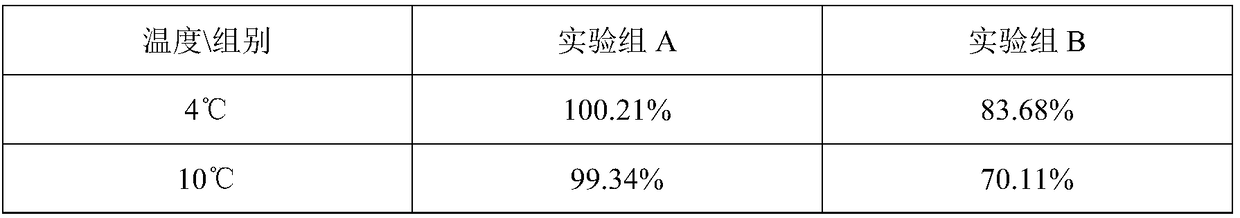
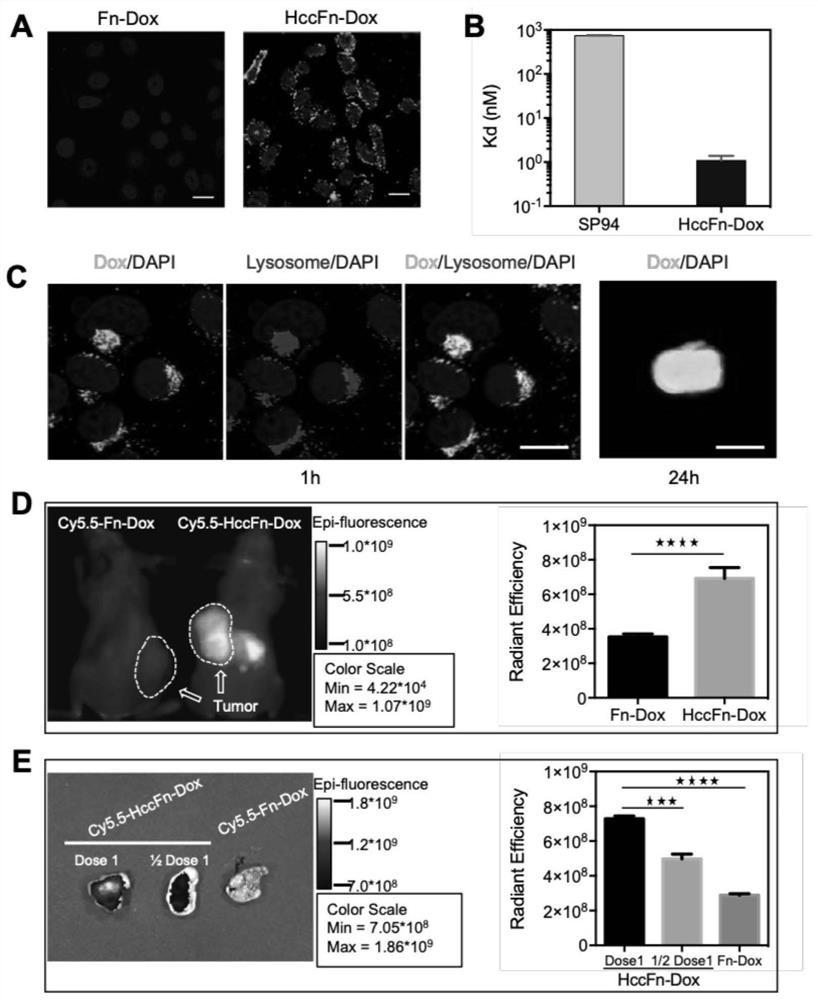
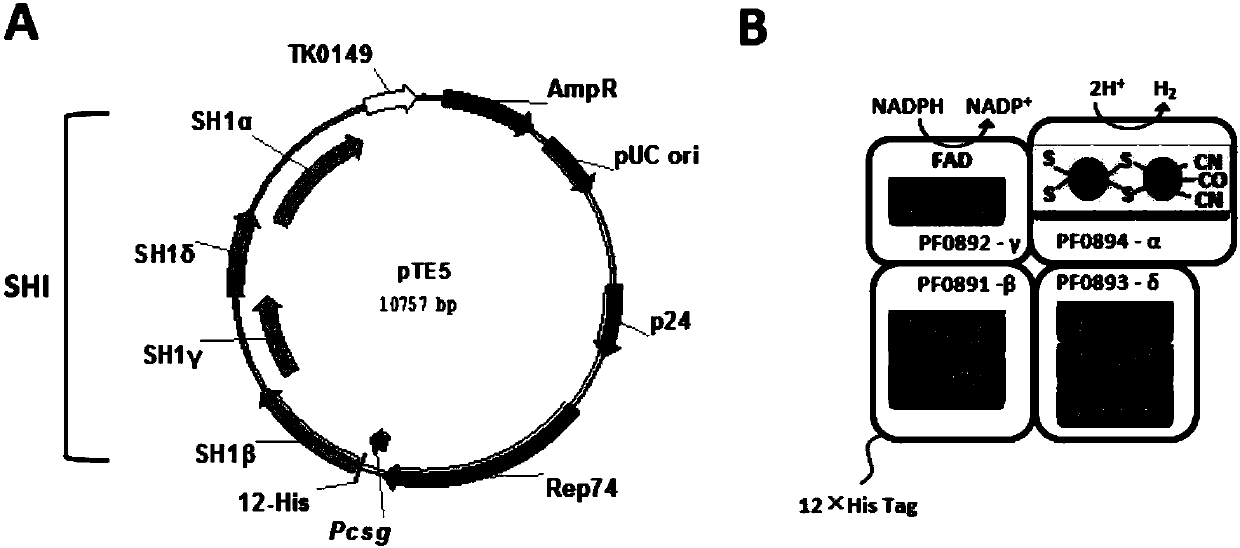
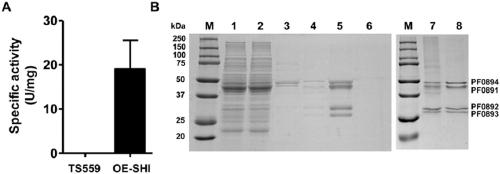
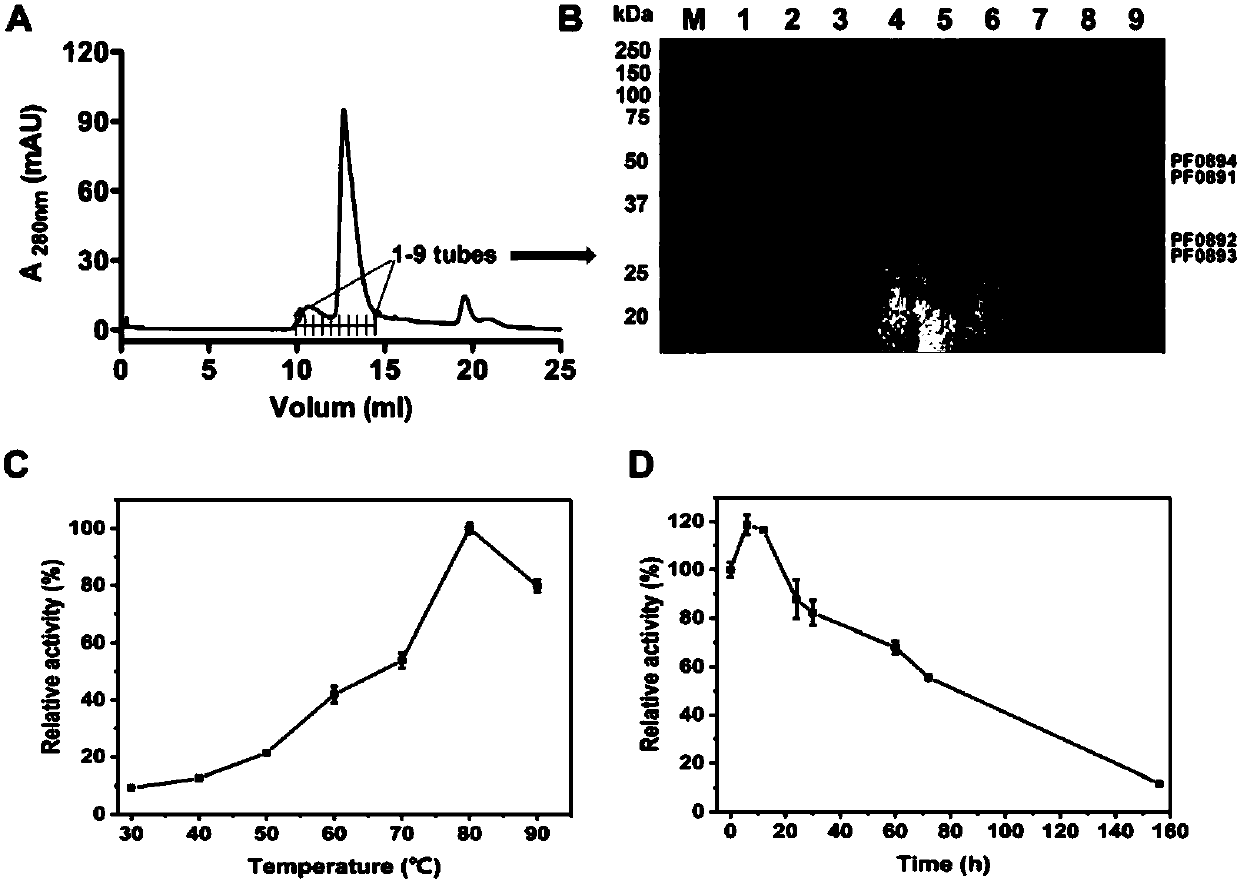
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Pyrococcus furiosus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pyrococcus furiosus is an extremophilic species of Archaea. It can be classified as a hyperthermophile because it thrives best under extremely high temperatures—higher than those preferred of a thermophile. It is notable for having an optimum growth temperature of 100 °C (a temperature that would destroy most living organisms), and for being one of the few organisms identified as possessing aldehyde ferredoxin oxidoreductase enzymes containing tungsten, an element rarely found in biological molecules.
Dideoxynucleotide-triphosphate utilization by the hyper-thermophilic DNA polymerase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus
InactiveUS6333183B1High sensitivityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesBinding site
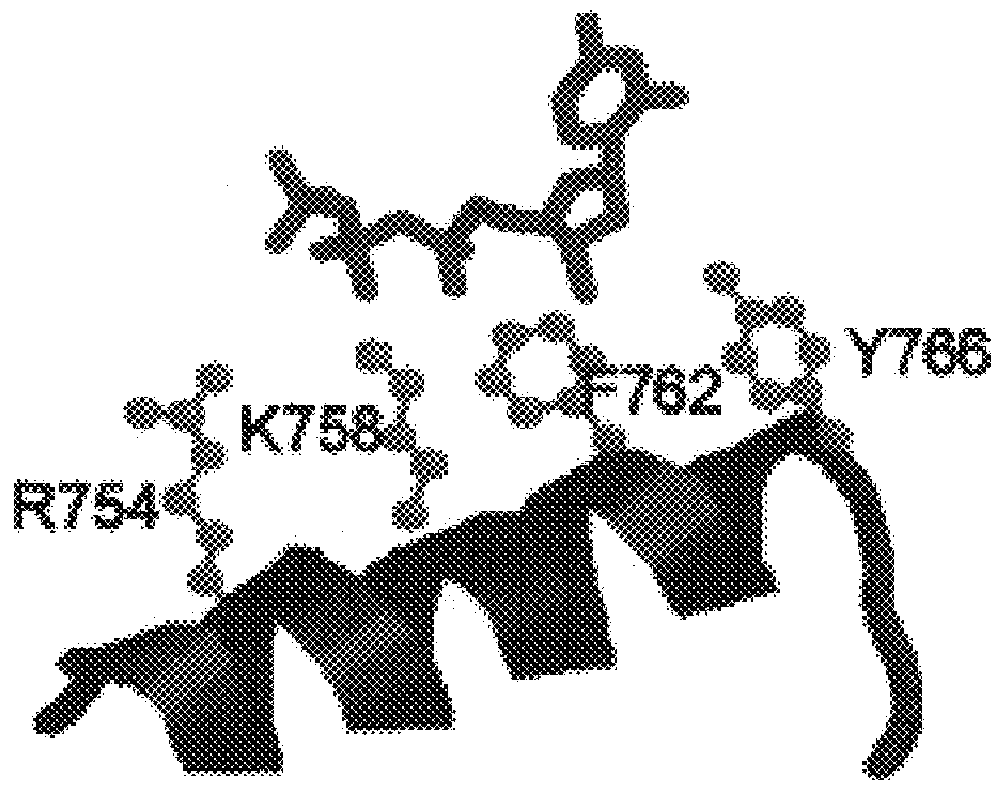
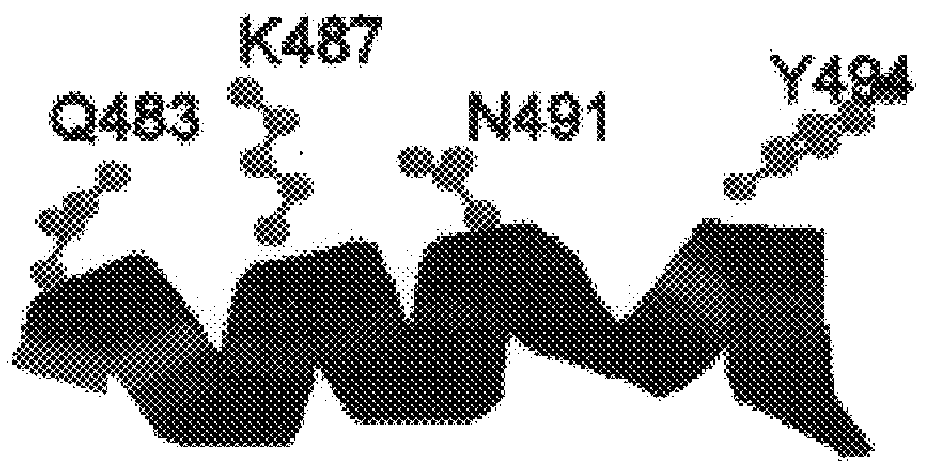
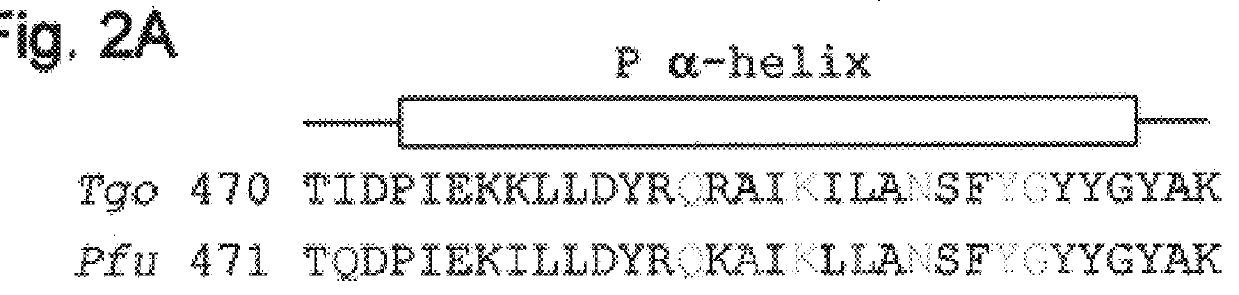
Polymerases from the Pol I family which are able to efficiently use ddNTPs have demonstrated a much improved performance when used to sequence DNA. A number of mutations have been made to the gene coding for the Pol II family DNA polymerase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus with the aim of improving ddNTP utilisation. "Rational" alterations to amino acids likely to be near the dNTP binding site (based on sequence homologies and structural information) did not yield the desired level of selectivity for ddNTPs. However, alteration at four positions (Q472, A486, L490 and Y497) gave rise to variants which incorporated ddNTPs better than the wild type, allowing sequencing reactions to be carried out at lowered ddNTP:dNTP ratios. Wild type Pfu-Pol required a ddNTP:dNTP ratio of 30:1; values of 5:1 (Q472H), 1:3 (L490Y), 1:5 (A486Y) and 5:1 (Y497A) were found with the four mutants; A486Y representing a 150-fold improvement over the wild type. A486, L490 and Y407 are on an alpha-helix that lines the dNTP binding groove, but the side chains of the three amino acids point away from this groove; Q472 is in a loop that connects this alpha-helix to a second long helix. None of the four amino acids can contact the dNTP directly. Therefore, the increased selectivity for ddNTPs is likely to arise from two factors: 1) Small overall changes in conformation that subtly alter the nucleotide triphosphate binding site such that ddNTPs become favoured; 2) interference with a conformational change that may be critical both for the polymerisation step and discrimination between different nucleotide triphosphates.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
