Patents
Literature
30 results about "Xerophyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A xerophyte (from Greek ξηρός xeros dry, φυτόν phuton plant) is a species of plant that has adaptations to survive in an environment with little liquid water, such as a desert or an ice- or snow-covered region in the Alps or the Arctic. Popular examples of xerophytes are cacti, pineapple and some Gymnosperm plants.
Collecting device and method of root exudates from xerophyte
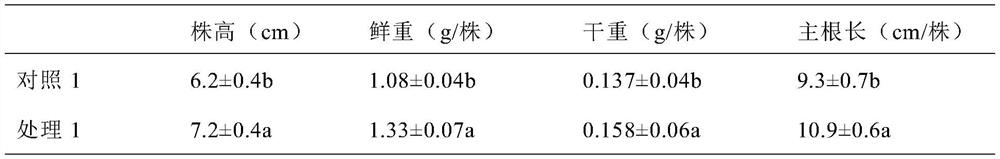
InactiveCN103776662AGuaranteed normal growthReflect the actual situationWithdrawing sample devicesRoot growthNormal growth
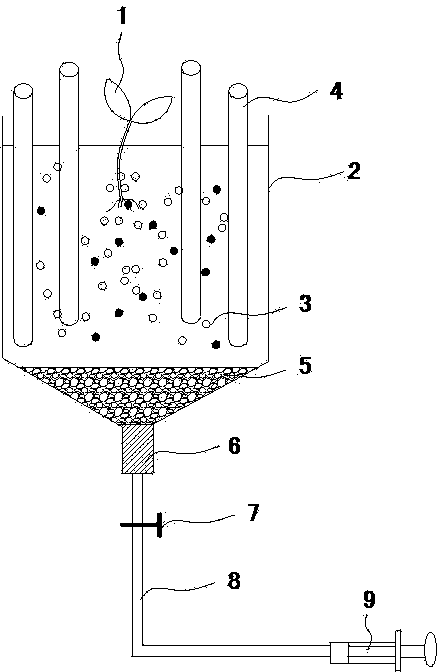
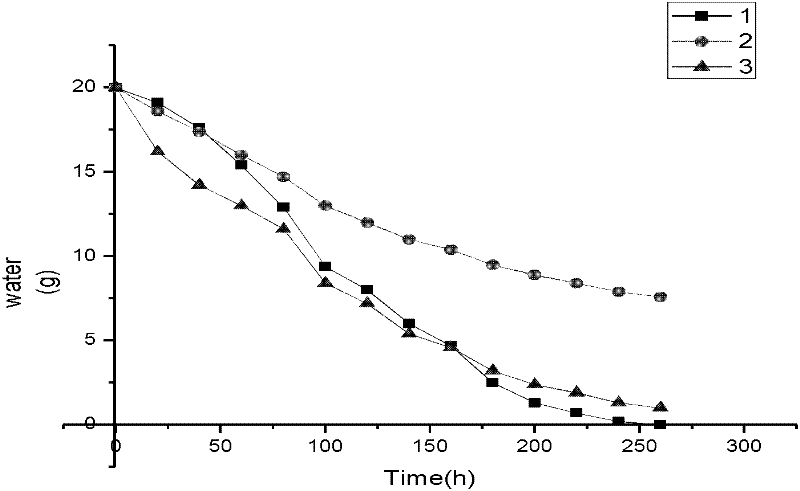
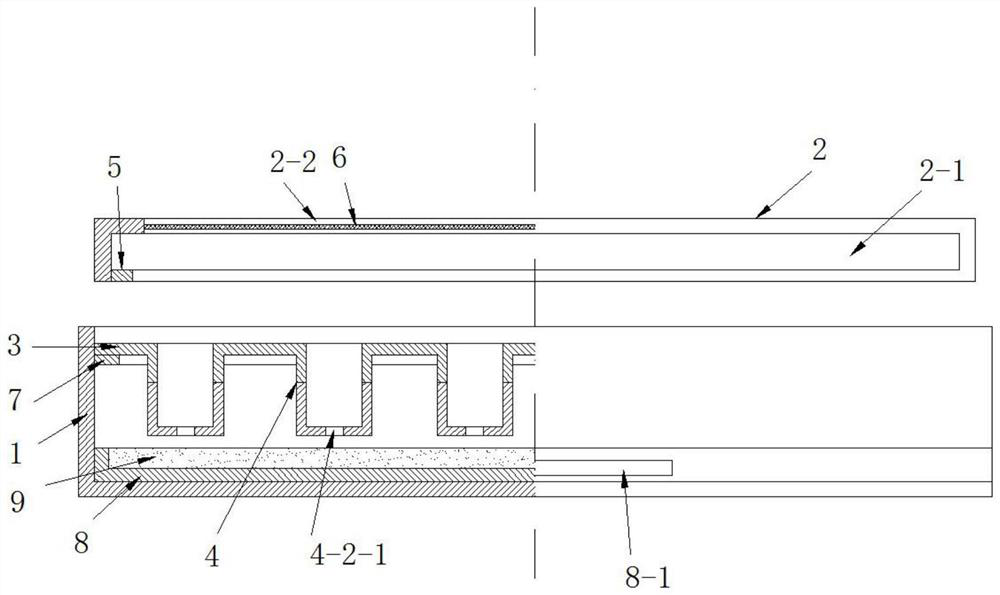
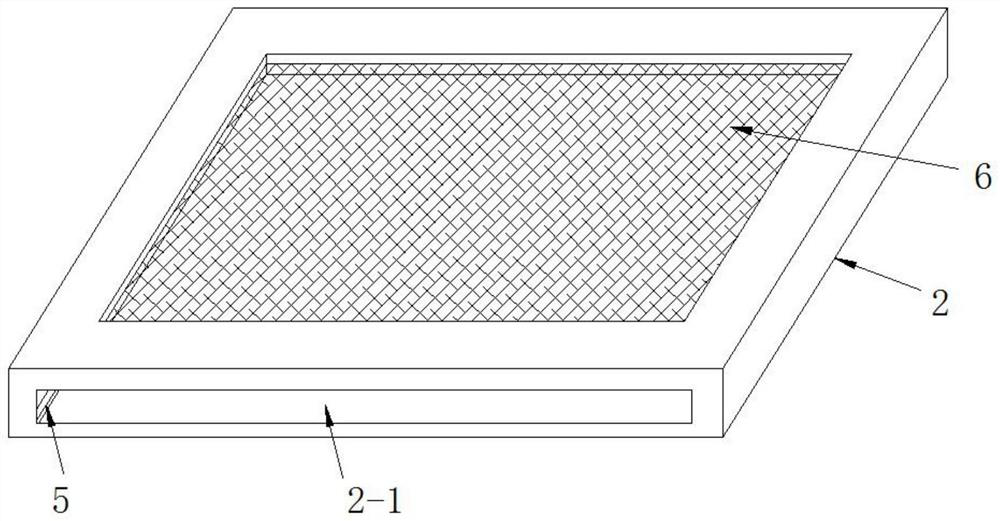
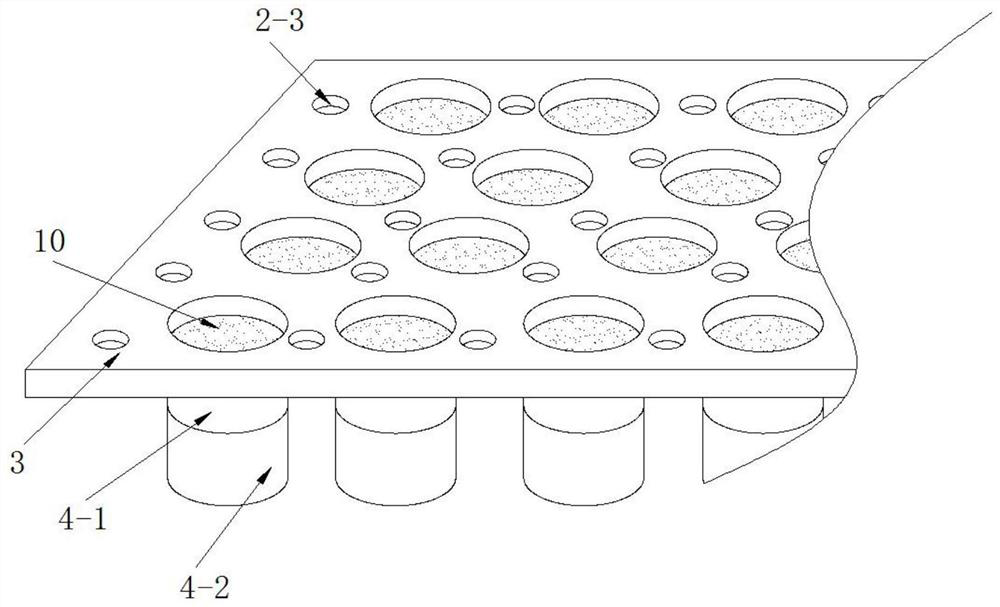
The invention provides a collecting device of root exudates from xerophytes. The collecting device comprises a cultivating bucket, wherein the bottom surface of the cultivating bucket is communicated with a rubber tube, and the other end of the rubber tube is connected with an injector, a soil vermiculite mixed culture medium layer and a filter layer are sequentially spread in the cultivating bucket from top to bottom, and an irrigation tube is further arranged in the cultivating bucket. The invention also provides a collecting method for the root exudates from xerophytes, which is designed according to the collecting device. The collecting device and method are suitable for research on plants under soil cultivation condition, especially the root exudates from xerophytes; compared with water-culture or simple medium cultivation method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that the actual condition of the root exudates from xerophytes under the natural condition can be better reflected; meanwhile, the collecting device cannot disturb the root growth or damage the rhizoapple environment in the premise of guaranteeing the normal growth of the plant, and the root damage and bleeding disturbance caused by collecting the root exudates through a traditional earth culture method are avoided.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Construction method for wet land artificial ecological island
InactiveCN101429758AReduce the degree of being washed outIncrease diversityArtificial islandsLand reclamationSludgeEngineering
The invention provides a method for constructing an artificial ecological island in wetland, which is to stack building waste and river mud or pond sludge into an island body according to the volume ratio of 2 to 3 on the basis of the prior natural island or a hard foundation in the wetland, and level and grind the island body layer by layer during the stacking; the circumference on the top of the island body is placed by stone and cement mortar, and xerophytes and hygrophytes are planted in the middle on the top of the island body; the stone and the cement mortar are used for placing vertically and horizontally frame bodies on the circumferential island slope of the surface of the island body; waste concrete bodies or gravel is filled into spaces of the frame bodies; slurry is sprayed or poured on the waste concrete bodies or the gravel, and the thickness of the slurry can cover the gravel or rubble; hygrophytes, emergent aquatic plants and submerged plants are planted on a slurry layer; and larger plants are planted before the waste concrete bodies or the gravel is filled. The method has low cost, is convenient to construct, is favorable for conserving water and soil, reduces the gradation degree of the island body, and makes a wetland ecosystem maintain stable.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for controlling desertification by adopting novel biological material gamma-polyglutamic acid (PGA)
InactiveCN102383415AControl liquidityReduce water transpirationOrganic fertilisersSoil conditioning compositionsXerophyteBlock structure
The invention relates to a method for controlling desertification by adopting a novel biological material and discloses a method for controlling desertification by adopting a novel biological material gamma-polyglutamic acid (PGA). The method comprises the step of spraying a gamma-PGA aqueous solution onto the surfaces of the roots of desert plants 1-10 times, wherein the concentration of the PGA aqueous solution is 0.5-10%. The method has the following beneficial effects: on the one hand, the loose sand soil is adhered into block structures by virtue of gamma-PGA, thus controlling the flowability of the sand soil in the deserts and playing a good role of stabilizing the sand; and on the other hand, the super-strong water retention and absorption of gamma-PGA is utilized to spontaneously form hydrogel by absorbing water poured manually and condensed dew formed at night, thus achieving the effect of moisture slow release and meeting the basic moisture demands of the plant seedlings with undeveloped root systems; and by combining the two hands, the transpiration and infiltration of the plant moisture can be furthest reduced and the soil environment in the deserts can be improved while the growth of the xerophytes in the deserts is promoted, thus finally achieving the effect of converting the sand into forests.
