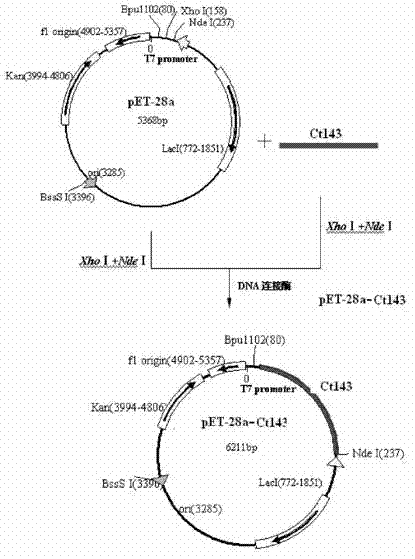
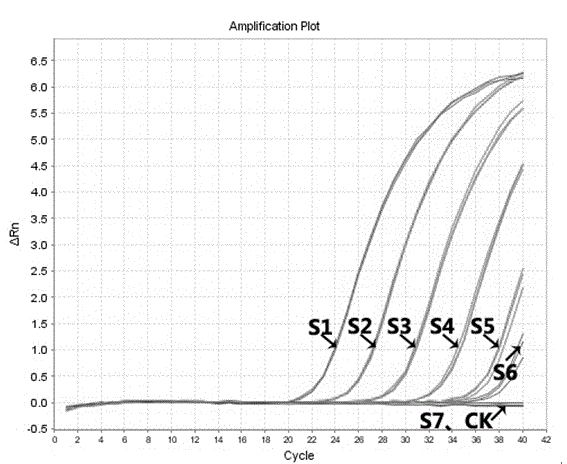
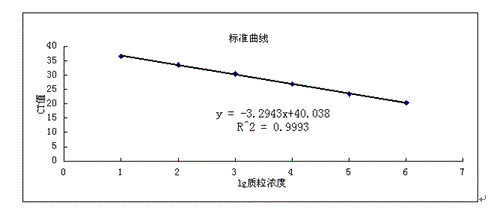
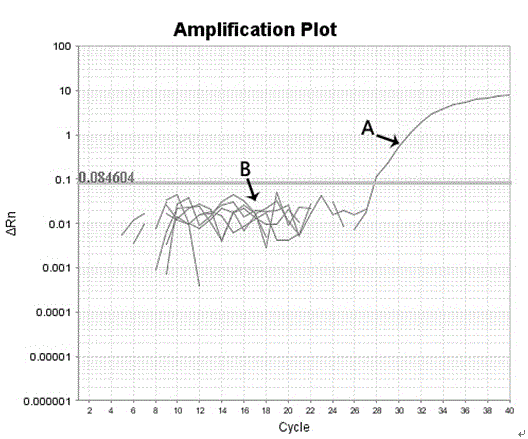
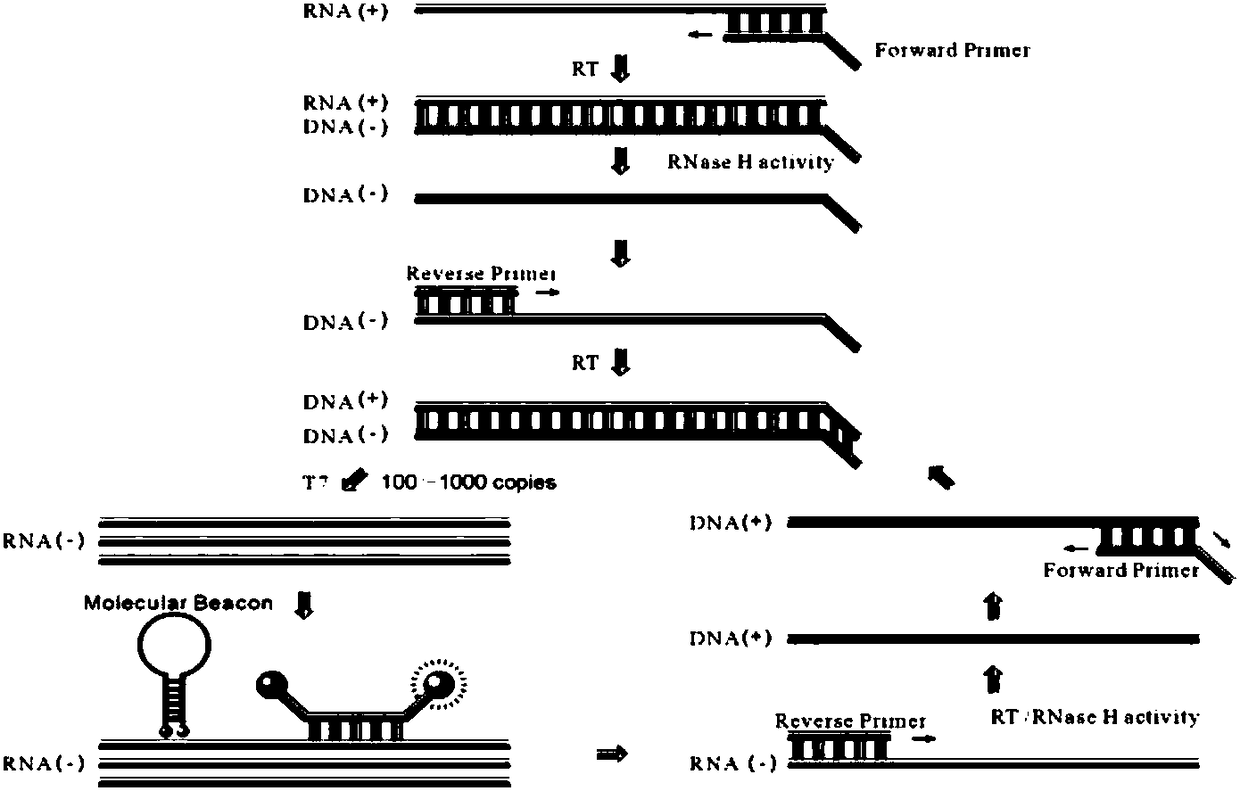
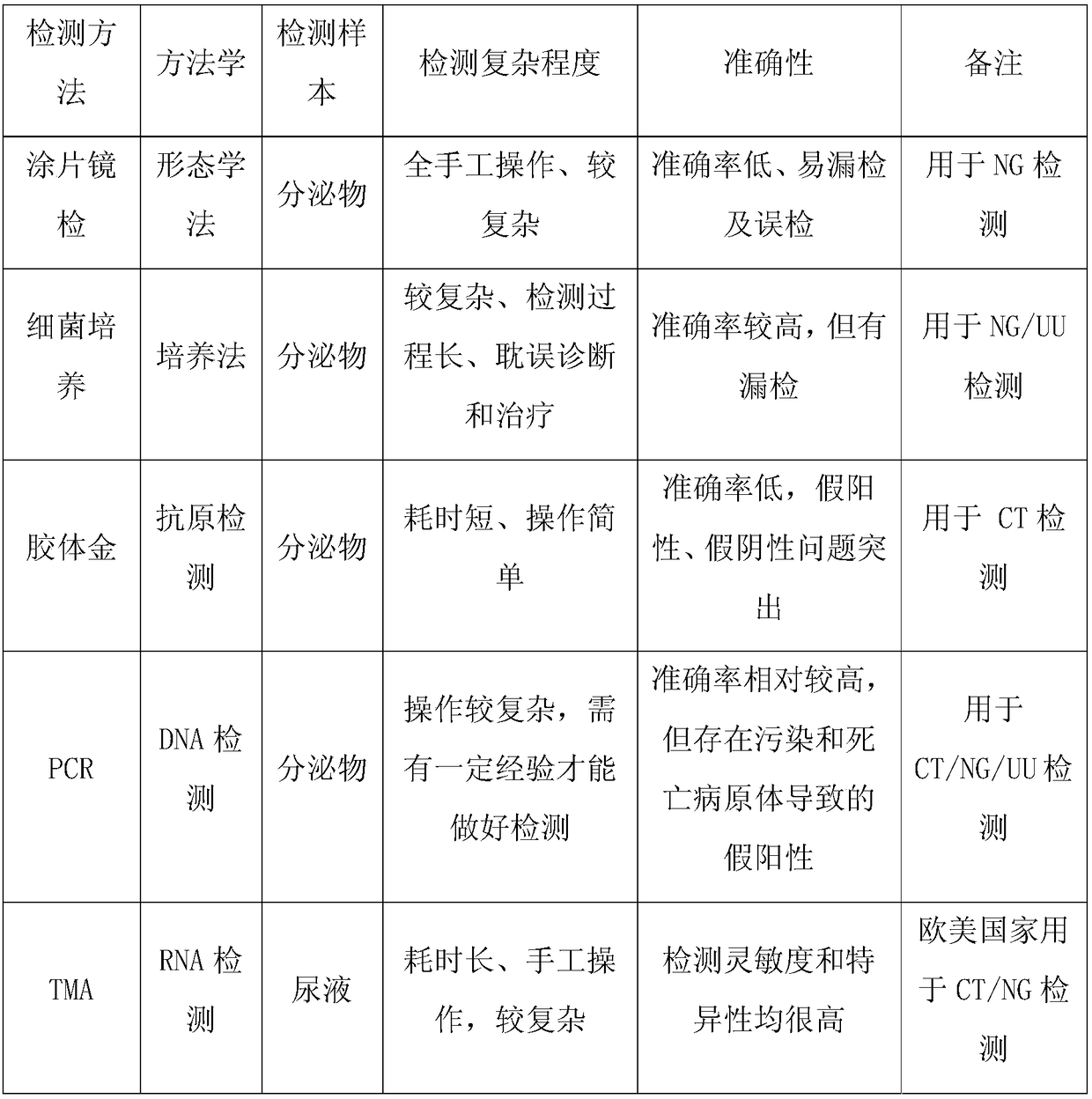
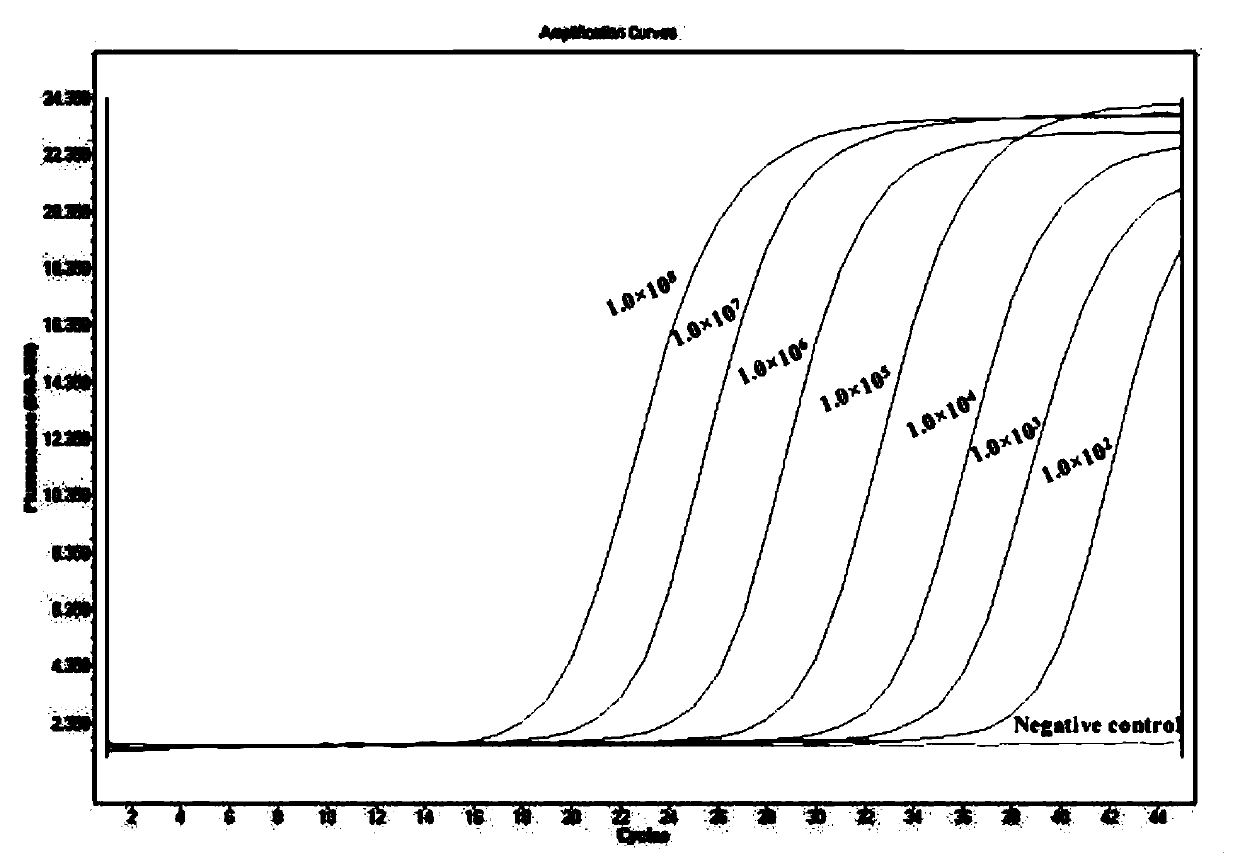
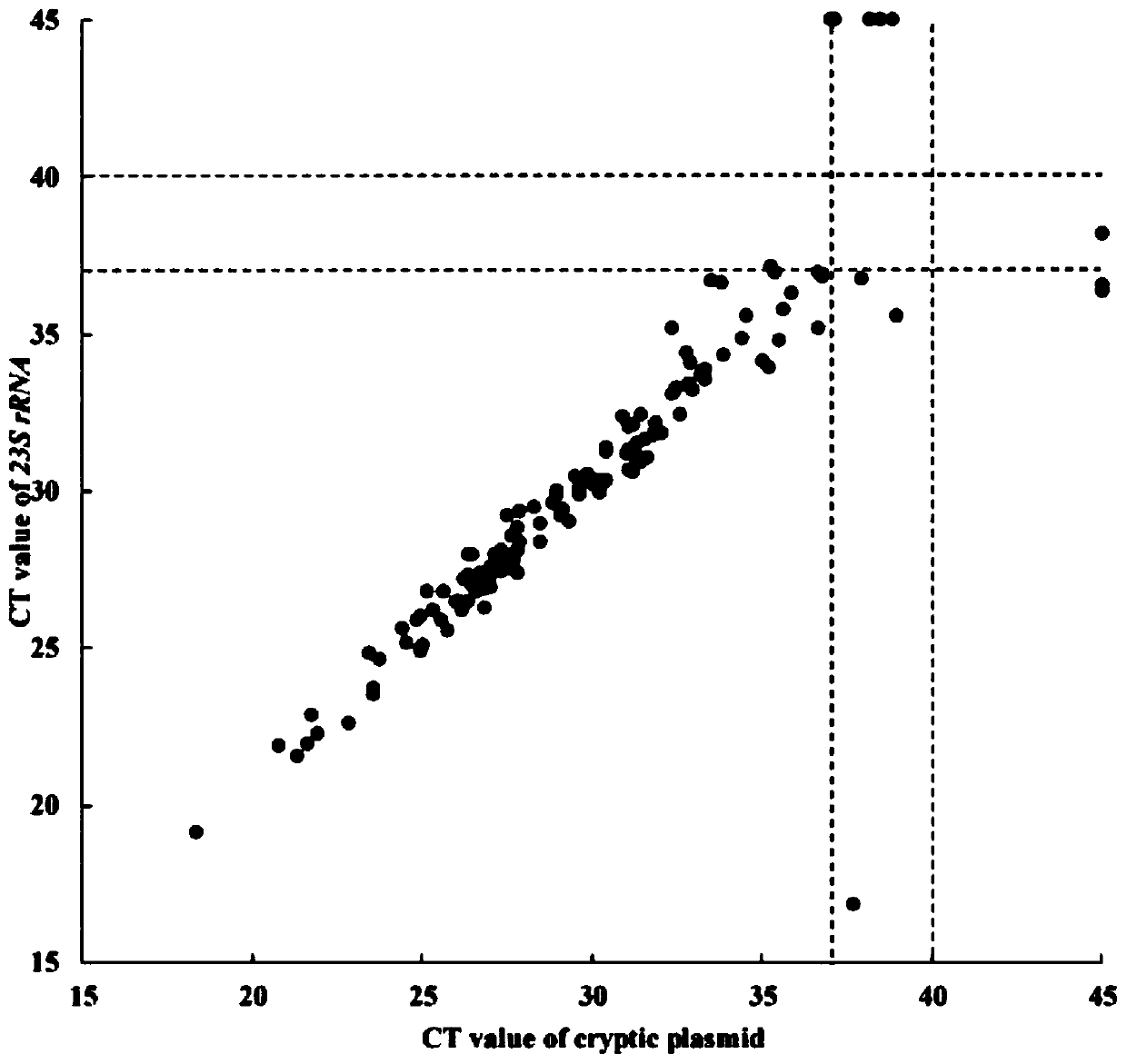
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Chlamydia trachomatis infection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
It is a disease caused by bacteria called Chlamydia trachomatis. Infection with C. trachomatis may result in urethritis, epididymitis, cervicitis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and other conditions.
Vaccines Against Chlamydial Infection
InactiveUS20100172927A1Improving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPolynucleotideImmunogenicity
Owner:CORIXA CORP +1
Kit for detecting chlamydia trachomatis (CT)
ActiveCN103060452AEasy to operateSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceForward primerPotassium
The invention provides a kit for detecting chlamydia trachomatis (CT). The kit comprises a nucleic acid releaser and a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) solution, wherein the nucleic acid releaser comprises 0.01-0.5mM / L of surfactin, 20-300mM / L of potassium chloride, 0.01-2% of sodium dodecyl sulfate and 0.05-1% of ethanol; and the PCR solution comprises a forward primer and a reverse primer which are used for amplifying targeted polynucleotide, and a probe for detecting the targeted polynucleotide. A method of releasing nucleic acid by using the nucleic acid releaser in the kit provided by the invention is not obviously different from a boiling method in the detection result, and a violent protein denaturant adopted for the nucleic acid extraction in the method provided by the invention quickly breaks a coat protein structure of a pathogen to release pathogen nucleic acid, so the release and extraction of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) can be realized without heating; besides, the sensitivity of the provided kit for detecting the CT can be 400 copies / ml, the linearity region of the detection is 400-4.00E+10 copies / ml; and moreover, CT-DNA in an unknown sample such as genital secretions can be quickly and precisely detected by using the kit, so a reliable experiment basis is provided for diagnosing CT infection.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
Immunization Against Chlamydia Infection
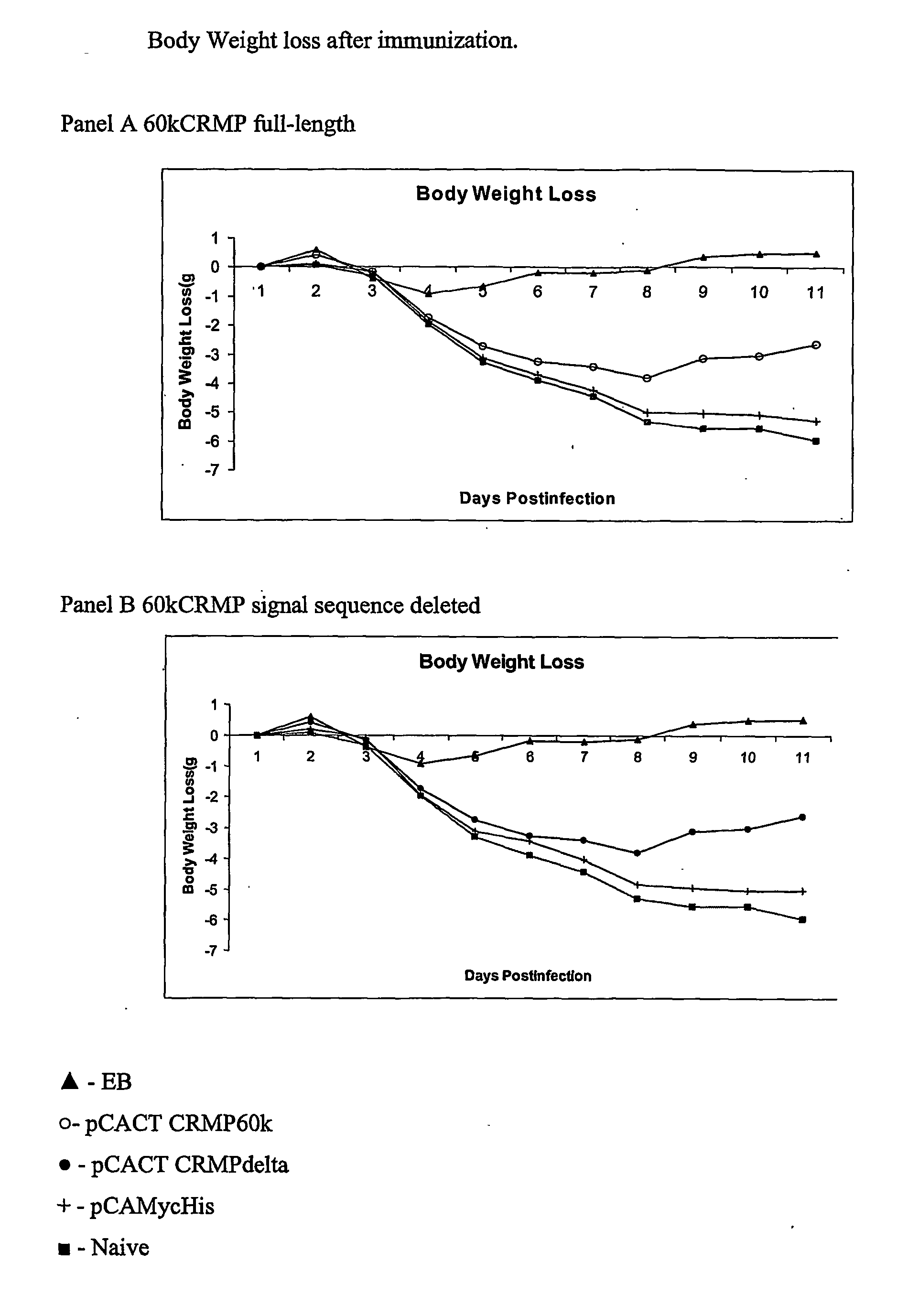
The present invention provides nucleic acids, proteins and vectors for a method of nucleic acid, including DNA, immunization of a host, including humans, against disease caused by infection by a strain of Chlamydia, specifically C. trachomatis. The method employs a vector containing a nucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide of a strain of Chlamydia operably linked to a promoter to effect expression of the gene product in the host. The polypeptides are derived from the Chalmydia gene 60kCRMP gene including truncated forms of the gene. The invention further provides recombinant 60kCRMP protein useful for protecting against disease caused by infection with Chlamydia.