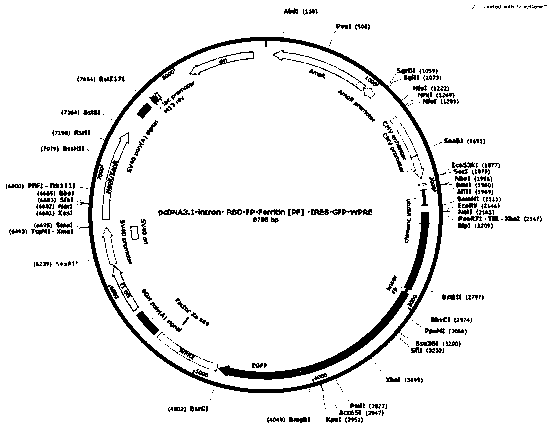
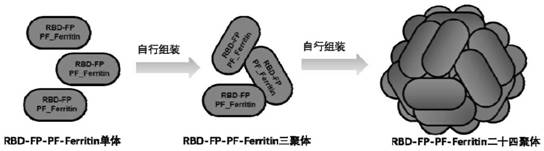
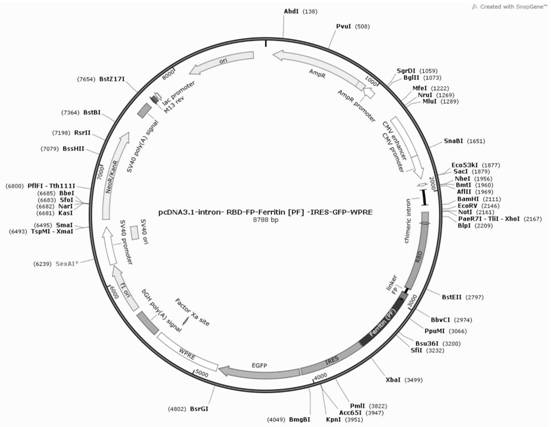
Novel coronavirus S protein two-region subunit nano vaccine based on pyrococcus furiosus ferritin
ActiveCN111217919AMultimerizationOvercoming the disadvantage of insufficient immunogenicitySsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsEucaryotic cellNeutralising antibody
The invention discloses a novel coronavirus S protein double-region subunit nano vaccine based on pyrococcus furiosus ferritin. The virus receptor binding domain (RBD) and fusion peptide (FP) are usedtogether as a double antigen, and are connected with pyrococcus furiosus ferritin (PF_Ferritin) to from a fusion protein RBD-FP-PF_Ferritin to realize antigen multimerization; and then an eukaryoticcell expression system is used for expressing, and a 24-mer nano antigen can be formed through self-assembly of PF_Ferritin. The scheme can overcome the shortcoming of insufficient immunogenicity of RBD monomers, the obtained vaccine can significantly increase the level of a neutralizing antibody against the virus of a host, and the produced antibody has the ability to strongly block the virus from invading target cells. In addition, the vaccine of the invention is simple in preparation method, is easy to purify, and is high in safety, and the vaccine can be relatively quickly applied to clinical trials.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
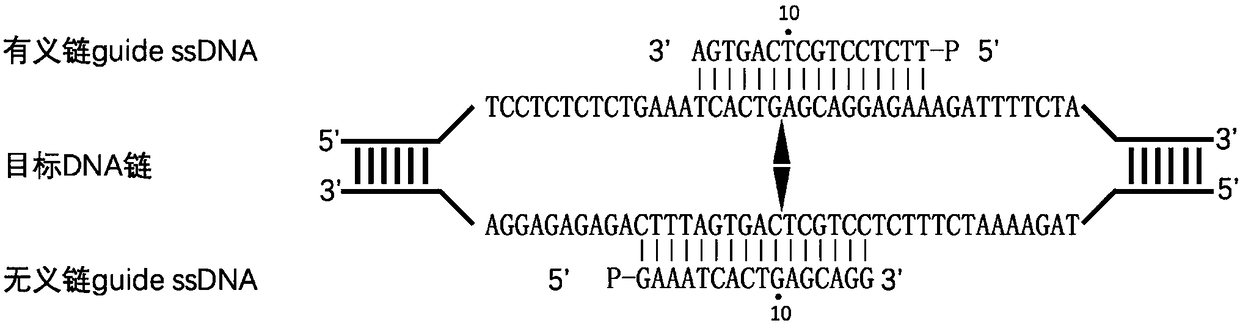
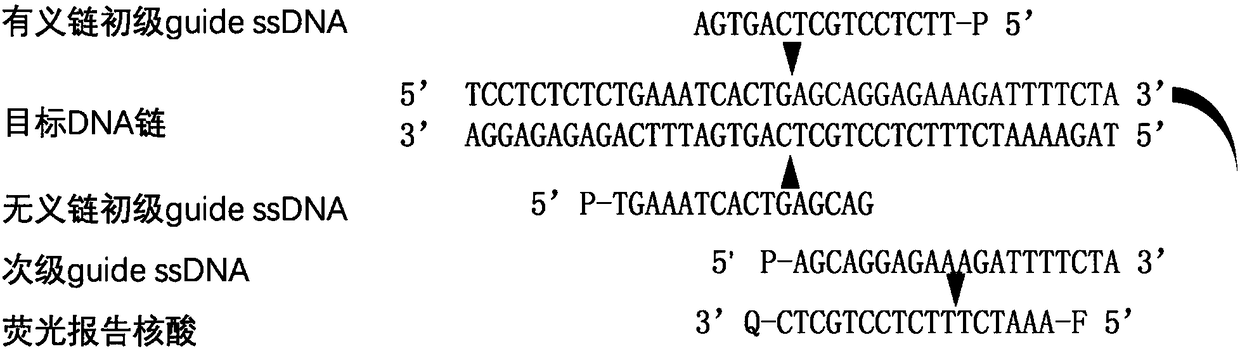
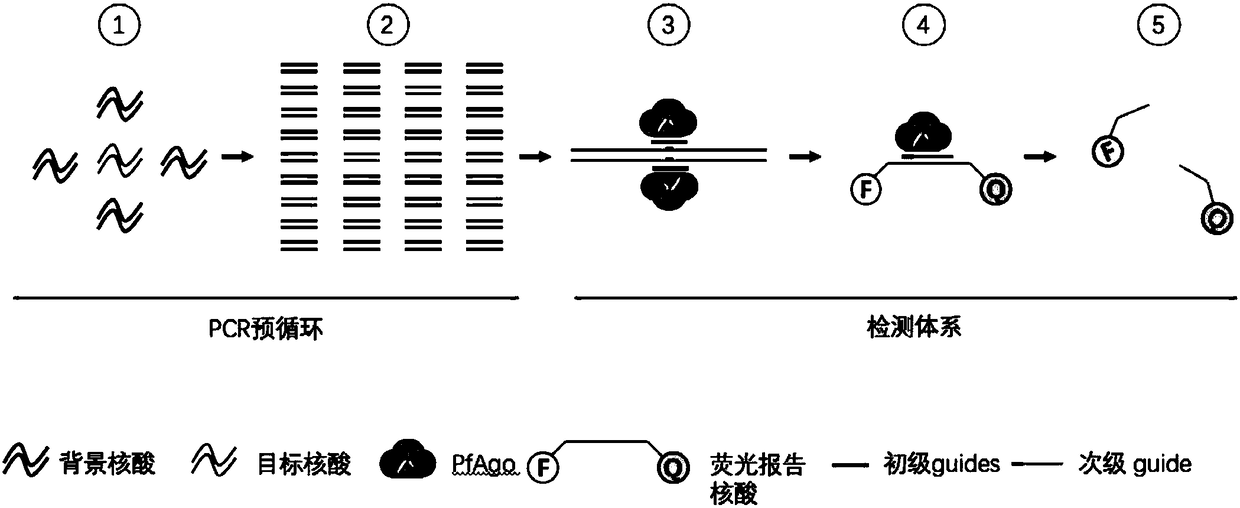
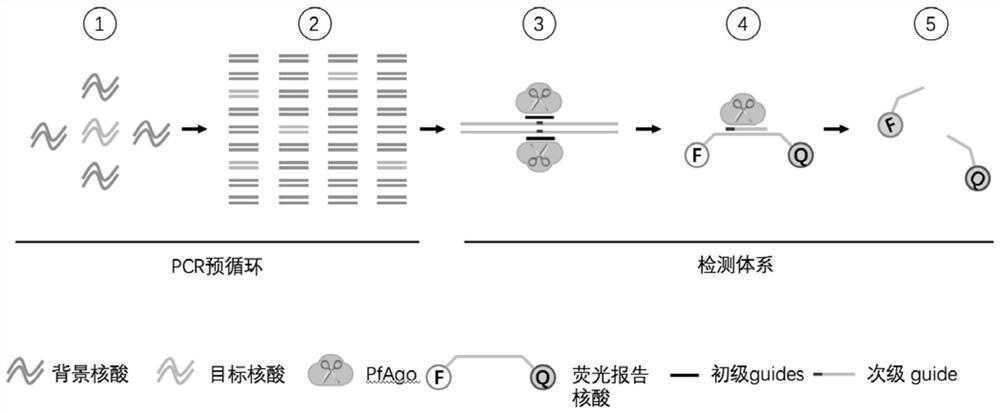
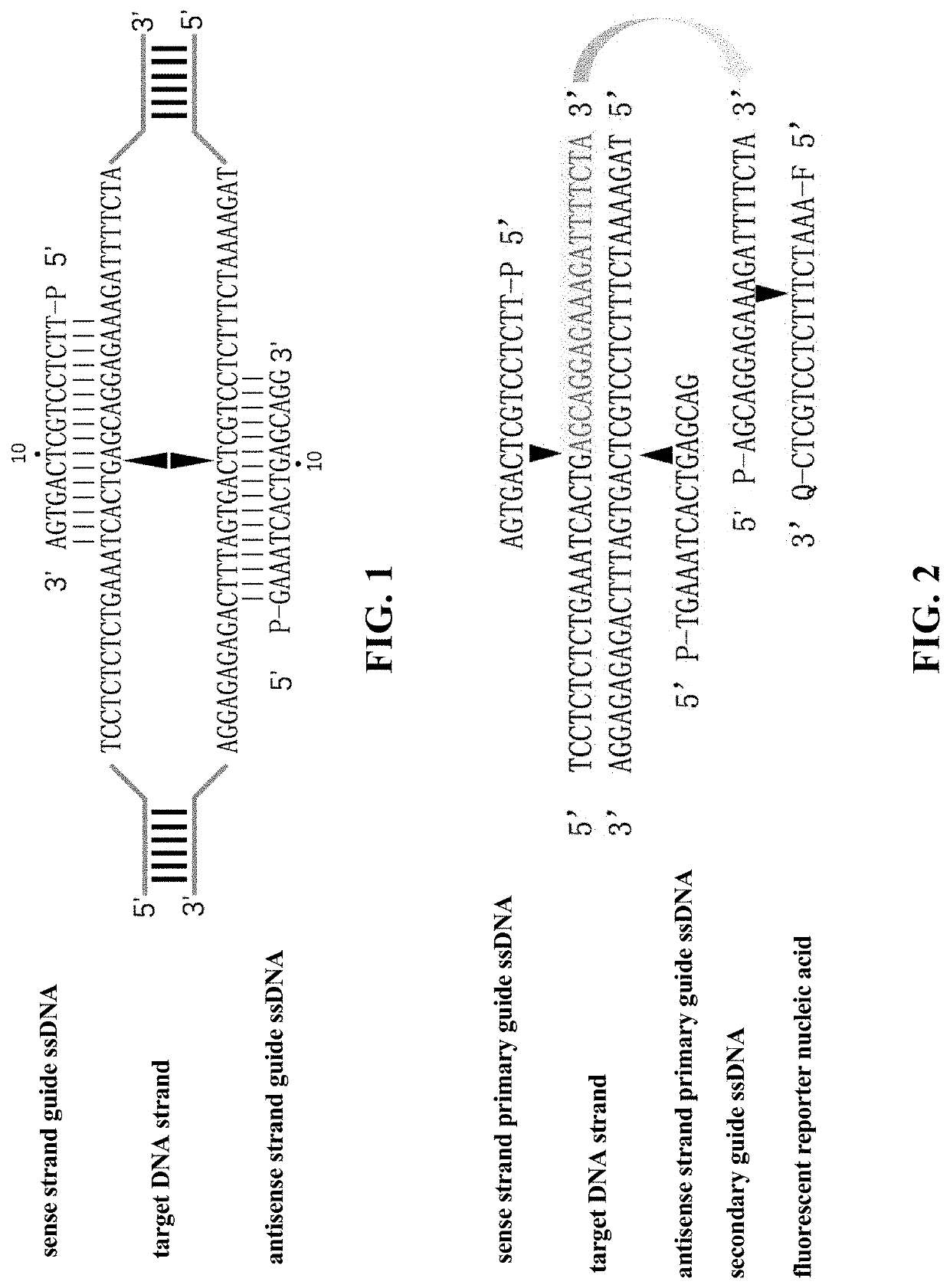
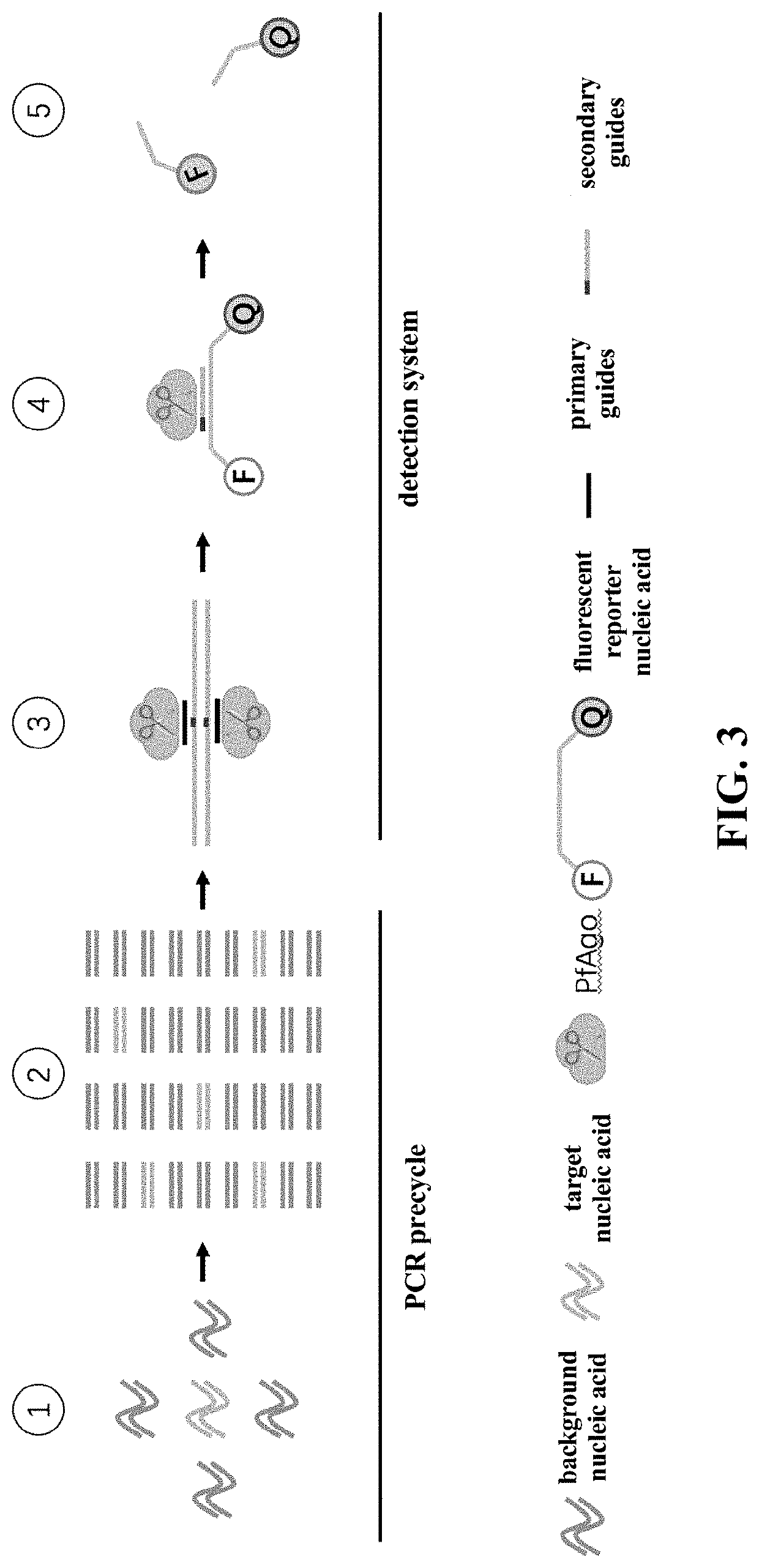
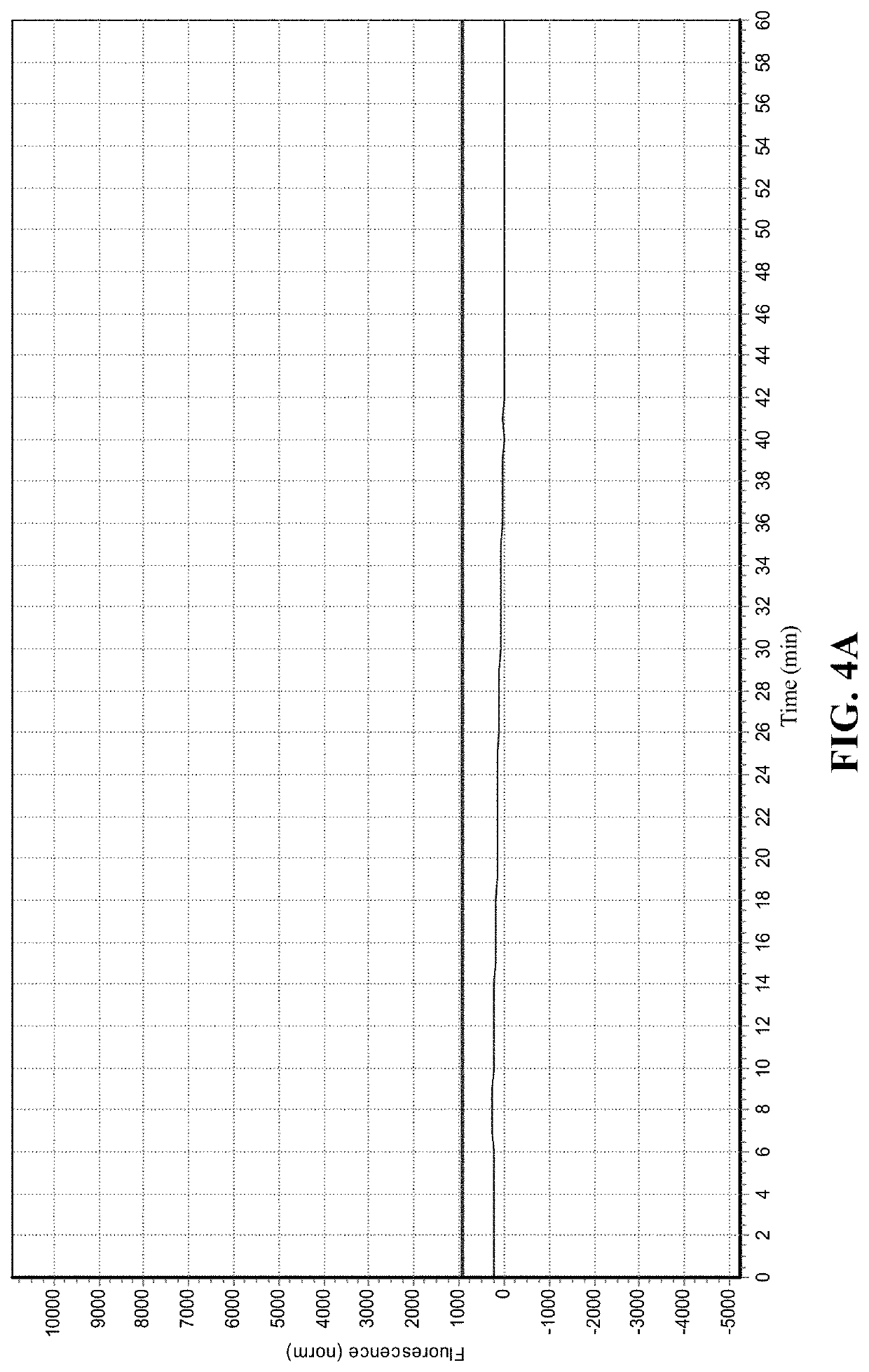
Nucleic acid testing method based on prokaryotic Argonaute protein and application of nucleic acid testing method
ActiveCN108796036AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceMedical diagnosis
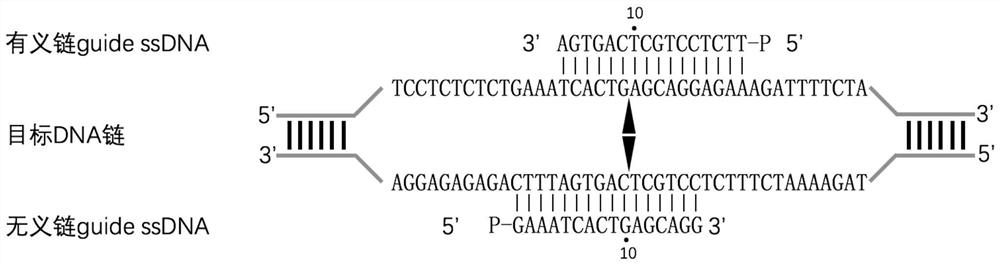
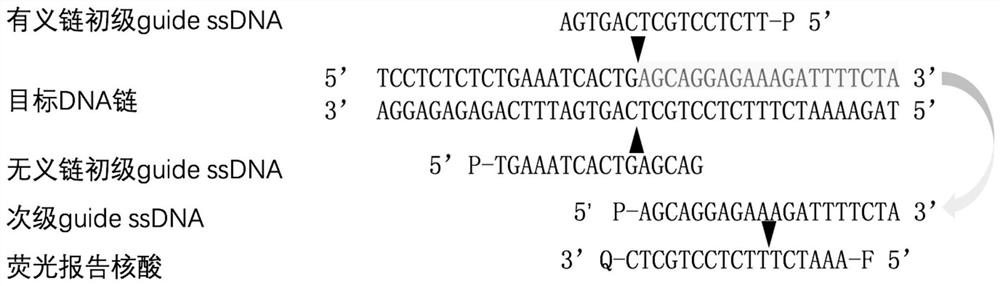
The invention provides a nucleic acid testing method based on a prokaryotic Argonaute protein and an application of the nucleic acid testing method, and particularly provides a system for detecting atarget nucleic acid molecule. The system comprises guide ssDNAs, gene editing enzyme Pyrococcus furiosus Argonaute (PfAgo) and a fluorescence reporter nucleic acid. The nucleic acid testing method ishigh in sensitivity, good in specificity and high in flux and can be widely applied to the fields of molecular medical diagnosis, food safety testing, environmental monitoring and the like.
