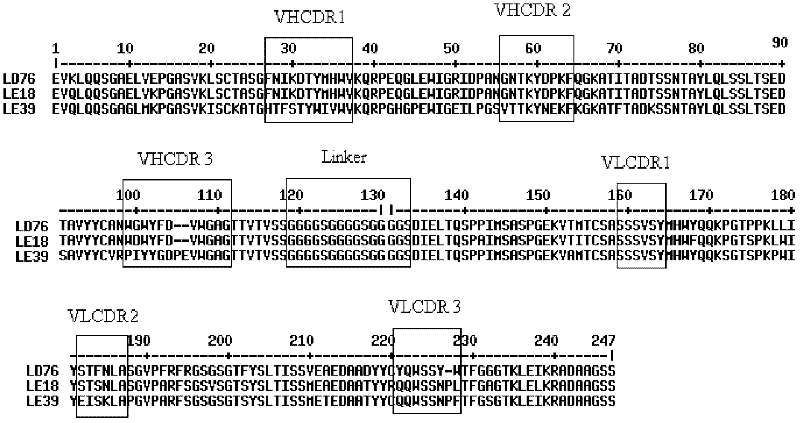
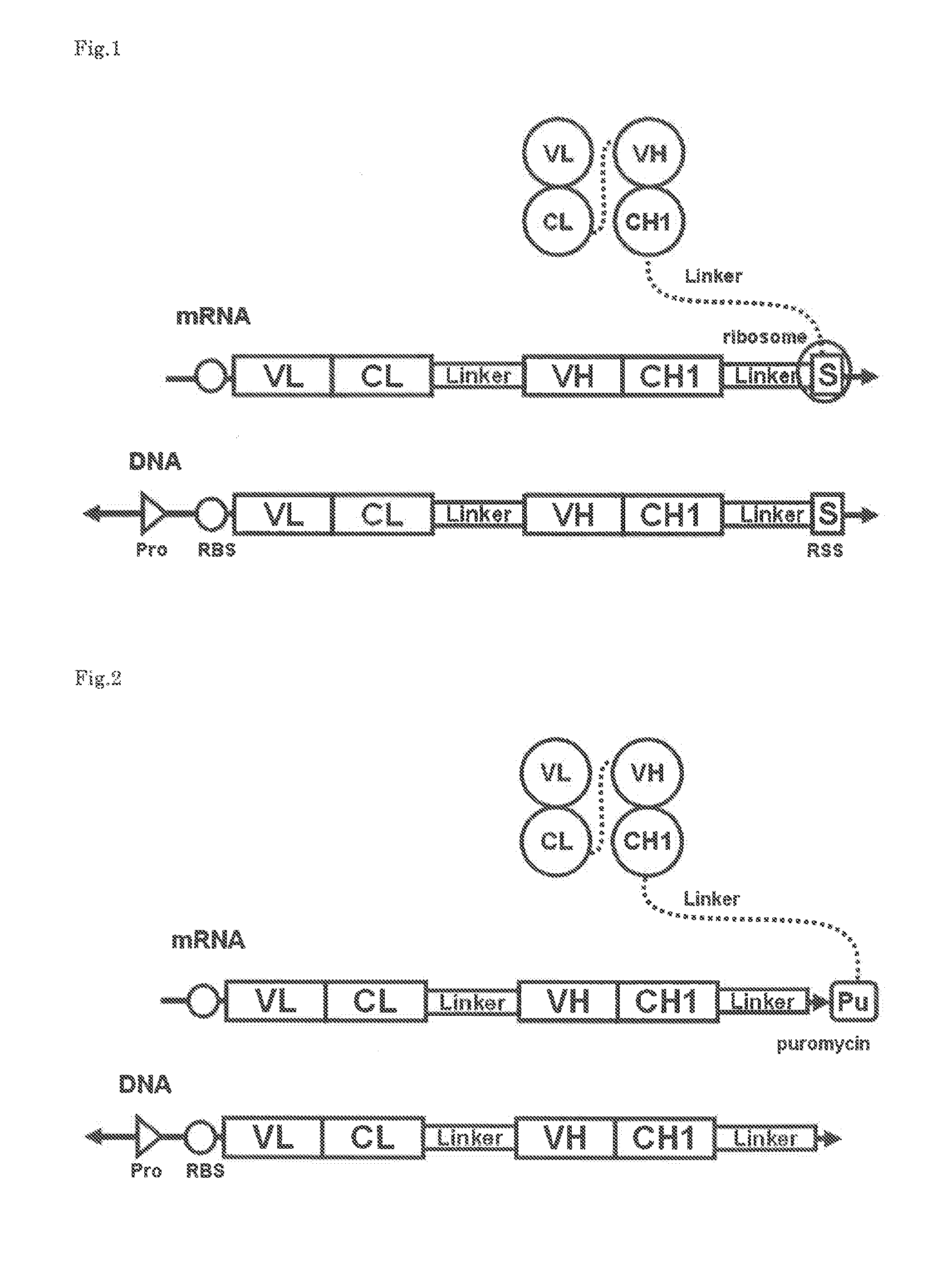
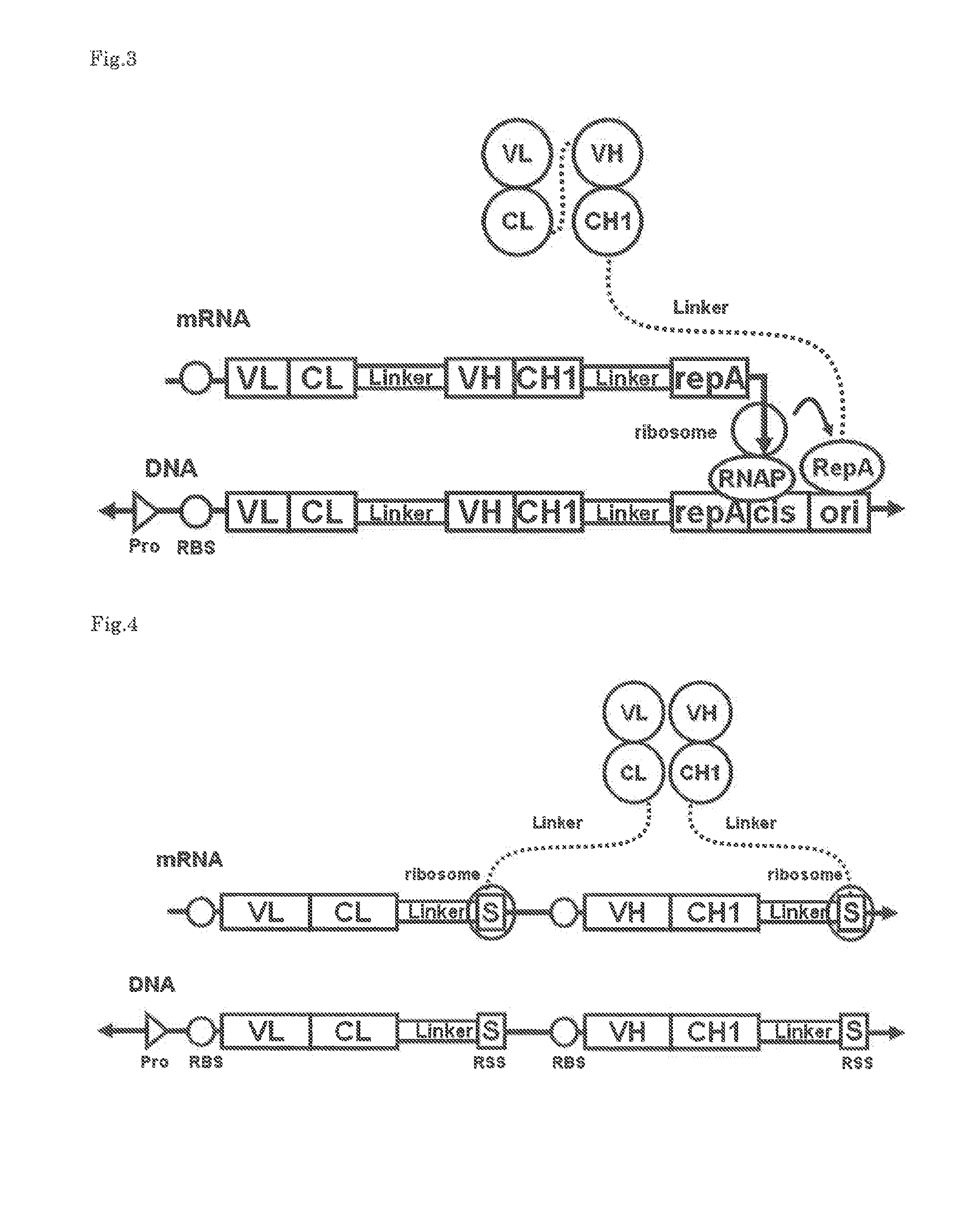
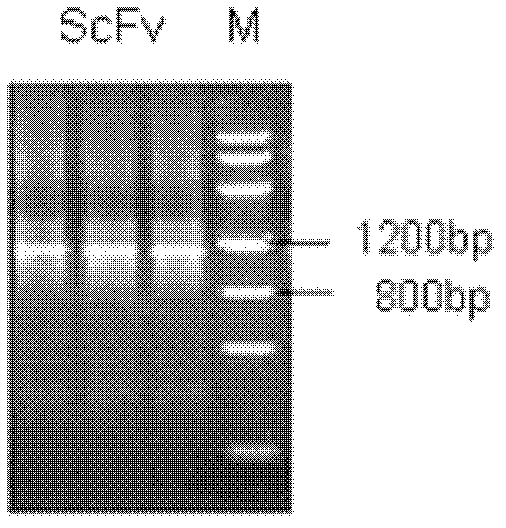Patents
Literature
38 results about "Ribosome display" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
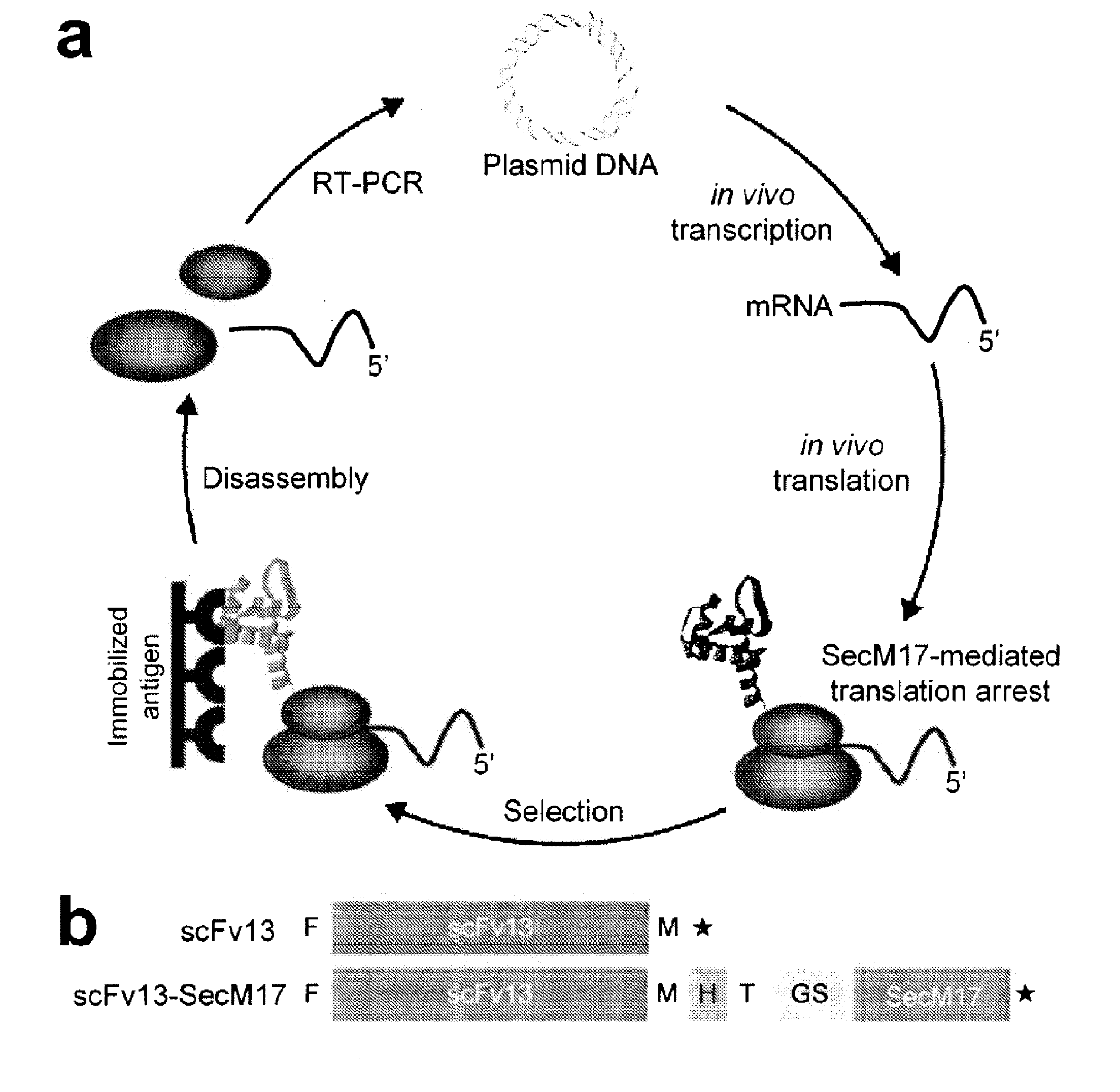
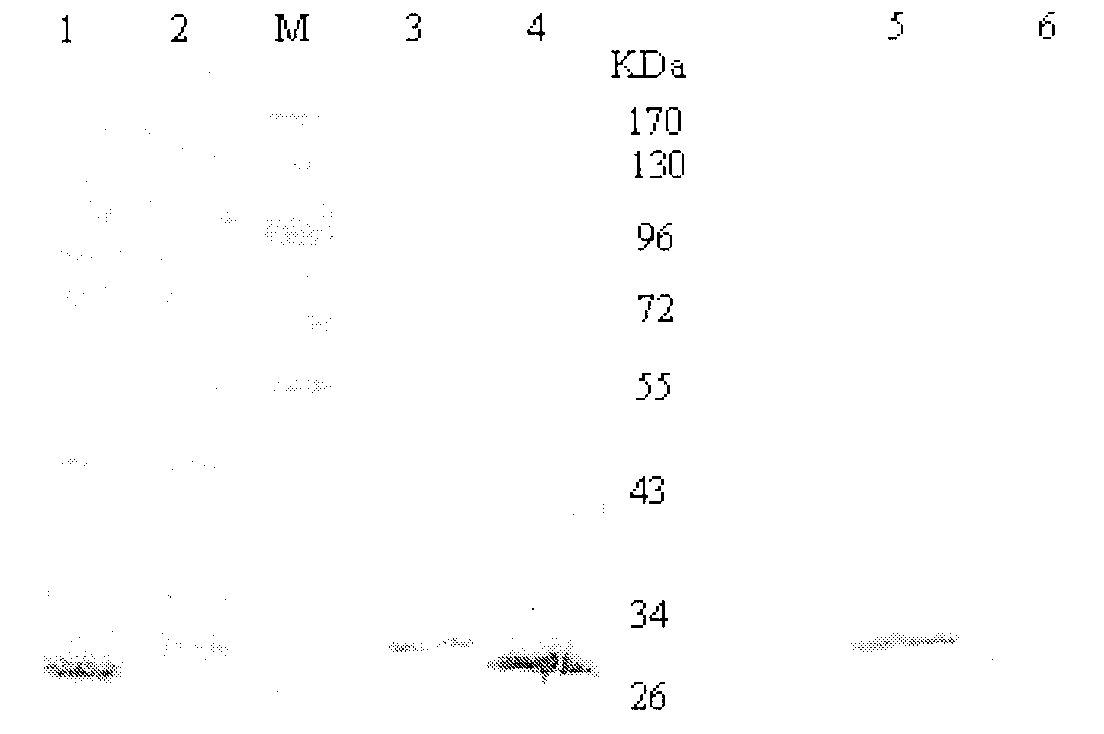
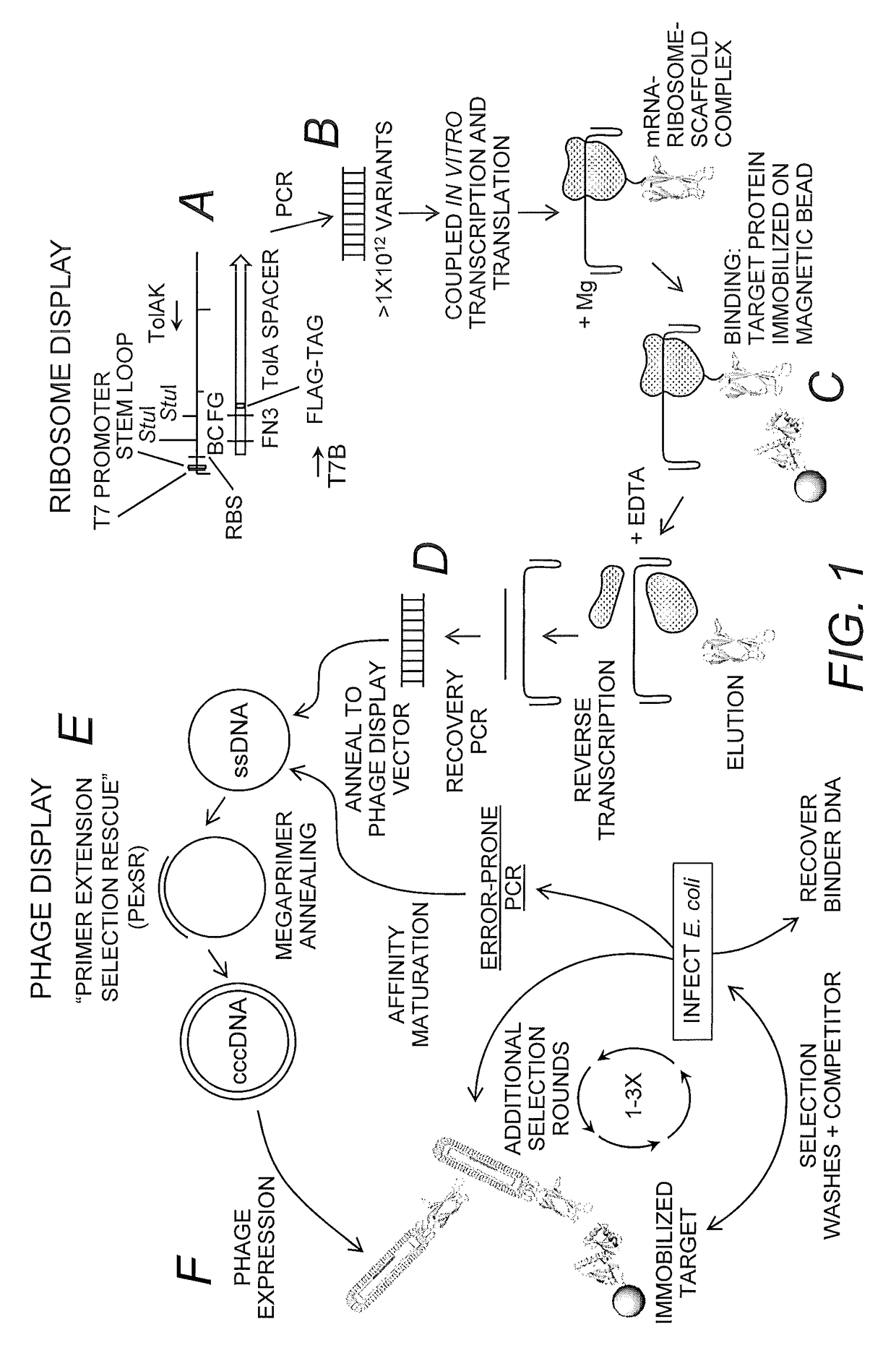
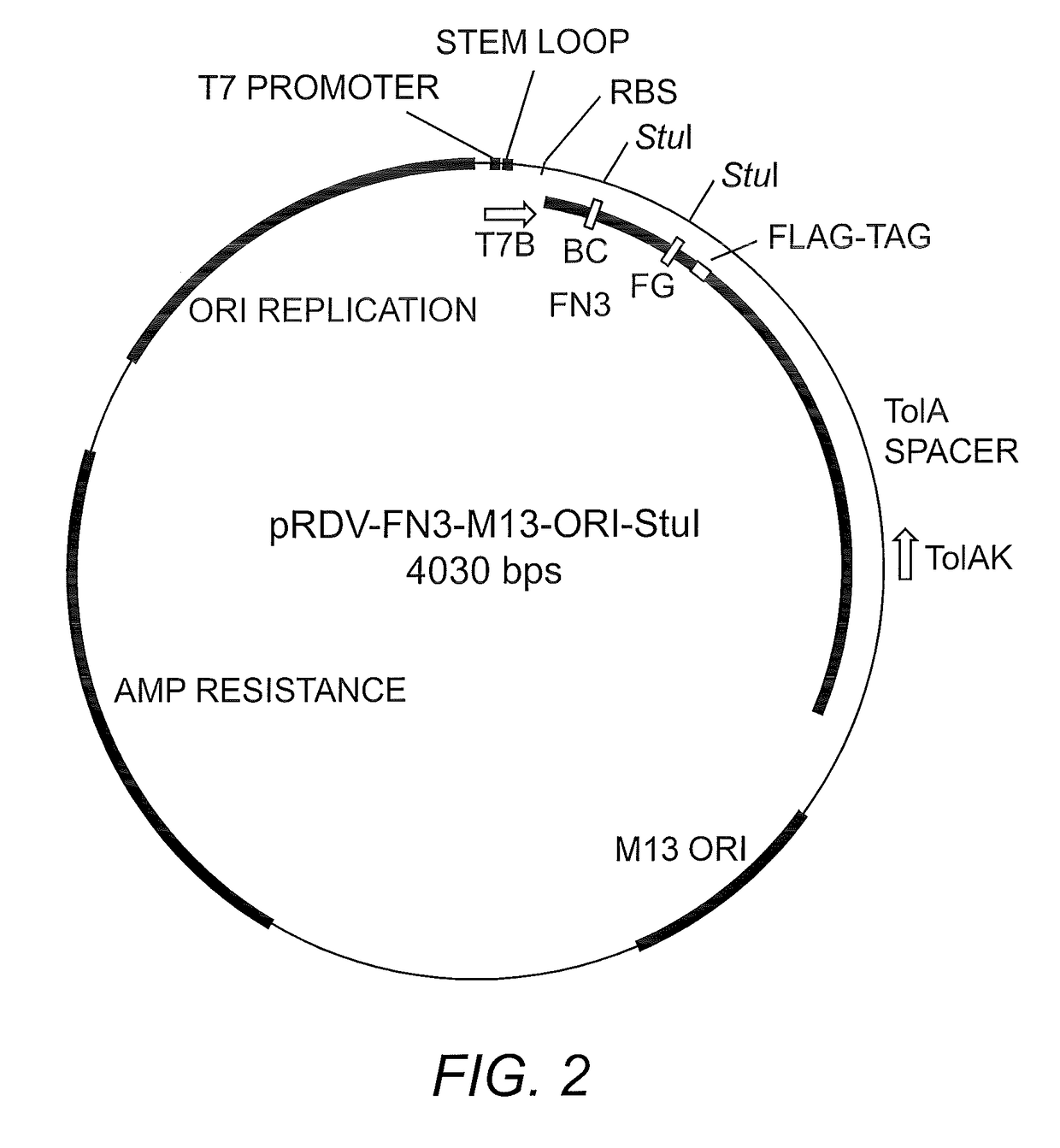
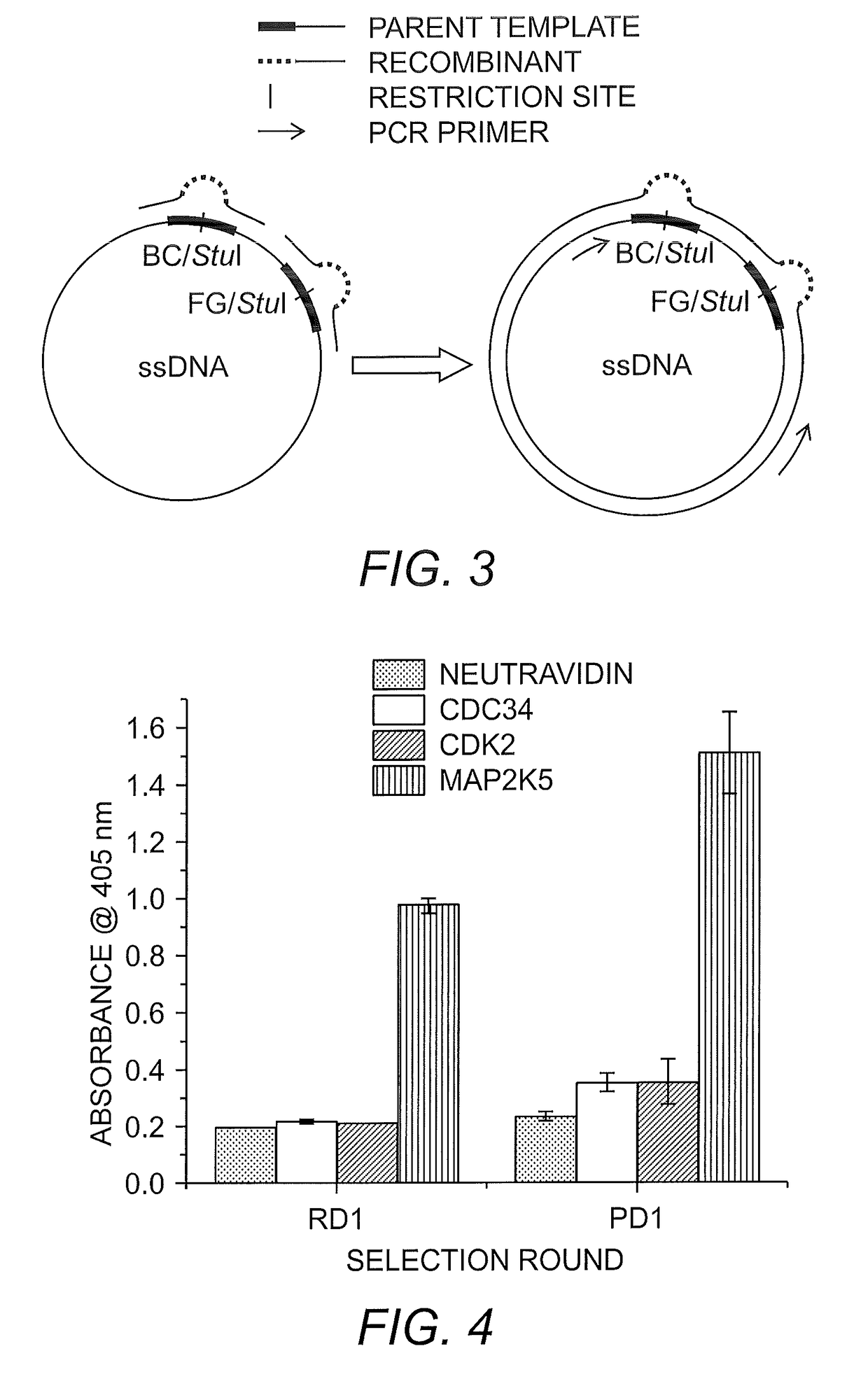
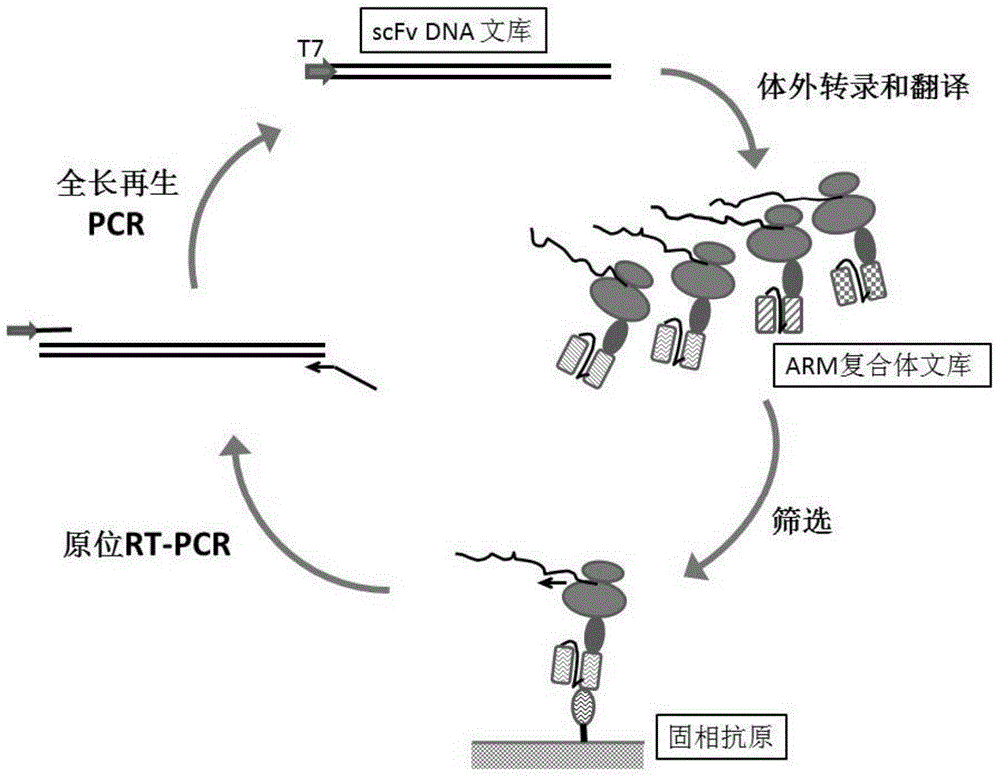
Ribosome display is a technique used to perform in vitro protein evolution to create proteins that can bind to a desired ligand. The process results in translated proteins that are associated with their mRNA progenitor which is used, as a complex, to bind to an immobilized ligand in a selection step. The mRNA-protein hybrids that bind well are then reverse transcribed to cDNA and their sequence amplified via PCR. The end result is a nucleotide sequence that can be used to create tightly binding proteins.
