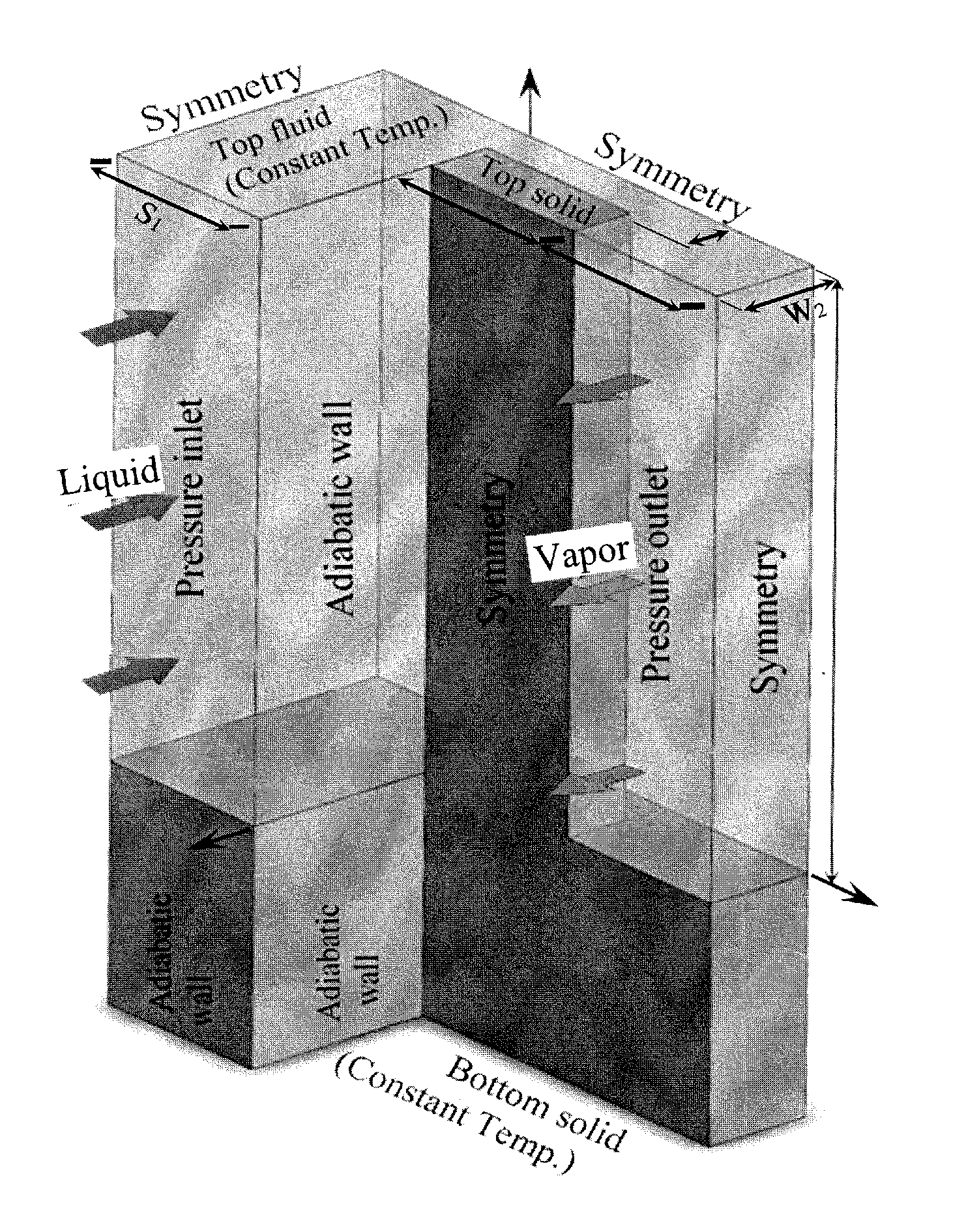
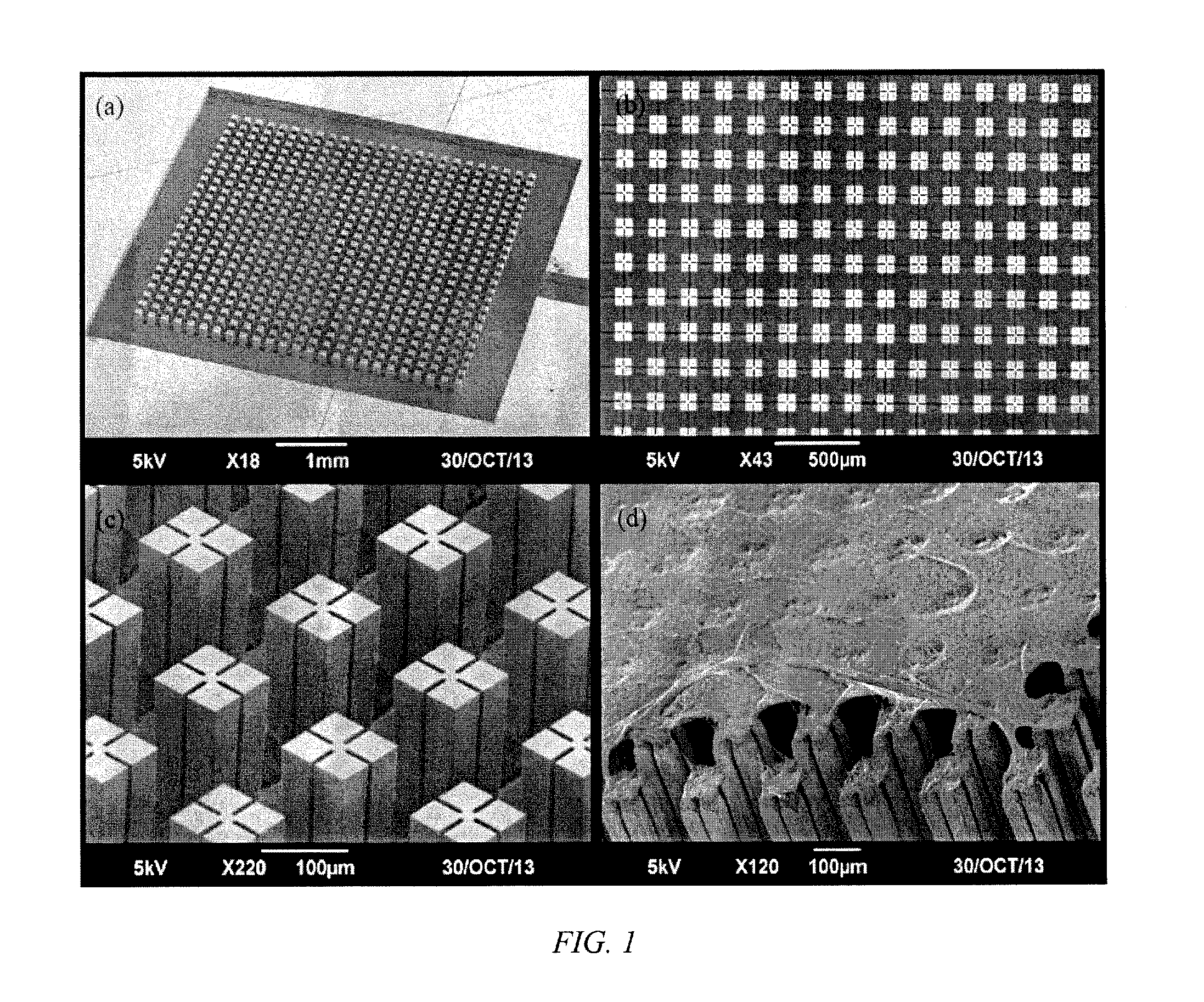
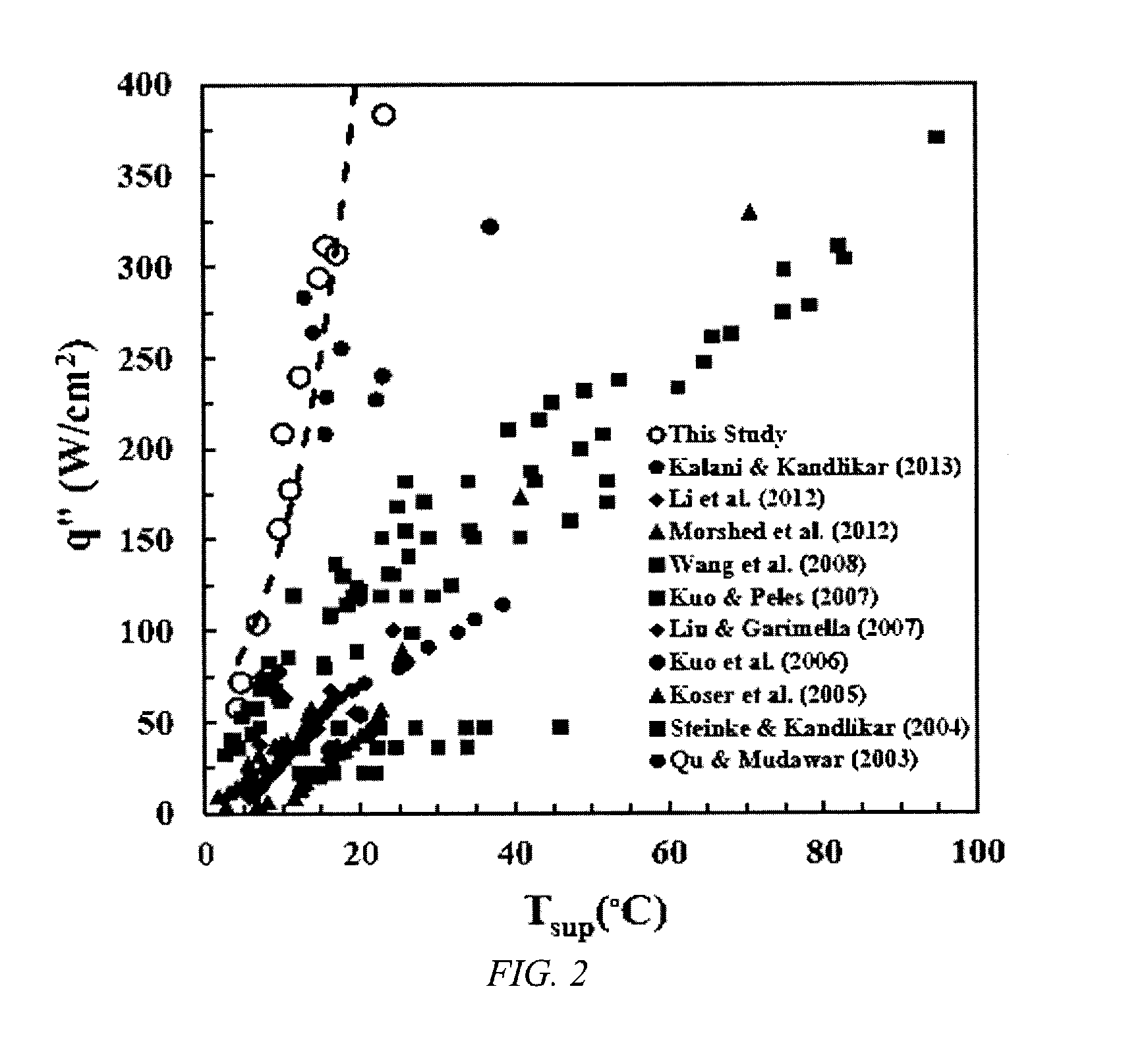
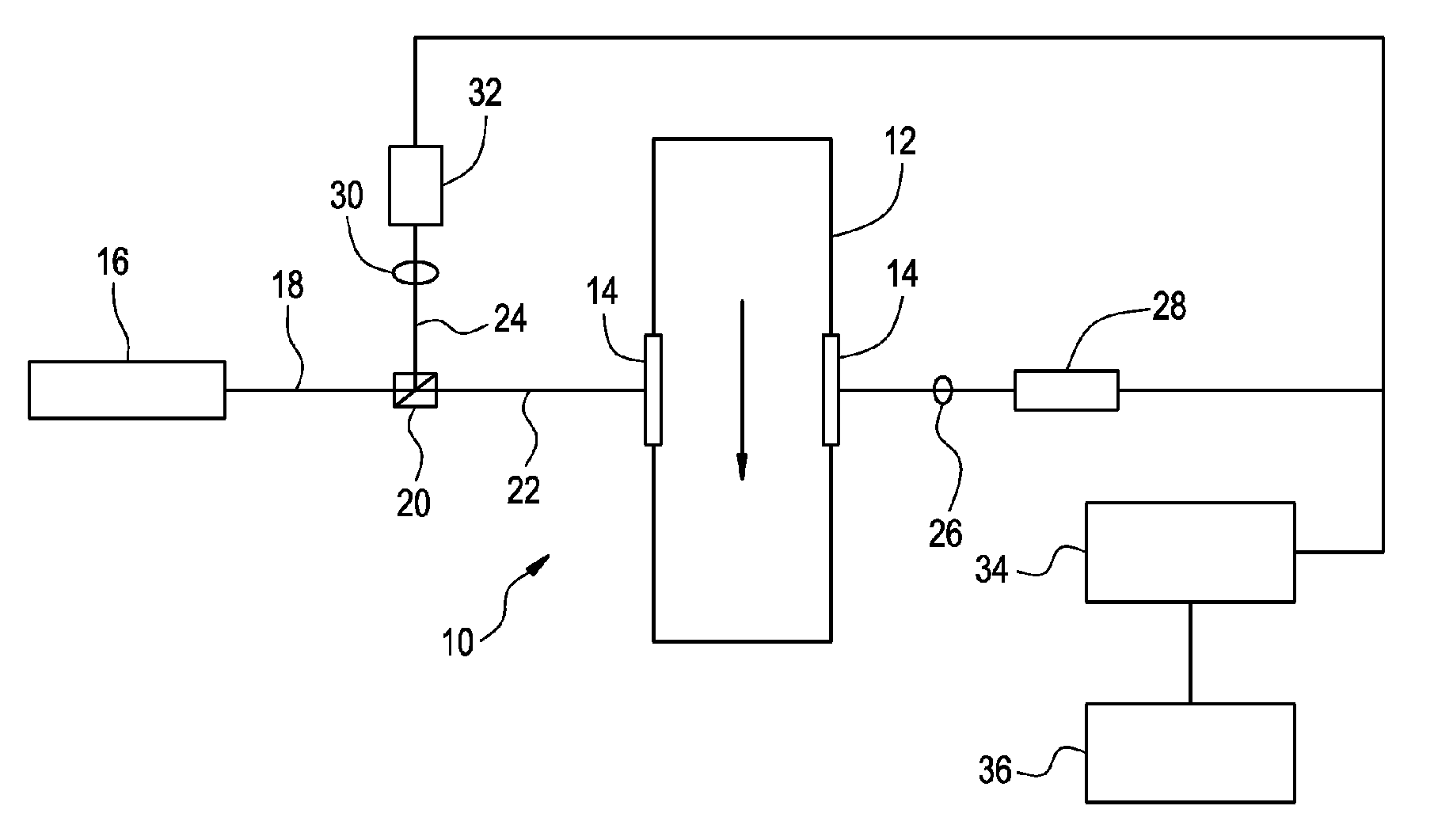
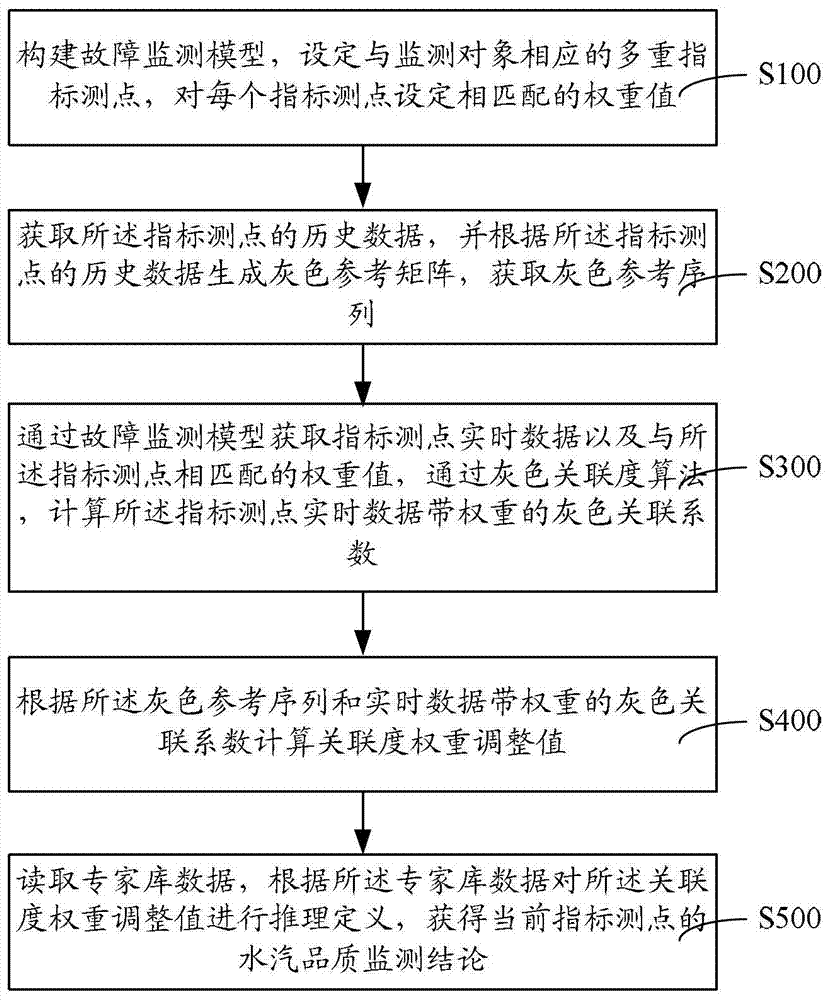
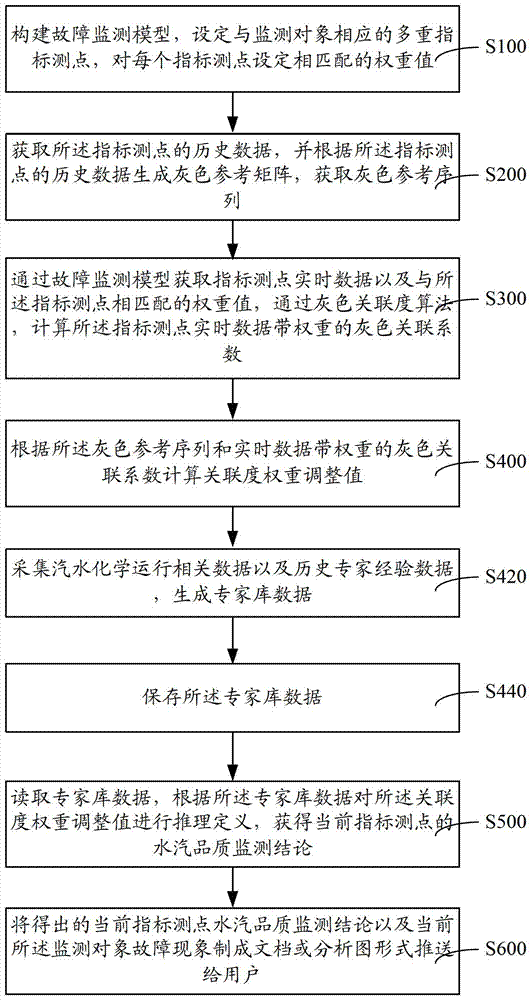
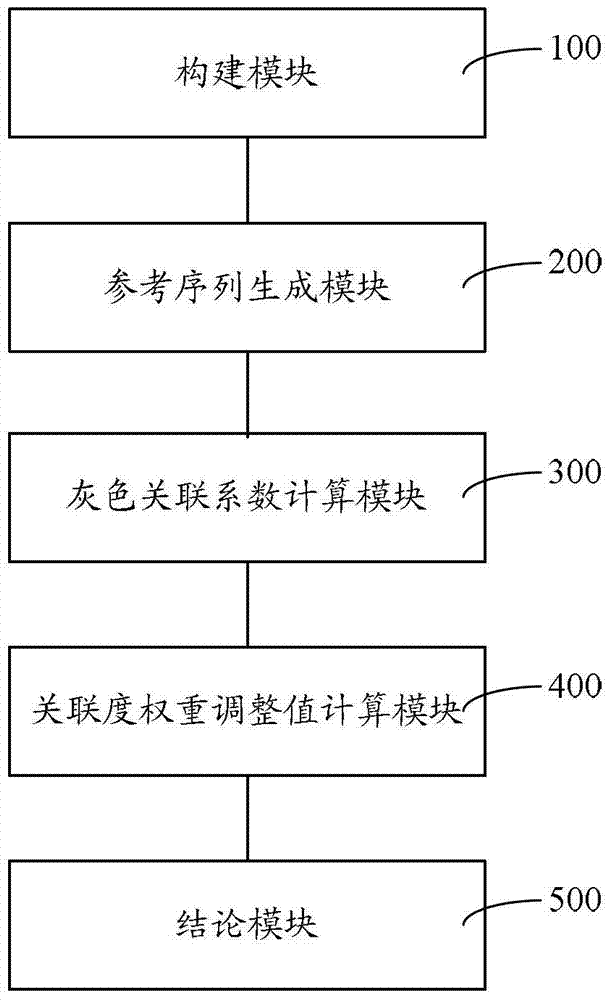
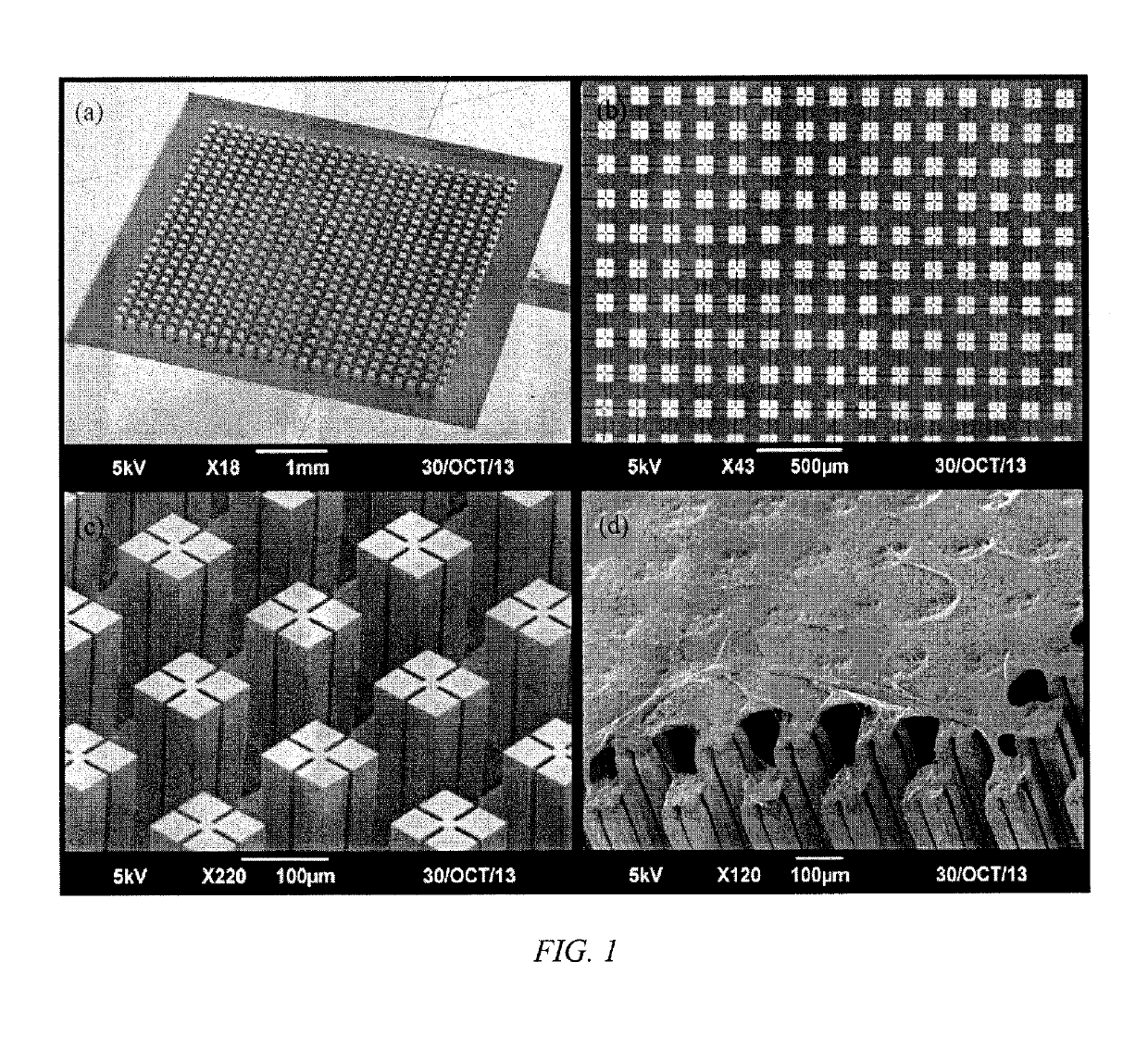
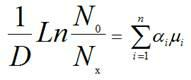Patents
Literature
55 results about "Vapor quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
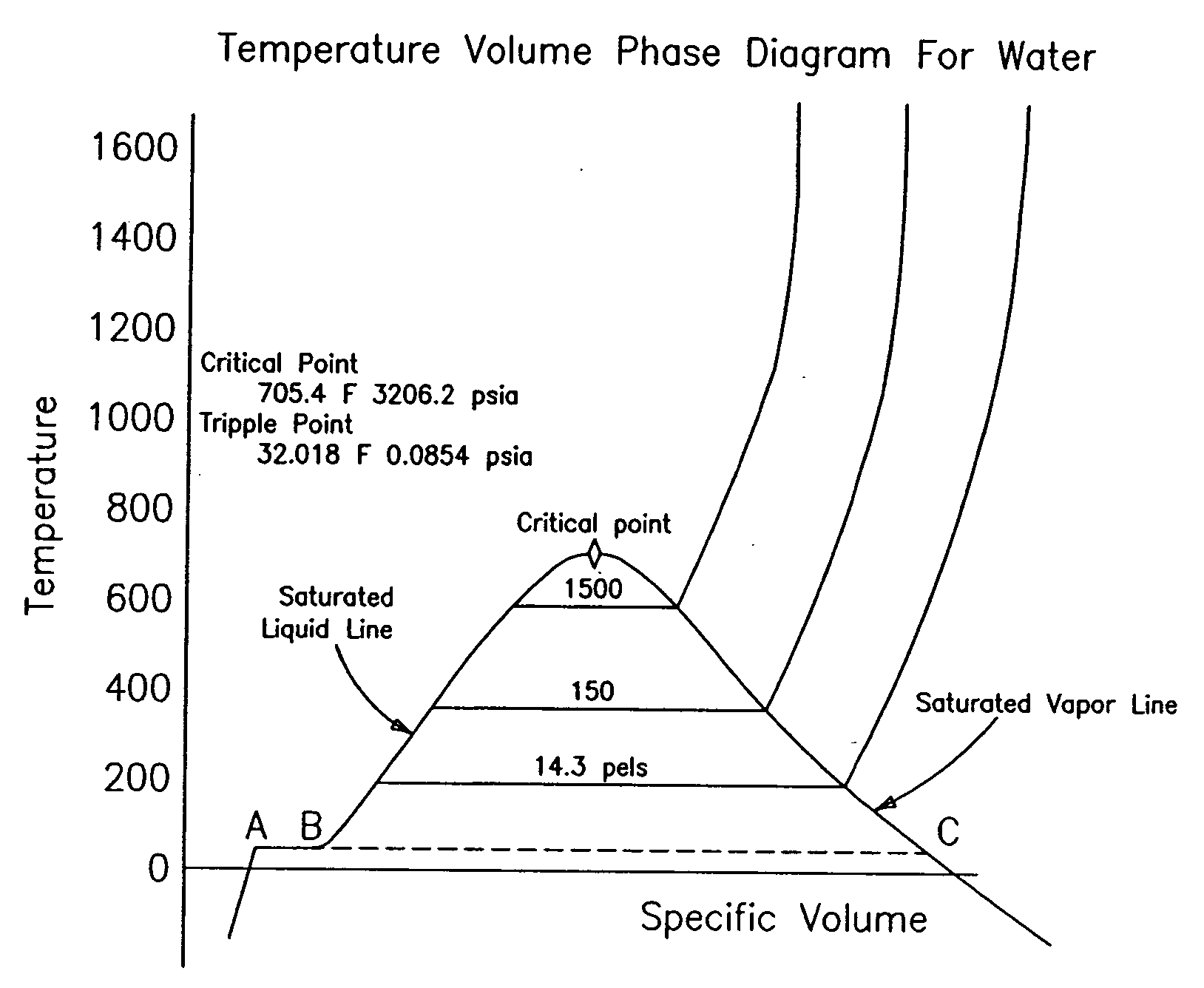
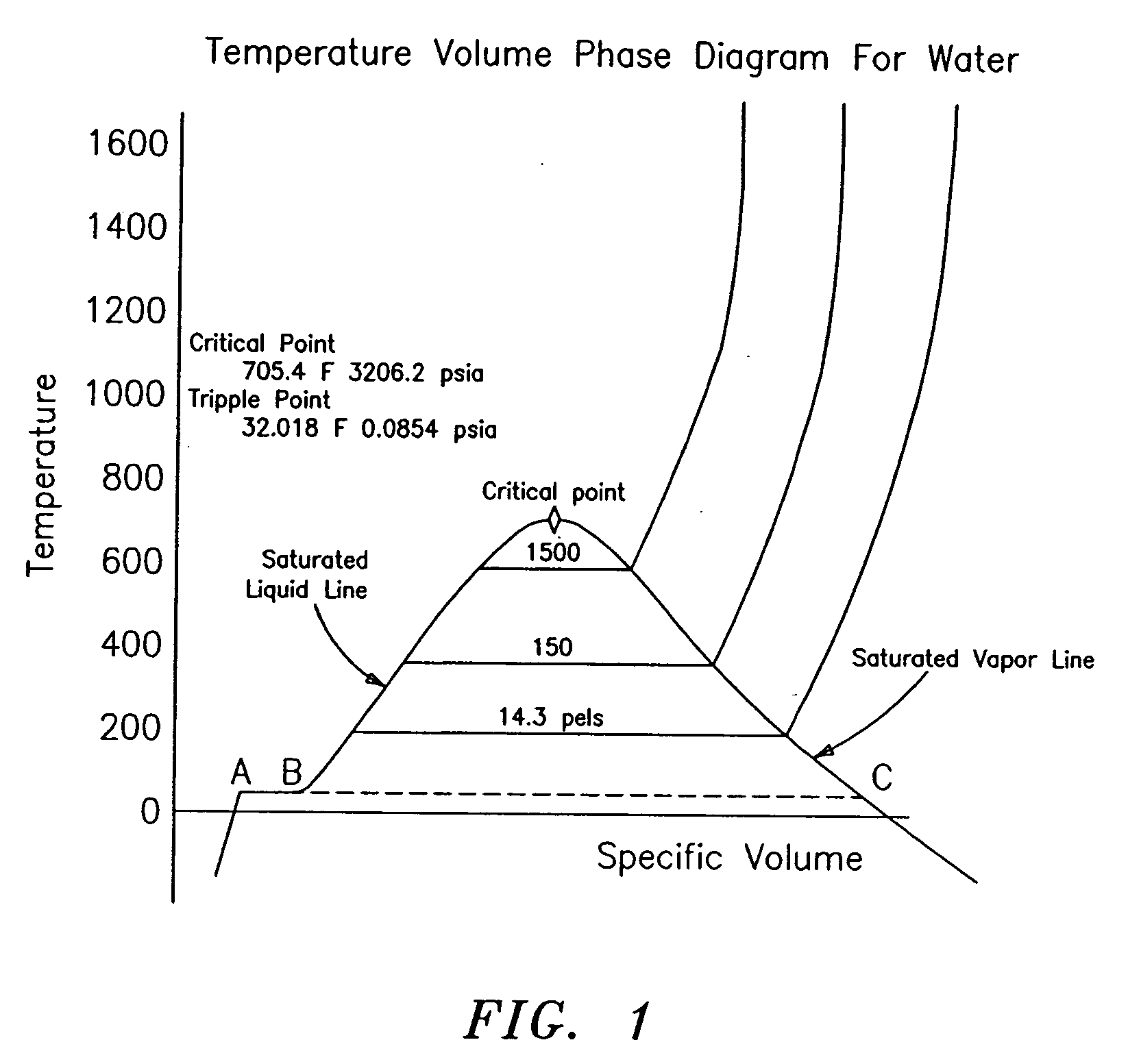
In thermodynamics, vapour quality is the mass fraction in a saturated mixture that is vapour; in other words, saturated vapour has a "quality" of 100%, and saturated liquid has a "quality" of 0%. Vapour quality is an intensive property which can be used in conjunction with other independent intensive properties to specify the thermodynamic state of the working fluid of a thermodynamic system. It has no meaning for substances which are not saturated mixtures (for example, compressed liquids or superheated fluids).
