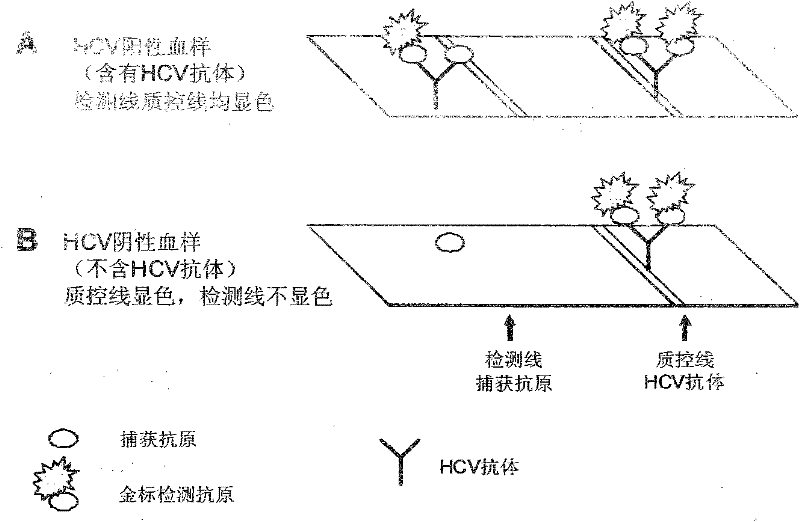
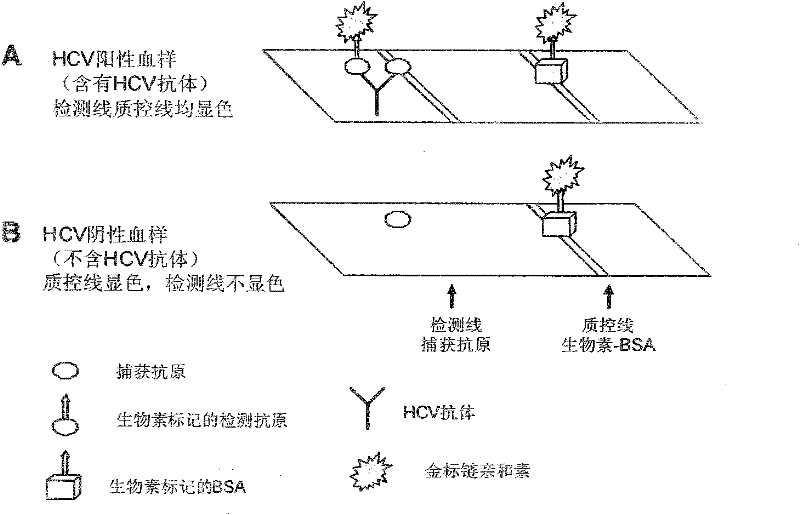
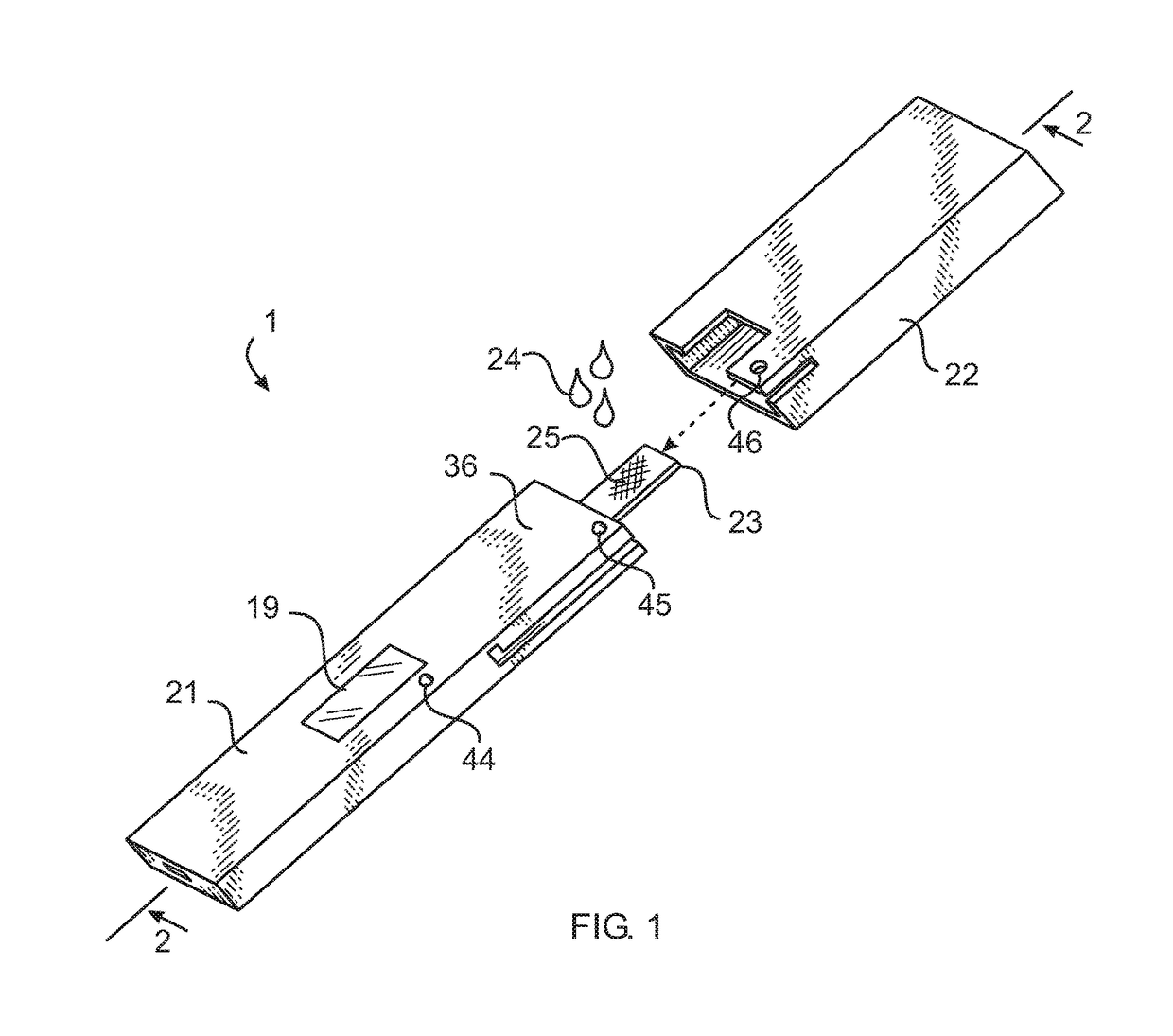
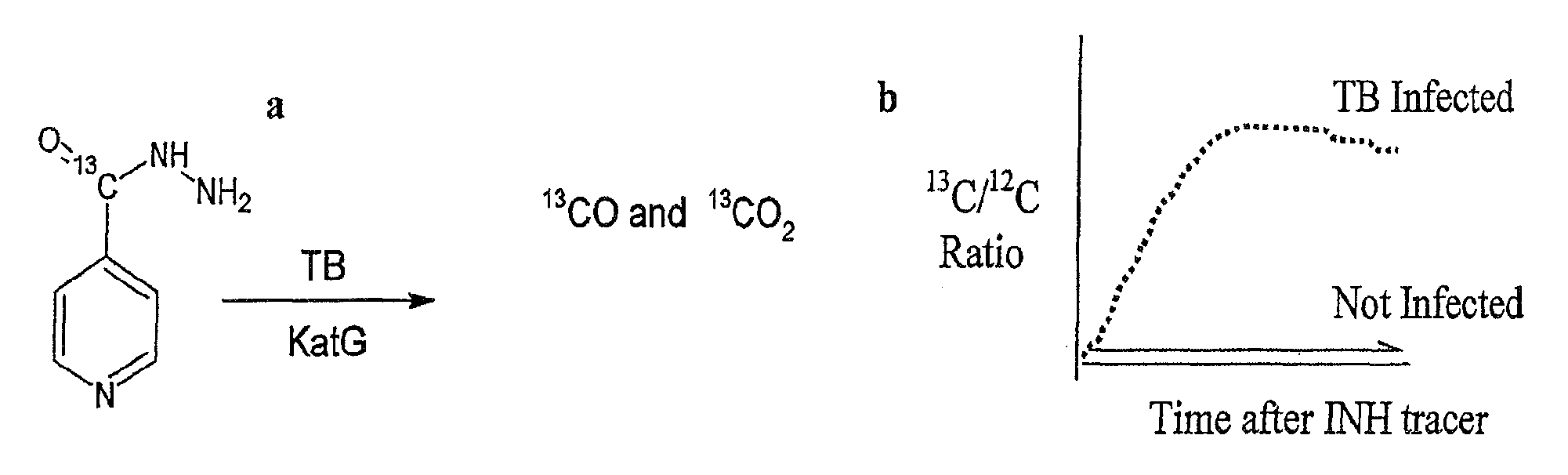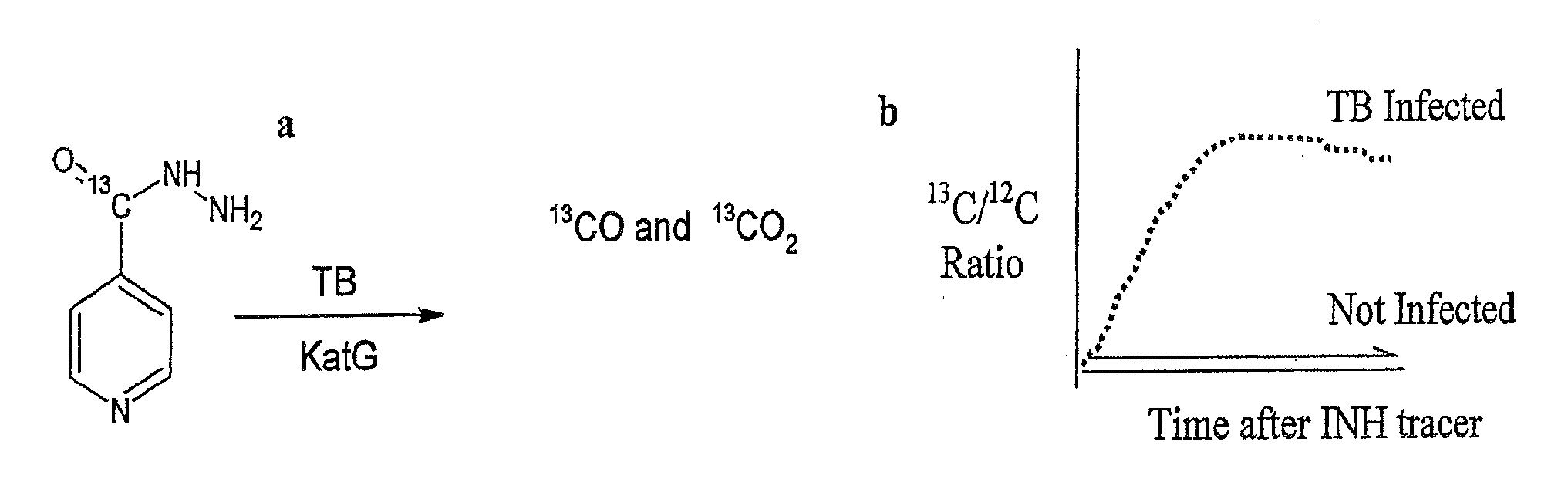Patents
Literature
50 results about "Rapid diagnostic test" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A rapid diagnostic test (RDT) is a medical diagnostic test that is quick and easy to perform. RDTs are suitable for preliminary or emergency medical screening and for use in medical facilities with limited resources. They also allow point-of-care testing in primary care for things that formerly only a laboratory test could measure. They provide same-day results within two hours, typically in approximately 20 minutes.
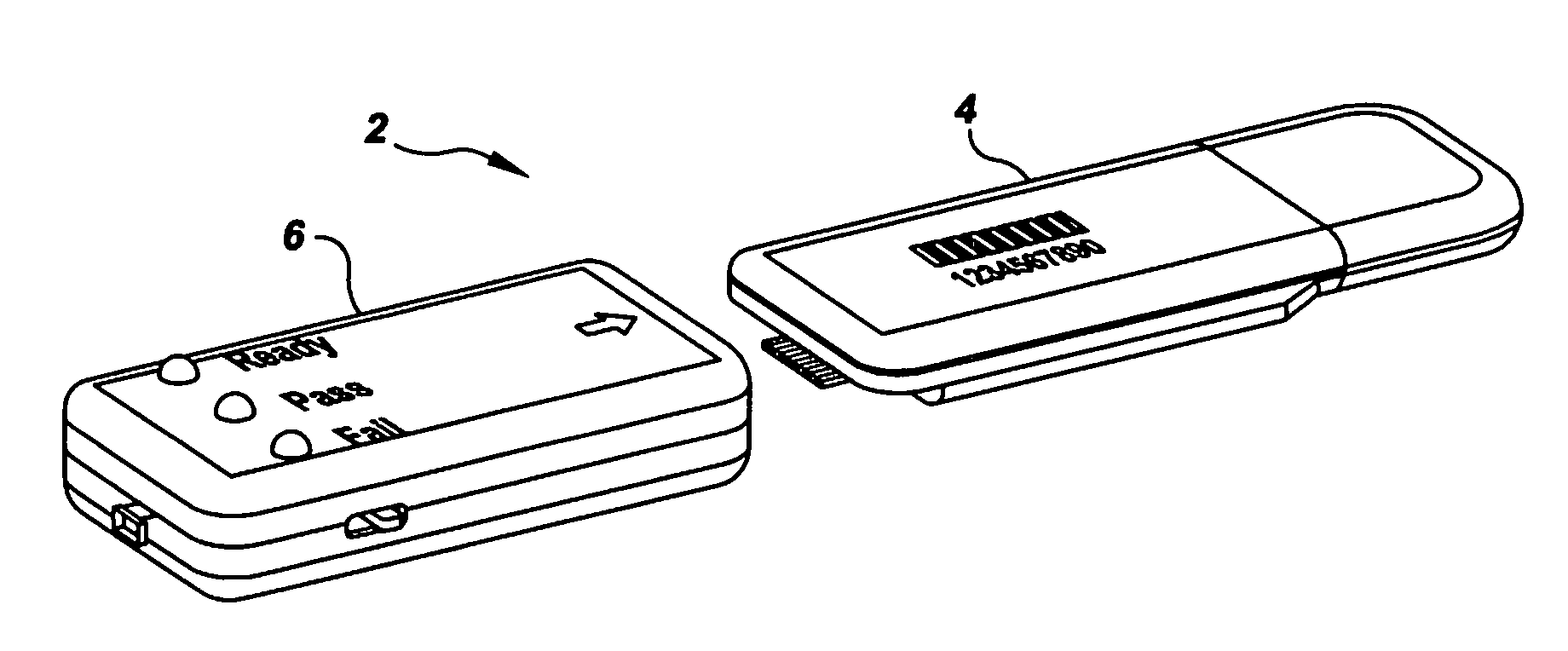
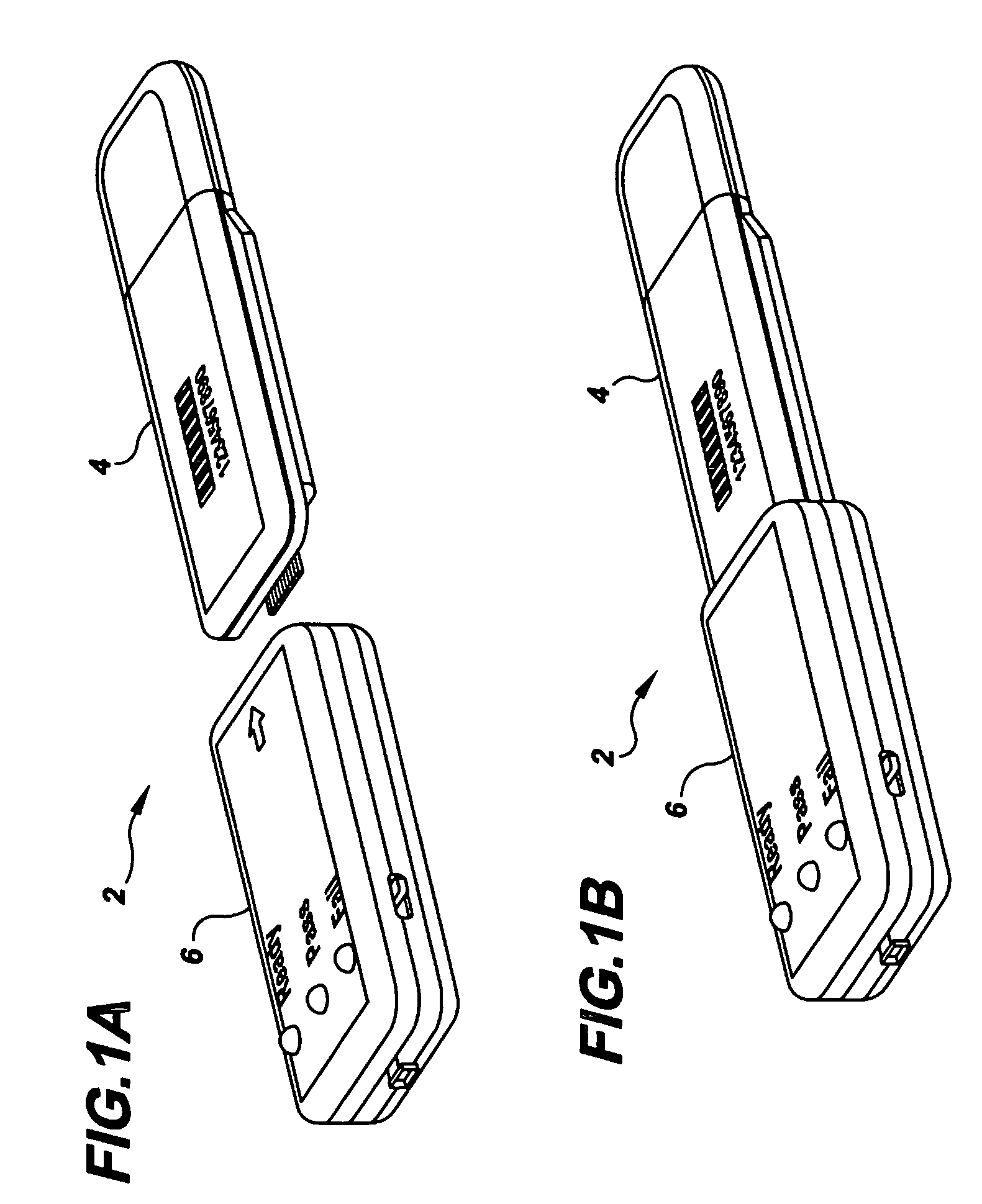
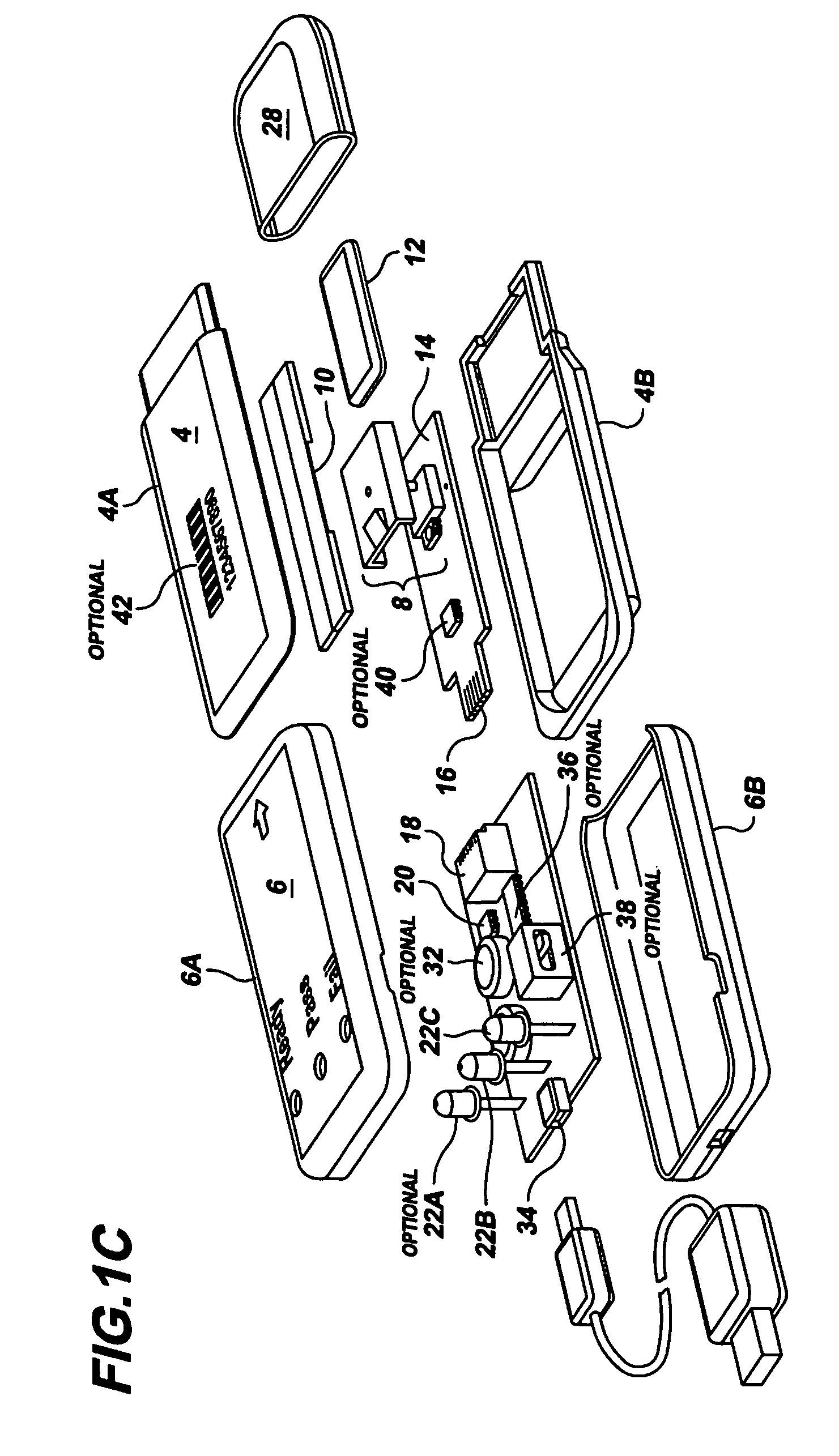
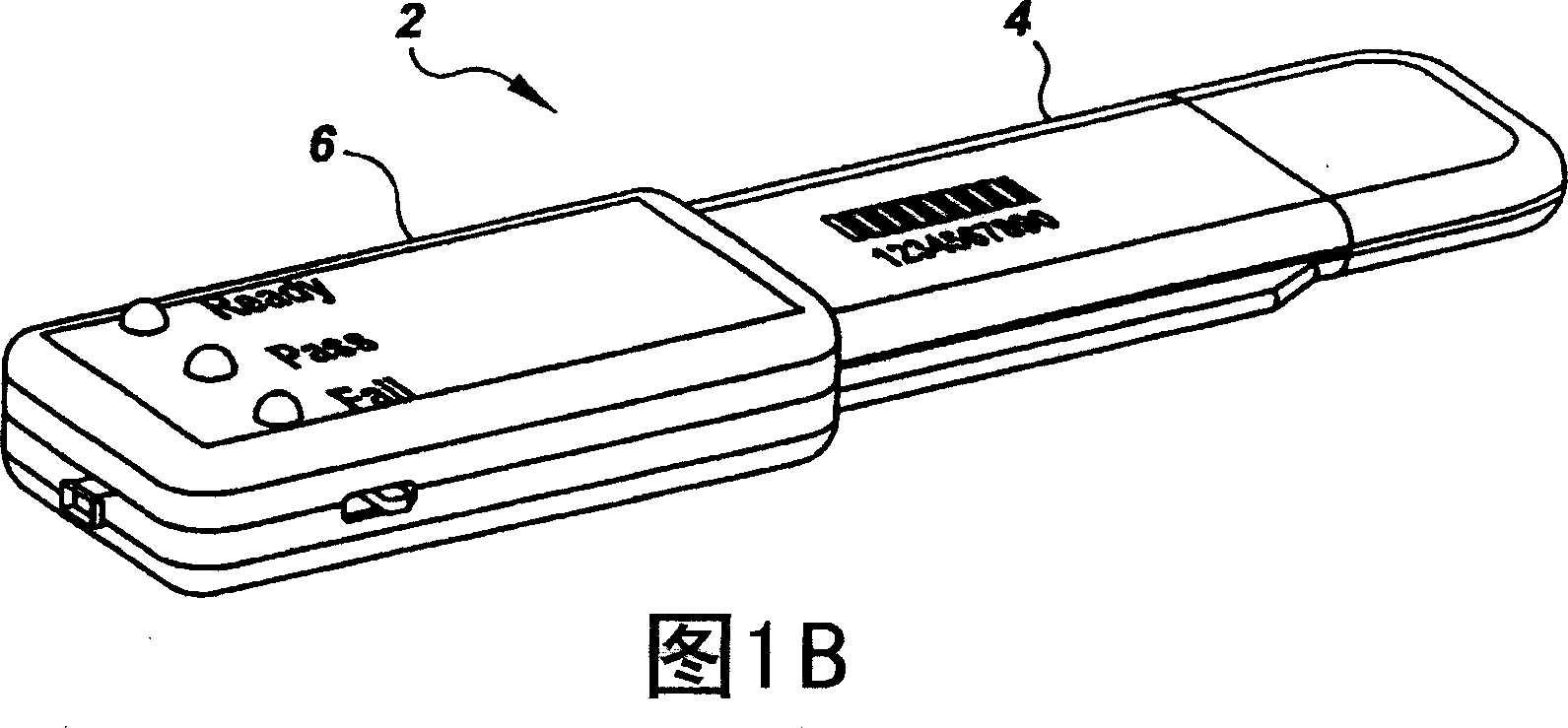
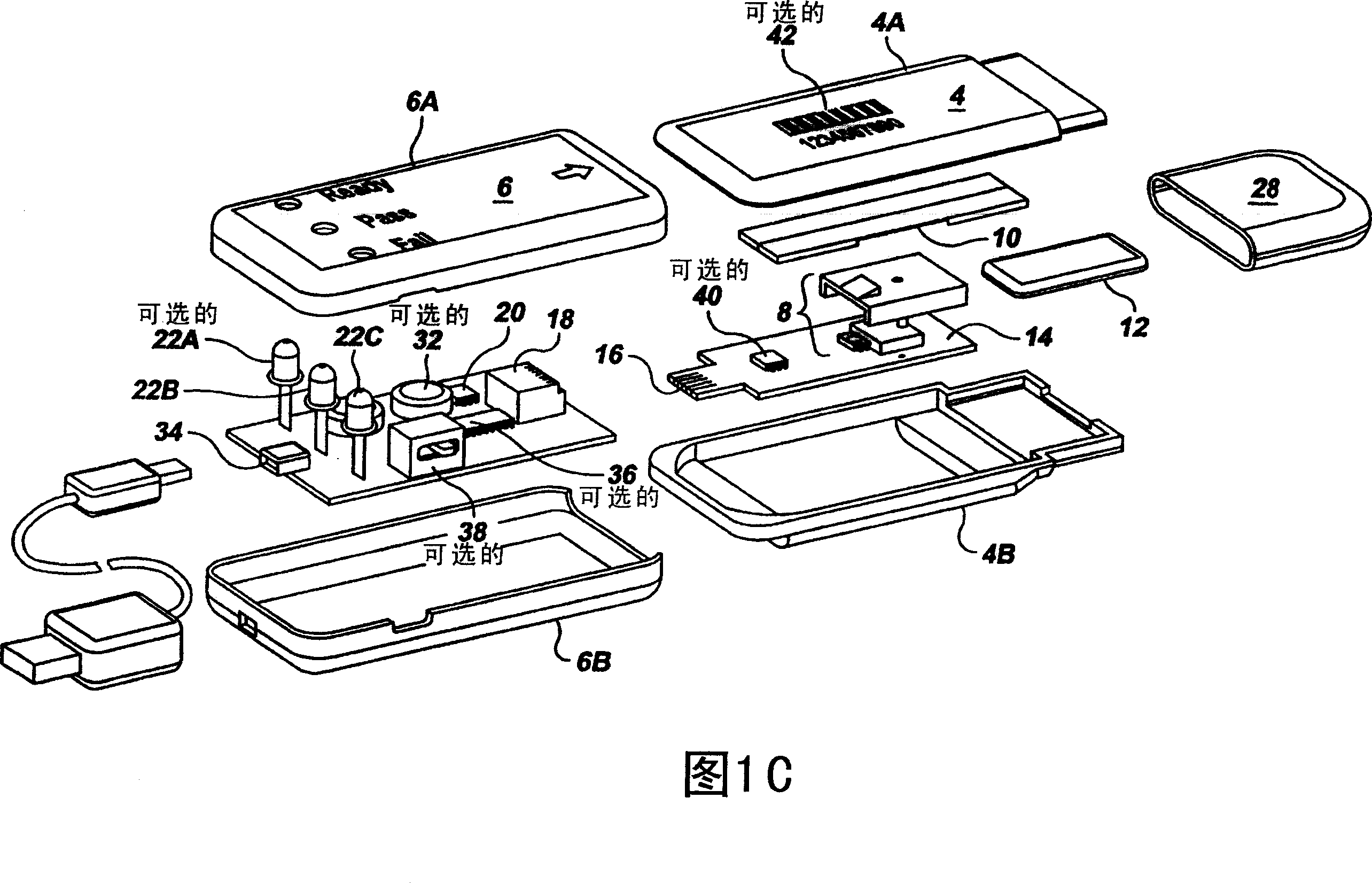
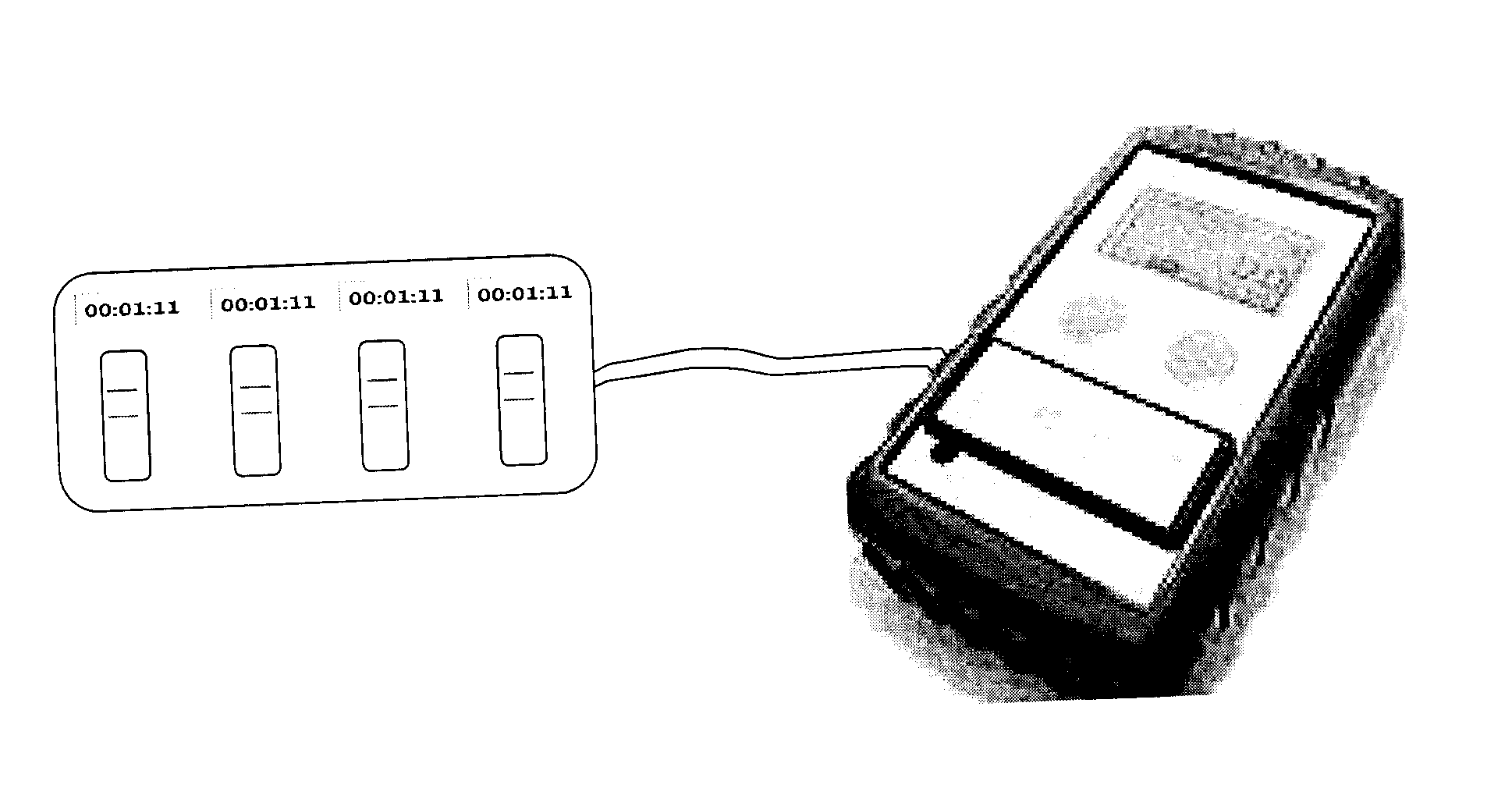
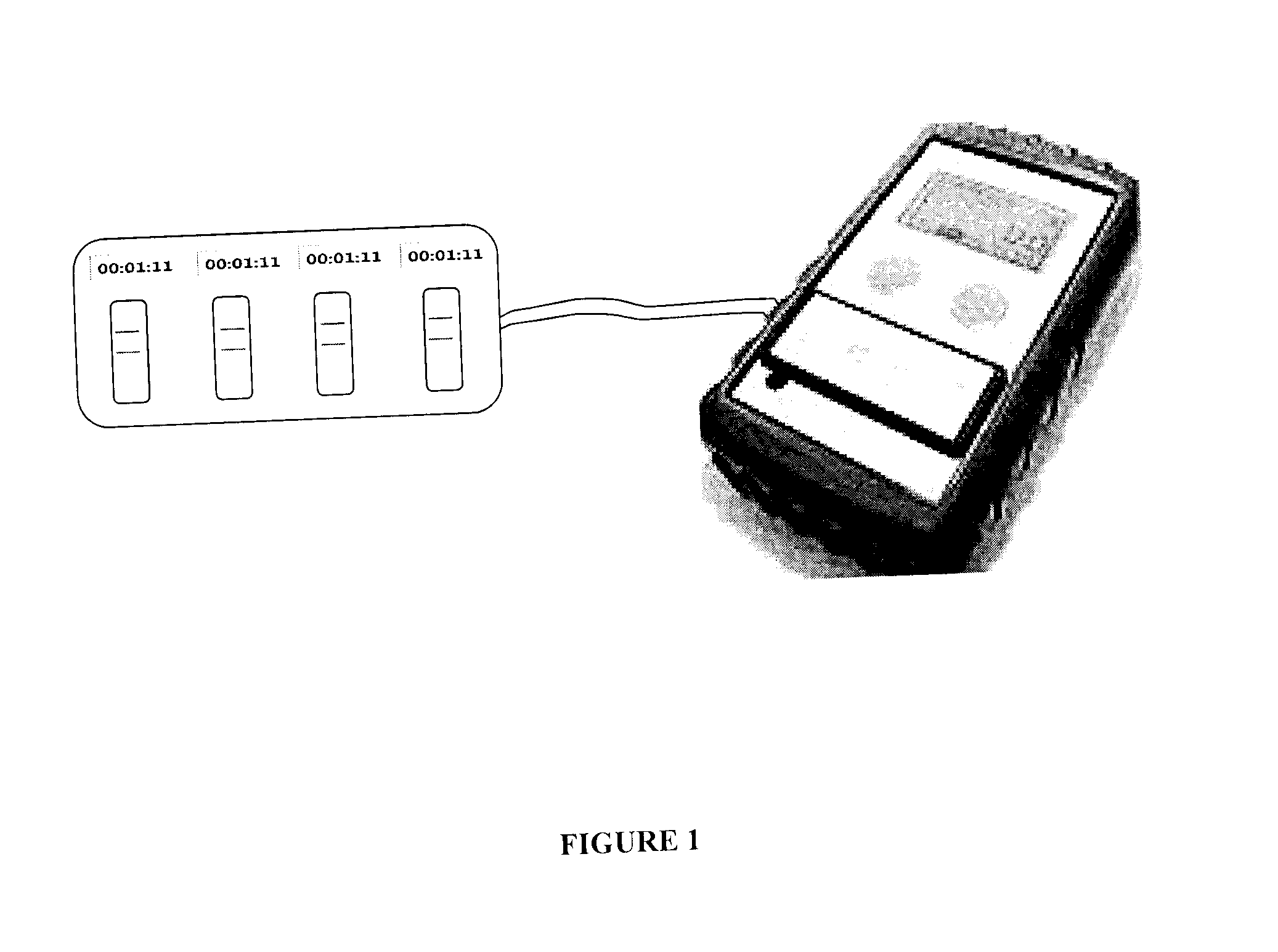
Semi-disposable optoelectronic rapid diagnostic test system
InactiveUS20070081920A1Wide and pointAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionRapid screening testHand held
A hand-held optoelectronic test system comprising a cartridge including at least one light source and sensors prealigned to permit acquisition of electro-optic data from a fluid sample reacted with a reagent, such as upon a test membrane in a reaction zone, and a reader which processes the acquired data to identify a physical change in the fluid sample. The cartridge and reader are operable for separate predetermined or controllable finite numbers of tests before becoming disposable.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
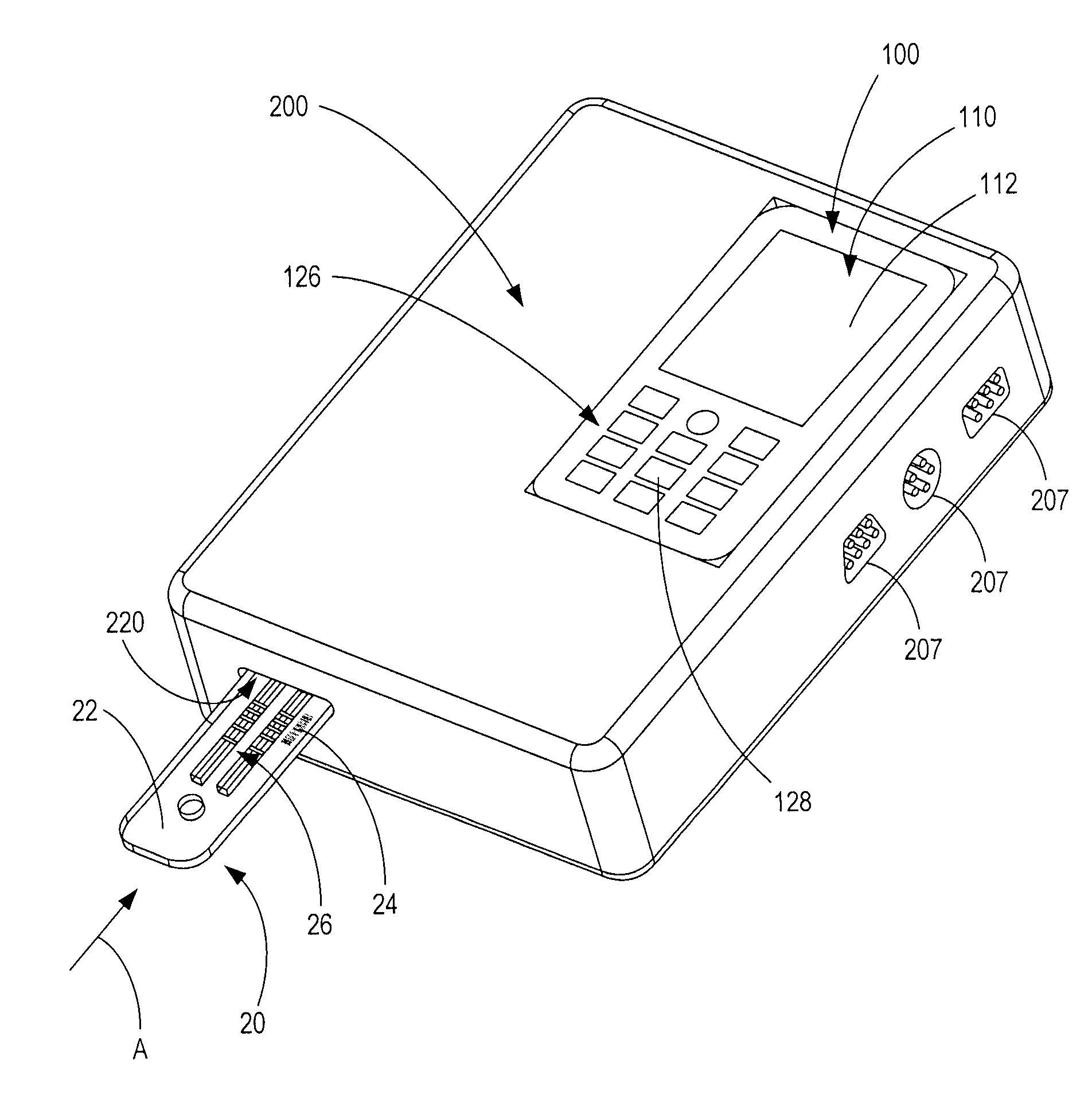
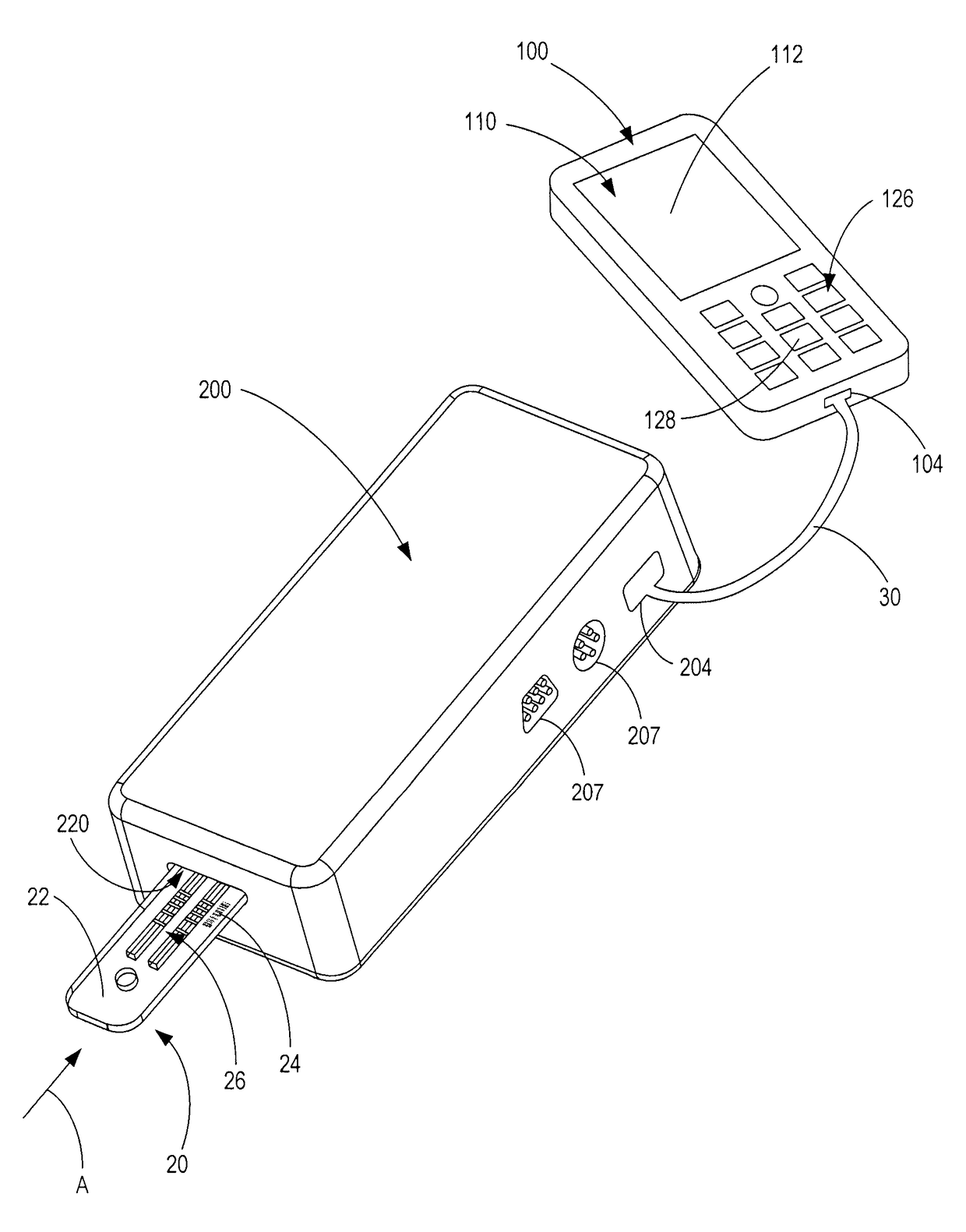
