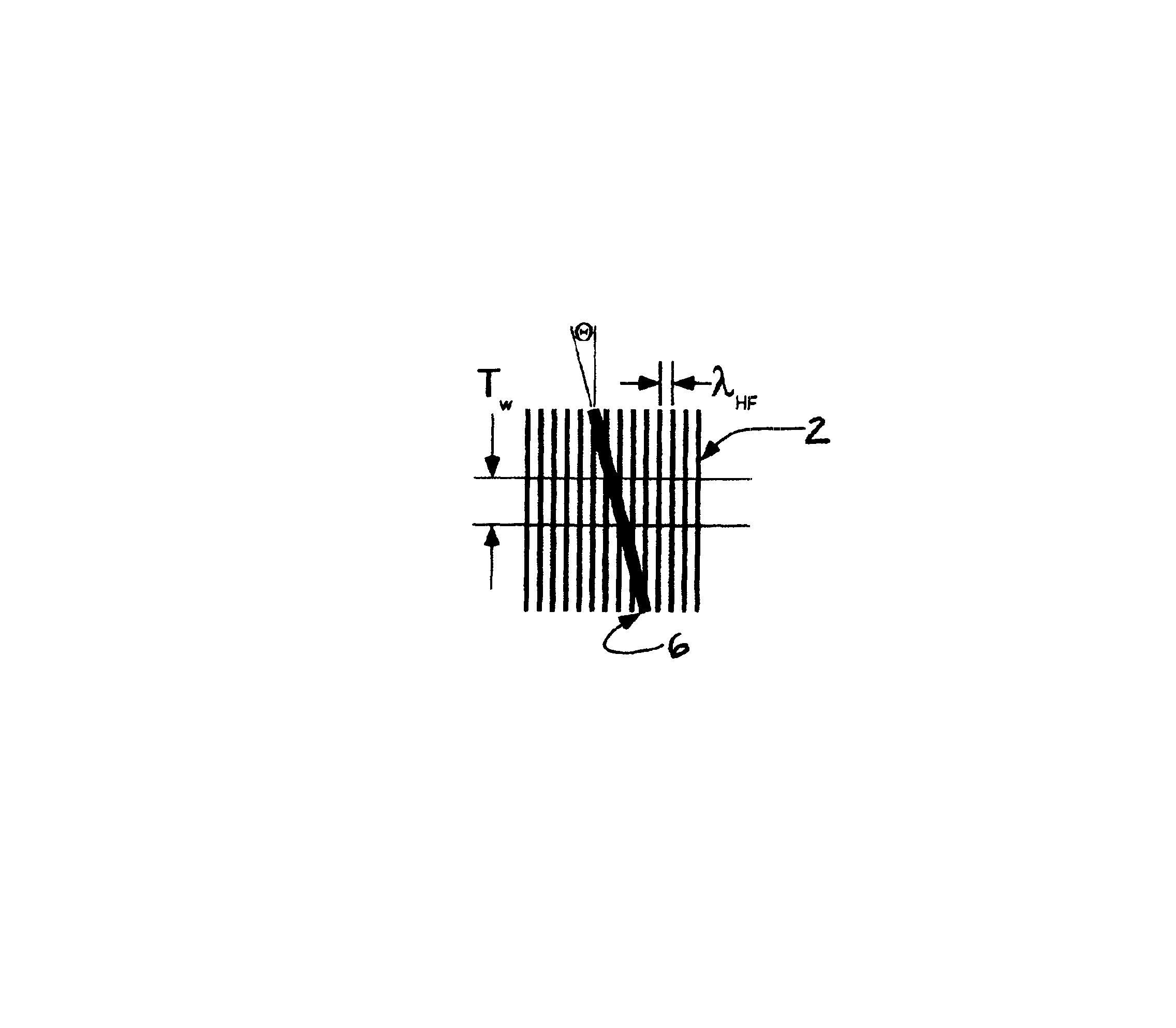Patents
Literature
161results about "Mounting heads on rotating support" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hybrid servopositioning systems
InactiveUS6873487B2Driving/moving recording headsHeads using thin filmsData recordingComputer science
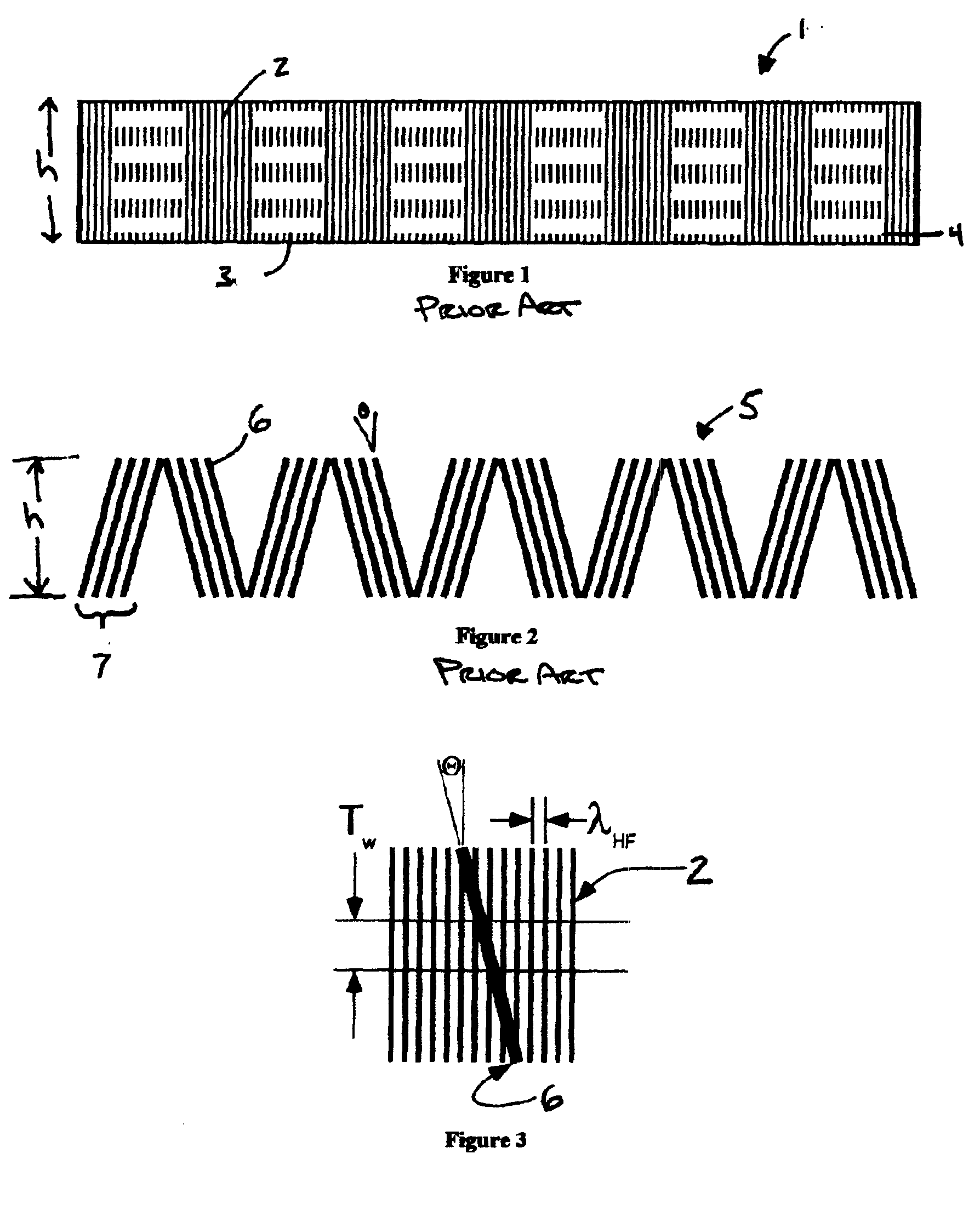
Servopositioning systems, methods, formats, and data recording media used in association with the same, employing both time-based and amplitude-based transverse tracking servo bands in the same or different locations on the medium.
Owner:SONY CORP
DSA suspension with microactuators extending to gimbal through flexible connectors
ActiveUS8879210B1Good stroke lengthHigh servo bandwidthArm with actuatorsRecord information storageDual stageEngineering
A dual stage actuated (DSA) suspension includes two PZT microactuators that are attached at their first ends to a non-gimbaled portion of the suspension such as the portion of the flexure that is rigidly attached to the load beam, and are attached at their second ends to the gimbaled portion of the suspension such as the gimbal tongue through flexible connectors that can be formed integrally with the suspension's flexure. The flexible connectors are flexible enough so as not to interfere with the suspension's gimballing action. The flexible connectors transmit force from the PZTs to the gimbal as the PZTs expand and contract in order to rotate the gimbal and thus effect fine movements of the head slider.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Flat servo bursts for arcuate track scanner
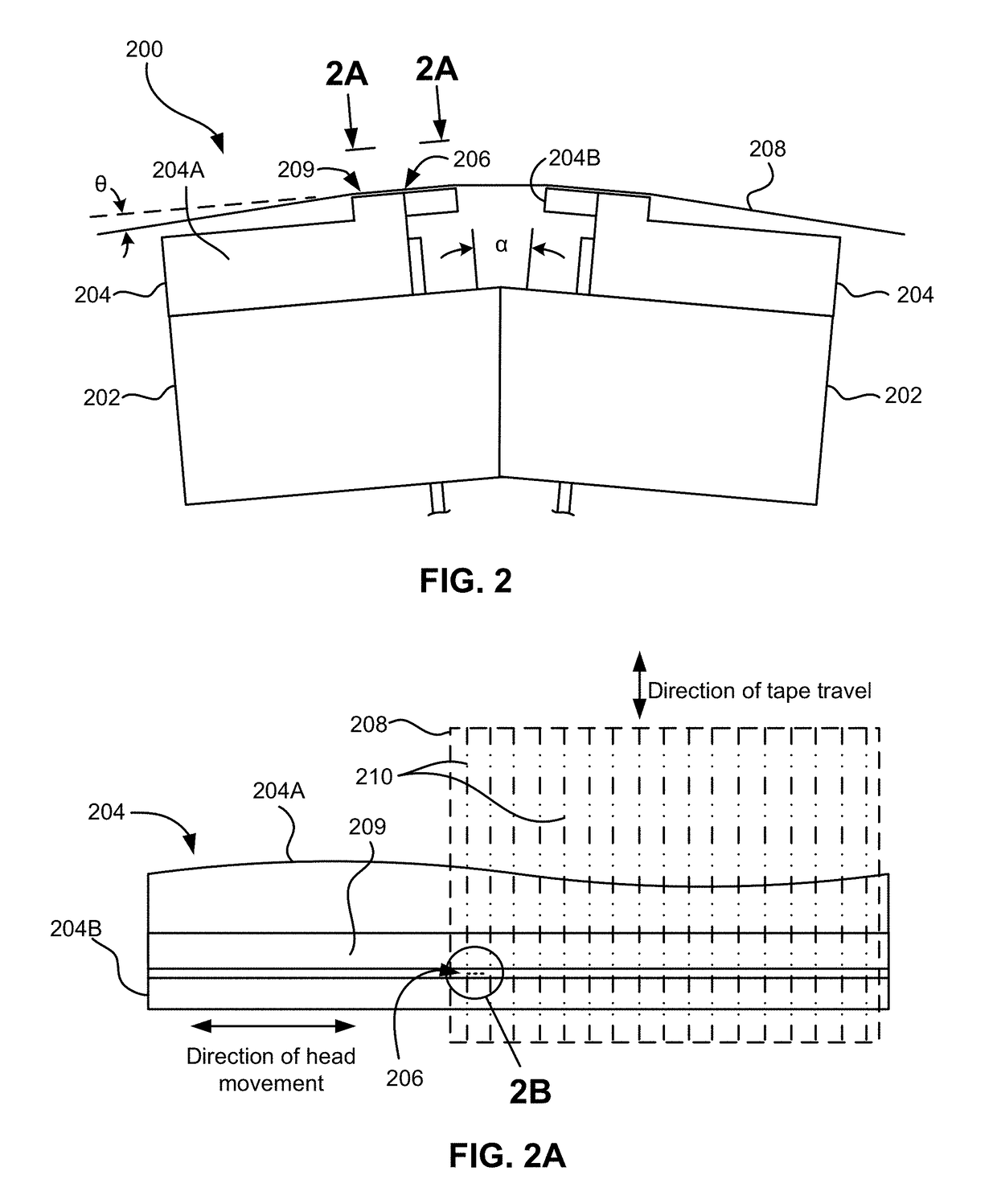
InactiveUS6285519B1Filamentary/web carriers operation controlAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeControl system
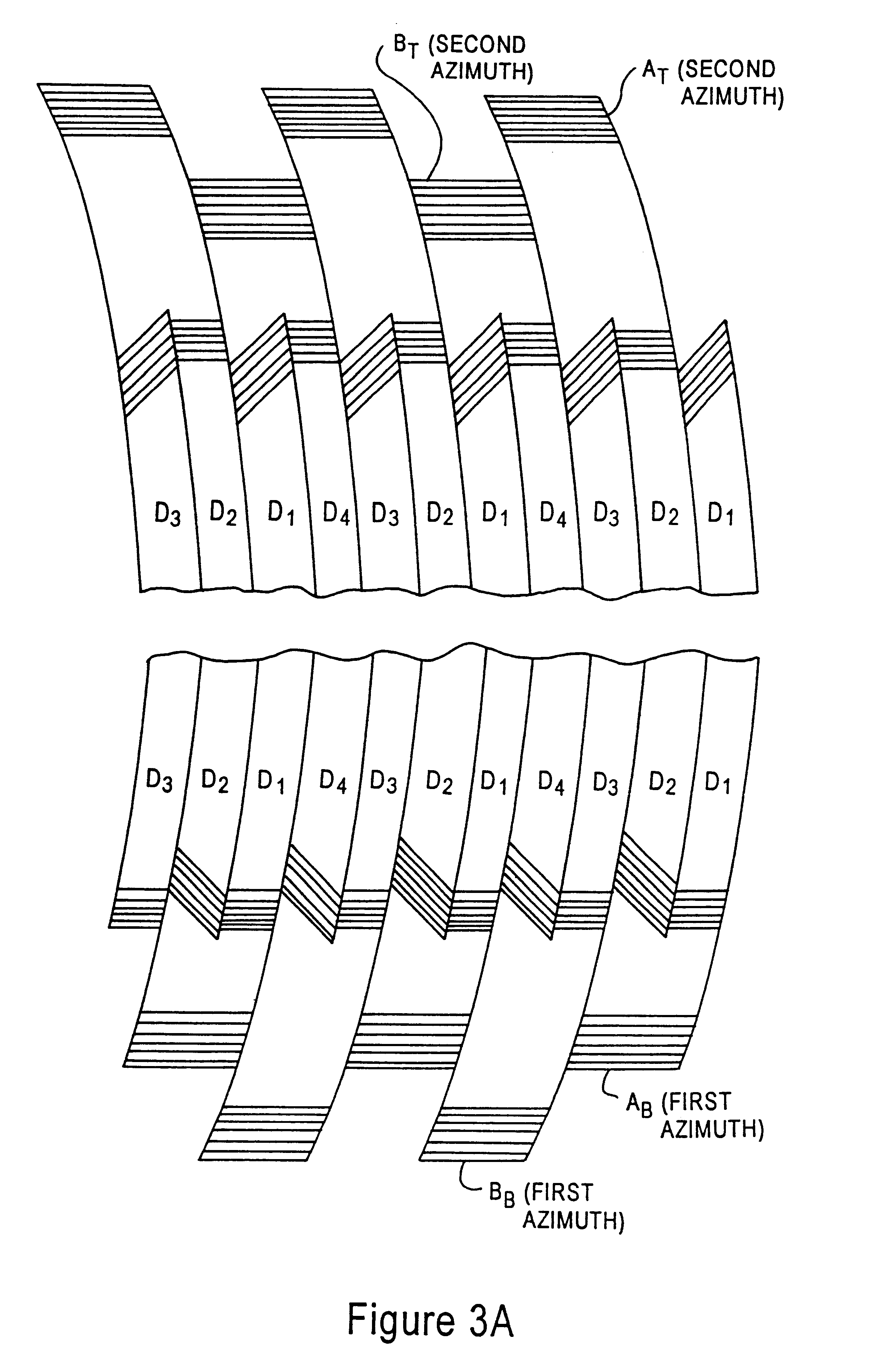
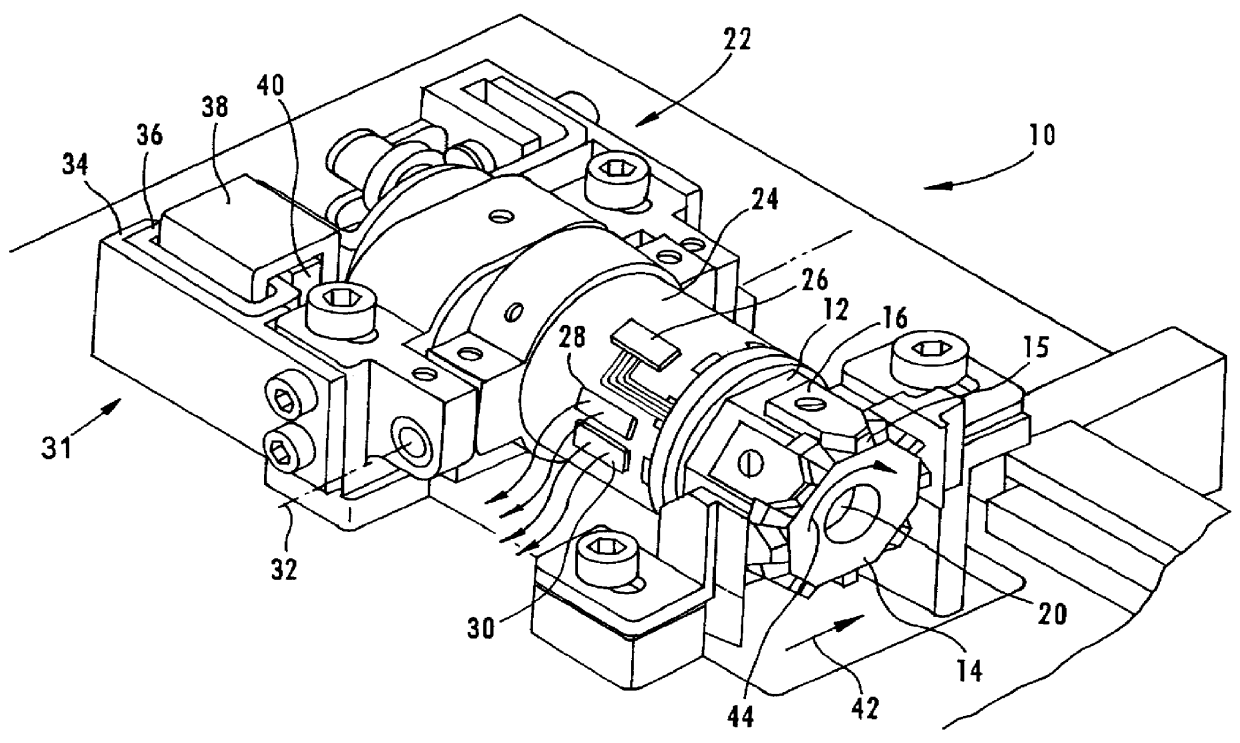
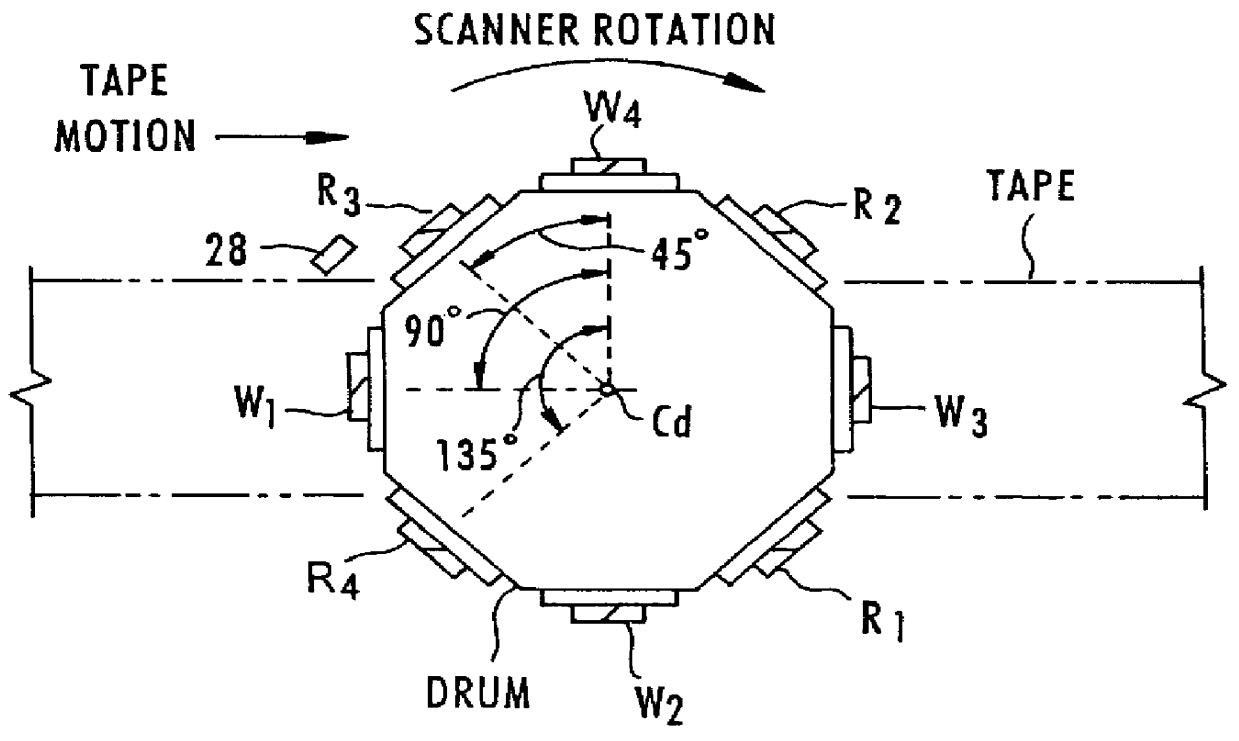
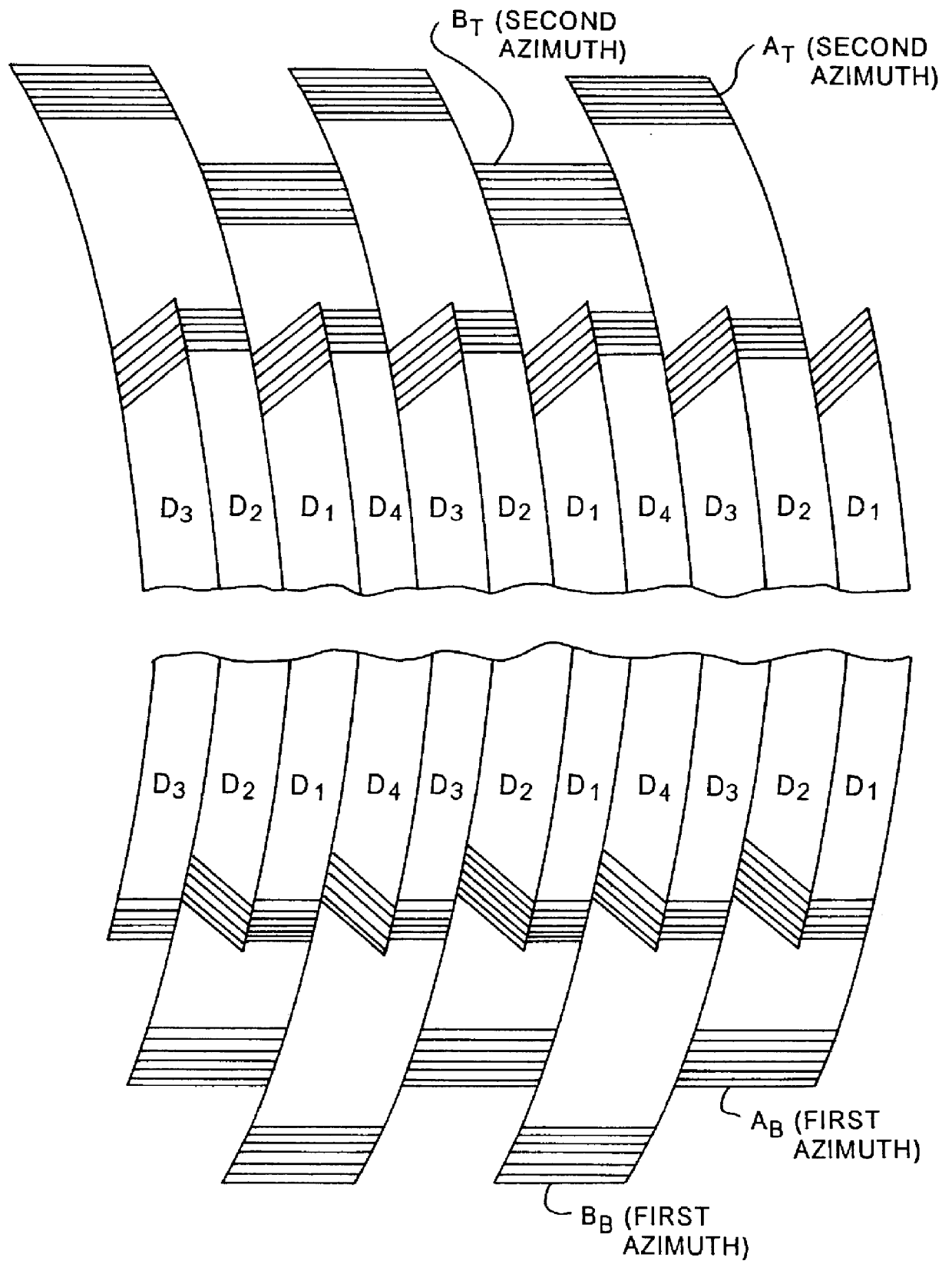
To control operations of an arcuate scanning head assembly, servo signals are written in one or more designated servo regions along a recording tape, for example along one or both edges of the recording area on the tape. To minimize the space occupied by the servo signals, the servo signals are always written with an azimuth that is substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis of the tape. In the preferred embodiment, servo signals aligned with adjacent tracks are written at two different positions within a servo region. As a read head passes over a track and the servo region, the head should overlap the servo signal aligned with that track and a portion of the servo signal aligned with the adjacent track. A control system samples the signal from the read head in a first time window corresponding to passage of the head across a burst aligned with the track and in a second time window corresponding to passage of the head across a burst aligned with the adjacent track. The system controls one or more parameters relating to the scanning operation as a function of a relationship of the two sampled amplitudes.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
Flat servo bursts for arcuate track scanner
InactiveUS6130792AFilamentary/web carriers operation controlAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeControl system
To control operations of an arcuate scanning head assembly, servo signals are written in one or more designated servo regions along a recording tape, for example along one or both edges of the recording area on the tape. To minimize the space occupied by the servo signals, the servo signals are always written with an azimuth that is substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis of the tape. In the preferred embodiment, servo signals aligned with adjacent tracks are written at two different positions within a servo region. As a read head passes over a track and the servo region, the head should overlap the servo signal aligned with that track and a portion of the servo signal aligned with the adjacent track. A control system samples the signal from the read head in a first time window corresponding to passage of the head across a burst aligned with the track and in a second time window corresponding to passage of the head across a burst aligned with the adjacent track. The system controls one or more parameters relating to the scanning operation as a function of a relationship of the two sampled amplitudes.
Owner:CERTANCE
Method and arrangement for servoing and formatting magnetic recording tape
InactiveUS6061199AFilamentary/web carriers operation controlDriving/moving recording headsMagnetic tapeComputer science
Owner:CERTANCE
Quasi-statically oriented head for recording non-legacy formats
InactiveUS20140334033A1Stable separationAlignment for track following on tapesTape carriersComputer hardwareMagnetic tape
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Angled flat-type recording head designed for near-constant resolution at varying type velocities
InactiveUS7193813B2Effective straighteningManufacture head surfaceManufacturing heads with multiple gapsImage resolutionMagnetic tape
