Patents
Literature
98results about How to "Accurate coordinates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
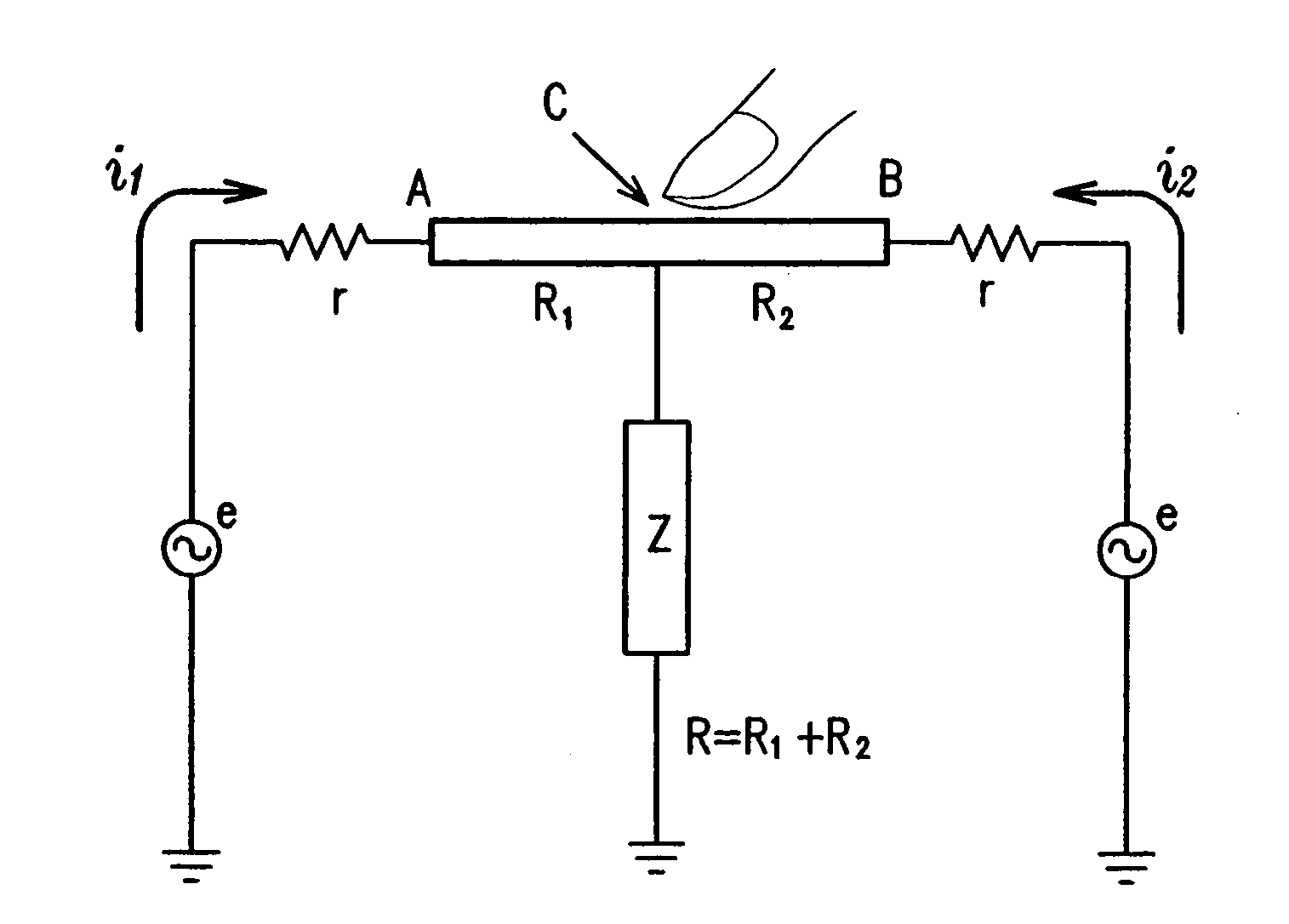
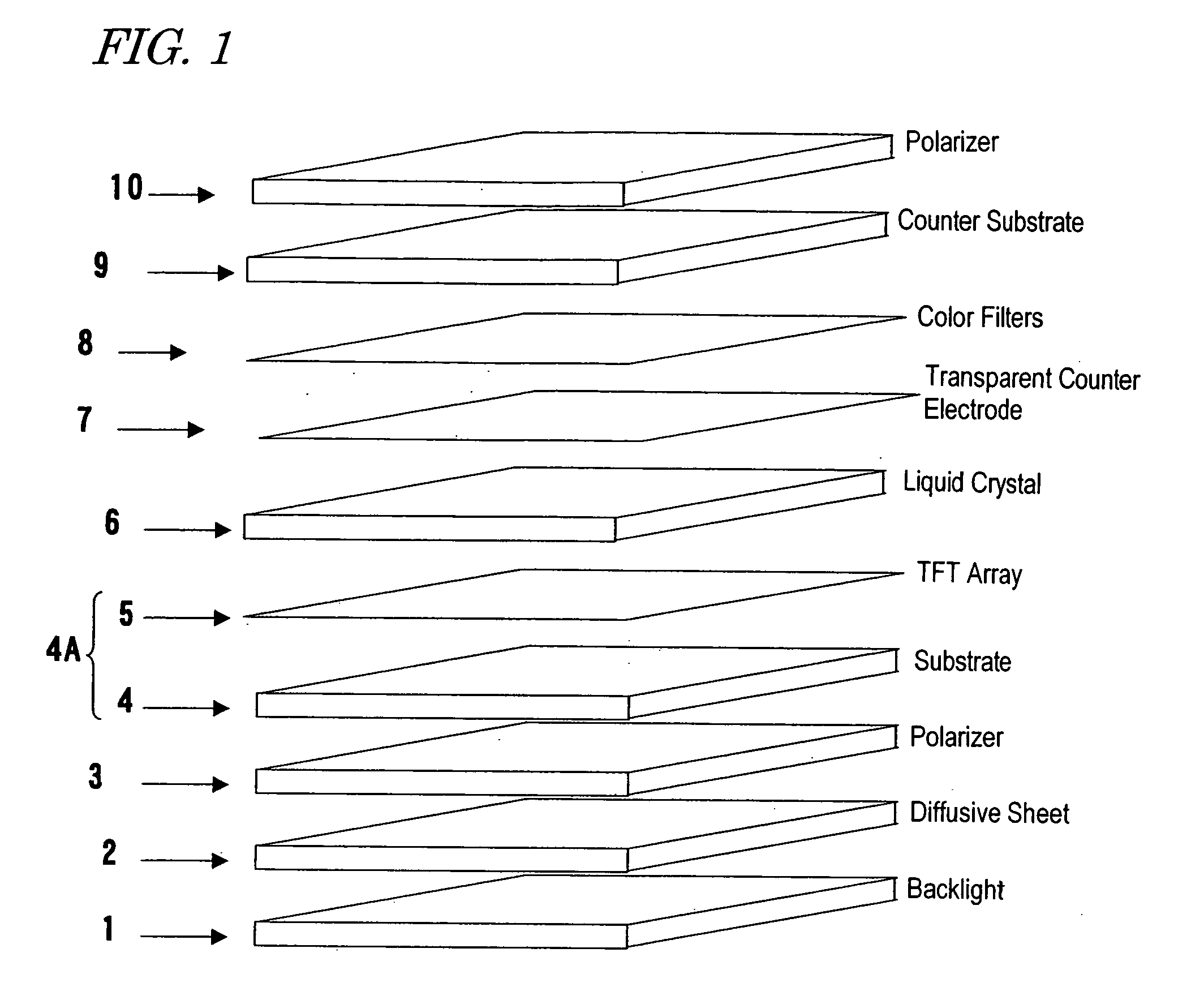
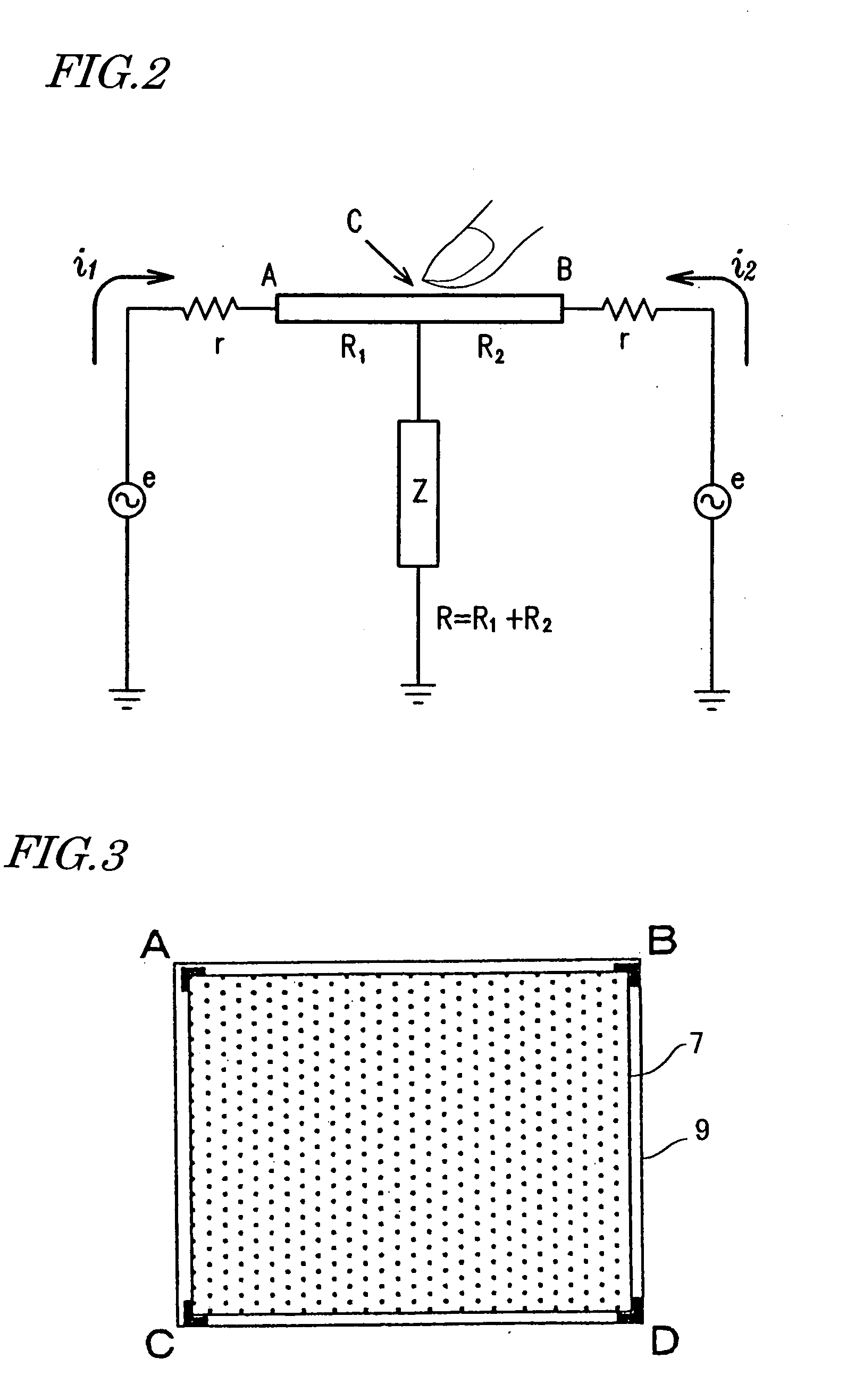
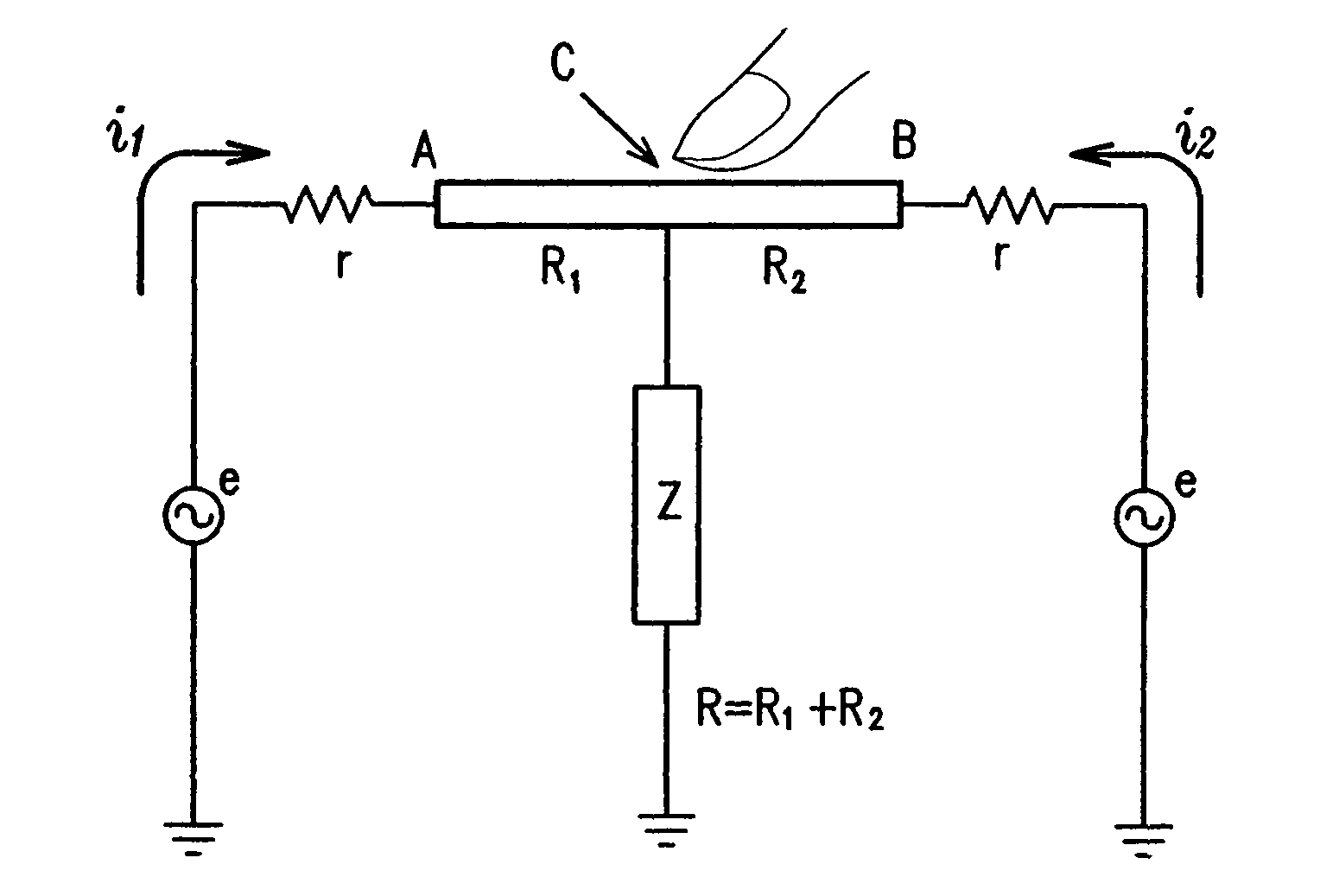
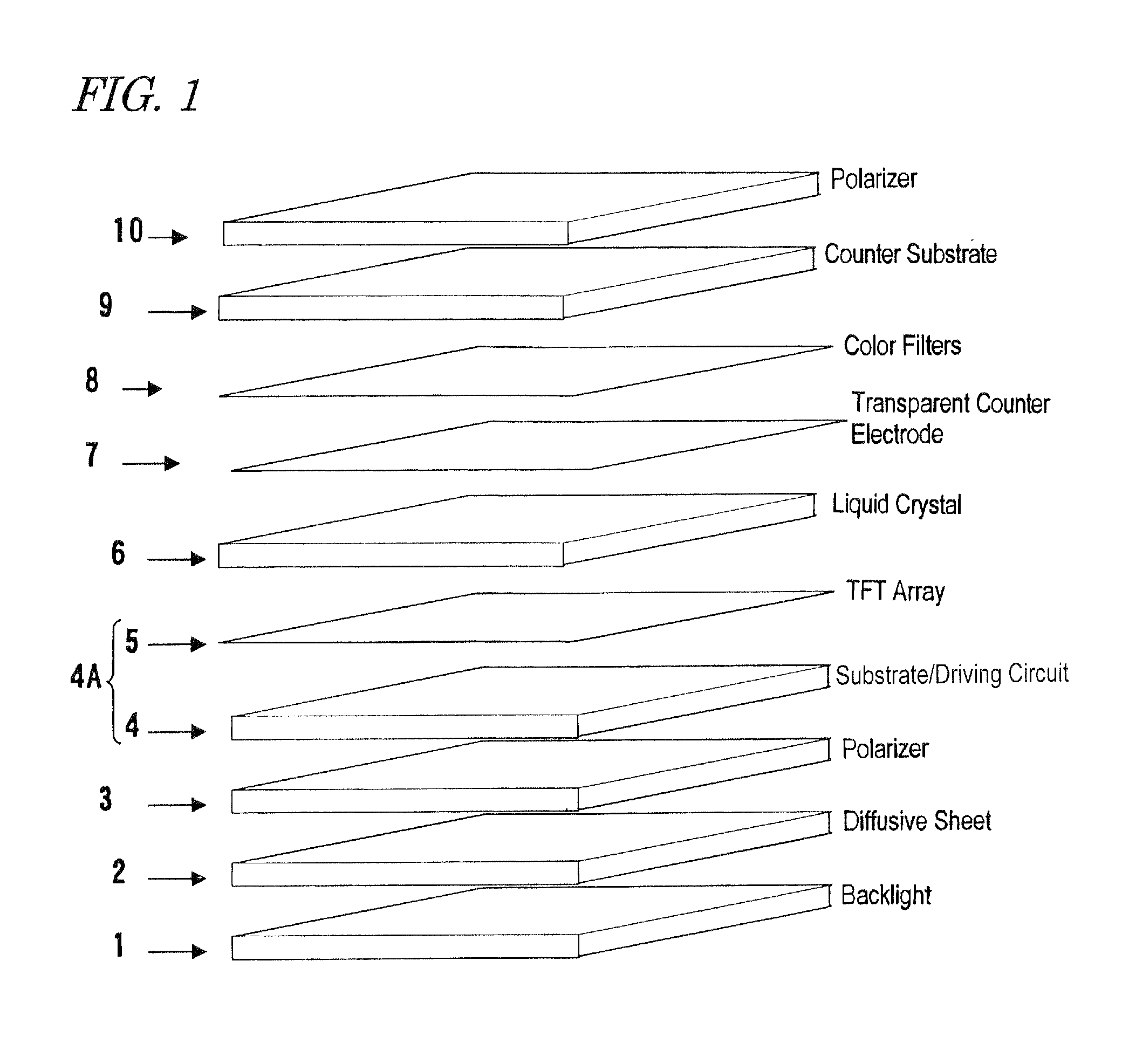
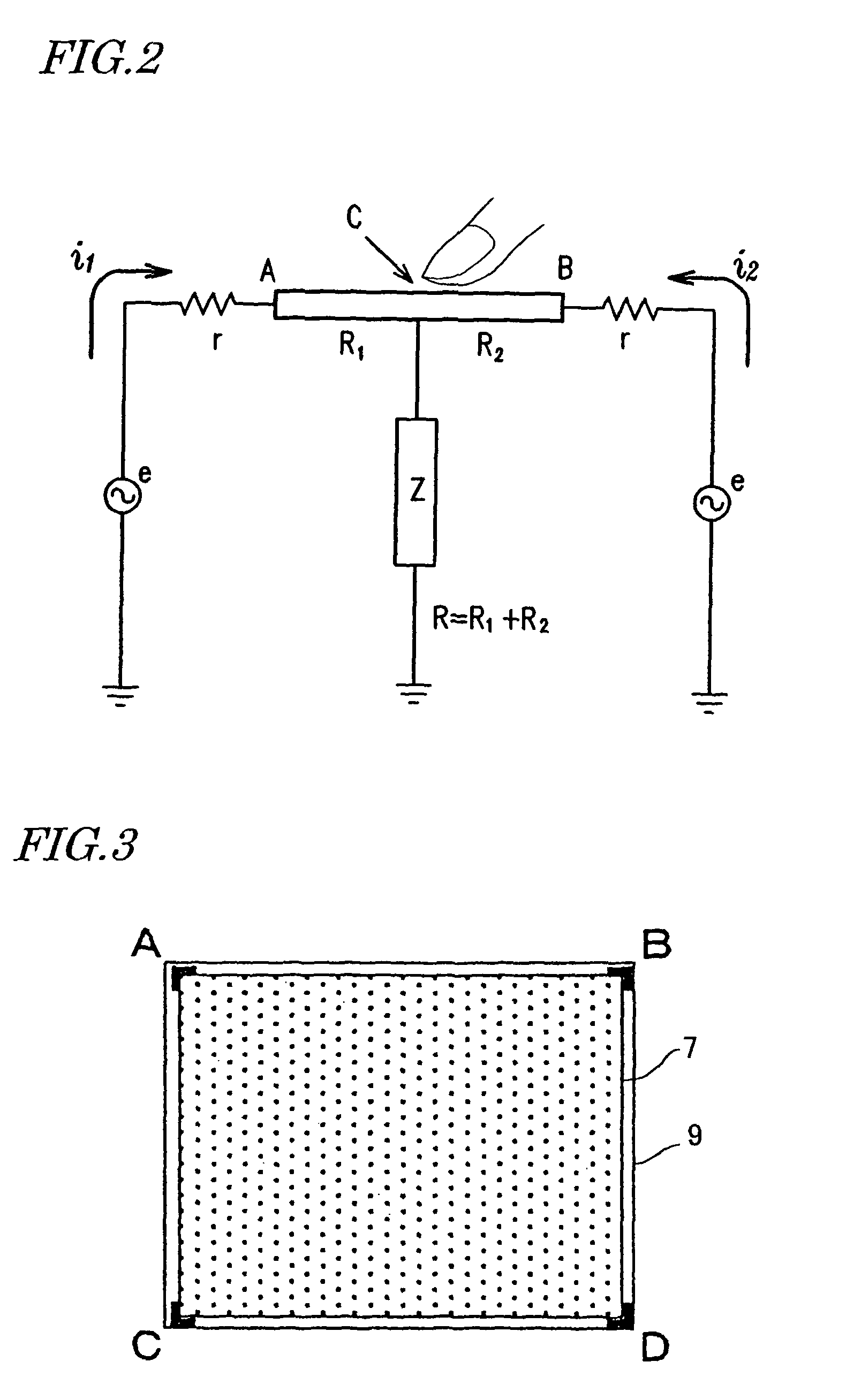
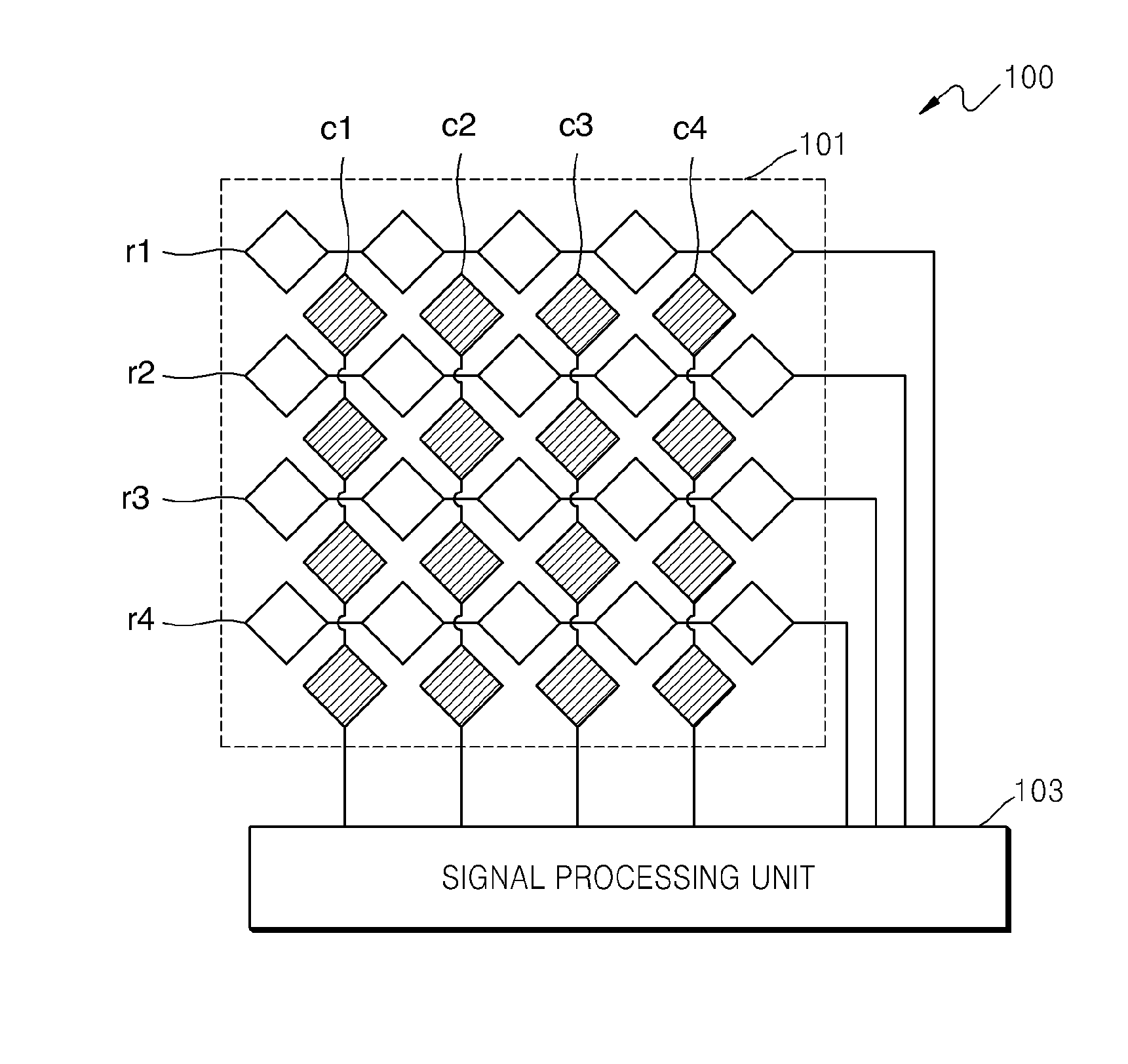
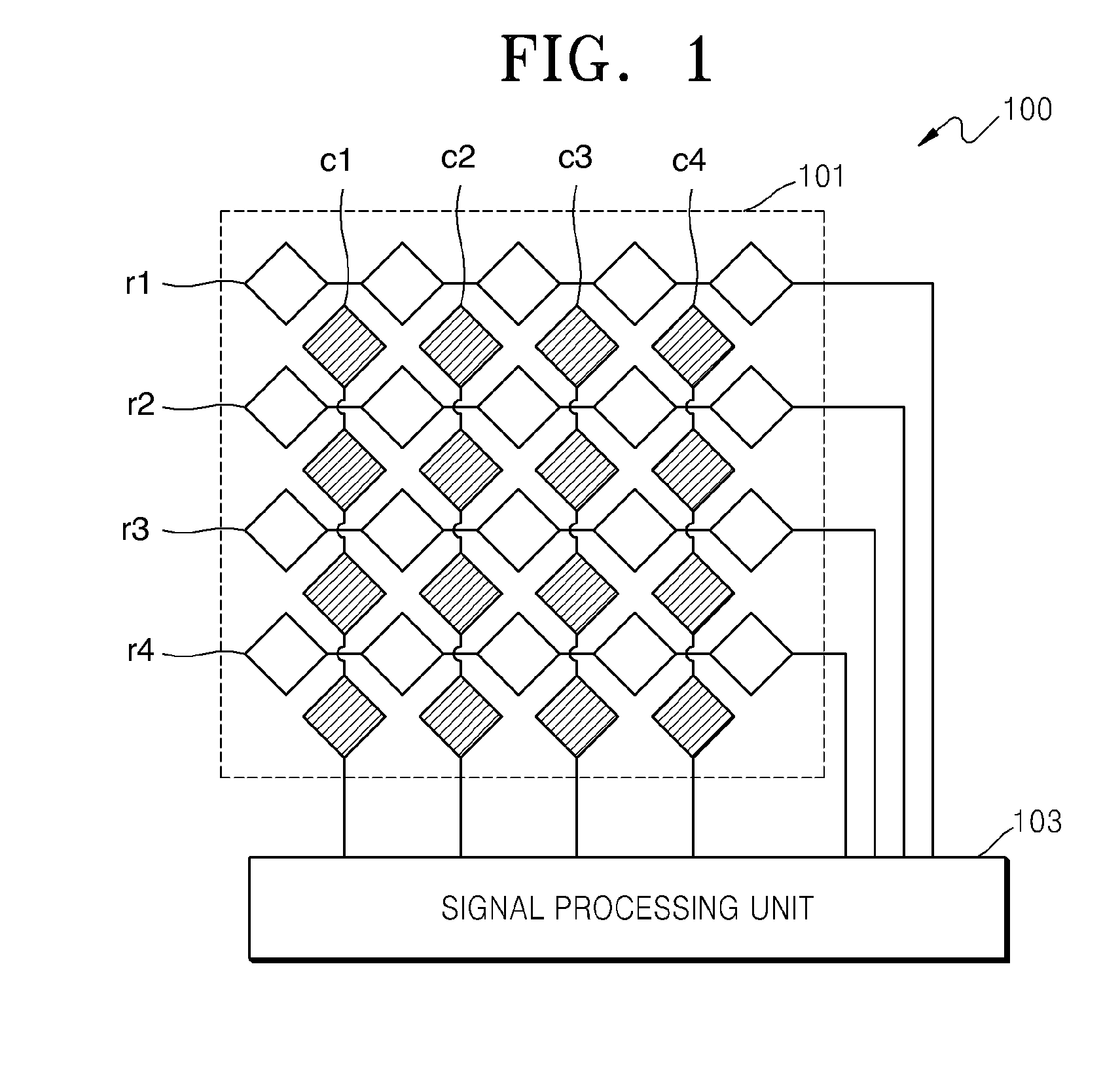
Touch sensor, display with touch sensor, and method for generating position data
ActiveUS20040217945A1Not deteriorate display performanceEffectively downsizedCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsElectricityVoltage
A display device with a touch sensor according to the present invention includes an active matrix substrate 4A and a transparent counter electrode 7. On a first surface of the active matrix substrate, multiple pixel electrodes are arranged in matrix. The transparent counter electrode is opposed to the first surface of the active matrix substrate. The display device further includes a first circuit, a second circuit and a switching circuit. The first circuit supplies a voltage or a current to the transparent counter electrode for display purposes. The second circuit detects currents flowing from a number of points on the transparent counter electrode. And the switching circuit selectively connects electrically one of the first and second circuits to the transparent counter electrode.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Touch sensor, display with touch sensor, and method for generating position data
ActiveUS8031180B2Not deteriorate display performanceEffectively downsizedCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsElectricityActive matrix
A display device with a touch sensor according to the present invention includes an active matrix substrate 4A and a transparent counter electrode 7. On a first surface of the active matrix substrate, multiple pixel electrodes are arranged in matrix. The transparent counter electrode is opposed to the first surface of the active matrix substrate. The display device further includes a first circuit, a second circuit and a switching circuit. The first circuit supplies a voltage or a current to the transparent counter electrode for display purposes. The second circuit detects currents flowing from a number of points on the transparent counter electrode. And the switching circuit selectively connects electrically one of the first and second circuits to the transparent counter electrode.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
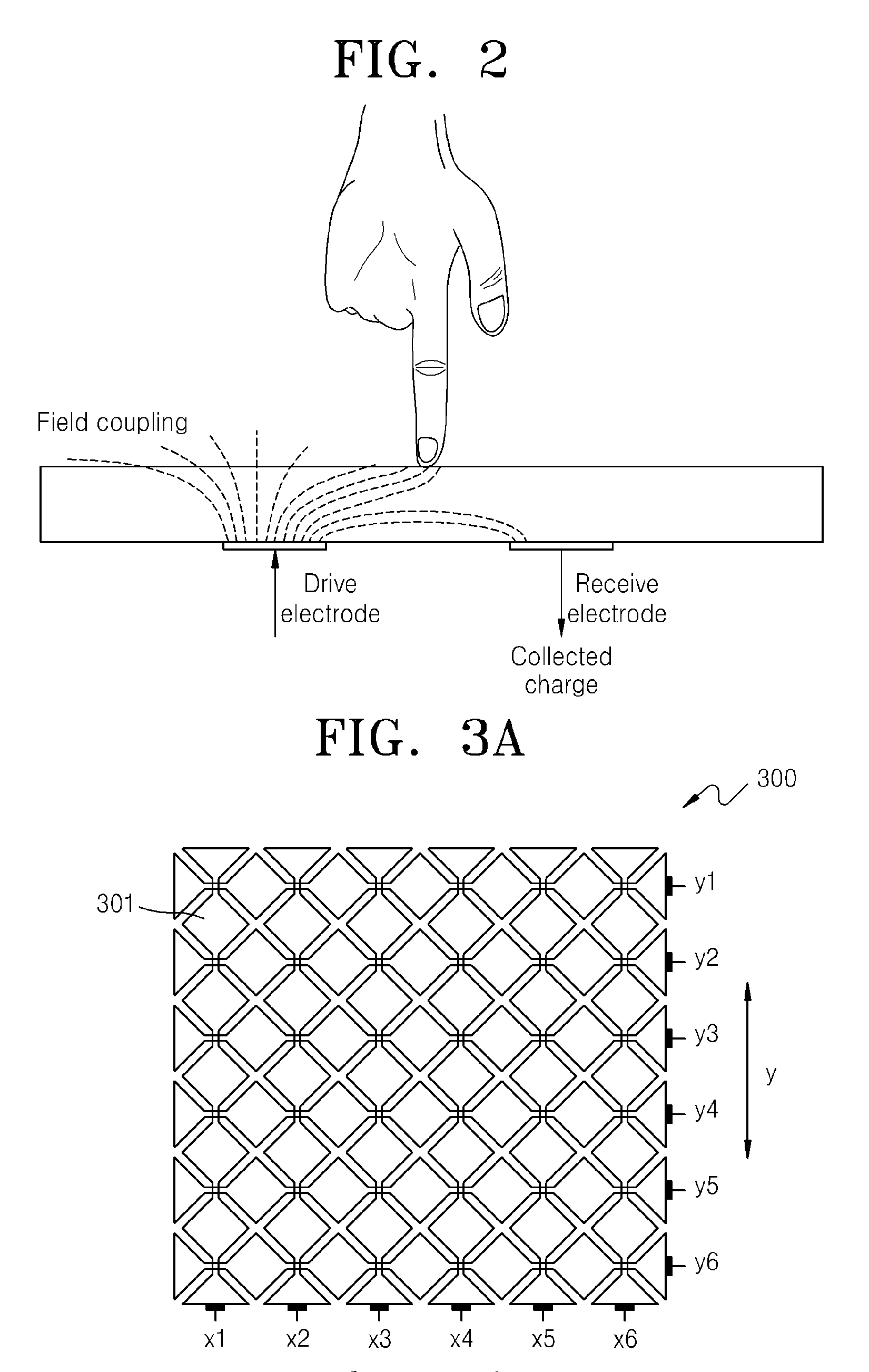
Method for detecting touch position
InactiveUS20100321337A1Accurate coordinatesInput/output processes for data processingSignal onPosition dependent
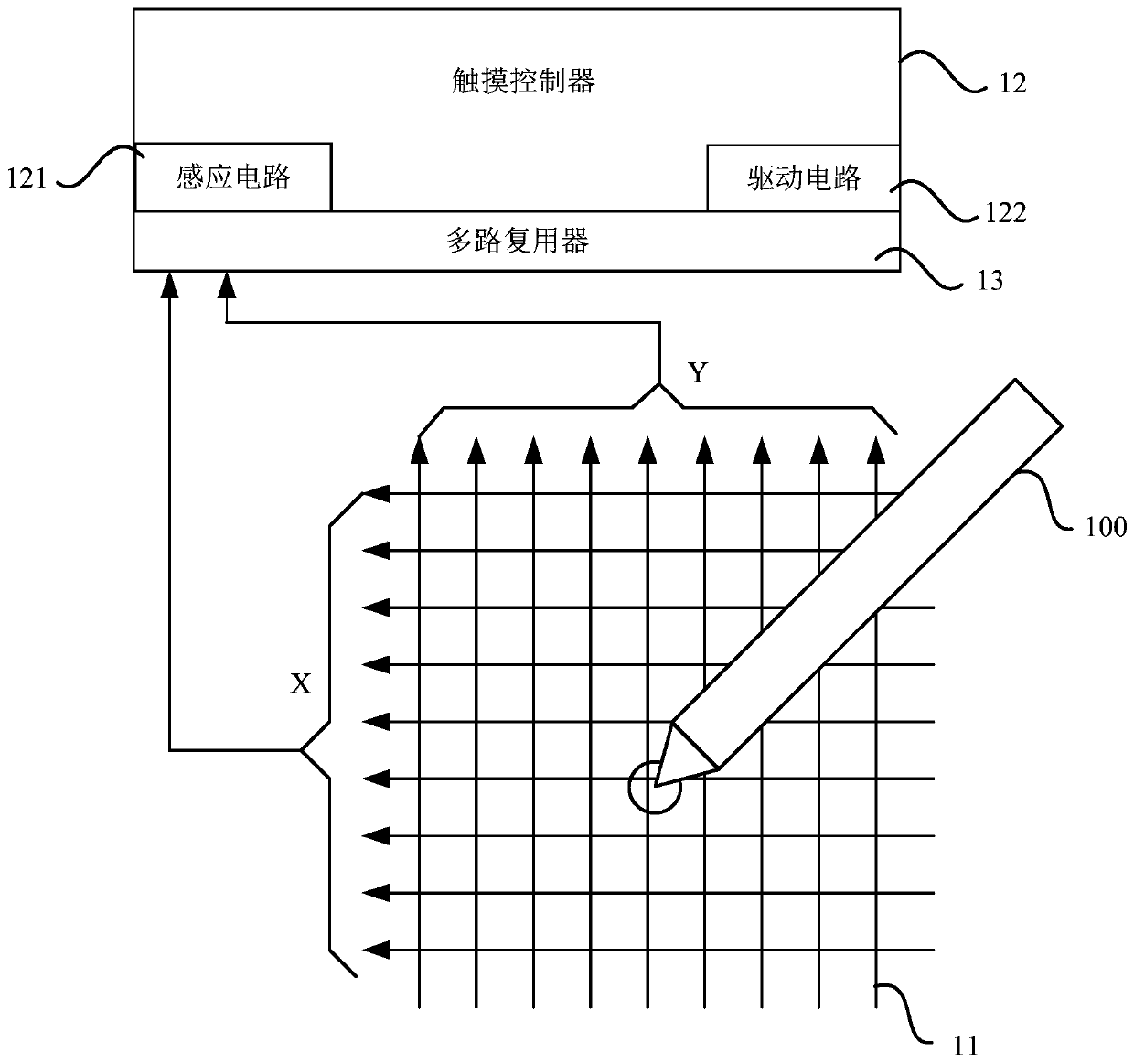
An exemplary method for detecting touch position includes the steps of: detecting a plurality of sensing points, obtaining at least one first signal and a plurality of second signals on the sensing points, wherein the at least one first signal each has an energy above a preset threshold, the second signals each has an energy below the preset threshold, positions of the sensing points where the second signals being detected are successive with a position(s) of the sensing point(s) where the at least one first signal being detected; performing a weighted averaging operation applied to the energies of the at least one first signal and the second signals and taking a result of the weighted averaging operation as a first dimension coordinate of a touching point, wherein weights of the respective energies are associated with the positions of the sensing points where the at least one first signal and the second signals being detected.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional surface scanning and measurement of a moving object