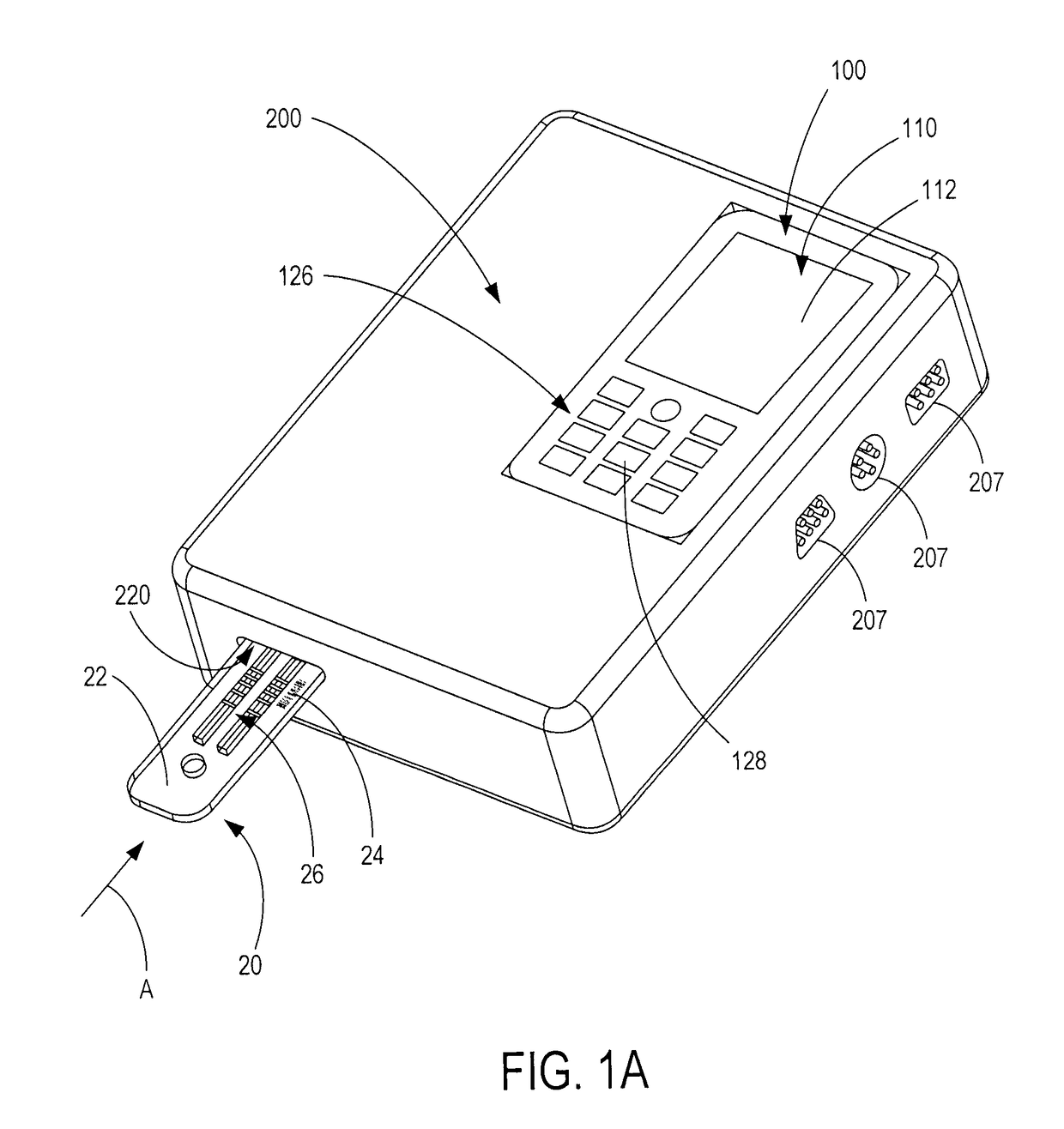
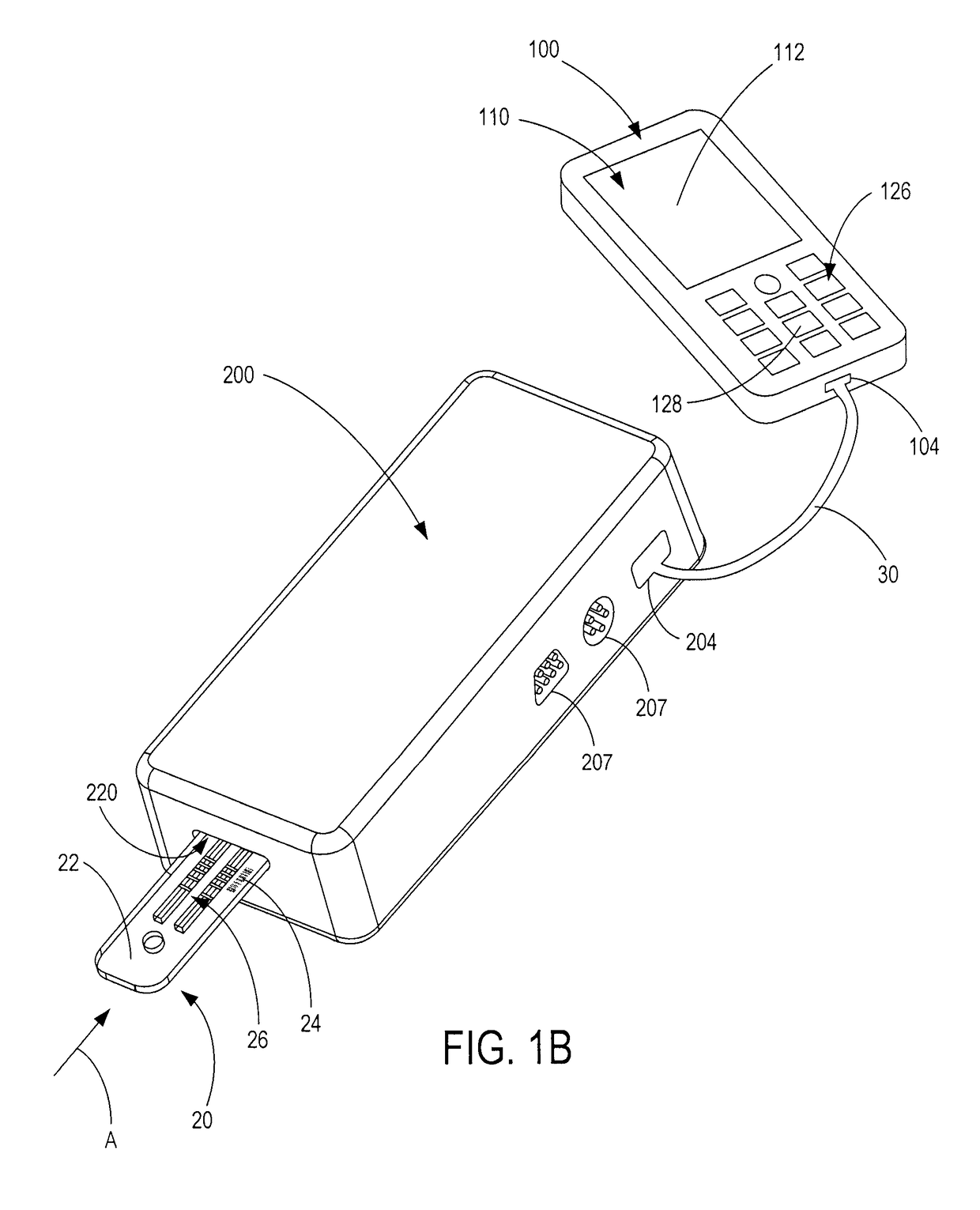
Handheld diagnostic test device and method for use with an electronic device and a test cartridge in a rapid diagnostic test
ActiveUS20120123686A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLocal control/monitoringRapid screening testHand held
A handheld diagnostic test device includes a port to removably receive a test cartridge, an element connected with an electronic device, and sensors for detection of test data from a biological or environment sample after reaction with reagents onboard the cartridge. The test device also includes memory storing algorithms for upload to the electronic device to enable a processor thereof: to await elapse of a pre-determined time following reaction of the sample with the reagents; to thereafter instruct the sensors to detect the test data; to generate presentation data based on the test data; and to present the presentation data from a presentation element of the electronic device to a user. A related method includes a connecting step, an up-loading step, a presentation step, a cartridge inserting step, a waiting step, a sensing step, and an electronic device processing step.
Owner:FIO CORP
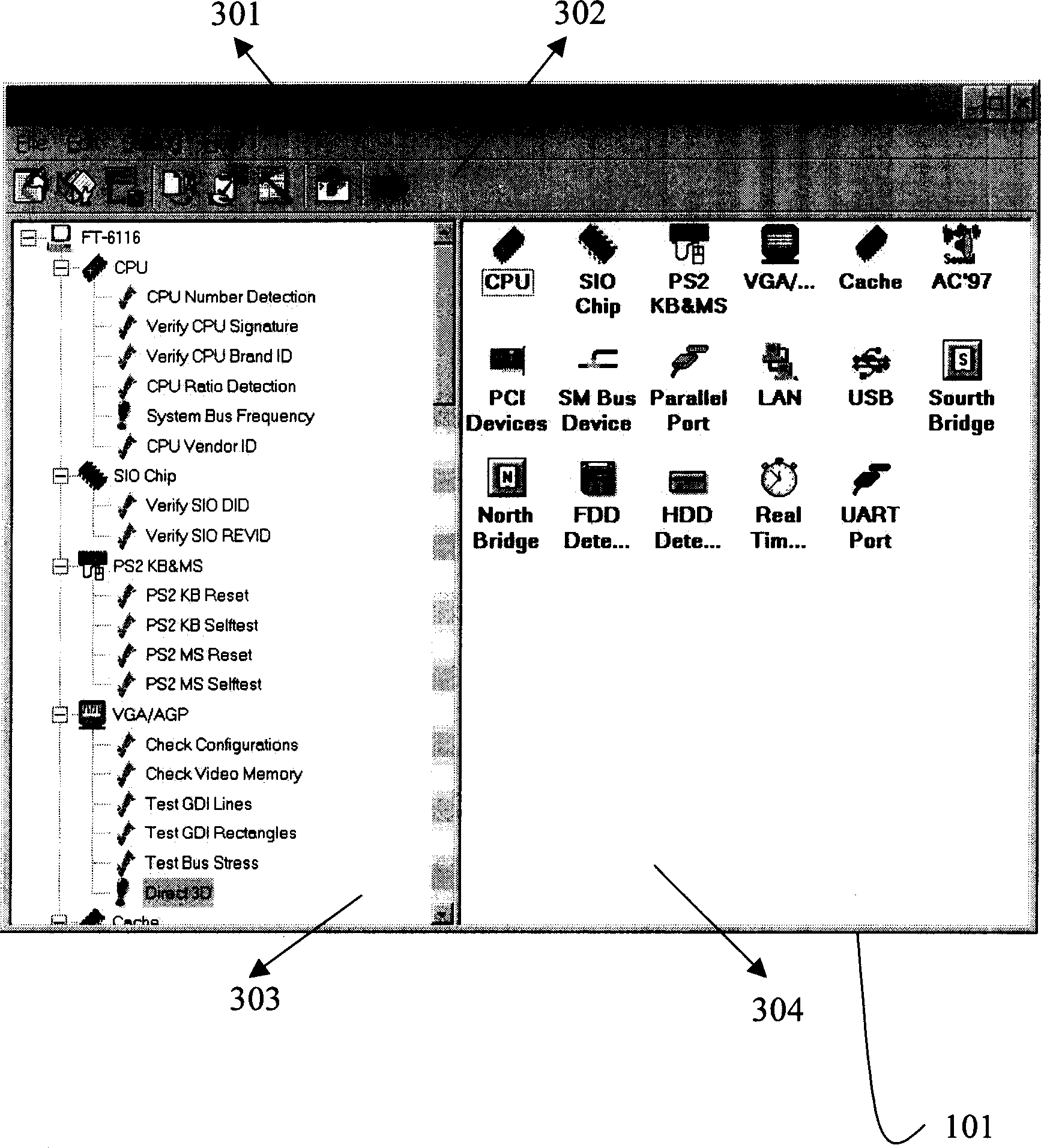
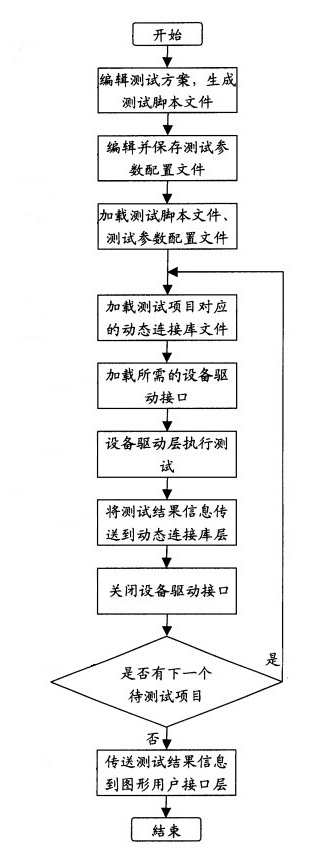
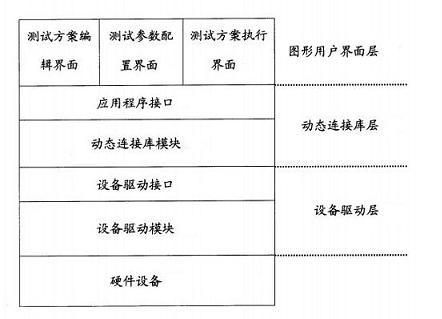
Rapid diagnosis testing system and method for computer hardware
InactiveCN1670710AAdd flexiblyGood hierarchyFunctional testingSpecific program execution arrangementsComputer hardwareGraphics
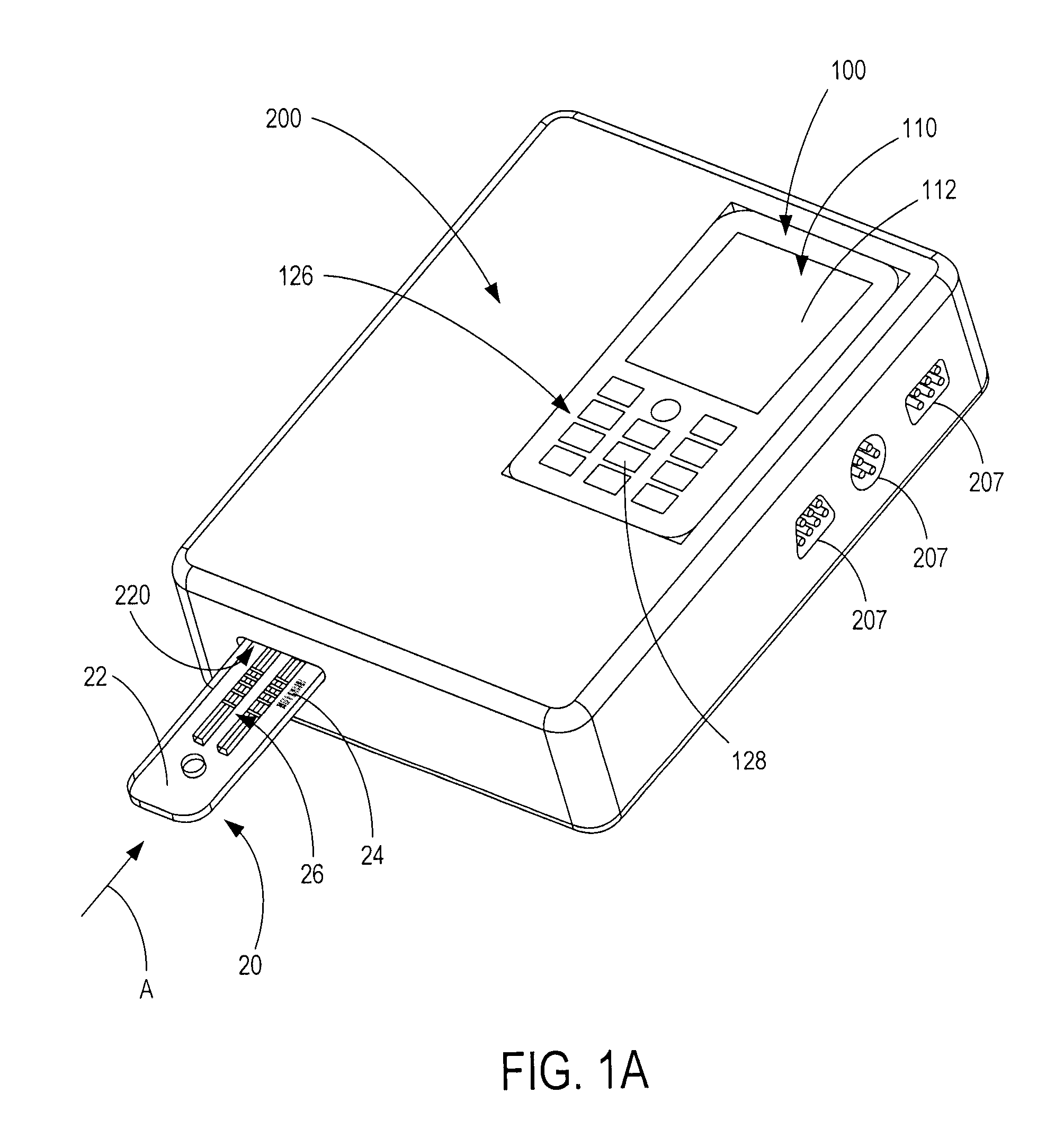
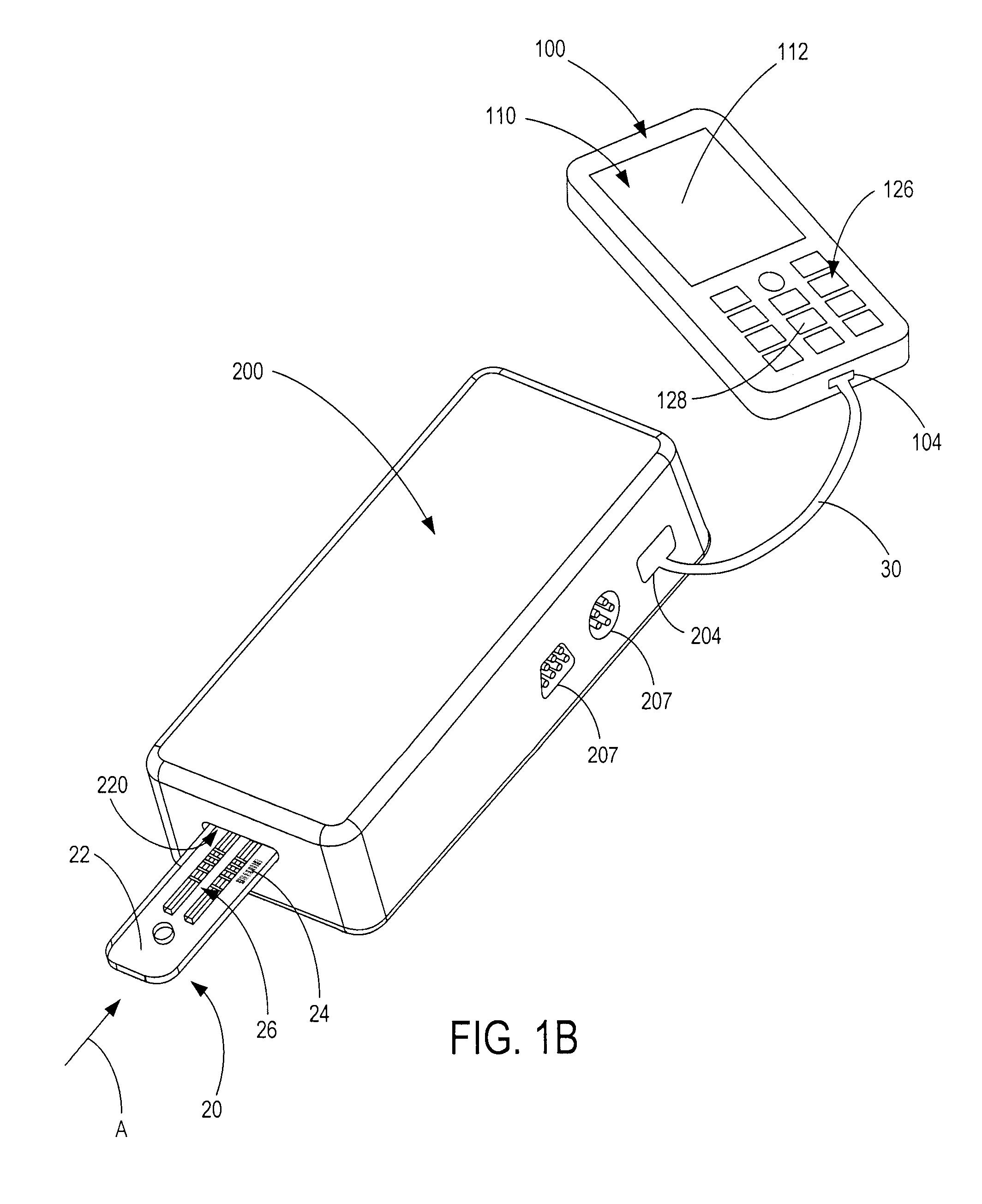
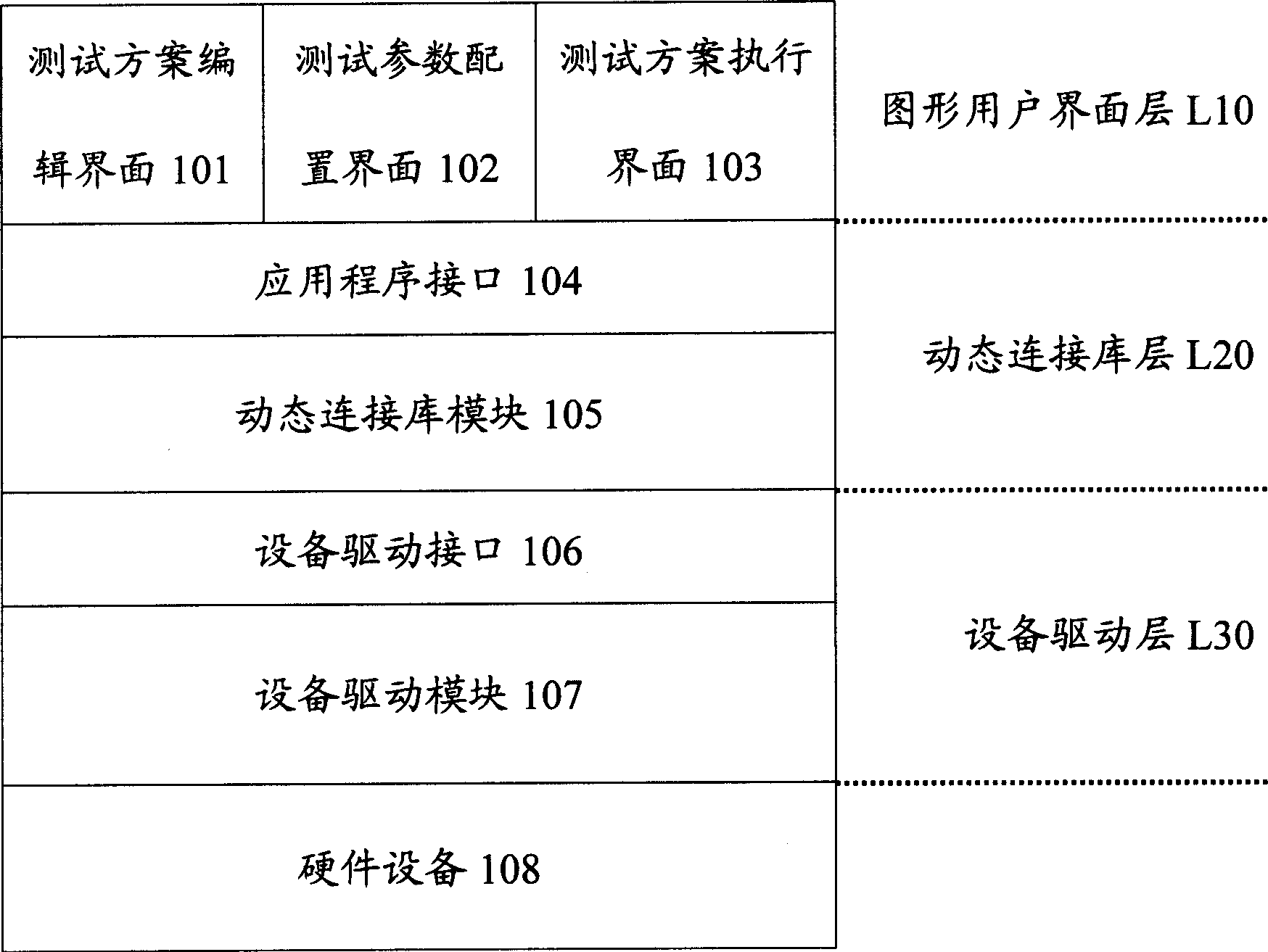
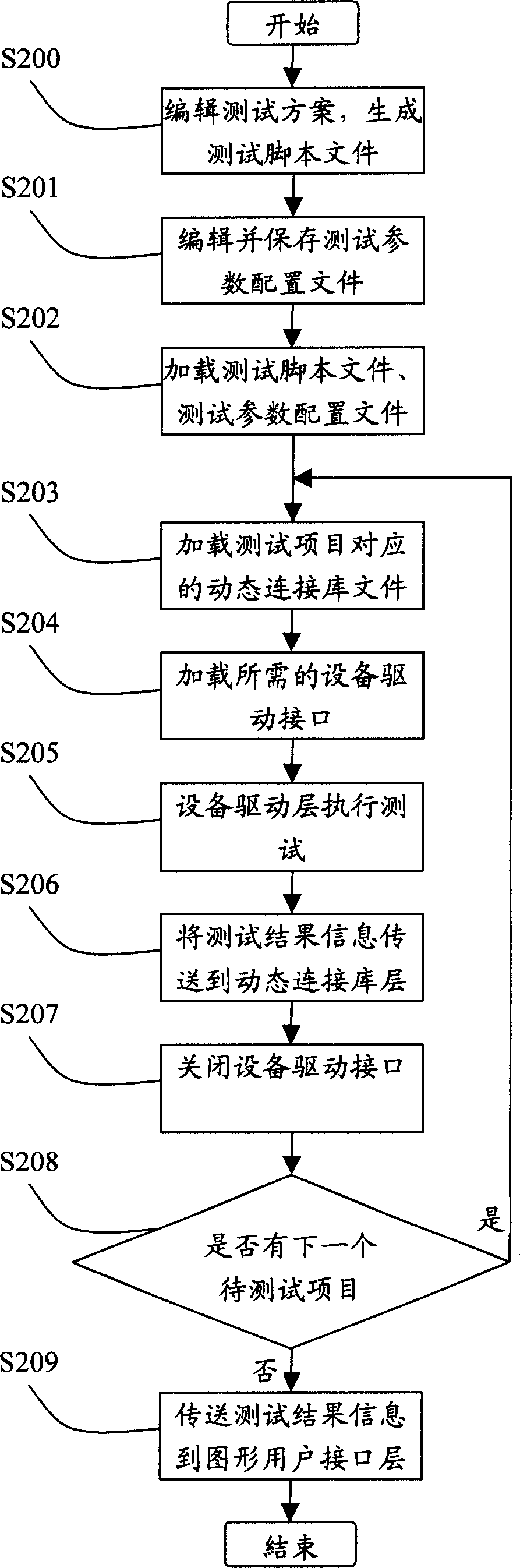
