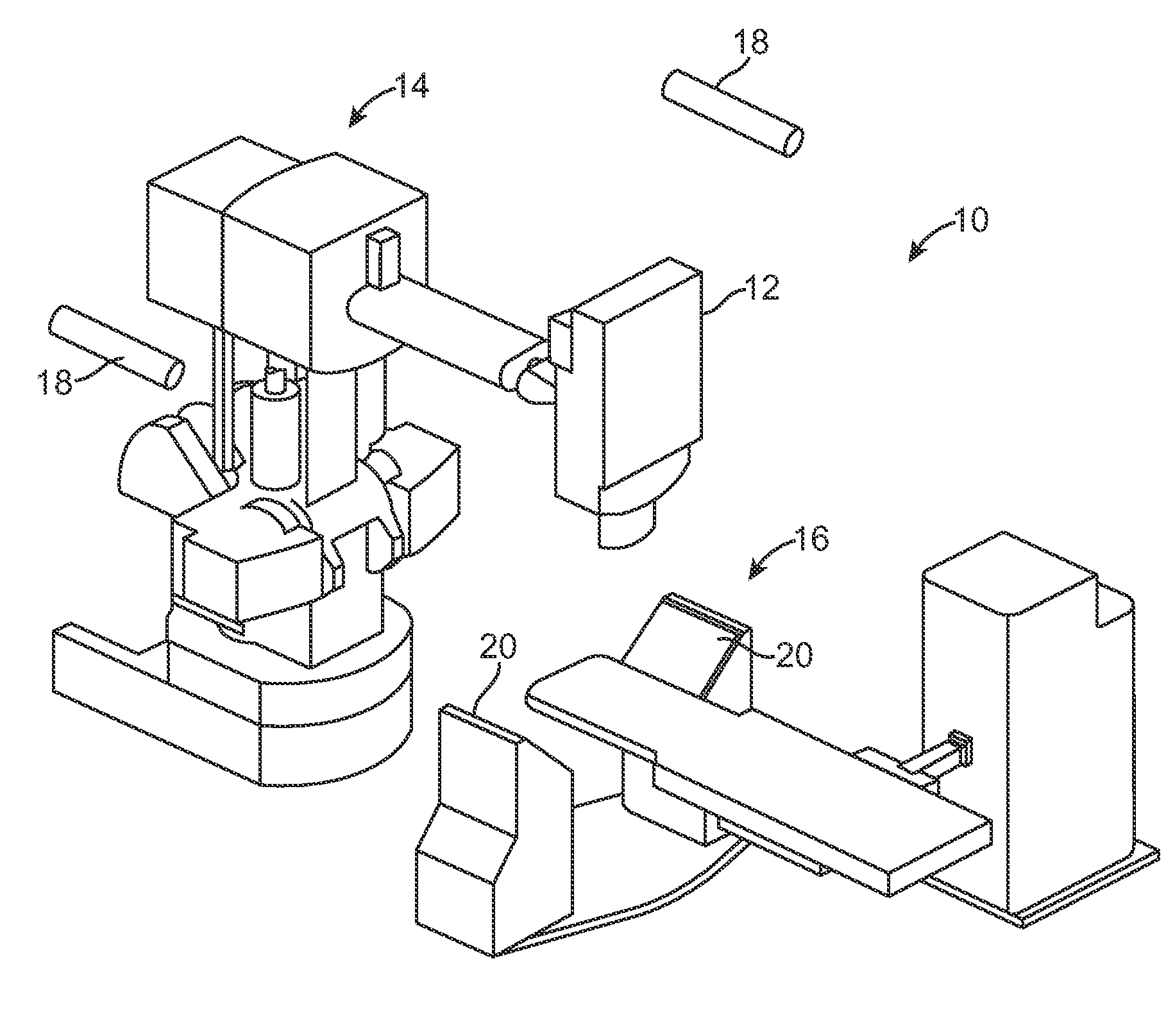
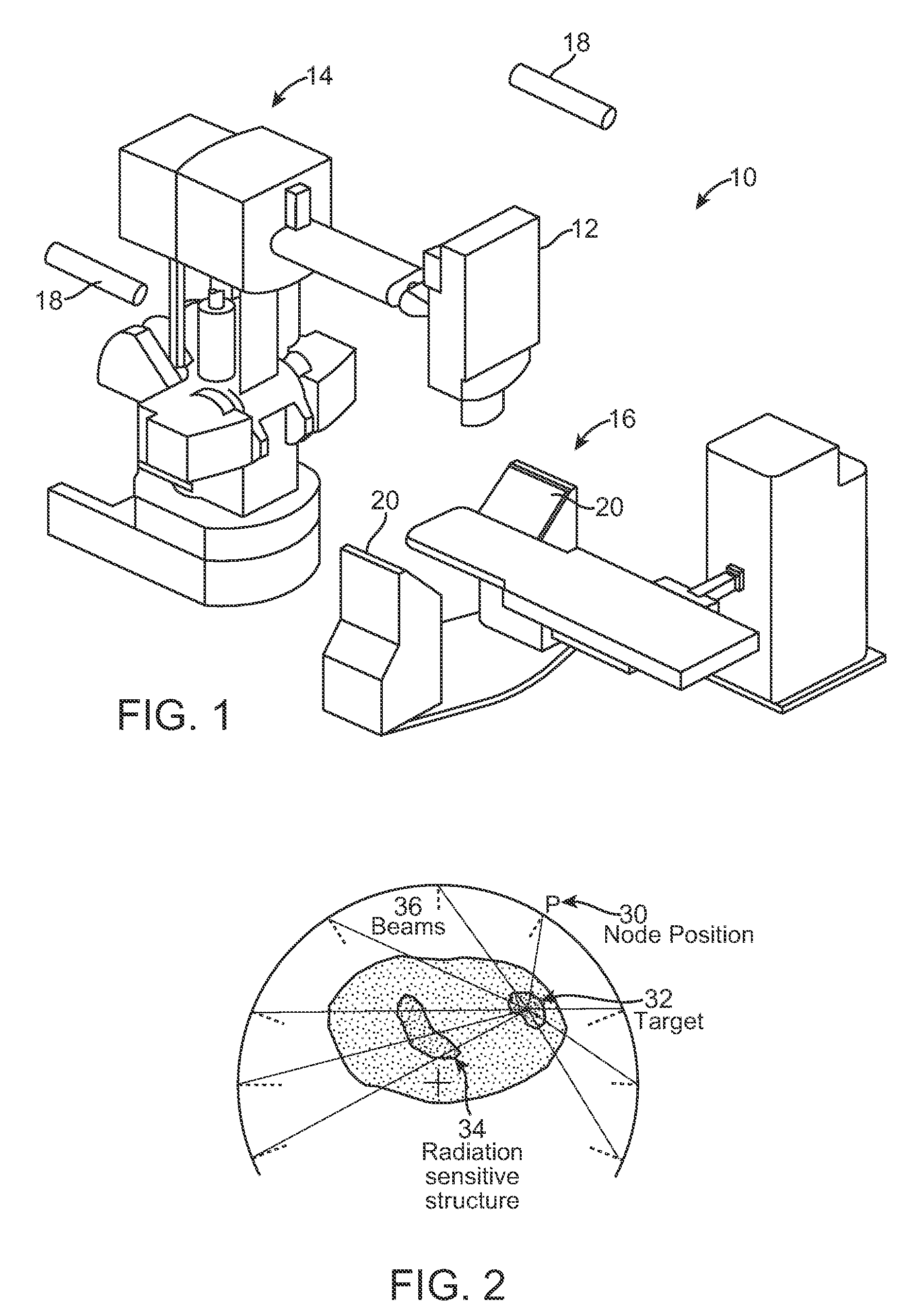
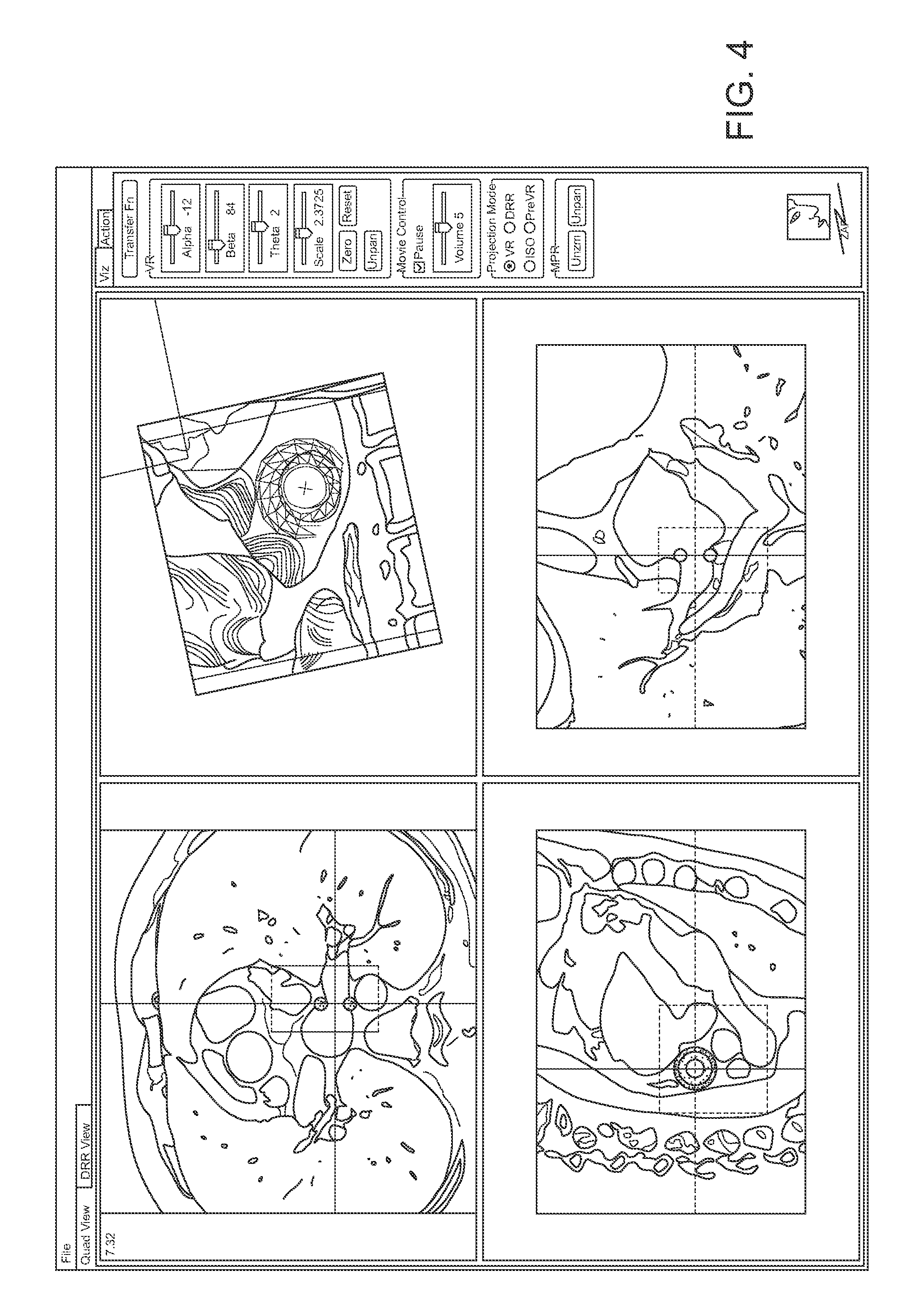
Radiation Treatment Planning and Delivery for Moving Targets in the Heart
ActiveUS20090257557A1Improved radiosurgical treatment of tissueReduce arrhythmiaX-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiation treatment planningTarget tissue
Method and systems are disclosed for radiating a moving target inside a heart. The method includes acquiring sequential volumetric representations of an area of the heart and defining a target tissue region and / or a radiation sensitive structure region in 3D for a first of the representations. The target tissue region and / or radiation sensitive structure region are identified for another of the representations by an analysis of the area of the heart from the first representation and the other representation. Radiation beams to the target tissue region are fired in response to the identified target tissue region and / or radiation sensitive structure region from the other representation.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
Radiation treatment planning and delivery for moving targets in the heart
ActiveUS7953204B2Improved radiosurgical treatment of tissueReduce arrhythmiaX-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiation treatment planningTarget tissue
Method and systems are disclosed for radiating a moving target inside a heart. The method includes acquiring sequential volumetric representations of an area of the heart and defining a target tissue region and / or a radiation sensitive structure region in 3D for a first of the representations. The target tissue region and / or radiation sensitive structure region are identified for another of the representations by an analysis of the area of the heart from the first representation and the other representation. Radiation beams to the target tissue region are fired in response to the identified target tissue region and / or radiation sensitive structure region from the other representation.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
Radiation Treatment Planning and Delivery for Moving Targets in the Heart
ActiveUS20110137158A1Improved radiosurgical treatment of tissueReduce arrhythmiaElectrocardiographyTomographyRadiologyNuclear medicine
Method and systems are disclosed for radiating a moving target inside a heart. The method includes acquiring sequential volumetric representations of an area of the heart and defining a target tissue region and / or a radiation sensitive structure region in 3D for a first of the representations. The target tissue region and / or radiation sensitive structure region are identified for another of the representations by an analysis of the area of the heart from the first representation and the other representation. Radiation beams to the target tissue region are fired in response to the identified target tissue region and / or radiation sensitive structure region from the other representation.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Method and device for calculating a cardiothoracic ratio
ActiveCN109801276AAccurate heart-to-chest ratio calculationImage analysisHuman bodyMinimum bounding box
The invention relates to the technical field of image processing, in particular to a method and device for calculating the cardiothoracic ratio of a chest medical image. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a chest medical image; obtaining a left lung bounding box, a right lung bounding box and a bounding box of the heart area; extracting a left lung region-of-interest, a right lungregion-of-interest and a heart region-of-interest in the bounding box; determining a minimum bounding box of the lung region of interest according to the left lung region of interest and the right lung region of interest; determining the long axis direction and the transverse axis direction of the human body according to the minimum bounding box of the lung region of interest; Determining a minimum bounding box of the region of interest of the heart; Calculating the ratio of the transverse diameter length of the minimum bounding box of the heart region to the transverse diameter length of theminimum bounding box of the lung, and calculating the ratio of the area of the heart region of interest to the area of the lung region of interest. According to the technical scheme, related tissuescan be accurately segmented, and the cardiothoracic ratio and the cardiothoracic area ratio can be automatically calculated.
Owner:沈阳联氪云影科技有限公司
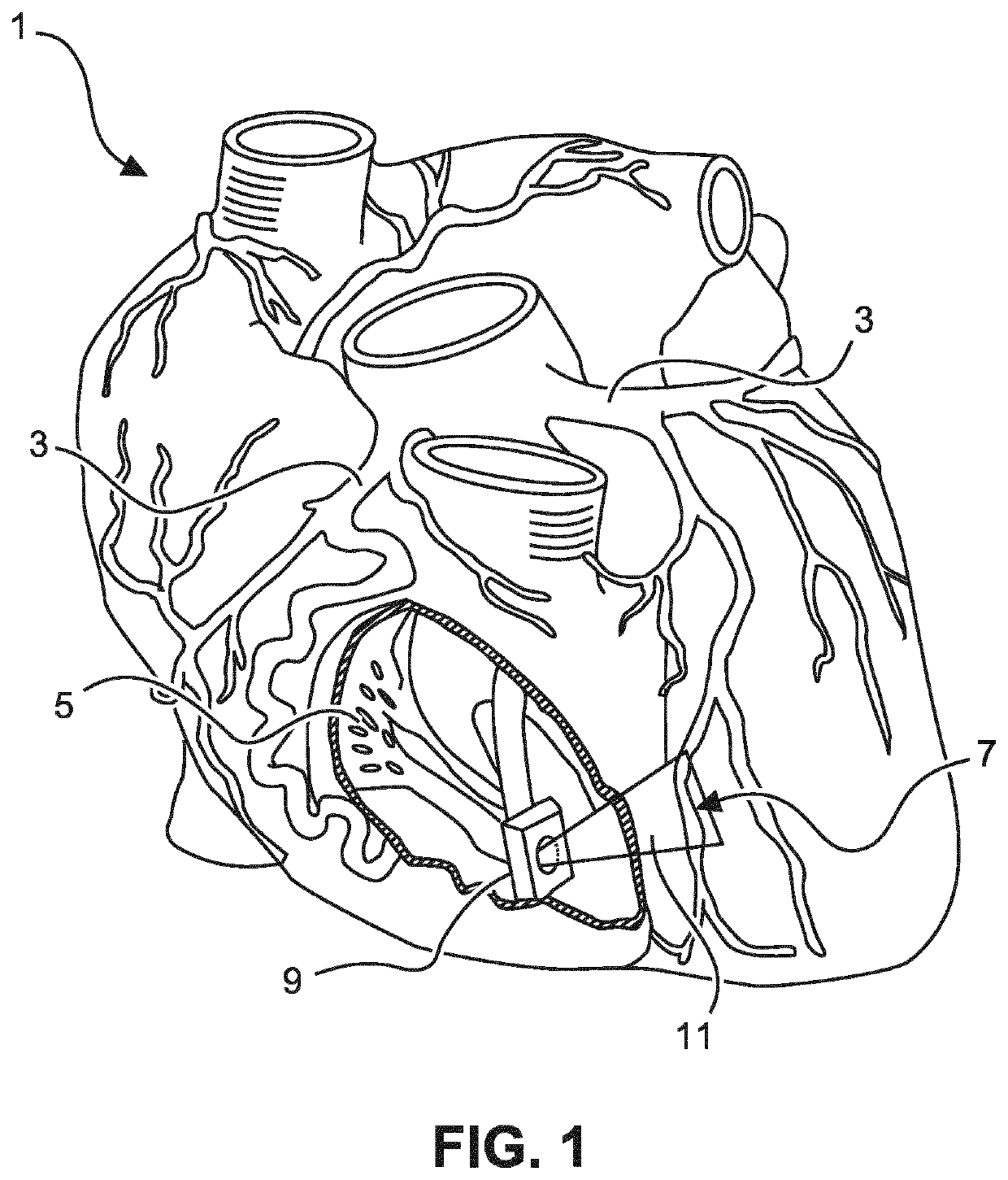
Shaped epicardial lead and placement system and method
ActiveUS10661080B2Function increaseAvoid displacementElectrocardiographyEpicardial electrodesLead systemPericardium
A cardiac lead system is provided. The lead is placed epicardially through the transverse pericardial sinus with integrated curvatures to prevent the lead from slipping out of the transverse pericardial sinus. Interaction with multiple chambers of the heart is facilitated in a single lead, without anchors that embed into the heart wall. Multiple electrodes can be grouped over each targeted heart area to ensure adequate electrical contact.