Owner:天津北洋百川生物技术有限公司
Artificial wetland for processing saliferous water body in northwest district
ActiveCN102616939AEfficient purificationSuitable ecological environmentSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentConstructed wetlandEngineering
The invention relates to an artificial wetland for processing a saliferous water body in northwest district. The artificial wetland is formed by a settling pond, an overland flow pond, a hygrophyte pond and a hydrophyte pond which are sequentially connected through an overflow dam, wherein one end of the settling pond is provided with a controlled inflow port, and the other end of the settling pond is provided with an abyssal region; the overland flow pond comprises a plurality of ridges; a channel is formed between each two adjacent ridges; salt-resistive xerophytes are planted on the ridges; salt-resistive hygrophytes are planted in the hygrophyte pond; salt-resistive hydrophytes are planted in the hydrophyte pond; and the bottom parts of the settling pond, the overland flow pond, the hygrophyte pond and the hydrophyte pond are respectively provided with a steady gradient in downward trend from each inlet and each outlet. The invention also provides a method for processing the saliferous water body in the northwest district by utilizing the artificial wetland. The artificial wetland is suitable to be used in the northwest district in China and the problem that a large number of lake water bodies have serious salinization can be solved.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST +1
Orchard soil ventilating and fertilizing method
ActiveCN104718866AImprove gas environmentGas environment maintenanceFertilising methodsFertilizer mixturesInsect pestXerophyte
The invention discloses an orchard soil ventilating and fertilizing method. The orchard soil ventilating and fertilizing method comprises the following steps: drilling fertilizing holes at certain intervals by a soil punching machine along the inner edges of tree disks of fruit trees, packing thick organic materials in the bottoms of the holes, inserting bundled corn straw or branches into the bottoms of the fertilizing holes, then filling with organic fertilizer, spraying chemical fertilizer in ratio when the added organic fertilizer reaches a certain height, further adding the organic fertilizer, irrigating after the fertilizing holes are full filled with the organic fertilizer, slightly shaking the corn straws or the branches which are inserted into the holes, and finally covering the fertilizing holes and the tree disks with straw carpets; removing the straw carpets during topdressing in summer, applying the chemical fertilizer in ratio and covering with the straw carpets again. According to the orchard soil ventilating and fertilizing method, the corn straws or the branches are inserted into the fertilizing holes; the air permeability is improved; with the combination of the straw carpets with few same plant diseases and insect pests as the xerophilous plants, the water, fertilizer, air and heat are obviously improved; the temperature and the humidity of the soil are stabilized; the plant diseases and insect pests are reduced; the root development and the nutrient absorption are promoted; the consumption of the chemical fertilizer is reduced; the labor efficiency is improved; the labor intensity is alleviated.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Gathering and cleaning method for extreme xerophyte undershrub reaumurta soongorica seeds
InactiveCN104686009AThe method is simpleHave twice the result with half the effortSeed and root treatmentXerophyteSprigging
The invention discloses a gathering and cleaning method for extreme xerophyte undershrub reaumurta soongorica seeds. The gathering and cleaning method for the extreme xerophyte undershrub reaumurta soongorica seeds includes that gathering, to be specific, shearing the current fruited branches with mature seeds, gathering the branches, tedding at a sunning ground, tedding under the sun to realize air drying, beating, and gathering the fallen seeds; cleaning, to be specific, placing the gathered seeds in a vessel, adding water to the seeds, stirring completely, and standing; air drying, to be specific, fishing out the full seeds at the bottom of the vessel, draining off the water, and tedding to realize air drying; dust removing, to be specific, removing dust from the air dried seeds through the gentle breeze of an electric fan; sealing and storing, to be specific, bagging the clean full seeds, and storing in a -20 degrees centigrade freezer for latter use. The gathering and cleaning method for extreme xerophyte undershrub reaumurta soongorica seeds is easy and convenient to operate, fast and effective, and twice the result is obtained with half the effort; a lot of full seeds used as germination experiment and seeding materials can be cleaned and selected in a short time, and the gathering and cleaning method for extreme xerophyte undershrub reaumurta soongorica seeds is very good for popularization in the production and significant for the reproduction of the eremophyte reaumurta soongorica.
Owner:GANSU DESERT CONTROL RES INST
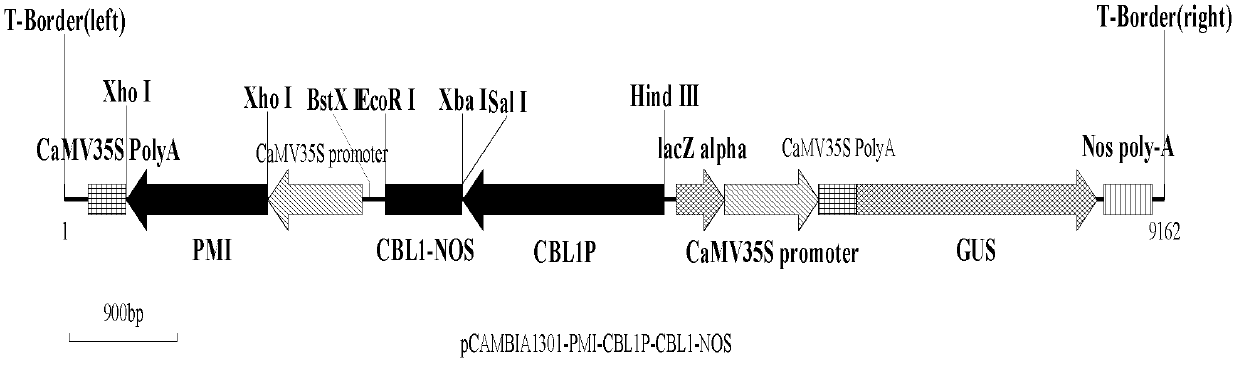
Transformation method of eucalyptus grandis
InactiveCN102660575AFix security issuesMicrobiological testing/measurementHorticulture methodsPhosphomannose IsomeraseXerophyte
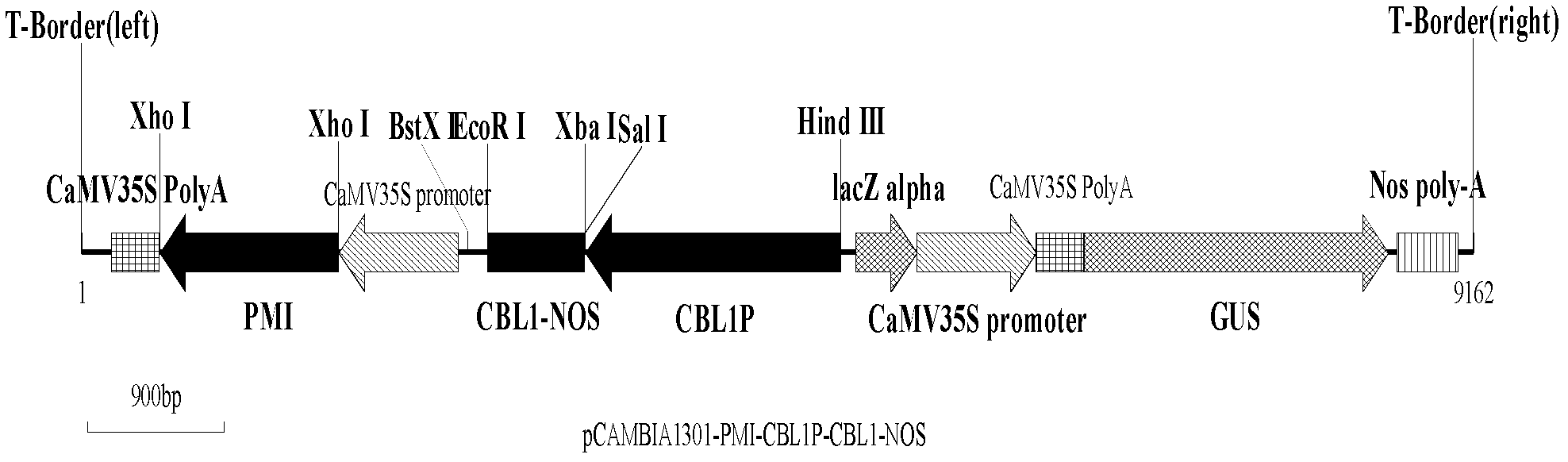
The invention provides a safe and efficient genetic transformation method of eucalyptus grandis in order to solve problems encountered during the process of transforming eucalyptus by using an agrobacterium-mediated method in the prior art. The method is to successfully transfer a target gene AmCBL1 into eucalyptus grandis by constructing an expression vector with a safety marker gene PMI (6-phosphomannose isomerase) as a selection marker, making a plurality of tissue culture experiments and improving genetic transformation methods. The target gene comes from super-xerophyte ammopiptanthus mongolicus (Ammopiptanthus mongolicus (Maxim.) Cheng F.), and is driven by its specific promoter AmCBL1P.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for planting greening plants in artificial shallow lake
InactiveCN102498909ATroubleshoot normal growthRich landscape connotationReceptacle cultivationSoil scienceEngineering
The invention discloses a method for planting greening plants in an artificial shallow lake. The method for planting greening plants in the artificial shallow lake is implemented through the following 9 steps: selection of an external waterproof container, selection of an internal planting container, container configuration, preparation of nutrient soil, filling of nutrient soil, selection of plants, selection of a corresponding external waterproof container, planting of plants, watering, maintenance, so that the problem of normal growth of xerophyte in shallow lakes can be solved, the connotation of the water landscape is enriched, and the landscape level is improved. In addition, the method for planting greening plants in the artificial shallow lake has the advantages of low investment,high efficiency, convenience in management, and the like, and can be applied to greening of artificial shallow lakes in cities in a large area.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
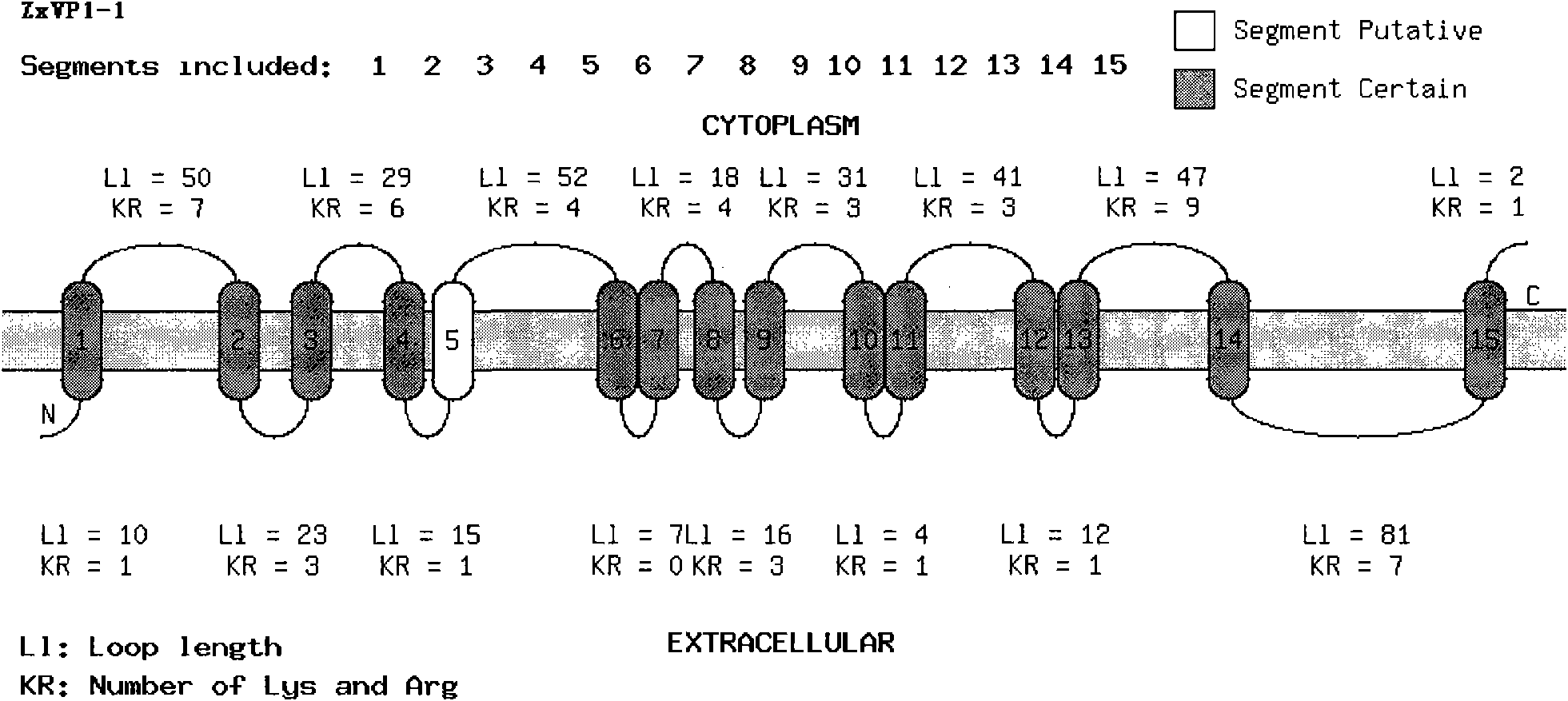
Tonoplast hydrogen pyrophosphatase gene of strong xerophyte zygophyllumxanthoxylum and plant expression vector as well as genetic plant transformation method thereof
The invention relates to tonoplast hydrogen pyrophosphatase gene ZxVP1-1 and two core segments ZxVP1-2 and ZxVP1-3 cloned from succulent xerophyte zygophyllumxanthoxylum peculiar to deserts in Central Asia, and a plant expression vector Pcambia1302-ZxVP1-1 of the gene as well as an engineering agrobacterium GV3101 containing the expression vector. The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and biology, and is mainly used for genetic improvement of crops, can improve characteristics of salinity tolerance, drought control, cold resistance, leanness resistance, biomass and the like of the crops, and has the important social benefit, economic benefit and biological benefit.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Collection device for plant root exudates and collection method for xerophyte root exudates
ActiveCN106989961AAvoid cloggingEffective dredgingWithdrawing sample devicesAgriculture gas emission reductionPlant rootsEngineering
The invention provides a collection device for plant root exudates. A filter plate is arranged in a nutrient liquid barrel to effectively filter solid impurities in liquid to prevent the blockage of a connecting pipe, furthermore, an air blowing device is arranged, so that through holes on the filter plate can be dredged to prevent the through holes on the filter plate from being blocked. The invention further provides a collection method for xerophyte root exudates. A method of combining soil culture and water culture is adopted to reduce the hydroponic time so as to effectively avoid phenomena of rotted roots and the like caused by long-term soaking of plant roots in the liquid, the collection method is suitable for xerophytes, and makes the culture environment more adapted to the growth environment of the xerophytes after carrying out the water culture transiently to further improve the connection accuracy and reliability of the root exudates.
