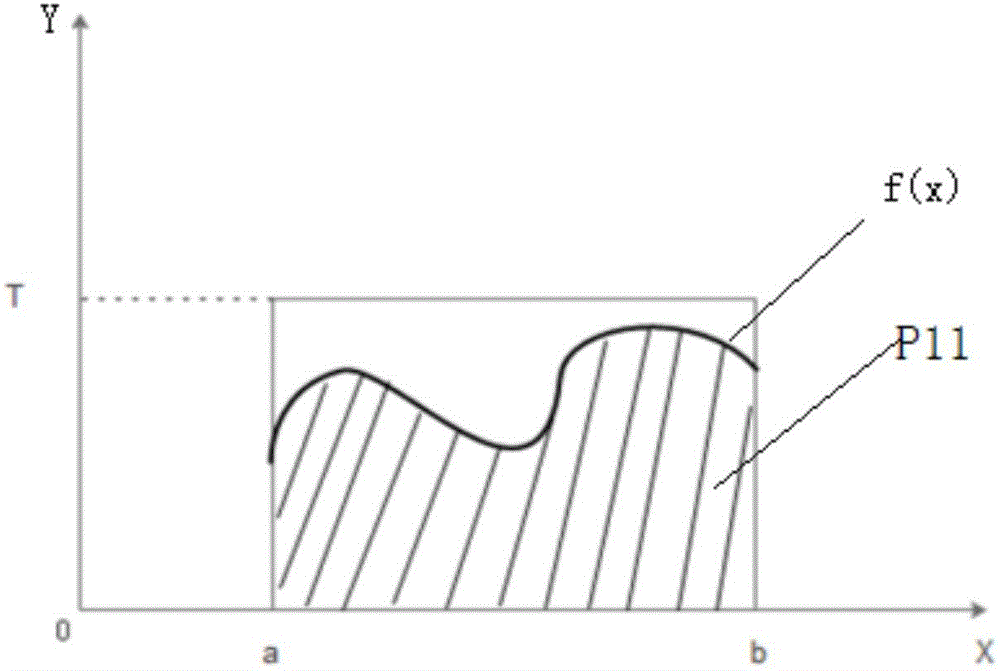
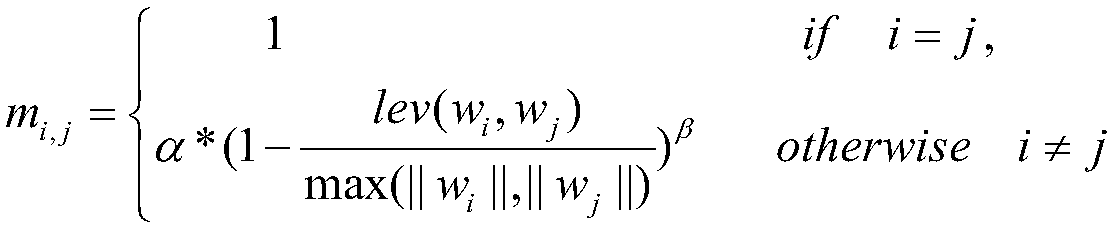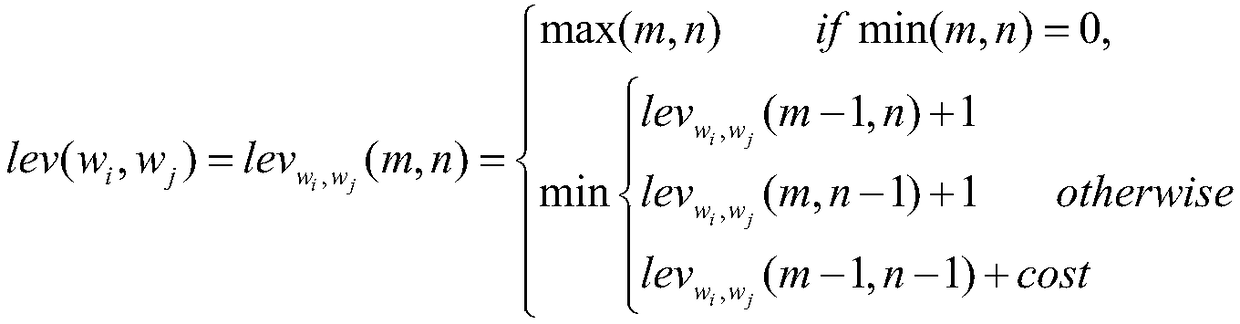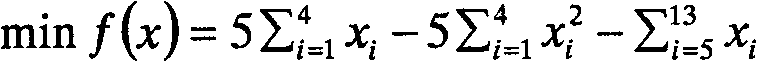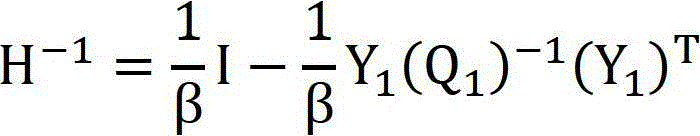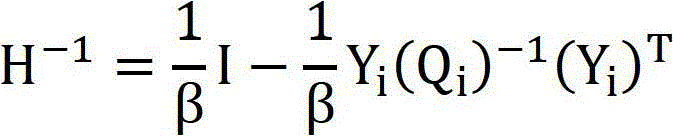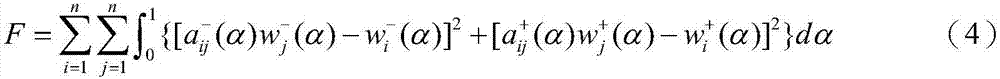Patents
Literature
87 results about "Problems involving arithmetic progressions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
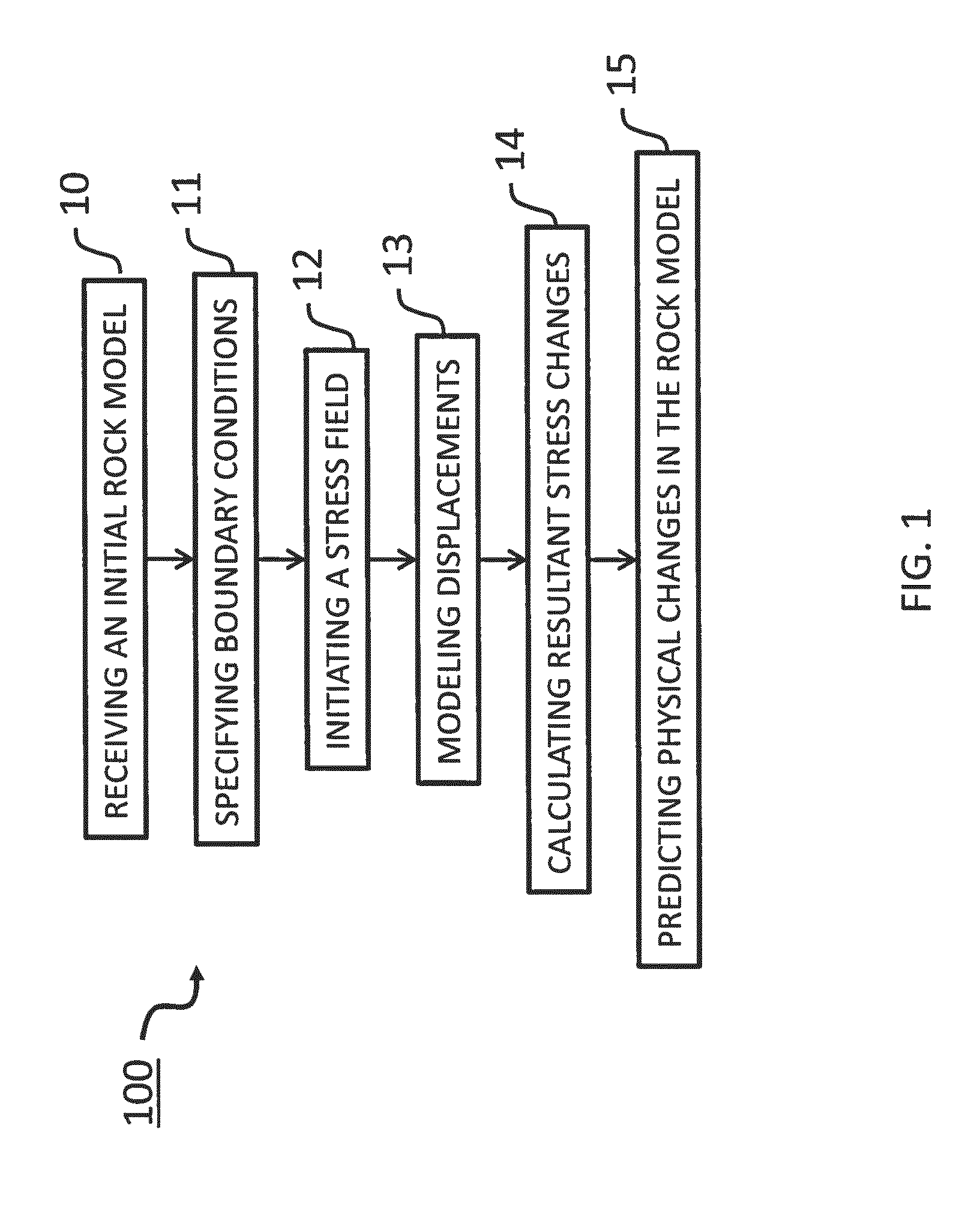
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
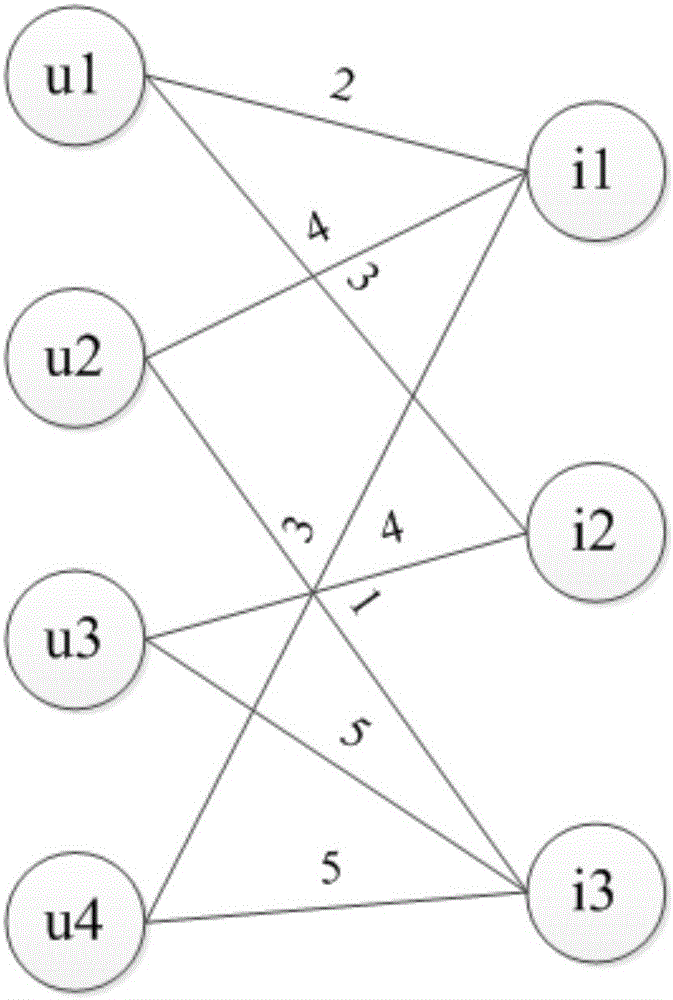
Problems involving arithmetic progressions are of interest in number theory, combinatorics, and computer science, both from theoretical and applied points of view.
Local Causal and Markov Blanket Induction Method for Causal Discovery and Feature Selection from Data
In many areas, recent developments have generated very large datasets from which it is desired to extract meaningful relationships between the dataset elements. However, to date, the finding of such relationships using prior art methods has proved extremely difficult especially in the biomedical arts. Methods for local causal learning and Markov blanket discovery are important recent developments in pattern recognition and applied statistics, primarily because they offer a principled solution to the variable / feature selection problem and give insight about local causal structure. The present invention provides a generative method for learning local causal structure around target variables of interest in the form of direct causes / effects and Markov blankets applicable to very large datasets and relatively small samples. The method is readily applicable to real-world data, and the selected feature sets can be used for causal discovery and classification. The generative method GLL-PC can be instantiated in many ways, giving rise to novel method variants. In general, the inventive method transforms a dataset with many variables into either a minimal reduced dataset where all variables are needed for optimal prediction of the response variable or a dataset where all variables are direct causes and direct effects of the response variable. The power of the invention and significant advantages over the prior art were empirically demonstrated with datasets from a diversity of application domains (biology, medicine, economics, ecology, digit recognition, text categorization, and computational biology) and data generated by Bayesian networks.