Owner:BRUNHAM ROBERT +3
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) fluorescence quantitative rapid test kit and method for chlamydia trachomatis
ActiveCN102329866AEfficient removalQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceReference product
The invention aims at providing a kit which is suitable for rapid test of chlamydia trachomatis in clinical samples and can be used for auxiliary diagnosis and efficacy monitoring of chlamydia trachomatis infection. The technical scheme of the invention is as follows: an PCR (polymerase chain reaction) fluorescence quantitative rapid test kit of the chlamydia trachomatis is provided and comprisesa PCR reaction solution, wherein the PCR reaction solution contains primers and a fluorescence probe; and the primers comprise an upstream primer and a downstream primer, and the kit further comprises a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase, a strong positive quality control product, a weak positive quality control product, a negative quality control product, a positive quantitative reference product and a DNA extraction solution. According to the CT (chlamydia trachomatis) fluorescence PCR quantitative test kit and method provided by the invention, a Taqman core technology platform and an arabidopsis internal reference system are utilized, thus the test sensitivity is higher. Furthermore, the accuracy, specificity, repeatability, stability, sensitivity and precision are improved compared with those of the existing product.
Owner:泰普生物科学(中国)有限公司
Fluorescent polymerase chain reaction (PCR) kit for detecting chlamydia trachomatis infection by SYBR Green method
InactiveCN102094073AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceControl substancesBiology
The invention discloses a fluorescent polymerase chain reaction (PCR) kit for detecting chlamydia trachomatis infection by an SYBR Green method and belongs to the field of in-vitro nucleic acid diagnosis kits. The kit comprises a negative reference and control substance, a negative reference substance, fluorescent PCR reaction liquid, Taq enzyme and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) extraction liquid. The kit comprises a PCR reaction system in which a fluorescent PCR technology is taken as basis, forward and reverse primers and fluorescent dye SYBR Green aiming at the specific sequence of chlamydia trachomatis, can detect chlamydia trachomatis infection in a clinical sample conveniently and quickly, and has high specificity and great clinical value for early detection of the chlamydia trachomatis.
