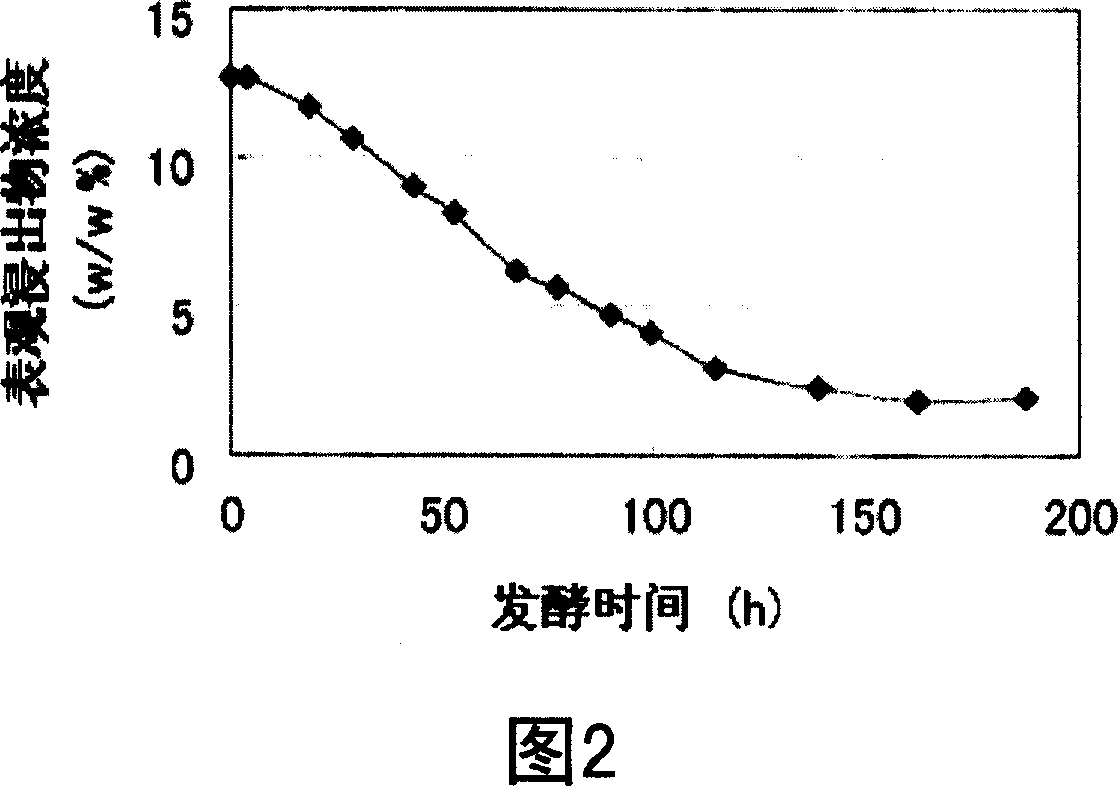
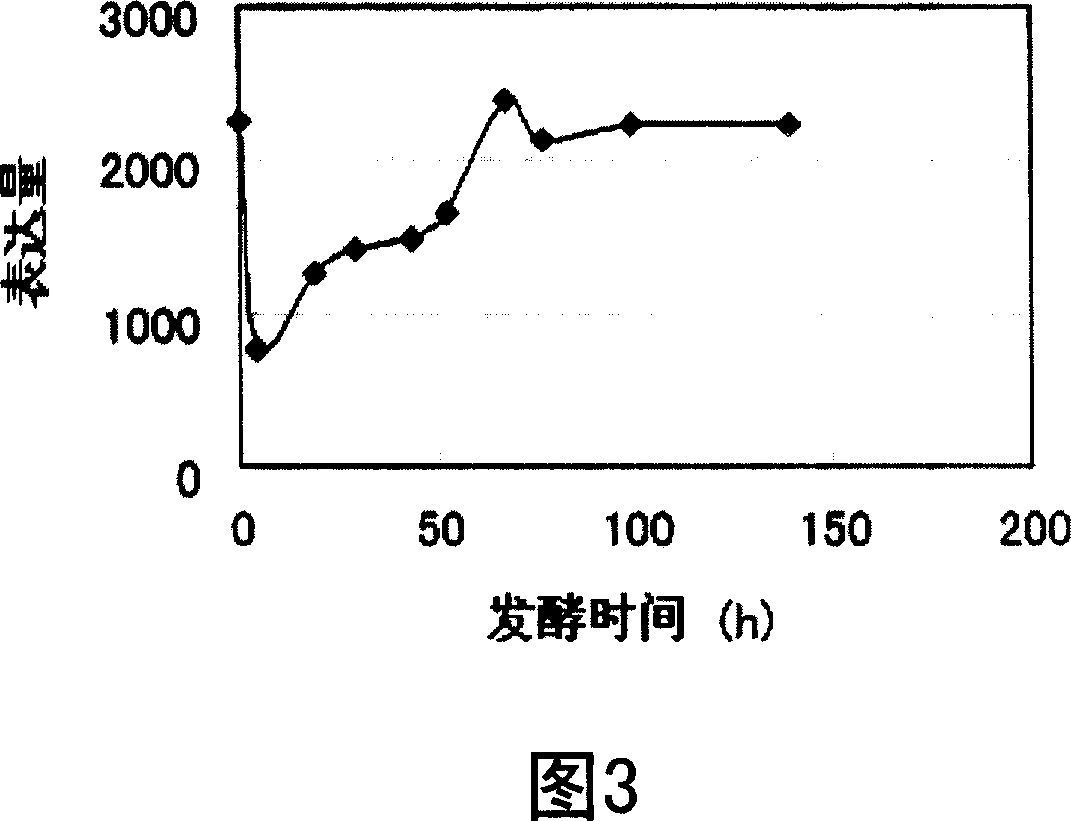
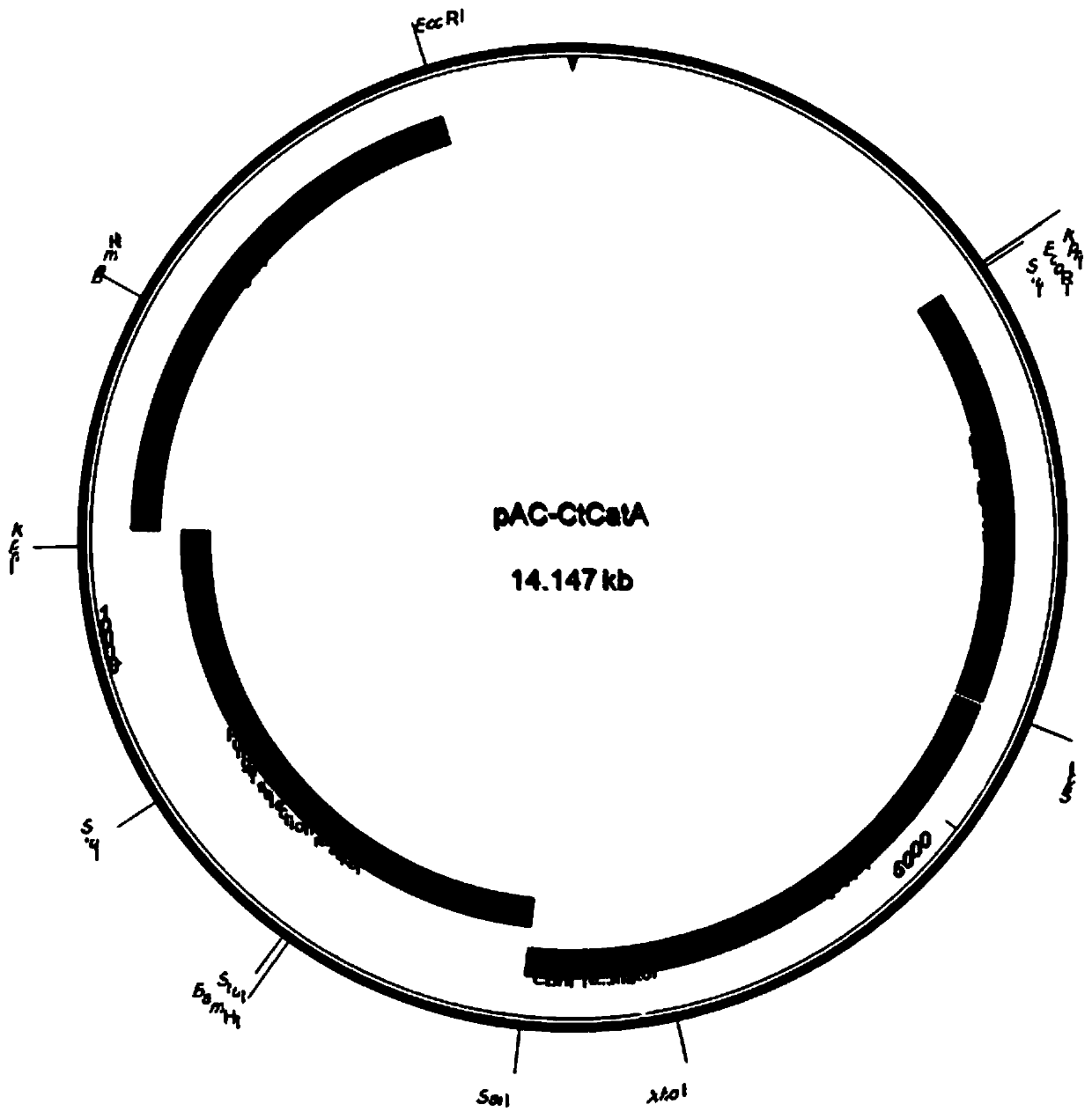
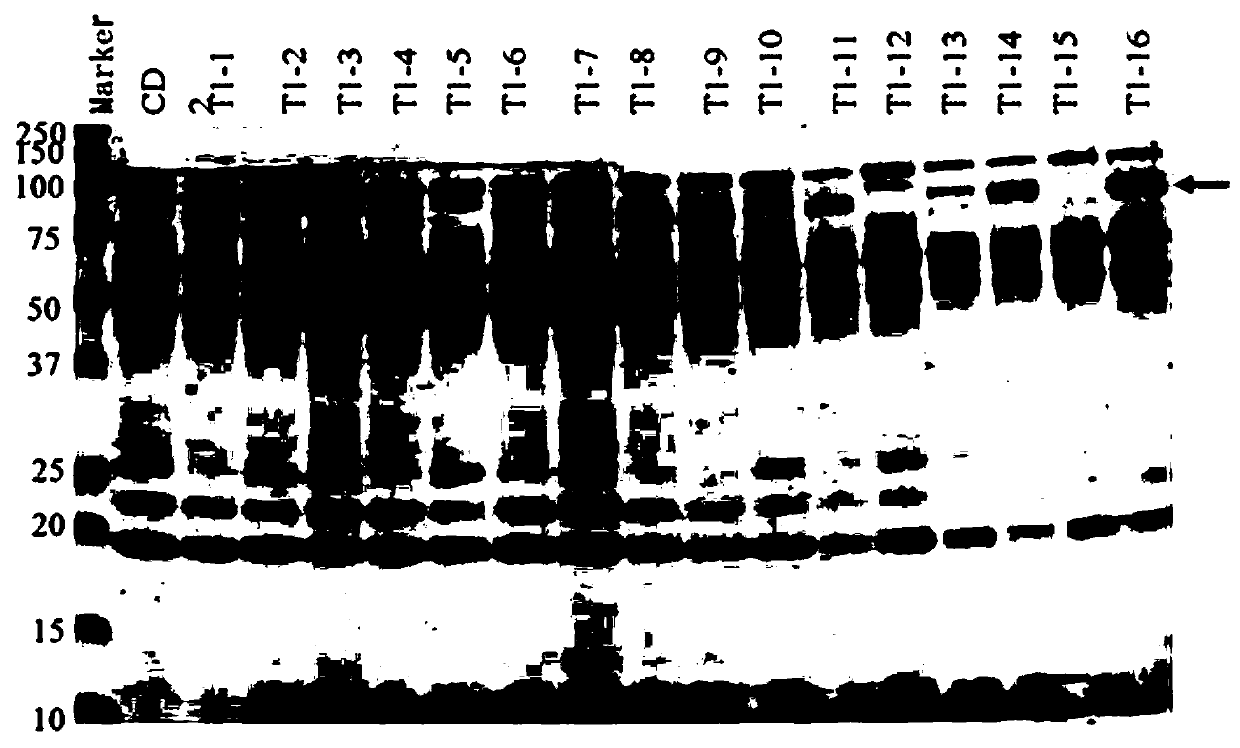
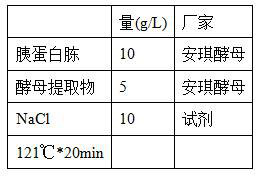
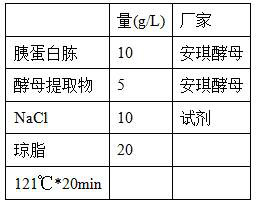
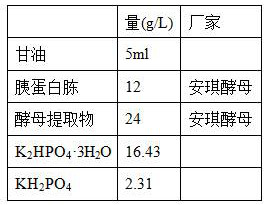
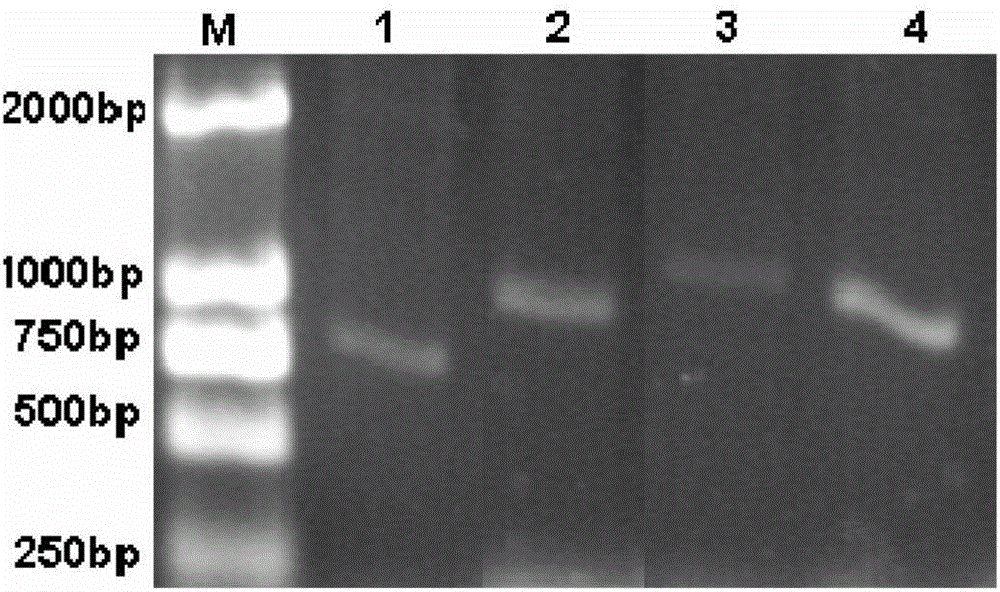
Patents
Literature
46 results about "Catalase Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This gene encodes catalase, a key antioxidant enzyme in the bodies defense against oxidative stress. Catalase is a heme enzyme that is present in the peroxisome of nearly all aerobic cells.