InactiveUS6974964B1Eliminate sensitivityIncrease areaImpression capsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMobile objectImage sensor
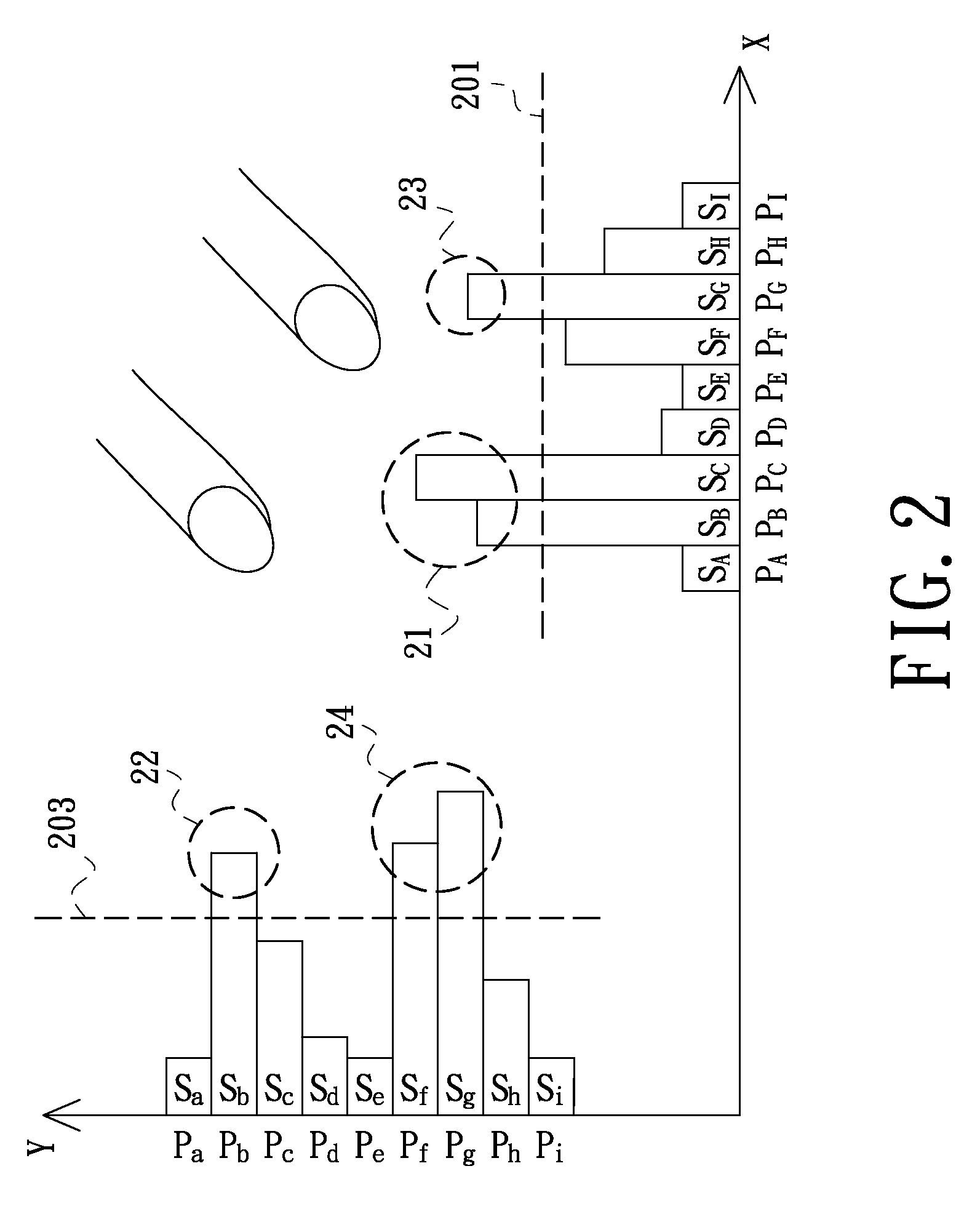
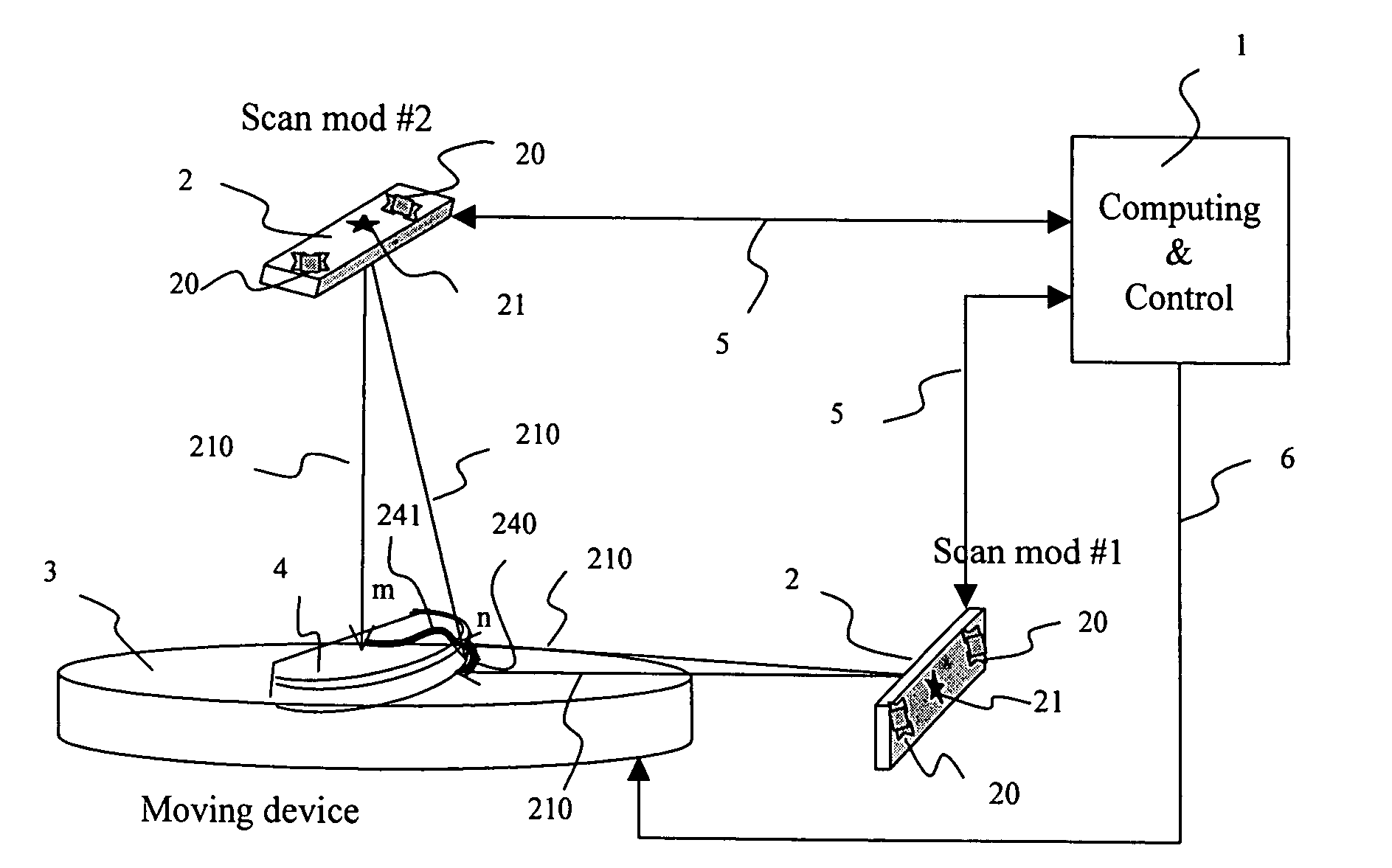
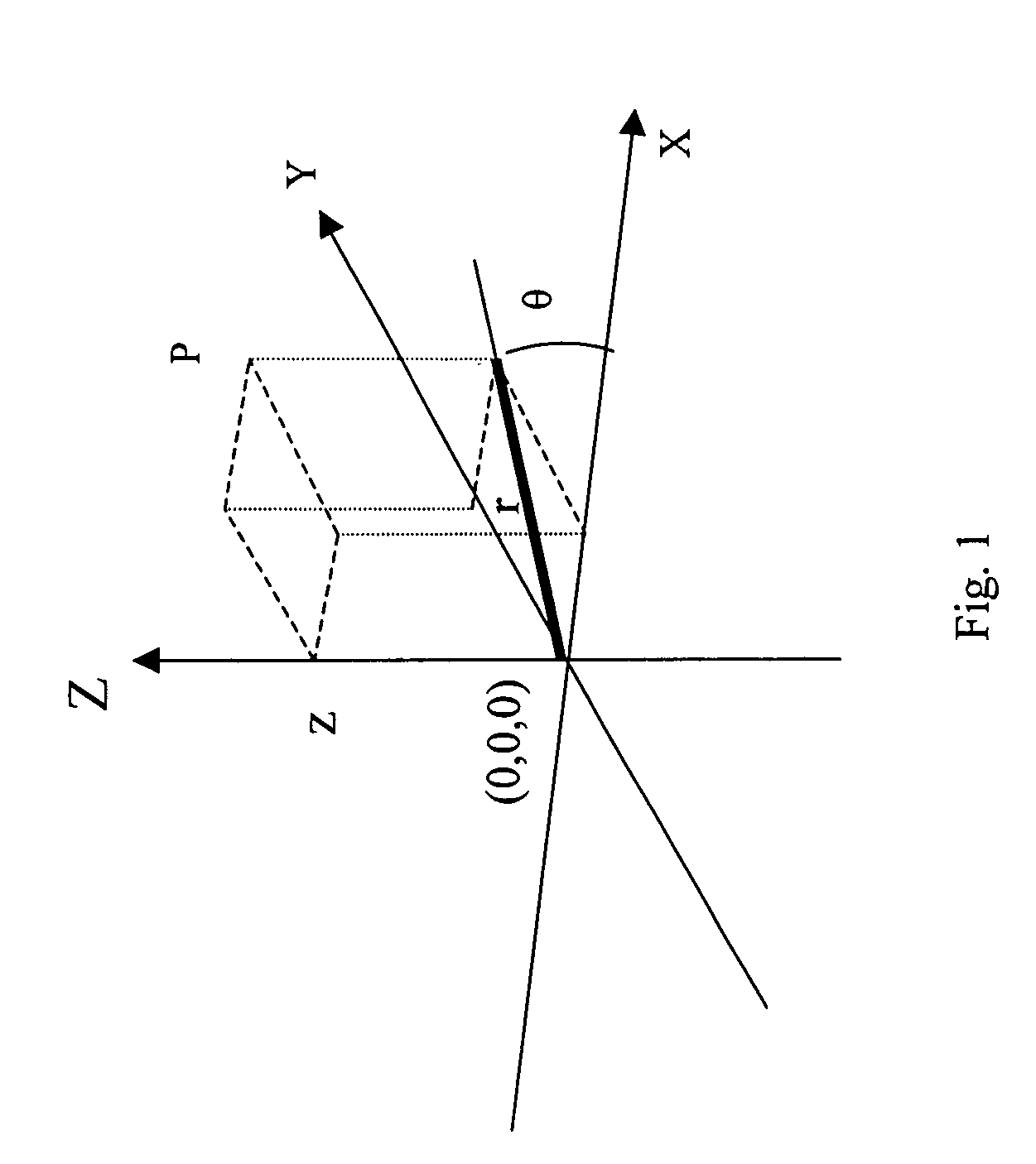
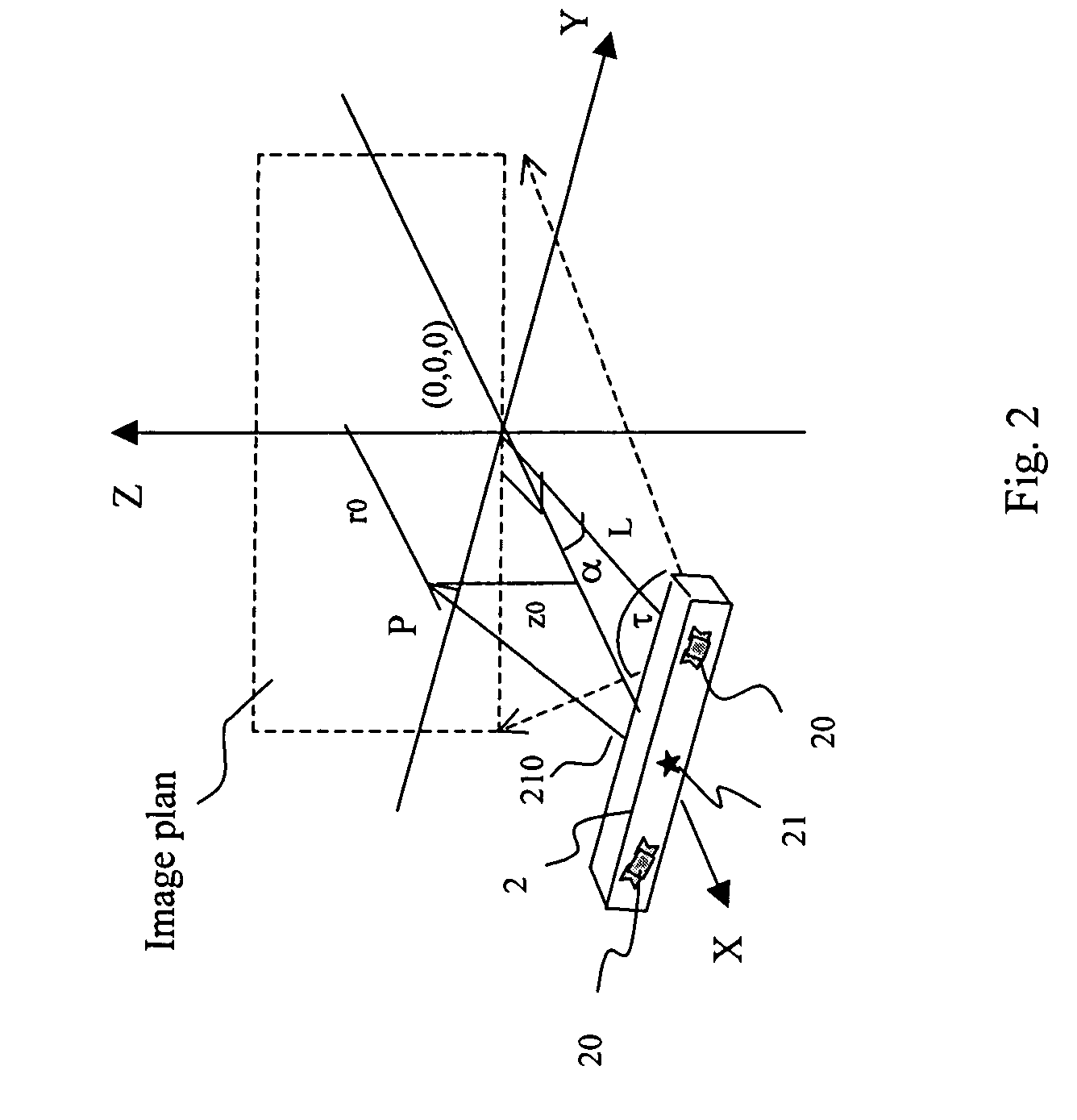
An apparatus and method to scan and collect data relative to the position of a moving object. The method includes the calibration, equations, and algorithm needed to compute the surface coordinates of an object. The preferred embodiment of the apparatus includes two light sources and four area array image sensors, one moving device, and one computing device. The device scans the object, generates data, computes the position, and provides a complete measure of the 3D surface coordinates of an object. The methodology includes calibration of a known pattern to the area array image sensor, equations to map the physical points to the image sensor, algorithms to determine a best estimate of the coordinates of occluded points, and techniques to merge the computed coordinates from different sections of the object.
Owner:WANG BU CHIN
Method and apparatus for forming electrode pattern on touch panel
InactiveUS20110242028A1Accurate coordinatesInput/output processes for data processingTouch SensesEngineering
A touch sense panel includes a first set of individual sensing units for sensing a location along a first axis. The first set of individual sensing units includes a first plurality of strings of individual sensing units, each string including at least two of the individual sensing units of the first set. The at least two individual sensing units are electrically connected to each other and arranged in a direction perpendicular to the first axis. A first individual sensing unit of a first string of the first plurality of strings is electrically connected to a first individual sensing unit of a second string of the first plurality of strings, the second string adjacent to the first string, such that the first string and the second string form a single, first electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
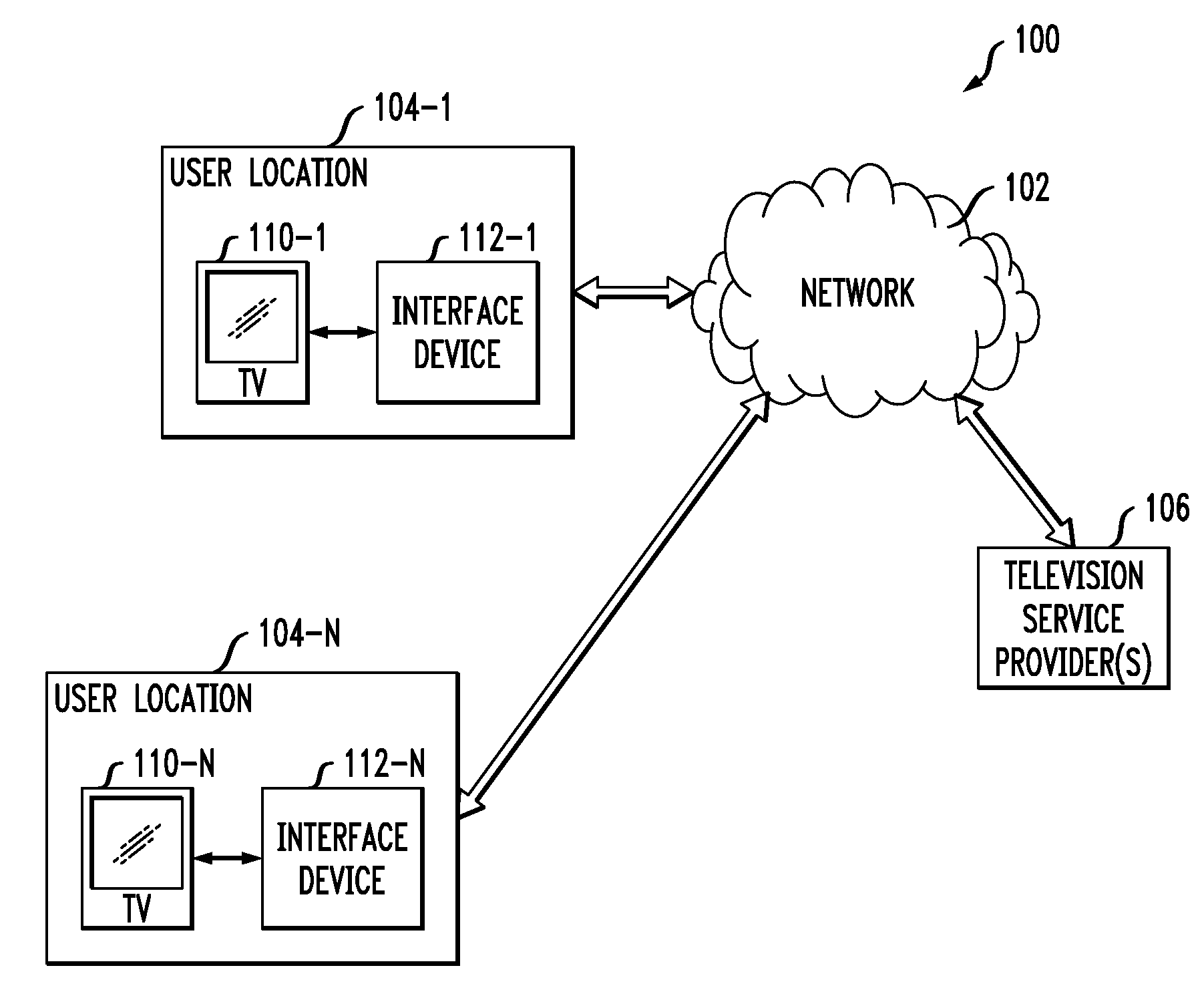
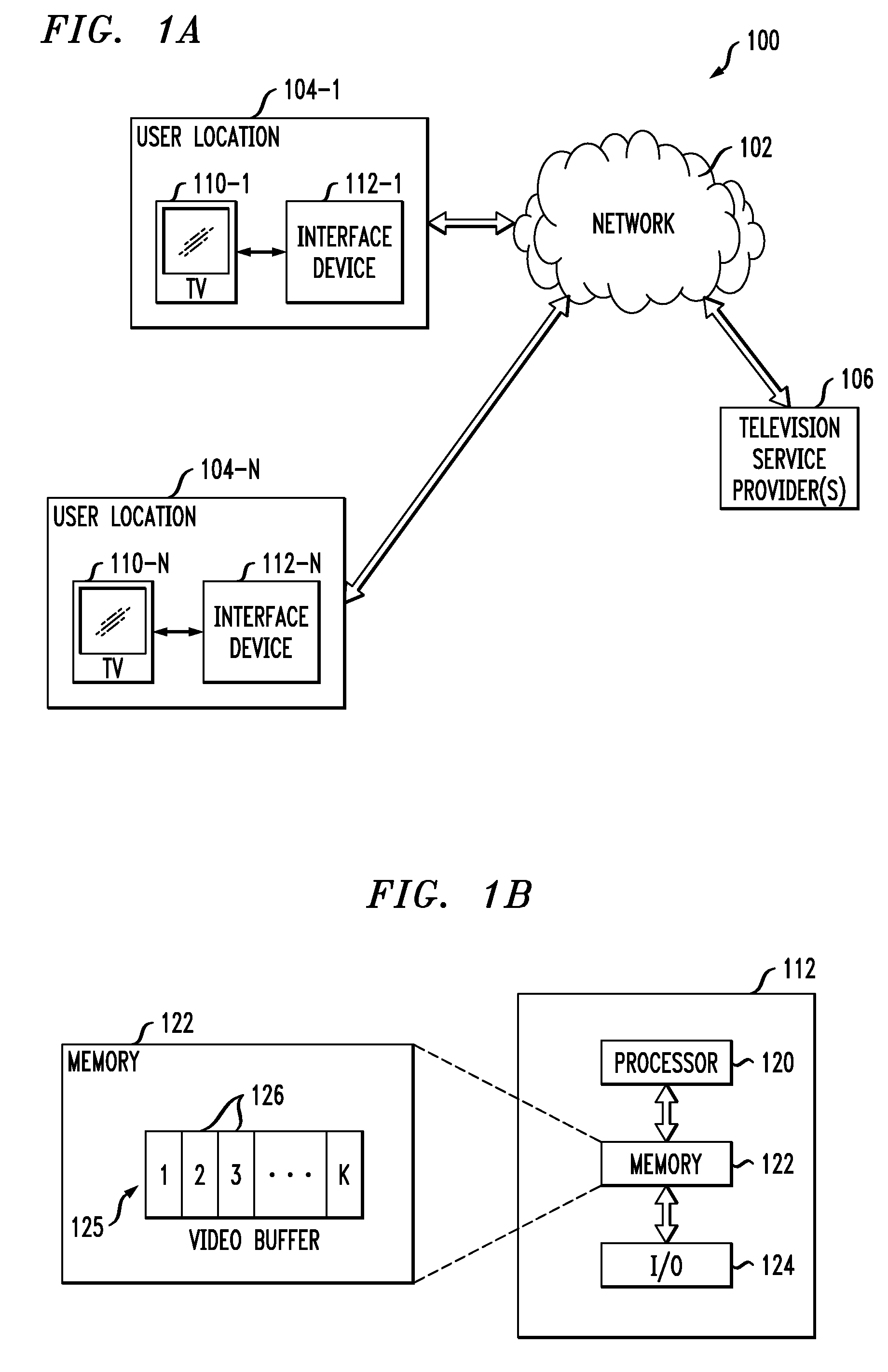
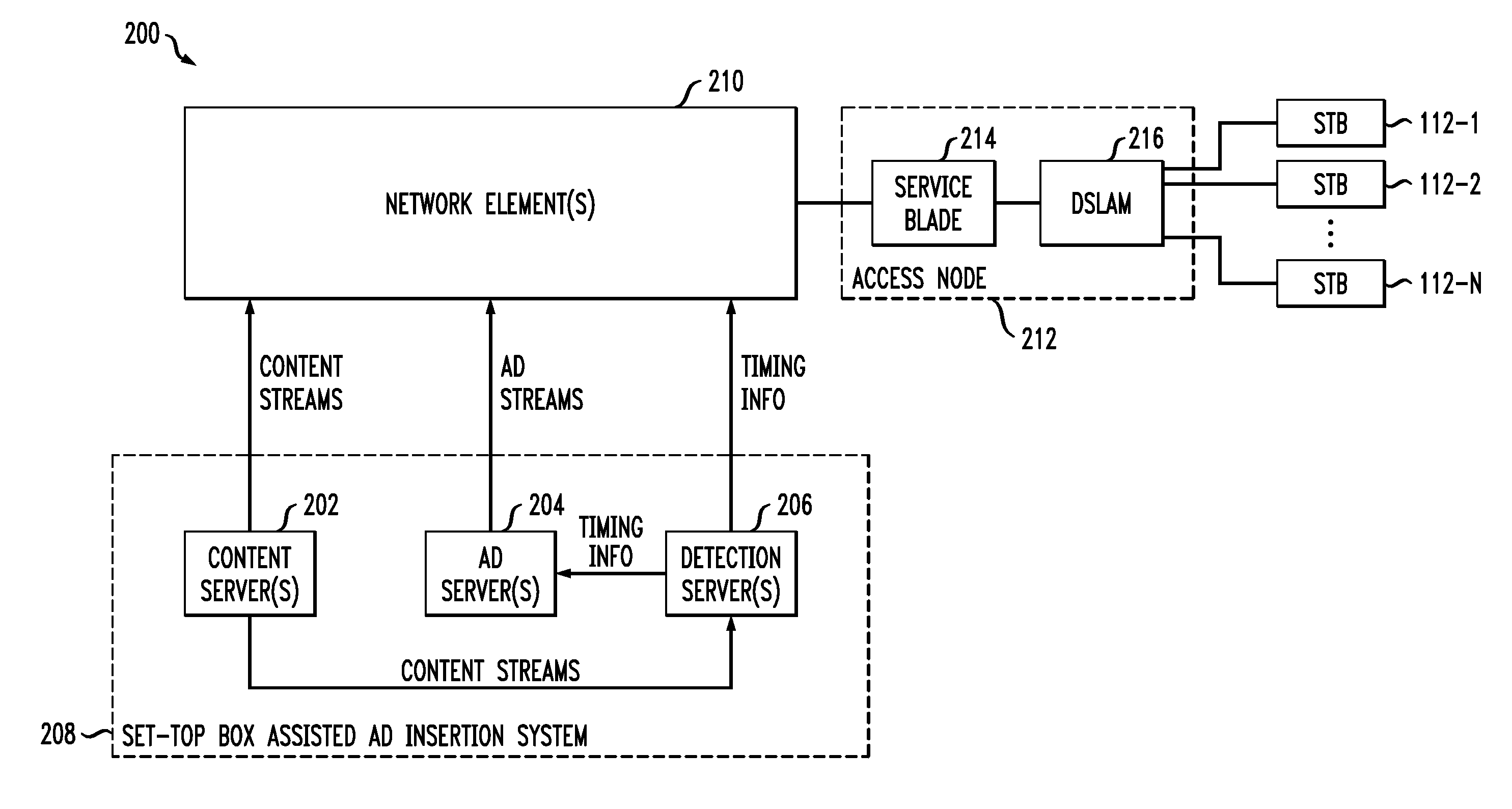
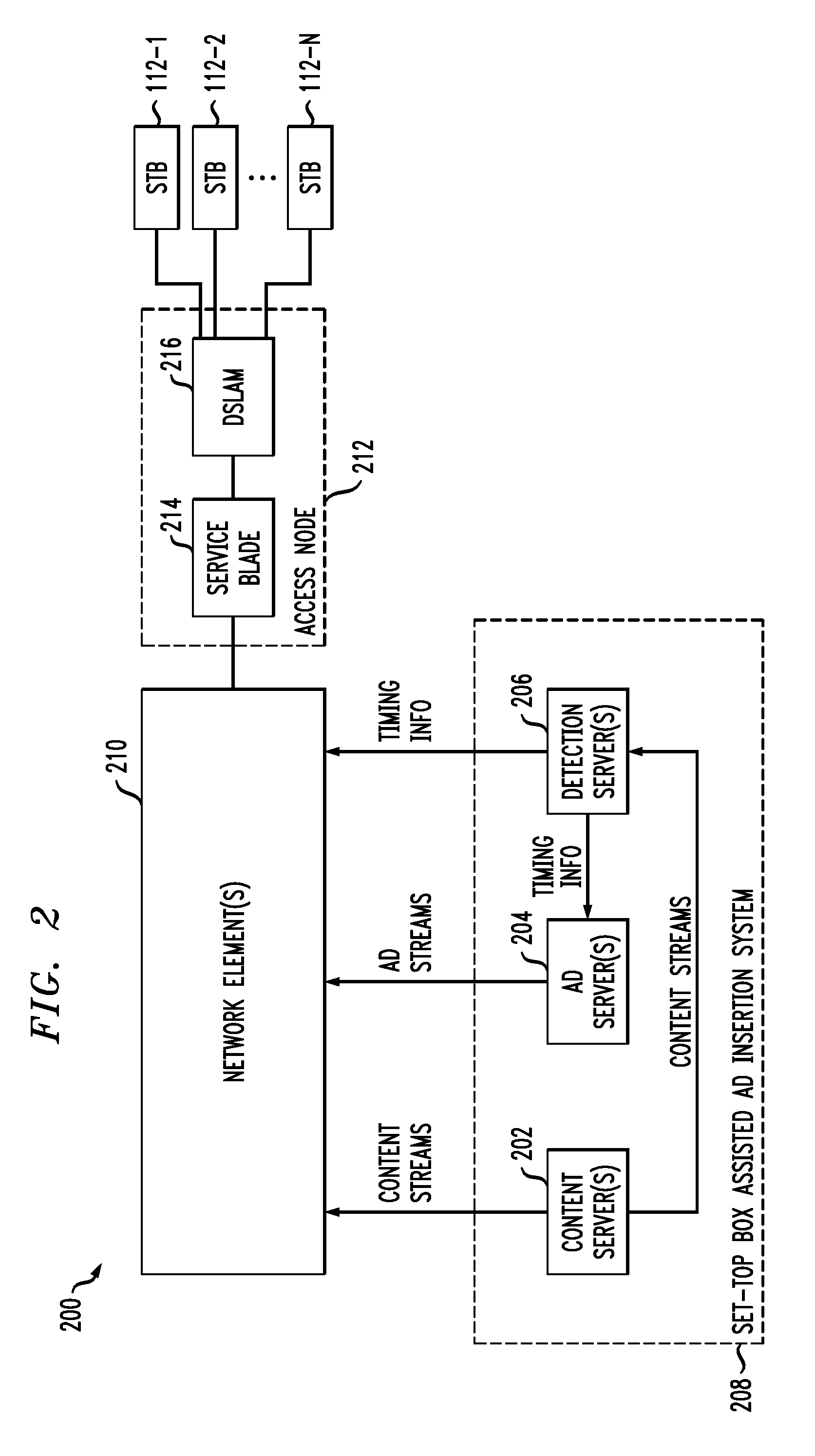
Interface Device Having Multiple Software Clients to Facilitate Display of Targeted Information
InactiveUS20100083305A1To offer comfortAccurate coordinatesSelective content distributionElectrical cable transmission adaptationObjective informationDistribution system
Advertisements or other types of targeted information are delivered to set-top boxes or other user interface devices of a signal distribution system. In one aspect of the invention, a user interface device comprises at least first and second software clients and a video buffer. The first software client receives packets associated with a first media stream, and the second software client receives packets associated with a second media stream containing the targeted information. The first software client delivers at least a portion of the packets associated with the first media stream to the video buffer. The second software client delivers at least a portion of the packets associated with the second media stream to the video buffer while one or more packets of the first media stream are still in the video buffer. The user interface device switches from the first media stream to the second media stream based on timing information which may be received from an external detection server.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
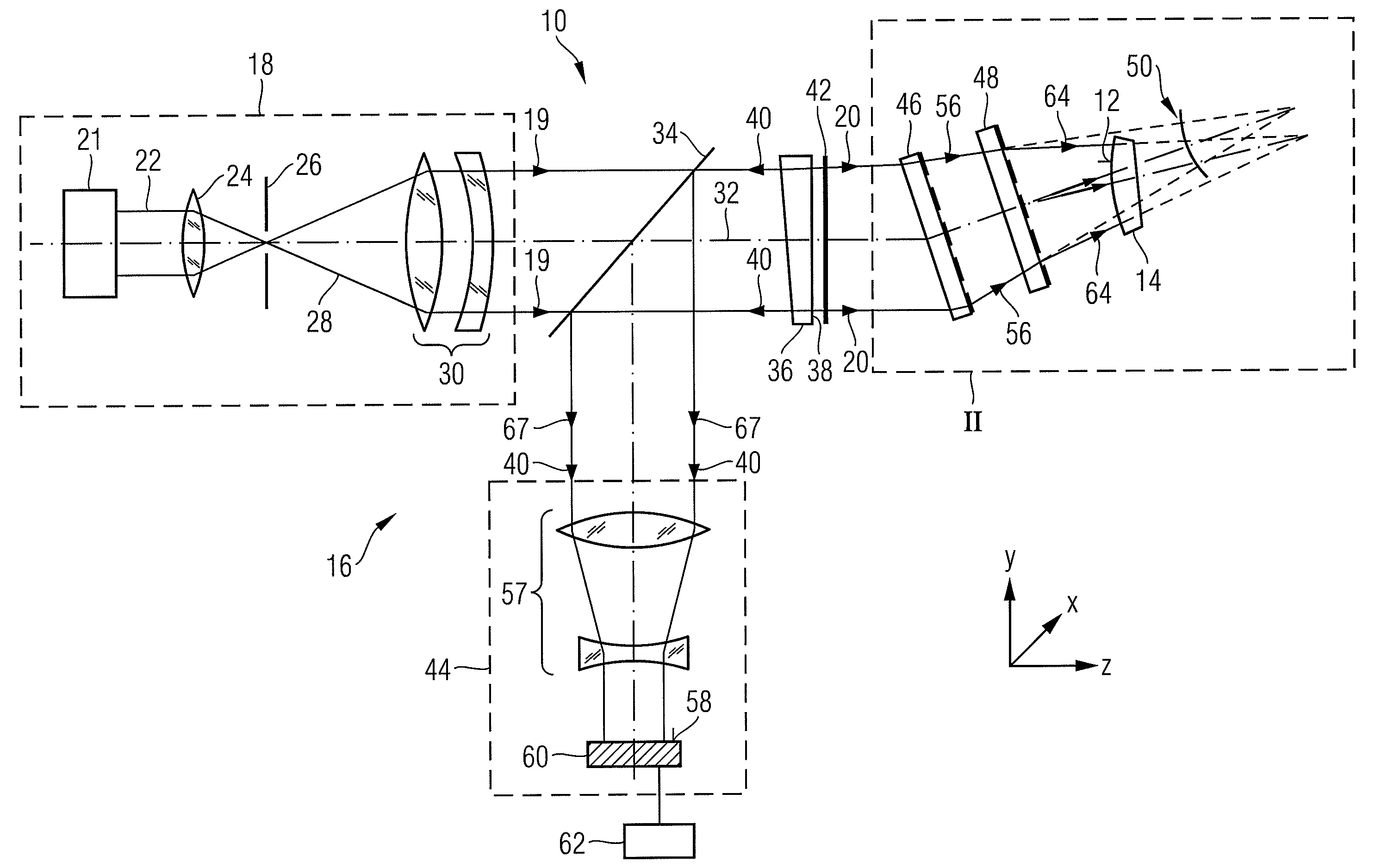
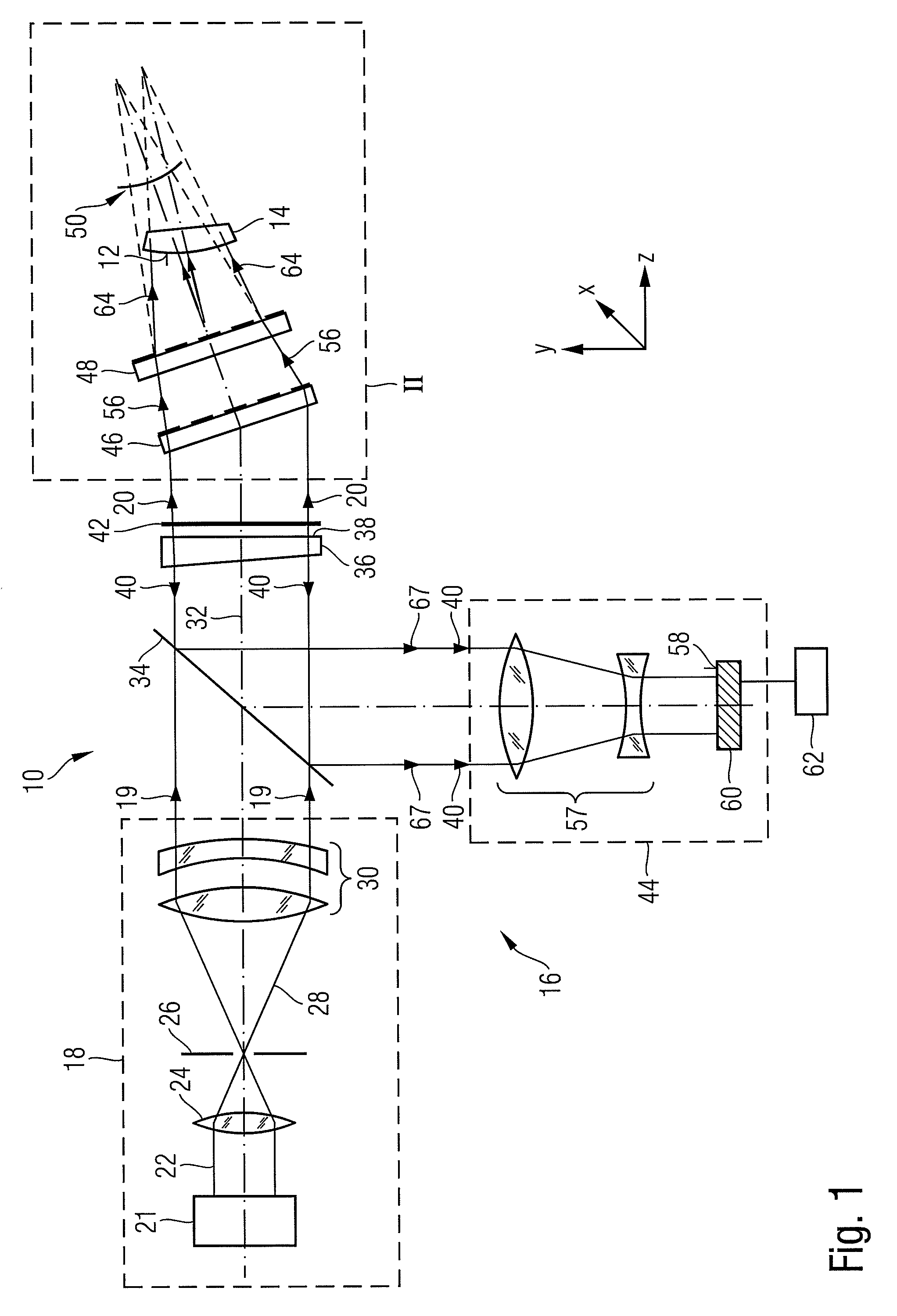