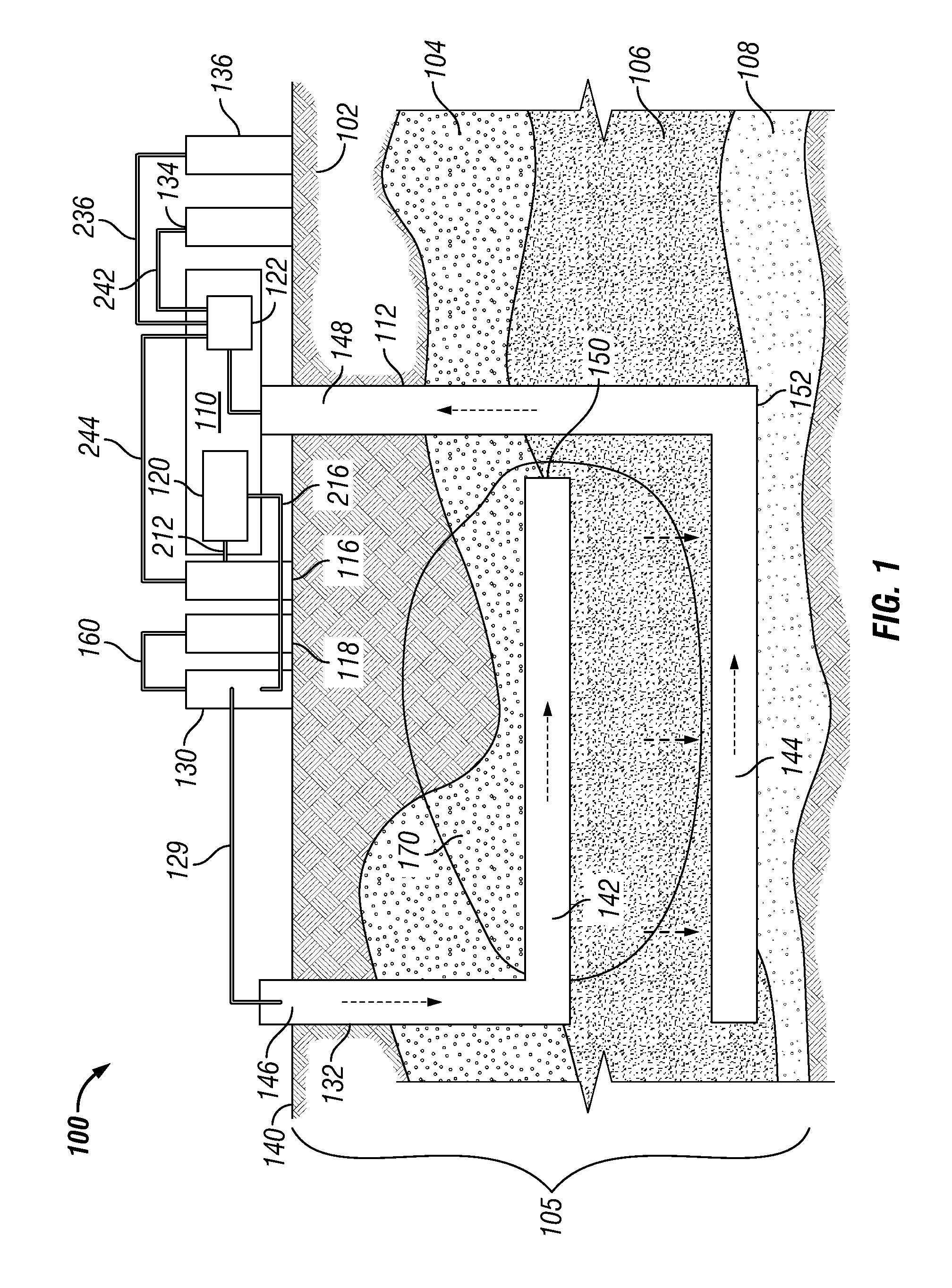
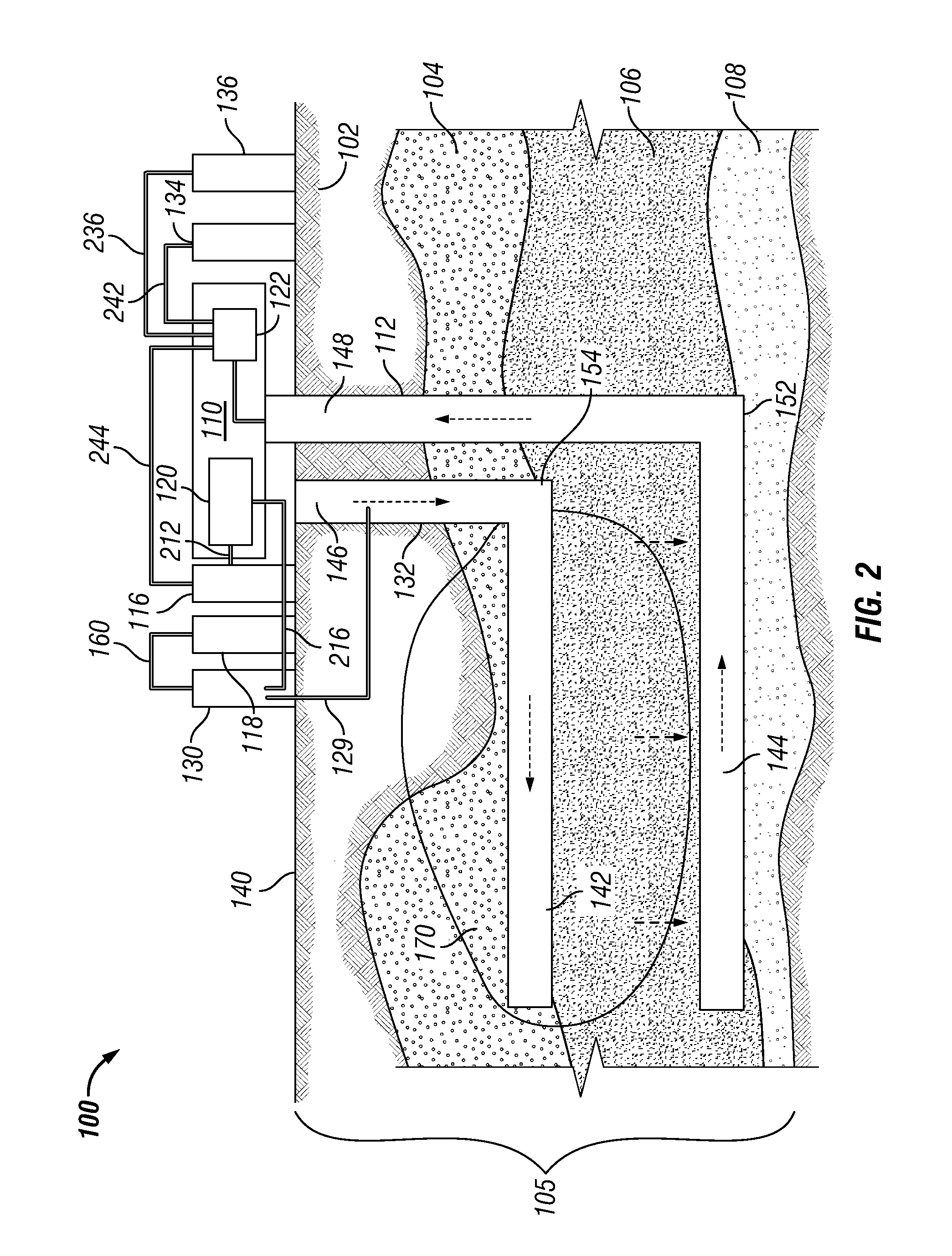
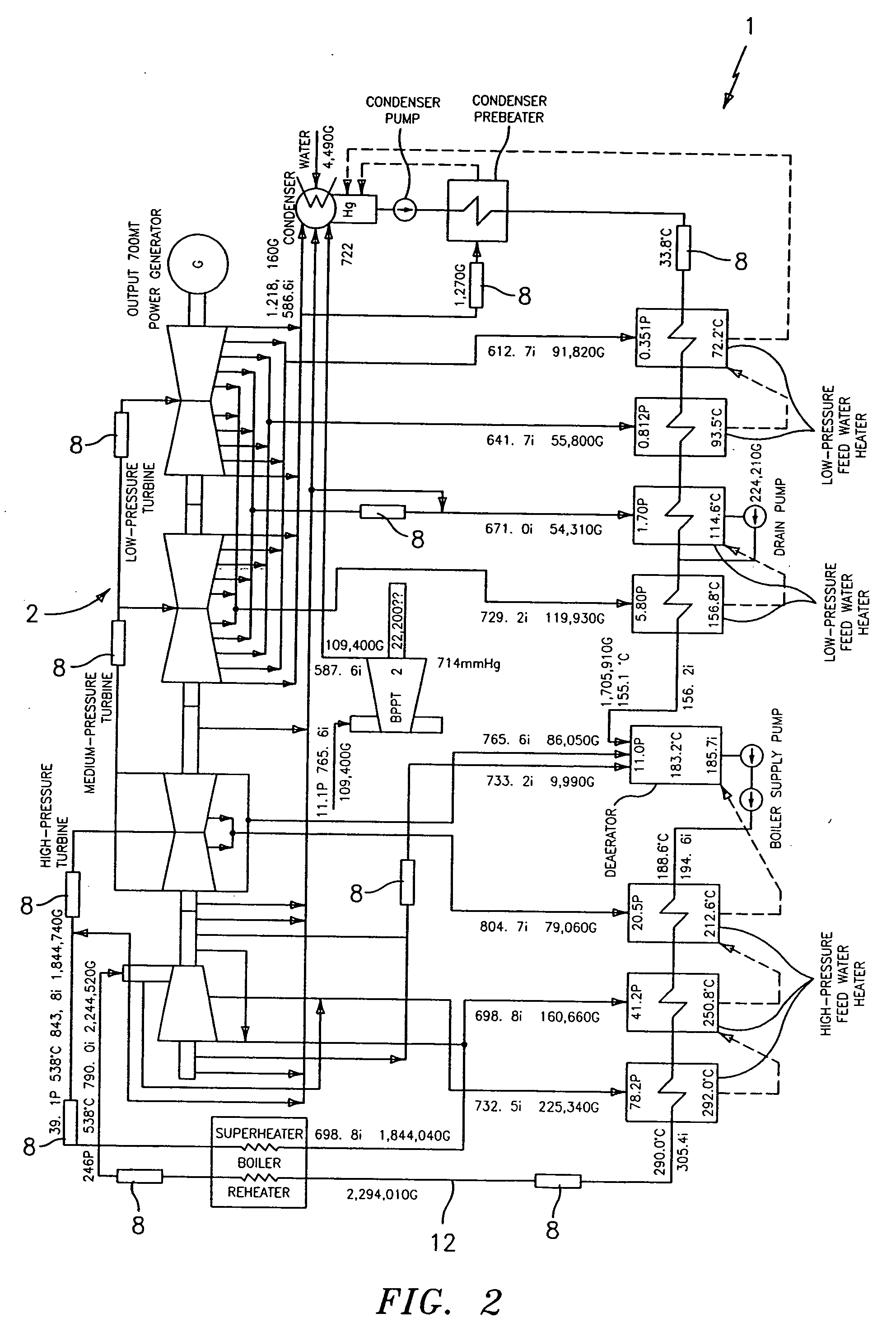
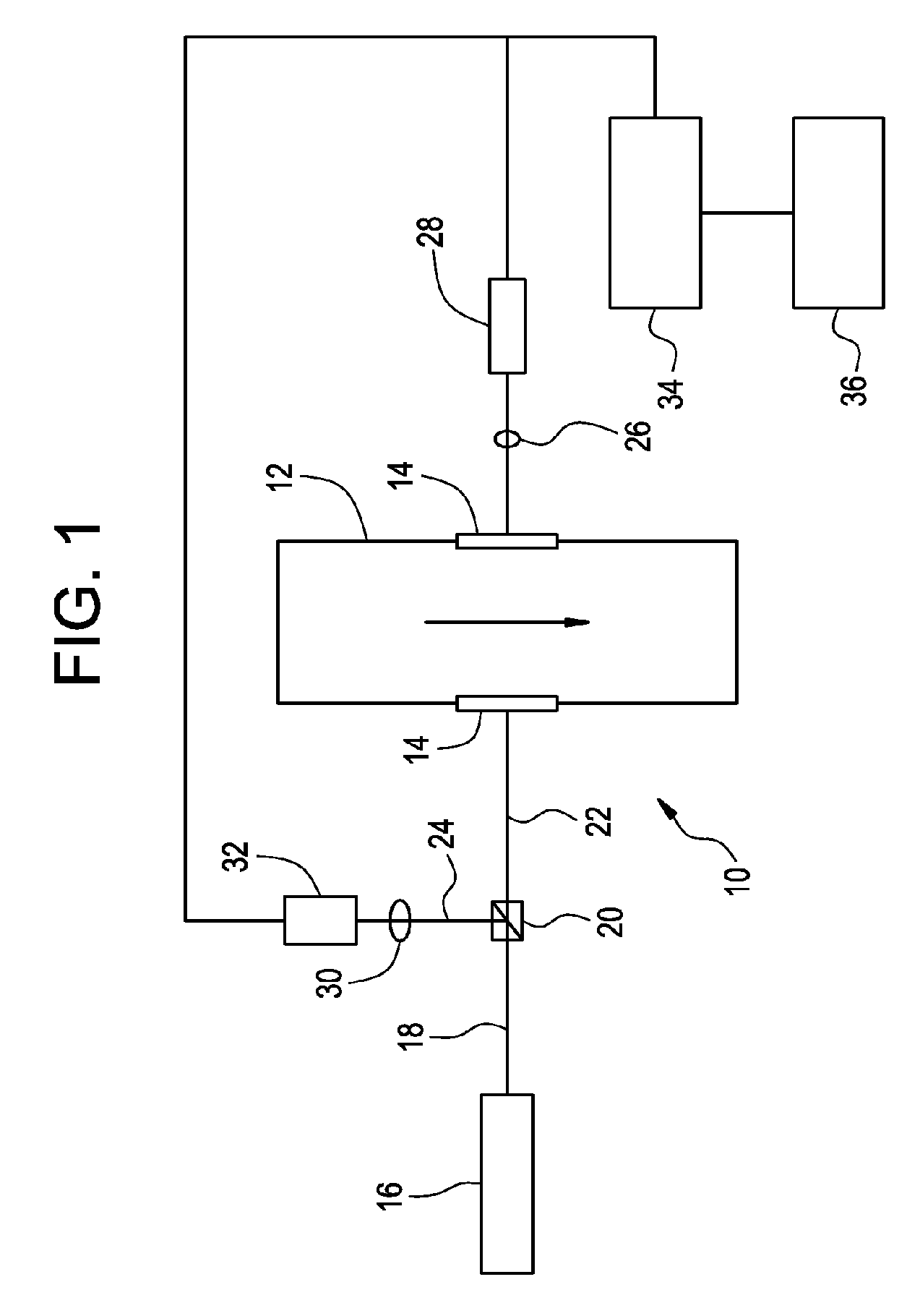
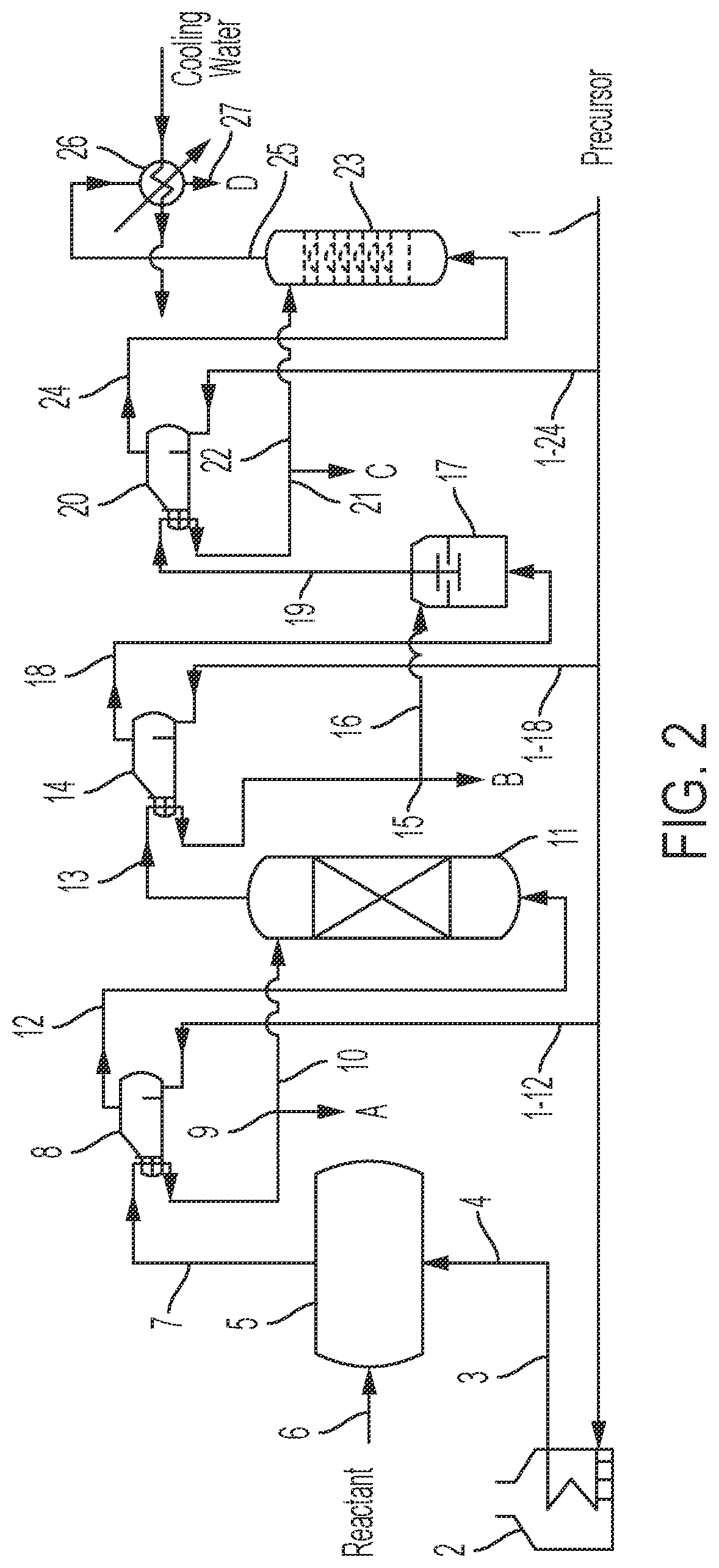
Steam flow measuring device and method
ActiveCN102435245AFluid speed measurementVolume/mass flow by differential pressureComputerized systemVolumetric Mass Density
The invention relates to a steam flow measuring device and method for measuring steam flow and heat values on time. The device mainly comprises a monoenergetic gamma sensor, a Venturi flow meter, a temperature transmitter, a pressure transmitter, a steam inlet connecting pipe section and a steam outlet connecting pipe section, and is used for effectively measuring saturated water amount and saturated steam amount of steam in real time. The measuring method comprises the following steps of: measuring section saturated steam dryness by using the monoenergetic gamma sensor; measuring the total steam mass flow by using the Venturi flow meter; and considering possible slippage (relative speed difference) between saturated steam and saturated water. A gas-liquid annular flow slippage analytic solution method is adopted, so that the saturated steam amount, saturated water amount and corresponding heat values can be computed in real time by using a computer system. By adopting the measuring method, steam and liquid phases in steam can be distinguished and measured directly. Compared with the conventional single-phase measuring and density correcting method, the method has the advantages of no additional error, no influence by the flow form and gas-liquid phase change and higher measuring accuracy.
Owner:LANZHOU HAIMO TECH CO LTD
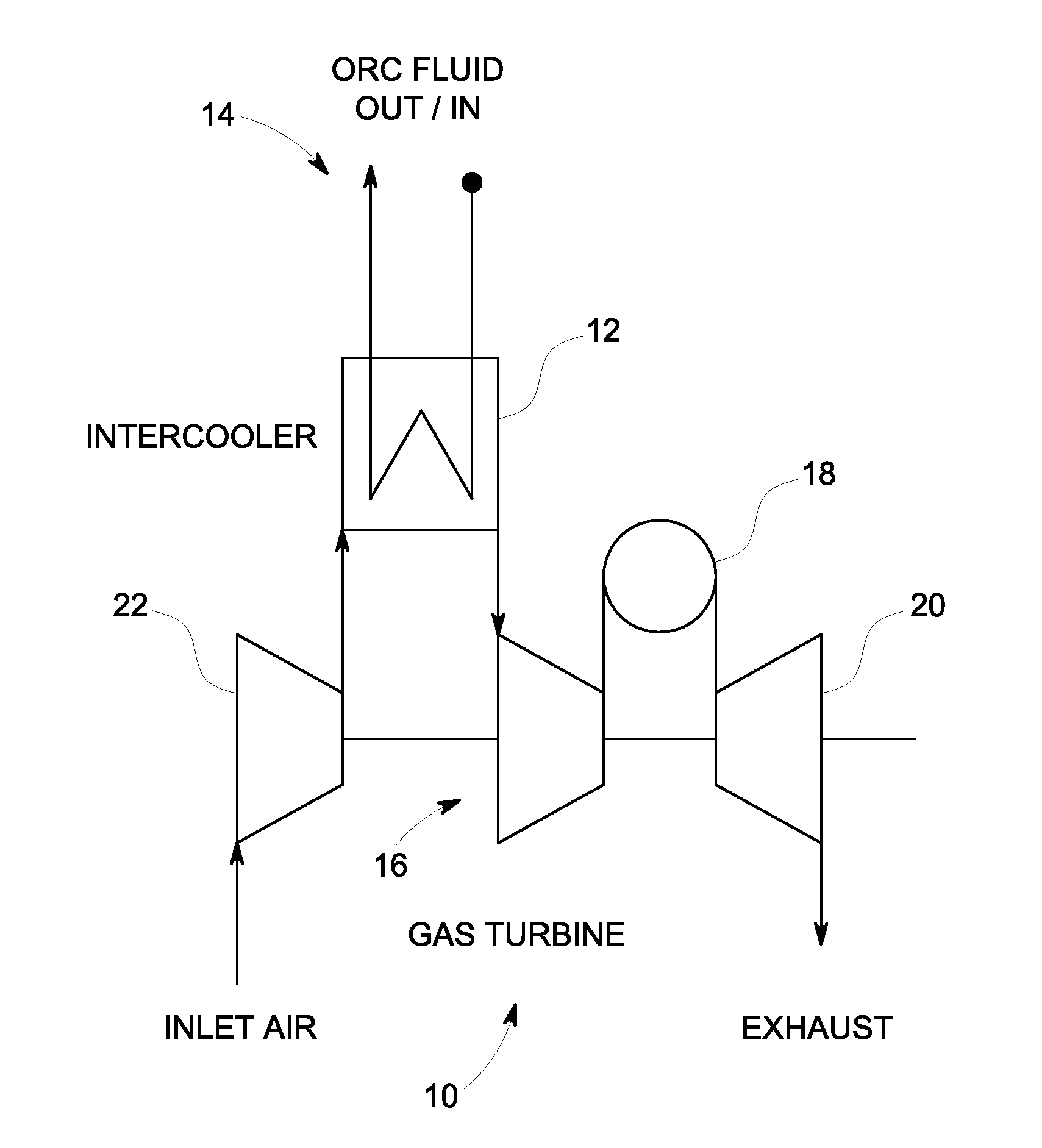
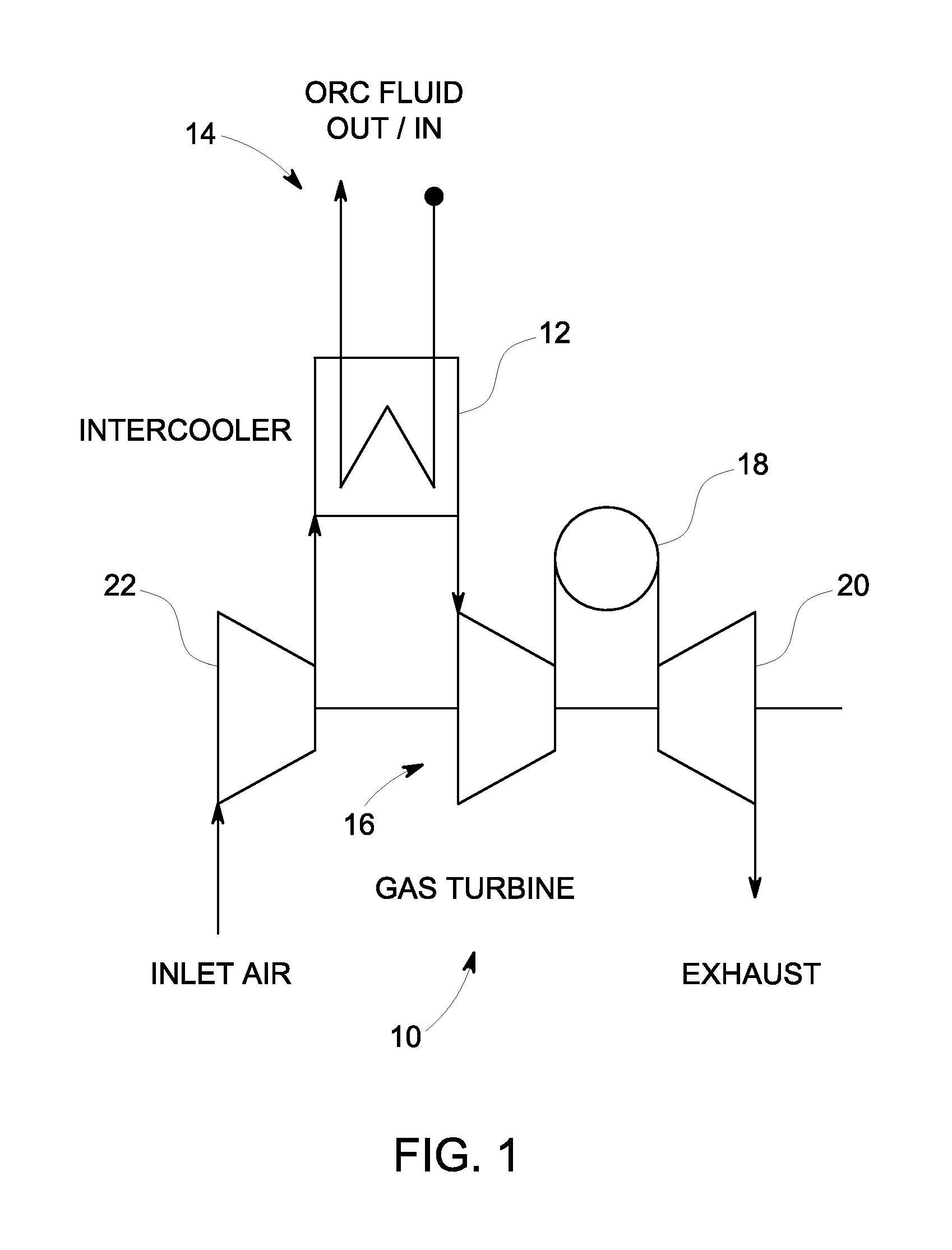
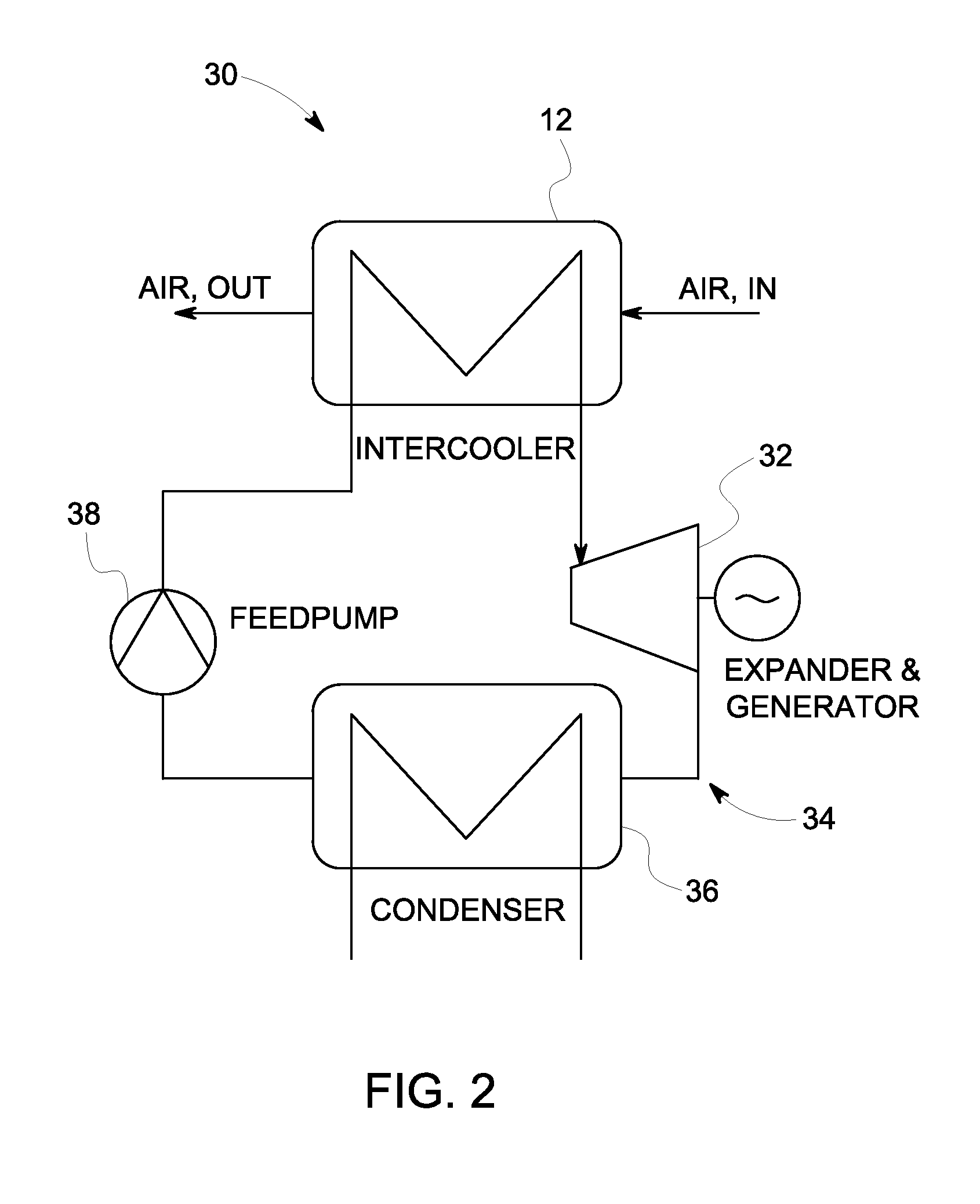
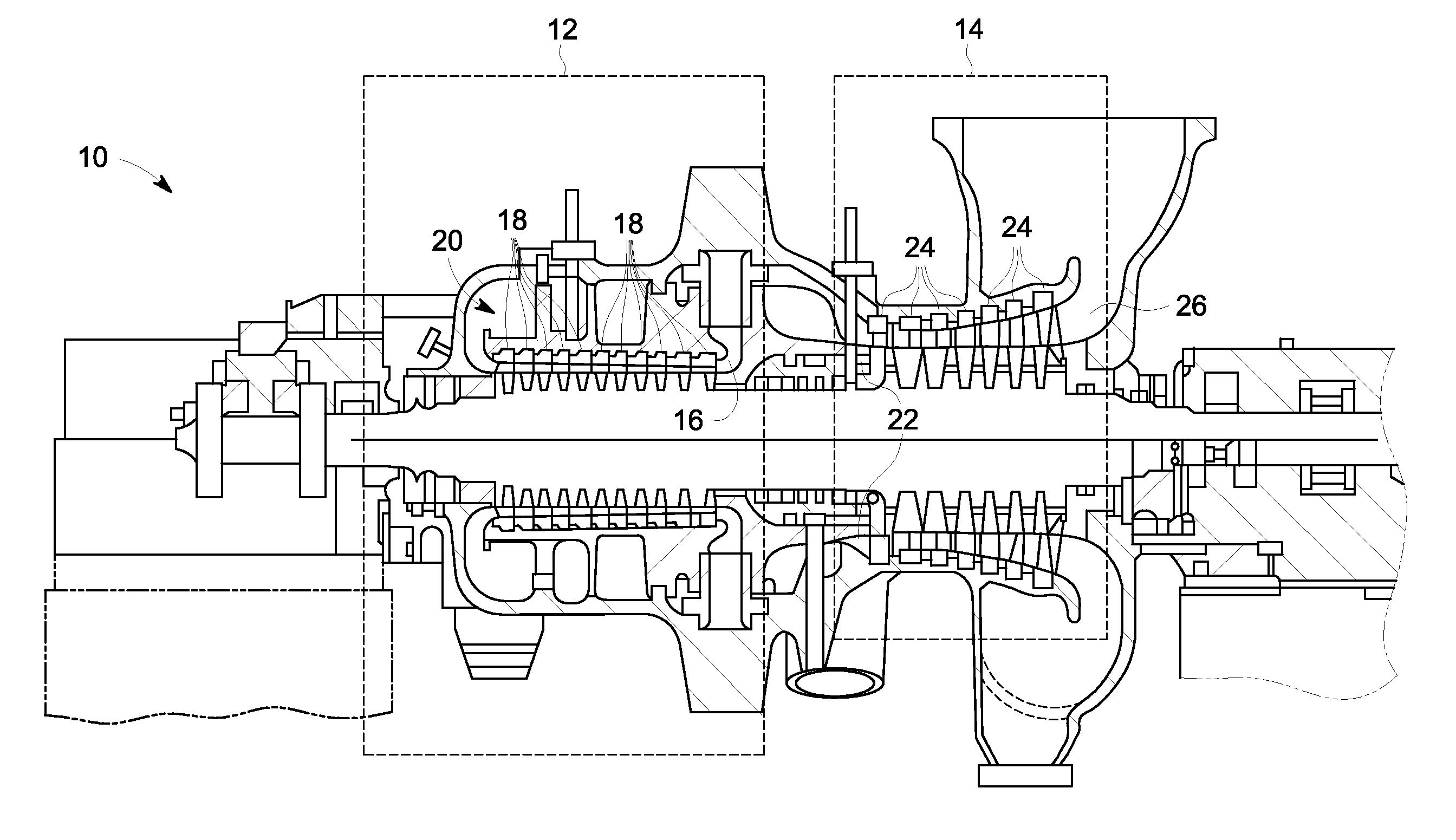
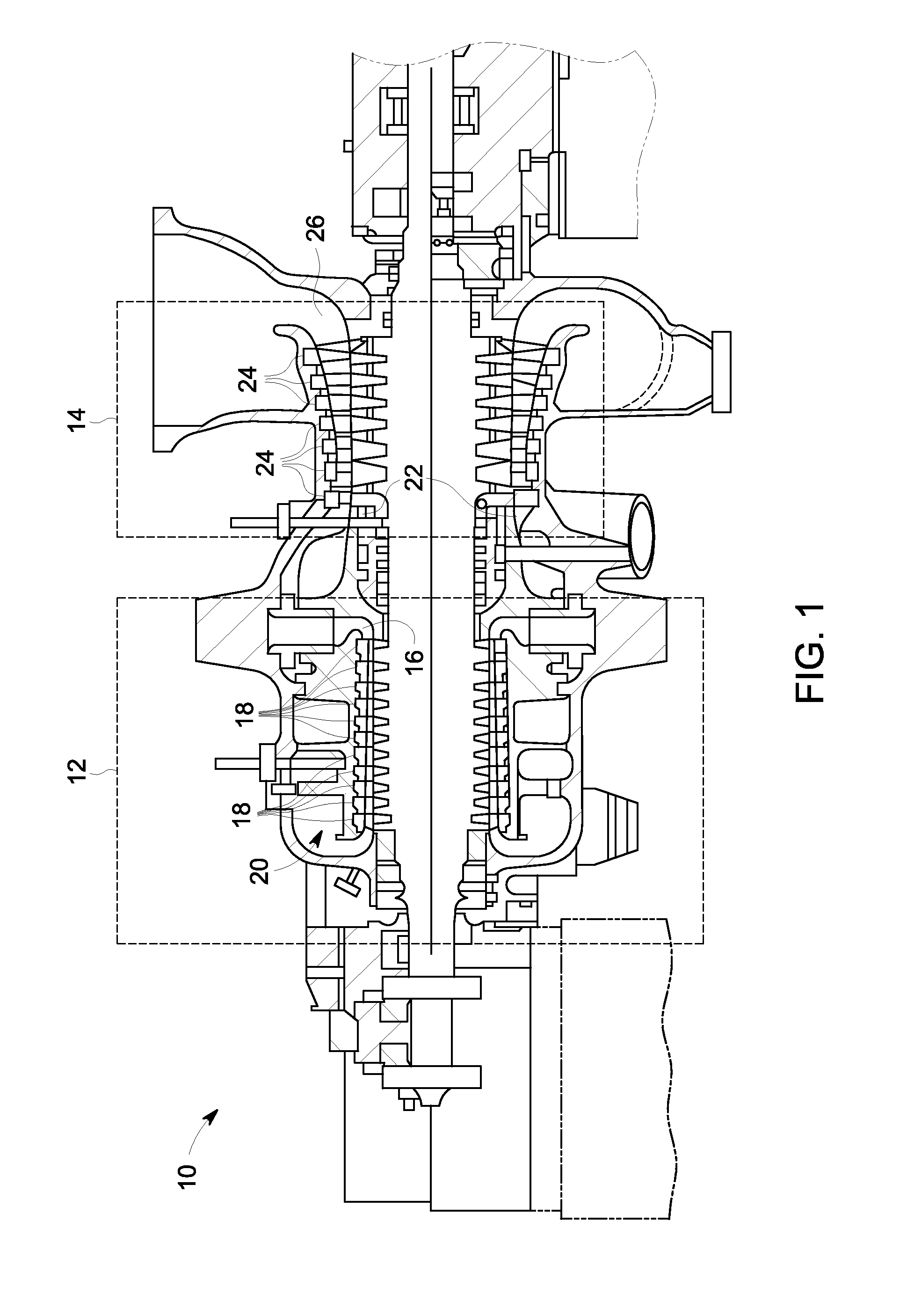
Gas turbine intercooler with tri-lateral flash cycle
InactiveUS20120216502A1Improve steaming qualityElectric power generatedGas turbine plantsSteam engine plantsIntercoolerVapor quality
A gas turbine intercooler operates to heat a predetermined organic fluid via heat generated by the gas turbine. The heated organic fluid remains in a partially evaporated or non-evaporated liquid phase to provide a heated organic fluid that reaches a state of saturation with a vapor quality less than unity. An expansion machine expands the heated organic fluid via a Tri-Lateral Flash cycle to increase the vapor quality and generate electrical power therefrom.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
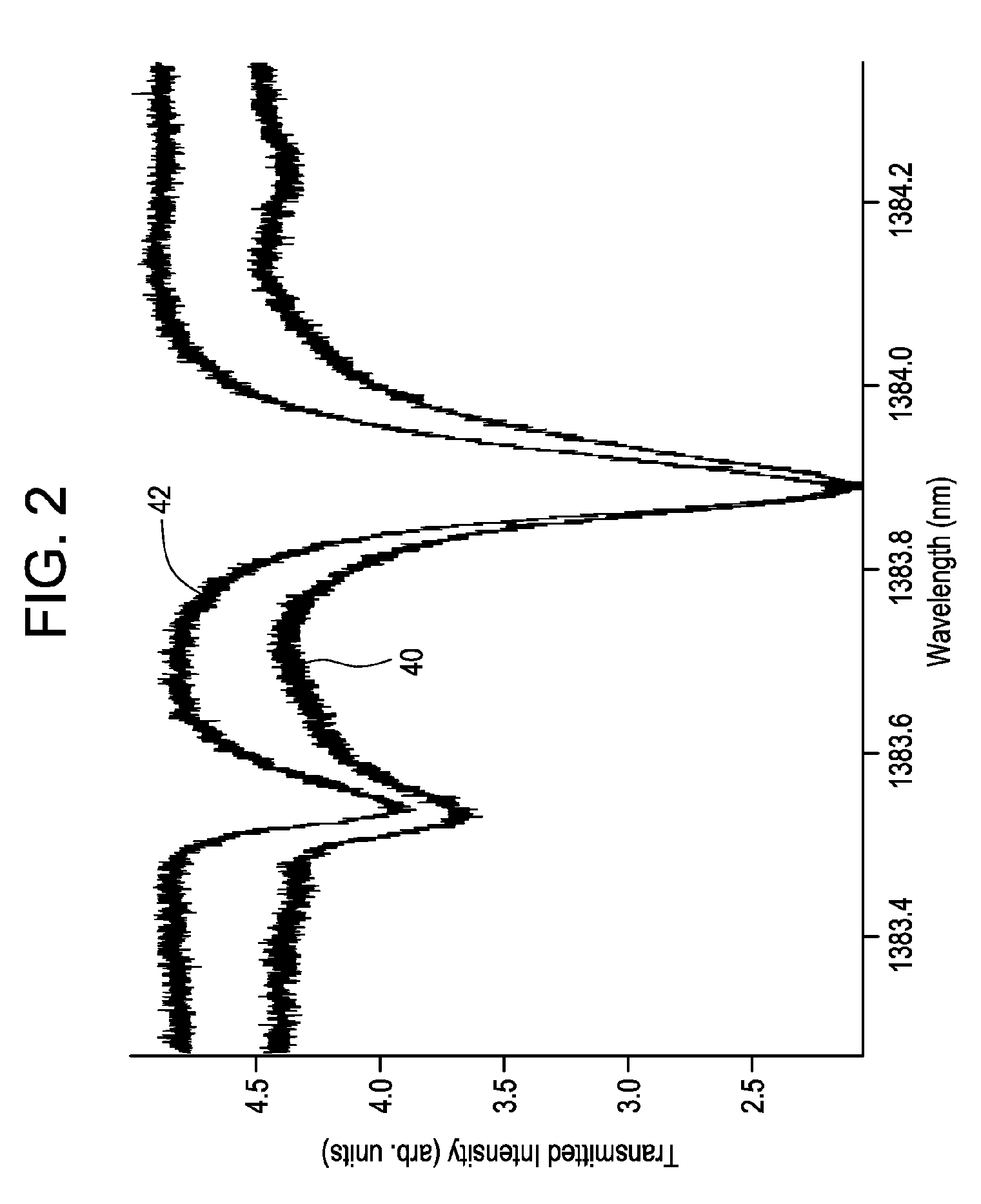
Apparatus and Method for Measuring Steam Quality
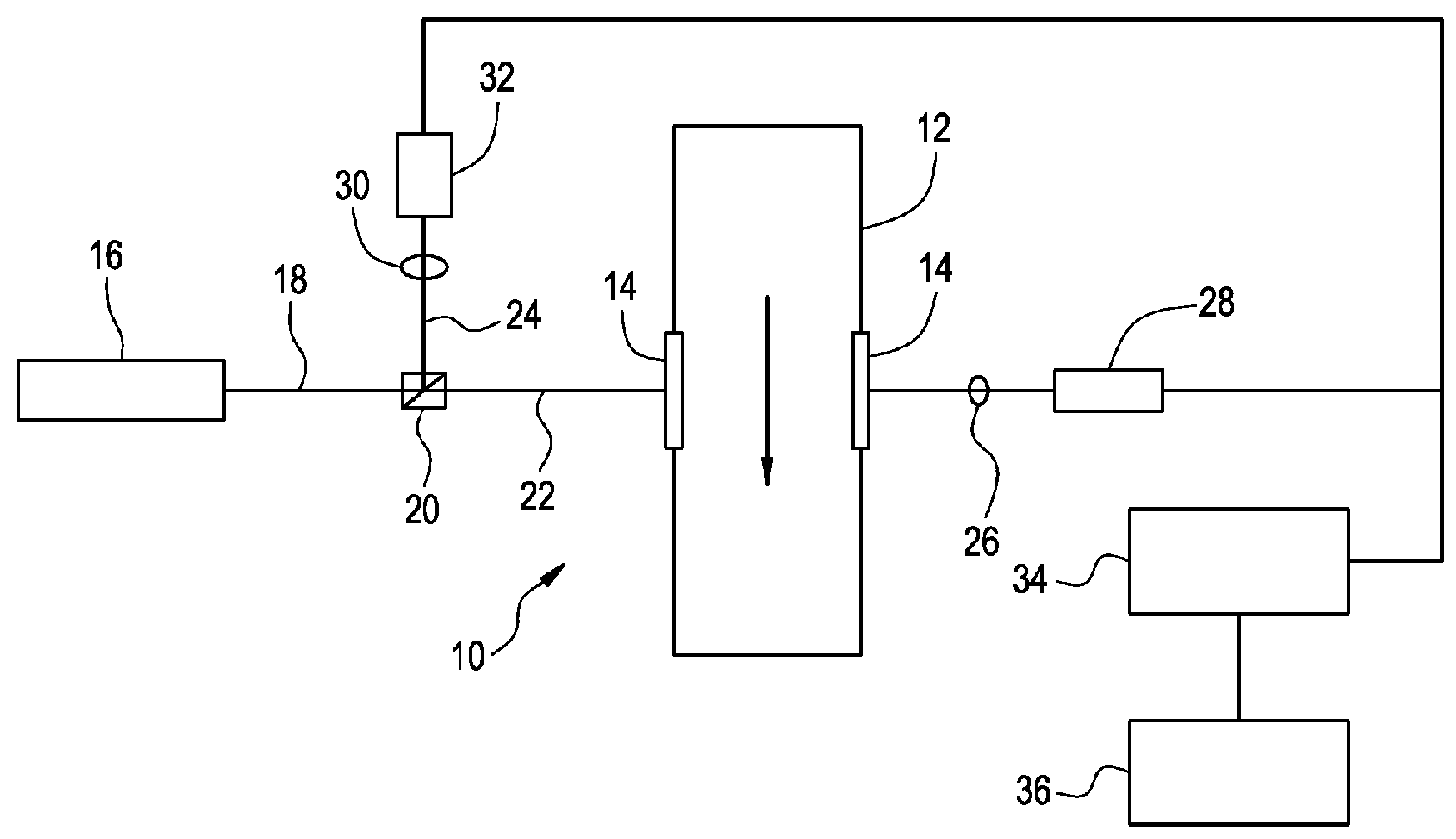
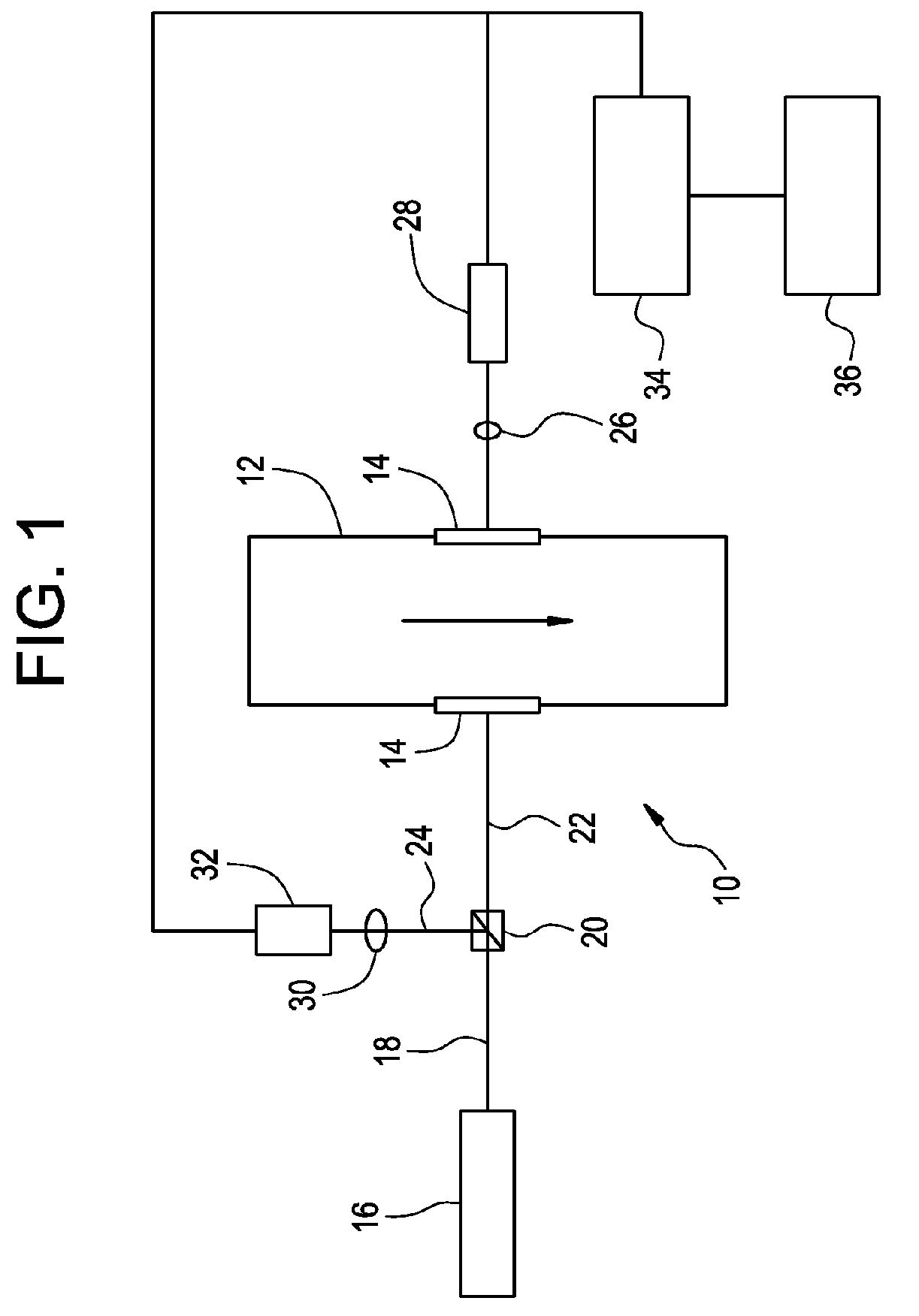
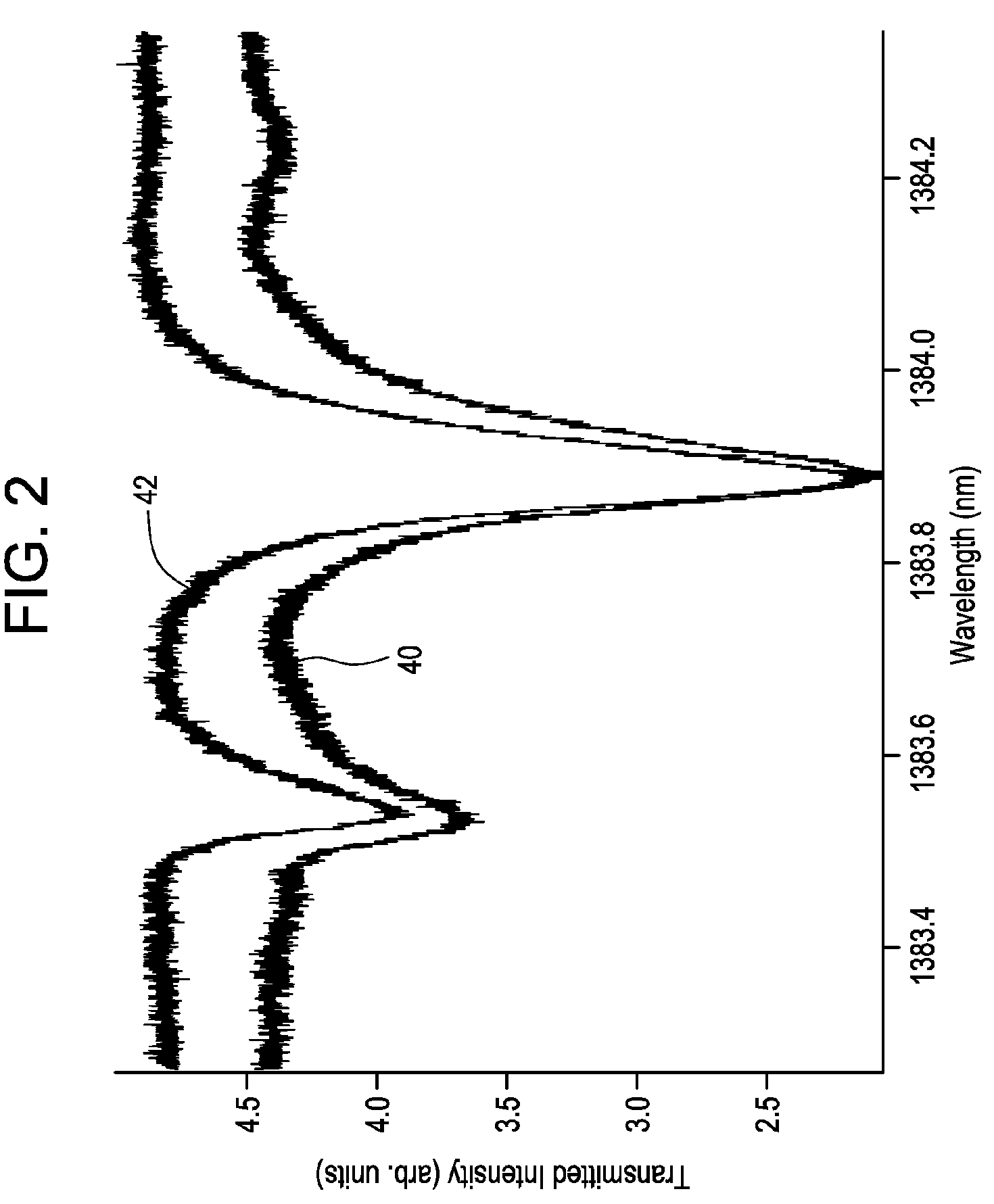
ActiveUS20070069131A1Economical and fastMeasure directlyRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsVapor qualityLiquid water
Determination of steam quality by passing one or more laser beams through steam in a steam chamber and directly determining a total number of vapor molecules and a total number of water molecules based on absorption of radiation in the one or more laser beams by the water vapor phase and the liquid water phase in the steam. Specific volumes of water vapor phase and liquid water phase in the steam using the total numbers of water vapor and liquid water molecules are determined and the quality of the steam is calculated based on the specific volumes of the water vapor phase and the liquid water phase in steam. One embodiment comprises a narrow linewidth laser for measuring steam quality and another embodiment comprises multiple broadband lasers for measuring steam quality.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for estimation of sagd process characteristics
InactiveUS20110288778A1Fast and accurate and efficientElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyVapor qualitySection plane