A magnetic tape head system and associated method are disclosed. Included is one or more head assemblies each including a base with a row bar coupled thereto with a head situated therein for defining a tape bearing surface defining a tape wrap angle with respect to a horizontal plane. A length of the tape bearing surface is between approximately 0.57 millimeters and 0.7 millimeters and the tape wrap angle is between approximately 0.5 degrees and 1.3 degrees such that a resolution of the magnetic tape head system is substantially independent of a velocity of the tape.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hard disc device
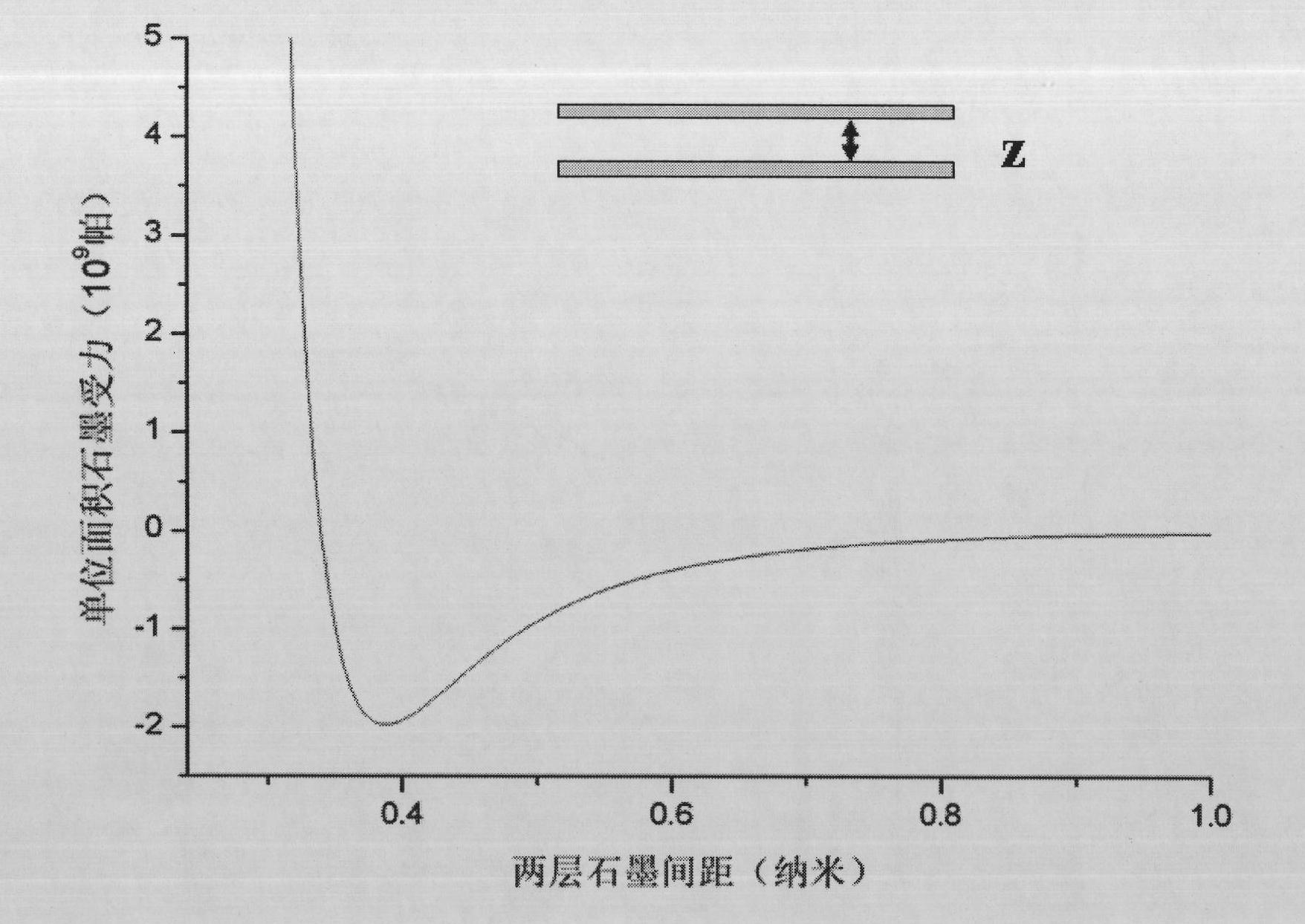
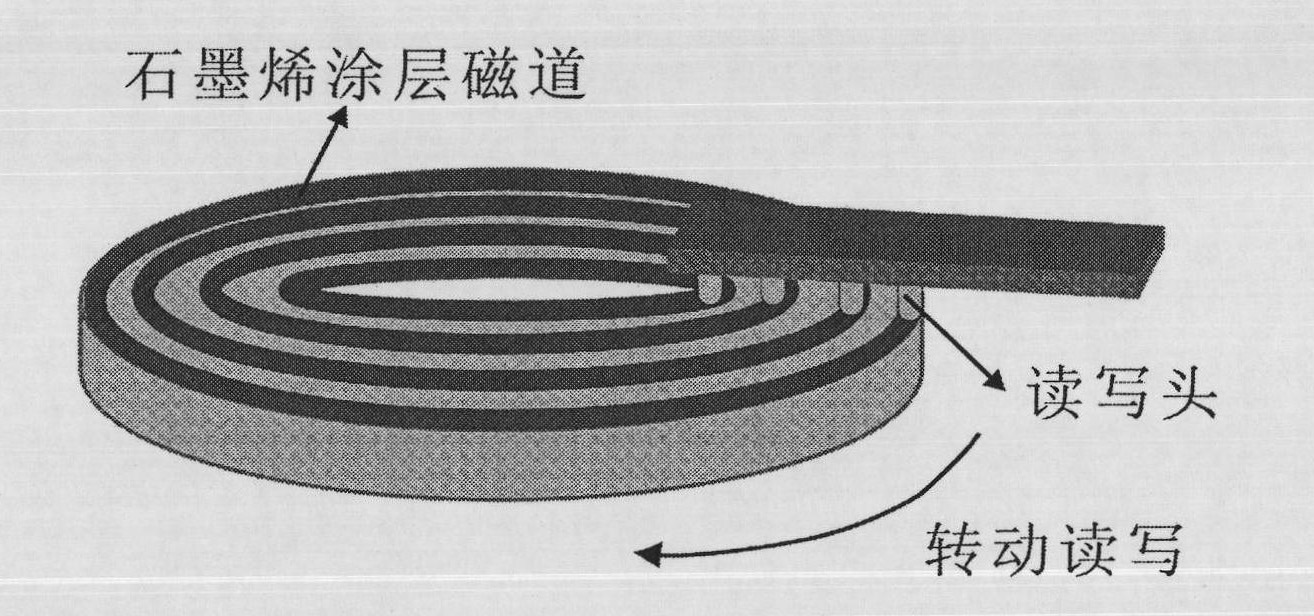
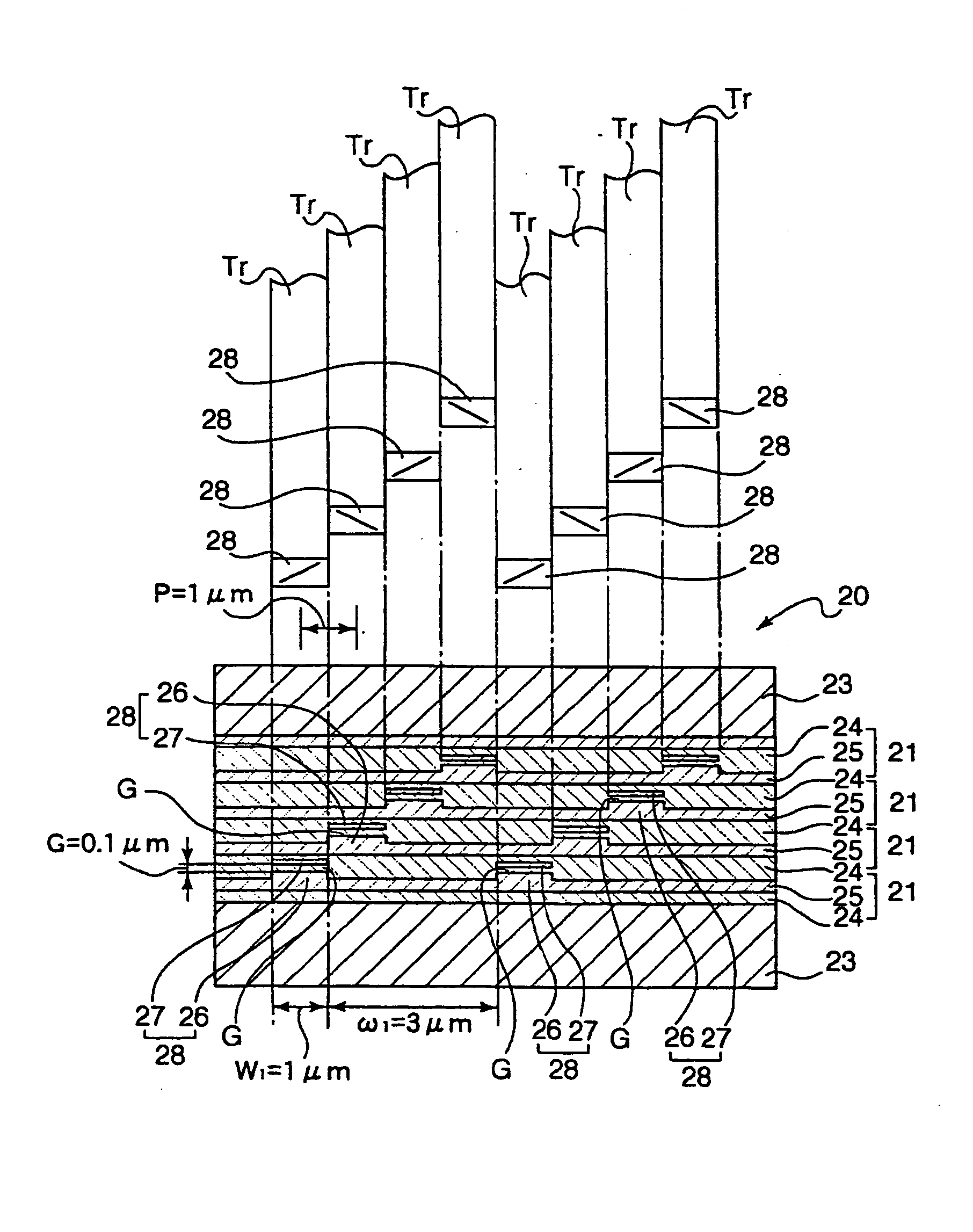
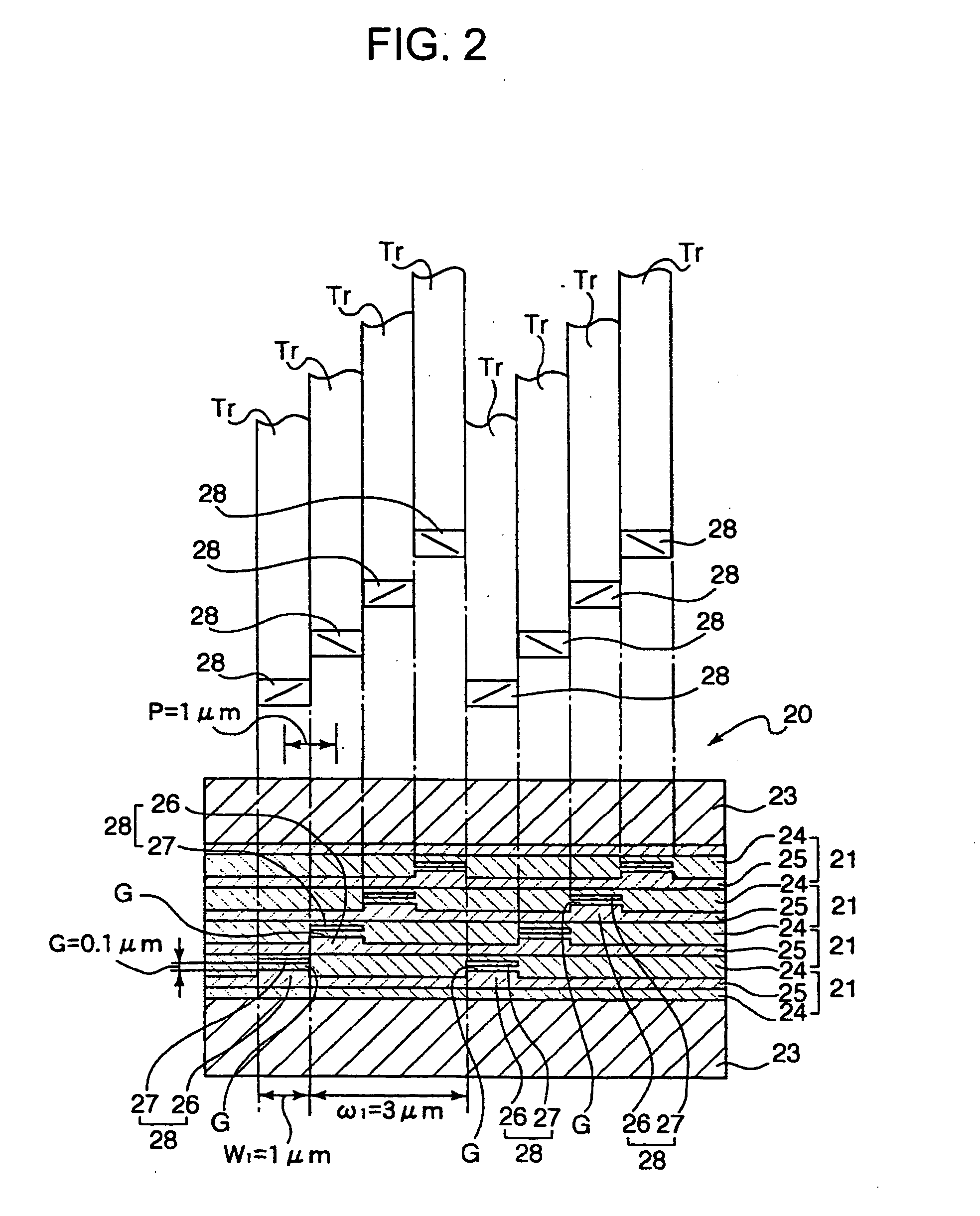
ActiveCN101794581AReduce spacingImprove storage densityManufacture head surfaceMounting heads on rotating supportFrictional coefficientMonolayer graphene
The invention provides a hard disc device, comprising a magnetic head and a disc body, wherein the magnetic head and the disc body are provided with low-friction atomic scale smooth surfaces; and each low-friction atomic scale smooth surface comprises monolayer graphene, molybdenium disulfide, bismuth, molybdenum, mica and the like. Vander wale force between the low-friction atomic scale smooth surfaces is used as soft support, thus greatly reducing the distance of the magnetic head and the disc body, correspondingly improving the storage density of a magnetic disc, and being capable of realizing contact reading and writing to a hard disc. Simultaneously, due to the extreme low friction coefficient between the atomic scale smooth surfaces, the extreme high rotating speed can be easily realized, so the reading and writing speed of data of the hard disc can be improved. In addition, the hard disc device can well solve the defects of the traditional hard disc in the aspects of high-low temperature resistance, vibration resistance, shock resistance and the like, and greatly improves the stability of the hard disc.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Magnetoresistive head with spin valve film magnetic sensor element
InactiveUS6970332B2Improve corrosion resistanceRaise the ratioNanoinformaticsRecord information storageMagnetic reluctanceNon magnetic
An improvement in the corrosion resistance of a magnetoresistive head is aimed for, and a high magnetoresistivity ratio is maintained. In a magnetoresistive head equipped with, as a magnetic sensor element for detecting magnetic signals while in contact with a magnetic recording medium, a spin-valve film, which has a structure where an anti-ferromagnetic layer, a pinned layer in which the direction of magnetization is pinned in a predetermined direction by an exchange-coupling magnetic field at work between itself and the anti-ferromagnetic layer, a free layer in which the direction of magnetization changes in accordance with an external magnetic field, and a non-magnetic layer for magnetically isolating the pinned layer and the free layer are layered, the corrosion potential of the spin-valve film relative to a standard hydrogen electrode measured while immersed in a NaCl solution of a concentration of 0.1 mol / L is specified at +0.4 [V vs. SHE] or above.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnetic recording/reproducing apparatus using a GMR head
InactiveUS6989974B2Improve corrosion resistanceHigh sensitivityNanoinformaticsHeads using thin filmsMagnetic reluctanceSpin valve
A highly reliable magnetic recording / reproducing apparatus is provided. In the magnetic recording / reproducing apparatus, a spin-valve film is used as a magnetic sensor element for detecting magnetic signals. By defining the corrosion potential of this spin-valve film, and further by specifying the residual magnetization of a magnetic recording medium used as well as the product of the residual magnetization and the thickness of the magnetic layer to a range that is numerically optimal, the occurrence of corrosion on the surface of a magnetoresistive head that contacts the medium is prevented, and the occurrence of electromagnetic discharge is avoided. Further, by numerically specifying the surface resistivity of the metal magnetic thin film of the magnetic recording medium, as well as the roughness of the surface on which the metal magnetic thin film is formed, electrostatic discharge preventing effects and wear resistance are improved.
Owner:SONY CORP
Process for producing an assembly having several magnetic heads and multiple head assembly obtained by this process
InactiveUS6256864B1Reduce the impactEnsure continuityElectrical transducersManufacturing heads with multiple gapsElectrical conductorPole piece