Owner:KOBARA MEDICAL INC
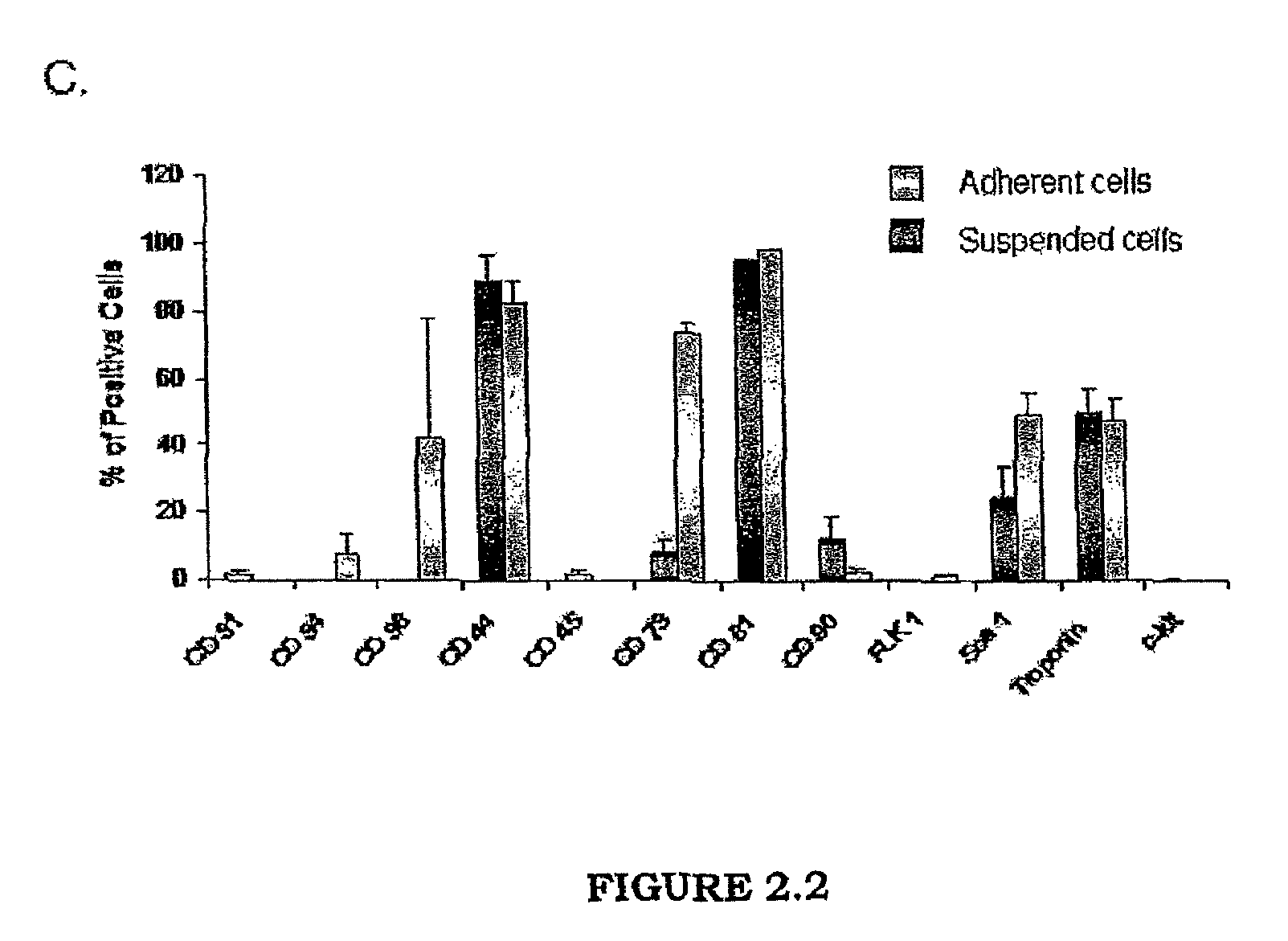
Method for culturing cells derived from the adipose tissue and uses thereof
The invention concerns a method for culturing cells derived from the adipose tissue and in particular the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) to induce formation of cardiomyocytes, the use of the cells obtained by said culture method to reconstitute an ischemized cardiac zone, in particular following an infarction, as well as a pharmaceutical composition containing said cells. The method for obtaining cardiac cells comprises at least the following steps: a) selecting cardiomyogenic cells from the stromal vascular fraction (SVF); b) culturing the cells selected at step a) in a liquid medium optimized for expanding ex vivo the cardiomyogenic cells; c) maintaining and expanding said cells by successive passes in the liquid medium; and d) obtaining cardiac cells.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Determining calcium content from spectral ct data
ActiveUS20190295249A1Good, efficient and/or robust methods and means for determiningImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionCardiovascular structure3d image
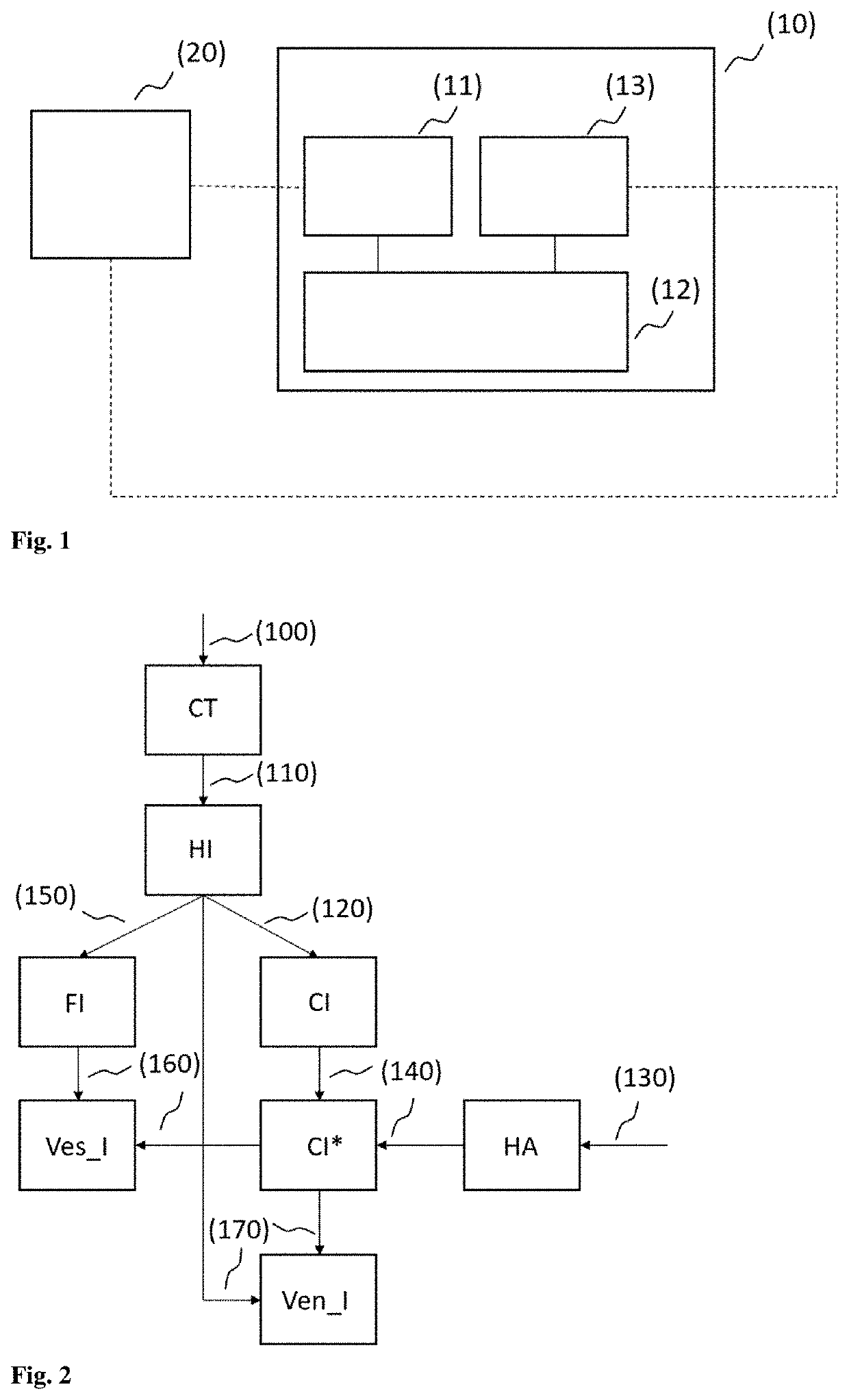
Present invention relates to devices and methods for determining a calcium content by analyzing cardiac spectral CT data. CT projection data (9), obtainable by scanning a cardiac region of a subject using a spectral CT scanning unit, is modelled (12) by applying a material decomposition algorithm to the projection data to provide a calcium-specific component. Tomographic reconstructions (13) of the projection data, to provide a first 3D image (8), and of the calcium-specific component, to provide a second 3D image (6), are performed. The first 3D image (8) is segmented (14) to provide an image mask (5) corresponding to a cardiovascular structure of interest, a part of the second 3D image (6) is selected (15) based on the image mask (5), and a calcium content is calculated (16) in the cardiovascular structure of interest based on the selected part of the second 3D image (6).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