This invention provides one computer hardware rapid diagnose system and method, which comprises three layers of structures: image user interface layer to provide interface with edit testing scheme, allocation test parameters and to execute test scheme and display test result information; dynamic connection database layer with several computer hardware dynamic connection database file to transfer the computer hardware driving program; device driving layer with several computer hardware driving programs to drive the hardware device and get the test result information.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
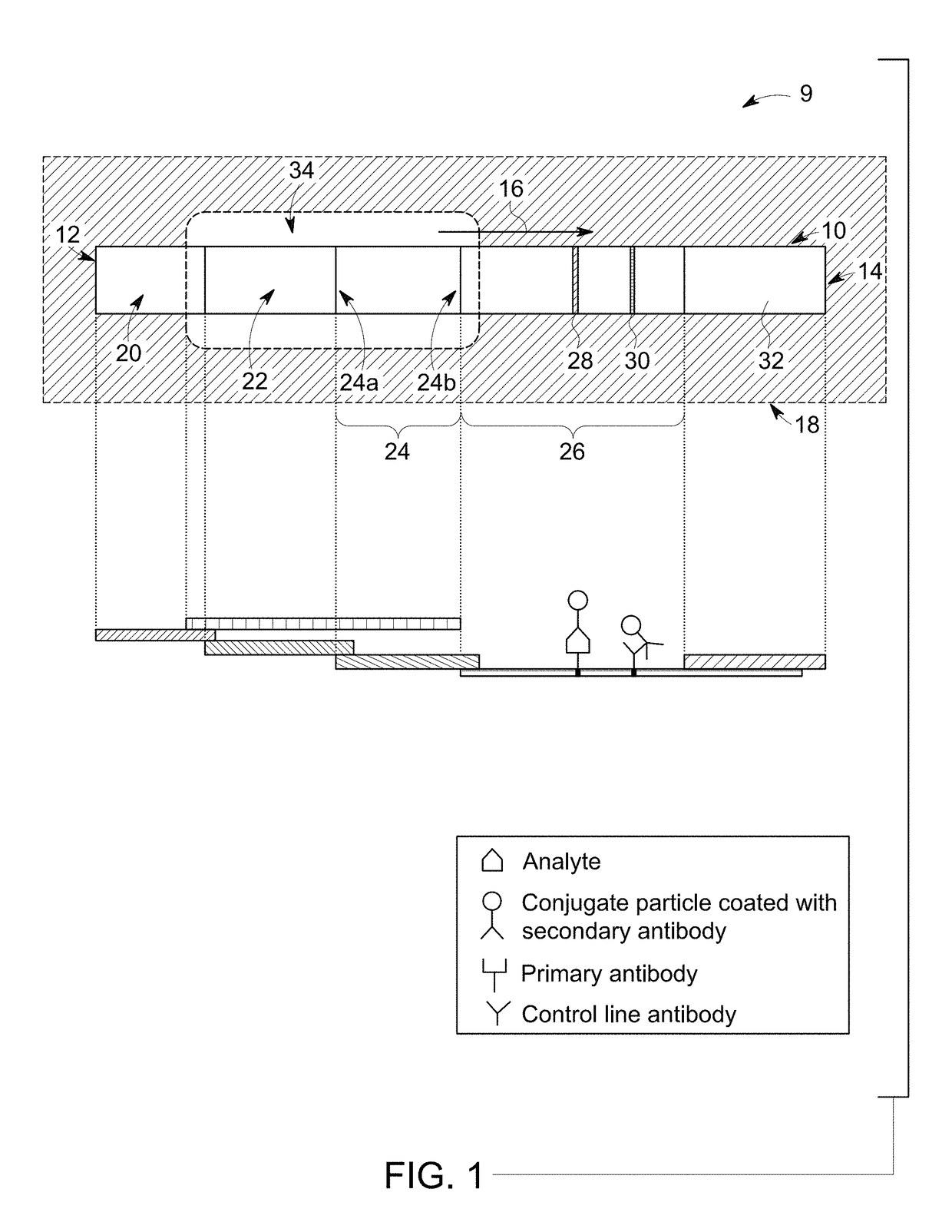
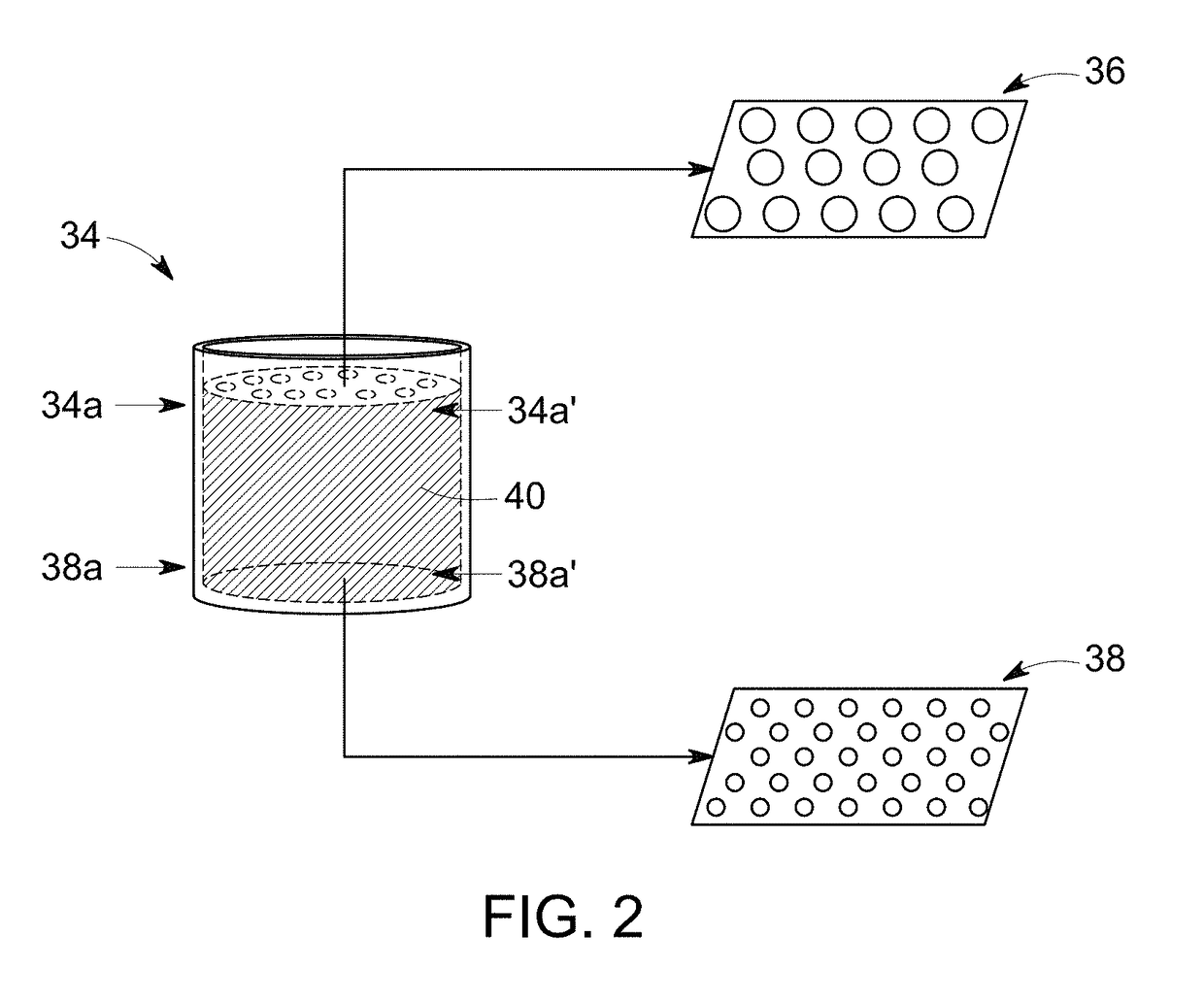
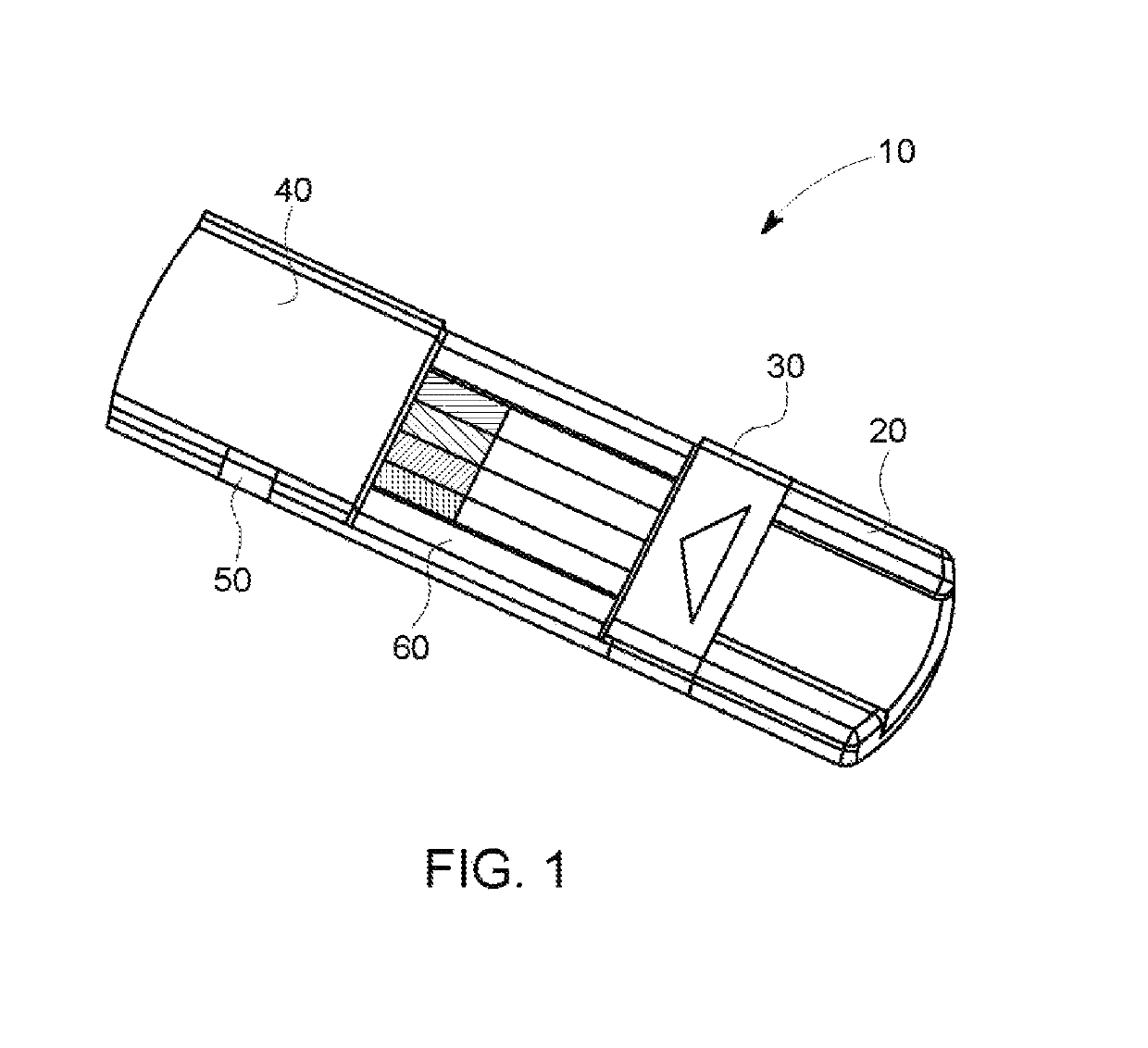
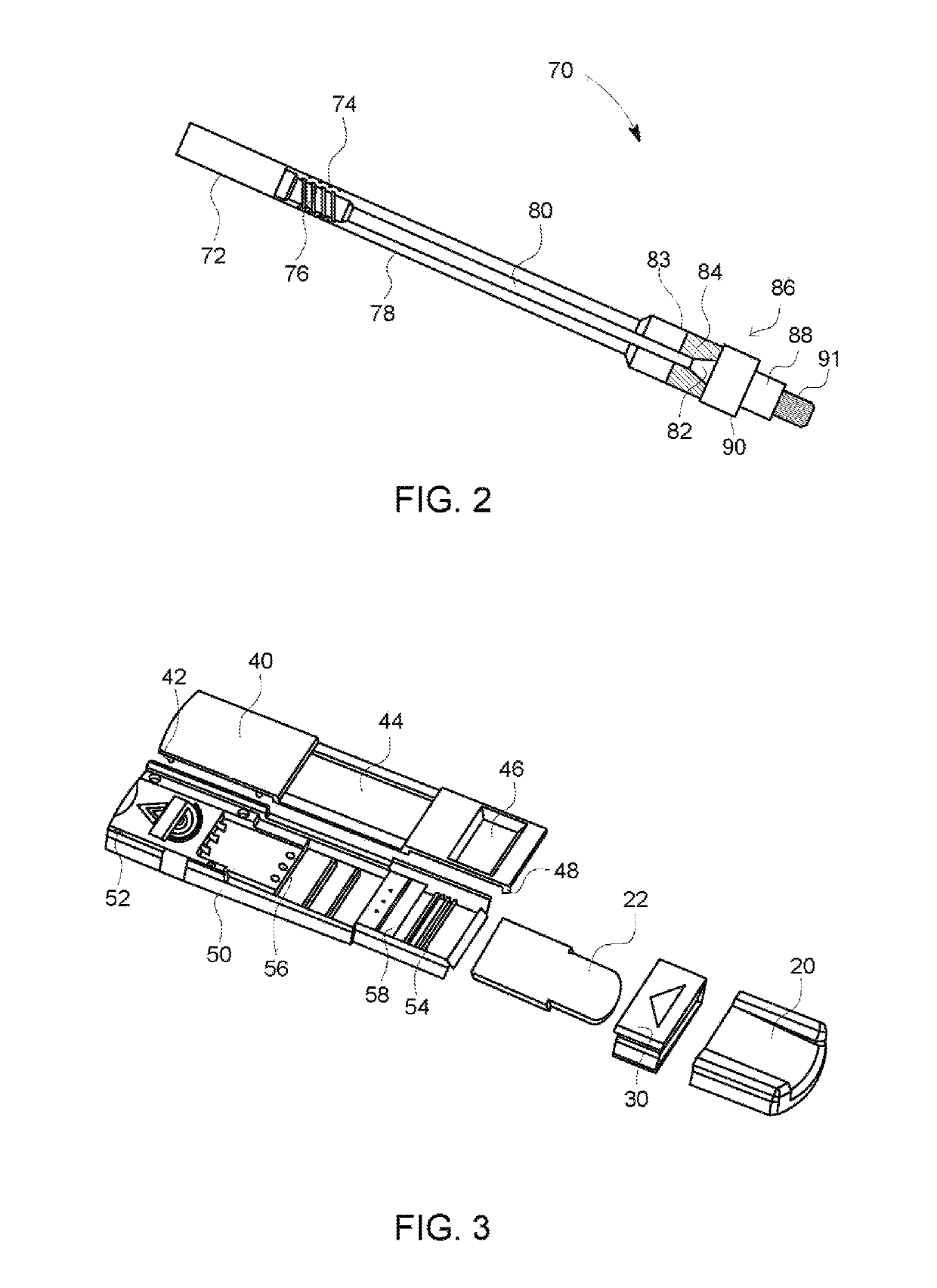
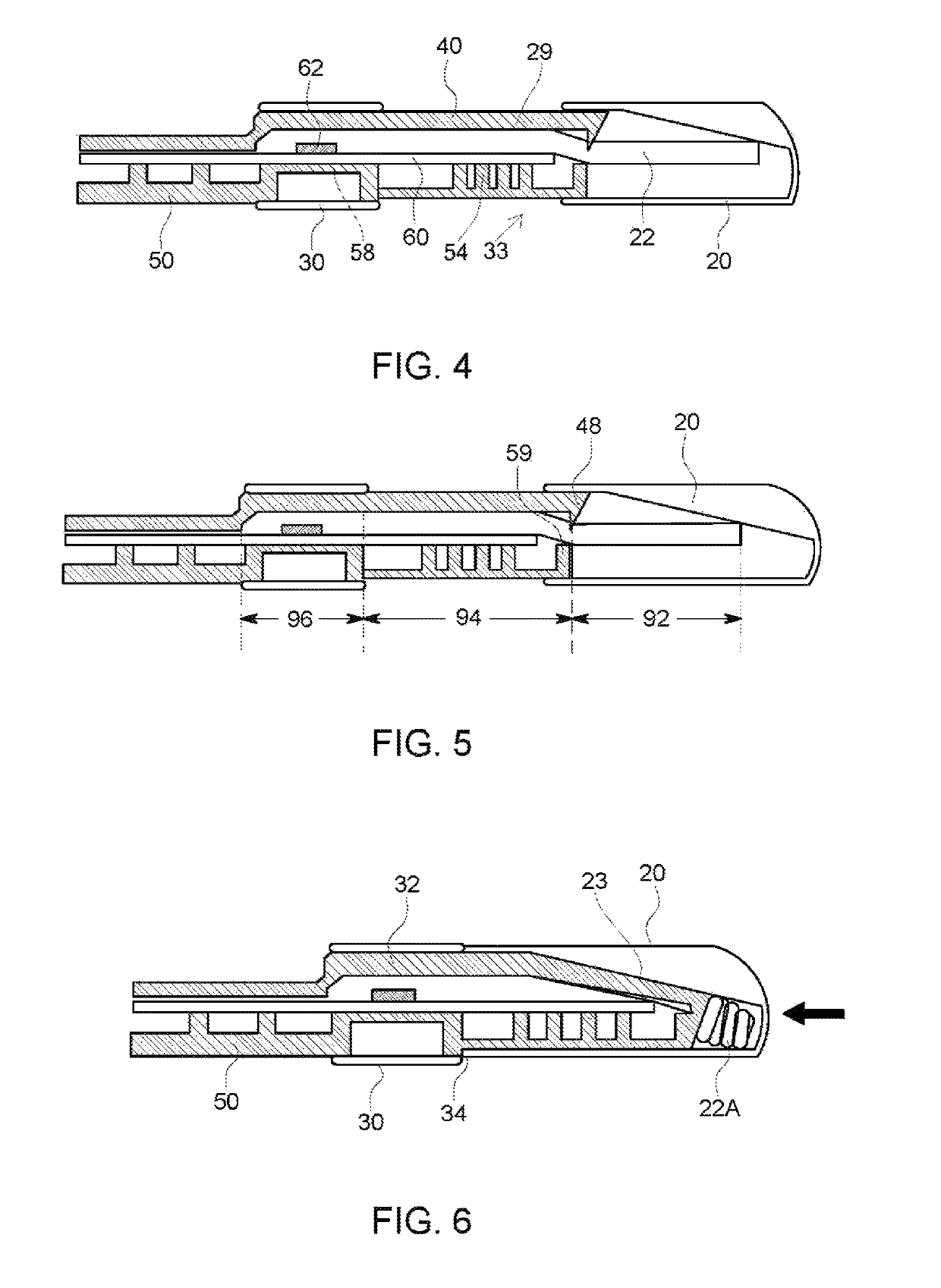
Device for rapid diagnostic tests to detect antigens with improved sensitivity
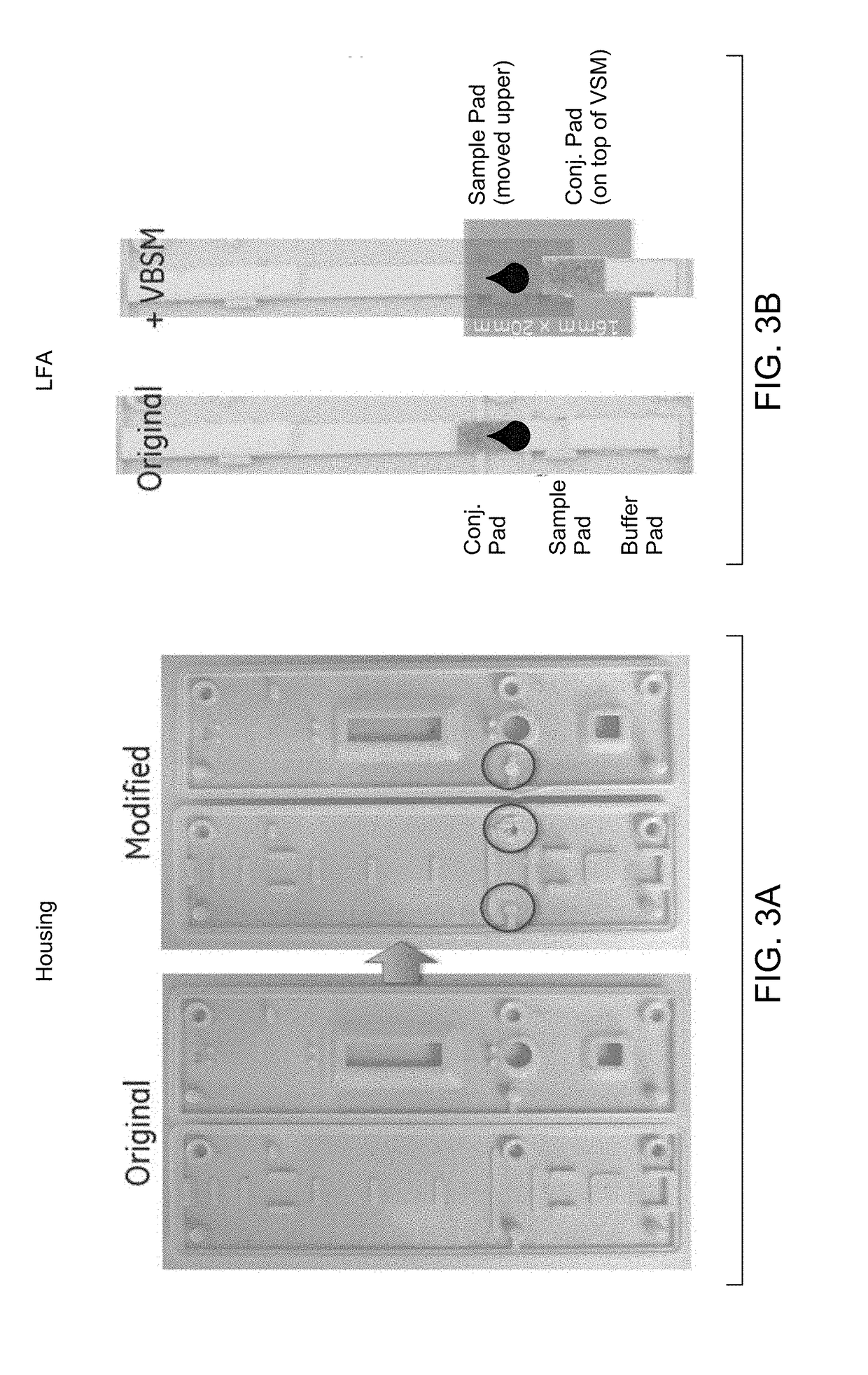
A rapid diagnostic testing device for testing of a biological sample is provided. The device comprises a channeled construct, at least one lateral flow unit, and a cassette housing. The channeled construct is configured to receive a biological sample to form at least partially purified biological sample. The lateral flow unit is at least partially disposed in the cassette housing. The lateral flow unit comprises: a sample receiving zone, a conjugate zone and a detection zone. The sample receiving zone is operatively coupled to the channeled construct for receiving the partially purified biological sample comprising at least one analyte. The conjugate zone comprising a conjugate particle to bind the analyte is disposed adjacent to the first side of the sample receiving zone. The detection zone is disposed adjacent to the second side of the sample receiving zone and comprises at least one binding agent for detecting the analyte.