Process for the production of an assembly having several magnetic heads and multiple head assembly obtained by said process.Production takes place of a first substrate (60) with first pole pieces (621, 622) and a second substrate (70) with second pole pieces (721, 733) and magnetic connectors (741, 742). One of the substrates is reversed and engaged on the other. The second substrate is thinned out so that the two pole pieces (721, 722) and the magnetic connectors (741, 742) are level or almost level. The assembly is completed by forming on the second thinned out substrate, magnetic circuit closing means and conductor coils.Application to the production of multiple magnetic head assemblies.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Tubular rotary head cleaner having a non-woven fabric for a magnetic recording and/or reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS6069776AFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageEngineeringMechanical engineering
A head cleaner for a magnetic recording and / or reproducing apparatus for cleaning rotary magnetic heads. The head cleaner includes a rotary spindle rotatably mounted on a support arm movable between an operative position, in which the head cleaner is in position to clean the magnetic heads, and an inoperative position separated from the magnetic heads. The head cleaner also includes a plurality of oblong webs of non-woven fabric with or without an abrasive material coated on one surface thereof. The oblong webs of non-woven fabric are fixedly secured to the rotary spindle so as to extend radially outwardly therefrom while being spaced an equal distance from each other in a direction circumferentially thereof.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Head system, recording and reproduction system, and magnetic recording method
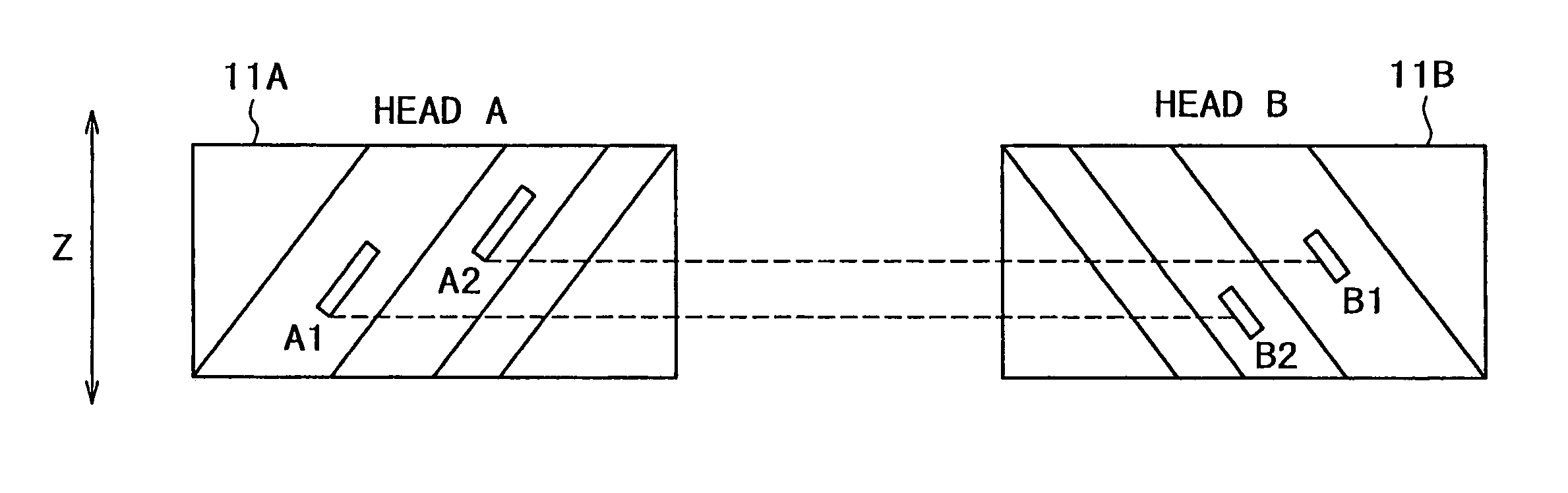
InactiveUS7420758B2Improve accuracyEliminate needAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageHigh densityMagnetization
Disclosed is a head system including a plurality of recording heads for azimuth recording. The system includes a first recording head having a plurality of magnetic gaps having a first azimuth angle, and a second recording head having a plurality of magnetic gaps having a second azimuth angle different from the first azimuth angle. After first magnetization patterns are formed on a recording medium by the first recording head, second magnetization patterns are formed by overwriting side edge portions in the formation direction of the first magnetization patterns by the second recording head. This makes it possible to prevent the worsening of the accuracy of the magnetization pattern width due to a relative height stagger (offset) between the heads, to thereby enhance the accuracy of the magnetization pattern width, and to achieve high-density recording.
Owner:SONY CORP
Current-assisted magnetic recording write head with improved write gap structure
ActiveUS20200005815A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImprove errorManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageHemt circuitsMechanical engineering
A current-assisted magnetic recording write head has an electrically conductive layer in the write gap between the write pole and the trailing shield. Electrical circuitry directs current from the write pole, through the conductive layer, to the trailing shield. The current through the conductive layer generates an Ampere field substantially orthogonal to the magnetization in the write pole to assist magnetization switching of the write pole. The write head's magnetic throat height (THm) is substantially the thickness of the trailing shield at the write gap, while the write head's electrical throat height (THe) is substantially the height of the conductive layer in the write gap. In embodiments of this invention, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the readback signal and the soft error rate (SER) of the recorded data can be improved with a write gap structure wherein THe is greater than THm.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Data card with a full circular track for alignment and amplitude calibration
InactiveUS6934098B2Conveniently determinedConveniently centeringApparatus for flat record carriersCode conversionLocking mechanismData signal
This invention discloses a flat data storage medium that includes a plurality of substantially parallel data arc-segments. The data arcs further include at least one full circle data track provided for obtaining a measurement of an average amplitude of data signals over the full circle data track for calibrating a pickup head implemented for reading data from the data arc-segments. This invention further discloses a data storage system for accessing data stored in a data storage medium. The data storage system includes dynamic head loading / unloading system that includes a handle for pushing a linkage connected to the handle for loading and unloading the data storage medium to an engaged and disengaged positions relative to a pickup head for accessing data disposed on the data storage medium. The dynamic head loading / unloading system further includes a locking mechanism for automatically locking the data storage medium inside the data storage system when the linkage is disposed at an engaged-position. The dynamic head loading / unloading system further includes a data-storage medium orientation-selection for cooperating and adapting the data storage medium inside the data storage system only when the data storage medium is inserted into the data storage system in a predefined orientation.