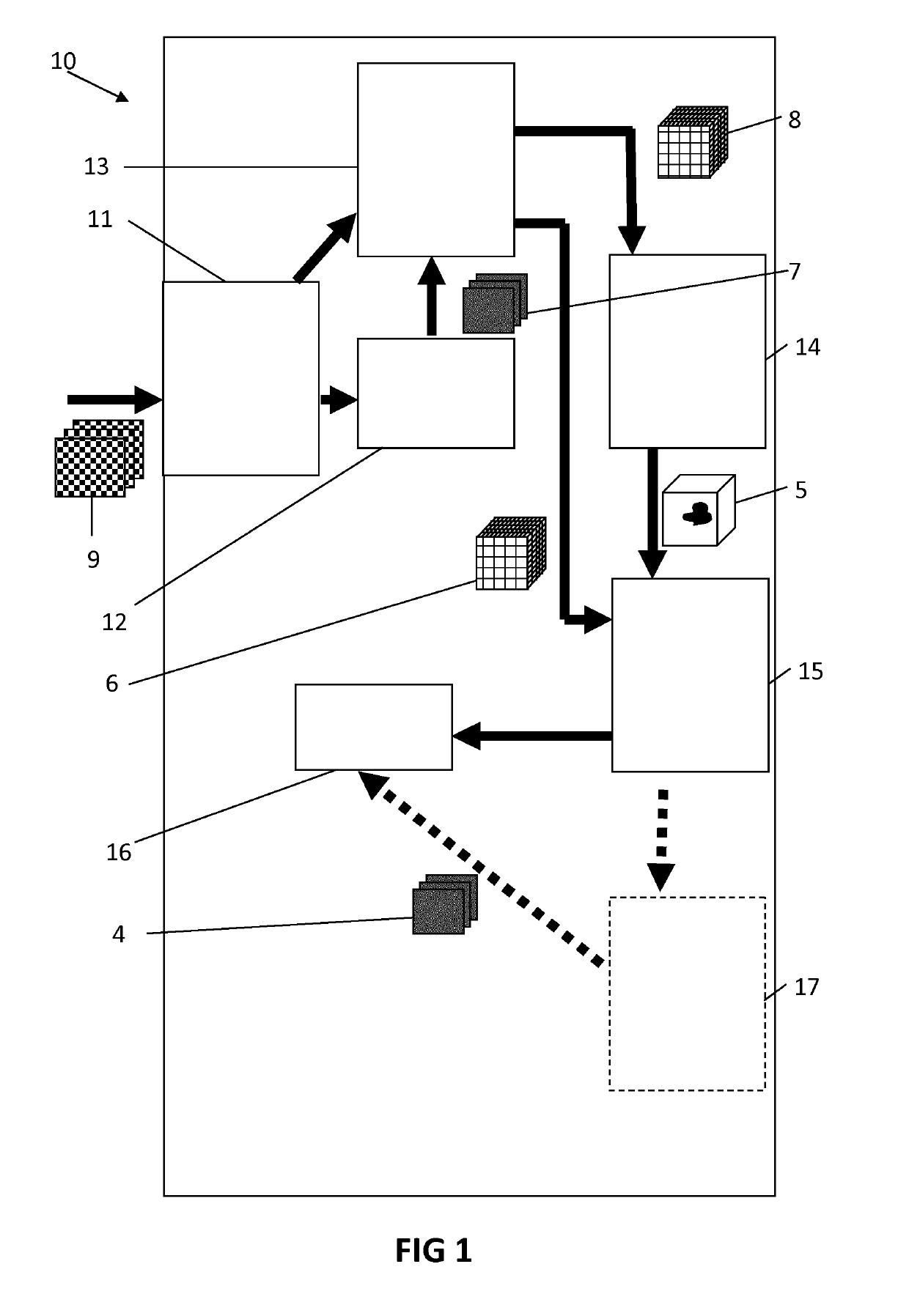
Device and process for electrical impedance tomography (EIT) with identification of a heart region
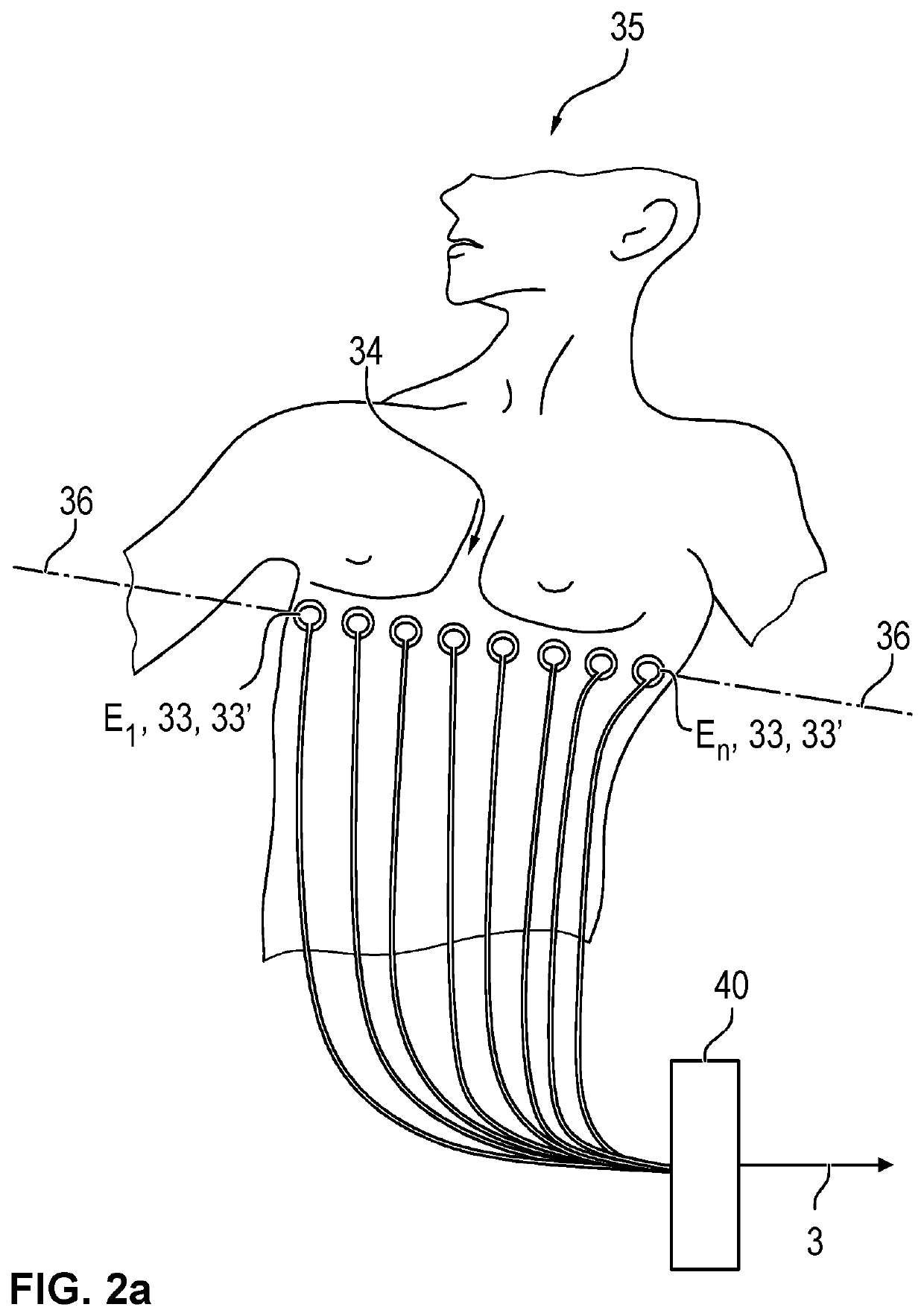
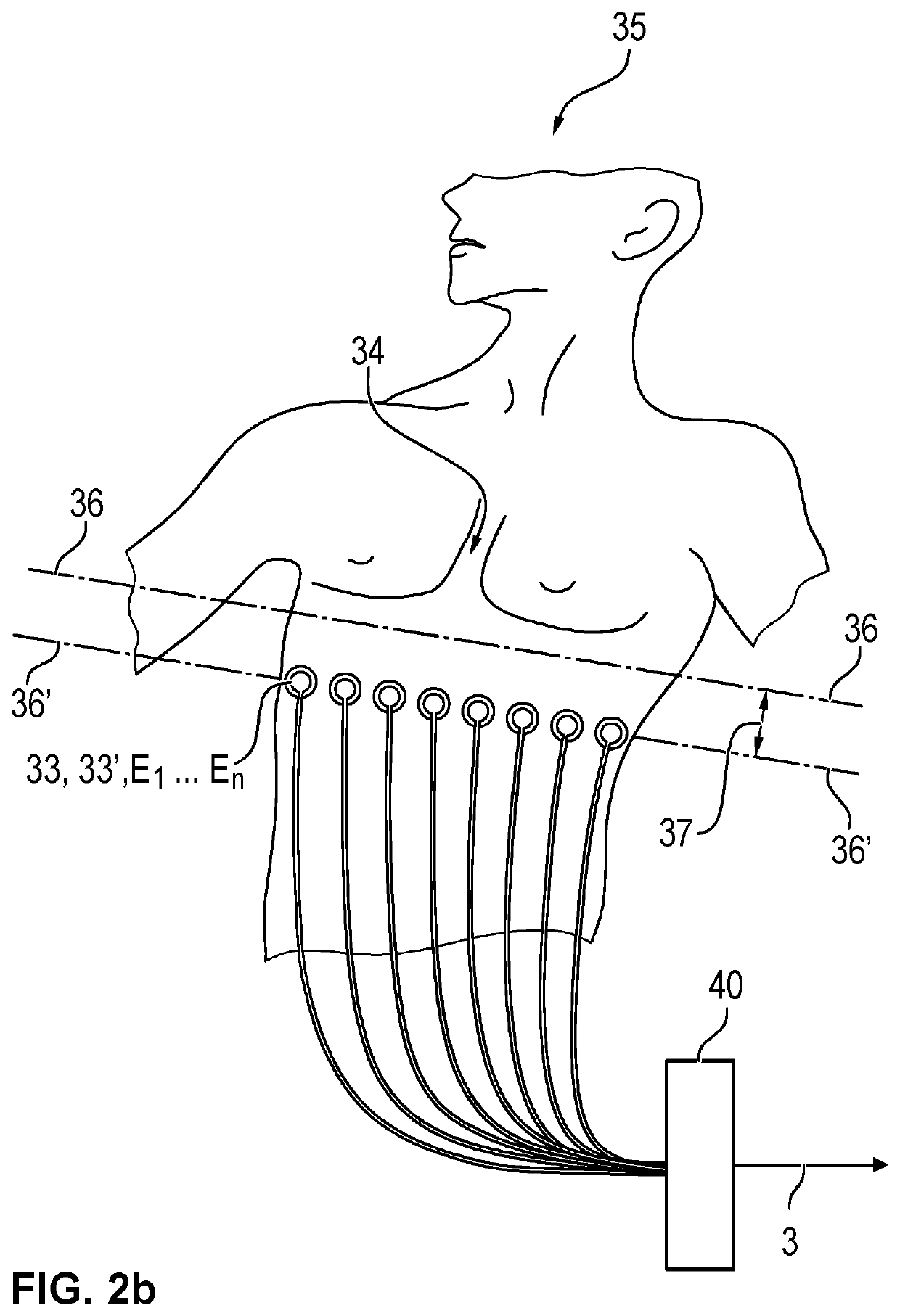
PendingUS20200138335A1Stable heart rate signalImprove robustnessMedical imagingRespiratory organ evaluationData acquisitionRat heart
An electrical impedance tomography (EIT) device (30) with an electrode array (33), with a measured value acquisition and feed unit (40), with a computing / control unit (70) and with a data input unit (50). The computing / control unit (70) coordinates the operation and the data acquisition of EIT data (3) and is configured to identify a heart region.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
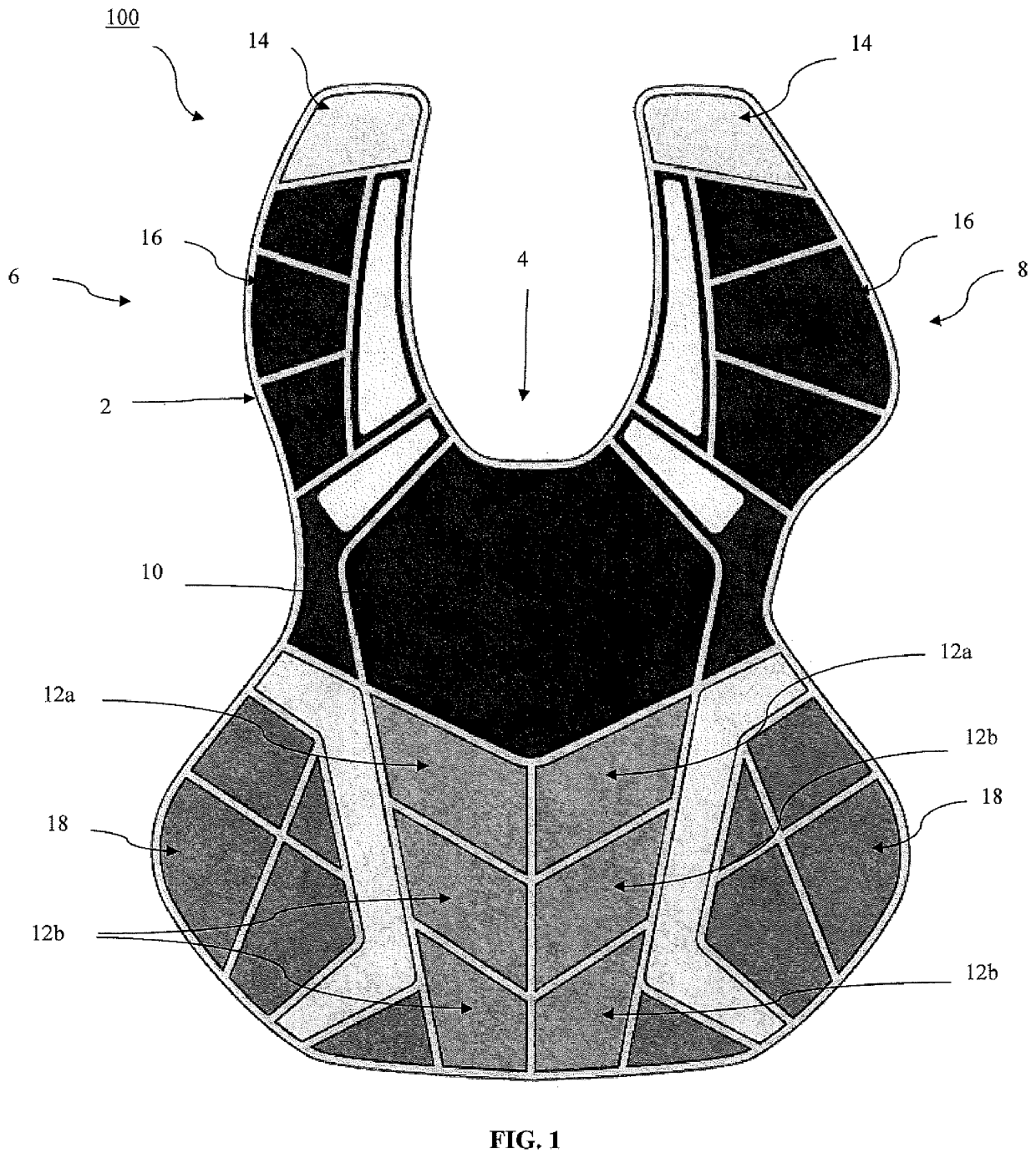
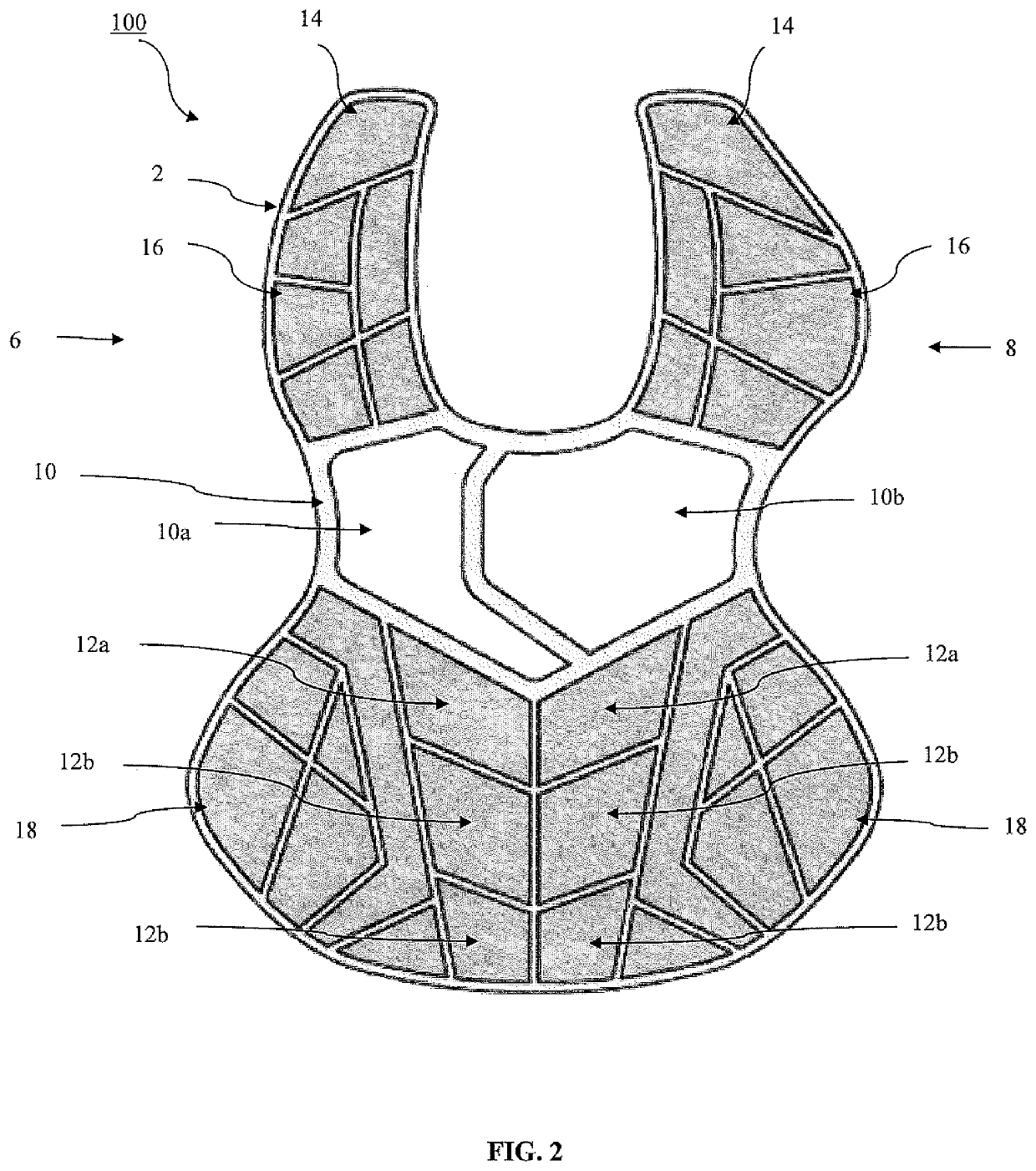
Chest protector
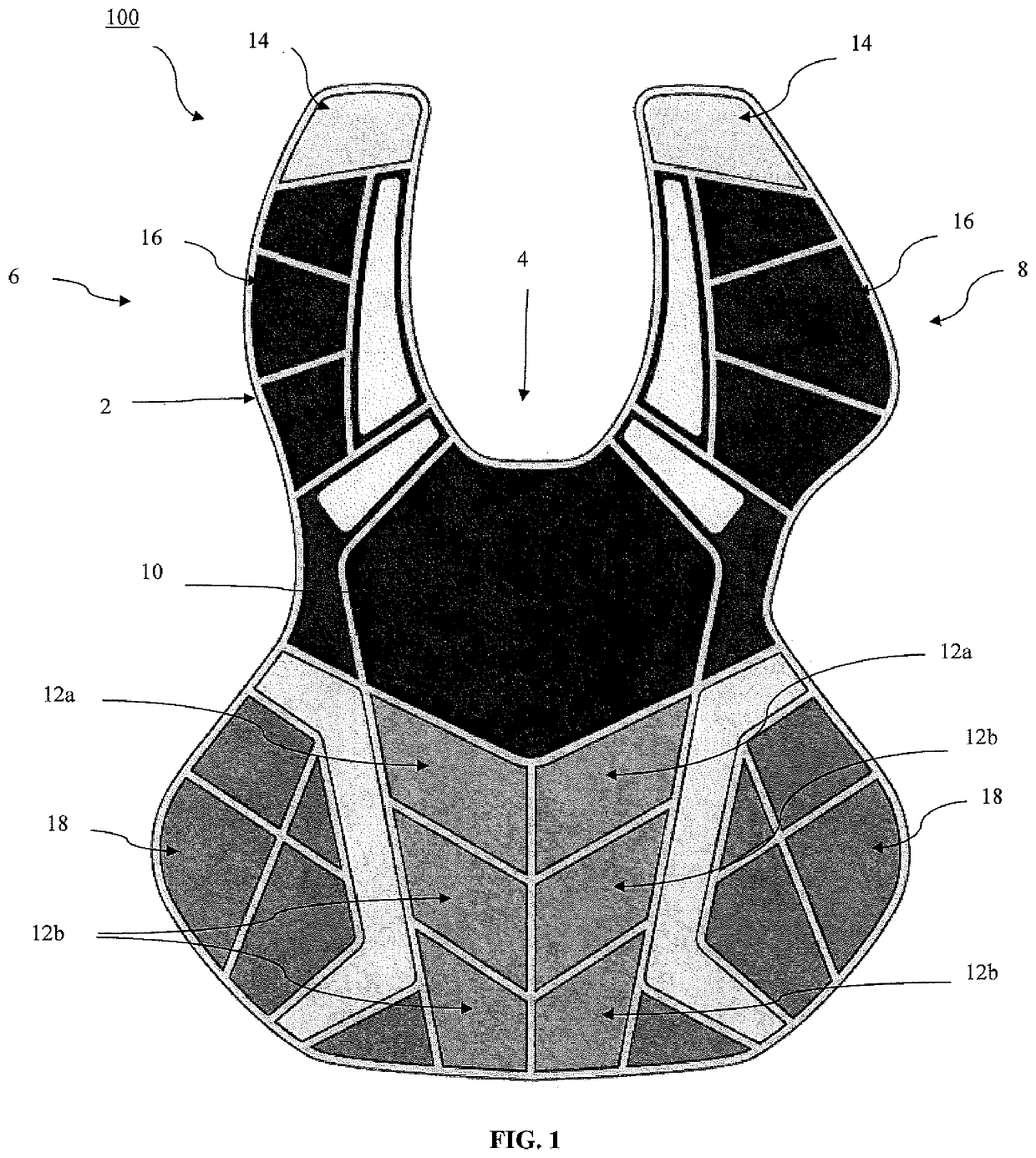
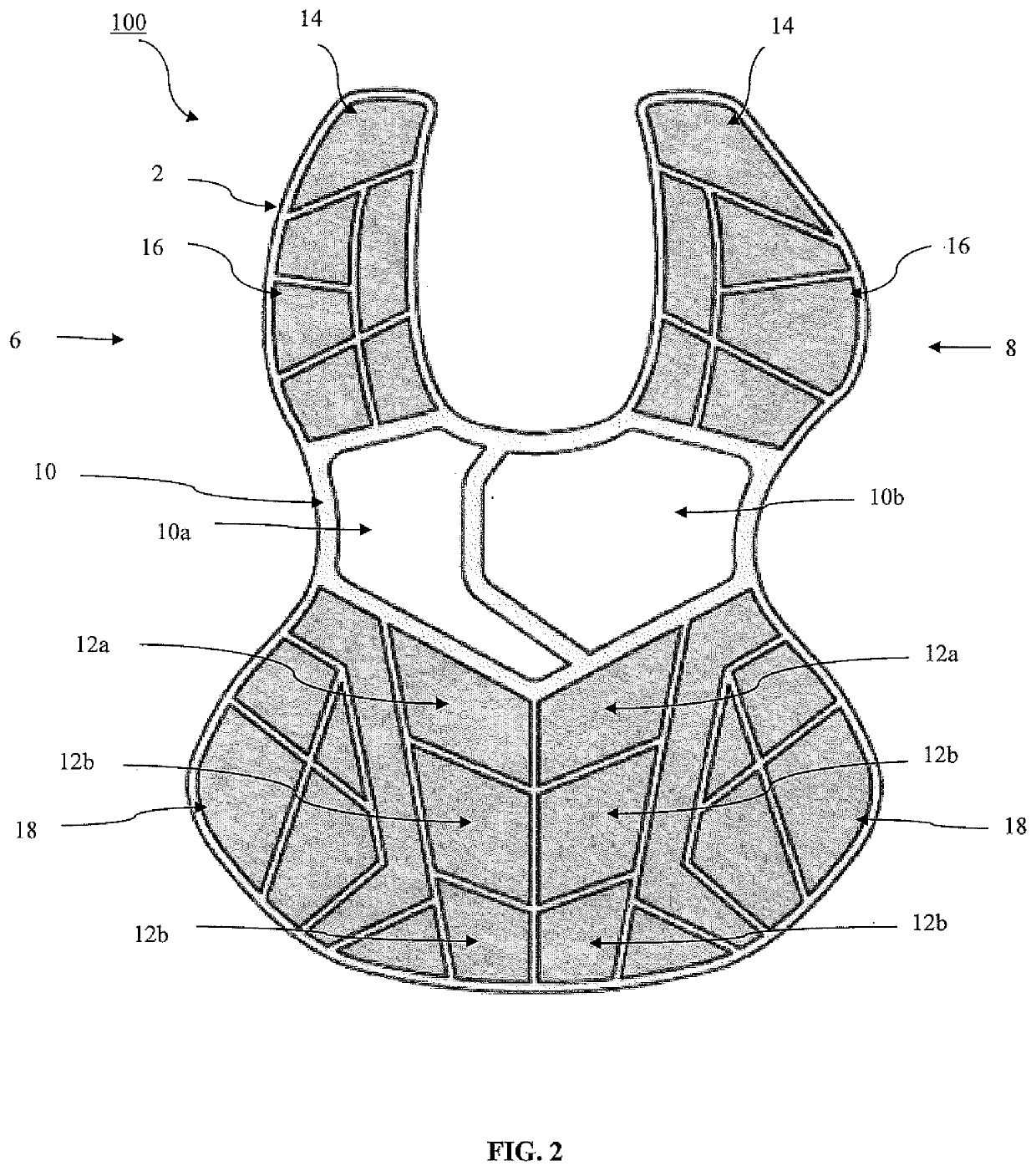
ActiveUS20200037680A1Reduce generationFull coverageSport apparatusProtective garmentChest protectorCommotio cordis
The present invention is directed to a chest pad that significantly reduces the occurrence of commotio cordis among athletes. The chest pad may be utilized as a stand-alone chest protector intended to provide coverage primarily for the upper chest wall and the cardiac area. The chest pad may also be implanted into or utilized in traditional chest protectors that provide full coverage of the user's torso. The chest pad of the present invention provides additional protection to the heart of the wearer such that impact in the heart area with a projectile is absorbed by the chest pad.