Method by using co-expression recombinant bacteria strain to convert and produce alpha-ketoglutarate
ActiveCN107686850AHigh yieldSolve the problem that a large amount of catalase needs to be added from an external sourceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliStreptomyces
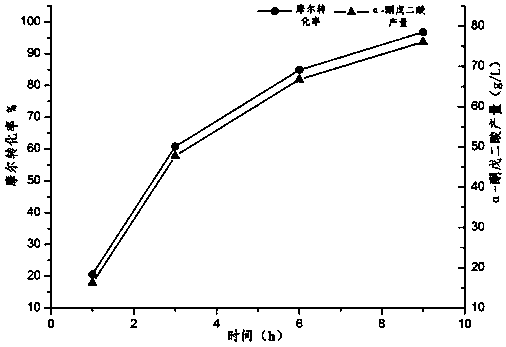
The invention discloses a method by using a co-expression recombinant bacteria strain to convert and product alpha-ketoglutarate, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The method is characterized in that novel L-glutamic oxidase is screened from streptomycete and is induced to express and purify in escherichia coli, and the enzymatic property is studied; when the pH (potential of hydrogen) value is 5.5 to 7.0, the enzyme has higher activity, the most suitable reaction temperature is 30 to 45 DEG C, Vmax is 100 to 150U / mg, and Km is 8 to 10mM; the original gene sequence of the L-glutamic oxidase is subject to codon optimization, and the plasmid co-expression with a catalase gene from the escherichia coli is performed, so as to construct the co-expression recombinant bacteria strain; the recombinant bacteria strain is used as a whole-cell catalyst to convert the L-glutamic acid (salt), the output of alpha-ketoglutarate reaches 76.08g / L after reacting for 9h, and the molar conversion rate is 96.8%. The method has the advantages that the problems of complicated production steps, low yield, pollution to environment and the like in the alpha-ketoglutarate production process aresolved, the high-yield and one-step type production of the alpha-ketoglutarate is realized, and the industrial application value is higher.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
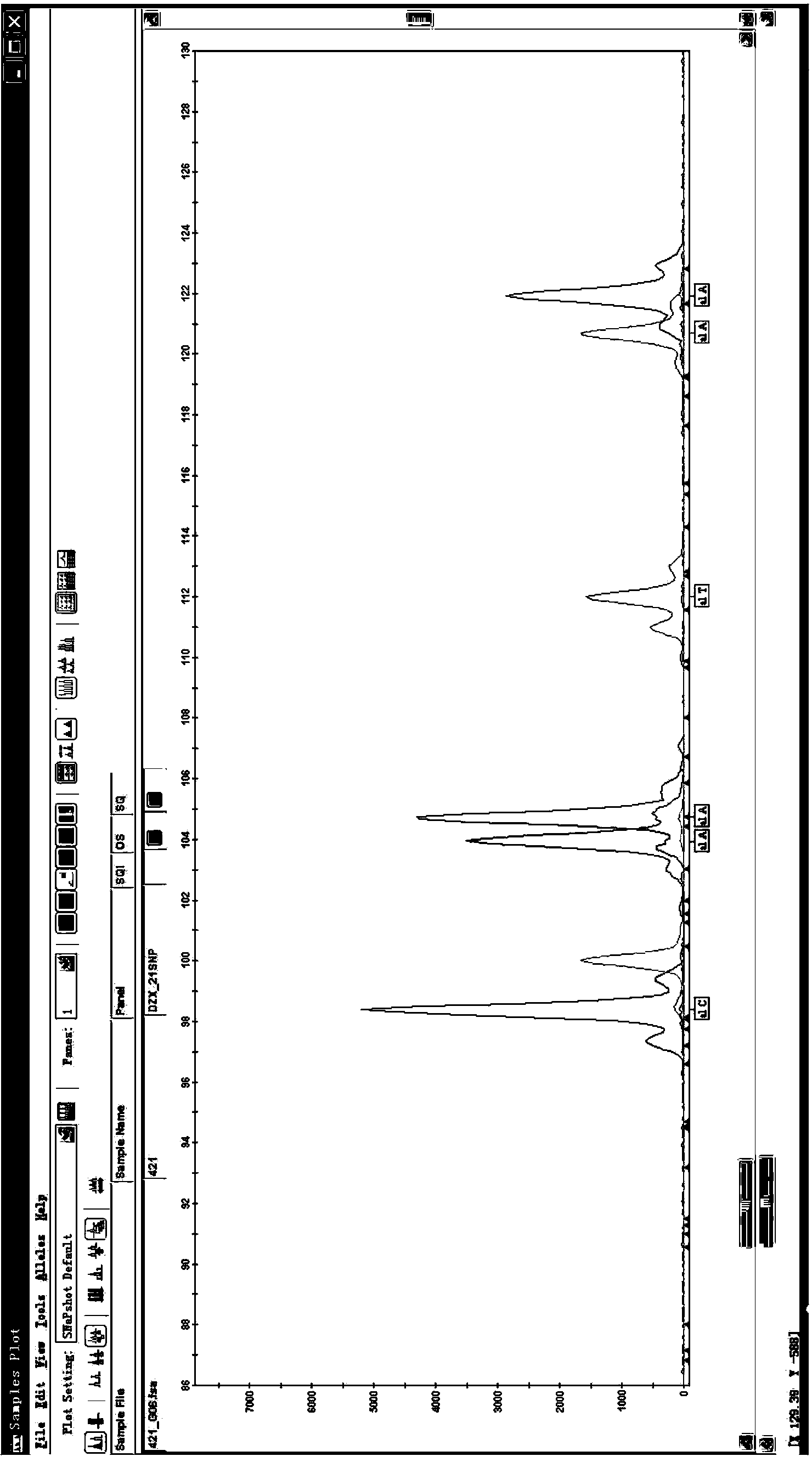
Selection, detection and application of catalase gene tagging single nucleotide polymorphic sites
InactiveCN103642921AReduce inductionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideHaplotype
The design of the invention relates to selection, detection and application of tagging single nucleotide polymorphic sites of a catalase (CAT) gene, and further relates to a haplotype consisting of the tagging single nucleotide polymorphic (SNP) sites of the CAT gene, a detection method of the haplotype and a kit for detecting the tagging single nucleotide polymorphic sites of the CAT gene. According to the selection, detection and application disclosed by the invention, 6 tagging SNP sites of the CAT gene related to noise-induced deafness are screened, wherein risk of an individual carrying an rs769217 site C allelic gene and suffering from the noise-induced deafness is greatly increased when noise intensity is 85-92dB, and risk of an individual carrying an rs208679 site A allelic gene and suffering from the noise-induced deafness is greatly increased when noise intensity is less than 85dB; a specific combined haplotype A-G-T-C-A-C individual carrying six tagging SNP sites, compared to other haplotype individuals, is higher in risk of suffering from the noise-induced deafness.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Catalase and high-yielding genetic engineering strains thereof