Owner:DCARD
Backward compatible head for quasi-static tilted reading and/or recording
InactiveUS20150187379A1Driving/moving recording headsManufacturing heads with multiple gapsMagnetic mediaTransducer
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Magnetic tape recording apparatus for recording tracks having same track pitch
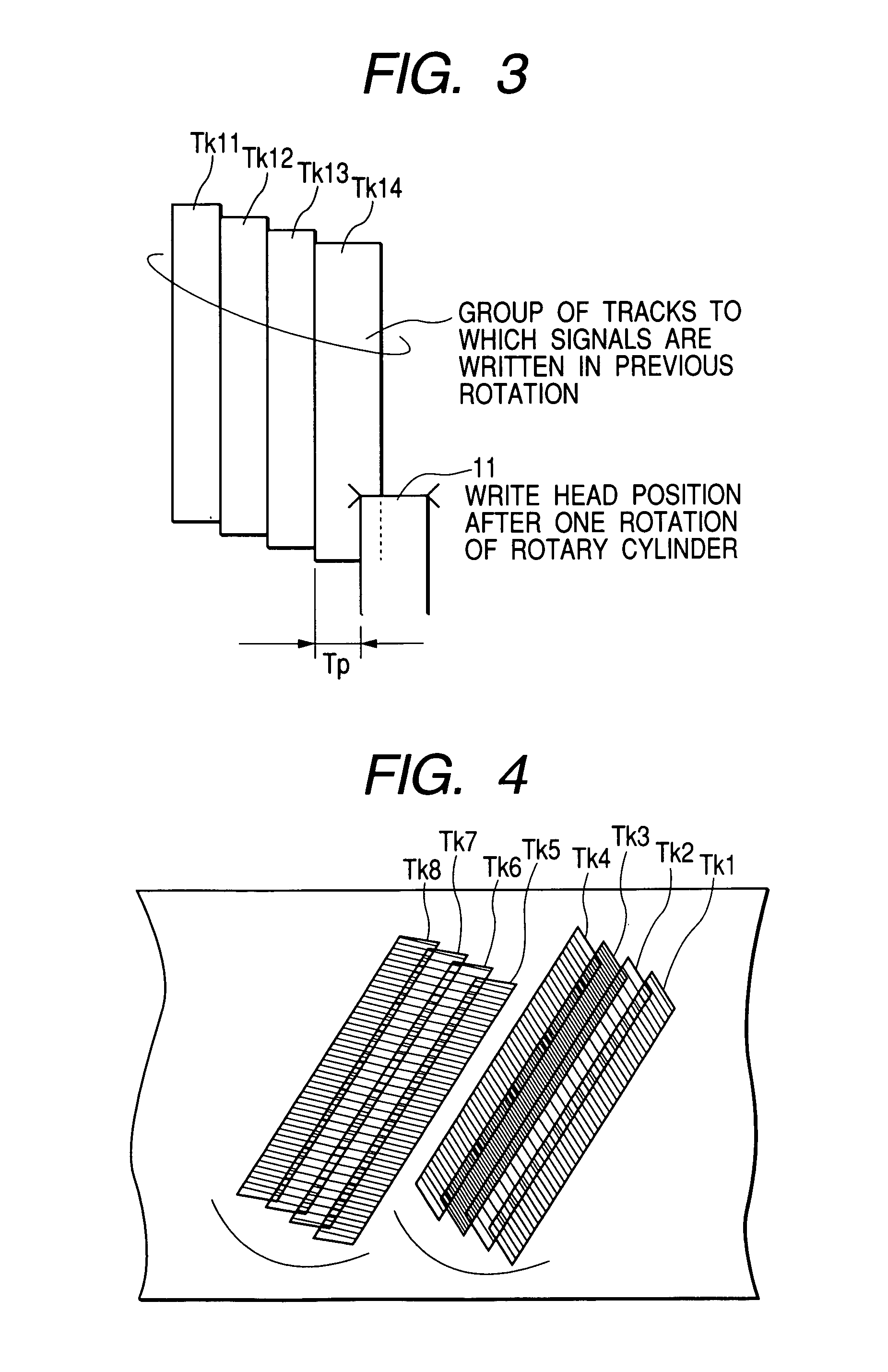
InactiveUS6922298B2Eliminating and reducing causeEliminate or reduce the cause of deterioration in accuracy of recording track widthFilamentary/web carriers operation controlDriving/moving recording headsHelical scanTape speed
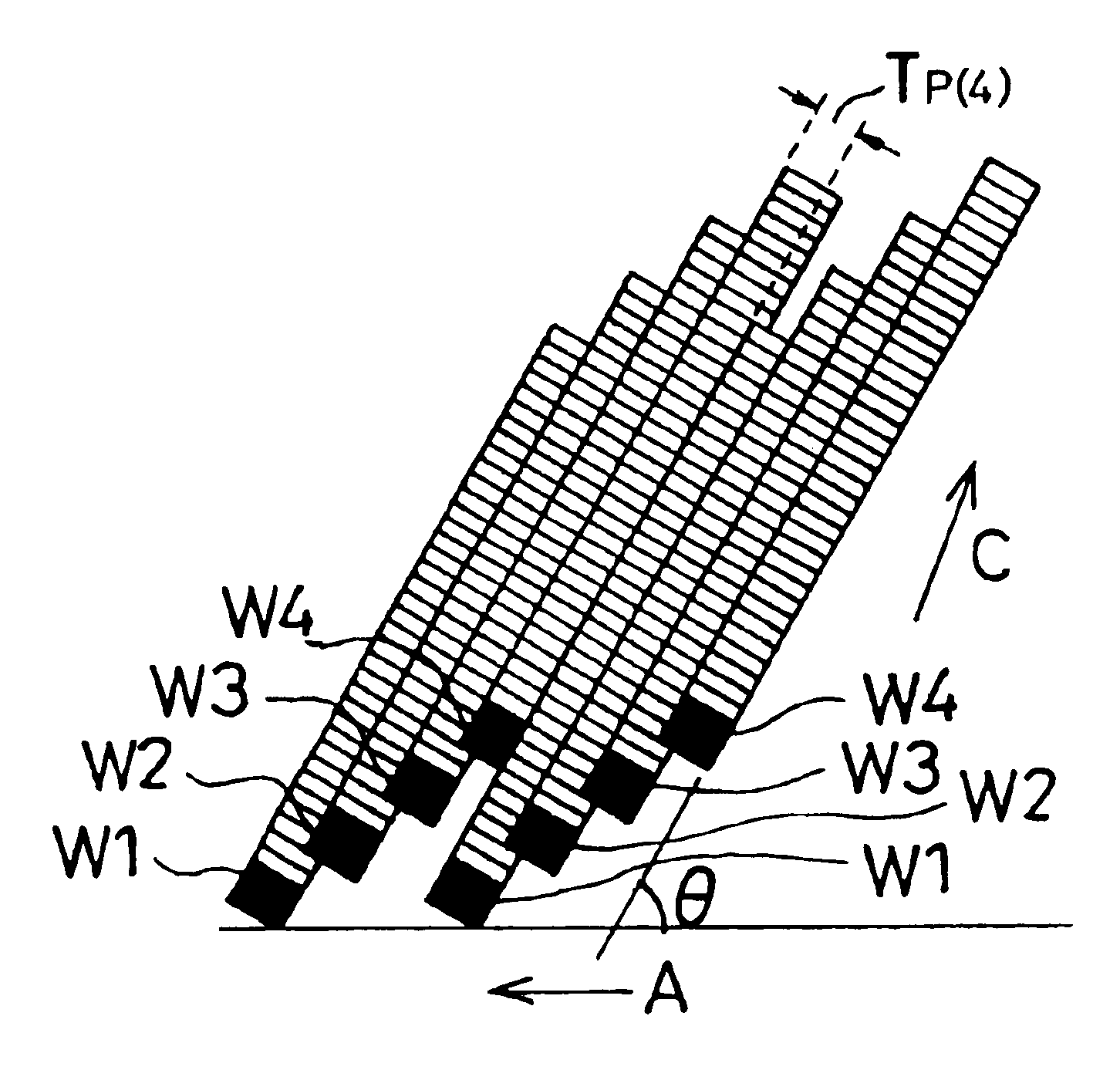
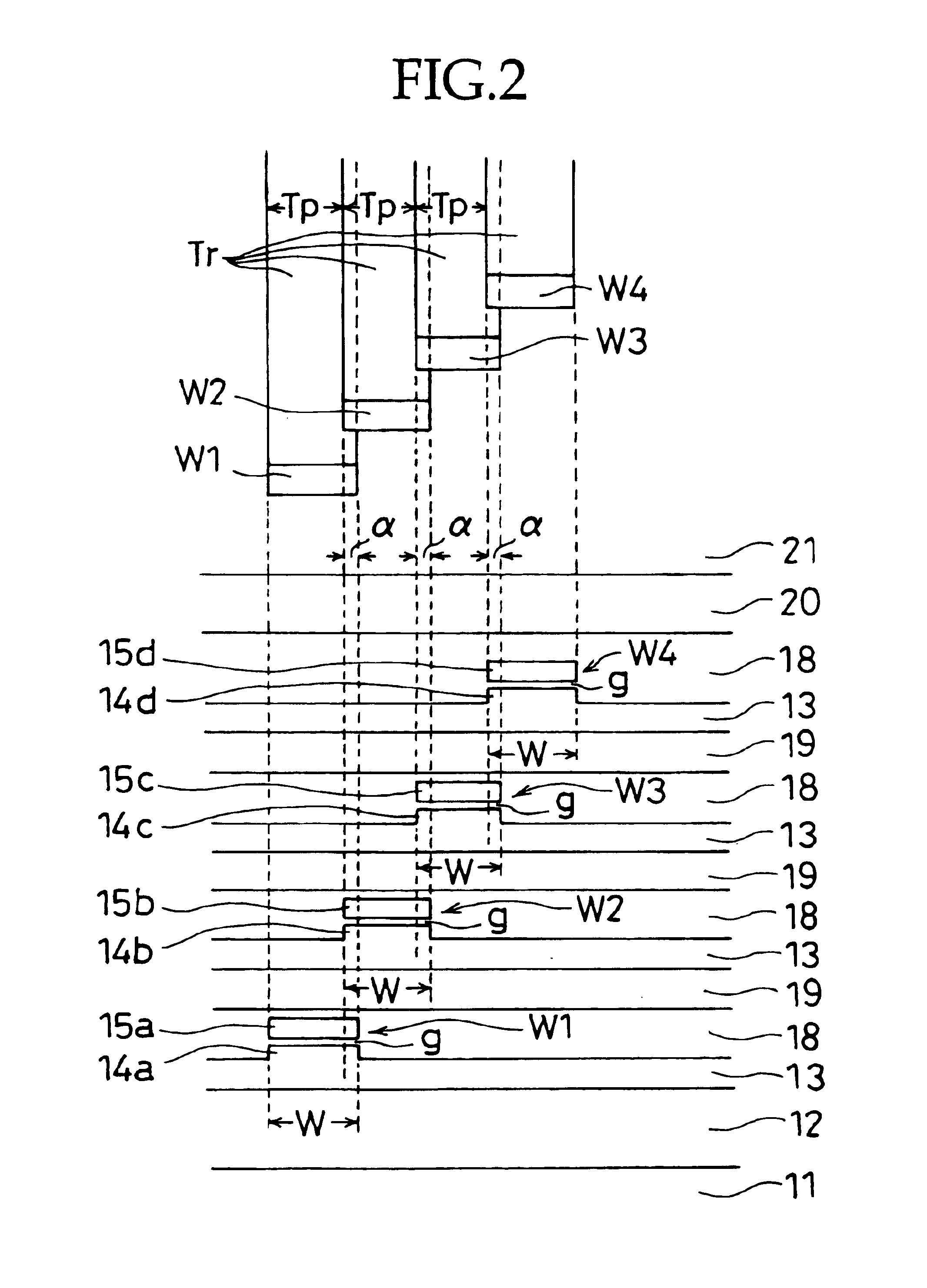
In a helical scan type magnetic tape recording apparatus, one thin film multi-recording head is mounted on a rotary drum, wherein the multi-recording head includes N recording heads for recording N recording tracks at a predetermined track angle on a magnetic tape by one rotation of the rotary drum to perform recording for forming continuous recording tracks having the same track pitches, by determining rotary drum rotation and a tape speed in accordance with equation V1=Tp·N·(RPS) / sin θ, such that (N−1) recording tracks having the same track pitches narrower than the head width and one recording track having a wider track width than that are formed by a first rotation of the drum, then by a second rotation, a preceding recording head overwrites the recording track having the wider track width to form a recording track having a track width equal to the track width of the recording track.
Owner:SONY CORP
Head stack assembly with suspension supporting head slider and hard disc drive including the same
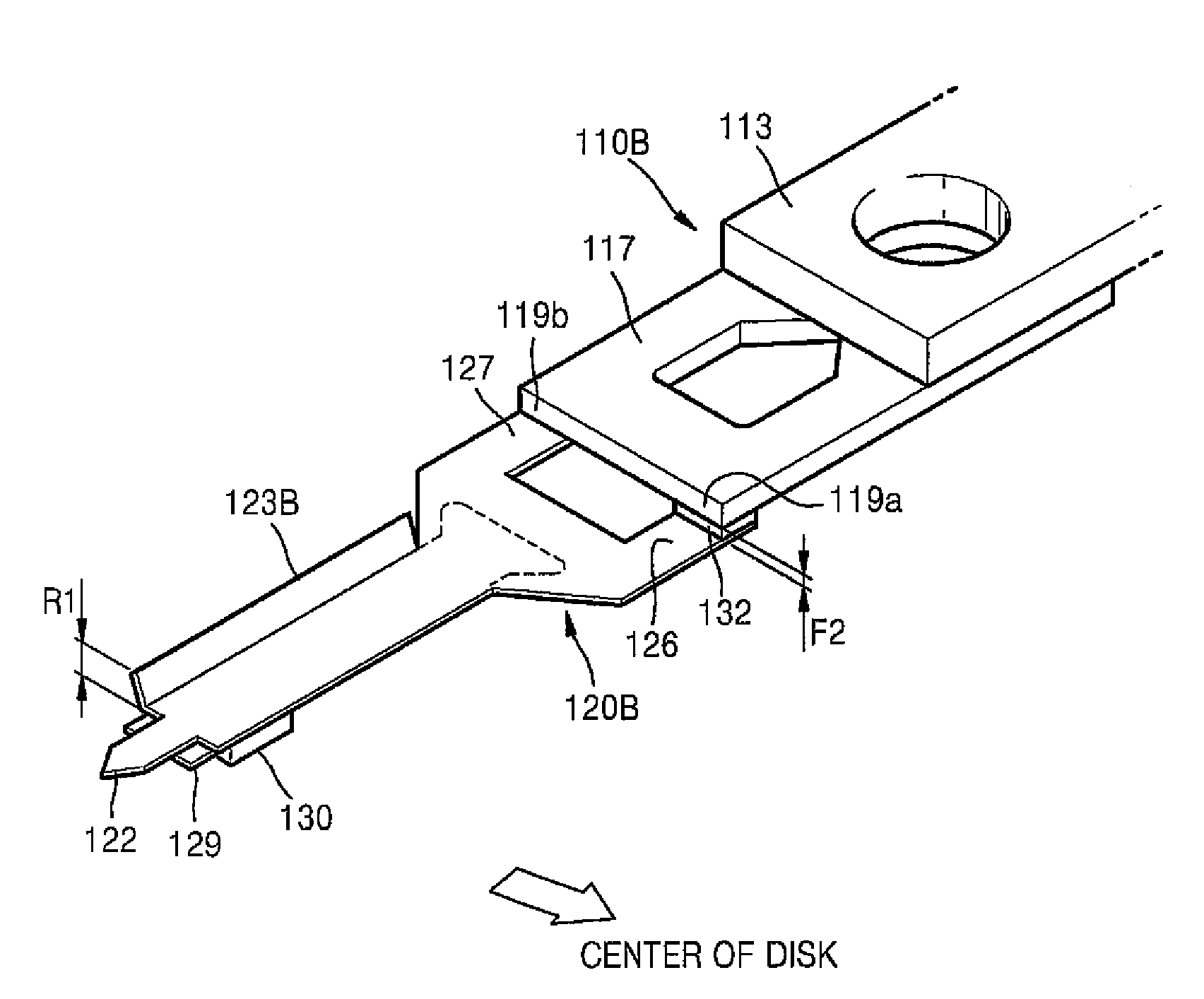
InactiveUS7952835B2Minimize extentHigh speed machiningTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageHard disc driveEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic recording head having longitudinally spaced offset arrays
ActiveUS20170372735A1Record information storageMounting heads on rotating supportMagnetic tapeTransducer
Owner:IBM CORP