Owner:INST OF SOIL FERTILIZER & RESOURCE ENVIRONMENT JIANGXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Artificial wetland for processing saliferous water body in northwest area
ActiveCN102616939BEfficient purificationSuitable ecological environmentSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentConstructed wetlandEngineering
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST +1
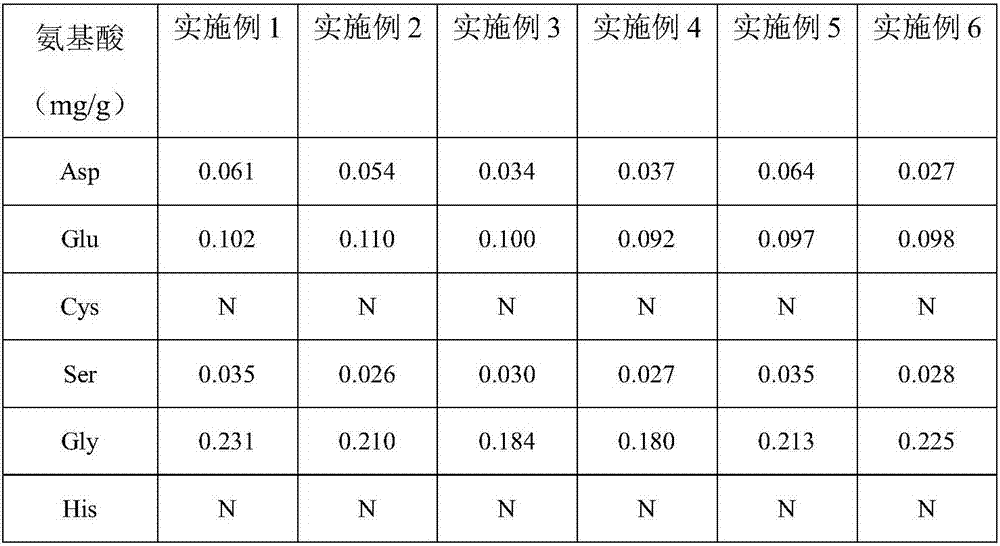
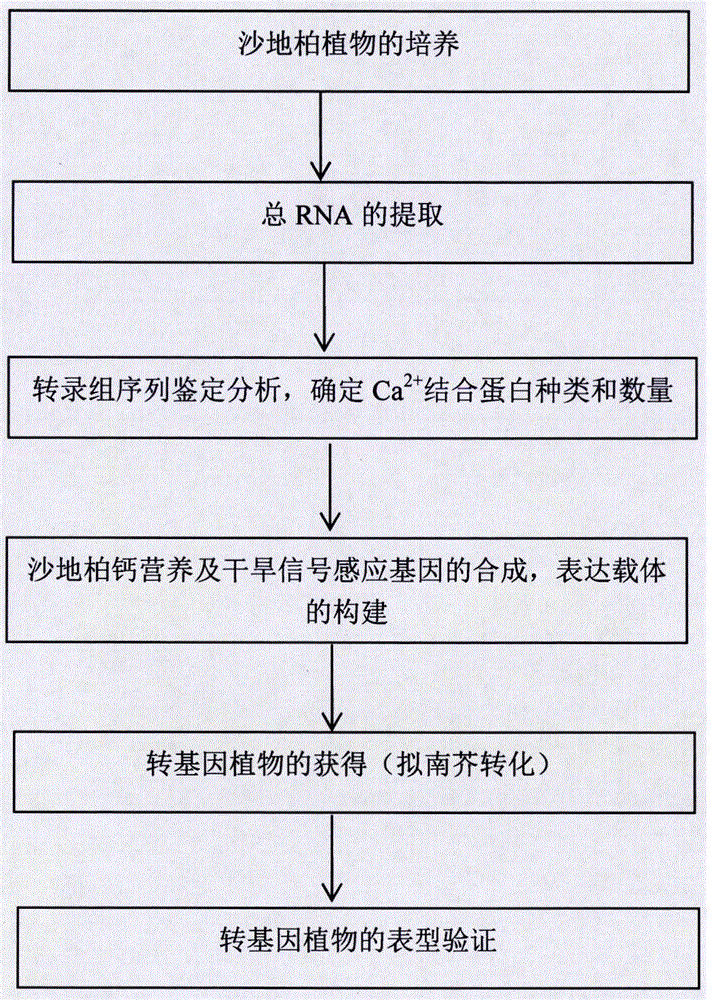
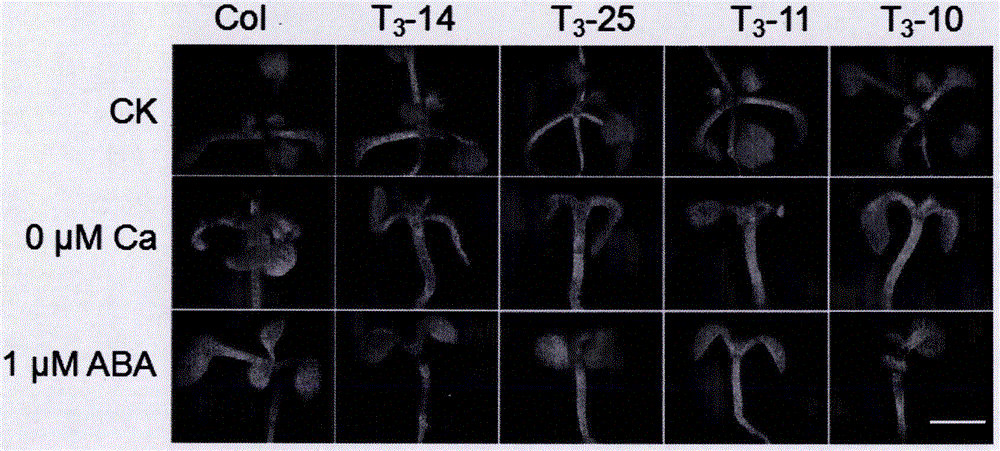
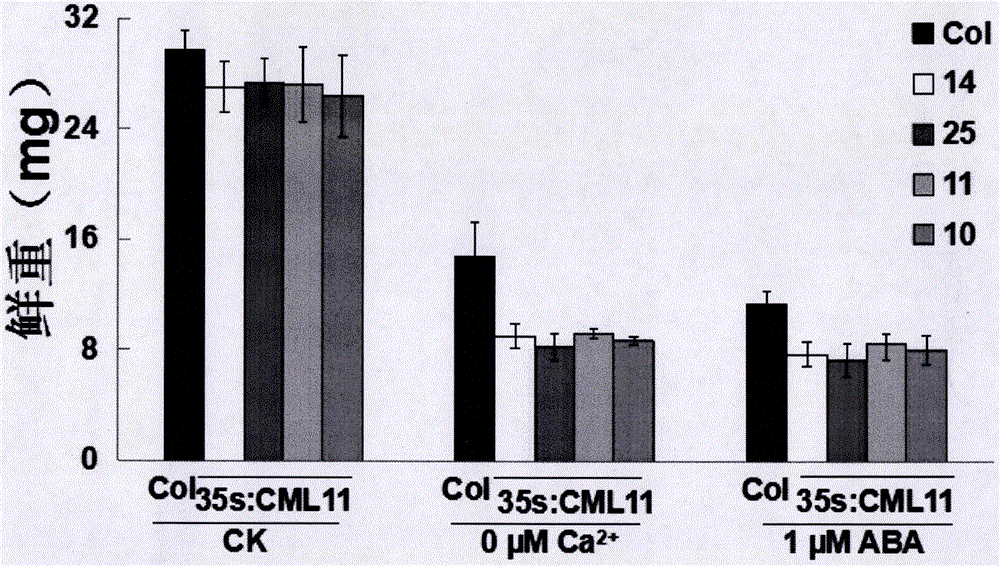
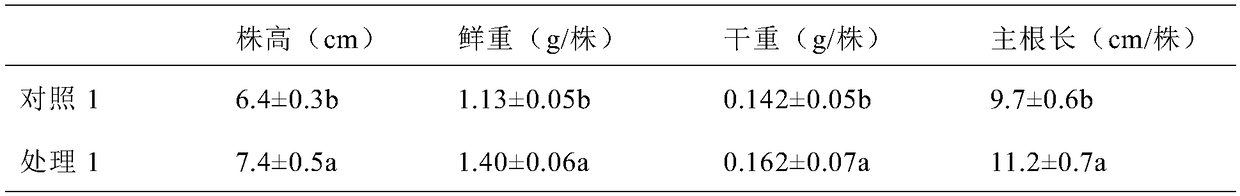
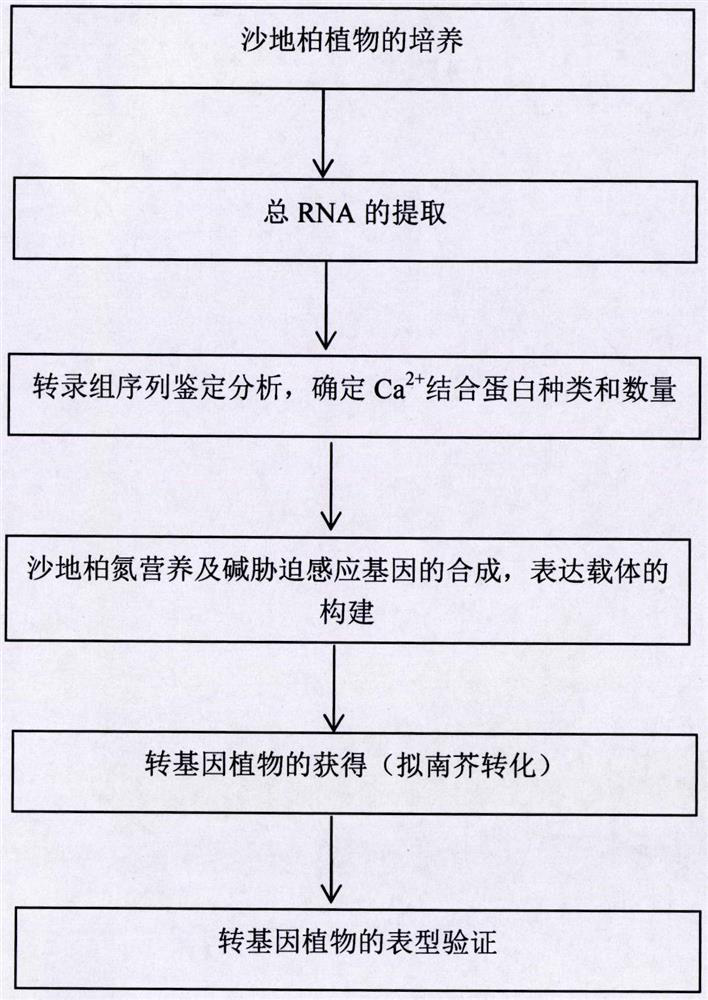
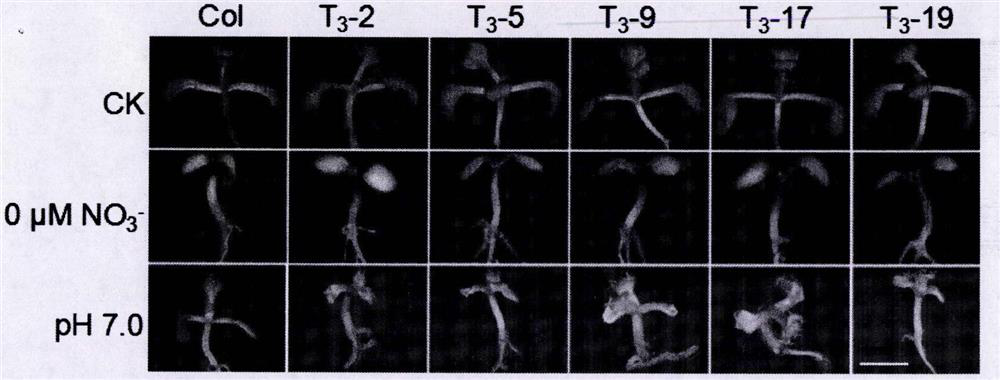
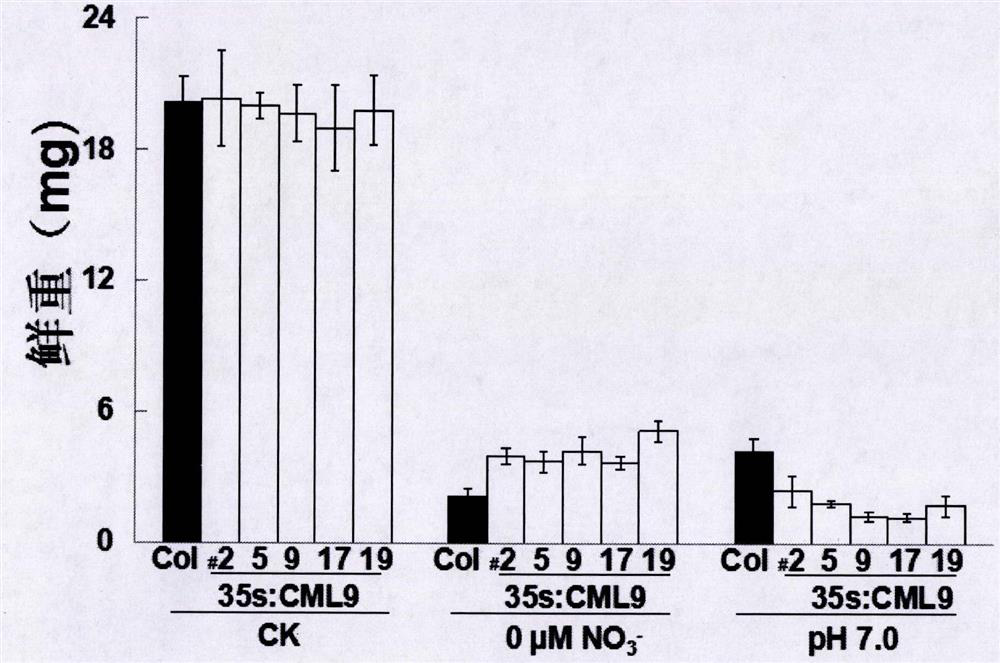
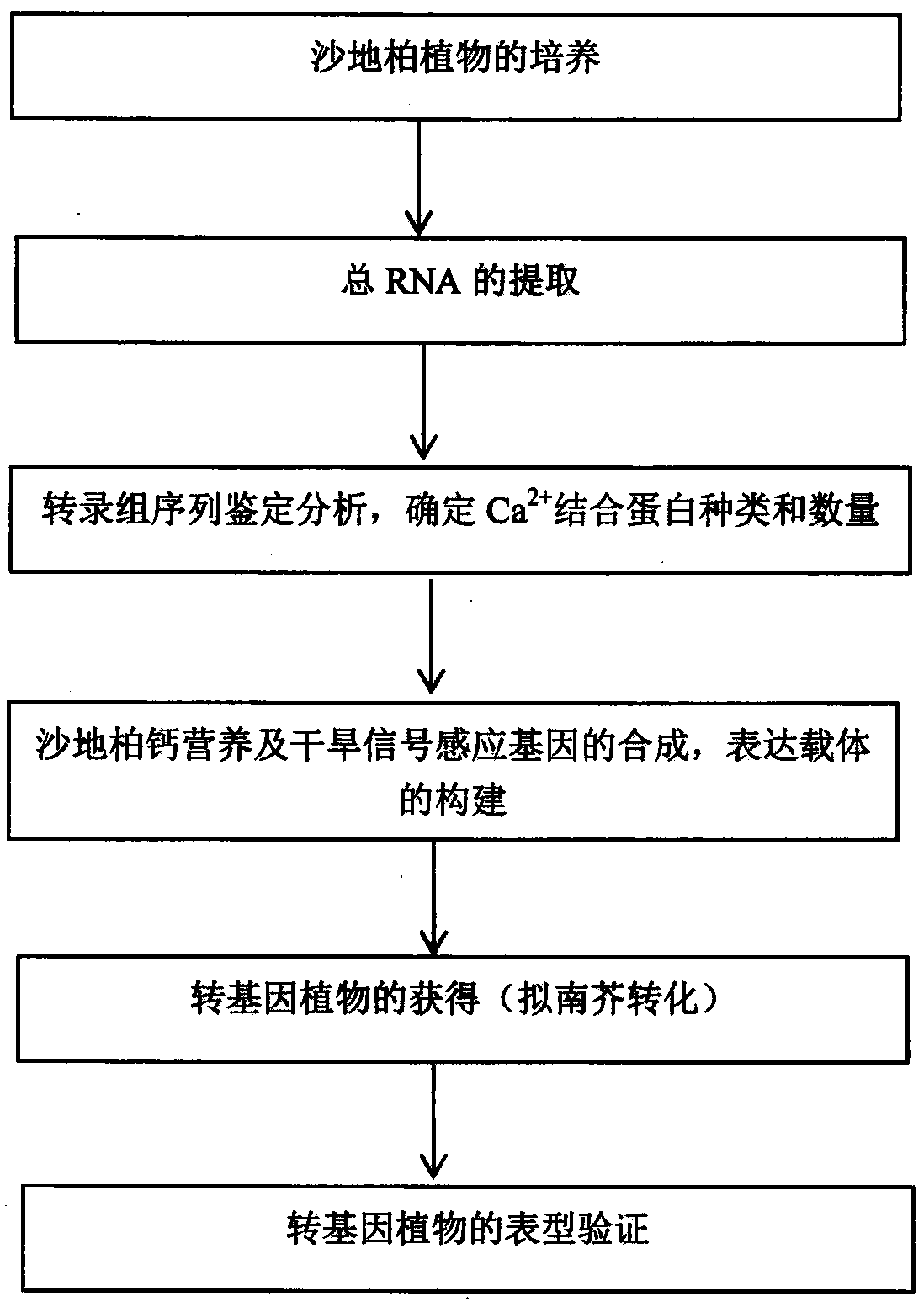
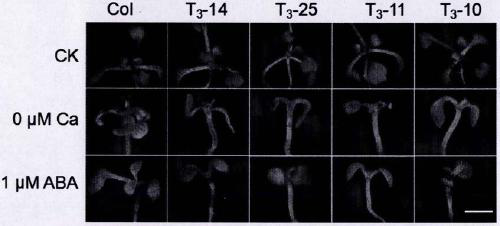
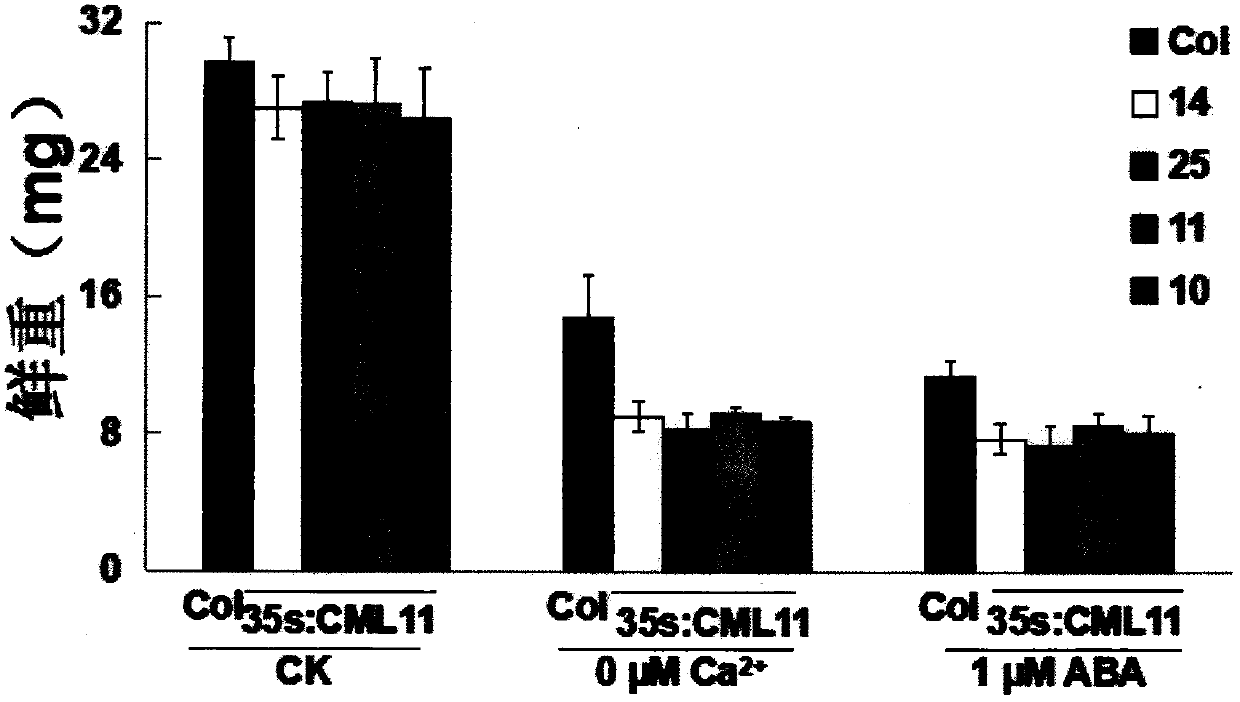
Sensing gene CML11 capable of adjusting plant calcium nutrient and drought signal from Sabina vulgaris and application thereof
The invention relates to a sensing gene CML11 capable of adjusting plant calcium nutrient and drought signal from Sabina vulgaris of strong xerophytes of northwestern region of Inner Mongolia. The encoded protein of the gene has a calcium ion bonding site. The gene has the advantages that by preparing material, cloning gene and building subsequent plant expression carriers, the gene is delivered into an arabidopsis thaliana wild type of a model plant by an agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated feature infection method, and a resistant plant is screened, so as to finally obtain multiple single-gene inserted and purified T3 transgenic plants; the transgenic plant and the wild control plant are subjected to different element expression analysis under the sterile culture condition, and compared with the wild control plant, the transgenic plant has the sensitive features of short root, fresh leaf and light weight under the low-calcium condition and drought hormone ABA