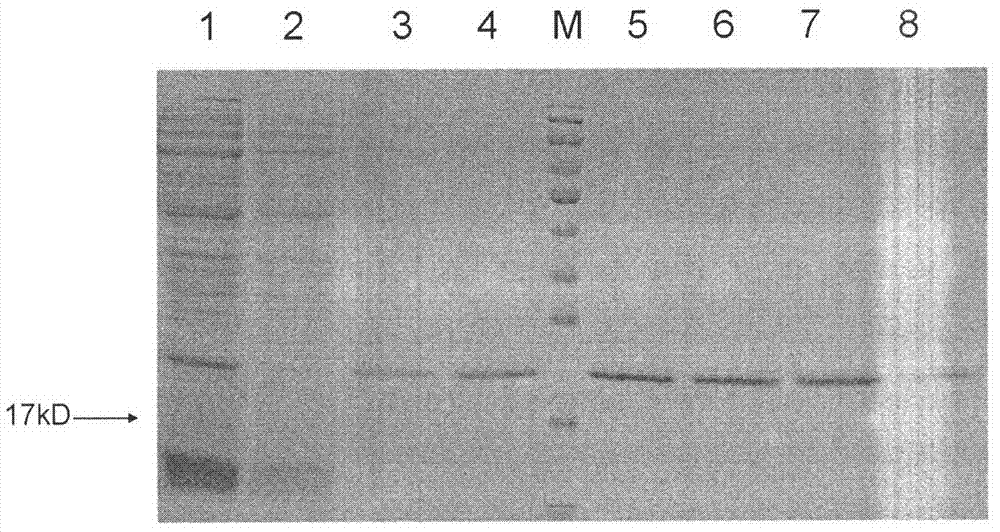
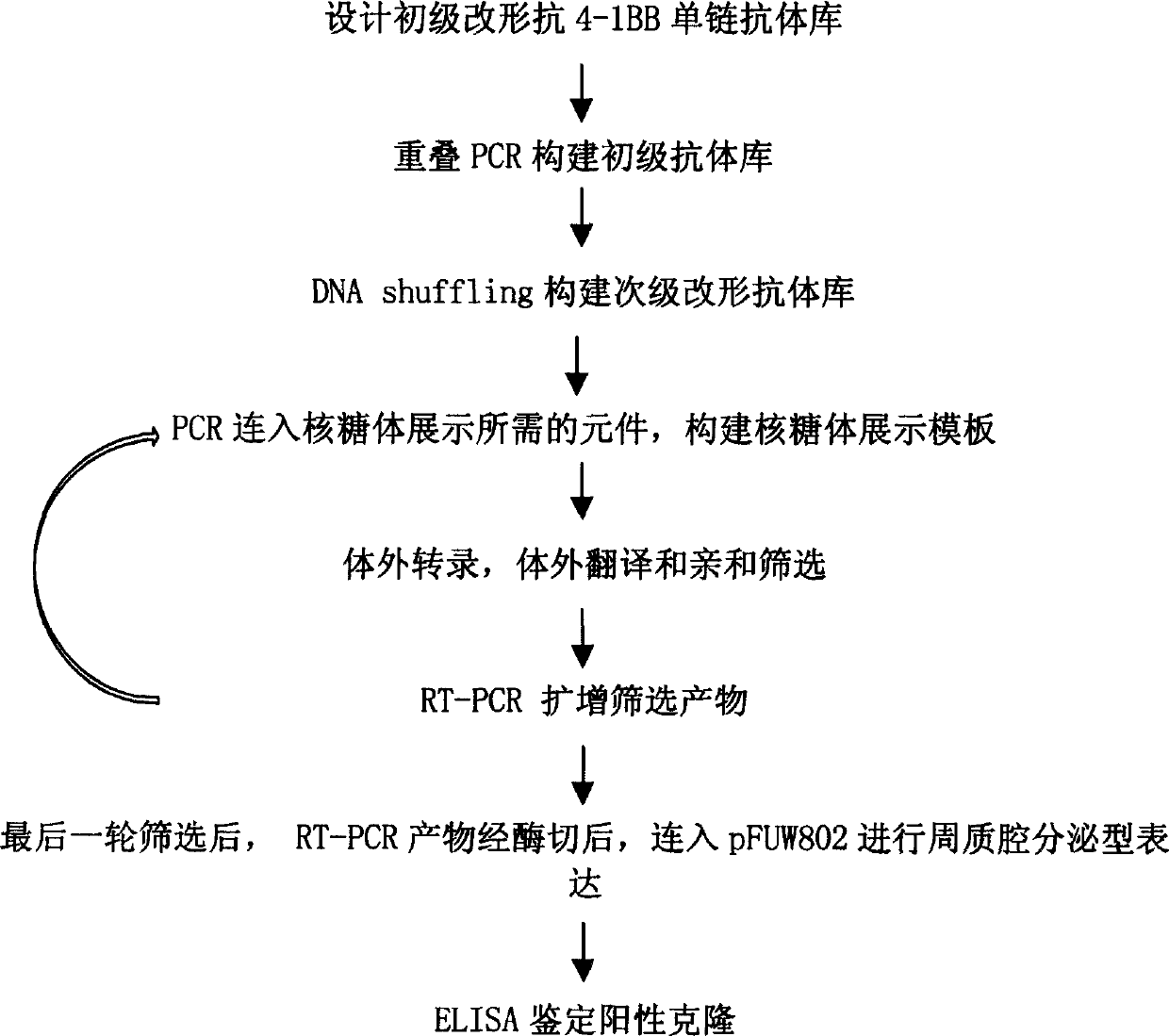
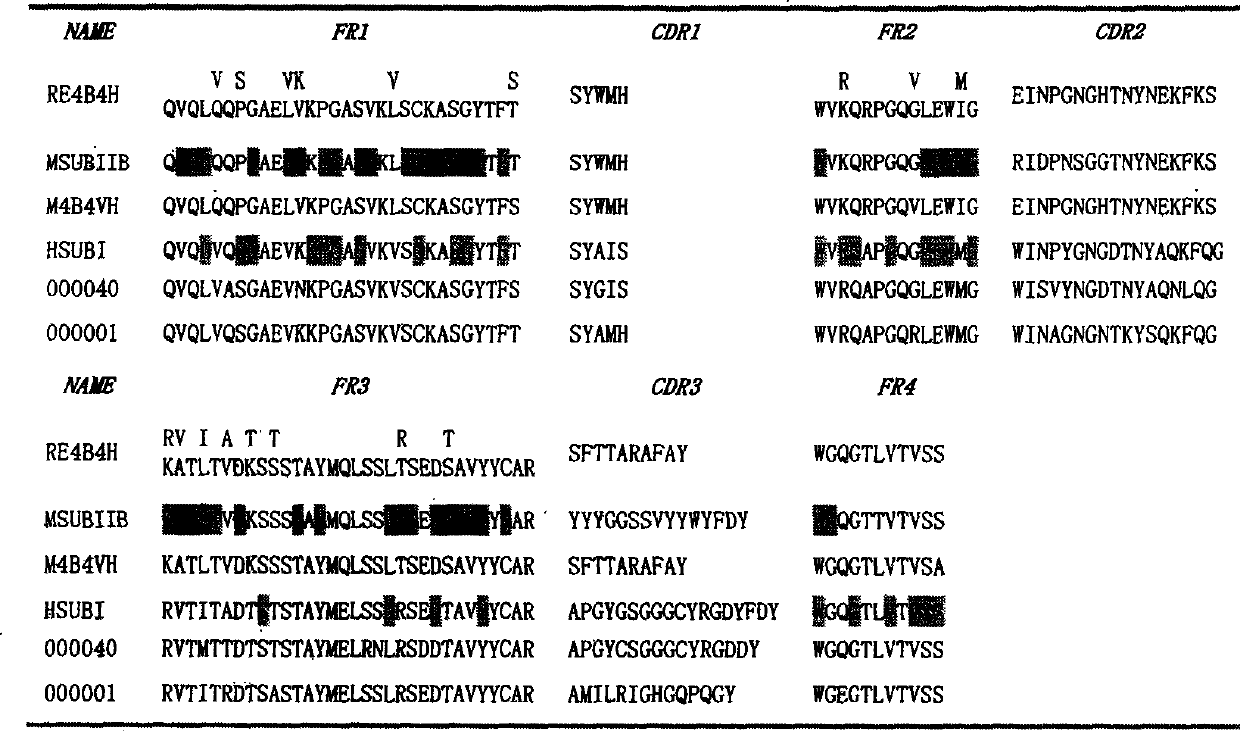
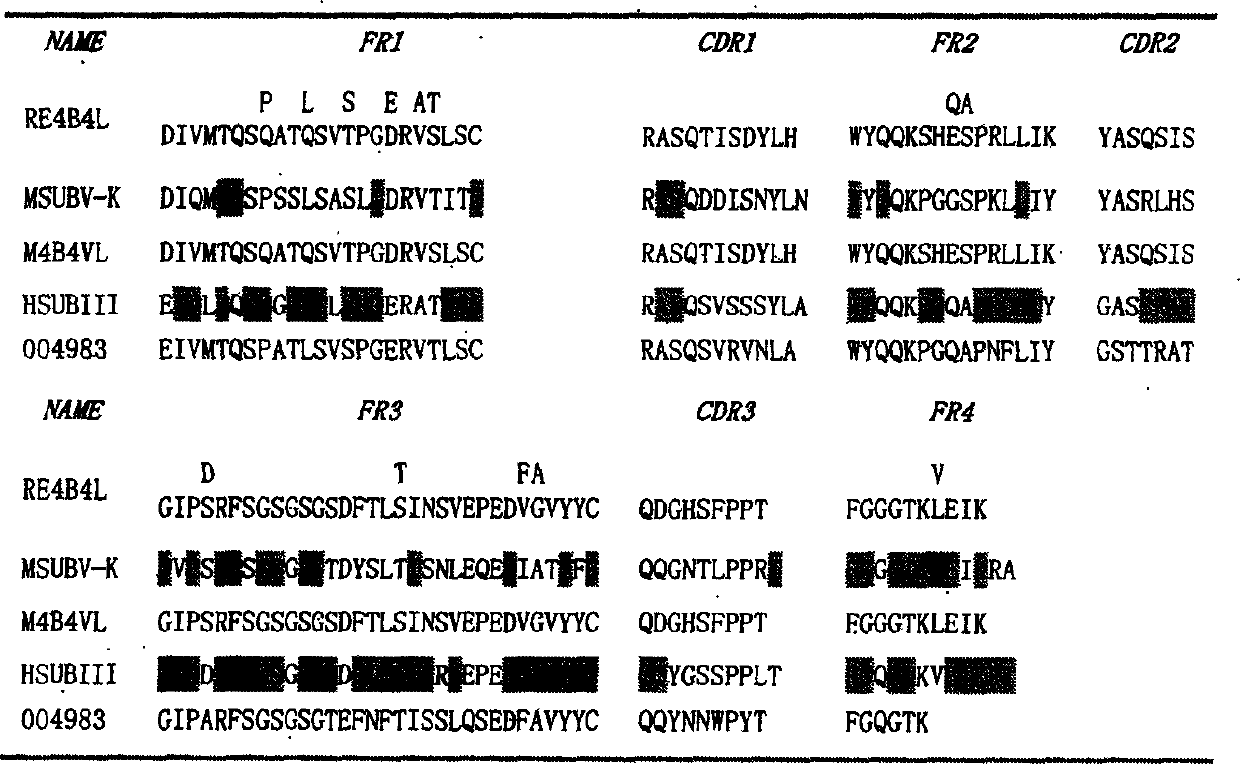
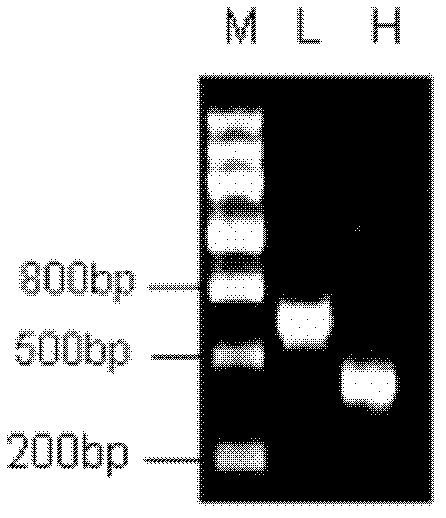
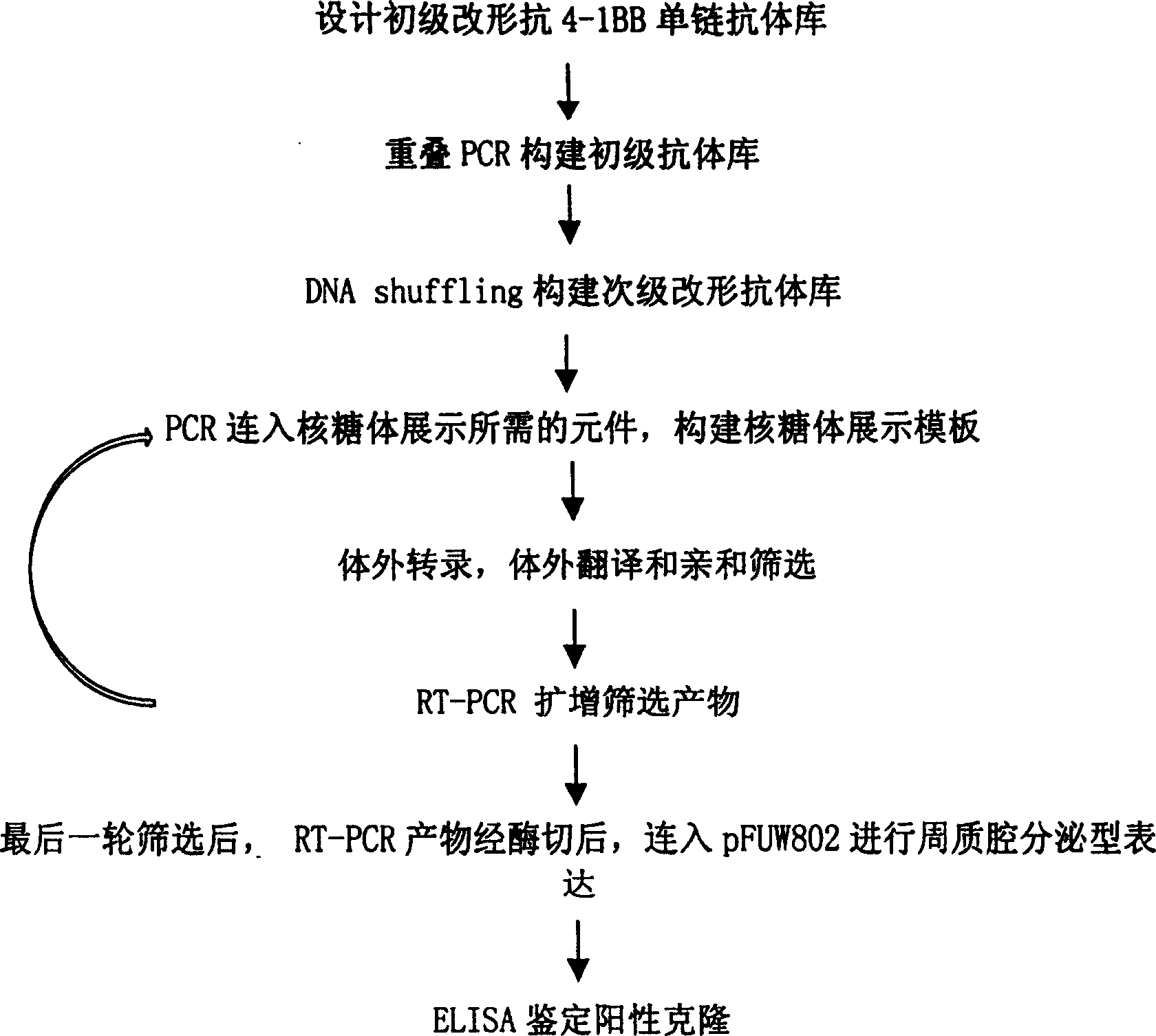
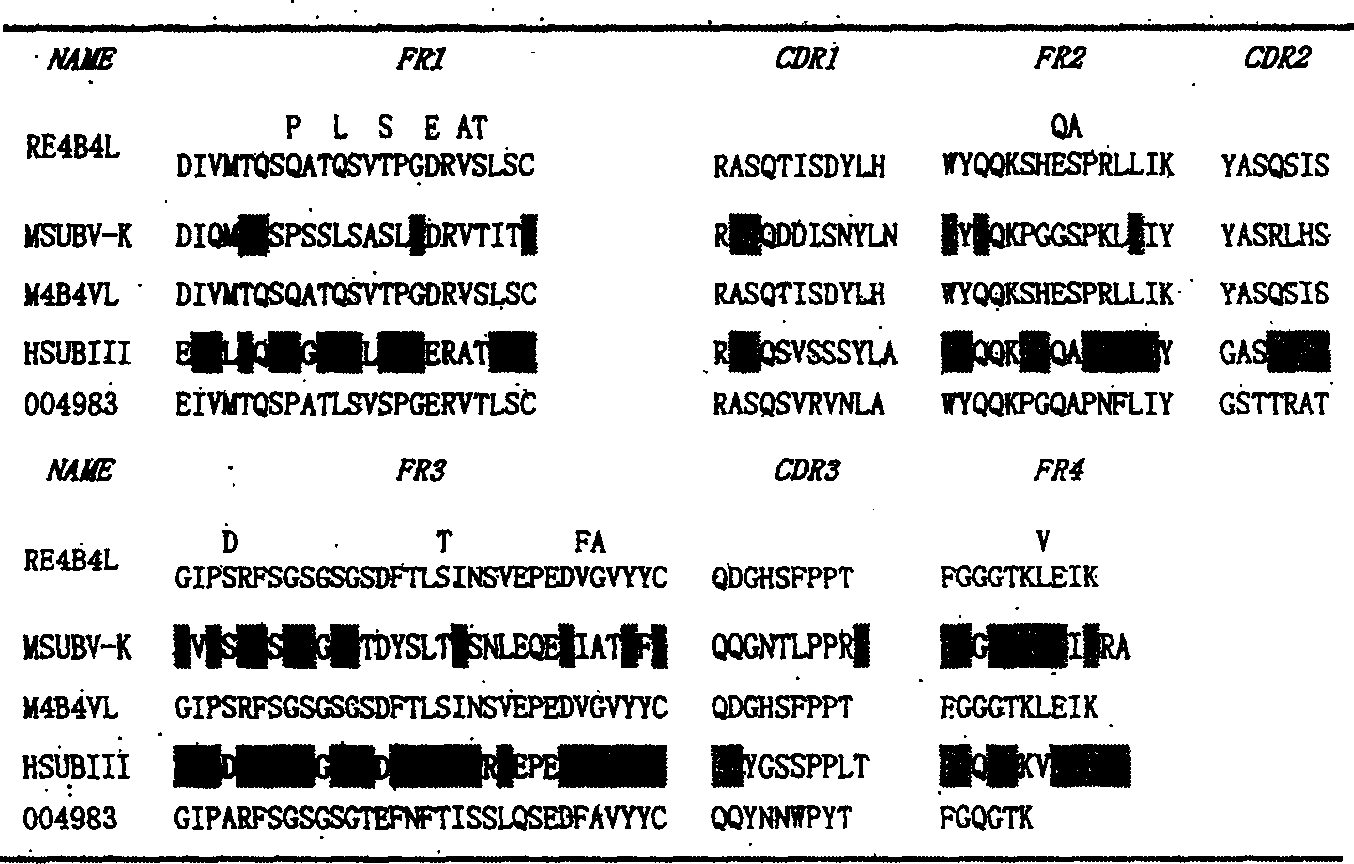
In vitro molecular directed evolution method for reshaping antibody
InactiveCN1566341AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionSingle-Chain AntibodiesNucleotide
The invention relates to an in vitro molecular directed evolution method for reshaping antibody, which integrates ribosome displaying technology with DNA reorganization technology by designing reshaped antibody molecules, thus directly obtaining the extracorporal molecules of the single-chain antibody reshaped orientation.