Owner:TOKITAE LLC +1
Methods and compositions for multivalent binding and methods for manufacture of rapid diagnostic tests
InactiveUS20100143905A1High affinityConstant gainMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresRapid screening testMultivalent binding
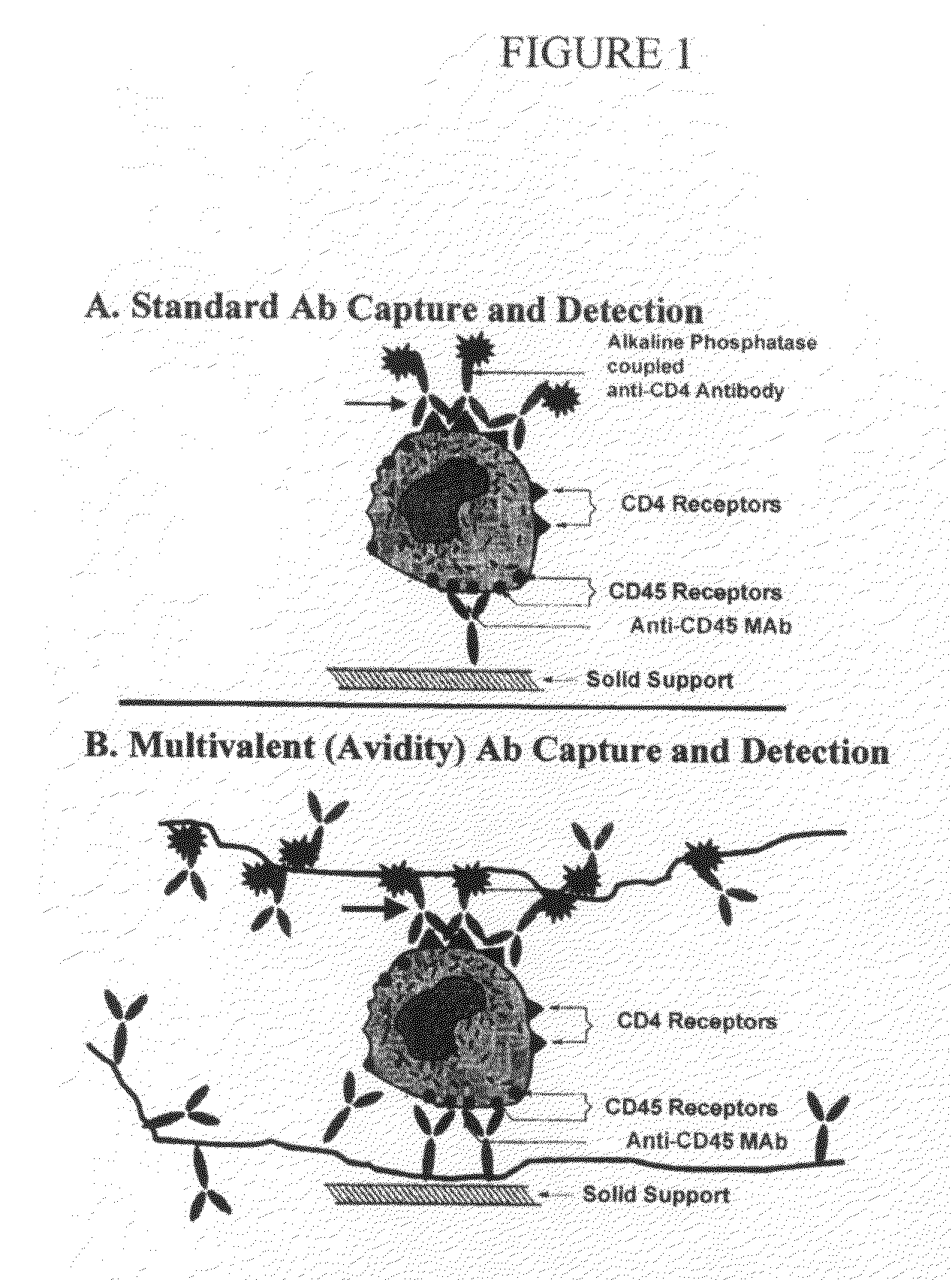
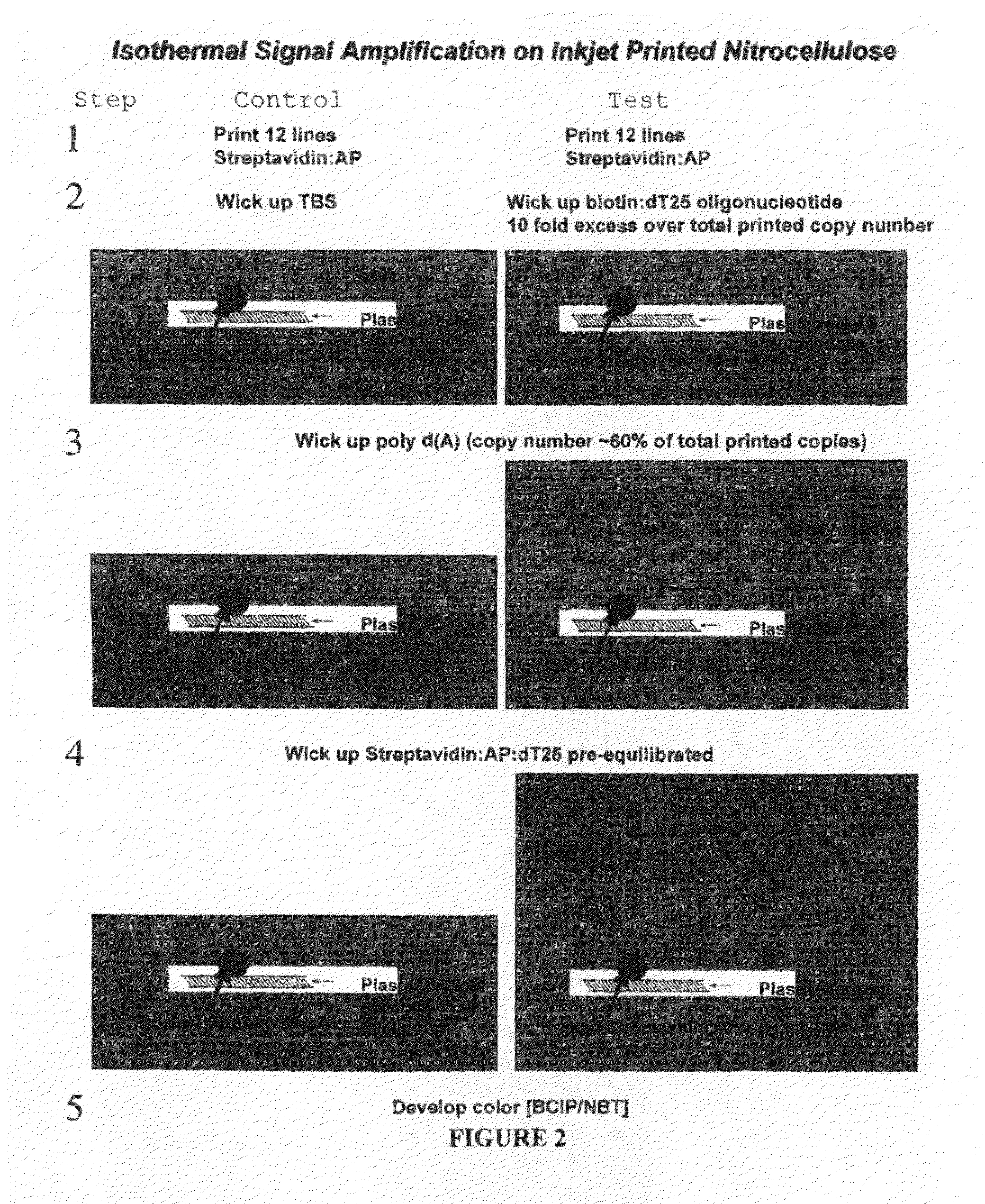
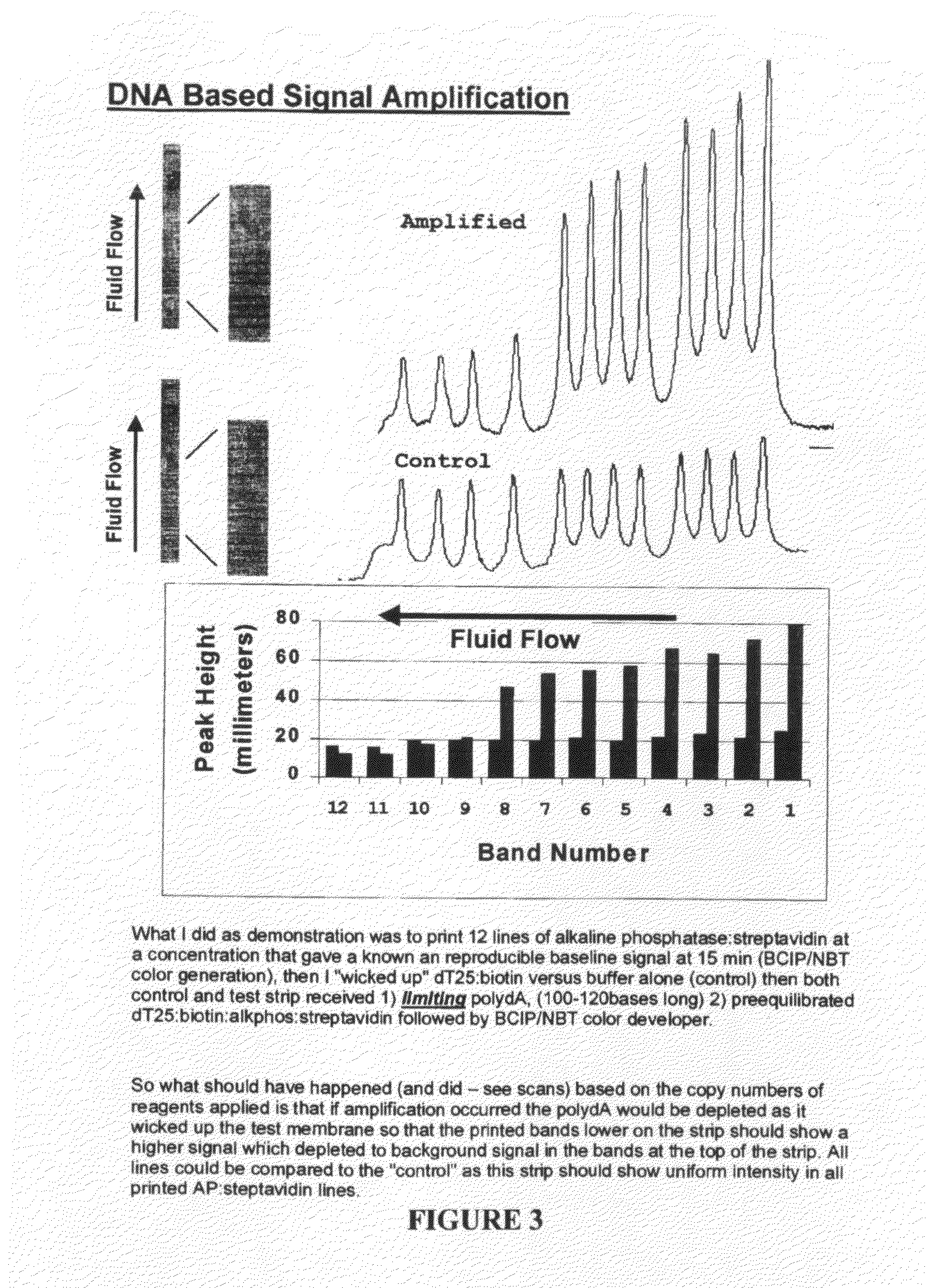
The invention provides reagents and methods for multivalent binding and quantitative capture of components in a sample. In one aspect, reagents and methods for diagnostic assay for antigen, ligand, binding agent, or antibody are provided. Compositions of a non-natural or deliberately constructed nucleic acid-like polymeric scaffold are provided, to which multiple antibodies, peptides or other binding agents can be affixed by hybridization of a oligonucleotide: binding agent complex such that the nucleic acid: binding agent construction displays multivalent behavior when interacting with a multivalent analyte. Methods for constructing and using the scaffolds are described. Such compositions may include assembly of mixed specificity binding agents such that the composition displays multivalent binding behavior against a target containing mixed analytes which can be bound by the construct to effect a binding affinity increase such as is observed in avidity reagents against single analytes expressed multiply on the target analyte. A manufacturing method for producing rapid diagnostic assays in a decentralized manner is also described. The method generates net economic advantages over conventional diagnostic manufacturing practices.
Owner:LANE MICHAEL J +2
Semi-disposable optoelectronic rapid diagnostic test system
InactiveCN1948952AColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingRapid screening testSoftware engineering
A hand-held optoelectronic test system comprising a cartridge including at least one light source and sensors prealigned to permit acquisition of electro-optic data from a fluid sample reacted with a reagent, such as upon a test membrane in a reaction zone, and a reader which processes the acquired data to identify a physical change in the fluid sample. The cartridge and reader are operable for separate predetermined or controllable finite numbers of tests before becoming disposable.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System for quickly diagnosing and testing computer hardware
InactiveCN102214133ARapid diagnostic testAdd flexiblyDetecting faulty computer hardwareGraphicsComputer hardware
The invention provides a system for quickly diagnosing and testing computer hardware. The system is used for quickly diagnosing and testing the computer hardware and displaying information of a test result. A test system of the invention is divided into three layers of structures, namely a graphical user interface layer for providing a graphical user interface for editing a test scheme, configuring a test parameter, performing the test scheme and displaying the information of the test result, a dynamic linkbase layer which comprises dynamic linkbase files of a plurality of pieces of computer hardware and is used for calling a driver of the computer hardware, and an equipment driving layer which comprises drivers of the plurality of pieces of computer hardware and is used for driving computer hardware equipment and acquiring the information of the test result of the computer hardware equipment. By the system, a new test module can be added flexibly without changing a main program of the system.
Owner:苏州工业园区七星电子有限公司
Handheld diagnostic test device and method for use with an electronic device and a test cartridge in a rapid diagnostic test
ActiveUS9805165B2Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLocal control/monitoringRapid screening testHand held
Owner:FIO CORP
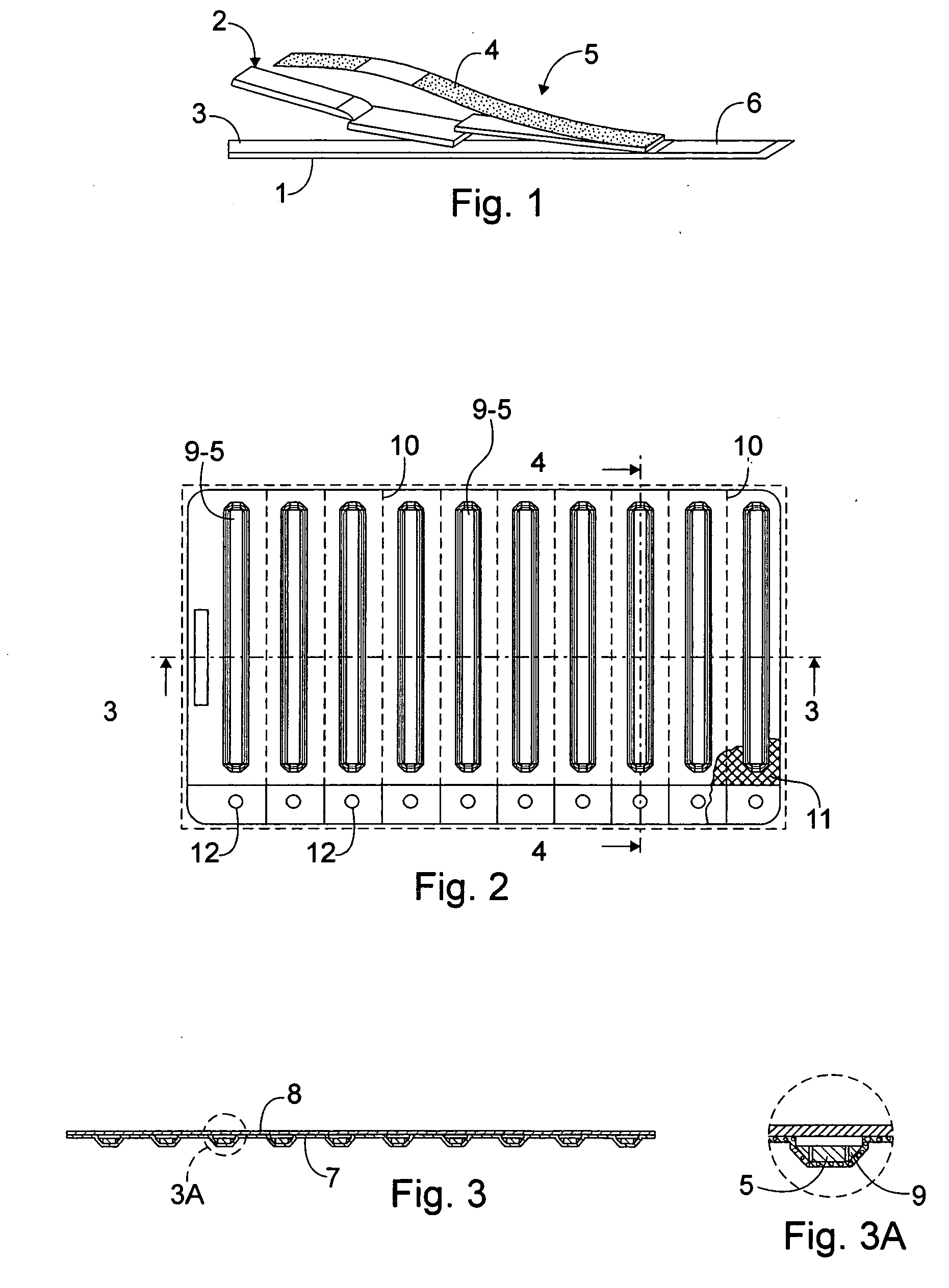
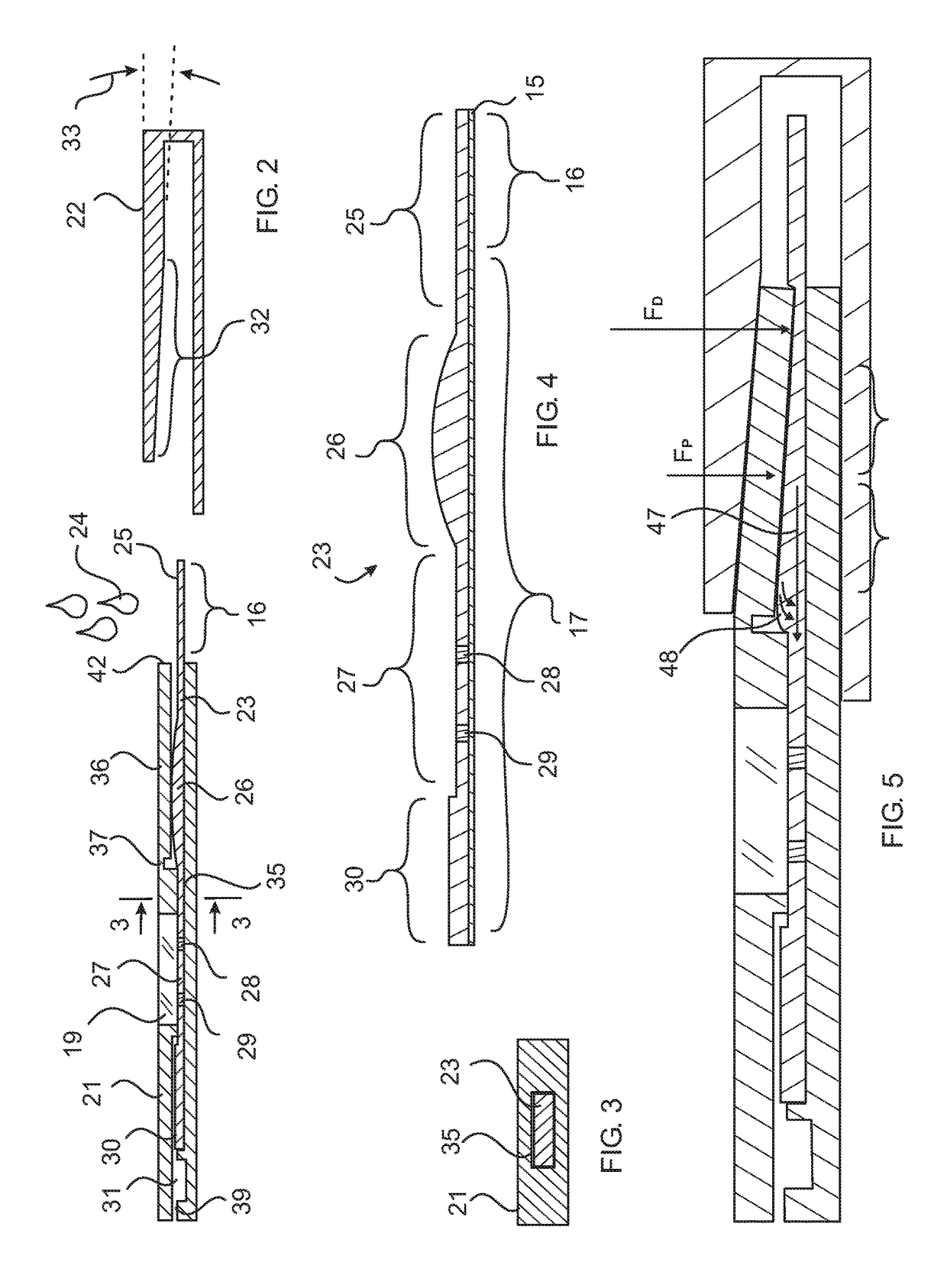
Blistered rapid diagnostic test with incorporated moisture absorbent material
InactiveUS20070056873A1Easy to holdImprove sealingSurgeryPharmaceutical containersRapid screening testEngineering
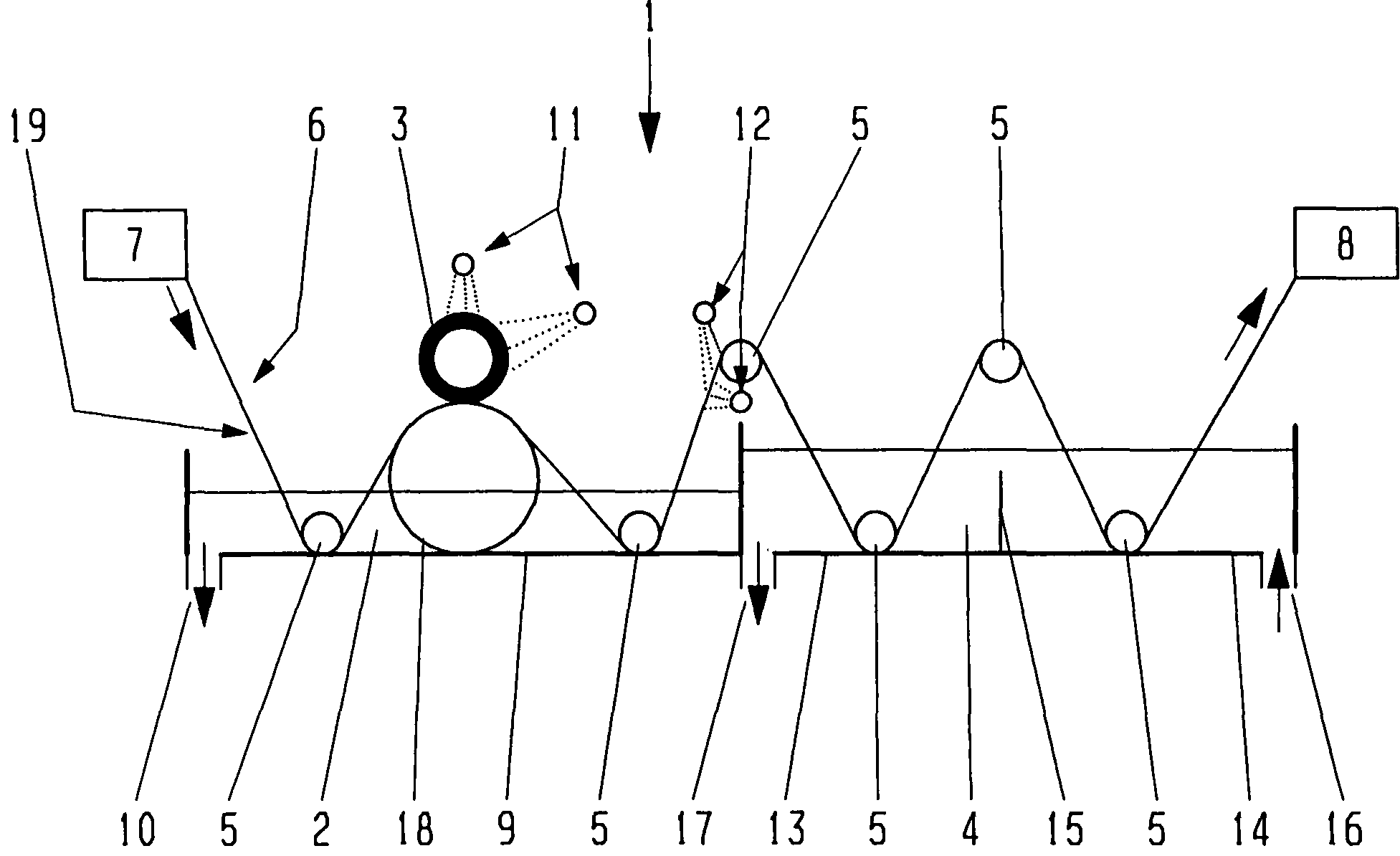
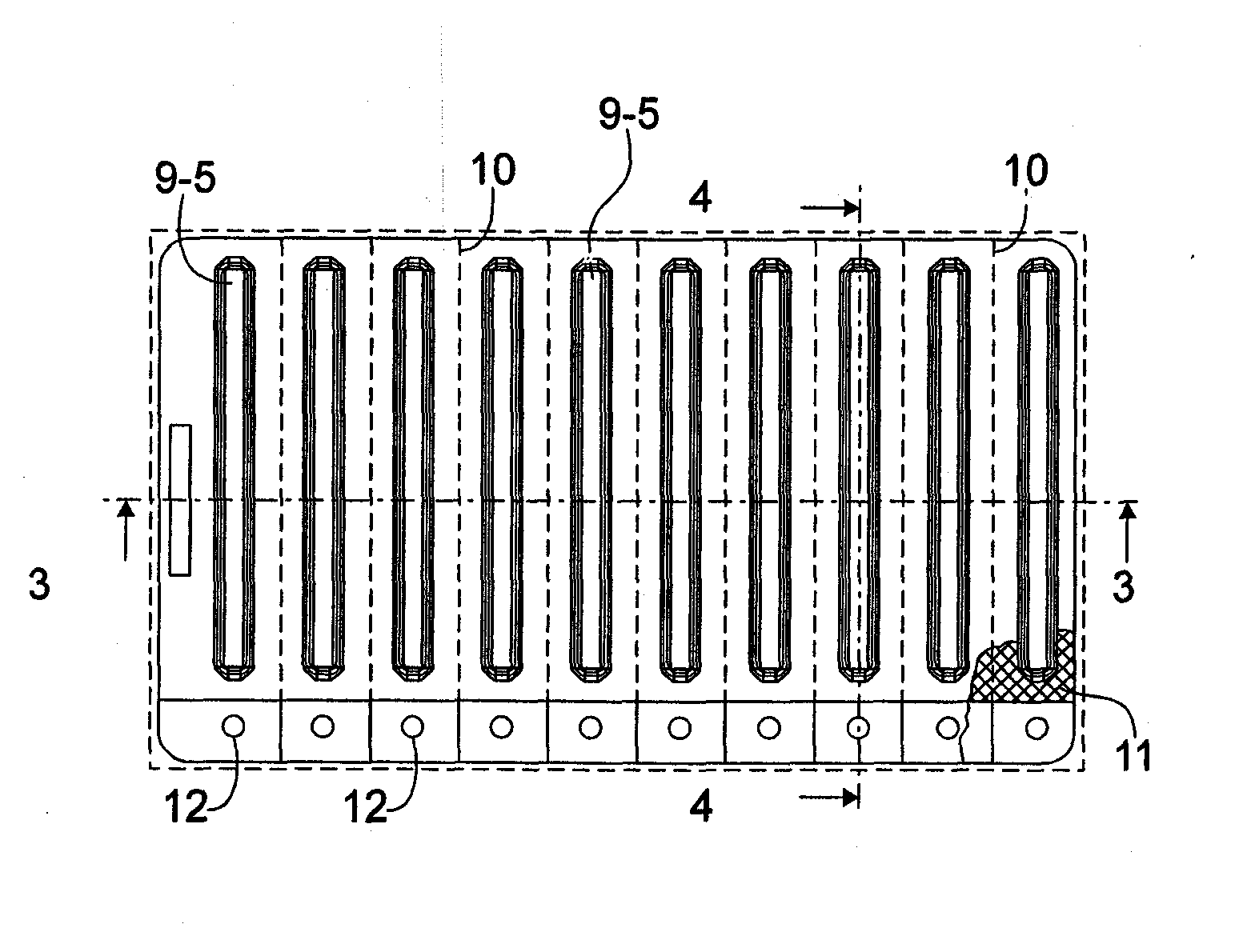
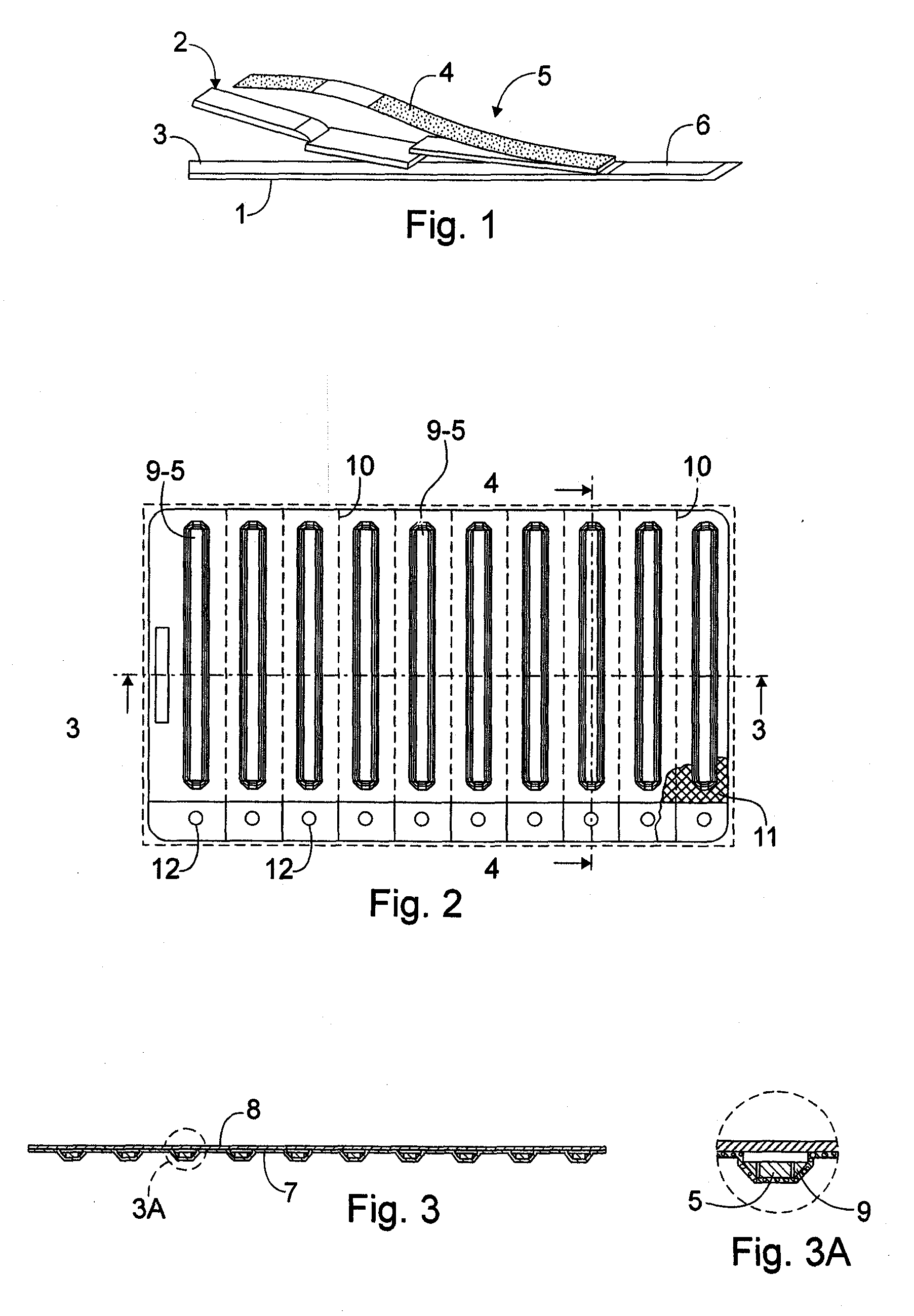
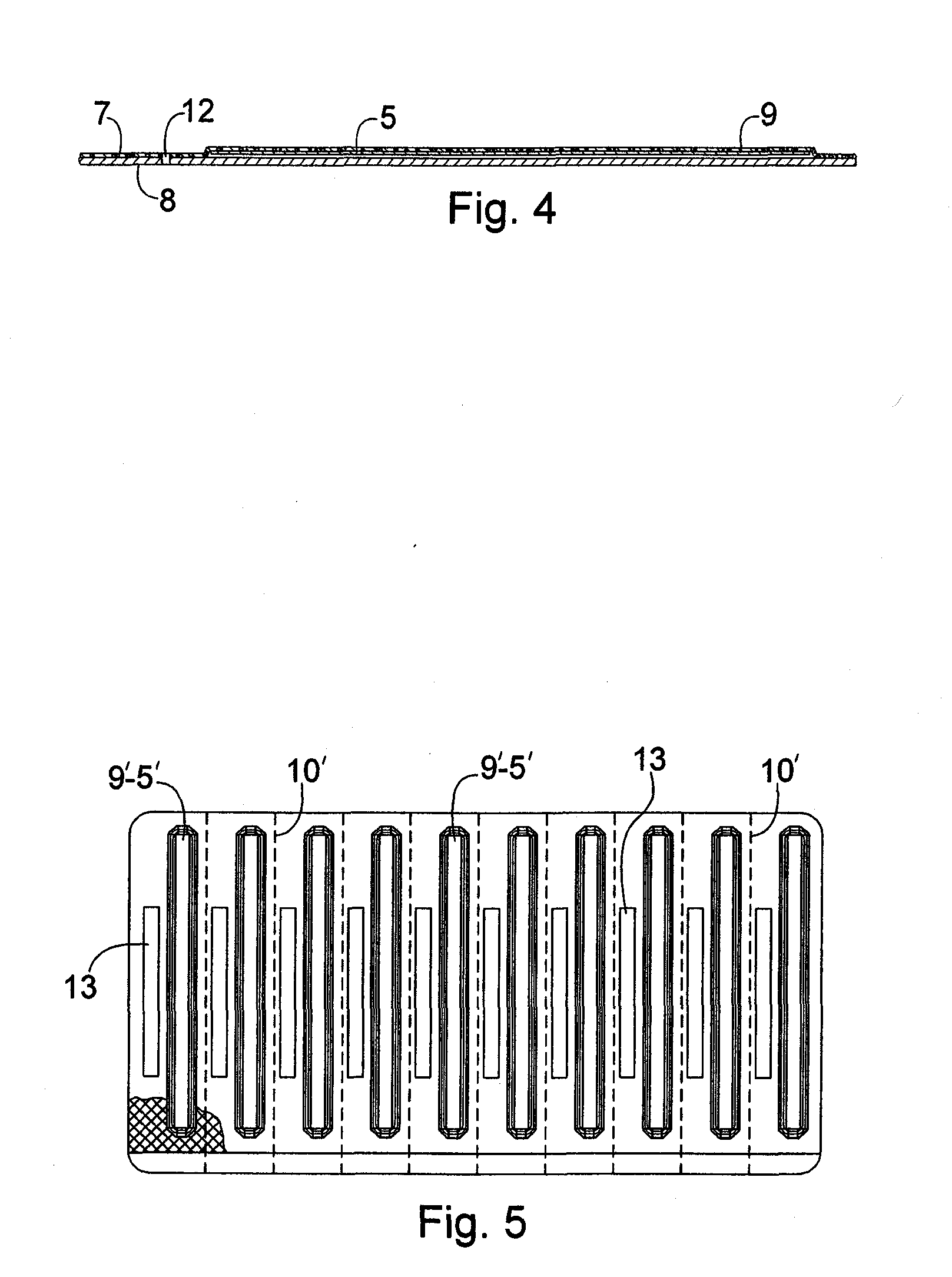
A package which incorporates, integrated in the composition of one of the components of the test's package, a plastic base (1), a moisture absorbing agent, so that this does not affect them, in combination with one or more polymers, which may be packaged in a blister produced by a base sheet (7) with structures which give rise to cavities (9), in each one whereof a rapid diagnostic test (5) is placed, whose base sheet (7) is complemented with a cover sheet (8) which seals the previous by heat fusion, achieving the hermeticity of each cavity.