ActiveCN106047829AEasy to synthesizeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousEscherichia coli
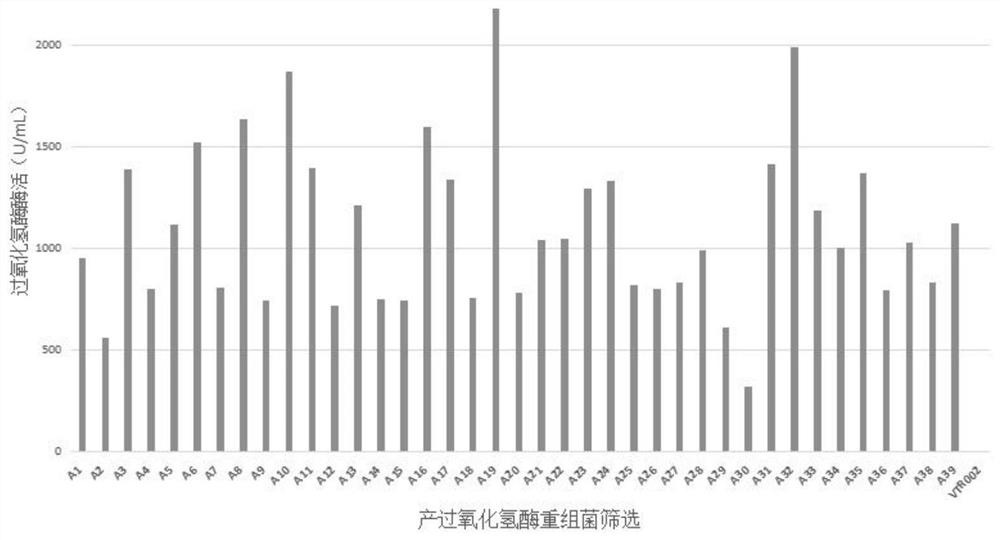
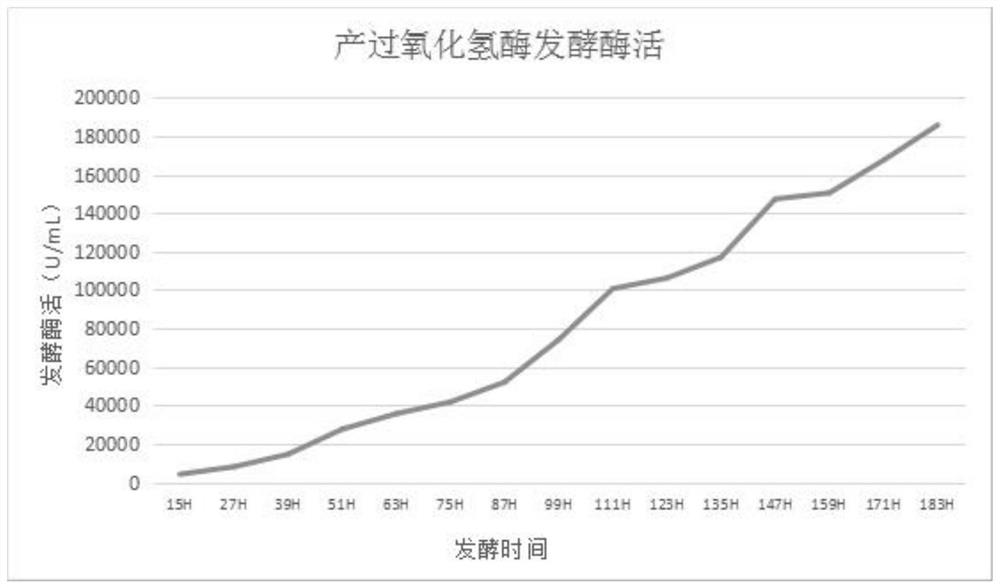
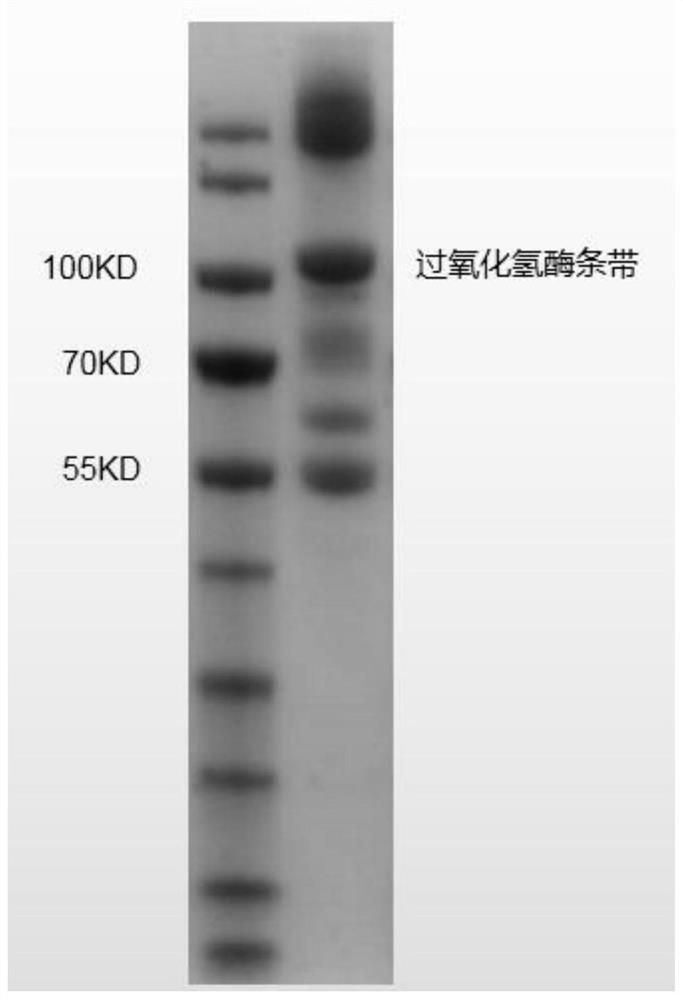
The invention relates to a novel-originated catalase and the construction of recombinant engineering strains of the catalase. The construction is characterized in that primers are designed according to a catalase gene of bacillus pumilus for the first time, and recombinant expression vectors are constructed; the vectors are converted to genetic engineering strains, i.e., Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis for heterologous expression; the recombinant engineering strains are subjected to fermented cultivation through a 5L fermentation tank by using a fermentation culture medium, wherein catalase of recombinant Escherichia coli is mainly subjected to intracellular expression and has the enzyme activity of 6645U / mL, catalase of recombinant B. subtilis 168 has the total enzyme activity of 23,263U / mL and the extracellular enzyme activity of 15,368U / mL, catalase of B. subtilis WB600 has the total enzyme activity of 26,635U / mL and the extracellular enzyme activity of 20,128U / mL, the extracellular synthesis of the catalase is better facilitated by using the B. subtilis WB600 as a host, and thus the B. subtilis WB600 has an important industrial application value. The invention achieves the maximum yield compared with currently-reported methods which are used for producing the catalase by using microbes, so that a practical and effective policy for industrial production of the catalase is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
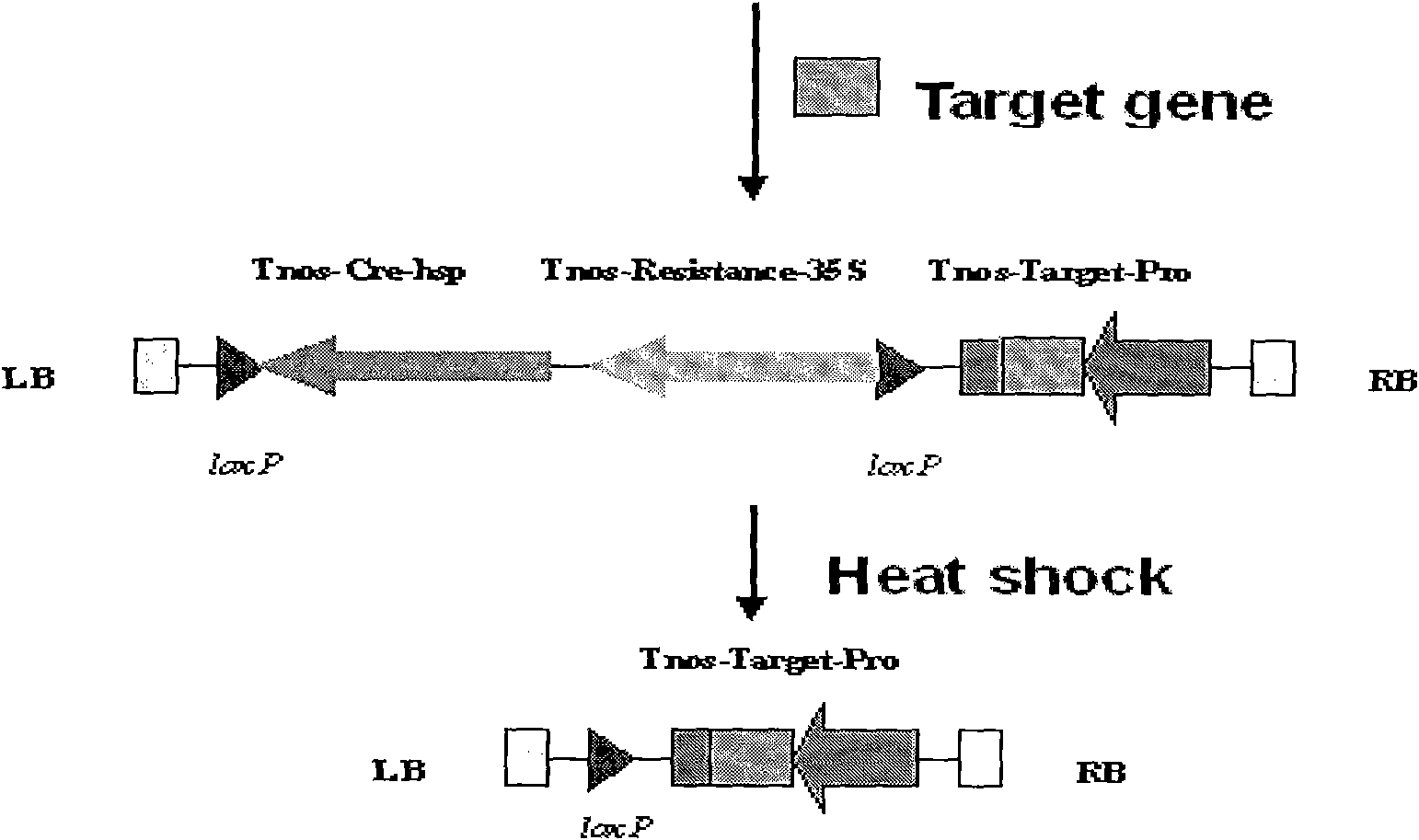
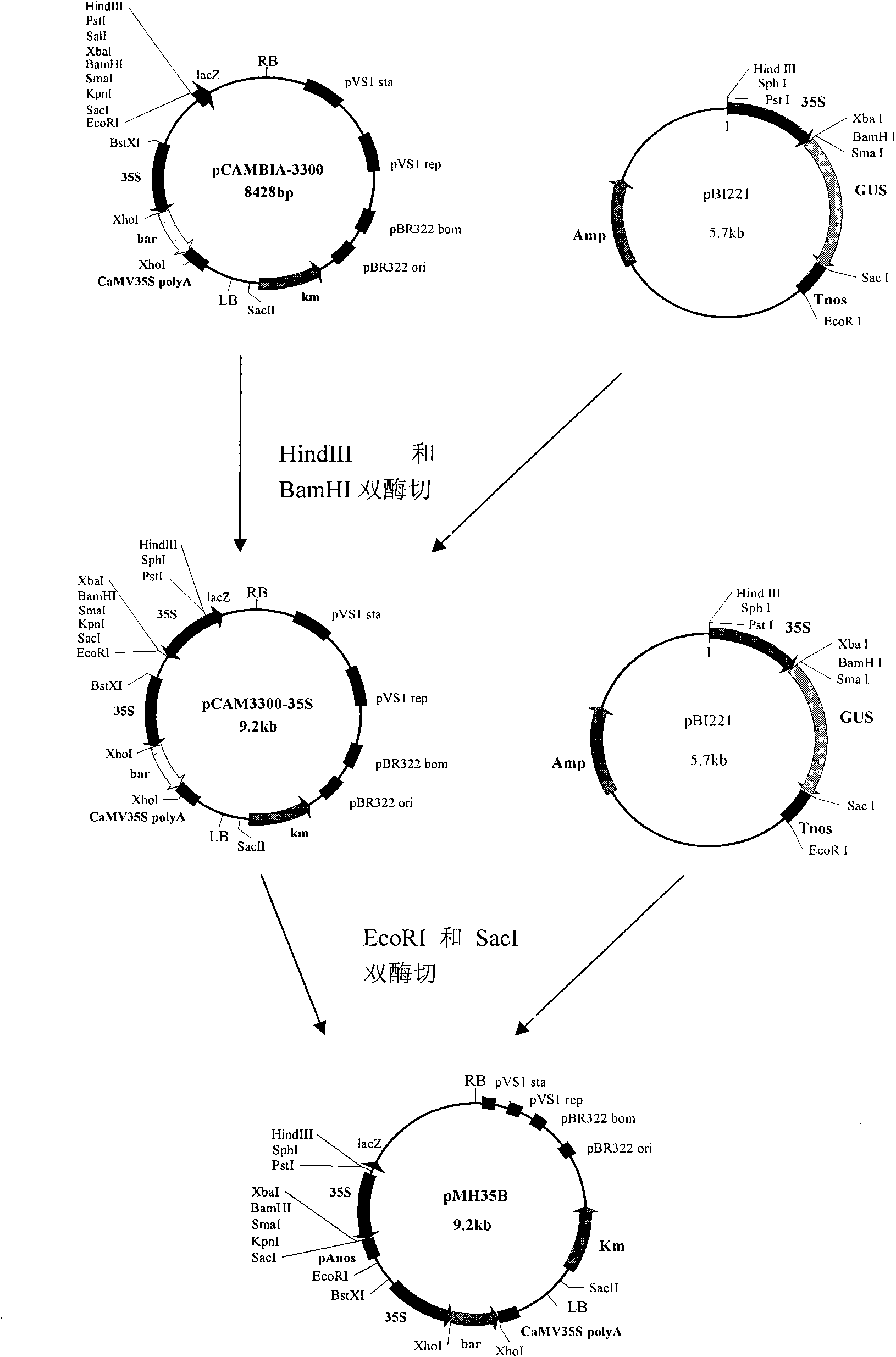
Expression vector capable of efficiently deleting selectable marker gene of transgenic plant and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102311971AImprove breeding efficiencyAvoid difficultiesVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsInteinPlant genetic engineering
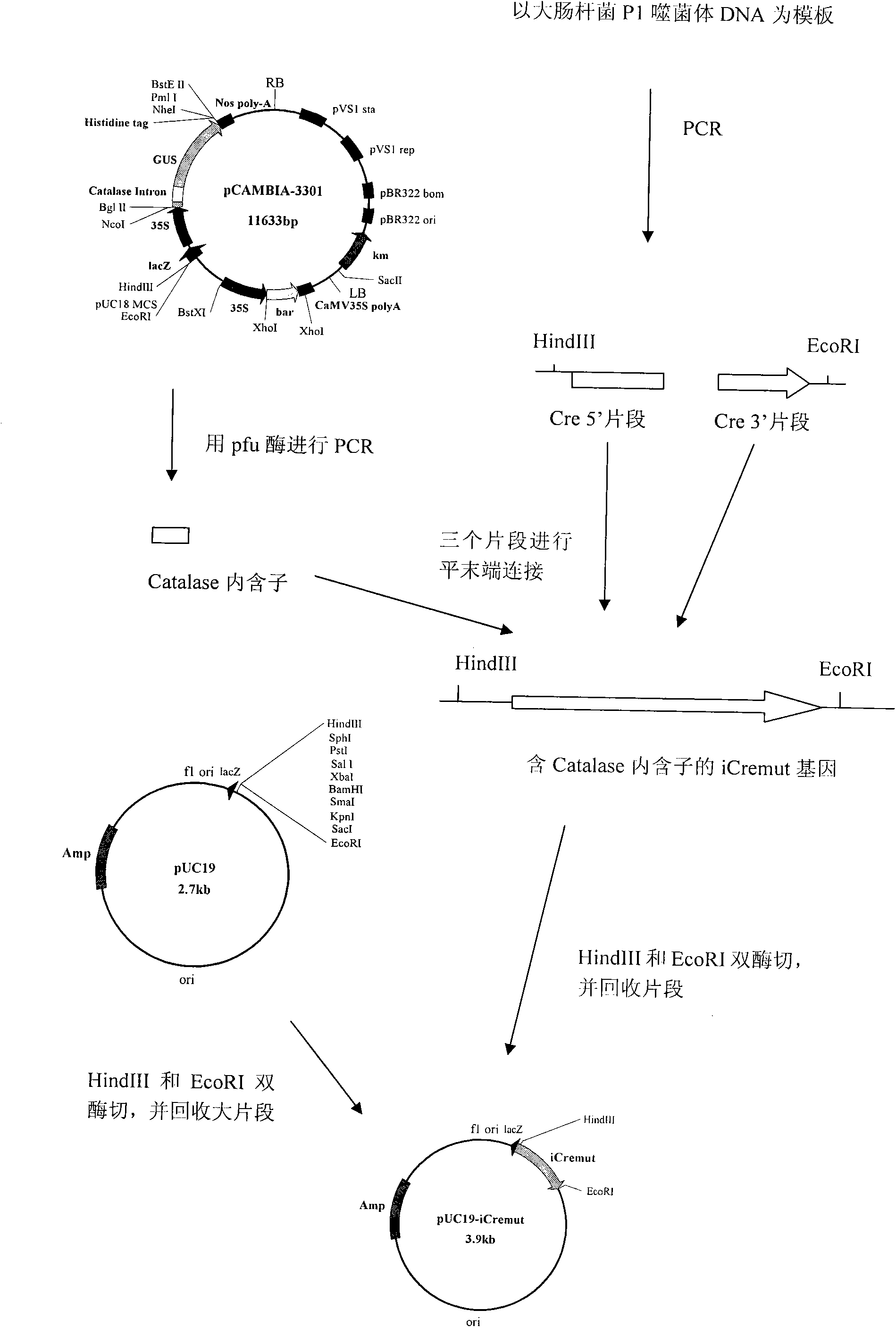
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering and provides an expression vector capable of efficiently deleting a selectable marker gene of a transgenic plant. The expression vector contains a Cre gene expression box, a selectable marker gene expression box, a promoter for driving a target gene, a terminator of the target gene and a polyclone site for inserting the target gene; the base sequence of the Cre gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1; and the Cre gene expression box and the selectable marker gene expression box are located between two equidirectional loxP sites. An introne of a catalase gene from a castor-oil plant is inserted to the Cre gene so that the expression of the Cre gene in microorganisms is prevented, the difficulty of constructing the expression vector is overcome, the efficiency of transforming plants by Agrobacterium tumefaciens is increased, and the cultivating efficiency of the transgenic plants is greatly increased.