Method and apparatus for determining a deviation of an actual shape from a desired shape of an optical surface
ActiveUS20090128829A1Good effectSuitable for measuringMirrorsUsing optical meansWavefrontOptical surface
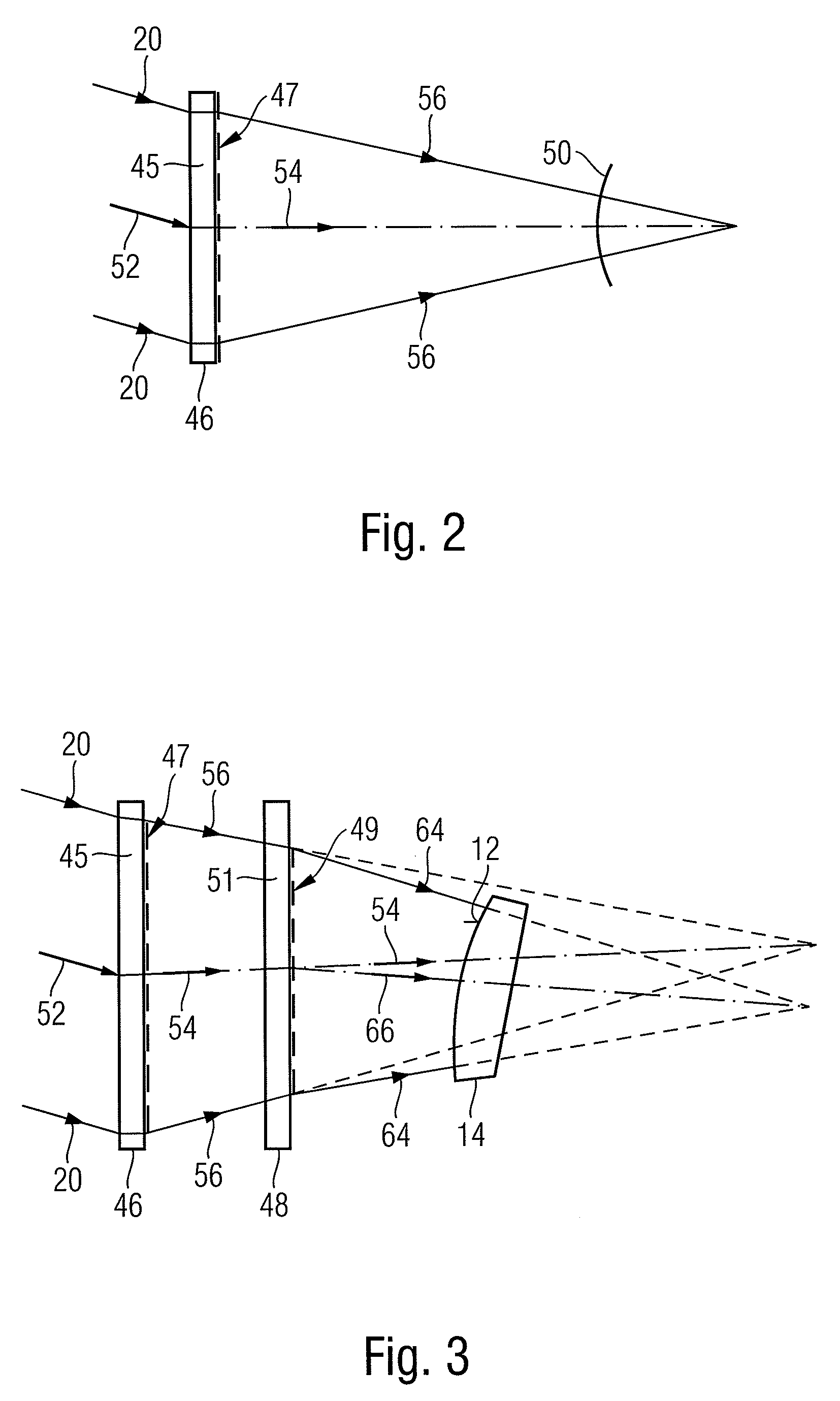
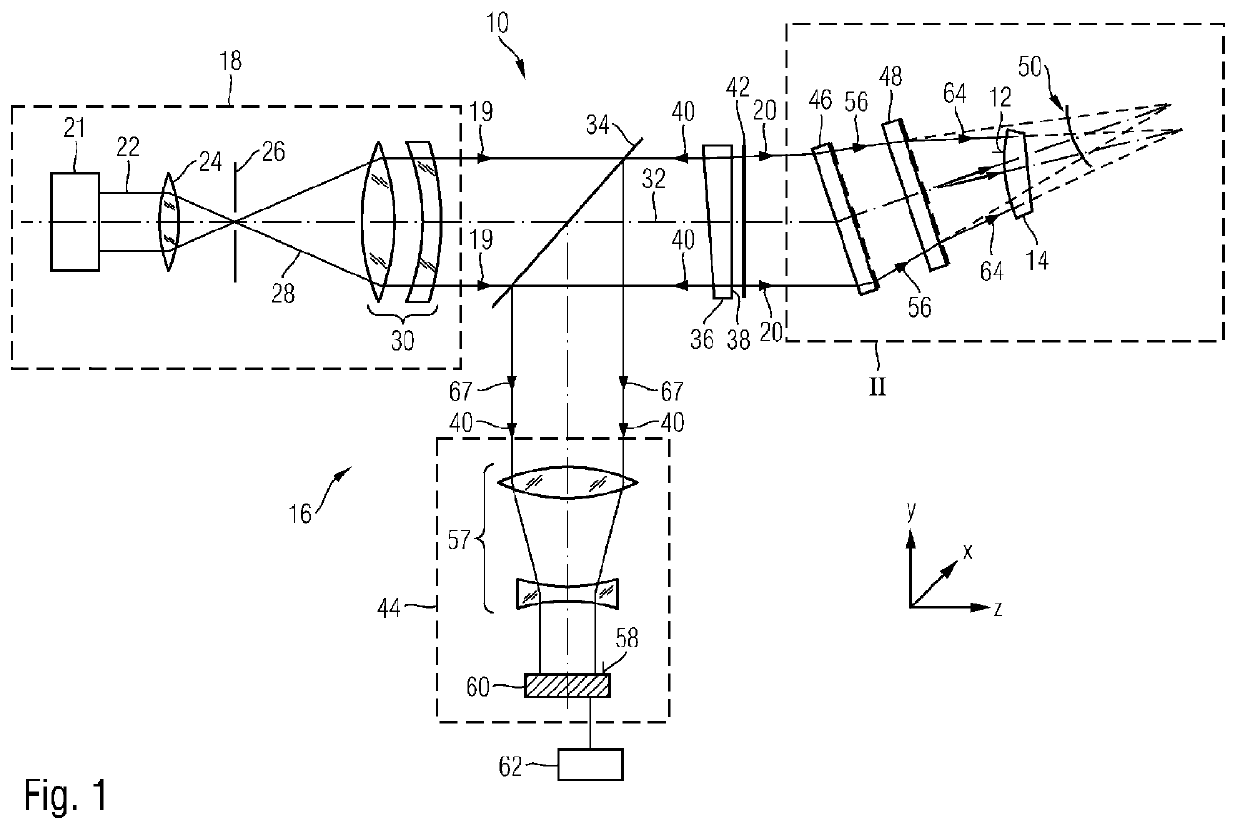
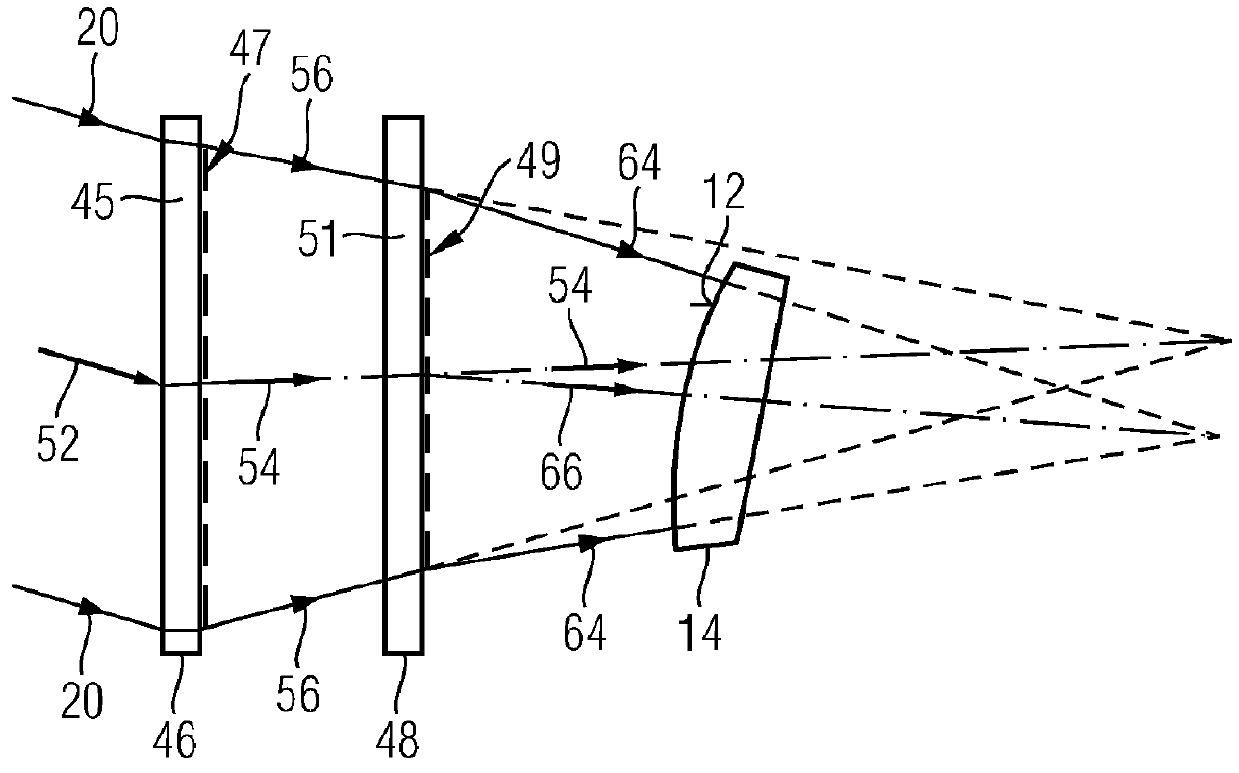
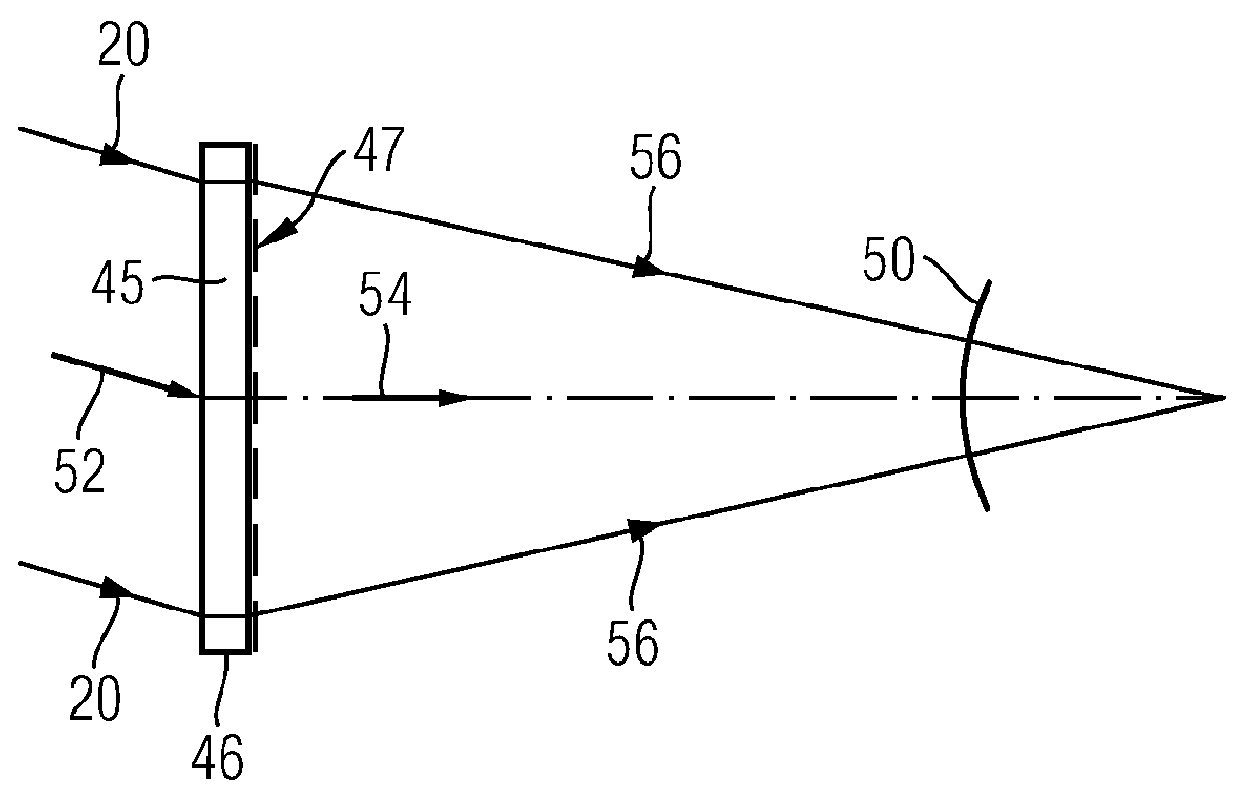
A method of determining a deviation of an actual shape from a desired shape of an optical surface (12; 103) includes: providing an incoming electromagnetic measuring wave (20; 113), providing two diffractive structures (47, 49; 145, 146, 141, 143) which are respectively designed to reshape the wavefront of an arriving wave, calibrating one of the two diffractive structures (47, 49; 145, 146, 141, 143) by radiating the incoming measuring wave (20; 113) onto the at least one diffractive structure to be calibrated (47, 49; 145, 146, 141, 143) and determining a calibration deviation of the actual wavefront from a desired wavefront of the measuring wave (20; 113) after interaction of the latter with the at least one diffractive structure to be calibrated (47, 49; 145, 146, 141, 143), positioning the two diffractive structures (47; 49; 145, 146, 141, 143) in the optical path of the incoming measuring wave (20; 113) such that individual rays of the measuring wave radiate through both diffractive structures (47; 49; 145, 146, 141, 143), and reshaping the incoming measuring wave (20; 113) by means of the two diffractive structures (47; 49; 145, 146, 141, 143) to form an adapted measuring wave (64; 114), the wavefront of which is adapted to the desired shape of the optical surface (12; 103), positioning the optical surface (12; 103) in the optical path of the adapted measuring wave (64, 114) so that the adapted measuring wave (64; 114) interacts with the optical surface (12; 103) and measuring the wavefront of the adapted measuring wave (64; 114) after interaction of the latter with the optical surface (12; 103).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
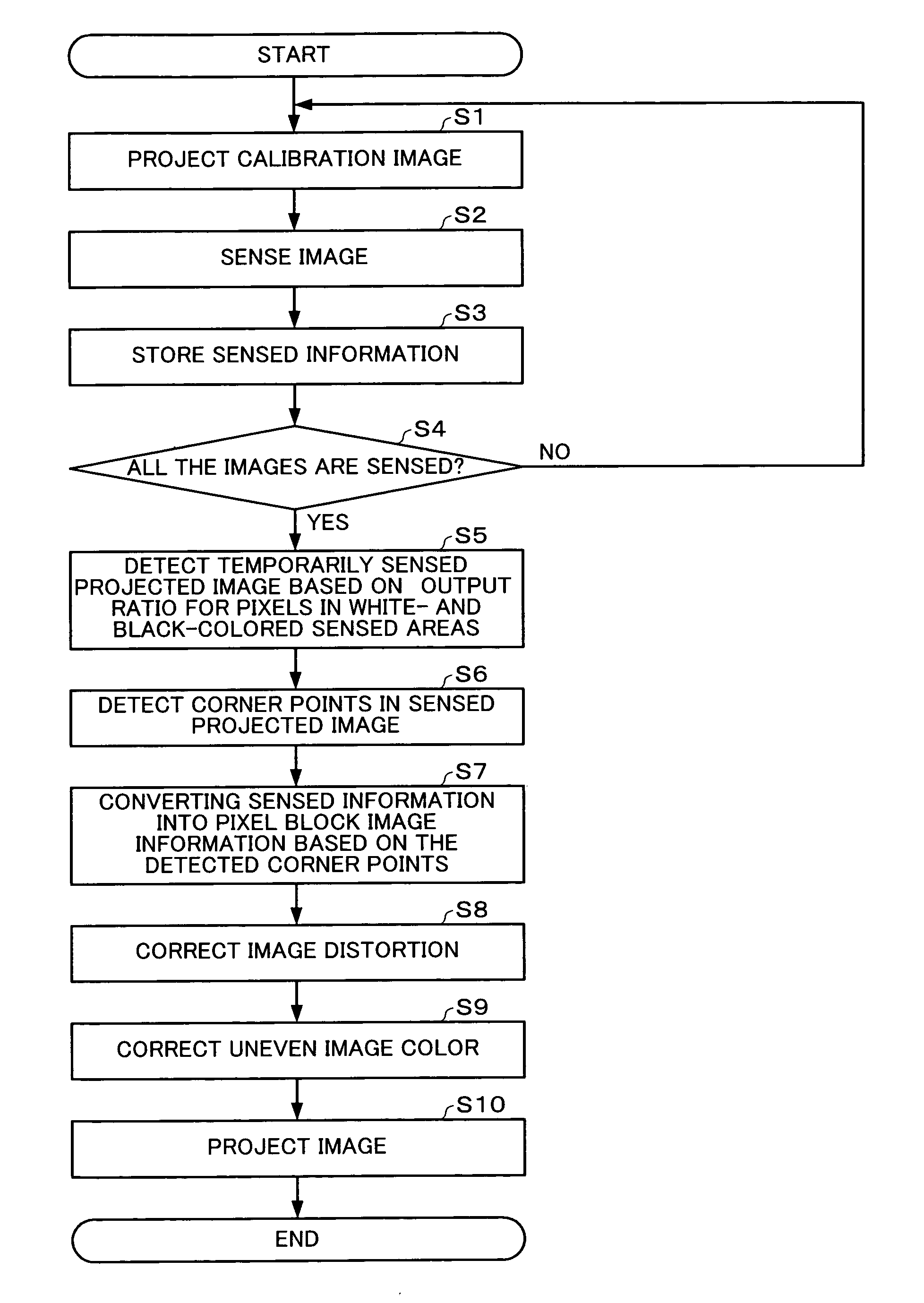
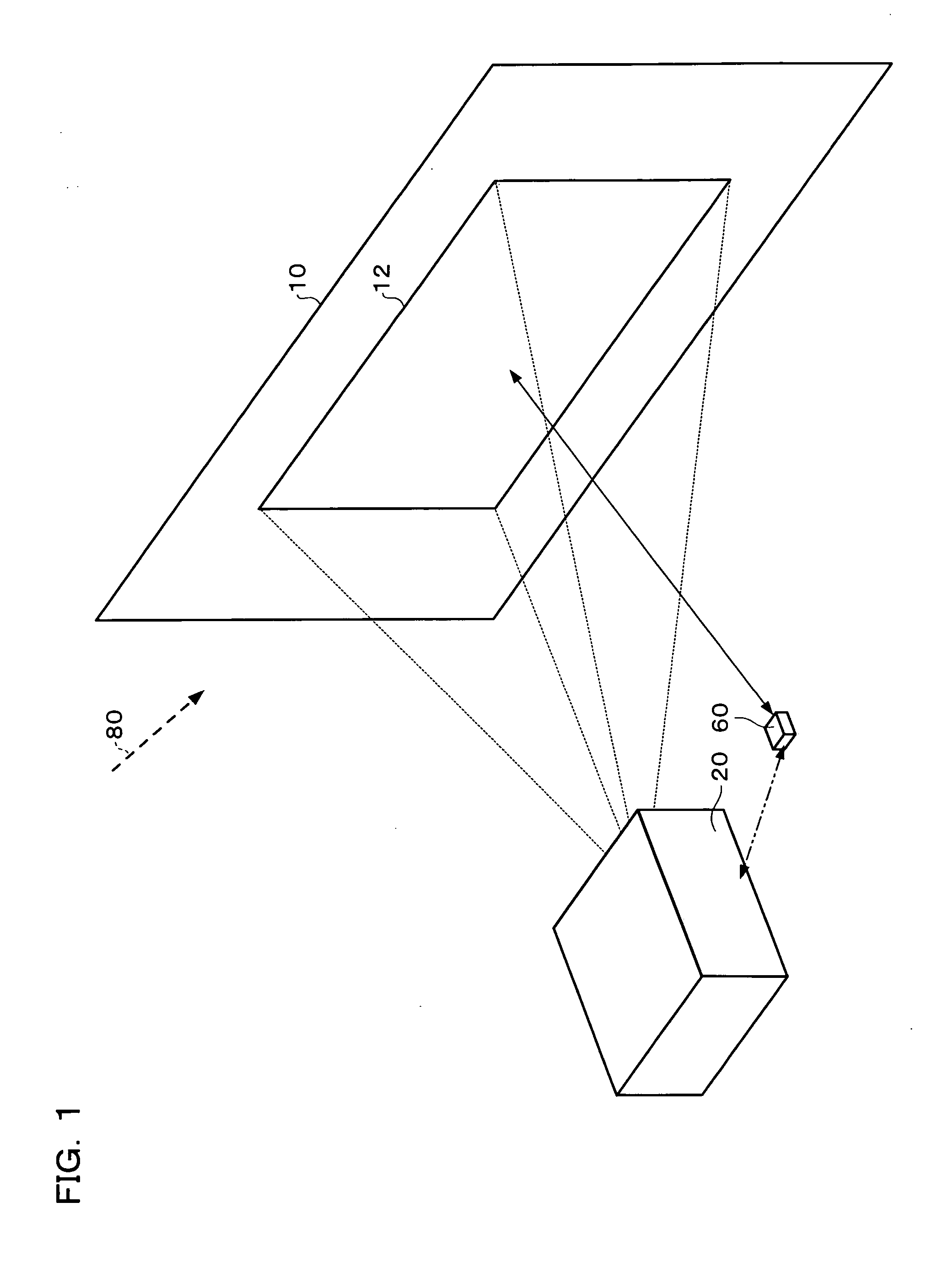
Image processing system, projector, computer-readable medium, and image processing method
InactiveUS7266240B2Accurate coordinatesEfficient detectionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSpatial light modulatorImaging processing
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for mapping touch screen based on five points calibration
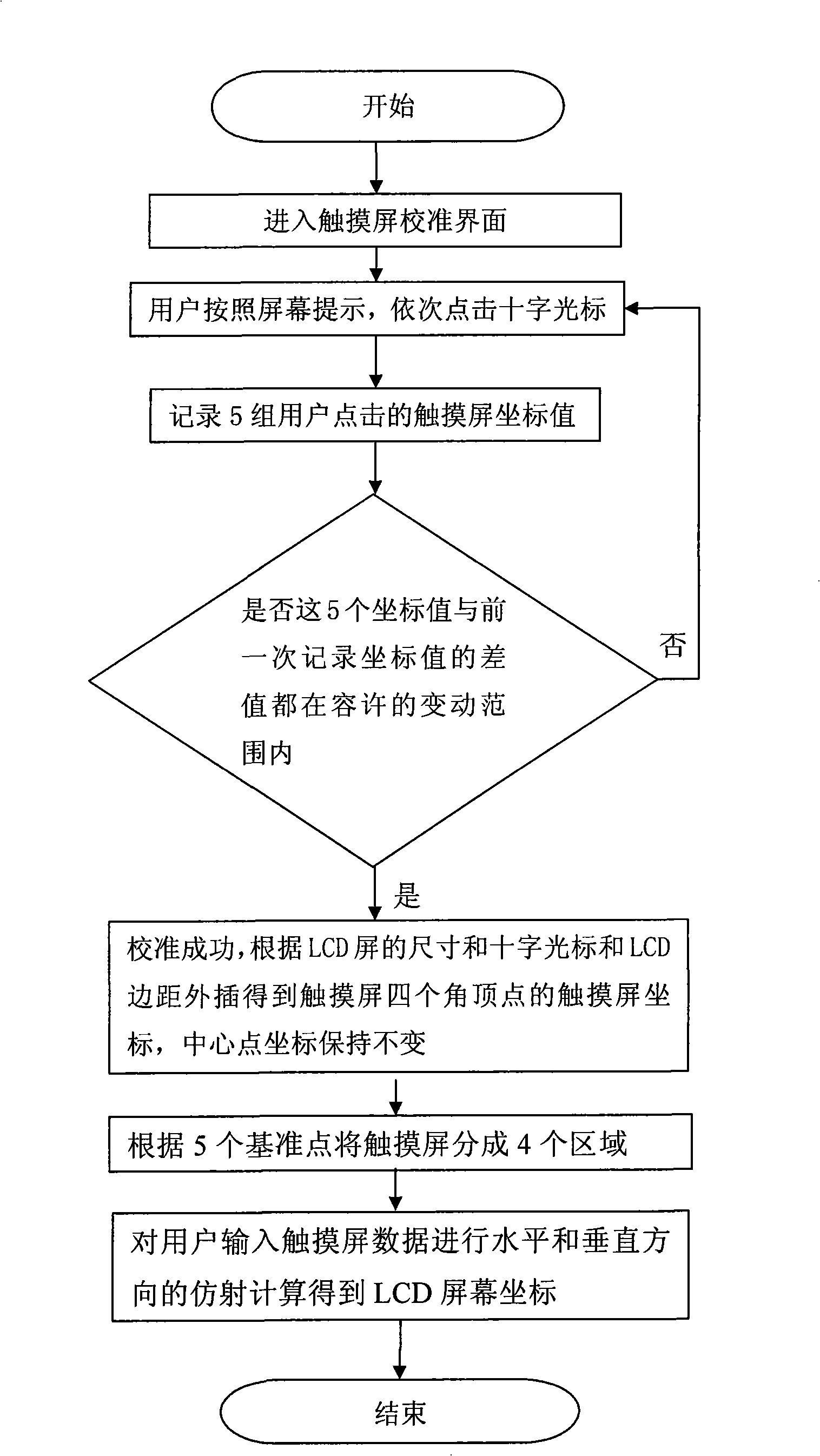
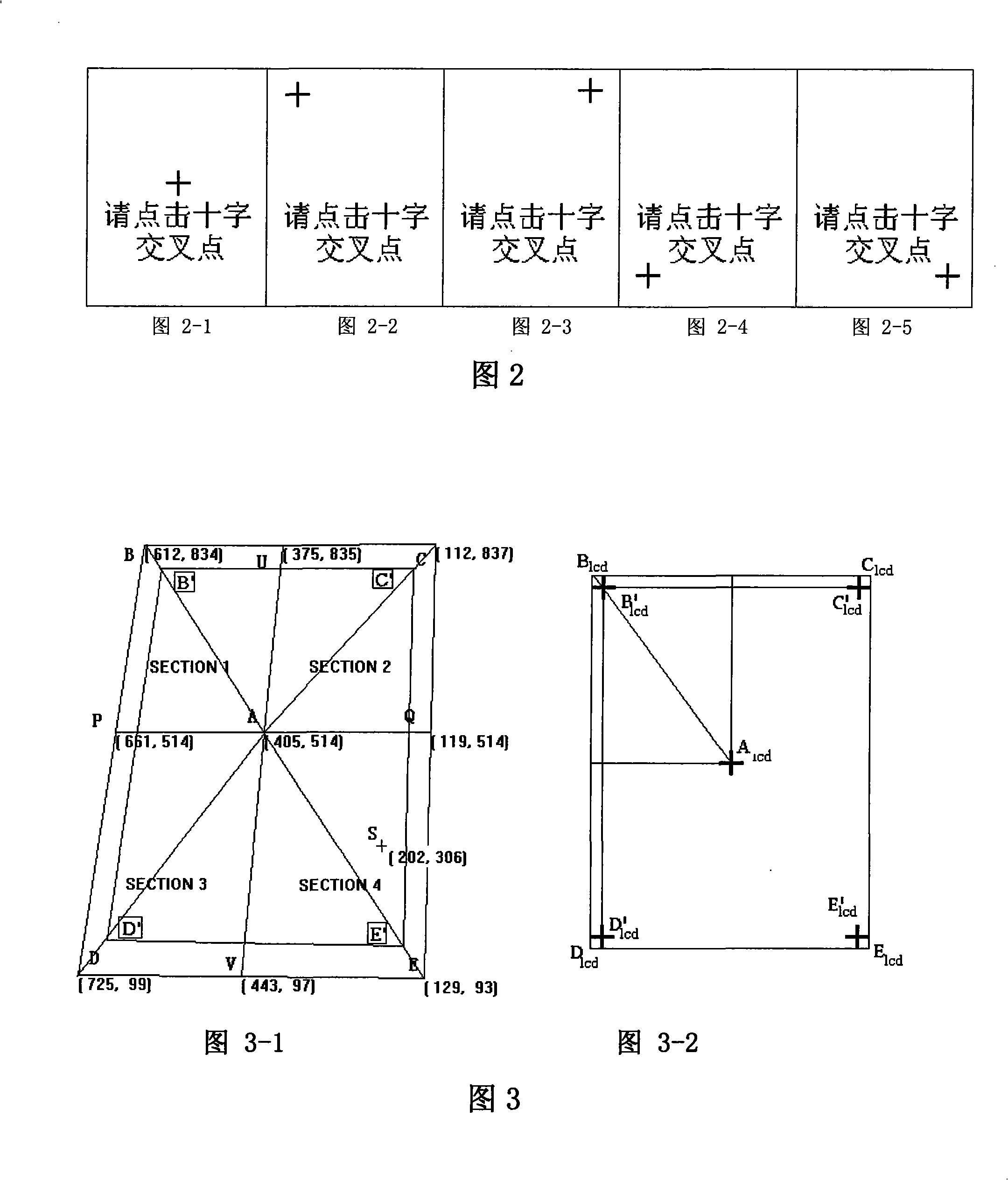
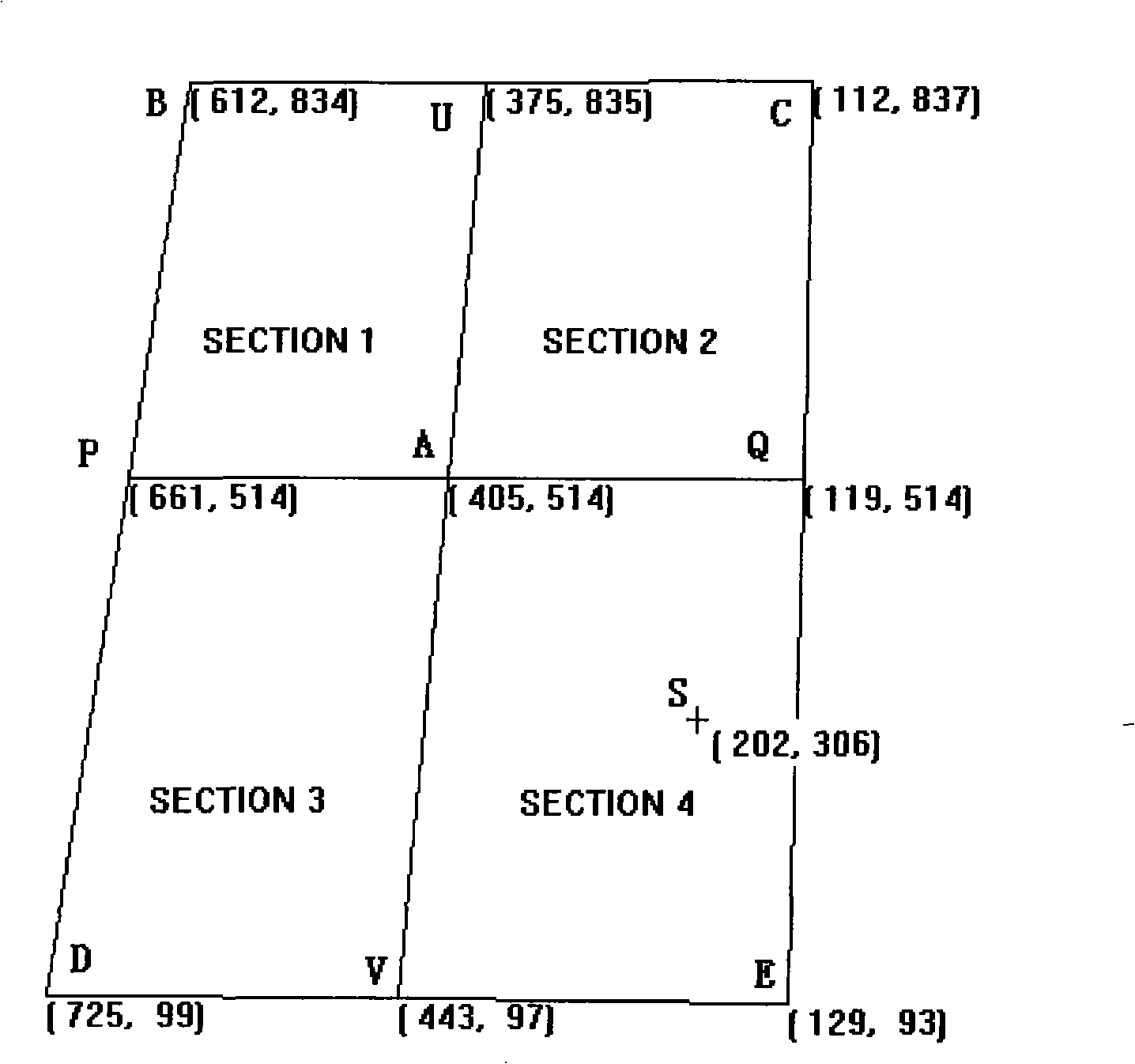
ActiveCN101349955AAccurate coordinatesSolve the inaccurate patchInput/output processes for data processingTouchscreenParallelogram
The invention relates to a touch screen mapping method based on five point calibration, which uses dynamic ratio to calculate the mapping value from the touch screen coordinate and LCD coordinates according to the different coordinates on the touch screen, to compensate the deformation of trapezium and parallelogram, to resolve the deflection problem of touch points caused by the serious inclination at the horizontal and vertical directions of the touch screen, and uses the coordinates of five points to divide the screen into a plurality of mapping areas one-to-one, to realize accurate coordinates of the touch screen mapped to a LCD screen, to resolve the problem of inaccurate point caused by inaccurate pasting and aging of the touch screen, effectively reduces the problem of traditional algorisms which not consider the fine rotation of the four corner coordinates relative to the center coordinates, to cause the left and right inclination of horizontal strokes and the upper and lower inclination of vertical strokes and resolves the inaccurate point problem of small touch points of small LCD screens (128x160).
