Patents
Literature
40results about How to "Inhibition of PID effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
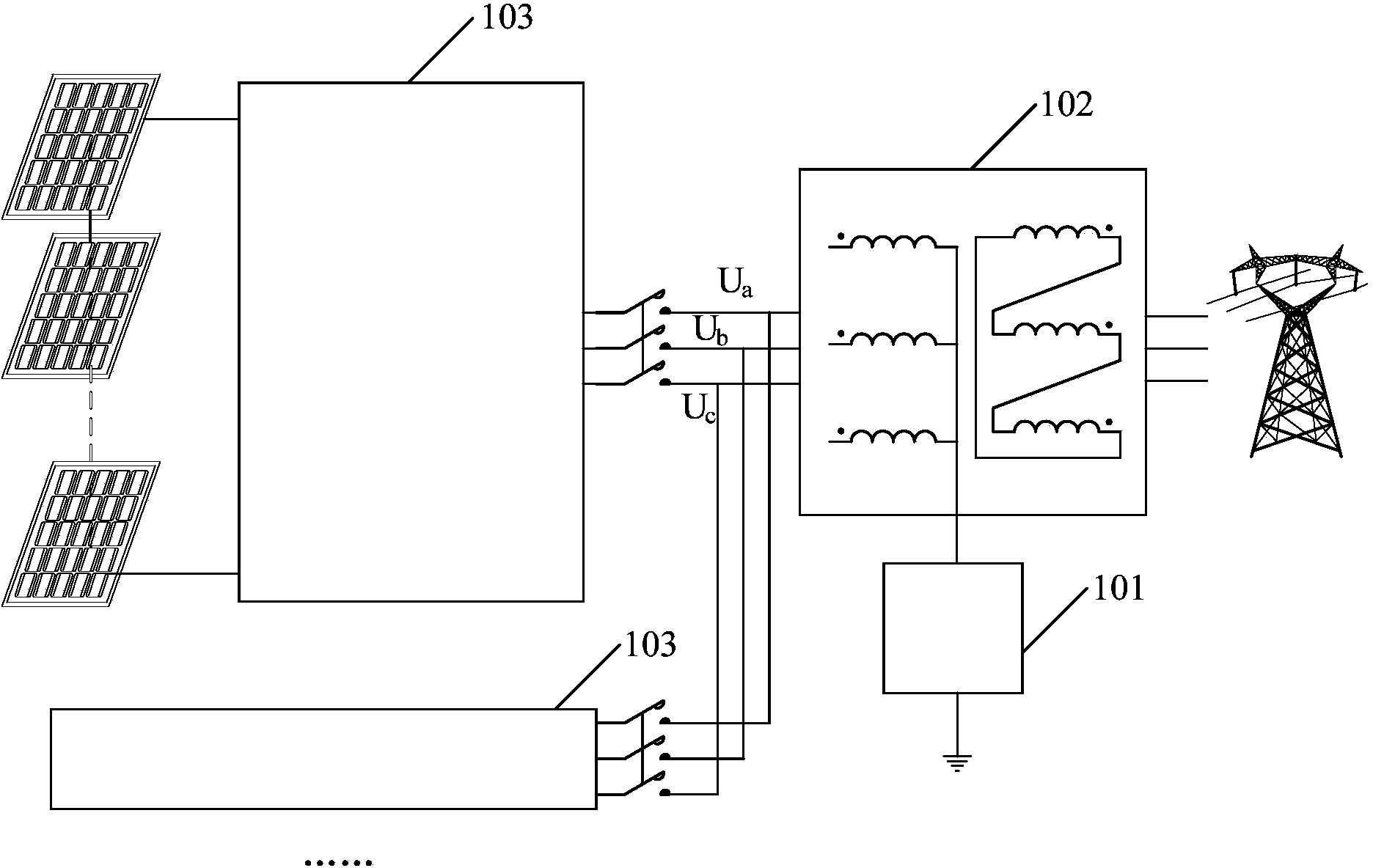
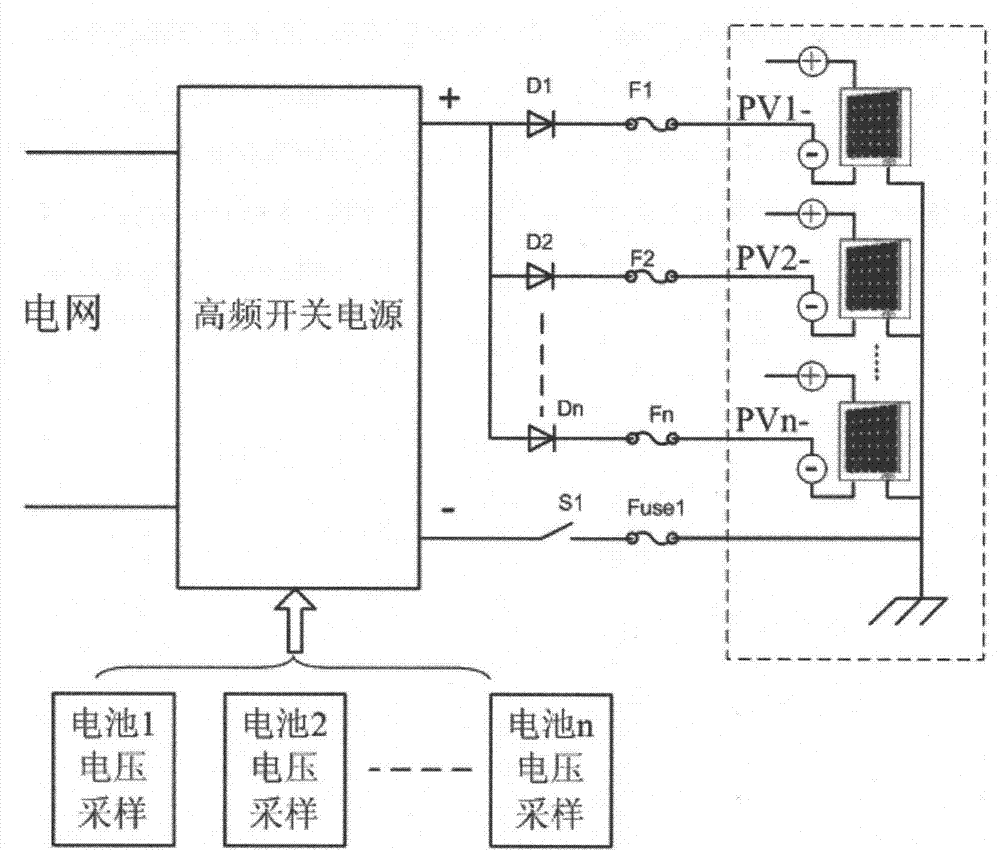
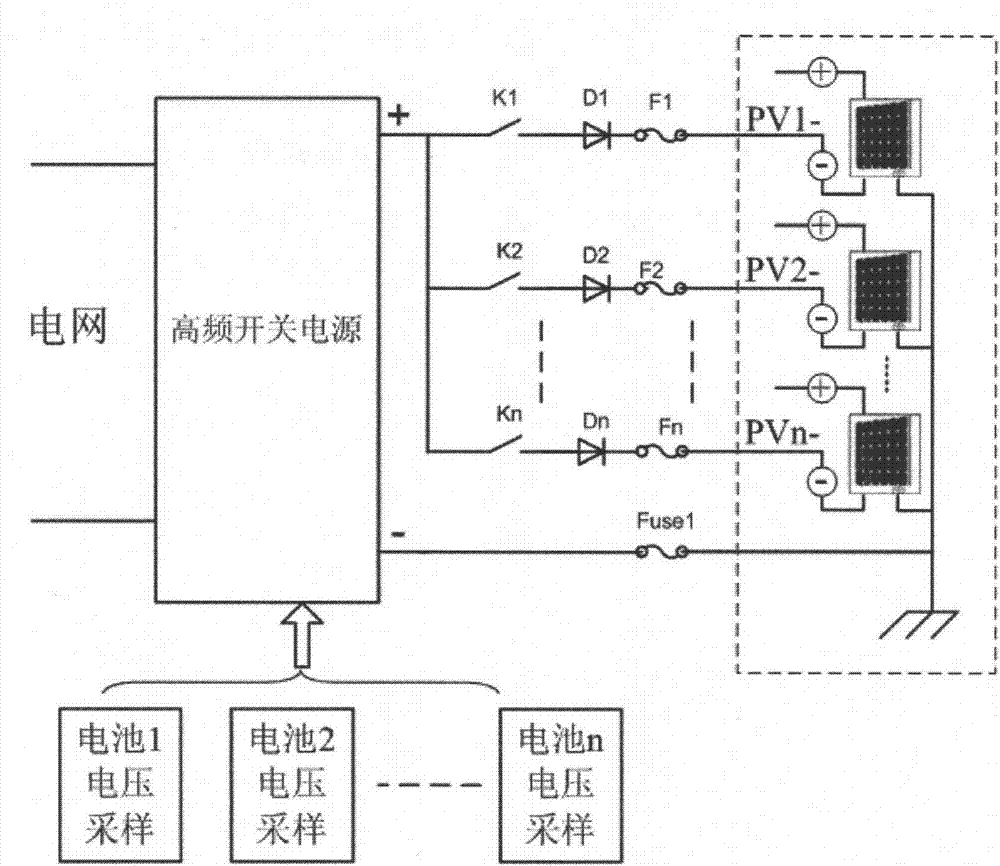
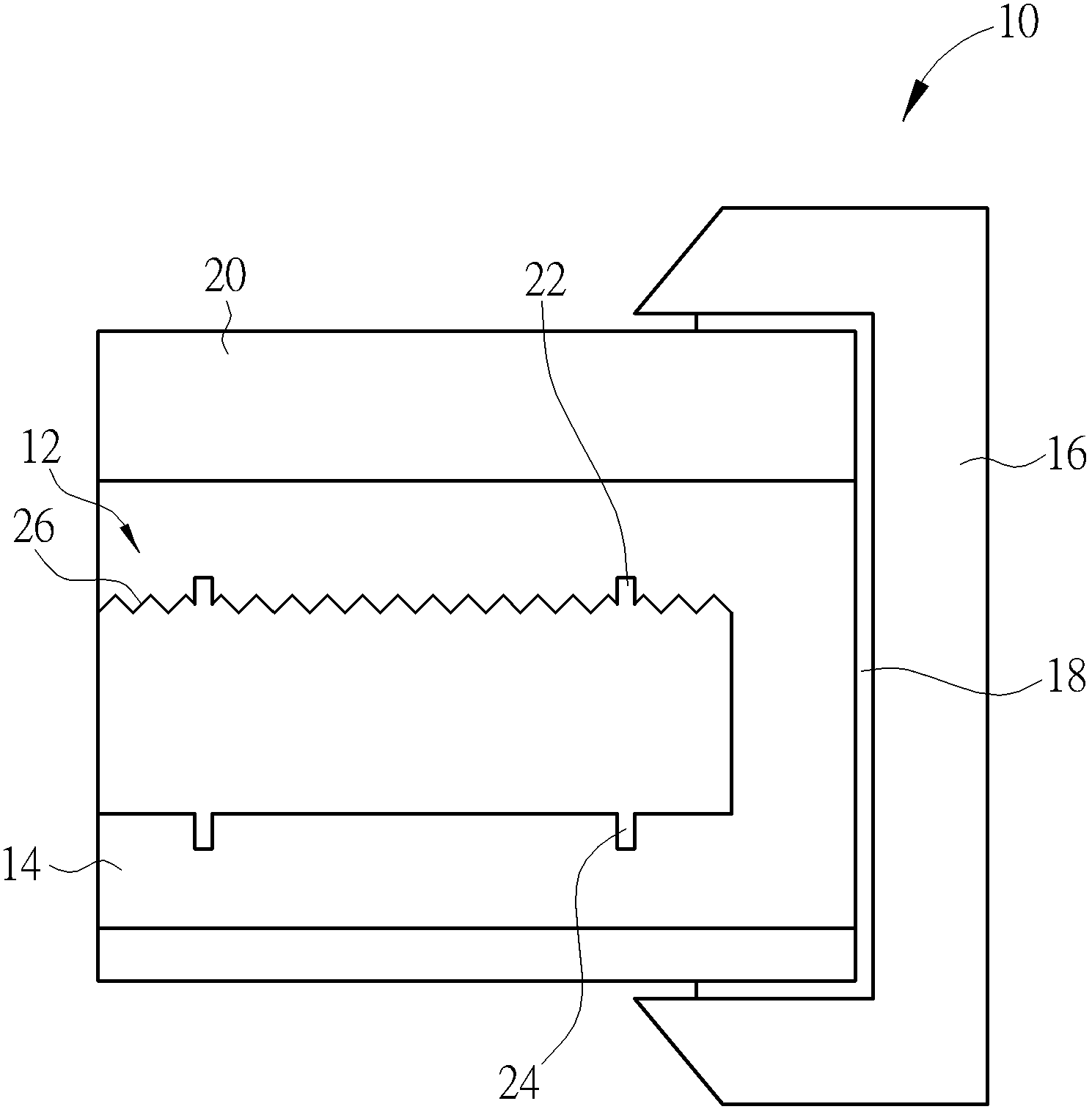
Device for restraining PID effect of photovoltaic panel
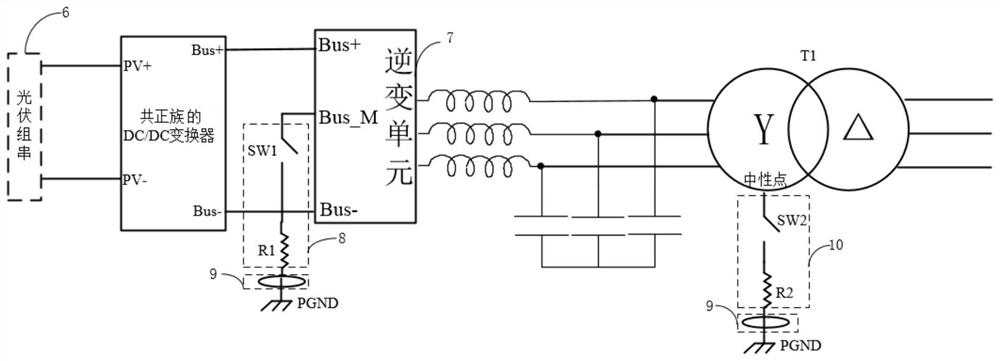
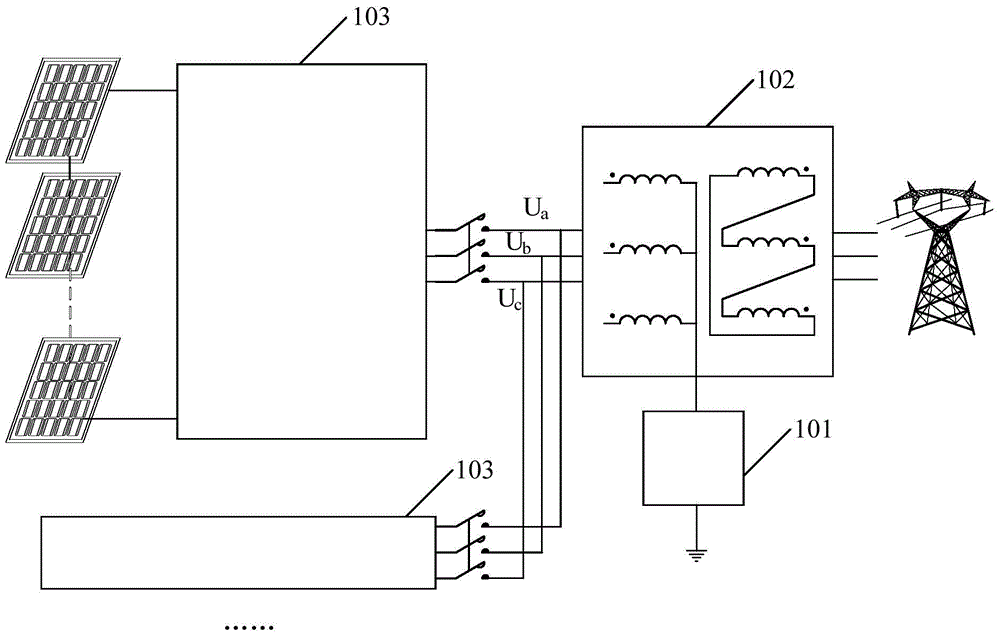
ActiveCN103973217AInhibition of PID effectIncreased voltage to groundPhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationPower inverterPhotovoltaic power station
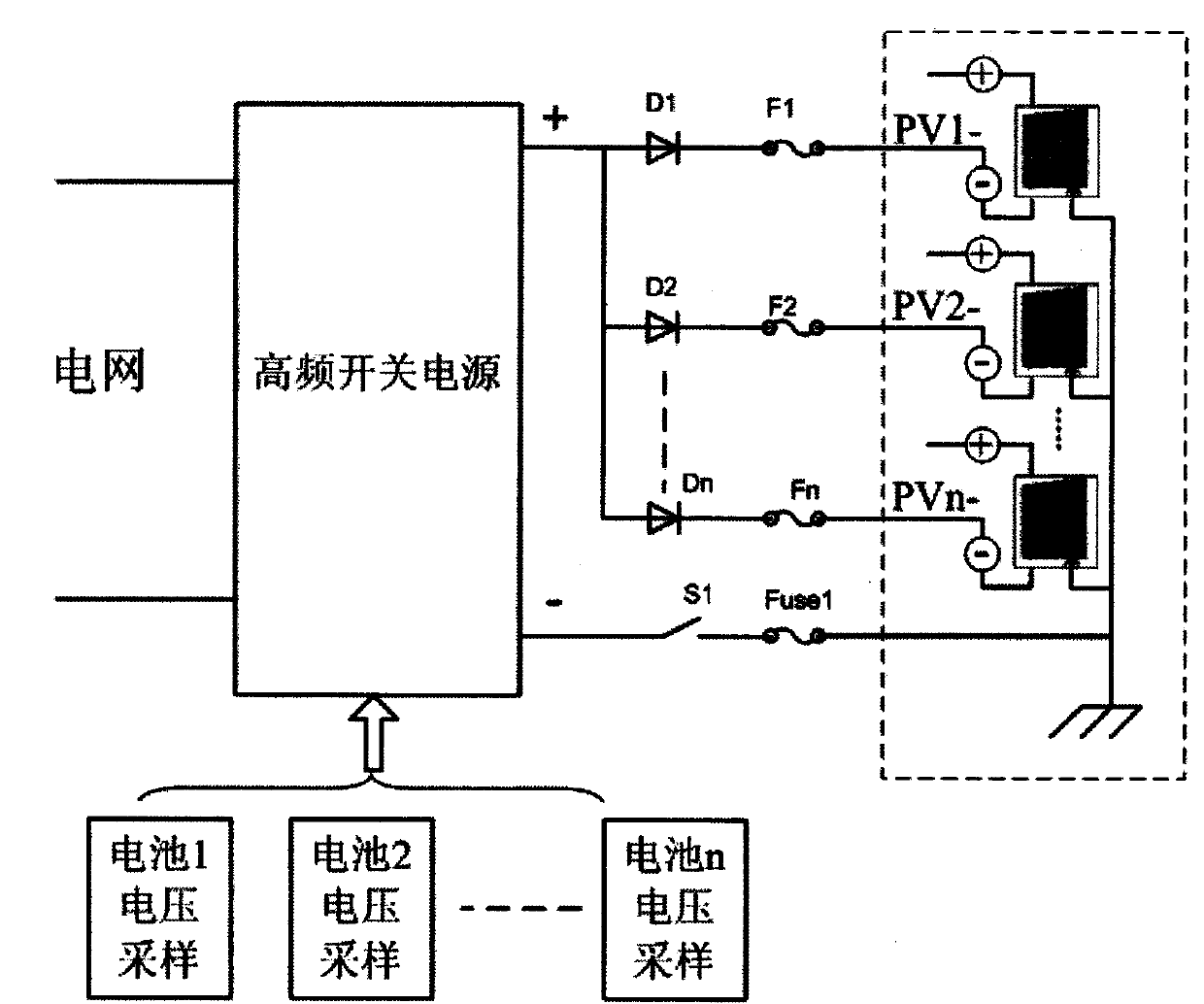
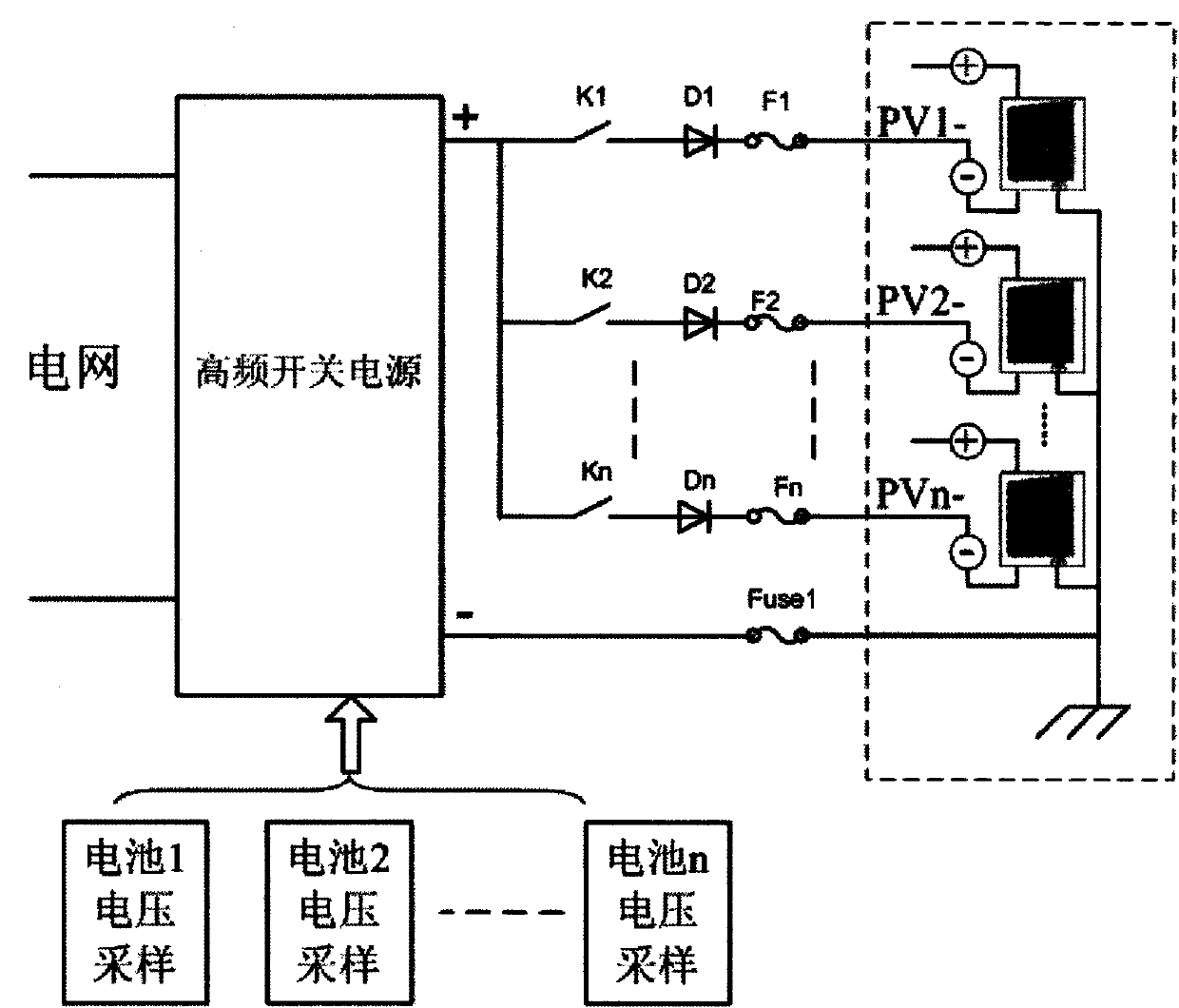
The invention discloses a device for restraining the PID effect of a photovoltaic panel. According to the device, the voltage to ground of a neutral point on the alternating-current boosting side of a photovoltaic power station is boosted through a voltage boosting circuit so that the voltage to ground of the preceding photovoltaic panel of an inverter can be boosted, the photovoltaic panel has positive bias relative to the ground, and the PID effect of the photovoltaic panel can be restrained. According to the device, not all the inverters or photovoltaic panels need to be processed, and the device has the advantages that the device is easy to implement and low in cost, detection of insulation resistance is not influenced, and the device is particularly suitable for the application that serial-type photovoltaic inverters are used for building a photovoltaic power station.
Owner:SINENG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Short-fiber-reinforced pultrusion composite material solar energy assembly frame and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104761880AImprove efficiencyImprove lateral strengthPhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationUltimate tensile strengthFiber orientation