Owner:林忠平
Catalase with high enzyme activity, gene, recombinant strain with high catalase yield and application
ActiveCN112522227AEfficient productionOvercome the problem of low expression efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyGenetic engineering
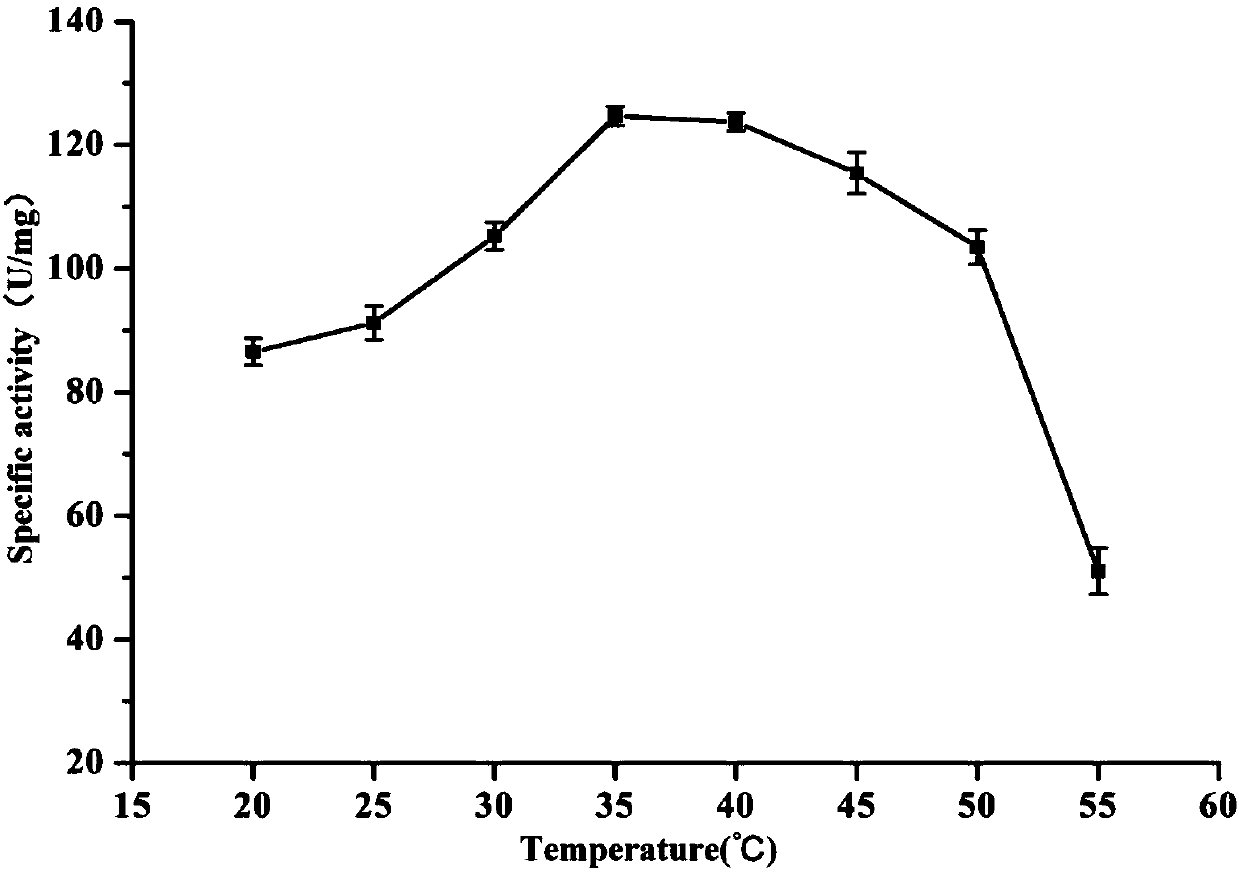
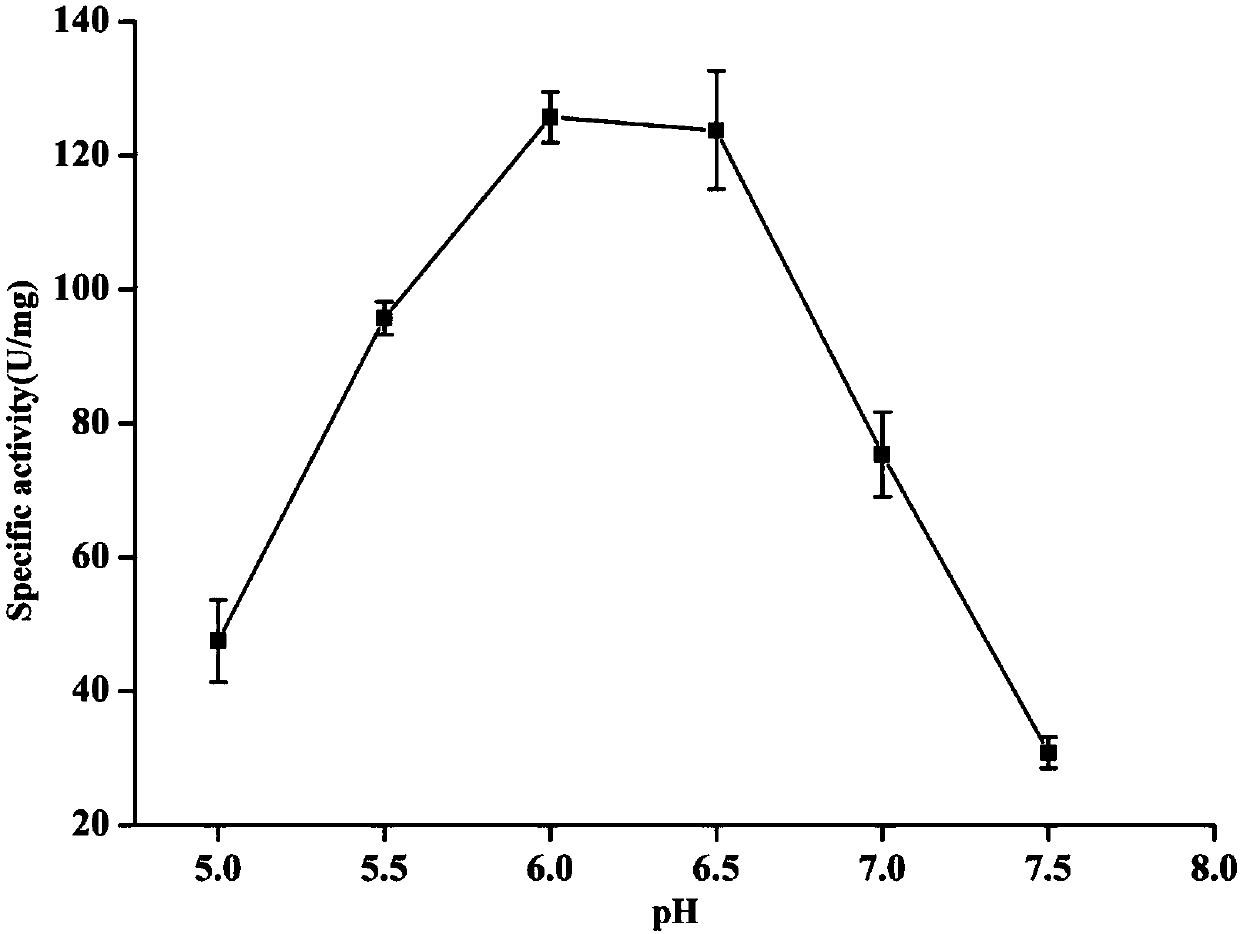
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to catalase with high enzyme activity, a gene, a recombinant strain with high catalase yield and application. The amino acid sequence of catalase catR is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The catalase with high enzyme activity and the gene of the catalase are provided, and the recombinant strain for efficiently expressing the catalase isobtained. The recombinant strain produced by fermentation can efficiently produce the catalase. The catalase disclosed by the invention is widely applied to production of sodium gluconate.
Owner:GUANGDONG VTR BIO TECH
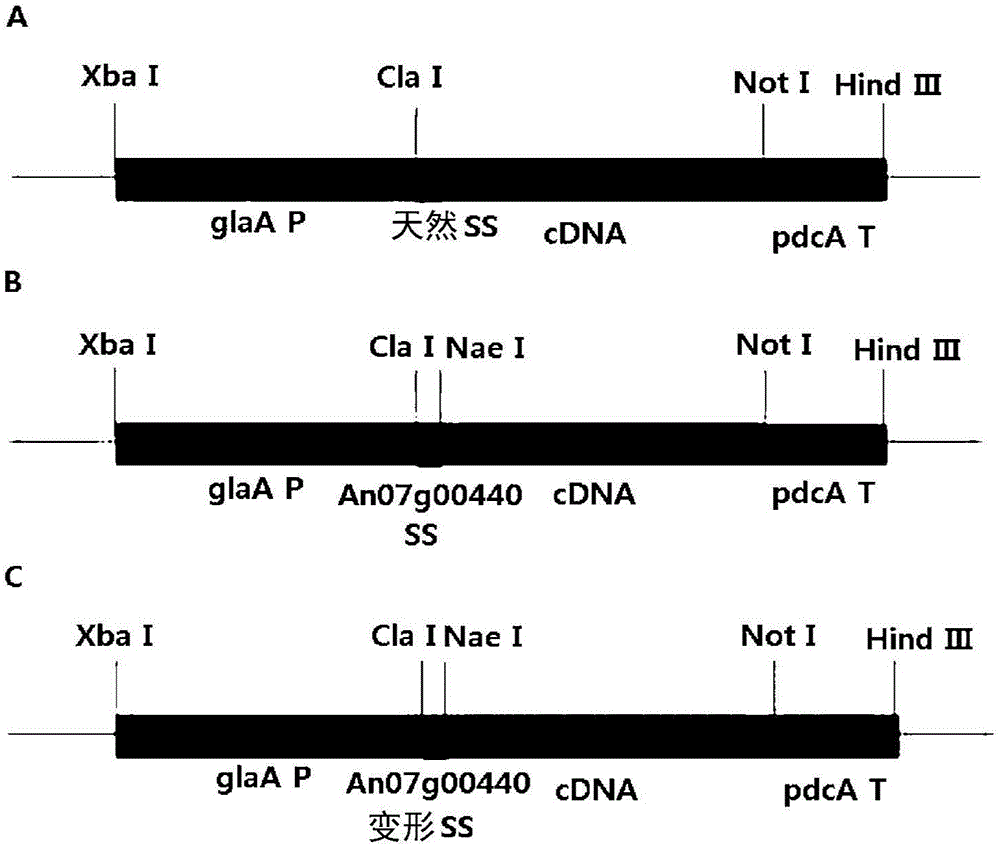
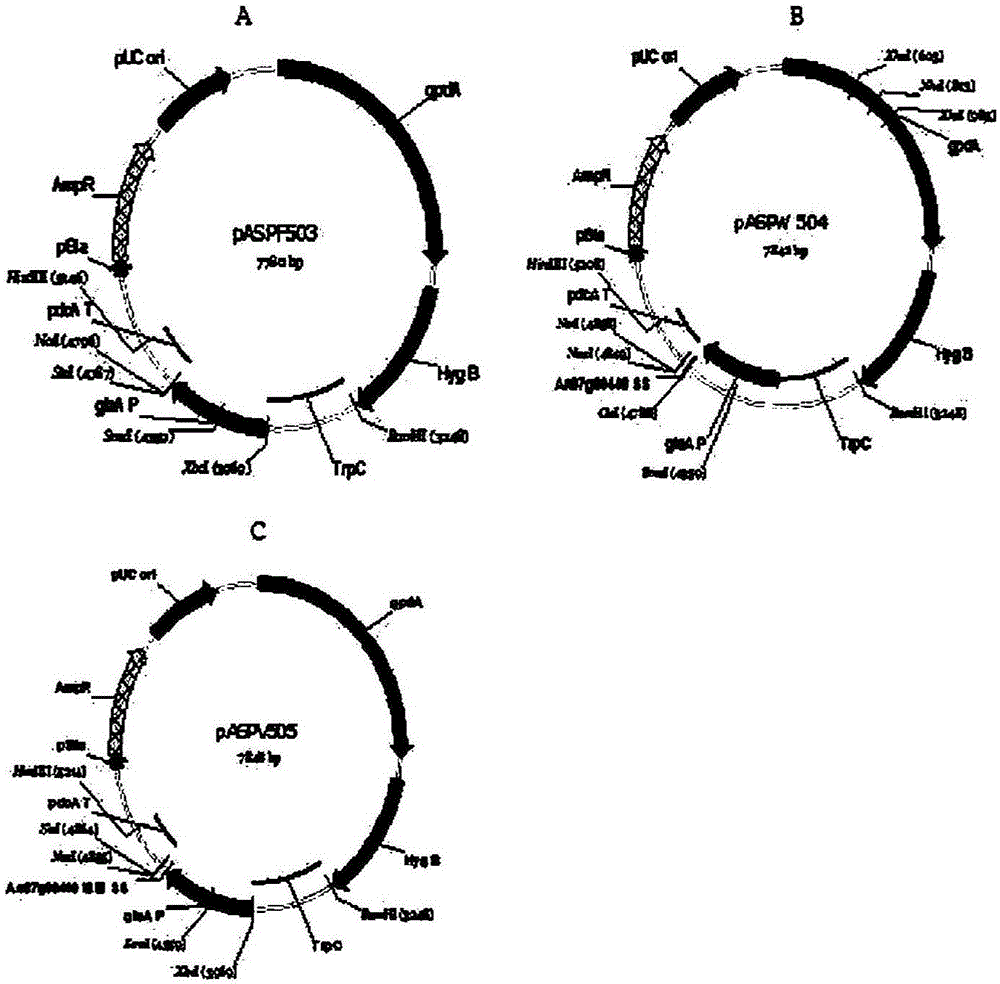
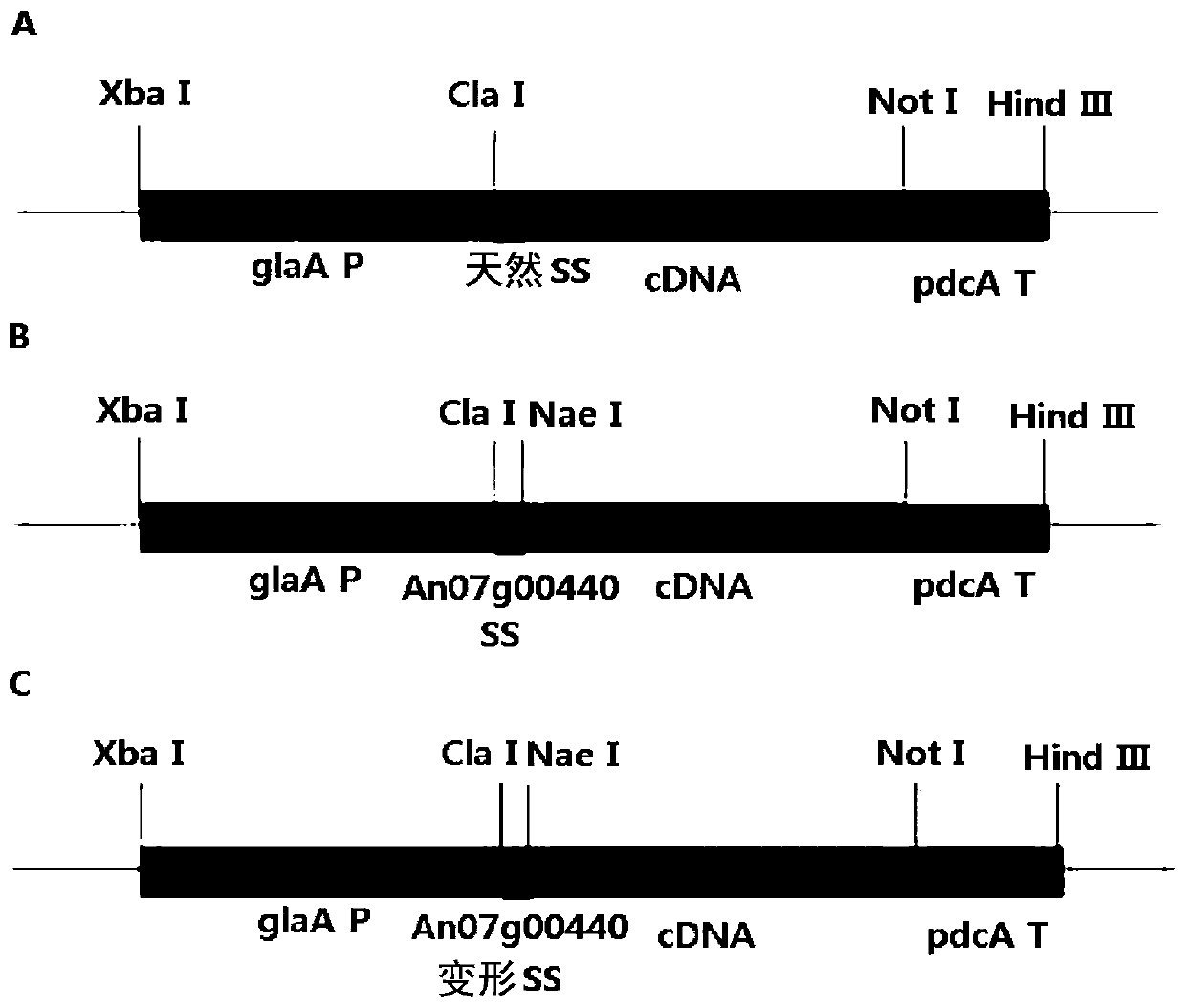
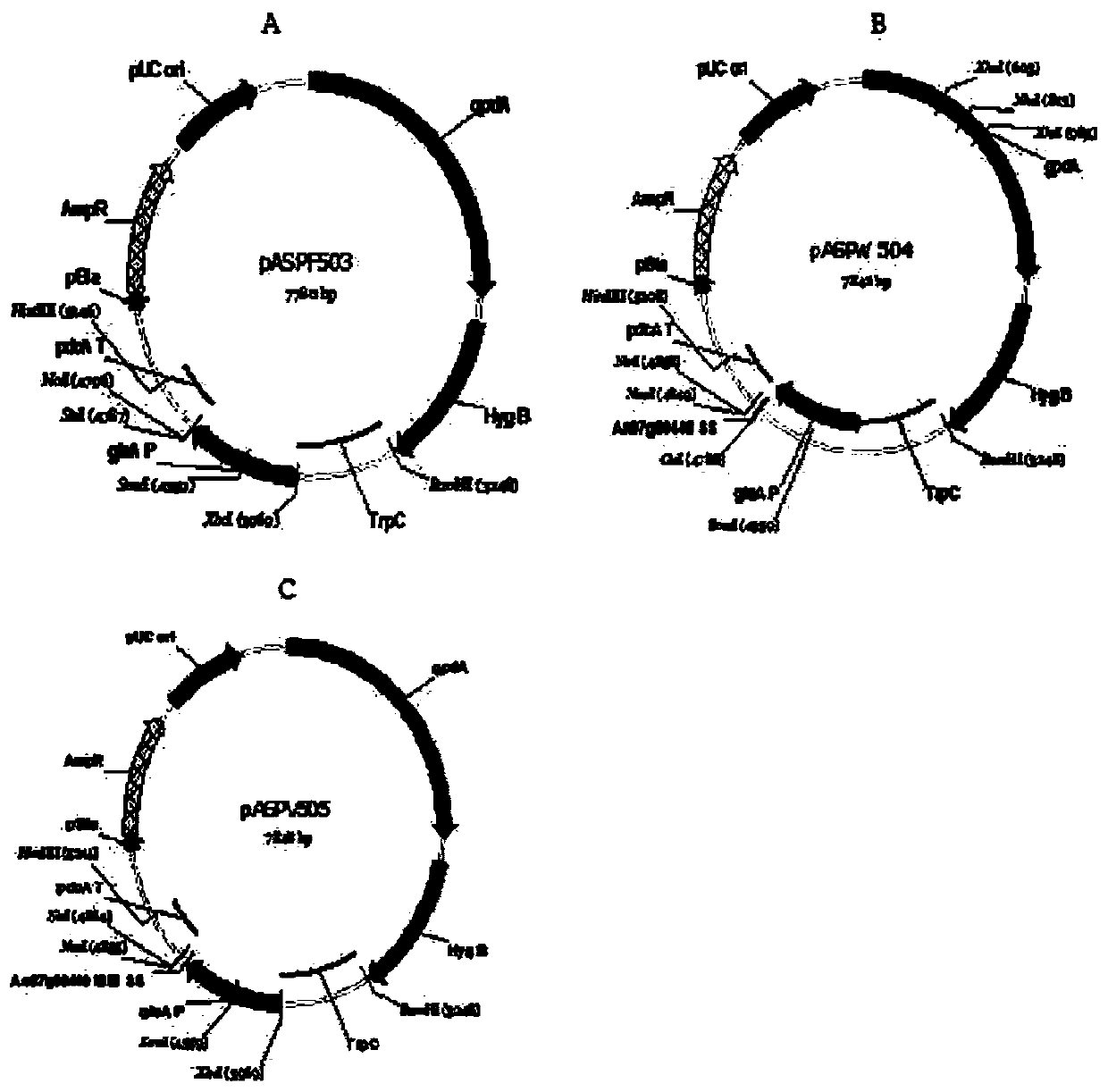
Novel catalase signal sequence and method for catalase expression using same
The present invention relates to a novel signal sequence for mass-expression of catalase and a use thereof and, more specifically, to a novel lipase signal sequence; an expression vector comprising the signal sequence and a catalase gene; a recombinant microorganism into which the expression vector is introduced; and a method for mass-producing catalase by culturing the recombinant microorganism. The use of the expression vector comprising the novel signal sequence, according to the present invention, can induce mass expression and secretion of particular catalase and other target proteins, and thus the expression vector is very useful in the stable mass production of the particular catalase and other target proteins.
Owner:GENOFOCUS CO LTD
Relativity between gene of catalase and essential hypertension
A process for testing the susceptibility of primary hypertension includes detecting if there are variations in hydrogen peroxidase gene CAT, transcript and / or protein of an individual, and determining its high susceptibility of there are. Its reagent kit is also disclosed.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Catalase gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101029312AExcellent aroma stabilityExtended shelf lifeFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyYeast
The present invention relates to a gene encoding a catalase and use thereof, in particular, a brewery yeast having high sulfite-producing capability, alcoholic beverages produced with said yeast, and a method for producing said beverages. More particularly, the present invention relates to a yeast, whose capability of producing sulfite, that contribute to stability of flavor in products, is enhanced by amplifying expression level of CTT1 gene encoding a catalase Ctt1p, especially non-ScCTT1 gene or ScCTT1 gene specific to a lager brewing yeast, and to a method for producing alcoholic beverages with said yeast.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Chaetomium thermophilum temperature-resistant catalase and application
InactiveCN110373396ALow commercial priceLow costFungiMicroorganism based processesHigh humidityAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses chaetomium thermophilum temperature-resistant catalase and application. An amino acid sequence of chaetomium thermophilum temperature-resistant catalase is shown as SEQ ID No.1. Chaetomium thermophilum temperature-resistant catalase is obtained through heterogeneous expression and fermenting production of chaetomium thermophilum temperature-resistant catalase CatA gene, hashigh resistance to high temperature and high humidity and can be used for replacing antibiotics in livestock-poultry breeding.
Owner:SHANGHAI YOUTELL BIOCHEM +1
Recombinant food-grade lactobacillus containing catalase genes
The invention relates to recombinant food-grade lactobacillus containing catalase genes. The lactobacillus is the food-grade lactobacillus which contains the catalase genes of a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and is constructed through recombining gene engineering by taking lactococcus lactis NZ9000 as a strain. In the invention, colon bacillus gene group libraries with different sizes of segments are constructed by using a shotgun method, clones containing complete catalase genes are screened through heart brain dipping culture medium containing gallotannic acid, and the catalase genes are inserted into a lactococcus lactis carrier pGK12 or pRV300 to convert the lactococcus lactis NZ9000 to construct the recombinant food-grade engineering recombinant lactobacillus containing the catalase genes. The recombinant lactococcus lactis has certain anti-oxidization capability and capability for resisting environmental stress, thereby providing novel food-grade engineering recombinant lactococcus lactis.