Owner:ELORZ OSCAR LANDETA +1
Rapid diagnostic test systems and methods
ActiveUS7625763B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRapid screening testAssay
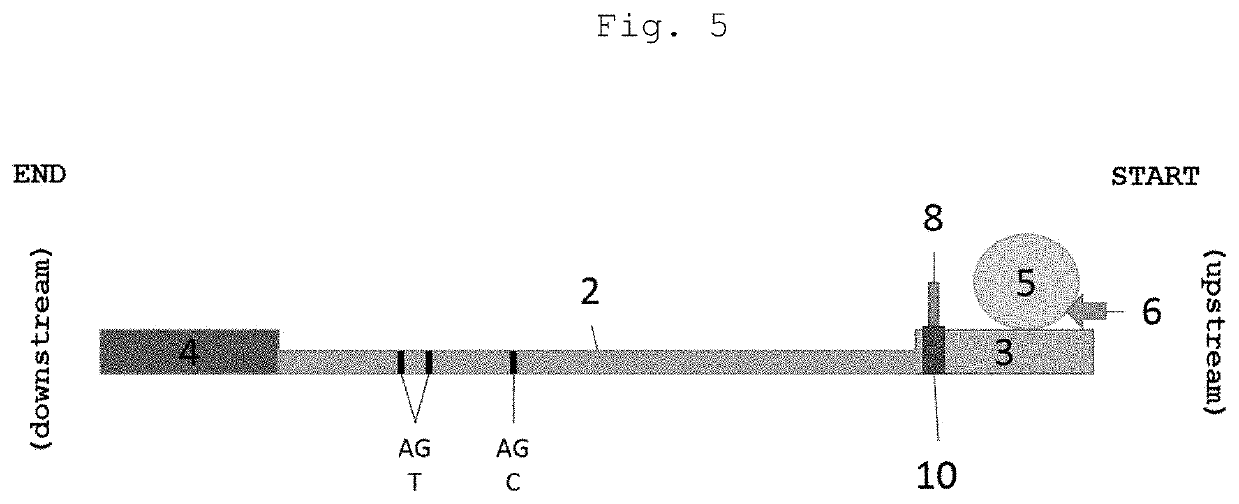
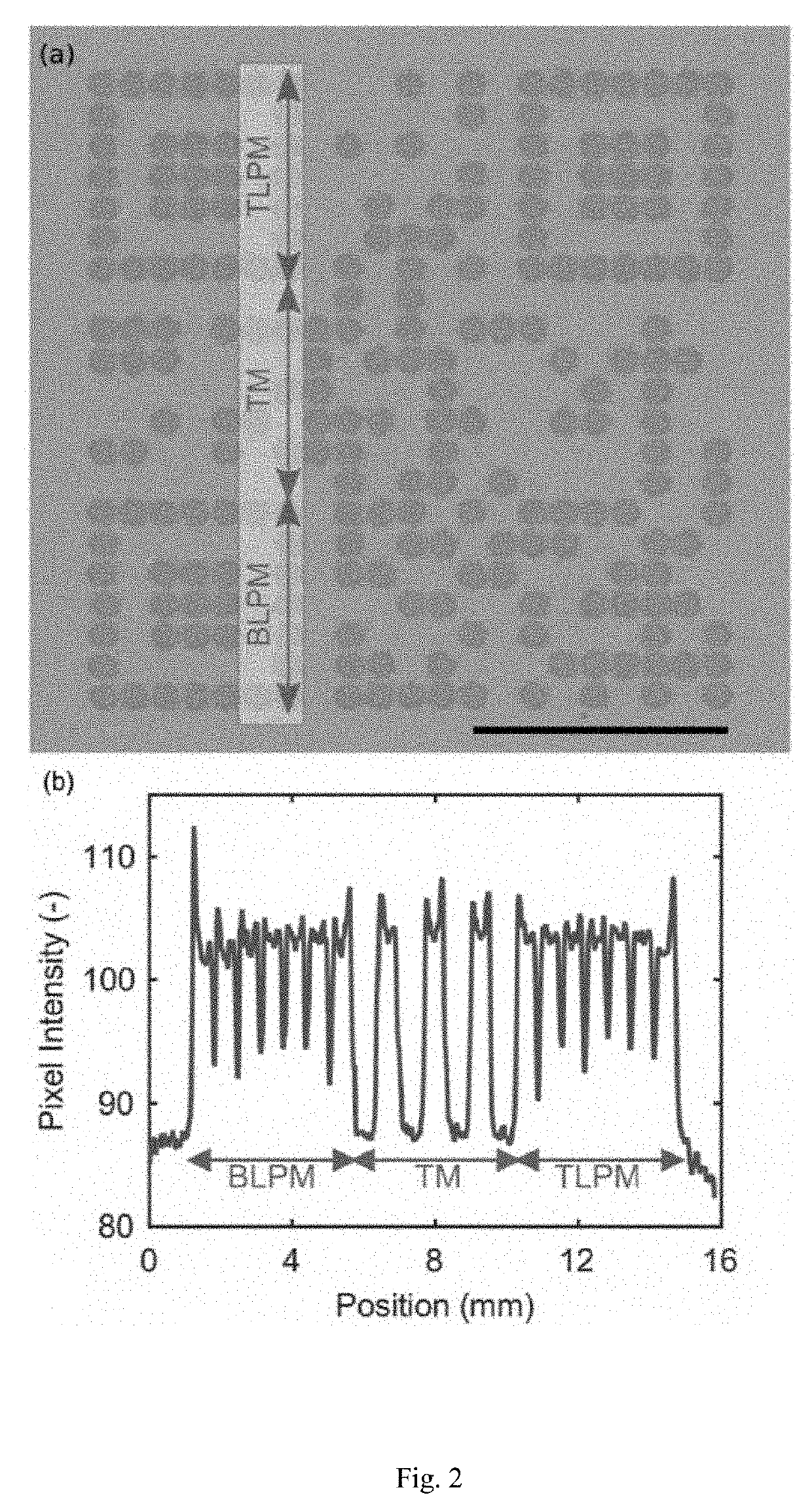
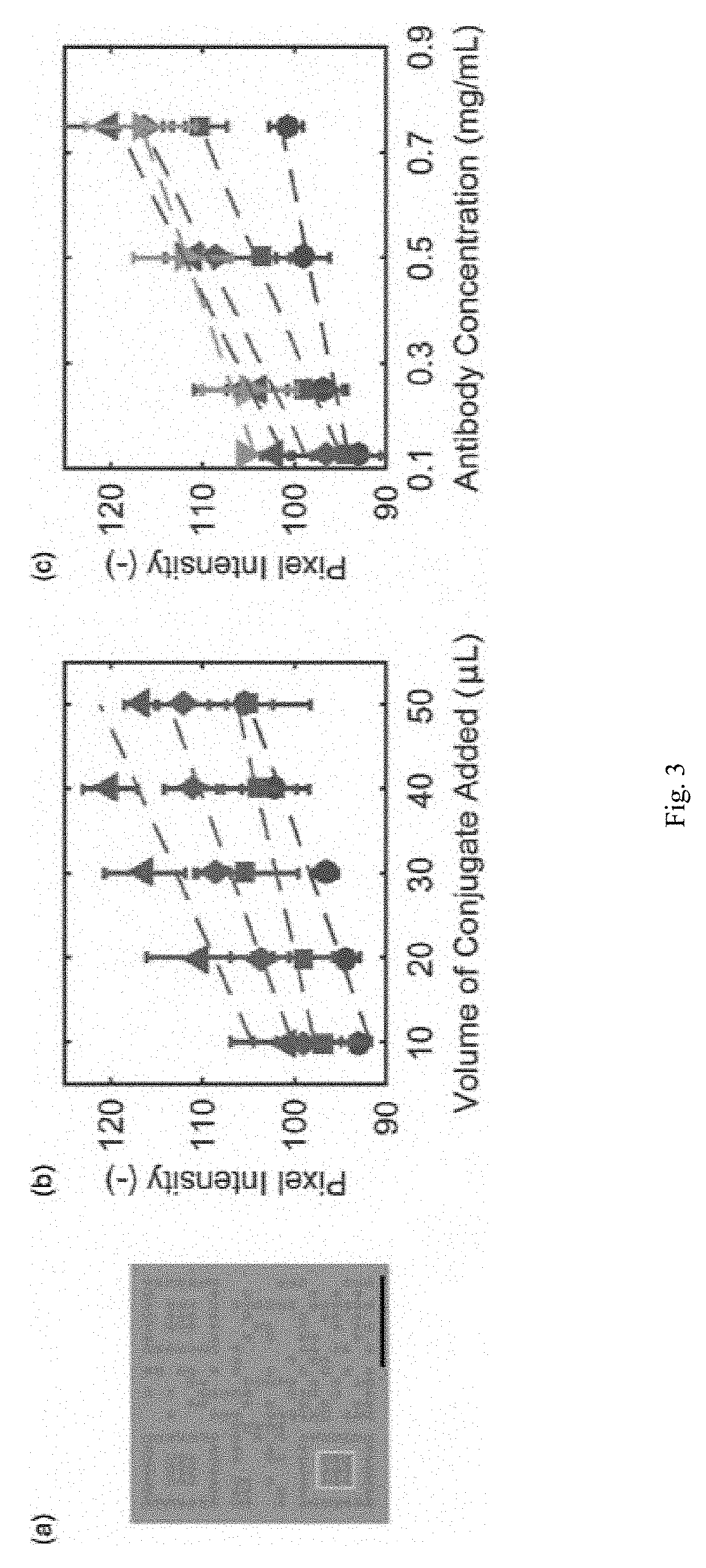
A rapid diagnostic test system includes a lateral-flow strip for performing a binding assay. The lateral-flow strip contains a binding agent having a deposition density that varies periodically along at least a portion of the lateral-flow strip. The test system further includes an imaging system that is used to capture an image of the portion of the lateral-flow strip.
Owner:ALVERIX
Portable fluorescence immunity analyzer and portable fluorescence analysis method
PendingCN107884571AEasy to carryRapid sample testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceRapid screening testFluorescence immunoassay analyzer
The invention discloses a portable fluorescence immunity analyzer. The portable fluorescence immunity analyzer comprises a test strip bin, an excitation light source, a camera, a communication moduleand a processing module, wherein the test strip bin is used for being inserted with a fluorescence chromatography rapid diagnosis test strip; the excitation light source is arranged right above a color developing region of the fluorescence chromatography rapid diagnosis test strip and used for exciting a fluorescent substance on the fluorescence chromatography rapid diagnosis test strip to producefluorescence emitting lights; the camera is arranged at an entrance above an acquisition channel on the excitation light source and used for acquiring the fluorescence emitting lights of a fluorescence test strip; the communication module is used for sending an image acquired by the camera; and the processing module is used for controlling the excitation light source, the camera and the communication to work harmoniously.
Owner:北京安百胜诊断科技有限公司 +1
Semiconductor device, diagnostic test, and diagnostic test circuit
ActiveCN104977523AElectronic circuit testingRedundant data error correctionPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
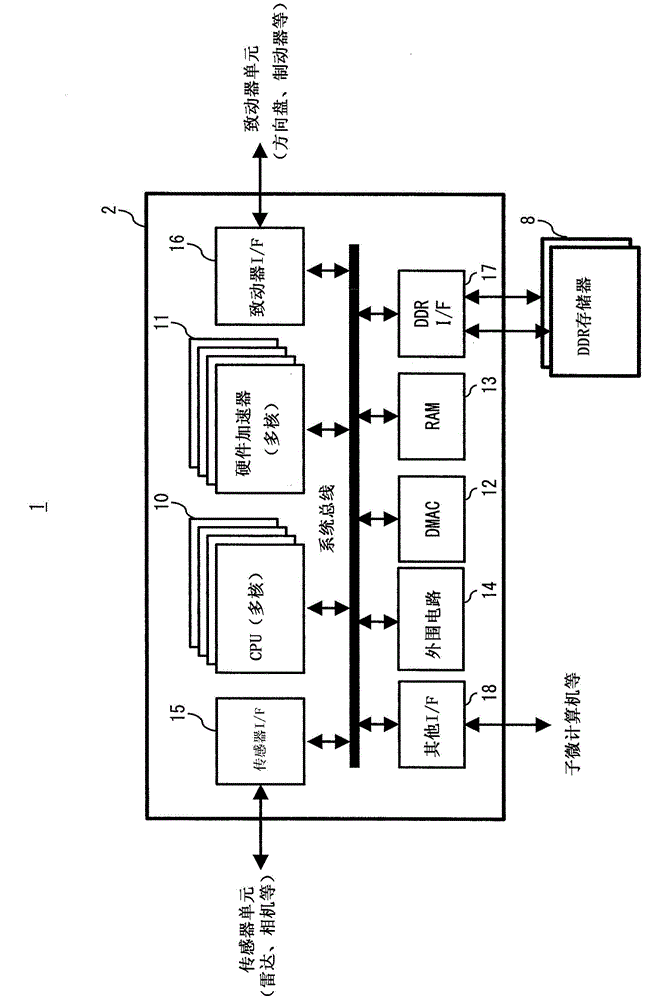
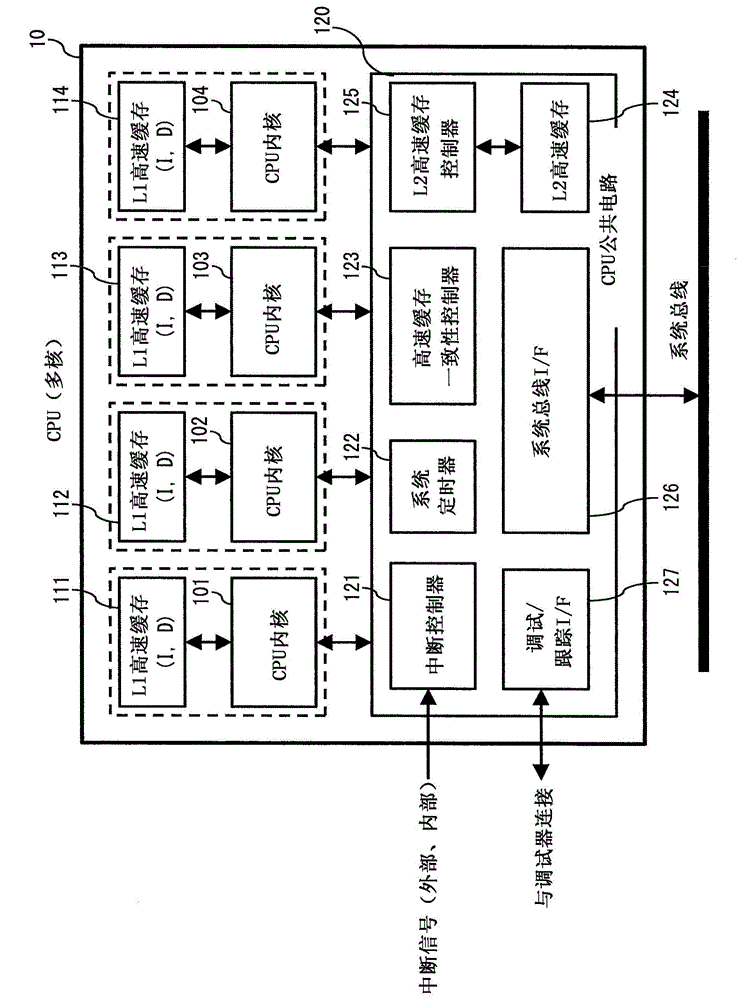
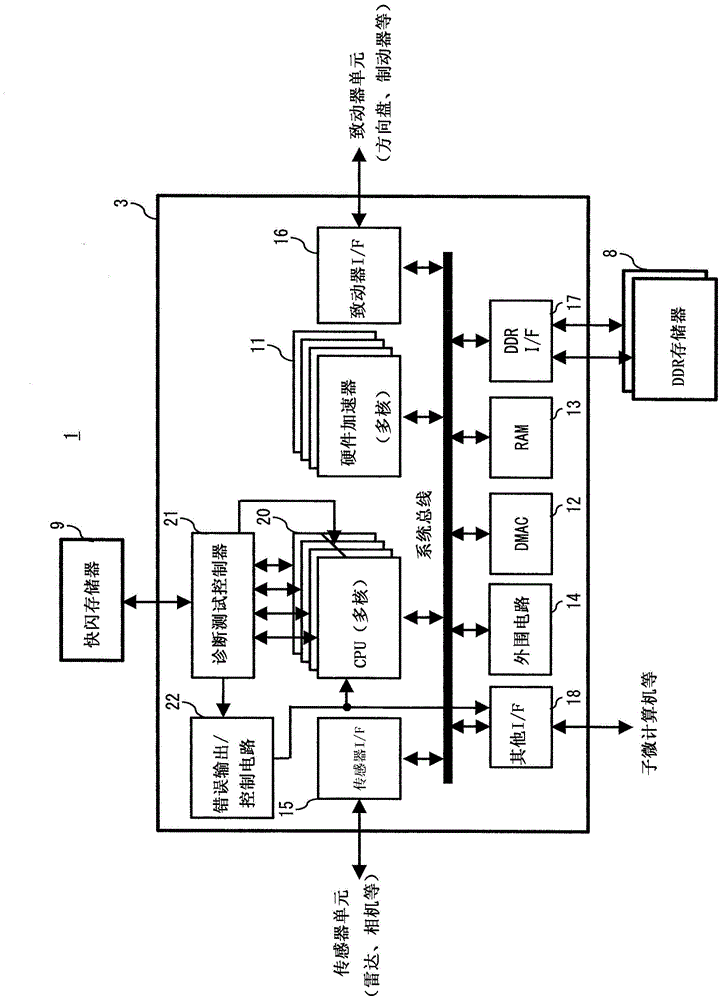
Deterioration in operation performance due to a fault diagnosis is prevented. A semiconductor device (90) according to the present invention includes a plurality of CPU cores (91 to 94) each including a scan chain, and a diagnostic test circuit (95) that performs a scan test for the plurality of CPU cores (91 to 94) by using the scan chain of the CPU core. The diagnostic test circuit (95) performs a scan test for each of the plurality of CPU cores (91 to 94) in a predetermined order on a periodic basis so that execution time periods of the scan tests do not overlap each other.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Non-invasive rapid diagnostic test for M. tuberculosis infection
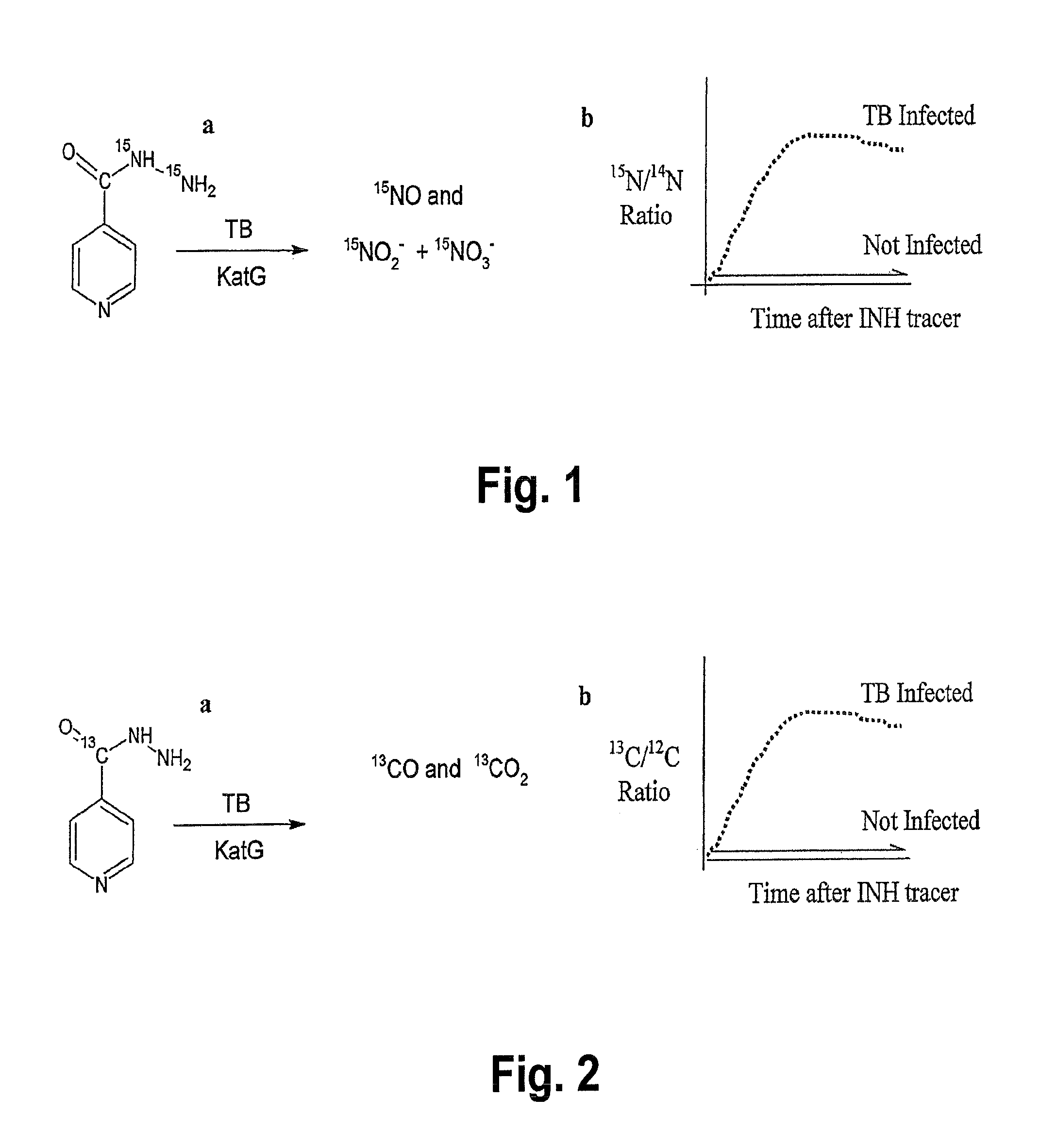
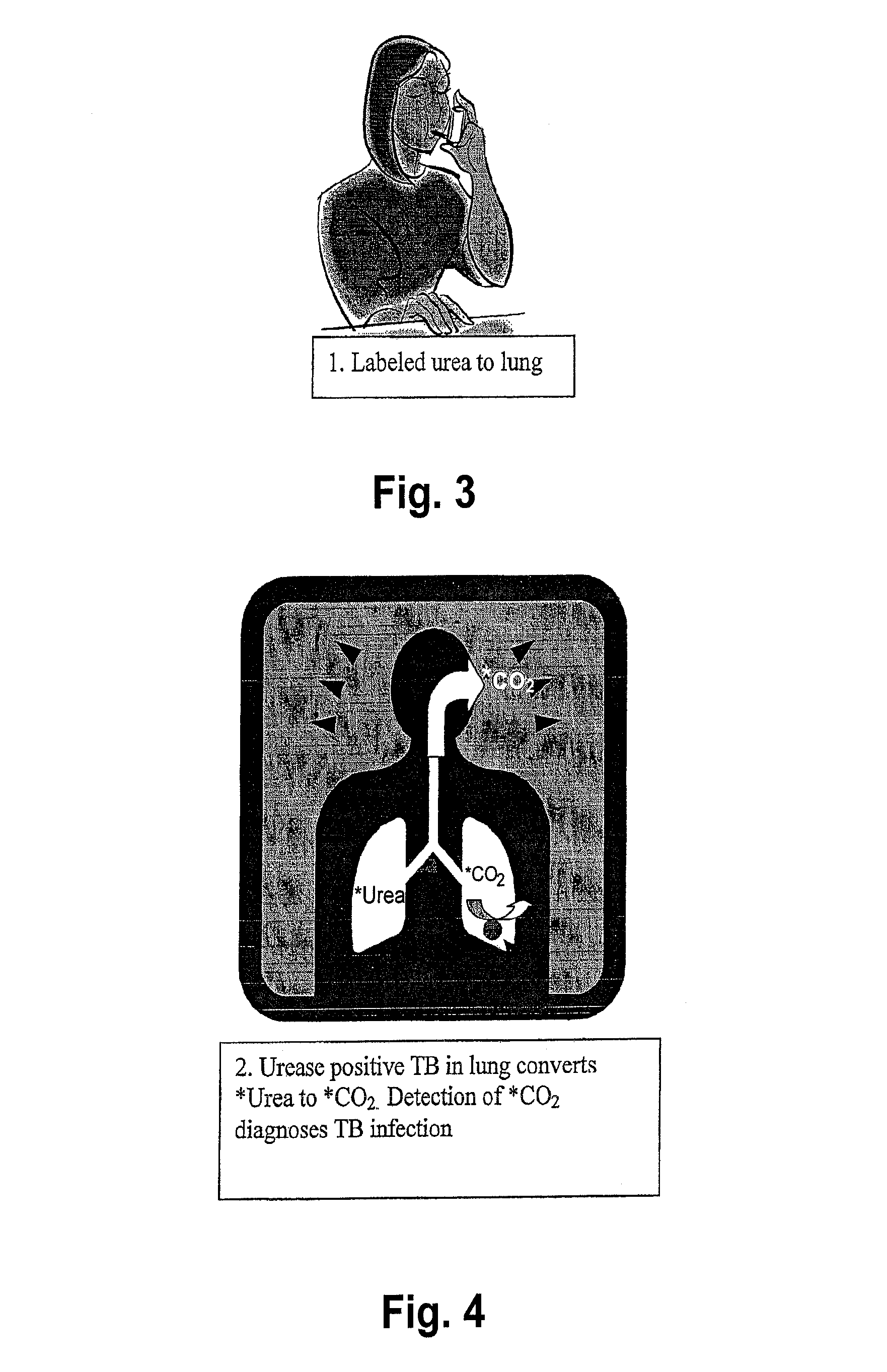
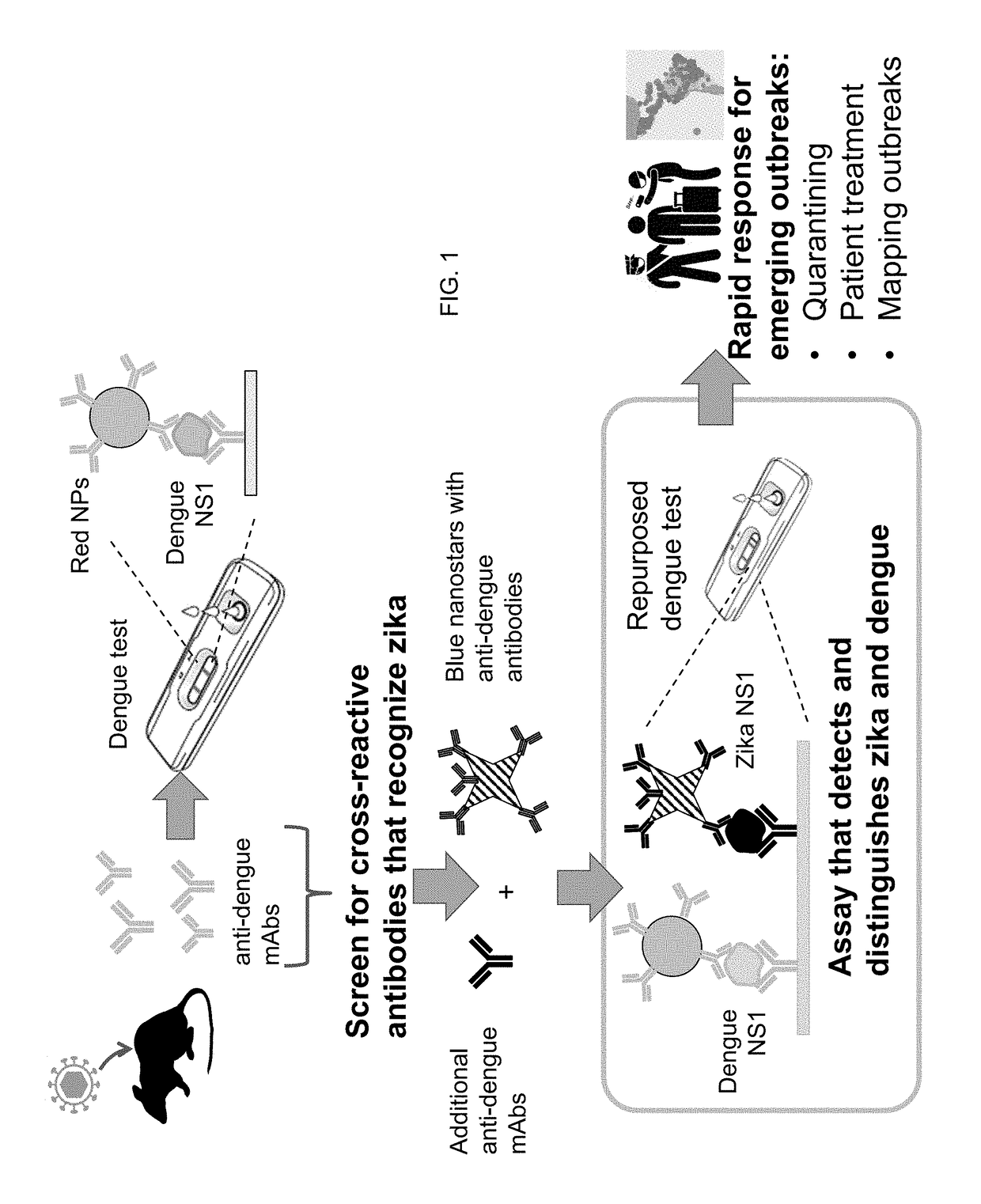
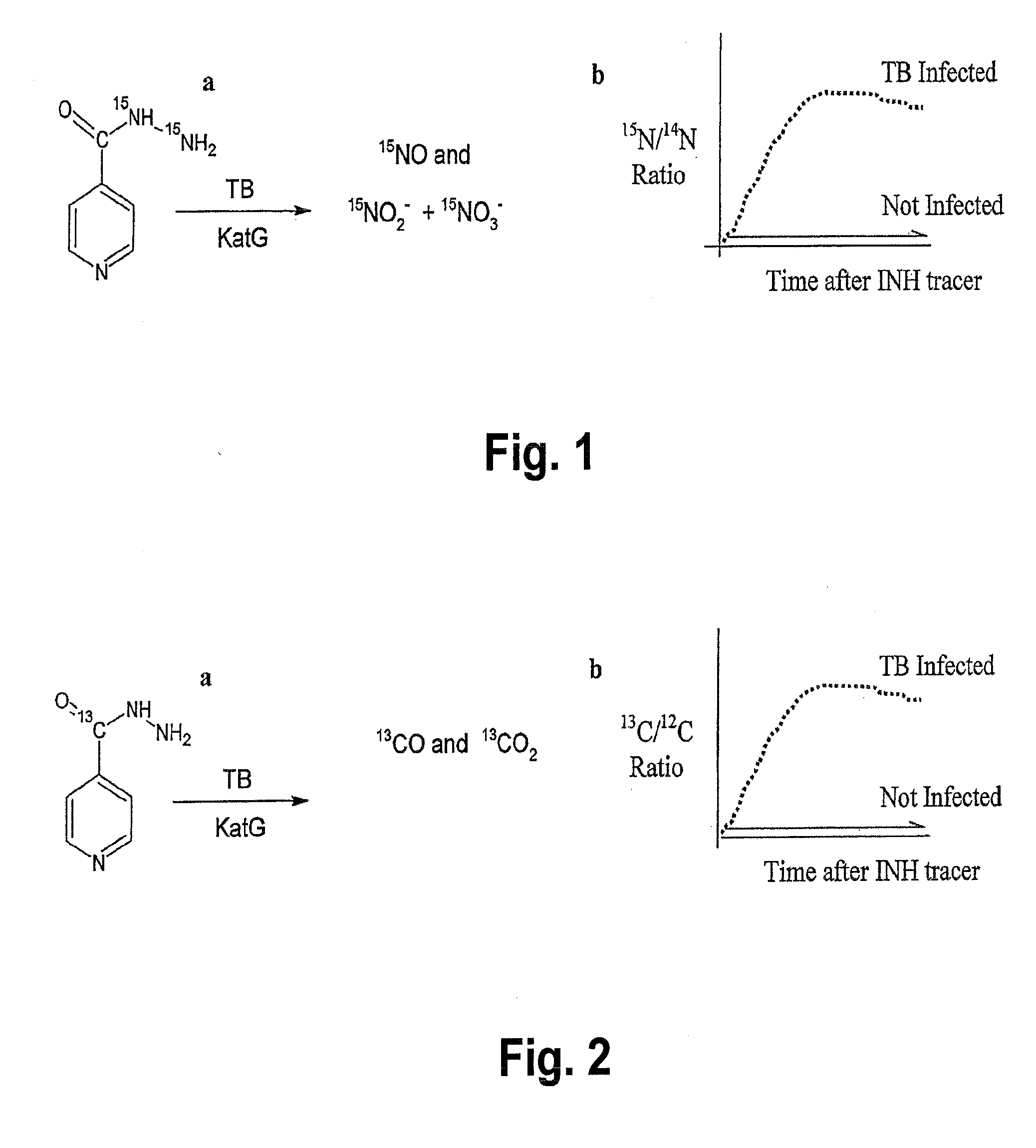
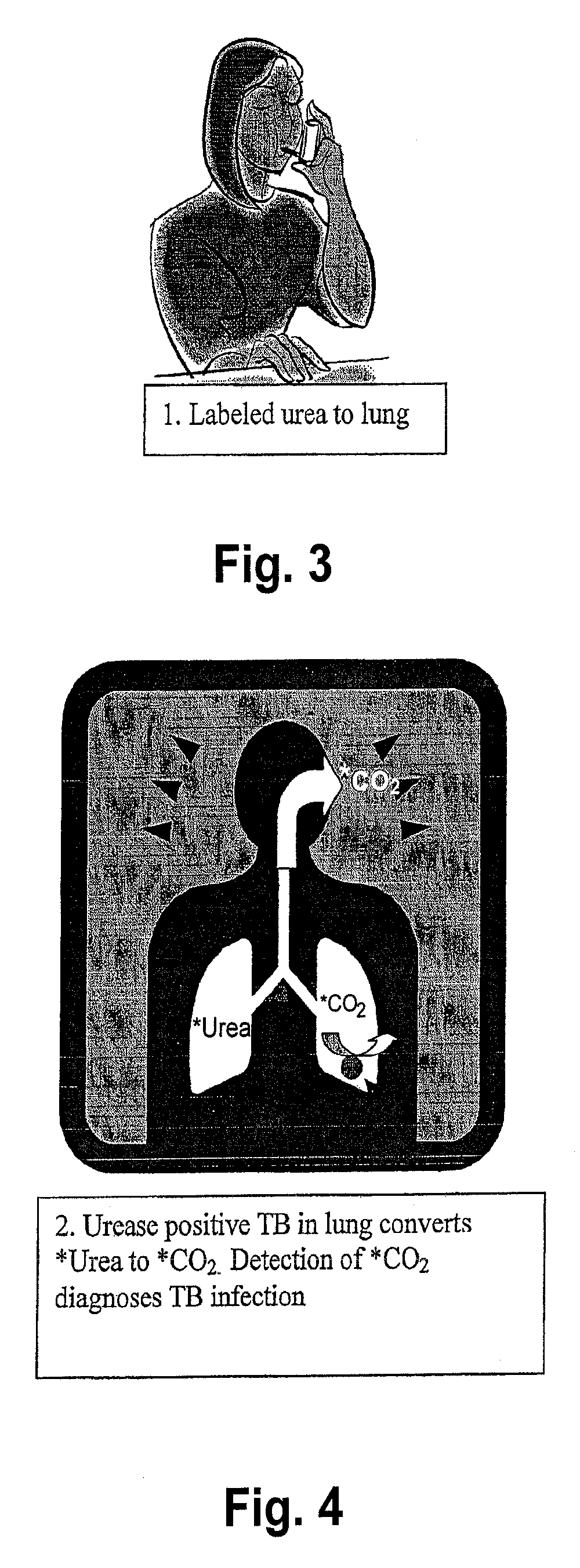
This invention relates to a test for detecting a Mycobacterium tuberculosis (tuberculosis or TB) infection in a patient or subject, specifically a diagnostic test, including a breath test, whereby patients are provided a small dose of an isotopically labeled TB drug, Isoniazid (INH) orally or directly to the lungs of the patient or subject. If TB is present, a TB enzyme mycobacterial peroxidase KatG oxidizes the INH; and KatG specific metabolites, in particular, isotopically labeled nitric oxide (NO), nitrites, nitrates, carbon monoxide (CO) or carbon dioxide converted from carbon monoxide of INH cleavage are measured. Other embodiments relate to a diagnostic breath test for detecting TB utilizing isotopically labeled urea (preferably, carbon-13 labeled urea), alone or in combination with isotopically labeled isoniazid (preferably, nitrogen-15 labeled isoniazid), wherein M. tuberculosis organism, if present in the patient or subject's lungs (or other tissues), will metabolize the isotopically labeled urea to isotopically labeled carbon dioxide (CO2) such that a determination of the residence of M. tuberculosis, including residence of an isoniazid resistant strain of M. tuberculosis, may be made.