Owner:上海裕隆医学检验所股份有限公司
Recombined chlamydia trachomatis protein and application thereof
InactiveCN103820471AMeet the needs of clinical diagnosis of infectionStrong specificityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyClinical diagnosis
The invention relates to a recombined chlamydia trachomatis protein and also relates to application of the recombined chlamydia trachomatis protein in preparation of detection kits. The diagnosis kit prepared by using the recombined chlamydia trachomatis protein has advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, and simple operation and better meets the requirement of clinical diagnosis of chlamydia trachomatis infection.
Owner:英诺特(唐山)生物技术有限公司
Nano-gold test paper for detecting major outer membrane protein antigen of chlamydia trachomatis as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102411055AHigh sensitivityEasy to storeMaterial analysisNitrocelluloseChlamydia trachomatis Antigen
The invention relates to test paper for detecting chlamydia trachomatis infection, and the test paper comprises a baseplate, a sample pad, a conjugate pad, a nitrocellulose membrane and an absorption pad, wherein a detection line and a quality control line are arranged on the nitrocellulose membrane, the detection line on the nitrocellulose membrane is coated by mouse anti-human monoclonal protein antibody IgG (antibody II) of major outer membrane protein antigen of chlamydia trachomatis in the concentration of greater than or equal to 1mg / mL, and the quality control line is coated by goat anti-mouse IgG polyclonal antibody in the concentration of greater than or equal to 1.5mg / mL; the conjugate pad is coated by mouse anti-human monoclonal protein antibody IgG (antibody I) of the MOMP (major outer membrane protein) antigen of the chlamydia trachomatis, which is labeled by nano-gold and is in the concentration of not less than 6 mu g / mL; the sensitivity of detecting the MOMP of the chlamydia trachomatis of the test paper is 0.1ng / ml, the detection value range is 0-200ng / ml and the specificity is 98.5%; and the detection can be completed within 5 minutes.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Chlamydia trachomatis serotype D genes
A plasmid isolated from Clamydia trachomatis is described, which comprises 8 genes encoding proteins useful in the formulation of vaccines or diagnostic test for determining the bacterium or specific antibodies generated during C. trachomatis infections; in particular the recombinant fusion MS2-pgp3D protein is described comprising polypeptidic sequences encoded by pCT and immunogenic in the course of infections in man. A method for preparing said protein in E. coli further described.
Owner:SCLAVO SPA
Vaccines against chlamydial infection
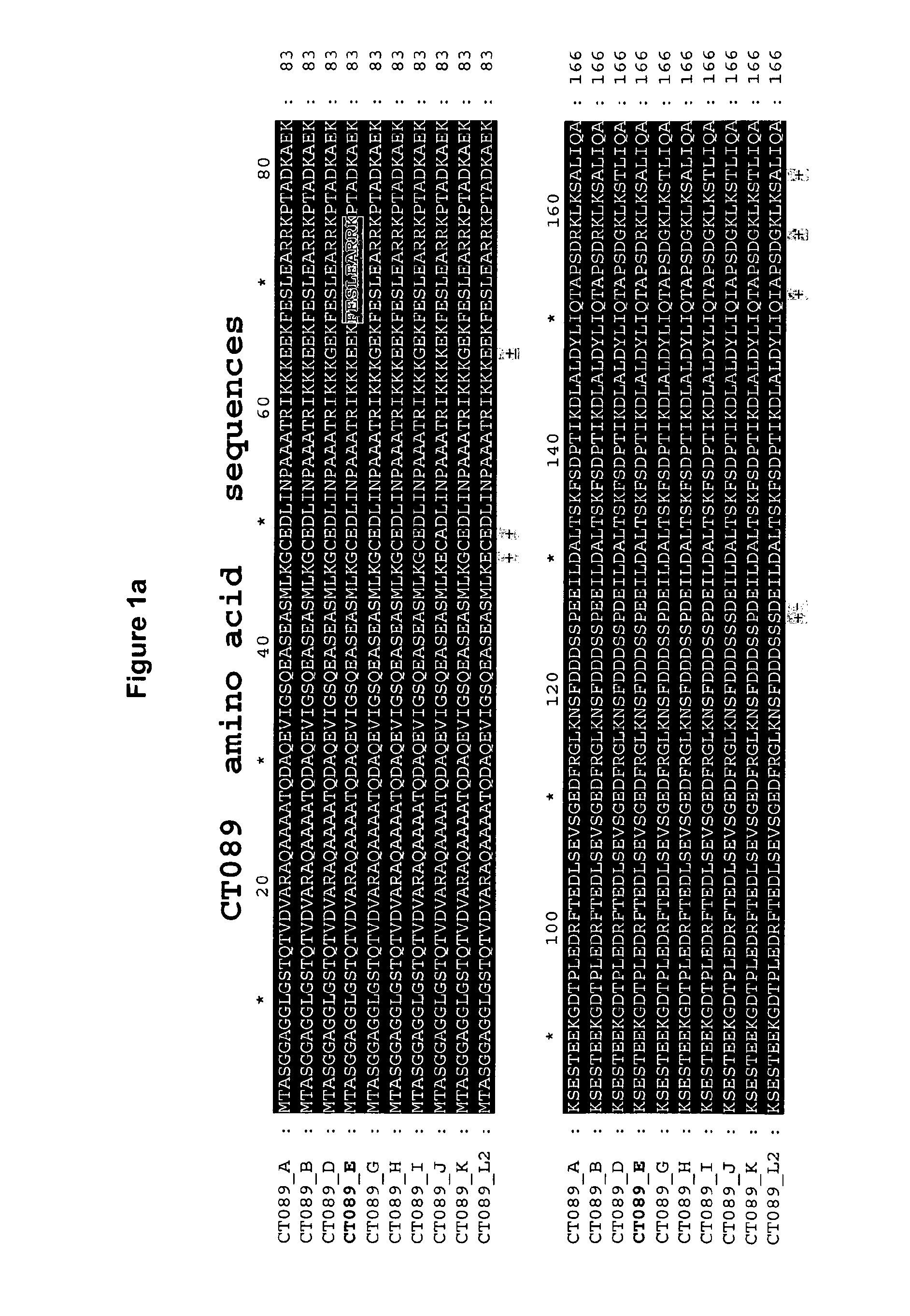
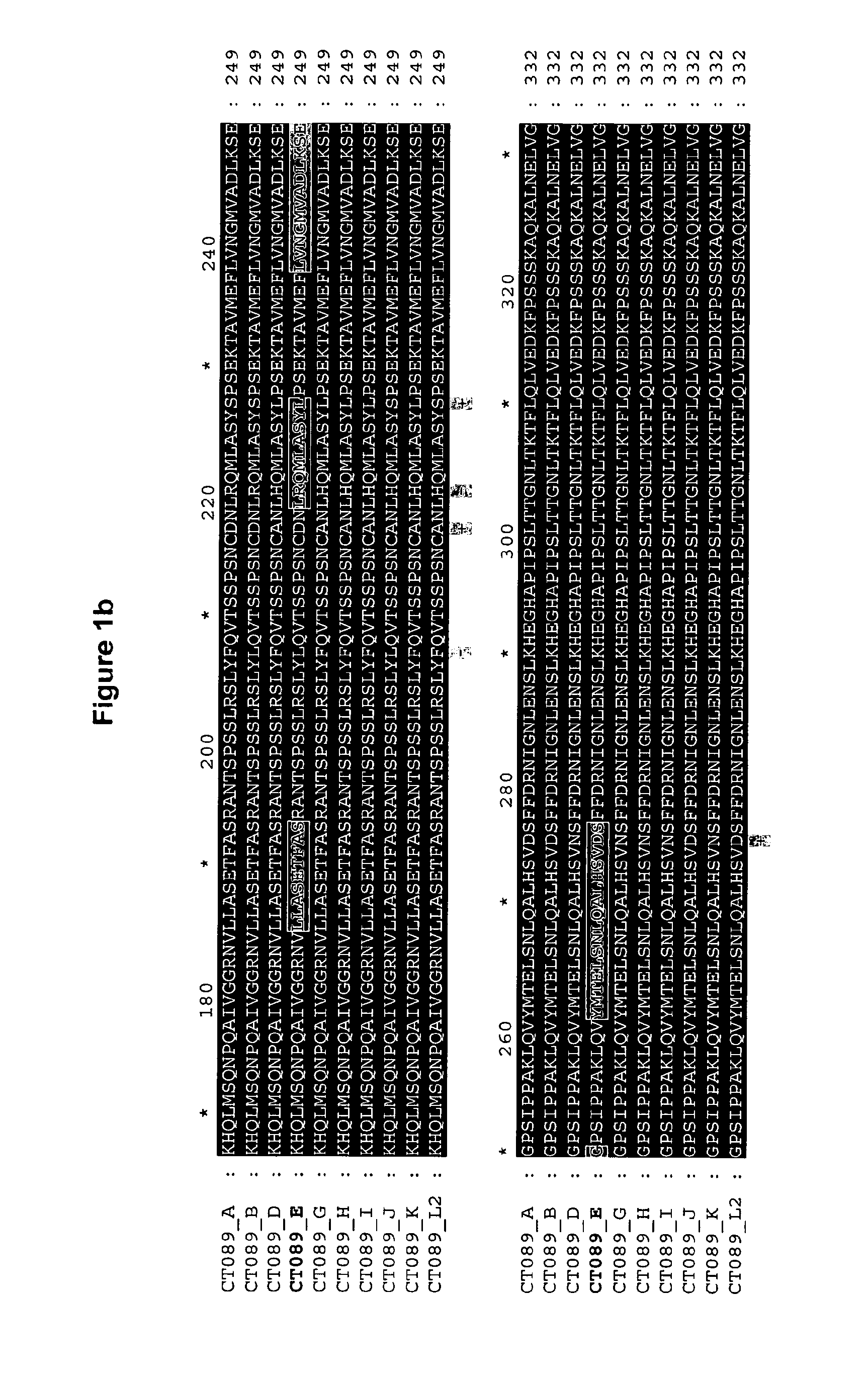
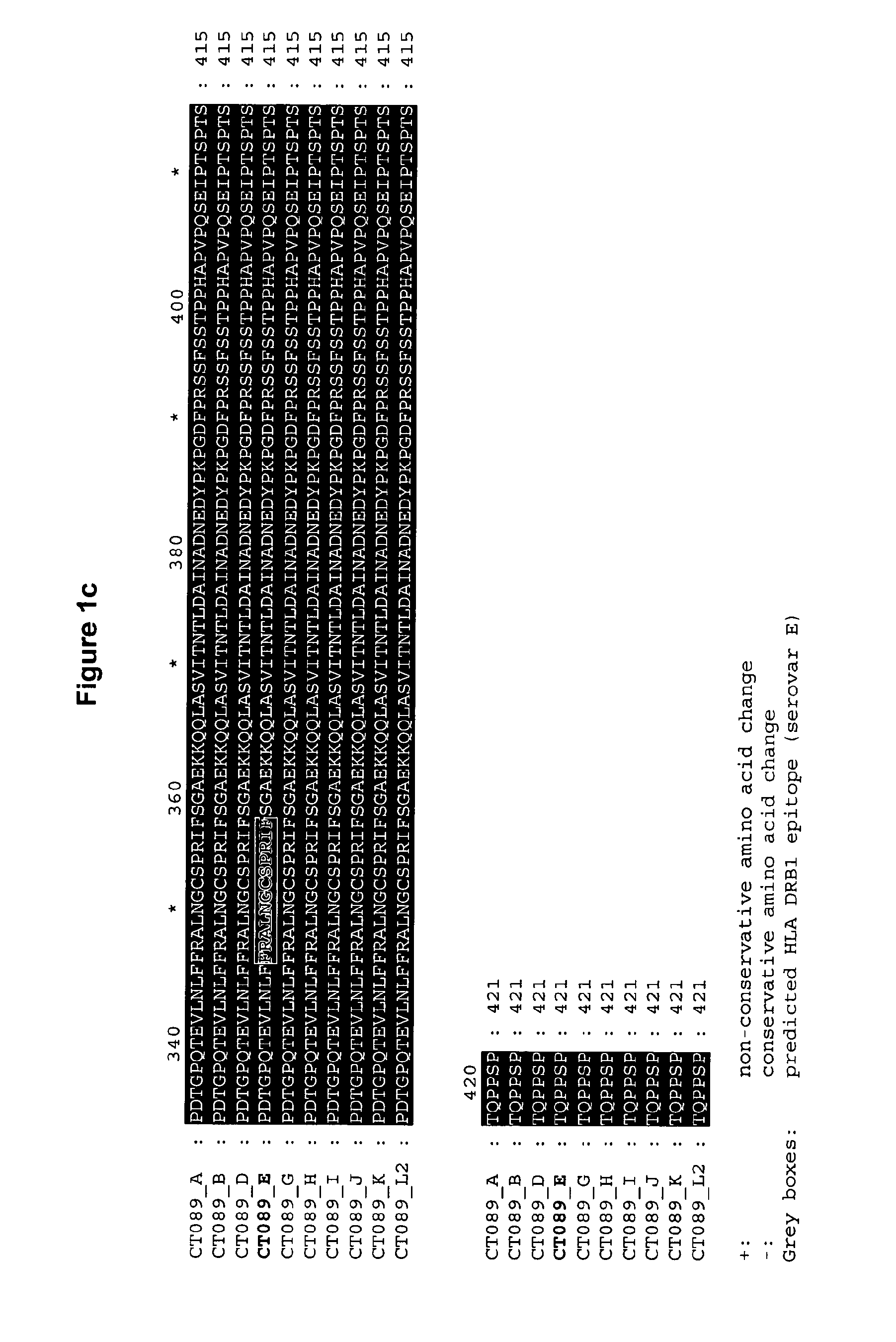
The invention discloses a method for the treatment or prevention of ocular Chlamydia trachomatis infection by the administration of a safe and effective amount of an immunogenic composition comprising one or more Chlamydia trachomatis proteins, immunogenic fragments thereof or polynucleotides encoding said proteins or fragments, selected from the list consisting of Swib, Momp, Ct-858, Ct-875, Ct-622, Ct-089, passenger domain of PmpG (PmpGpd) and passenger domain of PmpD (PmpDpd).