Owner:AMPAC ENTERPRISES
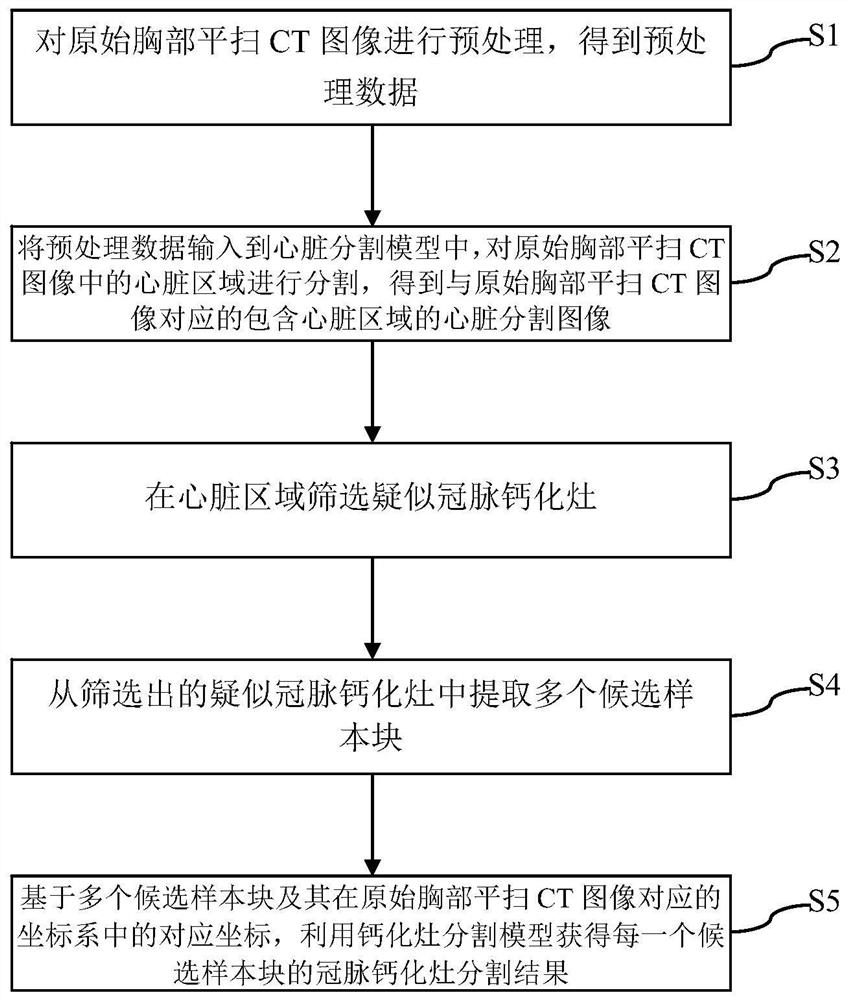
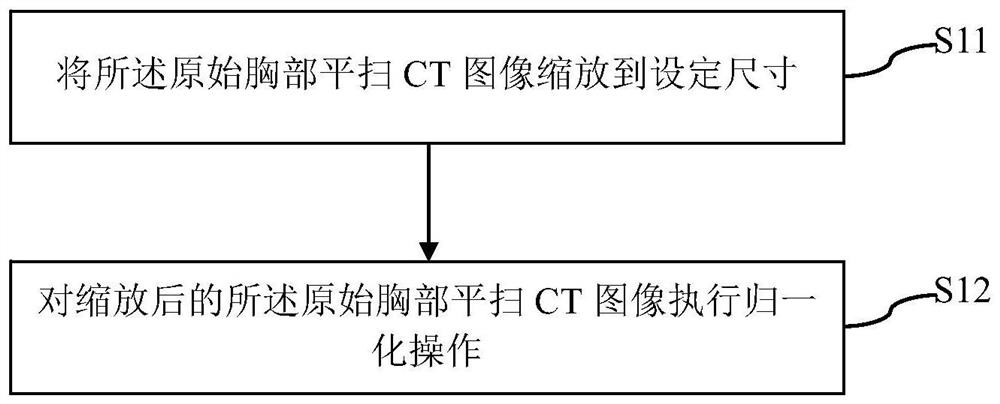
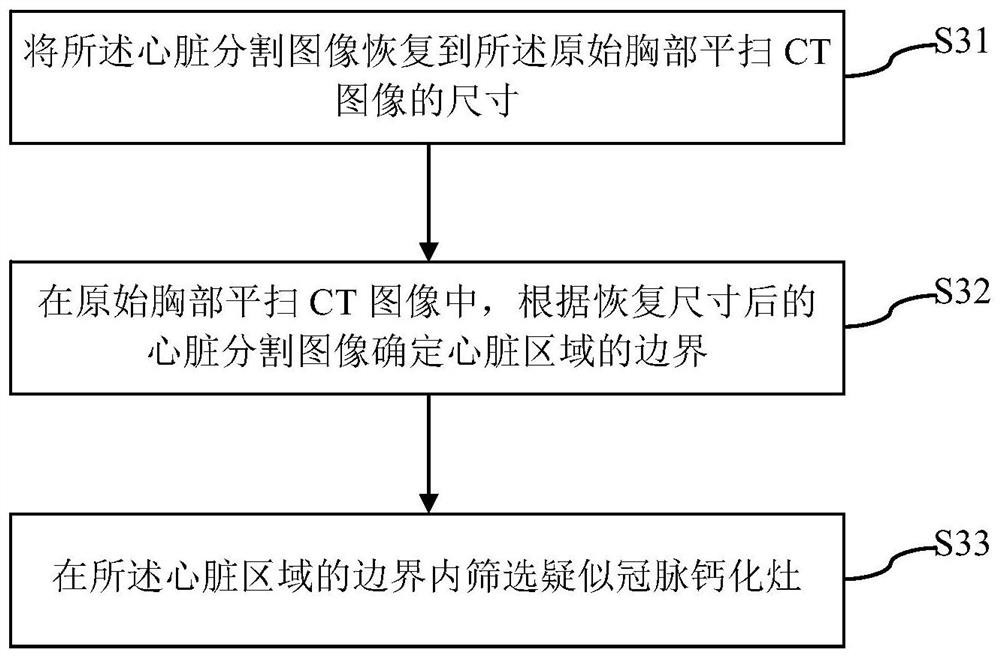
Coronary artery calcification lesion full-automatic segmentation method based on chest flat scanning CT
ActiveCN112288752AImprove accuracyGood forecastImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationRadiology
The invention discloses a coronary artery calcification lesion full-automatic segmentation method based on chest flat scanning CT, and the method comprises the following steps: carrying out the preprocessing of an original chest flat scanning CT image, and obtaining preprocessing data; inputting the preprocessed data into a heart segmentation model, and segmenting a heart region in the original chest flat-scanning CT image to obtain a heart segmentation image which corresponds to the original chest flat-scanning CT image and contains the heart region; screening suspected coronary artery calcification lesions in the heart area; extracting a plurality of candidate sample blocks from the screened suspected coronary artery calcification lesions; and based on the plurality of candidate sample blocks and the corresponding coordinates of the candidate sample blocks in the coordinate system corresponding to the original chest horizontal scanning CT image, obtaining coronary artery calcification focus segmentation results of the candidate sample blocks by using a calcification focus segmentation model. According to the method, a coarse-to-fine strategy is adopted, a two-stage deep neural network is used for achieving full-automatic coronary artery calcification focus segmentation based on chest flat scanning CT, and a good segmentation result can also be obtained for data with large noise.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Method and system for patient-specific virtual percutaneous structural heart intervention
PendingUS20210022806A1Reliable measurementConvenient timeHeart valvesComputer-aided planning/modellingRat heartBiomedical engineering
A system and method for selecting, from a series of cardiac implants having different sizes, the cardiac implant having optimum size for implantation in a patient. The method includes obtaining data representative of a patient-specific cardiac region and predicting the optimum size of the cardiac implant best matching a predefined criterion when deployed in the cardiac region. The predicting includes querying a database; determining parameter values for a parametric model representation of the patient-specific cardiac region; and / or entering the data representative of the patient-specific cardiac region into an artificial intelligence device.