The invention relates to thermally stimulated oil recovery in horizontal wells, namely to the methods for estimation of Steam Assisted Gravity Drainage (SAGD) process characteristics. Method for estimation of SAGD process characteristics is characterized by the steps of measuring temperature along the injection well, measuring steam quality and injection rate at the inlet of the injection well, estimating the pressure distribution profile by using the data obtained, estimating steam injection profile by using the obtained pressure profile and injection rate combined with ID injection well model for pressure losses in the wellbore and heat exchange between injection well tubing and annulus. The obtained steam injection profile is used as an input parameter for a set of 2D cross-sectional analytical SAGD models taking into account reservoir and overburden formation properties impact on production parameters and SAGD characteristics. SAGD process characteristics are estimated on the basis of energy conservation law for condensed steam taking into account heat losses into the reservoir and overburden formation and hence the fluid production rate changing in time.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Apparatus and method for measuring steam quality
ActiveUS7381954B2Economical and fastMeasure directlyRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsVapor qualityWater vapor
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Process for producing oil
Heavy oil or bitumen is recovered by injecting an oil recovery formulation comprising ammonia and steam having a vapor quality of from greater than 0 to less than 0.7, or injecting components thereof, into an underground oil-bearing formation comprising oil or bitumen having a total acid number of at least 0.1 and producing oil or bitumen from the formation after injection of the oil recovery formulation, or components thereof, into the formation.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
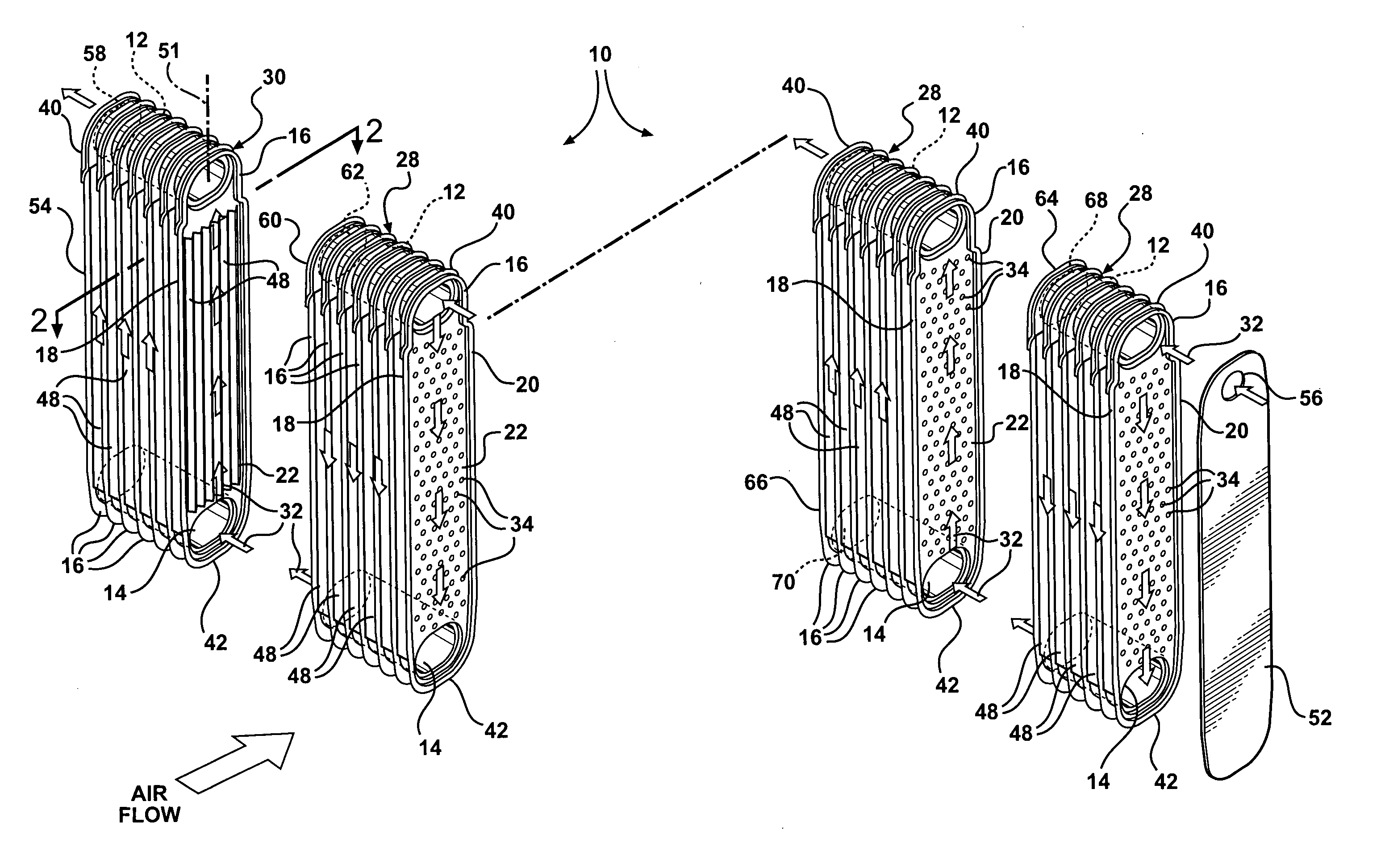
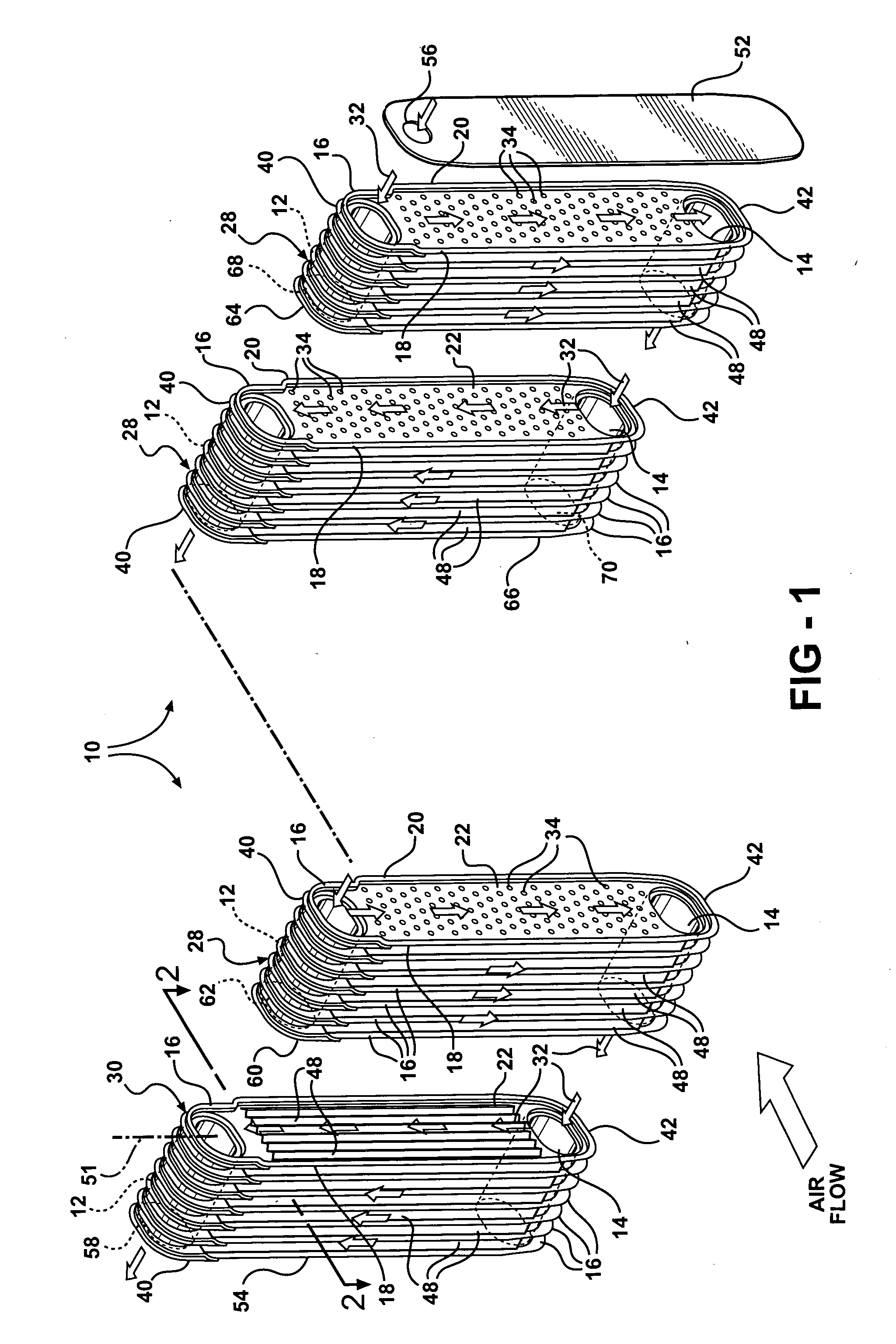
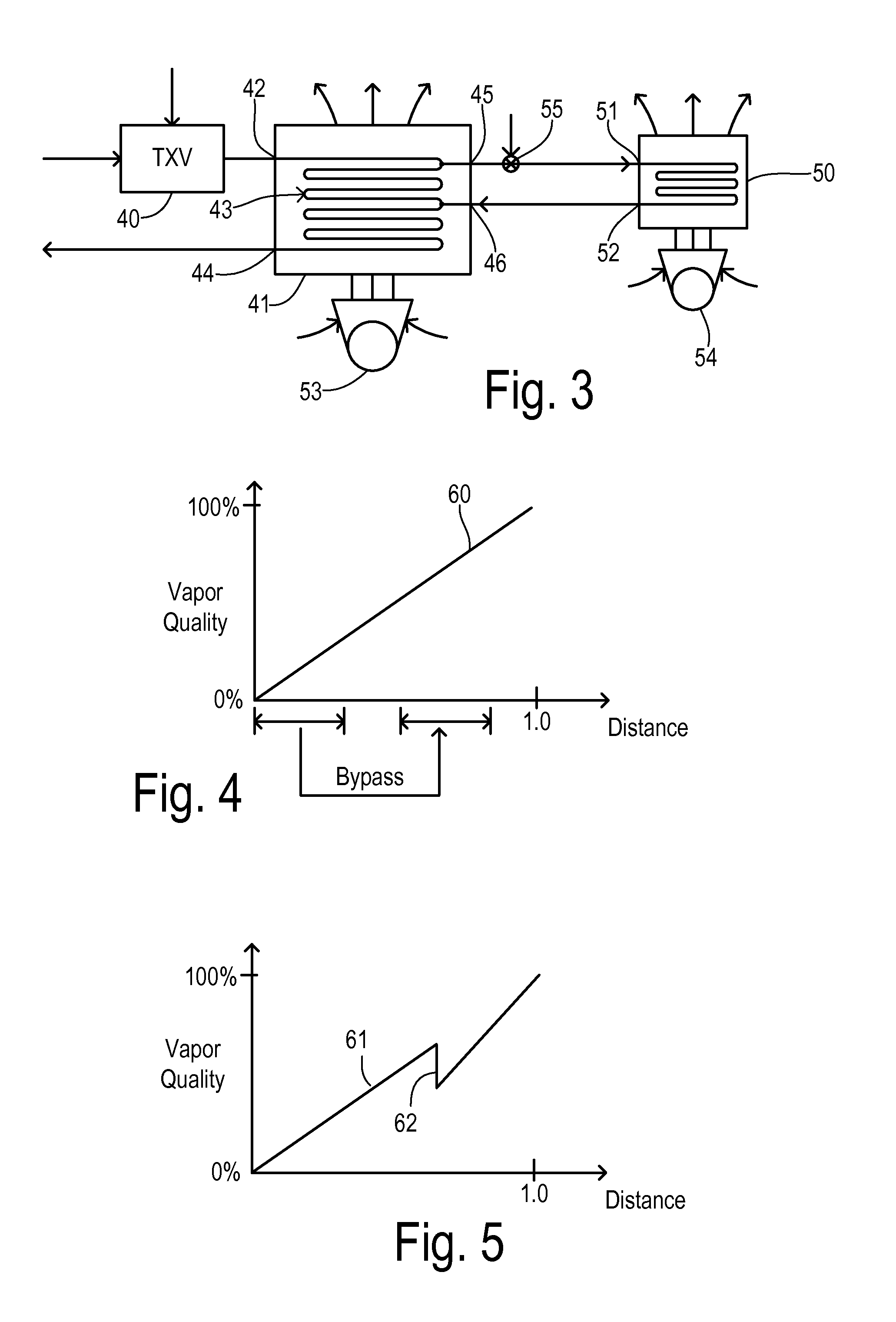
Evaporator designs for achieving high cooling performance at high superheats
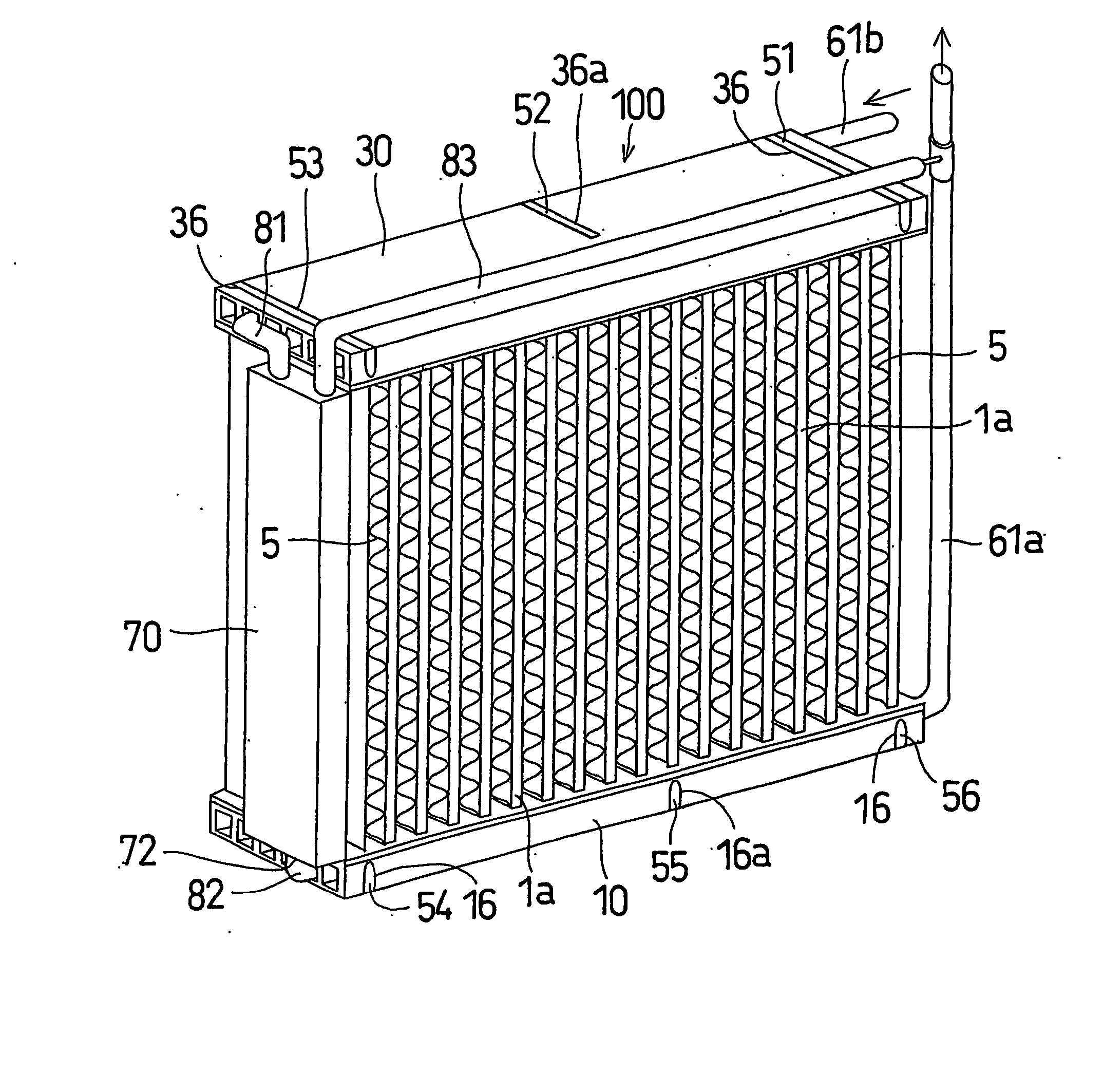
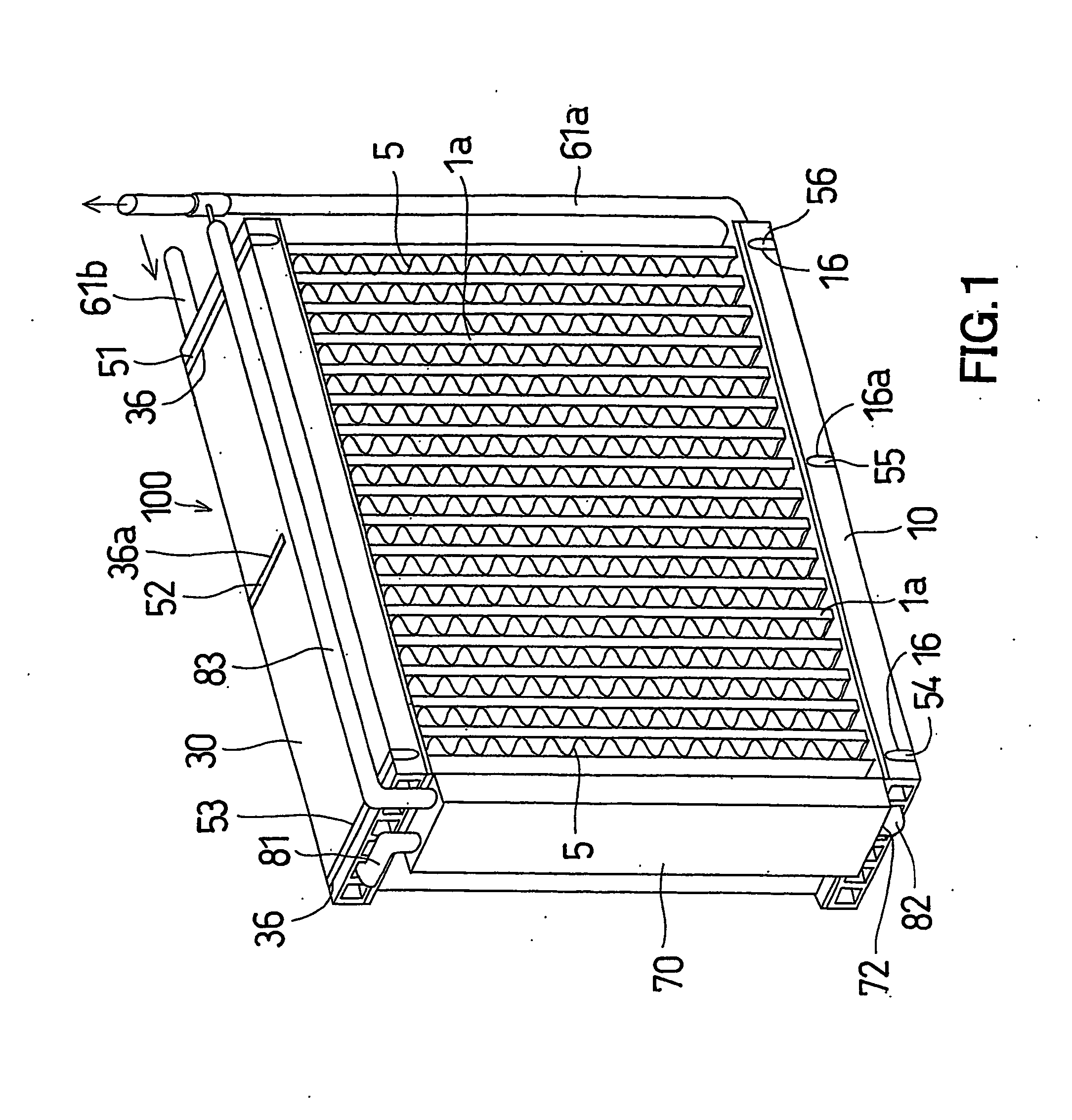
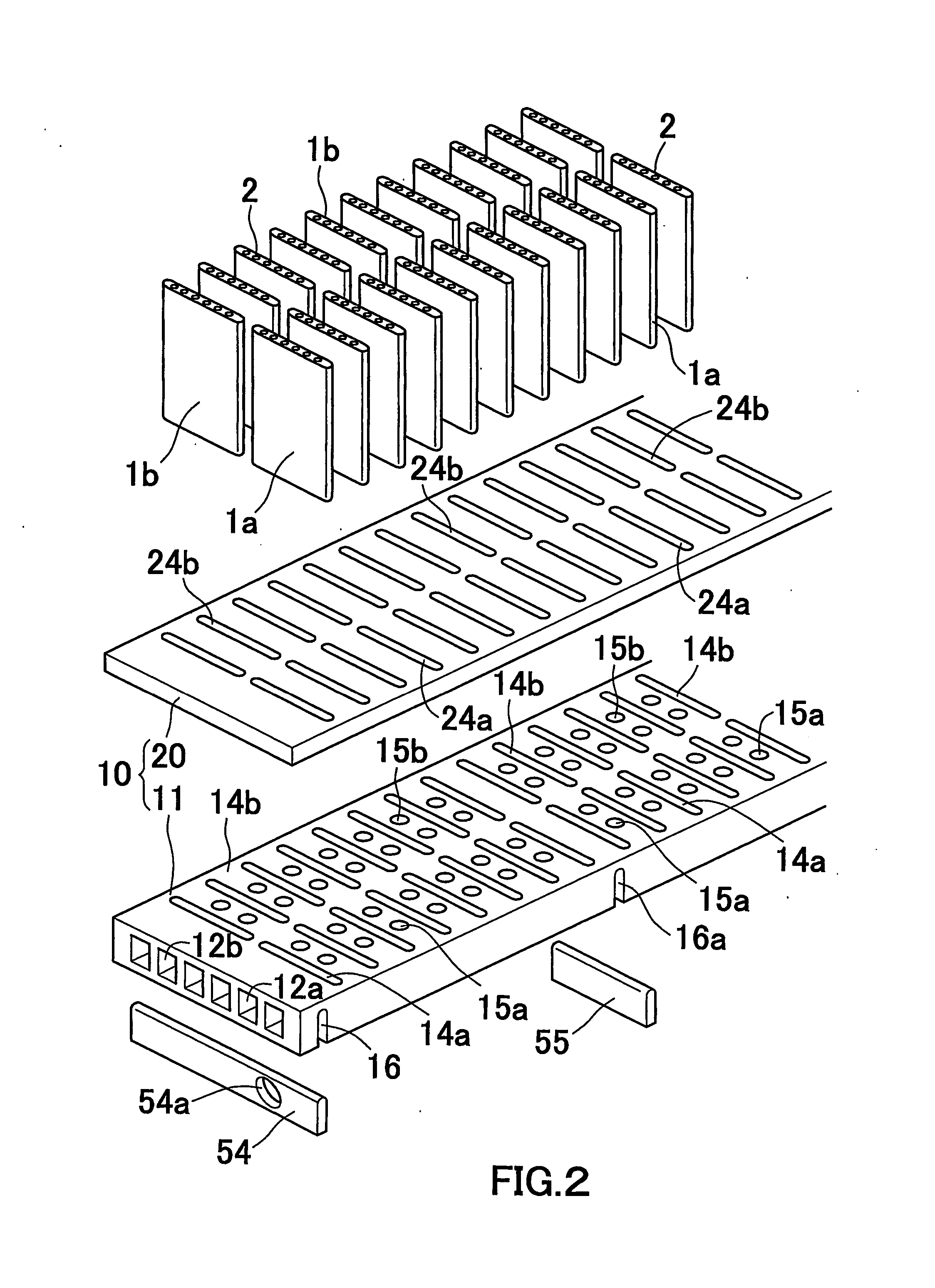
InactiveUS20060144051A1Speed up heat exchangeReduce thermal resistanceEvaporators/condensersStationary conduit assembliesThermal energyVapor quality
An evaporator includes plates disposed in pairs in first and second groups, along spaced tanks. Dimples extend from the interior portions in the first group, and interior fins are disposed against the interior portions of the second group. The dimples enhance the distribution of liquid refrigerant in the passageways and the thermal energy exchange between ambient air and an upstream, low vapor quality flow of fluid passing between upstream and downstream side edges, of the first group of plates. The evaporator also eliminates the tonal noise or whistle under certain transient operating conditions.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
High purity carbon dioxide delivery system using dewars
In delivery of bulk liquefied gas under pressure from portable containers, the claimed invention provides a system and process for directing the evaporated vapor from one or more satellite pressure vessels through a master vessel. The gas transfer operates passively to provide for longer unattended run times for a downstream application. The master vessel serves as a trap for the incoming gas vapor, and thereby improves the overall vapor quality by re-equilibrating the vapor with the colder bulk liquid in the master vessel before delivery to the destination application.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Evaporator refrigeration system vehicle equipped with said system and method of evaporating refrigerant
InactiveUS20060288733A1Improve heat transfer efficiencyPrevents deterioration of coefficientAir-treating devicesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleVapor qualityEngineering
An evaporator using a CO2 refrigeration that prevents a raise in vapor quality of refrigeration in an evaporator passage to obtain heat exchanging efficiency. The evaporator for use in a refrigeration system includes a refrigerant inlet for introducing a refrigerant, a refrigerant outlet for discharging the refrigerant, and an evaporator passage for causing the refrigerant introduced via the refrigerant inlet to evaporate and leading the refrigerant to the refrigerant outlet. An intermediate outlet is provided at an intermediate portion of the evaporator passage. A refrigerant high in vapor quality among the refrigerant passing through the intermediate portion from the refrigerant inlet flows out of the intermediate outlet to prevent a raise in vapor quality of refrigerant.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
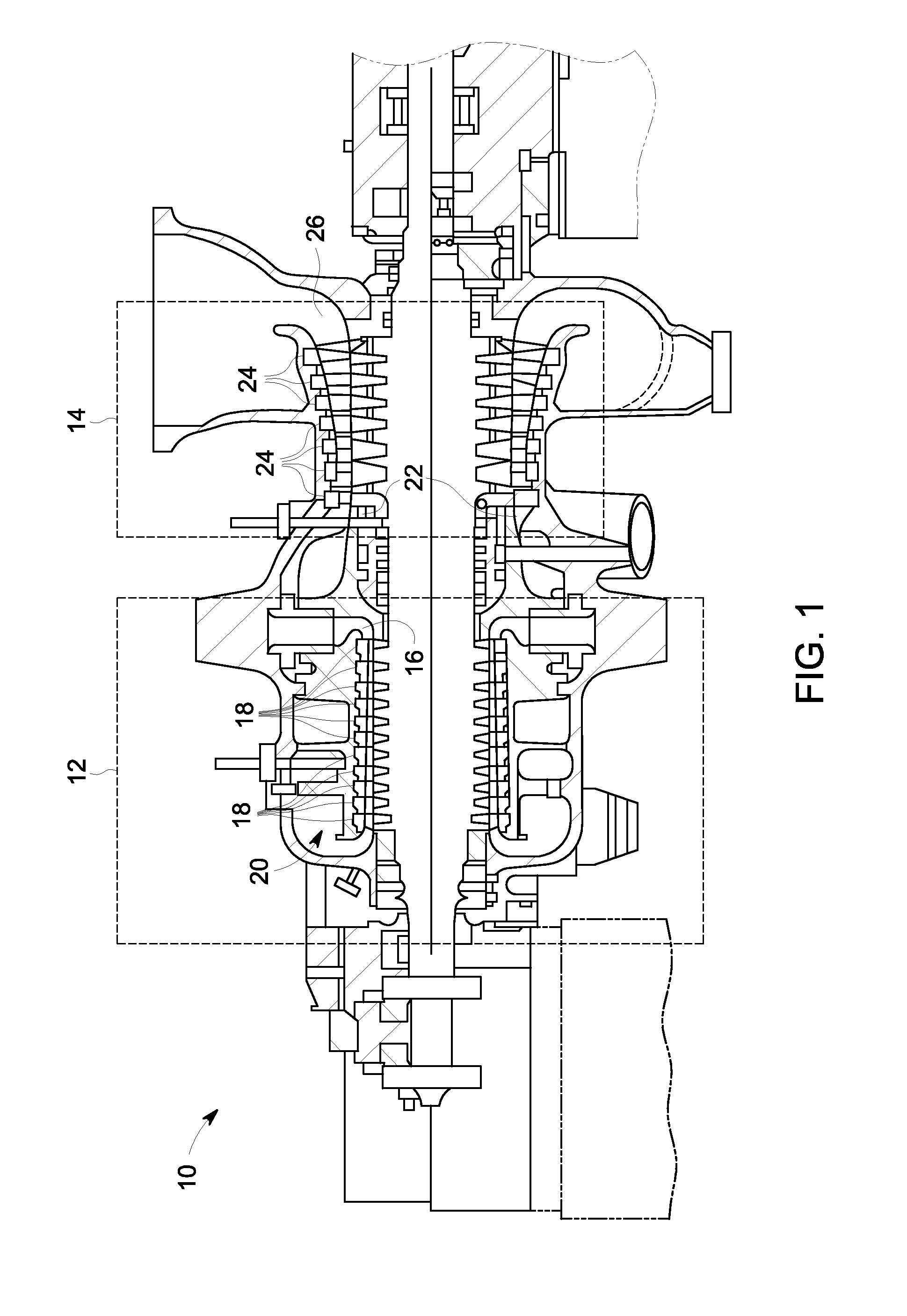
Apparatus and method for measuring parameters of a mixture having liquid droplets suspended in a vapor flowing in a pipe