The invention discloses a short-fiber-reinforced pultrusion composite material solar energy assembly frame, which is characterized by being produced through a pultrusion method and being composed of following components, by volume: 5-10% of short fibers, 50-80% of continuous fibers and 10-40% of resin. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the solar energy assembly frame. In the method, a short fiber reinforcement body is added for solving a problem of insufficient strength in the vertical direction of the fiber when a continuous reinforced pultrusion composite material is used as the solar energy assembly frame. The continuous fiber is impregnated in the resin mixture, in which 5-10% by volume of the short fibers is dispersed homogeneously, and then the impregnated continuous fiber is injected into a die for obtain the solar energy assembly frame through pultrusion. The short fibers can form an overlap joint structure among the continuous fiber so that the performance in the vertical direction of the fibers in the material can be improved. Not only is the excellent performance in the direction in parallel with the fibers ensured, but also an excellent mechanical performance in the vertical direction of the fibers can be ensured at the same time.
Owner:哈尔滨生材新材料科技发展有限公司
PID-resistant encapsulation adhesive film used for photovoltaic cell
ActiveCN104530994ANo hydrolysis reactionCohesive solutionNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesivesPolyolefinAlpha-olefin
The invention discloses a PID-resistant encapsulation adhesive film used for a photovoltaic cell. The PID-resistant encapsulation adhesive film comprises, by mass, polyolefin resin 80%-95%, polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane 1%-20%, a peroxide crosslinking agent 0.1-2%, an auxiliary crosslinking agent 0.01-1%, a light stabilizing agent and an ultraviolet absorber, wherein the polyolefin resin is an ethylene / alpha-olefin copolymer or a composition of the ethylene / alpha olefin copolymer; the polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane contains a hydrolysable radical which is selected from one or more of a methoxy group, an ethoxy group, a methoxyethoxy group and an acetoxyl group. The PID-resistant encapsulation adhesive film has good adhesive performance and ageing-resistant performance while having excellent PID-resistant performance, thereby having positive practical significance.