Owner:JIAOHONG BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
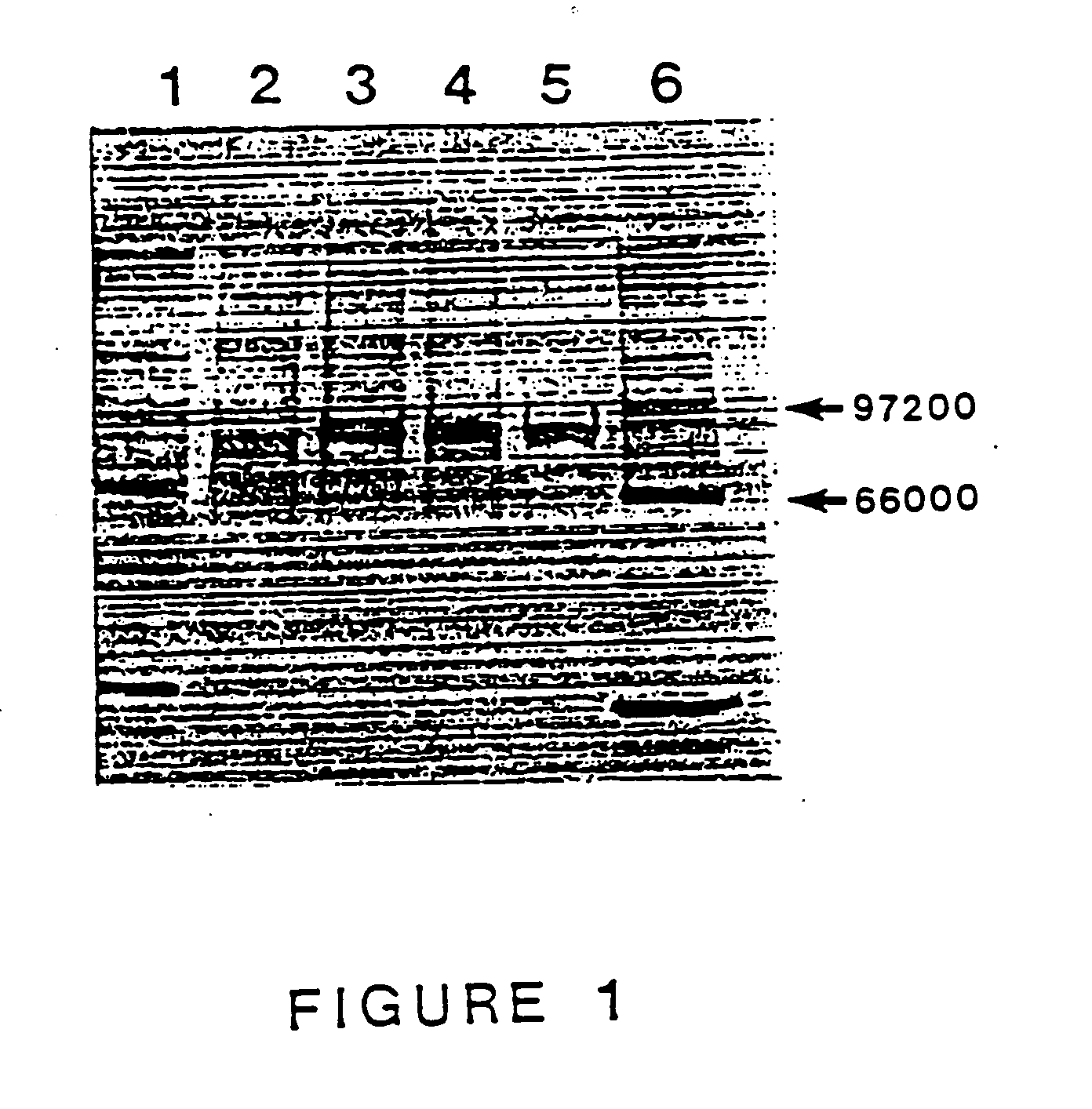
Purified thermostable Pyrococcus furiosus DNA polymerase I
Purified thermostable Pyrococcus furiosus DNA polymerase that migrates on a non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel faster than phosphorylase B and Taq polymerase and more slowly than bovine serum albumin and has an estimated molecular weight of 90,000–93,000 daltons when compared with a Taq polymerase standard assigned a molecular weight of 94,000 daltons.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
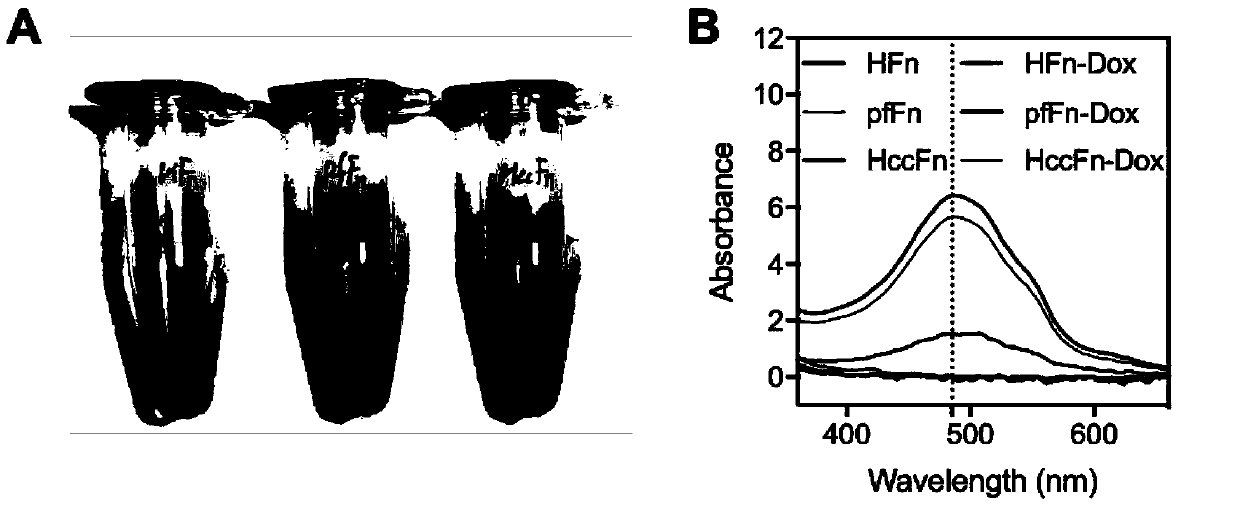
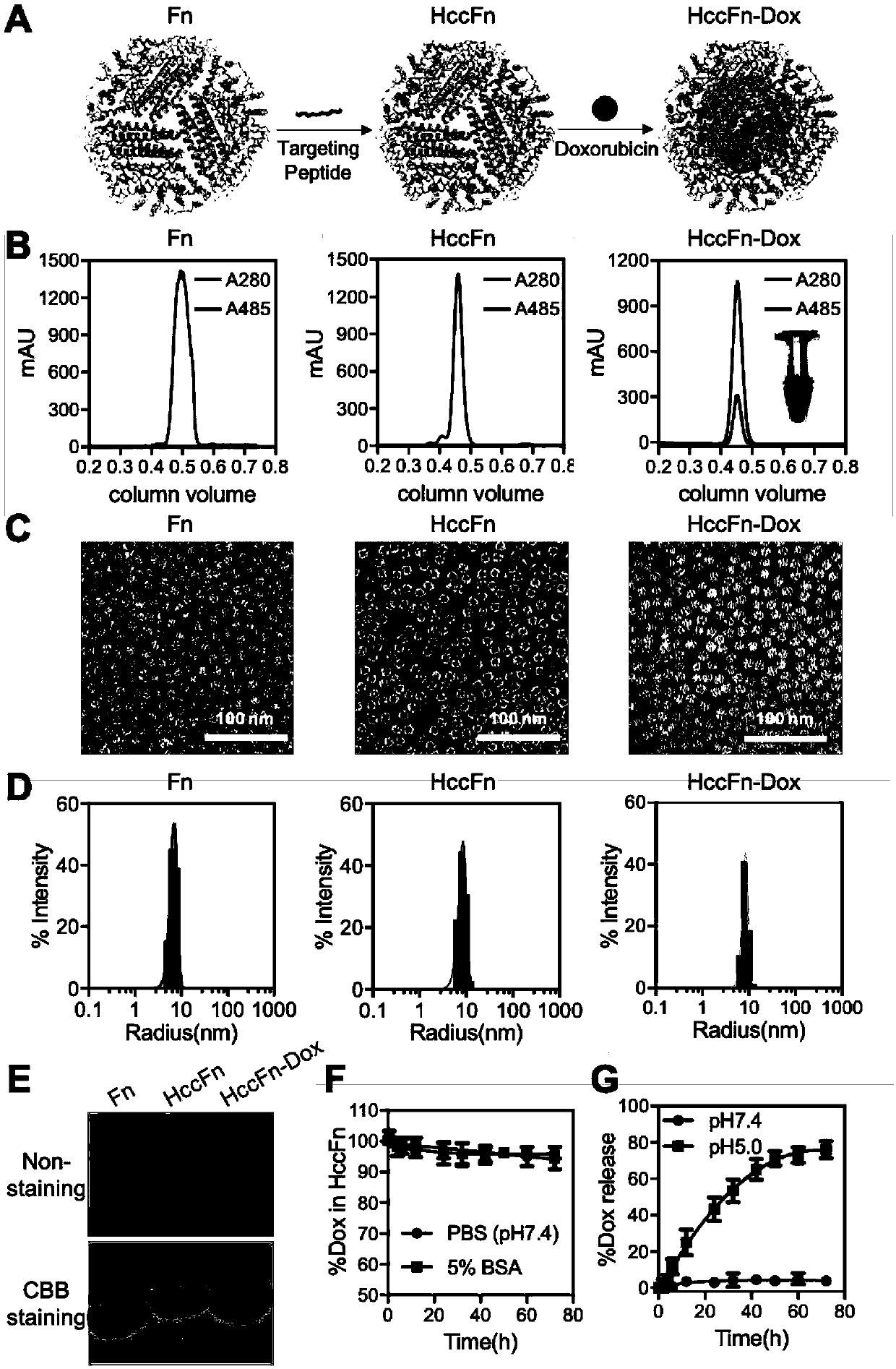
Nano-drug carrier loading anticancer drugs, and preparation method and application of nano-drug carrier
The invention relates to a nano-drug carrier loading anticancer drugs, and a preparation method and application of the nano-drug carrier. The nano-drug carrier is a physiological polymer of pyrococcusfuriosus ferritin and a derivative thereof, wherein the derivative comprises fusion proteins modified based on the pyrococcus furiosus ferritin, and ferritin modified based on the amino acid sequenceof a protein shell inner cavity of the pyrococcus furiosus ferritin; and the anticancer drugs include but are not limited to small molecule drugs, oligonucleotides and functional peptide fragments.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Purified thermostable pyrococcus furiosus DNA polymerase i