InactiveUS20060260384A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume/mass flow measurementVapor qualityEngineering
An apparatus 10,70 and method is provided that includes a spatial array of unsteady pressure sensors 15-18 placed at predetermined axial locations x1-xN disposed axially along a pipe 14 for measuring at least one parameter of a saturated vapor / liquid mixture 12, such as steam, flowing in the pipe 14. The pressure sensors 15-18 provide acoustic pressure signals P1(t)-PN(t) to a signal processing unit 30 which determines the speed of sound amix propagating through of the saturated vapor / liquid mixture 12 in the pipe 14 using acoustic spatial array signal processing techniques. The primary parameters to be measured include vapor / liquid concentration (i.e., steam wetness or steam quality), vapor / liquid mixture volumetric flow, mass flow, enthalpy, density and liquid droplet size. Frequency based sound speed is determined utilizing a dispersion model to determine the parameters of interest.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
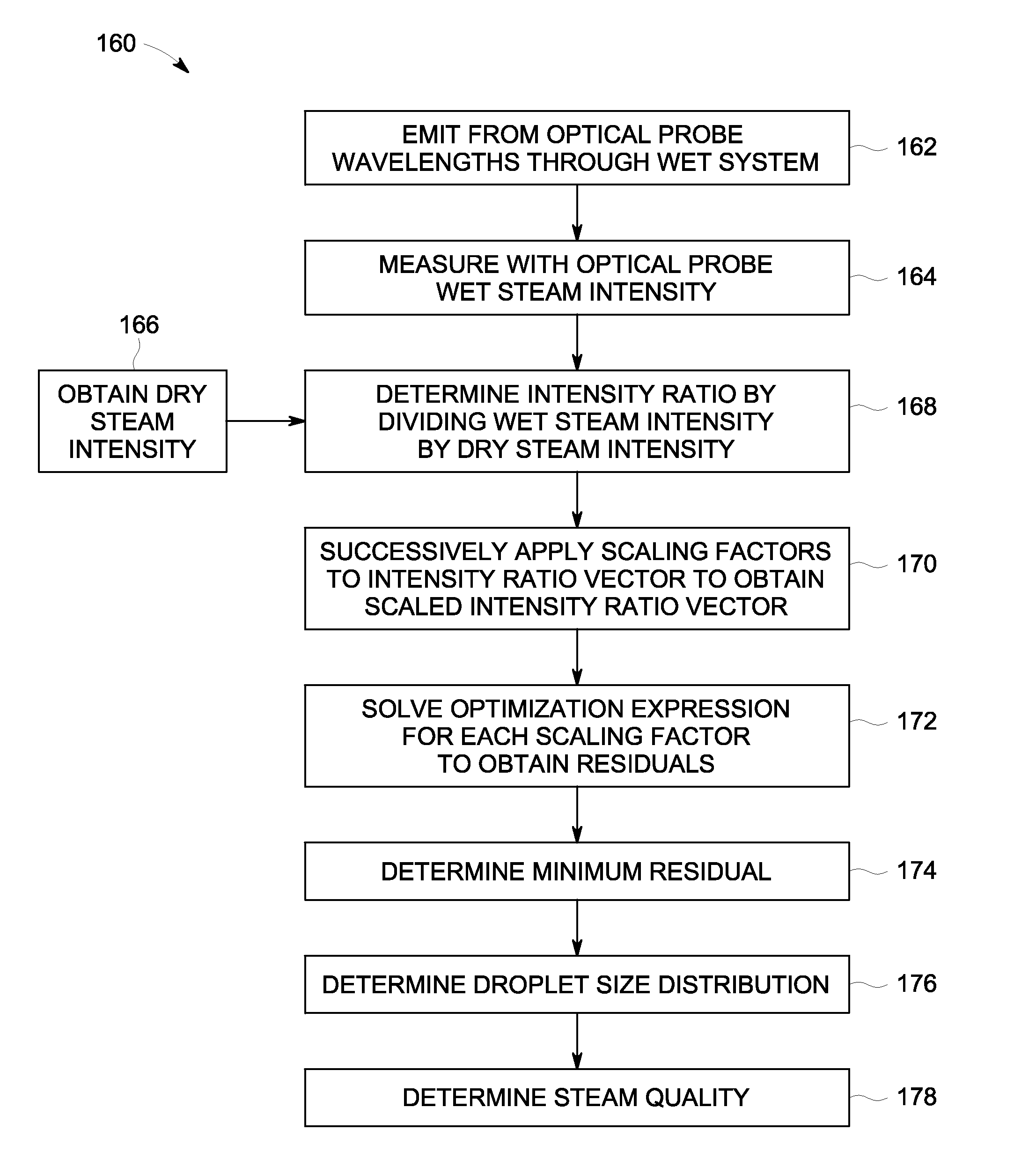
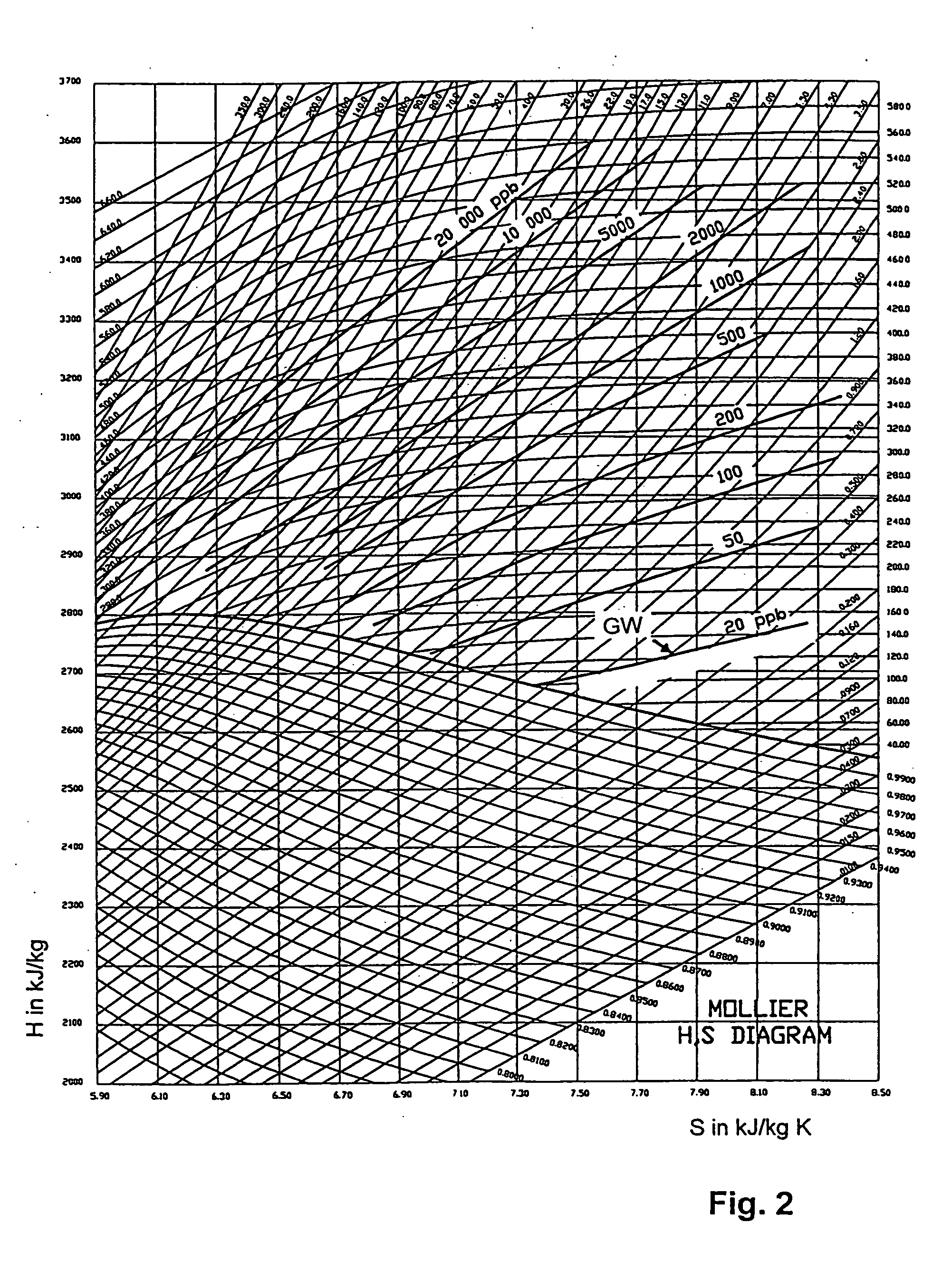
Method and system for steam quality monitoring
A method of determining a steam quality of a wet steam located in an interior of a steam turbine includes emitting from an optical probe a plurality of wavelengths through the wet steam, measuring with the optical probe a wet steam intensity corresponding to each of the plurality of wavelengths emitted through the wet steam, determining an intensity ratio vector by dividing the wet steam intensity by a corresponding dry steam intensity for each of the plurality of wavelengths, successively applying scaling factors to the intensity ratio vector to obtain a scaled intensity ratio vector, calculating a suitable value for each of the scaling factors to obtain a plurality of residuals, determining a minimum residual of the plurality of residuals, determining a droplet size distribution by calculating the droplet number density corresponding to the minimum residual, and determining the steam quality based on the droplet size distribution.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
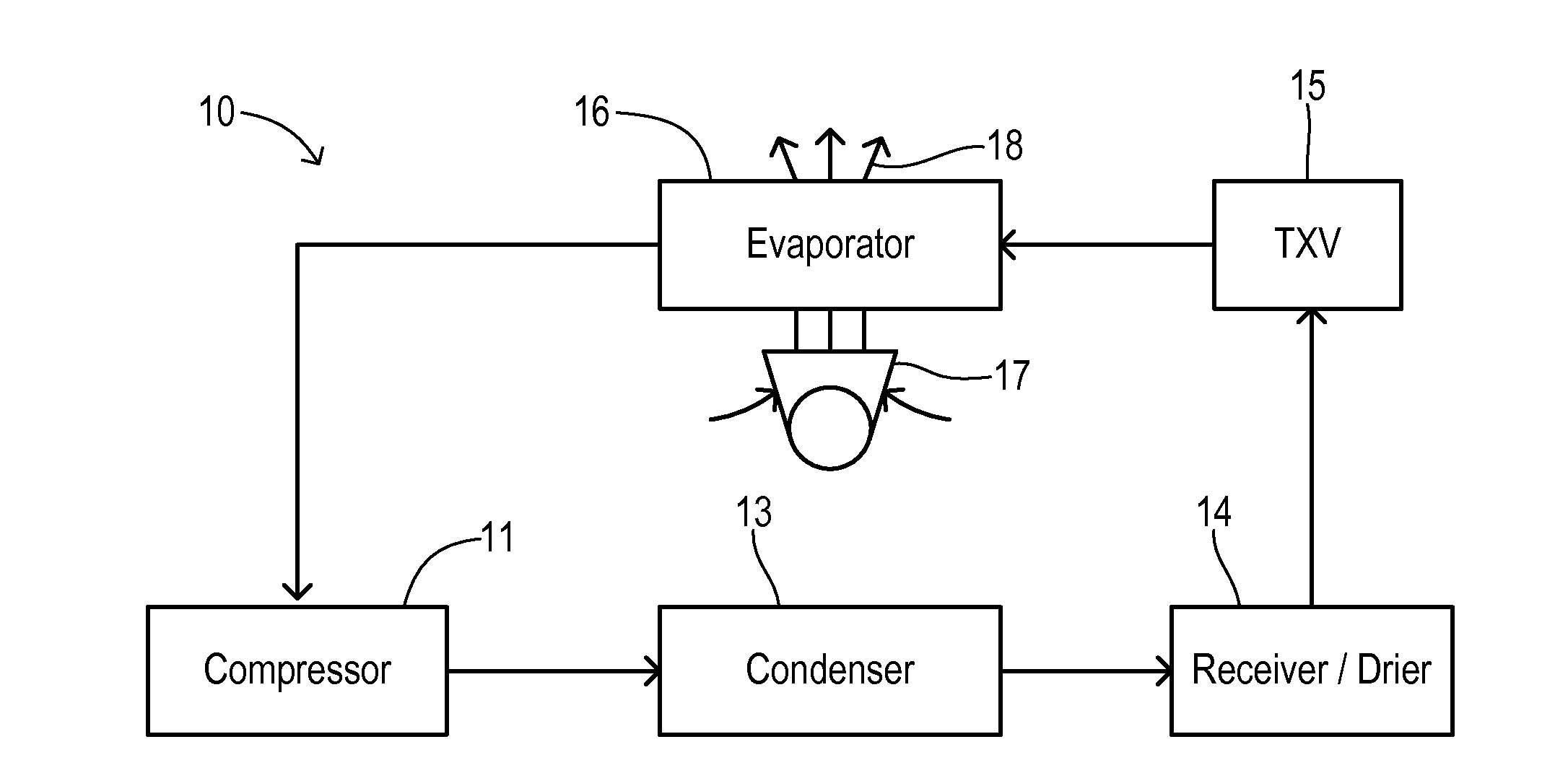
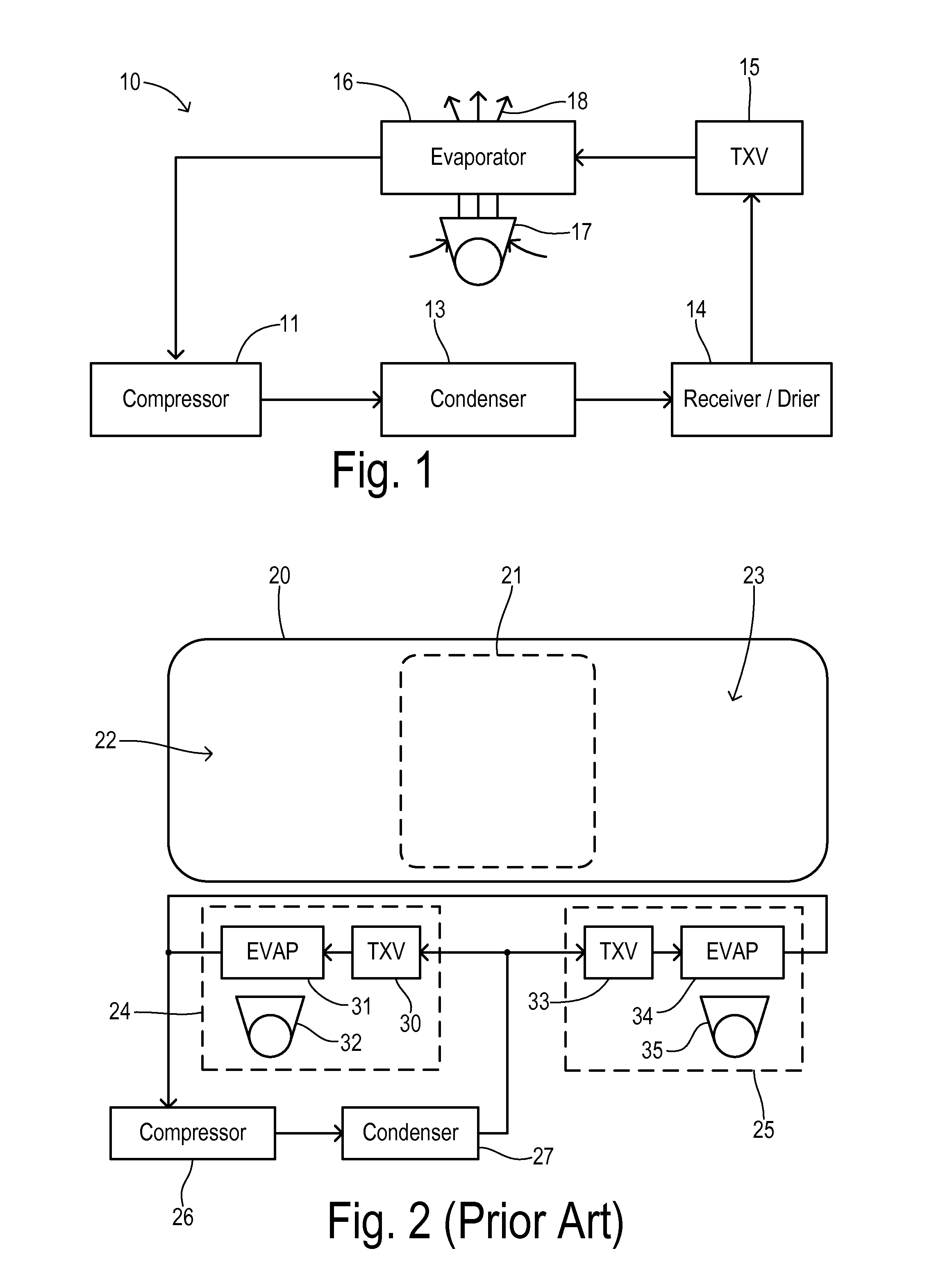
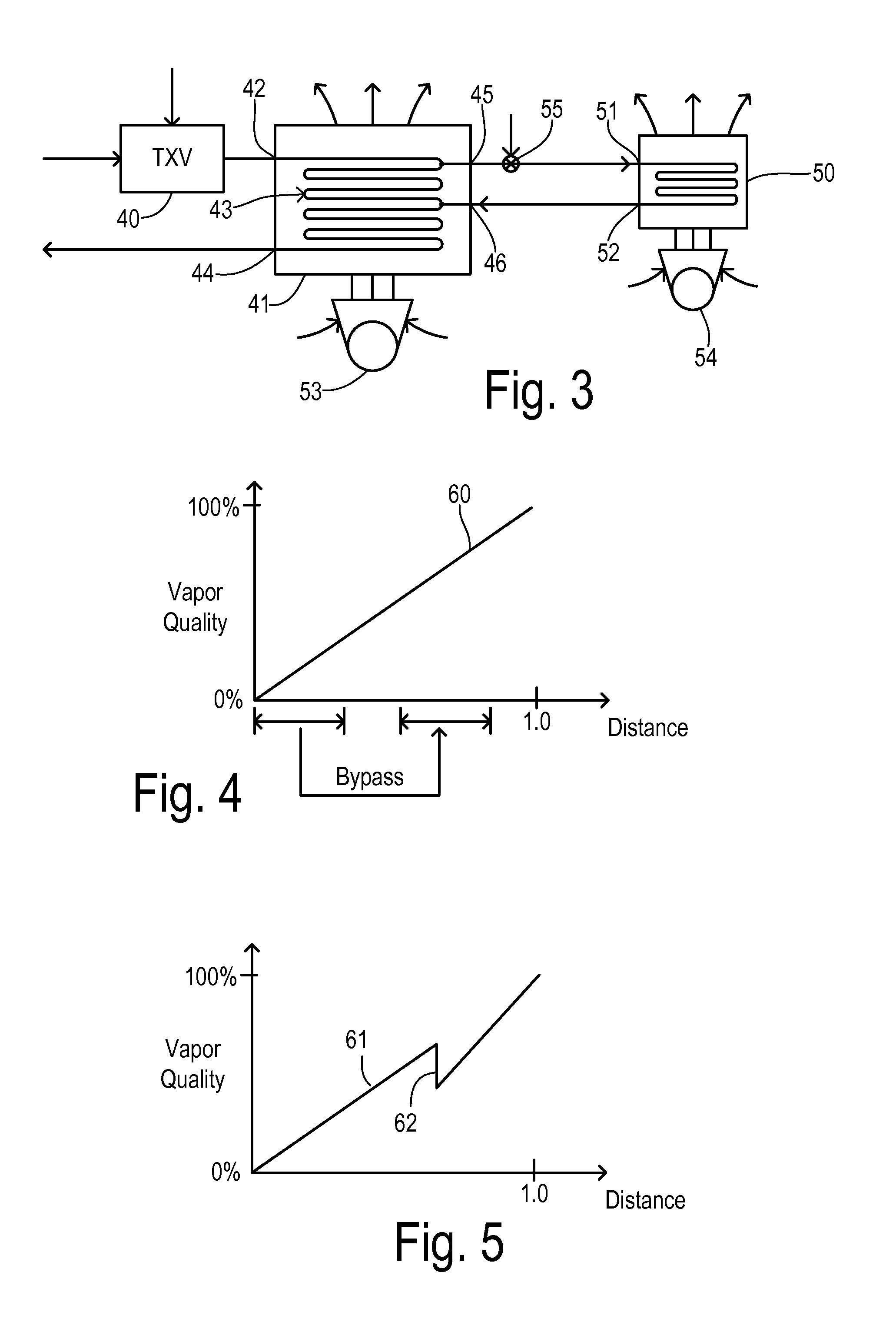
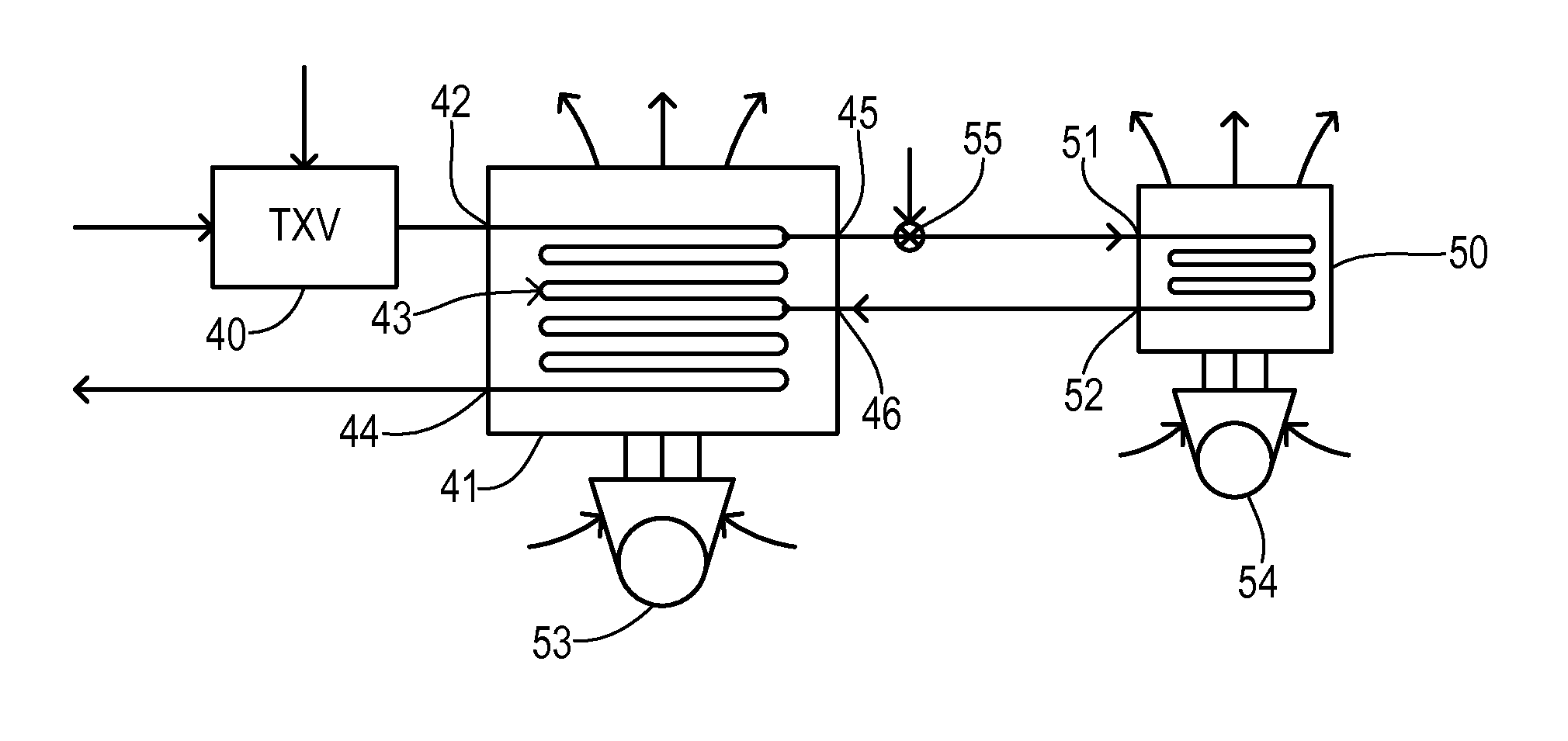
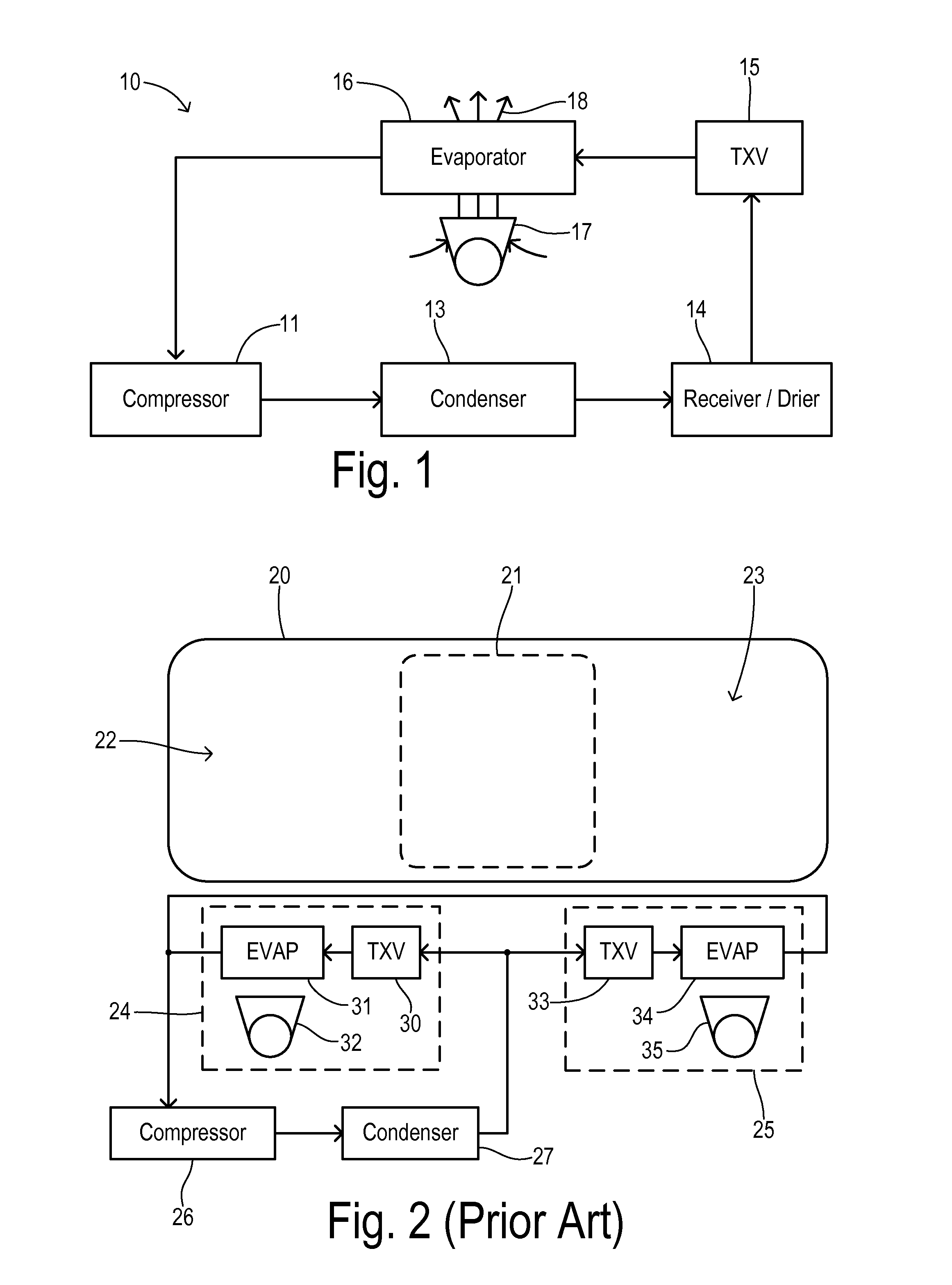
Air Conditioner with Series/Parallel Secondary Evaporator and Single Expansion Valve
ActiveUS20130104589A1Evaporators/condensersCompression machines with several evaporatorsVapor qualityAir conditioning
An air conditioning system has one expansion valve supplying refrigerant to two evaporators. A vapor quality of a refrigerant has an initial value at a primary inlet of a primary evaporator, and has a resultant value at the primary outlet. The primary evaporator has a bypass inlet at a first location where the vapor quality of the refrigerant is less than about 80% of the resultant value. A secondary evaporator has a secondary inlet receiving a bypass portion of the metered flow of refrigerant split-off at a second location of the primary evaporator between the first location and the expansion valve. The secondary outlet is connected to the bypass inlet. Thus, cooling can be achieved for two different zones using only one expansion valve.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Hierarchical Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Micro/Nanostructures for Pushing the Limits of Critical Heat Flux
ActiveUS20160295742A1Improve balanceReduce instabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesVapor qualityMicrometer
A high efficiency heat sink for the cooling of microelectronic devices involves a phase change from liquid fluid to fluid vapor with a vapor quality of 100%. The liquid fluid is provided to an active area that contains fins having micrometer dimension that support a membrane that is nanoporous. The membrane is effectively impermeable to liquid fluid but permeable to fluid vapor. The heat sink provides very high heat flux and coefficient of heat transfer at low mass flux over a broad range of surface superheat temperatures. The heat sink can be constructed of equi-spaced posts that separate liquid microchannels from vapor microchannels that are connected through capillary forced valves formed between adjacent equi-spaced posts.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
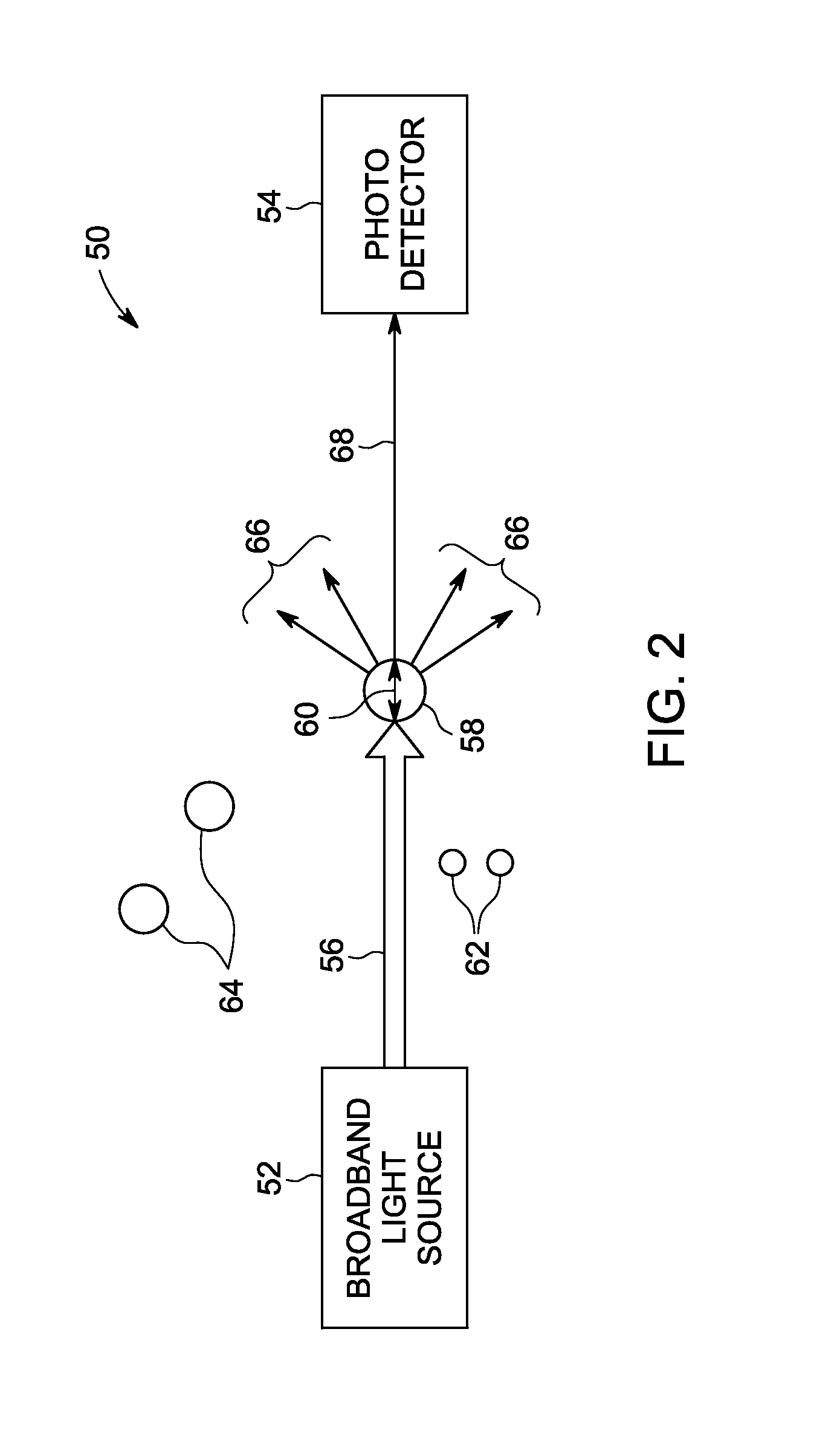
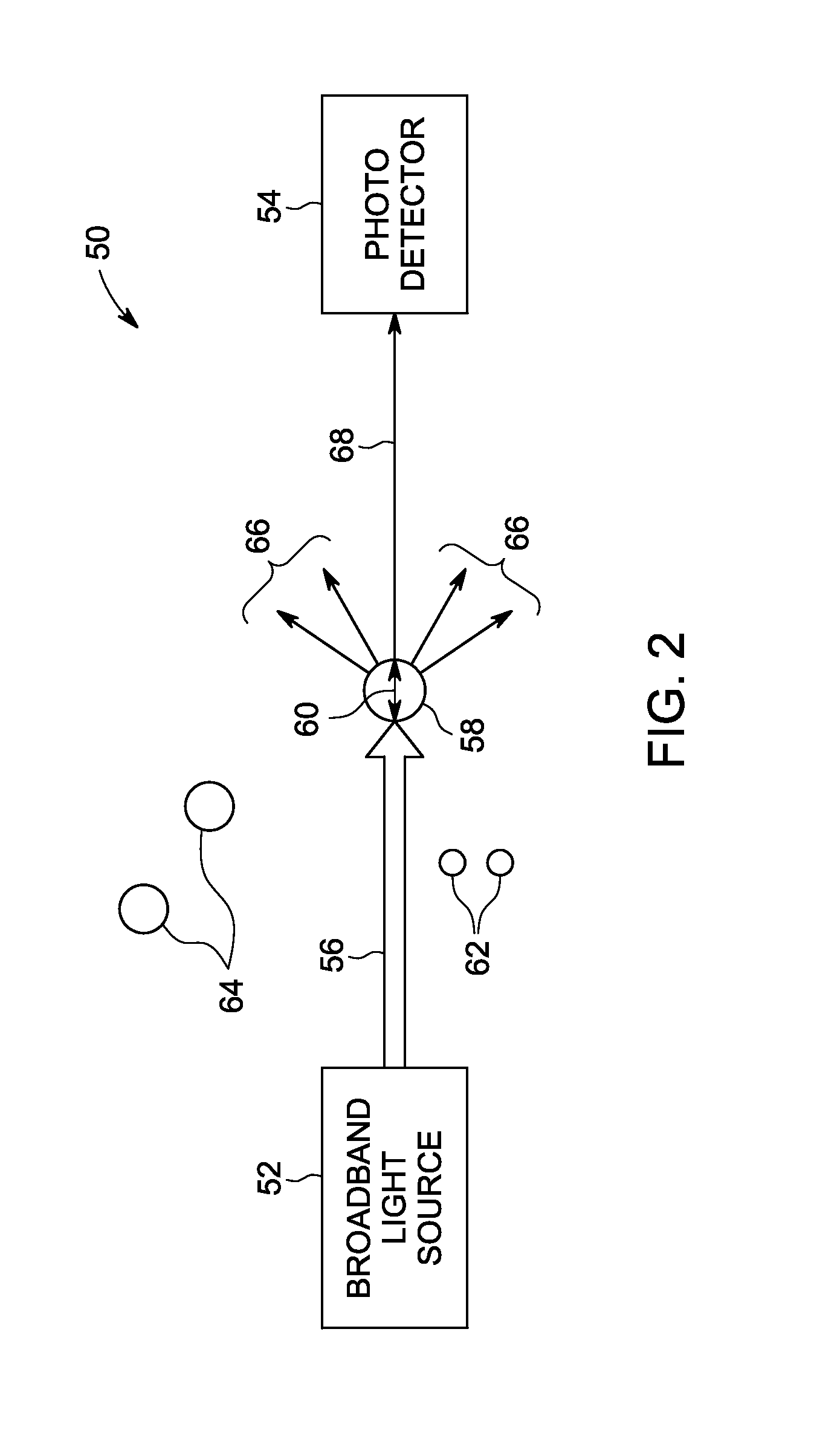