Owner:ALIFERIS KONSTANTINOS CONSTANTIN F +1
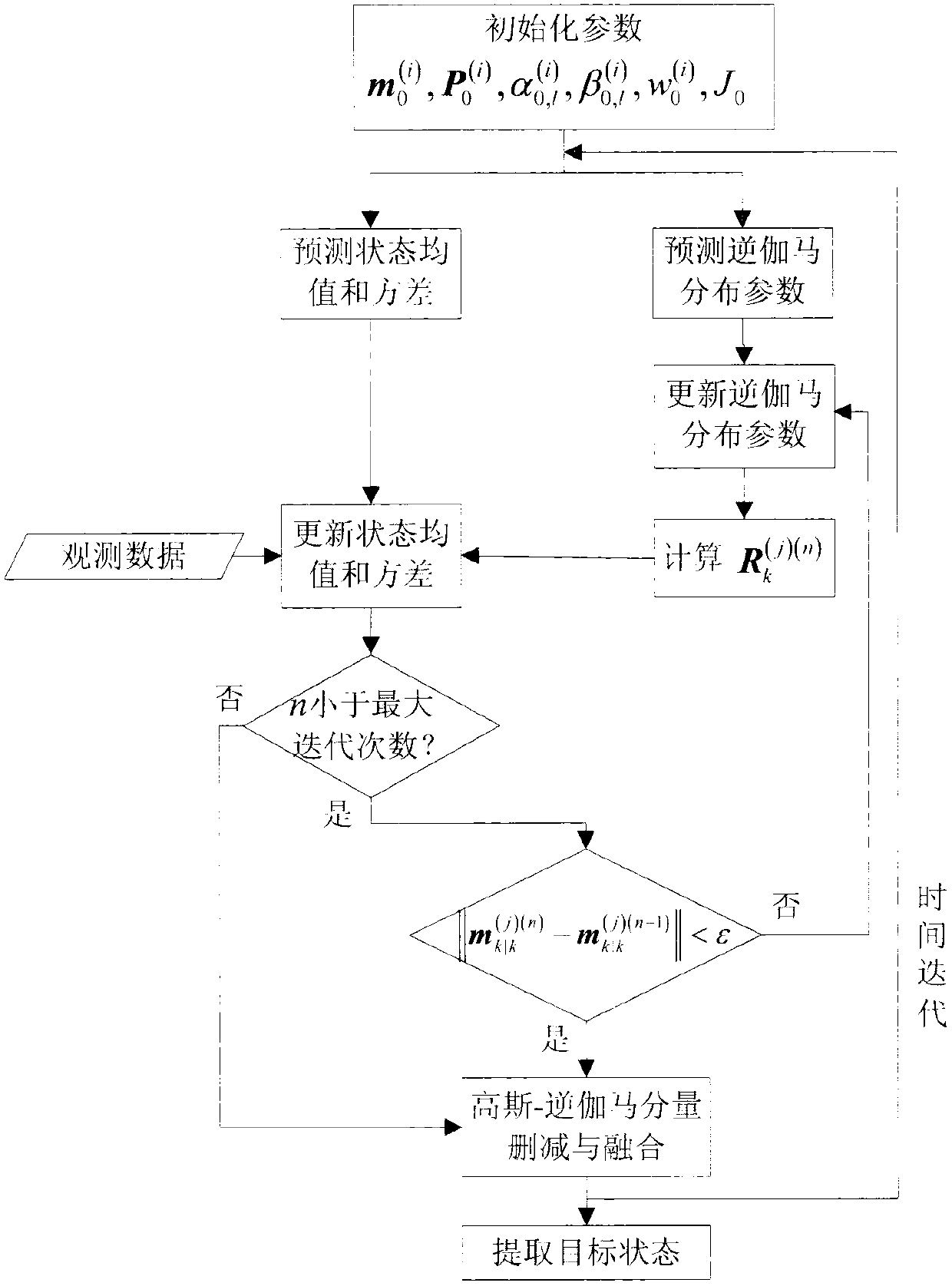
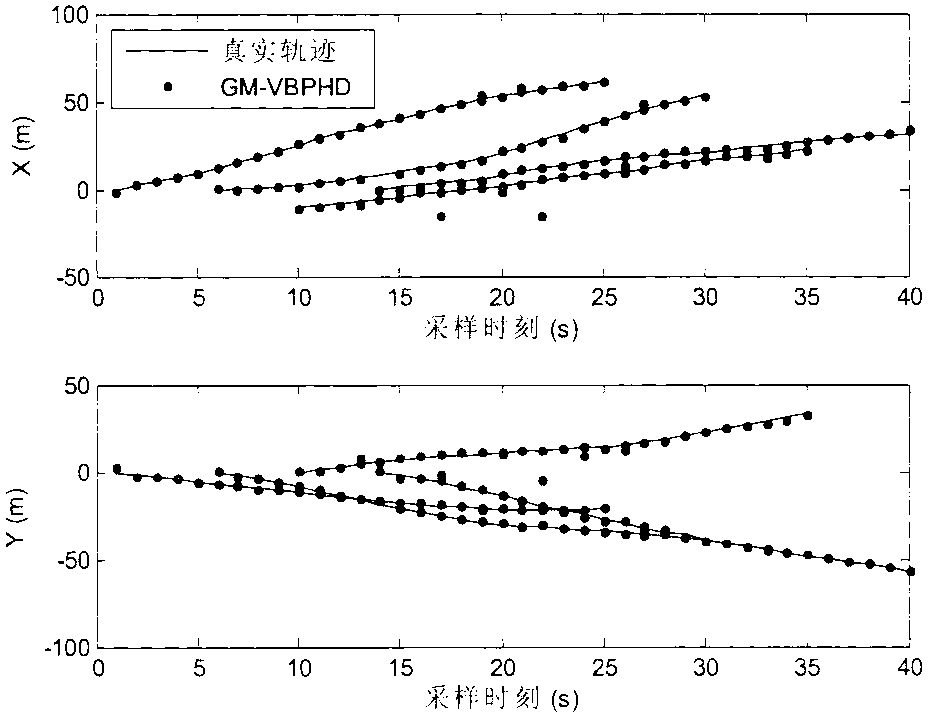
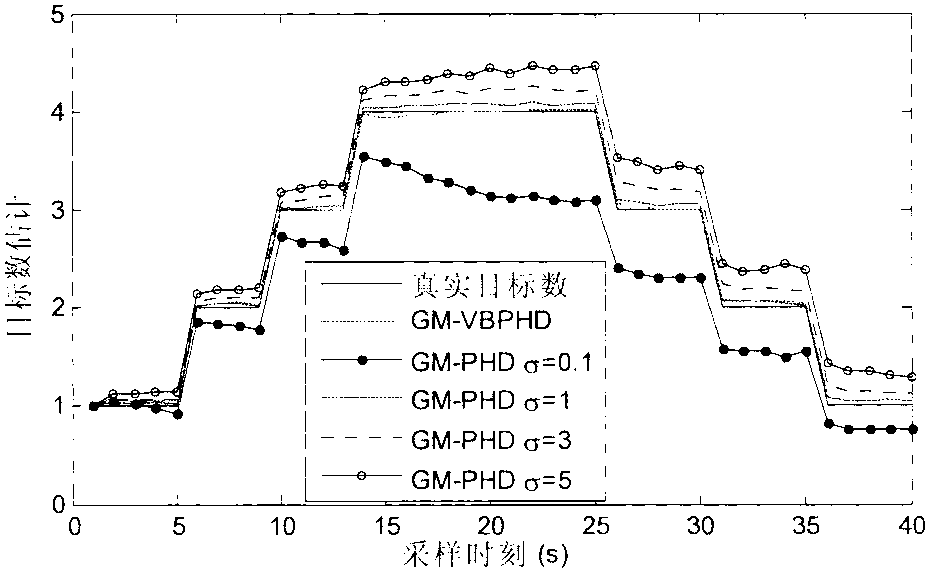
Probability hypothesis density multi-target tracking method based on variational Bayesian approximation technology
ActiveCN103345577AEfficient estimation of true measurement noiseAchieve goal trackingSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingHypothesis
The invention discloses a probability hypothesis density multi-target tracking method based on a variational Bayesian approximation technology, and belongs to the technical field of guidance and intelligent information processing. The probability hypothesis density multi-target tracking method based on the variational Bayesian approximation technology mainly solves the problem that an existing random set filtering method can not achieved varied number multi-target tracking under an unknown quantity measurement noise environment. According to the method, the variational Bayesian approximation technology is introduced, posterior probability hypothesis density of target states and measurement noise covariance is estimated in a combination mode, a Gaussian mixture inverse gamma distribution recurrence closed solution is adopted, and thus the varied number multi-target tracking under the unknown quantity measurement noise environment is achieved. The probability hypothesis density multi-target tracking method based on the variational Bayesian has a good tracking effect and robustness, is capable of meeting the design demands on practical engineering systems and has good engineering application value.
Owner:江苏华文医疗器械有限公司
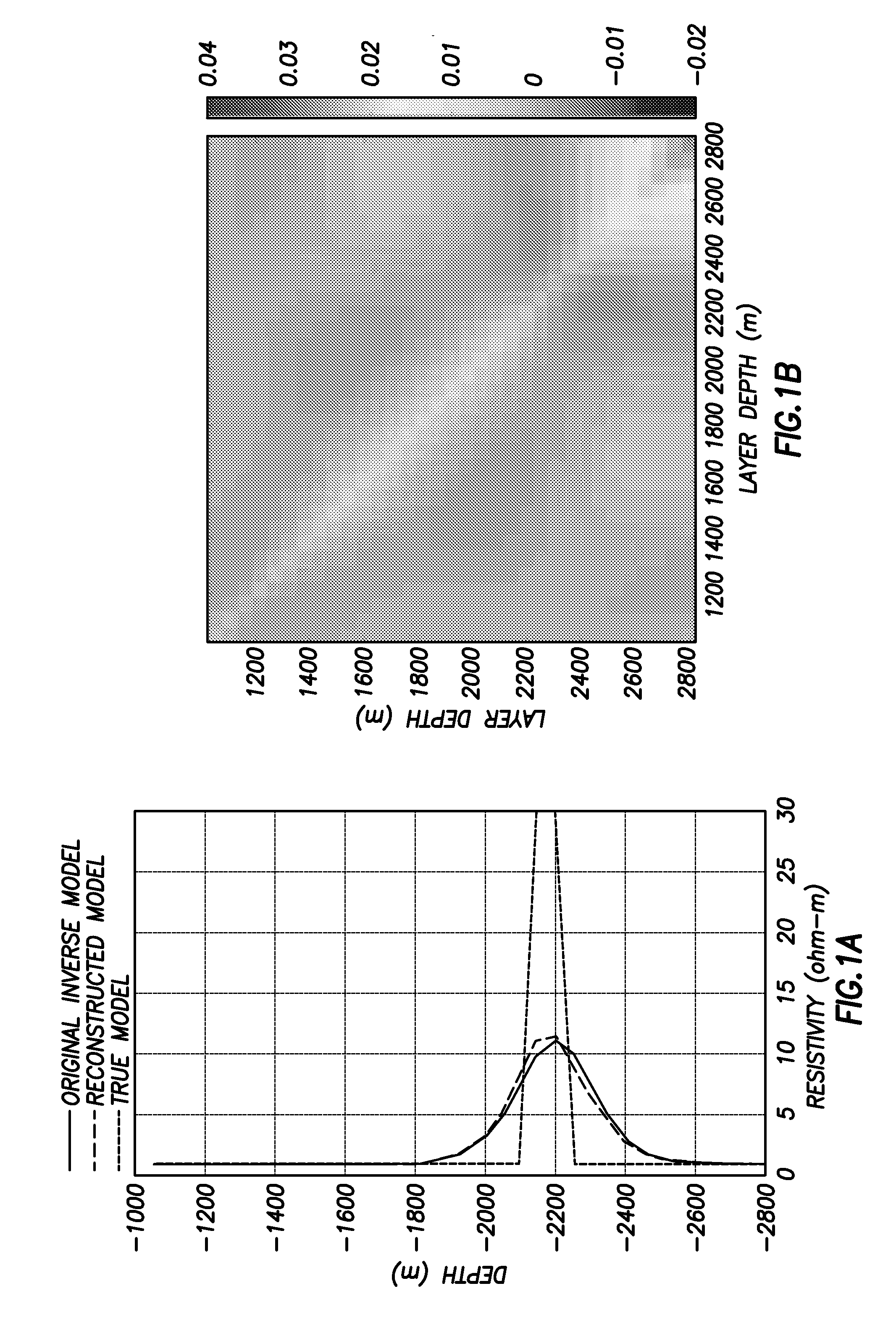
Uncertainty estimation for large-scale nonlinear inverse problems using geometric sampling and covariance-free model compression
ActiveUS20130185033A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationModel sampleModel parameters
A method for uncertainty estimation for nonlinear inverse problems includes obtaining an inverse model of spatial distribution of a physical property of subsurface formations. A set of possible models of spatial distribution is obtained based on the measurements. A set of model parameters is obtained. The number of model parameters is reduced by covariance free compression transform. Upper and lower limits of a value of the physical property are mapped to orthogonalspace. A model polytope including a geometric region of feasible models is defined. At least one of random and geometric sampling of the model polytope is performed in a reduced-dimensional space to generate an equi-feasible ensemble of models. The reduced-dimensional space includes an approximated hypercube. Probable model samples are evaluated based on data misfits from among an equi-feasible model ensemble determined by forward numerical simulation. Final uncertainties are determined from the equivalent model ensemble and the final uncertainties are displayed in at least one map.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
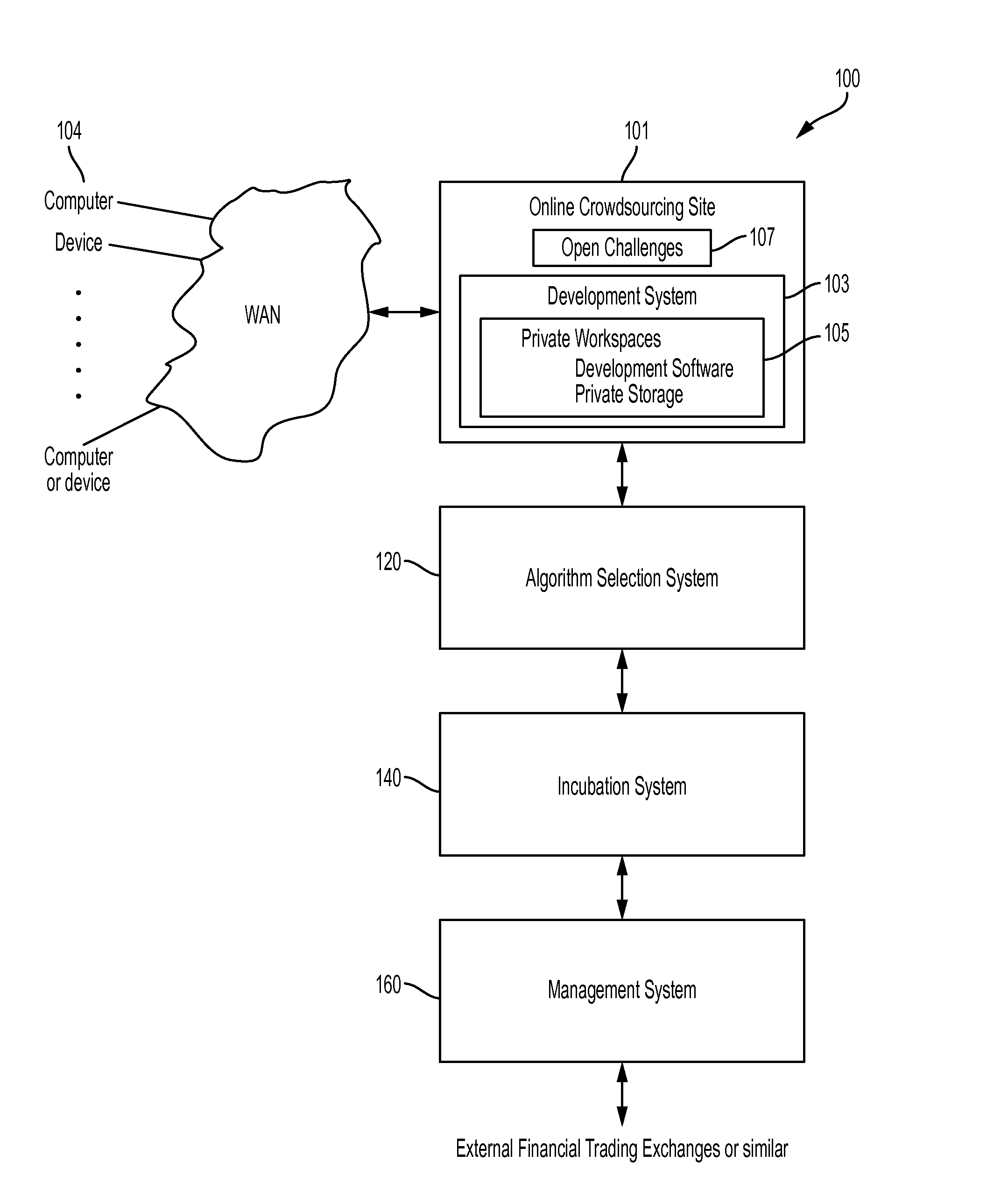
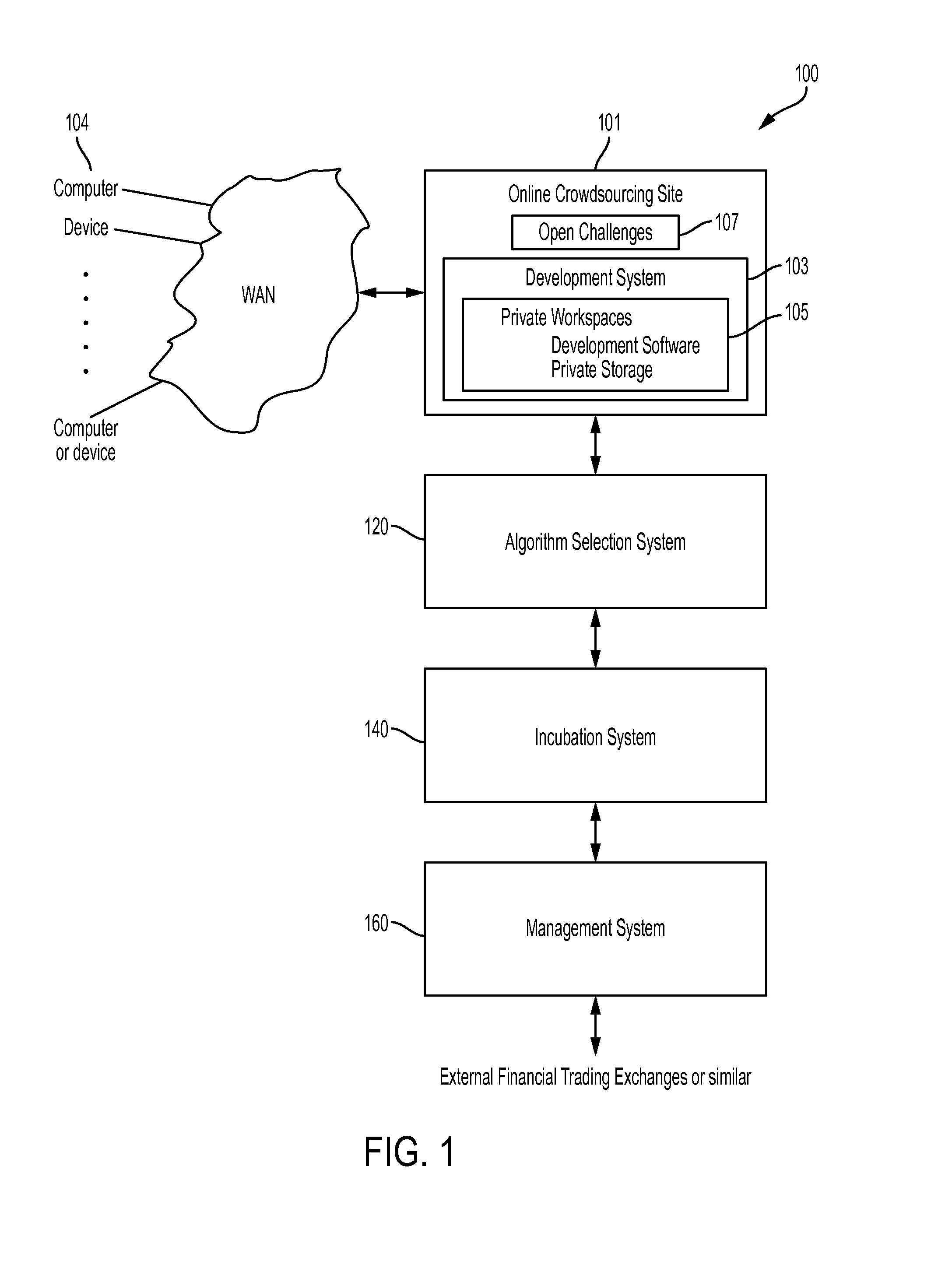
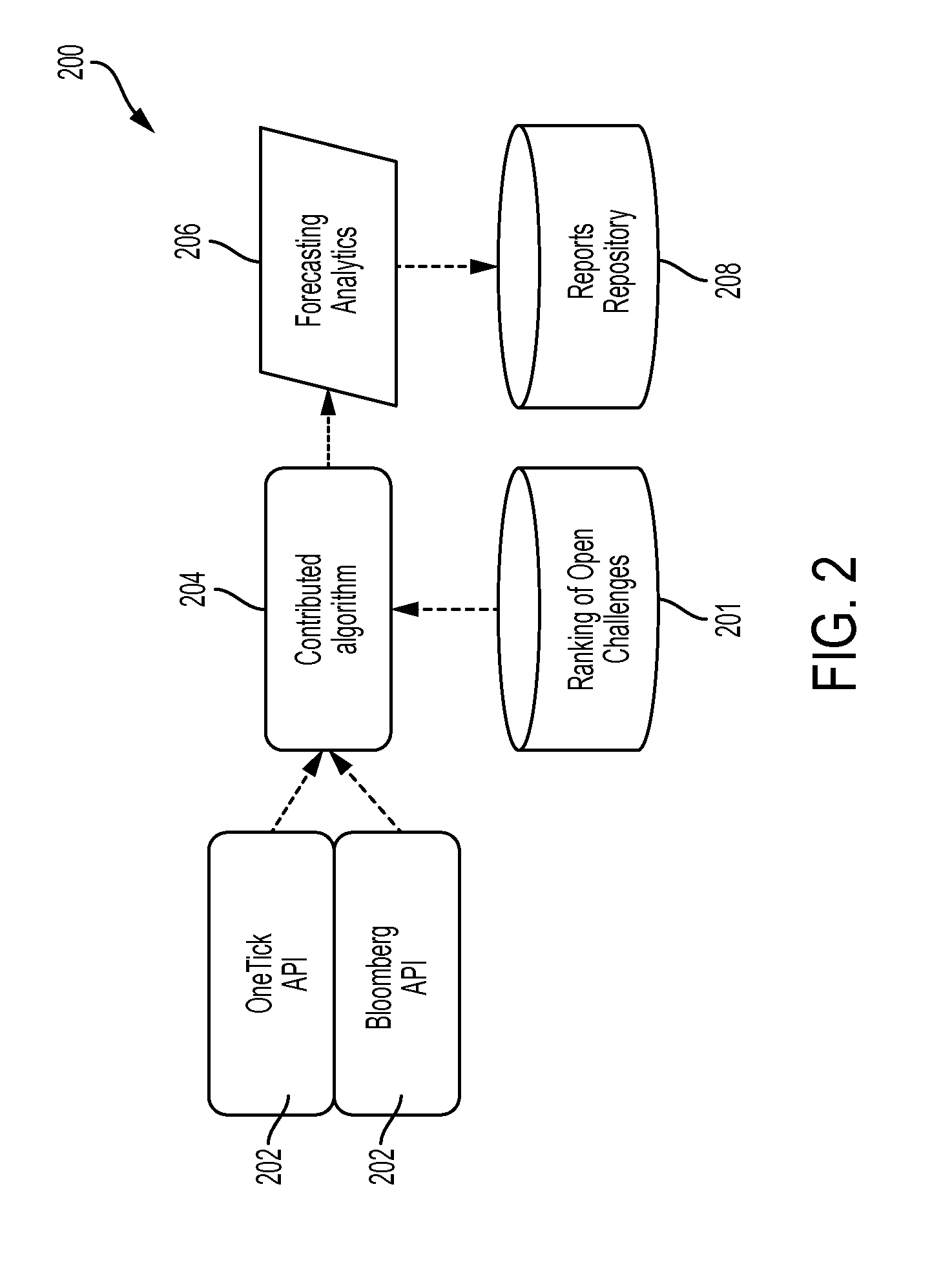
Systems and methods for crowdsourcing of algorithmic forecasting
New computational technologies generating systematic investment portfolios by coordinating forecasting algorithms contributed by researchers are provided. Work on challenges is efficiently facilitated by the algorithmic developer's sandbox (“ADS”). Second, the algorithm selection system performs a batch of tests that selects the best developed algorithms, updates the list of open challenges and translates those scientific forecasts into financial predictions. The algorithm controls for the probability of backtest overfitting and selection bias, thus providing for a practical solution to a major flaw in computational research involving multiple testing. Third, the incubation system verifies the reliability of those selected algorithms. Fourth, the portfolio management system uses the selected algorithms to execute investment recommendations. A dynamically optimal portfolio trajectory is determined by a quantum computing solution to combinatorial optimization representation of the capital allocation problem. Fifth, the crowdsourcing of algorithmic investments controls the workflow and interfaces between all of the hereinabove introduced components.