InactiveUS20060040370A1Efficient workLess mutationSugar derivativesBacteriaPyrococcus furiosusPolyacrylamide
Purified thermostable Pyrococcus furiosus DNA polymerase that migrates on a non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel faster than phosphorylase B and Taq polymerase and more slowly than bovine serum albumin and has an estimated molecular weight of 90,000-93,000 daltons when compared with a Taq polymerase standard assigned a molecular weight of 94,000 daltons.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Pfu replication accessory factors and methods of use
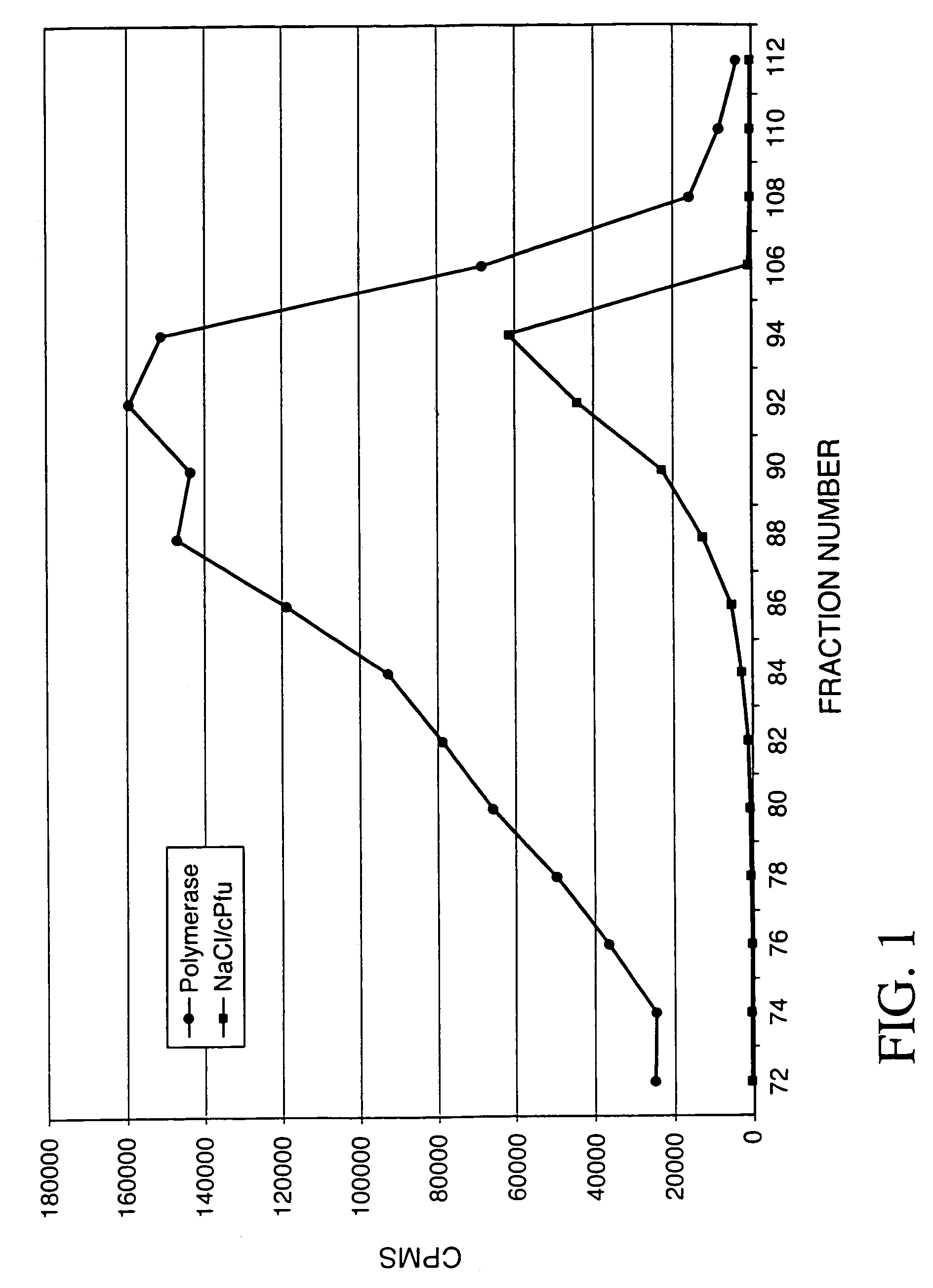
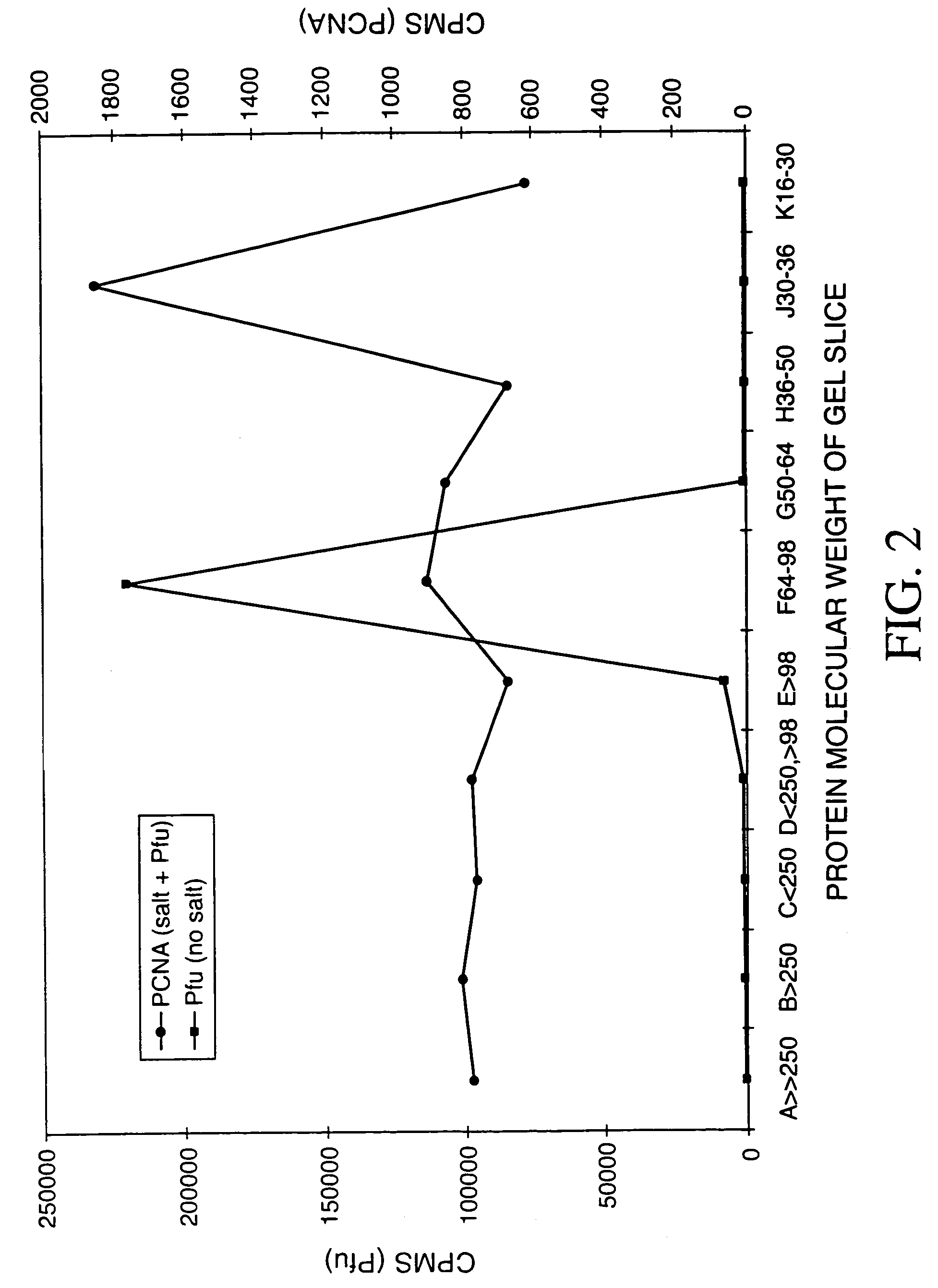
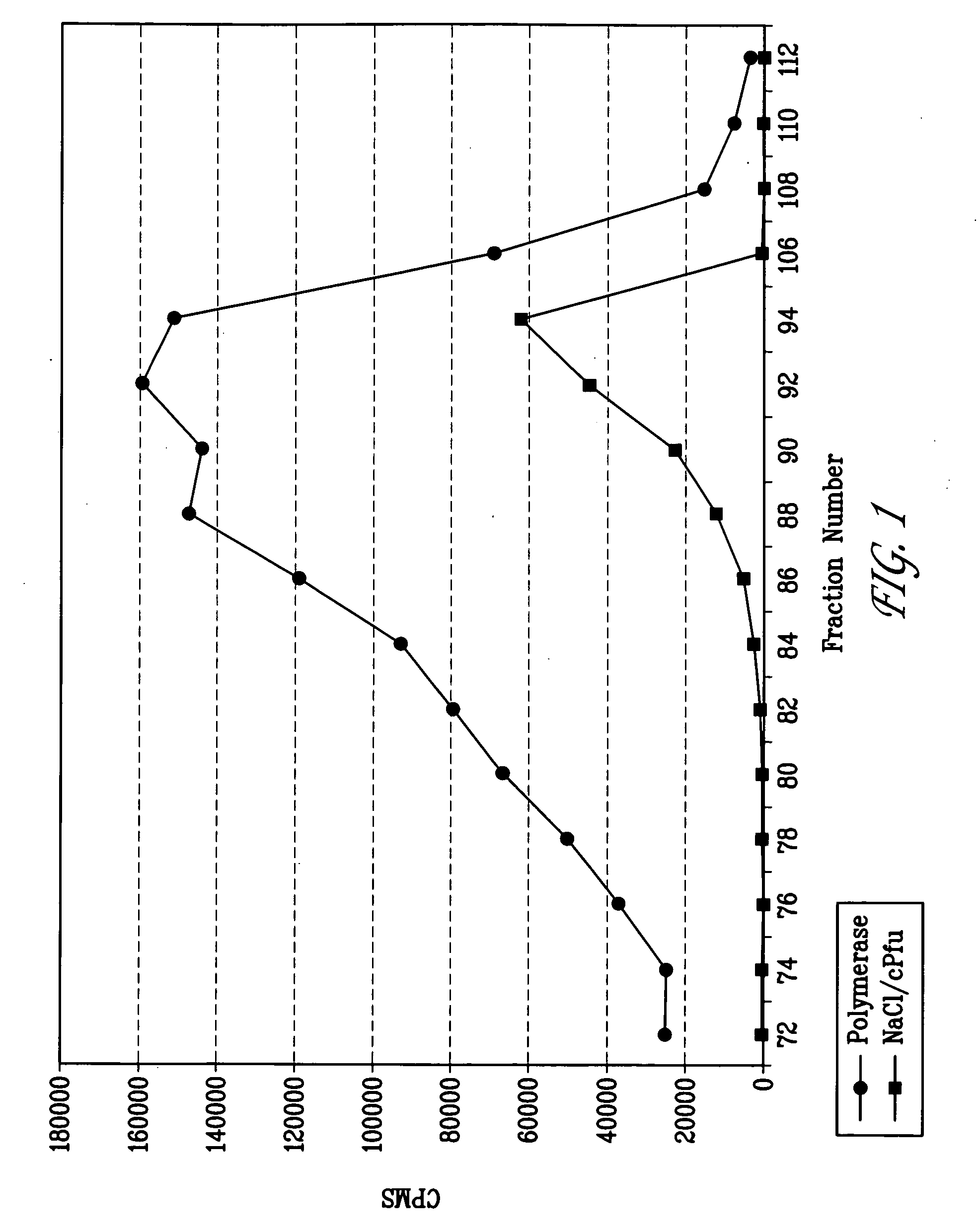
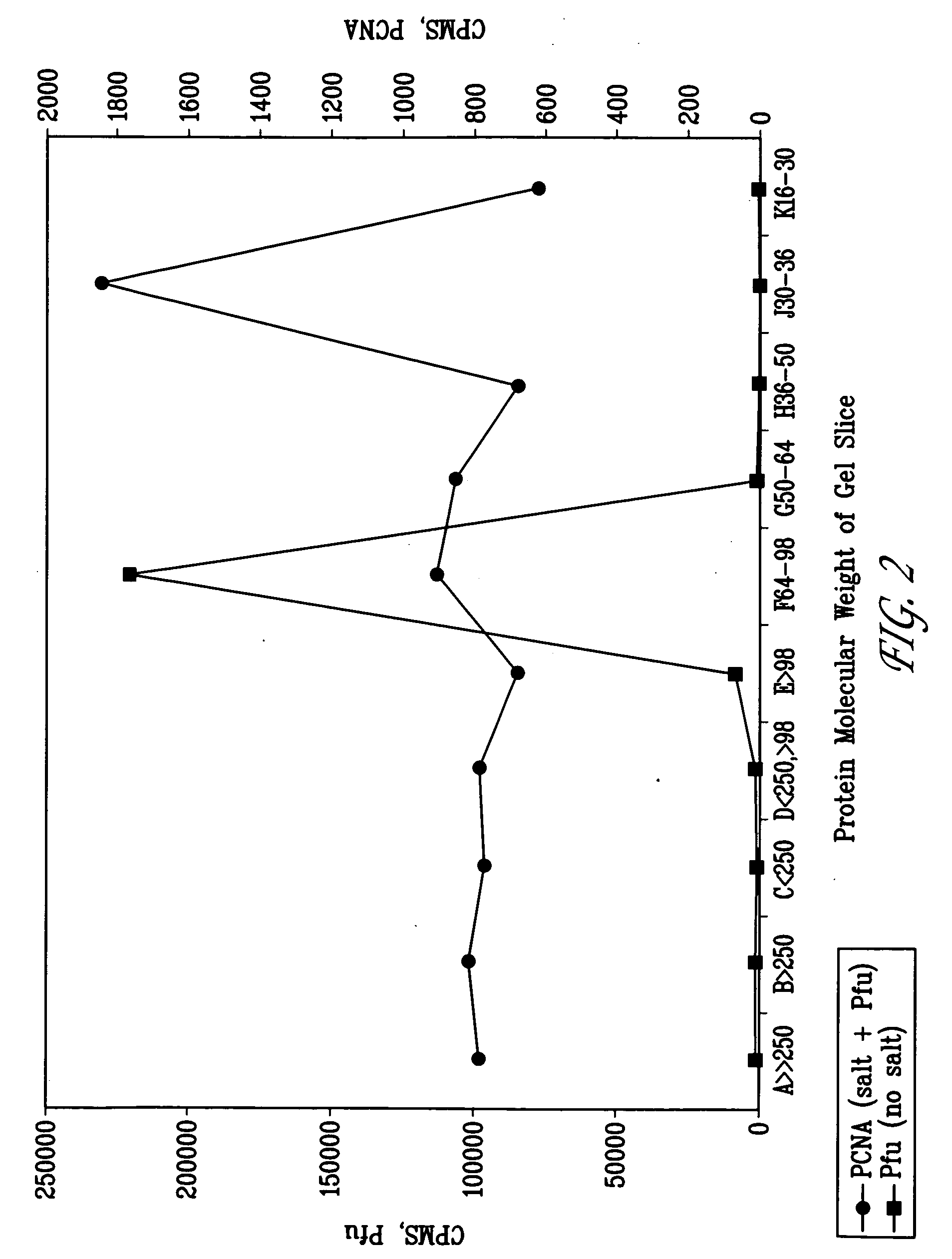
This invention provides isolated polynucleotides that encode replication accessory factors. The invention also provides novel DNA replication accessory factors, which have been isolated and purified from the hyperthermophilic archaea Pyrococcus furiosus. The invention also provides various methods of enhancing a nucleic acid polymerase reaction comprising the addition of the replication accessory factors to the reaction. This invention further provides methods of synthesizing, amplifying, and mutagenizing nucleic acids of interest employing the replication accessory factors. This invention also provides kits comprising at least one of the replication accessory factors. This invention also provides kits useful for various methods that comprise at least one replication accessory factor.