Measurement of Steam Quality Using Multiple Broadband Lasers
ActiveUS20070069132A1Economical and fastMeasure directlyRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsVapor qualityWater vapor
Determination of steam quality by passing one or more laser beams through steam in a steam chamber and directly determining a total number of vapor molecules and a total number of water molecules based on absorption of radiation in the one or more laser beams by the water vapor phase and the liquid water phase in the steam. Specific volumes of water vapor phase and liquid water phase in the steam using the total numbers of water vapor and liquid water molecules are determined and the quality of the steam is calculated based on the specific volumes of the water vapor phase and the liquid water phase in steam. One embodiment comprises a narrow linewidth laser for measuring steam quality and another embodiment comprises multiple broadband lasers for measuring steam quality.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
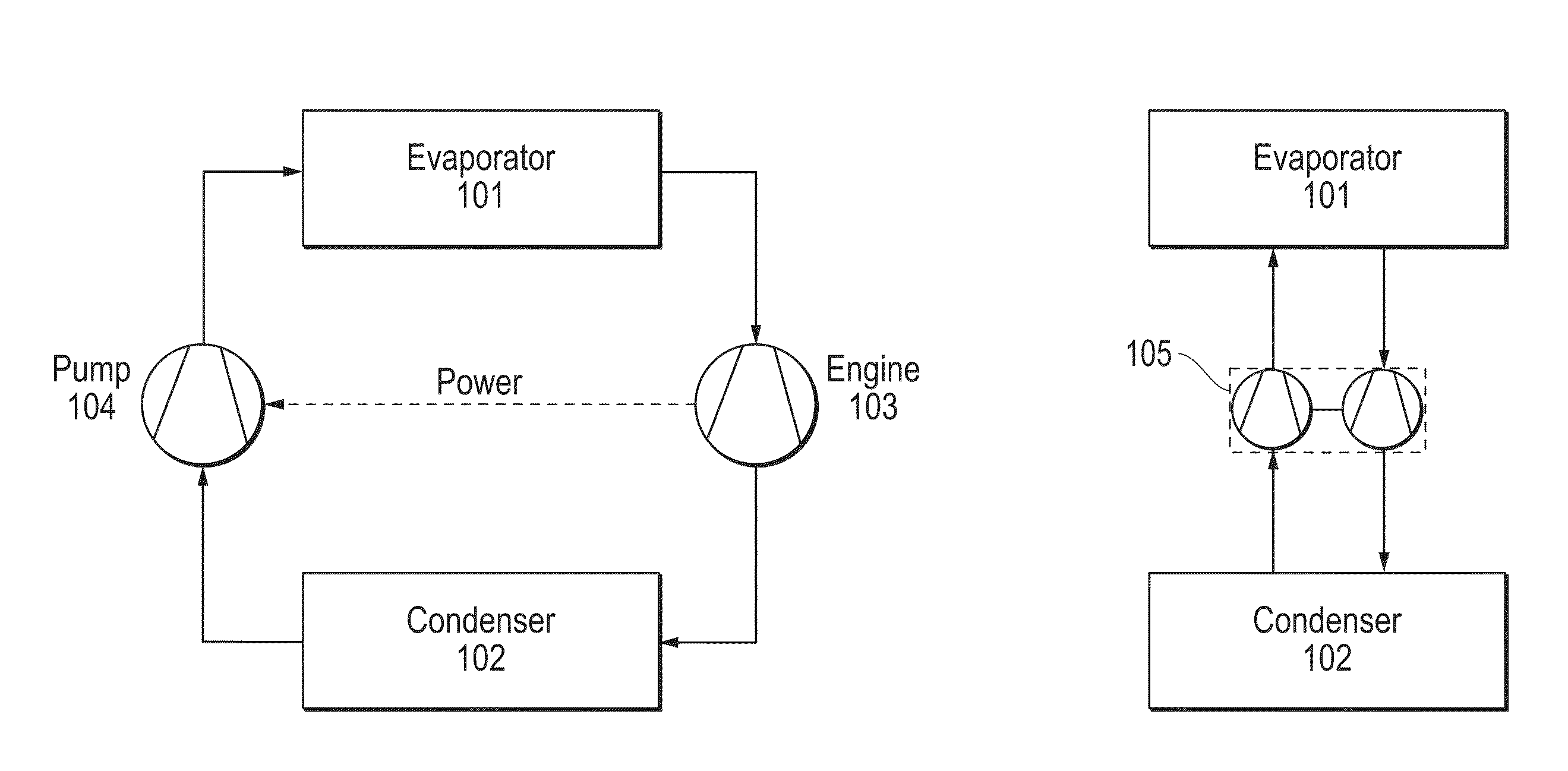
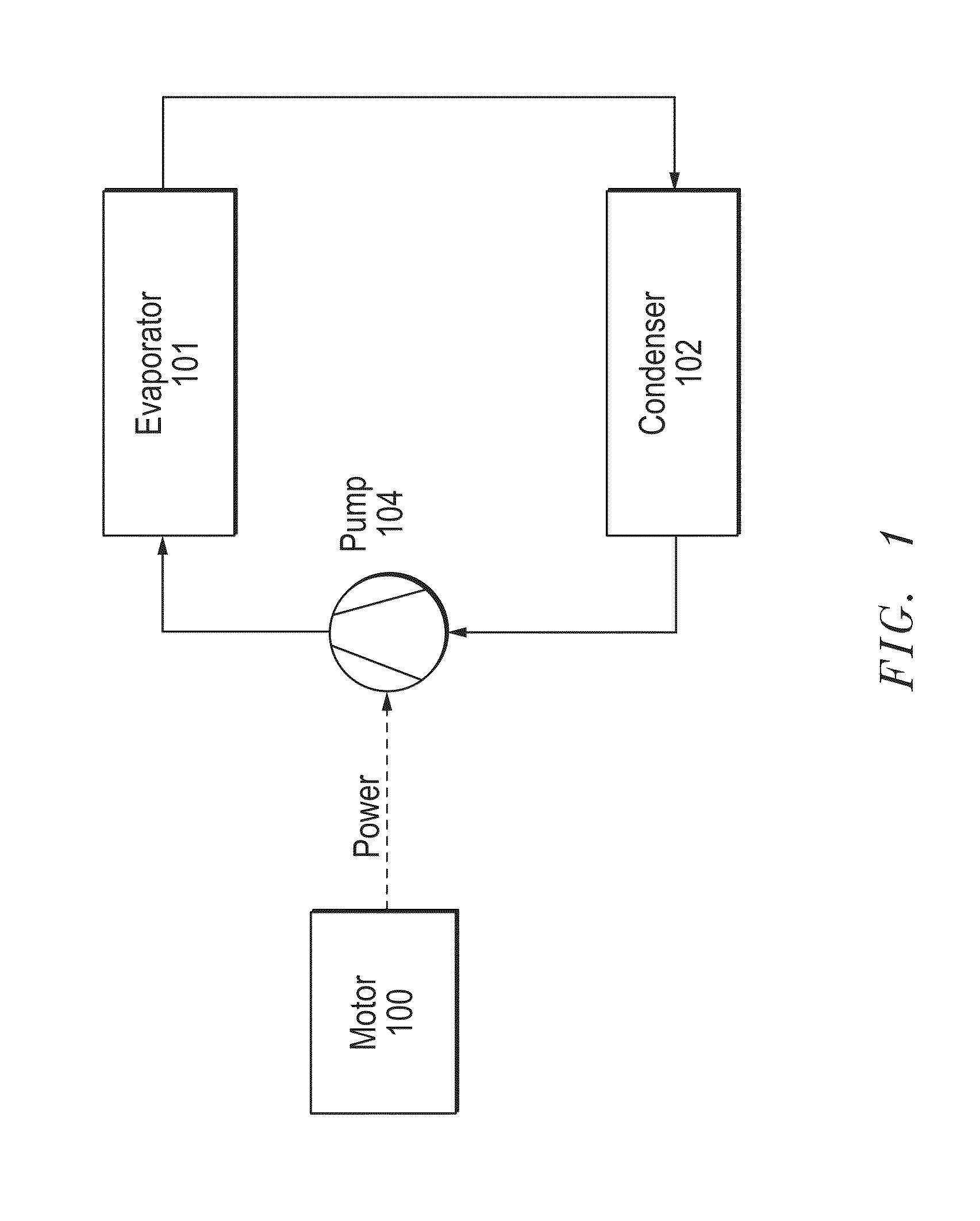
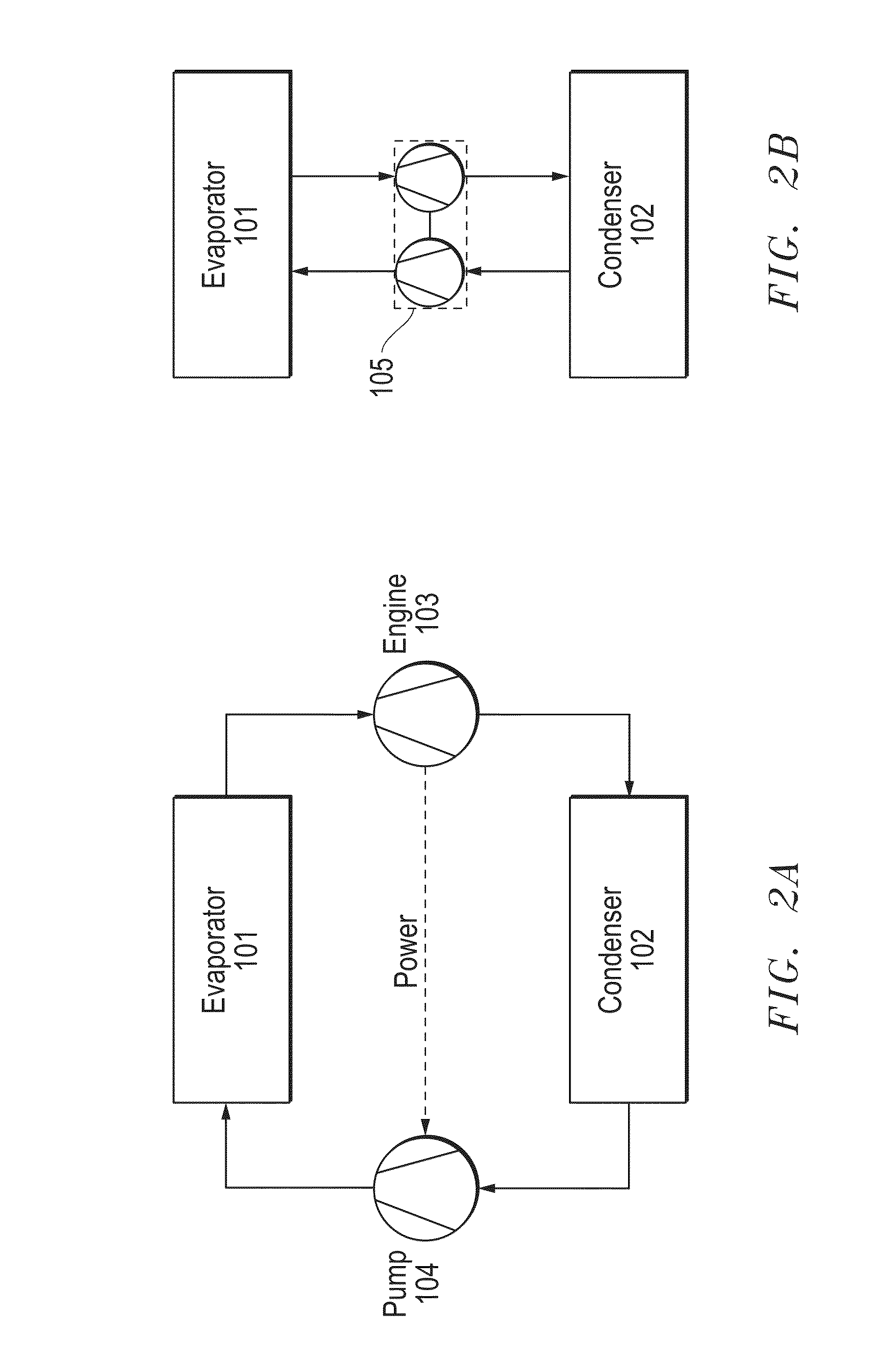
Heat transfer engine
InactiveUS20150101330A1Eliminating external power overheadReduce needIndirect heat exchangersSteam engine plantsWorking fluidVapor quality
The invention provides a method for a thermally activated closed loop heat transfer system, and requires no other external power source other than the heat which it is transferring. The system is based on a two-phase (liquid / vapor) working fluid, with heat input through an evaporator and heat rejected through a condenser. All of the mechanical power produced by an engine, driven by the high vapor quality fluid leaving the evaporator, is consumed by the pump. The pump drives the low vapor quality fluid leaving the condenser back to the evaporator. Nearly isothermal heat transport can be achieved when using a pure or azeotropic working fluid, since the operation only requires the evaporator pressure to be marginally higher than the condensers pressure.
Owner:J R THERMAL LLC
Process for producing oil
Heavy oil or bitumen is recovered by injecting an oil recovery formulation comprising ammonia and steam having a vapor quality of from greater than 0 to less than 0.7, or injecting components thereof, into an underground oil-bearing formation comprising oil or bitumen having a total acid number of at least 0.1 and producing oil or bitumen from the formation after injection of the oil recovery formulation, or components thereof, into the formation.
Owner:SHELL INT RES MAATSCHAPPIJ BV
Measurement of Steam Quality in Steam Turbine
A solution for measuring steam quality in a steam turbine is disclosed. A steam quality measurement (SQM) device and an ejector are coupled to a steam turbine through an appropriate piping configuration to draw steam emitted from the turbine through the SQM device for measurement of the steam quality, for example, continuously, during operation of the turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Air conditioner with series/parallel secondary evaporator and single expansion valve
ActiveUS8677779B2Evaporators/condensersCompression machines with several evaporatorsVapor qualityAir conditioning
An air conditioning system has one expansion valve supplying refrigerant to two evaporators. A vapor quality of a refrigerant has an initial value at a primary inlet of a primary evaporator, and has a resultant value at the primary outlet. The primary evaporator has a bypass inlet at a first location where the vapor quality of the refrigerant is less than about 80% of the resultant value. A secondary evaporator has a secondary inlet receiving a bypass portion of the metered flow of refrigerant split-off at a second location of the primary evaporator between the first location and the expansion valve. The secondary outlet is connected to the bypass inlet. Thus, cooling can be achieved for two different zones using only one expansion valve.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
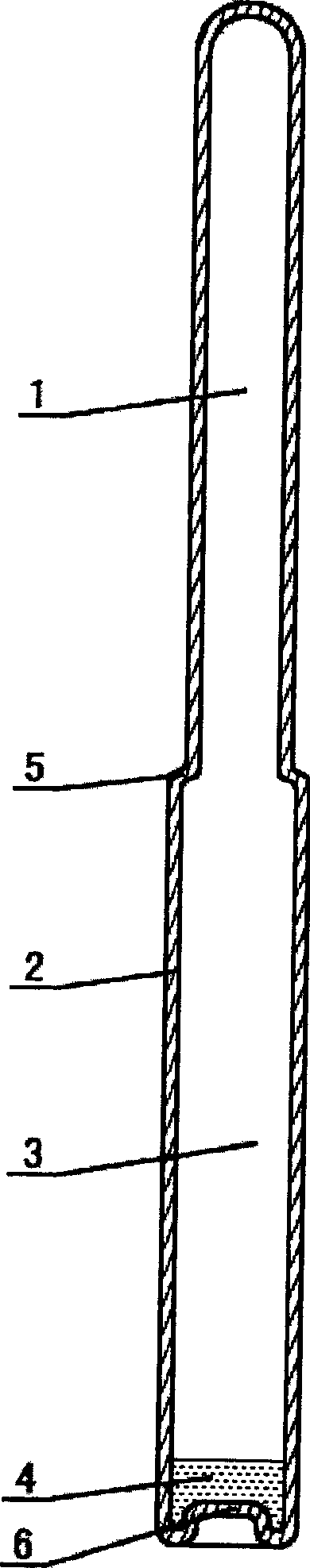
Heat pipe of glass shell
InactiveCN1661315AReduce corrosionLow wear resistanceIndirect heat exchangersHeat exchange apparatusWorking fluidHigh rate