Owner:AQR CAPITAL MANAGEMENT LLC
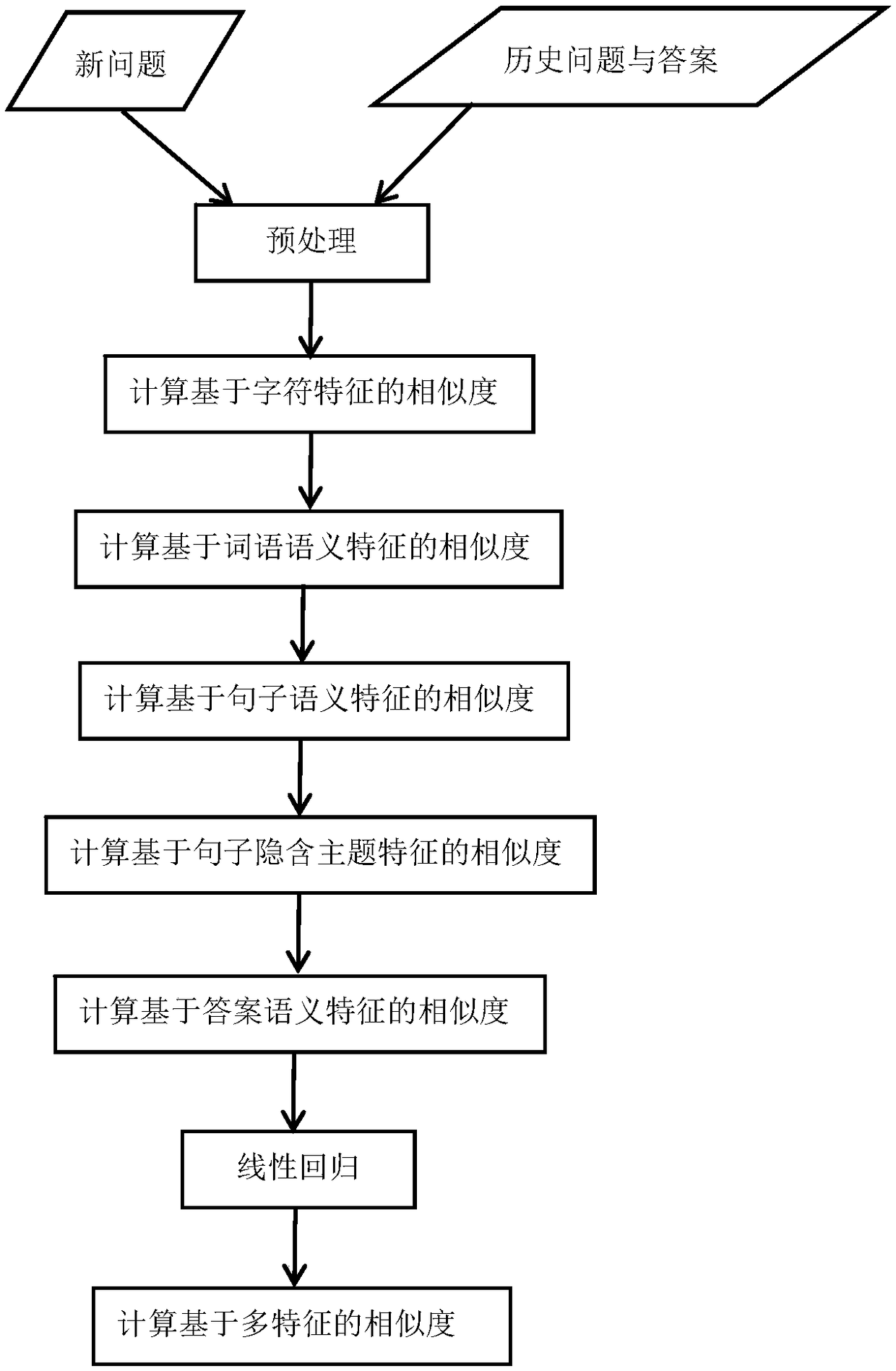
Problem similarity calculation method based on a plurality of features
ActiveCN109344236AIncrease diversityImprove generalization abilityDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisSemantic gapSemantic feature
The invention discloses a problem similarity calculation method based on a plurality of features, includes steps: For the input new question sentence, Compared with the stored historical questions andcorresponding answers, the similarities between the new questions and the historical questions are calculated based on character features, semantic features of words, semantic features of sentences,implied topic features of sentences and semantic features of answers. The final similarity is the product of the above five similarities and their corresponding weights, which are trained by linear regression method. The invention adopts a plurality of features to increase the diversity of sample attributes, and improves the generalization ability of the model. At that same time, the soft cosine distance is utilized to convert the TF-IDF is fused with editing distance, word semantics and other information, which overcomes the semantic gap between words and improves the accuracy of similarity calculation.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Computer Implemented Method for Discovery of Markov Boundaries from Datasets with Hidden Variables
InactiveUS20110202322A1Character and pattern recognitionComputation using non-denominational number representationLocal methodData set
Methods for Markov boundary discovery are important recent developments in pattern recognition and applied statistics, primarily because they offer a principled solution to the variable / feature selection problem and give insight about local causal structure. Currently there exist two major local method families for identification of Markov boundaries from data: methods that directly implement the definition of the Markov boundary and newer compositional Markov boundary methods that are more sample efficient and thus often more accurate in practical applications. However, in the datasets with hidden (i.e., unmeasured or unobserved) variables compositional Markov boundary methods may miss some Markov boundary members. The present invention circumvents this limitation of the compositional Markov boundary methods and proposes a new method that can discover Markov boundaries from the datasets with hidden variables and do so in a much more sample efficient manner than methods that directly implement the definition of the Markov boundary. In general, the inventive method transforms a dataset with many variables into a minimal reduced dataset where all variables are needed for optimal prediction of some response variable. The power of the invention was empirically demonstrated with data generated by Bayesian networks and with 13 real datasets from a diversity of application domains.
Owner:STATNIKOV ALEXANDER +1
Multi-model fused house property evaluation method
InactiveCN107230113AImprove comparabilityImprove efficiencyProduct appraisalMathematical modelNetwork model
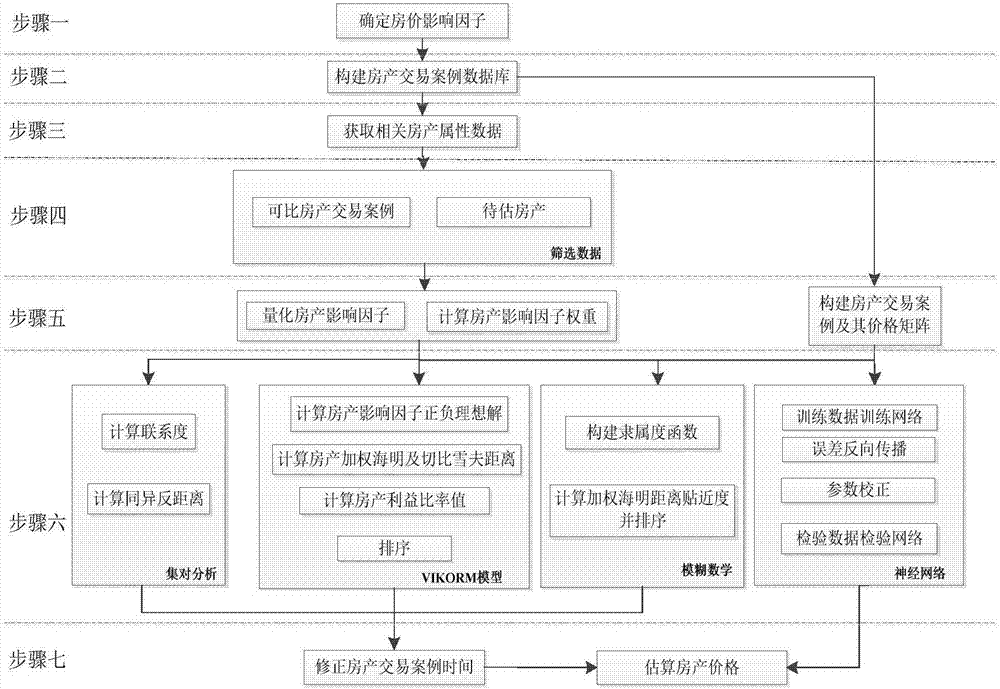
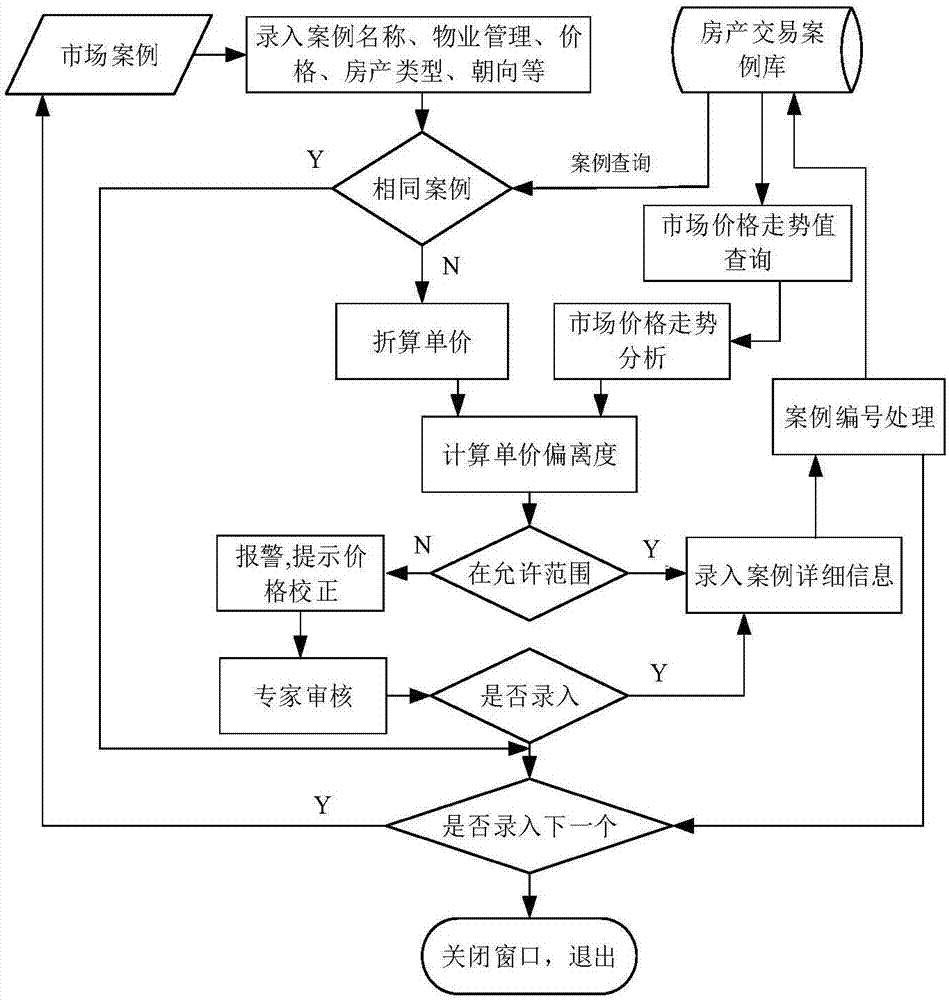
The present invention provides a real estate evaluation method with multi-model integration, which includes the following steps: determining the real estate price influencing factor; constructing a real estate transaction case database according to the determined real estate price influencing factor; obtaining real estate transaction cases in relevant areas through the real estate to be evaluated; screening the real estate data to obtain comparable transaction cases; quantify the housing price impact factors and calculate the weights of housing price impact factors; use set pair analysis model, VIKOR model, fuzzy mathematical model, and neural network model to calculate relevant parameters respectively; correct the time of real estate transaction cases, and estimate Property prices to be appraised. The present invention adopts spatial information technology to establish a real estate database, and based on this, constructs a precise quantification method for real estate valuation factors and a batch evaluation mode for real estate prices fused with multiple mathematical models, which overcomes the subjective nature of price influencing factors in traditional single-model valuation methods The problem of uniqueness and the singleness of the valuation model.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
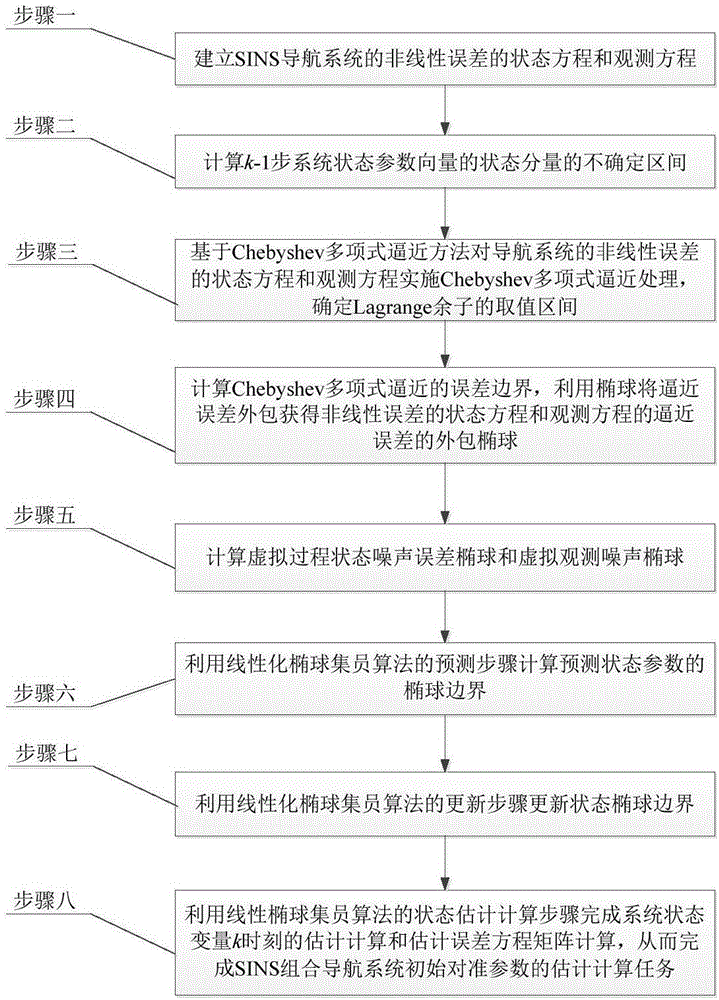
Expanded ellipsoid set-membership filtering method based on Chebyshev interpolation polynomial approximation
ActiveCN106767780AGuaranteed calculation stabilityReduce computational complexityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsComputation complexityState parameter
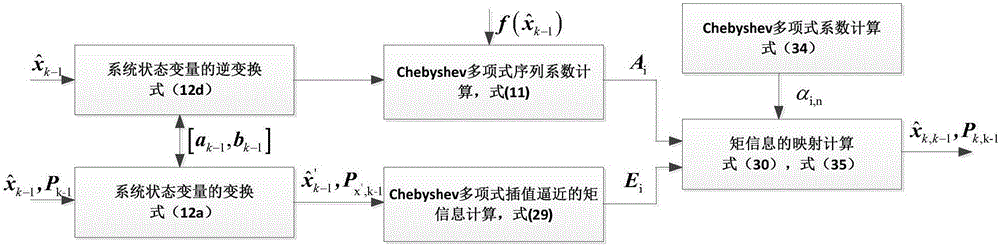