Owner:FEOPS NV
Ultrasonic image processing method and equipment
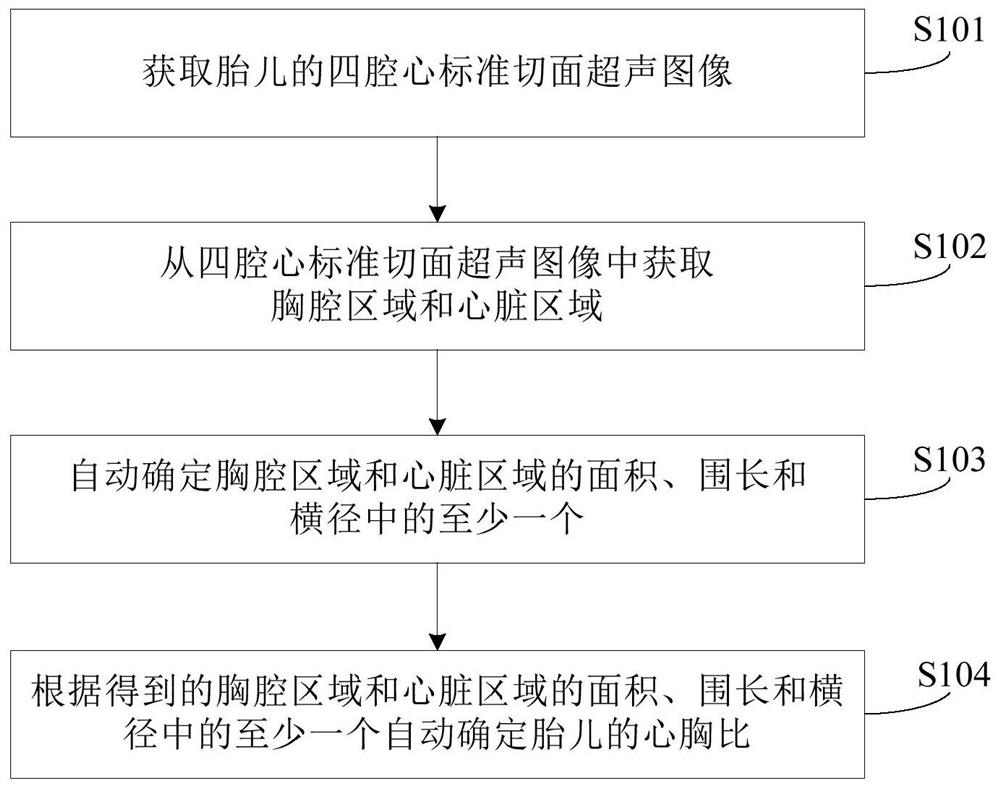
PendingCN114699106ARealize automatic measurementImprove work efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisThoracic structureImaging processing
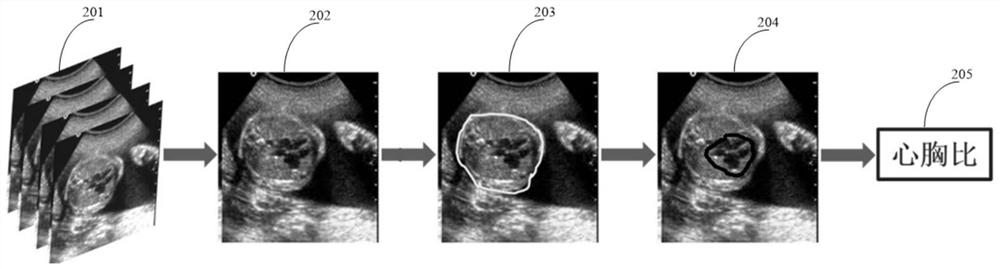
The embodiment of the invention provides an ultrasonic image processing method and equipment. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a four-cavity heart standard section ultrasonic image of a fetus; obtaining a thoracic cavity area and a heart area from the four-cavity heart standard section ultrasonic image; automatically determining at least one of an area of the thoracic cavity region and the heart region, a girth of the thoracic cavity region and the heart region, and a transverse diameter of the thoracic cavity region and the heart region; a cardiothoracic ratio of the fetus is automatically determined based on at least one of an area of the thoracic and cardiac regions, a girth of the thoracic and cardiac regions, and a transverse diameter of the thoracic and cardiac regions. According to the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, the automatic measurement of the heart-chest ratio of the fetus is realized based on the ultrasonic image of the fetus, the operation is simplified, and the working efficiency of a clinician is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of estimation physiological parameters using medical image data
PendingUS20210012887A1Reduce volatilityImprove stabilityMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesImaging heartTissue architecture
A method (12) of estimating one or more physiological parameters, in particular of a cardiac region, based on medical imaging data. An input time series of three-dimensional medical images is received (14), representative of a cardiac region of a patient. A meshless simulation frame-work is applied (16) for simulating blood flow through at least a portion of the anatomical area captured by the images. The simulation framework comprises in particular simulating force interactions between individual elements of a simulated fluid (representing blood) and individual patches of a tissue structure of the imaged cardiac region. One or more physiological parameters (18) are derived based on the simulated blood flow.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
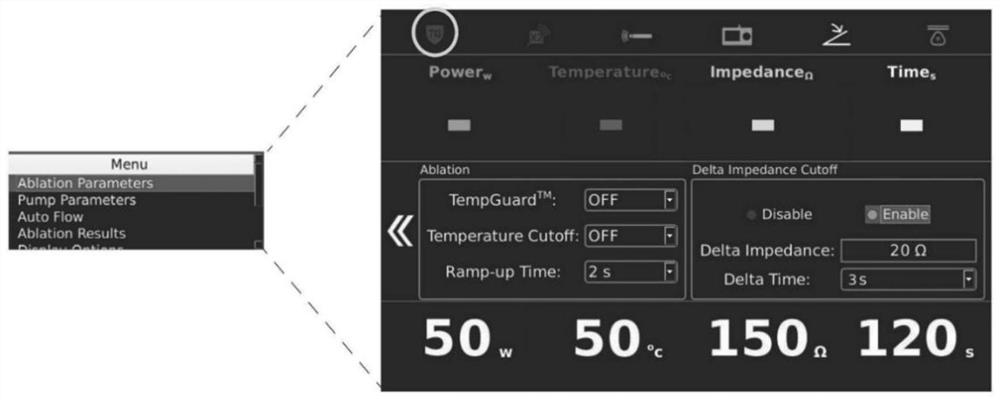
Regulating system of arrhythmia radio frequency catheter
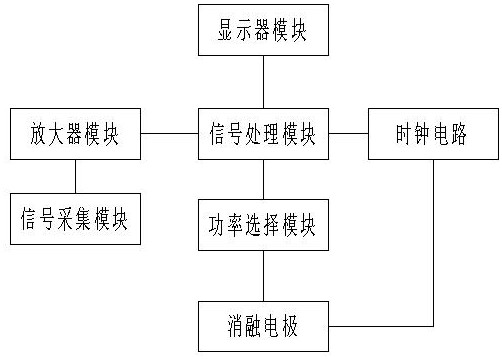
PendingCN113855222ATo achieve the purpose of continuous ablationGood treatment effectCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringDisplay deviceCatheter
The invention discloses a regulating system of an arrhythmia radio frequency catheter. The regulating system comprises a signal acquisition module, a signal processing module, an amplifier module, a display module, a power selection module and an ablation electrode, wherein the signal acquisition module is used for acquiring an impedance signal of a heart, the impedance signal is amplified by virtue of the amplifier module and is transmitted to the signal processing module, the signal processing module is used for processing and calculating the signal so as to obtain impedance information, and the power selection module is used for selecting working power of the ablation electrode according to a processing result of the signal processing module; and the display module is used for displaying a heart impedance result and the working power of the ablation electrode, and the ablation electrode is used for carrying out ablation treatment on a heart region. The regulating system disclosed by the invention can detect impedance of a focus region in real time, judge an impedance value and carry out ablation on the focus region, so that the aim of continuous ablation of the radio frequency catheter is achieved, and a treatment effect is improved.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV
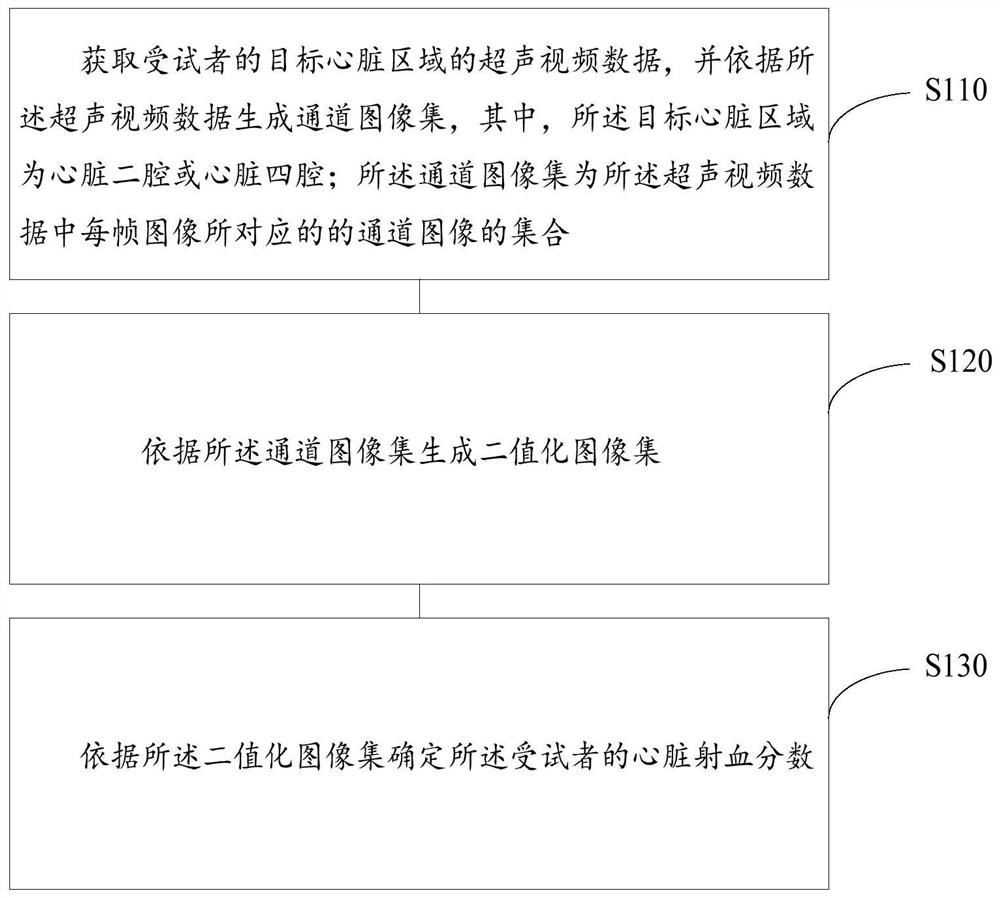
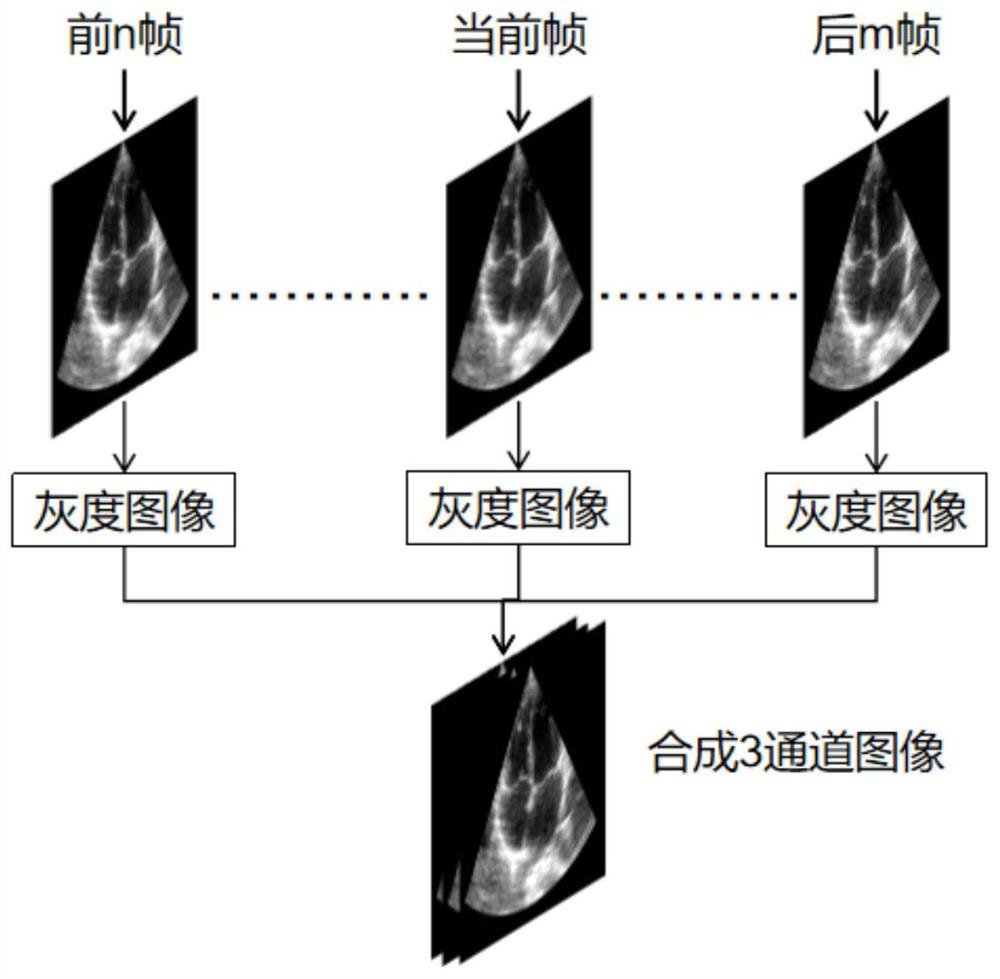
Cardiac ejection fraction calculation method and device
PendingCN112381895ARealize automatic calculationImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac cycleMagnetocardiography device
The embodiment of the invention provides a cardiac ejection fraction calculation method and device, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining ultrasonic video data of a target cardiac region of asubject, and generating a channel image set according to the ultrasonic video data, wherein the target heart region is a cardiac two-cavity or heart four-cavity; wherein the channel image set is a setof channel images corresponding to each frame of image in the ultrasonic video data; generating a binary image set according to the channel image set; and determining the cardiac ejection fraction ofthe subject according to the binarized image set. By utilizing the self-learning function of the neural network, the cardiac ejection fractions of multiple cardiac cycles are automatically calculated, the defects of a traditional calculation method are overcome, the method does not depend on other devices such as electrocardiogram devices and cross-cardiac cycle analysis devices, and the invention has the advantages of being high in accuracy, high in usability, repeatable and the like. Sufficient and accurate reference data is provided for classification, diagnosis and treatment of heart failure.
Owner:深圳蓝影医学科技股份有限公司
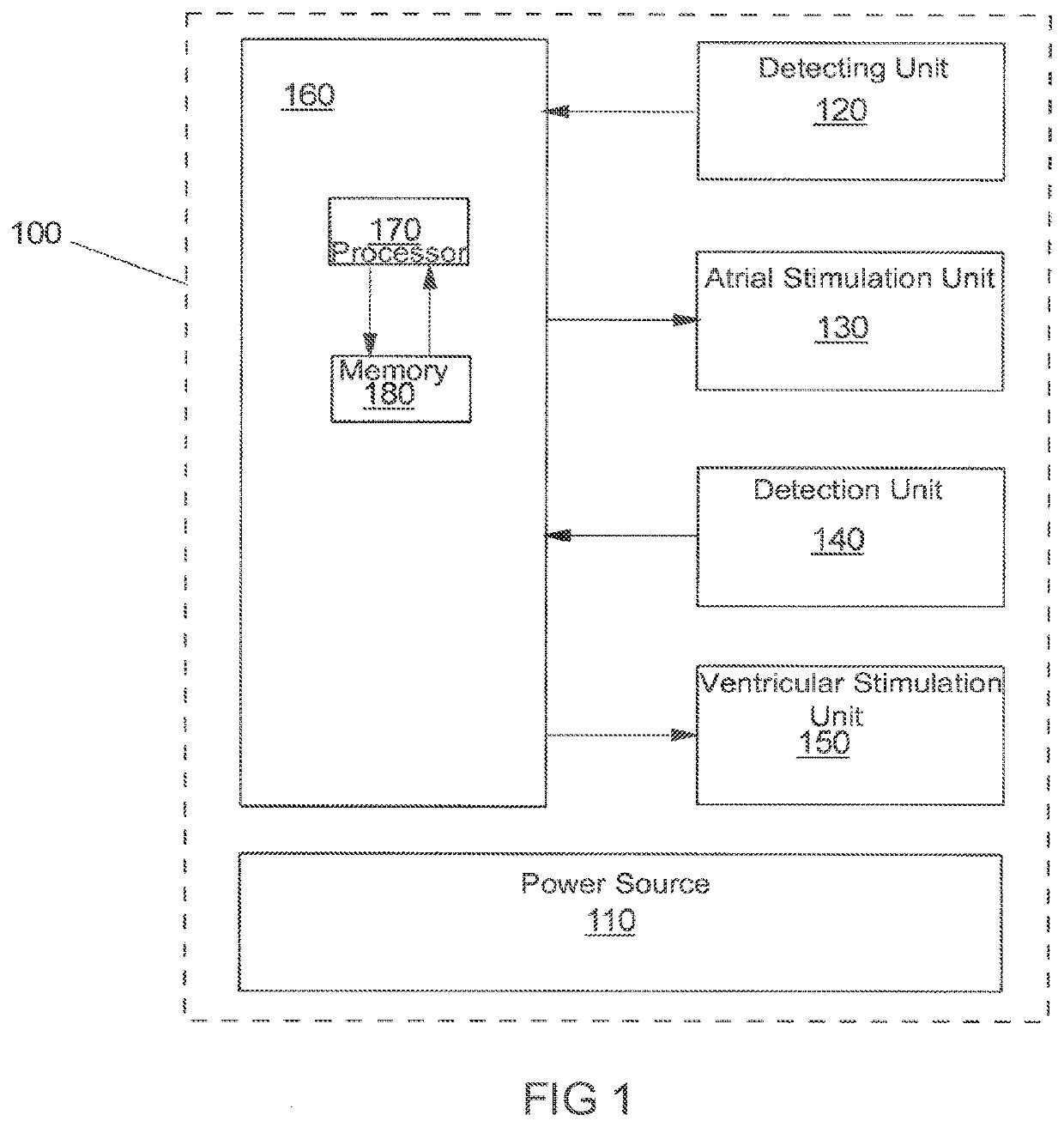
Implantable system for stimulating a human heart or an animal heart
PendingUS20220212021A1Convenient treatmentReduce power consumptionHealth-index calculationHeart defibrillatorsRat heartBiomedical engineering
An implantable system for stimulating a heart contains a processor, a memory, a stimulator, and a first detection unit for detecting a cardiac rhythm disturbance of a cardiac region. The memory includes a computer-readable program, which prompts the processor to carry out the following steps: a) detecting via the first detection unit whether a cardiac rhythm disturbance is present in a cardiac region of a heart of a patient; b) when a cardiac rhythm disturbance is present, selecting a stimulation strategy based on a selection criterion; c) stimulating the cardiac region in which the cardiac rhythm disturbance was detected by way of the stimulator, using the selected stimulation strategy; d) detecting a success and / or an efficiency of the conducted stimulation; e) comparing the success and / or the efficiency to a predefinable success and / or efficiency criterion; and f) if the predefinable success and / or efficiency criterion was not achieved, optimizing the stimulation strategy.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Chest protector
ActiveUS11388938B2Reduce generationFull coverageSport apparatusProtective garmentCommotio cordisCardiac arrhythmia
A chest pad that significantly reduces the occurrence of commotio cordis among athletes is disclosed. The chest pad may be utilized as a stand-alone chest protector intended to provide coverage primarily for the upper chest wall and the cardiac area. The chest pad may also be implanted into or utilized in traditional chest protectors that provide full coverage of the user's torso. The chest pad provides additional protection to the heart of the wearer such that impact in the heart area with a projectile is absorbed by the chest pad.