Rotary magnetic head device and method of producing a rotary magnetic head device
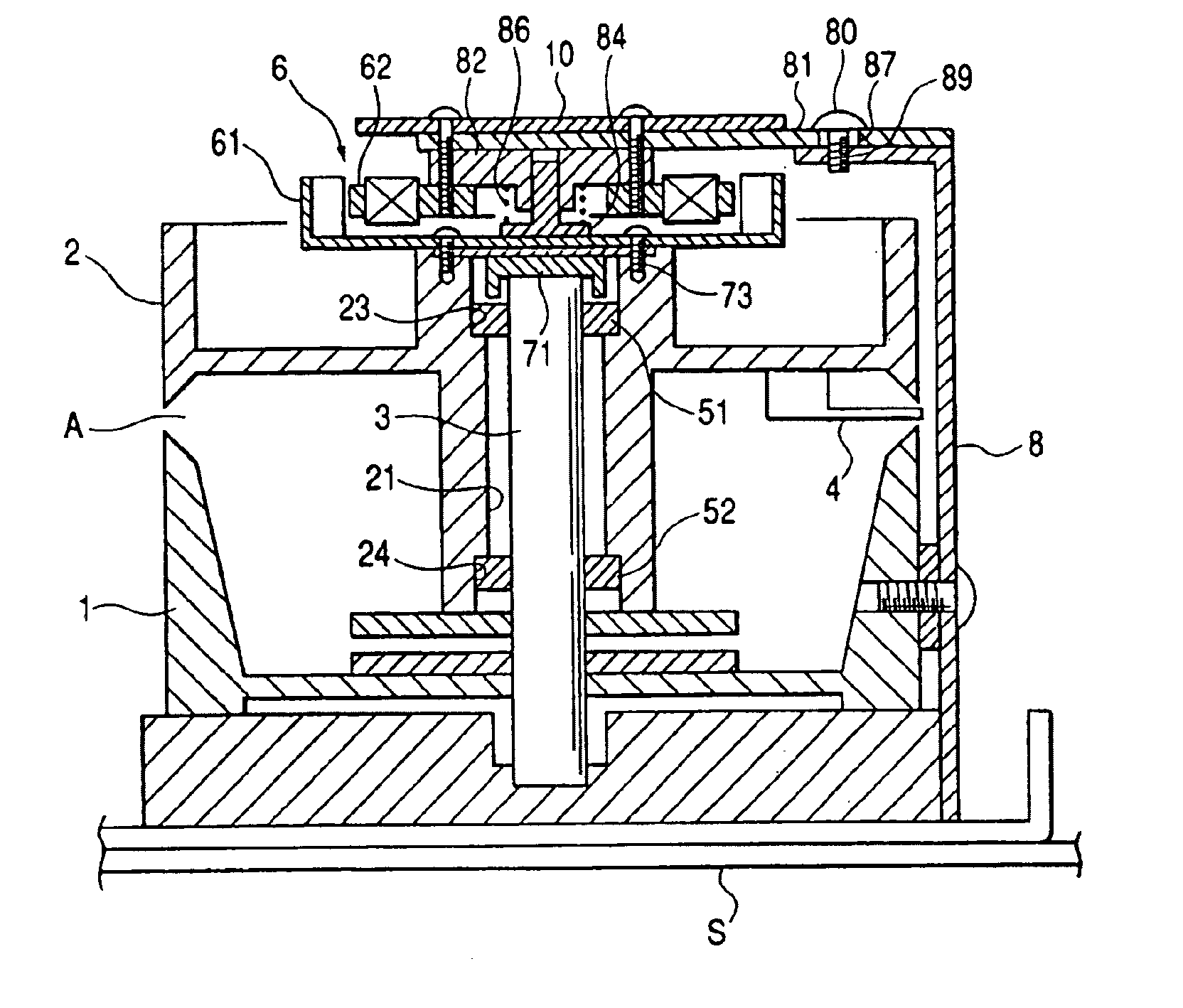
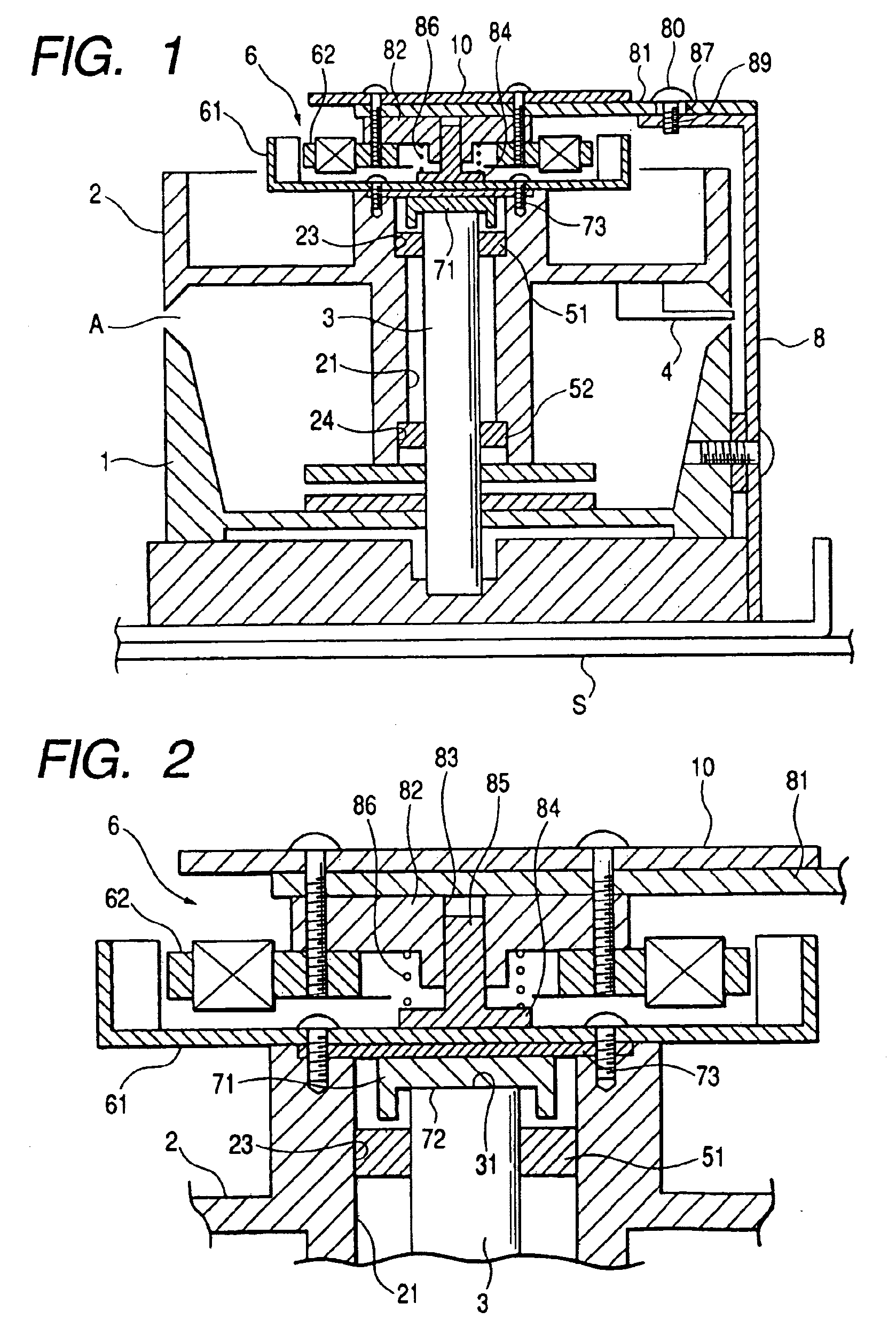
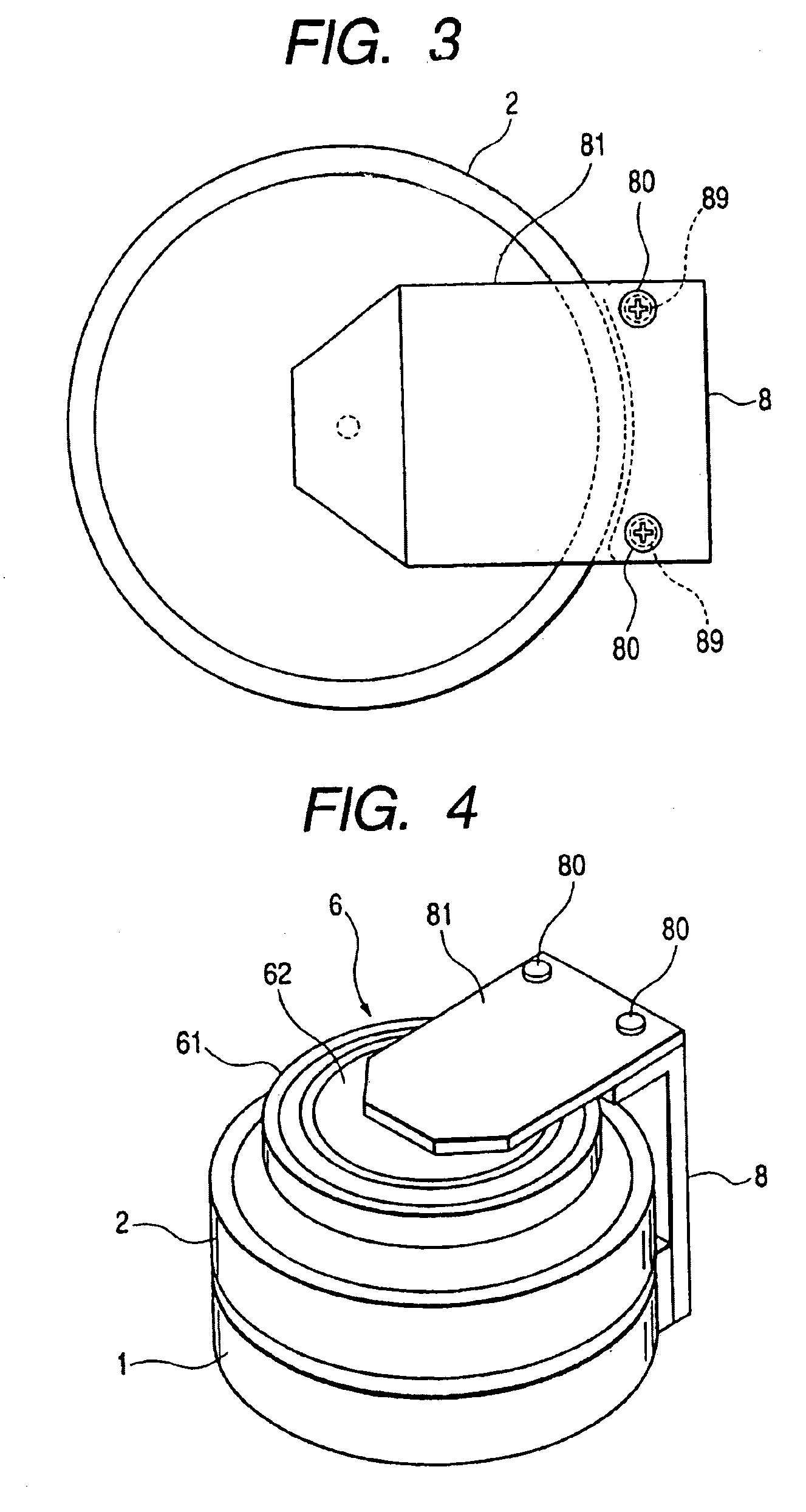
InactiveUS7009817B2Easy to adjustAvoid influenceDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageThrust bearingEngineering
A rotary magnetic head device includes a stationary drum; a rotary drum having a rotary magnetic head; a rotor of a motor fixed to the rotary drum; a support shaft for pivotally supporting the rotary drum, the support shaft having a receiving face; a radial bearing for receiving a radial load, interposed between the rotary drum and the support shaft; a thrust bearing for receiving a thrust load, being slidably put on the receiving face; an urging member for urging the thrust bearing against the receiving face by pushing the rotary drum downward; and a reverse L-shaped support fixed to the stationary drum. The urging member is supported by the reverse L-shaped support and arranged on the rotary drum.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Magnetic recording head, magnetic reproducing head, magnetic head, tape drive and disk drive
InactiveUS20050174689A1Reduce widthMinimizes alignment errorManufacture unitary devices of plural headsHeads using thin filmsHigh densityEngineering
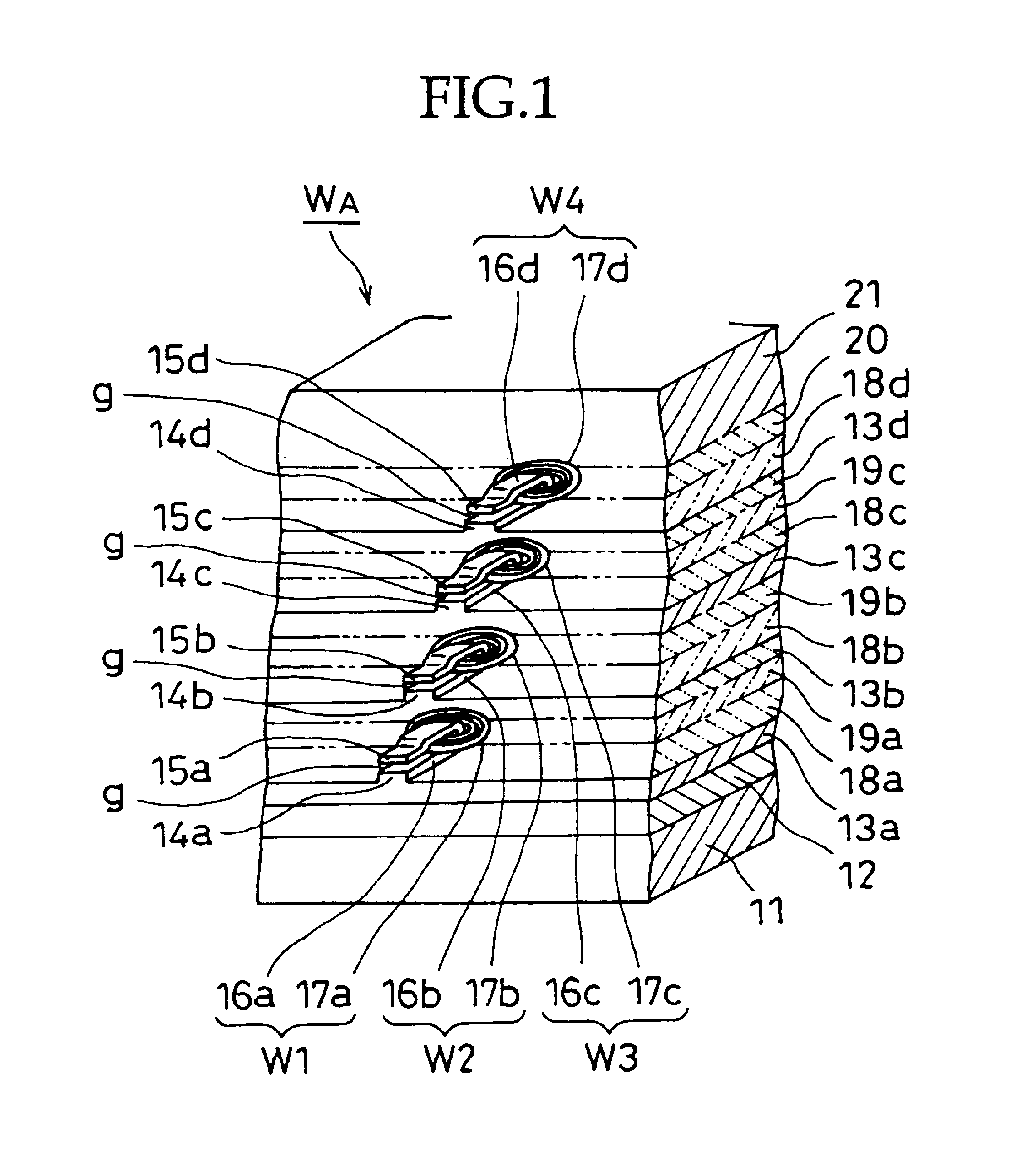
A magnetic recording / reproducing head having a plurality of magnetic head elements for multi-channeling capable of achieving high density recording / reproducing capability, including: a plurality of magnetic recording / reproducing head layers each including magnetic recording / reproducing head elements fabricated by a thin film process and interposed between two insulating / magnetic shielding layers laminated on a non-magnetic substrate; the total of magnetic recording / reproducing head elements formed therein are displaced from each other in a head width direction, and each magnetic recording / reproducing head layer has a plurality of magnetic recording / reproducing head elements formed at a predetermined pitch.