A heat pipe with a glass shell is composed of a glass shell, a heat-conducting working fluid, and the like. Its glass shell heat pipe is fully sealed by a glass tube head at one end, and then connected to a full glass tube cavity that is exhausted and filled with a heat-conducting working fluid tailpipe after being closed by a glass tube head at the other end. The heat-conducting working medium tailpipe is evacuated, filled with heat-conducting working medium, and then the glass is welded and sealed to form an all-glass circular tubular container. The heat-conducting working medium filled in the heat pipe of the glass shell has the characteristics of large vaporization enthalpy, good thermal conductivity and stable physical and chemical properties. The heat-conducting working medium is either water, an aqueous solution, or a liquid organic substance; the filling amount of the heat-conducting working medium in the heat pipe of the glass shell: the heat-conducting working medium corresponding to the saturated heat-conducting working medium vapor volume of the glass-shell heat pipe under the maximum rated working temperature and pressure steam quality. The heat-conducting working medium steam above the maximum rated working temperature and pressure is superheated steam, and the relationship between its corresponding temperature and pressure follows Charles' law in gas experiments.
Owner:ZIBO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD +1
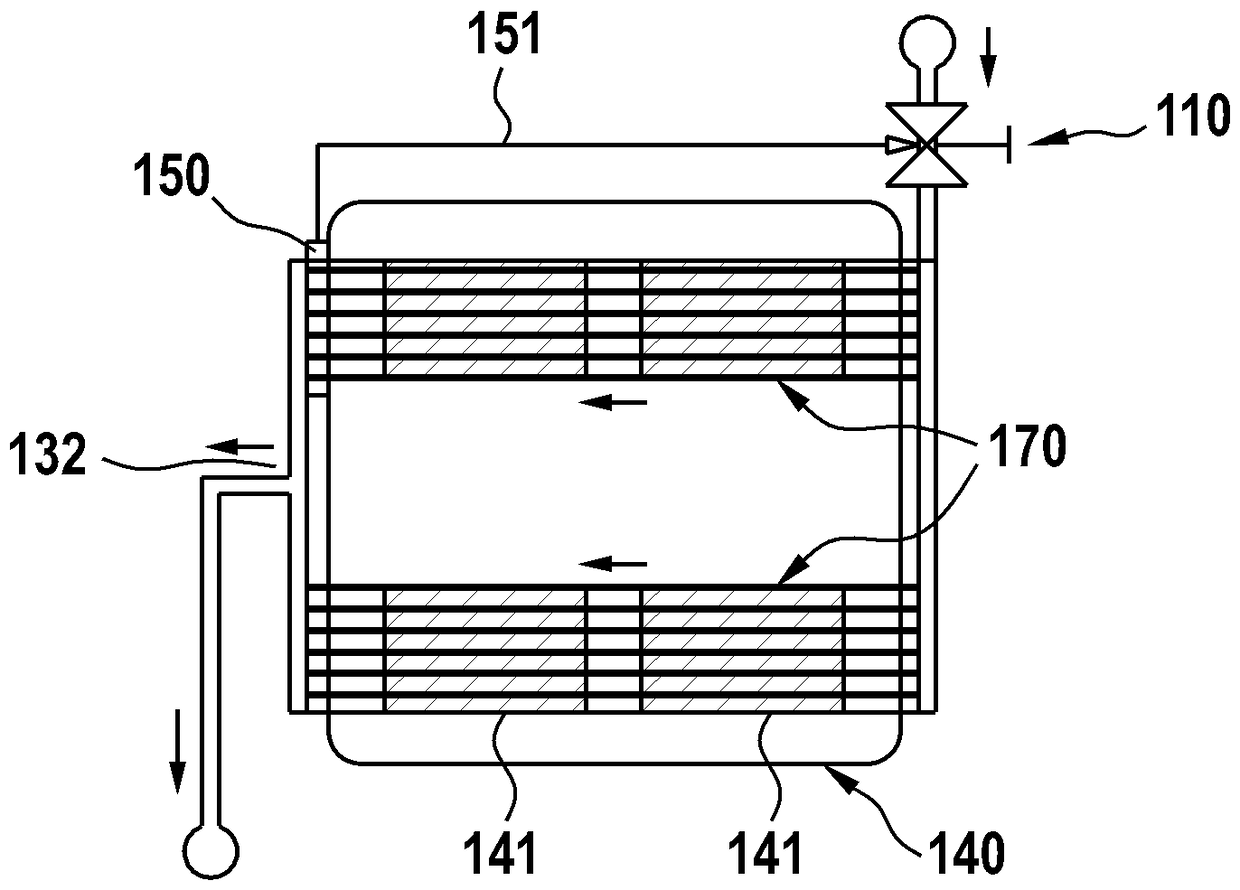
Cooling regulation system and method for cooling regulation
ActiveCN108458519AObvious benefitsObvious featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesVapor qualityEngineering
A cooling regulation system (100) is described which includes: a valve (110) having an control device (120) configured for controlling an opening of an orifice (111) provided between a valve inlet (112) and a valve outlet (113) such that a flow of a coolant from the valve inlet to the valve outlet can be regulated; an evaporator (130) with a contact surface that is adapted to be thermally connected to a heat source (140, 141) such that a thermal load from the heat source is dissipated by the evaporator in an operating state of the cooling regulation system; and a regulation device (150) configured for regulating a position of the control device in order to regulate the flow of the coolant, wherein the regulation device is in thermal contact with the evaporator at a position at which a vapor quality [chi] of the coolant is [chi]<=[chi]cr, wherein [chi]cr is the critical vapor quality.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Method and system for steam quality monitoring
A method of determining a steam quality of a wet steam located in an interior of a steam turbine includes emitting from an optical probe a plurality of wavelengths through the wet steam, measuring with the optical probe a wet steam intensity corresponding to each of the plurality of wavelengths emitted through the wet steam, determining an intensity ratio vector by dividing the wet steam intensity by a corresponding dry steam intensity for each of the plurality of wavelengths, successively applying scaling factors to the intensity ratio vector to obtain a scaled intensity ratio vector, calculating a suitable value for each of the scaling factors to obtain a plurality of residuals, determining a minimum residual of the plurality of residuals, determining a droplet size distribution by calculating the droplet number density corresponding to the minimum residual, and determining the steam quality based on the droplet size distribution.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
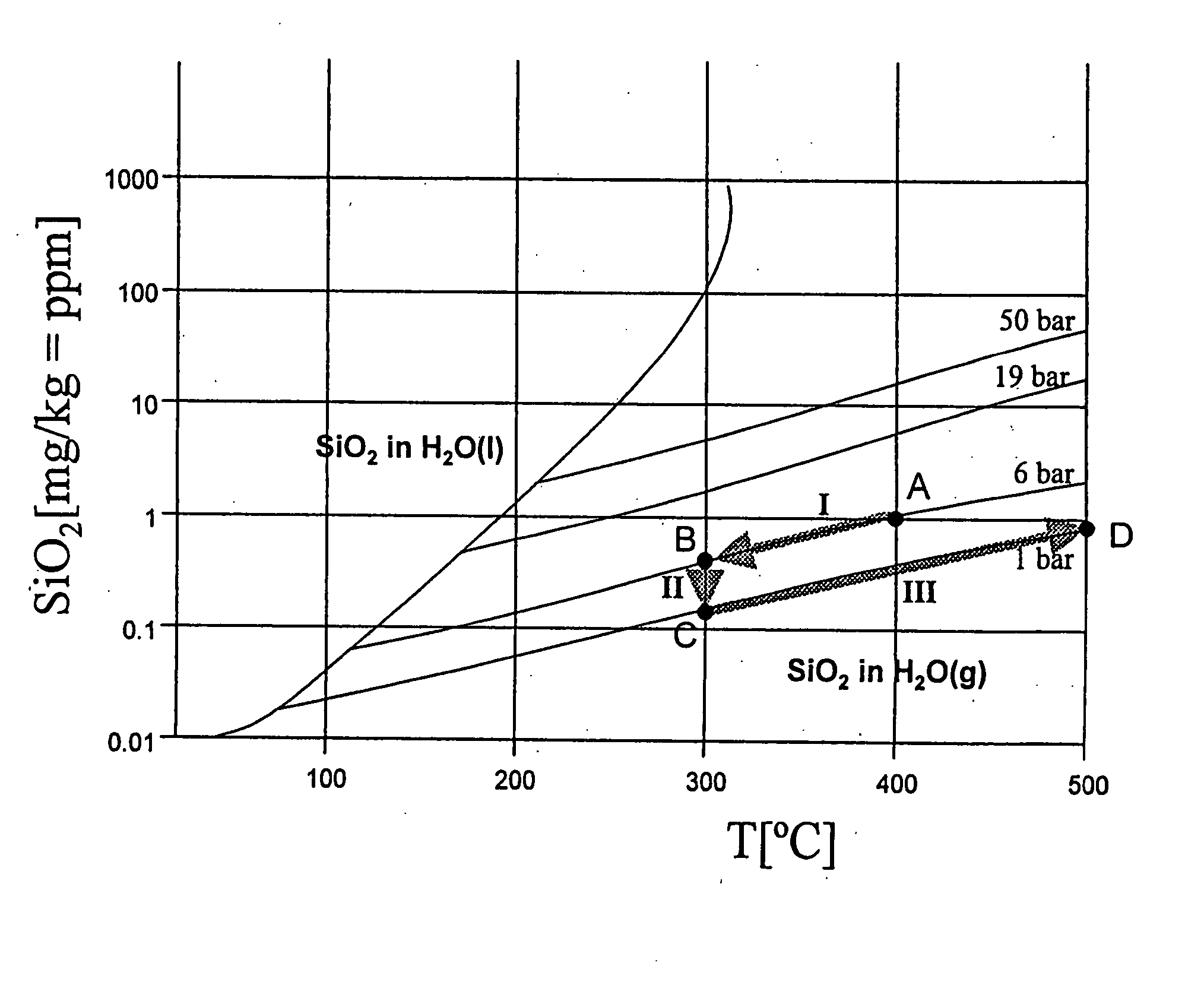
Method for the prevention of deposits in steam systems
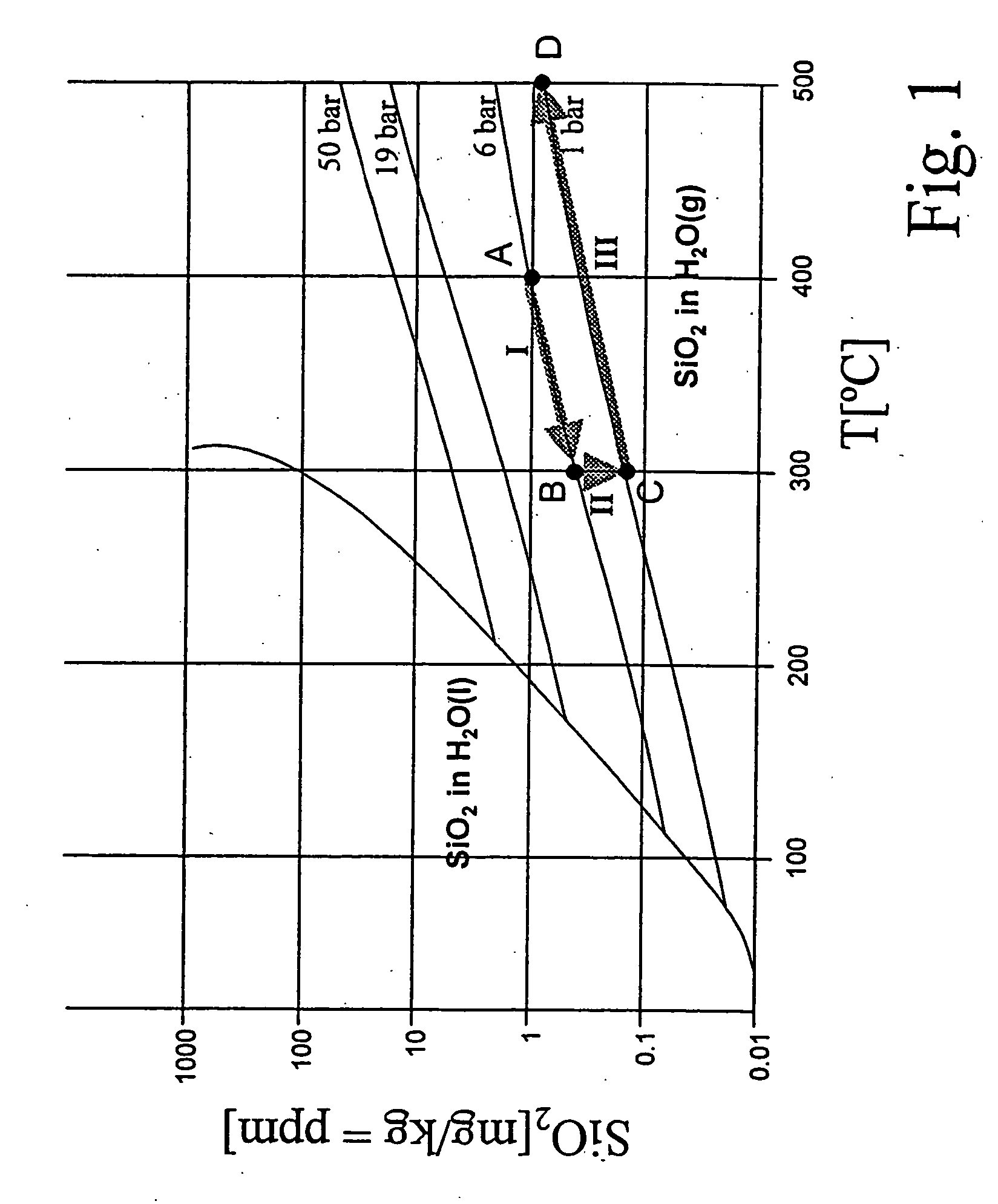
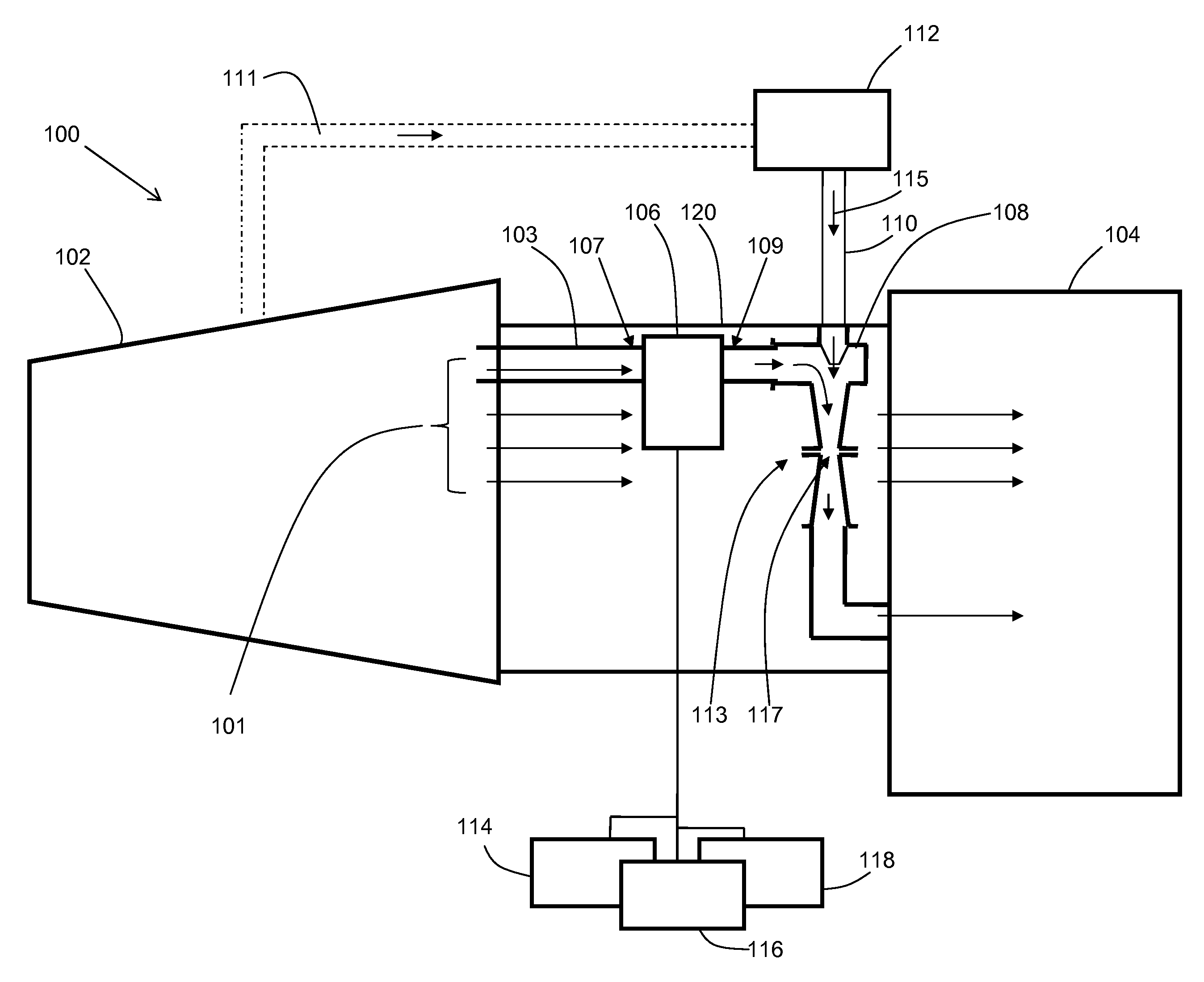
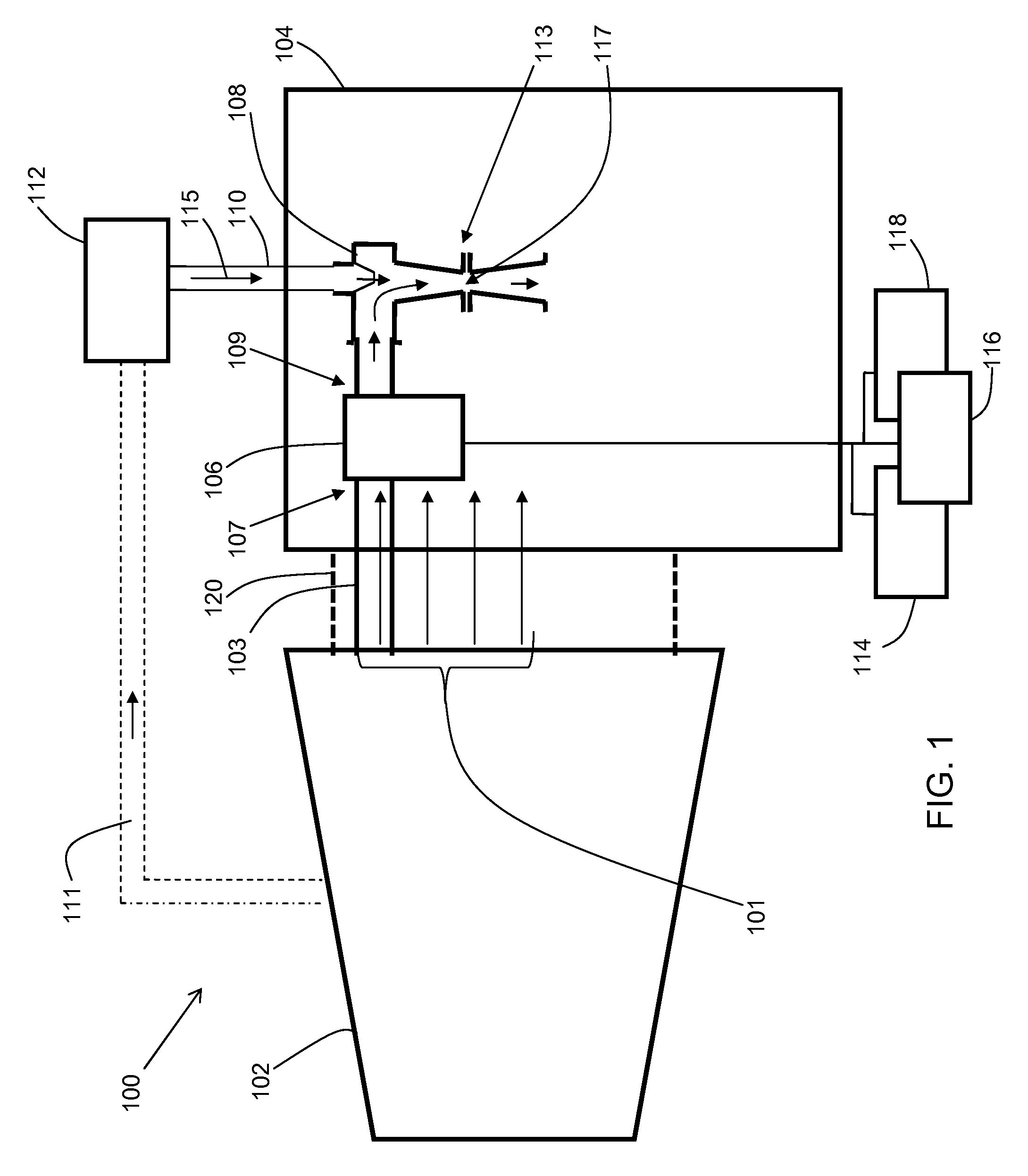
InactiveUS20060010877A1Avoid impuritiesAvoid disadvantagesGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsSolubilityVapor quality
In a method for preventing the deposition of impurities in steam systems, in which steam of a given steam quality flowing in them is subject to temperature and / or pressure changes, a simple prevention of deposits is achieved in that an appropriate structural configuration and design of the steam systems prevents the steam solubility of the impurities present in specific concentrations in the steam from being exceeded as a result of changes in the temperature and / or pressure conditions.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
Measurement of steam quality in steam turbine
A solution for measuring steam quality in a steam turbine is disclosed. A steam quality measurement (SQM) device and an ejector are coupled to a steam turbine through an appropriate piping configuration to draw steam emitted from the turbine through the SQM device for measurement of the steam quality, for example, continuously, during operation of the turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