Owner:WINGTECH COMM
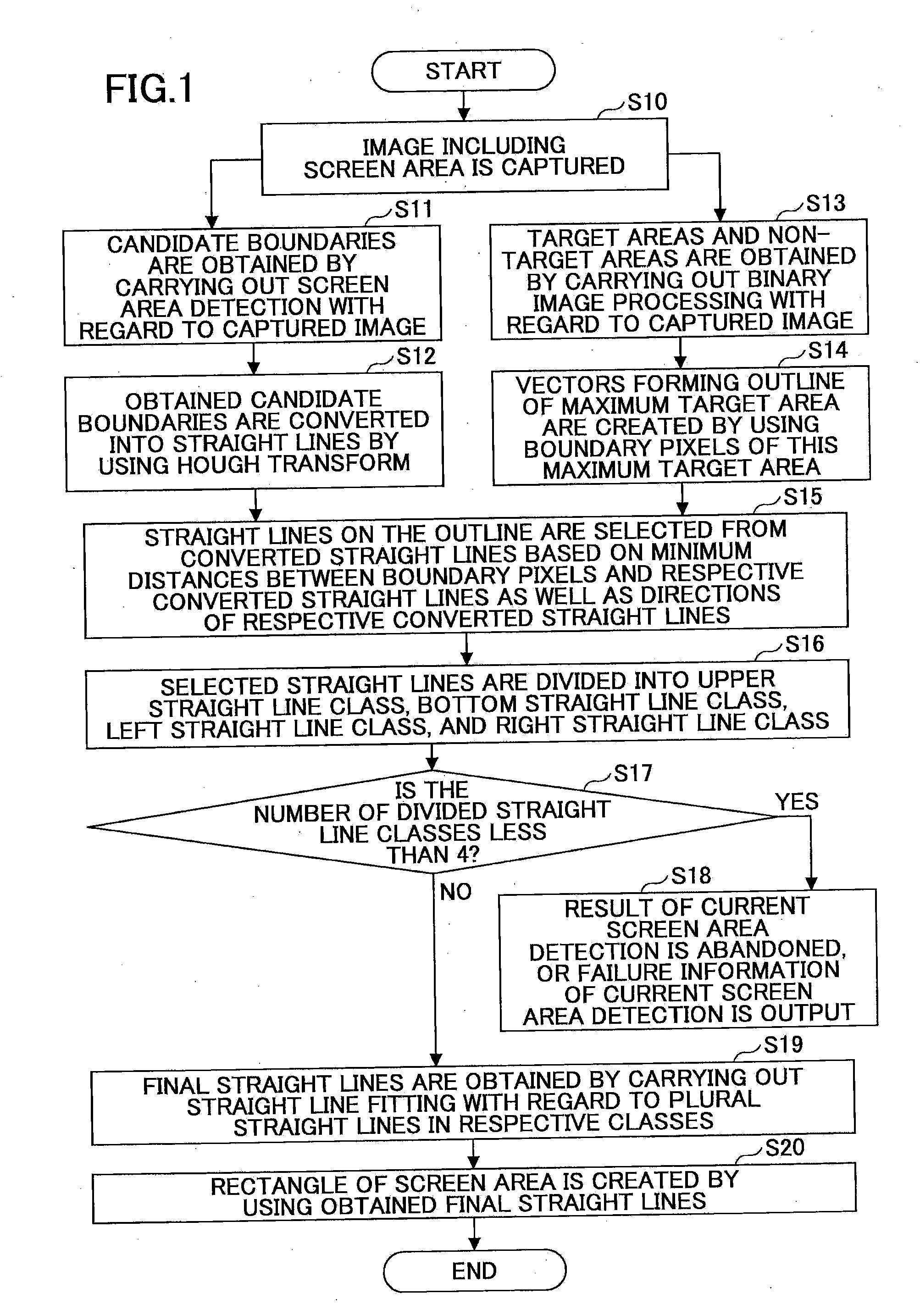
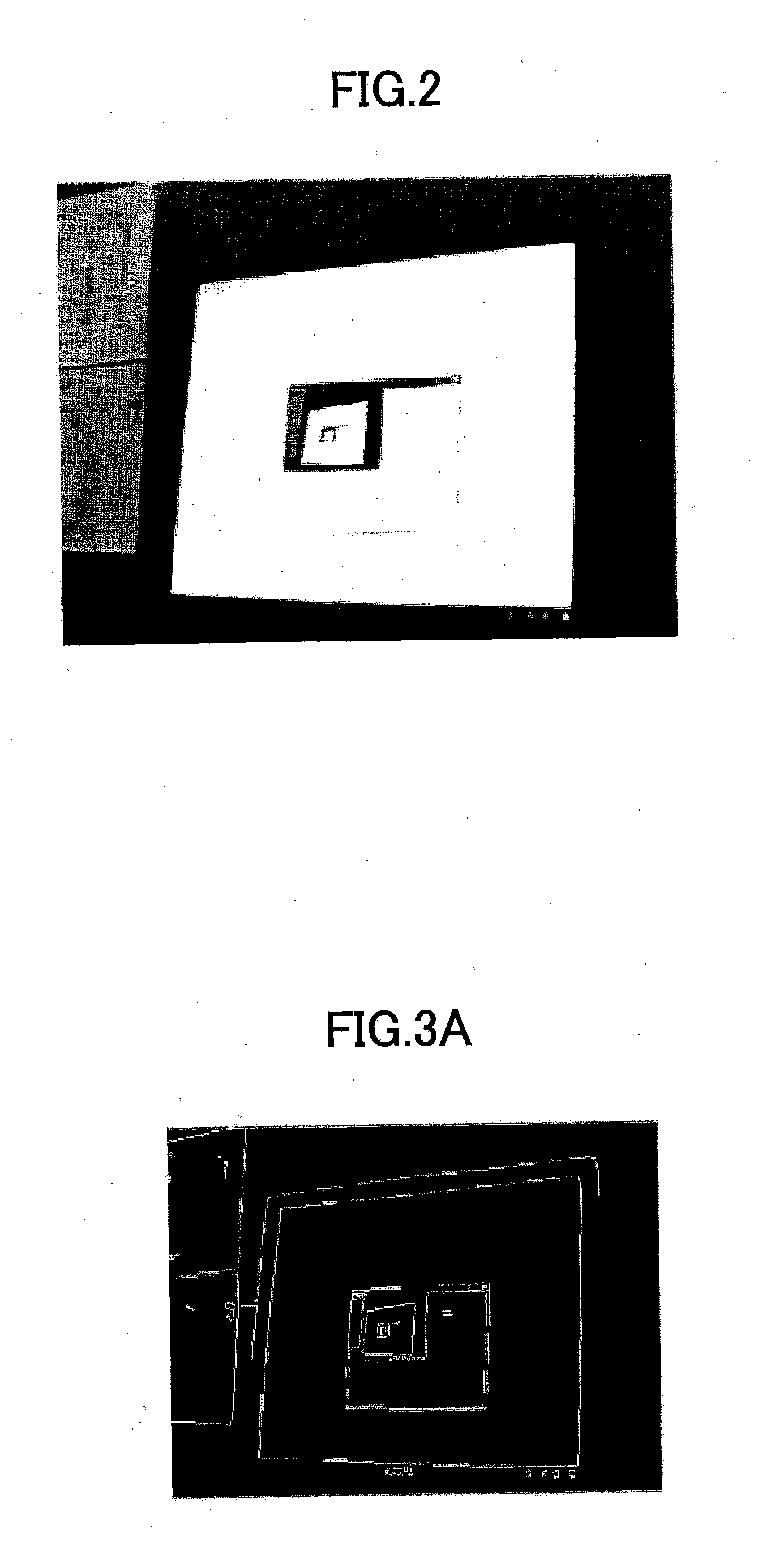
Screen area detection method and screen area detection system
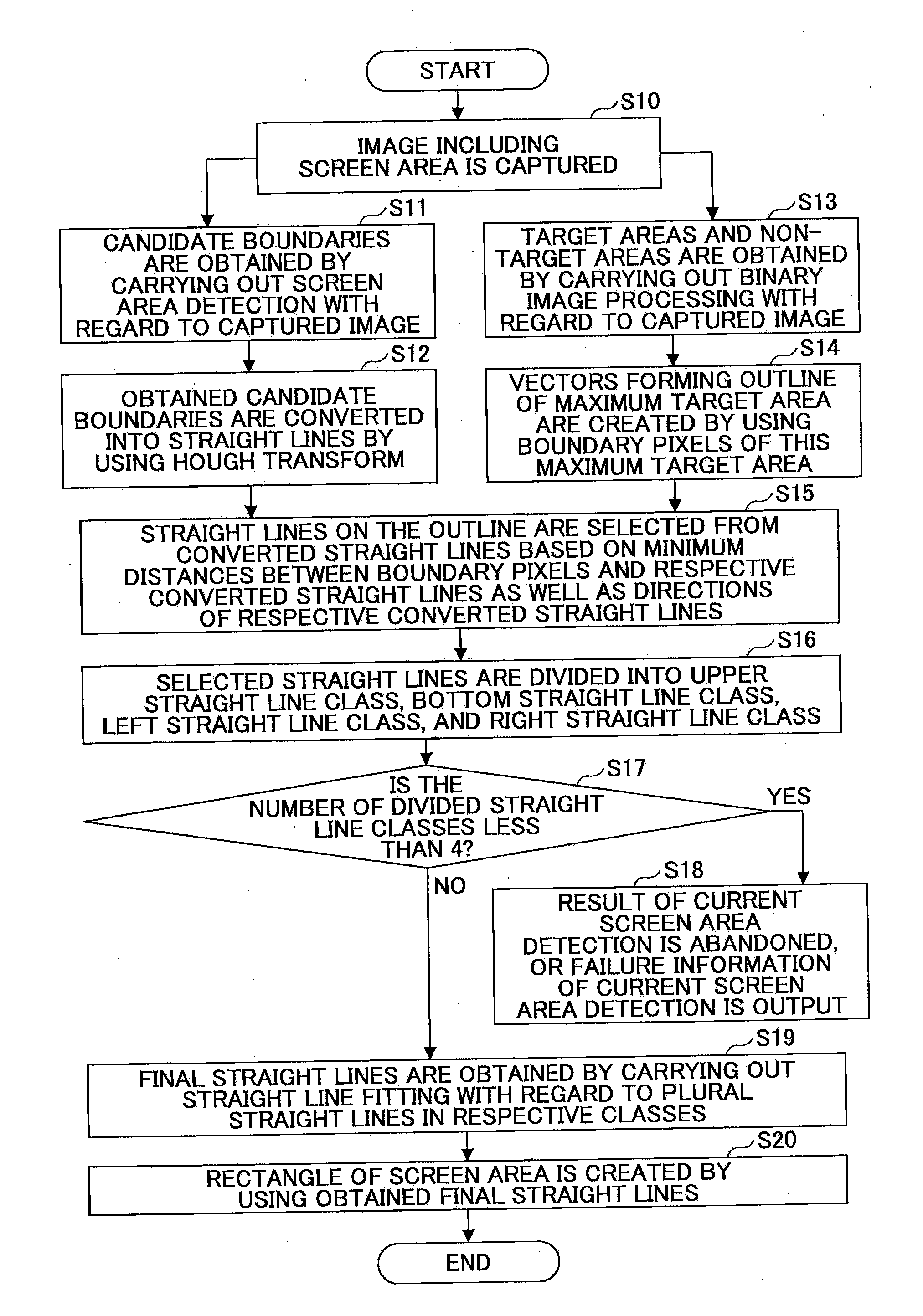
InactiveUS20110274353A1High positionAccurate acquisitionImage enhancementImage analysisRegion detectionBinary image
Disclosed are a method and a system for detecting a screen area. The method comprises a step of capturing an image including the screen area; a step of obtaining candidate boundaries of the screen area; a step of converting the candidate boundaries into straight lines; a step of carrying out binary image processing with regard to the captured image; a step of obtaining boundary pixels of a maximum target area, and letting the boundary pixels serve as an outline of the maximum target area; a step of selecting straight lines on the outline from the converted straight lines; a step of dividing the selected straight lines into four classes; and a step of obtaining final straight lines by carrying out straight line fitting with regard to straight lines in the respective classes so as to obtain four boundaries of the screen area.
Owner:RICOH KK
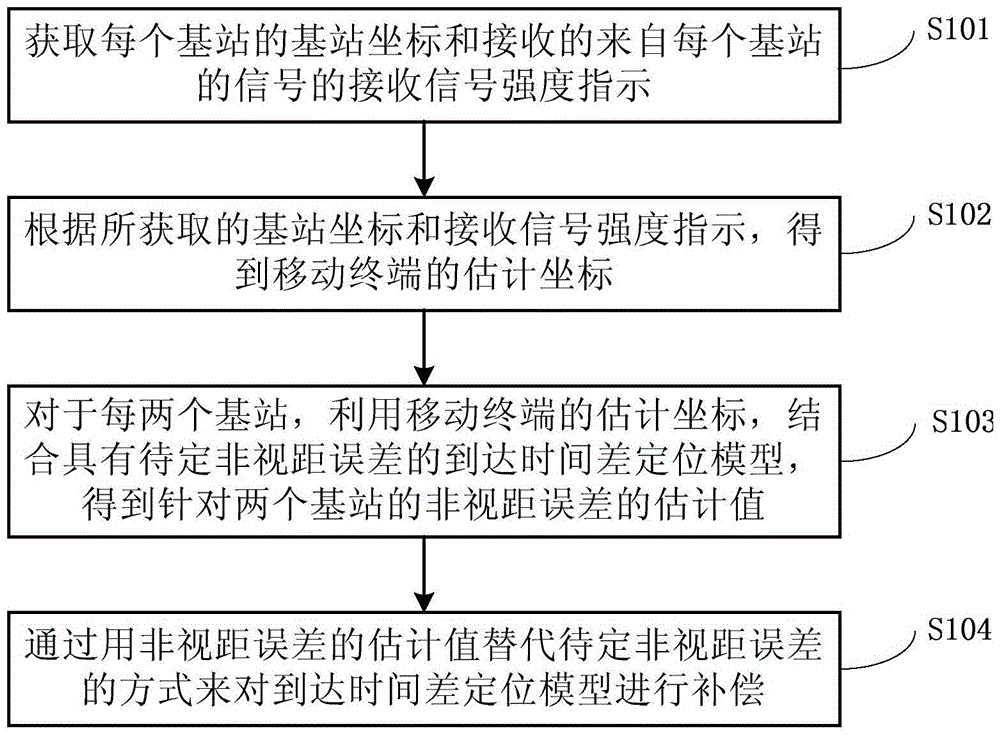
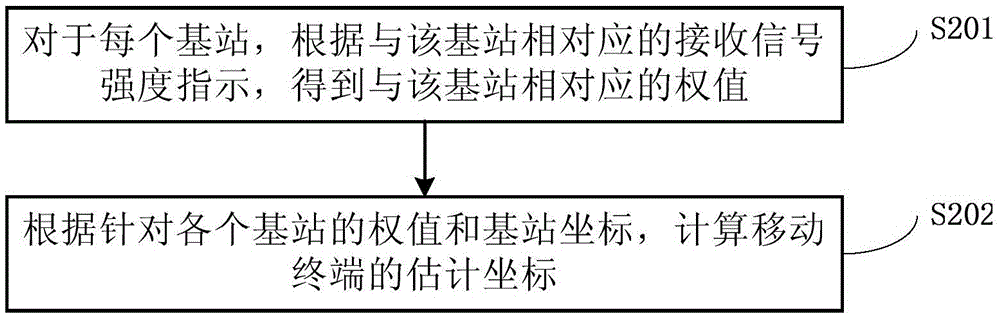
Indoor location non line of sight compensation method
InactiveCN105491659AAccurate coordinatesPosition fixationWireless communicationReceived signal strength indicationEngineering
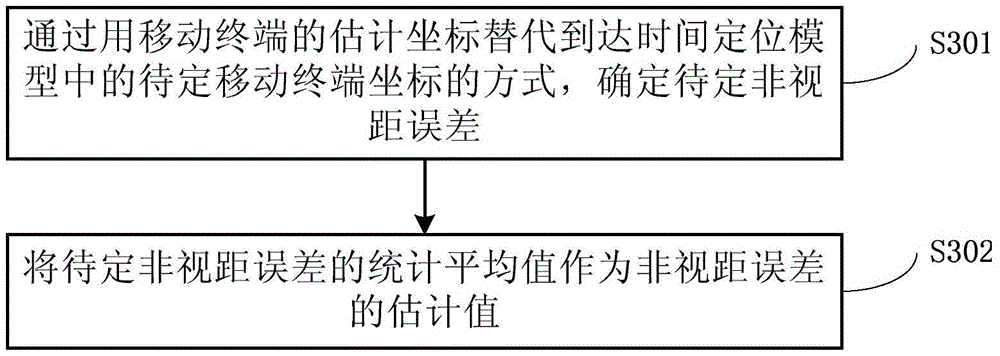
The invention discloses an indoor location non line of sight compensation method and an indoor location method. The compensation method comprises the steps of acquiring base station coordinates of each base station arranged indoor and received signal strength indication of a received signal from each base station; obtaining estimated coordinates of a mobile terminal according to the acquired base station coordinates and received signal strength indication; obtaining an estimation value of a non line of sight error for every two base stations by use of the estimated coordinates of the mobile terminal according to the mobile terminal and a time difference of arrival location model having a specific non line of sight error of the two base stations; and replacing an undetermined non line of sight error with the estimated value of the non line of sight error so as to compensate the time difference of arrival location model. Through adoption of the method, the technical problem that the coordinates of the mobile terminal cannot be resolved due to overlarge time difference of arrival (TDOA) caused by the non line of sight error is solved, and accurate coordinates of the mobile terminal are obtained through non line of sight compensation for the TDOA.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for positioning multiple moving targets by wireless sensor network syncretized with radio frequency identification
InactiveCN101945472AReduce work intensityImprove responseNetwork topologiesRadio frequencyReal-time computing
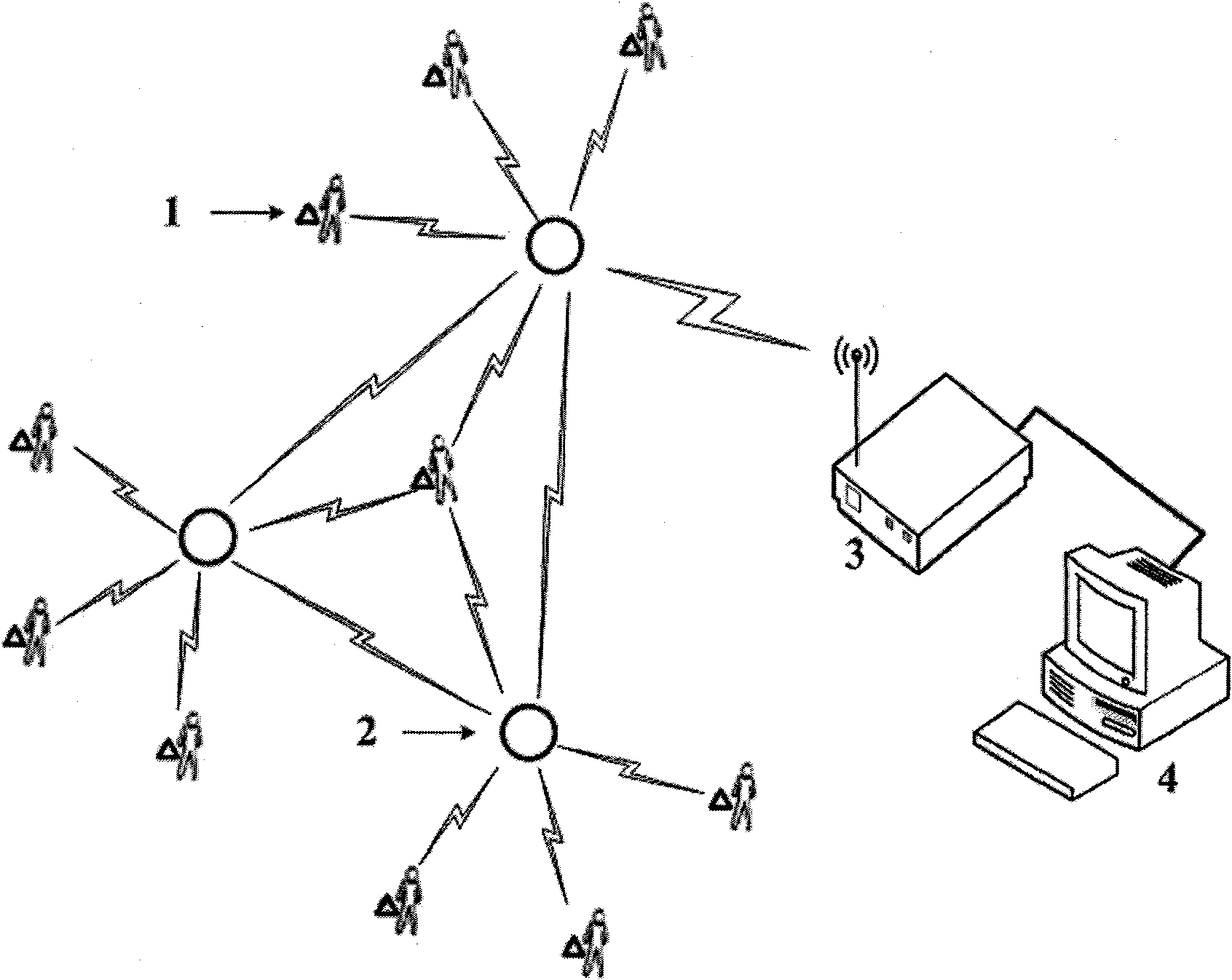
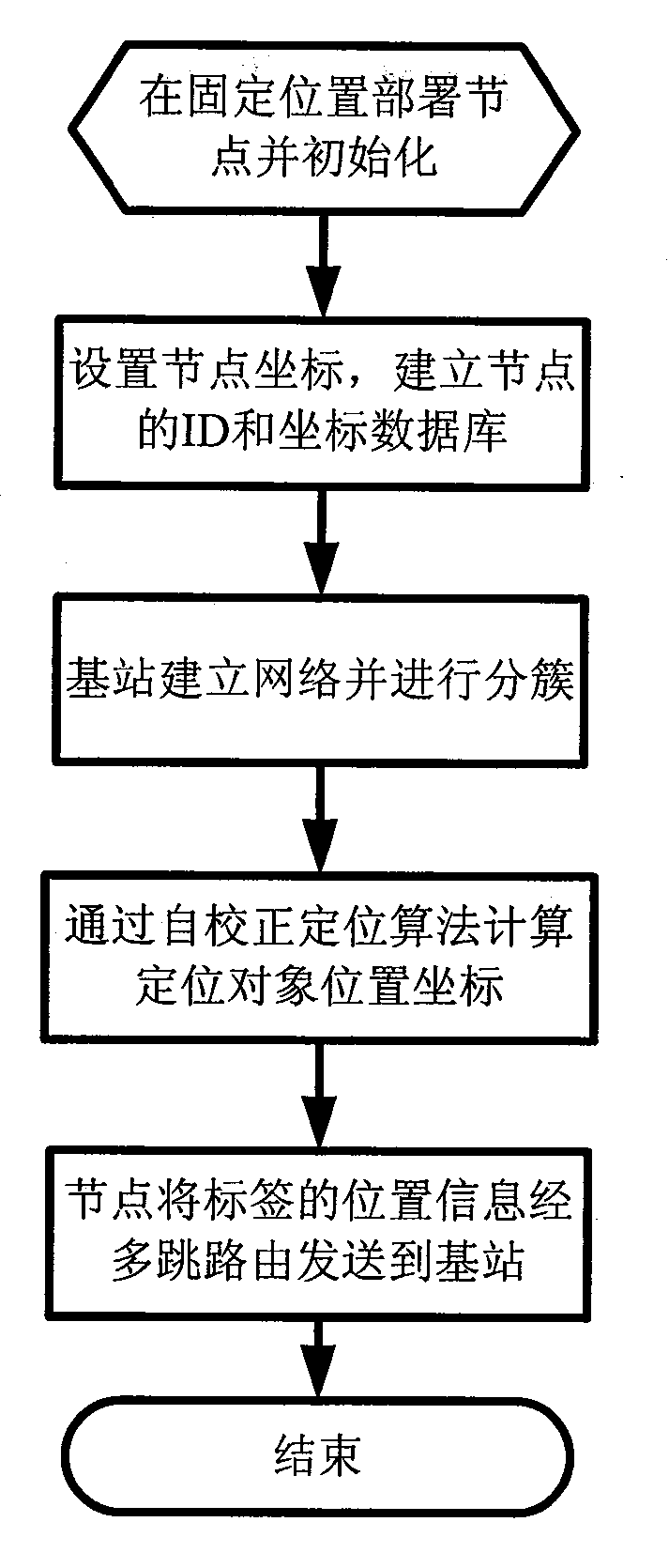
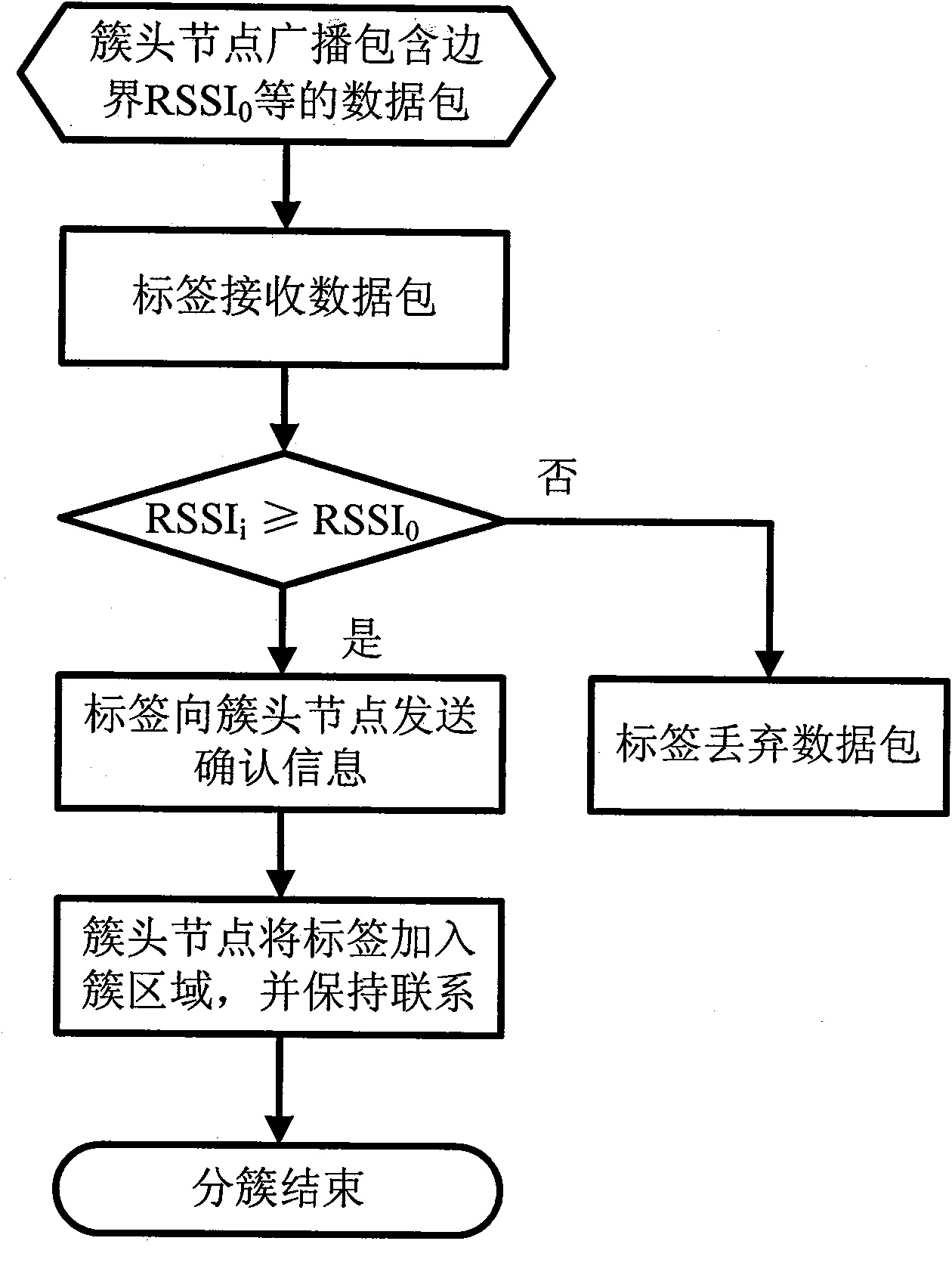
The invention discloses a method for positioning multiple moving targets by a wireless sensor network syncretized with radio frequency identification (WSID), which comprises the following steps of: fixedly deploying WSID nodes at preset positions, electrifying and initiating the WSID nodes; configuring identification (ID) for each node by a base station respectively, establishing a position relation database of all nodes, and sending the ID of all the nodes and the position relation database to each node respectively; sending a data packet for establishing a network to each node by the base station, establishing the network, sending a data packet for establishing a cluster and determining a cluster head, and clustering the network; setting a WSID tag on a moving target, electrifying and initiating the tag, and computing the position coordinates of the moving target by self-correction positioning algorithm by the node and the tag on the moving target once the moving target provided with the tag enters a positioning area; and allowing the tag to send the position information of the moving target to the base station through the node by multi-hop routing, and sending the position information of the moving target to a monitoring terminal through networks such as Internet or GPRS or TD-SCDMA after the base station acquires the position information of the moving target.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
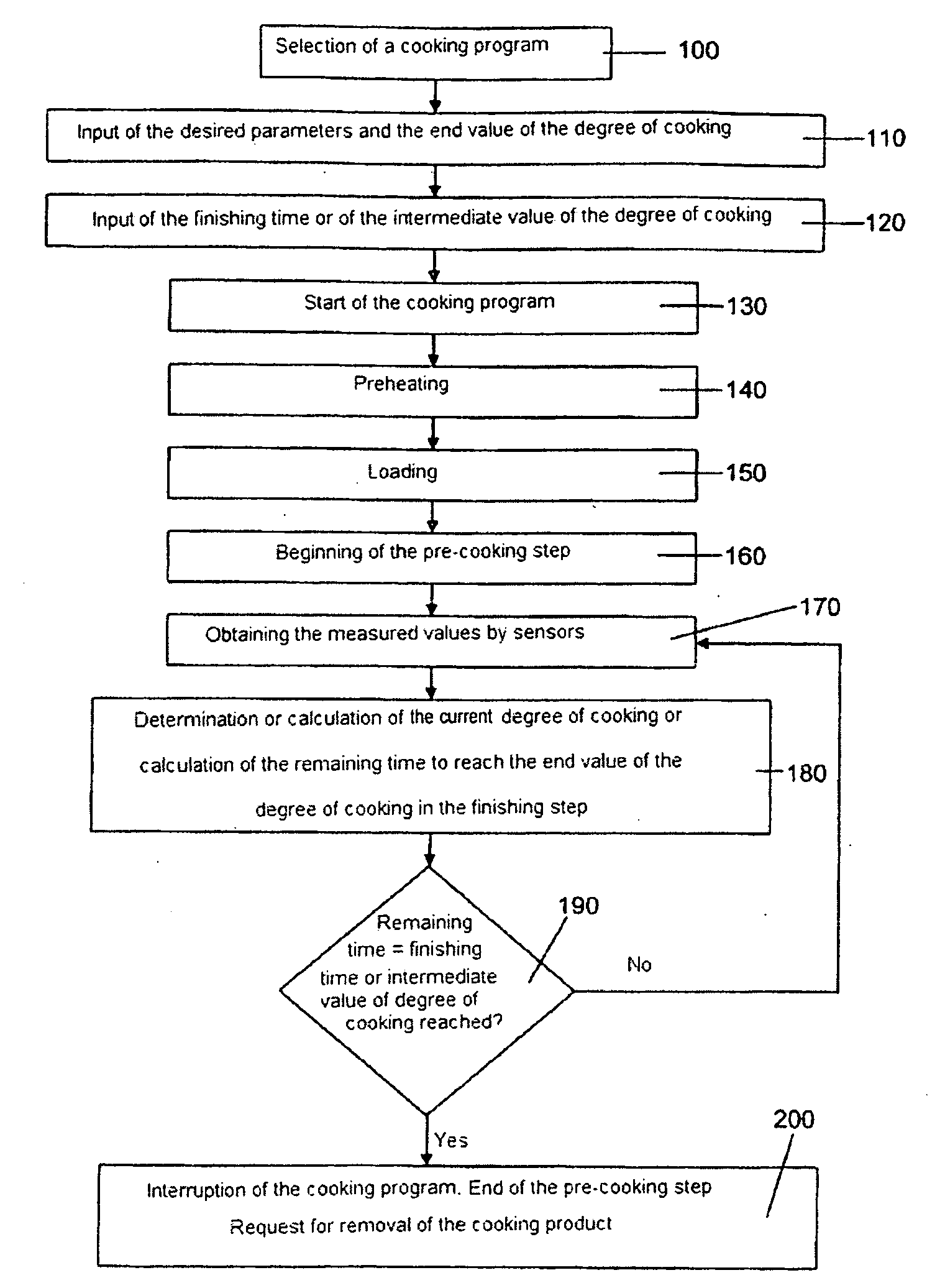
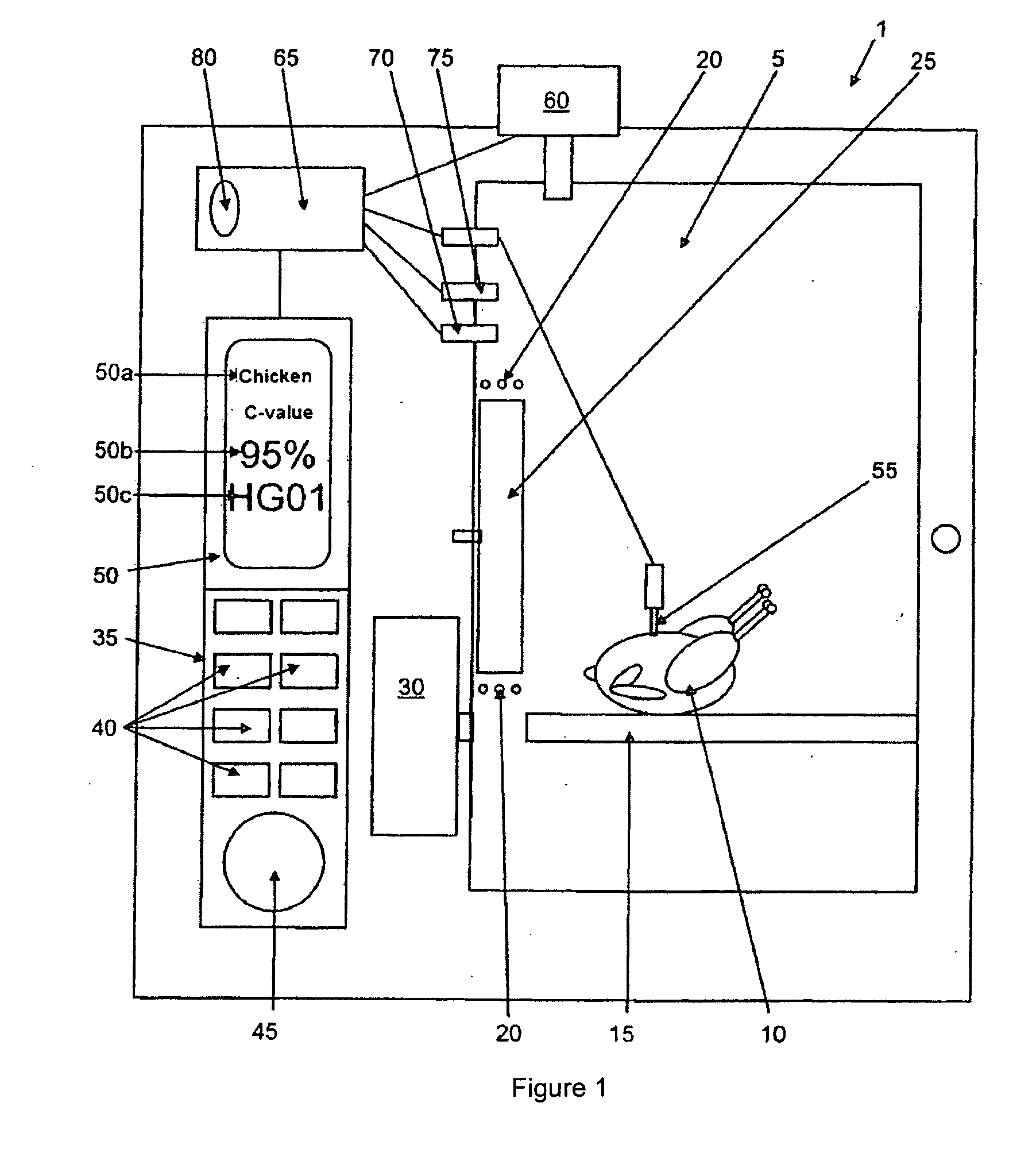
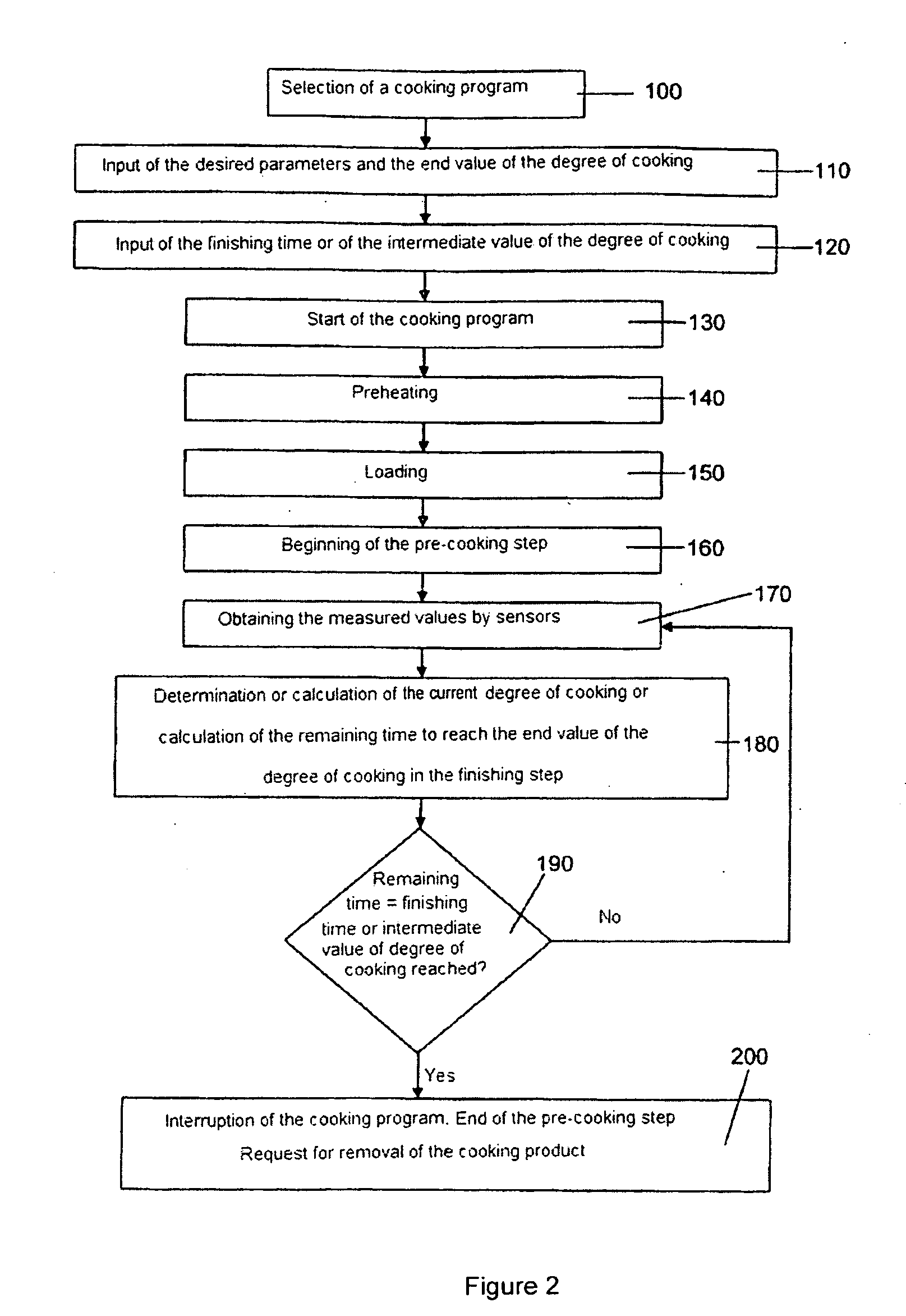