Owner:STRATAGENE INC US
Protein stabilization by domain insertion into a thermophilic protein
ActiveUS8592192B2Improve dynamic stabilityCompromise in its activityEnzyme stabilisationImmunoglobulinsProtein targetADAMTS Proteins
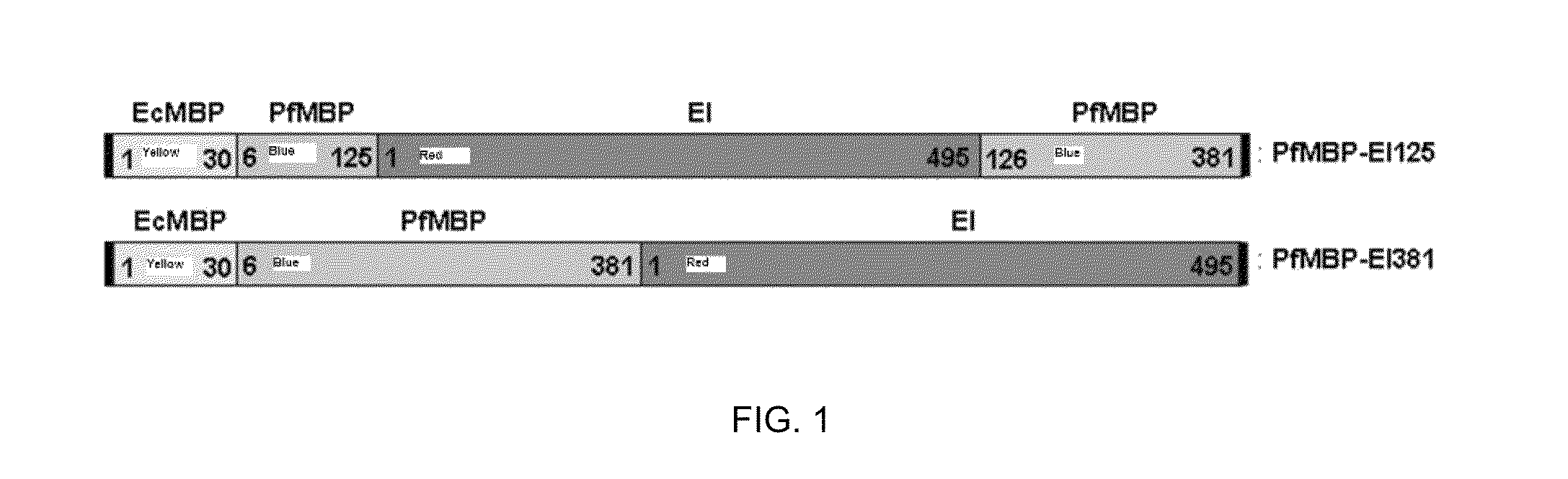
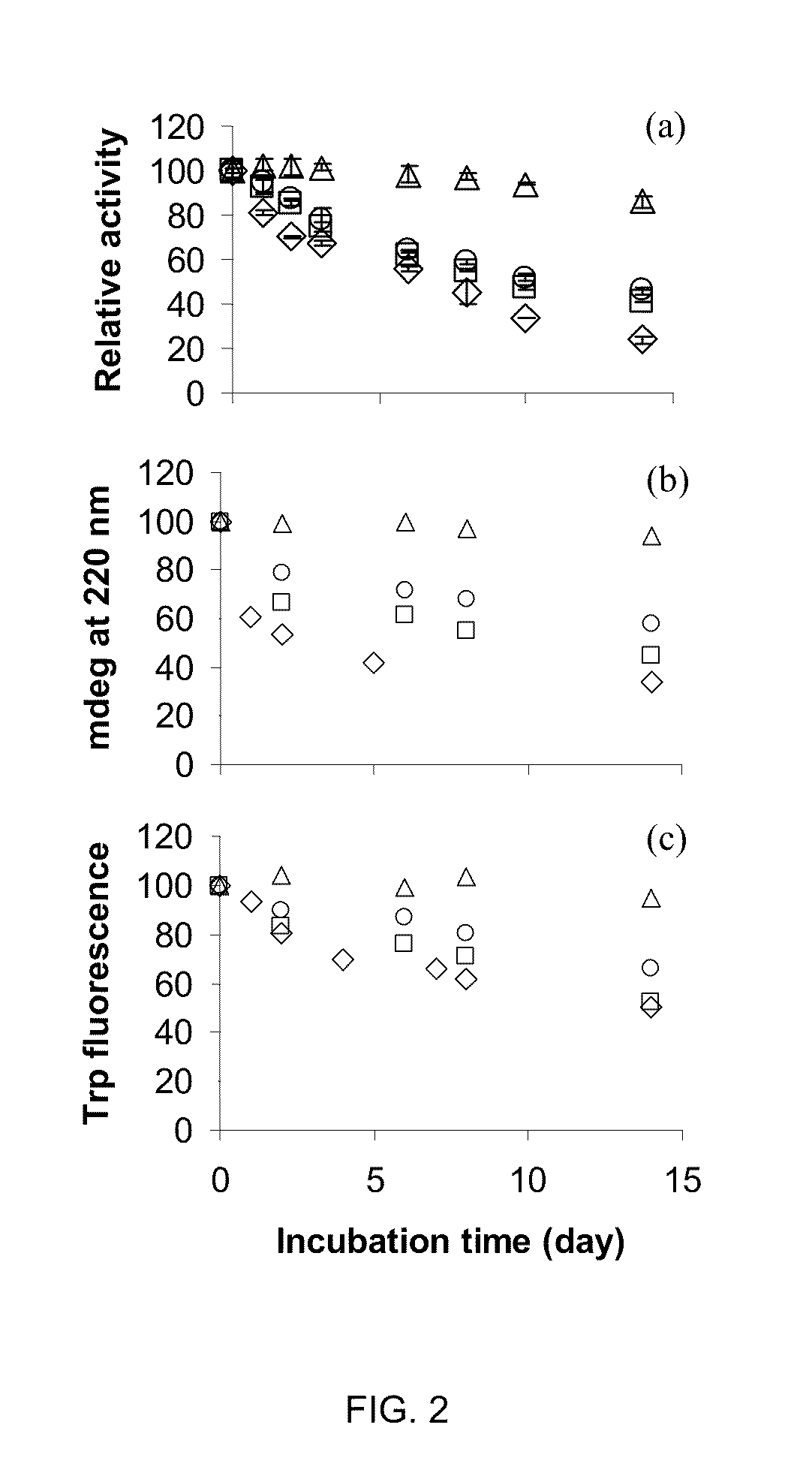
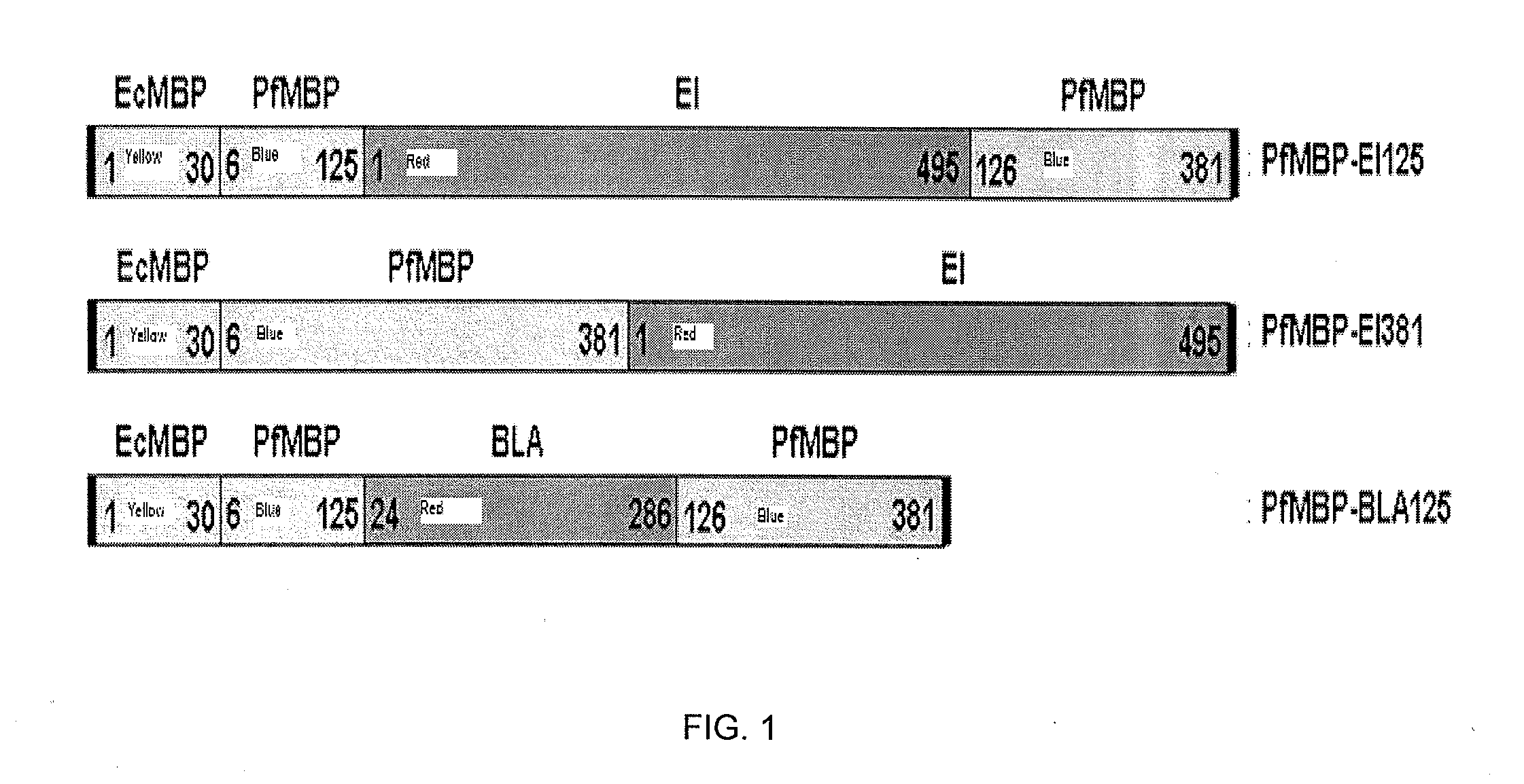
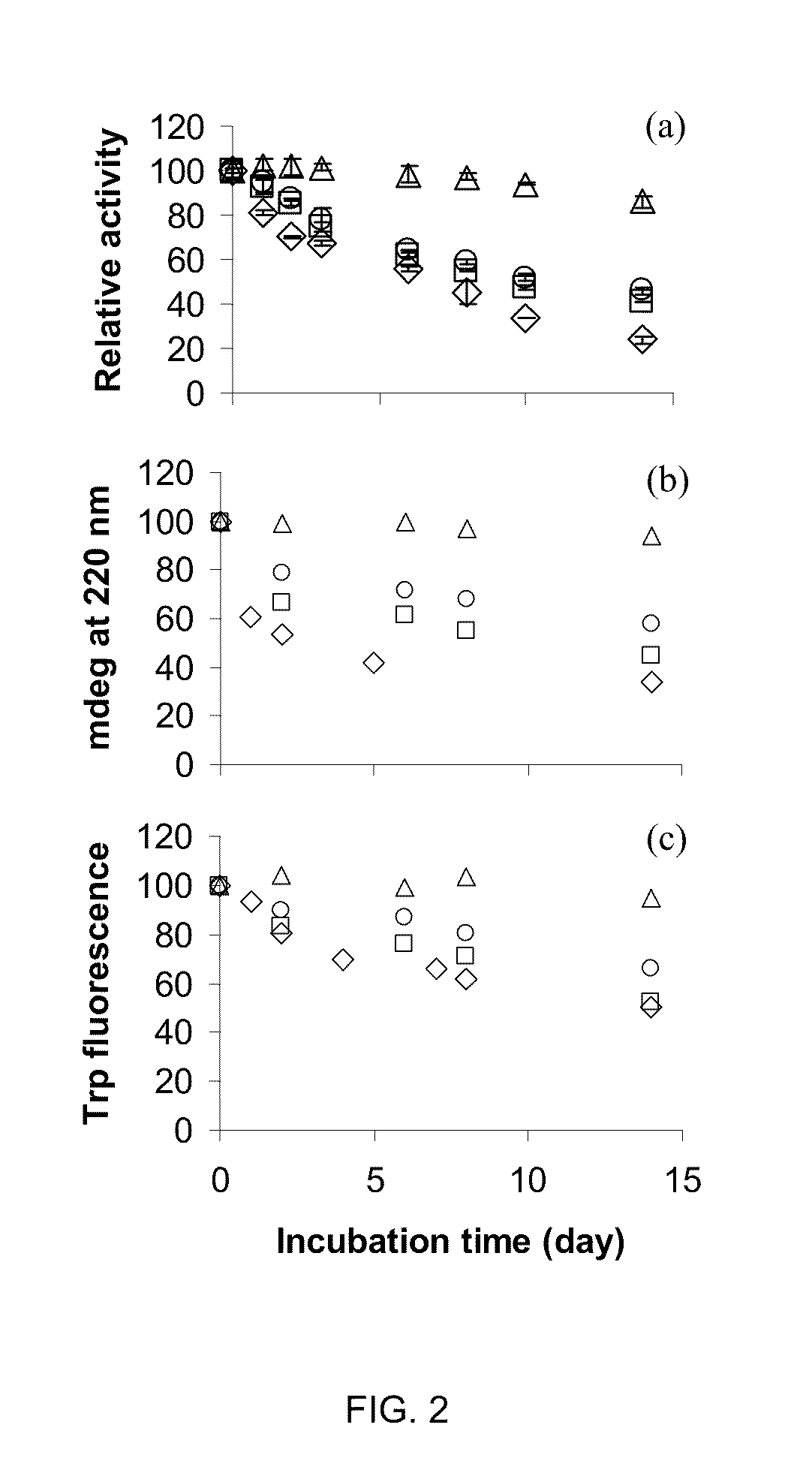
A strategy to improve protein stability by domain insertion. TEM 1 beta-lactamase (BLA) and exo-inulinase, as model target enzymes, are inserted into a hyperthermophilic maltose binding protein from Pyrococcus furiosus (PfMBP). Unlike conventional protein stabilization methods that employ mutations and recombinations, the inventive approach does not require any modification on a target protein except for its connection with a hyperthermophilic protein scaffold. For that reason, target protein substrate specificity was largely maintained, which is often modified through conventional protein stabilization methods. The insertion was achieved through gene fusion by recombinant DNA techniques.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Thermostable endo-beta-1,4-glucanase
An enzyme preparation having optimum endo- beta -1,4-glucanase activity at a temperature of at least 90 DEG C is obtainable from or endogeneous to a strain belonging to Archaea, e.g. an endo- beta -1,4-glucanase cloned from the species Pyrococcus furiosus, DSM 3638 and being encodable by the DNA sequence of SEQ ID NO:1.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Pyrococcus furiosus strains and methods of using same
InactiveUS20120135411A1MicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementOrigin of replicationPolynucleotide
Provided herein are methods for transforming a Pyrococcus furiosus with a polynucleotide. In one embodiment, the method includes contacting a P. furiosus with a polynucleotide under conditions suitable for uptake of the polynucleotide by the P. furiosus, and identifying transformants at a frequency of, for instance, at least 103 transformants per microgram DNA. Also provided are isolated Pyrococcus furiosus having the characteristics of Pyrococcus furiosus COM1, and plasmids that include an origin of replication that functions in a Pyrococcus furiosus. The plasmid is stable in a recipient P. furiosus without selection for more than 100 generations and is structurally unchanged after replication in P. furiosus for more than 100 generations.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Protein stabilization by domain insertion into a thermophilic protein
ActiveUS20100227374A1Improve dynamic stabilityImprove stabilityEnzyme stabilisationImmunoglobulinsProtein targetProtein insertion
A strategy to improve protein stability by domain insertion. TEM 1 beta-lactamase (BLA) and exo-inulinase, as model target enzymes, are inserted into a hyperthermophilic maltose binding protein from Pyrococcus furiosus (PfMBP). Unlike conventional protein stabilization methods that employ mutations and recombinations, the inventive approach does not require any modification on a target protein except for its connection with a hyperthermophilic protein scaffold. For that reason, target protein substrate specificity was largely maintained, which is often modified through conventional protein stabilization methods. The insertion was achieved through gene fusion by recombinant DNA techniques
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
pyrococcus furiosus strains and methods of using same
Provided herein are methods for transforming a Pyrococcus furiosus with a polynucleotide. In one embodiment, the method includes contacting a P. furiosus with a polynucleotide under conditions suitable for uptake of the polynucleotide by the P. furiosus, and identifying transformants at a frequency of, for instance, at least 103 transformants per microgram DNA. Also provided are isolated Pyrococcus furiosus having the characteristics of Pyrococcus furiosus COM1, and plasmids that include an origin of replication that functions in a Pyrococcus furiosus. The plasmid is stable in a recipient P. furiosus without selection for more than 100 generations and is structurally unchanged after replication in P. furiosus for more than 100 generations.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Shuttle vector based transformation system for pyrococcus furiosus
InactiveUS20110262954A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove actionMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementPyrococcusShuttle vector
The present invention relates to vectors for transforming archaea and to transformed archaea, and in particular to shuttle vector systems for transformation of members of the genus Pyrococcus.
Owner:UNIV REGENSBURG
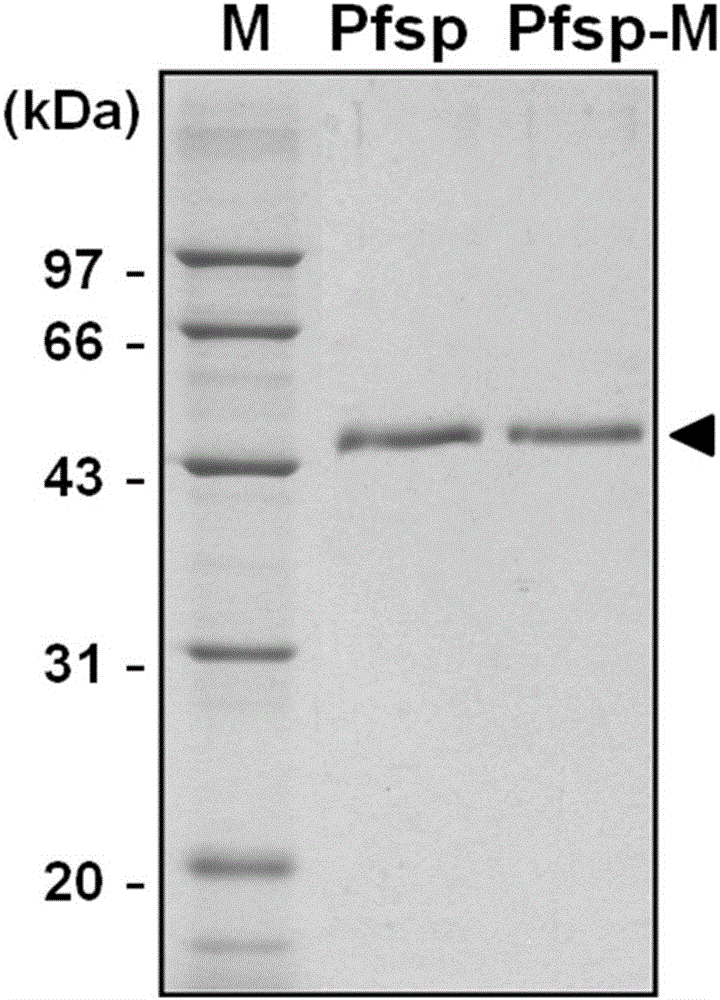
Protease with improved high-temperature activity and thermal stability as well as preparation method and applications of protease
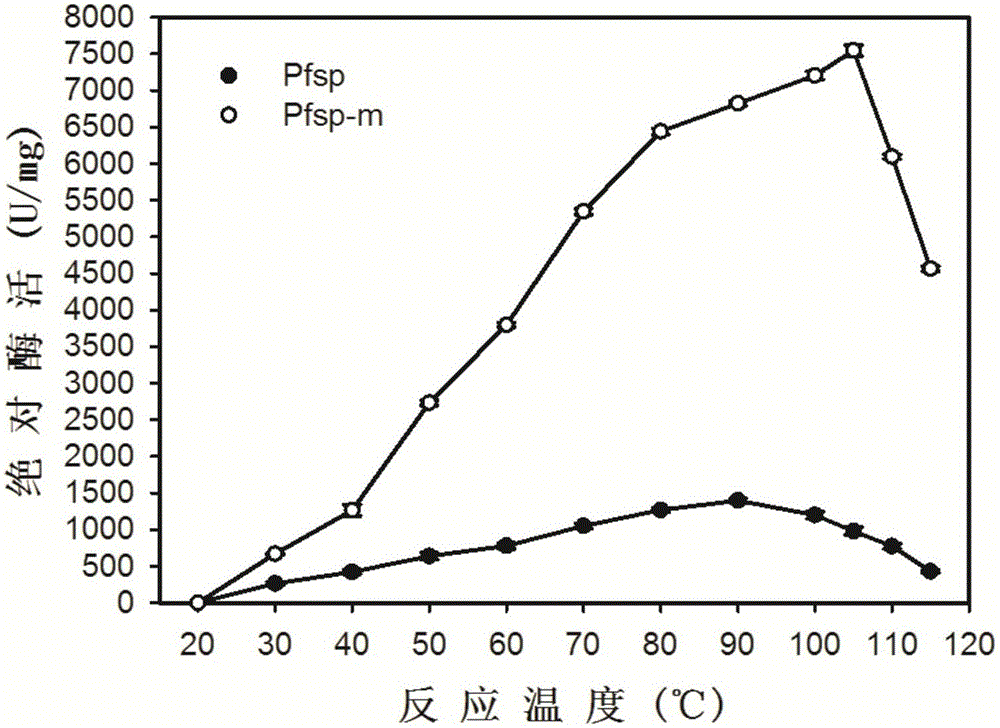
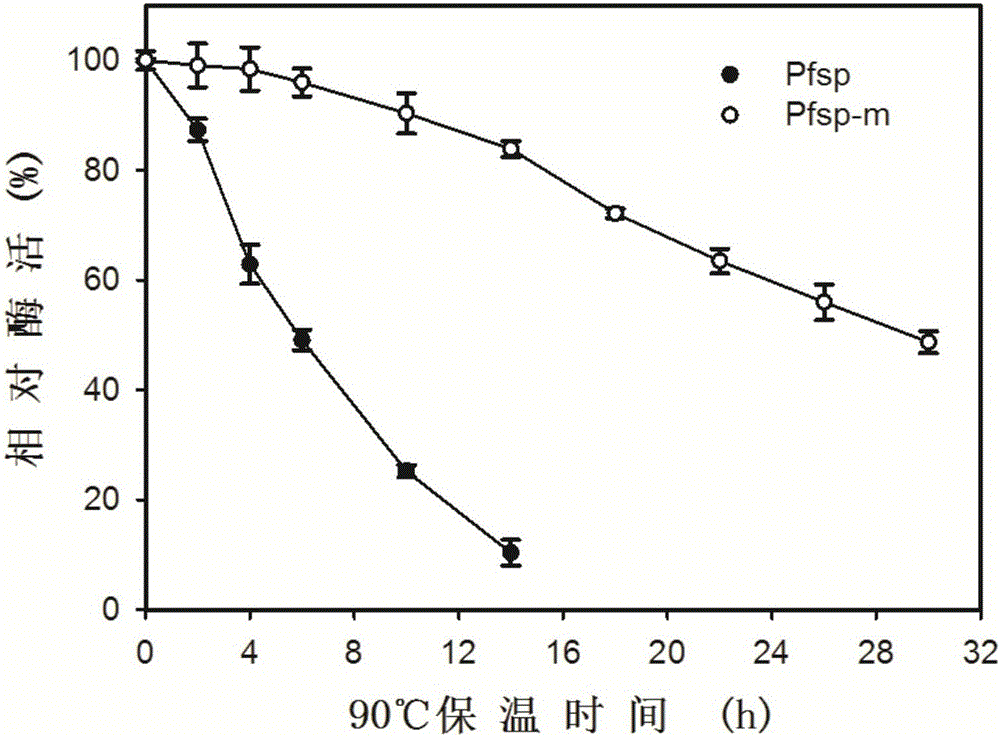
ActiveCN106085990AImprove activity stabilityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsProteinase activityHalf-life
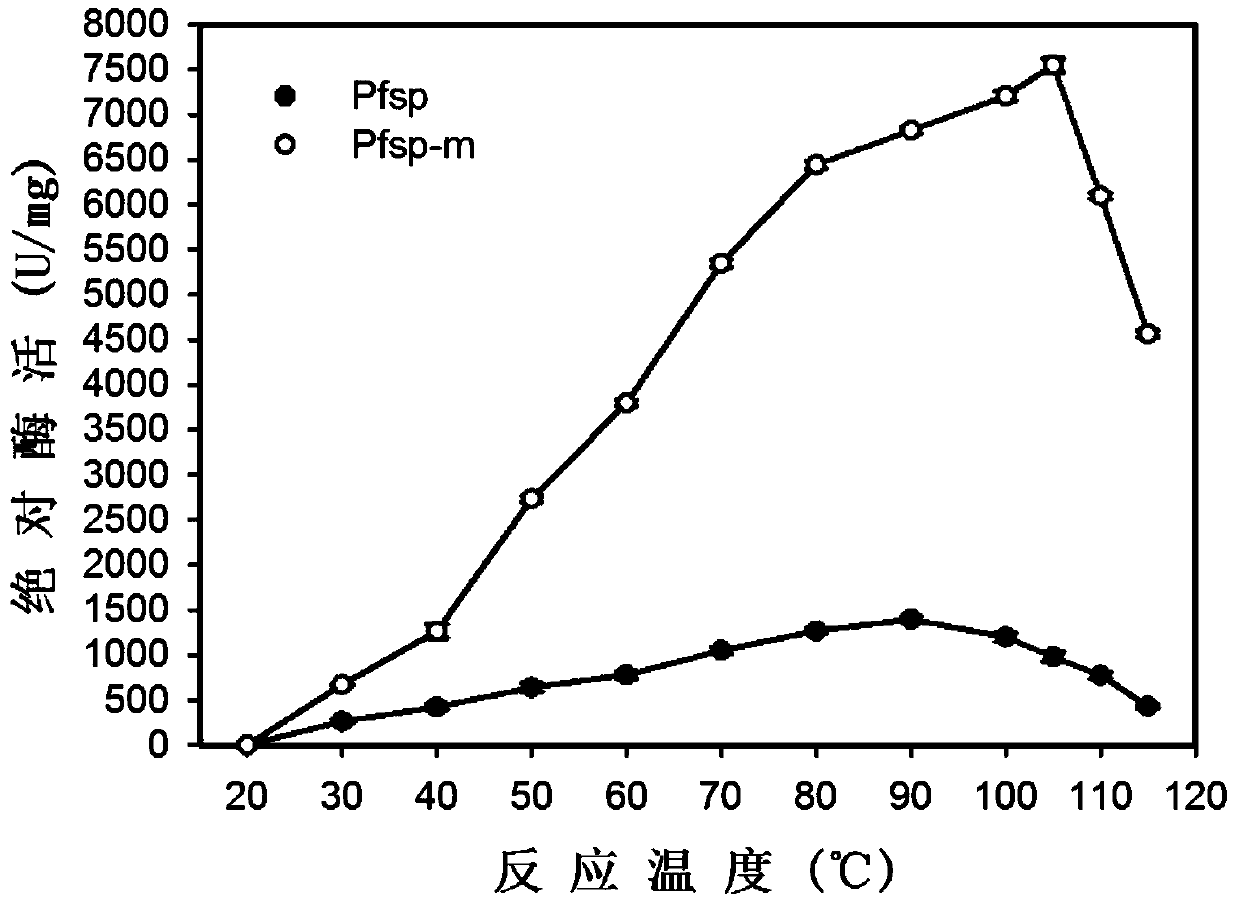
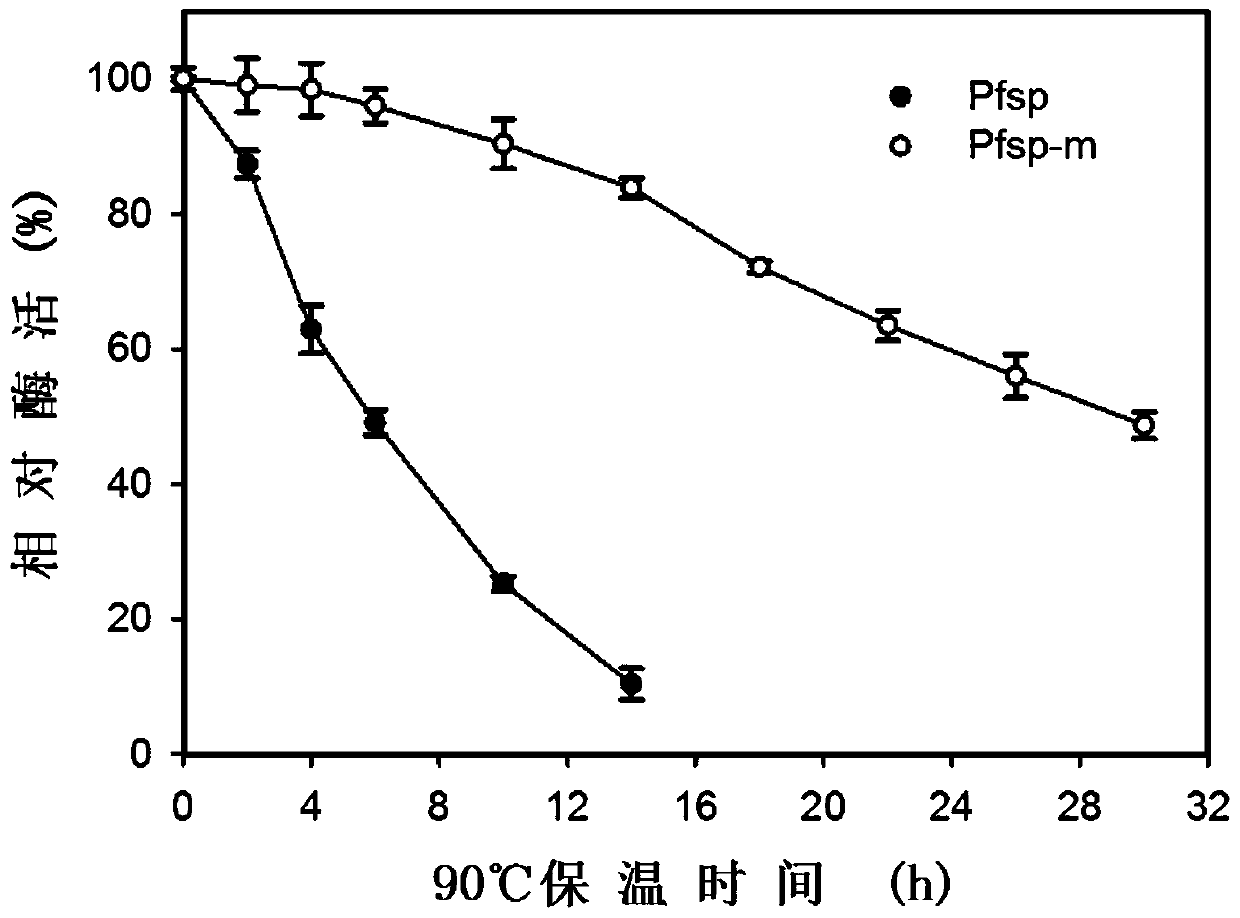
The invention discloses a protease with improved high-temperature activity and thermal stability and an encoded gene of the protease. According to the protease, protease Pfsp derived from Pyrococcus furiosus is taken as a female parent, the amino acid sequence of Pfsp is transformed by adopting the molecular biological technology, and the protease Pfsp-m with wide industrial application prospect is obtained. The optimal reaction temperature of Pfsp-m is improved to 105 DEG C from the contrast 90 DEG C; the absolute enzyme activity at 90 DEG C is improved to 6823.32 U / mg from the contrast 1396.24U / mg, which is improved by 4.89 times; the absolute keratinase enzyme activity at 90 DEG C is improved to 6140.99U / mg from the contrast 1116.99U / mg, which is improved by 5.50 times; the half-life period at 90 DEG C is prolonged to 28h from the contrast 6h, which is improved by 4.67 times.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Novel polymerase compositions and uses thereof