conditions, so that the encoded protein of the gene has the function of adjusting plant calcium nutrient and drought signal; a new orientation is provided for the culture of anti-drought plants by the gene engineering technique, and the important significance is realized for the molecular seed breeding threatened by the drought.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA M GRASS ECOLOGY & ENVIROMENT GRP CO LTD
Method for planting greening plants in artificial shallow lake
InactiveCN102498909BTroubleshoot normal growthRich landscape connotationReceptacle cultivationSoil scienceEngineering
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Mechanical sowing, drip irrigation and seedling raising method for haloxylon ammodendron
PendingCN114287284AAvoid quality impactReduce laborFertilising methodsCultivating equipmentsSeederHaloxylon ammodendron
The invention provides a mechanical sowing, drip irrigation and seedling raising method for haloxylon ammodendron, and belongs to the technical field of xerophyte cultivation. According to the method, a seeder comprising a seeder and a soil covering box is selected for drilling and sand covering, drip irrigation belts are laid between rows, and the water yield of the drip irrigation belts per meter per hour is 2.4-2.5 kg. Through mechanical seeding, the consistency and precision of seeding and soil covering are improved, and the mechanization degree is greatly improved. Water and fertilizer management is conducted through the drip irrigation tape, irrigation is more uniform, the water resource utilization rate is higher, the method is not limited by the terrain, and the requirement for the land flatness degree is lowered. According to the method, the sowing time is saved, the labor efficiency is improved, the quality of the obtained haloxylon ammodendron seedlings is better, the seedling rate is higher, and the method is suitable for all areas capable of supporting arrangement of drip irrigation belts.