Owner:AMPAC ENTERPRISES
Heart image acquisition method and device, magnetic resonance equipment and storage medium
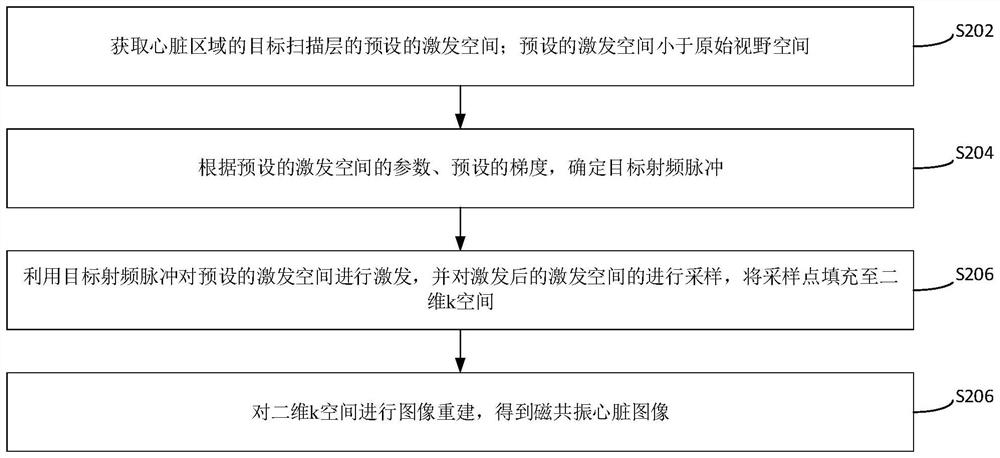
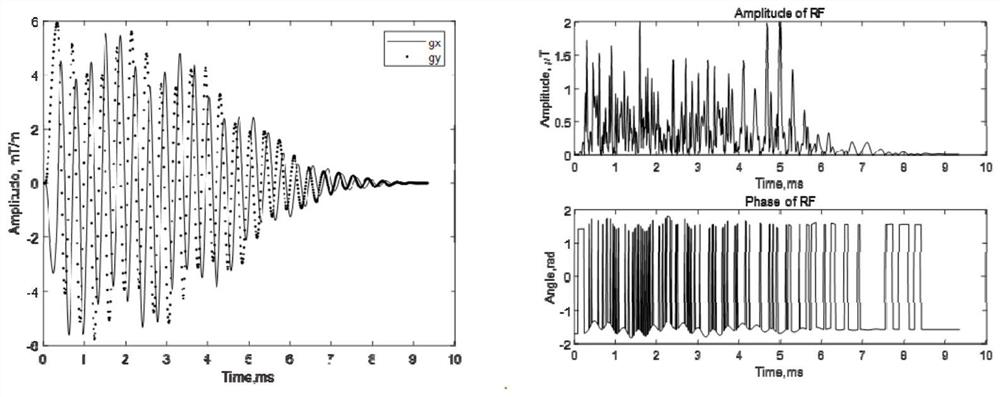
PendingCN114114115AAvoid Motion ArtifactsReduce sizeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsK-spaceRat heart
The invention relates to a heart image acquisition method and device, magnetic resonance equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a preset excitation space of a target scanning layer of a heart area, determining a target radio frequency pulse according to parameters of the preset excitation space and a preset gradient, exciting the preset excitation space by using the target radio frequency pulse, sampling the excited excitation space, filling a two-dimensional k space with sampling points, and obtaining a target scanning layer of the heart area; according to the method, the two-dimensional k space is subjected to image reconstruction to obtain the magnetic resonance heart image, the size of the original view space is reduced, it is ensured that the image in the systolic period can be scanned, and the two-dimensional k space is selected, so that motion artifacts generated during systole when a traditional three-dimensional k space is excited for scanning can be avoided.
Owner:UNITED IMAGING RES INST OF INNOVATIVE MEDICAL EQUIP
Using method of radiofrequency ablation device
PendingCN113598930ASuddenImprove securitySurgical instruments for heatingRf ablationRadiofrequency ablation device
The invention provides a use method of a radiofrequency ablation device. When a catheter radiofrequency ablation operation is started, the initial impedance value of the heart of a patient is detected and recorded as a, the change impedance value on a radiofrequency ablation instrument is set as b, and the change time zone on the radiofrequency ablation instrument is set as c; in the catheter radiofrequency ablation operation process, the heart impedance change rate delta d of the patient on the radiofrequency ablation instrument is observed in real time; when the catheter for catheter radiofrequency ablation performs continuous radiofrequency ablation on the heart of the patient, when the time is not longer than the change time zone c and the change rate delta d of the impedance value of the heart of the patient in real time is larger than the change impedance value b, the radiofrequency ablation action is stopped immediately; after ablation is stopped, the position of the catheter for catheter radiofrequency ablation in the heart continues to be transferred, and the heart area where the change rate delta d of the real-time patient heart impedance value is larger than the change impedance value b is avoided. According to the method, tiny gas explosion of heart tissues can be avoided, and the operation safety is improved.
Owner:罗剑锋
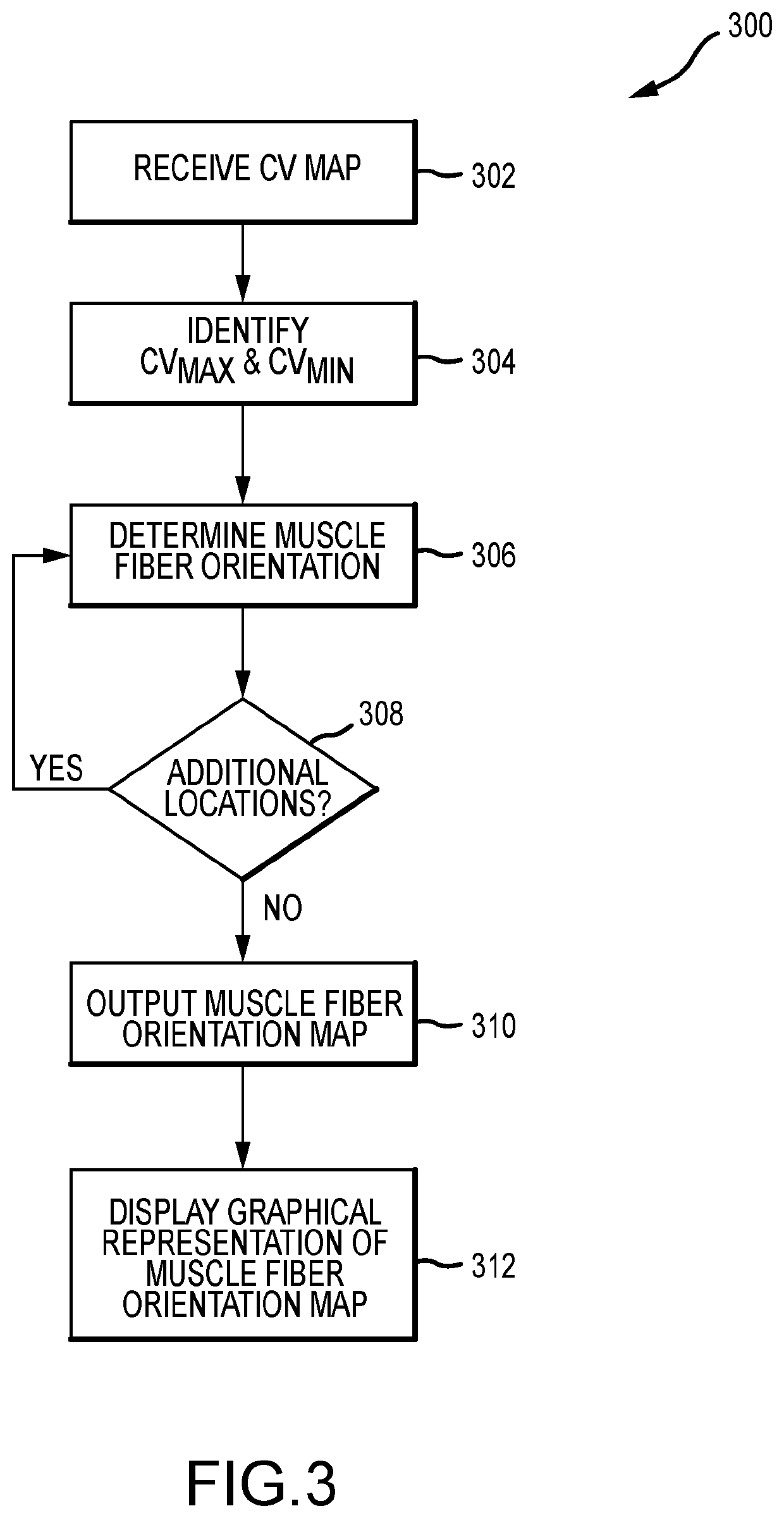
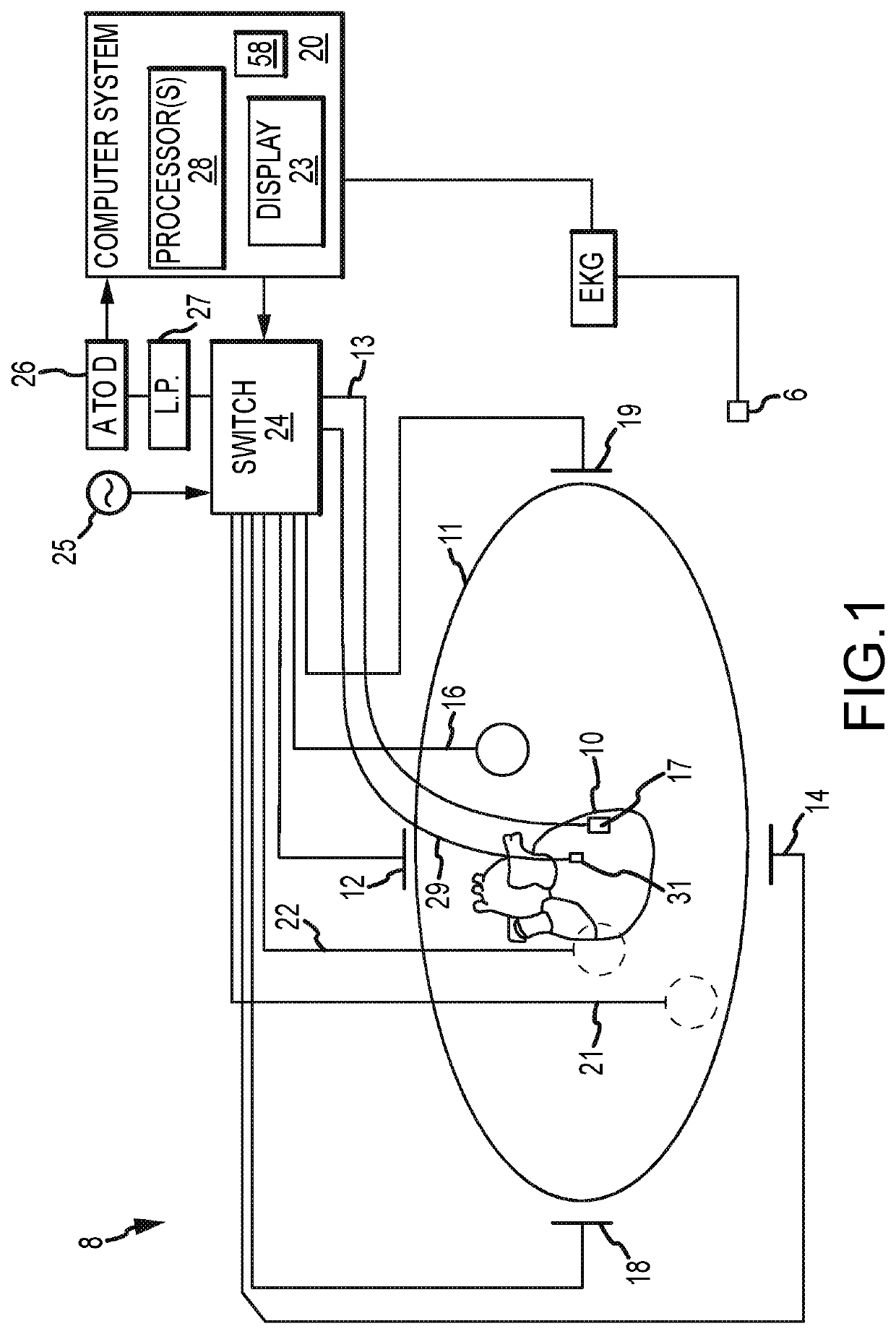
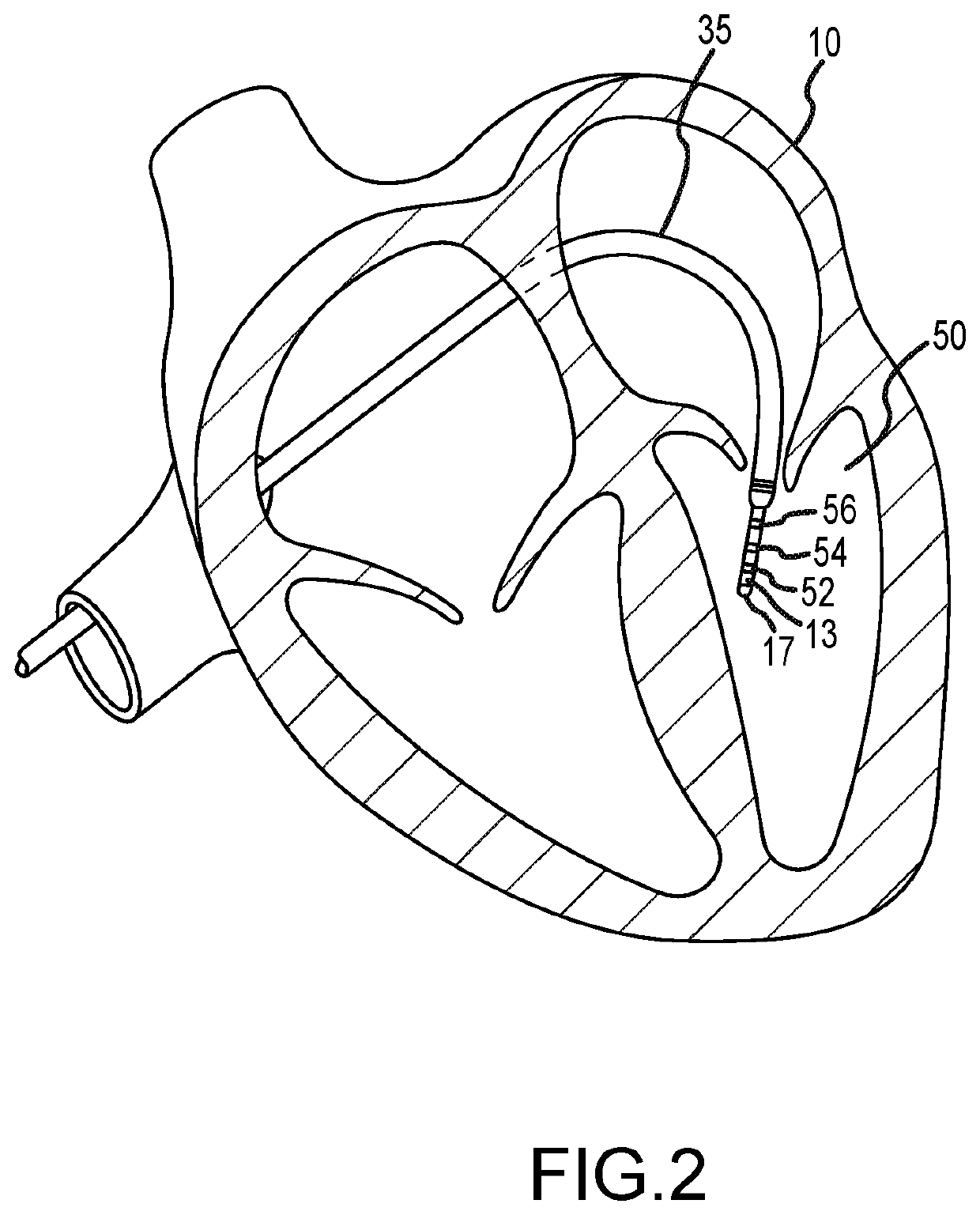
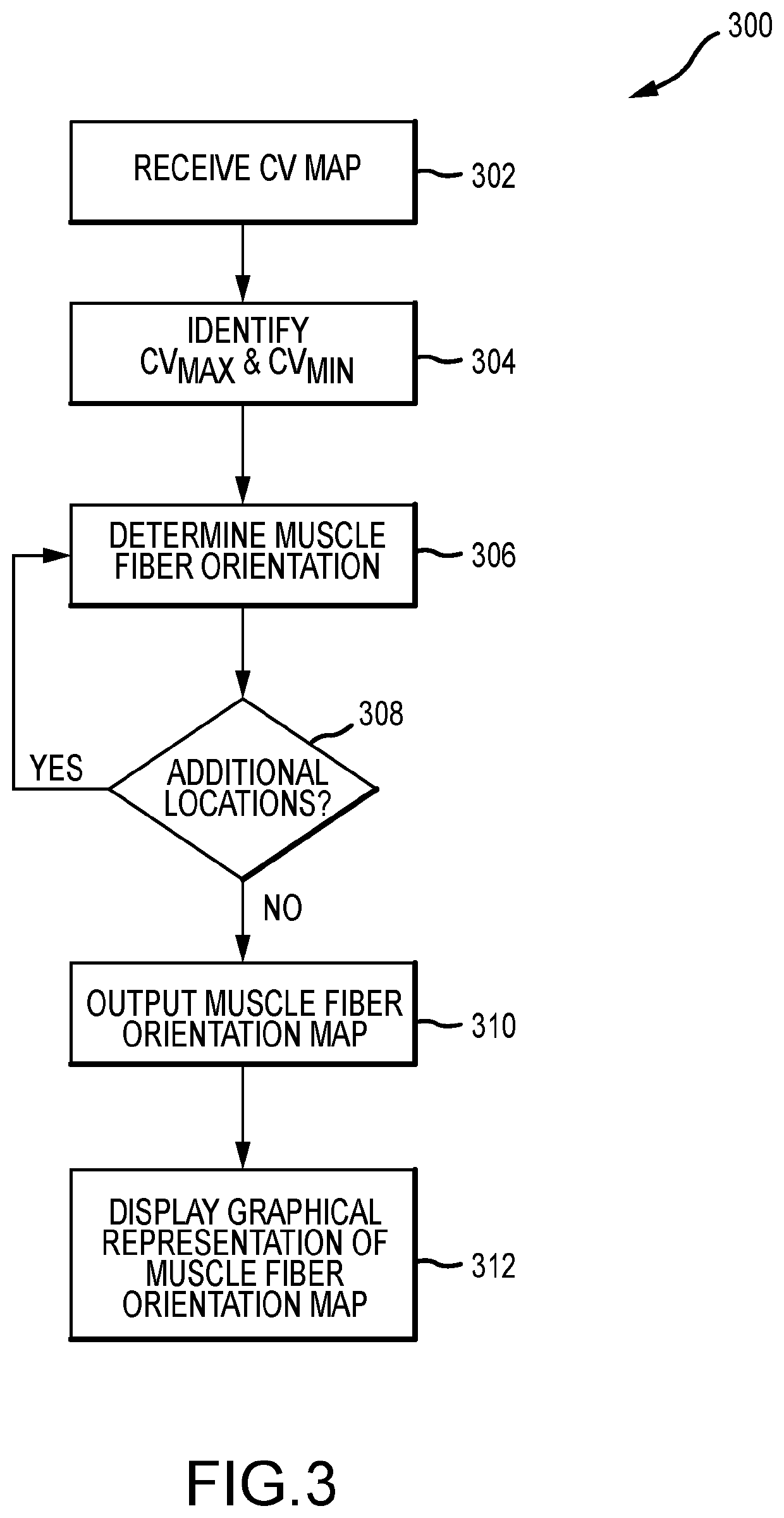
System and method for mapping cardiac muscle fiber orientation