Owner:BEIJING ABT GENETIC ENG TECH +1
Single-chain antibody against fenitrothion and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102229672AStrong specificityHigh affinityMicroorganism based processesImmunoglobulinsEscherichia coliSingle-Chain Antibodies
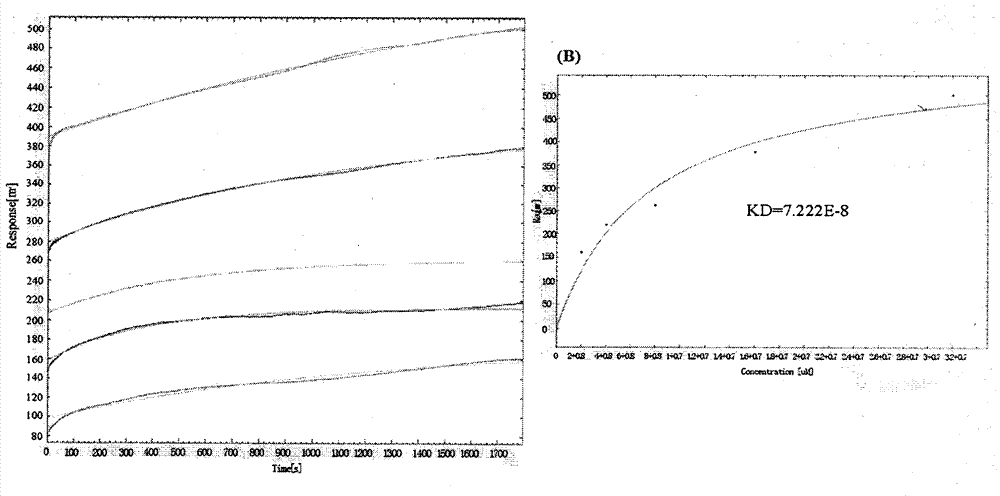
The invention relates to a single-chain antibody against fenitrothion and a preparation method thereof. A ribosome display library of a whole set of single-chain antibody genes against the fenitrothion is constructed by using a ribosome display technology and rounding a hybrid tumor technology, and three single-chain antibody genes with high affinity and high specificity for the fenitrothion are screened from the library. After the single-chain antibody genes are connected with vectors PPOW3.0 and then subjected to soluble expression in escherichia coli, three soluble proteins with molecular weights of about 30KDa are obtained; and by enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA) and Biacore analysis, the three antibody proteins have high affinity and high specificity for the fenitrothion, so excellent single-chain antibody genes and antibody proteins are provided for establishing ELISA and immune sensors. The invention has significance for realizing quick, simple, convenient and accurate detection of organic phosphorus pesticide residue, and provides a new direction.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
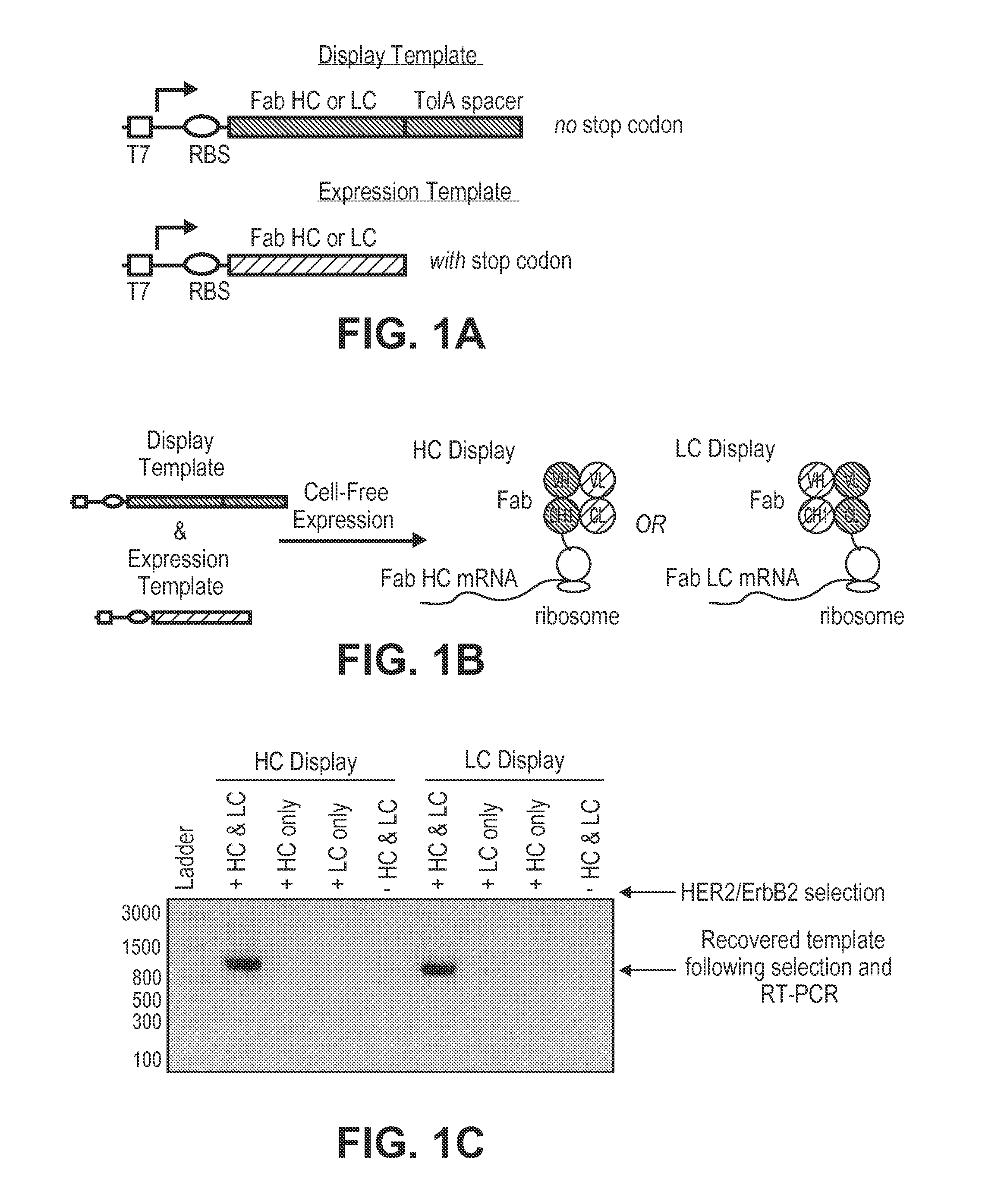
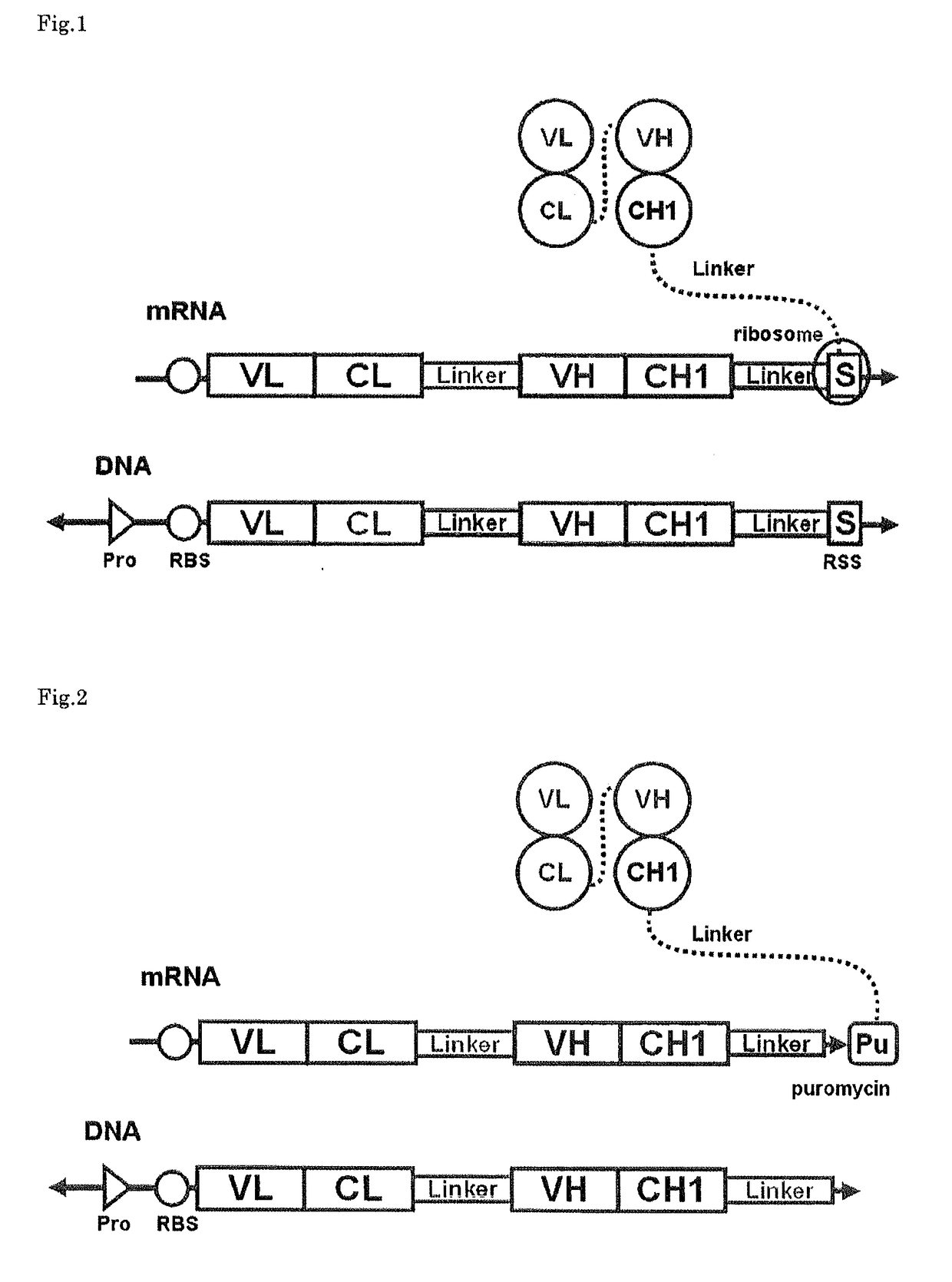
Polynucleotide construct capable of displaying fab in a cell-free translation system, and method for manufacturing and screening fab using same
InactiveUS20130288908A1Maximizing affinityHigh affinitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigenCell free
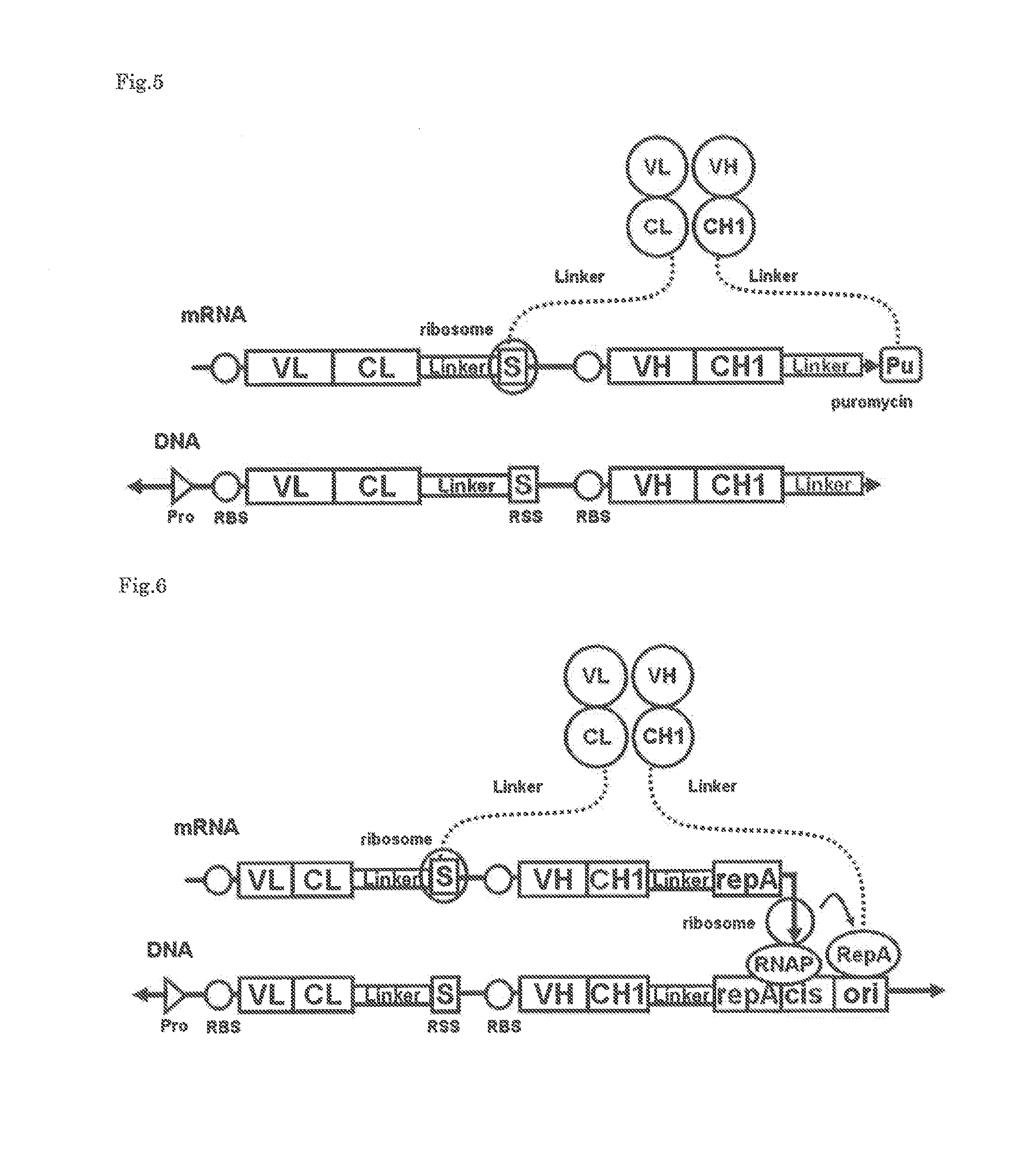
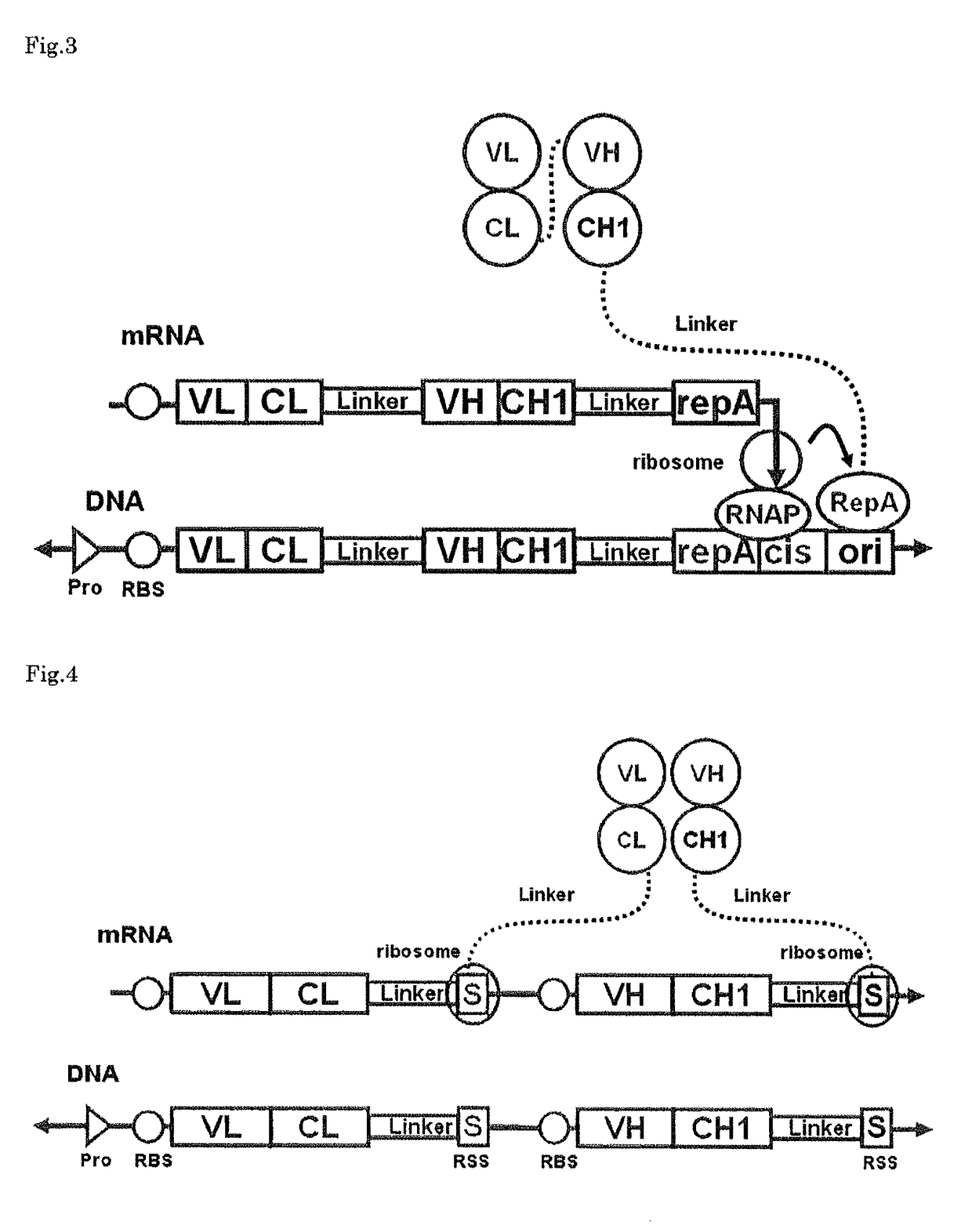
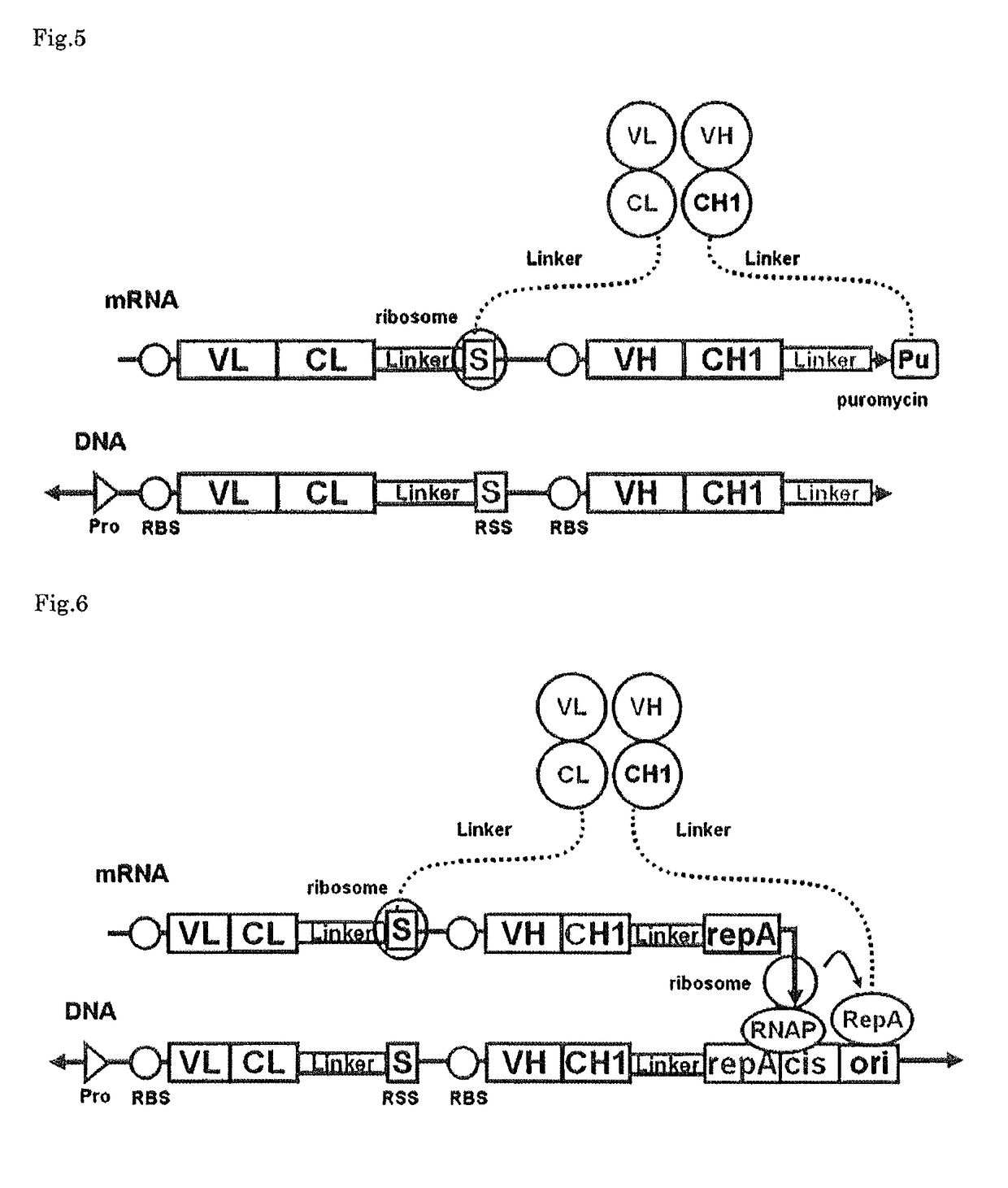
The polynucleotide construct of (1) or (2) below is used to perform ribosome display, CIS display and / or mRNA display in order to screen a Fab against an antigen of interest: (1) a polynucleotide construct which monocistronically comprises a ribosome-binding sequence, Fab first chain-coding sequence, linker peptide-coding sequence, Fab second chain-coding sequence and scaffold-coding sequence in this order, and further comprises at its 3′-end a structure necessary for maintaining a complex with the Fab encoded by itself, and (2) a polynucleotide construct which comprises a Fab first chain-expressing cistron and a Fab second chain-expressing cistron each containing a ribosome-binding sequence, a Fab first chain-coding sequence or Fab second chain-coding sequence, and a scaffold-coding sequence in this order, the first Fab-expressing cistron further comprising at its 3′-end a ribosome stall sequence, said Fab second chain-expressing cistron further comprising at its 3′-end a structure necessary for maintaining a complex with the Fab encoded by itself.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