Owner:STC UNM
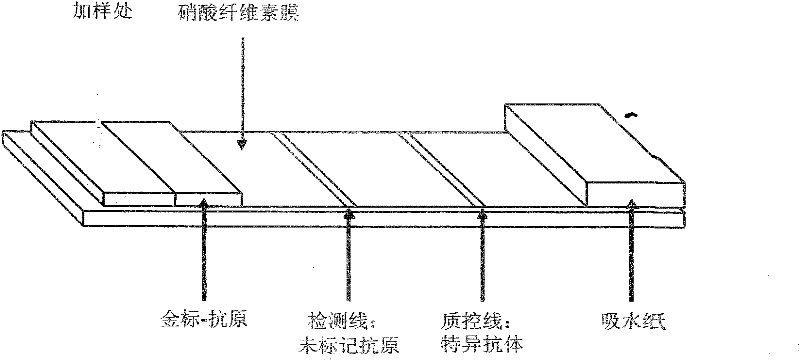
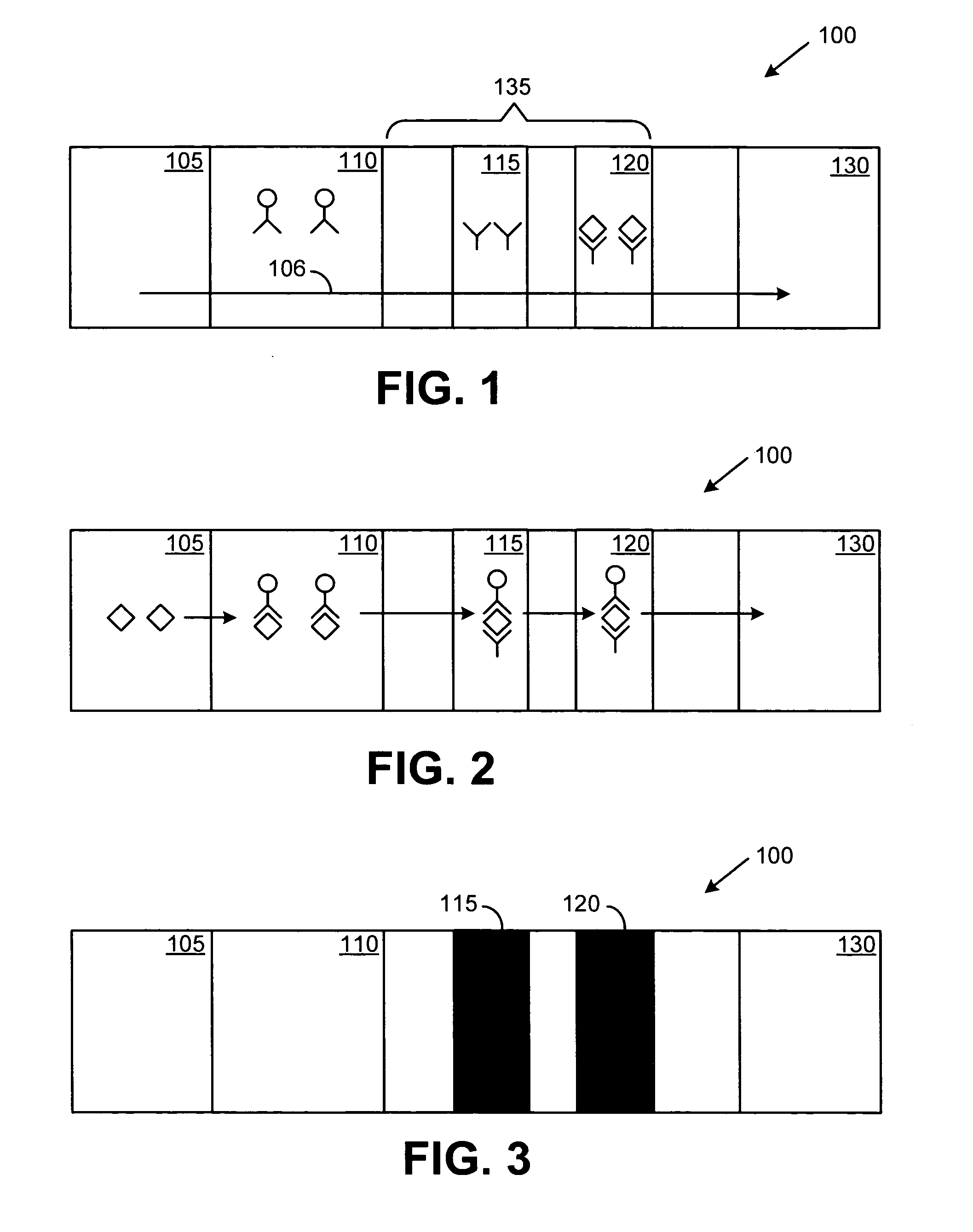
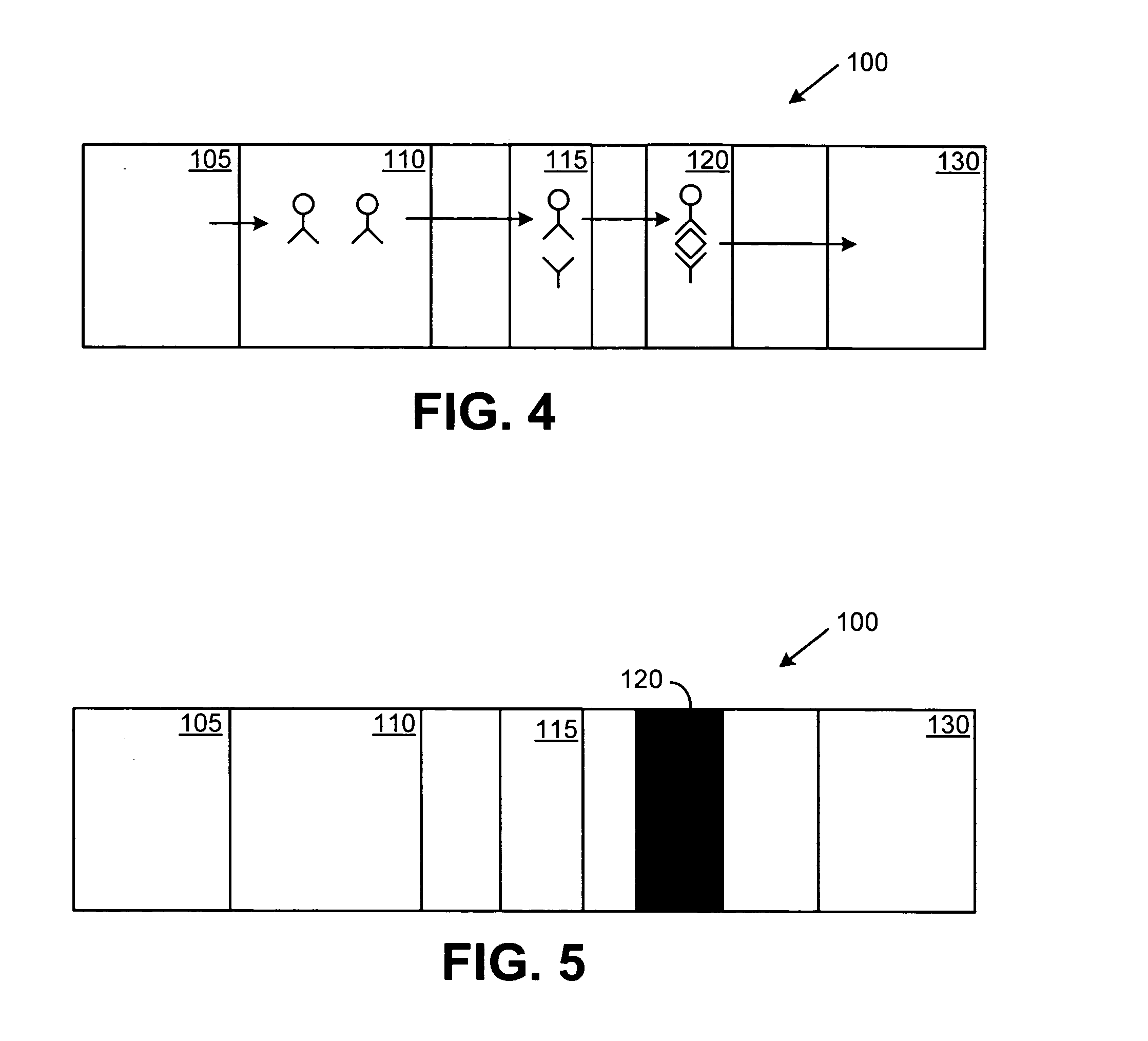
Multiplexed Immunoassay for Detecting Biomarkers of Disease
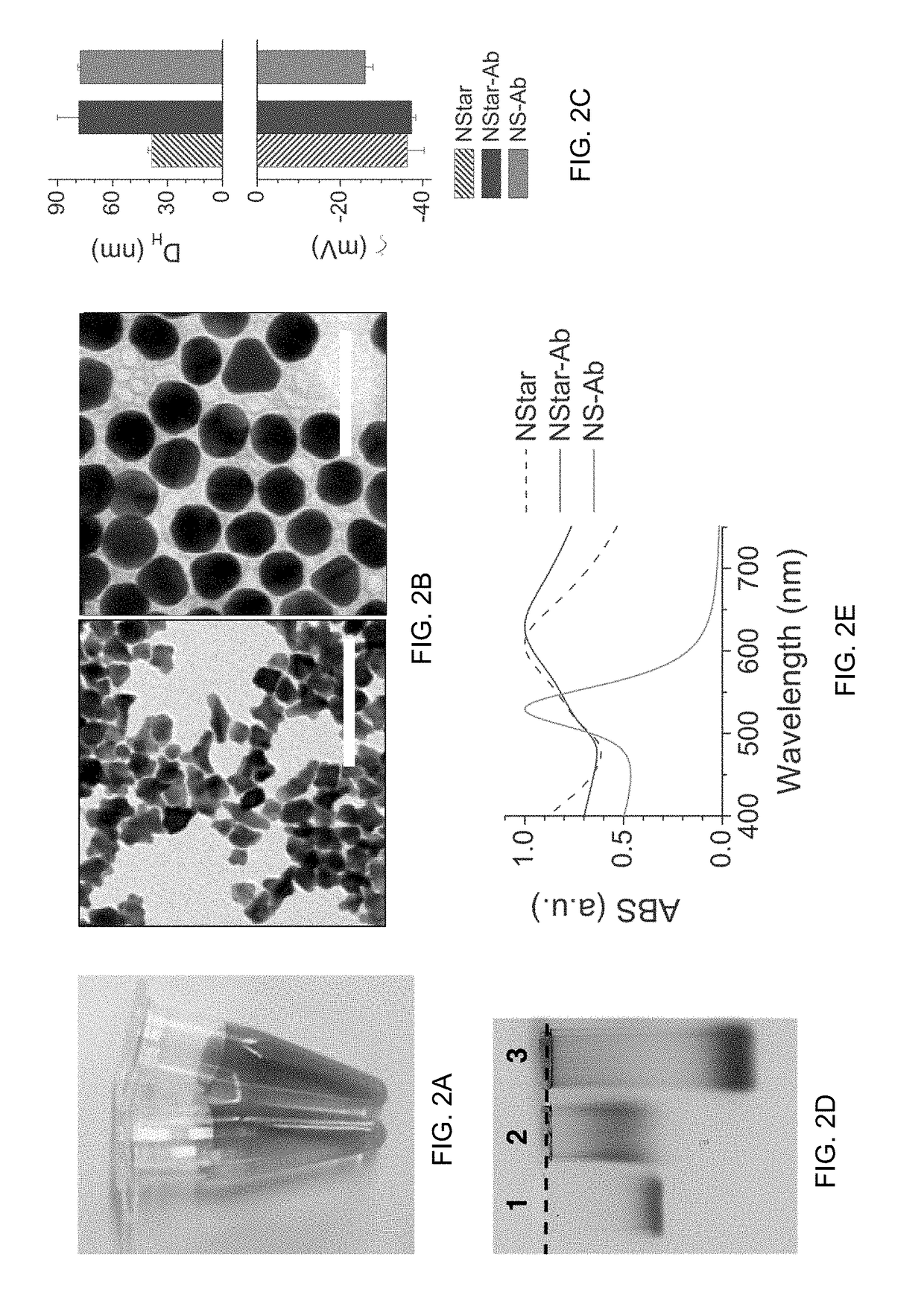
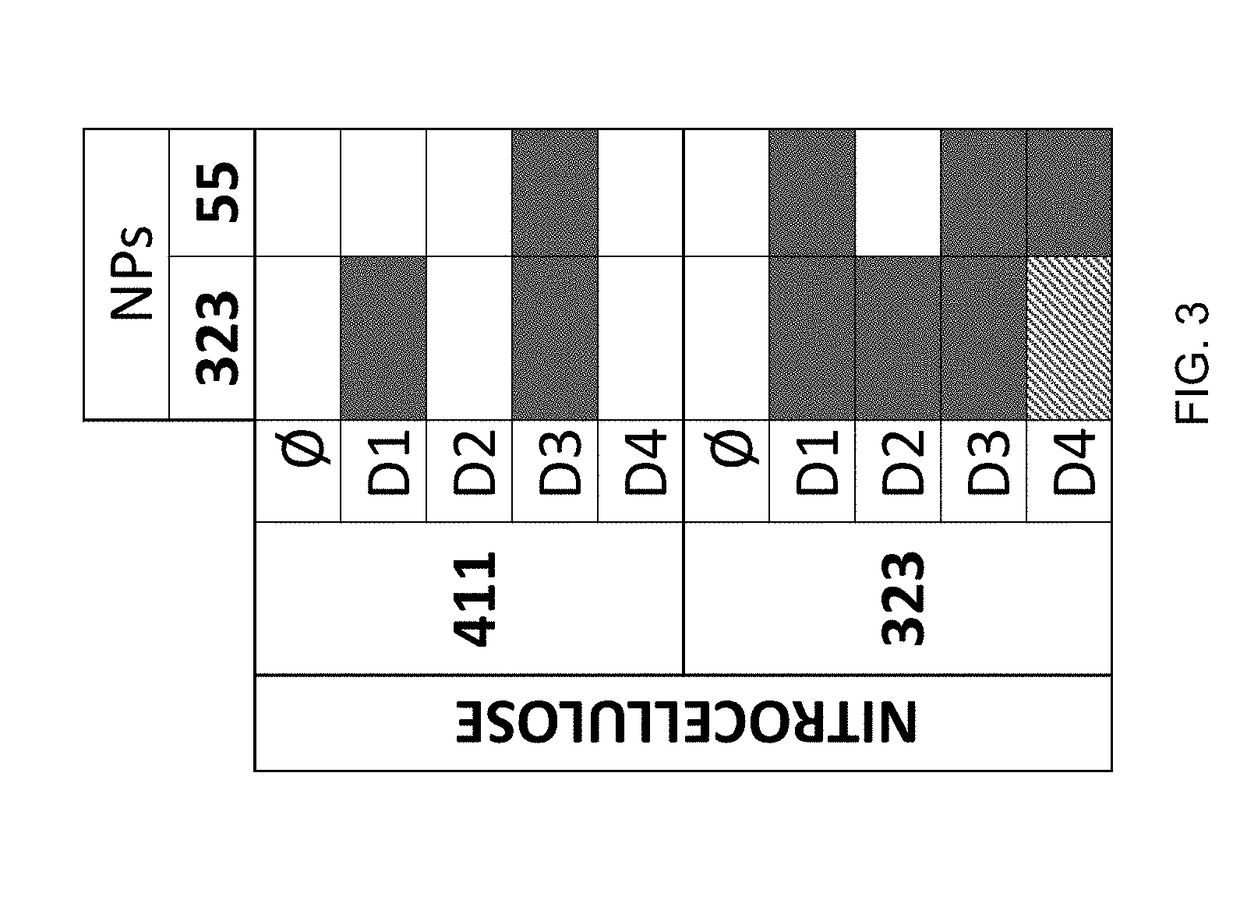
The present invention provides a multiplexed immunoassay which leverages stockpiled antibodies to detect whether a patient has been infected with an emerging disease which does not have specific antibodies raised against it (FIG. 1). The assay is preferably designed as a paper-based assay, which allows diagnosis at point of care (POC) and readout by eye or mobile phone. Paper-based rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) are convenient, robust, and can be read out within minutes. The immunoassay of the invention combines the strategic use of nanoparticles of assorted colors with readily available stockpiled antibodies to one or more biomarkers of disease, particularly viral diseases.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Immunoassay rapid diagnostic test universal analysis device, system, method and computer readable medium
InactiveUS20150212074A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsBiological testingRapid screening testComputer science
A device, system, method, and computer readable medium is provided for universal analysis of immunoassay rapid diagnostic tests. They permit different tests, from varied manufacturers, to be read even though such tests may be associated with reflection and / or emission types of signals. The device, system, method, and computer readable medium use one or more rapid diagnostic test databases, including information on products commercially available on the market and on customized rapid tests. The device, system, method, and computer readable medium identify the type of test to be analyzed by matching it with the test database(s). They capture a corresponding reflection and / or emission signal from the test, as appropriate. The device, system, method, and computer readable medium may transform the signal to an image, or vice-versa, and / or analyze the image to interpret the test result.
Owner:FIO CORP
Non-Invasive Rapid Diagnostic Test For M.Tuberculosis Infection
ActiveUS20090191639A1Improve protectionImprove the immunityCompounds screening/testingBiocideRapid screening testMetabolite
This invention relates to a test for detecting a Mycobacterium tuberculosis (tuberculosis or TB) infection in a patient or subject, specifically a diagnostic test, including a breath test, whereby patients are provided a small dose of an isotopically labeled TB drug, Isoniazid (INH) orally or directly to the lungs of the patient or subject. If TB is present, a TB enzyme mycobacterial peroxidase KatG oxidizes the INH; and KatG specific metabolites, in particular, isotopically labeled nitric oxide (NO), nitrites, nitrates, carbon monoxide (CO) or carbon dioxide converted from carbon monoxide of INH cleavage are measured. Other embodiments relate to a diagnostic breath test for detecting TB utilizing isotopically labeled urea (preferably, carbon-13 labeled urea), alone or in combination with isotopically labeled isoniazid (preferably, nitrogen-15 labeled isoniazid), wherein M. tuberculosis organism, if present in the patient or subject's lungs (or other tissues), will metabolize the isotopically labeled urea to isotopically labeled carbon dioxide (CO2) such that a determination of the residence of M. tuberculosis, including residence of an isoniazid resistant strain of M. tuberculosis, may be made.
