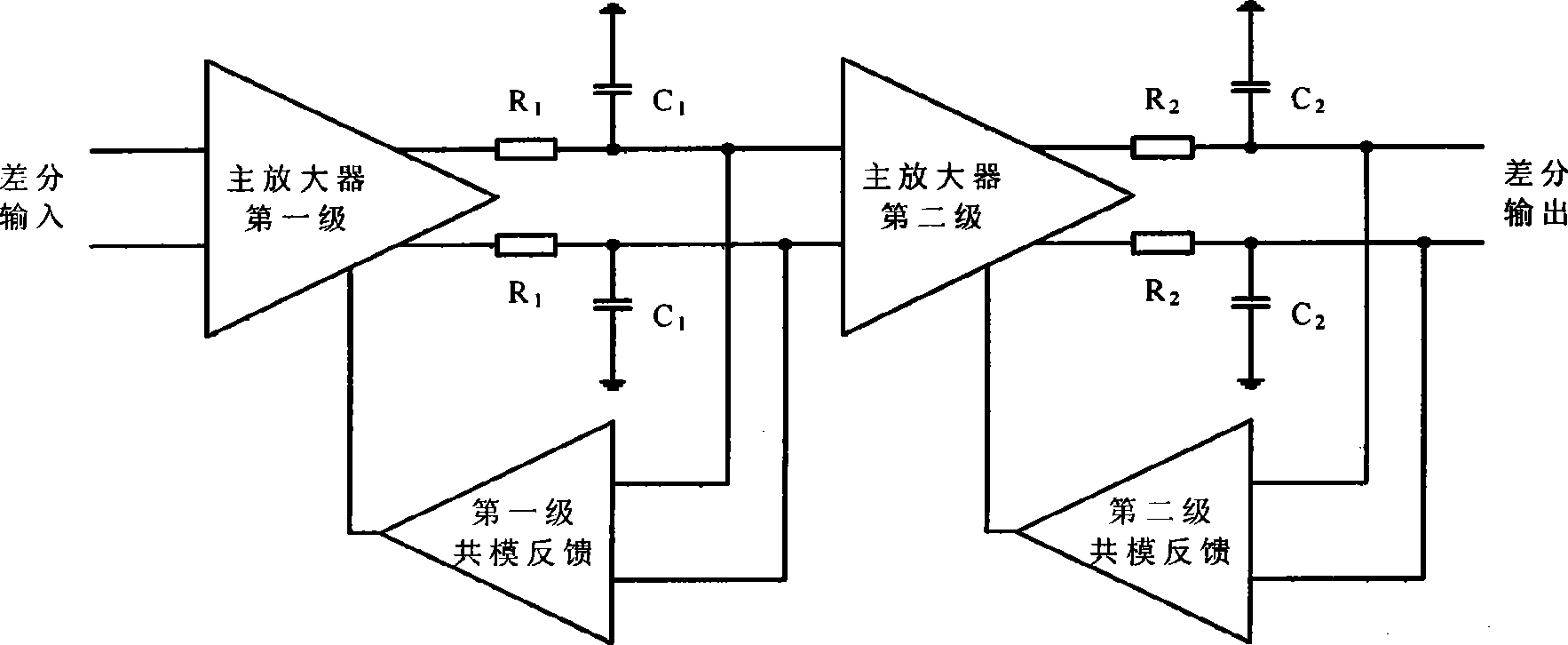
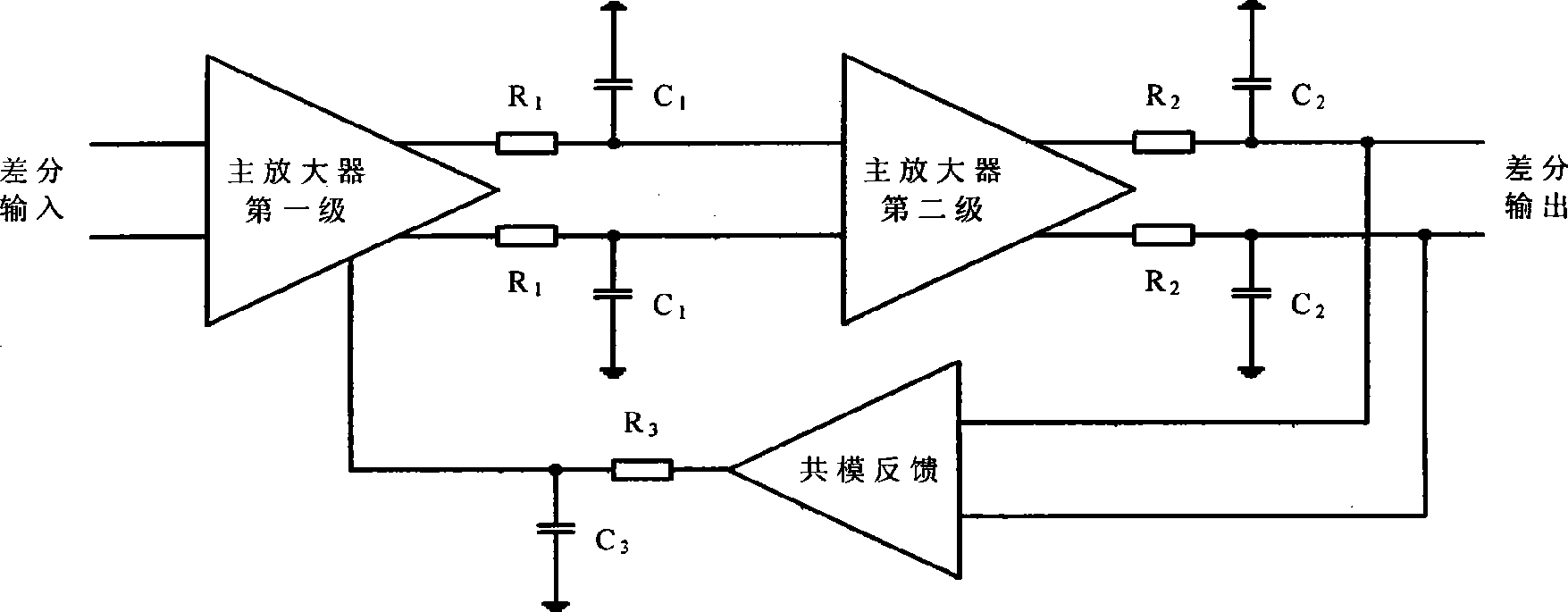
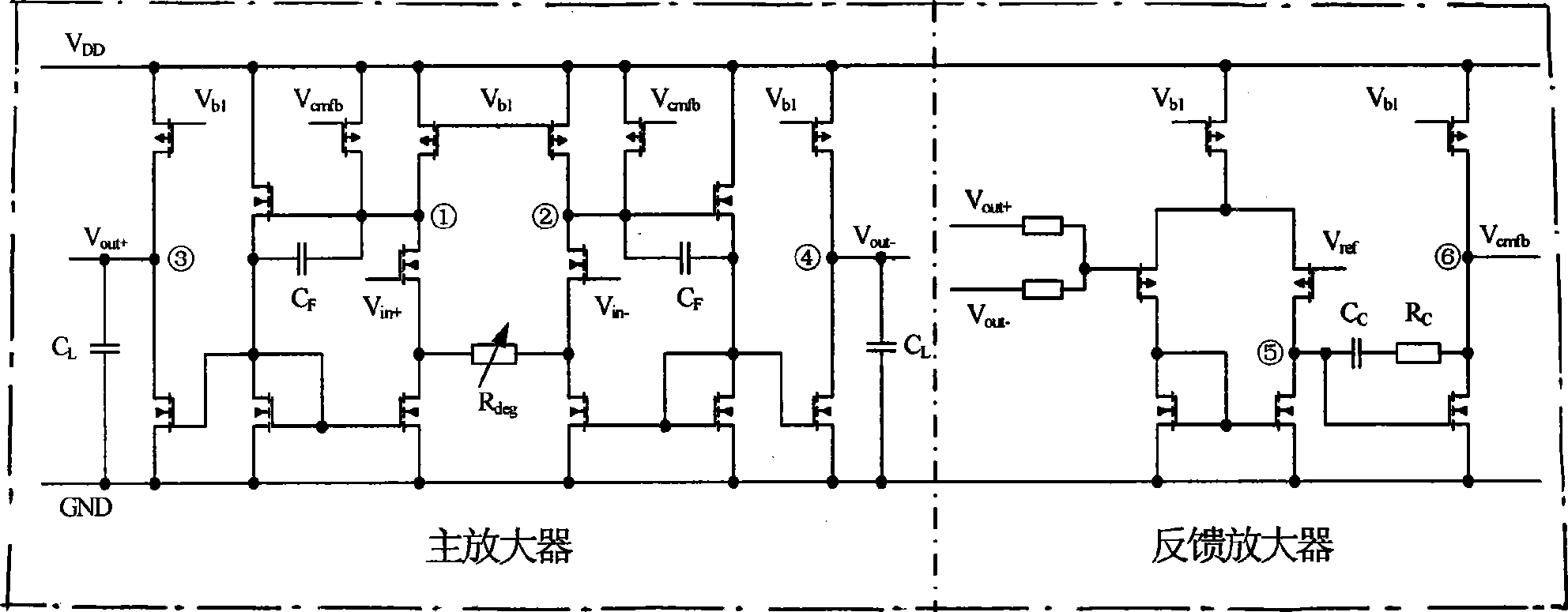
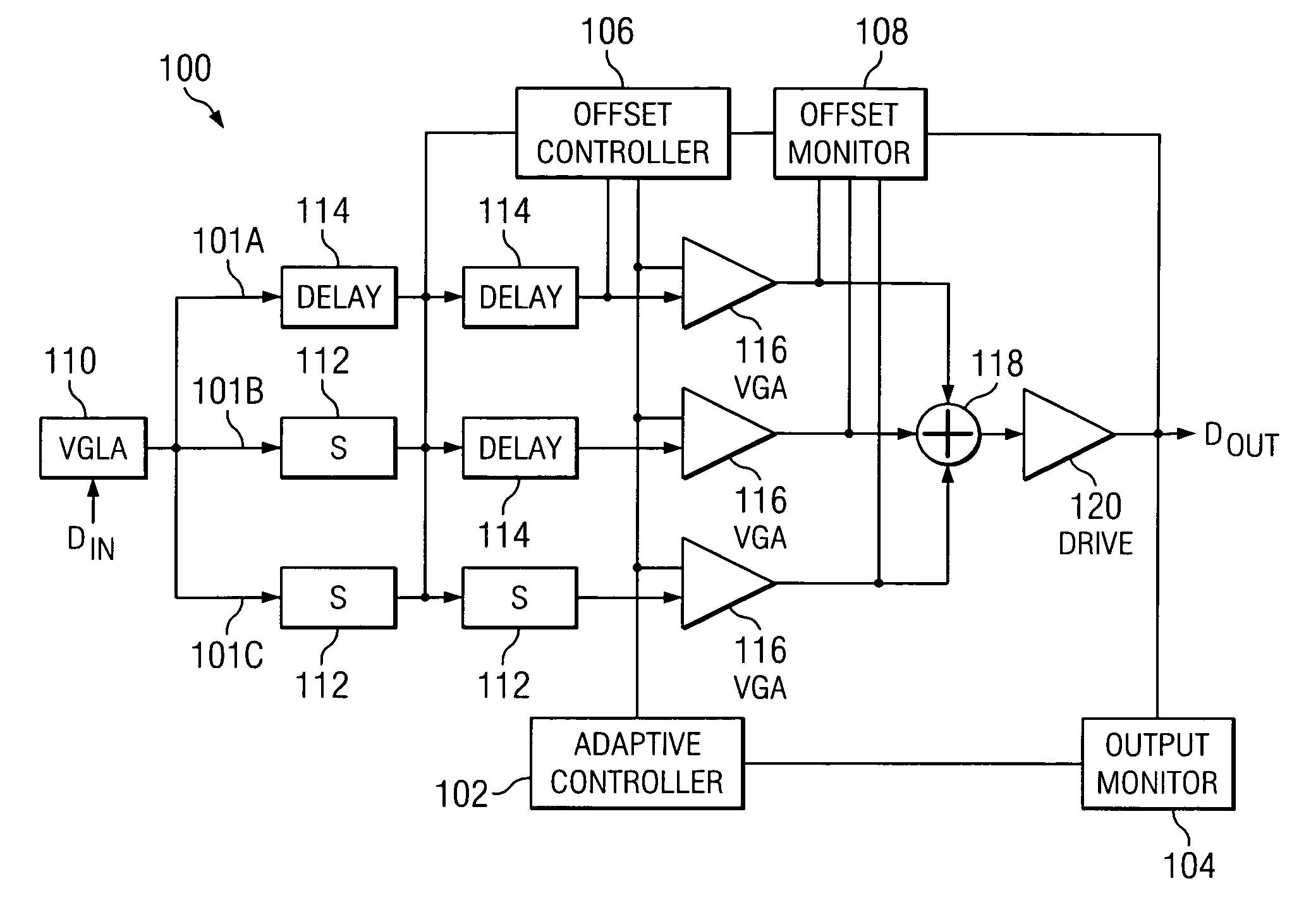
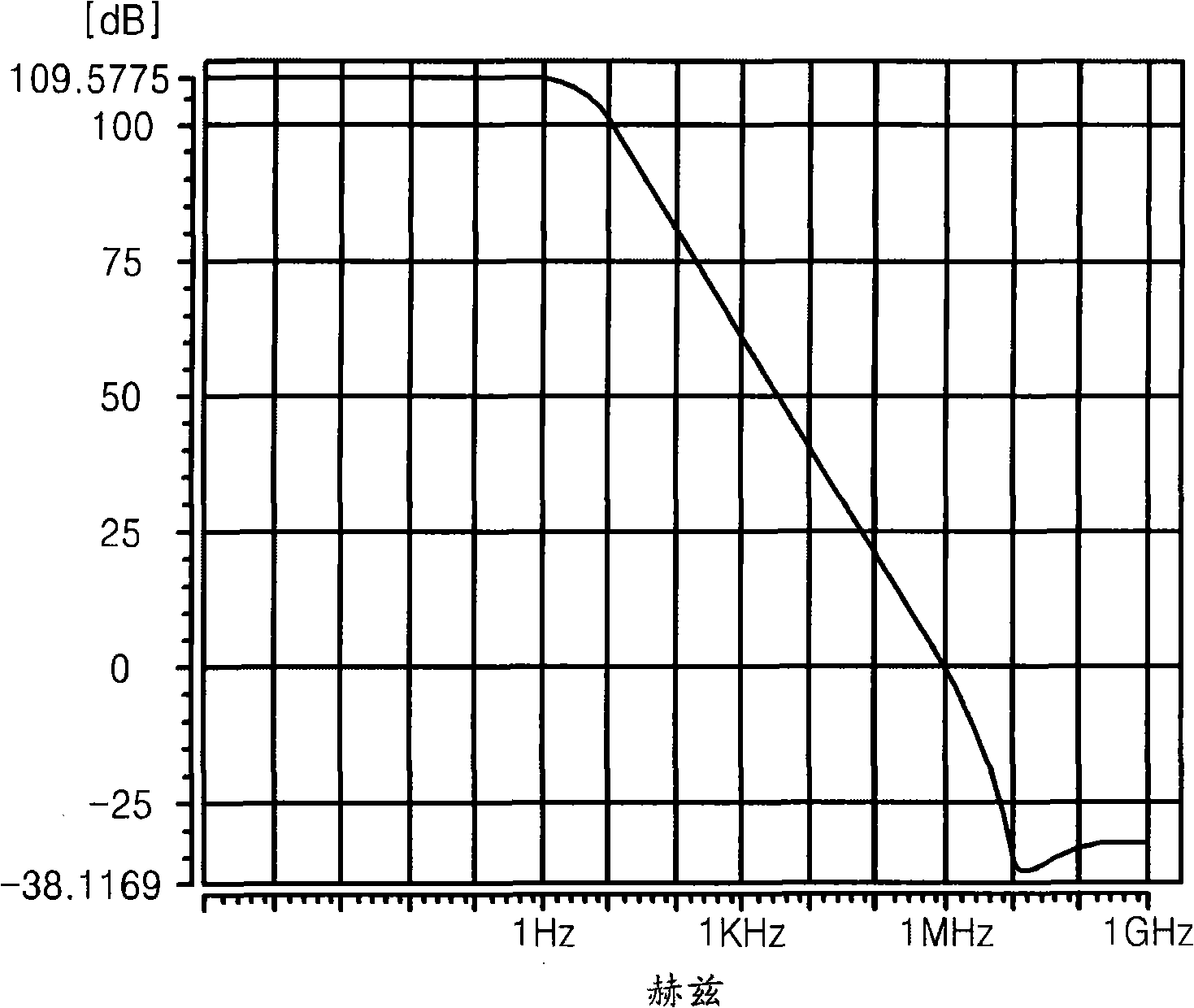
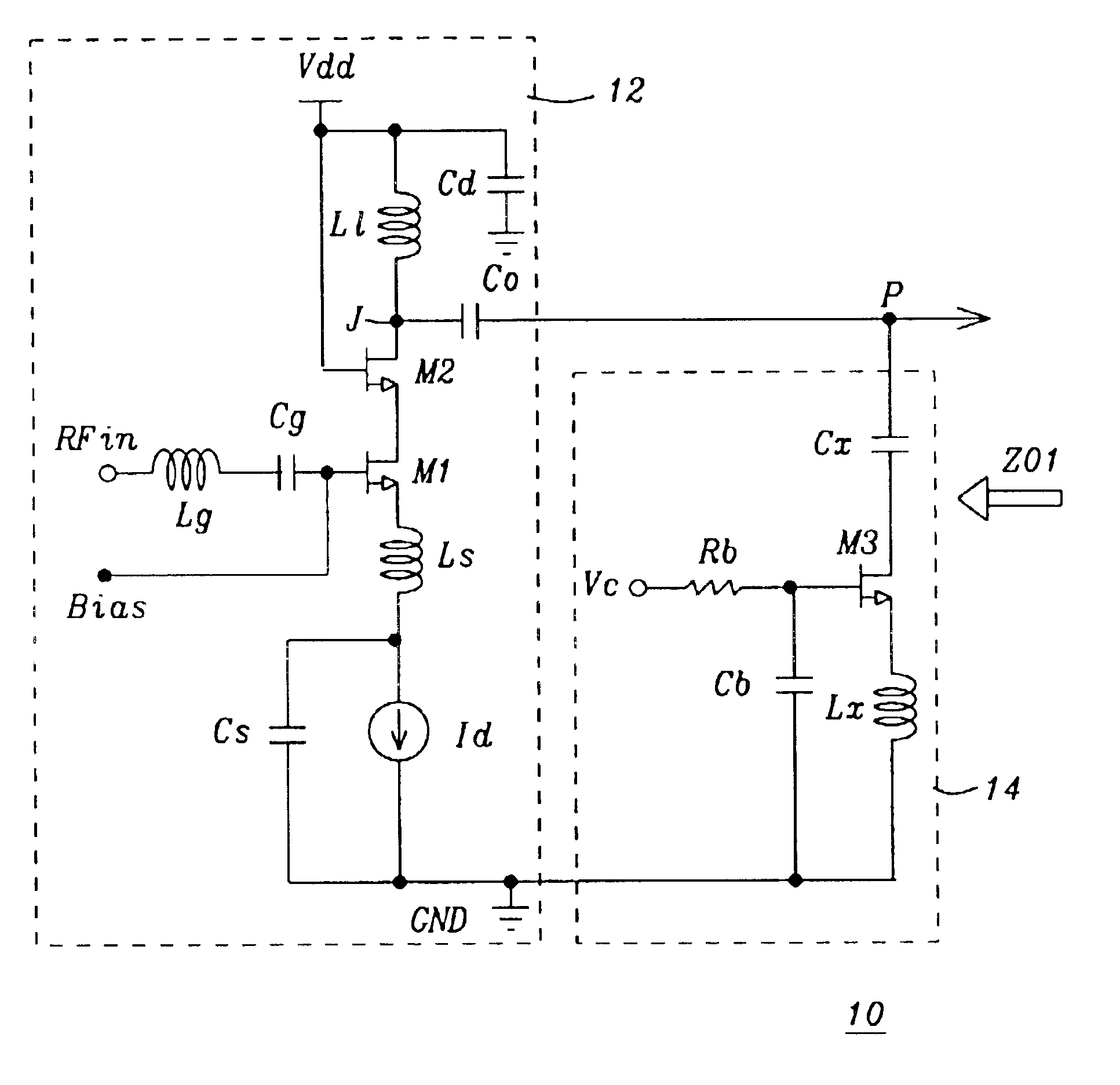
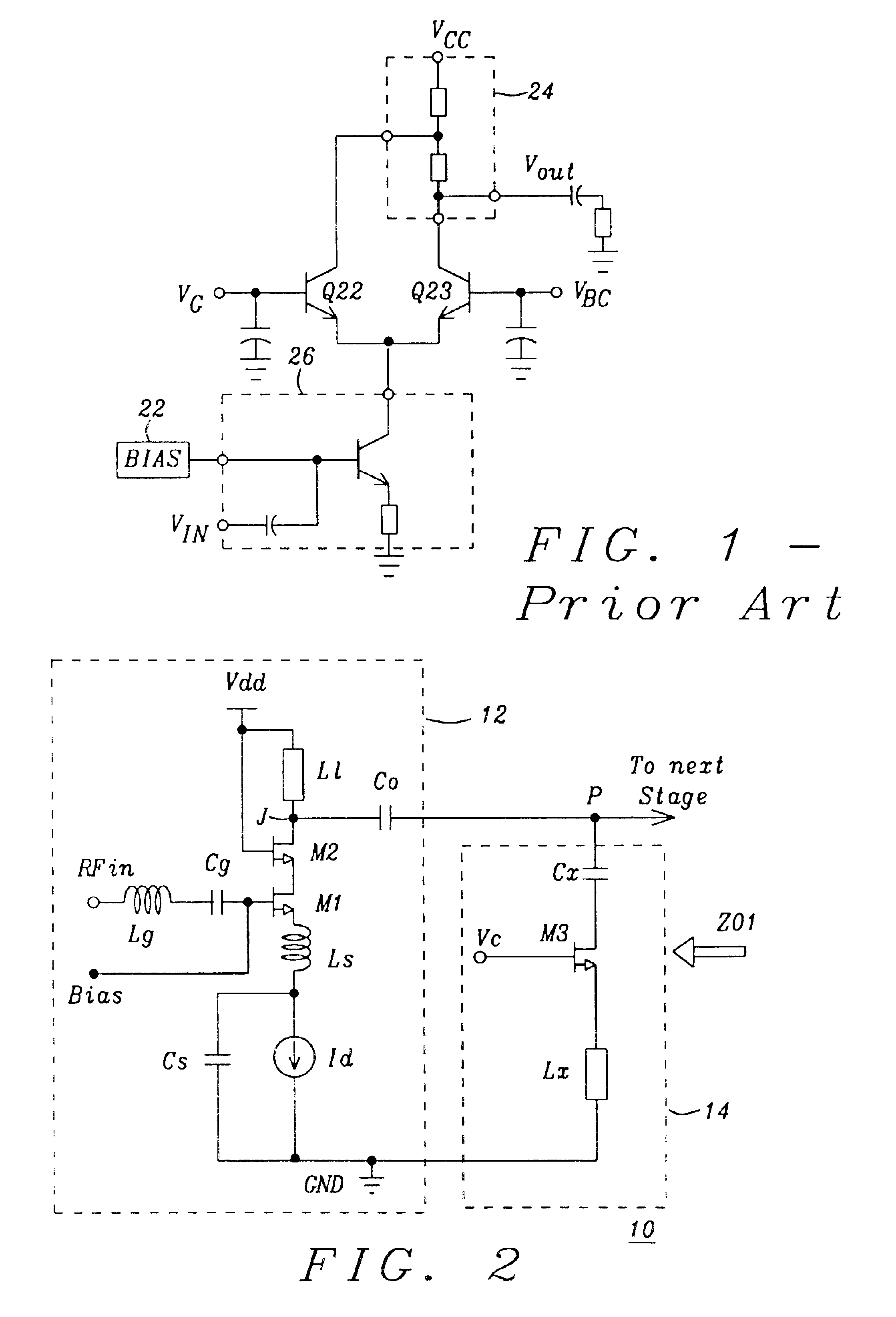
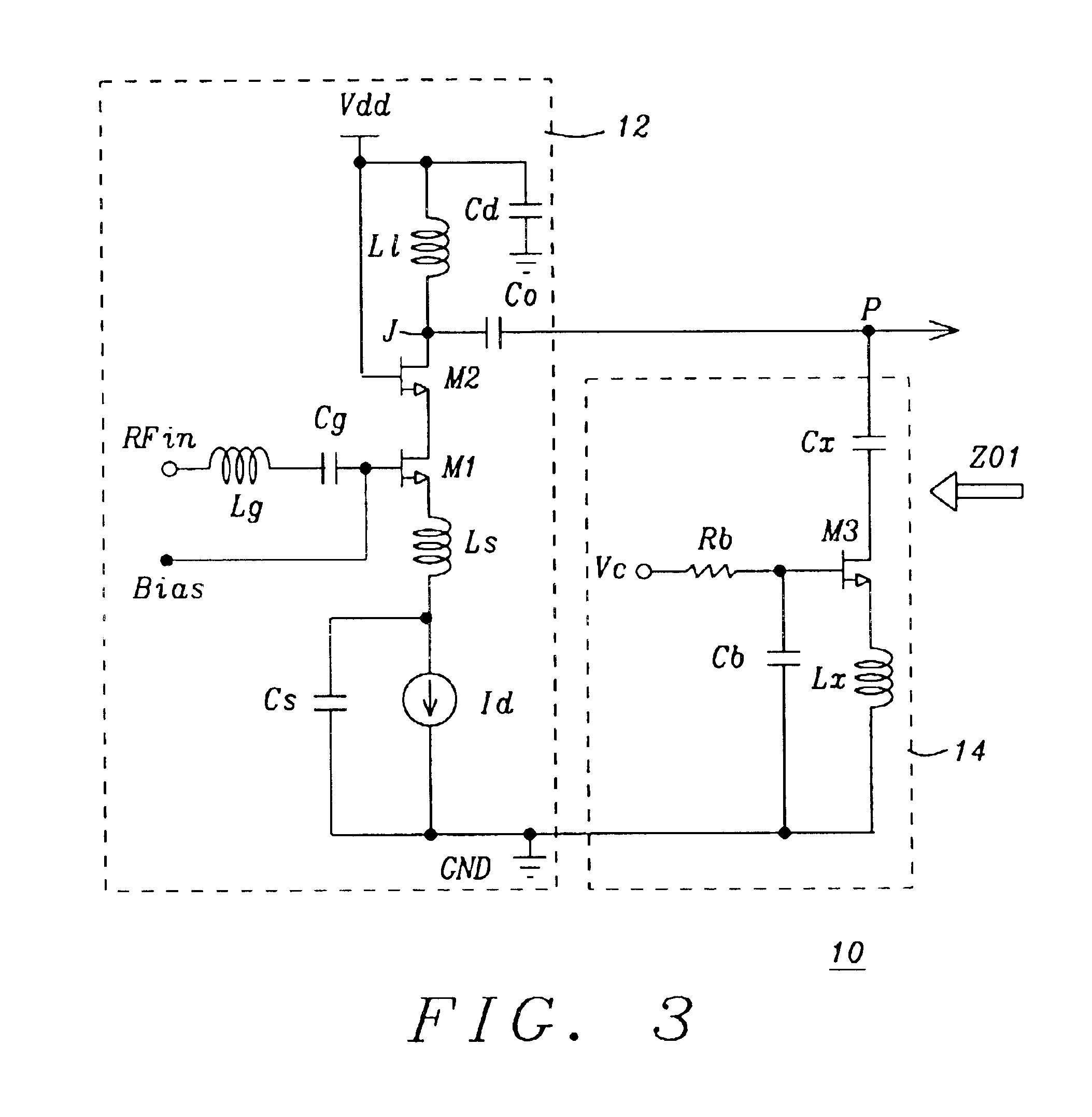
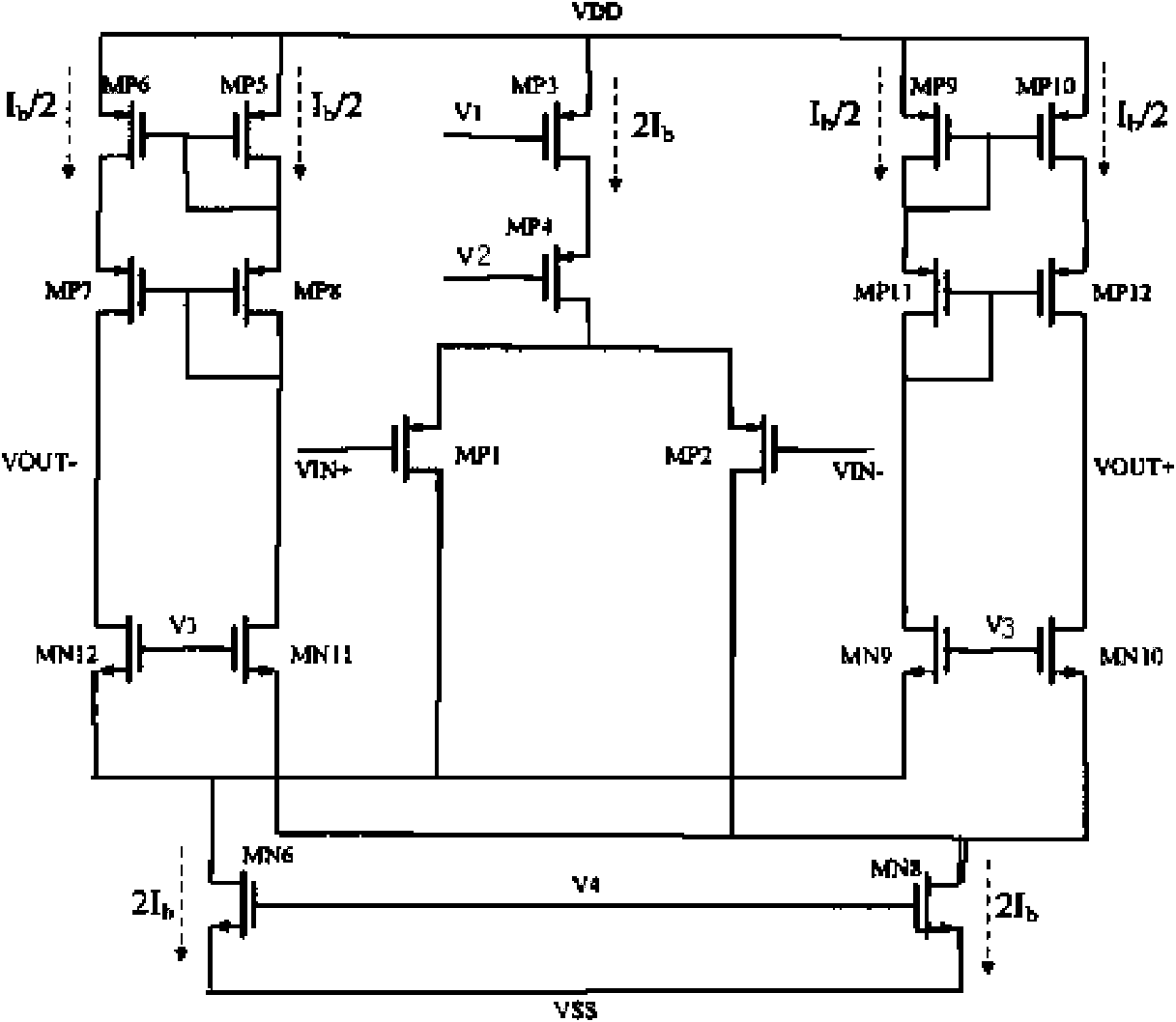
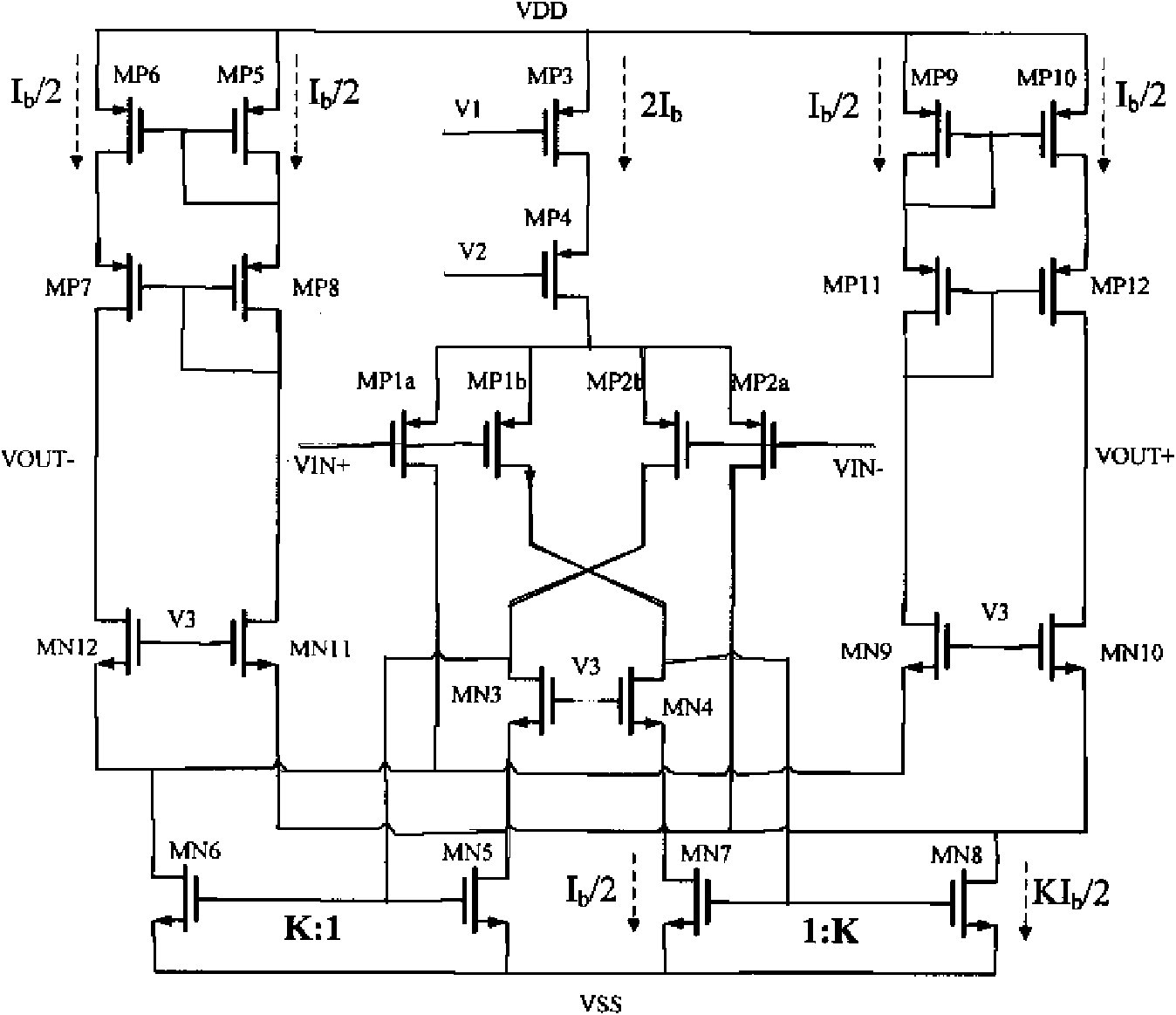
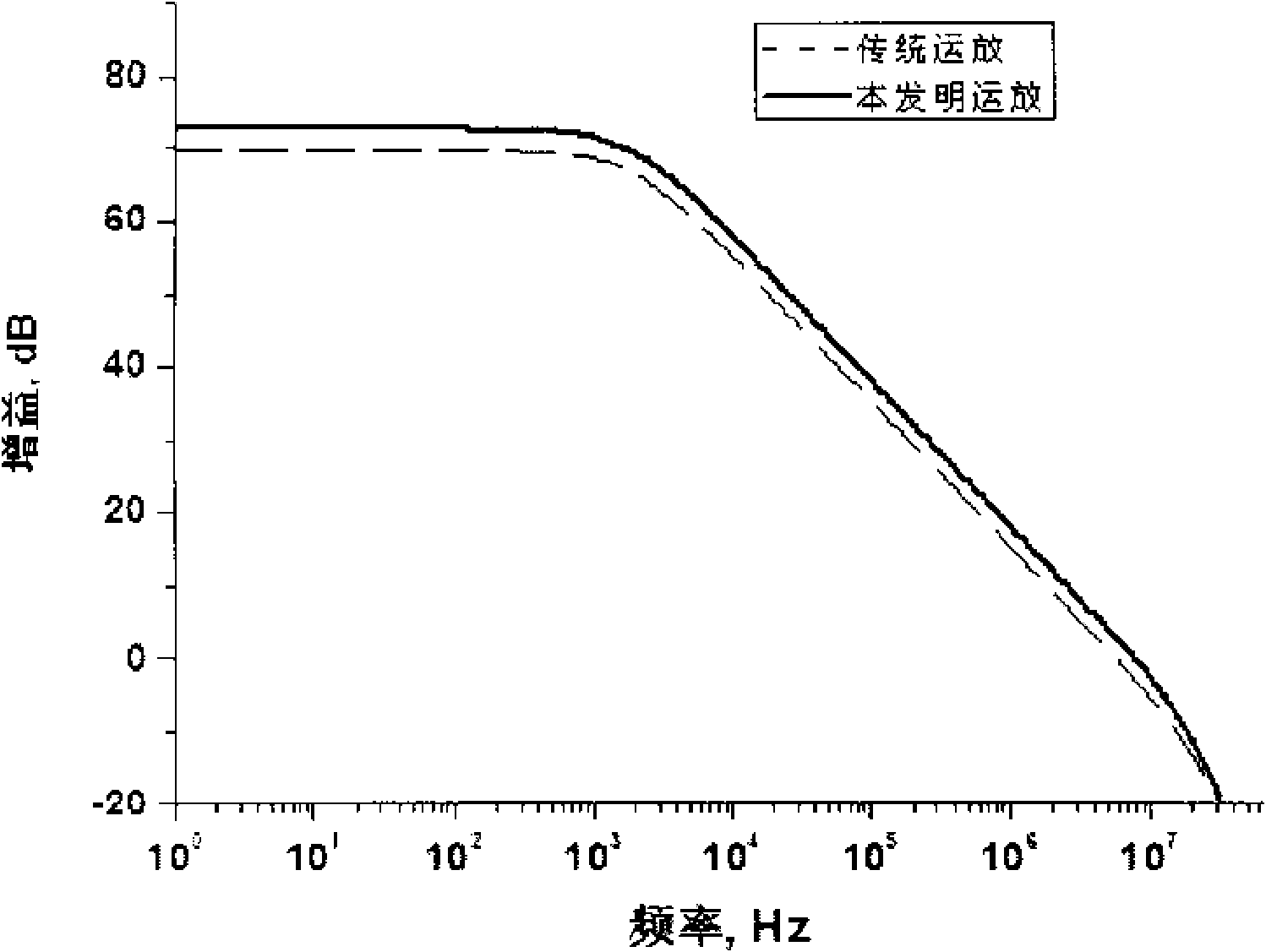
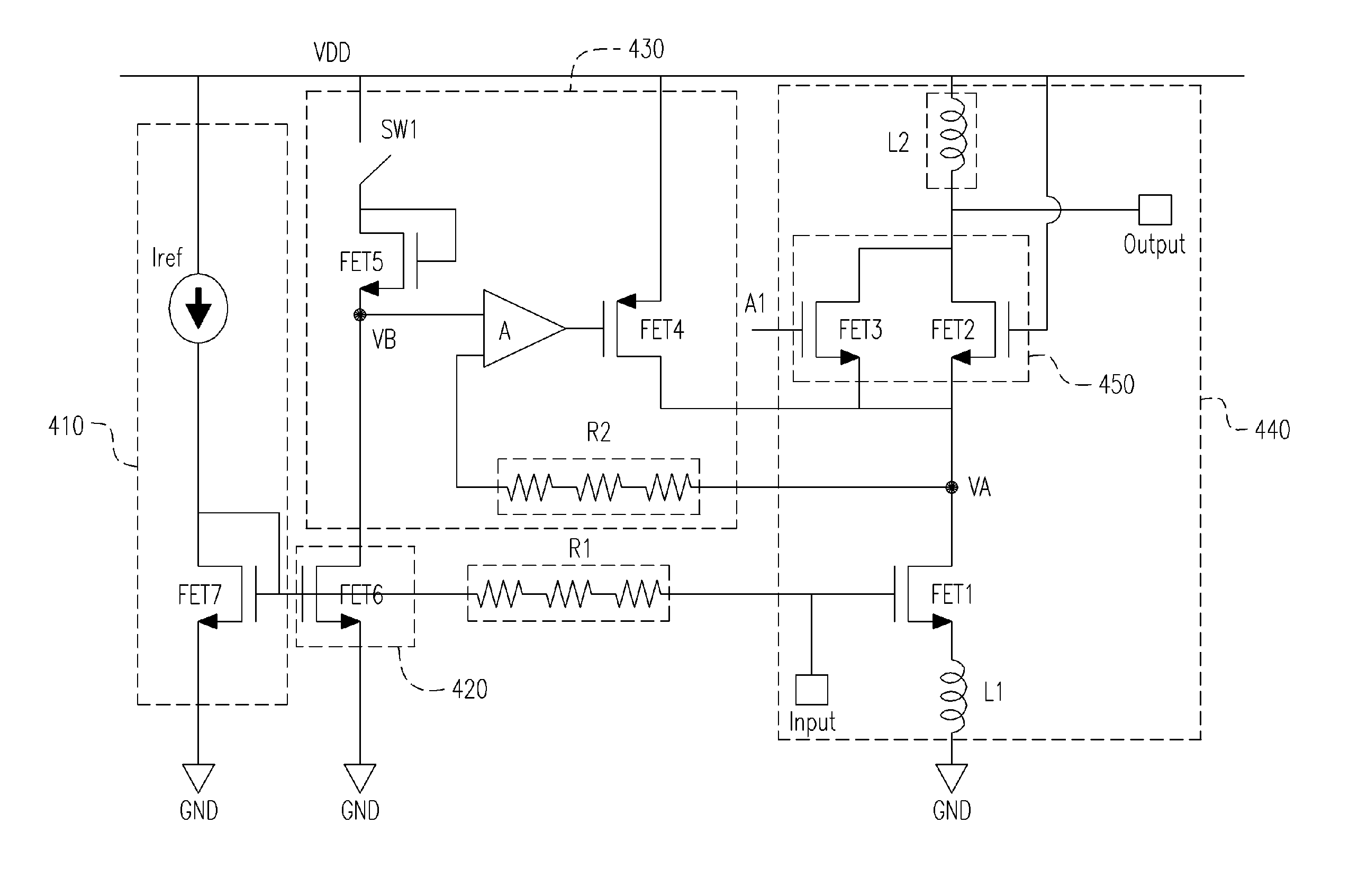
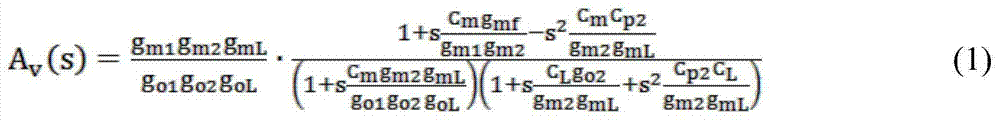Patents
Literature
108 results about "Cascade amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
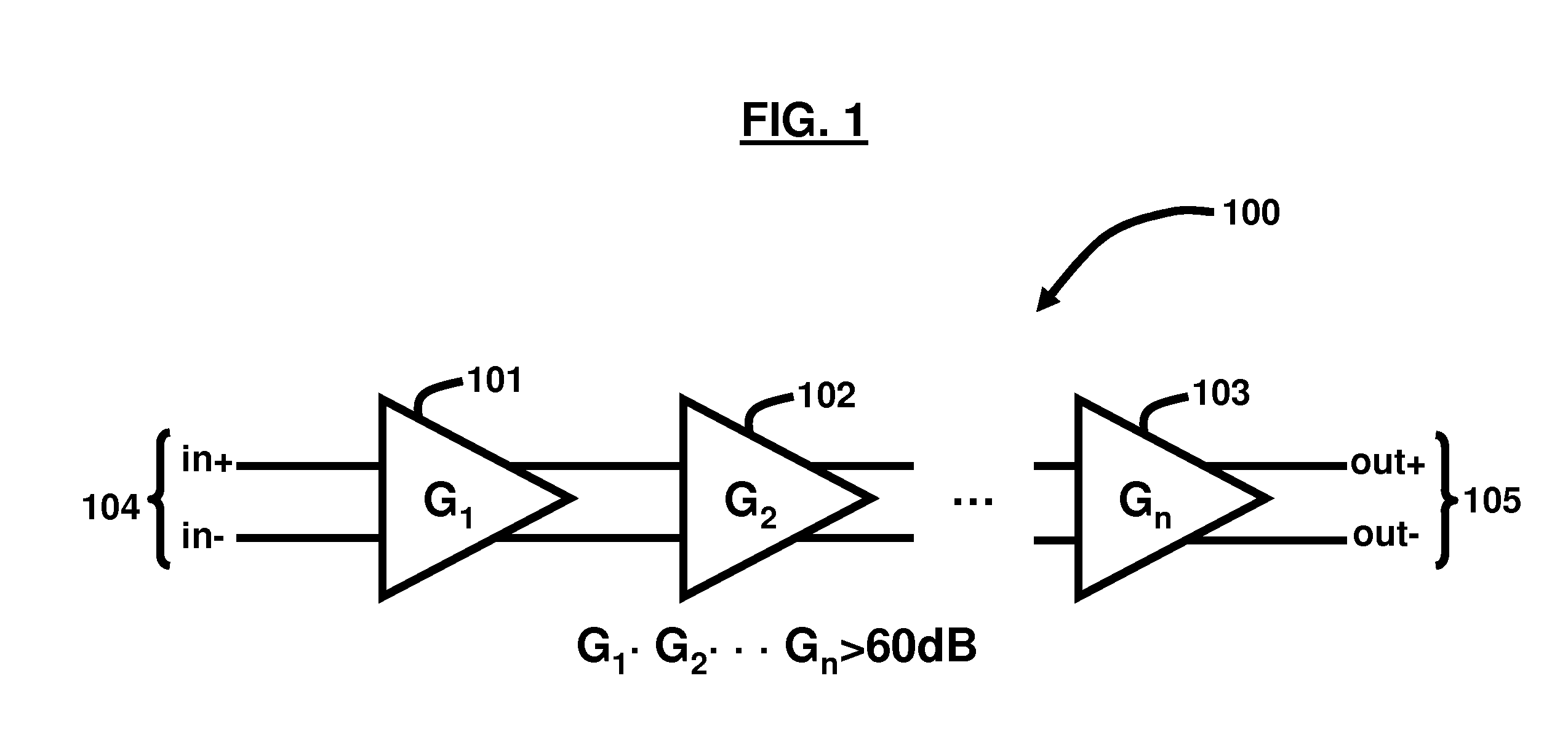
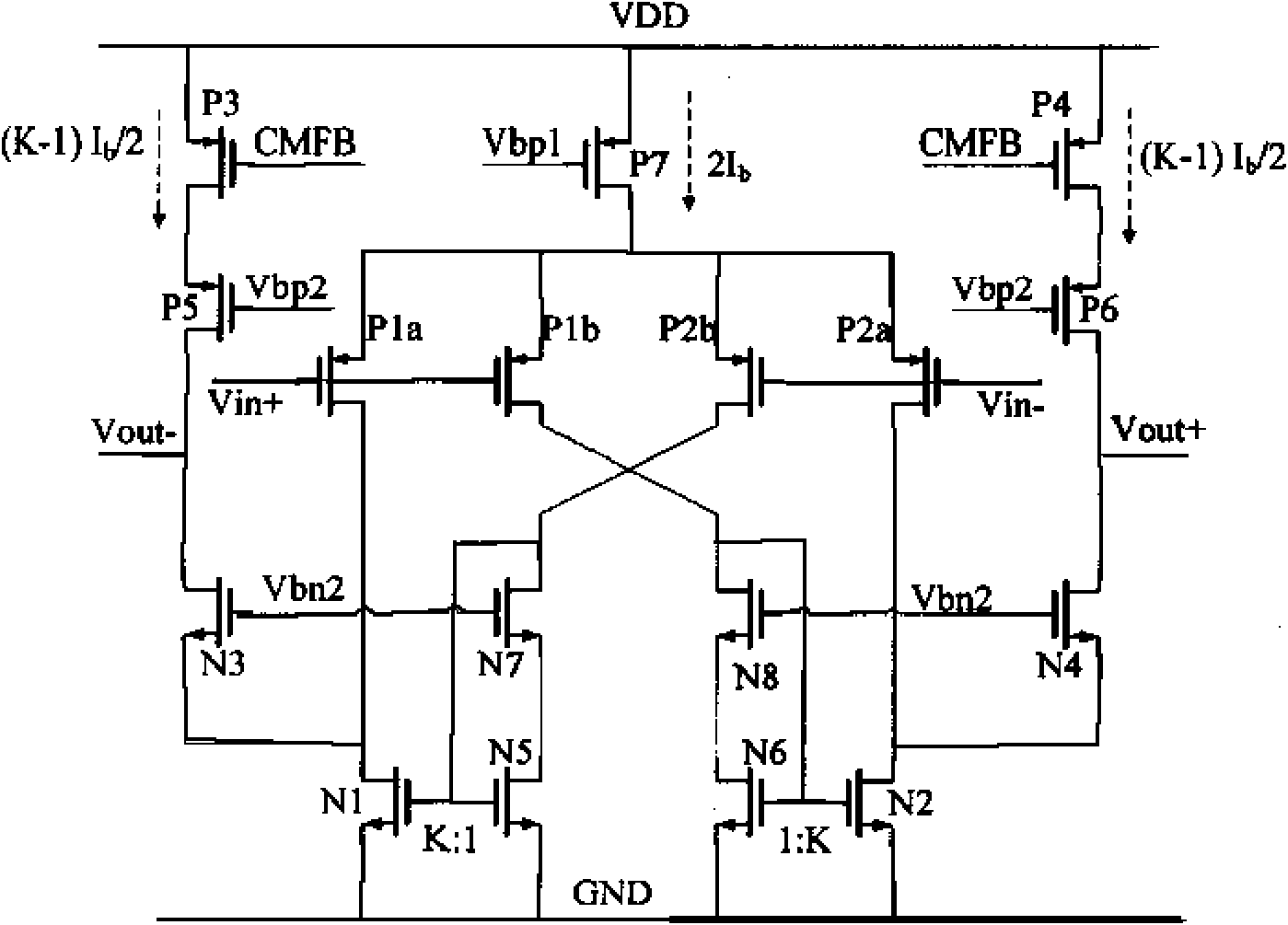
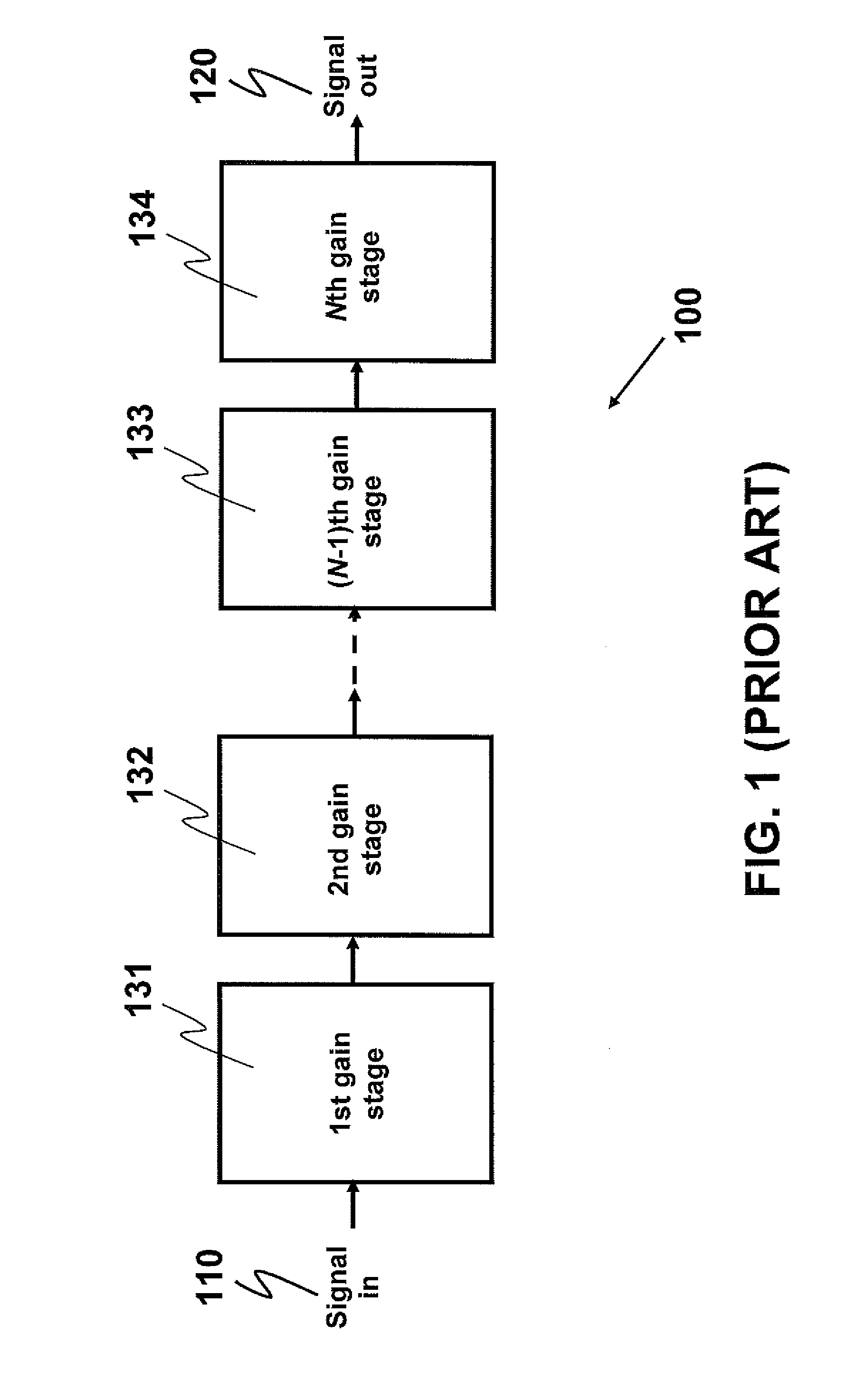
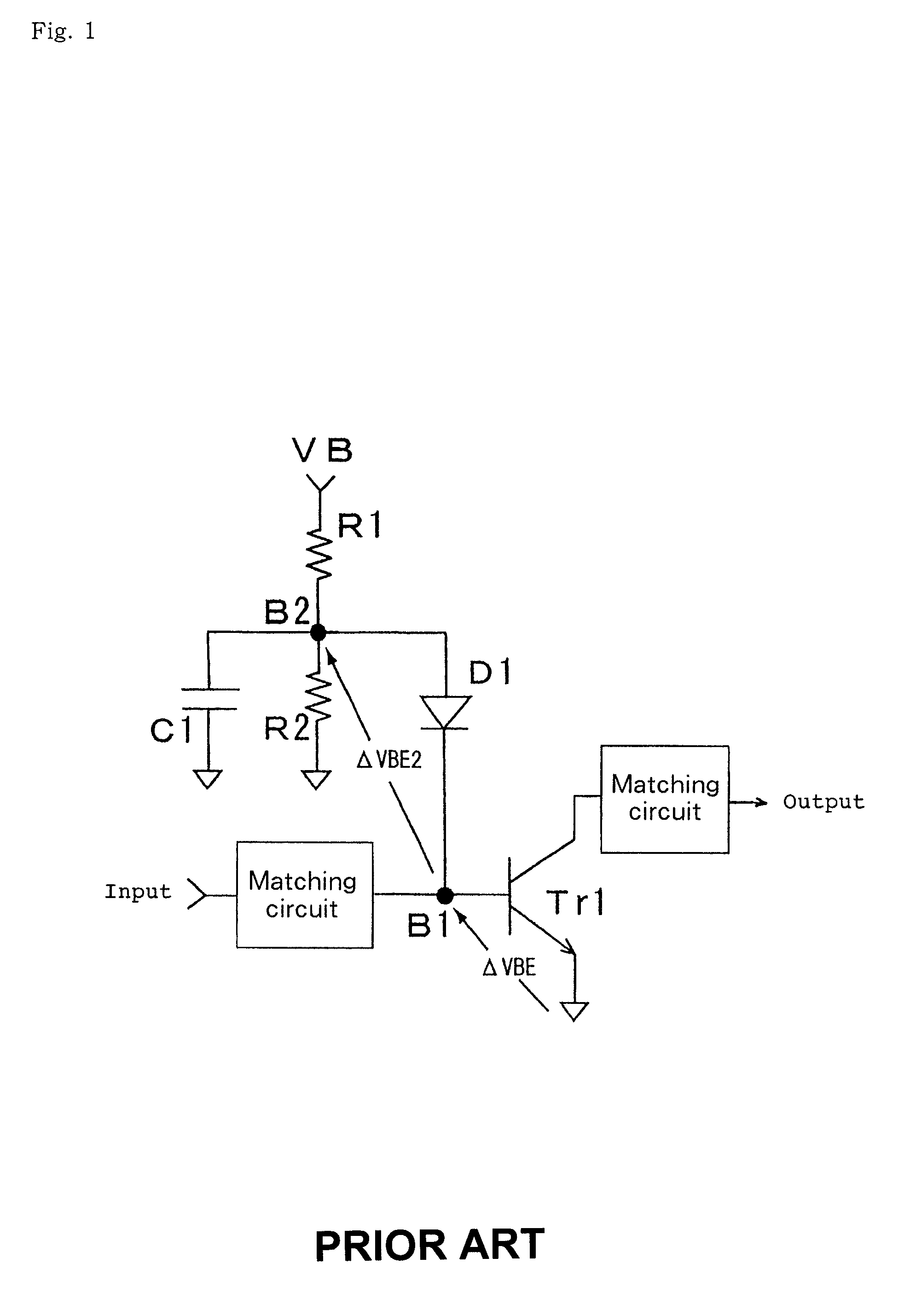
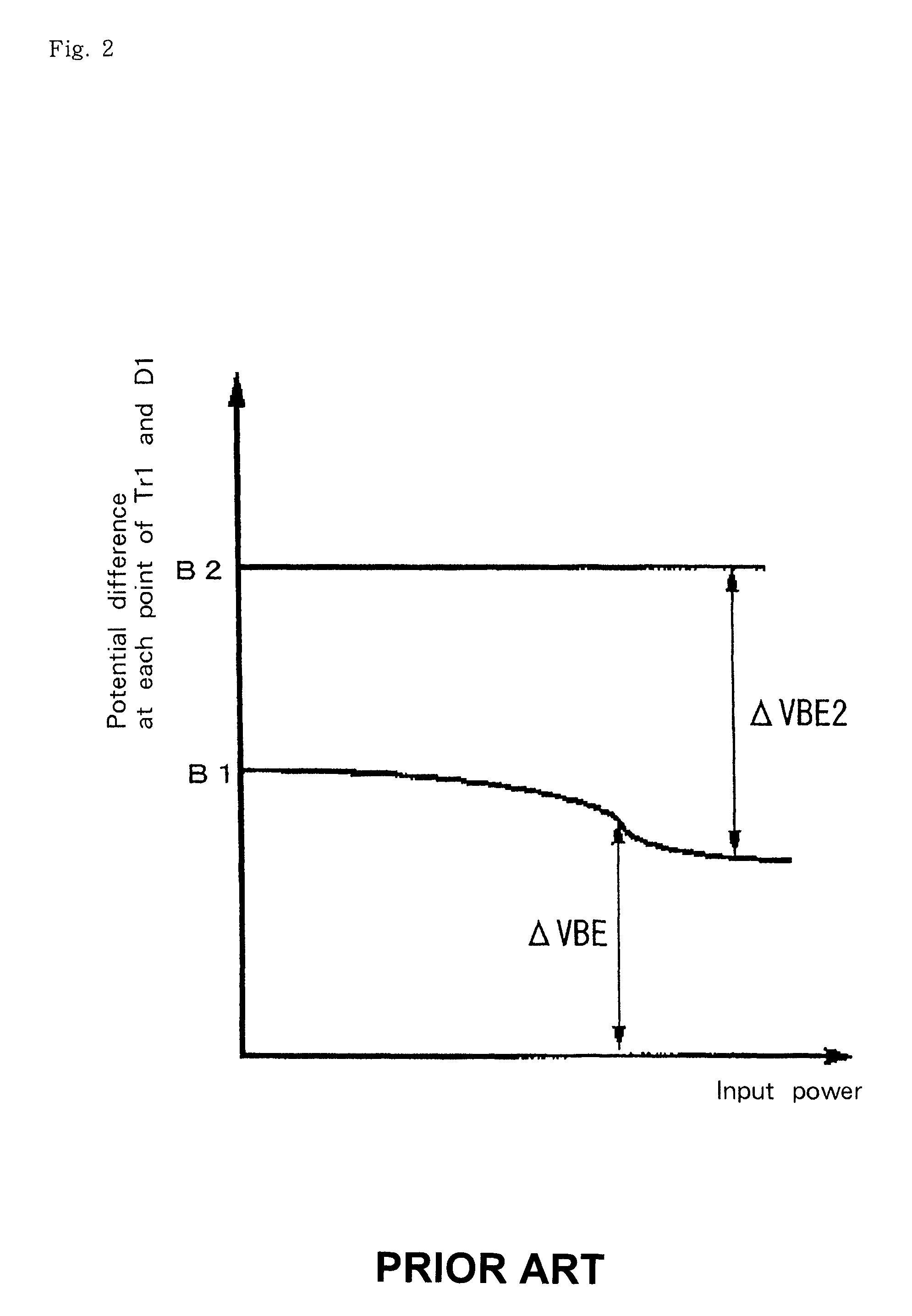
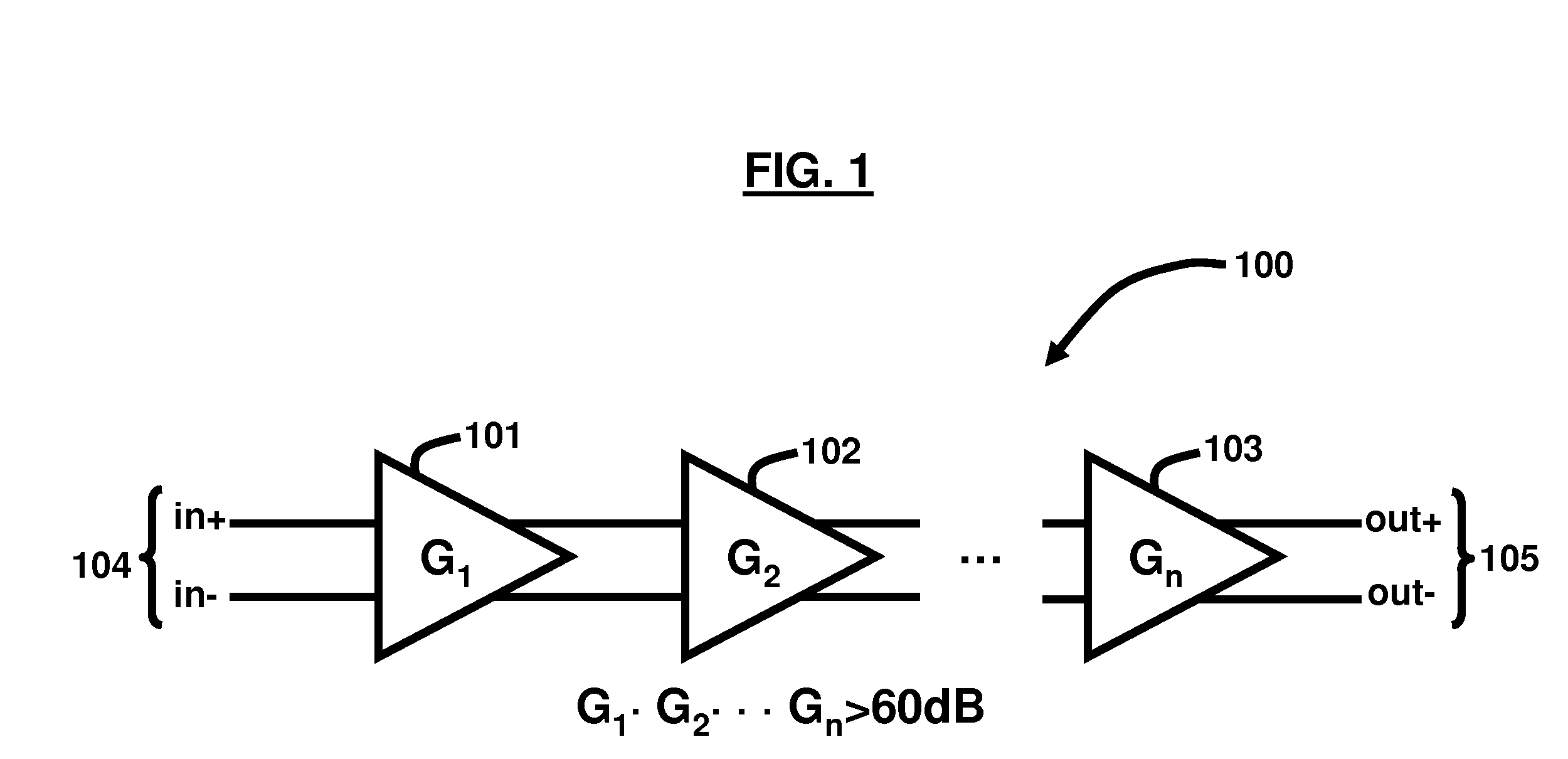
A cascade amplifier is any two-port network constructed from a series of amplifiers, where each amplifier sends its output to the input of the next amplifier in a daisy chain. A cascade is basically a differential amplifier with one input grounded and the side with the real input has no load. It can also be seen as a common collector followed by a common base. Since the input side has no load there is no gain on that side and the Miller effect does not come into play. In addition, Vds or Vce stays fairly constant which reduces distortion. Its advantage over the cascade is that it does not require as much voltage headroom. Its disadvantage is since it has two legs it requires twice as much current as a cascade for similar performance. The complication in calculating the gain of cascaded stages is the non-ideal coupling between stages due to loading. Two cascaded common emitter stages are shown below. Because the input resistance of the second stage forms a voltage divider with the output resistance of the first stage, the total gain is not the product of the individual stages.