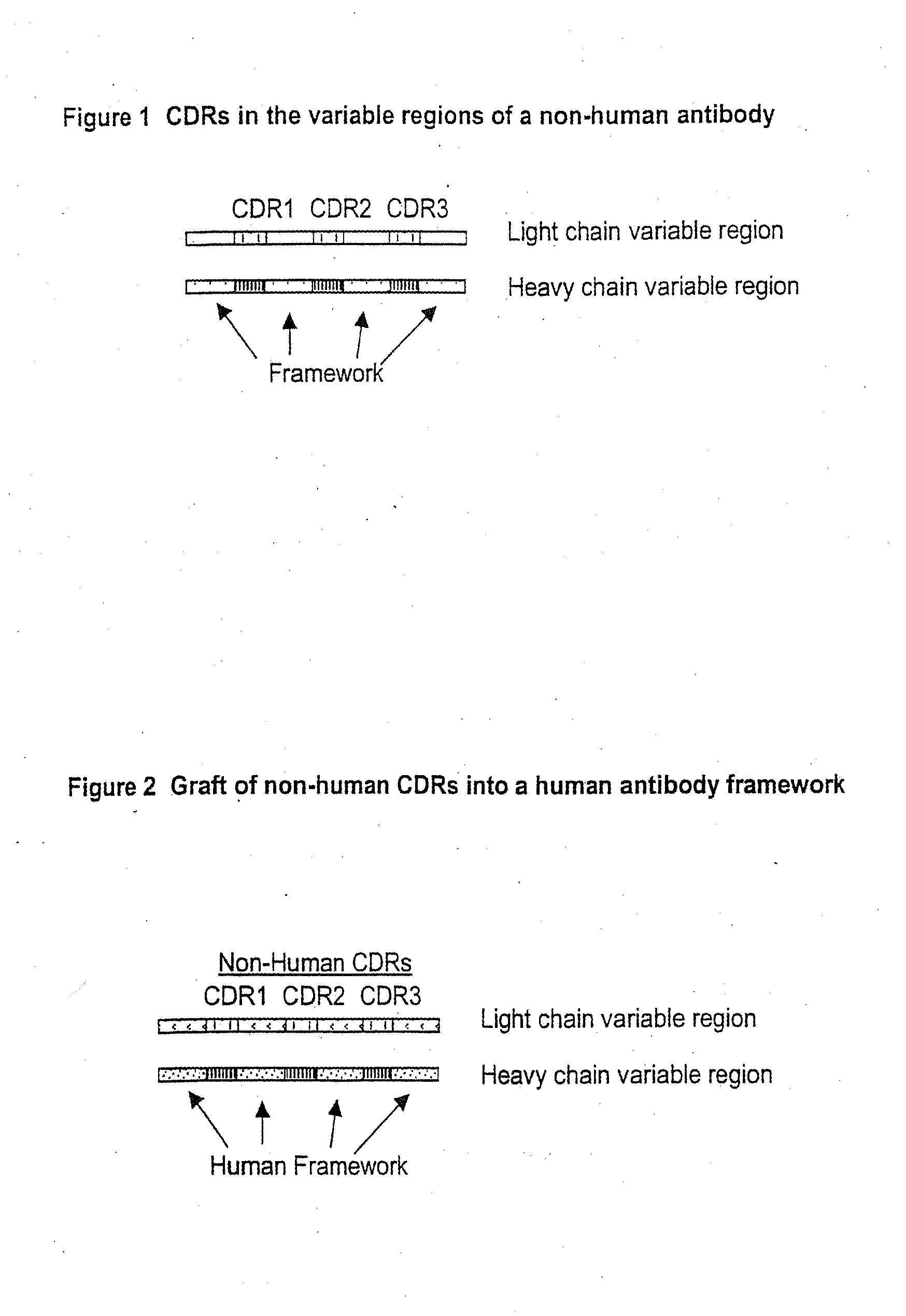
High throughput generation and affinity maturation of humanized antibody
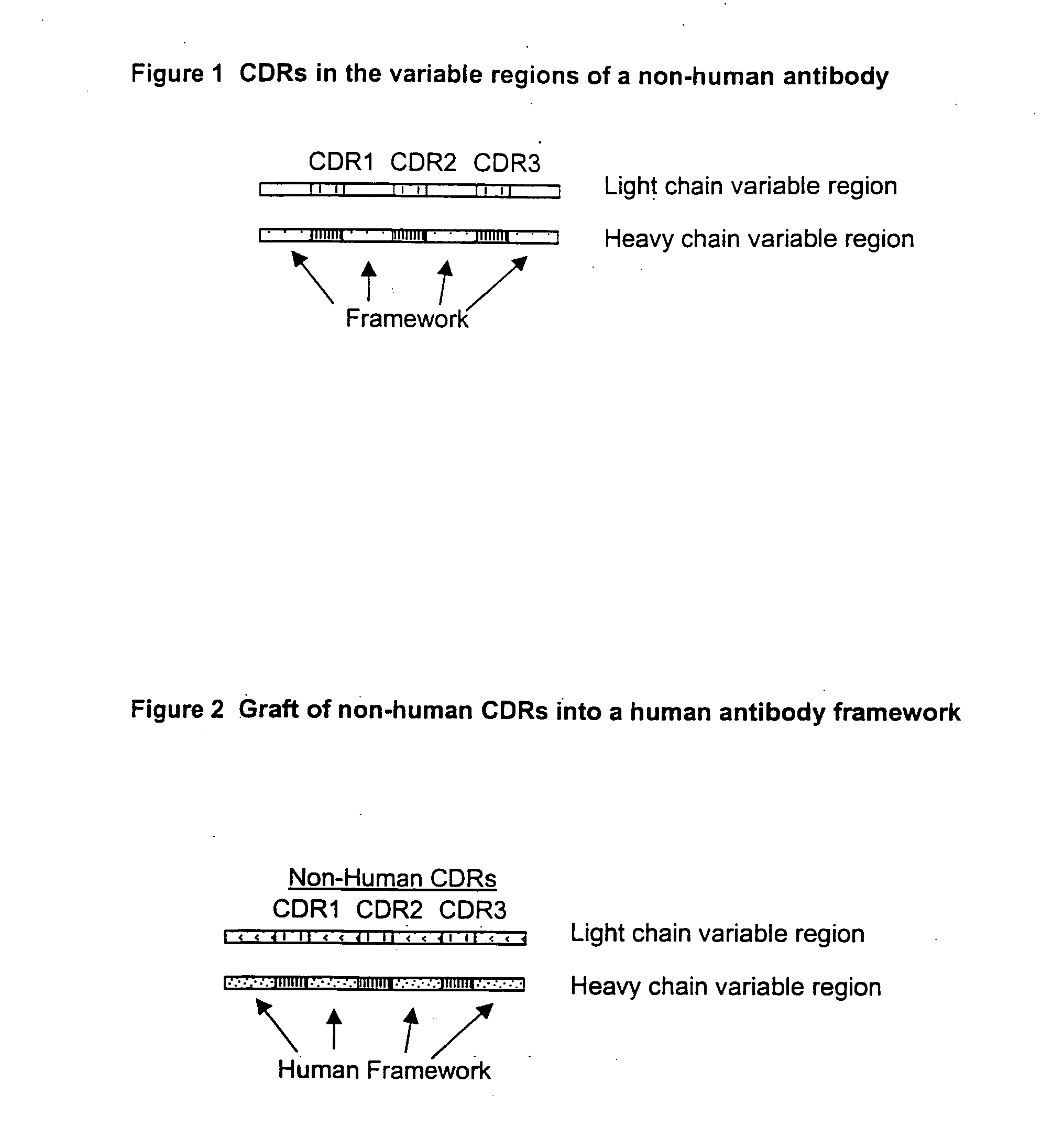
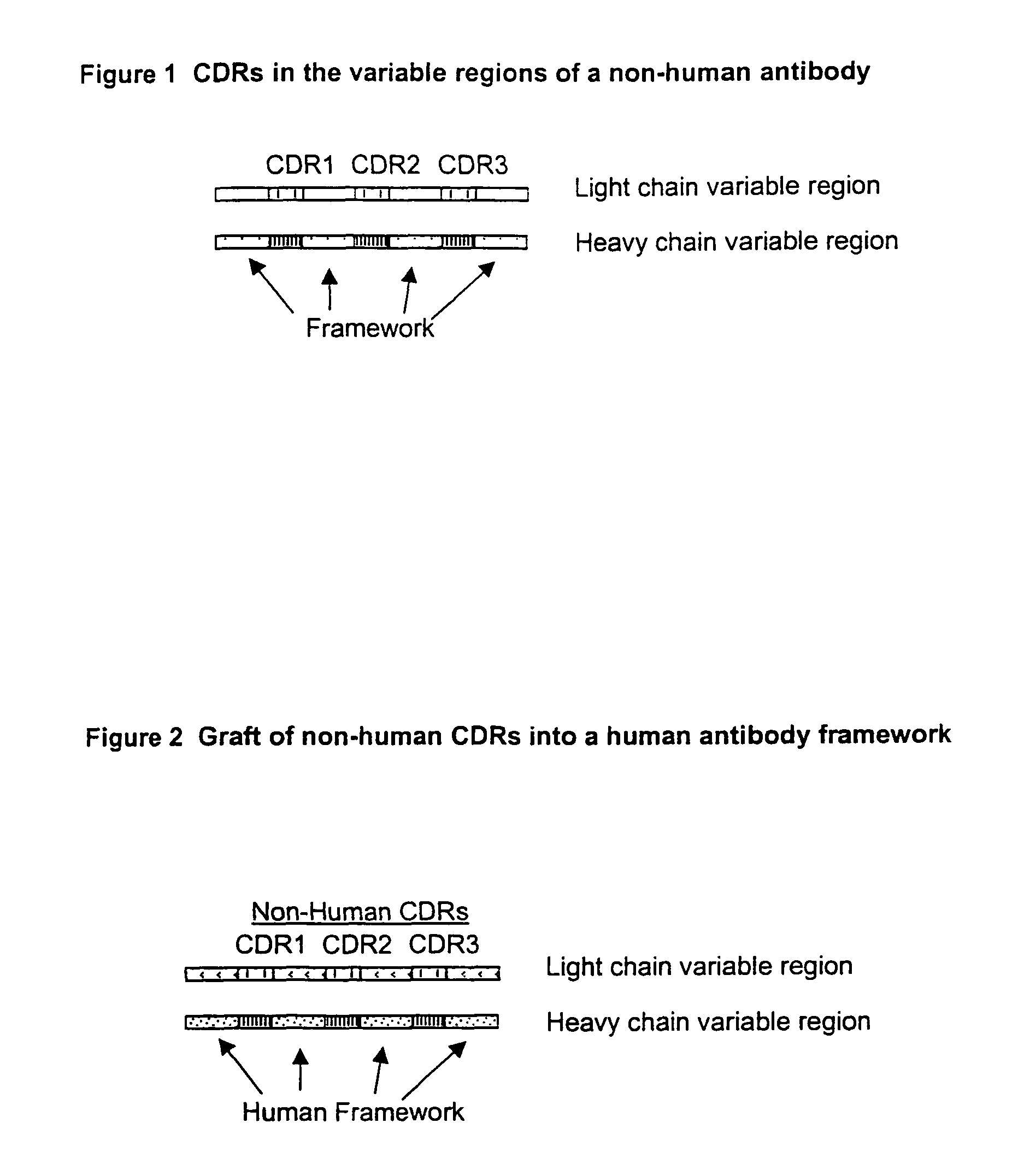
Compositions, methods, and kits are provided for efficiently generating and screening humanized antibody with high affinity against a specific antigen. The library of humanized antibody is generated by mutagenizing a chimeric antibody template that combines human antibody framework and antigen binding sites of a non-human antibody. Alternatively, the library of humanized antibody is generated by grafting essential antigen-recognition segment(s) such as CDRs of the non-human antibody into the corresponding position(s) of each member of a human antibody library. This library of humanized antibody is then screened for high affinity binding toward a specific antigen in vivo in organism such as yeast or in vitro using techniques such as ribosome display or mRNA display. The overall process can be efficiently performed in a high throughput and automated manner, thus mimicking the natural process of antibody affinity maturation.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
High throughput generation and affinity maturation of humanized antibody
InactiveUS9464286B2Generate efficientlyEfficient screeningMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigen bindingHumanized antibody
Compositions, methods, and kits are provided for efficiently generating and screening humanized antibody with high affinity against a specific antigen. The library of humanized antibody is generated by mutagenizing a chimeric antibody template that combines human antibody framework and antigen binding sites of a non-human antibody. Alternatively, the library of humanized antibody is generated by grafting essential antigen-recognition segment(s) such as CDRs of the non-human antibody into the corresponding position(s) of each member of a human antibody library. This library of humanized antibody is then screened for high affinity binding toward a specific antigen in vivo in organism such as yeast or in vitro using techniques such as ribosome display or mRNA display. The overall process can be efficiently performed in a high throughput and automated manner, thus mimicking the natural process of antibody affinity maturation.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Protein discovery using intracellular ribosome display