Owner:SUZHOU DUCHAMPS ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
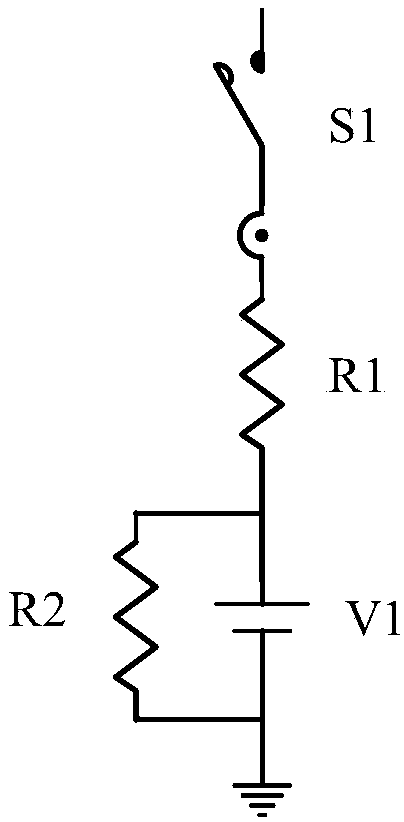
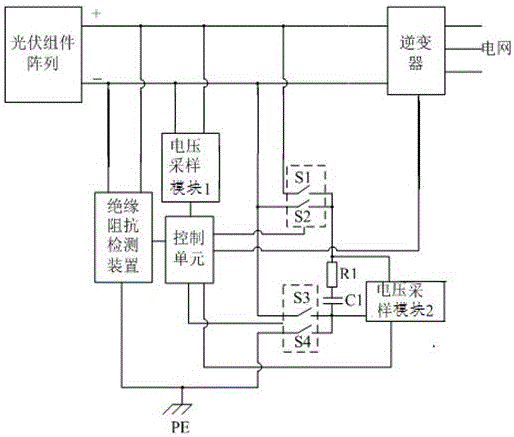
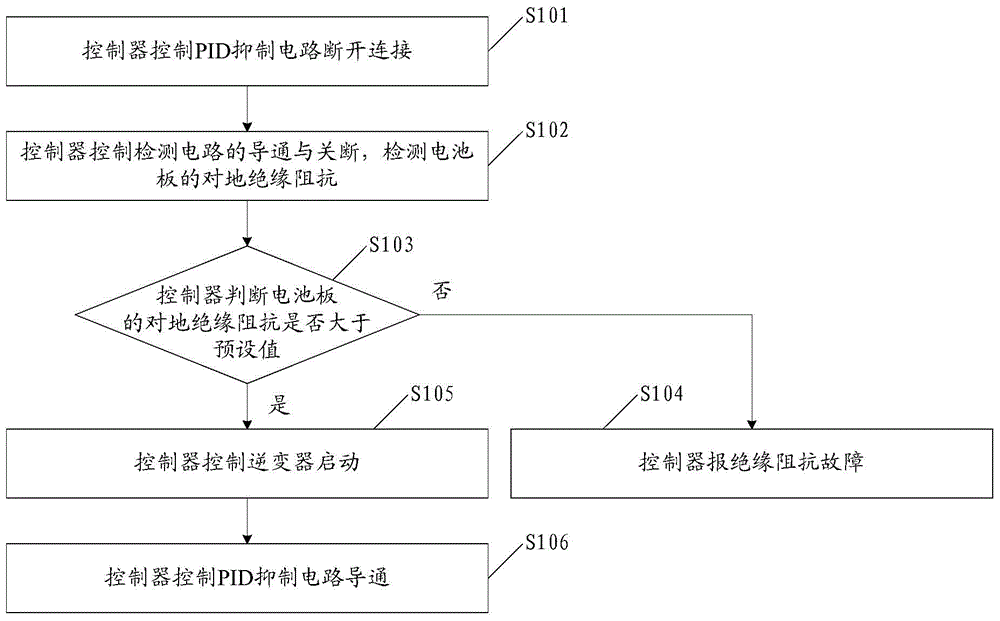
Method and circuit for detecting insulation resistance
ActiveCN103983855AAchieving PID suppressionRealize the suppression functionImpedence measurementsInsulation resistanceCells panel
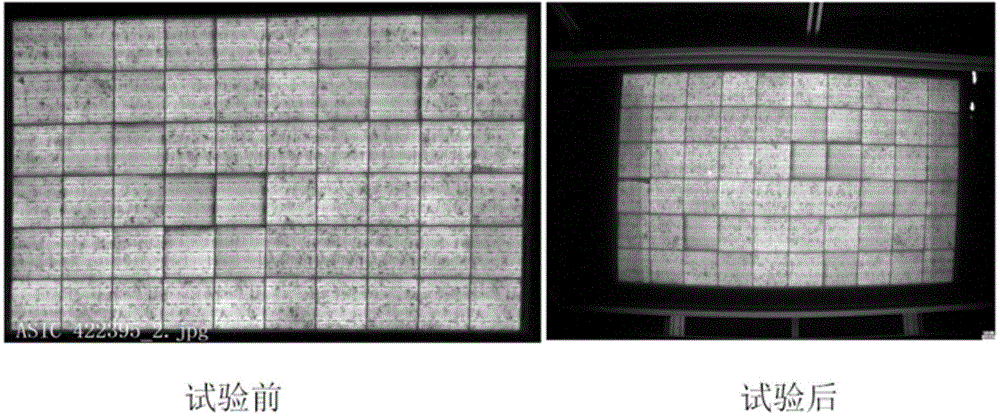
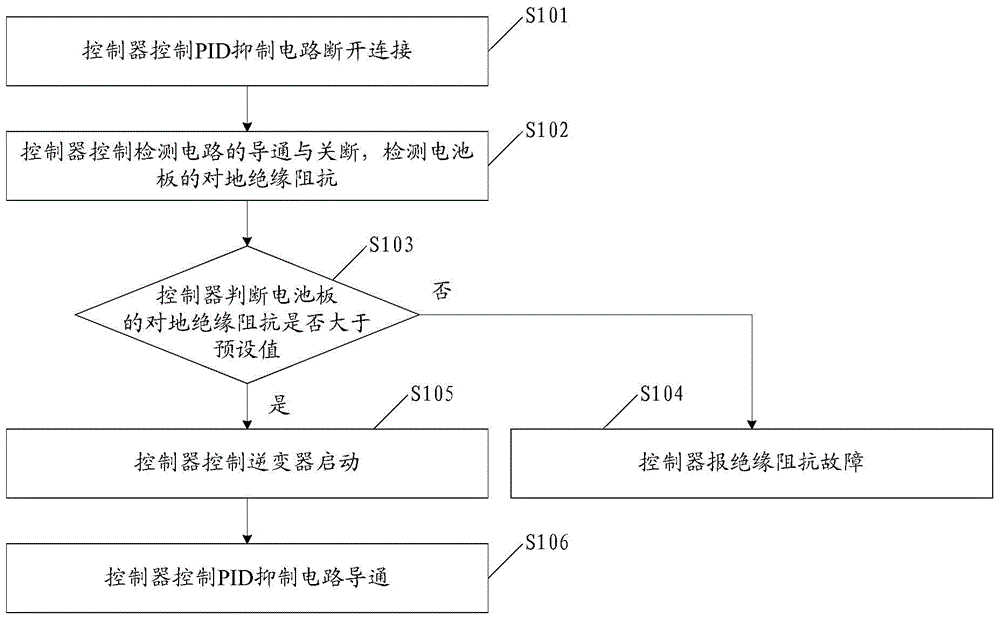
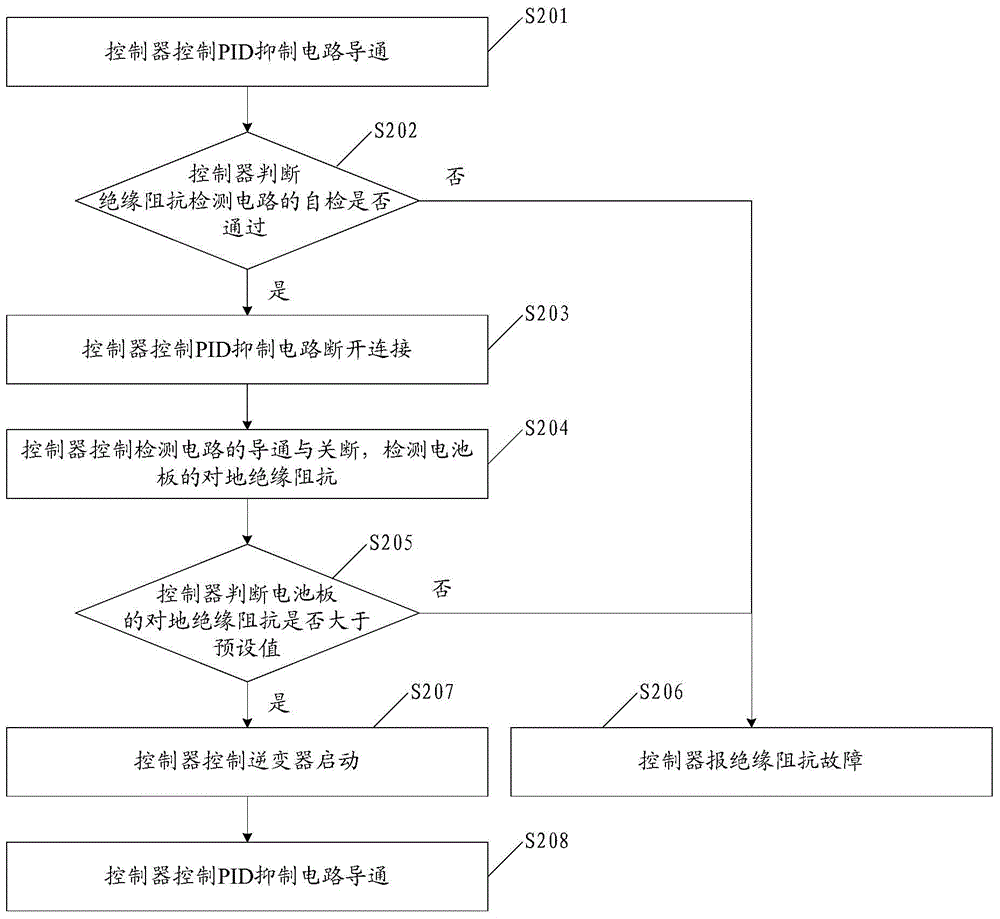
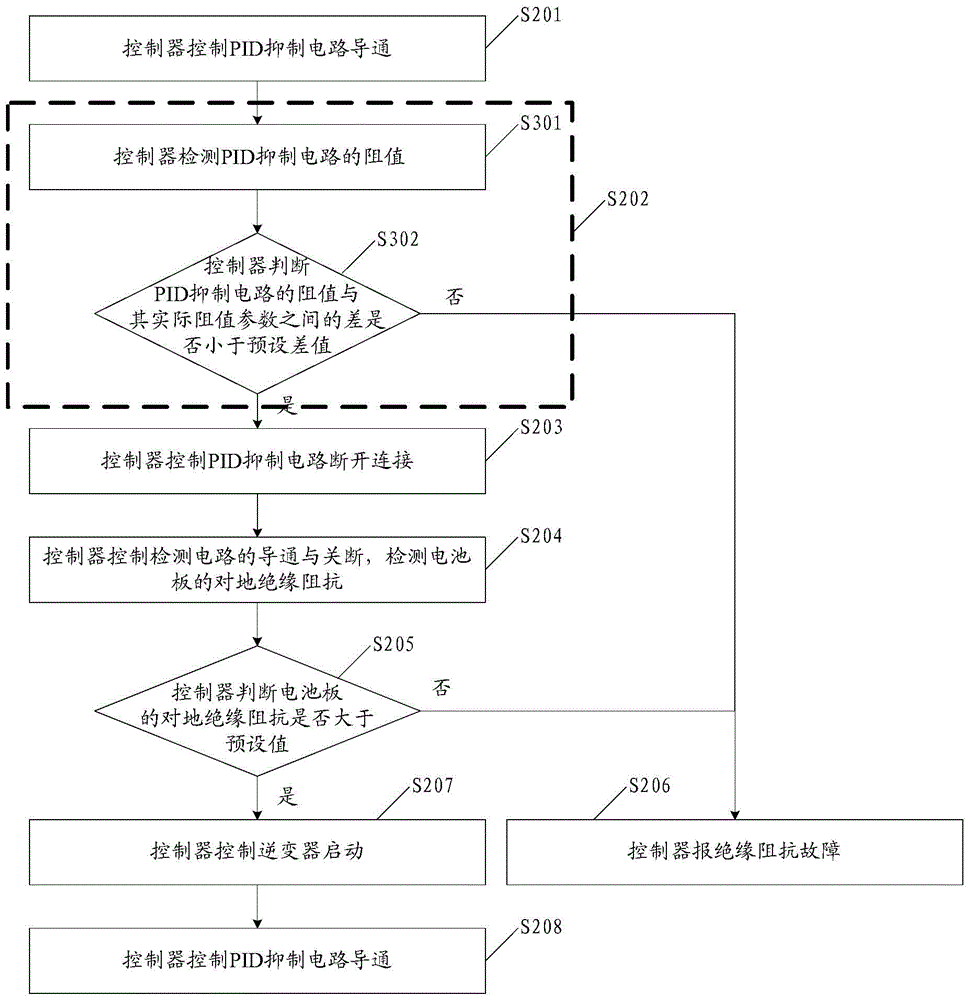
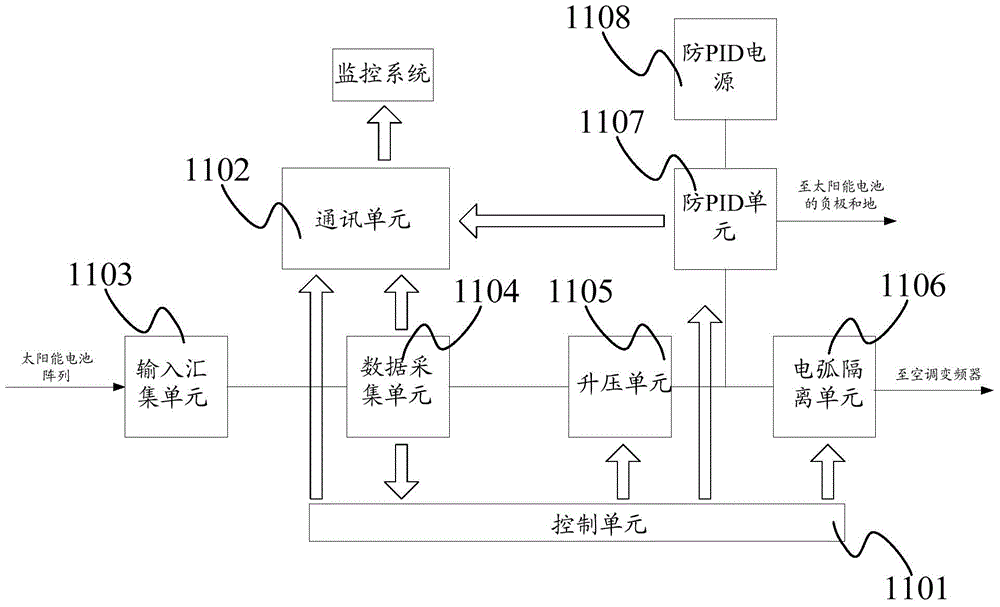
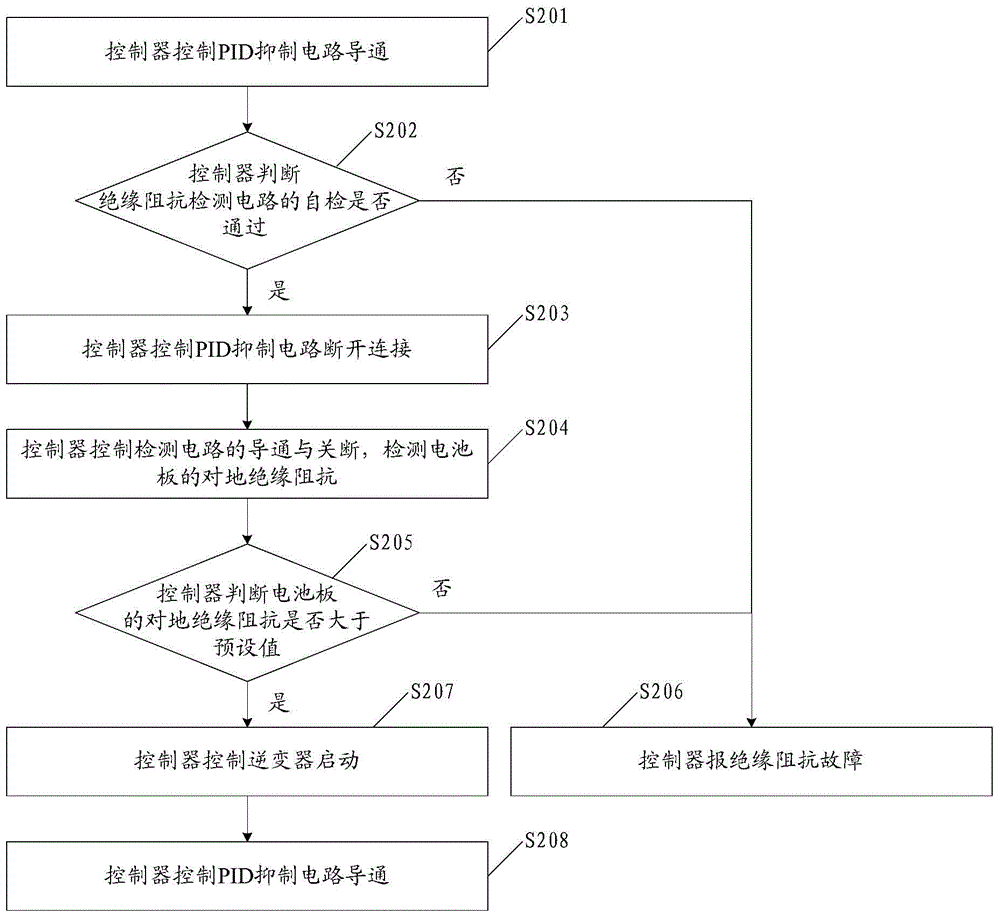
The invention discloses a method and circuit for detecting insulation resistance. A controller controls turn-on and turn-off of a PID suppression circuit and then controls turn-on and turn-off of the circuit for detecting insulation resistance, and then insulation resistance against the ground of a cell panel can be detected; whether the insulation resistance against the ground of the cell panel is larger than a preset value or not is judged; when it is judged that the insulation resistance against the ground of the cell panel is smaller than or equal to the preset value, insulation resistance faults are reported; when it is judged that the insulation resistance against the ground of the cell panel is larger than the preset value, an inverter is controlled to be started, then the PID suppression circuit is controlled to be turned on, and then suppression of the PID effect is achieved. Detection on the insulation resistance against the ground of the cell panel is achieved before grid connection of the inverter, the function of suppressing PID is achieved, and the problems in the prior art are solved.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
PID (potential induced degradation) resistible solar cell passivated antireflective film
The invention discloses a PID (potential induced degradation) resistible solar cell passivated antireflective film. The PID resistible solar cell passivated antireflective film can be of two structures. One structure includes that the bottom layer of the passivated antireflective film is a passivated antireflective layer SiNx with refraction rate 2.0-2.1 and the thickness ranging from 70nm to 80nm; and the top layer of the passivated antireflective film is a conductive amorphous silicon layer with the thickness ranging from 3nm to 10nm. The other structure includes that the bottom layer of the passivated antireflective film is a passivated layer SiNx with the refraction rate 2.2-2.3 and the thickness ranging from 9nm to 11nm; an intermediate layer of the passivated antireflective film is a conductive amorphous silicon layer with the thickness ranging from 3nm to 10nm; and the top layer of the passivated antireflective film is an antireflective layer SiNx with refraction rate 2.0-2.1 and the thickness ranging from 60nm to 70nm. A battery end of a solar battery with the passivated antireflective film can effectively prevent PID effect. Further, based on existing conventional battery process, combination of ingredients and thickness of the antireflective film can be changed only, the antireflective film can be compatible with existing battery process and easy to realize. The PID resistible solar cell passivated antireflective film is applicable to conventional P-type batteries and also applicable to efficient back-passivation batteries, EWT (emitter wrap through) batteries, MWT (metal wrap through) batteries, and N-type IBC (interdigitated back contact) batteries and the like.
Owner:TRINASOLAR CO LTD
Fiber-felt-reinforced composite material solar energy assembly frame and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104760299ALow costLight in massPhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationFiber bundleEngineering
The invention discloses a fiber-felt-reinforced composite material solar energy assembly frame and a preparation method thereof and aims to solve a problem of poor strength of a solar energy assembly frame structure in the prior art. In the invention, two solar energy assembly frames are jointed to each other to form a regular rectangular outer side, wherein the two solar energy assembly frames can be produced at the same time. Meanwhile, during a moulding process, the external side of unidirectional fiber bundles arranged in a preset shape is wrapped by fiber felt, and then the solar energy assembly frame is sent to a heating die for pultrusion. By means of cooperation with a pulling apparatus at the outer side and a cutting machine for cutting the material, the required solar energy assembly frame is formed. By means of addition of the continuous fiber felt at the outer side, the transversal strength of the solar energy assembly frame can be enhanced so that the solar energy assembly frame is excellent in comprehensive performances. By means the production of the two frames at the same time, the preparation method is increased in production efficiency, is simplified in processes and can promote an application of the composite material in photovoltaic field.
Owner:哈尔滨生材新材料科技发展有限公司
Achieving method for preventing photovoltaic cell panel PID effect