Owner:SONY CORP
Negative pressure type rotary head drum unit and magnetic tape drive using the same
InactiveUS7050265B2Reduce contact pressureSuppress mutationDriving/moving recording headsFluid-dynamic spacing of headsContact pressureMagnetic tape
Disclosed herein is a rotary head drum unit including a cylindrical drum surface and a magnetic head for recording / reproducing a signal to / from a magnetic tape running along the drum surface. The magnetic head has a tape sliding surface adapted to come into sliding contact with the magnetic tape. The tape sliding surface of the magnetic head is positioned at a level lower than the height of the magnetic tape flying above the drum surface. The magnetic tape is brought into contact with the tape sliding surface by negative pressure. With this configuration, an increase in contact pressure of the magnetic tape sliding on the tape sliding surface of the magnetic head can be prevented and the contact pressure can be uniformed to thereby prevent a reduction and variations in magnetic recording or reproduction output.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus and method and thin film magnetic head used therein
InactiveUS7092187B2Increase transfer rateDifficult to achieveFilamentary/web carriers operation controlHeads using thin filmsMagnetic tapeRecording density
The present invention provides a magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus, a magnetic recording and reproducing method, and a thin film magnetic head that enable a good contact between elements and a recording medium with a reduced track pitch even if the number of head channels is increased, thereby realizing high recording density and high transfer rate.At least one multitrack write head having N (N is an integer of 2 or more) write elements arranged along a track width direction in an integral fashion and at least one multitrack read head having L (L is an integer equal to or more than N) read elements arranged along the track width direction in an integral fashion are formed on the rotary drum. The multitrack write head writes signals to a group of N tracks aligned parallel on the magnetic tape during one rotation of the rotary drum, and the multitrack read head reads the group of N signal tracks by the use of any one of the L read elements.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Energy conserving disc drive
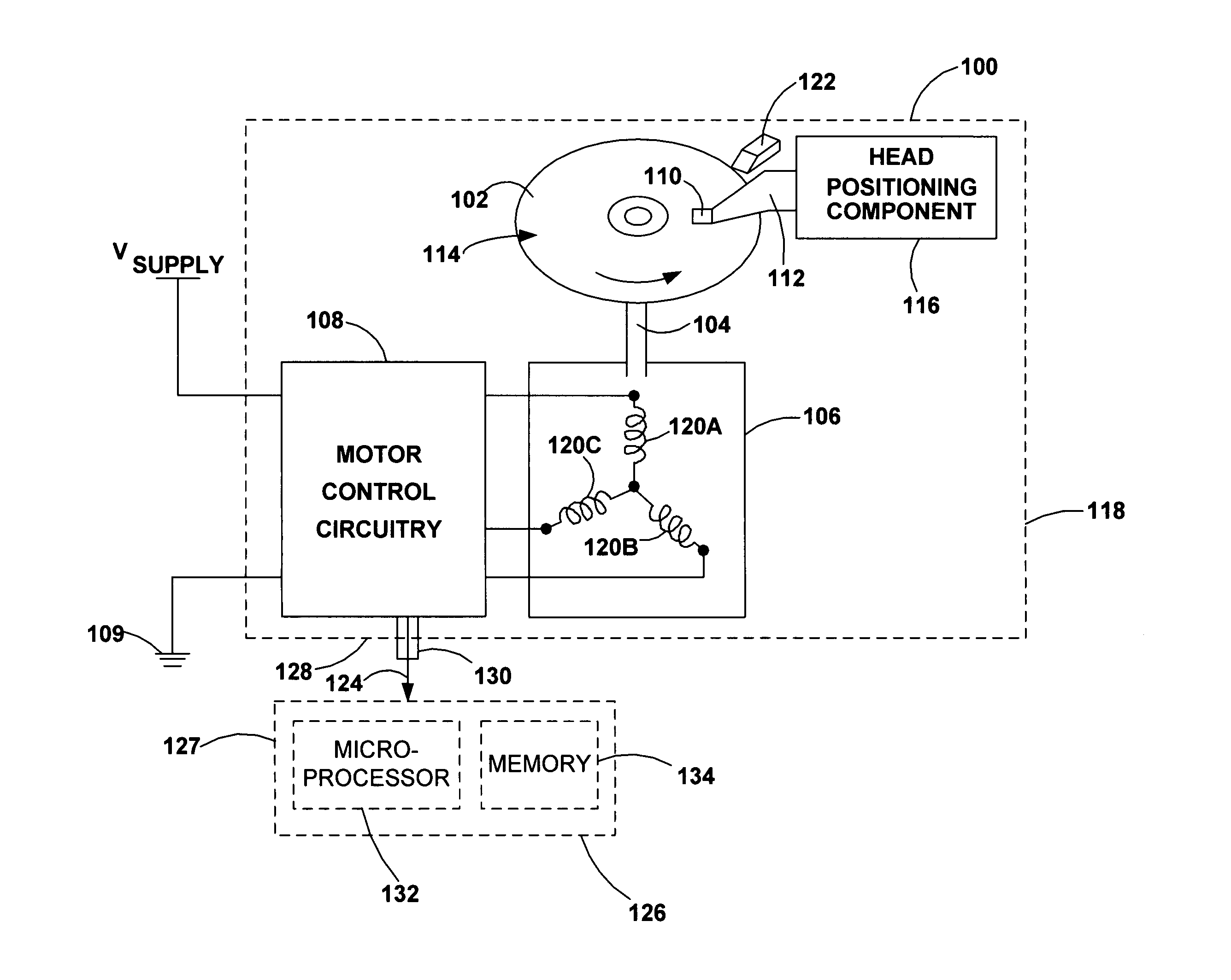
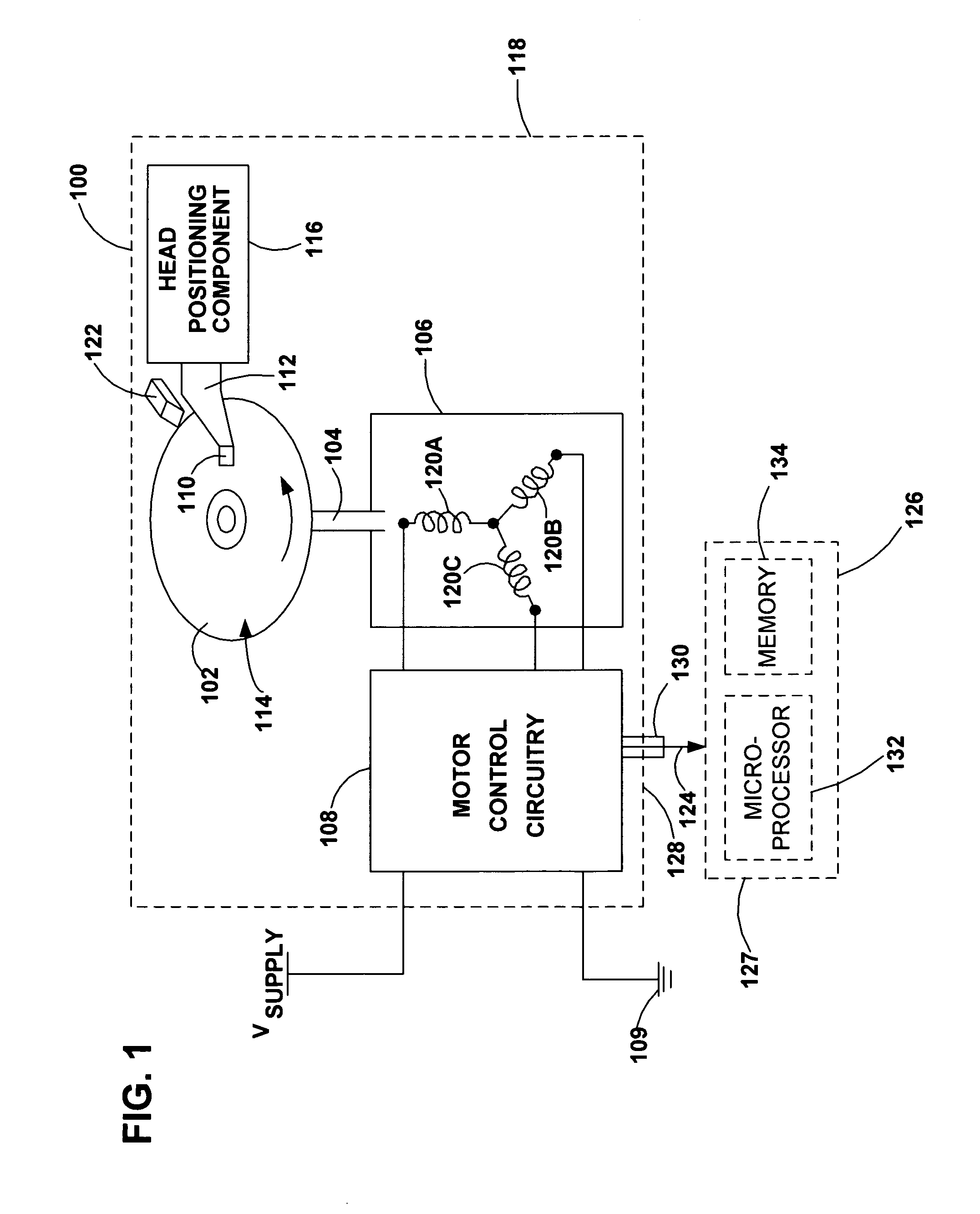
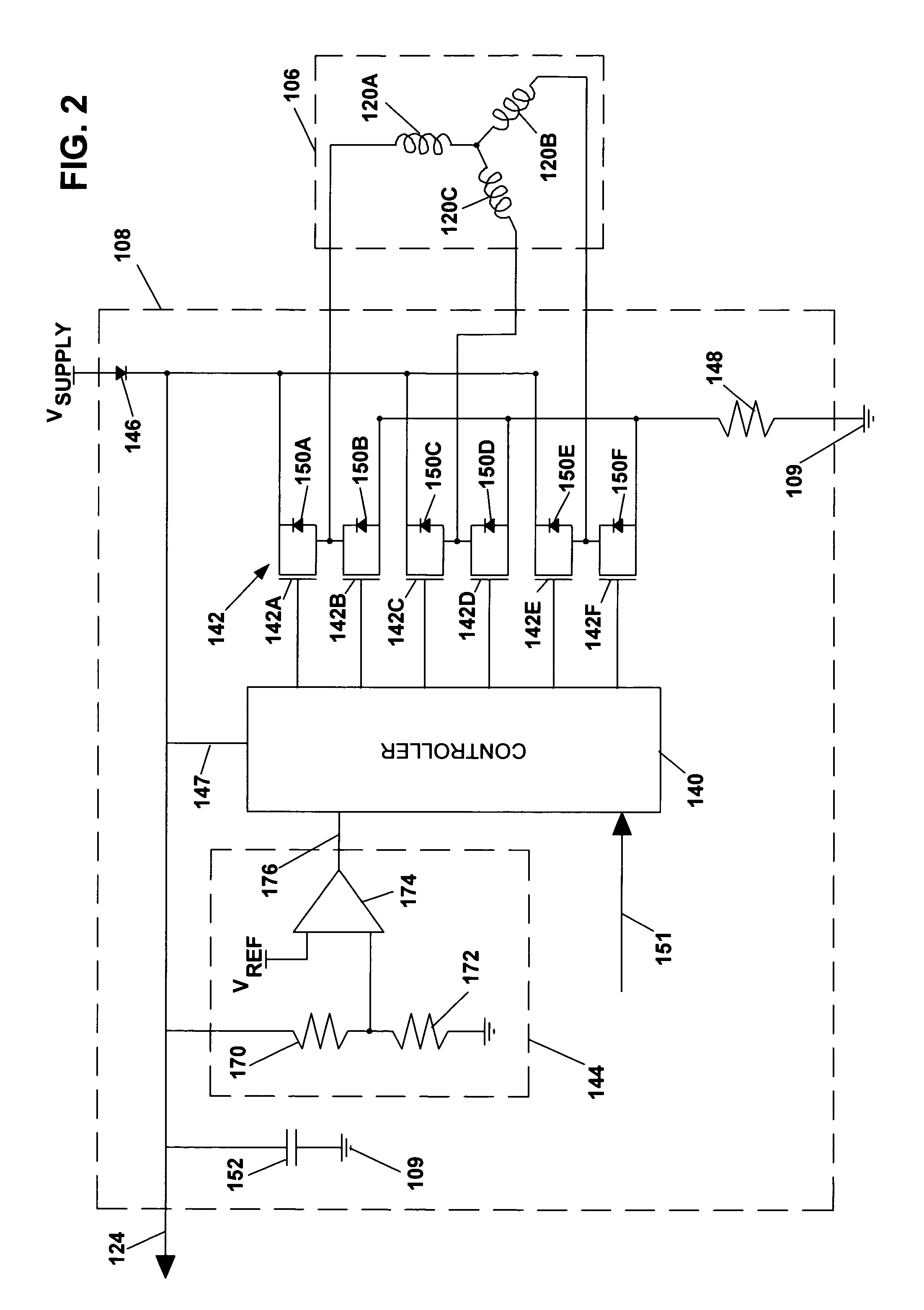
InactiveUS7005817B2Electronic commutation motor controlSynchronous motors startersMotor controlElectronic component
A disc drive includes a disc mounted to a rotatable spindle, a motor coupled to the spindle, and motor control circuitry. The motor has a motoring mode in which it rotates the spindle and a braking mode in which is decelerates the rotating spindle and generates power. The motor control circuitry is adapted to control the modes of the motor. The disc drive also includes an auxiliary power output that is generated while operating the motor in the braking mode. The auxiliary power output is made accessible to electronic components that are collateral to the disc drive.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Method of fabricating a magnetic head device
InactiveUS6898840B1Temperature increase can be substantially suppressedImprove cooling effectReducing temperature influence on carrierPrinted circuit assemblingBiomedical engineeringThermal conduction
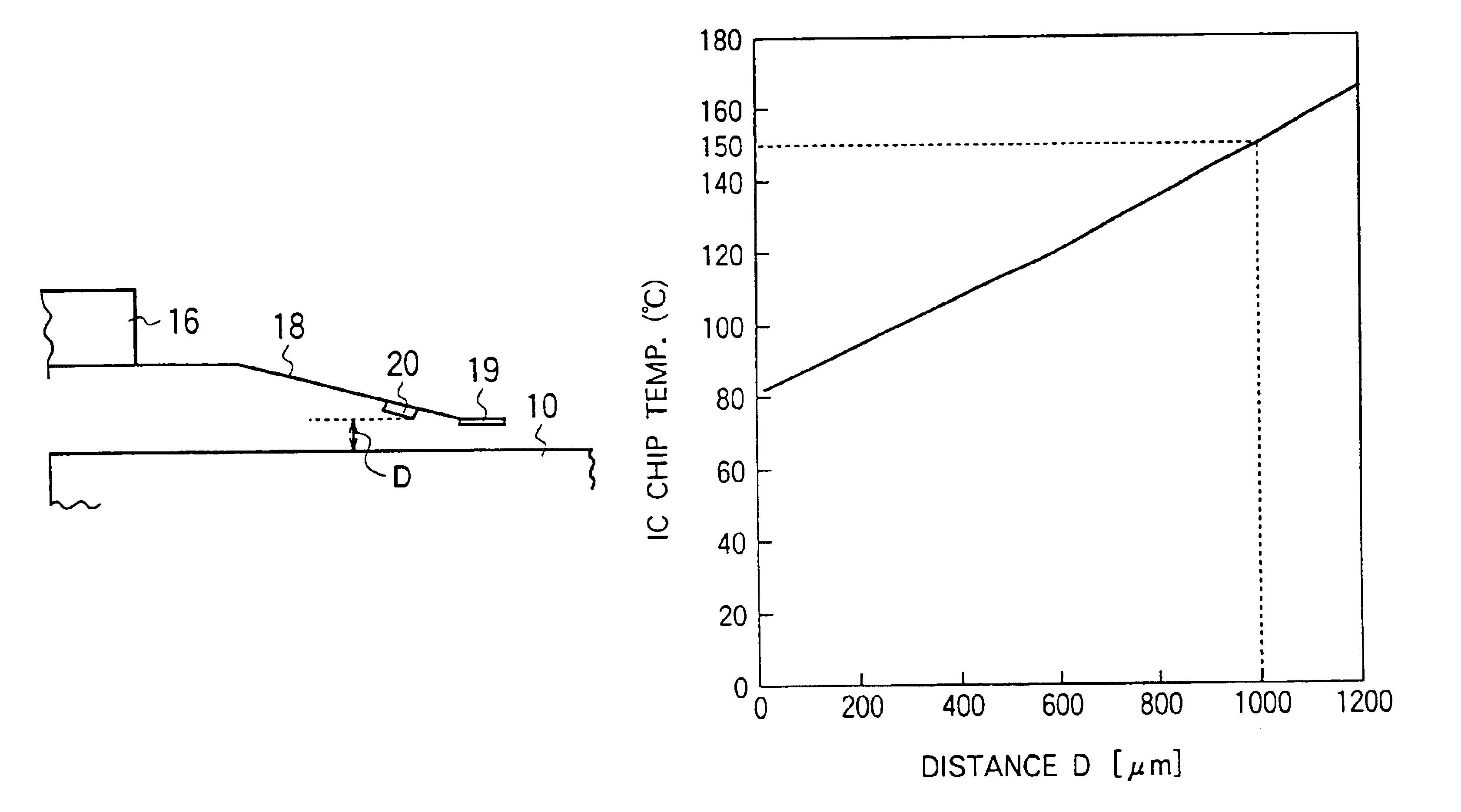
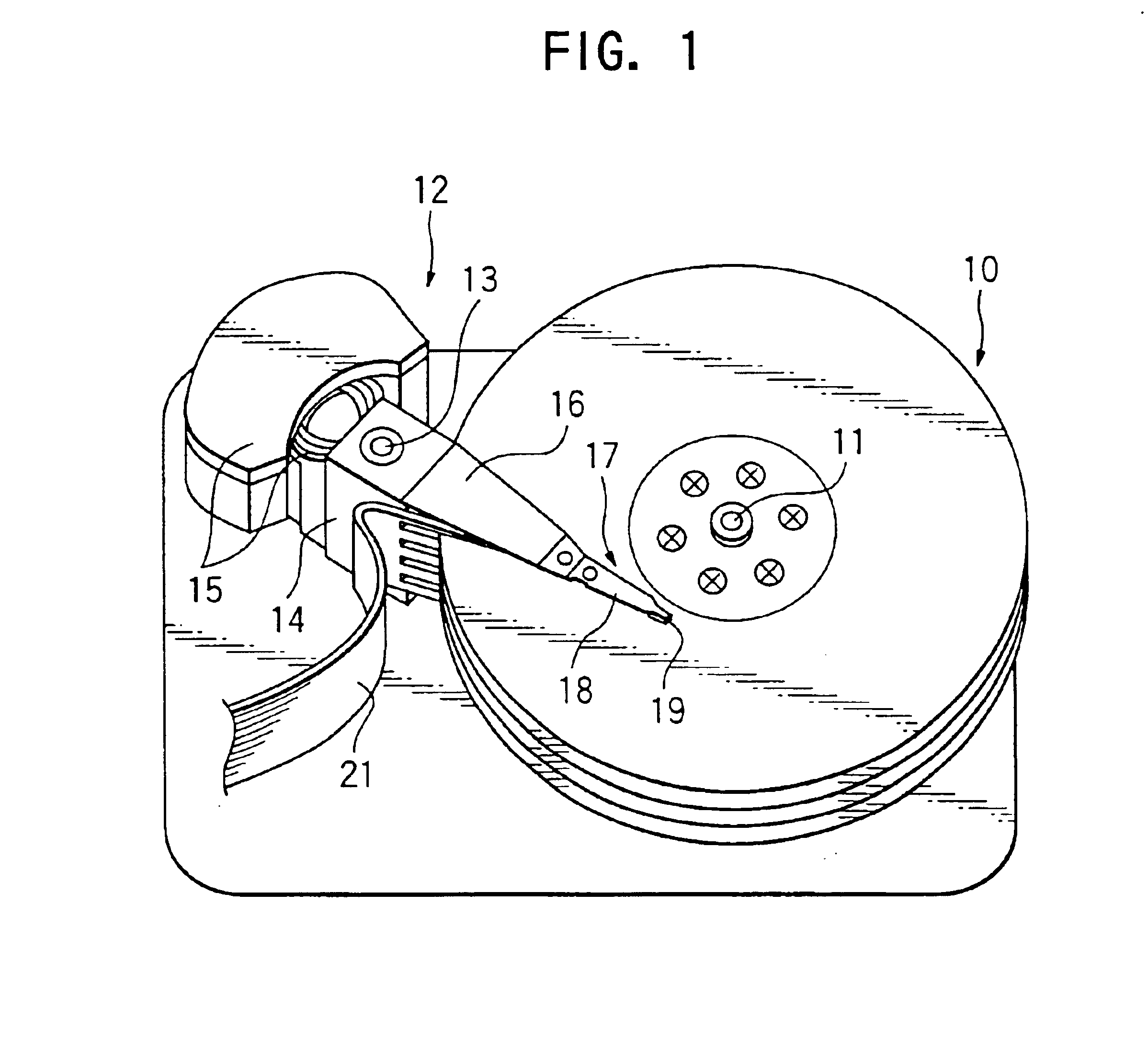