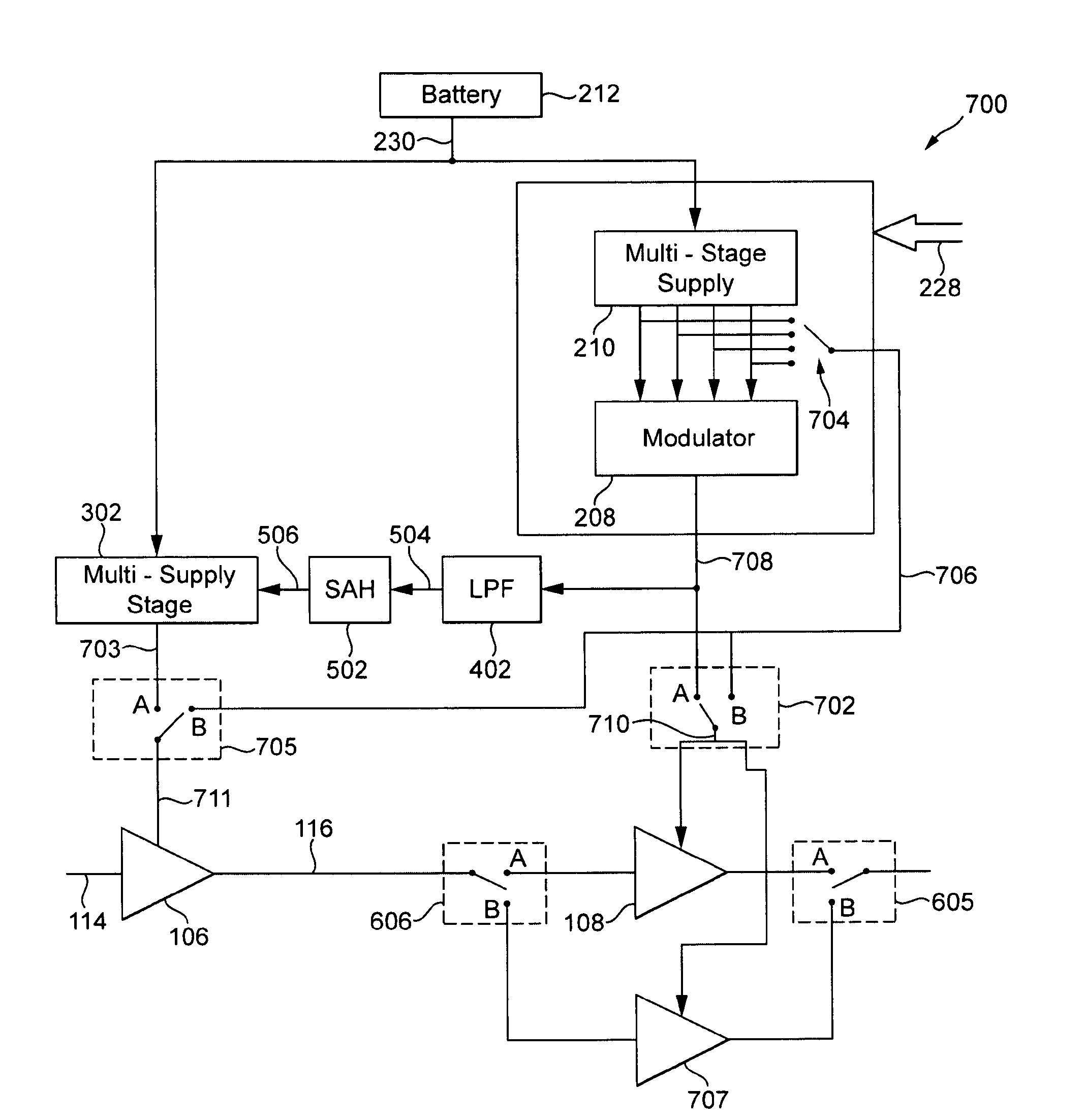
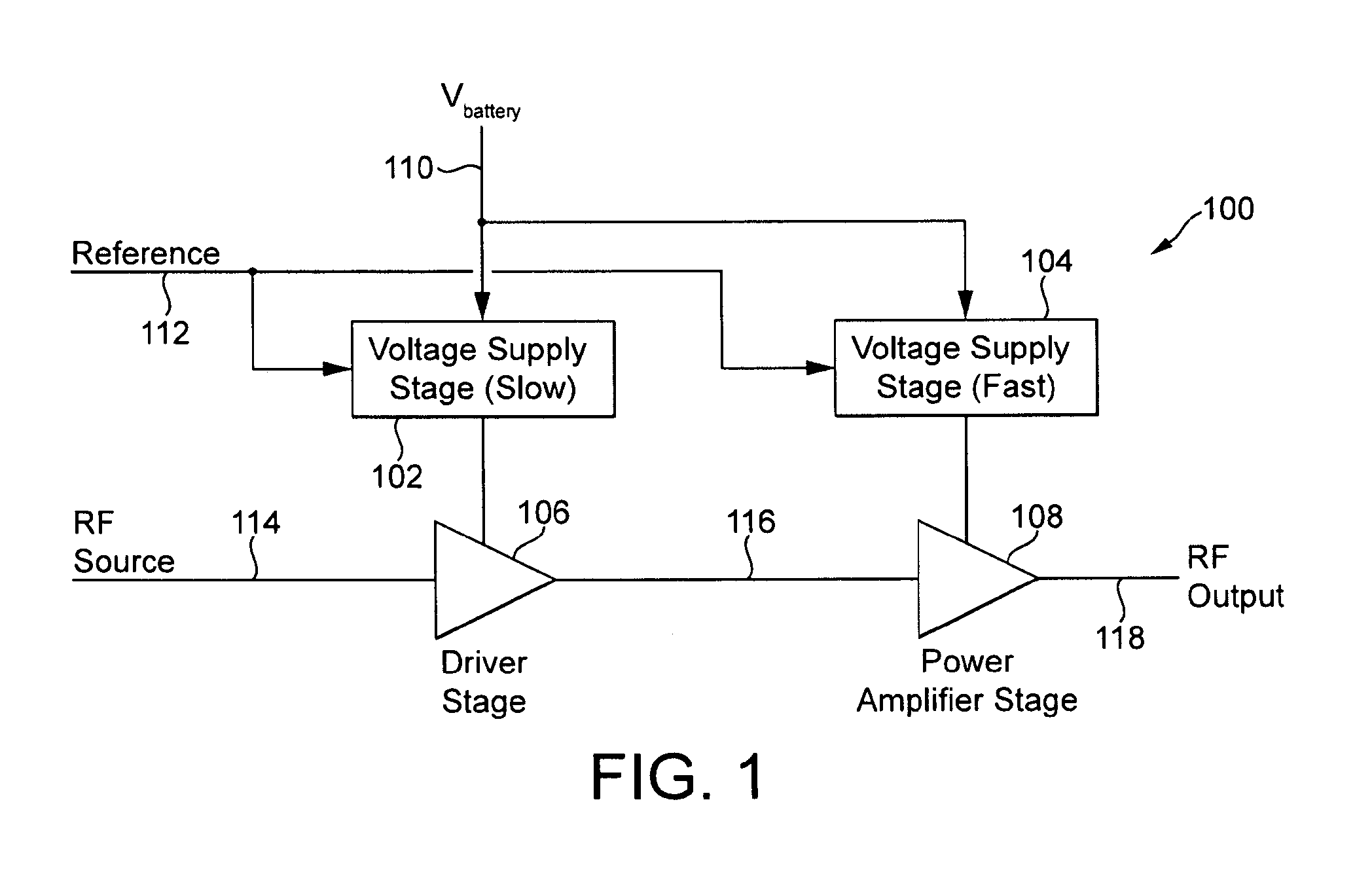
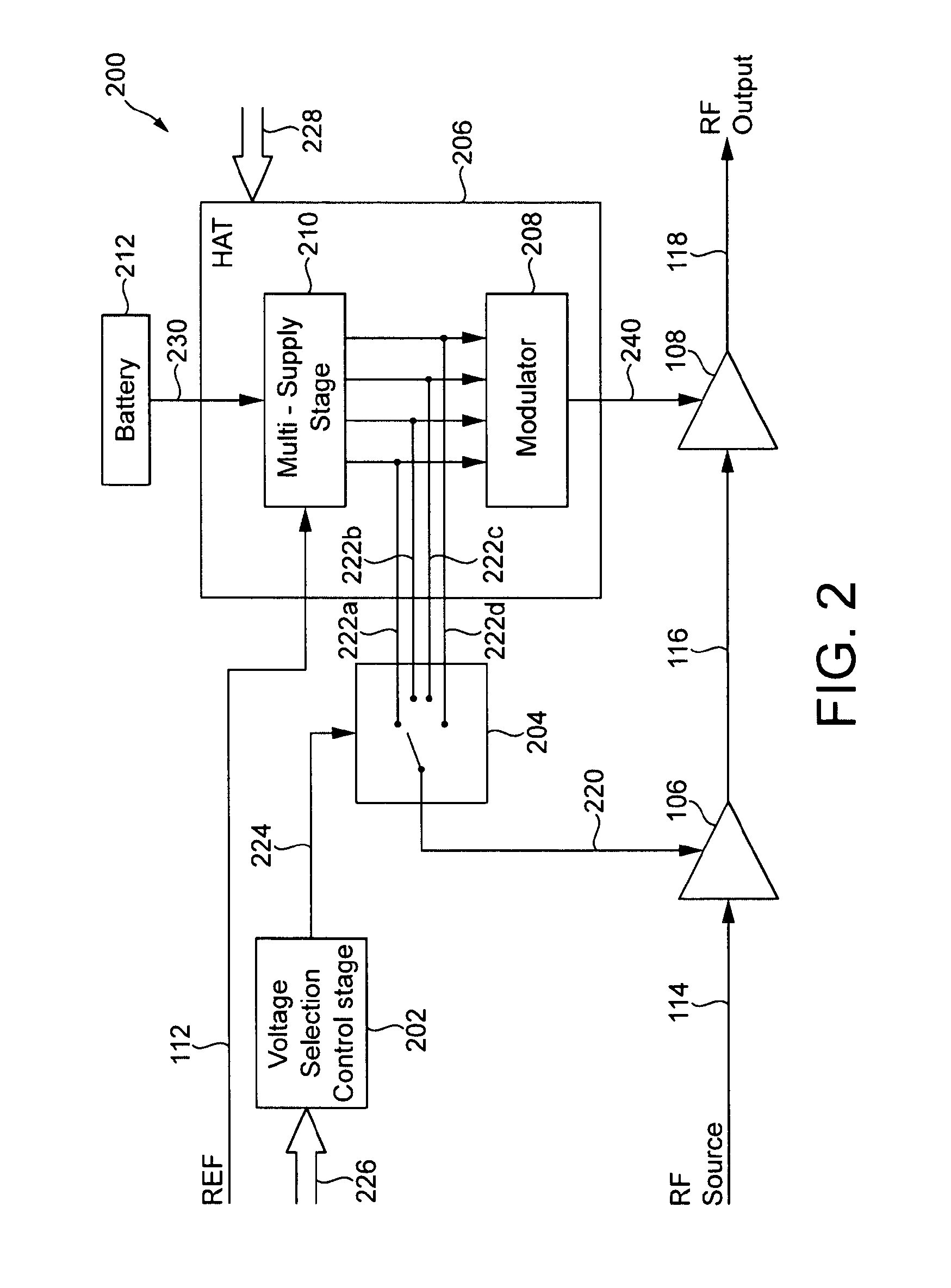
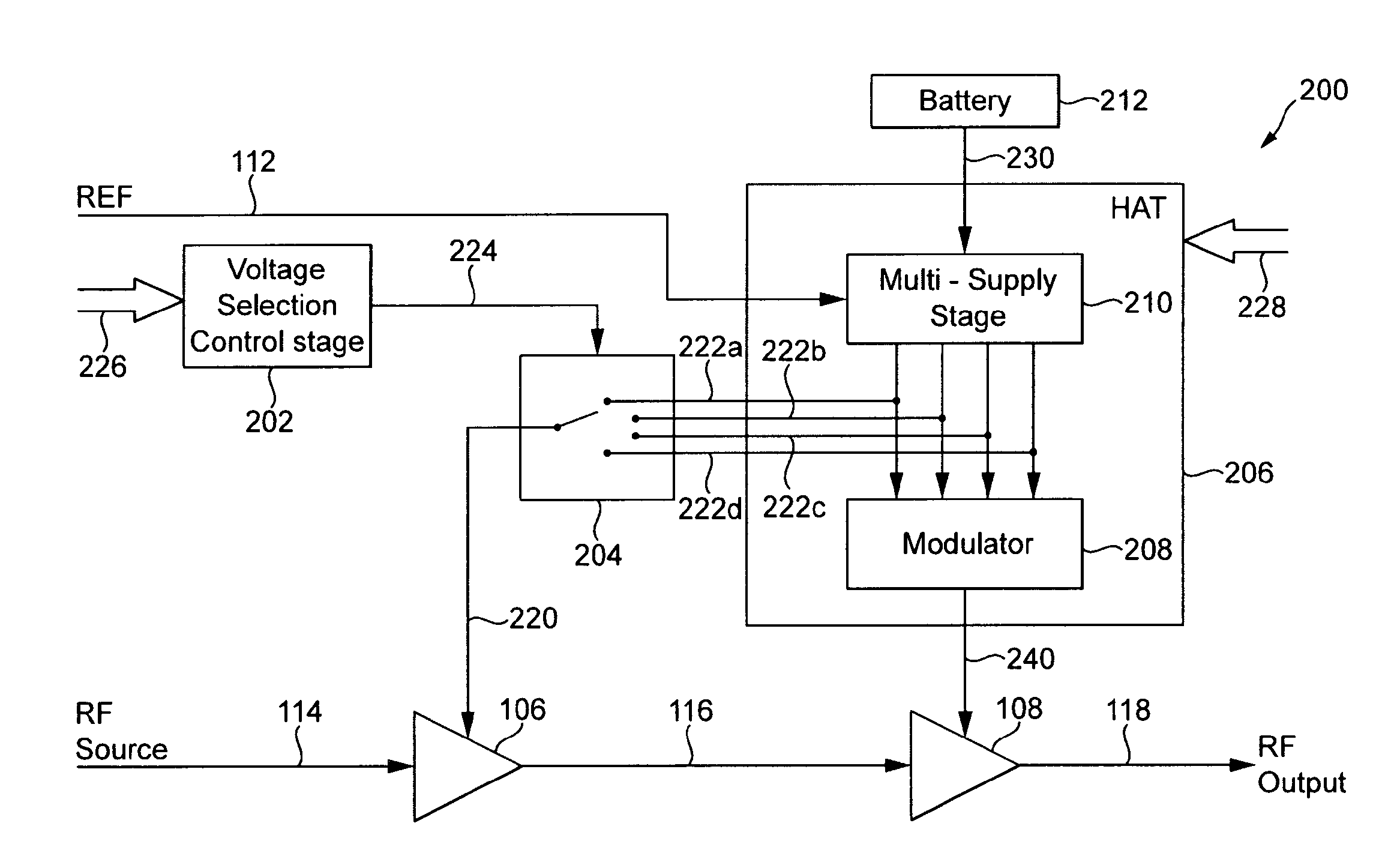
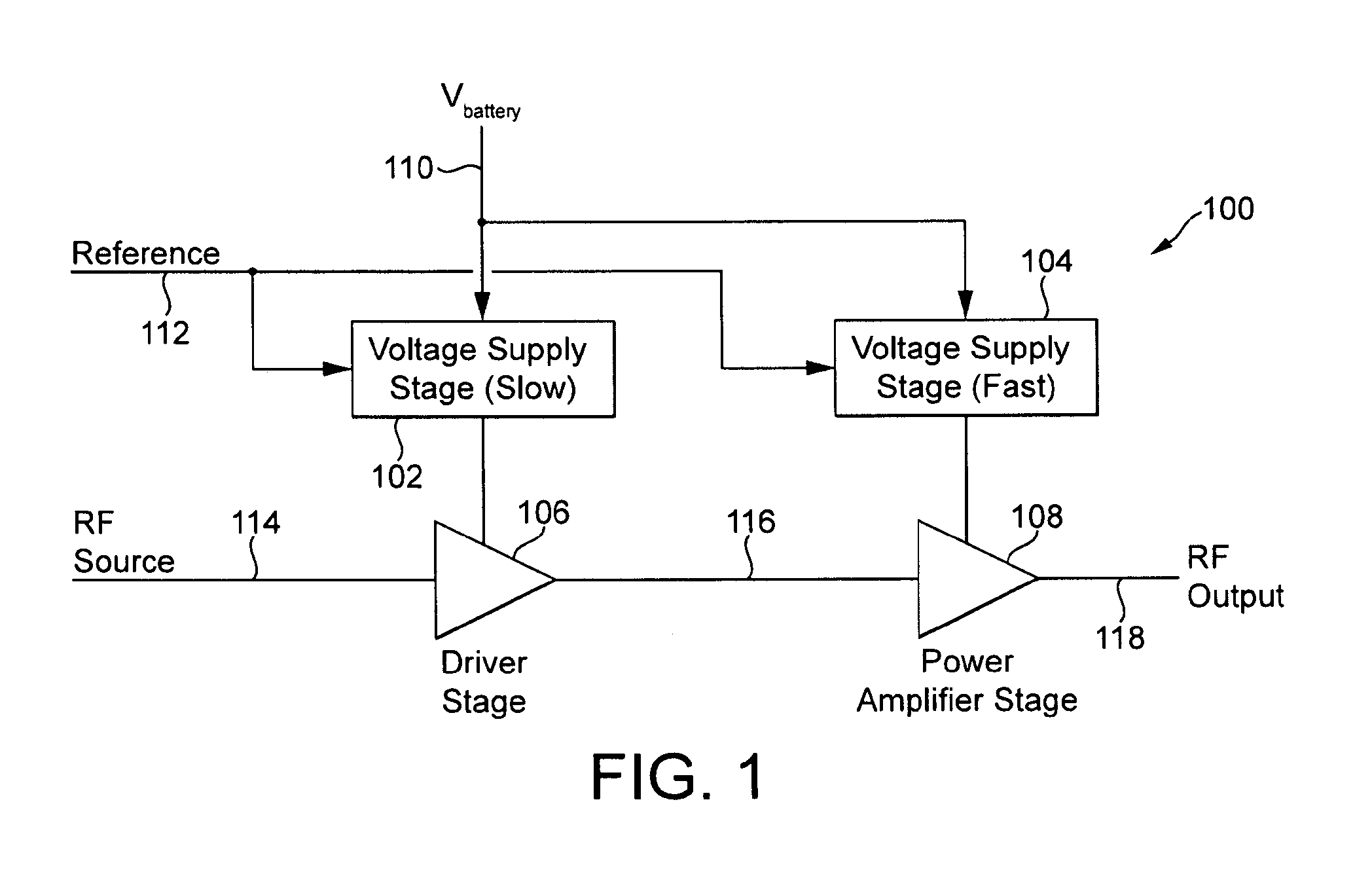
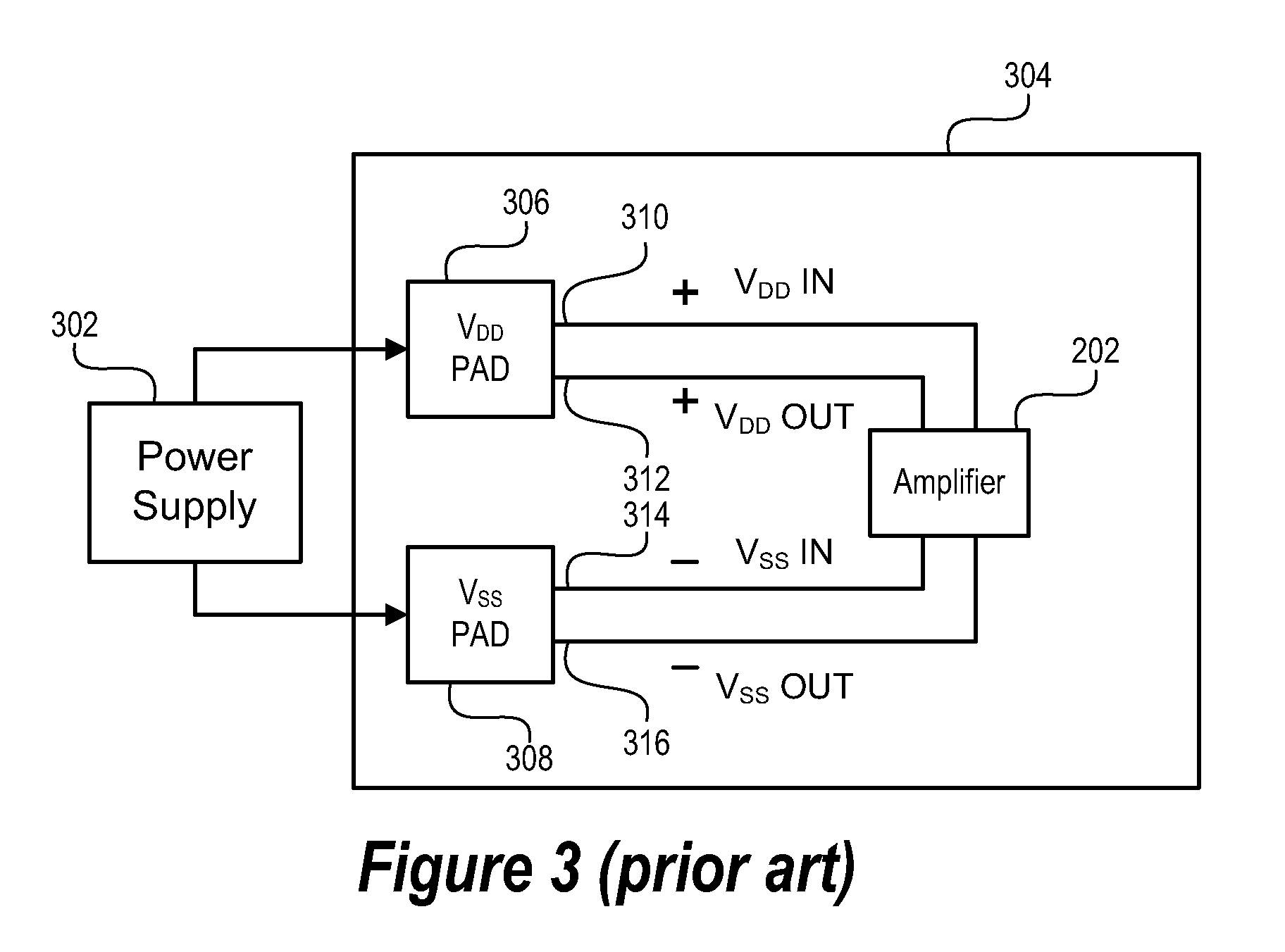
Power supply arrangement for multi-stage amplifier
There is disclosed a multi-stage amplifier comprising: a first amplifier stage; a second amplifier stage; a first voltage supply stage arranged to provide a supply voltage to the first amplifier in dependence on an average power of a signal to be amplified; and a second voltage supply stage arranged to provide a supply voltage to the second amplifier in dependence on an instantaneous power of a signal to be amplified.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Power supply arrangement for multi-stage amplifier
There is disclosed a multi-stage amplifier comprising: a first amplifier stage; a second amplifier stage; a first voltage supply stage arranged to provide a supply voltage to the first amplifier in dependence on an average power of a signal to be amplified; and a second voltage supply stage arranged to provide a supply voltage to the second amplifier in dependence on an instantaneous power of a signal to be amplified.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
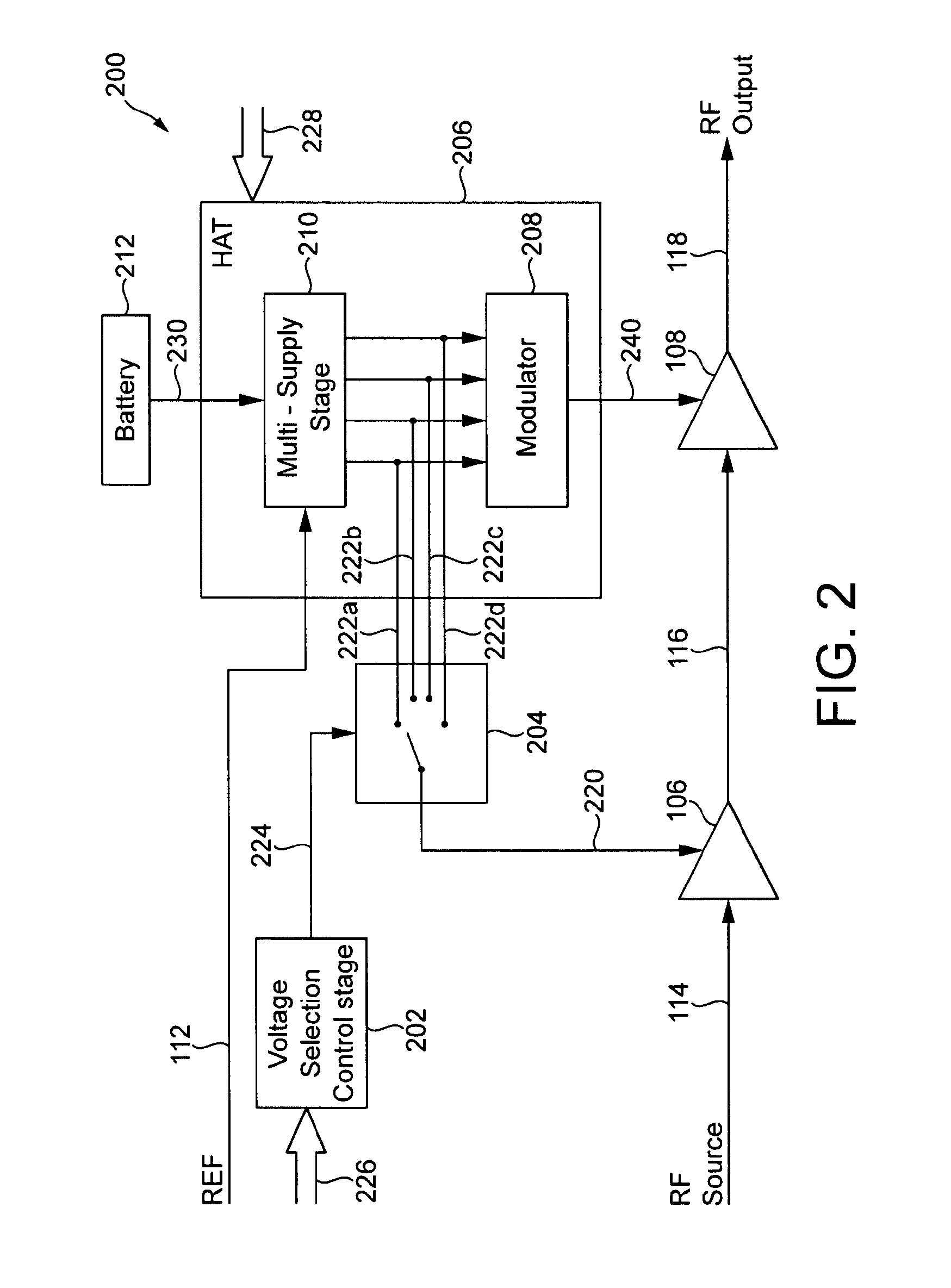
Multi-stage amplifier with multiple sets of fixed and variable voltage rails
A signal processing system and method utilizes a multi-stage amplifier to amplify an input signal. The multi-stage amplifier uses a mixed set of voltage rails to improve the operating efficiency of at least one of the amplification stages while allowing other amplification stages to operate in a predetermined operating mode. Efficiency of at least one of the stages is improved by supplying at least one variable voltage rail to an amplification stage of the multi-stage amplifier. The variable voltage rail varies in response to changes in an input signal voltage to the amplification stage. Accordingly, at least one amplification stage utilizes a variable voltage rail, and all amplification stages are supplied with a set of voltage rails that provides sufficient input signal headroom, thus, providing amplification stage efficiency and adequate voltage to allow operation of all amplification stages.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
DC-coupled multi-stage amplifier using all-pass resistive/capacitive network for level shifting
InactiveUS6943631B2Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAmplifier combinationsLevel shiftingCapacitance
A resistive level-shifting biasing network is used with a capacitor in parallel to couple FET-based amplifier stages from DC to several GHz in a multi-stage amplifier. The output of the first amplifier stage is connected to the input of the second amplifier stage without a blocking capacitor or level-shifting diodes, allowing a portion of the drain current for the first amplifier stage to be supplied from the second amplifier stage. In a particular embodiment, a distributed amplifier achieved over 20 dB gain from DC to about 80 GHz using three traveling wave amplifier chips.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
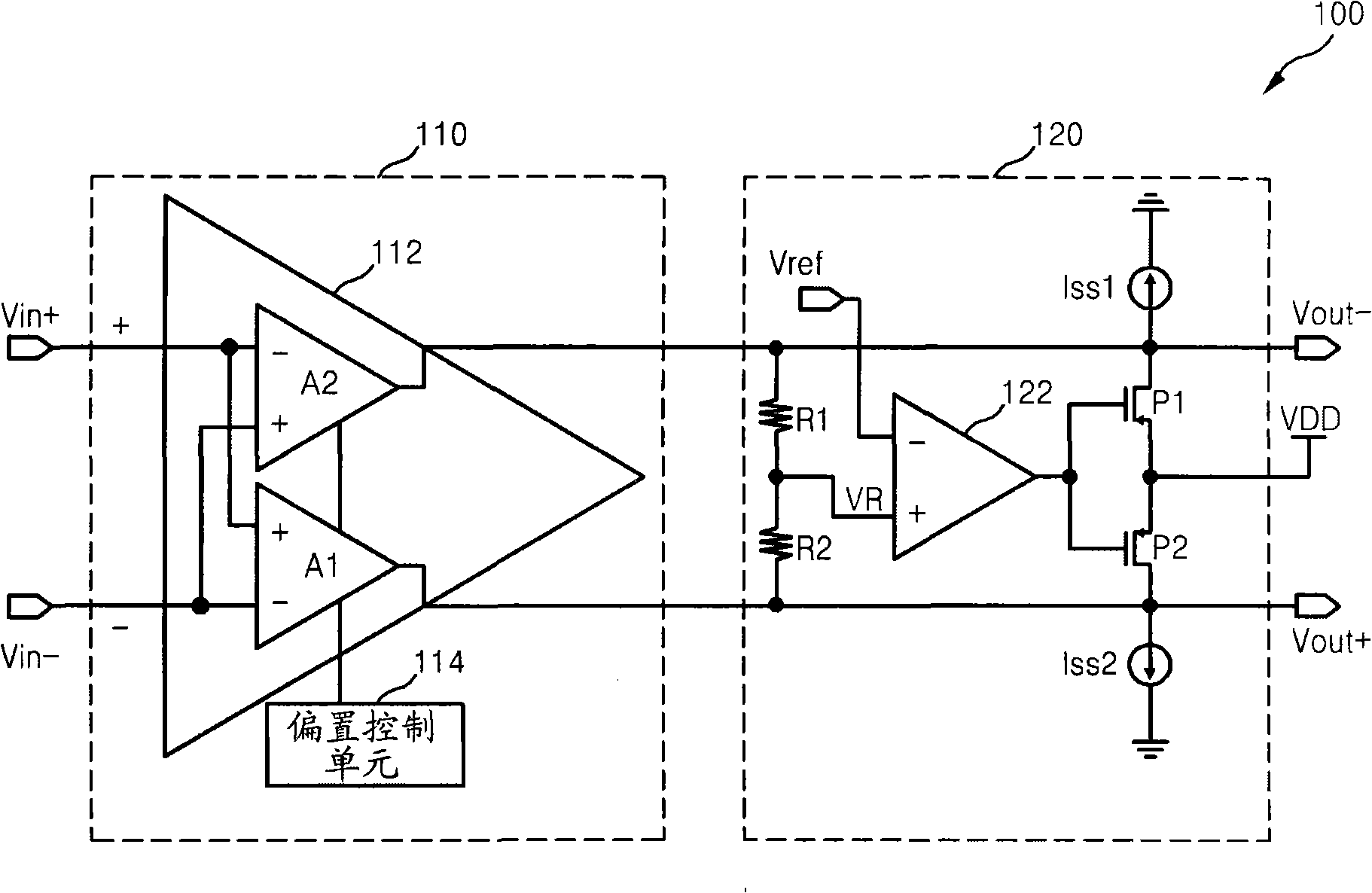
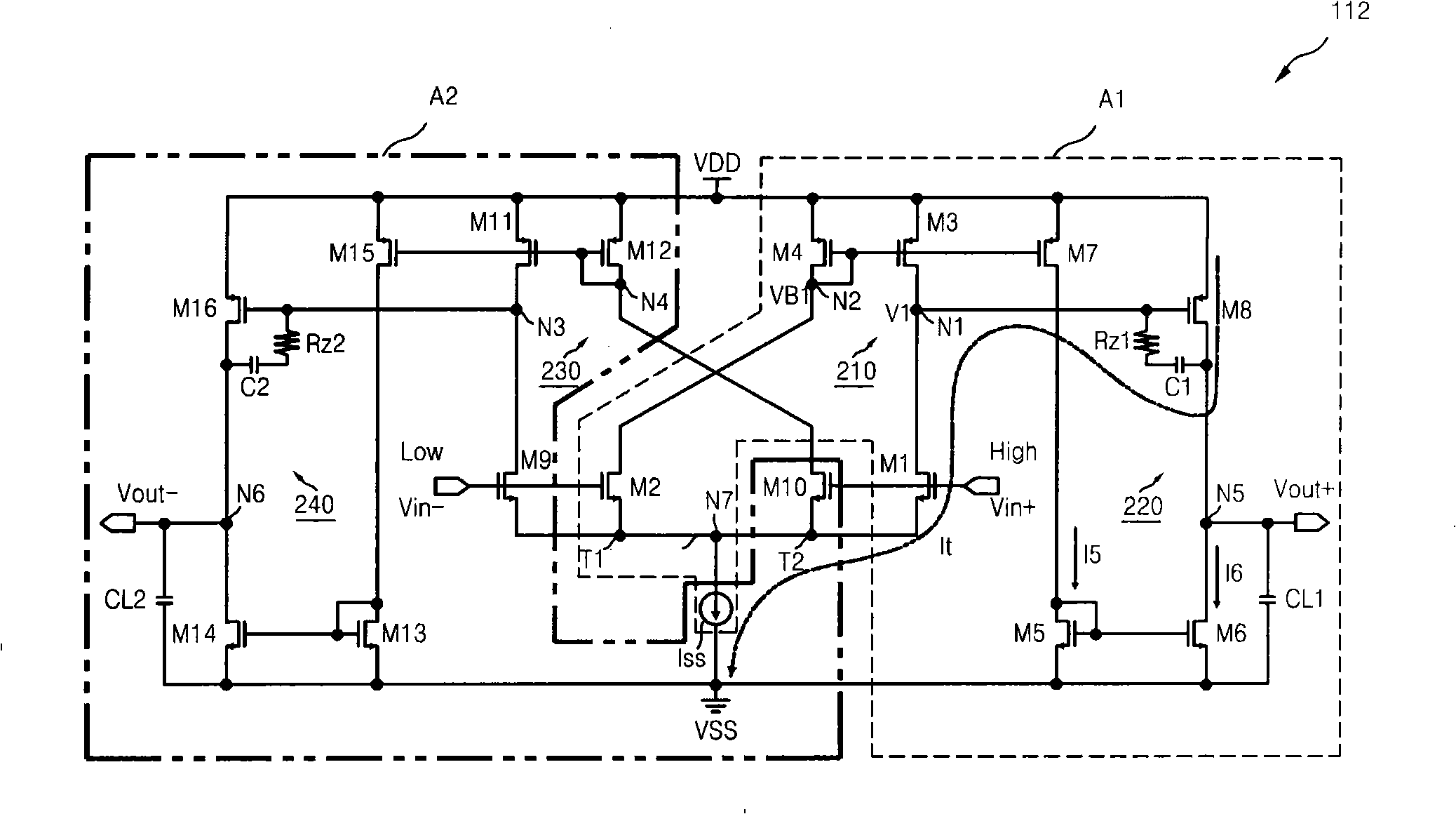
Method for compensating common mode feedback circuit frequency of two-stage amplifier
InactiveCN101373956AImprove phase marginImprove stabilityDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesDual stageControl signal
The invention discloses a common-mode feedback circuit frequency compensation method of a dual-stage amplifier, which belongs to the analog integrated circuit design field. One common-mode feedback circuit is adopted in the dual-stage amplifier to reduce the area and the power consumption of the feedback circuit; the dual-stage amplifier adopts a fully-differential input / output structure; a differential output terminal is used for sampling the common-mode output level; a first-stage amplifying circuit thereof comprises a controllable biasing circuit; a common-mode feedback control signal controls the first-stage common-mode output level and the second-stage common-mode output level of the amplifier at the same time through the controllable biasing circuit; a feedback amplifier is realized by adopting a dual-stage operational amplifier with miller compensation. The left half plane zero point generated by the feedback amplifier in a loop circuit counteracts a certain left half plane pole in a prime amplifier, thereby forming a stable compensation loop circuit. The common-mode feedback circuit frequency compensation method has the advantages of less feedback circuit elements, lower feedback circuit power consumption, high low-frequency loop gain and better compensation phase margin.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