ActiveCN103888052ADoes not affect workRestoring the problem of output power attenuationPhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationUltrasound attenuationCells panel
The invention provides an achieving method for preventing photovoltaic cell panel PID effect. The method comprises the steps that first, a PID effect energy recovering unit is established; second, when voltages of N photovoltaic cell pack strings sampled by the PID effect energy recovering unit are lower than a set threshold value, the PID effect energy recovering unit is cut into a photovoltaic generating system; and any photovoltaic cell pack string voltage of the N photovoltaic cell pack string voltages sample by the PID effect energy recovering unit is larger than the set threshold value, the PID effect energy recovering unit is cut out of the photovoltaic generating system. Under the premise that working of a photovoltaic inverter is not affected, the problem of photovoltaic cell panel output power attenuation caused by a photovoltaic cell component PID phenomenon is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHINT POWER SYST +1
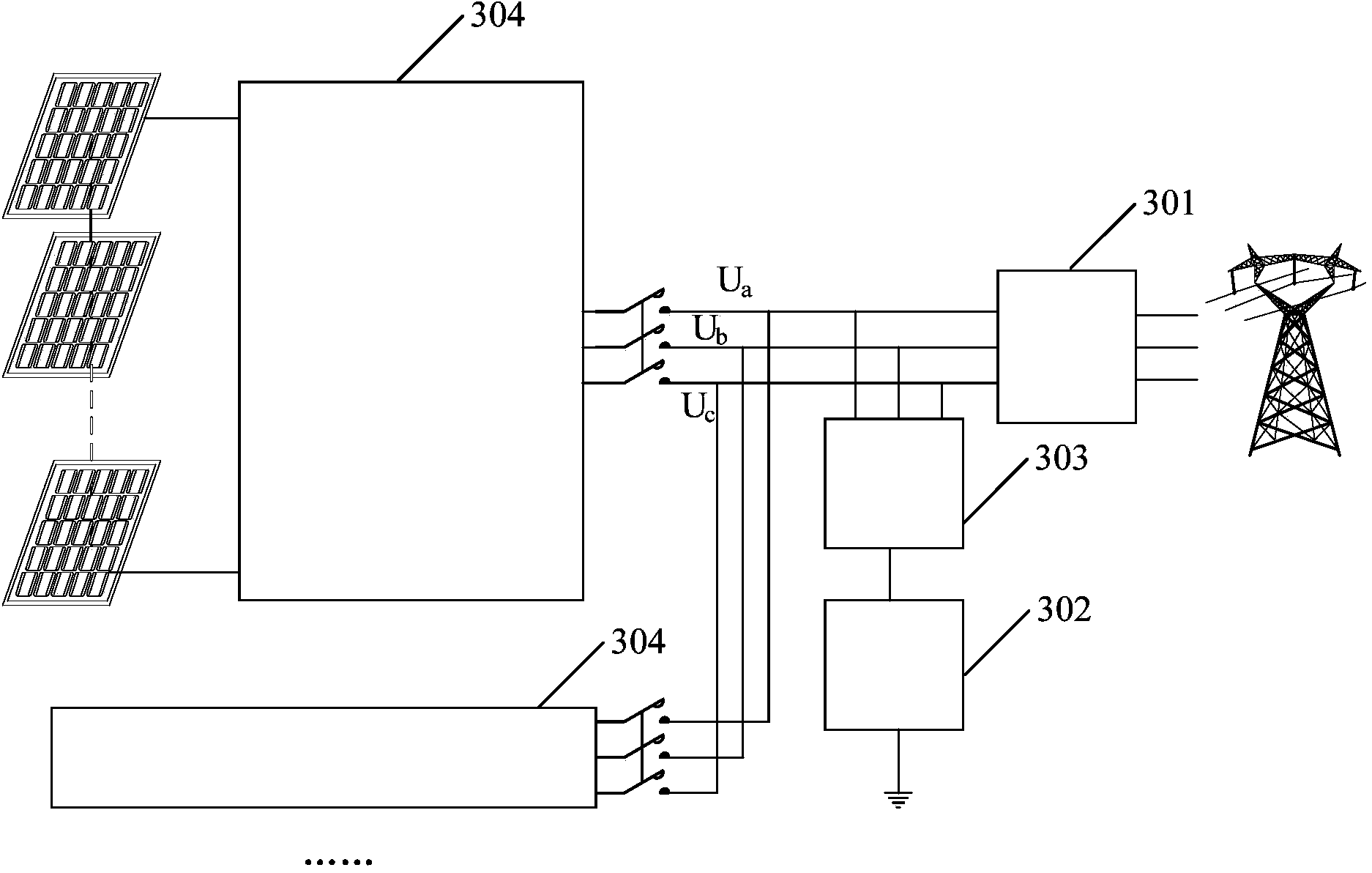
Method and device for inhibiting PID effect of photovoltaic module in inverter
ActiveCN105720907AInhibition of PID effectSimple structurePhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationControl theoryForward voltage
The invention discloses a method and device for inhibiting the PIED effect of a photovoltaic module in an inverter.The method comprises the steps that when the inverter is shut down, electric energy emitted by the photovoltaic module is used for applying a forward voltage to the position between a negative electrode of the photovoltaic module and the ground, and an ionized layer on the photovoltaic module is eliminated.According to the method and device, the electric energy emitted by the photovoltaic module is fully utilized, a forward electric field is applied to the position between the negative electrode and the ground, and the PID effect can be effectively inhibited.The device is simple in structure, safe and reliable, and the defects in the prior art are overcome.
Owner:NANJING SCIYON AUTOMATION GRP
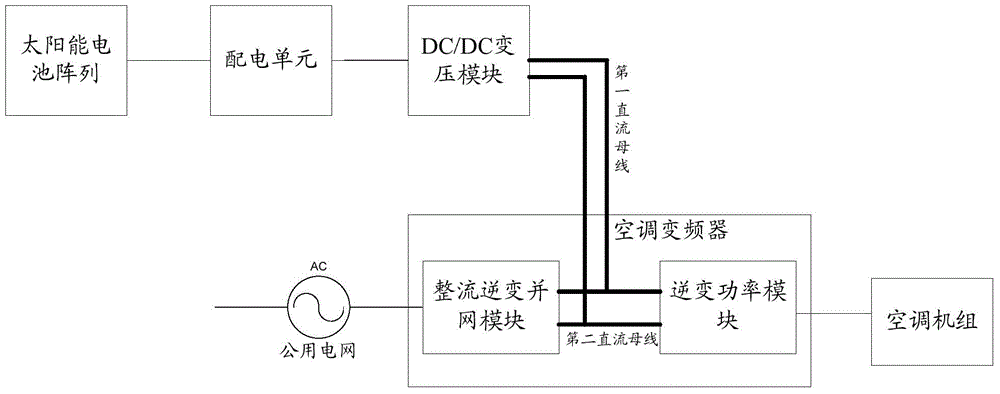
Solar energy variable-frequency air conditioner system
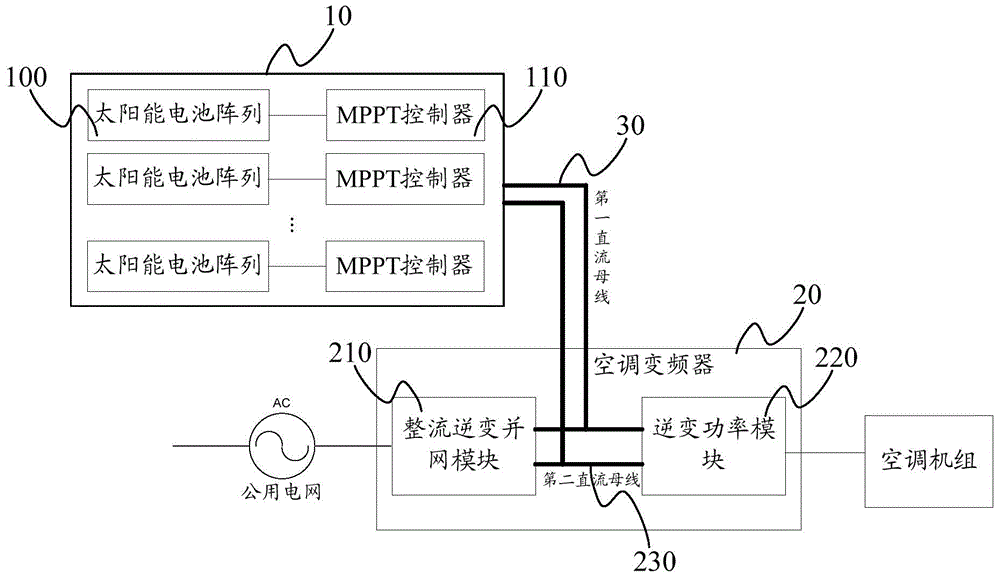
InactiveCN104949246AInhibition of PID effectRealize functionLighting and heating apparatusAir conditioning systemsElectrical batteryGrid connection
The invention provides a solar energy variable-frequency air conditioner system. The solar energy variable-frequency air conditioner system comprises a solar cell array group, an air conditioner frequency converter and a first direct current bus, wherein the solar cell array group comprises multiple solar cell arrays and multiple MPPT controllers; each MPPT controller is connected with one or more solar cell arrays; the MPPT controllers are connected with the air conditioner frequency converter through the first direct current bus and used for increasing and stabilizing voltage of direct current generated by the solar cell arrays, tracking and controlling the MPPT output of each solar cell array and restraining the PID effect of the solar cell arrays; the air conditioner frequency converter comprises a rectification and inversion grid connection module, an inversion power module and a second direct current bus; the rectification and inversion grid connection module is connected with the inversion power module through the second direct current bus; the first direct current bus and the second direct current bus are connected in parallel; accordingly, the MPPT function of the multiple paths of solar cell arrays and the function of restraining the PID effect can be achieved.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
Novel non-metallic photovoltaic module and assembling method thereof
InactiveCN106026888ALow costExtended service lifePhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationMechanical engineeringMaterials science
The invention provides a novel non-metallic photovoltaic module and an assembling process thereof. The novel non-metallic photovoltaic module comprises a photovoltaic module and a solar module insulated frame for fixing the photovoltaic module, wherein a composite material is adopted to be subjected to pultrusion to form the solar module insulated frame; and the photovoltaic module and the solar module insulated frame are bonded into an integrated structure by adopting an adhesive layer at the joint place. The structure is delicate; the process is concise; the photovoltaic module and the insulated frame formed by adopted the composite material through pultrusion are combined to form the photovoltaic module, no stop bar exists on the front face of the module frame, no accumulated dust exists in the bottom of the front face of the module, no hot spot effects are generated, and the service life of the module is prolonged, and the power generation amount of the module is ensured; and, as the insulated frame of the module adopts the composite material, no PID phenomenon is generated, the module efficiency and the service life are not reduced in the case of long-time power generation work of the module, and the cost of the whole system is reduced.