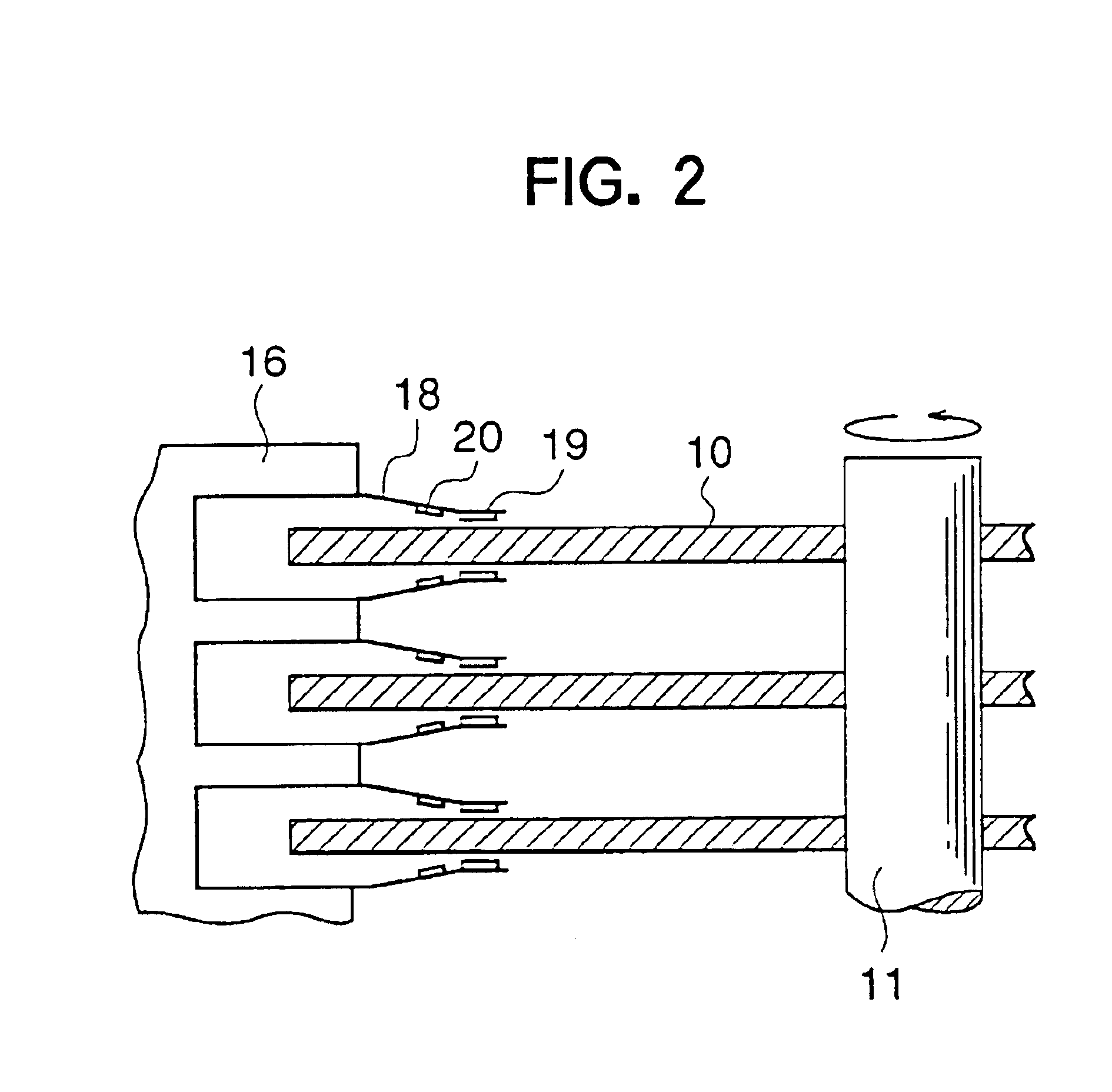
A method of fabricating a magnetic head device comprising a slider having a magnetic head element, a suspension structure made of a thin resilient material and having one end supporting the slider and the other end to be attached to another member, and a head IC chip. The head IC chip is mounted on the suspension structure so as to face a magnetic recording disc and at a position spaced from the slider-supporting one end of the suspension structure by an intervening portion of the suspension structure. The position is selected so that the intervening portion is effective to suppress a temperature increase in the head IC chip due to at least thermal conduction through the intervening portion.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Head drum assembly for magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
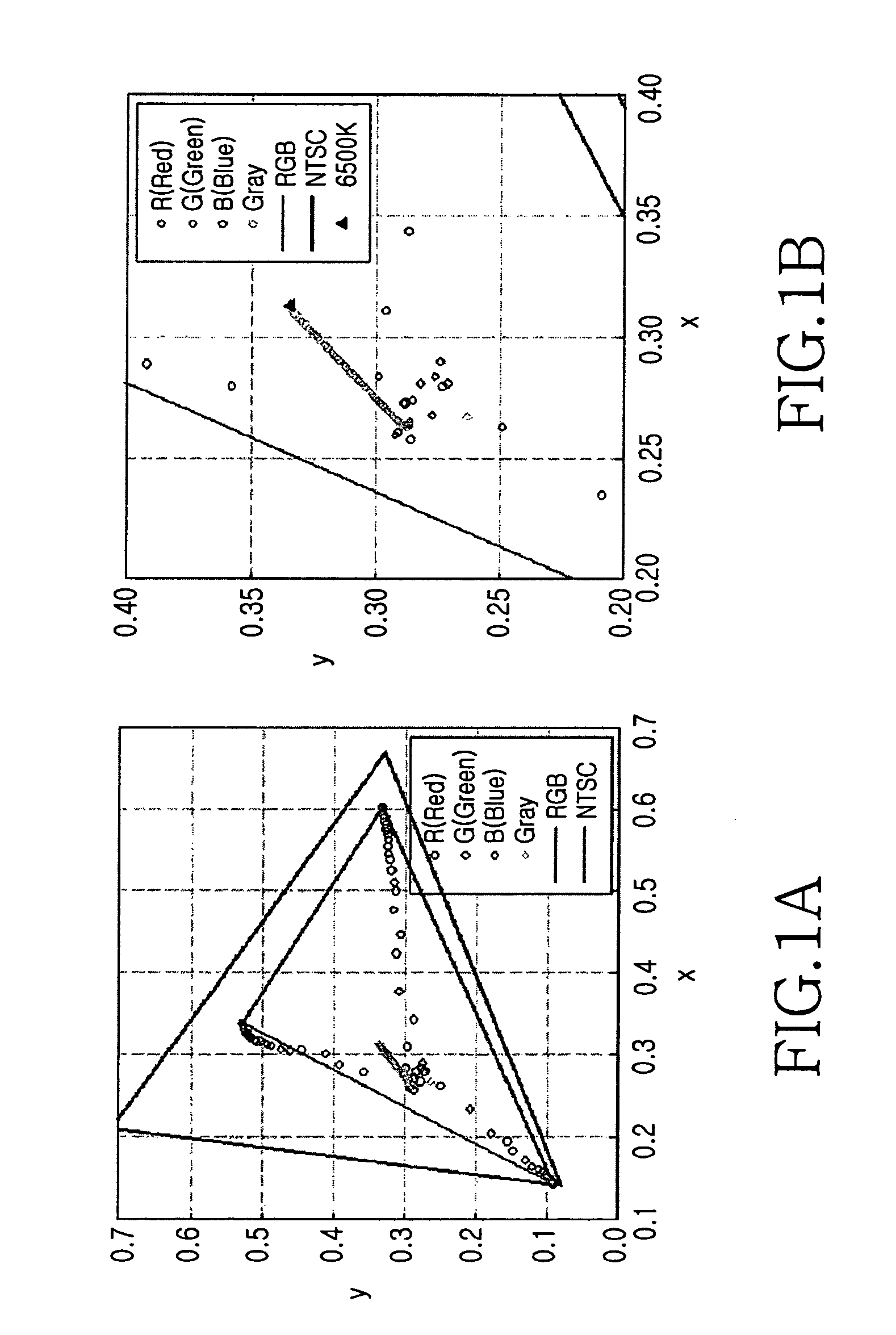
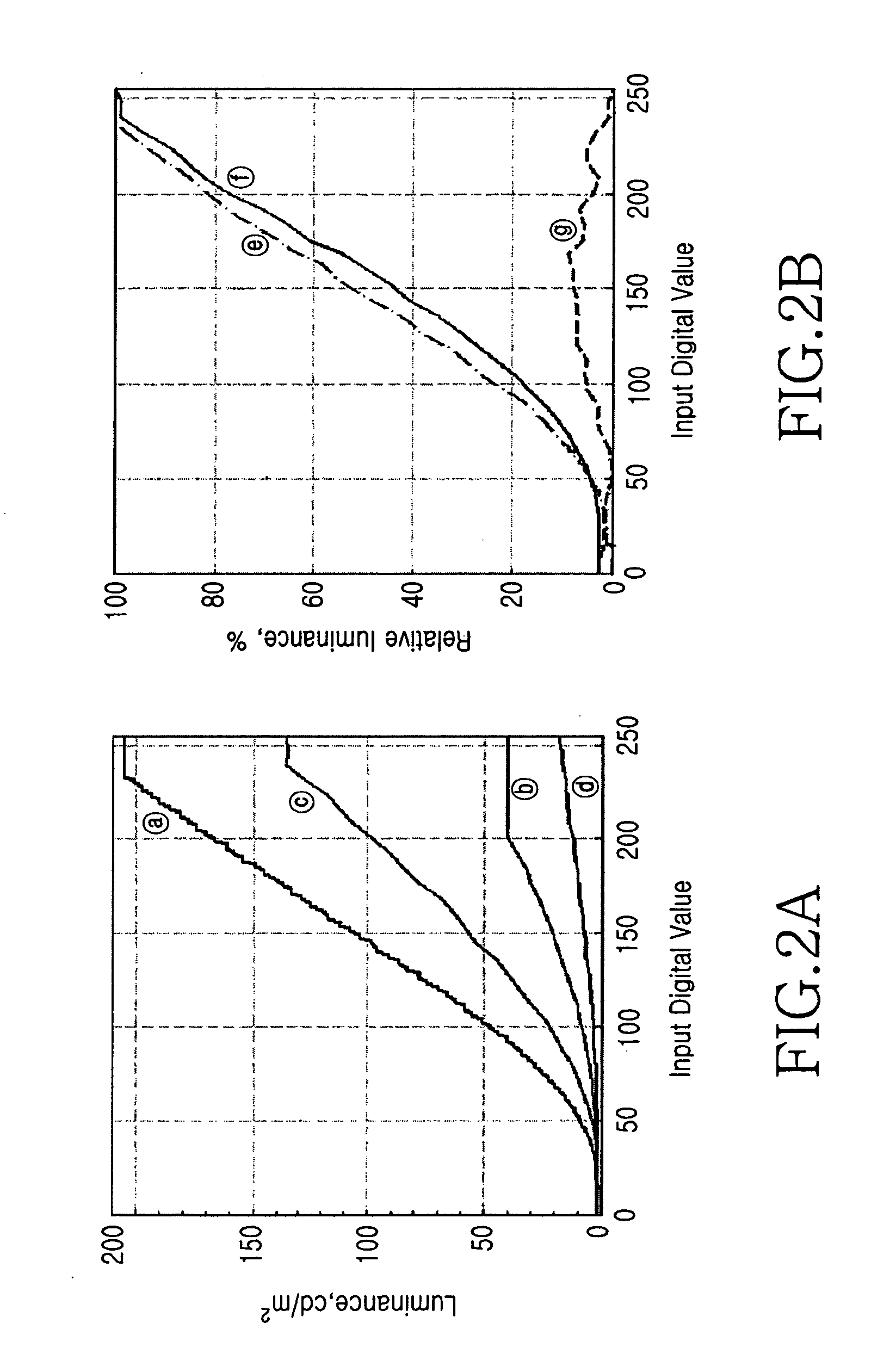
InactiveUS20060022924A1Accurate color reproductionStatic indicating devicesMounting heads on rotating supportControl signalVideo processing
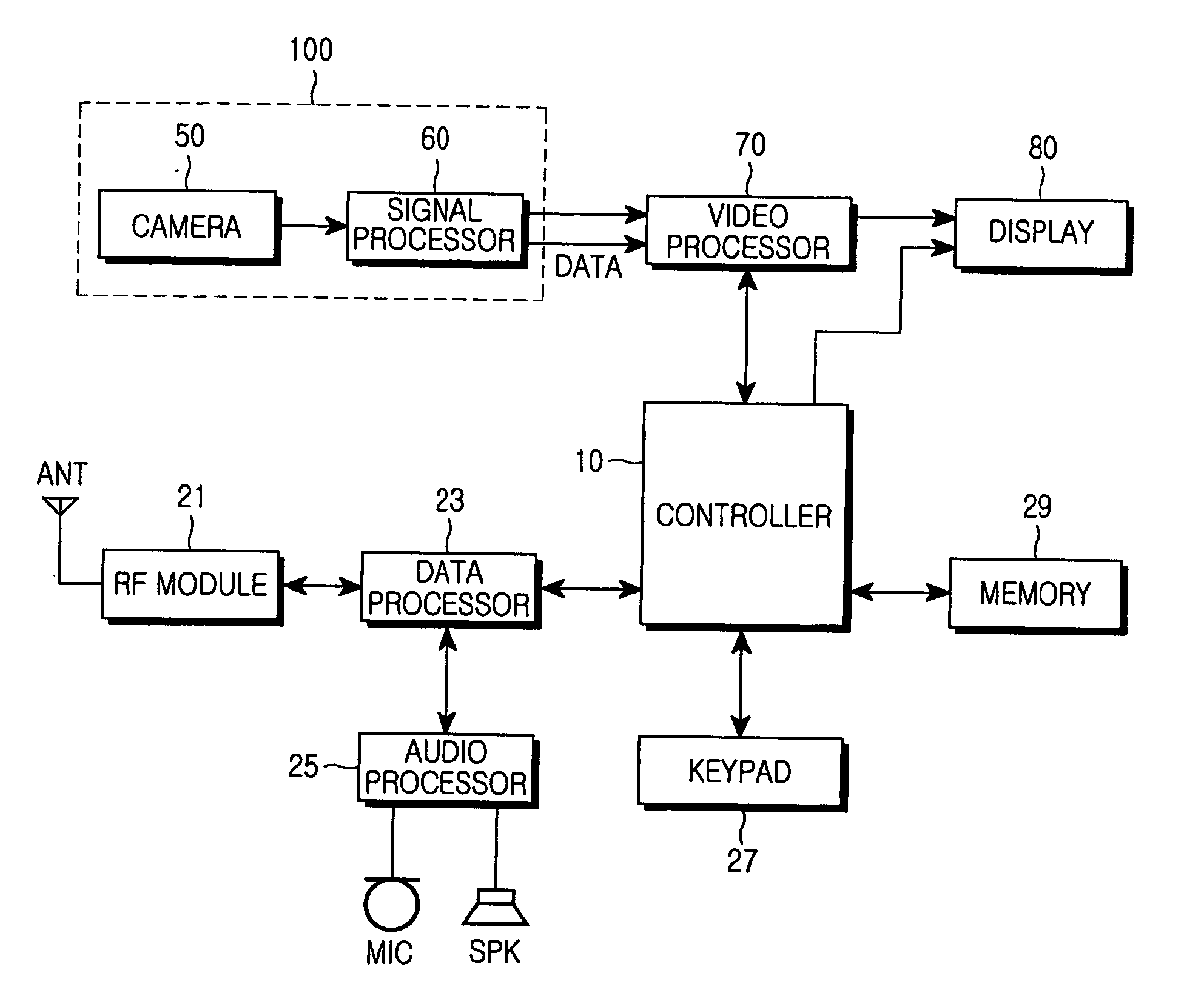
An apparatus and method for compensating a gray-scale CCT in an LCD are provided. In the apparatus, a camera captures an external image, a memory stores the captured image and other image data, and a video processor compensates the correlated color temperature (CCT) of the image received from the camera and the image data read from the memory according to a gray-scale CCT compensation control signal, and outputs a compensated RGB signal. A display receives the compensated RGB signal and displays the image on the LCD according to the RGB colors. A controller controls the video processor by the gray-scale CCT compensation control signal for the image data received from the camera and the memory.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Etching method and a method of manufacturing a magnetic head
A magnetic gap is formed to be vertical to the film forming surface of a substrate with high accuracy by a simple method. The method comprises a non-magnetic film forming step of forming a non-magnetic film made of the non-magnetic material on the substrate, a high selectivity film forming step of forming a high selectivity film made of a material which has a higher selectivity ratio with respect to reactive ion etching than the non-magnetic material, on the non-magnetic film formed, a patterning step of patterning the high-selectivity film into a predetermined shape, and an etching step of etching the non-magnetic film by reactive ion etching, using the high selectivity film as a mask.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnetically erecorded data reproduction apparatus and method
InactiveUS20040021970A1Eliminate the effects ofReduce error rateModification of read/write signalsSignal processing for reducing noiseViterbi decoderAudio power amplifier
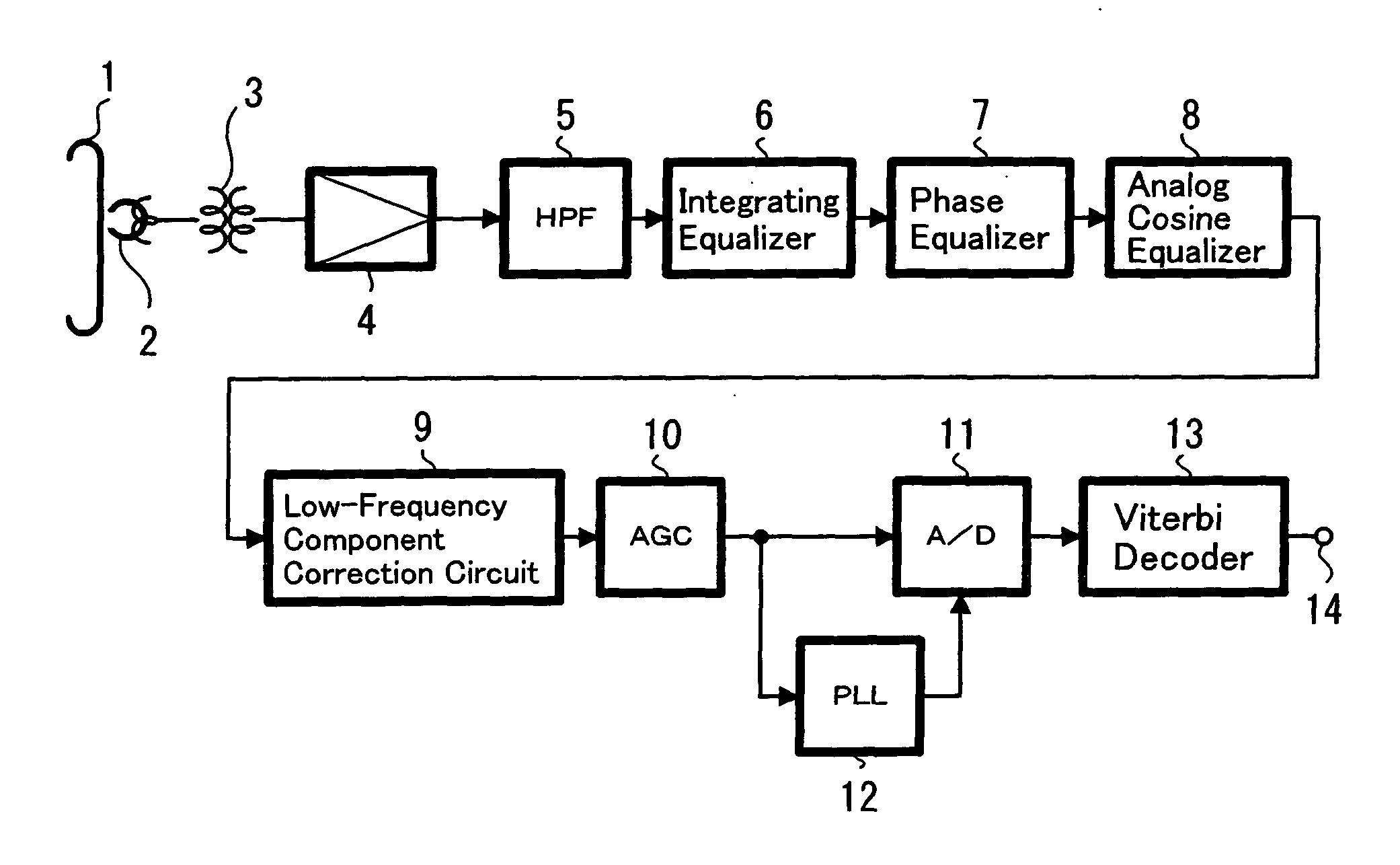
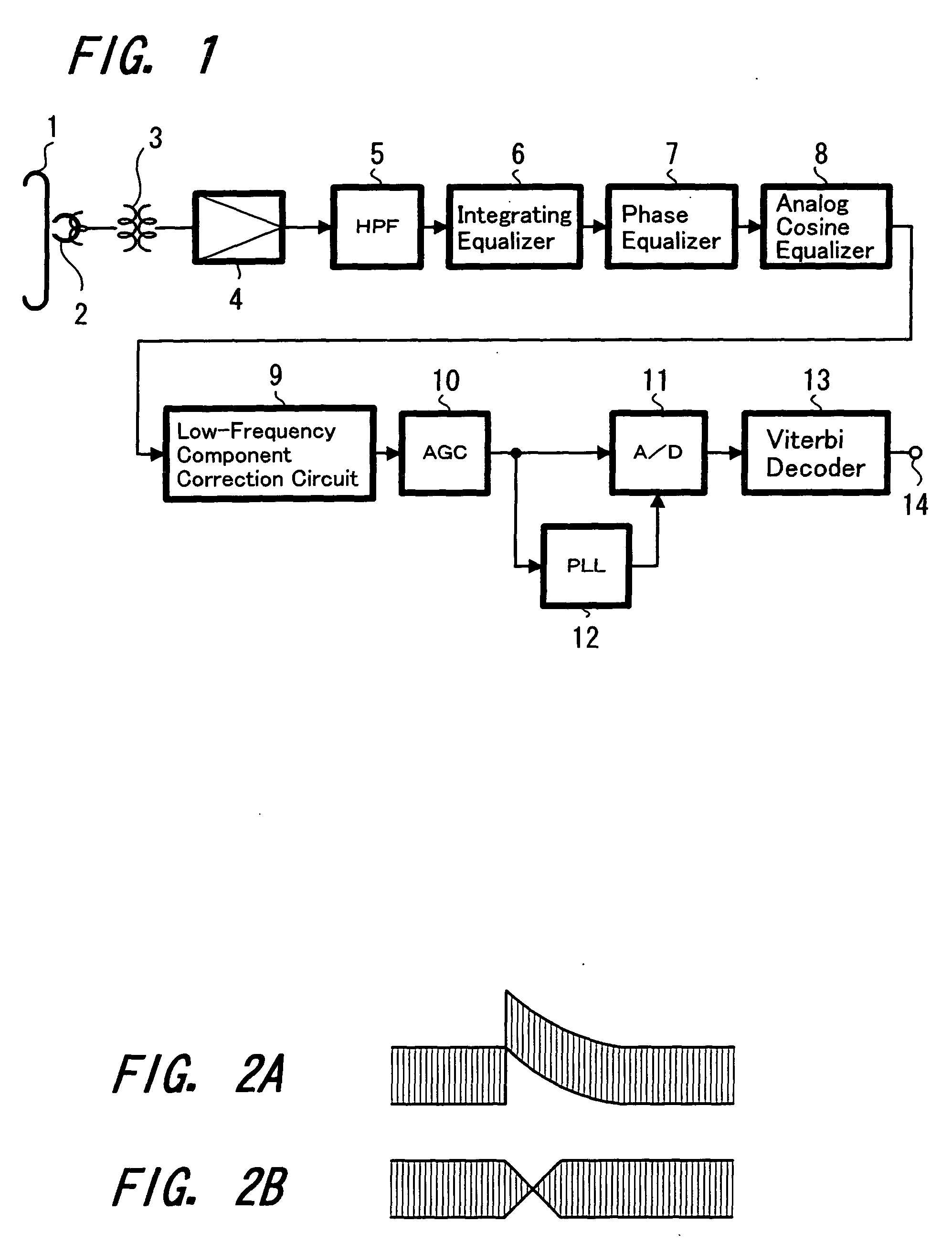
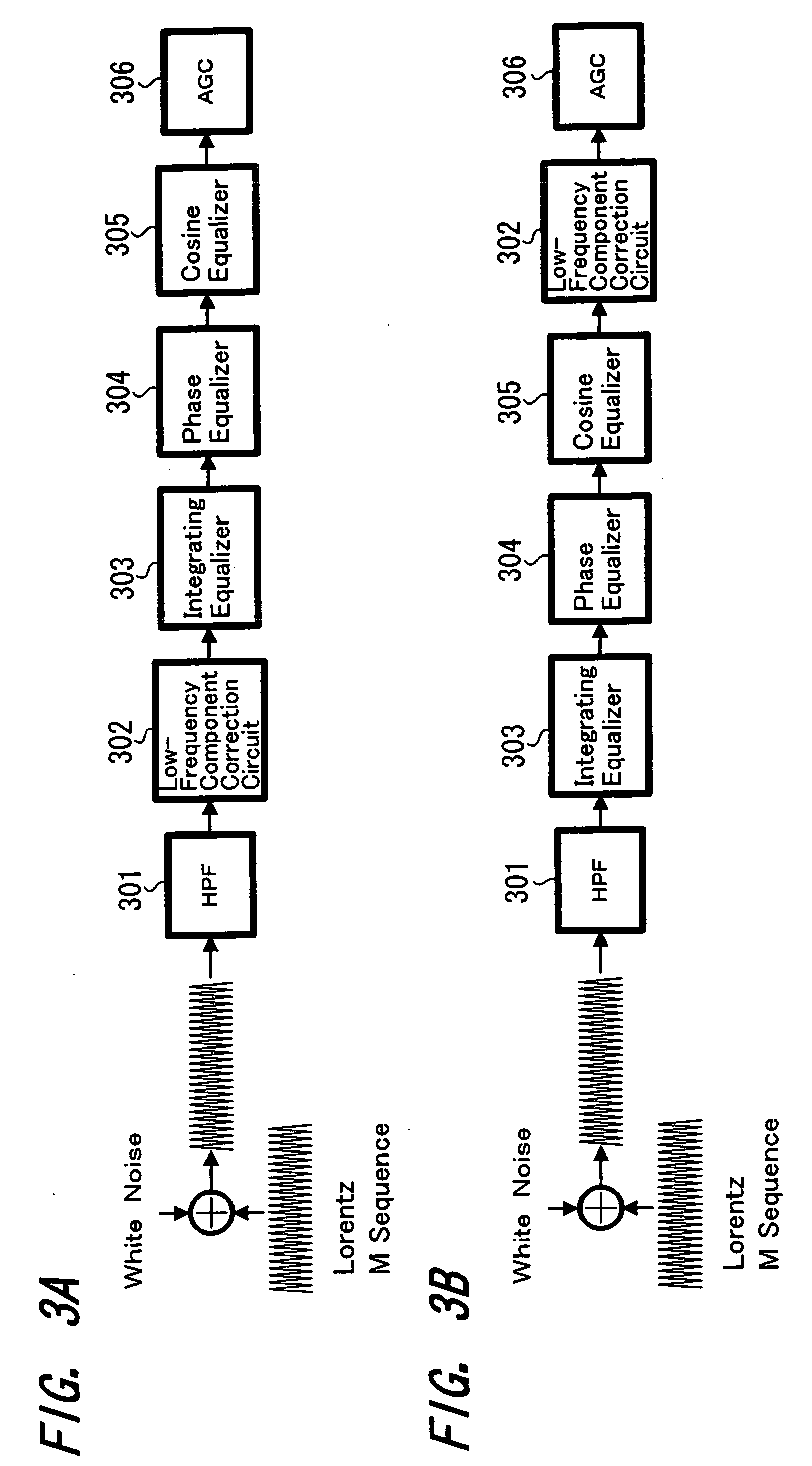
The present invention relates to a magnetically recorded data reproduction apparatus which reproduces magnetically recorded data using a magnetoresistive head and method thereof. In this invention the recorded data are reproduced by a magnetoresistive head 2 and supplied to a reproduction amplifier 4. The signal from the reproduction amplifier 4 is then supplied to a high-pass filter 5 and a frequency component of, for example, 1 MHz or lower, is cut off. The signal from the HPF 5 is supplied to an integrating equalizer 6, a phase equalizer 7 and an