Owner:STC UNM
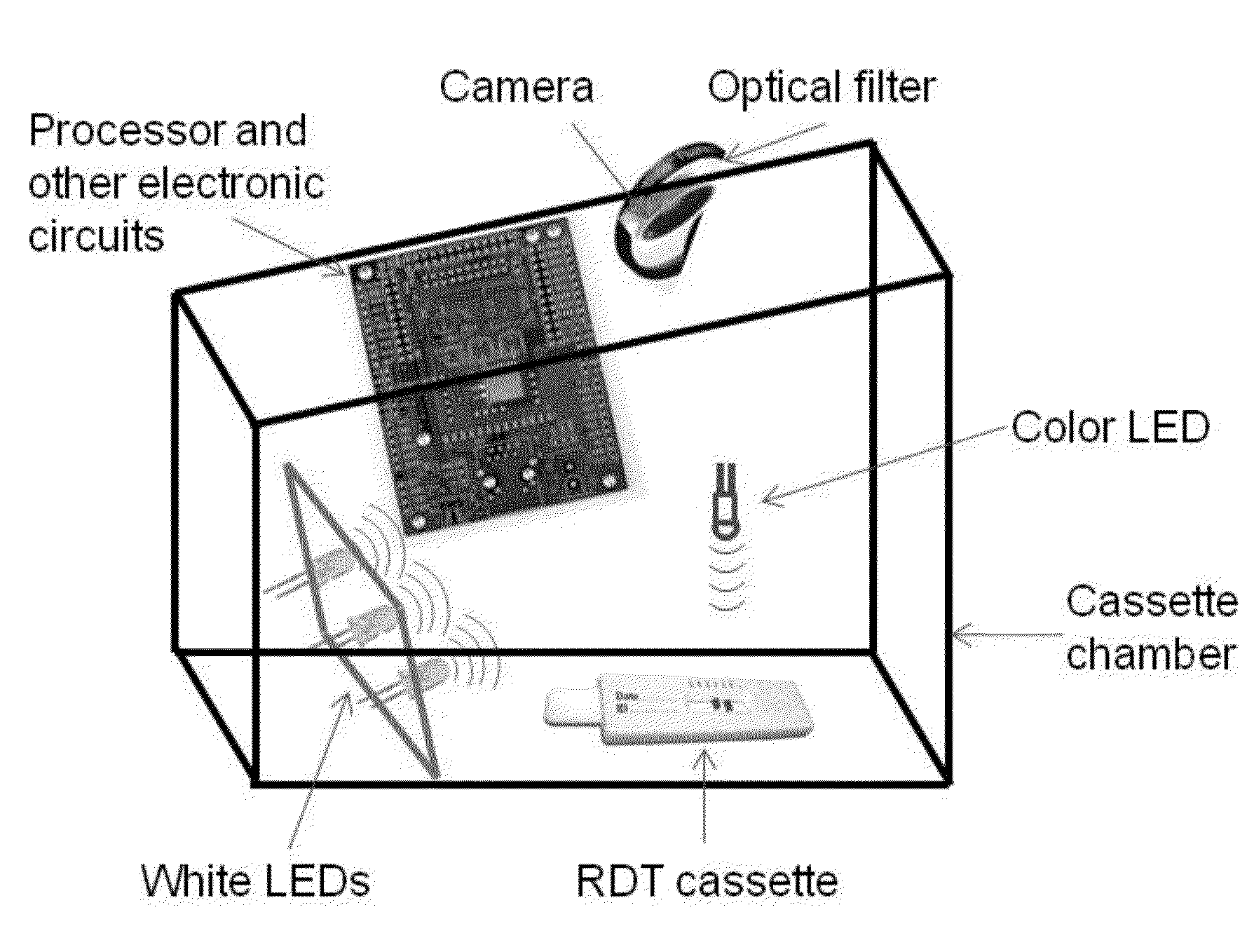
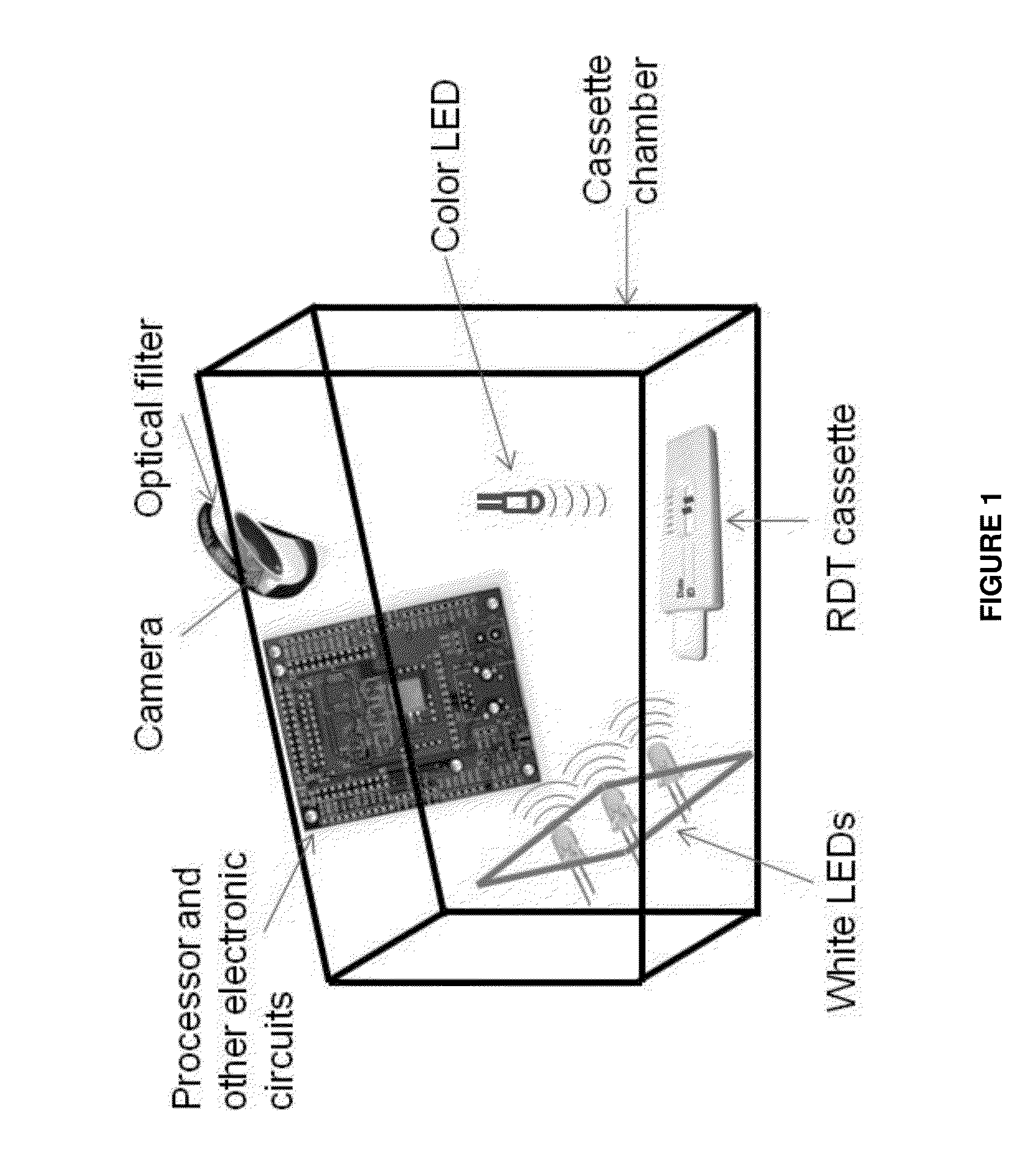
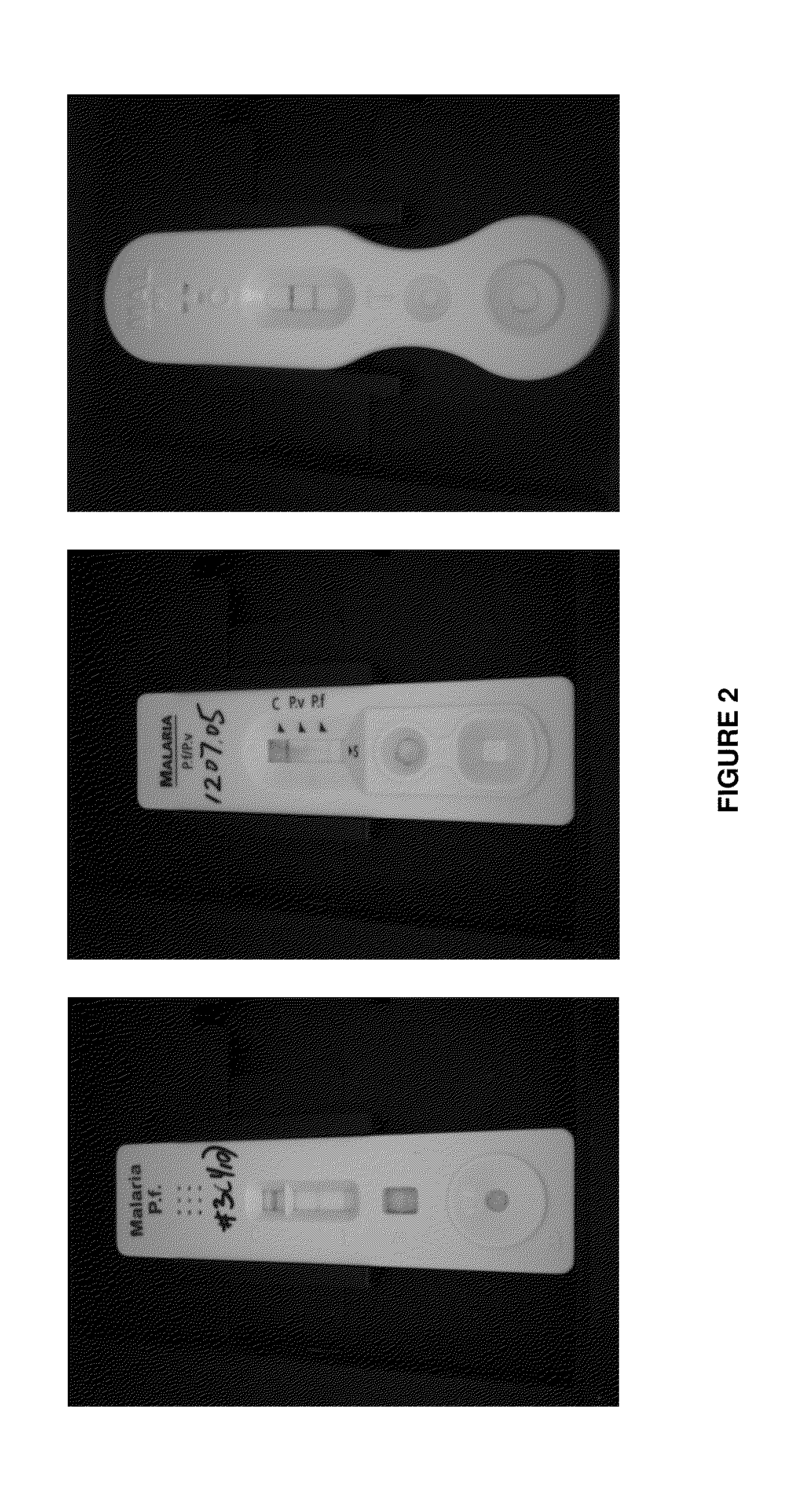
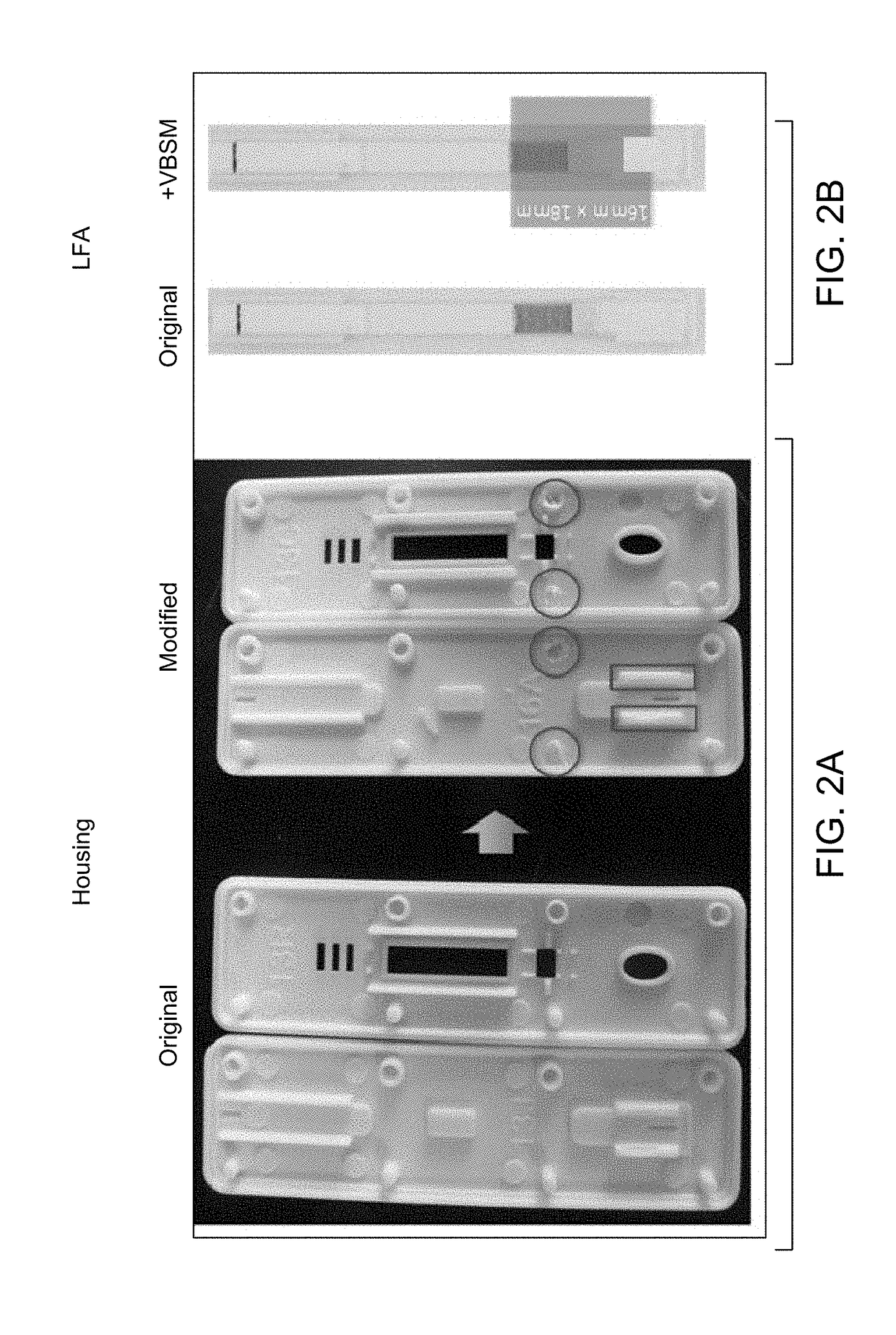
A quality control sensor method, system and device for use with biological/environmental rapid diagnostic test devices
InactiveCN104303212ARegistering/indicating quality control systemsThermometers using physical/chemical changesRapid screening testImaging analysis
Quality control (QC) sensor methods, systems and devices are for use with biological / environmental rapid diagnostic test (RDT) devices and provide for automatic timers, reminders and RDT cassette images. Sensors are calibrated and optimized, and provide for quality control of the RDT devices. Image analysis identifies cassette and patient information, and evaluates the processing and conditions of the RDT devices, cassettes and RDTs. Results may be accessed and analyzed remotely from the RDT devices. RDT chain of custody and workflow, incubation and reading sequences are tracked. A QC score for each unique patient RDT is determined based on QC criteria.
Owner:FIO CORP
Process for producing surface enhanced membrane
InactiveUS7807475B2Speed up the processEfficient productionSemi-permeable membranesMembranesRapid screening testLiquid medium
Owner:SARTORIUS STEDIM BIOTECH GMBH
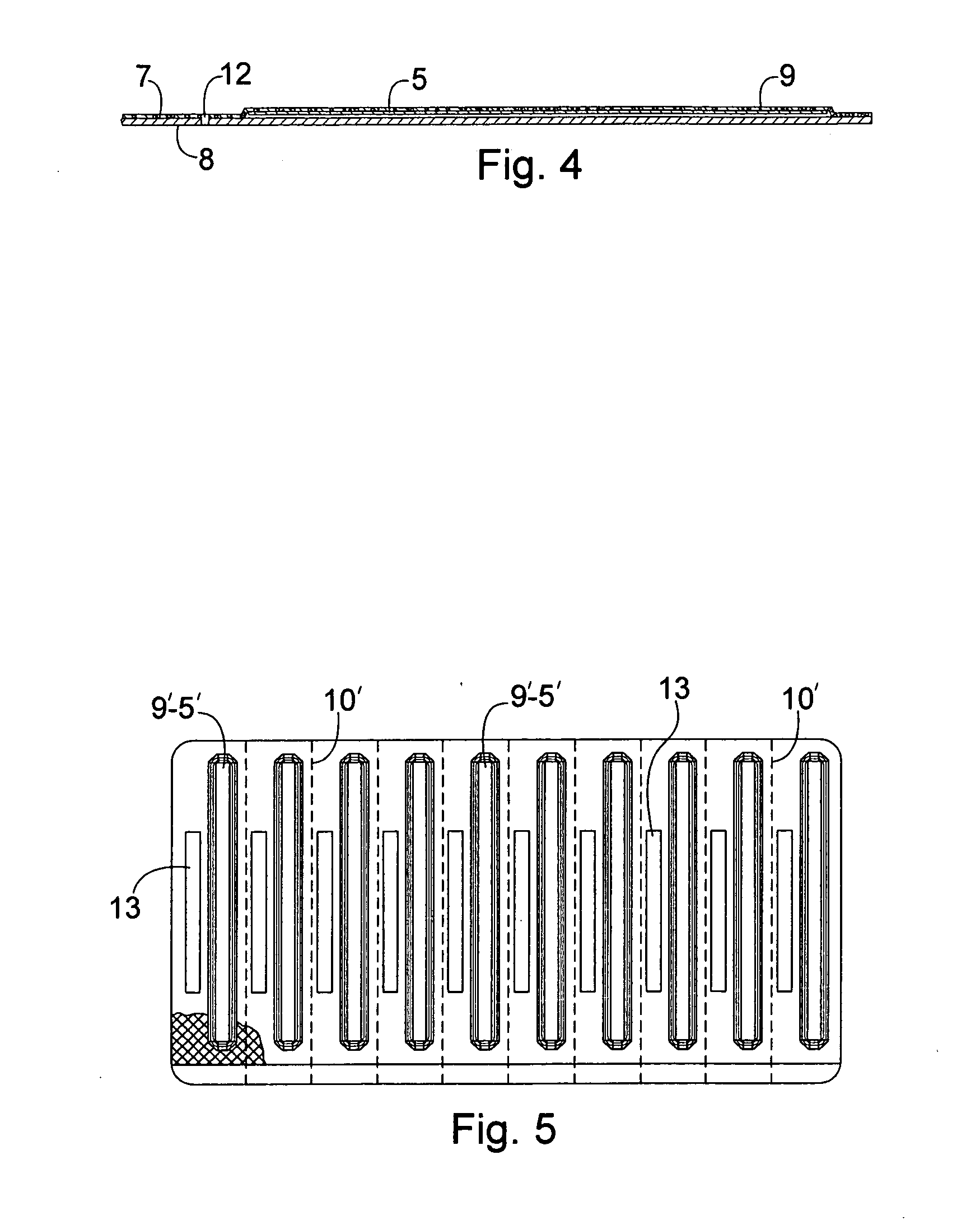
Blistered rapid diagnostic test with incorporated moisture absorbent material
InactiveUS20100025266A1Improve sealingReduced dimensionVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsLaboratory glasswaresRapid screening testAbsorbent material
A package which incorporates, integrated in the composition of one of the components of the test package, a plastic support (1), a moisture absorbing agent, so that this does not affect them, in combination with one or more polymers, which may be packaged in a blister produced by a base sheet (7) with cavities (9), in each one whereof a rapid diagnostic test (5) is placed, whose base sheet (7) is complemented with a cover sheet (8) which seals the base sheet by heat fusion, achieving the hermeticity of each cavity.
Owner:LANDETA ELORZ OSCAR +1
Quality control sensor method, system and device for use with biological/environmental rapid diagnostic test devices
InactiveUS20140324373A1Thermometers using physical/chemical changesSpecial data processing applicationsRapid screening testImaging analysis
Quality control (QC) sensor methods, systems and devices are for use with biological / environmental rapid diagnostic test (RDT) devices and provide for automatic timers, reminders and RDT cassette images. Sensors are calibrated and optimized, and provide for quality control of the RDT devices. Image analysis identifies cassette and patient information, and evaluates the processing and conditions of the RDT devices, cassettes and RDTs. Results may be accessed and analyzed remotely from the RDT devices. RDT chain of custody and workflow, incubation and reading sequences are tracked. A QC score for each unique patient RDT is determined based on QC criteria.
Owner:FIO CORP
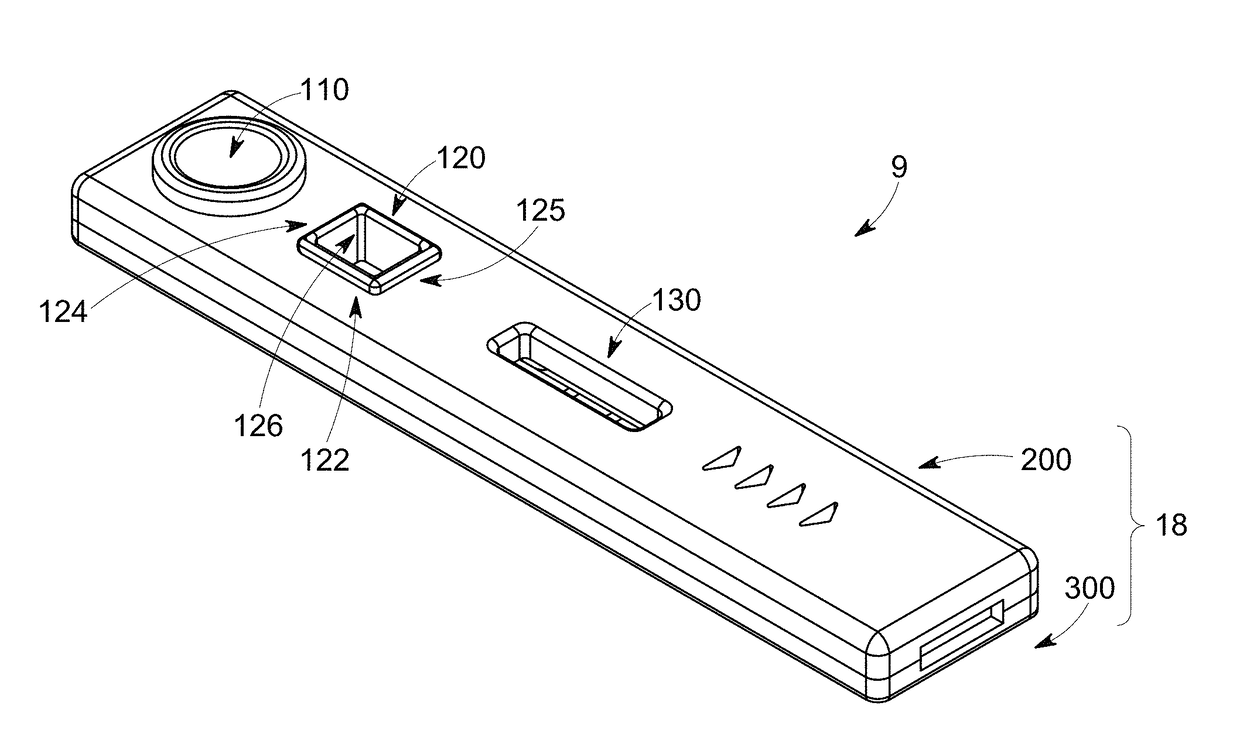
Cassette device for quick test of diagnosis, method for detecting a ligand in a biological sample and kit
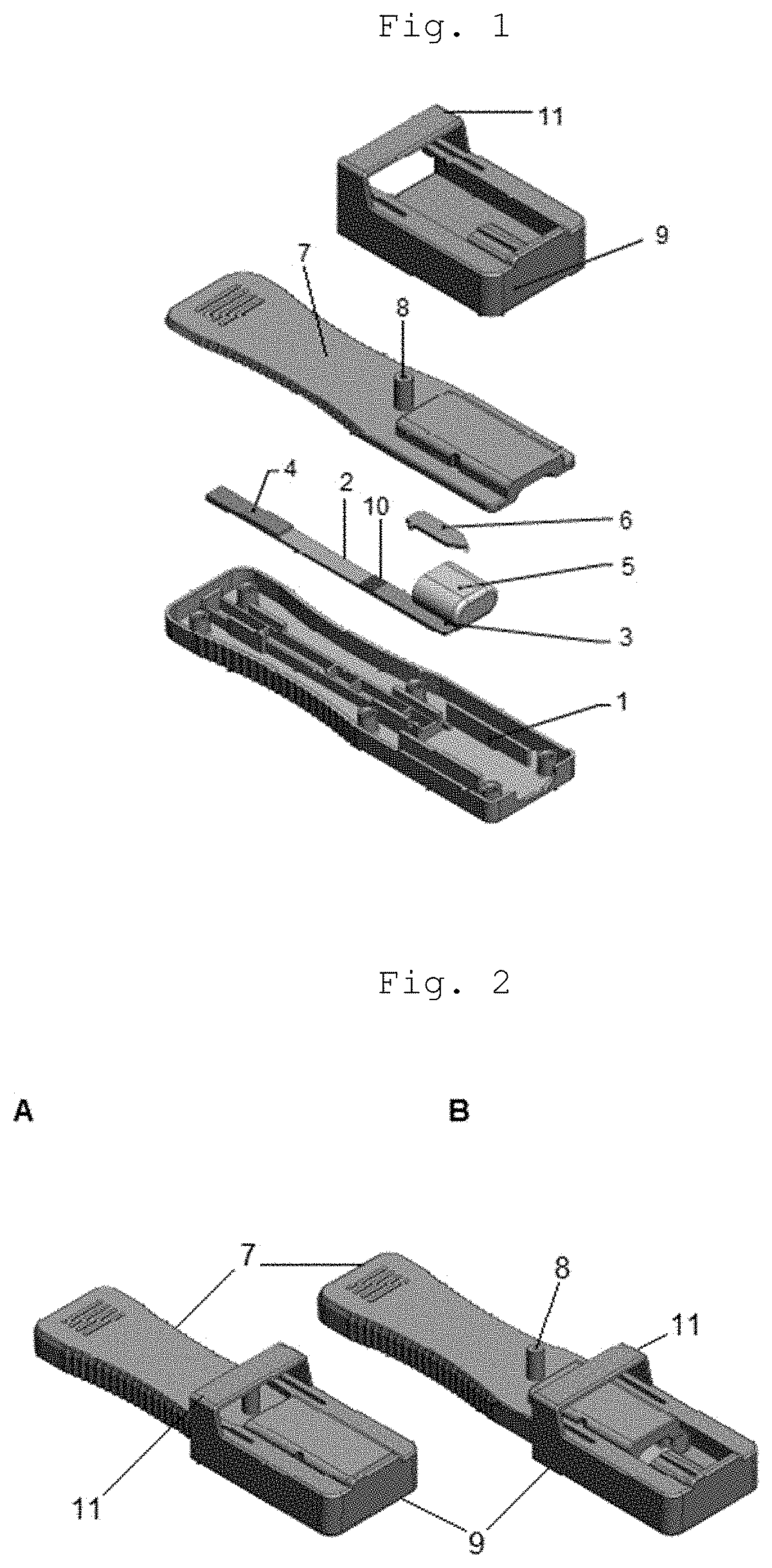
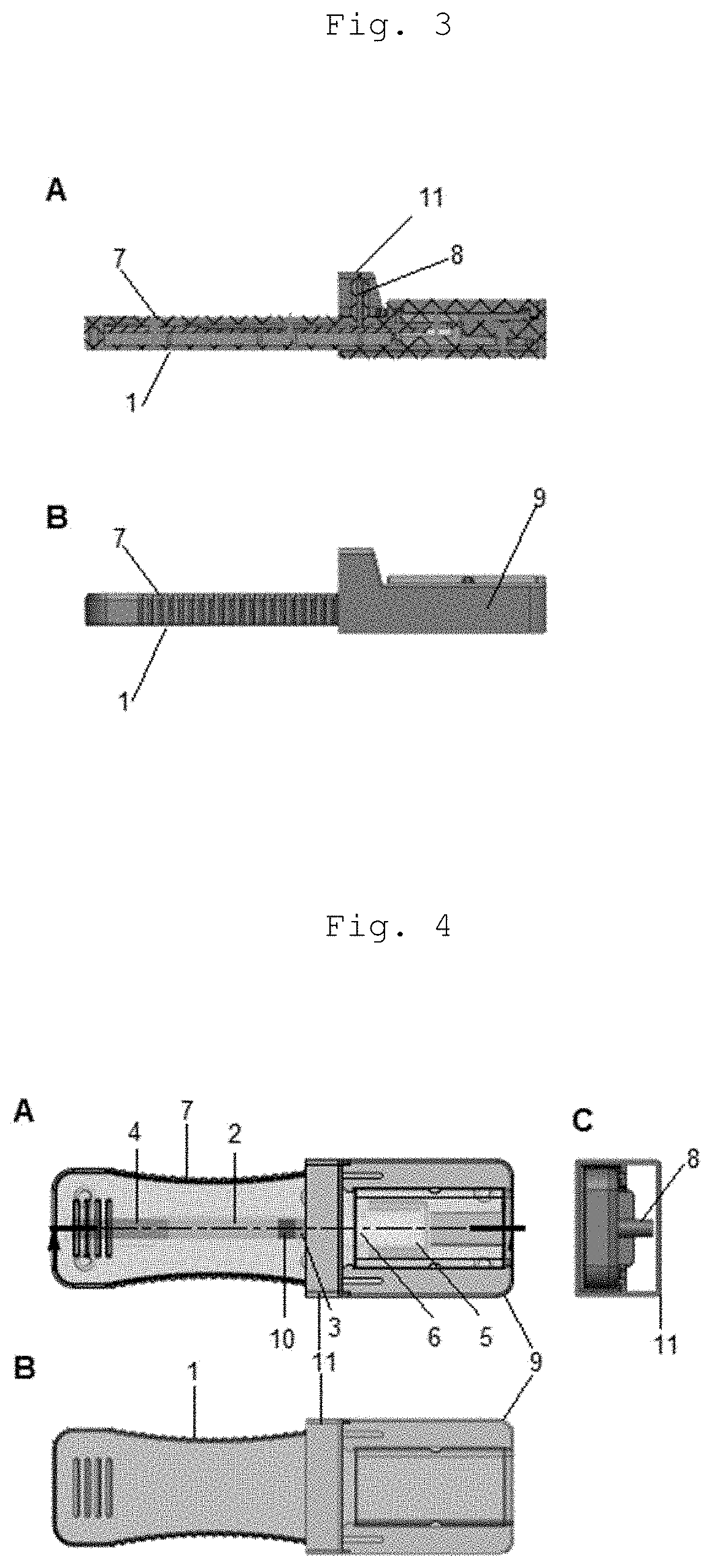
InactiveUS20200345286A1Promote migrationAvoid pollutionLaboratory glasswaresSensorsRapid screening testCapillary Tubing
A cassette device for rapid diagnostic test in a single step. More specifically, an immunochromatographic rapid test for identifying antibodies present in a biological sample, such as human blood, is disclosed. The device has a lower cassette (1) and an upper cassette (7) containing a capillary-tube-shaped structure (8). The capillary-shaped structure holds the sample amount needed for the rapid test, preventing waste and sample dilution. Lower (1) and upper (7) cassettes are attached by a movable cover (9), which when pressed causes the capillary-tube-shaped structure closure (8), and a disruption of a capsule (5) containing buffer solution by pressing thereof using a spear-shaped structure (6). Disruption of the capsule (5) by this mechanism allows the buffer solution to be poured in a controlled manner over an absorbent pad (3) located on a test strip (2) in a point anterior the point receiving the sample (10).