Owner:JIANGYIN UTT SOLAR EQUIP
Novel anti-PID device
PendingCN109617126AImprove power generation efficiencyInhibition of PID effectSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationElectrical resistance and conductanceInstability
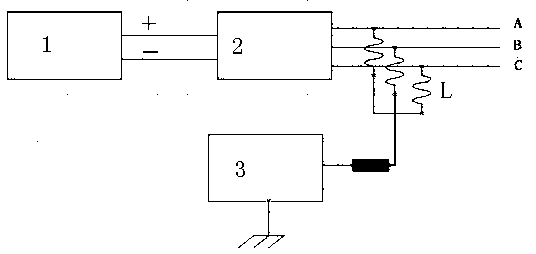
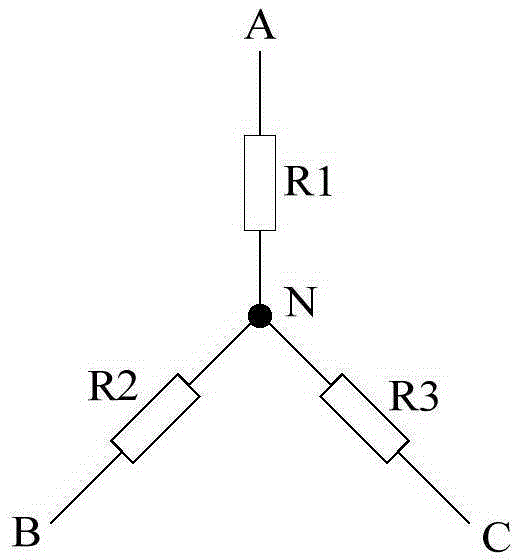
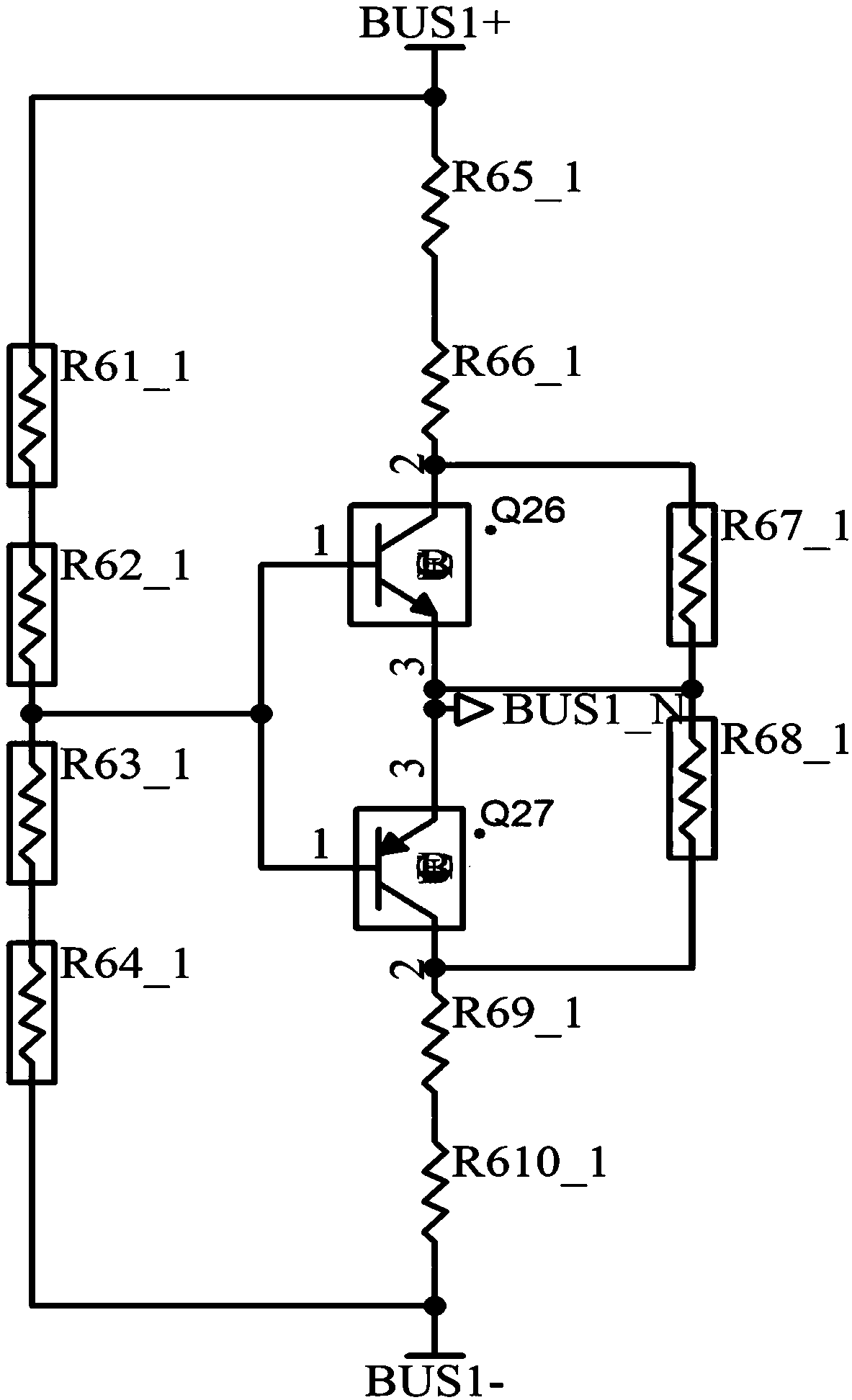
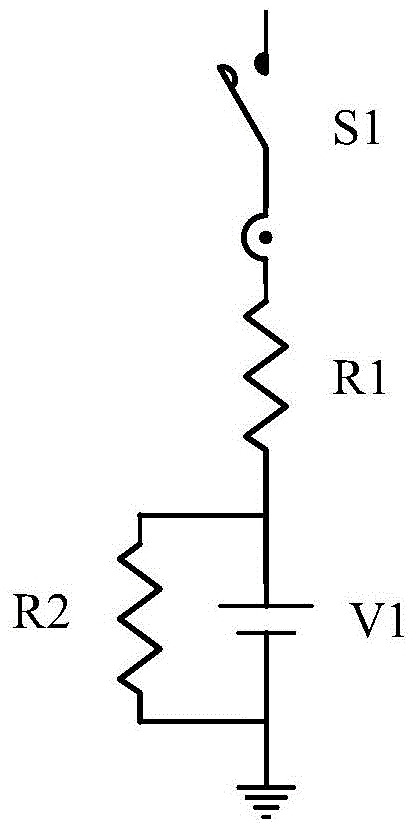
The invention discloses a novel anti-PID device. The novel anti-PID device adopts a three-phase power grid for power supply, and is characterized by being connected with an AC output end of a power supply of an inverter; a virtual midpoint is constructed through inductance and resistance; output of an anti-PID controller is connected between the virtual midpoint and the ground to provide isolationvoltage output, sampling power supply and logic comparison level; the anti-PID controller increases voltage to ground of the virtual midpoint; when the inverter is connected to the grid, the voltageto ground of a PV battery panel is increased, so as to inhibit the generation of a PID effect. The device has the advantages of inhibiting the PID effect and being low in power consumption and good instability, accords with safety standard requirements, and is capable of greatly enhancing the power generation efficiency of photovoltaic grid-connected systems and prolonging the service life of thesystems.
Owner:NINGBO GINLONG TECH
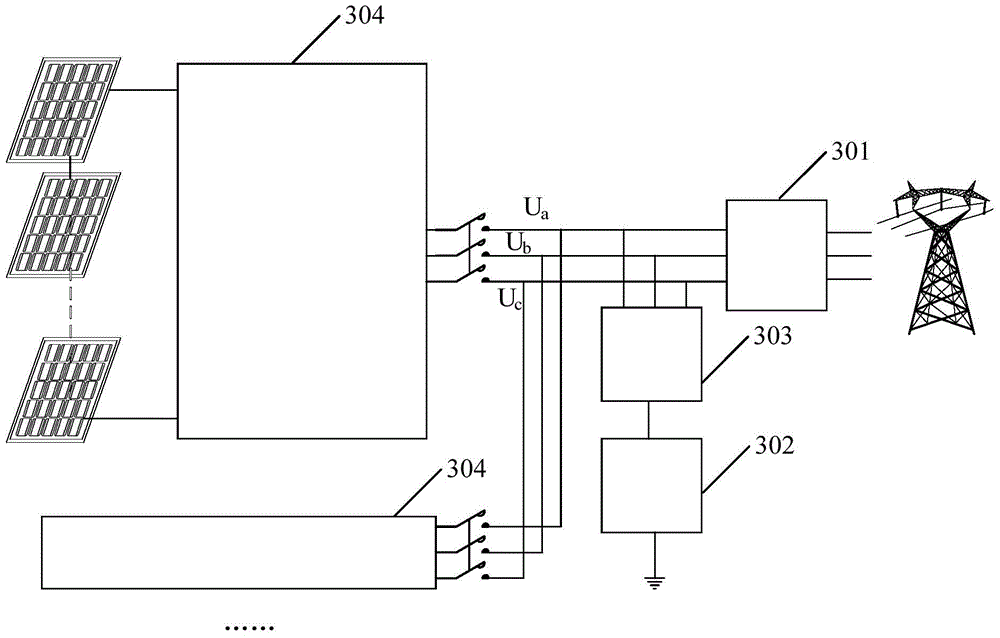
Anti-PID device, anti-PID photovoltaic grid-connected power generation system and anti-PID method
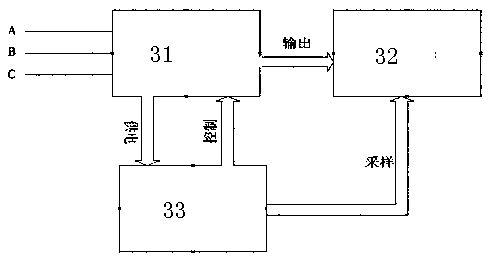
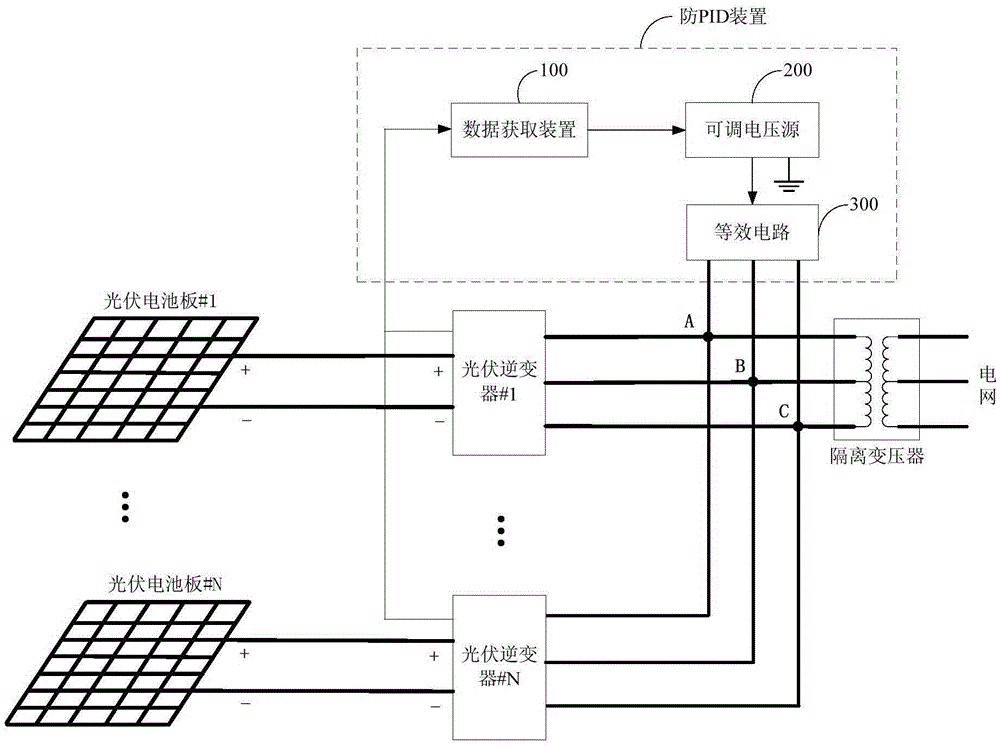
ActiveCN105406516AAvoid PID EffectsAvoid negative pressureContigency dealing ac circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsBusbarData acquisition
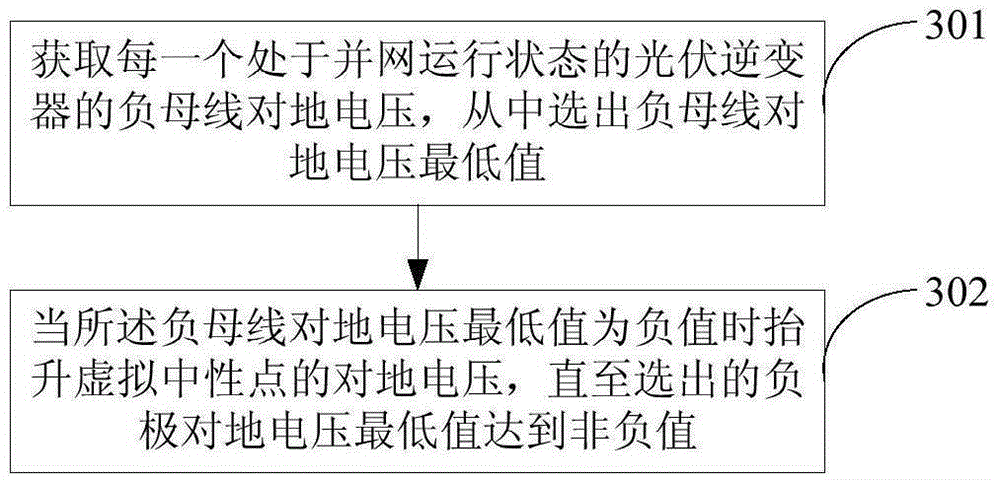
The invention discloses an anti-PID device, an anti-PID photovoltaic grid-connected power generation system and an anti-PID method. The anti-PID device is applied to a direct current-side ungrounded photovoltaic grid-connected power generation system. The anti-PID device includes a data acquisition device, an adjustable voltage source and an equivalent circuit, wherein the data acquisition device is used for acquiring negative busbar voltage to earth of each photovoltaic inverter in a grid-connected operation state, the equivalent circuit is used for constructing an equivalent neutral point of the photovoltaic grid-connected power generation system, the adjustable voltage source is used for selecting out the minimum value of the negative busbar voltage to earth which is transmitted by the data acquisition device in real time; the electric energy output end of the adjustable voltage source is connected with the equivalent neutral point constructed by the equivalent circuit; when the minimum value of the negative busbar voltage to earth is a negative value, the adjustable voltage source boosts the output voltage to earth of the adjustable voltage source itself until the minimum value of the negative busbar voltage to earth becomes a non-negative value. With the anti-PID device, the anti-PID photovoltaic grid-connected power generation system and the anti-PID method adopted, a photovoltaic panel will not generate a PID effect.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
Illite/smectite clay containing anti-PID functional master batch for photovoltaic packaging film and preparation method for illite/smectite clay containing anti-PID functional master batch
ActiveCN109705442AGood anti-PID functionImprove high temperature resistanceNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesives without carriersMasterbatchSilanes
The invention relates to the field of photovoltaic packaging materials and particularly relates to an illite / smectite clay containing anti-PID functional master batch for a photovoltaic packaging filmand a preparation method for the illite / smectite clay containing anti-PID functional master batch. The master batch is prepared from the following ingredients in percentage by weight: 50% to 88% of EVA resin, 4% to 20% of modified zirconium phosphate crystal, 0.5% to 10% of cross-linker, 0.5% to 2.5% of silane coupler, 5% to 15% of nano illite / smectite clay and the balance of auxiliaries. According to the illite / smectite clay containing anti-PID functional master batch for the photovoltaic packaging film and the preparation method for the illite / smectite clay containing anti-PID functional master batch, the defect in the prior art that master batches for photovoltaic packaging films do not have an anti-PID function and thus performance of batteries is low is overcome; the illite / smectiteclay containing anti-PID functional master batch for the photovoltaic packaging film, prepared by the method, has a good anti-PID function; meanwhile, a top-class flame-retardant effect is achieved under the condition of not additionally adding flame retardants; and furthermore, the illite / smectite clay containing anti-PID functional master batch further has the advantages that the antibacterial and mildewproof effect is good, meanwhile, toxic and harmful substances in the functional master batch can be remarkably reduced, and the like.
Owner:NINGBO NENGZHIGUANG NEW MATERIALS TECH