Method and cooking appliance for cooking according to the c-value
ActiveUS20090061070A1Overcome disadvantagesSuitable for processingDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusProcess engineeringCore temperature
A method for the cooking of a cooking product in a cooking appliance with a cooking chamber that comprises at least one heating device, a computer device, a memory device and at least one sensor device, is carried out, in dependence on a degree of cooking of a cooking product and / or of a cooking duration, in particular determined by the core temperature, the browning, the pH value and / or the cooking value, from values measured by the sensor device with consideration of the at least occasionally deposited values in the memory device via the computer device, wherein at least two steps separated from one another in time, comprising a pre-cooking step, which is interrupted when a determined intermediate value of the degree of cooking and / or of the duration of cooking, in particular a determined remaining time for reaching the cooking duration is reached, and a finishing cooking step, in particular a finishing step that is recalled at a later time point in order to end the cooking of the cooking product with consideration of the intermediate value.
Owner:RATIONAL AG
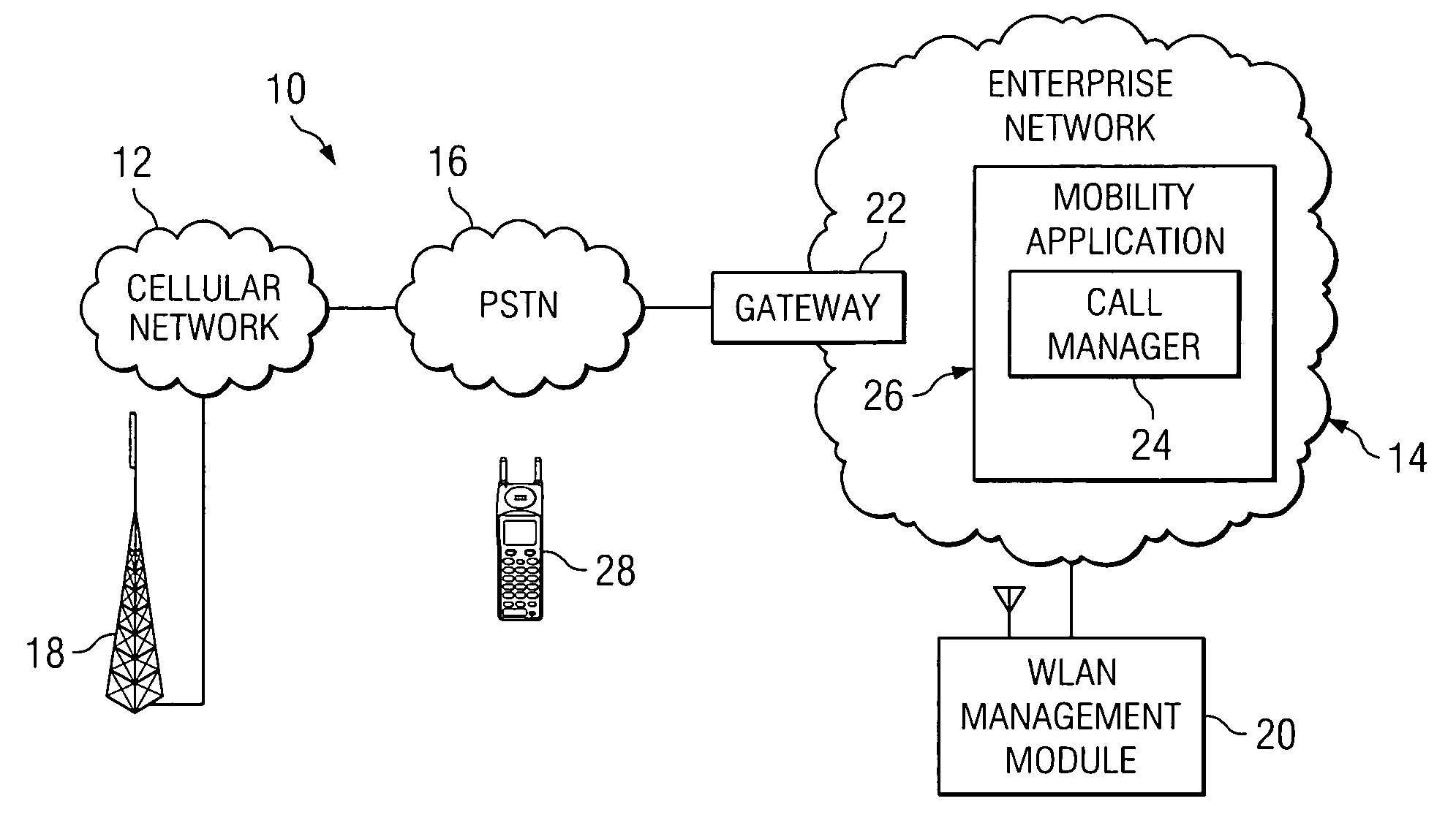
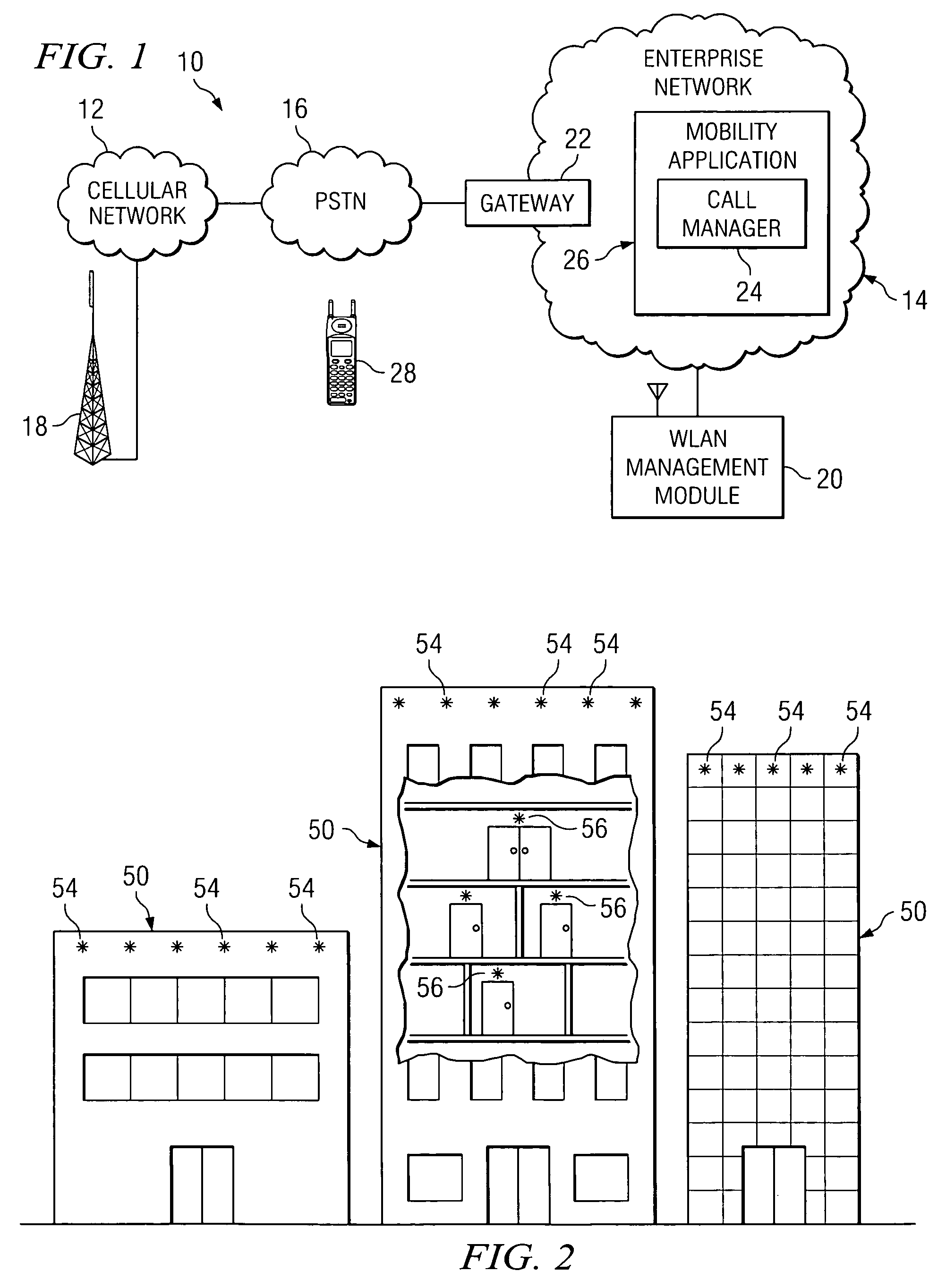
System and method for providing access points to assist in a handoff decision in a wireless environment
ActiveUS7383046B2Maximize battery lifeMinimize consumptionAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile stationCellular network
According to a particular embodiment, a method for assisting in a handoff is provided that includes receiving signaling from one or more access points, which may transmit information to a mobile station. The information may be used to execute a handoff from an enterprise network to a cellular network or from the cellular network to the enterprise network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Image processing system, projector, program, information storage medium and image processing method
InactiveUS20040240748A1Accurate displayAccurate coordinatesImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSpatial light modulatorImaging processing
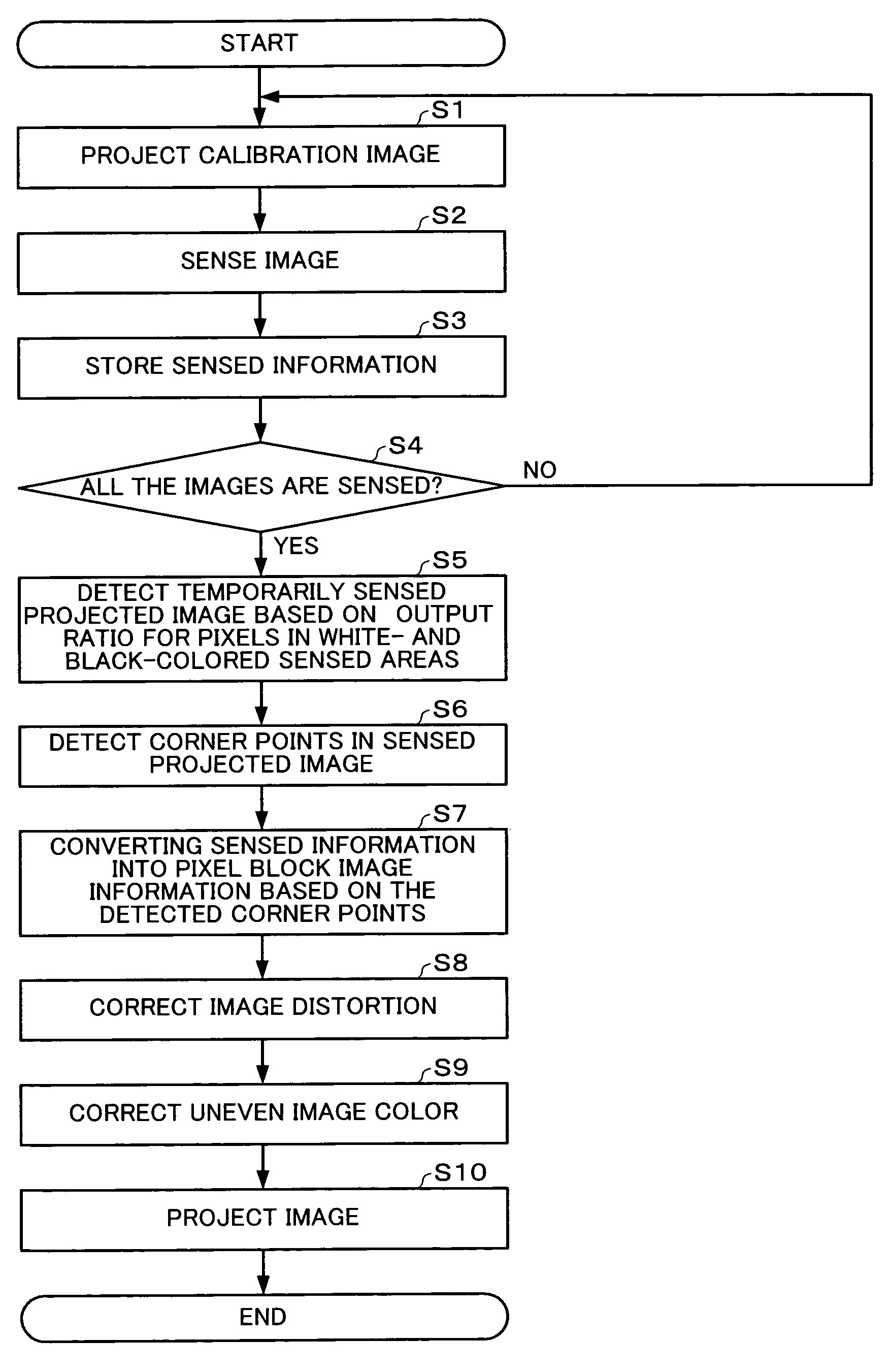
To provide an image processing system enabling association of the coordinates of a sensed projected image in a sensing area with the coordinates of the spatial light modulator, a projector is formed of: an image projecting section which projects calibration images; a ratio information generating section which computes a ratio of image signal values or luminance values for each pixel in the sensing area obtained by sensing the calibration images, based on sensed information from a sensor which senses the calibration images, to generate ratio information; an edge point detecting section which searches the ratio information to detect corner points of a sensed projected image for each pixel having a ratio equal to or larger than a predetermined value; a pixel block image information generating section which converts sensed information of an area defined by the detected corner points into pixel block image information representing a ratio of image signal values or luminance values for each pixel block including one or more pixels.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
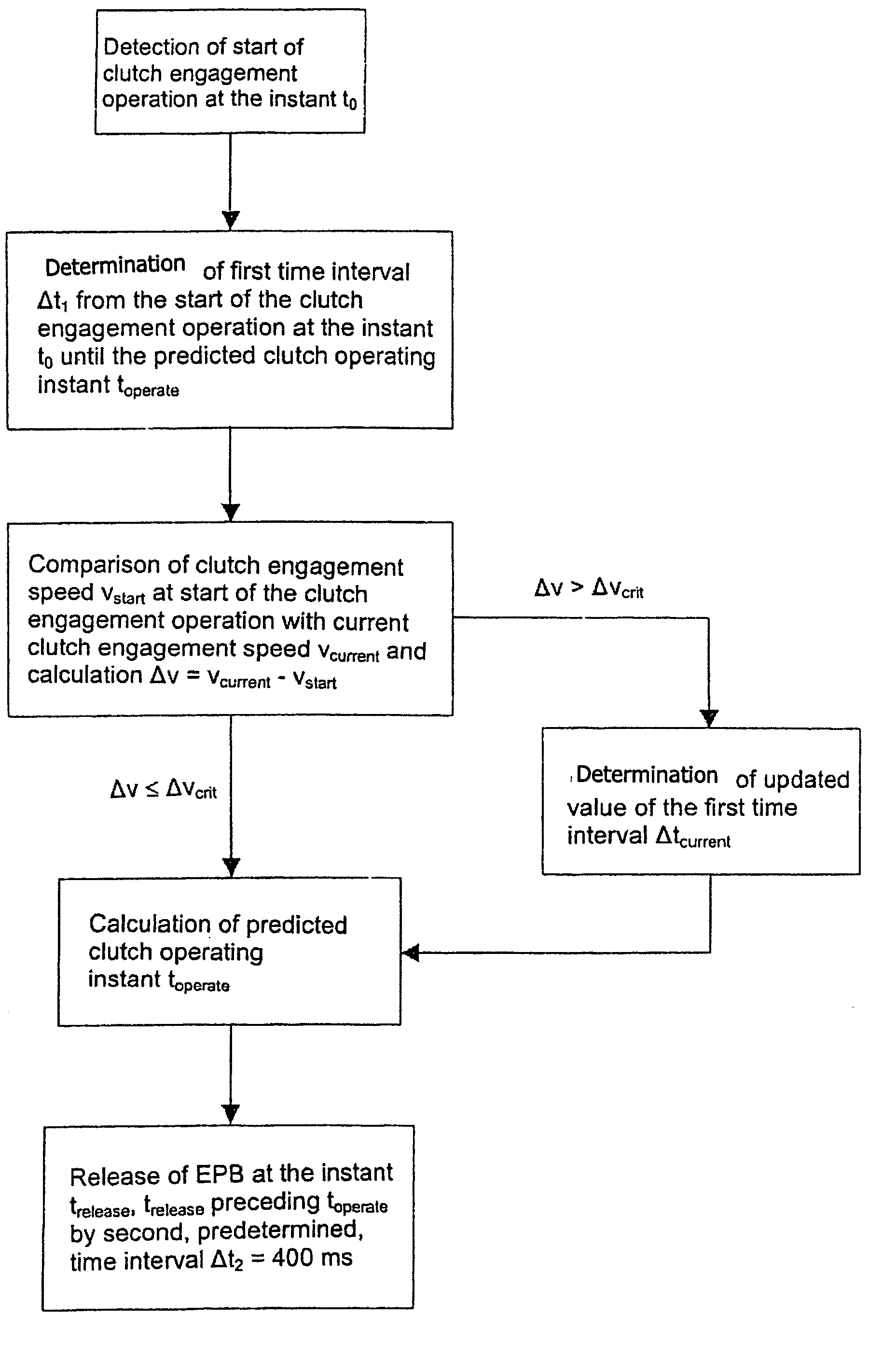
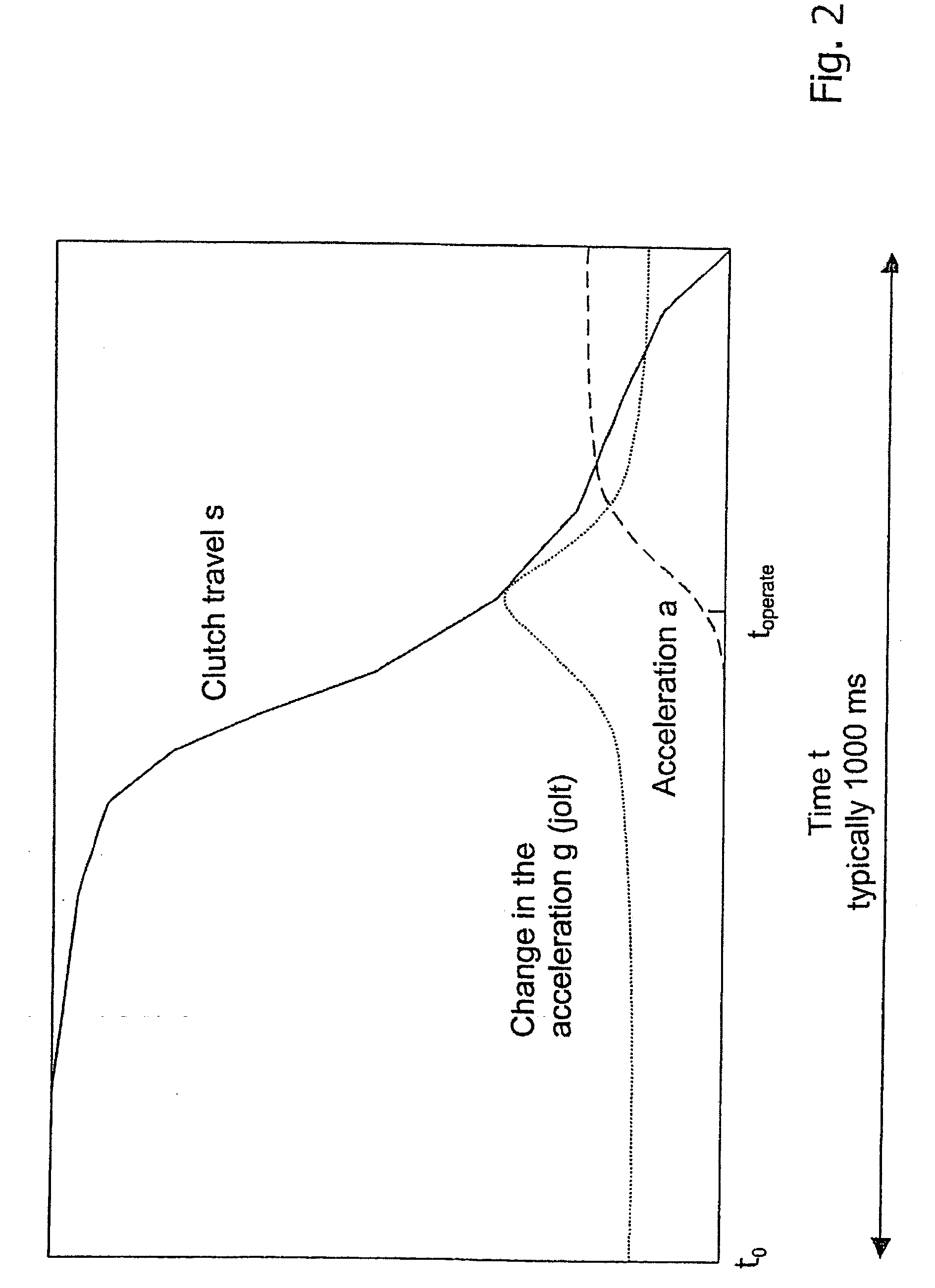
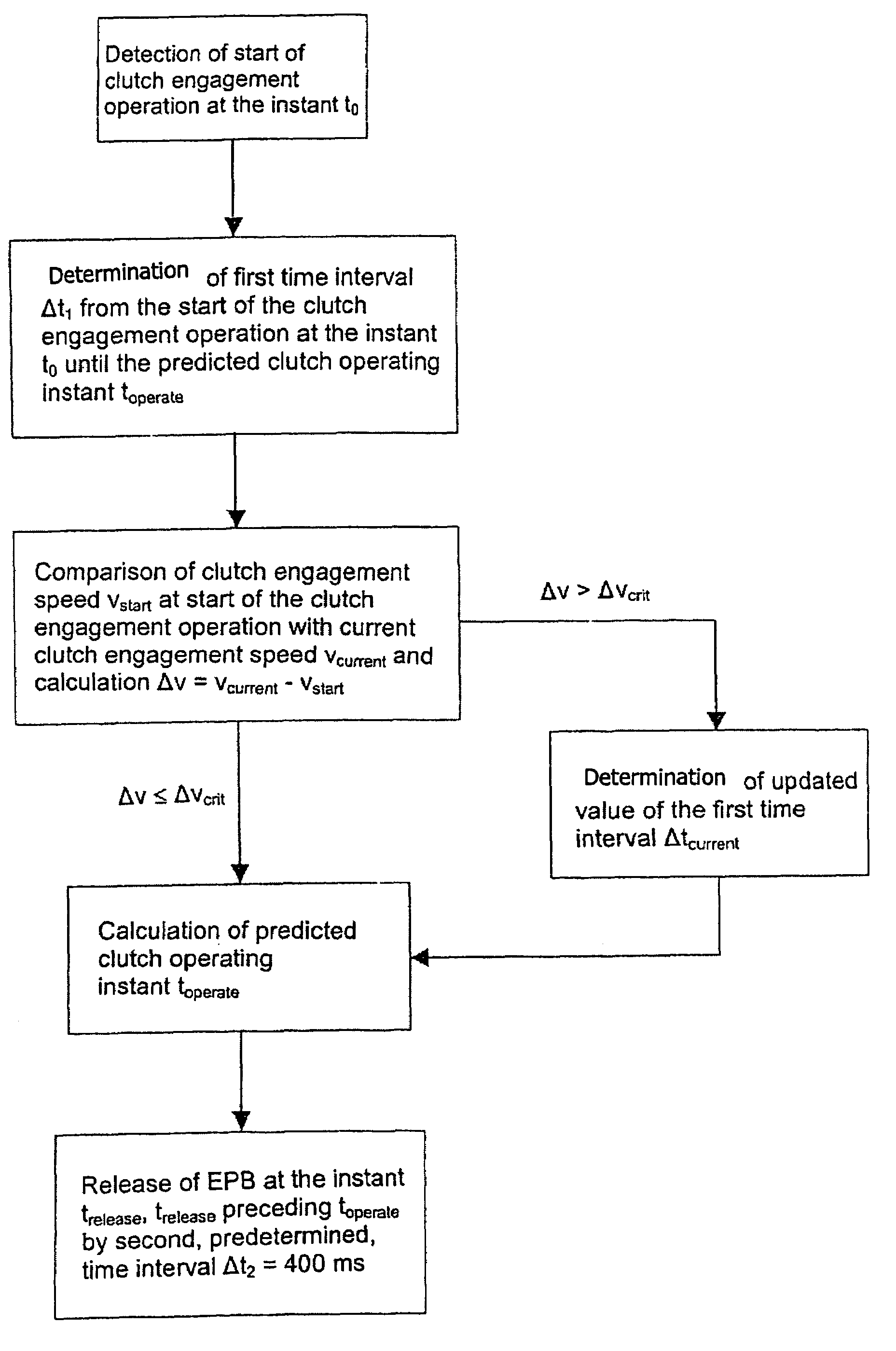
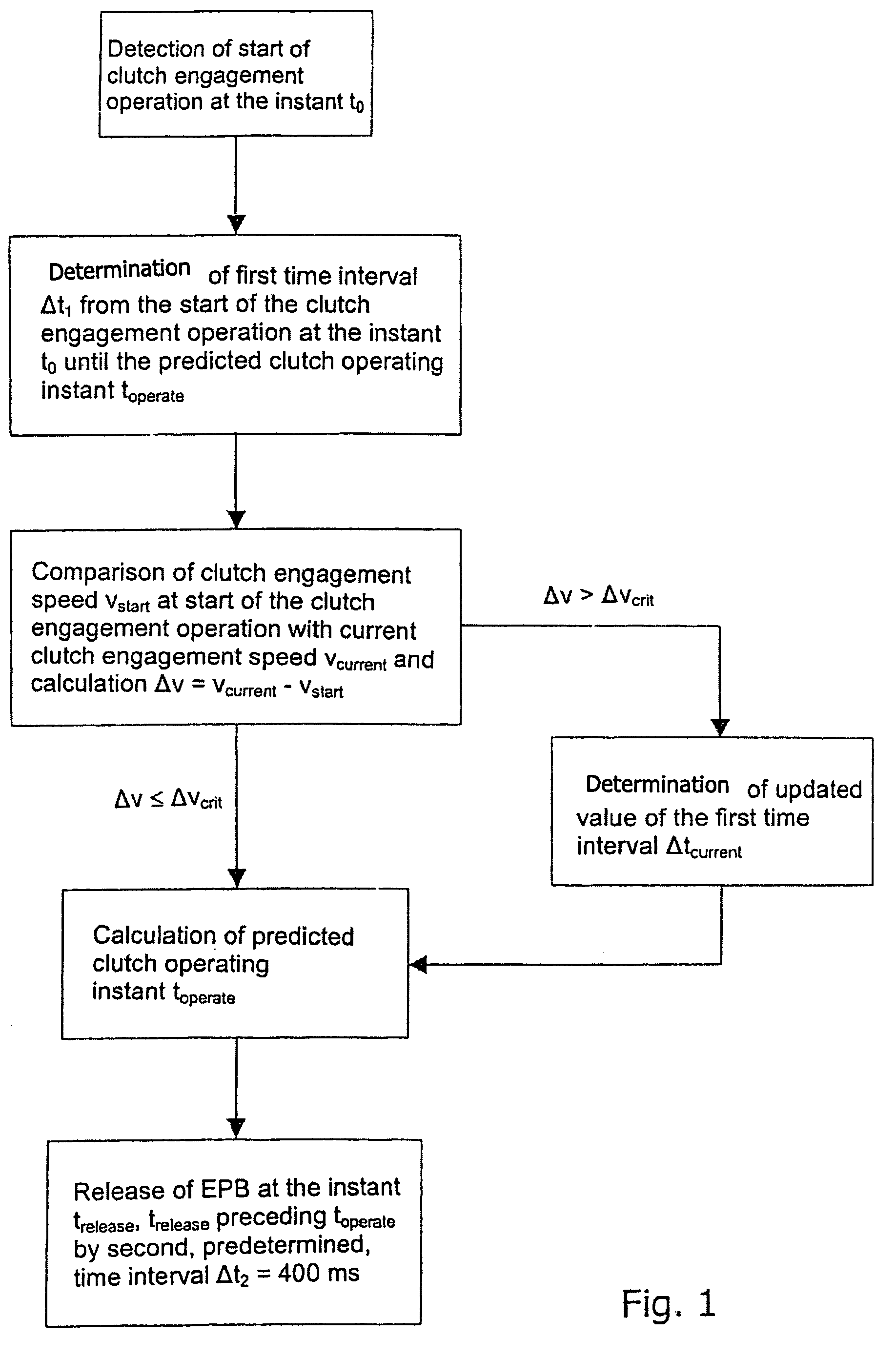
Method and system for controlling a braking system equipped with an electric parking brake
ActiveUS20060076204A1Accurate coordinatesBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsElectric parking brakeMobile vehicle
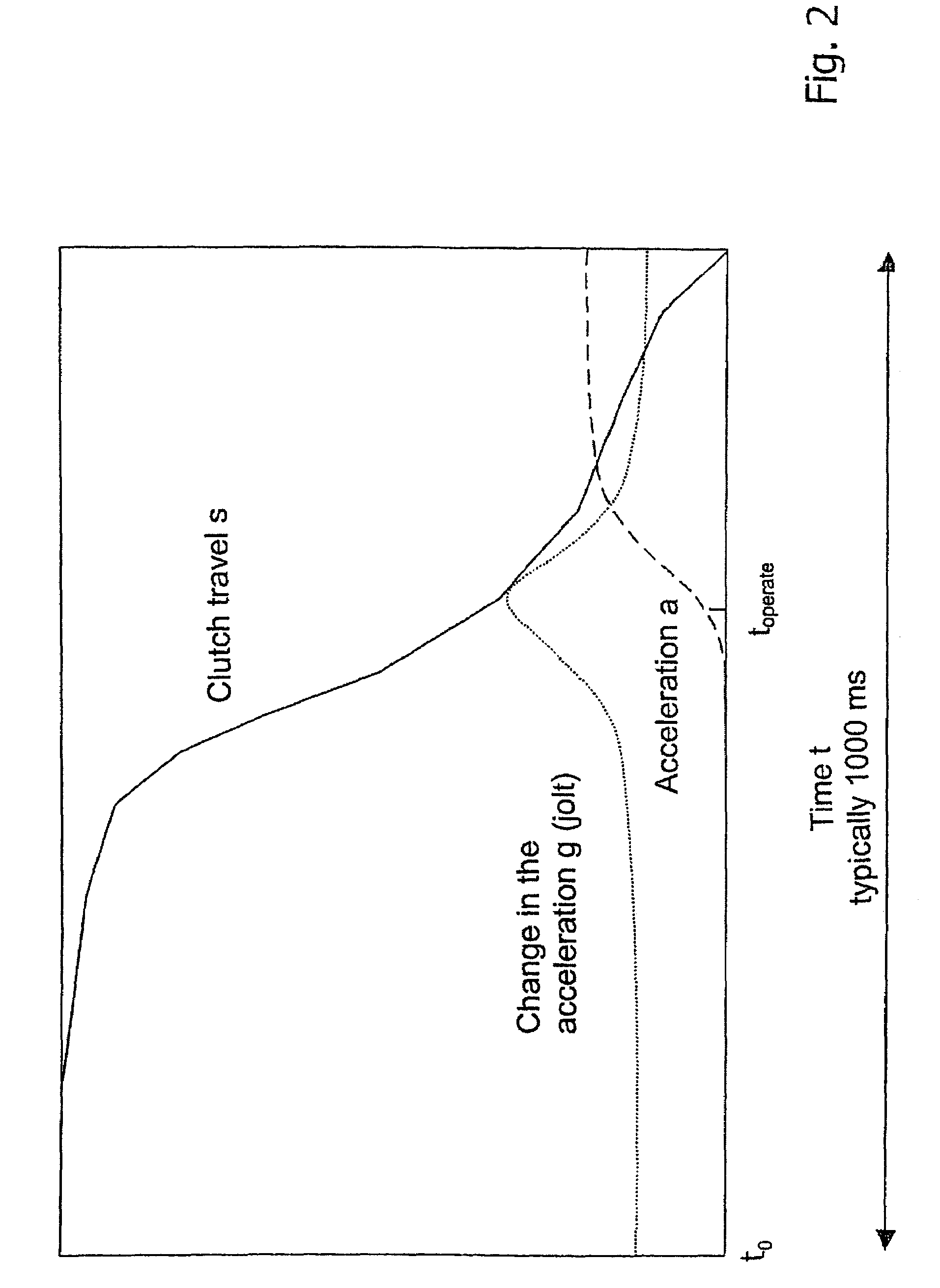
In a method and system for controlling a braking system, equipped with an electric parking brake, for a motor vehicle, the electric parking brake is released in response to an identification of a moving-off operation. A release instant of the electric parking brake is defined in dependence on at least one measured parameter of a clutch engagement operation. In comparison with a method and system in which, for example, the electric parking brake is released in dependence on the actuation of the accelerator by a driver, the method and system permit a more precise coordination of the deactivation of the electric parking brake with the clutch engagement operation, and thus with the moving-off operation of the vehicle, particularly in the case of a vehicle equipped with a manual transmission.