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA +1
Chlamydia trachomatis recombinant protein and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102925462AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideImmunogenicity
The invention provides a chlamydia trachomatis recombinant protein and a preparation method thereof, relating to the field of gene engineering technology and diagnostic reagent and vaccine development. The invention relates to a chlamydia trachomatis fusion protein which can be applied to the clinical diagnosis of chlamydia trachomatis infection; and a nucleotide sequence coding the protein comprises plasmids of the nucleotide sequence and pronucleus host cells. The invention also relates to a method for preparing the protein and application thereof. The recombinant protein has high specificity and strong immunogenicity, and can improve the sensitivity and specificity of a detection reagent; and compared with the same kind of kits on the market, the recombinant protein has the advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity and the like, and perfectly meets the needs in the clinical diagnosis of human chlamydia trachomatis infection.
Owner:英诺特(唐山)生物技术有限公司
Fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit for chlamydia trachomatis
InactiveCN105018573AStrong specificityShort detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluoProbesA-DNA
The invention provides a fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit for chlamydia trachomatis in clinic samples, used for assisted diagnosis of chlamydia trachomatis. The kit comprises a PCR solution, a DNA polymerase solution, positive quality control, weakly positive quality control, negative quality control, positive quantitative reference, lysate and protease K, wherein the PCR solution contains forward and reverse primers and the fluorescence probe are specific primers and probe designed for the specific sequence of chlamydia trachomatis and are capable of amplifying a target DNA sequence specifically so as to conveniently and quickly detect chlamydia trachomatis infection in clinic samples. The kit has the characteristics of high specificity and high sensitivity.
Owner:兰州安康伯乐生物技术有限公司
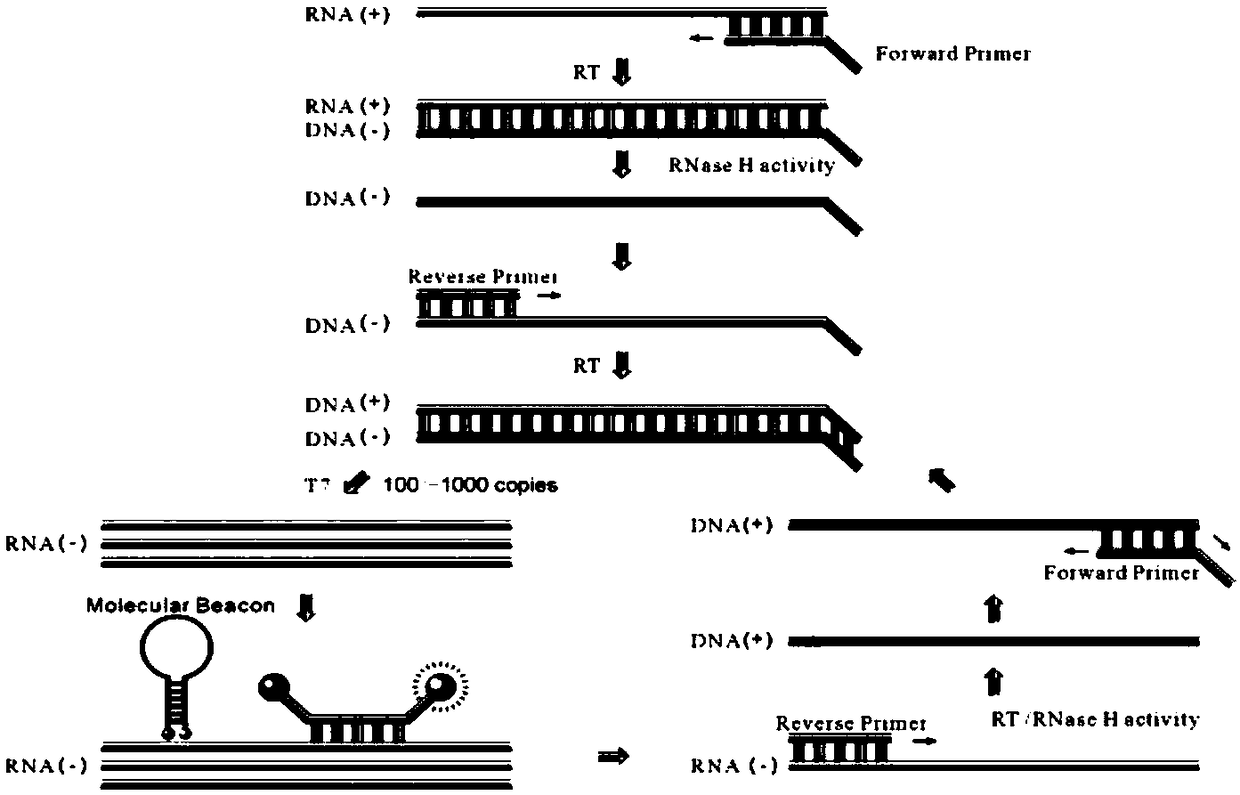
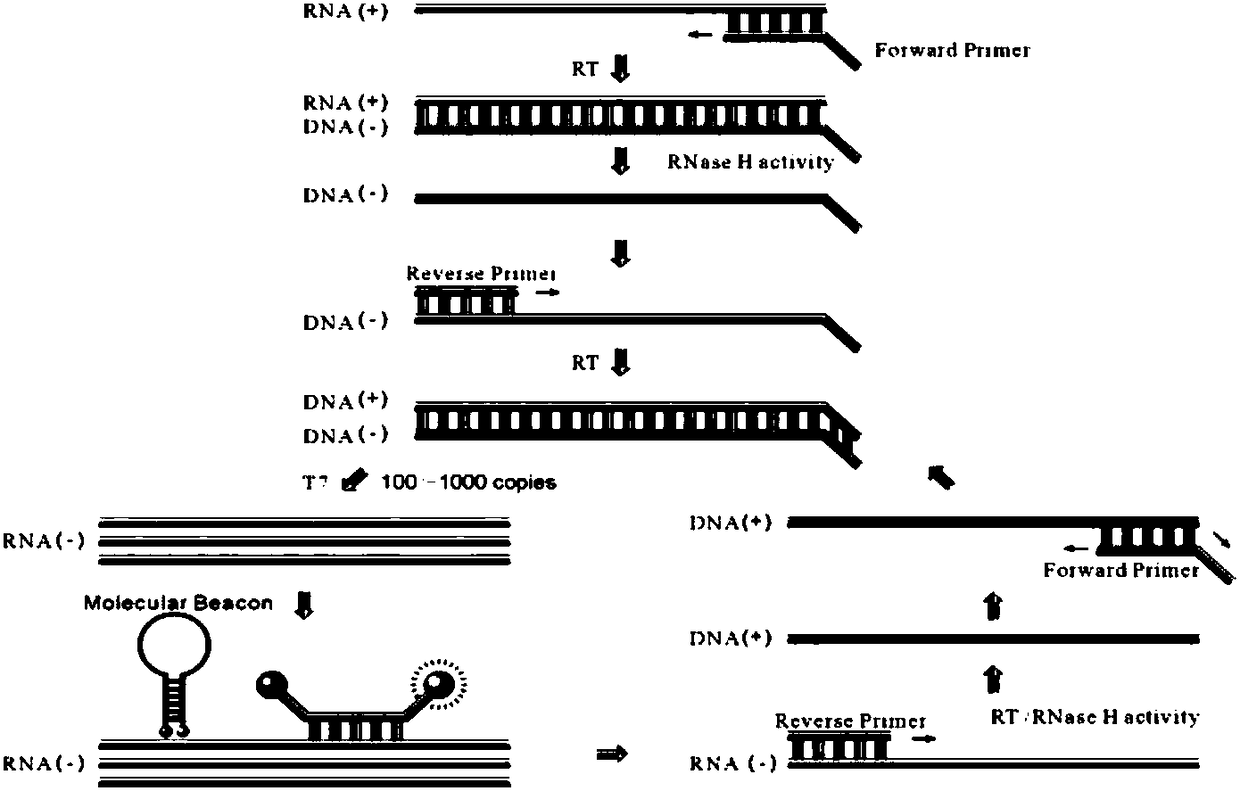
Molecular-biological detection method for neisseria gonorrhoeae infection based on SAT (Simultaneous Amplification and Testing) of RNA target
InactiveCN108546744ASave medical resourcesReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlFluorescence
The invention provides a molecular-biological detection method for neisseria gonorrhoeae infection based on SAT (Simultaneous Amplification and Testing) of a RNA target. The molecular-biological detection method comprises the following steps: step (1) adopting a specific target capture technology and a magnetic-bead method to extract pure cell target nucleic acid, i.e., adopting RNA as a target, wherein comprising (1-1) the specificity of the target nucleic acid is manually extracted; (1-2) the pure cell target nucleic acid is obtained, i.e., RNA is used as the target; step (2) adopting a RNAreal-time fluorescent constant-temperature amplification detection technology to obtain a detection result for neisseria gonorrhoeae infection, wherein comprising (2-1) M-MLV reverse transcriptase generates a DNA copy of the target nucleic acid; (2-2) T7RNA polymerase generates multiple RNA copies from the DNA copy; (2-3) an optimizing probe with fluorescence labeling is specifically combined withthe extracted RNA copy, so that a fluorescence signal generated is captured by a detection instrument, and the detection result for the neisseria gonorrhoeae infection is obtained according to the occurring time and the intensity of the signal; step (3) judging the detection result by combination with positive control and negative control.
Owner:一零零二信息科技(沧州)有限责任公司
Nutritional digestive juice for chlamydia neutralization
InactiveCN101565728AAvoid difficultiesAvoid overgrowthMicrobiological testing/measurementPatient needUrethritis
The invention relates to a Nutritional digestive juice for chlamydia neutralization, in particular to a prescription of a cell culture medium used when a urethritis patient needs the examination of the chlamydia cell culture after using a large amount of clinical antibiotics and a preparation method of the cell culture medium. The genital tract chlamydia trachomatis infection is one of the most common diseases which are sexually transmitted. Chlamydia trachomatis is also regarded as the important cause of the pelvic inflammatory disease and the sequelae (tubal infertility and ectopic pregnancy) thereof. The chlamydia cell culture method is the most sensitive and the most reliable method used for examining the chlamydia. The culture medium can detect out the positive result of the genital tract chlamydia after the large amount of clinical antibiotics is used, thereby having the function of the clinical diagnosis guidance and the clinical treatment and the important meaning of preventing the abuse of the antibacterial drugs.