The invention provides an expanded ellipsoid set-membership filtering method based on Chebyshev interpolation polynomial approximation. According to the expanded ellipsoid set-membership filtering method, the problems of complexness in computation and low efficiency and computational accuracy in a method based on Taylor-series linear approximation are solved. The expanded ellipsoid set-membership filtering method comprises the following steps: establishing a nonlinear strapdown inertial navigation system equation and an observation equation; computing an indeterminate interval of a system state parameter component of a (k-1) step; carrying out Chebyshev polynomial approximation computation on the nonlinear equation and the observation equation of the inertial navigation system; computing an error boundary of the Chebyshev polynomial approximation computation, so as to acquire outsourcing ellipsoids of the Chebyshev interpolation polynomial approximation computation errors of the nonlinear system equation and the observation equation; and by virtue of a linear ellipsoid set-membership filtering method, computing and predicting an ellipsoid boundary of a state variable, updating a computation state ellipsoid boundary, computing an estimation value of a state parameter variable of a k step, and estimating variance matrix. The expanded ellipsoid set-membership filtering method has the beneficial effects that a computational accuracy is relatively high, the computational complexness of an algorithm is reduced, and the computational stability of the expanded ellipsoid set-membership filtering method is effectively guaranteed.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Method for synchronously reconstructing dynamic PET image and tracer kinetic parameter on the basis of TV and sparse constraint
ActiveCN105894550ASolve the estimation problemHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionImage generationSequence reconstructionSparse constraint
The invention discloses a method for synchronously reconstructing a dynamic PET image and a tracer kinetic parameter on the basis of TV (total variation) and sparse constraint. The method introduces a dictionary based on sparse constraint and a TV operator to carry out a whole reconstruction process by establishing a mathematic model for synchronously estimating the dynamic PET image and the kinetic parameter, wherein a dynamic PET sequence reconstruction subproblem provided with the total variation operator is subjected to iterative optimization solution by an ADMM algorithm, and a PET kinetic parameter estimation subproblem in combination with the dictionary based on sparse constraint is solved by a soft threshold iterative algorithm. The method solves a problem for simultaneously estimating the dynamic PET image sequence and the kinetic parameter, introduces the TV operator to improve the low result resolution and noise interference proneness in the PET image reconstruction process, and may obtain a better reconstruction result compared with other algorithms which individually reconstructs the PET image or estimates the kinetic parameter.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
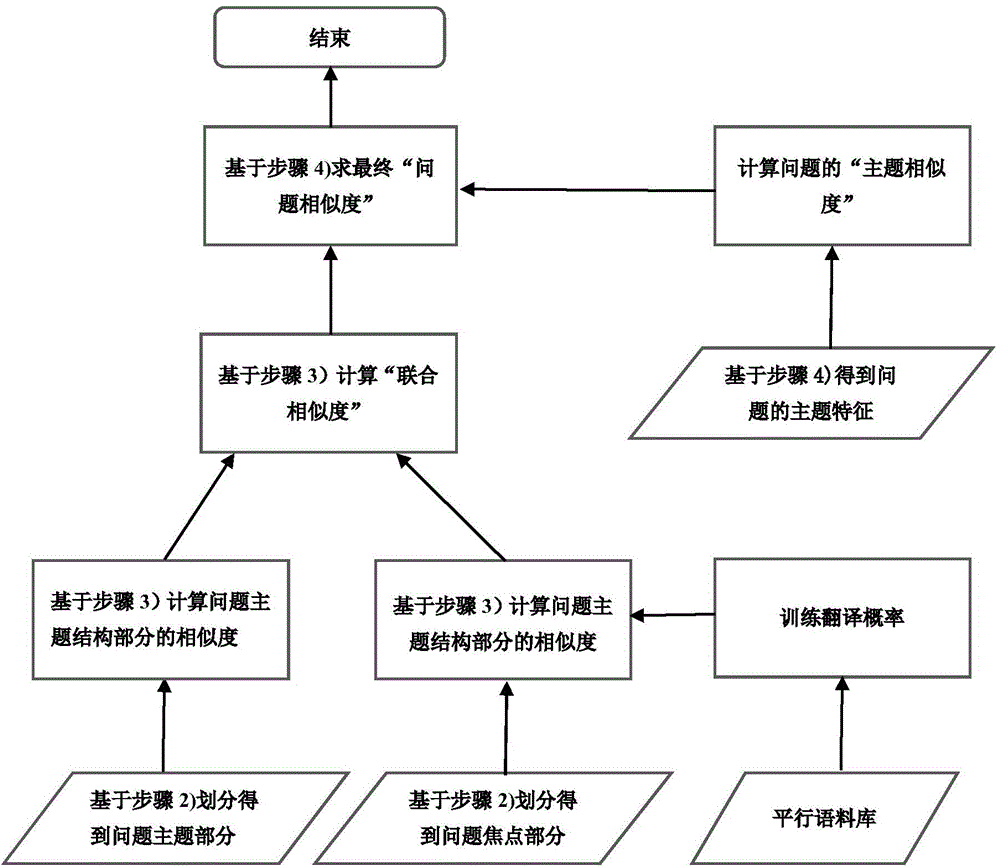
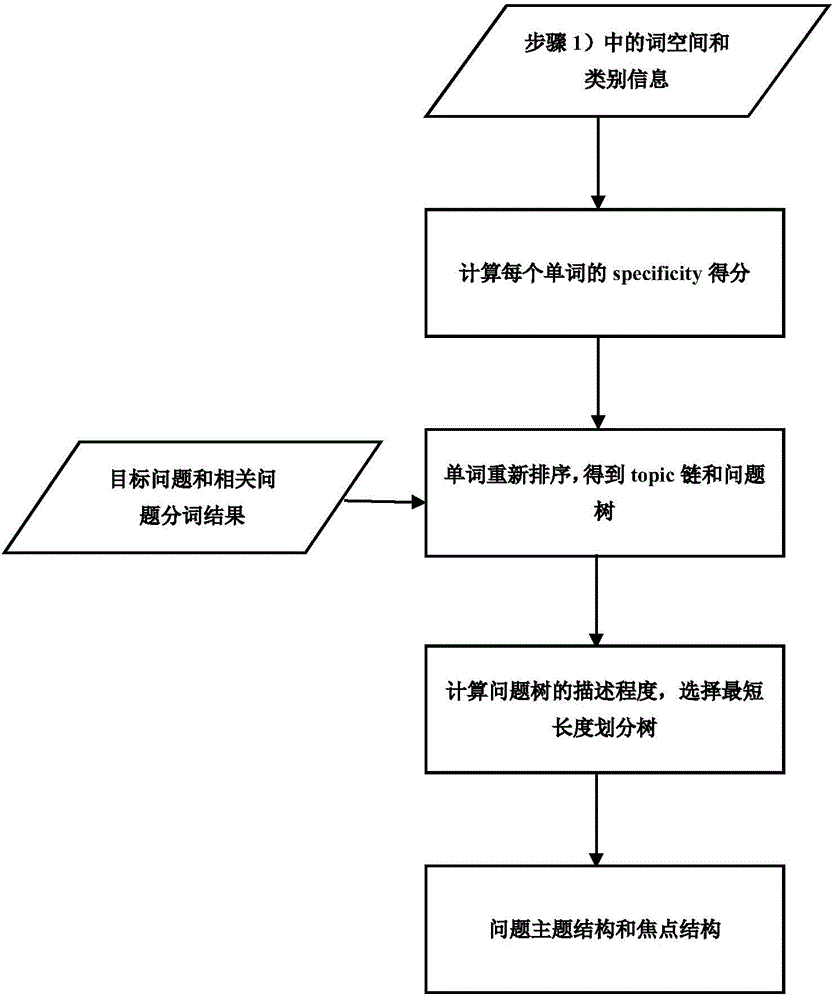
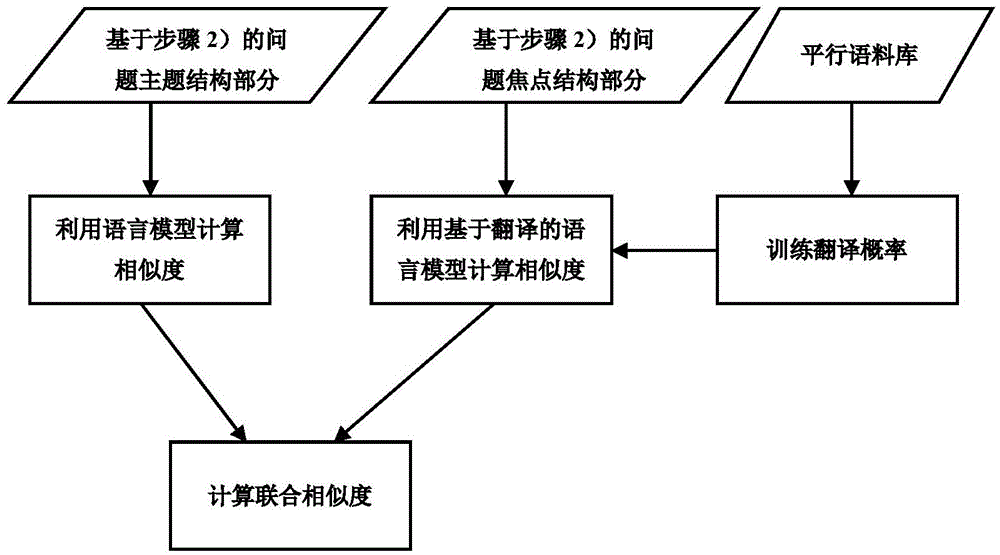
Problem similarity calculation method based on subjects and focuses of problems
InactiveCN104899188ATake advantage ofThe calculation result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum description lengthCalculation methods
The present invention discloses a problem similarity calculation method based on subjects and focuses of problems Basic preprocessing, such as word segmentation and the like, is carried out on problem data by using a tokenizer, and based on the basic preprocessing, a tree tailor model based on the minimum description length divides each problem into a problem subject and a problem focus; with respect to subject structures and focus structures of two problems, a language model and a language model based on translation are respectively used to calculate a similarity score, and a joint similarity is obtained by means of weighted summation; and a subject similarity between the two problems is calculated by using a method based on a BTM subject model, and two similarities are finally subjected to weighted summation to obtain the final problem similarity. According to the present invention, architectural features and subject information of the problems are introduced into the problem similarity calculation, the information of the problems is more sufficiently used, and by introducing the subject information of the problems besides word statistics information into the problem similarity calculation, accuracy of the problem similarity calculation is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
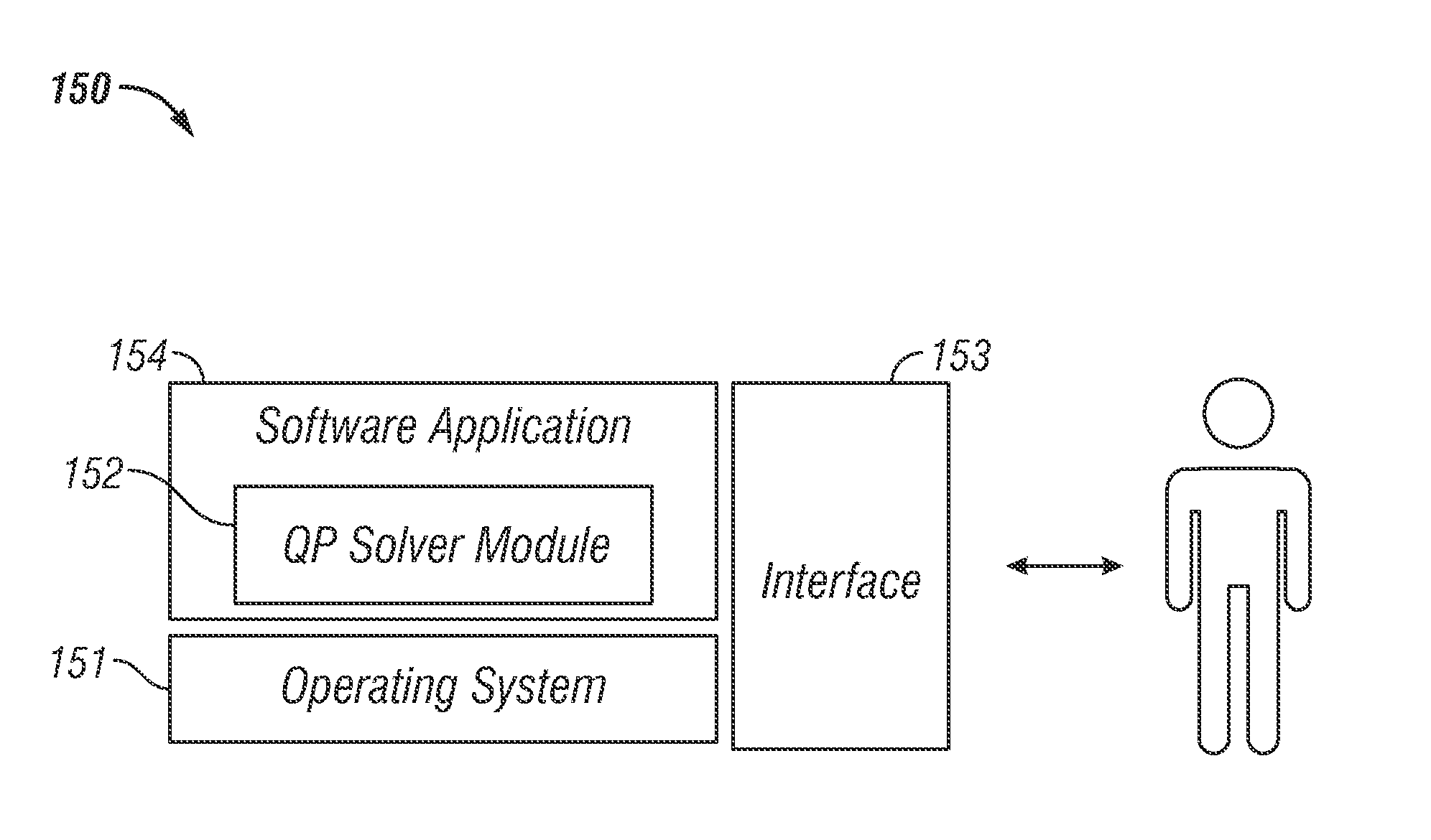
System and method for solving quadratic programming problems with bound constraints utilizing a semi-explicit quadratic programming solver
ActiveUS20120059782A1Knowledge representationComplex mathematical operationsTheoretical computer scienceOptimization problem
A system and method for solving a quadratic programming optimization problem with bound constraints using a semi-explicit QP solver with respect to an embedded platform is presented. A linear system of equations associated with a matrix (e.g., a Karush-Kuhn-Tucker matrix, KKT system) can be solved at each iteration of the solver based on a factorization approach. A set of partial factors with respect to the QP problem can be pre-computed off-line and stored into a memory. The factorization process of the KKT matrix can then be finished on-line in each iteration of the semi-explicit QP solver in order to effectively solve the QP optimization problems. The QP problem can be solved utilizing a standard active-set approach and / or a partial explicit approach based on a processor utilization and memory usage.