Owner:LUCAS AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Method for point cloud data processing and crossover object obtaining of transmission line
InactiveCN106503060AMany measuring pointsHigh measurement accuracyGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsTerrainLaser scanning
Provided is a method for point cloud data processing and crossover object obtaining of a transmission line. A terrain and ground object information database is established according to actual information of terrain and ground objects in three-dimensional point cloud data; original three-dimensional point cloud data is obtained by utilizing three-dimensional laser scanning; and the ground objects are obtained. On the original basis of not changing the original point cloud data, no modeling rendering processing is performed, spatial information at any point is not changed, he point cloud data of the various ground objects is obtained accurately; and according to concrete requirements of design disciplines, a topographic map suitable for three-dimensional design of a high-voltage transmission line is formed, which is achieved internationally for the first time and is a breakthrough in the technical field of track design.
Owner:山东东电电气工程技术有限公司
High-intensity focused ultrasound device
ActiveUS10639504B2Extended service lifeReduce maintenance costsUltrasound therapySurgical navigation systemsUltrasound deviceHigh intensity
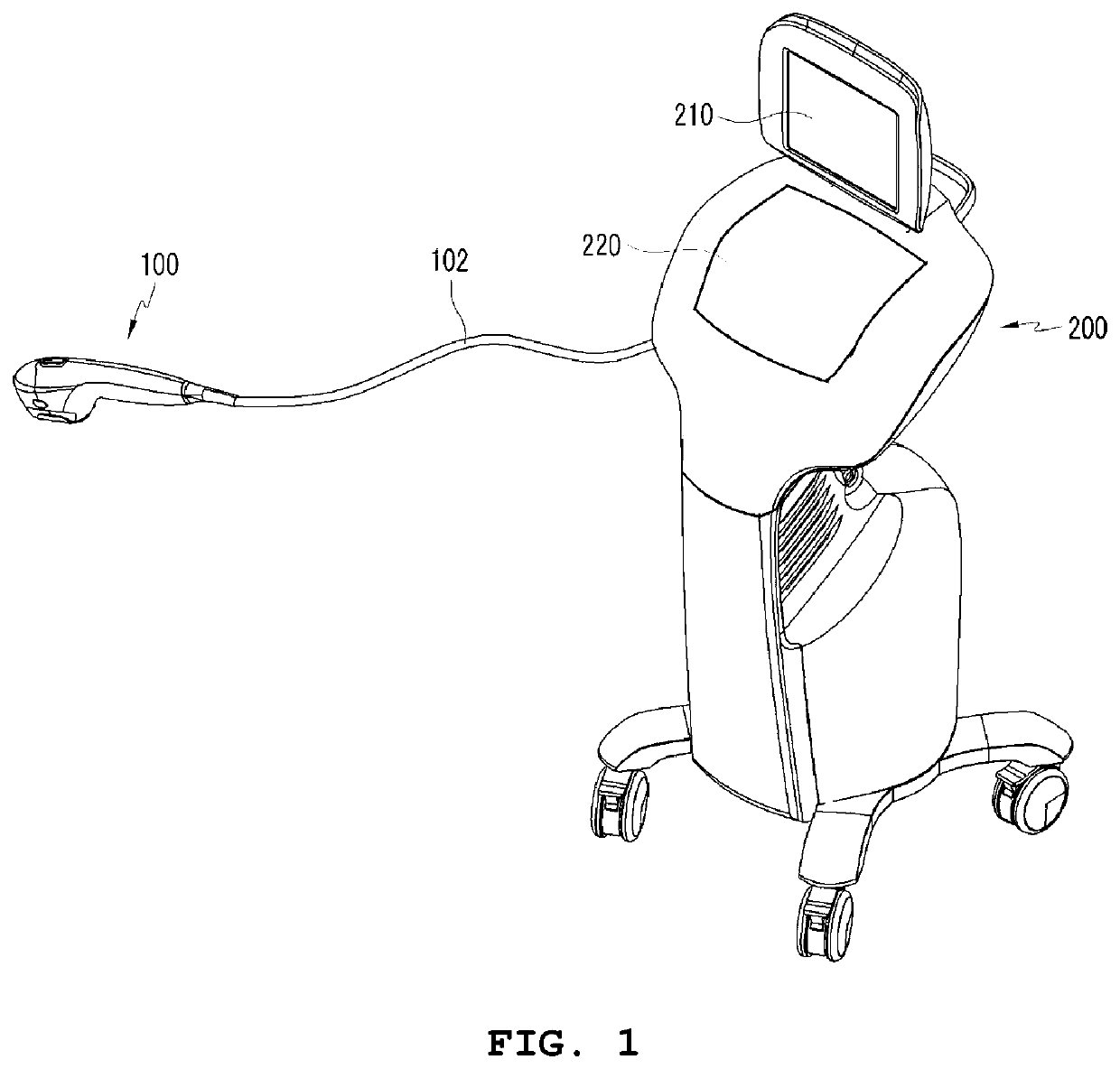
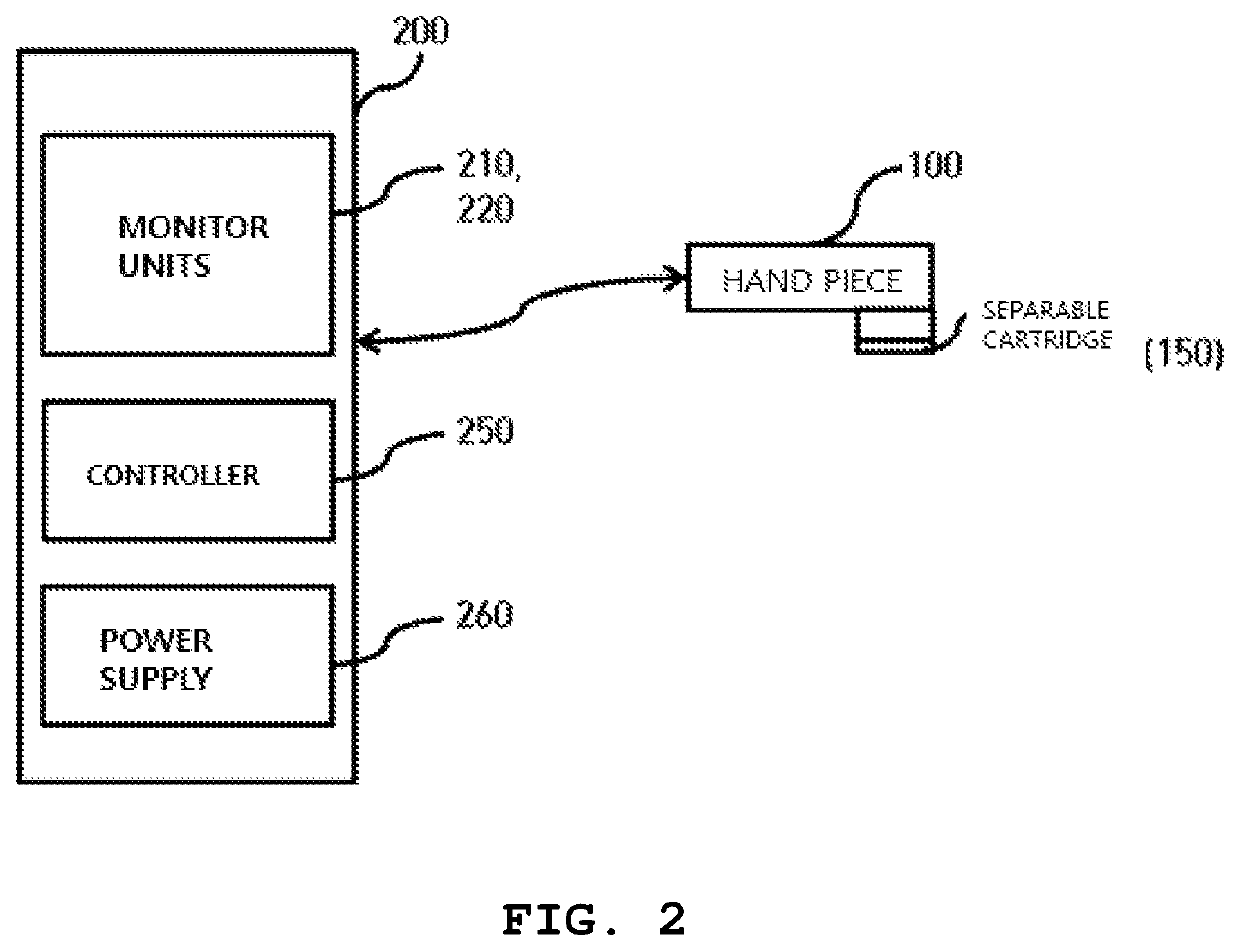
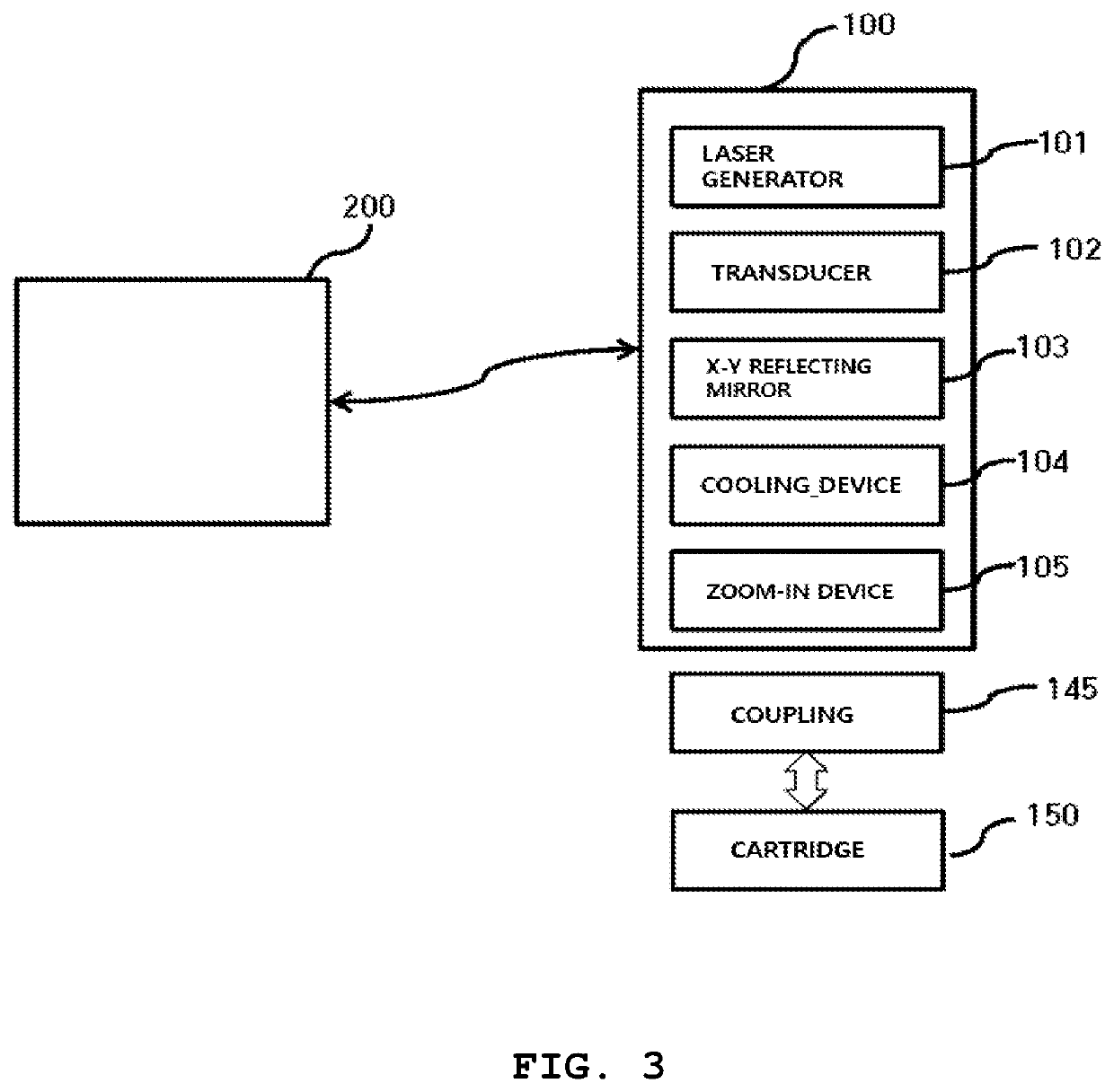
A high-intensity focused ultrasound is configured such that a disposable separable cartridge is attached to and detached from the ultrasound device, so that a practitioner, i.e. a doctor, can obtain coordinates of a skin tissue of a subject using a scanner of an ultrasonic transducer and locate an accurate procedure point in real time. A procedure can be performed on the accurate procedure point of the skin tissue without repeated procedures.
Owner:KIM YOU IN
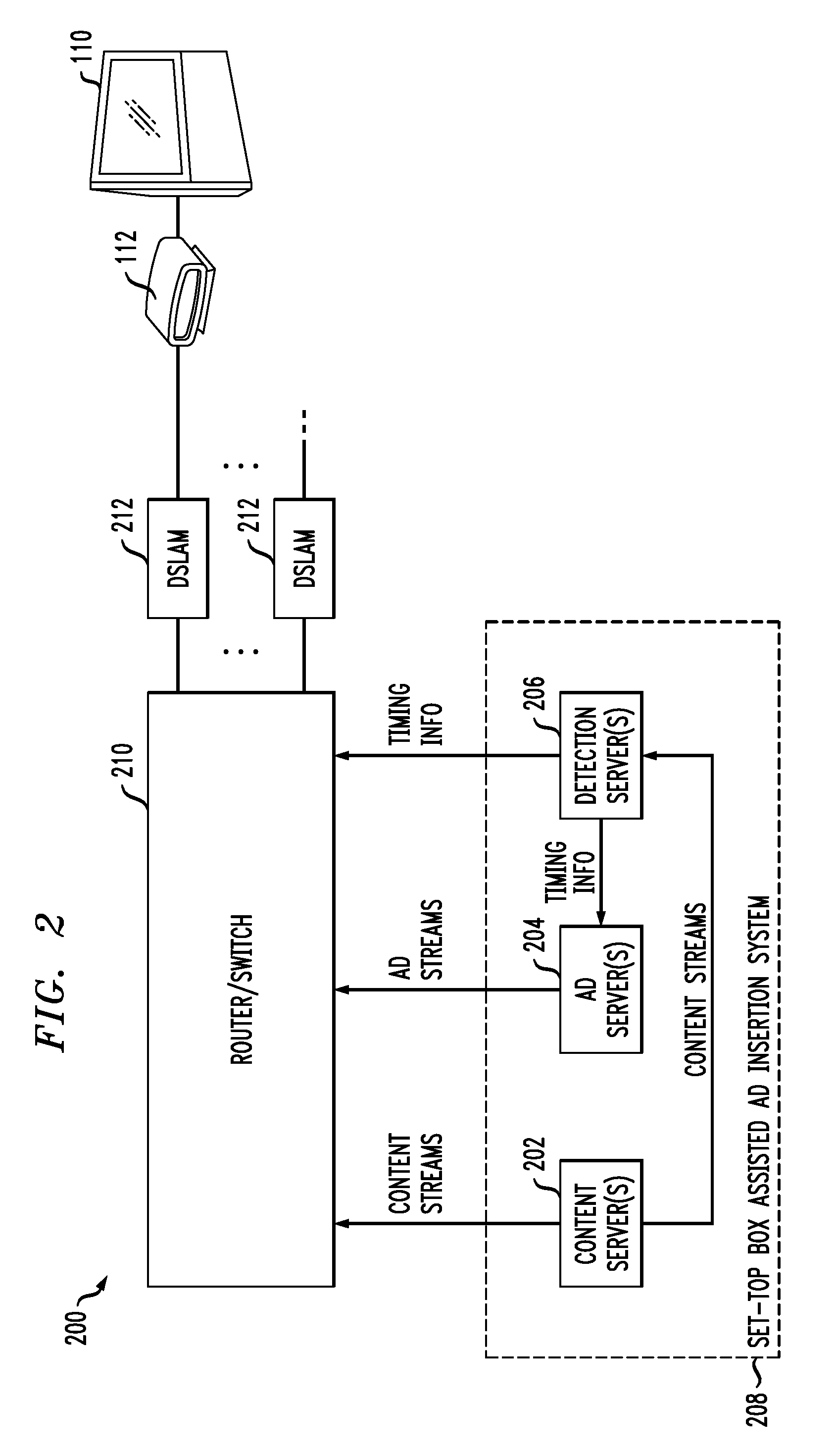
Access Node Based Targeted Information Insertion
ActiveUS20100217885A1Reduce latencyFacilitate provisionMultiple digital computer combinationsSelective content distributionDistribution systemReceipt
Advertisements or other types of targeted information are delivered to set-top boxes or other user interface devices of a signal distribution system. In one aspect of the invention, an access node sends a message to the user interface device directing the user interface device to switch from a content stream to a targeted information stream at a specified time. Responsive to the message, the access node receives a request from the user interface device to join a targeted multicast group associated with the targeted information stream. Without requiring receipt of a subsequent request from the user interface device to leave a content multicast group associated with a content stream, the access node causes the user interface device to be dropped from the content multicast group prior to the specified time. The access node then delivers the targeted information stream to the user interface device via the targeted multicast group.
Owner:RPX CORP
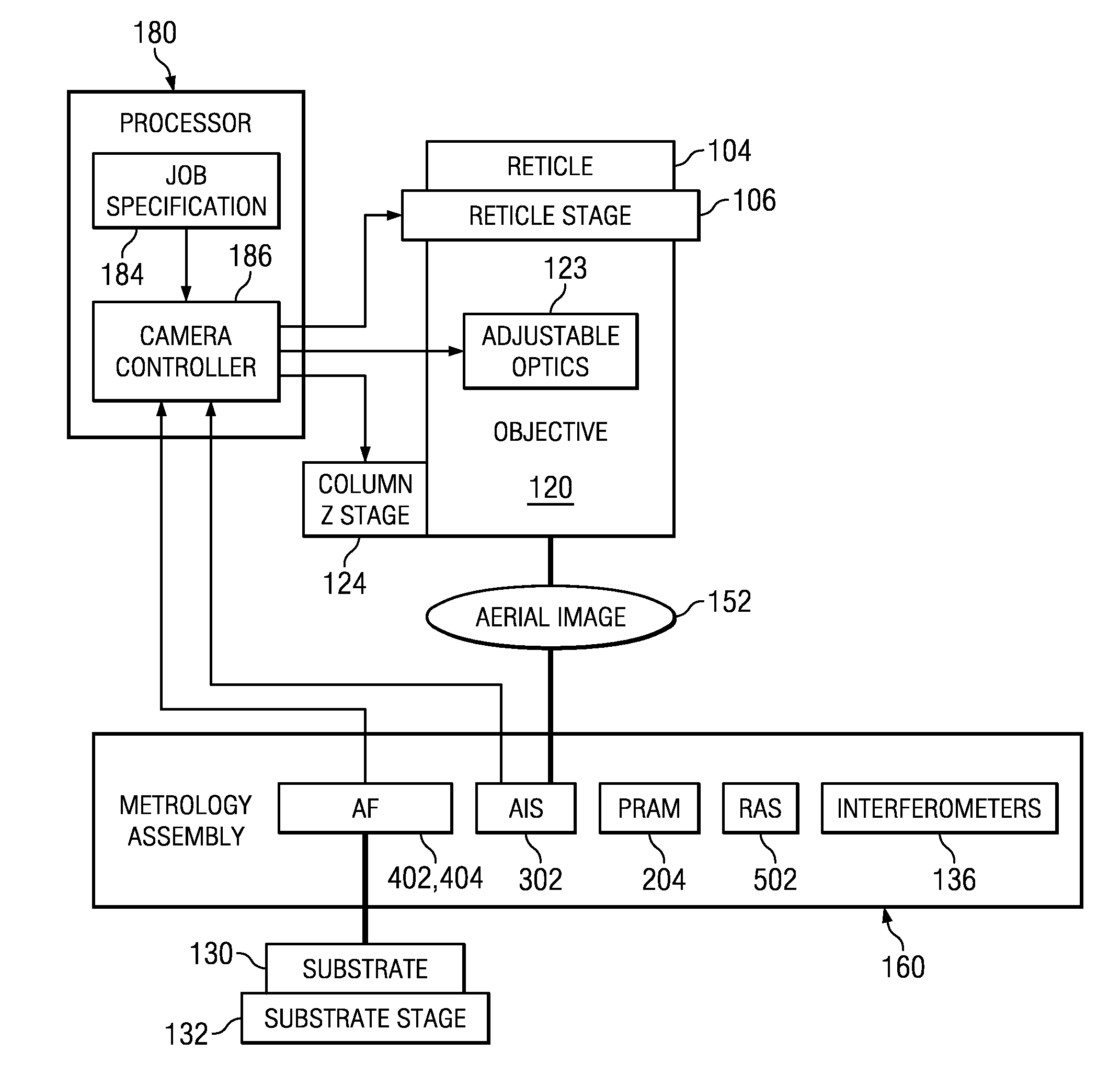
System and Method for Estimating Field Curvature
ActiveUS20120015460A1Accurate coordinatesRelaxes constraintImage analysisSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementProjection opticsMetrology
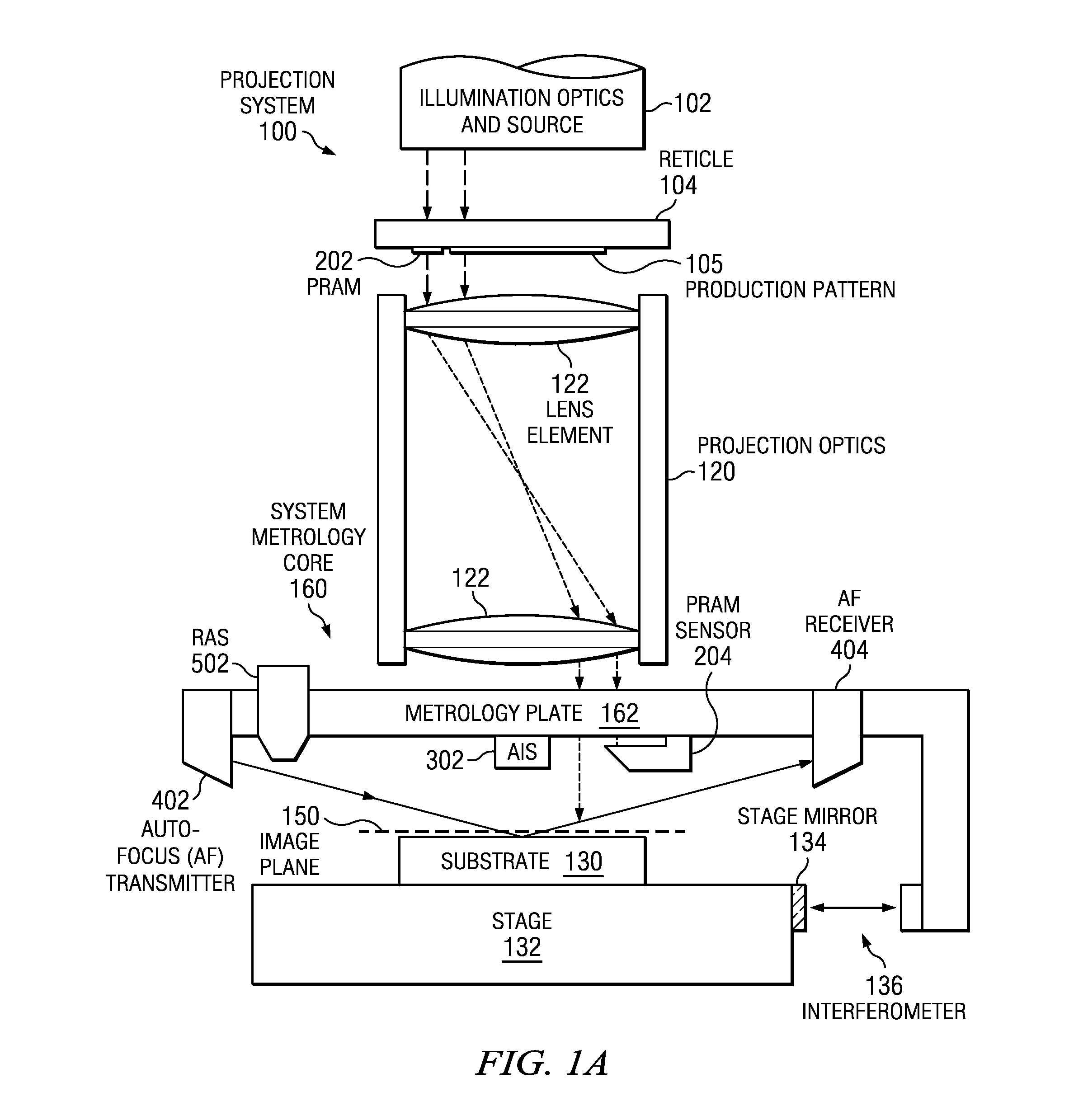
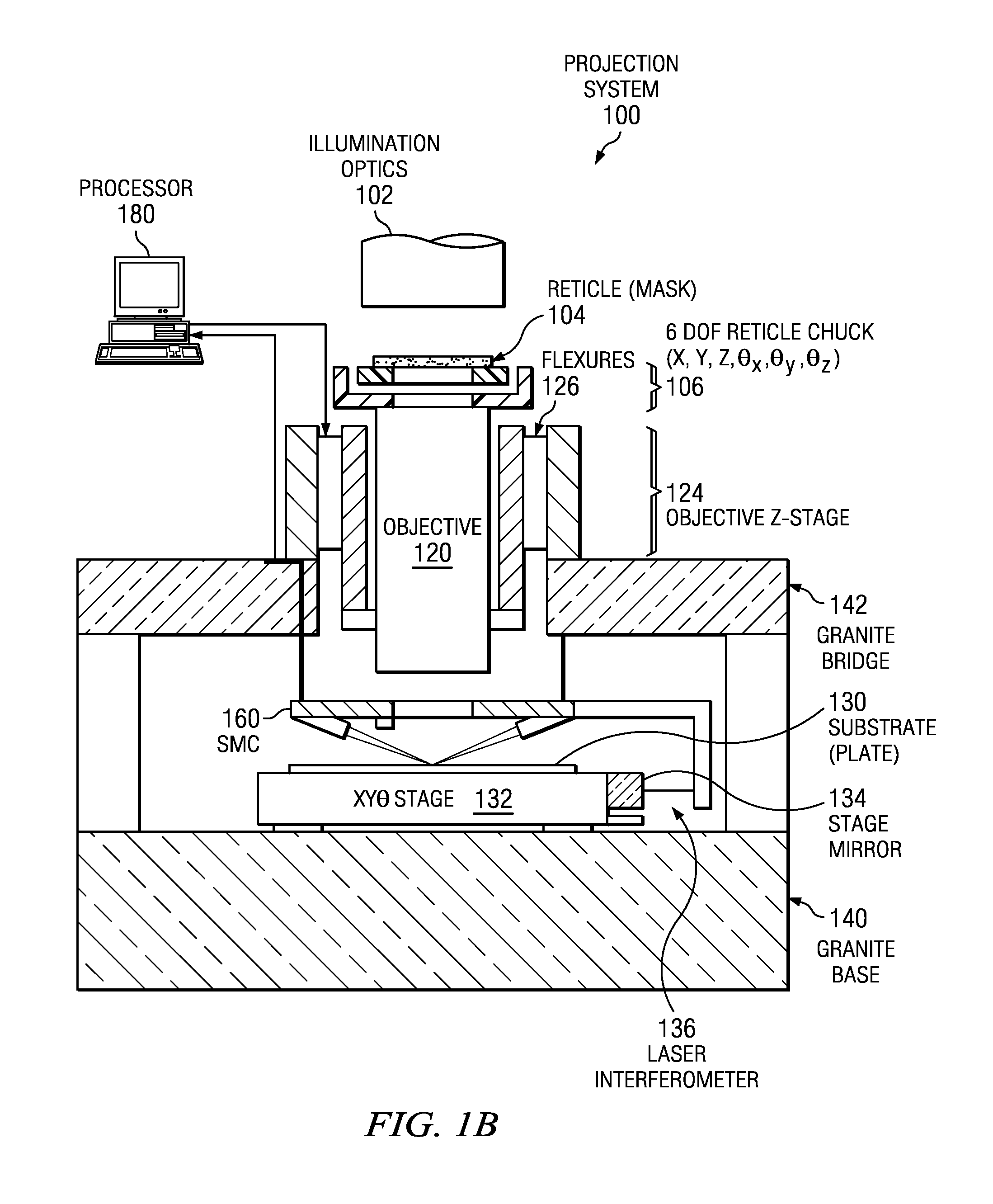
Projection systems and methods with mechanically decoupled metrology plates according to embodiments of the present invention can be used to characterize and compensate for misalignment and aberration in production images due to thermal and mechanical effects. Sensors on the metrology plate measure the position of the metrology plate relative to the image and to the substrate during exposure of the substrate to the production image. Data from the sensors are used to adjust the projection optics and / or substrate dynamically to correct or compensate for alignment errors and aberration-induced errors. Compared to prior art systems and methods, the projection systems and methods described herein offer greater design flexibility and relaxed constraints on mechanical stability and thermally induced expansion. In addition, decoupled metrology plates can be used to align two or more objectives simultaneously and independently.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Automatic plugging-in device of connector pin
ActiveCN105870761AIncrease productivityEasy loadingContact member assembly/disassemblyInsertion deviceConnector Pin
The invention discloses an automatic plugging-in device of a connector pin. The automatic plugging-in device comprises a machine frame, an emptying device, a plugging device, a plurality of terminal conveying devices, a feeding device, a discharging device, a CCD photographing device and a terminal supporting device, wherein the emptying device is fixed to the machine frame, the plugging device is connected with the emptying device in a butted mode, the multiple terminal conveying devices are arranged in front of the plugging device, the feeding device and the discharging device are arranged at the two ends of the terminal conveying devices, the CCD photographing device is arranged on the side of the plugging device, and the terminal supporting device is used for fixing mobile terminals. On the one hand, automatic conveying of other stations can be achieved; on the other hand, the automatic plugging-in device can be connected with a plurality of automatic plugging-in devices in a butted mode, so that the production efficiency is improved exponentially; the feeding device and the discharging device are arranged at the two ends of the terminal conveying devices, so that automatic feeding and discharging are achieved; due to the fact that the CCD photographing device is arranged for photographing, position coordinates of each jack in the terminals are obtained, and precise coordinates are provided for follow-up plugging-in of pins.