Owner:阿拉善盟林业草原研究所(阿拉善盟林业调查规划中心阿拉善荒漠研究中心)
Transformation method of eucalyptus grandis
InactiveCN102660575BFix security issuesMicrobiological testing/measurementHorticulture methodsPhosphomannose IsomeraseXerophyte
The invention provides a safe and efficient genetic transformation method of eucalyptus grandis in order to solve problems encountered during the process of transforming eucalyptus by using an agrobacterium-mediated method in the prior art. The method is to successfully transfer a target gene AmCBL1 into eucalyptus grandis by constructing an expression vector with a safety marker gene PMI (6-phosphomannose isomerase) as a selection marker, making a plurality of tissue culture experiments and improving genetic transformation methods. The target gene comes from super-xerophyte ammopiptanthus mongolicus (Ammopiptanthus mongolicus (Maxim.) Cheng F.), and is driven by its specific promoter AmCBL1P.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
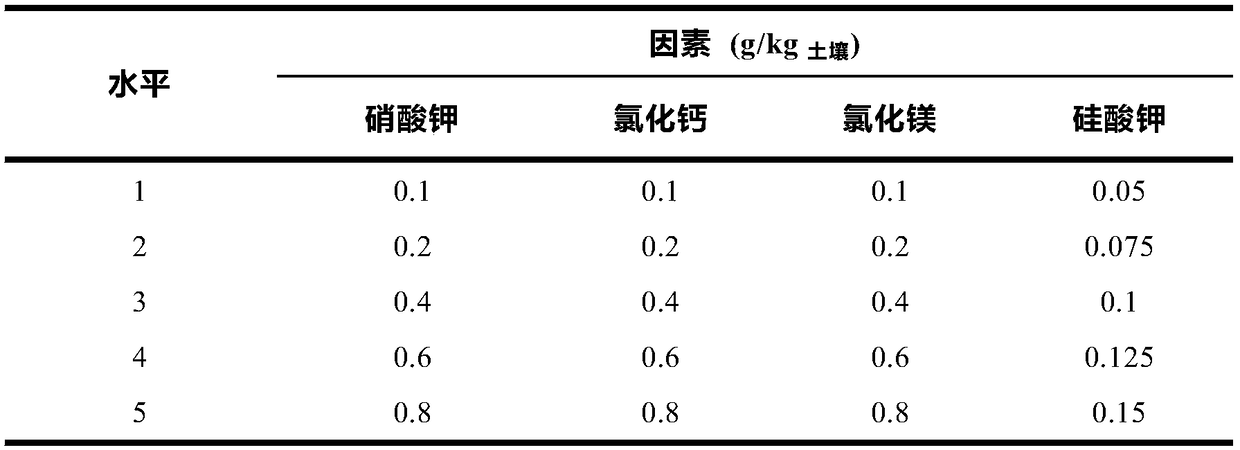
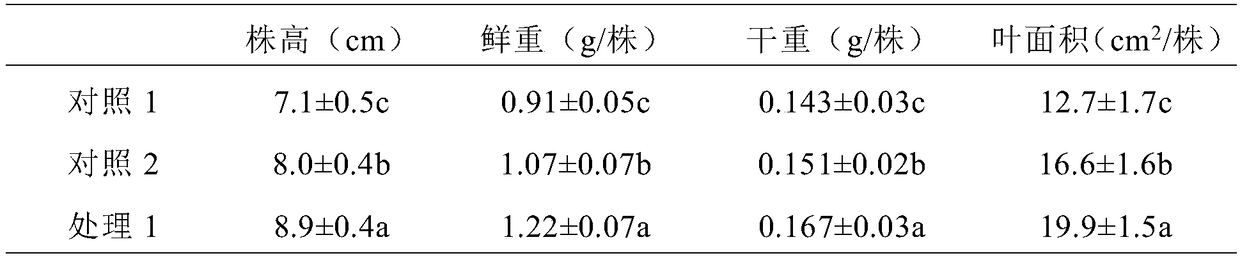
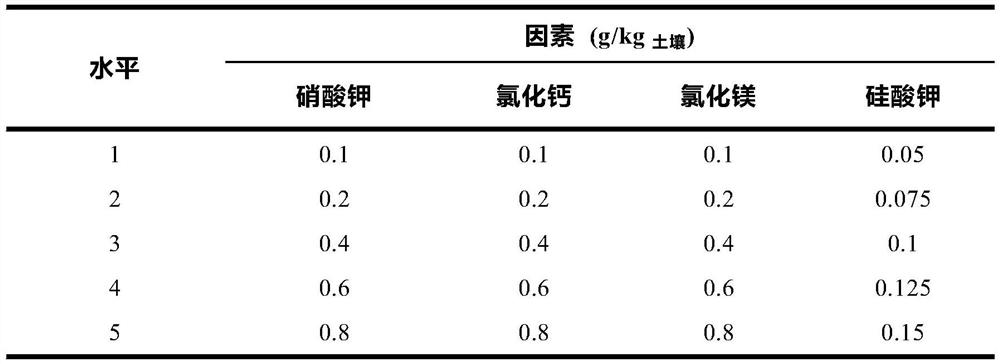
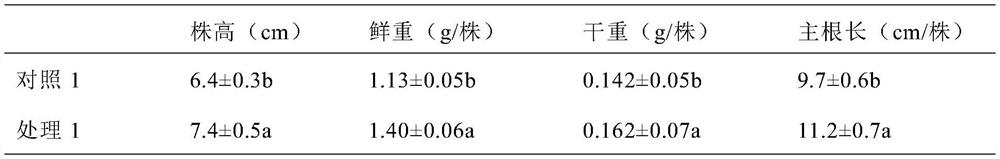
Mineral compound fertilizer for desert sclerophyllous xerophytes and application of mineral compound fertilizer
ActiveCN109354564APromote growthProtect and improve the ecological environmentCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersAridEcological environment
The invention provides a mineral compound fertilizer for desert sclerophyllous xerophytes. The mineral compound fertilizer comprises potassium nitrate, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride and potassium silicate. The invention further provides application of the mineral compound fertilizer for the desert sclerophyllous xerophytes. The fertilizer application rate of the mineral compound fertilizeris 99.3-206.9 kilograms / mu when the mineral compound fertilizer is directly applied into soil in desert regions; a mass ratio of the mineral compound fertilizer for the desert sclerophyllous xerophytes to soil is (0.6-1.25 g):1 kg when the mineral compound fertilizer is applied to earth culture seedlings; the fertilizer application rate of the mineral compound fertilizer is 12-25 g / L when the mineral compound fertilizer is applied to sand culture seedlings or water culture seedlings. The mineral compound fertilizer for the desert sclerophyllous xerophytes and the application have the advantages that the mineral compound fertilizer can be popularized and applied to the desert regions and can be used for culturing seedlings with strong drought resistance in the desert regions, accordingly, degraded desert vegetation can be rejuvenated and regenerated, growth of the degraded vegetation in the desert regions can be promoted, ecological environments can be protected and improved, and novelresearch prospects can be developed for ways for exploring the drought resistance of desert plants in arid desert regions; soil structures can be improved by the mineral compound fertilizer, the soilfertility can be enhanced by the mineral compound fertilizer, growth of the desert sclerophyllous xerophytes can be promoted by the mineral compound fertilizer, and the drought resistance of the desert sclerophyllous xerophytes can be improved by the mineral compound fertilizer.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
A kind of desertification land vegetation restoration method
ActiveCN110859066BReduce the degree of desertificationImprove germination rateGrowth substratesCulture mediaRevegetationWater storage
The invention discloses a method for restoring vegetation in sandy land, which comprises the following steps: step a, dig out round pits arranged horizontally and vertically on the sandy land to be treated, and four adjacent round pits are used as a planting unit; step b, in the The round pit is covered with mixed matrix sand; step c, making a plant seed protection bag; step d, burying most of the plant seed protection bag in the above-mentioned round pit mixed matrix sand, and then laying a layer of local sand on the surface of the above-mentioned round pit, and the above-mentioned The upper end of the protective bag can be flush; step e, every four planting units form a grid to form a grid, and build a sandbag retaining wall outside the grid; step f, open a cross groove in the grid, and fill the groove The above-mentioned mixed substrate sandy soil is then evenly spread and sprinkled xerophyte herbaceous plant seeds in the trench, and finally a layer of local sandy soil is laid on the surface of the trench. The desertified land vegetation recovery method of the present invention can cope with the harsh conditions of the desertified land, achieve a good water storage effect, and improve the vegetation survival rate.
Owner:JIANGSU LVYAN ECOLOGY TECH CO LTD
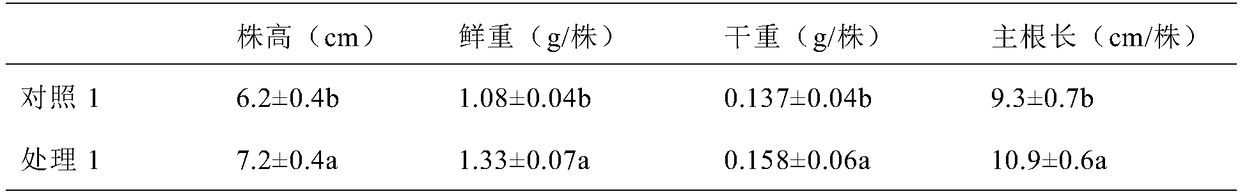
Regulating Plant Nitrogen Nutrition and Alkali Stress Sensing Gene cml9(q6-1) and Its Application
The invention relates to a sensing gene CML9 (Q6-1) for adjusting plant nitrogen nutrition and alkaline stress from strong xerophyte Sabina vulgaris. in northwest part of Inner Mongolia. The encoding protein of the gene has a calcium ion binding site. A preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing a material, cloning the gene, building a subsequent plant expression carrier, and further guiding the gene into a mode plant arabidopsis thaliana wild model by an agrobacterium-mediated floc infection method; screening a resistance seedling, so as to obtain a T3 transgenic plant with insertion and purification of multiple single genes. Compared with the wild type, the transgenetic plant can well grow under the low nitrogen condition, and poorly grow under the alkaline stress condition, so that the encoding protein of the gene has the function of adjusting the plant nitrogen nutrient and the alkaline stress. The gene has the advantages that a new direction is provided for the culturing of drought-resistant plants by the gene engineering technique, and the important meaning is realized for the molecular seed breeding under the drought stress.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA M GRASS ECOLOGY & ENVIROMENT GRP CO LTD