Owner:GARRETT TRANSPORATION I INC
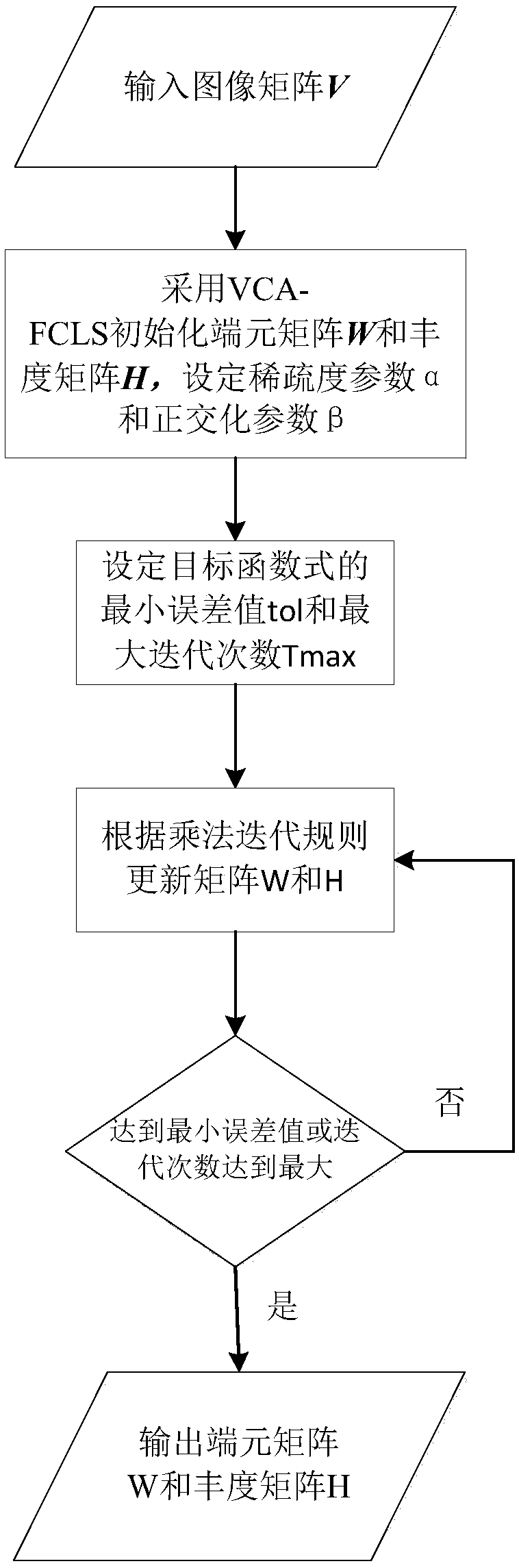
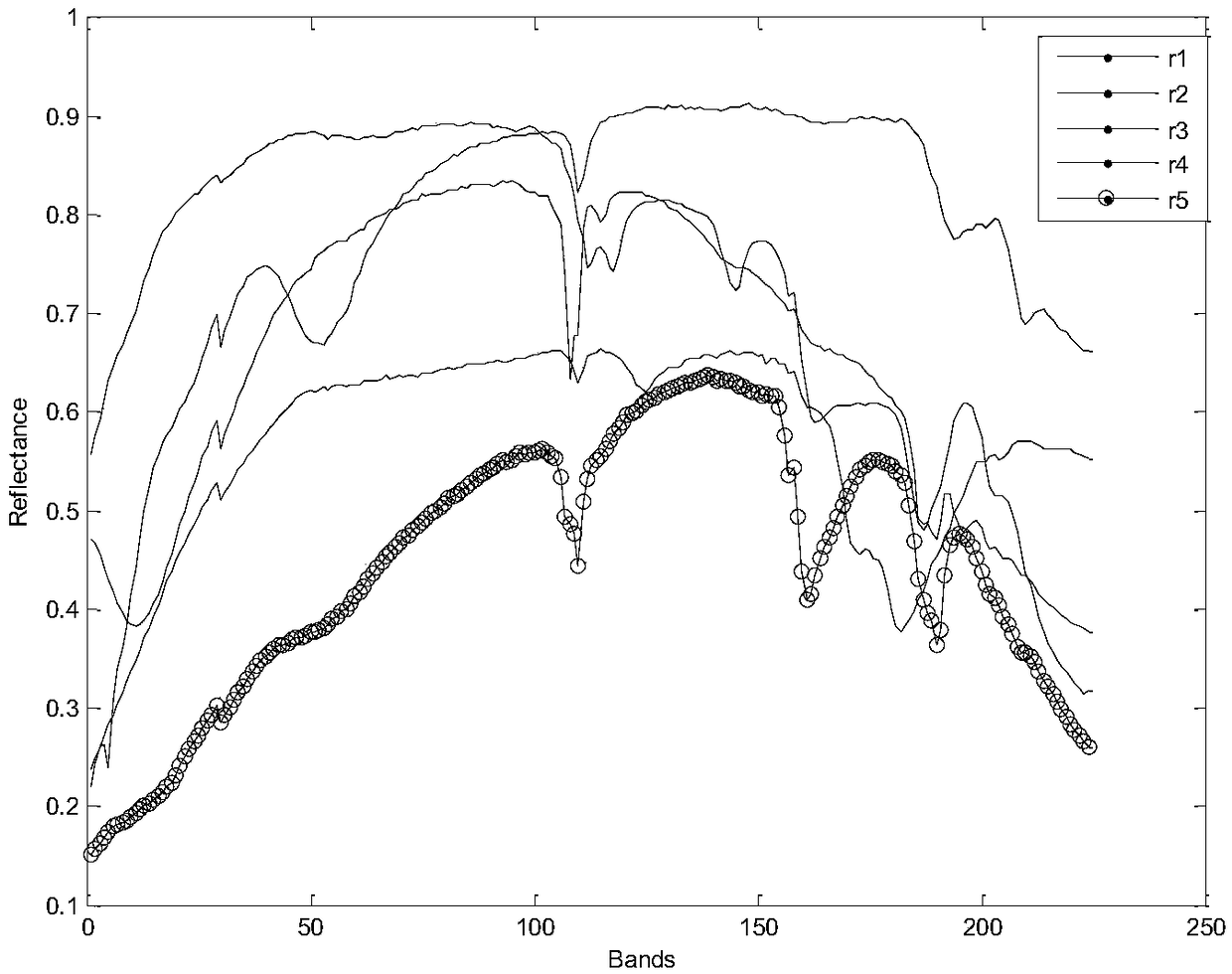
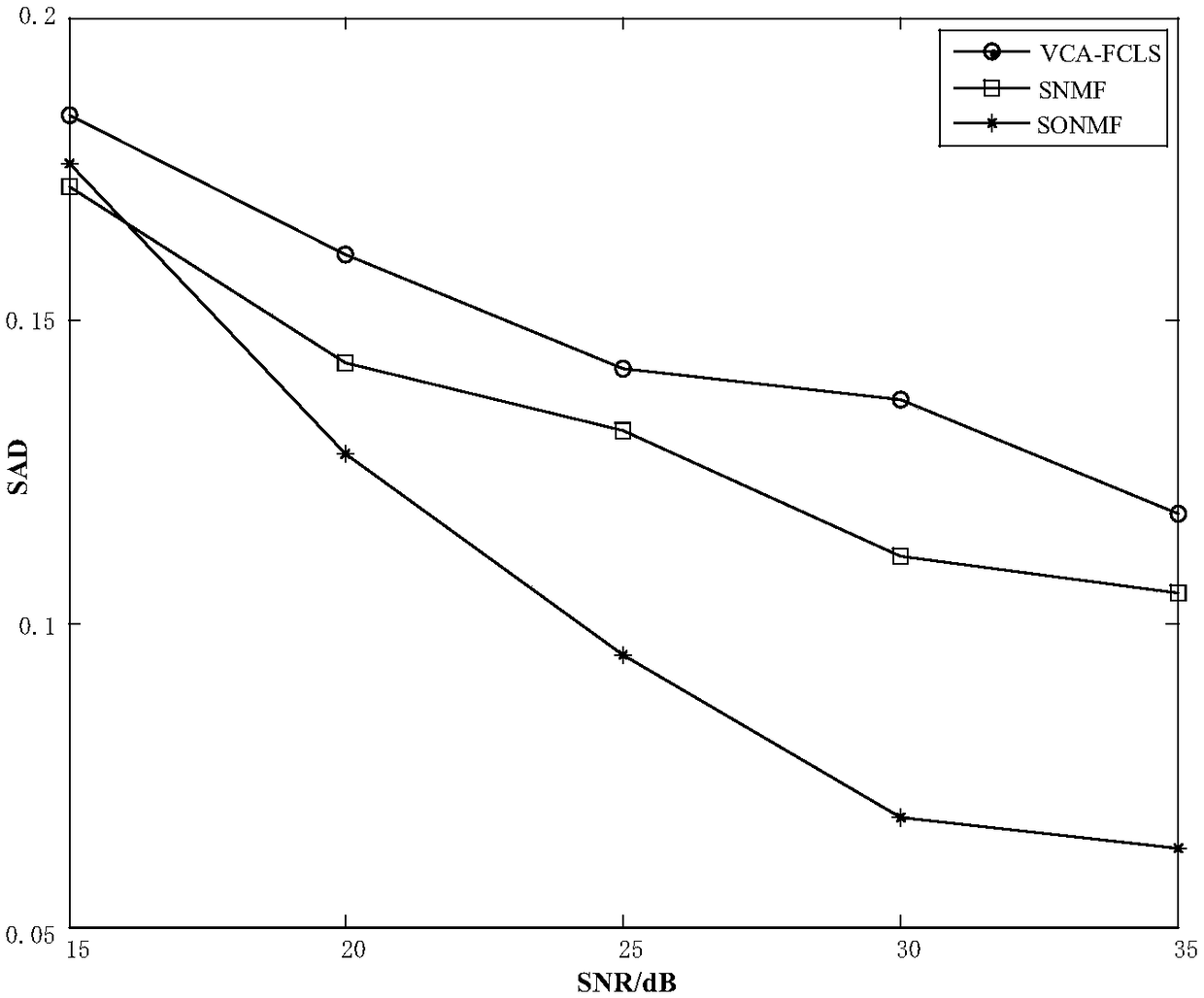
Spectral unmixing scheme based on abundance sparse and endmember orthogonal constraint NMF(Non-negative Matrix Factorization)
InactiveCN109085131AGuaranteed independenceGood unmixing effectColor/spectral properties measurementsAlgorithmDecomposition
A spectral unmixing scheme based on abundance sparse and endmember orthogonal constraint NMF(Non-negative Matrix Factorization) is an algorithm of a spectral image decomposition field. A classical NMFtarget function is a non-convex function, and a constraint condition needs to be added into the target function for solving the problems. The characteristics of spectral images are combined to put forward the spectral image unmixing algorithm which combines endmember orthogonality with abundance sparse constrains NMF on the basis of a linear spectral mixture model. The endmember orthogonal constraint guarantees independence among spectral endmembers, meanwhile, the abundance sparsity fully utilizes the sparsity of spectral data, two constraint conditions are introduced into the target function, a least square method is adopted to obtain the iteration rules of an endmember matrix and an abundance matrix, and a final result is obtained through the setting of an iterative termination condition. Through the experiments of simulation data and truthful data, the effectiveness of the algorithm is verified.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
An Optimization Method for Constrained Problems Based on Evolutionary Optimization Algorithms
The invention relates to an optimization method for constrained problems based on an evolutionary optimization algorithm. For constrained optimization problems, this method adopts the method of penalty function to deal with constrained problems, and uses swarm intelligence optimization algorithm to optimize the function with penalty items. Using this optimization method, the penalty coefficient of each constraint item in the algorithm iteration process is jointly determined by the number of all individuals in the population that meet the constraint conditions, the degree of violation of constraints, and the sum of the objective functions of all individuals in the population. This avoids the problem that the penalty coefficient is too large or too small, prompts the algorithm to achieve a balance between the satisfaction of the constraints and the non-satisfaction of the individuals in the population as much as possible in each iteration, and avoids that the optimization of practical engineering problems cannot give a suitable penalty coefficient The problem.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Matrix decomposition parallelization method based on graph calculation model
The invention discloses a matrix decomposition parallelization method based on a graph calculation model. Matrix decomposition can be flexibly brought into more user information. The matrix decomposition deduces the hidden semantic vectors of a user and an article according to the score of the article by the user, and then, recommendation is carried out according to the hidden semantic vectors of the user and the article. However, in a practical application scene, the implementation of a matrix decomposition recommendation algorithm needs to consume a great quantity of time, and traditional commercial requirements can not be met. A distributed calculation platform can be used for carrying out parallelization on the matrix decomposition recommendation algorithm to effectively solve the problem, and meanwhile, a multiple-iteration calculation problem is in the presence in the implementation of the matrix decomposition recommendation algorithm. The invention puts forward the Spark-based GraphX graph calculation frame to realize matrix decomposition parallelization. Compared with a traditional MapReduce calculation graph model, the graph calculation frame has the obvious advantages on the aspect of the solving of multiple-iteration problems and execution efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for solving influence maximization problem based on user behavior propagation model
InactiveCN108182640AEffective eliminationImprove rankingData processing applicationsSoftware designSocial circleInfluence propagation
The invention discloses a method for solving an influence maximization problem based on a user behavior propagation model. According to the method, the individual user influence is calculated based onuser behaviors of the social network, the influence propagation probability is calculated based on the individual user influence, and the maximization scope of influenced users in a special social circle is calculated based on the influence propagation probability. Compared with a propagation model based on the network topology structure, a more considerable influence node set can be more easilyacquired in the social network, nodes with the larger influence can better influence other adjacent nodes, the success probability is correspondingly larger, the individual user influence can be solved through a PageRank method based on the time distribution user liveness to effectively eliminate zombie nodes, compared with a PageRank method based on the network topology structure, the acquired influence has greater timelines and accuracy, ranking of active users can be better improved, and ranking of inactive users can be reduced.