Owner:昆山市德来福工业自动化有限公司
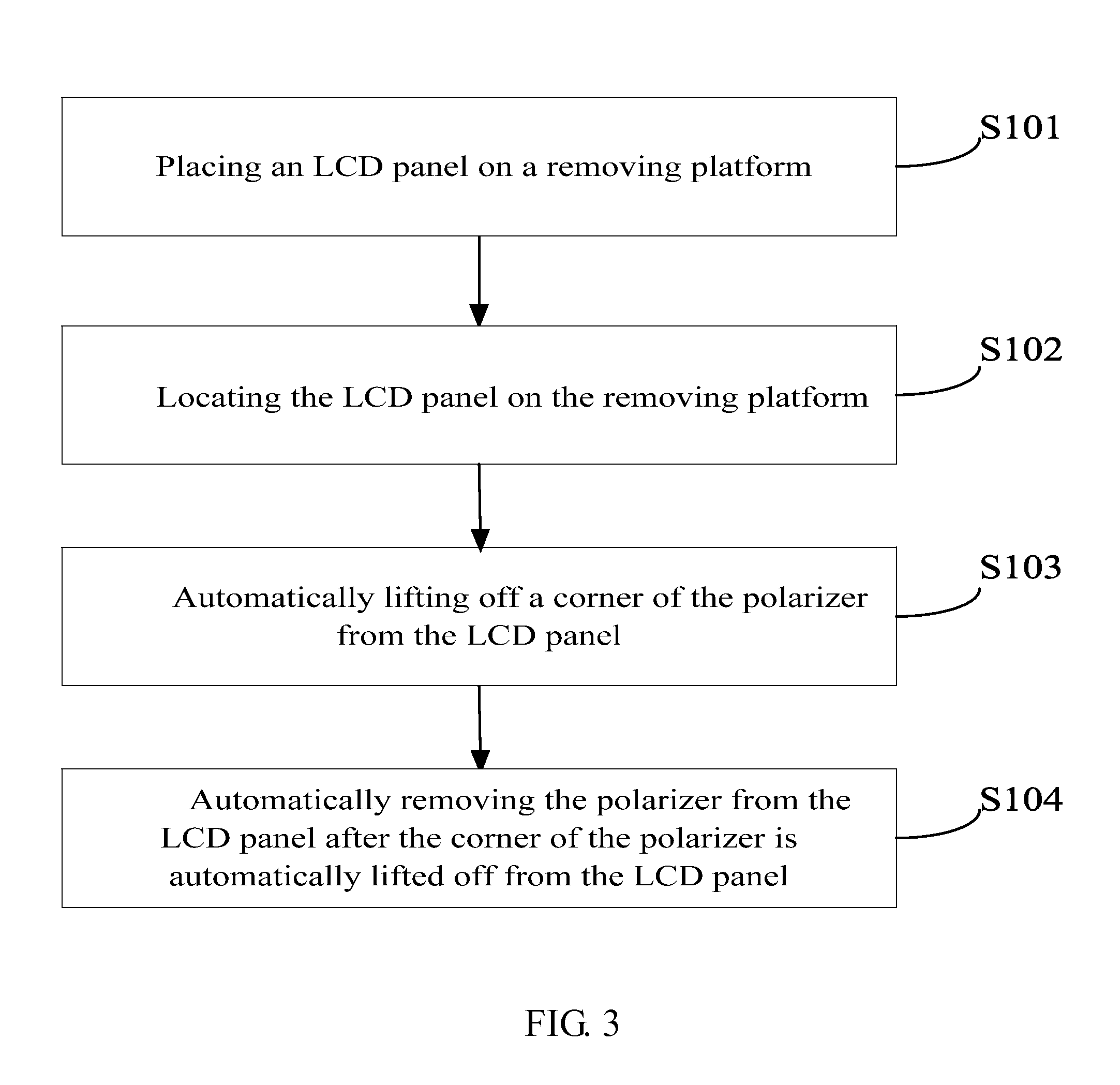
Method of fully, automatically removing a polarizer of an LCD panel
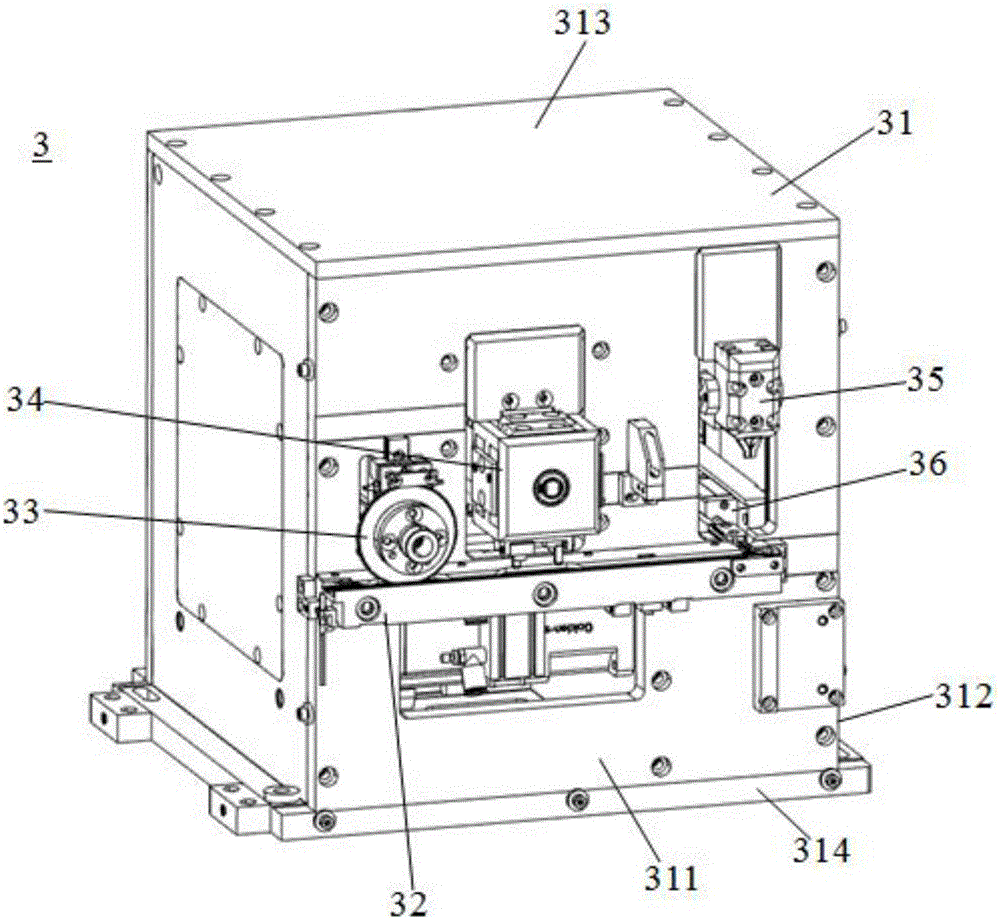
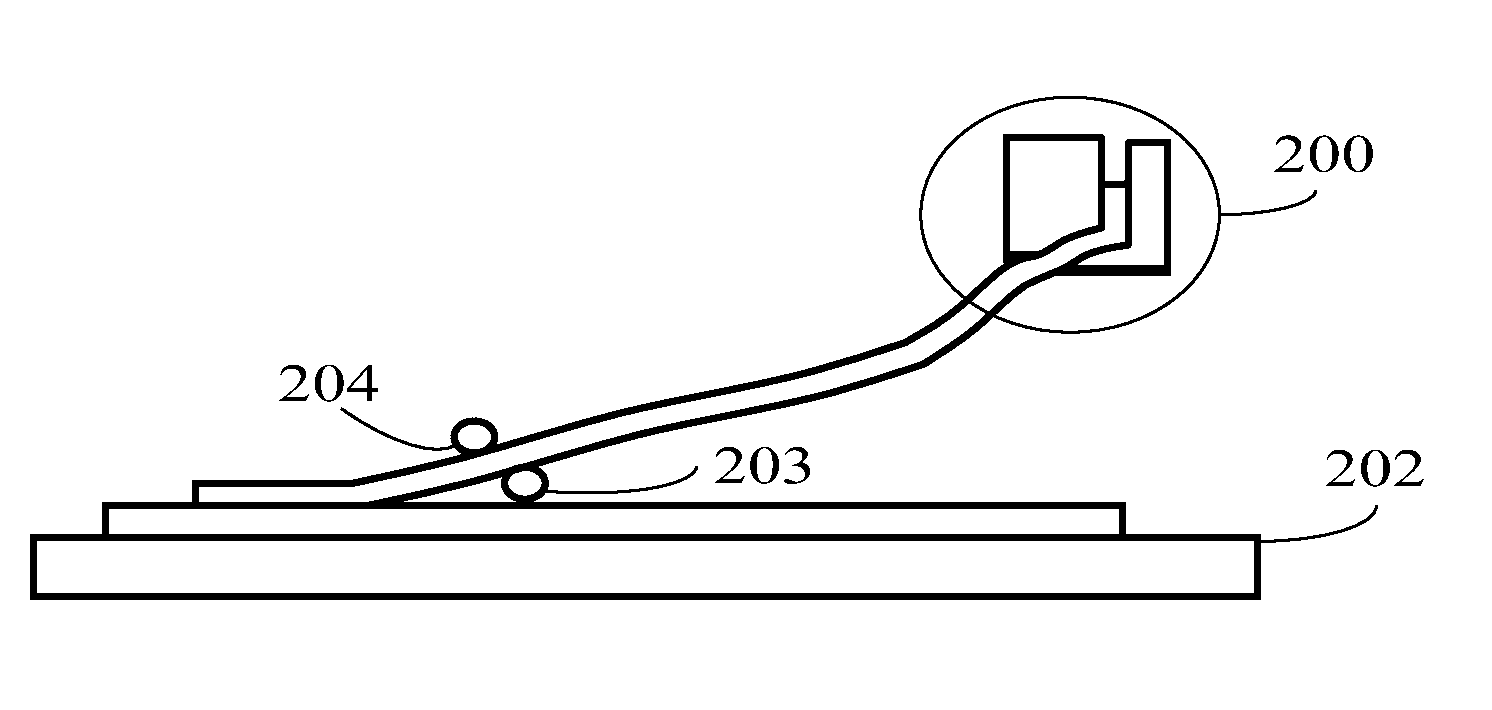
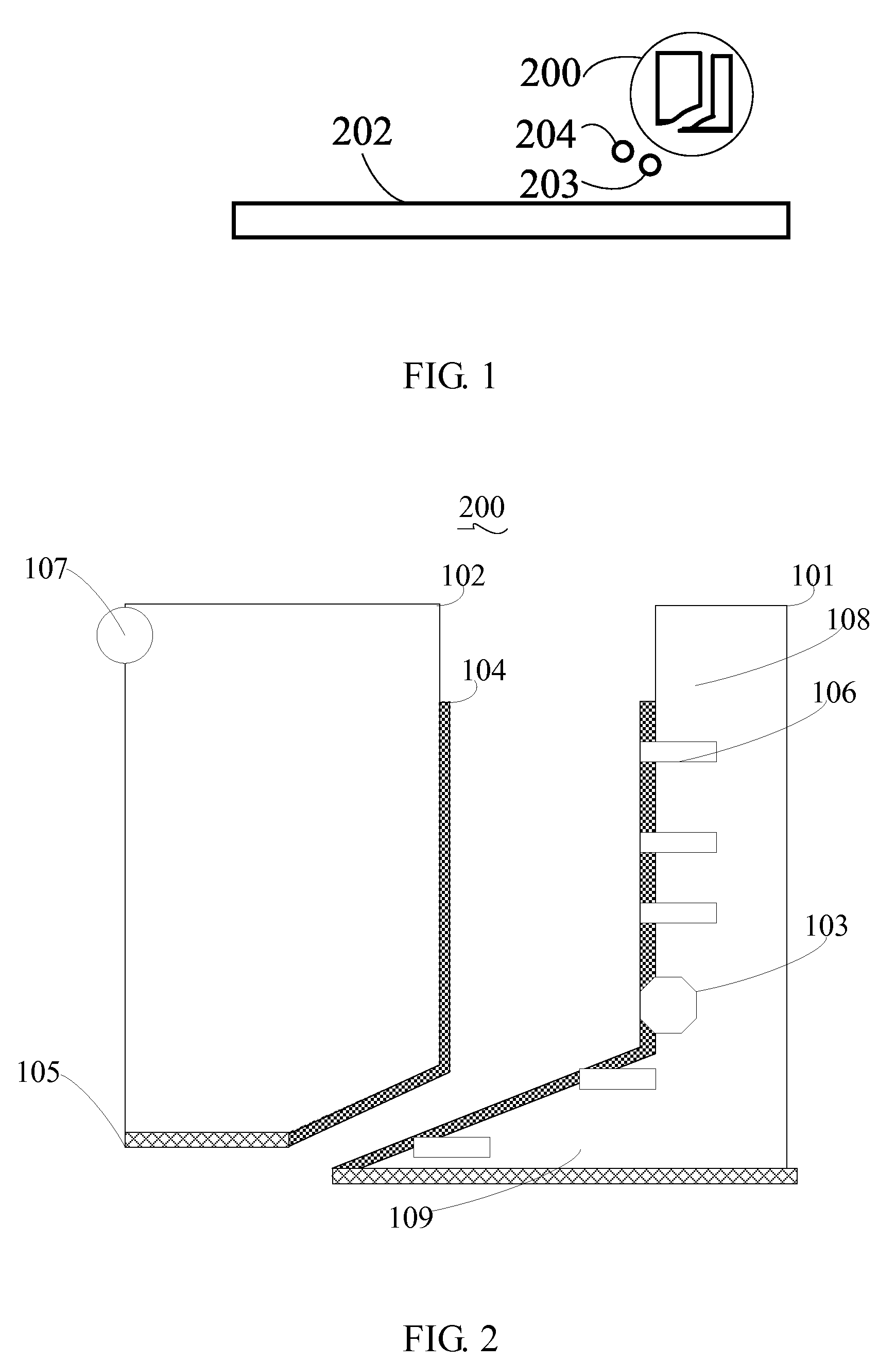
ActiveUS8756783B2Improve efficiencyRaise the ratioLamination ancillary operationsWave amplification devicesLiquid-crystal displayClipping - action
An automatic corner lift-off apparatus for a polarizer of a liquid crystal display (LCD) panel is disclosed, which is suitable for use in a process of removing a polarizer during manufacturing of an LCD panel and comprises: a front clip, comprising a long arm and a short arm which intersect with each other to substantially form an “L” shape; a back clip, spaced apart from the front clip and being capable of cooperating with the front clip to perform a clipping action; and at least one sensor disposed on the front clip or the back clip, being configured to sense whether the polarizer has been successfully lifted off. Thereby, the present disclosure allows for fully automatic polarizer removing operations and can reduce work-related injuries and improve the success ratio of and efficiency of removing the polarizer.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
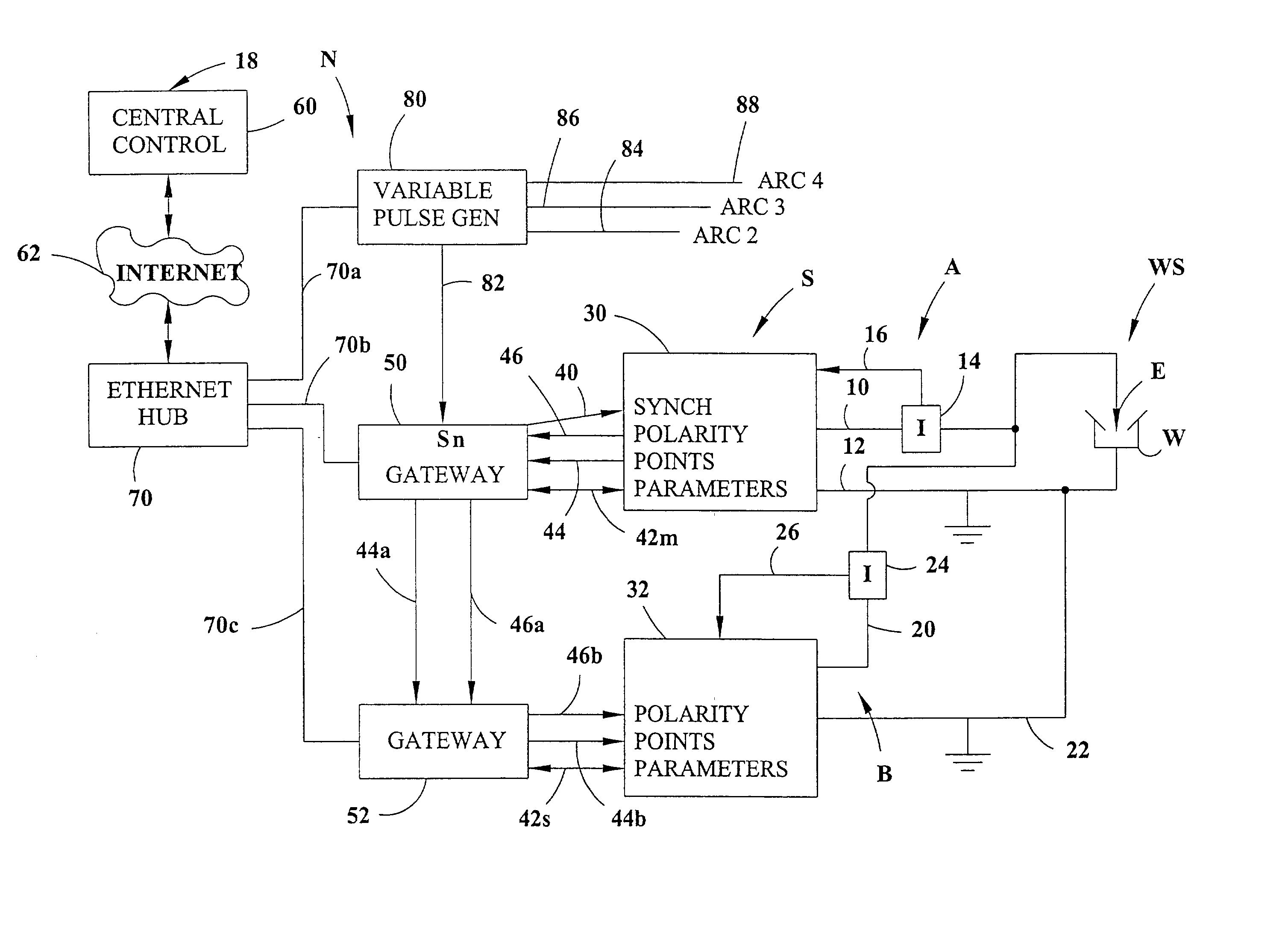
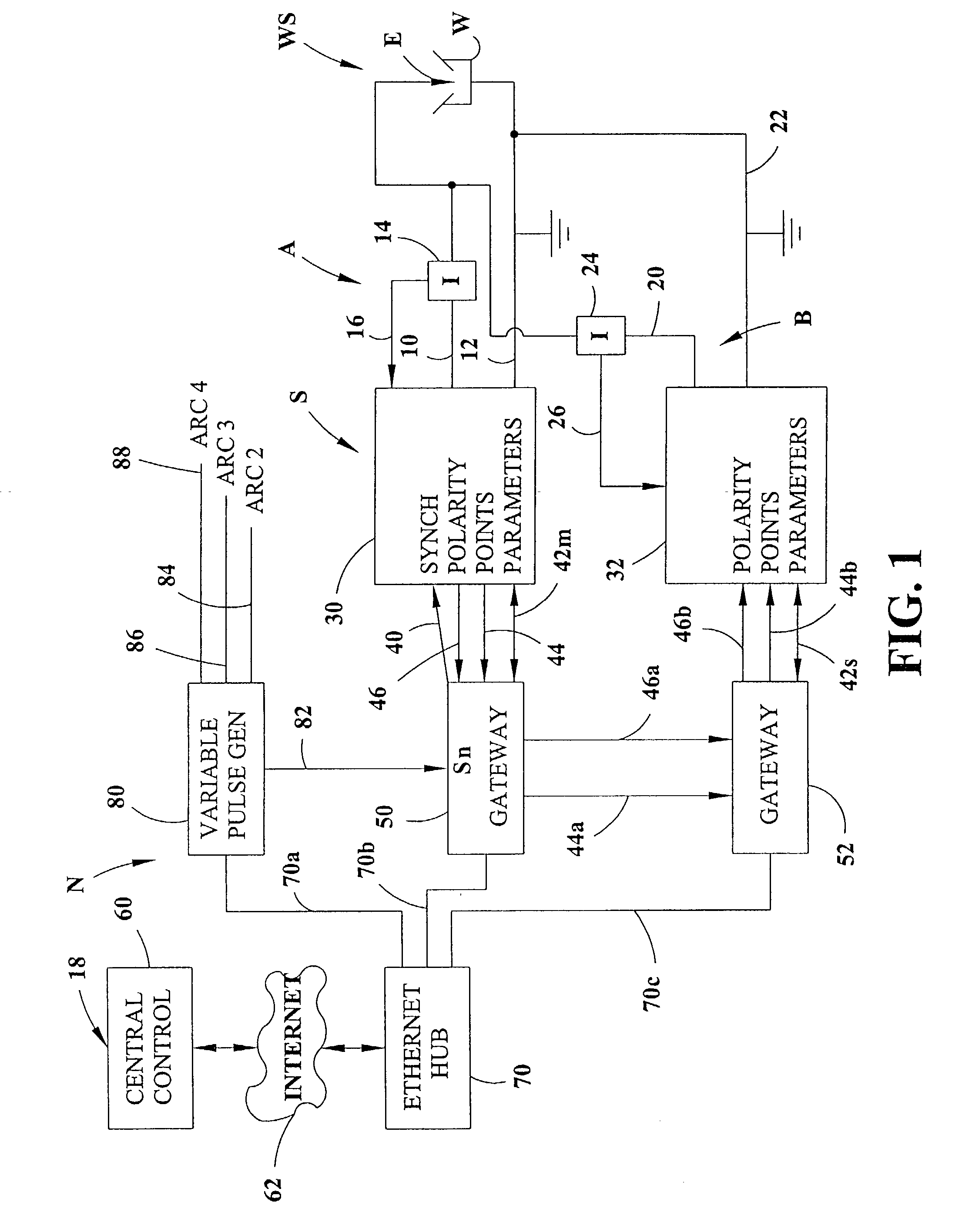
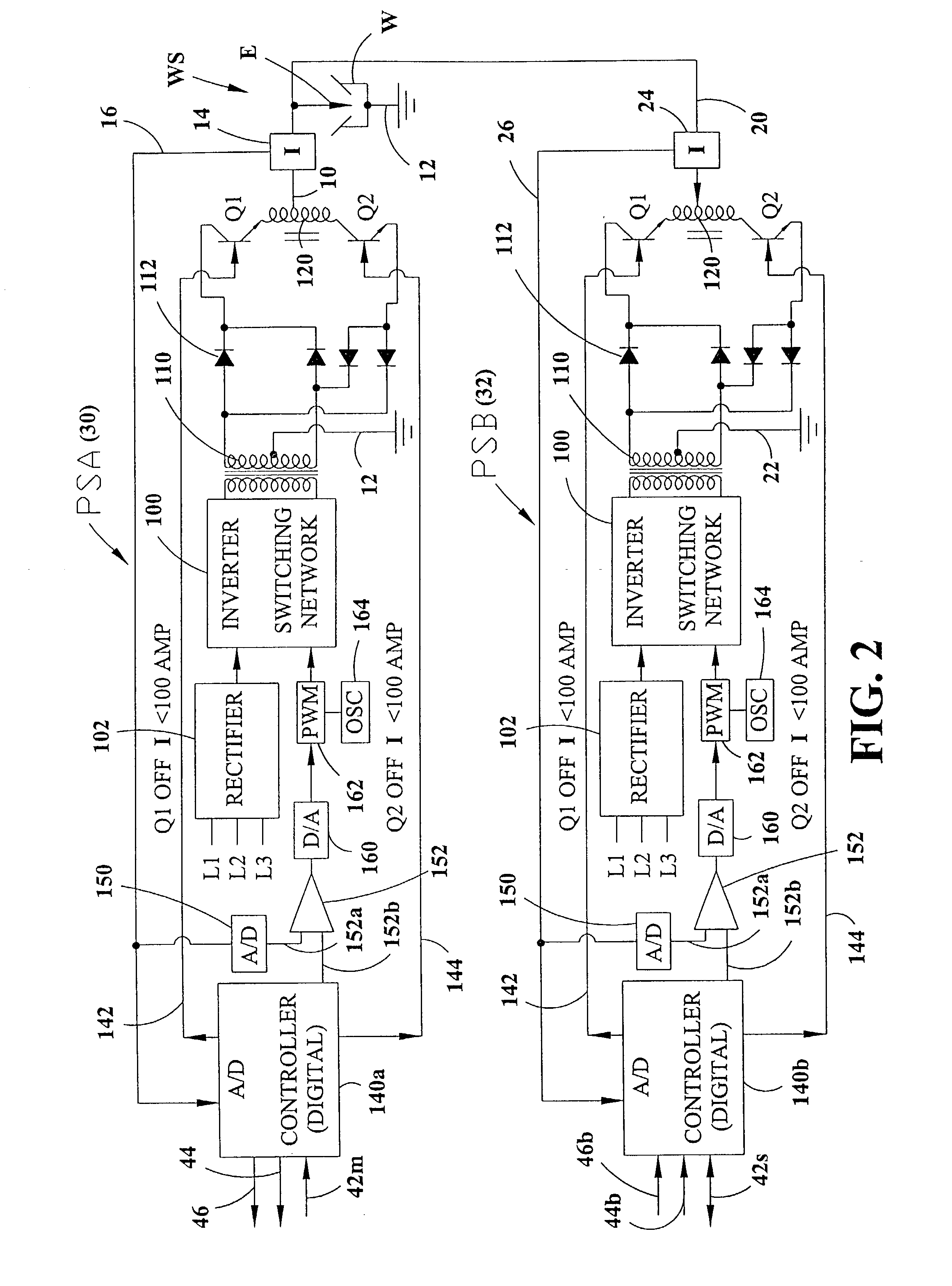
Electric arc welding system
An electric arc welding system for creating an AC welding arc between an electrode and a workpiece wherein the system comprises a first controller for a first power supply to cause the first power supply to create an AC current between the electrode and workpiece by generating a switch signal or command with polarity reversing switching points in the first controller, with the first controller operated at first welding parameters in response to first power supply specific parameter signals to the first controller. The system has at least one slave controller for operating a slave power supply to create an AC current between the electrode and workpiece by reversing polarity of the AC current at switching points where the slave controller is operated at second welding parameters in response to second power supply specific parameter signals to the slave controller. An information network connected to the first controller and the slave controller and containing digital first and second power supply specific parameter signals for the first controller and the slave controller and a digital interface connects the first controller with the slave controller to control the switching points of said second power supply by the switch signal or command from the first controller.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
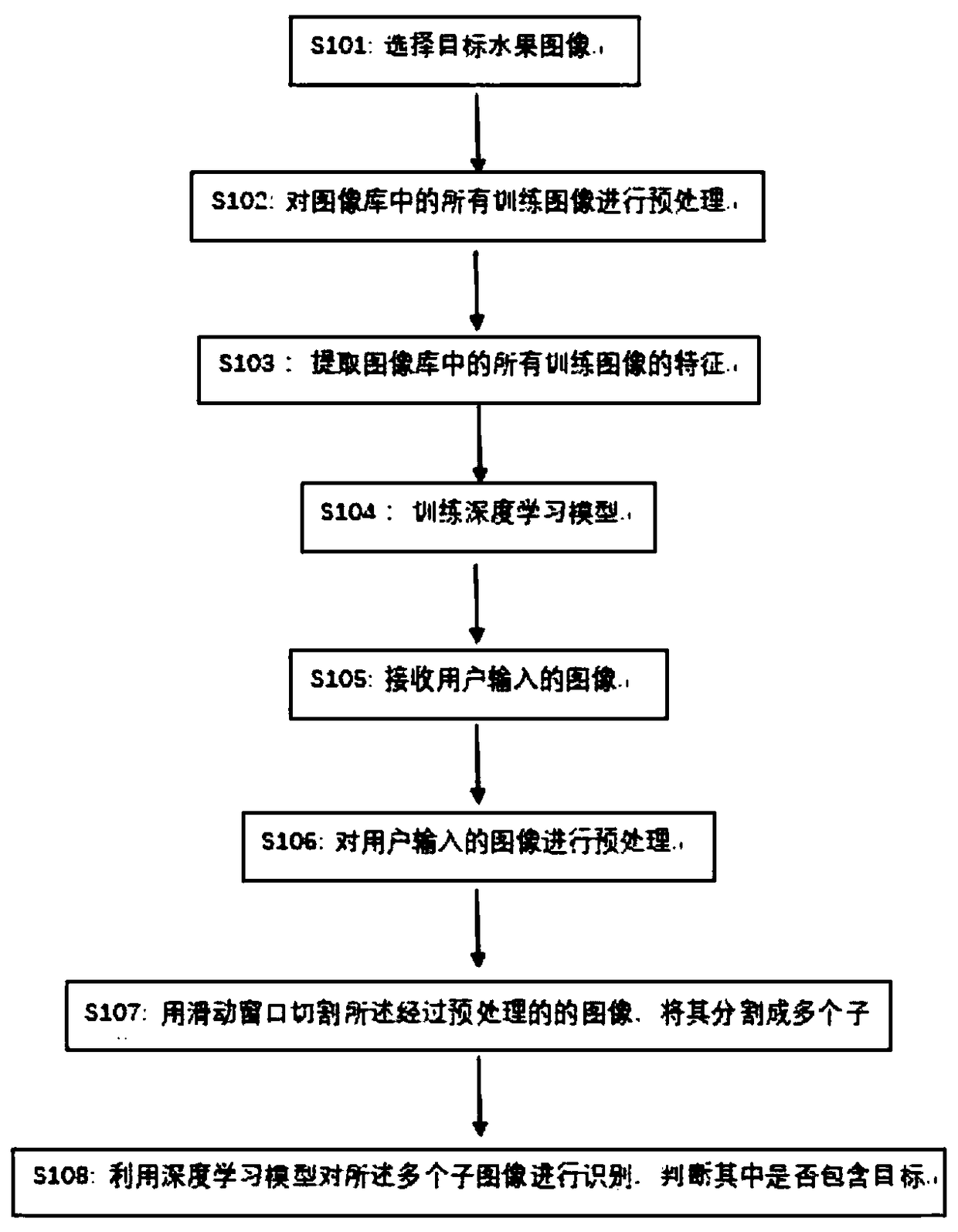
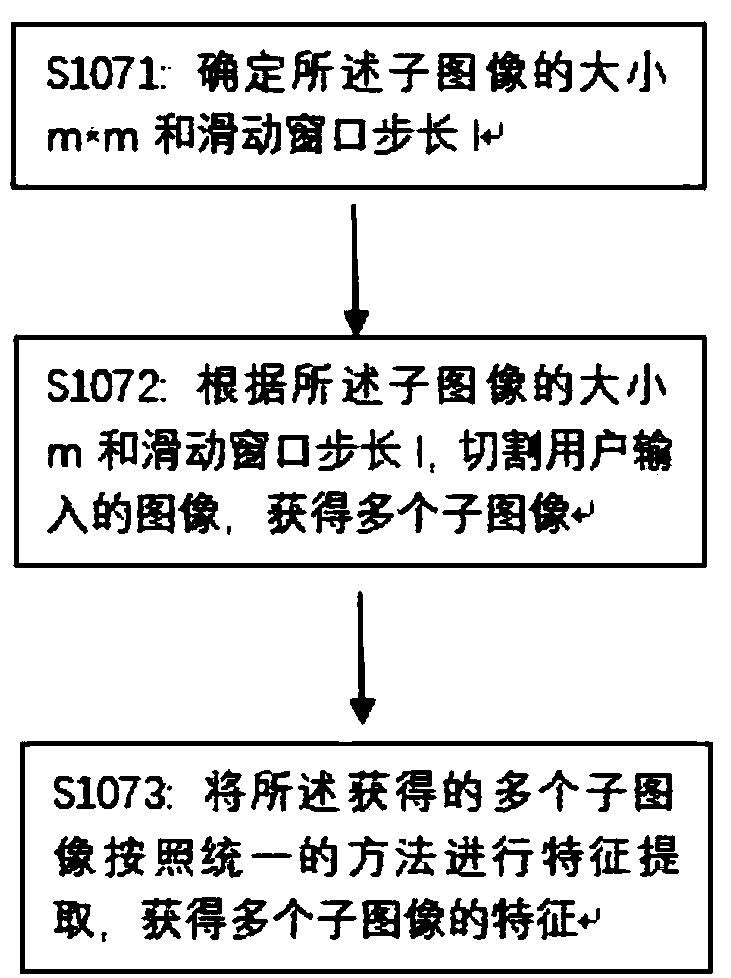
Fruit recognition method and device based on deep learning
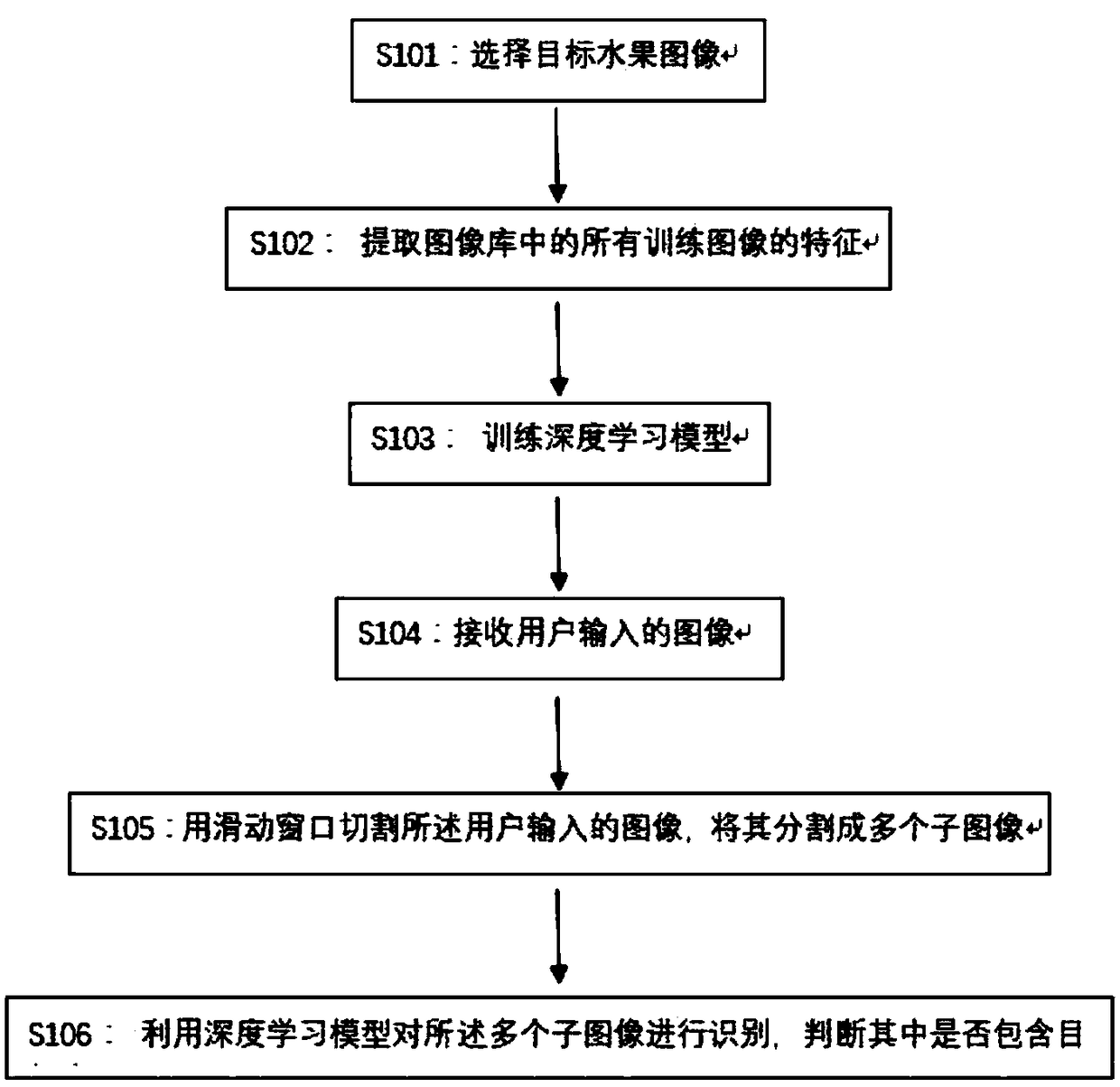
InactiveCN108319894AAccurate coordinatesSolve the "where" problemImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorComputer science
The invention provides a fruit recognition method and device based on deep learning. The method comprises the steps of selecting a target fruit image library, extracting the features of all training images in the image library, inputting obtained feature vectors of all training images into a deep learning model and training the deep learning model, and identifying images inputted by a user by using the trained deep learning model, judging whether target fruits are included and identifying the specific locations of all the target fruits in the images. Compared with the prior art, the modification and training are carried out based on a traditional deep learning model and fruit images are identified, the recognition of obtained fruit image data has higher accuracy, information such as position information is included, and thus a better recognition effect is obtained.