Owner:ZHAOQING UNIV
Recombinant lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101948856AImprove survival rateImprove antioxidant capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDismutase
The invention relates to a recombinant lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain and a preparation method thereof. The lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain carries expression vectors of a catalase gene and a superoxide dismutase gene which are connected in series. The method for preparing the engineering strain comprises the following steps of: 1) amplifying catalase gene segments and superoxide dismutase gene segments from genomes of lactobacillus sake and streptococcus thermophiles by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method; 2) designing a specific restriction enzyme site, wherein the restriction enzyme site is connected in series with an escherichia coli-lactobacillus shuttle plasmid vector pSIP502; and 3) transforming a recombinant plasmid into lactobacillus rhamnosus by an electroporation method. The recombinant lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain prepared by the method can remarkably enhance oxidation resistance and can be applied to the fermented food industry.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
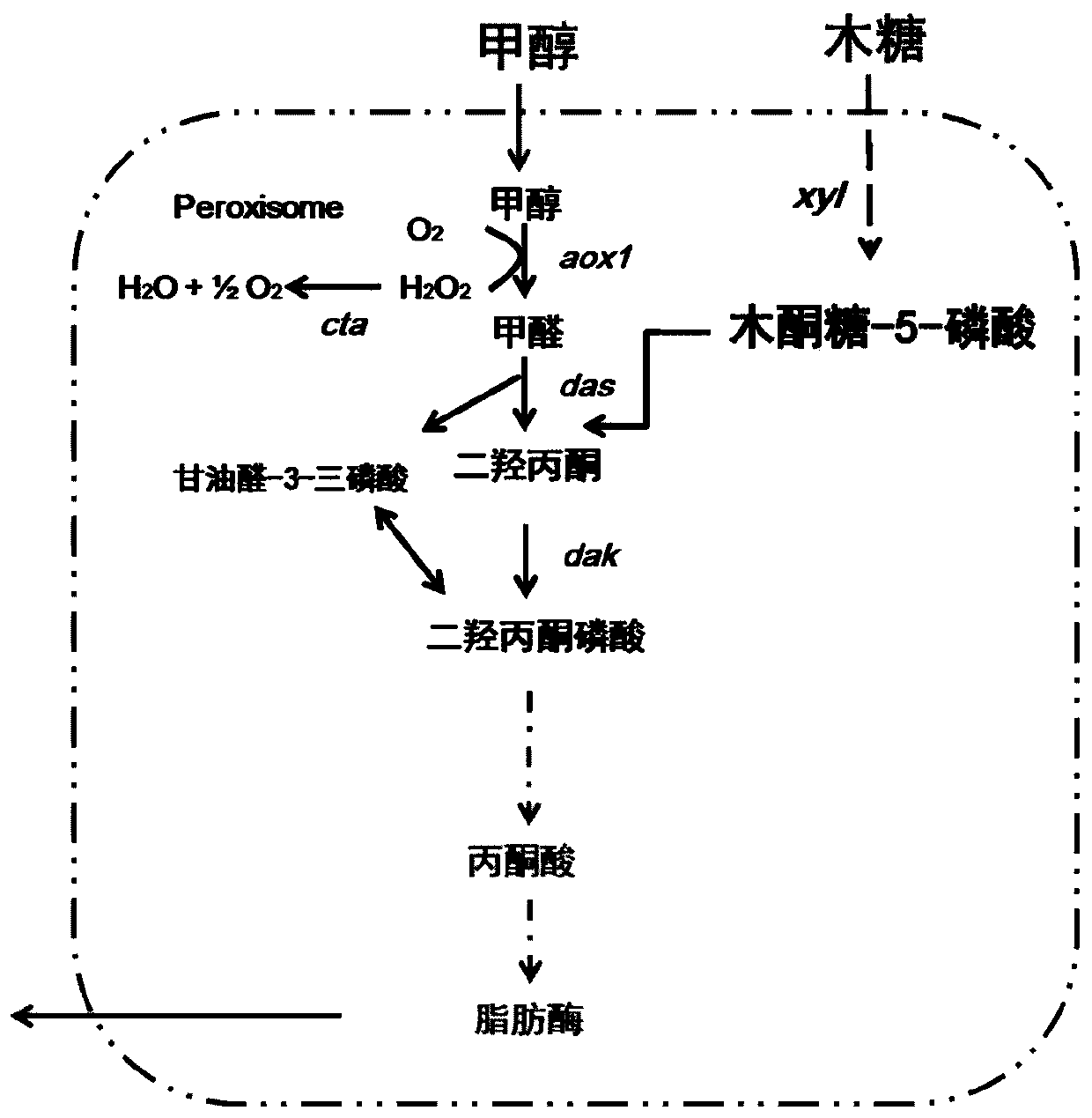
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing lipase by using methanol and xylose co-substrate and application of genetically engineered bacterium
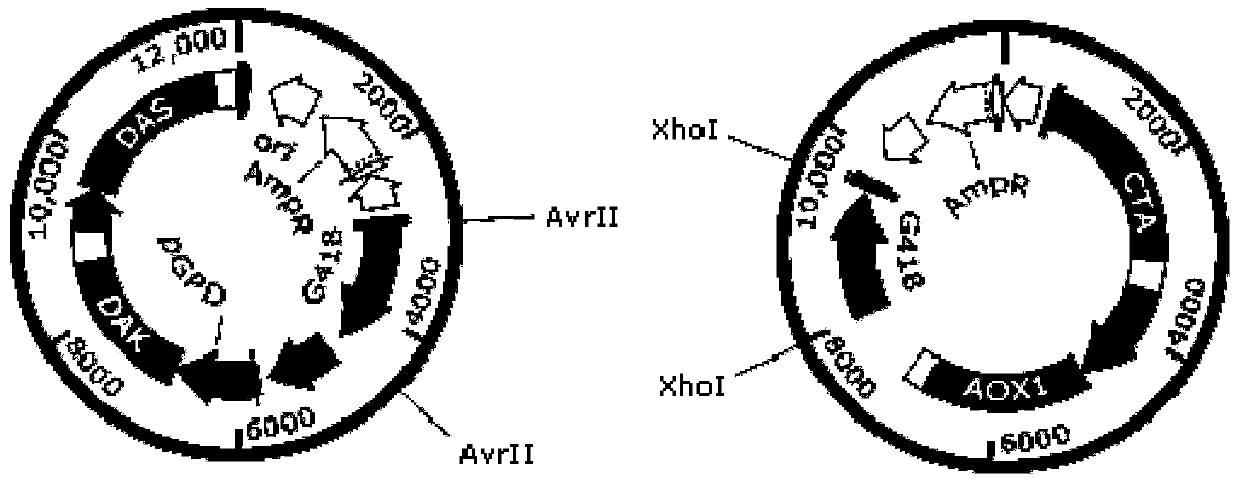
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing lipase by using a methanol and xylose co-substrate and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. A methanol oxidasegene aox1, a dihydroxyacetone synthase gene das, a catalase gene cta and a dihydroxyacetone kinase gene dak are introduced into host bacteria; and the host bacteria are Candida antarctica capable ofproducing the lipase by utilizing xylose. According to the invention, a methanol metabolic pathway is introduced into the Candida antarctica by utilizing a synthetic biology way, so that the Candida antarctica can produce the lipase by taking non-food-grade raw materials, namely the methanol and the xylose, as a co-substrate, the production cost is reduced to a certain extent, and the applicationhas great significance and economic value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
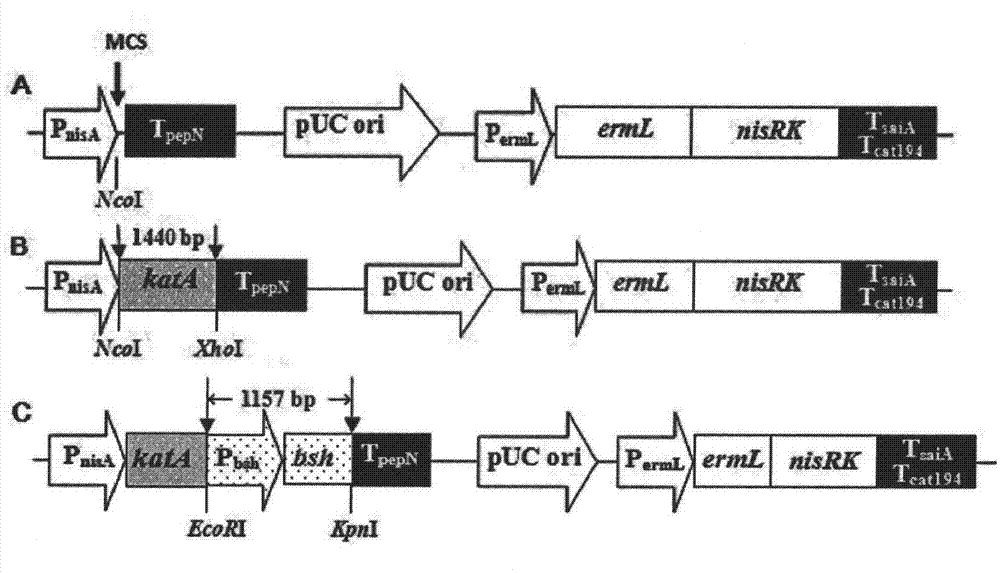
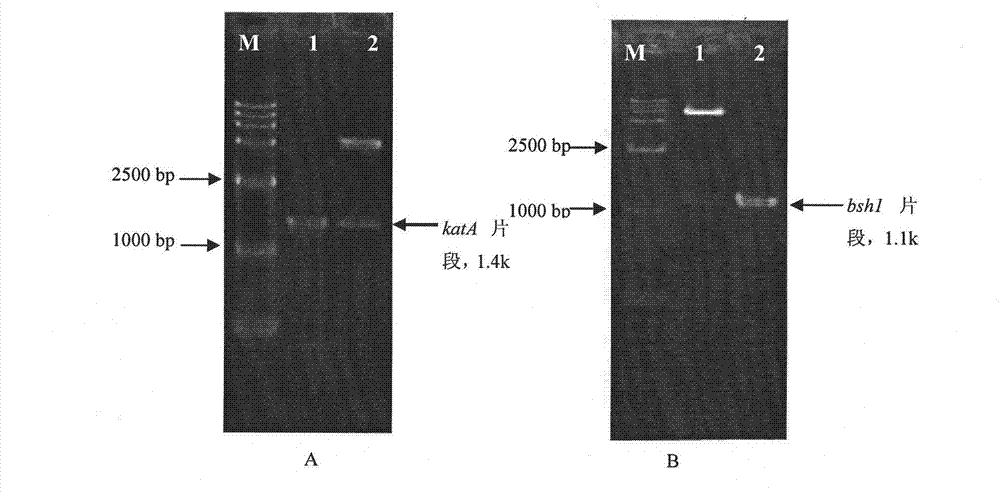
Recombinant lactobacillus casei engineering strain and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a recombinant lactobacillus casei engineering strain and a preparation method thereof. The lactobacillus casei engineering strain carries an expression vector of a catalase gene and a bile salt hydrolase gene which are connected in series. The preparation method of the engineering strain comprises the following steps of: 1) respectively amplifying segments of the catalase gene and the bile salt hydrolase gene in genomes of lactobacillus sake and lactobacillus plantarum by a PCR method; 2) designing a specific restriction enzyme cutting site and constructing the specific restriction enzyme cutting site in an Escherichia coli-lactobacillus shuttle plasmid vector pSIP502 by series connection; and 3) converting a recombinant plasmid to lactobacillus casei by an electroporation method. The recombinant lactobacillus casei engineering strain prepared by the method can obviously improve oxidation resistance and bile salt resistance and can be applied to the fermented food industry.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method of preparing recombination human source catalase and application thereof
The present invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and is especially process of preparing recombinant humanized catalase. The process of obtaining humanized catalase in high yield includes cloning humanized catalase gene by means of gene engineering technology, constructing its expression plasmid and transforming to cell. The process is simple and has no disease contamination and high yield of humanized catalase, and the prepared humanized catalase has high activity. The present invention includes also the new recombinant plasmid and transformant. Experiments show that the expressed recombinant humanized catalase may be applied in preparing medicine for resisting infection, resisting oxidation, resisting senility and antagonizing tumor.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method utilizing degenerate primer to detect diversity of bacteria catalase in seawater
InactiveCN102851380AGood varietyAccurate methodMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a method utilizing degenerate primer to detect the diversity of bacteria catalase in seawater. Four types of combination of degenerate primer are designed in a bacteria catalase conserved region; catalase gene segments in seawater total DNA are amplified through polymerase chain reaction; then a library of the catalase gene segments is established through coliform bacteria; the catalase gene segments in the library are subjected to enzyme digestion through restriction enzyme; the molecular weight distribution of the segments is detected through cataphoresis, so as to determine different types of electrophoretic bands; and finally different types of the catalase genes are respectively subjected to order-checking, so that information of the diversity of catalase gene can be obtained. The method is accurate, reliable and rapid, uses degenerate primer to detect the diversity of bacteria catalase in seawater, and can be used for detecting the diversity of bacteria catalase in seawater.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
A kind of catalase and its high-yielding genetically engineered bacteria
ActiveCN106047829BEasy to synthesizeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a novel-originated catalase and the construction of recombinant engineering strains of the catalase. The construction is characterized in that primers are designed according to a catalase gene of bacillus pumilus for the first time, and recombinant expression vectors are constructed; the vectors are converted to genetic engineering strains, i.e., Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis for heterologous expression; the recombinant engineering strains are subjected to fermented cultivation through a 5L fermentation tank by using a fermentation culture medium, wherein catalase of recombinant Escherichia coli is mainly subjected to intracellular expression and has the enzyme activity of 6645U / mL, catalase of recombinant B. subtilis 168 has the total enzyme activity of 23,263U / mL and the extracellular enzyme activity of 15,368U / mL, catalase of B. subtilis WB600 has the total enzyme activity of 26,635U / mL and the extracellular enzyme activity of 20,128U / mL, the extracellular synthesis of the catalase is better facilitated by using the B. subtilis WB600 as a host, and thus the B. subtilis WB600 has an important industrial application value. The invention achieves the maximum yield compared with currently-reported methods which are used for producing the catalase by using microbes, so that a practical and effective policy for industrial production of the catalase is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cordyceps militaris activity RT-PCR detection primers and detection method
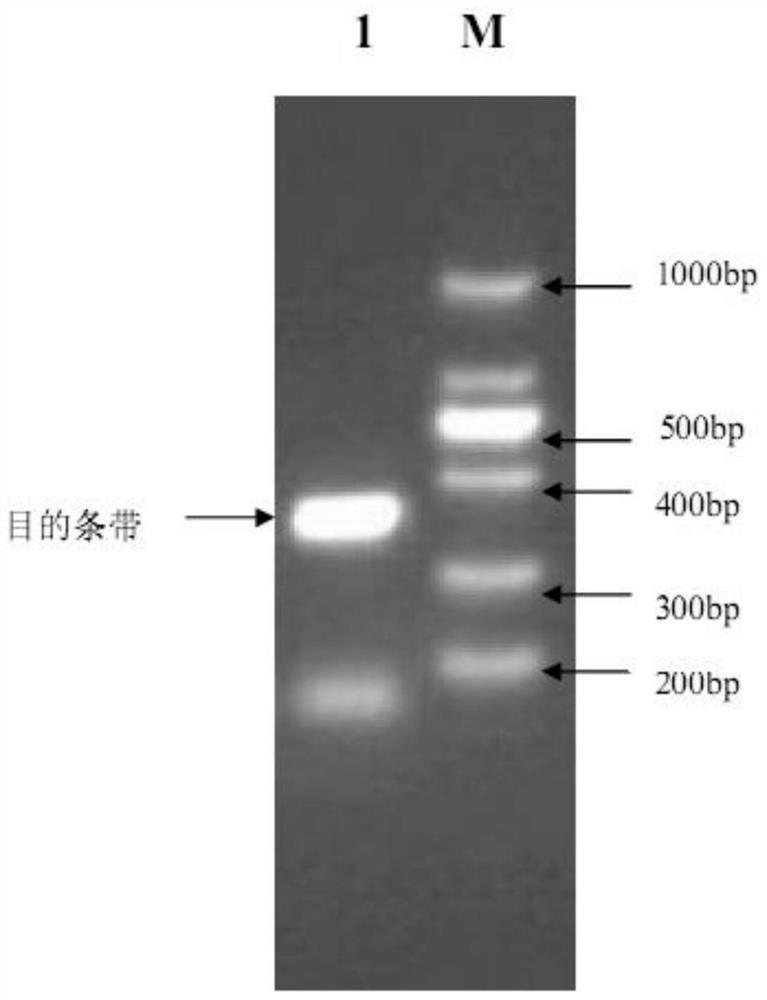
PendingCN112501340AAmplified catalase gene fragmentReliable test resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
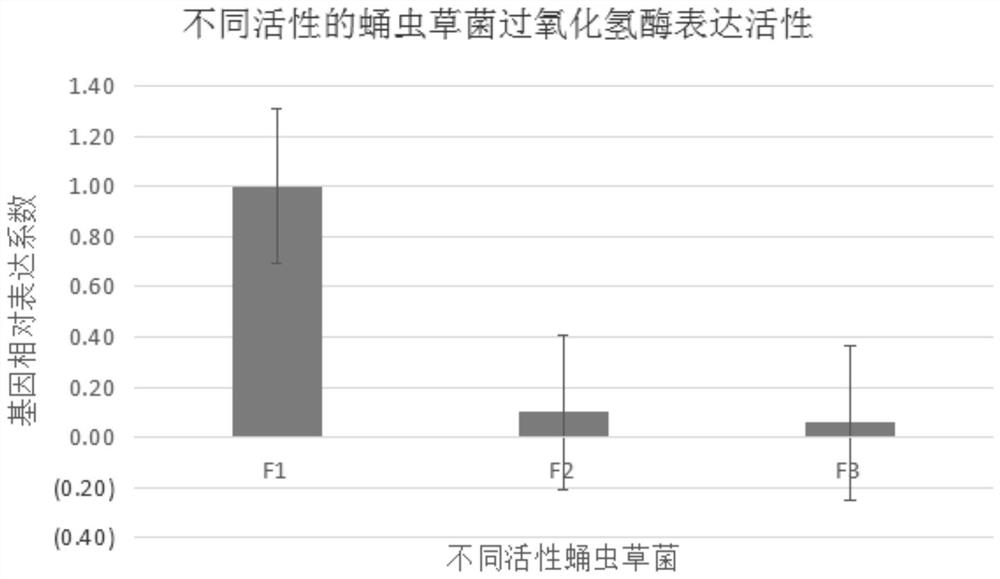
The invention discloses cordyceps militaris activity RT-PCR detection primers and a detection method, and belongs to the technical field of molecular detection and identification. The primers have nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. By adopting the specific primers SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, a catalase gene fragment of cordyceps militaris can be effectively amplified, and the fragment is 341 bp in size and can be used for RT-PCR detection. 2-delta delta CT statistical analysis is adopted for detection results, compared with a control strain, sample value / control value is used as a judgment standard, when the ratio is larger than or equal to 1, the detected strain can be used for production; when the ratio is less than 1 and greater than 0.1, the detected strainhas weak activity and should be used with caution; and when the ratio is less than 1 / 10, the detected strain basically cannot be used for production of cordyceps militaris and cordyceps flowers. The detection result can be used to predict relative activity of cordyceps militaris, and provide technical basis for screening strains in production.