The subject invention provides novel compositions containing a mixture of (a) an enzyme that possesses substantial 3′-5′ exonuclease activity (b) a DNA polymerase with less 3′-5′ exonuclease activity than the enzyme with substantial 3′-5′ exonuclease activity. Preferably, the DNA polymerase for inclusion in the compositions are DNA polymerases that substantially lack 3′-5′ exonuclease activity. A preferred embodiment of the invention is a composition comprising the Taq DNA polymerase (isolated from Thermus aquaticus) and the Pfu DNA polymerase (isolated from Pyrococcus furiosus). Another aspect of the invention is to provide methods for synthesizing polynucleotides, typically DNA, using compositions comprising an enzyme that possesses substantial 3′-5′ exonuclease activity and a DNA polymerase with less 3′-5′ exonuclease activity than the enzymes possessing substantial 3′-5′ exonuclease activity, preferably a DNA polymerase that substantially lacks 3′-5′ exonuclease activity. Another aspect of the invention involves the use the subject method of polynucleotide synthesis to carry out the synthesis step in a polymerase chain reaction experiment. Yet another aspect of the invention is to provide kits for the synthesis of polynucleotides, wherein the kits comprise an enzyme that possesses substantial 3′-5′ exonuclease activity and a DNA polymerase with less 3′-5′ exonuclease activity than the enzyme possessing substantial 3′-5′ exonuclease activity.
Owner:STRATAGENE INC US
Nucleic acid detection method based on prokaryotic argonaute protein and its application
ActiveCN108796036BMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceNucleic acid detectionFood safety
The invention provides a prokaryotic Argonaute protein-based nucleic acid detection method and application thereof. Specifically, the present invention provides a detection system for detecting target nucleic acid molecules, the system comprising guide ssDNAs, gene editing enzyme Pyrococcus furiosus Argonaute (PfAgo) and fluorescent reporter nucleic acid. The nucleic acid detection method of the invention has high sensitivity, good specificity, and high throughput, and can be widely used in many fields such as molecular medical diagnosis, food safety detection, and environmental monitoring.
Owner:JIAOHONG BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
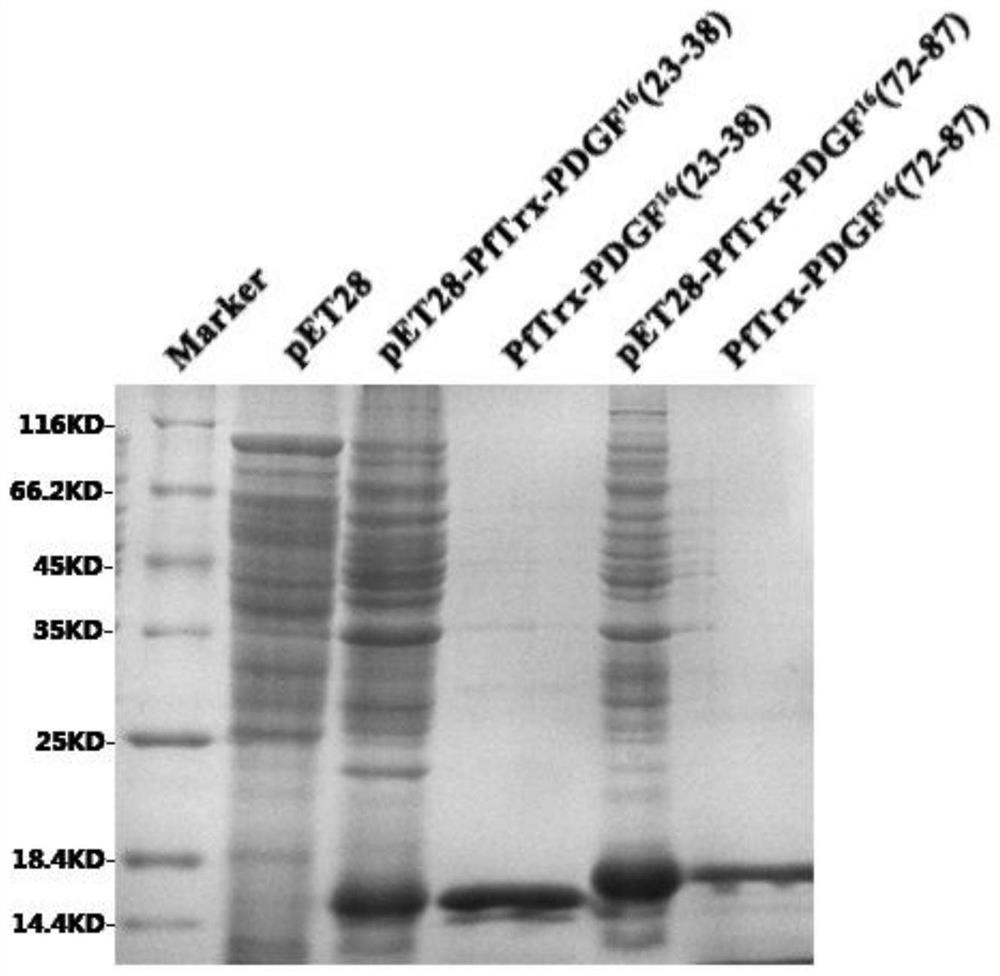
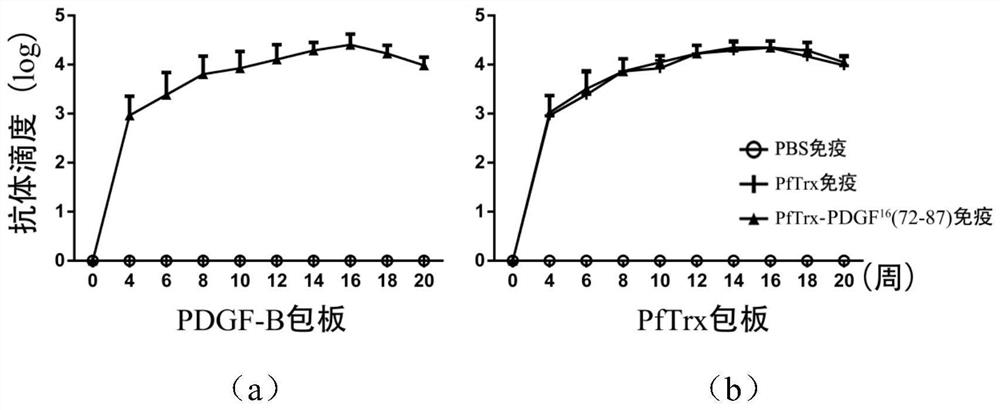
A platelet-derived growth factor recombinant vaccine for treating pulmonary fibrosis and its application
ActiveCN111303271BReduce pulmonary fibrosisLower levelVertebrate antigen ingredientsRespiratory disorderAntigen epitopeAntigen
The invention discloses a platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) recombinant vaccine for treating pulmonary fibrosis, wherein the PDGF epitope (aa72‑87, QVRKIEIVRKKPIFKK) is inserted into the prokaryotic prokaryotic of Pyrococcus furiosus thioredoxin (PfTrx) In the plasmid pET28‑PfTrx, express and purify the recombinant vaccine PfTrx‑PDGF 16 (72‑87), the recombinant vaccine can successfully stimulate the body to produce high-titer anti-PDGF neutralizing antibodies, and significantly reduce the lung fibrosis in mice induced by bleomycin (BLM). PfTrx‑PDGF 16 (72‑87) Recombinant vaccine immunization can significantly reduce the inflammatory response of the lung tissue in the acute stage after tracheal infusion of bleomycin, inhibit the production of collagen and the increase and deposition of cell matrix in the mouse lung; at the same time, it can also reduce the TGF in the lung tissue of the mouse ‑β1, CTGF, α‑SMA, Col1a2, Col3a1 expression levels, these characteristics are extremely beneficial to slow down the process of pulmonary fibrosis.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF MEDICAL COLLEGE OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
A novel coronavirus S protein dual-region subunit nanovaccine based on pyrococcal ferritin
ActiveCN111217919BMultimerizationOvercoming the disadvantage of insufficient immunogenicitySsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsEucaryotic cellPyrococcus
The invention discloses a novel coronavirus S protein double-region subunit nano vaccine based on pyrococcus furiosus ferritin. The virus receptor binding domain (RBD) and fusion peptide (FP) are usedtogether as a double antigen, and are connected with pyrococcus furiosus ferritin (PF_Ferritin) to from a fusion protein RBD-FP-PF_Ferritin to realize antigen multimerization; and then an eukaryoticcell expression system is used for expressing, and a 24-mer nano antigen can be formed through self-assembly of PF_Ferritin. The scheme can overcome the shortcoming of insufficient immunogenicity of RBD monomers, the obtained vaccine can significantly increase the level of a neutralizing antibody against the virus of a host, and the produced antibody has the ability to strongly block the virus from invading target cells. In addition, the vaccine of the invention is simple in preparation method, is easy to purify, and is high in safety, and the vaccine can be relatively quickly applied to clinical trials.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A protease with improved high-temperature activity and thermal stability, its preparation method and application
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Purified thermostable Pyrococcus furiosus DNA polymerase I
Purified thermostable Pyrococcus furiosus DNA polymerase that migrates on a non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel faster than phosphorylase B and Taq polymerase and more slowly than bovine serum albumin and has an estimated molecular weight of 90,000-93,000 daltons when compared with a Taq polymerase standard assigned a molecular weight of 94,000 daltons.