Owner:山东爱城市网信息技术有限公司
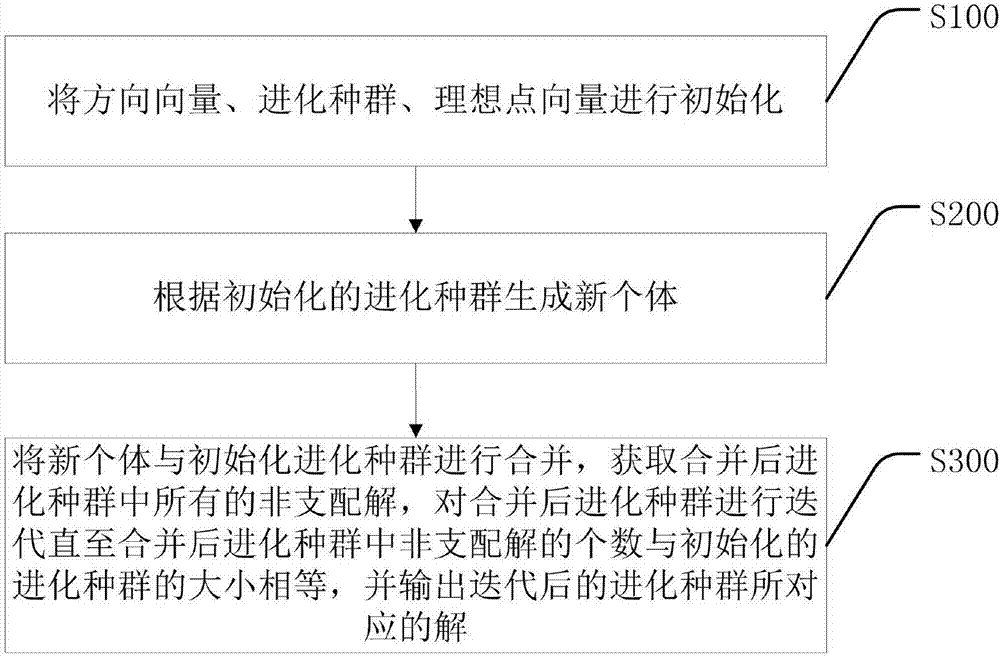
Index and direction vector-combined multi-objective optimization method and system
InactiveCN107122844AAlleviate the problem of less selection pressureReduce computational complexityForecastingArtificial lifePressure decreaseComputation complexity
The invention discloses an index and direction vector-combined multi-objective optimization method and system. The method includes the following steps that: a direction vector, an evolutionary population and an ideal point vector are initialized; new individuals are generated according to the initialized evolutionary population; and the new individuals and the initialized evolutionary population are merged, so that non-dominated solutions in the merged evolutionary population are obtained, the merged evolutionary population is iterated until the number of the non-dominated solutions in the merged evolutionary population in equal to the size of the initialized evolutionary population, and solutions corresponding to the iterated evolutionary population are outputted. According to the method and system of the invention, the Pareto dominance relation can be replaced, the problem of selective pressure decrease caused by the large proportion of non dominated individuals can be effectively alleviated; dual epsilon indexes strictly accord with the consistency of the Pareto dominance, and the computational complexity of the method of the invention is relatively low compared to the indexes; and additional parameter settings are not needed, and therefore, calculation is simple.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
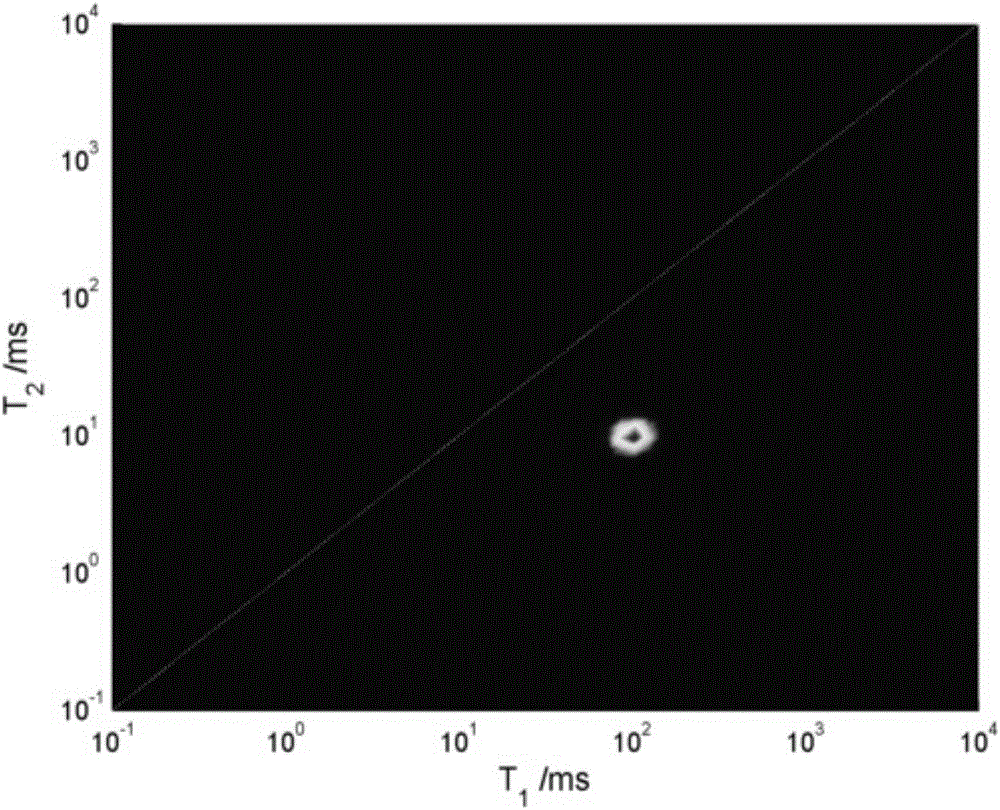
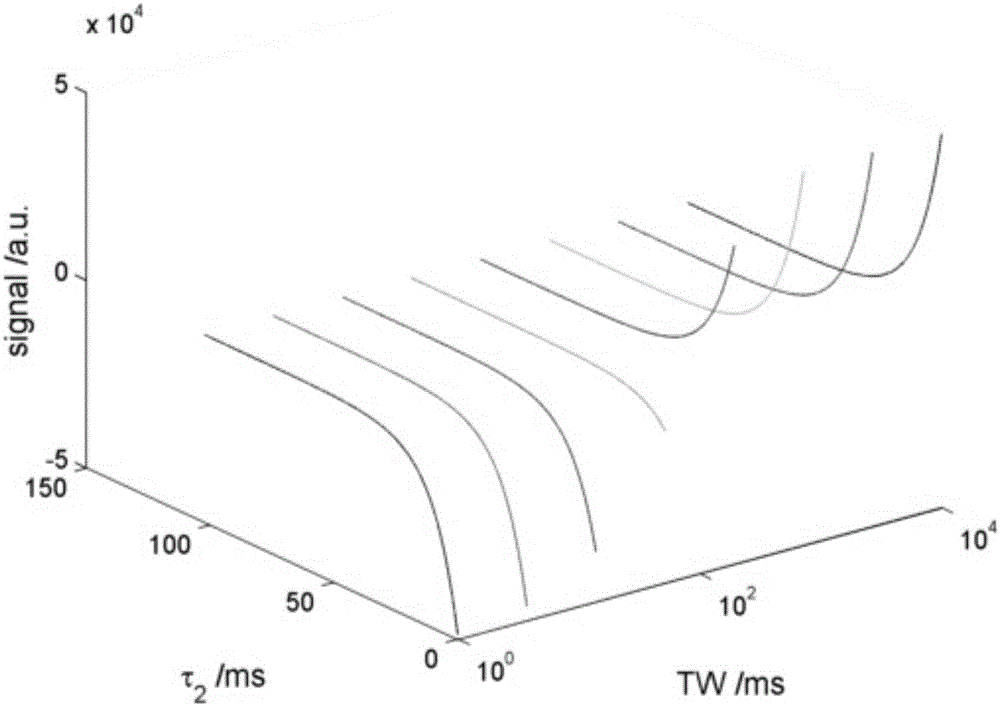
Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional spectrum inversion algorithm
ActiveCN106199474AGuaranteed non-negativitySimplify the inversion processMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsRobustificationSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention relates to a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) two-dimensional spectrum inversion algorithm which extends a PDCO (a primitive dual interior point method for convex objectives) to two-dimensional space for solving a two-dimensional inversion problem. Compared with other low-field NMR inversion algorithms reported in domestic and foreign literatures, the inversion algorithm of the invention uses L1 regularization and L2 regularization instead of just the L2 regularization, thereby getting closer to the sparseness of an original signal and acquiring spectral distribution that may more reflect a reality. The PDCO can ensure the non-negativity of a solution, and does not need additional nonnegative constraint calculation, which simplifies an inversion process. The inversion algorithm of the invention can also distinguish closely adjacent peaks and achieves high computational accuracy. The inversion algorithm of the invention has good robustness and may obtain stable inversion results under different SNR data.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
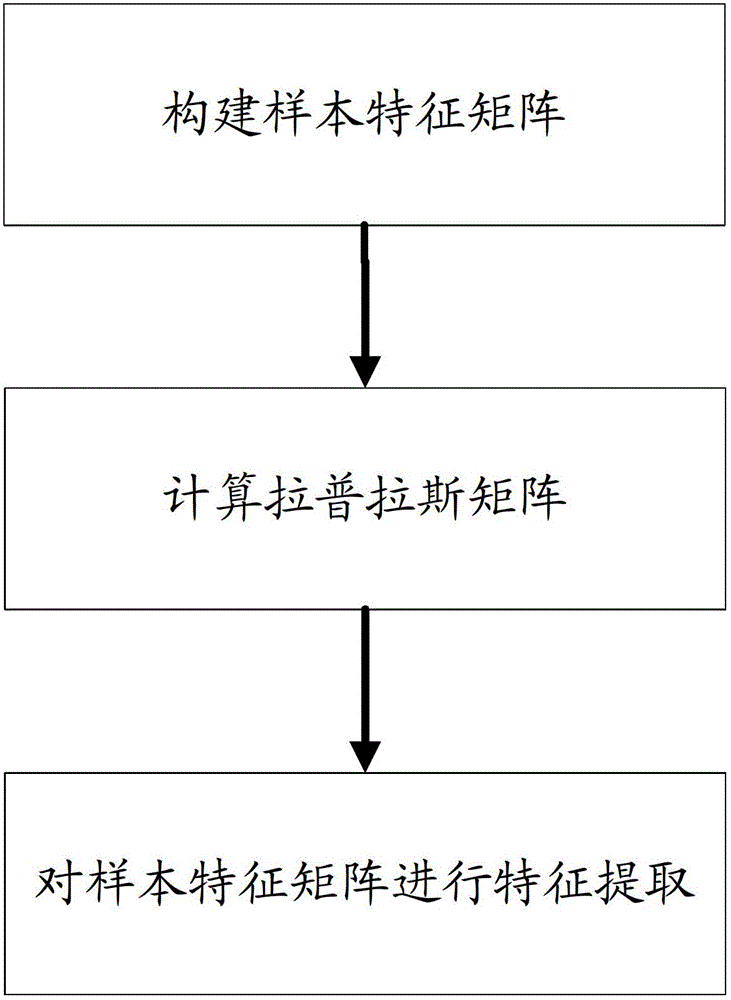
Unsupervised cluster characteristic selection method based on Laplace regularization
InactiveCN102722578AImprove effectivenessSubsequent learning predicts improved resultsSpecial data processing applicationsFeature extractionUnsupervised clustering
The invention discloses an unsupervised cluster characteristic selection method based on Laplace regularization. The unsupervised cluster characteristic selection method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a sample characteristic matrix, (2) calculating a Laplace matrix, and (3) extracting the characteristics of the sample characteristic matrix. The unsupervised cluster characteristic selection method disclosed by the invention selects the characteristics through directly measuring the variance of follow-up study prediction results, and can directly enhance the follow-up study prediction results. Influence of the selected characteristics to predicted values of the study problems is taken into the consideration in the characteristic extraction process, so that the follow-up study efficiency can be efficiently improved. In addition, the modeling of data of the unsupervised cluster characteristic selection method disclosed by the invention is on the basis of a Laplace method of manifold geometry of the data. The unsupervised cluster characteristic selection method can efficiently reflect distribution information of the data in the space so as to calculate the maximum dimensionality of the information amount.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
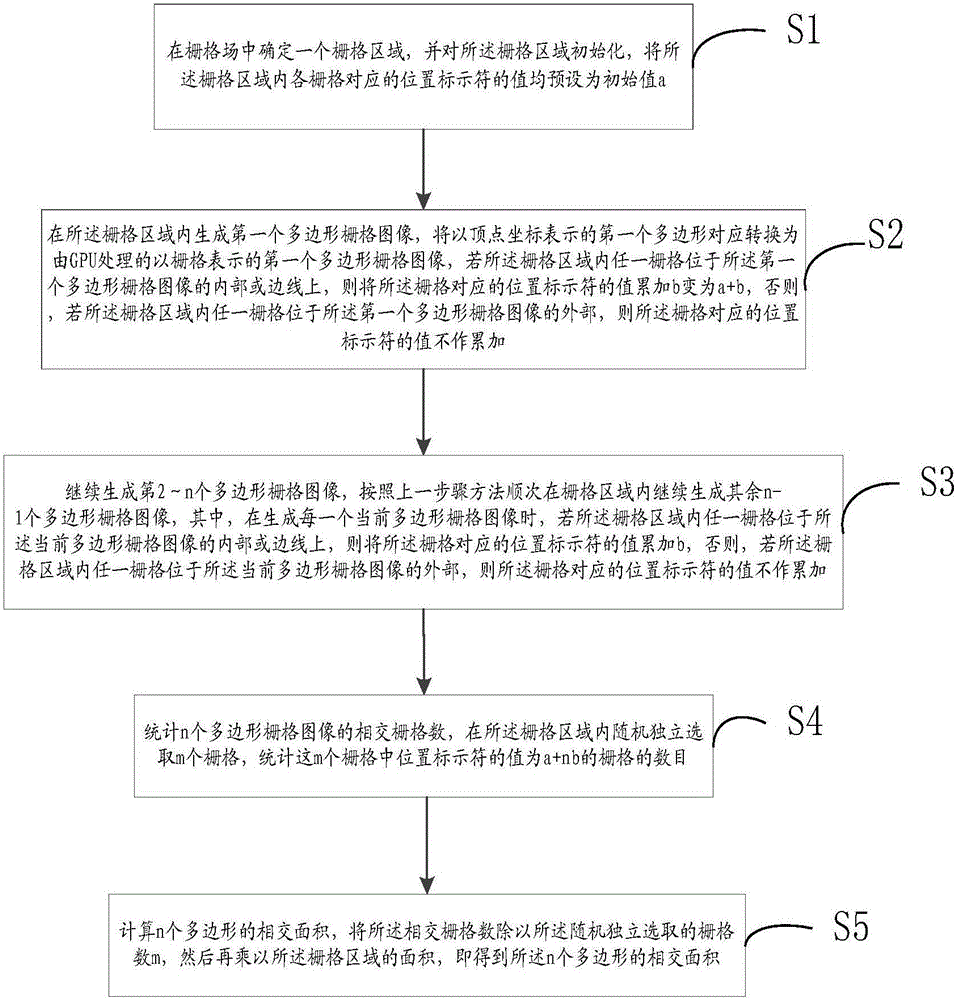
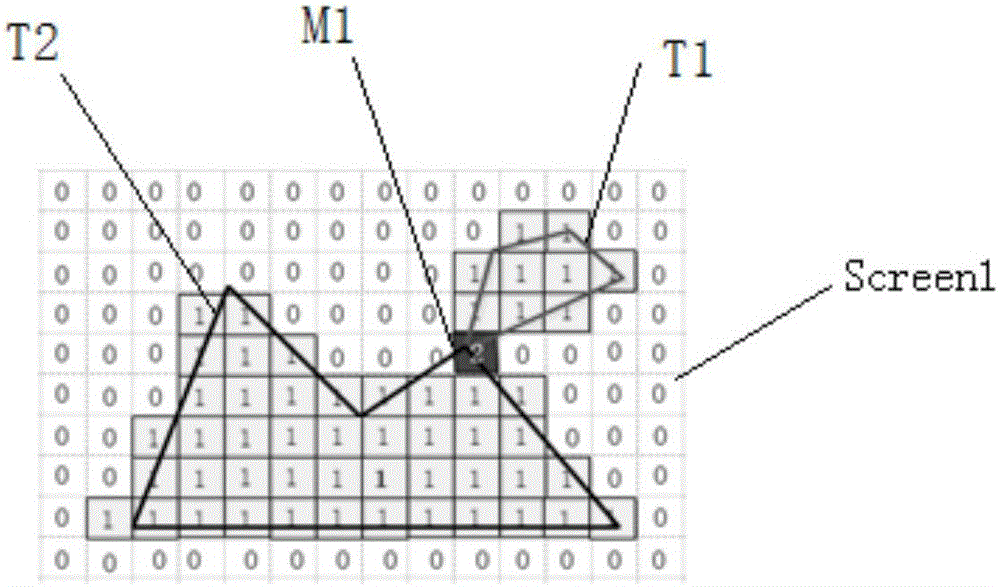
Arbitrary polygon intersection area calculation method based on probability statistics
ActiveCN106709857AEasy to handleProcessing speedProcessor architectures/configurationRasterisationComputer science
The invention discloses an arbitrary polygon intersection area calculation method based on probability statistics. The arbitrary polygon intersection area calculation method comprises steps that with help of a GPU, rasterization of arbitrary polygons is realized, and the polygons expressed by vertex coordinates are converted into polygon raster images expressed by rasters; the valuation and the correction of the position identifiers of the rasters are carried out according to the intersection condition of the raster images; the arbitrary rasters are selected from a raster field to simulate the whole raster area to improve time performance; the number of the intersection rasters in the arbitrary rasters is counted, and then the intersection area is calculated. The above mentioned calculation method is not restricted by the concavity and the convexity of the polygons, and the parallelism feature of the GPU is adopted, and by comparing with the calculation methods with the help of the GPU, a processing speed is greatly improved, a principle is simple, and realization is convenient. According to an experimental result, the calculation method is suitable for the arbitrary complicated polygons, and the singularity problems of the conventional calculation methods are prevented, and therefore good robustness is provided.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
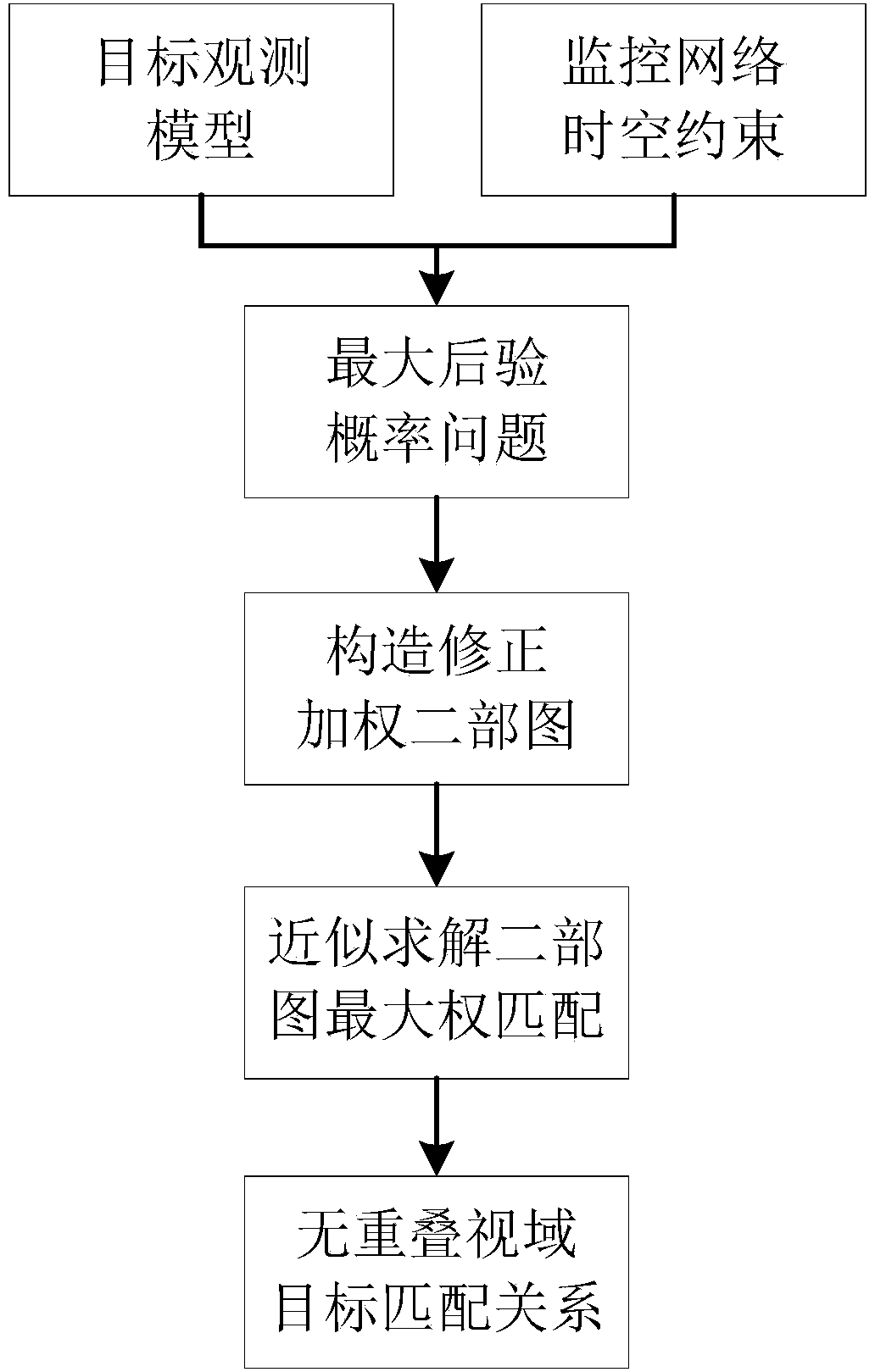
Disjoint-view object matching method based on corrected weighted bipartite graph