Owner:NANTONG TEXTILE & SILK IND TECH RES INST +1
Pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacterium for heterologous expression of recombinant catalase and application of pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacterium
PendingCN114164221ASimple production processEasy to getFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousEngineered genetic
The invention discloses pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacteria for heterologous expression of recombinant catalase and application, and belongs to the technical field of industrial biology. The invention relates to a pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacterium for heterologous expression of recombinant catalase. The pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacterium carries a recombinant expression vector of an alkali-resistant catalase gene which is derived from Bacillus subtilis 168 and is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. Compared with catalase extracted from animal livers or obtained by using a prokaryotic expression system, the recombinant catalase obtained by using pichia pastoris heterologous secretory expression has the advantages that the separation and purification process is simple and convenient, and pure enzyme is easier to obtain, so that the production process of the enzyme is simplified, and the production and use cost is reduced; and a novel method is provided for scientific research and production practice requiring recombination of pure catalase.
Owner:李宪臻
Relativity between gene of catalase and essential hypertension
A process for testing the susceptibility of primary hypertension includes detecting if there are variations in hydrogen peroxidase gene CAT, transceipt and / or protein of an individual, and determining its high susceptibility if there are. Its reagent kit is also disclosed.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Relativity between gene of catalase and essential hypertension
A process for testing the susceptivity of primary hypertension includes detecting if there are variations in hydrogen peroxidase gene CAT, transcript and / or protein of an individual, and determining its high susceptibility if there are. Its reagent kit is also disclosed.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
A method for improving the enzyme activity of l-amino acid deaminase heterologous expression
ActiveCN109022380BIncrease enzyme activityReduce the amount of solutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and relates to a method for improving the enzyme activity of heterologous expression of L-amino acid deaminase, which uses L-amino acid deaminase (L-amino acid deaminase, LAAD) gene and catalase (Catalase) Gene expression in tandem. The present invention adopts L-amino acid deaminase to be expressed in series with catalase, which increases the enzyme activity per unit cell and increases the amount of cell per unit fermentation volume, thereby having high industrial application value.
Owner:浙江正硕生物科技有限公司
Method utilizing degenerate primer to detect diversity of bacteria catalase in seawater
InactiveCN102851380BGood varietyAccurate methodMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a method for detecting the diversity of bacterial catalase in seawater by using degenerate primers, designing a combination of four kinds of degenerate primers based on the conserved region of bacterial catalase, and using polymerase chain reaction to amplify the diversity of bacterial catalase in seawater. Catalase gene fragments, and then use Escherichia coli to construct a library of enzyme gene fragments, use restriction endonucleases to digest the enzyme genes in the library, detect the molecular weight distribution of the fragments by electrophoresis, and determine the types of different electrophoresis bands, and finally Different types of catalase genes were sequenced separately to obtain information on the diversity of catalase genes. This method is an accurate, reliable, rapid, new method using degenerate primers to detect the diversity of bacterial catalase in seawater, and can be used to detect the diversity of bacterial catalase in seawater.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Low-temperature catalase and its preparation method and application
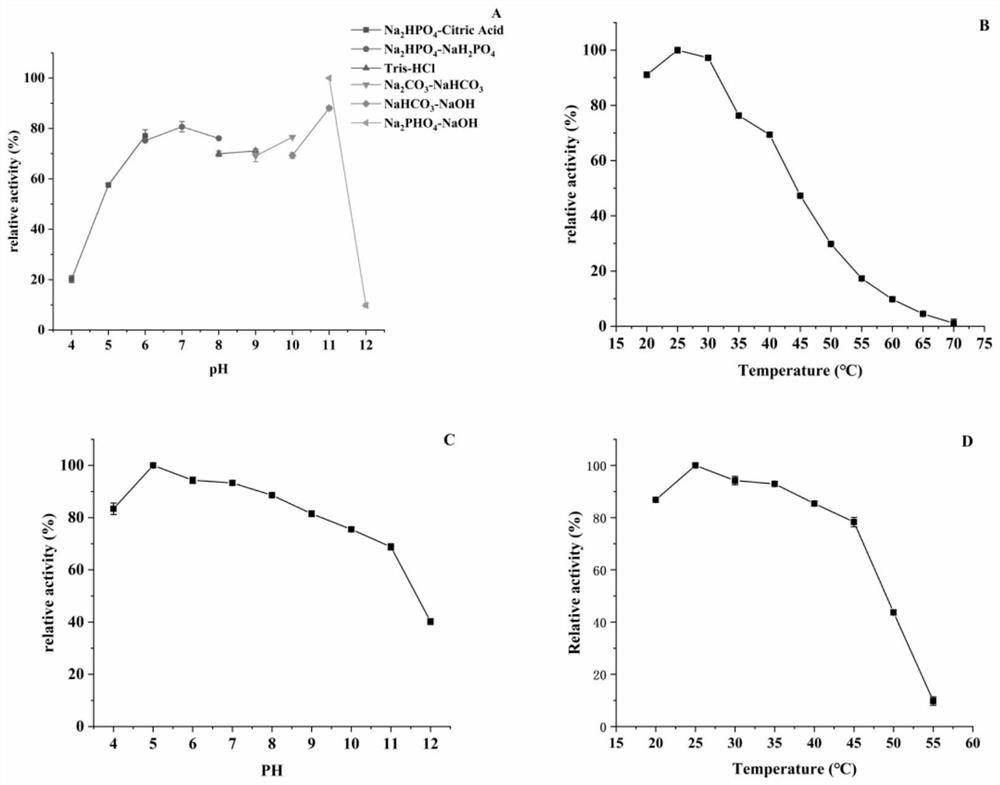
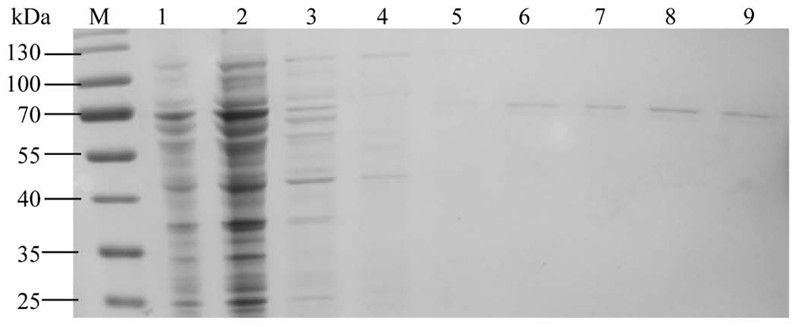
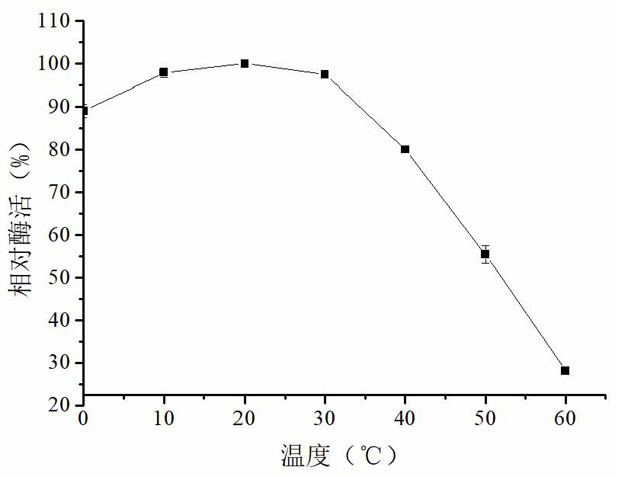
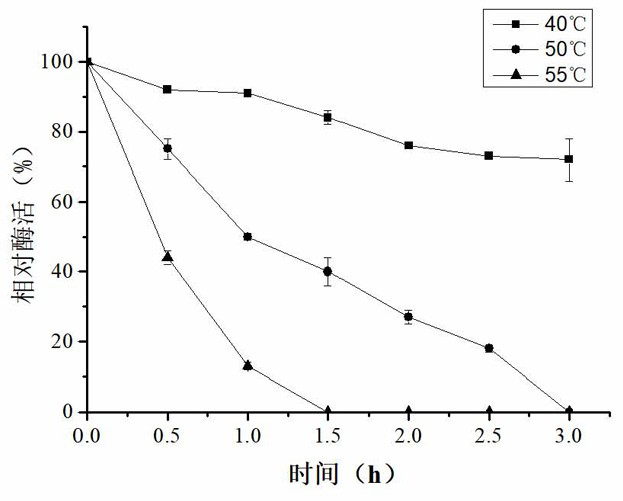
The invention discloses low-temperature catalase, its preparation method and application. The present invention separates the catalase gene from the Tianshan soil macrogene, and its polynucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1, encoding 502 amino acids and a stop codon. The optimal temperature of the catalase of the present invention is 10-20°C, and it has high enzyme activity in the low temperature range of 0-30°C, has the characteristics of a low-temperature enzyme, and can play a role in removing H in a low-temperature environment. 2 o 2 role. The catalase of the present invention has good thermal stability, and has good thermal stability at 40°C. After 3 h of treatment, 74% of the enzyme activity still remains, and has certain thermal stability at 50°C. After 0.5 h of treatment 78% of the enzyme activity still remained. The optimal pH of the catalase of the present invention is 8.0. The present invention further provides the catalase as an antioxidant in removing H 2 o 2 in the application.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Catalase gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101029311AExcellent aroma stabilityExtended shelf lifeFungiBeer fermentationBiotechnologyYeast
The present invention relates to a gene encoding a catalase and use thereof, in particular, a brewery yeast having high sulfite-producing capability, alcoholic beverages produced with said yeast, and a method for producing said beverages. More particularly, the present invention relates to a yeast, whose capability of producing sulfite, that contribute to stability of flavor in products, is enhanced by amplifying expression level of CTA1 gene encoding a catalase Cta1p, especially non-ScCTA1 gene or ScCTA1 gene specific to a lager brewing yeast, and to a method for producing alcoholic beverages with said yeast.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
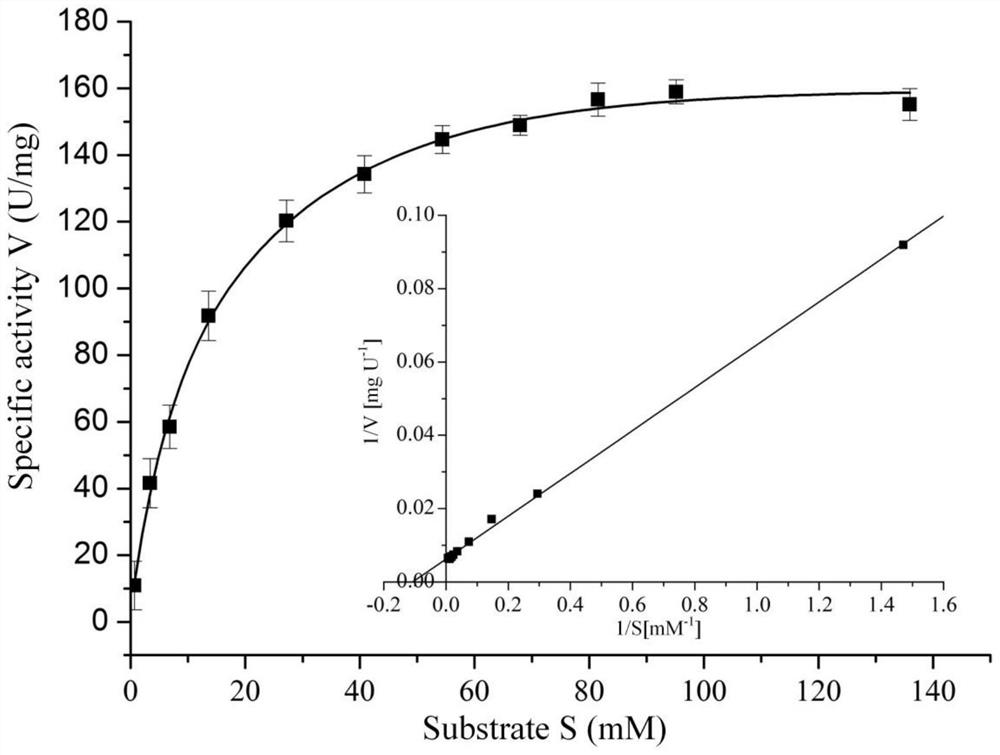
A kind of method that utilizes co-expression recombinant strain to transform and produce α-ketoglutarate
ActiveCN107686850BHigh yieldSolve the problem that a large amount of catalase needs to be added from an external sourceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliOxidative enzyme
The invention discloses a method for transforming and producing α-ketoglutarate by using a co-expression recombinant strain, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The present invention selects a new type of L-glutamate oxidase from Streptomyces, induces expression and purifies it in Escherichia coli, and conducts enzymatic properties research. The optimum reaction temperature is 30~45℃, V max 100~150 U / mg, K m 8~10 mM. The original gene sequence of L-glutamate oxidase was codon-optimized and co-expressed with the catalase gene derived from Escherichia coli to construct a co-expression recombinant strain. The recombinant strain was used as the whole cell catalyst to convert L-glutamic acid (salt), and the yield of α-ketoglutarate reached 76.08 g / L after 9 h of reaction, and the molar conversion rate was 96.8%. The invention solves the problems of cumbersome production steps, low yield and environmental pollution of α-ketoglutaric acid, realizes high-yield and one-step production of α-ketoglutaric acid, and has high industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Catalase Gene and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20090130255A1Good flavor stabilityExtended shelf lifeFungiSugar derivativesYeastBiotechnology
The present invention relates to a gene encoding a catalase and use thereof, in particular, a brewery yeast having high sulfite-producing capability, alcoholic beverages produced with said yeast, and a method for producing said beverages. More particularly, the present invention relates to a yeast, whose capability of producing sulfite, that contribute to stability of flavor in products, is enhanced by amplifying expression level of CTT1 gene encoding a catalase Ctt1p, especially non-ScCTT1 gene or ScCTT1 gene specific to a lager brewing yeast, and to a method for producing alcoholic beverages with said yeast.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Novel catalase signal sequence and catalase expression method using the same
The present invention relates to a novel signal sequence for mass-expression of catalase and a use thereof and, more specifically, to a novel lipase signal sequence; an expression vector comprising the signal sequence and a catalase gene; a recombinant microorganism into which the expression vector is introduced; and a method for mass-producing catalase by culturing the recombinant microorganism. The use of the expression vector comprising the novel signal sequence, according to the present invention, can induce mass expression and secretion of particular catalase and other target proteins, and thus the expression vector is very useful in the stable mass production of the particular catalase and other target proteins.