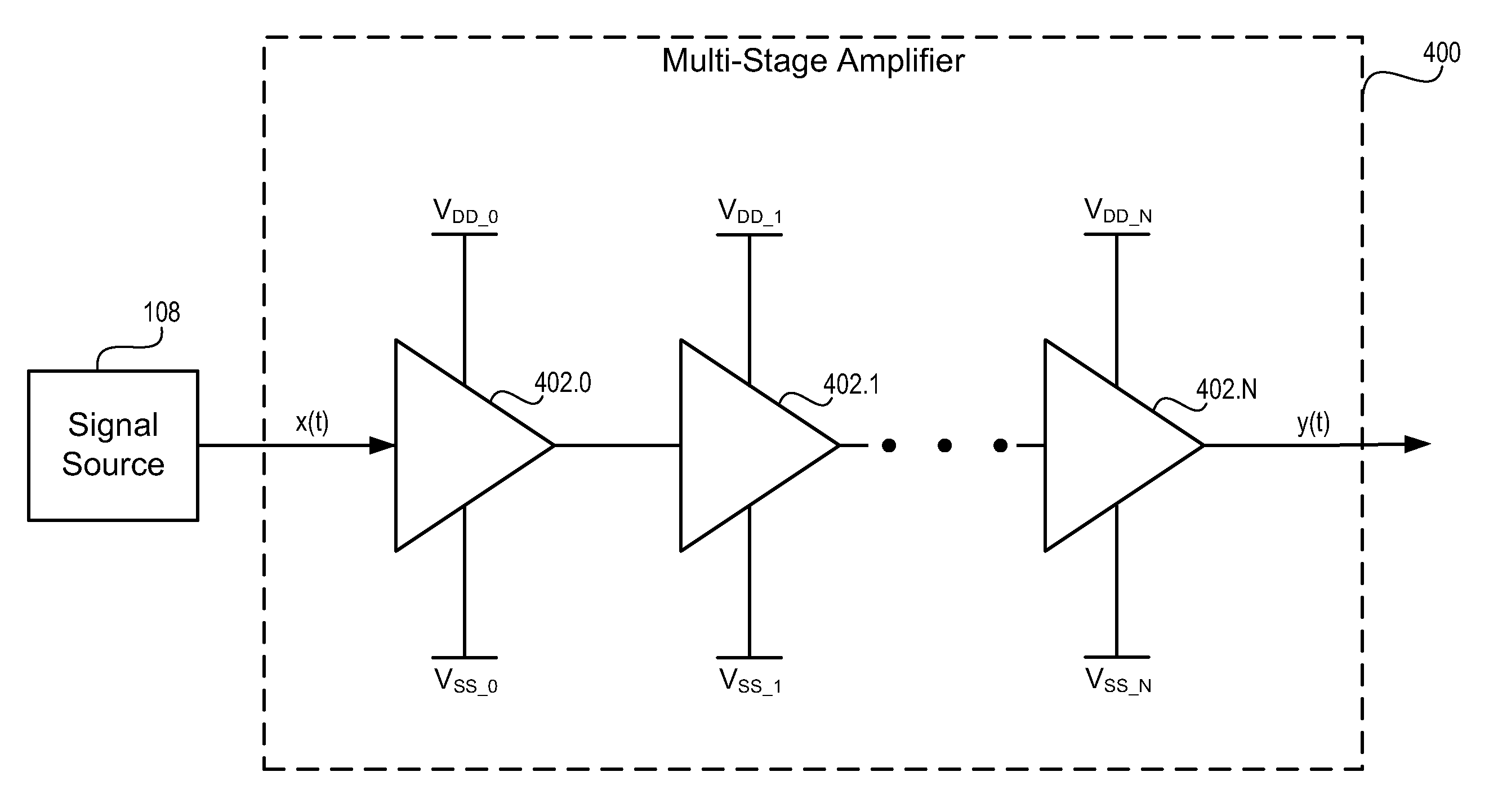
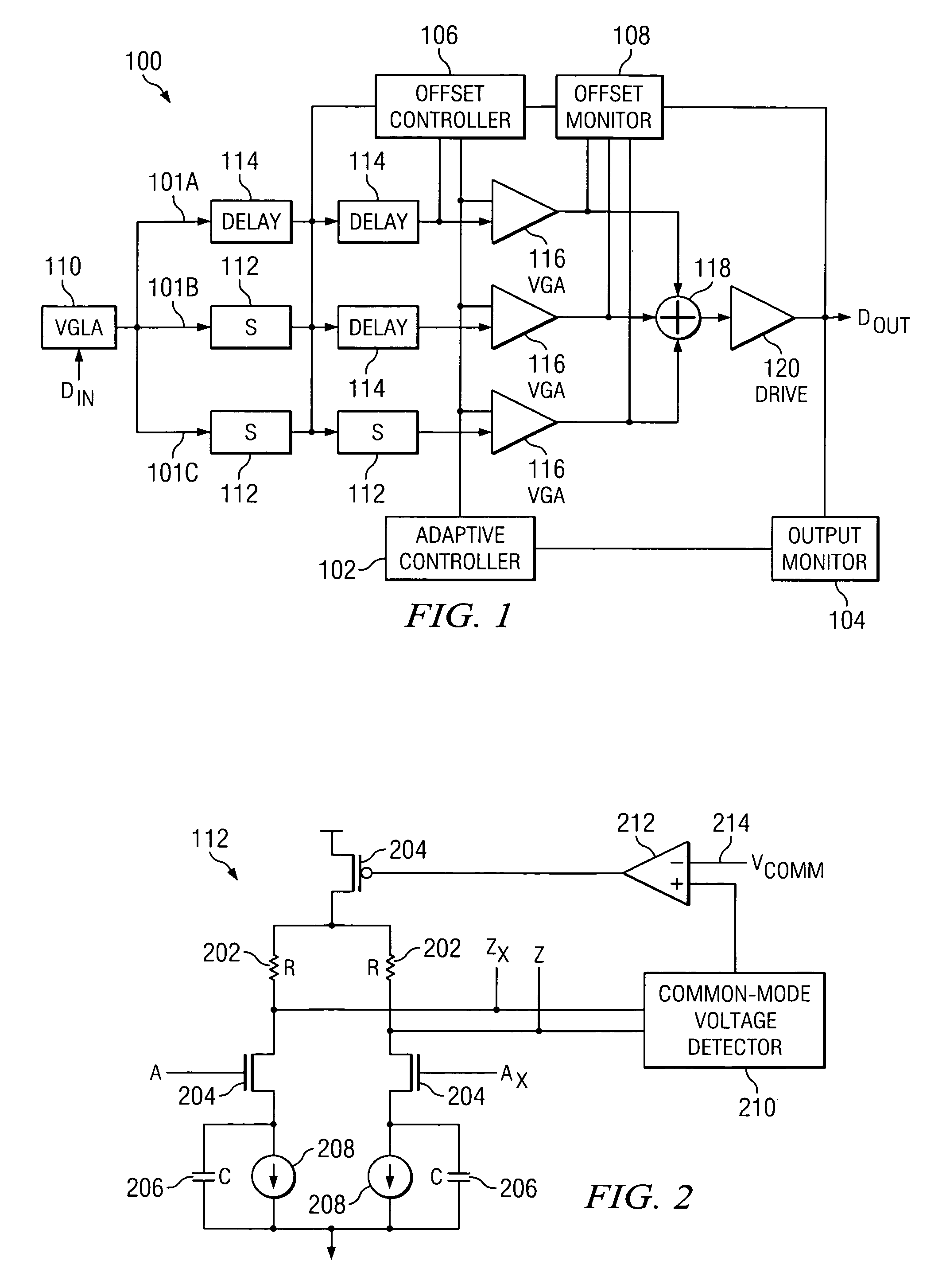
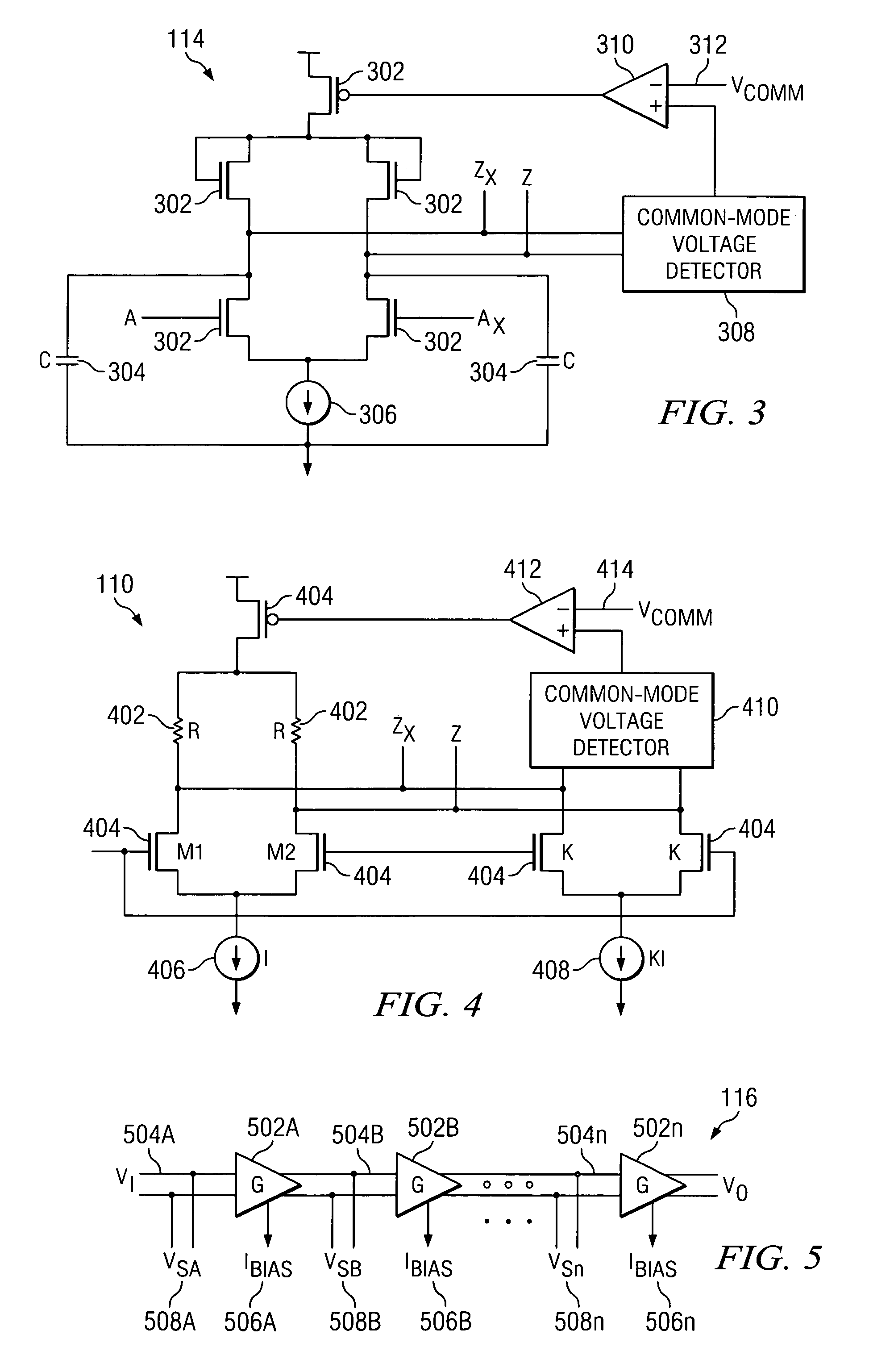
Correcting DC offsets in a multi-stage amplifier
ActiveUS7034608B2Improve responseAdequate levelTransmission control/equlisationNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierEngineering
A method for correcting DC offsets in a multi-stage amplifier includes determining a DC offset imparted by a multi-stage amplifier to an input signal. The method further includes applying a correction voltage to a plurality of selected stages in the multi-stage amplifier. The total correction voltage applied substantially negates the DC offset imparted by the multi-stage amplifier.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Fully differential class AB amplifier and amplifying method using single-ended, two-stage amplifier
InactiveCN101277095AHigh gainIncrease conversion rateDifferential amplifiersSingle-ended push-pull amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
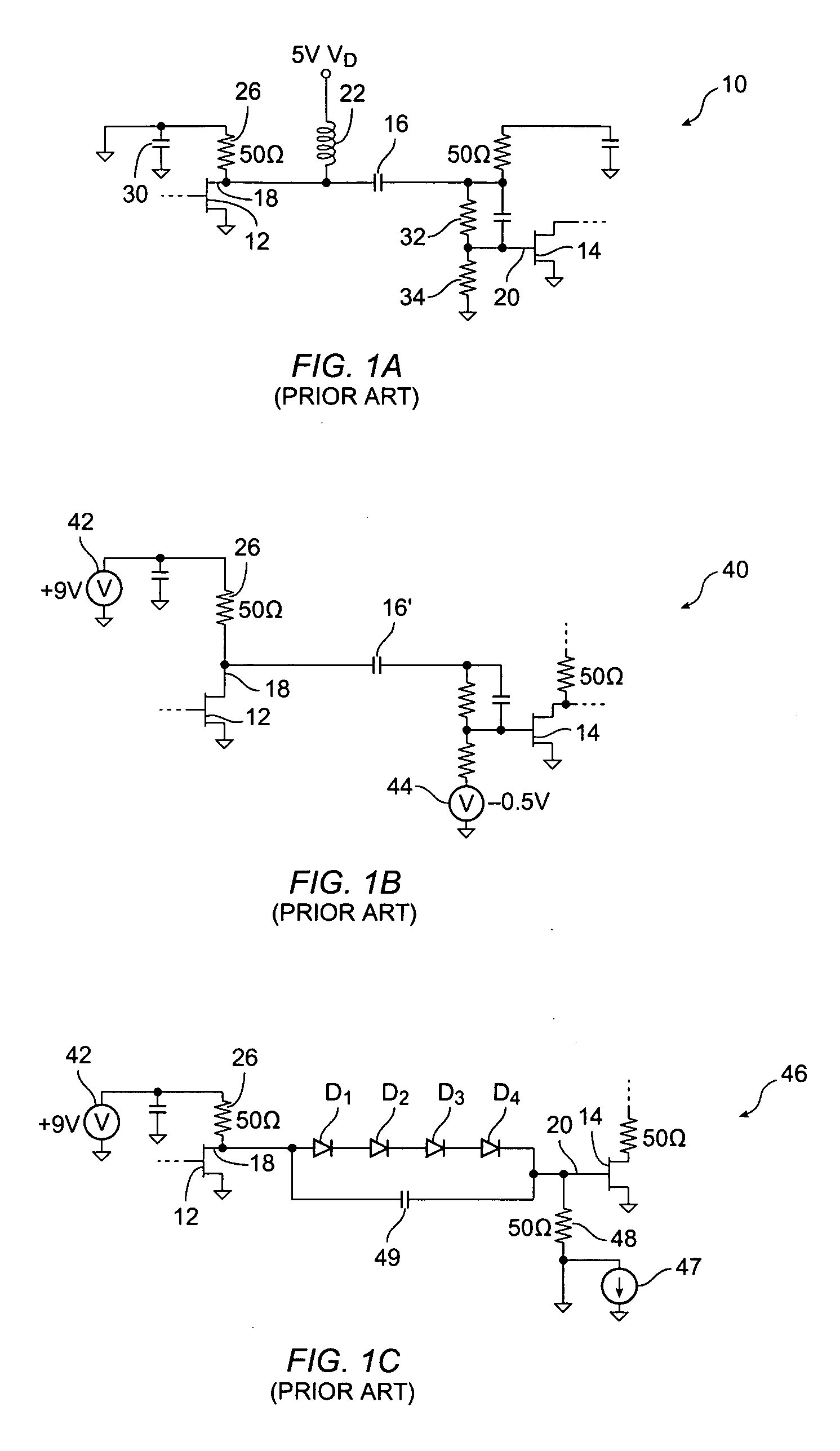
Variable gain low noise amplifier
InactiveUS6819179B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceMOSFETCascade amplifier
The load of the cascode amplifier is varied by connecting another (secondary) load in parallel with the original load. The secondary load is connected through a MOSFET switch. During the High Gain Mode the MOSFET switch is OFF and the secondary load is electrically isolated from the main load, whereas in the Low Gain Mode the switch is turned ON and the secondary load appears across the primary load, reducing the effective load impedance. The secondary load is AC coupled such that the DC bias current does not pass through the secondary load and hence the Noise Figure (NF) and linearity (IIP3) performance are better in the Low Gain Mode. A number of such switchable loads can be connected across the load to obtain programmability.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
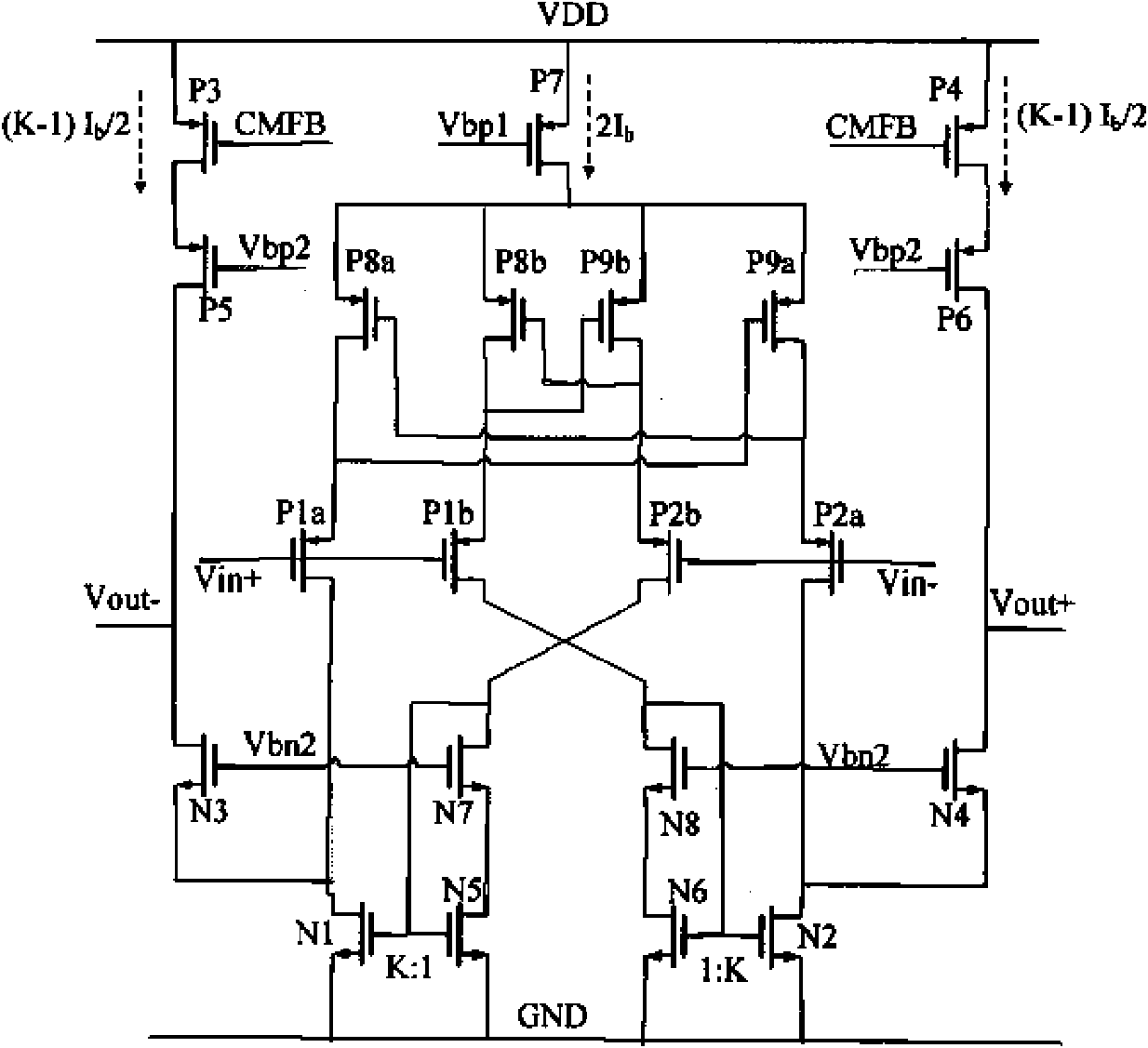
Multistage operational amplifier
ActiveCN103780213AReduce areaEliminate the effects ofDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
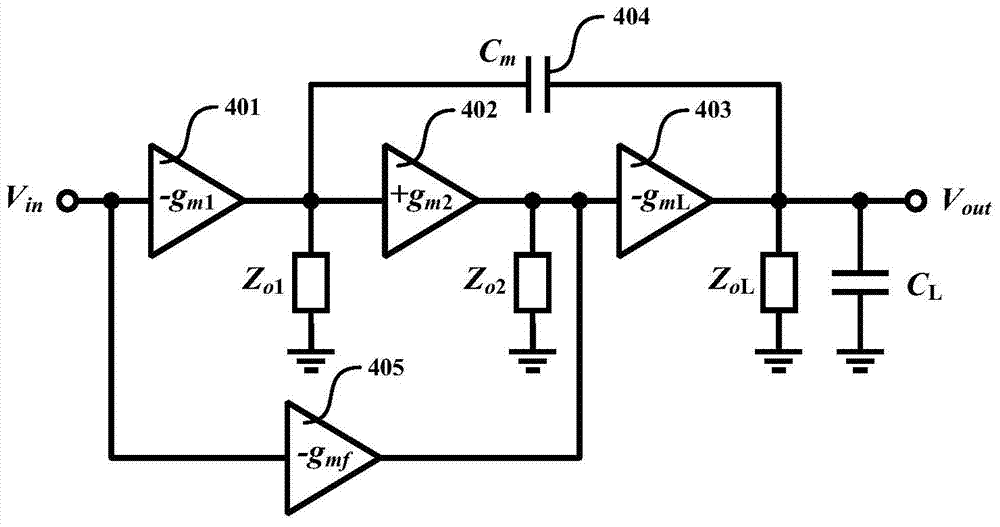
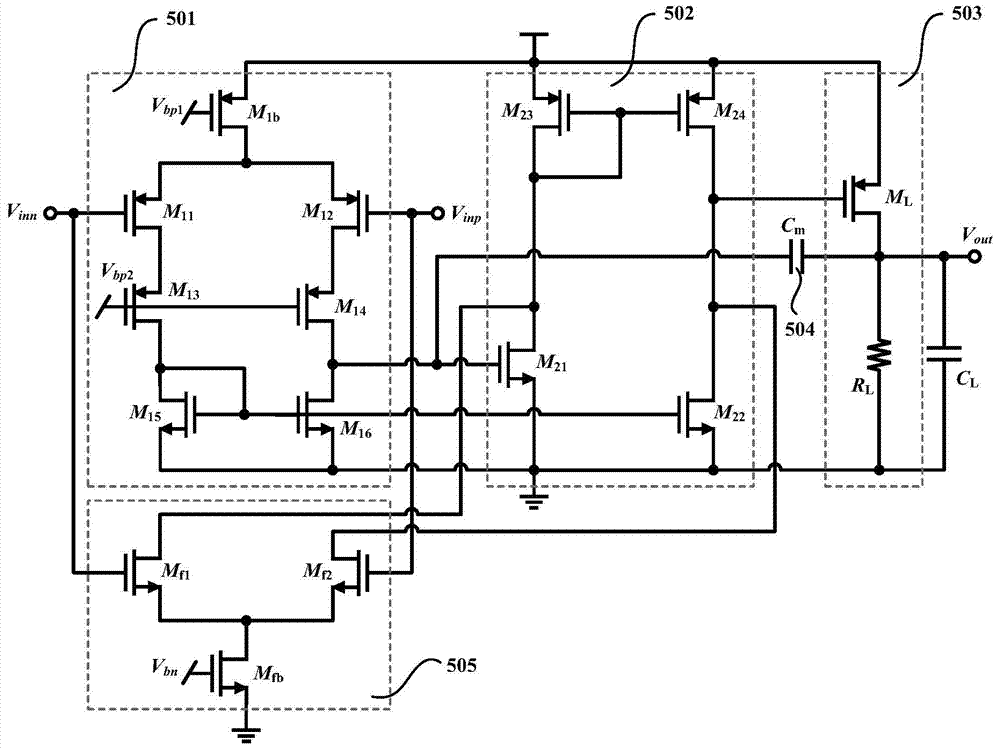
The invention relates to the technical field of amplifiers, in particular to a multistage operational amplifier which adopts a multipath single Miller capacitance frequency compensation method. The multistage operational amplifier comprises a first-stage amplifier, a second-stage amplifier, a third-stage amplifier, a Miller compensation capacitor and a feedforward transconductance amplifier. The first-stage amplifier, the second-stage amplifier and the third-stage amplifier are in series connection in sequence, one end of the Miller compensation capacitor is connected with the output end of the first-stage amplifier, the other end of the Miller compensation capacitor is connected with the output end of the third-stage amplifier, the input end of the feedforward transconductance amplifier is connected with the input end of the first-stage amplifier, and the output end of the feedforward transconductance amplifier is connected with the output end of the second-stage amplifier. Only one Miller compensation capacitor is adopted in the multistage operational amplifier, the chip area can be greatly saved, power consumption can be reduced, due to the introduction of the feedforward transconductance amplifier, the effect caused by a first non-dominant pole is eliminated, the bandwidth of the operational amplifier is further increased, and stability is improved.