ActiveUS20110008774A1Efficient foldingImprove stabilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein-protein complexDNA
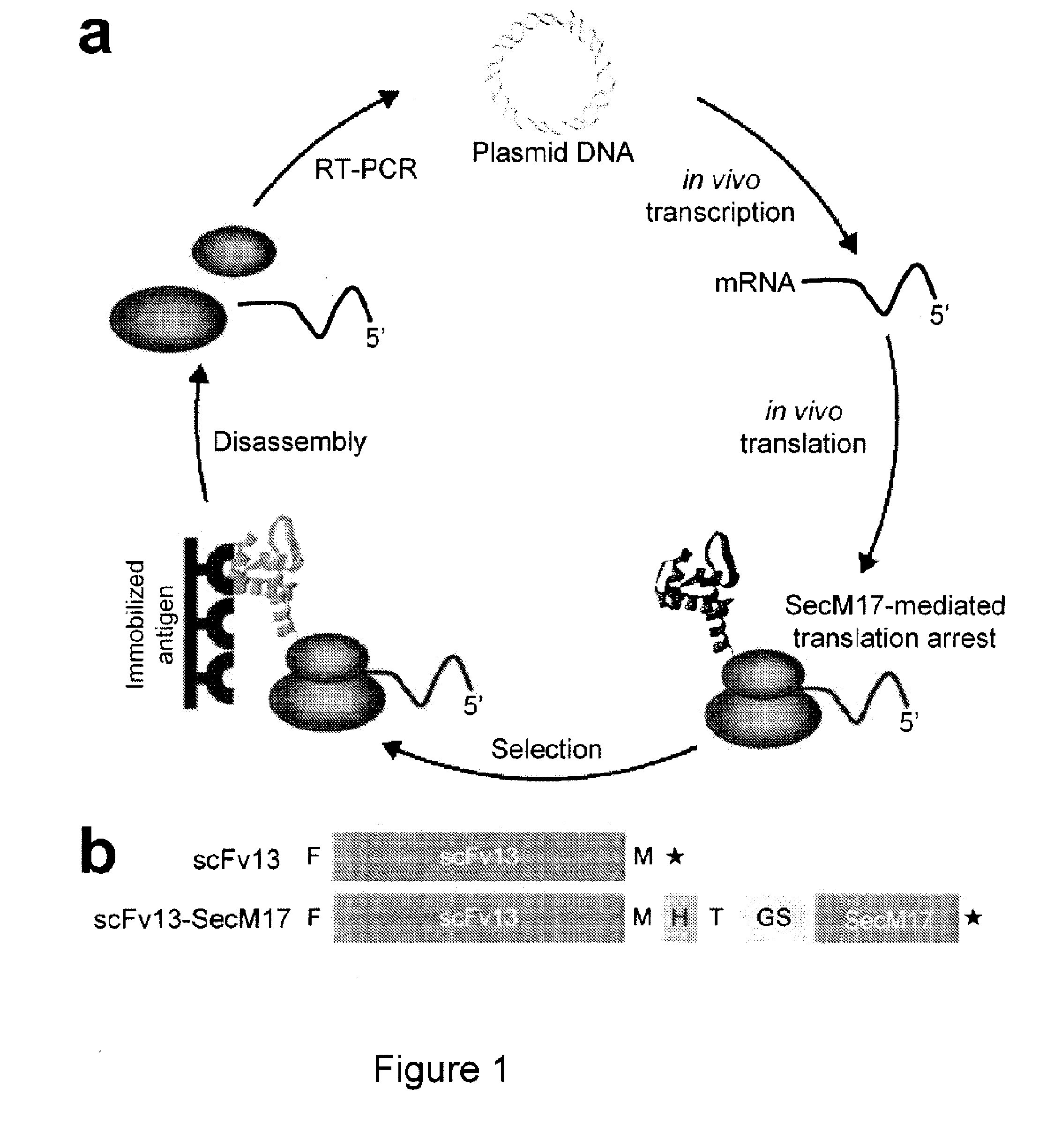
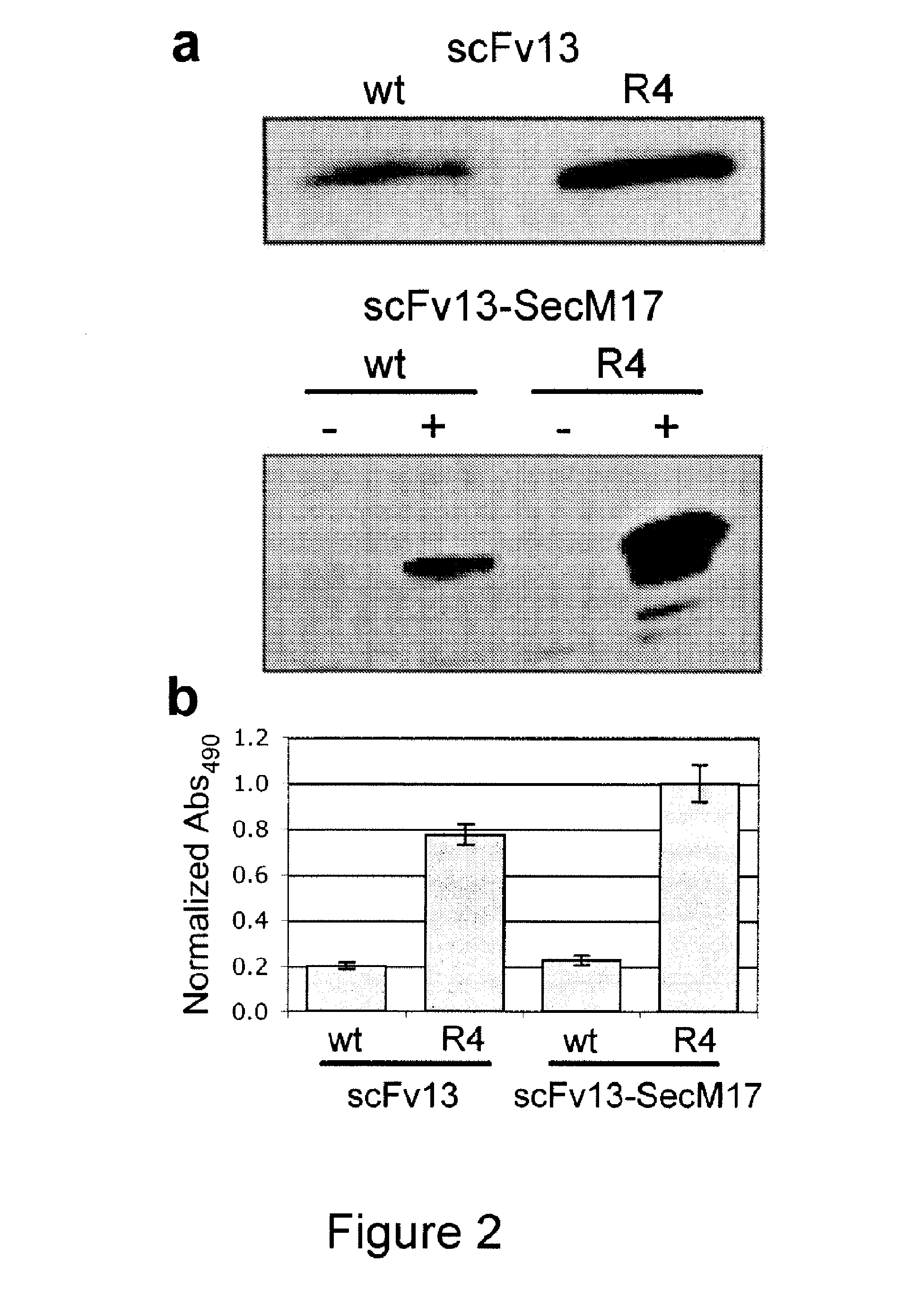
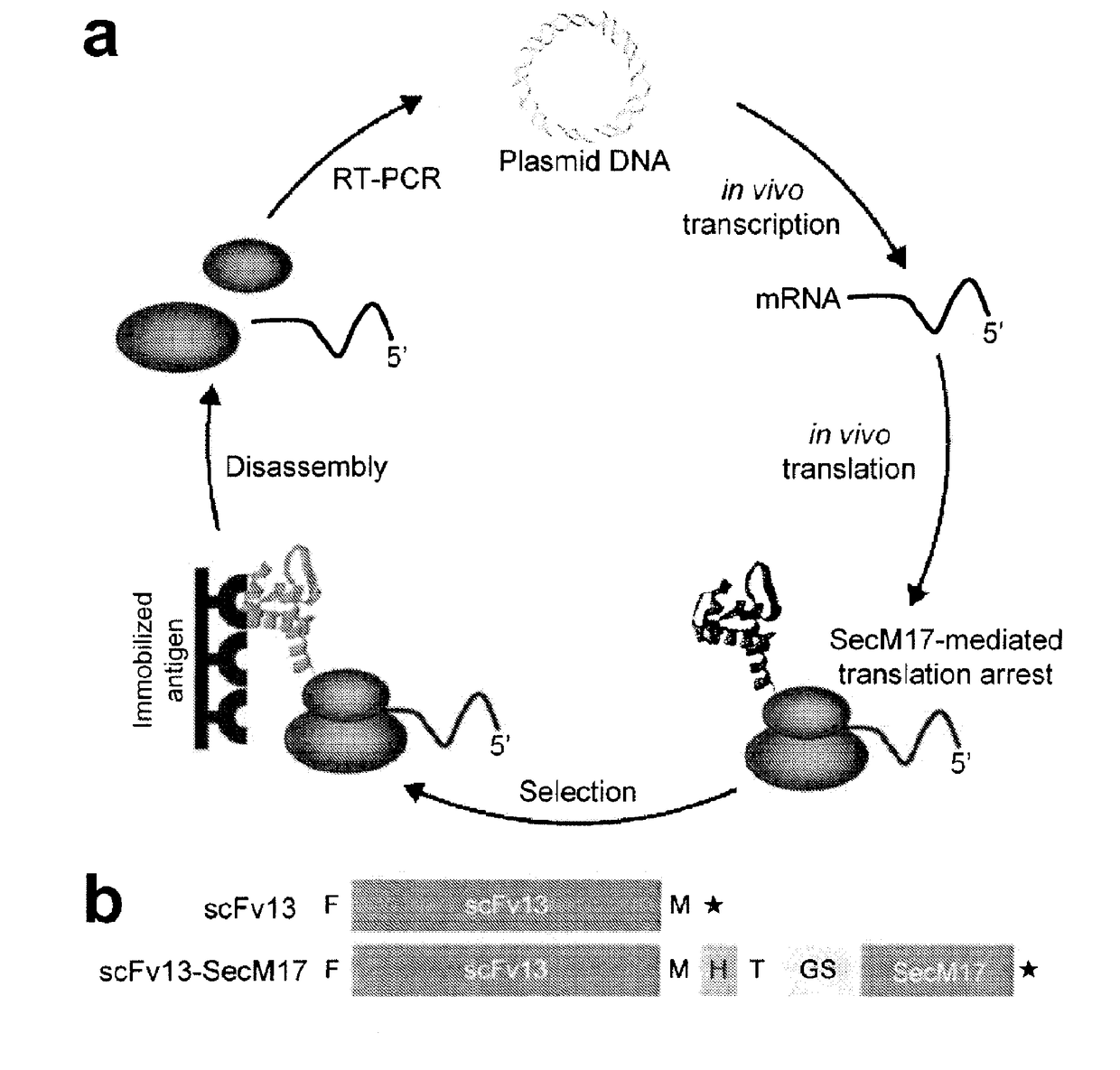
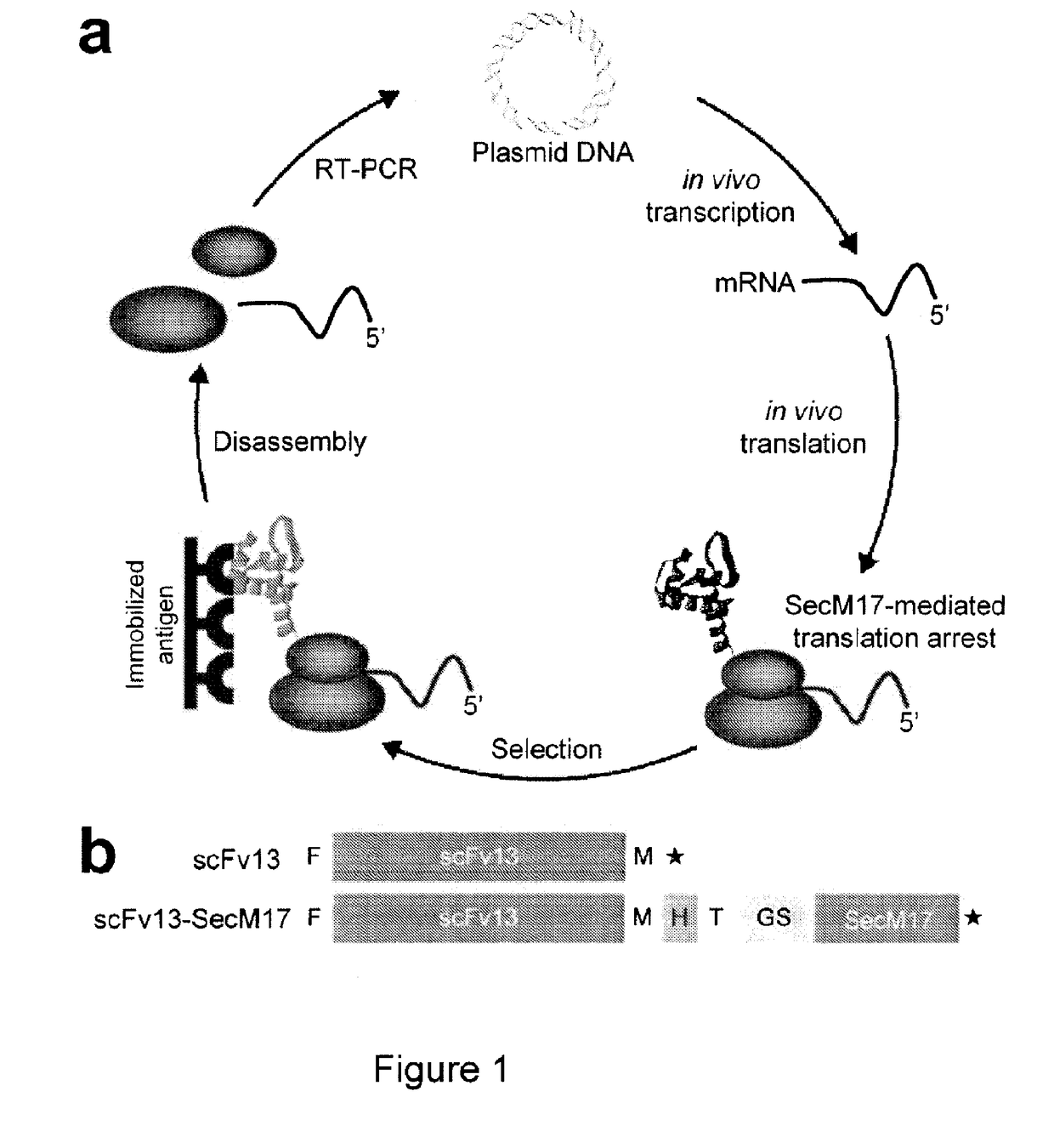
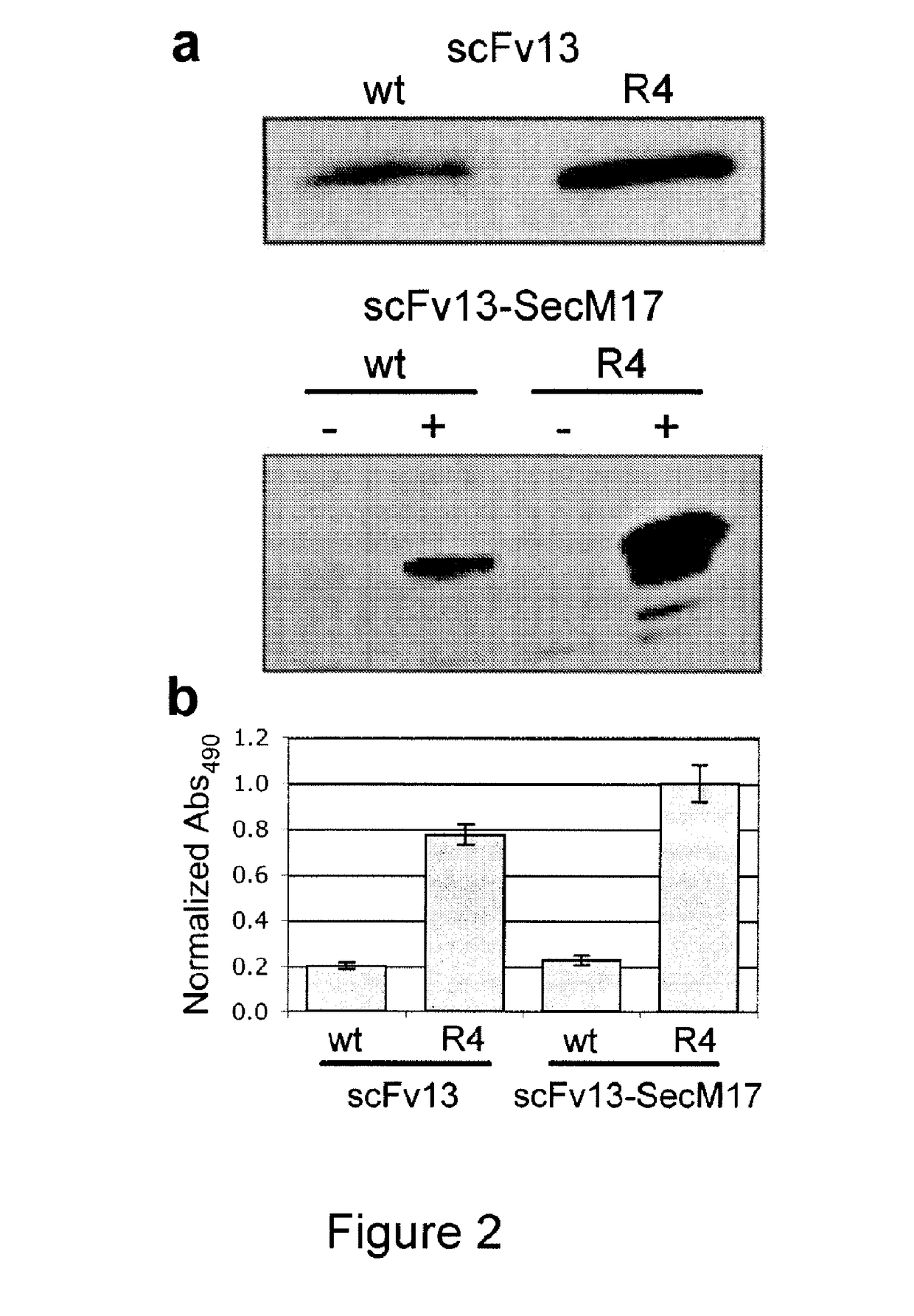
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a protein that binds to a target molecule and has intracellular functionality. This method includes providing a construct comprising a deoxyribonucleic acid molecule encoding the protein which binds to the target molecule, with the deoxyribonucleic acid molecule being coupled to a stall sequence. A host cell is transformed with the construct and then cultured under conditions effective to form, within the host cell, a complex of the protein whose translation has been stalled, the mRNA encoding the protein, and ribosomes. The protein in the complex is in a properly folded, active form and the complex is recovered from the cell. This method can be carried out with a cell-free extract preparation containing ribosomes instead of a host cell. The present invention also relates to a construct which includes a deoxyribonucleic acid molecule encoding a protein that binds to a target molecule and an SecM stalling sequence coupled to the deoxyribonucleic acid molecule. The deoxyribonucleic acid molecule and the SecM stalling sequence are coupled with sufficient distance between them to permit expression of their encoded protein, within the cell, in a properly folded, active form.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
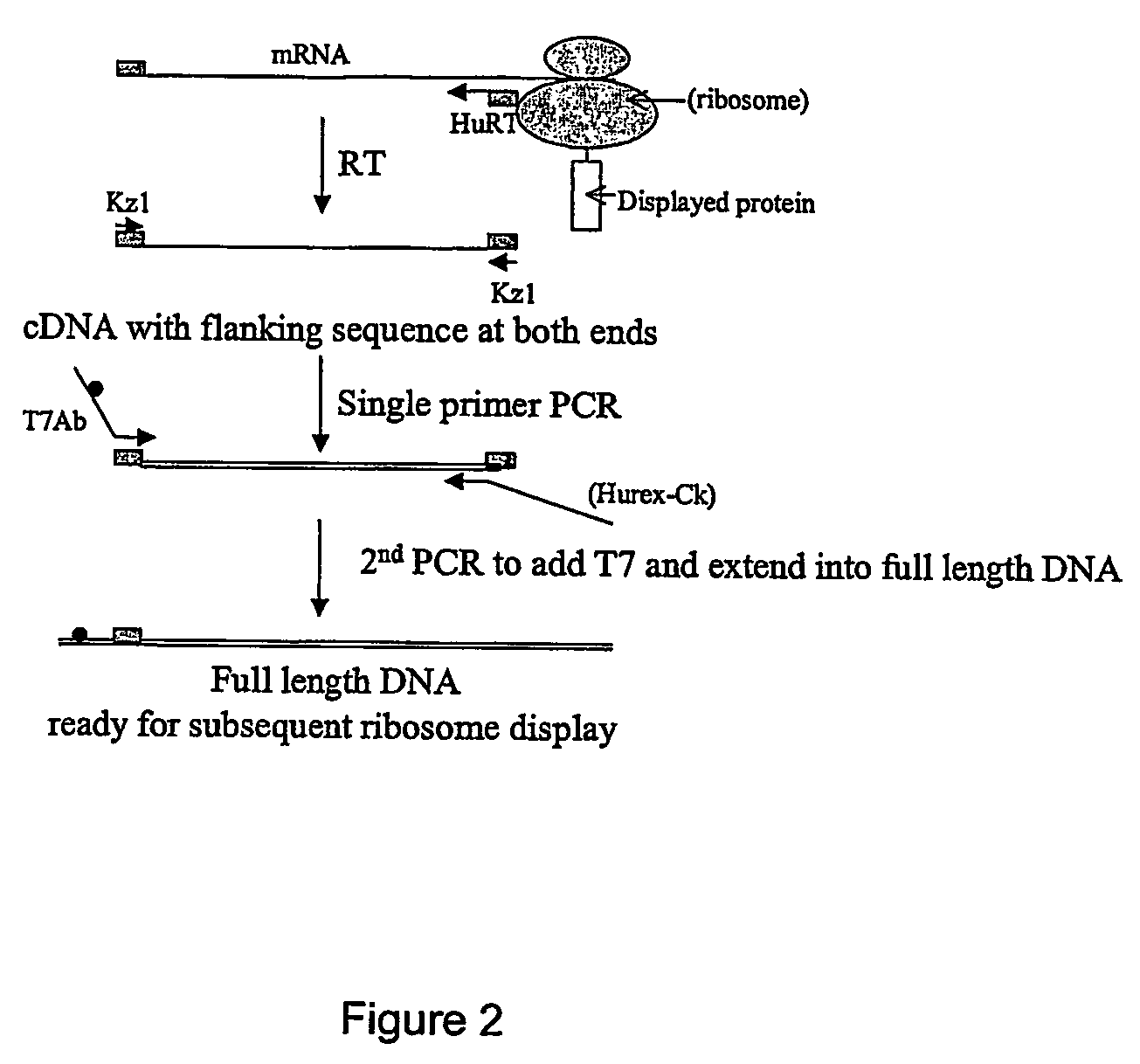
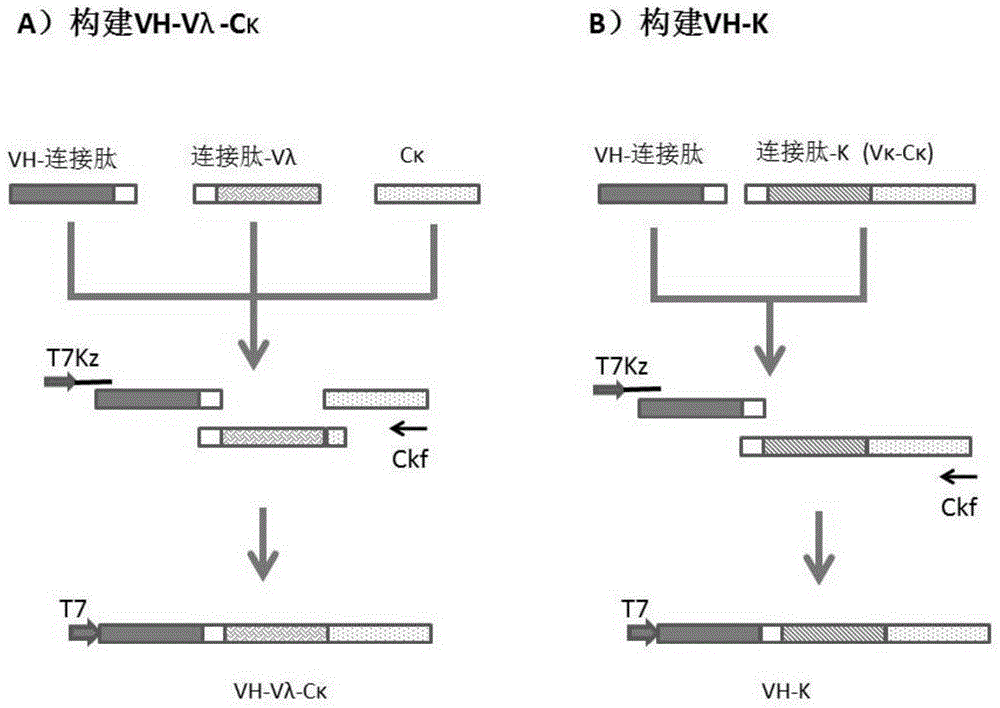
Methods for recovery of DNA from mRNA in ribosome display complexes
InactiveUS7572577B2High sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDNABioinformatics
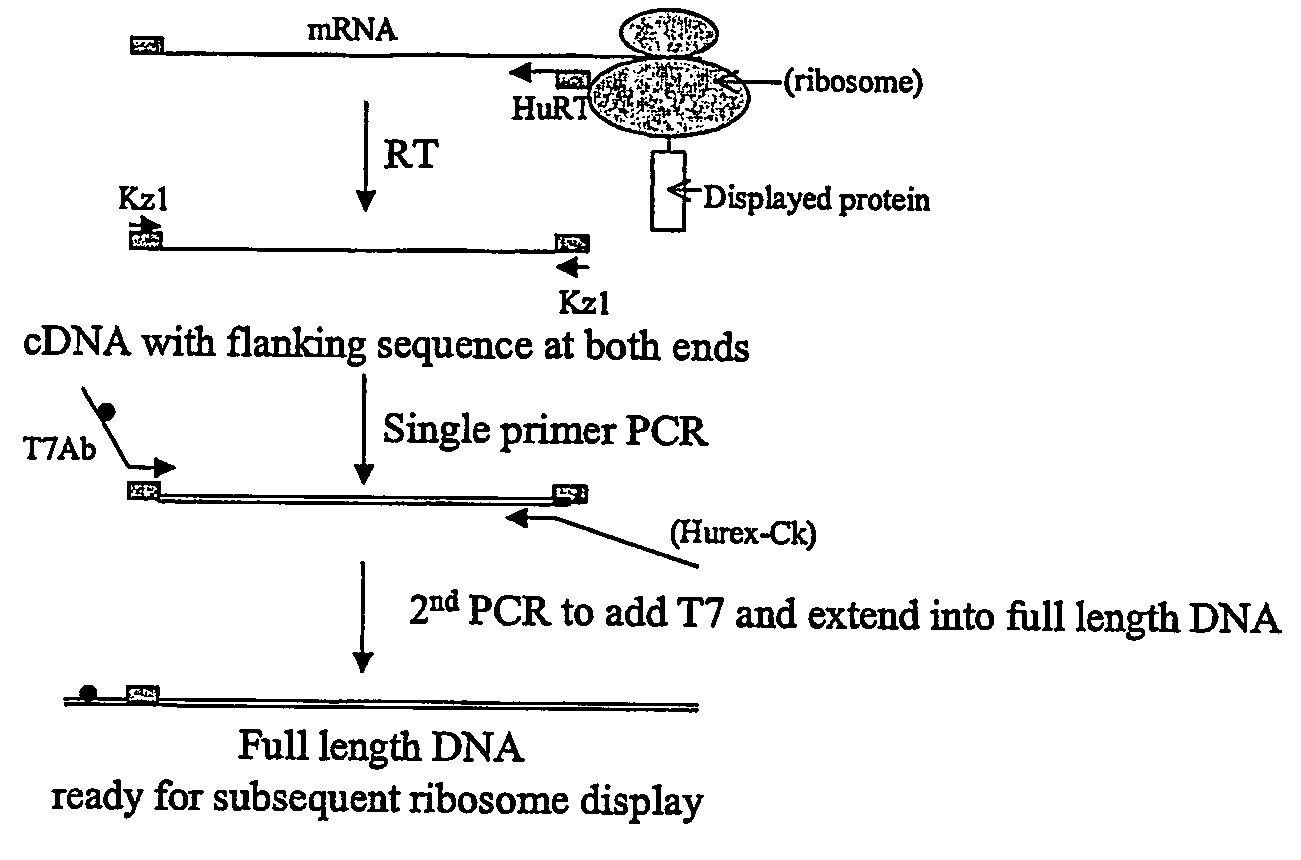
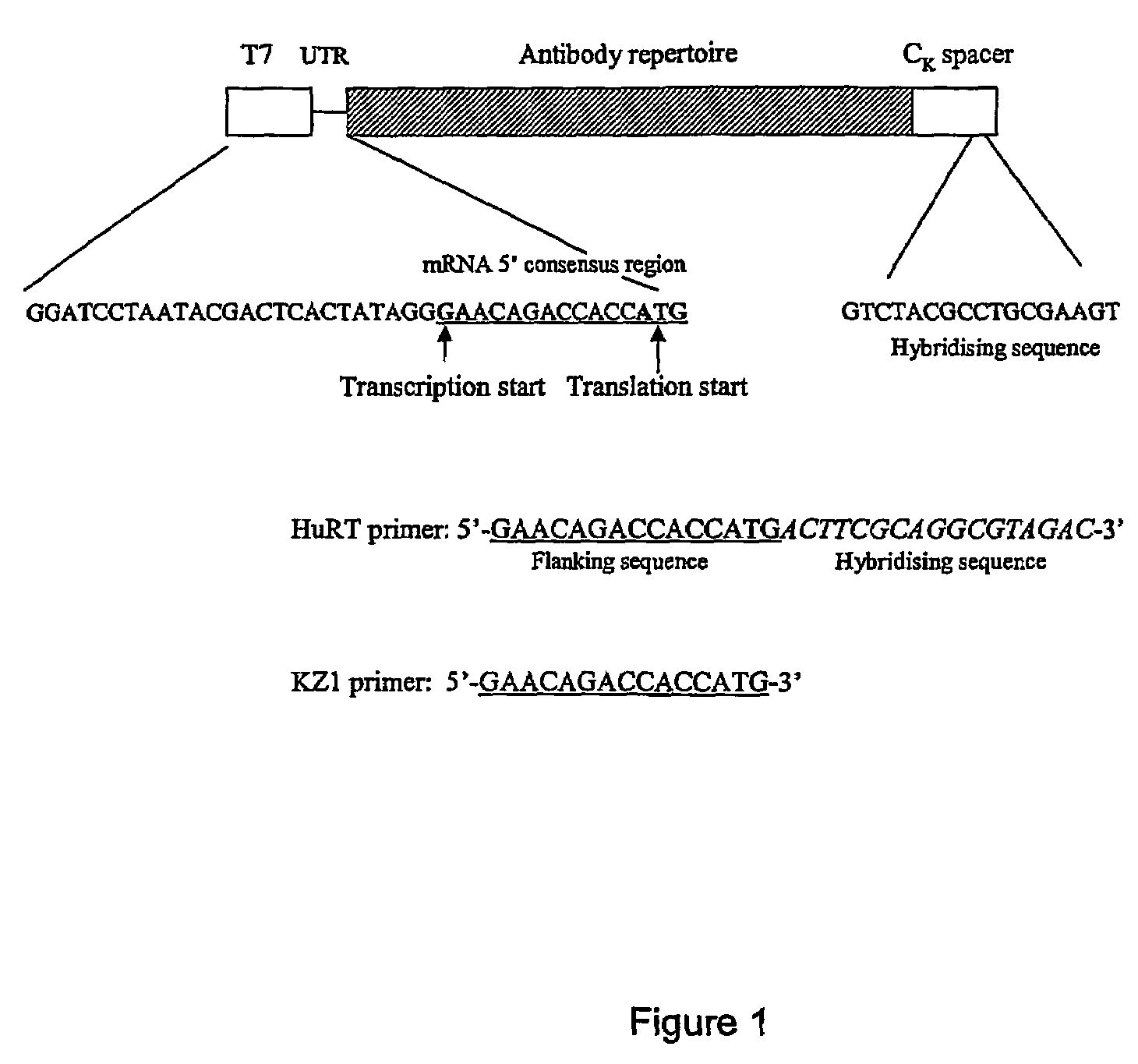
The invention provides a method for recovery of cDNA from mRNA, comprising reverse transcription (RT) of mRNA using a RT primer which includes a sequence based on the 5′ consensus region of the mRNA which is identical or similar to 5′ consensus region of the mRNA and which includes a sequence capable of specifically hybridising to the 3′ region of the mRNA, followed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using a single primer to generate ss cDNA, ds cDNA and amplify the cDNA. Primers for use in methods of the invention and kits for performing methods of the invention are also provided. The methods of the invention can partially or fully automated.