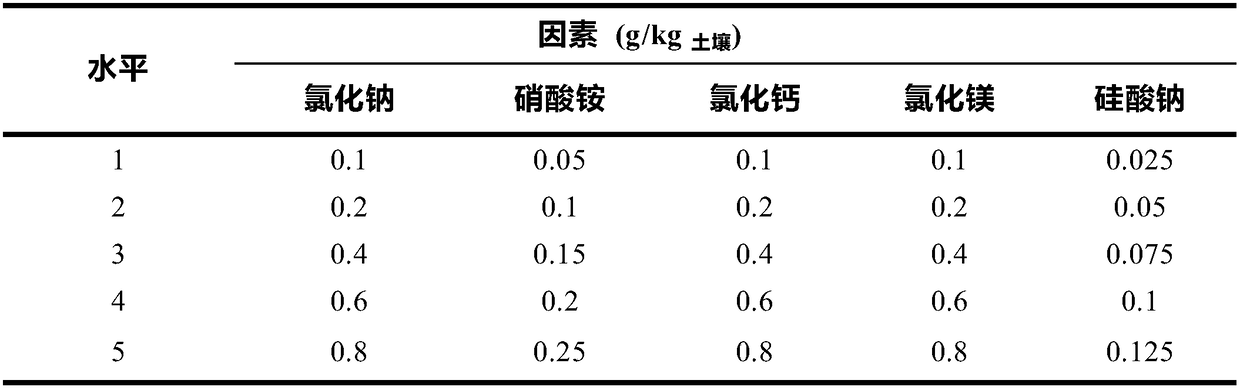
Mineral compound fertilizer for desert succulent xerophytes and application of mineral compound fertilizer
ActiveCN109354525ASolve the survival rateSolve the problem of slow rejuvenation updateCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersAridEcological environment
The invention provides a mineral compound fertilizer for desert succulent xerophytes. The mineral compound fertilizer comprises sodium chloride, ammonium nitrate, calcium chloride, magnesium chlorideand sodium silicate. The invention further provides application of the mineral compound fertilizer for the desert succulent xerophytes. The fertilizer application rate of the mineral compound fertilizer is 157.2-210.9 kilograms / mu when the mineral compound fertilizer is directly applied into soil in desert regions; a mass ratio of the mineral compound fertilizer for the desert succulent xerophytesto soil is (0.95-1.275 g):1 kg when the mineral compound fertilizer is applied to earth culture seedlings; the fertilizer application rate of the mineral compound fertilizer is 9.5-12.75 g / L when themineral compound fertilizer is applied to sand culture seedlings or water culture seedlings. The mineral compound fertilizer for the desert succulent xerophytes and the application have the advantages that the mineral compound fertilizer can be popularized and applied to the desert regions and can be used for culturing seedlings with strong drought resistance in the desert regions, accordingly, degraded desert vegetation can be rejuvenated and regenerated, growth of the degraded vegetation in the desert regions can be promoted, ecological environments can be protected and improved, and novelresearch prospects can be developed for ways for exploring the drought resistance of desert plants in arid desert regions; soil structures can be improved by the mineral compound fertilizer, the soilfertility can be enhanced by the mineral compound fertilizer, growth of the desert succulent xerophytes can be promoted by the mineral compound fertilizer, and the drought resistance of the desert succulent xerophytes can be improved by the mineral compound fertilizer.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO-ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Cypress sativa regulates plant calcium nutrition and drought signal sensing gene cml11 and its application
The invention relates to a sensing gene CML11 capable of adjusting plant calcium nutrient and drought signal from Sabina vulgaris of strong xerophytes of northwestern region of Inner Mongolia. The encoded protein of the gene has a calcium ion bonding site. The gene has the advantages that by preparing material, cloning gene and building subsequent plant expression carriers, the gene is delivered into an arabidopsis thaliana wild type of a model plant by an agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated feature infection method, and a resistant plant is screened, so as to finally obtain multiple single-gene inserted and purified T3 transgenic plants; the transgenic plant and the wild control plant are subjected to different element expression analysis under the sterile culture condition, and compared with the wild control plant, the transgenic plant has the sensitive features of short root, fresh leaf and light weight under the low-calcium condition and drought hormone ABA conditions, so that the encoded protein of the gene has the function of adjusting plant calcium nutrient and drought signal; a new orientation is provided for the culture of anti-drought plants by the gene engineering technique, and the important significance is realized for the molecular seed breeding threatened by the drought.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA M GRASS ECOLOGY & ENVIROMENT GRP CO LTD
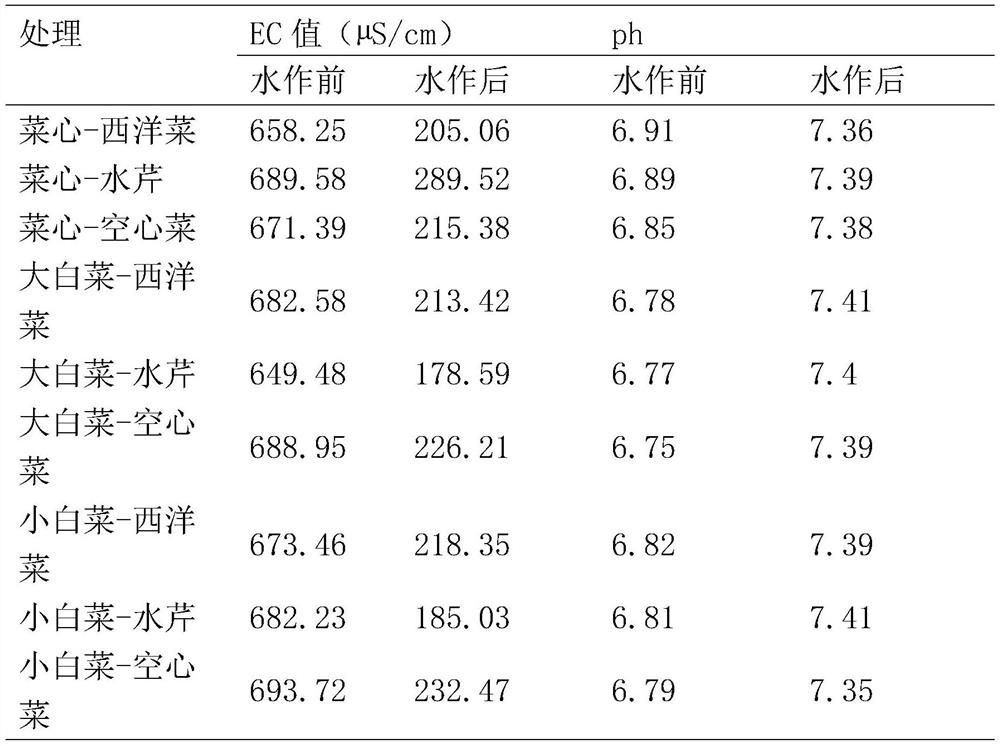
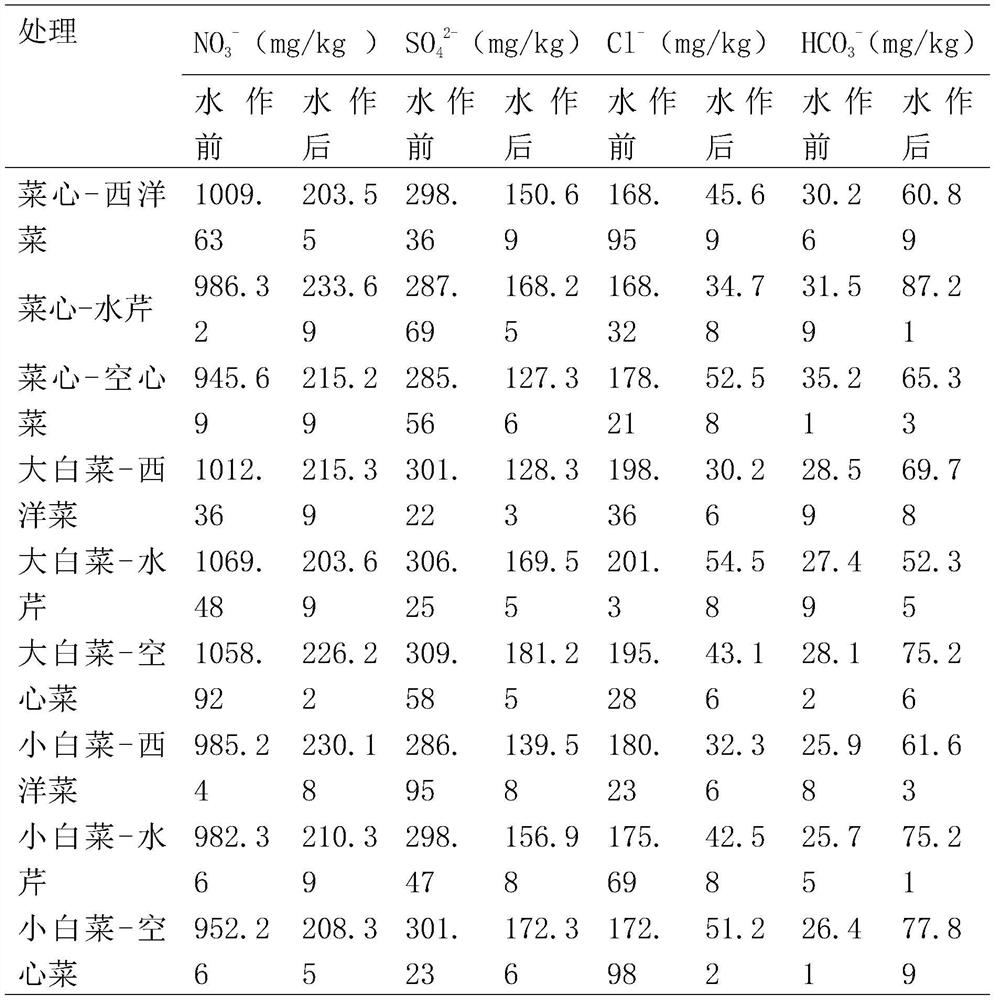
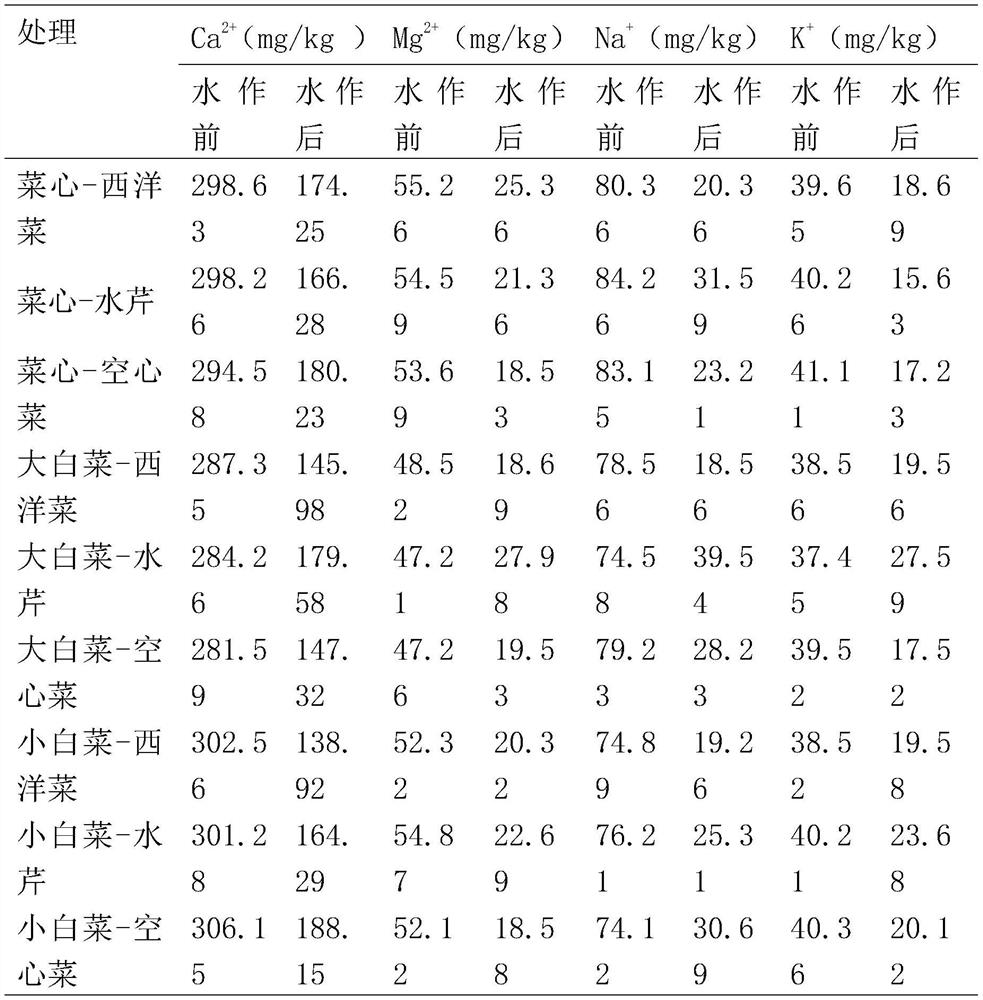
Method for improving soil by rice field-upland field rotation of leaf vegetables and aquatic vegetables and detection method thereof
InactiveCN111742796AEC value improvementLower EC valueEarth material testingLeaf crop cultivationXerophyteWatercress
The invention discloses a method for improving soil by rice field-upland field rotation of leaf vegetables and aquatic vegetables, and relates to the field of agricultural planting. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, performing planting of aquatic vegetables in a dry land where xerophyte crops are planted for a long time from July to December in Hainan, performing planting of a season of leaf vegetables after planting a season of aquatic vegetables in the same year, and repeating the steps for three times, wherein complete random block arrangement is adopted for each planting. The aquatic vegetables comprise watercress, cress, water spinach and watercress. The leaf vegetables comprise flowering cabbages, Chinese cabbages and pakchoi cabbages, the EC value, the pH value, theanion content and the cation content of plough layer soil are all improved through the method, and the improvement effect is obvious.