Owner:南京中科微电子有限公司
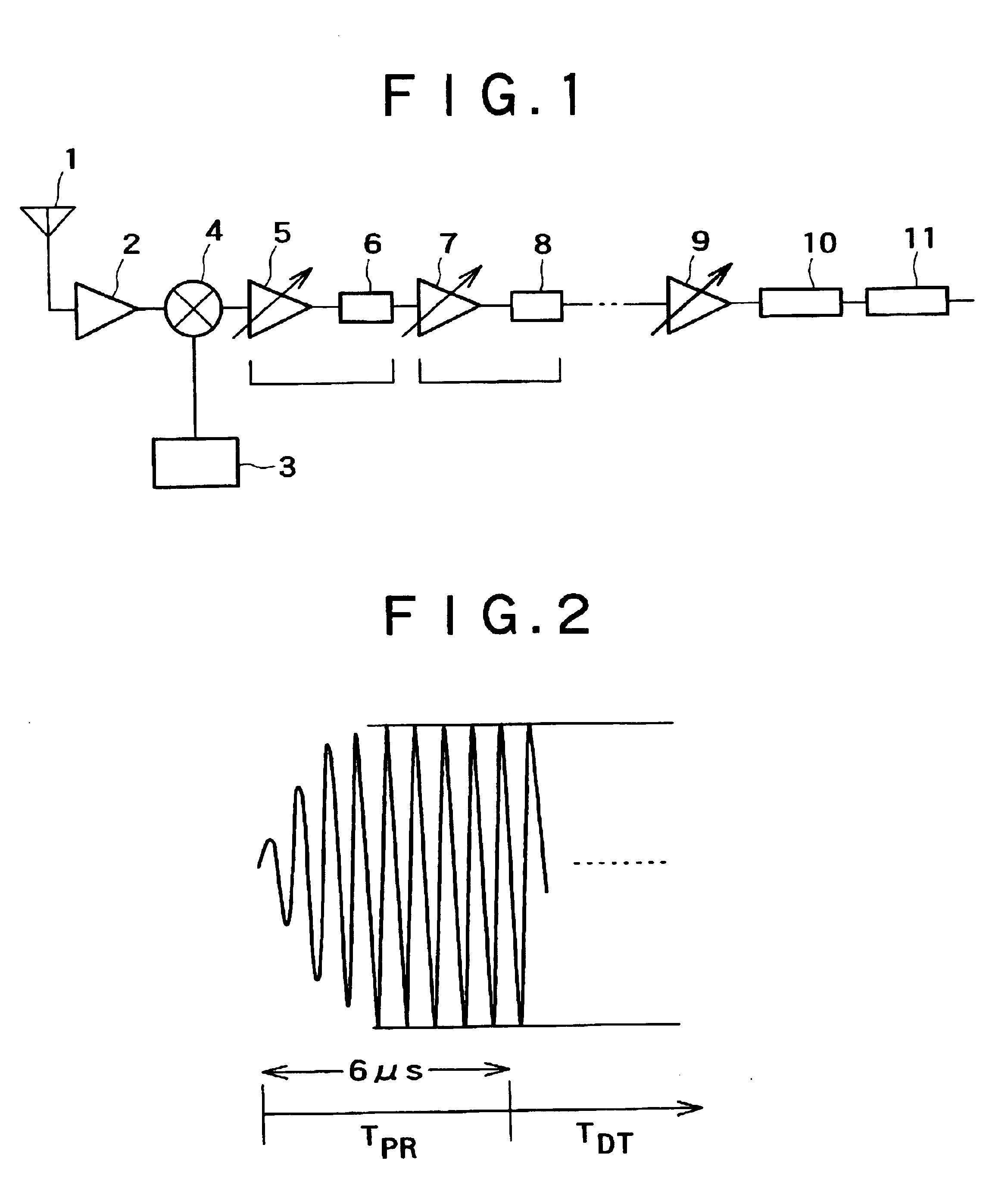
Gain-control method and device for cascaded amplifiers
InactiveUS6927628B2Easy to switchLow costGain controlAmplifier combinationsGain-switchingEngineering
A gain-control method and device that enable high-speed gain switching of cascaded programmable gain amplifiers (PGA) without a high-resolution A / D converter is provided. In one example, the gain-control method for cascaded PGAs detects all the input levels of the PGAs, calculates the optimum gains of the PGAs each on the basis of the detection results, and sets the obtained optimum gains of each of the PGAs at one time, whereby high-speed gain switching becomes possible. The gain-control device for cascaded PGAs that implements this gain-control method includes peak hold circuits that retain the input levels of each of the PGAs, a switch group that sequentially switches outputs of the peak hold circuits, an A / D converter that sequentially detects the outputs from the switch group, and a control and operation device that calculates the optimum gains of the PGAs from the detection results by the A / D converter to set the calculated optimum gains simultaneously to each of the PGAs.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
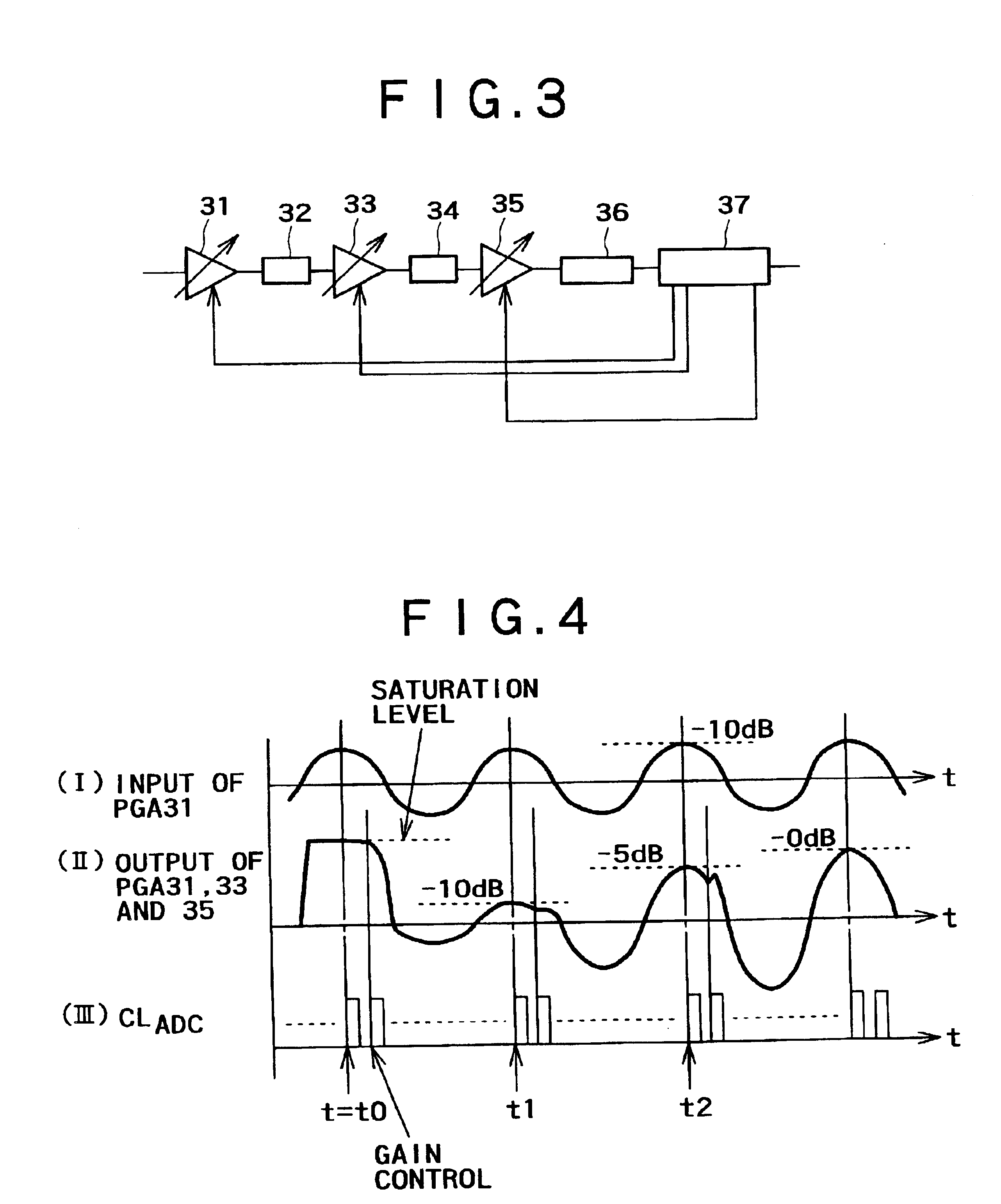
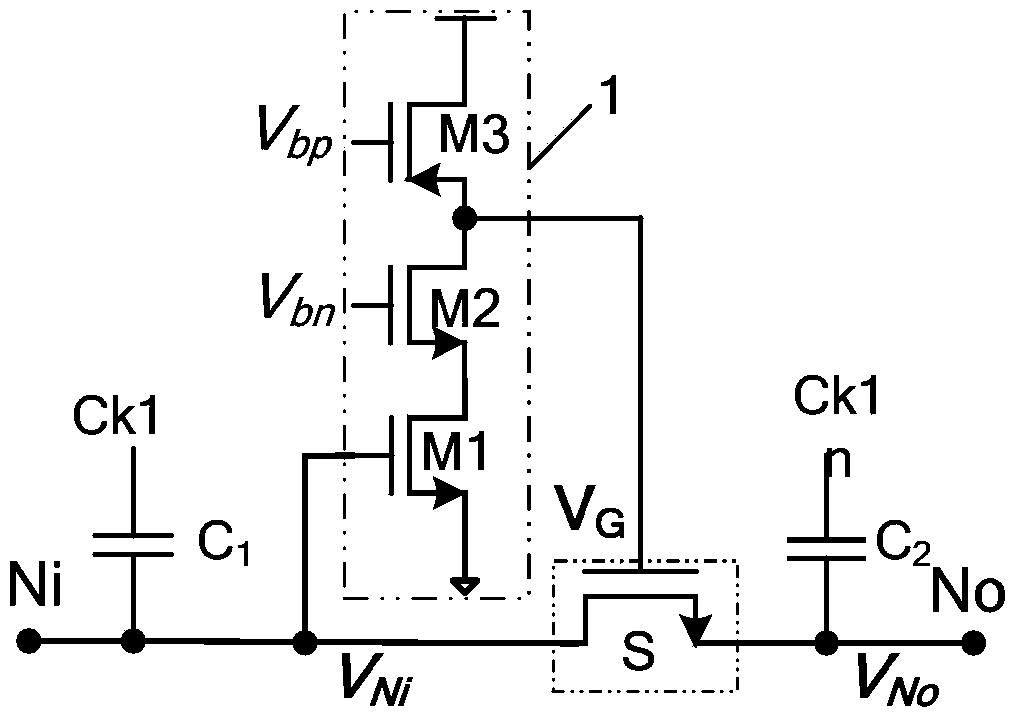
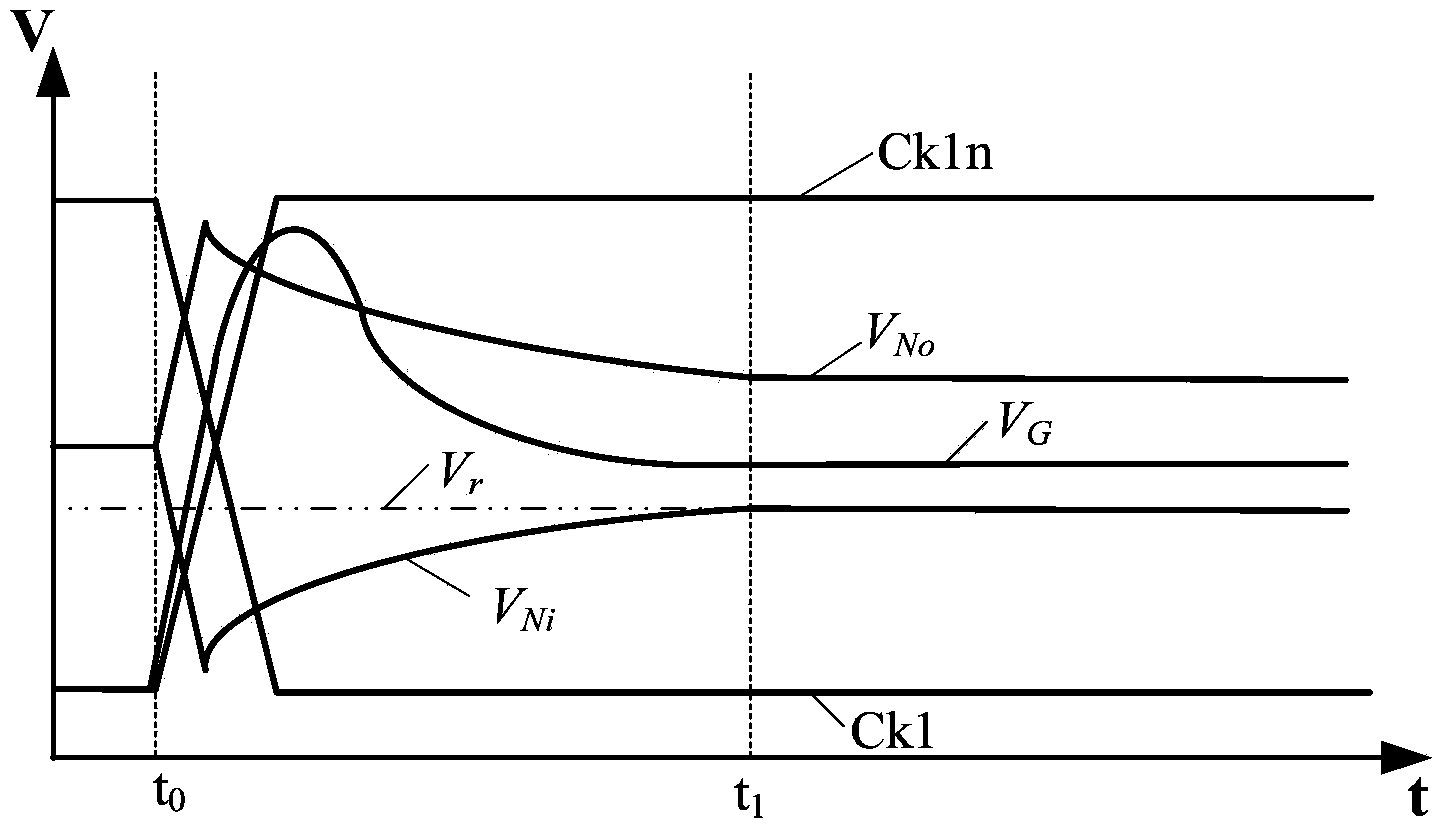
Method and apparatus for DC offset cancellation in amplifiers
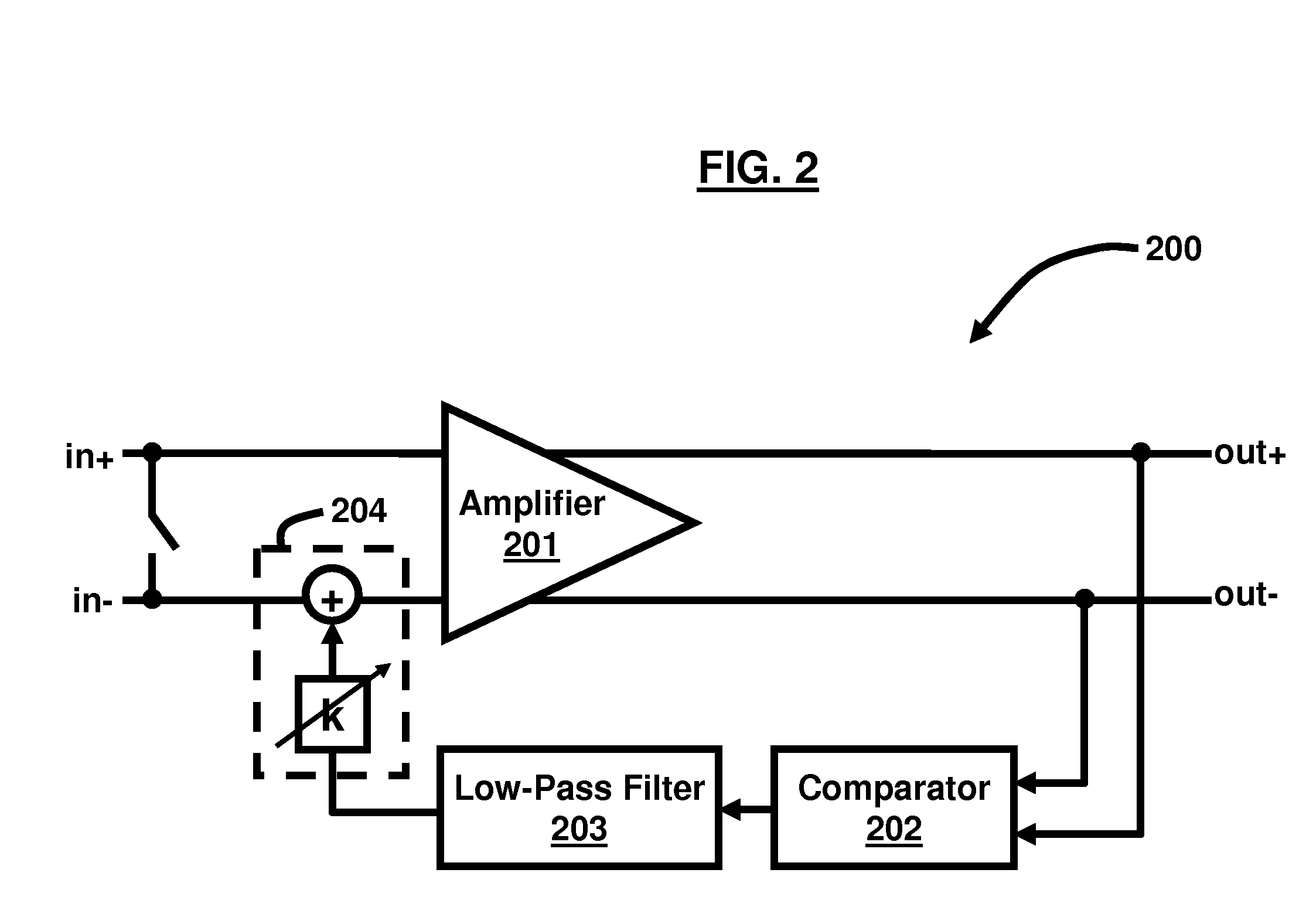
ActiveUS20080048773A1Offset errorAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierOffset cancellation
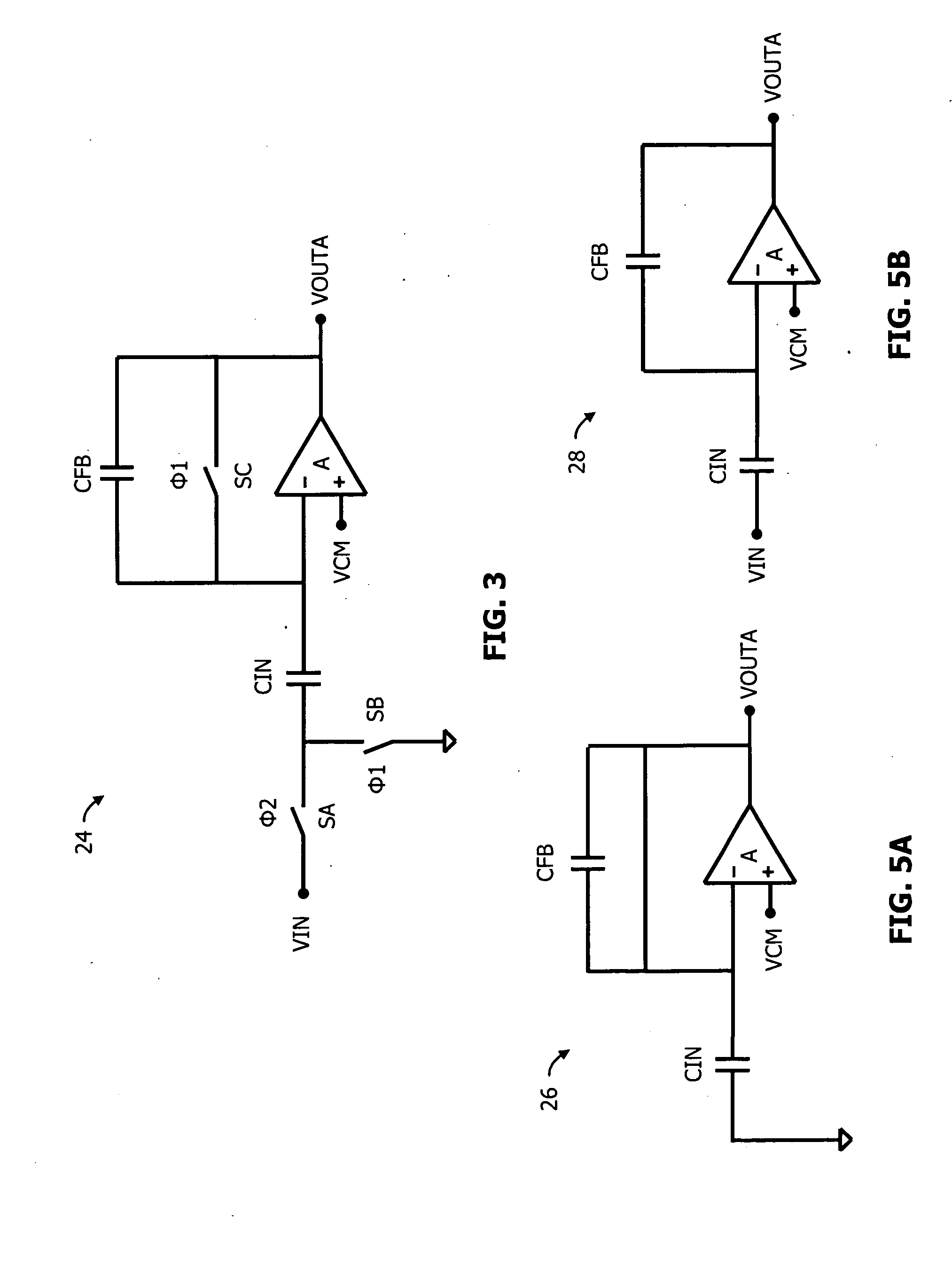
A system, circuit, and method of canceling DC offset errors in cascaded amplifiers comprises arranging a plurality of any of analog voltage and analog current amplifier stages in any of cascaded and parallel configurations; operatively connecting a feedback comparator and digital logic in a feedback path around a given amplifier, wherein the digital logic comprises a finite state machine implementing an adaptive search algorithm comprising fixed switching and modulated switching; operatively connecting a switch at a differential input of the amplifier to short both input terminals of the amplifier; performing fixed switching on binary weighted elements generating discrete analog steps used to vary any of DC offset voltage and current at the input of the amplifier; and performing modulated switching on at least one lower least significant bit (LSB) of all bits used to vary the any of the DC offset voltage and current.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
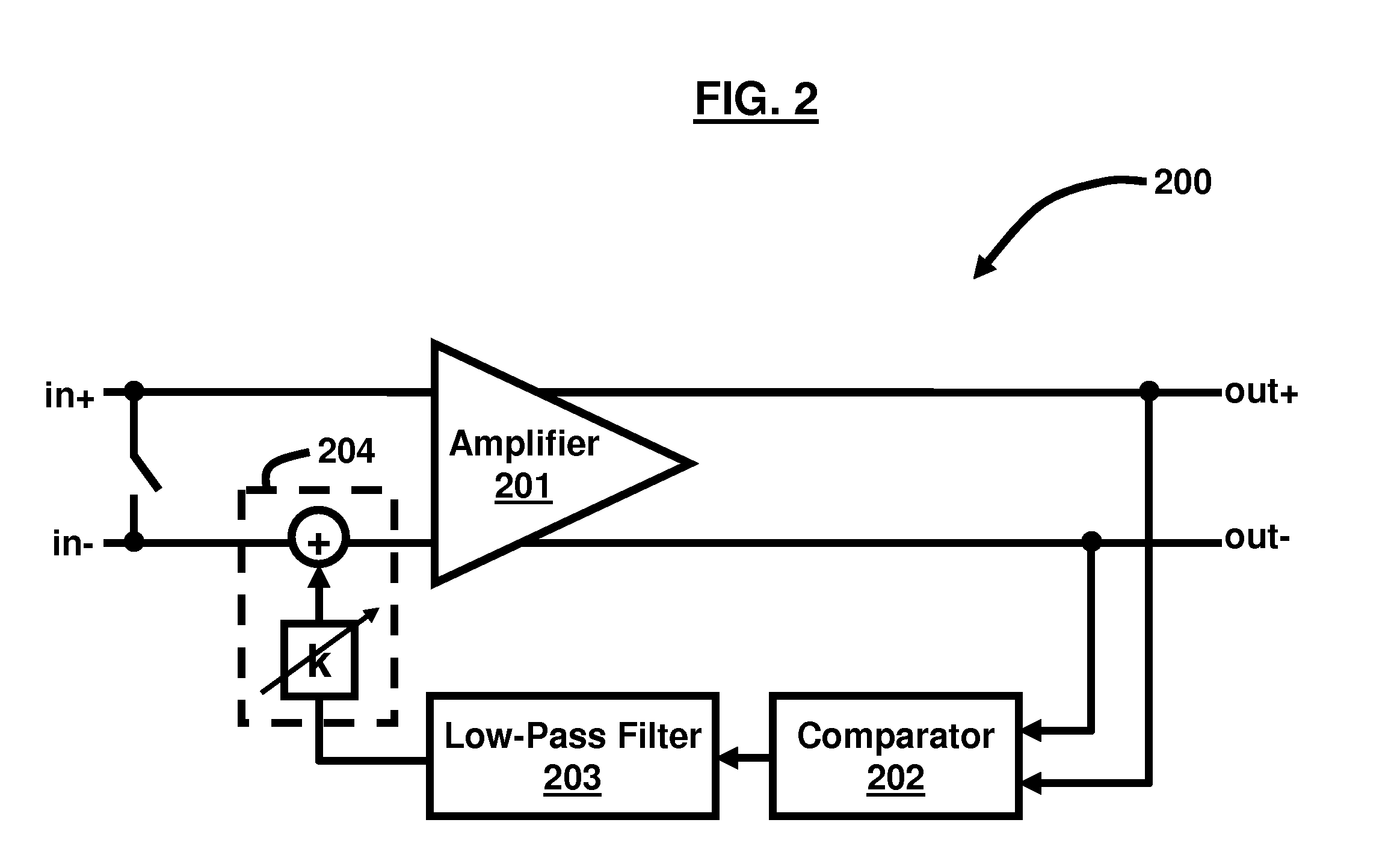
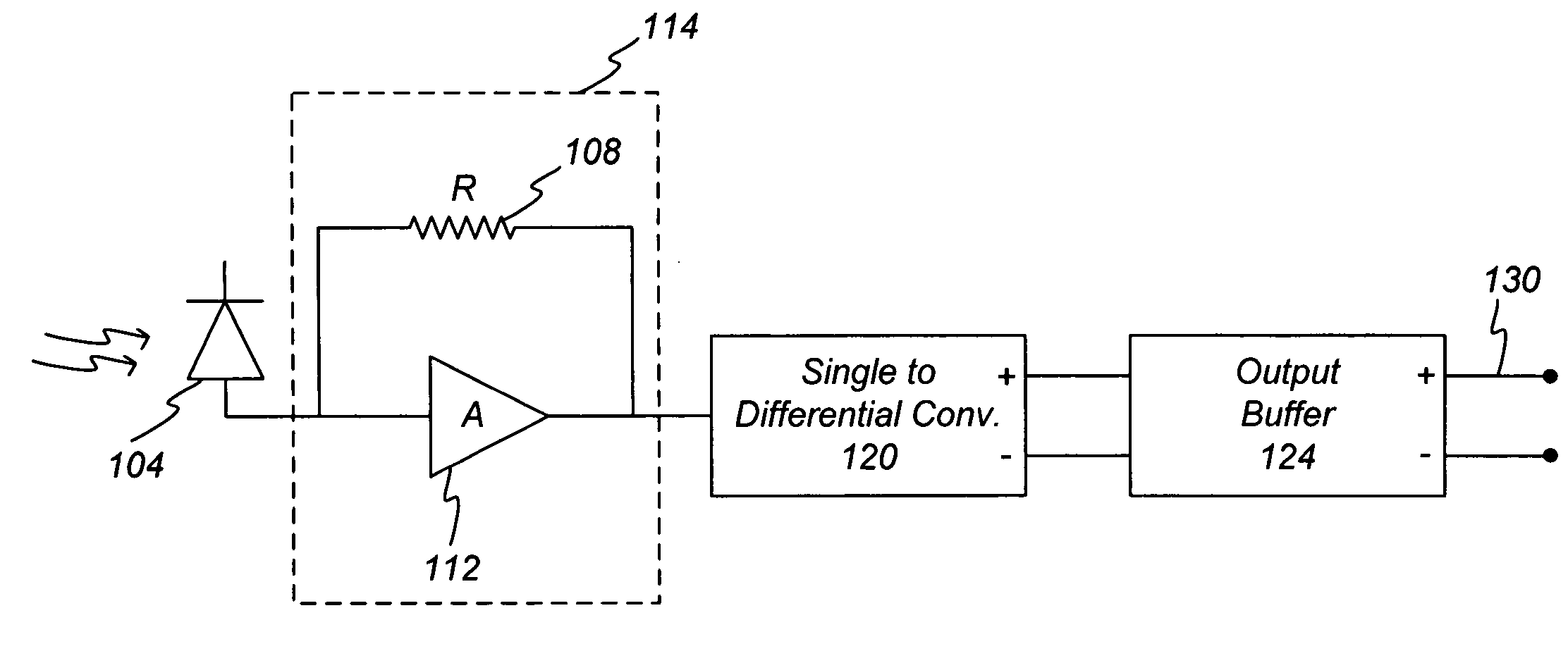
High sensitivity two-stage amplifier
ActiveUS8509629B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsNegative feedbackHigh rate
The invention relates to amplifiers and in particular, to a transimpedance amplifier for high rate applications. Disclosed is a two stage transimpedance amplifier having a first stage comprising an amplifier and a load and a second stage comprising an amplifier and a resistor. Negative feedback is provided through a feedback resistor. Only two voltage conversions occur which reduces phase distortion, as compared to three stage transimpedance amplifiers which perform 3 voltage conversions.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
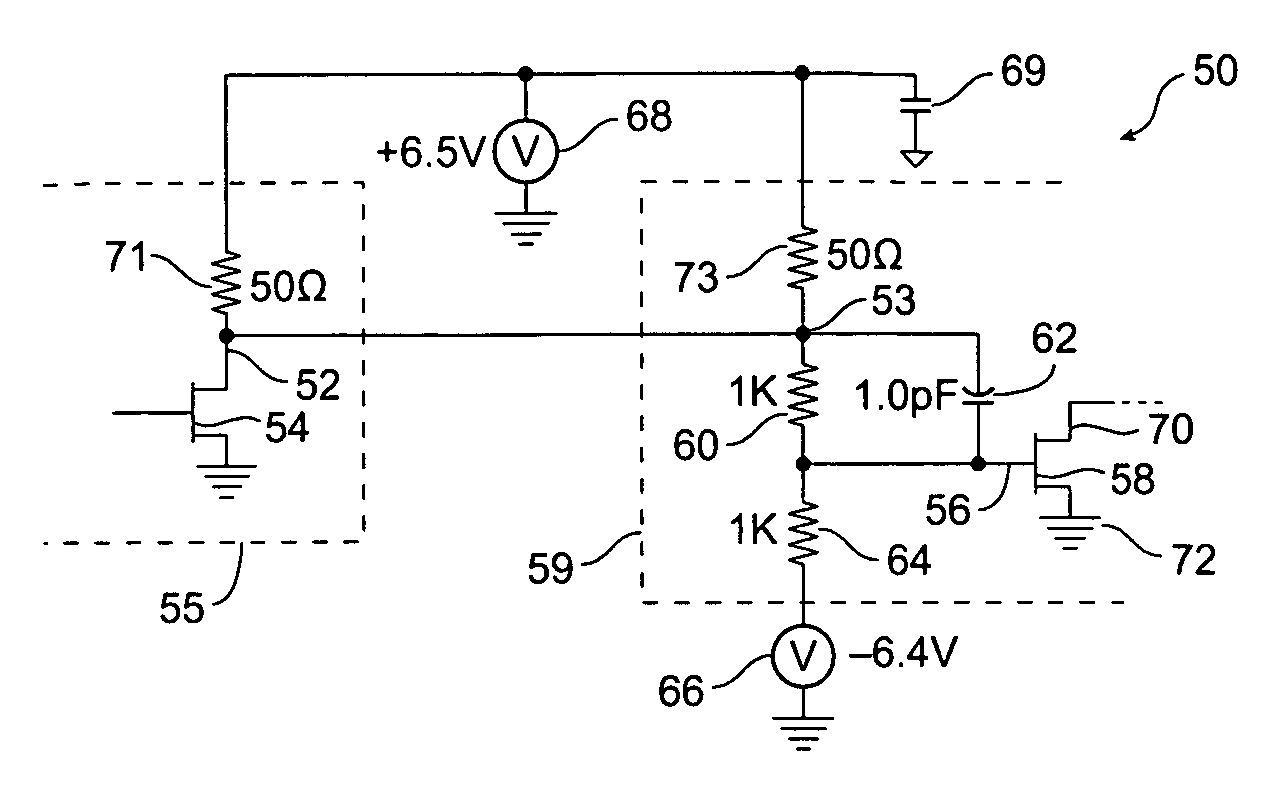
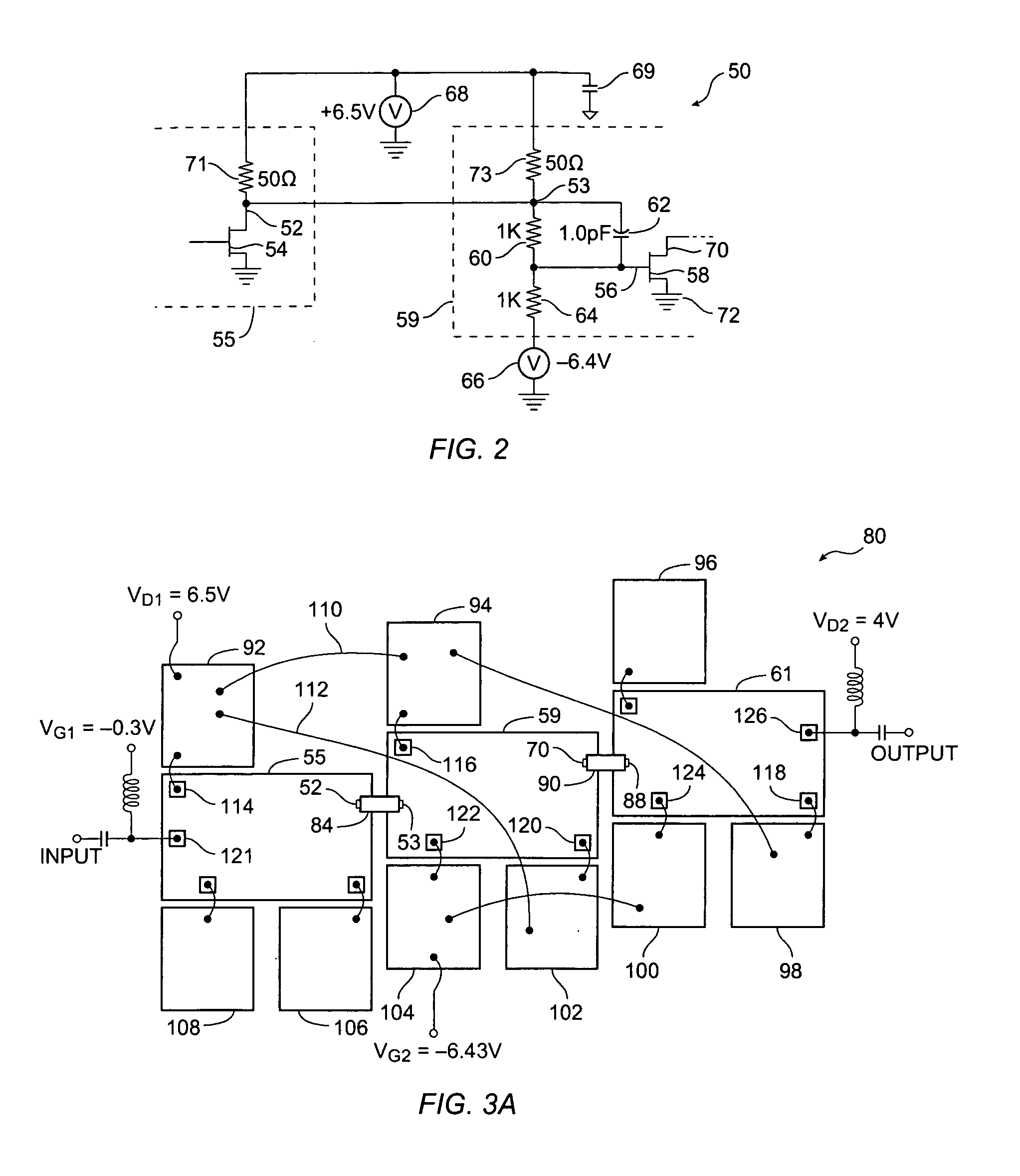
Transconductance-enhanced recovery current folded MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) transistor cascade amplifier
ActiveCN102176659AIncreased large signal slew rateExtension of timeNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersLow voltageCascode
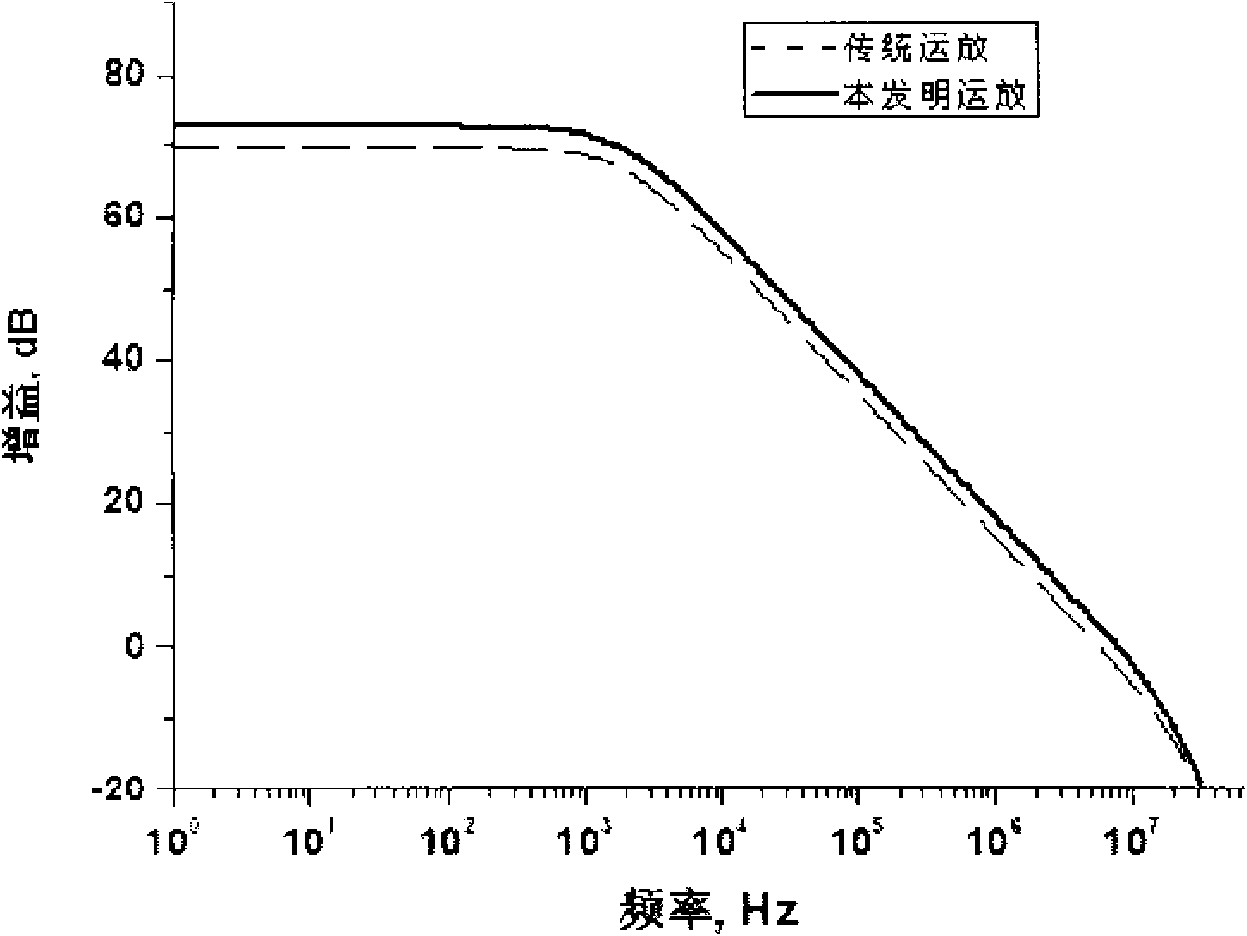