Owner:CRESCENDO BIOLOGICS
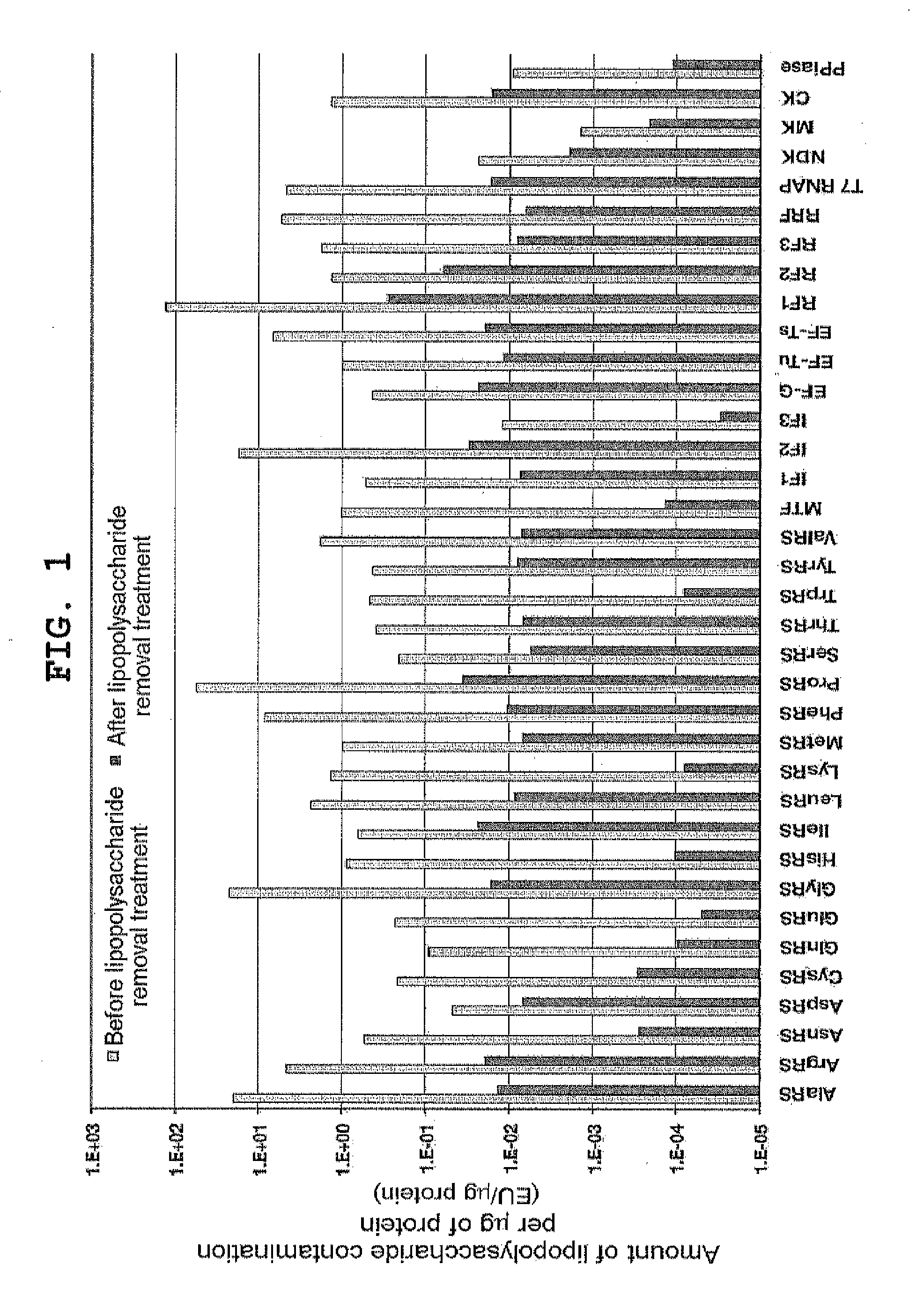
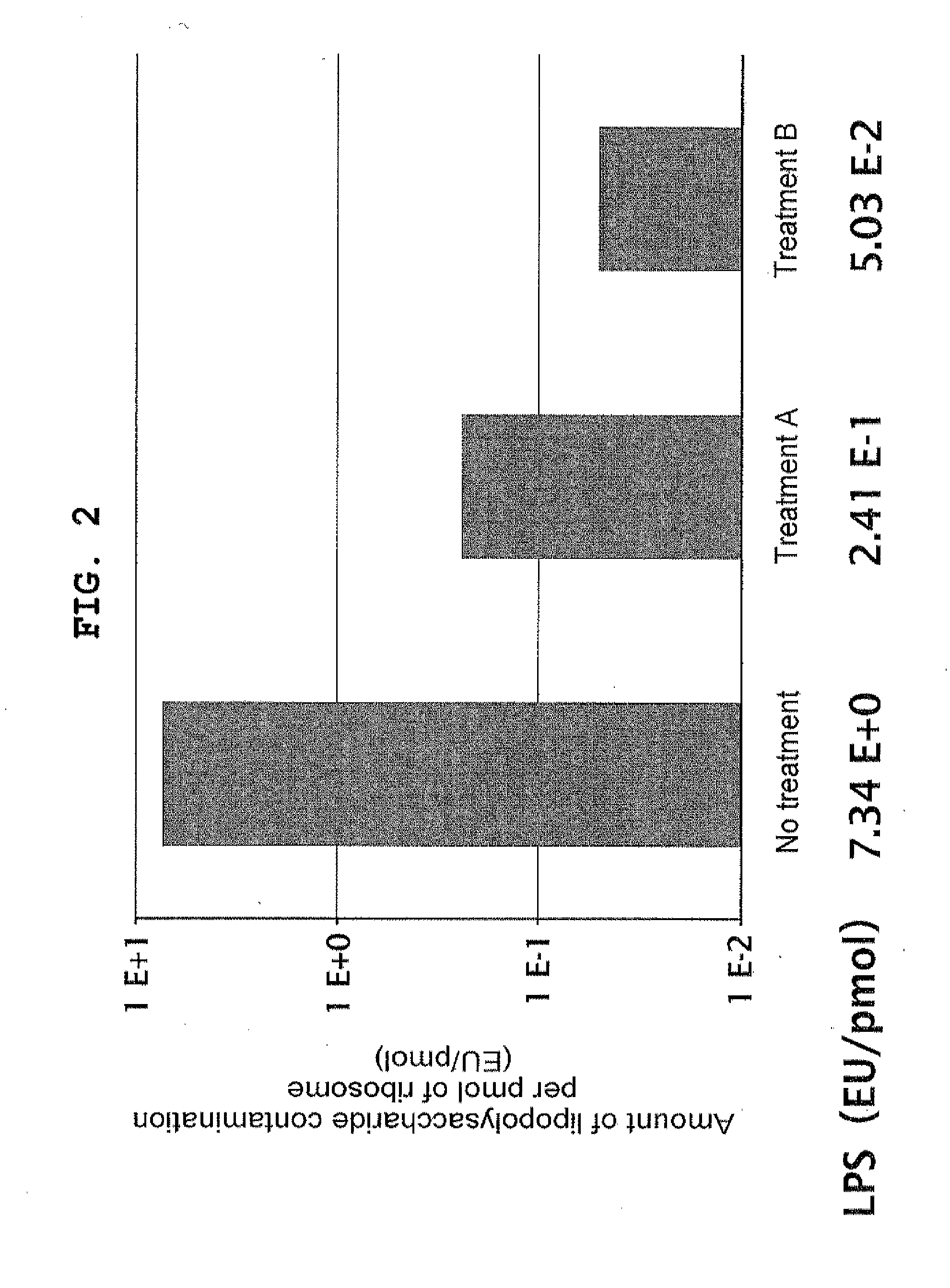
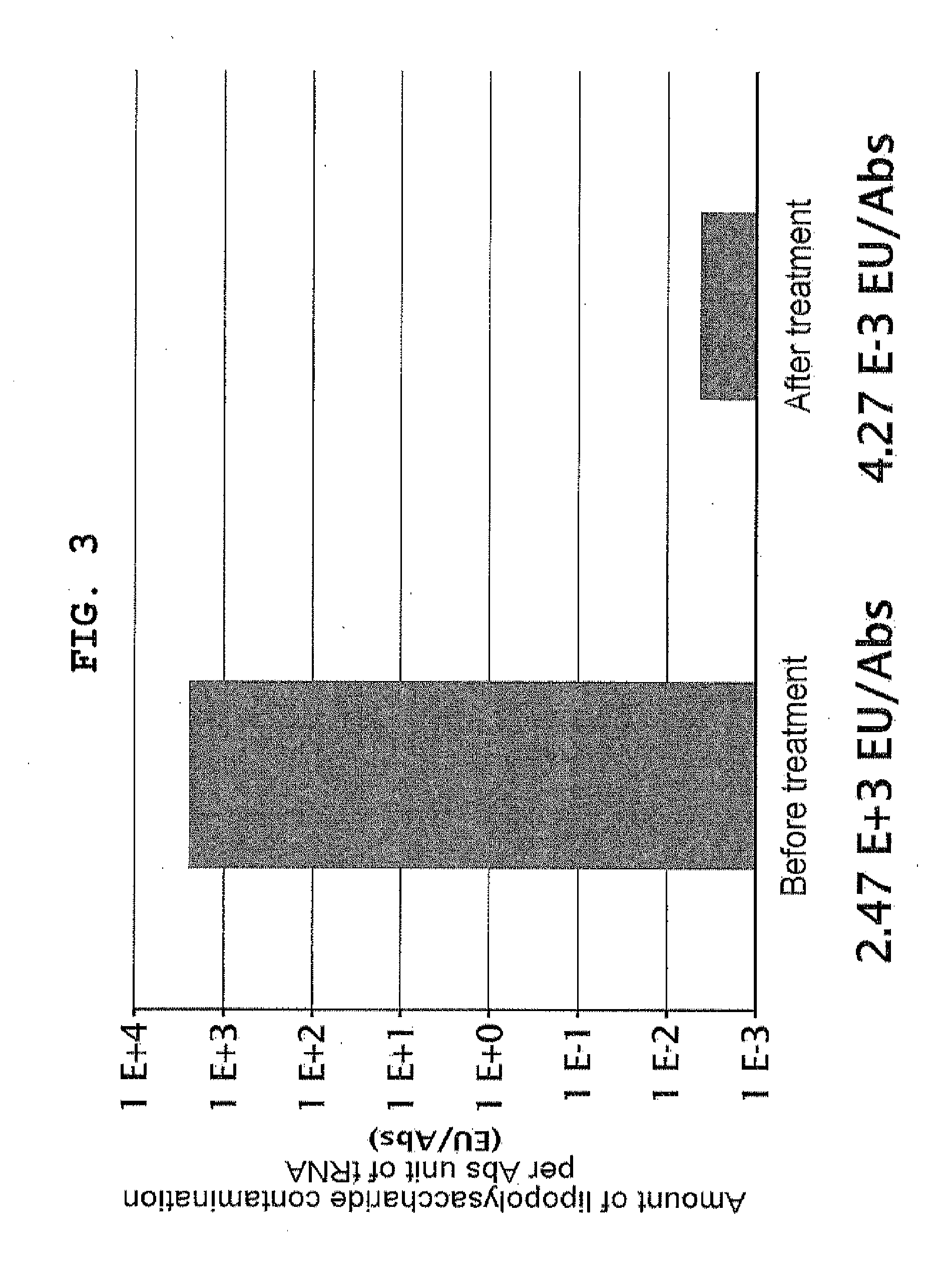
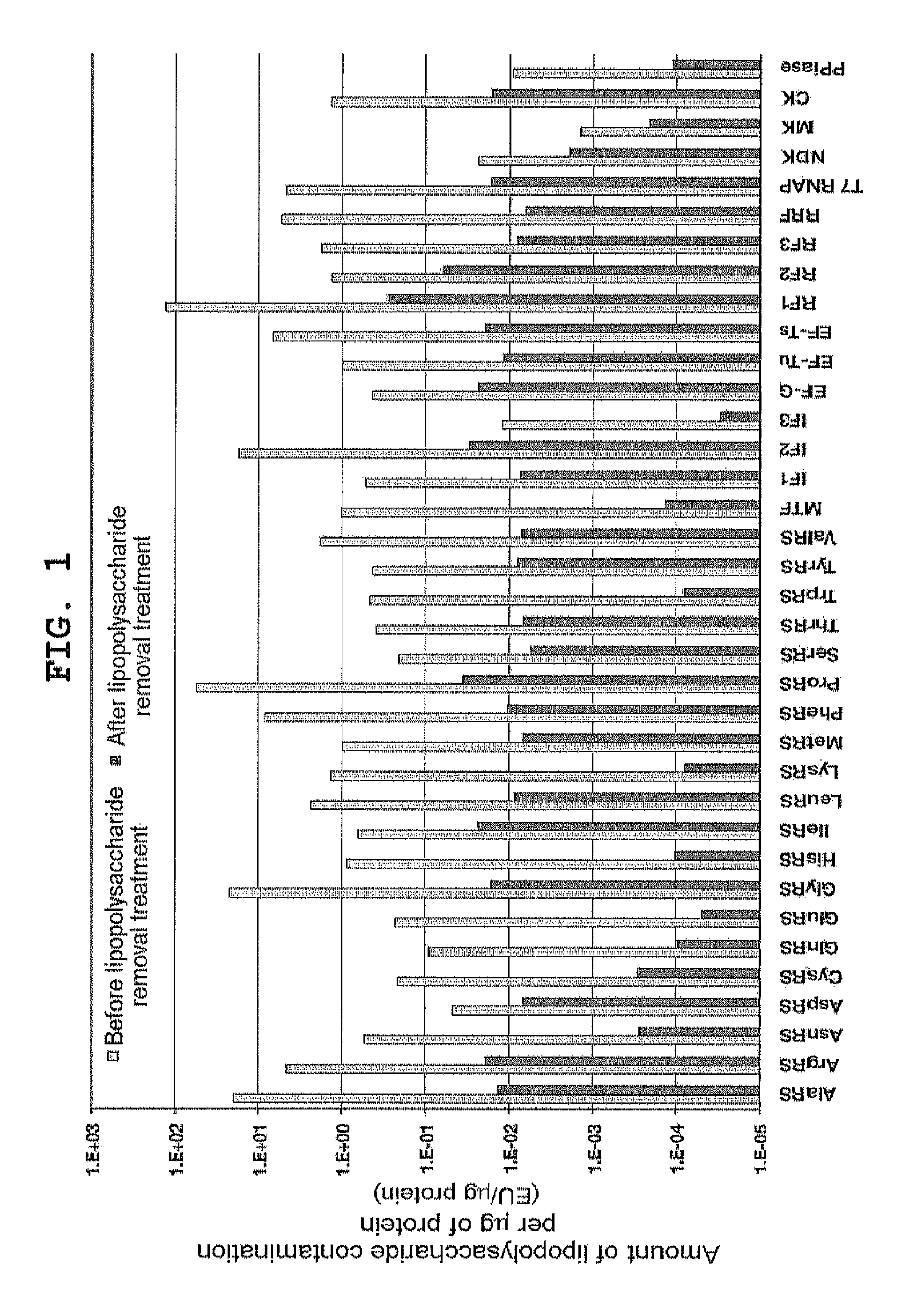
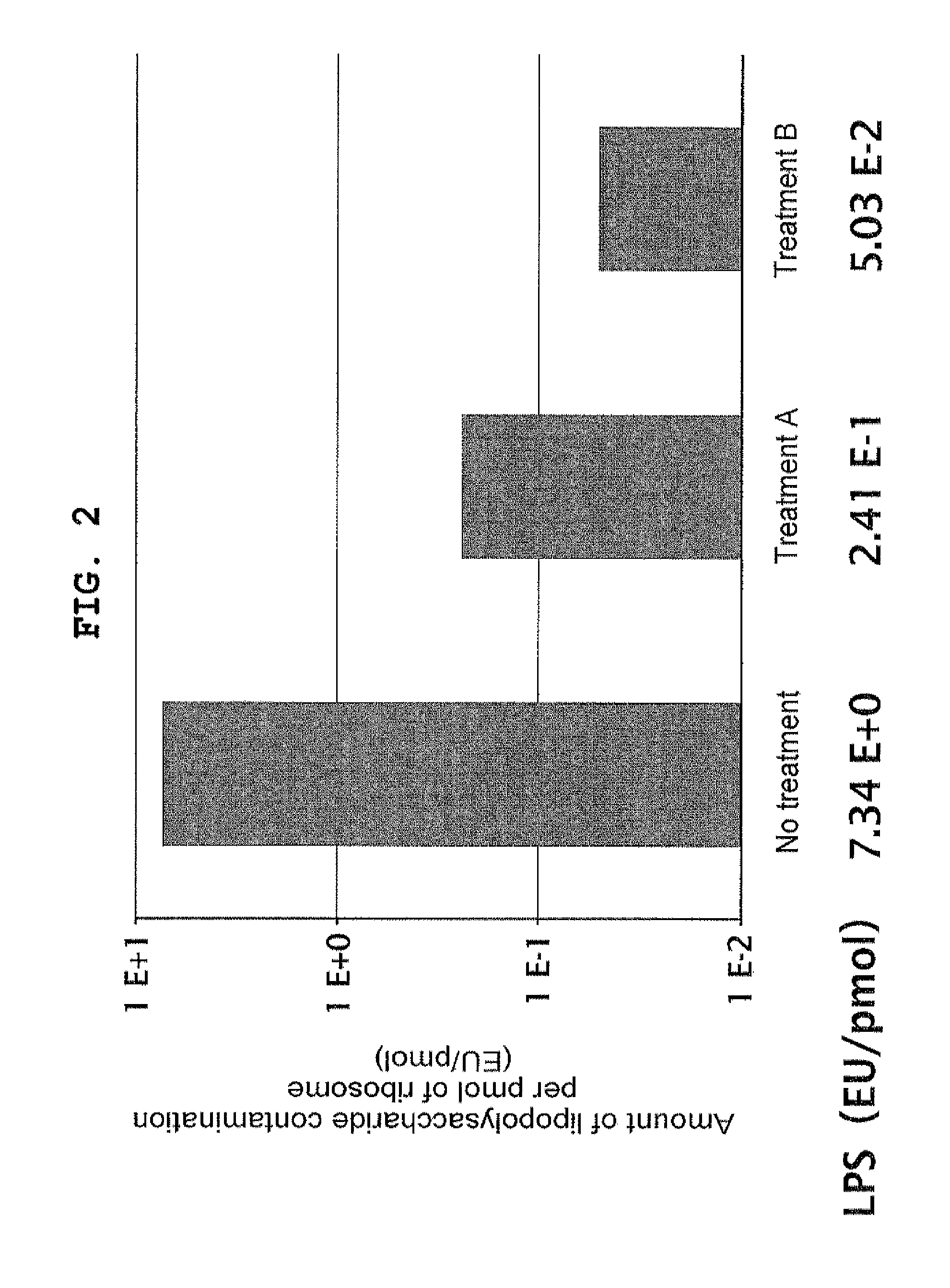
Composition for synthesizing protein with reduced lipopolysaccharide contamination, method for producing protein using said composition
ActiveUS20120231496A1Reduce pollutionImprove accuracySugar derivativesMicroorganismsCell-free protein synthesisContamination
According to the present invention, a composition possessing cell-free protein synthesis activity with reduced contaminating lipopolysaccharide, and a method for producing a protein using the same are provided. When ribosome display is performed using the composition and method for protein production of the present invention, the background that is caused by non-specific binding is reduced, so that a nucleic acid that encodes the desired polypeptide can be selected with high accuracy and high efficiency.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
High throughput generation and affinity maturation of humanized antibody
InactiveUS20160237424A1Generate efficientlyEfficient screeningLibrary screeningBiological testingAntigen bindingAntibody affinity
Compositions, methods, and kits are provided for efficiently generating and screening humanized antibody with high affinity against a specific antigen. The library of humanized antibody is generated by mutagenizing a chimeric antibody template that combines human antibody framework and antigen binding sites of a non-human antibody. Alternatively, the library of humanized antibody is generated by grafting essential antigen-recognition segment(s) such as CDRs of the non-human antibody into the corresponding position(s) of each member of a human antibody library. This library of humanized antibody is then screened for high affinity binding toward a specific antigen in vivo in organism such as yeast or in vitro using techniques such as ribosome display or mRNA display. The overall process can be efficiently performed in a high throughput and automated manner, thus mimicking the natural process of antibody affinity maturation.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Screening method for paraquat simulation antibody and application thereof
InactiveCN104513316AAffect specific recognitionAffect spatial conformationImmunoglobulinsBiological testingLipocalinAntibody screens
Belonging to the field of biotechnologies, the invention relates to a screening method for a paraquat simulation antibody and application thereof. The simulation antibody is screened out from a ribosome display Lipocalin simulation antibody library and is subjected to soluble functional expression. The invention also relates to a method of screening the paraquat simulation antibody by a ribosome display technology. The paraquat simulation antibody screened out in the invention can be used for paraquat residual monitoring and development of a kit for rapid detection of pesticide paraquat residual.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Selection of fab fragments using ribosomal display technology
The invention relates to a method for generating and selecting Fab fragments using ribosomal display and cell-free protein synthesis. The invention also provides a ribosomal display reaction system for generating Fab fragment complexes. The compositions of a Fab fragment complex and a library thereof are also provided.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
Antitumor peptide with pH selectivity and application of antitumor peptide
InactiveCN103936834AHigh selectivityEasy to quantifyPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesSide chainMicroscopic observation
The invention relates to an antitumor peptide with efficient pH selectivity and an application of the antitumor peptide, belonging to the technical field of antitumor drug research and development and application. A series of peptides which are rich in histidine and have membrane lysis and antitumor activities are constructed by adopting the ribosome display technology and a series of antitumor peptides with normal physiological condition and tumor characteristic acidic condition selectivity are constructed by utilizing the special acidity coefficient of the imidazole side chain of histidine. The peptides have killing effects on lung cancer cells and breast cancer cells and can selectively kill the tumor cells in acidic conditions, inhibit tumor growth in mice xenotransplantation models and especially inhibit tumor growth in acidic conditions highly selectively. Microscopic observation, lactic dehydrogenase experiments, fluorescence quenching and circular dichroism spectrums of the peptides prove that the permeability of the peptides is increased by inserting and carrying out lysis on cell membranes, thus leading cell activity reduction and cell death.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
12 peptide ZA for inhibiting hepatitis c virus to infect human cell and preparation method and application
InactiveCN101456901AQuick combinationPrevent invasionPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemAntigenHepacivirus
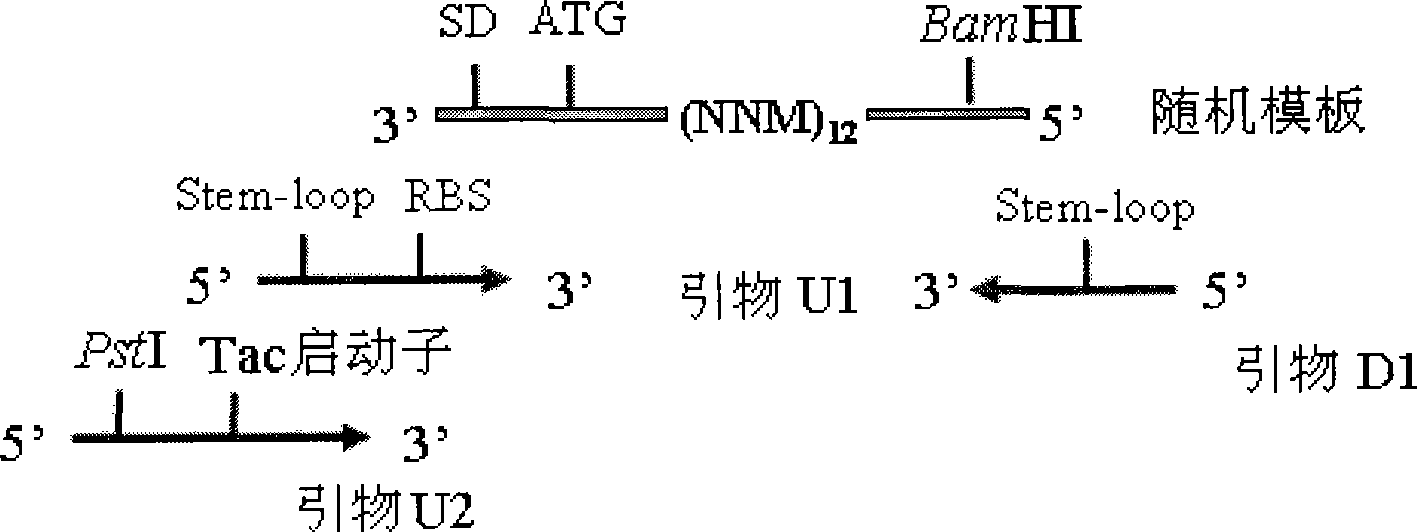
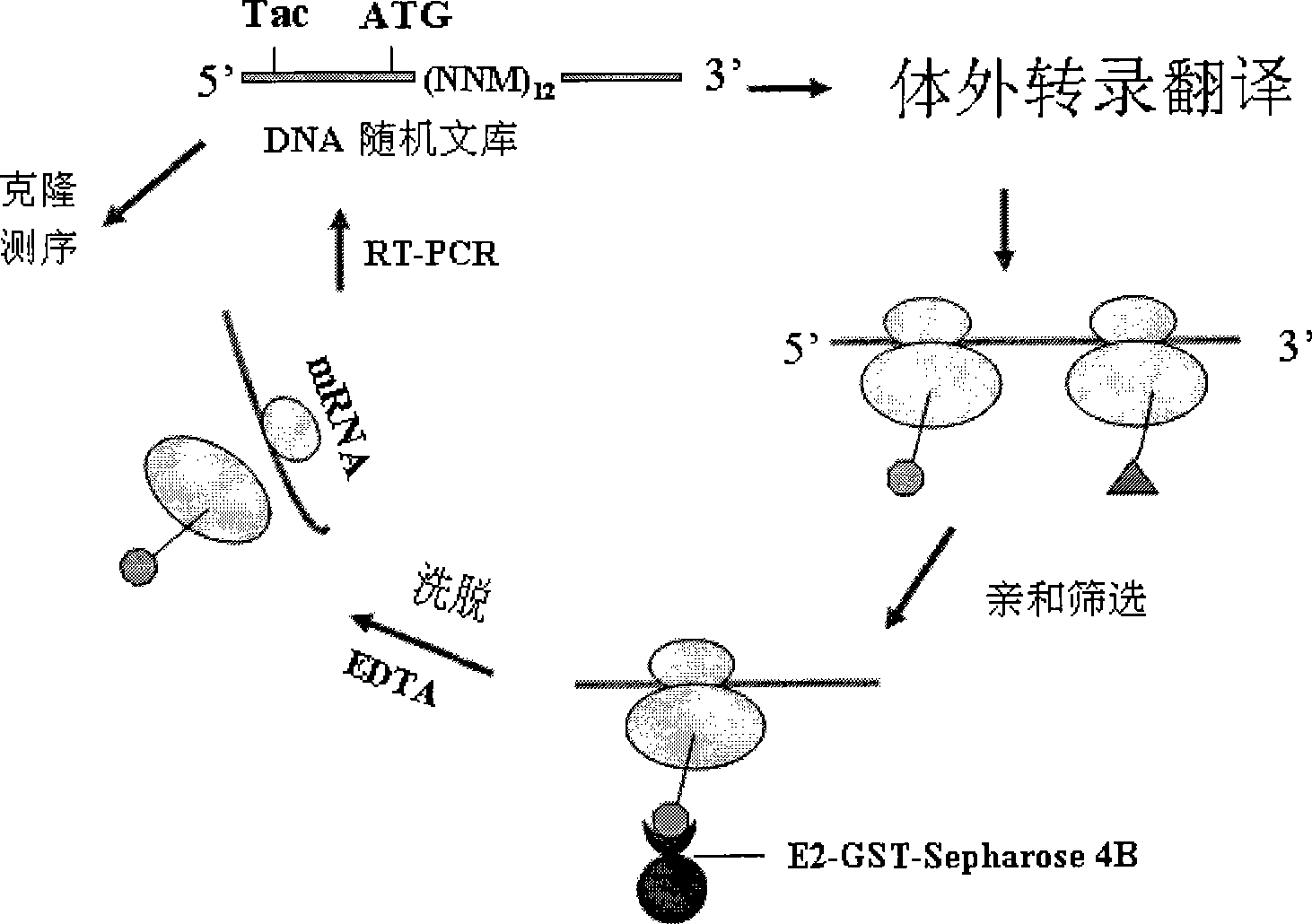
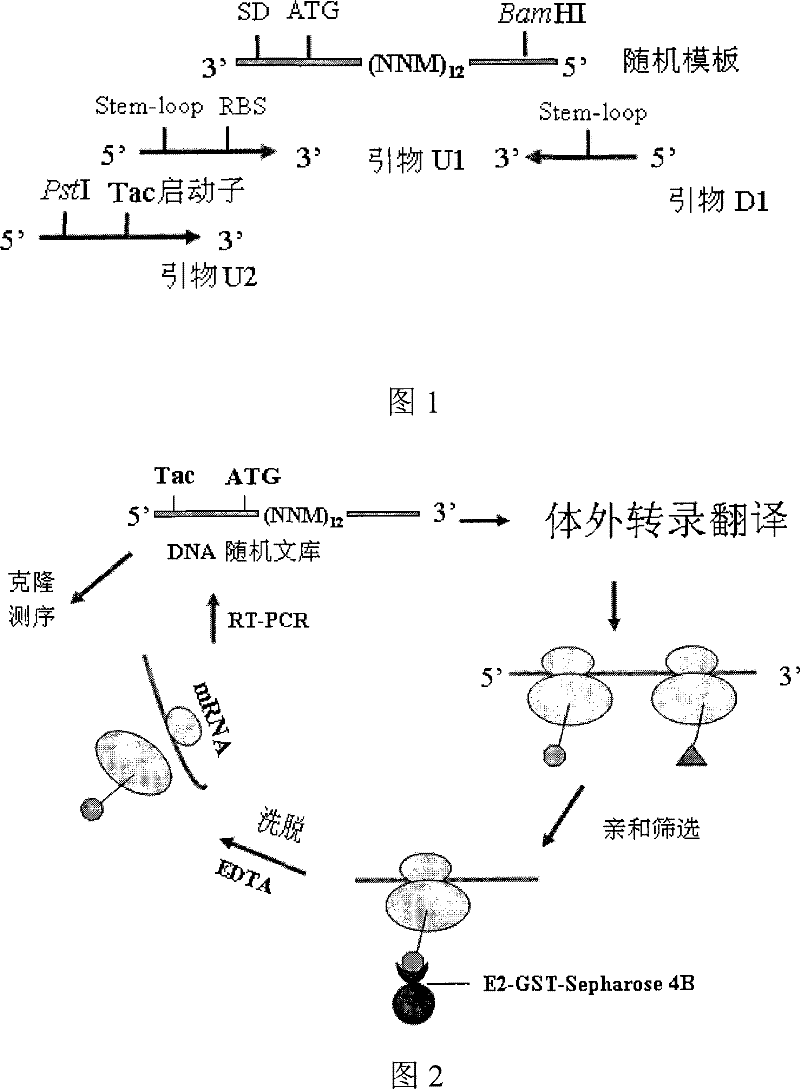
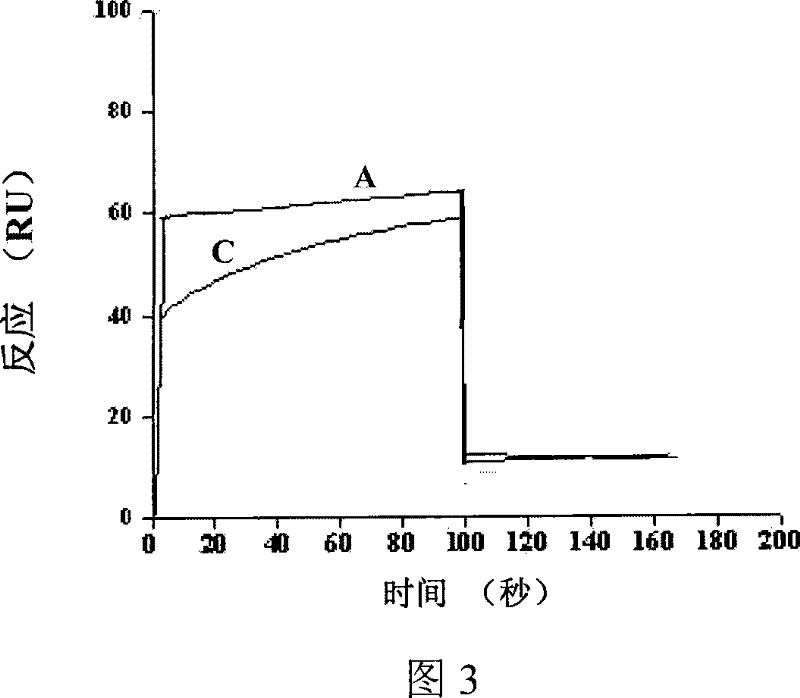
The invention discloses a dodecapeptide ZA capable of inhibiting the hepatitis C virus from infecting human body cells and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing an E2-GST fusion protein; then preparing an E2-GST fusion protein antibody; thirdly establishing a random DNA library; fourthly preparing a ribosome library; and fifthly screening the polypeptide bonded with the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein through the ribosome display library so as to obtain the dodecapeptide (ZA) specially bonded with the E2 protein. Due to the high affinity of the polypeptide ZA with the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein, the polypeptide ZA can remarkably alleviate the intrusion of HCV into the human body cells and DC cells, inhibit the integration of the E2 protein with human body cells, and have a high inhibition capacity. The dodecapeptide ZA is used for preparing the medicines capable of treating and preventing hepatitis C virus infection. The polypeptide is applied to a kit for detecting the hepatitis C virus envelope antigen.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Polynucleotide construct capable of displaying fab in a cell-free translation system, and method for manufacturing and screening fab using same