Owner:STRATAGENE INC US
Thermostable endo-beta-1,4-glucanase
An enzyme preparation having optimum endo- beta -1,4-glucanase activity at a temperature of at least 90 DEG C is obtainable from or endogeneous to a strain belonging to Archaea, e.g. an endo- beta -1,4-glucanase cloned from the species Pyrococcus furiosus, DSM 3638 and being encodable by the DNA sequence of SEQ ID NO:1.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
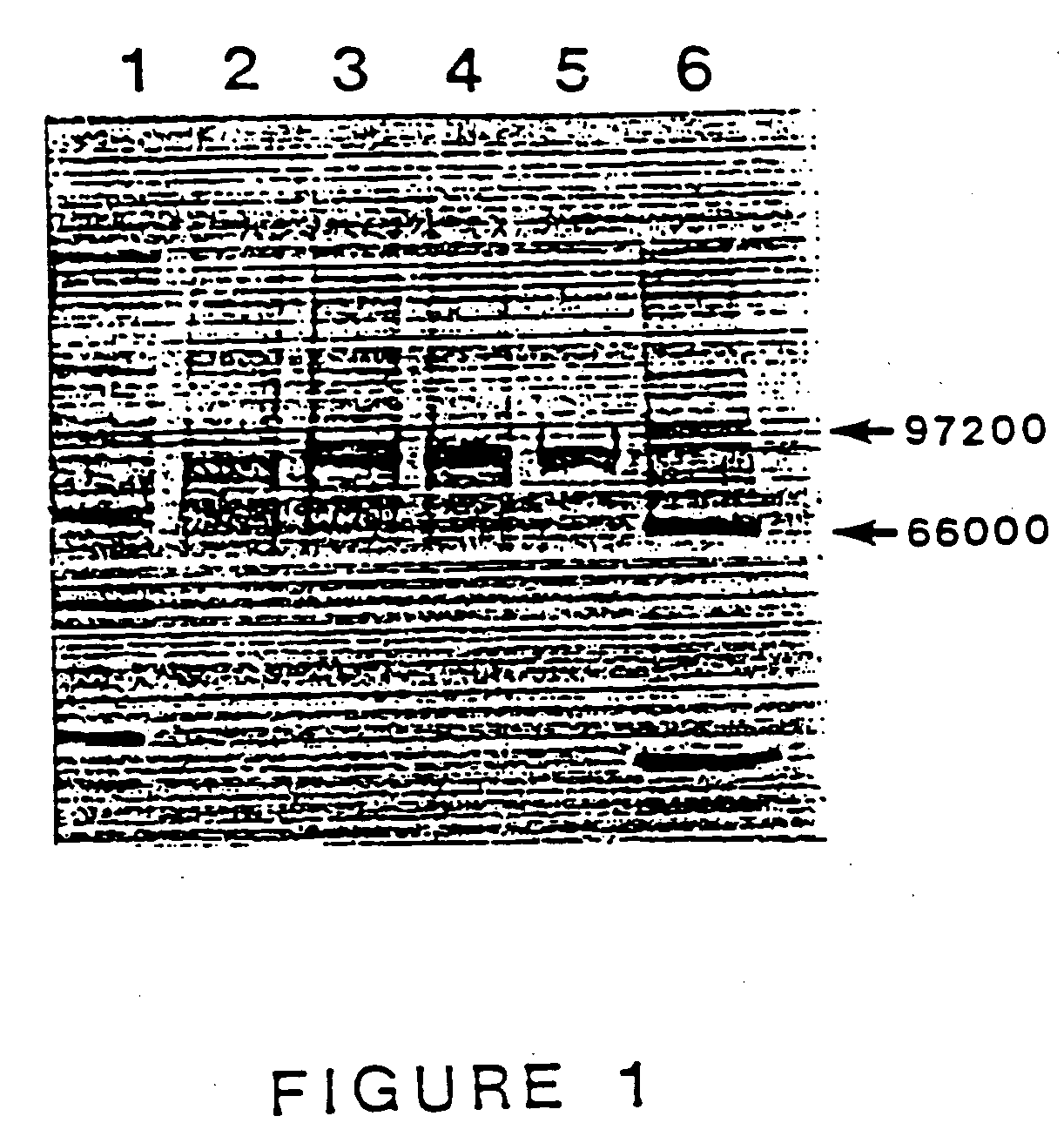
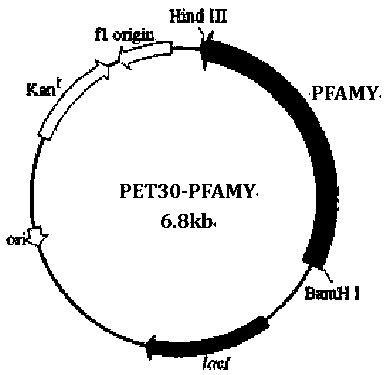
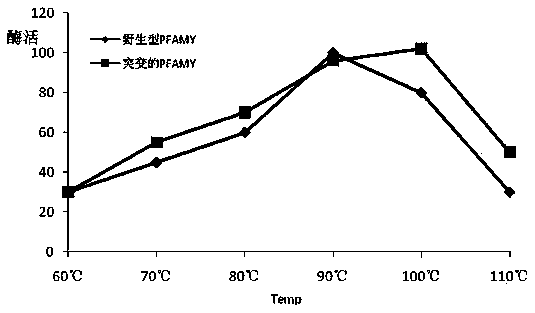
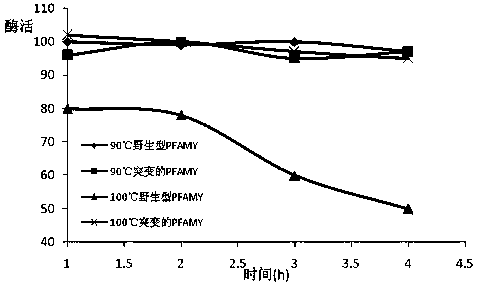
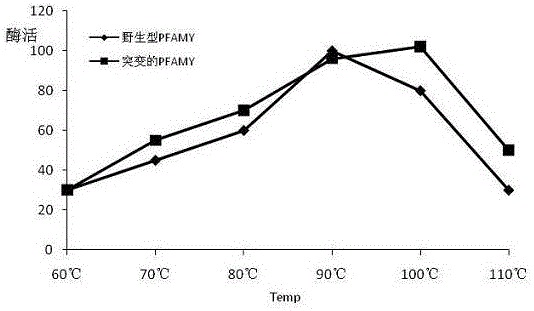
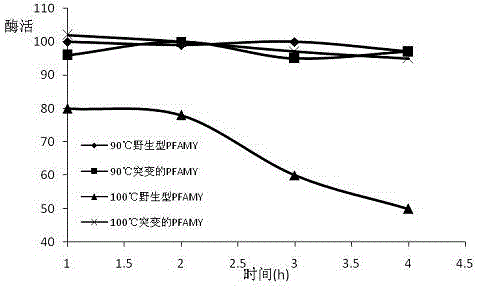
A mutant α-amylase and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN106434601BIncrease enzyme activitySimplify industrial post-processingNucleic acid vectorFermentationEscherichia coliWild type
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering, and in particular relates to mutational alpha-amylase as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The mutational alpha-amylase provided by the invention has a high-temperature-resistant amino acid sequence, amino acids at the following one or more sites of the amino acid sequence are replaced with other amino acids on the basis of an amino acid sequence of wild type pyrococcus furiosus alpha-amylase (PFAMY), the replaced amino acid sites are W65, C204 and N366, the expression quantity of mutated PFAMY genes reaches 10000u / l in escherichia coli, and the enzyme activity of the mutational alpha-amylase is greatly improved compared with the wild type PFAMY; the heat stability of the mutated PFAMY is improved, and the optimum temperature is changed to 100 DEG C from the original 90 DEG C, so that the mutational alpha-amylase is higher in heat stability and more stable in enzyme activity; therefore, the mutational alpha-amylase has better industrial application prospect.
Owner:河北华石生物科技有限公司
Pfu replication accessory factors and methods of use
Owner:STRATAGENE INC US
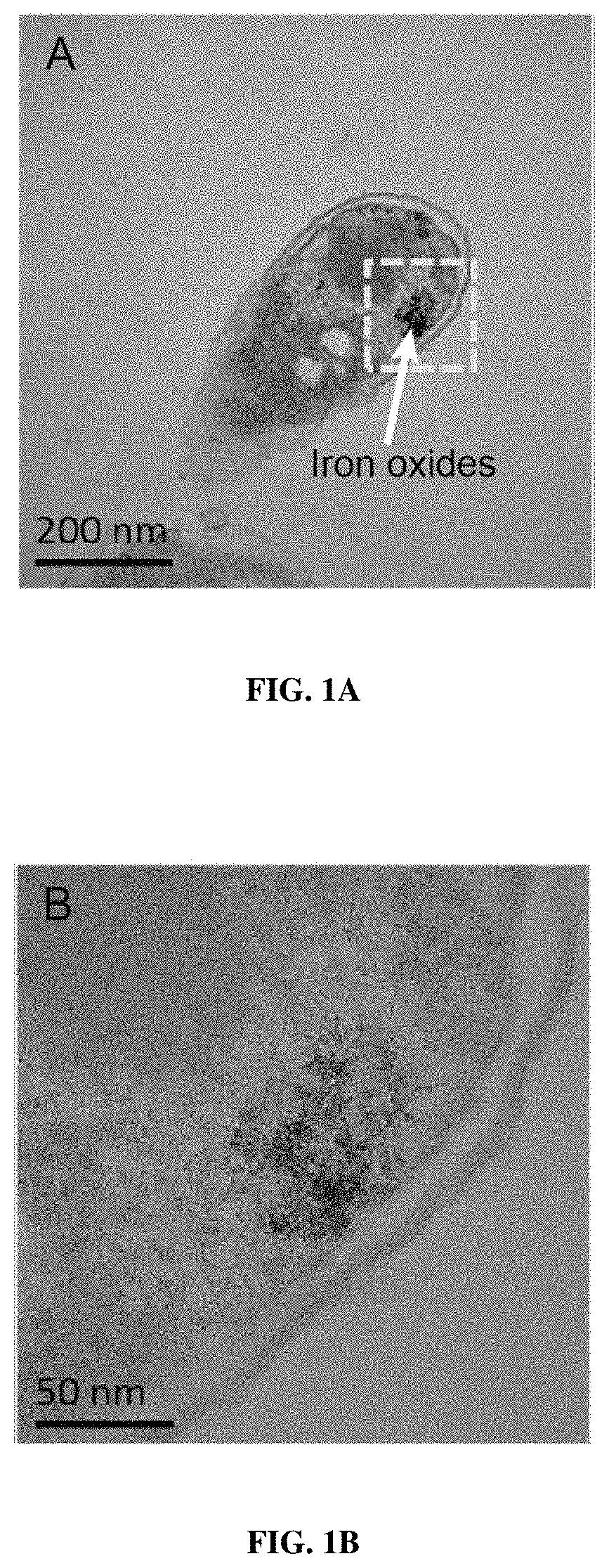
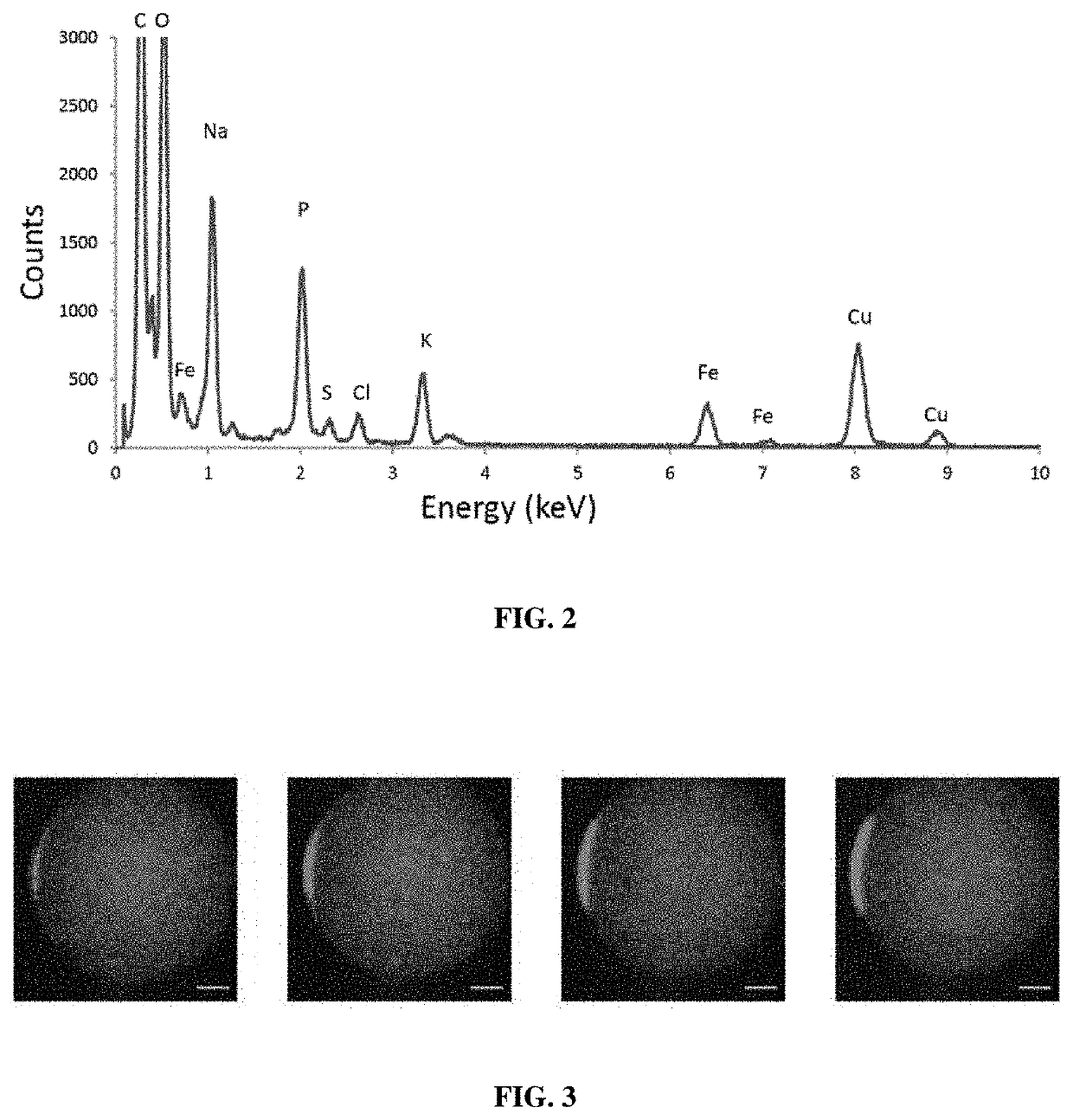
Magnetic bacteria, non-therapeutic and therapeutic uses thereof
PendingUS20220257671A1Reduce chanceAvoid delayBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsHeterologousAntigen
Recombinant, alive and metabolically active bacteria including a heterologous prokaryotic biomineralized ferritin. In particular, the inventors have shown that naturally non-magnetic Escherichia coli may be engineered to become magnetic by the expression and the biomineralization of the ferritin of Pyrococcus furiosus. Moreover, the inventors have shown that a fixed number of magnetic E. coli strains keep their magnetic properties through cell division by asymmetrical division. The inventors have also shown that magnetic bacteria according to the invention may be of use in both non-therapeutic and therapeutic uses, such as, e.g., the biosensing of target substance, the depollution of complex environments, the display of antibodies, nanobodies and antigens, the delivery of therapeutic substance to target cells, the targeting and infection of target cells.