Owner:ORANGELIFE COMERCIO E IND LTDA ME
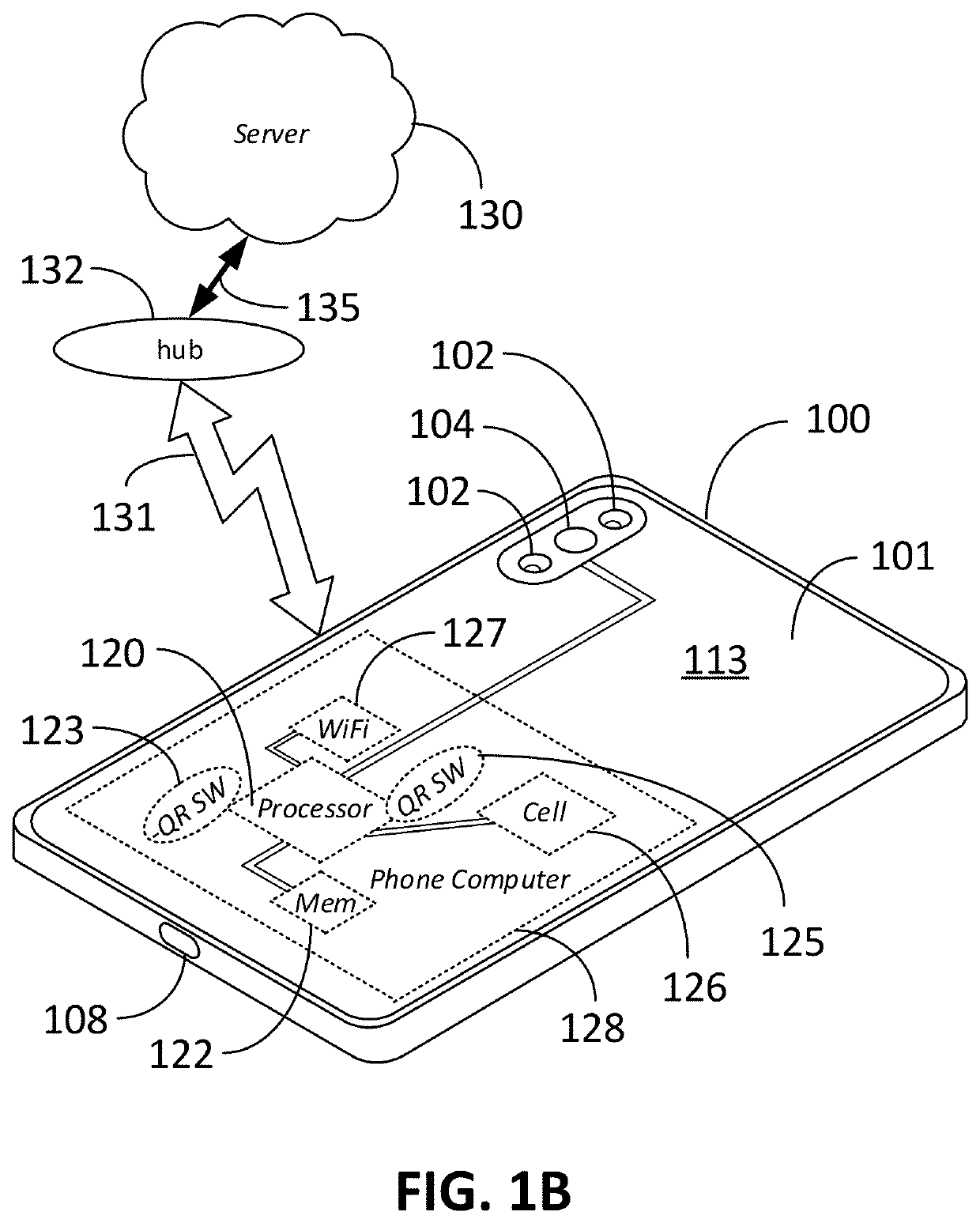
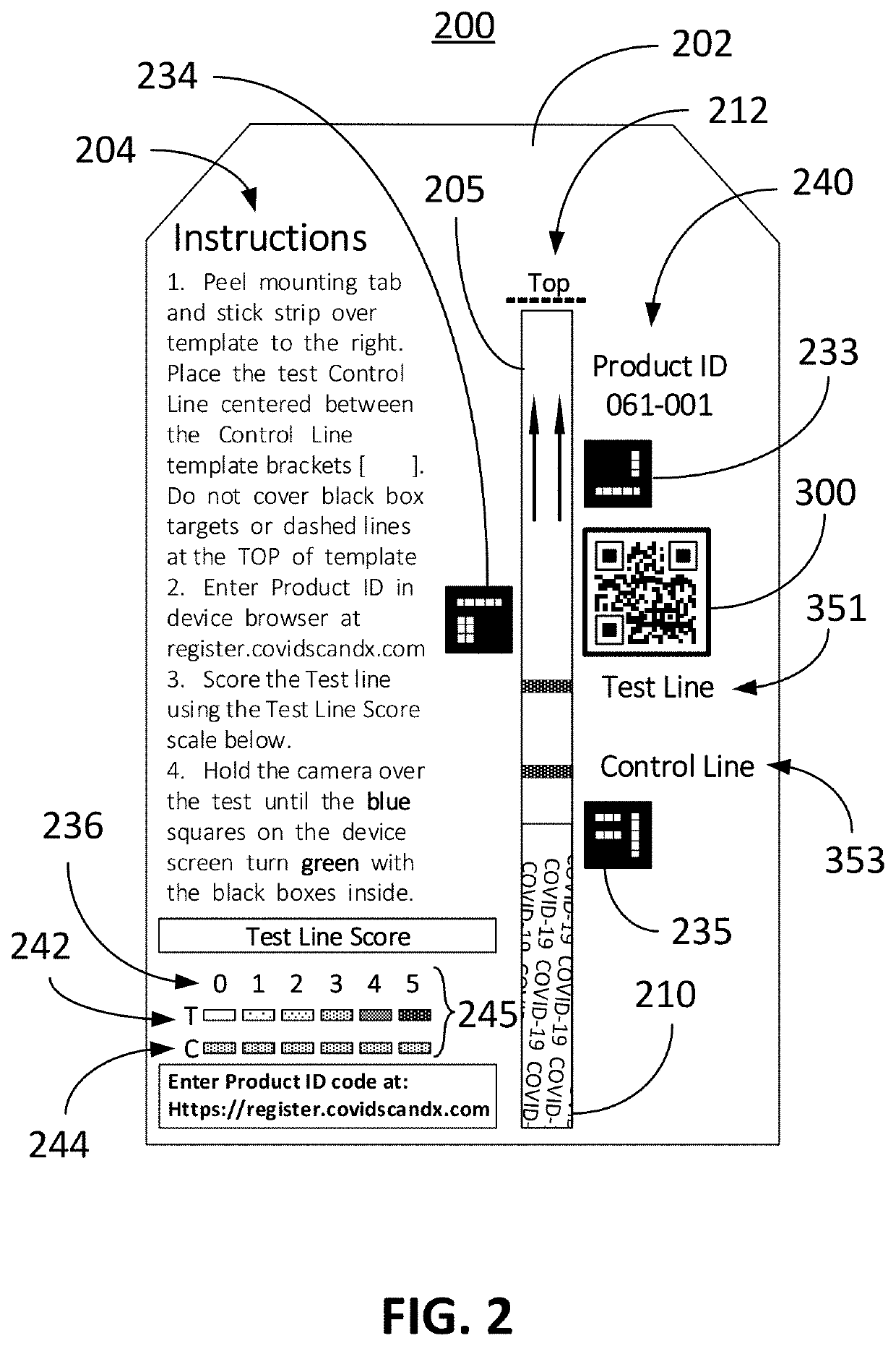
Secure machine readable code-embedded diagnostic test
InactiveUS20190257822A1Facilitate accurate quantitative image processingSimple processCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing record carriersRapid screening testApplication software
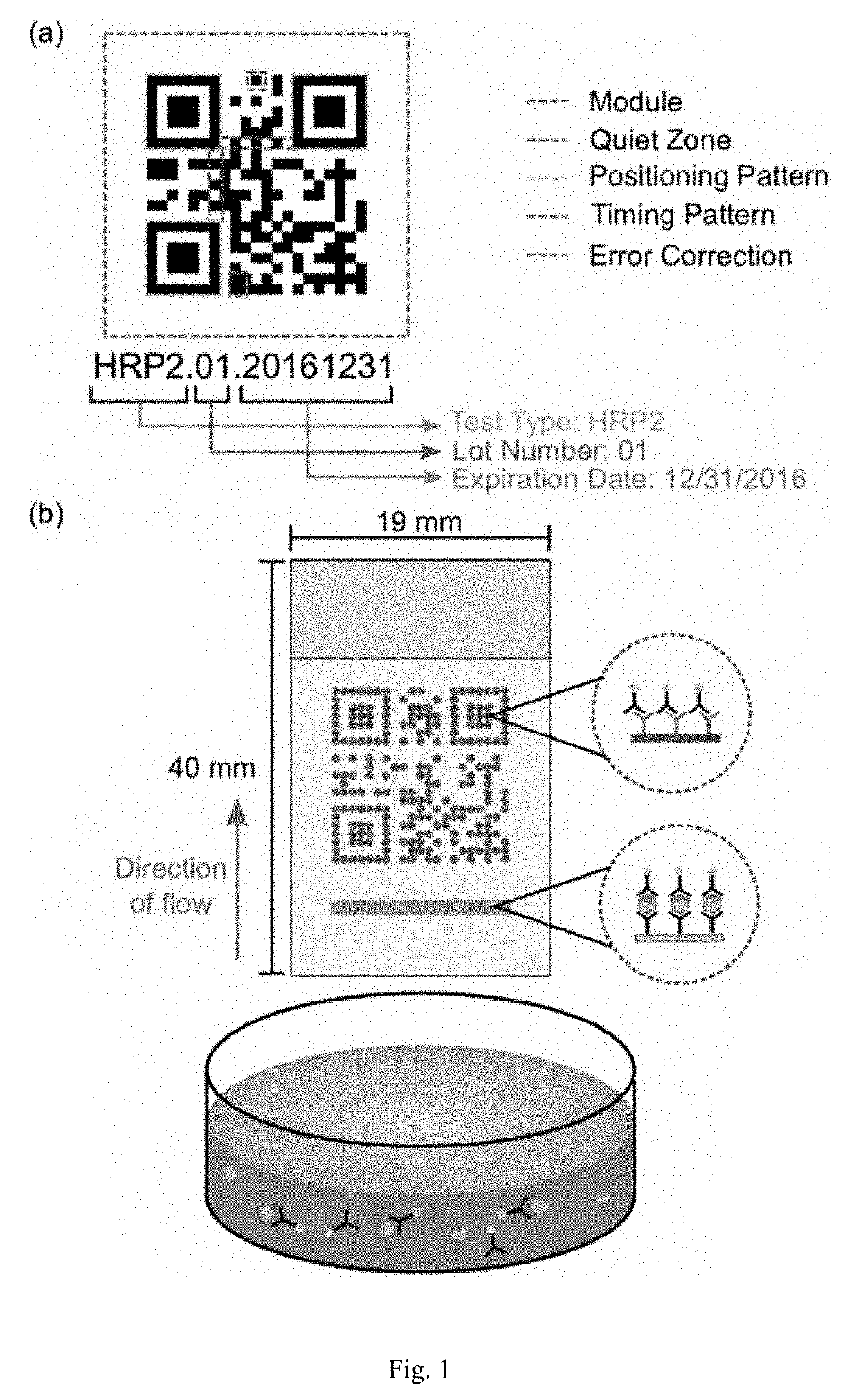
Disclosed herein is an information-augmented rapid diagnostic test in which control and test modules of a barcode, such as a QR code, are responsive to biomarkers in an analyte to become visible and form at least a portion of the barcode upon detection of the presence of such biomarkers. The barcode embeds test manufacturing details, serves as a trigger for image capture, enables registration for image analysis, and corrects for lighting effects. An accompanying mobile application preferably automatically captures an image of the test when the QR code is recognized, decodes the QR code, performs image processing to determine the concentration of the particular biomarker that is being diagnosed, and transmits the test results and QR code payload to a secure web portal.
Owner:PRAGMADX INC
Rapid diagnostic test device and sampling method using driven flow technology
A progressive compression driven flow cartridge for analyzing liquids is coupled with convenient sampling methods for different applications. A one-step device provides for direct sample collection upon a sample pad annexed to the cartridge. The sample pad can deliver sample to the test strips, while saving a portion of the sample pad for further laboratory confirmation use. If the sample collecting pad is not suitable to collect the sample, such as the case of biological substances inside the human body, such as within the nose or throat, a two-step device can include a long-arm swab applicator and a specialized chamber in which some amount of liquid can dissolve biological substances as specimen. The specimen can then be transferred onto the cartridge, either by application to the sample pad, or into the device through a sample window. Each method provides a qualitative analysis much faster than traditional rapid diagnostic devices.
Owner:DNT SCI RES
Direct Application of Recombinant Fusion Proteins in Rapid Diagnostic Tests
InactiveCN102262158AEasy to purifyGood water solubilityBiological testingHybrid peptidesDiseaseAntigen
The invention belongs to the field of bioengineering technology. Based on the common problems in the field of rapid antibody detection at home and abroad, such as poor antigen water solubility, weak detection signal, low sensitivity, and poor specificity, the invention proposes to directly use the overall fusion protein carrying a fusion label to detect the analyte Rapid detection of planar flow type. 1. The main points of the present invention are: constructing the recombinant gene of the fusion protein; expressing and purifying the recombinant fusion protein; preparing detection reagents and capture reagents with the recombinant fusion protein. 2. The present invention shows that the fusion protein has the advantages of good water solubility, easy purification, natural configuration, high activity, and high labeling efficiency, and the rapid detection reagent made from it has high sensitivity and specificity. 3. The rapid detection reagent constructed according to the present invention can detect one or two analytes simultaneously. 4. The present invention has broad application prospects in the field of application and basic research such as disease diagnosis, epidemiological survey, medical identification, new drug development, agriculture, animal husbandry and veterinary medicine.
Owner:戴国祯 +1
Rapid diagnostic test device by driven flow technology
ActiveUS9702872B1Increase speedPredictable rate of uptakeMaterial analysis using immobilised reagentsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical mixturesRapid screening test
A rapid diagnostic test device uses driven flow technology to significantly expedite the testing time of a sample. The rapid diagnostic test device can be used to analyze liquids, such as some body fluids, by using labeled molecular affinity binding, such as immunochromatography. The test device can detect an analyte, such as an antibody or antigen, which may indicate a particular condition, the presence of a particular drug, or the like. The device includes a cover and base that combine to form an internal cavity for receiving a test strip. Compression bars in the cover and a compression cushion in the base sandwich a conjugate pad of the test strip to accelerate chemical mixtures to flow from the conjugate pad of the test strip toward fixed sites along the strip from which readings are taken.
Owner:DNT SCI RES
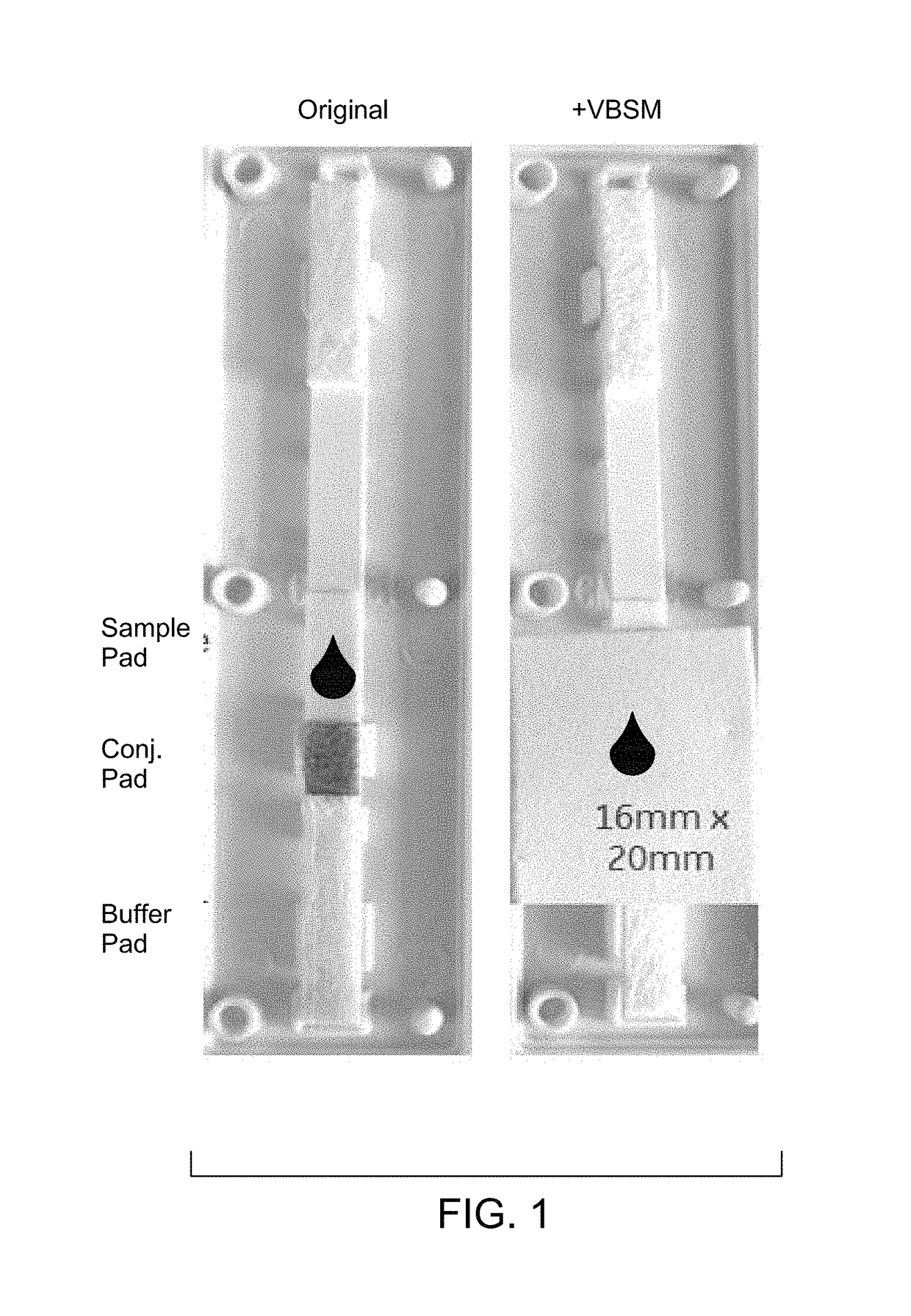
Integration of sample separation with rapid diagnostic tests for improved sensitivity
InactiveUS20170212112A1Reduce distractionsEasy to detectBiological material analysisRapid screening testUltimate tensile strength
Provided herein are integrated devices that improve sensitivity of rapid diagnostic tests. The devices described herein integrate sample separation with rapid diagnostic tests and improve signal intensity of the rapid diagnostic tests.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Process for Producing Surface Enhanced Membrane
ActiveUS20100330691A1Speed up the processEfficient productionMembranesSemi-permeable membranesRapid screening testLiquid medium
Owner:SARTORIUS STEDIM BIOTECH GMBH
Method and associated device for rapid detection of target biomolecules with enhanced sensitivity
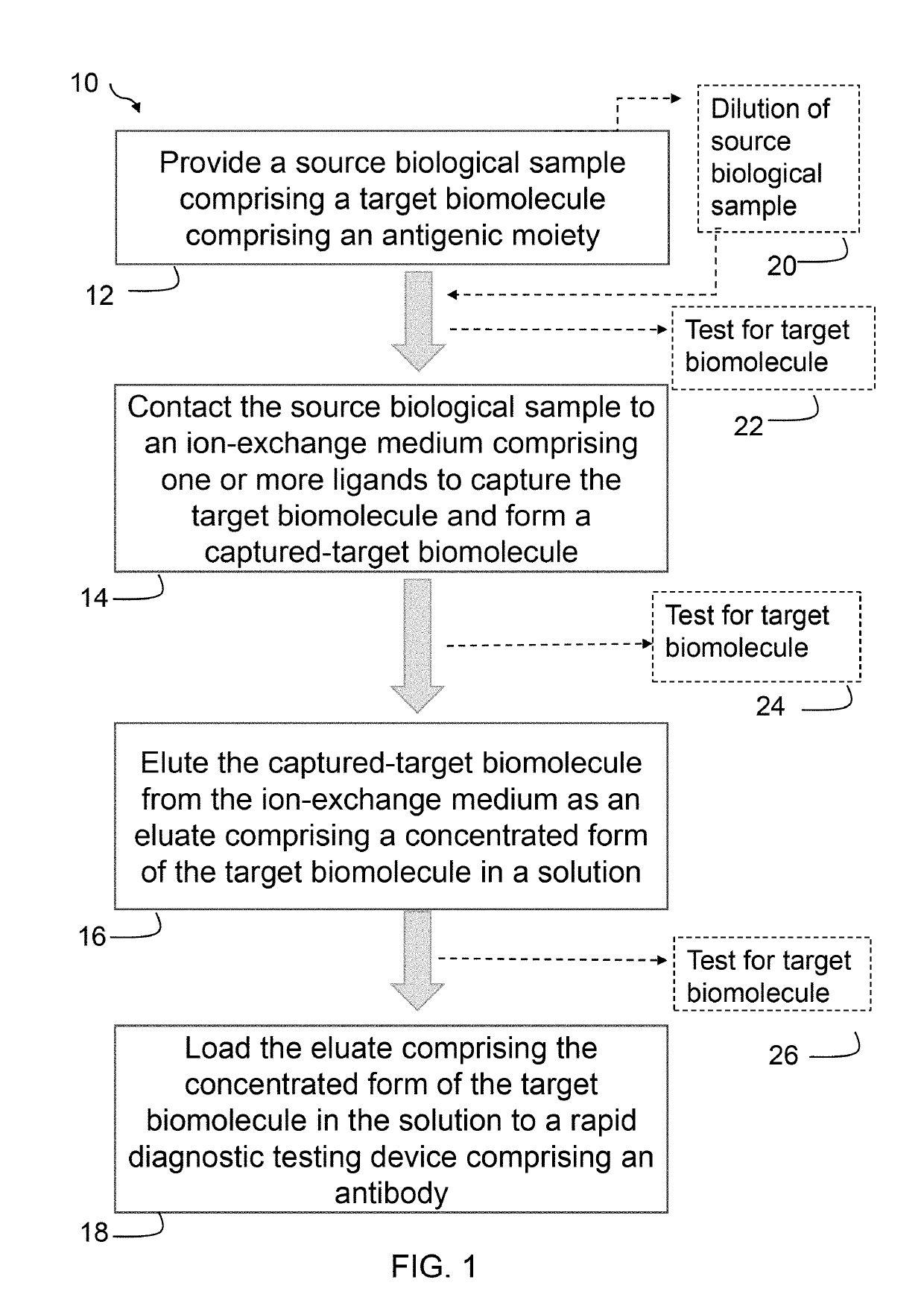
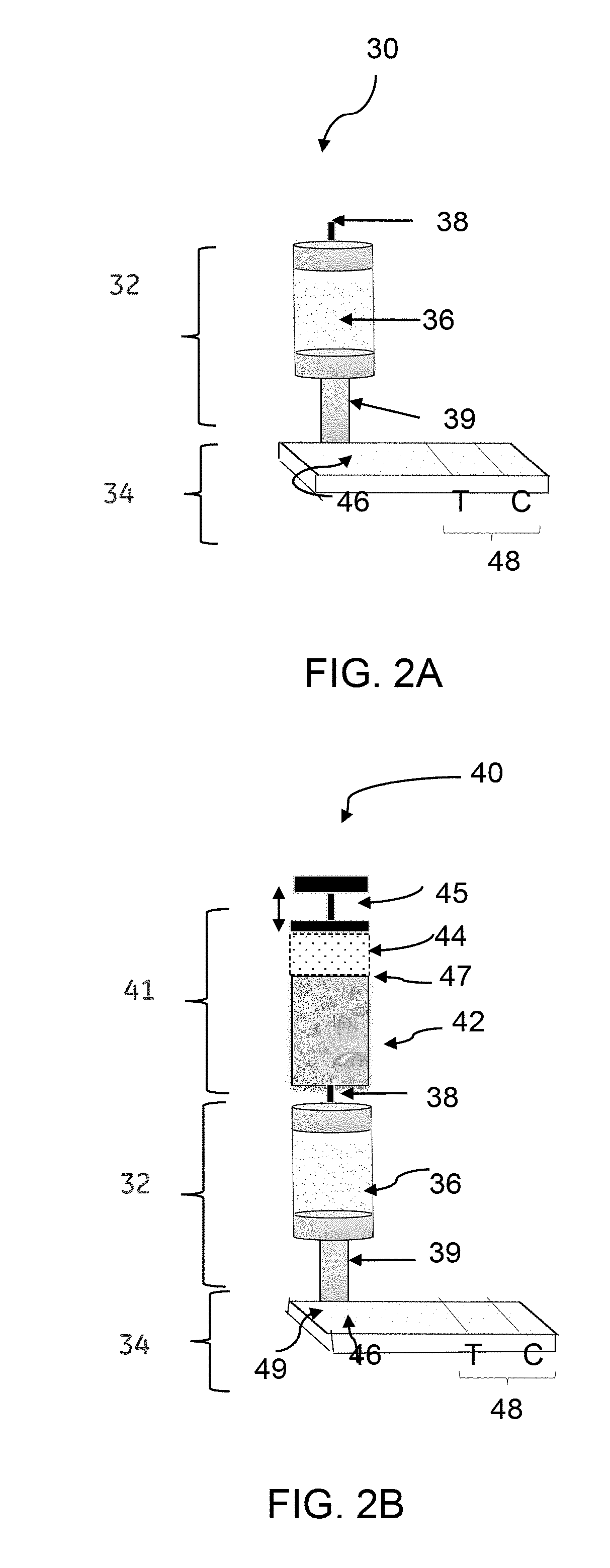
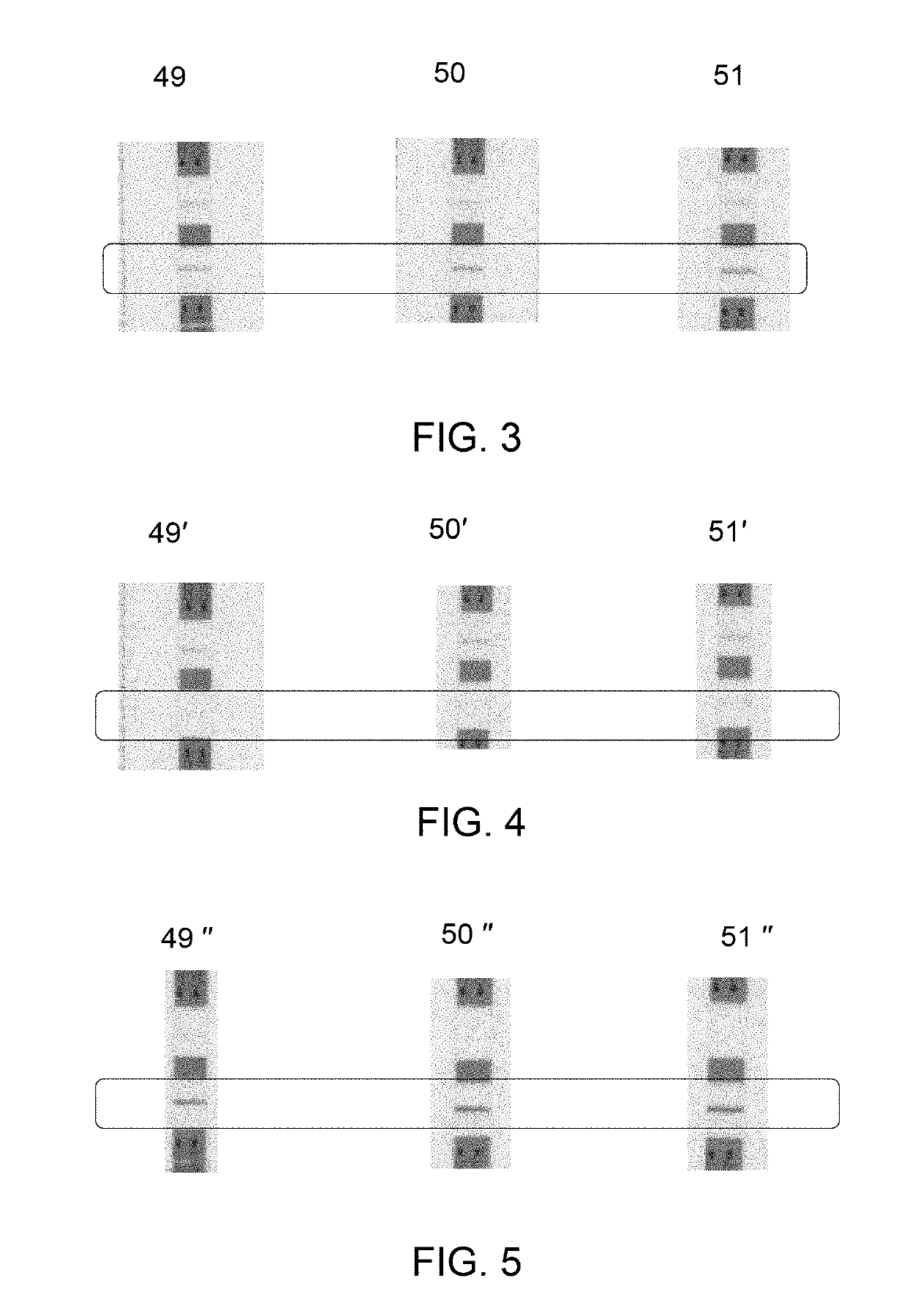
A rapid detection method of a target biomolecule comprising an antigenic moiety is provided. The method includes providing a source biological sample comprising the target biomolecule; contacting the source biological sample to an ion-exchange medium; eluting the captured-target biomolecule from the ion-exchange medium as an eluate, and loading the eluate to a rapid diagnostic testing device comprising an antibody. The eluate comprises a concentrated form of the biomolecule in a solution having a salt concentration greater than 150 mM. A concentration of the target biomolecule in the eluate is in a range from about 2× to 25× compared to a concentration of the biomolecule in the source biological sample. The target biomolecule binds to the antibody under the salt concentration of greater than 150 mM. A device for rapid detection of target biomolecule is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Computer vision method for improved automated image capture and analysis of rapid diagnostic test devices
ActiveUS20220027587A1Low efficacyImprove accuracyHealth-index calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionRapid screening testAntigen
The disclosed embodiments are generally directed to improving feature detection of rapidly acquired images using camera-enabled mobile devices involving a 2-D decal code, such as a QR code, for improving the reading accuracy of a rapid diagnostic antigen or antibody or enzymatic colorimetric directed test, such as for COVID-19 diagnosis. One primary issue with evaluating a Covid-19 rapid test is detecting and quantifying positive test lines from sampled test strips based on digital images of the test strip. Aspects of the present invention contemplate masking a QR code to improve the sample image resolution and contrast. Other aspects of the present invention contemplate methods and techniques to evaluate a test line on the sample image by enhancing an intensity curve along the test line and control line containing area by way of calculating the instantaneous change in pixel intensity and evaluating the position and intensity of those signals.
Owner:NEUROGANICS DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Rapid diagnostic test systems and methods
A rapid diagnostic test system includes a lateral-flow strip for performing a binding assay. The lateral-flow strip contains a binding agent having a deposition density that varies periodically along at least a portion of the lateral-flow strip. The test system further includes an imaging system that is used to capture an image of the portion of the lateral-flow strip.
Owner:ALVERIX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com