InactiveUS20180017573A1Maximizing affinityHigh affinityHybrid immunoglobulinsBiological testingAntigenCell free
The polynucleotide construct of (1) or (2) below is used to perform ribosome display, CIS display and / or mRNA display in order to screen a Fab against an antigen of interest: (1) a polynucleotide construct which monocistronically comprises a ribosome-binding sequence, Fab first chain-coding sequence, linker peptide-coding sequence, Fab second chain-coding sequence and scaffold-coding sequence in this order, and further comprises at its 3′-end a structure necessary for maintaining a complex with the Fab encoded by itself; and (2) a polynucleotide construct which comprises a Fab first chain-expressing cistron and a Fab second chain-expressing cistron each containing a ribosome-binding sequence, a Fab first chain-coding sequence or Fab second chain-coding sequence, and a scaffold-coding sequence in this order, the first Fab-expressing cistron further comprising at its 3′-end a ribosome stall sequence, said Fab second chain-expressing cistron further comprising at its 3′-end a structure necessary for maintaining a complex with the Fab encoded by itself.
Owner:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP +1
12 peptide ZB for inhibiting hepatitis c virus to infect human cell and preparation method and application
InactiveCN101456900AQuick combinationPrevent invasionPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemAntigenBinding force
The invention discloses a dodecapeptide ZB capable of inhibiting the hepatitis C virus from infecting human body cells and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing an E2-GST fusion protein; then preparing an E2-GST fusion protein antibody; thirdly establishing a random DNA library; fourthly preparing a ribosome library; and fifthly screening the polypeptide bonded with the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein through the ribosome display library so as to obtain the polypeptide specially bonded with the E2 protein. Due to the high affinity of the polypeptide ZB with the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein, the polypeptide ZB can remarkably alleviate the intrusion of HCV into the human body cells, inhibit the binding force of HCV with human body hepatocytes, have a high inhibition capacity, and competitively inhibit the integration of a virus HCVE2 and a receptor CD81 after having an action with the E2 protein. The dodecapeptide is used for preparing the medicines capable of treating and preventing hepatitis C virus infection. In addition, the polypeptide is applied to a kit for detecting the hepatitis C virus envelope antigen.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Molecular constructs and uses thereof in ribosomal translational events
ActiveUS9006393B1Promote recoveryFacilitate targeted insertionPeptide/protein ingredientsFusion with degradation motifRibosome displayTransformed cell
Stalled ribosome:nascent molecule of interest complexes and methods of using same are provided. Plasmids, particularly DNA plasmids, comprising a stall segment are also disclosed. The methods provide for the facile and stable formation of stalled ribosome:nascent molecule of interest complexes that may be used to examine protein synthesis and protein conformational events, as well as in the creation of desired ribosomal displays. Cells transformed with these plasmids are also provided, and include both eukaryotic and prokaryotic transformed cells. Stall elements that provide for ribosomal stalling of eukaryotic and prokaryotic ribosomes are also disclosed. Various therapeutic and clinical applications of these methods are also provided and used in diseases associated with defects in protein accumulation in vivo.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Methods of B-cell epitope antigenic systems-discovery
ActiveUS20090226899A1Reduce physical stressEnhances viability of assaying immunogenicityImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFc(alpha) receptorADAMTS Proteins
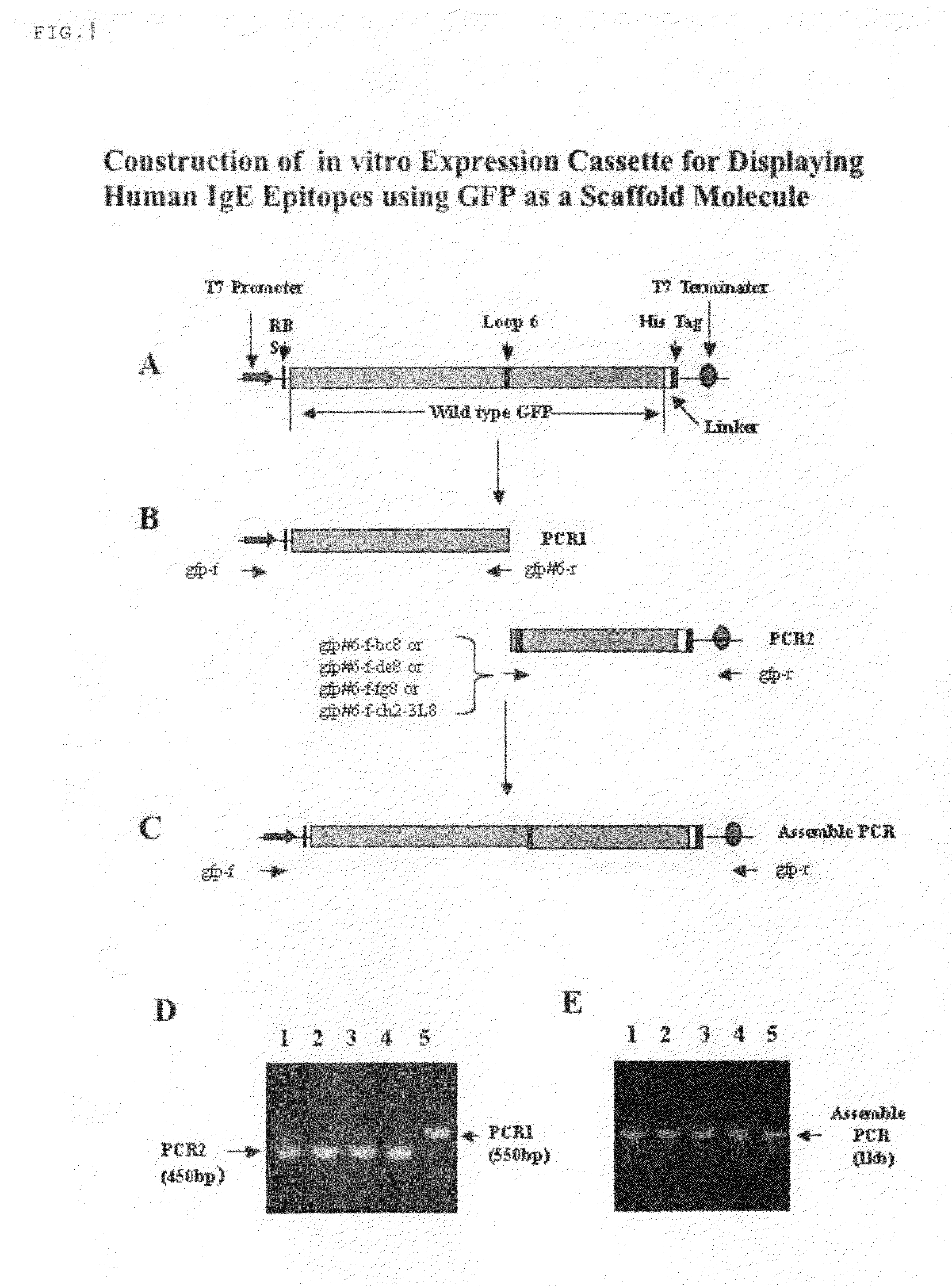
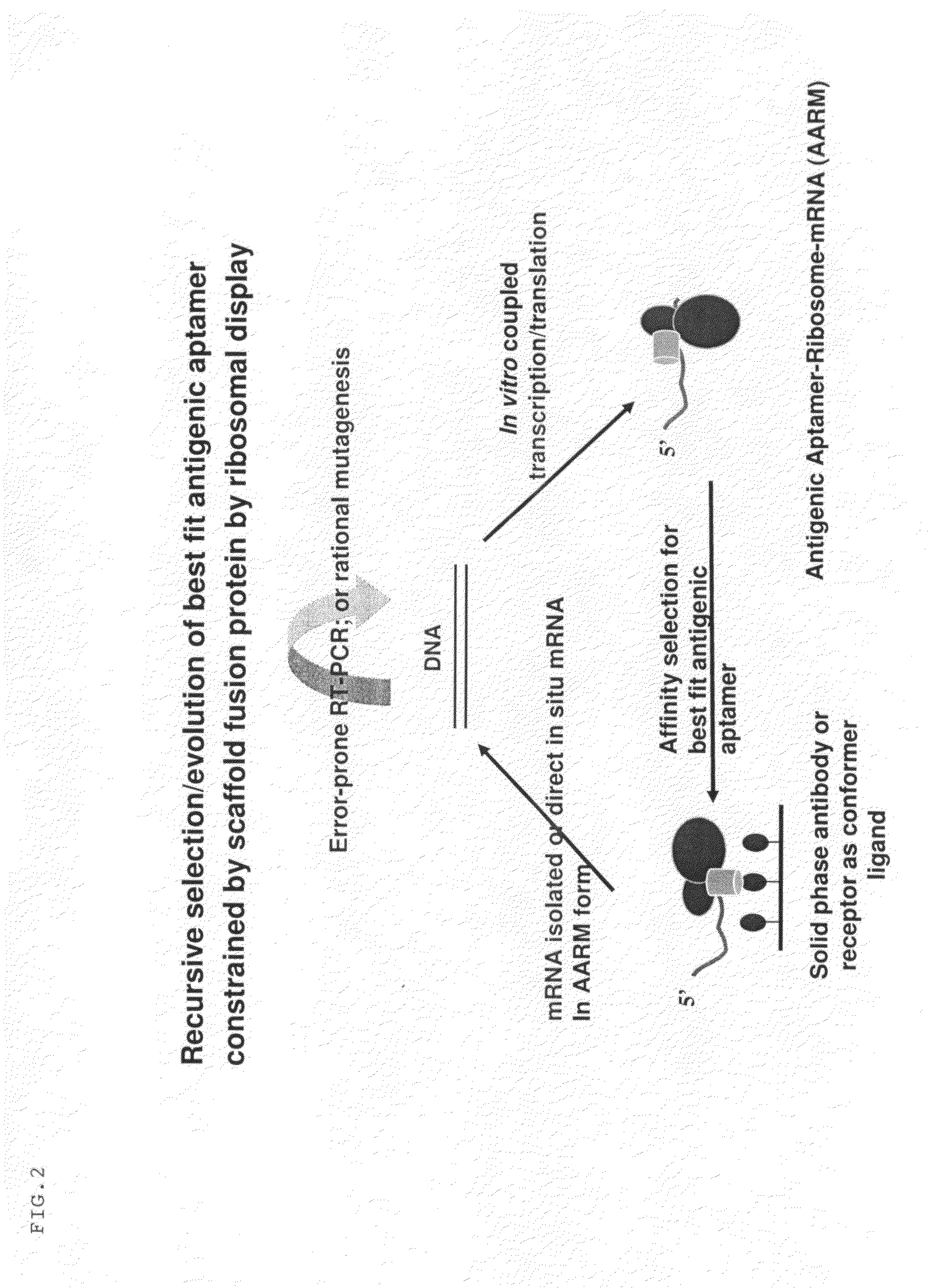
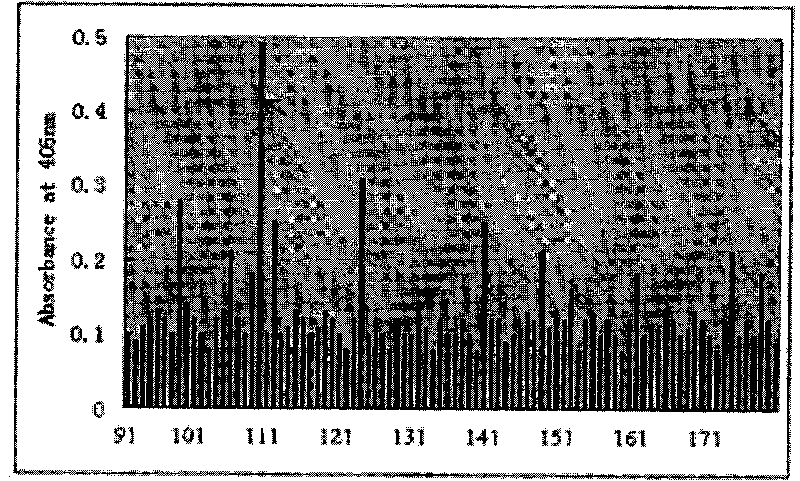
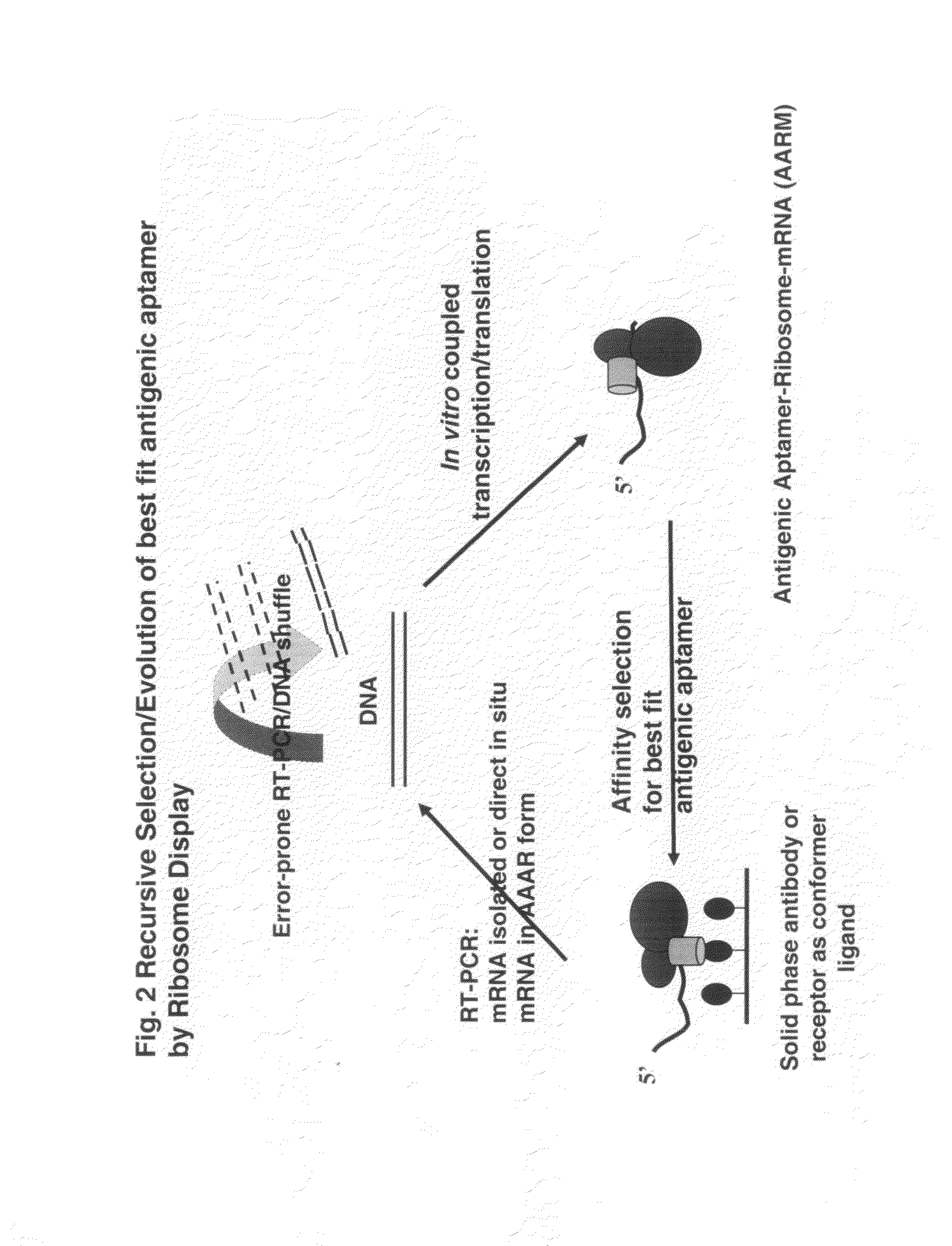
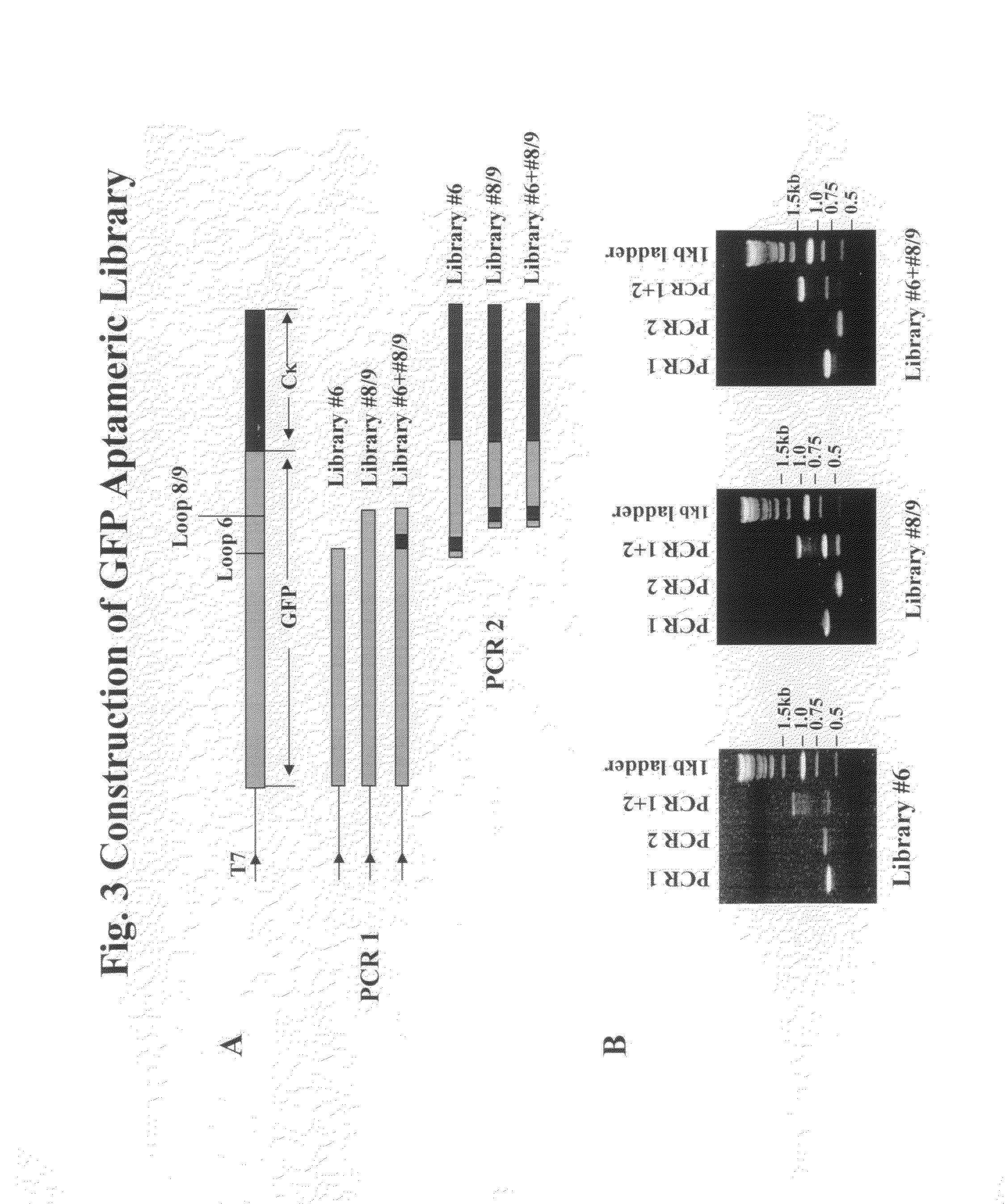
A method is disclosed wherein an antigenic B-cell epitope is discovered by in vitro transcription and translation of pre-determined sequence on thermostable protein scaffolds detected by antibodies to a native protein. Immune reactivities of IgE B-cell epitopes from pre-determined IgE sequences from the constant region, engaged in binding to high affinity IgE Fc receptors, placed in a loop of green fluorescent protein (GFP) were shown immuno-reactive with anti-IgE. Moreover, the antigenic B-cell epitope can be further optimized by molecular evolution, selected by conformer antibody and receptor on solid phase via ribosome display. Alternatively, a random aptameric antigenic sequence inserted into a loop of the protein scaffold, mimicking a pre-determined sequence of a native protein, can be selected by solid phase conformer antibody and receptor via ribosome display. High affinity binding of B-cell epitopes selected from the random aptameric library with antibodies to native pre-determined B-cell epitope of a native protein can be optimized by molecular evolution with error-prone RT-PCR by ribosome display.