Photovoltaic module based on slide-in track
InactiveCN109586658ALow costInhibition of PID effectPhotovoltaic supportsPhotovoltaic energy generationRare earthBlock structure
The invention discloses a photovoltaic module based on a slide-in track. The photovoltaic module comprises a support frame and a photovoltaic power generation panel, wherein the support frame comprises a base, a support column and a mounting plate; two first hydraulic oil cylinders in conjunction are arranged on the left side of the support column; two second hydraulic oil cylinders in conjunctionare arranged on the right side of the support column; a slide rail is arranged on the mounting plate; the photovoltaic power generation panel includes a frame and a photovoltaic module body; the outer side of the vertical plate of the frame is provided with a slide block structure having a T-shaped cross section; The photovoltaic module body comprises a tempered glass layer, a quartz glass layercontaining a rare earth europium ion complex, a high-volume-resistivity EVA film, a solar panel, an EVA film, a heat dissipation sheet and a high-strength steel wire mesh. The support frame can be adjusted timely to make the photovoltaic module body face the sun, thereby achieving high power generation efficiency, simple structure and low cost. The photovoltaic module suppresses a PID effect, hasa good heat dissipation effect, high photoelectric conversion efficiency, a thin thickness, high strength, and a long service life.
Owner:西藏学伦科技有限公司
Anti-PID (Potential Induced Degradation) assembly and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN108615774AAvoid gatheringNo performance impactPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesPotential induced degradationEngineering
The invention relates to an anti-PID (Potential Induced Degradation) assembly and a manufacturing method thereof. The anti-PID assembly comprises front panel glass, a first packaging layer, at least one photovoltaic solar cell, a second packaging layer, a backplane and an assembly frame, wherein ultrathin two-dimensional electrical nano material layers are arranged between the front panel glass and the first packaging layer and between the second packaging layer and the backplane; and the side edges of the ultrathin two-dimensional electrical nano material layers are connected with the assembly frame. The ultrathin two-dimensional electrical nano material layer is adopted as an insertion layer of a solar module, the layer has strong absorbability, good conductivity and high transmittance and can thus play a good role of adsorbing ions, the ions are transferred to the assembly frame, and thus, accumulation of charges on the surface of the cell caused by ion migration to generate PID effects can be avoided; and due to the high transmittance, application of the two-dimensional nano material can be ensured not to affect the performance of the solar module.
Owner:TAIZHOU ZHONGLAI PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
Double-glass double-faced photovoltaic car shed power generation system with rainproof function
InactiveCN105450147AImprove space utilization efficiencyTake advantage ofPhotovoltaic supportsRoof covering using slabs/sheetsPurlinEngineering
The invention relates to a double-glass double-faced photovoltaic car shed power generation system with a rainproof function. The system comprises a bracket, a purlin, a double-glass double-faced photovoltaic module and a charging box, wherein the purlin is arranged on the bracket; the double-glass double-faced photovoltaic module is arranged on the purlin; and the charging box is connected with the double-glass double-faced photovoltaic module and is used for charging the vehicles. The double-glass double-faced photovoltaic car shed power generation system has the rainproof and power generation functions at the same time, so that the efficient utilization of space is realized and the power generation cost is reduced; due to the rainproof protection, the service life of the charging box can be effectively prolonged.
Owner:JIANGSU ST SOLAR
High-frequency isolation inverter and solar power generating system
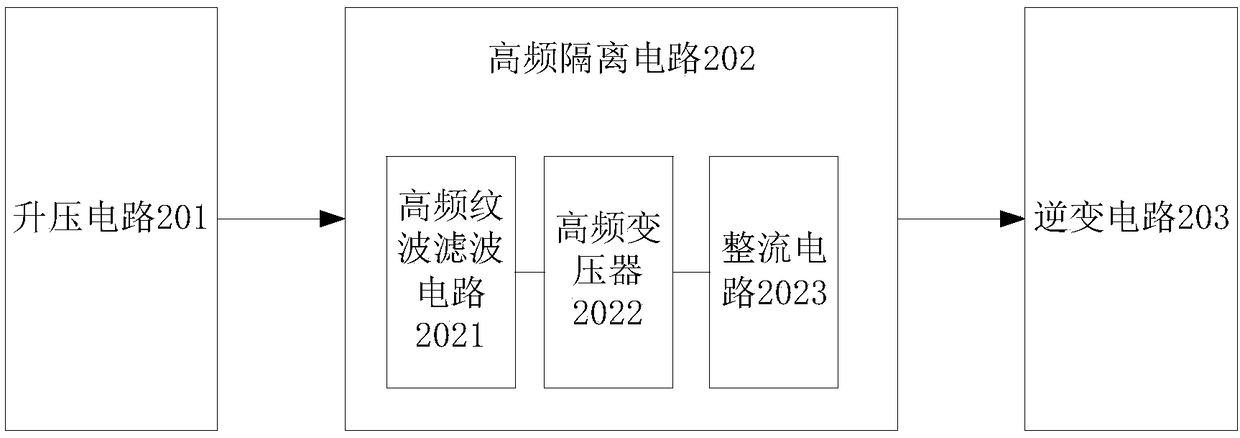
PendingCN108649830ASuppresses Common Mode Leakage CurrentAvoid PID EffectsAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionPower inverterEngineering
The invention discloses a high-frequency isolation inverter and a solar power generating system. The high-frequency isolation inverter comprises a booster circuit connected with a solar power generating device and conducting filtering and pumping on direct voltage output by the solar power generating device, a high-frequency isolation circuit connected with the booster circuit and conducting direct-current isolation conversion on the voltage output by the booster circuit, and an inversion circuit connected with the high-frequency isolation circuit and conducting inverting transformation and filtering on the output voltage of the high-frequency isolation circuit and then outputting alternating current. The high-frequency isolation inverter can effectively inhibit common-mode leakage currentof a thin film module power generating system and prevent the PID effect of a glass-based thin film module and is small in occupied area, low in cost and convenient to install.