Owner:HANGZHOU QOGORI TECH
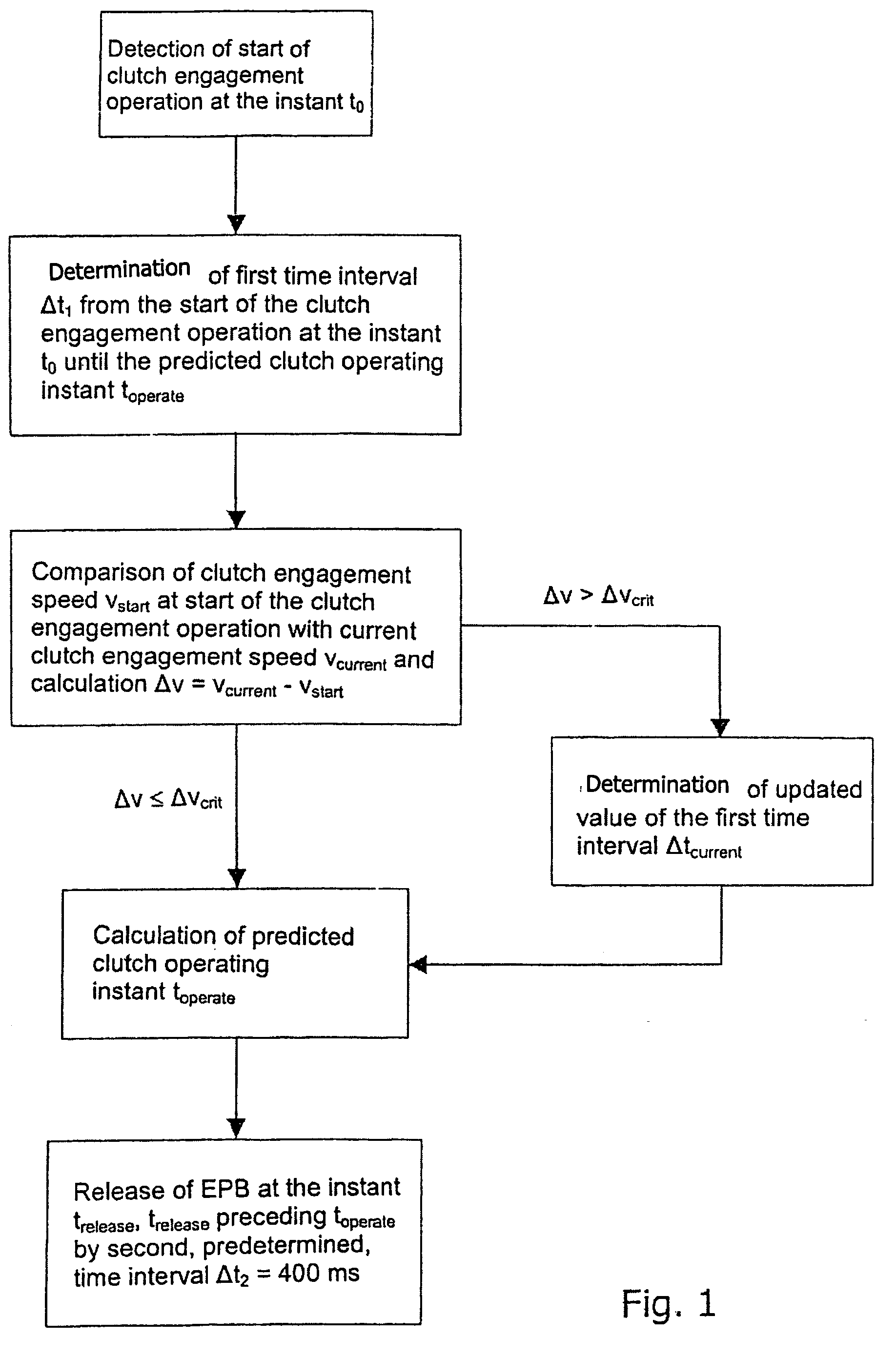
Method and system for controlling a braking system equipped with an electric parking brake
ActiveUS7407463B2Accurate coordinatesBraking action transmissionEngine controllersMobile vehicleElectric parking brake
In a method and system for controlling a braking system, equipped with an electric parking brake, for a motor vehicle, the electric parking brake is released in response to an identification of a moving-off operation. A release instant of the electric parking brake is defined in dependence on at least one measured parameter of a clutch engagement operation. In comparison with a method and system in which, for example, the electric parking brake is released in dependence on the actuation of the accelerator by a driver, the method and system permit a more precise coordination of the deactivation of the electric parking brake with the clutch engagement operation, and thus with the moving-off operation of the vehicle, particularly in the case of a vehicle equipped with a manual transmission.
Owner:LUCAS AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Method and apparatus for determining a deviation of an actual shape from a desired shape of an optical surface
ActiveUS20120127481A1Accurate coordinatesImprove accuracyUsing optical meansFree formClassical mechanics
An optical element having an optical surface (12; 103), which optical surface has an actual shape, the actual shape deviating from a desired shape by maximum 0.2 nm, wherein the desired shape is either: a free-form surface having a deviation from its best-fitting sphere of at least 5 μm or a substantially rotationally symmetrical surface having a deviation from its best-fitting sphere of at least 0.5 mm.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
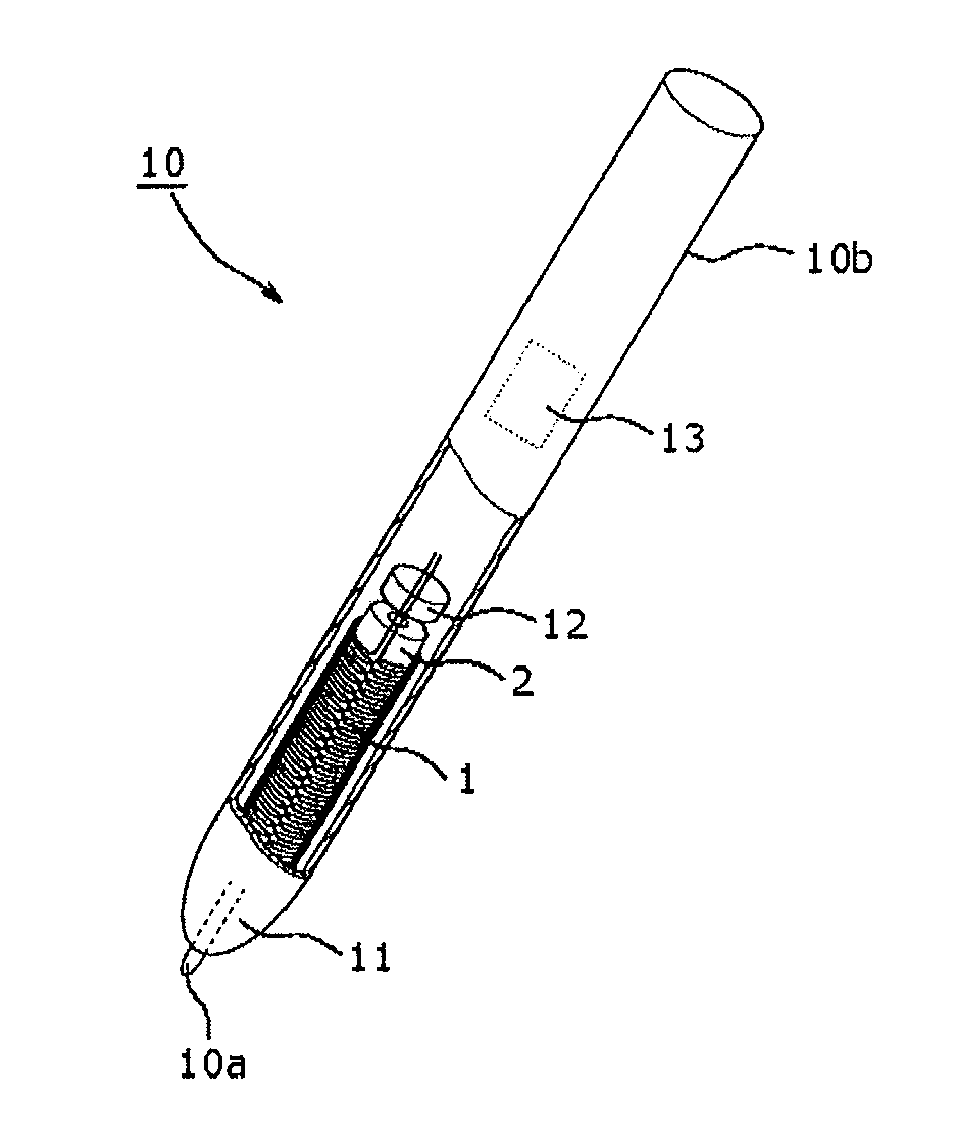
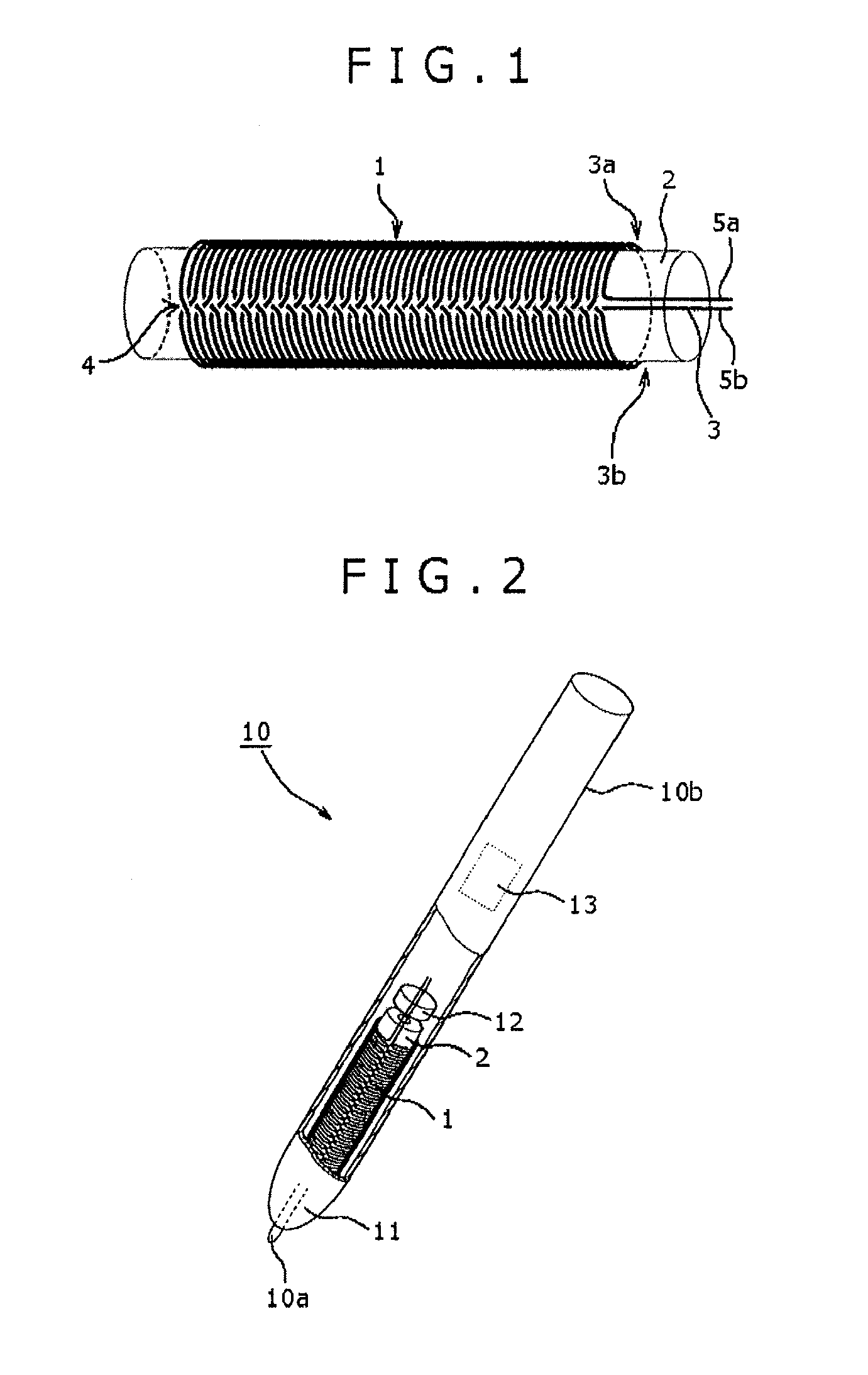
Coil, position indicator, position detecting device, and coil winding method
InactiveUS20110115753A1Suppress radiationRadiation suppressionLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreTransmission systemsConductor CoilElectrical and Electronics engineering
A position indicator for use in a pen tablet device includes a coil for emitting a position indicating signal. The coil includes: a first conductive wire wound from a distal end portion thereof to a proximal end portion thereof in a predetermined rotational direction; and a second conductive wire wound from a proximal end portion thereof to a distal end portion thereof in the predetermined rotational direction, wherein the first conductive wire and the second conductive wire are connected to each other at the proximal end portions thereof, and the wound first conductive wire and the wound second conductive wire are disposed alternately adjacent to each other.
Owner:WACOM CO LTD
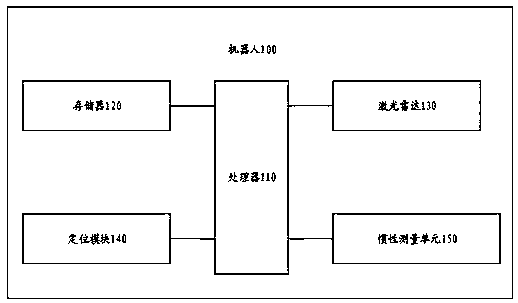
Robot mapping method and device, robot and storage medium
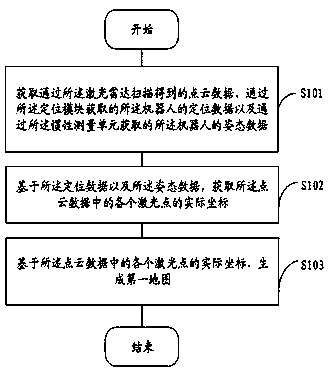
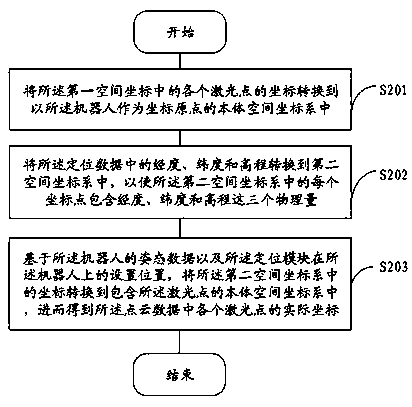
InactiveCN111427061AAccurate mapReduce unlocatableNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsInertial measurement unitLocation data
The invention provides a robot mapping method and device, a robot and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps that point cloud data obtained through laser radar scanning, positioning data, obtained through a positioning module, of a robot and posture data, obtained through an inertia measurement unit, of the robot are obtained; actual coordinates of each laser point in the point cloud data are obtained based on the positioning data and the posture data; and a first map is generated based on the actual coordinates of each laser point in the point cloud data. According to the robot mapping method provided by the embodiment of the invention, loopback detection is not needed. Besides, the position data of the robot and the posture data of the robot are obtained through the positioningmodule and the inertial measurement unit respectively; compared with the robot position data and posture data reversely determined through the point cloud data, so that the constructed map is more accurate, and the laser mapping mode can be suitable for the outdoor strong light environment.
Owner:北京云迹科技股份有限公司
Signal transmitting and receiving method, processor chip, active pen, touch screen
ActiveCN110832447ARealize transmissionShorten detection timeInput/output processes for data processingActive penTouchscreen
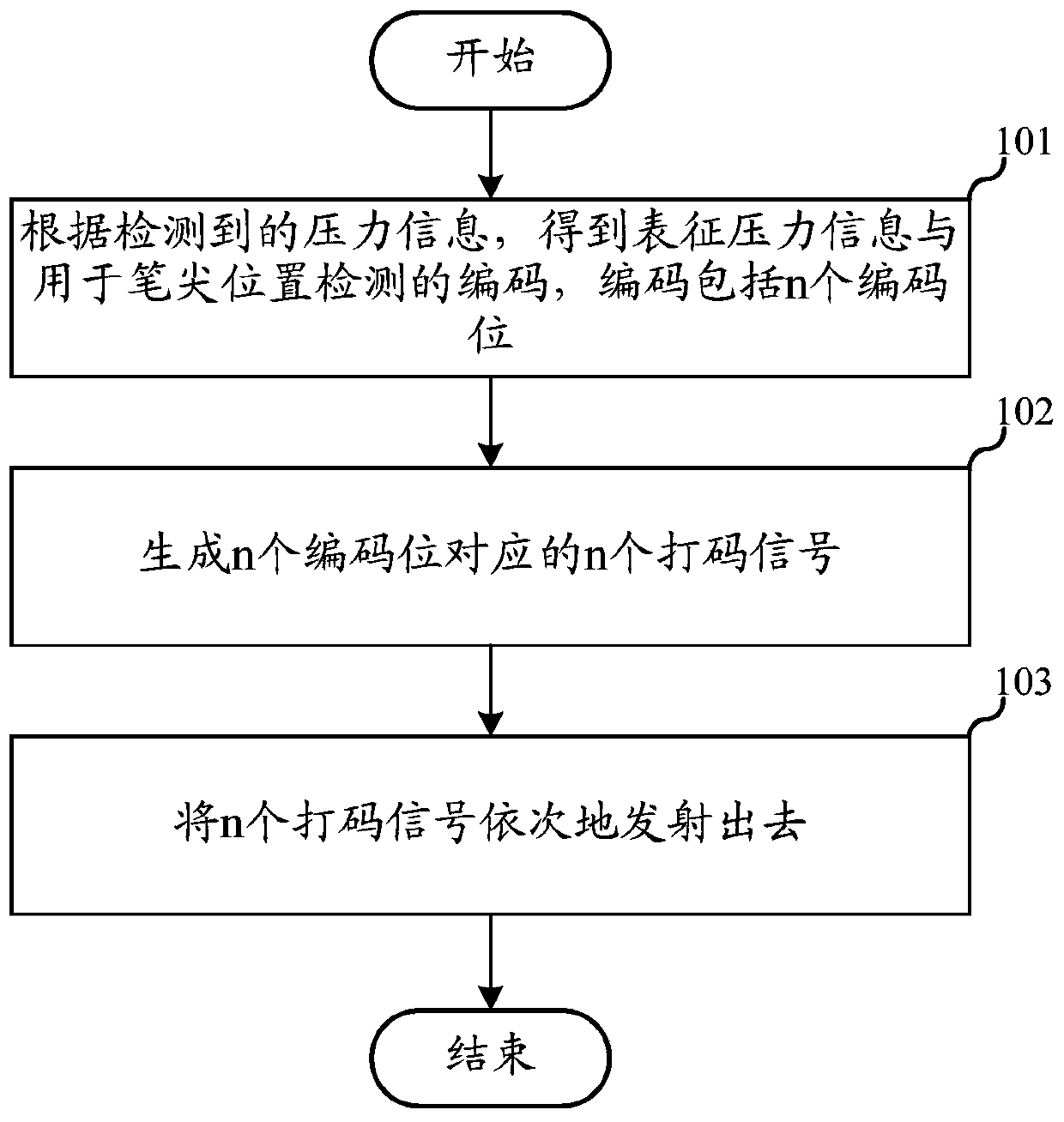
Some embodiments of the present application provide a signal transmitting and receiving method, a processor chip, an active pen, and a touch screen. The signal transmission method includes: obtainingcharacterizing pressure information and a code for detecting the position of the pen tip according to the detected pressure information, wherein the encoding includes n encoding bits, where n is an integer greater than 1 (101); generating n coded signals (102) corresponding to n coded bits; transmitting each coded signal of the n coded signals at a preset first frequency, a preset second frequency, or a transmission prohibited manner, wherein the first frequency, the second frequency of the n coded signals, and the prohibited transmission are related to pressure information (103); with the above solution, the active pen can output more coordinates of the nib position in unit time, and the touch screen can detect more coordinates of the nib position in unit time, which improves the reporting rate.
Owner:SHENZHEN GOODIX TECH CO LTD
Liquid ejecting apparatus and method for adjusting positions of nozzle rows
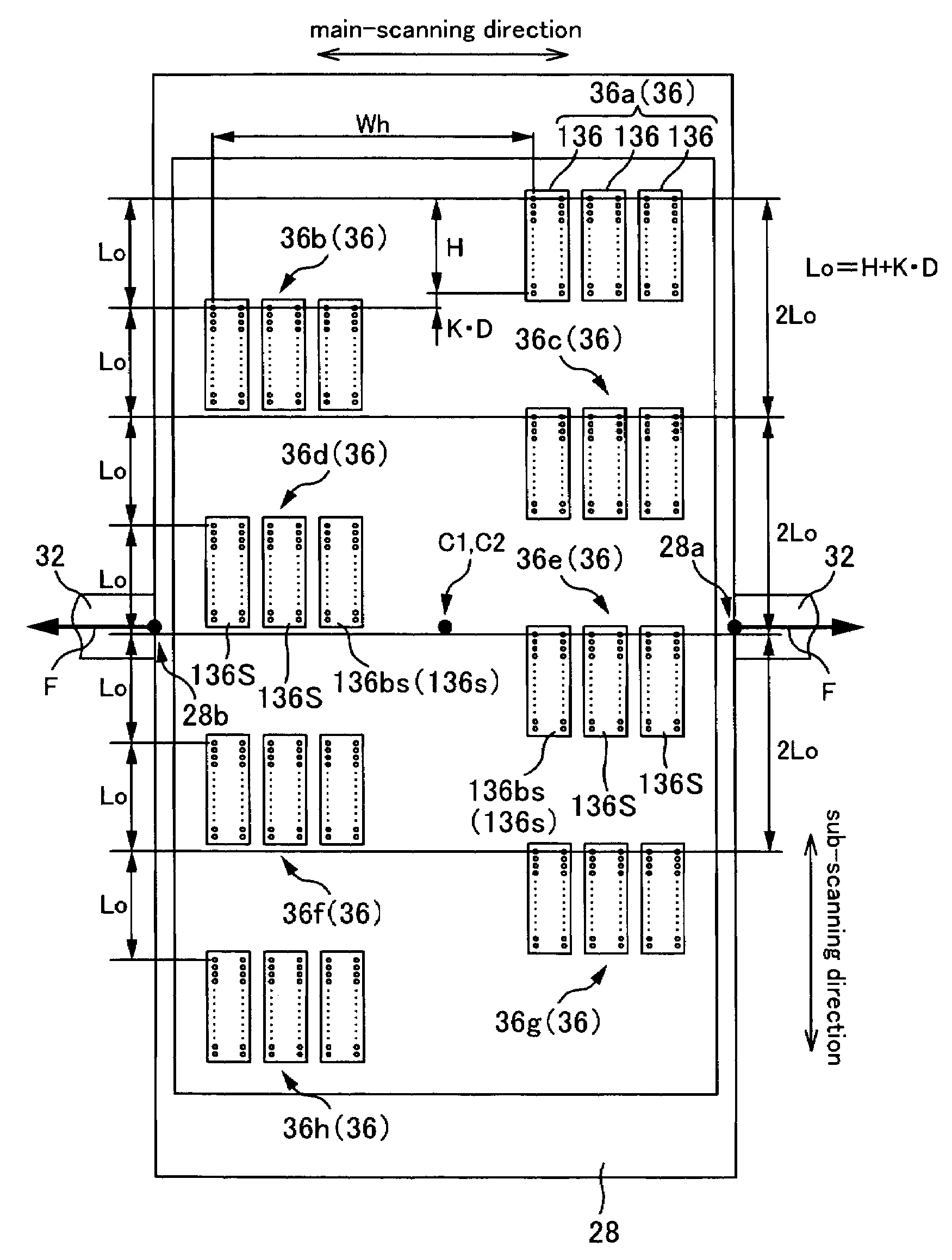
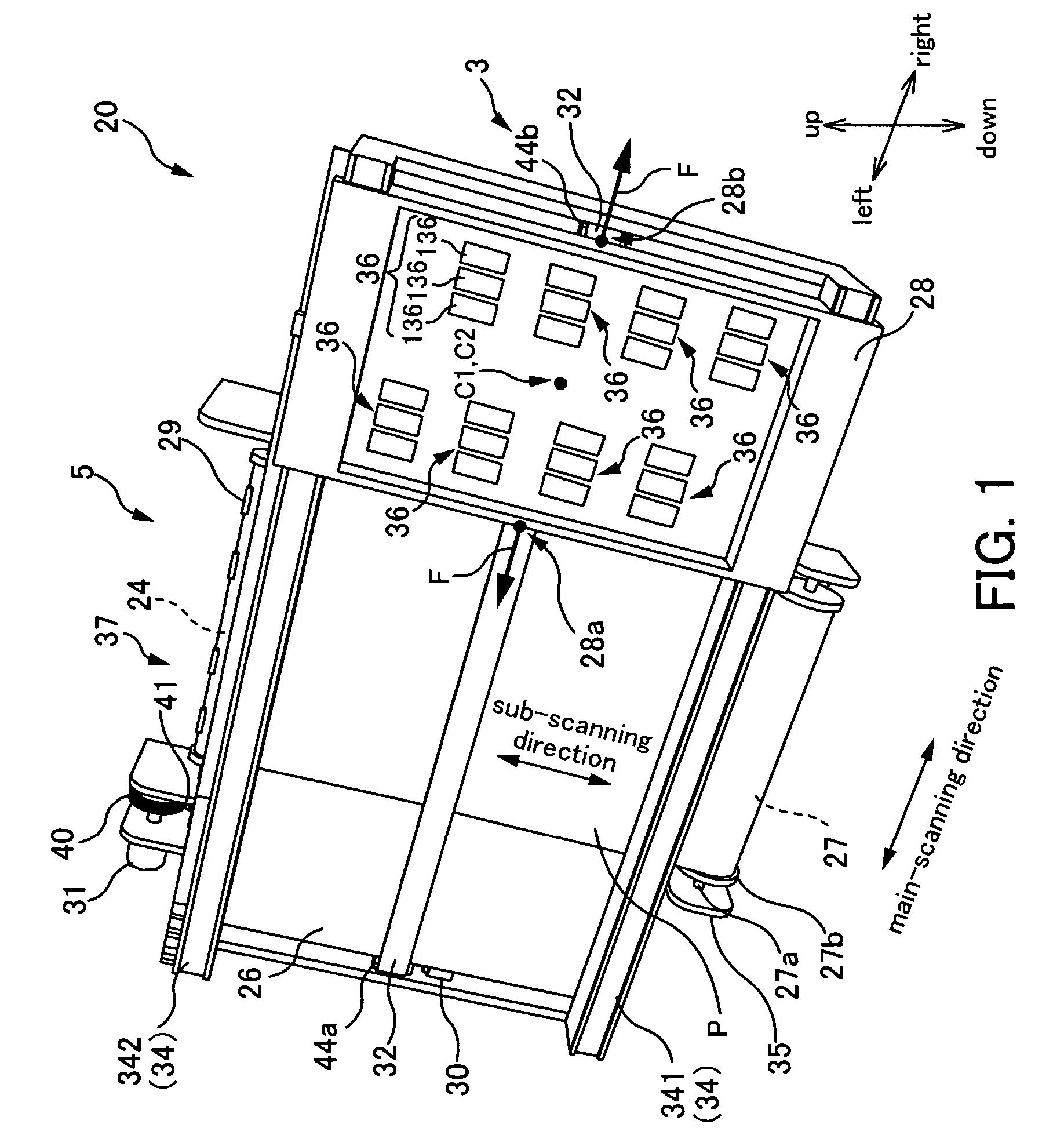
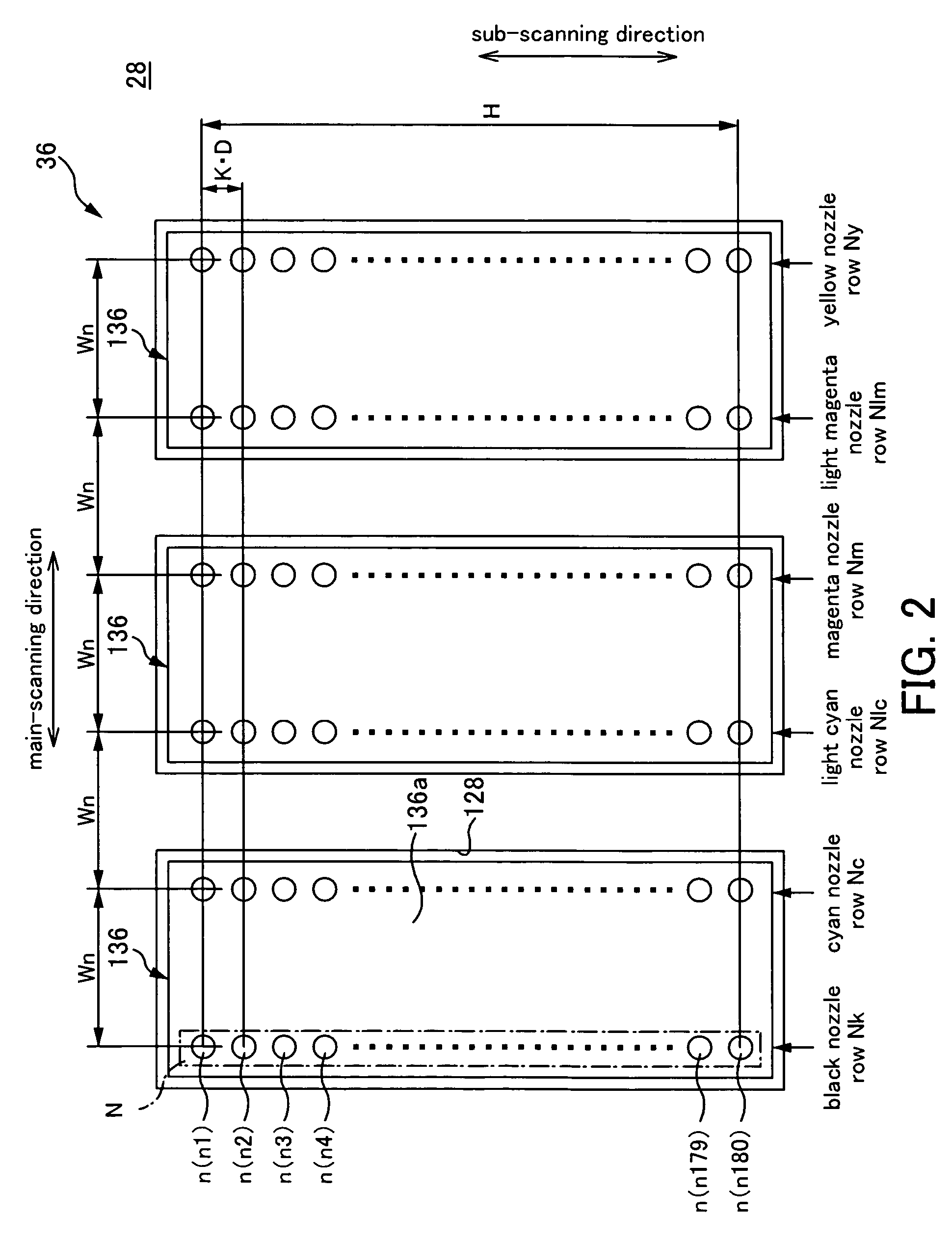
InactiveUS7591526B2Accurate coordinatesLiquid surface applicatorsInking apparatusLiquid jetLine of action
A liquid ejecting apparatus comprises a moving unit that moves by receiving a moving force, and a plurality of nozzle rows for ejecting liquid onto a medium, wherein each of the nozzle rows is adjusted in its position on the moving unit, taking a nozzle row that is arranged on a side close to a line of action of the moving force as a reference.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com