Owner:曲奕
Rapid fluorescence PCR detection kit for Chlamydia trachomatis
InactiveCN105018574AReduce the risk of contaminationSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionProteinase K
The invention belongs to the field of in-vitro nucleic acid detection and aims to provide a rapid detection kit applicable to Chlamydia trachomatis in a clinical sample and used for assisted diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis. A rapid fluorescence PCR detection kit for Chlamydia trachomatis comprises a PCR liquid, a negative quality control material, a positive quality control material, a weak positive quality control material, lysate and proteinase K, wherein the PCR liquid contains TaqDNA polymase for hot starting, forward and reverse primers and SYBRGreenI pigment, and the forward and reverse primers are specific primers designed for specific sequence of Chlamydia trachomatis and are capable of specifically amplifying a target DNA sequence, so that the clinical diagnosis purpose is achieved. The kit disclosed by the invention can be used for simply and rapidly detecting the infection of Chlamydia trachomatis in the clinical sample and has the characteristics of high specificity and high sensitivity.
Owner:兰州安康伯乐生物技术有限公司
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) target SAT (Simultaneous Amplification and Testing) based molecular biological detection method for ureaplasma urealyticum infection
InactiveCN108611403ASave medical resourcesReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesReverse transcriptaseFluorescence
The invention provides an RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) target SAT (Simultaneous Amplification and Testing) based molecular biological detection method for ureaplasma urealyticum infection. The method comprises the following steps: I, by using a specific target capturing technique, extracting pure cell target nucleic acid by using a magnetic bead method, that is, taking RNA as a target, namely (1-1) manually extracting target nucleic acid specificity, and (1-2) extracting pure cell target nucleic acid, that is, taking RNA as the target; II, obtaining detection results of chlamydia trachomatis infection by using an RNA real-time fluorescent constant-temperature amplification detection technique, namely (2-1) generating one DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) copy of the target nucleic acid RNA through M-MLV reverse transcriptase, (2-2) generating multiple RNA copies from the DNA copy by using T7RNA polymerase, and (2-3) specifically combining an optimized probe with a fluorescent marker and the extracted RNA copies so as to generate a fluorescent signal which is captured by using a detector, and obtaining a detection result of chlamydia trachomatis infection according to signal appearance time andintensity; III, with the combination of a positive reference and a negative reference, judging detection results, and carrying out bacterium testing.
Owner:一零零二信息科技(沧州)有限责任公司
Kit for detecting chlamydia trachomatis (CT)
ActiveCN103060452BEasy to operateSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceForward primerPotassium
The invention provides a kit for detecting chlamydia trachomatis (CT). The kit comprises a nucleic acid releaser and a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) solution, wherein the nucleic acid releaser comprises 0.01-0.5mM / L of surfactin, 20-300mM / L of potassium chloride, 0.01-2% of sodium dodecyl sulfate and 0.05-1% of ethanol; and the PCR solution comprises a forward primer and a reverse primer which are used for amplifying targeted polynucleotide, and a probe for detecting the targeted polynucleotide. A method of releasing nucleic acid by using the nucleic acid releaser in the kit provided by the invention is not obviously different from a boiling method in the detection result, and a violent protein denaturant adopted for the nucleic acid extraction in the method provided by the invention quickly breaks a coat protein structure of a pathogen to release pathogen nucleic acid, so the release and extraction of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) can be realized without heating; besides, the sensitivity of the provided kit for detecting the CT can be 400 copies / ml, the linearity region of the detection is 400-4.00E+10 copies / ml; and moreover, CT-DNA in an unknown sample such as genital secretions can be quickly and precisely detected by using the kit, so a reliable experiment basis is provided for diagnosing CT infection.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) fluorescence quantitative rapid test kit and method for chlamydia trachomatis
ActiveCN102329866BEfficient removalQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceReference product
The invention aims at providing a kit which is suitable for rapid test of chlamydia trachomatis in clinical samples and can be used for auxiliary diagnosis and efficacy monitoring of chlamydia trachomatis infection. The technical scheme of the invention is as follows: an PCR (polymerase chain reaction) fluorescence quantitative rapid test kit of the chlamydia trachomatis is provided and comprises a PCR reaction solution, wherein the PCR reaction solution contains primers and a fluorescence probe; and the primers comprise an upstream primer and a downstream primer, and the kit further comprises a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase, a strong positive quality control product, a weak positive quality control product, a negative quality control product, a positive quantitative reference product and a DNA extraction solution. According to the CT (chlamydia trachomatis) fluorescence PCR quantitative test kit and method provided by the invention, a Taqman core technology platform and an arabidopsis internal reference system are utilized, thus the test sensitivity is higher. Furthermore, the accuracy, specificity, repeatability, stability, sensitivity and precision are improved compared with those of the existing product.
Owner:泰普生物科学(中国)有限公司
Immunization Against Chlamydia Infection
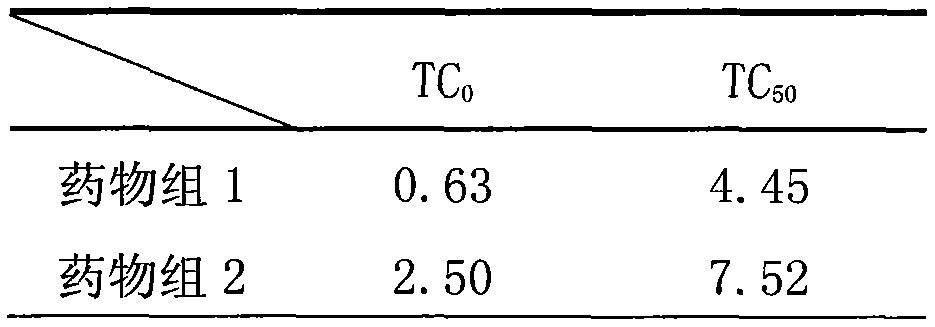
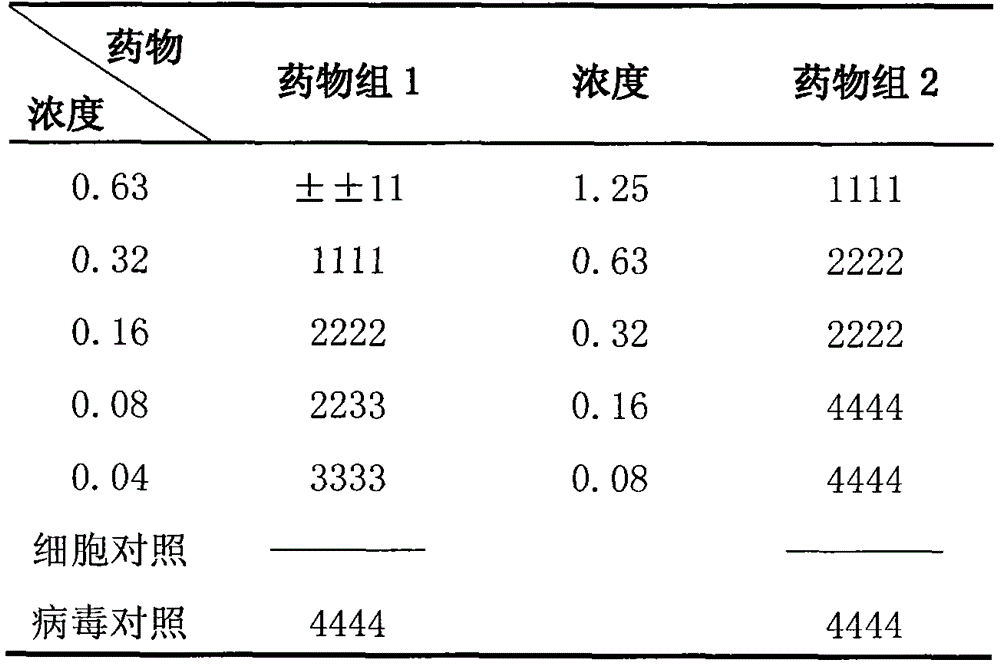
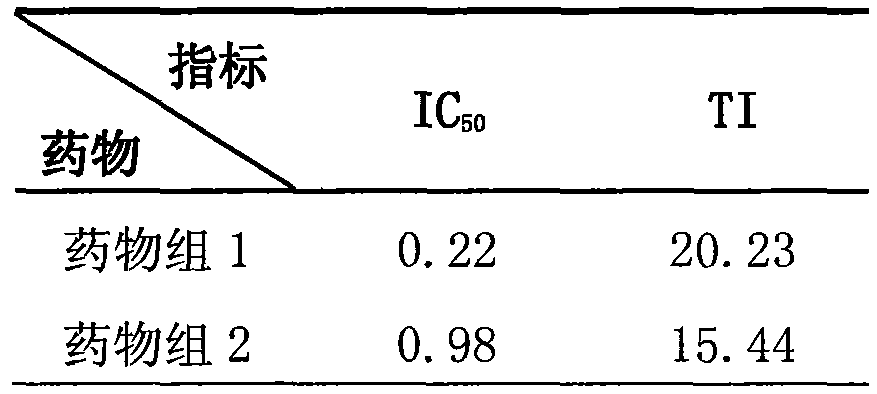
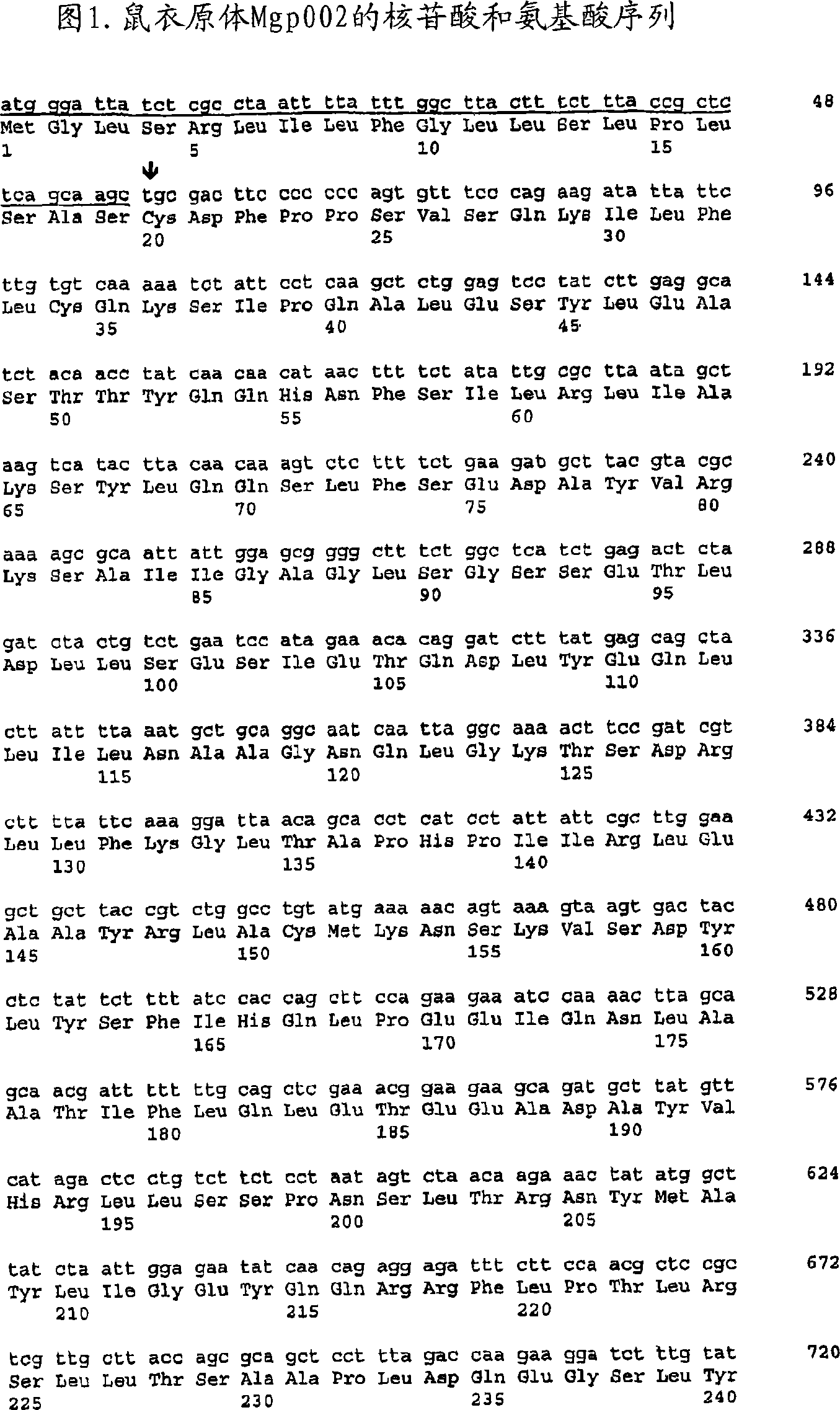
The present invention provides nucleic acids, proteins and vectors for a method of nucleic acid, including DNA, immunization of a host, including humans, against disease caused by infection by a strain of Chlamydia, specifically C. trachomatis. The method employs a vector containing a nucleotide sequence encoding a Mgp002 polypeptide of a strain of Chlamydia operably linked to a promoter to effect expression of the gene product in the host. Truncated forms of the full-length Mgp002 gene are useful immunogens for protecting against disease caused by infection with Chlamydia. The invention further provides recombinant Mgp002 protein useful for protecting against disease caused by infection with Chlamydia.