Owner:海南省农业科学院蔬菜研究所
A kind of desert less pulp xerophyte mineral compound fertilizer and its application
InactiveCN109354564BPromote growthProtect and improve the ecological environmentCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersAridPotassium nitrate
The present invention provides a kind of mineral compound fertilizer for xerophyte with little pulp in desert, which is composed of potassium nitrate, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride and potassium silicate. In the soil of desert areas, the amount of fertilizer applied is 99.3 kg / mu to 206.9 kg / mu; when it is applied to the soil to cultivate seedlings, the mass ratio of mineral compound fertilizer and soil of xerophyte with less pulp in desert is (0.6g~1.25g): 1kg ; When used in sand or water cultivation, the amount of fertilizer applied is 12g / L-25g / L. The mineral compound fertilizer for xerophytes with less pulp in deserts of the present invention is popularized and applied in desert areas, and is used for cultivating strong drought-resistant seedlings in desert areas, rejuvenating and renewing degraded desert vegetation, promoting the growth of degraded vegetation in desert areas, protecting and improving the ecological environment, and providing Exploring the pathways of drought resistance of desert plants in arid desert areas opens up new research prospects, which can improve soil structure, increase soil fertility, promote the growth of desert xerophytes and increase their drought resistance.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Orchard soil aeration and fertilization method
ActiveCN104718866BImprove gas environmentGas environment maintenanceFertilising methodsFertilizer mixturesInsect pestXerophyte
The invention discloses an orchard soil ventilating and fertilizing method. The orchard soil ventilating and fertilizing method comprises the following steps: drilling fertilizing holes at certain intervals by a soil punching machine along the inner edges of tree disks of fruit trees, packing thick organic materials in the bottoms of the holes, inserting bundled corn straw or branches into the bottoms of the fertilizing holes, then filling with organic fertilizer, spraying chemical fertilizer in ratio when the added organic fertilizer reaches a certain height, further adding the organic fertilizer, irrigating after the fertilizing holes are full filled with the organic fertilizer, slightly shaking the corn straws or the branches which are inserted into the holes, and finally covering the fertilizing holes and the tree disks with straw carpets; removing the straw carpets during topdressing in summer, applying the chemical fertilizer in ratio and covering with the straw carpets again. According to the orchard soil ventilating and fertilizing method, the corn straws or the branches are inserted into the fertilizing holes; the air permeability is improved; with the combination of the straw carpets with few same plant diseases and insect pests as the xerophilous plants, the water, fertilizer, air and heat are obviously improved; the temperature and the humidity of the soil are stabilized; the plant diseases and insect pests are reduced; the root development and the nutrient absorption are promoted; the consumption of the chemical fertilizer is reduced; the labor efficiency is improved; the labor intensity is alleviated.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of container seedling raising method of sand xerophyte
InactiveCN110100607BQuick transplant cultivationGuaranteed water supplyPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsWater storagePlant cultivation
A method for raising seedlings of sandy xerophytes in a container, the invention relates to the technical field of plant cultivation; filling a cultivation bucket with nutrient soil, planting sandy xerophyte seedlings into the nutrient soil in the cultivation bucket; planting several seedlings into the bottom box of the seedlings The arrays are distributed on the cultivation racks of the nursery, and the cultivation hardware facilities in the nursery are adjusted so that the temperature, humidity and light meet the growth needs of the sandy xerophyte seedlings; after a period of cultivation, the mesh water storage tray is pulled out from the bottom box, Add nutrient solution or water to the water storage cotton to supplement the nutrients and water needed for seedling growth. It can quickly transplant and cultivate the sand xerophytes cultivated in the container, ensures the water supply on the way from the nursery to the planting site, helps to improve the survival rate after transplanting, and has stronger practicability.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Construction method for wet land artificial ecological island
InactiveCN101429758BReduce the degree of being washed outIncrease diversityArtificial islandsLand reclamationSludgeEngineering
The invention provides a method for constructing an artificial ecological island in wetland, which is to stack building waste and river mud or pond sludge into an island body according to the volume ratio of 2 to 3 on the basis of the prior natural island or a hard foundation in the wetland, and level and grind the island body layer by layer during the stacking; the circumference on the top of theisland body is placed by stone and cement mortar, and xerophytes and hygrophytes are planted in the middle on the top of the island body; the stone and the cement mortar are used for placing vertically and horizontally frame bodies on the circumferential island slope of the surface of the island body; waste concrete bodies or gravel is filled into spaces of the frame bodies; slurry is sprayed orpoured on the waste concrete bodies or the gravel, and the thickness of the slurry can cover the gravel or rubble; hygrophytes, emergent aquatic plants and submerged plants are planted on a slurry layer; and larger plants are planted before the waste concrete bodies or the gravel is filled. The method has low cost, is convenient to construct, is favorable for conserving water and soil, reduces thegradation degree of the island body, and makes a wetland ecosystem maintain stable.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Promoter of efficient expression Zmzf gene for water flooding of corn root