The invention discloses a transconductance-enhanced recovery current folded MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) transistor cascade amplifier, belonging to the design field of analogue integrated circuits. The amplifier comprises a transconductance-enhanced input stage, an intermediate stage for amplifying a recovery current and a rail-to-rail output stage, wherein the transconductance-enhanced input stage is formed by four shunted PMOS (P-channel metal oxide semiconductor) transistors and four (two pairs of) PMOS transistors constituting negative resistance enhanced transconductance, and used forconverting input voltage signals into four paths of currents and multiplying transconductance of input tubes; the intermediate stage for amplifying the recovery current mainly comprises two low-voltage current mirrors and is used for realizing the amplification of the recovery current; and the rail-to-rail output stage mainly comprises two PMOS transistors and two NMOS (N-channel metal oxide semiconductor) transistors and is used for realizing the rail-to-rail output of signals. The amplifier is capable of improving the bandwidth capability by over two times under the condition of not increasing power consumption, greatly increases low-frequency gains and large-signal slew rate, improves phase margin and enhances performances of a circuit.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
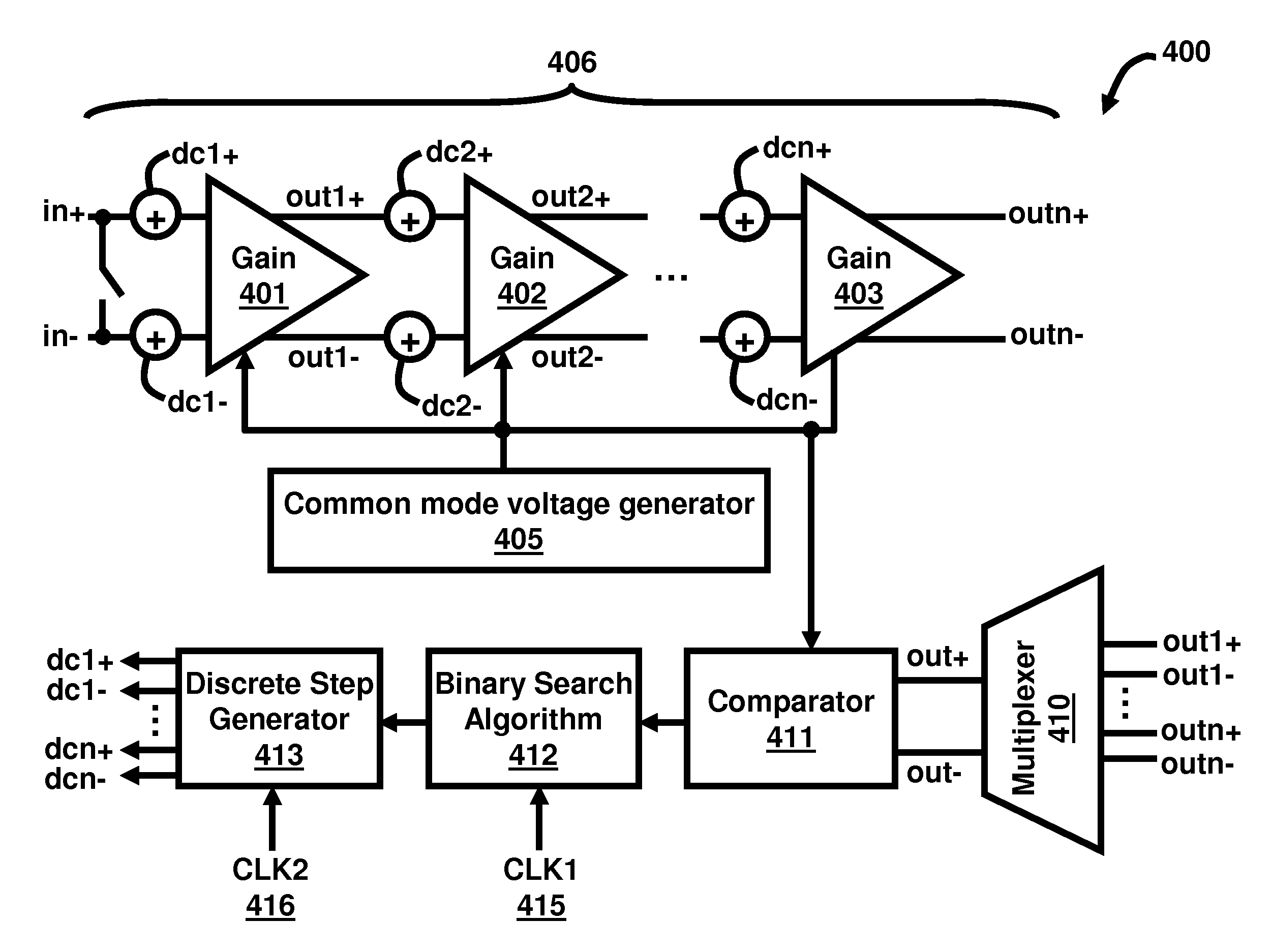
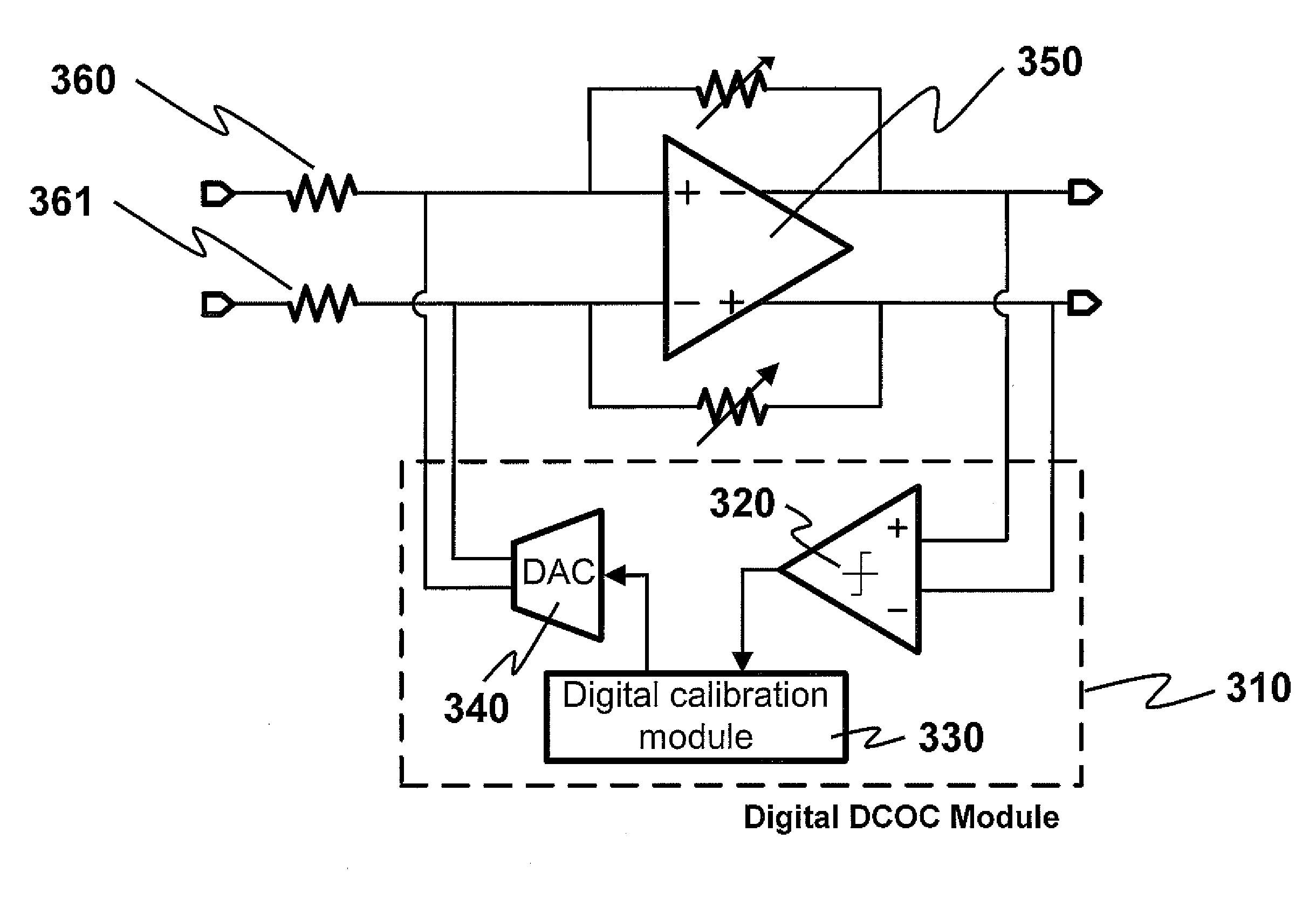
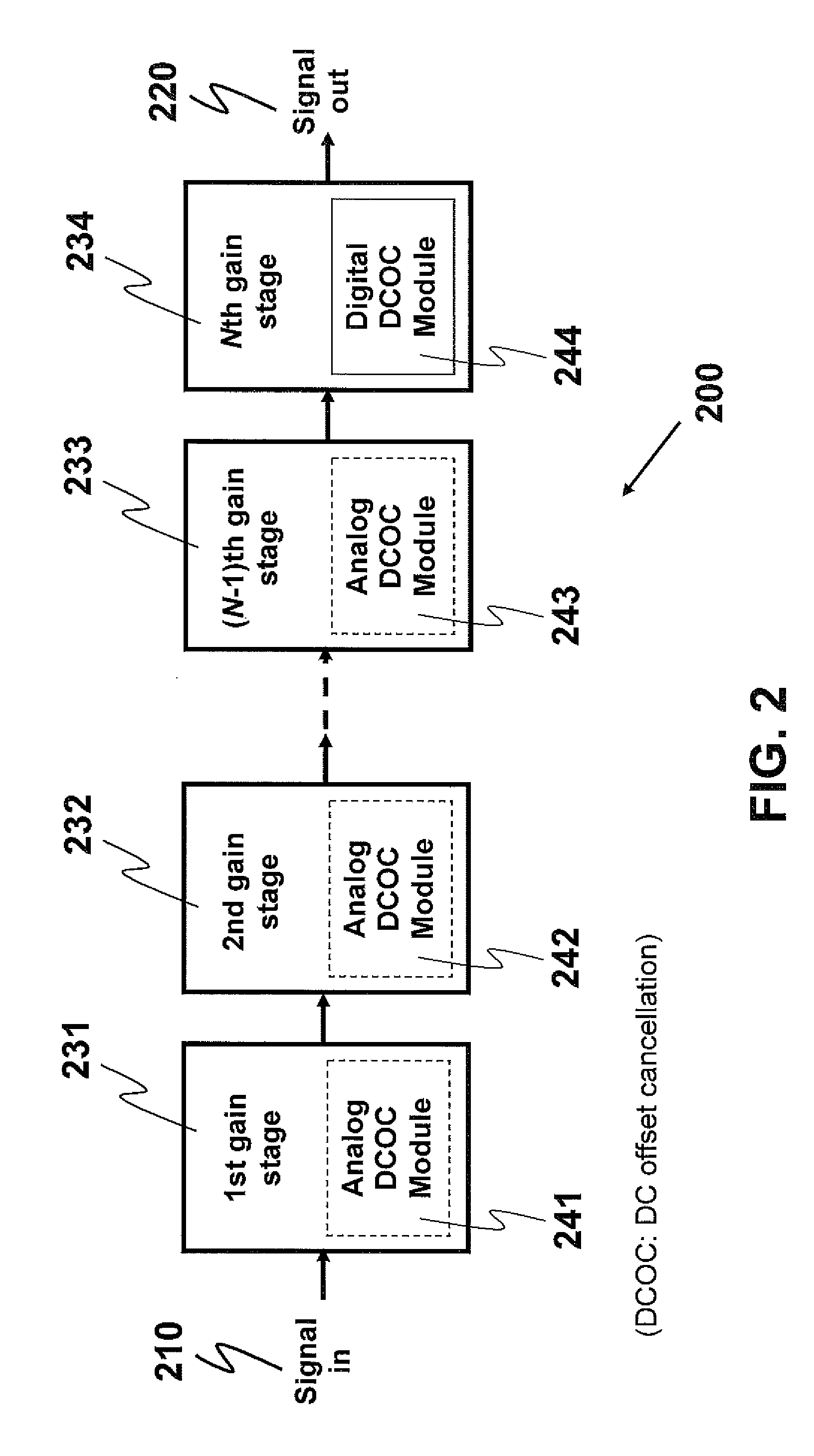
DC offset cancellation for a multi-stage amplifier
InactiveUS20140176238A1Differential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAudio power amplifierOffset cancellation
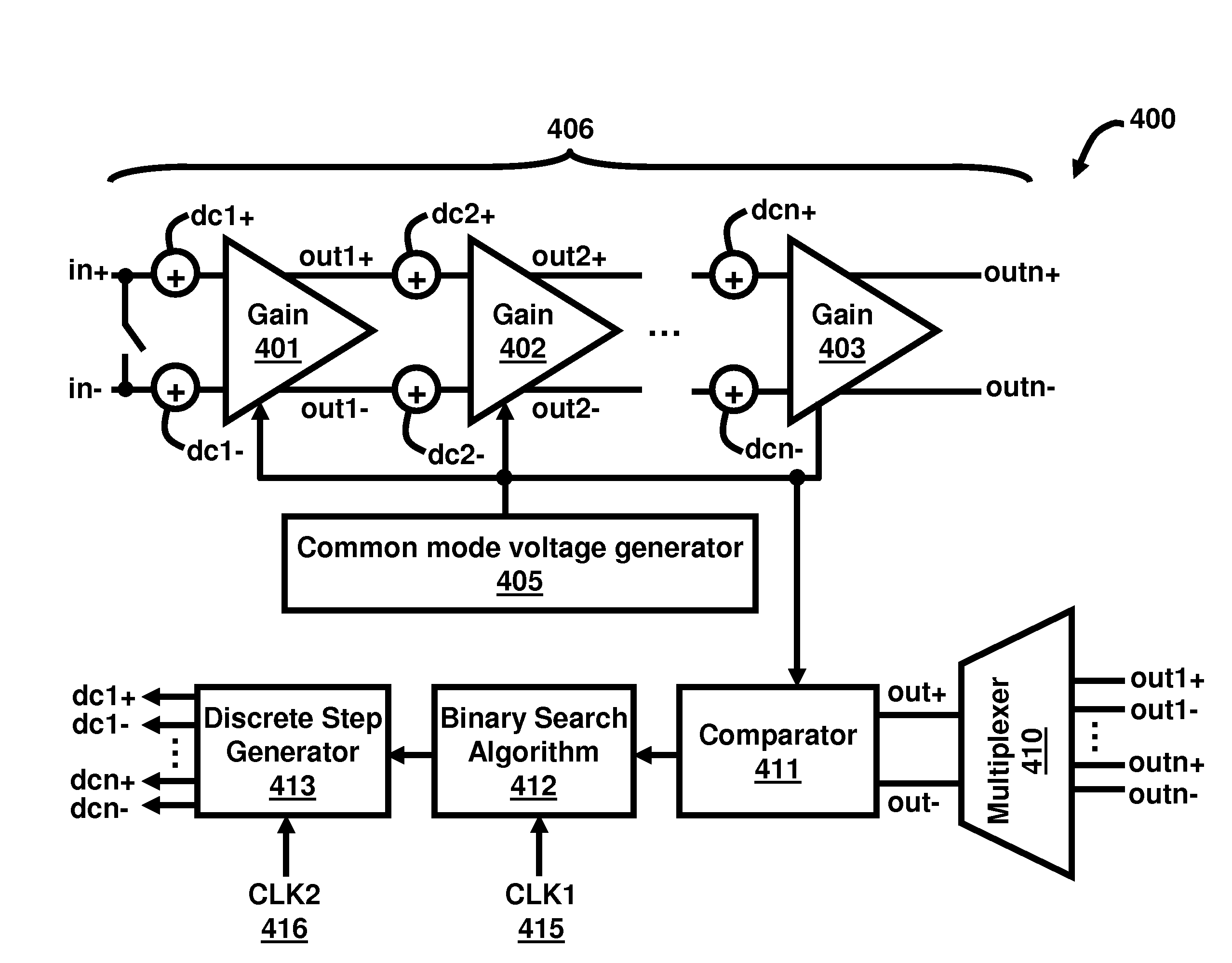
This invention provides a multi-stage amplifier incorporating DC offset cancellation. The amplifier has a plurality of series-connected gain stages each of which comprises a differential amplifier unit generating a pair of differential outputs from a pair of differential inputs. In particular, a trailing stage in the plurality of gain stages comprises a digital DC offset cancellation module configured to compensate for a DC offset of the trailing stage's differential amplifier unit. The digital DC offset cancellation module comprises a comparator coupled to the pair of differential outputs of the trailing stage's differential amplifier unit for receiving such differential outputs as inputs for the comparator. Preferably, the comparator has an inherent DC offset that is substantially small. It is preferable that a non-trailing stage of the amplifier comprises an analog DC offset cancellation module for compensating for a DC offset of the non-trailing stage.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
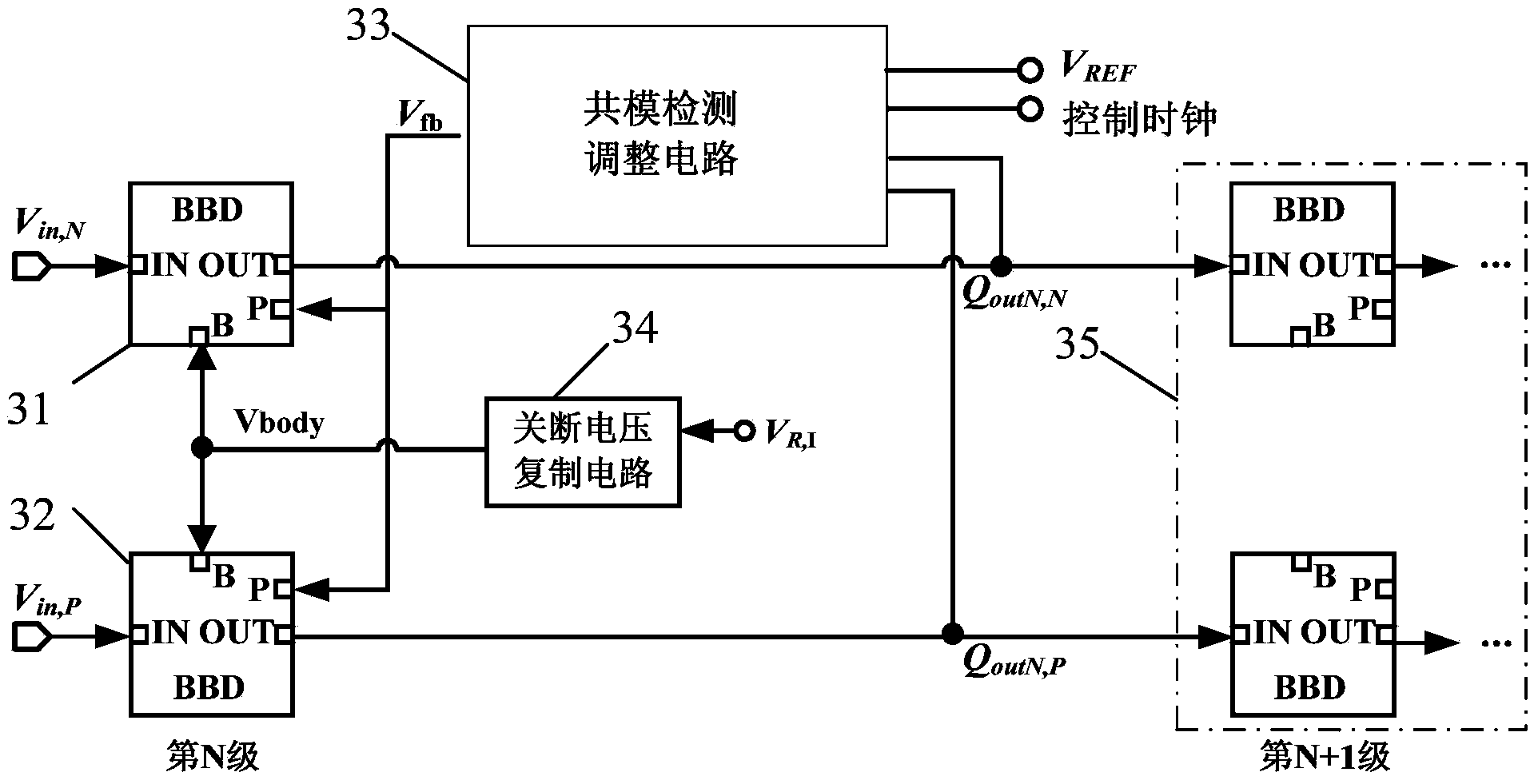
PVT insensitive common mode charge control device for charge coupling assembly line analog-digital converter
ActiveCN104270152AChanging the Large Signal CharacteristicsChange the cut-off point voltageAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCharge controlCascode
The invention relates to a circuit device used for controlling common mode charges in a charge coupling assembly line analog-digital converter. The circuit device comprises two output common mode adjusting charge transmission circuits (BBD), a common mode detection adjusting circuit and a voltage turning-off copy circuit. According to the aim of the circuit device, a common mode charge problem caused by an existing charge transmission technology is restrained, and the purpose of adjusting common mode charges precisely is achieved through two adjusting modes. According to the first adjusting mode, the large-signal characteristic of a cascade amplifier is changed by adjusting voltage of a substrate of an input tube of the cascade amplifier, and therefore on-off point voltage of a whole BBD is changed. According to the second mode, the large-signal characteristic of the cascade amplifier is changed by changing grid voltage of a parallel-connection tube M4, and the on-off point voltage of the whole BBD can be changed. The two modes are respectively used for dealing with errors of the two common mode charges.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
Multi-stage amplifier with switching circuitry
InactiveUS7199654B1Reducing parasitic chargeAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifiers using switched capacitorsAudio power amplifierTuned amplifier
Disclosed are a multi-stage amplifier circuit, a method of operating a multi-stage amplifier circuit, and a device with the multi-stage amplifier circuit. The amplifier circuit technology includes an operational amplifier shared among multiple stages and switching circuitry. The various switching circuitry switches among elements to provide different input signals and different feedback to the shared operational amplifier at the different stages of operation of the amplifier circuit. The various switching circuitry also stores and discharges charge at one or more operational amplifier inputs.