ActiveCN104065932AImprove robustnessSolve matching problemsImage analysisClosed circuit television systemsMaximum a posteriori estimationTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a disjoint-view object matching method based on a corrected weighted bipartite graph. The method relates to the field of computer vision. The method expresses a disjoint-view object matching problem as a maximum posterior probability problem, so that an object observation model and time-space constraints of a surveillance network are combined, and the maximum posterior probability problem is resolved through solving the maximum weight matching of a weighted bipartite graph. To solve the problem that construction of a common weighted bipartite graph is liable to introduction of incorrect matching, the method provides a corrected weighted bipartite graph construction method based on an adaptive threshold, so that incorrect matching is prevented from being introduced during construction of the weighted bipartite graph as much as possible. Aimed at the defect of a conventional KM method that the amount of computation is too large during large-scale weighted bipartite graph matching problem solving, the method brings forward a MH sampling-based method for approximating and solving the maximum weight matching of the weighted bipartite graph, so that a disjoint-view object matching relationship is obtained.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
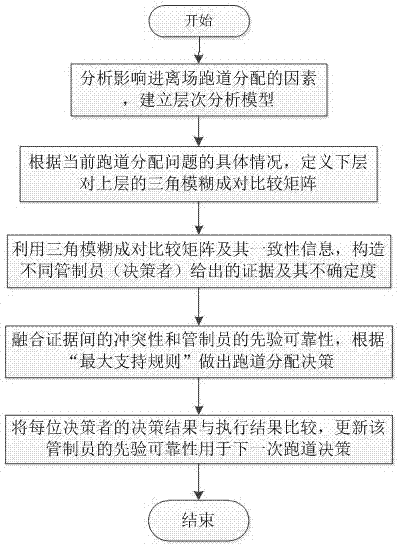
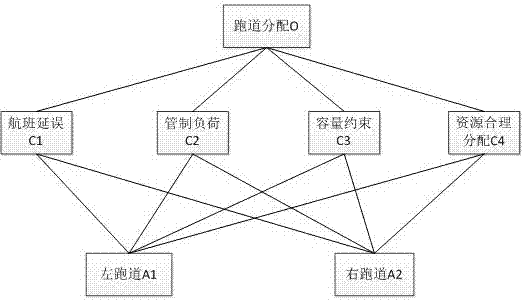
Airport runway allocation decision method based on fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and evidence theory
The invention discloses an airport runway allocation decision method based on a fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and an evidence theory, belonging to the technical field of runway distribution. The method includes analyzing factors influencing the distribution of the approach and departure runways, and establishing an analytic hierarchy model; according to the specific situation of the current runway distribution problem, defining a triangular fuzzy pairwise comparison matrix of the hierarchical model; constructing the evidences given by different controllers and uncertainty by means of the triangular fuzzy pairwise comparison matrix and the consistency information; comprehensively considering the conflict between evidences and the prior reliability of the controllers, and fusing differentevidences by using an evidence theory; calculating a trust interval of the fusion result and making a decision; finally, comparing the decision result of each decision maker with an execution result,and updating the prior reliability of the controllers for the next runway allocation decision. According to the method, the subjective factors in the runway distribution process are fully considered,and the subjective factors are converted into the uncertainty of the evidence for decision, so that the runway distribution result is more consistent with reality.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
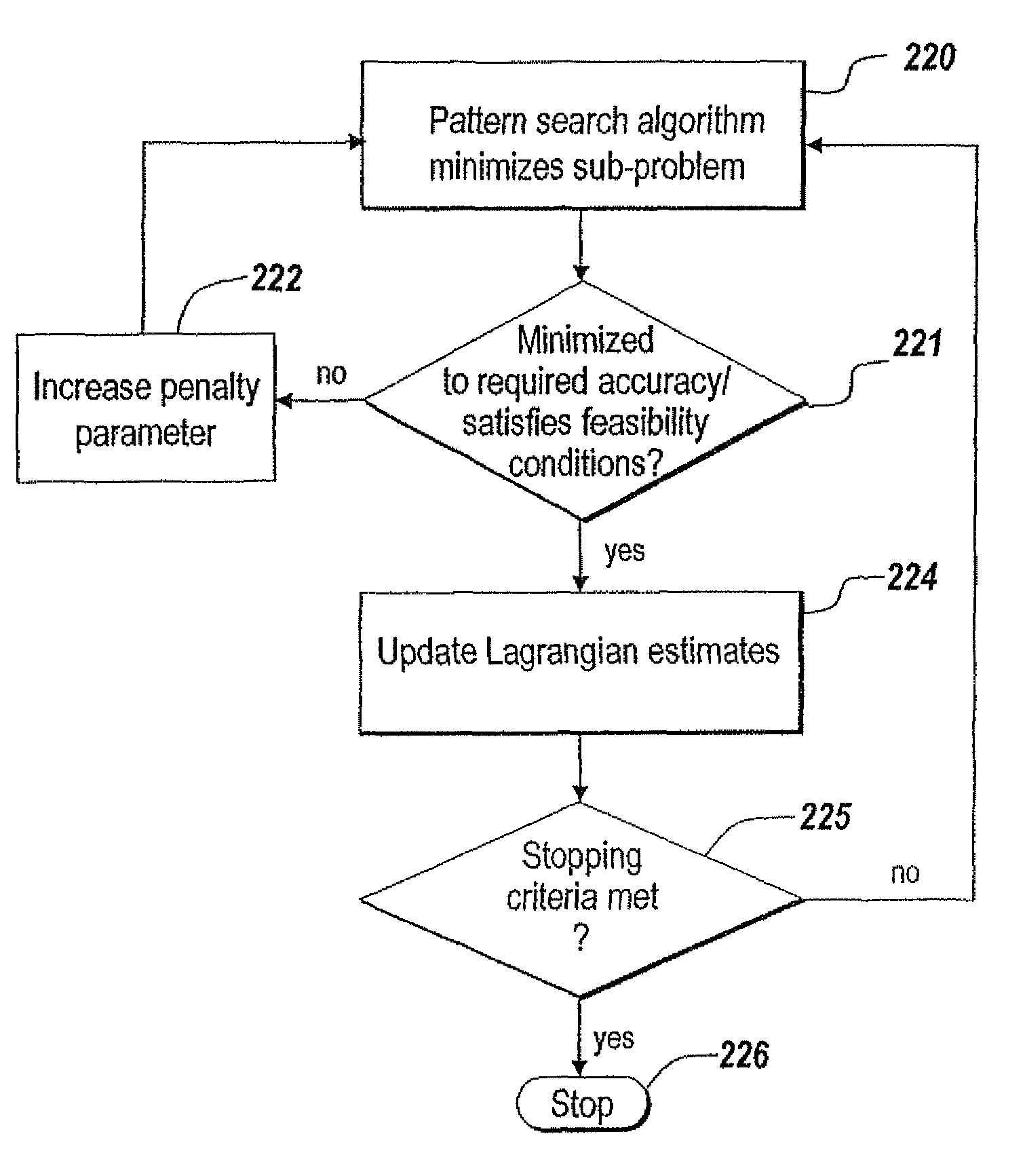
System and method for performing non-linear constrained optimization with an augmented lagrangian pattern search
InactiveUS8290892B1Constraint-based CADFuzzy logic based systemsProblems involving arithmetic progressionsMethod of undetermined coefficients
An Augmented Lagrangian Pattern Search (ALPS) algorithm that attempts to solve a non-linear optimization problem subject to non-linear, linear, and, bound constraints is discussed. The present invention utilizes information from the linear and bound constraints, formulates sub-problems using Lagrange parameter estimates and appropriate penalty parameters (using a log barrier), and provides a robust update formulae for parameters which guides the algorithm towards a minimum. The present invention solves a general non-linear optimization problem without using any slack variables to convert the inequality constraints to equality constraints or equality constraints to inequality constraints.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
PPI network comparison-oriented graph matching constraint solving symbol method
ActiveCN107704578AReduce complexityImprove solution efficiencyBiostatisticsProteomicsConstraint satisfaction problemGraph match
The invention discloses a PPI network comparison-oriented graph matching constraint solving symbol method. According to the method, a CSP model is established (a constraint condition with a shortest path is established) by utilizing a constraint relationship in a graph structure; by adoption of a graph-based backtracking algorithm, an OBDD symbol technology and each included symbol operation, theaim of solving subgraph isomorphism problems is achieved; and finally, the technology is imported in to a PPI network comparison problem, the problem is solved and a PPI network comparison-oriented graph matching constraint solving symbol technology is given. According to the method, the graph-based backtracking algorithm which is used for solving constraint satisfaction problems is combined, theOBDD symbol technology is adopted, advantages of an operation method are developed, and a graph matching symbol algorithm is applied to the protein mutual action network comparison problems in the field of biological information according to a constraint symbol solving technology which is used for solving sub-graph isomorphism, so that the problem solving efficiency can be improved to a certain extent and the state space complexity is reduced.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
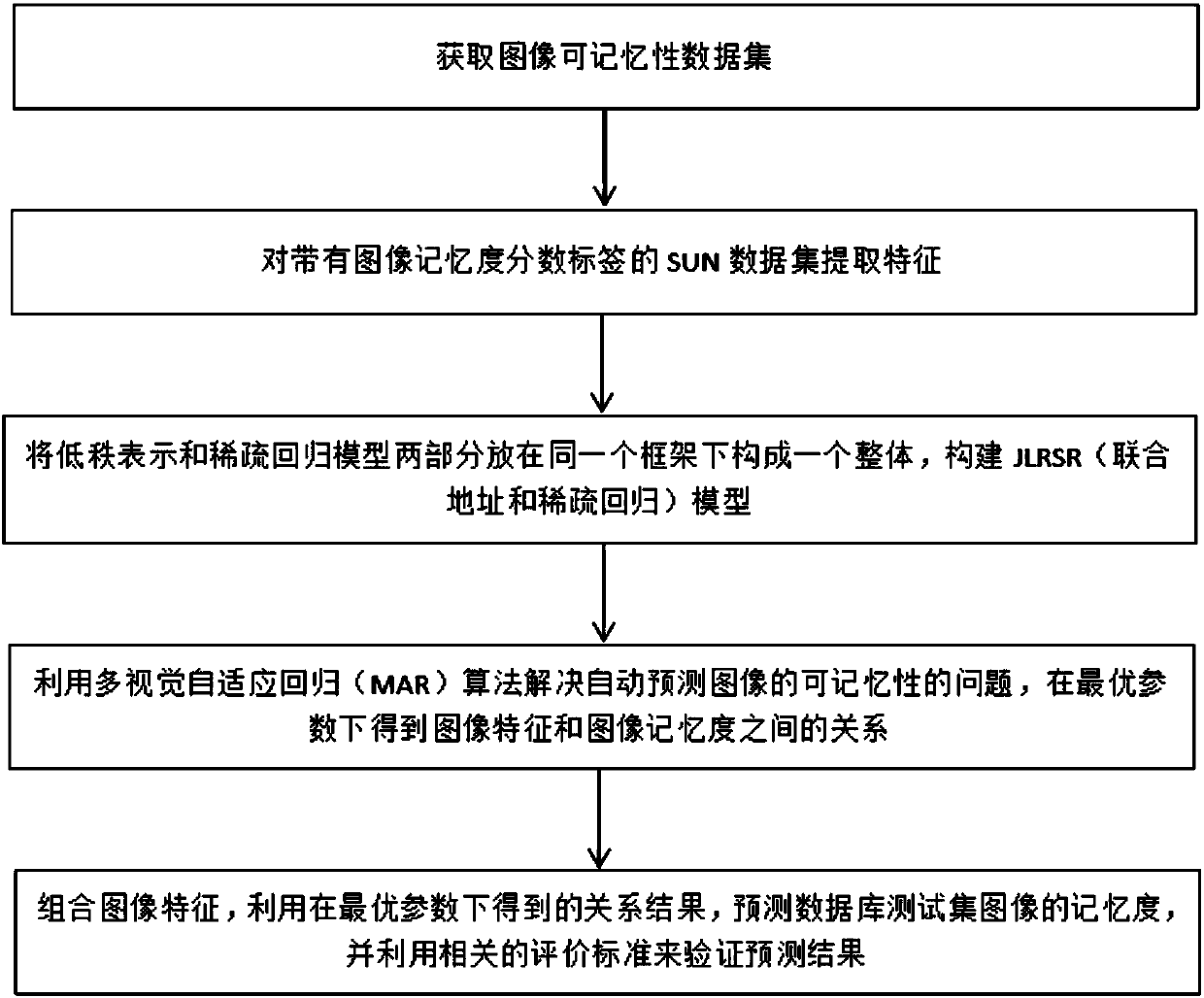
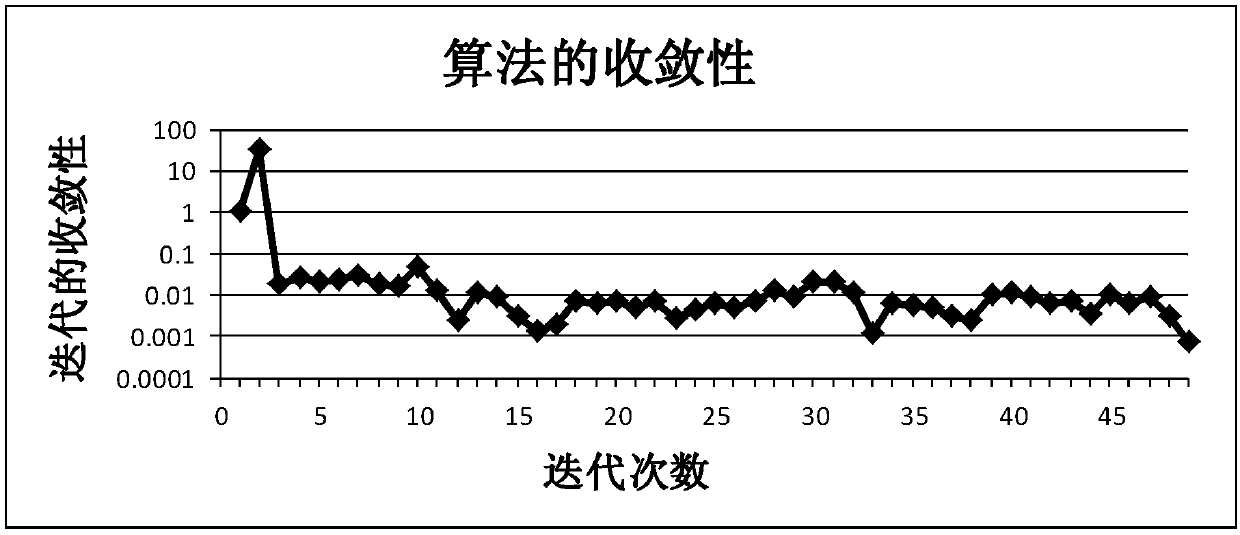
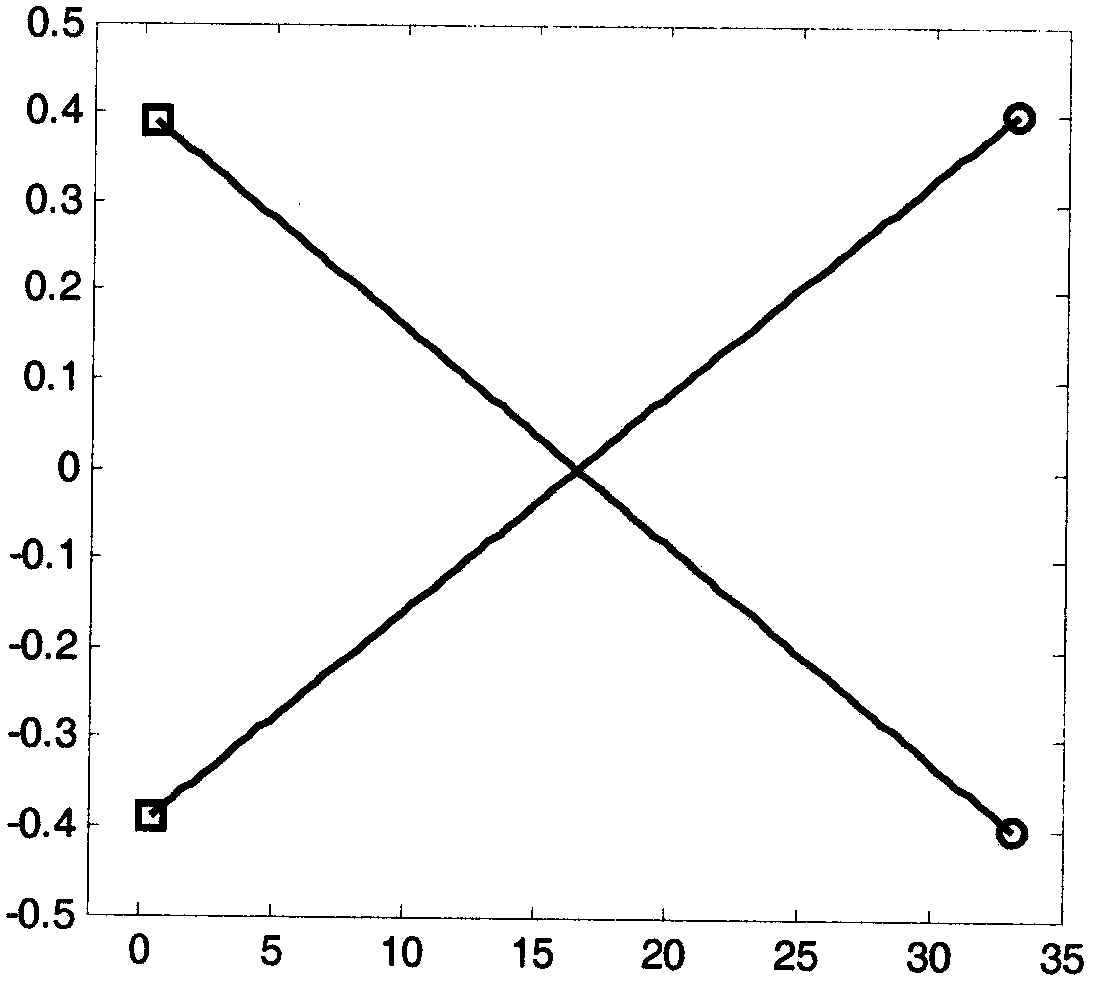
Learning method for joint low-rank representation and sparse regression
ActiveCN107590505AImprove accuracySolve optimization problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setFeature extraction
The invention discloses a learning method for joint low-rank representation and sparse regression. The method comprises the following steps: extracting the features of a SUN data set with an image memory score label; putting low-rank representation and a sparse regression model under the same framework to form a whole, and constructing a joint low-rank representation and sparse regression model; and solving the automatic image prediction memorability problem using a multi-vision adaptive regression algorithm, getting the relationship between image features and image memory under optimal parameters, getting a relationship result under optimal parameters, predicting the image memory of a test set in a database, and verifying the prediction result based on relevant evaluation criteria. The memorability of an image area can be accurately predicted through a low-rank learning framework of joint low-rank representation and sparse regression.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Anti-flight path merging combined probability data association algorithm
InactiveCN107561528AImplement trackingThe estimated bias is smallRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHypothesisMachine learning