Owner:DONGJUN NEW ENERGY CO LTD
Potential-induced degradation prevention circuit and photovoltaic system using same
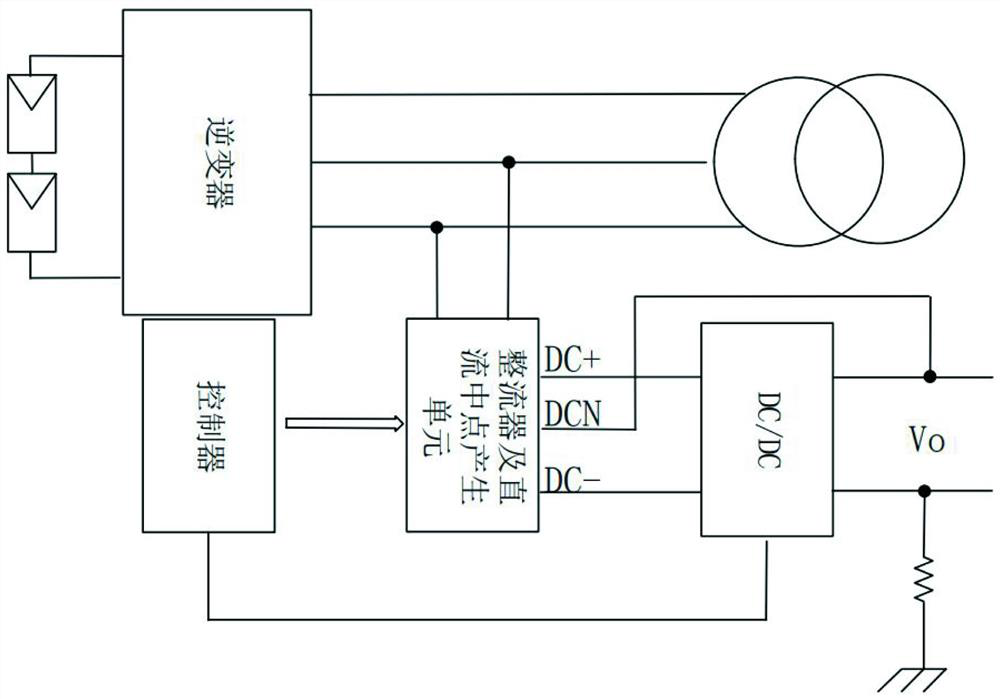
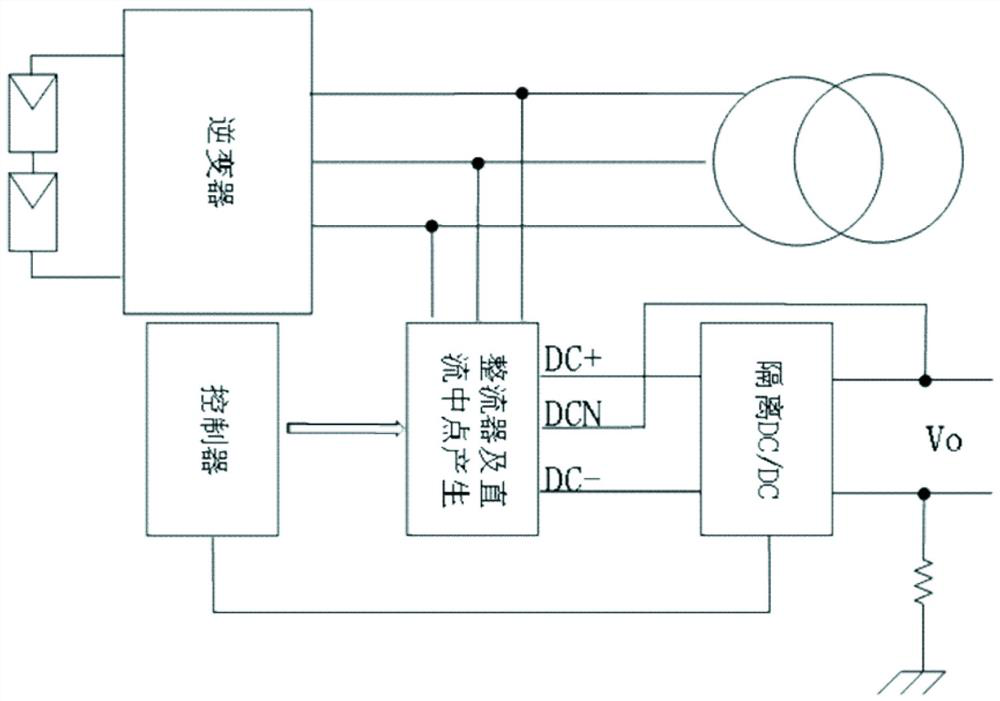
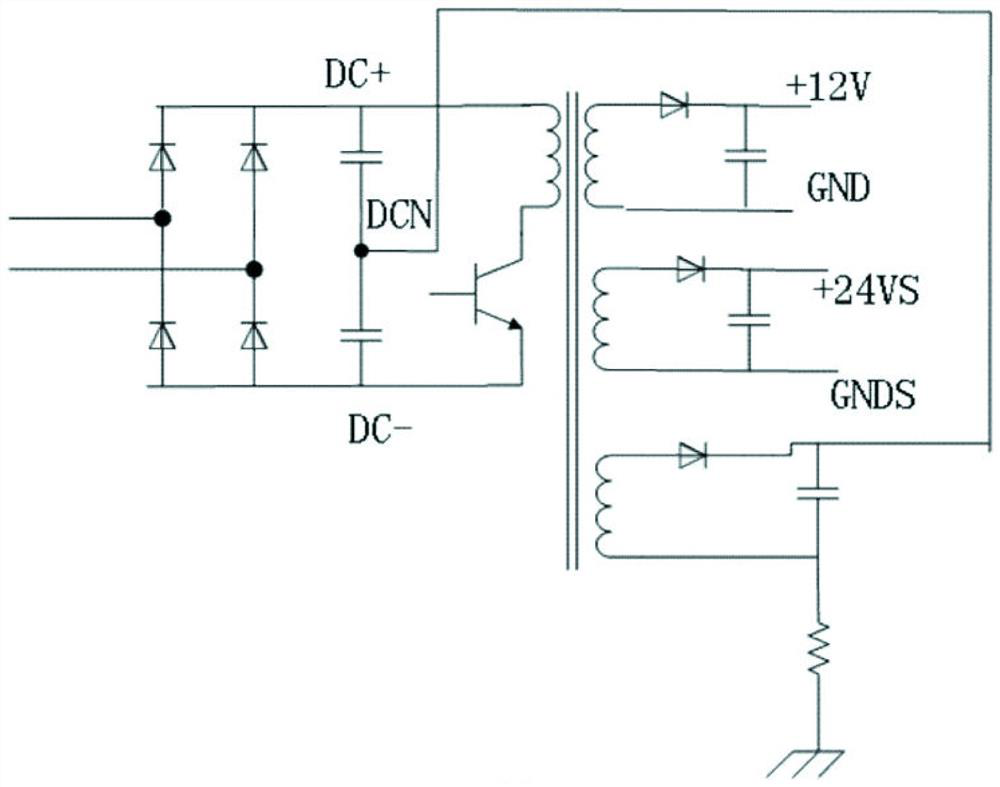
PendingCN114400912ASimple structureImprove performanceAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionPhysicsPower station
The invention relates to a potential induced degradation prevention circuit and a photovoltaic system using the same. The potential-induced degradation prevention circuit comprises a rectifier and a DC / DC converter. The input end of the rectifier is connected with the output end of the inverter, and the rectifier is provided with a positive output port, a negative output port and a voltage midpoint port. And the input end of the DC / DC converter is connected with the positive output port and the negative output port of the rectifier, and the output end of the DC / DC converter is connected to the voltage midpoint port of the rectifier and the ground respectively, and is used for raising the PV-to-ground voltage of the photovoltaic module when the inverter works so as to enable the PV-to-ground voltage to be greater than or equal to 0V. The photovoltaic system comprises a photovoltaic module, an inverter, an isolation transformer and the potential induced degradation prevention circuit. The circuit is simple in structure and reliable in performance, the PID effect of the photovoltaic module can be effectively prevented, meanwhile, the site construction complexity of a power station is reduced, the manual input of the system is reduced, and the operation and maintenance cost is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU GOODWE POWER SUPPLY TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Short fiber reinforced pultrusion composite material solar module frame and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104761880BImprove efficiencyImprove lateral strengthPhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationFiber orientationUltimate tensile strength
Owner:哈尔滨生材新材料科技发展有限公司
Photovoltaic module
InactiveCN104425640AAvoid PID EffectsGuaranteed output powerPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesUltrasound attenuationPotential induced degradation
The invention relates to a photovoltaic module, which comprises a photovoltaic back plate, a first packaging adhesive layer, a solar cell, a second packaging adhesive layer and a transparent cover plate which are stacked in sequence, wherein the volume resistivity of the first packaging adhesive layer and the volume resistivity of the second packaging adhesive layer are not less than 1.2*1014omega.cm. According to the photovoltaic module, by arranging the first packaging adhesive layer and the second packaging adhesive layer, which are high in volume resistivity, at two sides of the solar cell, the PID (potential induced degradation) effect can be effectively avoided, and therefore power attenuation cannot be caused even if the reverse bias phenomenon occurs in a photovoltaic module system during the operation of a photovoltaic power station, and the output power and the generating effect of the photovoltaic module are further ensured.
Owner:CSG PVTECH
Solar cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103178135AAvoid surface recomposition problemsAvoiding Current Recombination ProblemsFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationElectrical conductorSolar cell
The utility provides a solar cell comprising a substrate, a soft doped zone, a semiconductor layer, a first electrode and a second electrode. The substrate is provided with a first surface and a second surface which are arranged oppositely. The soft doped zone is located on the first surface of the substrate, and a doping type of the soft doped zone is opposite to that of the substrate. The semiconductor layer is arranged above the soft doped zone, and the doping type of the semiconductor layer is identical to that of the substrate. The first electrode is located on the first surface of the substrate, and the bottom of the first electrode is cut to align to a port between the soft doped zone and the first surface. The second electrode is arranged on the second surface of the substrate.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
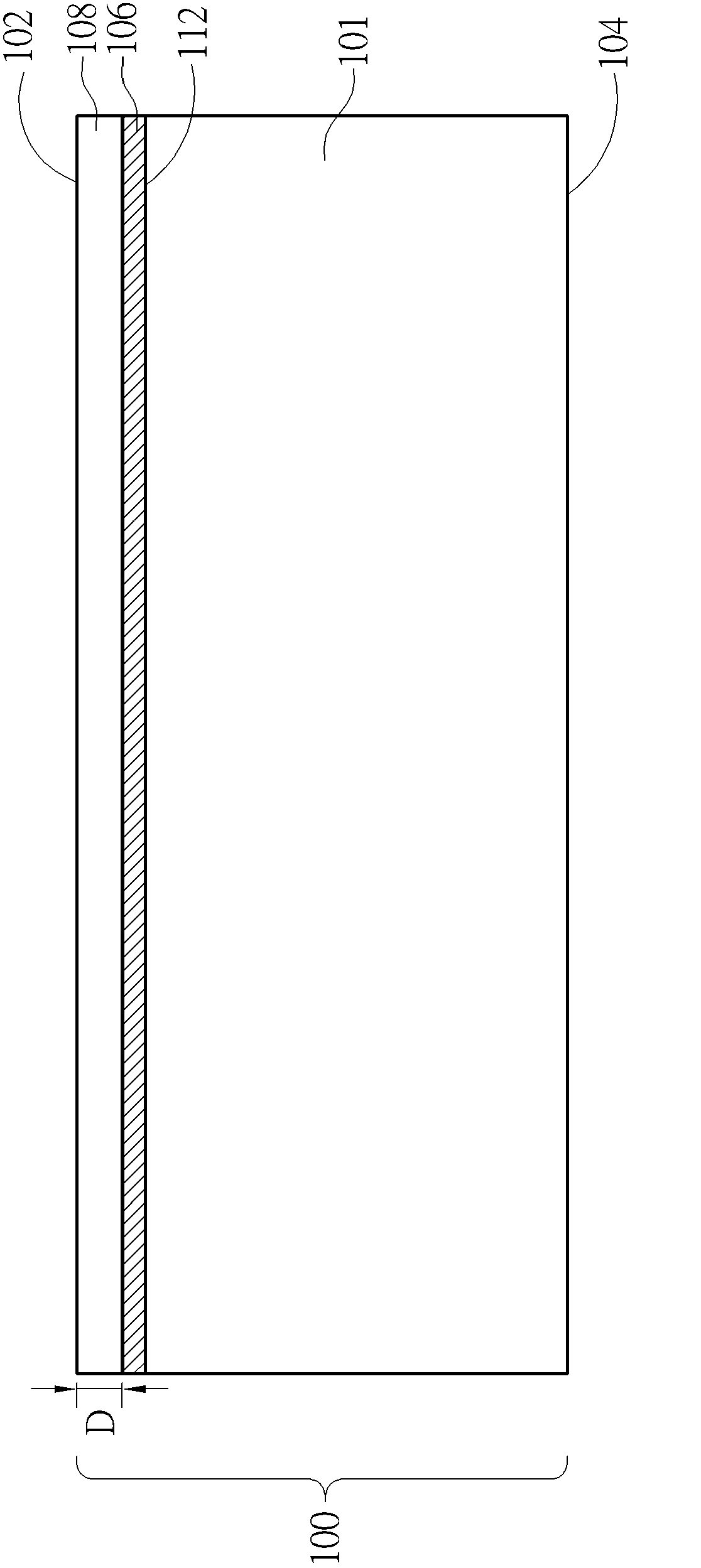
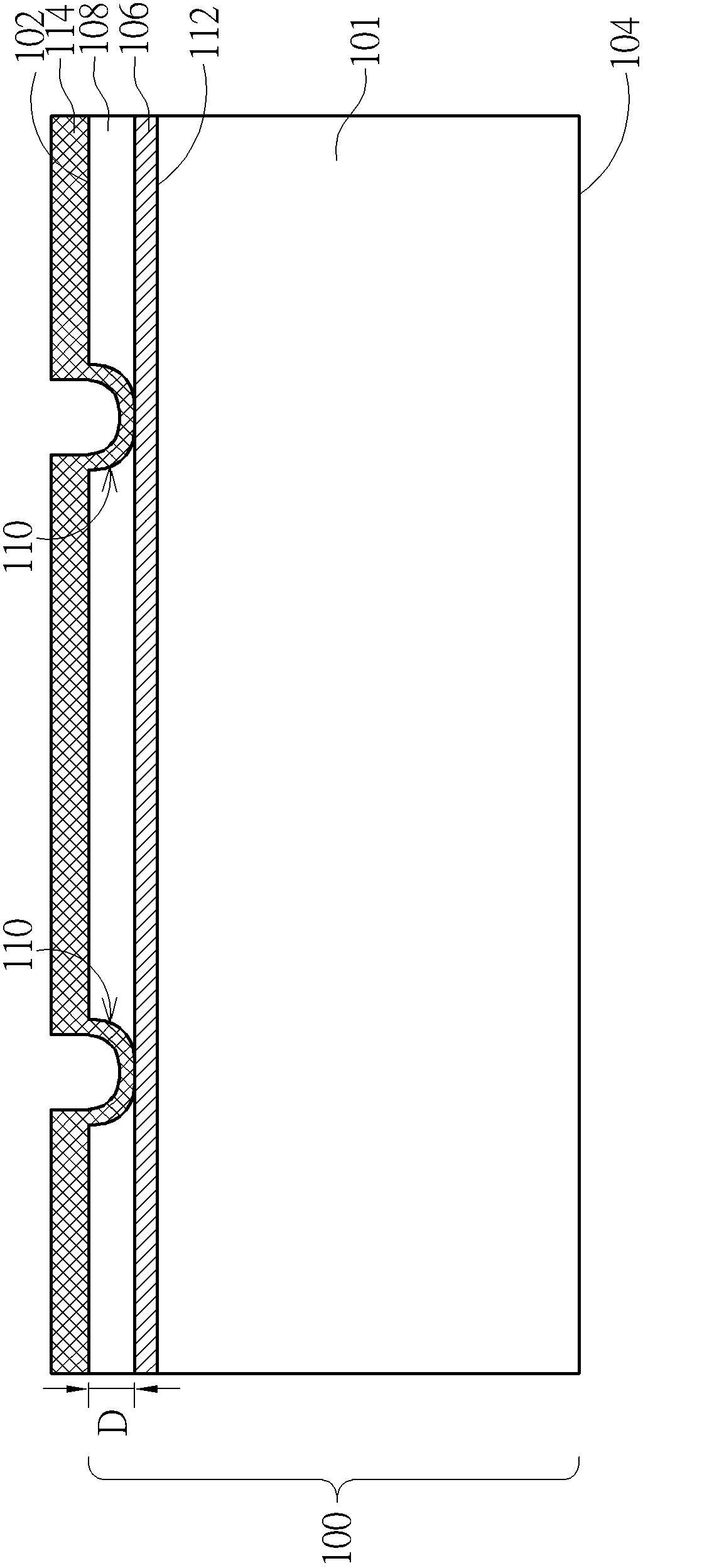
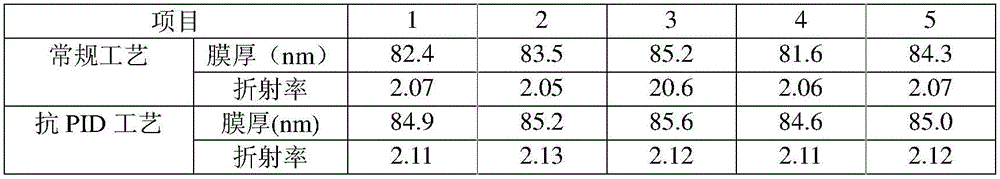
Dual-layer antireflection film plating process capable of resisting PID effect of monocrystal solar cell
ActiveCN106024973AInhibition of PID effectFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationGraphiteSolar cell
The invention relates to a dual-layer antireflection film plating process capable of resisting a PID effect of a monocrystal solar cell. The process is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1) enabling an oxide layer to be grown on a silicon wafer after the phosphorosilicate glass is removed by adopting an ultraviolet oxidization process specifically at the technological temperature of 350-400 DEG C with the oxygen flow of 4-10L / min for 20-50s to form a compact oxide layer on the surface of the silicon wafer; (2) inserting the silicon wafer into a graphite boat and putting the graphite boat into a furnace tube; (3) vacuumizing the furnace tube to reduce the pressure in the furnace pipe to be less than 35mtorr; and (4) pumping 6,000-6,200sccm of ammonia gas to the furnace tube, controlling the pressure in the furnace tube to be 1,600-1,700mtorr, controlling the temperature to be 425 DEG C, and opening a radio frequency power supply. Trials prove that the PID effect of the solar cell can be well solved by the ultraviolet oxidization and a PECVD (plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition) process.