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering and is characterized by cloning a promoter of an efficient expression Zmzf gene for water flooding of a corn root from a corn inbred line Mo17; and the nucleotide sequence of the promoter is shown as SEQ ID No. 1. By connecting the promoter of the Zmzf gene with target genes of insect resistance, disease-resistance, resilience and the like and applying the genes to genetic transformation of xerophyte, the promoter can promote the efficient expression of the downstream target gene under the anaerobic conditions of water-logging, water flooding and the like and improve the capacities of the root of a transgenic plant, such as insect resistance, disease-resistance, resilience and the like; and meanwhile, the promoter is only expressed at the root and does not relate to the problem of food safety of the part of an edible transgenic plant above the ground; and thus the promoter has good application prospect in genetic improvement on water-logging tolerance of the xerophyte.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Ecological riverway restoration method based on riverbed structure transformation
InactiveCN114045779AImprove the ecological environmentMeet water requirementsWater resource protectionBreakwatersPlant rootsEdaphic
The invention discloses an ecological riverway restoration method based on riverbed structure transformation. The method comprises a riverbed 1 and a river embankment road 5, wherein a first-stage river bank 2 and a second-stage river bank 3 are sequentially constructed from the riverbed 1 to two sides to the river embankment road 5, and the riverbed 1, the first-stage river bank 2, the second-stage river bank 3 and the natural river embankment road 5 are sequentially connected through inclined protection slopes 4; the heights of the first-stage river bank 2 and the second-stage river bank 3 are set according to hydraulic conditions of a river, aquatic plant reeds are planted on the first-stage river bank 2, xerophyte green bristlegrass and chloris virgata are planted on the second-stage river bank 3, and poplars and willows are planted on the two sides of the river embankment road 5; and a layered soil structure with alternate sandy soil and clay is constructed on a root system layer below the river bank according to the distribution of corresponding vegetation root systems. According to the method, water flow is promoted to advance, water retention, water holding and water storage performance of plant root layer soil can be achieved, and ecological restoration of a riparian zone is facilitated. The method is suitable for ecological restoration of seasonal sandy wide and shallow rivers in plain areas.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of mineral compound fertilizer of desert succulent xerophyte and its application
ActiveCN109354525BPromote growthProtect and improve the ecological environmentCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersAridEcological environment
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
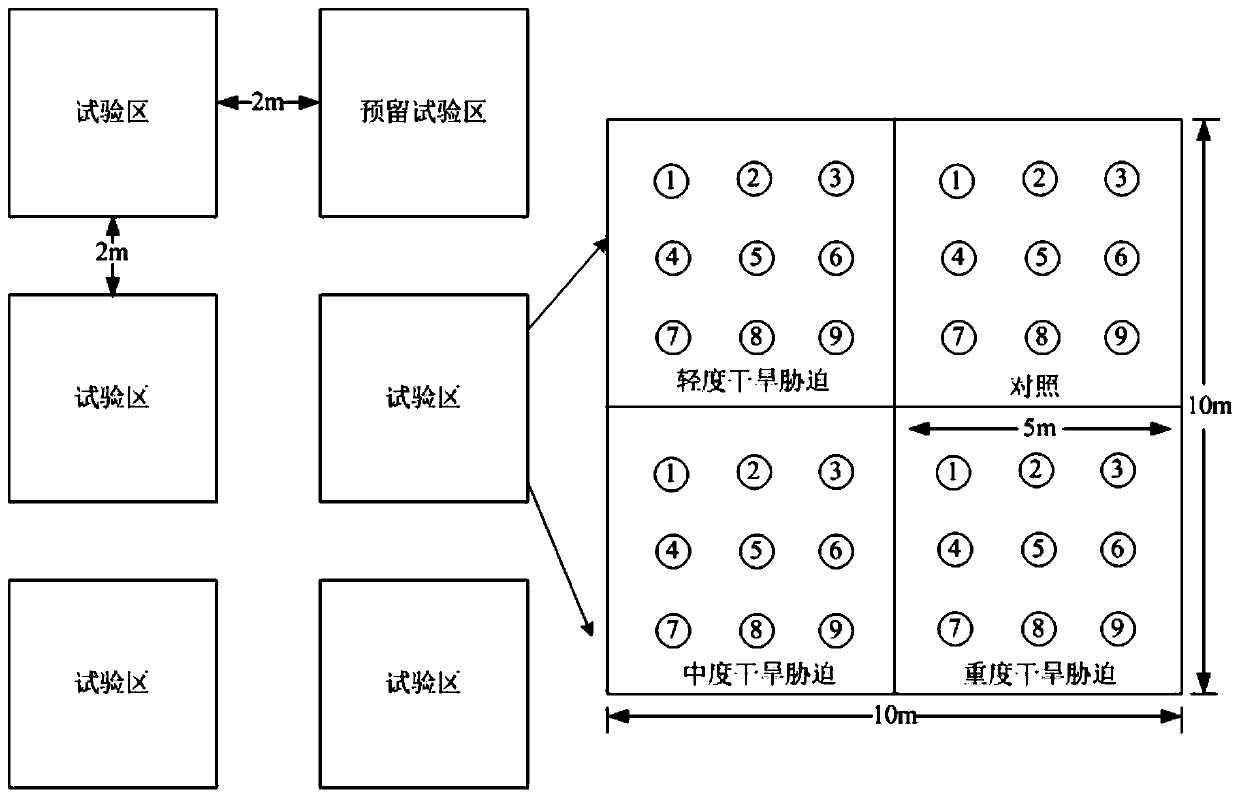
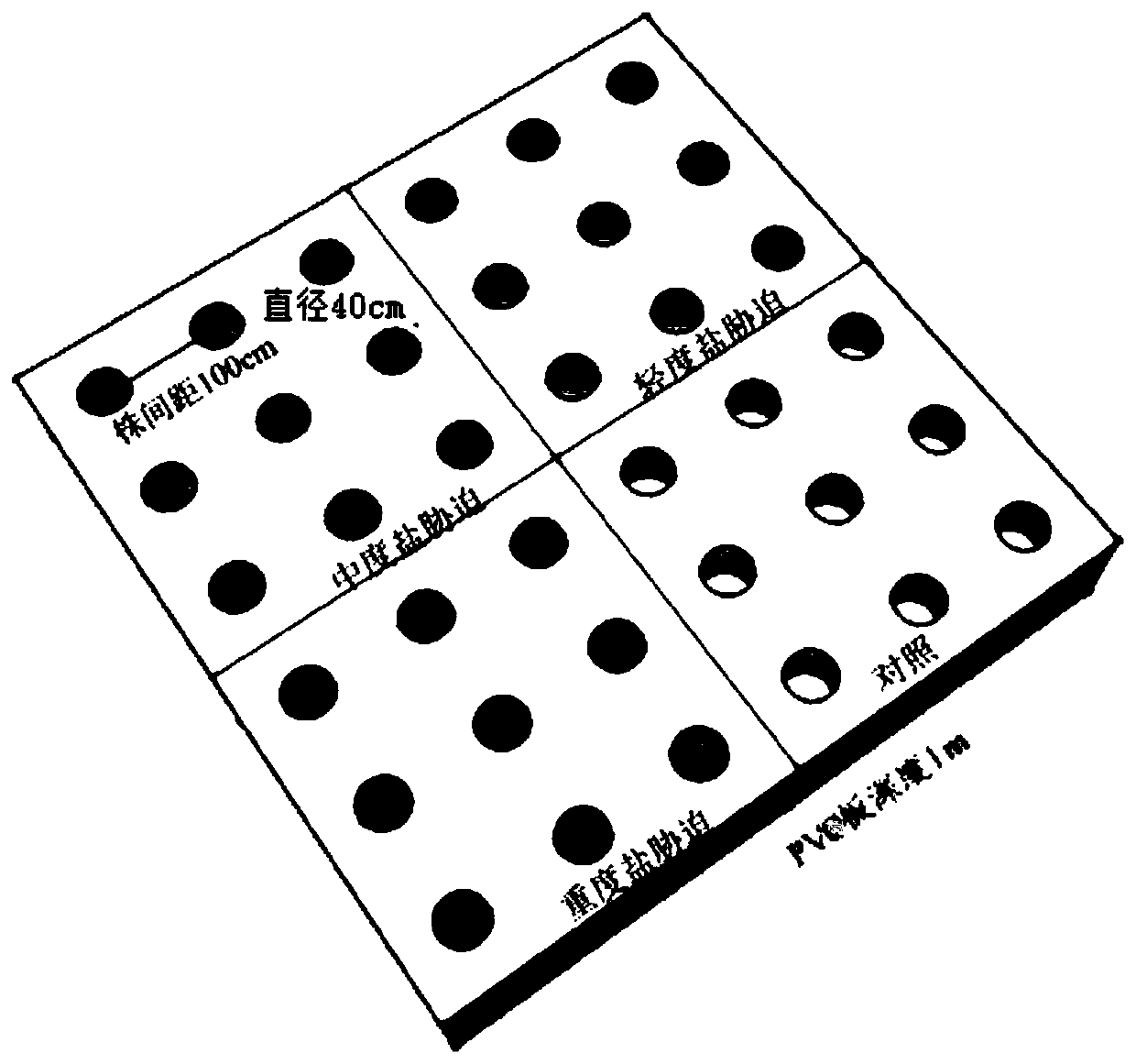
Field herbaceous plant environment control test method
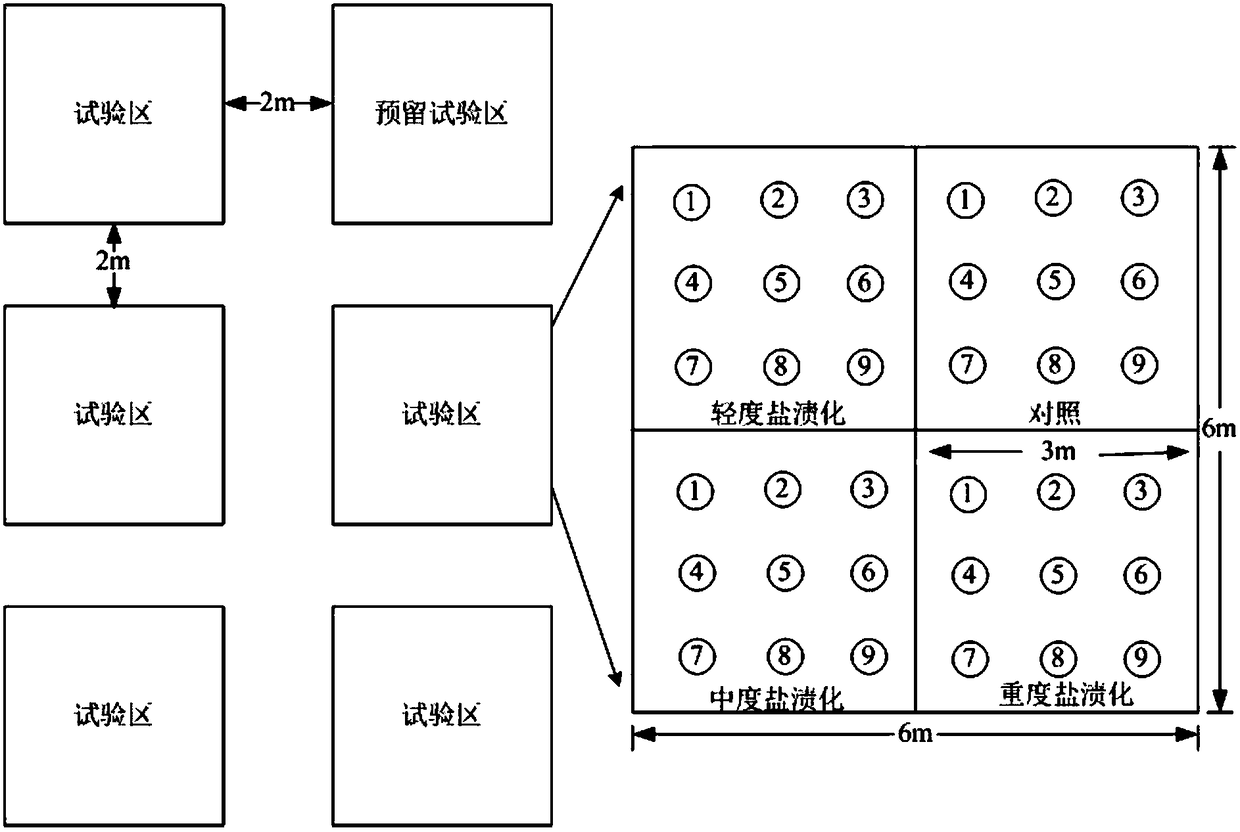
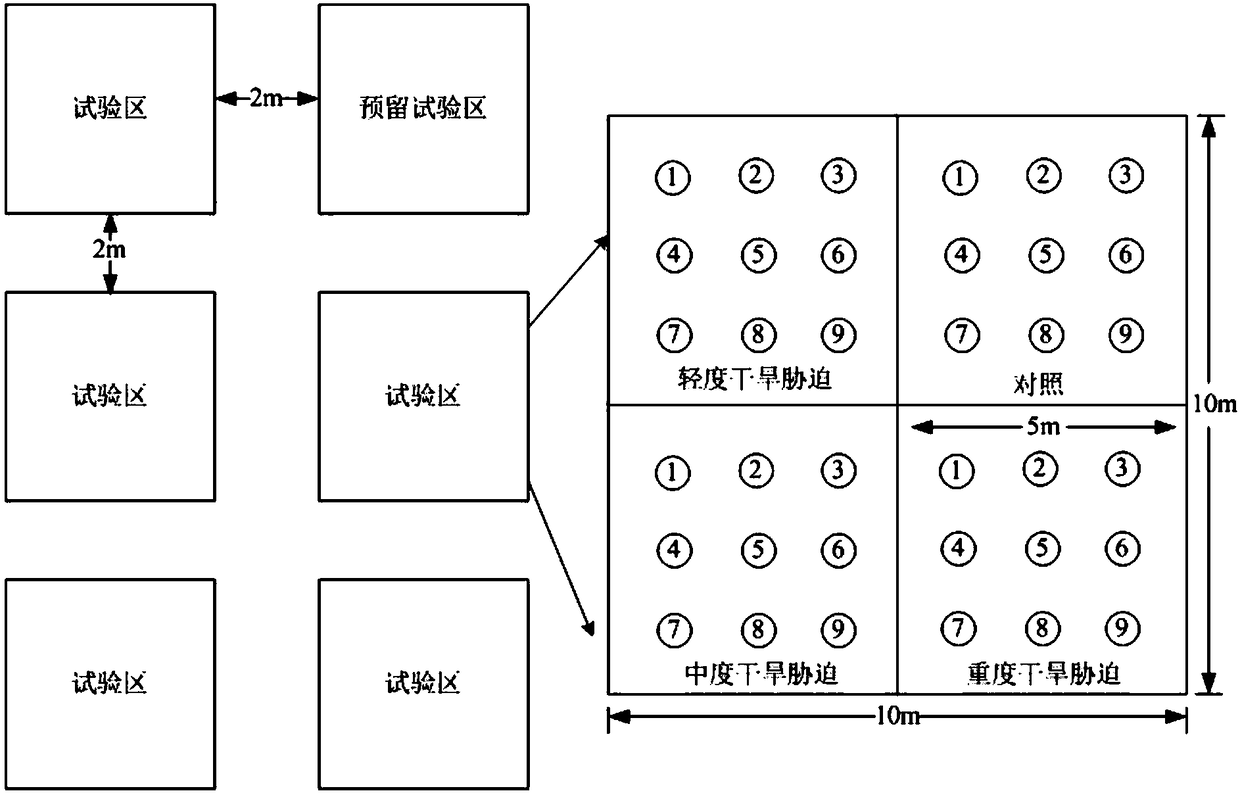
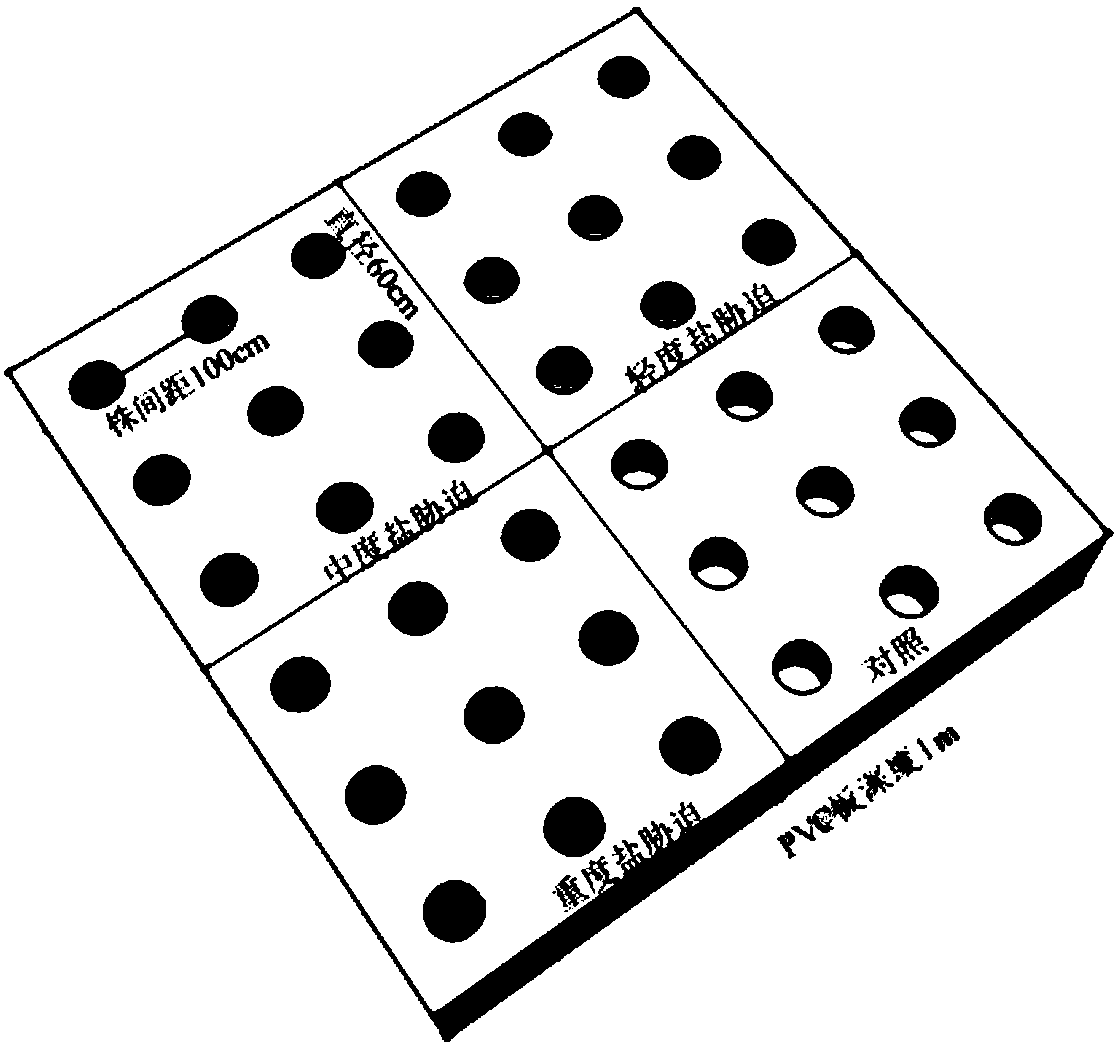
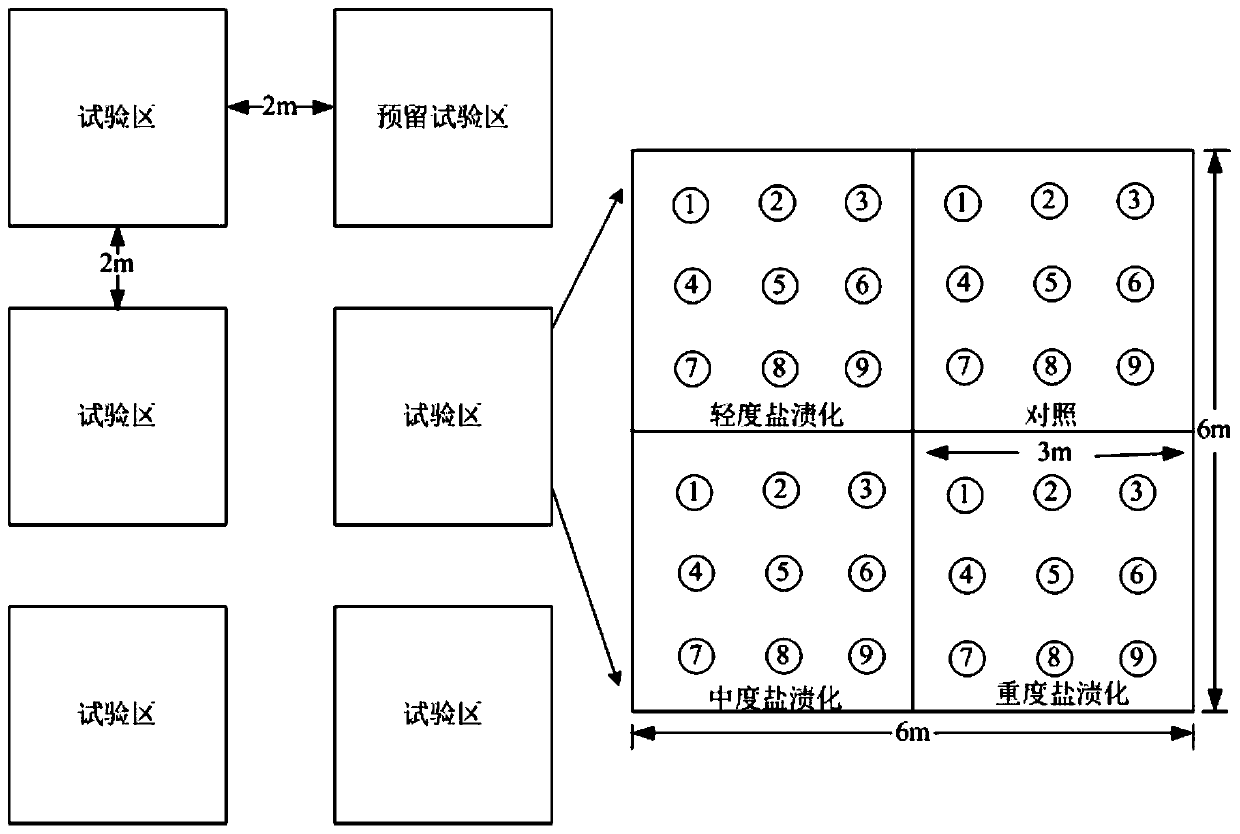
InactiveCN108513882AEasy to build experimental gradientsAvoid cross contaminationFabaceae cultivationCultivating equipmentsHalophyteSample plot
The invention discloses a field herbaceous plant environment control test method. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a planting sample plot is selected; 2, plants to be planted are selected; 3, halophyte and xerophyte seedlings are planted in the sample plot in the first ten-day period of April of the first year, irrigation is conducted after the halophyte and xerophyte seedlings areplanted, and it is ensured that the water content of soil after irrigation reaches the saturation water content; 4, irrigation is carried out once after planting at the end of April, and it is ensured that seedling planting is successful through manual management; 5, salt and drought gradient test processing is completed in early May, and then field observation test and plant and soil sample collection are carried out according to requirements of research purposes in growth seasons including May, July and September; 6, in the middle ten days of April of the second growth year, irrigation is conducted once, and it is ensured that the saturation water content of the soil is reached after each time of irrigation. The method is low in cost, the salt and water gradient is obvious, control samples are easy to select, and the effect is good.
Owner:新疆维吾尔自治区环境保护科学研究院
A kind of method of field herbaceous plant environmental control test
InactiveCN108513882BEasy to surviveIn line with natural conditionsFabaceae cultivationCultivating equipmentsHalophyteSample plot
The invention discloses a field herbaceous plant environment control test method. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a planting sample plot is selected; 2, plants to be planted are selected; 3, halophyte and xerophyte seedlings are planted in the sample plot in the first ten-day period of April of the first year, irrigation is conducted after the halophyte and xerophyte seedlings areplanted, and it is ensured that the water content of soil after irrigation reaches the saturation water content; 4, irrigation is carried out once after planting at the end of April, and it is ensured that seedling planting is successful through manual management; 5, salt and drought gradient test processing is completed in early May, and then field observation test and plant and soil sample collection are carried out according to requirements of research purposes in growth seasons including May, July and September; 6, in the middle ten days of April of the second growth year, irrigation is conducted once, and it is ensured that the saturation water content of the soil is reached after each time of irrigation. The method is low in cost, the salt and water gradient is obvious, control samples are easy to select, and the effect is good.
Owner:新疆维吾尔自治区环境保护科学研究院
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com