Owner:BE INTPROP
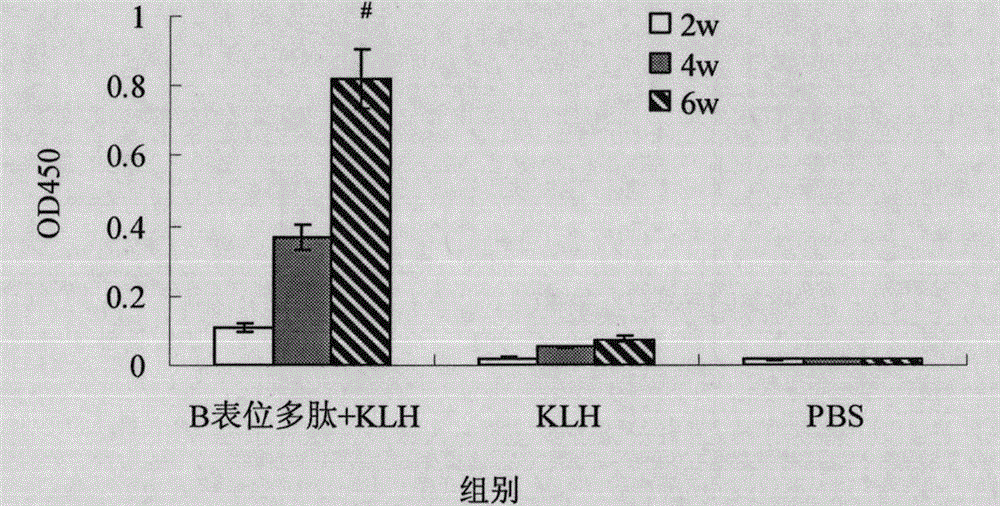
B cell epitope of Tarp protein of chlamydia trachomatis and application of B cell epitope
InactiveCN104558118AImproving immunogenicityGood antigenicityAntibacterial agentsChlamydiaceae ingredientsDiseaseNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly discloses a B cell epitope which is obtained by screening on the basis of full-length Tarp protein of chlamydia trachomatis. The invention further discloses an encoding nucleotide and an amino acid sequence of the B cell epitope, and further discloses an application of the B cell epitope in prevention of chlamydia trachomatis infection diseases. The B cell epitope disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high immunogenicity and antigenicity, and good application prospect.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
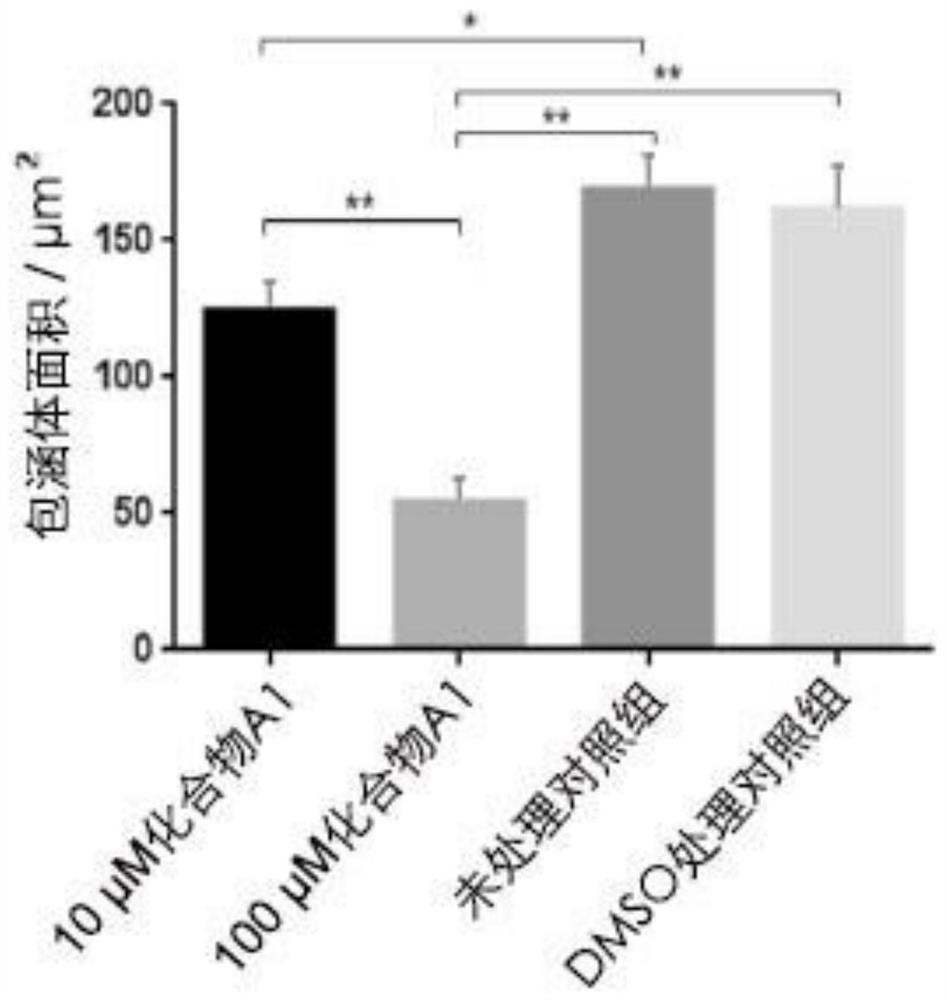
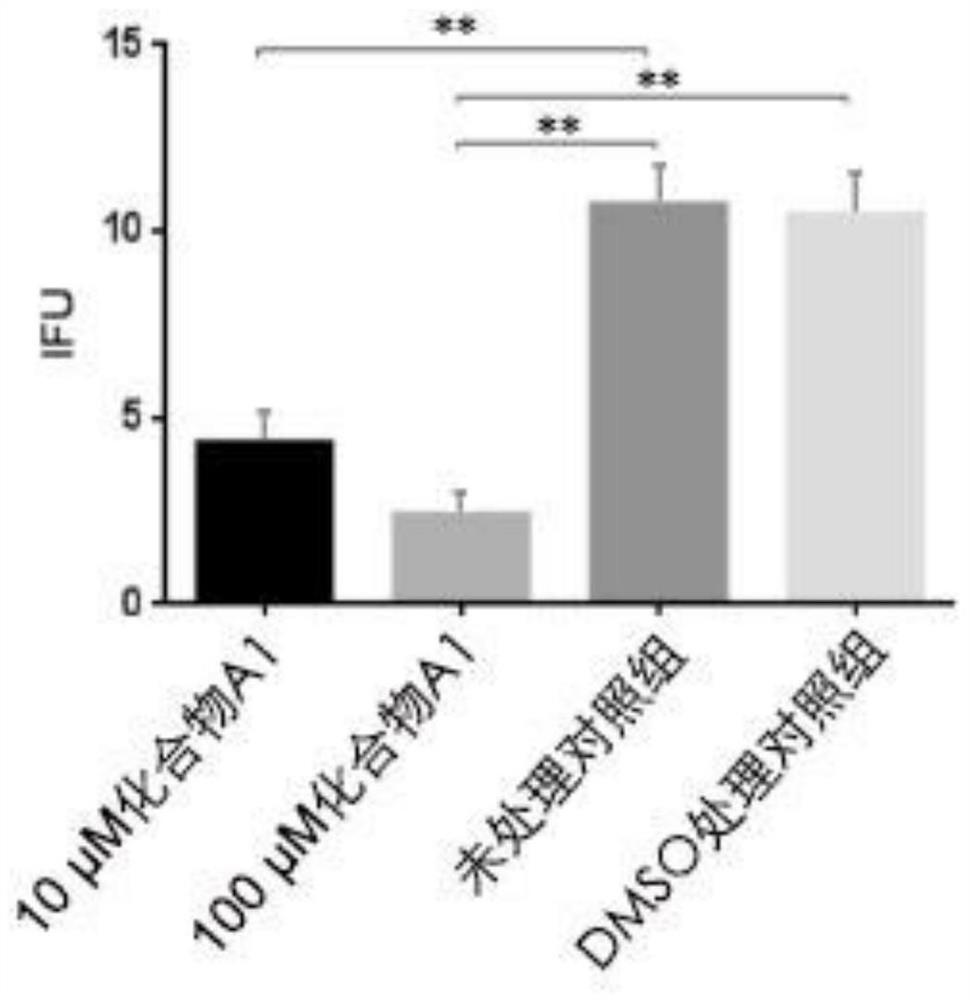
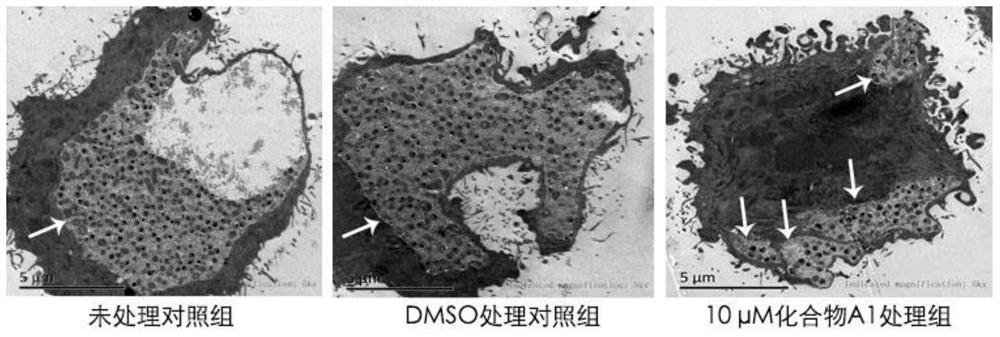
Use of peptidomimetic compounds in the preparation of drugs for inhibiting intracellular growth of Chlamydia trachomatis
ActiveCN109675014BReduce in quantityReduce areaAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderPharmaceutical drugMicrobiology
The invention provides application of a mimetic peptide compound in preparing a drug for inhibiting intracellular growth of chlamydia trachomatis. The mimetic peptide compound can directly act on HtrA(High Temperature Requirement A) protein of the chlamydia trachomatis and is capable of inhibiting intracellular growth of the chlamydia trachomatis in the level of 10 muM, the quantity and the areaof chlamydia trachomatis inclusion bodies are reduced, and a new path is provided for treating chlamydia trachomatis infection.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating gynecological diseases and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105617175AHeat-clearing and detoxifyingWith blood circulation and dampnessAntibacterial agentsSexual disorderDiseaseThirst
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating gynecological diseases and a preparation method thereof. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from gentian, hedyotis diffusa, radix stemonae, ligusticum wallichii and cortex dictamni according to a certain weight ratio. The traditional Chinese medicine composition can be processed to form a common preparation. The traditional Chinese medicine composition has functions of clearing heat and removing toxins, and invigorating circulation of blood and eliminating dampness, is used for treating damp-poison-static-caused leukorrheal diseases with symptoms of leukorrhagia, leucorrhea yellowing, peculiar smell of leucorrhea, pruritus vulvae or burning heat and pain sensation, dysphoria and thirst, and fatigue and treating mucopurulent cerricitis (caused through Chlamydia trachomatis infection) with the above symptoms.
Owner:江西百神昌诺药业有限公司
Immunization against chlamydia infection
The present invention provides nucleic acids, proteins and vectors for a method of nucleic acid, including DNA, immunization of a host, including humans, against disease caused by infection by a strain of Chlamydia, specifically C. trachomatis. The method employs a vector containing a nucleotide sequence encoding a Mgp002 polypeptide of a strain of Chlamydia operably linked to a promoter to effect expression of the gene product in the host. Truncated forms of the full-length Mgp002 gene are useful immunogens for protecting against disease caused by infection with Chlamydia. The invention further provides recombinant Mgp002 protein useful for protecting against disease caused by infection with Chlamydia.