Owner:宁夏银星能源光伏发电设备制造有限公司
A kind of anti-pid packaging adhesive film for photovoltaic cells
ActiveCN104530994BNo hydrolysis reactionImprove anti-PID performanceNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesivesPolyolefinAlpha-olefin
The invention discloses a PID-resistant encapsulation adhesive film used for a photovoltaic cell. The PID-resistant encapsulation adhesive film comprises, by mass, polyolefin resin 80%-95%, polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane 1%-20%, a peroxide crosslinking agent 0.1-2%, an auxiliary crosslinking agent 0.01-1%, a light stabilizing agent and an ultraviolet absorber, wherein the polyolefin resin is an ethylene / alpha-olefin copolymer or a composition of the ethylene / alpha olefin copolymer; the polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane contains a hydrolysable radical which is selected from one or more of a methoxy group, an ethoxy group, a methoxyethoxy group and an acetoxyl group. The PID-resistant encapsulation adhesive film has good adhesive performance and ageing-resistant performance while having excellent PID-resistant performance, thereby having positive practical significance.
Owner:SUZHOU DUCHAMPS ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Photovoltaic element and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104037242BInhibition of PID effectFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationUltrasound attenuationSemiconductor structure
The present invention provides a photovoltaic element and a manufacturing method thereof. The photovoltaic element comprises a semiconductor structure composition and a protection layer. The semiconductor structure composition comprises a plurality of side surfaces, a p-n junction, an n-p junction, a p-i-n junction, an n-i-p junction, a double junction and a multiple junction. In particular, the protection layer is formed to cover the plurality of side surfaces of the semiconductor structure composition. Therefore, the protection layer is allowed to prevent the photovoltaic element from generating a potential induced attenuation effect.
Owner:SINO AMERICAN SILICON PROD
A kind of insulation resistance detection method and circuit
ActiveCN103983855BRealize the suppression functionRealize detectionImpedence measurementsCells panelGrid connection
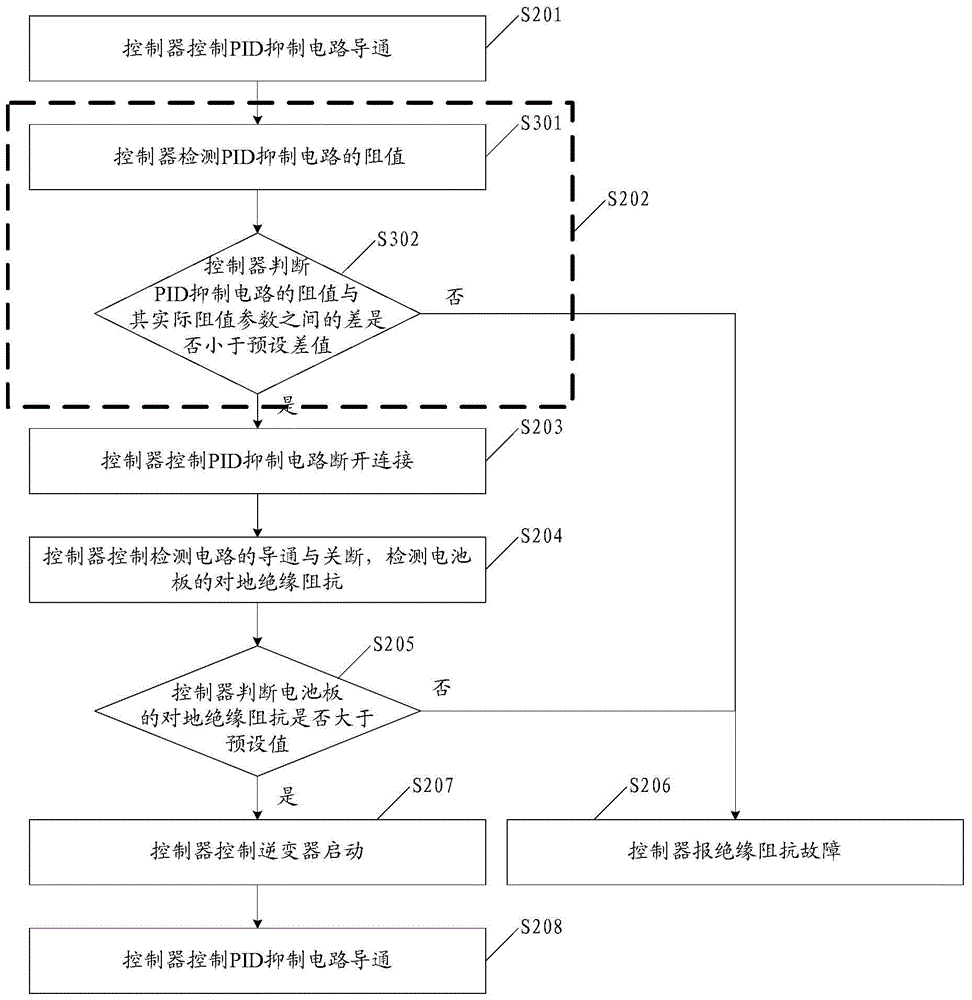
The invention discloses a method and circuit for detecting insulation resistance. A controller controls turn-on and turn-off of a PID suppression circuit and then controls turn-on and turn-off of the circuit for detecting insulation resistance, and then insulation resistance against the ground of a cell panel can be detected; whether the insulation resistance against the ground of the cell panel is larger than a preset value or not is judged; when it is judged that the insulation resistance against the ground of the cell panel is smaller than or equal to the preset value, insulation resistance faults are reported; when it is judged that the insulation resistance against the ground of the cell panel is larger than the preset value, an inverter is controlled to be started, then the PID suppression circuit is controlled to be turned on, and then suppression of the PID effect is achieved. Detection on the insulation resistance against the ground of the cell panel is achieved before grid connection of the inverter, the function of suppressing PID is achieved, and the problems in the prior art are solved.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
A realization method of preventing pid effect of photovoltaic panels
ActiveCN103888052BInhibition of PID effectDoes not affect workPhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationUltrasound attenuationCells panel
Owner:SHANGHAI CHINT POWER SYST +1
A kind of preparation method of crystalline silicon solar cell
ActiveCN103199153BShield breachFulfil requirementsPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesDielectricPotential induced degradation
Disclosed is a method for preparing a crystalline silicon solar cell. The method comprises the following steps: (1) cleaning the surface of a silicon slice, and performing texturing, diffusion, junction making and edge etching on the surface of the silicon slice; (2) forming a layer of silicon dioxide dielectric film on a light-receiving surface or a double surfaces of the silicon slice, the thickness of the layer of silicon dioxide dielectric film is 1.0 to 10 nm; and (3) performing antireflective film coating, silk-screen printing and sintering to obtain the crystalline silicon solar cell. In this way, a method for preparing a crystalline silicon solar cell resisting potential induced degradation is developed. The formed silicon dioxide dielectric film well blocks ion migration, prevents the ion migration from damaging a PN junction and effectively restrains a PID effect and can meet requirements on a PID Free cell plate.
Owner:CSI CELLS CO LTD
Common positive electrode DC/DC converter and photovoltaic inverter system formed by common positive electrode groups of common anode DC/DC converter
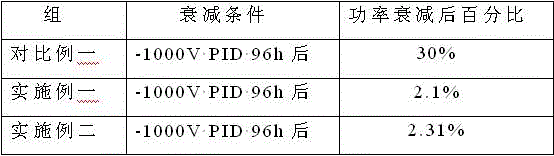
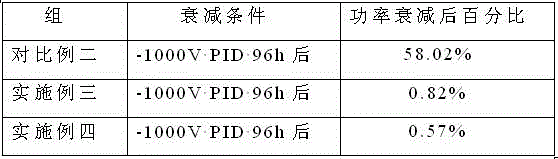
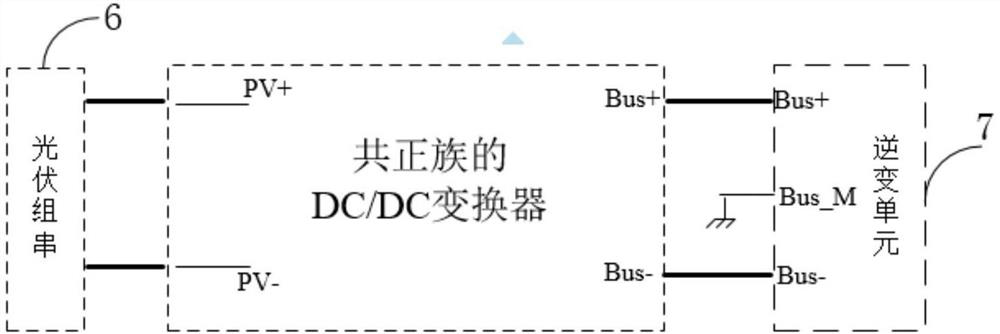
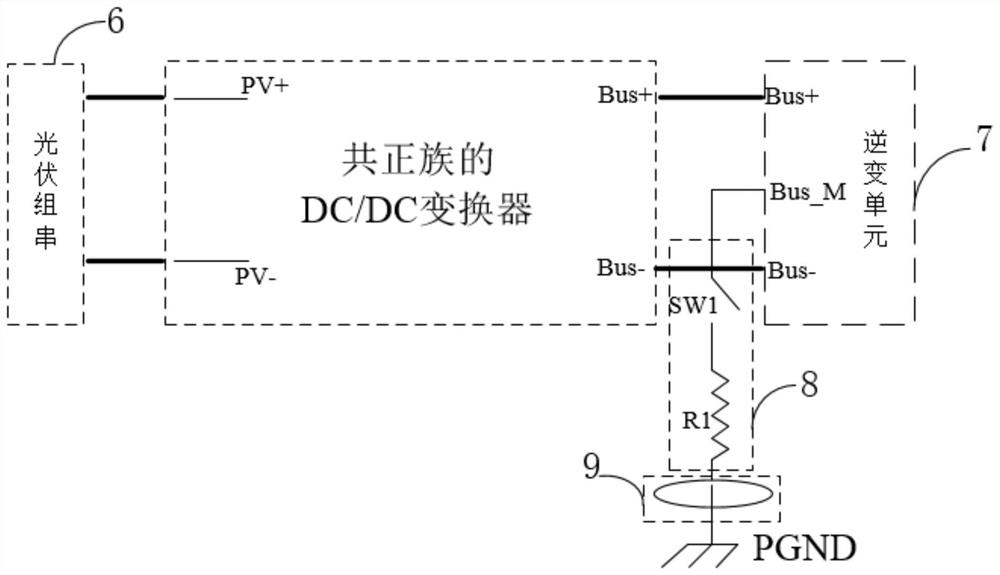
PendingCN113315373AHave the ability to protectInhibition of PID effectDc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectrical polarityEngineering
The invention discloses a common positive electrode DC / DC converter and a photovoltaic inverter system formed by the common positive electrode groups of the common positive electrode DC / DC converter. The common positive electrode DC / DC converter comprises a photovoltaic connecting unit, a switch control unit, an energy storage unit, a polarity output control unit and an inverter connecting unit, one end of the switch control unit and a bus positive electrode end of the inversion connection unit are both connected with a photovoltaic positive electrode end of the photovoltaic connection unit, a photovoltaic negative electrode end of the photovoltaic connection unit is connected with one end of the energy storage unit, and the other end of the energy storage unit and a negative electrode end of the polarity output control unit are both connected with the other end of the switch control unit. The positive electrode end of the polarity output control unit is connected with the bus negative electrode end of the inversion connection unit, the midpoint of the bus positive electrode end and the bus negative electrode end of the inversion connection unit is grounded, and the photovoltaic inversion system formed by the common positive group comprises a plurality of photovoltaic group strings, inversion units and at least one common positive electrode DC / DC converter. The common positive electrode DC / DC converter is applied to a photovoltaic inverter system of 1000V-3000V and higher voltage level, and effectively inhibits the PID effect of a photovoltaic panel.
Owner:SINENG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Photovoltaic module frame and material thereof, and photovoltaic module
PendingCN112636682AReduce performanceIncrease output powerPhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationFiberEngineering
The invention discloses a photovoltaic module frame and a material thereof, and a photovoltaic module, relates to the technical field of solar photovoltaic modules, and aims to solve the problems that the PID effect of the photovoltaic module is caused and the generating capacity of the photovoltaic module is influenced due to the fact that water vapor permeates into the photovoltaic module. The photovoltaic module frame material comprises a thermoplastic polymer material, an inorganic fiber material and a dispersing agent. Specifically, the thermoplastic polymer material accounts for 64%-72% of the photovoltaic module frame material by mass percentage, the inorganic fiber material accounts for 24%-32% of the photovoltaic module frame material by mass percentage, and the dispersing agent accounts for 2.5%-4% of the photovoltaic module frame material by mass percentage. The photovoltaic module frame comprises the photovoltaic module frame material provided by the technical scheme. The photovoltaic module frame material provided by the invention is used for manufacturing the photovoltaic module frame.
Owner:滁州隆基乐叶光伏科技有限公司
A device for suppressing the pid effect of a solar panel
ActiveCN103973217BInhibition of PID effectIncreased voltage to groundPhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationPhotovoltaic power stationAlternating current
Owner:SINENG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com