analog cosine equalizer 8. The signal from the equalizer 8 is supplied to an AGC amplifier 10 through a low-frequency component correction circuit 9. The signal from the AGC amplifier 10 is supplied to an A / D converter 11. Further, the signal from the AGC amplifier 10 is supplied to the digital PLL circuit 12 and the extracted clock signal is supplied to the A / D converter 11. The digitized signal is then supplied to, for example, a Viterbi decoder 13 and the decoded signal is obtained at an output terminal 14. Thus, the effect of noise due to the so-called thermal asperity (TA noise) is removed, thereby preventing increases in the error rate of the reproduction signals due to the effect of TA noise and the occurrence of problems in equipment.
Owner:SONY CORP
Head drum assembly of a tape recorder having a resilient body to preload bearings thereof
InactiveUS7139155B2Improve assembly efficiencyReduce manufacturing costRolling contact bearingsDriving/moving recording headsElastomerMagnetic tape
A head drum assembly of a tape recorder in which an inner race and an outer race of an upper bearing are press-fitted onto a shaft and a rotary drum, respectively, thereby applying a preload. A resilient body, such as a compressed coil spring, is disposed between a lower bearing disposed between the rotary drum and the shaft and a stationary drum. The resilient body upwardly presses the inner race of the lower bearing, thereby applying a preload. Accordingly, the head drum assembly of the tape recorder provides enhanced assembling efficiency and reduced manufacturing costs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flexible assembly magnetic header, magnetic header folding combination and disk driving unit with static protection structure
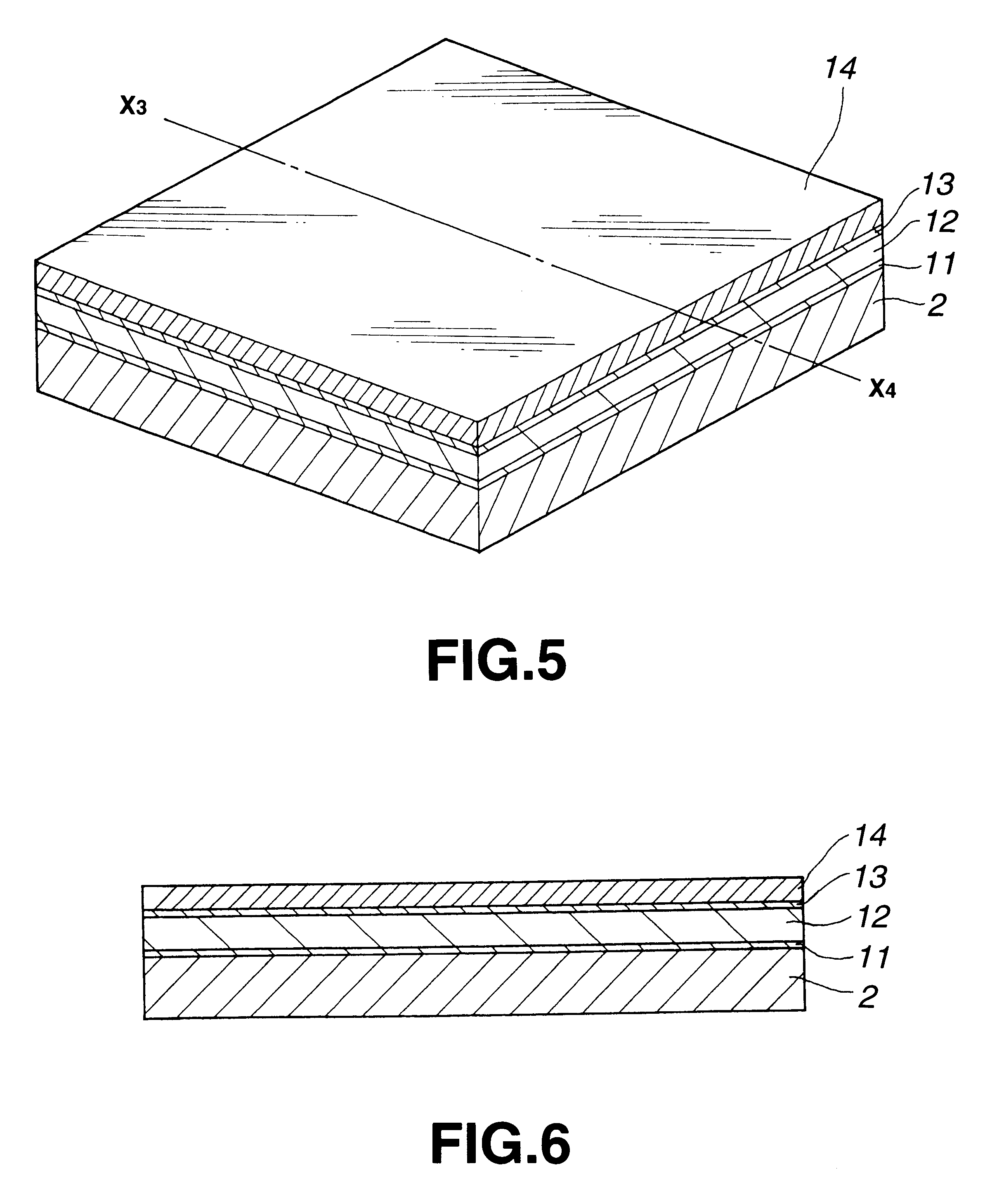
InactiveCN101241707AAvoid the impact of the assembly processAvoid burnsRecord information storageMounting heads on rotating supportEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A flexible assembling magnetic head with electrostatic protection structure, includes a magnetic head body which is arranged with an air load-bearing surface, a magnetic head reverse facing to the air load-bearing as well as a cauda edge connected to the air load-bearing surface and the magnetic head reverse, a pair of magnetic head contacts are formed on the cauda edge; an electrostatic protection structure settong on the magnetic head reverse comprises an insulating disc setting on the magnetic head reverse, an electrostatic resistance disc setting on the insulating disc and composed of the insulating layer as well as an electrostatic resistance layer, and an earthing element contacting electrically to the electrostatic resistance of the electrostatic resistance disc as well as the magnetic head reverse; as well as a wire layer locating between the insulating disc and the insulating layer of the electrostatic resistance disc, and contacting electrically to the magnetic head contact of the magnetic head body. The present invention discloses a magnetic head disc-folding combination containing the flexible assembling magnetic as well as a magnetic disk drive unit.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Popular searches
Manufacture of flux-sensitive heads Alignment for track following on disks Digital recording Heads relative to moving tape Mounting/attachment of transducer head Structure of arm assembly Support for heads Recording signal processing Track changing/selection Carrier speed control/regulation/indication
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com