Owner:GENOFOCUS CO LTD
Recombinant lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101948856BImprove survival rateImprove antioxidant capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a recombinant lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain and a preparation method thereof. The lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain carries expression vectors of a catalase gene and a superoxide dismutase gene which are connected in series. The method for preparing the engineering strain comprises the following steps of: 1) amplifying catalase gene segments and superoxide dismutase gene segments from genomes of lactobacillus sake and streptococcus thermophiles by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method; 2) designing a specific restriction enzyme site, wherein the restriction enzyme site is connected in series with an escherichia coli-lactobacillus shuttle plasmid vector pSIP502; and 3) transforming a recombinant plasmid into lactobacillus rhamnosus by an electroporation method. The recombinant lactobacillus rhamnosus engineering strain prepared by the method can remarkably enhance oxidation resistance and can be applied to the fermented food industry.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Catalase gene and use thereof
The present invention relates to a gene encoding a catalase and use thereof, in particular, a brewery yeast having high sulfite-producing capability, alcoholic beverages produced with said yeast, and a method for producing said beverages. More particularly, the present invention relates to a yeast, whose capability of producing sulfite, that contribute to stability of flavor in products, is enhanced by amplifying expression level of CTA1 gene encoding a catalase Cta1p, especially non-ScCTA1 gene or ScCTA1 gene specific to a lager brewing yeast, and to a method for producing alcoholic beverages with said yeast.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
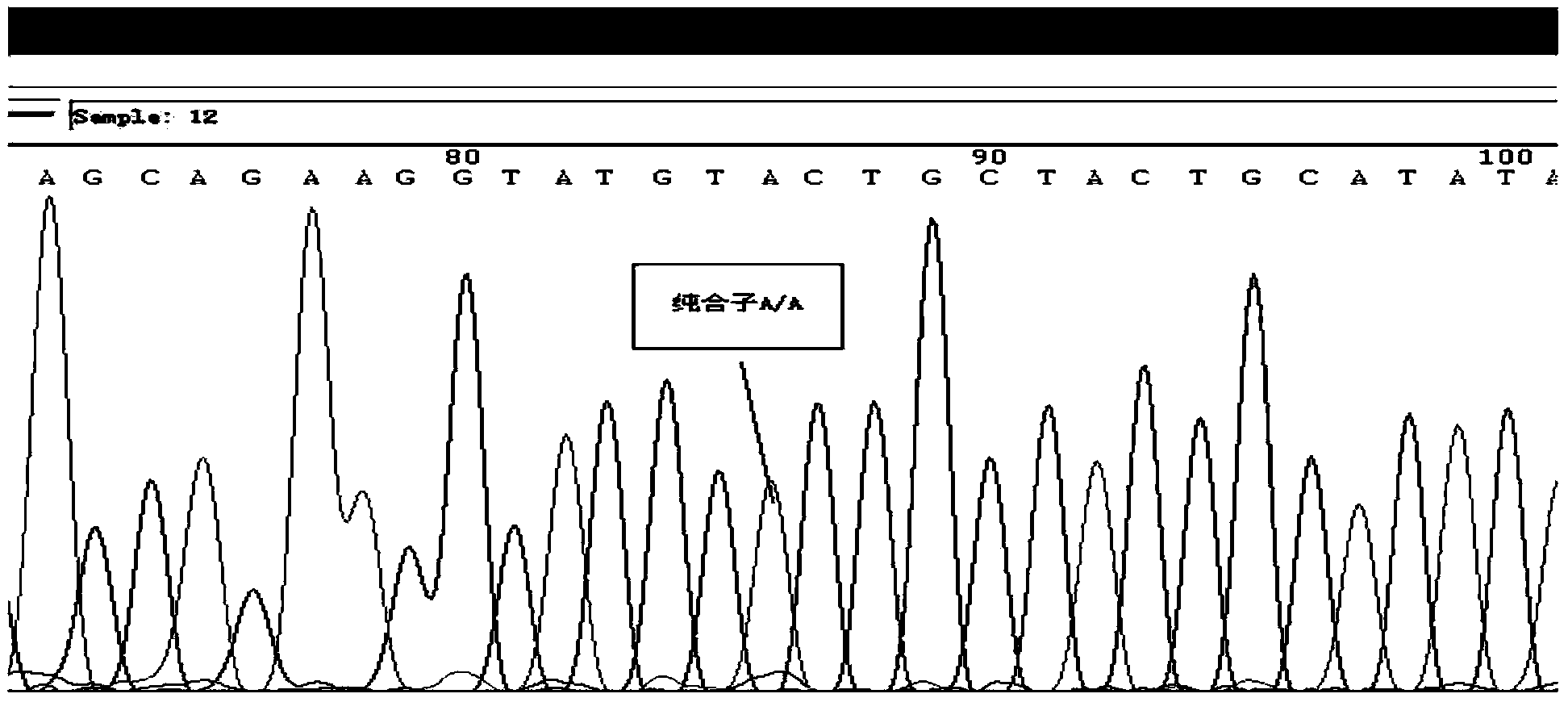
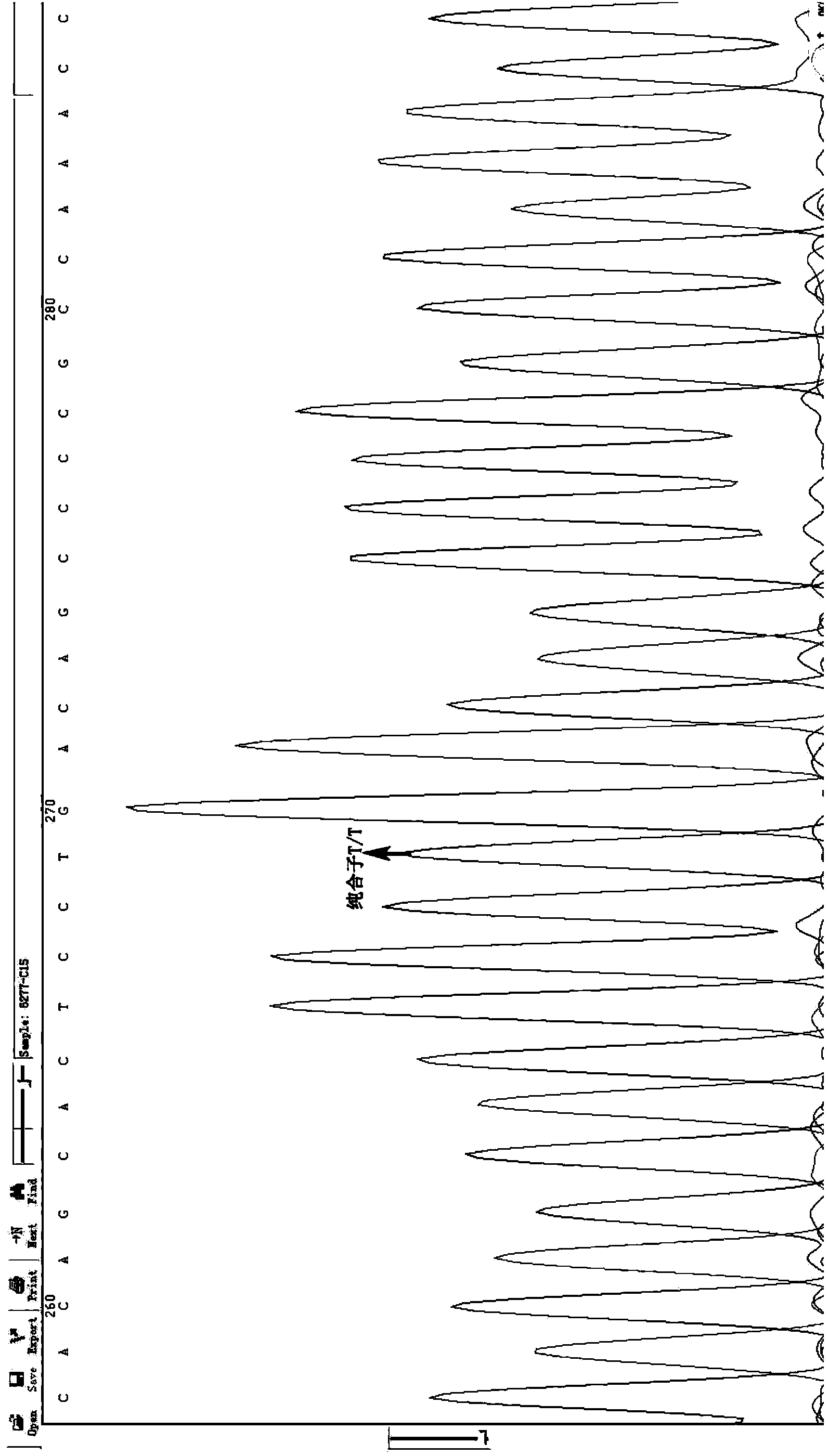
Selection, detection and application of catalase gene tagging single nucleotide polymorphic sites
InactiveCN103642921BReduce inductionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideHaplotype
The design of the invention relates to selection, detection and application of tagging single nucleotide polymorphic sites of a catalase (CAT) gene, and further relates to a haplotype consisting of the tagging single nucleotide polymorphic (SNP) sites of the CAT gene, a detection method of the haplotype and a kit for detecting the tagging single nucleotide polymorphic sites of the CAT gene. According to the selection, detection and application disclosed by the invention, 6 tagging SNP sites of the CAT gene related to noise-induced deafness are screened, wherein risk of an individual carrying an rs769217 site C allelic gene and suffering from the noise-induced deafness is greatly increased when noise intensity is 85-92dB, and risk of an individual carrying an rs208679 site A allelic gene and suffering from the noise-induced deafness is greatly increased when noise intensity is less than 85dB; a specific combined haplotype A-G-T-C-A-C individual carrying six tagging SNP sites, compared to other haplotype individuals, is higher in risk of suffering from the noise-induced deafness.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com