Owner:RE SECURED NETWORKS LLC
Symmetrically-folded MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) transistor cascade amplifier with broadband and low-power consumption
ActiveCN102176658AHigh bandwidthIncrease low frequency gainAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthLow voltageHemt circuits
The invention discloses a symmetrically-folded MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) transistor cascade amplifier with broadband and low-power consumption, belonging to the design field of analogue integrated circuits. The amplifier comprises a shunt input stage, a recovery-current amplifying intermediate stage and a rail-to-rail output stage, wherein the shunt input stage is formed by four PMOS (P-channel metal oxide semiconductor) transistors; the recovery-current amplifying intermediate stage is used for converting input voltage signals into four paths of small signal currents and formed by two low-voltage current mirrors as well as is used for amplifying recovery currents; and the rail-to-rail output stage is formed by four PMOS transistors and two NMOS (N-channel metal oxide semiconductor)transistors and used for realizing rail-to-rail output of signals. The amplifier is capable of improving the bandwidth capability by over two times under the condition of not adding power consumption, has the advantages of higher common-mode rejection ratio, symmetrical positive-negative conversion rate, higher low-frequency gain and the like, and can improve performances of a circuit.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Current-matching variable gain amplifier
ActiveUS20060261893A1Simple circuitReduce power wasteDifferential amplifiersAmplification control detailsMOSFETAudio power amplifier
A current-matching variable gain amplifier is provided. The amplifier comprises a reference current source, at least one cascode amplifier, a matching circuit, a control circuit, and at least one first blocking circuit. The reference current source provides a reference current. Each of the cascode amplifiers amplifies an input signal according to the reference current. The matching circuit equalizes the voltage level at a first node in each cascode amplifier and the voltage level at a second node in the matching circuit. The matching circuit also equalizes the current of a main MOSFET of each cascode amplifier and the current of a first MOSFET of the matching circuit. The control circuit controls the current of the first MOSFET of the matching circuit. Each of the first blocking circuit(s) corresponds with the cascode amplifier, and is coupled between the reference current source and the corresponding cascode amplifier, for blocking RF signals.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Current-matching variable gain amplifier
A current-matching variable gain amplifier is provided. The amplifier comprises a reference current source, at least one cascode amplifier, a matching circuit, a control circuit, and at least one first blocking circuit. The reference current source provides a reference current. Each of the cascode amplifiers amplifies an input signal according to the reference current. The matching circuit equalizes the voltage level at a first node in each cascode amplifier and the voltage level at a second node in the matching circuit. The matching circuit also equalizes the current of a main MOSFET of each cascode amplifier and the current of a first MOSFET of the matching circuit. The control circuit controls the current of the first MOSFET of the matching circuit. Each of the first blocking circuit(s) corresponds with the cascode amplifier, and is coupled between the reference current source and the corresponding cascode amplifier, for blocking RF signals.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Variable-gain amplifier
ActiveUS20070296501A1Reduce voltageImprove featuresGain controlAmplifier combinationsVariable-gain amplifierAudio power amplifier
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
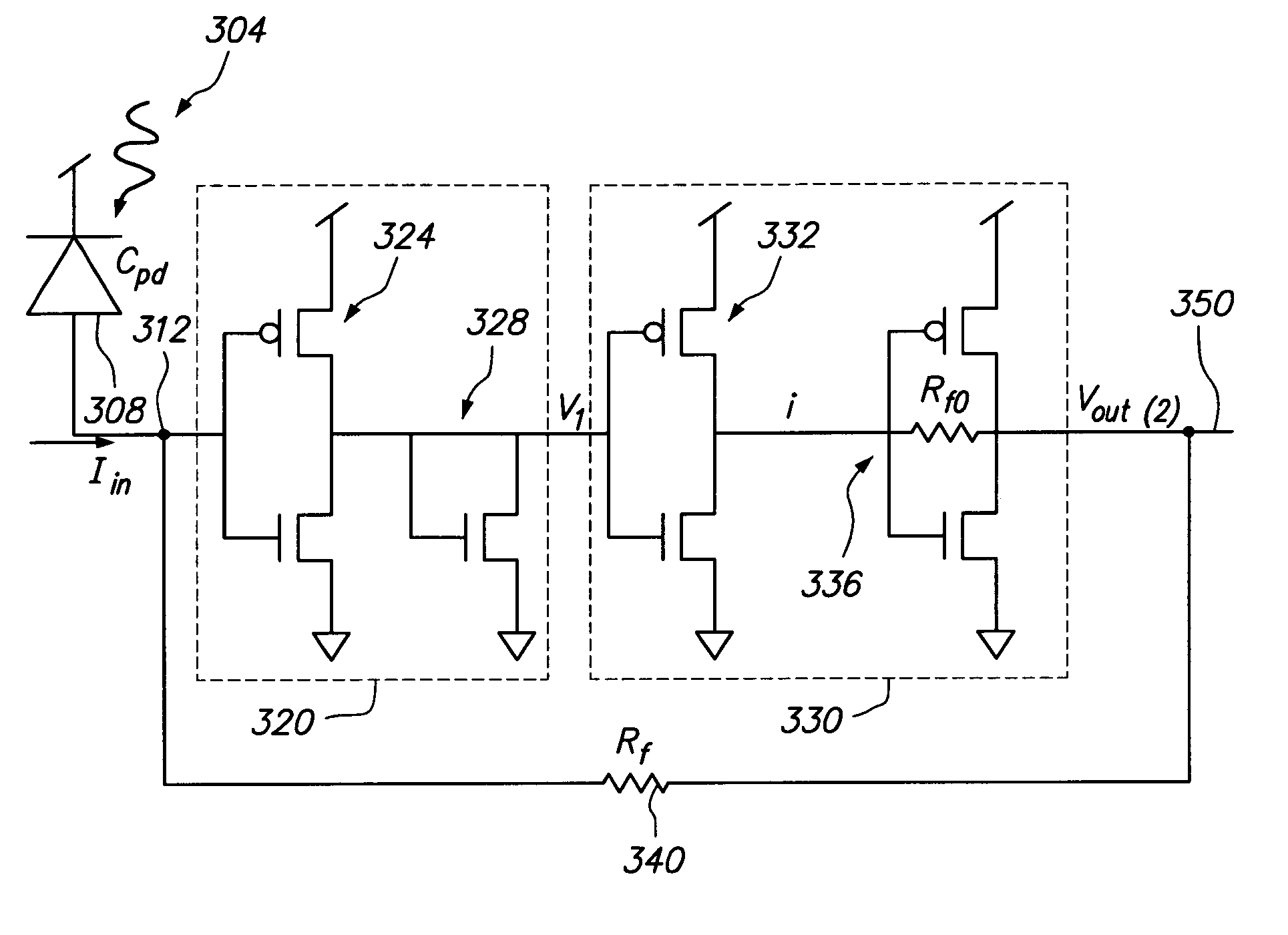
High-gain low-noise optimal bias regulating type cascode trans-impedance amplifier
InactiveCN106253856AHigh gainHigh bandwidthAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlLow noiseCascode
The invention discloses a cascode transimpedance amplifier with high gain, low noise and optimal bias adjustment, which includes: a main amplifier and an auxiliary amplifier, and also includes: a connection between the output terminal of the auxiliary amplifier and the gate of the main amplifier In between, a bias circuit with a high-pass filter structure is added to isolate the DC bias of the main amplifier and the auxiliary amplifier, so that both work in the best bias state; a cascode amplifier is used to replace the DC bias in the auxiliary amplifier Common-source stage amplifier, providing higher gain-bandwidth product; series inductor L at the input 1 , the series inductor L between the common-source and common-gate devices of the cascode amplifier 2 , the two inductances, the photodetector capacitance at the input end and the parasitic capacitance of the MOS tube form two π-type matching networks respectively. On the premise of ensuring that the overall bandwidth of the transimpedance amplifier is not reduced, the present invention improves the circuit gain and reduces noise, and finally realizes the RGC transimpedance amplifier with high gain and low noise.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
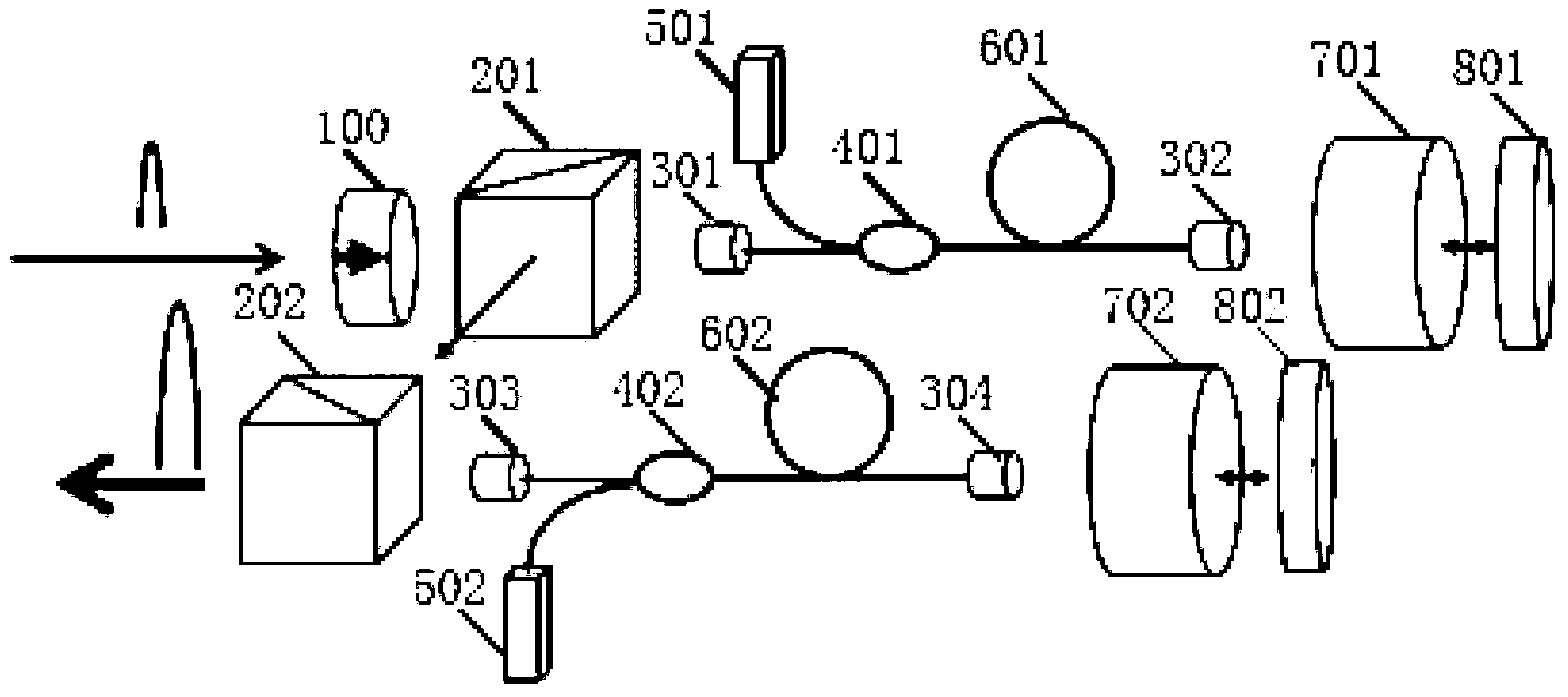
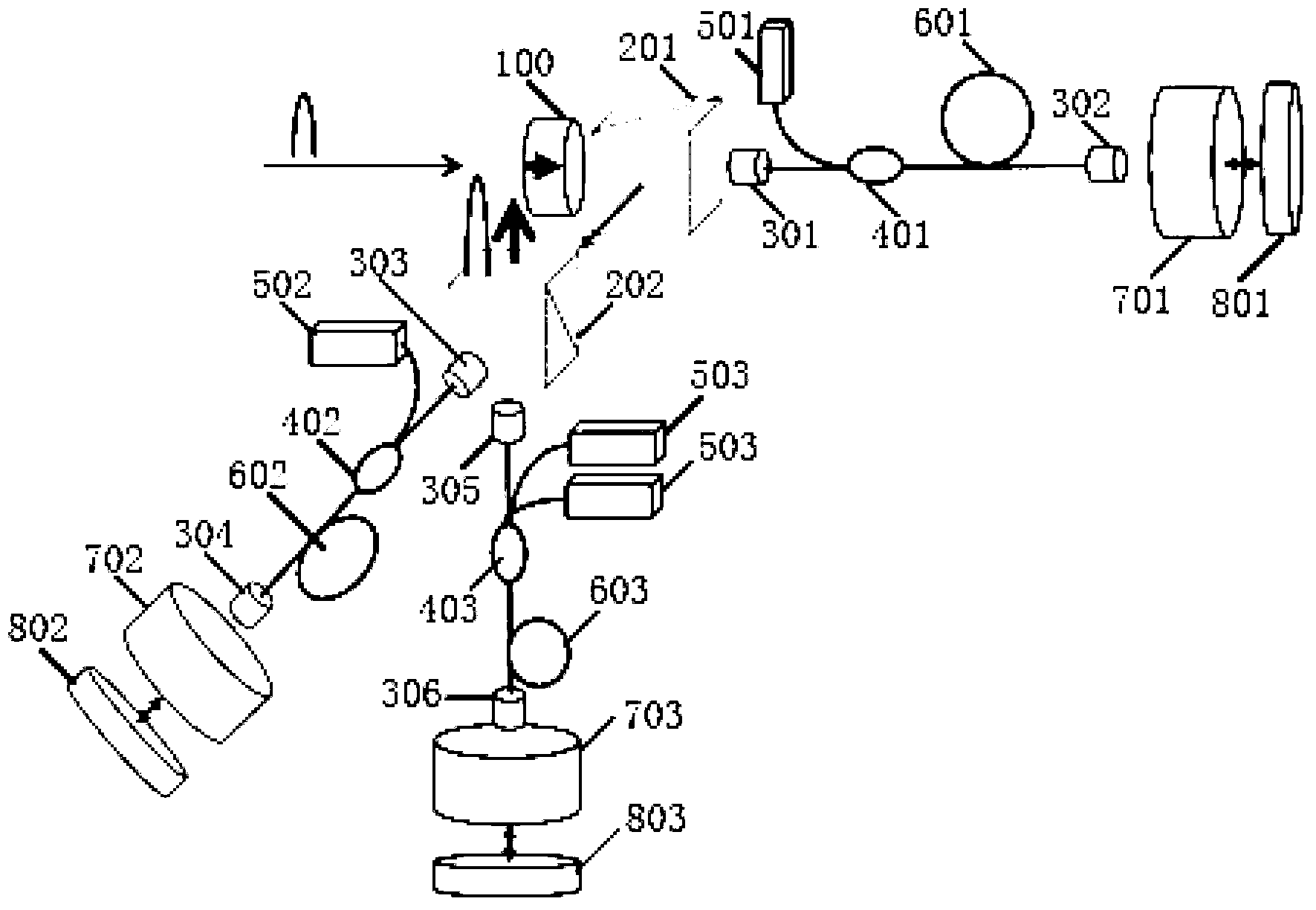
Polarization-stable optical fiber laser cascade amplifier
ActiveCN103236629AEnhanced couplingEasy to useOptical resonator shape and constructionCoupling light guidesBeam splitterHigh power lasers
The invention discloses a polarization-stable optical fiber laser cascade amplifier, which comprises a laser space isolator for preventing return seed laser from damaging a seed source, the laser space isolator is connected with a first polarizing beam splitter for splitting laser in different directions, the first polarizing beam splitter is connected with a first optical fiber collimator, the first optical fiber collimator is connected with a first combiner, the first combiner is connected with a first gain optical fiber for generating population inversion, the first gain optical fiber is connected with a second optical fiber collimator, the second optical fiber collimator is connected with a Faraday rotator mirror for rotating the laser polarization angle by 45 degrees, the Faraday rotator mirror is connected with a total-reflection mirror for returning incident light along the original path, the pumping input end of the first combiner is connected with a first pumping source, and one reflecting end of the first polarizing beam splitter servers as a polarization-maintaining pulse output end. The polarization-stable optical fiber laser cascade amplifier has the advantage that the polarization-stable optical fiber laser cascade amplifier can always keep the polarization state of amplified and outputted high-power laser stable in the process of amplification.
Owner:广东华快光子科技有限公司 +1
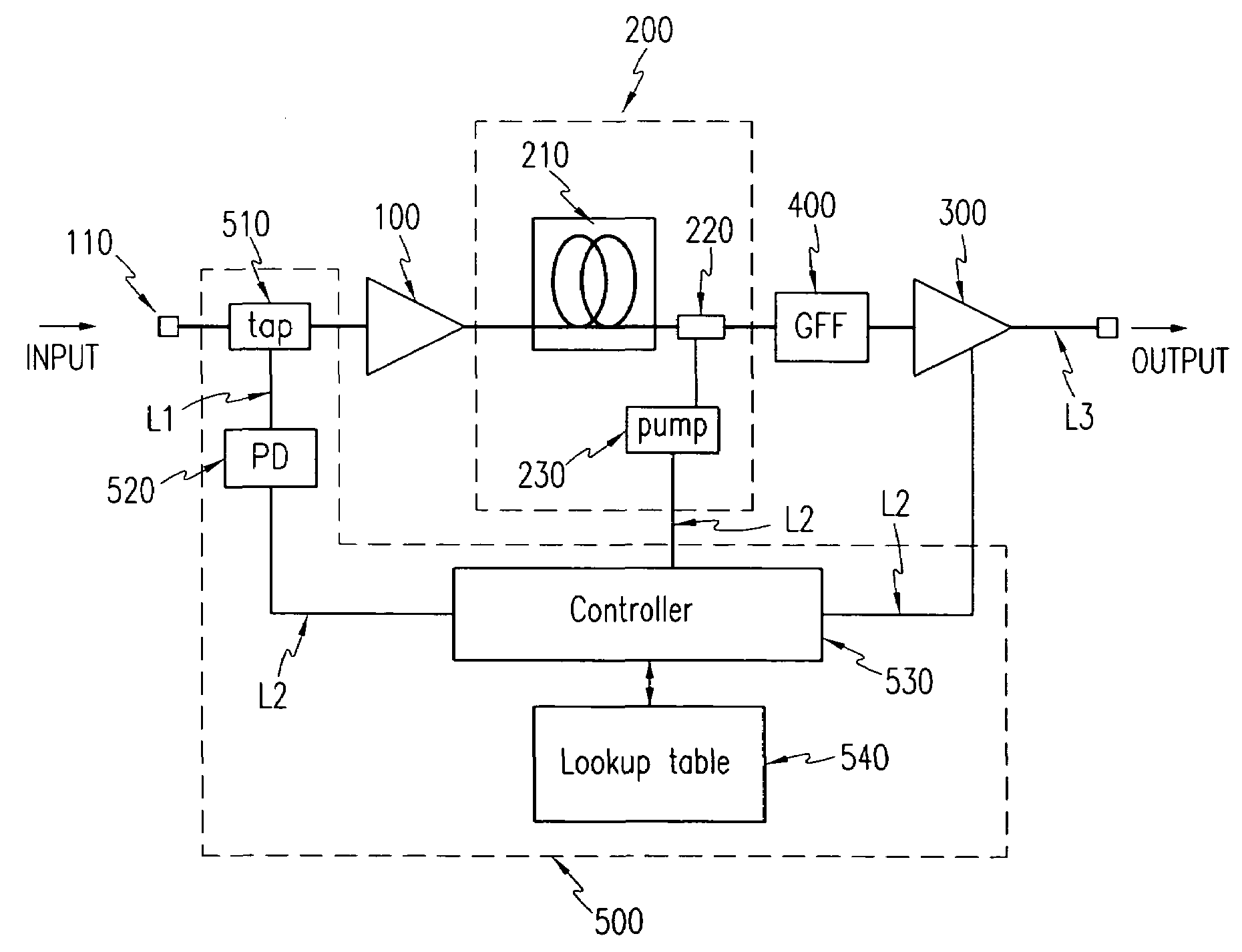
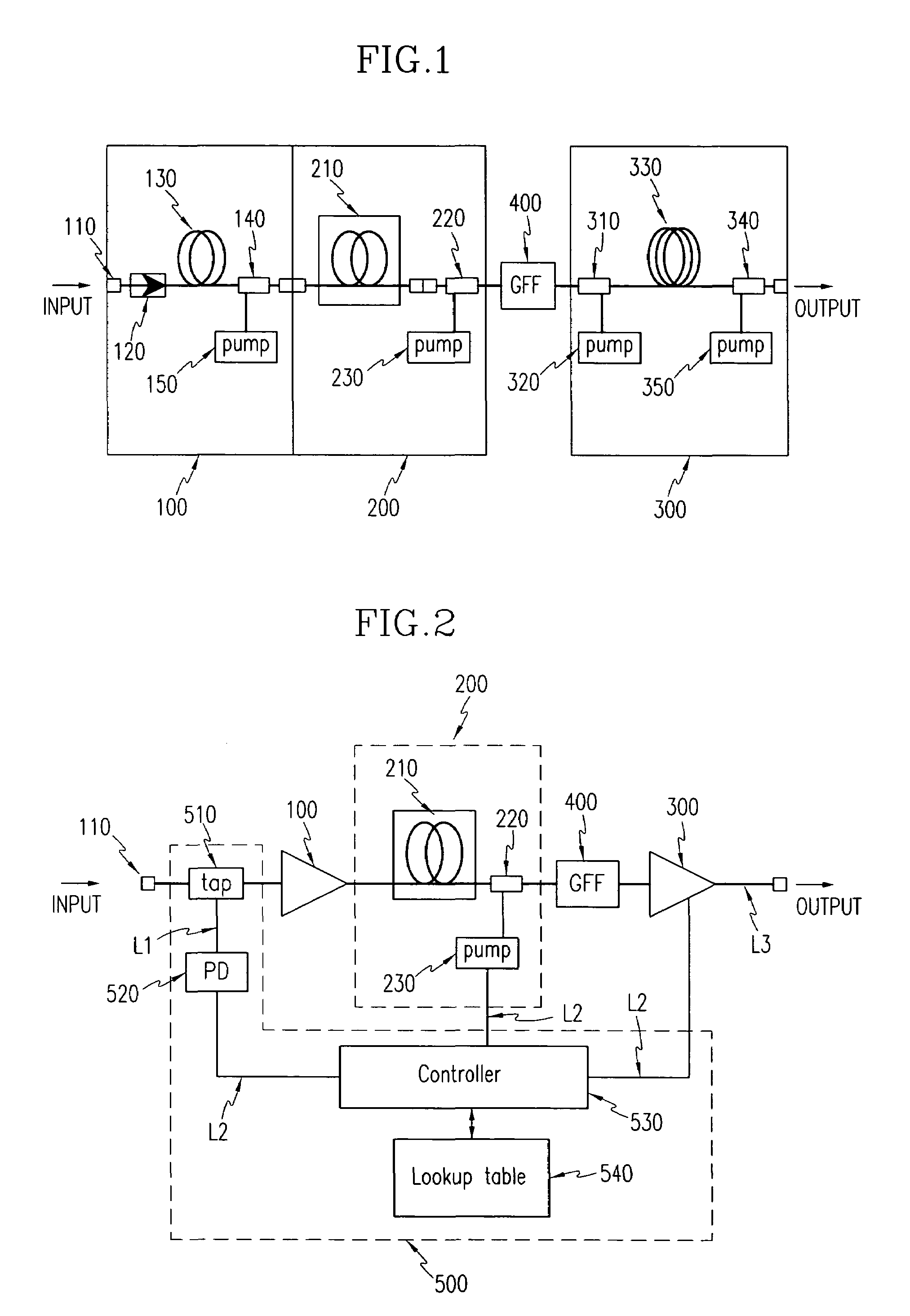
Fiber amplifier and control method thereof
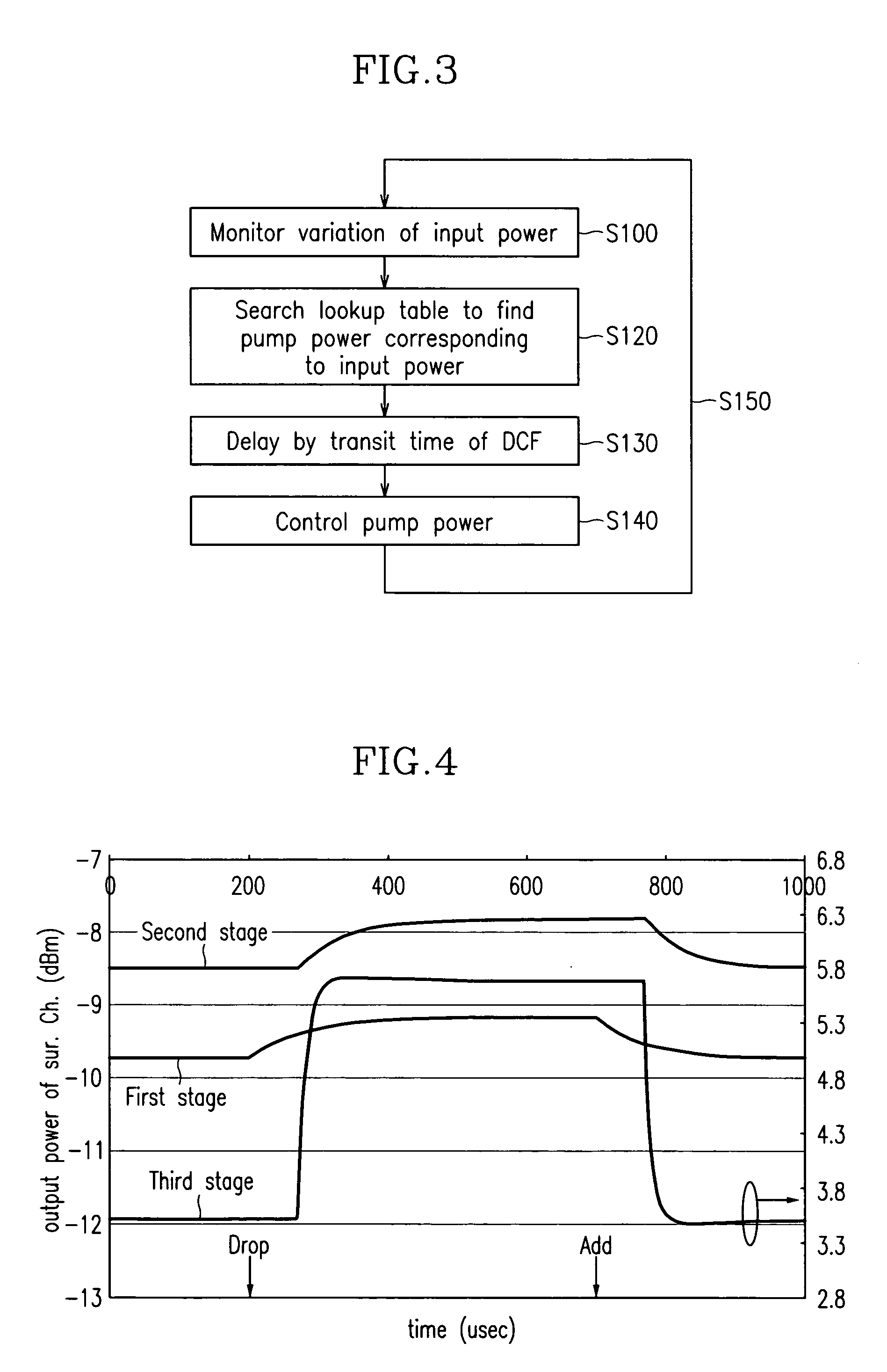
InactiveUS7038841B2Constant outputReduce transient effectsLaser using scattering effectsWavelength-division multiplex systemsAudio power amplifierThree stage
A method for realizing, in a fiber amplifier with three stages of amplifiers, automatic gain control in which a constant gain is obtained when channels are varied, and automatic level control in which a constant output per channel is obtained when a light power is varied because of variations in span loss. A light power or another light power of a specific wavelength is monitored to determine when variations in these light powers take place, current values of pump laser diodes appropriate for an input is read from a lookup table, and pump laser diodes are driven. During this operation, a pump power of the first stage amplifier is constantly maintained, and those of the second or third stage amplifier are controlled.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
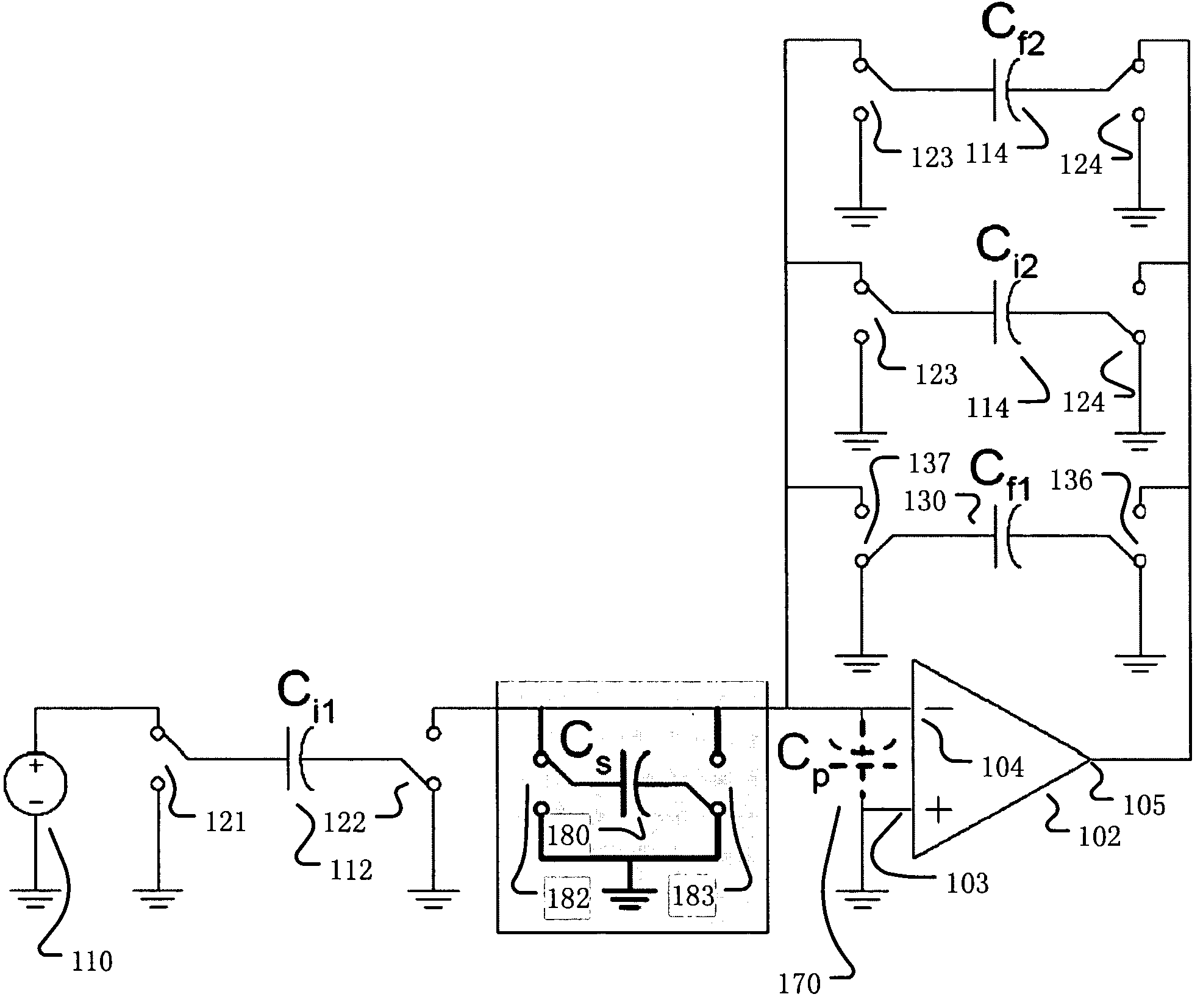
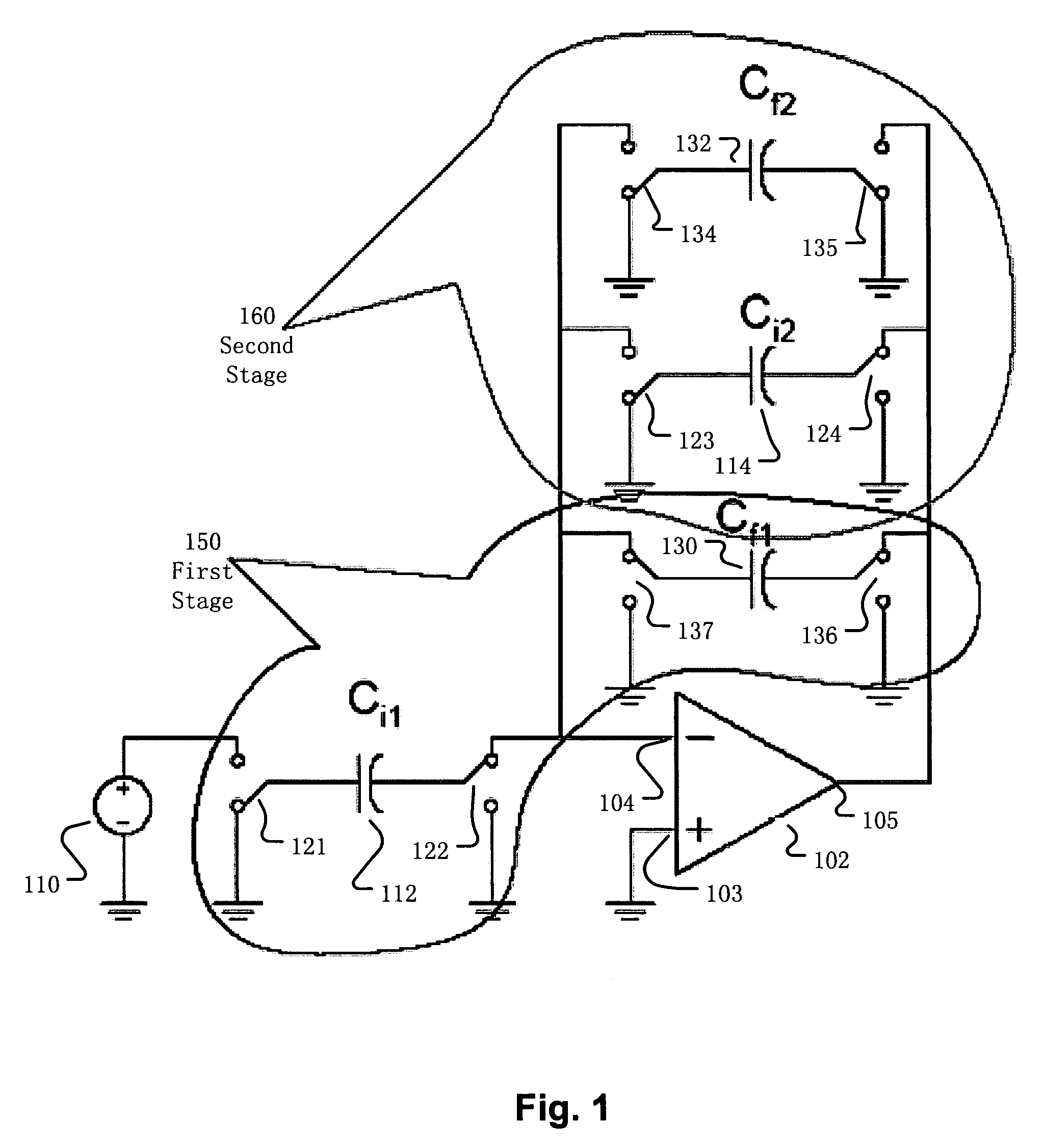
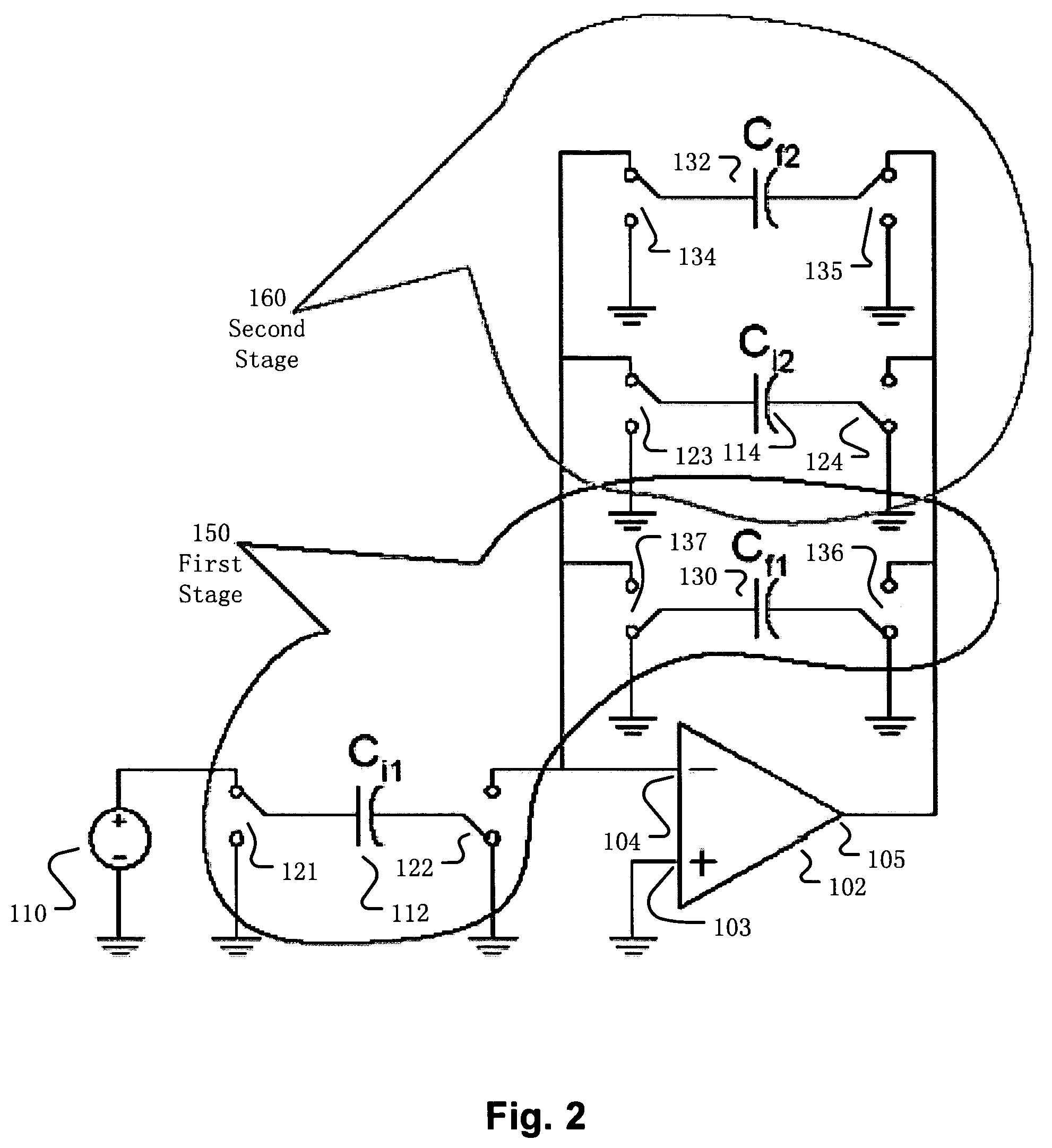
Switched-capacitor circuit having switch-less feedback path
ActiveUS7795959B2Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier combinationsNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
A switched-capacitor circuit includes a plurality of cascaded differential-input, single-ended-output amplifiers. A negative feedback path, from an output terminal of a last of the cascaded amplifiers to an input terminal of a first of the cascaded amplifiers, is configured to exclude, and not be shorted out by, any switches.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Amplifier
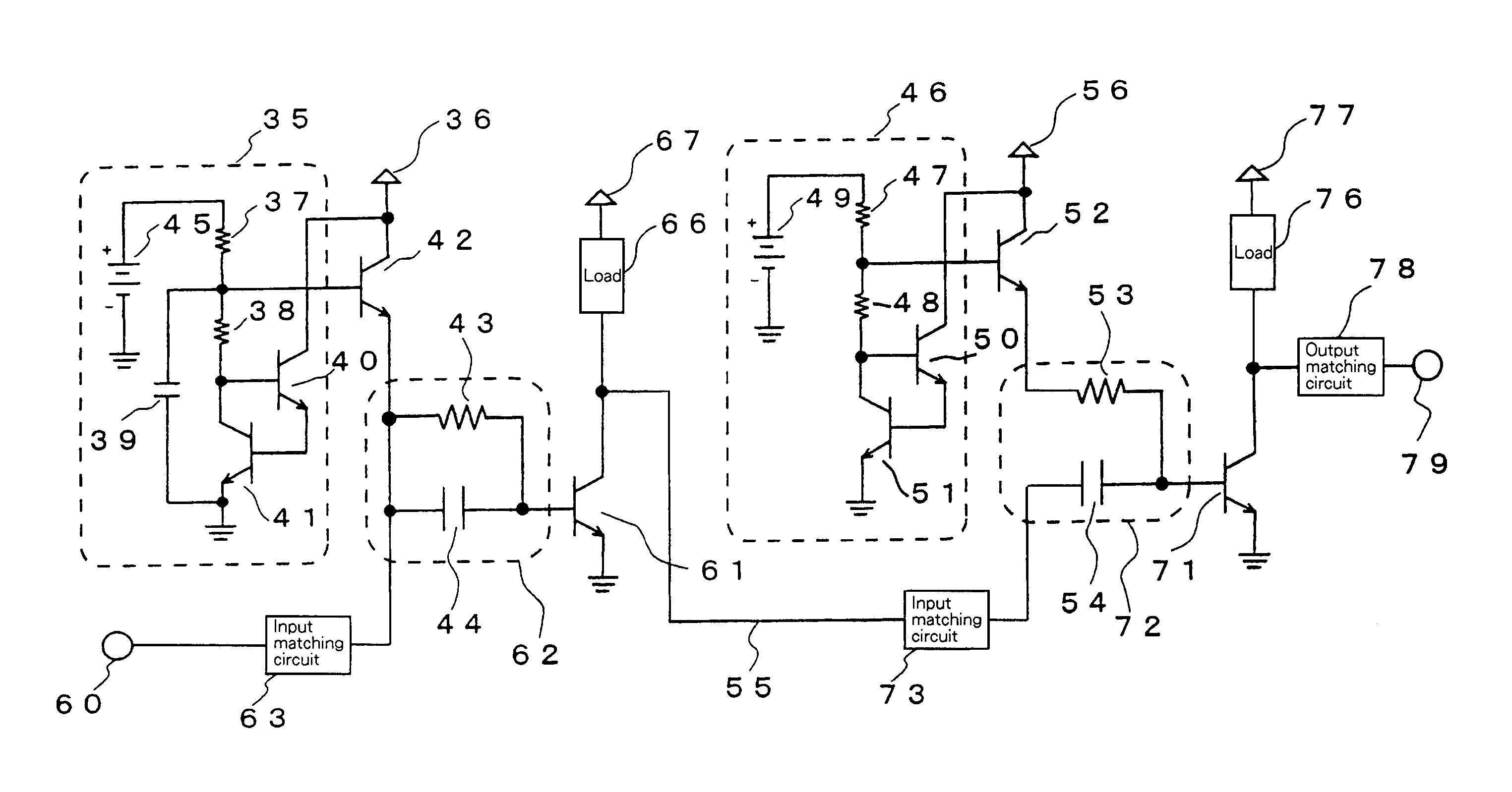
ActiveUS7768345B2Improve power added efficiencyReduce outputAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlEngineeringMultistage amplifier
The present invention provides compensation for distortions in a multi-stage amplifier having a gain expansion characteristic. The present invention also provides an approach for using an amplification stage biased in a state close to B-class, which exhibits high power with added efficiency at low output, in order to have a gain expansion characteristic in all stages of a multi-stage amplifier. The amplifier of the present invention has a gain expansion characteristic which presents an increase in gain in response to an increase in input power or output power in a certain range of the input power or the output power. The amplifier is characterized in that an emitter grounded amplifier circuit comprising a first bipolar transistor has a base terminal to which an input matching circuit and a cathode of a first diode for supplying a bias voltage are connected through a first impedance element which does not block a direct current, and the first diode has an anode which is connected to a reference power supply which presents a sufficiently low impedance at high frequencies.