On-line testing method for sodium analyzer
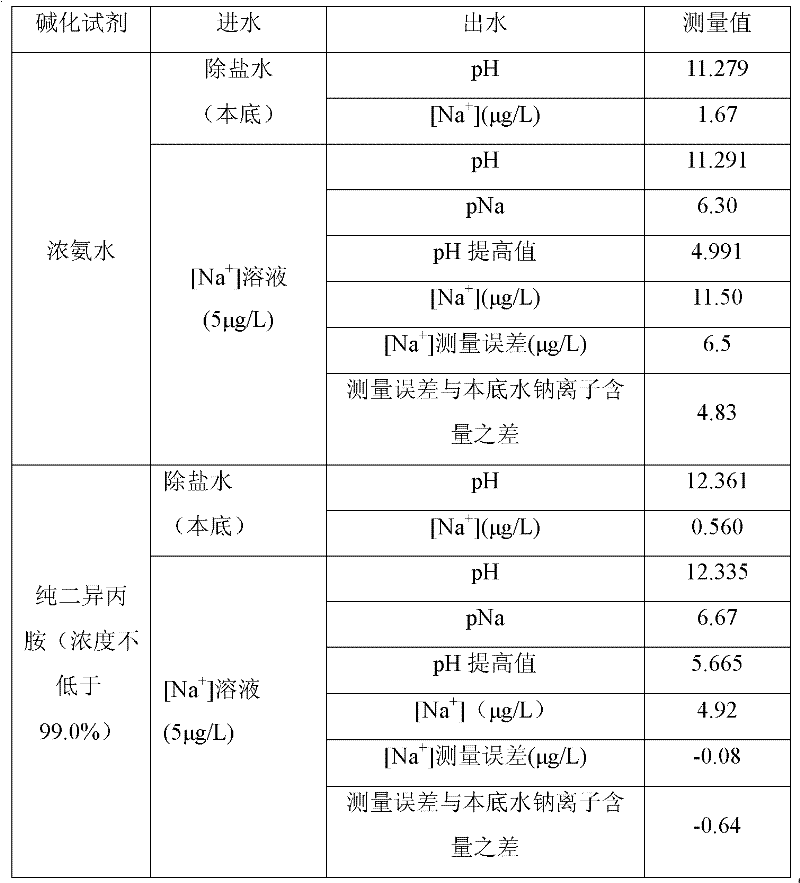
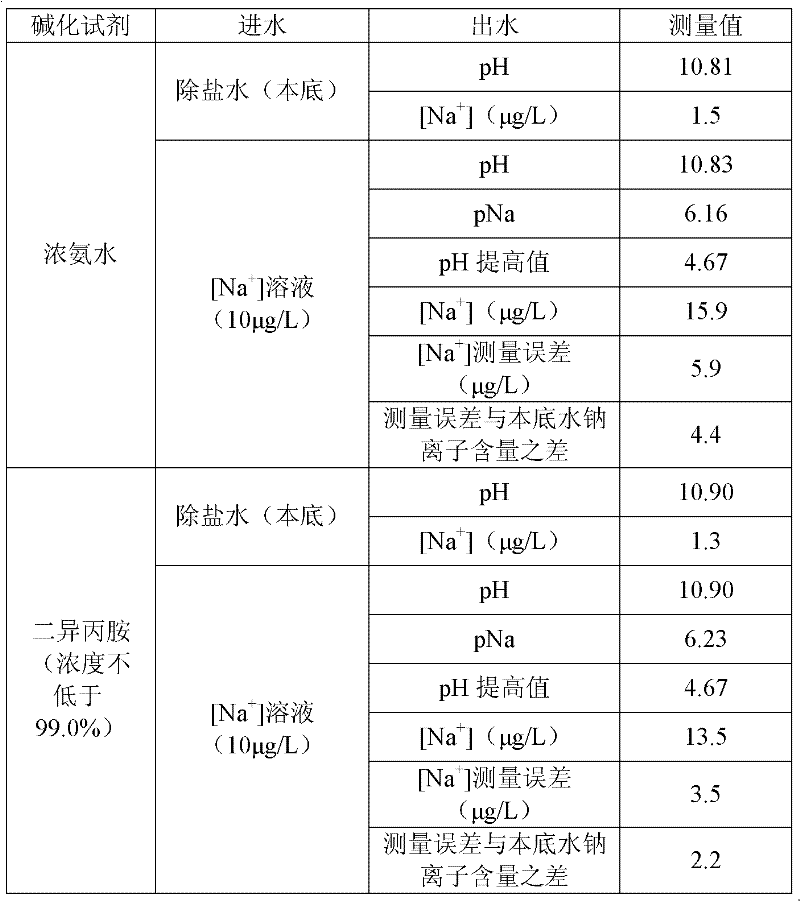
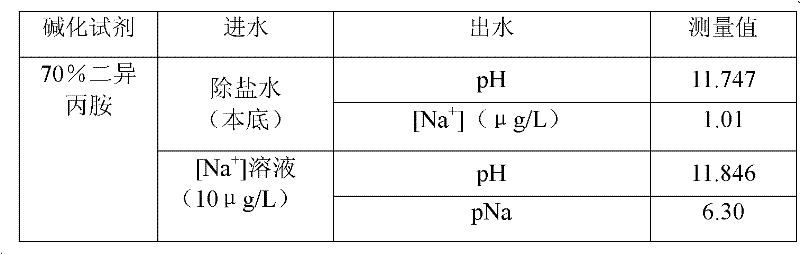
InactiveCN102230858AReduce measurement errorReduce economic lossPreparing sample for investigationObservational errorAlkalinity
The invention provides an on-line testing method for a sodium analyzer. 65-75wt% diisopropylamine and 45-55wt% diisopropylamine are respectively used as the alkali agents for air-ventilating and alkali-adding on-line testing for the sodium analyzer and air-evacuating and alkali-adding on-line testing for the sodium analyzer. The method is capable of not only meeting the requirement of the sodium ions testing for water alkalinity but also reducing the instrument testing error so as to improve the instrument testing reliability. In addition, the correct values of sodium ions testing can help an operator to discover the problems of aqueous vapor quality control and adjust the work mode promptly, thereby reducing the corrosion, scale formation and salification of each machine set each year, so as to avoid an economic loss of millions of Yuan, have a significant importance in the safe and economical operation of a power plant as well as save energy and reduce consumption.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF STATE GRID ANHUI ELECTRIC POWER +1
Thermal power plant vapor quality monitoring method and system
The invention provides a thermal power plant vapor quality monitoring method and system. Through introduction of gray system indexes and combination of a weight adjustment algorithm, a gray system including the weight adjustment algorithm no longer depends on single index measuring points and expert database data for inferring equipment faults, however, other multi-index measuring points are added to serve as characteristic parameters for unified inferential analysis, a gray relational coefficient of set weight values and a parameter sequence is calculated, then an expert system infers and defines calculated relational coefficient weight adjustment value, and a monitoring analysis conclusion is obtained finally to enable fault information covered by vapor quality change to be deeper, so that a thermal power plant vapor quality monitoring conclusion is more accurate.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Hierarchical hydrophilic/hydrophobic micro/nanostructures for pushing the limits of critical heat flux
ActiveUS10492333B2Improve balanceReduce instabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesVapor qualityMicrometer
A high efficiency heat sink for the cooling of microelectronic devices involves a phase change from liquid fluid to fluid vapor with a vapor quality of 100%. The liquid fluid is provided to an active area that contains fins having micrometer dimension that support a membrane that is nanoporous. The membrane is effectively impermeable to liquid fluid but permeable to fluid vapor. The heat sink provides very high heat flux and coefficient of heat transfer at low mass flux over a broad range of surface superheat temperatures. The heat sink can be constructed of equi-spaced posts that separate liquid microchannels from vapor microchannels that are connected through capillary forced valves formed between adjacent equi-spaced posts.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method and device for determining temperatures of upper end and lower end of gas injection well packer
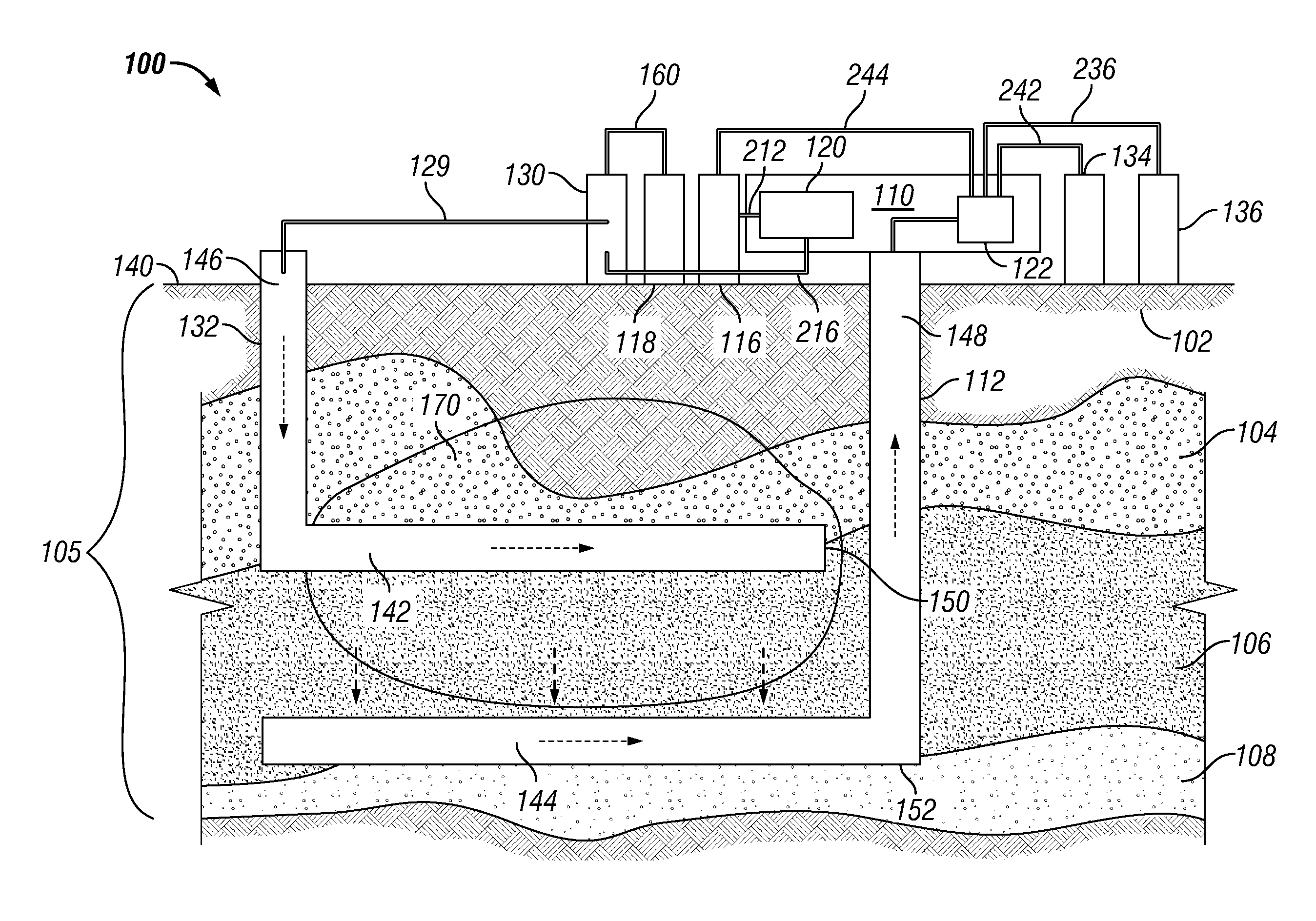
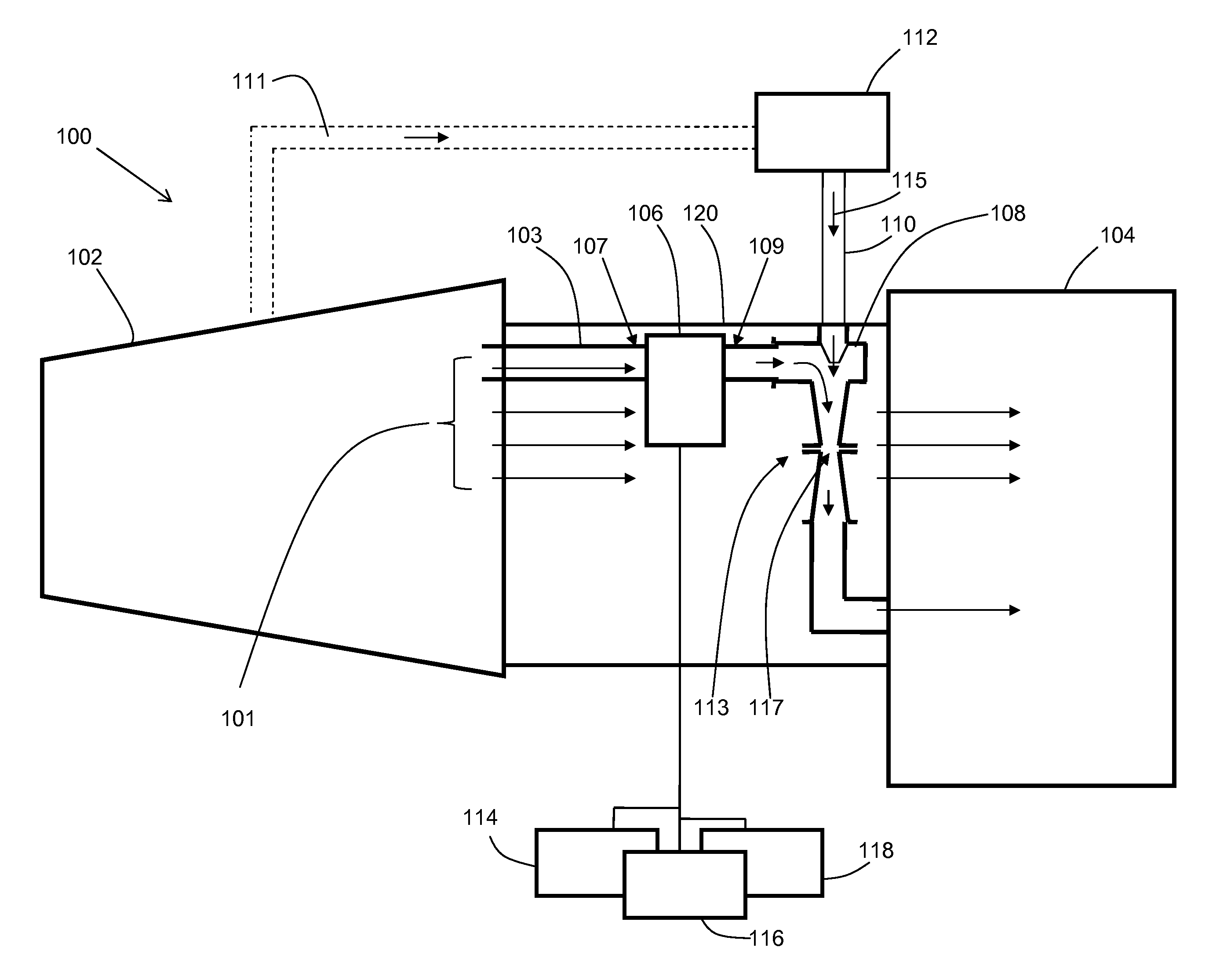
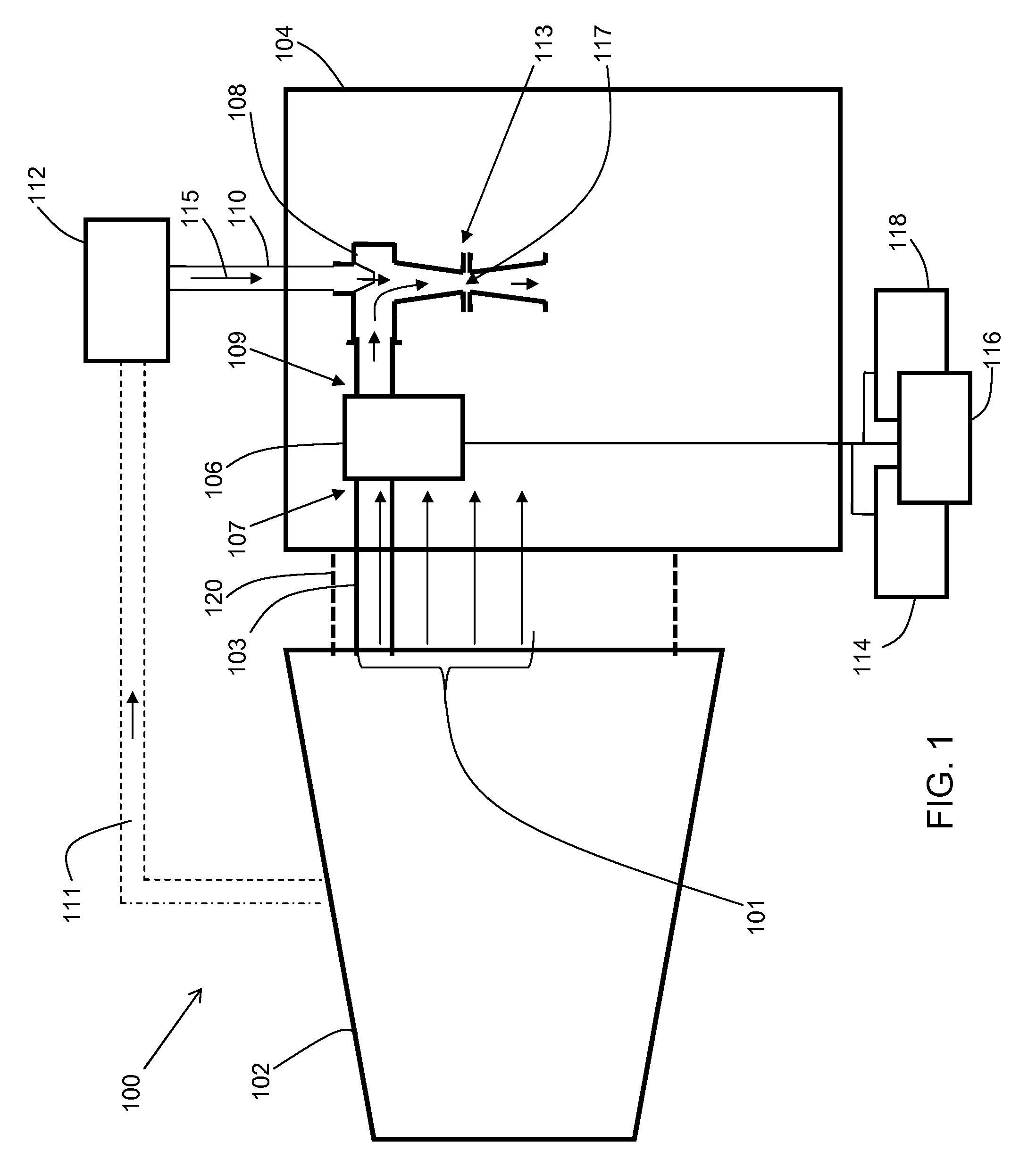
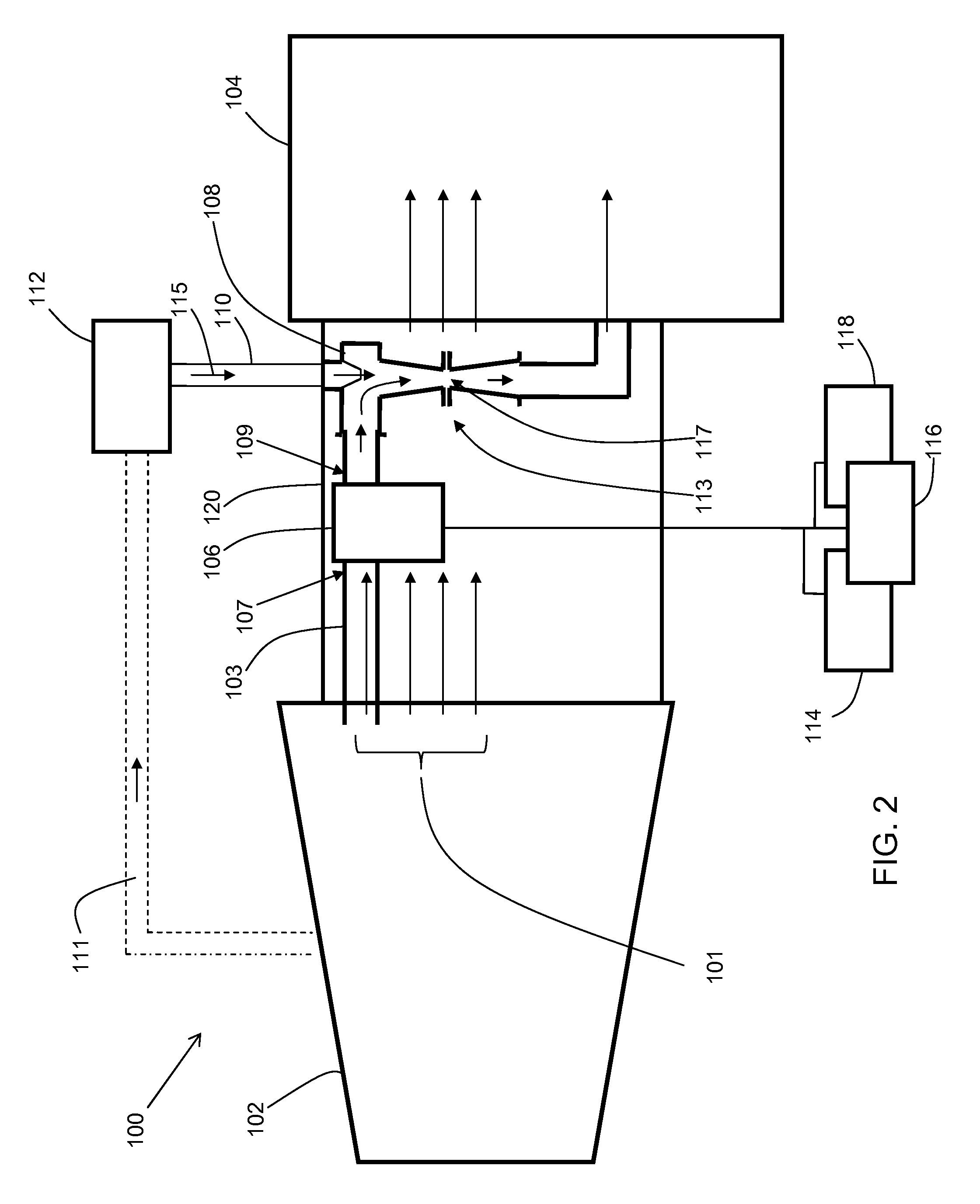
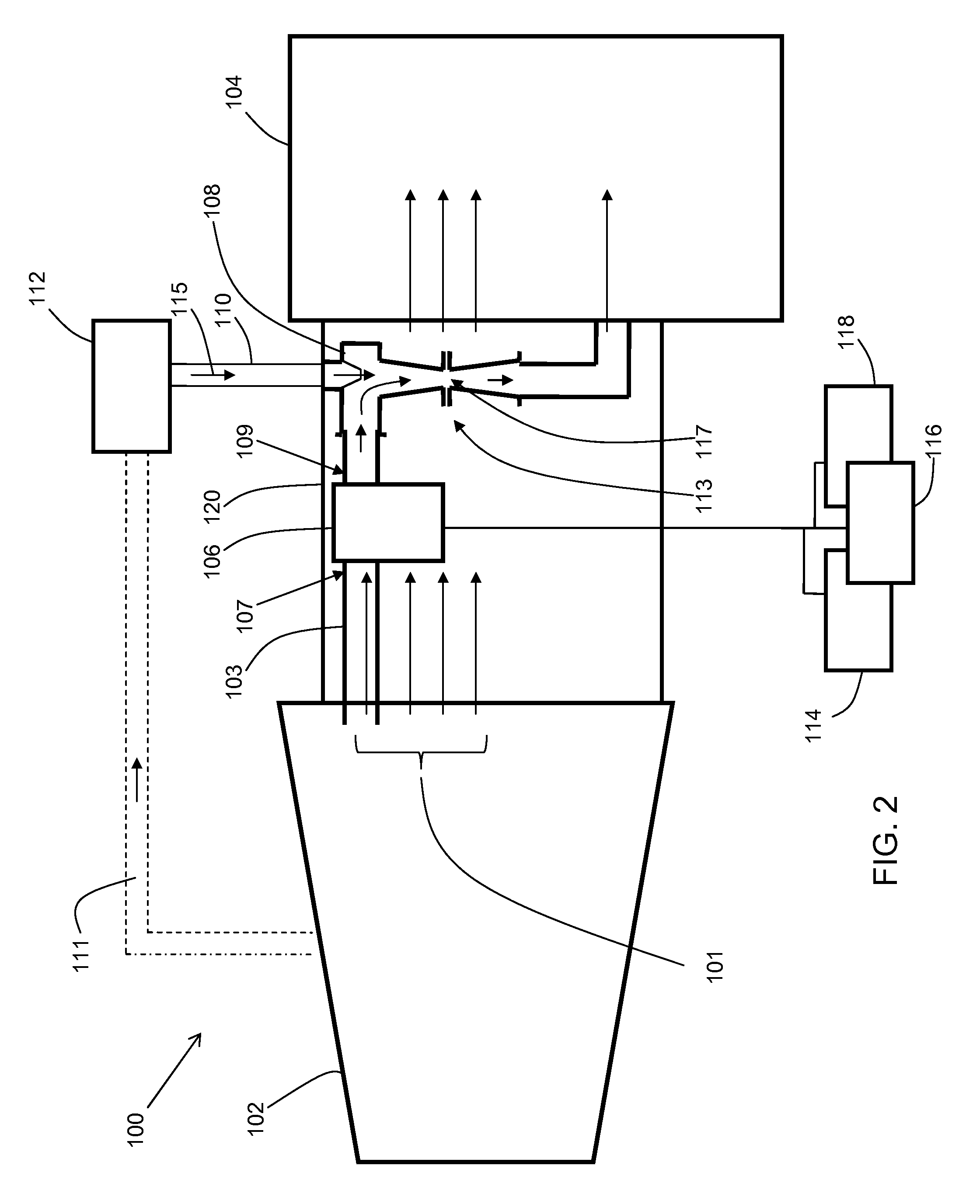
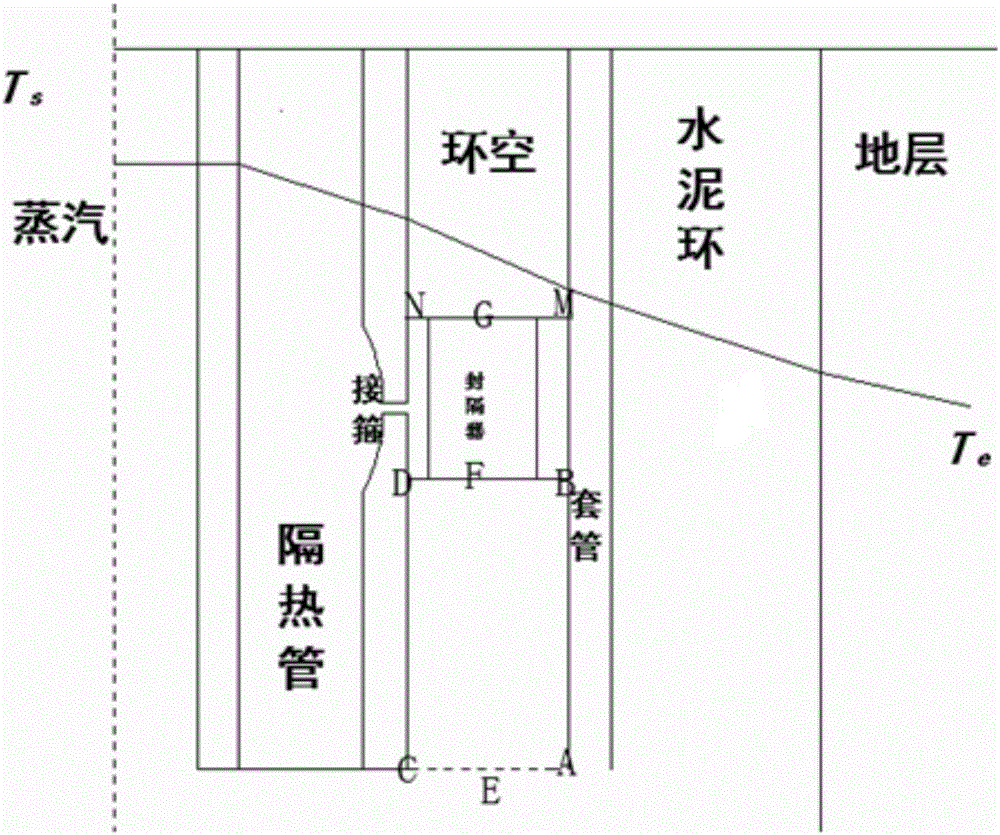
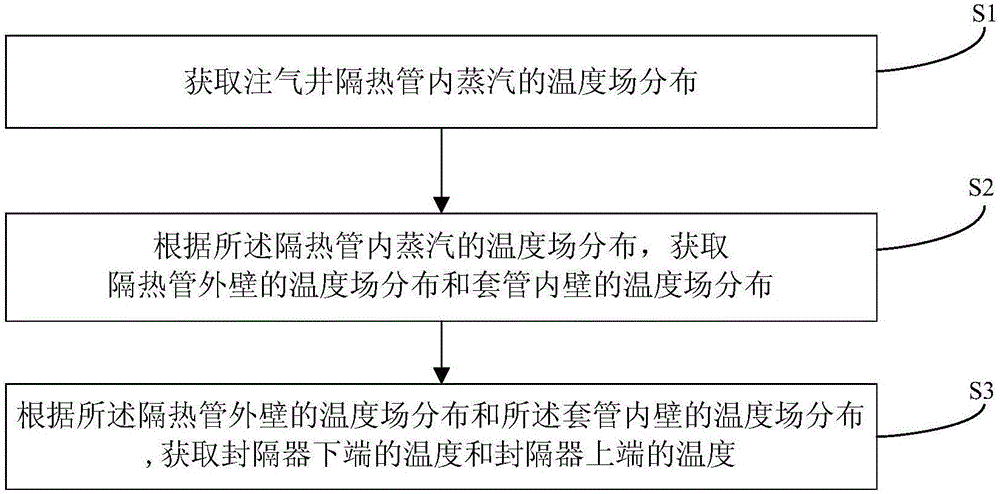
ActiveCN106021958AImprove steaming qualityImprove thermal recovery effectSurveyConstructionsEngineeringInjection well