The invention relates to an anti-flight path merging combined probability data association algorithm, belongs to the data association, target tracking and statistics signal processing field, and aimsto solve the flight path merging problems of a classic jointed probability data association algorithm (JPDA) under the target spatial domain dense conditions; the method comprises the following steps:firstly analyzing the essence reasons of the JPDA algorithm flight path merging phenomenon, deriving to get the problem keys, and observing adjacent targets to as to watch the mutual state intersectupdates; analyzing each feasible association hypothesis of the original JPDA algorithm, confirming certain hypothesis that may cause state intersect updates, avoiding the certain hypothesis accumulation effects on the corresponding target-flight path association probability, thus effectively preventing intersect updates, and finally solving the flight path merging problems.
Owner:中国人民解放军63870部队
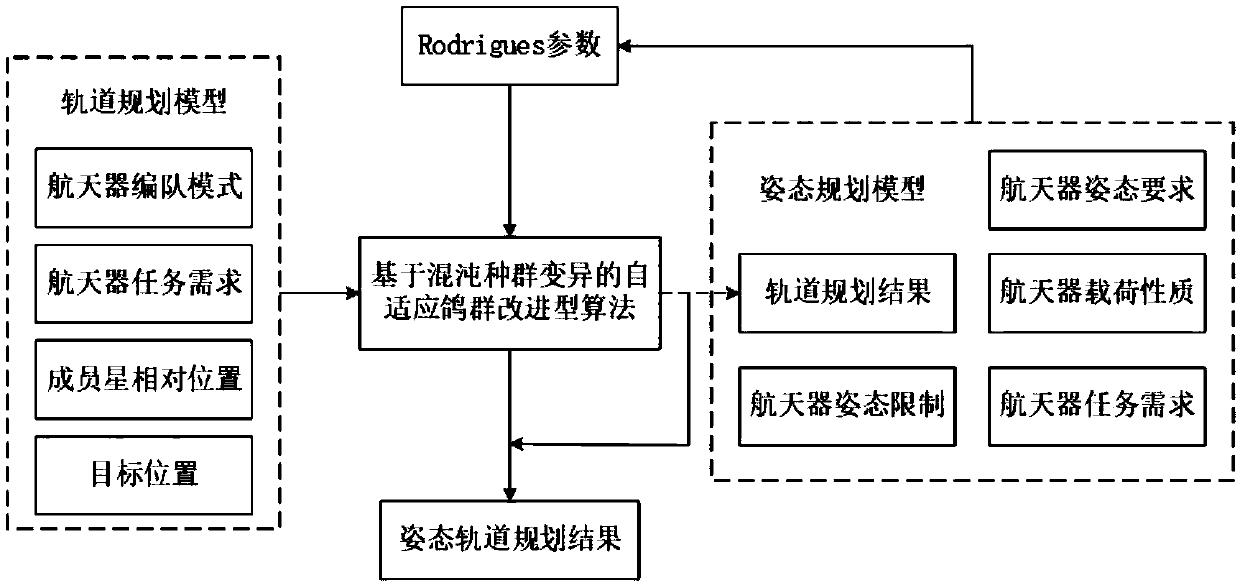
Spacecraft attitude and orbit collaborative planning method based on chaotic population variation pigeon-inspired optimization (PIO)
ActiveCN108919818AFast convergenceAchieve optimal planningCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsAlgorithmPlanning method
The invention discloses a spacecraft attitude and orbit collaborative planning method based on chaotic population variation pigeon-inspired optimization (PIO), and belongs to the technical field of satellite attitude and orbit control. According to the spacecraft attitude and orbit collaborative planning method, the pigeon dynamic optimization strategy of exploring, searching, variation and homingis adopted at the evolution stage of an algorithm; at the map compass stage, initialization operation is conducted by adding chaotic operators aiming at the population initialization problem, after the population is initialized, adaptive operators are added, and thus the population can evolve in an adaptive mode according to the current population evolution state, and meanwhile the problem that the population is caught in the local optimal solution is solved by adding mutation operators; and at the landmark operator stage, contracting operators are added aiming at the problem of population contracting, the problems that superior individuals run away too fast, and the population degenerates are solved, thus the planning result is smoother, population evolution is deeper, the local optimalsolution problem and the algorithm divergence problem are solved, and the calculated quantity of the algorithm is further reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Arbitrary Lagrange Euler method based on multi-dimensional Riemann solution
InactiveCN103823916AClear resolutionImprove robustnessSpecial data processing applicationsShock waveInstability
The invention discloses an arbitrary Lagrange Euler method based on the multi-dimensional Riemann solution. The method is used for solving two-dimensional compressible fluid mechanics equation sets and relevant issues based on the same. The arbitrary Lagrange Euler method based on the multi-dimensional Riemann solution includes: grid generation and physical quantity initial distribution; determination of a strategy and a manner of grids at a next moment; determination of a two-dimensional Riemann solution implement algorithm of grid cell frontier flux; expression form of the grid cell frontier flux; acquisition of a numerical method of a calculation result at the next moment. The novel two-dimensional Riemann solution implement algorithm for determining the grid cell frontier flux is provided, conditions such as proneness to distortion of grids, instability of numerical value impact waves and the like resulted from a traditional one-dimensional Riemann solution can be overcome, and the defect that an existing two-dimensional Riemann solution method is too complicated to implement is corrected. The arbitrary Lagrange Euler method based on the multi-dimensional Riemann solution is a simple, robust and precise numerical algorithm component, suitable for numerical simulation of multimedium large-deformation problems, and further suitable for currently popular forms of finite differences, finite volume and finite element methods.
Owner:沈智军 +2
A method for distinguishing similarity of middle and small river basin
InactiveCN109388664AQuality improvementIncrease differentiationCharacter and pattern recognitionGeographical information databasesData dredgingCluster algorithm
A method for distinguish similaritying of middle and small river basin includes such steps: constructing a dataset clustering collective; selecting characteristic index to construct characteristic subset, inputting the characteristic subset into basic clustering algorithm to obtain a clustering subset; constructing the similarity matrix of the clustering collectivity; using the similarity matrix of the clustering collectivity as the input matrix of the preset clustering fusion algorithm; finally, performing matrix clustering fusion: using the preset clustering fusion algorithm to perform clustering fusion of the similarity matrix to realize similarity judgment. The invention fully utilizes the characteristics of the geographic data and the hydrological data of the small and medium-sized watershed, and realizes similarity analysis of the small and medium-sized watershed by using the data mining technology, so as to solve the technical problem that the similarity of the hydrological watershed is difficult to be judged.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
System and method for geomechanical and rock physics elastostatic modeling
ActiveUS20160161634A1Well formedGeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationVirial theoremBoundary values
A method for geomechanical and rock physics modeling of a geologic volume of interest may include solving for the elastostatic boundary value problems using a finite-difference method which applies the Virial Theorem.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
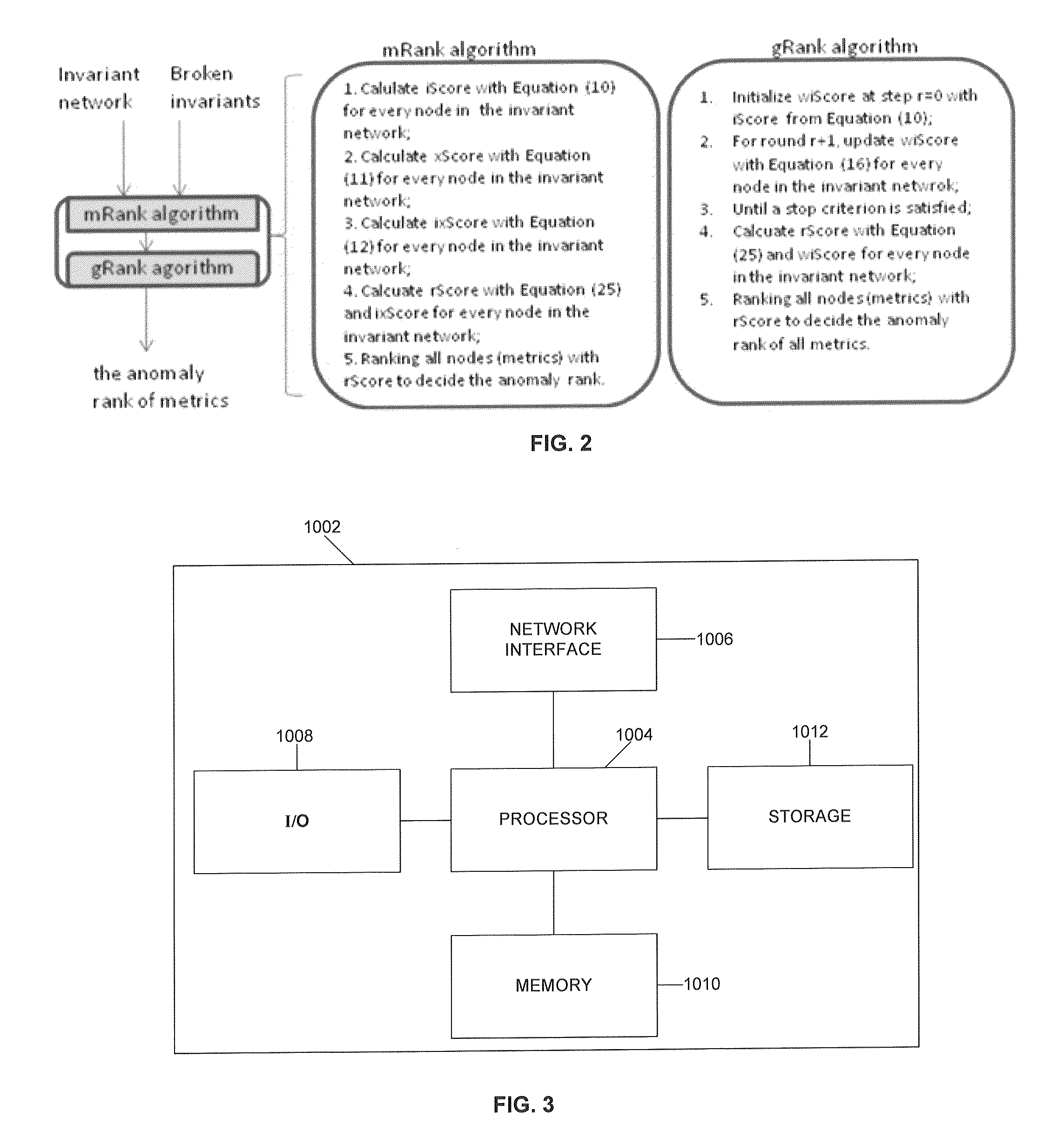
Method for metric ranking in invariant networks of distributed systems
A method for metric ranking in invariant networks includes, given an invariant network and a set of broken invariants, two ranking processes are used to determine and rank the anomaly scores of each monitoring metrics in large-scale systems. Operators can follow the rank to investigate the root-cause in problem investigation. In a first ranking process, given a node / metric, the method determines multiple scores by integrating information from immediate neighbors to decide the anomaly score for metric ranking. In a second ranking process, given a node / metric, an iteration process is used to recursively integrate the information from immediate neighbors at each round to determine its anomaly score for metric ranking.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com