Owner:NEC CORP
High sensitivity two-stage amplifier
ActiveUS20090110409A1Less phase distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsNegative feedbackPhase distortion
The invention relates to amplifiers and in particular, to a transimpedance amplifier for high rate applications. Disclosed is a two stage transimpedance amplifier having a first stage comprising an amplifier and a load and a second stage comprising an amplifier and a resistor. Negative feedback is provided through a feedback resistor. Only two voltage conversions occur which reduces phase distortion, as compared to three stage transimpedance amplifiers which perform 3 voltage conversions.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
Switched-capacitor circuit having switch-less feedback path
ActiveUS20090195306A1Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier combinationsNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
A switched-capacitor circuit includes a plurality of cascaded differential-input, single-ended-output amplifiers. A negative feedback path, from an output terminal of a last of the cascaded amplifiers to an input terminal of a first of the cascaded amplifiers, is configured to exclude, and not be shorted out by, any switches.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Method and apparatus for DC offset cancellation in amplifiers
ActiveUS7348839B2Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierOffset cancellation
A system, circuit, and method of canceling DC offset errors in cascaded amplifiers comprises arranging a plurality of any of analog voltage and analog current amplifier stages in any of cascaded and parallel configurations; operatively connecting a feedback comparator and digital logic in a feedback path around a given amplifier, wherein the digital logic comprises a finite state machine implementing an adaptive search algorithm comprising fixed switching and modulated switching; operatively connecting a switch at a differential input of the amplifier to short both input terminals of the amplifier; performing fixed switching on binary weighted elements generating discrete analog steps used to vary any of DC offset voltage and current at the input of the amplifier; and performing modulated switching on at least one lower least significant bit (LSB) of all bits used to vary the any of the DC offset voltage and current.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Sense amplifier with input offset compensation
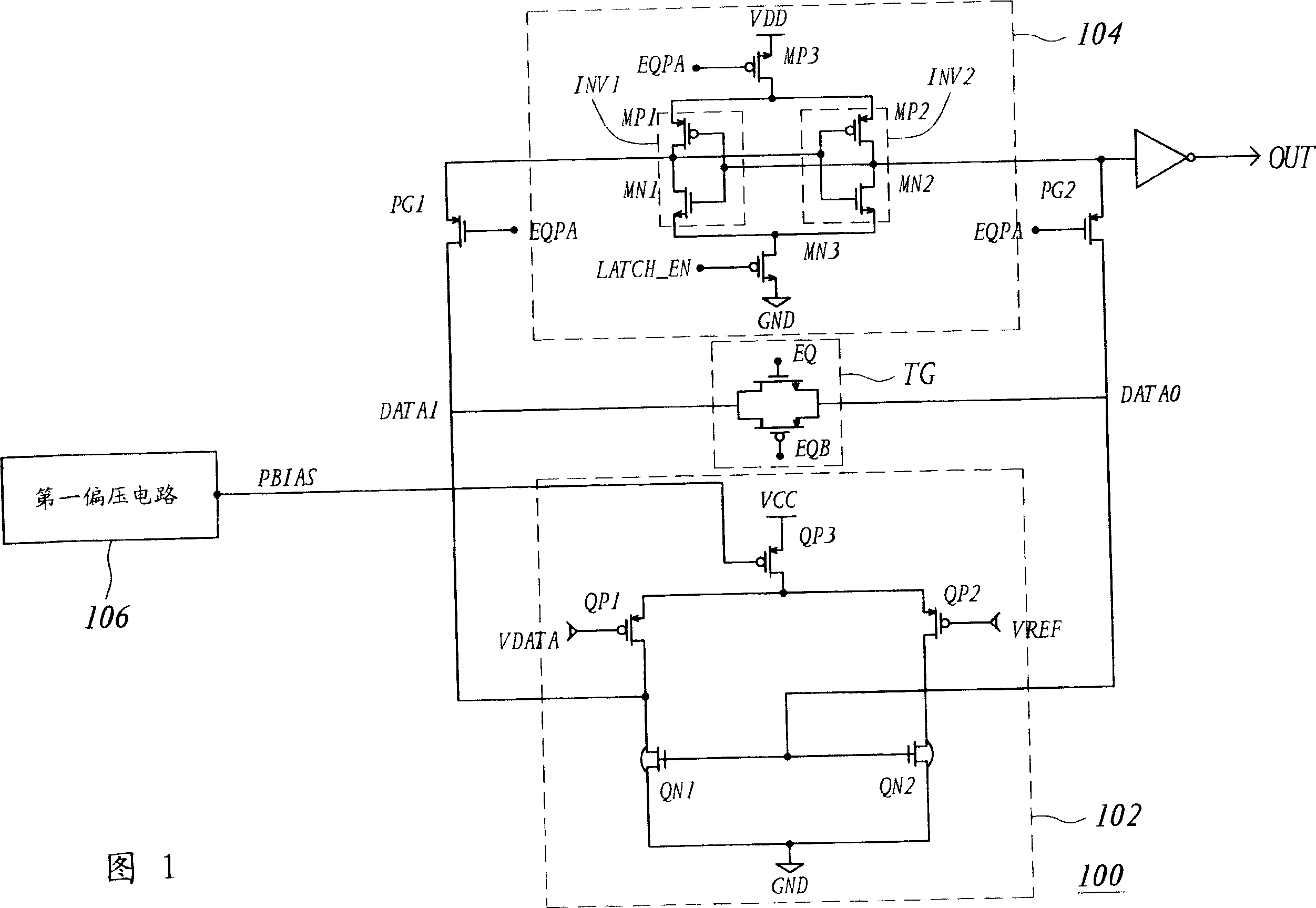
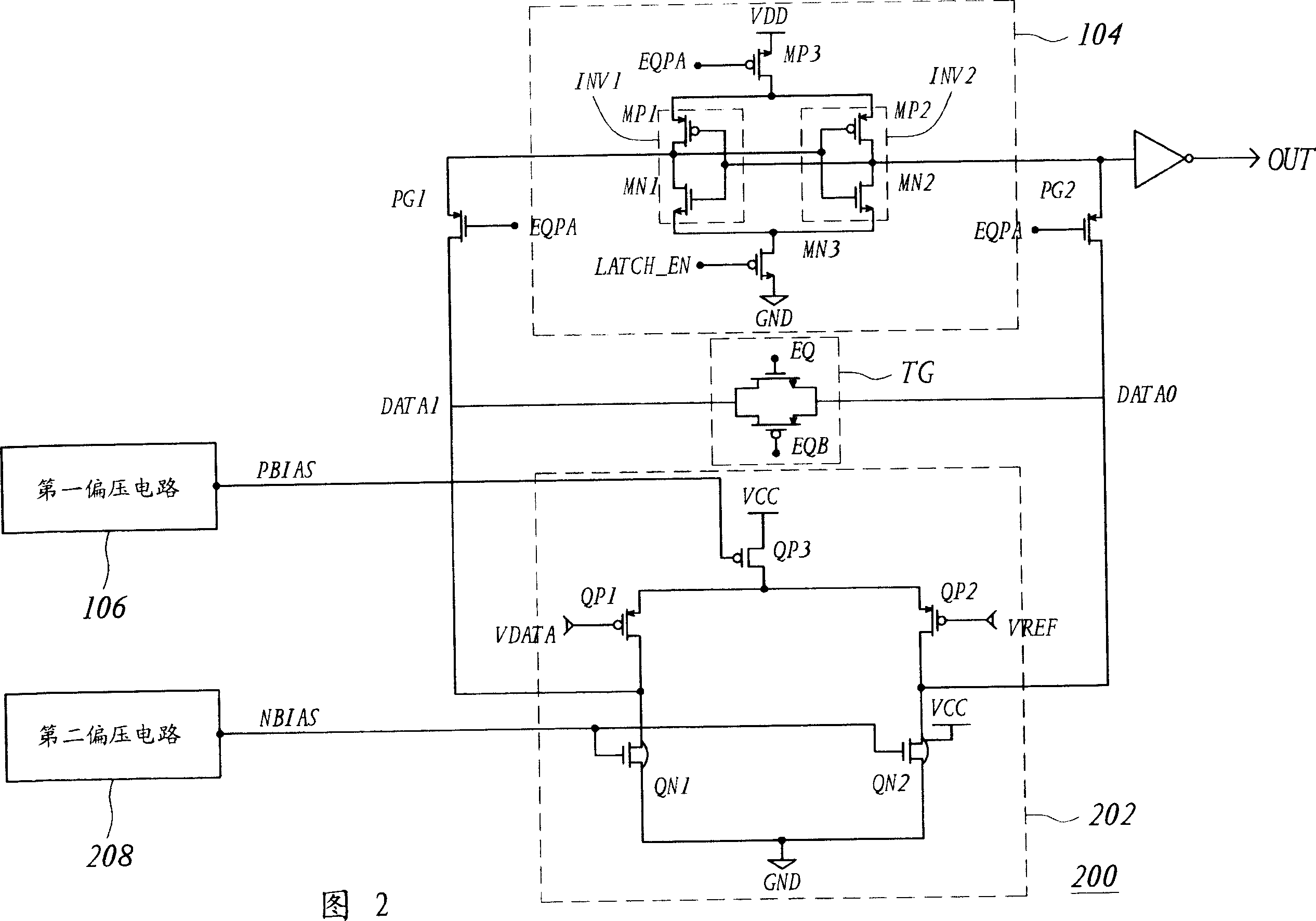
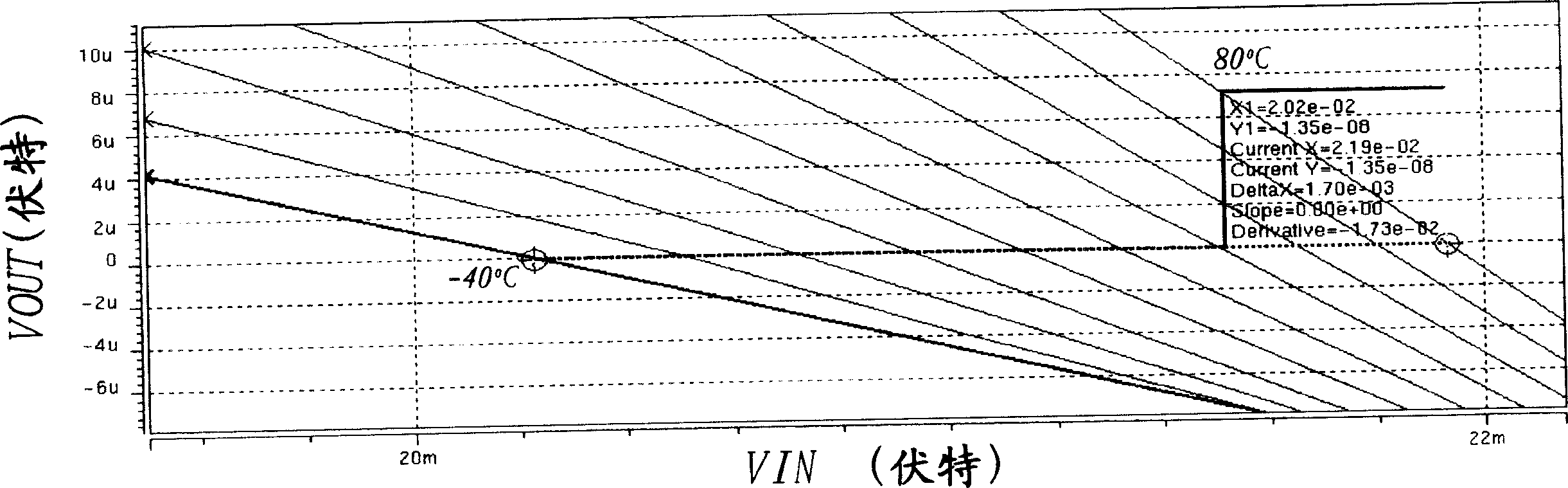
A sense amplifier, including a first stage amplifier and a second stage amplifier, for compensating input offset voltage changes due to temperature variation of the sense amplifier. The first stage amplifier receives a data voltage and a reference voltage, and outputs a first data output and a second data output. The first stage amplifier receives an adjusted voltage, and is biased at an internal voltage. The second stage amplifier includes a latch, for level-shifting and amplifying the first and second data output, and is biased at an external voltage. The sense amplifier further includes a bias circuit, for generating the adjusted voltage according to temperature variation of the sense amplifier, to reduce the input offset voltage changes.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
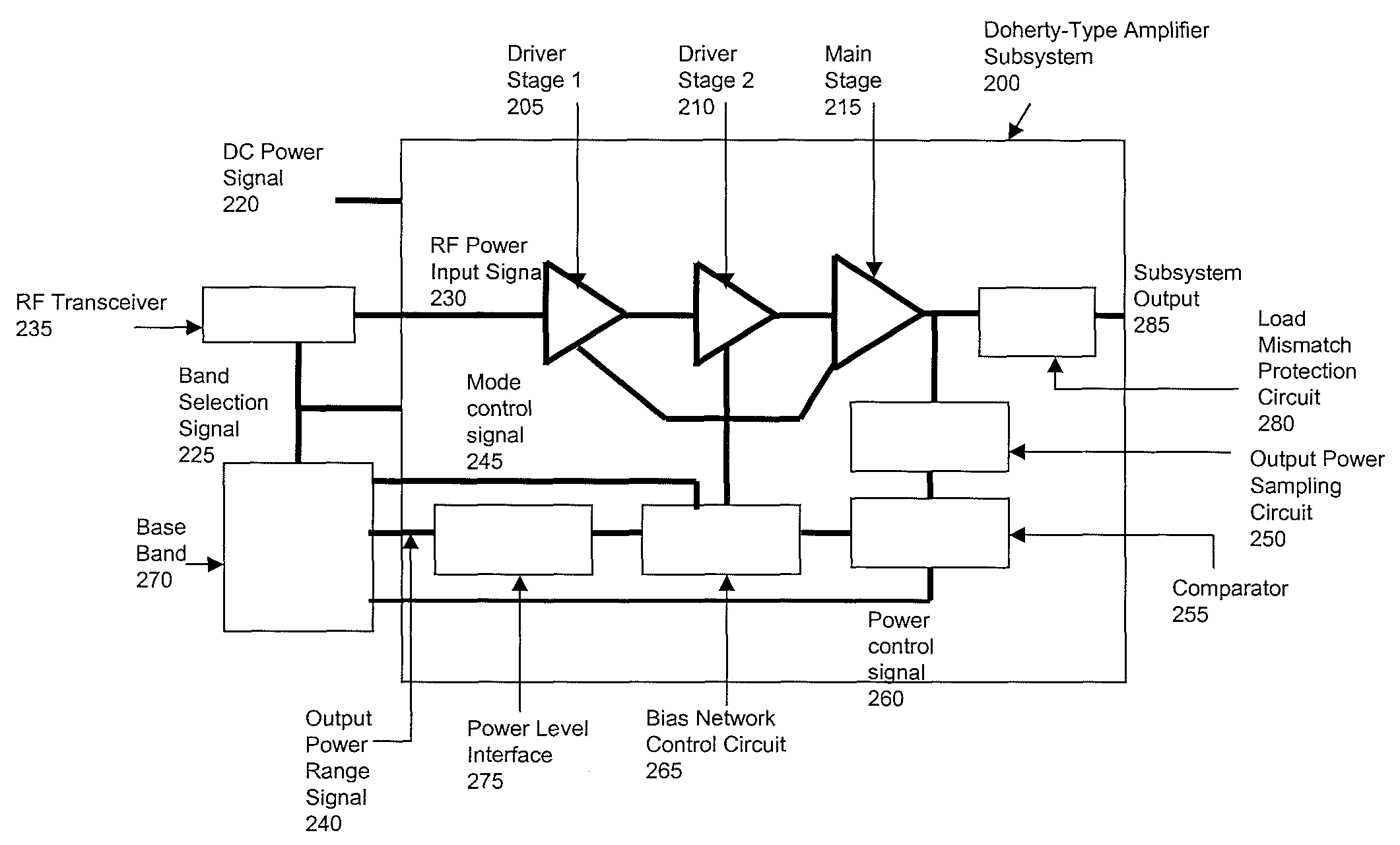
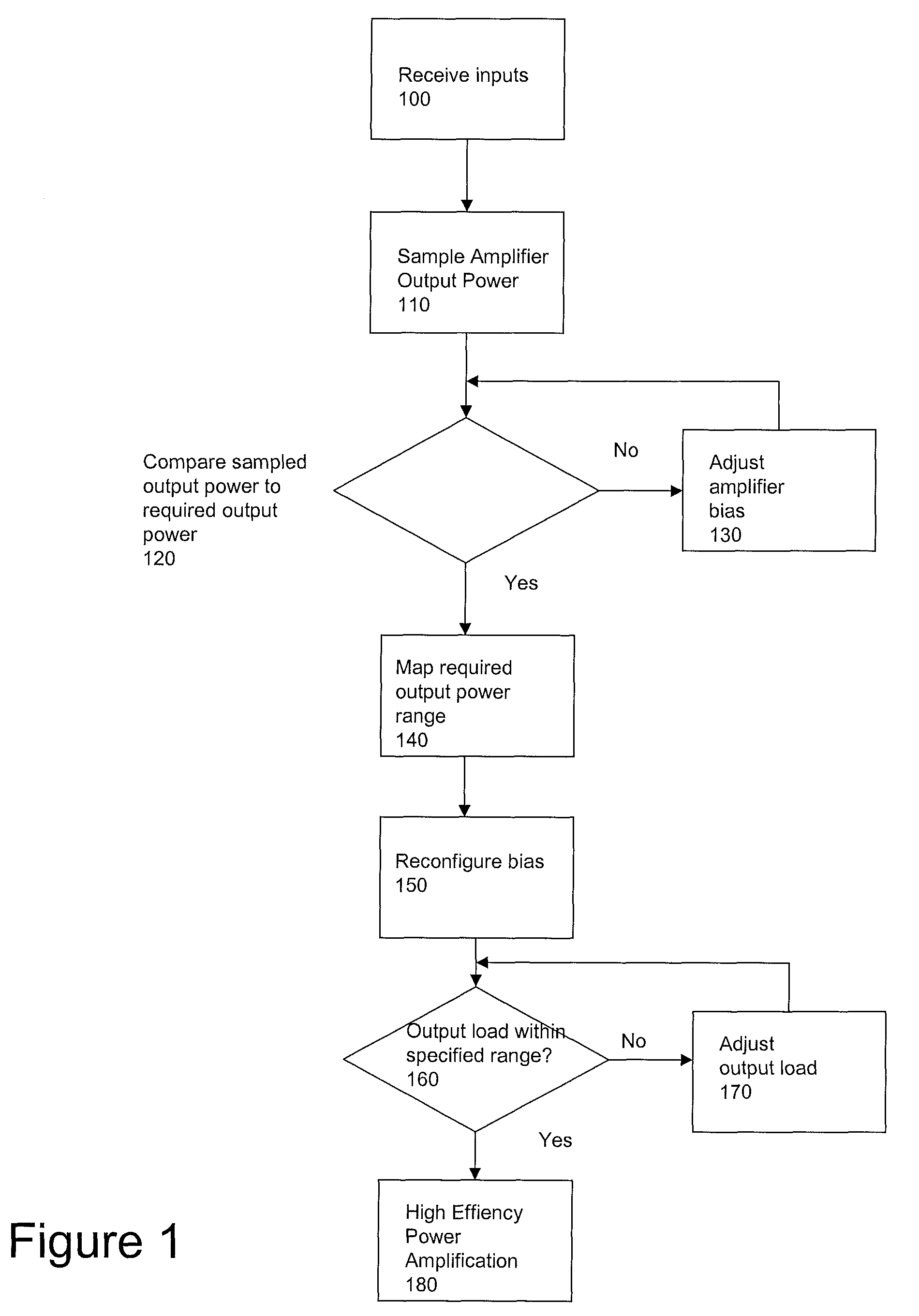
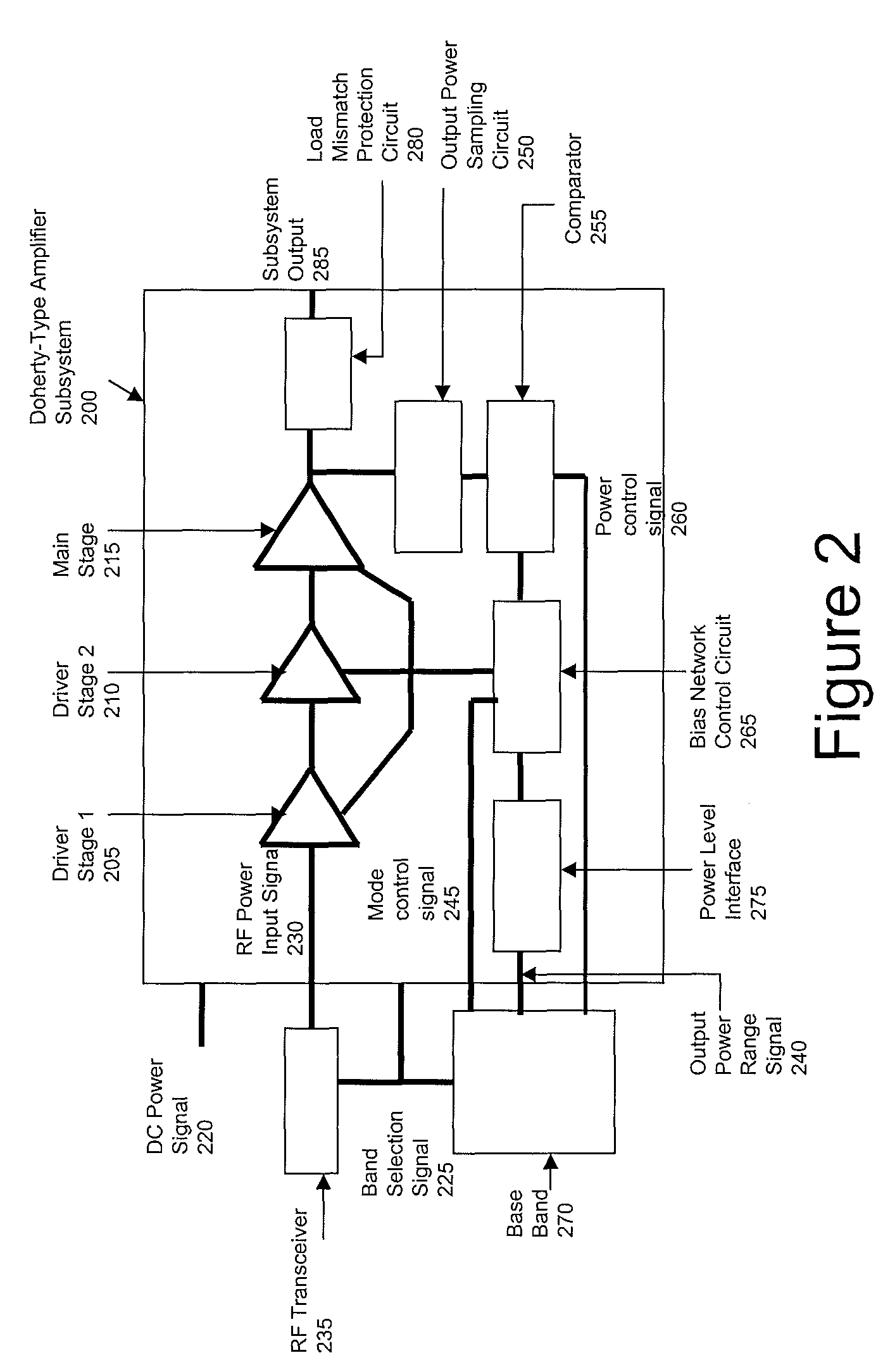
Method and apparatus of Doherty-type power amplifier subsystem for wireless communications systems
InactiveUS7817973B1High-efficiency RF powerImprove battery lifeEnergy efficient ICTResonant long antennasRadio frequencyWireless communication systems
Method and apparatus for high-efficiency radio frequency (RF) power amplification. A method high-efficiency RF power amplification comprises receiving control and power signals, sampling power output of a main stage amplifier, comparing sampled amplifier output power with output power requirement information, reconfiguring bias of the cascaded amplifiers based on power adjustment information, coupling the output of a main stage power amplifier to a load mismatch protection circuit. An electronic apparatus for a Doherty-type high-efficiency RF power amplifying subsystem comprising a power interface circuit coupled to a bias network control circuit, an output power sampling circuit, the comparator comparing signal representing amplifier output power with the power control signal, the bias network control circuit adapts bias condition of the amplifier block, a load mismatch protection circuit provides well-controlled load, thereby the amplifier block amplifies RF input signal transmitted to the subsystem output.
Owner:TUO XIHE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com