Owner:PARIS SCI & LETTRES +3
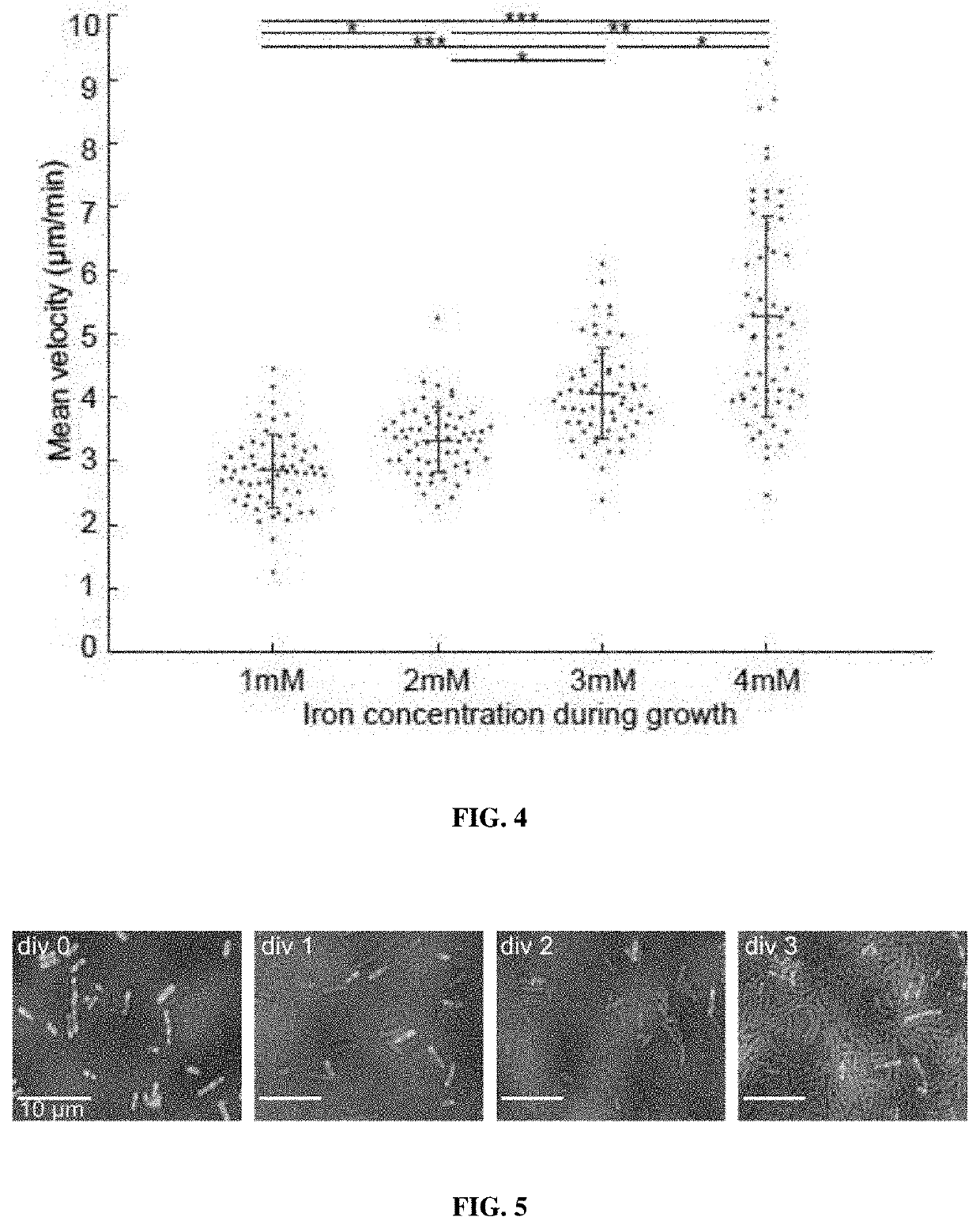
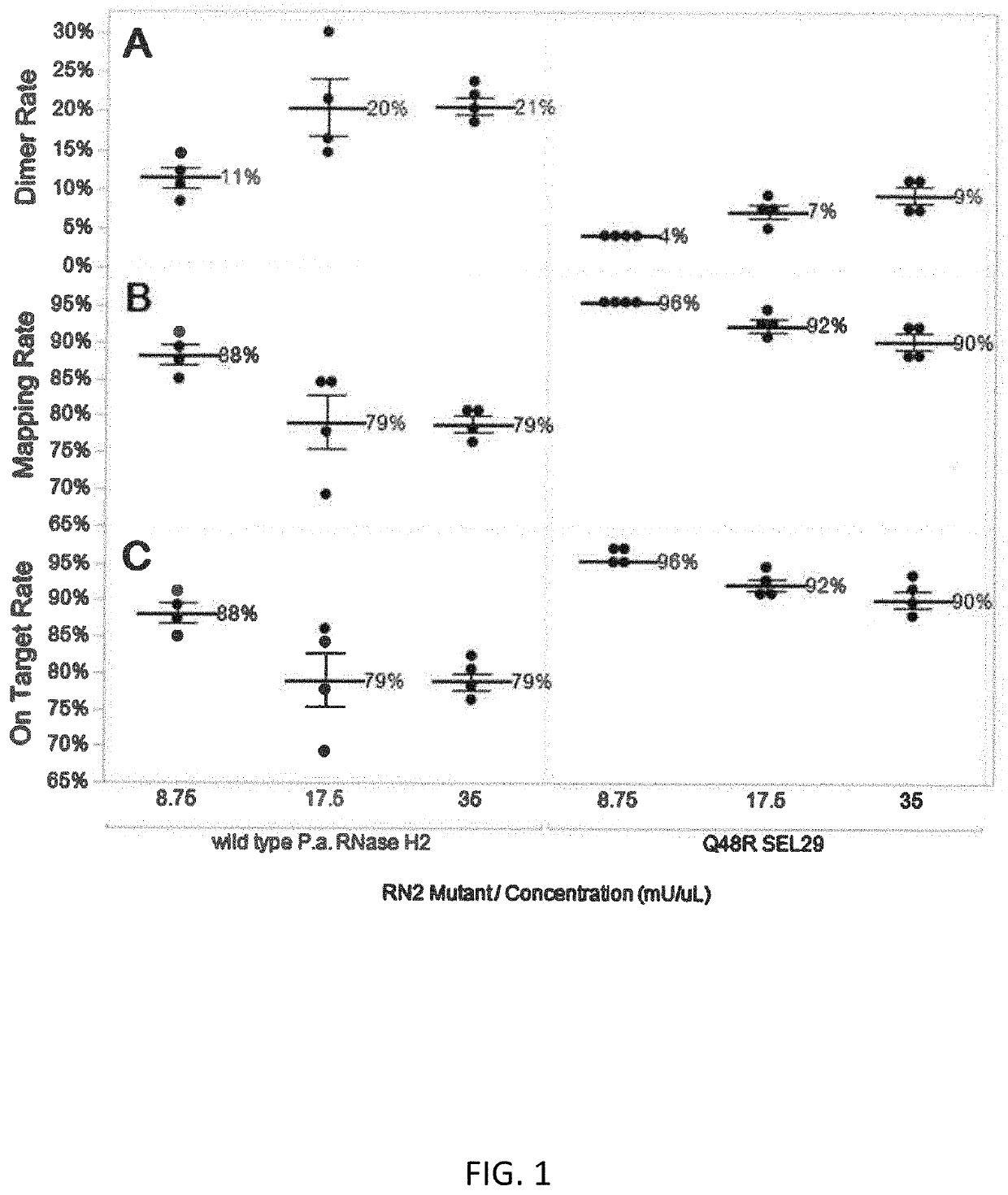
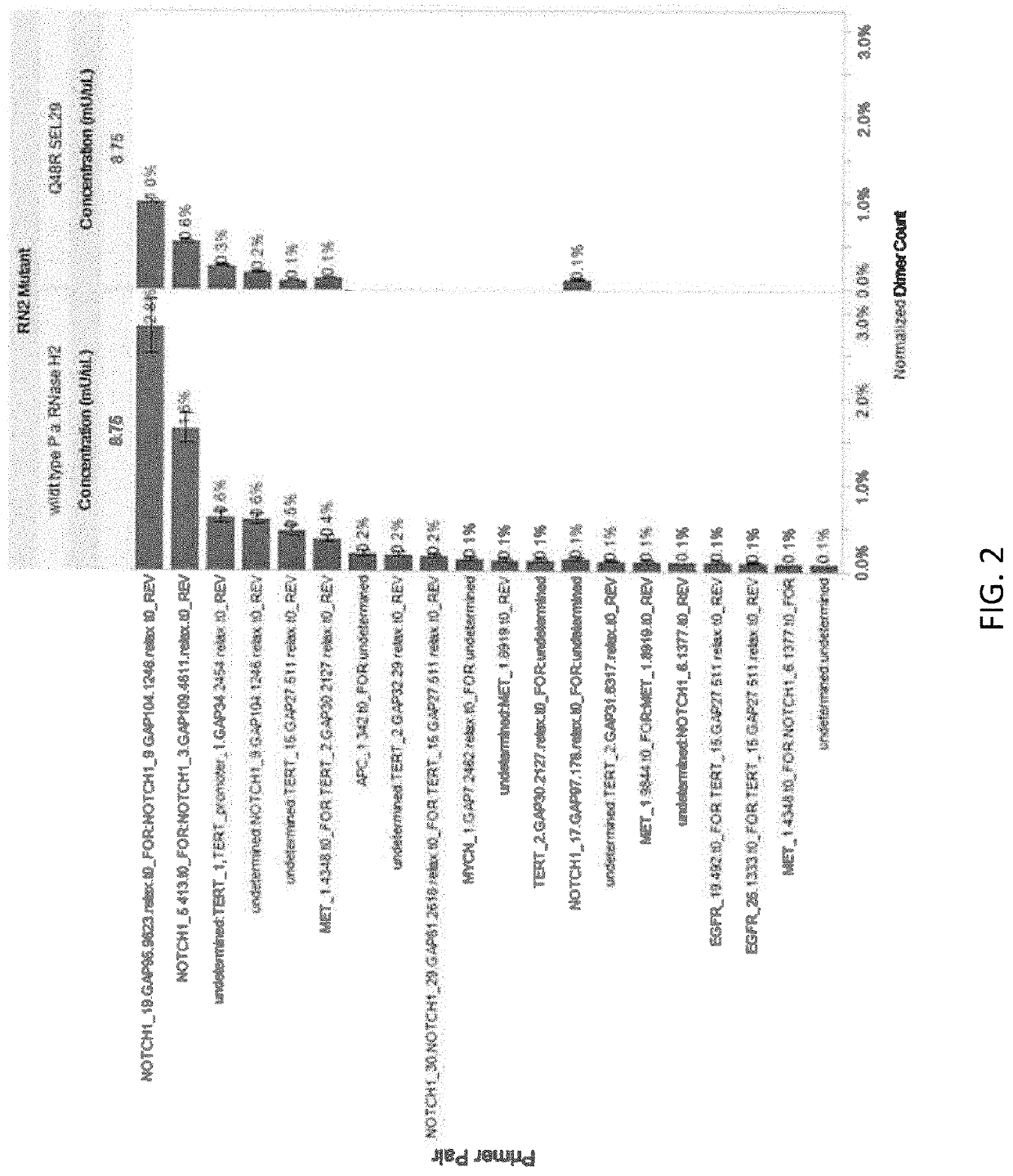
Rnase h2 mutants that reduce primer dimers and off-target amplification in rhpcr-based amplicon sequencing with high-fidelity DNA polymerases
PendingUS20220348997A1Improved mapping rate and on-target rateEasy mappingHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDimerMutant
The present invention pertains to hybrid RNase H2 proteins that include fragments of amino acid sequences from Pyrococcus abyssi (P.a.), Thermococcus kodakarensis (T.kod), and Pyrococcus furiosus organisms, as well as methods of using the same to improve mismatch discrimination and activity in a high-fidelity DNA polymerase buffer.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
Probiotic honey grapefruit tea and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108887437AGuaranteed accumulationDoes not affect flavorTea substituesMethanosarcina barkeriStreptococcus fecalis
The invention provides a probiotic honey grapefruit tea and a preparation method thereof. In the technical scheme, lactobacillus casei and streptococcus faecium are taken as probiotic components and are blended with a conventional beverage, so that an intestinal tract probiotic effect is achieved. On such basis, the invention researches an approach for inhibiting growth of two probiotics, in orderto prevent the lactobacillus casei and streptococcus faecium from propagating in the beverage and influencing the flavor of the beverage. An experiment proves that an antagonism effect on propagationefficiency can be achieved when two probiotics are co-cultured with pyrococcus furiosus and methanosarcina barkeri; on such basis, an intergrowth environment and a nutritional condition of four microorganisms are researched; a treating method according to the invention can guarantee the biomass accumulation in early stage and can achieve the balance of flora scale of four microorganisms after mixed cultivation; the blending of the beverage and the mixed bacteria acquired according to the method is capable of keeping bacteria propagation basically stagnated under storage and transportation environments, so that the flavor of the beverage is prevented from being influenced.
Owner:江西韩金实业有限公司
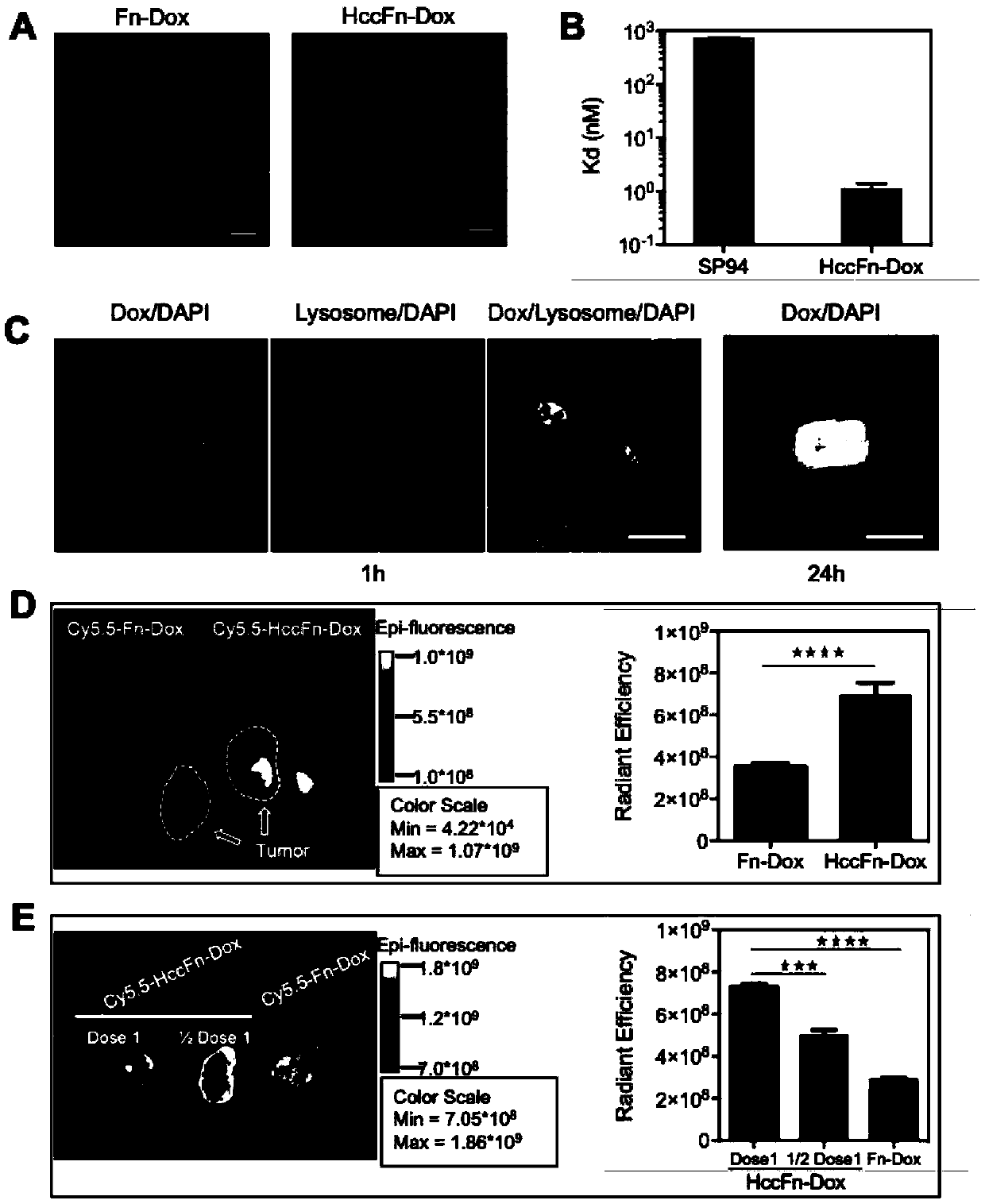
A nano-drug carrier loaded with anti-tumor drugs, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN109512799BBacteria peptidesMacromolecular non-active ingredientsPharmaceutical SubstancesAnti neoplastic
The invention relates to a nano drug carrier loaded with antitumor drugs, a preparation method and application thereof. The nano-drug carrier is a physiological polymer of Pyrococcus ferritin and its derivatives (including fusion proteins modified based on it, and ferritin modified based on the amino acid sequence of its protein shell lumen), and the anti-tumor Drugs include, but are not limited to, small molecule drugs, oligonucleotides, and functional peptides.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Heterologous expression purification method for recombination high temperature nickel and iron hydrogenase and application thereof
ActiveCN109666689AIncrease productionSimple stepsOxidoreductasesFermentationHeterologousShuttle vector
The invention discloses a heterologous expression purification method for a recombination high temperature nickel and iron hydrogenase and application thereof, and belongs to the field of expression purification and application of the nickel and iron hydrogenase. The disclosed high temperature nickel and iron hydrogenase is from pyrococcus furiosus, thermococcus kodakarensis at the other end of ashuttle vector is used for performing recombination over-expression, by means of combination and a histidine label and the specificity of a nickel column, the purifying process of the recombination hydrogenase is simplified, and the yield of the hydrogenase is increased; by coupling with diaphorase DI containing FMN, the novel electron transmission way is formed, and NADH regeneration is achievedby means of hydrogen. The expression purification method for the recombination high temperature nickel and iron hydrogenase has the advantages of being simplified in steps, high in enzyme yield, low in production cost and the like; in addition, according to the built coenzyme regeneration system, hydrogen (gas) is adopted as a substrate, the influence on a reaction system is small, the pH value ofthe solution cannot be changed, and products are easily separated.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for detecting nucleic acid based on prokaryotic argonaute protein and application thereof
PendingUS20210164024A1High sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansNucleic acid detectionGenetics
Owner:JIAOHONG BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Mutational alpha-amylase as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106434601AIncrease enzyme activitySimplify industrial post-processingNucleic acid vectorFermentationEscherichia coliWild type
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering, and in particular relates to mutational alpha-amylase as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The mutational alpha-amylase provided by the invention has a high-temperature-resistant amino acid sequence, amino acids at the following one or more sites of the amino acid sequence are replaced with other amino acids on the basis of an amino acid sequence of wild type pyrococcus furiosus alpha-amylase (PFAMY), the replaced amino acid sites are W65, C204 and N366, the expression quantity of mutated PFAMY genes reaches 10000u / l in escherichia coli, and the enzyme activity of the mutational alpha-amylase is greatly improved compared with the wild type PFAMY; the heat stability of the mutated PFAMY is improved, and the optimum temperature is changed to 100 DEG C from the original 90 DEG C, so that the mutational alpha-amylase is higher in heat stability and more stable in enzyme activity; therefore, the mutational alpha-amylase has better industrial application prospect.
Owner:河北华石生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com