Conduction velocity information for a cardiac region can be used to map the cardiac muscle fiber orientation of that region. In particular, for a plurality of locations within the cardiac region, a relationship between a local conduction velocity, a maximum local conduction velocity within the region, and a minimum local conduction velocity within the region is used to determine the cardiac muscle fiber orientation at the respective location. Even more particularly, when the local conduction velocity at the respective location equals the maximum local conduction velocity, the cardiac muscle fiber orientation is parallel to a direction of a conduction velocity vector at the respective location, and when the local conduction velocity at the respective location equals the minimum local conduction velocity, the cardiac muscle fiber orientation is perpendicular to a direction of a conduction velocity vector at the respective location.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
System and Method for Mapping Cardiac Muscle Fiber Orientation
Conduction velocity information for a cardiac region can be used to map the cardiac muscle fiber orientation of that region. In particular, for a plurality of locations within the cardiac region, a relationship between a local conduction velocity, a maximum local conduction velocity within the region, and a minimum local conduction velocity within the region is used to determine the cardiac muscle fiber orientation at the respective location. Even more particularly, when the local conduction velocity at the respective location equals the maximum local conduction velocity, the cardiac muscle fiber orientation is parallel to a direction of a conduction velocity vector at the respective location, and when the local conduction velocity at the respective location equals the minimum local conduction velocity, the cardiac muscle fiber orientation is perpendicular to a direction of a conduction velocity vector at the respective location.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
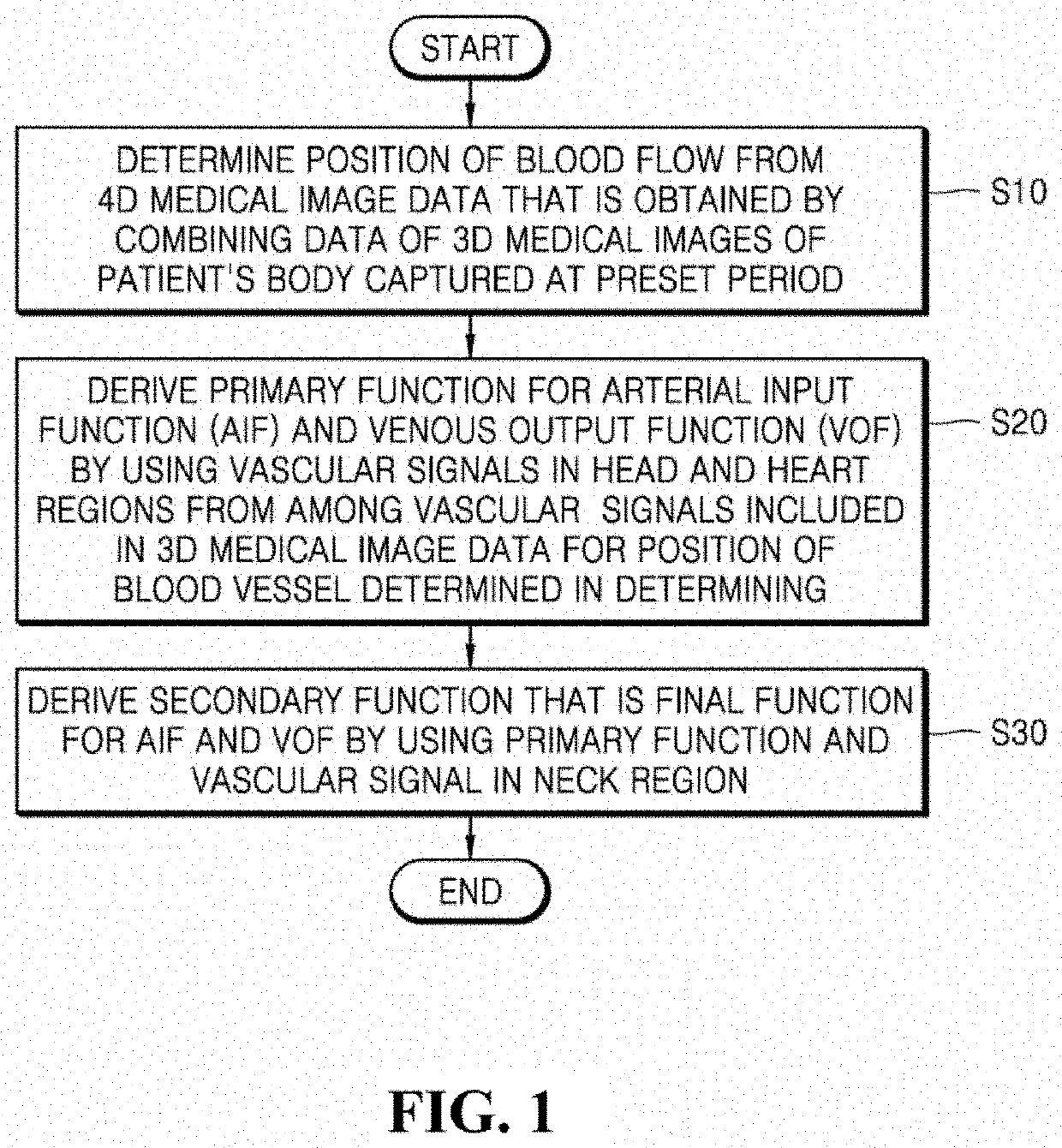
Method for analyzing blood flow by using medical image
ActiveUS10750964B2Accurate detectionAccurate analysisImage enhancementImage analysisVeinVenous blood flow
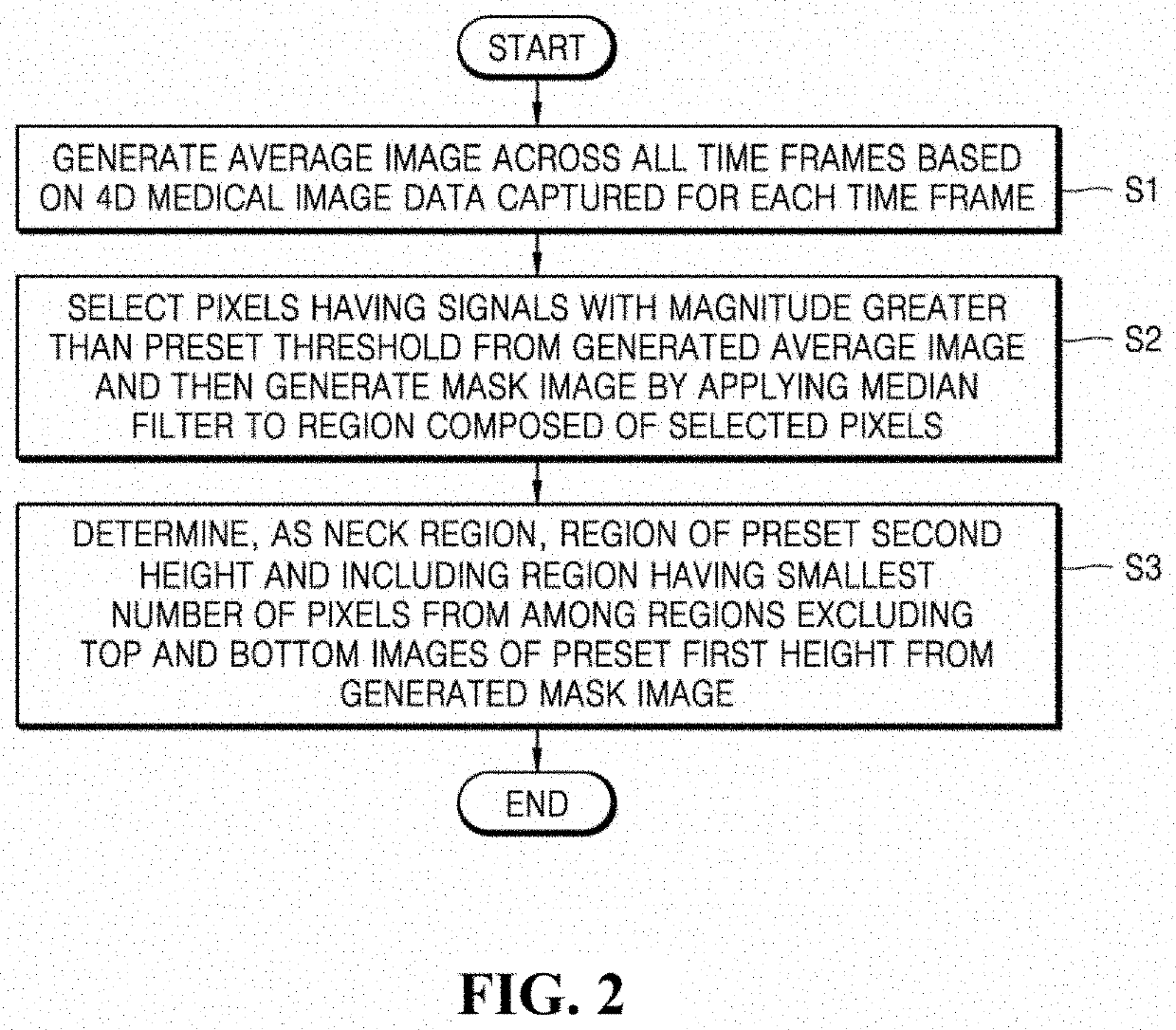
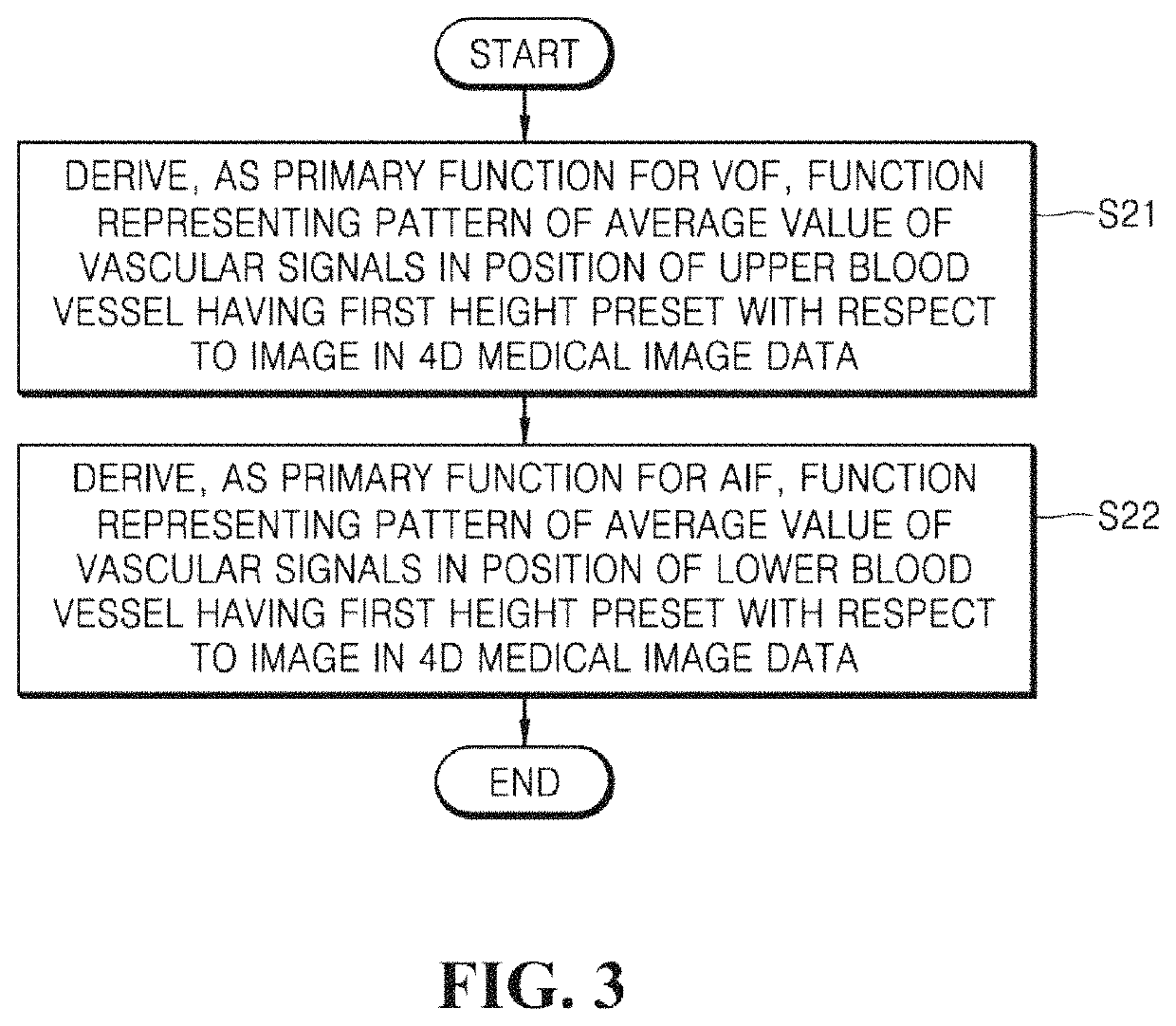
Provided is a technique for deriving a mathematical function for defining arterial and venous blood flow in the body by using a four-dimensional medical image. A method of analyzing blood flow by using a medical image according to an embodiment of the present disclosure includes: determining a position of a blood vessel from four-dimensional medical image data that is obtained by combining data of three-dimensional medical images of a patient's body captured at a preset period; deriving a primary function for an arterial input function and a venous output function by using a vascular signal in a head region and a vascular signal in a heart region from among vascular signals included in three-dimensional medical image data for the position of the blood vessel determined in the determining; and deriving a secondary function that is a final function for the arterial input function and the venous output function by using the primary function and a vascular signal in a neck region.