The invention relates to the field of steam injection thermal recovery of thickened oil, in particular to a method and device for determining the temperatures of the upper end and the lower end of a gas injection well packer. The method includes the steps that the temperature field distribution of steam in a gas injection well heat insulation pipe is acquired; the temperature field distribution of the outer wall of the heat insulation pipe and the temperature field distribution of the inner wall of a casing pipe are acquired according to the temperature field distribution of the steam in the heat insulation pipe; the temperature of the lower end of the packer and the temperature of the upper end of the packer are acquired according to the temperature field distribution of the outer wall of the heat insulation pipe and the temperature field distribution of the inner wall of the casing pipe. According to the method, the temperature of the upper end of the packer and the temperature of the lower end of the packer are calculated, and therefore the position of the packer can be optimized; the method is of great guiding significance on improvement of the heat insulation effect of a gas injection well, prolonging of the thermal recovery life of an oil well and improvement of the quality of steam and the oil well thermal recovery effect.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Once through steam generator with 100% quality steam output
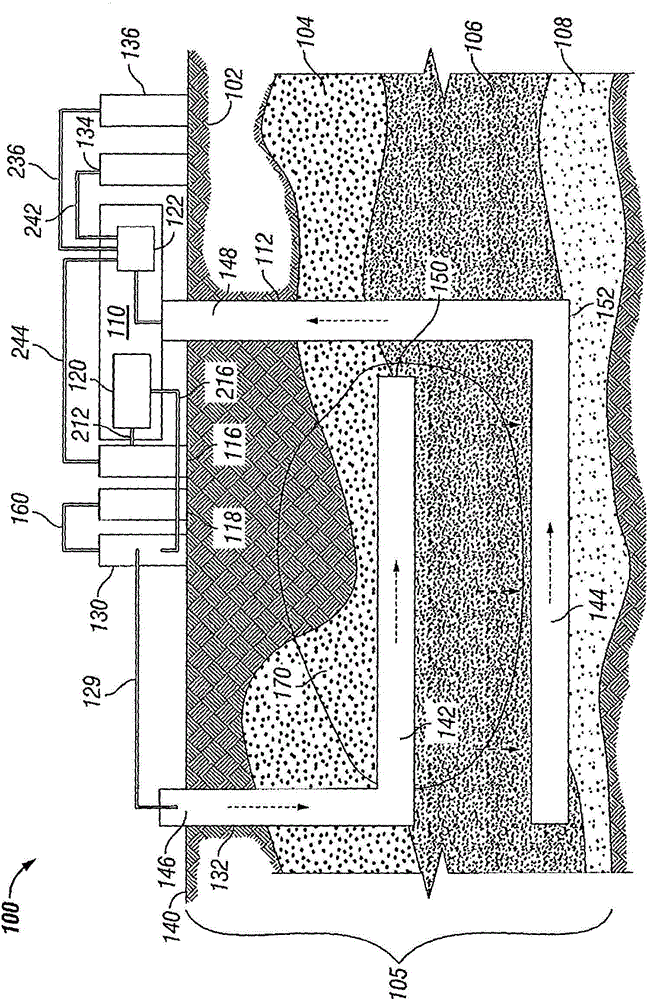
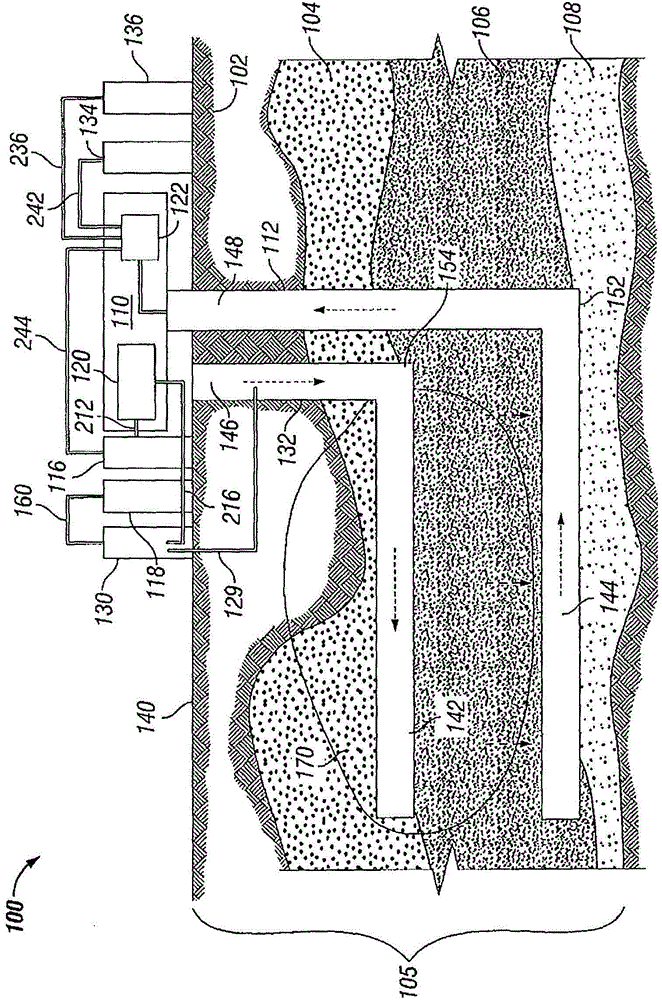
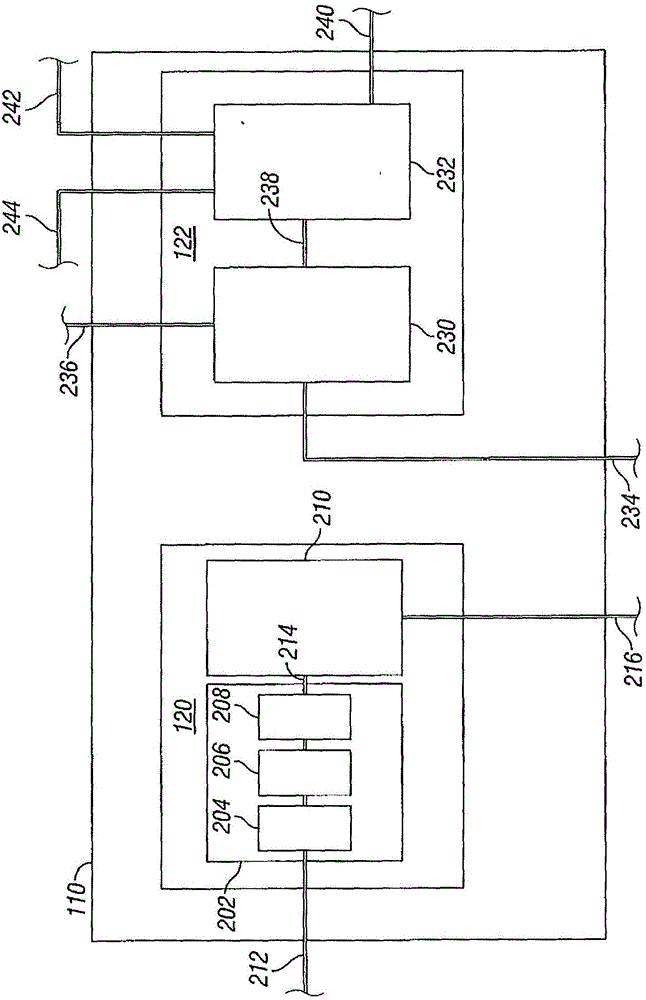
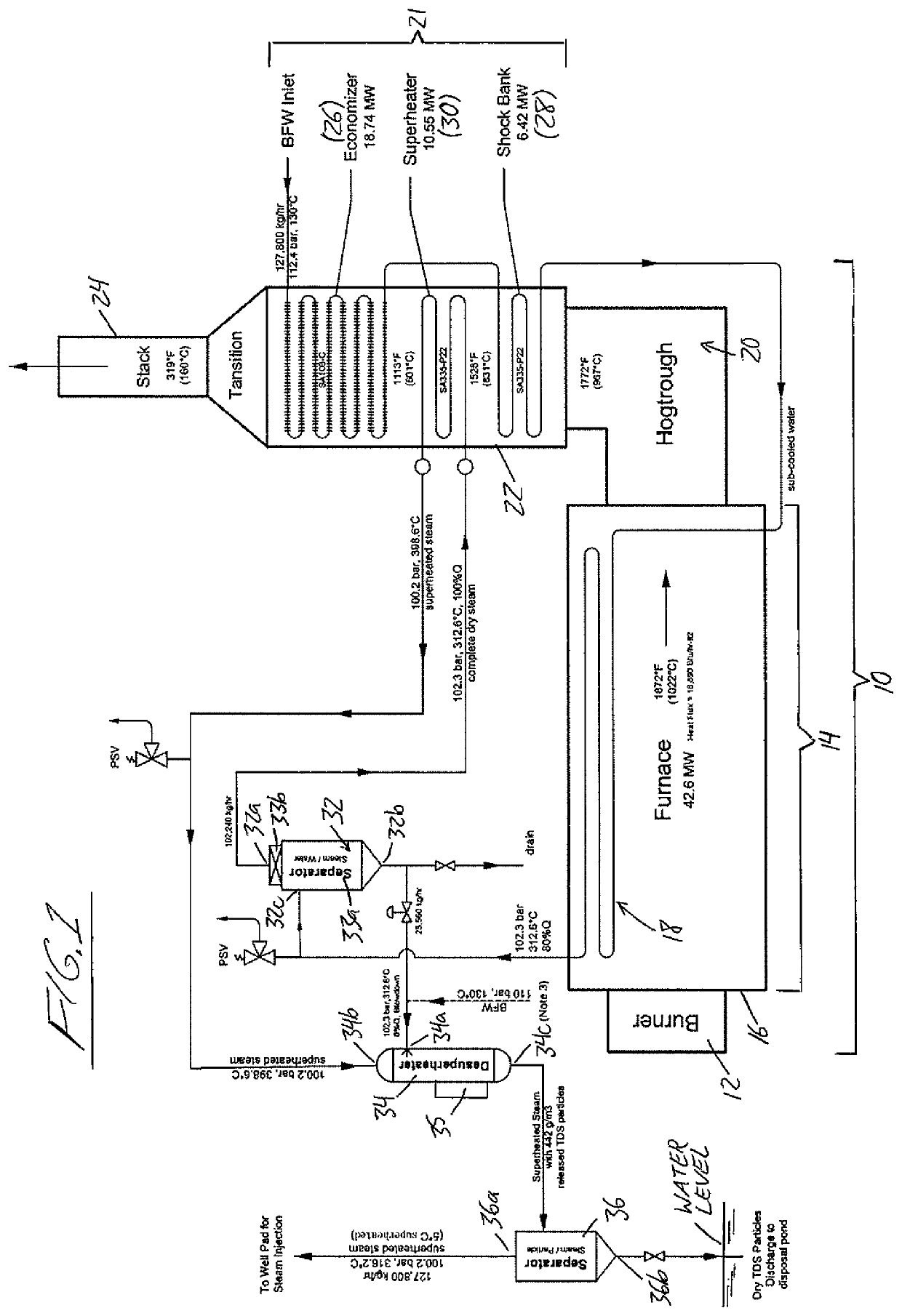
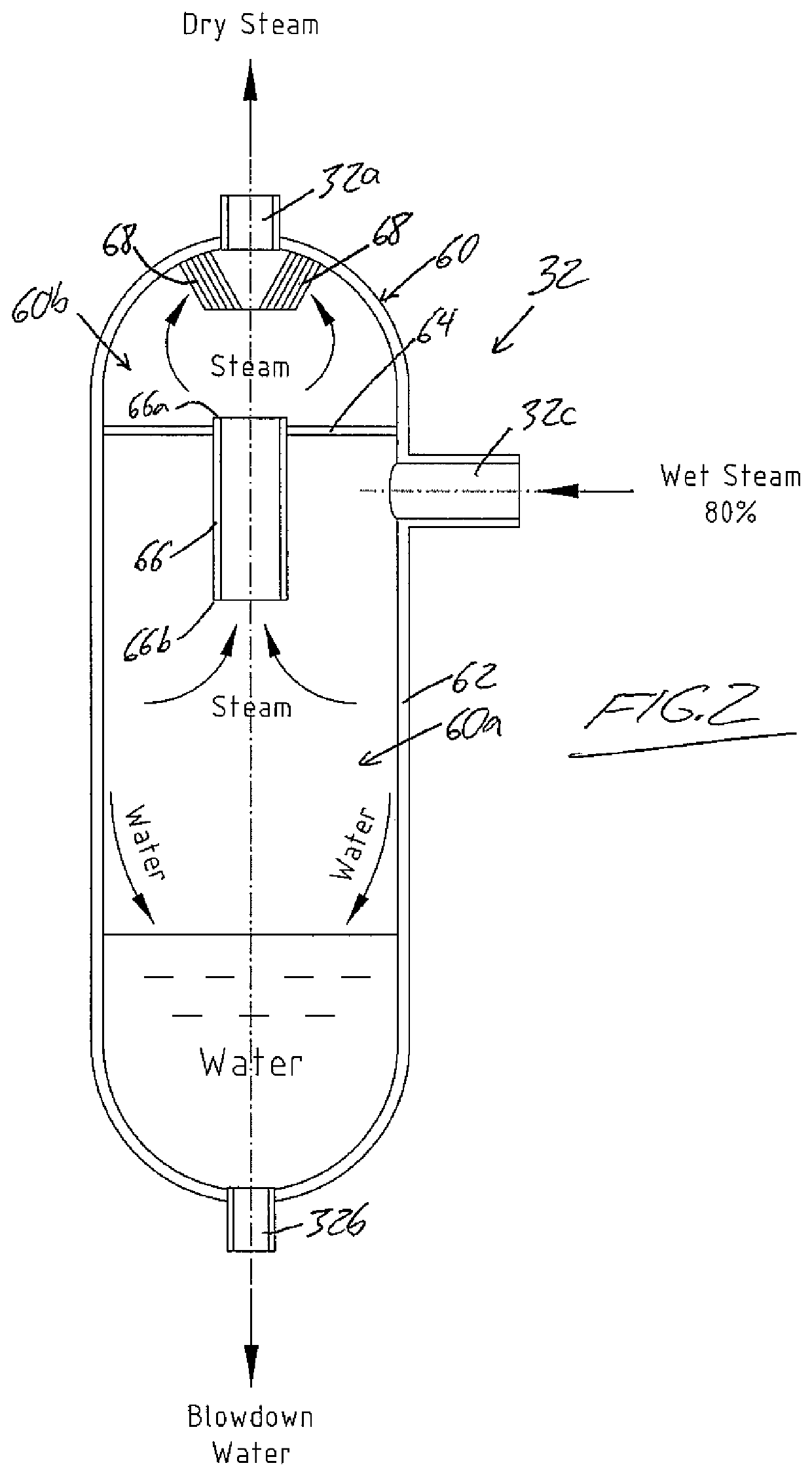
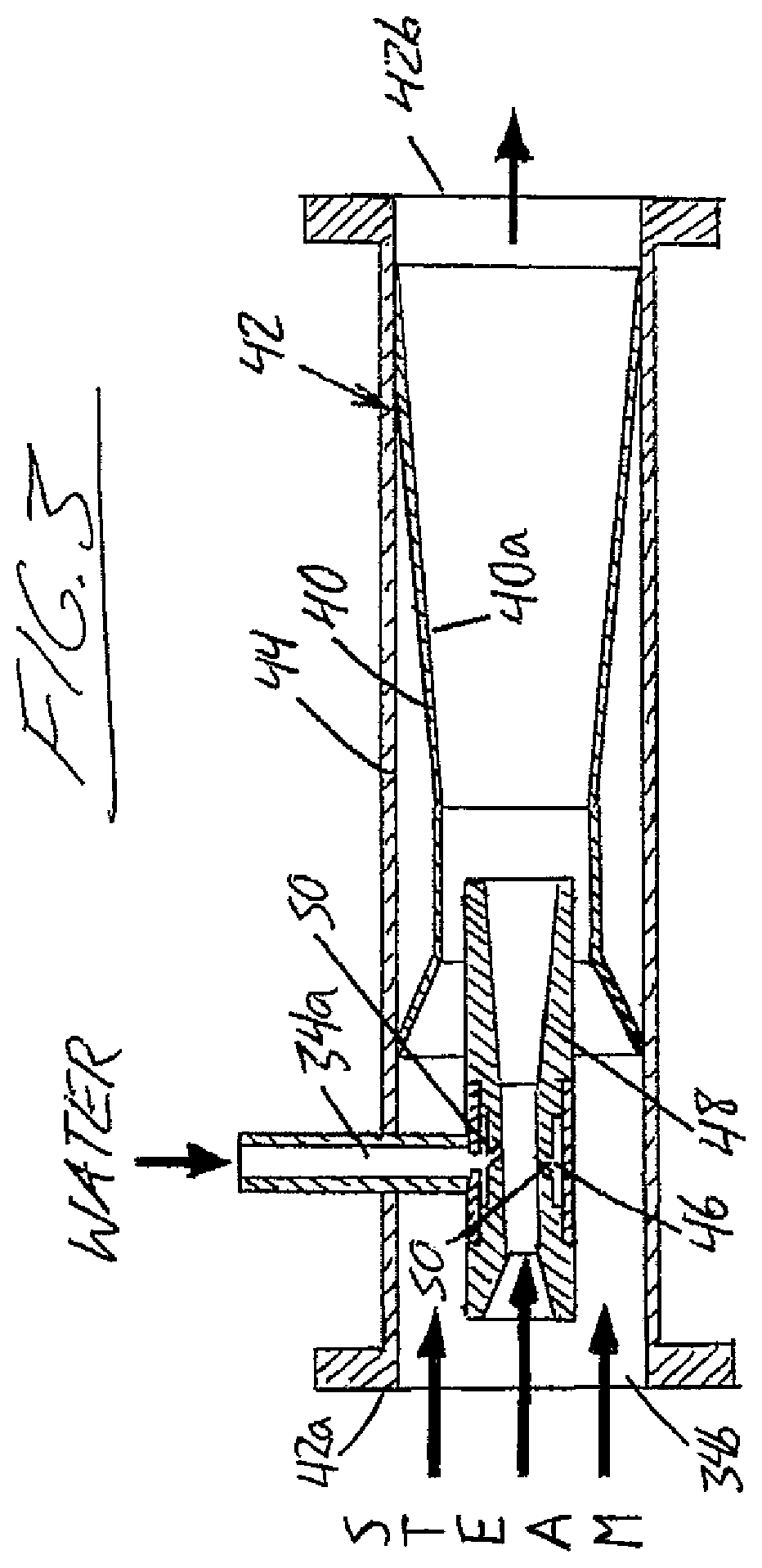
ActiveUS10830431B2Improve steaming qualitySuperheating controlSteam generation using pressureThermodynamicsVapor quality
A system for deriving 100% quality steam for steam assisted gravity drainage (SAGD) injection or other applications features a once through steam generator (OTSG), a steam-water separator connected downstream of the OTSG's radiant tubes to separate steam and water from a two-phase flow received therefrom, superheater tubes installed in the convection section and connected to a steam outlet of the steam-water separator in downstream relation thereto to receive and heat dried steam therefrom to a superheated state, and a desuperheater connected downstream of the superheater tubes to receive the superheated steam therefrom and use same to vaporize blowdown water from the steam-water separator, whereby the vaporized blowdown water and the superheated steam collectively form a superheated steam output for the intended application, typically after additional separation of solid particles therefrom for optimal steam quality.
Owner:CANADA J R CONSULTING INC
Storage system for fuels
InactiveUS20180003431A1Well mixedQuality improvementSolidificationLiquefactionVapor qualityDistillation
A condensation system for a reservoir, which stores fuel cryogenically, is disclosed. A portion of the fuel exists as a boil-off gas with a first vapor quality. The condensation system includes an absorption unit coupled to the reservoir and is configured to receive and mix the boil-off gas with a refrigerant, forming a liquid solution. A distillation unit is coupled to the absorption unit to receive the liquid solution at a supplemented pressure, and is configured to separate the fuel to a gaseous state from the liquid solution. Further, a cooling circuit is configured to receive the fuel in the gaseous state from the distillation unit at the supplemented pressure and a supplemented temperature, and deliver the fuel to the reservoir at a lower pressure and a temperature, with a vapor quality lower than the first vapor quality.
Owner:ELECTRO-MOTIVE DIESEL
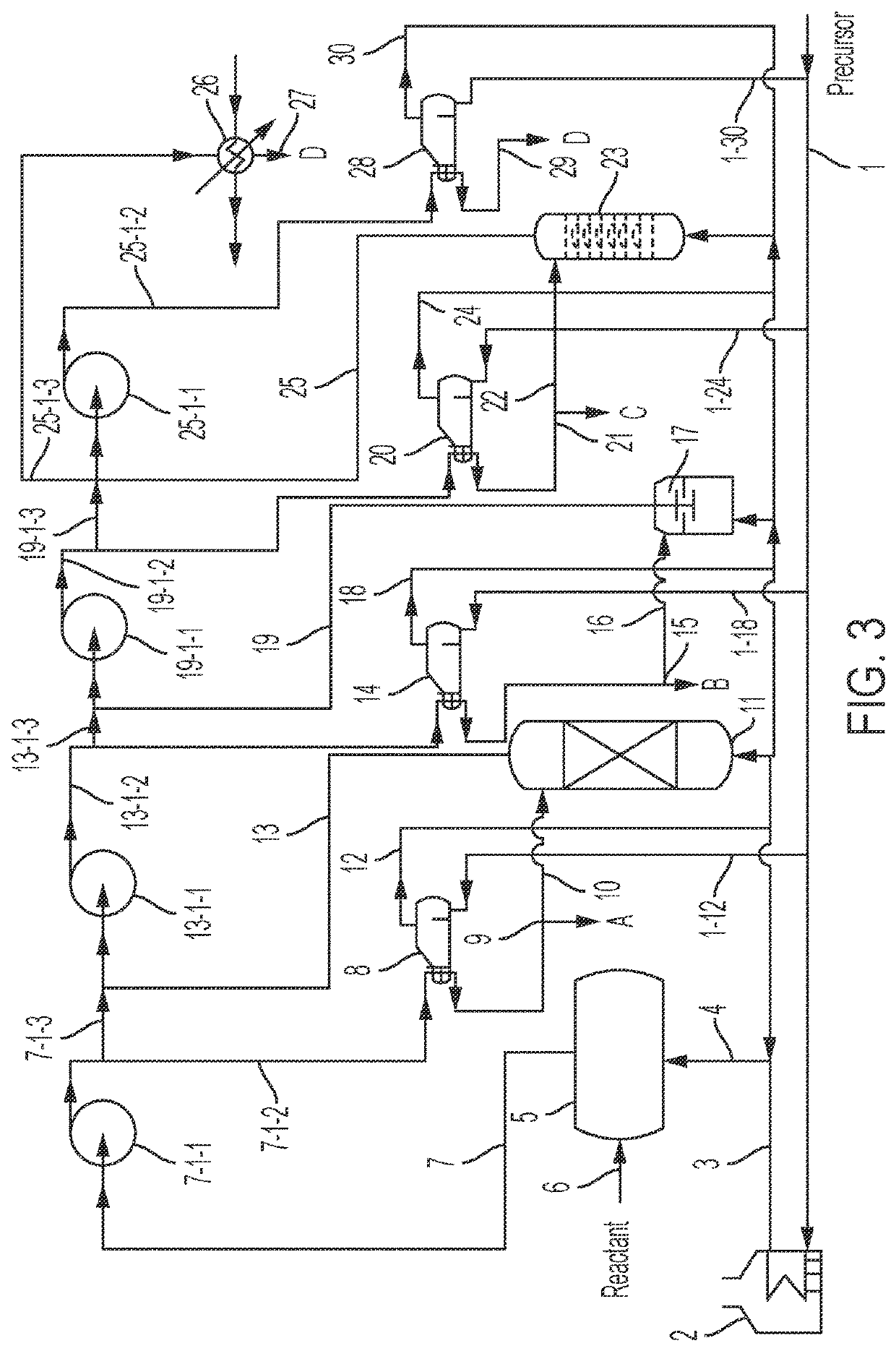
Methods and systems for optimizing mechanical vapor compression and/or thermal vapor compression within multiple-stage processes
ActiveUS20220016542A1Increase pressureIncrease temperatureThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingThermodynamicsVapor quality
The present invention utilizes mechanical vapor compression and / or thermal vapor compression integrating compression loops across multiple process stages. A sequential network of compressors is utilized to increase the pressure and condensing temperature of the vapors within each process stage, as intra-vapor flow, and branching between process stages, as inter-vapor flow. Because the vapors available are shared among and between compressor stages, the number of compressors can be reduced, improving economics. Balancing vapor mass flow through incremental compressor stages which traverse multiple process stages by splitting vapors between compressor stages enables the overall vapor-compression system to be tailored to individual process energy requirements and to accommodate dynamic fluctuations in process conditions.
Owner:ENERGY INTEGRATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com