Owner:圣诺菲·帕斯图尔公司
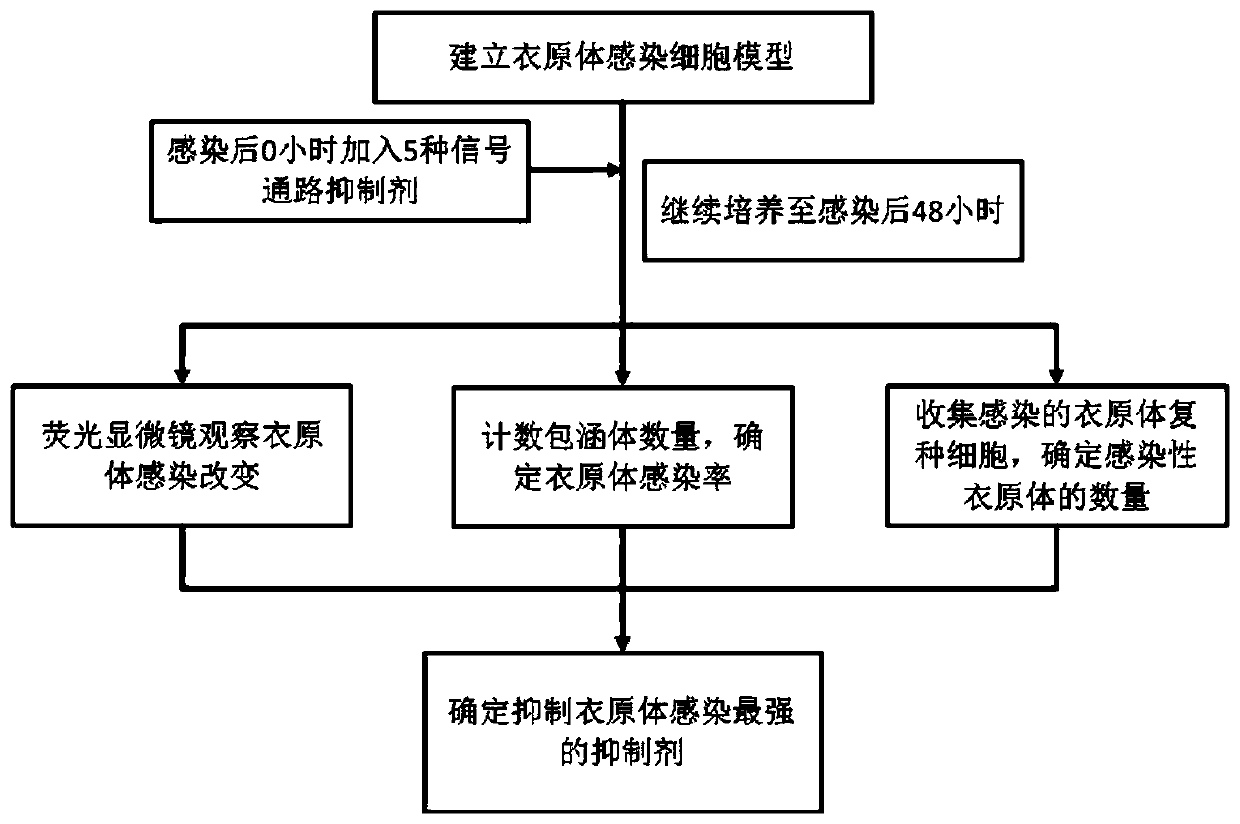
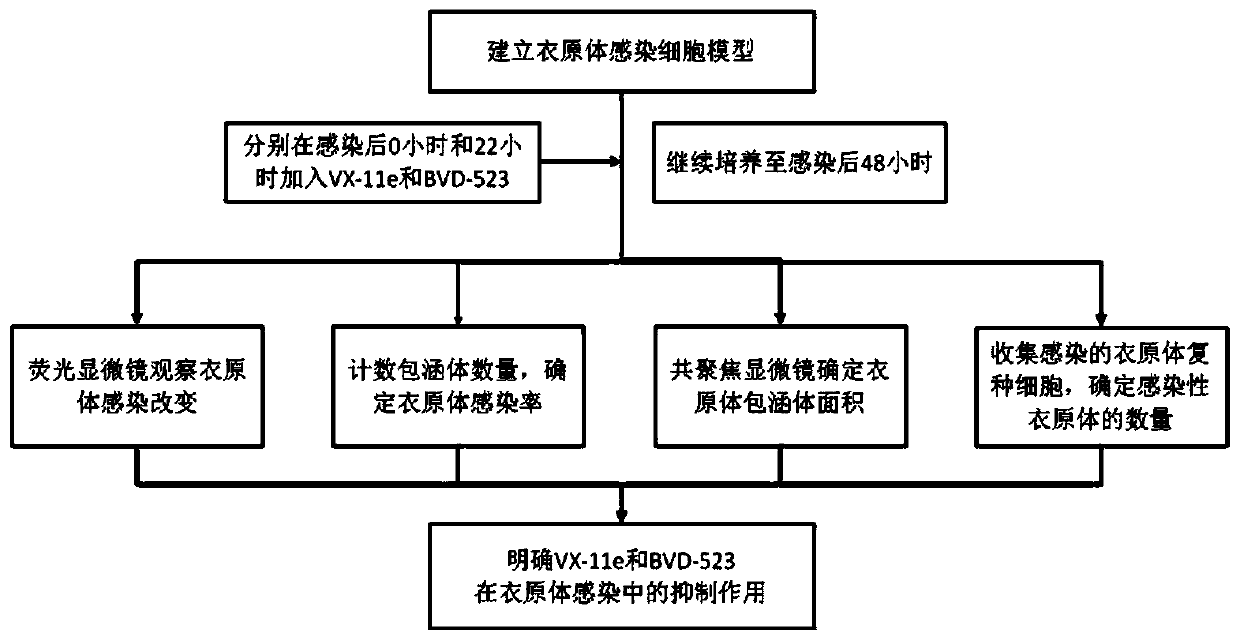
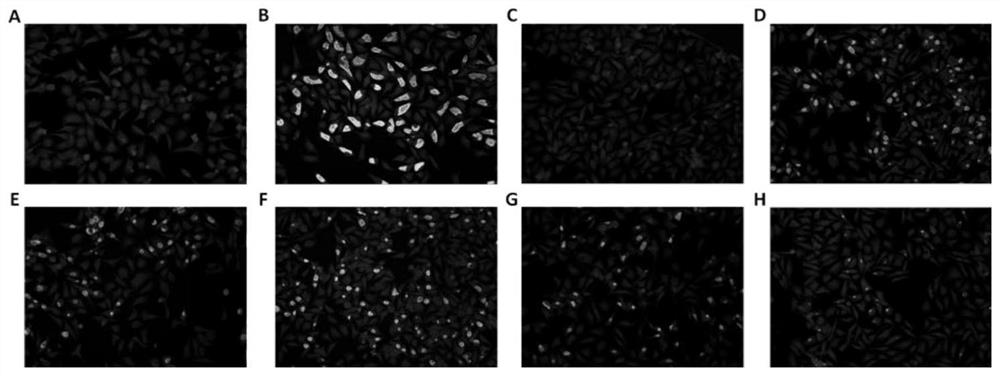
Application of ERK signal pathway small molecule inhibitor in inhibiting chlamydia infection
ActiveCN109745562AAvoid infectionStrong anti-infection effectOrganic active ingredientsAntiinfectivesSignalling pathwaysCHLAMYDIAL INFECTIONS
The invention discloses an application of small molecule inhibitors VX-11e and BVD-523 in inhibiting chlamydia infection. The research found that the signal pathway inhibitors VX-11e and BVD-523 can obviously inhibit the infection of the chlamydia trachomatis, and have significant difference compared with the reported MEK inhibitor U0126; according to the application of small molecule inhibitors VX-11e and BVD-523 in inhibiting chlamydia infection, the small molecule inhibitors VX-11e and BVD-523 are applied to chlamydia infection for the first time, and are expected to be new drugs for chlamydia targeting host therapy; the research also found that inhibitors VX-11e and BVD-523 had synergistic effect with azithromycin. After chlamydia infection, VX-11e and BVD-523 could promote the anti-infection effect of azithromycin, which was of great value in the treatment of chlamydia infection. The application of small molecule inhibitors VX-11e and BVD-523 in inhibiting chlamydia infection hasimportant significance for the development of new drugs for chlamydia trachomatis infection and the search of new targets for auxiliary host therapy.
Owner:DERMATOLOGY HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV (GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL DERMATOLOGY HOSPITAL GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL CENT FOR STI & SKIN DISEASES CONTROL & PREVENTION RES CENT FOR LEPROSY CONTROL & PREVENTION CHINA)
Molecular-biological detection method for chlamydia trachomatis infection based on SAT (Simultaneous Amplification and Testing) of RNA target
InactiveCN108546746ASave medical resourcesReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlTarget capture
The invention provides a molecular-biological detection method for chlamydia trachomatis infection based on SAT (Simultaneous Amplification and Testing) of a RNA target. The molecular-biological detection method comprises the following steps: step (1) adopting a specific target capture technology and a magnetic-bead method to extract pure cell target nucleic acid, i.e., adopting RNA as the target,wherein comprising (1-1) the specificity of the target nucleic acid is manually extracted; (1-2) the pure cell target nucleic acid is obtained, i.e., RNA is used as a target; step (2) adopting a RNAreal-time fluorescent constant-temperature amplification detection technology to obtain a detection result for chlamydia trachomatis infection, wherein comprising (2-1) M-MLV reverse transcriptase generates a DNA copy of the target nucleic acid; (2-2) T7RNA polymerase generates multiple RNA copies from the DNA copy; (2-3) an optimizing probe with fluorescence labeling is specifically combined withthe extracted RNA copy, so that a fluorescence signal generated is captured by a detection instrument, and the detection result for the chlamydia trachomatis infection is obtained according to the occurring time and the intensity of the signal; step (3) judging the detection result by combination with positive control and negative control.
Owner:一零零二信息科技(沧州)有限责任公司
A traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating gynecological diseases and its preparation method
ActiveCN105617175BHeat-clearing and detoxifyingWith blood circulation and dampnessAntibacterial agentsSexual disorderDiseaseThirst
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating gynecological diseases and a preparation method thereof. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from gentian, hedyotis diffusa, radix stemonae, ligusticum wallichii and cortex dictamni according to a certain weight ratio. The traditional Chinese medicine composition can be processed to form a common preparation. The traditional Chinese medicine composition has functions of clearing heat and removing toxins, and invigorating circulation of blood and eliminating dampness, is used for treating damp-poison-static-caused leukorrheal diseases with symptoms of leukorrhagia, leucorrhea yellowing, peculiar smell of leucorrhea, pruritus vulvae or burning heat and pain sensation, dysphoria and thirst, and fatigue and treating mucopurulent cerricitis (caused through Chlamydia trachomatis infection) with the above symptoms.
Owner:江西百神昌诺药业有限公司
Application of small molecule inhibitors of erk signaling pathway in inhibiting chlamydia infection
ActiveCN109745562BAvoid infectionStrong anti-infection effectOrganic active ingredientsAntiinfectivesChlamydiaceae InfectionsCHLAMYDIAL INFECTIONS
The invention discloses the application of small molecule inhibitors VX-11e and BVD-523 in inhibiting chlamydia infection. The study of the present invention found that the signaling pathway inhibitors VX‑11e and BVD‑523 can significantly inhibit the infection of Chlamydia trachomatis, compared with the reported MEK inhibitor U0126, there is a significant difference; the present invention is the first small molecule inhibitor VX‑11e and BVD‑523 applied to chlamydia infection, which is expected to become a new drug for chlamydia targeted host therapy; at the same time, the study also found that the combined application of inhibitors VX‑11e and BVD‑523 with azithromycin has a synergistic effect, after chlamydia infection, VX‑11e and BVD‑523 can promote the anti-infective effect of azithromycin, and have important application value for the treatment of chlamydia infection. The invention is of great significance for the development of new drugs for chlamydia trachomatis infection and for finding new targets for assisting host treatment.