Owner:THE CATHOLIC UNIV OF KOREA IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Myocardial CT perfusion image synthesis
The present invention relates to image processing devices and related methods. The image processing device (10) comprises a data input (11) for receiving spectral computed tomography volumetric image data organized in voxels. The image data comprises a contrast-enhanced volumetric image of a cardiac region in a subject's body and a baseline volumetric image of that cardiac region, e.g. a virtual non-contrast image, wherein the contrast-enhanced volumetric image conveys anatomical information regarding coronary artery anatomy of the subject. The device comprises a flow simulator (12) for generating, or receiving as input, a three-dimensional coronary tree model based on the volumetric image data and for simulating a coronary flow based on the three-dimensional coronary tree model. The device comprises a perfusion synthesis unit (13) for generating a perfusion image representative of a blood distribution in tissue at at least one instant in time taking at least the baseline volumetric image and said coronary flow simulation into account.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Coronary circulation using intra-cardiac echo
PendingUS20210307722A1Precise positioningReduce needOrgan movement/changes detectionCatheterCoronary arteriesCardiac echo
The present invention relates to an intra cardiac echo imaging device, an intra cardiac echo imaging system and method for assessing coronary circulation using an intra cardiac echo probe. An image of a cardiac region is received, wherein the image provides at least one or more coronary vessels and / or at least one heart chamber; at least one region of interest within the image is defined; imaging parameters of an intra cardiac echo probe are received; and at least one of a location, an orientation and access path of the intra cardiac echo probe relative to the region of interest is calculated based on: anatomical content in the region of interest and / or in the cardiac region and the imaging parameters of the intra cardiac echo probe; a roadmap and the at least one of the calculated location, orientation and access path of the intra cardiac echo probe is output to a display.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Segmentation of the cardiac region in CT images
The present disclosure pertains to the analysis of the cardiac region in CT images. Provided herein are a method, a computer system and a computer program product for the segmentation of the cardiac region in CT images.
Owner:BAYER AG
Determining calcium content from spectral CT data
ActiveUS10929974B2Good, efficient and/or robust methods and means for determiningImage enhancementReconstruction from projection3d imageCardiovascular structure
Present invention relates to devices and methods for determining a calcium content by analyzing cardiac spectral CT data. CT projection data (9), obtainable by scanning a cardiac region of a subject using a spectral CT scanning unit, is modelled (12) by applying a material decomposition algorithm to the projection data to provide a calcium-specific component. Tomographic reconstructions (13) of the projection data, to provide a first 3D image (8), and of the calcium-specific component, to provide a second 3D image (6), are performed. The first 3D image (8) is segmented (14) to provide an image mask (5) corresponding to a cardiovascular structure of interest, a part of the second 3D image (6) is selected (15) based on the image mask (5), and a calcium content is calculated (16) in the cardiovascular structure of interest based on the selected part of the second 3D image (6).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
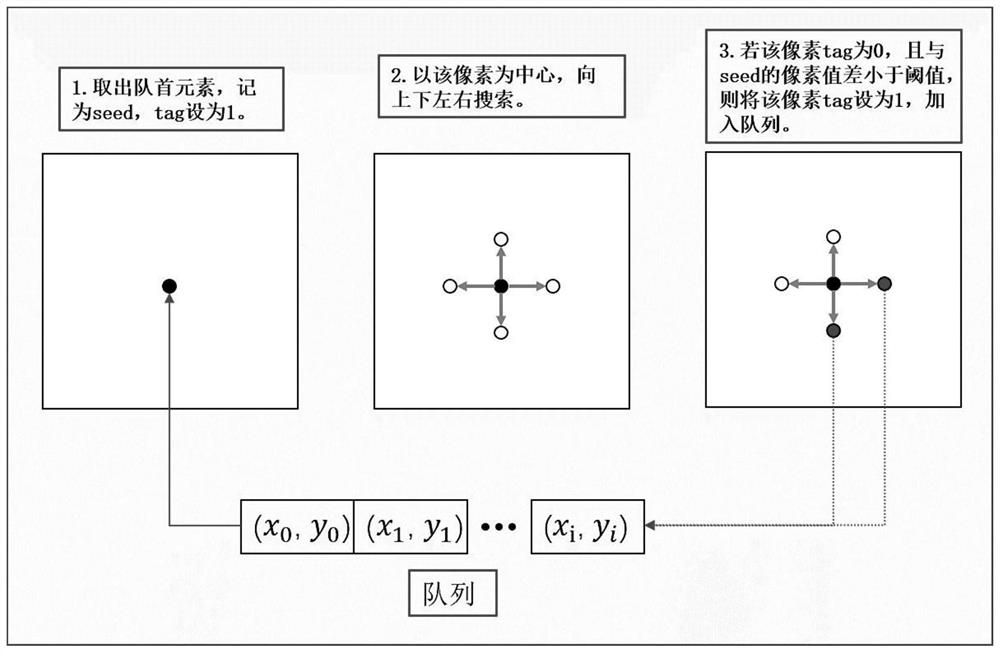
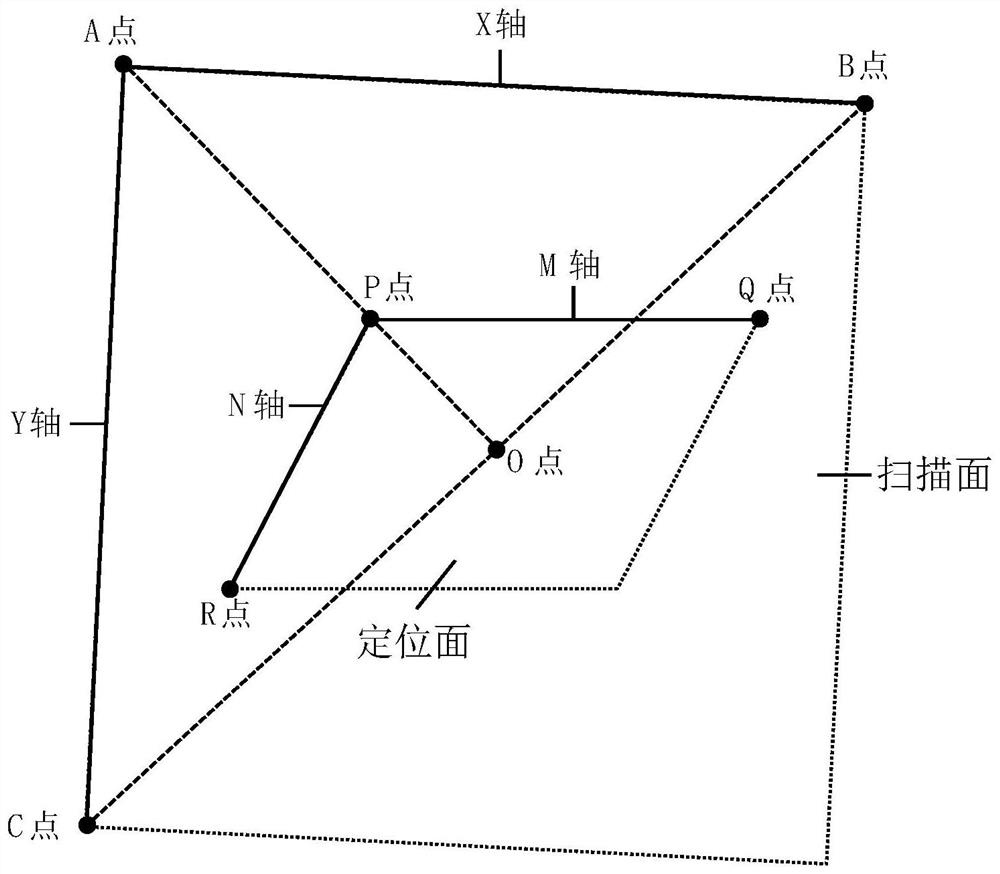
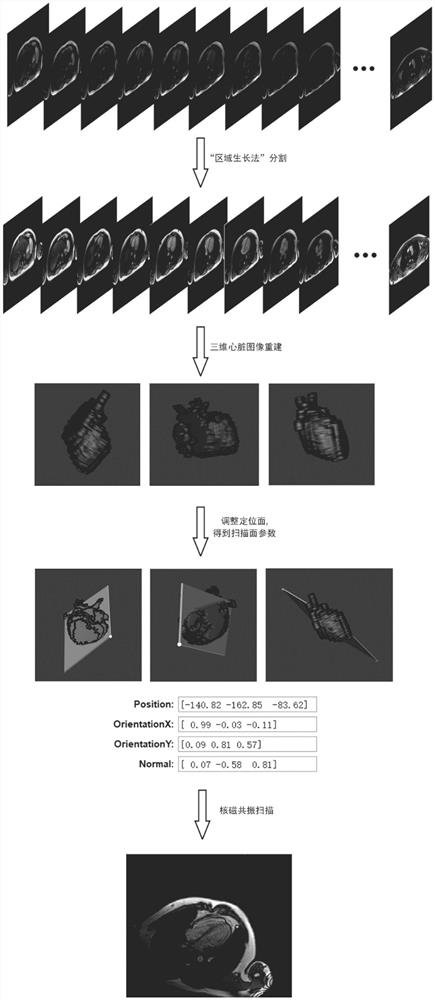
Heart three-dimensional positioning method based on MR horizontal axis image segmentation
PendingCN114419071AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisThoracic structureRadiology
The invention discloses a heart three-dimensional positioning method based on MR horizontal axis image segmentation, which comprises the following steps: scanning multiple layers of MR horizontal axis images, segmenting a heart region by using a region growing segmentation algorithm, reconstructing a three-dimensional heart image, manually adjusting a positioning surface, calculating parameters of a scanning surface, and inputting the parameters into a scanning instrument to complete scanning of four-cavity heart, horizontal axis and long axis of the heart. Compared with a manual positioning method, the method has the advantages that scanning surfaces such as a long axis, a short axis and a four-cavity heart of the heart can be directly scanned only by scanning a thoracic cavity image at a horizontal axis position, obtaining scanning surface parameters through post-processing and inputting the scanning surface parameters into a magnetic resonance scanning system, so that the time consumed by a positioning process is shortened, and the accuracy of heart positioning is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method of estimating physiological parameters using medical image data
PendingCN111902879AMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesTissue architectureMedical imaging data
A method (12) of estimating one or more physiological parameters, in particular of a cardiac region, based on medical imaging data. An input time series of three-dimensional medical images is received(14), representative of a cardiac region of a patient. A meshless simulation framework is applied (16) for simulating blood flow through at least a portion of the anatomical area captured by the images. The simulation framework comprises in particular simulating force interactions between individual elements of a simulated fluid (representing blood) and individual patches of a tissue structure ofthe imaged cardiac region. One or more physiological parameters (18) are derived based on the simulated blood flow.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
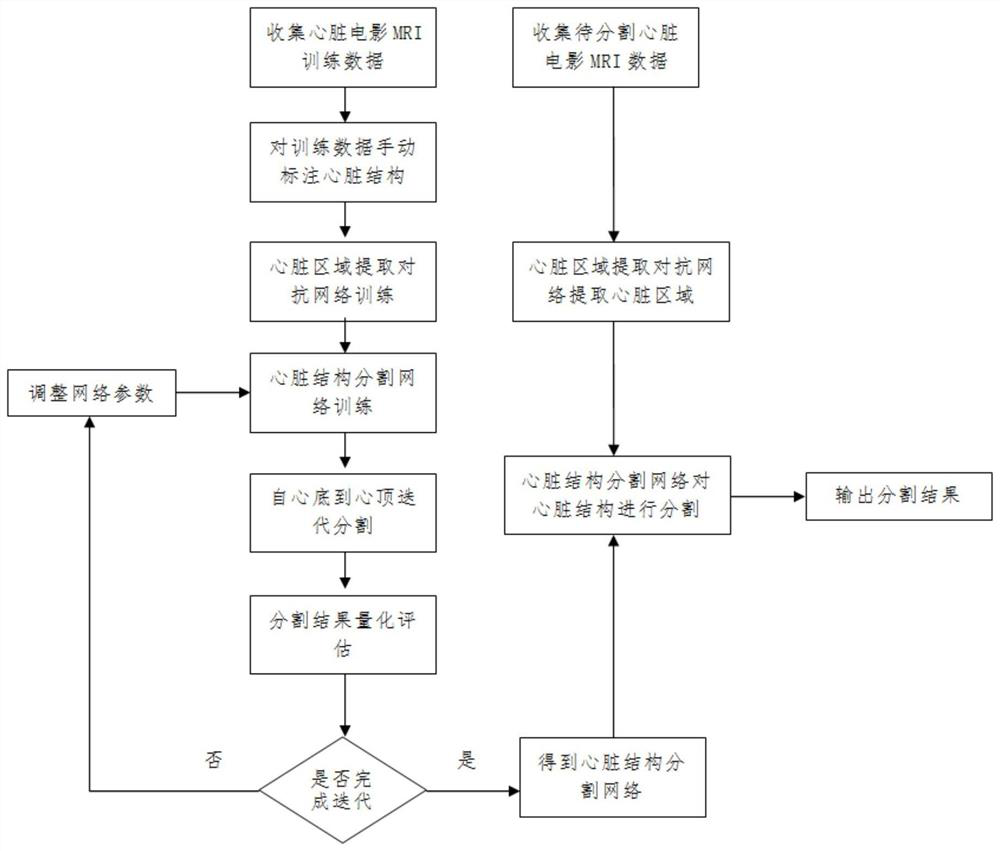
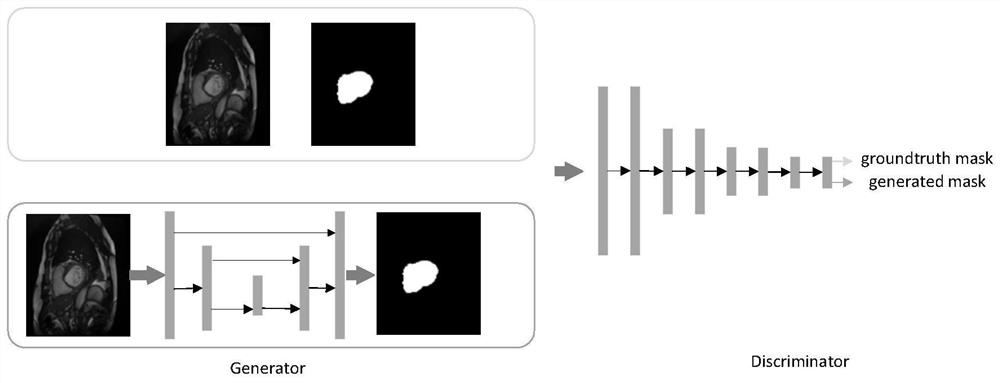
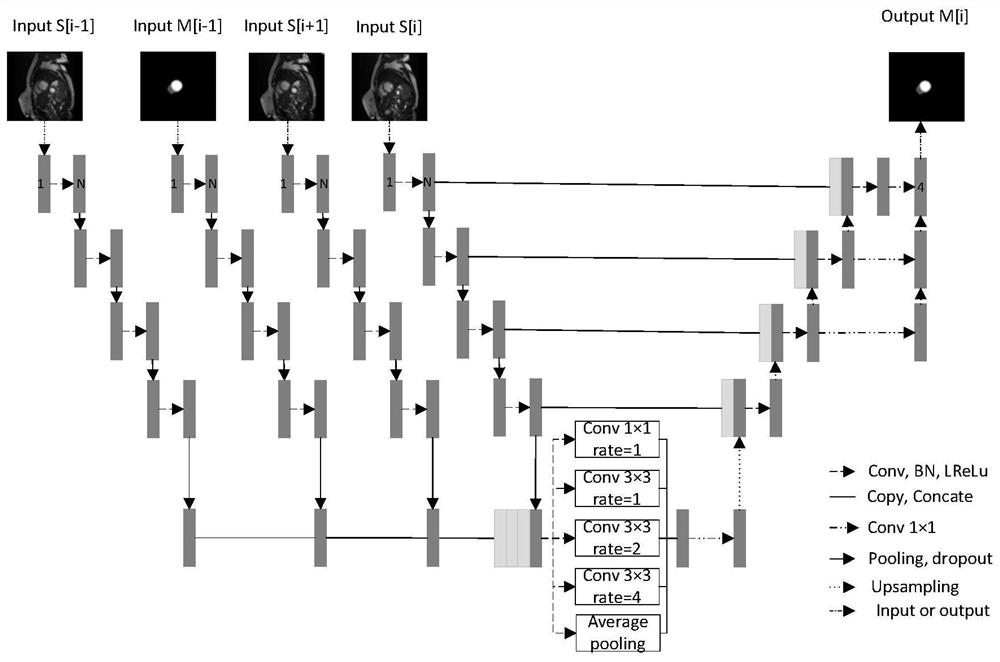
Segmentation method of cardiac structure in MRI images based on multi-channel convolutional neural network
ActiveCN110599499BExtract automaticallyAccurate extractionImage enhancementImage analysisHeart diseaseComputer vision
The present invention relates to a method for segmenting cardiac structures in MRI images based on a multi-channel convolutional neural network, which includes collecting heart movie MRI training data of normal people and heart patients, and manually marking the cardiac structures in the training data by experienced doctors as Heart segmentation labeling results, based on the training data to train the heart region extraction model, so that the heart region extraction model can accurately extract the heart region, and train the heart segmentation network according to the heart region extracted from the training data to segment the heart Structure, using the standard segmentation labeling results as a standard to measure the segmentation performance of the constructed heart segmentation network. The present invention uses a heart region extraction model based on a generative confrontation network to extract the heart, which improves the accuracy of the heart region extraction; at the same time, the context information between adjacent layers is used through a multi-channel convolutional neural network, which improves the segmentation accuracy and accuracy. Spend.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com