Owner:SWEY SHEN ALEXCHEN
Human genetic engineering antibody TRD 109 as well as preparation method and application thereof
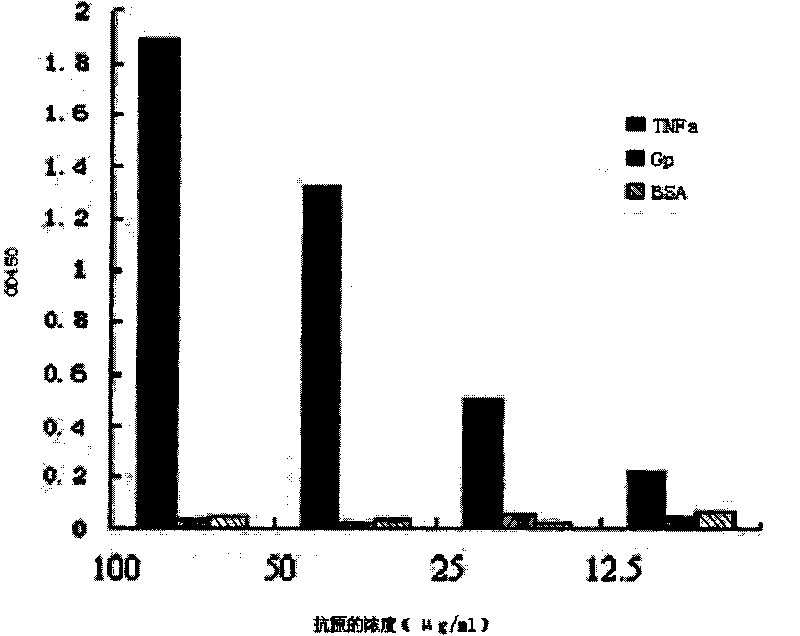
The invention provides a human genetic engineering antibody TRD 109 which is screened by utilizing a molecular biological technology-ribosome display technology, aims to TNF-alpha and realizes high-efficiency expression of the antibody to a prokaryotic system. A biological characteristic research demonstrates that the TRD 109 is a human genetic engineering antibody which has high affinity, better stability, simple structure and easy construction and can specifically neutralize the TNF-alpha, inhibit the generation of multiple kinds of cell factors, block the generation and development of AR in the source and is a human anti TNF-alpha antibody which can reduce the infiltration of eosinophils in a mouse nasal mucous membrane and relieve mouse allergic rhinitis symptom; and a gene and a gene product of the human anti TNF-alpha antibody can be used for preparing a medicaments for diagnosing and treating diseases caused by overexpression of the TNF-alpha, such as preparing a medicament for treating diseases including allergic rhinitis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
In vitro molecular directed evolution method for reshaping antibody
InactiveCN1289668CFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionSingle-Chain AntibodiesAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to an in vitro molecular directed evolution method for reshaping antibody, which integrates ribosome displaying technology with DNA reorganization technology by designing reshaped antibody molecules, thus directly obtaining the extracorporal molecules of the single-chain antibody reshaped orientation.
Owner:BEIJING ABT GENETIC ENG TECH +1
Diethylstilbestrol single-chain antibody screening method and purpose of diethylstilbestrol single-chain antibody
InactiveCN103130893AStrong specificitySequence clearImmunoglobulins against hormonesBiological testingDiseaseNatural antibody
The invention relates to a diethylstilbestrol single-chain antibody screening method and a purpose of a diethylstilbestrol single-chain antibody, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The single-chain antibody is screened from a ribosome showing mouse source natural antibody base and is subjected to soluble expression. The invention further relates to a diethylstilbestrol antibody screening method with a ribosome showing technology. The diethylstilbestrol single-chain antibody screened through the method can be used for pollution detection, development of immune quick test kits used for quick test of diethylstilbestrol residual and treatment of relevant diseases, and a foundation is laid for future detection and research on the diethylstilbestrol single-chain antibody.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Method and kit for generating high affinity binding agents
A combined ribosome-display and phage-display method and kit for carrying out the method are provided. The method includes screening a ribosome-display library of binding agents to identify binding agents that interact with one or more target molecules of interest, converting the RNA encoding the binding agents to a phage-display format by amplification and primer extension, and the screening the phage-display library to enrich for binding agents that interact with one or more target molecules of interest.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Aptameric IgE peptides in a protein scaffold as an allergy vaccine
ActiveUS8865179B2Reduce physical stressEnhances viability of assaying immunogenicityImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFc(alpha) receptorADAMTS Proteins
A method is disclosed wherein an antigenic B-cell epitope is discovered by in vitro transcription and translation of pre-determined sequence on thermostable protein scaffolds detected by antibodies to a native protein. Immune reactivities of IgE B-cell epitopes from pre-determined IgE sequences from the constant region, engaged in binding to high affinity IgE Fc receptors, placed in a loop of green fluorescent protein (GFP) were shown immuno-reactive with anti-IgE. Moreover, the antigenic B-cell epitope can be further optimized by molecular evolution, selected by conformer antibody and receptor on solid phase via ribosome display. Alternatively, a random aptameric antigenic sequence inserted into a loop of the protein scaffold, mimicking a pre-determined sequence of a native protein, can be selected by solid phase conformer antibody and receptor via ribosome display. High affinity binding of B-cell epitopes selected from the random aptameric library with antibodies to native pre-determined B-cell epitope of a native protein can be optimized by molecular evolution with error-prone RT-PCR by ribosome display.
Owner:SWEY SHEN ALEXCHEN
Citrinin-resisting single-chain antibody as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105037539ASimplify the screening processSimplify the manufacturing processImmunoglobulins against fungi/algae/lichensBiological testingBiotechnologyAntigen
The invention provides a single-chain antibody resisting citrinin. Artificial coupling antigen citrinin-BSA / BSA and citrinin-OVA / OVA antigen are combined to perform affinity screening for an antibody-ribosome-mRNA triplet complex, an RT-PCR method is used for recovering an affinity screened product, a ribosome display technology is used for screening a single-chain antibody, a screened gene fragment is expressed by virtue of pronucleus and then is identified by utilizing an ELISA method to obtain the citrinin-resisting single-chain antibody. The screening and preparation process of the antibody is greatly simplified, interference of a protein carrier is alleviated, and a probability for obtaining a specificity single-chain antibody is increased; the recovery yield is increased. Due to renal toxicity, teratogenicity and carcinogenicity, the citrinin poses a severe threat to the health of human beings and livestock, and the citrinin-resisting single-chain antibody can be used as a reagent for detecting citrinin pollution residue in an agricultural product and a food sample.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Protein discovery using intracellular ribosome display
ActiveUS9879252B2Efficient foldingImprove stabilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementIntracellularMolecular binding
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a protein that binds to a target molecule and has intracellular functionality. This method includes providing a construct comprising a deoxyribonucleic acid molecule encoding the protein which binds to the target molecule, with the deoxyribonucleic acid molecule being coupled to a stall sequence. A host cell is transformed with the construct and then cultured under conditions effective to form, within the host cell, a complex of the protein whose translation has been stalled, the mRNA encoding the protein, and ribosomes. The protein in the complex is in a properly folded, active form and the complex is recovered from the cell.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
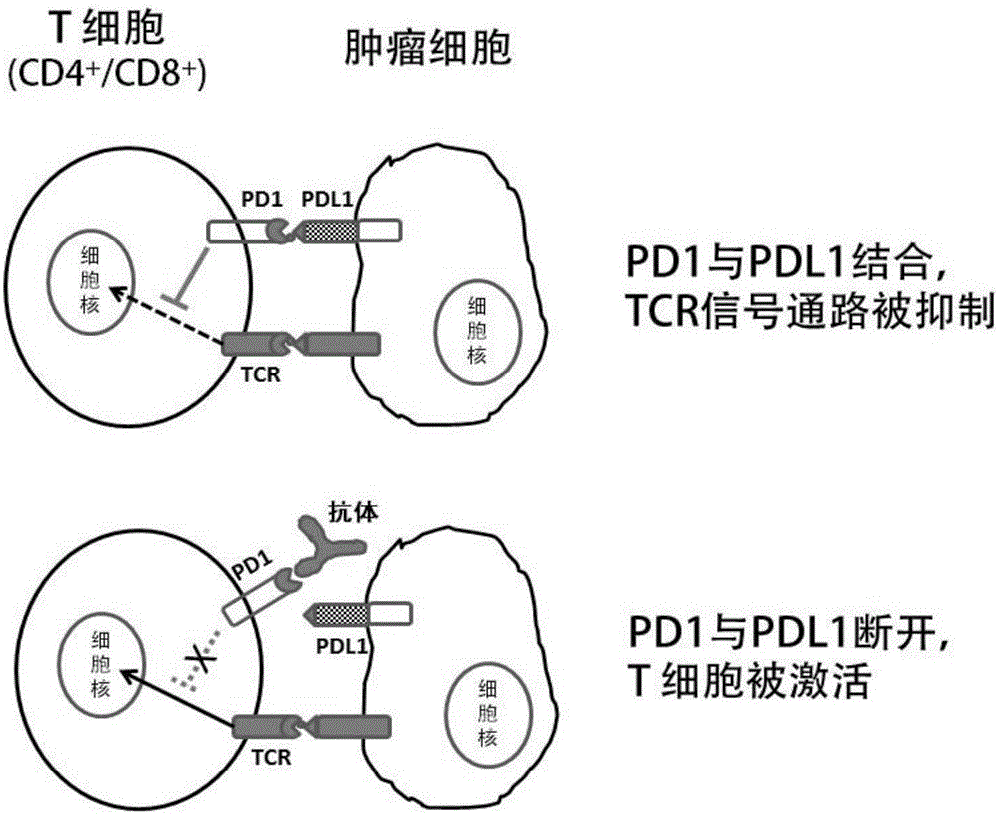
Anti-human PD-1 protein antibody as well as encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN106699887AEffective treatmentHigh affinityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesHeavy chain
The invention discloses an anti-human PD-1 protein antibody as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. The antibody comprises a heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region, wherein amino acid sequences of three hypervariable regions CDRH1, CDRH2 and CDRH3 of the heavy chain variable region are shown as GFTFSSYAMS, AISGSGGTTYYADSVKG and AWAPFVNSIVVVTANDL respectively; amino acid sequences of three hypervariable regions CDRL1, CDRL2 and CDRL3 of the light chain variable region are shown as RASQGISTWLA, AASSLQS and QQANSFPI respectively. A human single-chain antibody library is established, single-chain antibodies are screened with a ribosome display technology, and the obtained anti-human PD-1 protein antibody can be specially bonded with human PD-1 protein, has high affinity, can be used for detecting cells expressing PD-1, can be used as a fully-human anti-human PD-1 antibody for treating human diseases and effectively prevents and treats tumor diseases.
Owner:杭州贝颐药业有限公司
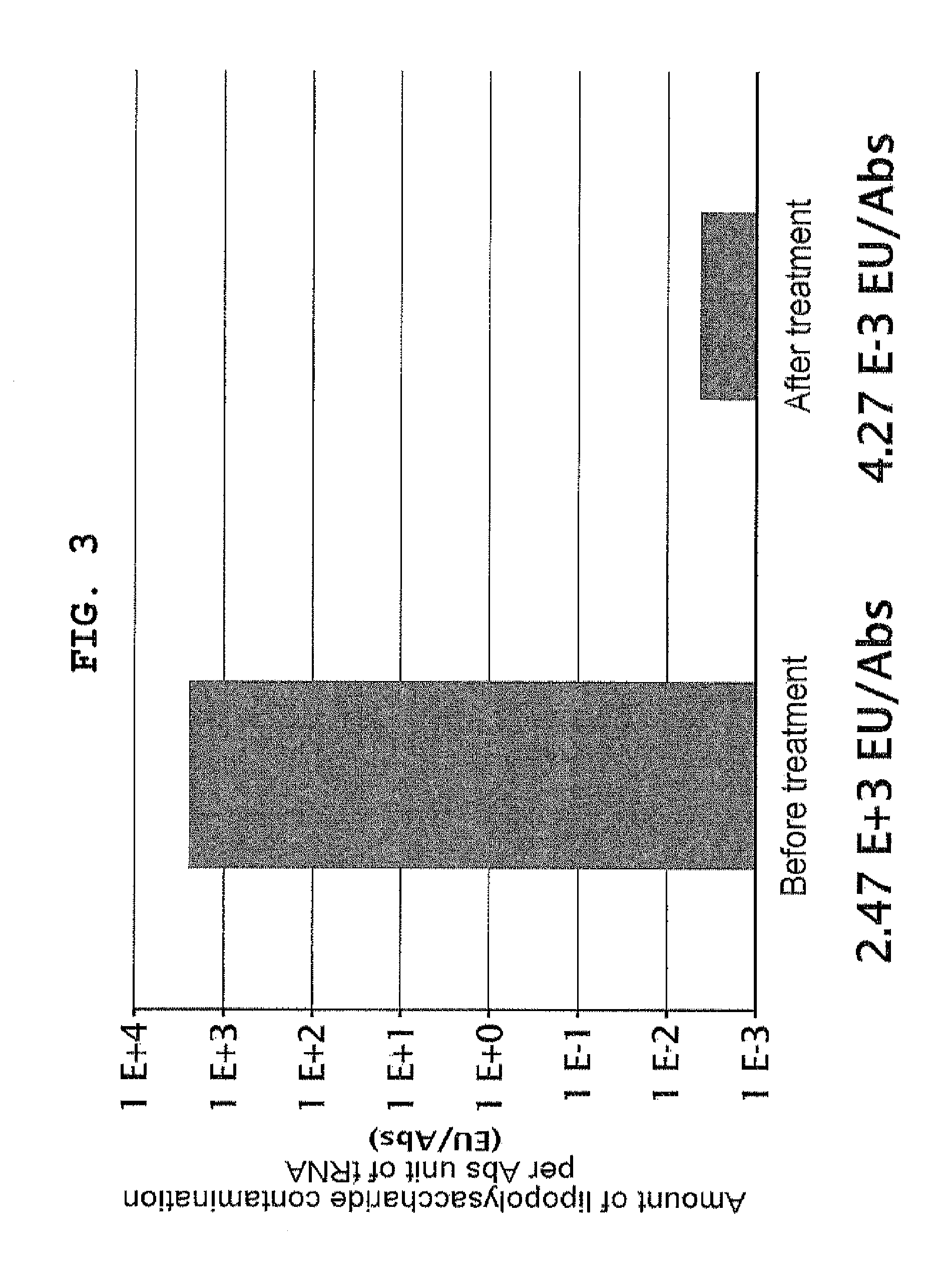
Composition for synthesizing protein with reduced lipopolysaccharide contamination, method for producing protein using said composition
ActiveUS9175327B2Reduce pollutionBackground due to the non-specific binding is reducedSugar derivativesMicroorganismsCell-free protein synthesisContamination
According to the present invention, a composition possessing cell-free protein synthesis activity with reduced contaminating lipopolysaccharide, and a method for producing a protein using the same are provided. When ribosome display is performed using the composition and method for protein production of the present invention, the background that is caused by non-specific binding is reduced, so that a nucleic acid that encodes the desired polypeptide can be selected with high accuracy and high efficiency.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
ph selective anti-tumor polypeptide and its application
InactiveCN103936834BHigh selectivityPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesSide chainMicroscopic observation
The invention relates to a high-efficiency pH-selective anti-tumor polypeptide and its application, and belongs to the technical field of research and development and application of anti-tumor drugs. The present invention uses ribosome display technology to construct a series of histidine-rich polypeptides with membrane cleavage and anti-tumor activity, and uses the special acidity coefficient of histidine imidazole side chain to construct a series of polypeptides that are effective for normal physiological conditions and tumors. Selective anti-tumor polypeptides in characteristic acidic conditions. They have killing effects on both lung cancer cells and breast cancer cells, and can selectively kill tumor cells under acidic conditions; inhibit the growth of tumors in mouse xenograft models, especially highly selectively inhibit tumor cells under acidic conditions Tumor growth. Through microscope observation, lactate dehydrogenase experiment, fluorescence quenching and polypeptide circular dichroism, it is proved that these polypeptides increase their permeability by inserting and cleaving the cell membrane, resulting in decreased cell activity and death.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Human genetic engineering antibody TRD 109 as well as preparation method and application thereof
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Ribosome display technology-based rabbit monoclonal antibody preparation method
The invention discloses a rabbit monoclonal antibody preparation method. The preparation method is characterized in that a ribosome display technology is adopted to prepare a rabbit monoclonal antibody, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out PCR amplification on the gene library of the target antibody, adding a promoter, a ribosome binding site and a stem loop, carrying out incubation in a cell-free translation system with couple transcription and translation to make the translation product of the target antibody gene be displayed on the surface of the ribosome and to form an mRNA-protein-ribosome ternary complex, directly screening the target ribosome from the ternary complex through an immobilized target molecule by using a routine immunological detection technology, carrying out next-cycle enrichment and amplification by using RT-PCR amplification, and finally screening the target antibody with high affinity. The preparation method of the rabbit monoclonal antibody has the following advantages: 1, the method is more convenient and fast than the prior art; 2, the screened antibody can be stably reduplicated; and 3, high-flux screening can be realized in order to obtain the antibody with high affinity.
Owner:江苏佰润医疗科技有限公司 +1
12 peptide ZA for inhibiting hepatitis c virus to infect human cell and preparation method and application
InactiveCN101456901BQuick combinationPrevent invasionPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemAntigenHepacivirus
The invention discloses a dodecapeptide ZA capable of inhibiting the hepatitis C virus from infecting human body cells and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing an E2-GST fusion protein; then preparing an E2-GST fusion protein antibody; thirdly establishing a random DNA library; fourthly preparing a ribosome library; and fifthly screening the polypeptide bonded with the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein through the ribosome display library so as to obtain the dodecapeptide (ZA) specially bonded with the E2 protein. Due to the high affinity of the polypeptide ZA with the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein, the polypeptide ZA can remarkably alleviate the intrusion of HCV into the human body cells and DC cells, inhibit the integration of the E2 protein with human body cells, and have a high inhibition capacity. The dodecapeptide ZA is used for preparing the medicines capable of treating and preventing hepatitis C virus infection. The polypeptide is applied to a kit for detecting the hepatitis C virus envelope antigen.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com