Owner:DERMATOLOGY HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV (GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL DERMATOLOGY HOSPITAL GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL CENT FOR STI & SKIN DISEASES CONTROL & PREVENTION RES CENT FOR LEPROSY CONTROL & PREVENTION CHINA)
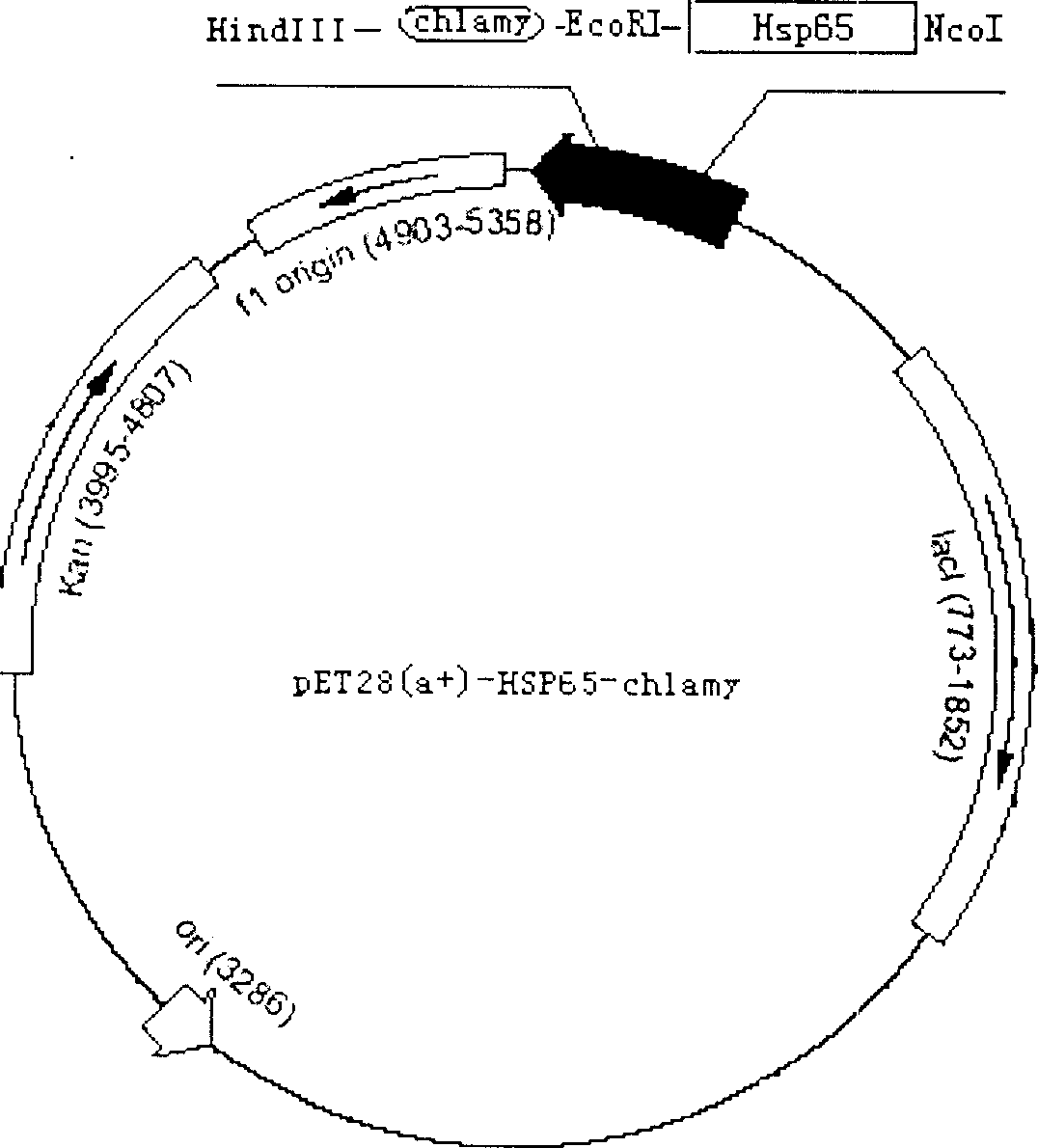
Recombination protein for preventing human trachoma bedsnia infestation and its use
A recombinant protein vaccine for preventing the infection of human chlamydia trachomatis, which is a fusion protein recombined by linking the heat shock protein 65 of BCG vaccine with the epitope of main outer membrane protein of chlamydia trachomatis, the nucleotide sequence for coding it, the expression carrier containing said nucleotide sequence, the host cell containing said expression carrier, and the process for preparing said recombinant protein vaccine are disclosed.
Owner:BEIJING HYDVAX BIOTECH
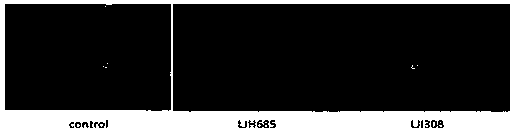
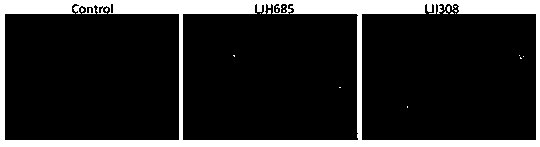
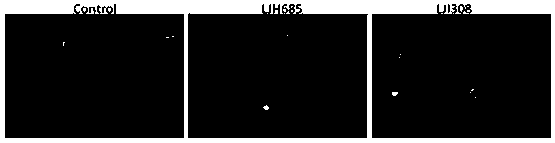
Application of RSK signal channel inhibitors to restraining chlamydia trachomatis infection
ActiveCN109847063AAvoid infectionStrong anti-infection effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAzithromycinSerotype
The invention discloses an application of RSK signal channel inhibitors to restraining chlamydia trachomatis infection. Through research, the inventor finds that RSK signal channel inhibitors LJH685 and LJI308 can restrain chlamydia trachomatis infection and are effective on the chlamydia trachomatis of different cell types and different serotypes, and the RSK signal channel inhibitors are appliedto the chlamydia trachomatis infection for the first time, and hopefully become new medicines for chlamydia trachomatis targeted host treatment. Besides, through research, the inventor also finds that when the RSK signal channel inhibitors LJH685 and LJI308 and azithromycin are in united application, synergistic effects can be achieved, after the chlamydia trachomatis infection, the LJH685 and the LJI308 can promote the anti-infection effect of the azithromycin, and the RSK signal channel inhibitors have important application value on treating the chlamydia trachomatis infection. The RSK signal channel inhibitors have important significance on developing the new medicines for the chlamydia trachomatis infection and seeking new target points for auxiliary host treatment.
Owner:DERMATOLOGY HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV (GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL DERMATOLOGY HOSPITAL GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL CENT FOR STI & SKIN DISEASES CONTROL & PREVENTION RES CENT FOR LEPROSY CONTROL & PREVENTION CHINA)
Main outer membrane protein epitope vaccine of chlamydia trachomatis based on HBcAg vector and application of main outer membrane protein epitope vaccine
The invention relates to a chimeric vaccine of a hepatitis B virus and chlamydia trachomatis, and an application of the chimeric vaccine, and particularly relates to a recombinant protein containing one or more epitopes with a main outer membrane protein epitope vaccine of the chlamydia trachomatis. The epitope peptides are inserted into the same or different permissive sites of hepatitis B virus core antigen (HBcAg) protein in a form of a single epitope or a plurality of epitopes which are combined together; the recombinant fusion protein capable of stimulating the organism to generate humoral immunity and cellular immunity with respect to the chlamydia trachomatis is formed; the immunogenicity and the immunoprotecive property of various fusion proteins are primarily evaluated; and a foundation is laid for further research and application of preventing and treating chlamydia trachomatis infection and related diseases employing the epitope vaccine based on an HBcAg vector. The vaccine disclosed by the invention has efficient and safe immunoprophylaxis and treatment effects on the related diseases of the chlamydia trachomatis, and is simple in preparation process and immunologic process, obvious in effect and high in repeatability.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
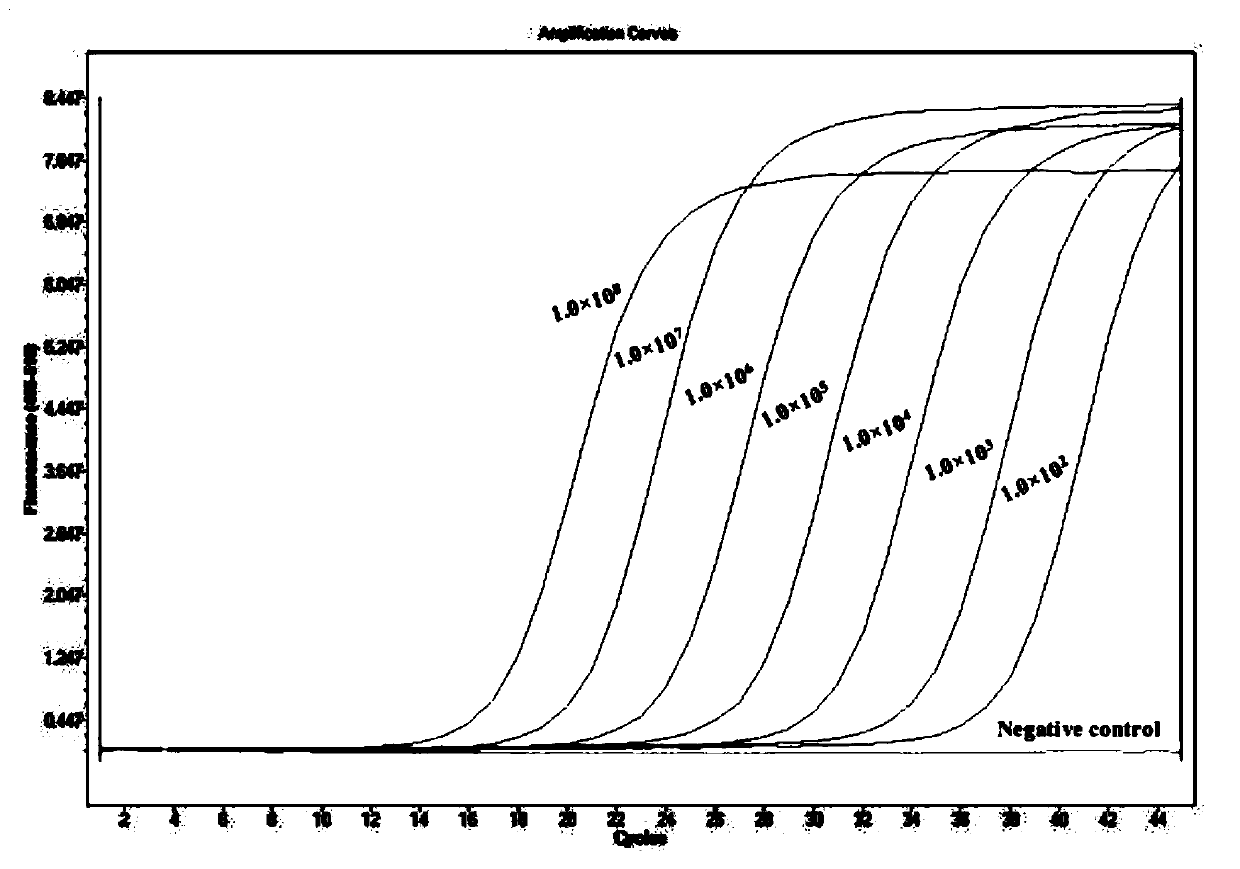
Double qPCR method for rapidly detecting chlamydia trachomatis, primer and probe
PendingCN109750115AImprove diagnostic capabilitiesEasy patentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesLower limitTrue positive rate
The invention provides a double qPCR method for rapidly detecting chlamydia trachomatis, a primer and a probe, wherein the method comprises the following steps: (1) preliminary preparation procedure;(2) extraction and purification of nucleic acid; (3) primer / probe design, synthesis and labeling; (4) qPCR amplification and result judgment; (5) testing the detection lower limit and the amplification linear range; (6) calculation of diagnostic sensitivity and specificity; (7) statistical methods; the double qPCR method for rapidly detecting chlamydia trachomatis has the advantages that the detection lower limit is as low as 2copies / PCR, the amplification linear range reaches 1.0*102-1.0*108 copies / mL, the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for the chlamydia trachomatis are 100.0%(134 / 134) and 99.3%(1142 / 1150) respectively, and the report result is less than or equal to 2.0 hours from sample treatment; the method has the advantages of simplicity, convenience, rapidness, high sensitivity and good specificity, not only can improve the diagnosis capability of chlamydia trachomatis infection, but also can achieve rapid detection and gain time for early accurate treatment.
Owner:深圳市宝安区沙井人民医院 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com